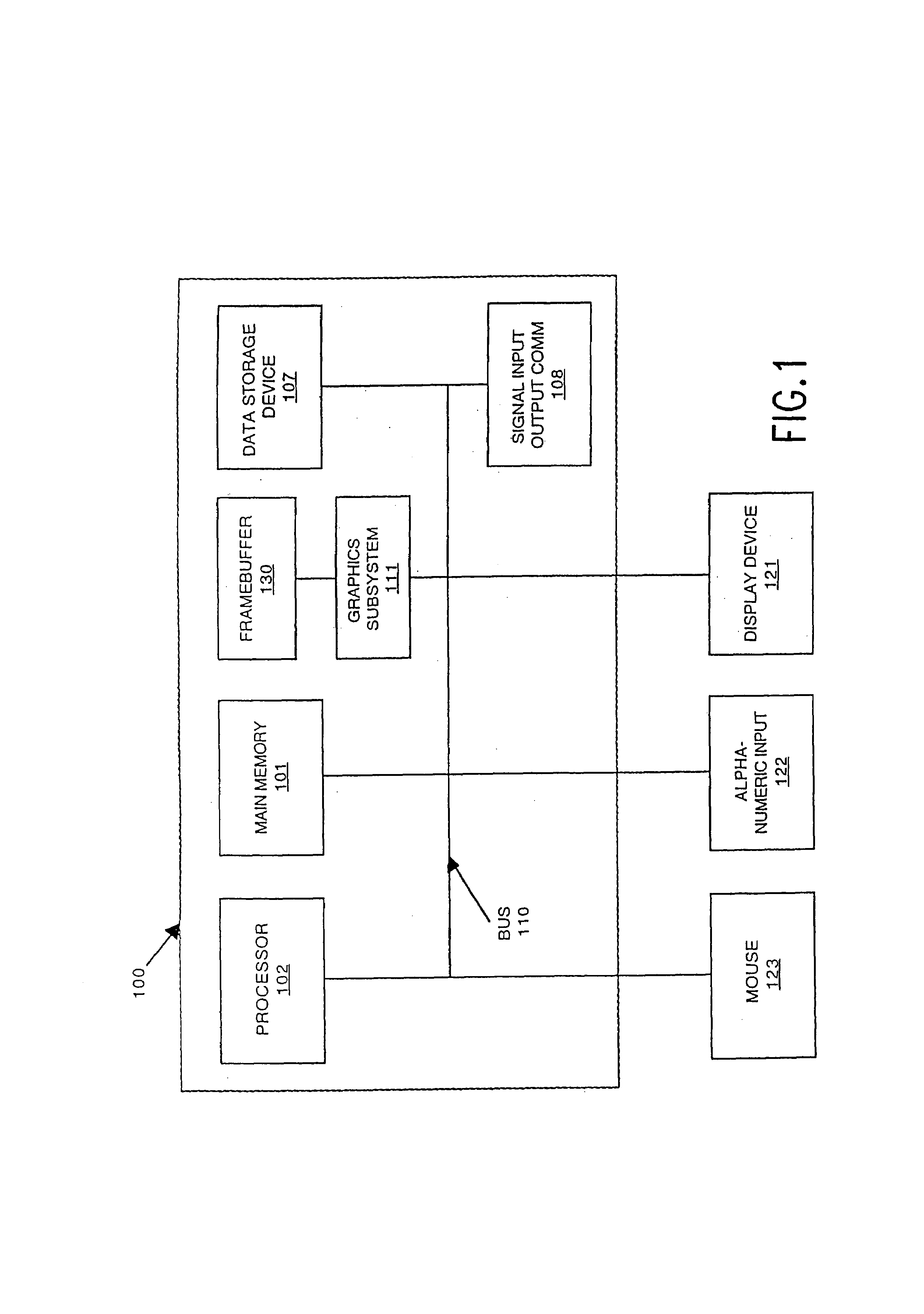
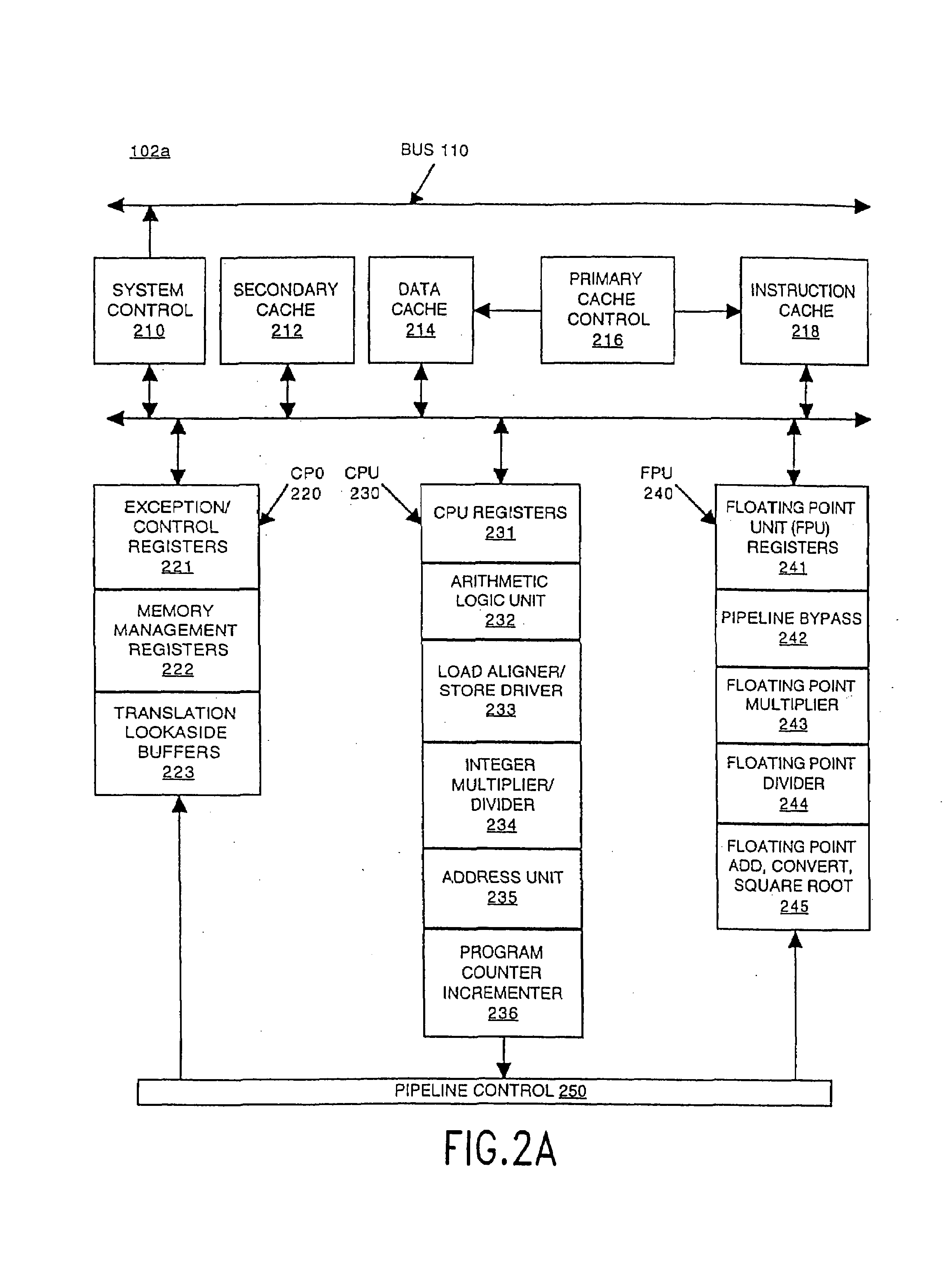
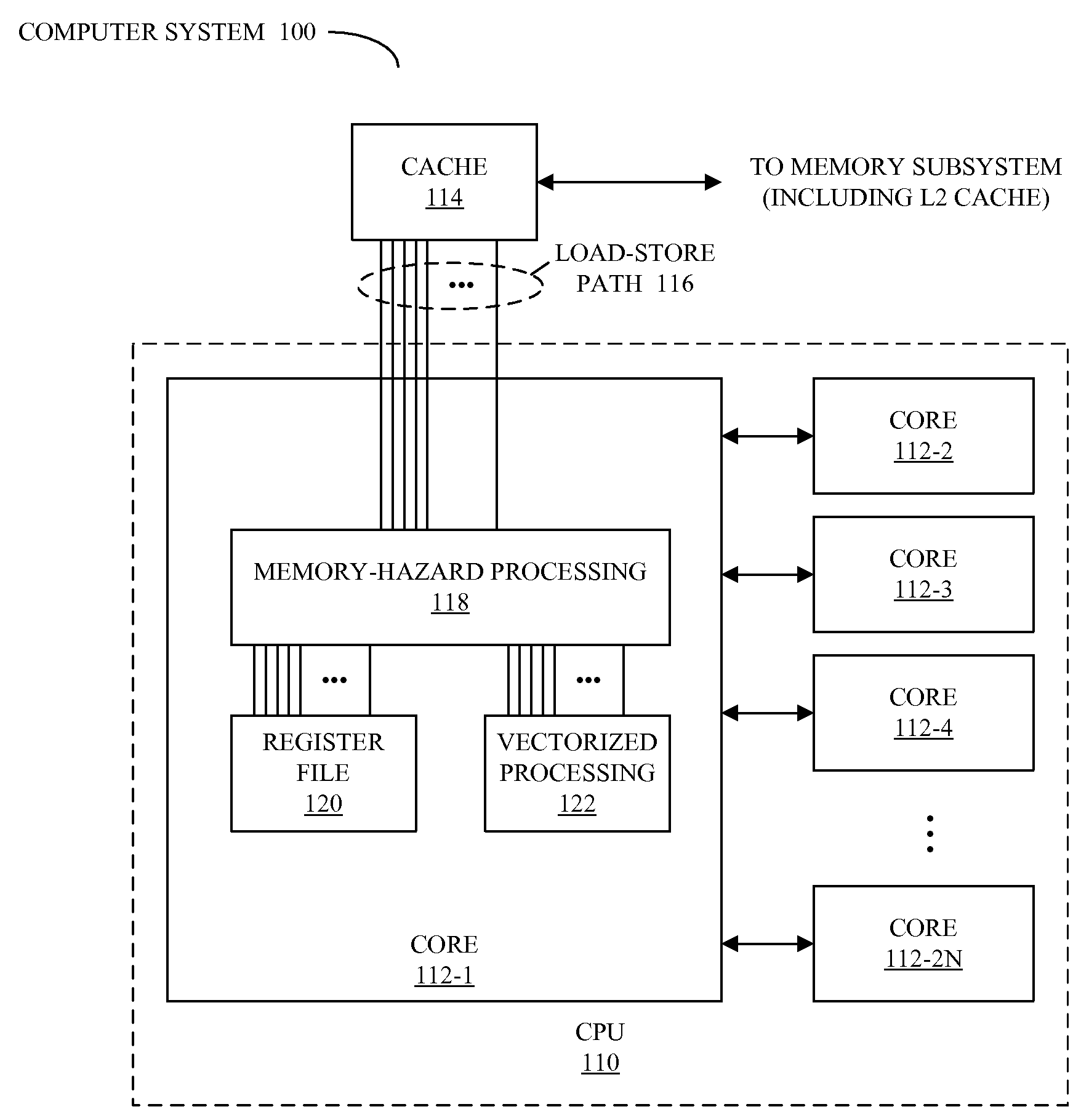
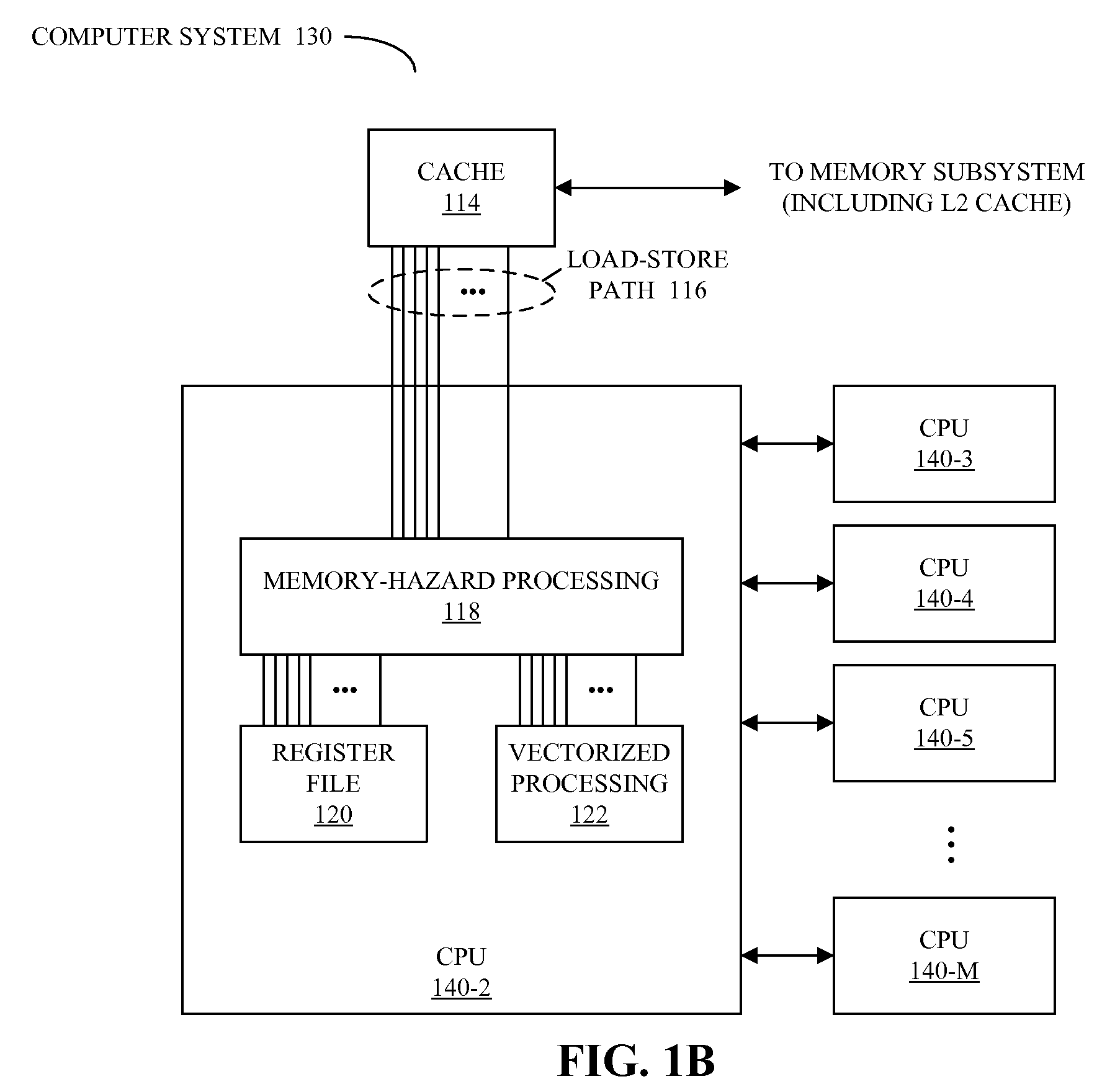
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
456results about "Conditional code generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
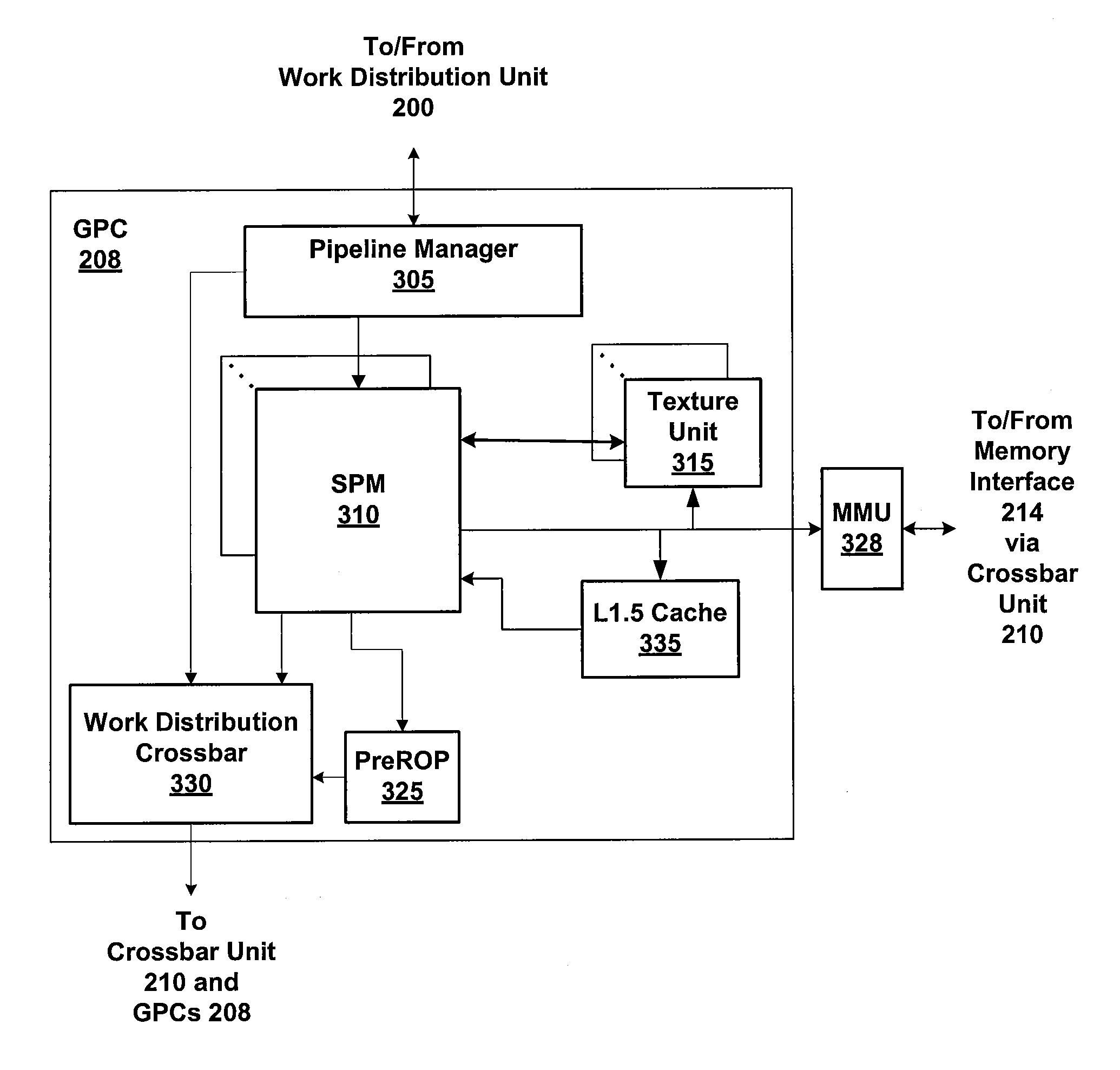
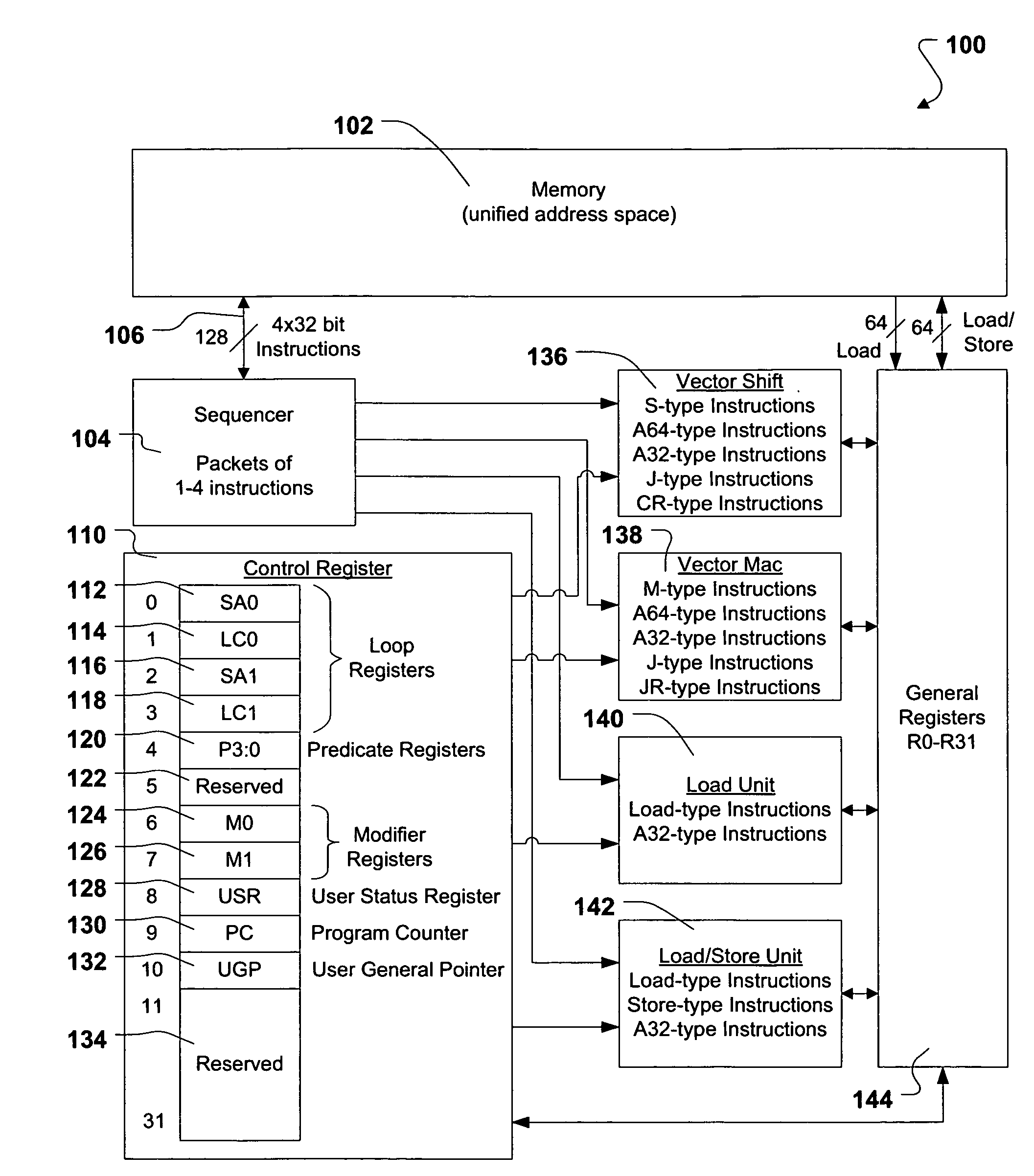
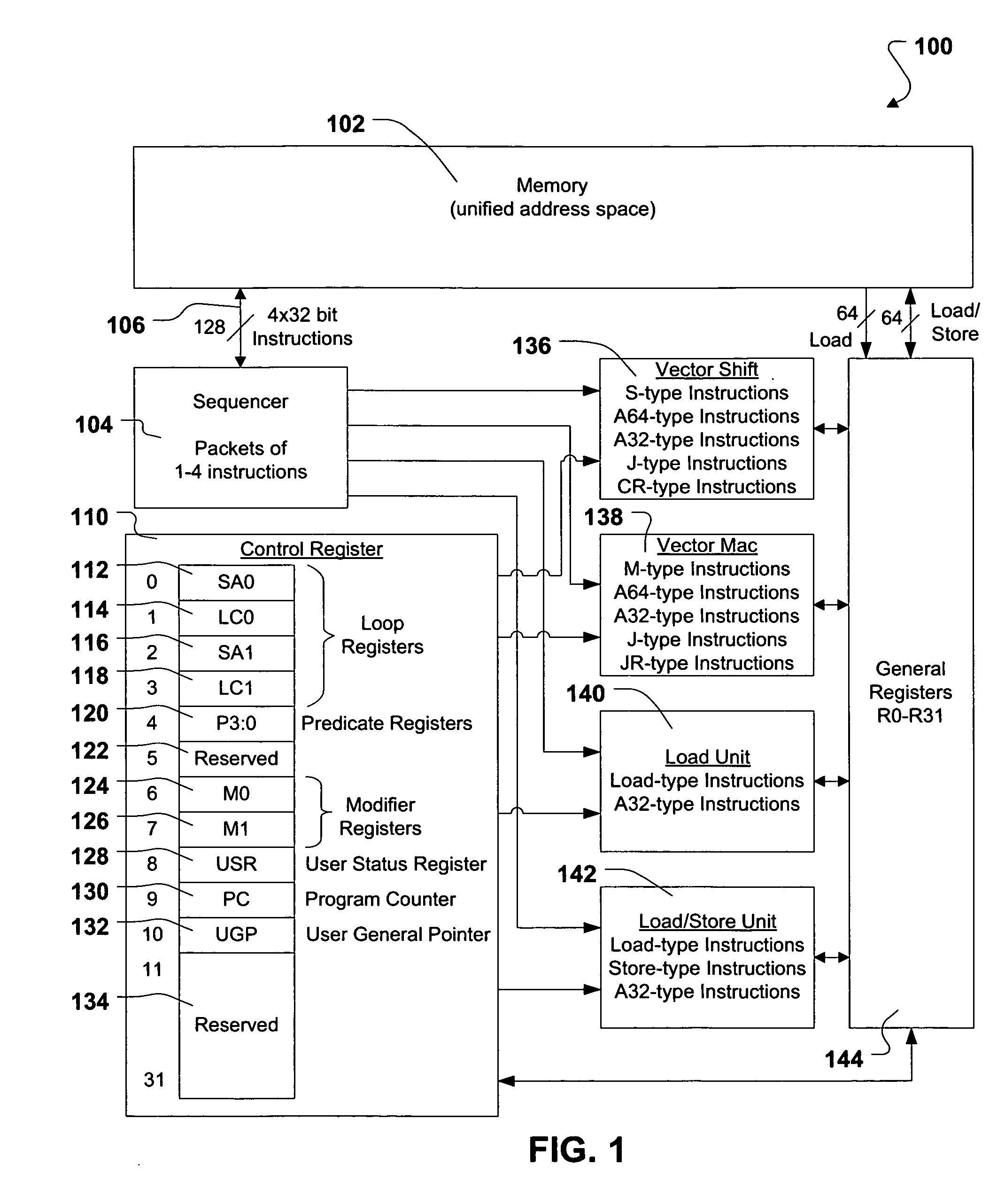
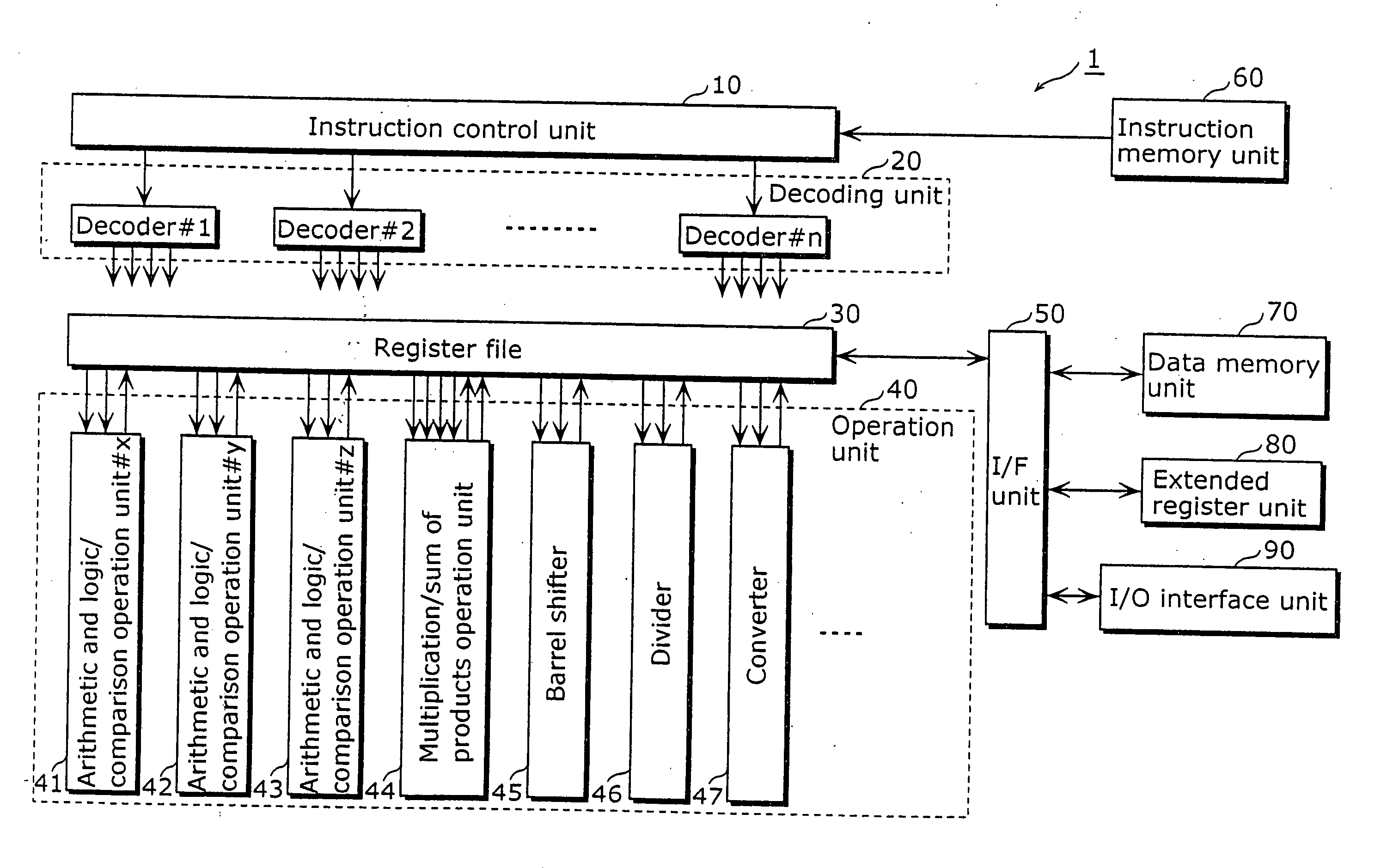
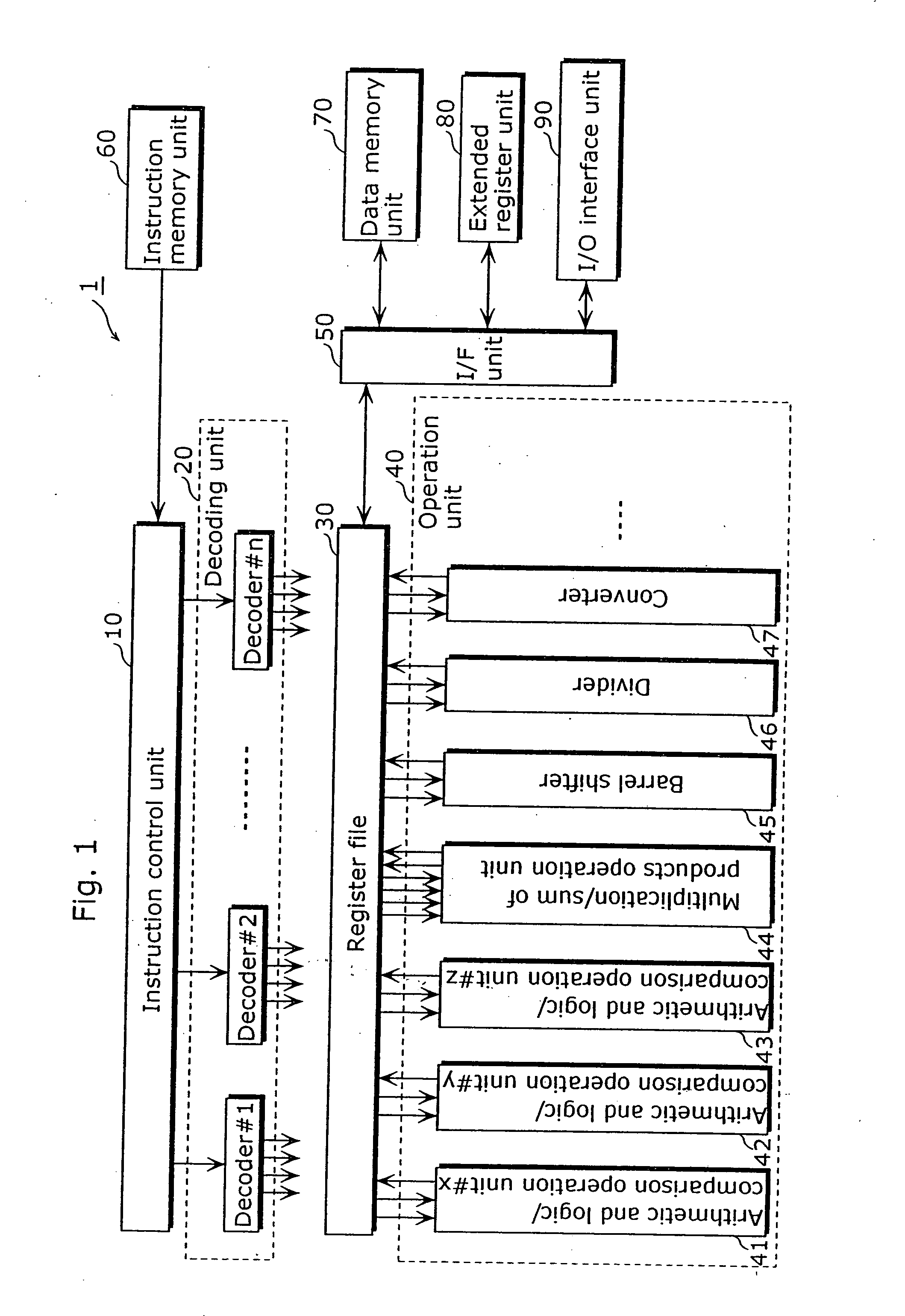
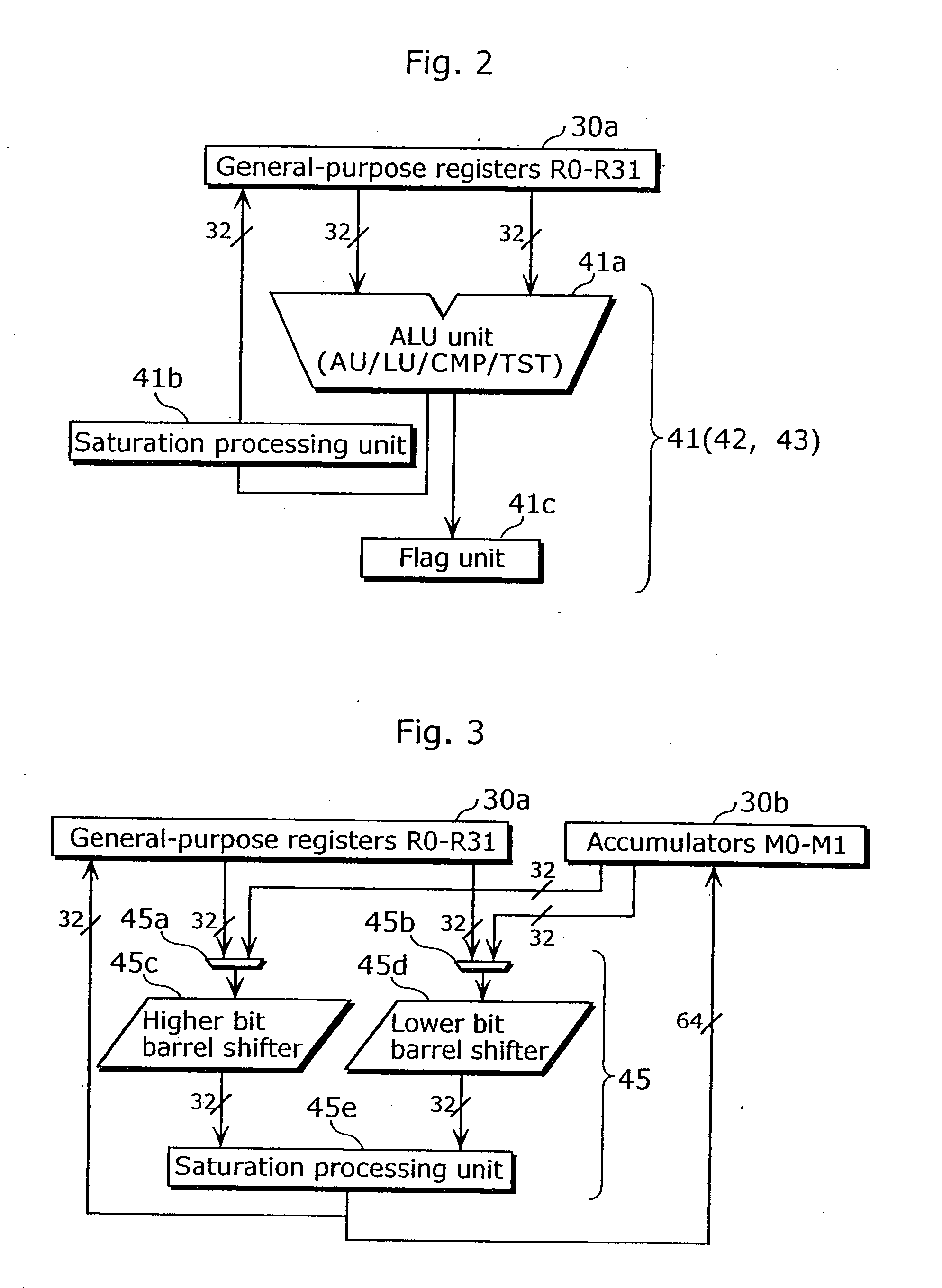
Programmable system for processing a partitioned network infrastructure
InactiveUS6859841B2Many timesMinimize movementConditional code generationInstruction analysisGeneral purposeNetwork interface controller
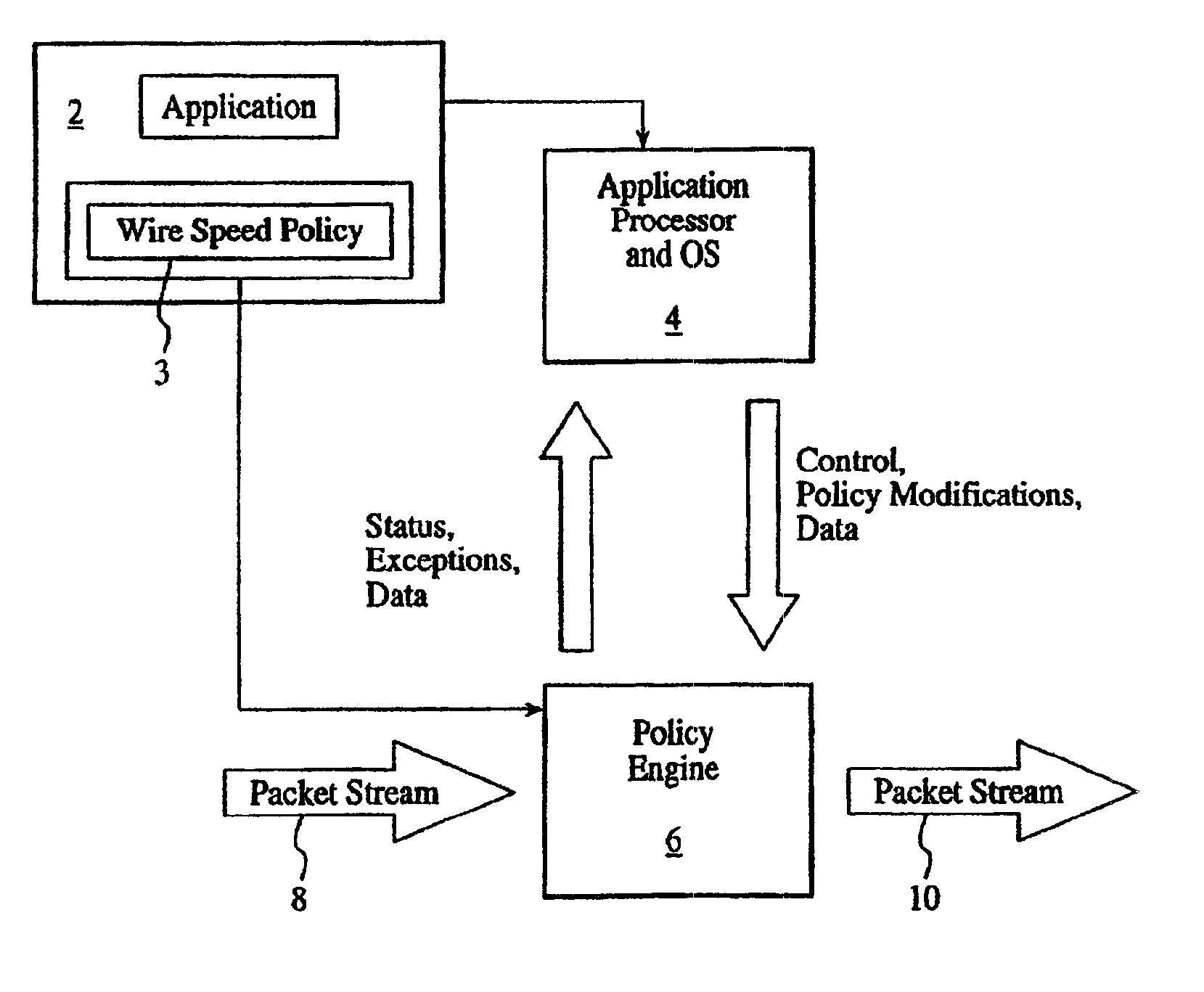
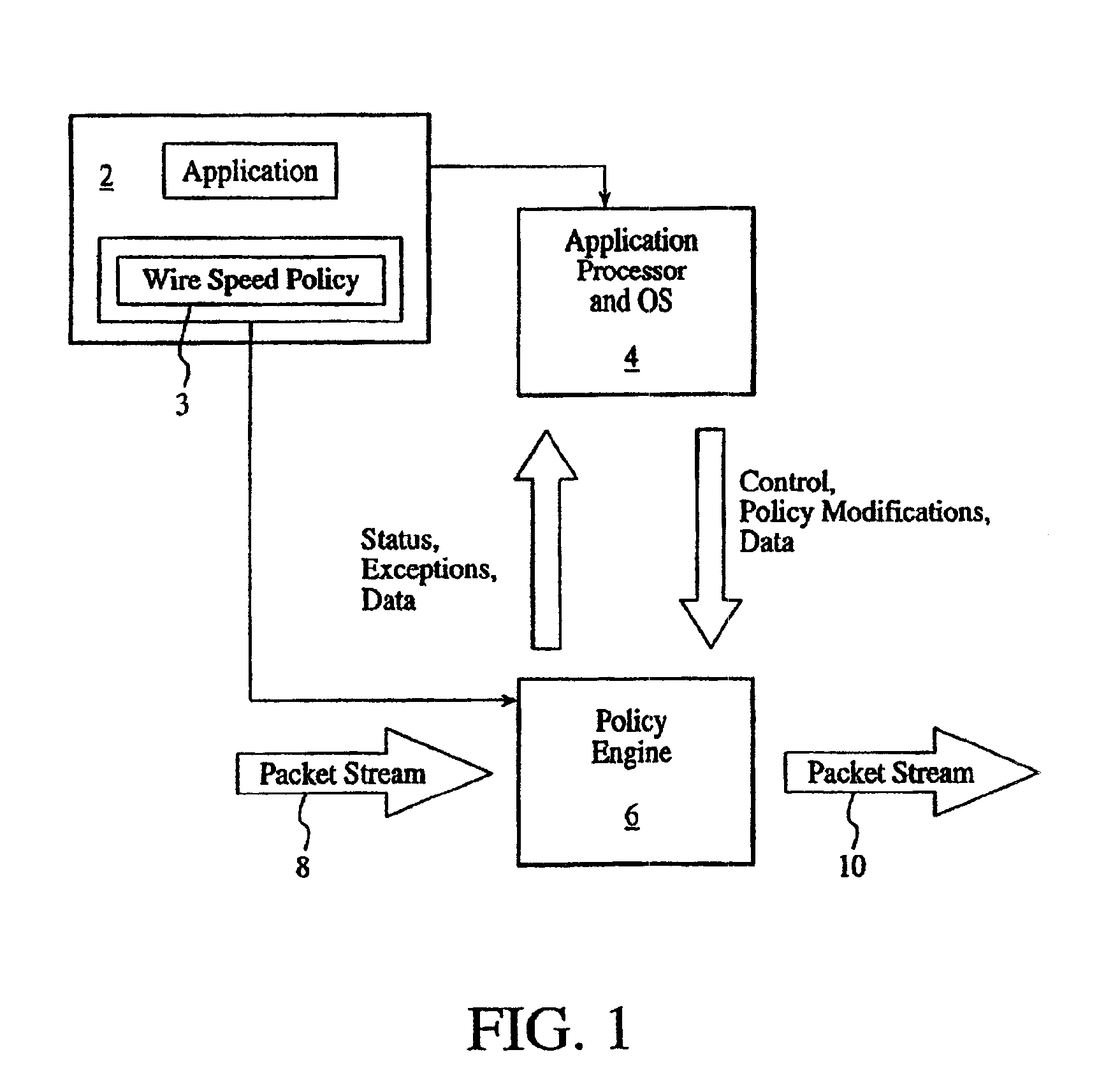
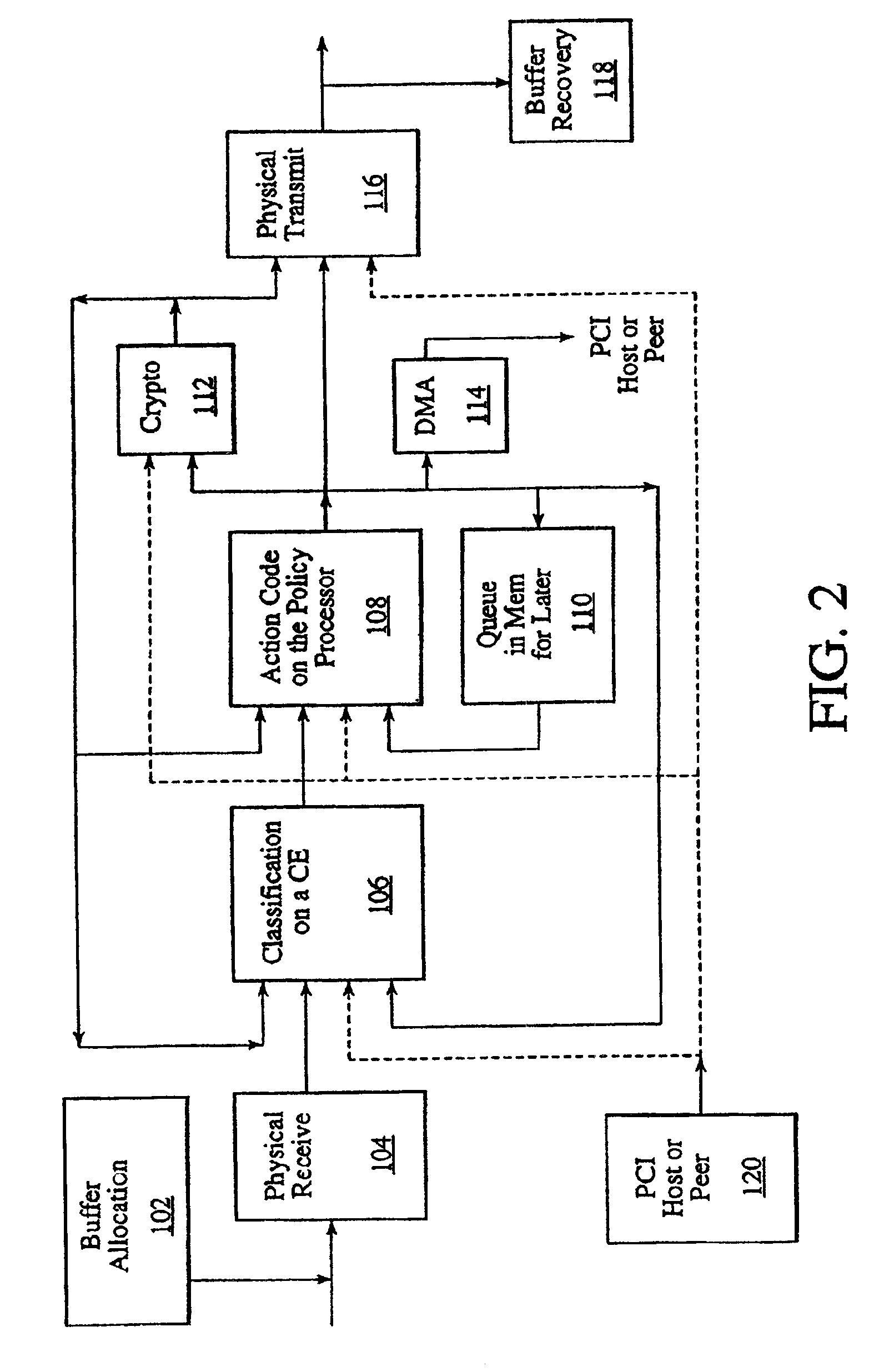
The present invention relates to a general-purpose programmable packet-processing platform for accelerating network infrastructure applications which have been structured so as to separate the stages of classification and action. Network packet classification, execution of actions upon those packets, management of buffer flow, encryption services, and management of Network Interface Controllers are accelerated through the use of a multiplicity of specialized modules. A language interface is defined for specifying both stateless and stateful classification of packets and to associate actions with classification results in order to efficiently utilize these specialized modules.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Reconfigurable data path processor
InactiveUS6883084B1Eliminates branchingCycle simpleEnergy efficient ICTConditional code generationMultiplexerProcessing element
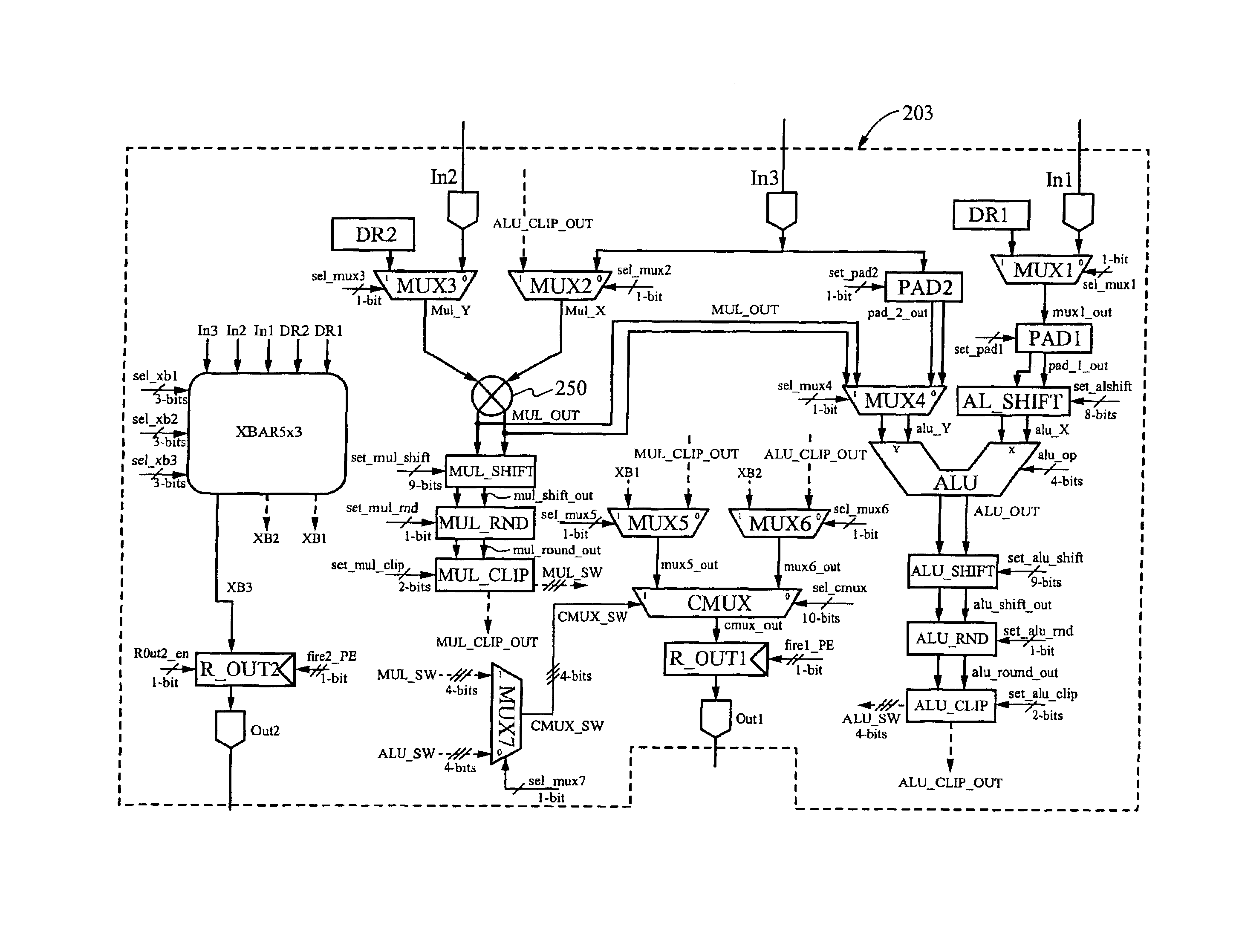
A reconfigurable data path processor comprises a plurality of independent processing elements. Each of the processing elements advantageously comprising an identical architecture. Each processing element comprises a plurality of data processing means for generating a potential output. Each processor is also capable of through-putting an input as a potential output with little or no processing. Each processing element comprises a conditional multiplexer having a first conditional multiplexer input, a second conditional multiplexer input and a conditional multiplexer output. A first potential output value is transmitted to the first conditional multiplexer input, and a second potential output value is transmitted to the second conditional multiplexer output. The conditional multiplexer couples either the first conditional multiplexer input or the second conditional multiplexer input to the conditional multiplexer output, according to an output control command. The output control command is generated by processing a set of arithmetic status-bits through a logical mask. The conditional multiplexer output is coupled to a first processing element output. A first set of arithmetic bits are generated according to the processing of the first processable value. A second set of arithmetic bits may be generated from a second processing operation. The selection of the arithmetic status-bits is performed by an arithmetic-status bit multiplexer selects the desired set of arithmetic status bits from among the first and second set of arithmetic status bits. The conditional multiplexer evaluates the select arithmetic status bits according to logical mask defining an algorithm for evaluating the arithmetic status bits.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100293342A1Simple structureSmall spacingConditional code generationRegister arrangementsInstruction setContent-addressable memory
