Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
635results about "Active element network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
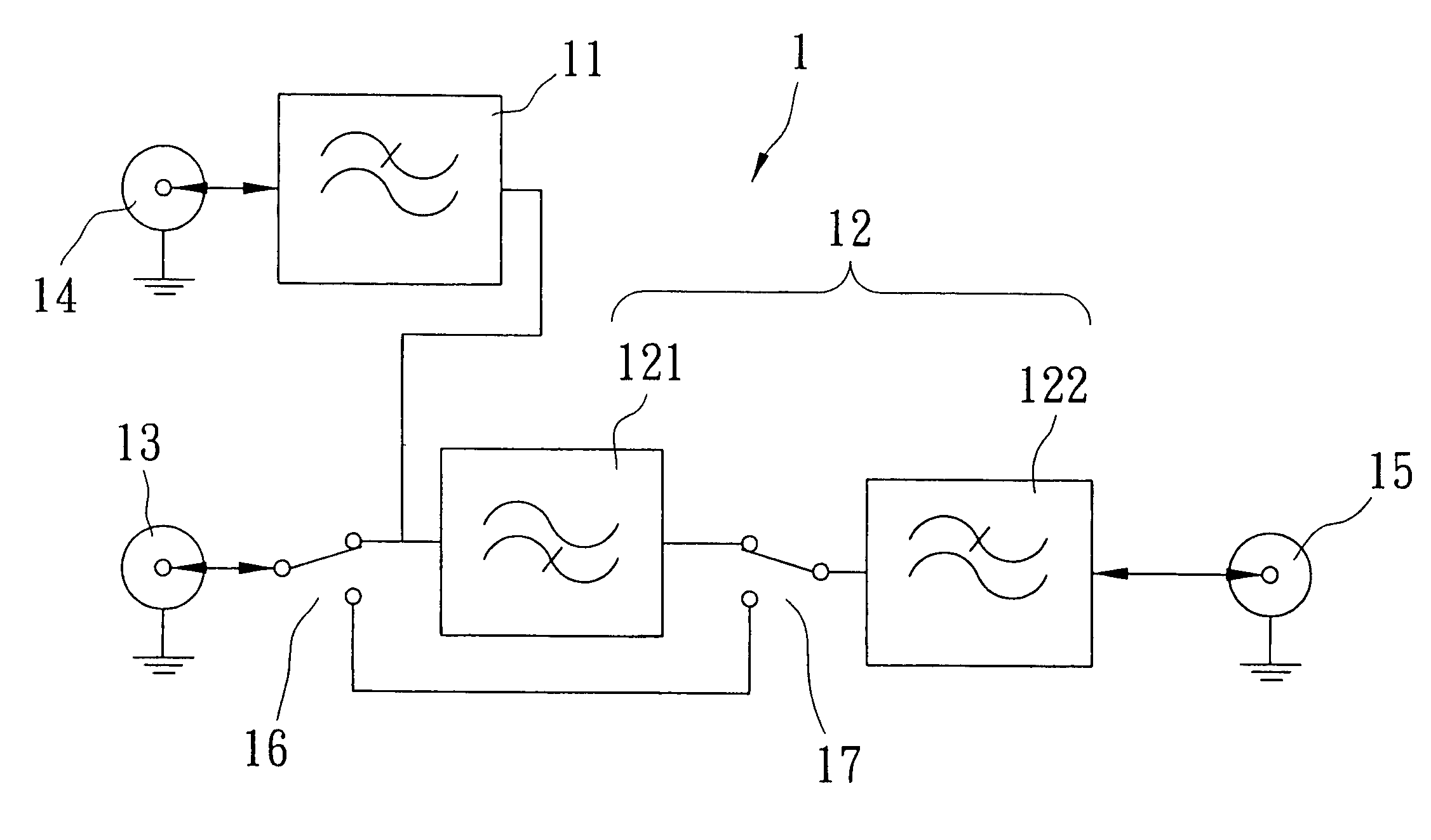
