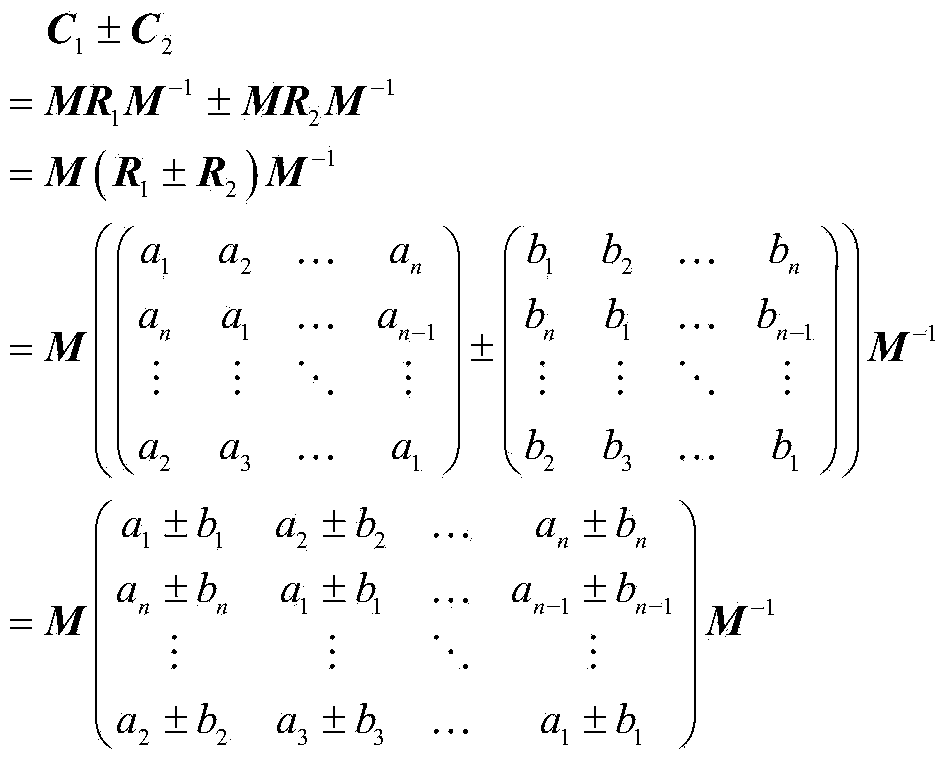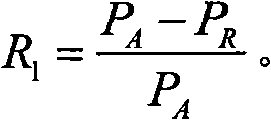Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
181 results about "Arithmetic computation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computation | arithmetic |. is that computation is the act or process of ; calculation; reckoning while arithmetic is the mathematics of numbers (integers, rational numbers, real numbers, or complex numbers) under the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
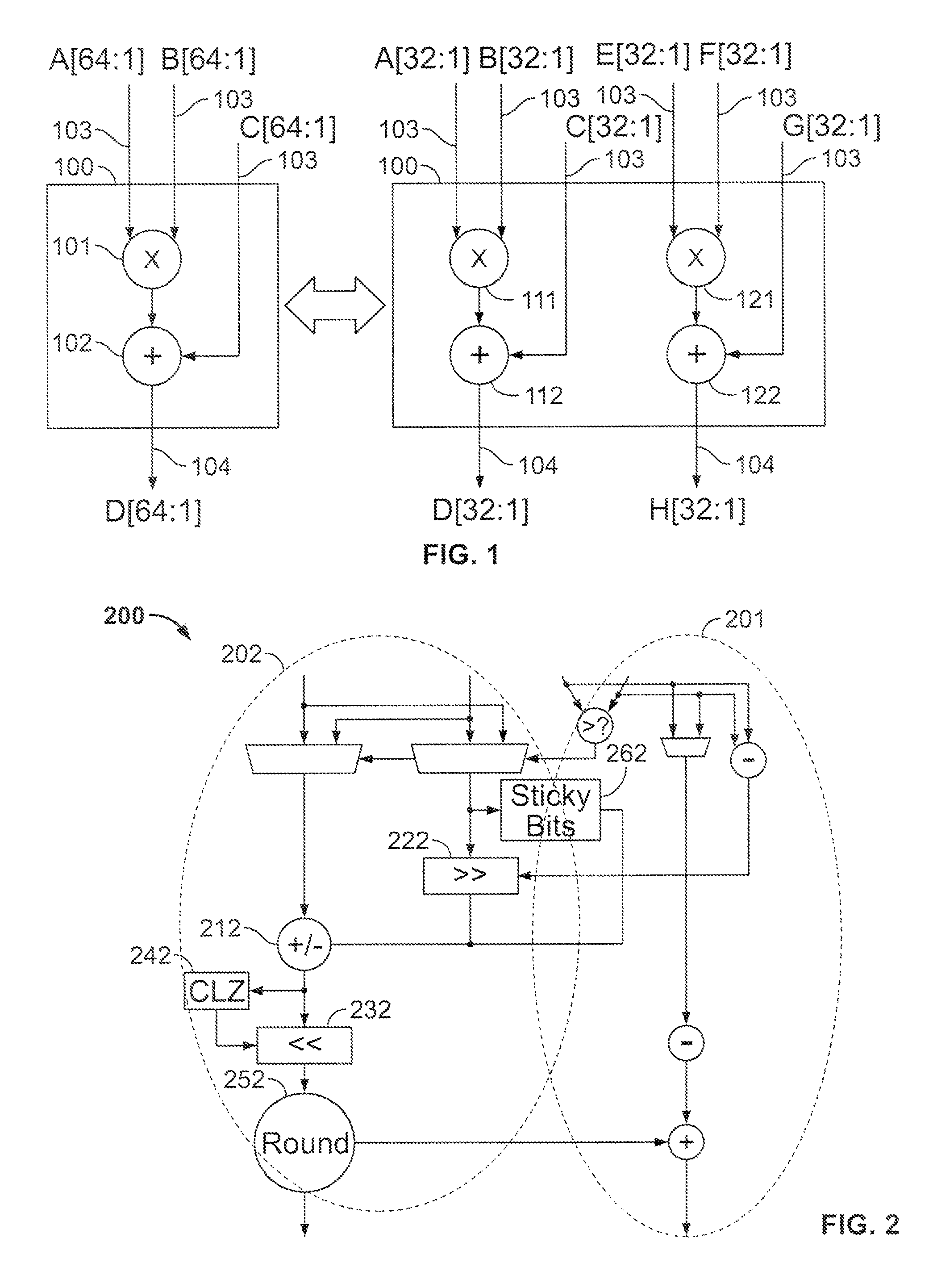
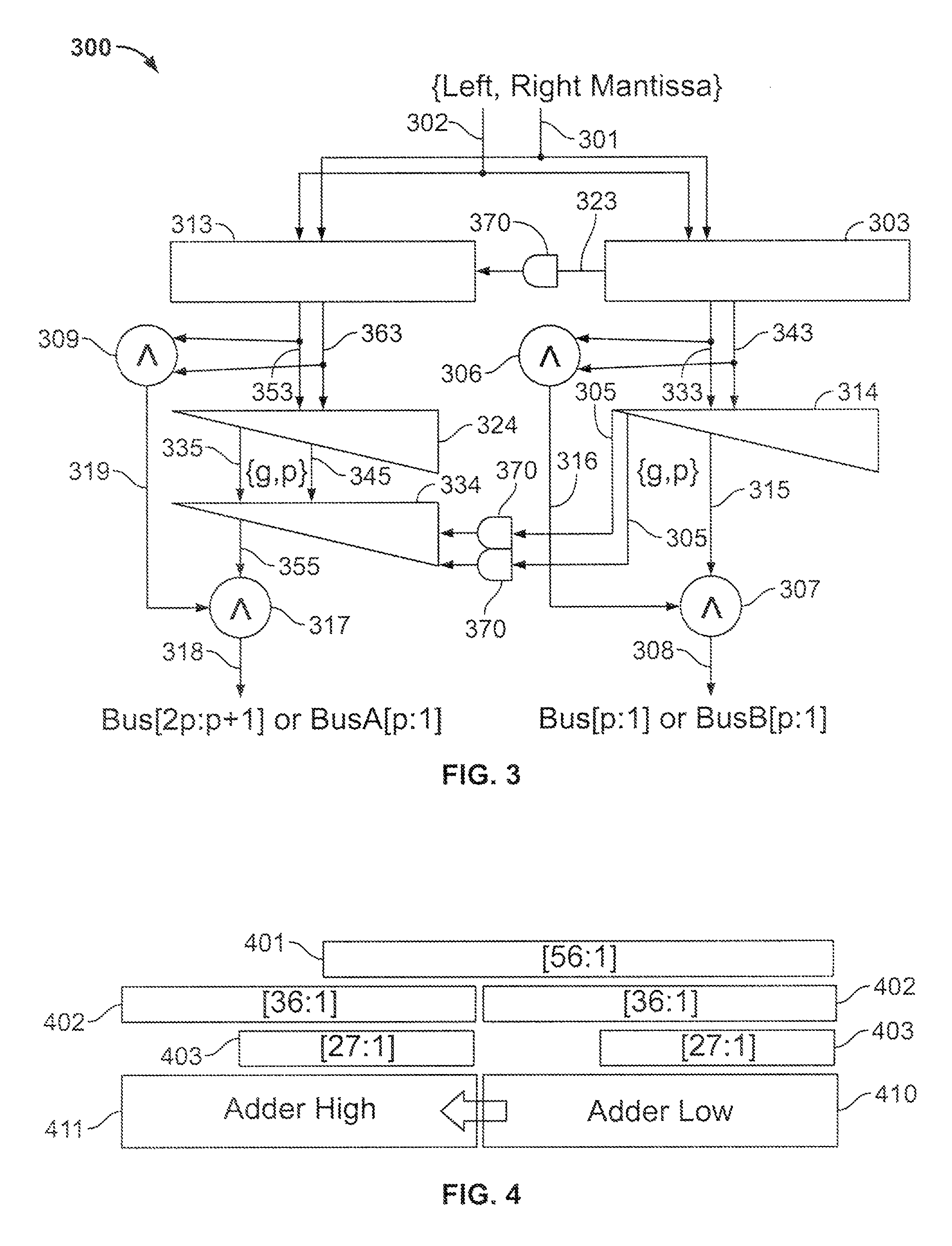
Shared FP and SIMD 3D multiplier
InactiveUS6490607B1Computations using contact-making devicesRuntime instruction translationComputerized systemTheoretical computer science
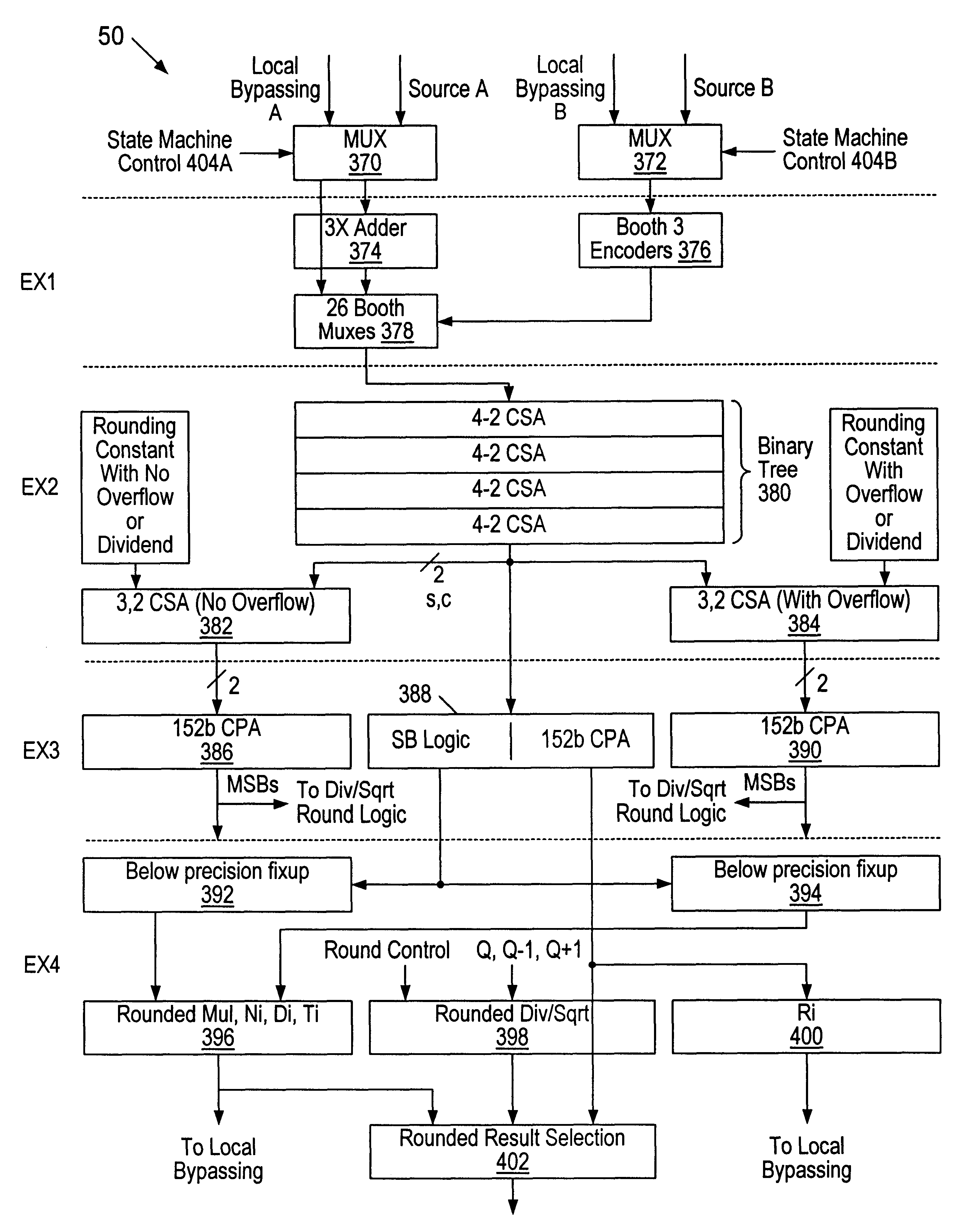
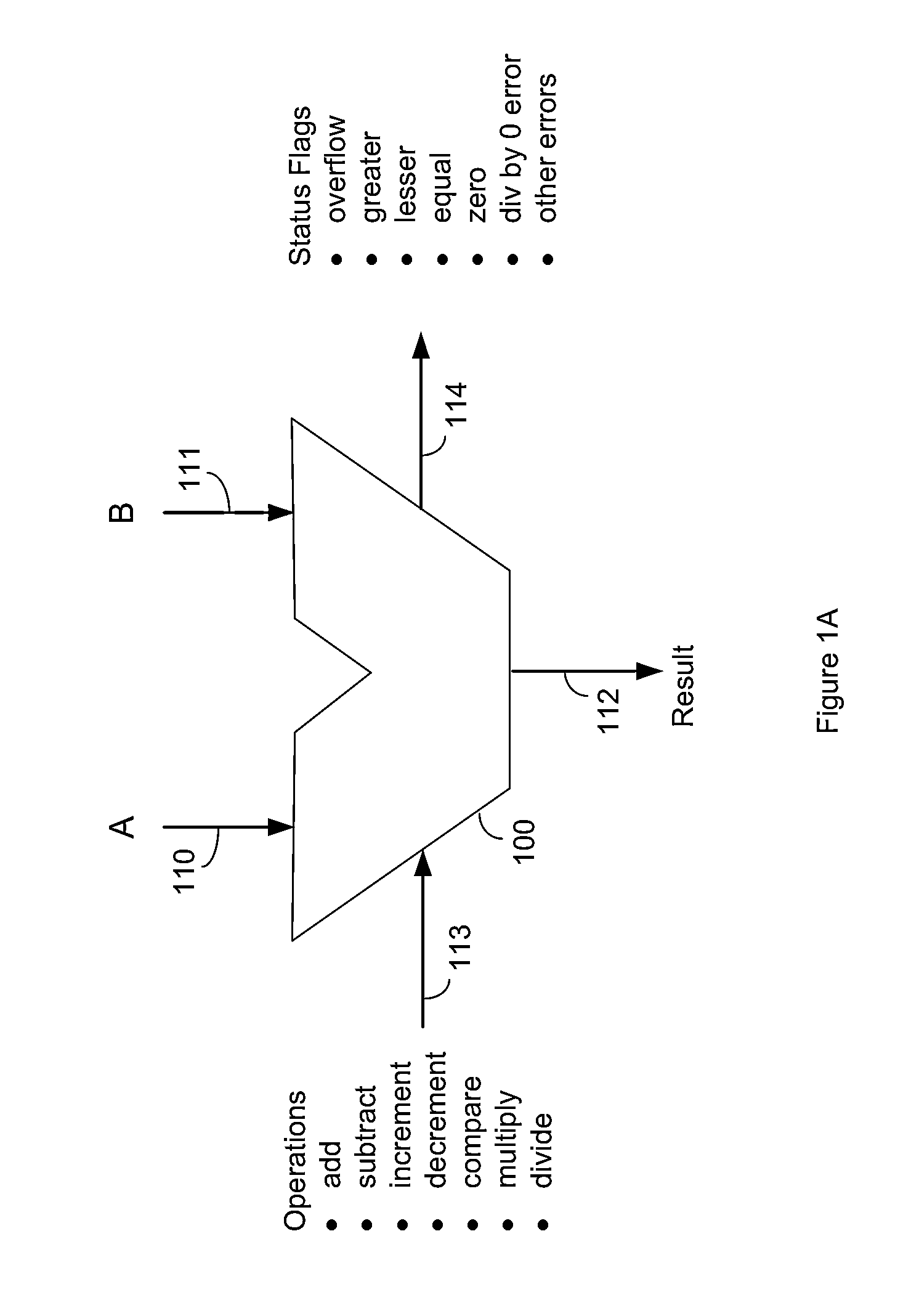
A multiplier configured to perform multiplication of both scalar floating point values (XxY) and packed floating point values (i.e., X1xY1 and X2xY2). In addition, the multiplier may be configured to calculate XxY-Z. The multiplier comprises selection logic for selecting source operands, a partial product generator, an adder tree, and two or more adders configured to sum the results from the adder tree to achieve a final result. The multiplier may also be configured to perform iterative multiplication operations to implement such arithmetical operations such as division and square root. The multiplier may be configured to generate two versions of the final result, one assuming there is an overflow, and another assuming there is not an overflow. A computer system and method for performing multiplication are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Computer processor for higher precision computations using a mixed-precision decomposition of operations
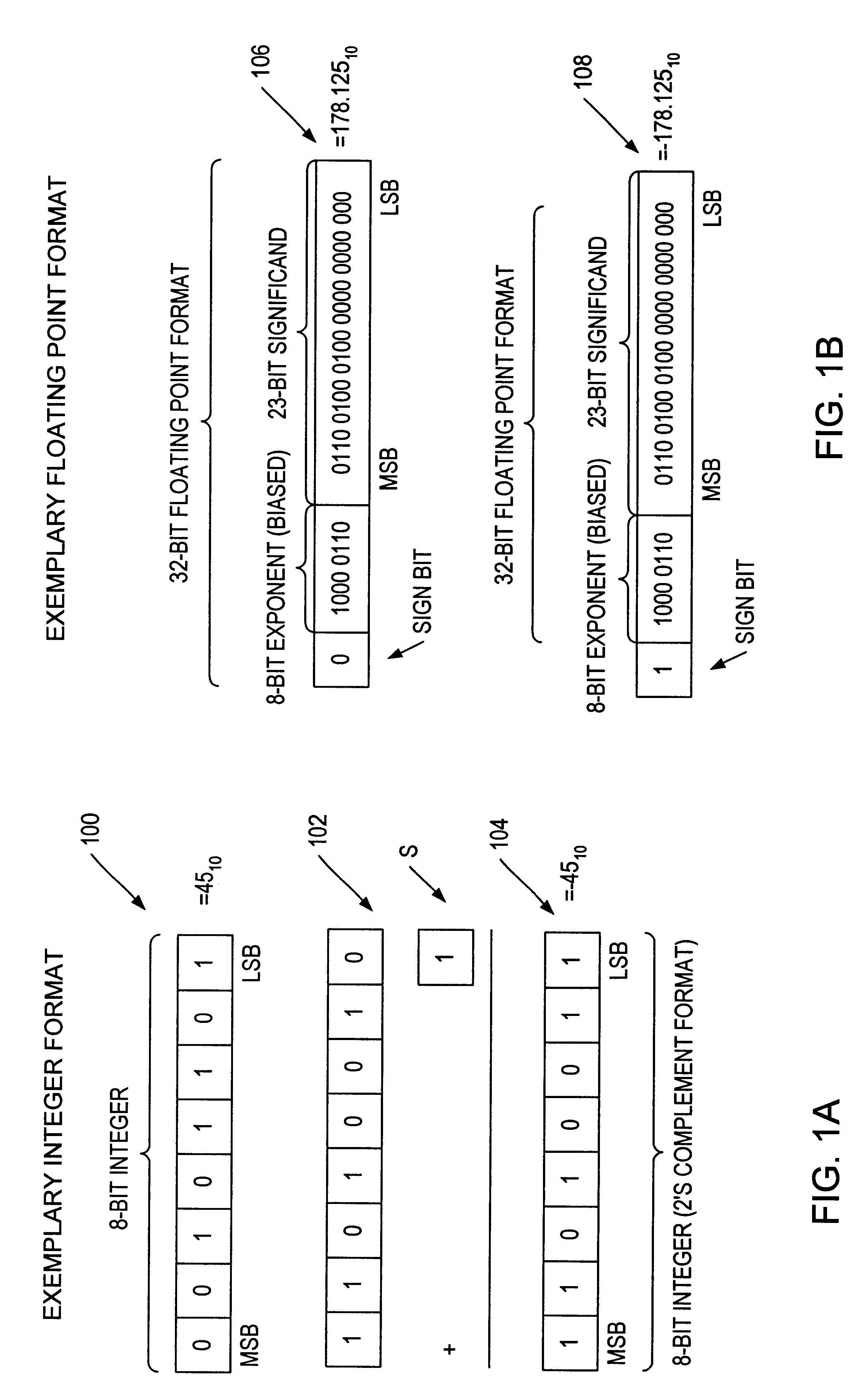
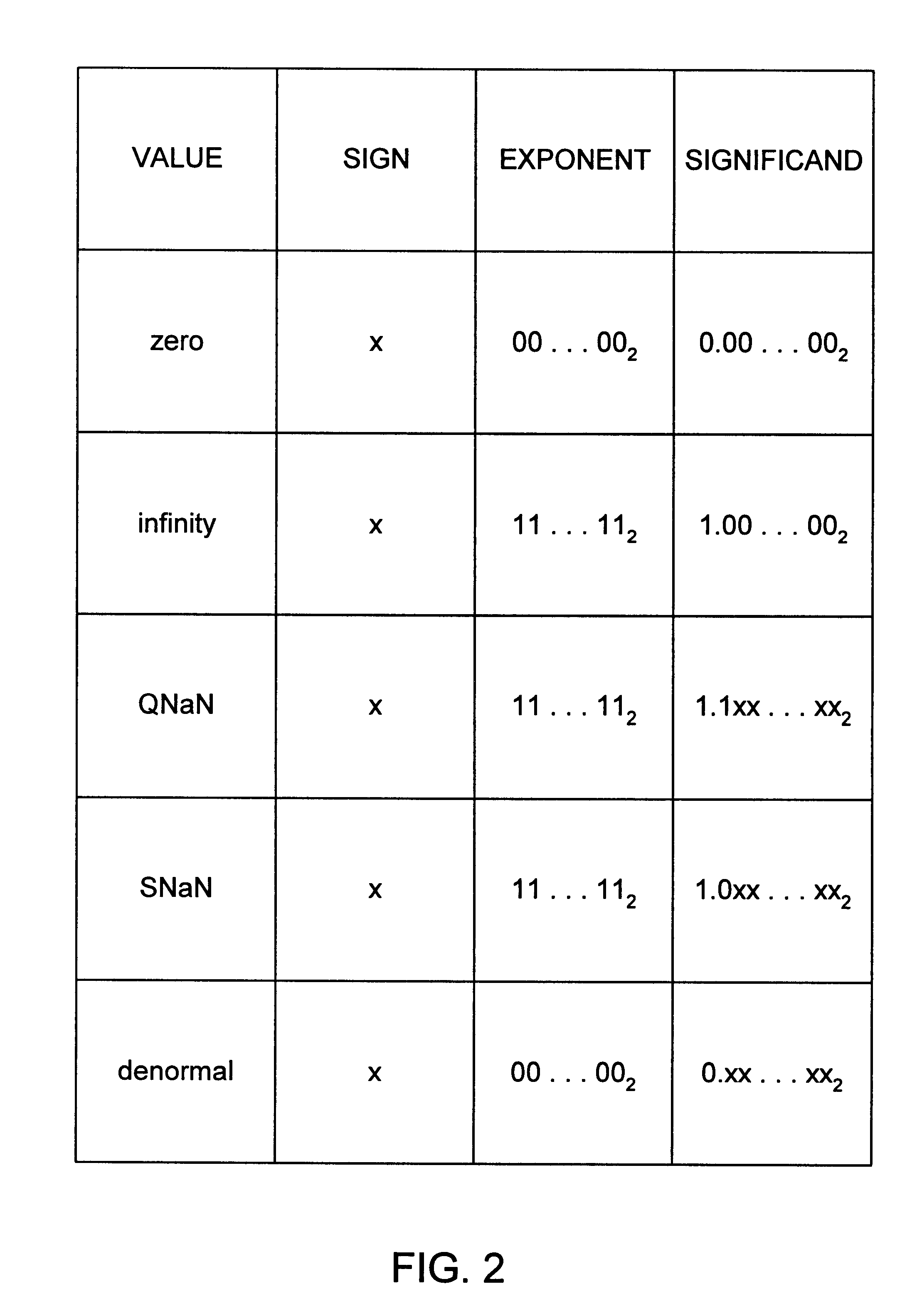
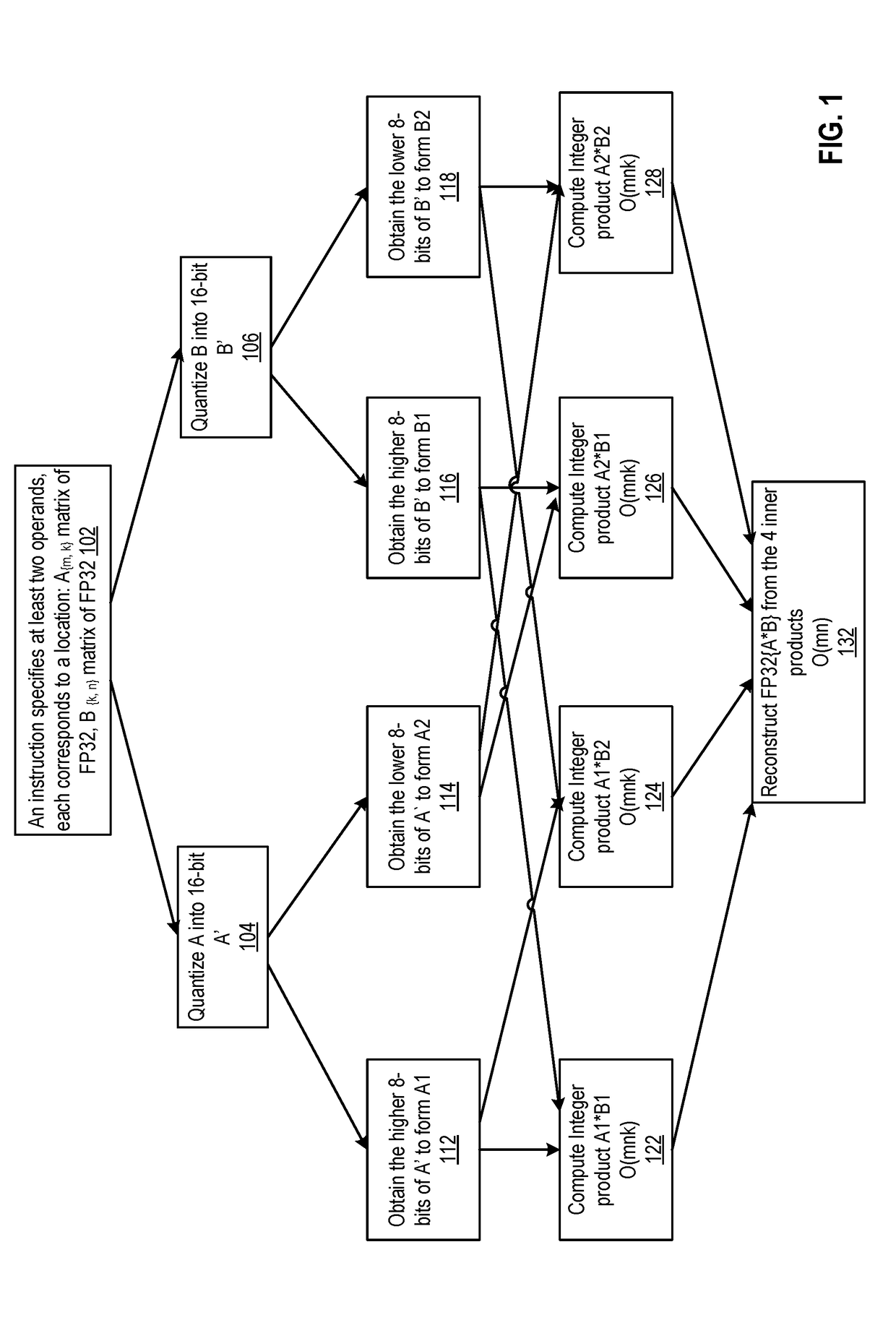
Embodiments detailed herein relate to arithmetic operations of float-point values. An exemplary processor includes decoding circuitry to decode an instruction, where the instruction specifies locations of a plurality of operands, values of which being in a floating-point format. The exemplary processor further includes execution circuitry to execute the decoded instruction, where the execution includes to: convert the values for each operand, each value being converted into a plurality of lower precision values, where an exponent is to be stored for each operand; perform arithmetic operations among lower precision values converted from values for the plurality of the operands; and generate a floating-point value by converting a resulting value from the arithmetic operations into the floating-point format and store the floating-point value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
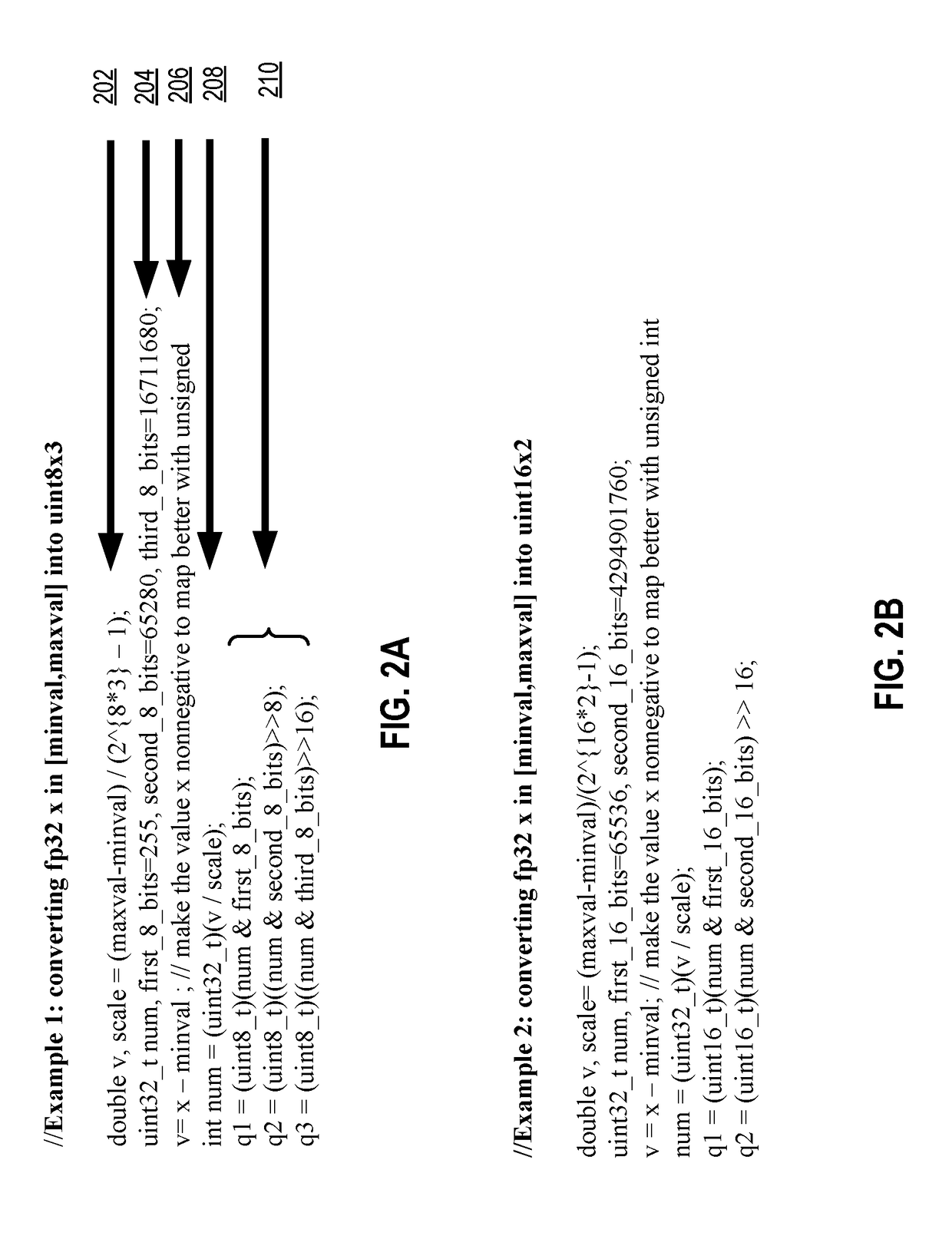
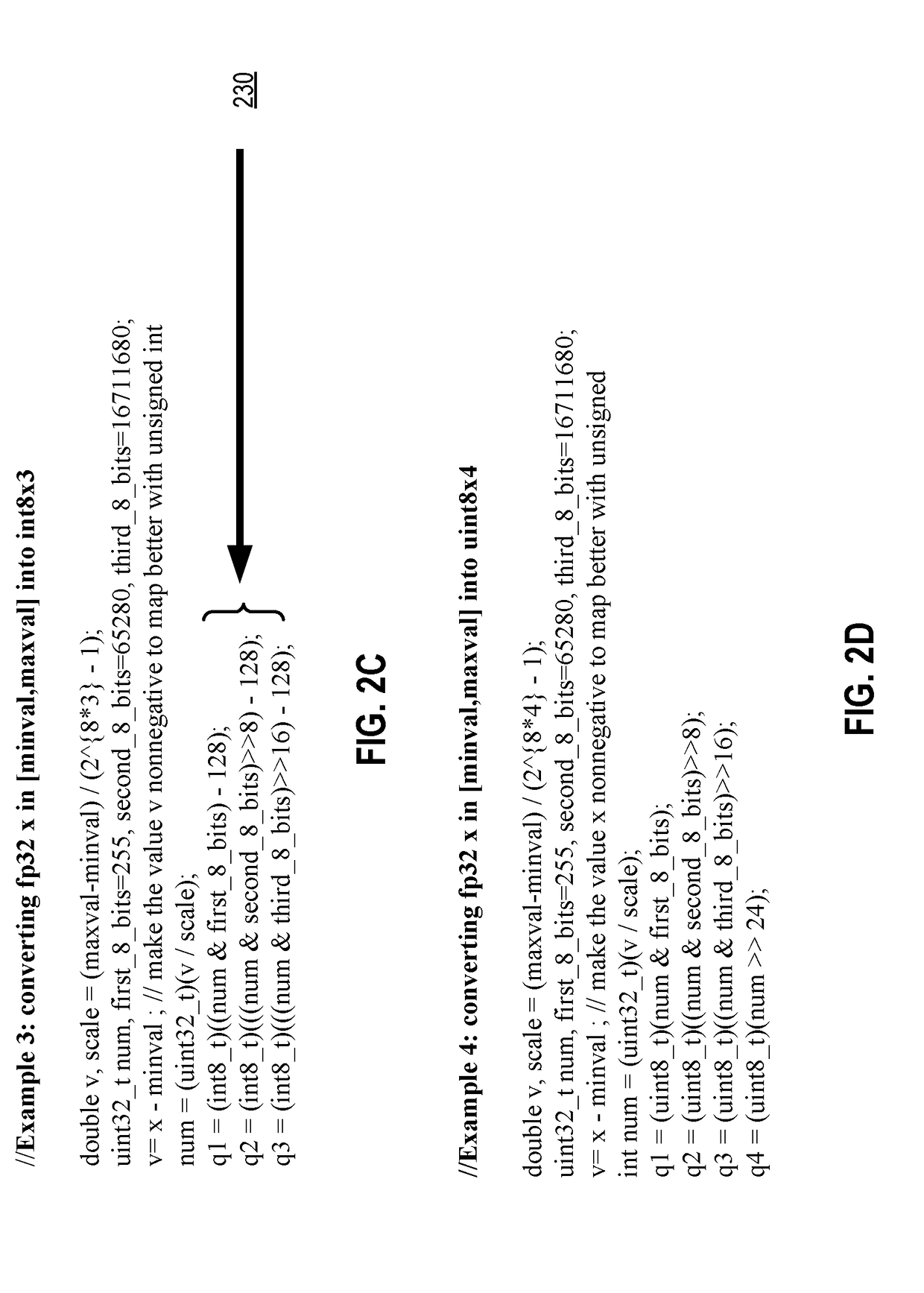
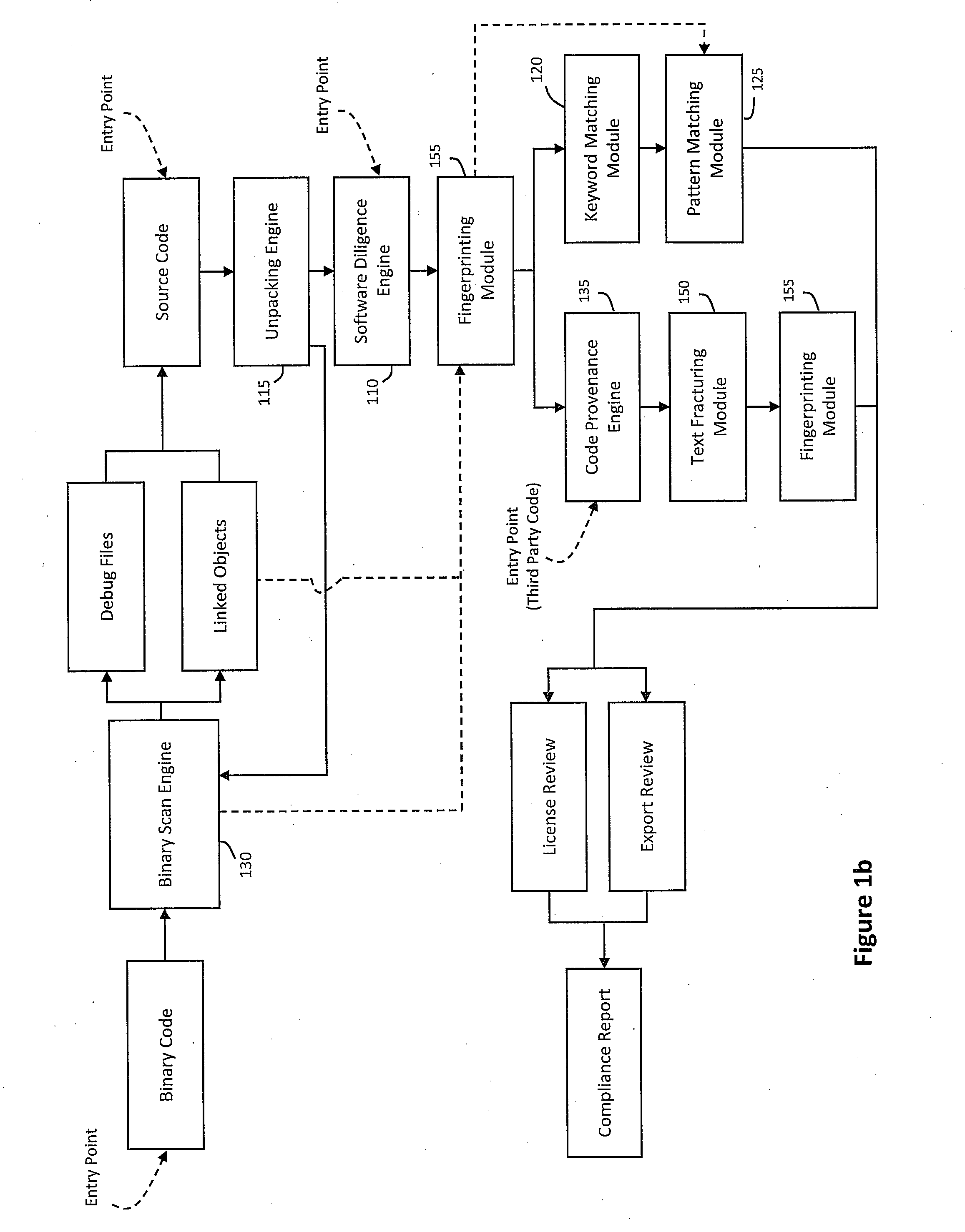
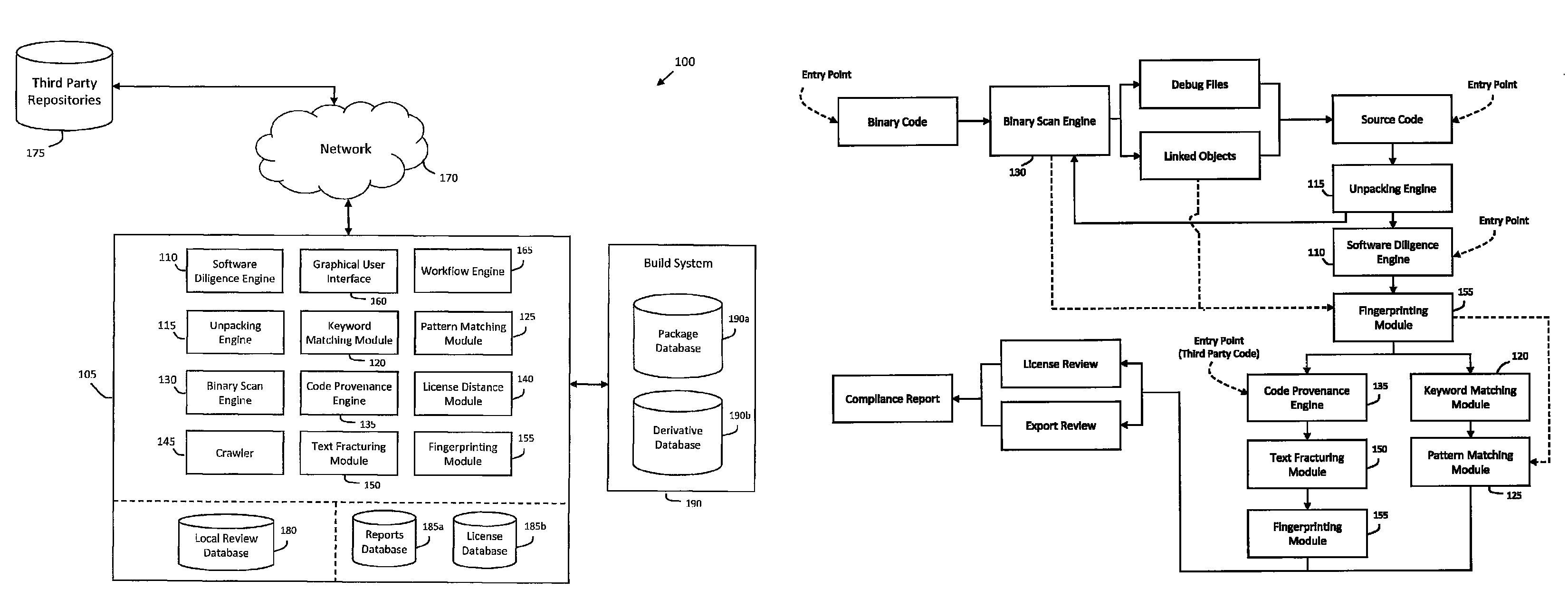
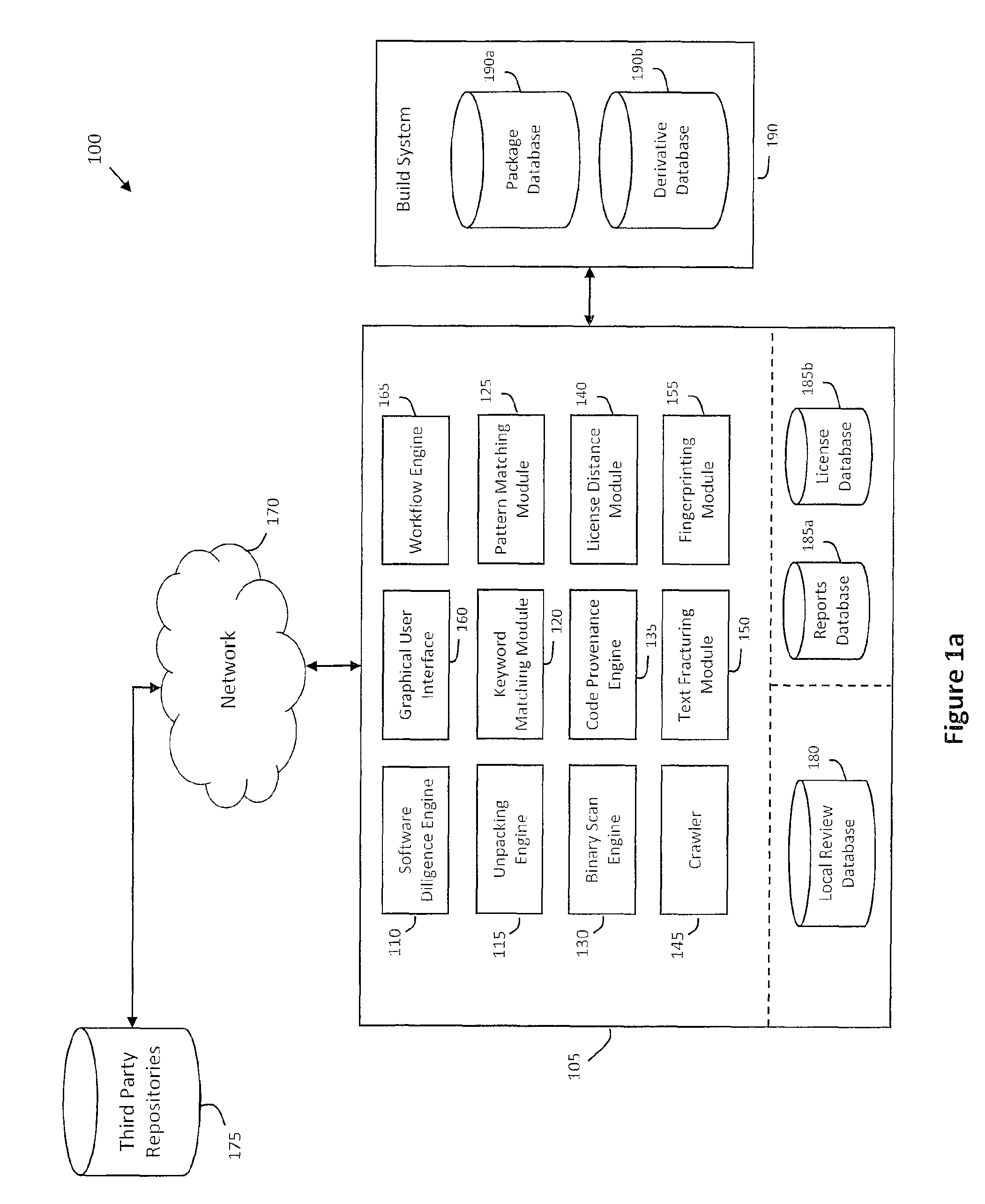
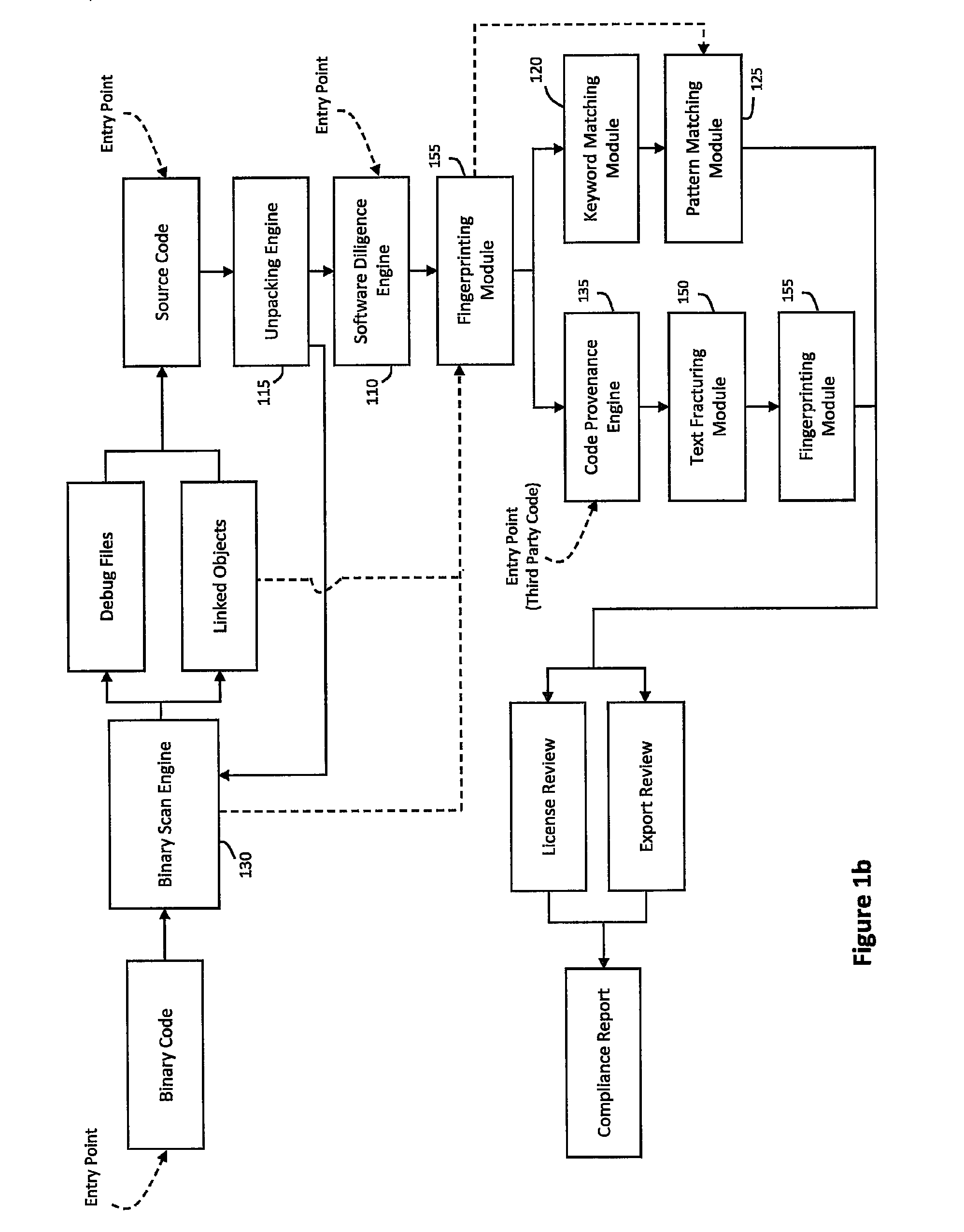
System and method for performing code provenance review in a software due diligence system
ActiveUS20100242028A1Lack of precisionProgram/content distribution protectionSpecific program execution arrangementsSource codeArithmetic computation
A system and method is provided for performing code provenance review in a software due diligence system. In particular, performing code provenance review may include sub-dividing source code under review and third-party source into logical fragments using a language-independent text fracturing algorithm. For example, the fracturing algorithm may include a set of heuristic rules that account for variations in coding style to create logical fragments that are as large as possible without being independently copyrightable. Unique fingerprints may then be generated for the logical fragments using a fingerprint algorithm that features arithmetic computation. As such, potentially related source code may be identified if sub-dividing the source code under review and the third-party source code produces one or more logical fragments that have identical fingerprints.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
