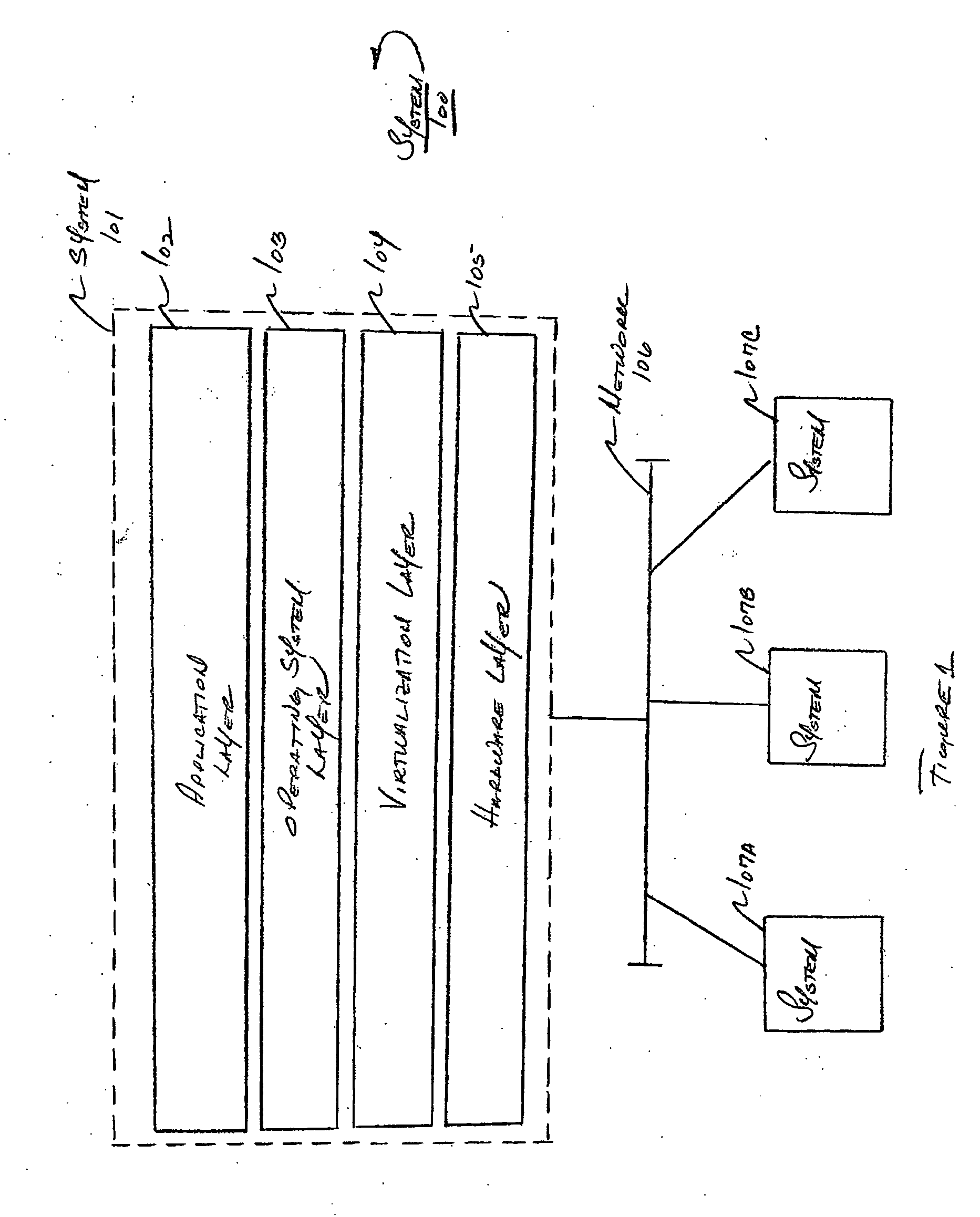
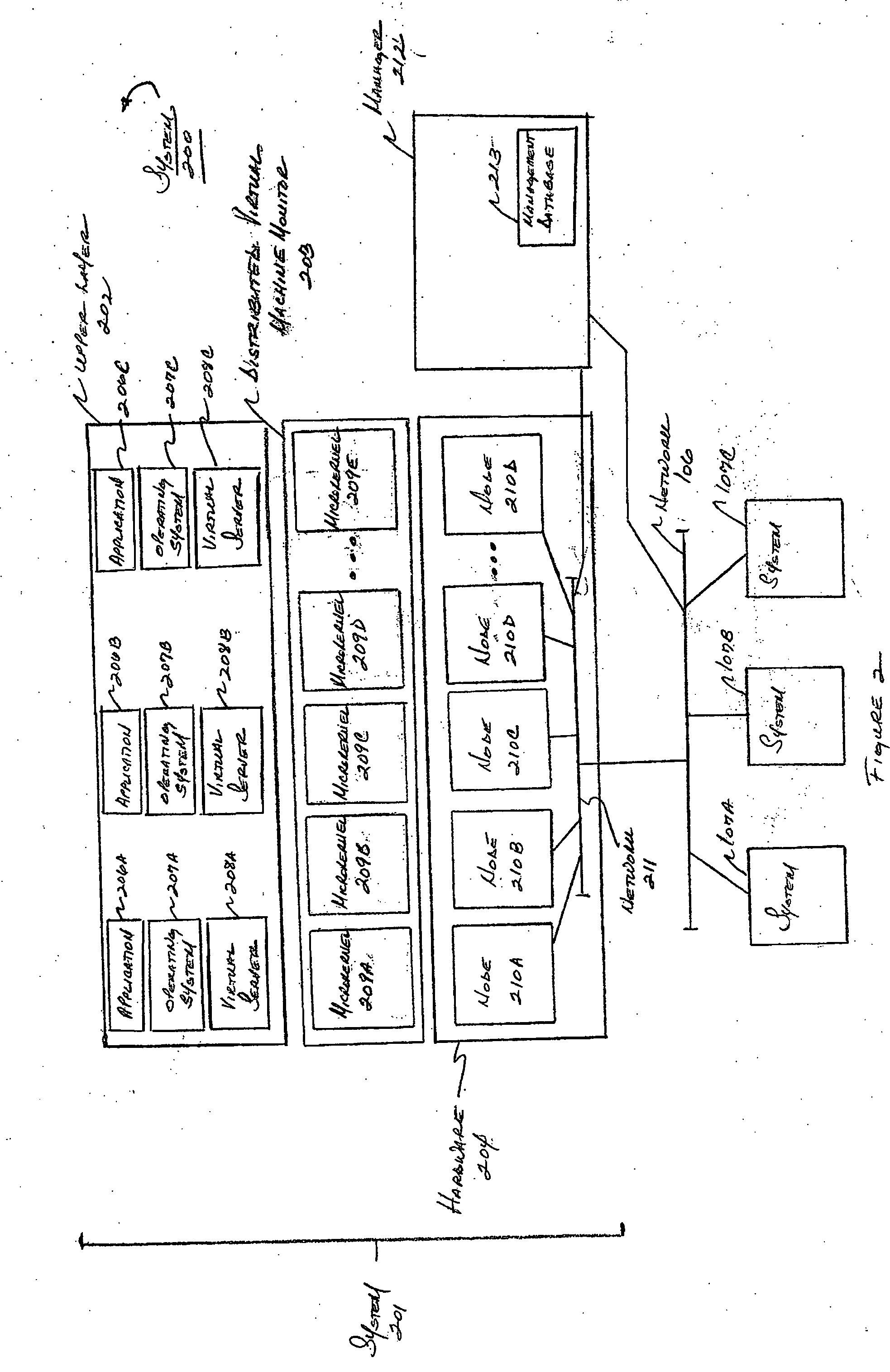
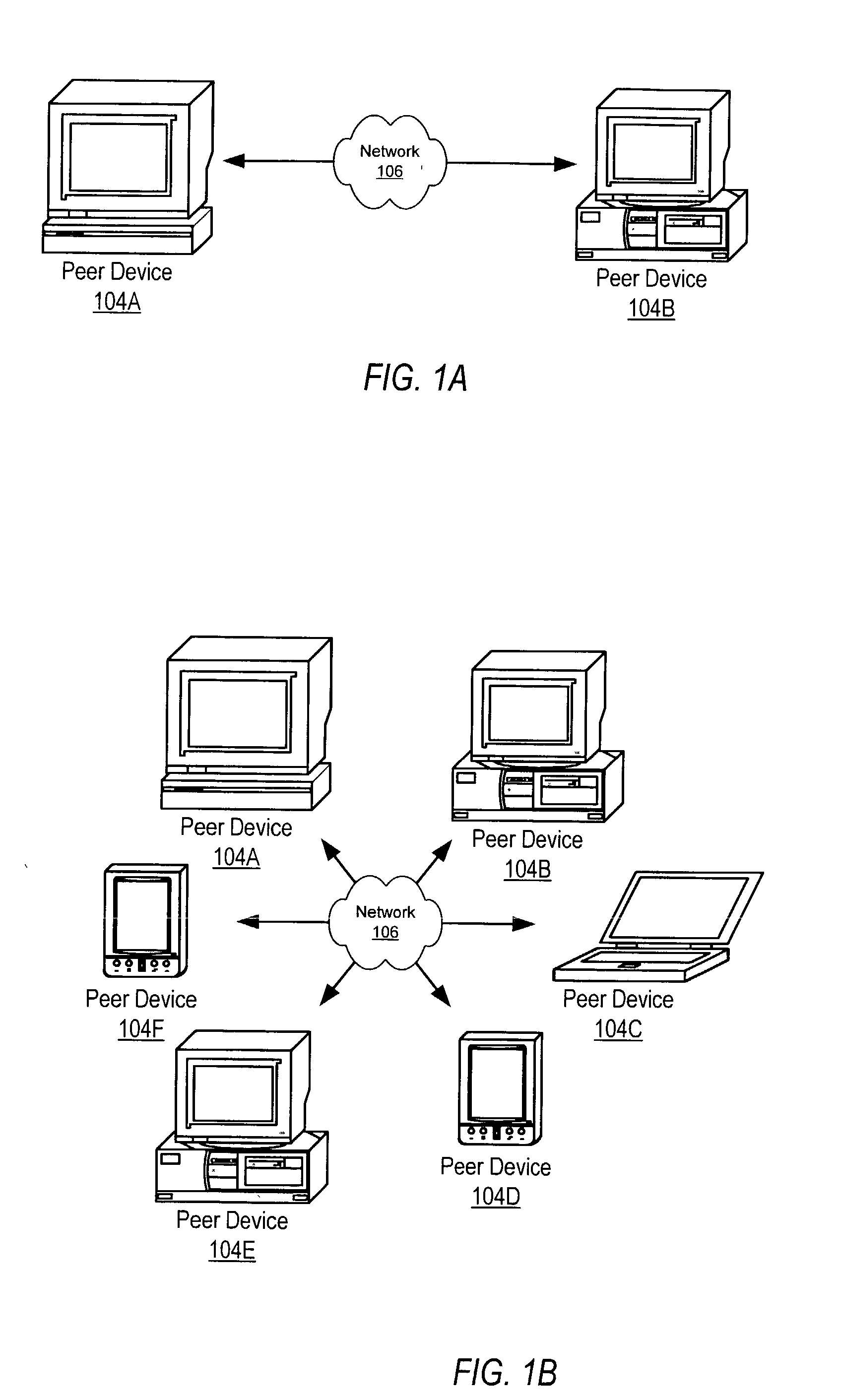
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33145results about "Resource allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
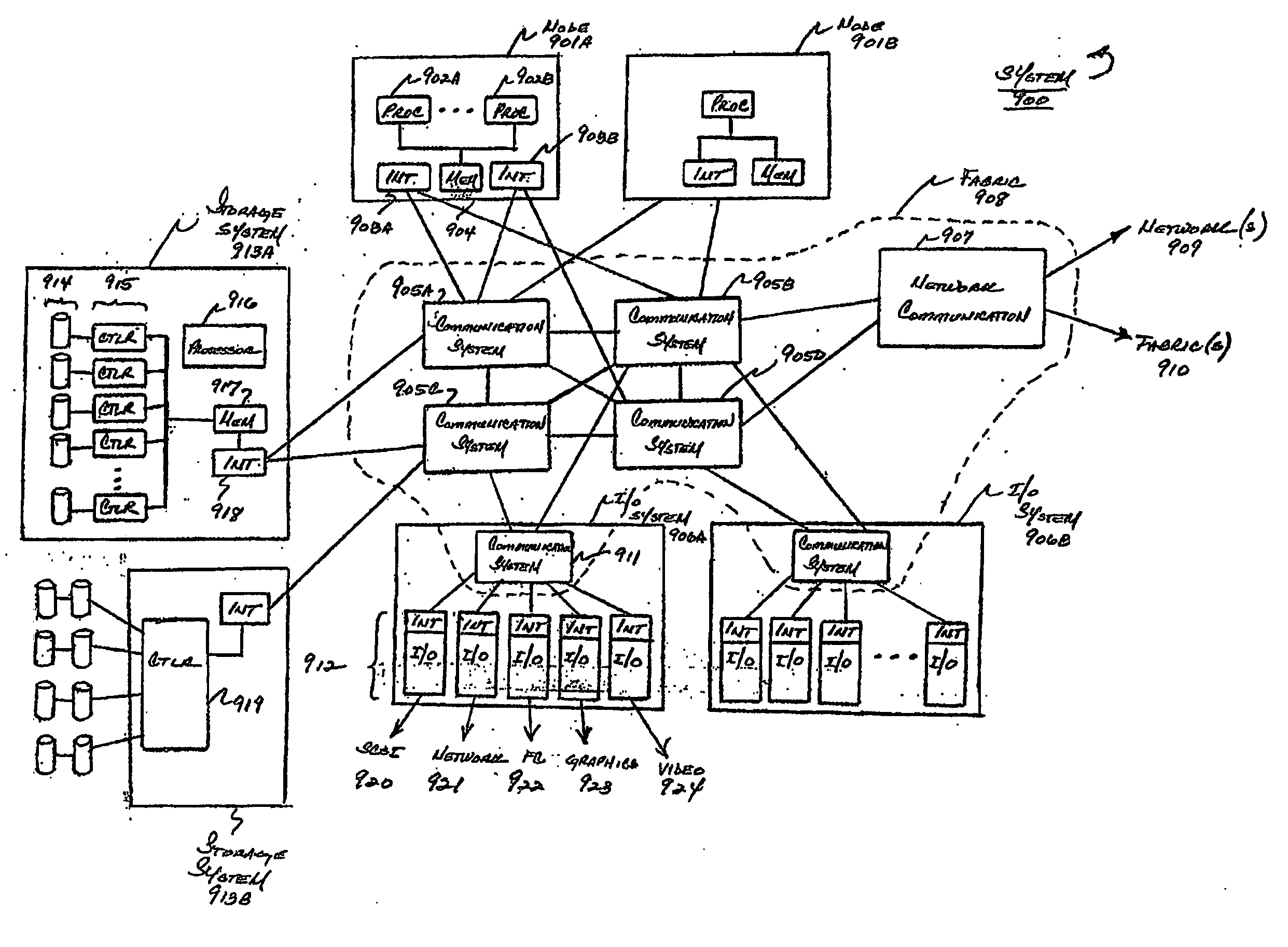
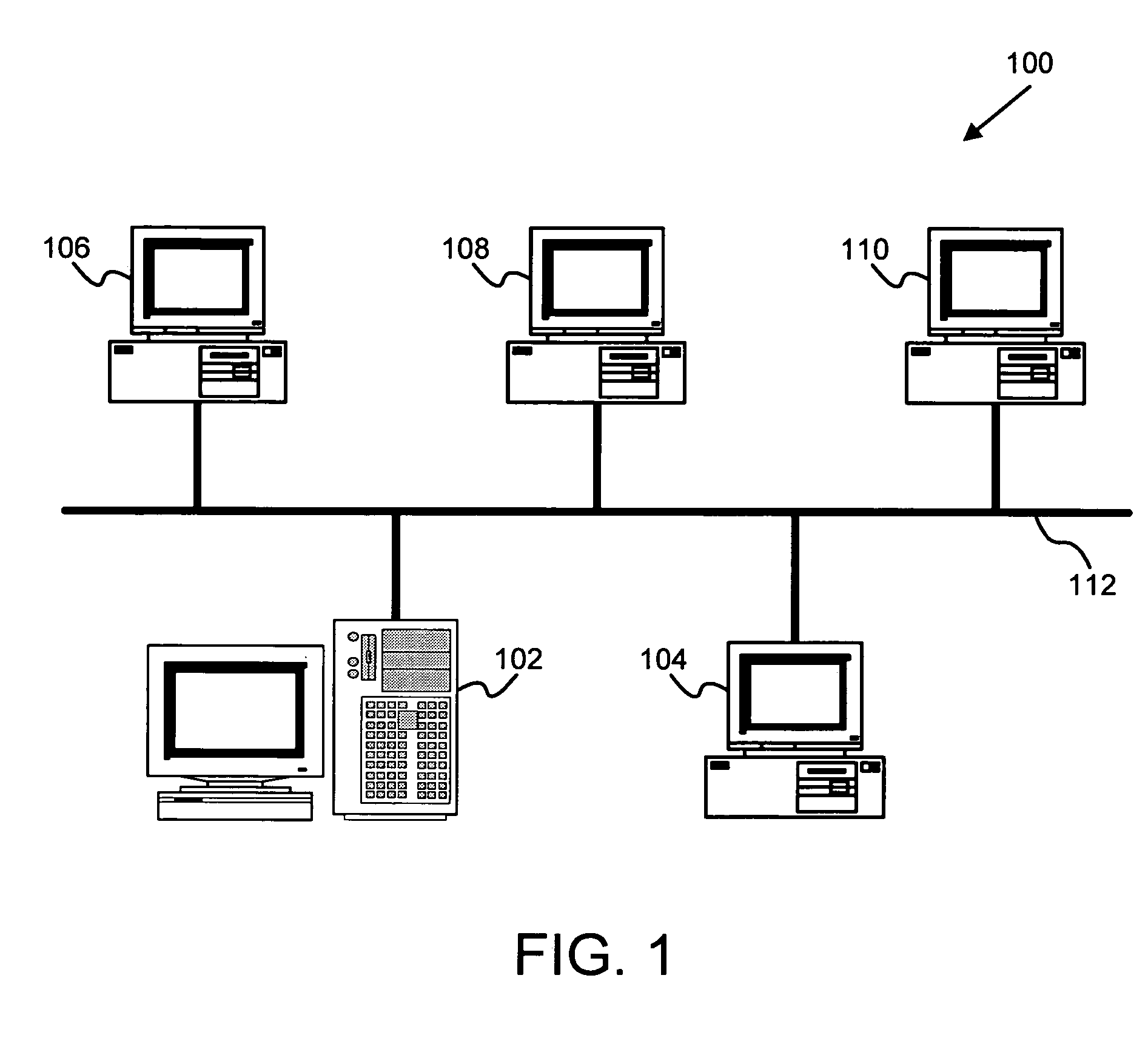
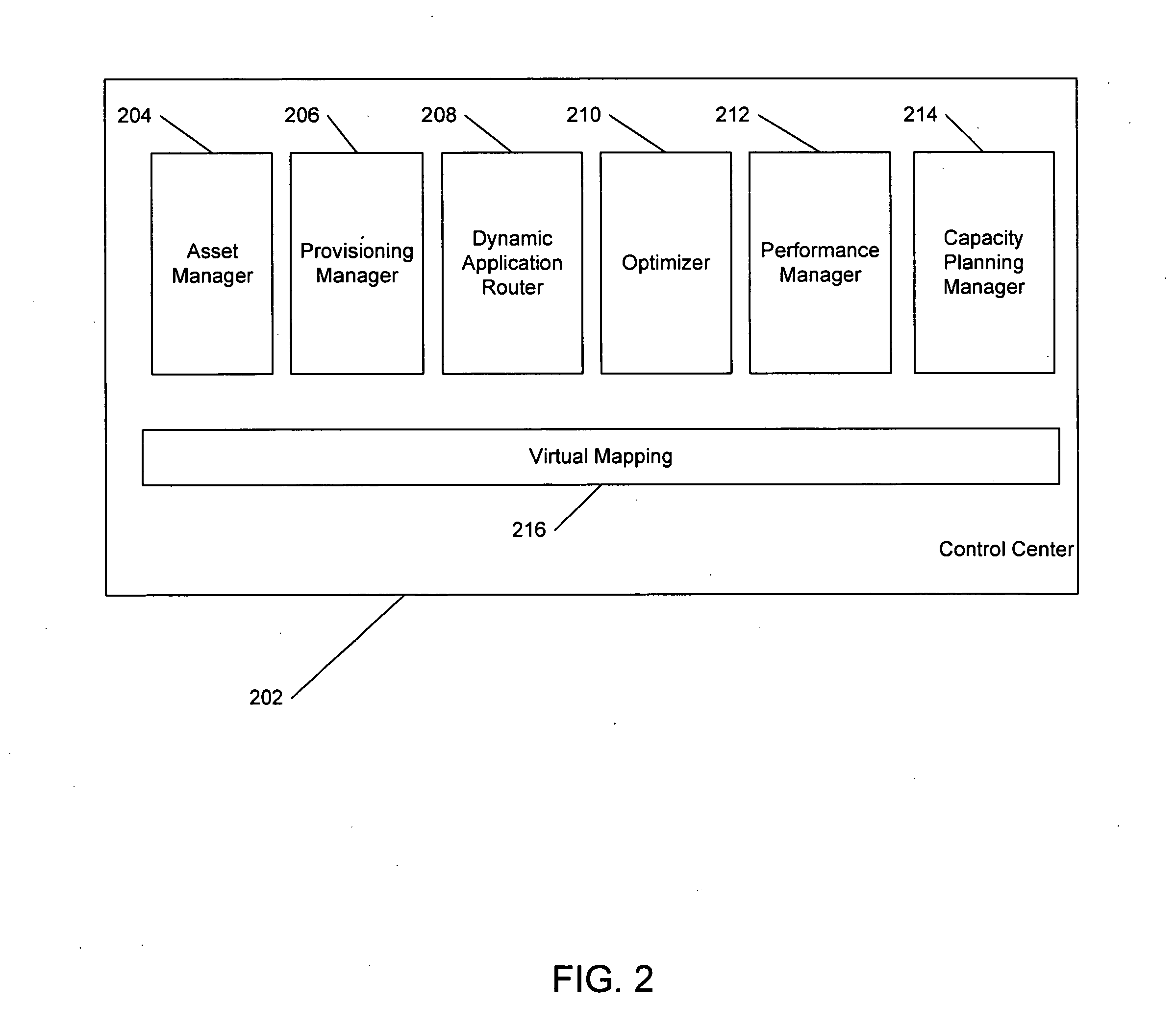
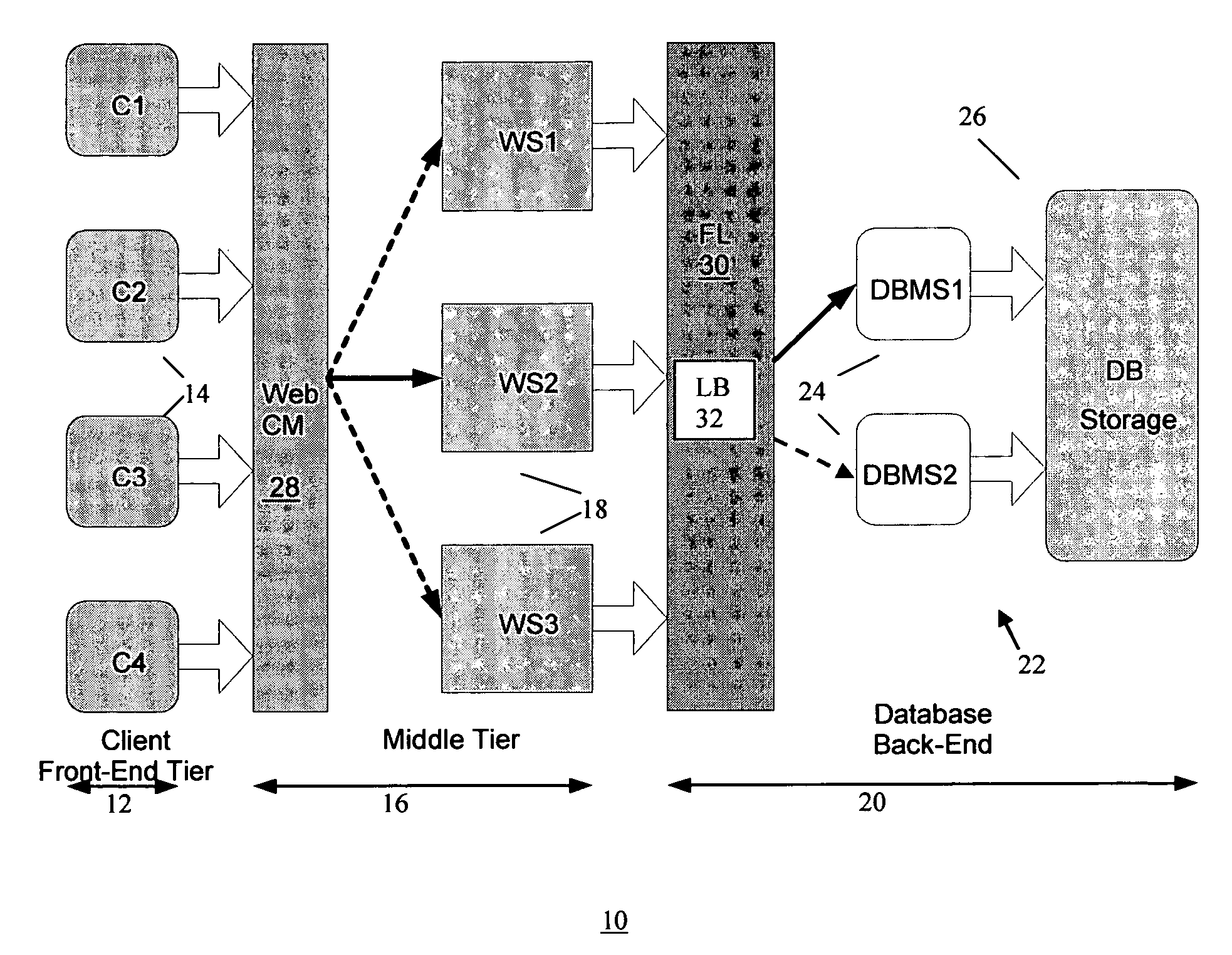
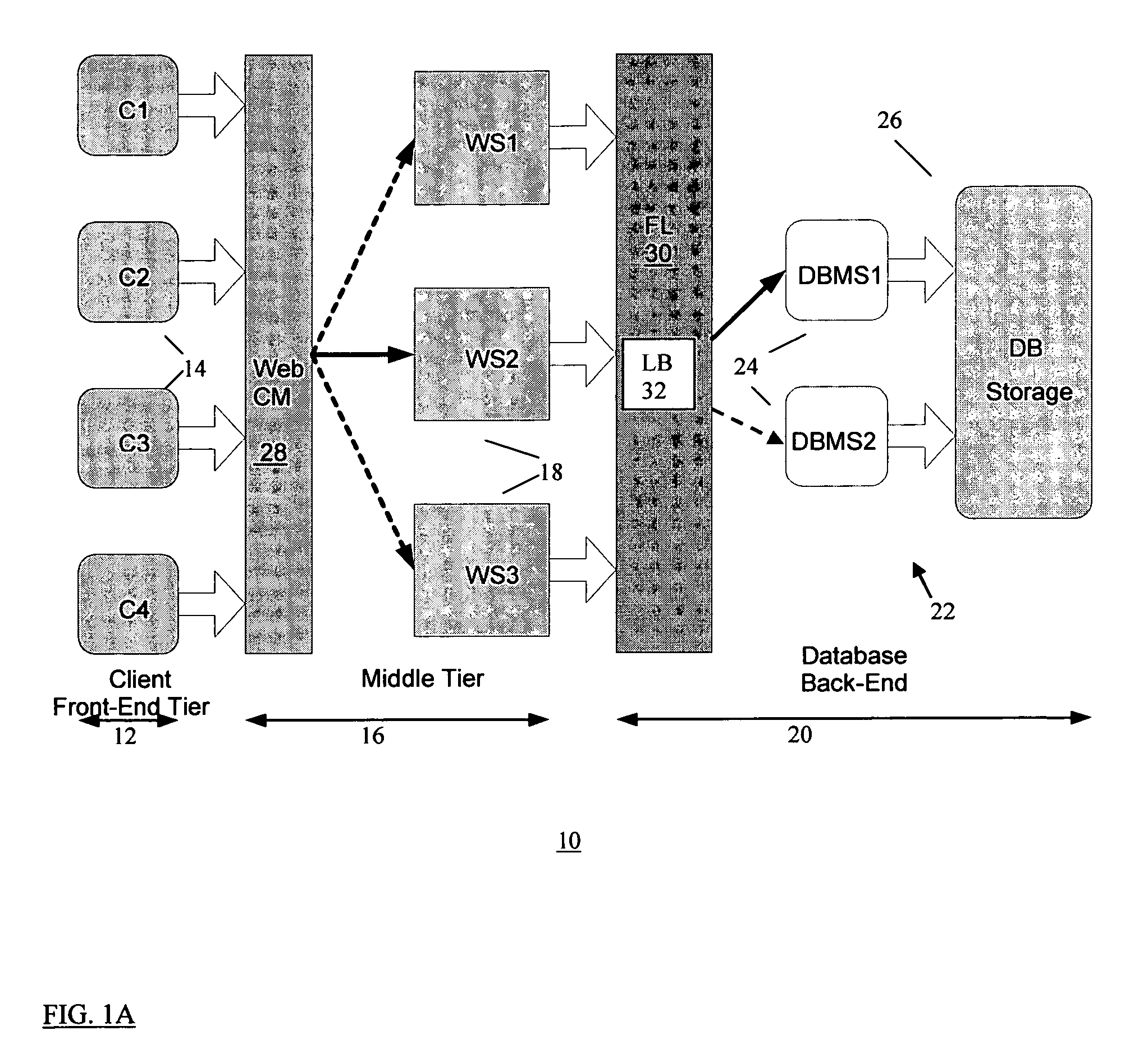
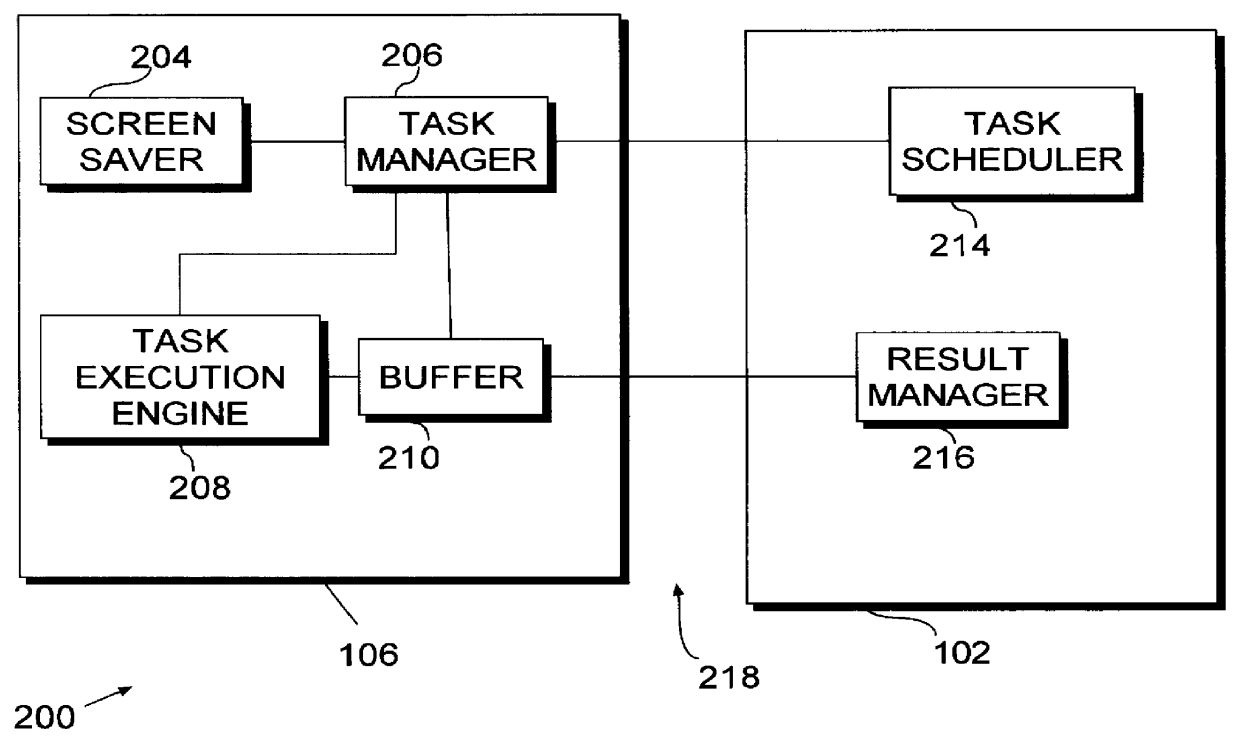
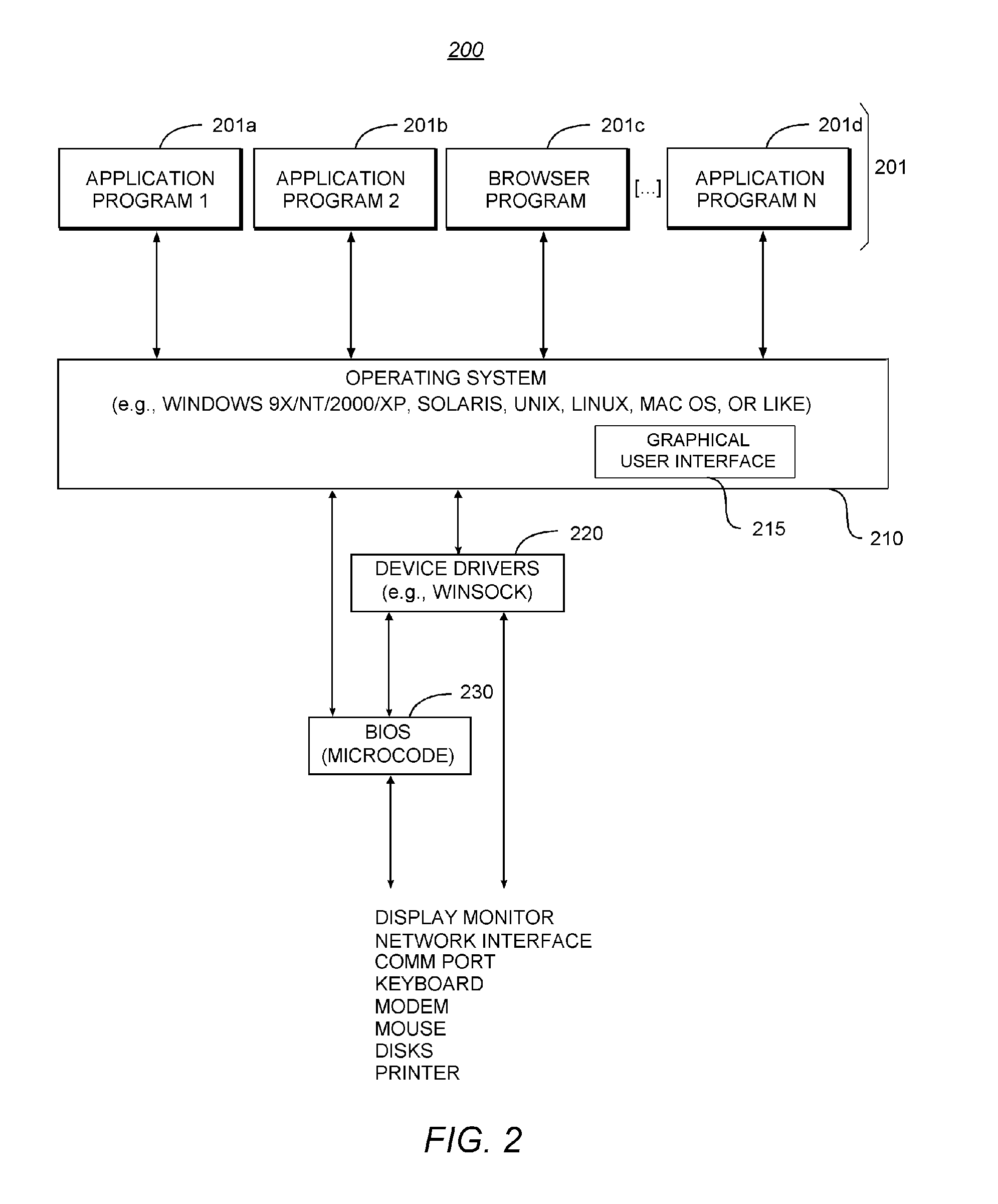
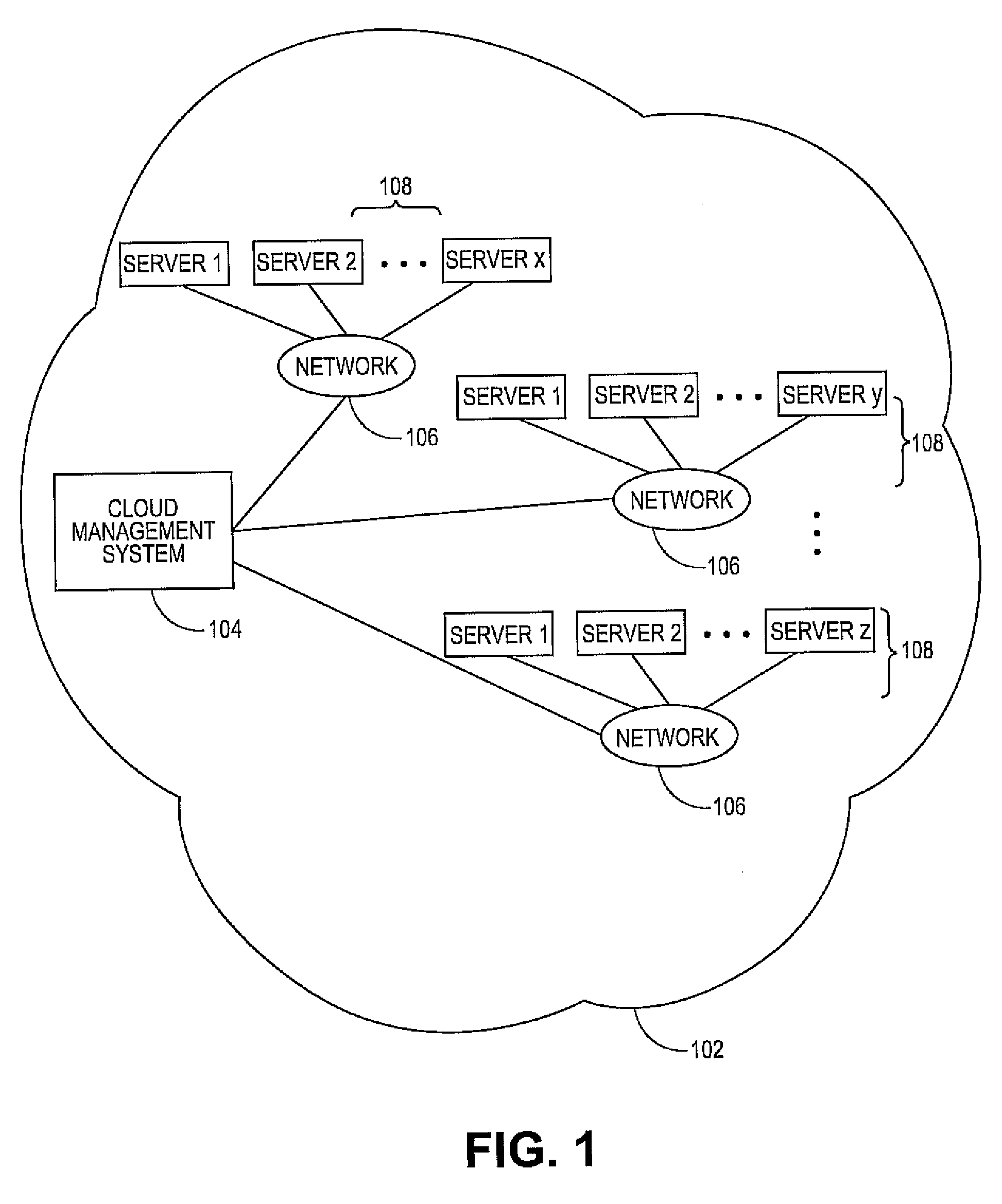
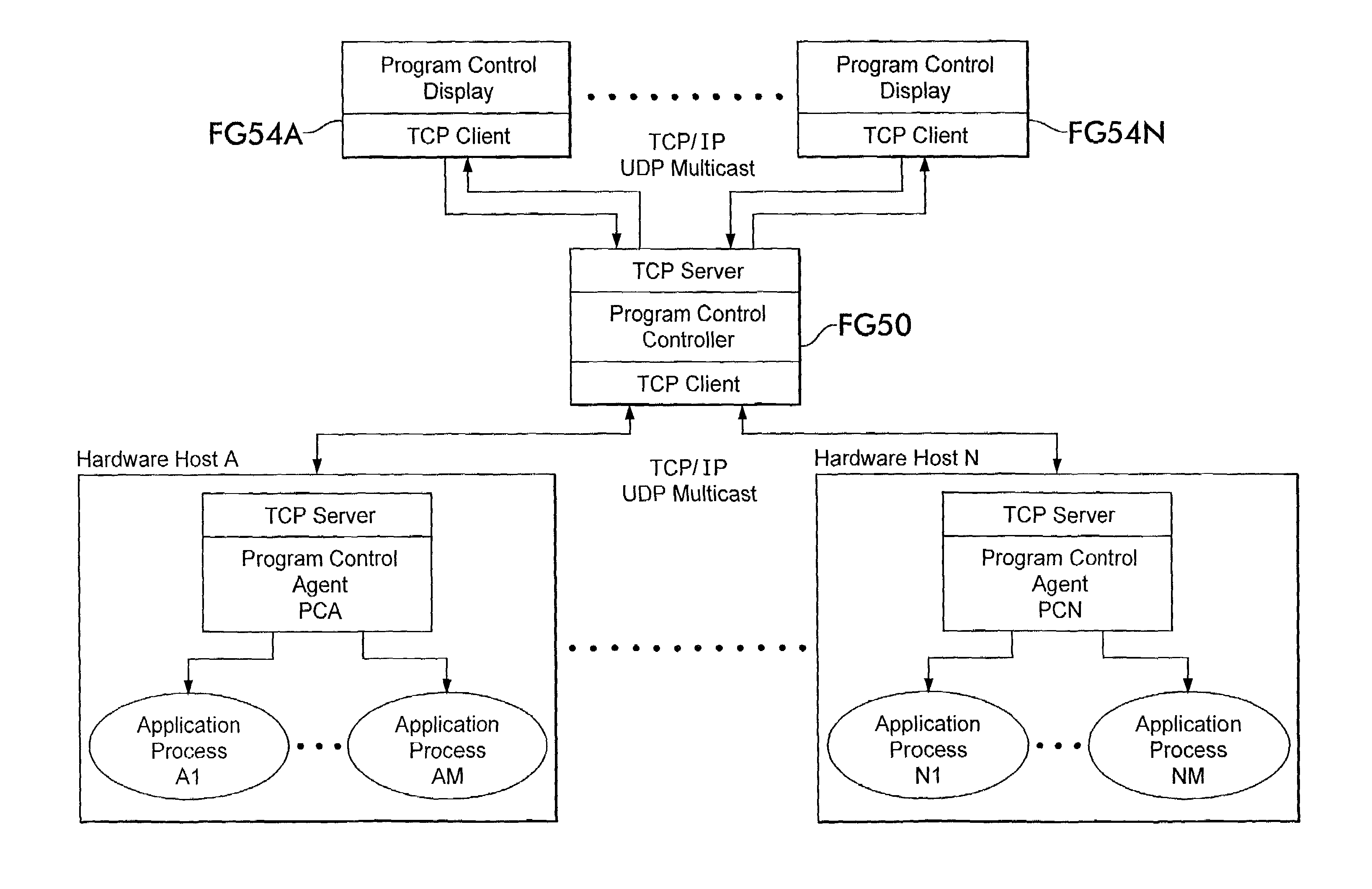
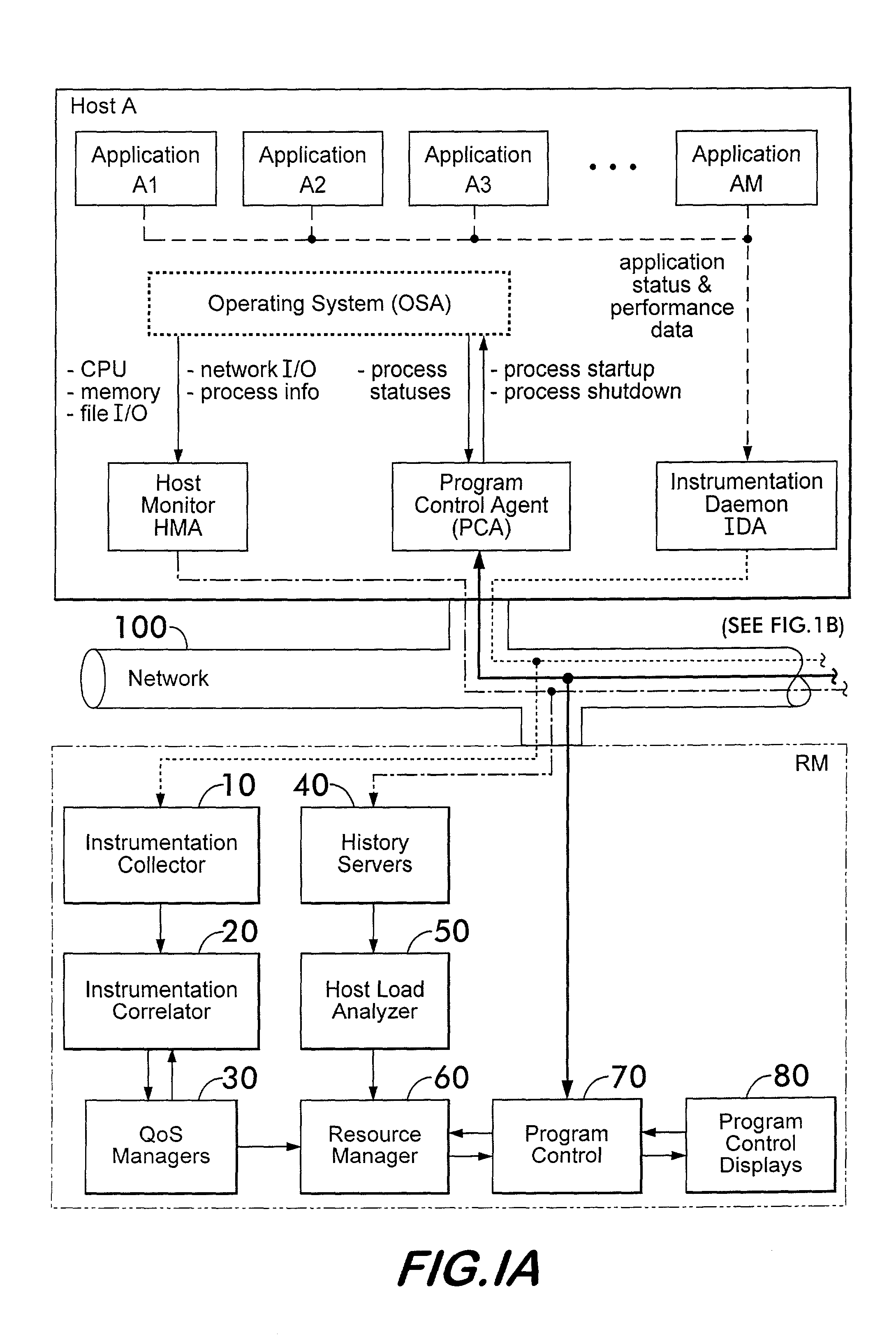
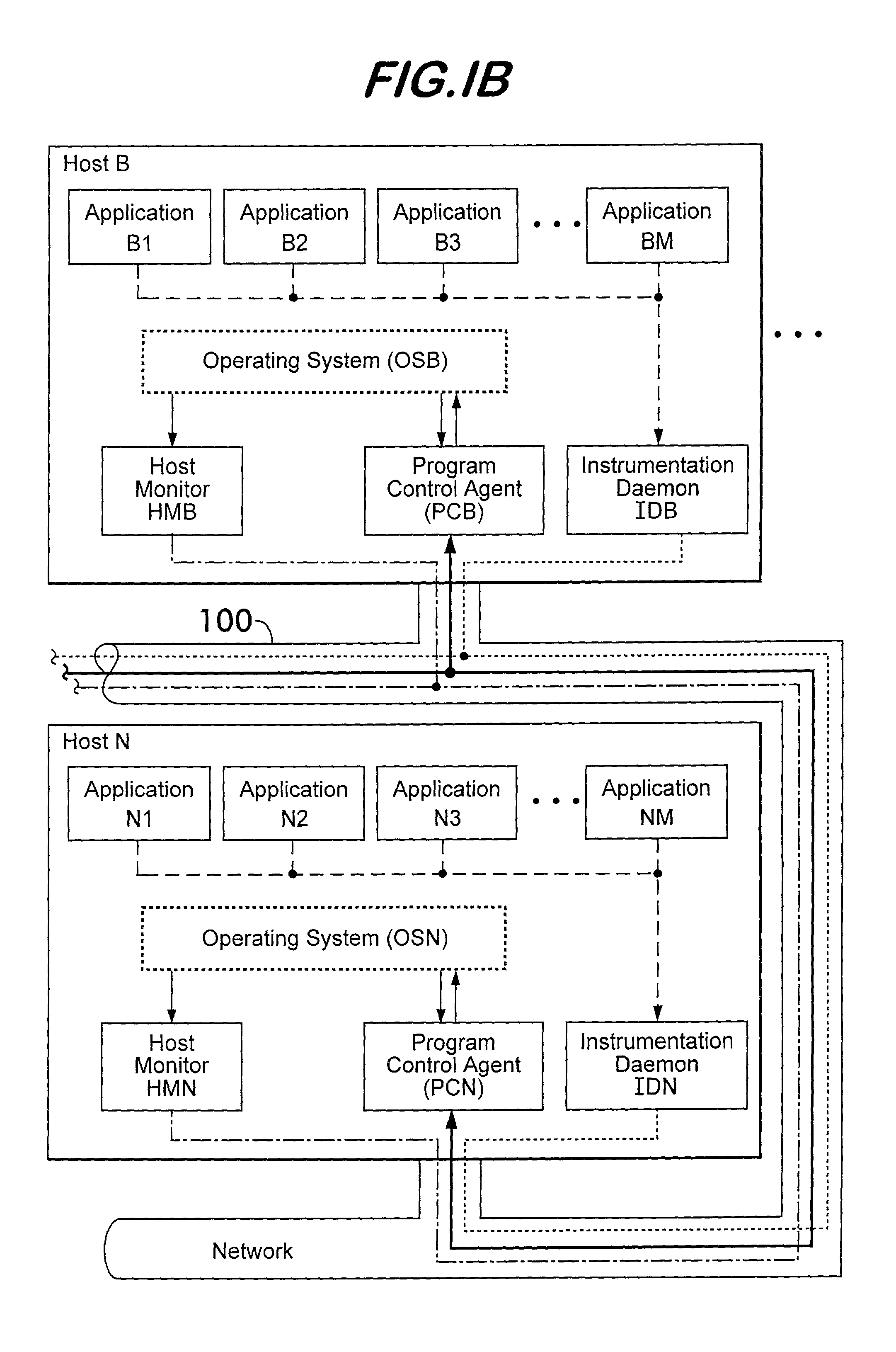
System and method for managing virtual servers
ActiveUS20050120160A1Grow and shrink capabilityMaximize useResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemPrimitive state
A management capability is provided for a virtual computing platform. In one example, this platform allows interconnected physical resources such as processors, memory, network interfaces and storage interfaces to be abstracted and mapped to virtual resources (e.g., virtual mainframes, virtual partitions). Virtual resources contained in a virtual partition can be assembled into virtual servers that execute a guest operating system (e.g., Linux). In one example, the abstraction is unique in that any resource is available to any virtual server regardless of the physical boundaries that separate the resources. For example, any number of physical processors or any amount of physical memory can be used by a virtual server even if these resources span different nodes. A virtual computing platform is provided that allows for the creation, deletion, modification, control (e.g., start, stop, suspend, resume) and status (i.e., events) of the virtual servers which execute on the virtual computing platform and the management capability provides controls for these functions. In a particular example, such a platform allows the number and type of virtual resources consumed by a virtual server to be scaled up or down when the virtual server is running. For instance, an administrator may scale a virtual server manually or may define one or more policies that automatically scale a virtual server. Further, using the management API, a virtual server can monitor itself and can scale itself up or down depending on its need for processing, memory and I / O resources. For example, a virtual server may monitor its CPU utilization and invoke controls through the management API to allocate a new processor for itself when its utilization exceeds a specific threshold. Conversely, a virtual server may scale down its processor count when its utilization falls. Policies can be used to execute one or more management controls. More specifically, a management capability is provided that allows policies to be defined using management object's properties, events and / or method results. A management policy may also incorporate external data (e.g., an external event) in its definition. A policy may be triggered, causing the management server or other computing entity to execute an action. An action may utilize one or more management controls. In addition, an action may access external capabilities such as sending notification e-mail or sending a text message to a telephone paging system. Further, management capability controls may be executed using a discrete transaction referred to as a “job.” A series of management controls may be assembled into a job using one or management interfaces. Errors that occur when a job is executed may cause the job to be rolled back, allowing affected virtual servers to return to their original state.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Apparatus, system, and method for autonomic control of grid system resources
ActiveUS20050131993A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsAutomatic controlData operations
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for autonomic management of data operations and performance resources on a grid computing system. An autonomic management apparatus includes a monitor module, a policy module, and a regulation module. The monitor module is configured to monitor the grid computing system for a trigger event. The policy module is configured to access one of a plurality of system policies. Each of the plurality of system policies corresponds to an operational control parameter of a system resource of the grid computing system. The regulation module is configured to autonomically regulate the system resource in response to a recognized trigger event according to one of the plurality of system policies. The trigger event may be a prediction trigger event, an initiation trigger event, a regulation trigger event, or a termination trigger event.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Virtual systems management
Automatic configuration management of a network is provided by determining an inventory of resources at a virtualization layer of a node of the network, assigning prioritization to members of a set of network configuration elements, allocating virtual resources among the set of network configuration elements, establishing a network configuration. The configuration is managed by determining real time performance metrics for the configuration, producing a reallocation of the virtual resources based on the performance metrics that are estimated to change the established configuration, change the performance metrics, and initiating the reallocation of the virtual resources. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement that allows a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:TOUTVIRTUAL