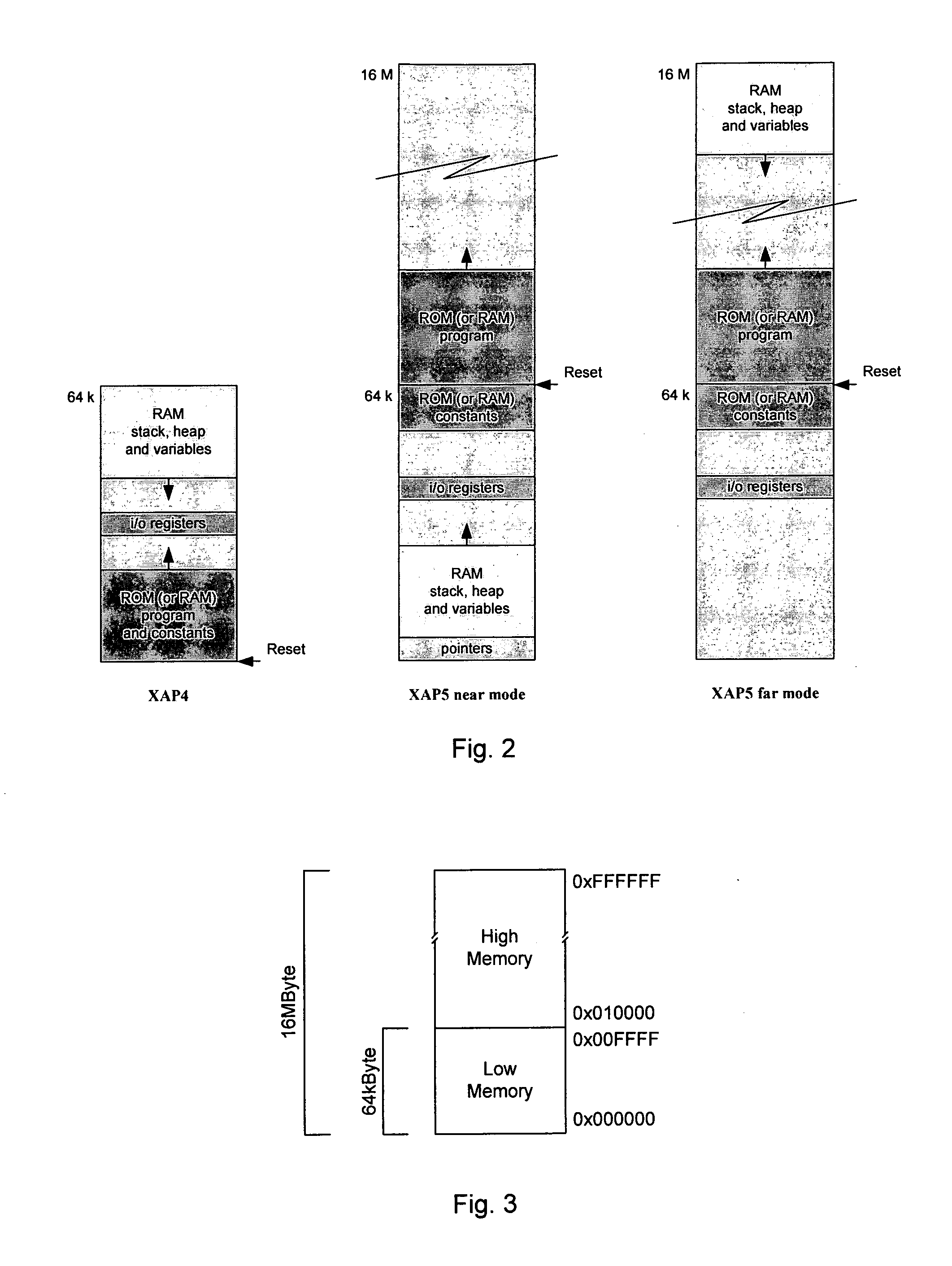
Apparatus comprises a processor configured for operation under a sequence of instructions from an instruction set, wherein said processor comprises: means for conditionally inhibiting at least one type of trap, interrupt or exception (TIE) event, wherein, when operating under a sequence of instructions, said inhibition means is inaccessible by said instructions to inhibit the or each type of TIE event, without interrupting said sequence. A data processing apparatus includes a processor adapted to operate under control of program code comprising instructions selected from an instruction set, the apparatus comprising: a predefined memory space providing a predefined addressable memory for storing program code and data, a larger memory space providing a larger addressable memory, means for accessing program code and data within the predefined memory space, and means for controlling the access means so as to enable the access means to access program code located within the larger memory space.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
System for processing a cluster of instructions where the instructions are issued to the execution units having a priority order according to a template associated with the cluster of instructions
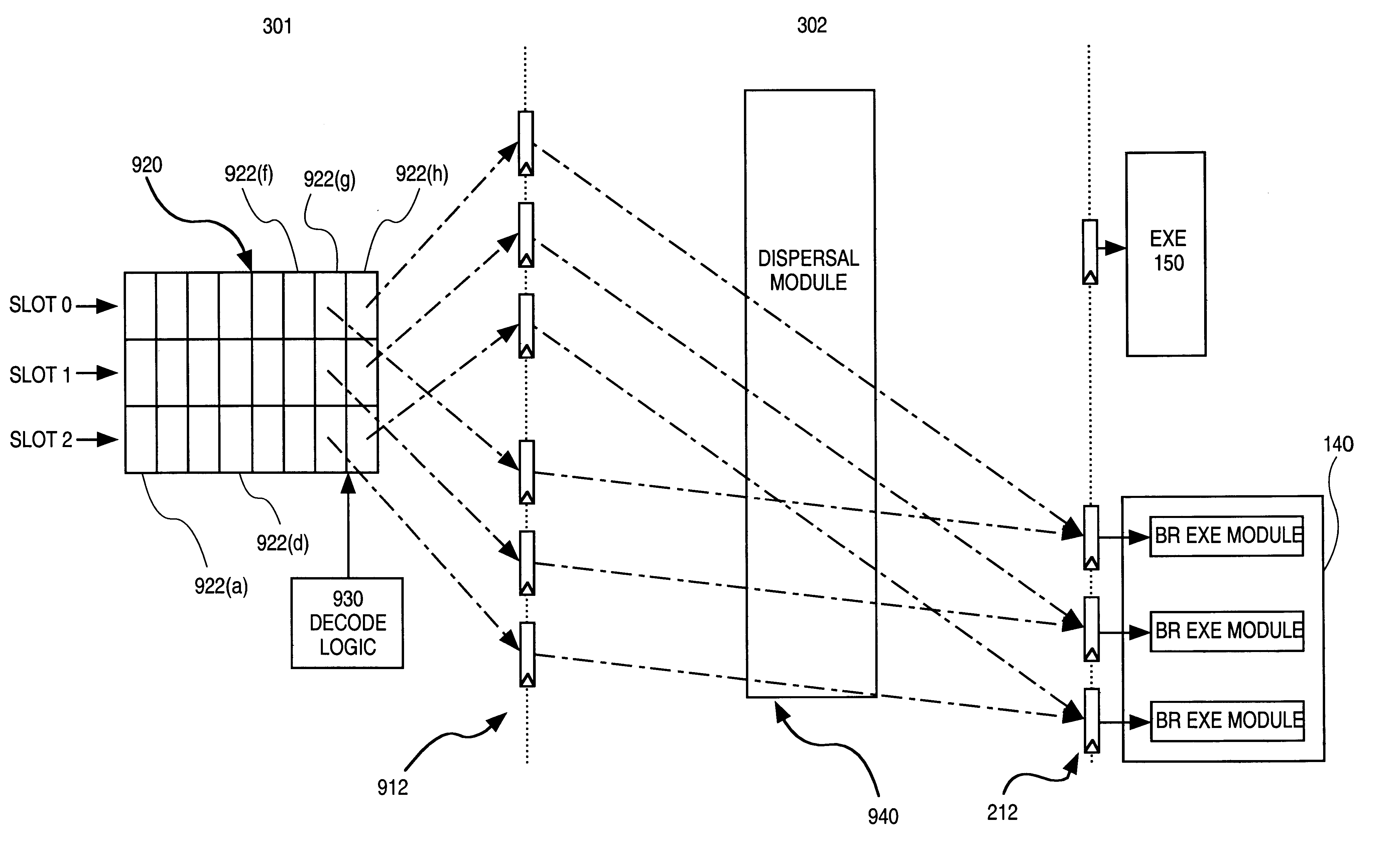
InactiveUS6240510B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsProcessing InstructionParallel computing
A system is provided for processing concurrently one or more branch instructions in an instruction bundle. The system includes multiple branch execution pipelines, each capable of executing a branch instruction to determine a branch direction, target address, and any side effects. Linking logic receives the resolved branch information and identifies a first branch instruction in execution order for which the branch direction is taken.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Shared register architecture for a dual-instruction-set CPU to facilitate data exchange between the instruction sets
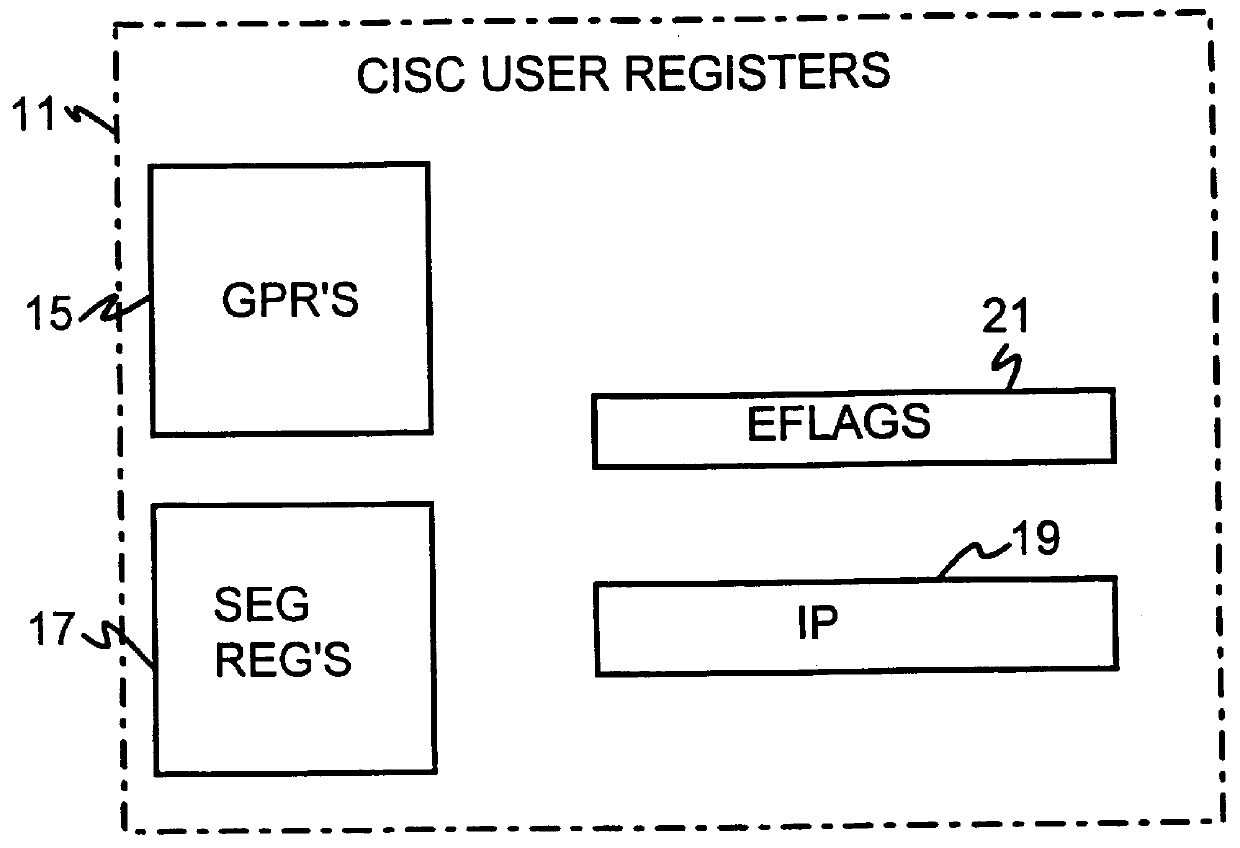
A dual-instruction set central processing unit (CPU) is capable of executing instructions from a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set and from a complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set. Data and address information may be to transferred from a CISC program to a RISC program running on the CPU by using shared registers. The architecturally-defined registers in the CISC instruction set are merged or folded into some of the architecturally-defined registers in the RISC architecture so that these merged registers are shared by the two instructions sets. In particular, the flags or condition code registers defined by each architecture are merged together so that CISC instructions and RISC instructions will implicitly update the same merged flags register when performing computational instructions. The RISC and CISC registers are folded together so that the CISC flags are at one end of the register while the frequently used RISC flags