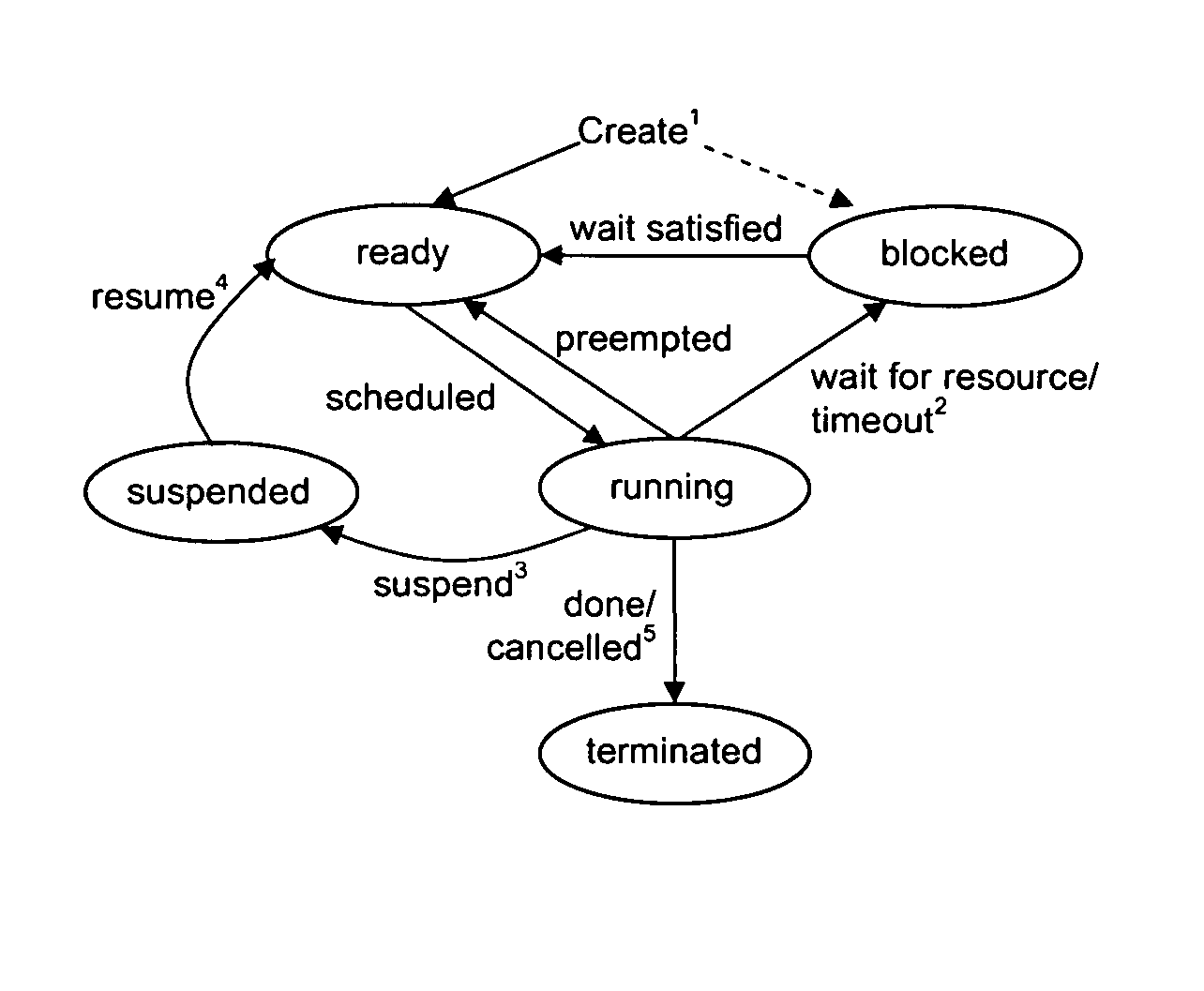
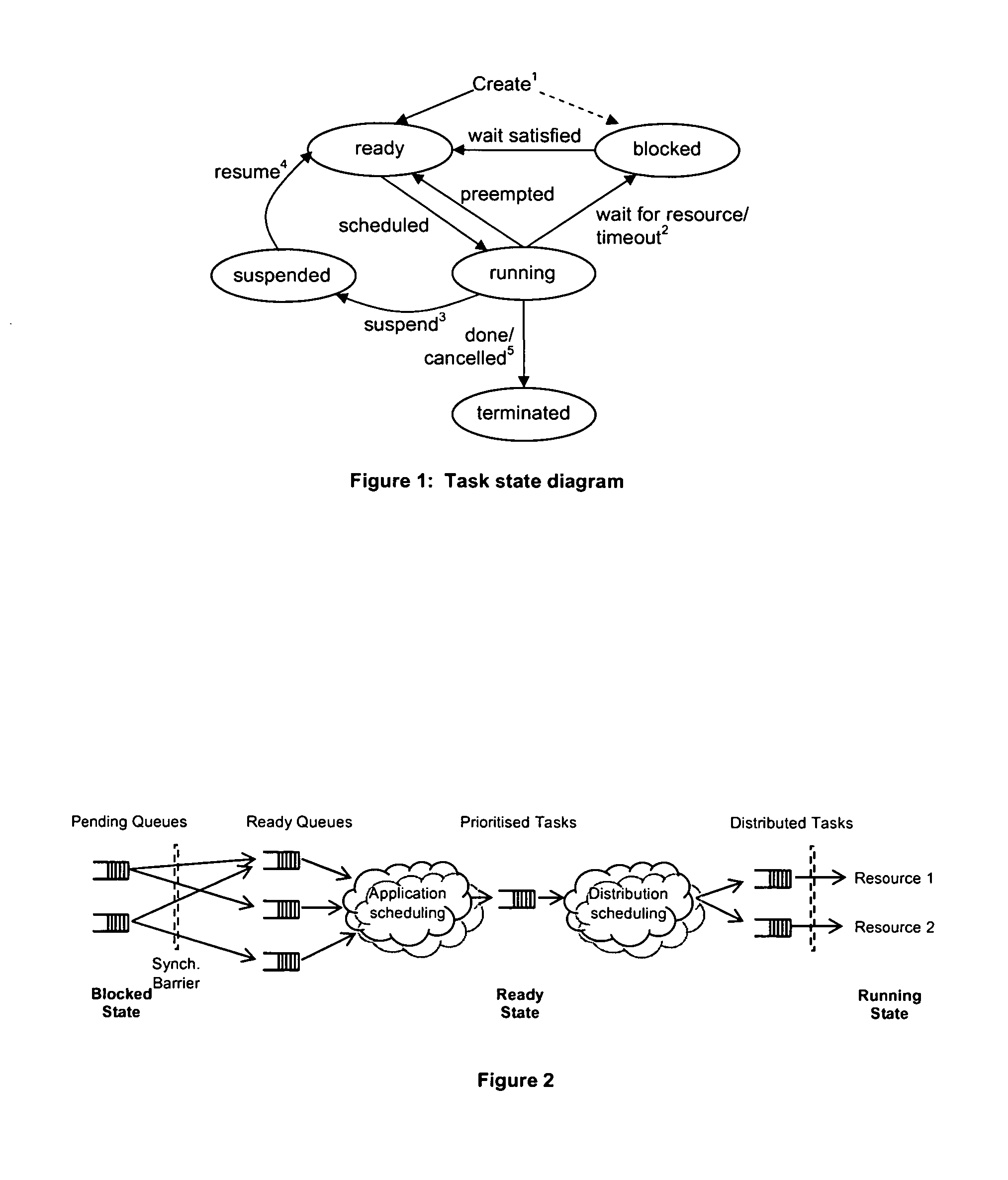
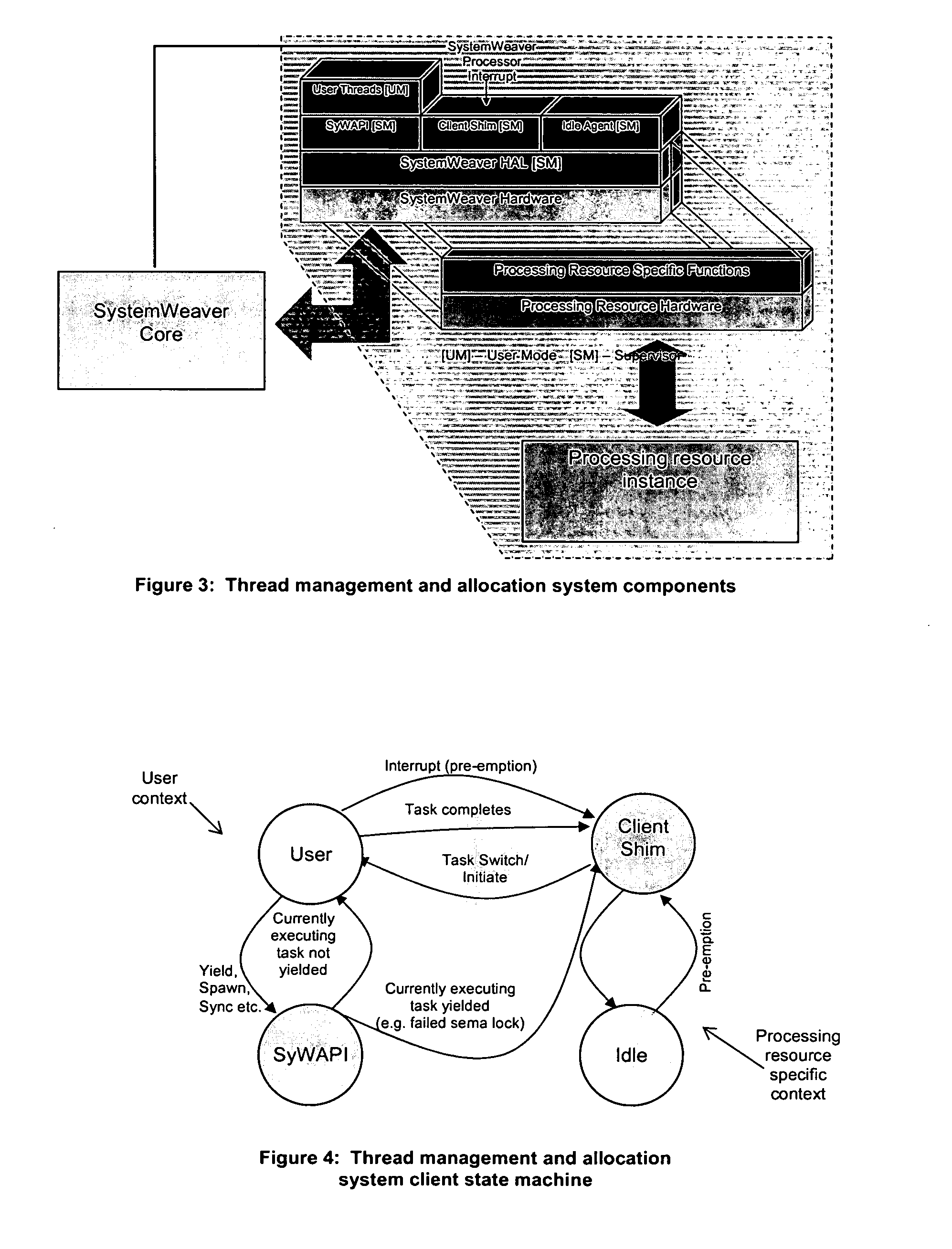
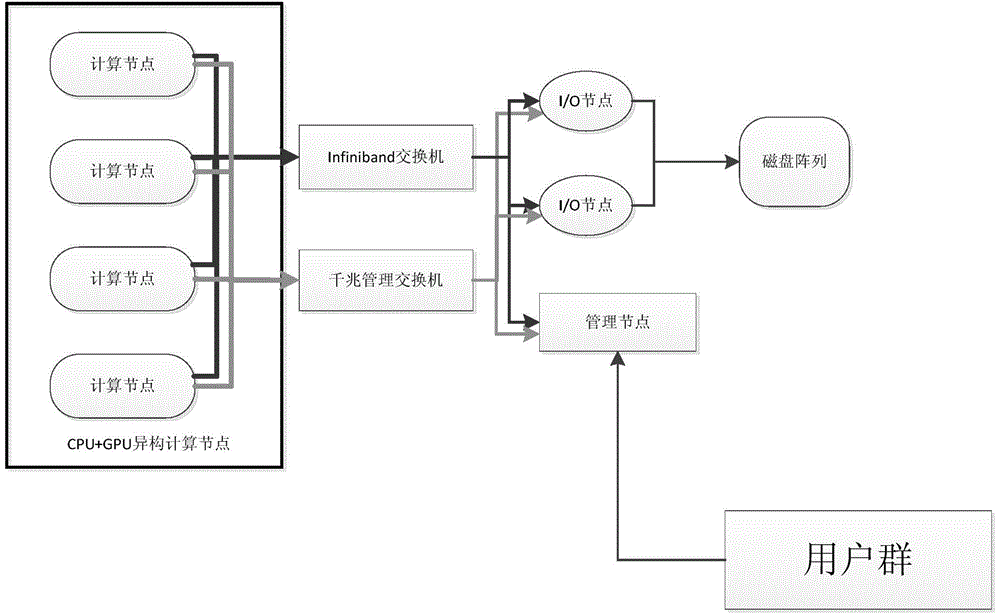
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9788results about "Concurrent instruction execution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single-chip microcomputer
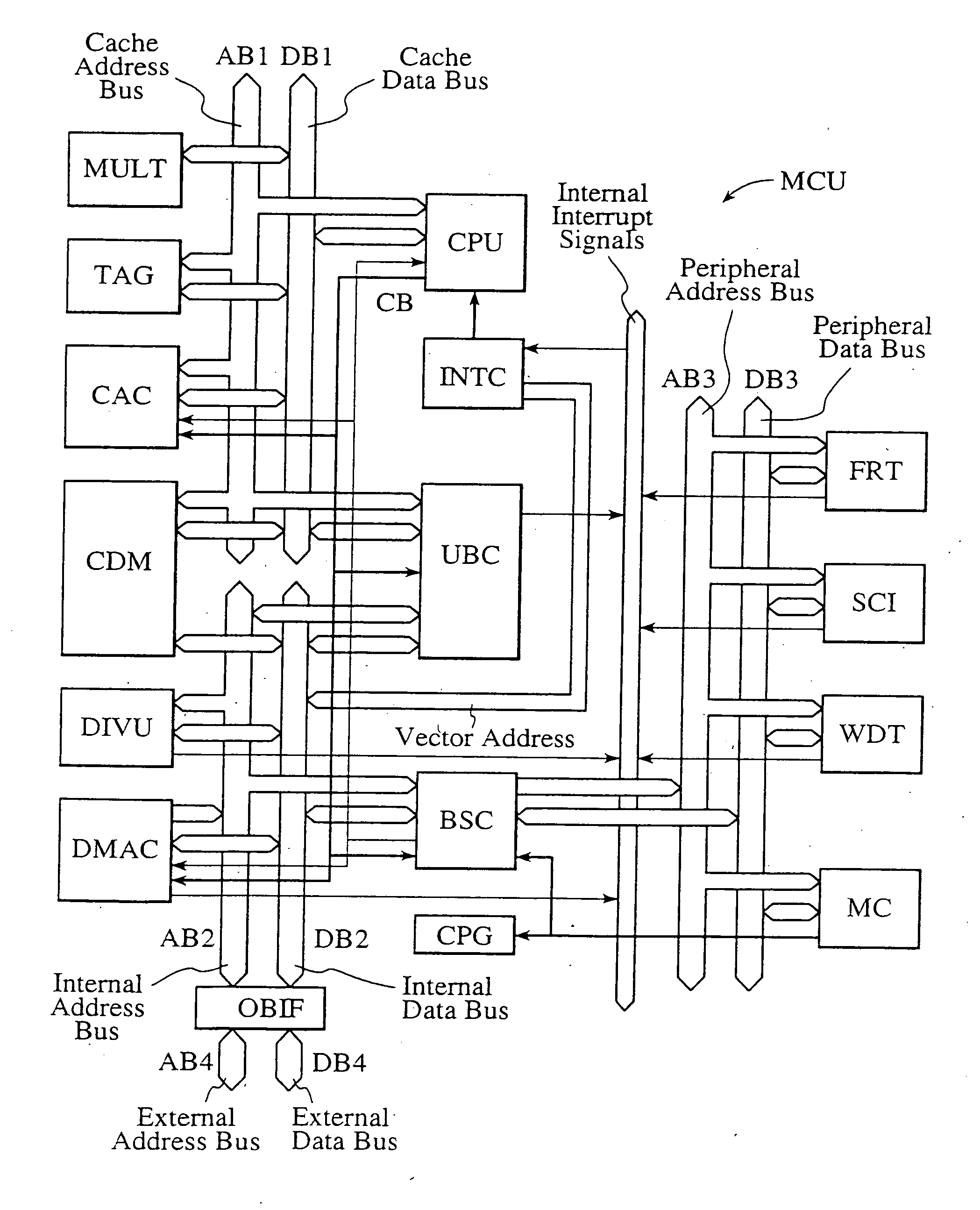
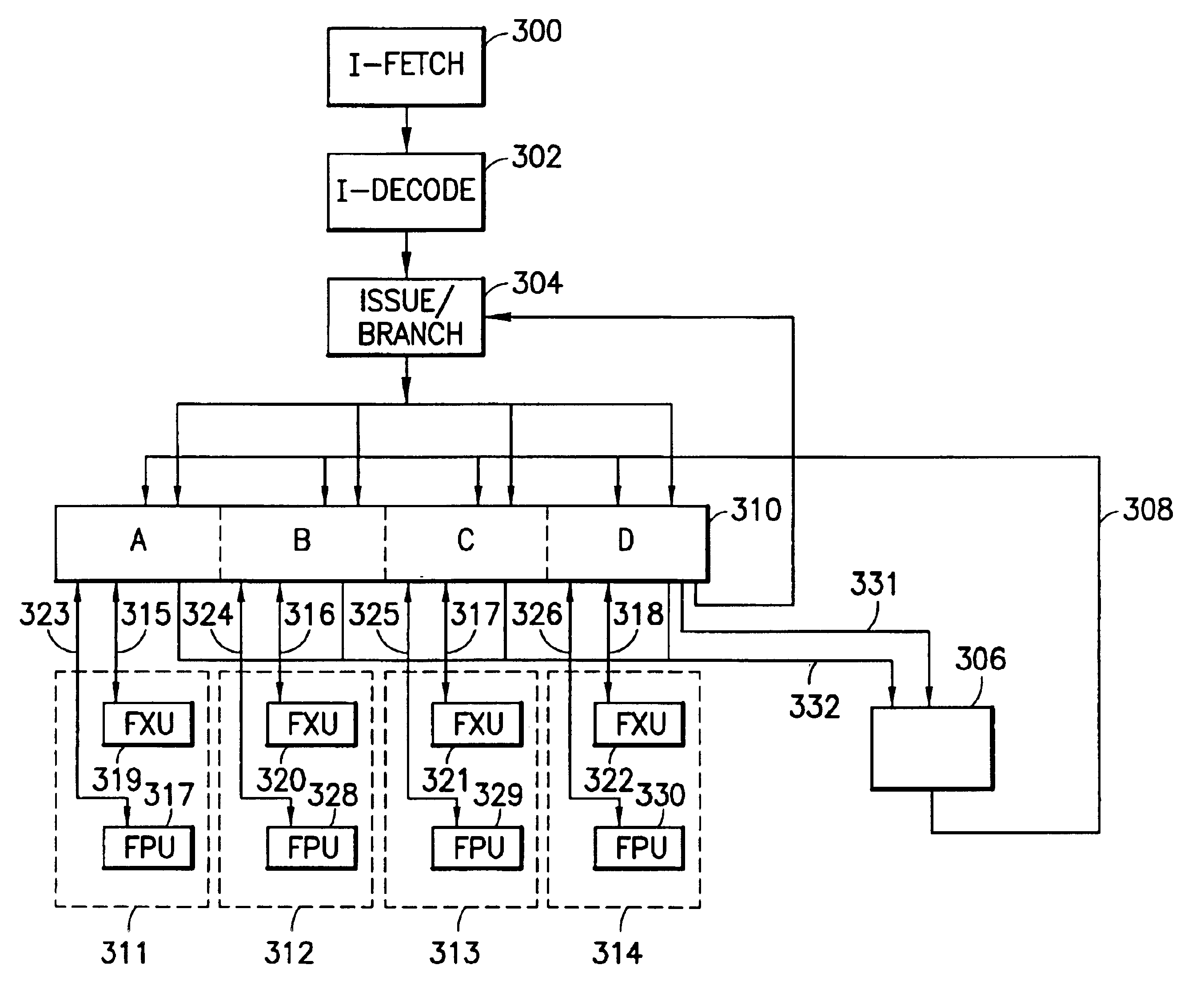
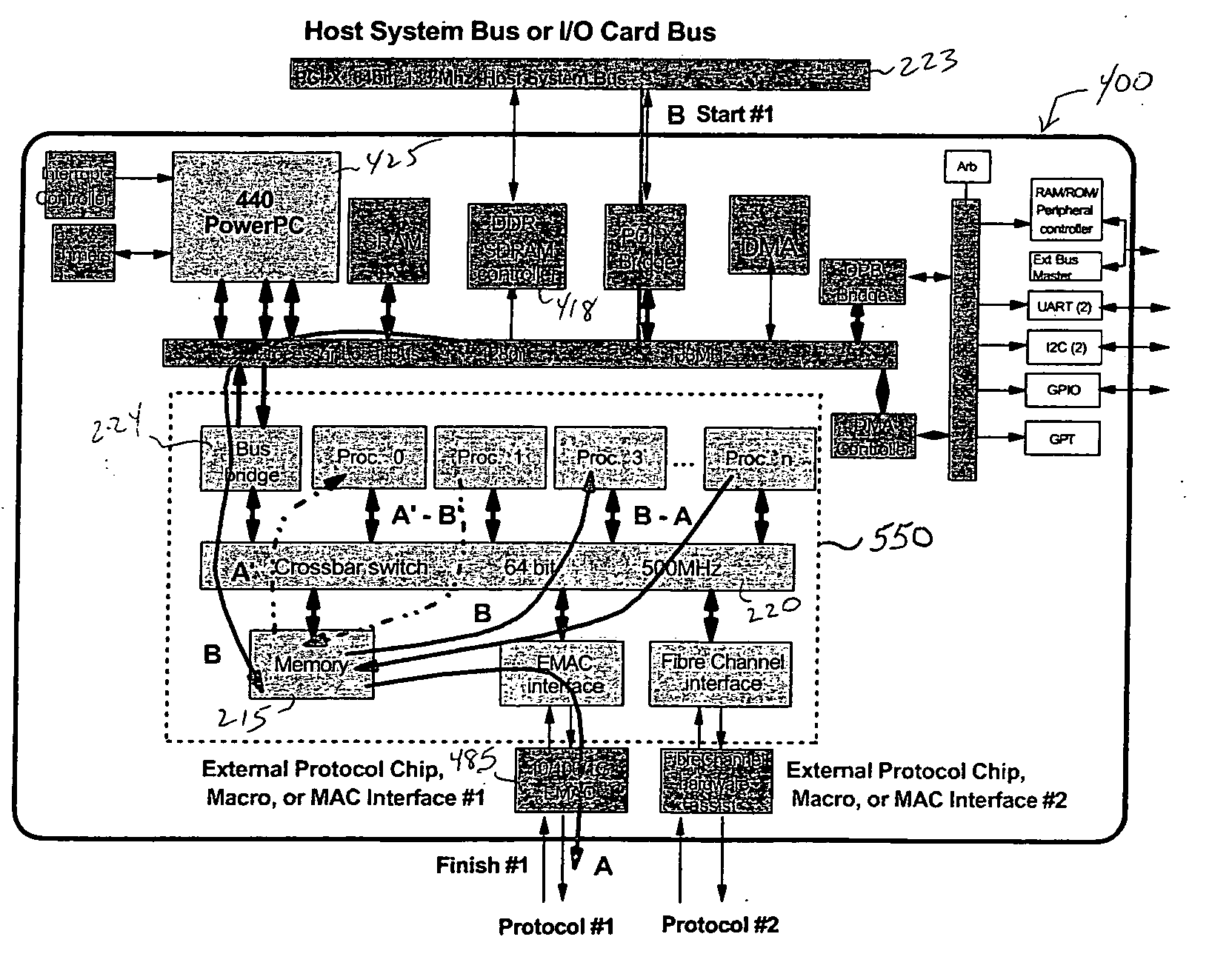
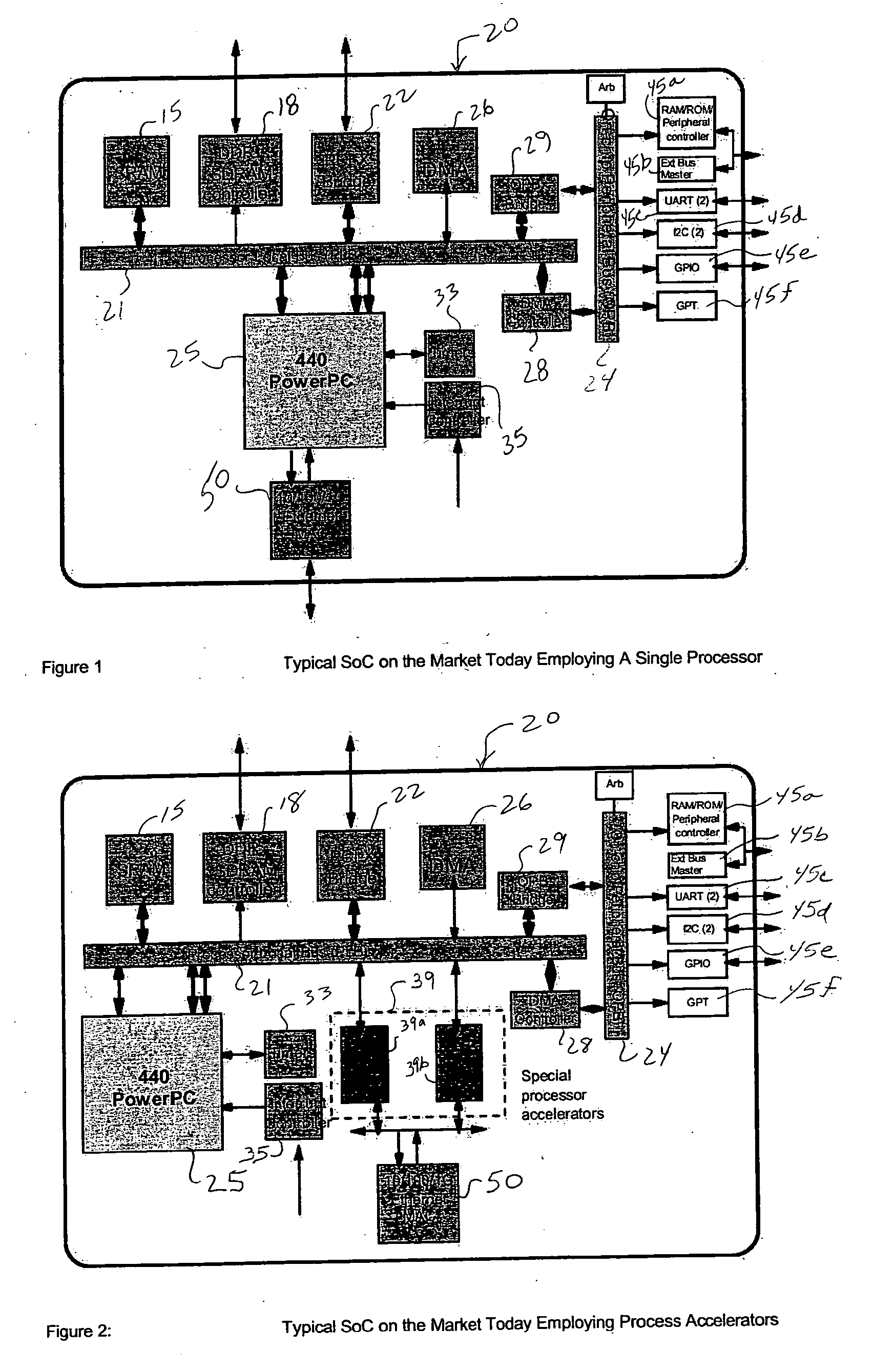
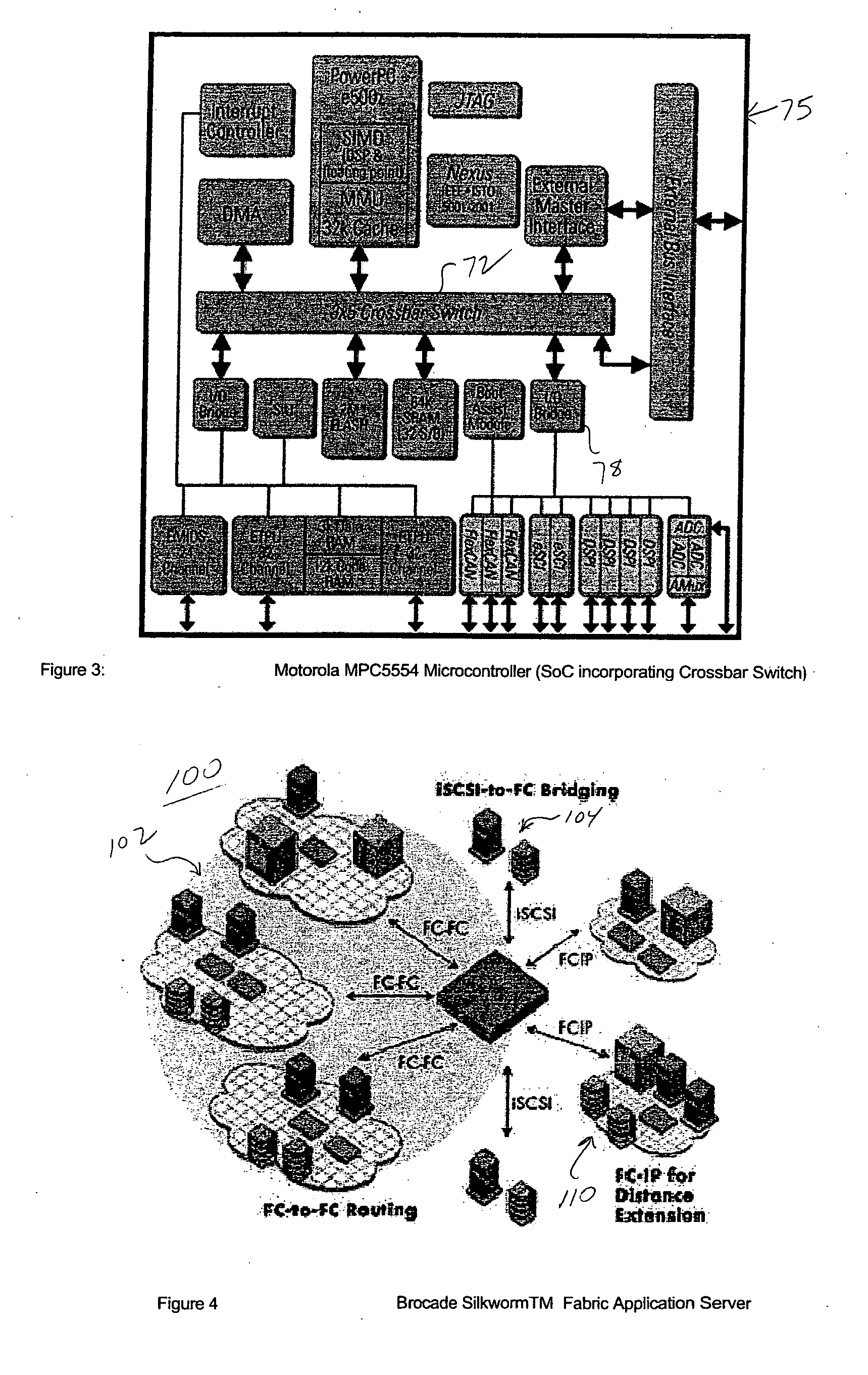
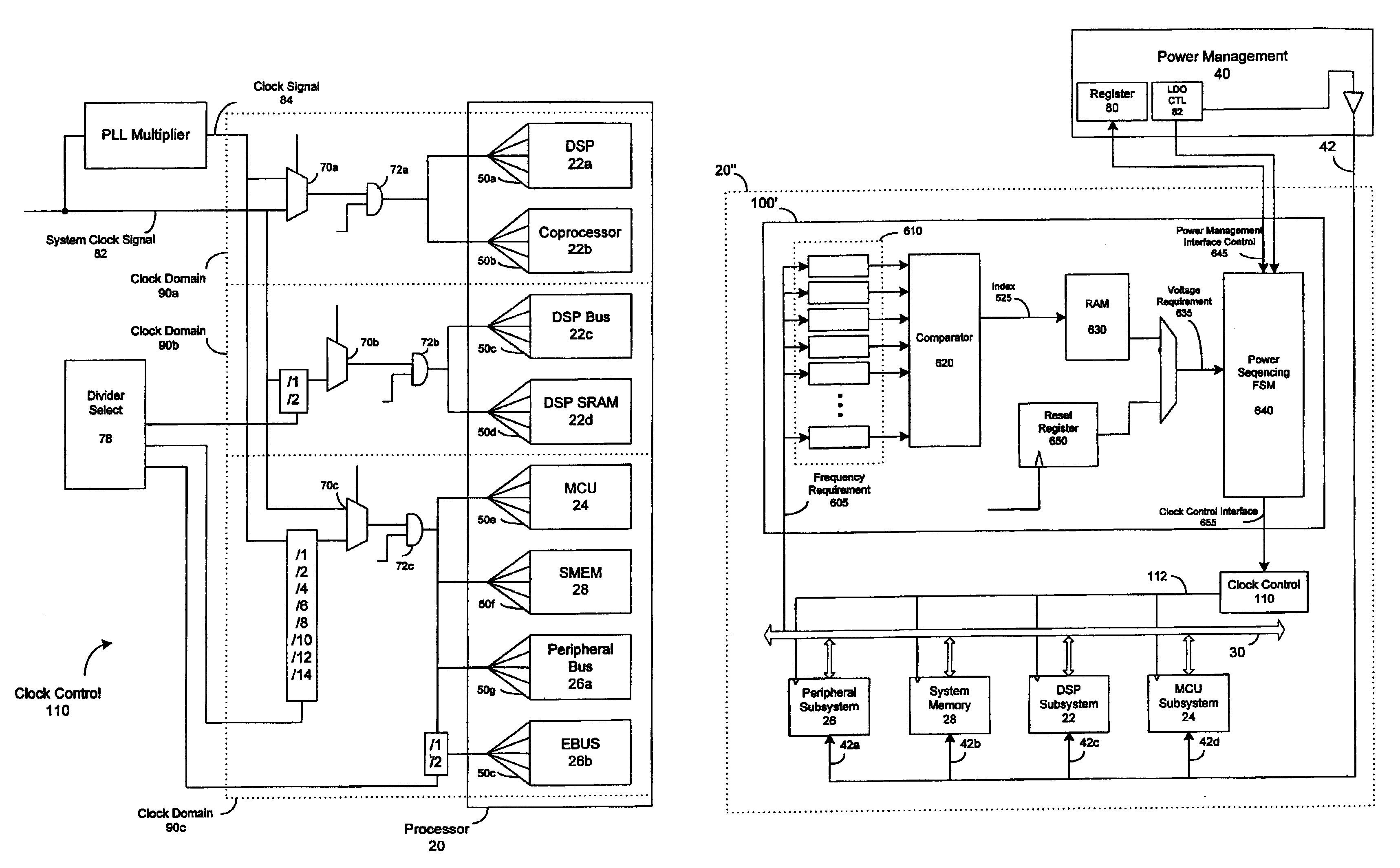
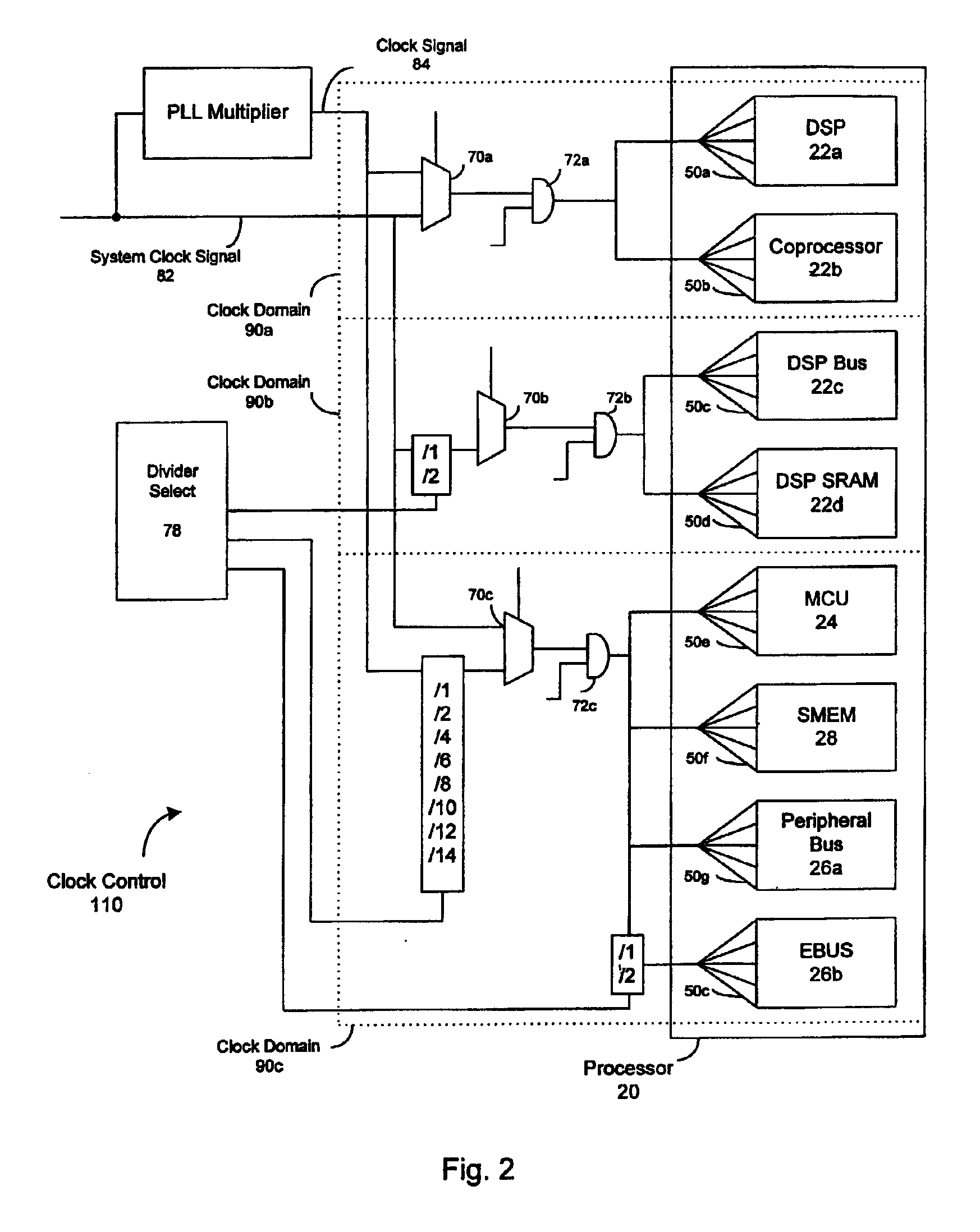
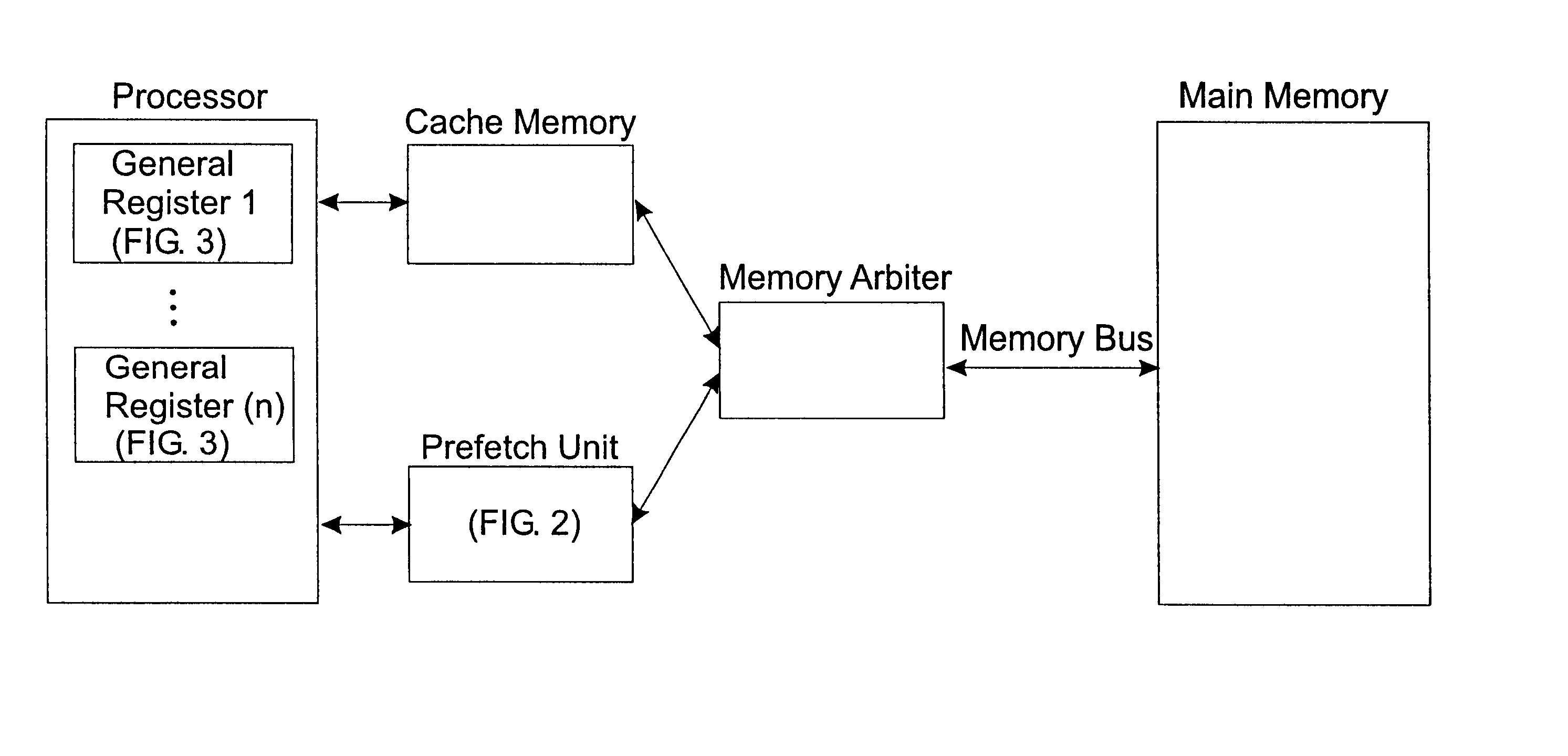
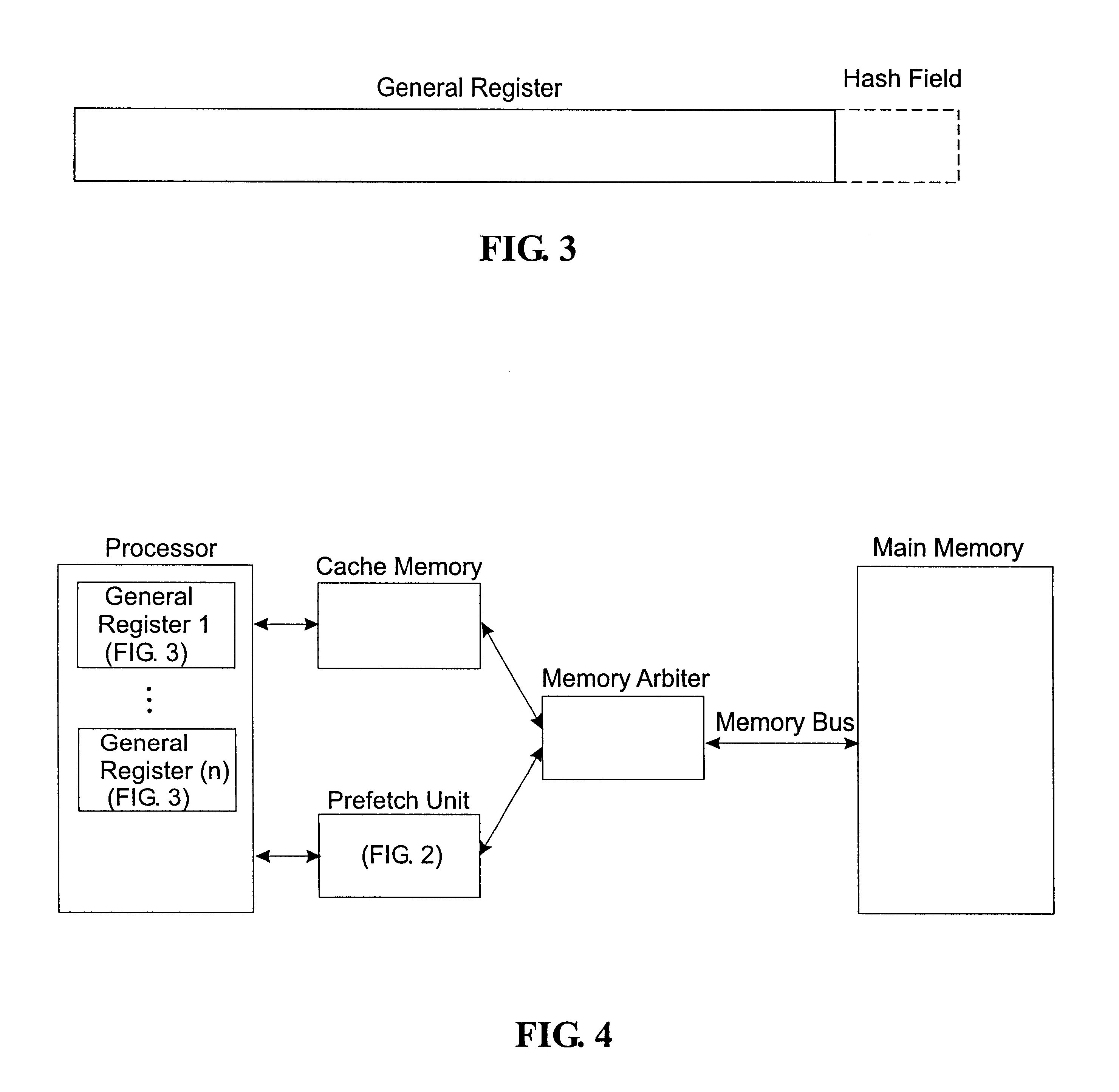
InactiveUS20120023281A1Multiple functionsPerformance multiplePower managementEnergy efficient ICTMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
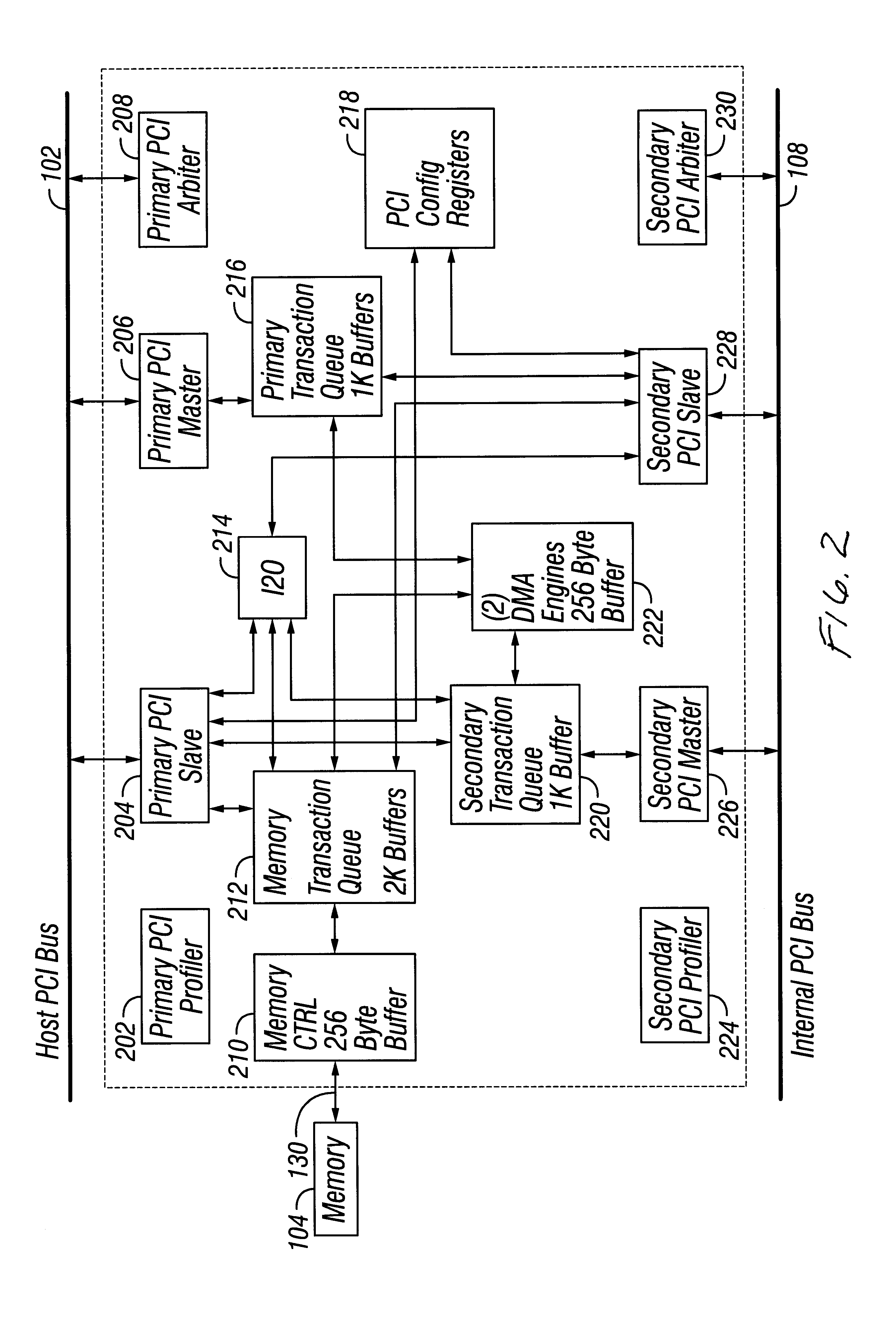
A single-chip microcomputer comprising: a first bus having a central processing unit and a cache memory connected therewith; a second bus having a dynamic memory access control circuit and an external bus interface connected therewith; a break controller for connecting the first bus and the second bus selectively; a third bus having a peripheral module connected therewith and having a lower-speed bus cycle than the bus cycles of the first and second buses; and a bus state controller for effecting a data transfer and a synchronization between the second bus and the third bus. The single-chip microcomputer has the three divided internal buses to reduce the load capacity upon the signal transmission paths so that the signal transmission can be accomplished at a high speed. Moreover, the peripheral module required to have no operation speed is isolated so that the power dissipation can be reduced.
Owner:KAWASAKI SHUMPEI +8
Active memory data compression system and method
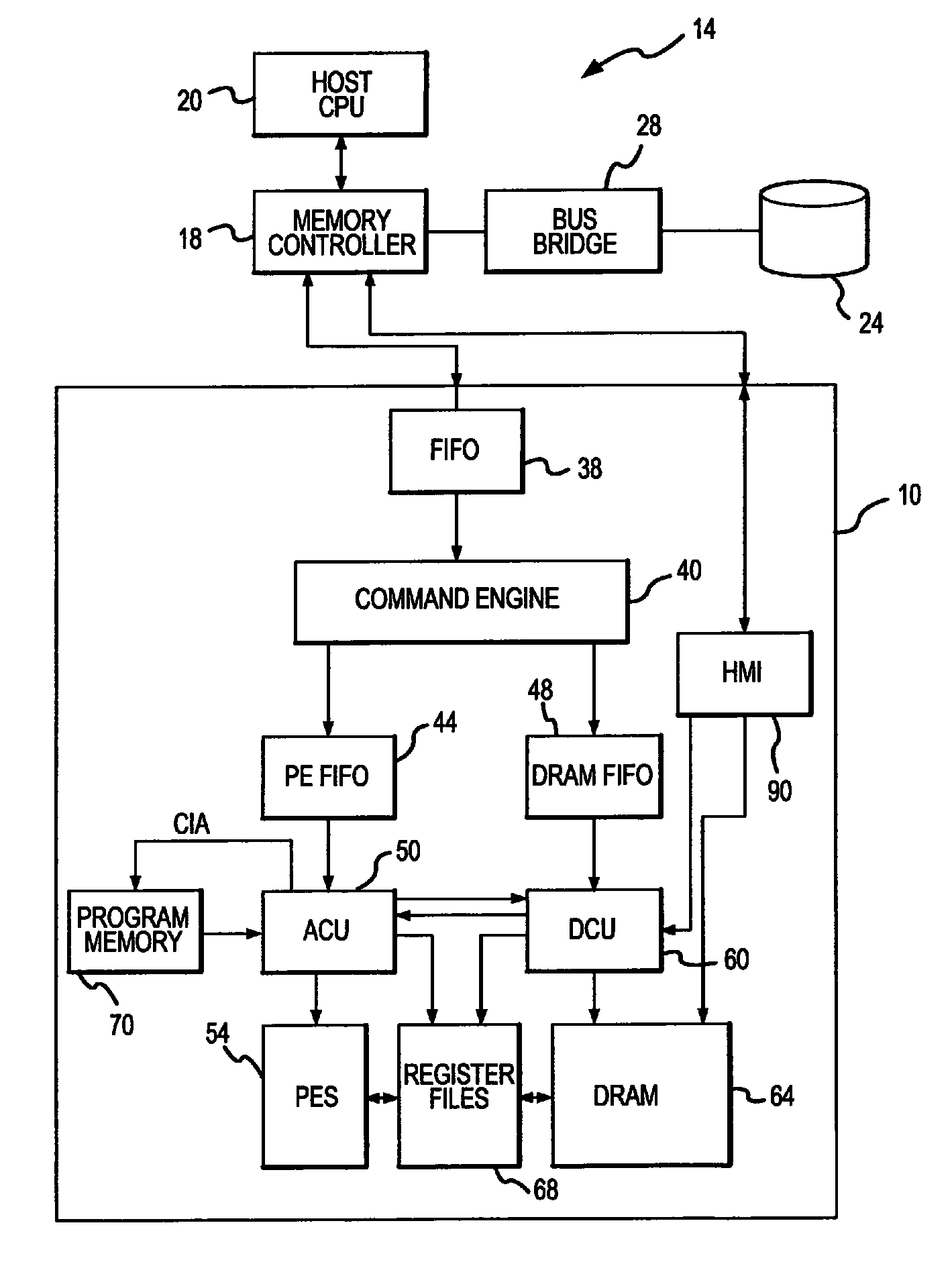
ActiveUS9015390B2Concurrent instruction executionArchitecture with single central processing unitMass storageData compression
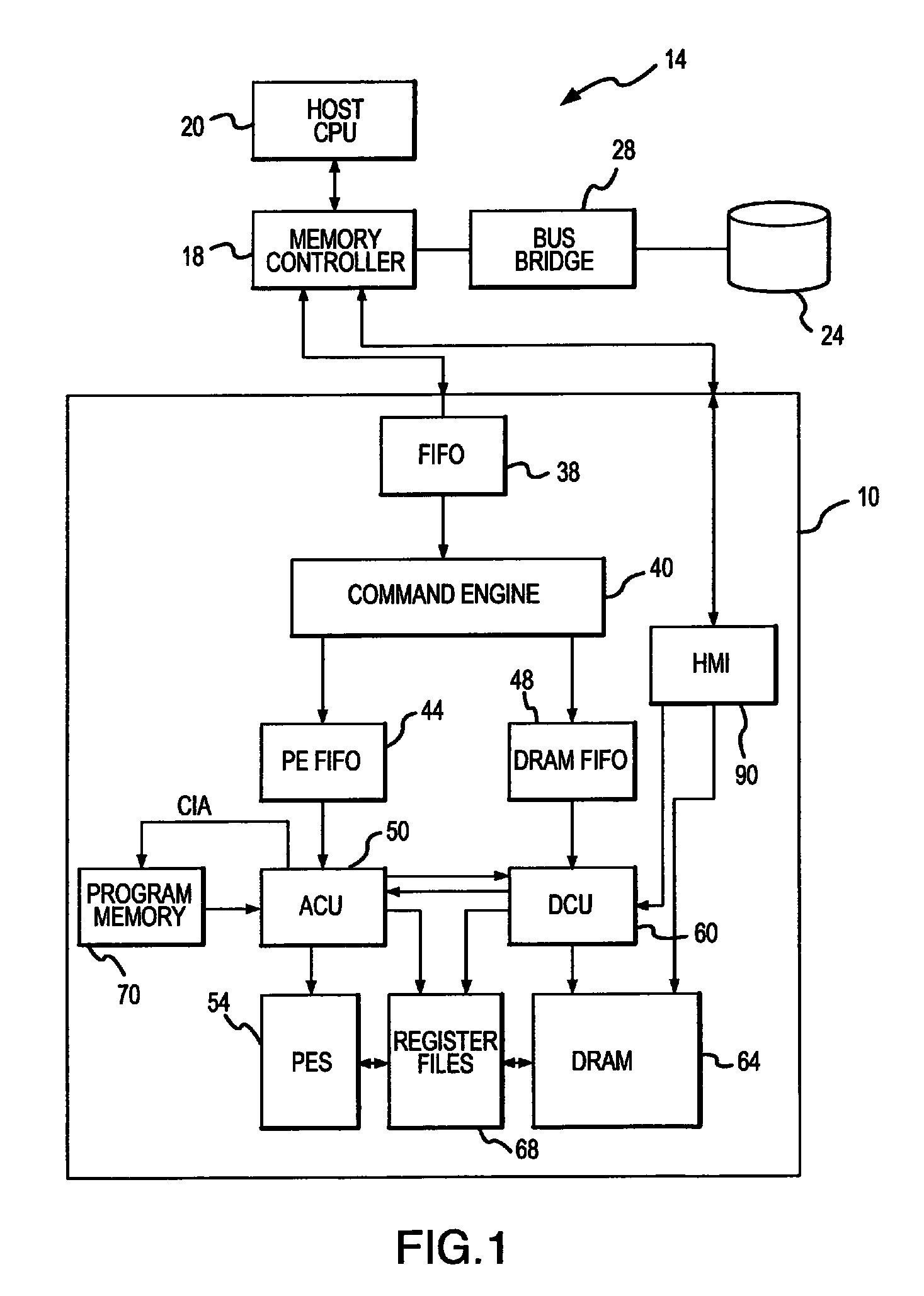
An integrated circuit active memory device receives task commands from a component in a host computer system that may include the active memory device. The host system includes a memory controller coupling the active memory device to a host CPU and a mass storage device. The active memory device includes a command engine issuing instructions responsive to the task commands to either an array control unit or a DRAM control unit. The instructions provided to the DRAM control unit cause data to be written to or read from a DRAM and coupled to or from either the processing elements or a host / memory interface. The processing elements execute instructions provided by the array control unit to decompress data written to the DRAM through the host / memory interface and compress data read from the DRAM through the host / memory interface.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
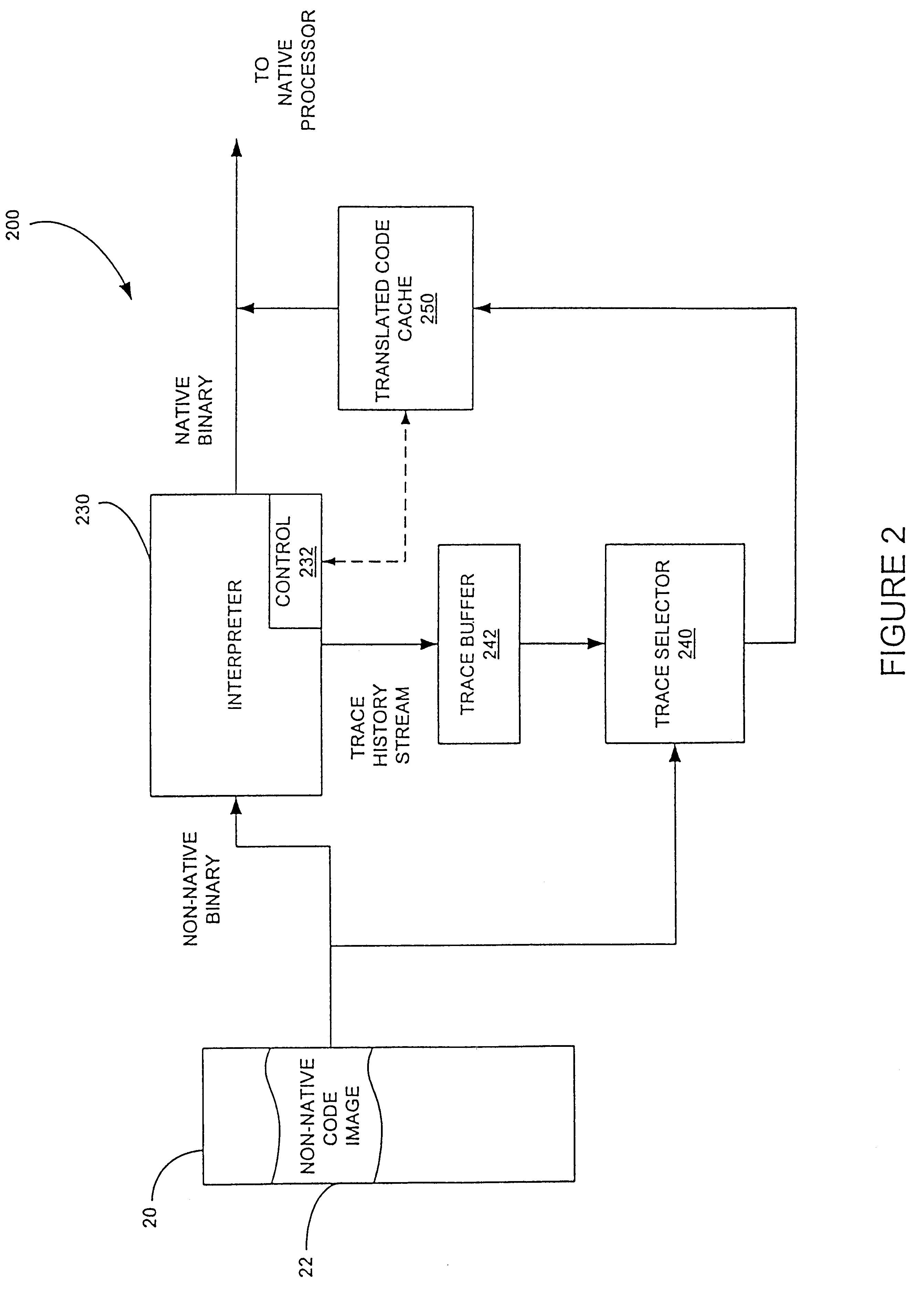
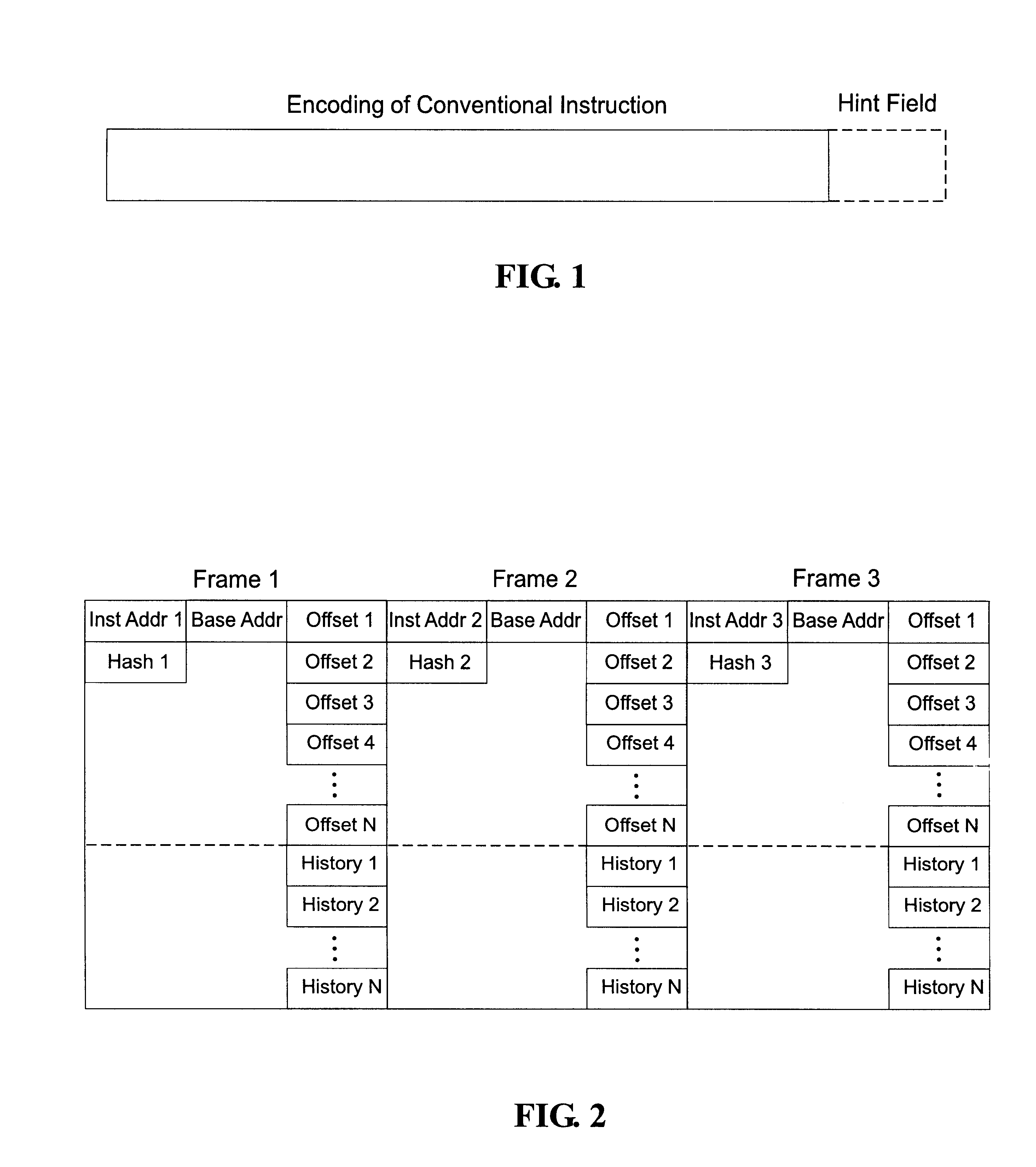
Method for selecting active code traces for translation in a caching dynamic translator
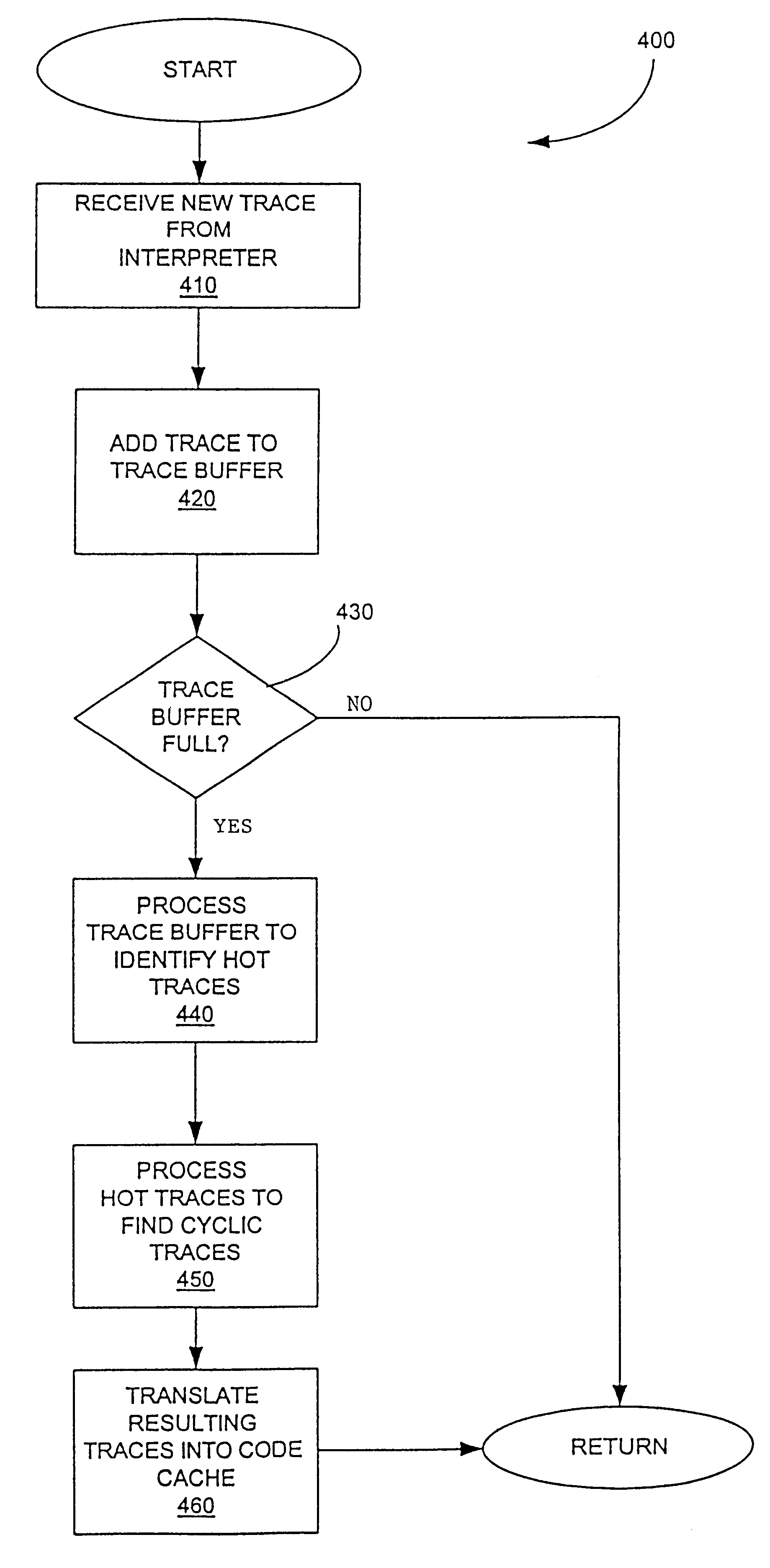
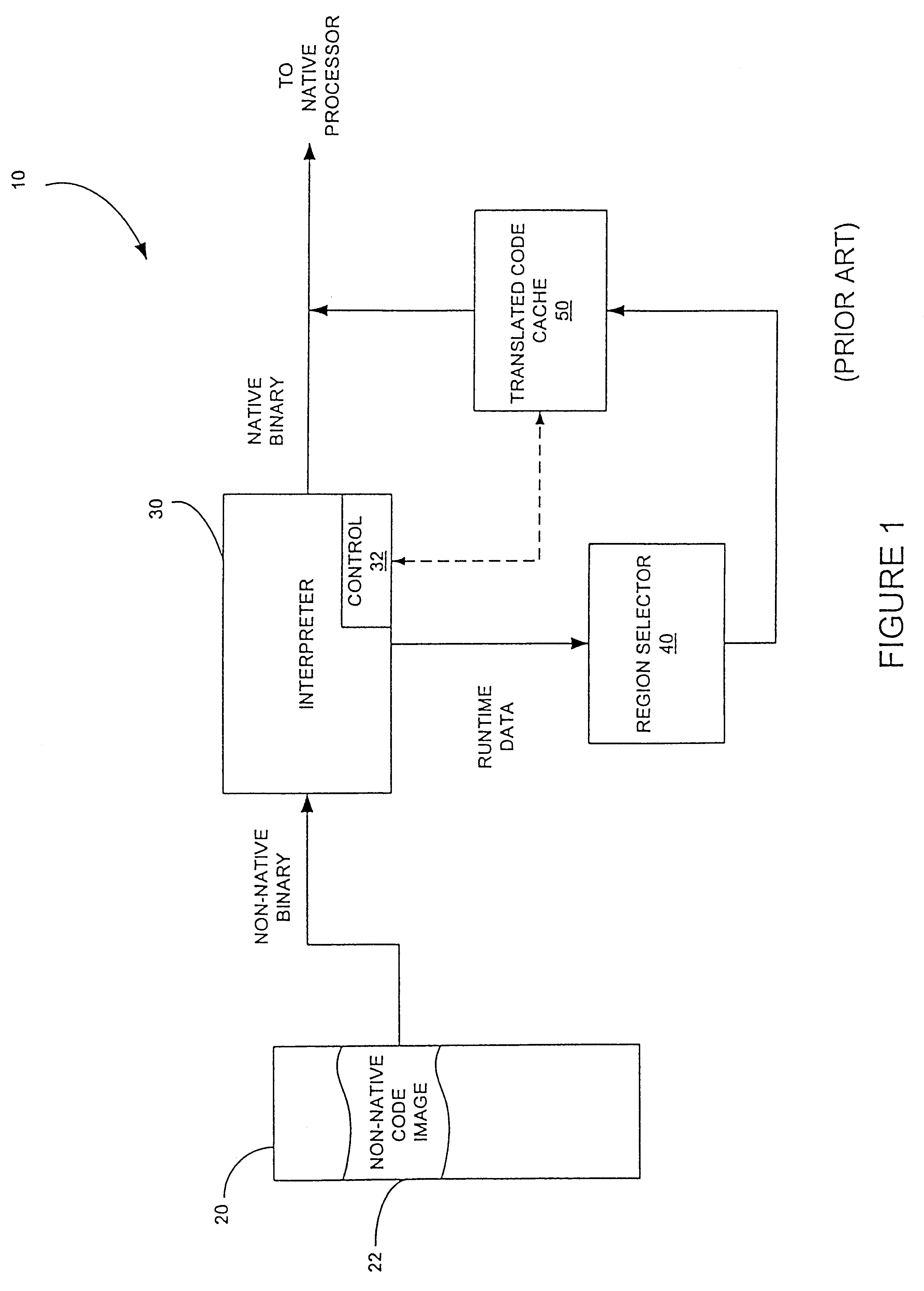
A method is shown for selecting active, or hot, code traces in an executing program for storage in a code cache. A trace is a sequence of dynamic instructions characterized by a start address and a branch history which allows the trace to be dynamically disassembled. Each trace is terminated by execution of a trace terminating condition which is a backward taken branch, an indirect branch, or a branch whose execution causes the branch history for the trace to reach a predetermined limit. As each trace is generated by the executing program, it is loaded into a buffer for processing. When the buffer is full, a counter corresponding to the start address of each trace is incremented. When the count for a start address exceeds a threshold, then the start address is marked as being hot. Each hot trace is then checked to see if the next trace in the buffer shares the same start address, in which case the hot trace is cyclic. If the start address of the next trace is not the same as the hot trace, then the traces in the buffer are checked to see they form a larger cycle of execution. If the traces subsequent to the hot trace are not hot themselves and are followed by a trace having the same start address as the hot trace, then their branch histories are companded with the branch history of the hot trace to form a cyclic trace. The cyclic traces are then disassembled and the instructions executed in the trace are stored in a code cache.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