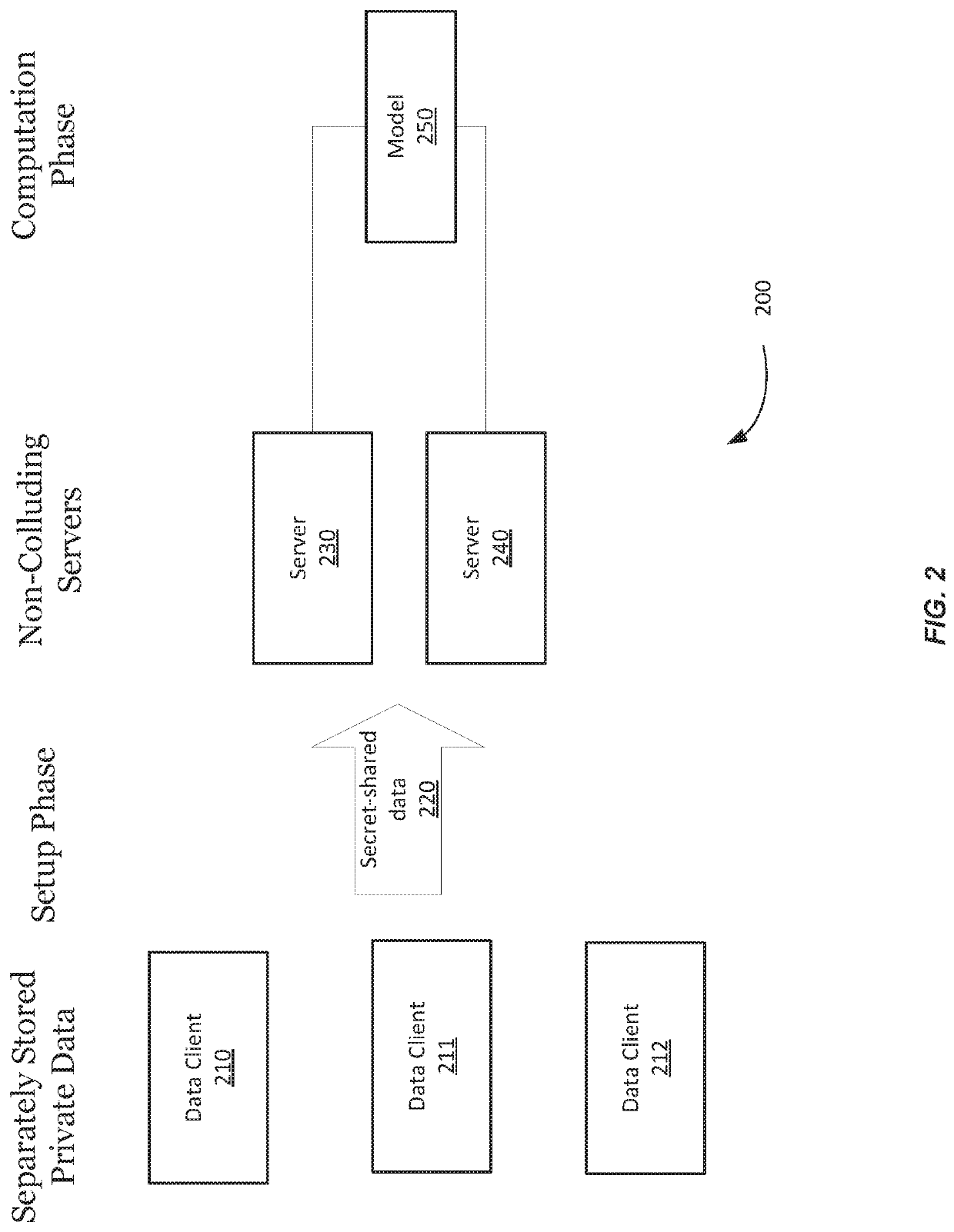
Privacy-preserving machine learning
ActiveUS20200242466A1Efficiently determinedLimited amount of memoryKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data protectionStochastic gradient descentAlgorithm
New and efficient protocols are provided for privacy-preserving machine learning training (e.g., for linear regression, logistic regression and neural network using the stochastic gradient descent method). A protocols can use the two-server model, where data owners distribute their private data among two non-colluding servers, which train various models on the joint data using secure two-party computation (2PC). New techniques support secure arithmetic operations on shared decimal numbers, and propose MPC-friendly alternatives to non-linear functions, such as sigmoid and softmax.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
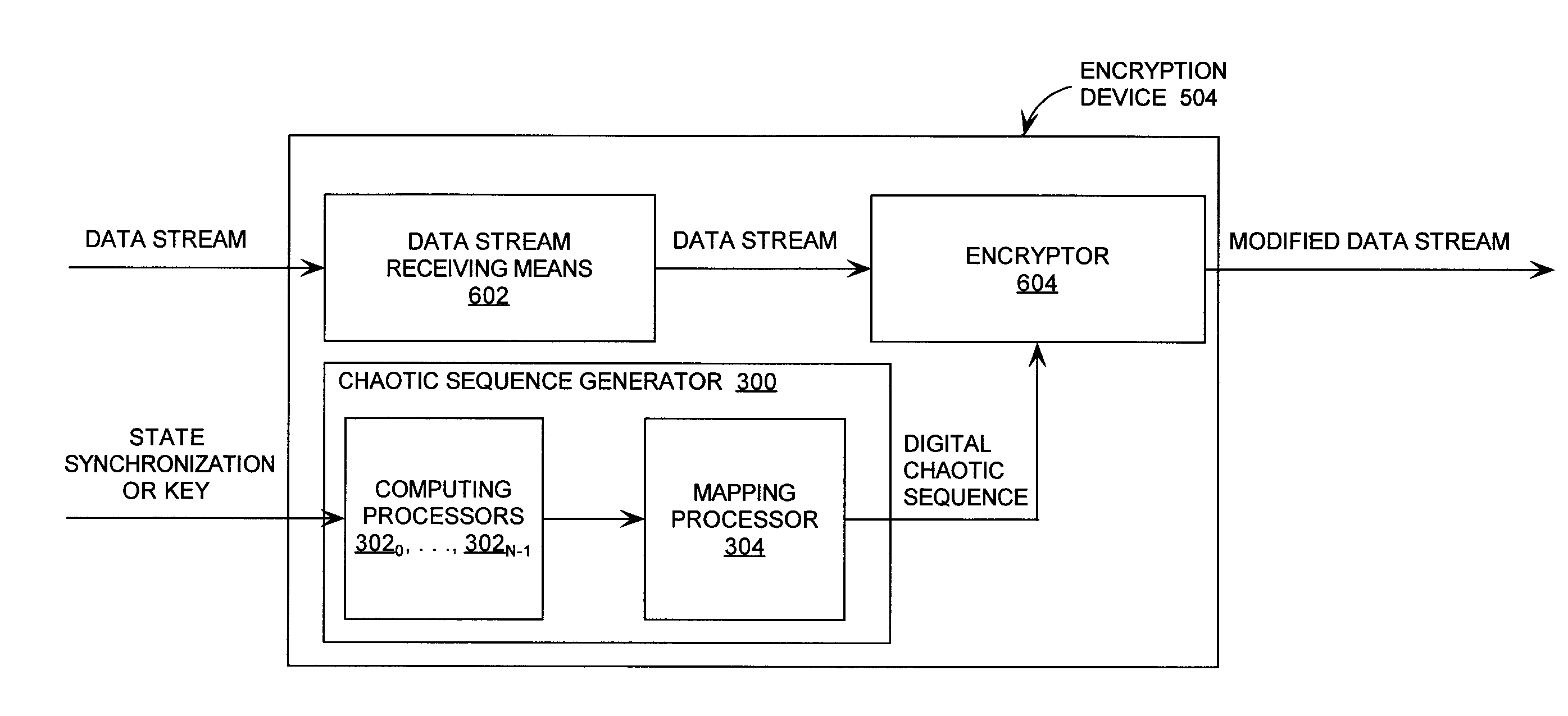
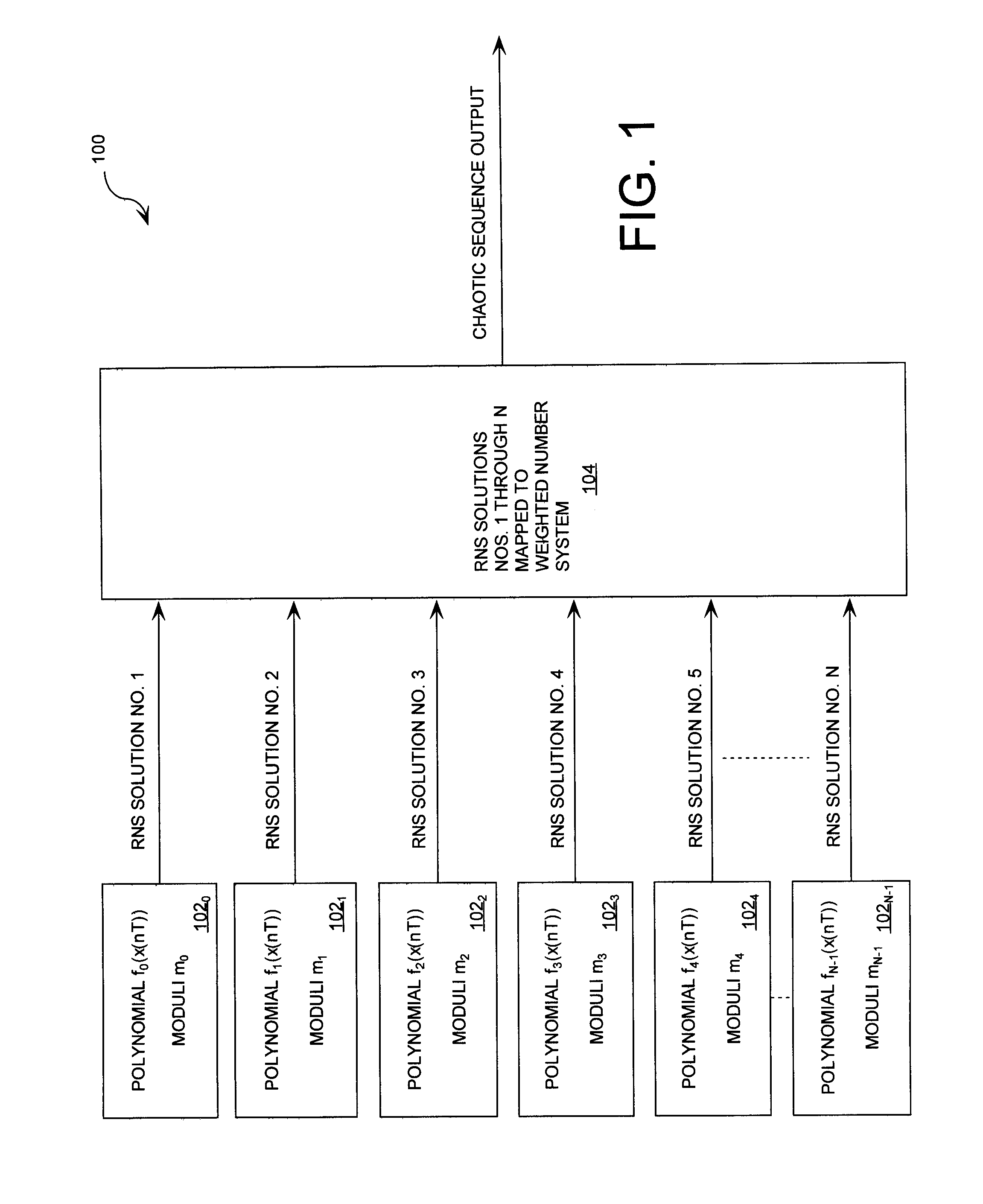
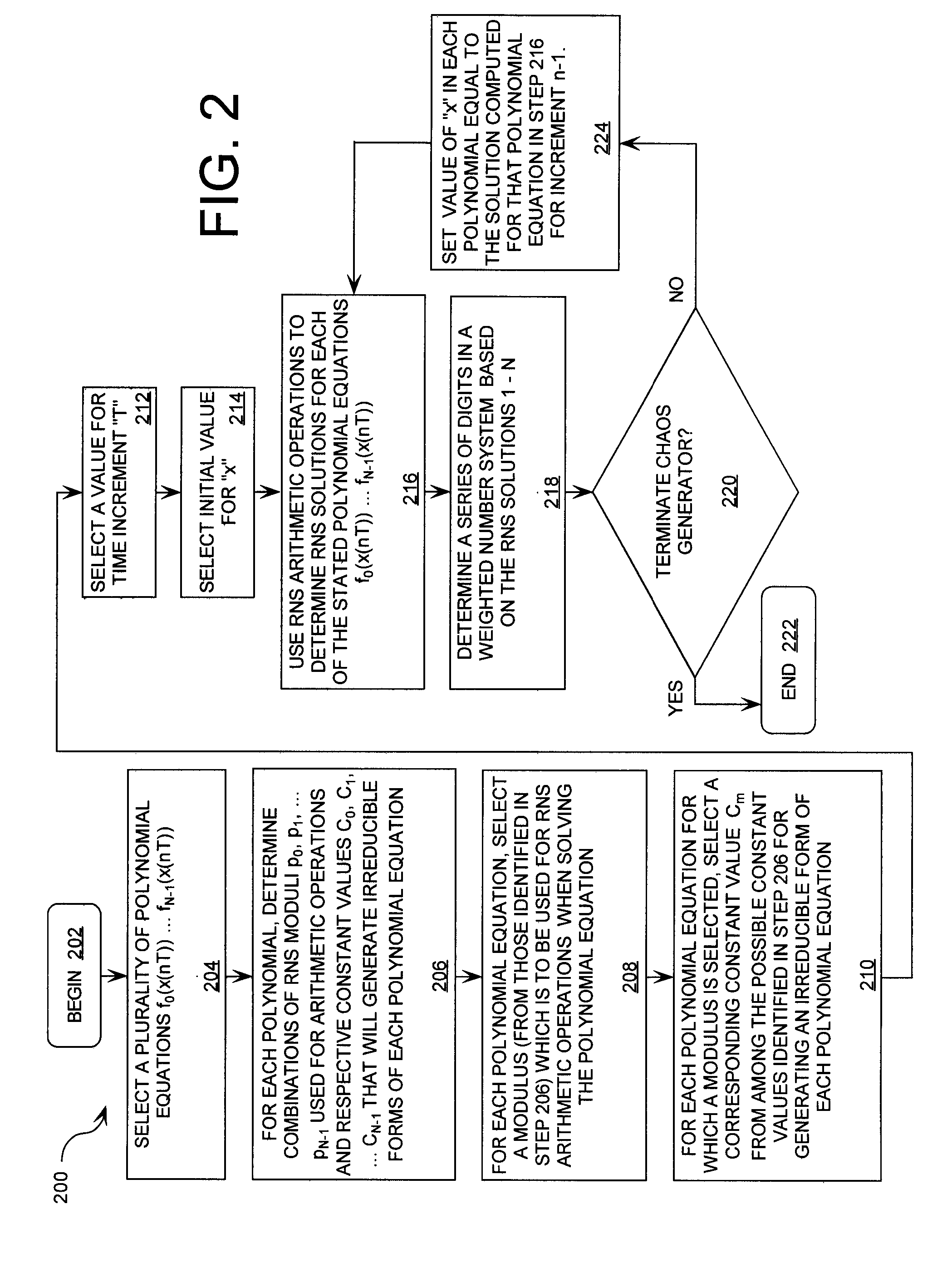
Cryptographic system incorporating a digitally generated chaotic numerical sequence
ActiveUS20090196420A1Data stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationNumbering systemData stream
A cryptographic system (CS) is provided. The CS (500) is comprised of a data stream receiving device (DSRD), a chaotic sequence generator (CSG) and an encryptor. The DSRD (602) is configured to receive an input data stream. The CSG (300) includes a computing means (3020, . . . , 302N-1) and a mapping means (304). The computing means is configured to use RNS arithmetic operations to respectively determine solutions for polynomial equations. The solutions are iteratively computed and expressed as RNS residue values. The mapping means is configured to determine a series of digits in the weighted number system based on the RNS residue values. The encryptor is coupled to the DSRD and CSG. The encryptor is configured to generate a modified data stream by incorporating or combining the series of digits with the input data stream.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
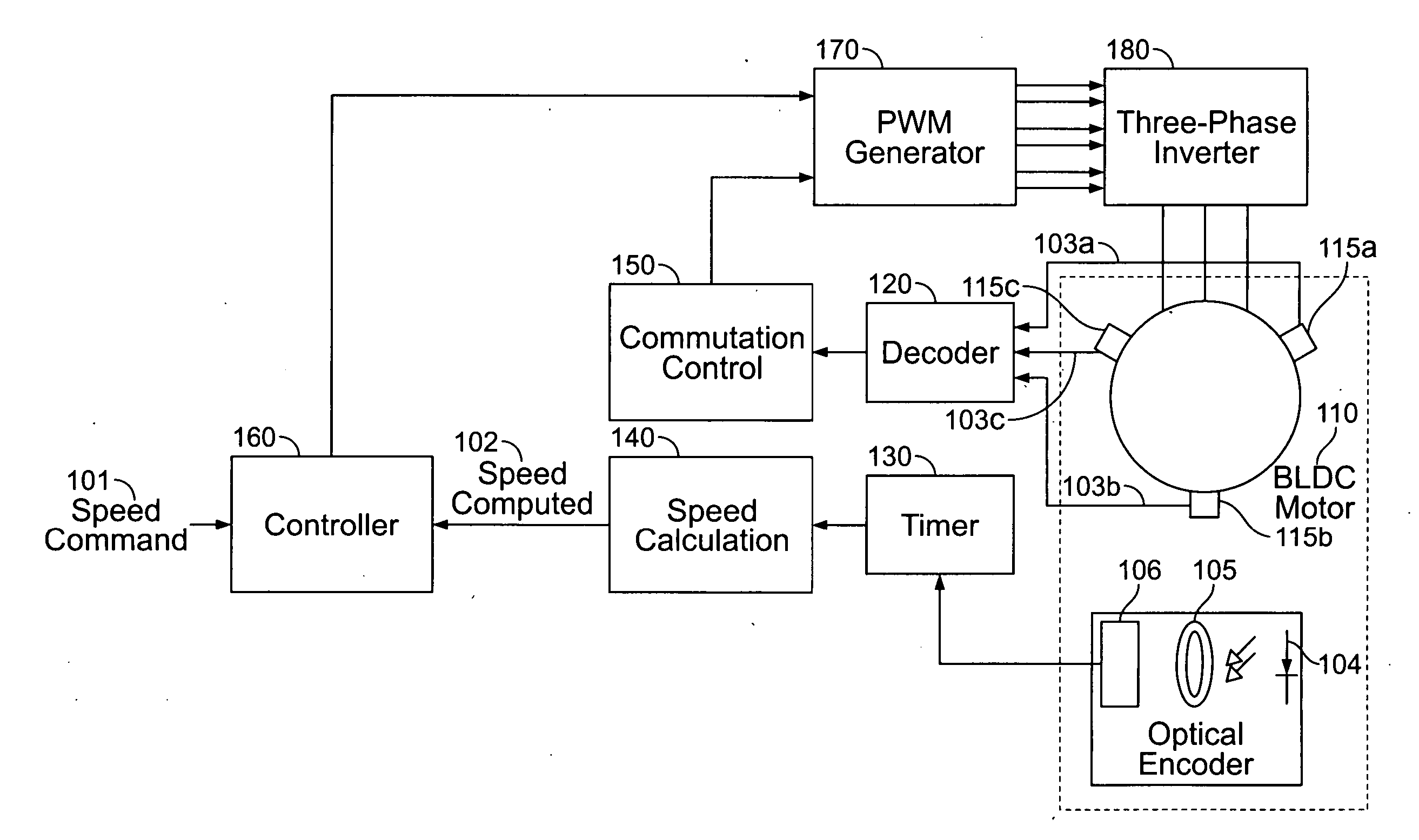
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
ActiveUS20050031322A1Small and cost-efficient packageRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
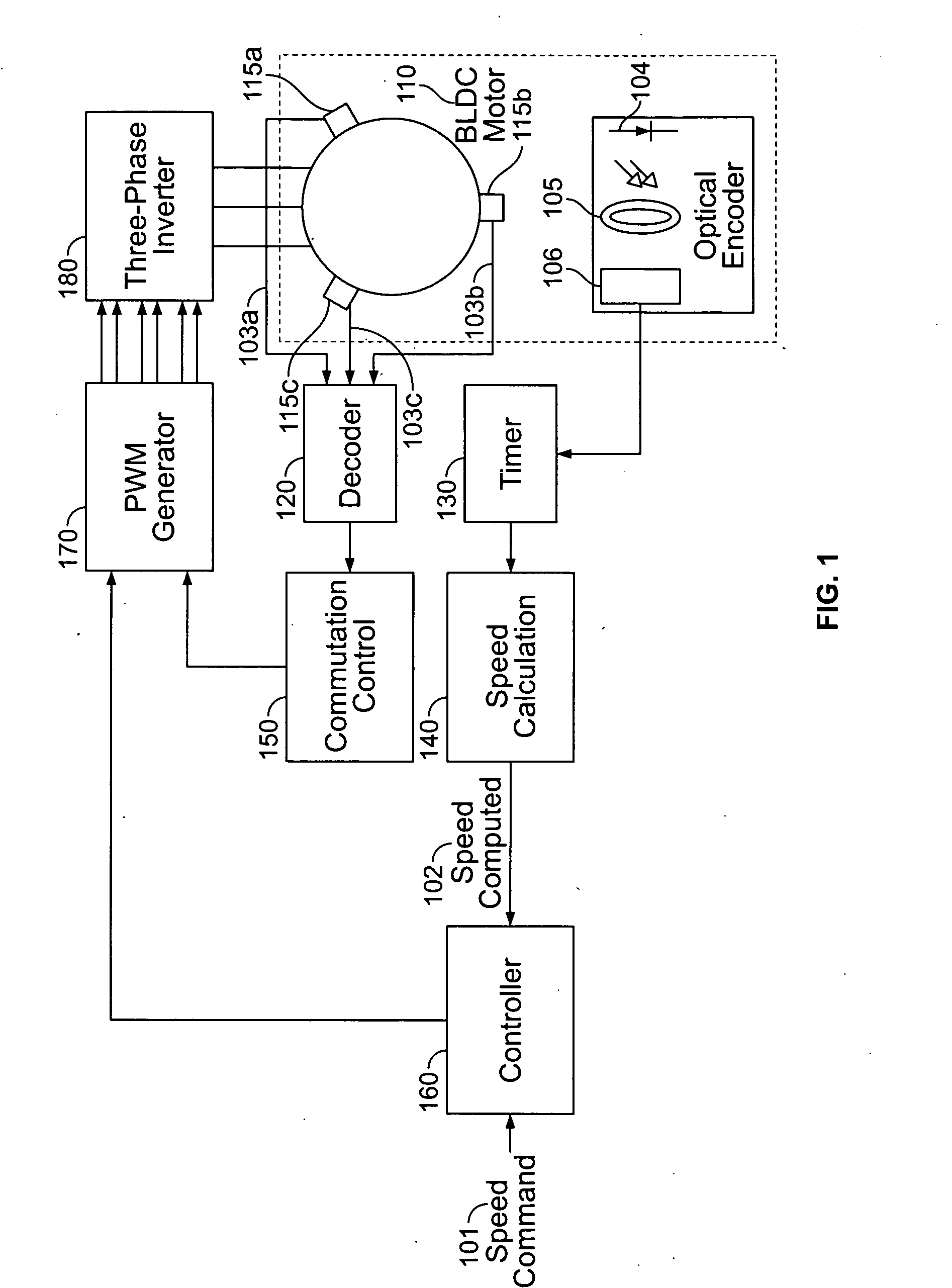
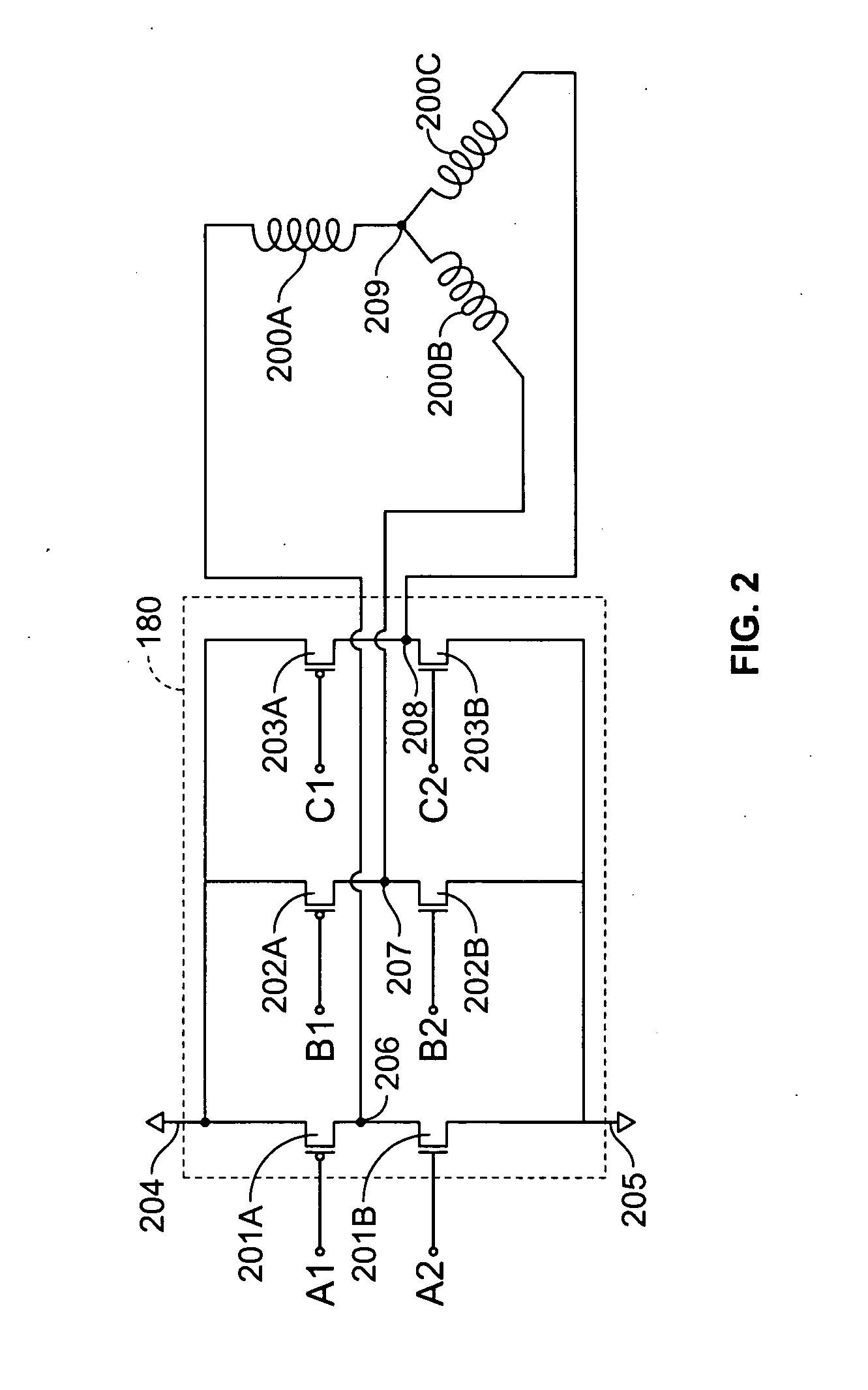
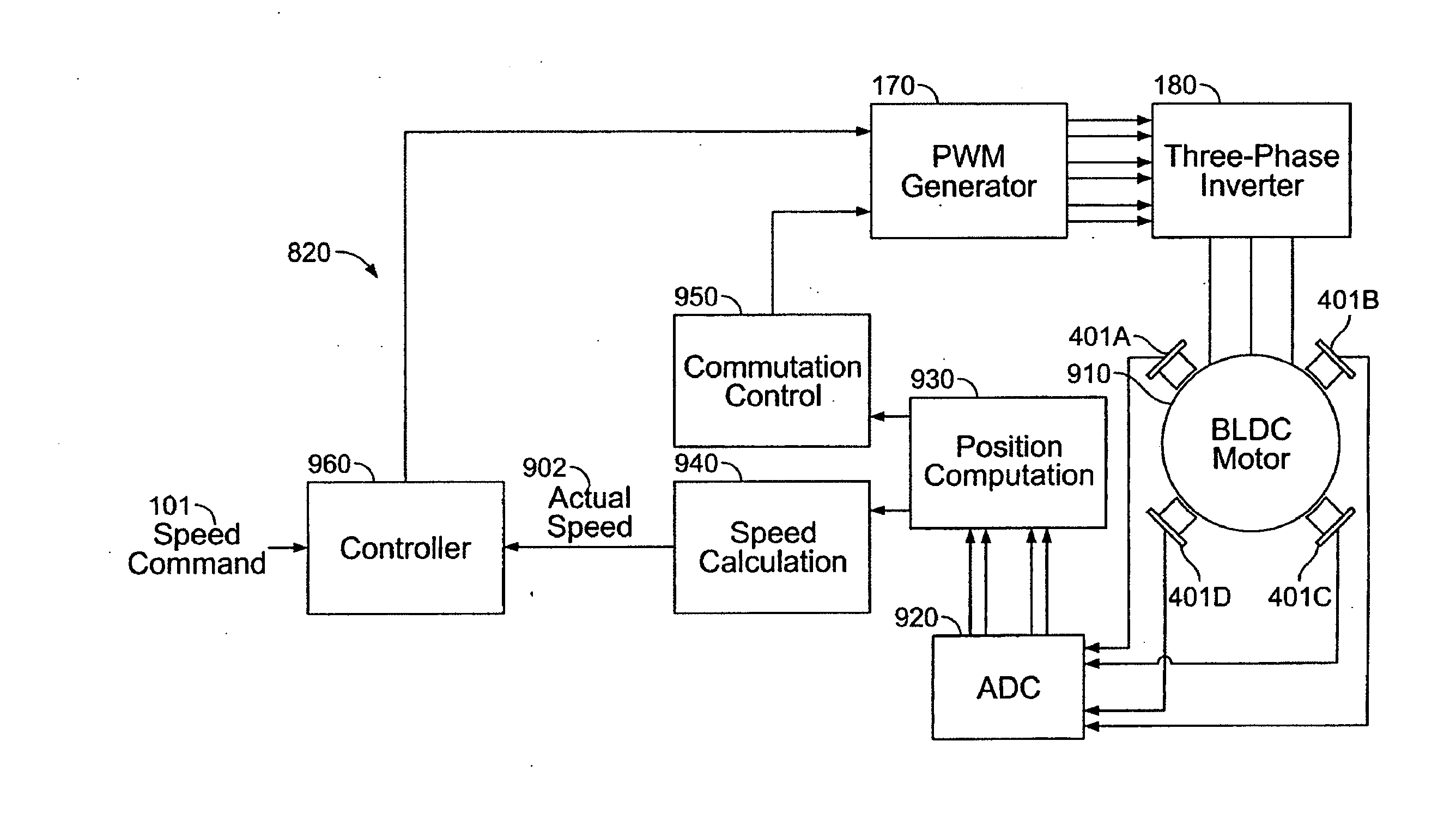
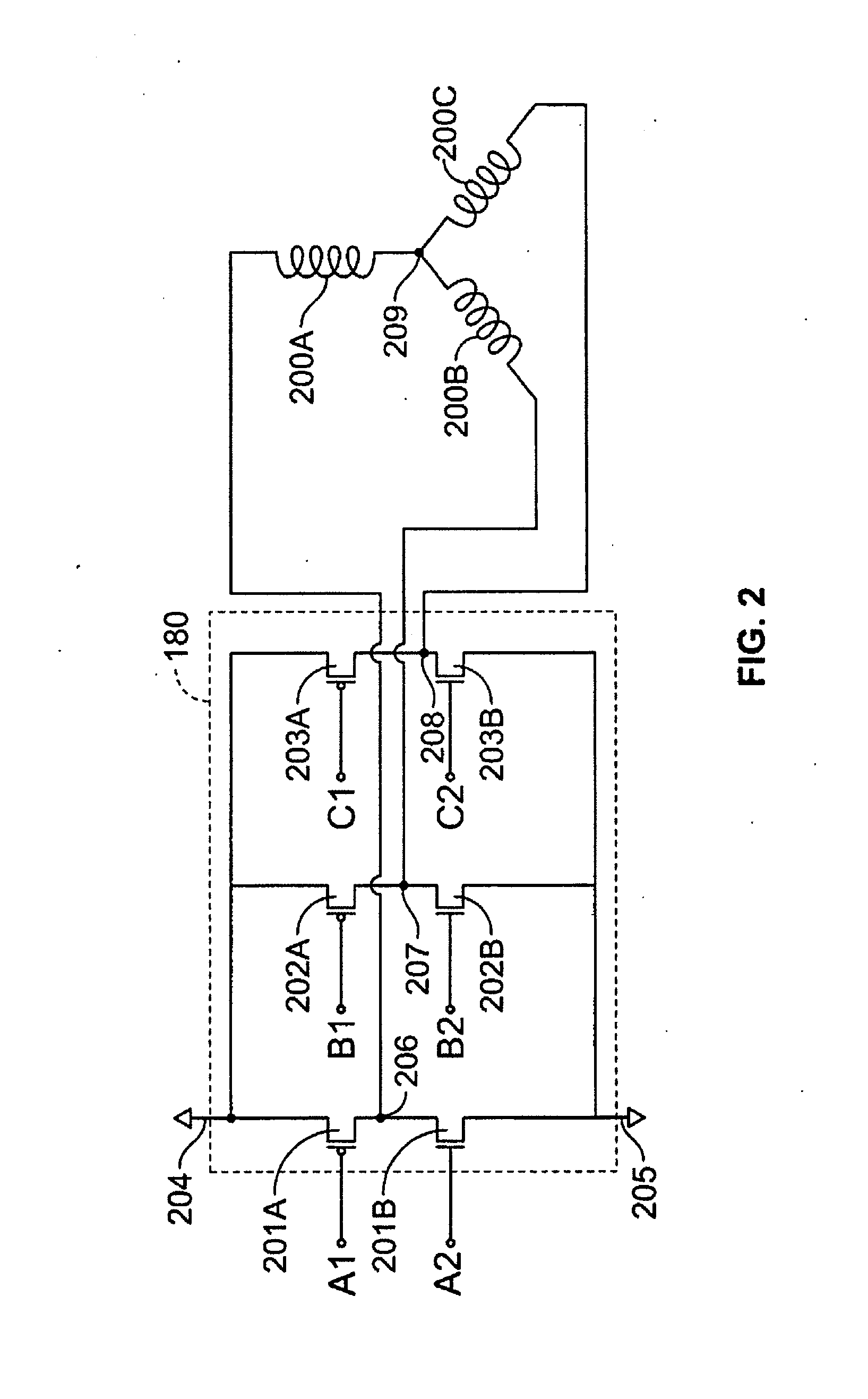
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
Apparatus and method for efficient arithmetic in finite fields through alternative representation
InactiveUS6199087B1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticTheoretical computer scienceOperand
A method and apparatus are shown for performing efficient arithmetic on binary vectors in a finite field. Typically, there is an efficient algorithm within an execution context, such as hardware or software, for performing a selected arithmetic operation on an operand. When the operand is in a first representative format and the efficient algorithm operates in an alternative representation format, then the operand is permutated from the first representative format to the alternative representation format. The efficient algorithm is then performed on the operand in the alternative representation format in order to obtain a result in the alternative representation format. The result is then permutated from the alternative representation format to the first representation format. Thus, efficient arithmetic is obtained by using the most efficient algorithm available in either the first representation format or the alternative representation format and permuting operands and results to the representation format corresponding to the most efficient algorithm available.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