are at the other end, but the RISC instructions can read or write any bit in the merged register. The CISC code segment base address is stored in the RISC branch count register, while the CISC floating point instruction address is stored in the RISC branch link register. The general-purpose registers (GPR's) are also merged together, allowing a CISC program to pass data to a RISC program merely by writing one of its GPR's, switching control to the RISC program, and the RISC program reading one of its GPR's that is merged with and corresponds to the CISC GPR that was written to by the CISC program.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mechanisms to avoid inefficient core hopping and provide hardware assisted low-power state selection
InactiveUS20110161627A1Energy efficient ICTConditional code generationPower Management UnitComputer science
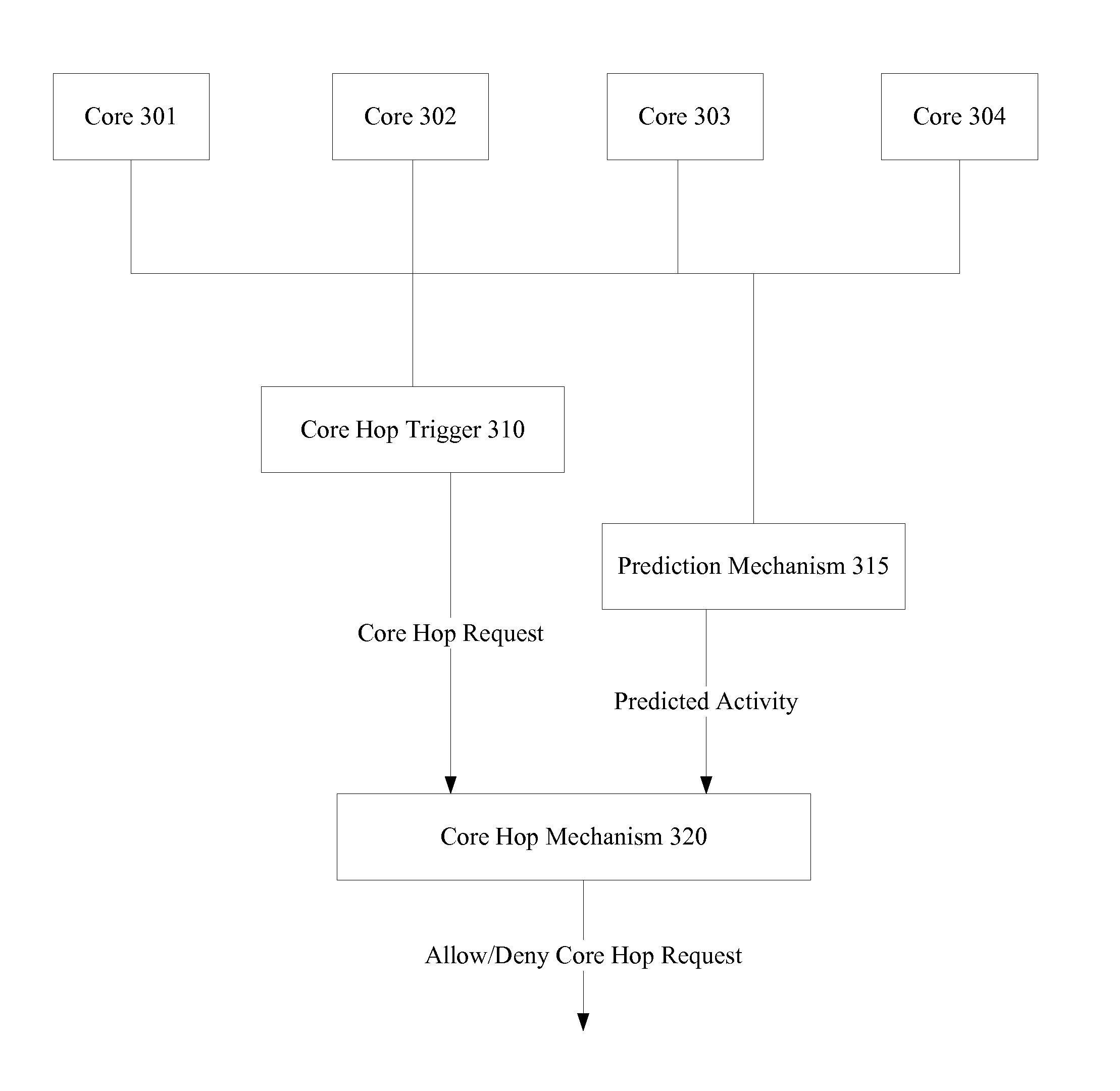
An apparatus and method is described herein for avoiding inefficient core hopping and providing hardware assisted power state selection. Future idle-activity of cores is predicted. If the residency of activity patterns for efficient core hop scenarios is predicted to be large enough, a core is determined to be efficient and allowed. However, if efficient activity patterns are not predicted to be resident for long enough—inefficient patterns are instead predicted to be resident for longer—then a core hop request is denied. As a result, designers may implement a policy for avoiding core hops that weighs the potential gain of the core hop, such as alleviation of a core hop condition, against a penalty for performing the core hop, such as a temporal penalty for the core hop. Separately, idle durations associated with hardware power states for cores may be predicted in hardware. Furthermore, accuracy of the idle duration prediction is determined. Upon receipt of a request for a core to enter a power state, a power management unit may select either the hardware predicted power state, if the accuracy is high enough, or utilize the requested power state, if the accuracy of the hardware prediction is not high enough.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processor and method that accelerate evaluation of pairs of condition-setting and branch instructions
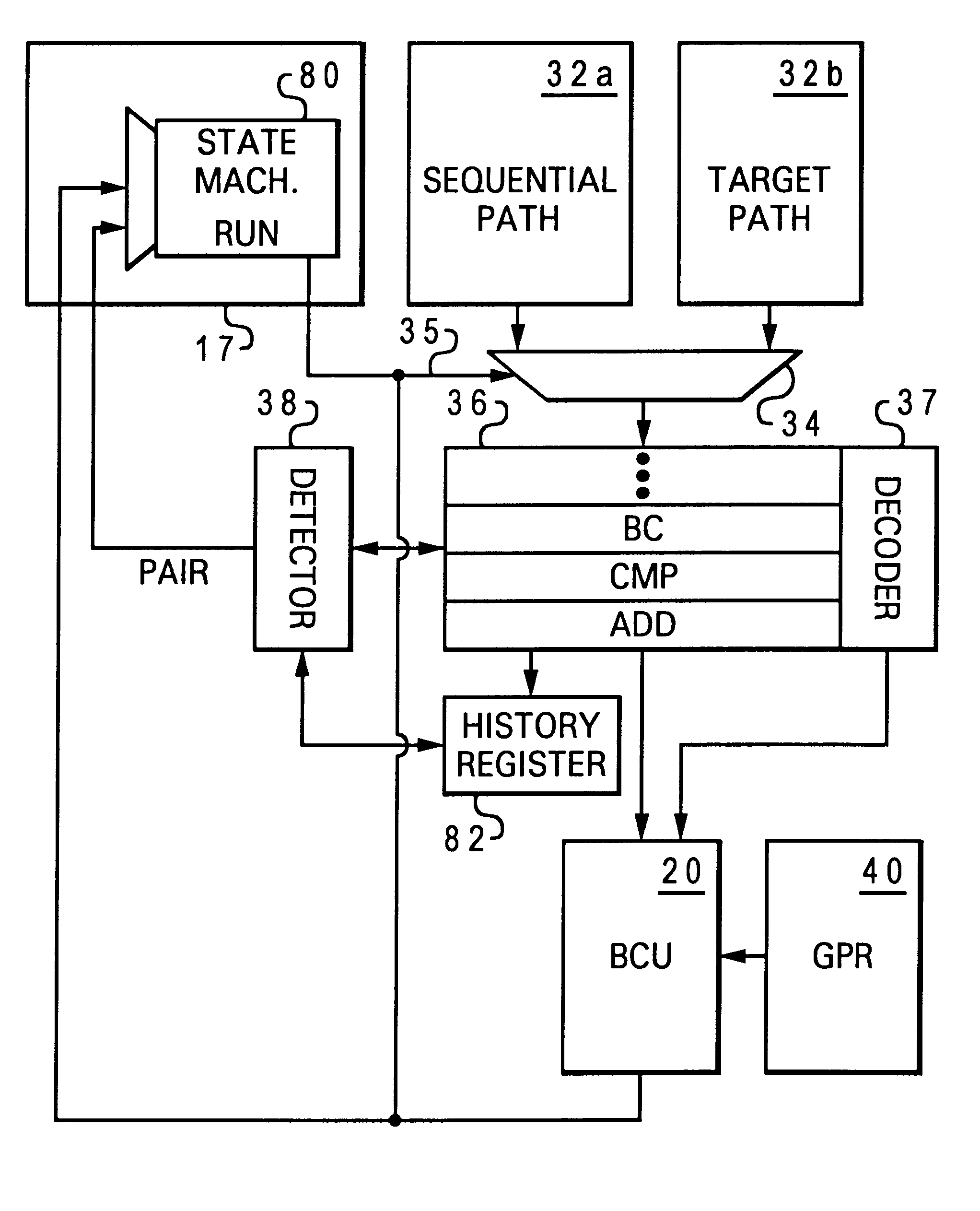
InactiveUS6598153B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsImage resolutionExecution unit
A processor that promotes accelerated resolution of conditional branch instructions includes an instruction sequencer that fetches a plurality of instructions and a detector that detects, among the plurality of fetched instructions, a condition-setting instruction and a conditional branch instruction that depends upon the condition-setting instruction. The processor further includes a decoder that decodes the conditional branch instruction to produce a decoded condition type and an execution unit. In response to the detection of the condition-setting instruction and the conditional branch instruction, the execution unit resolves the conditional branch instruction by evaluating the condition-setting instruction and the decoded condition type in a single operation. Because the condition code bits are not computed or stored as an intermediate result as in prior art processors, branch resolution is accelerated.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Rapid execution of FCMOV following FCOMI by storing comparison result in temporary register in floating point unit