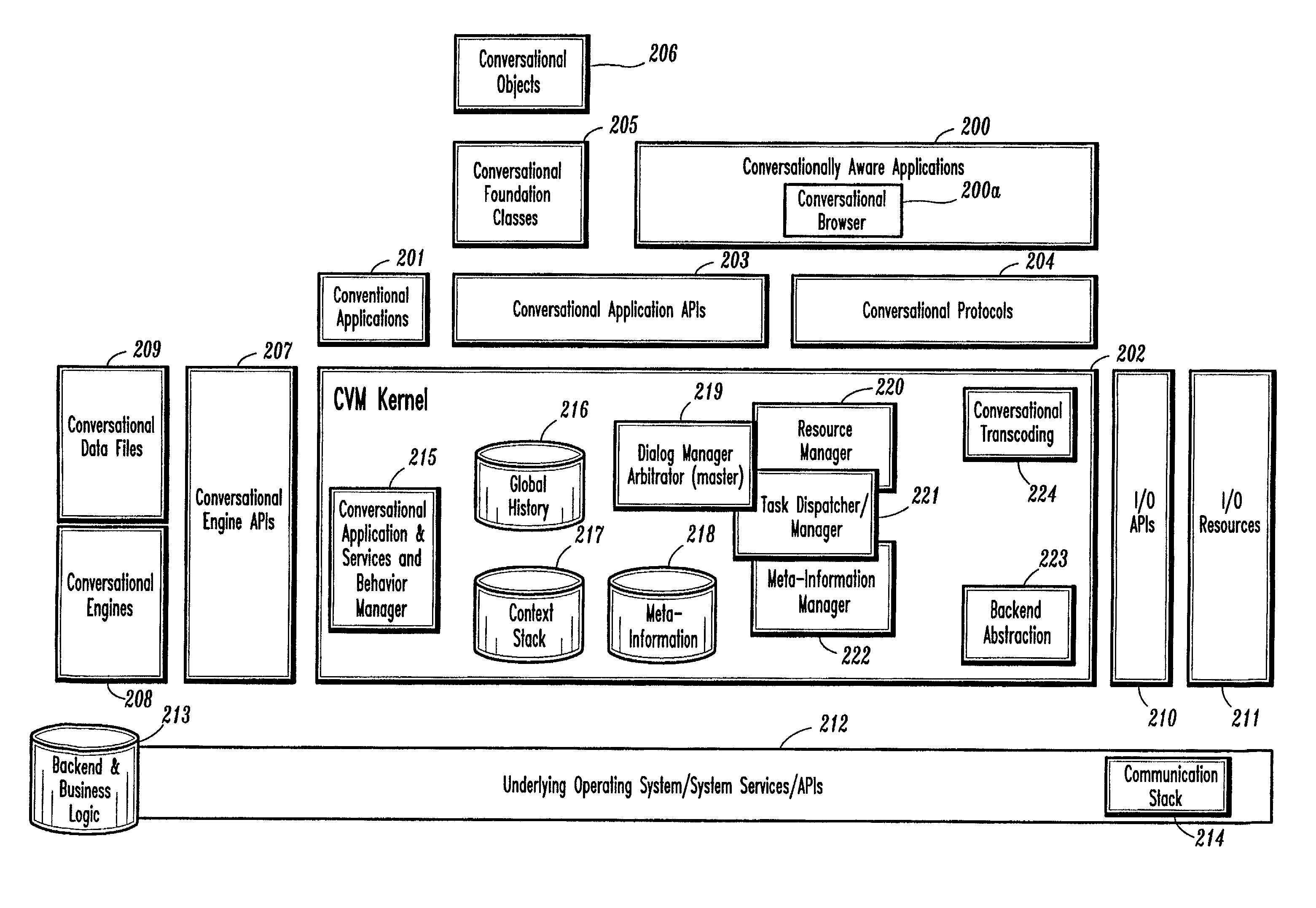
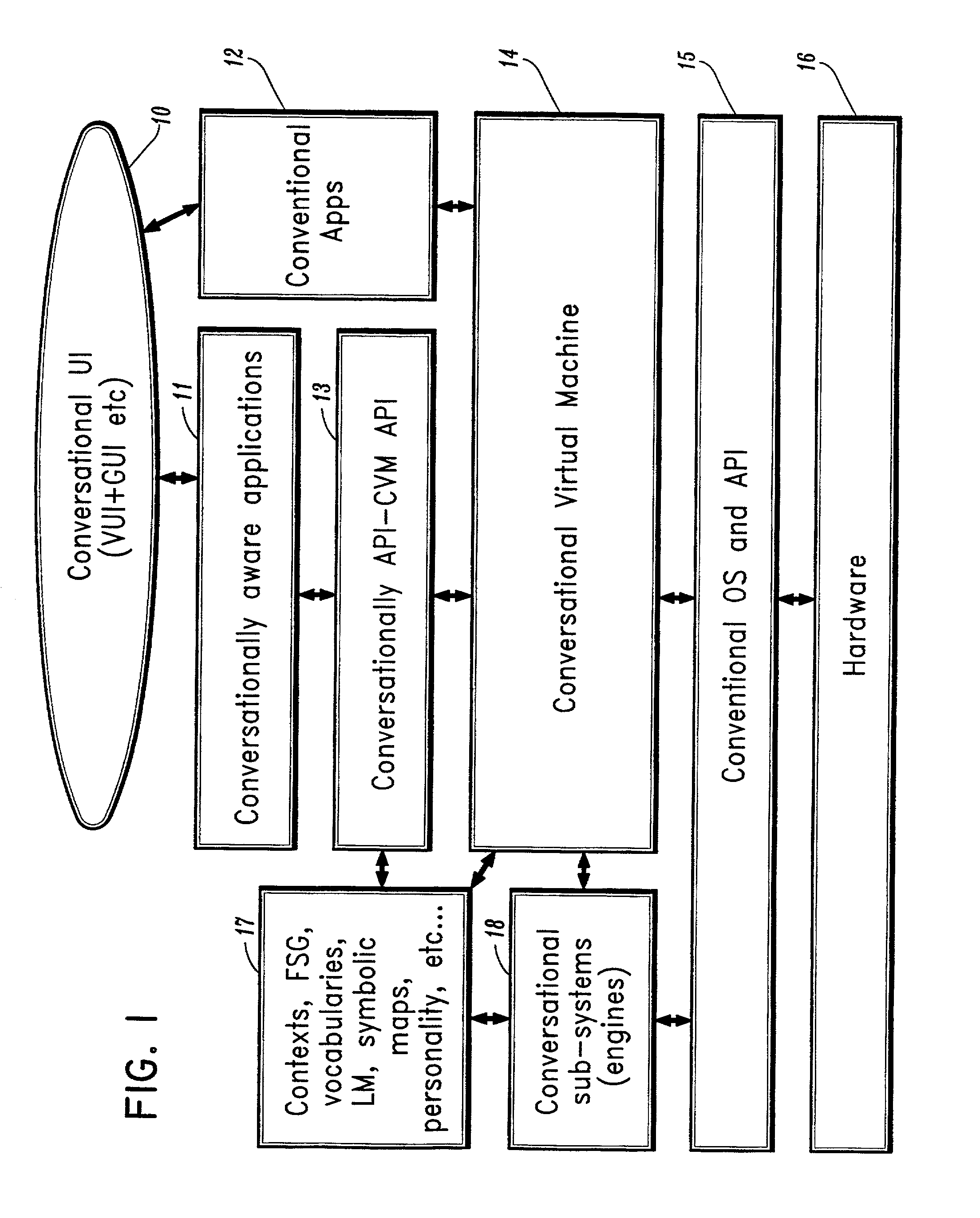
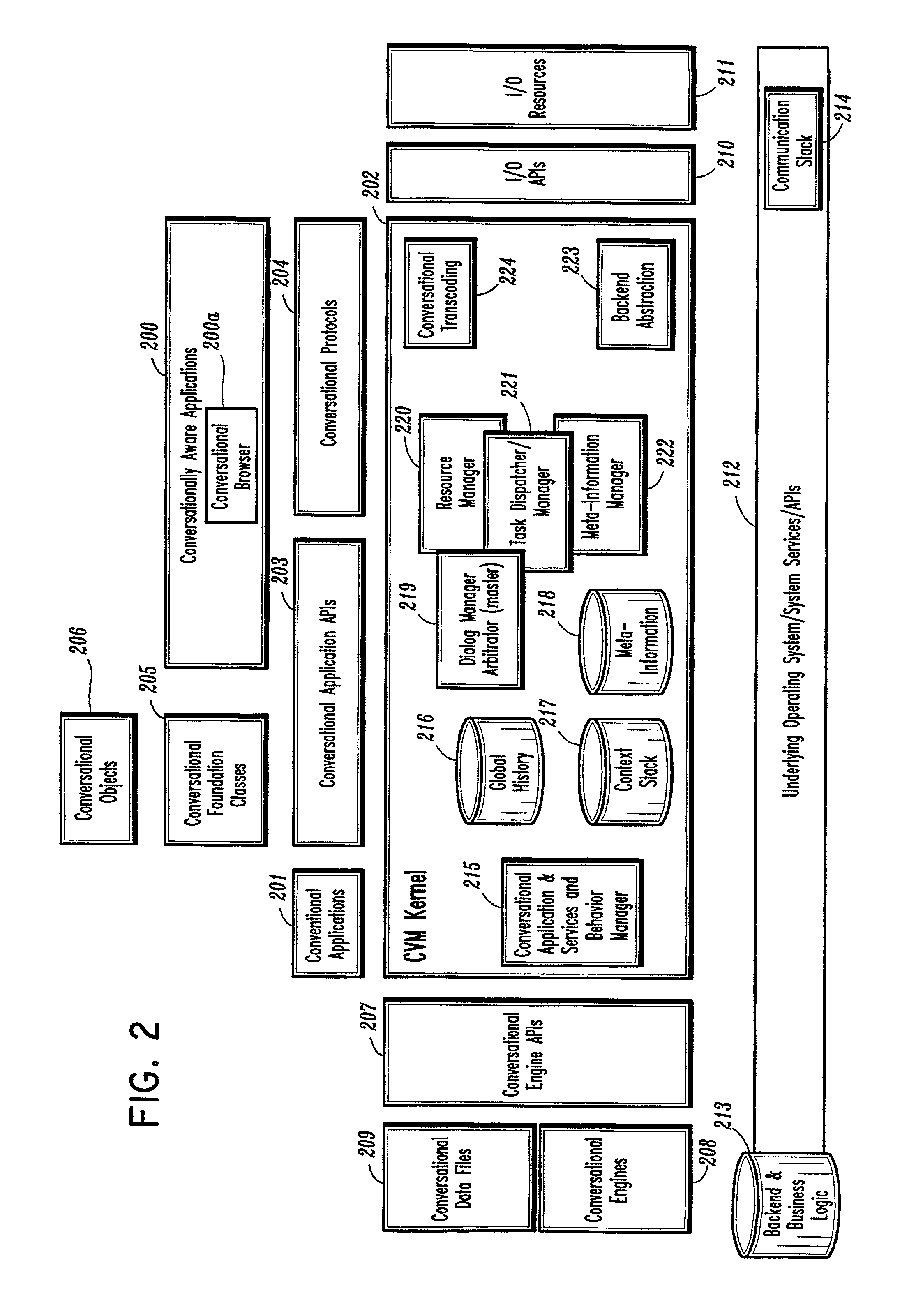
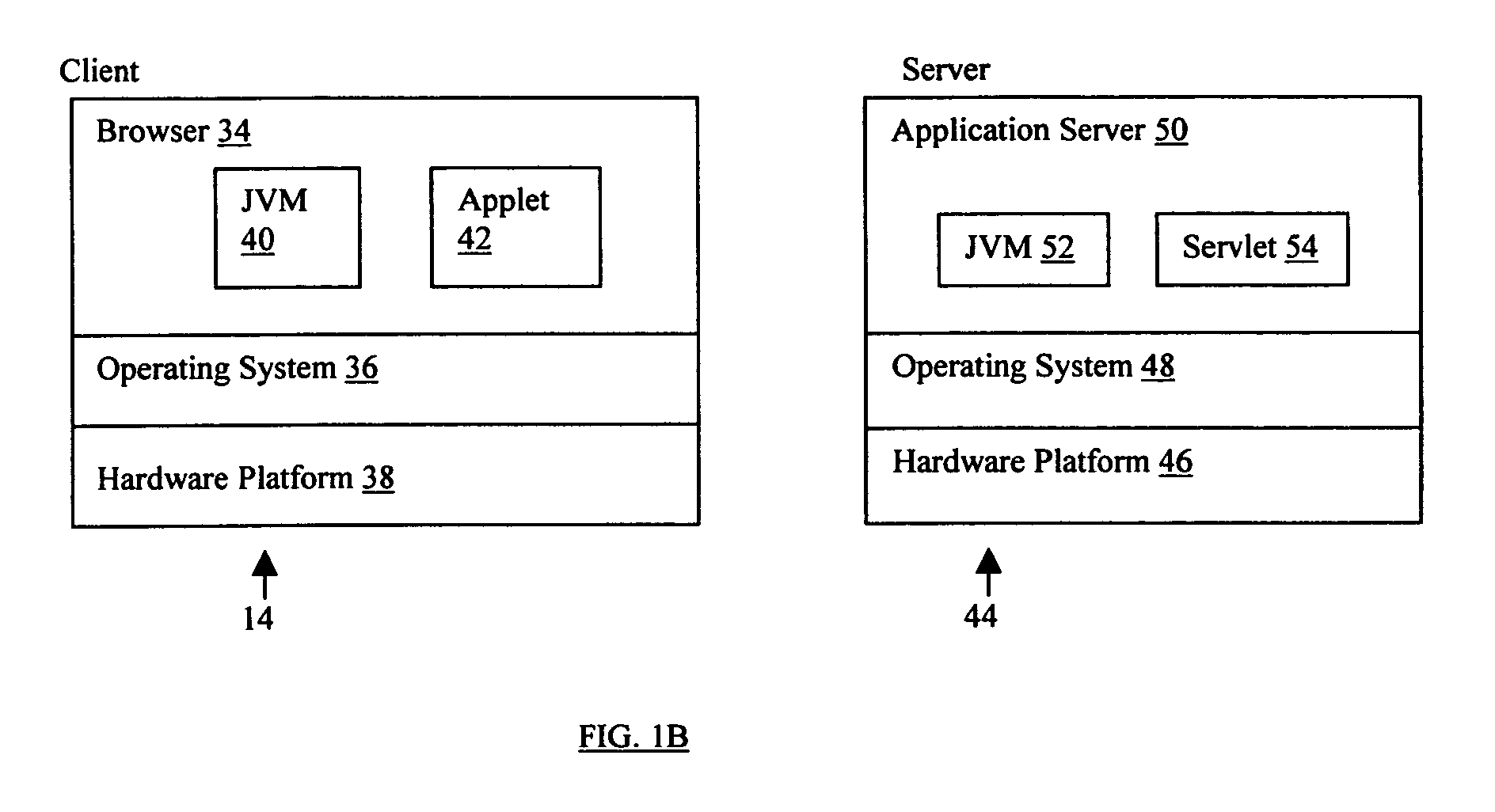
Conversational computing via conversational virtual machine
InactiveUS7137126B1Limitation for transferReduce degradationInterconnection arrangementsResource allocationConversational speechApplication software
A conversational computing system that provides a universal coordinated multi-modal conversational user interface (CUI) (10) across a plurality of conversationally aware applications (11) (i.e., applications that “speak” conversational protocols) and conventional applications (12). The conversationally aware maps, applications (11) communicate with a conversational kernel (14) via conversational application APIs (13). The conversational kernel (14) controls the dialog across applications and devices (local and networked) on the basis of their registered conversational capabilities and requirements and provides a unified conversational user interface and conversational services and behaviors. The conversational computing system may be built on top of a conventional operating system and APIs (15) and conventional device hardware (16). The conversational kernel (14) handles all I / O processing and controls conversational engines (18). The conversational kernel (14) converts voice requests into queries and converts outputs and results into spoken messages using conversational engines (18) and conversational arguments (17). The conversational application API (13) conveys all the information for the conversational kernel (14) to transform queries into application calls and conversely convert output into speech, appropriately sorted before being provided to the user.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Storage mapping and partitioning among multiple host processors in the presence of login state changes and host controller replacement
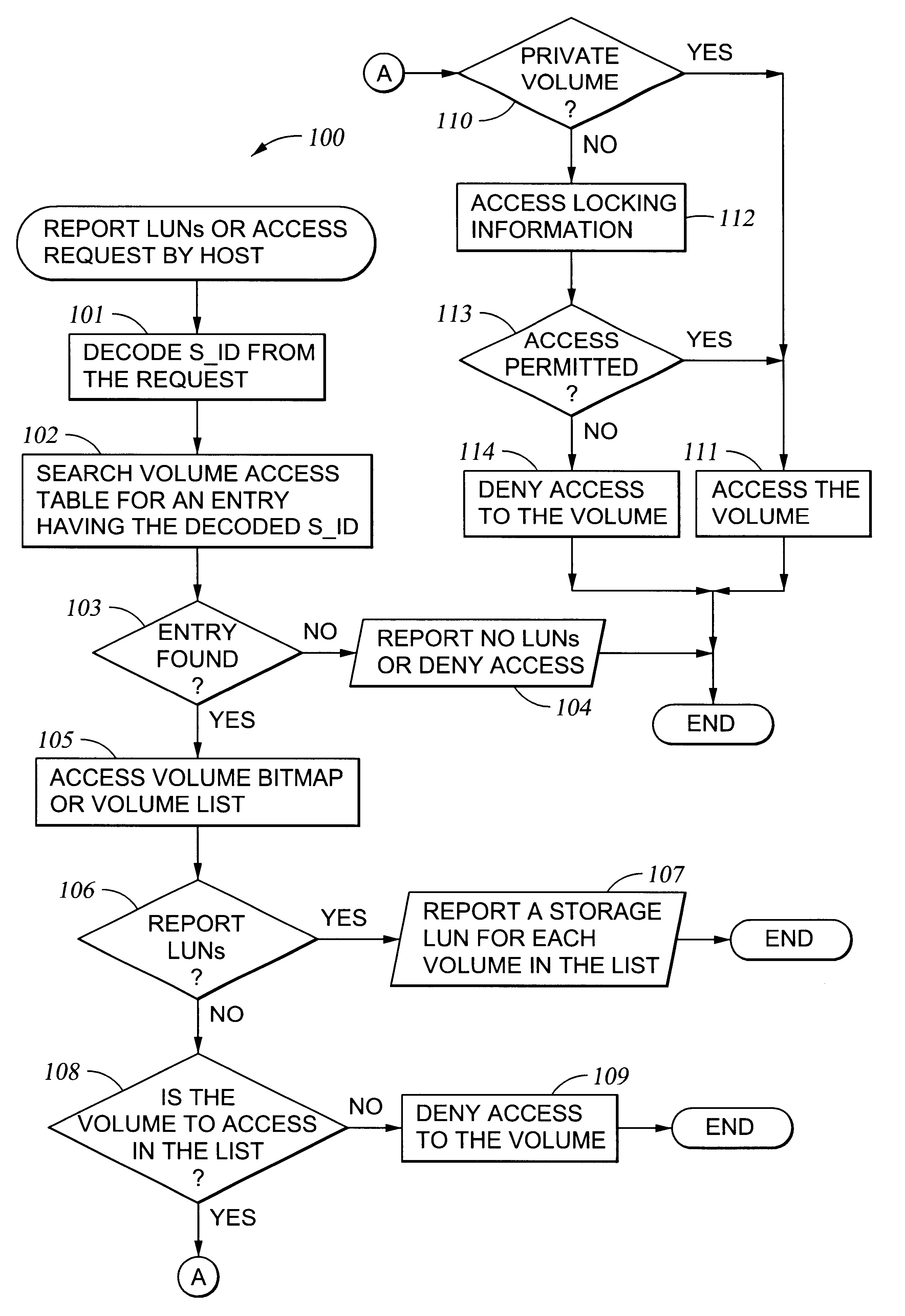
InactiveUS6260120B1Input/output to record carriersData processing applicationsData portControl store
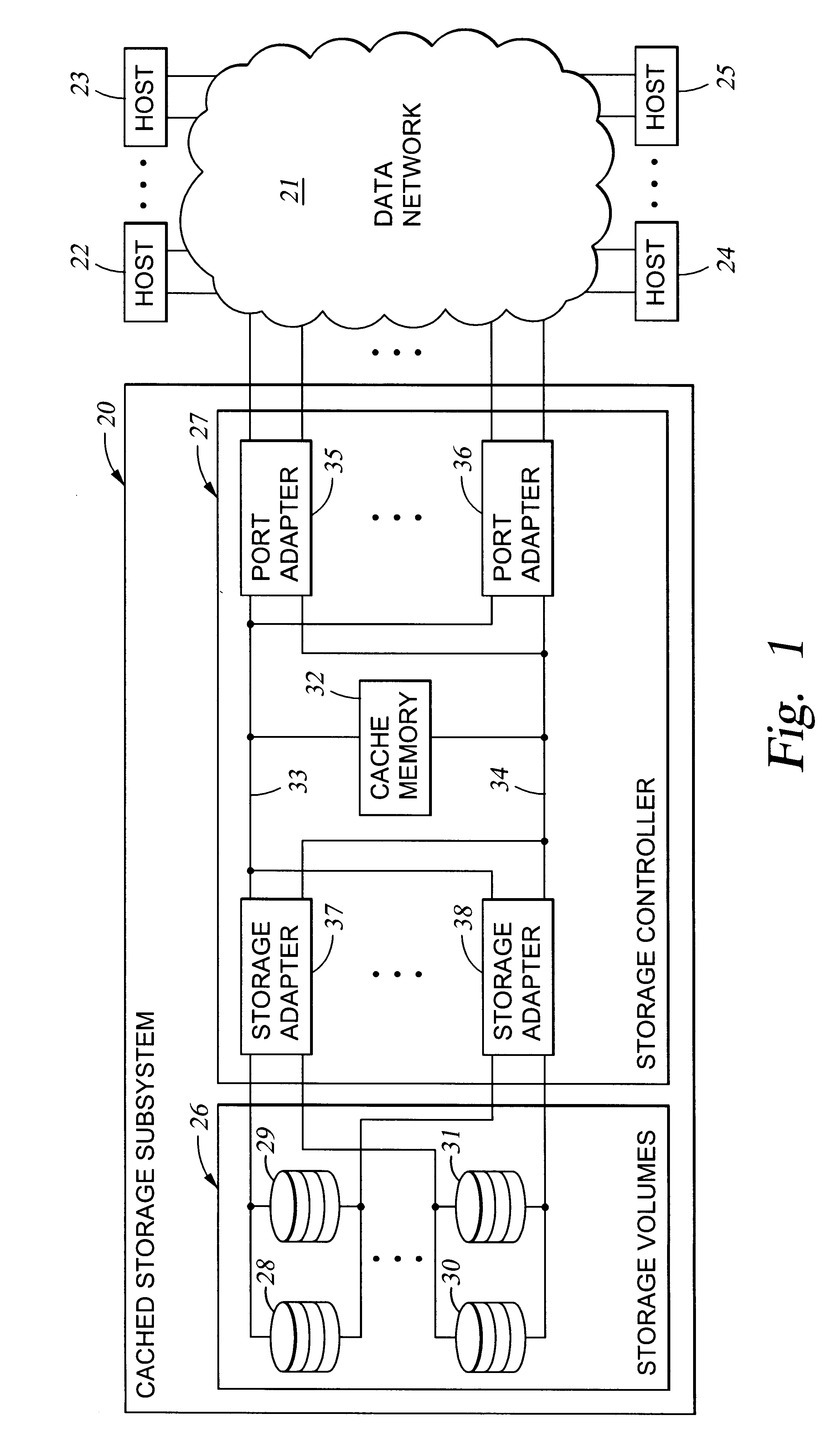
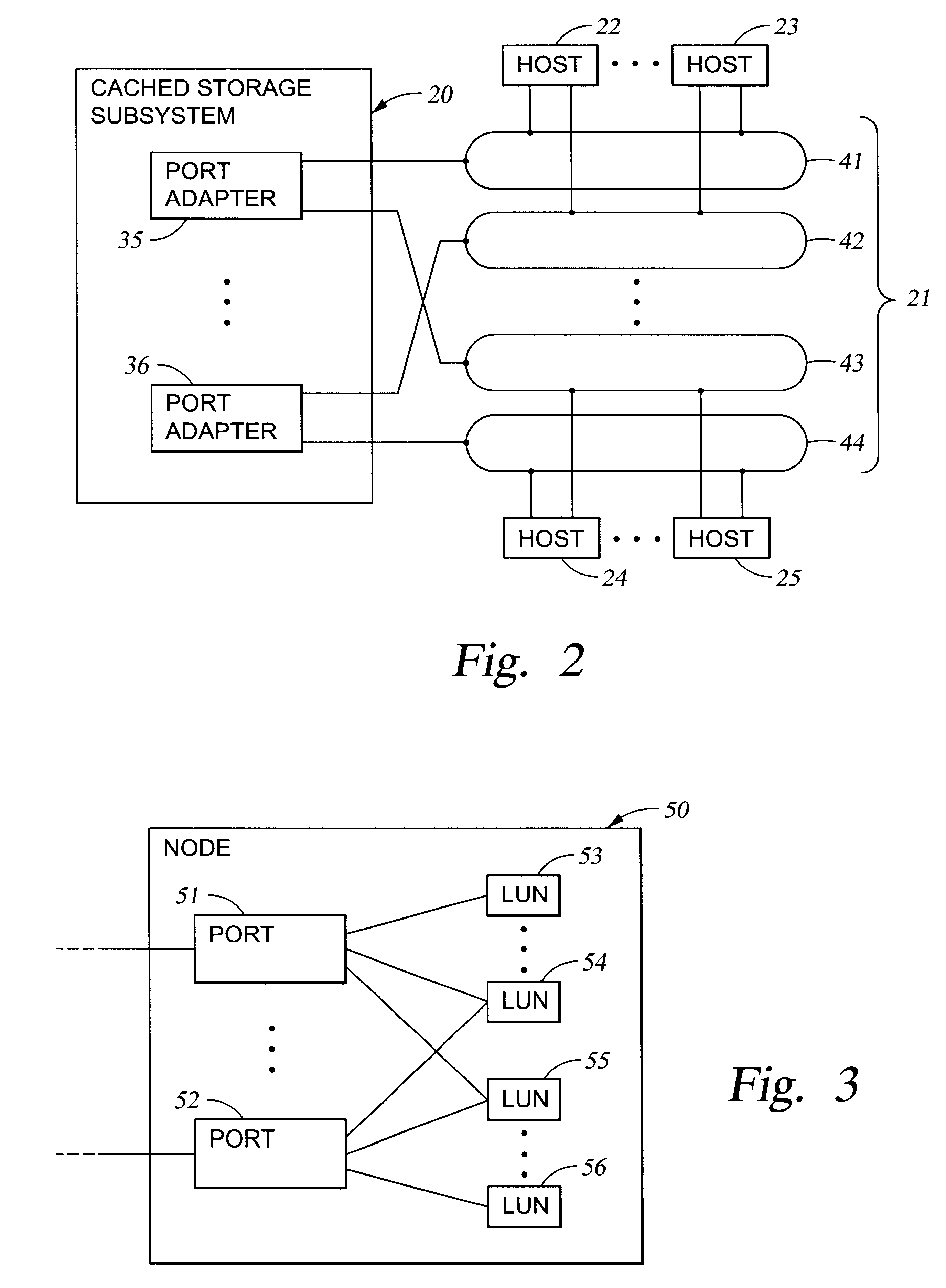
A storage controller for controling access to data storage has a memory and at least one data port for a data network including host processors. The memory is programmed to define a respective specification for each host processor of a respective subset of the data storage to which access by the host processor is restricted, and each specification is associated with a host identifier stored in the memory. When the storage controller receives a data access request from a host processor, it decodes a host identifier from the data access request, and searches the memory for a host identifier matching the host identifier decoded from the request. Upon finding a match, the respective specification of the respective subset for the host processor is accessed to determine whether or not storage specified by the storage access request is contained in the respective subset. If so, then storage access can continue, and otherwise, storage access is denied. Preferably the host identifier decoded from the request is a temporary address assigned by the network, and also stored in the memory in association with each respective specification is a relatively permanent identifier for the host processor.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
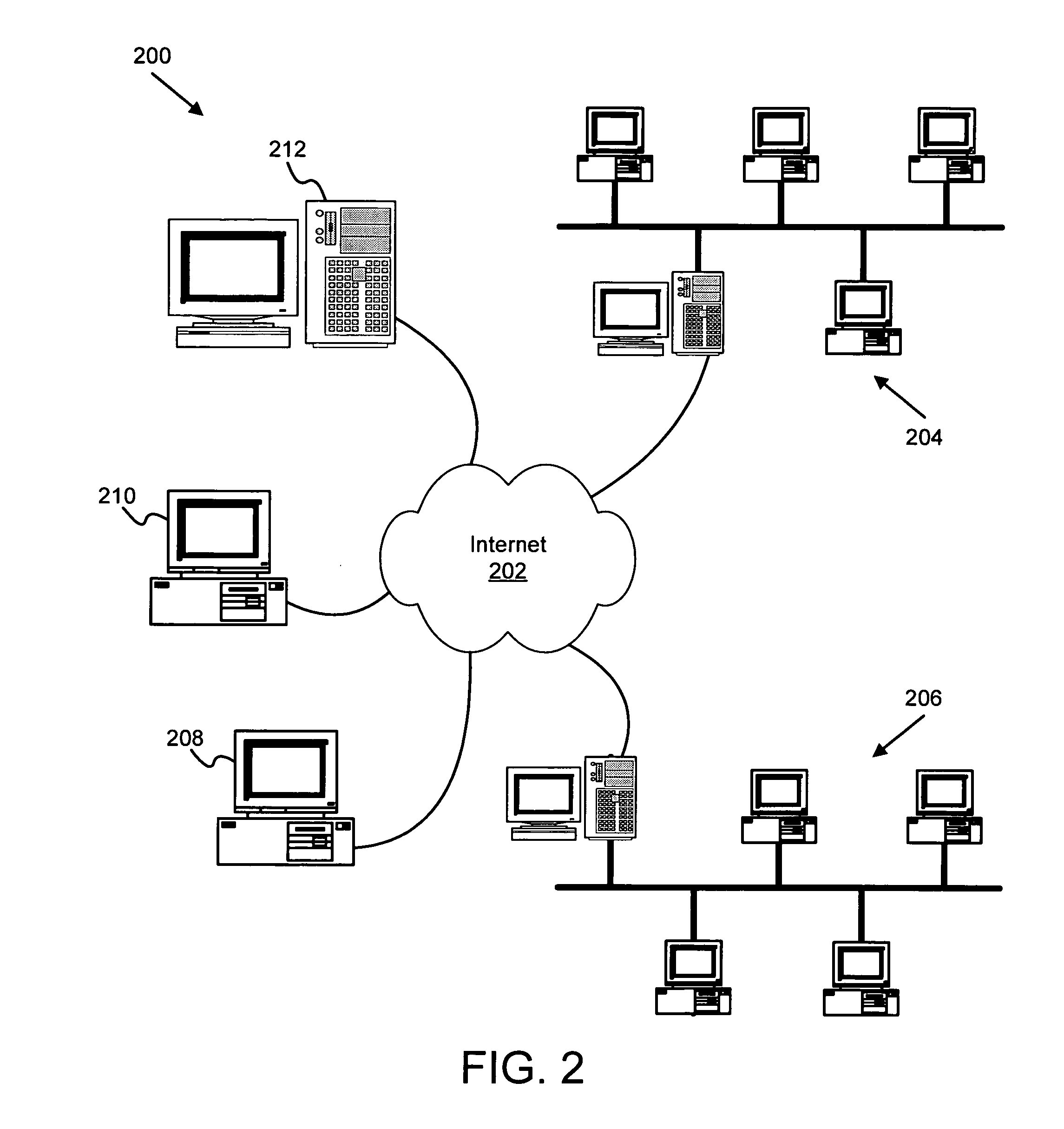
Method and apparatus for providing virtual computing services
InactiveUS20050044301A1Easy to manageLow costResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtualizationOperational system
A level of abstraction is created between a set of physical processors and a set of virtual multiprocessors to form a virtualized data center. This virtualized data center comprises a set of virtual, isolated systems separated by a boundary referred as a partition. Each of these systems appears as a unique, independent virtual multiprocessor computer capable of running a traditional operating system and its applications. In one embodiment, the system implements this multi-layered abstraction via a group of microkernels, each of which communicates with one or more peer microkernel over a high-speed, low-latency interconnect and forms a distributed virtual machine monitor. Functionally, a virtual data center is provided, including the ability to take a collection of servers and execute a collection of business applications over a compute fabric comprising commodity processors coupled by an interconnect. Processor, memory and I / O are virtualized across this fabric, providing a single system, scalability and manageability. According to one embodiment, this virtualization is transparent to the application, and therefore, applications may be scaled to increasing resource demands without modifying the application.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
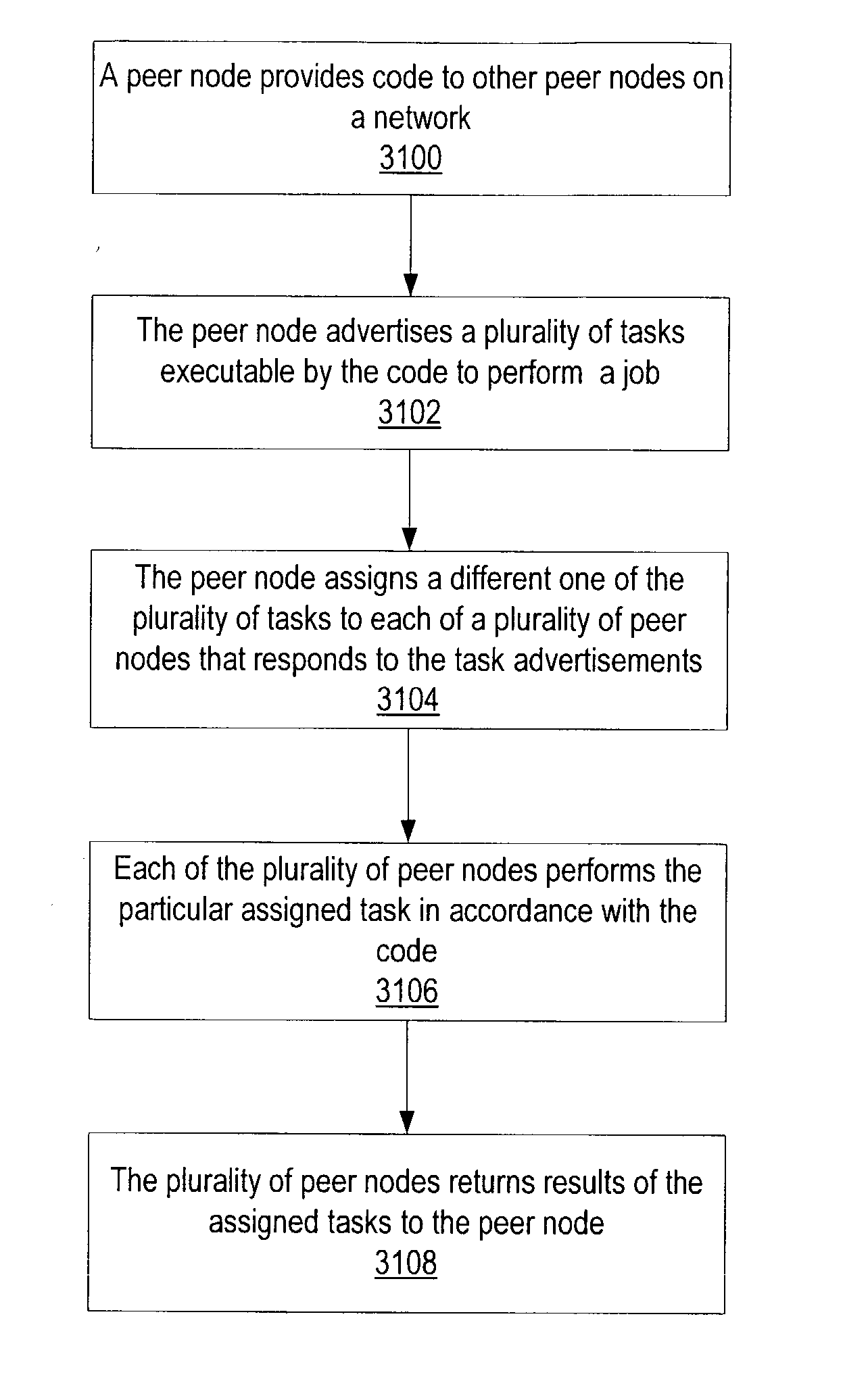