Residue number arithmetic logic unit
ActiveUS20130311532A1Improve performanceConservingProgram controlComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitNumbering system
Methods and systems for residue number system based ALUs, processors, and other hardware provide the full range of arithmetic operations while taking advantage of the benefits of the residue numbers in certain operations. In one or more embodiments, an RNS ALU or processor comprises a plurality of digit slices configured to perform modular arithmetic functions. Operation of the digit slices may be controlled by a controller. Residue numbers may be converted to and from fixed or mixed radix number systems for internal use and for use in various computing systems.
Owner:OLSEN IP RESERVE
Generic implementations of ellipitic curve cryptography using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030208518A1Digital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticBinary multiplierOperand
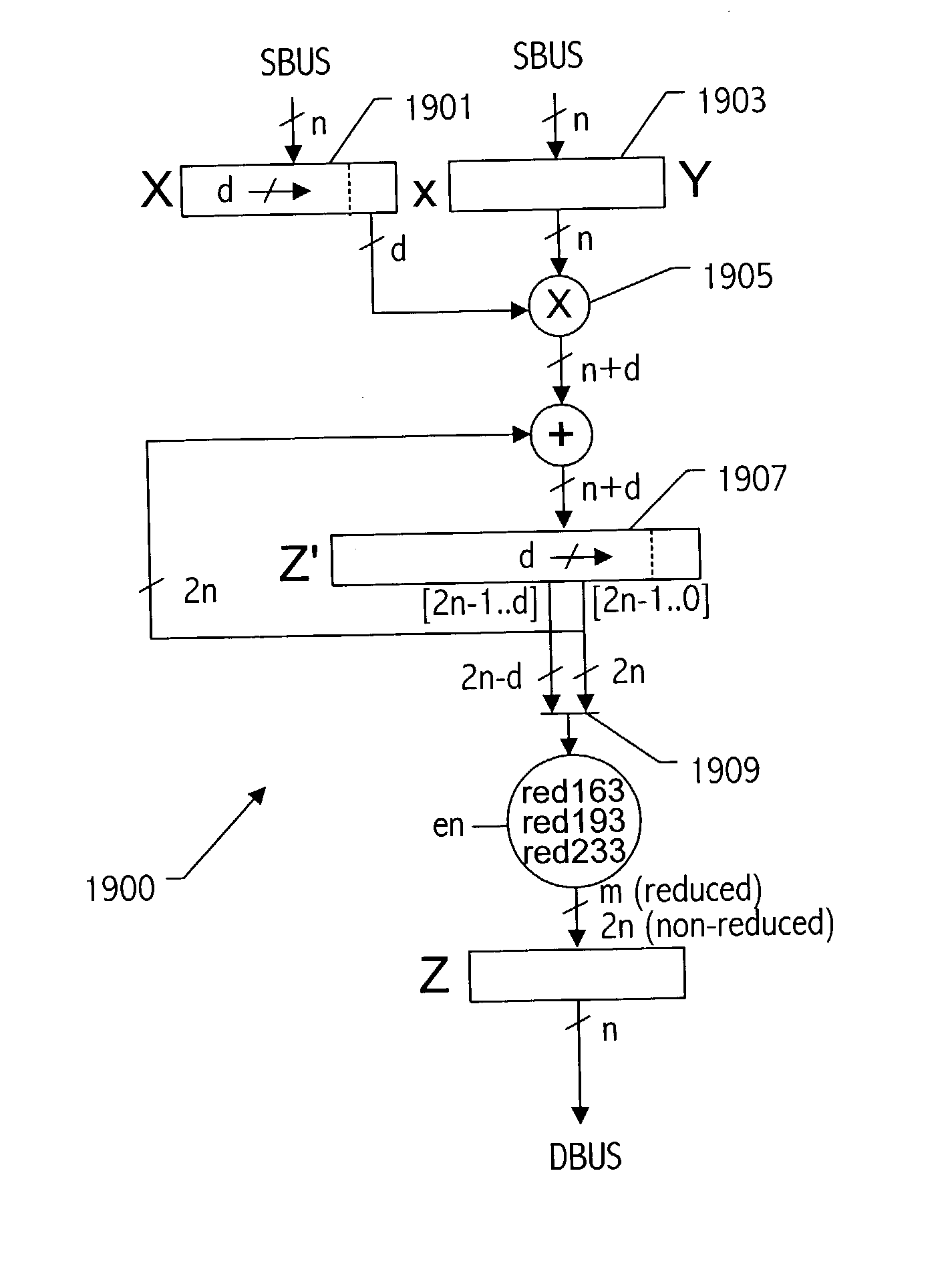
A reduction operation is utilized in an arithmetic operation on two binary polynomials X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, where the coefficients as are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The reduction operation includes partially reducing a result of the arithmetic operation on the two binary polynomials to produce a congruent polynomial of degree less than a chosen integer n, with m<=n. The partial reduction includes using a polynomial M'=(Mm(t)-t<m>)*t<n-m>, or a polynomial M''=Mm(t)*t<n-m >as part of reducing the result to the degree less than n and greater than or equal to m. The integer n can be the data path width of an arithmetic unit performing the arithmetic operation, a multiple of a digit size of a multiplier performing the arithmetic operation, a word size of a storage location, such as a register, or a maximum operand size of a functional unit in which the arithmetic operation is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for performing code provenance review in a software due diligence system
ActiveUS8307351B2Lack of precisionProgram/content distribution protectionSpecific program execution arrangementsThird partySource code
A system and method is provided for performing code provenance review in a software due diligence system. In particular, performing code provenance review may include sub-dividing source code under review and third-party source into logical fragments using a language-independent text fracturing algorithm. For example, the fracturing algorithm may include a set of heuristic rules that account for variations in coding style to create logical fragments that are as large as possible without being independently copyrightable. Unique fingerprints may then be generated for the logical fragments using a fingerprint algorithm that features arithmetic computation. As such, potentially related source code may be identified if sub-dividing the source code under review and the third-party source code produces one or more logical fragments that have identical fingerprints.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multiple-precision processing block in a programmable integrated circuit device
