Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1491 results about "Ring oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A ring oscillator is a device composed of an odd number of NOT gates in a ring, whose output oscillates between two voltage levels, representing true and false. The NOT gates, or inverters, are attached in a chain and the output of the last inverter is fed back into the first.
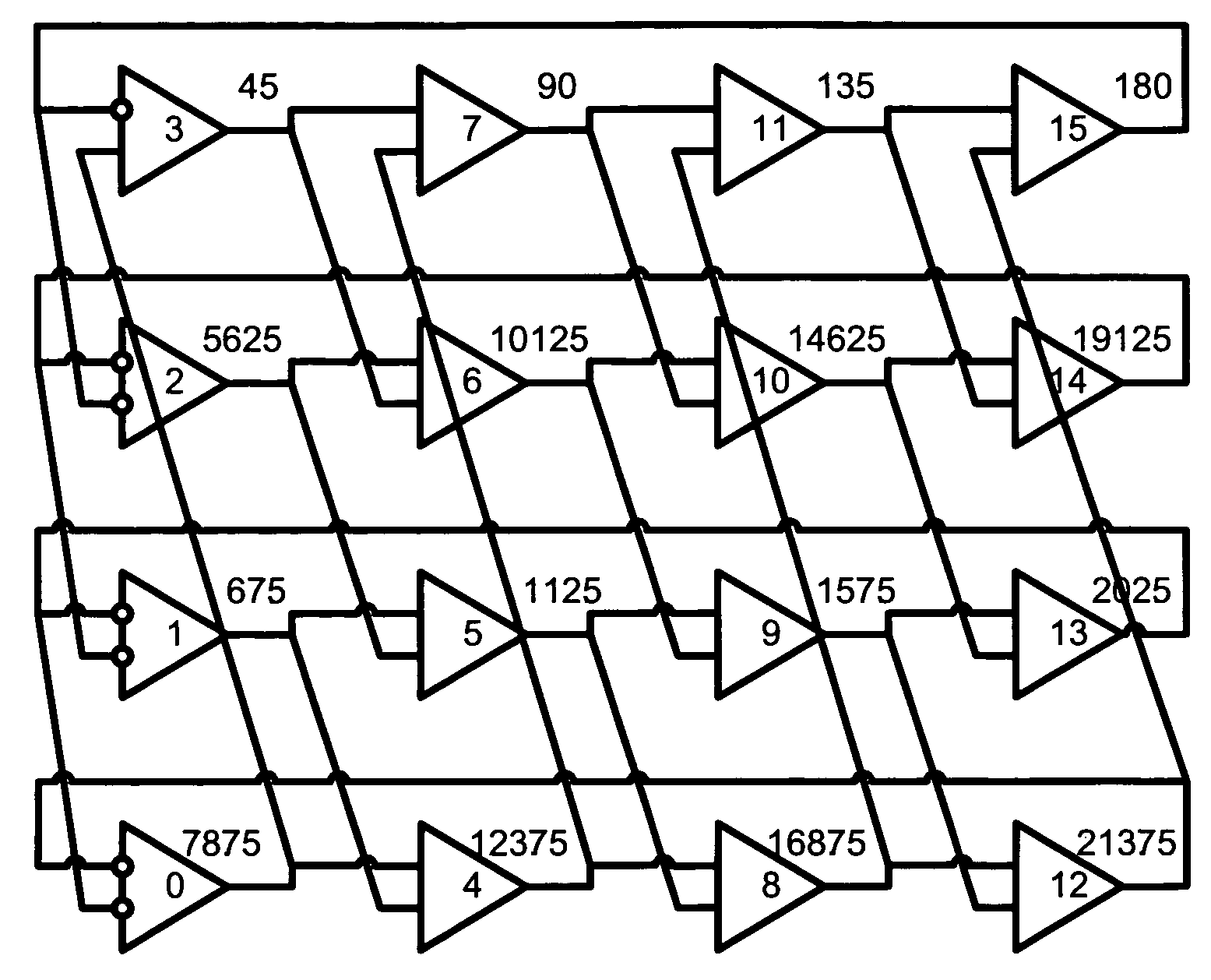
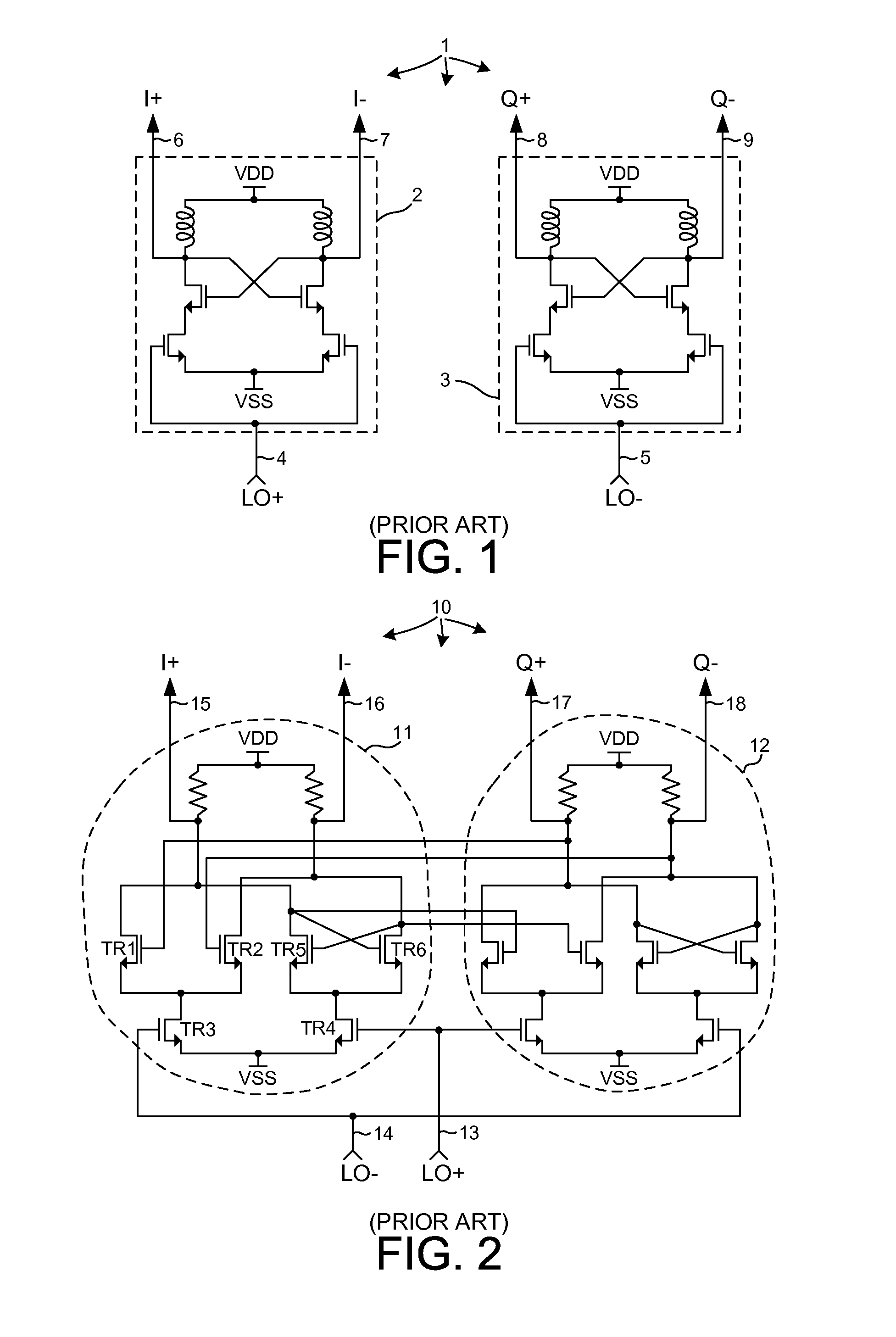
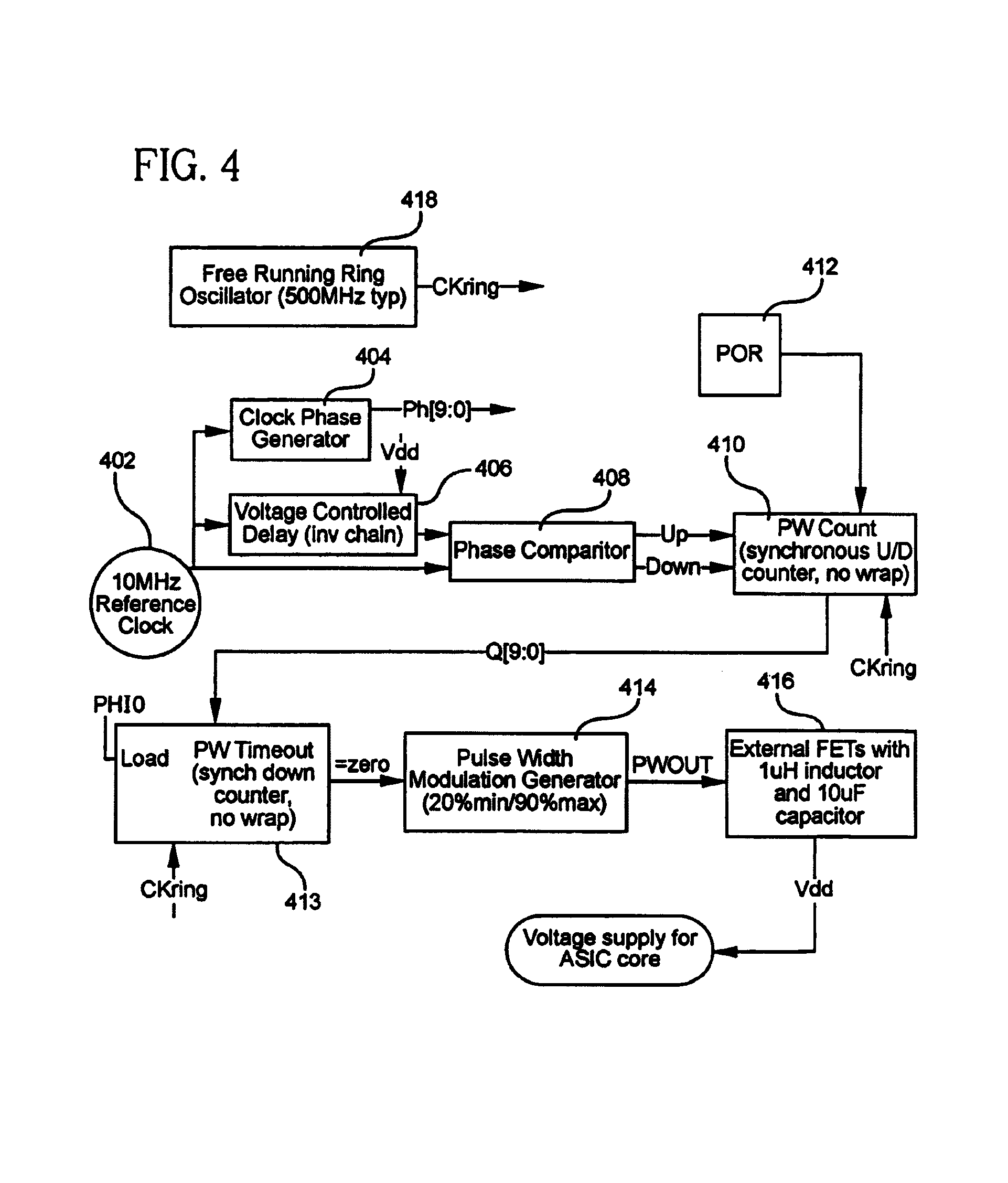
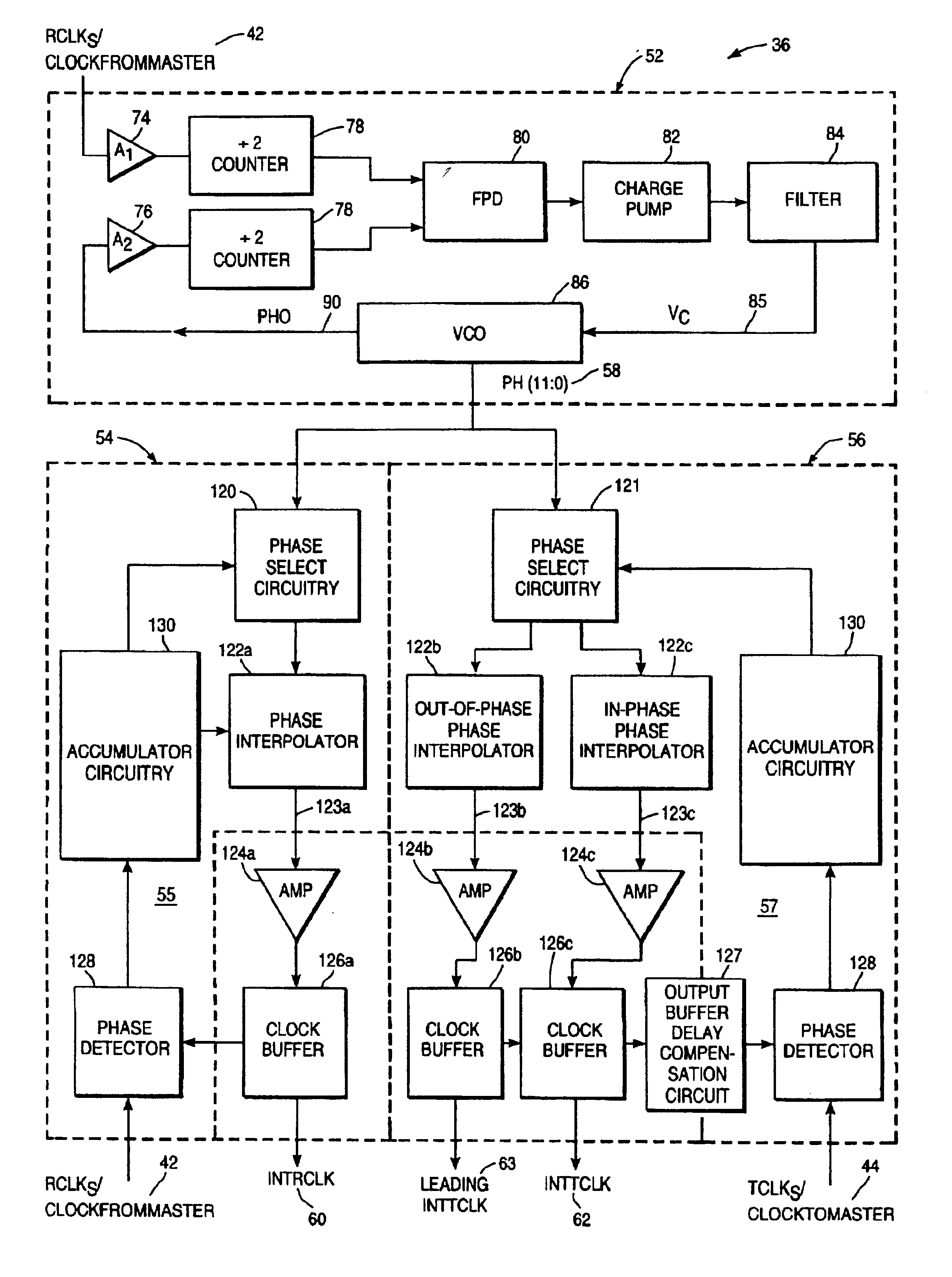
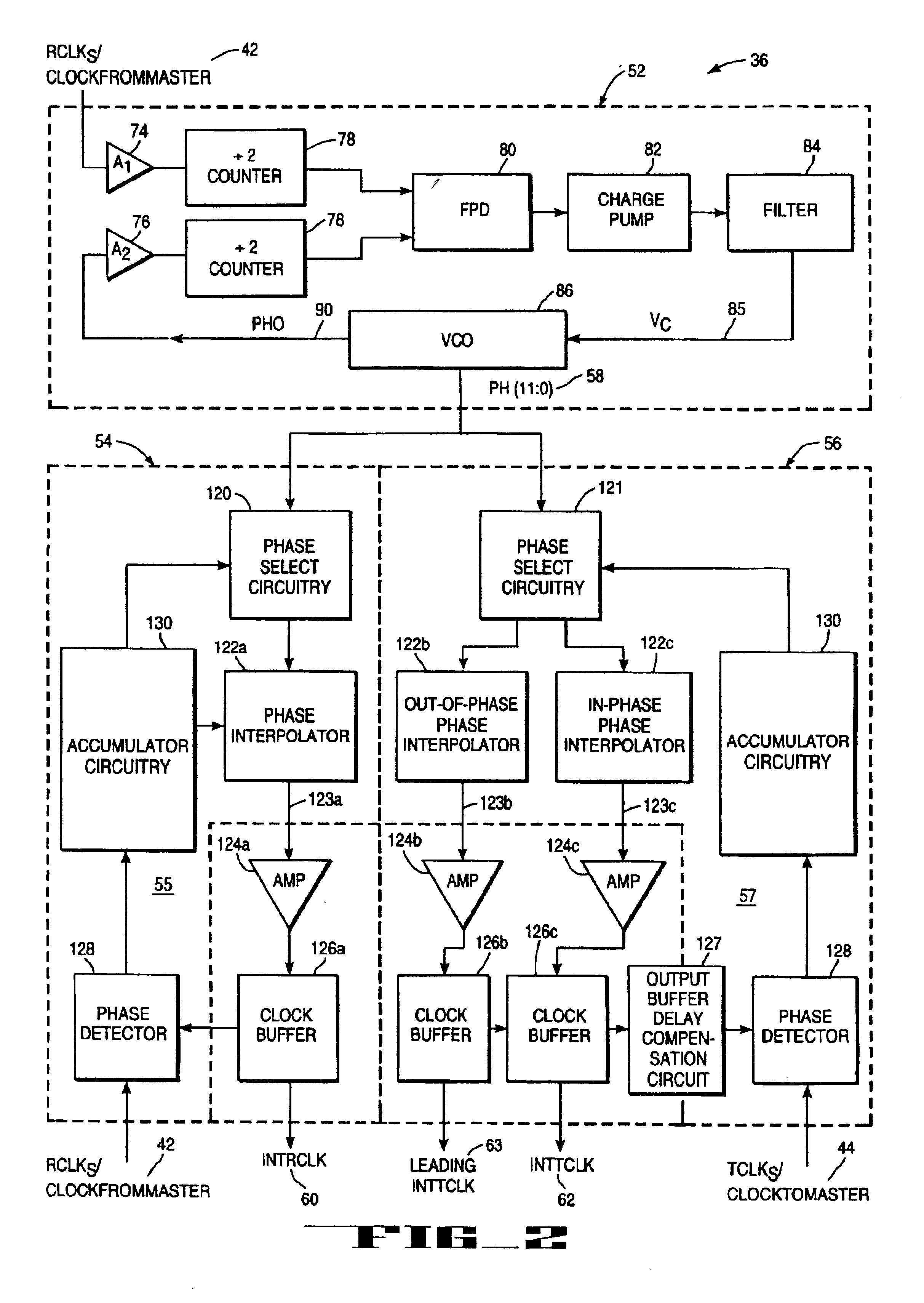
Array oscillator and polyphase clock generator
InactiveUS20060001496A1Increase speedReduce jitterPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsMOSFETMultiplexing
The present invention relates generally to array oscillator circuits for use as phase delay generators. More particularly, the present invention relates to a novel array oscillator for providing a plurality of phases which have stable phase relationships. The present invention is particularly applicable to the generation of poly-phase clocks for receivers of very high speed interfaces which employ an over-sampling technique, or multiplexing, and for high speed logic. The array oscillator according to the invention comprises at least one ring oscillator having a plurality of at least two interconnected buffer stages including at least one, or any integer odd number of inverting stages and a series of non-inverting stages, wherein the buffer stages are formed of N-type MOSFET transistors.
Owner:ACUID +1
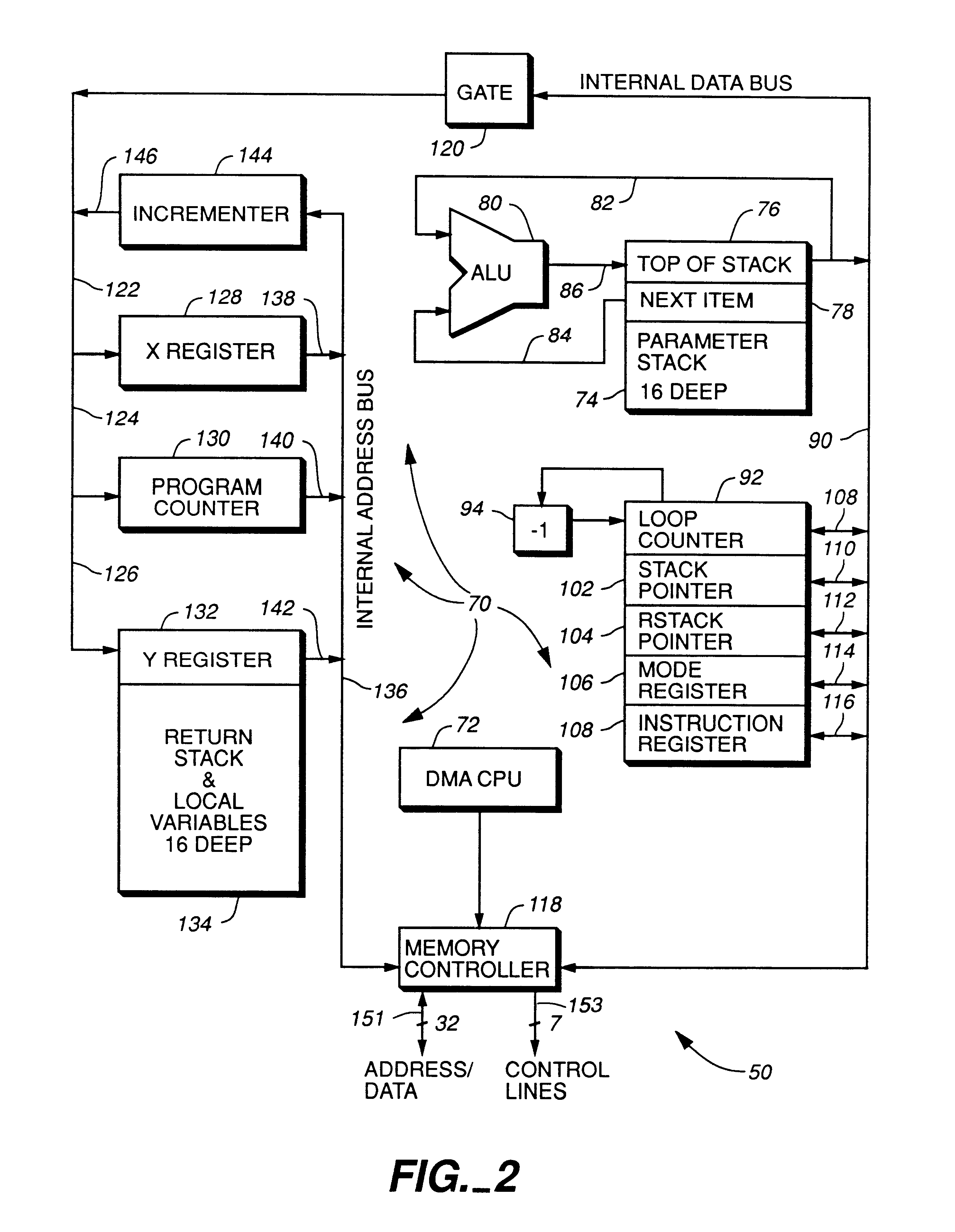
High performance microprocessor having variable speed system clock
InactiveUS6598148B1Improve performanceWithout sacrificing microprocessor speedRandom number generatorsInstruction analysisComputer architectureStatic random-access memory
A microprocessor integrated circuit including a processing unit disposed upon an integrated circuit substrate is disclosed herein. The processing unit is designed to operate in accordance with a predefined sequence of program instructions stored within an instruction register. A memory, capable of storing information provided by the processing unit and occupying a larger area of the integrated circuit substrate than the processing unit, is also provided within the microprocessor integrated circuit. The memory may be implemented using, for example dynamic or static random-access memory. A variable output frequency system clock, such as generated by a ring oscillator, is also disposed on the integrated circuit substrate.