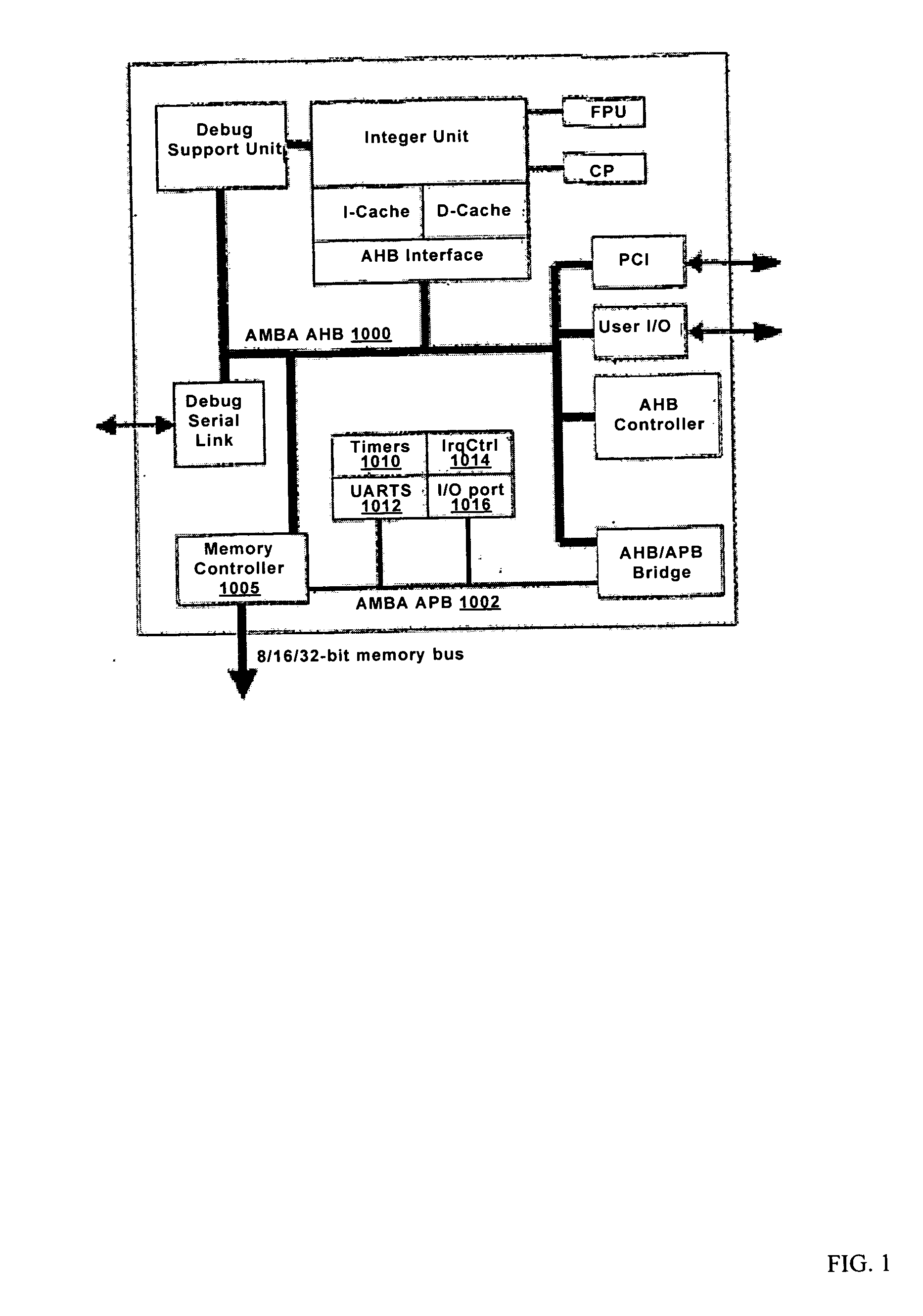
Microprocessors
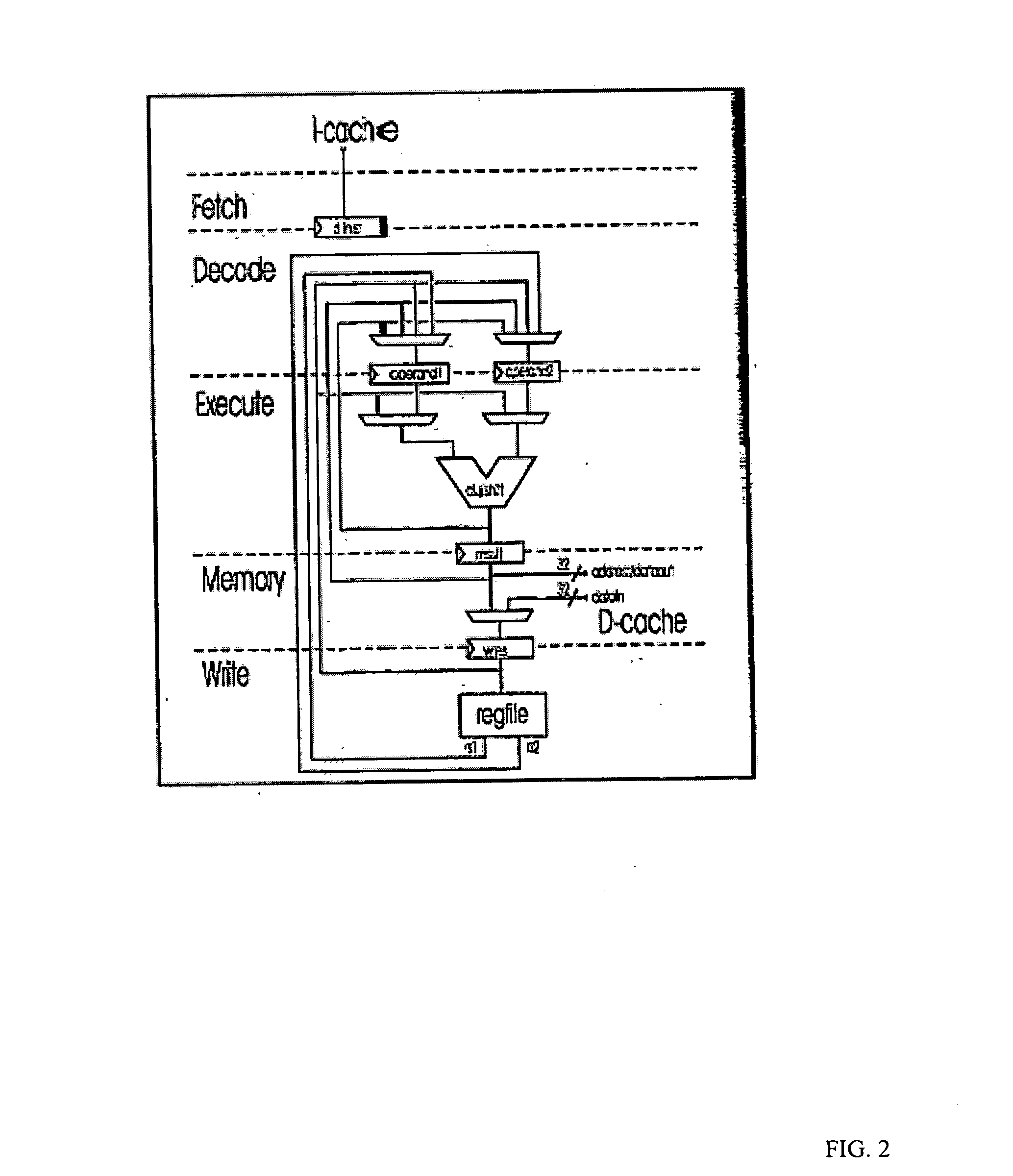
A processor (100) is provided that is a programmable fixed point digital signal processor (DSP) with variable instruction length, offering both high code density and easy programming. Architecture and instruction set are optimized for low power consumption and high efficiency execution of DSP algorithms, such as for wireless telephones, as well as pure control tasks. The processor includes an instruction buffer unit (106), a program flow control unit (108), an address / data flow unit (110), a data computation unit (112), and multiple interconnecting busses. Dual multiply-accumulate blocks improve processing performance. A memory interface unit (104) provides parallel access to data and instruction memories. The instruction buffer is operable to buffer single and compound instructions pending execution thereof. A decode mechanism is configured to decode instructions from the instruction buffer. The use of compound instructions enables effective use of the bandwidth available within the processor. A soft dual memory instruction can be compiled from separate first and second programmed memory instructions. Instructions can be conditionally executed or repeatedly executed. Bit field processing and various addressing modes, such as circular buffer addressing, further support execution of DSP algorithms. The processor includes a multistage execution pipeline with pipeline protection features. Various functional modules can be separately powered down to conserve power. The processor includes emulation and code debugging facilities with support for cache analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
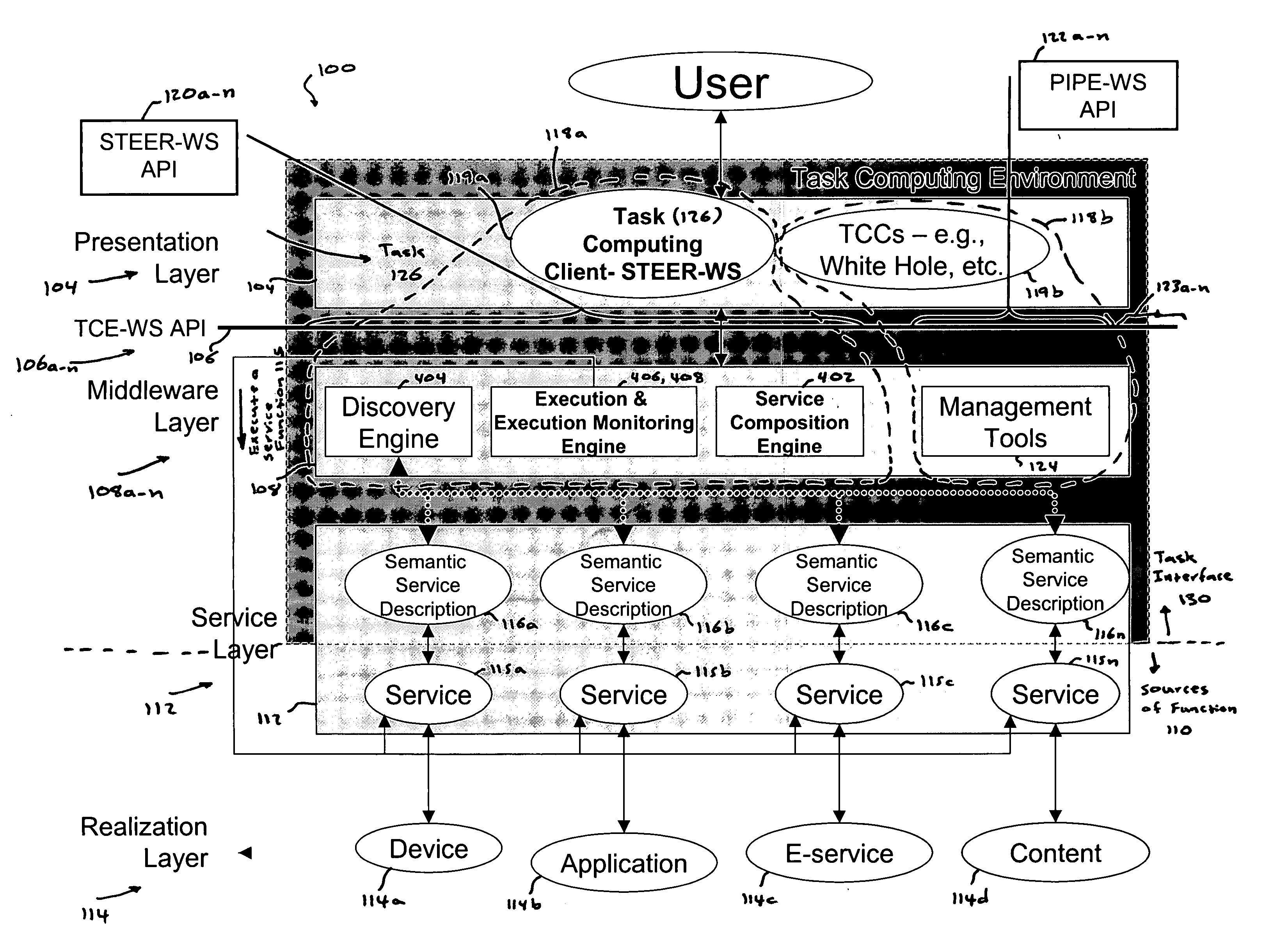
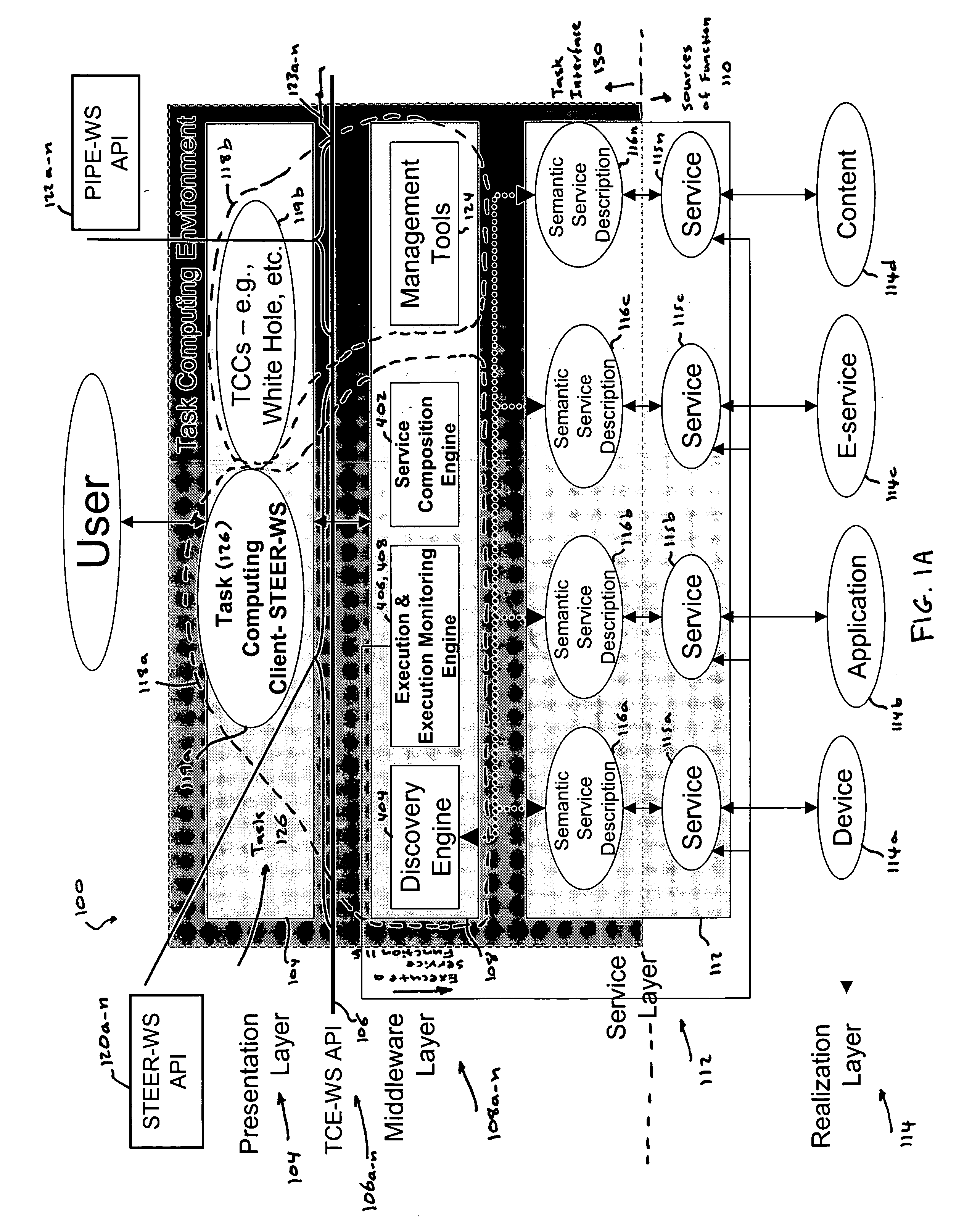
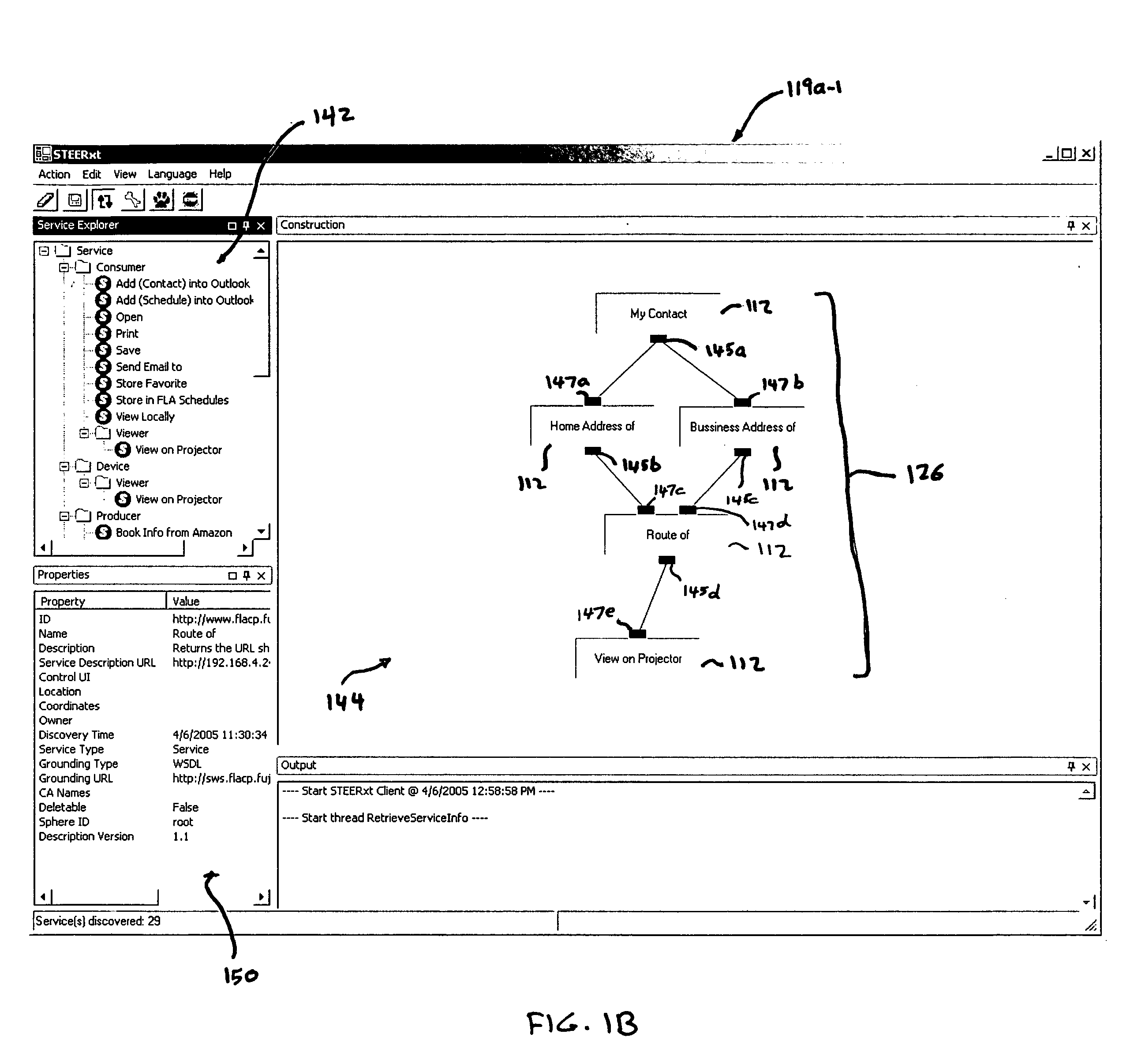
Task computing
InactiveUS20050246726A1Program control using stored programsConcurrent instruction executionLayer interfaceProcedure calls
Task Computing computer system by segmenting the system into a plurality of implementation tiers of a presentation layer, a remote procedure call programming interface (API), a middleware layer to which the presentation layer interfaces via the remote procedure call API to real-time, dynamically generate a computer implemented task interface at the presentation layer to a semantically described source of function as a service on a computer system, and a service layer and a function source realization layer providing the semantically described source of function as the service on the computer system to which the middleware layer interfaces. Real-time and dynamically composing an executable task that comprises one or more services using the generated task interface at the presentation layer to one or more services on the computer based upon the semantically described application-, device- and service-rich computer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
SIMD datapath coupled to scalar/vector/address/conditional data register file with selective subpath scalar processing mode
InactiveUS6839828B2Not compromise SIMD data processing performanceReduce consumptionRegister arrangementsDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerOperation mode