A specialized processing block in a programmable integrated circuit device is configurable to perform floating-point arithmetic operations at selectable different precisions. The specialized processing block includes a plurality of different respective types of floating-point arithmetic operator structures. For each respective type of floating-point arithmetic operator structure, respective control circuitry for partitions the respective type of floating-point arithmetic operator structure to select between a first precision for which the respective type of floating-point arithmetic operator structure is not partitioned, and at least a second precision, less than the first precision, for which the respective type of floating-point arithmetic operator structure is partitioned into at least two smaller ones of the respective type of floating-point arithmetic operator structure.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
InactiveUS20080092893A1RespiratorsDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:CAREFUSION 207 INC
Quasi-fully homomorphic ciphertext data operation method and system
InactiveCN107592195AAvoid insecuritySolving inefficienciesSecuring communicationThird partyCiphertext
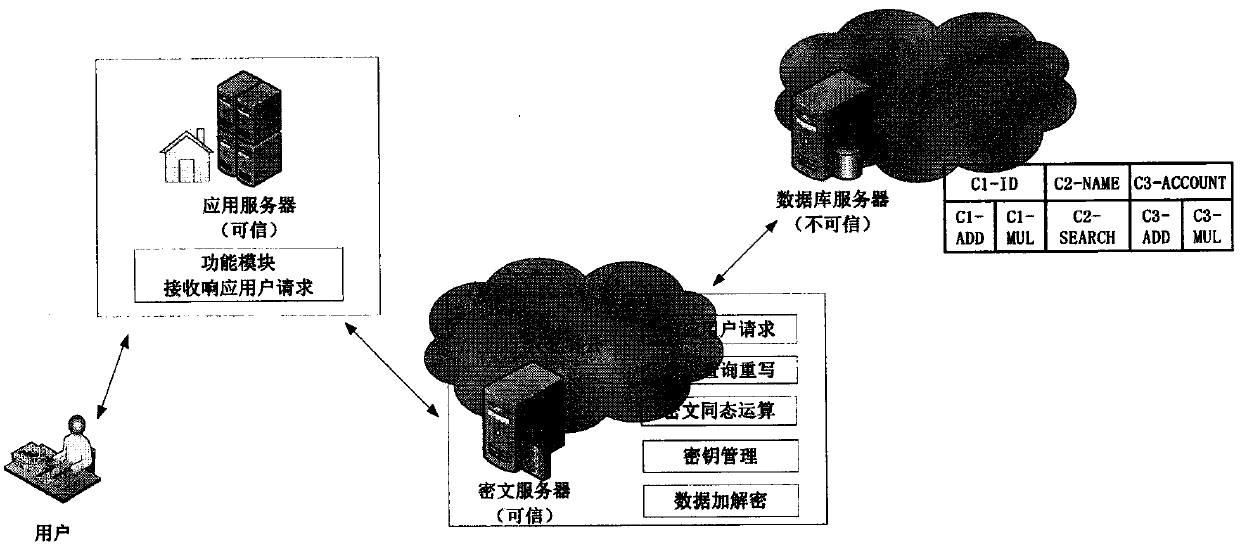
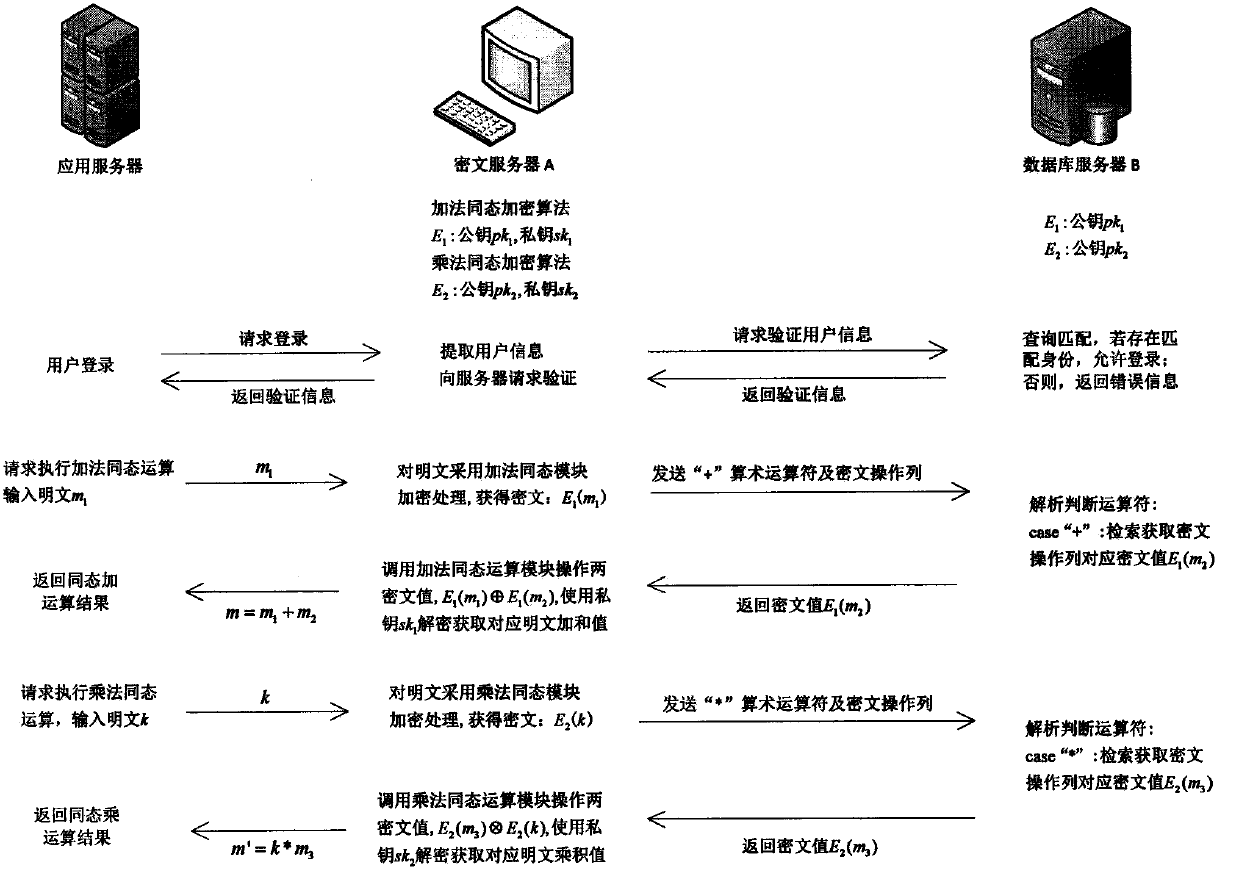
The present invention discloses a quasi-fully homomorphic ciphertext data operation method and system and belongs to the ciphertext database and network data privacy protection technical field. The fully homomorphic cipher operation-based hybrid cloud platform architecture is provided, existing database configurations are not needed to be drastically modified, and therefore, a construction mode issimple; a ciphertext server is defined to support homomorphic calculation, query interception rewriting, data encryption and decryption, key management and other functions, is deployed at the privatecloud platform of a local data center and can establish a connection between the local data center and a third-party public cloud platform; a classified field extension mode is adopted, field extension is performed on numerical value data and character type data; by means of mode innovation, quasi-fully homomorphic ciphertext conventional arithmetic calculation is performed on the numerical valuedata through a functional demand-based cipher service strategy; query / operation is directly performed on ciphertext data; and therefore, the processing efficiency of the data and the security of thestorage and retrieval of the data can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH INST
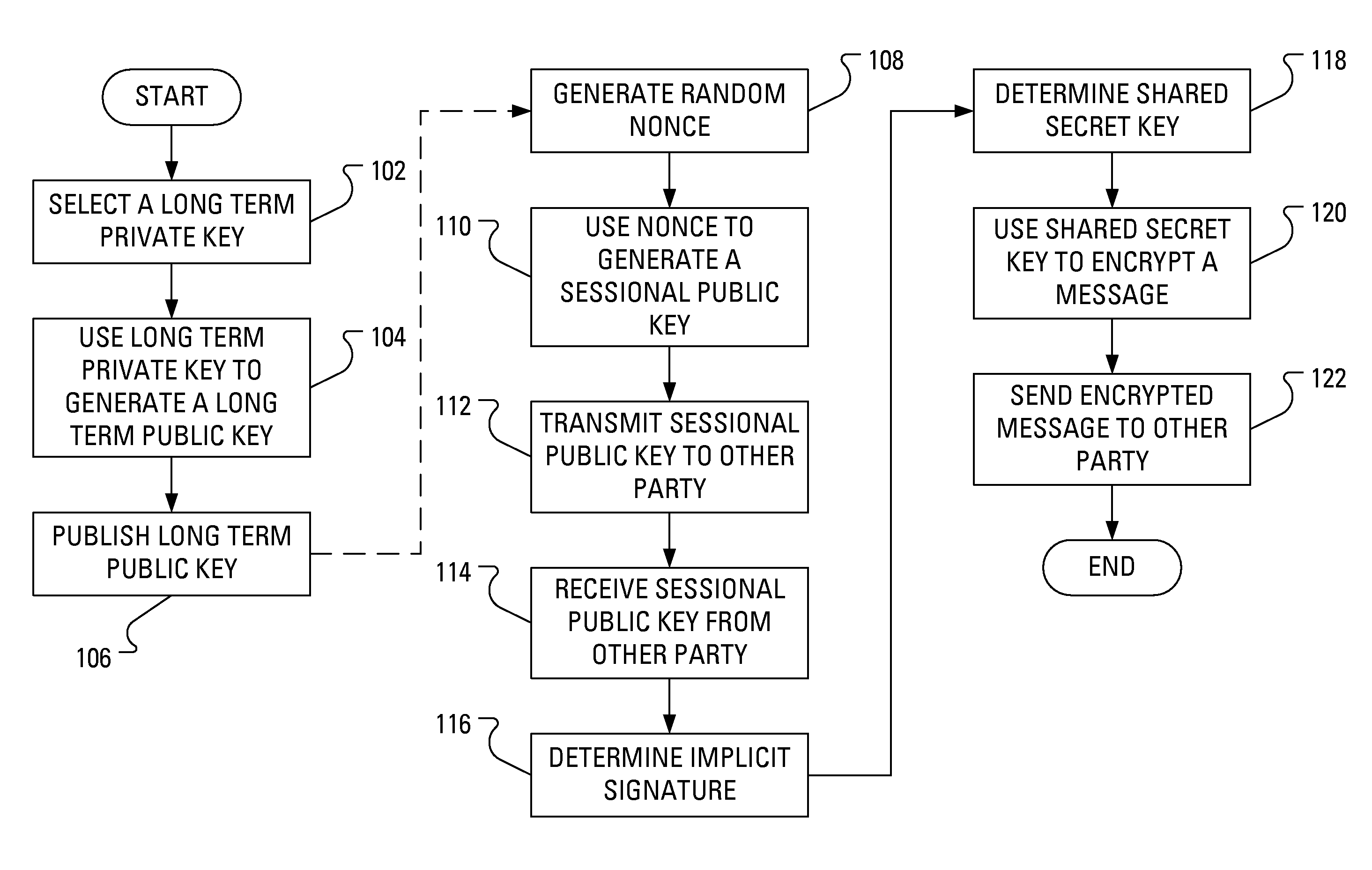
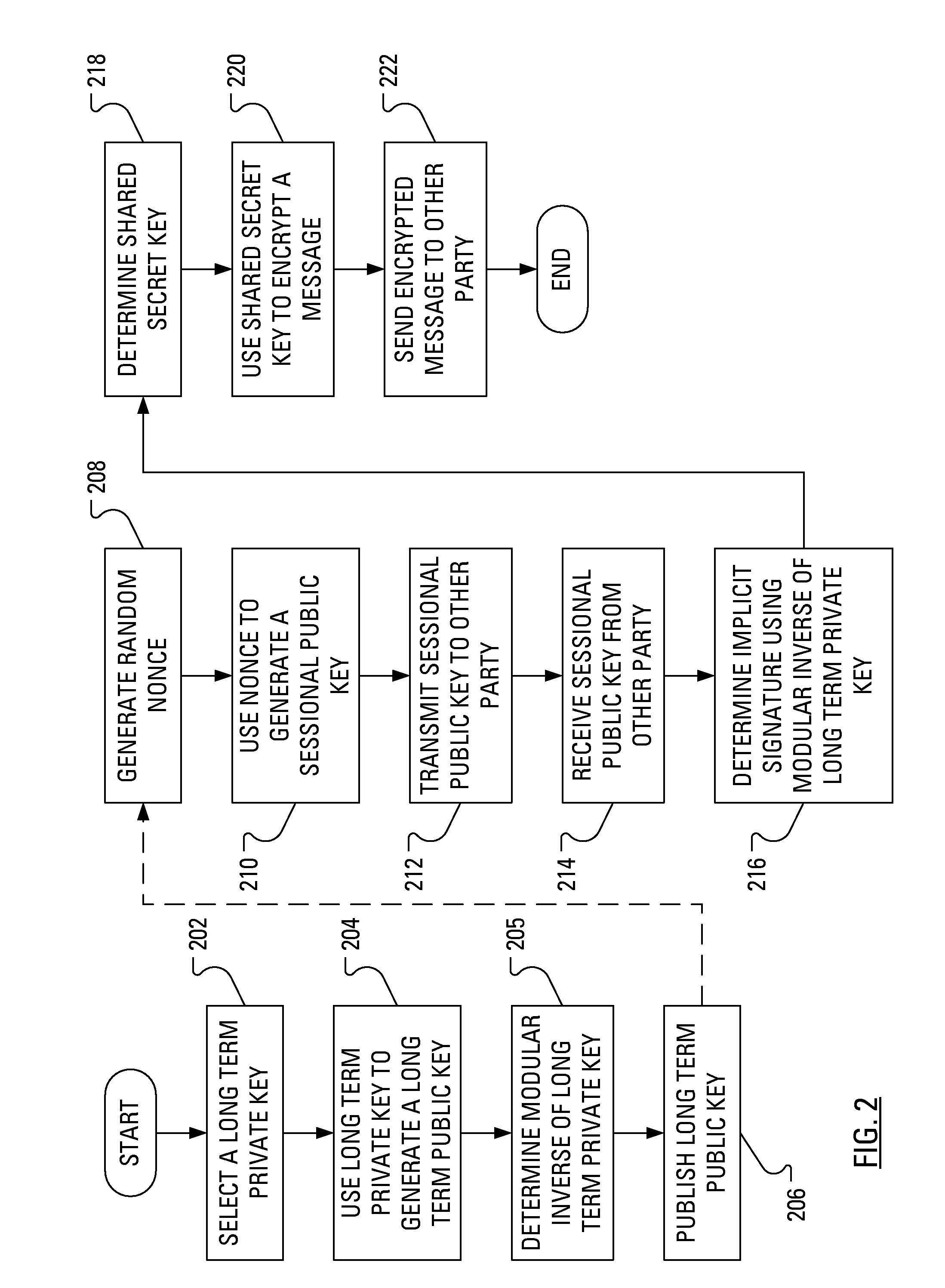
Power Analysis Countermeasure for the ECMQV Key Agreement Algorithm
ActiveUS20080301459A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPower analysisComputer hardware
Execution of the ECMQV key agreement algorithm requires determination of an implicit signature, which determination involves arithmetic operations. Some of the arithmetic operations employ a long-term cryptographic key. It is the execution of these arithmetic operations that can make the execution of the ECMQV key agreement algorithm vulnerable to a power analysis attack. In particular, an attacker using a power analysis attack may determine the long-term cryptographic key. By modifying the sequence of operations involved in the determination of the implicit signature and the inputs to those operations, power analysis attacks may no longer be applied to determine the long-term cryptographic key.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Raid-6 computation system and method
ActiveUS8037391B1Reduce computational complexityImprove system efficiencyError detection/correctionCode conversionGraphicsRAID