Owner:MOORE CHARLES H TTE UTD 03 21 2006 THE EQUINOX TRUST
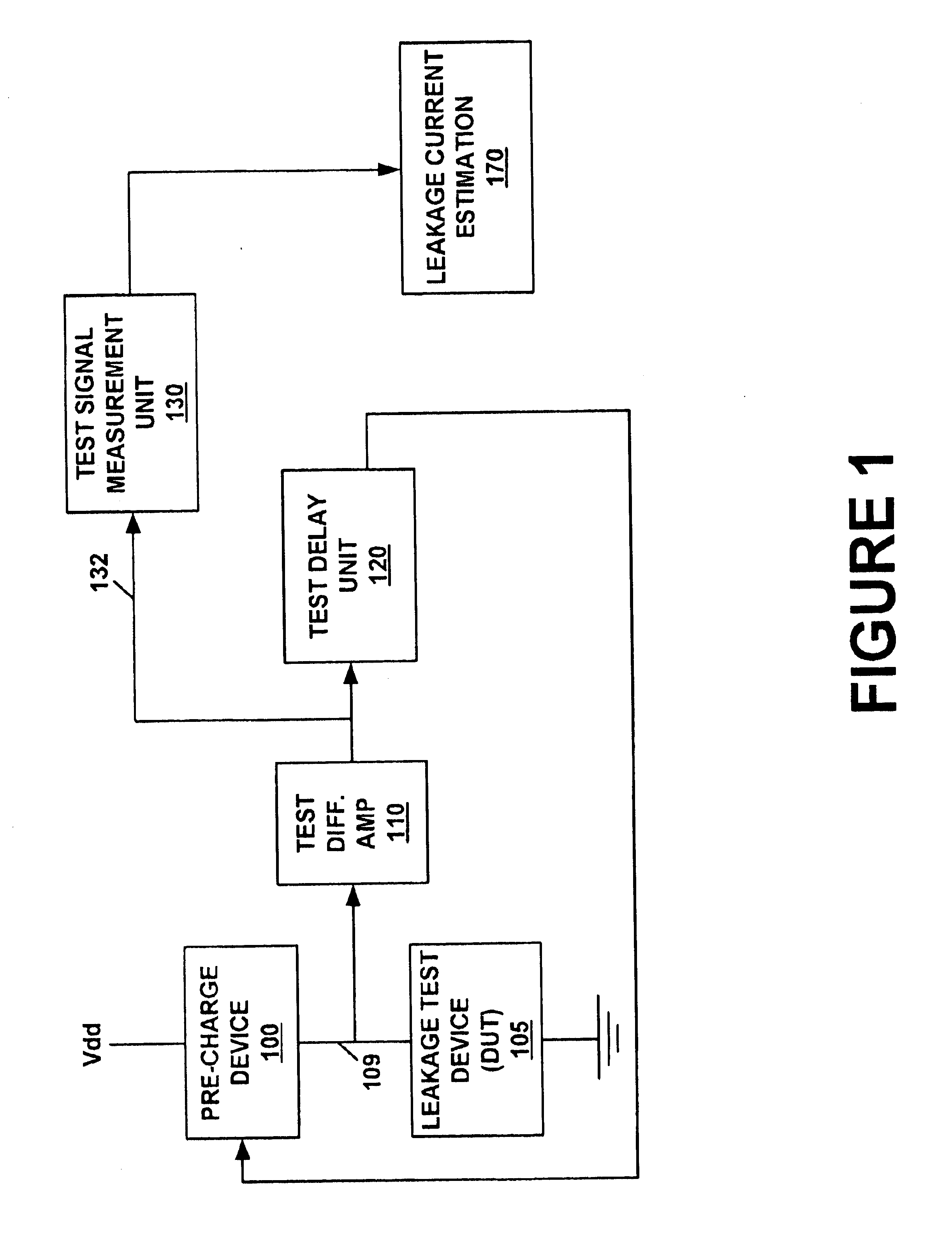
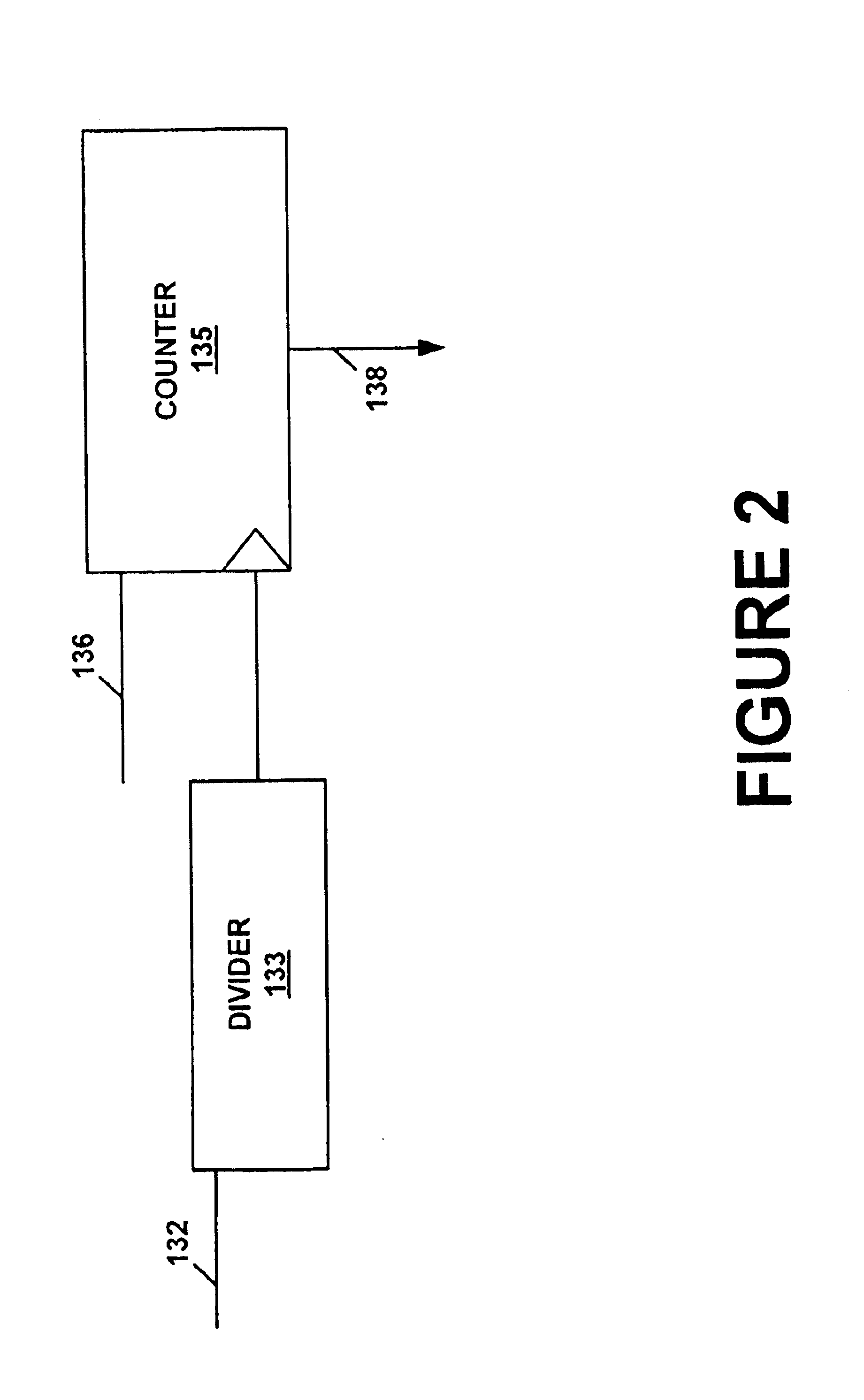
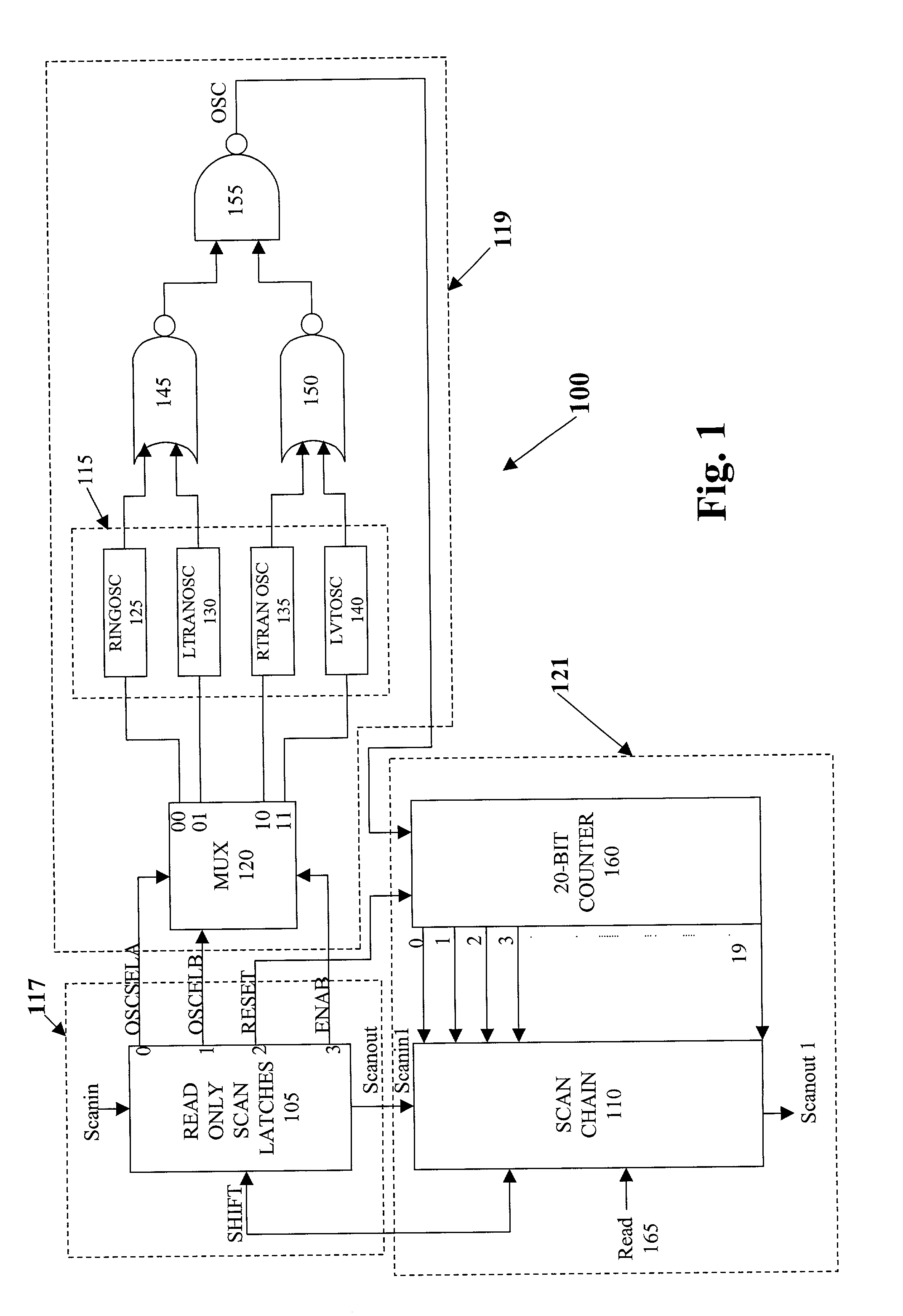
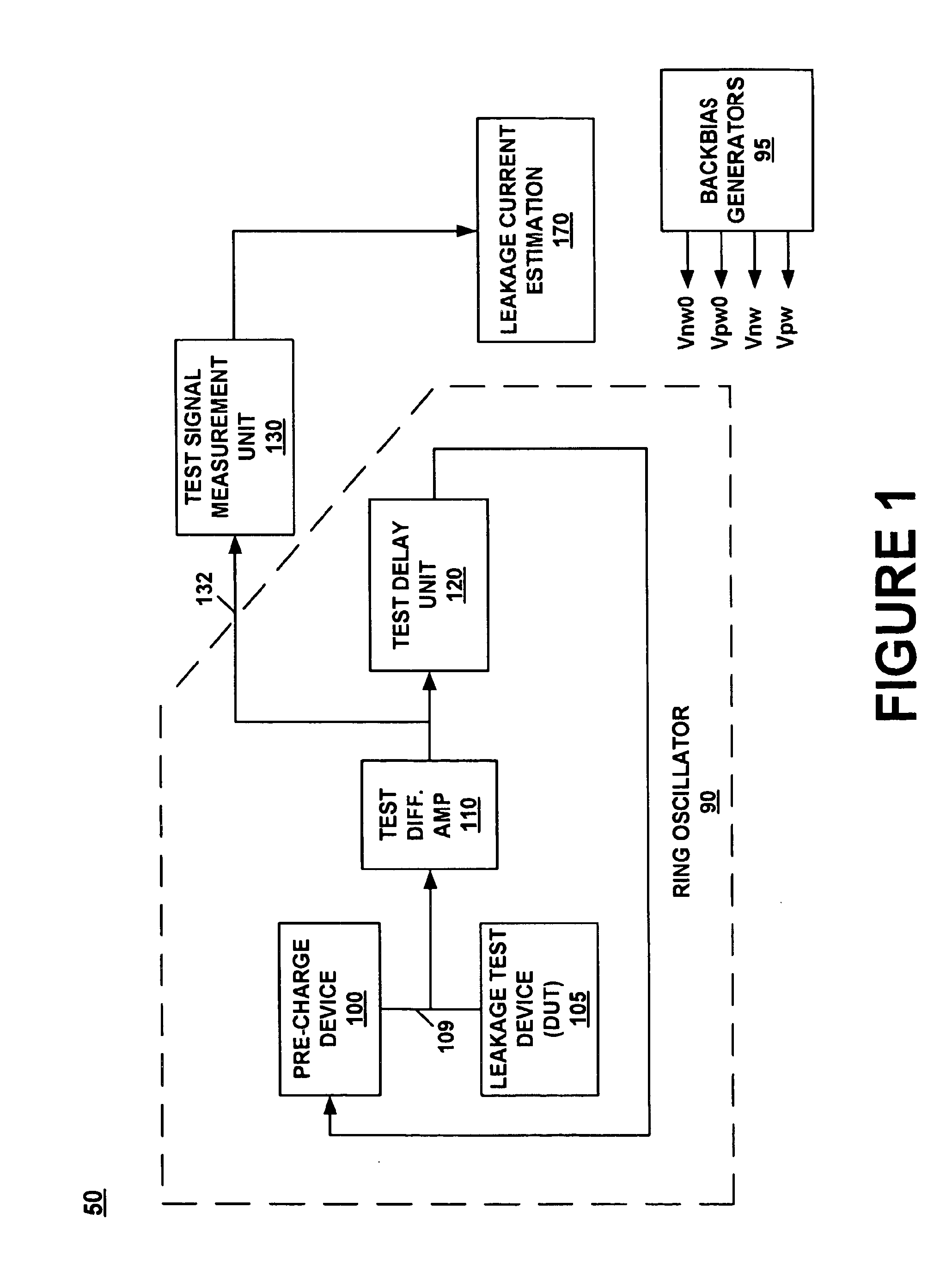
System and method for measuring transistor leakage current with a ring oscillator
InactiveUS6882172B1Accurate measurementAccurately leakage currentElectronic circuit testingShort-circuit testingLeakage testDrain current
A method of measuring the transistor leakage current. In one embodiment, the method involves driving a ring oscillator with a dynamic node driver having a leakage test device biased to an off state to produce a test signal. The test signal is extracted and the frequency is measured. The leakage current is estimated from the measured frequency.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
On-chip transistor degradation monitoring
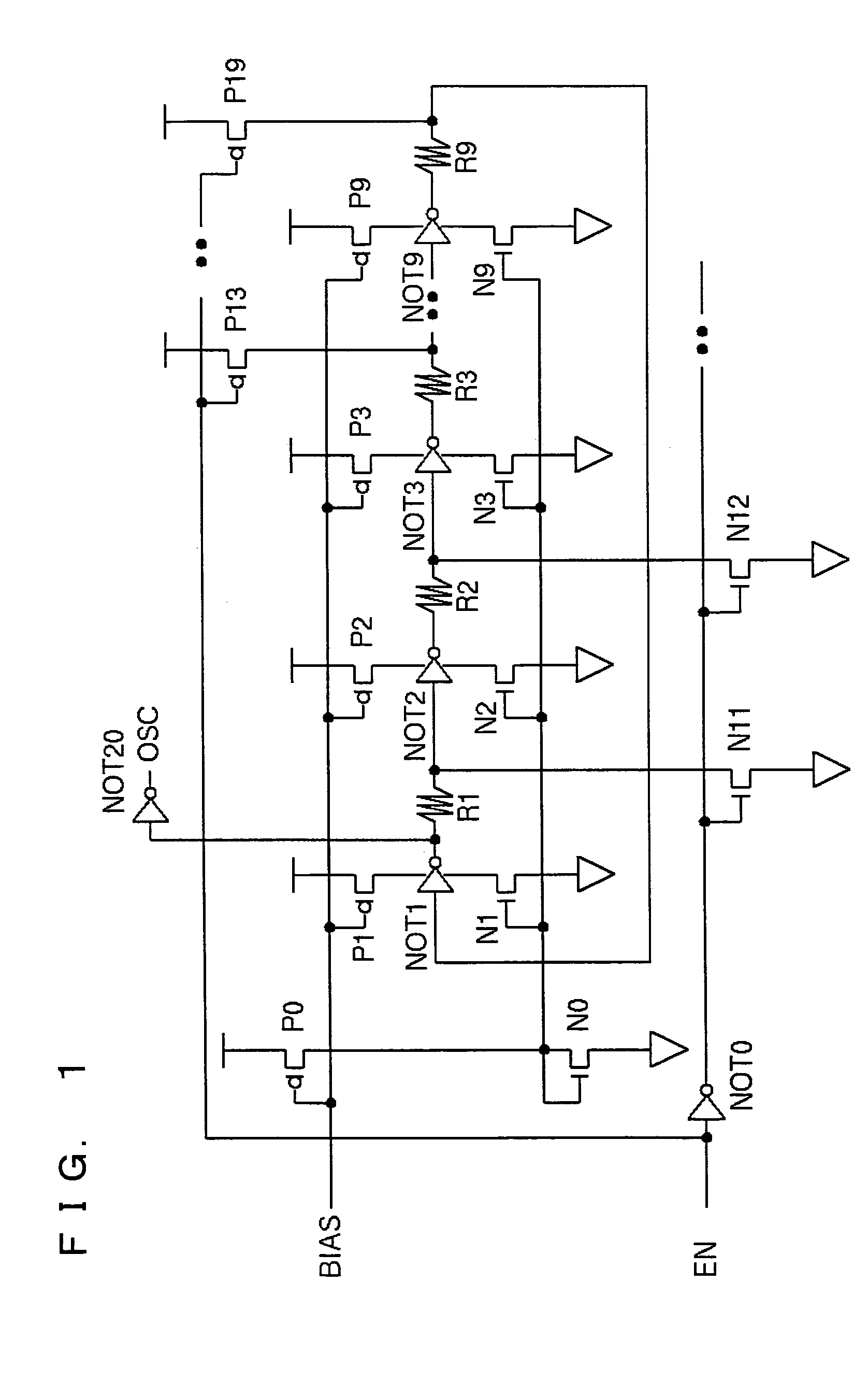
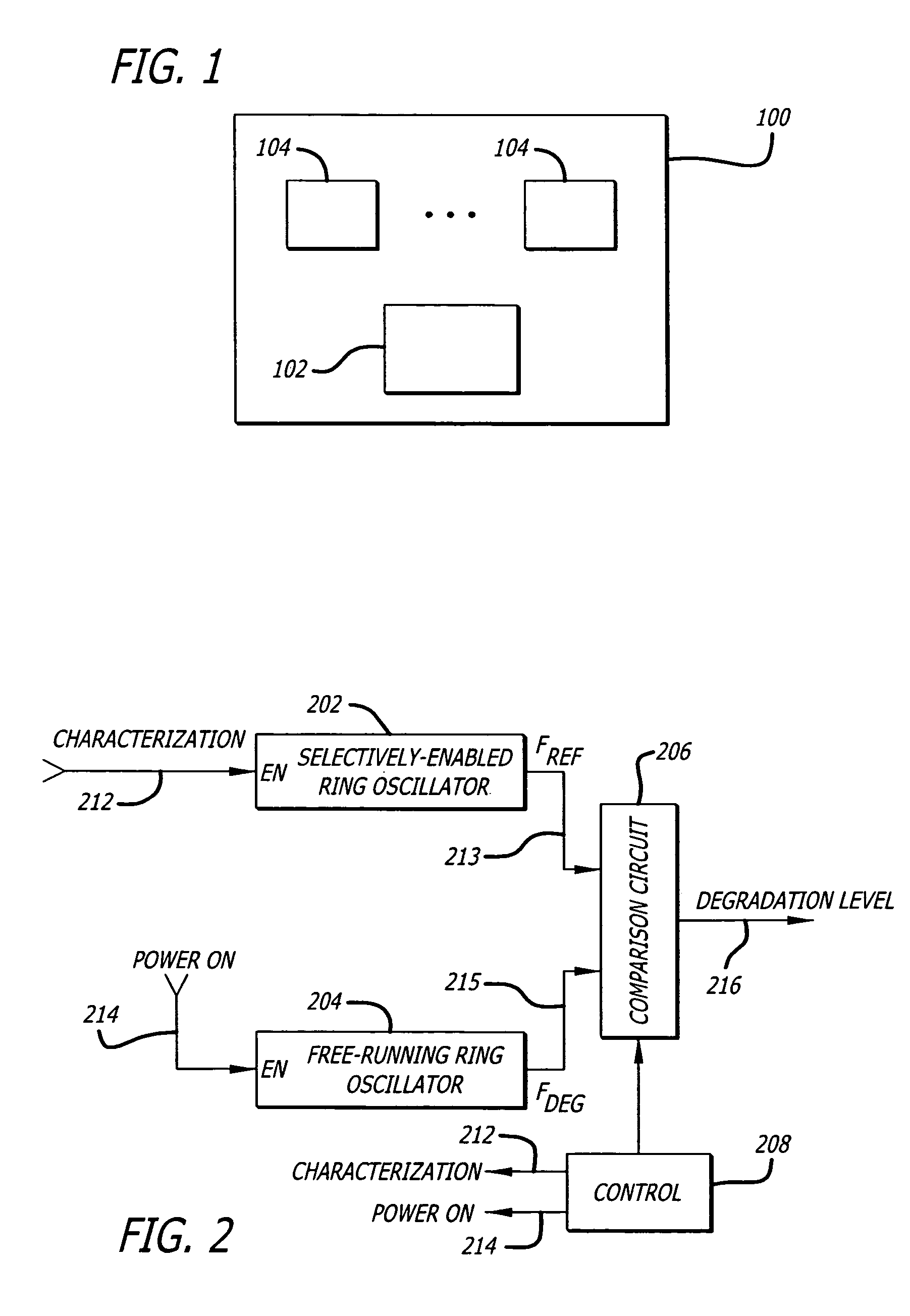
InactiveUS20050134394A1Digital circuit testingPulse generation by logic circuitsEngineeringRing oscillator
Embodiments of the invention include on-chip characterization of transistor degradation. In one embodiment, includes one or more functional blocks to perform one or more functions and an integrated on-chip characterization circuit to perform on-chip characterization of transistor degradation. The integrated on-chip characterization circuit includes a selectively enabled ring oscillator to generate a reference oscillating signal, a free-running ring oscillator to generate a free-running oscillating signal, and a comparison circuit coupled to the selectively enabled ring oscillator and the free-running ring oscillator. From the reference oscillating signal and the free-running oscillating signal, the comparison circuit determine a measure of transistor degradation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
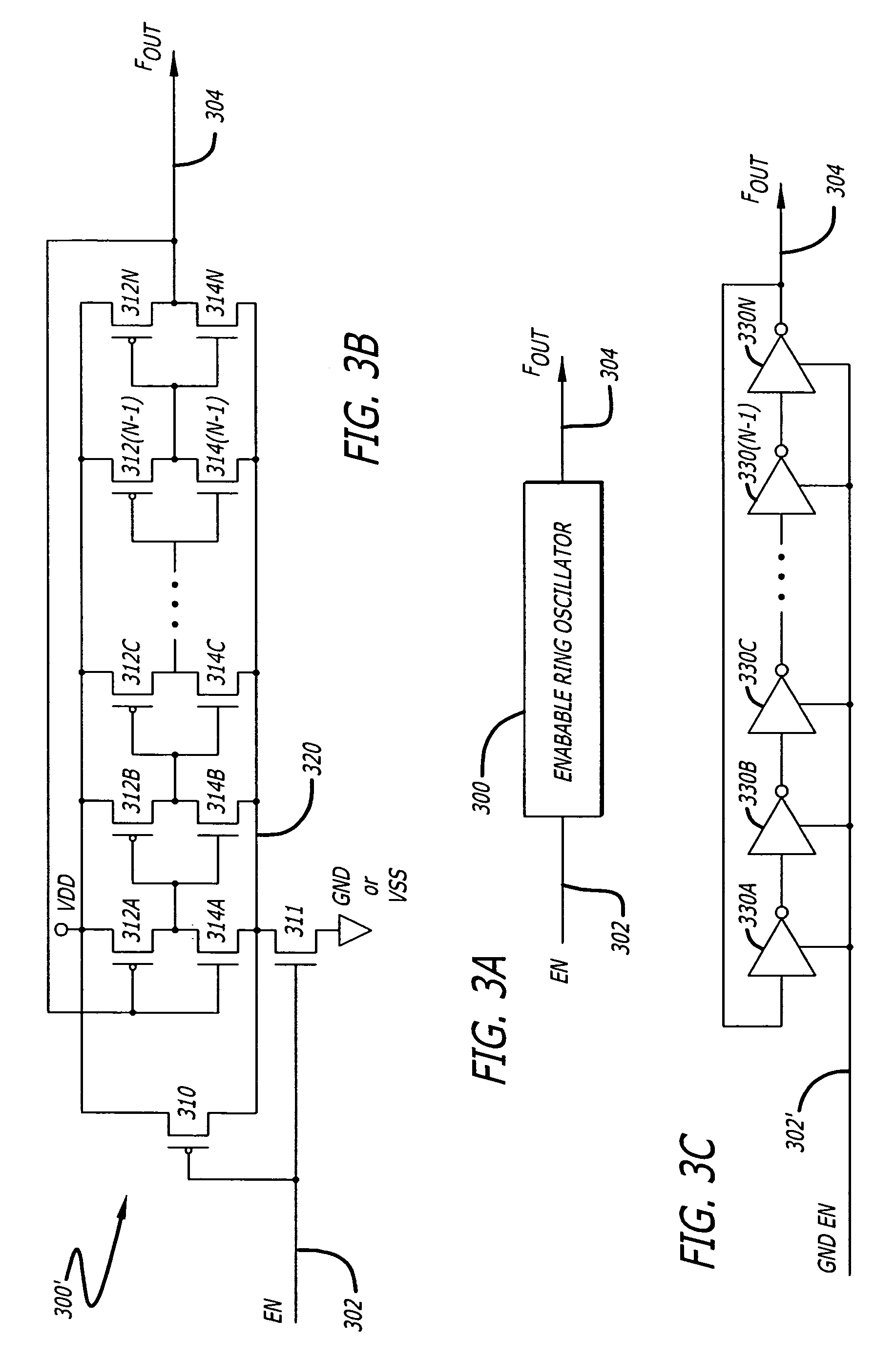
Scan based multiple ring oscillator structure for on-chip speed measurement
The present invention bundles four ring oscillators, a 20-bit ripple counter and the necessary control logic needed to implement a JTAG scan based interface. The present system can be located on every die, so that each location can be individually tested. It communicates with the outside world through a standard JTAG interface. It is accessible at wafer, package, and system test which allows for several methods of correlating the oscillator speed to the speed of a part in the actual system.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
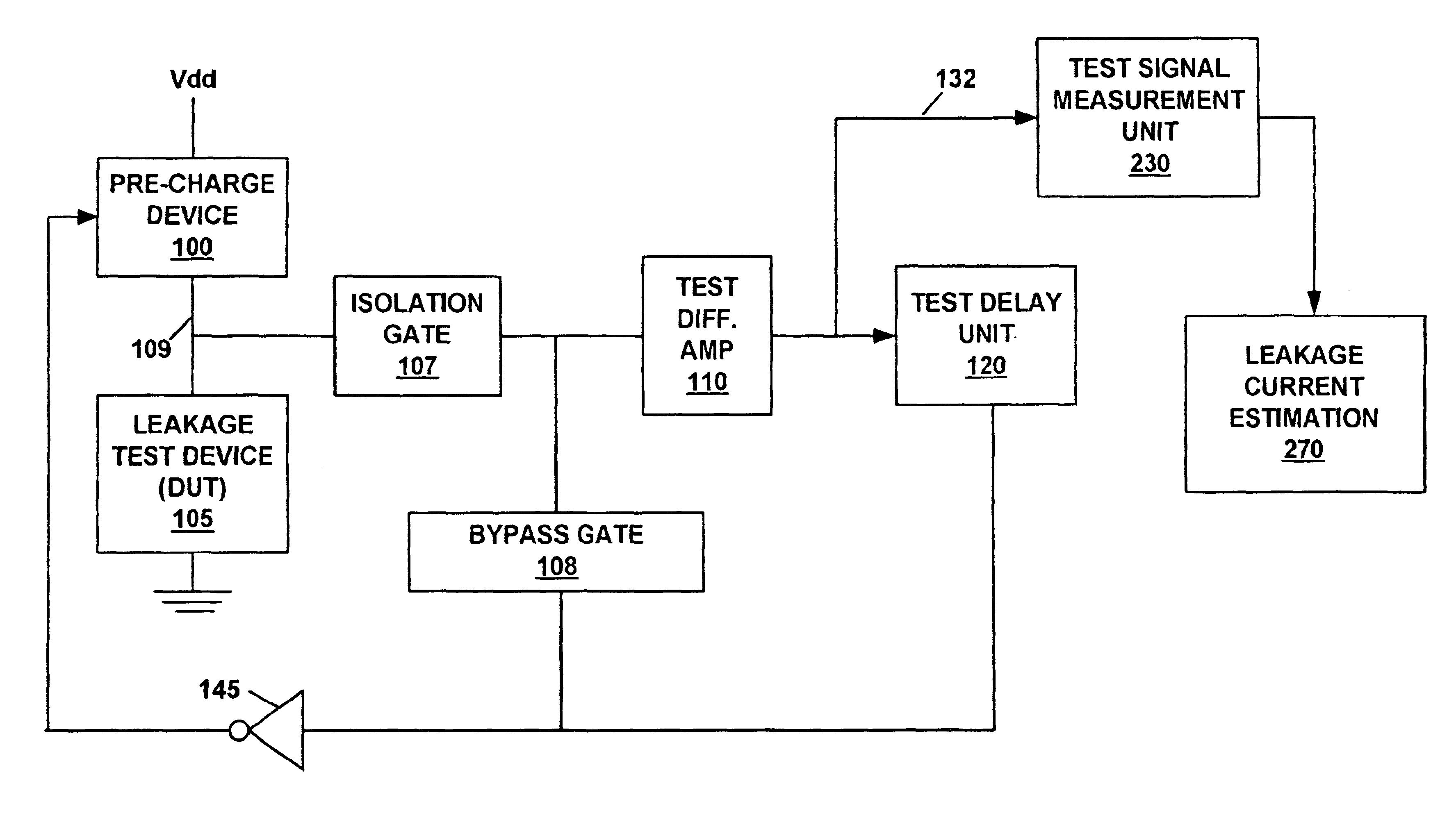
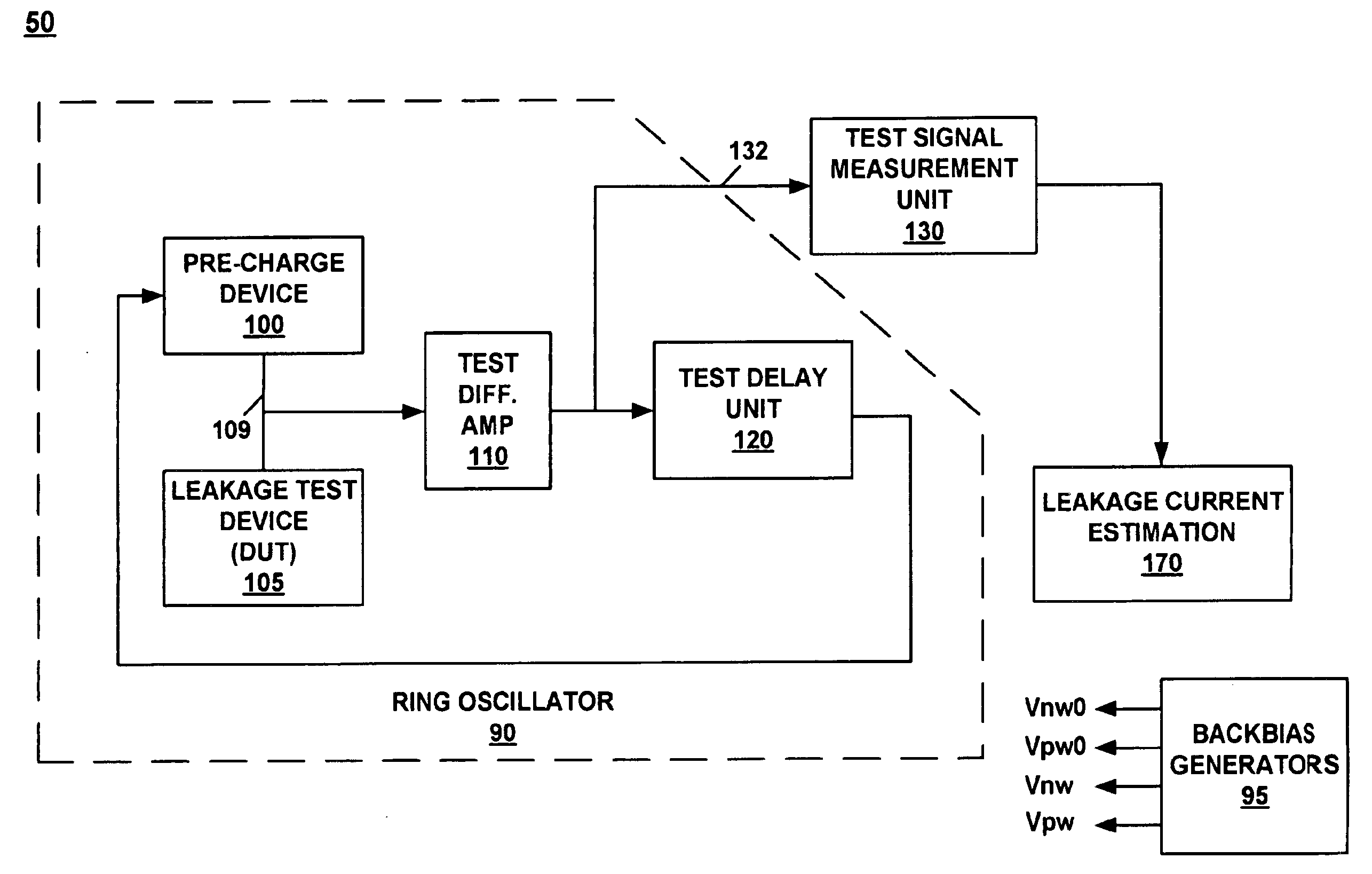
System and method for measuring transistor leakage current with a ring oscillator with backbias controls
A circuit and method thereof for measuring leakage current are described. The circuit includes a pre-charge device subject to a first backbias voltage and a leakage test device subject to a second backbias voltage. The leakage test device is coupled to the pre-charge device. The leakage test device is biased to an off state. A differential amplifier is coupled to the pre-charge device and the leakage test device. A delay unit is coupled to the differential amplifier and to an input of the pre-charge device. The pre-charge device is turned on and off at a frequency that corresponds to said leakage current.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
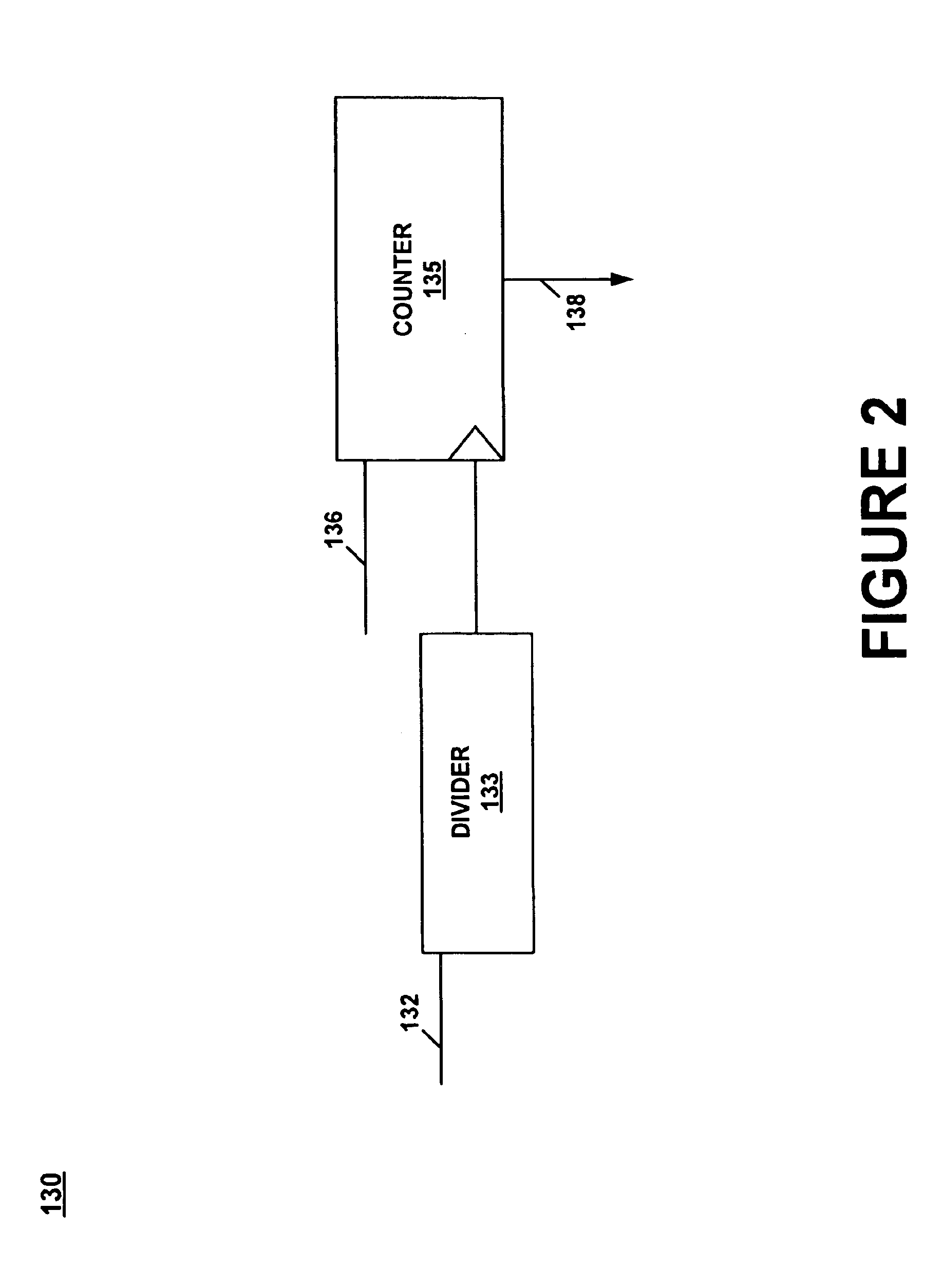
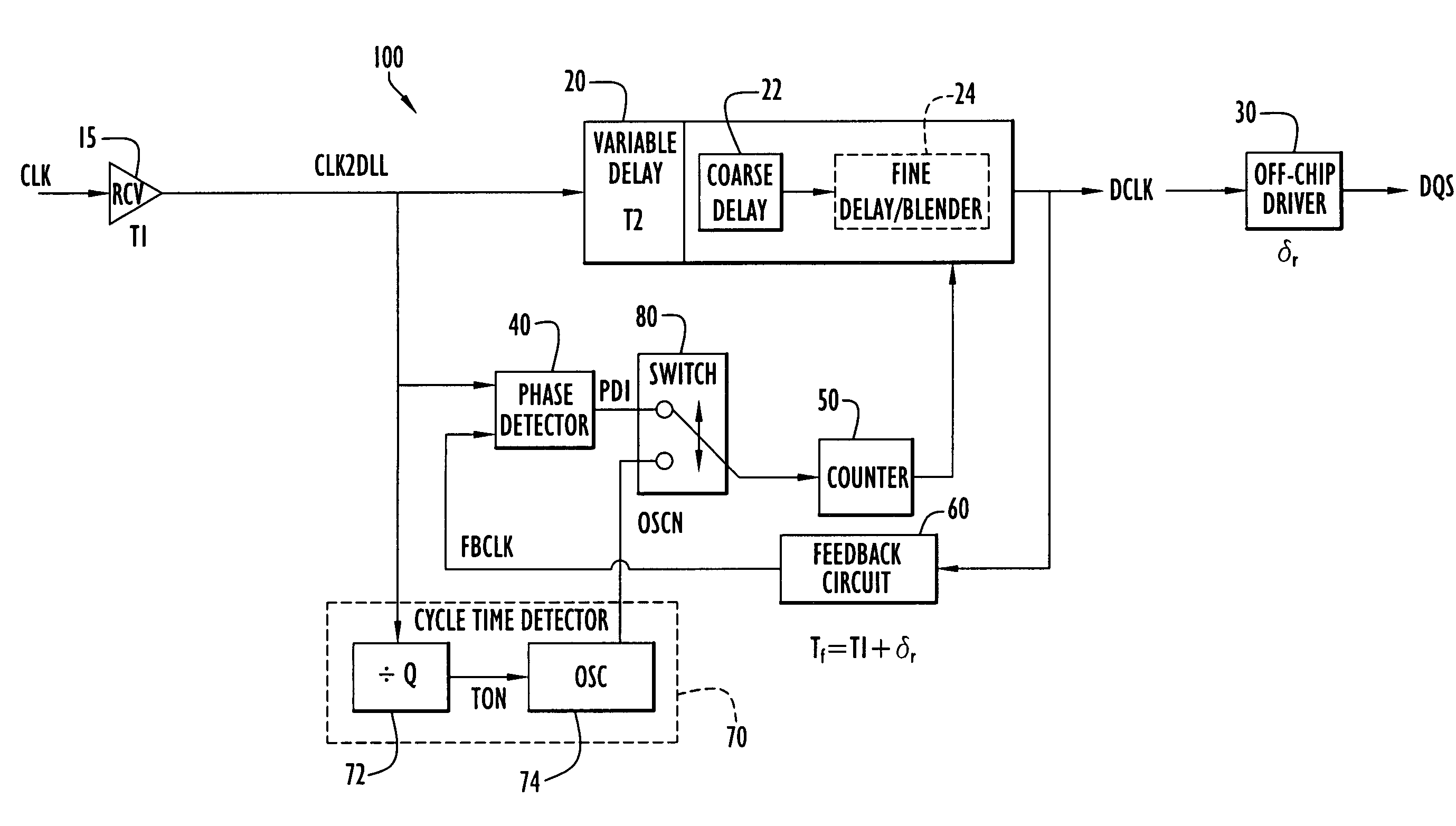
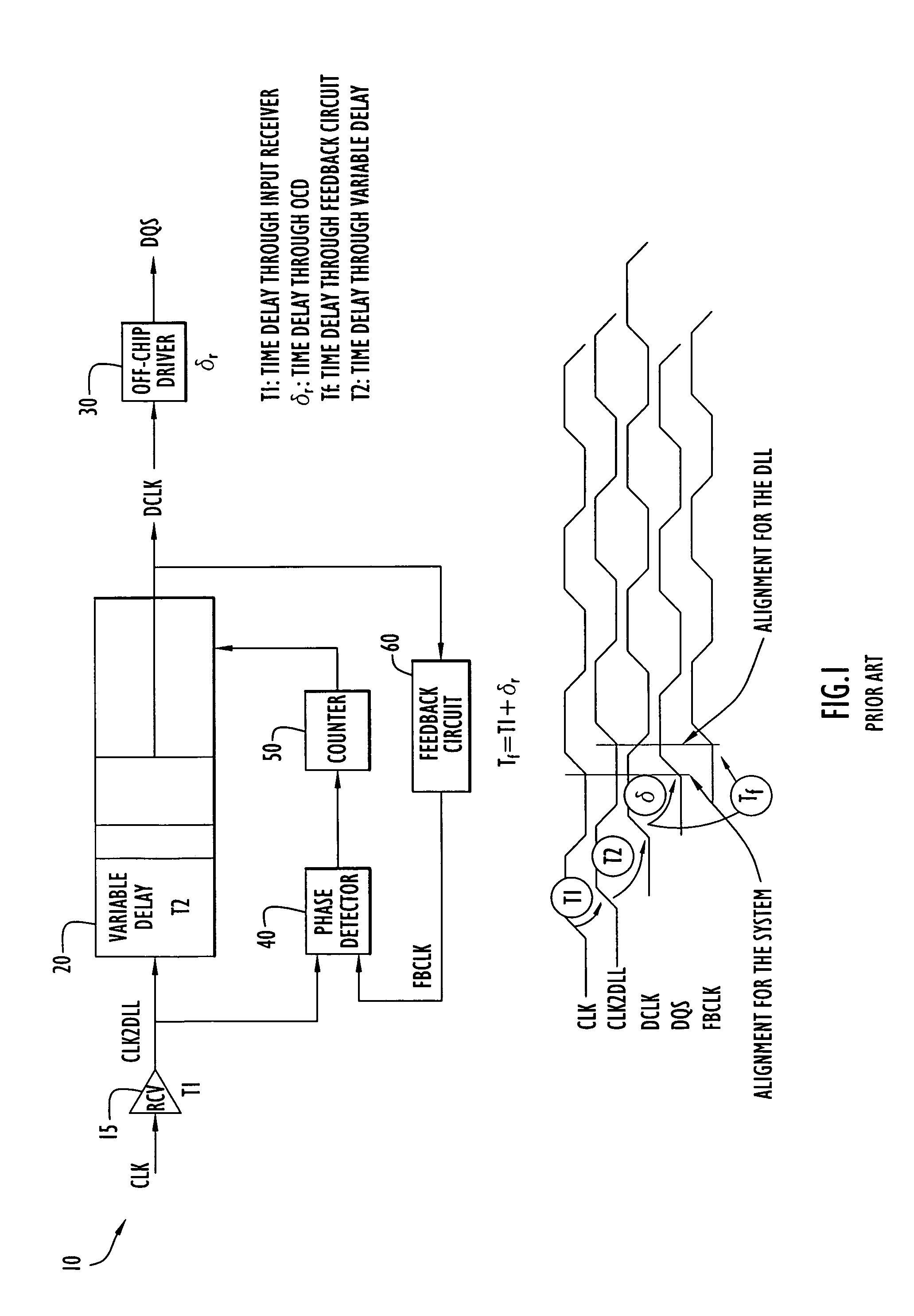
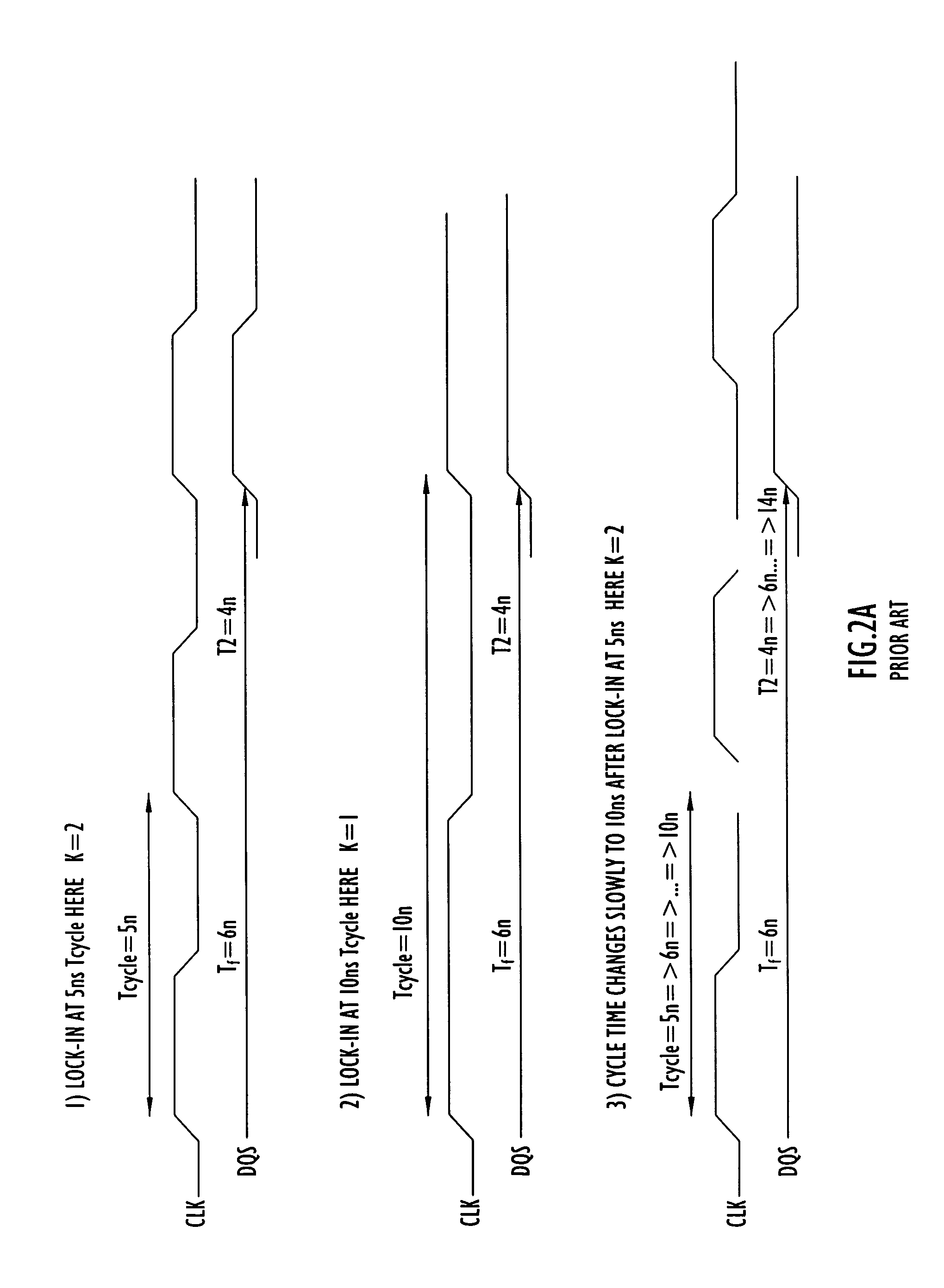
Method and apparatus compensating for frequency drift in a delay locked loop