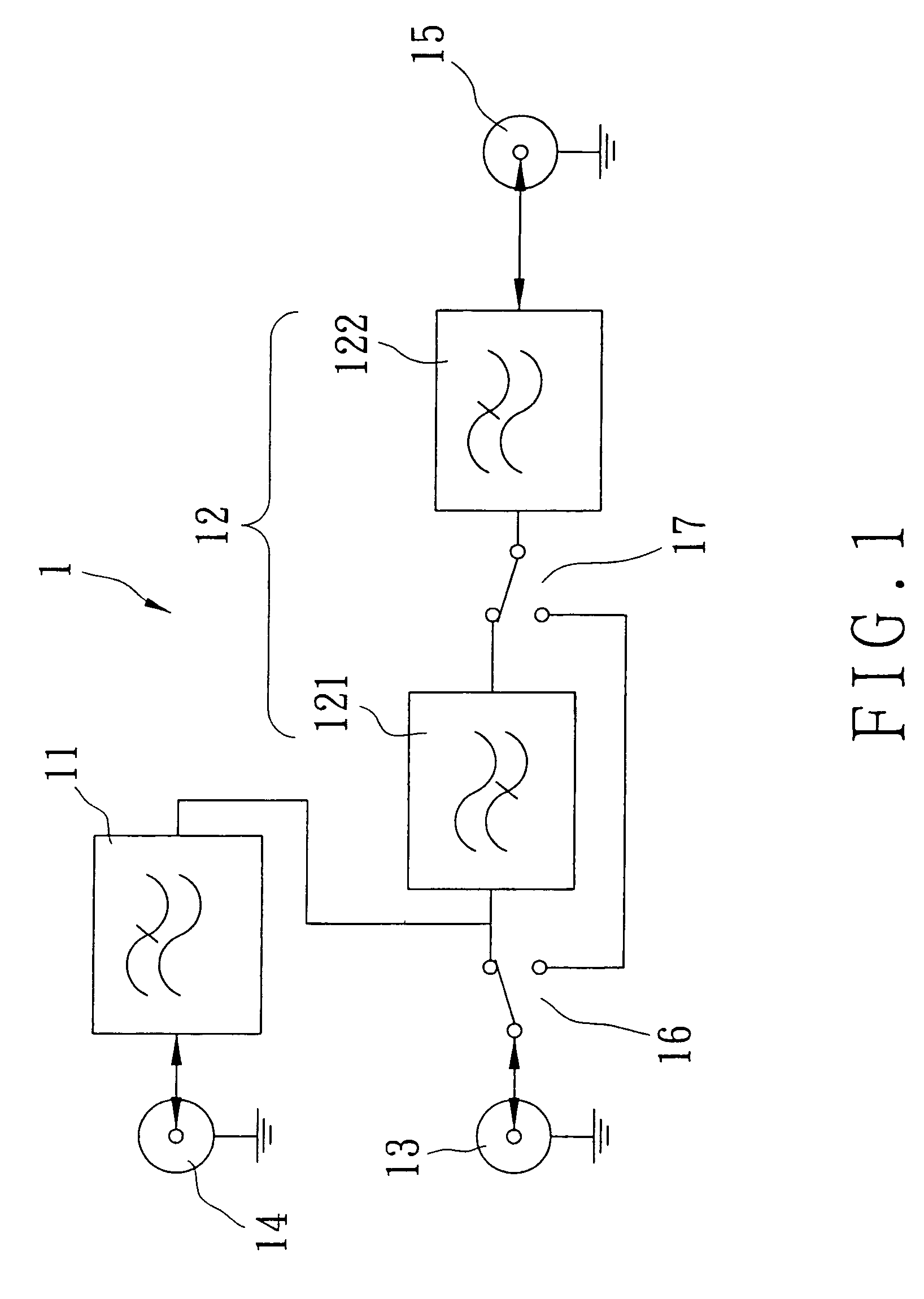
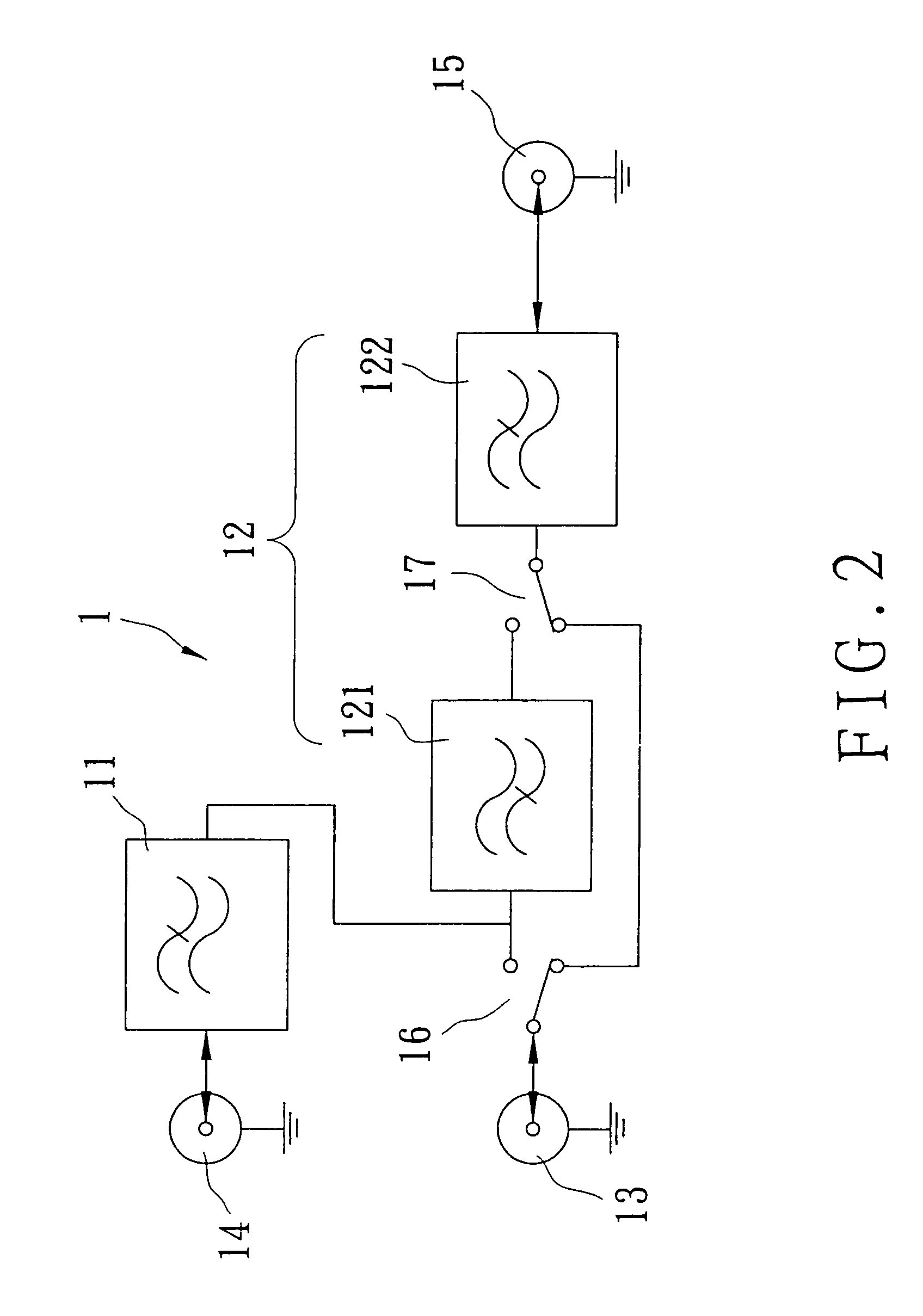