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for performing RAID-6 computations using simple arithmetic functions and two-dimensional table lookup operations. Four lookup tables are computed and saved prior to normal operation of a RAID-6 disk array. During normal operation of the RAID-6 disk array, all RAID-6 related computations may be performed using a small set of simple arithmetic operations and a set of lookup operations to three of the four previously saved lookup tables. Greater computational efficiency is gained by reducing the RAID-6 computations to simple operations that are performed efficiently on a typical central processing unit or graphics processing unit.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Parallel modulo arithmetic using bitwise logical operations
InactiveUS20040083251A1Efficient executionImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsCryptographic attack countermeasuresParallel computingTheoretical computer science
Parallel modulo arithmetic calculations are carried out on a device adapted to perform bitwise logical operations by storing the numbers to be operated upon in a vector form, and performing arithmetical operations on multiple numbers in parallel. The invention finds particular application in cryptosystems, as well as in other fields.
Owner:TAO GROUP
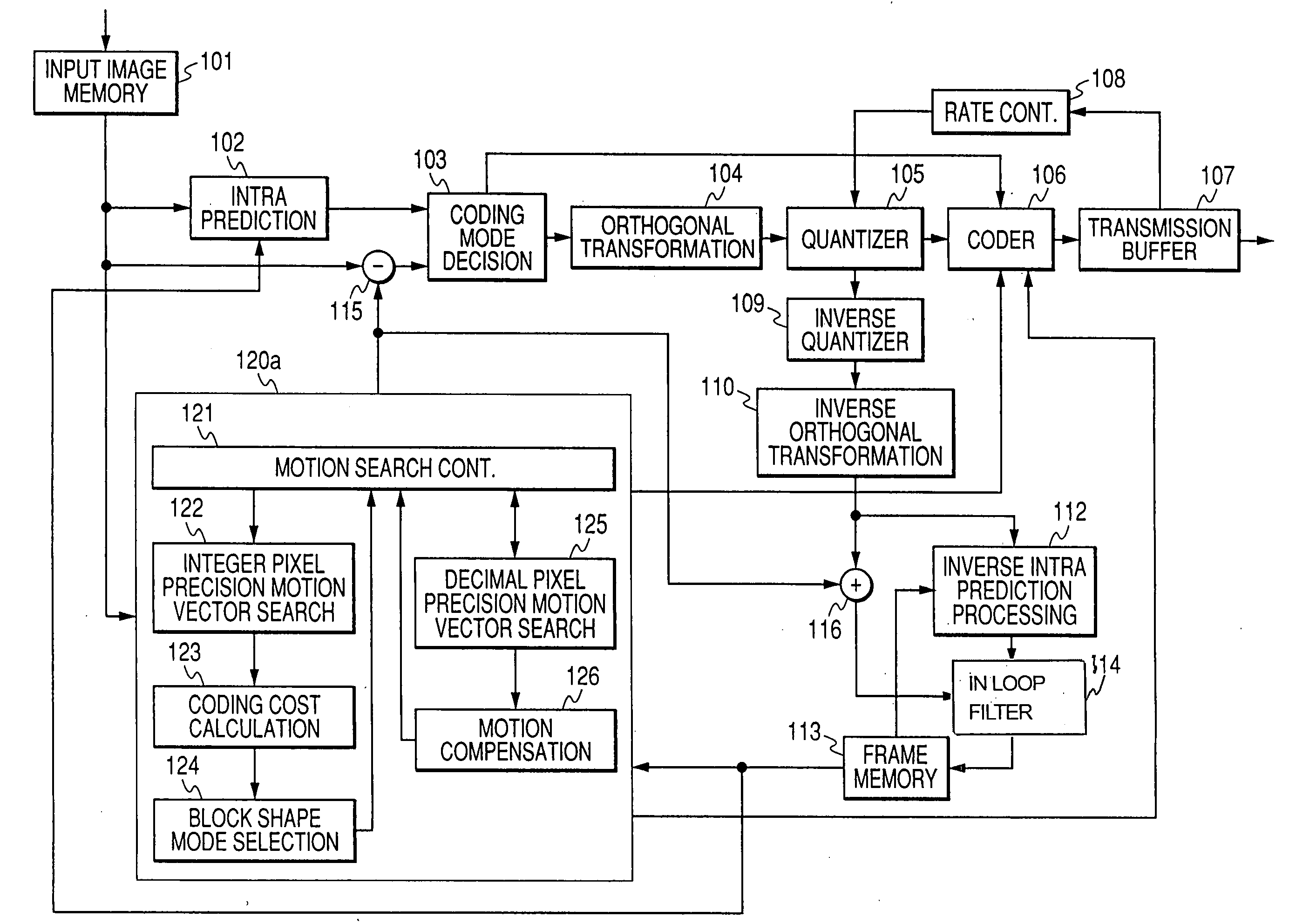
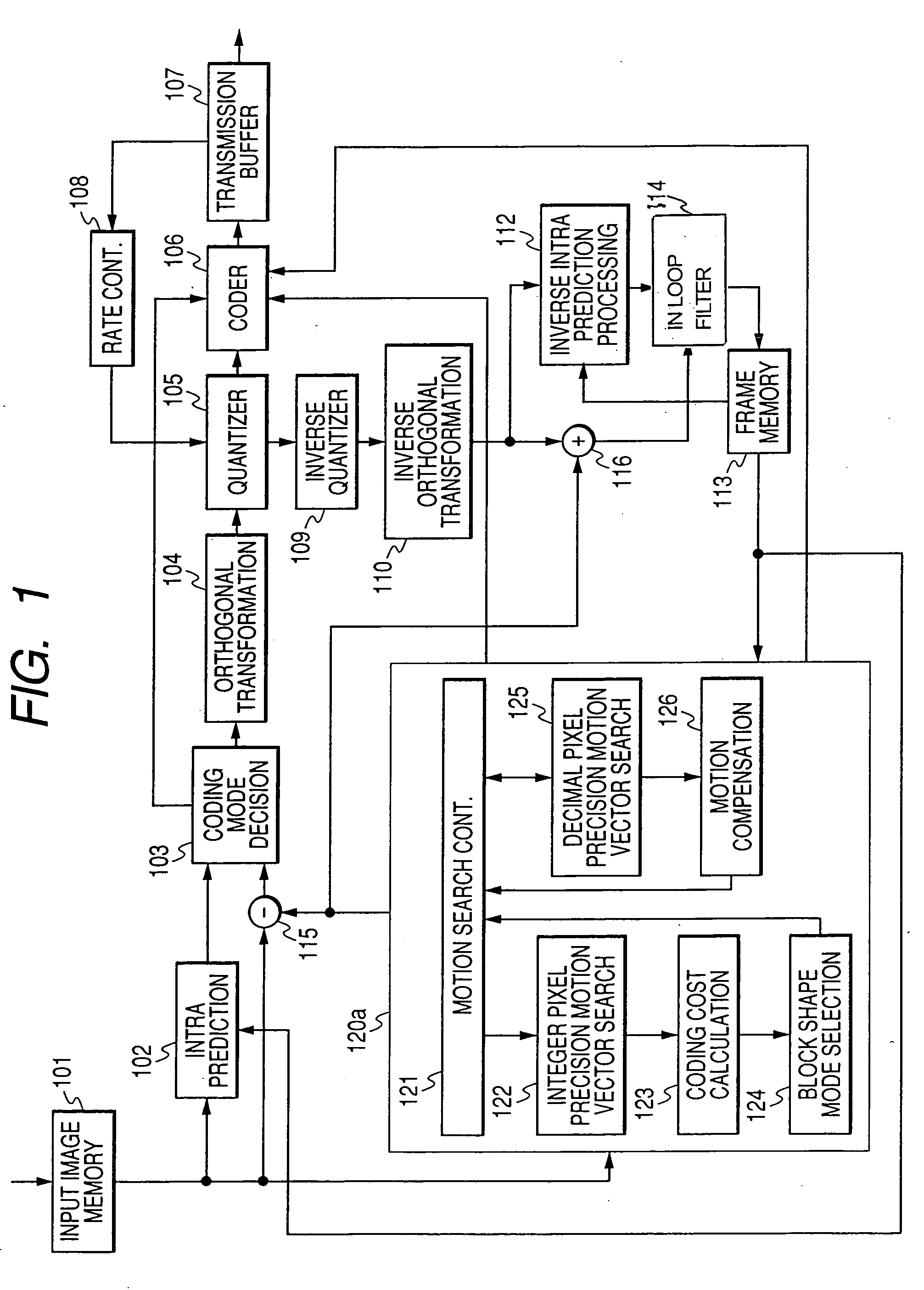
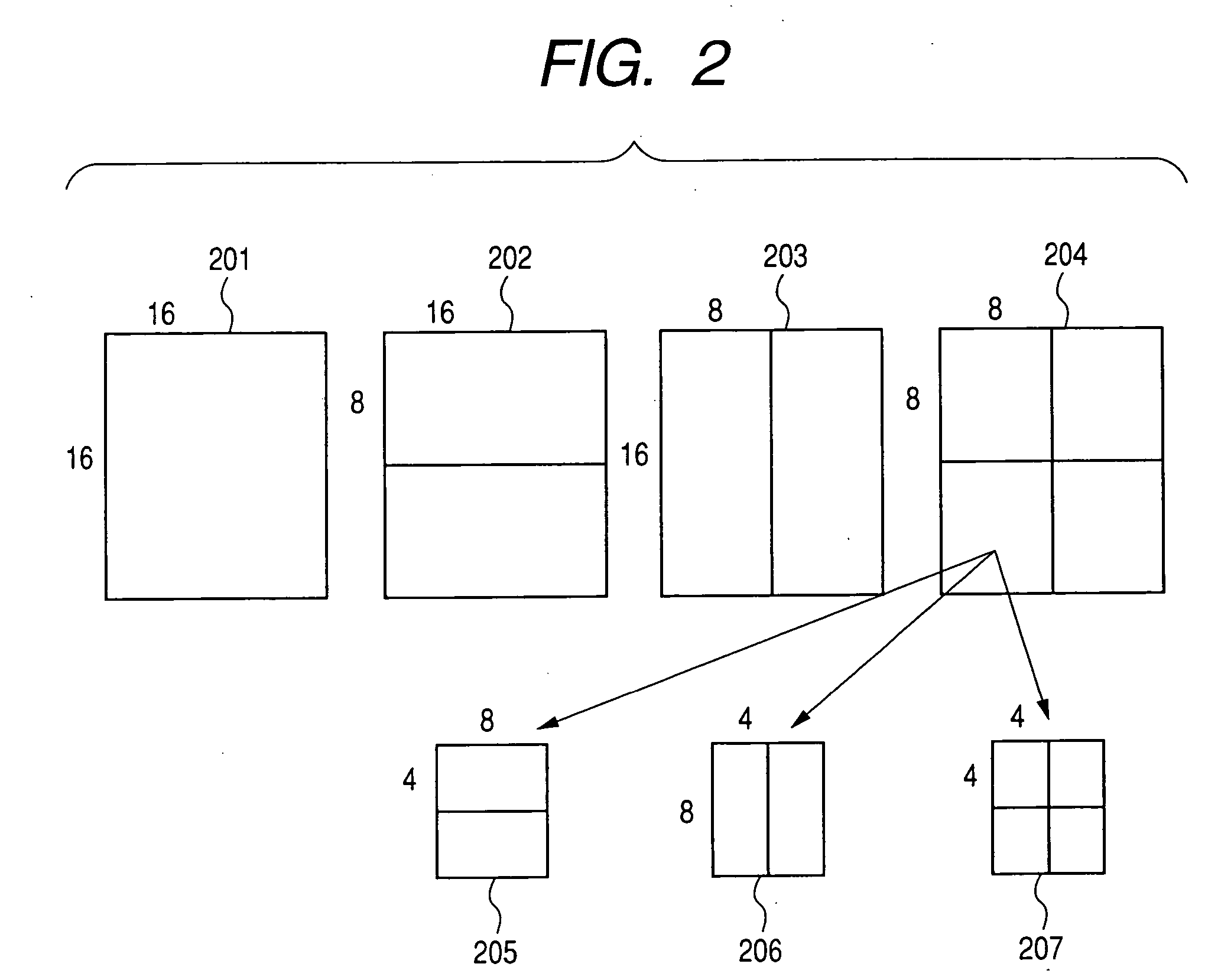
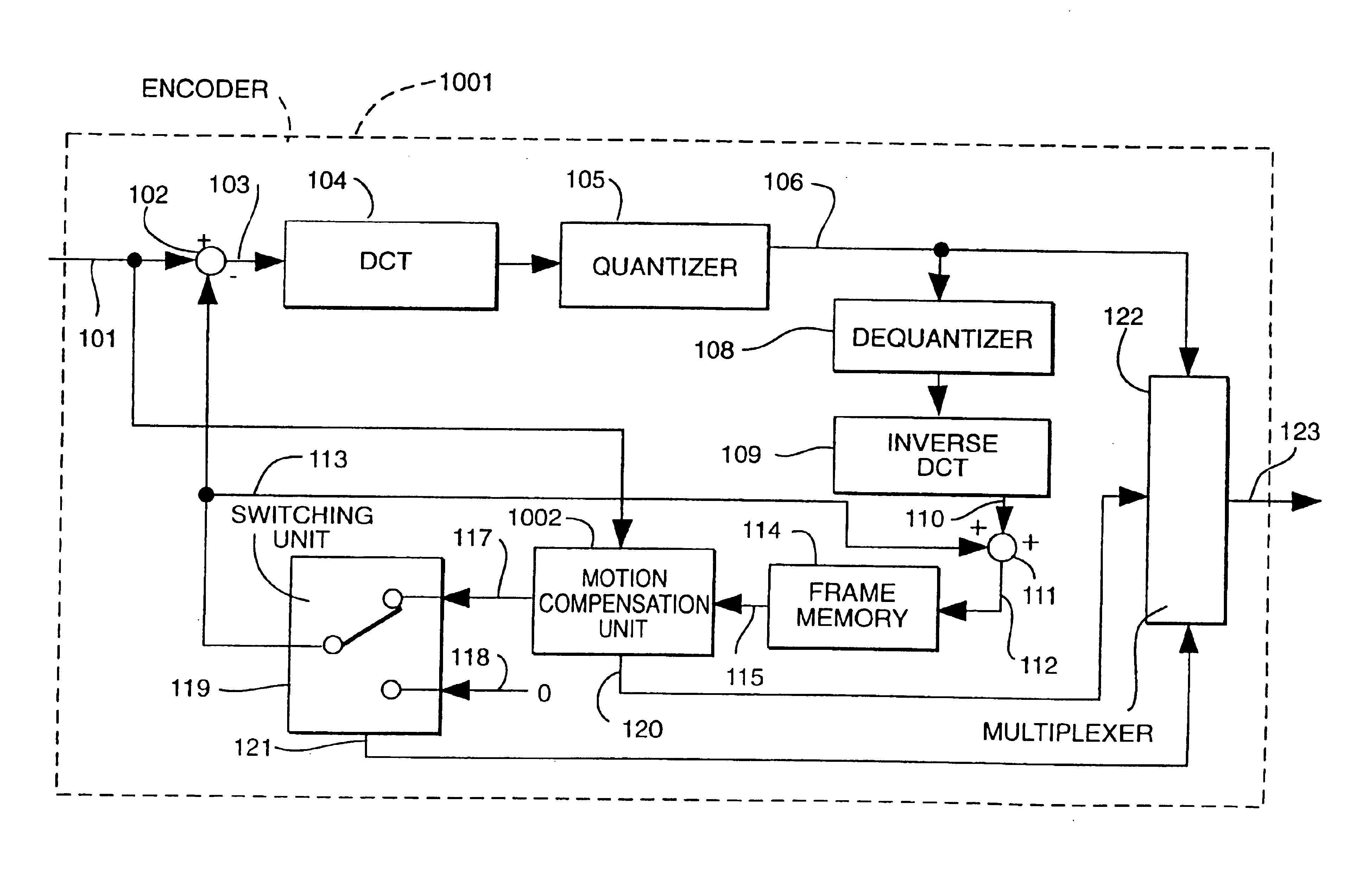
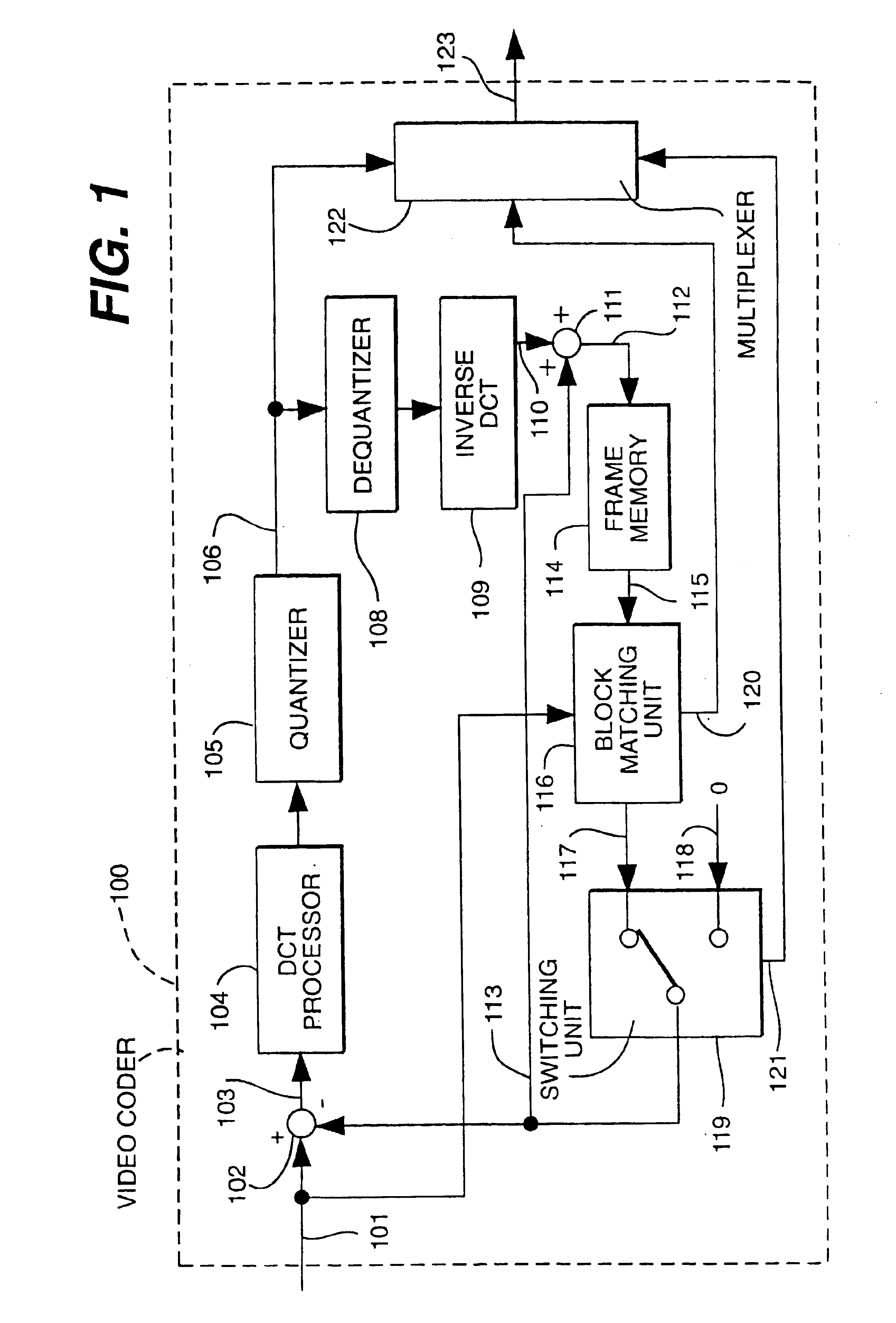
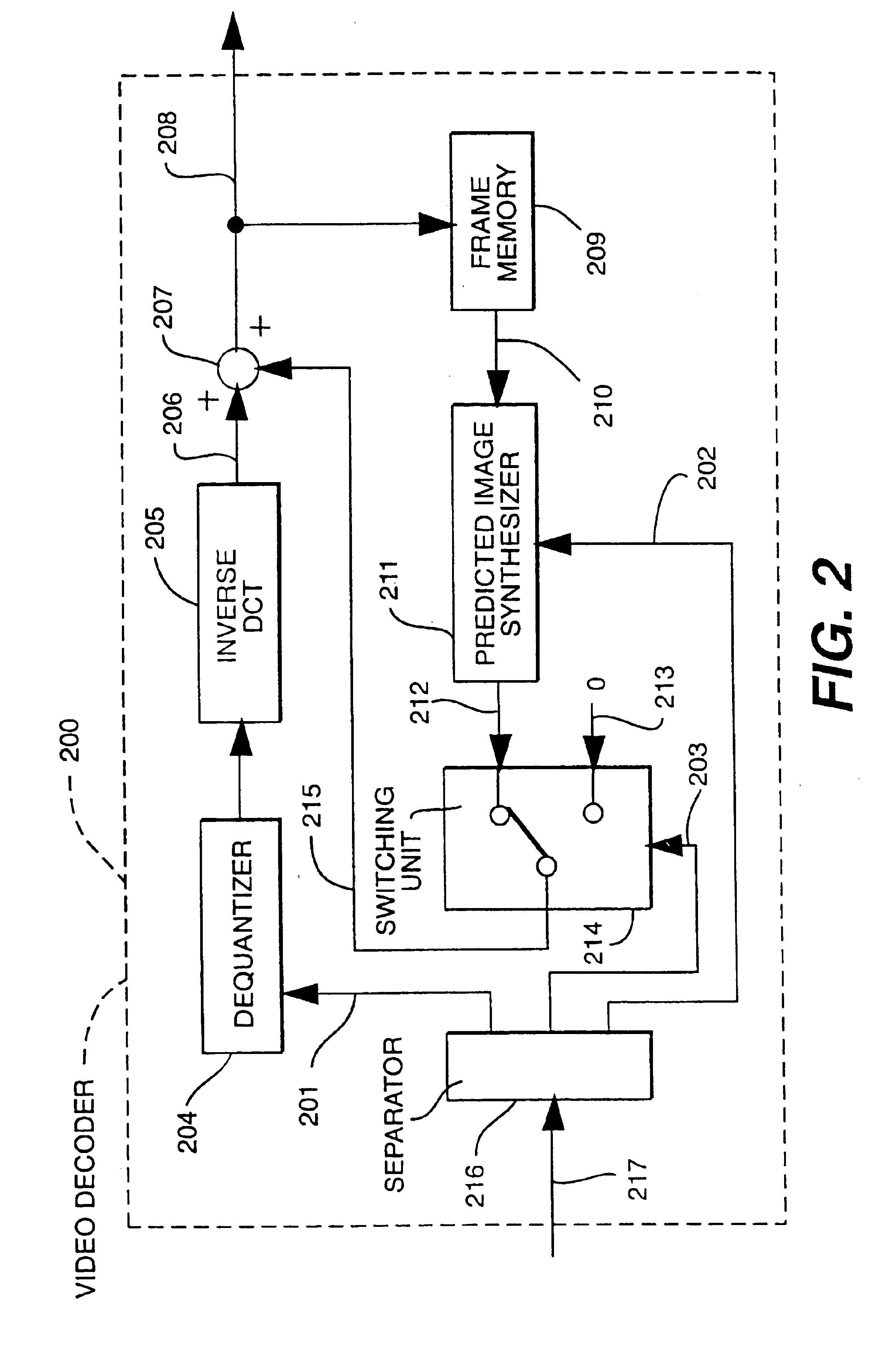
Motion compensation image coding device and coding method
ActiveUS20060126741A1Preventing numberPrecise cuttingTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationMotion vectorImage code
The present invention provides a technology that is implemented in a motion compensation image coding device or a coding method and intended to code motion picture data in real time by performing a decreased number of arithmetic operations so as to determine a motion vector. In motion compensation image coding, macroblocks and sub-blocks into which each of the macroblocks is divided are searched for a motion vector with integer pixel precision. Based on the results of the search, a shape of a block that should be searched for a motion vector with decimal pixel precision is determined as a shape mode. The block of the shape mode is searched for a motion vector with decimal pixel precision, whereby a motion vector needed to produce predictive image data is determined.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Circulant matrix transformation based and ciphertext computation supportive encryption method
The invention discloses a circulant matrix transformation based and ciphertext computation supportive encryption method. The method includes the steps: firstly, encrypting original data by means of converting the original data into vectors, then converting the vectors into a circulant matrix and encrypting through a key matrix to obtain an encrypted outsourcing matrix; secondly, encrypting computational parameters by means of converting the computational parameters into vectors, then converting the vectors into a circulant matrix and encrypting through a key matrix to obtain an encrypted computational parameter matrix; thirdly, performing arithmetic operation of an encrypting matrix to obtain an encrypted operation result; fourthly, decrypting the encrypted operation result through the key matrix to obtain a circulant matrix, and then selecting one line / column of the circulant matrix to be added to obtain a plaintext of the operation result. The method is particularly suitable for outsourcing storage and computation of confidential data in a cloud computing environment, and can be used for protecting the confidential data of persons or enterprises; the method is supportive to four-rule hybrid operation of infinite addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of encrypted numerical data.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A quantization circuit and a quantization method of a convolution neural network