A delay locked loop (DLL) according to the present invention includes a cycle time detector to determine the quantity of delay elements within a clock cycle and adjust a DLL counter controlling a DLL variable delay line to enable operation or locking in response to DLL overflow and underflow conditions. The cycle time detector includes a ring oscillator having a strong correlation between the oscillator period and the DLL delay elements. The output of the oscillator controls the counter to provide a new locking position for the DLL in the presence of overflow or underflow conditions. The oscillator is driven for an interval corresponding to the product of the external clock period and the quantity of delay elements in the ring oscillator. In effect, the delay of the DLL is adjusted to the preceding or succeeding external clock period to enable locking in response to overflow or underflow conditions.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Oscillating circuit, booster circuit, nonvolatile memory device, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS7180794B2Suppress the variation in the oscillating frequencies of an output signalChange in resistancesSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower inverterEngineering
In a ring oscillator constituting an oscillating circuit, resistor circuits are used as delay circuits to be connected to respective inverters. That is, the inverters and the resistors are connected in series so that the resistor is provided between the adjacent inverters. With the arrangement, it is possible to provide an oscillating circuit which is less dependent on any of power supply voltages, temperatures, and manufacturing variations, while maintaining a characteristic in which the oscillating frequency decreases as an output voltage of a booster circuit increases.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
On-chip transistor degradation monitoring
InactiveUS7205854B2Digital circuit testingPulse generation by logic circuitsEngineeringSelf excited oscillation
Embodiments of the invention include on-chip characterization of transistor degradation. In one embodiment, includes one or more functional blocks to perform one or more functions and an integrated on-chip characterization circuit to perform on-chip characterization of transistor degradation. The integrated on-chip characterization circuit includes a selectively enabled ring oscillator to generate a reference oscillating signal, a free-running ring oscillator to generate a free-running oscillating signal, and a comparison circuit coupled to the selectively enabled ring oscillator and the free-running ring oscillator. From the reference oscillating signal and the free-running oscillating signal, the comparison circuit determine a measure of transistor degradation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
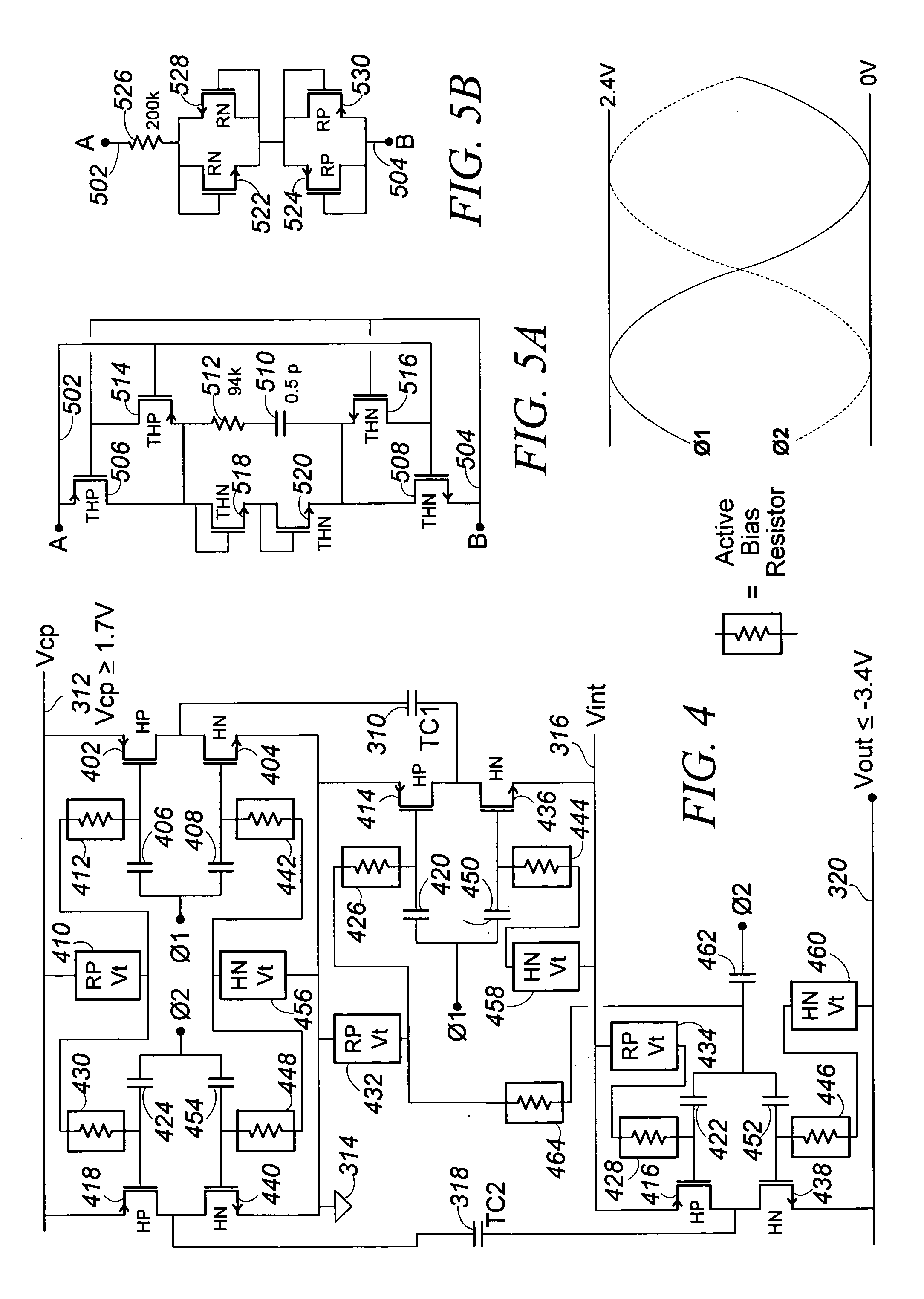
Low-Noise High Efficiency Bias Generation Circuits and Method
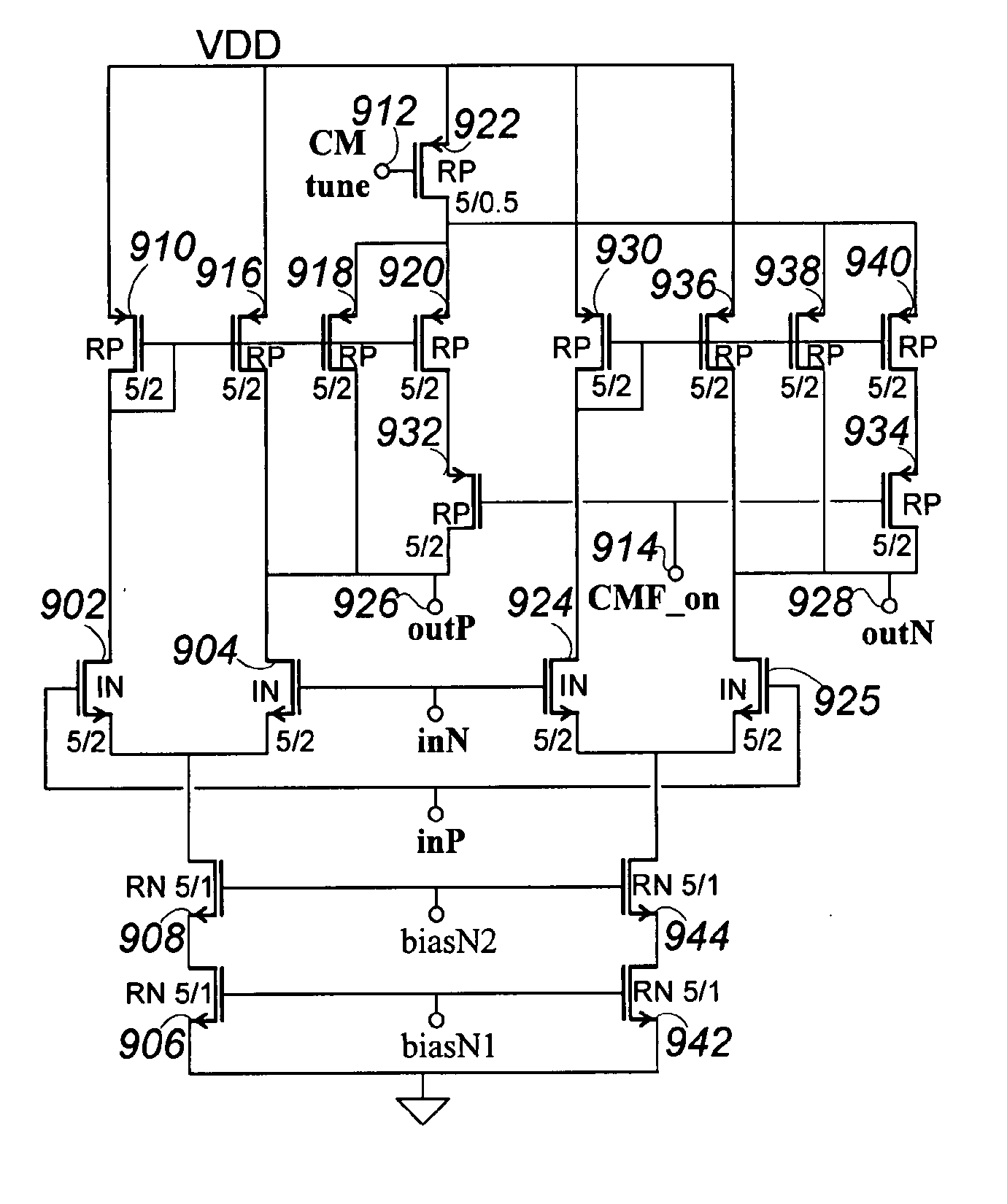
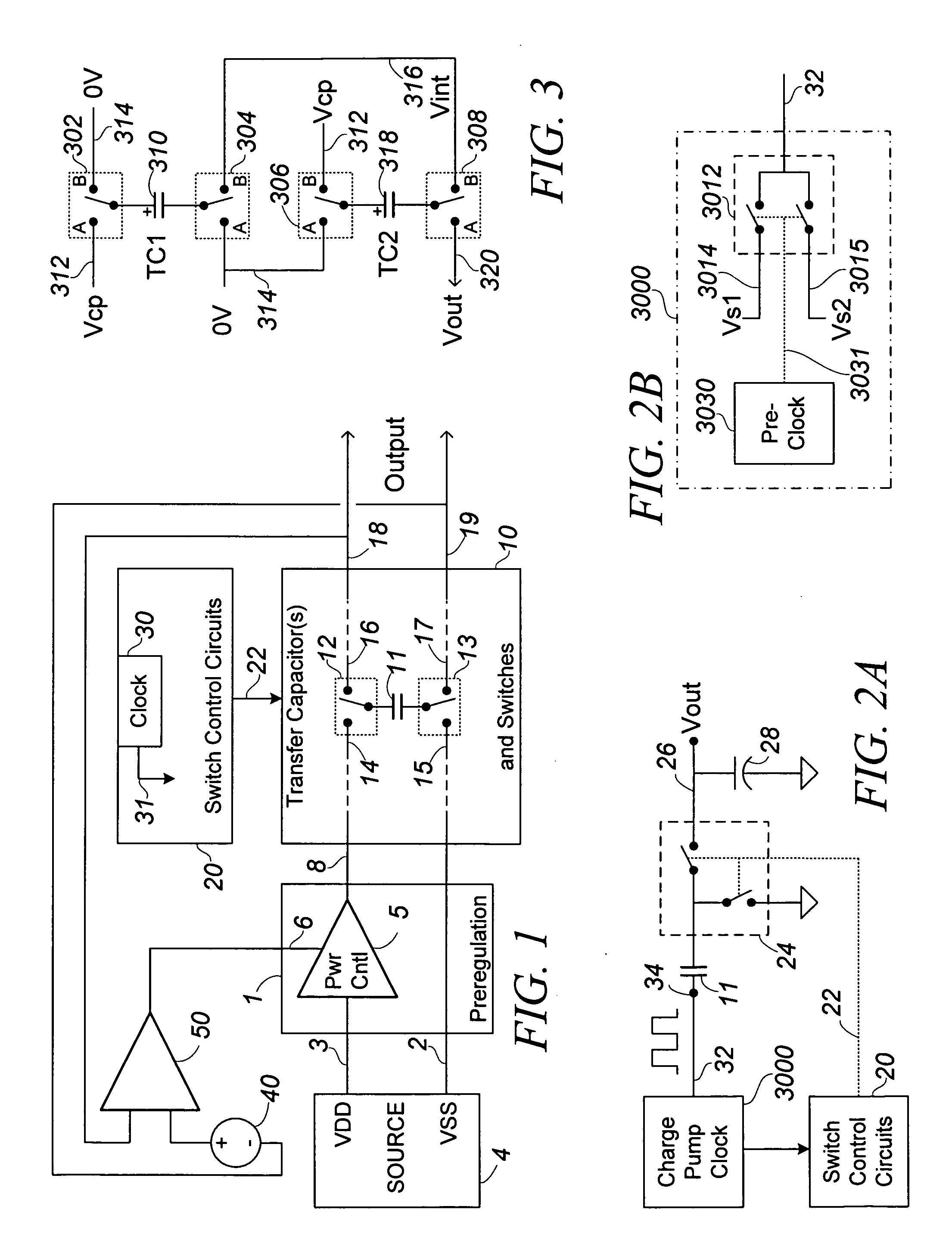
ActiveUS20110156819A1Reduce voltageAvoid problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceActive element networkLow noiseCapacitance
A bias generation method or apparatus defined by any one or any practical combination of numerous features that contribute to low noise and / or high efficiency biasing, including: having a charge pump control clock output with a waveform having limited harmonic content or distortion compared to a sine wave; having a ring oscillator to generating a charge pump clock that includes inverters current limited by cascode devices and achieves substantially rail-to-rail output amplitude; having a differential ring oscillator with optional startup and / or phase locking features to produce two phase outputs suitably matched and in adequate phase opposition; having a ring oscillator of less than five stages generating a charge pump clock; capacitively coupling the clock output(s) to some or all of the charge transfer capacitor switches; biasing an FET, which is capacitively coupled to a drive signal, to a bias voltage via an “active bias resistor” circuit that conducts between output terminals only during portions