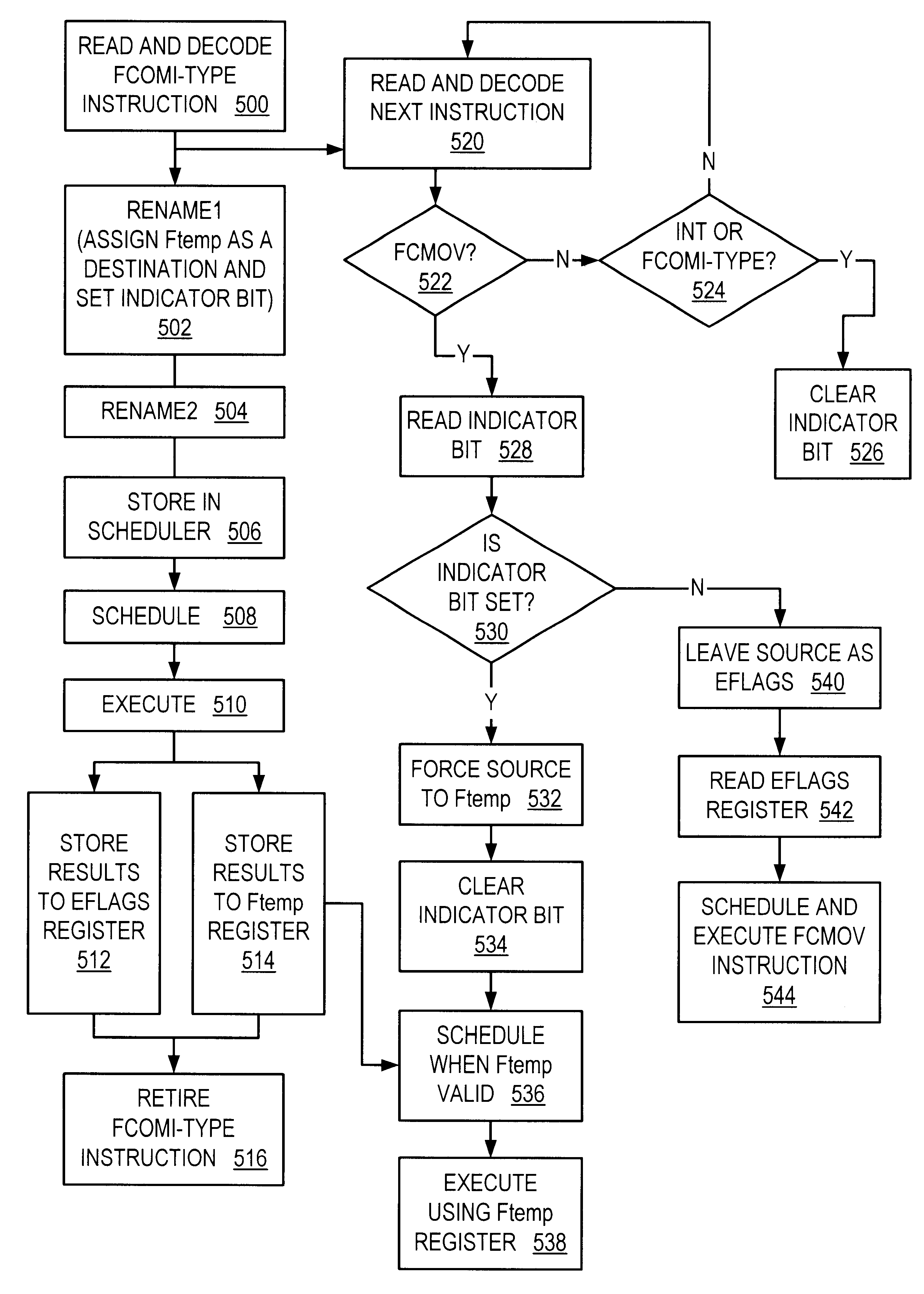
InactiveUS6393555B1Conditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerFloating-point unit
A microprocessor with a floating point unit configured to rapidly execute floating point compare (FCOMI) type instructions that are followed by floating point conditional move (FCMOV) type instructions is disclosed. FCOMI-type instructions, which normally store their results to integer status flag registers, are modified to store a copy of their results to a temporary register located within the floating point unit. If an FCMOV-type instruction is detected following an FCOMI-type instruction, then the FCMOV-type instruction's source for flag information is changed from the integer flag register to the temporary register. FCMOV-type instructions are thereby able to execute earlier because they need not wait for the integer flags to be read from the integer portion of the microprocessor. A computer system and method for rapidly executing FCOMI-type instructions followed by FCMOV-type instructions are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
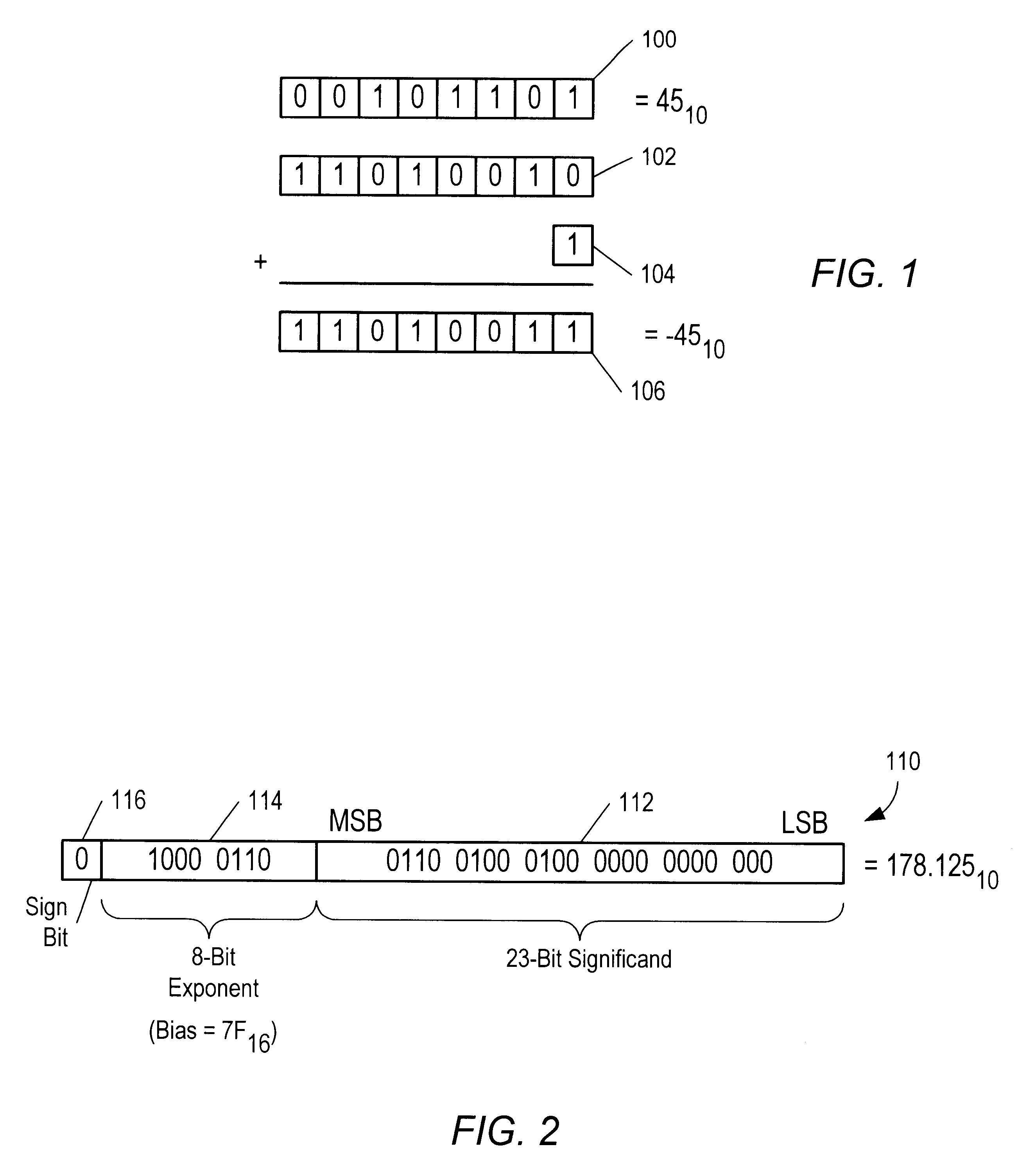
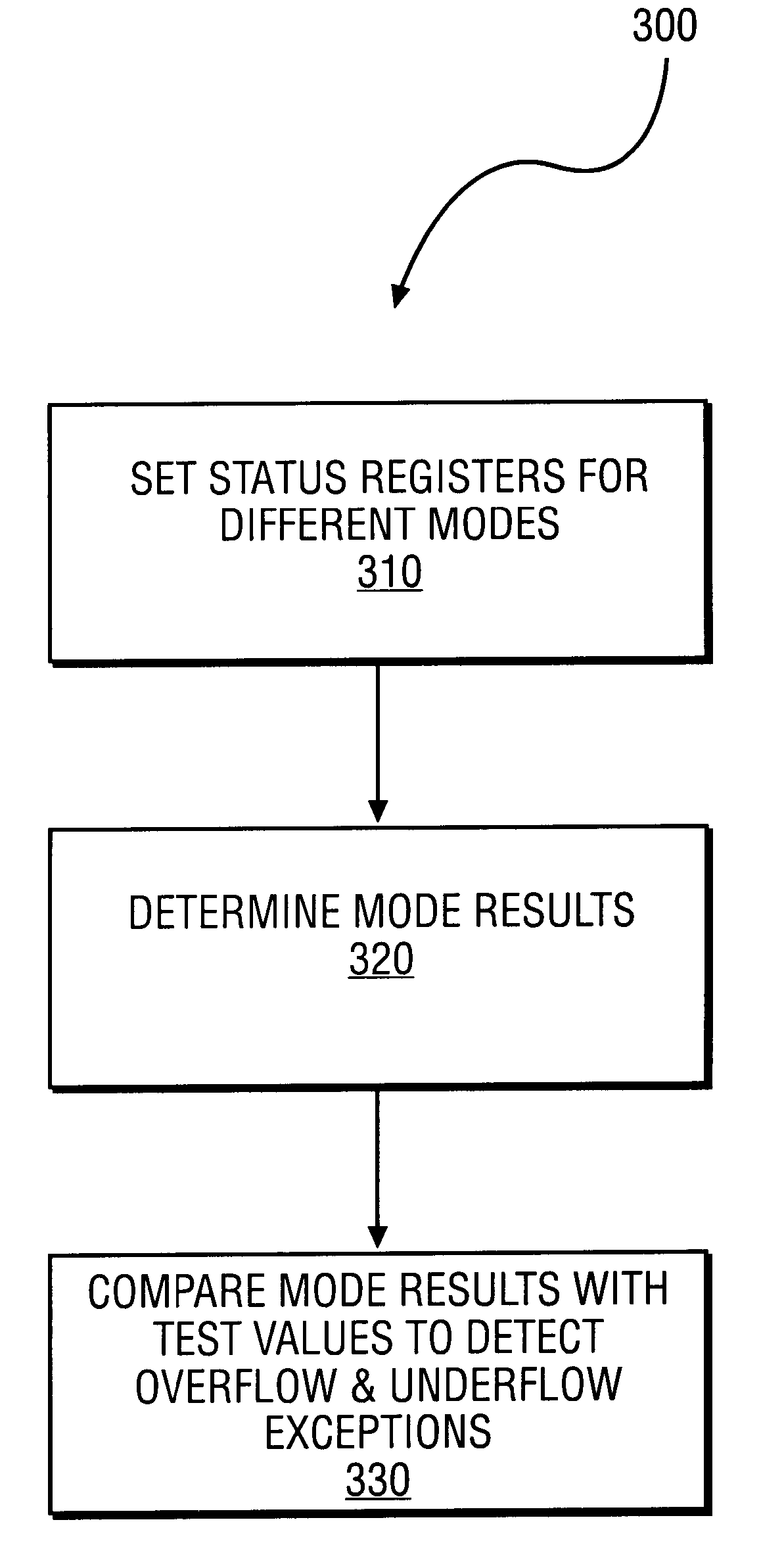
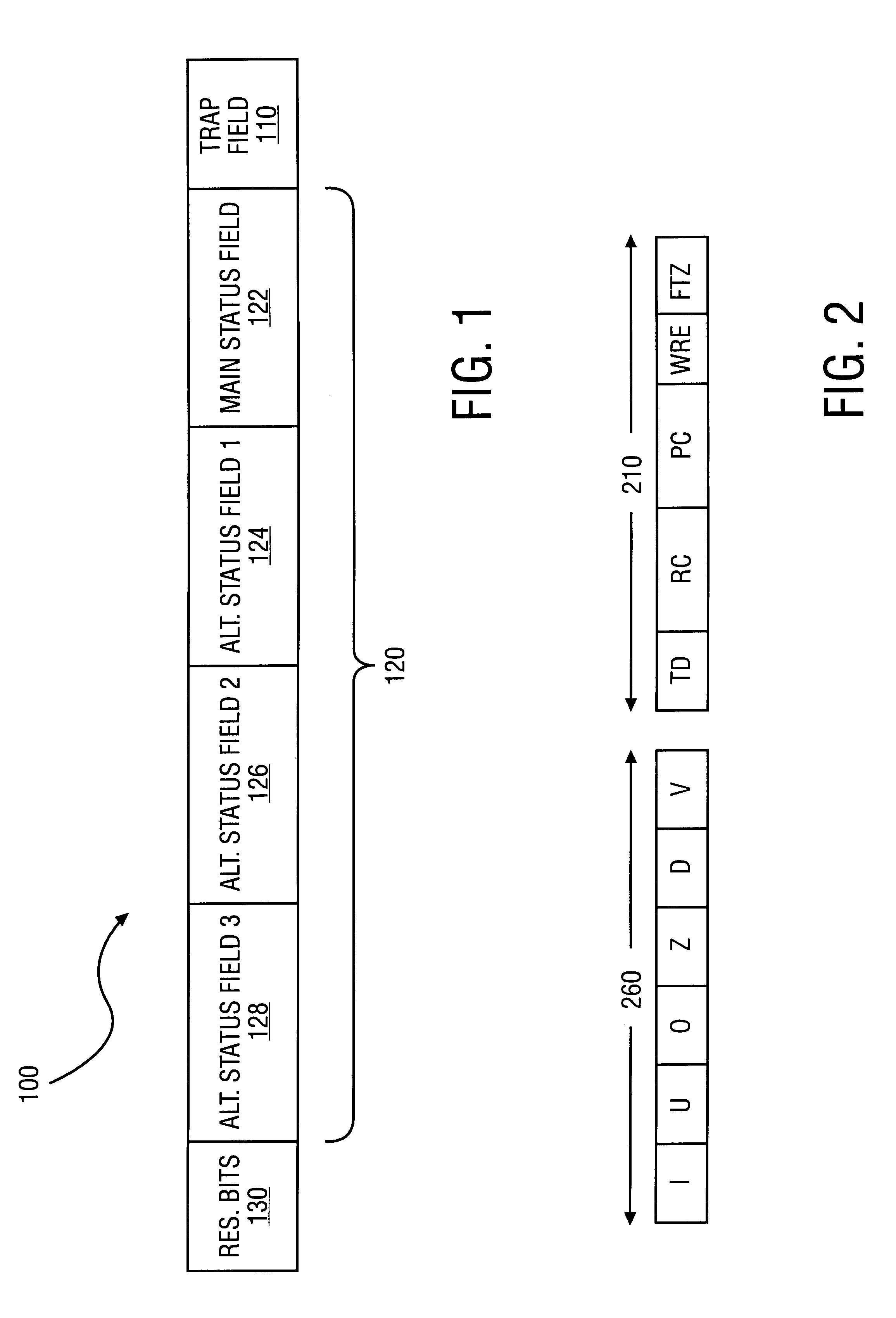
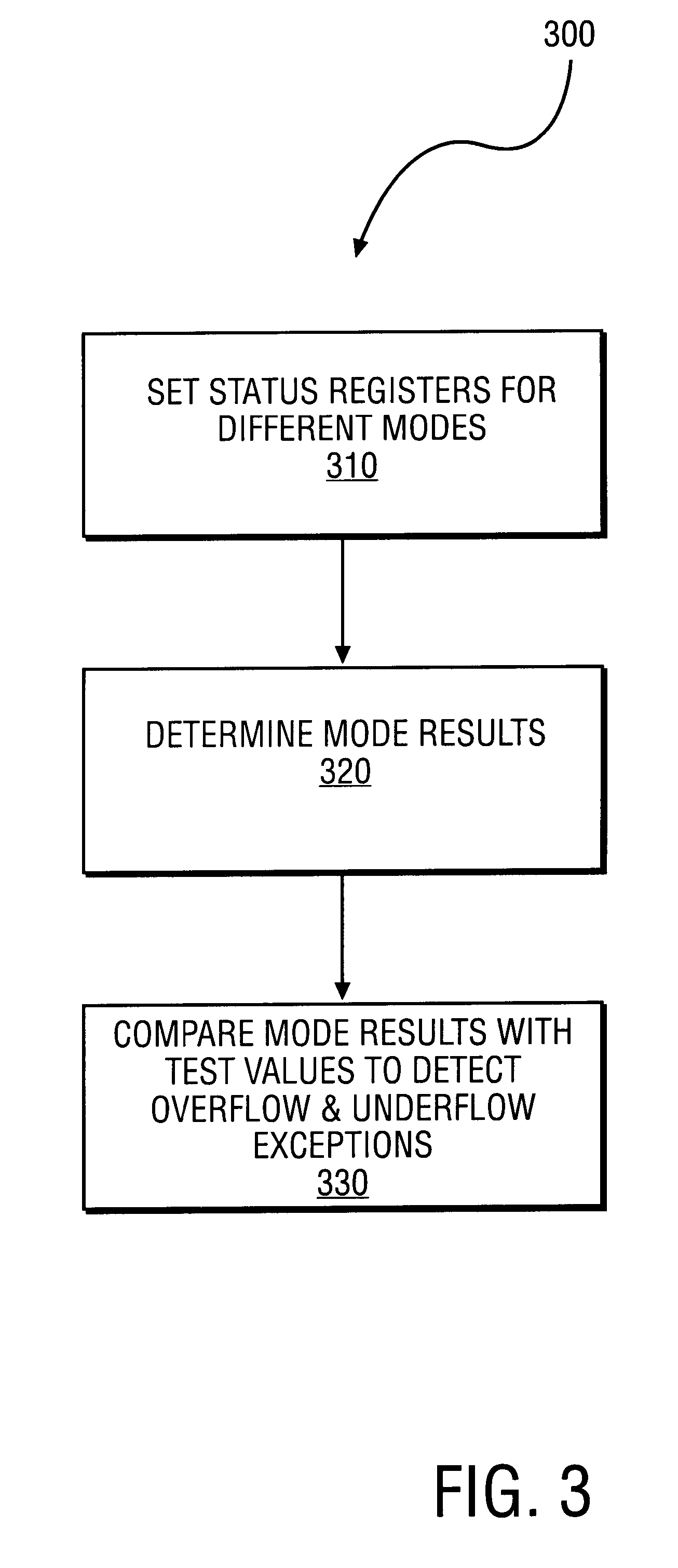
Method to detect IEEE overflow and underflow conditions
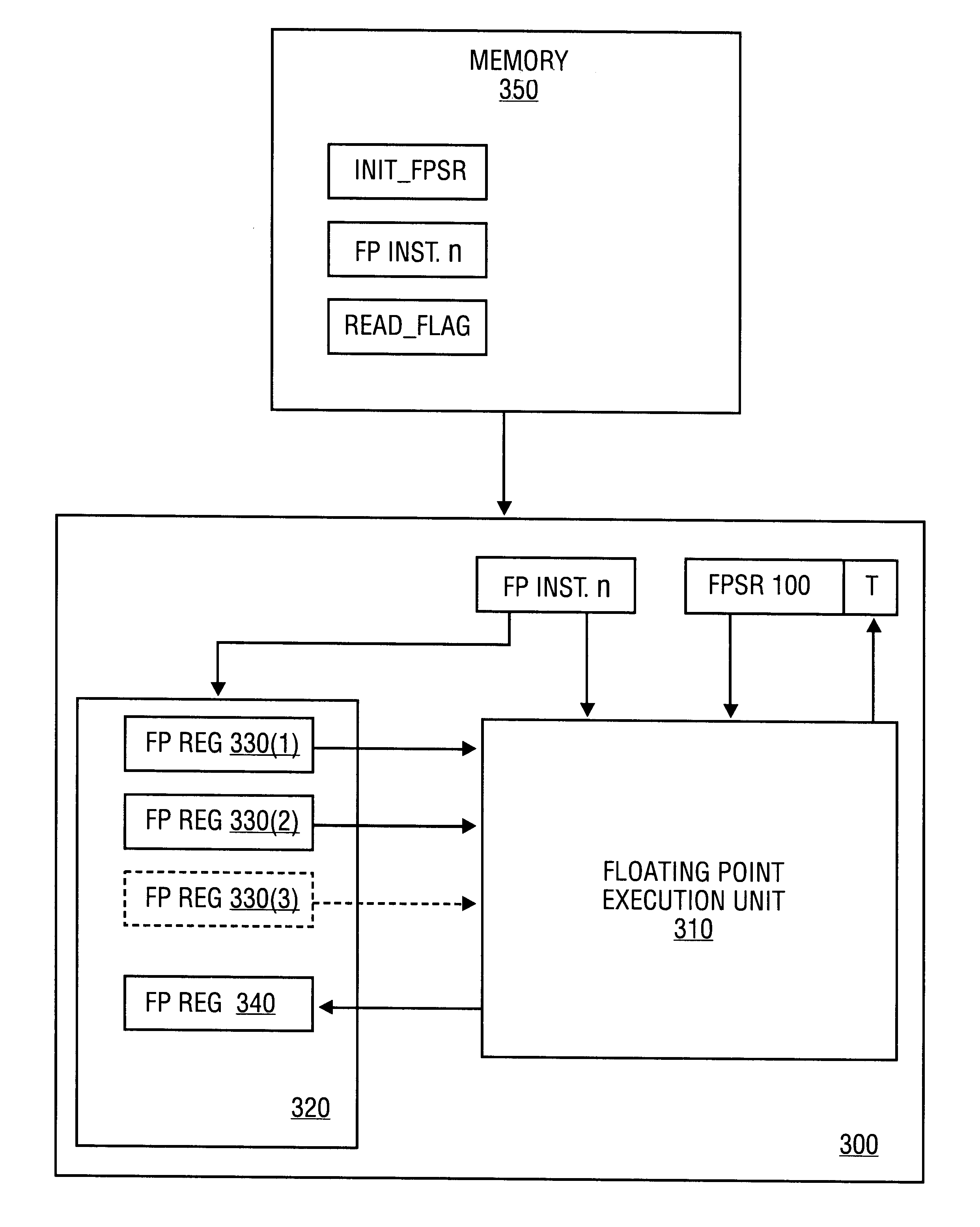
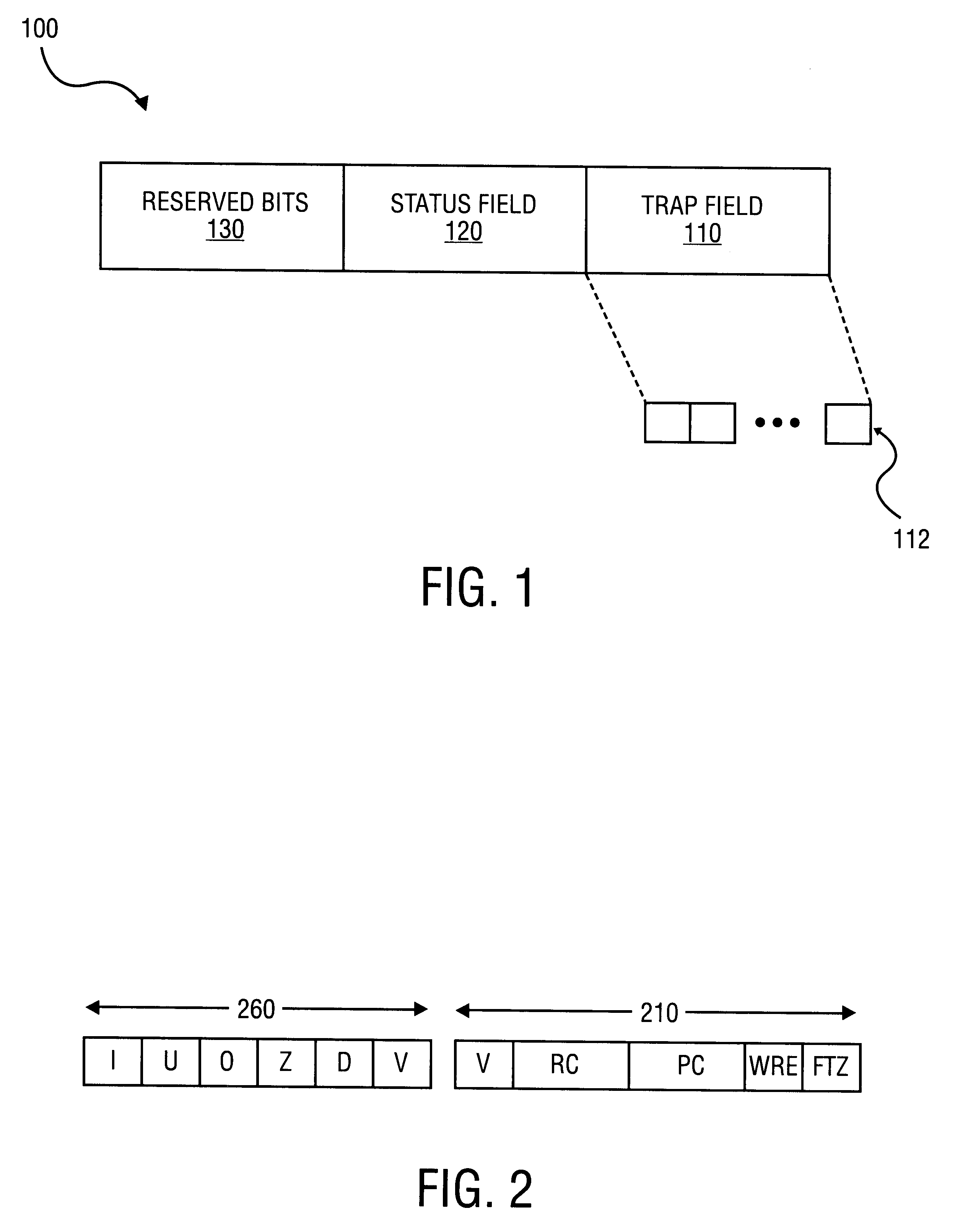
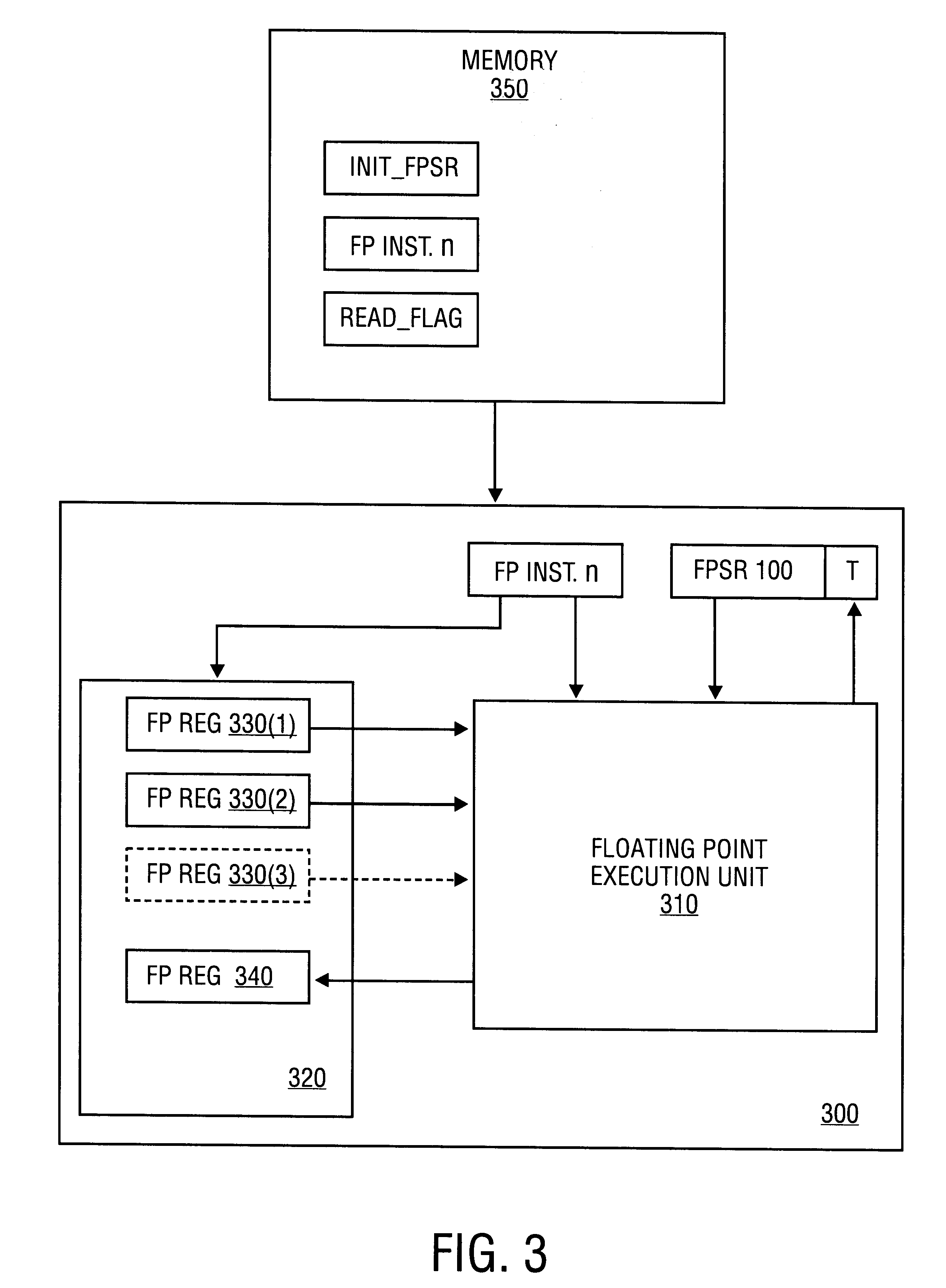
InactiveUS6219685B1Conditional code generationNext instruction address formationStatus registerComputer science
A method is disclosed for detecting overflow and underflow conditions using a status register having a main status field and first and second alternate status fields. The first and second alternate status fields are set to chop and wre modes, respectively, and chop and wre results are determined for an arithmetic operation using the first and second alternate status fields. The chop and wre results are tested against test values to determine whether an overflow or underflow condition exists.
Owner:INTEL CORP
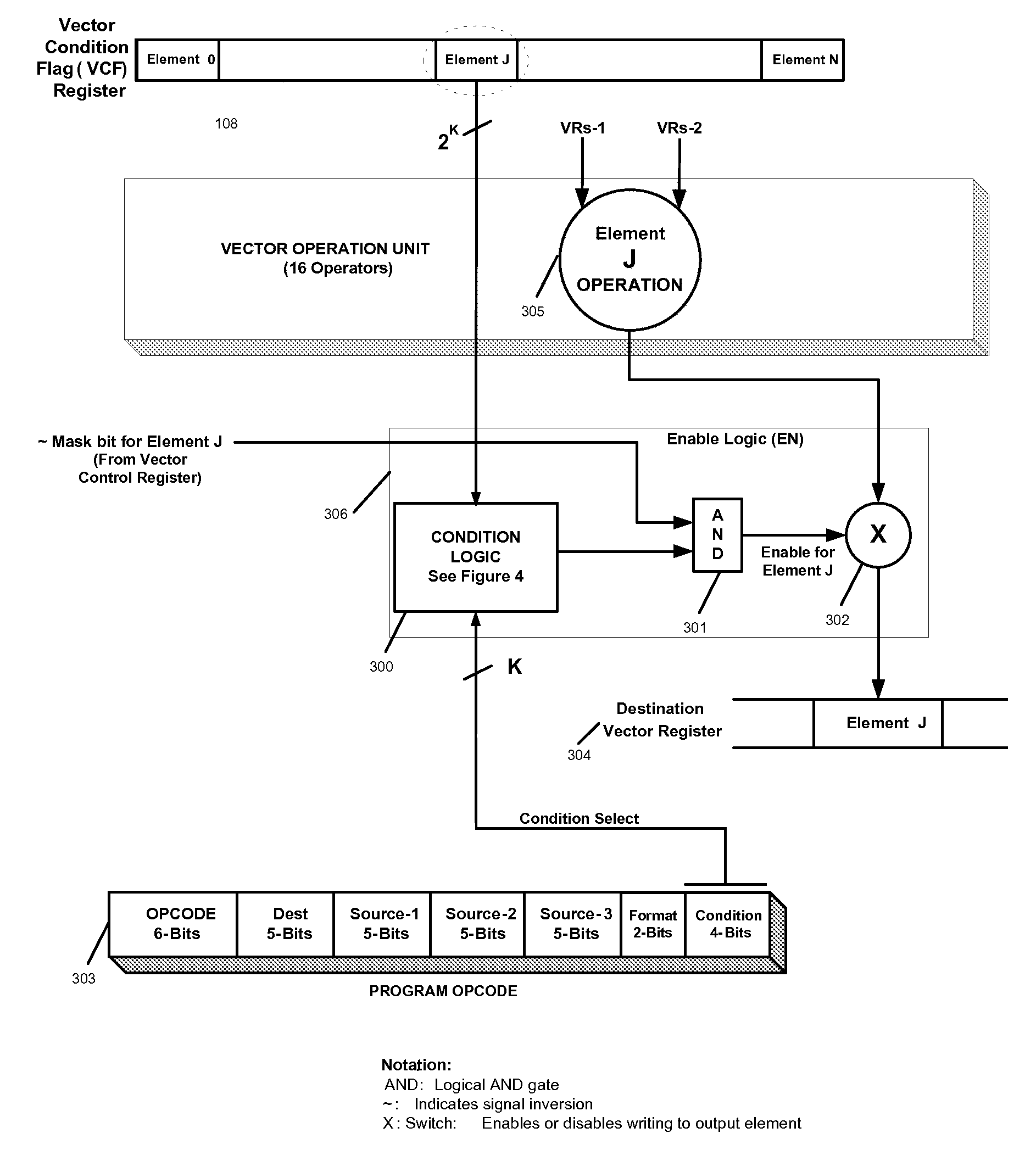
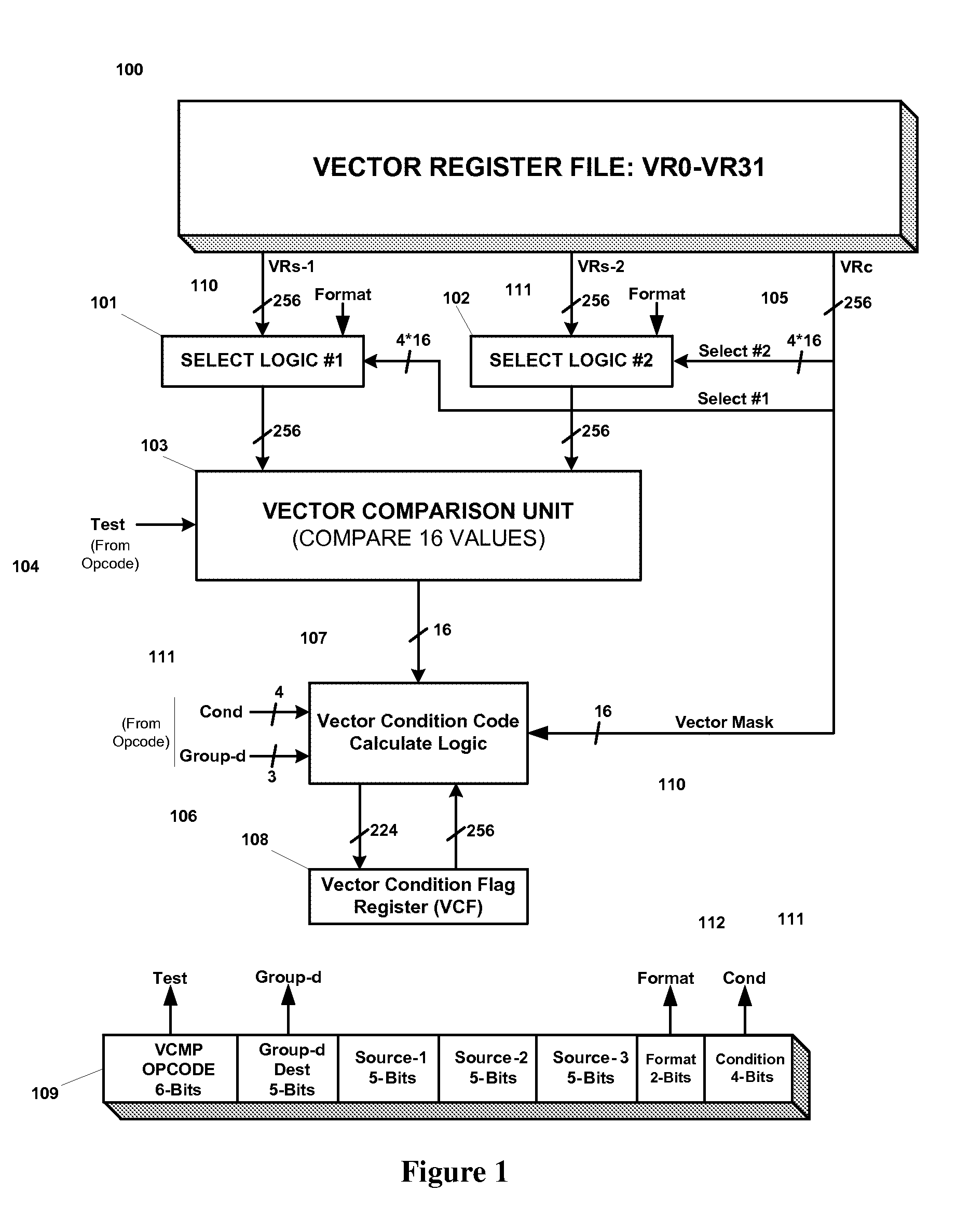
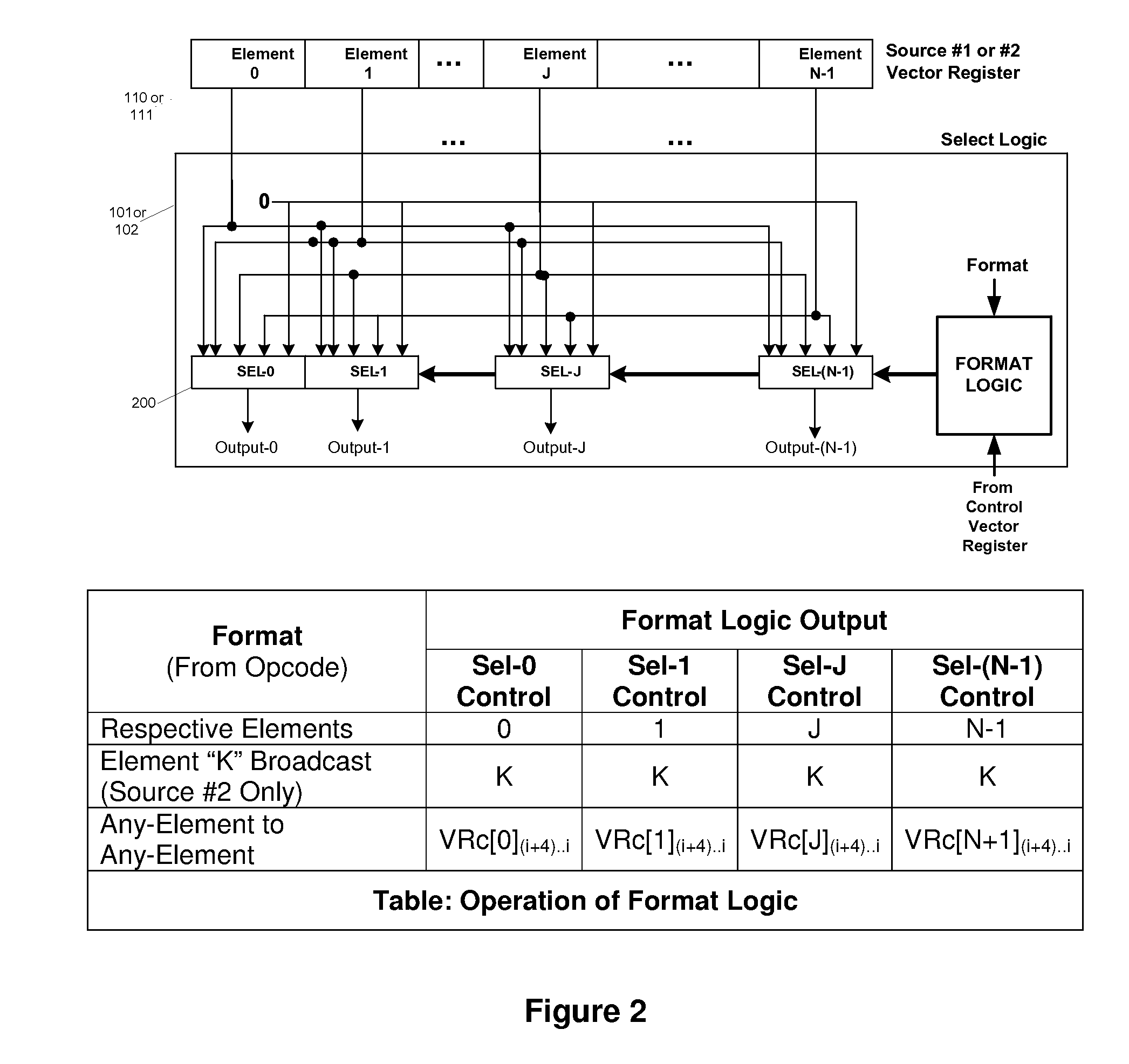
Efficient handling of vector high-level language conditional constructs in a SIMD processor
InactiveUS7793084B1Minimize the numberLow costConditional code generationDigital computer detailsVector elementSimd processing
The present invention provides an efficient method to implement nested if-then-else conditional statements in a SIMD processor, which requires only one vector compare instruction for both if and else parts of the conditional construct. No stack and stack-handling instructions are needed for vector condition codes. Two condition code flag bits representing if and else parts of testing per element provide for nesting of multiple if-then-else. All SIMD instructions are conditional including the vector compare instruction, and this provides a method for aggregating multiple conditions in nested if-then-else statements. M full levels of if-then-else nesting requires (2M−1) nodes or vector test instructions and 2M+1 condition code flags per vector element. Also, capability to compare any element of first source vector register with any element of second source vector is provided.