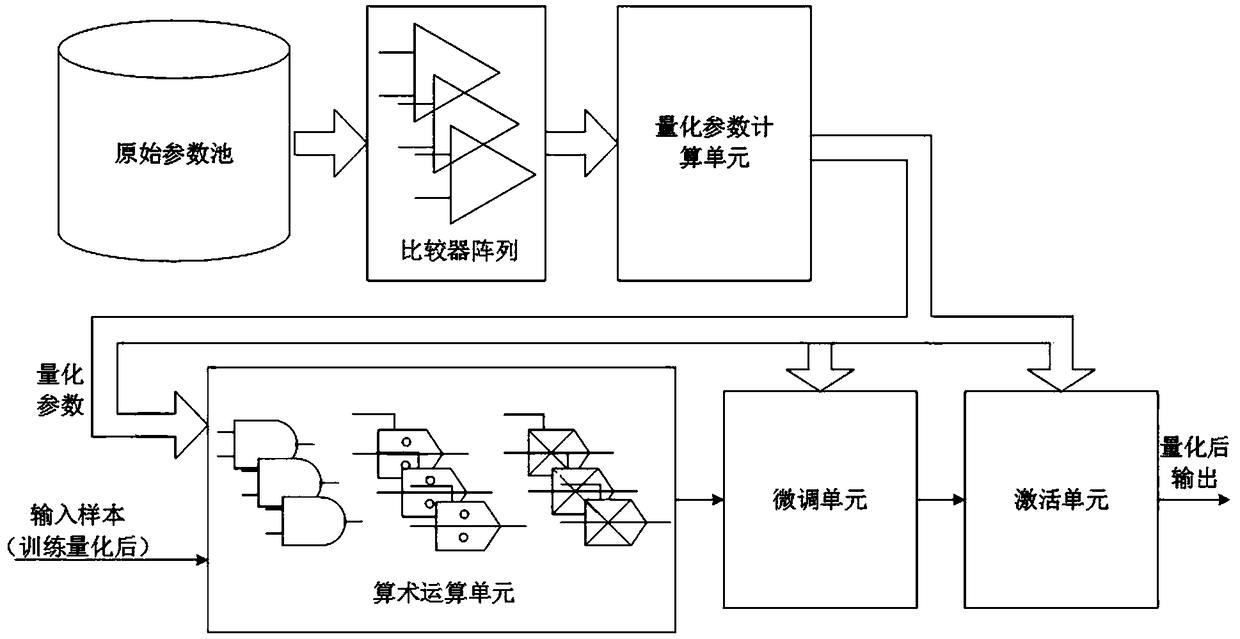
ActiveCN109472353AGuaranteed deploymentGuaranteed uptimeNeural architecturesPhysical realisationAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
A quantization circuit and a quantization method of a convolution neural network are disclosed, The invention belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence data processing, and comprises an original parameter pool, a comparator array, a quantization parameter calculation unit and an arithmetic operation unit. The original parameter pool is used for storing the original parameter data required for calculation of each layer of a convolution neural network, and comprises data of all channels and offset data of all convolution cores of each layer. The comparator array is used for performing statistical operation on the data in the original parameter pool, and iteratively comparing to obtain the maximum value and the minimum value of the parameters of each layer of the convolution neural network; The quantization parameter calculation unit is used for performing arithmetic operation on the maximum value and the minimum value to obtain each parameter used for model quantization;The arithmetic operation unit is used for quantifying the model, and the obtained results are expressed in an integer format of an unsigned bit specified number of bits. The invention can reduce the system power consumption through quantization, so that the deployment and operation of the convolution neural network on the terminal are more reliably guaranteed.
Owner:INSPUR GROUP CO LTD
Method and apparatus for low complexity spectral analysis of bio-signals
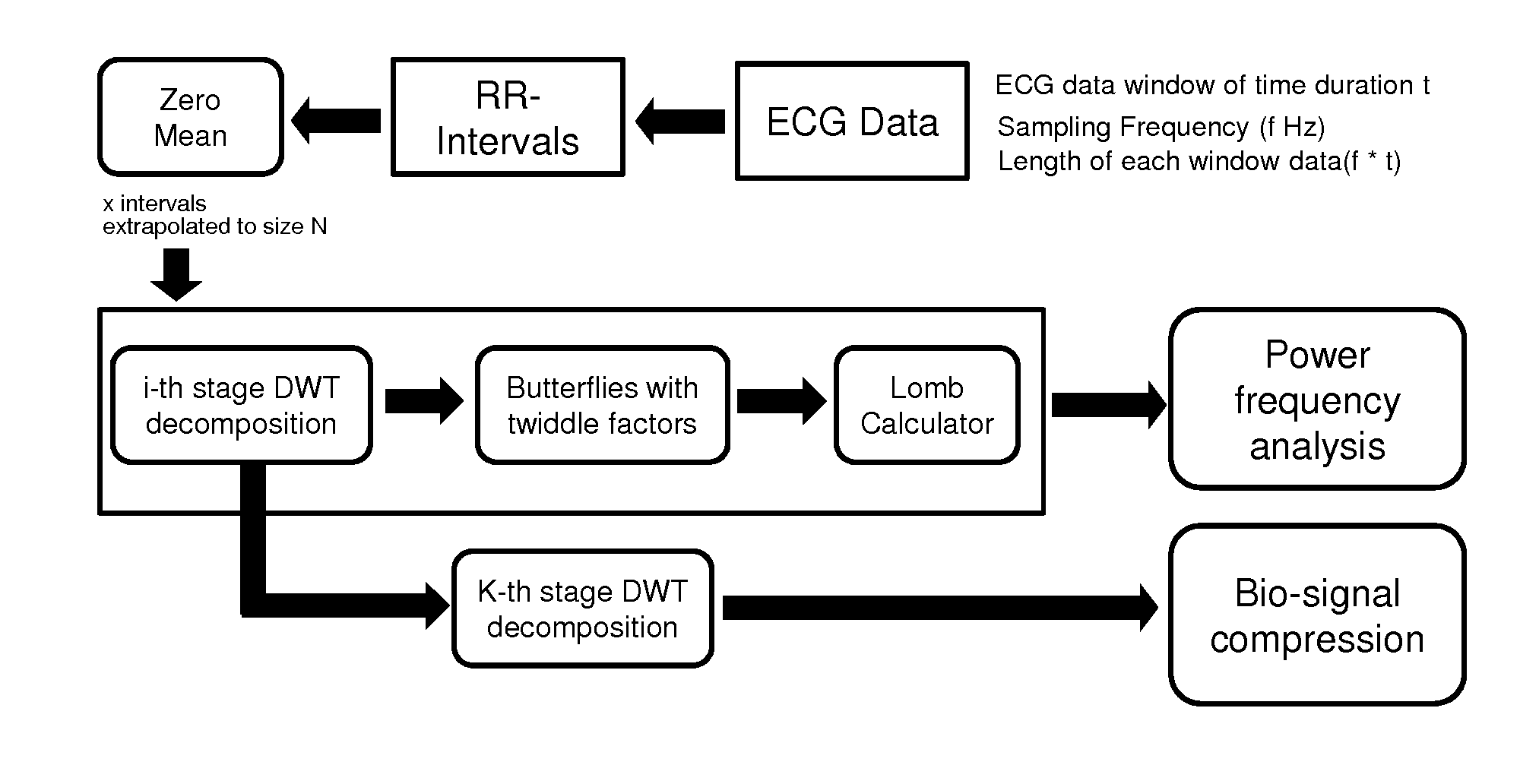
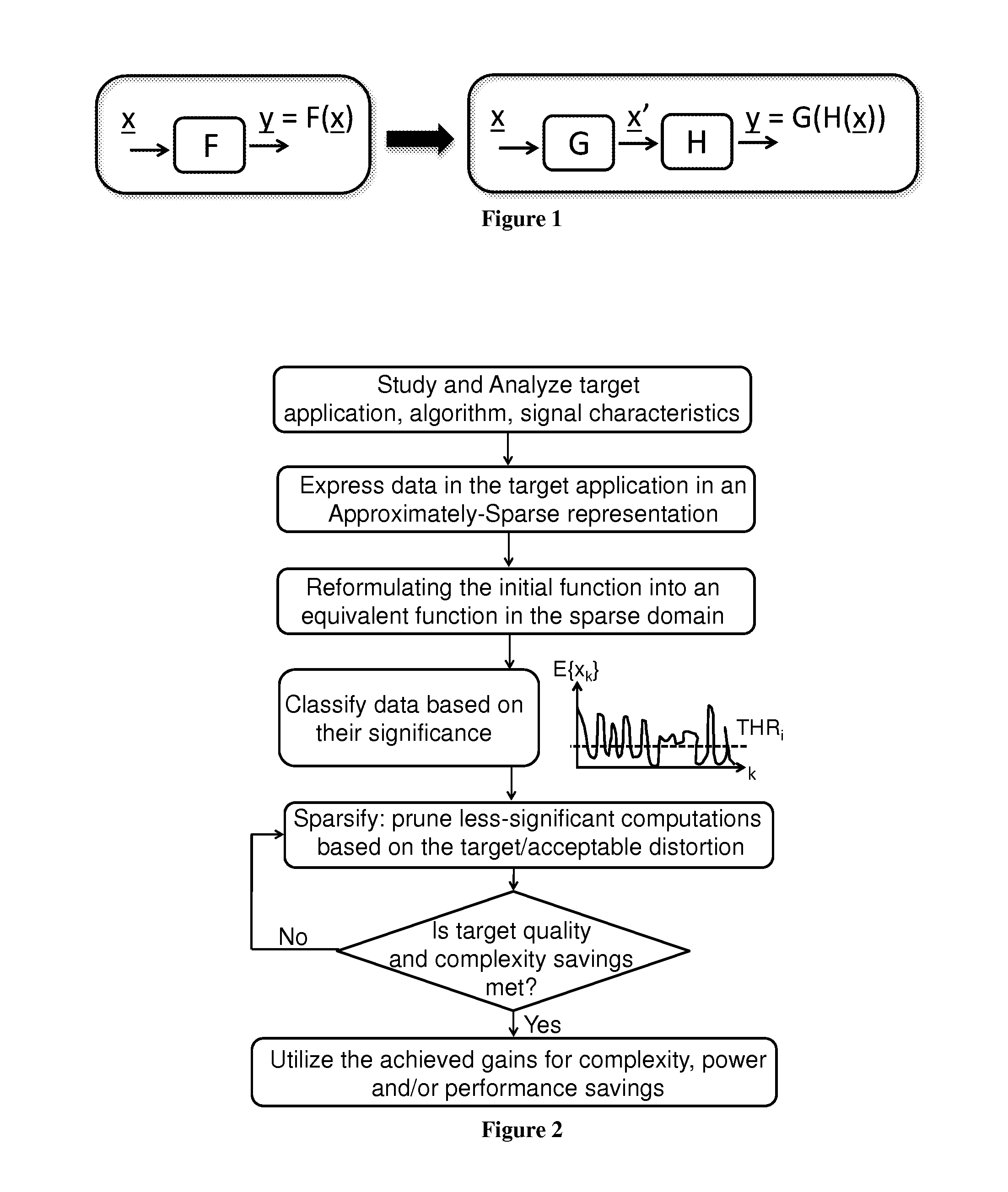
ActiveUS20150220486A1Reduce complexityWeaken energyDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsComputation complexityTheoretical computer science
A method and device for reducing the computational complexity of a processing algorithm, of a discrete signal, in particular of the spectral estimation and analysis of bio-signals, with minimum or no quality loss, which comprises steps of (a) choosing a domain, such that transforming the signal to the chosen domain results to an approximately sparse representation, wherein at least part of the output data vector has zero or low magnitude elements; (b) converting the original signal in the domain chosen in step (a) through a mathematical transform consisting of arithmetic operations resulting in a vector of output data; (c) reformulating the processing algorithm of the original signal in the original domain into a modified algorithm consisting of equivalent arithmetic operations in the domain chosen in step (a) to yield the expected result with the expected quality quantified in terms of a suitable application metric; (d) combining the mathematical transform of step (b) and the equivalent mathematical operations introduced in step (c) for obtaining the expected result within the original domain with the expected quality; (e) selecting a threshold value based on the difference in the mean magnitude value of the elements of the output data vector of the transform said in step (b) and the preferred complexity reduction and degree of output quality loss that can be tolerated in the expected result within the target application; (f) pruning a number of elements the magnitude of which is less than the threshold value selected in step (e); and / or eliminating arithmetic operations associated with the pruned elements of step (f) either in the mathematical transform of step (b) and / or in the equivalent algorithm of step (c).