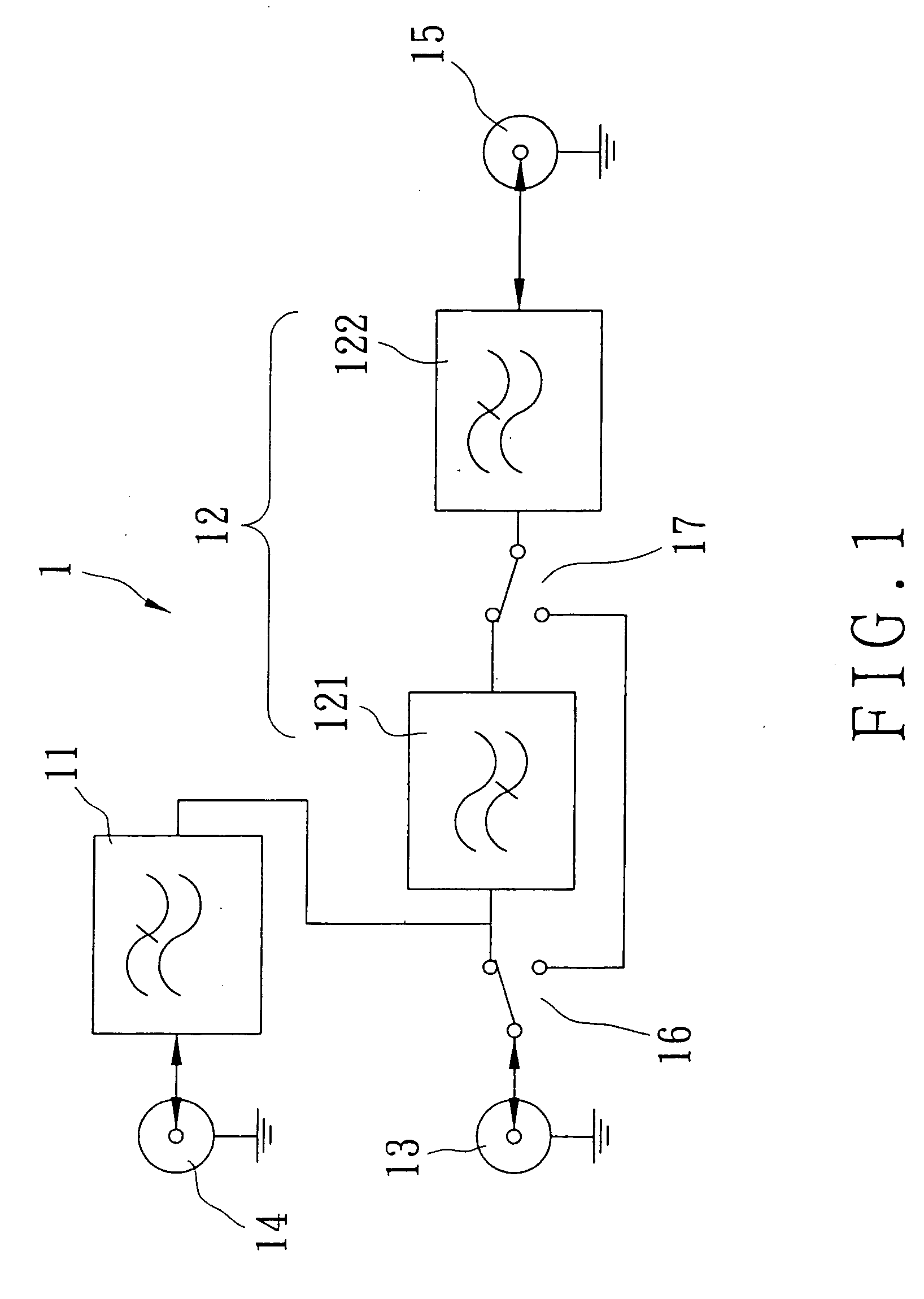
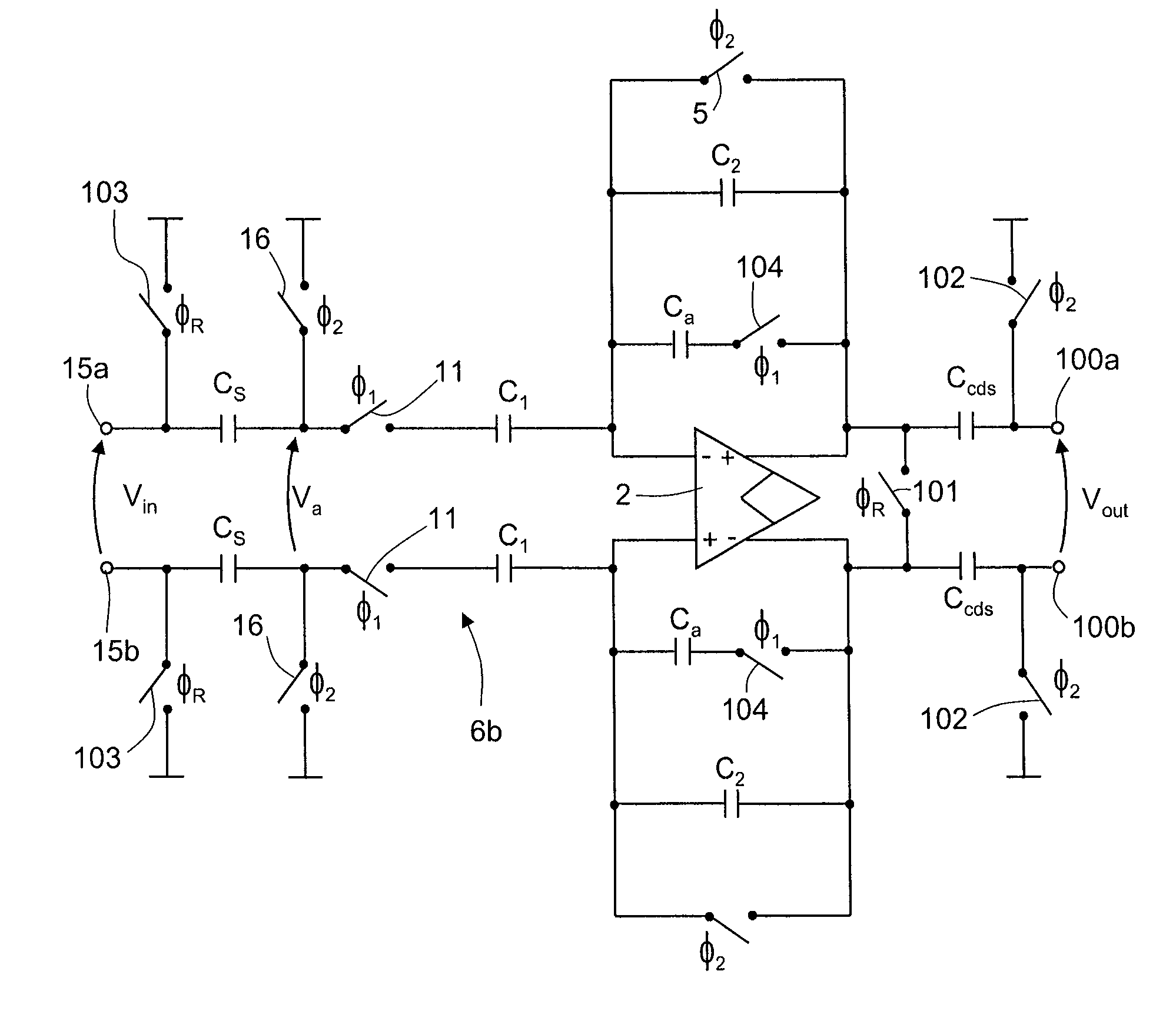