of a waveform appearing between the terminals, and / or wherein the bias voltage is generated by switching a small capacitance at cycles of said waveform. A charge pump for the bias generation may include a regulating feed back loop including an OTA that is also suitable for other uses, the OTA having a ratio-control input that controls a current mirror ratio in a differential amplifier over a continuous range, and optionally has differential outputs including an inverting output produced by a second differential amplifier that optionally includes a variable ratio current mirror controlled by the same ratio-control input. The ratio-control input may therefore control a common mode voltage of the differential outputs of the OTA. A control loop around the OTA may be configured to control the ratio of one or more variable ratio current mirrors, which may particularly control the output common mode voltage, and may control it such that the inverting output level tracks the non-inverting output level to cause the amplifier to function as a high-gain integrator.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) with a wide tuning range and substantially constant voltage swing over the tuning range
A wide tuning range and constant swing VCO is described that is based on a multipass Ring Oscillator enhanced with feed-backward connections. This VCO is designed to overcome tuning range limitations of prior-art “feed-forward” ring oscillators. The Feedback multipass Ring Oscillator of the invention provides decreasing frequency when tuned by increasing the feedback, thus covering a much wider tuning range irrespective of the speed limit of the technology while at the same time providing almost constant amplitude.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
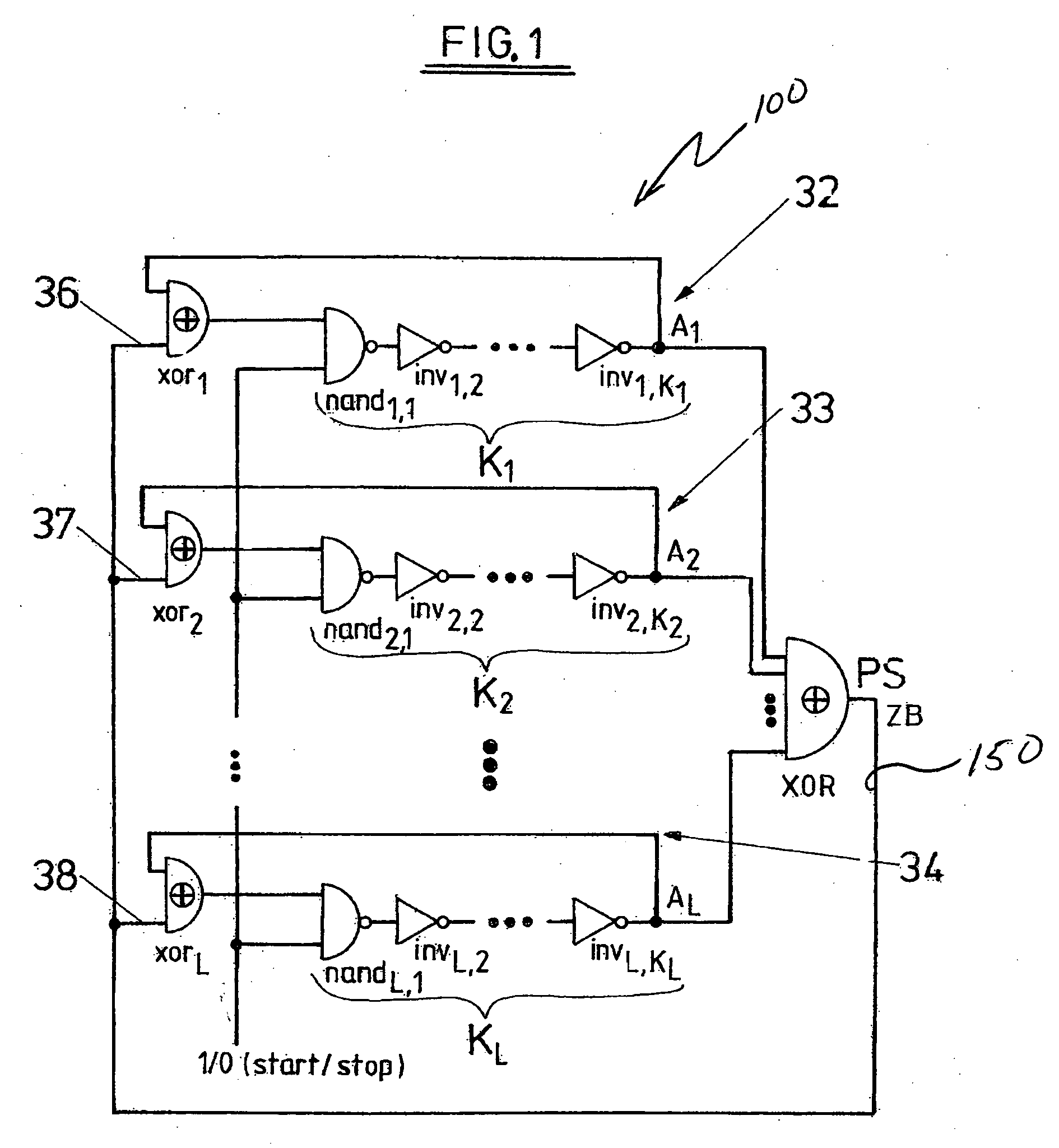
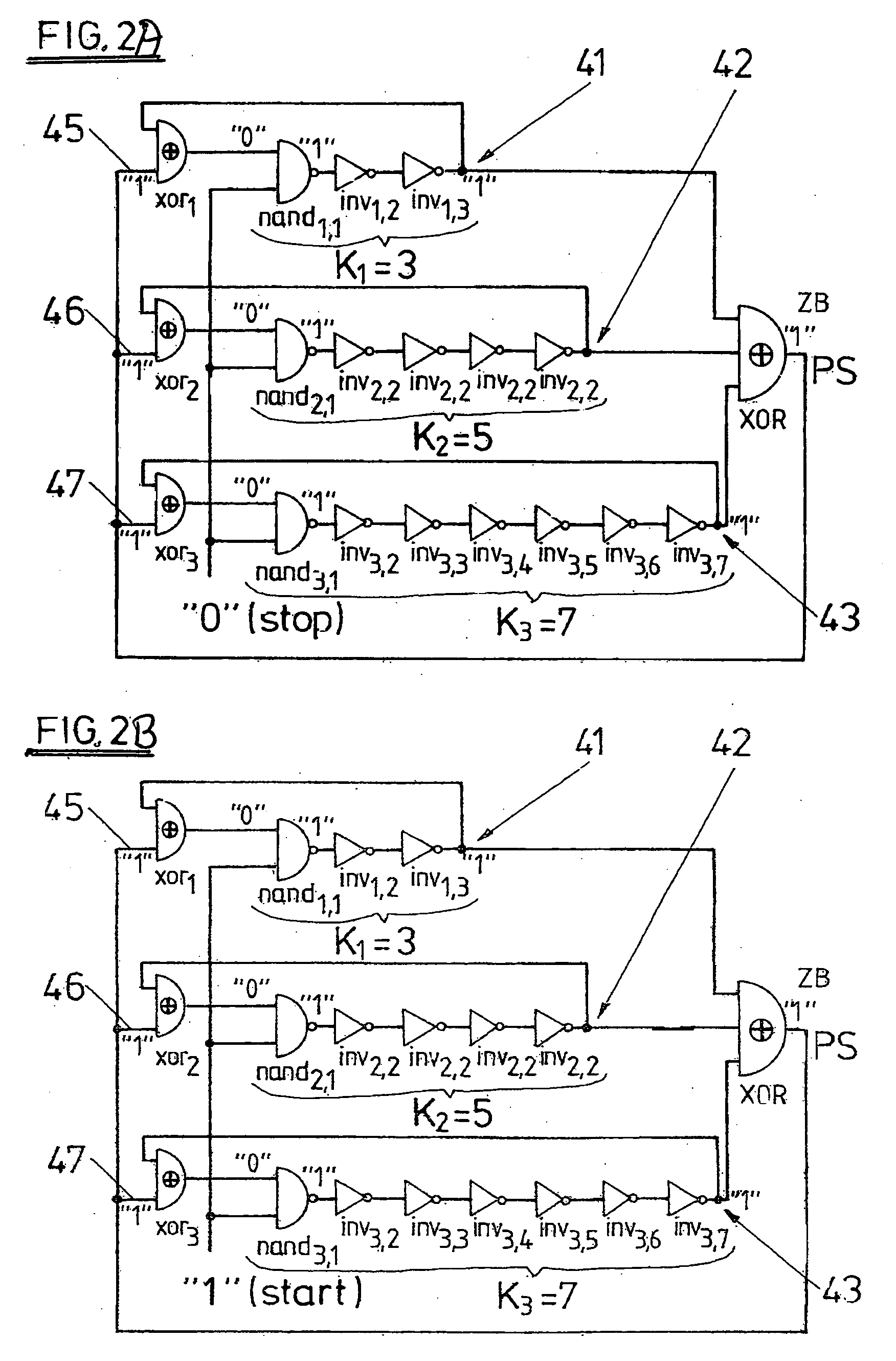
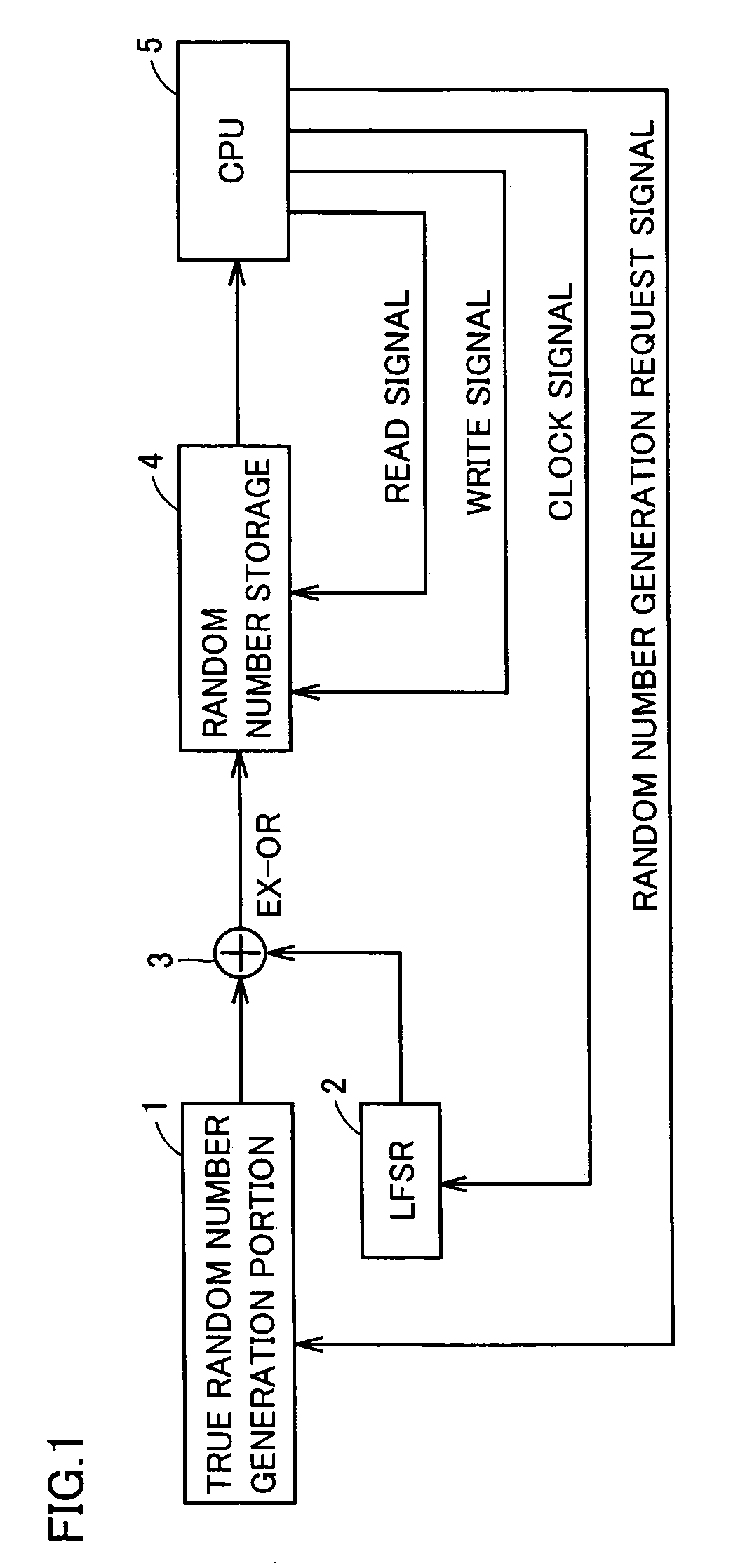
Random number generator and method for generating random numbers
InactiveUS20060069706A1AutocorrelationReduced sampling rate requirementsRandom number generatorsSecuring communicationNumber generatorComputer science
The invention relates to a method for generating random numbers in which oscillating digital output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) of unequal or equal periodicity are generated by at least two ring oscillators (32, 33, 34), an external parity signal (PS) representing a logical state (“0,”“1”) being generated when an odd number of the output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) take on a specified logical state (“1”). According to the invention, the external parity signal (PS) is fed back to an external parity input (36, 37, 38) of each of the respective ring oscillators (32, 33, 34). The invention further relates to a random number generator having at least two ring oscillators (32, 33, 34), made up in particular of independently free-running inverter chains with feedback having an odd number (K) of series-connected inverters (inv1,2, inv2,1, inv3,1, . . . , invi,j, . . . , invL,KL) that generate oscillating digital output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) of unequal or equal periodicity, and having first parity signal generating means (XOR) that generate an external parity signal (PS) representing a logical state (“0,”“1”) when an odd number of the output signals (A1, A2, . . . , AL) take on a specified logical state (“1”). According to the invention, there are feedback means (xor1, xor2, xor3, xor4, . . . , xorL) that feed back the external parity signal (PS) to an external parity input (36, 37, 38) of each of the respective ring oscillators (32, 33, 34). In this invention the cooperation of chaotic dynamics (feedback of the parity signal) and true randomness (jitter due to thermal noise) in digital circuits, a novel theoretical principle for generating random numbers, has been made into an efficient practical solution.