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
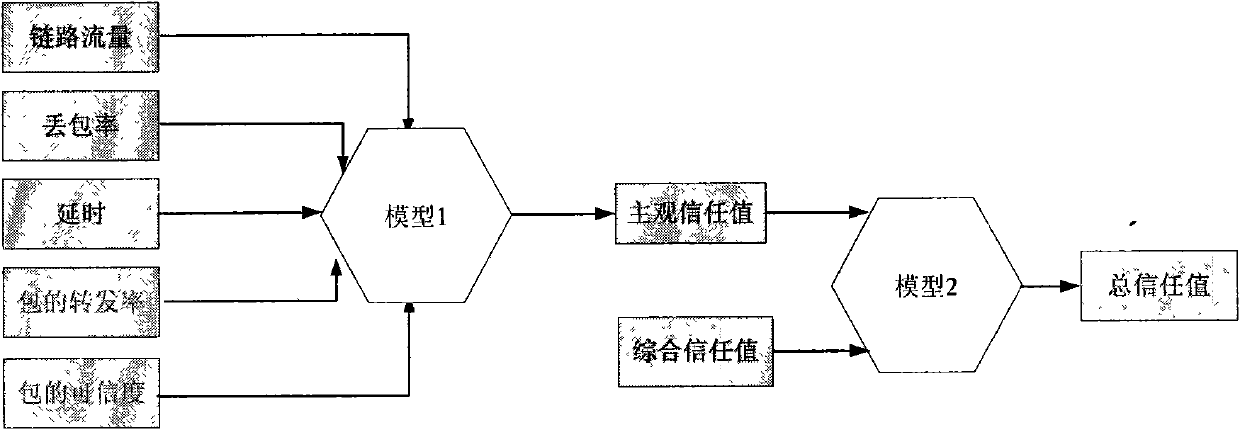
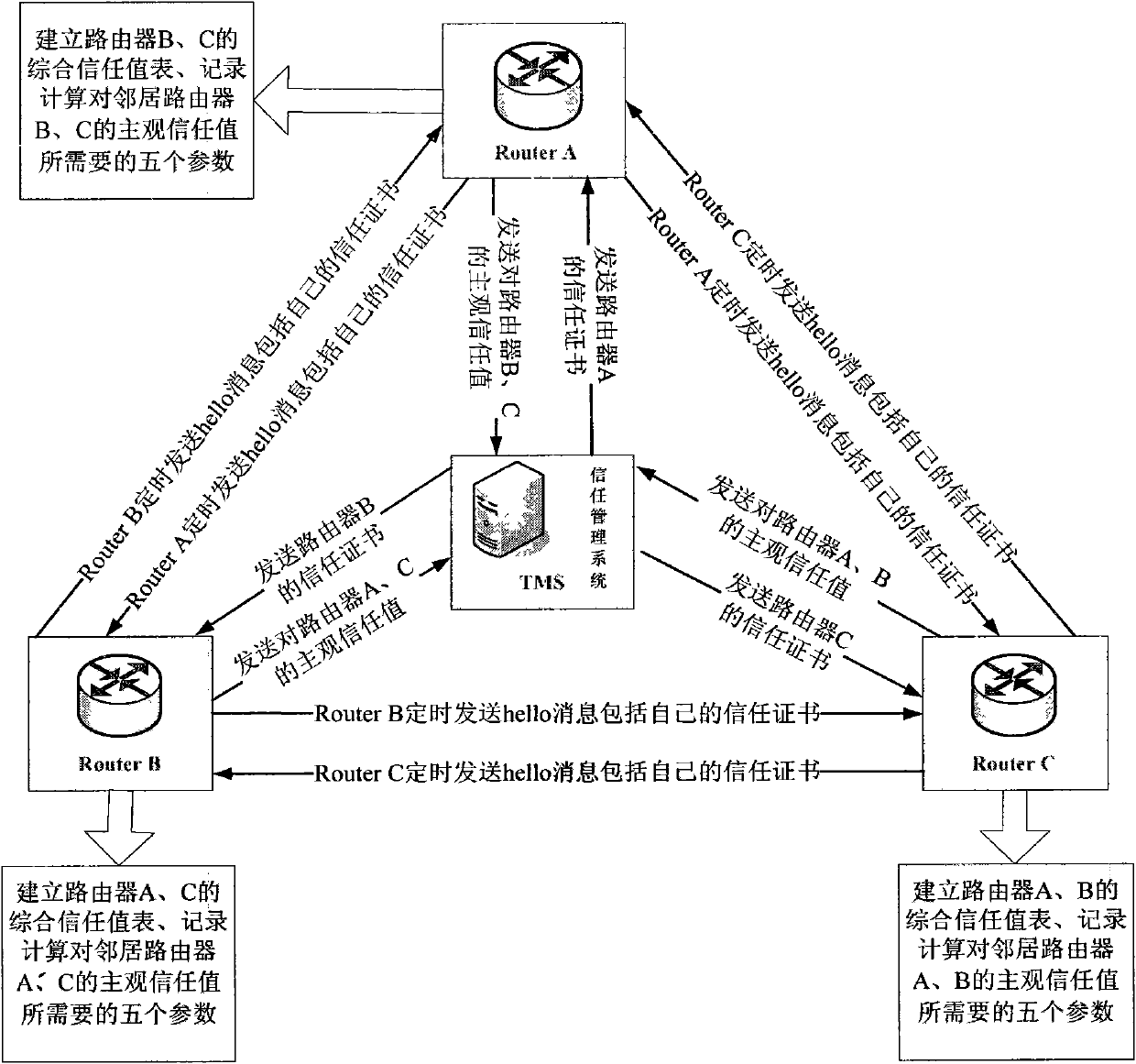
Trust management system based trusted reconstructing method of IP routing protocol
The invention discloses a trust management system based trusted reconstructing method of an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol, which comprises the following steps of: (1) before each router is added into a network, registering to the trust management system, and sending corresponding trust certificates to the routers by the trust management system, the trust certificates including comprehensive trust values of the routers and each being calculated according to safe parameters and configuration parameters of the routers and all the subjective trust value of the neighbor router to the routers by the trust management system; (2) transferring the trust certificates among the routers through hello information, wherein an adjacency relation is not established for the router without the trust certificate, all the routers in the network are ensured to have own trust certificates; (3) each router calculating the subjective trust value of the neighbor router based on network real time parameters including link flow, packet loss probability, retardation, transmission rate of the packet and reliability of the packet, during an interactive work with the neighbor router, calculating a total trust value of the neighbor router by using the comprehensive trust value and the subjective trust value of the neighbor router, and modifying a metric field of a link-state announcement Router_LSA packet as the total trust value and synchronizing a link-state data base;(4) modifying a Dijkstra algorithm, using a reciprocal of the total trust value between the routers as the parameter for the arithmetic computation, selecting the router with higher trust value to generate a shortest path tree, and forming a trust routing list; (5) periodically reporting the subjective trust value of the neighbor routers to the trust management system by each router, simultaneously obtaining the parameter required for computing the subjective trust value, updating the trust certificate of each router at fixed time, and eliminating the router with the overdue trust certificate out of the network to maintain the topological structure of the whole network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
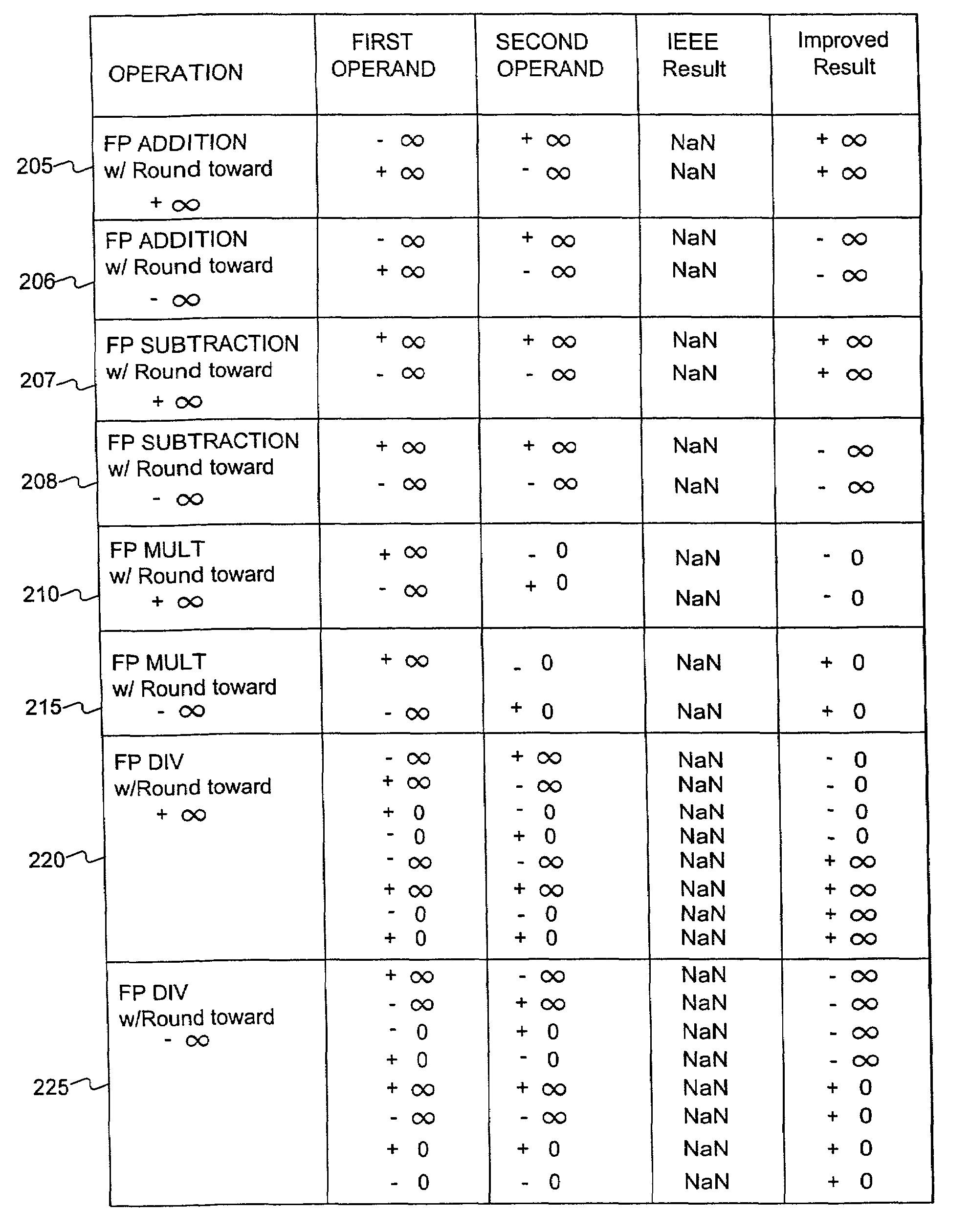
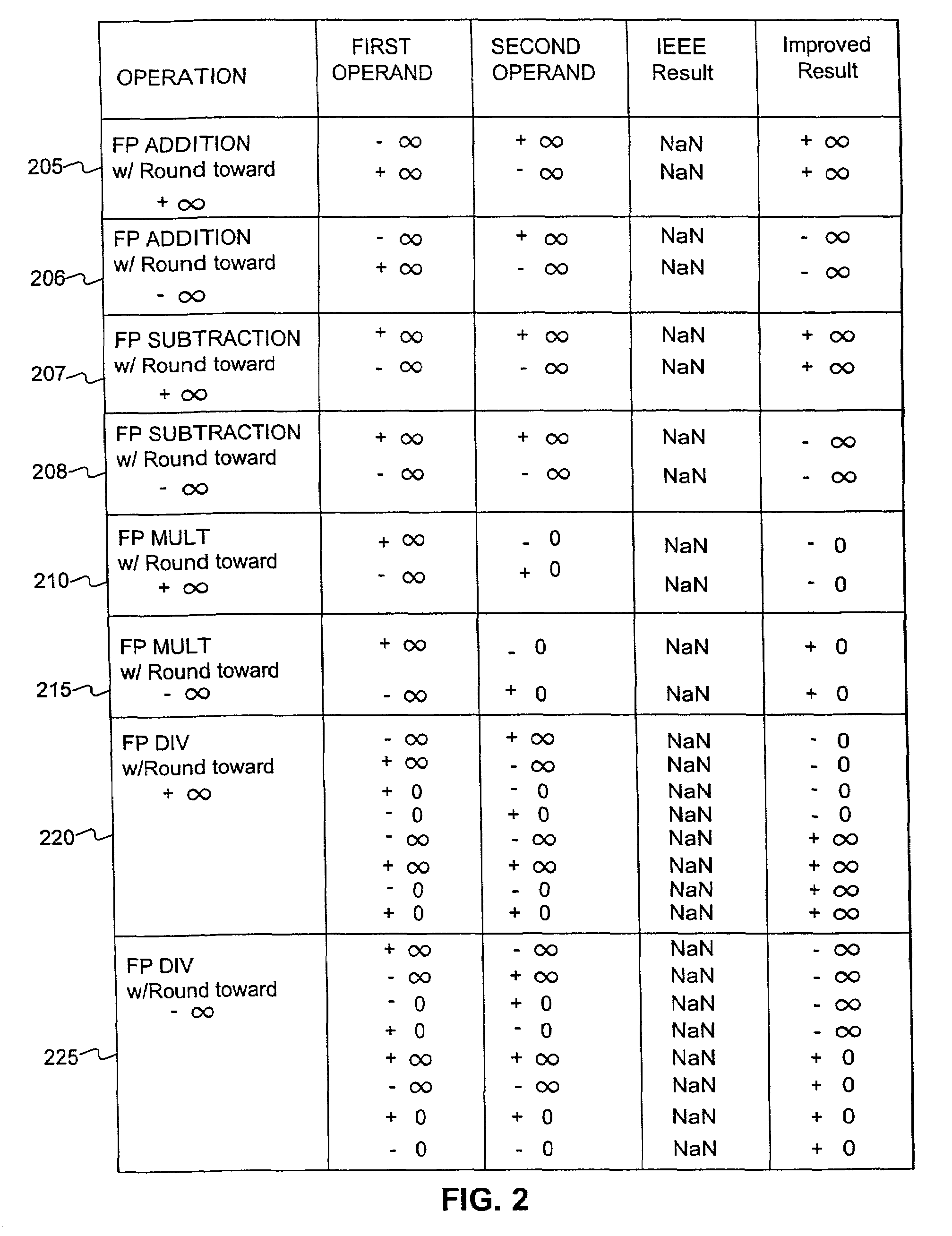
Floating point system with improved support of interval arithmetic
InactiveUS7069288B2Add supportPromote resultsConditional code generationComputation using non-contact making devicesInterval arithmeticOperand
Embodiments consistent with the principles of the present invention provide improved results, compared to IEEE Std. 754, for floating point operations used in interval arithmetic calculations. One embodiment consistent with the principles of the present invention provides a method of enhancing support of an interval computation when performing a floating point arithmetic operation, comprising the steps, performed by a processor, of receiving a first floating point operand, receiving a second floating point operand, executing the floating point arithmetic operation on the first floating point operand and the second floating point operand, determining whether a NaN substitution is necessary, producing a floating point result if the NaN substitution is determined to be unnecessary, and substituting an alternative value as the floating point result if the NaN substitution is determined to be necessary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Power Analysis Attack Countermeasure for the ECDSA
ActiveUS20080301458A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data processing detailsPower analysisCountermeasure
Execution of the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) requires determination of a signature, which determination involves arithmetic operations. Some of the arithmetic operations employ a long term cryptographic key. It is the execution of these arithmetic operations that can make the execution of the ECDSA vulnerable to a power analysis attack. In particular, an attacker using a power analysis attack may determine the long term cryptographic key. By modifying the sequence of operations involved in the determination of the signature and the inputs to those operations, power analysis attacks may no longer be applied to determine the long term cryptographic key.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Arithmetic functions in torus and tree networks
InactiveUS7313582B2Accelerated programImprove efficiencyError preventionDigital data processing detailsNODALAbsolute minimum
Methods and systems for performing arithmetic functions. In accordance with a first aspect of the invention, methods and apparatus are provided, working in conjunction of software algorithms and hardware implementation of class network routing, to achieve a very significant reduction in the time required for global arithmetic operation on the torus. Therefore, it leads to greater scalability of applications running on large parallel machines. The invention involves three steps in improving the efficiency and accuracy of global operations: (1) Ensuring, when necessary, that all the nodes do the global operation on the data in the same order and so obtain a unique answer, independent of roundoff error; (2) Using the topology of the torus to minimize the number of hops and the bidirectional capabilities of the network to reduce the number of time steps in the data transfer operation to an absolute minimum; and (3) Using class function routing to reduce latency in the data transfer. With the method of this invention, every single element is injected into the network only once and it will be stored and forwarded without any further software overhead. In accordance with a second aspect of the invention, methods and systems are provided to efficiently implement global arithmetic operations on a network that supports the global combining operations. The latency of doing such global operations are greatly reduced by using these methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
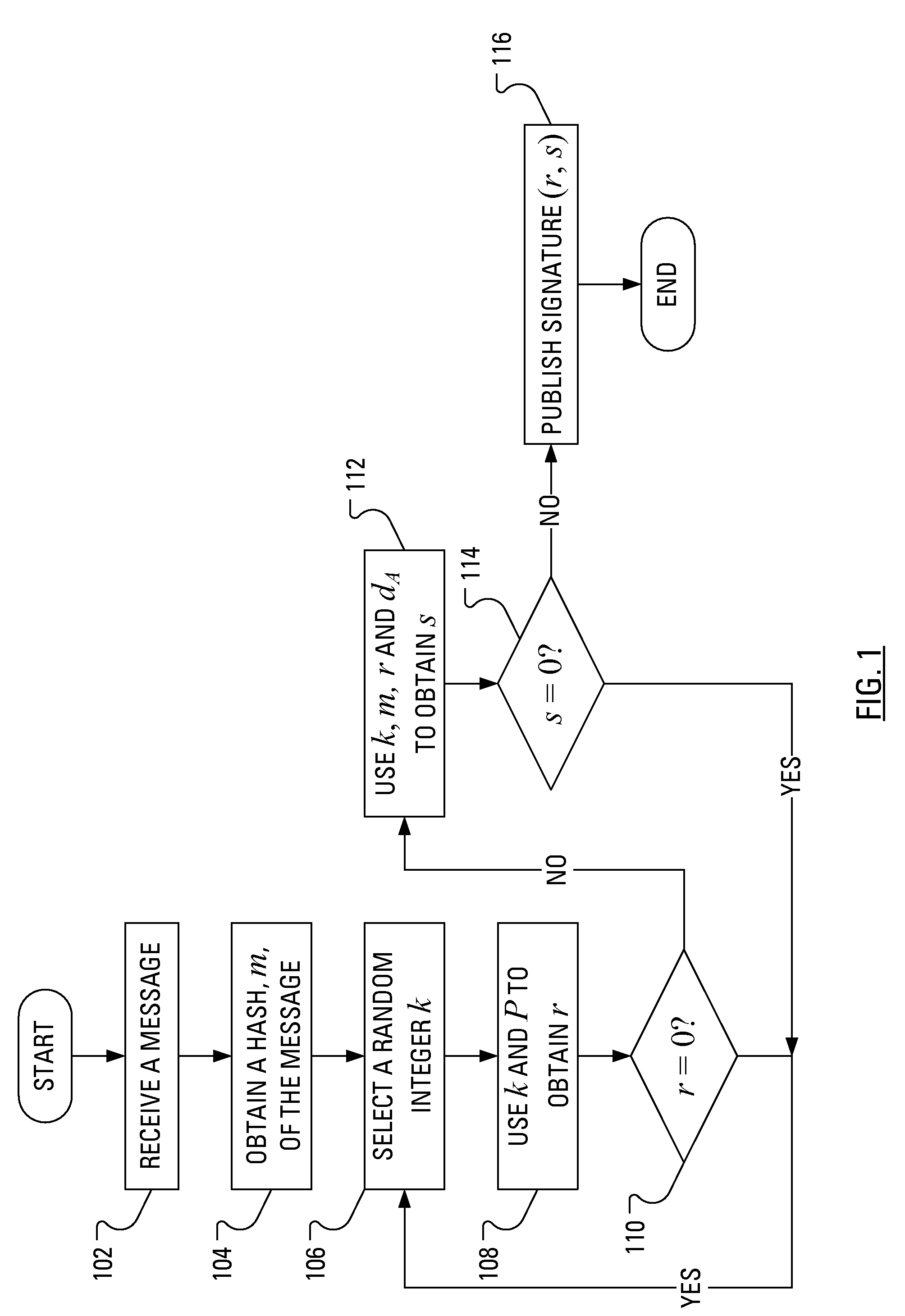
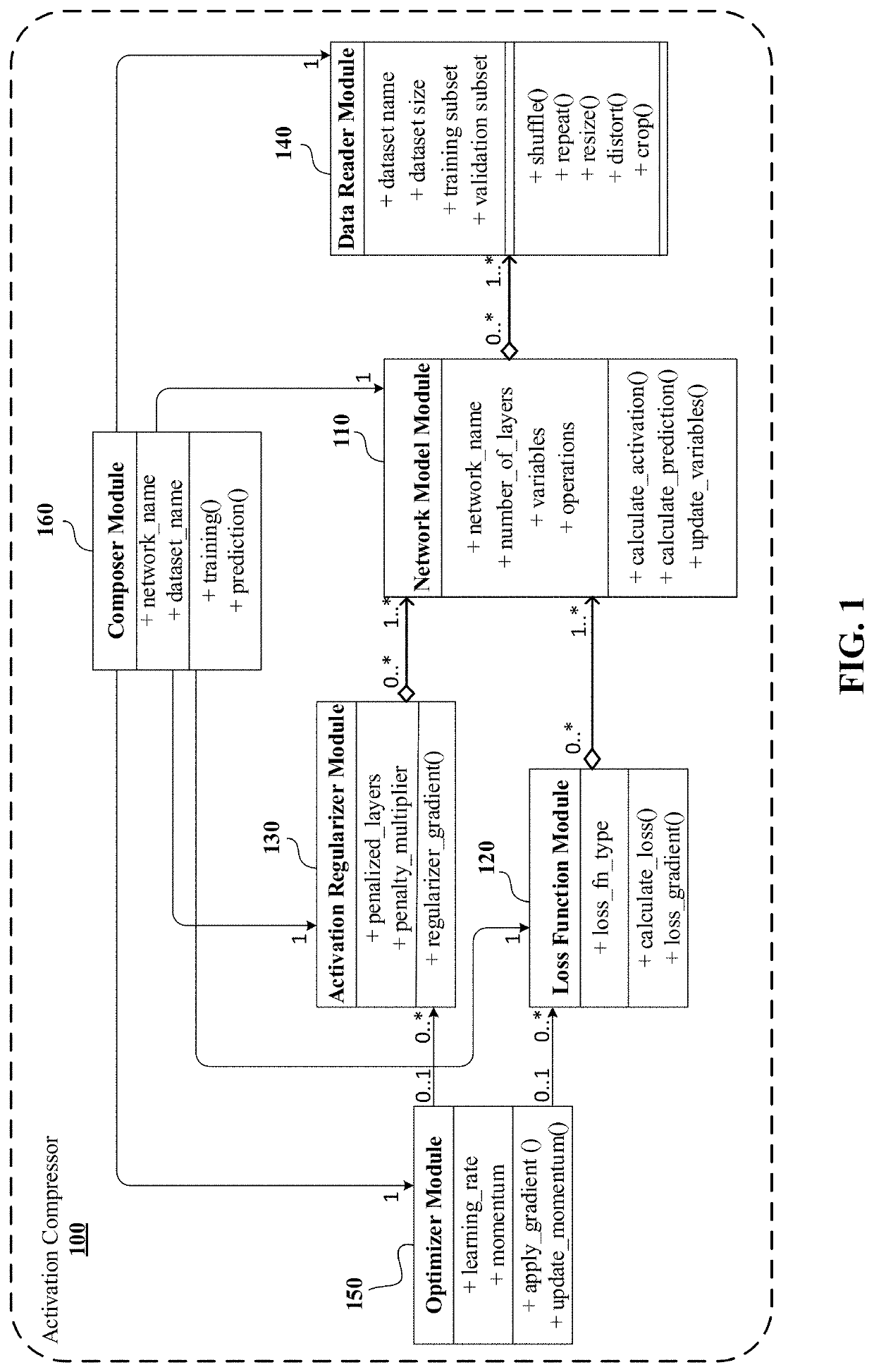
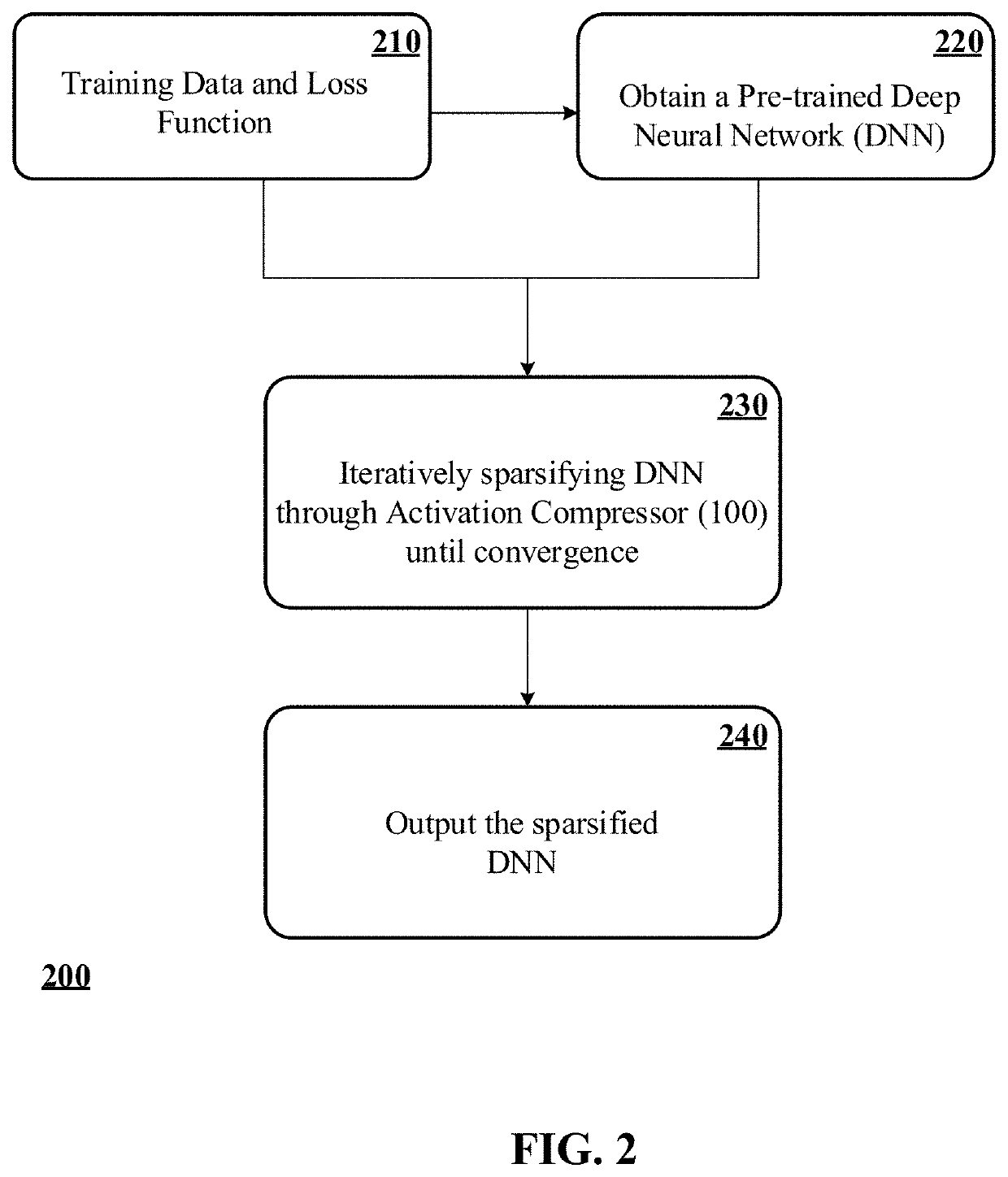
Neural network acceleration and embedding compression systems and methods with activation sparsification
ActiveUS10832139B2Inhibition of activationReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisData setEngineering