There is provided a processor designed to operate in a plurality of modes for processing vector and scalar instructions. Register files are each for storing scalar and vector data and address information. A parallel vector unit, coupled to the register files, includes functional units configurable to operate in a vector operation mode and a scalar operation mode. The vector unit includes an apparatus for tightly coupling the functional units to perform an operation specified by a current instruction. Under a vector operation mode, the vector unit performs, in parallel, a single vector operation on a plurality of data elements. The operations performed on the plurality of data elements are each performed by a different functional unit of the vector unit. Under a scalar operation mode, the vector unit performs a scalar operation on a data element received from the register files in a functional unit within the vector unit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Arithmetic processing apparatus
InactiveUS7412470B2MiniaturizationReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesProcessor registerComputer science
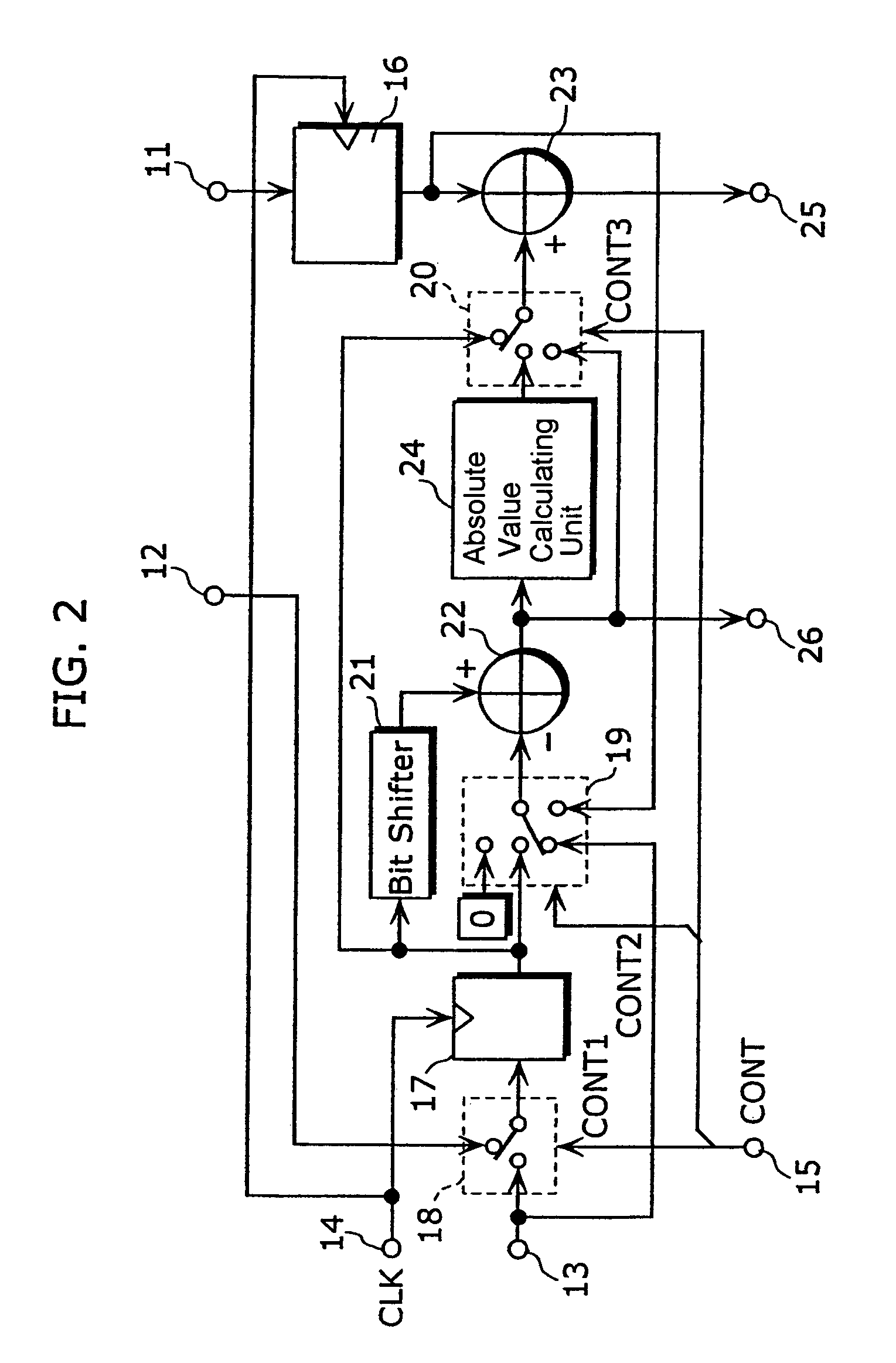
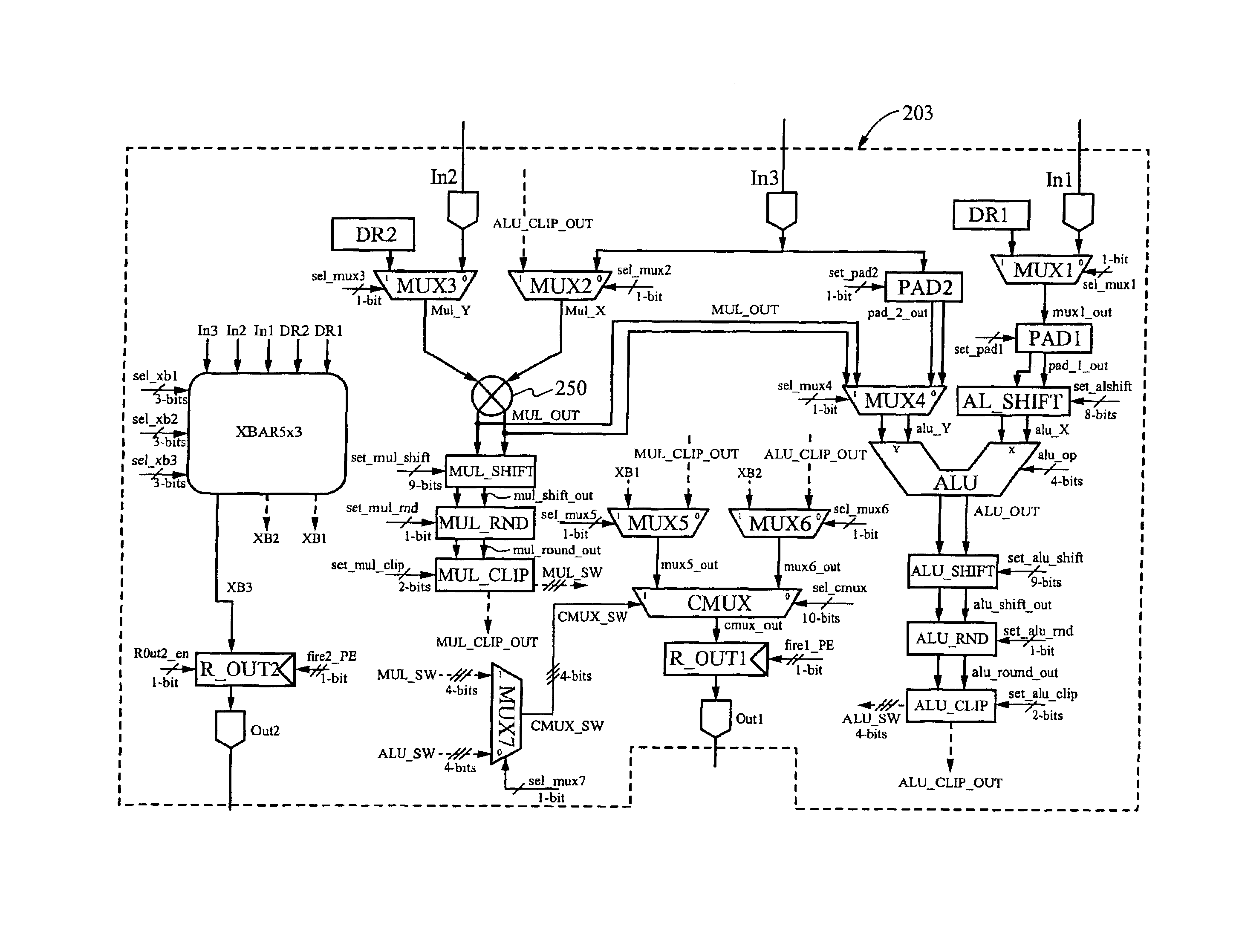
The arithmetic processing apparatus of the present invention is an arithmetic processing apparatus that can be reconfigured in accordance with a processing mode and has a plurality of arranged unit arithmetic circuits. Each unit arithmetic circuit includes at least one input terminal, at least one output terminal, a first register which holds data, an adder which calculates a sum of two pieces of data, a second register which holds data, a bit shifter which shifts data left or right, a subtractor which calculates a difference between two pieces of data, an absolute value calculating unit which calculates an absolute value of data, and a path setting unit which sets a path according to the processing mode connecting among these circuit elements.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Multiple tokenization for authentication
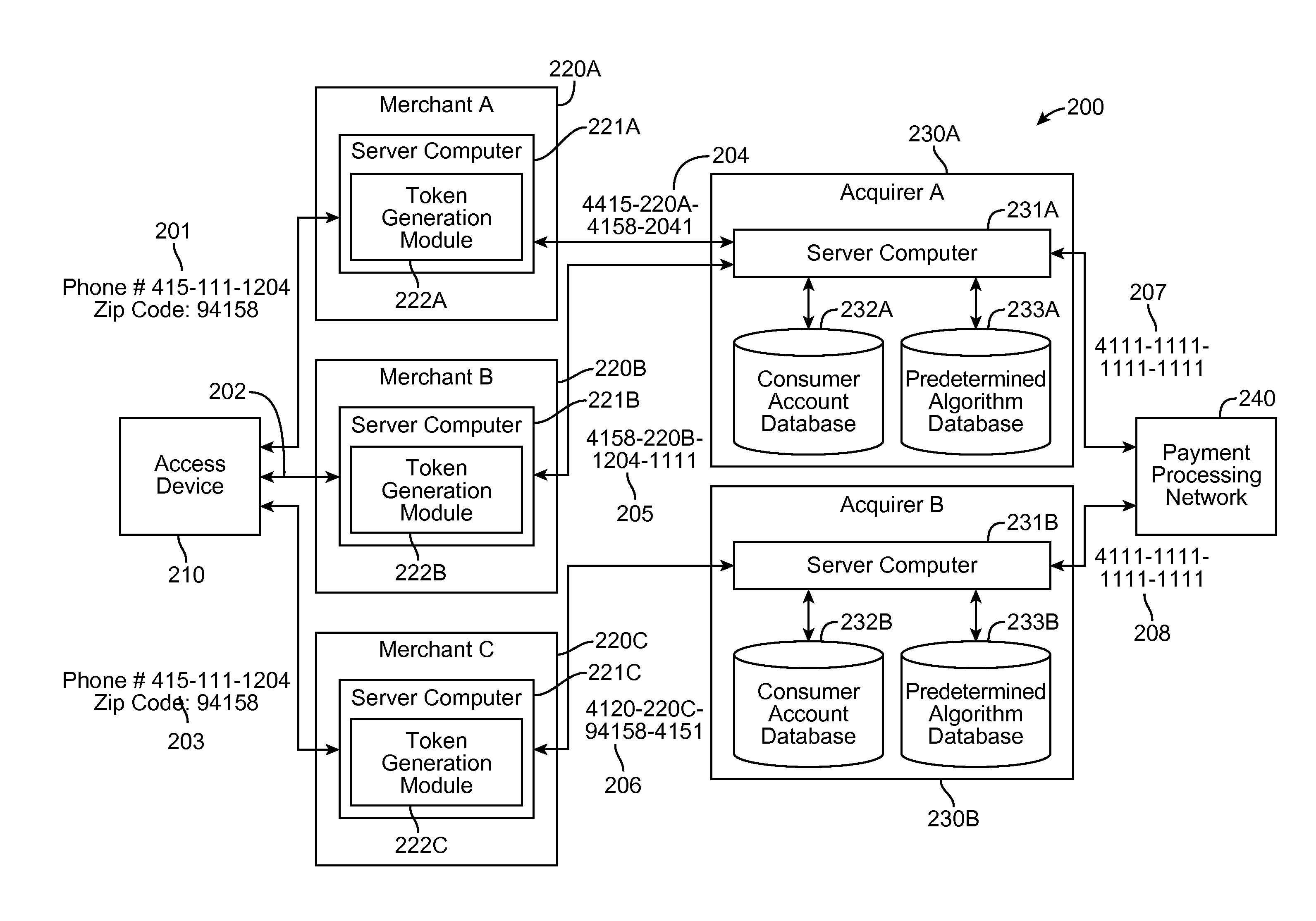
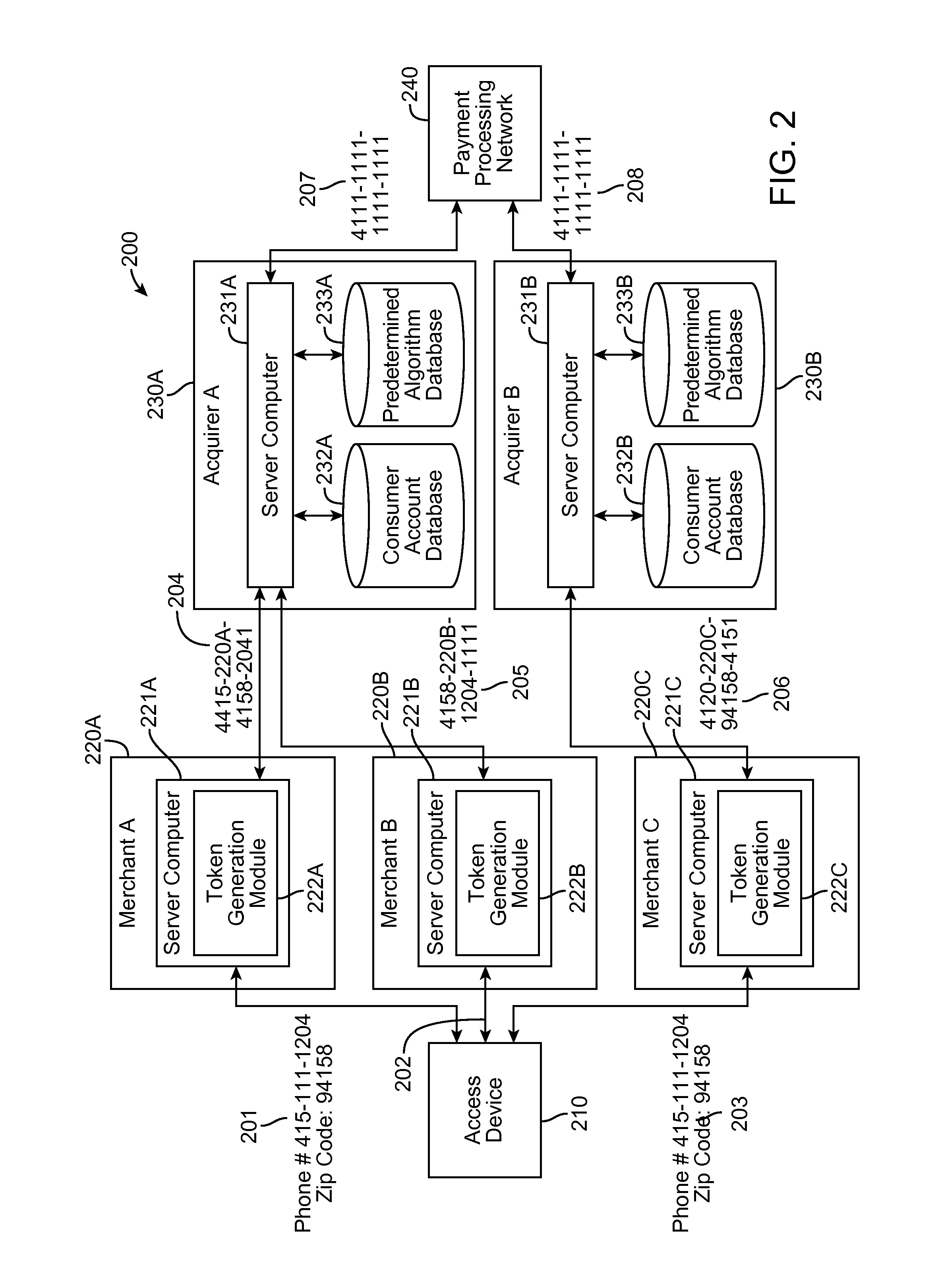
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to systems, methods, and apparatuses for authenticating a cardholder using multiple tokenization authentication. Embodiments of the invention are directed at a method. The method includes receiving at a first entity a first token from a consumer and determining a second token associated with the first token. Once the second token is determined, the second token is sent to a server computer at a second entity. The server computer then determines an account identifier associated with the second token and processes a transaction using the account identifier.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Single chip protocol converter
ActiveUS20050021874A1Increase the number ofHigh bandwidthConcurrent instruction executionMultiple digital computer combinationsSingle chipMultiprocessing
A single chip protocol converter integrated circuit (IC) capable of receiving packets generating according to a first protocol type and processing said packets to implement protocol conversion and generating converted packets of a second protocol type for output thereof, the process of protocol conversion being performed entirely within the single integrated circuit chip. The single chip protocol converter can be further implemented as a macro core in a system-on-chip (SoC) implementation, wherein the process of protocol conversion is contained within a SoC protocol conversion macro core without requiring the processing resources of a host system. Packet conversion may additionally entail converting packets generated according to a first protocol version level and processing the said packets to implement protocol conversion for generating converted packets according to a second protocol version level, but within the same protocol family type. The single chip protocol converter integrated circuit and SoC protocol conversion macro implementation include multiprocessing capability including processor devices that are configurable to adapt and modify the operating functionality of the chip.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
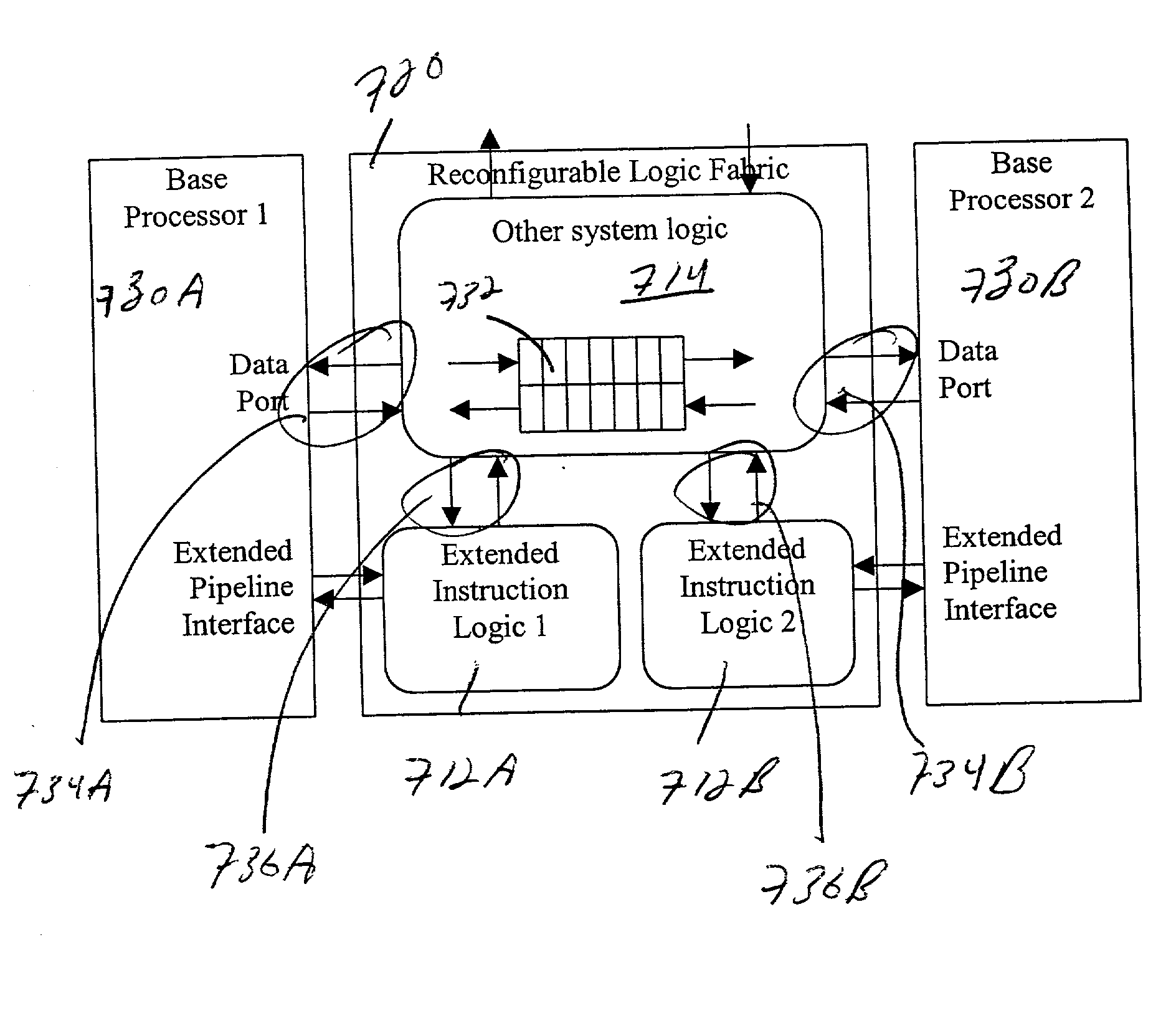
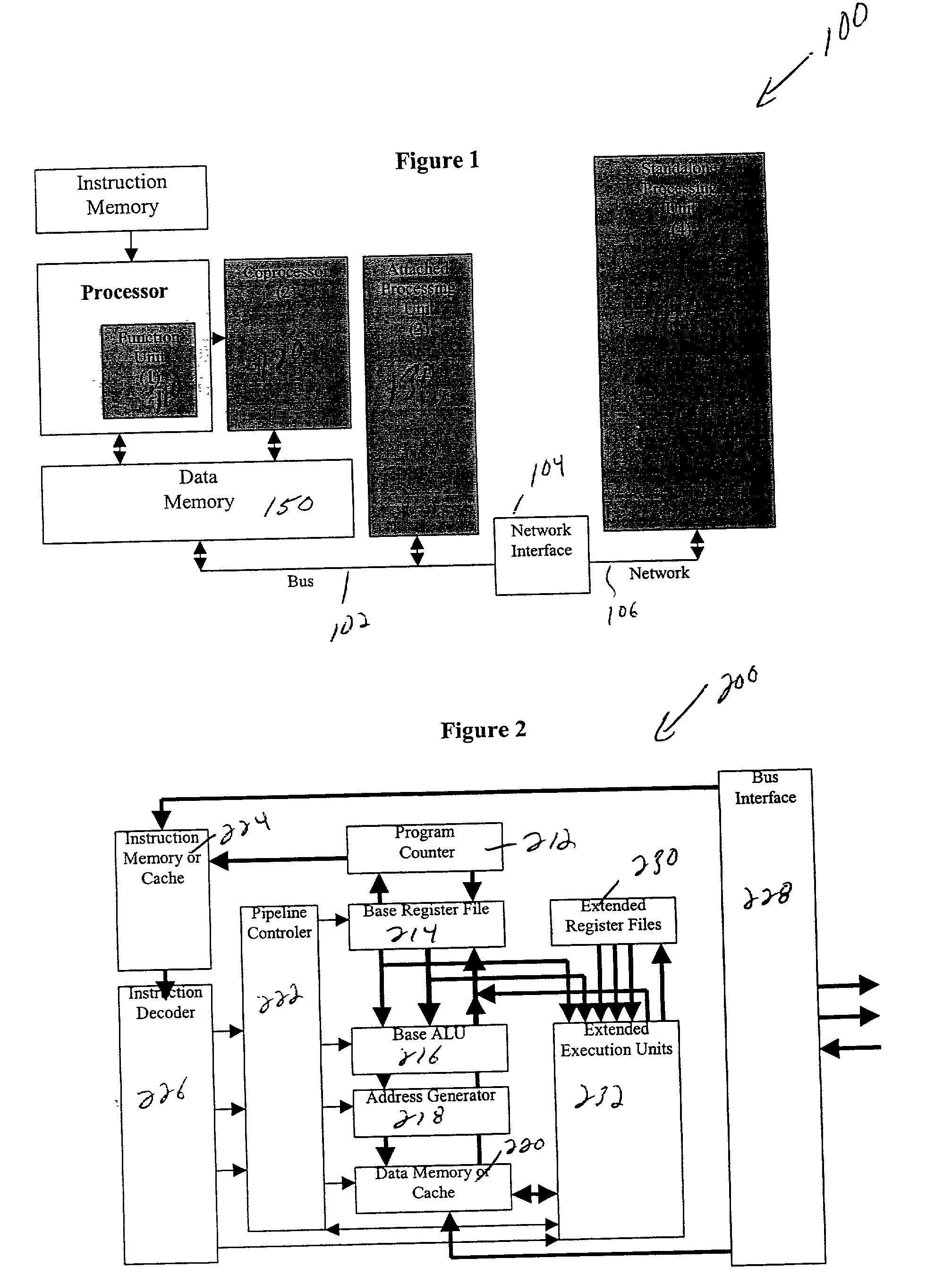
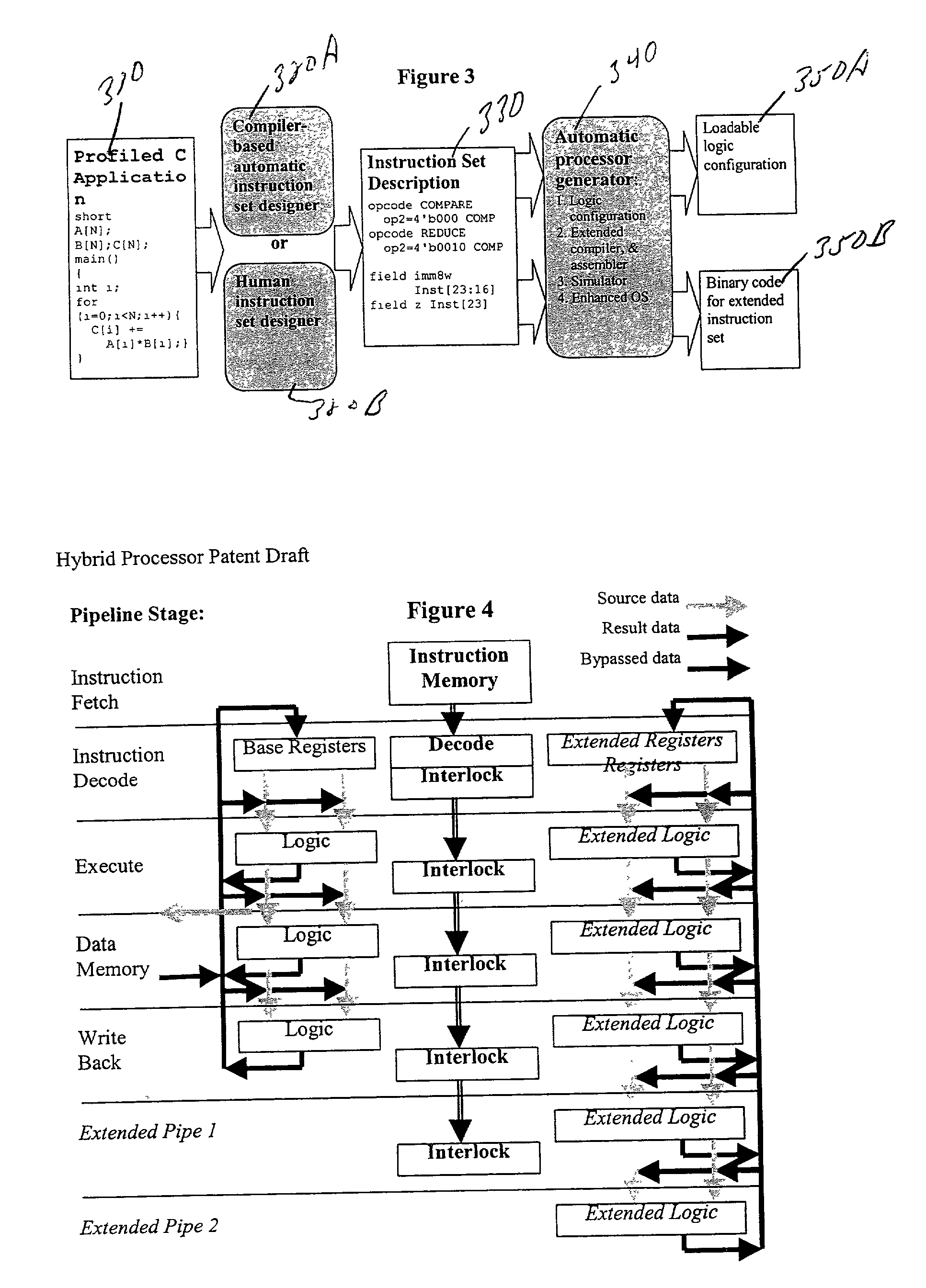
High-performance hybrid processor with configurable execution units
InactiveUS20050166038A1High bandwidthFlexibilityInstruction analysisConcurrent instruction executionHigh bandwidthLatency (engineering)