Owner:TDK MICRONAS GMBH
Multiphase receiver and oscillator
InactiveUS6385442B1Single output arrangementsPulse generation by logic circuitsLocal oscillator signalEngineering
A differential ring oscillator is provided with three differential amplifiers and provides three-phase output signals which can be used for synchronous detection of a received multi-phase modulated signal in a multi-phase receiver, wherein the phase of the local oscillator signals may be in other-than-quadrature relation. Two of the phase outputs of the local oscillator can be combined to provide a signal that is in quadrature with the remaining output. The oscillator is preferably controlled in coarse frequency control steps and using a fine voltage control signal responsive to a phase-locked loop to reduce frequency modulation of the oscillator signal arising out of leakage signals.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Divide-by-two injection-locked ring oscillator circuit
InactiveUS20110050296A1Improved output signal slew rateIncrease productivityPulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsInjection lockedLoad resistance
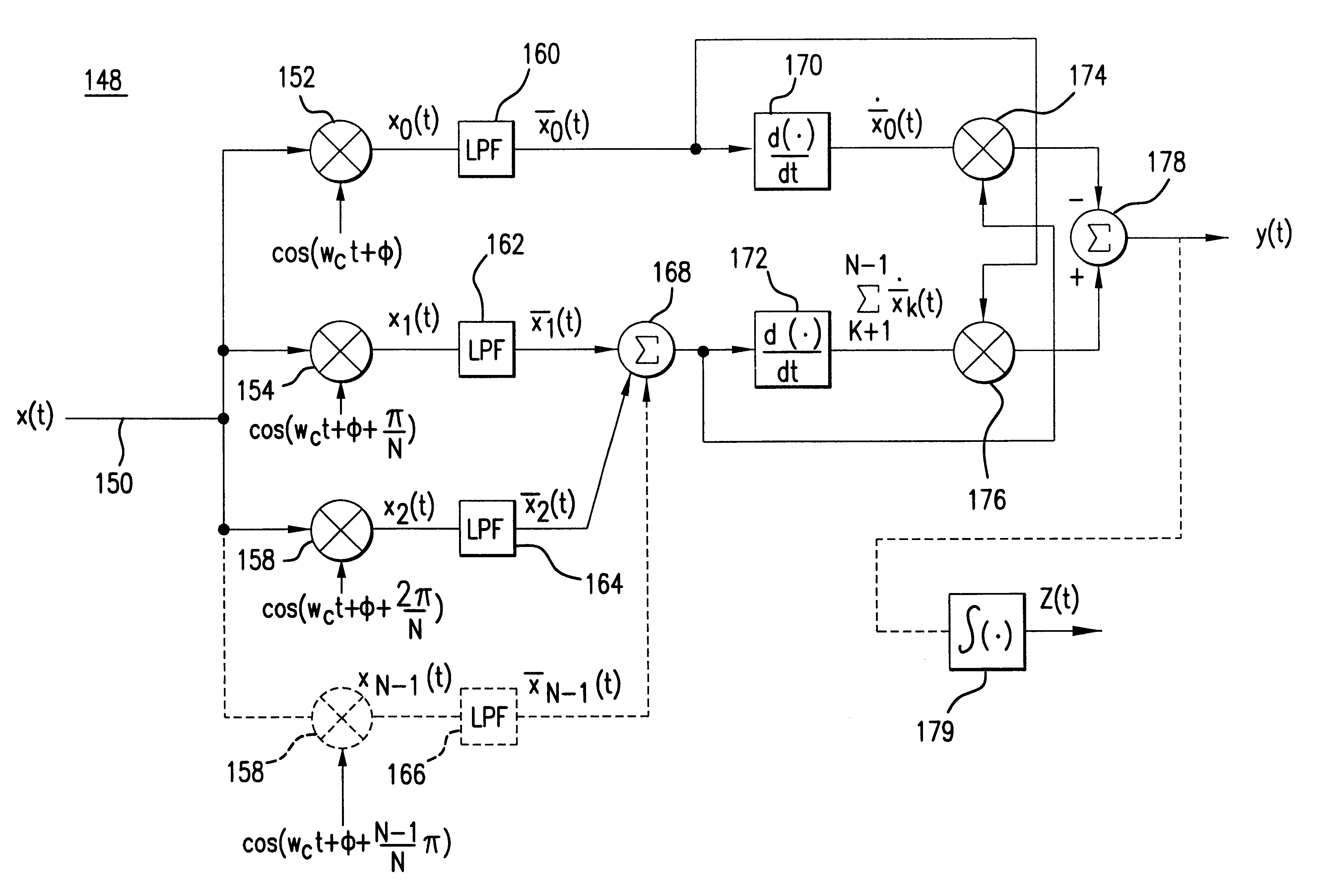
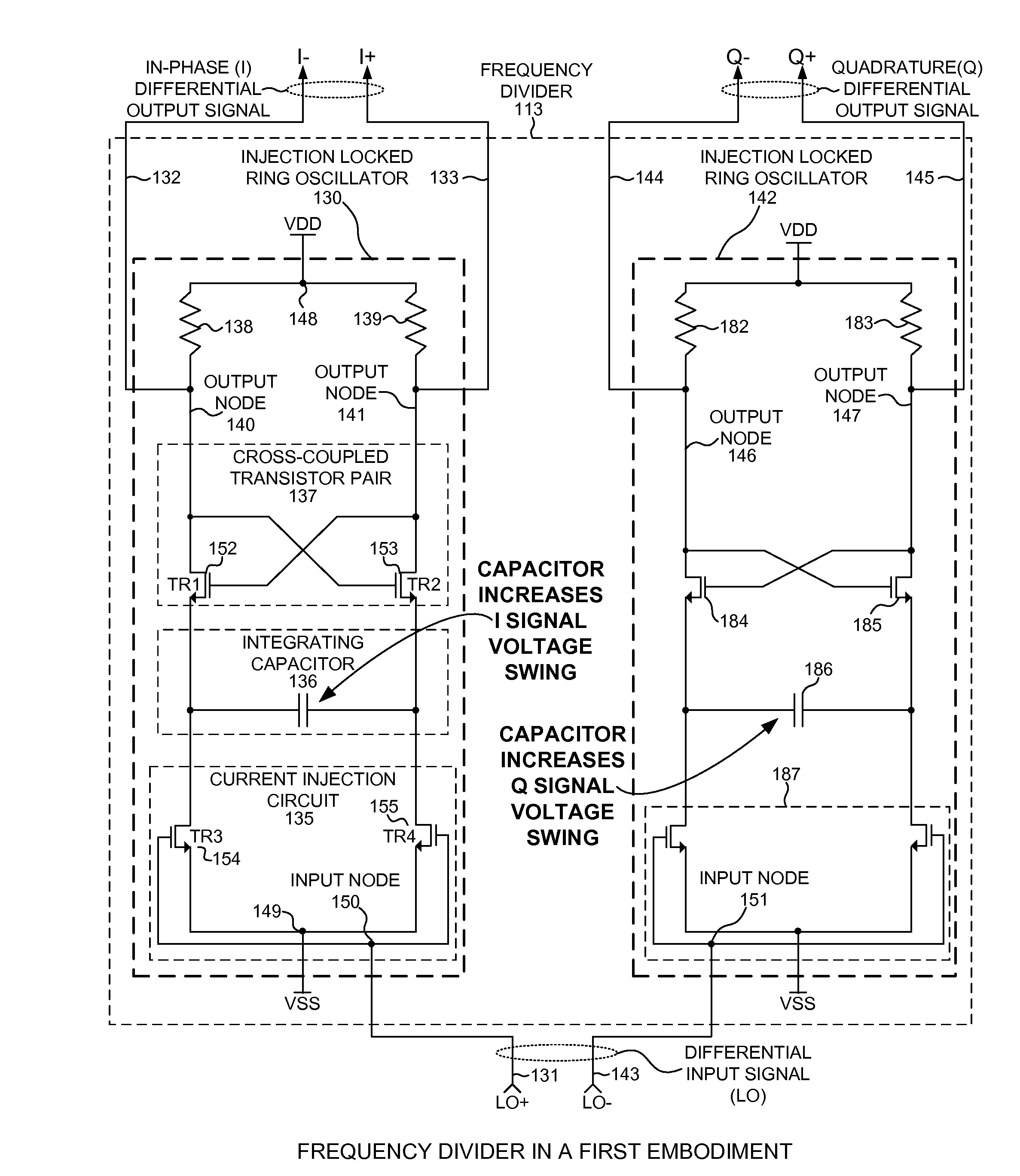
A frequency divider involves a plurality of Injection-locked Ring Oscillators (ILRO). A first ILRO includes a pair of cross-coupled N-channel transistors, a pair of load resistors, an integrating capacitor, and a current injection circuit. The drain of each transistor is coupled to the gate of the other transistor. Each load resistor couples the drain of each transistor to a circuit voltage source. The integrating capacitor couples the sources of each transistor. The current injection circuit alternately opens and closes a path from the source of each transistor to circuit ground in response to an oscillatory input signal of a first frequency. In response, the voltage state at the drain of each transistor is alternately latched and toggled, generating a differential pair of oscillating signals frequency divided by two. A first and second ILRO driven in antiphase generate two differential output signals in phase quadrature.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
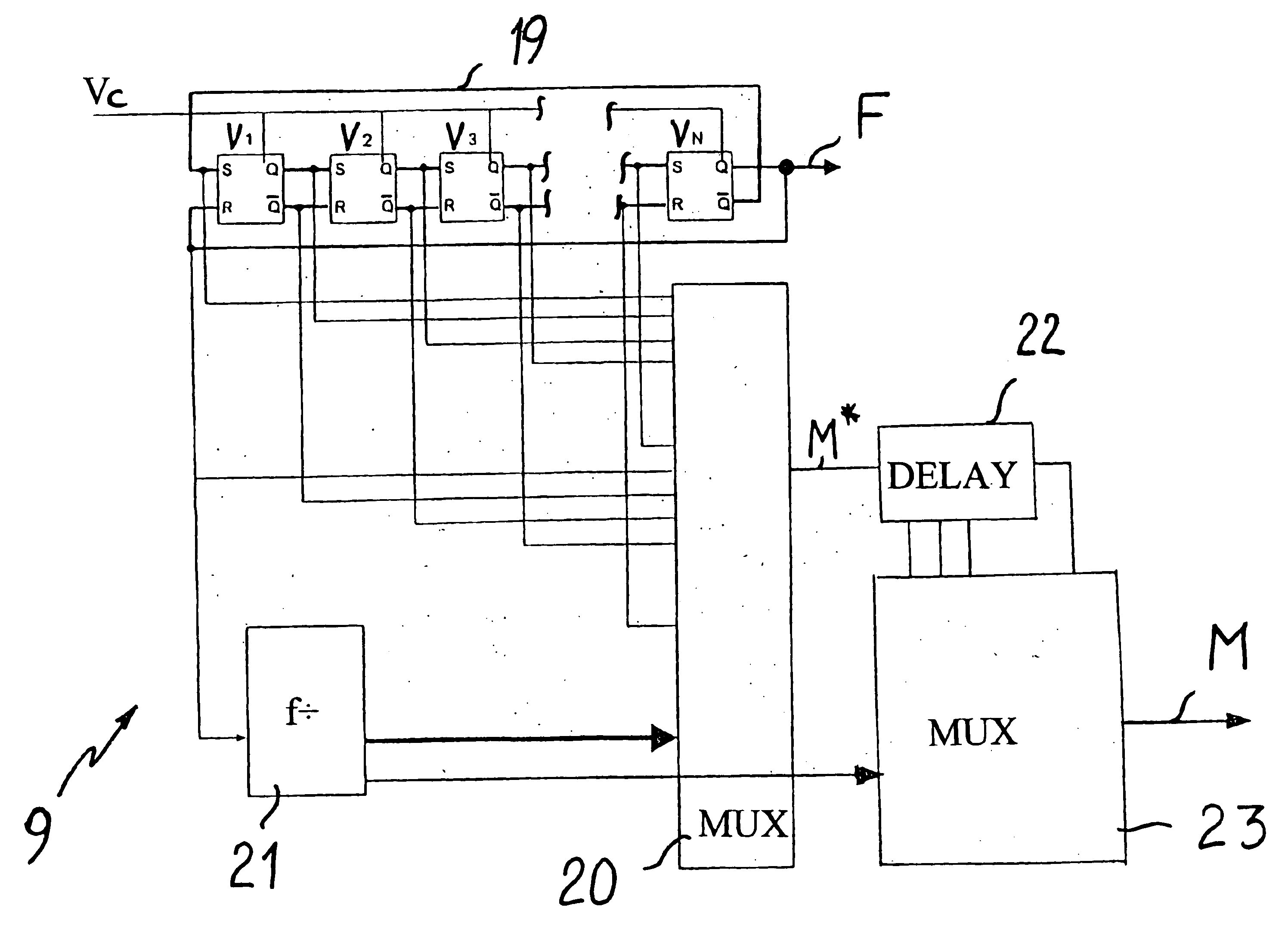
Method and device for carrying out frequency synthesis in a distance measuring device
InactiveUS6859744B2Reduce phase noiseReduce energy consumptionDigital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsMultiplexerElectromagnetic radiation
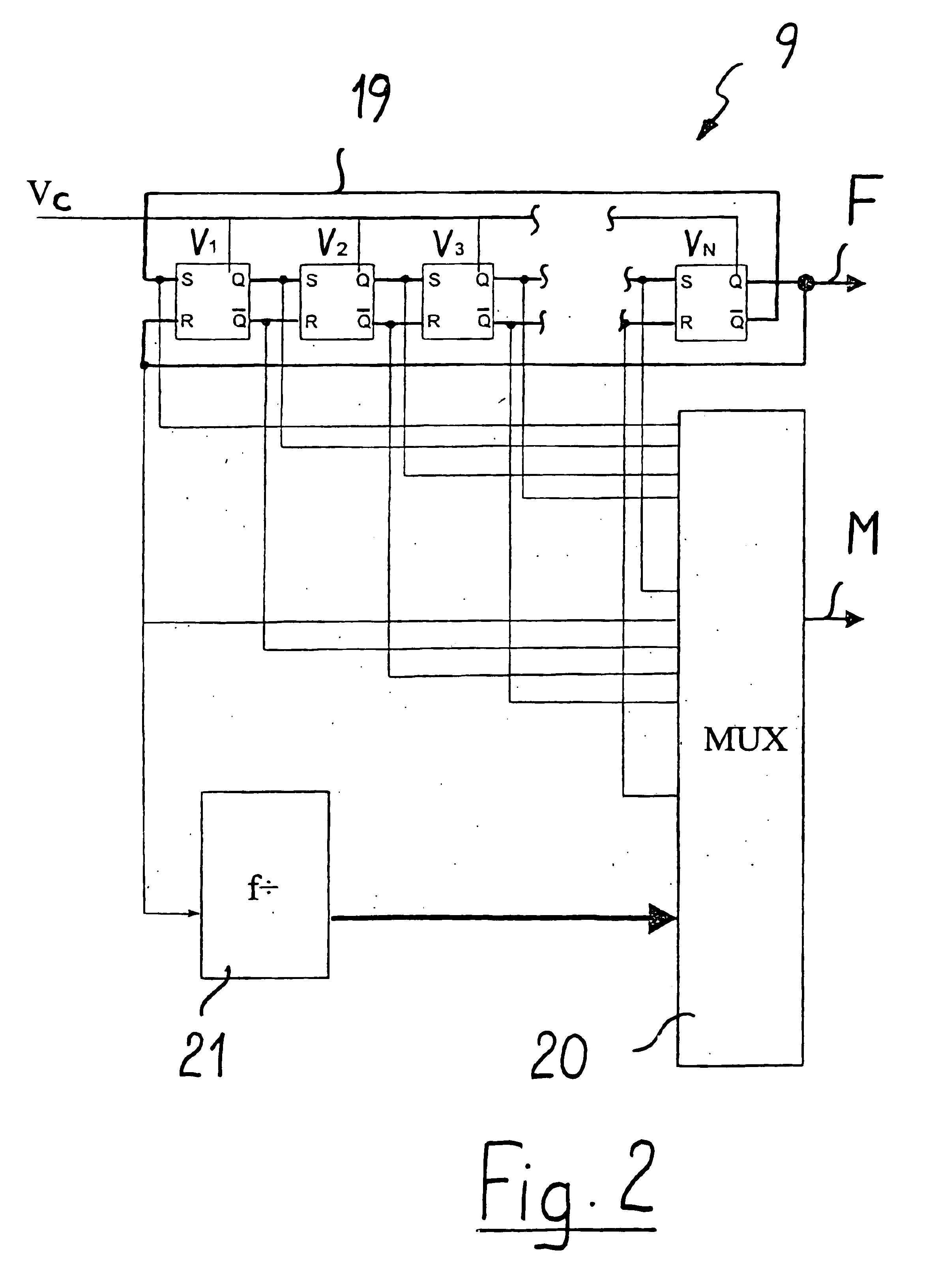
In a method and a device for carrying frequency synthesis, in particular in a distance measuring device based on the principle of evaluating the change over time in the phase of an electromagnetic radiation emitted by a radiation source and remitted by an object aimed at, a frequency, which is preferably furnished by a quartz oscillator, is regulated in a ring oscillator with N delay elements (V1, V2, V3, . . . , VN) to a desired first high frequency (F), which is used as a mixer frequency or as a modulation frequency. The signals at the N delay elements (V1, V2, V3, . . . , VN) are delivered to a multiplexer, which is switched over with a cadence that is equivalent to 2*N times the frequency of the low-frequency measurement signal to be evaluated to produce a modulation frequency or mixer frequency.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
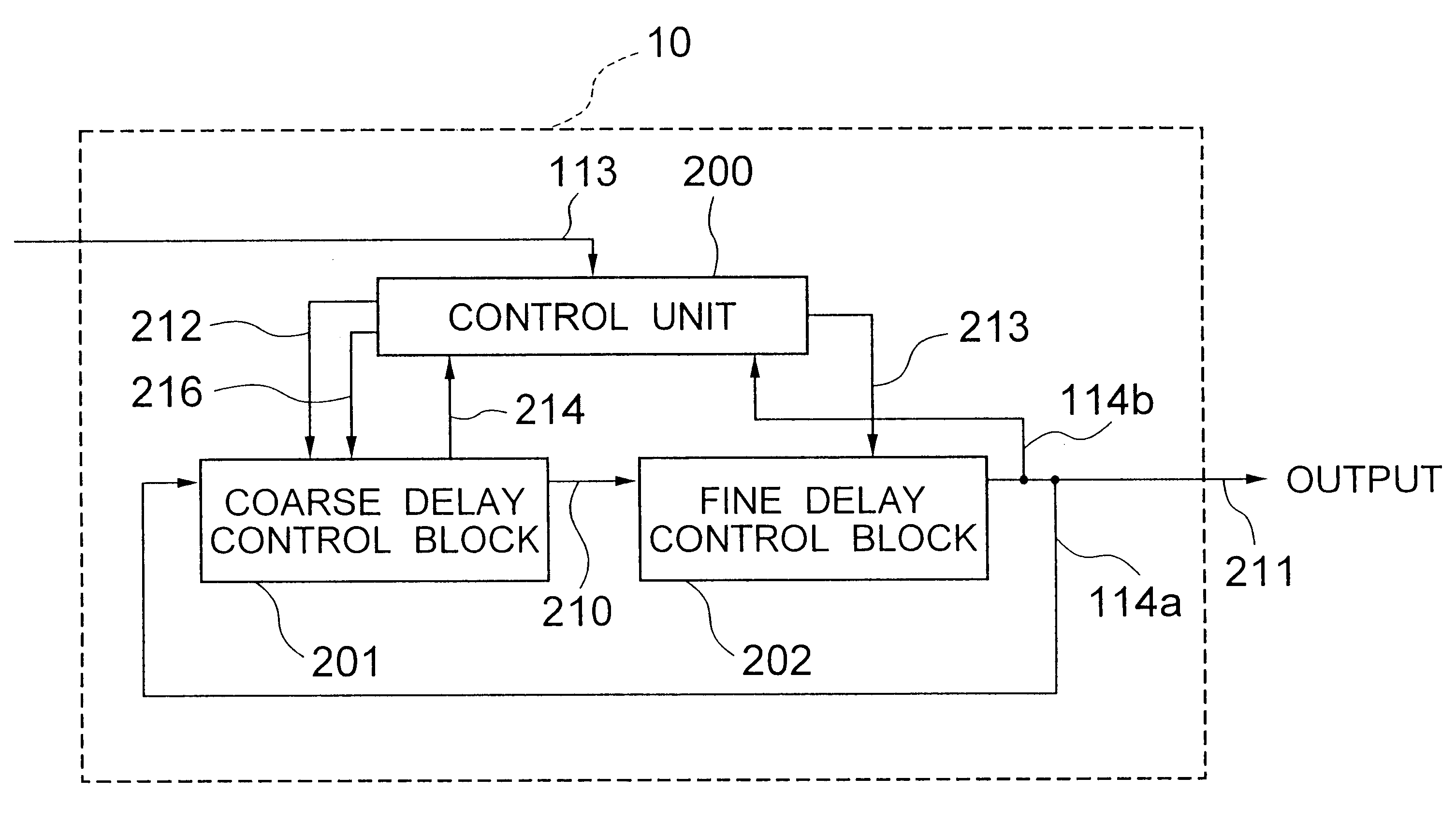
Ring oscillator having variable coarse and fine delays
A ring oscillator includes a coarse delay control block including a plurality of coarse delay gates, and a fine delay control block including a plurality of fine delay gates. The total delay of the fine delay control block is larger than a single delay step of the coarse delay control block, whereby variations of the delay step do not cause an adverse effect on the jitter characteristic of a PLL circuit having the ring oscillator. In a normal operation, the coarse delay control block increments the delay step after the total of the delay steps of the fine delay control block exceeds the delay step of the coarse delay control block.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
On-chip compensation control for voltage regulation
InactiveUS7075276B2Pulse automatic controlEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage regulator moduleControl signal
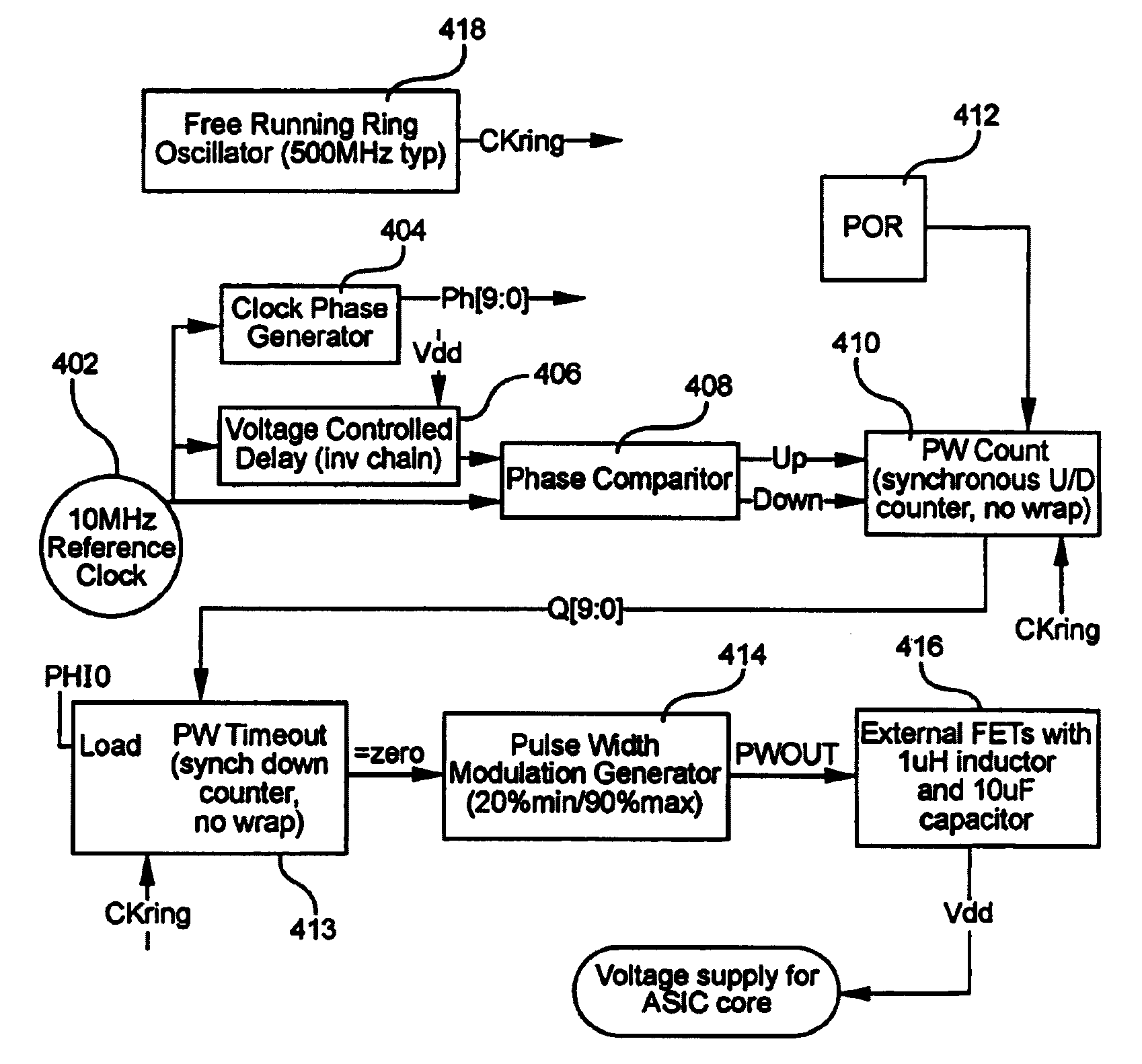
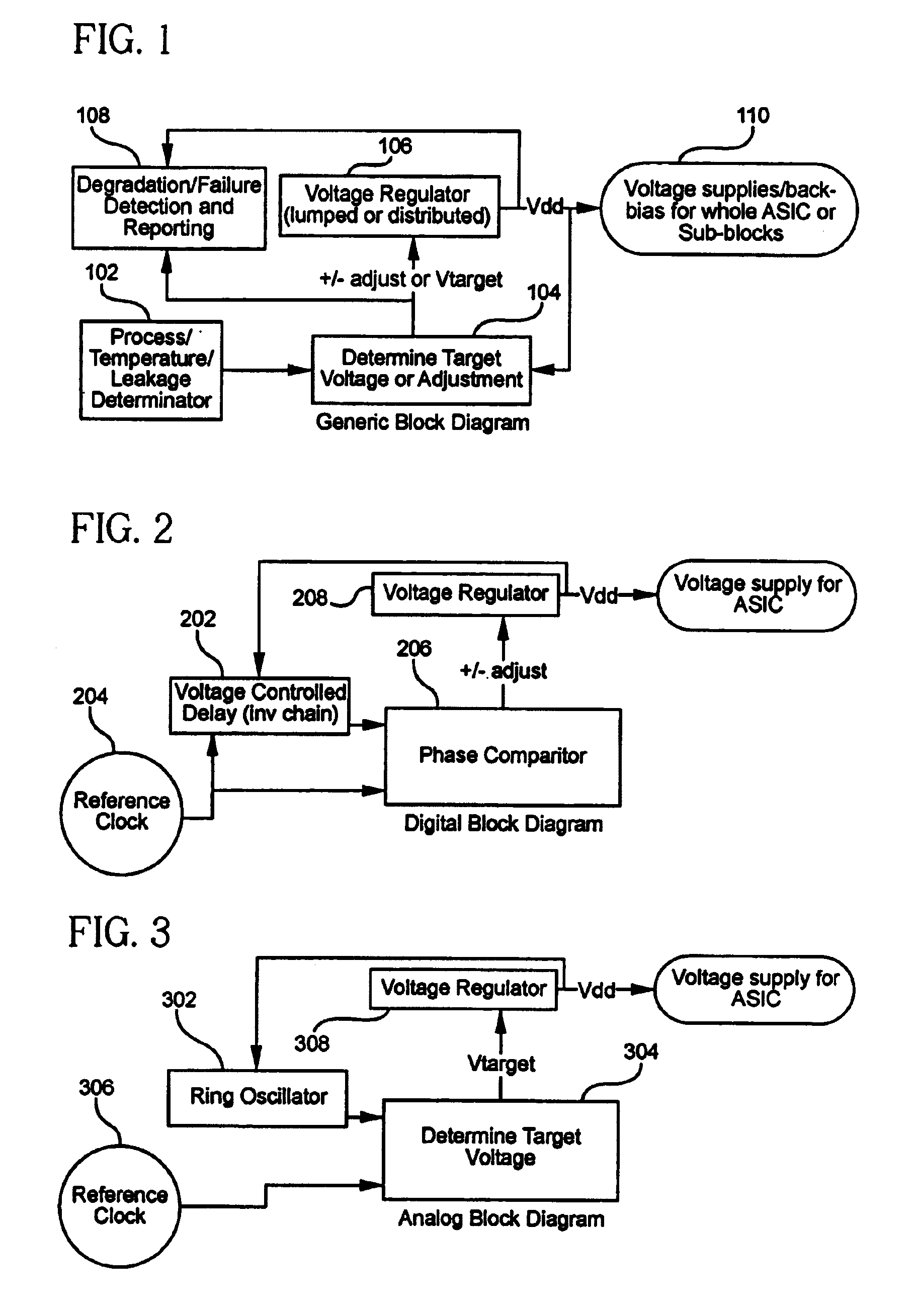
Manufacturing and / or operational variations that affect performance of an integrated circuit (IC) are at least partially compensated for, by determining the magnitude of these variations and providing one or more corresponding control signals to a voltage regulator, which, responsive thereto, increases or decreases the magnitude of the output voltage. The output voltage of the voltage regulator is typically provided to a power supply node of the IC. Similarly, the output of the voltage regulator may be provided to a substrate portion of the IC, so as to provide a substrate bias that is variable in response to changes in the performance of the IC. In various embodiments, a determination of the magnitude of the variations is made by comparing the performance of a digital delay circuit or a ring oscillator to a reference clock; speed characterization of the IC may be obtained from the voltage regulator control signals; and information regarding reliability degradation of the IC may be obtained from the control signals that are generated for control of the voltage regulation circuitry.