System and method for submitting and performing computational tasks in a distributed heterogeneous networked environment
ActiveUS20040098447A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsSymmetric multiprocessor systemOperating environment
System and method for submitting and performing computational tasks in a distributed heterogeneous networked environment. Embodiments may allow tasks to be submitted and run in parallel on a network of heterogeneous computers implementing a variety of operating environments. In one embodiment, a user on an originating node may advertise code on the network. Peer nodes that respond to the advertisement may receive the code. A job to be executed by the code may be split into separate tasks to distributed to the peer nodes that received the code. These tasks may be advertised on the network. Tasks may be assigned to peer nodes that respond to the task advertisements. The peer nodes may then work on the assigned tasks. Once a peer node's work on a task is completed, the peer node may return the results of the task to the originating node.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method, system, and program for determining a modification of a system resource configuration
InactiveUS20030135609A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsManagement systemReal-time computing
Provided are a method, system, and program for managing multiple resources in a system at a service level, including at least one host, network, and a storage space comprised of at least one storage system that each host is capable of accessing over the network. A plurality of service level parameters are measured and monitored indicating a state of the resources in the system. A determination is made of values for the service level parameters and whether the service level parameter values satisfy predetermined service level thresholds. Indication is made as to whether the service level parameter values satisfy the predetermined service thresholds. A determination is made of a modification to one or more resource deployments or configurations if the value for the service level parameter for the resource does not satisfy the predetermined service level thresholds.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Database load balancing for multi-tier computer systems
InactiveUS6950848B1Reduce disadvantagesMaximize server efficiencyResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDatabase serverComputerized system
A load balancing method and system for a transaction computer system having multiple database servers for at least one database, wherein database servers cooperate to provide a unified view of the data in the database. The method includes the steps of establishing connections to said multiple database servers for communicating with said database servers; and assigning transactions to respective ones of said multiple database servers to balance respective loads of said multiple database servers. Assigning each new transaction includes the steps of determining possible assignments of that new transaction to one or more of said multiple database servers, each said possible assignment to one of said multiple database servers being based on a load balancing scheme to balance respective loads of said multiple database servers; and assigning that new transaction to one of said multiple database servers as a function of said possible assignments of that new transaction, to balance respective loads of said multiple database servers.
Owner:YOUSEFIZADEH HOMAYOUN
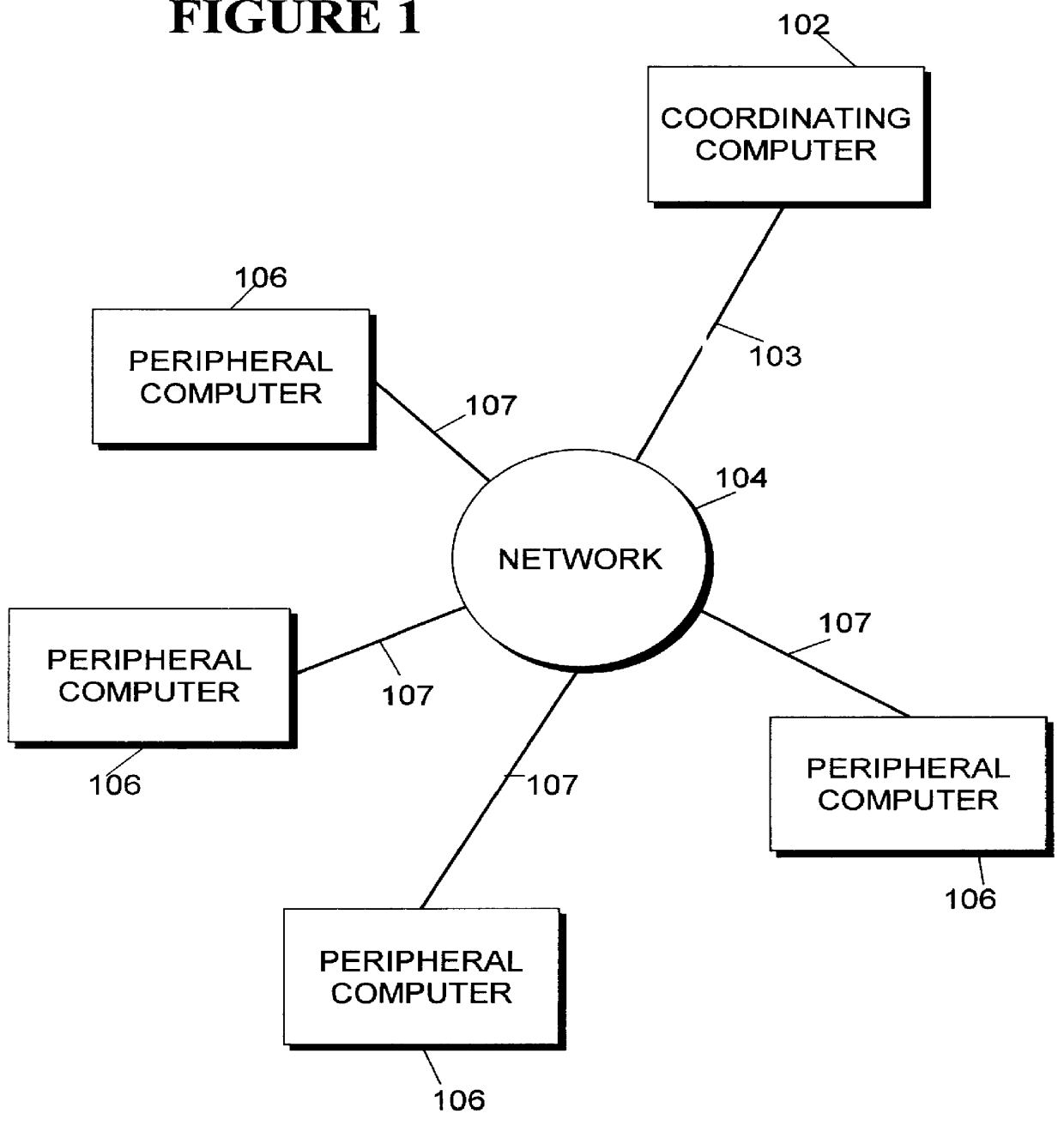
Task distribution processing system and the method for subscribing computers to perform computing tasks during idle time
InactiveUS6112225ALittle administrationLittle effortResource allocationGeneral purpose stored program computerAs DirectedTelecommunications link
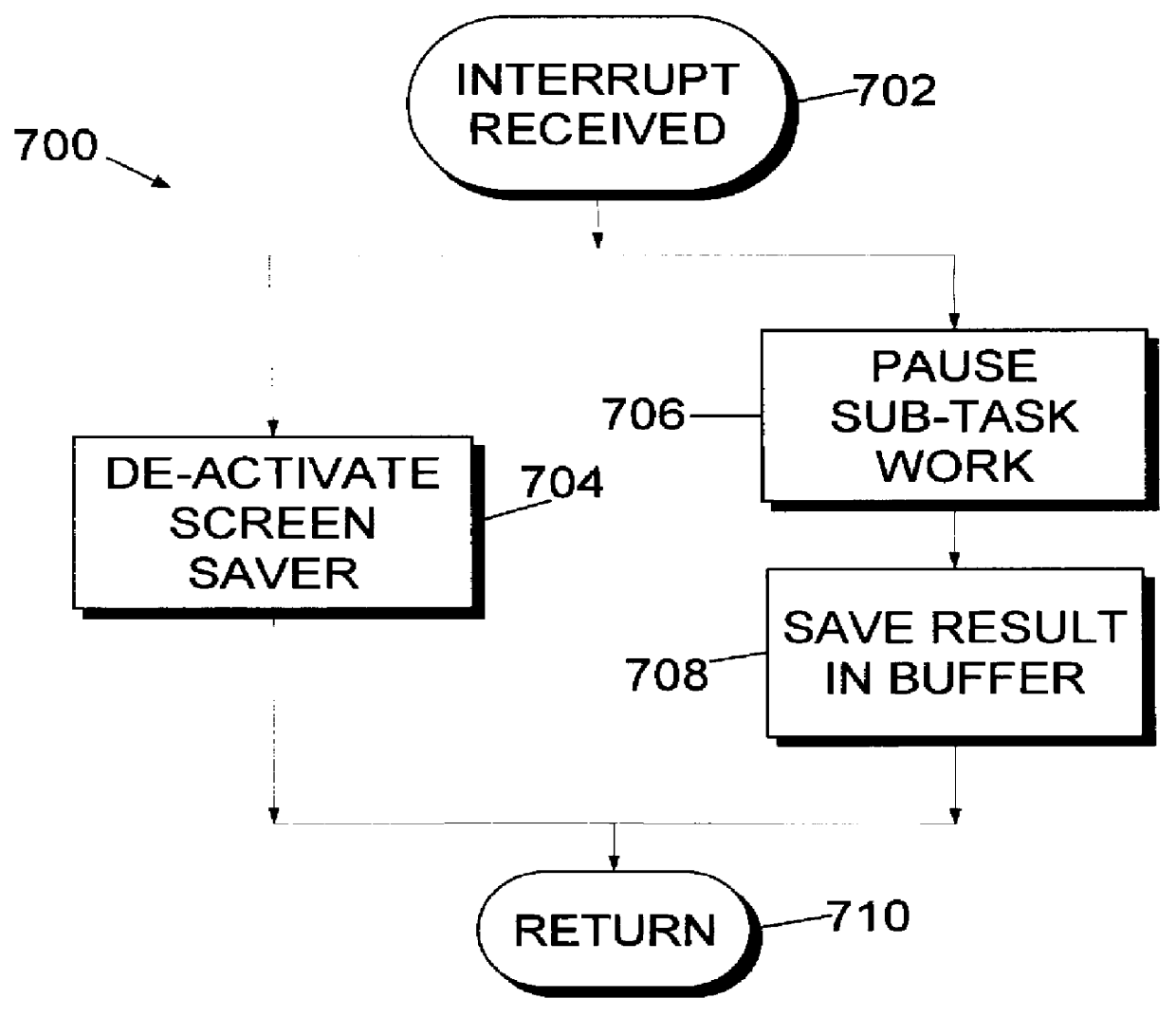
A computer executable "aggregate" task is processed by dividing it into subtasks and distributing the subtasks "on demand" to remotely located subscribing computers via a computer network. The aggregate task originates at a coordinating computer, coupled to one or more peripheral computers by appropriate communications links. The coordinating computer divides the aggregate task into multiple independent subtasks. Each peripheral computer begins to "subscribe" to the coordinating computer's aggregate task by obtaining an "idle time activation program" from the coordinating computer, and then installing the program locally. The idle time activation program which may include a screen saver, activates automatically when the subscribing computer is inactive. Continuing the subscription process, each peripheral computer requests a subtask from the coordinating computer. In response, the coordinating computer distributes different subtasks among the subscribing computers, completing the subscription process. The subscribing computers automatically work on their respective subtasks whenever they are idle, as directed by the local idle time activation program. When a subscribing computer completes its subtask, it transmits results back to the coordinating computer. When results of all subtasks have been received from subscribing computers, the coordinating computer compiles and stores these results, concluding the aggregate task.