Owner:CUE BIOTECH
Efficient Predicated Execution For Parallel Processors
ActiveUS20110078415A1Minimizes per-thread stateCost efficientConditional code generationRegister arrangementsOperandParallel processing
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
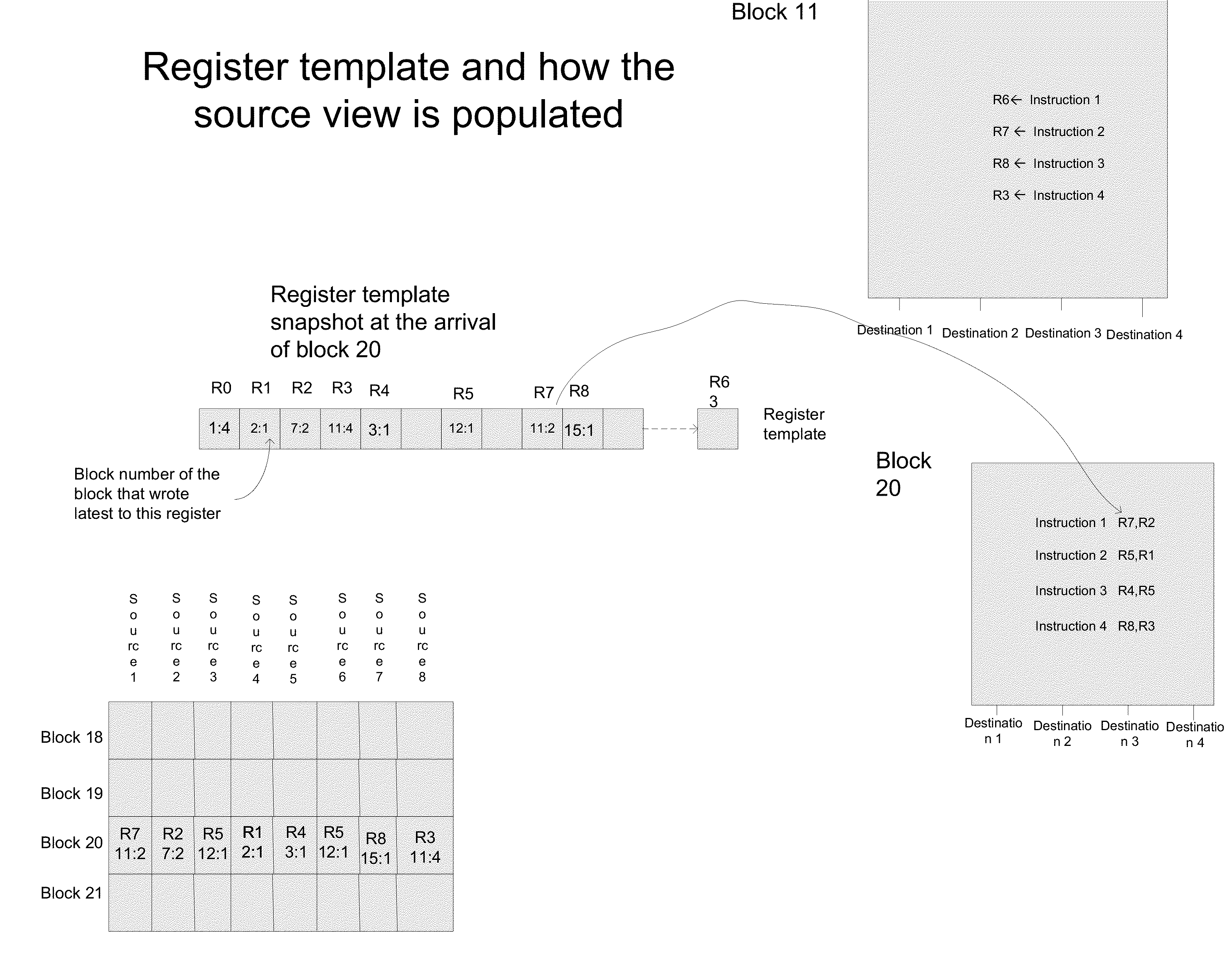
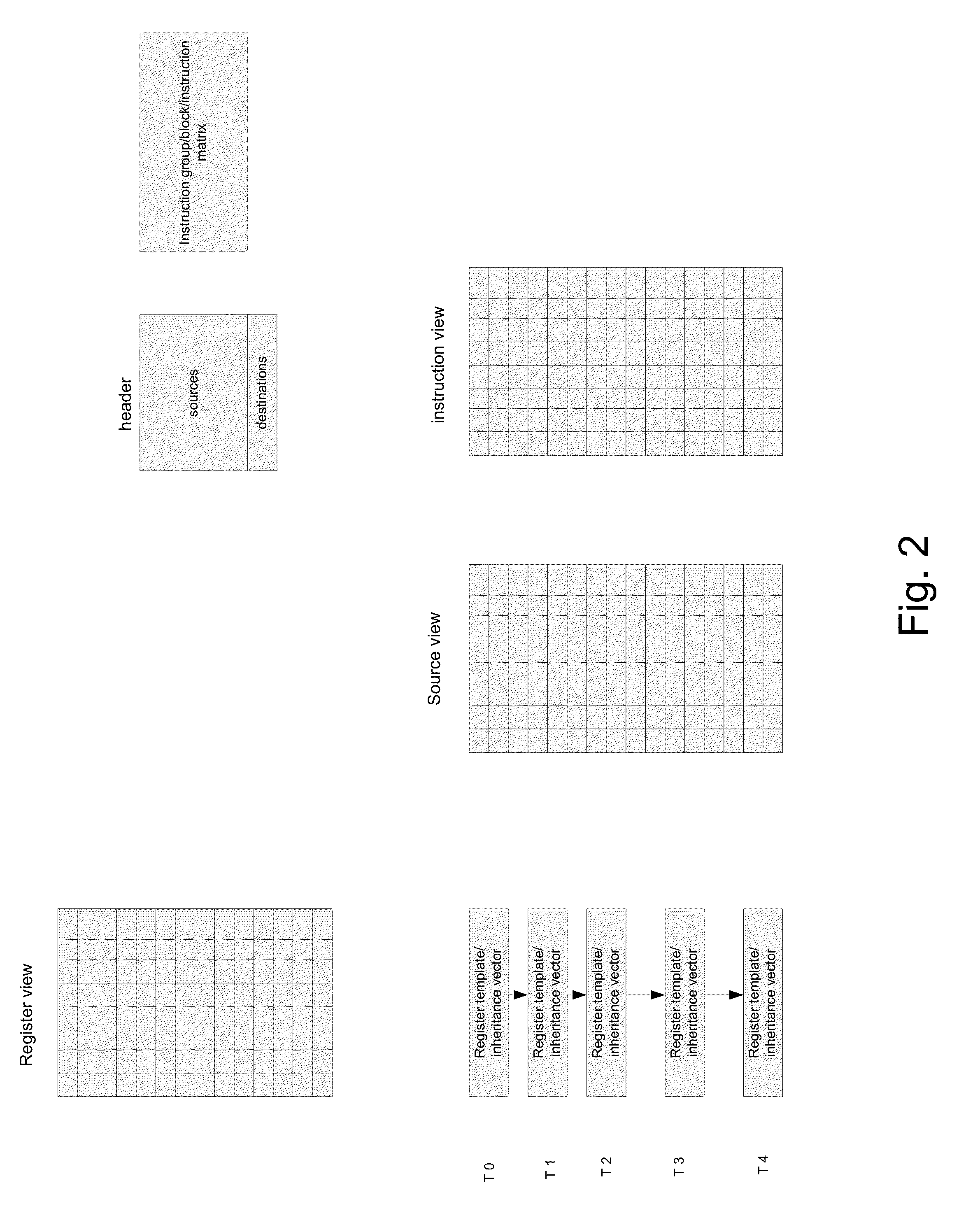
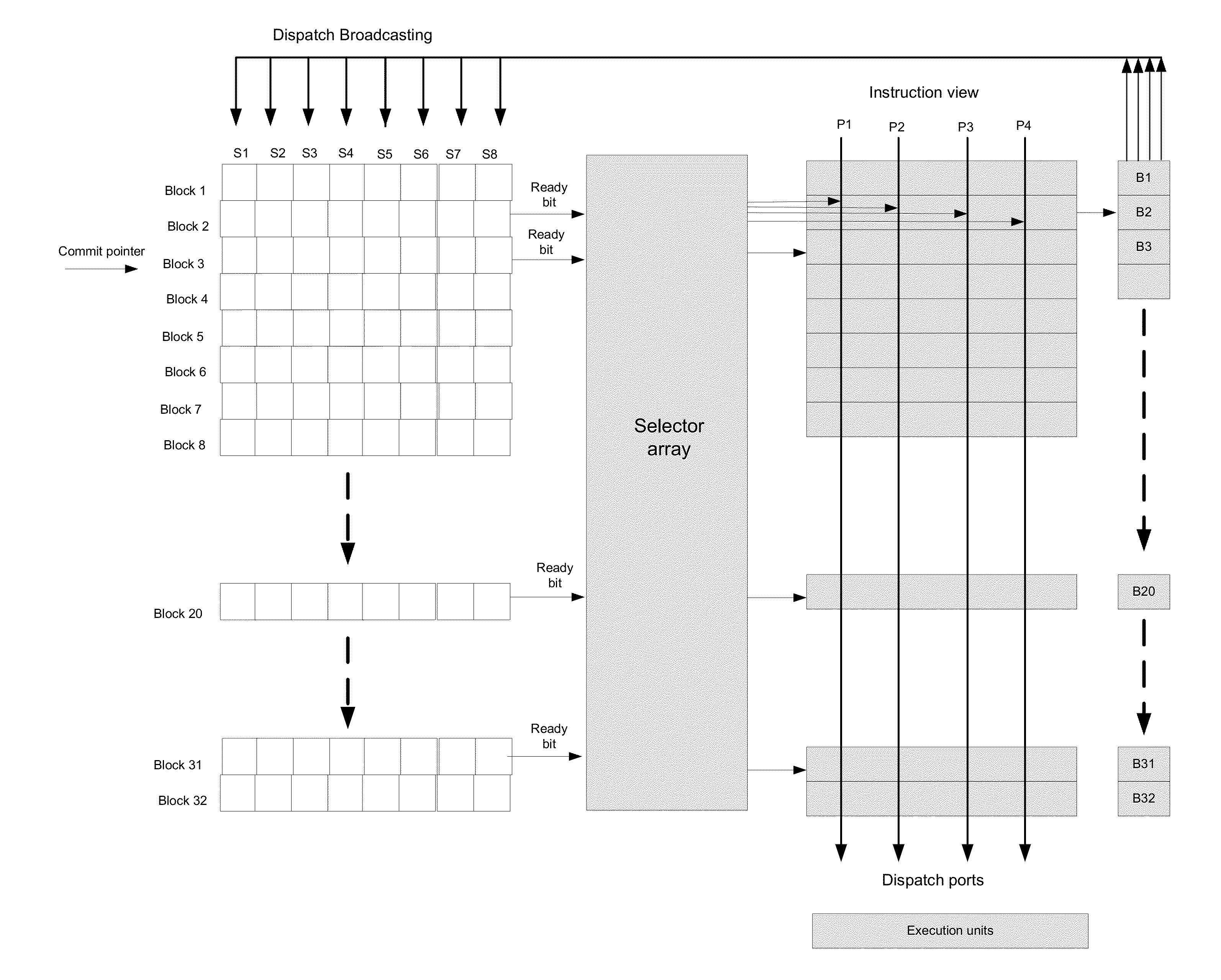
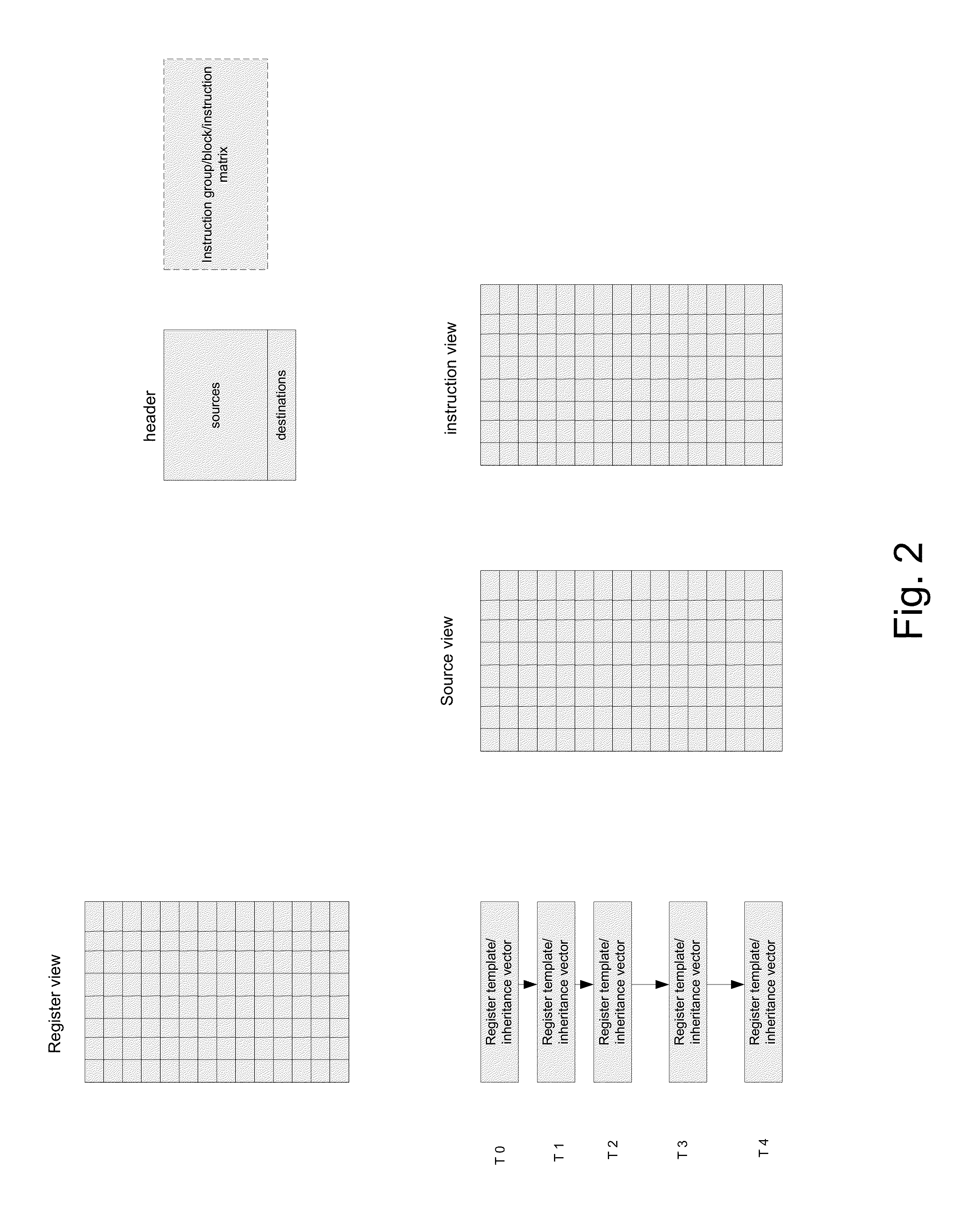
Method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure
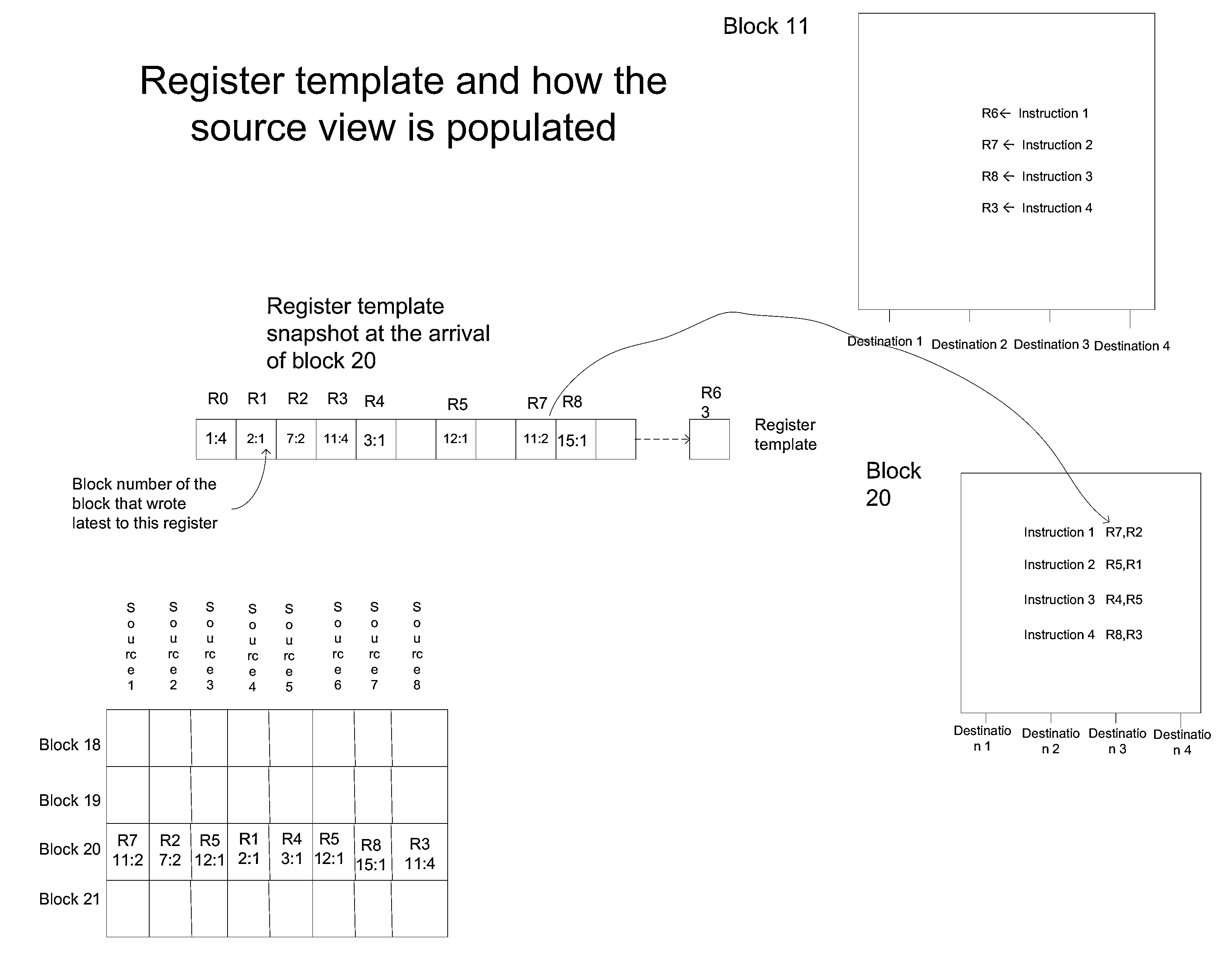
ActiveUS20140282601A1Conditional code generationProgram initiation/switchingParallel computingInstruction sequence
A method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; populating a block organized source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks as recorded by the plurality of register templates; upon dispatch of one block of the instruction blocks, broadcasting a number belonging to the one block to a column of the source view data structure that relates that block and marking the column accordingly; and updating the dependency information of remaining instruction blocks in accordance with the broadcast.
Owner:INTEL CORP
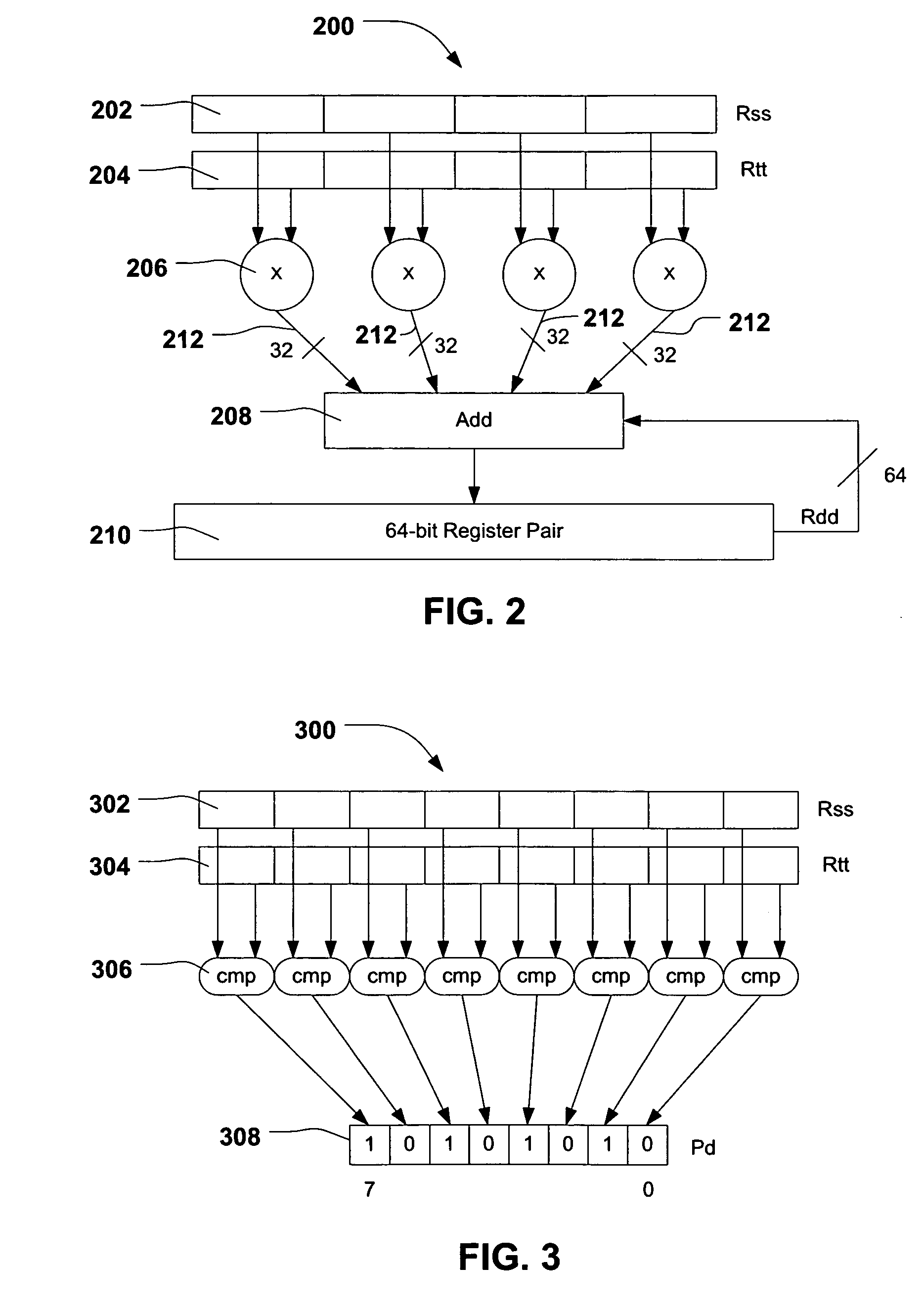
System and method of processing data using scalar/vector instructions
ActiveUS20080046683A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionConditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerCondition Code
A processor device is disclosed that includes a register file with a combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. The processor device utilizes the combined condition code register for scalar and vector operations. Further, a compare operation can store resulting bits in the combined condition code register and a conditional operation can utilize the combined condition code register bits for evaluating a condition.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Vector processor with special purpose registers and high speed memory access
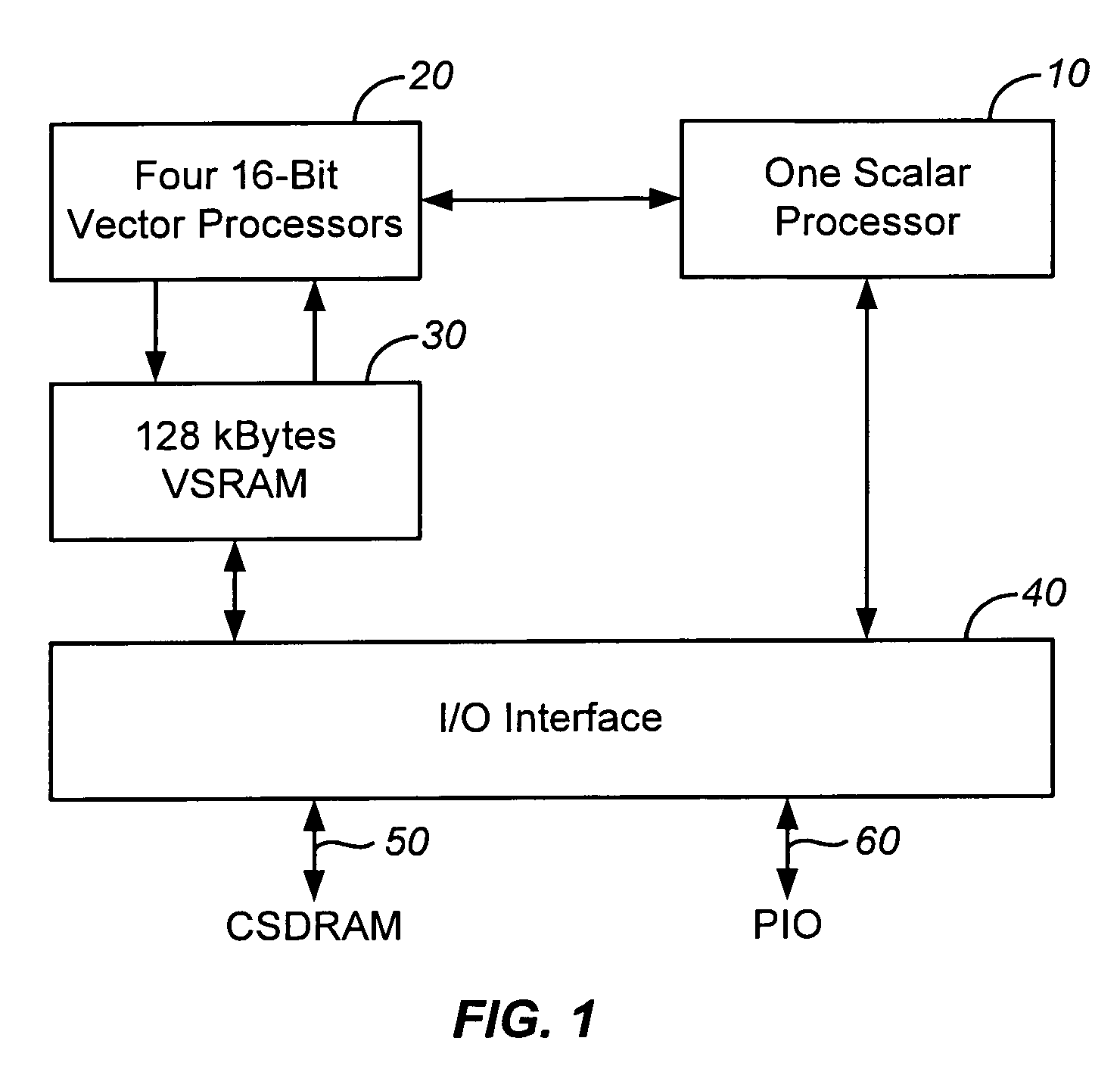
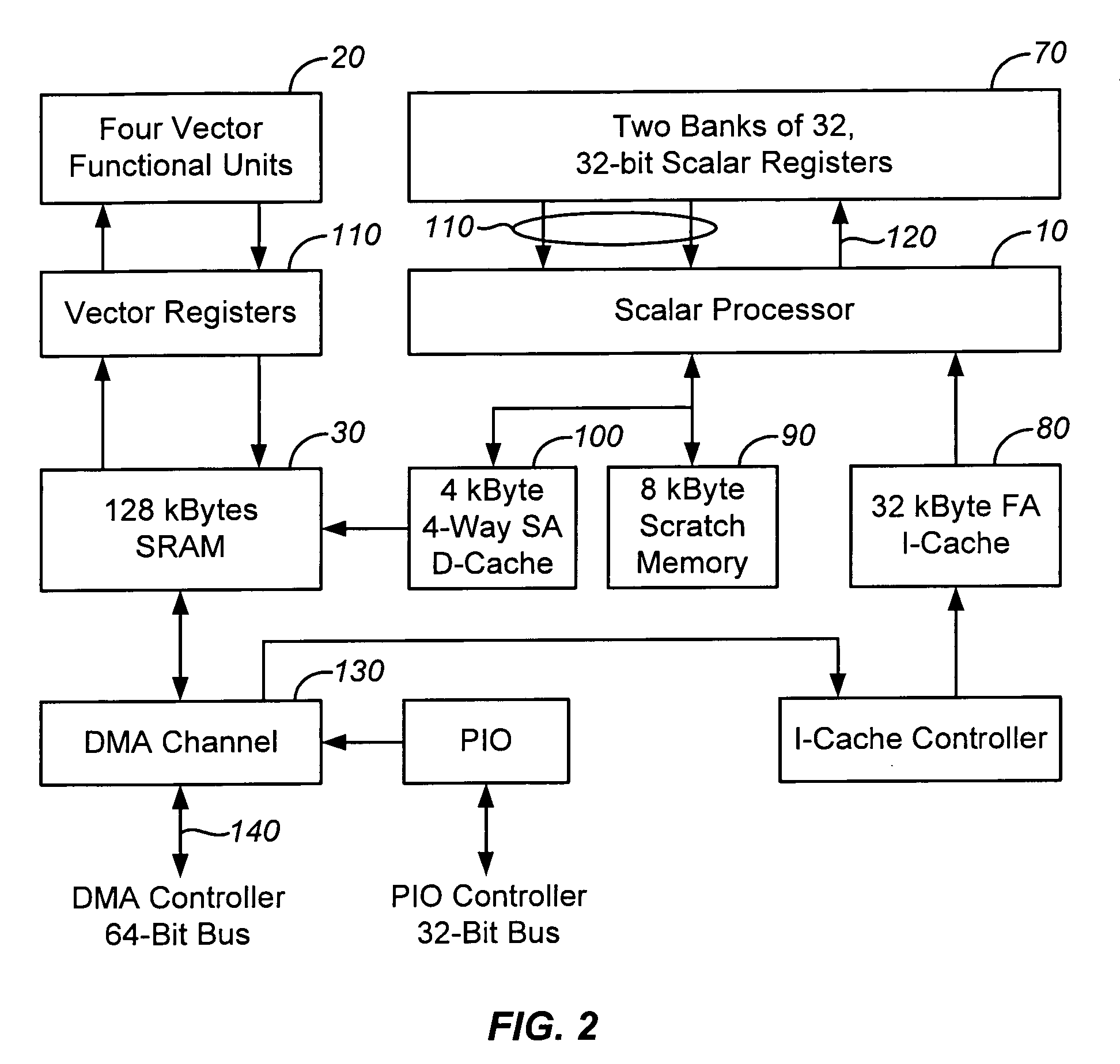
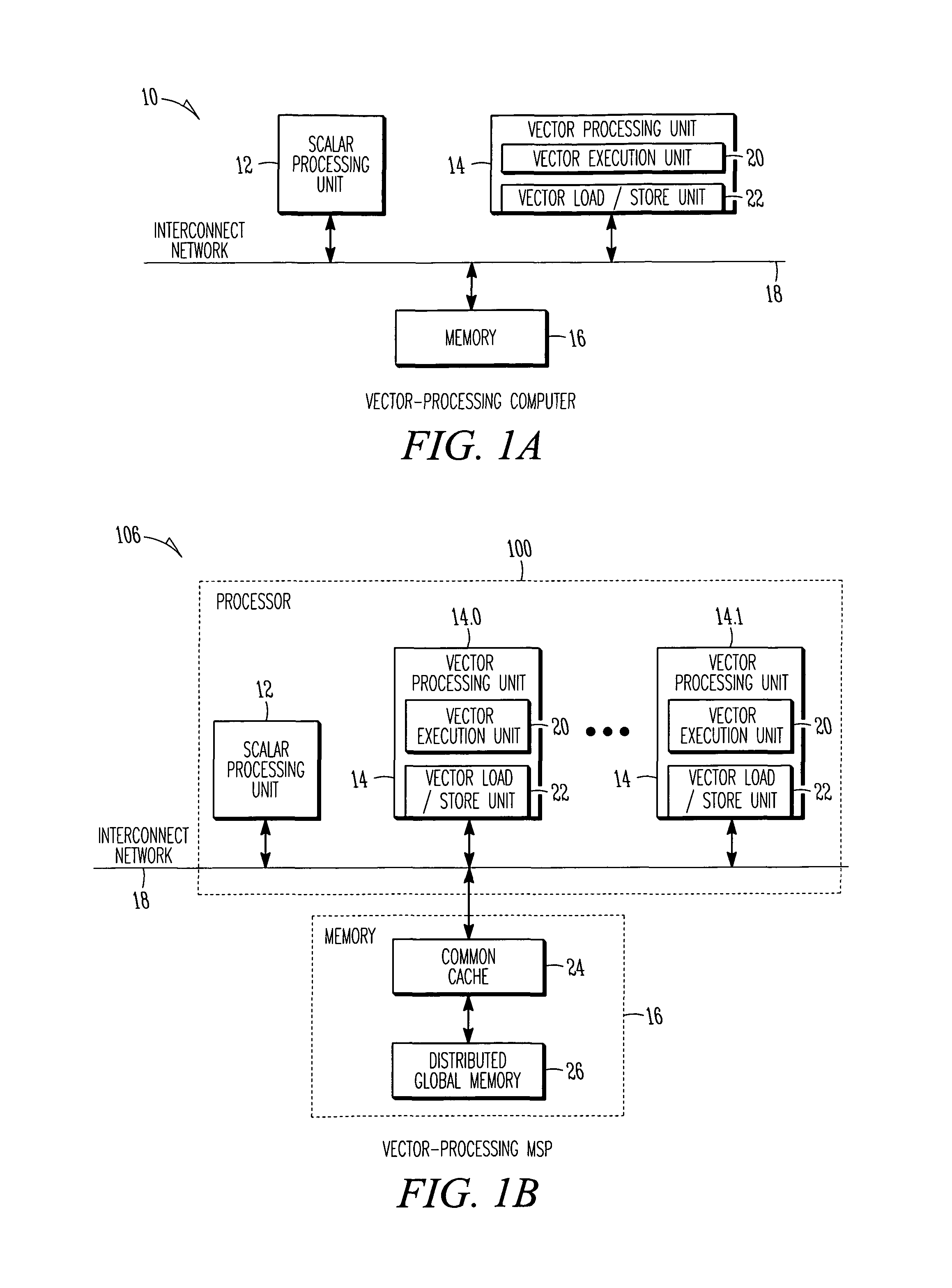
InactiveUS20060259737A1Limited instruction widthGreat instruction widthConditional code generationRegister arrangementsVector processorHigh speed memory
A vector processor includes a set of vector registers for storing data to be used in the execution of instructions and a vector functional unit coupled to the vector registers for executing instructions. The functional unit executes instructions using operation codes provided to it which operation codes include a field referencing a special register. The special register contains information about the length and starting point for each vector instruction. The processor includes a high speed memory access system to facilitate faster operation.