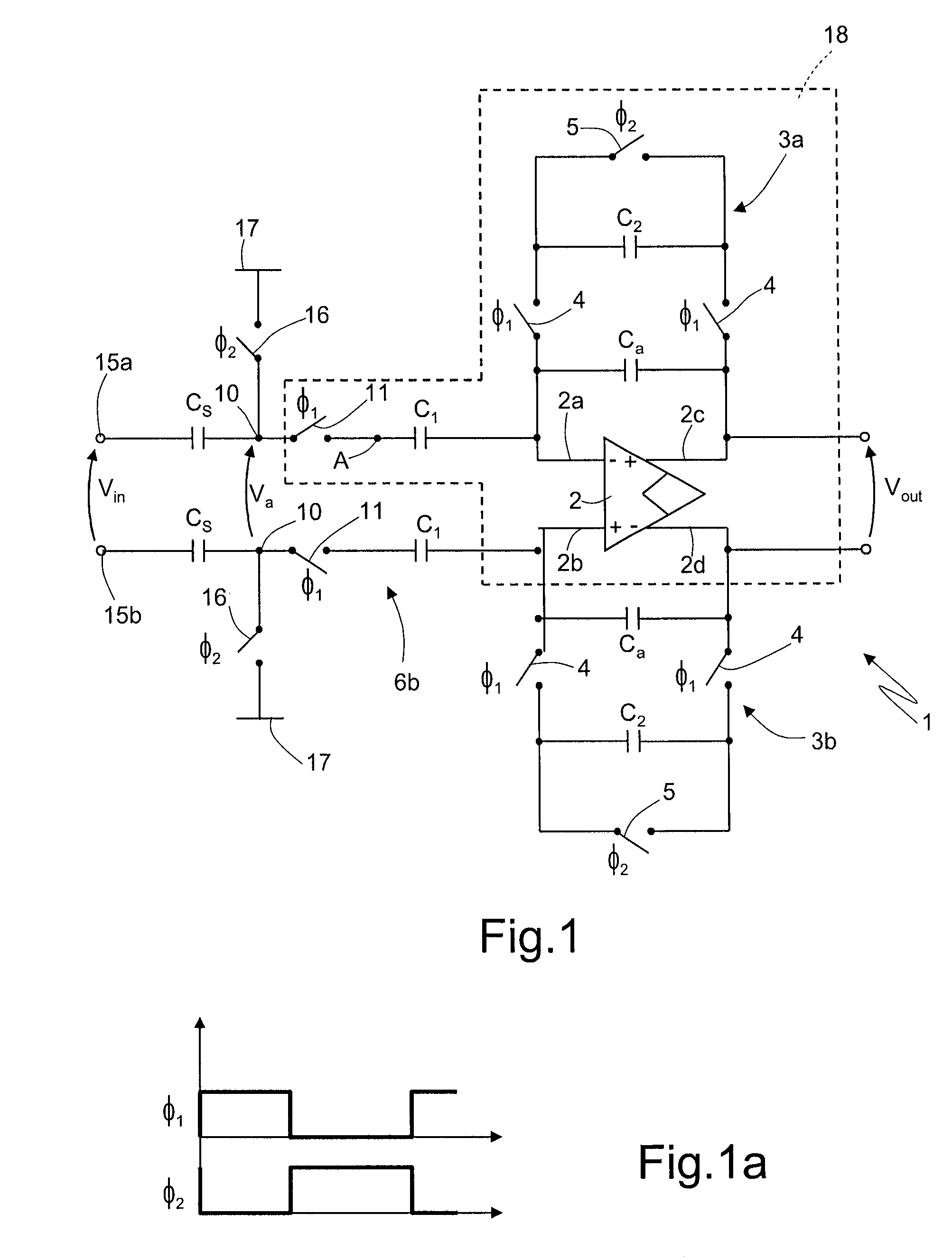
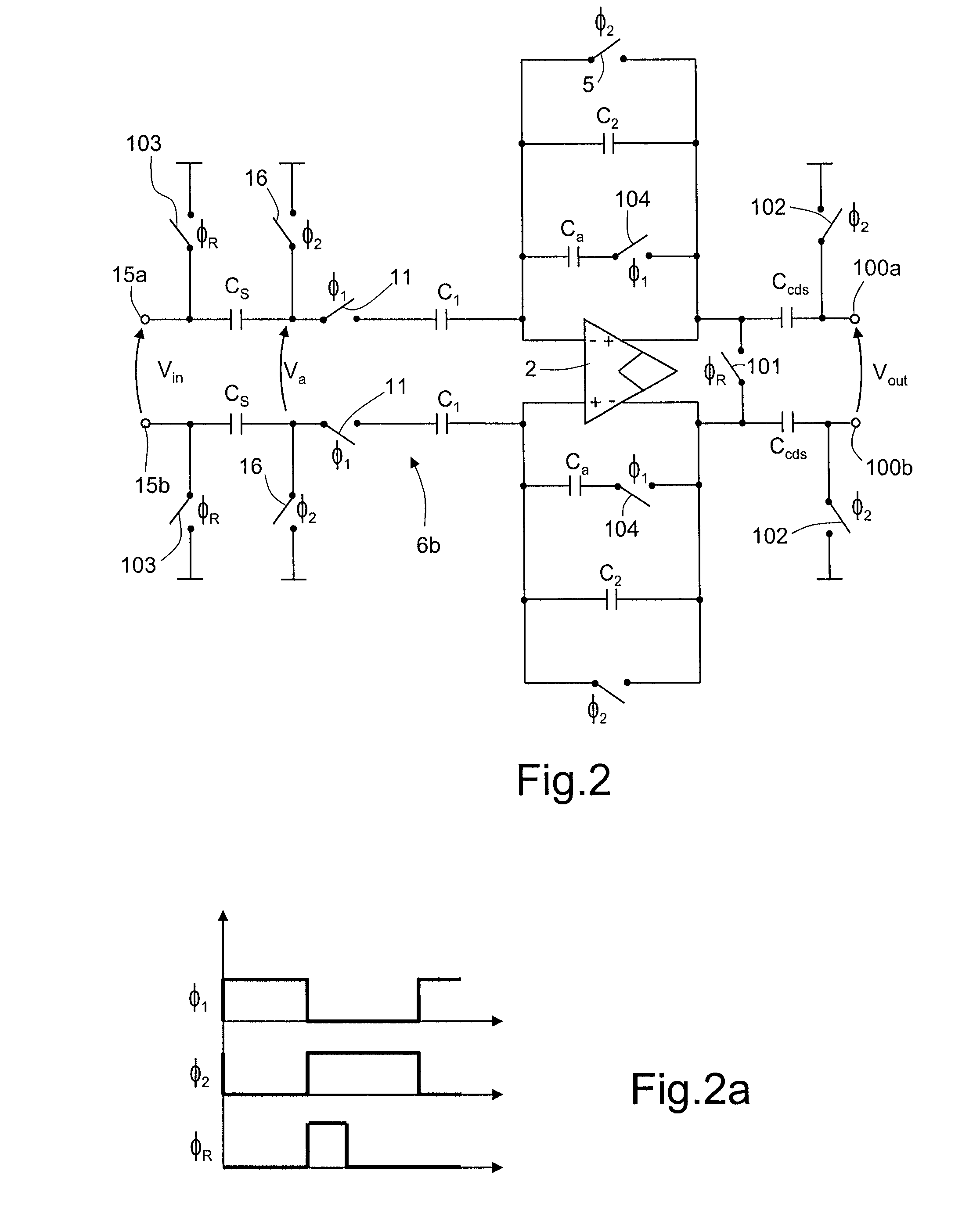