Owner:IBM CORP
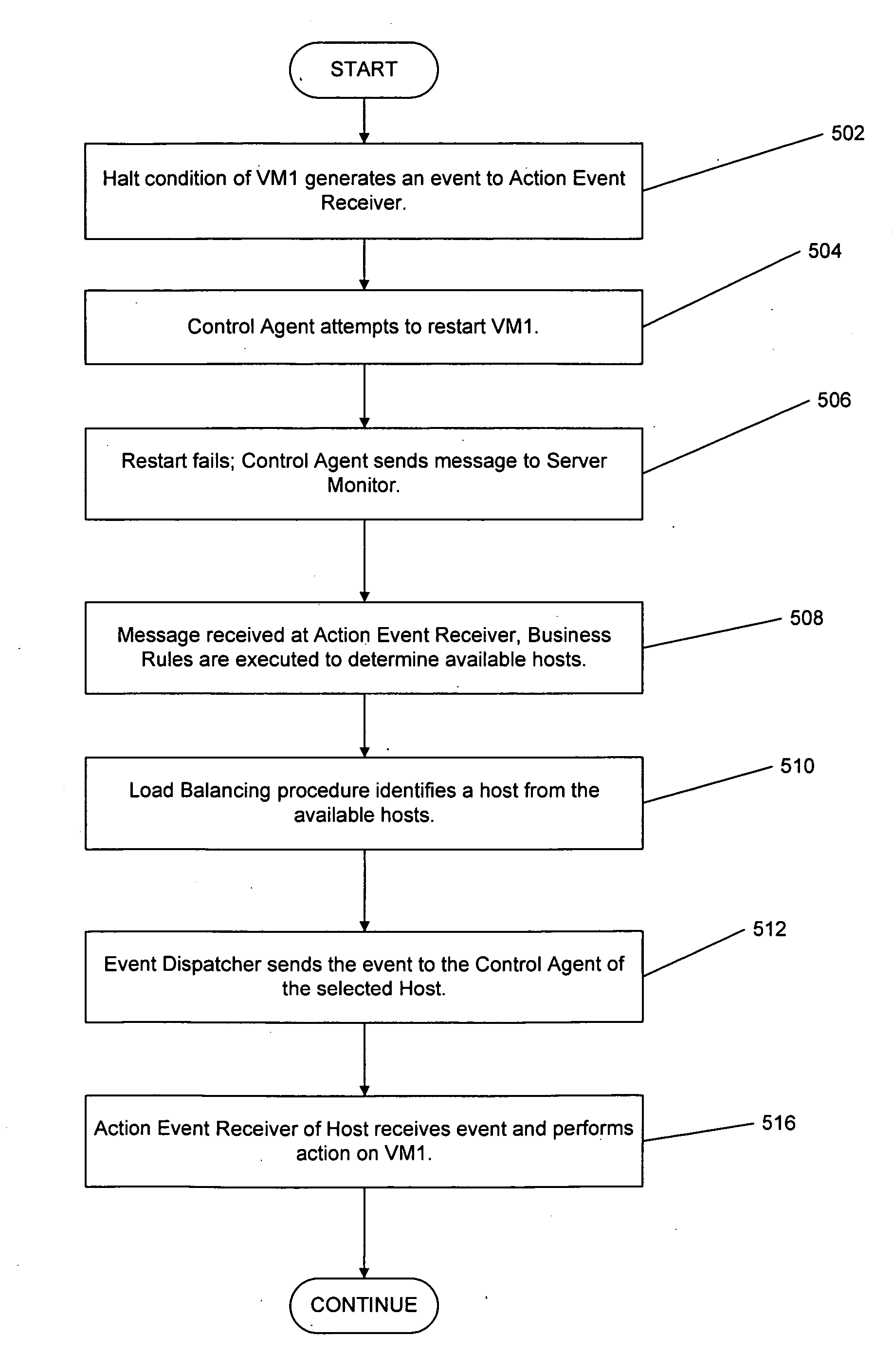
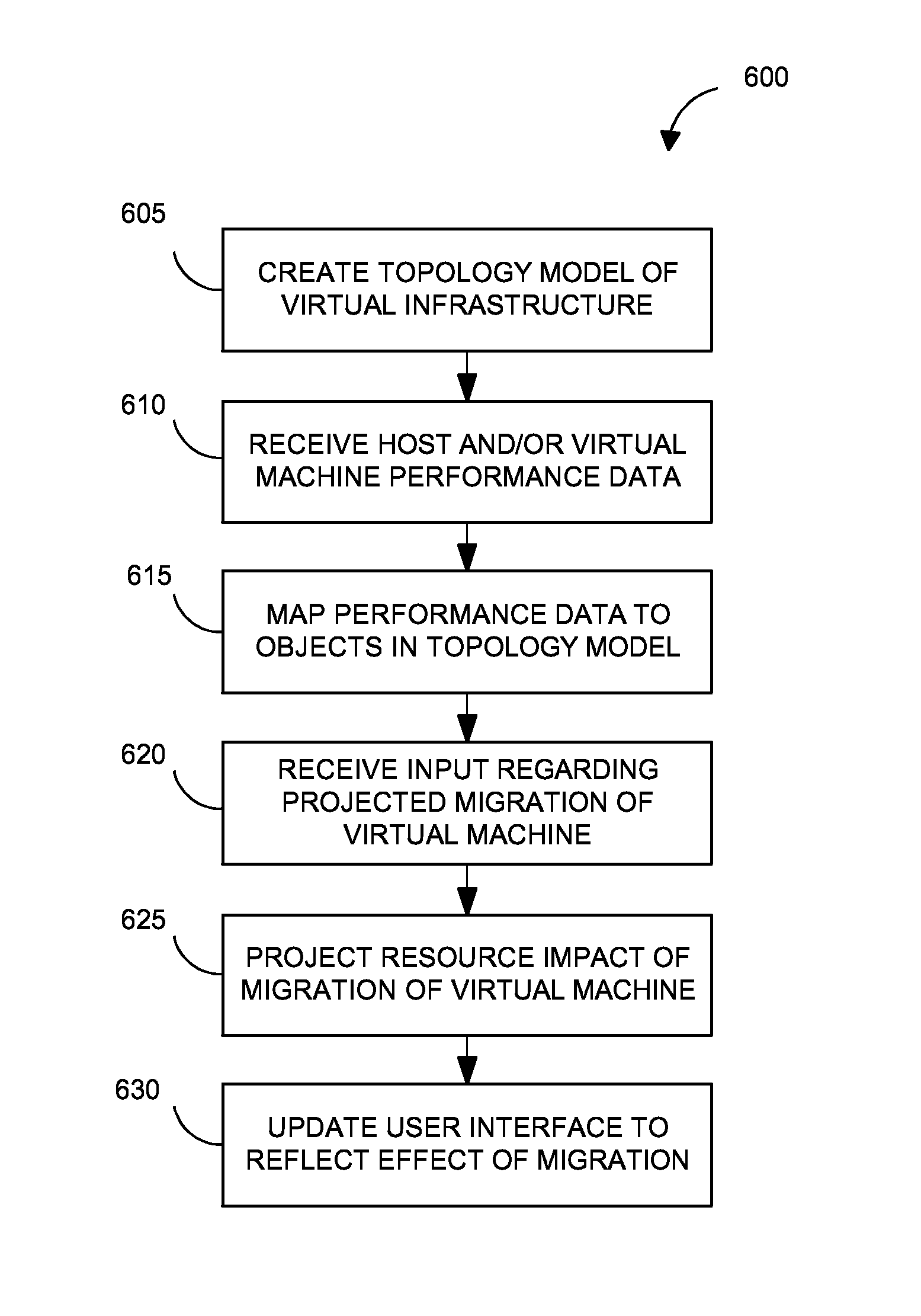
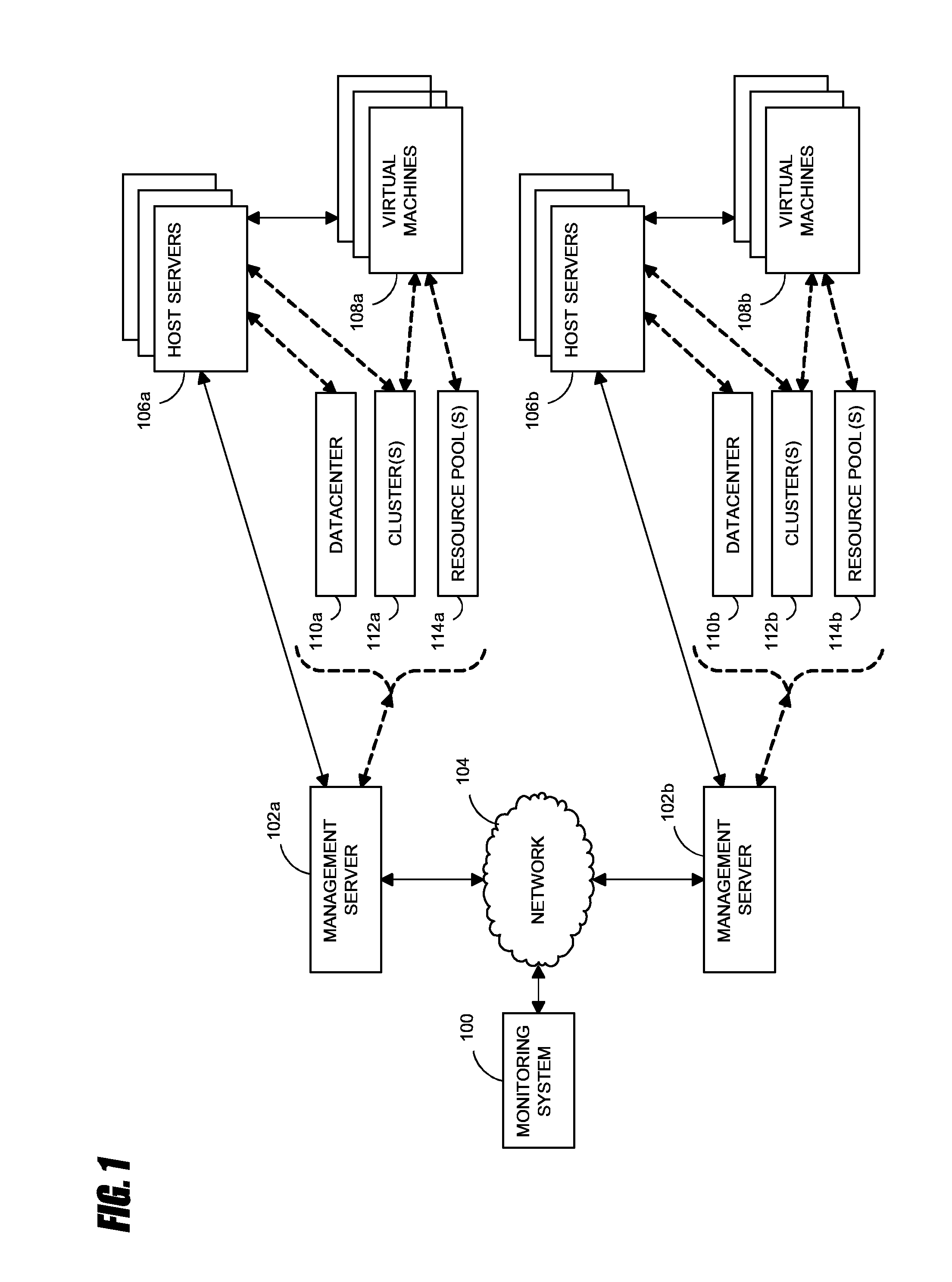
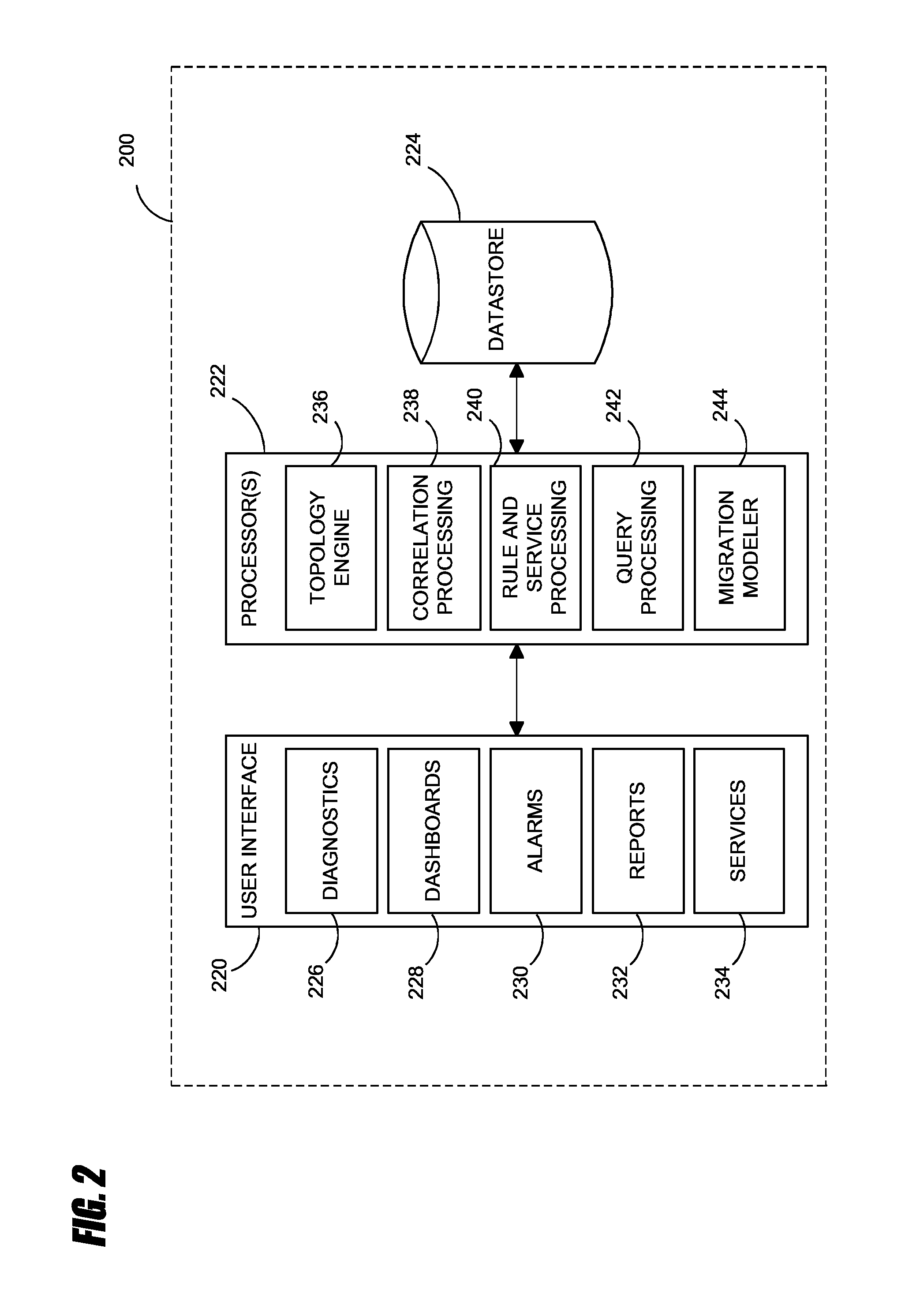
Systems and methods for analyzing performance of virtual environments
InactiveUS8175863B1Effective and efficient diagnosisResource allocationError detection/correctionMonitoring systemSmart surveillance
Intelligent monitoring systems and methods for virtual environments are disclosed that understand various components of a virtual infrastructure and how the components interact to provide improved performance analysis to users. In certain examples, a monitoring system assesses the performance of virtual machine(s) in the context of the overall performance of the physical server(s) and the environment in which the virtual machine(s) are running. For instance, the monitoring system can track performance metrics over a determined period of time to view changes to the allocation of resources to virtual machines and their location(s) on physical platforms. Moreover, monitoring systems can utilize past performance information from separate virtual environments to project a performance impact resulting from the migration of a virtual machine from one physical platform to another.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
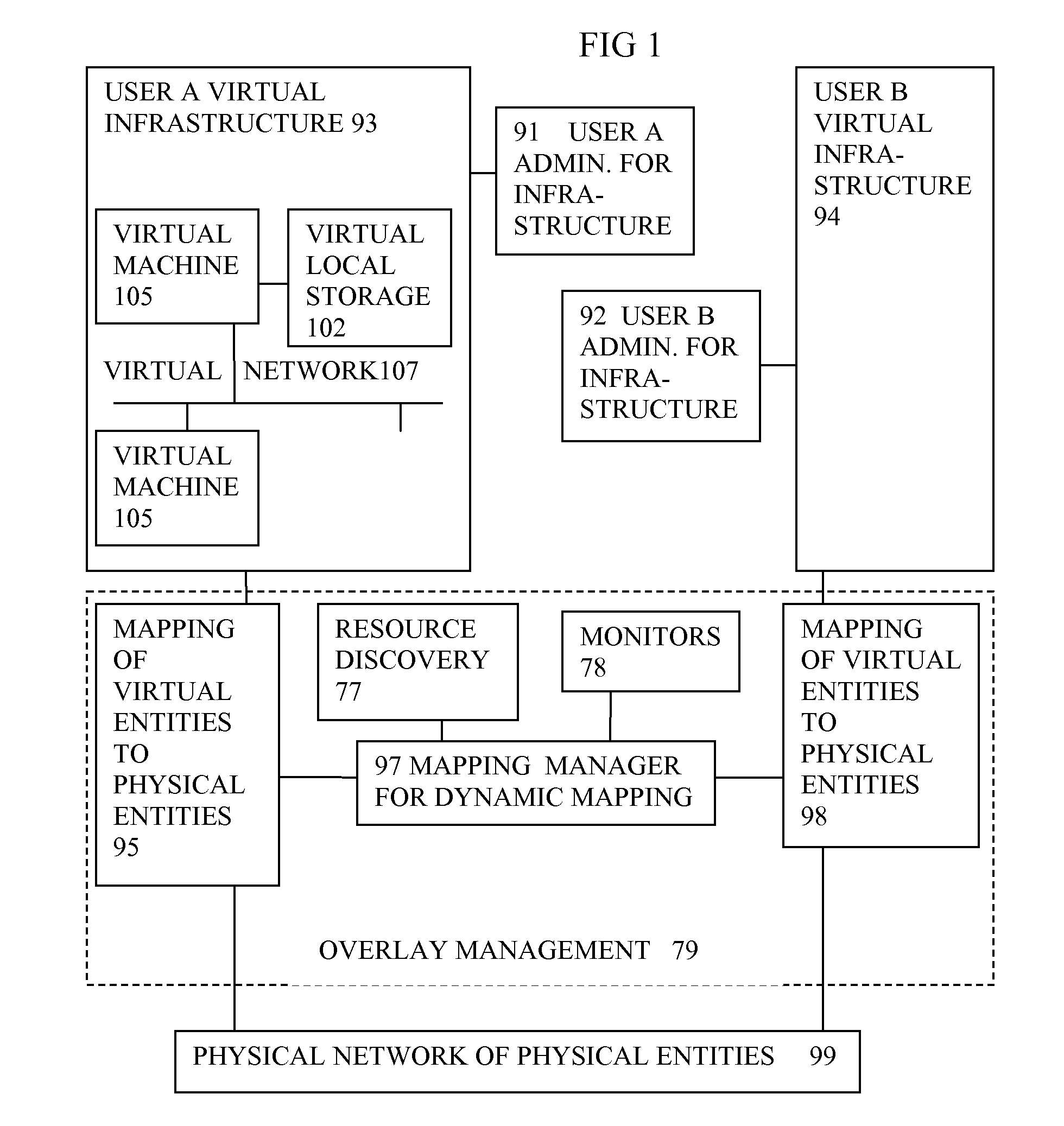
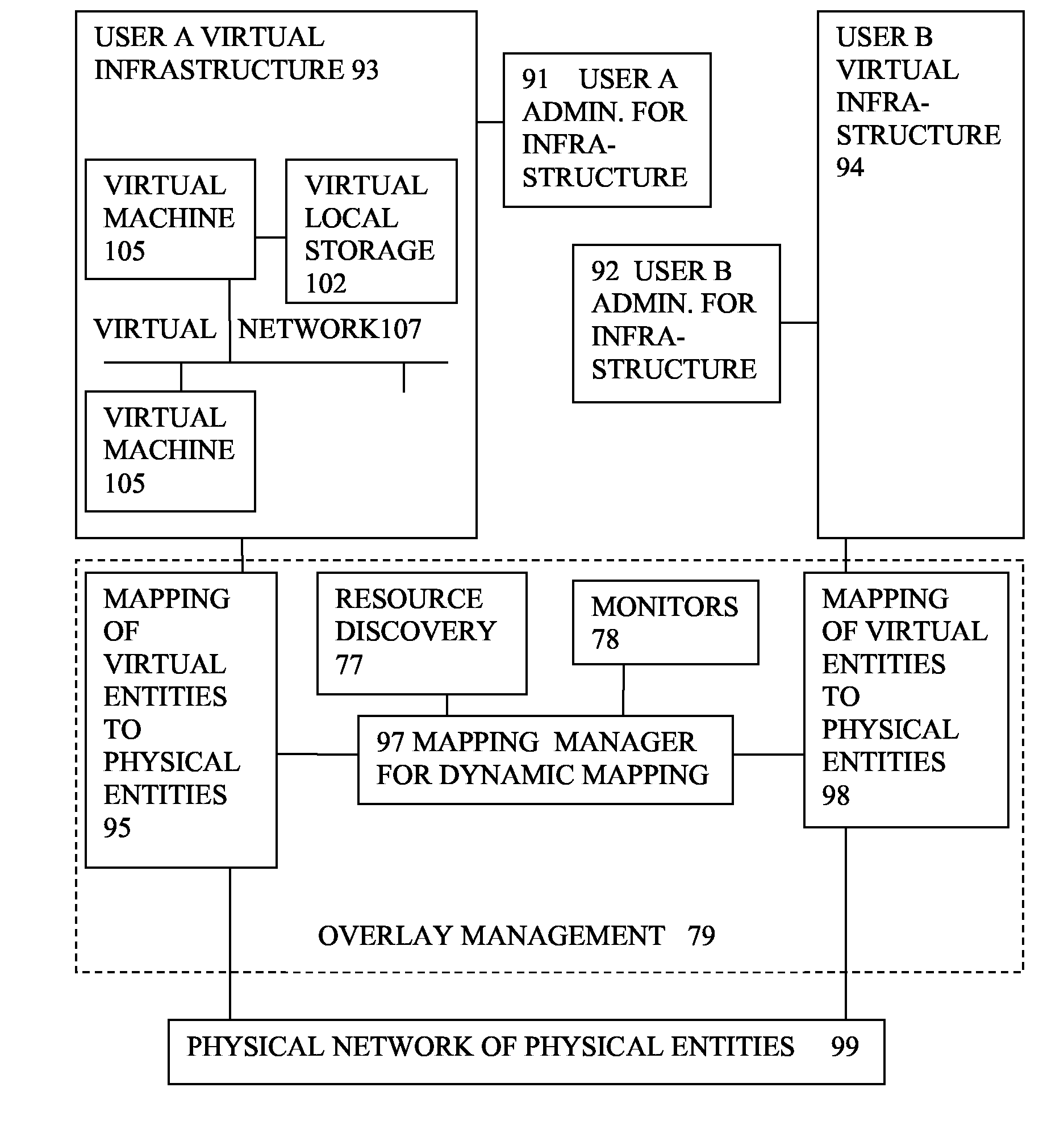
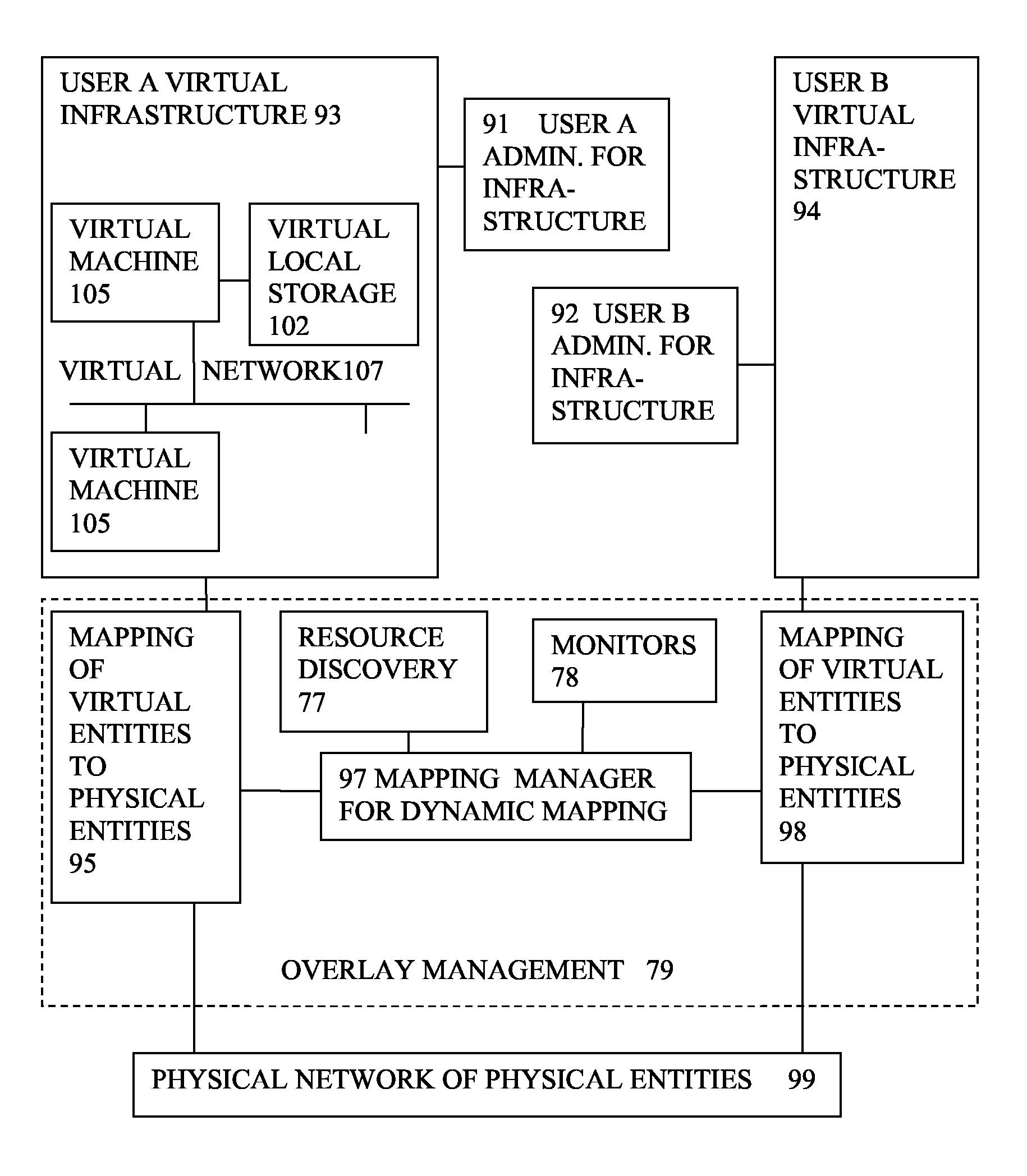
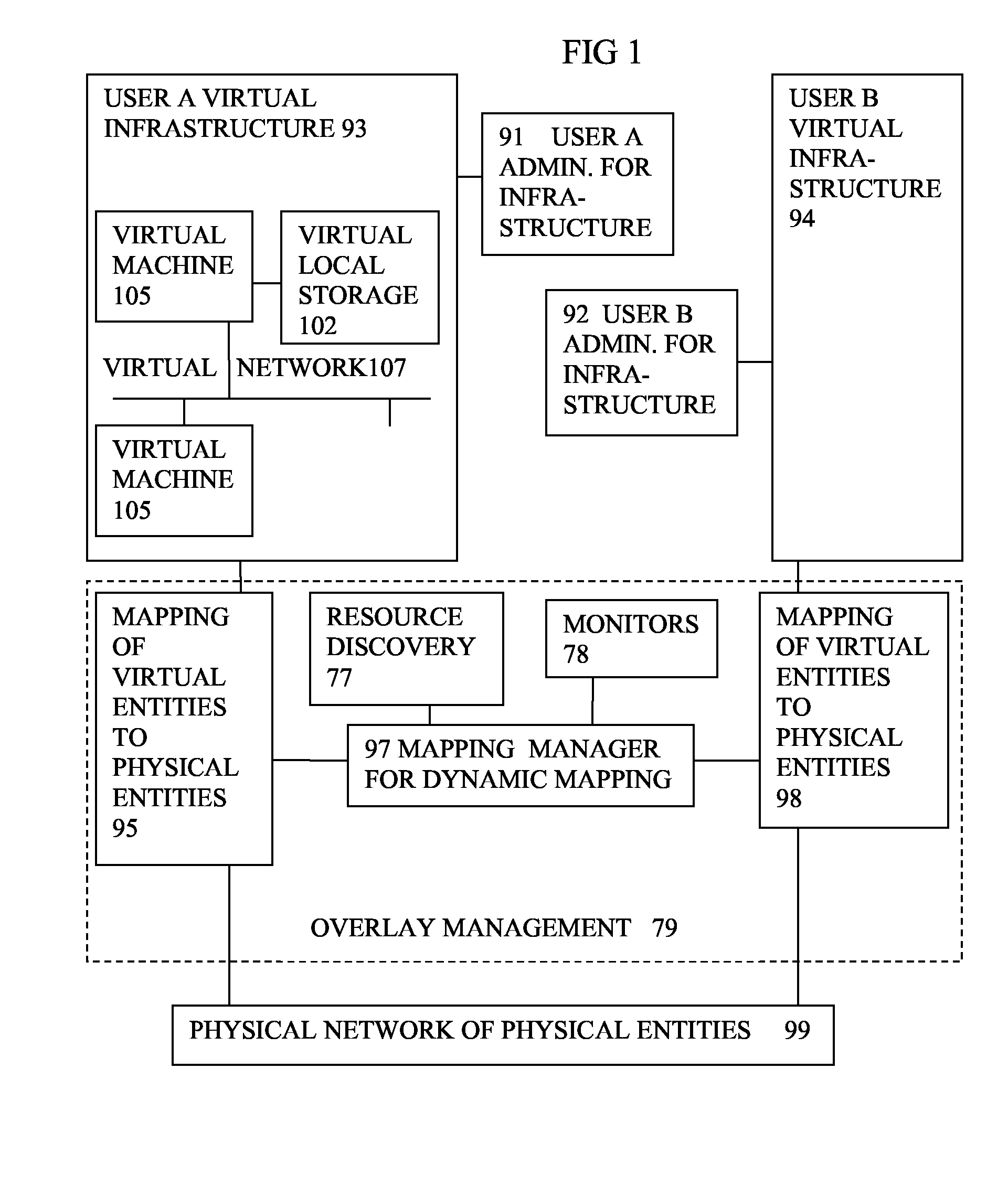
Virtual computing infrastructure
InactiveUS20090199177A1Overcome disadvantagesCritical applicationResource allocationTransmissionVirtualizationNetwork communication
A system has a virtual overlay infrastructure mapped onto physical resources for processing, storage and network communications, the virtual infrastructure having virtual entities for processing, storage and network communications. The system has a mapping manager to dynamically alter the mapping for balancing, performance, and redundancy. There can be more independence from the underlying physical configuration, compared to known methods of virtualizing only some of the entities. The mapping manager can be distributed across a number of entities on different physical servers arranged to cooperate with each other.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
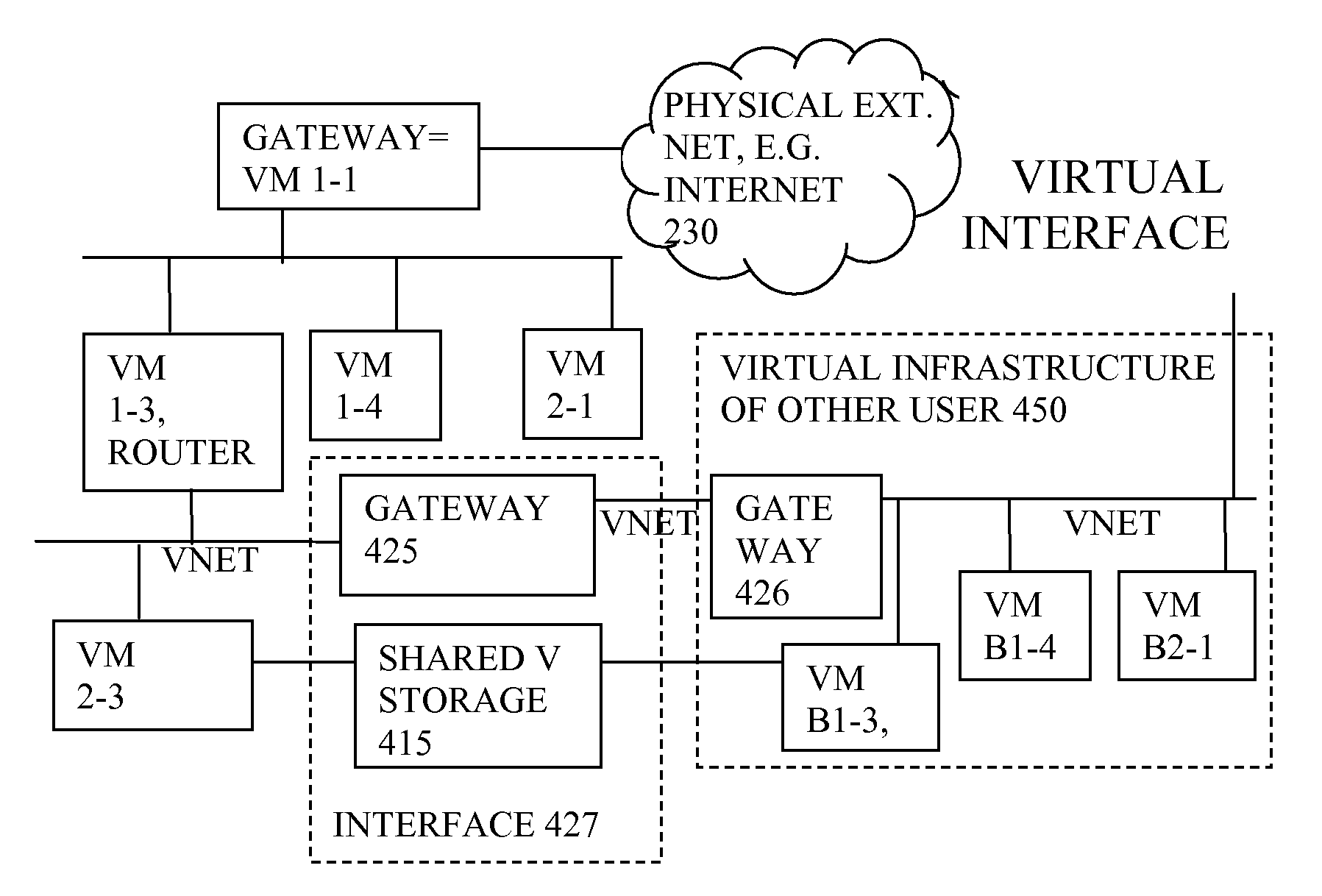
Virtual computing infrastructure
ActiveUS20110119748A1More separatedReduce hardware costsResource allocationComputer security arrangementsNetwork communicationApplication software
A system has a virtual overlay infrastructure mapped onto physical resources for processing, storage and network communications, the virtual infrastructure having virtual entities for processing, storage and network communications. Virtual infrastructures of different users share physical resources but are isolated and have their own management entities. An interface between infrastructures allows controlled relaxation of the isolation, using a gateway between virtual nets, or shared virtual storage devices. This can allow businesses to share data or applications, while maintaining control of security.
Owner:RED HAT +1
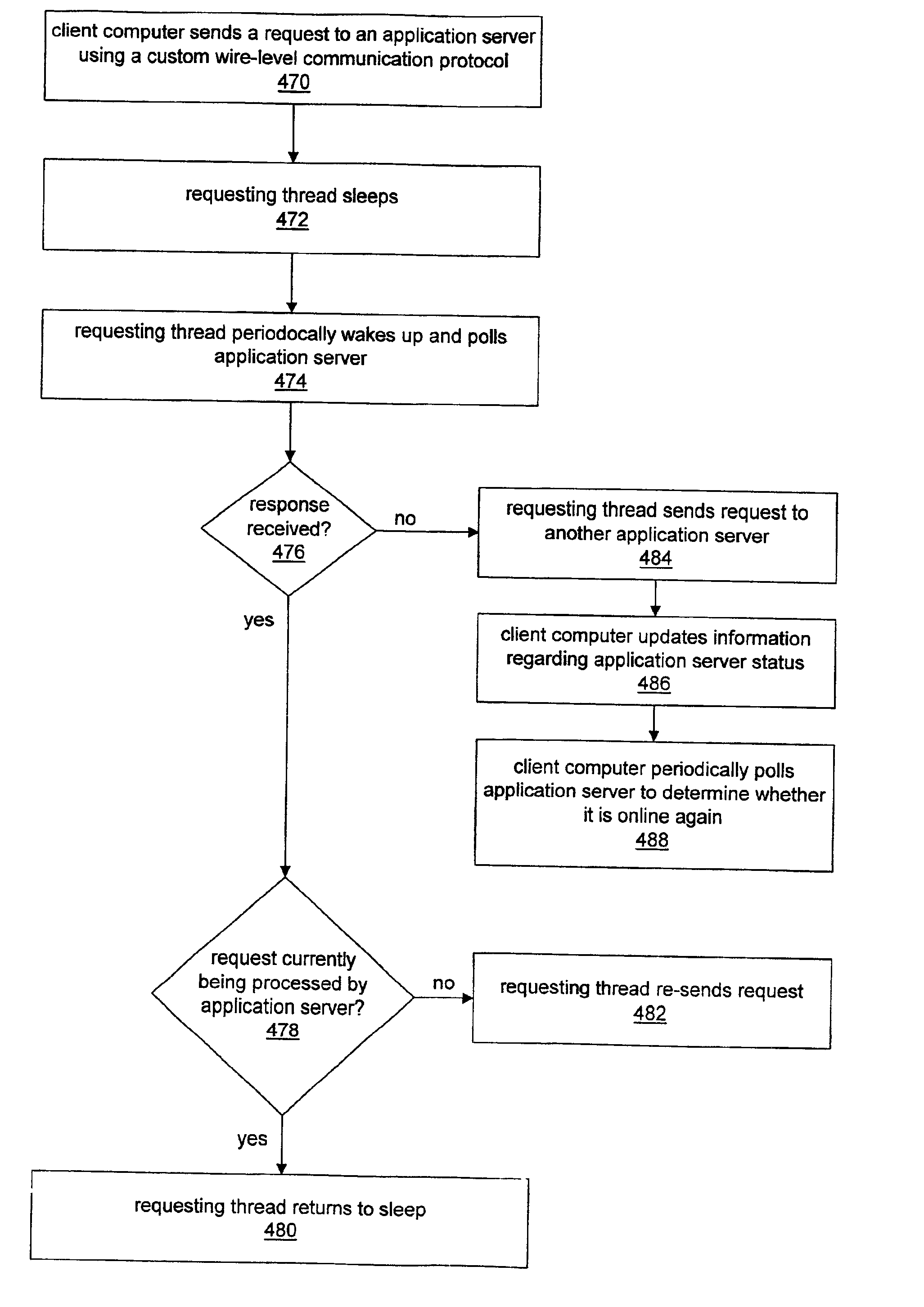
System and method for enabling application server request failover
InactiveUS6859834B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsFailoverApplication server
System and method for enabling application server request failover. For each application server request to be performed by a client computer, a requesting thread may be operable to utilize a custom wire-level communication protocol. Request failure detection mechanisms may be built into the custom wire-level communication protocol so that a requesting thread detects a failed request much sooner than if the thread utilized a standard communication protocol and relied on the client computer operating system for notification of failed requests. After sending a request to an application server, a requesting thread may be operable to “sleep” and then periodically wake up to poll the application server computer to determine whether the request has failed. If the requesting thread receives a response from the application server computer indicating that the request is not currently being processed, then the requesting thread may re-send the request. Receiving no response to the poll message may indicate that the application server computer is offline, e.g., due to a failure. The requesting thread may redirect the request to another application server computer if necessary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System Providing Methodology for Policy-Based Resource Allocation
A system providing methodology for policy-based resource allocation is described. In one embodiment, for example, a system for allocating computer resources amongst a plurality of applications based on a policy is described that comprises: a plurality of computers connected to one another through a network; a policy engine for specifying a policy for allocation of resources of the plurality of computers amongst a plurality of applications having access to the resources; a monitoring module at each computer for detecting demands for the resources and exchanging information regarding demands for the resources at the plurality of computers; and an enforcement module at each computer for allocating the resources amongst the plurality of applications based on the policy and information regarding demands for the resources.