Owner:MOFFETT TECH CO LTD
Ultrasonic wind speed and direction measurement device and measurement method
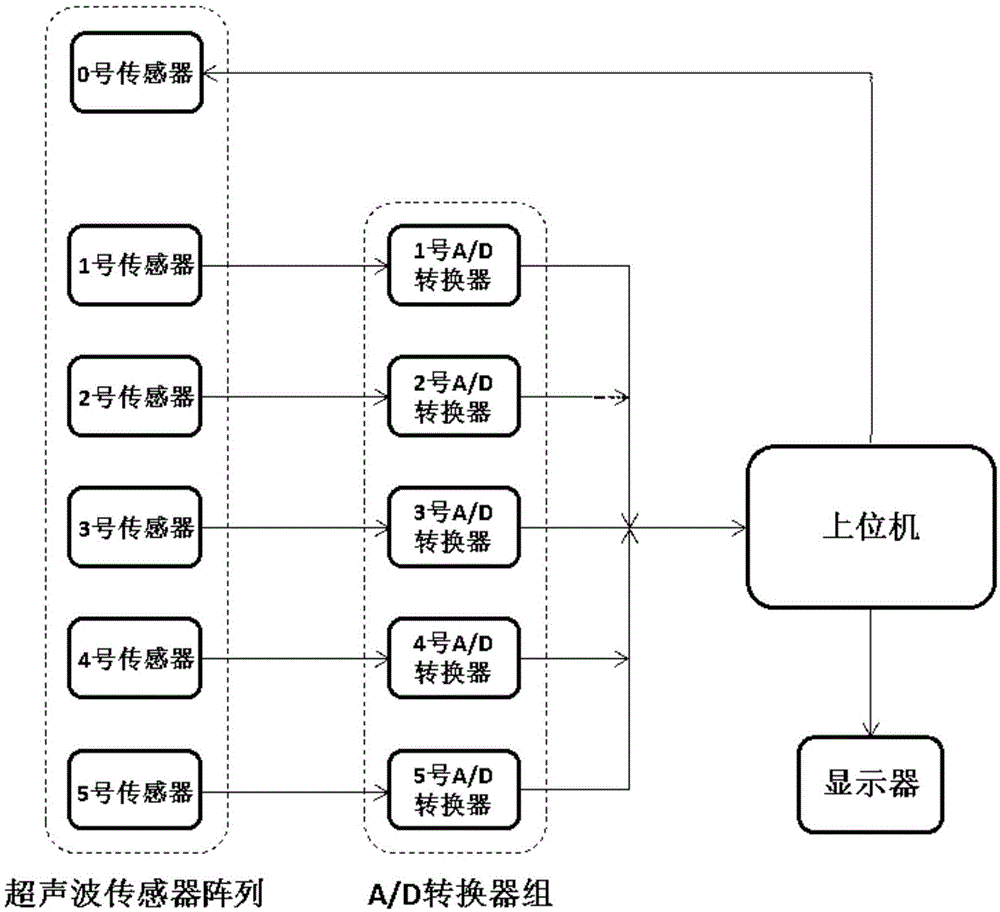
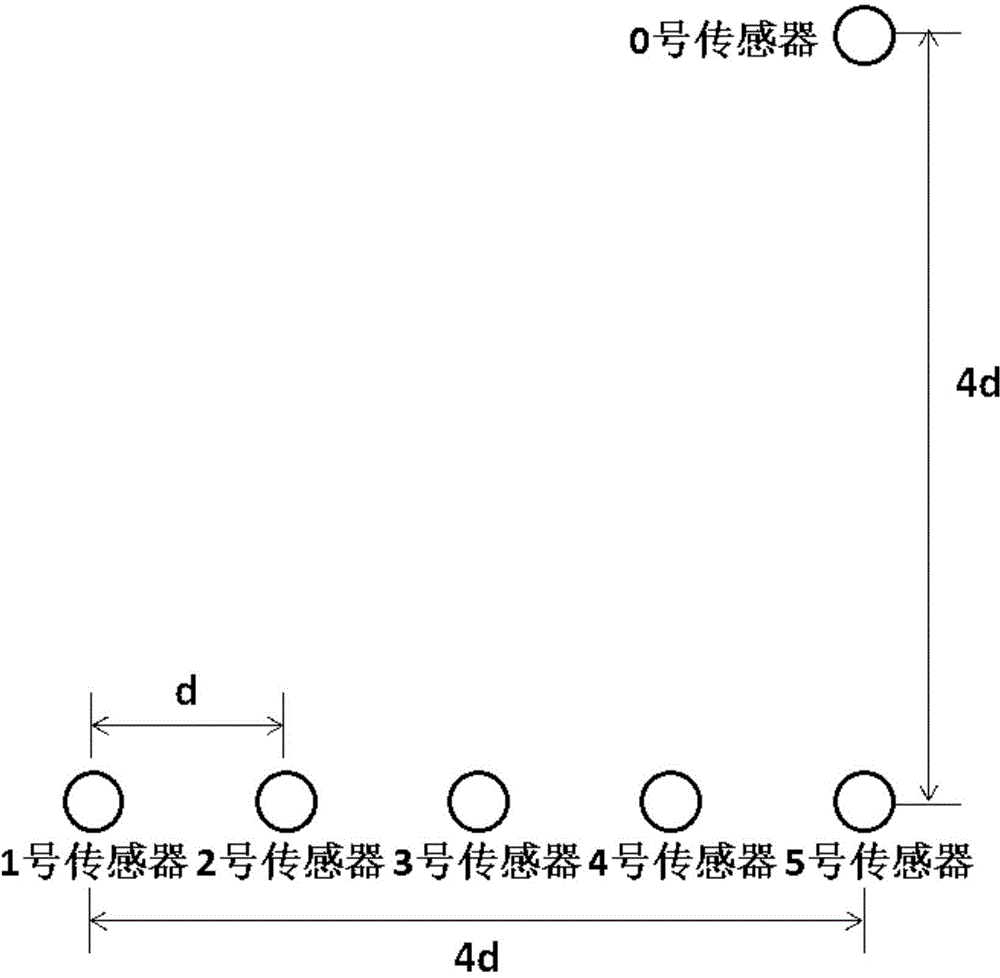
ActiveCN104897925AImprove anti-interference abilityHigh measurement accuracyIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceUltrasonic sensor
The present invention belongs to the field of ultrasonic measurement, and relates to an ultrasonic wind speed and direction measurement device and measurement method. Problems that conventional ultrasonic wind measurement devices are high in cost, opposite-type devices are large in mechanical structure and reflection-type devices are limited in precision are solved. The ultrasonic wind speed and direction measurement device comprises an ultrasonic sensor array, an A / D converter group, an upper computer and a display, wherein the ultrasonic sensor array is composed of six ultrasonic sensors. The measurement method of the ultrasonic wind speed and direction measurement device comprises controlling a NO. 0 ultrasonic sensor by the upper computer to send an ultrasonic single, the sent signal being S(t), the frequency f of the sent ultrasonic waves being 200 kHz; sampling signals received by NO. 1 to NO. 5 ultrasonic sensors by using the A / D converter group and inputting the sampled signals to the upper computer for arithmetic computation; controlling a display module by using the upper computer and outputting and displaying real-time wind speed and direction values after computation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Integer ciphertext arithmetic operation method based on homomorphic encryption
ActiveCN109412786AImprove algorithm efficiencyReduce frequencyCommunication with homomorphic encryptionAlgorithmNoise reduction
The invention provides an integer ciphertext arithmetic operation method based on homomorphic encryption, which comprises complement homomorphic calculation, addition subtraction homomorphic calculation, multiplication homomorphic calculation and division homomorphic calculation. This invention refers to the rules of complement, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of binary integersin computer, and transforms this rule into Boolean polynomials containing only logical AND and XOR operations. In multiplication and division, different calculations are made according to the information of special bits to correct the final calculation results. So we modify the form of Boolean polynomials to represent different computational results, that is, Boolean polynomials include all the inputs and mutually exclusive computational branches of this layer. Then Boolean polynomials are transformed into homomorphic polynomials which can be used in ciphertext computation, and the security of homomorphic polynomials is proved, which meets the requirement of semantic security. The multi-bit parallel operation of integer homomorphic arithmetic operation is realized, the algorithm efficiency of homomorphic operation is improved, the frequency of noise reduction operation is reduced, and the operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Cryptosystem and method using isogeny-based computations to reduce a memory footprint
ActiveUS20200259648A1Reduced footprintEfficient executionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPublic key for secure communicationMemory footprintParallel computing
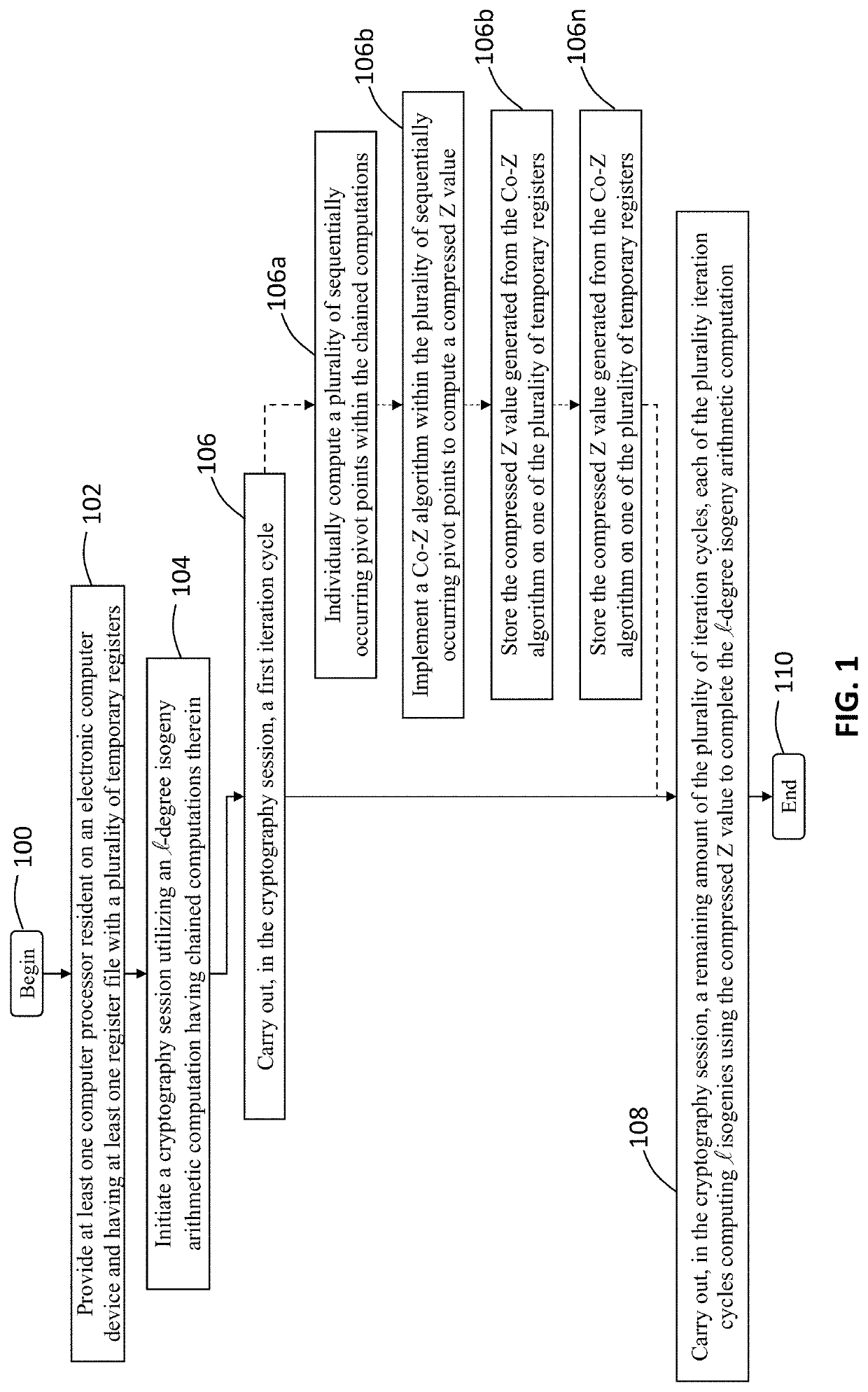
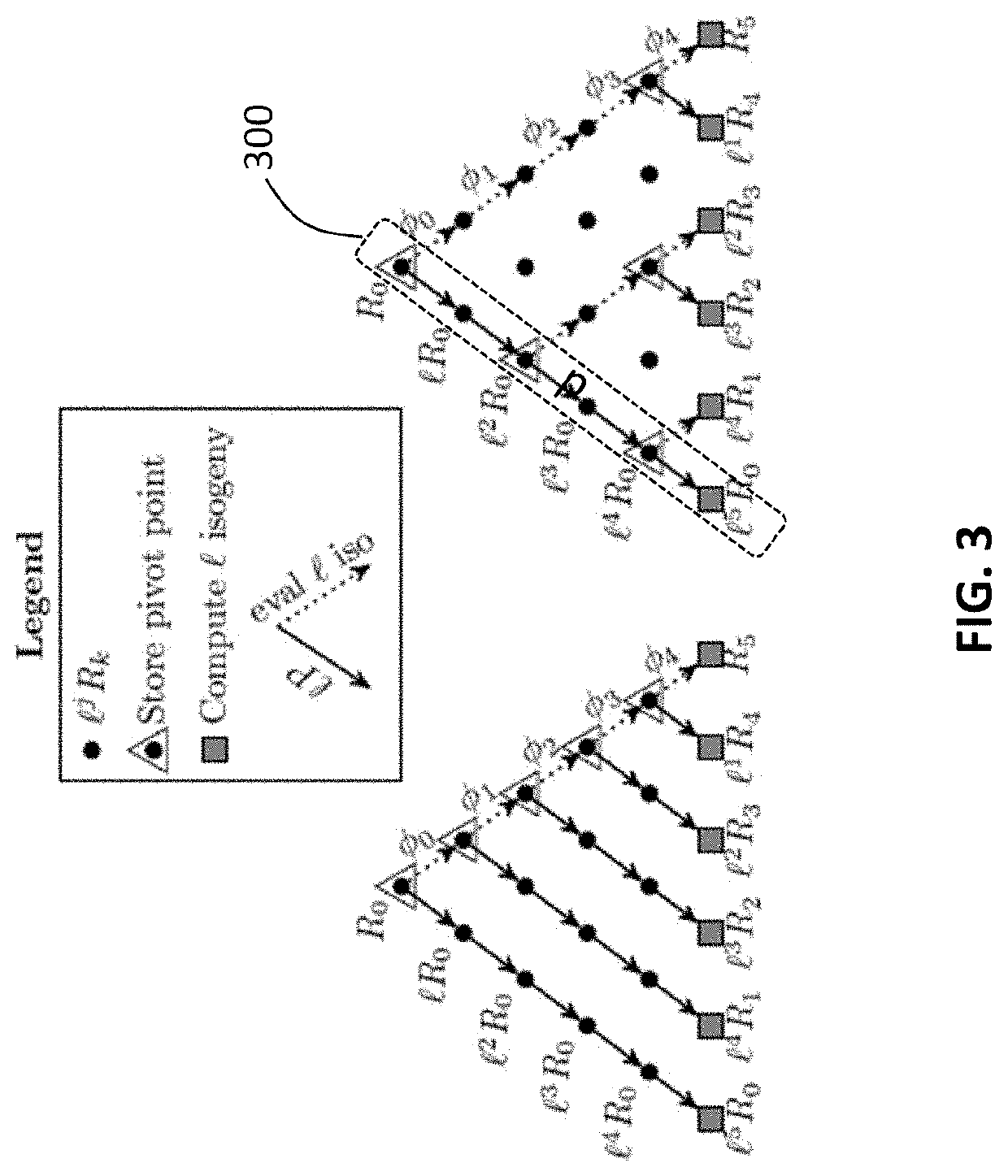
A computer processing system and method for reducing memory footprint that includes initiating, through at least one computer processor, a cryptography session utilizing an -degree isogeny arithmetic computation having chained computations therein. The cryptography session includes implementing a first iteration cycle, of a plurality of iteration cycles, and a implementing a remaining amount of the plurality of iteration cycles, each of the plurality iteration cycles computing isogenies using a compressed Z value to complete the -degree isogeny arithmetic computation. The first iteration cycle includes individually computing a plurality of sequentially occurring pivot points within the chained computations, implementing a Co-Z algorithm within the plurality of sequentially occurring pivot points to compute and store the compressed Z value on one of the plurality of temporary registers and computing a first isogeny of the -degree isogeny arithmetic computations using the compressed Z value.
Owner:PQSECURE TECH LLC
Digital Signal Processor Having Instruction Set With One Or More Non-Linear Functions Using Reduced Look-Up Table With Exponentially Varying Step-Size
InactiveUS20100138464A1Small sizeProgram controlComplex mathematical operationsLookup tableControl theory
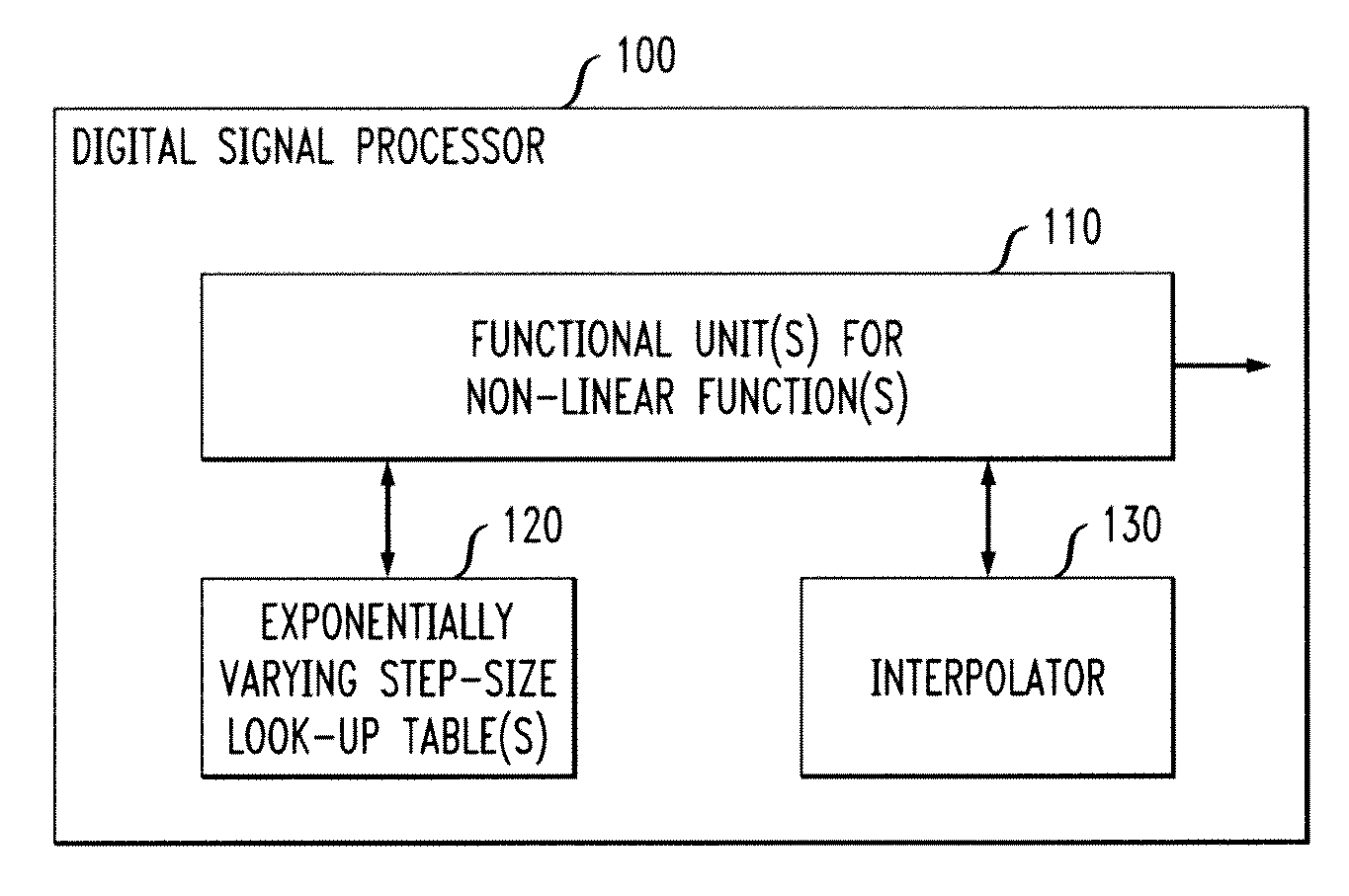
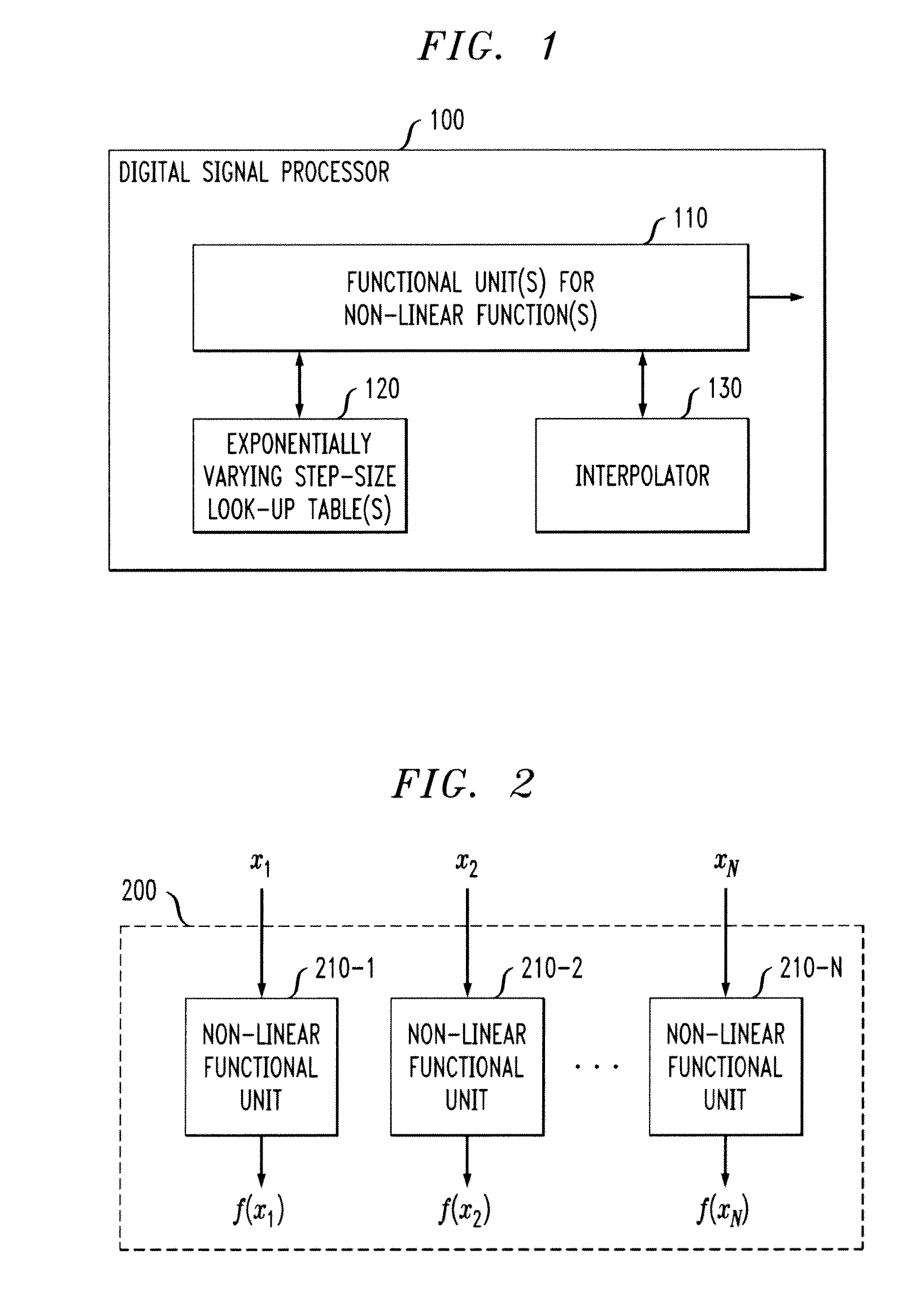
A digital signal processor and method are disclosed having an instruction set with one or more non-linear functions using a look-up table of reduced size and exponentially varying step-sizes. A digital signal processor evaluates a non-linear function for a value, x, by obtaining at least two values from at least one look-up table for the non-linear function that are near the value, x, wherein the at least one look-up table stores a subset of values for the non-linear function using exponentially-varying step sizes; and interpolating the at least two obtained values lo to obtain a result, y. A position of a leading zero in the value, x, can be used as an index into the at least one look-up table. The interpolation can comprise, for example, a linear interpolation or a polynomial interpolation. A modulo arithmetic operation can optionally be employed for a periodic non-linear function.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of coding and decoding image
InactiveUS6987810B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
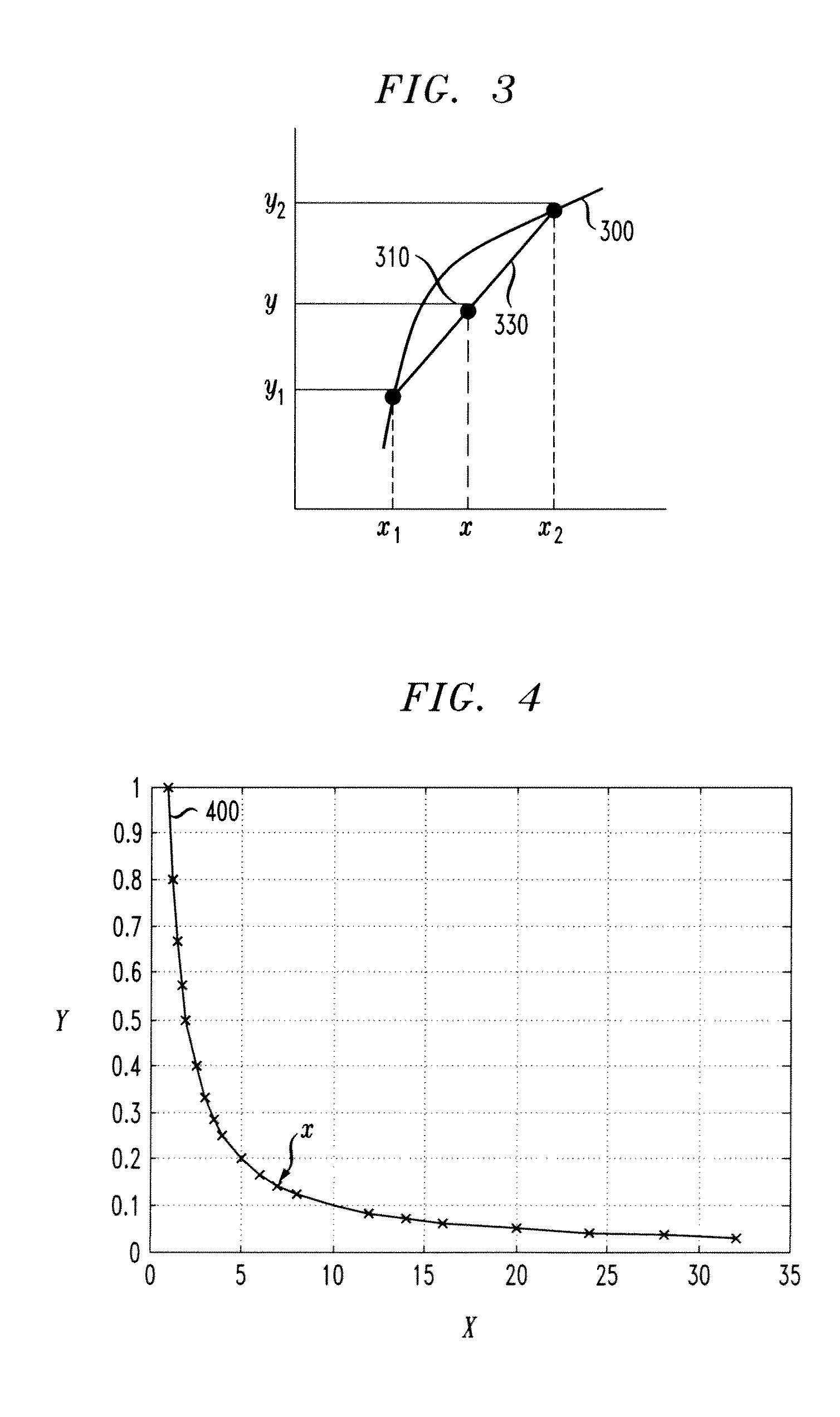
A method of simplifying the arithmetic operation in a global motion compensation process approximates the motion vector field of the whole image without using many parameters. Motion vectors in the global motion compensation are found by the interpolation and / or extrapolation of the motion vectors of a plurality of representative points 602, 603 and 604 having particular features in the spatial distance thereof. Since the shift operation can be substituted for the division for synthesizing a predicted image of global motion compensation, the processing using a computer or a dedicated hardware is simplified.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com