Owner:MEADLOCK JAMES W MEAD
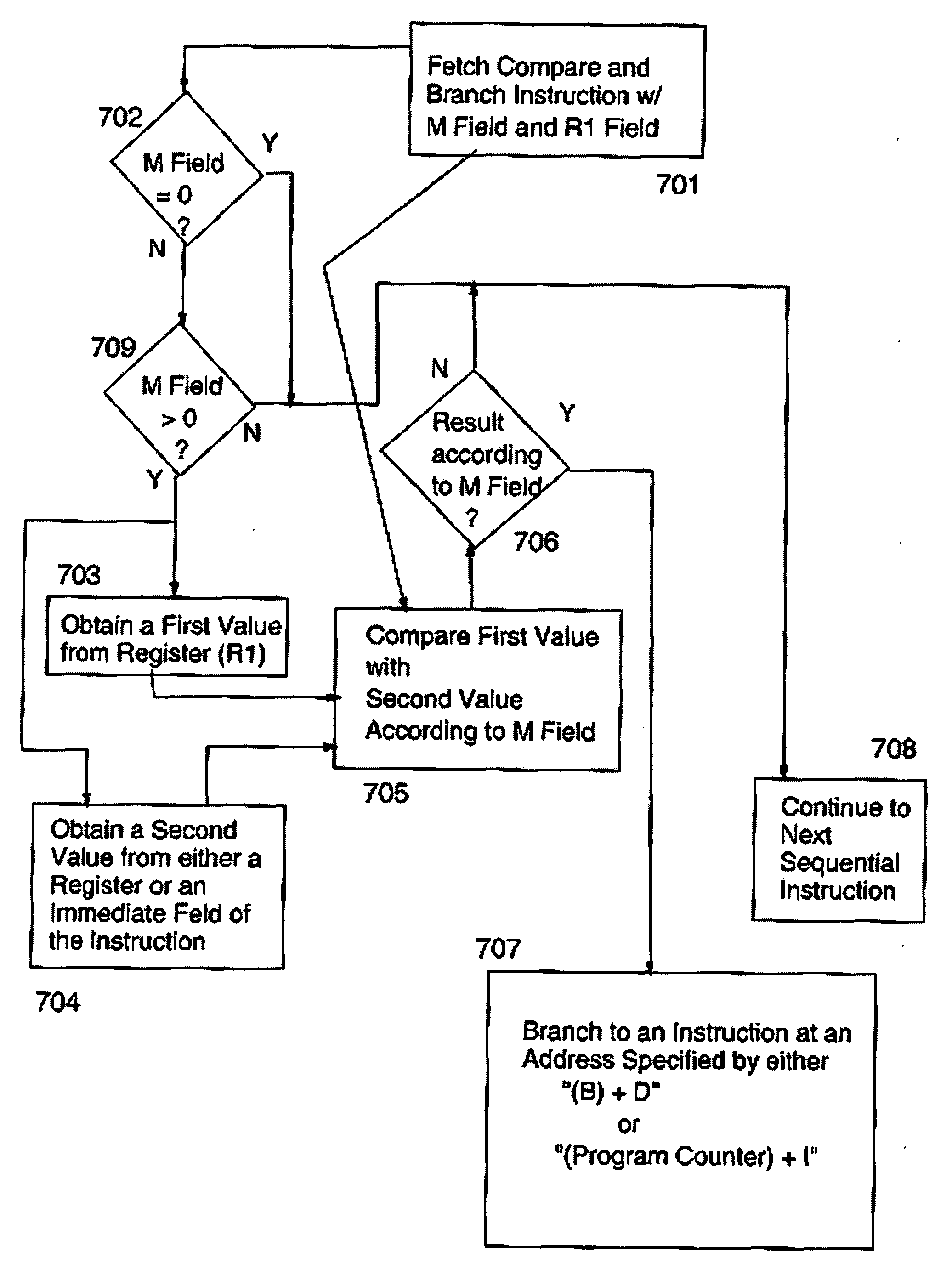
Compare and Branch Facility and Instruction Therefore
InactiveUS20090182983A1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsCondition CodeConditional branch
An atomic compare and branch instruction is executed that combines the function of a compare instruction having an option field with a conditional branch or jump instruction such that condition codes are preserved rather than setting condition codes to a value representative of the compare results. One comparand is obtained from any one of a memory location or an immediate field and the other comparand is obtained from a register field.
Owner:IBM CORP
Relaxed memory consistency model
ActiveUS8307194B1Conditional code generationProgram synchronisationData synchronizationClock synchronization
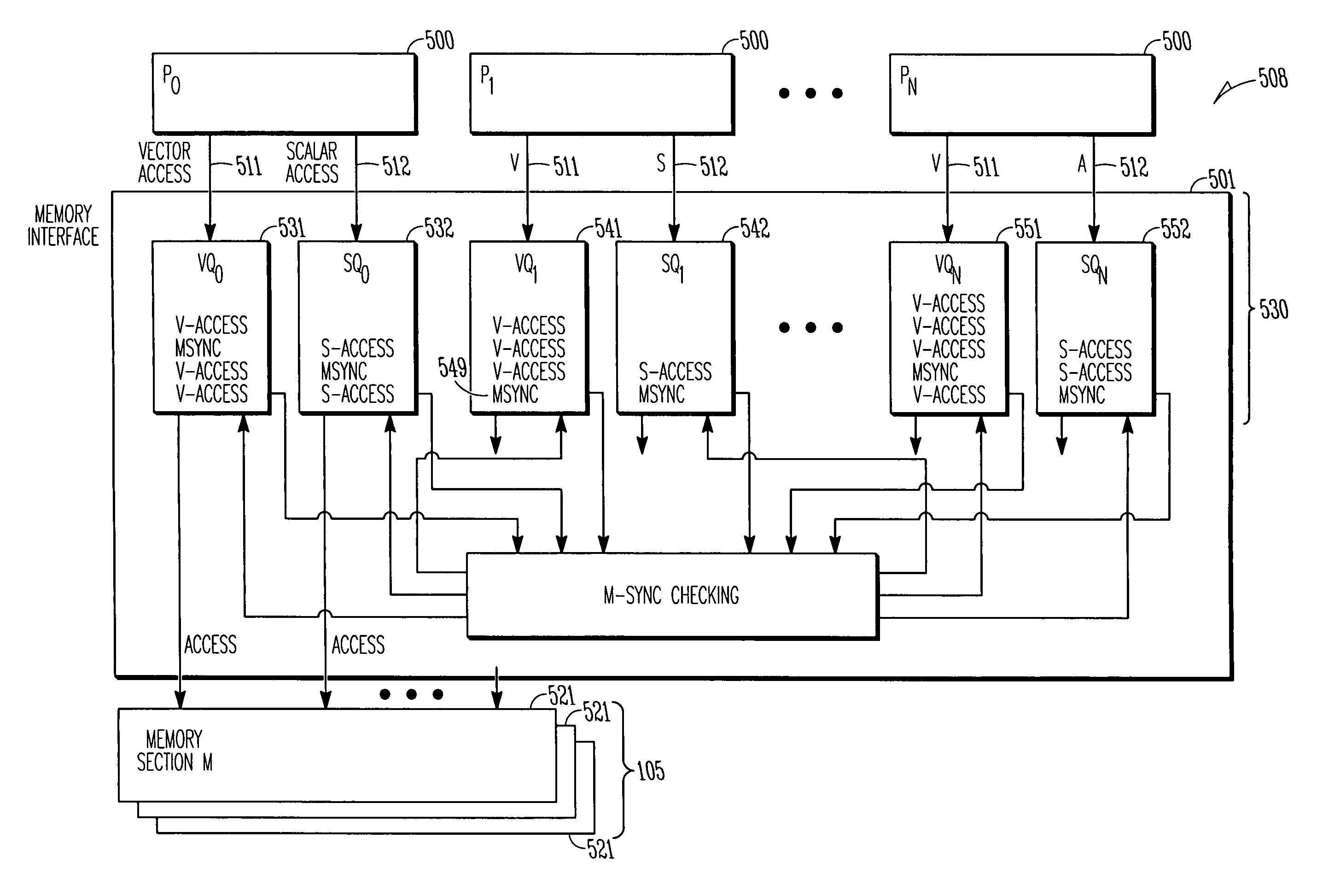
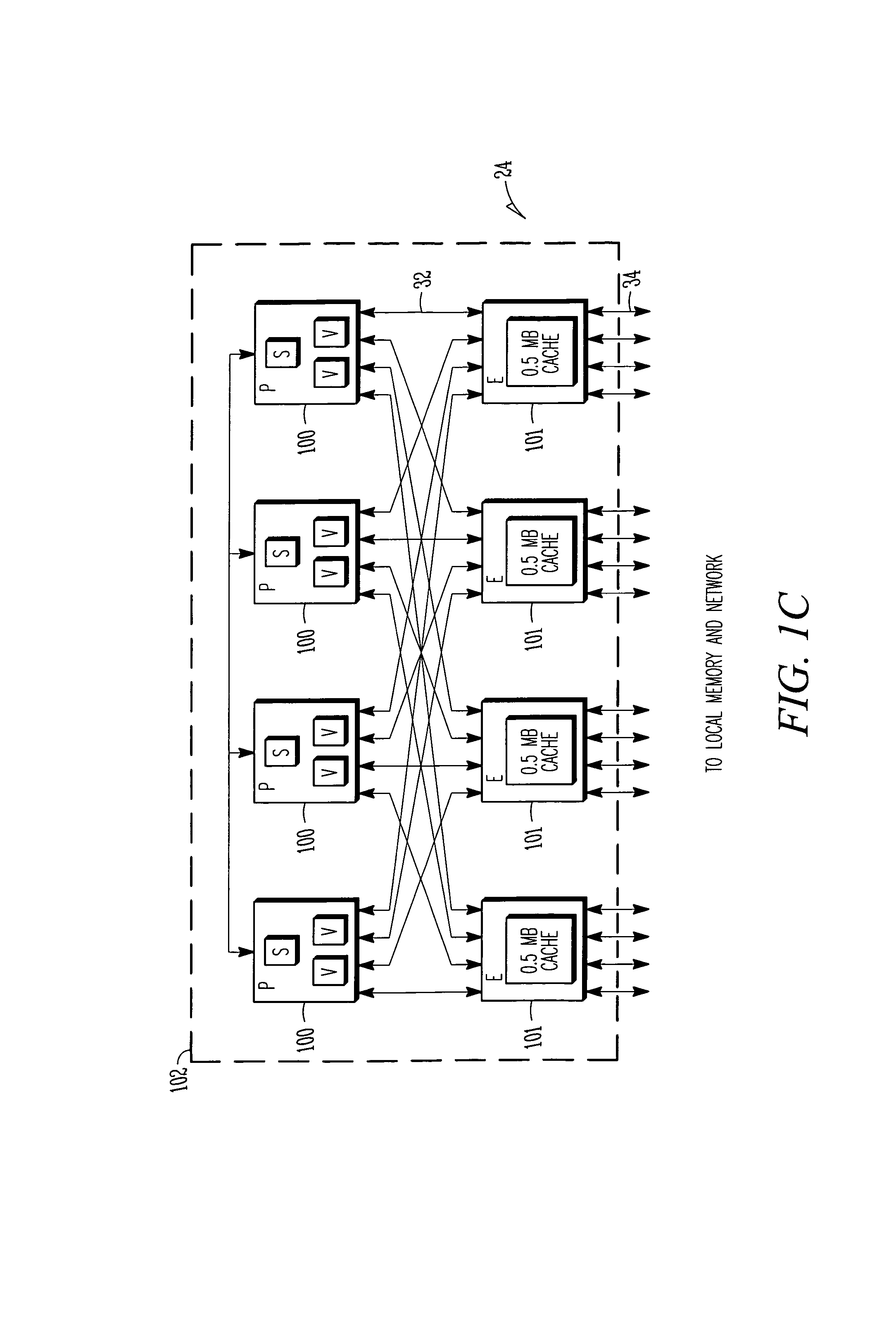
A method and apparatus to provide specifiable ordering between and among vector and scalar operations within a single streaming processor (SSP) via a local synchronization (Lsync) instruction that operates within a relaxed memory consistency model. Various aspects of that relaxed memory consistency model are described. Further, a combined memory synchronization and barrier synchronization (Msync) for a multistreaming processor (MSP) system is described. Also, a global synchronization (Gsync) instruction provides synchronization even outside a single MSP system is described. Advantageously, the pipeline or queue of pending memory requests does not need to be drained before the synchronization operation, nor is it required to refrain from determining addresses for and inserting subsequent memory accesses into the pipeline.
Owner:CRAY
Mechanism to detect IEEE underflow exceptions on speculative floating-point operations
InactiveUS6571265B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsFloating pointComputer science
A mechanism is disclosed for detecting underflow conditions for speculative floating-point operations. A floating-point status register includes a status flag which is set when a result generated by a floating-point instruction is "tiny". The status flag is cleared, all exceptions are masked, and the instruction is executed speculatively. The "tiny" exception flag is read to determine whether the speculatively executed instruction should raise an unmasked underflow exception. The exception may be raised if the processor reaches a point of registration associated with the instruction. The exception may be ignored if this point is not reached.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processor having a compare extension of an instruction set architecture
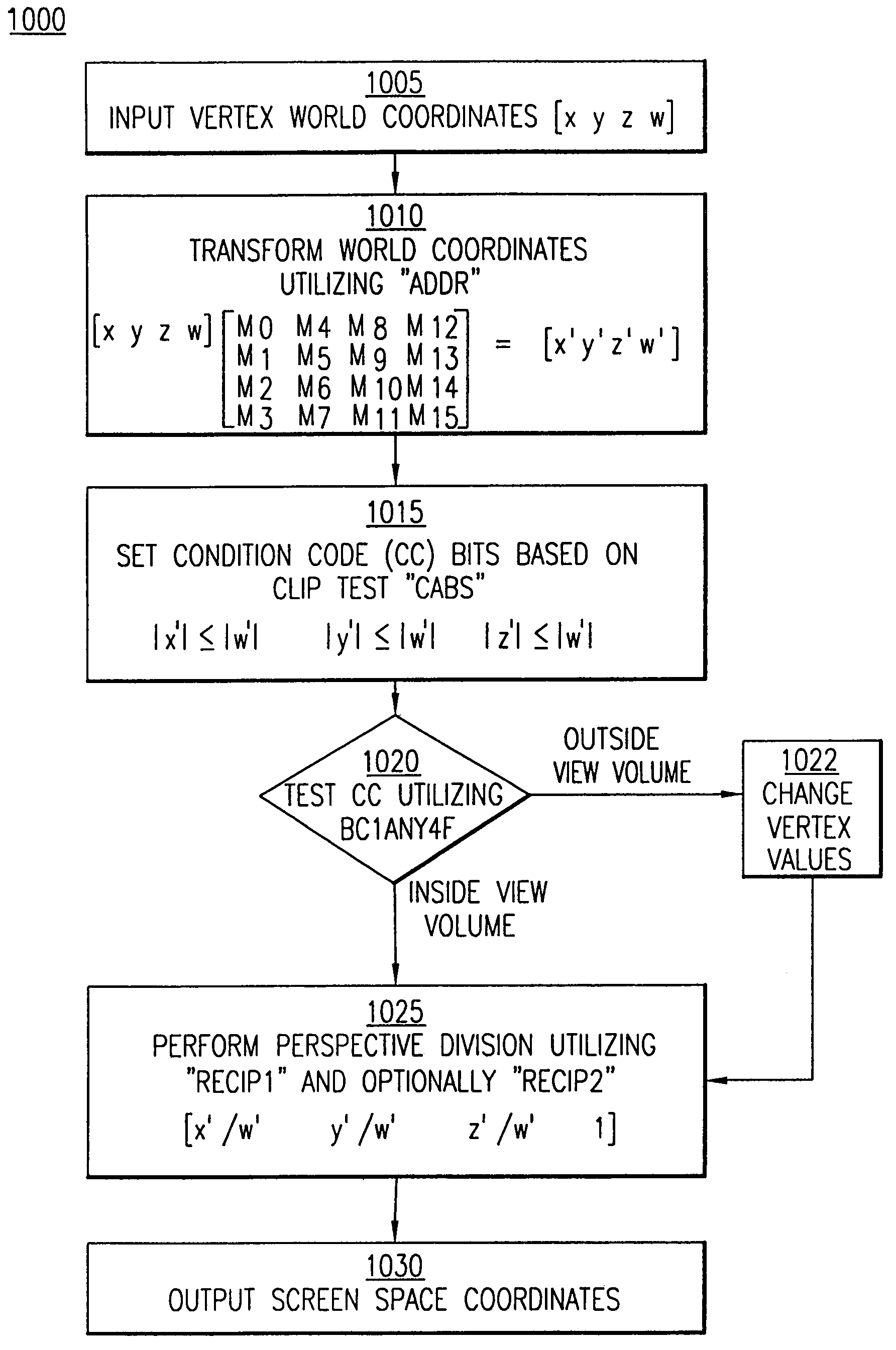
InactiveUS7242414B1Increase speedReduce in quantityConditional code generationRegister arrangementsOperandFloating point
A processor having a compare extension of an instruction set architecture which incorporates a set of high performance floating point operations. The instruction set architecture incorporates a variety of data formats including single precision and double precision data formats, as well as the paired-single data format that allows two simultaneous operations on a pair of operands. The extension includes instructions directed to a magnitude compare of floating point numbers and conversions between a pair of 32-bit fixed point integers and paired-single floating point format.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
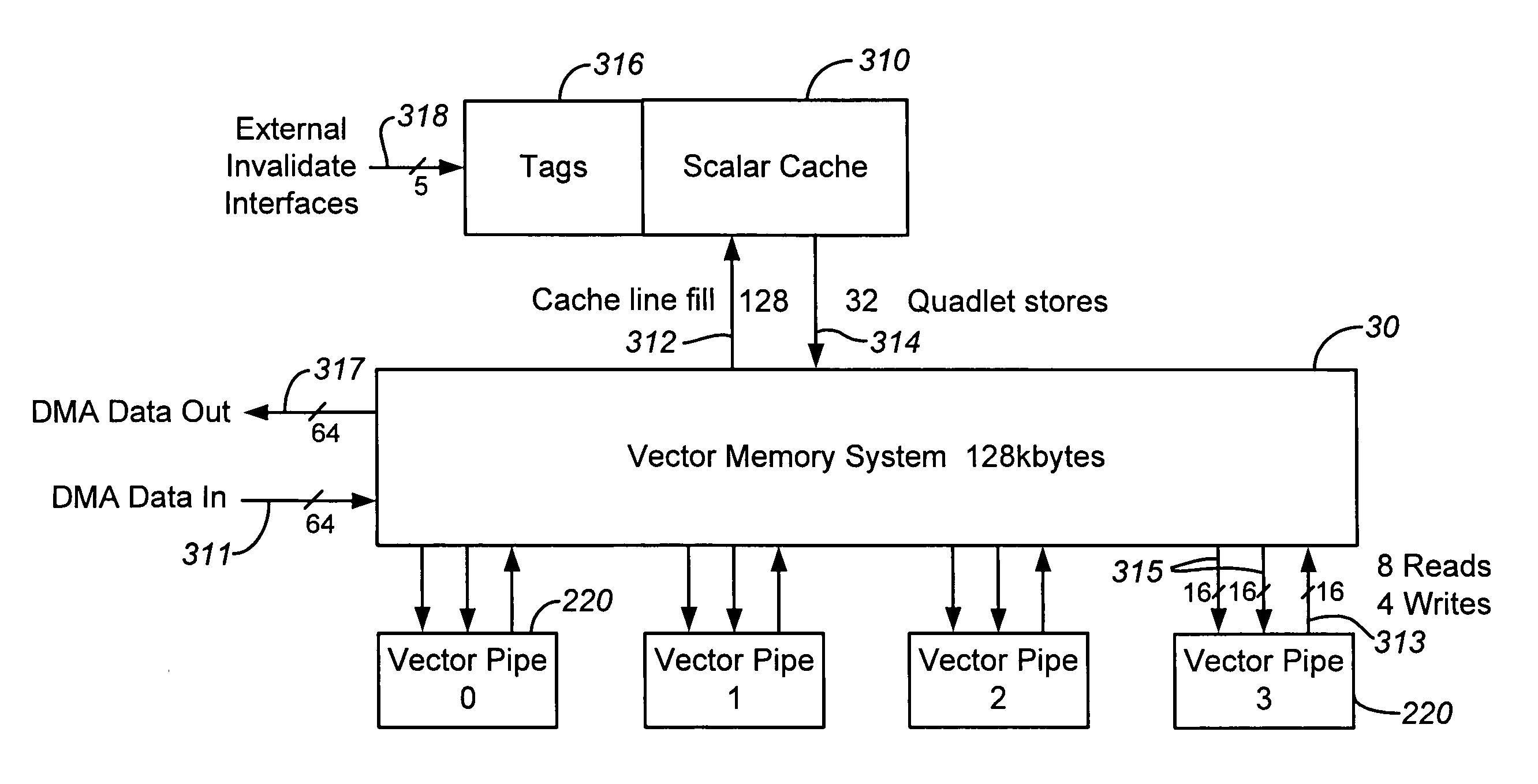
Detecting memory-hazard conflicts during vector processing
ActiveUS20080288744A1Operational speed enhancementConditional code generationMemory addressComputerized system
A method for performing parallel operations in a computer system when one or more memory hazards may be present, which may be implemented by a processor, is described. During operation, the processor receives instructions for detecting conflict between memory addresses in vectors when memory operations are performed in parallel using at least a portion of the vectors, and tracking positions in at least one of the vectors of any detected conflict between the memory addresses. Next, the processor executes the instructions for detecting the conflict between the memory addresses and tracking the positions.