Owner:CAVALIER NEWCO +1
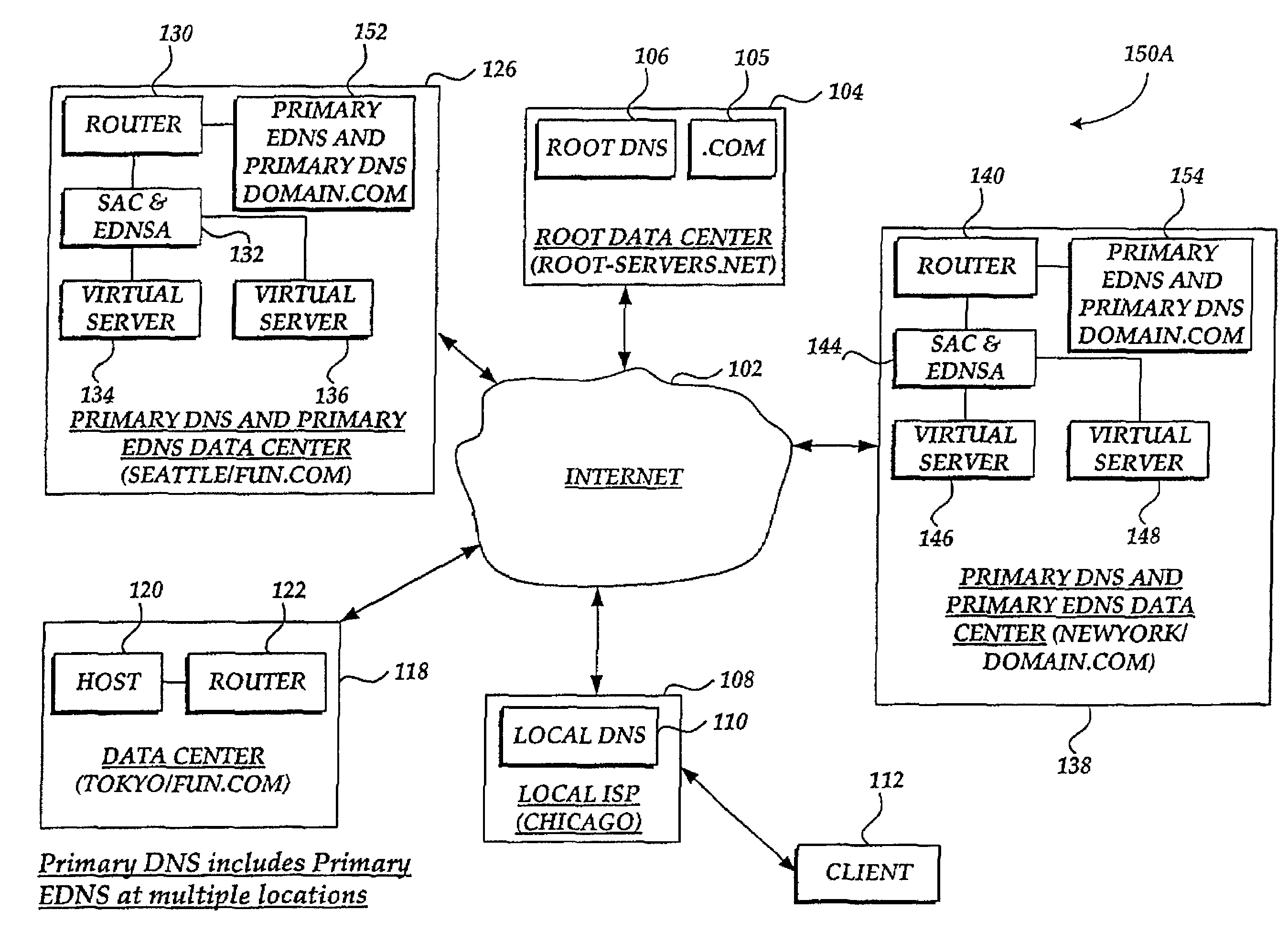
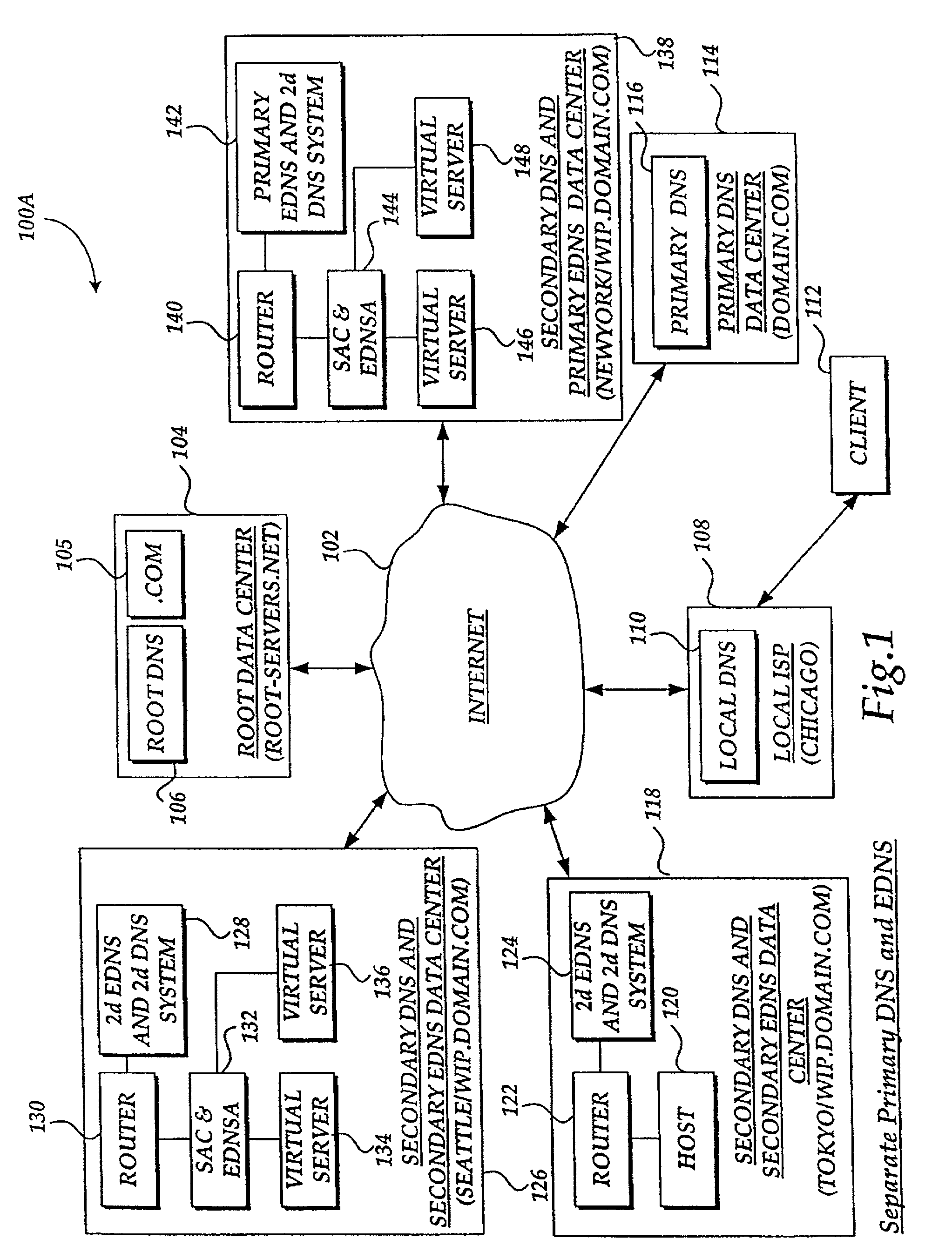
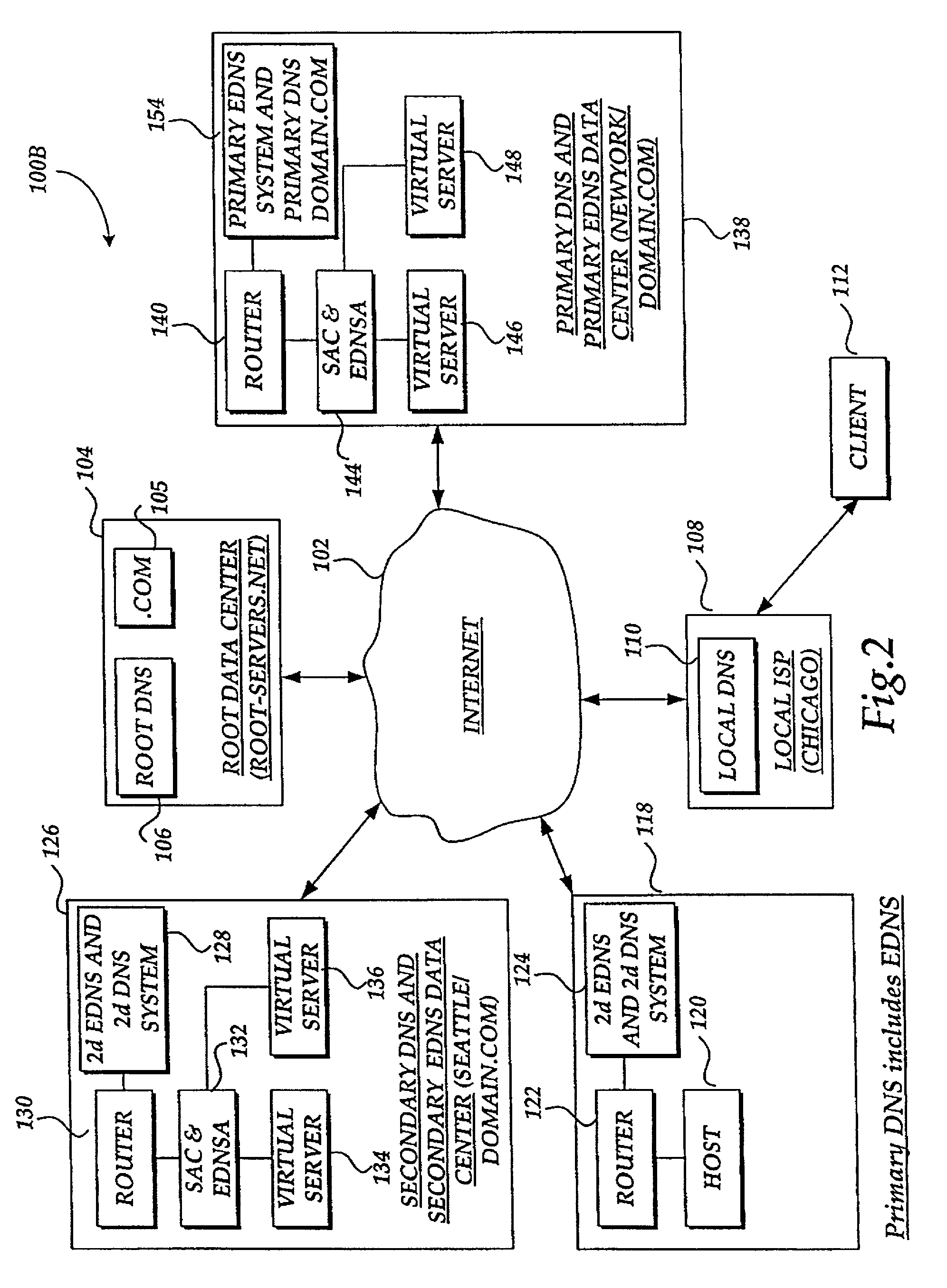
Method and system for balancing load distribution on a wide area network
InactiveUS7441045B2Close contactResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain nameIp address
A system and method for balancing the load on virtual servers managed by server array controllers at separate data centers that are geographically distributed on a wide area network such as the Internet is described. The virtual servers provide access to resources associated with a domain name request by a client program. When a Primary Domain Name System (DNS) determined the requested domain name is delegated to a EDNS, the EDNS employs metric information and statistics to resolve an IP address for a virtual server that is selected by the EDNS to optimally balance the load and provide access to resources associated with the domain name. The EDNS may load balance name servers. Additionally, the name server load balancing system may bridge disparate content delivery networks. Internet addresses are divided into geographical information that is used to delegate traffic. Also, metric information is collected and analyzed to help distribute the traffic.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
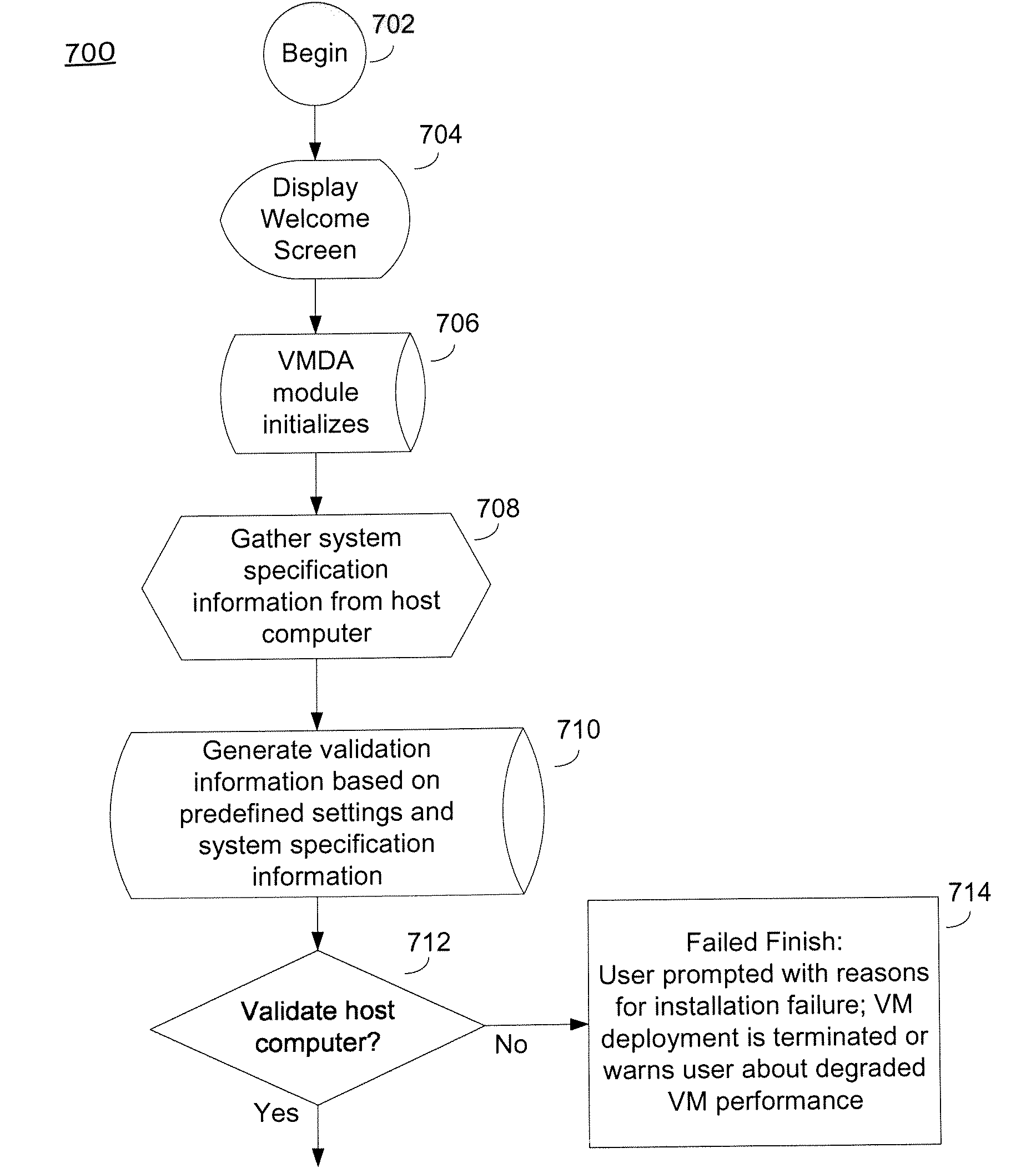
System and method for deploying a virtual machine
A system and method may include identifying a virtual machine setting associated with a virtual machine, obtaining system specification information associated with a computer, and generating validation information based on the system specification information and the virtual machine setting. The system and method may further include determining whether to deploy the virtual machine to the computer based on the validation information.
Owner:SMARTDEPLOY LLC
System and method for automatic workload characterization
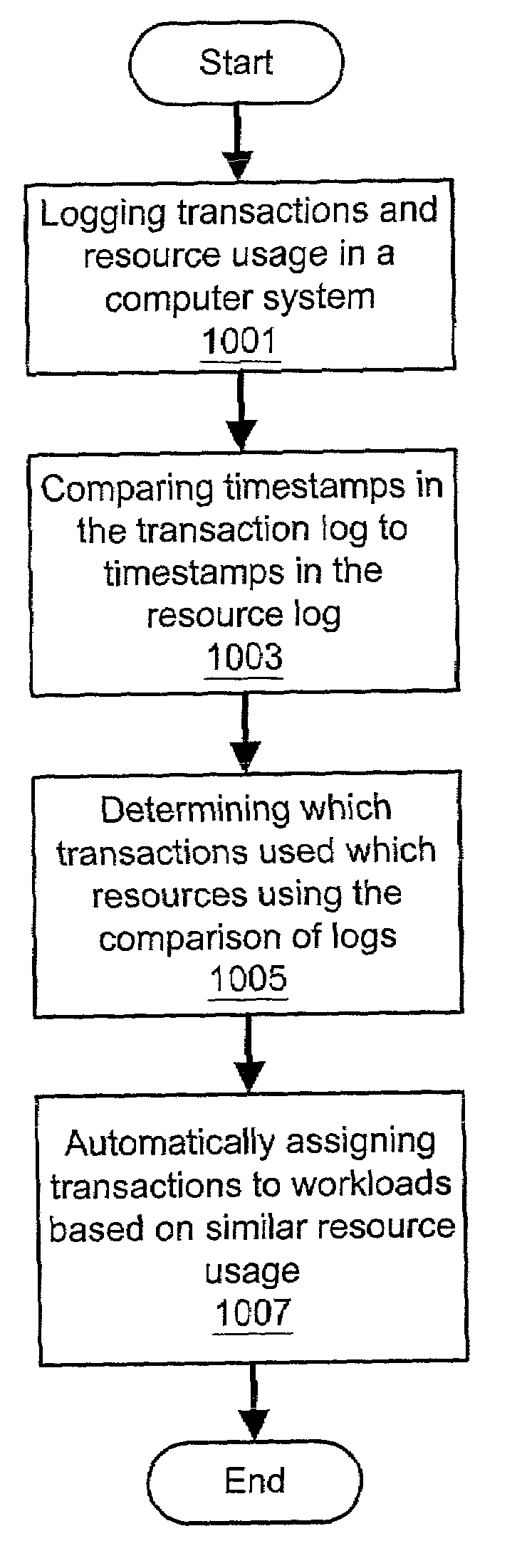
ActiveUS7028301B2Good precisionEasy accessResource allocationMemory systemsTimestampResource consumption
A system and method for automatic workload characterization are provided. Transactions performed in a computer system may be logged. The log of transactions comprises a timestamp for each transaction. Resource usage in the computer system may be logged. The log of resource usage comprises one or more periods of time during which each of a plurality of resources is used, and the log of resource usage comprises a plurality of system performance metrics which reflect resource consumption by one or more processes that performed the transactions. The timestamps in the log of transactions may be compared to the periods of time in the log of resource usage. It may be determined which transactions used which resources as a result of the comparing the timestamps in the log of transactions to the periods of time in the log of resource usage. One or more workloads may be determined using the determining which transactions used which resources. Heuristics may be used to group processes into workloads.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
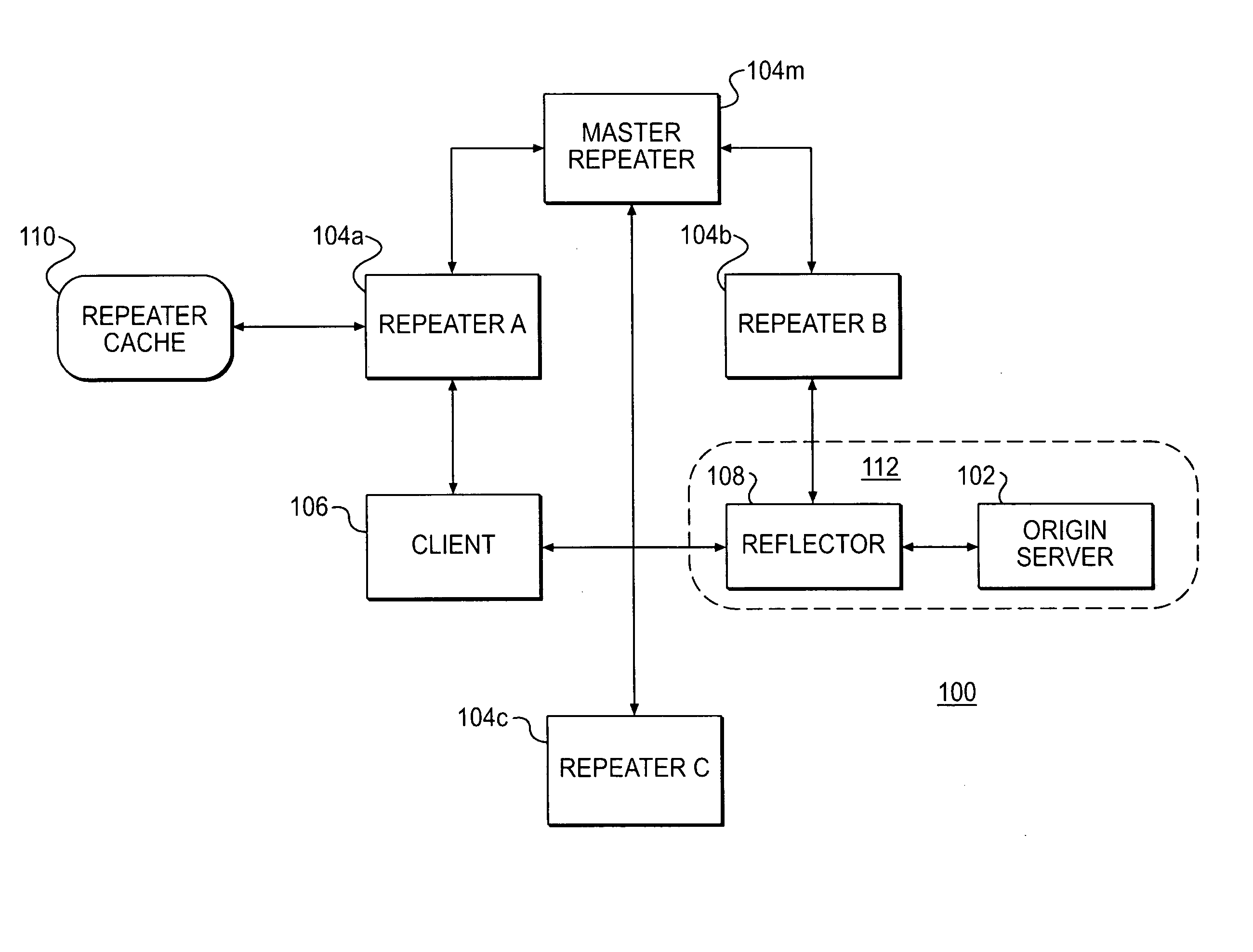
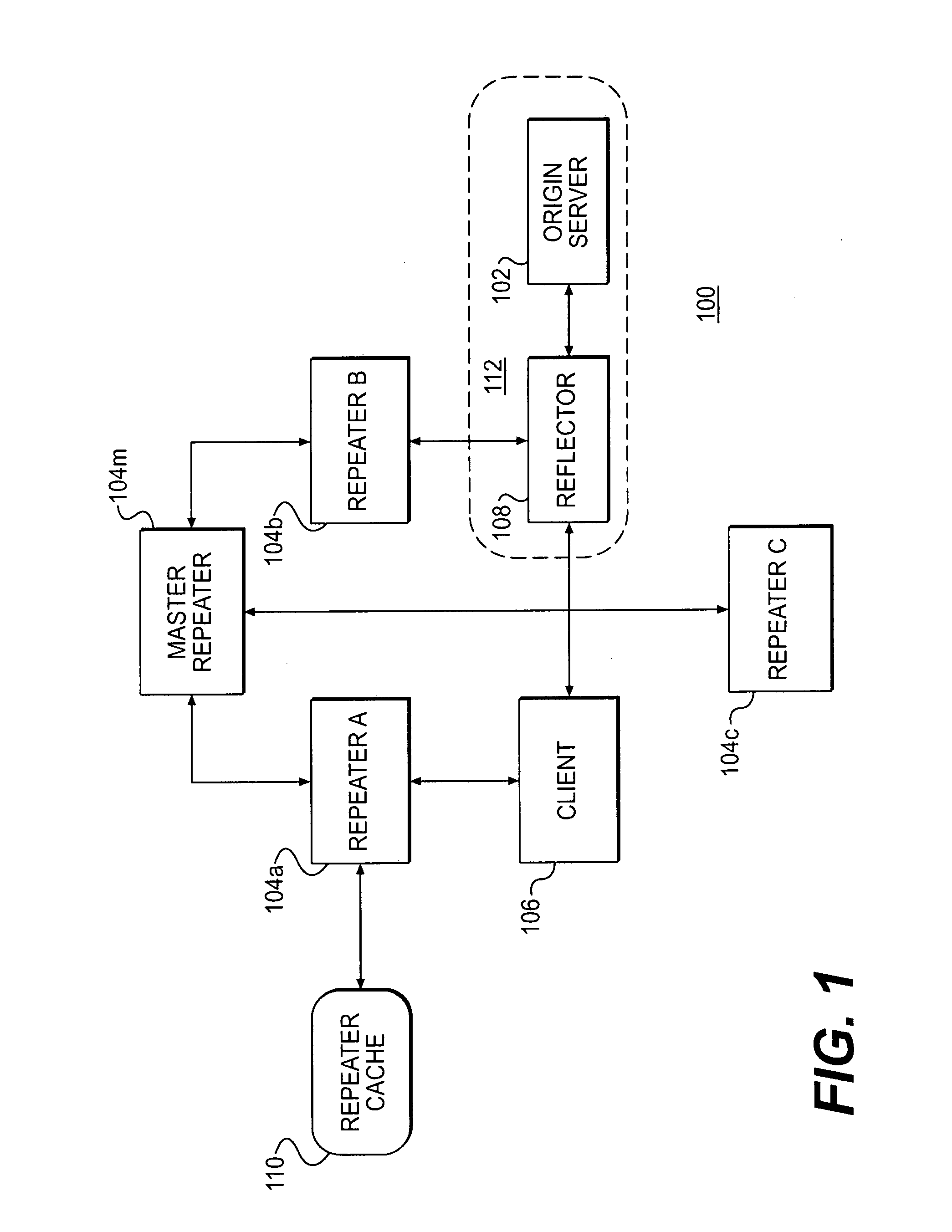
Controlling subscriber information rates in a content delivery network
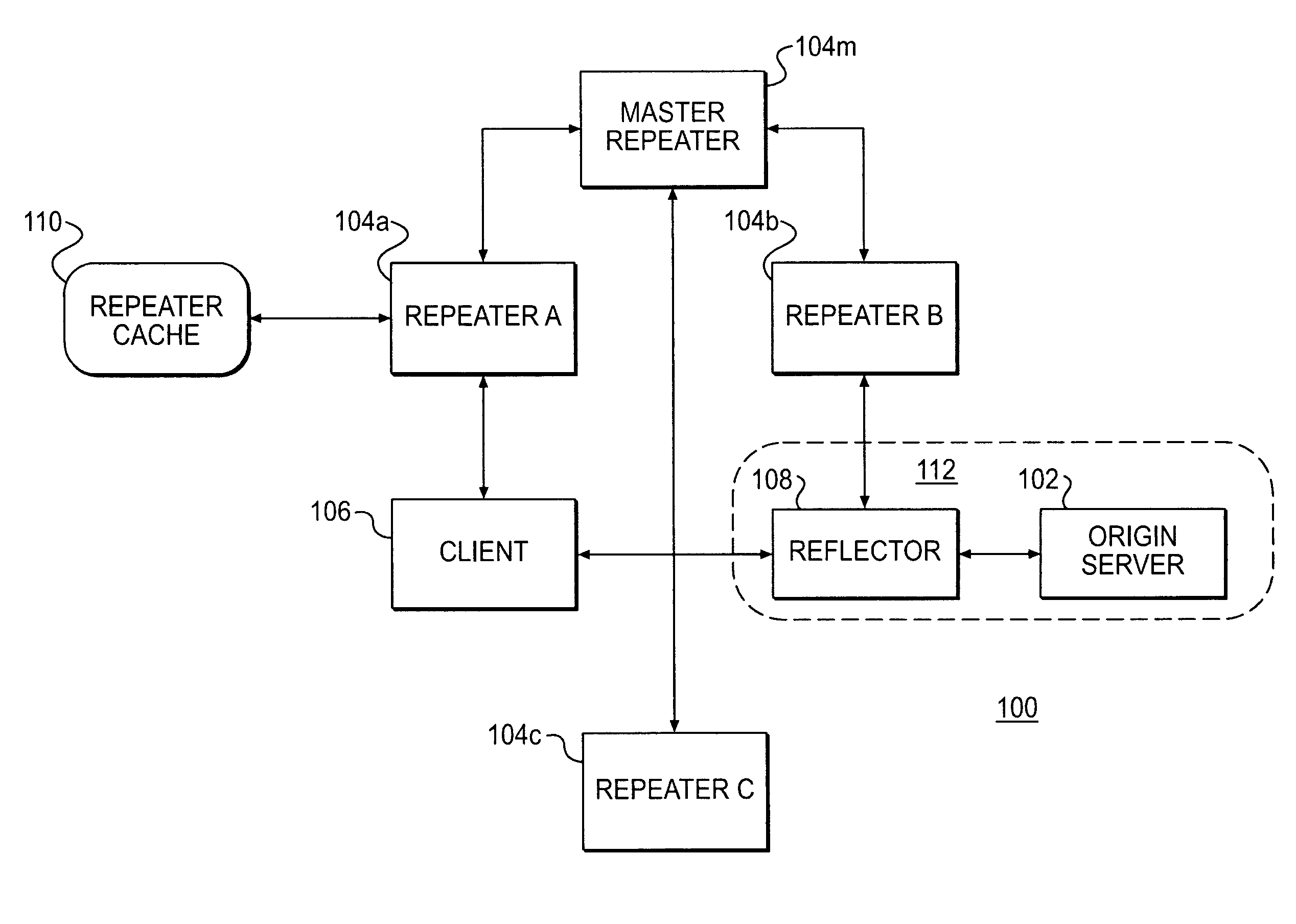
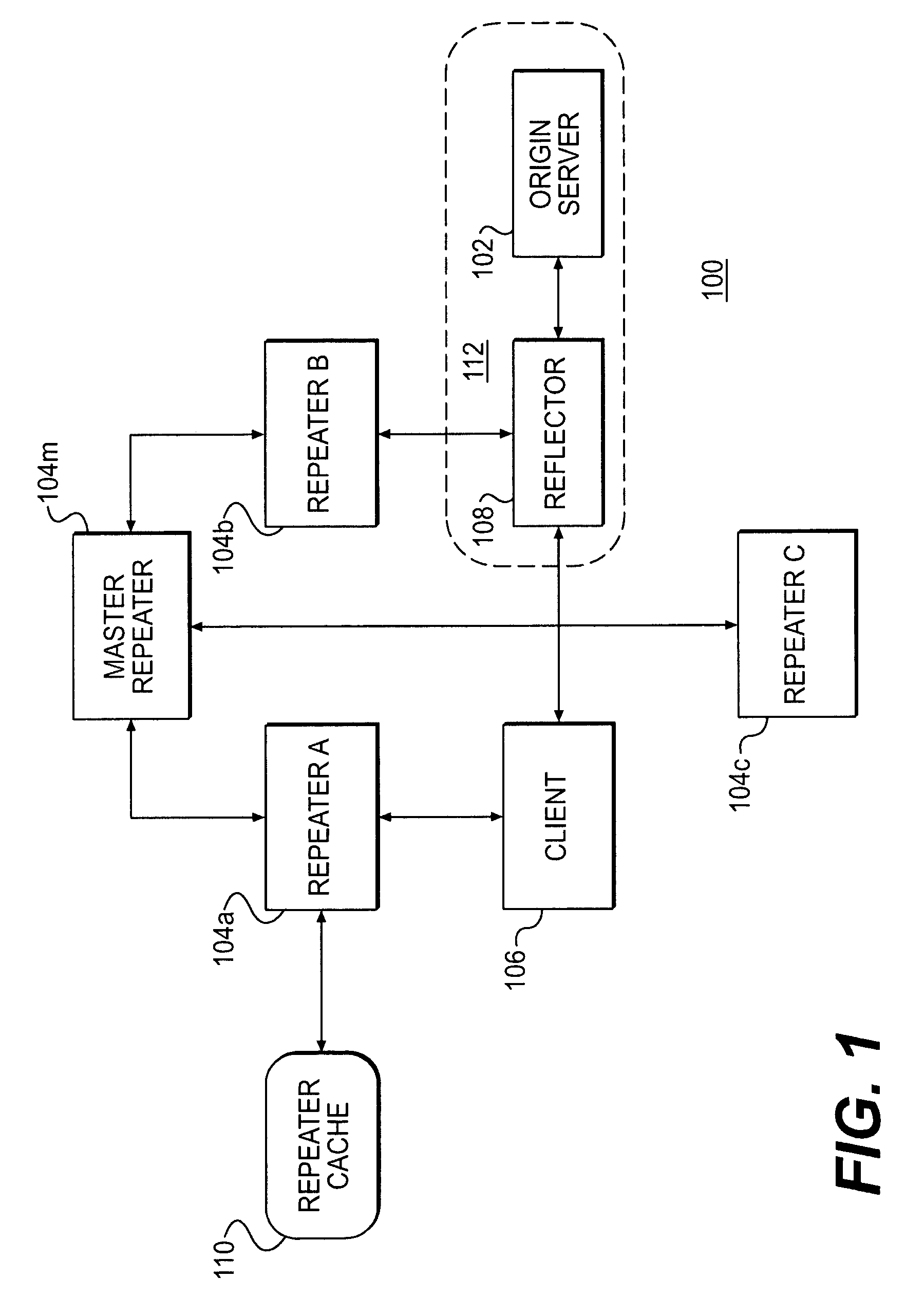
InactiveUS7949779B2Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed computingRepeater
A plurality of content providers provide multiple resources to multiple clients. At least some of said resources are to be served to clients from a shared content delivery network (CDN) formed by a plurality of repeater servers. Each content provider provides at least some resources via one or more content sources associated with that content provider. Amounts of data transmitted by the CDN on behalf of each of the plurality of content providers are monitored. Based at least in part on said monitoring, requests for resources are selectively delivered at a lower transmission rate. The lower transmission rate is achieved by generating pauses or delays in the transmission.