Owner:INNOTECH SYST
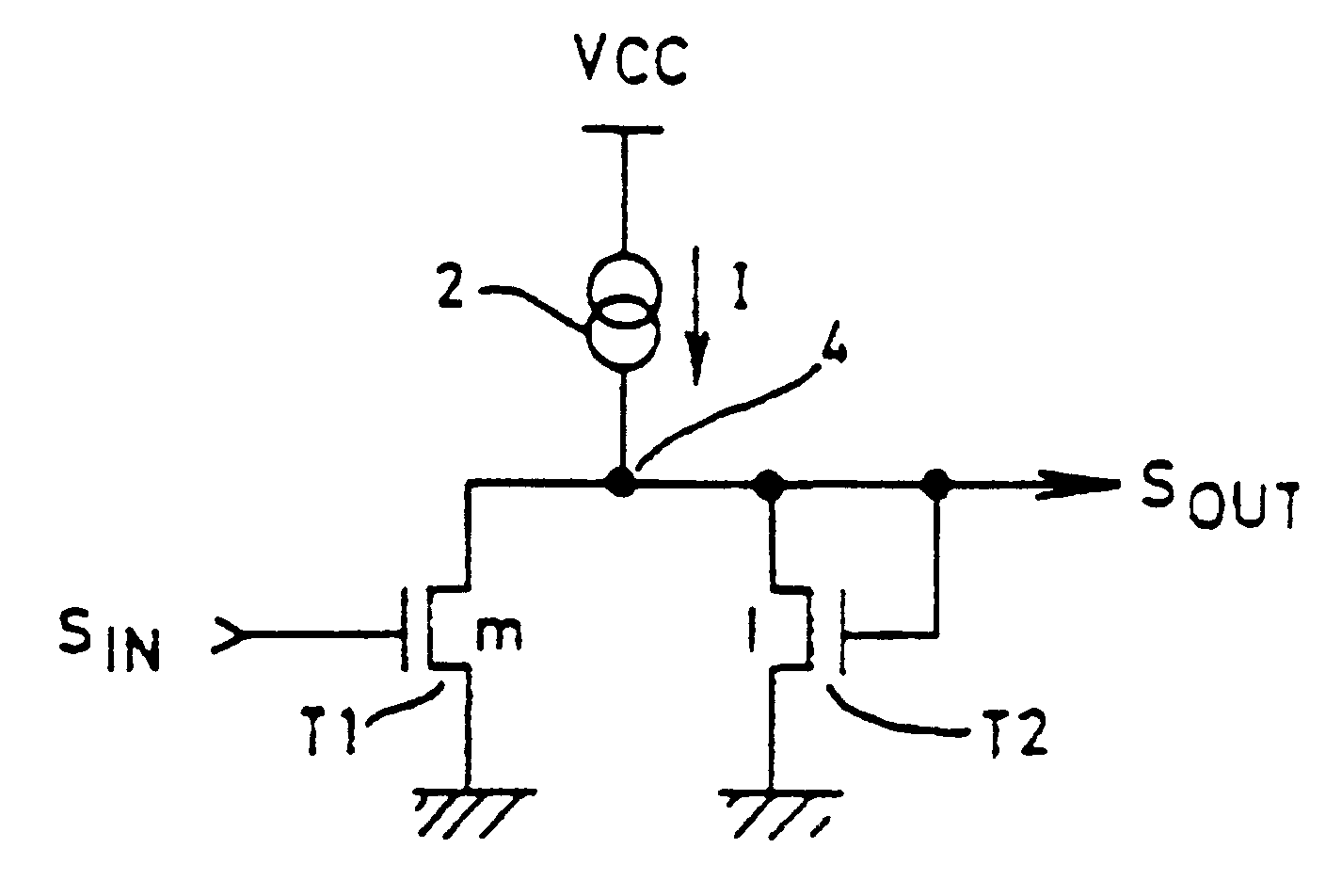
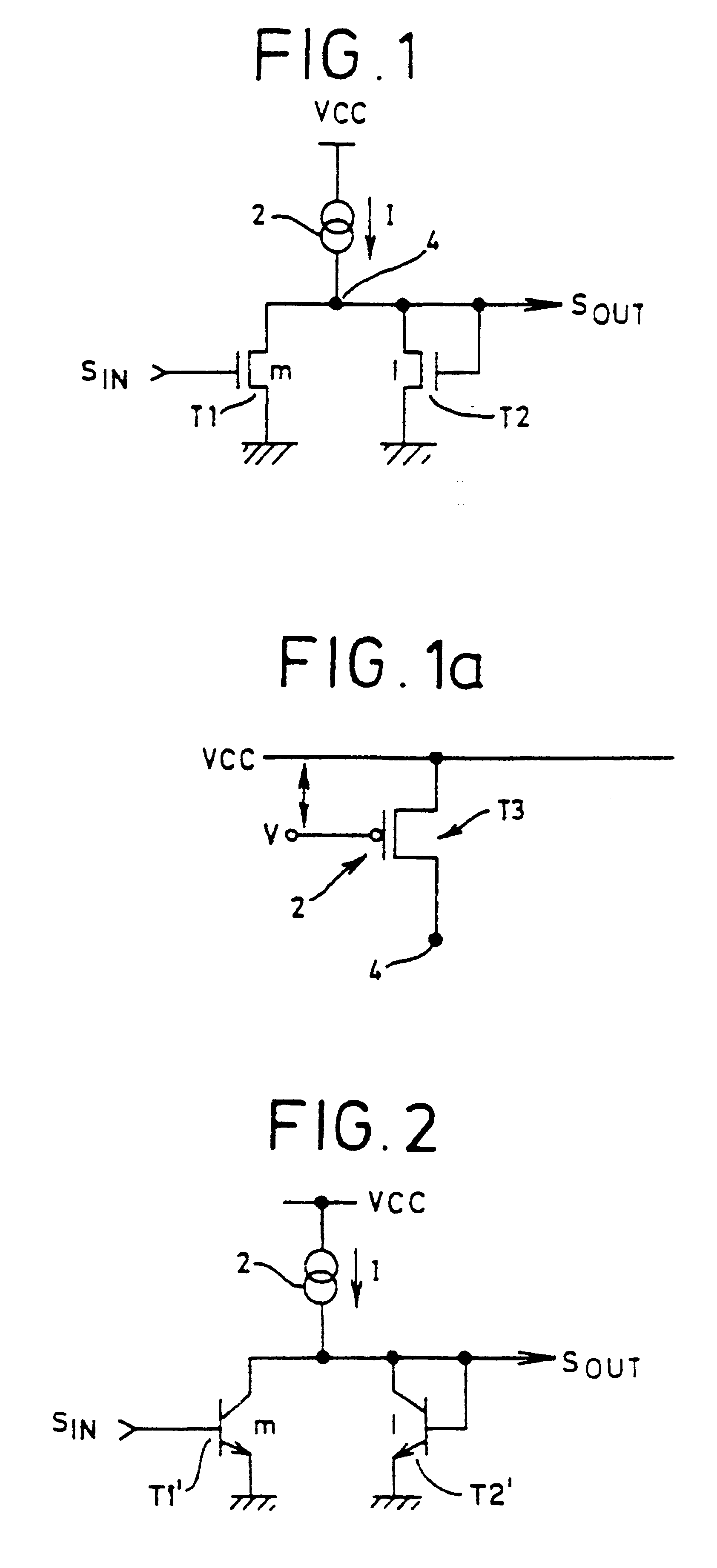
Ring oscillator using current mirror inverter stages
InactiveUSRE37124E1Limit maximum frequencyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsLow voltageEngineering
A ring oscillator having an odd number of single ended stages, each stage including two transistors connected as a current mirror. The stage provides for low-voltage performance and improved process tolerance characteristics.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Delay stage circuitry for a ring oscillator
InactiveUSRE38482E1Easy to optimizePulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexEngineeringVoltage clamp
A ring oscillator includes an even-numbered plurality of ring coupled delay stages. Each delay stage includes a differential amplifier, a voltage clamping circuit, and a current source. The differential amplifier receives first and second input signals from a preceding delay stage. The differential amplifier provides a first output signal and a complementary second output signal at first and second nodes, respectively. The voltage clamping circuit is coupled between the first and second nodes to limit a peak-to-peak voltage swing of each of the first and second output signals. The current source is coupled to the differential amplifier and varies a bias current in accordance with a delay bias voltage.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Test method and apparatus for verifying fabrication of transistors in an integrated circuit
ActiveUS6958659B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsEngineeringPositive feedback
A ring oscillator for a test apparatus and method for verifying fabrication of transistors in an integrated circuit on a die under test is implemented. The ring oscillator is fabricated on the die and includes a positive feedback loop between a circuit output terminal and a feedback input terminal. The feedback loop includes a plurality of delaying stages connected in cascade. A transfer gate is coupled to each delaying stage. Each of the transfer gates includes a pair of transistors of the first and second conductivity types connected in parallel. The ring oscillator is operable to provide a first oscillator output signal during a first test mode when the transistors of the first conductivity type are ON and the transistors of the second conductivity type are OFF. The ring oscillator is operable to provide a second oscillator output signal during a second test mode when the transistors of the first conductivity type are OFF and the transistors of the second conductivity type are ON. The ring oscillator is operable to provide a third oscillator output signal during a third test mode when the transistors of the first conductivity type are ON and the transistors of the second conductivity type are ON.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
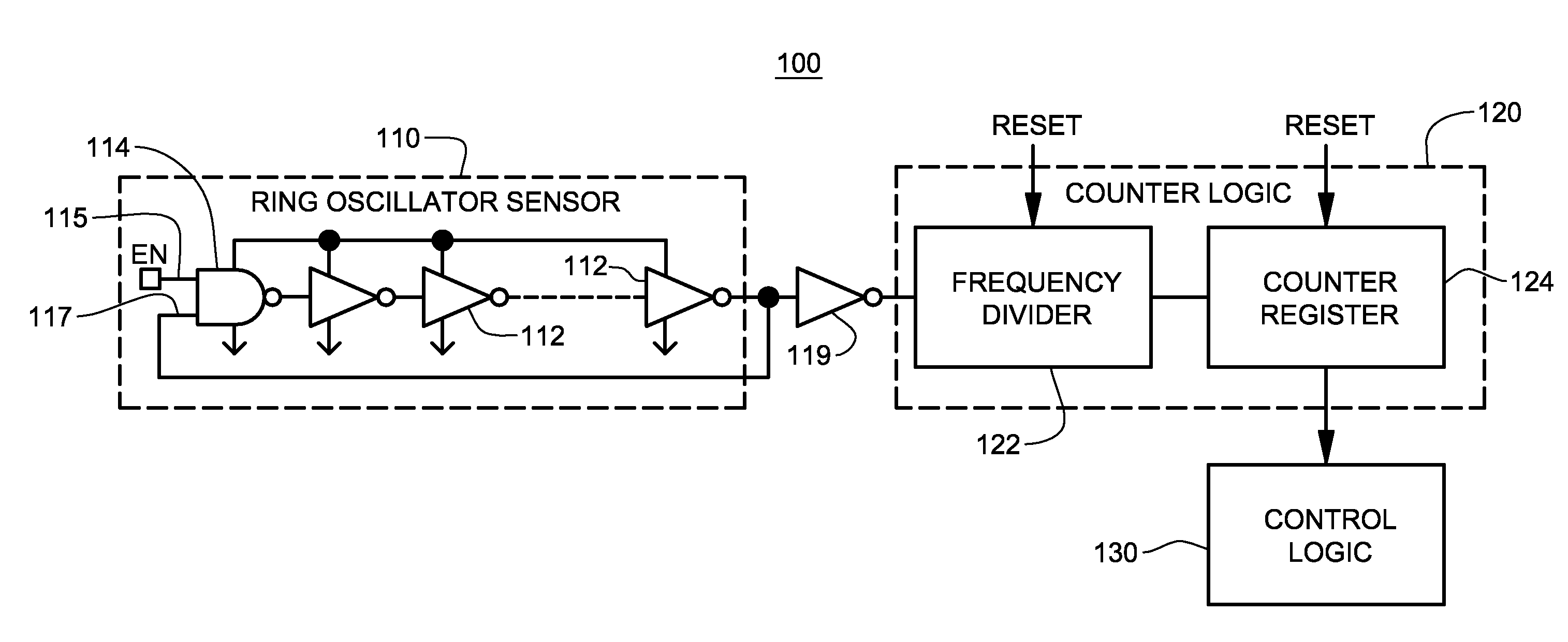
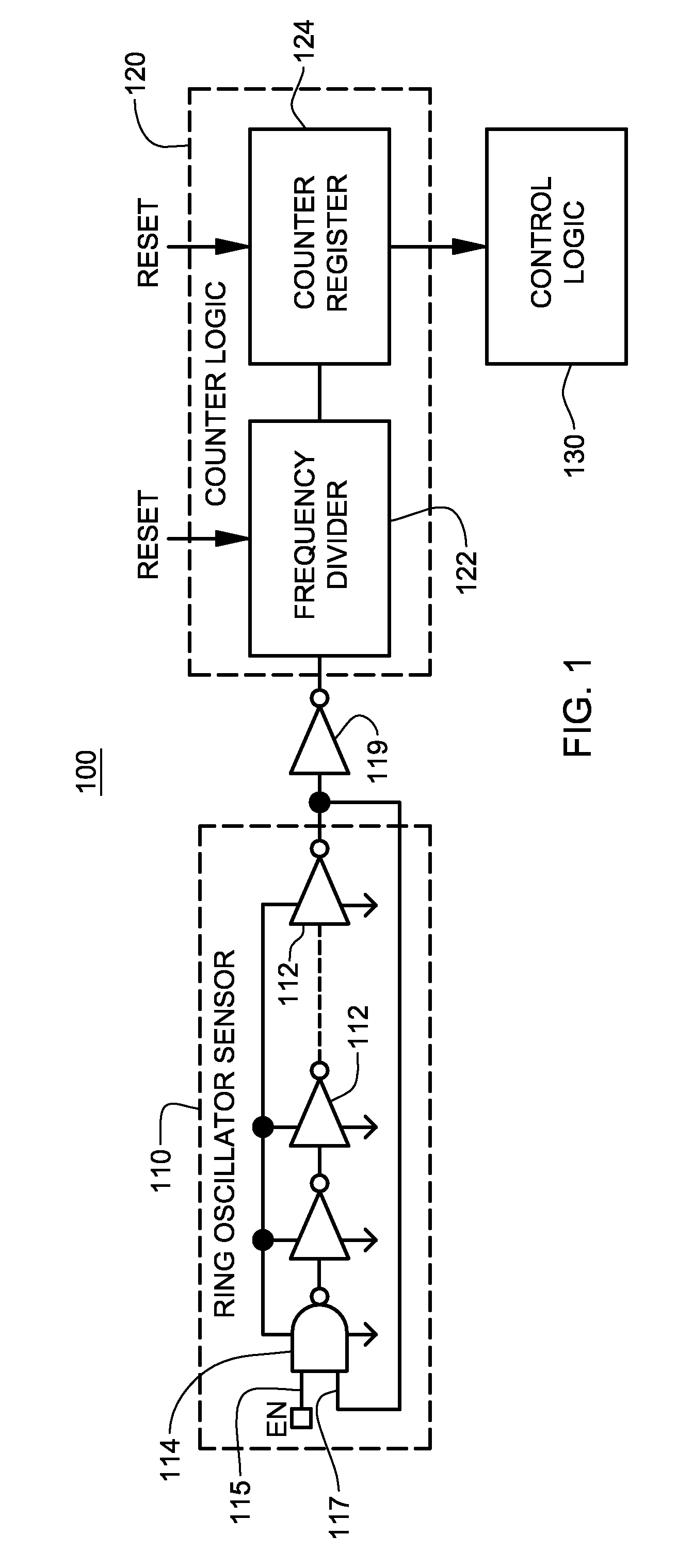
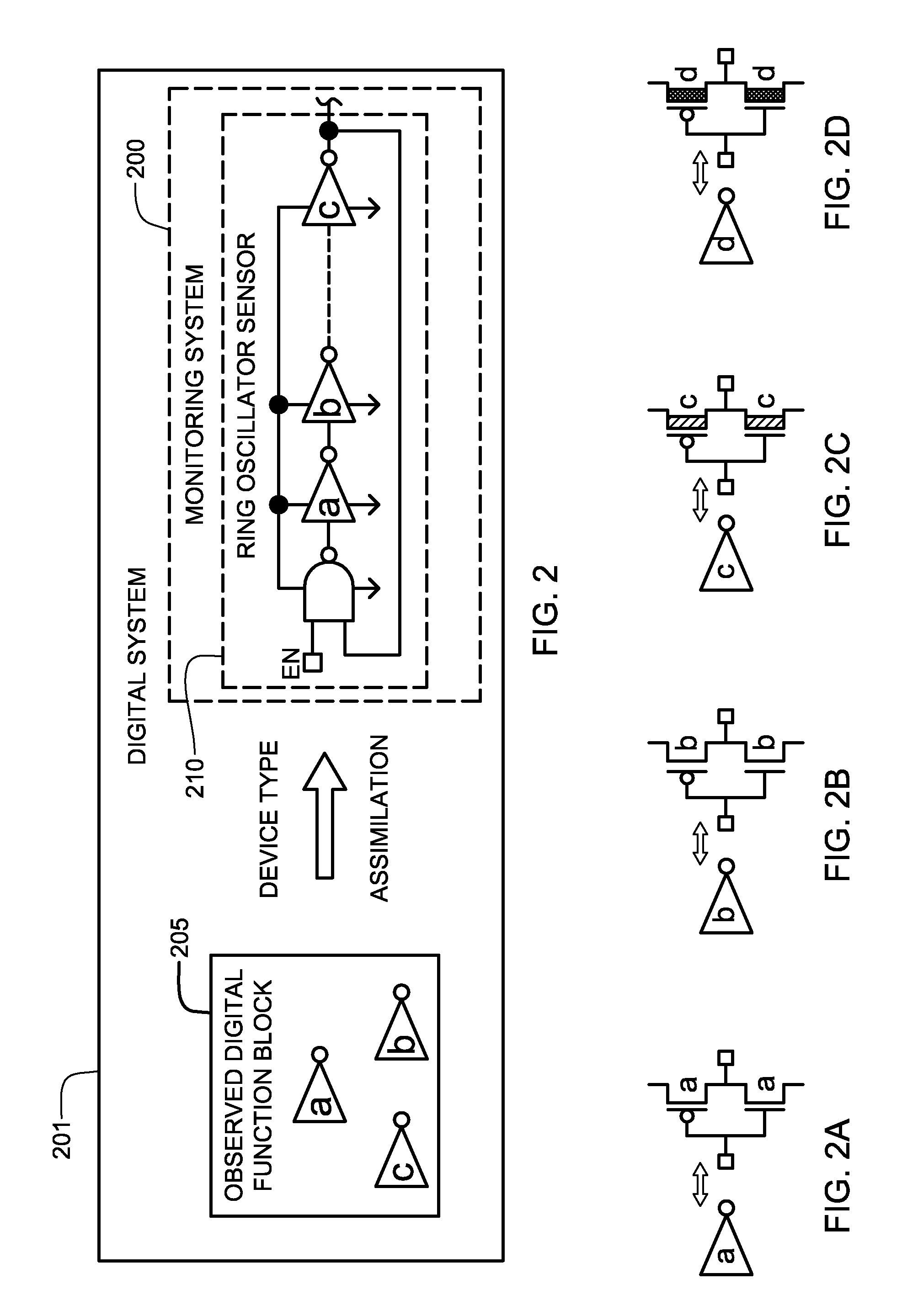
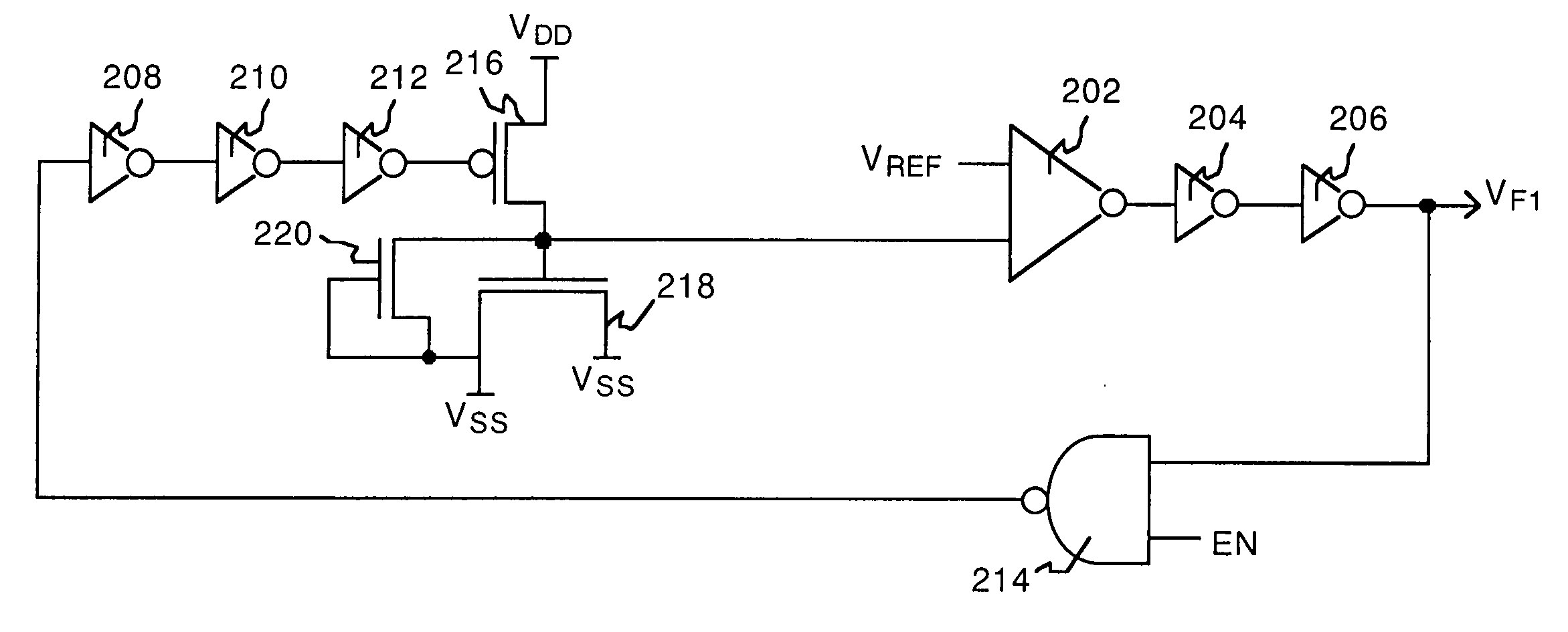
System and method for monitoring reliability of a digital system
System and method are provided for continually monitoring reliability, or aging, of a digital system and for issuing a warning signal if digital system operation degrades past a specified threshold. The technique includes implementing a ring oscillator sensor in association with the digital system, wherein logic and / or device percent composition of the ring oscillator sensor mirrors percent composition thereof within the digital system. Counter logic is coupled to the ring oscillator sensor for converting outputted count signals to an oscillation frequency, and control logic is coupled to the counter logic for periodically evaluating oscillation frequency of the ring oscillator sensor and generating a warning signal indicative of reliability degradation if at least one of: (i) a measured or estimated oscillation frequency is below a warning threshold frequency; or (ii) a measured or estimated rate of change in a difference between measured oscillation frequencies exceeds an acceptable rate of change threshold.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
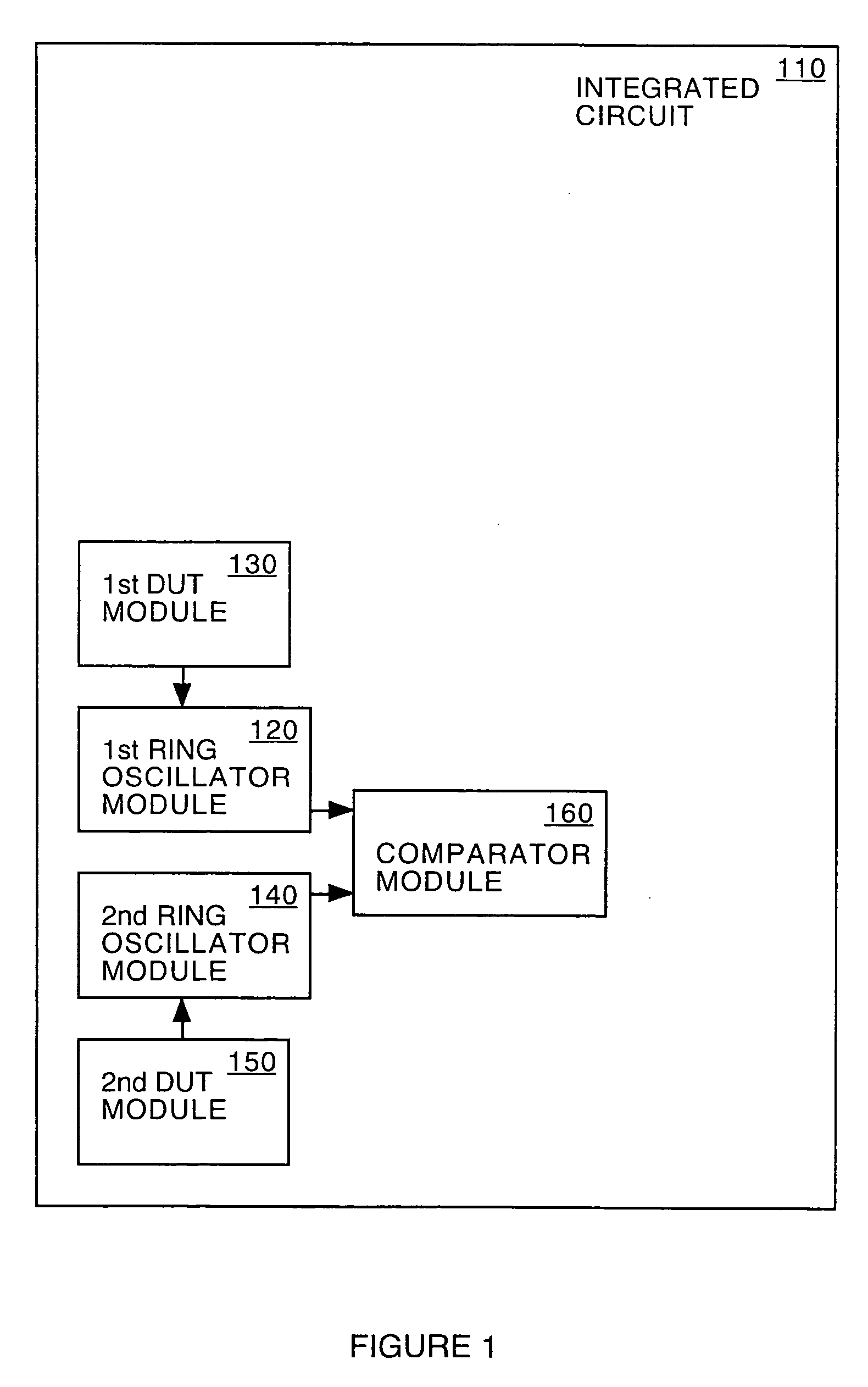
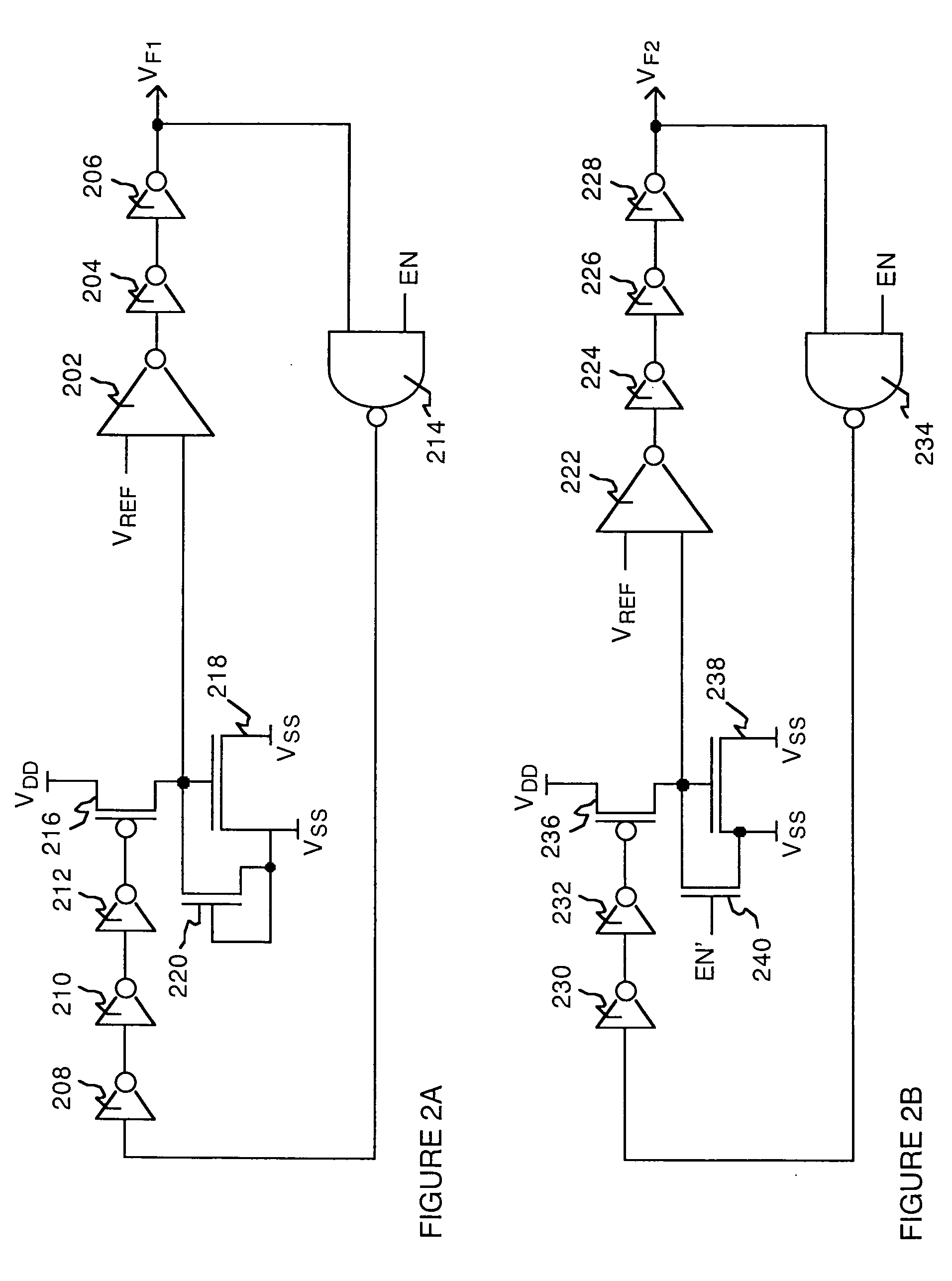
System and method for measuring time dependent dielectric breakdown with a ring oscillator
InactiveUS20050212547A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityGate leakage current