A new general method for building hybrid processors achieves higher performance in applications by allowing more powerful, tightly-coupled instruction set extensions to be implemented in reconfigurable logic. New instructions set configurations can be discovered and designed by automatic and semi-automatic methods. Improved reconfigurable execution units support deep pipelining, addition of additional registers and register files, compound instructions with many source and destination registers and wide data paths. New interface methods allow lower latency, higher bandwidth connections between hybrid processors and other logic.
Owner:TENSILICA
Data processing method and device
ActiveUS20070050603A1Improve data throughputDelay problemMemory adressing/allocation/relocationConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingData processing
In a data-processing method, first result data may be obtained using a plurality of configurable coarse-granular elements, the first result data may be written into a memory that includes spatially separate first and second memory areas and that is connected via a bus to the plurality of configurable coarse-granular elements, the first result data may be subsequently read out from the memory, and the first result data may be subsequently processed using the plurality of configurable coarse-granular elements. In a first configuration, the first memory area may be configured as a write memory, and the second memory area may be configured as a read memory. Subsequent to writing to and reading from the memory in accordance with the first configuration, the first memory area may be configured as a read memory, and the second memory area may be configured as a write memory.
Owner:SCIENTIA SOL MENTIS AG
Pipelined data relocation and improved chip architectures
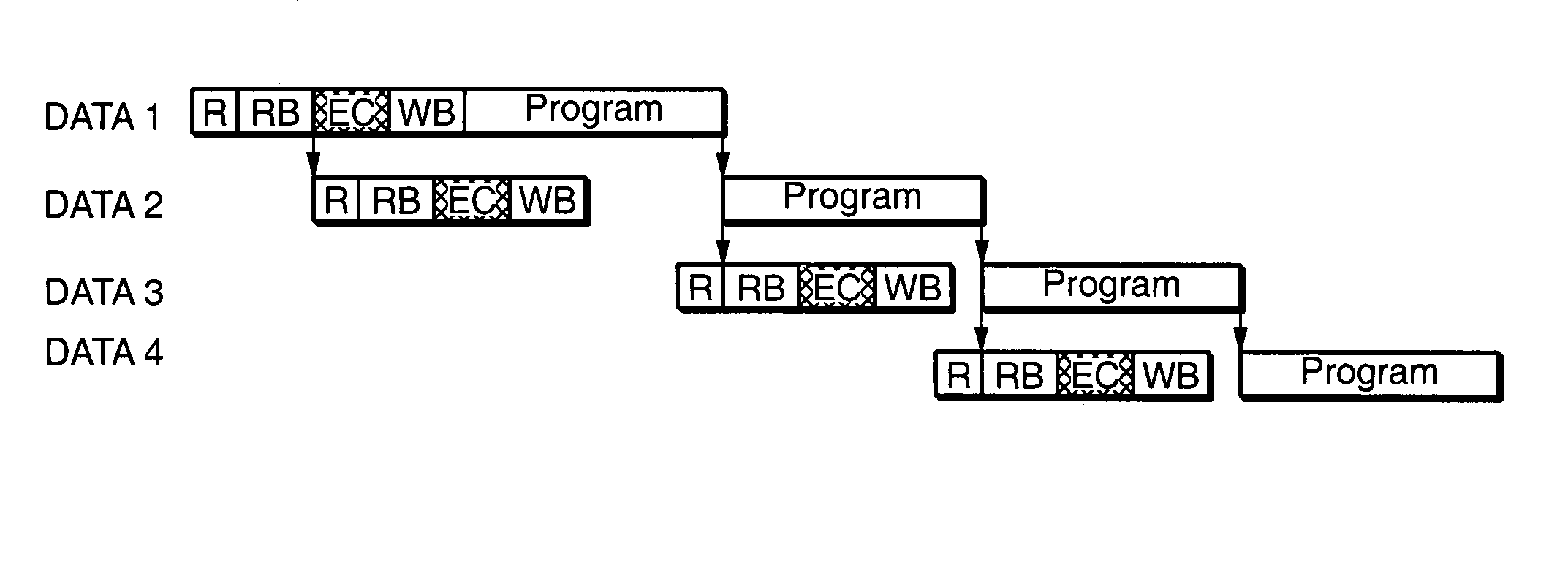
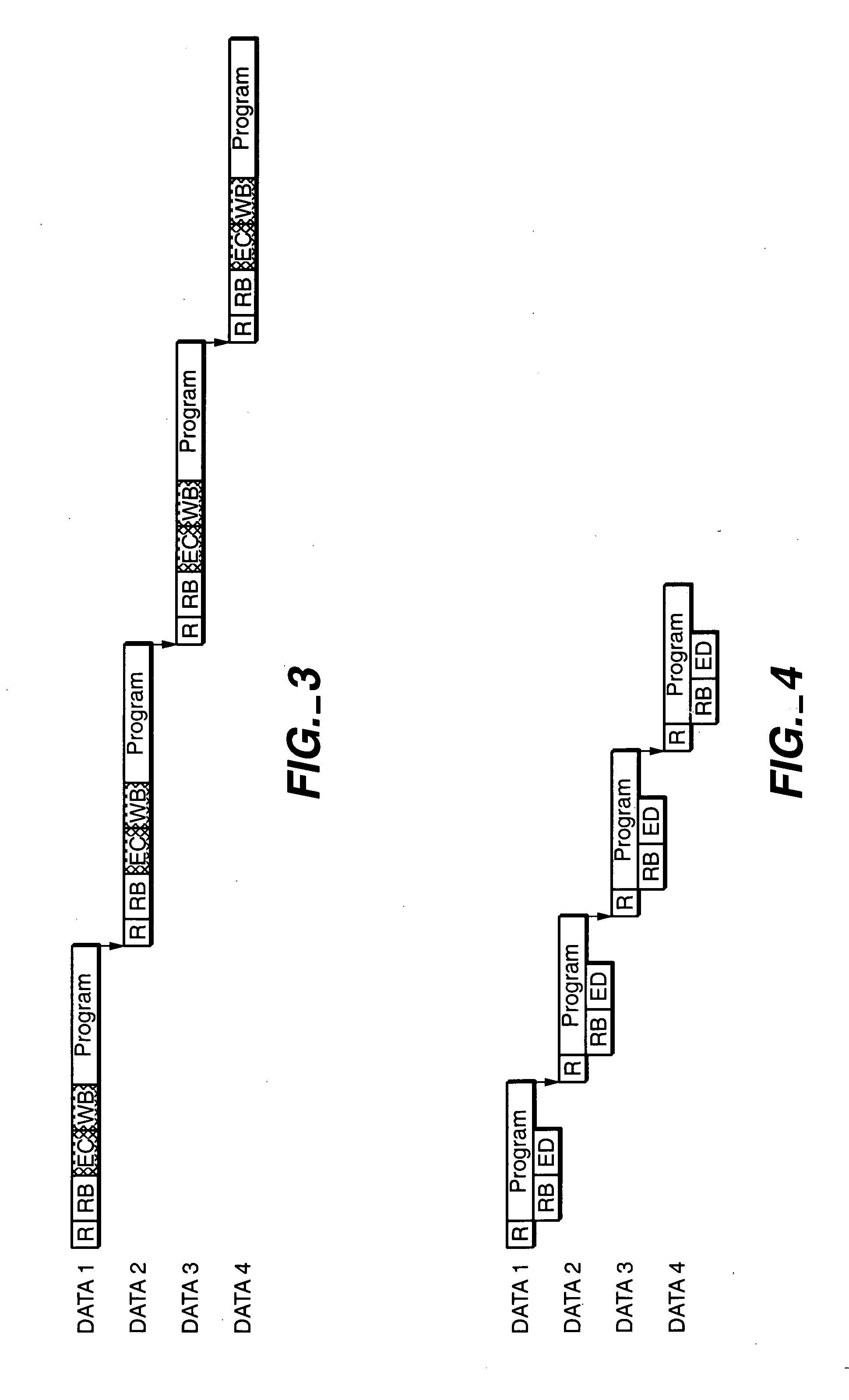
ActiveUS20050257120A1High error rateAccelerating complex data operationError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesPresent methodParallel computing
The present invention present methods and architectures for the pipelining of read operation with write operations. In particular, methods are presented for pipelining data relocation operations that allow for the checking and correction of data in the controller prior to its being re-written, but diminish or eliminate the additional time penalty this would normally incur. A number of architectural improve are described to facilitate these methods, including: introducing two registers on the memory where each is independently accessible by the controller; allowing a first memory register to be written from while a second register is written to; introducing two registers on the memory where the contents of the registers can be swapped.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
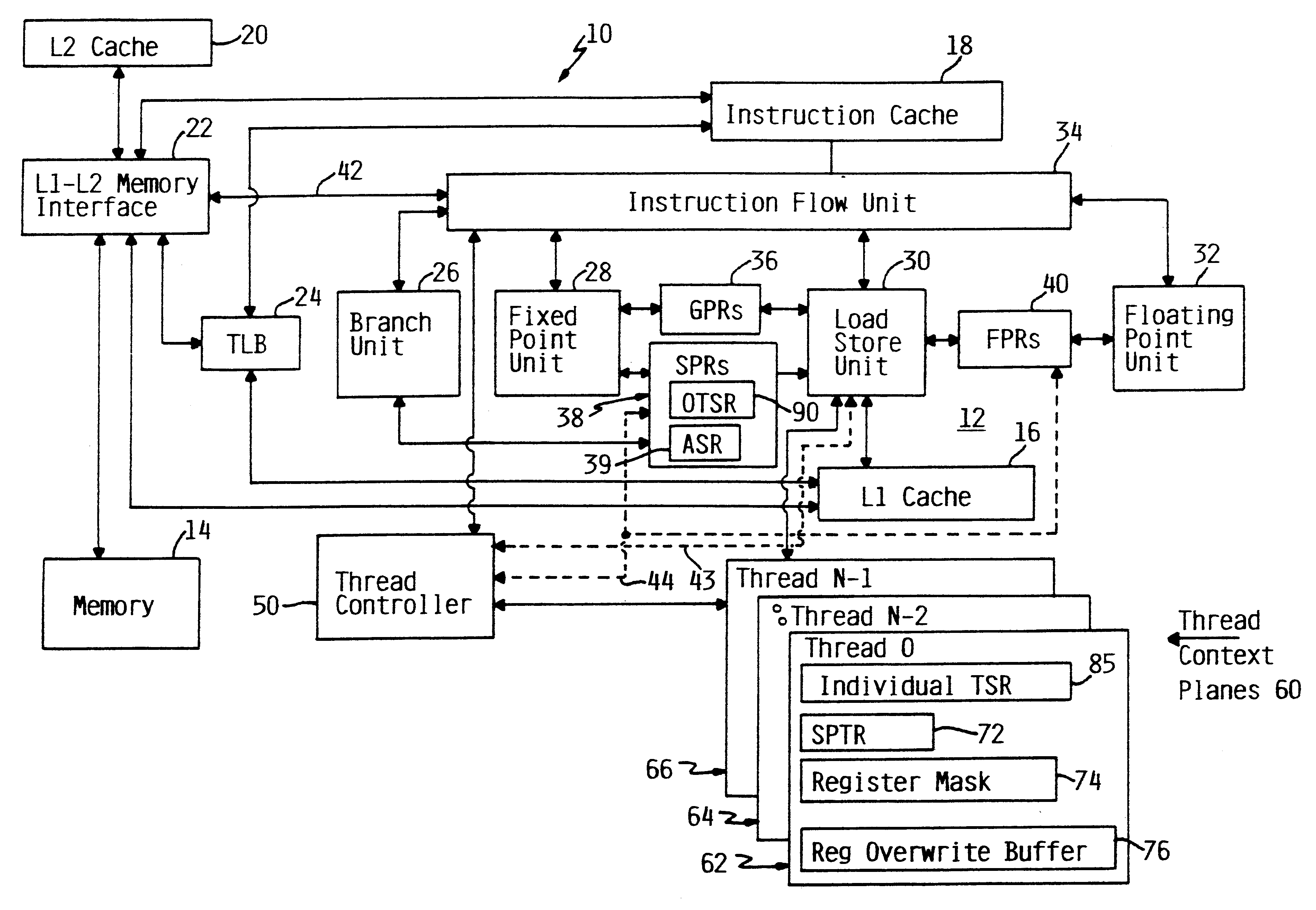
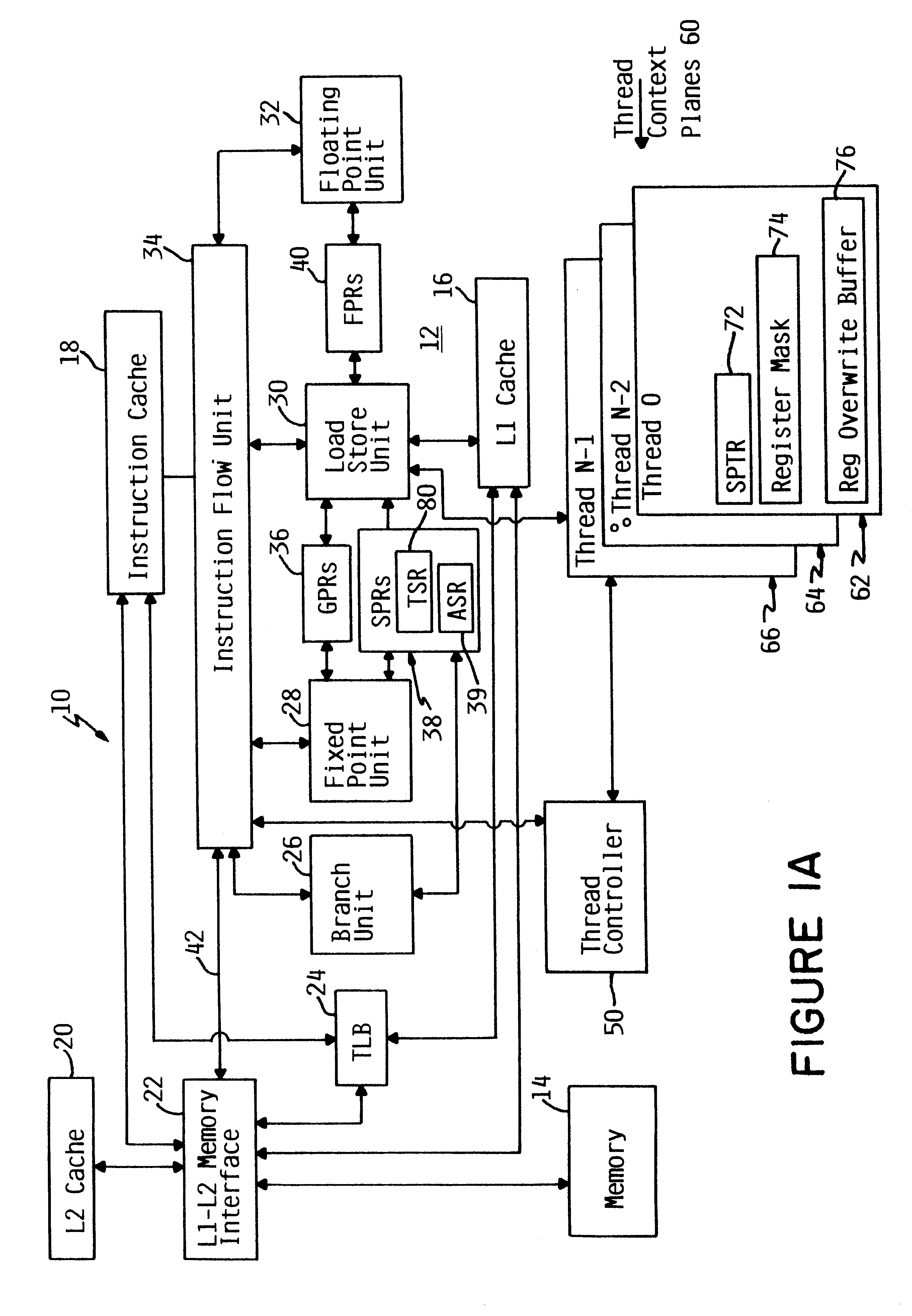
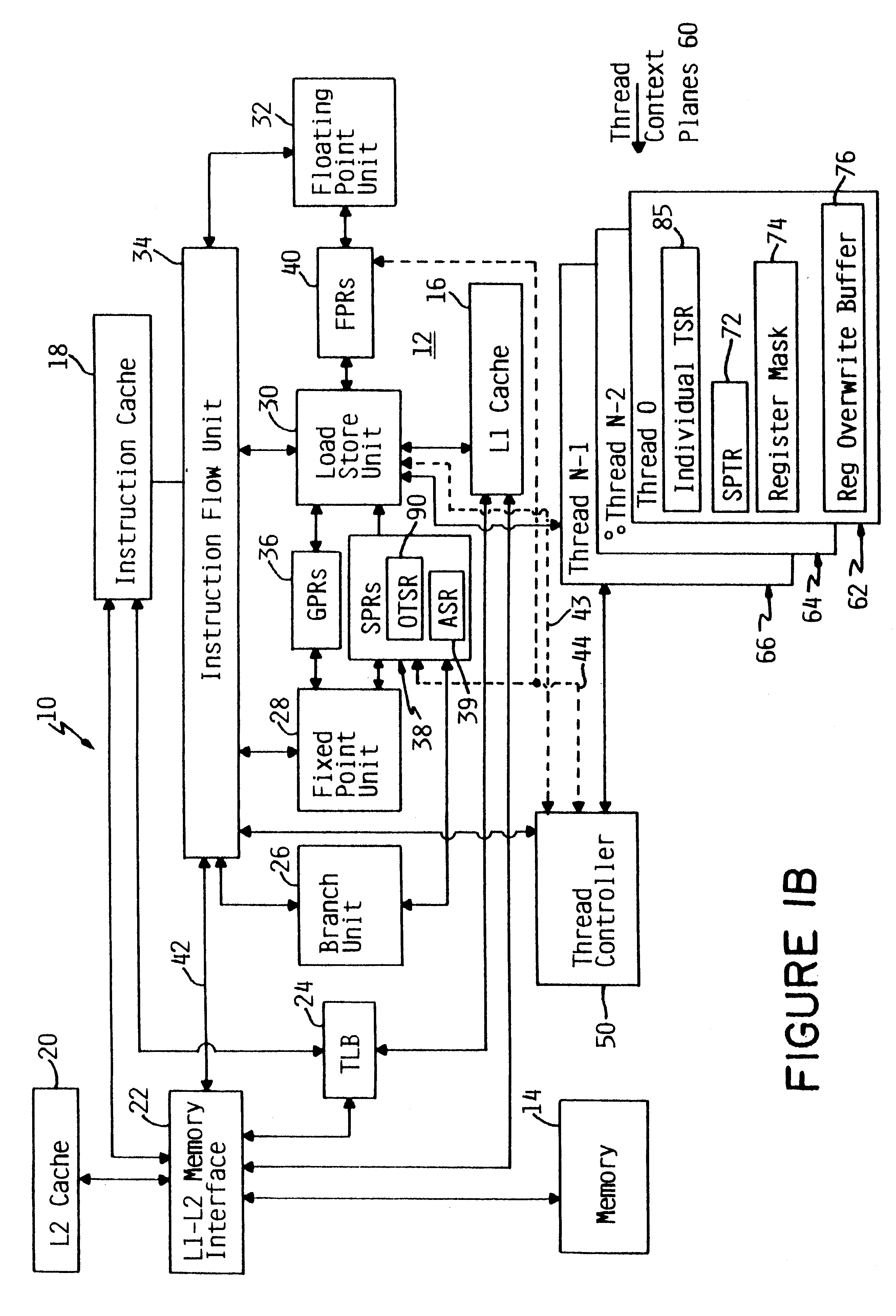
Apparatus and method for retrofitting multi-threaded operations on a computer by partitioning and overlapping registers
InactiveUS6233599B1Improve multithreading performance of processorImprove performanceResource allocationDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeProcessor register
An apparatus and method for performing multithreaded operations includes partitioning the general purpose and / or floating point processor registers into register subsets, including overlapping register subsets, allocating the register subsets to the threads, and managing the register subsets during thread switching. Register overwrite buffers preserve thread resources in overlapping registers during the thread switching process. Thread resources are loaded into the corresponding register subsets or, when overlapping register subsets are employed, into either the corresponding register subset or the corresponding register overwrite buffer. A thread status register is utilized by a thread controller to keep track of READY / NOT-READY threads, the active thread, and whether single-thread or multithread operations are permitted. Furthermore, the registers in the register subsets include a thread identifier field to identify the corresponding thread. Register masks may also be used to identify which registers belong to the various register subsets.