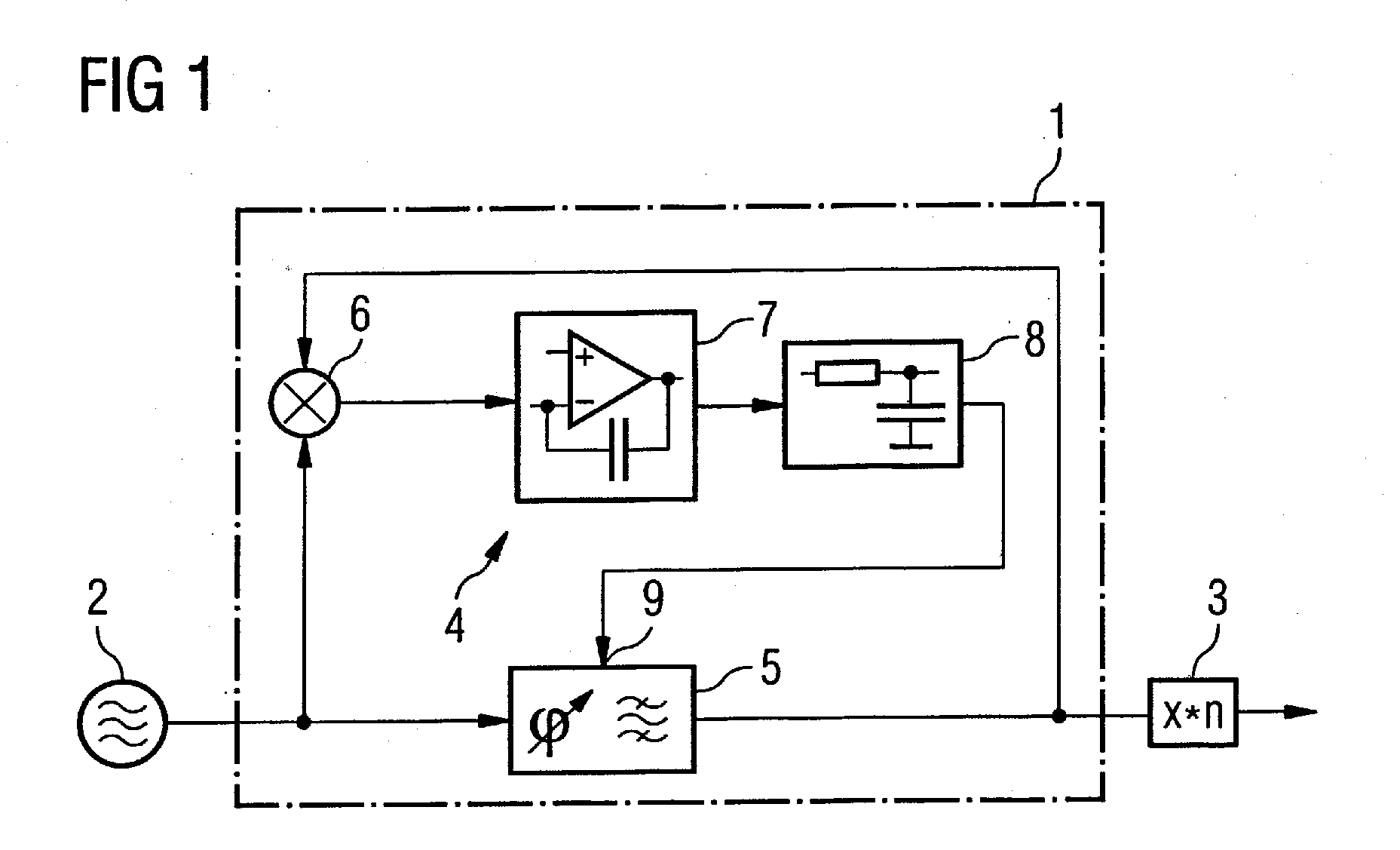
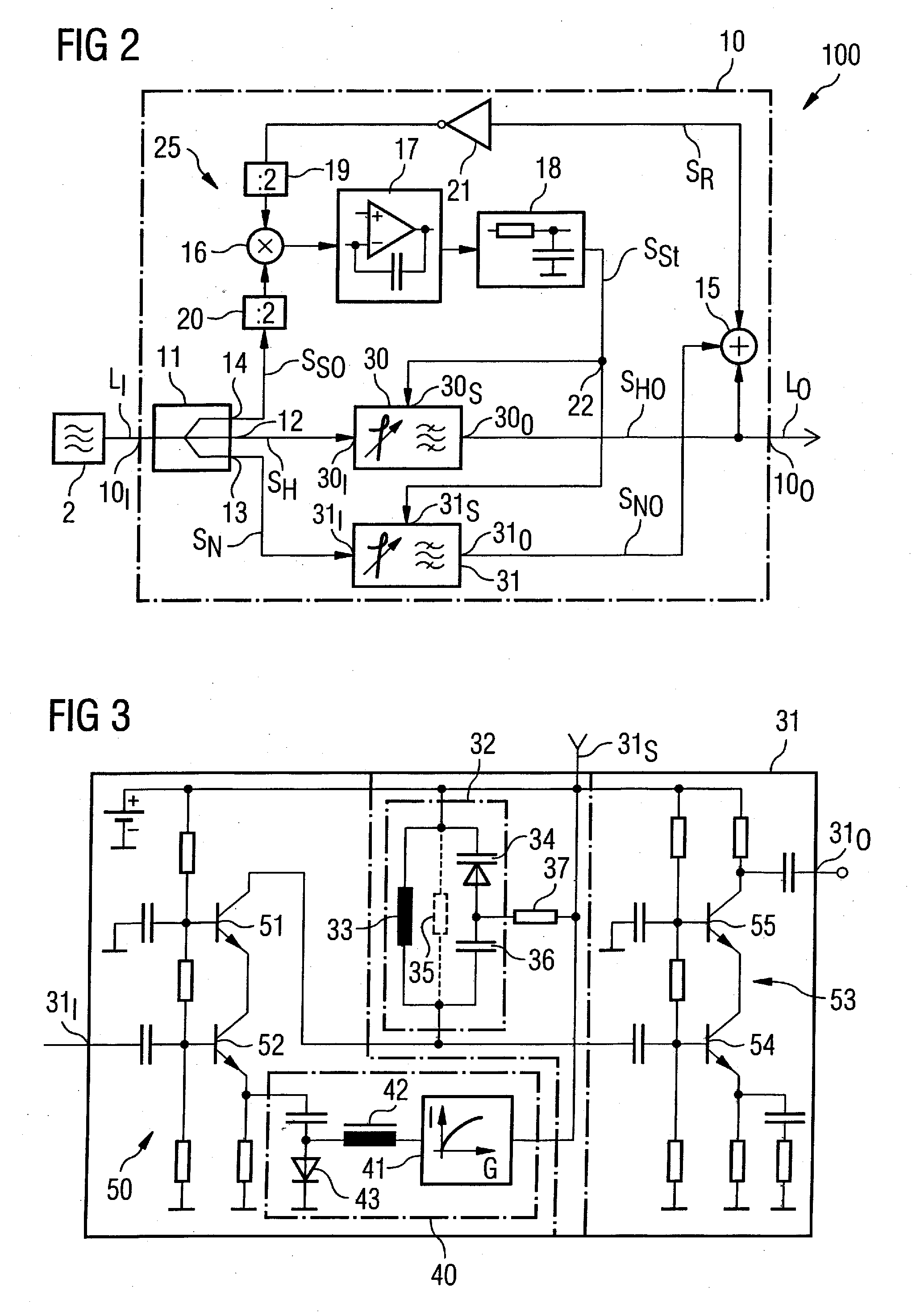
Notch filter for ripple