Owner:DIGITAL ISLAND +1
Method and apparatus for managing server load
InactiveUS6922724B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsBalancing networkTime information
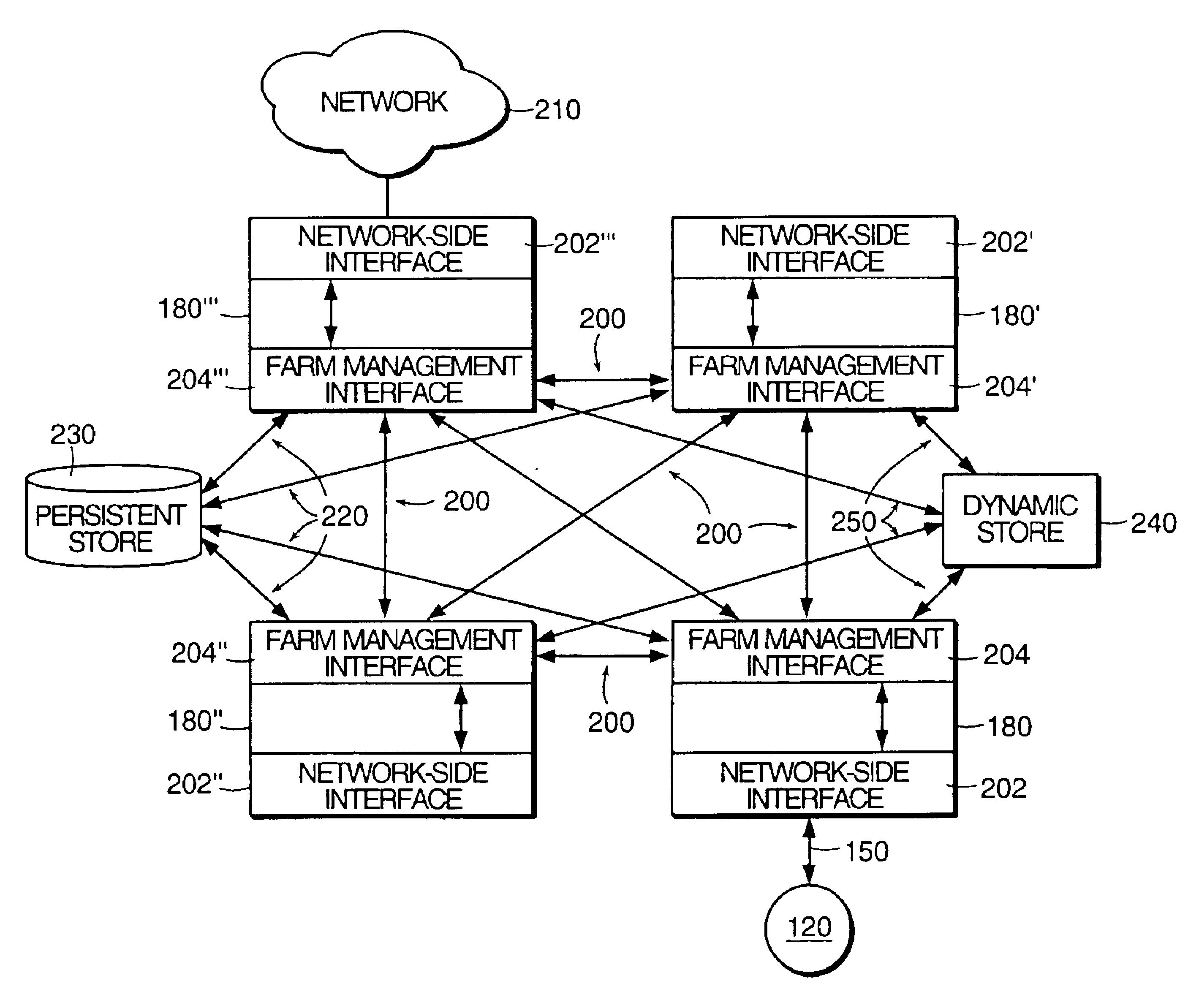
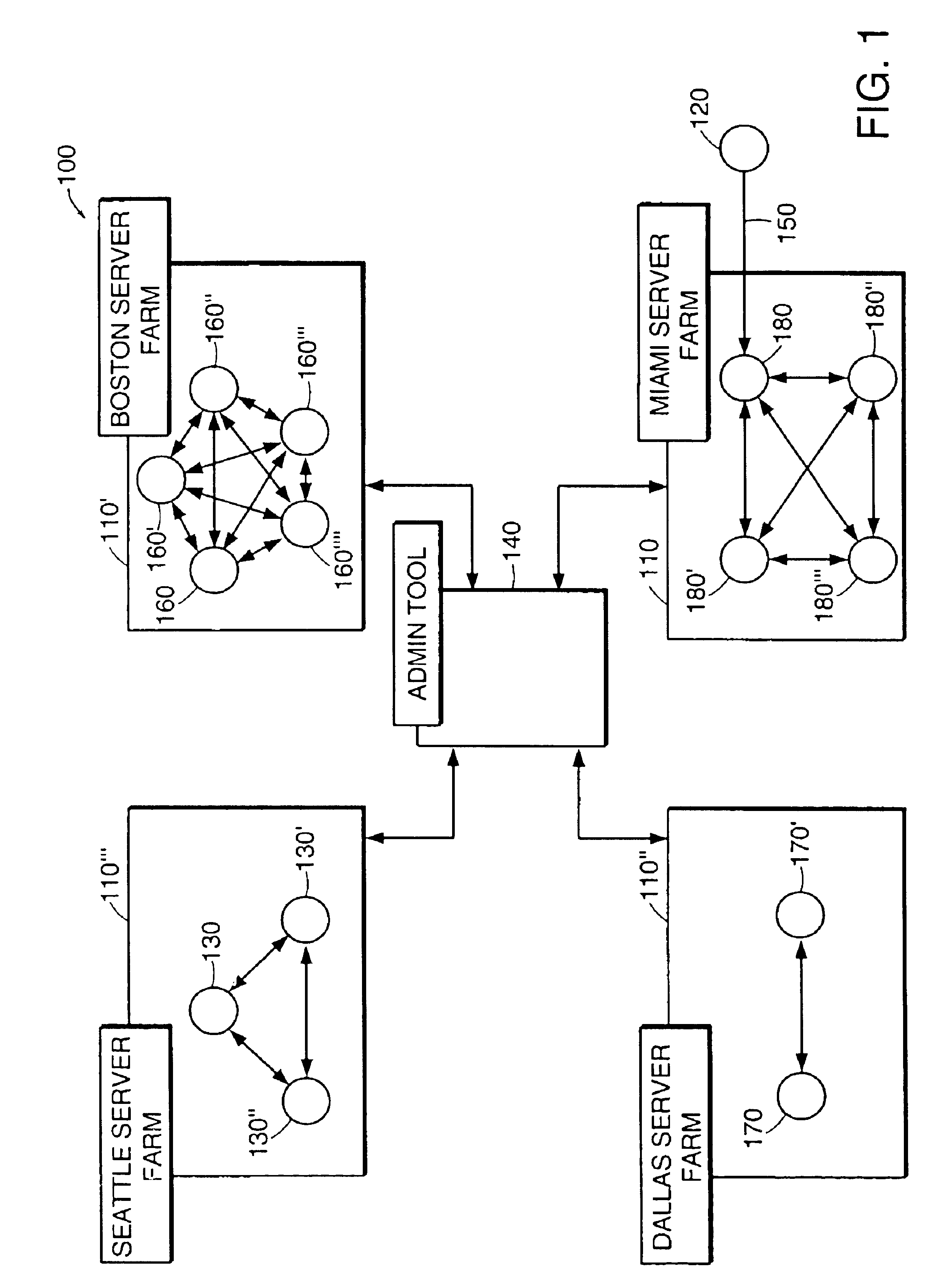
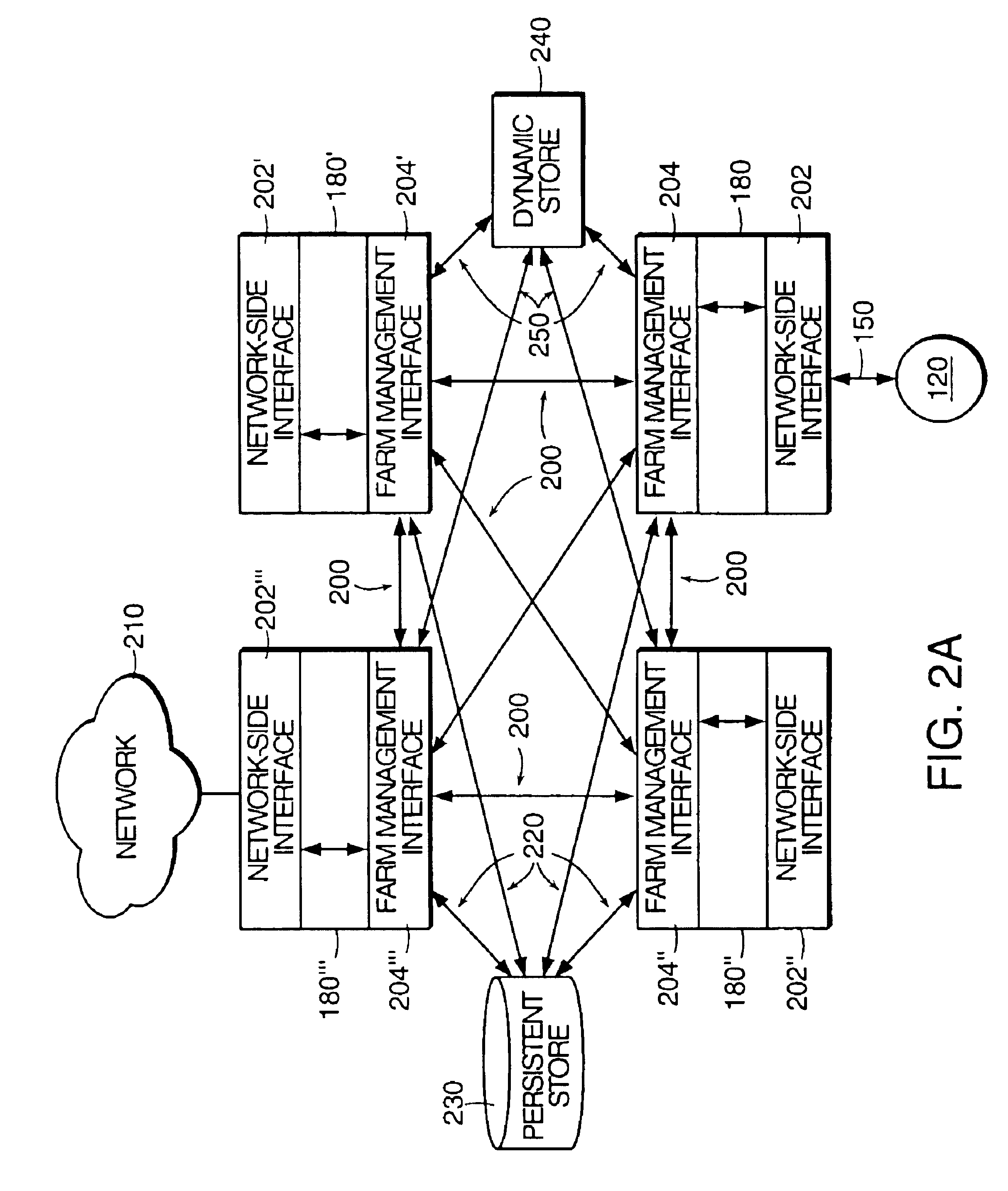
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for managing and balancing the load of each of the servers in the network. In one aspect, the invention relates to an apparatus for managing server load in a networked system of servers. The apparatus includes a dynamic store storing run-time information associated with a plurality of servers in a server farm. The apparatus also includes an event bus. The apparatus also includes a load management subsystem in communication with the dynamic store via the event bus. The load management subsystem receives a request from the event bus to identify a server and transmits a message to the event bus that includes an address of an identified server based on information from the dynamic store.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
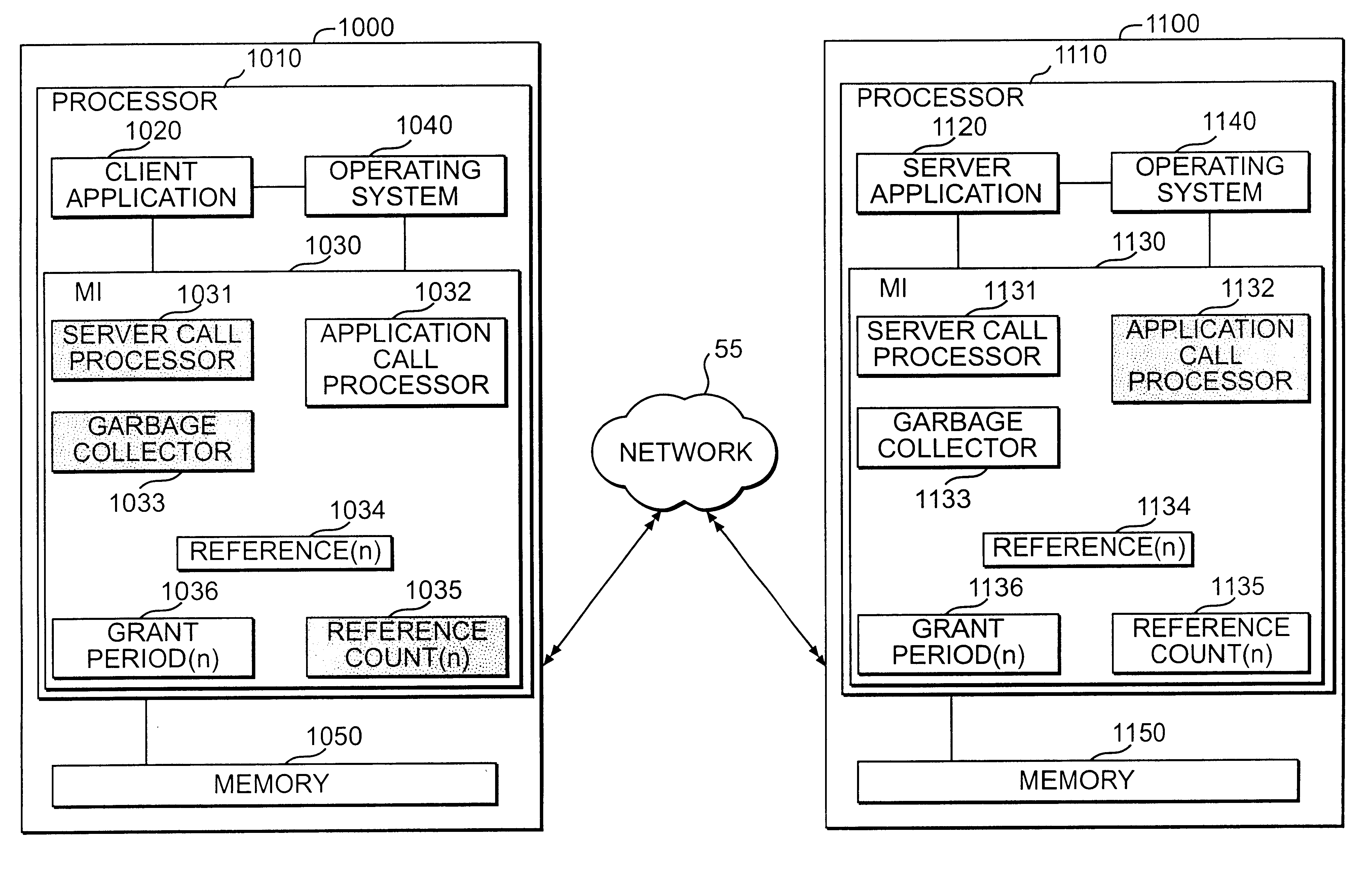
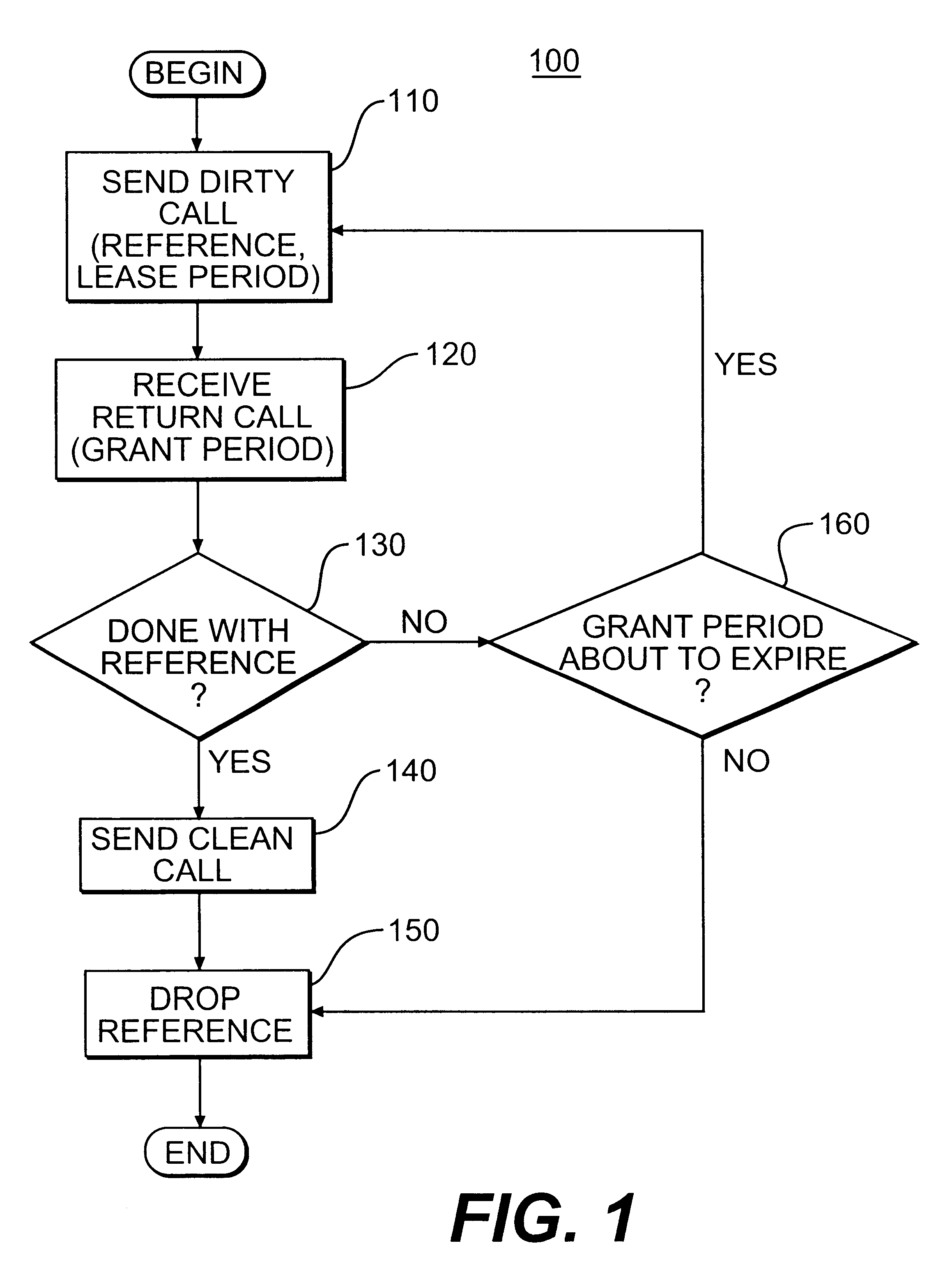
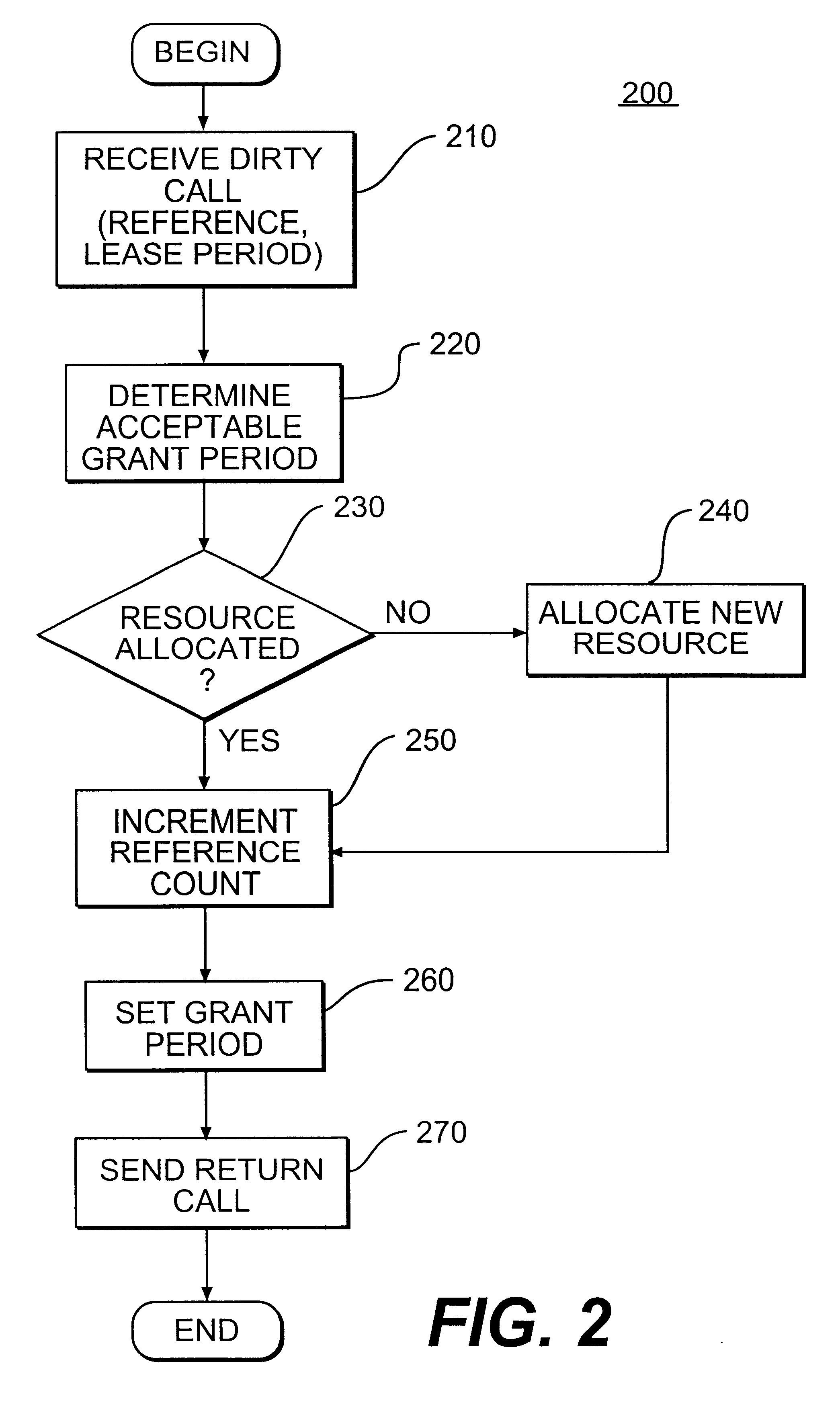
Method and system for leasing storage
A method and system for leasing storage locations in a distributed processing system is provided. Consistent with this method and system, a client requests access to storage locations for a period of time (lease period) from a server, such as the file system manager. Responsive to this request, the server invokes a lease period algorithm, which considers various factors to determine a lease period during which time the client may access the storage locations. After a lease is granted, the server sends an object to the client that advises the client of the lease period and that provides the client with behavior to modify the lease, like canceling the lease or renewing the lease. The server supports concurrent leases, exact leases, and leases for various types of access. After all leases to a storage location expire, the server reclaims the storage location.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
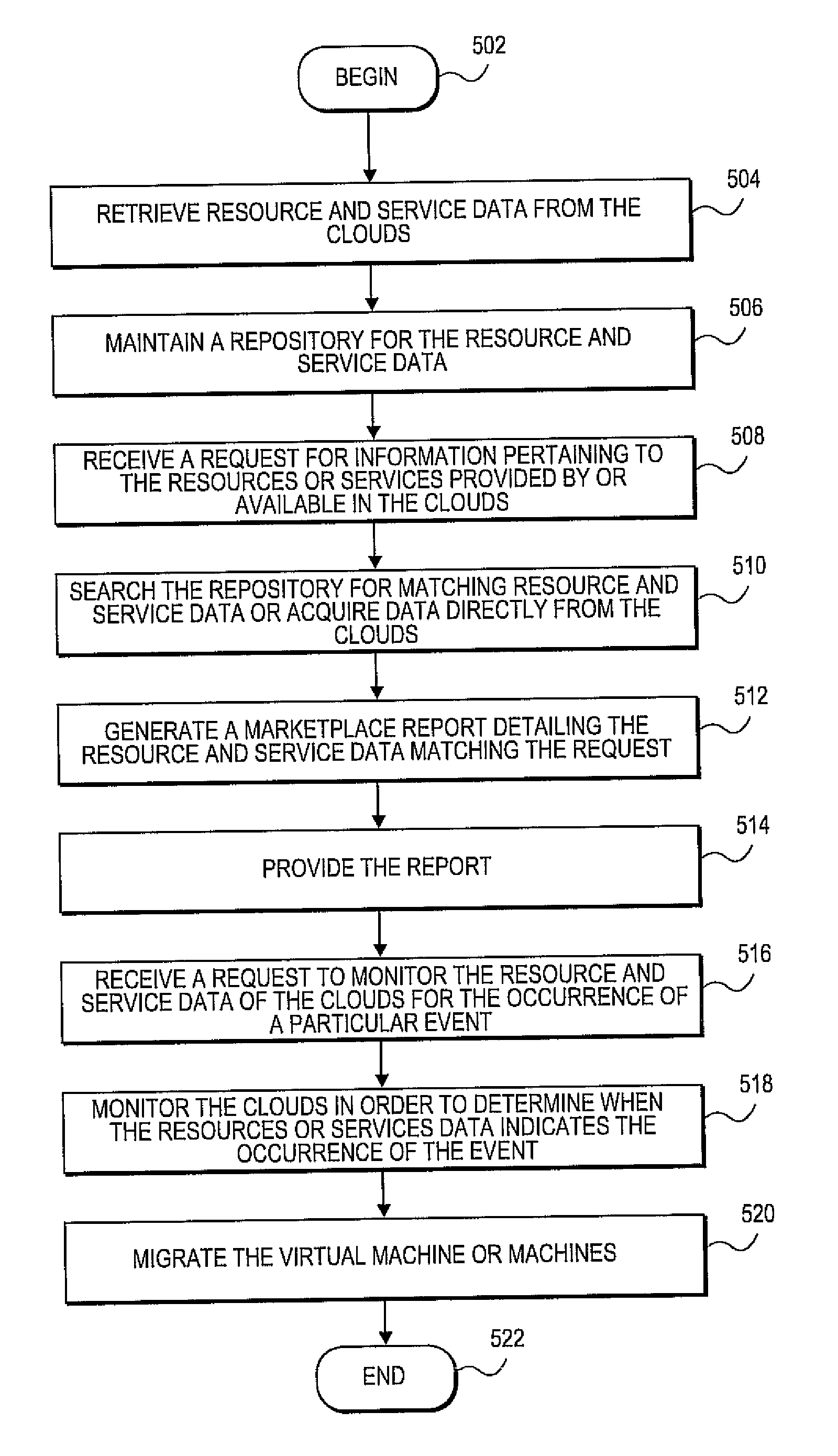
Methods and systems for providing a marketplace for cloud-based networks
A cloud marketplace system can be configured to communicate with multiple cloud computing environments in order to ascertain the details for the resources and services provided by the cloud computing environments. The cloud marketplace system can be configured receive a request for information pertaining to the resources or services provided by or available in the cloud computing environments. The cloud marketplace system can be configured to generate a marketplace report detailing the resource and service data matching the request. The cloud marketplace system can be configured to utilize the resource and service data to provide migration services for virtual machines initiated in the cloud computing environments.
Owner:RED HAT
Delivering resources to clients in a distributed computing environment with rendezvous based on load balancing and network conditions
InactiveUS20080215755A1Low costResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed Computing EnvironmentNetwork conditions
A plurality of repeater servers form a shared content delivery network (CDN) to serve resources to clients on behalf of a plurality of content providers. First and second resources are associated with a first content provider, the first resource referencing the second resource. The second resource is associated with a domain of the shared CDN. Responsive to a request that causes the first resource to be served to a client from a server in a domain associated with the first content provider, a CDN server is identified in the domain associated with the shared CDN to serve the second resource to the client. The CDN server is selected based, at least in part, on load conditions on at least some of the CDN servers, and on the client's location. Responsive to the CDN server being requested to serve the second resource: if a copy of the second resource is available on the CDN server, the copy is served to the client from the CDN server; otherwise, the second resource is replicated on the CDN server and then served to the client from the CDN server.
Owner:MOUNT SHASTA ACQUISITION +1
Virtual computing infrastructure
ActiveUS20090300605A1More separatedReduce hardware costsResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationOperational systemNetwork communication
A system has a virtual overlay infrastructure mapped onto physical resources for processing, storage and network communications, the virtual infrastructure having virtual entities for processing, storage and network communications. Each virtual infrastructure can be passivated by suspending applications, stopping operating systems, and storing state, to enable later reactivation. This is simpler for a complete virtual infrastructure than for groups of virtual entities and physical entities. It enables cloned virtual infrastructure to be created for testing, upgrading or sharing without risk to the parent. On failure, reversion to a previous working clone is feasible.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Resource invalidation in a content delivery network
InactiveUS20080215735A1Low costResource allocationDigital computer detailsComputer networkComputer science
A repeater server in a content delivery network (CDN) maintains a list of resources that are no longer valid. When the server gets a request for a resource, it checks whether that resource is on the list, and, if so, it replicates the resource from a content provider's content source such as an origin server. Otherwise the repeater server tries to serve a copy of the requested resource or to obtain a copy from another location in the CDN.