Owner:IBM CORP
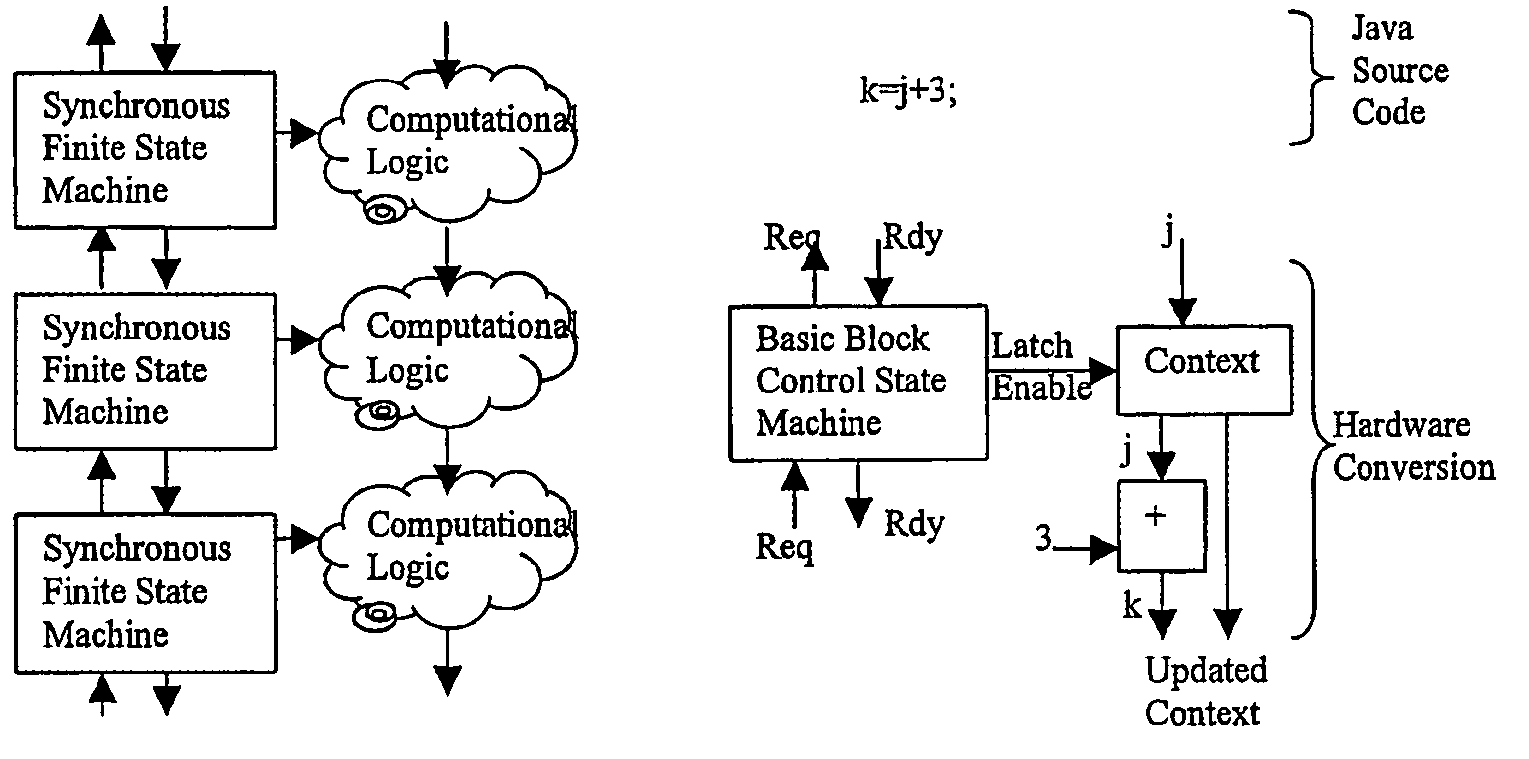
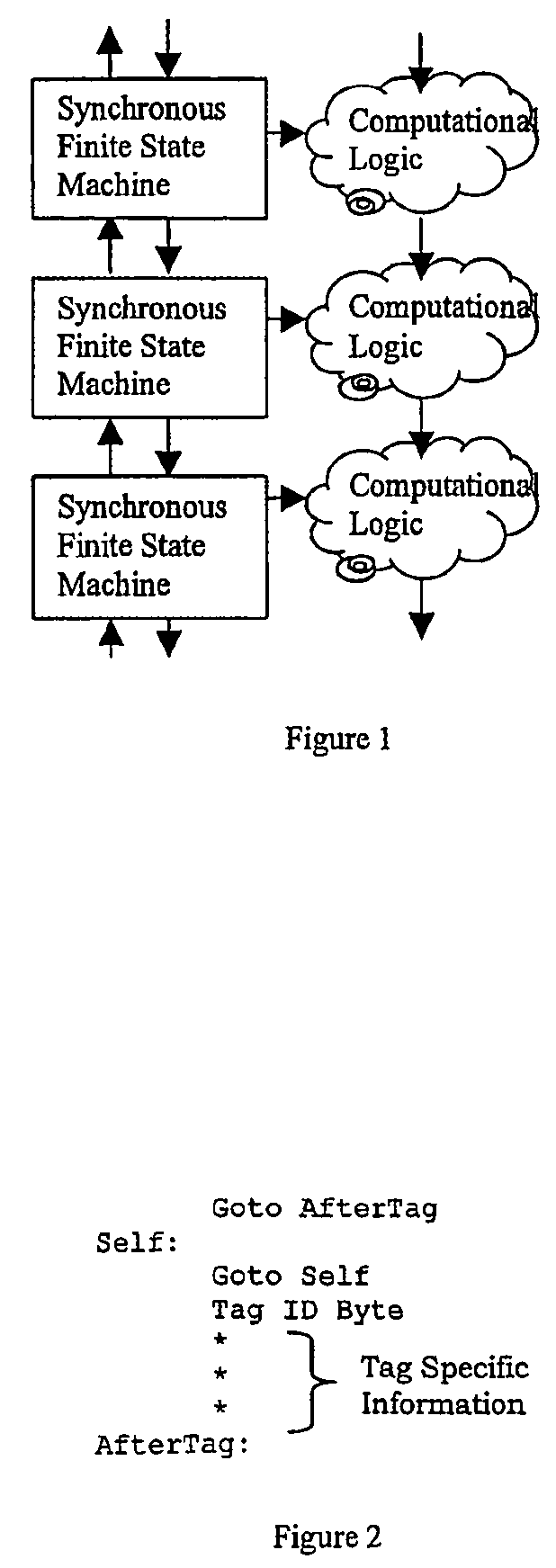
System of finite state machines
InactiveUS7224185B2Enough timeConcurrent instruction executionMultiple digital computer combinationsSufficient timeComputational logic
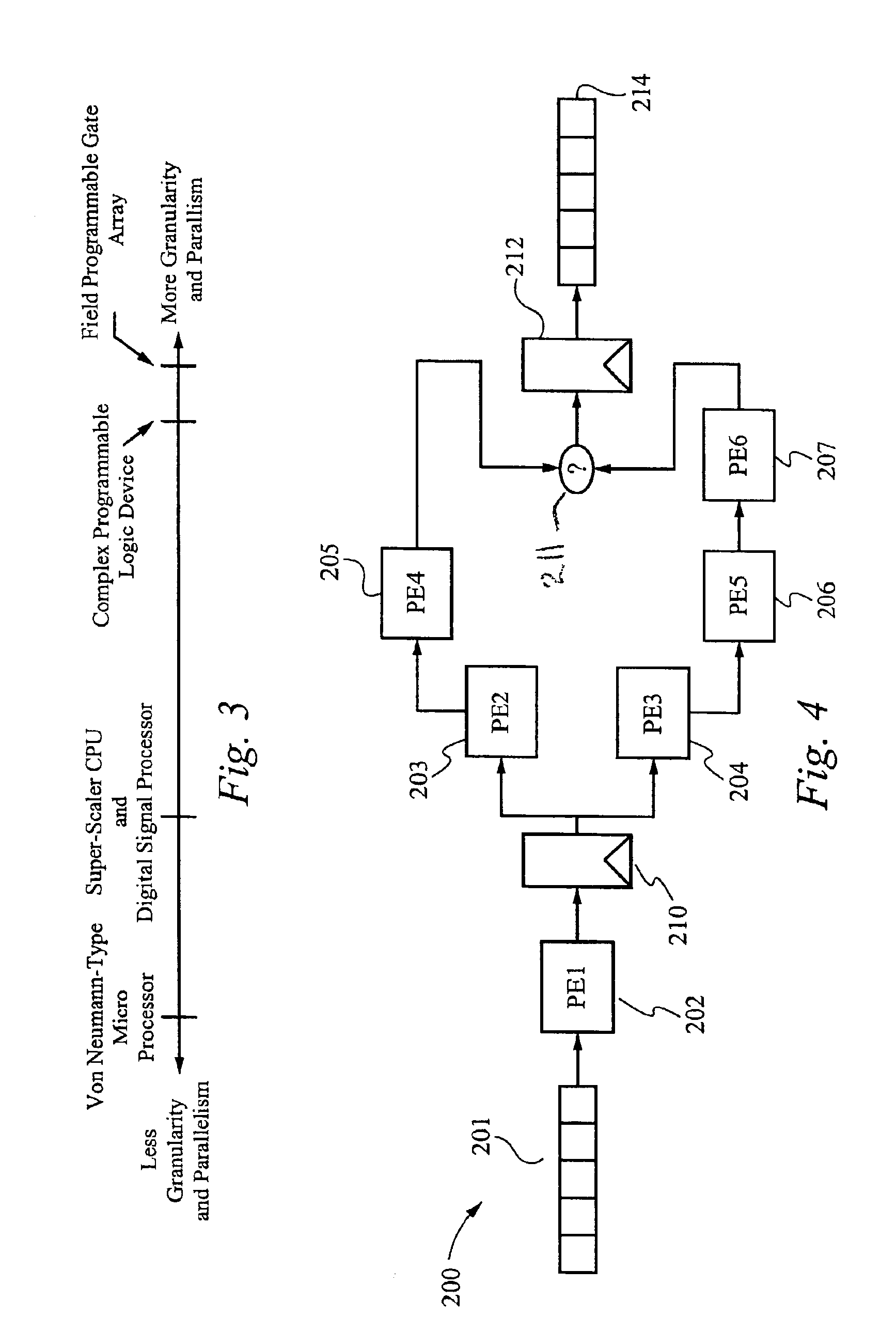
A system of finite state machines built with asynchronous or synchronous logic for controlling the flow of data through computational logic circuits programmed to accomplish a task specified by a user, having one finite state machine associated with each computational logic circuit, having each finite state machine accept data from either one or more predecessor finite state machines or from one or more sources outside the system and furnish data to one or more successor finite state machines or a recipient outside the system, excluding from consideration in determining a clock period for the system logic paths performing the task specified by the user, and providing a means for ensuring that each finite state machine allows sufficient time to elapse for the computational logic circuit associated with that finite state to perform its task.
Owner:CAMPBELL JOHN +1
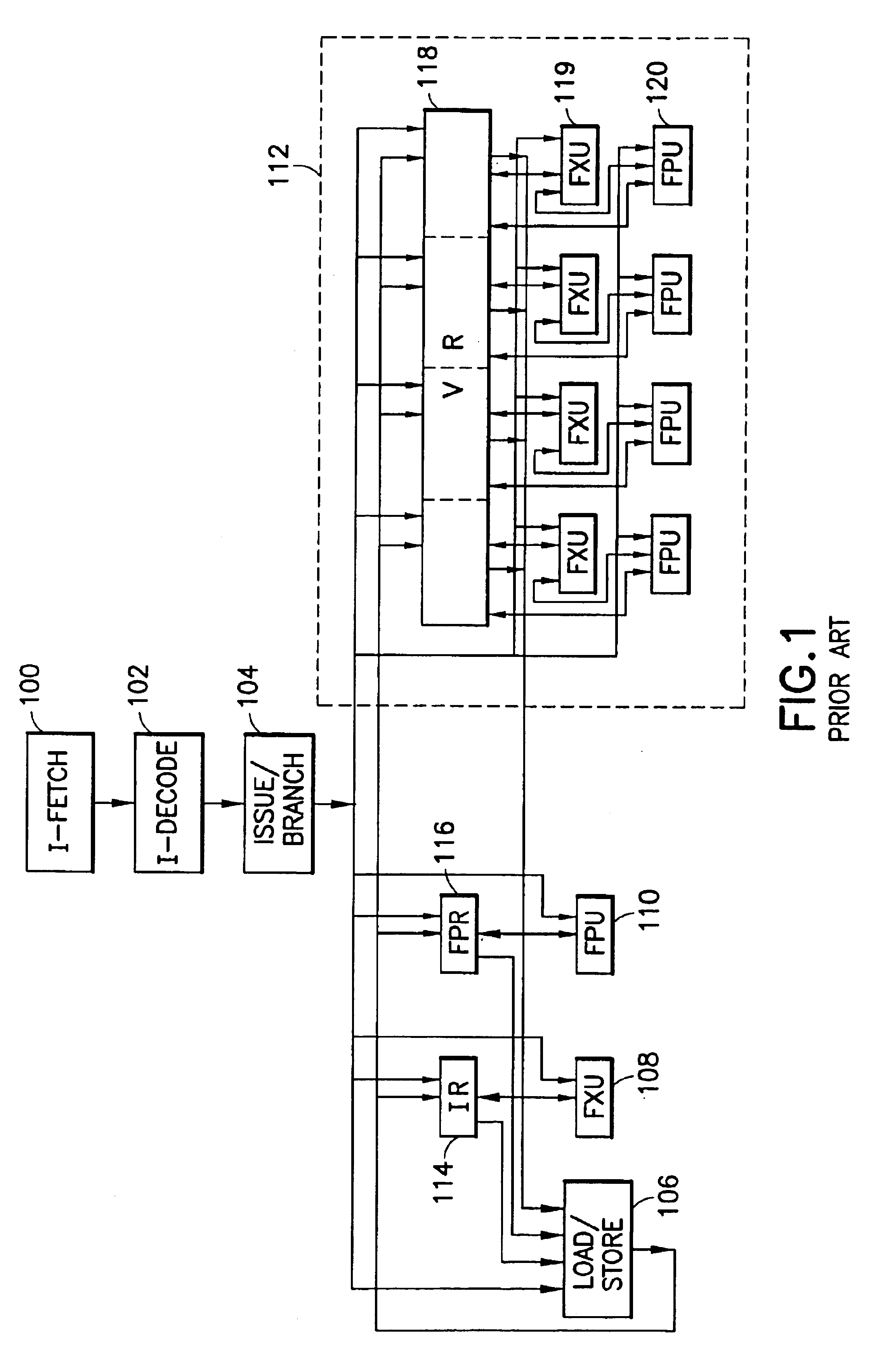
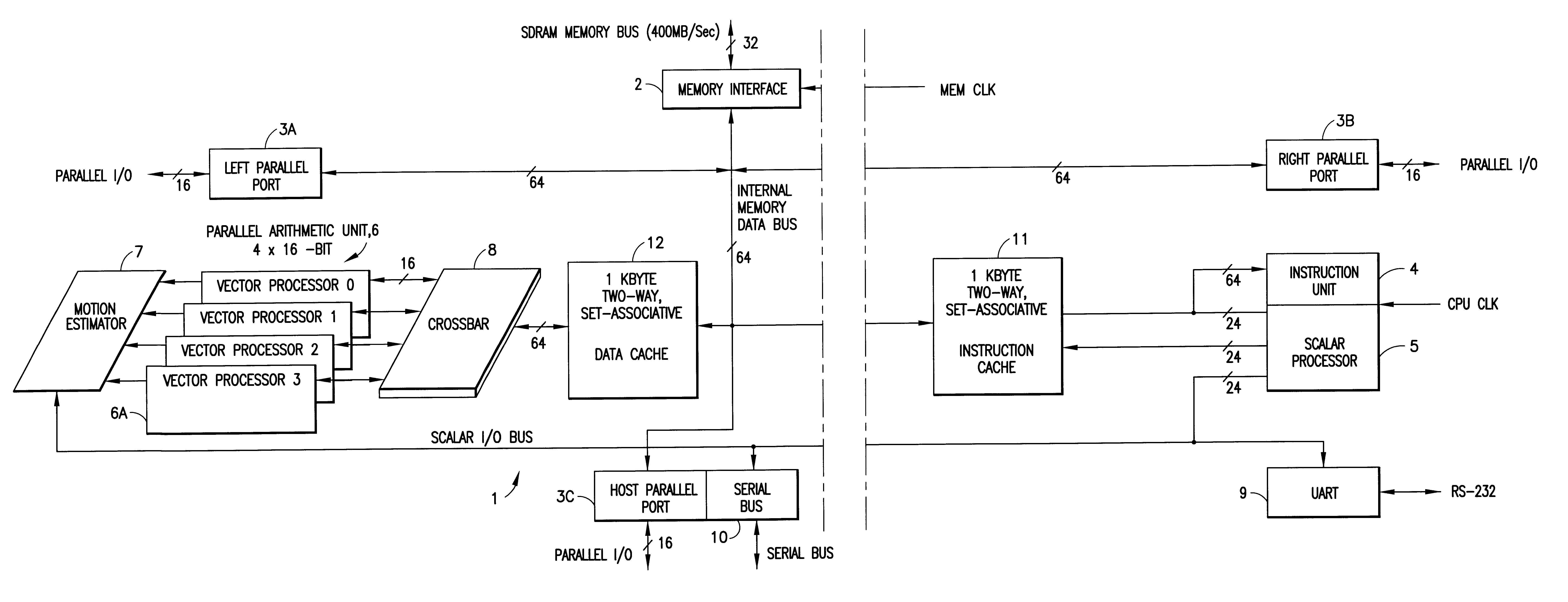
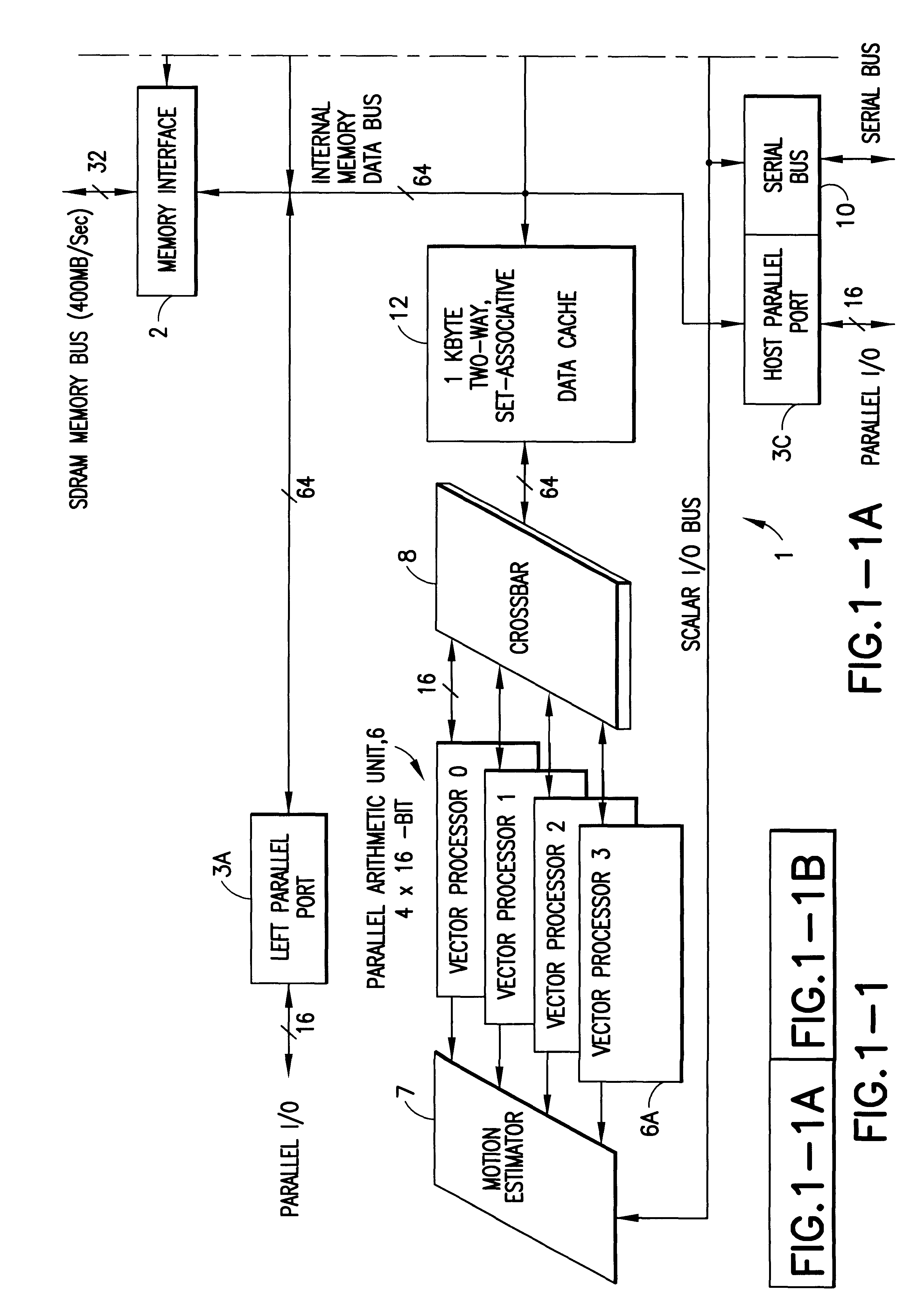
Digital signal processor containing scalar processor and a plurality of vector processors operating from a single instruction
InactiveUS6317819B1Register arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCrossbar switchDigital data
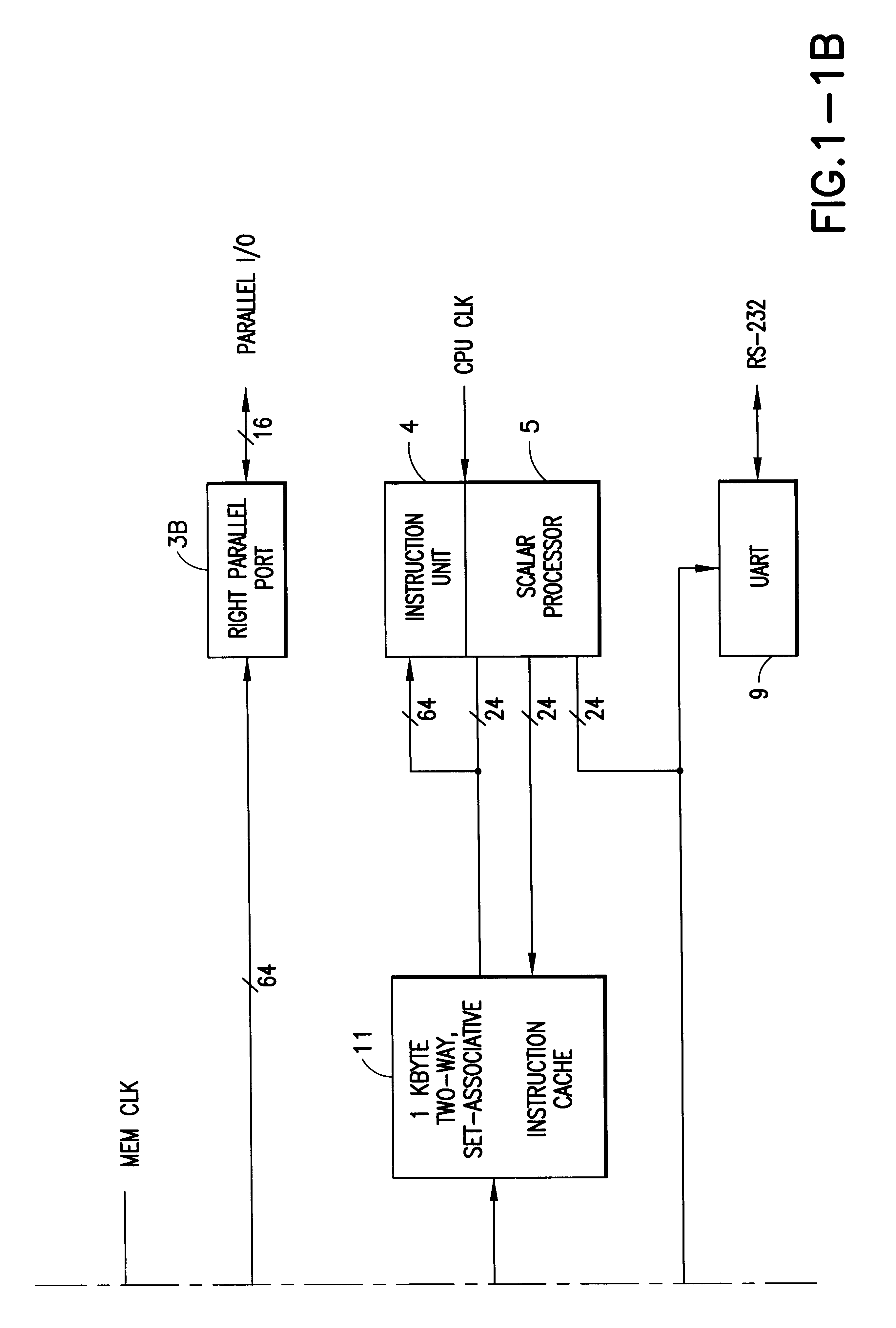
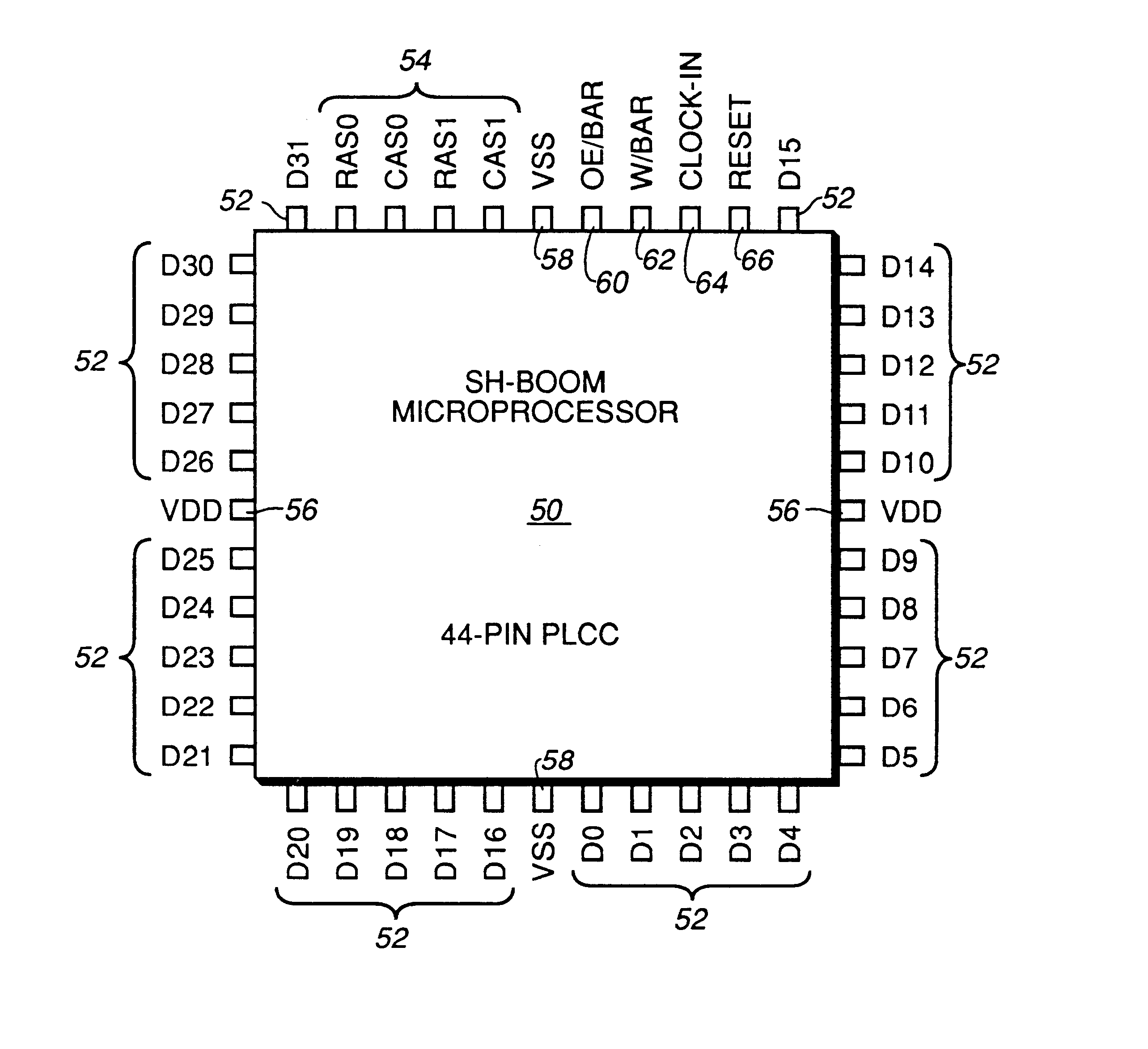
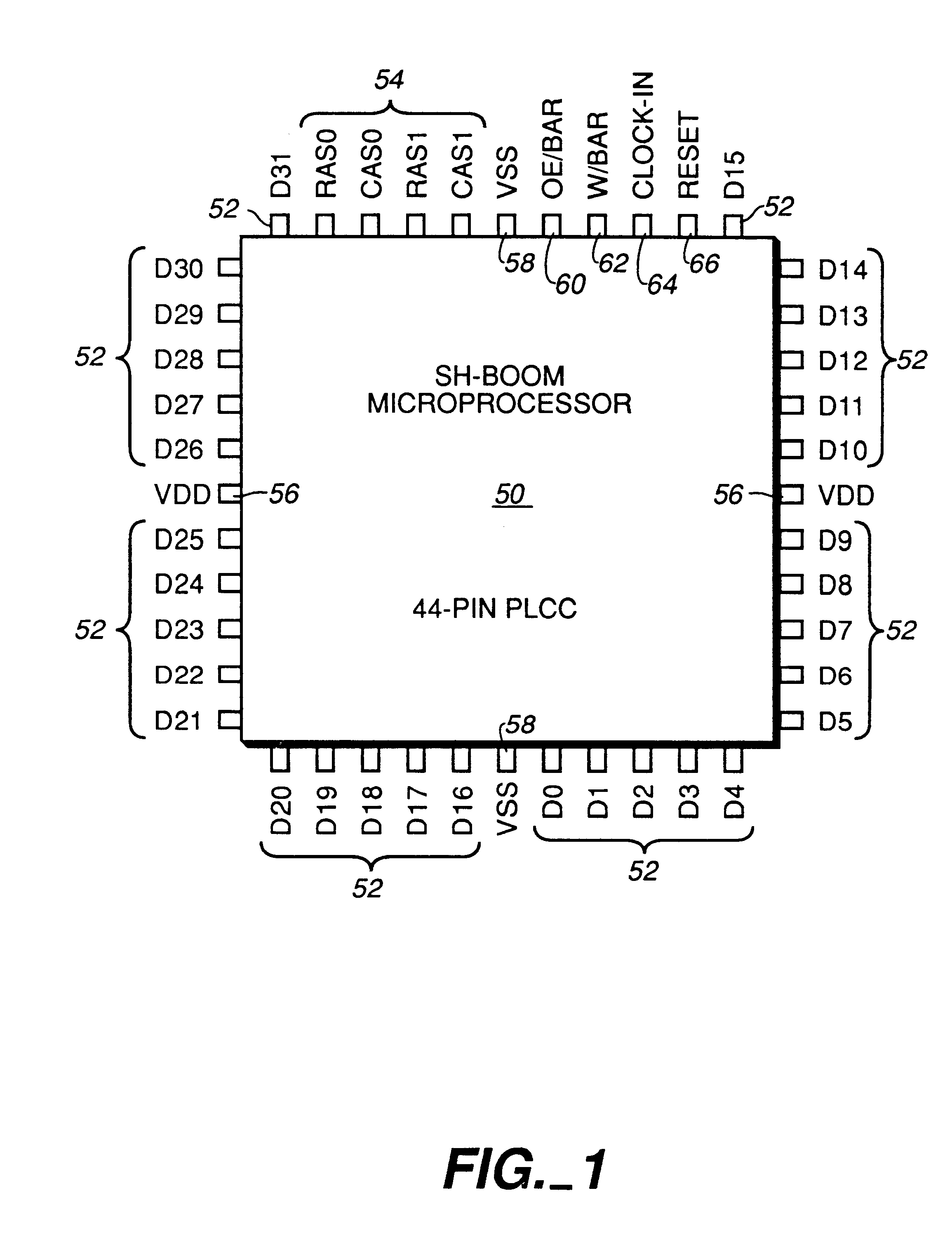
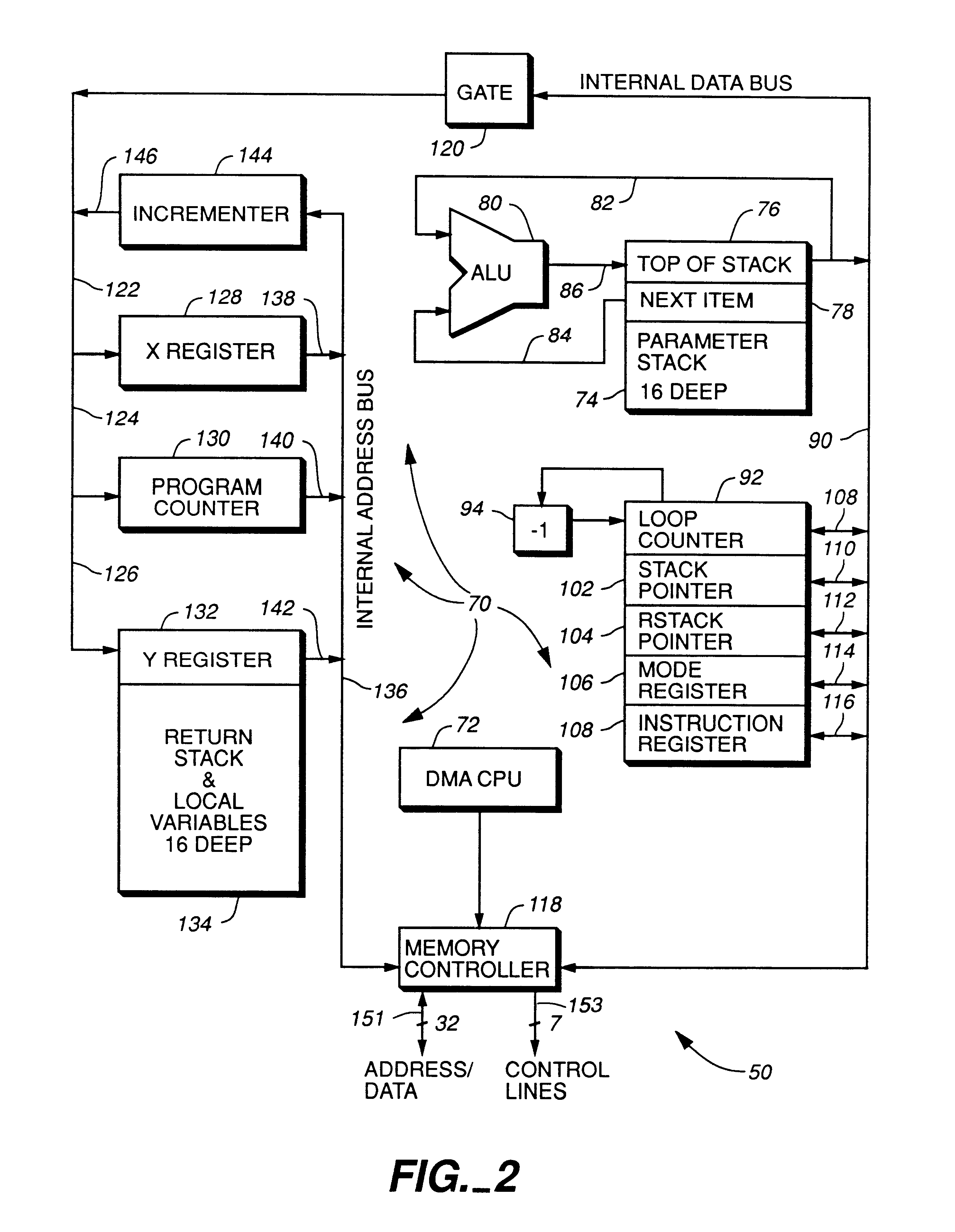
A digital data processor integrated circuit (1) includes a plurality of functionally identical first processor elements (6A) and a second processor element (5). The first processor elements are bidirectionally coupled to a first cache (12) via a crossbar switch matrix (8). The second processor element is coupled to a second cache (11). Each of the first cache and the second cache contain a two-way, set-associative cache memory that uses a least-recently-used (LRU) replacement algorithm and that operates with a use-as-fill mode to minimize a number of wait states said processor elements need experience before continuing execution after a cache-miss. An operation of each of the first processor elements and an operation of the second processor element are locked together during an execution of a single instruction read from the second cache. The instruction specifies, in a first portion that is coupled in common to each of the plurality of first processor elements, the operation of each of the plurality of first processor elements in parallel. A second portion of the instruction specifies the operation of the second processor element. Also included is a motion estimator (7) and an internal data bus coupling together a first parallel port (3A), a second parallel port (3B), a third parallel port (3C), an external memory interface (2), and a data input / output of the first cache and the second cache.
Owner:CUFER ASSET LTD LLC
High performance microprocessor having variable speed system clock
InactiveUS6598148B1Improve performanceWithout sacrificing microprocessor speedRandom number generatorsInstruction analysisComputer architectureStatic random-access memory