Owner:APPLE INC
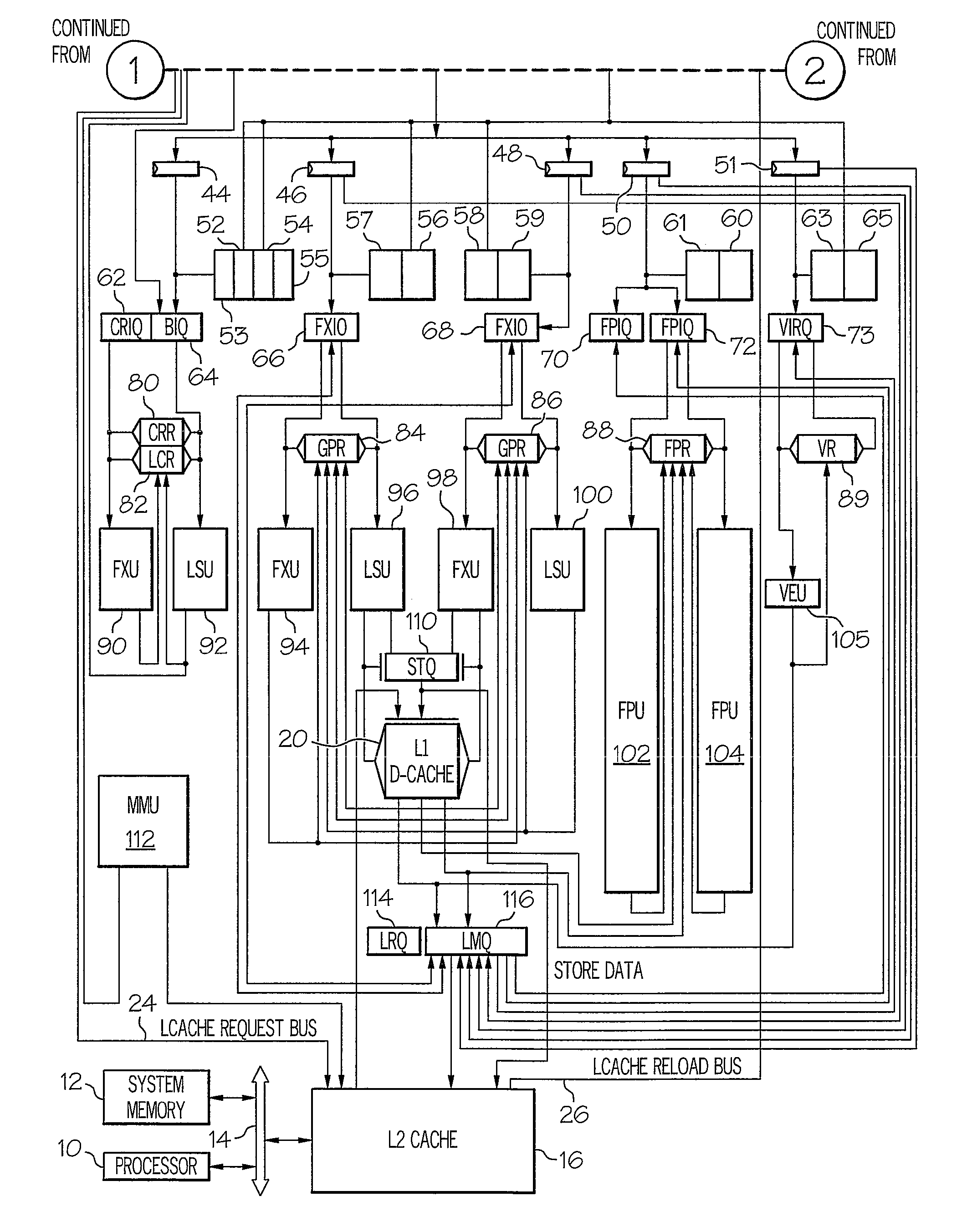
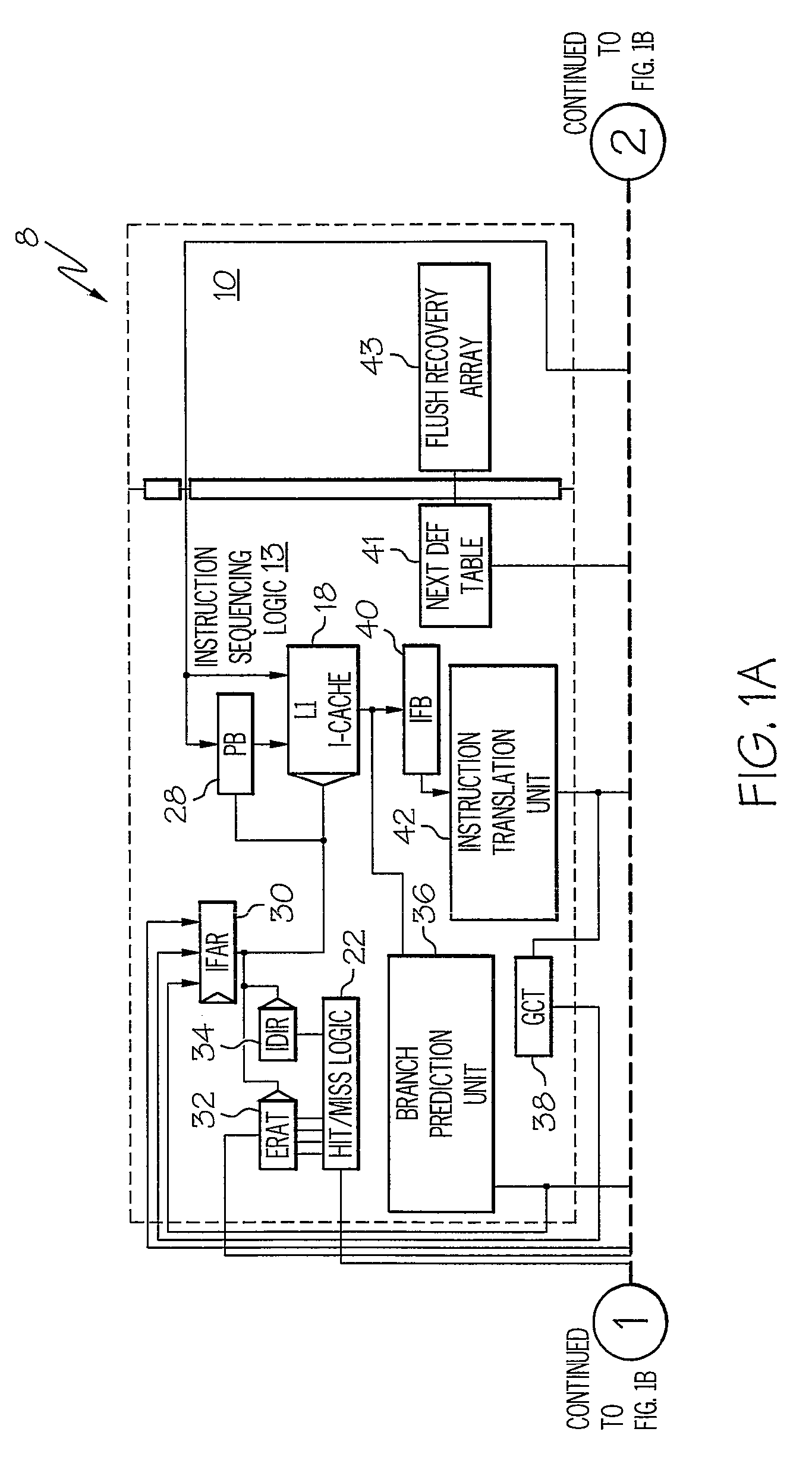
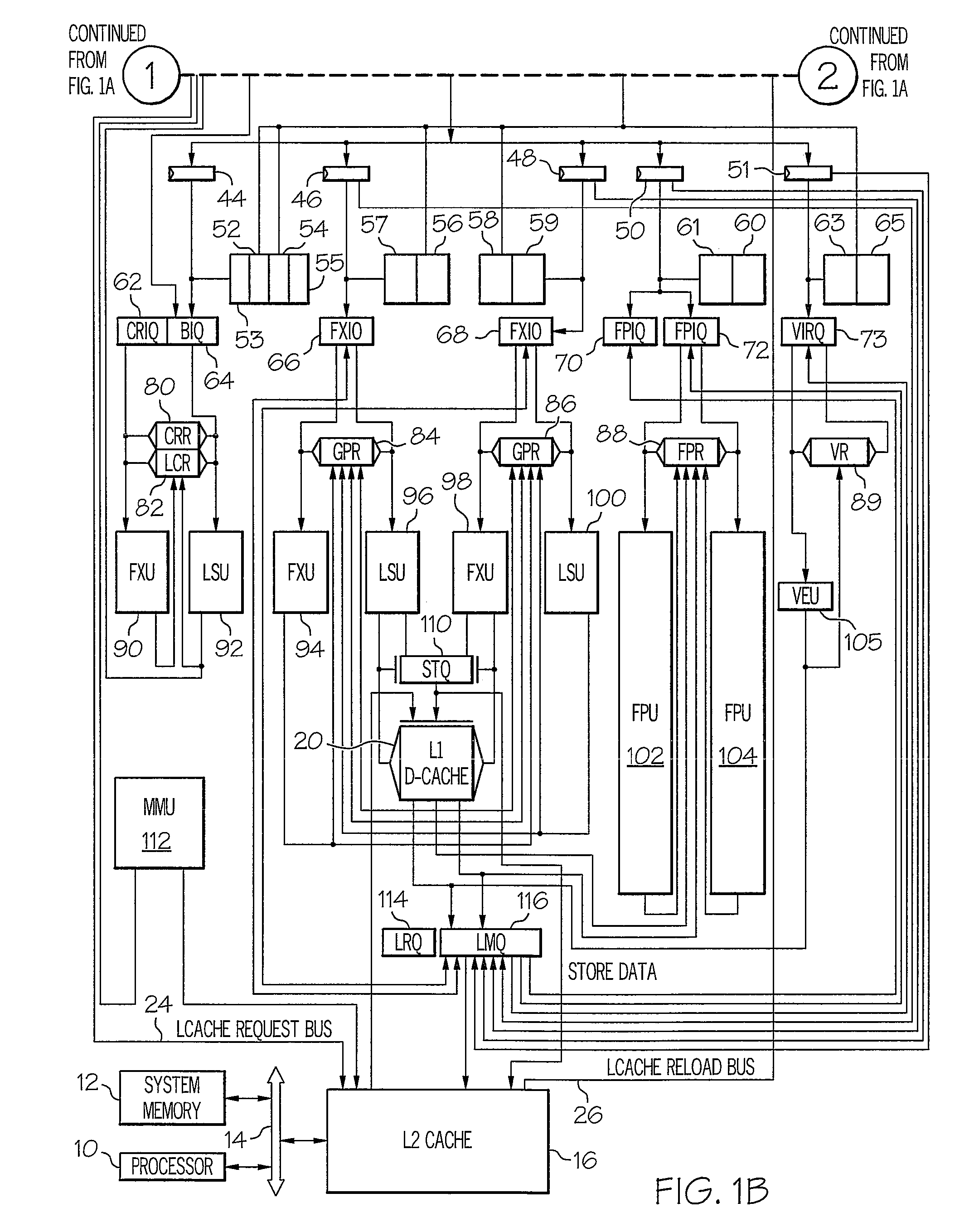
System and Method for Issuing Load-Dependent Instructions from an Issue Queue in a Processing Unit
InactiveUS20090113182A1Conditional code generationRegister arrangementsData processing systemMemory hierarchy
A system and method for issuing load-dependent instructions from an issue queue in a processing unit in a data processing system. In response to a LSU determining that a load request from a load instruction missed a first level in a memory hierarchy, a LMQ allocates a load-miss queue entry corresponding to the load instruction. The LMQ associates at least one instruction dependent on the load request with the load-miss queue entry. Once data associated with the load request is retrieved, the LMQ selects at least one instruction dependent on the load request for execution on the next cycle. At least one instruction dependent on the load request is executed and a result is outputted.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for executing multithreaded instructions grouped into blocks
ActiveUS20140282592A1Conditional code generationProgram initiation/switchingParallel computingInstruction sequence
A method for executing multithreaded instructions grouped into blocks. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks, wherein the instructions of the instruction blocks are interleaved with multiple threads; scheduling the instructions of the instruction block to execute in accordance with the multiple threads; and tracking execution of the multiple threads to enforce fairness in an execution pipeline.
Owner:INTEL CORP
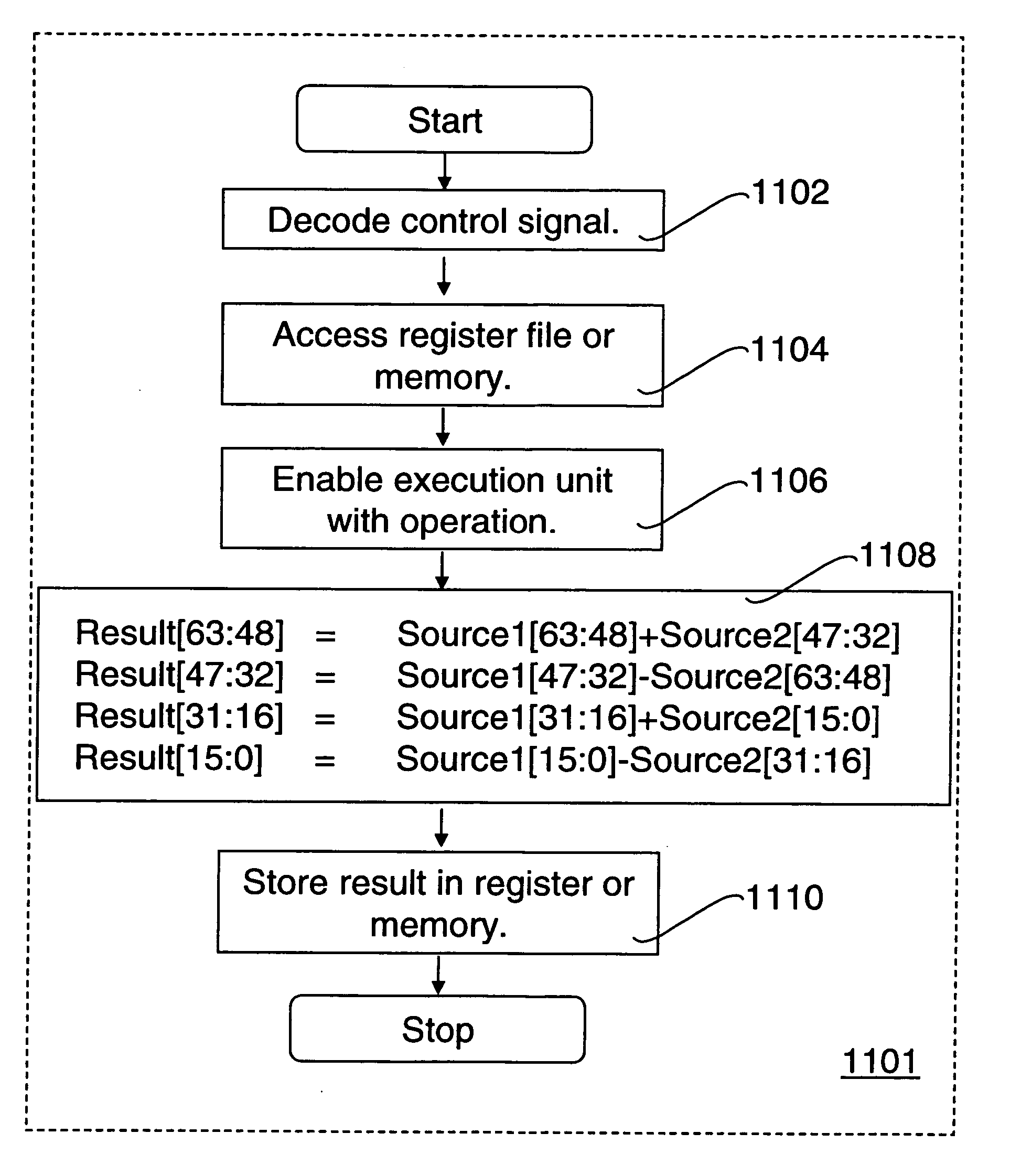
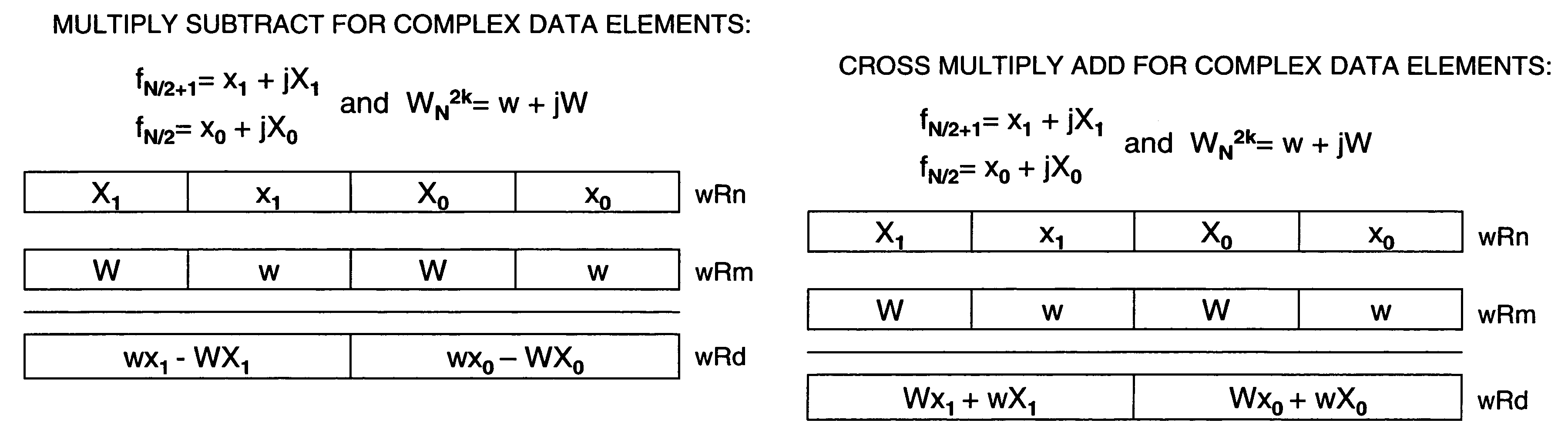
Method and apparatus for SIMD complex arithmetic
Methods and apparatus for calculating Single-Instruction-Multiple-Data (SIMD) complex arithmetic. A coprocessor instruction has a format identifying a multiply and subtract instruction to generate real components for complex multiplication of first operand complex data and corresponding second operand complex data, a cross multiply and add instruction to generate imaginary components for complex multiplication of the first operand complex data and the corresponding second operand complex data, an add-subtract instruction to add real components of the first operand to imaginary components of the second operand and to subtract real components of the second operand from imaginary components of the first operand, and a subtract-add instruction to subtract the real components of the second operand from the imaginary components of the first operand and to add the real components of the first operand to the imaginary components of the second operand.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for fusing instructions to provide or-test and and-test functionality on multiple test sources
ActiveUS20140281389A1Binary to binaryConditional code generationJust-in-time compilationMicro-operation
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for fusing instructions to provide OR-test and AND-test functionality on multiple test sources. Some embodiments include fetching instructions, said instructions including a first instruction specifying a first operand destination, a second instruction specifying a second operand source, and a third instruction specifying a branch condition. A portion of the plurality of instructions are fused into a single micro-operation, the portion including both the first and second instructions if said first operand destination and said second operand source are the same, and said branch condition is dependent upon the second instruction. Some embodiments generate a novel test instruction dynamically by fusing one logical instruction with a prior-art test instruction. Other embodiments generate the novel test instruction through a just-in-time compiler. Some embodiments also fuse the novel test instruction with a subsequent conditional branch instruction, and perform a branch according to how the condition flag is set.
Owner:INTEL CORP
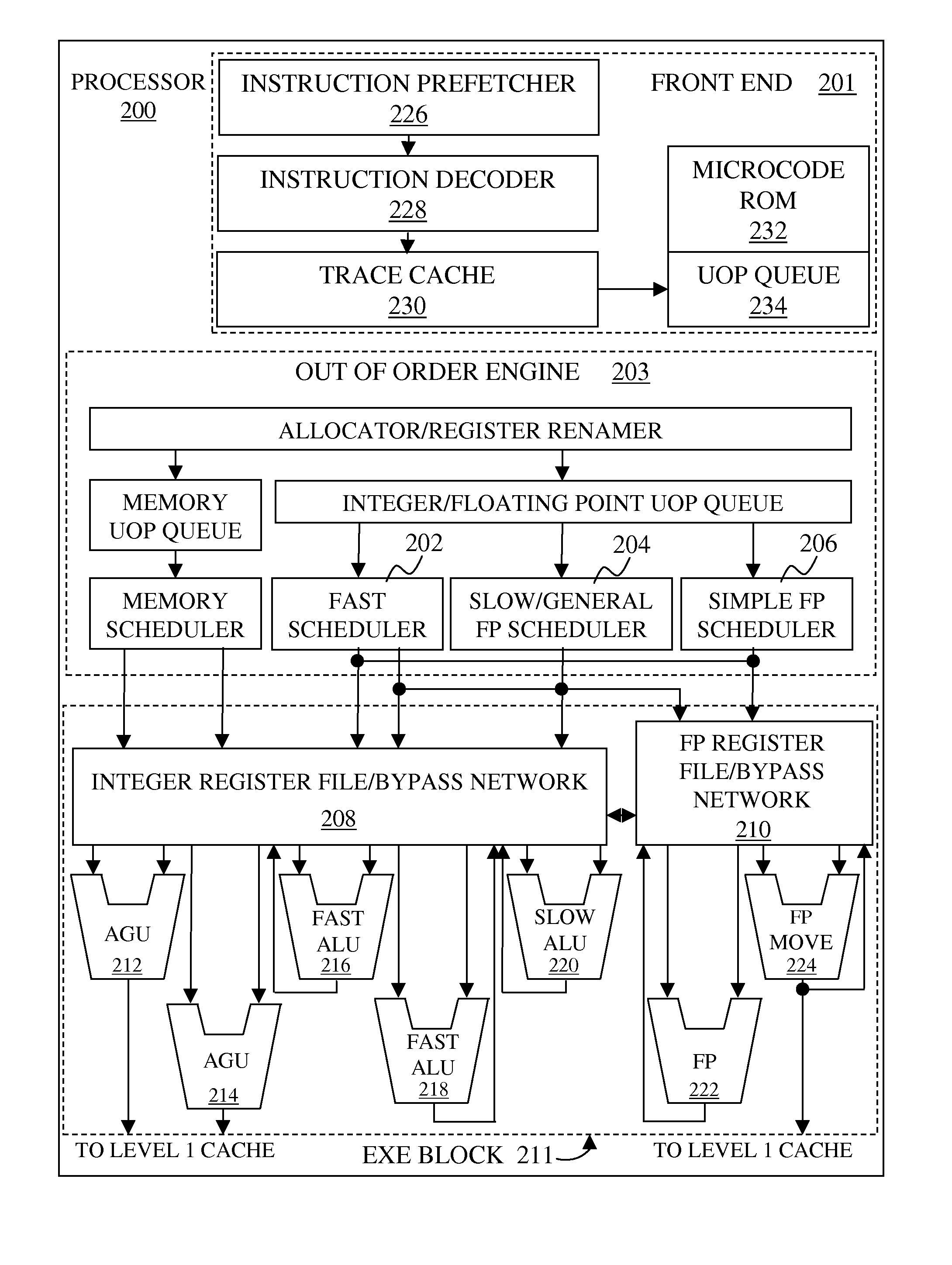
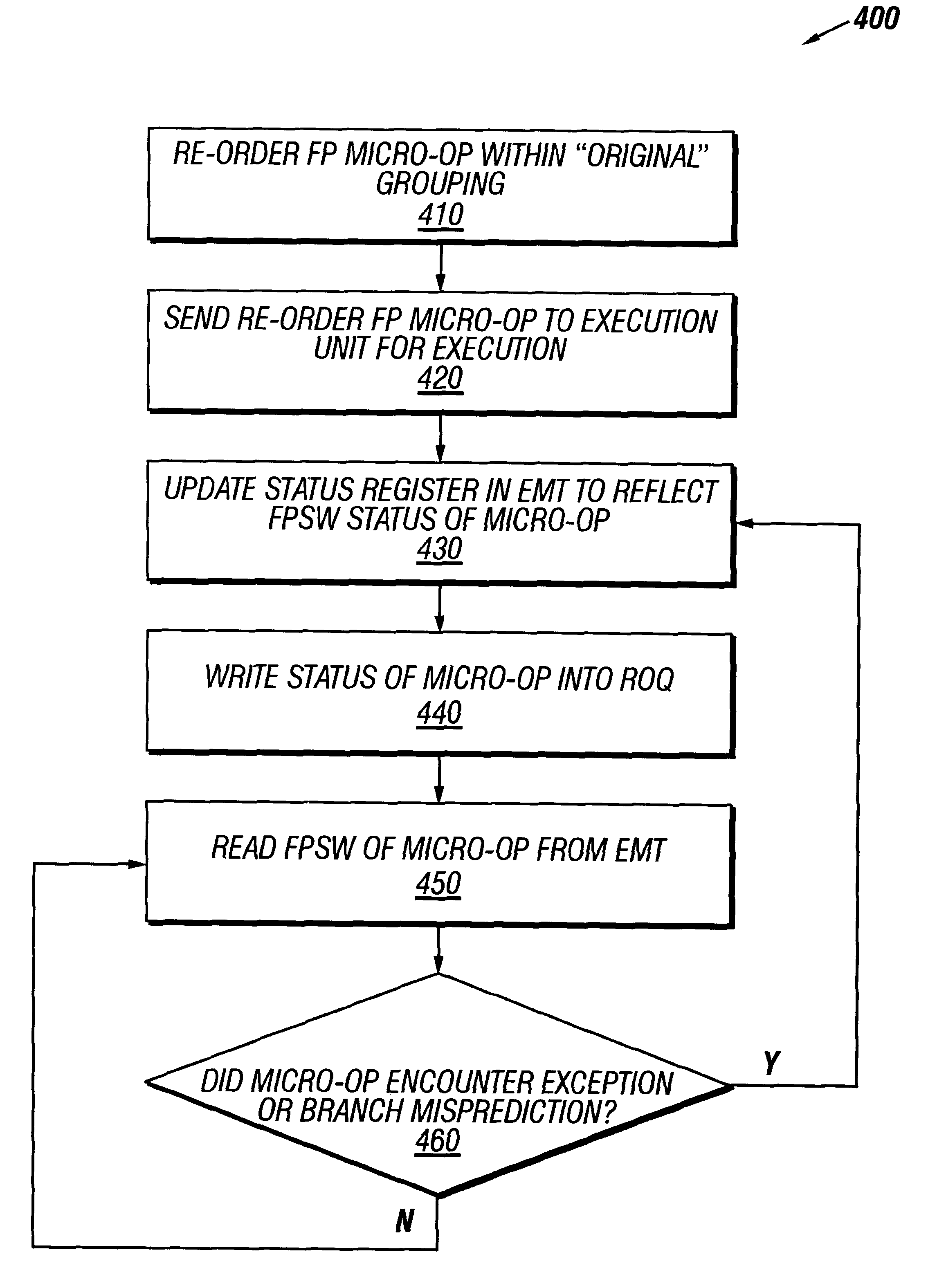
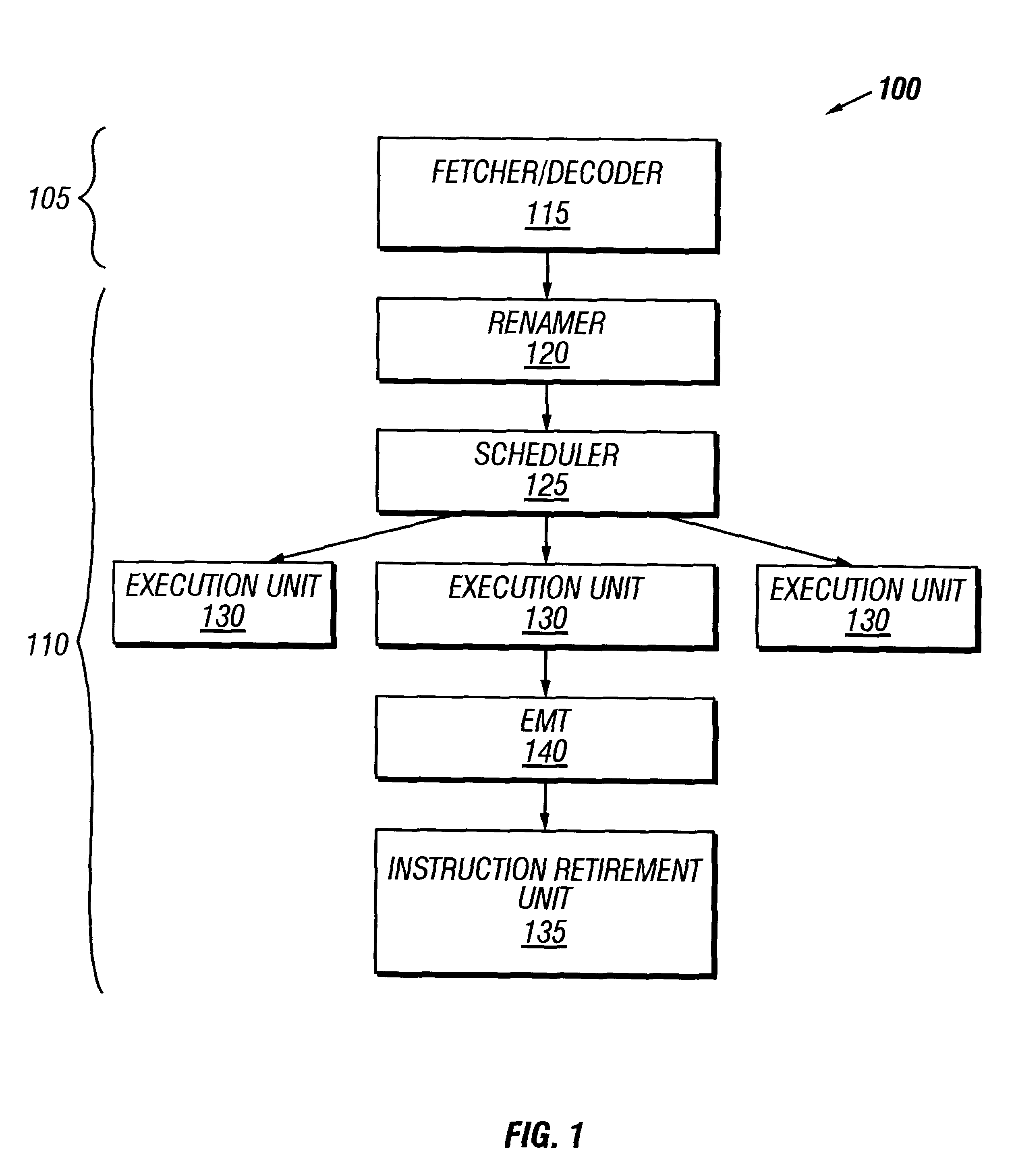
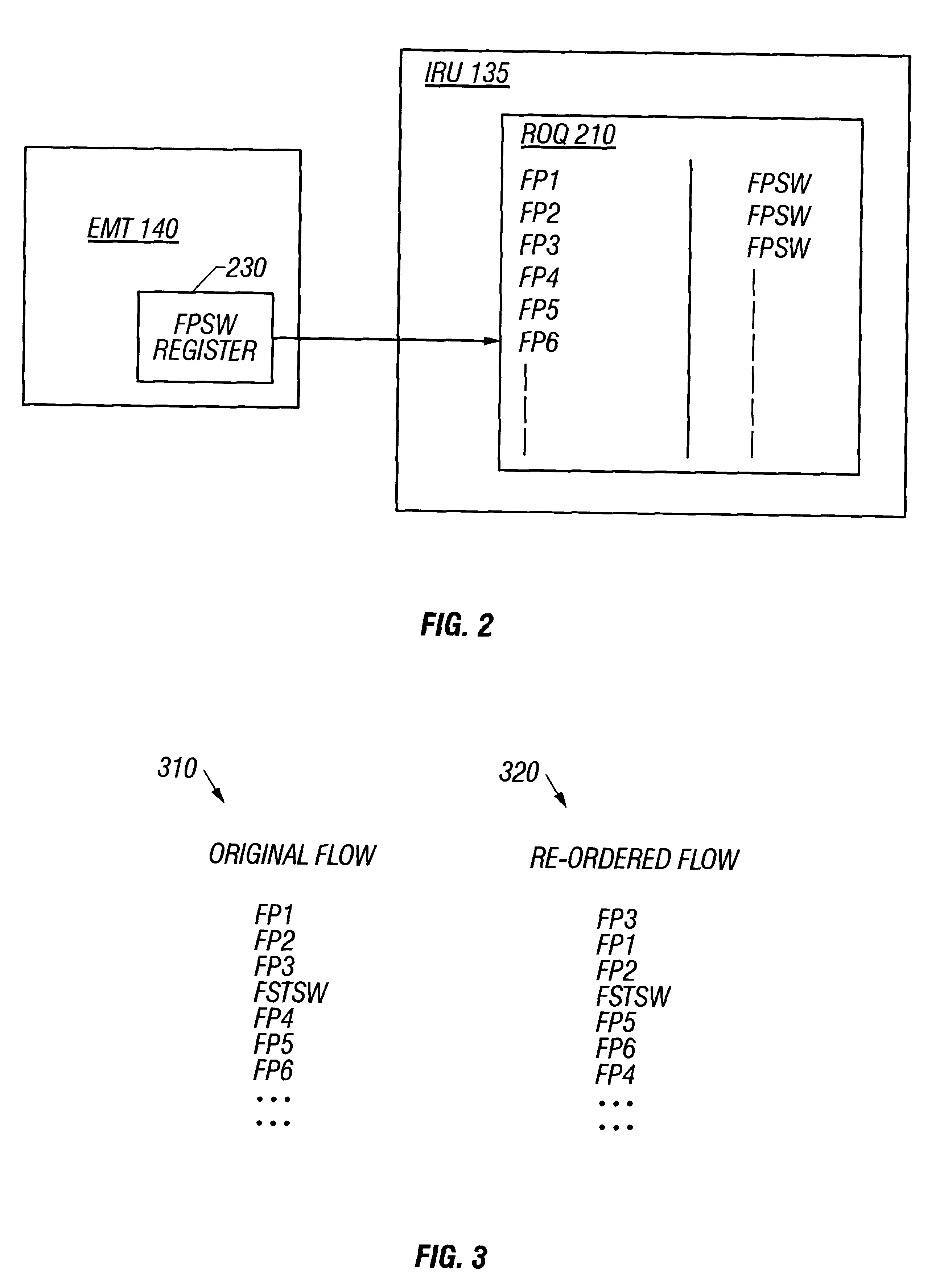
Method and apparatus for floating point (FP) status word handling in an out-of-order (000) Processor Pipeline
InactiveUS6223278B1Conditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingFloating point
A method for performing floating point (FP) instruction handling is provided. A floating point store status word (FSTSW) instruction is inserted within a plurality of micro-ops corresponding to a plurality of FP instructions and the plurality of micro-ops are ordered for execution. In another aspect, a processor is provided for executing a plurality of floating point (FP) instructions. The processor includes a fetcher / decoder unit to retrieve a plurality of FP instructions from a memory structure and generate a plurality of micro-ops from the FP instructions. The processor further generates a floating point store status word (FSTSW) instruction and includes a scheduler unit to re-order the micro-ops for execution.