An integrated circuit, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, includes a first device under test (DUT) module coupled to a first ring oscillator module and a second DUT module coupled to a second ring oscillator module. A dielectric layer of the first DUT is stressed during a first mode, thereby causing time dependent dielectric breakdown in the first dielectric layer. A dielectric layer of the second DUT is maintained as a reference. The operating frequency of the first ring oscillator module, during a second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current of the stressed dielectric layer. The operating frequency of the second ring oscillator module, during the second mode, is a function of a gate leakage current the reference dielectric layer. The integrated circuit may also include a comparator module for generating an output signal as a function of a difference between the operating frequency of the first and second ring oscillator modules.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
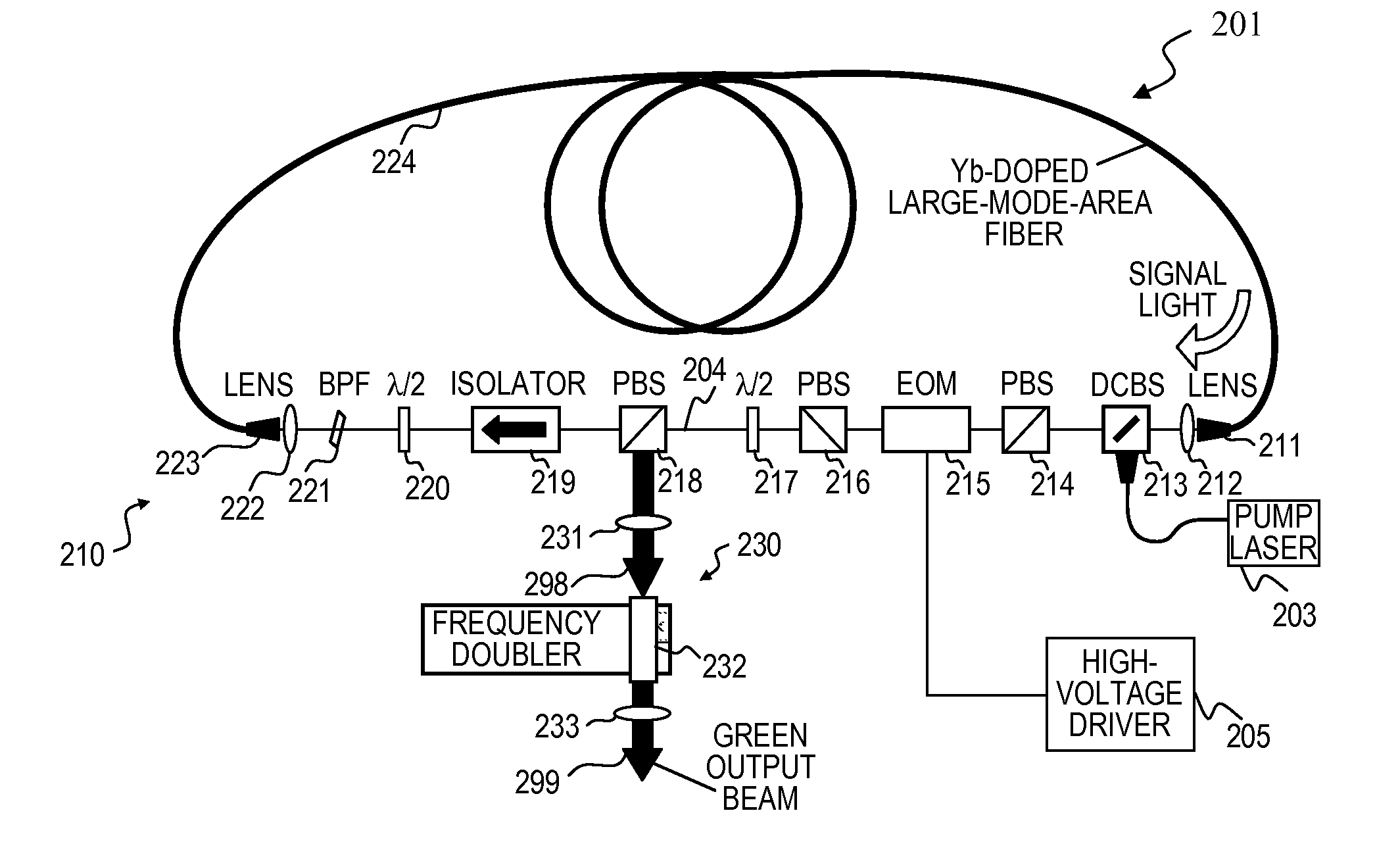
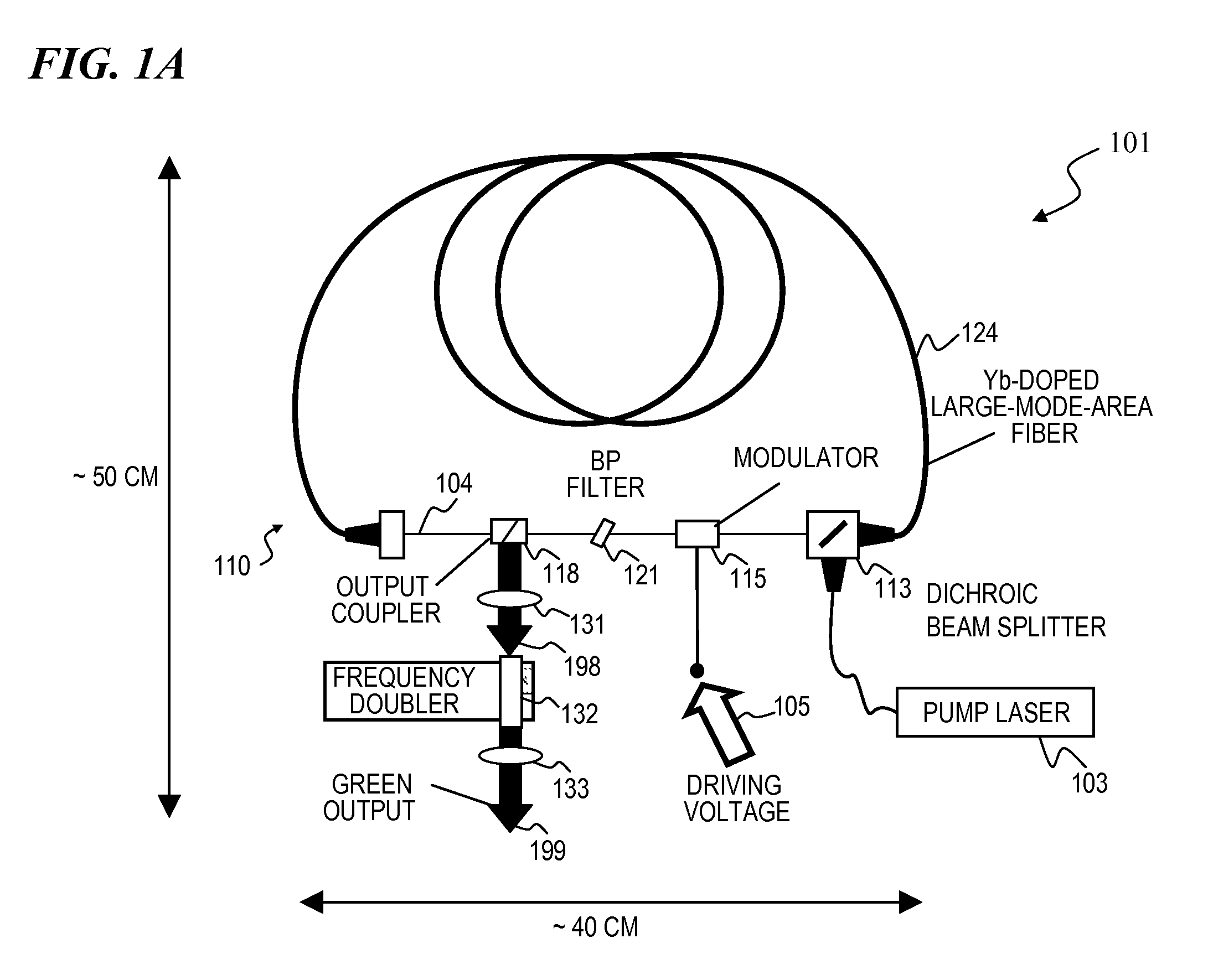
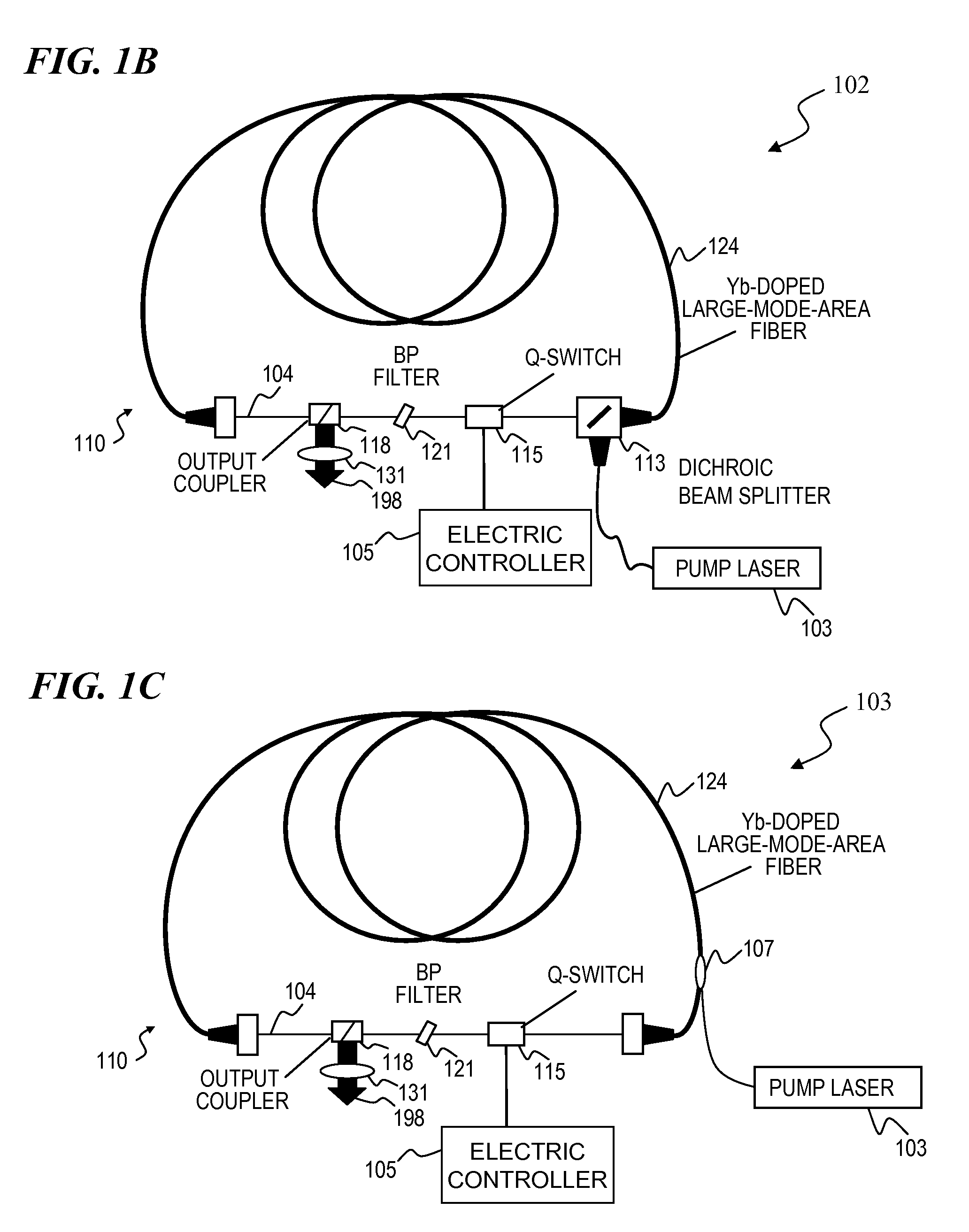
High-power, pulsed ring fiber oscillator and method
InactiveUS7876803B1Low costSmall footprintLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsBand-pass filterUltraviolet
A ring laser includes a large-core rare-earth-doped fiber ring-connected with a free-space path having an electro-optic switch, output coupler, and intracavity band-pass filter to enforce lasing operation in narrow wavelength range. In some cavity-dumped modes, the laser is configured in a similar manner, except that an output coupler is omitted since the optical power is extracted from the laser cavity by the electro-optic switch itself. The same laser can be configured to operate in Q-switched and / or cavity-dumping modes as well as in hybrid modes (e.g., partial Q-switch, followed by cavity dumping, or even CW). In some embodiments, the laser can be used as, or inject laser light into, a regenerative solid-state amplifier, or a Raman laser, or can be also used to generate visible, ultra-violet, mid-infrared, and far-infrared (THz) radiation via nonlinear wavelength conversion processes. The various embodiments can use a power oscillator or seed-plus-amplifier MOPA configuration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
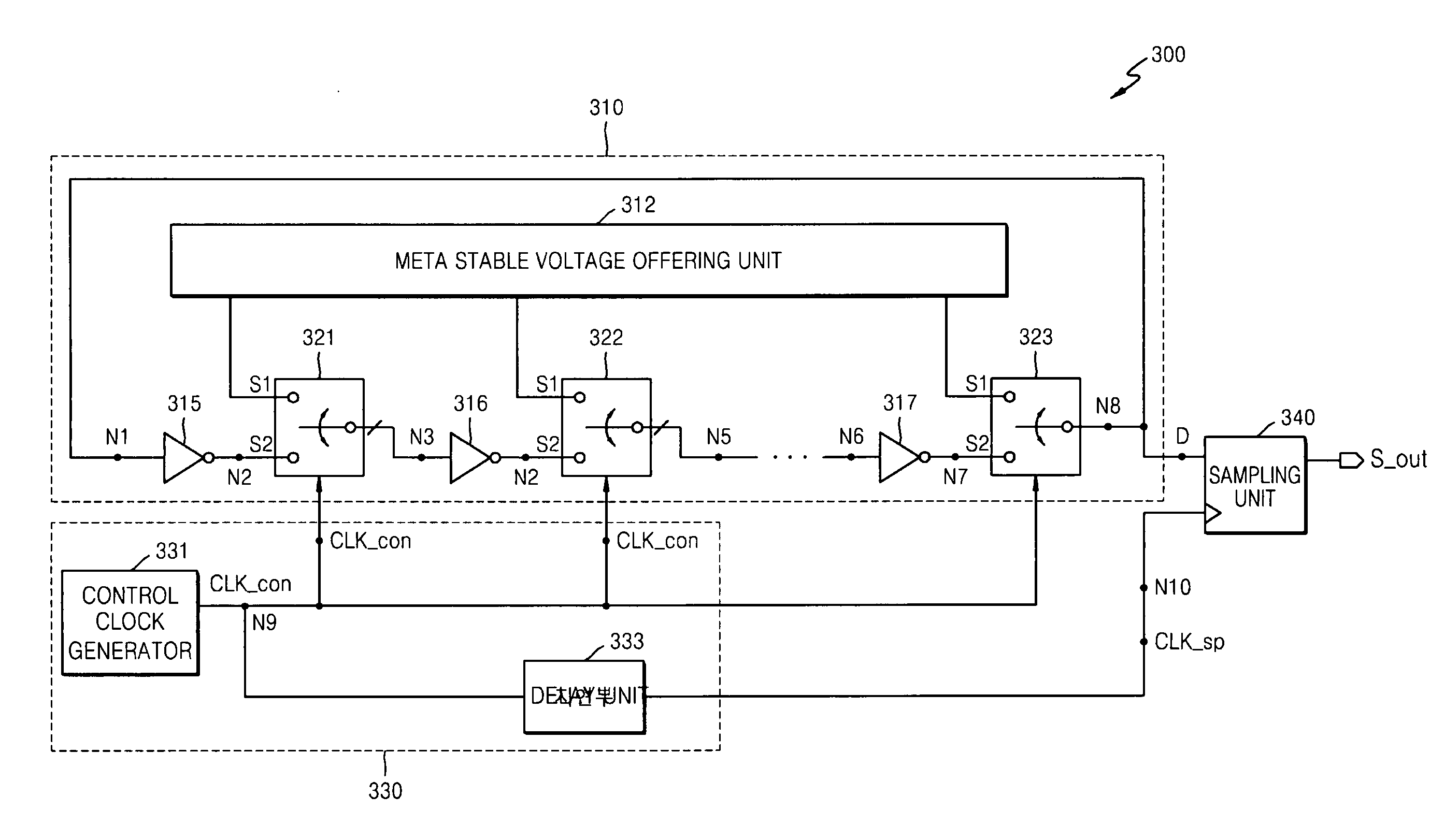
Random number generator
ActiveUS20090106339A1Improve throughputIncrease in areaRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsControl signalEngineering
Provided is a random number generator including: a clock generator outputting first and second control signals; a ring oscillator (RO) block receiving a meta stable voltage and performing an oscillation operation using the meta stable voltage in response to the first control signal; and a sampling unit sampling an output signal according to the oscillation operation in response to the second control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ring oscillator delta sigma ADC modulator with replica path nonlinearity calibration
ActiveUS20120194369A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionNonlinear distortionIntegrator
An embodiment provides a continuous-time delta-sigma modulator for analog-to-digital conversion. The modulator includes a signal path generating including a ring voltage controlled oscillator driven by an analog input signal. The signal path produces digital values by sampling the ring voltage controlled oscillator. A calibration circuit measures nonlinear distortion coefficients in a replica of the signal path. A nonlinearity corrector corrects the digital values based upon determined nonlinear distortion coefficients. Preferred embodiment ADC ΔΣ modulators do not require any analog integrators, feedback DACs, comparators, or reference voltages, and do not require a low jitter clock.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
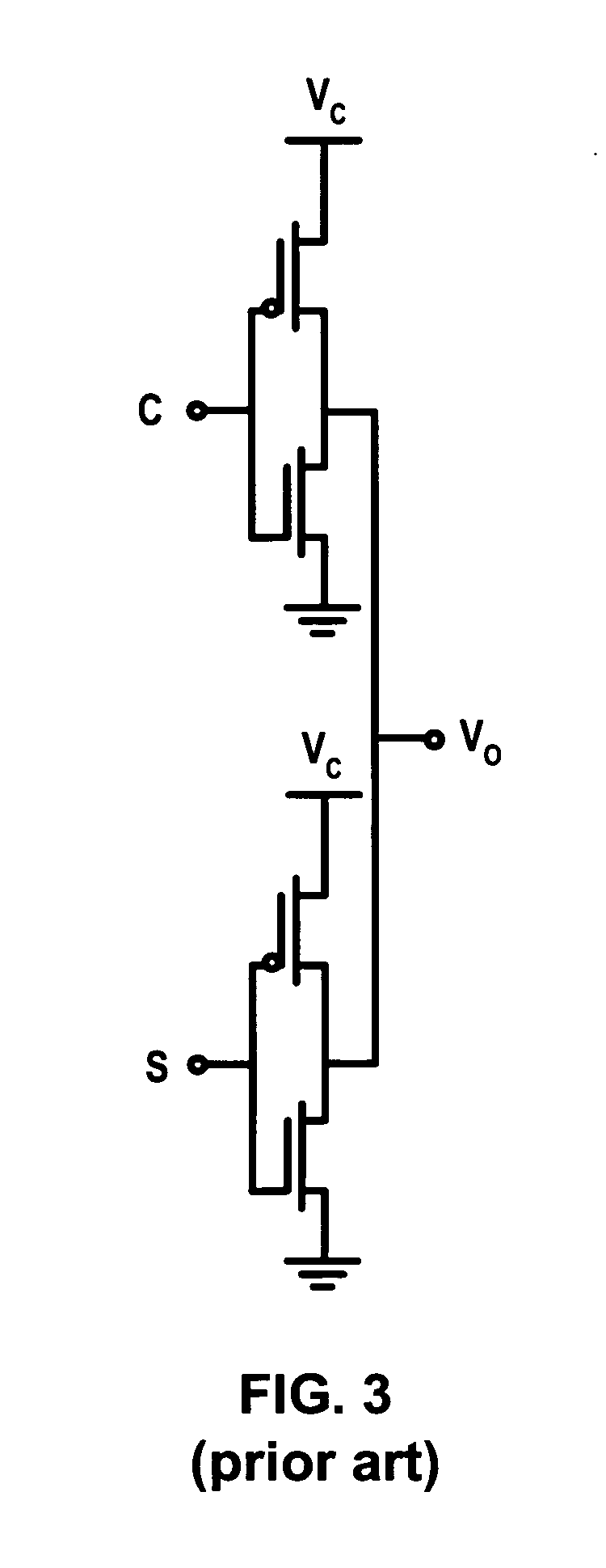
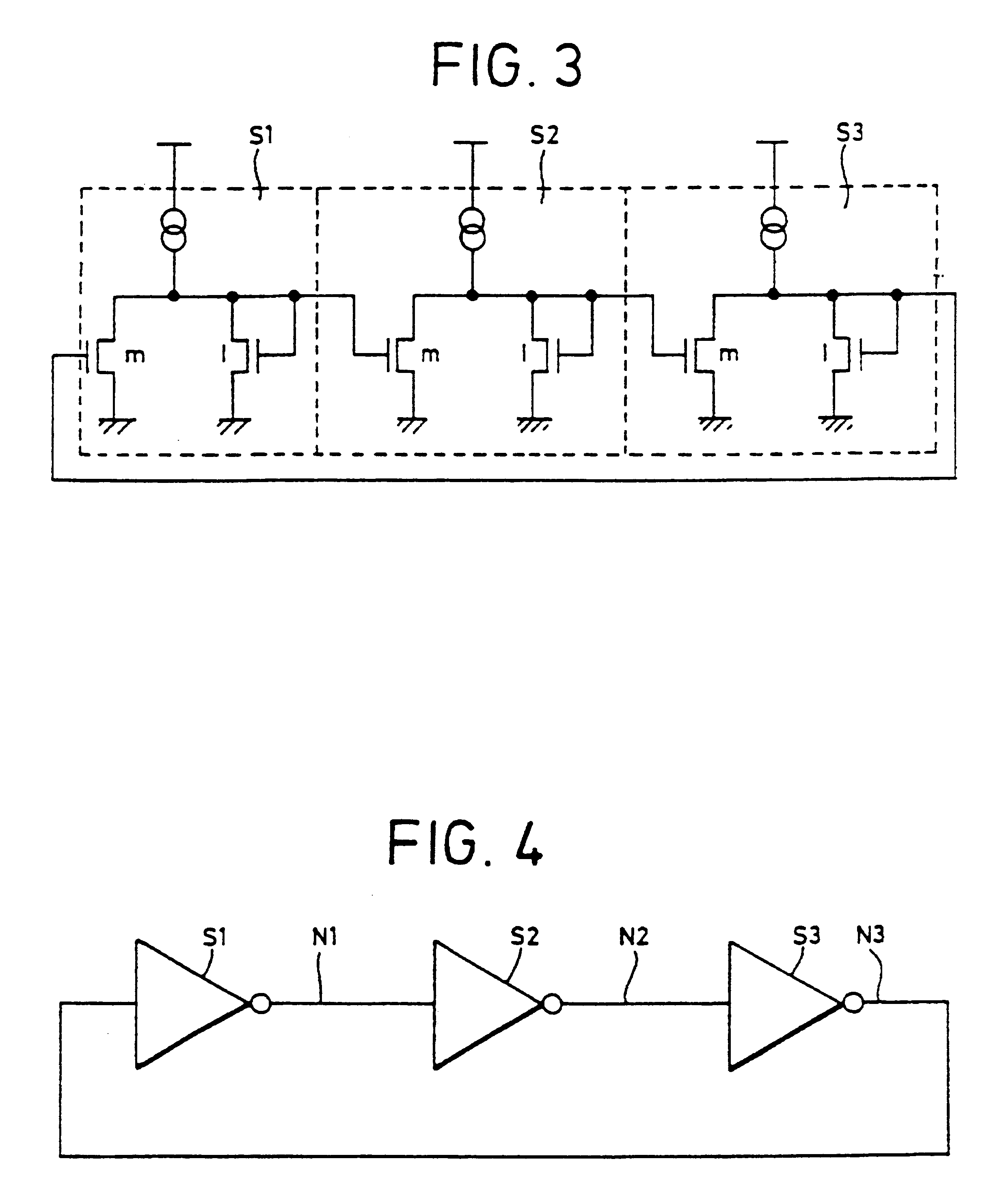
Ring oscillators having inverting and delay elements
InactiveUS6028490APulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsCharge currentDelayed time