A microprocessor integrated circuit including a processing unit disposed upon an integrated circuit substrate is disclosed herein. The processing unit is designed to operate in accordance with a predefined sequence of program instructions stored within an instruction register. A memory, capable of storing information provided by the processing unit and occupying a larger area of the integrated circuit substrate than the processing unit, is also provided within the microprocessor integrated circuit. The memory may be implemented using, for example dynamic or static random-access memory. A variable output frequency system clock, such as generated by a ring oscillator, is also disposed on the integrated circuit substrate.
Owner:MOORE CHARLES H TTE UTD 03 21 2006 THE EQUINOX TRUST
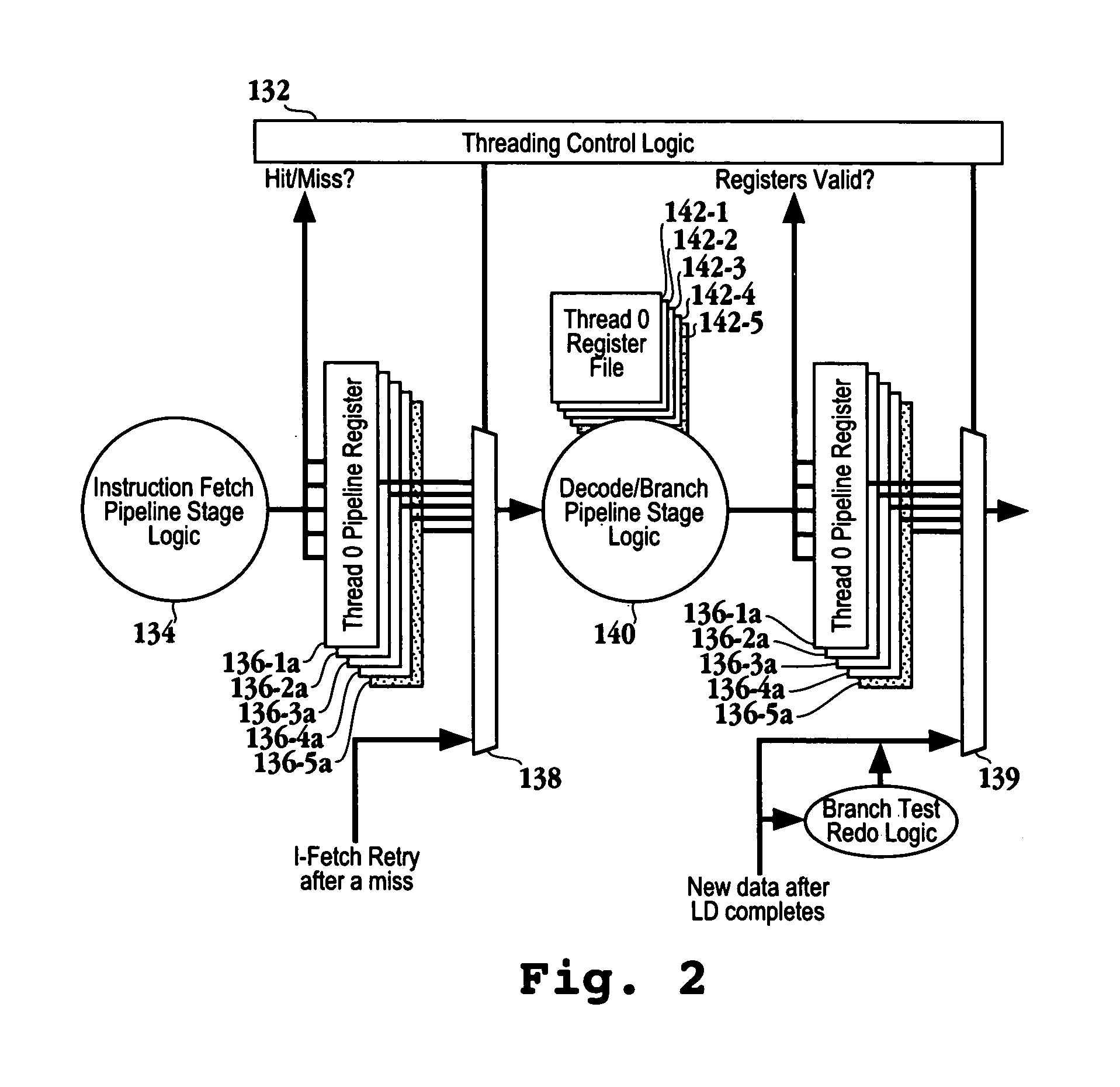
Switching method in a multi-threaded processor
InactiveUS6507862B1Program initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsOperational systemEmbedded system
A processor includes logic for attaining a very fast exception handling functionality while executing non-threaded programs by invoking a multithreaded-type functionality in response to an exception condition. The processor, while operating in multithreaded conditions or while executing non-threaded programs, progresses through multiple machine states during execution. The very fast exception handling logic includes connection of an exception signal line to thread select logic, causing an exception signal to evoke a switch in thread and machine state. The switch in thread and machine state causes the processor to enter and to exit the exception handler immediately, without waiting to drain the pipeline or queues and without the inherent timing penalty of the operating system's software saving and restoring of registers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multi-core multi-thread processor
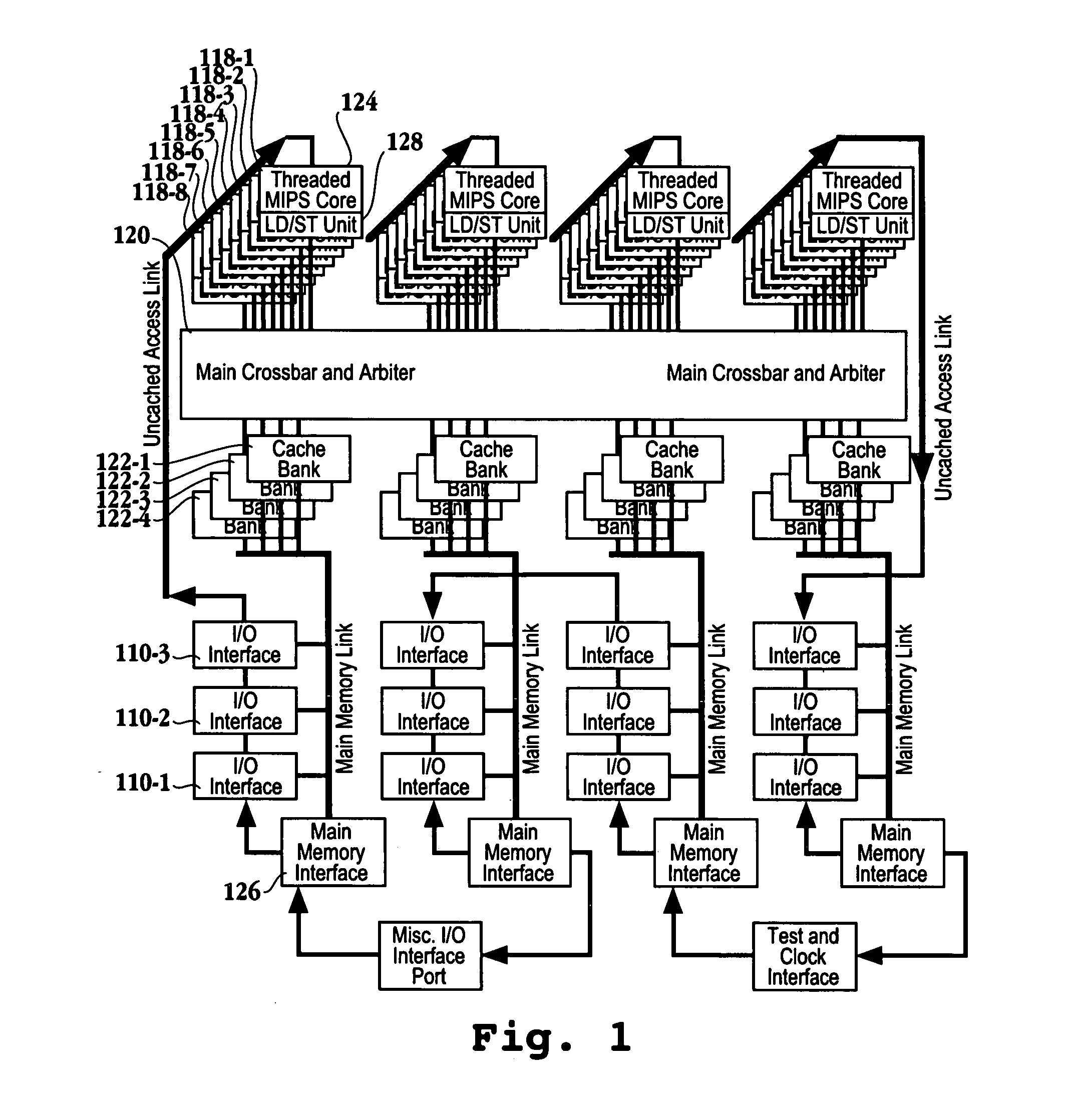
ActiveUS20050044319A1Easy accessRegister arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory interfaceParallel computing
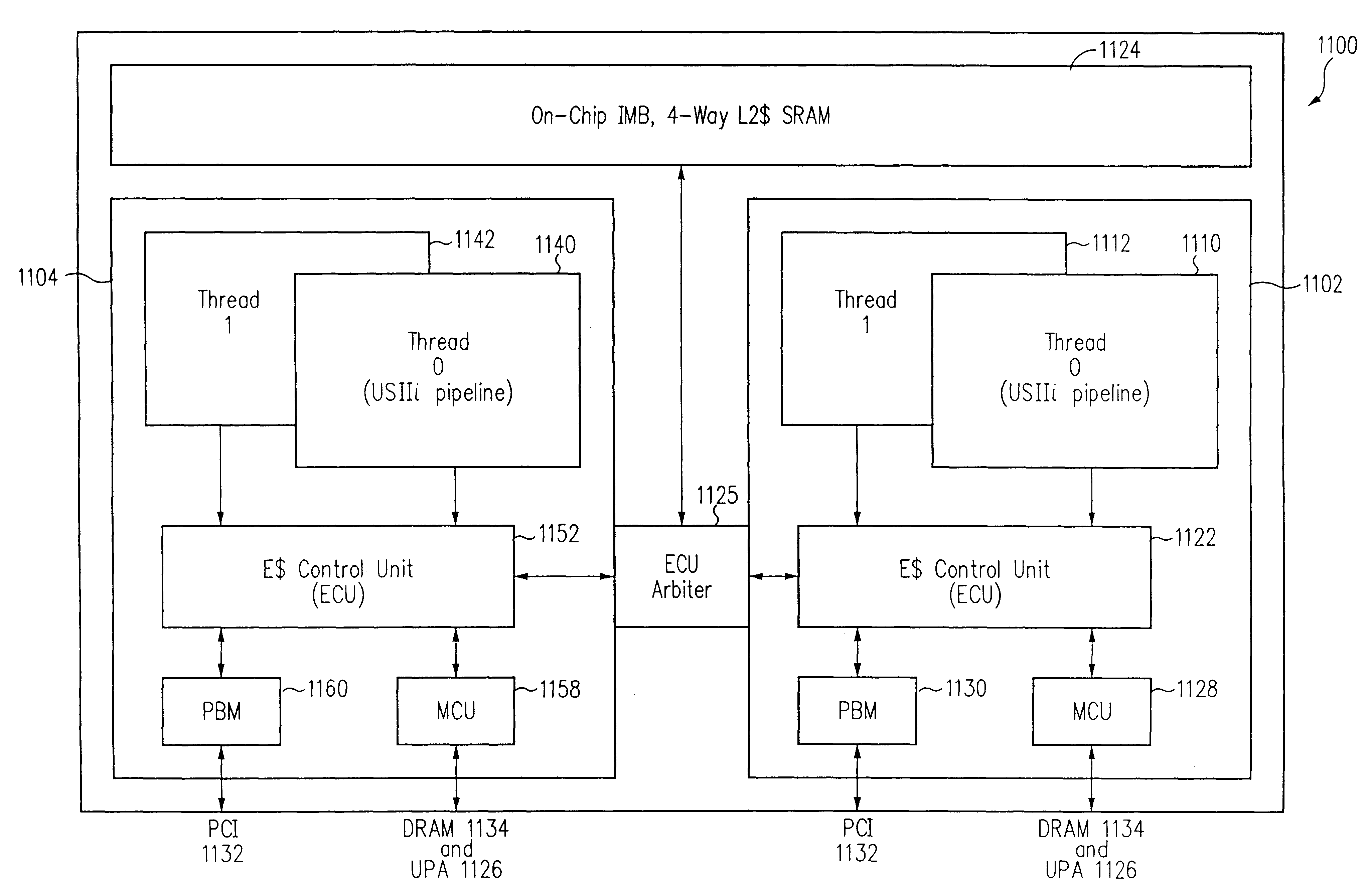
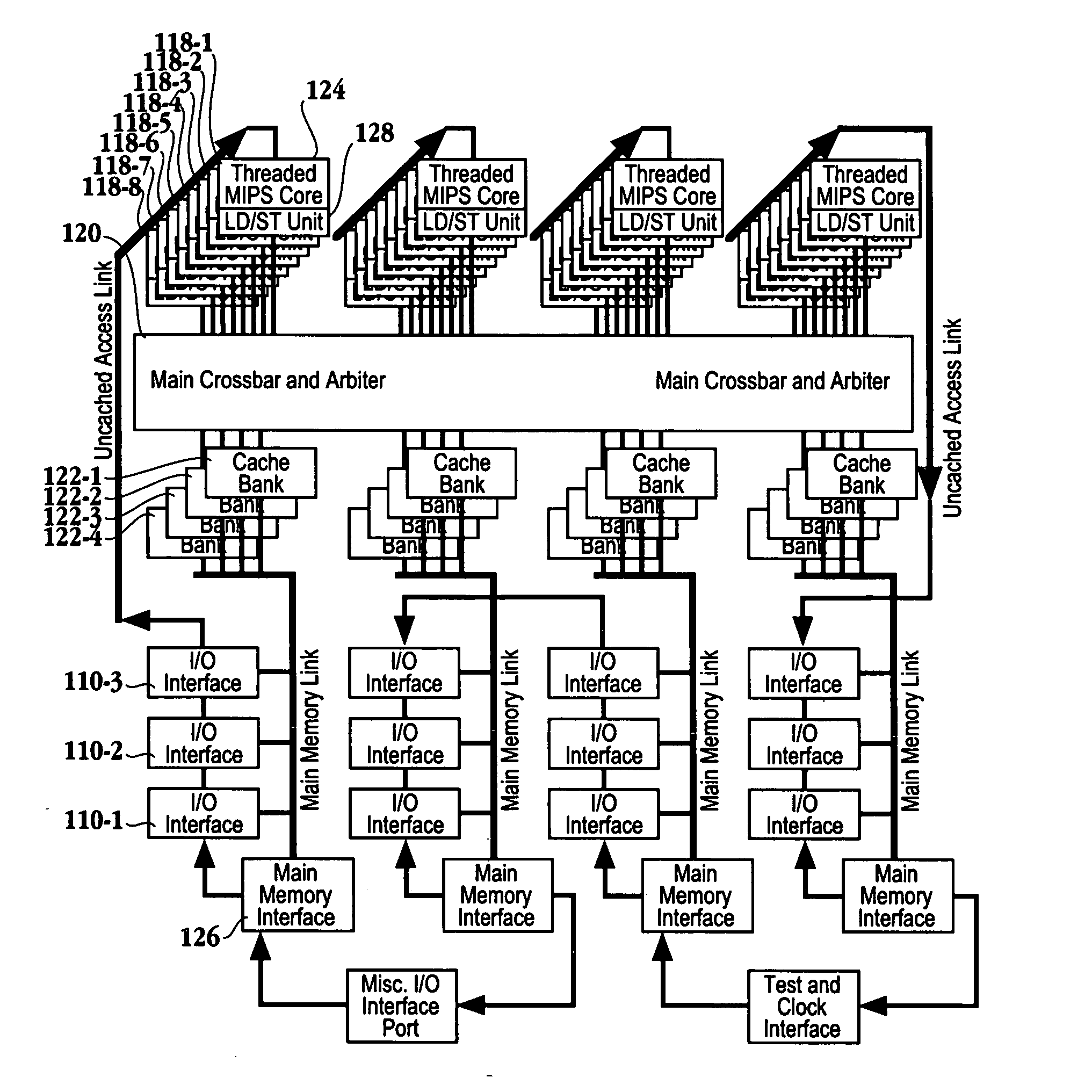
A processor is provided. The processor includes at least two cores. The at least two cores have a first level cache memory and are multi-threaded. A crossbar is included. A plurality of cache bank memories in communication with the at least two cores through the crossbar is provided. Each of the plurality of cache bank memories communicates with a main memory interface. A plurality of input / output interface modules in communication with the main memory interface and providing a link to the at least two cores are included. The link bypasses the plurality of cache bank memories and the crossbar. Threading hardware configured to enable the at least two cores to switch from a first thread to a second thread in a manner hiding delays caused by cache accesses is included. A server and a method for determining when to switch threads in a multi-core multi-thread environment are included.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Analyzing and transforming a computer program for executing on asymmetric multiprocessing systems
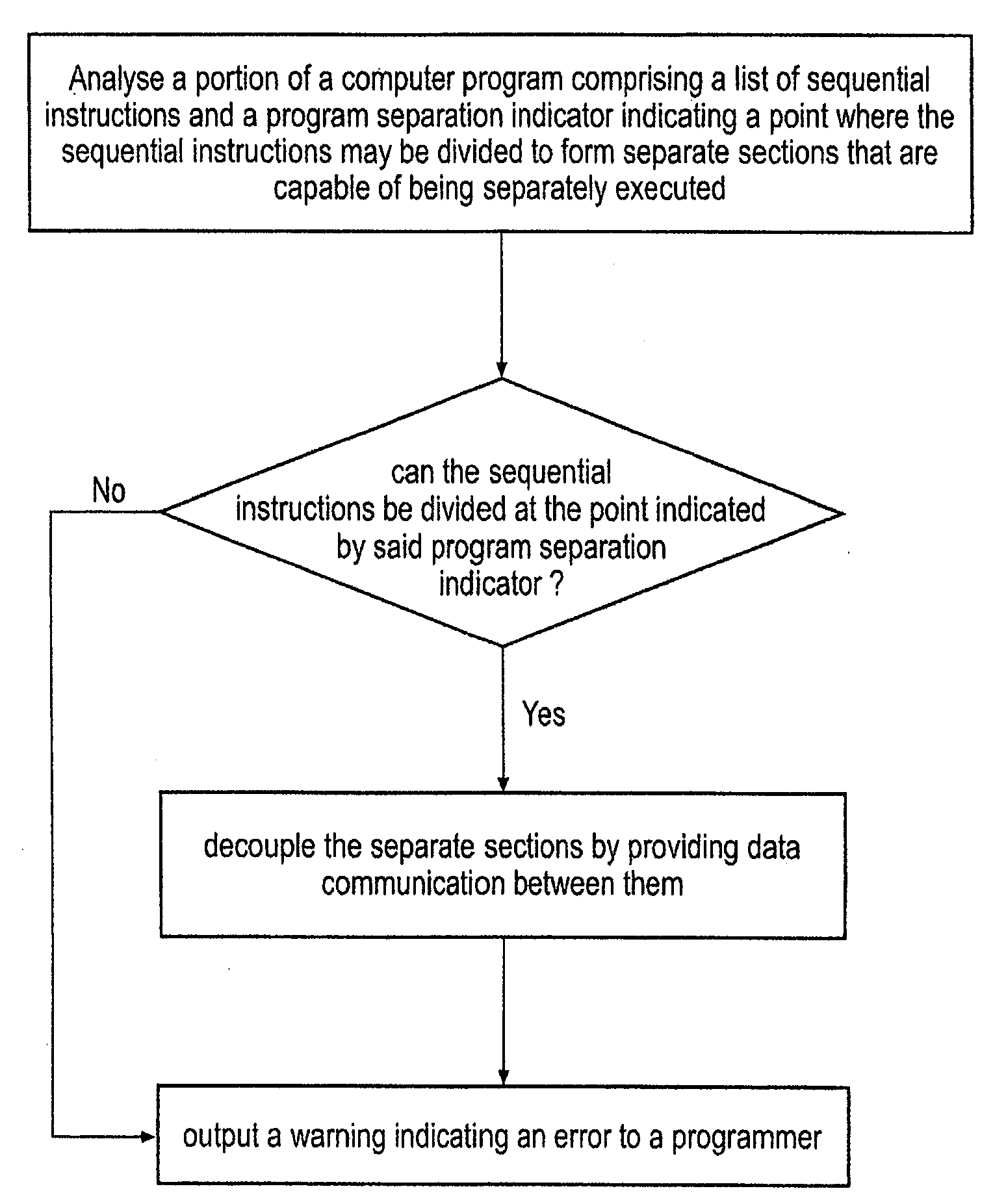
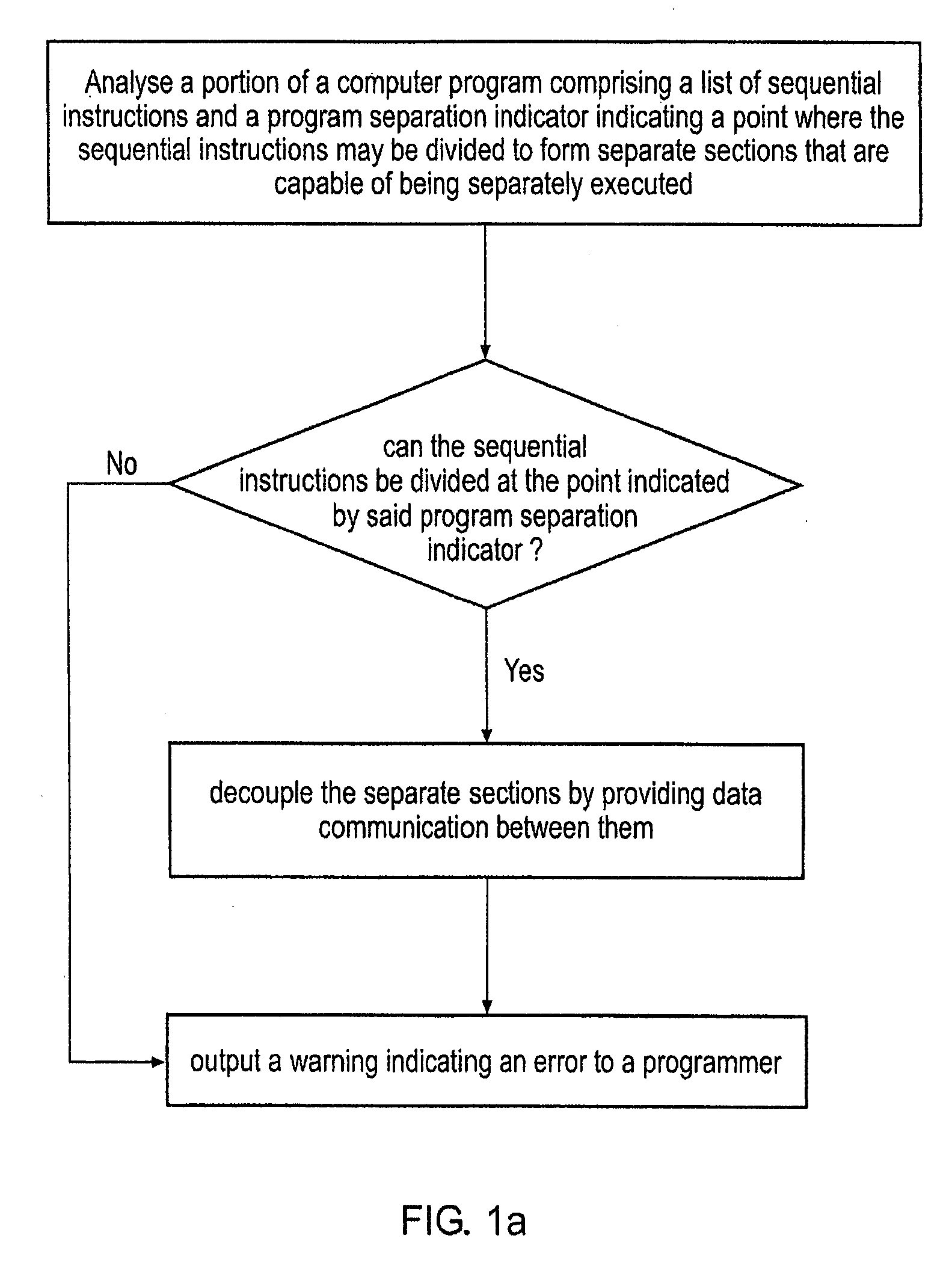
InactiveUS20080098208A1Easy to implementImprove system performanceDetecting faulty computer hardwareDigital computer detailsParallel computingData shipping
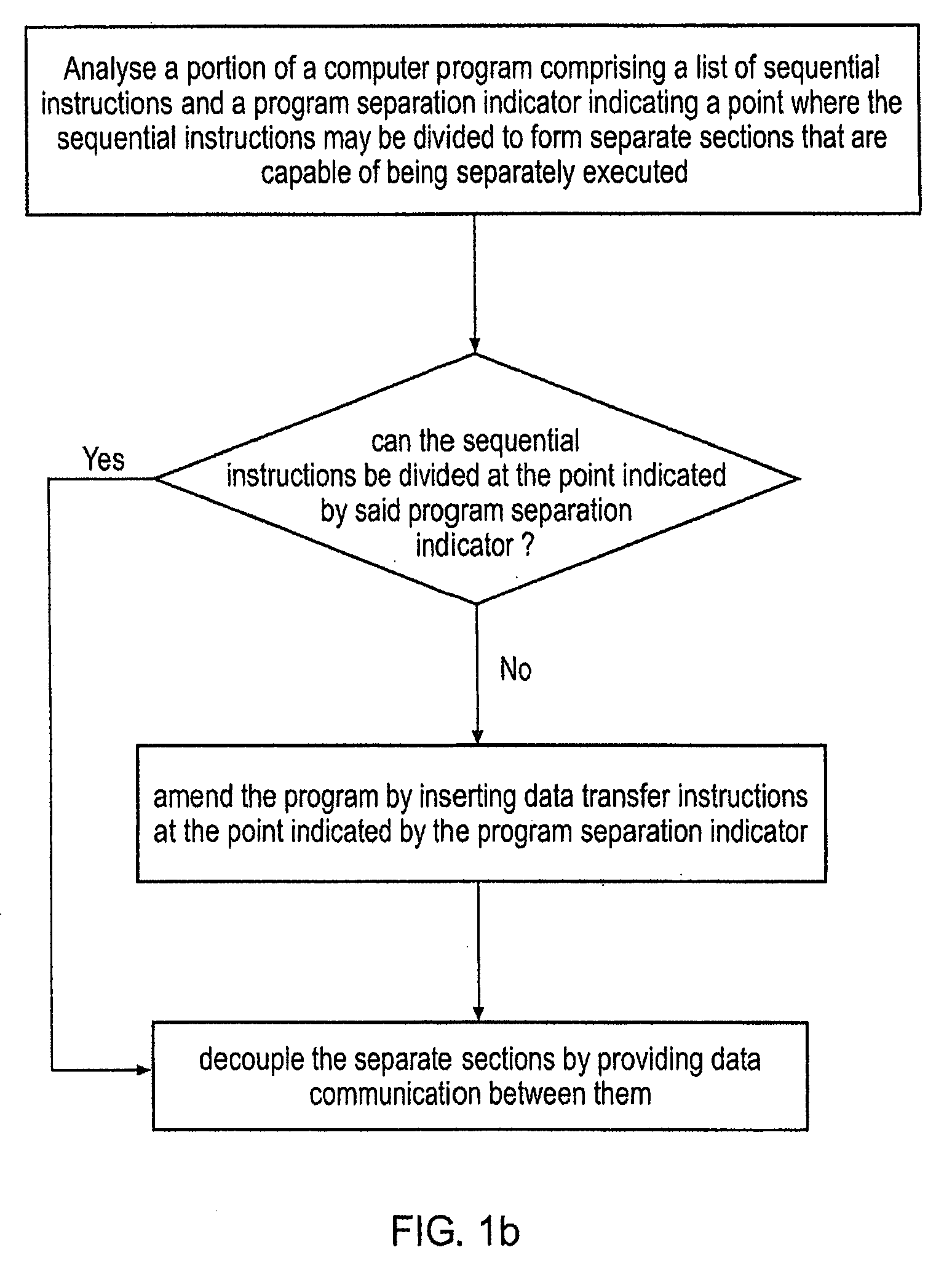