Owner:INTEL CORP
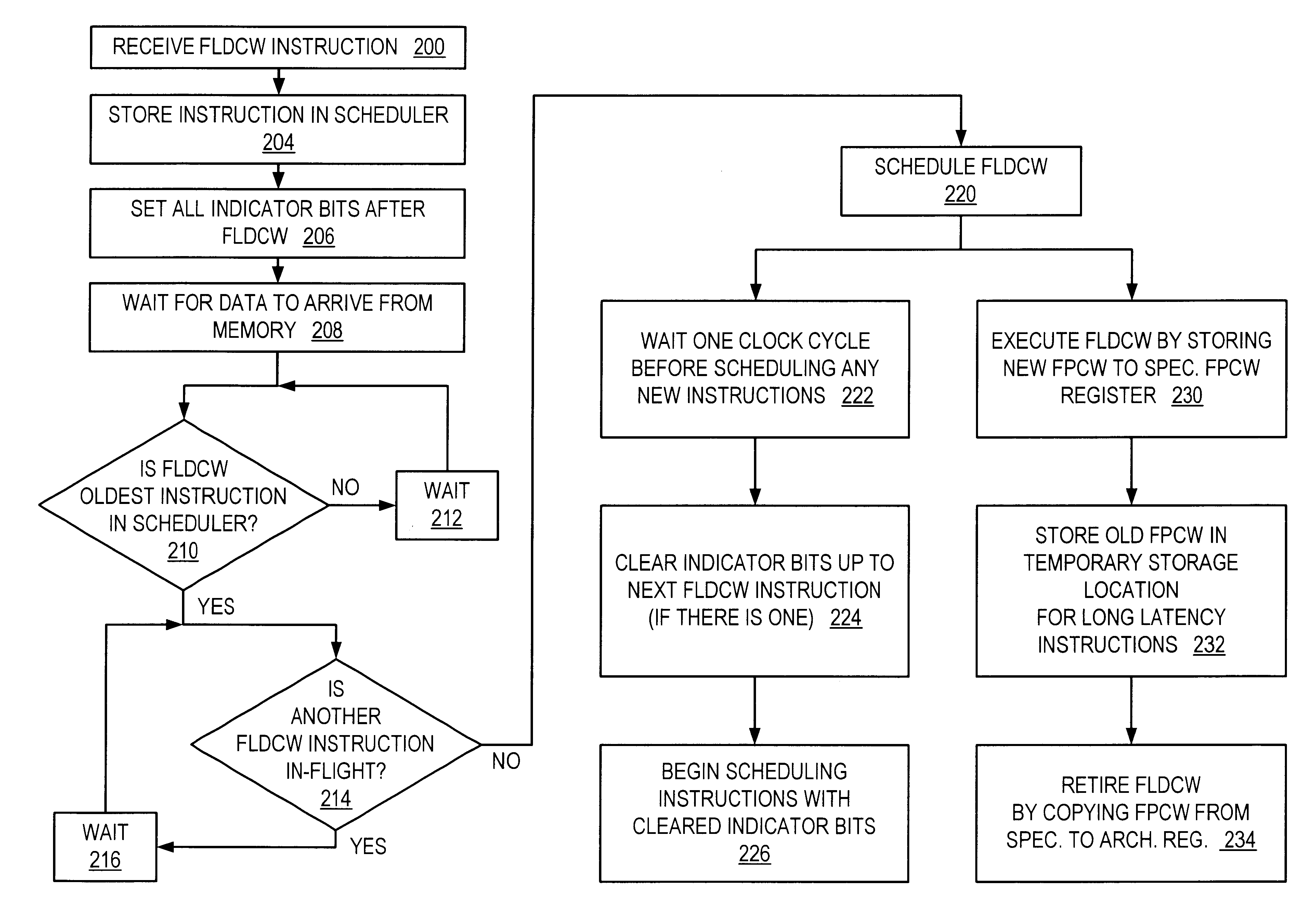
Rapid execution of floating point load control word instructions
InactiveUS6405305B1Conditional code generationDigital computer detailsScheduling instructionsParallel computing
A microprocessor with a floating point unit configured to rapidly execute floating point load control word (FLDCW) type instructions in an out of program order context is disclosed. The floating point unit is configured to schedule instructions older than the FLDCW-type instruction before the FLDCW-type instruction is scheduled. The FLDCW-type instruction acts as a barrier to prevent instructions occurring after the FLDCW-type instruction in program order from executing before the FLDCW-type instruction. Indicator bits may be used to simplify instruction scheduling, and copies of the floating point control word may be stored for instruction that have long execution cycles. A method and computer configured to rapidly execute FLDCW-type instructions in an out of program order context are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
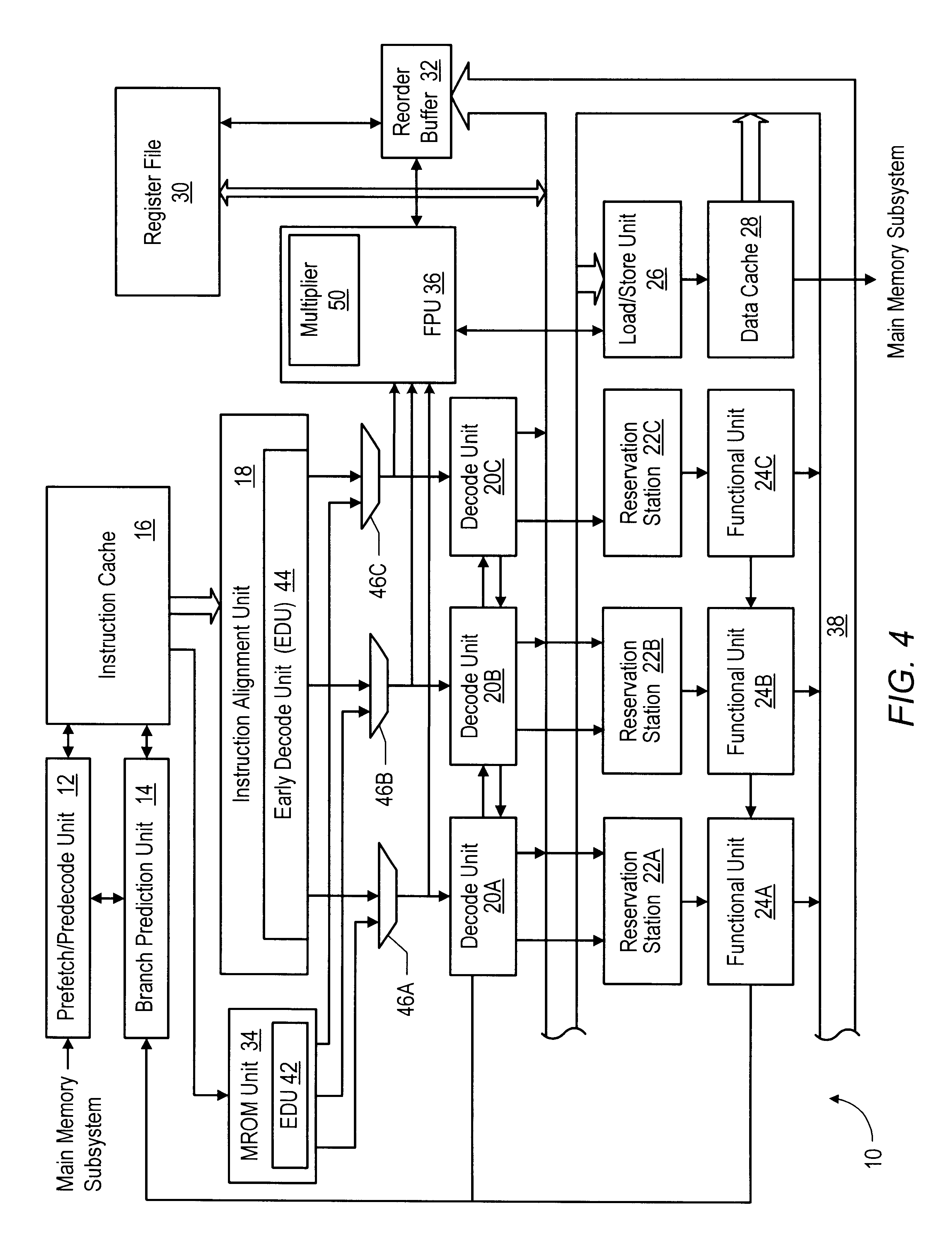
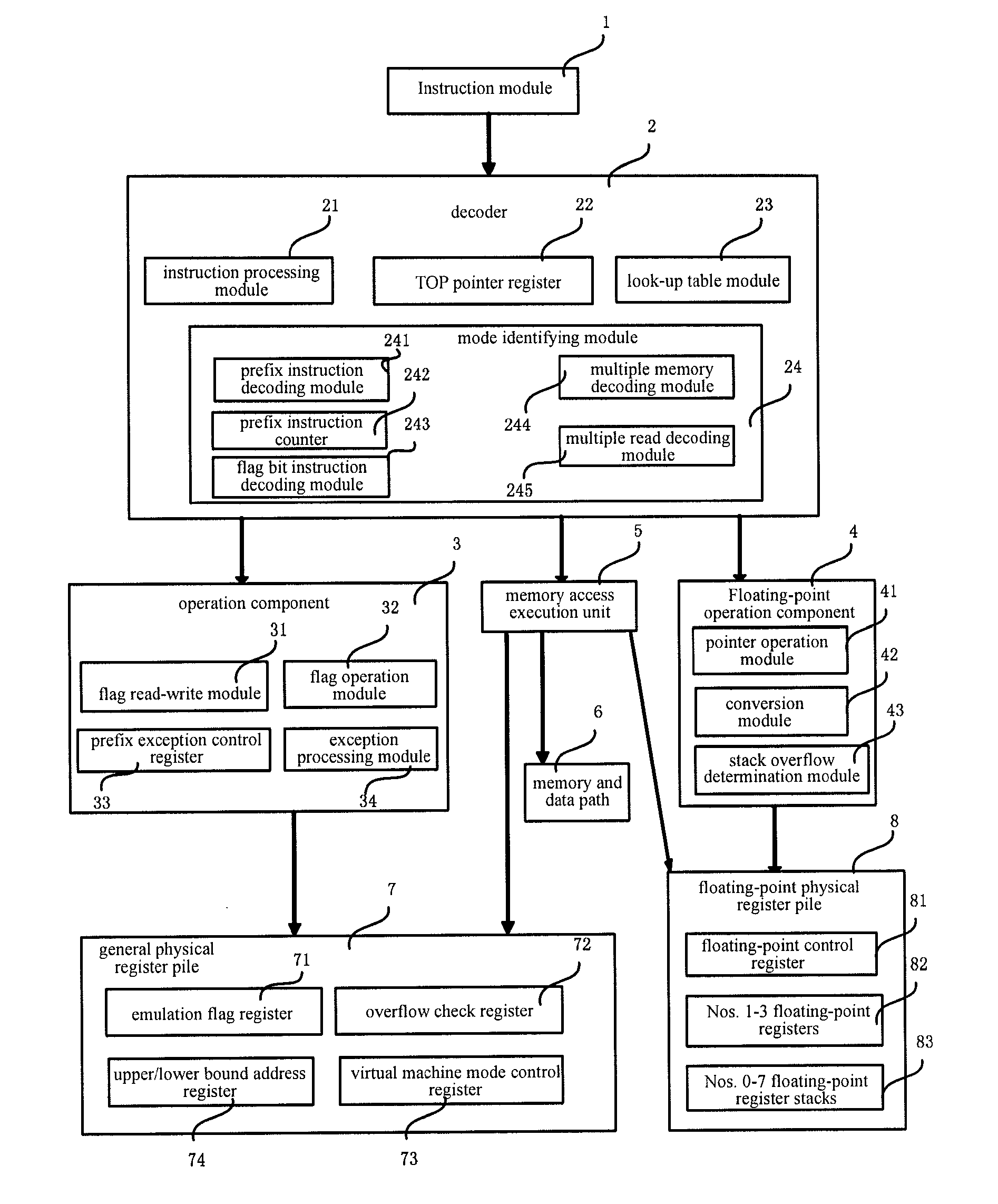
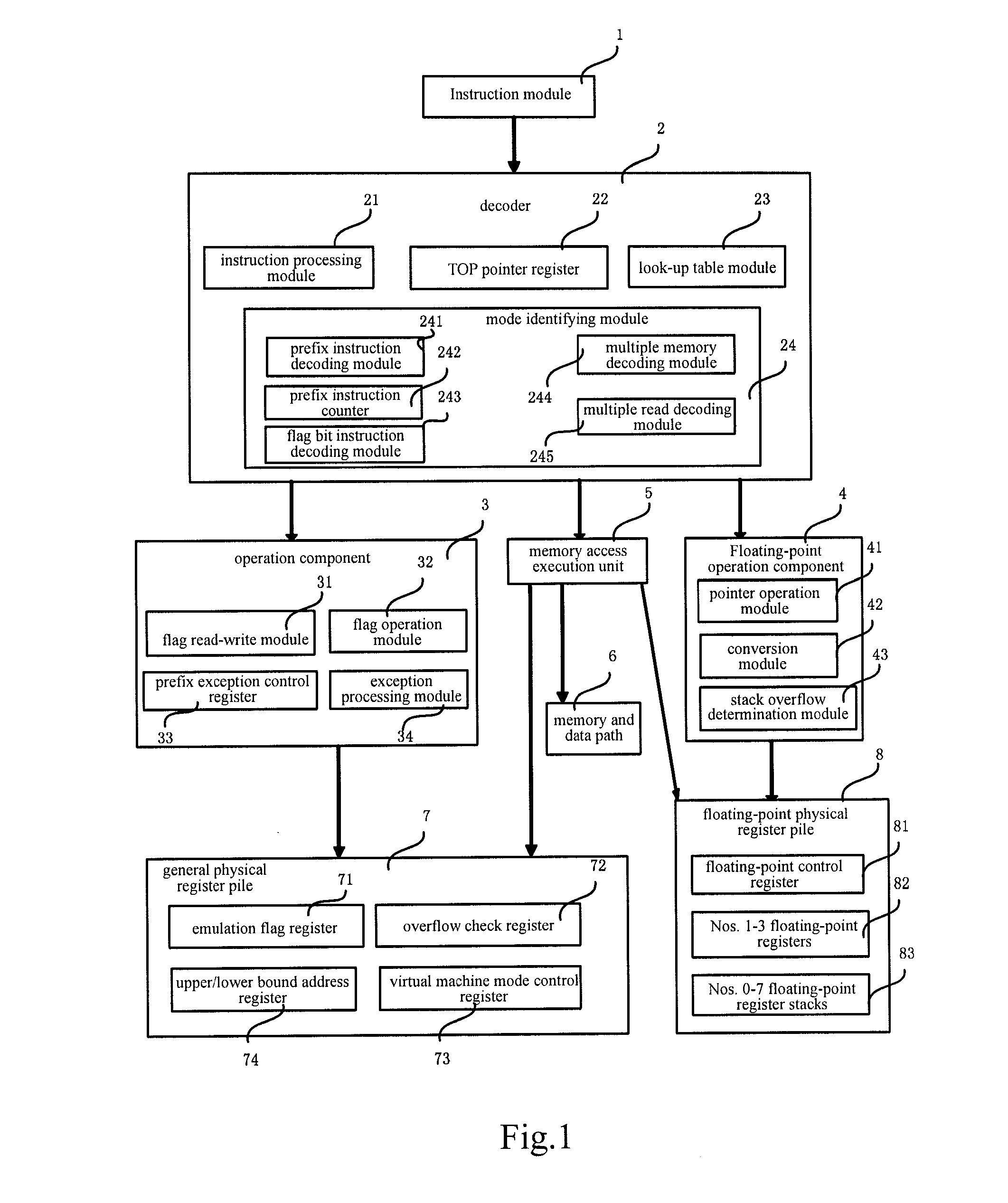
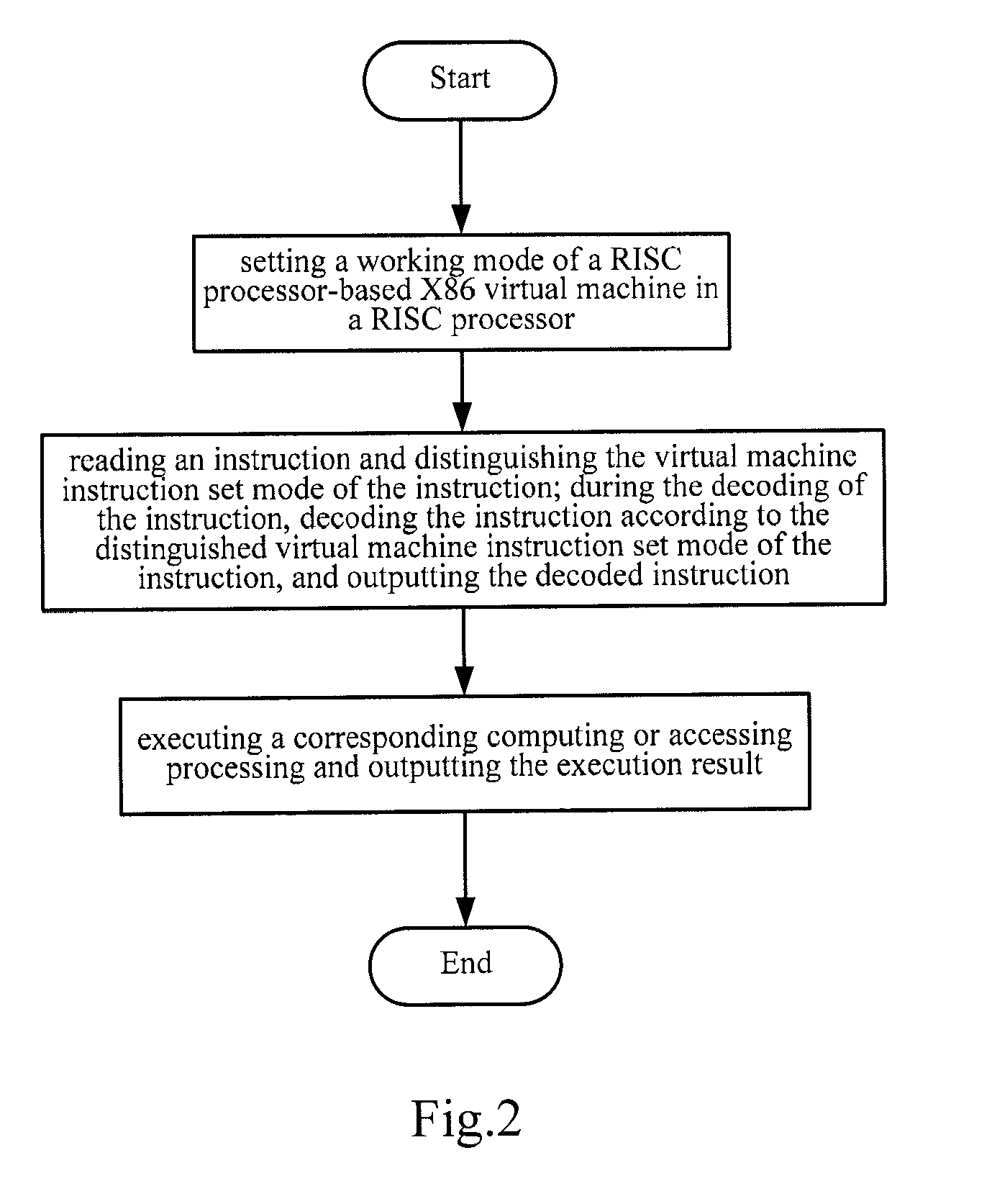
Risc processor apparatus and method for supporting x86 virtual machine
ActiveUS20110035745A1Improve performanceConditional code generationGeneral purpose stored program computerFloating pointInstruction set
A RISC processor apparatus and method for supporting an X86 virtual machine. The RISC processor includes: an instruction module for storing a virtual machine instruction set that supports the X86 virtual machine; a decoder for, during the decoding of an instruction of the virtual machine instruction set, distinguishing the virtual machine instruction set mode of the instruction, decoding the instruction according to the distinguished virtual machine instruction set mode, and outputting the decoded instruction to a fixed-point operation component or a floating-point operation component according to the distinguished virtual machine instruction set mode; the fixed-point operation component for processing the fixed-point instruction of the virtual machine instruction set according to the output of the decoder and outputting the execution result; the floating-point operation component for processing the floating-point instruction of the virtual machine instruction set according to the output of the decoder and outputting the execution result.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
Cross multiply and add instruction and multiply and subtract instruction SIMD execution on real and imaginary components of a plurality of complex data elements
Methods and apparatus for calculating Single-Instruction-Multiple-Data (SIMD) complex arithmetic. A coprocessor instruction has a format identifying a multiply and subtract instruction to generate real components for complex multiplication of first operand complex data and corresponding second operand complex data, a cross multiply and add instruction to generate imaginary components for complex multiplication of the first operand complex data and the corresponding second operand complex data, an add-subtract instruction to add real components of the first operand to imaginary components of the second operand and to subtract real components of the second operand from imaginary components of the first operand, and a subtract-add instruction to subtract the real components of the second operand from the imaginary components of the first operand and to add the real components of the first operand to the imaginary components of the second operand.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method for populating a source view data structure by using register template snapshots
ActiveUS20140281426A1Conditional code generationInstruction analysisProcessor registerParallel computing
A method for populating a source view data structure by using register template snapshots. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; populating a source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks as recorded by the plurality of register templates; and determining which of the plurality of instruction blocks are ready for dispatch by using the populated source view data structure.
Owner:INTEL CORP
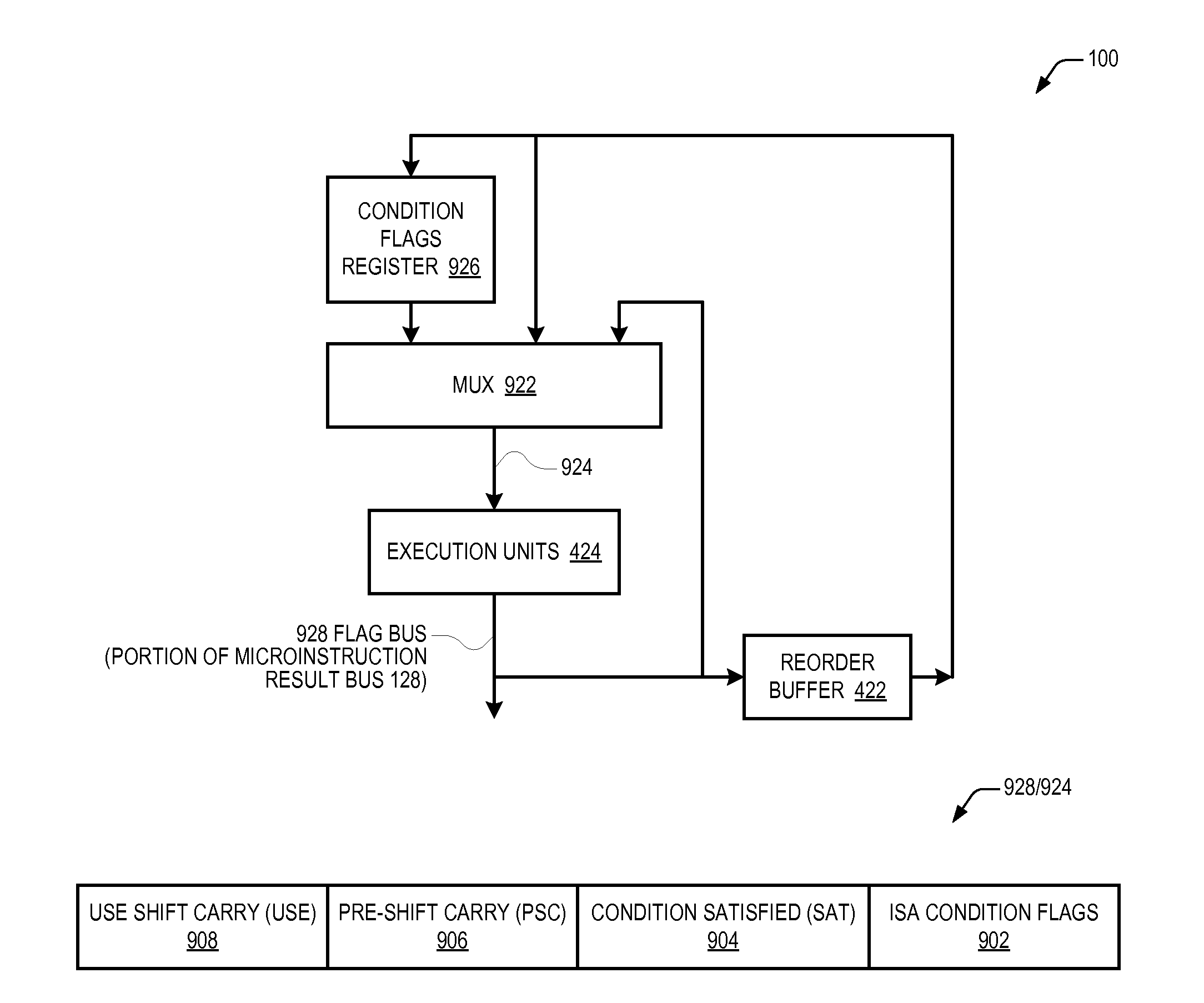
Conditional alu instruction pre-shift-generated carry flag propagation between microinstructions in read-port limited register file microprocessor
A microprocessor includes a hardware instruction translator that translates an architectural instruction into first and second microinstructions. To execute the first microinstruction, an execution pipeline performs the shift operation on the first source operand to generate the first result and a carry flag value and updates a non-architectural carry flag with the generated carry flag value. To execute the second microinstruction, it performs the second operation on the first result and the second operand to generate the second result and new condition flag values based on the second result. If a architectural condition flags satisfy the condition, it updates the architectural carry flag with the non-architectural carry flag value and updates at least one of the other architectural condition flags with the corresponding generated new condition flag values; otherwise, it updates the architectural condition flags with the current value of the architectural condition flags.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Processor executing SIMD instructions
InactiveUS20080046704A1Fast resultsFast processingConditional code generationInstruction analysisProcessor registerParallel computing
Owner:TANAKA TETABUYA +8
Popular searches
Multiple digital computer combinations Data switching networks Securing communication Concurrent instruction execution Architecture with single central processing unit Energy efficient computing Memory systems Specific program execution arrangements Computation using denominational number representation Interprogram communication
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com