An oscillator circuit constituted by connecting in a ring an odd number of stages of inverting delay circuits comprising inverting elements, for example, inverters INV1, INV2, and INV3, and delay elements D1, D2, and D3 connected to the output terminals of the inverting elements. In each delay element, the capacitor is charged and discharged in accordance with the output signal level from the inverter, the voltage of the capacitor and the reference voltage are compared by a comparison circuit, and a signal in accordance with the result of comparison is input to the inverting delay circuit of the next stage, therefore the delay time can be controlled by controlling the charging current of the delay element and the oscillation frequency can be controlled in accordance with this. Accordingly, the control property thereof is good, the range of variation can be broadened, and a reduction of jitter can be realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
Ring oscillator for temperature sensor, temperature sensor circuit, and semiconductor device having the same
InactiveUS20090096495A1Substrate temperature can be accuratelyAccurate measurementPulse automatic controlThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsMOSFETPower semiconductor device
A ring oscillator includes an odd number of unit circuits connected in series each of which includes an inverter. Each of the unit circuits includes the inverter and a MOSFET. The MOSFET is an FET which is a temperature sensor, and uses a drain-source leakage current in a state that the FET is normally turned off.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Digitally controlled oscillator and associated method
ActiveUS7330081B1Reduce riskReduce noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceDigital controlled oscillator
A digitally controlled oscillator circuit is provided that comprises a ring oscillator including multiple inverters; multiple digitally controlled capacitors (DCCs), each coupled to apply a digitally controllable amount of capacitance to an output of a different one of the inverters; and control circuitry operable to change an amount of capacitance applied to each inverter during operation of the ring oscillator and to cause the multiple DCCs to apply substantially the same amounts of capacitance to each of the inverter throughout operation of the ring oscillator.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
Gated ring oscillator for a time-to-digital converter with shaped quantization noise
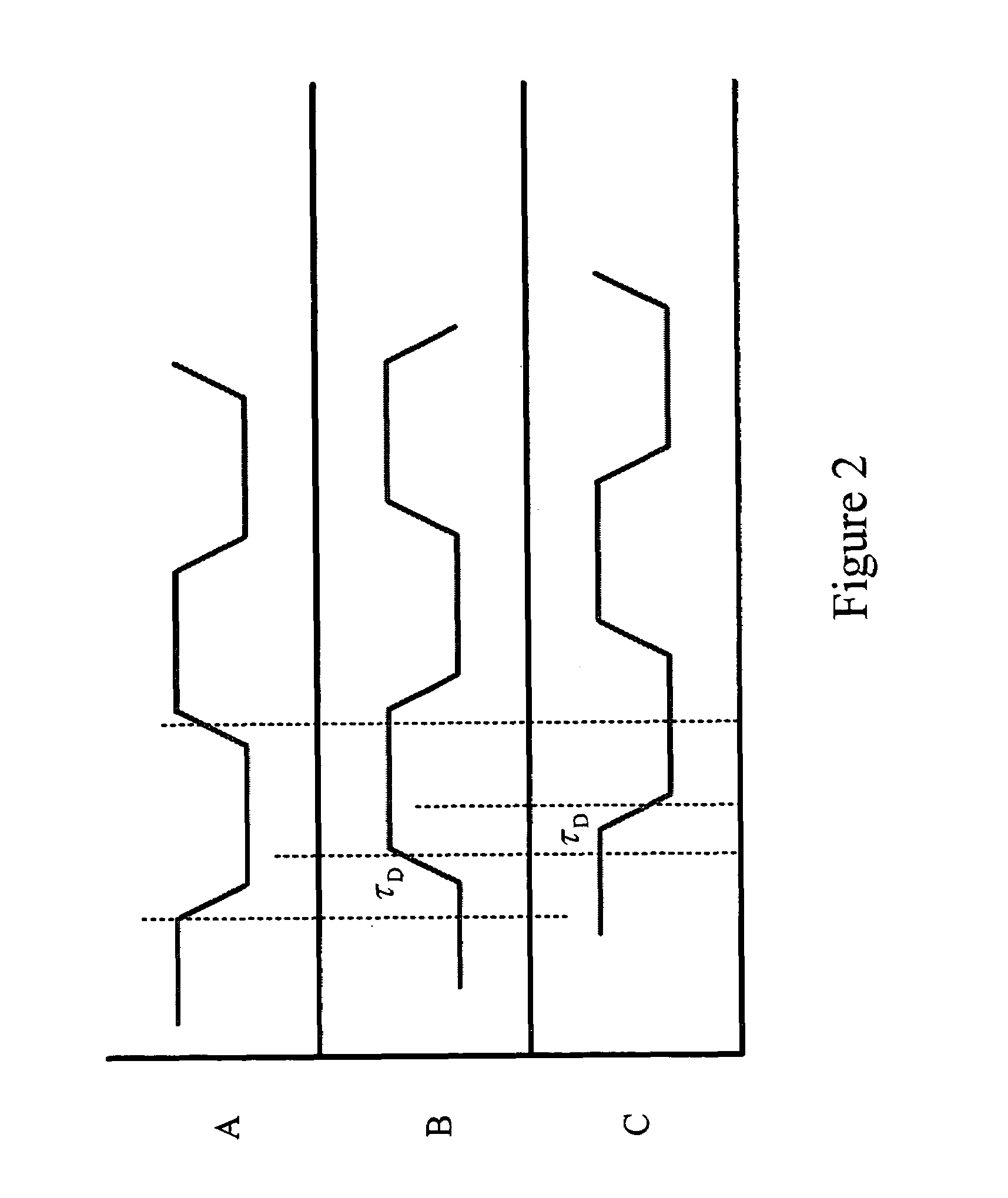
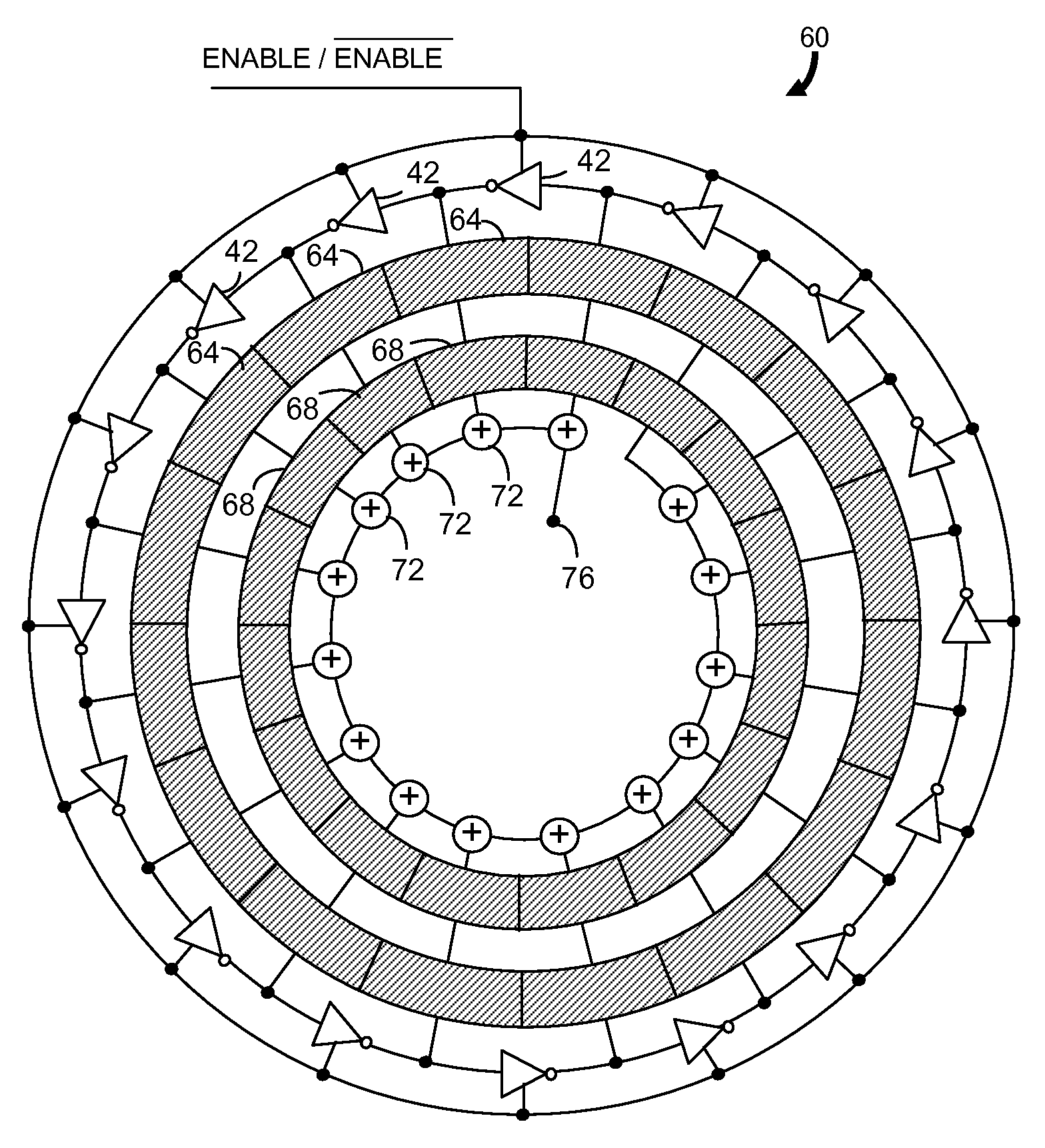
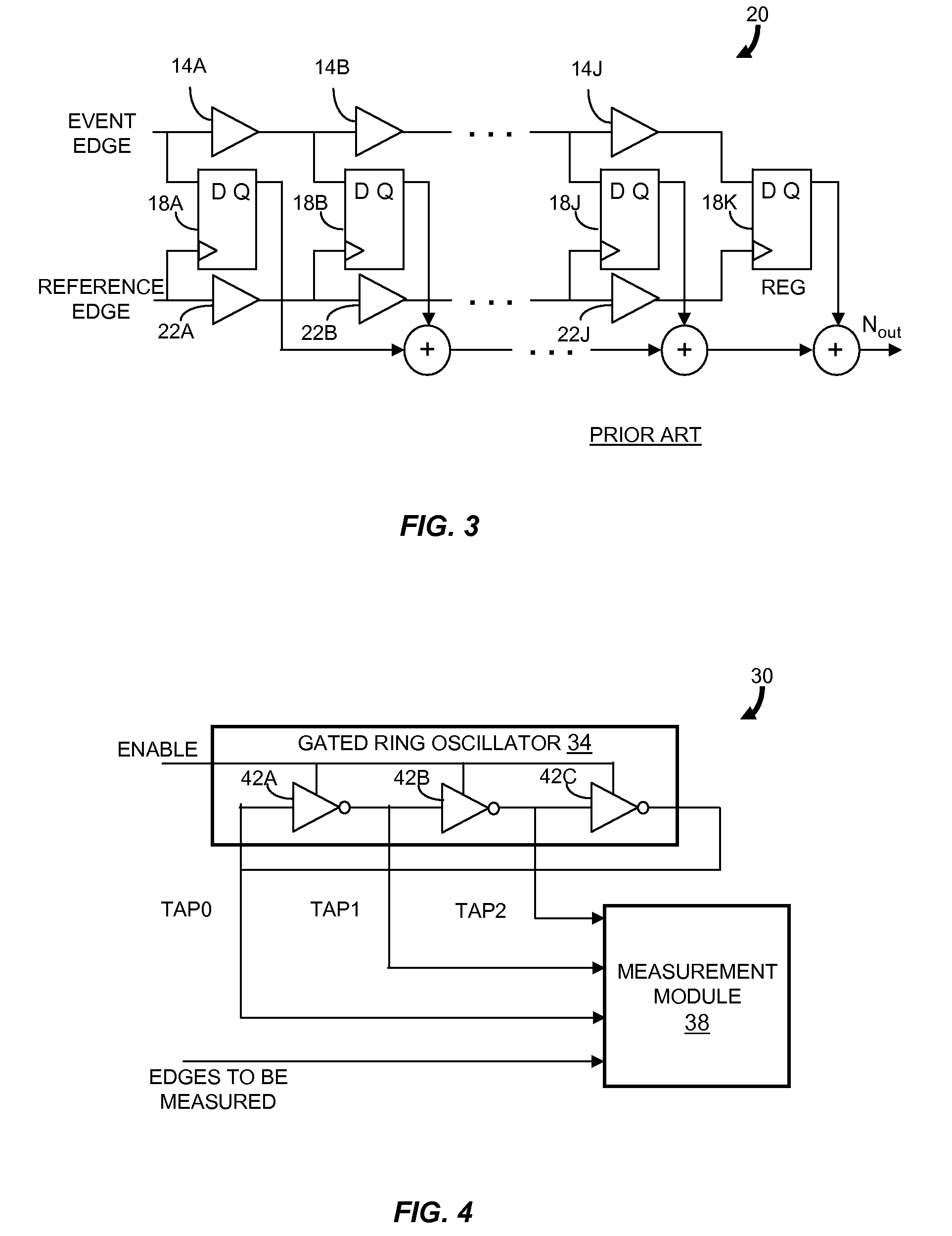
ActiveUS20080069292A1Resolution timeContinuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersImage resolutionNoise shaping
Described is a compact, lower power gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter that achieves first order noise shaping of quantization noise using a digital implementation. The gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter includes a plurality of delay stages configured to enable propagation of a transitioning signal through the delay stages during an enabled state and configured to inhibit propagation of the transitioning signal through the delay stages during a disabled state. Delay stages are interconnected to allow sustained transitions to propagate through the delay stages during the enabled state and to preserve a state of the gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter during the disabled state. The state represents a time resolution that is finer than the delay of at least one of the delay stages. A measurement module determines the number of transitions of the delay stages.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Random number generator with ring oscillation circuit
ActiveUS7424500B2Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceRandom number generatorsElectrical apparatusStable stateDelayed time
A random number generator includes a ring oscillator having an EX-OR gate and four inverters together forming a loop. This loop enters stable state for a start signal having the low level and oscillates for the start signal having the high level. When the start signal has a pulse of a width shorter than the loop's delay time, output nodes responsively, sequentially enter metastable state hovering between the high and low levels. The metastable waveform becomes smaller with time and finally disappears. As metastable state cannot be controlled in longevity, it disappears at any random number node. A counter thus outputs a signal serving as true random number data depending on the longevity of the metastable state. A random number generator miniaturized and having reduced power consumption, and of high performance can thus be implemented.
Owner:RENESAS LSI DESIGN CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com