A method is disclosed for transforming a portion of a computer program comprising a list of sequential instructions comprising control code and data processing code and a program separation indicator indicating a point where said sequential instructions may be divided to form separate sections that are capable of being separately executed and that each comprise different data processing code. The m method comprises the steps of: (i) analysing said portion of said program to determine if said sequential instructions can be divided at said point indicated by said program separation indicator and in response to determining that it can: (iia) providing data communication between said separate sections indicated by said program separation indicator, such that said separate sections can be decoupled from each other, such that at least one of said sections is capable of being separately executed by an execution mechanism that is separate from an execution mechanism executing another of said separate sections, said at least one of said sections being capable of generating data and communicating said data to at least one other of said separate sections; and in response to determining it can not: (iib) not performing step (iia). If step (iia) is not performed then a warning may be output, or the program may be amended so it can be separated at that point, or the program separation indicator may be removed and the sections that were to be separated merged.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Online search system, method and computer program
ActiveUS8452745B2Lower latencyReduce degradationWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsClient-sideSearch terms
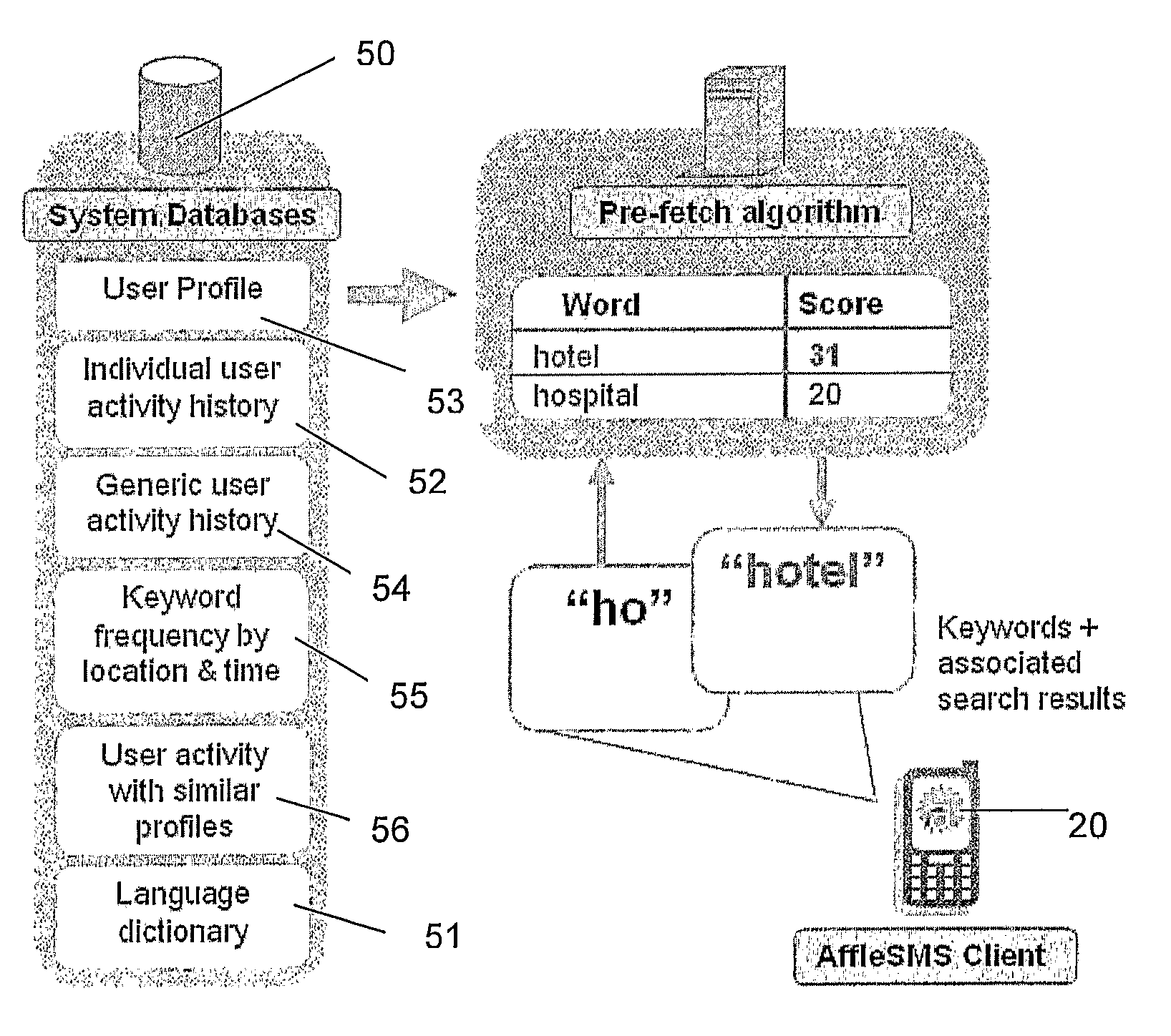
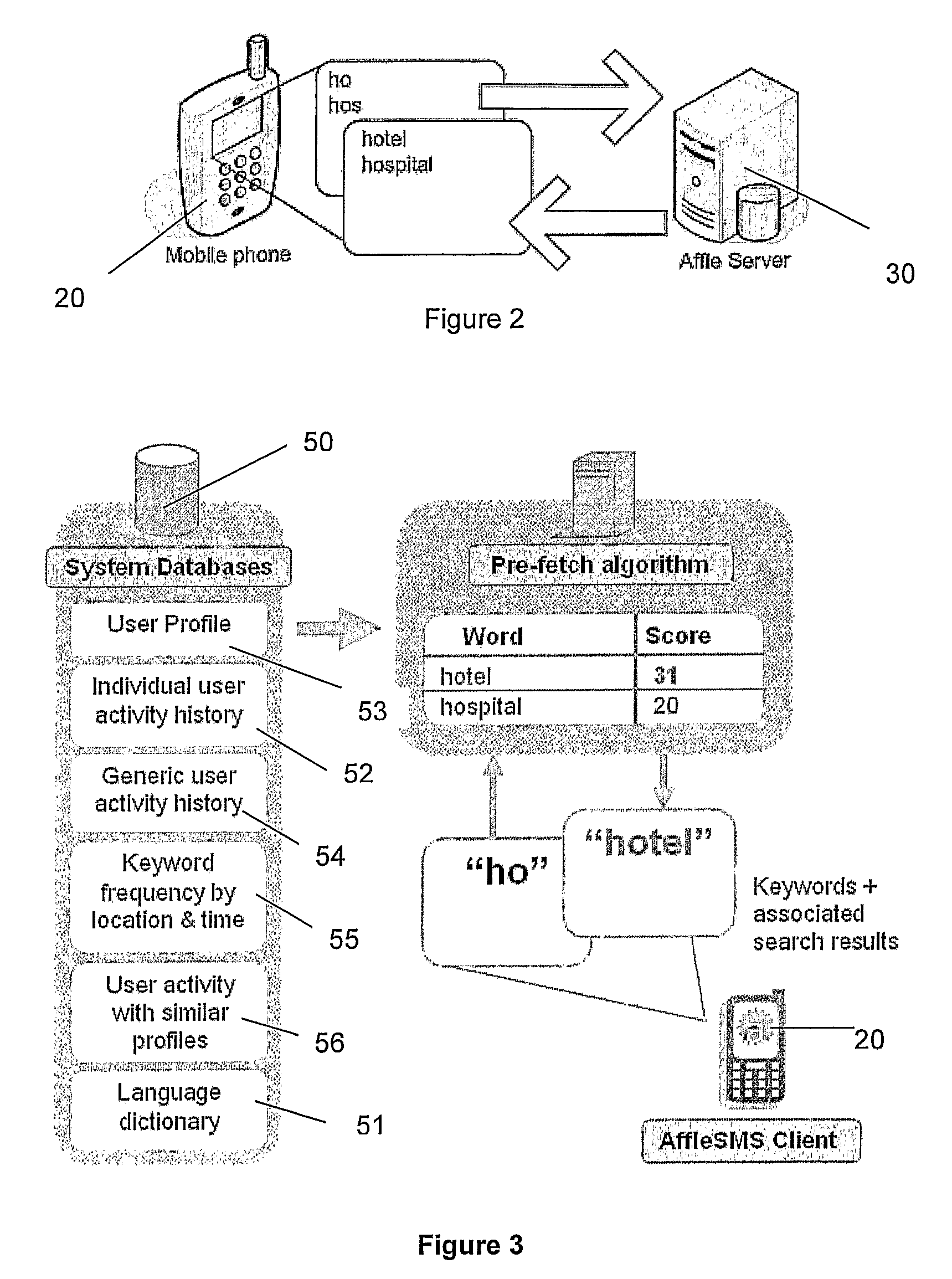
A search system, method and computer program are disclosed in which characters of a search term are captured as they are entered into a client system (20) and used to predict search terms. Search results are obtained for a predetermined number of the predicted search terms and cached at the client system (20). Upon determining the complete search term has been entered, search results corresponding to the complete search term are displayed.
Owner:AFFLE INT PTE LTD
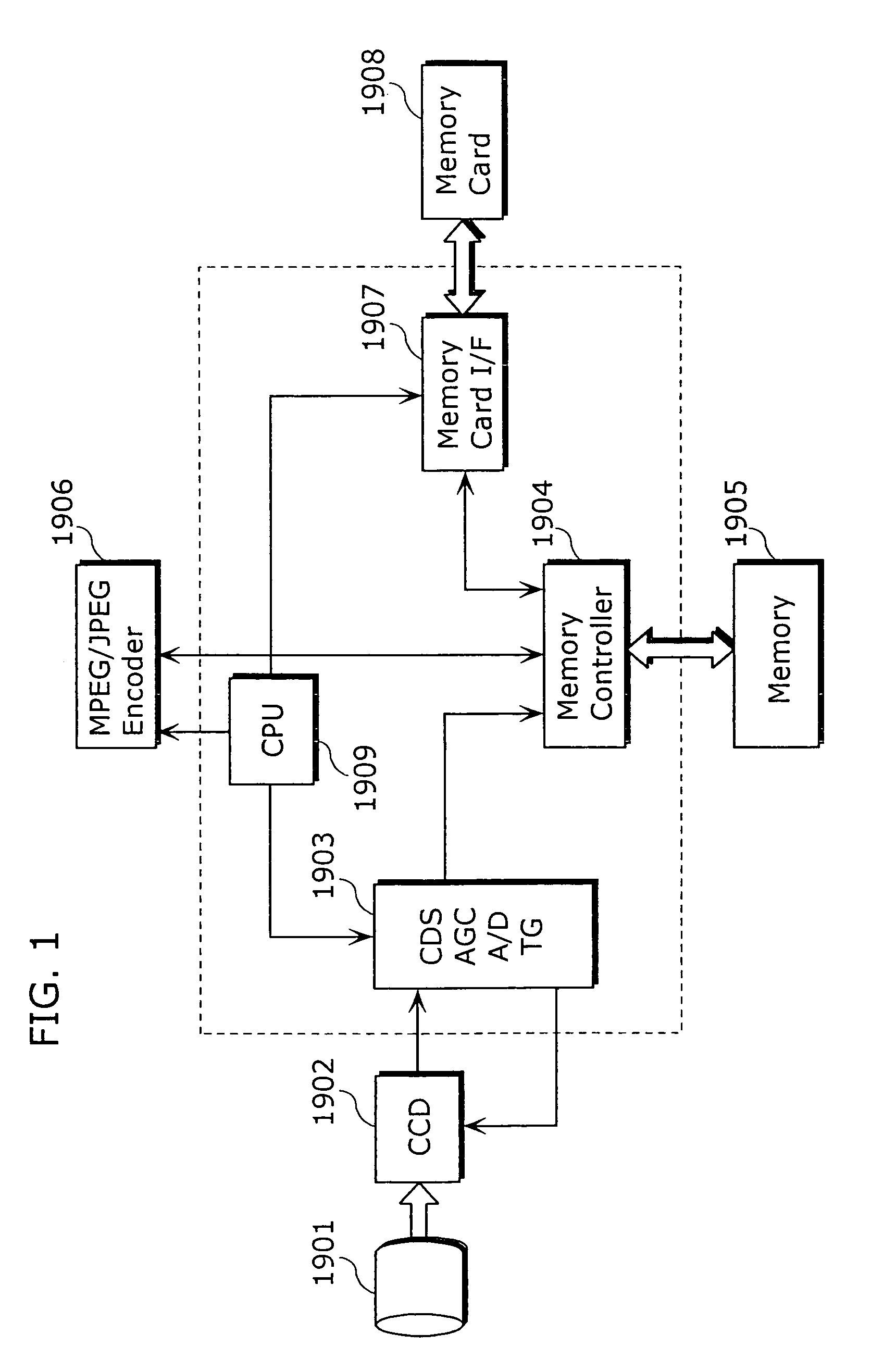
Dynamic voltage control method and apparatus
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
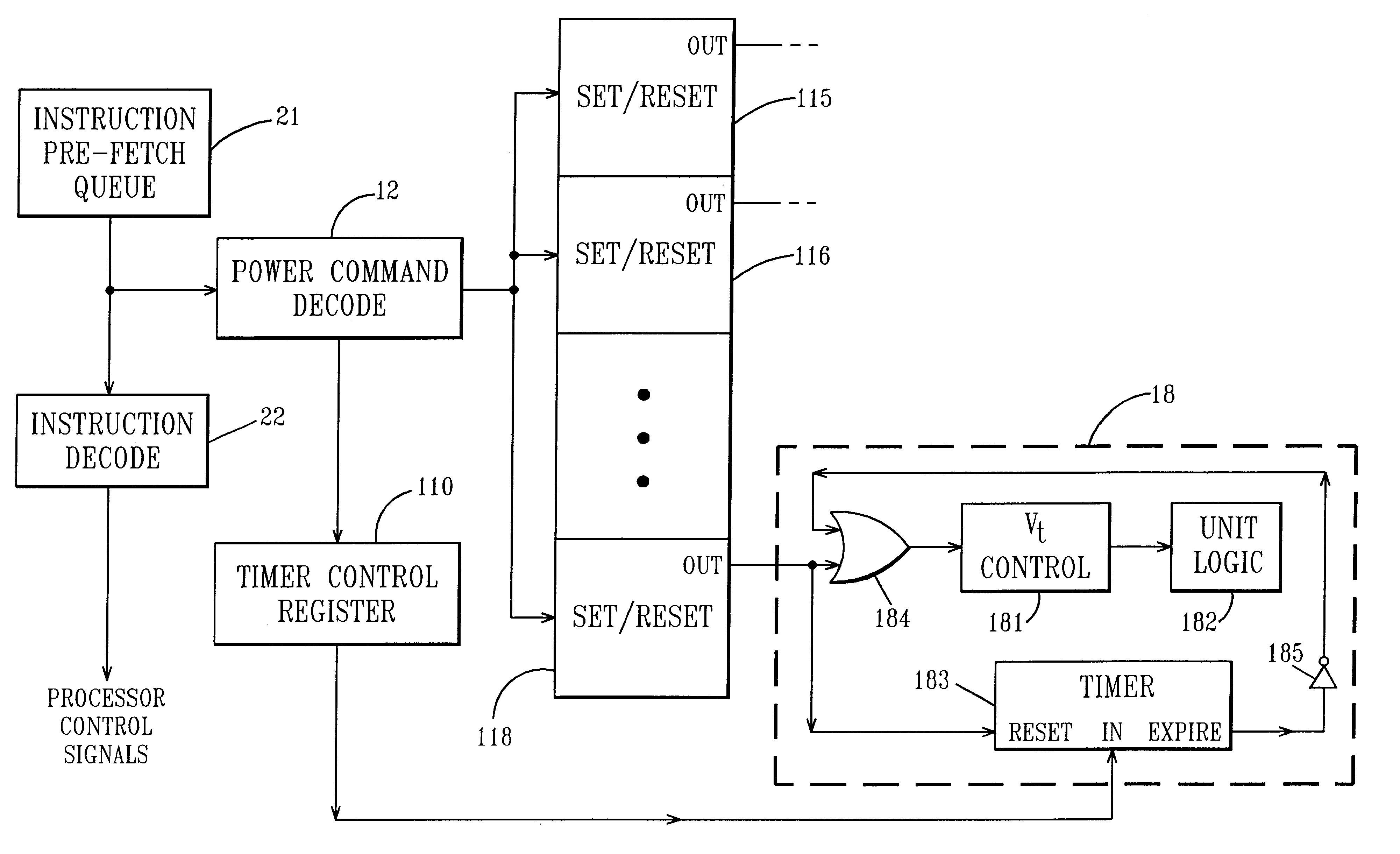
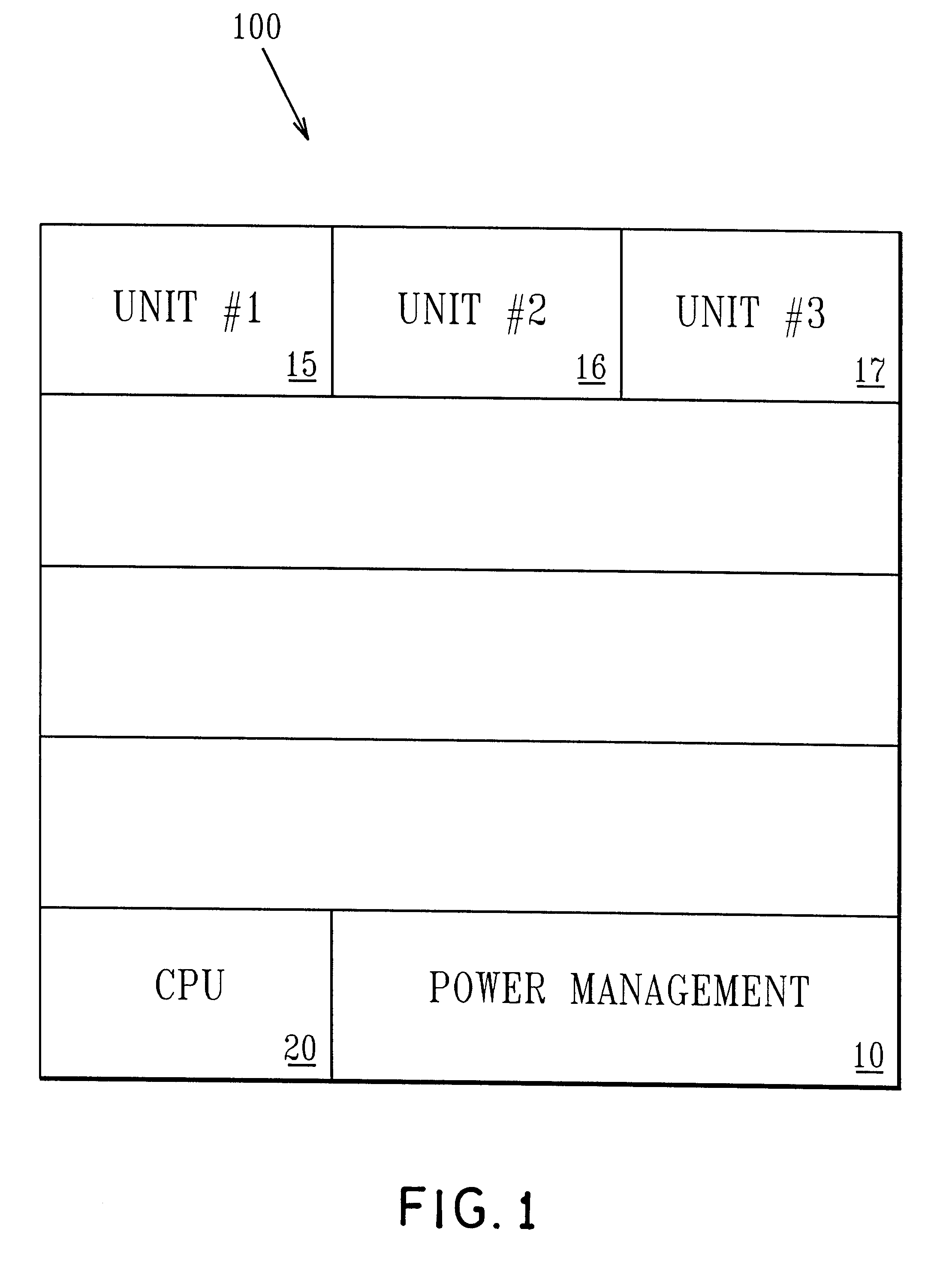
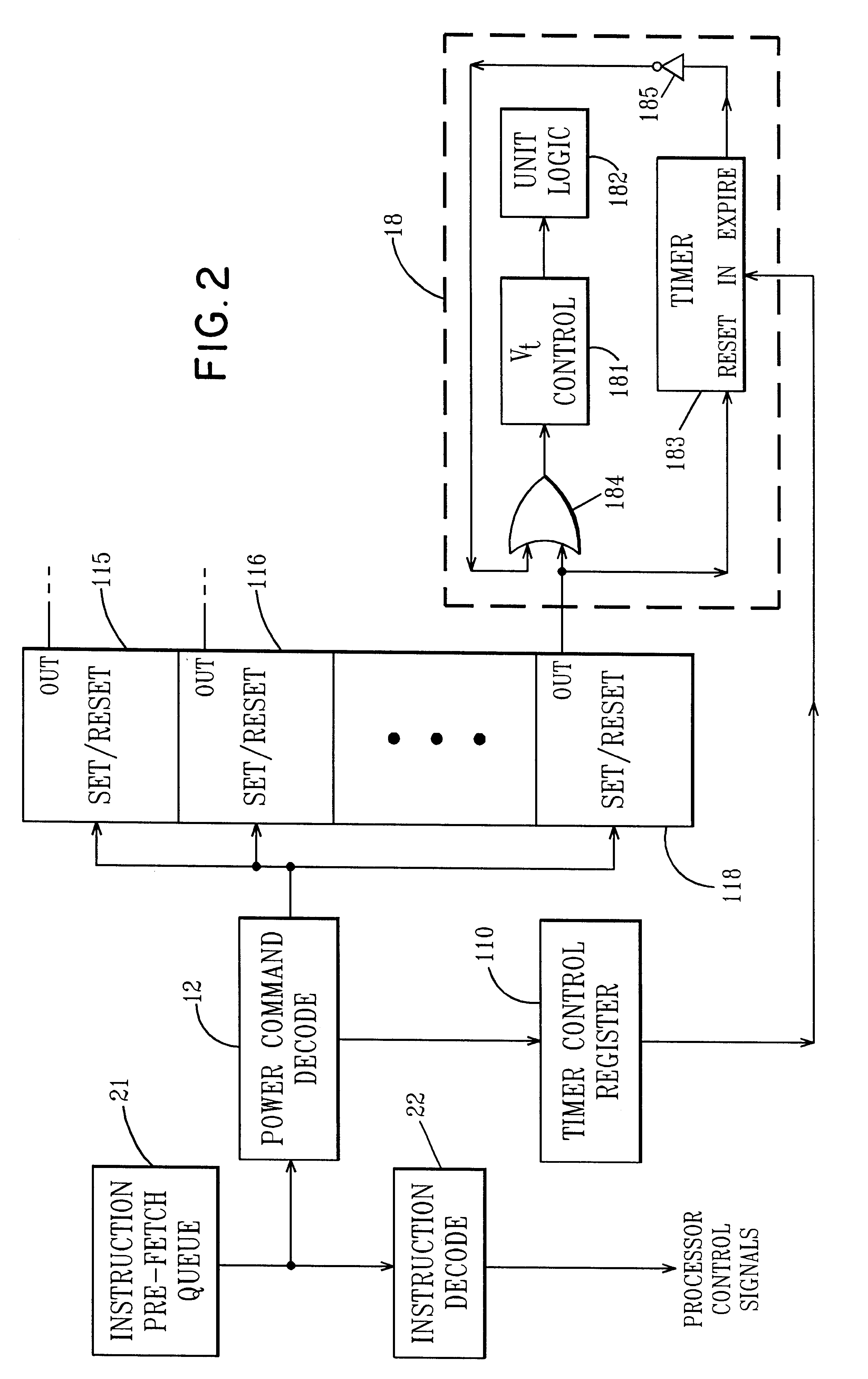
Managing VT for reduced power using power setting commands in the instruction stream
InactiveUS6477654B1Improve performanceSpeed maximizationEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringEmbedded systemInstruction stream
An integrated circuit includes a plurality of functional units which are capable of operating at more than one power / performance level and a power control unit. The power control unit controls the power / performance consumption of the different functional units to optimize operation of the integrated circuit. Special power control instructions are added to user applications in order to control via the power control unit, the power consumption of the different functional units.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method, apparatus and computer program product for efficient per thread performance information
InactiveUS6925424B2Solve excessive overheadAvoid interactionDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringProcessor registerComputer science
A value in a counter on a processor is incremented for occurrences of a monitored event, providing a measured value for the event. The value of the counter register for a first thread is saved responsive to a switch from the first thread to a second thread. The value is saved in an accumulator in system memory. Then, responsive to a switch back to the first thread, the value for the first thread is restored from the accumulator. In this way, a counter may be read, and its value, for the first thread, for example, remains consistent despite any intervening thread switches. Since the counter register may be read directly, in the user state, this provides a faster and more consistent way to update performance counts.