Owner:MOUNT SHASTA ACQUISITION +1
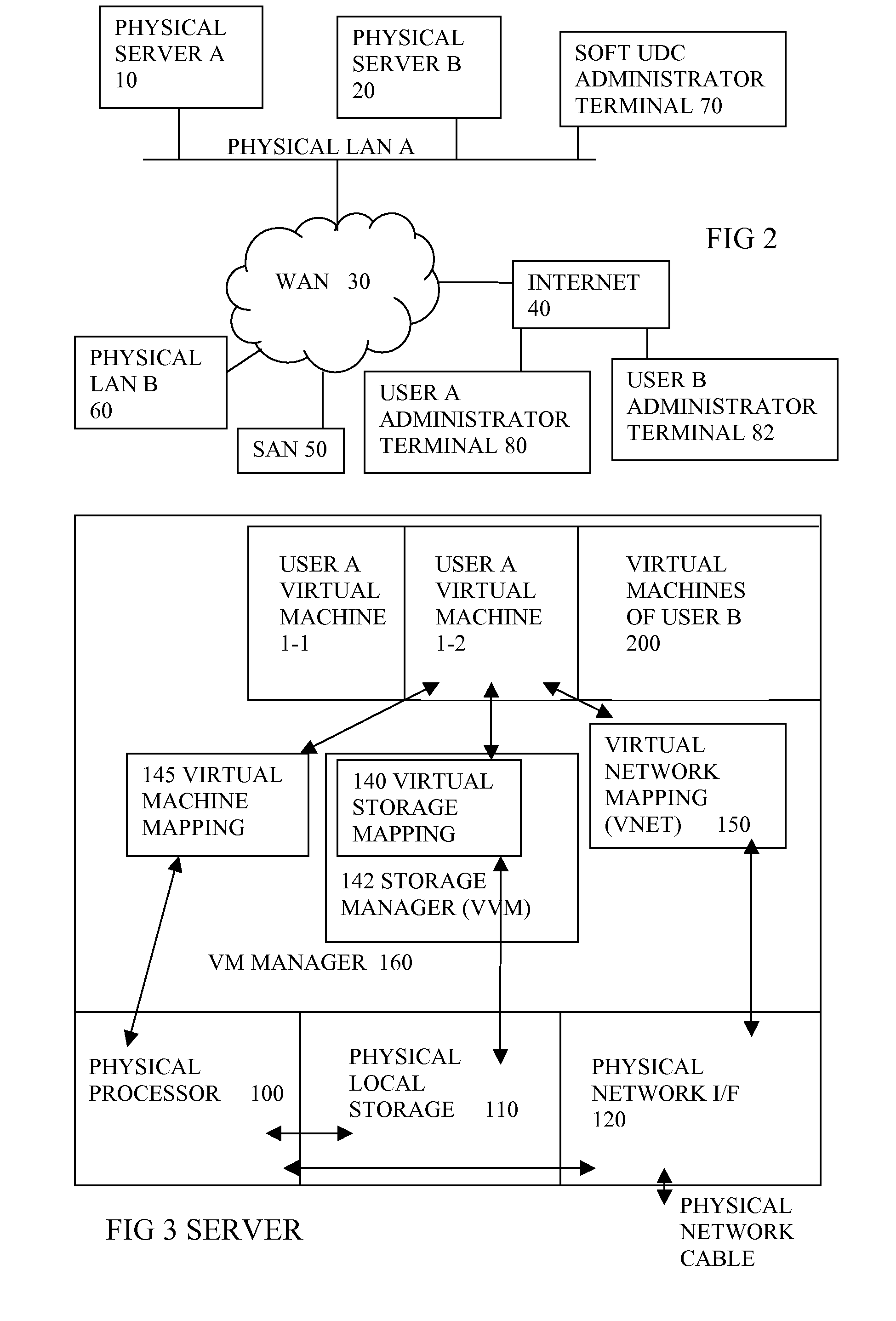
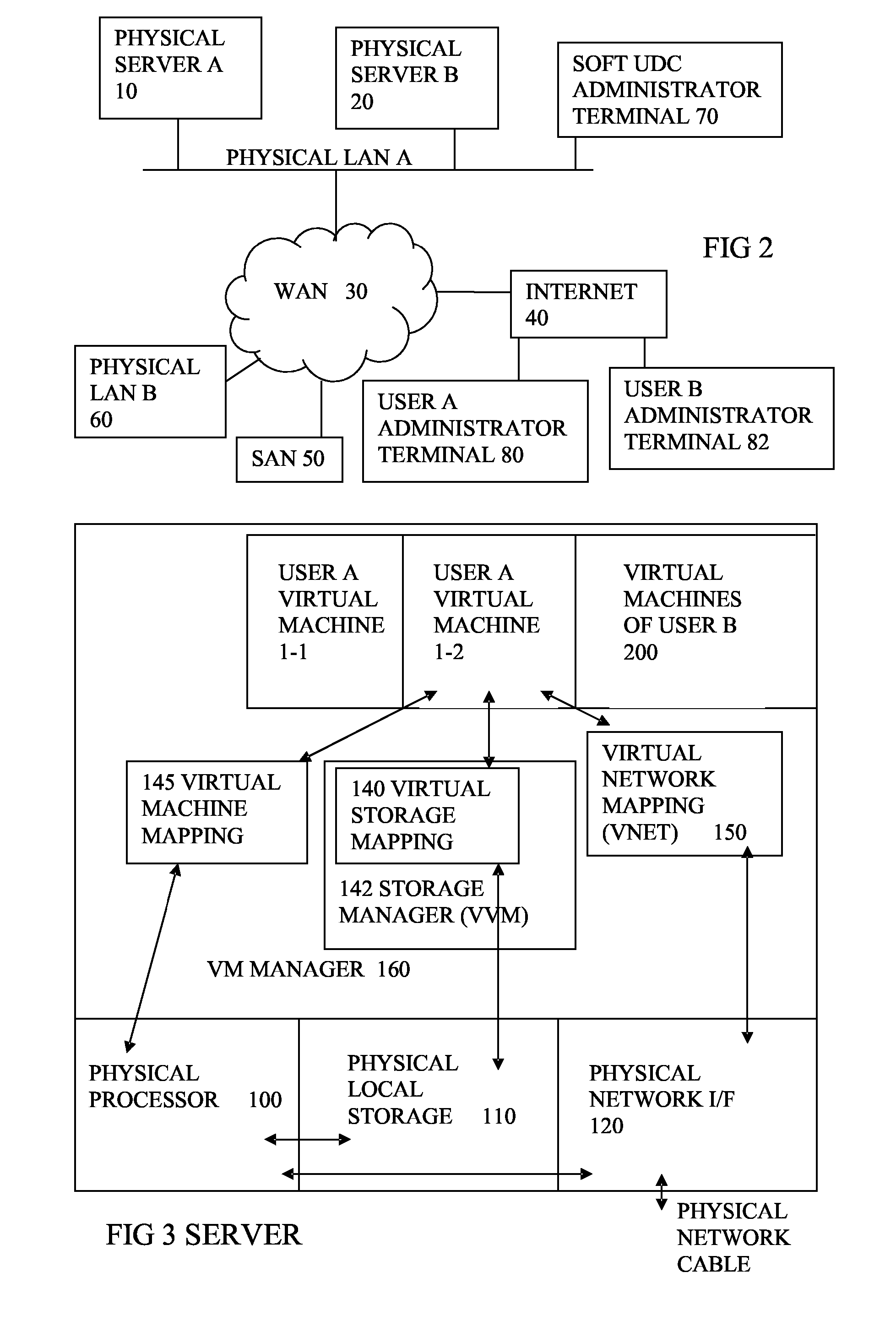
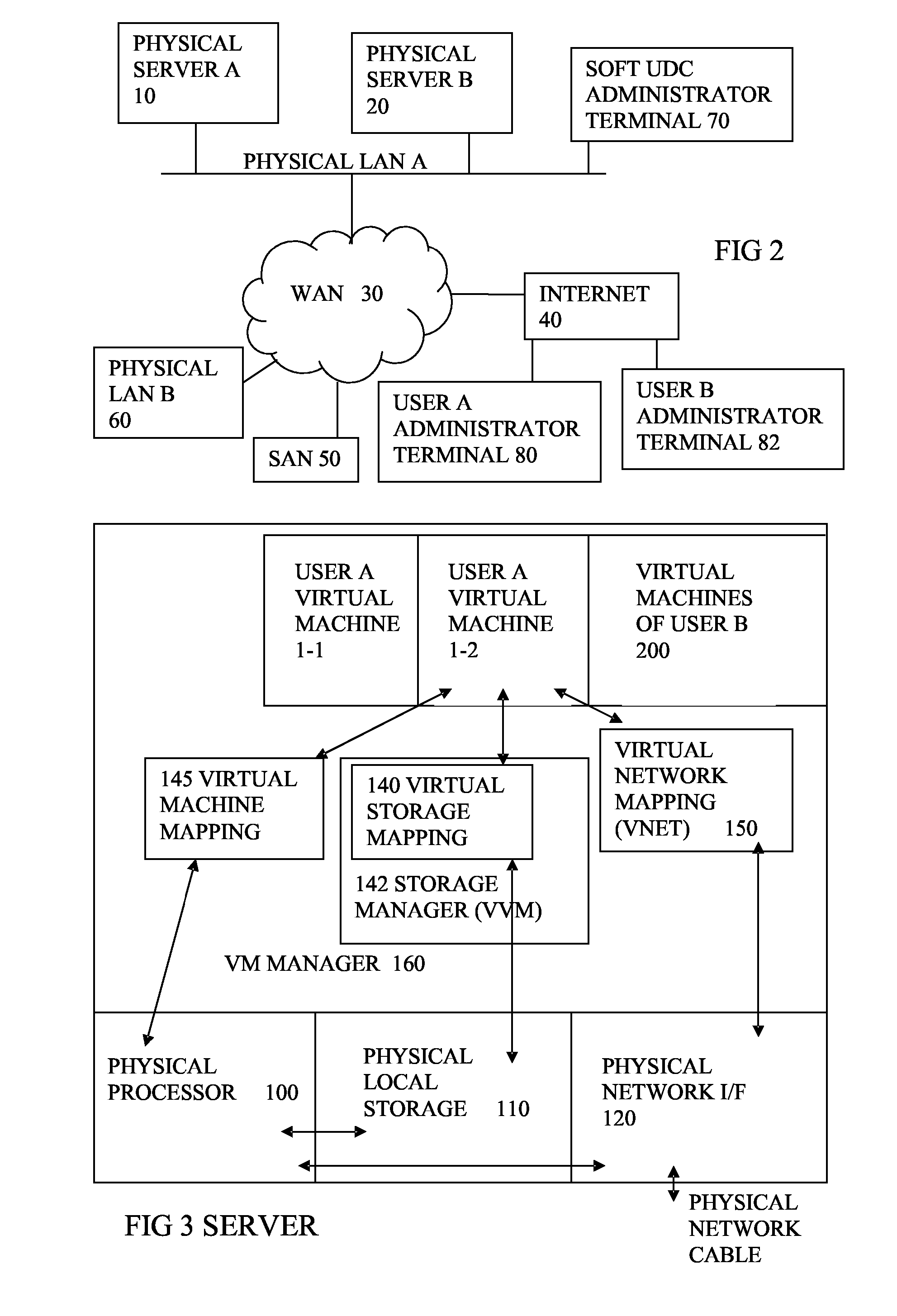
Method and apparatus for providing computer services
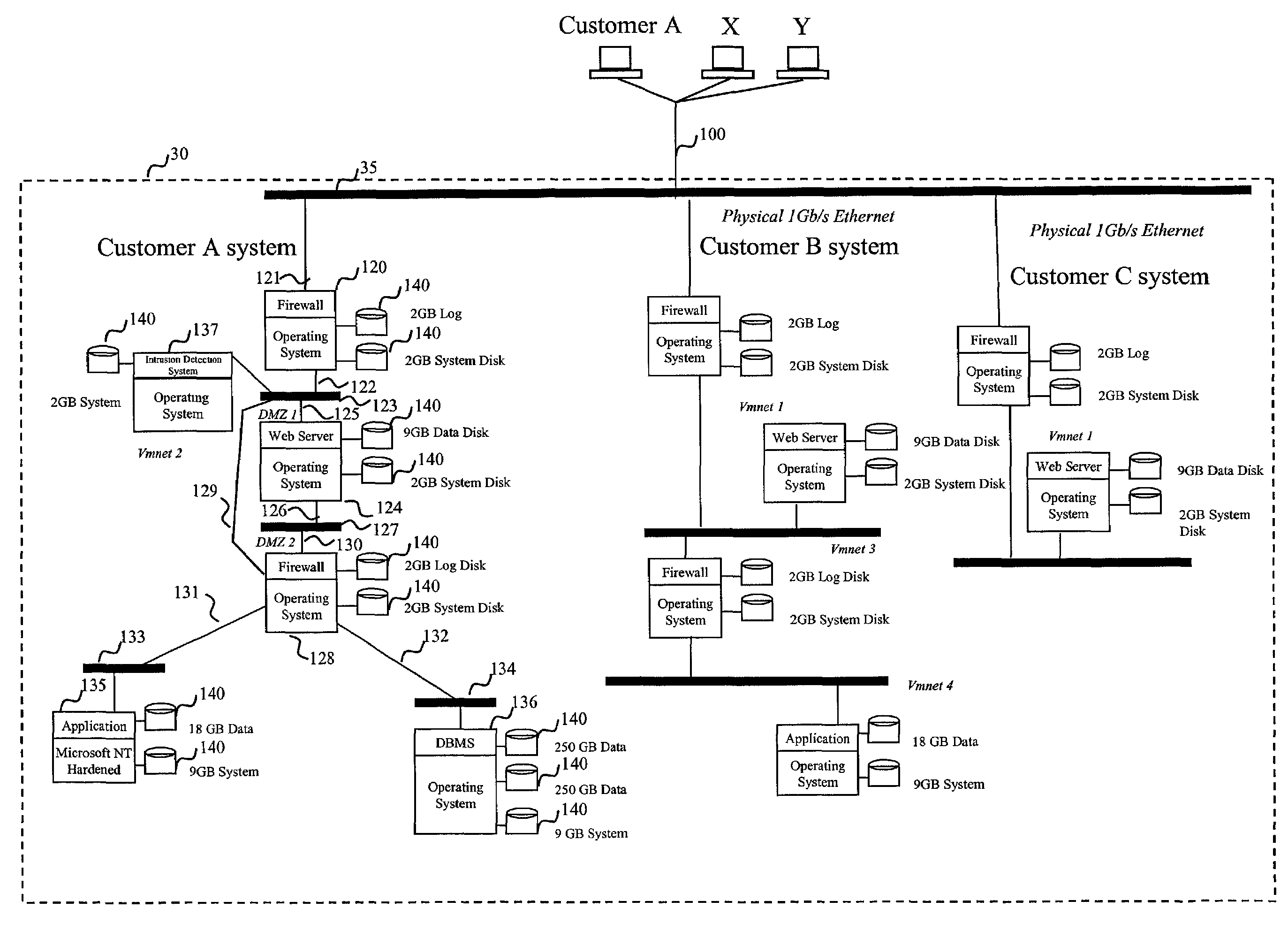
InactiveUS7448079B2Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceVirtual machine
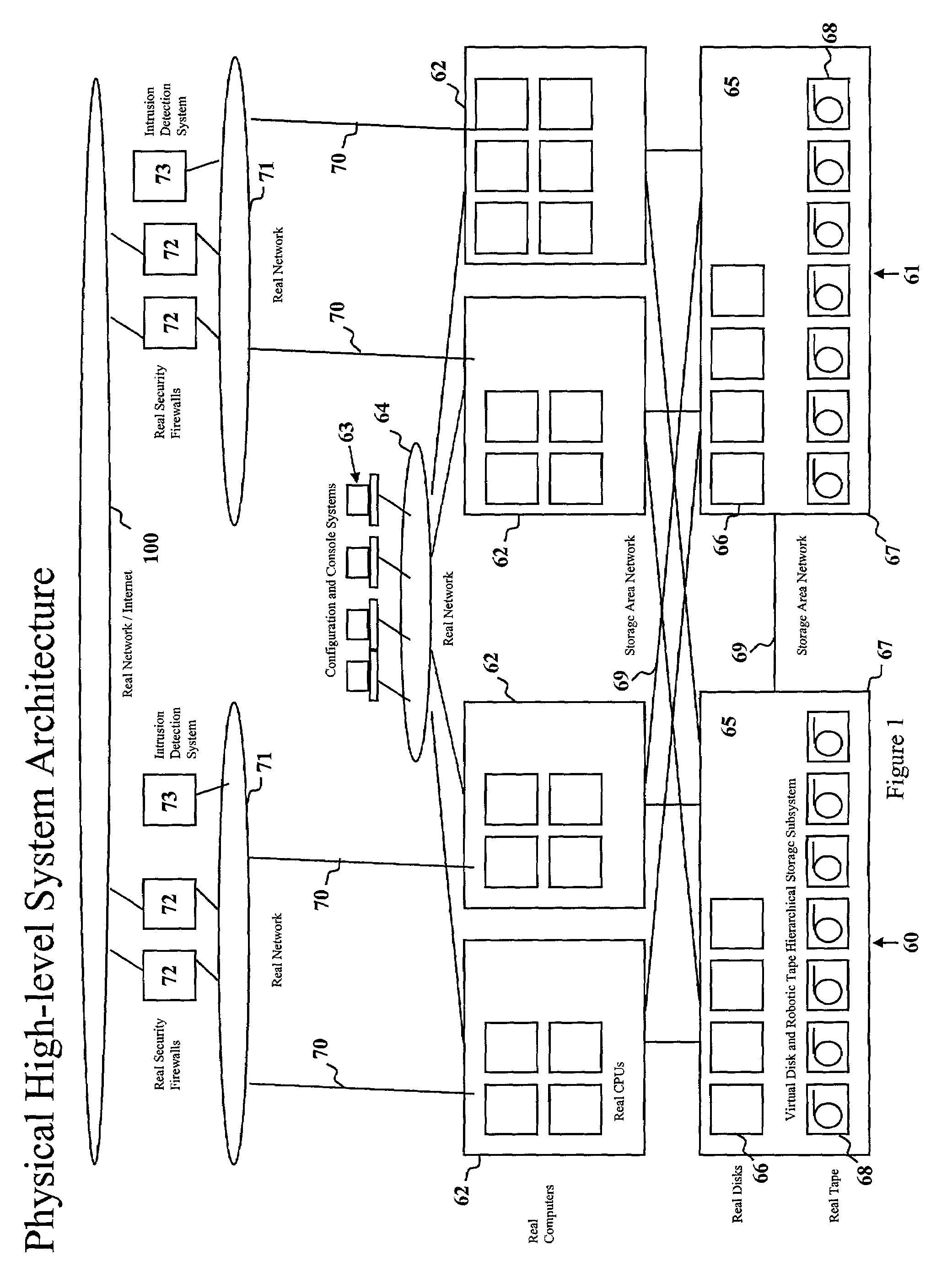
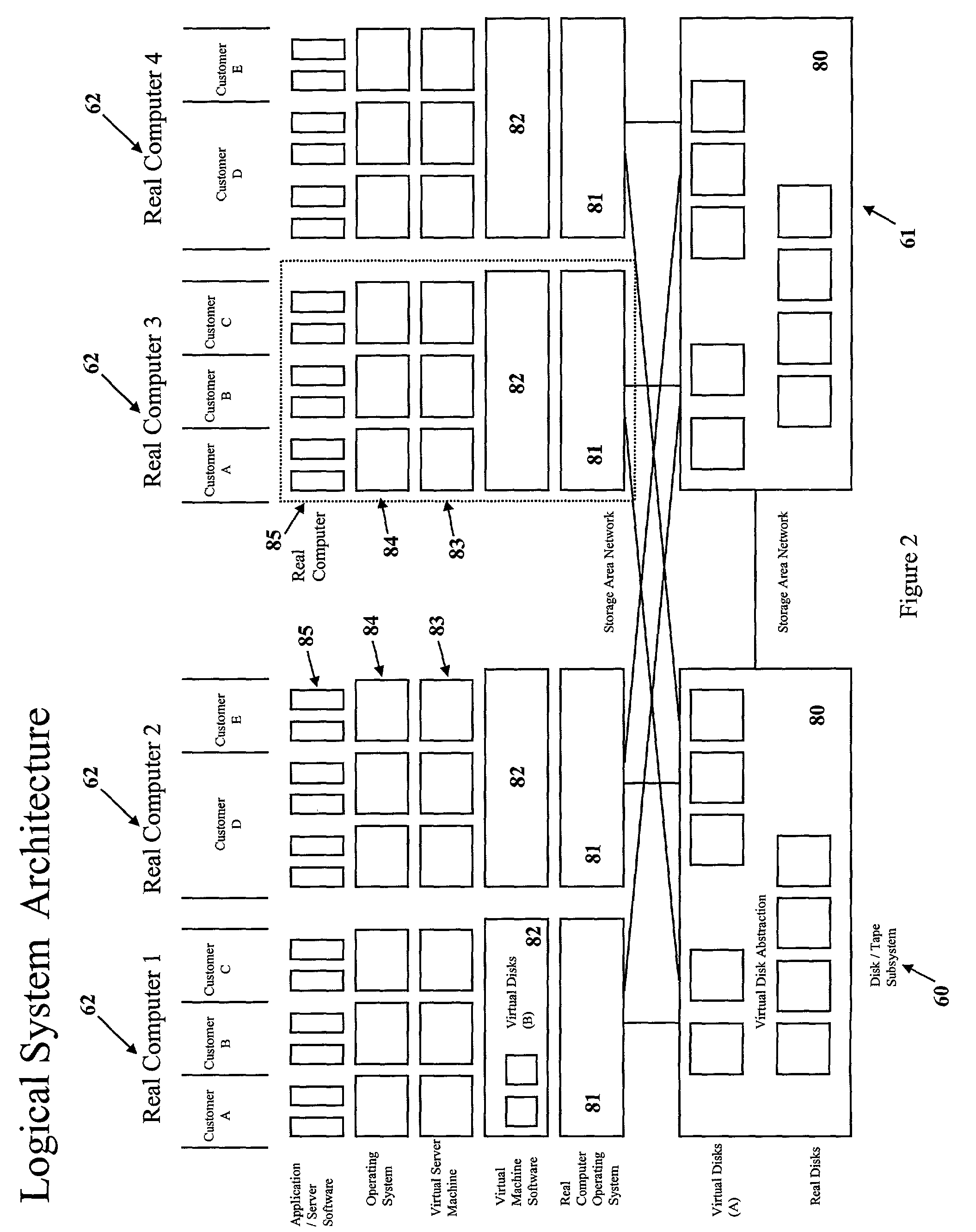
An apparatus and method are disclosed for providing one or more computer services to a plurality of customers (A,B,C). At least one virtual machine (VS) is set up on a real computer (30) for each of the customers (A,B,C) at the request of each of the customers (A,B,C). The or each virtual machine (VS) for each of the customers (A,B,C) has a specification specified by the respective customer (A,B,C).
Owner:ERNST & YOUNG
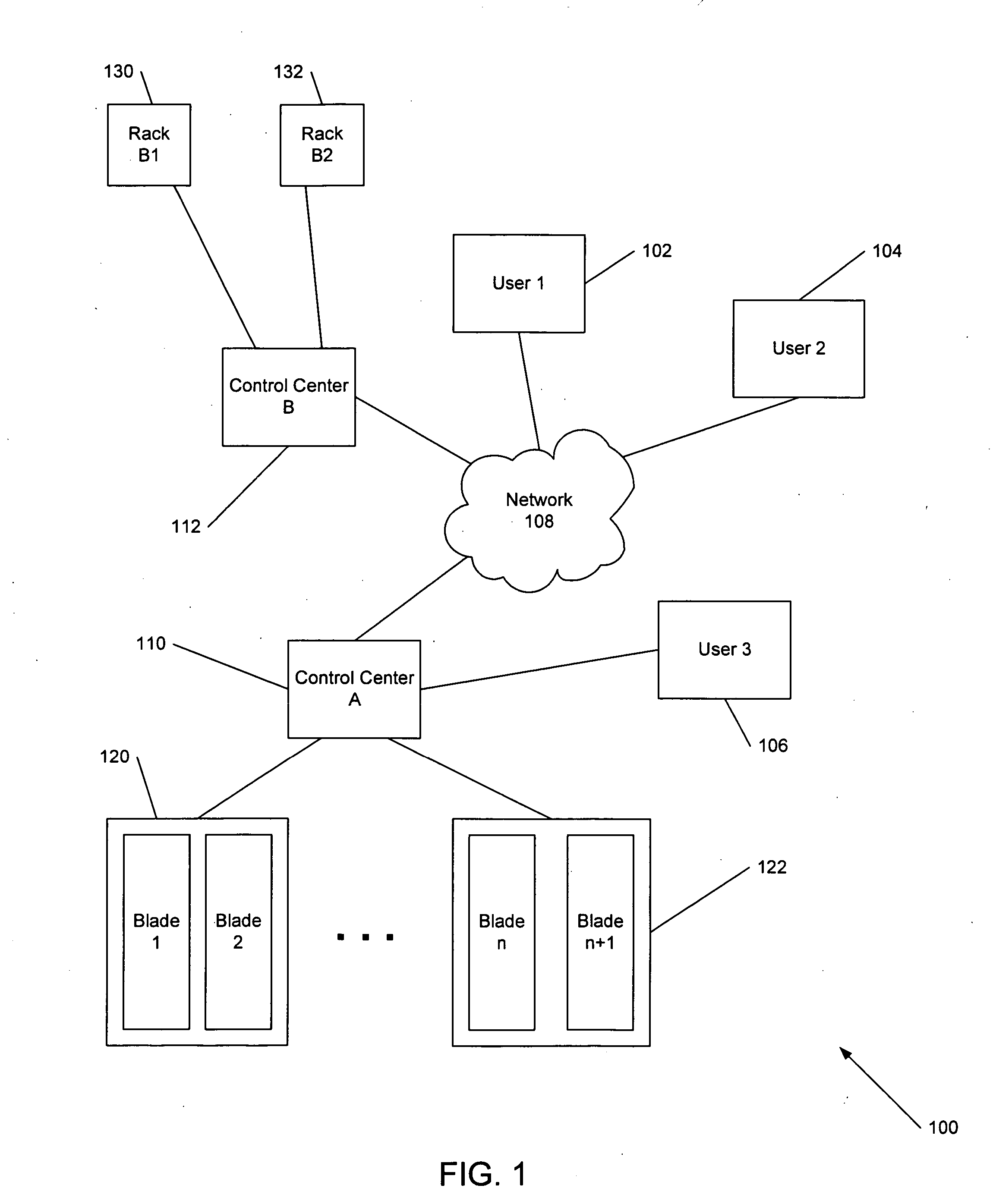
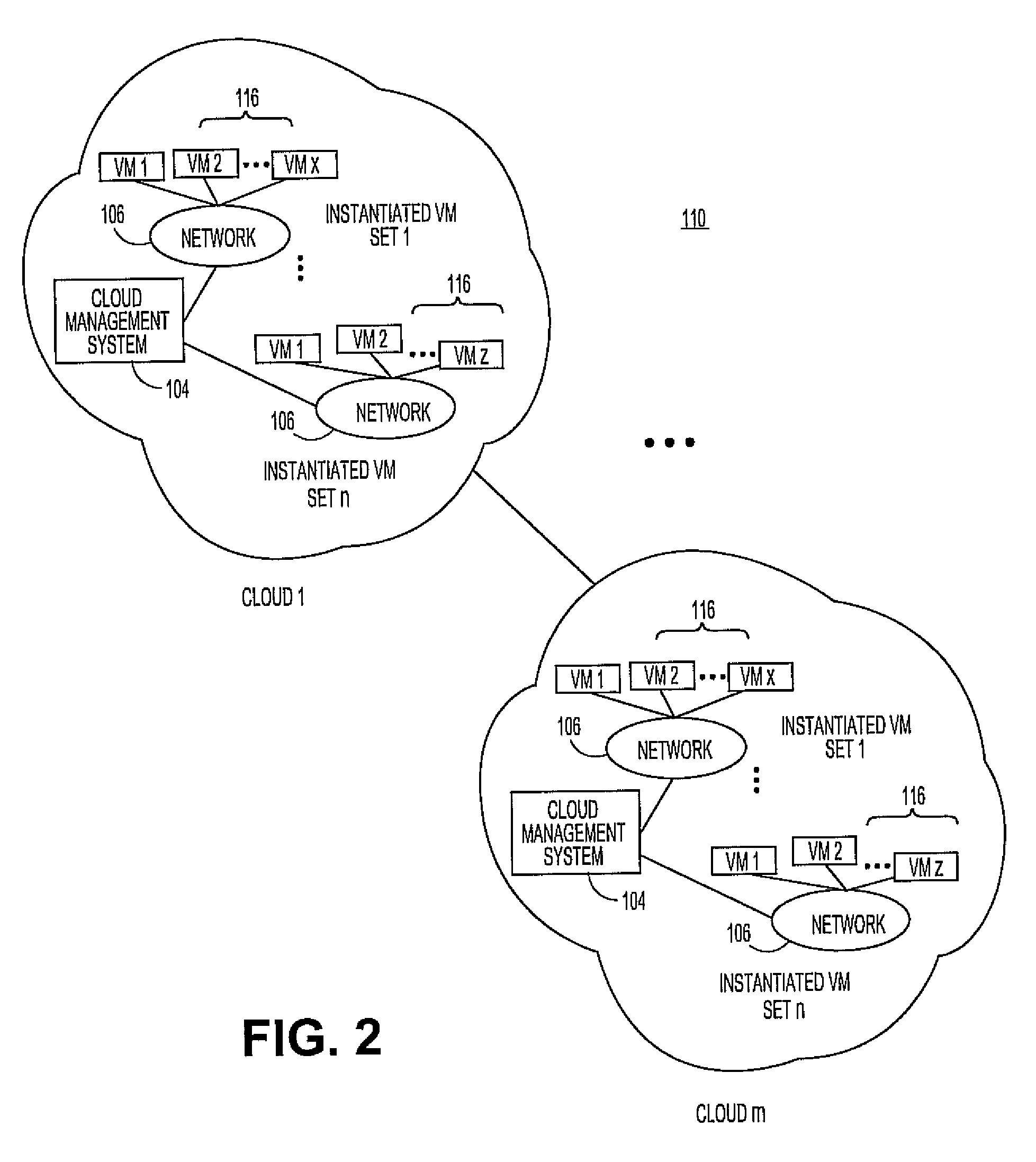
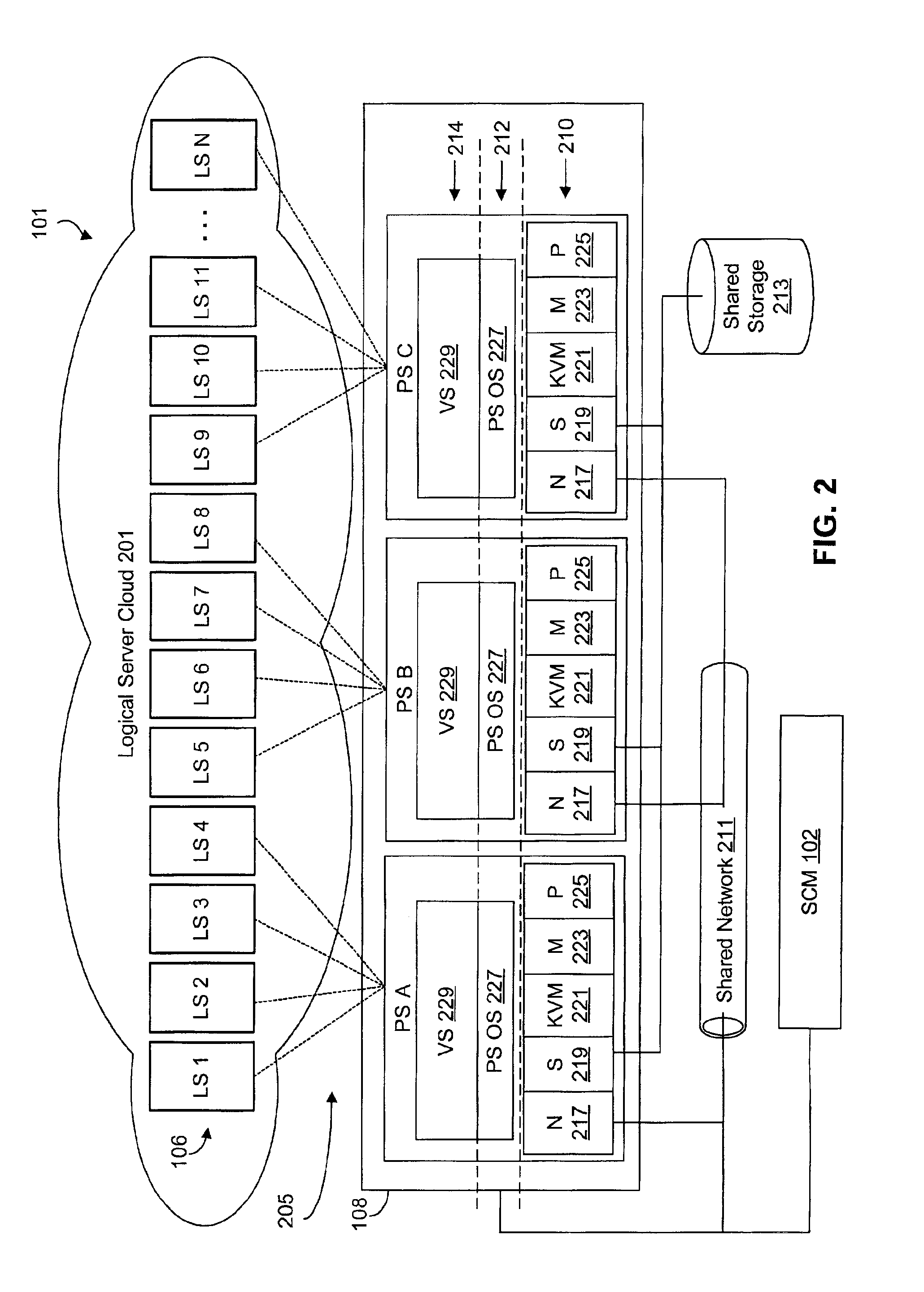
Virtualized logical server cloud providing non-deterministic allocation of logical attributes of logical servers to physical resources
InactiveUS6880002B2Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtualizationData store
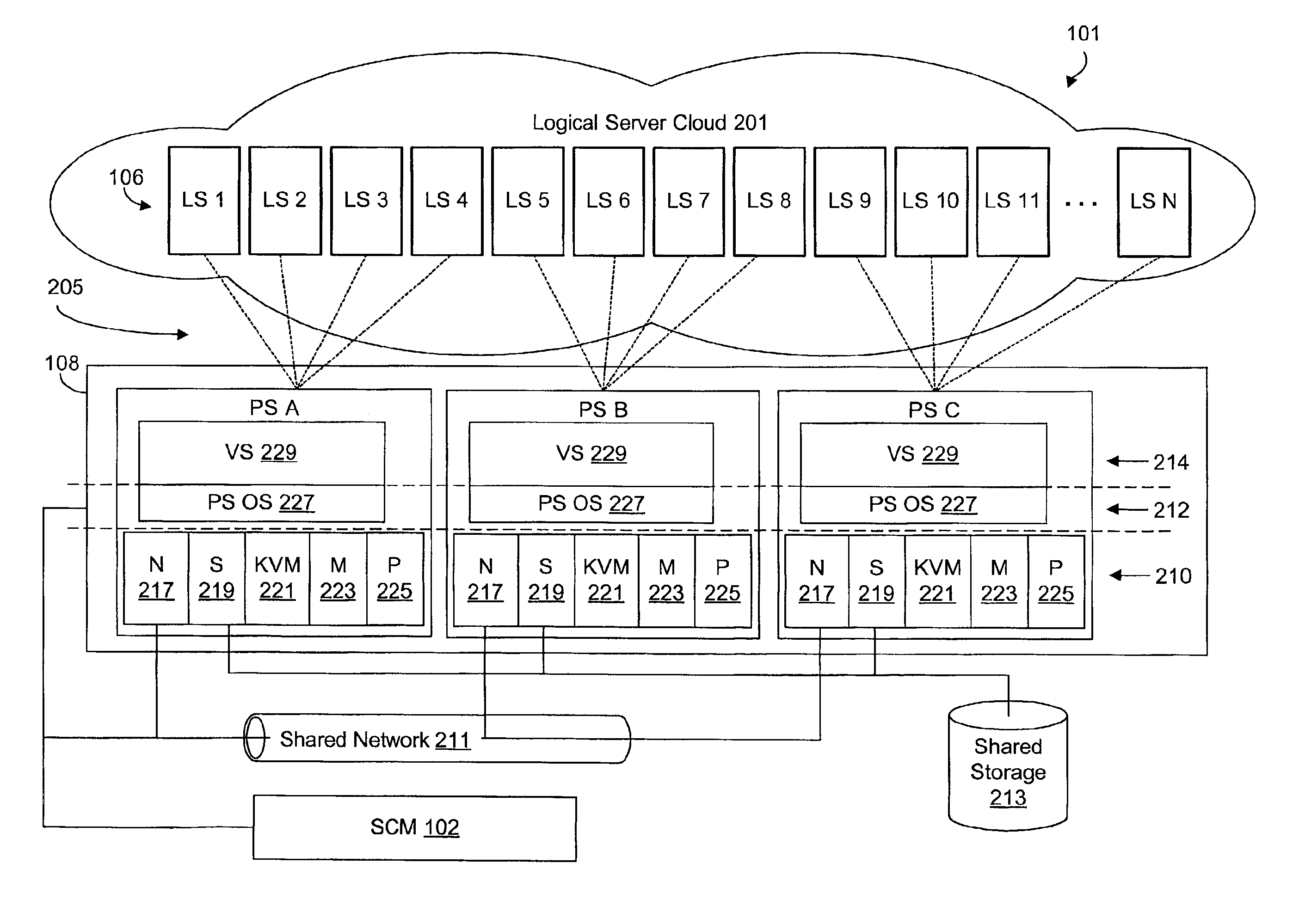
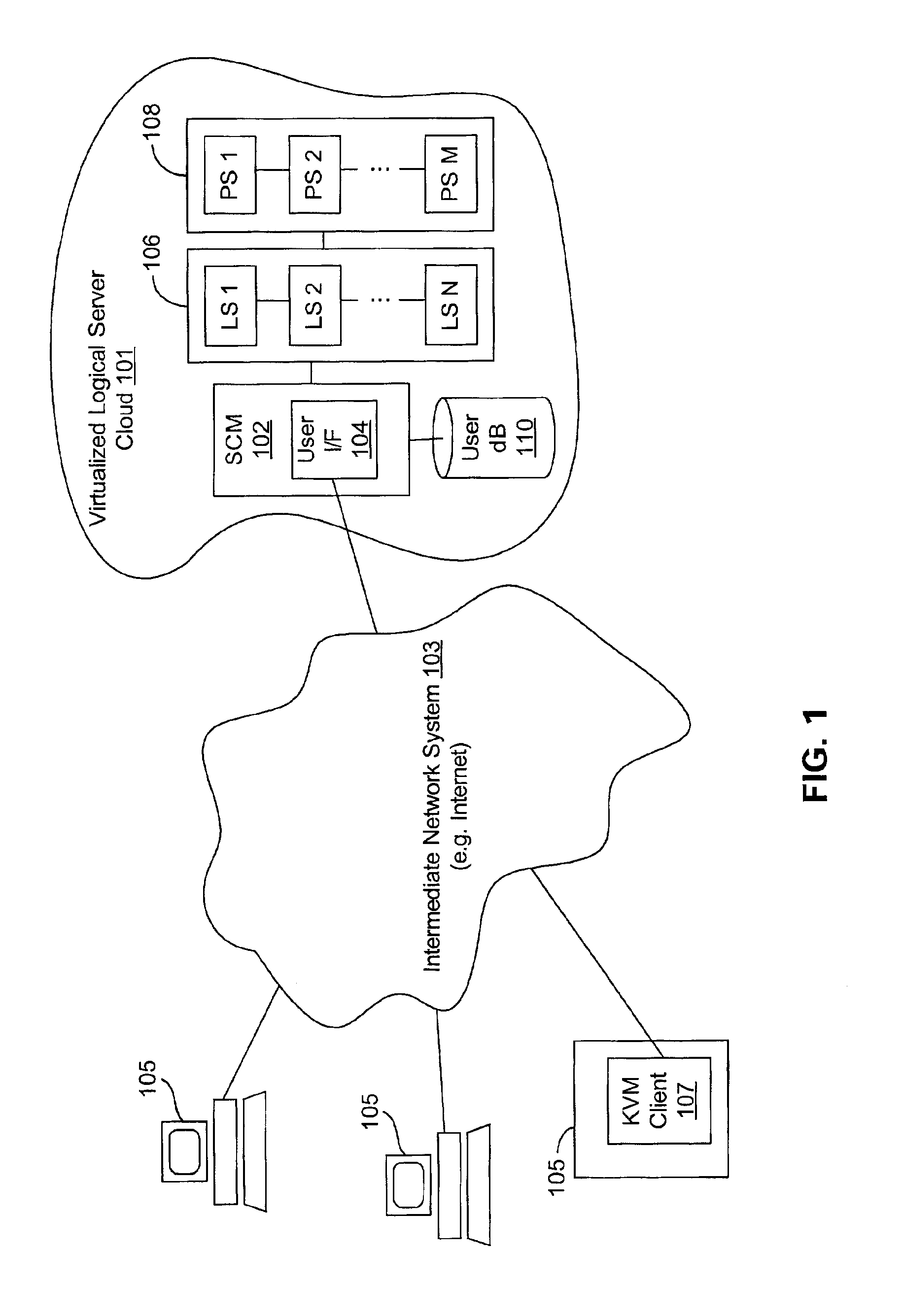
A virtualized logical server cloud that enables logical servers to exist independent of physical servers that instantiate the logical servers. Servers are treated as logical resources in order to create a logical server cloud. The logical attributes of a logical server are non-deterministically allocated to physical resources creating a cloud of logical servers over the physical servers. Logical separation is facilitated by the addition of a server cloud manager, which is an automated multi-server management layer. Each logical server has persistent attributes that establish its identity. Each physical server includes or is coupled to physical resources including a network resource, a data storage resource and a processor resource. At least one physical server executes virtualization software that virtualizes physical resources for logical servers. The server cloud manager maintains status and instance information for the logical servers including persistent and non-persistent attributes that link each logical server with a physical server.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
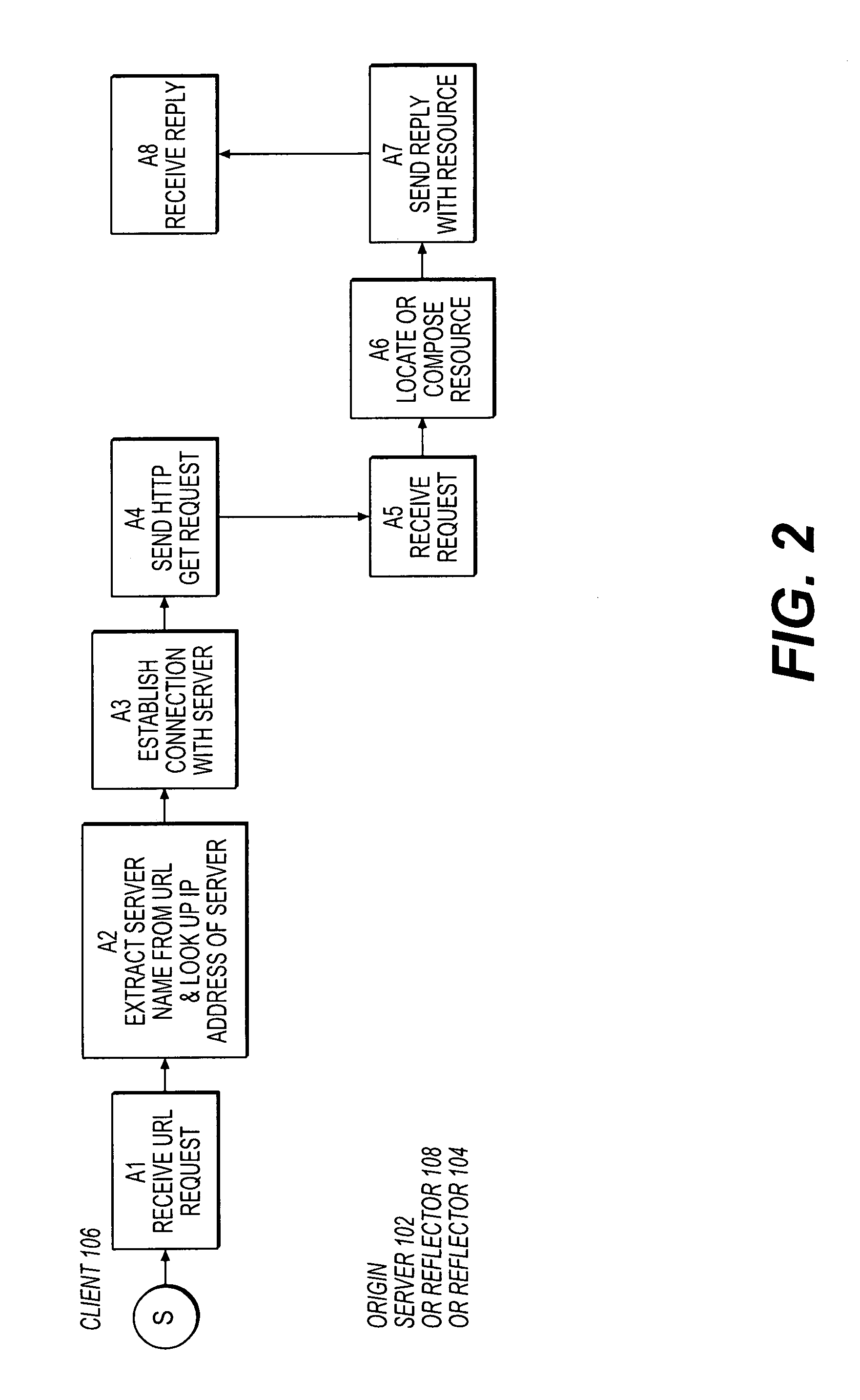
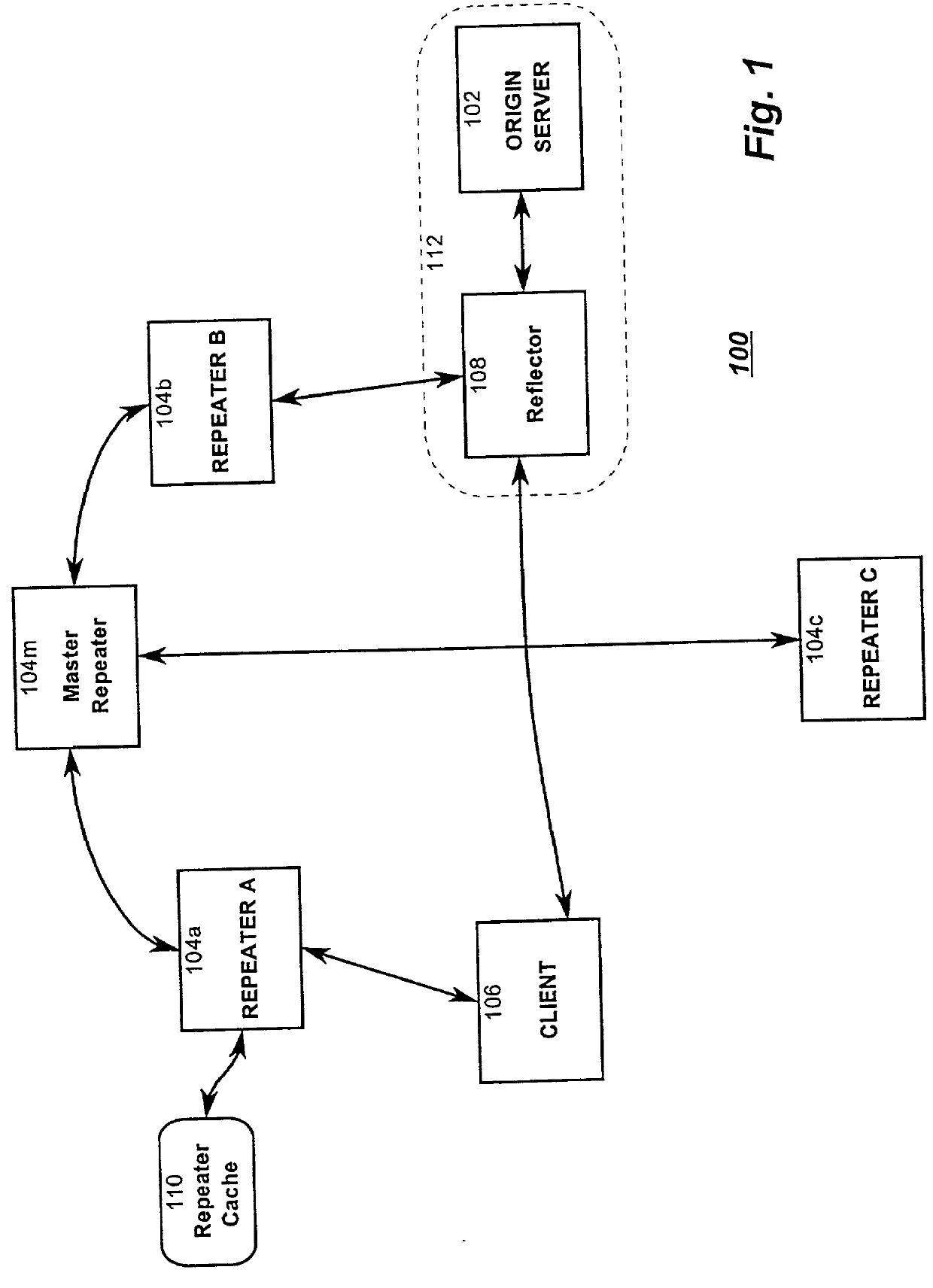
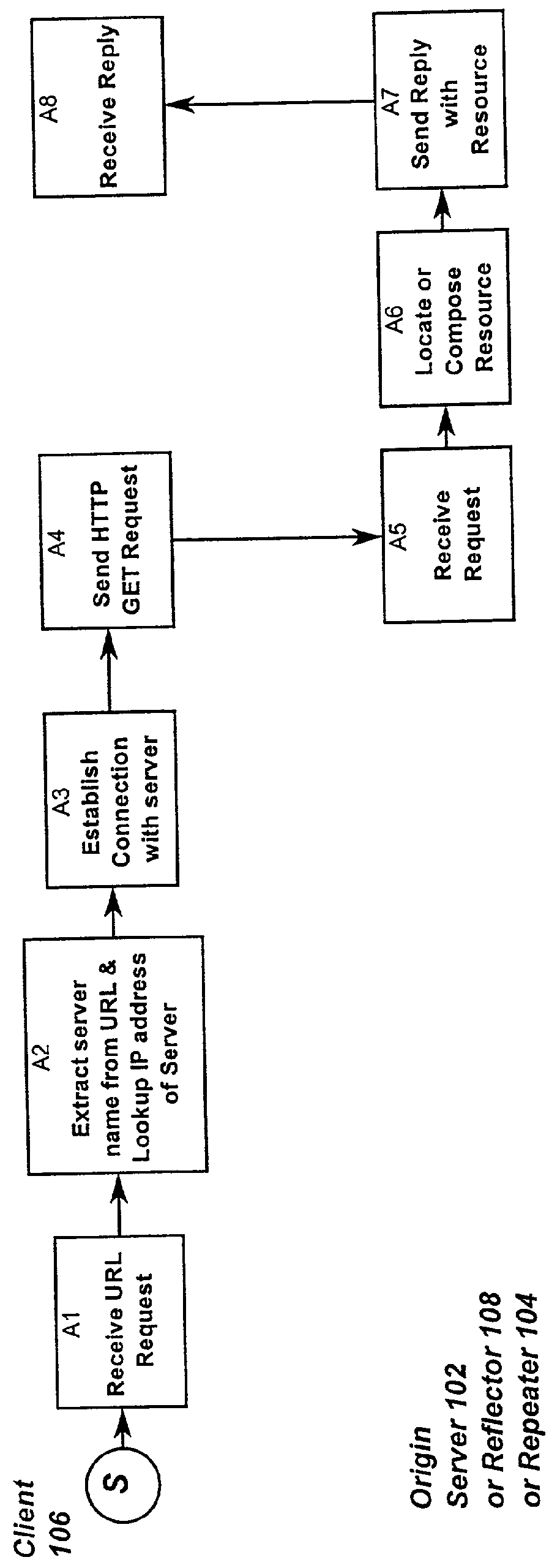
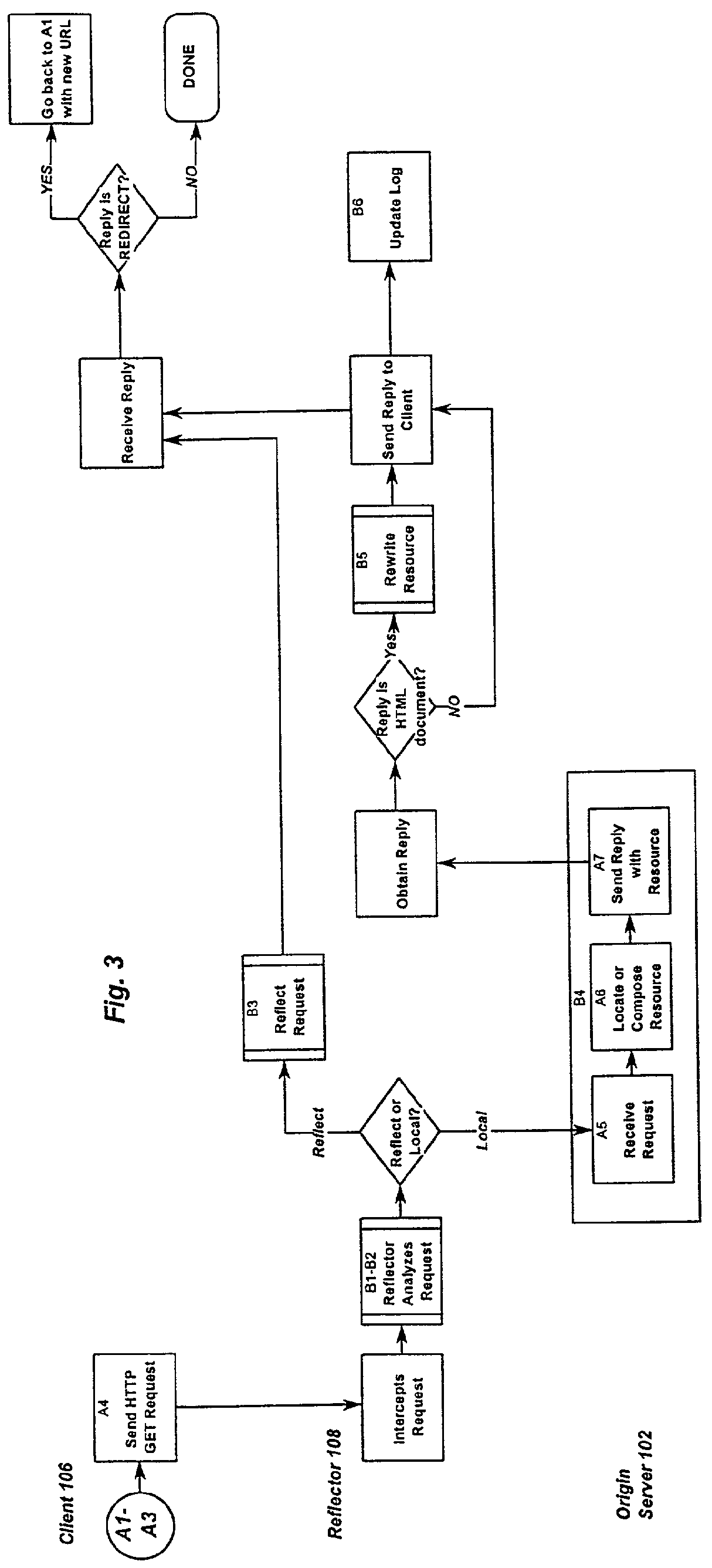
Optimized network resource location
InactiveUS20010056500A1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsEngineeringDistributed computing
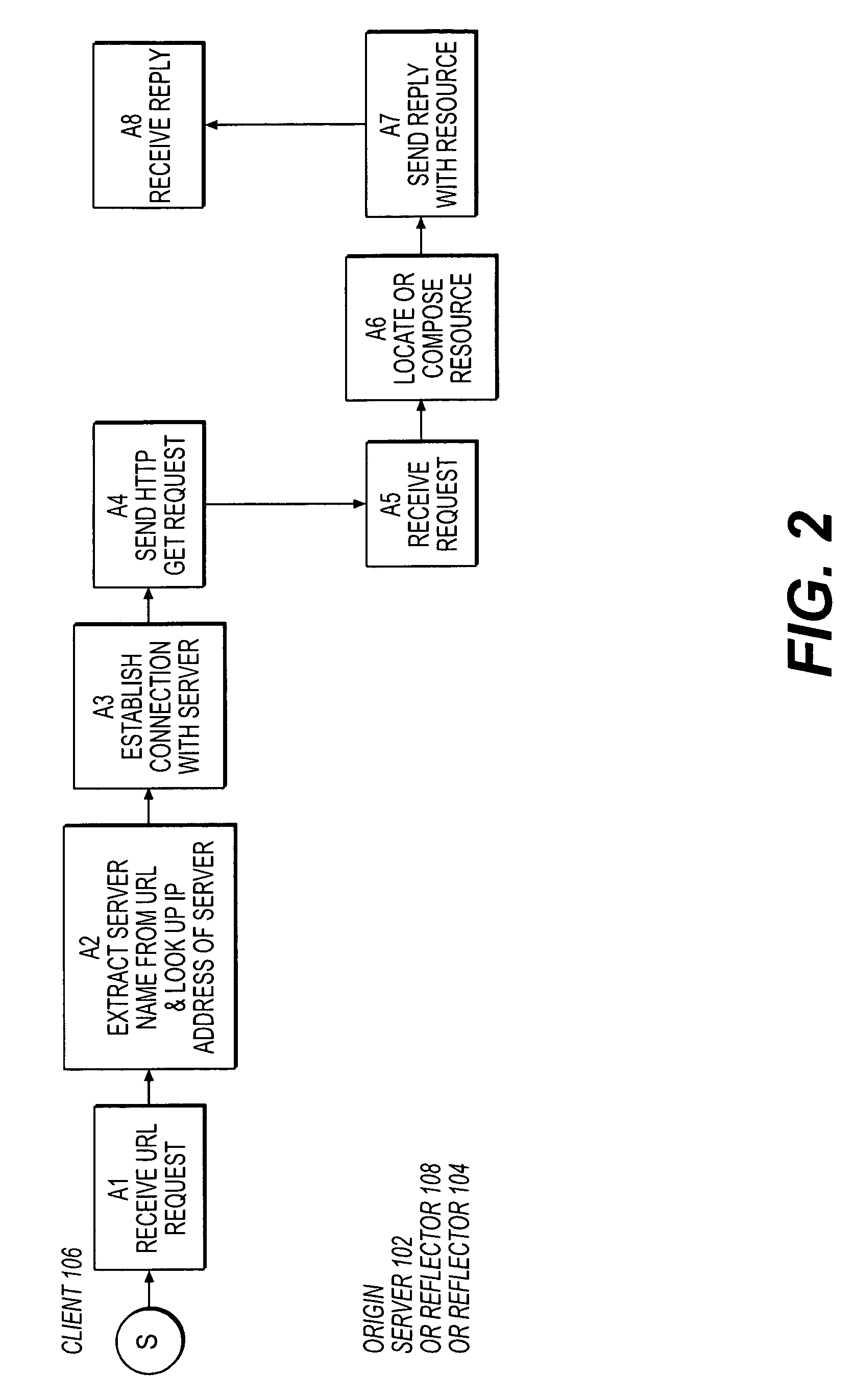
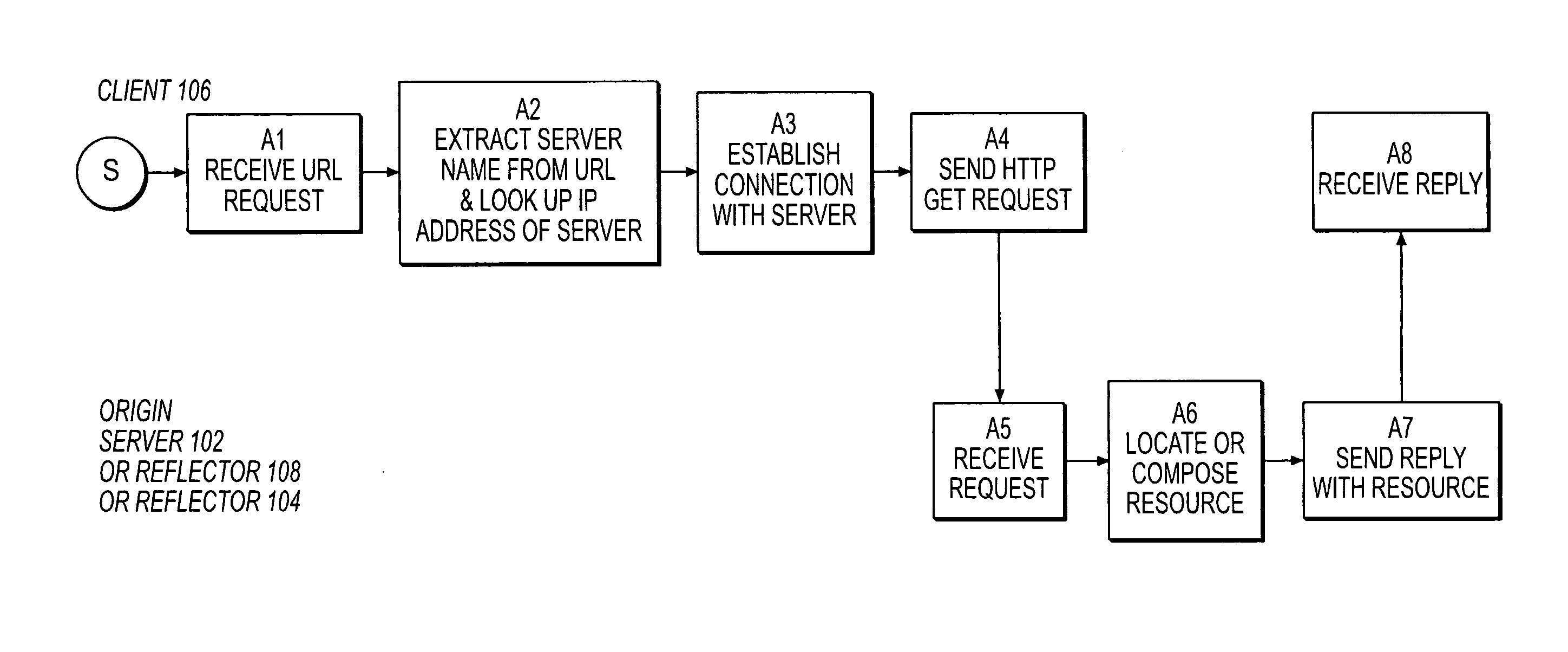
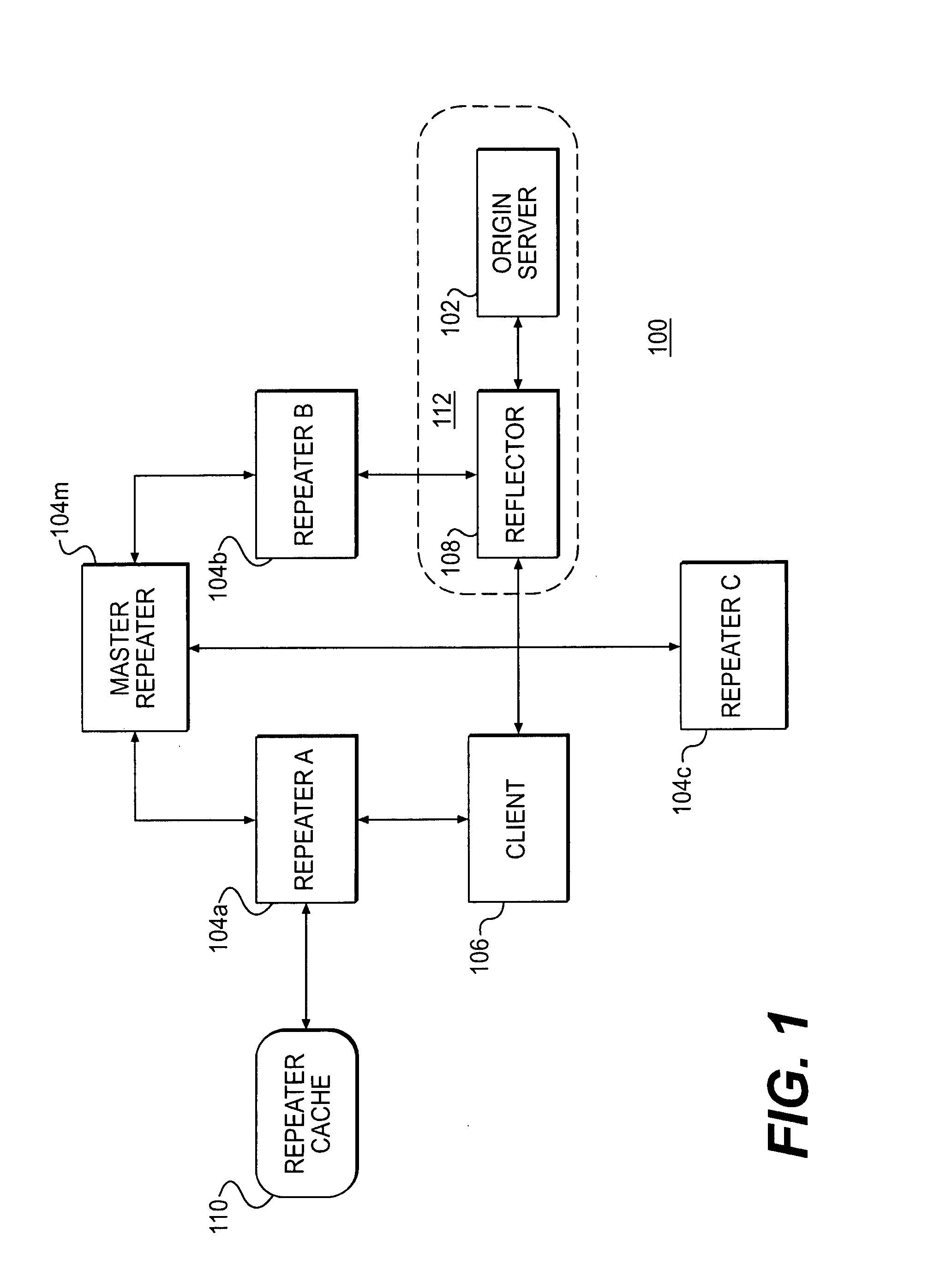
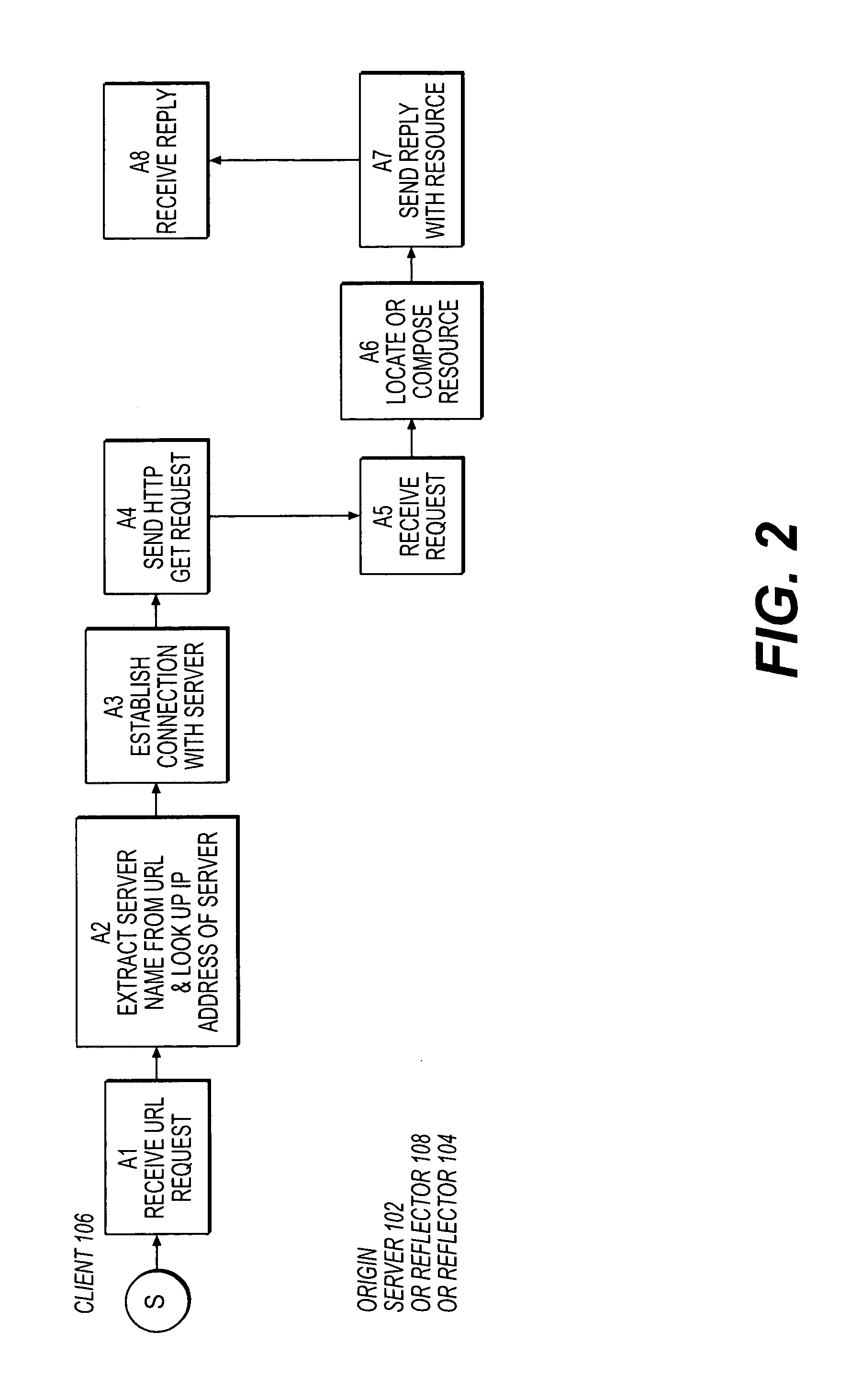