Owner:IBM CORP
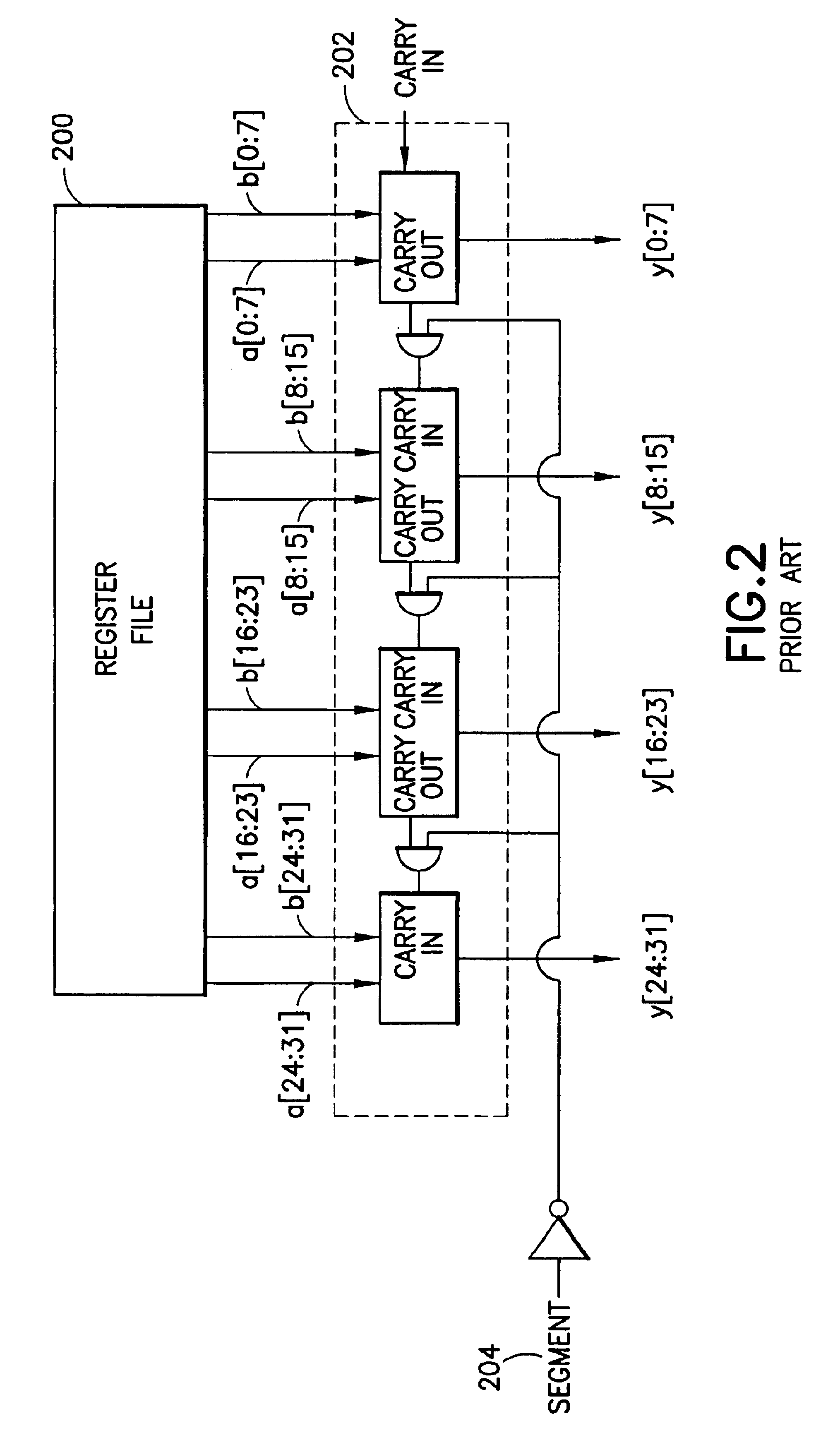
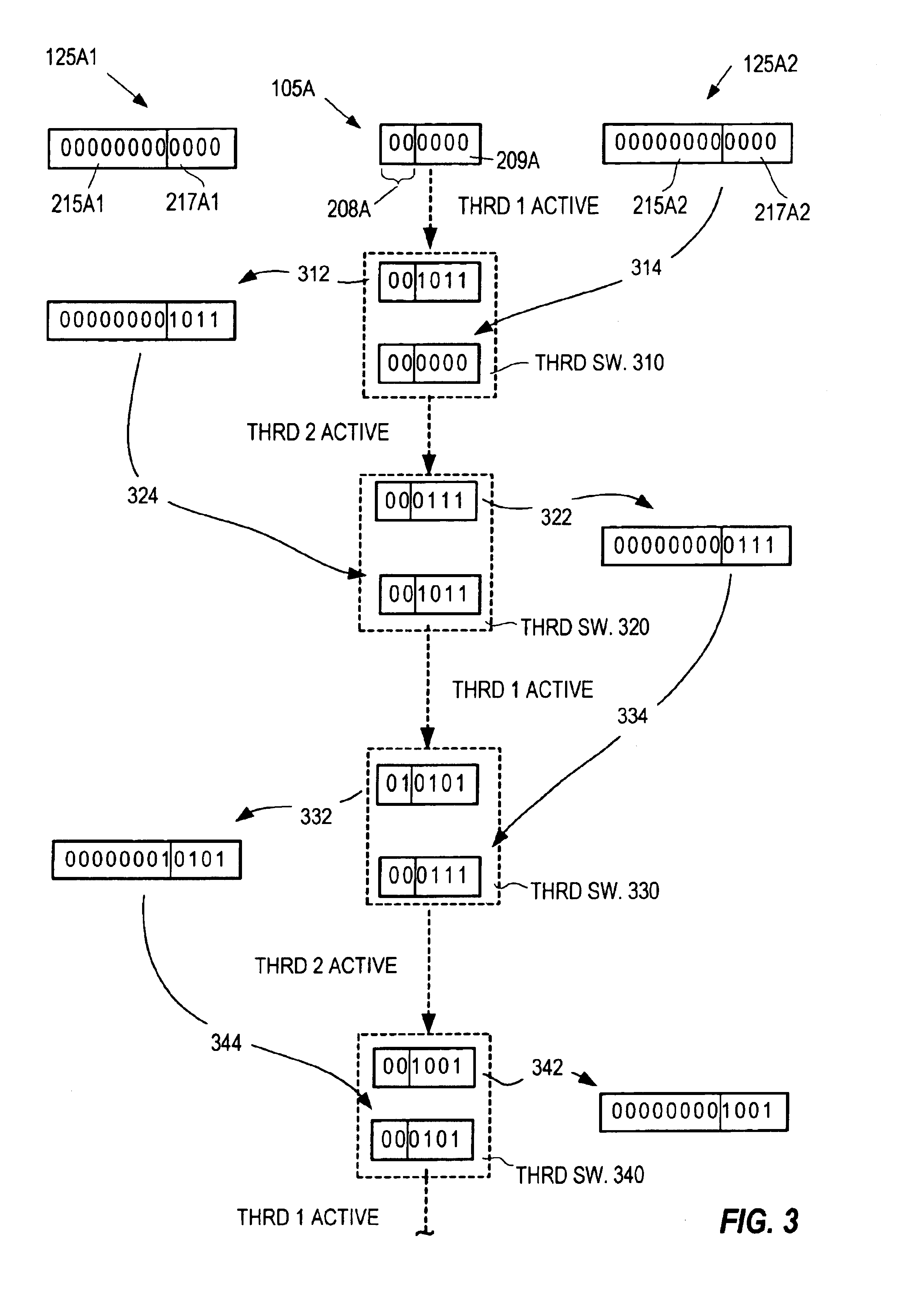
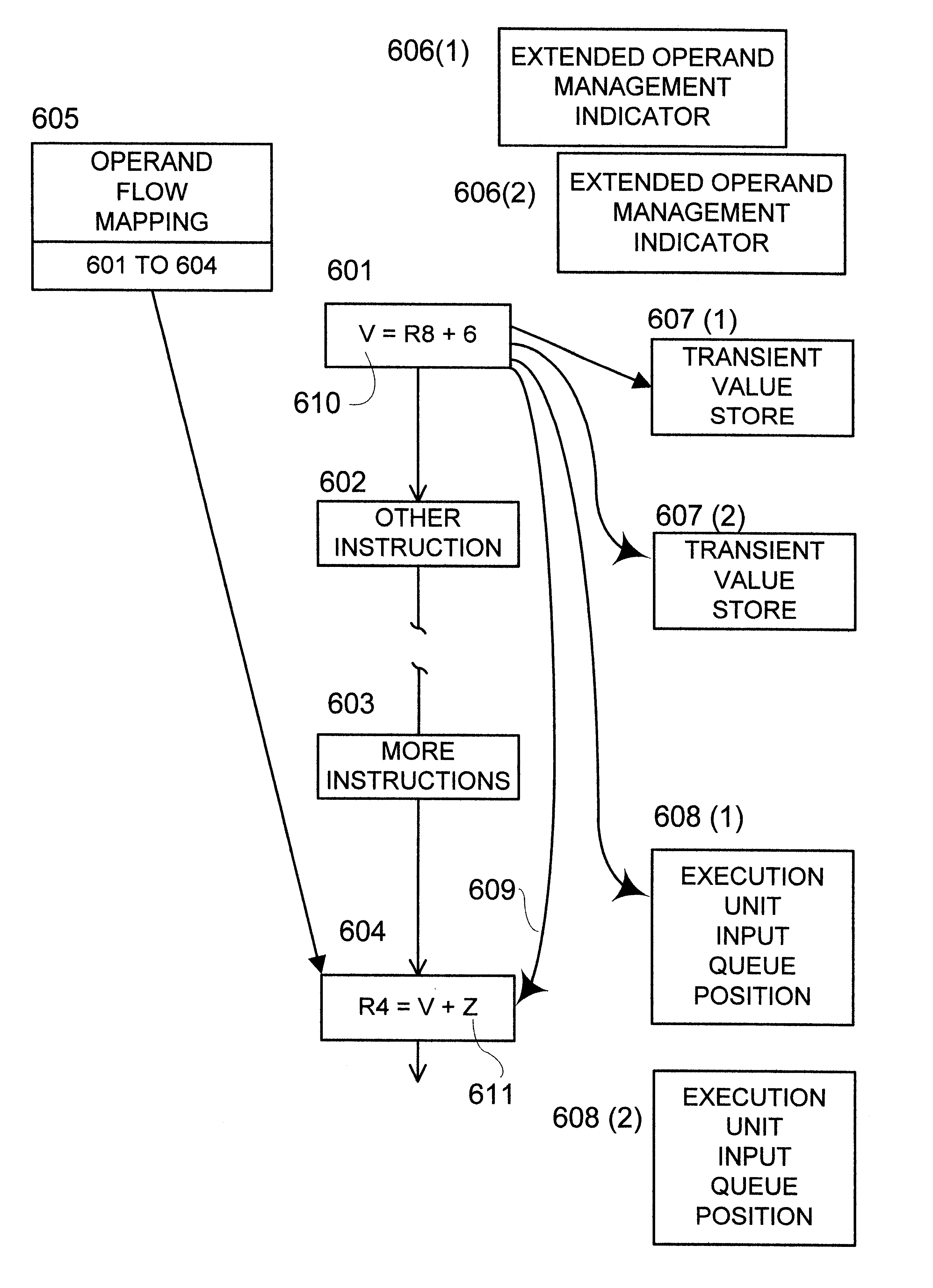
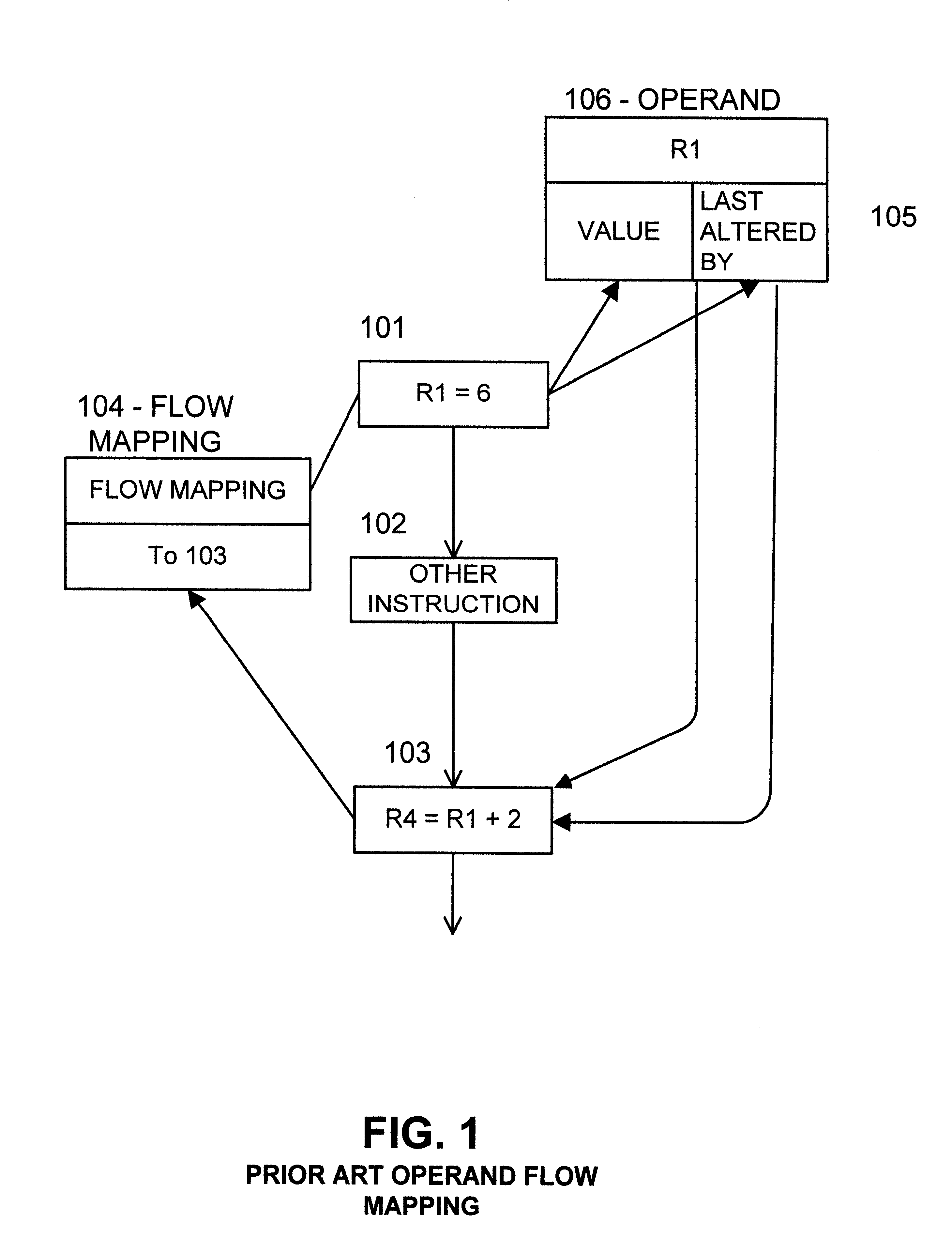
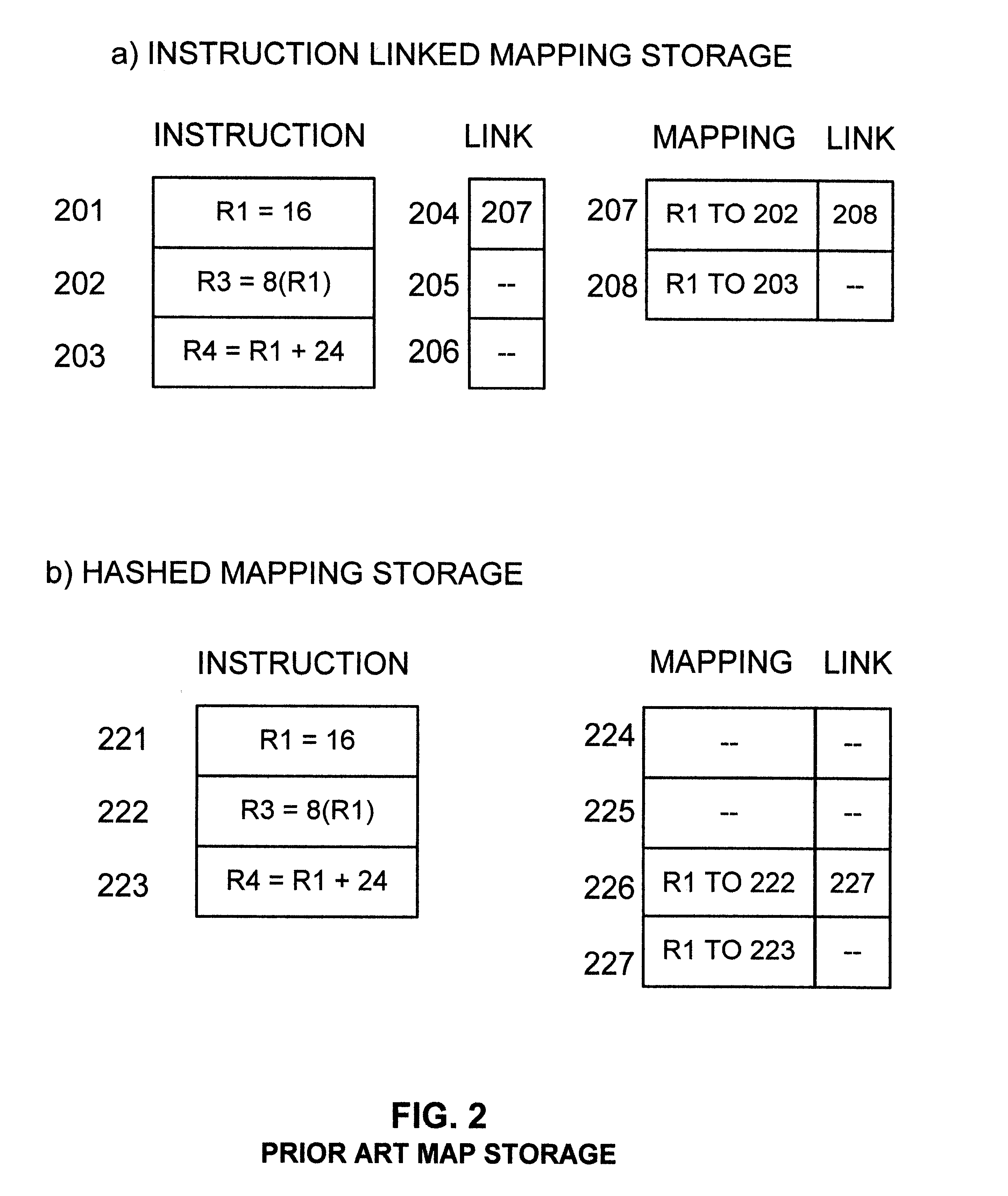
Extended operand management indicator structure and method
InactiveUS6615340B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionManagement indicatorsOperand forwarding
Extended operand management indicators stored during initial program execution enable management and regulation of operand values and streamline their handling. Operand values are stored in new types of stores. Operand location management indicators indicate current operand value locations among various store types for selected operands. Indicated operand-forwarding policies for selected operands streamline forwarding of operand values from source instructions to value receiving target instructions. Indicated loop iterations of operand source instructions enable forwarding of operands over more than one loop iteration. Stride indicators indicate strides of program loop accesses to matrix operands. Inter-loop indicators enable forwarding of operand values from source loop instructions directly to target loop instructions. Constant or nearly constant operands are indicated to enable their storage in special caches. Operands used for cross-CPU serialization are indicated for special handling and storage in spin lock cache. Indicators of farthest back and farthest forward branches since operand last update are used to enhance the prediction of longer-range branch directions. Virtual predicate operand indicators streamline execution of densely branching program code. Stack operand indicators enable nullification of paired stack pointer increment-decrement operations to avoid serious operand serialization bottlenecks in very high issue rate machines.
Owner:WILMOT II RICHARD BYRON
Scheduling in a multicore processor
ActiveUS20070220517A1Improve application performanceIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTConcurrent instruction executionProcessor elementMulti-core processor
A method and computer-usable medium including instructions for performing a method for scheduling executable transactions within a multicore processor comprising a plurality of processor elements. The method includes listing, using at least one distribution queue, a portion of the executable transactions in order of eligibility for execution. A plurality of executable transaction schedulers are provided, wherein each executable transaction scheduler includes a scheduling process for determining a most eligible executable transaction for execution from at least one candidate executable transaction ready for execution. The executable transaction schedulers are linked together to provide a multilevel scheduler. The most eligible executable transaction is output from the multilevel scheduler to the at least one distribution queue.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC +1
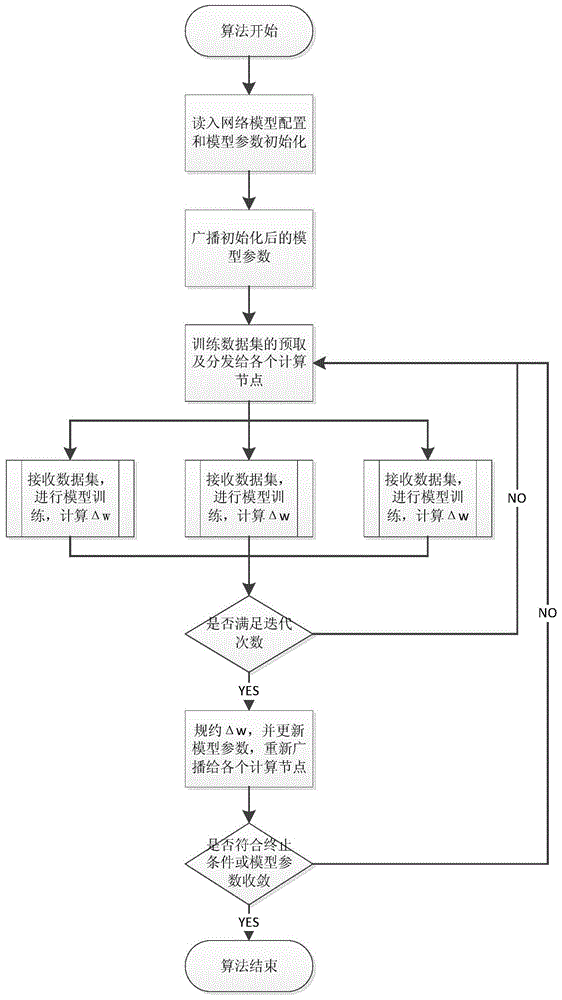
Convolution neural network parallel processing method based on large-scale high-performance cluster
InactiveCN104463324AReduce training timeImprove computing efficiencyBiological neural network modelsConcurrent instruction executionNODALAlgorithm
The invention discloses a convolution neural network parallel processing method based on a large-scale high-performance cluster. The method comprises the steps that (1) a plurality of copies are constructed for a network model to be trained, model parameters of all the copies are identical, the number of the copies is identical with the number of nodes of the high-performance cluster, each node is provided with one model copy, one node is selected to serve as a main node, and the main node is responsible for broadcasting and collecting the model parameters; (2) a training set is divided into a plurality of subsets, the training subsets are issued to the rest of sub nodes except the main mode each time to conduct parameter gradient calculation together, gradient values are accumulated, the accumulated value is used for updating the model parameters of the main node, and the updated model parameters are broadcast to all the sub nodes until model training is ended. The convolution neural network parallel processing method has the advantages of being capable of achieving parallelization, improving the efficiency of model training, shortening the training time and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHA MASHA ELECTRONICS TECH
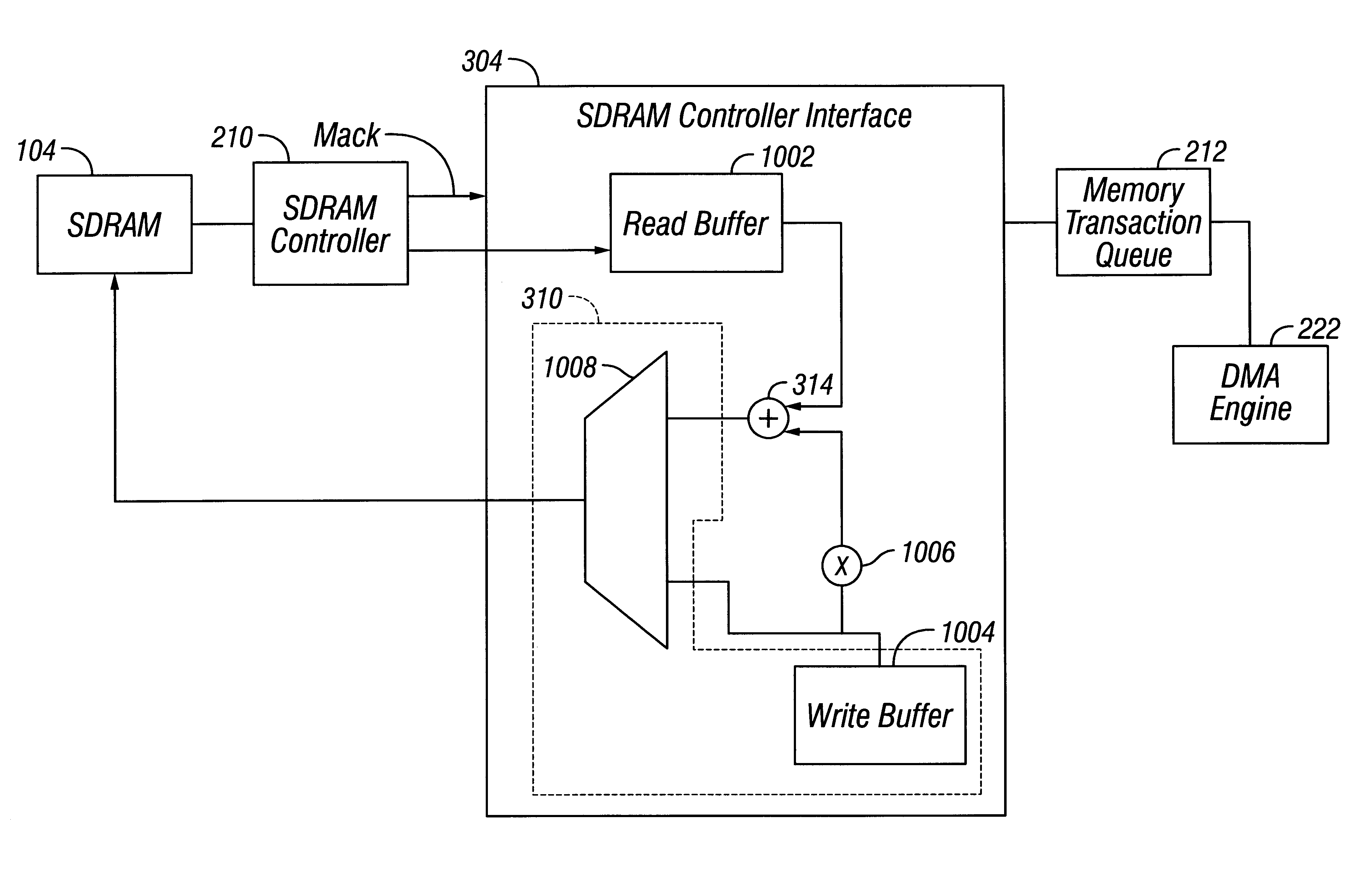
Raid XOR operations to synchronous DRAM using a read buffer and pipelining of synchronous DRAM burst read data
A memory interface controller includes a read buffer to pipeline data from a synchronous dynamic random access memory (DRAM) in response to a plurality of consecutive SDRAM burst read requests, a write buffer to store write data, an exclusive or (XOR) engine to XOR the write data with the data from the read buffer, and a write interface to write resulting data from XORing the write data and the data from the read buffer to the synchronous DRAM. Data is pipelined in the read buffer by repeatedly issuing an SDRAM burst read request before data is transferred out of the synchronous DRAM in response to a previous SDRAM burst read request until a desired amount of data is stored in the read buffer. The memory interface controller thus can perform an external read-modify-write cycle for the synchronous DRAM. The synchronous DRAM can serve as a RAID (Redundant Array s of Inexpensive Disks) memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Reconfigurable data path processor
InactiveUS6883084B1Eliminates branchingCycle simpleEnergy efficient ICTConditional code generationMultiplexerProcessing element
A reconfigurable data path processor comprises a plurality of independent processing elements. Each of the processing elements advantageously comprising an identical architecture. Each processing element comprises a plurality of data processing means for generating a potential output. Each processor is also capable of through-putting an input as a potential output with little or no processing. Each processing element comprises a conditional multiplexer having a first conditional multiplexer input, a second conditional multiplexer input and a conditional multiplexer output. A first potential output value is transmitted to the first conditional multiplexer input, and a second potential output value is transmitted to the second conditional multiplexer output. The conditional multiplexer couples either the first conditional multiplexer input or the second conditional multiplexer input to the conditional multiplexer output, according to an output control command. The output control command is generated by processing a set of arithmetic status-bits through a logical mask. The conditional multiplexer output is coupled to a first processing element output. A first set of arithmetic bits are generated according to the processing of the first processable value. A second set of arithmetic bits may be generated from a second processing operation. The selection of the arithmetic status-bits is performed by an arithmetic-status bit multiplexer selects the desired set of arithmetic status bits from among the first and second set of arithmetic status bits. The conditional multiplexer evaluates the select arithmetic status bits according to logical mask defining an algorithm for evaluating the arithmetic status bits.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Method for perfetching structured data
InactiveUS6311260B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsIdle timeComputer science
A method for prefetching structured data, and more particularly a mechanism for observing address references made by a processor, and learning from those references the patterns of accesses made to structured data. Structured data means aggregates of related data such as arrays, records, and data containing links and pointers. When subsequent accesses are made to data structured in the same way, the mechanism generates in advance the sequence of addresses that will be needed for the new accesses. This sequence is utilized by the memory to obtain the data somewhat earlier than the instructions would normally request it, and thereby eliminate idle time due to memory latency while awaiting the arrival of the data.
Owner:NEC CORP
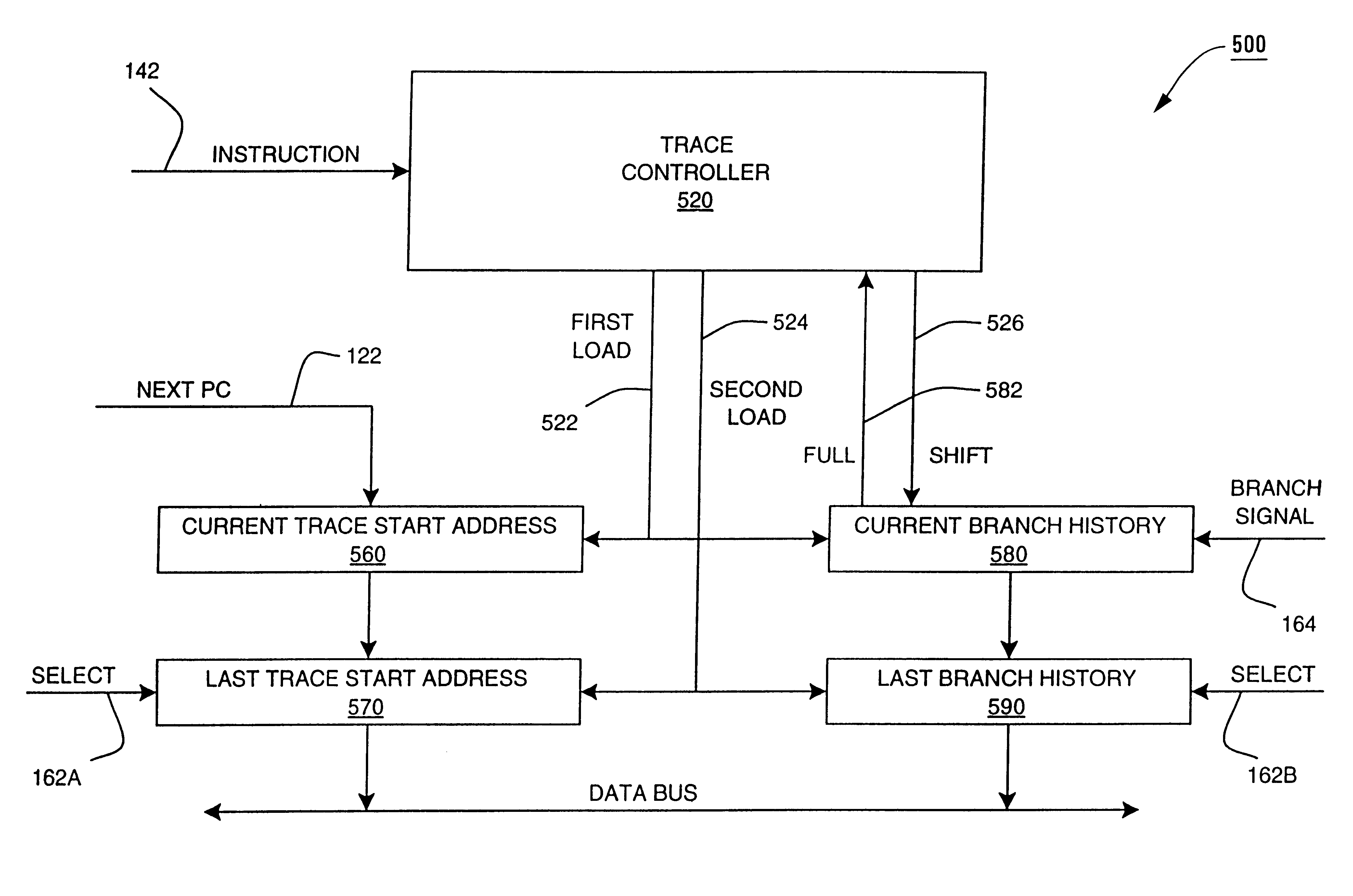
Method and apparatus for profiling of non-instrumented programs and dynamic processing of profile data
InactiveUS6233678B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationProcessor registerParallel computing
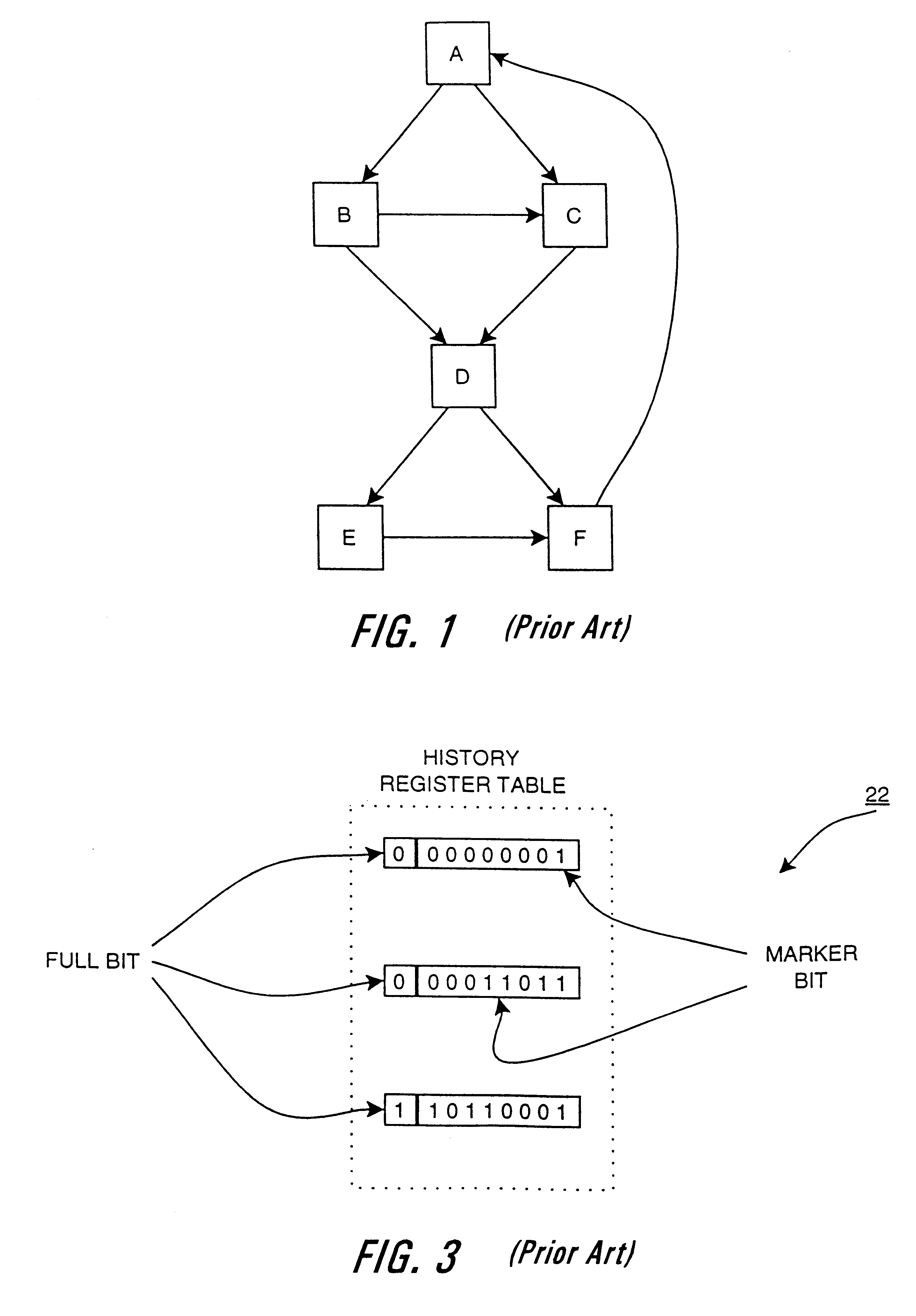
An apparatus and method are shown for collecting a branch history value of a program executing in a processor. A current start address register latches a program count value in response to a trace termination condition, such as an indirect branch instruction. A current branch history register is cleared in response to the trace termination condition and shifts in a branch outcome value of the processor in response to a conditional direct branch instruction. A last trace start address latches the content of the current trace start address and a last branch history register latches the content of the current branch history register when a trace termination condition occurs.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
Popular searches
Network traffic/resource management Data switching by path configuration Digital storage Energy efficient computing High level techniques Memory systems Input/output processes for data processing Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Computation using denominational number representation Handling data according to predetermined rules
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com