Resource requests made by clients of origin servers in a network are intercepted by reflector mechanisms and selectively reflected to other servers called repeaters. The reflectors select a best repeater from a set of possible repeaters and redirect the client to the selected best repeater. The client then makes the request of the selected best repeater. The resource is possibly rewritten to replace at least some of the resource identifiers contained therein with modified resource identifiers designating the repeater instead of the origin server.
Owner:DIGITAL ISLAND
System for monitoring and reporting performance of hosts and applications and selectively configuring applications in a resource managed system
ActiveUS7051098B2Program initiation/switchingResource allocationResource Management SystemMonitoring system
A monitoring system for a distributed environment including a plurality of hosts capable of executing multiple copies of a scalable application includes a first device for generating first data corresponding to performance of all copies of the scalable application; a second device for generating second data corresponding to performance of all host in the distributed environment; and a third device for generating performance metrics based on the first and second data.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Load balancing method in a communication network
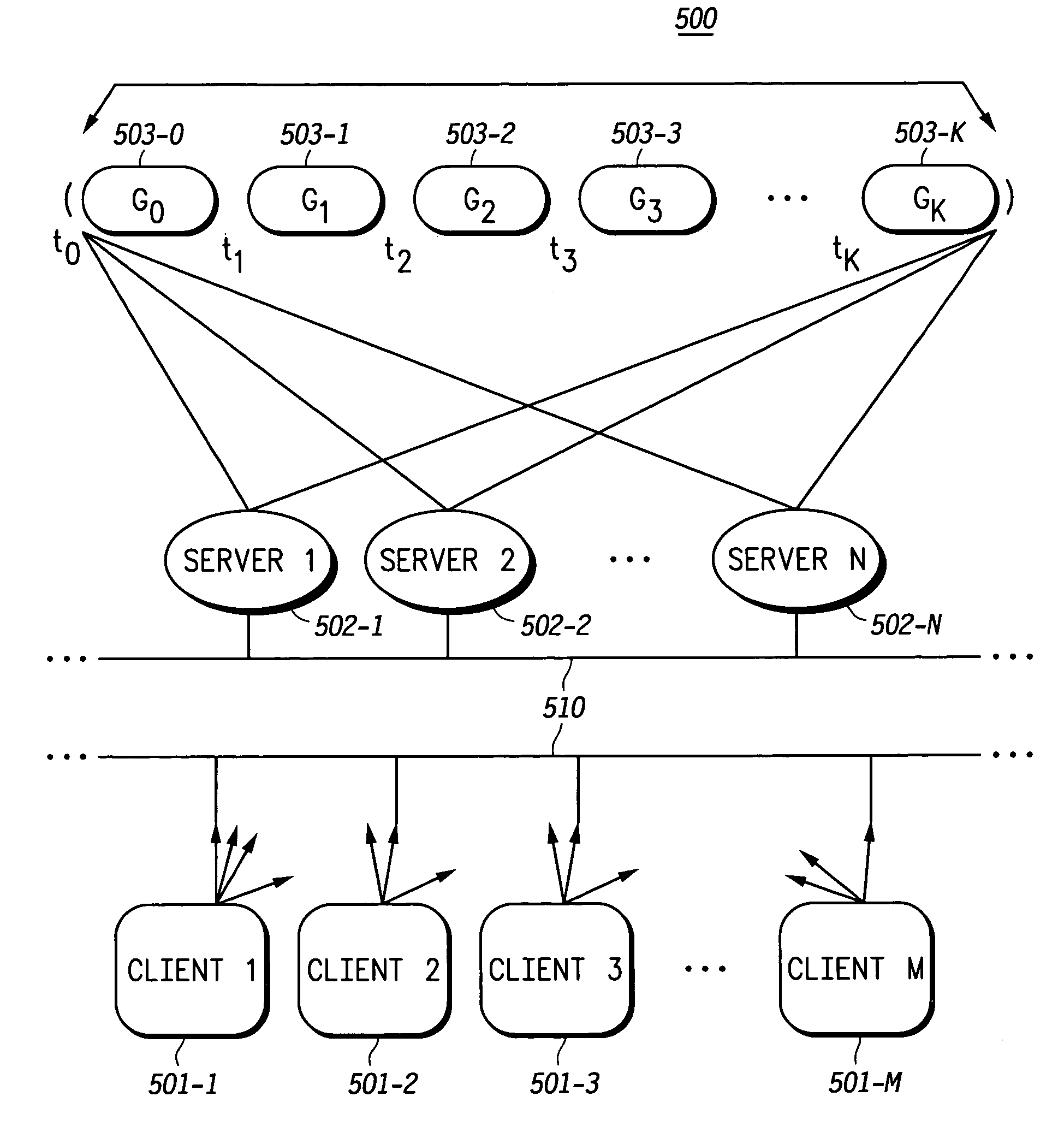
InactiveUS7062556B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemServer allocation
A communication system network (500) having a plurality of servers (502-1 through N), each having a load level based on serving a number of clients (501-1 through M), a method includes grouping plurality of servers (502-1 through N) into a plurality of server groups G0 through Gk (503-0 through k) respectively having load levels progressively from a least amount of load level to a most amount of load level, calculating a plurality of time periods T1 through Tk corresponding to the server groups G1 through Gk, assigning load to a server selected from the servers in the server group G0 from an initial time until expiration of the time period T1, after expiration of each of the time periods T1 through Tk measured from the initial time, load assignment takes place by assigning load to a server selected from the servers in the server groups from G0 and and at least one other server group, in server groups G1 through Gk, corresponding to an expiring time period.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Popular searches
Data switching by path configuration Interprogram communication Subscriber signalling identity devices Speech recognition Digital voice transmission telephone sets Special data processing applications Speech synthesis Web data browsing optimisation Devices with voice recognition Special service for subscribers
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com