reduction in chopper stabilized amplifiers
ActiveUS7292095B2Reduce ripple noiseFast signalAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
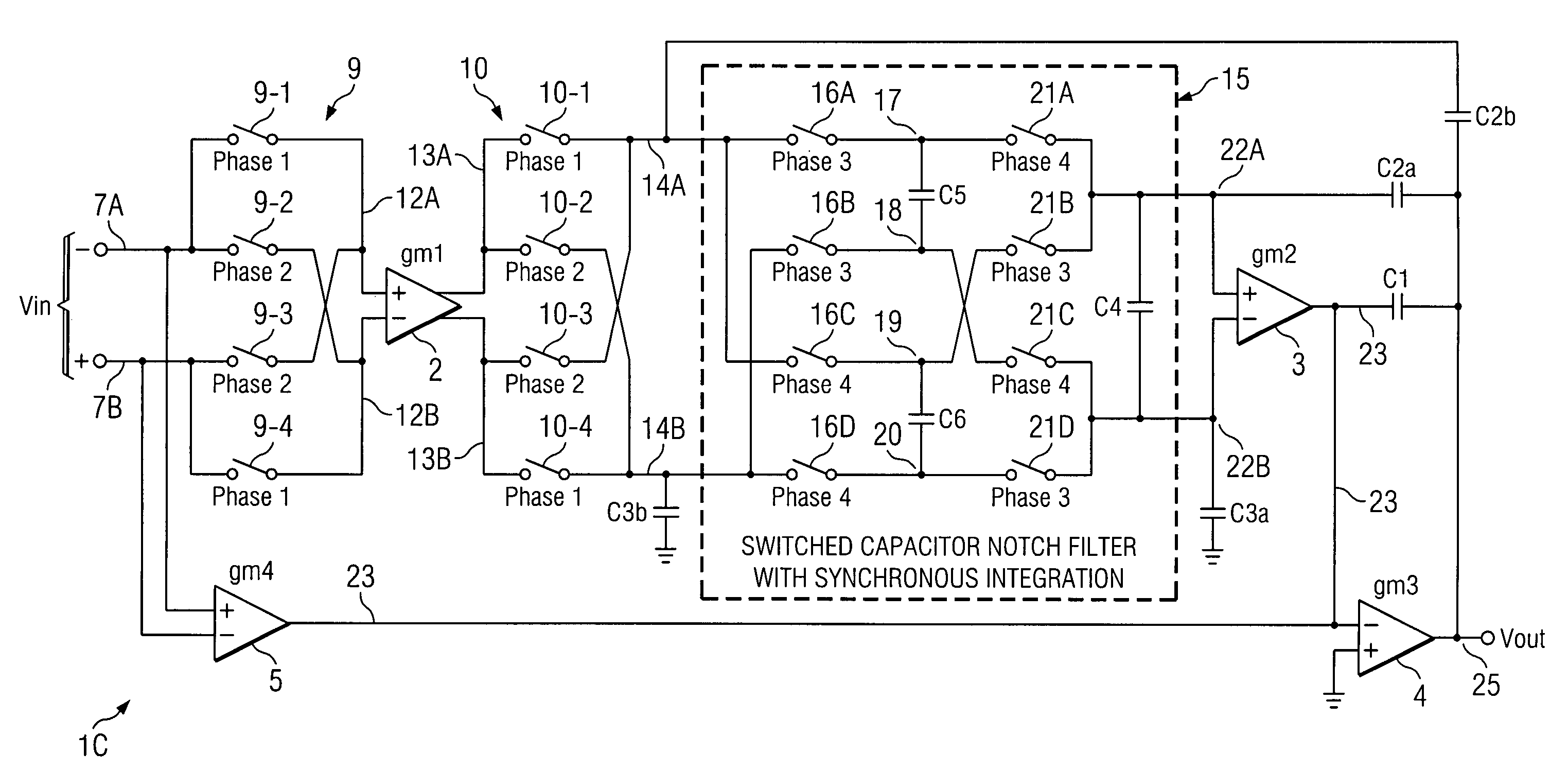
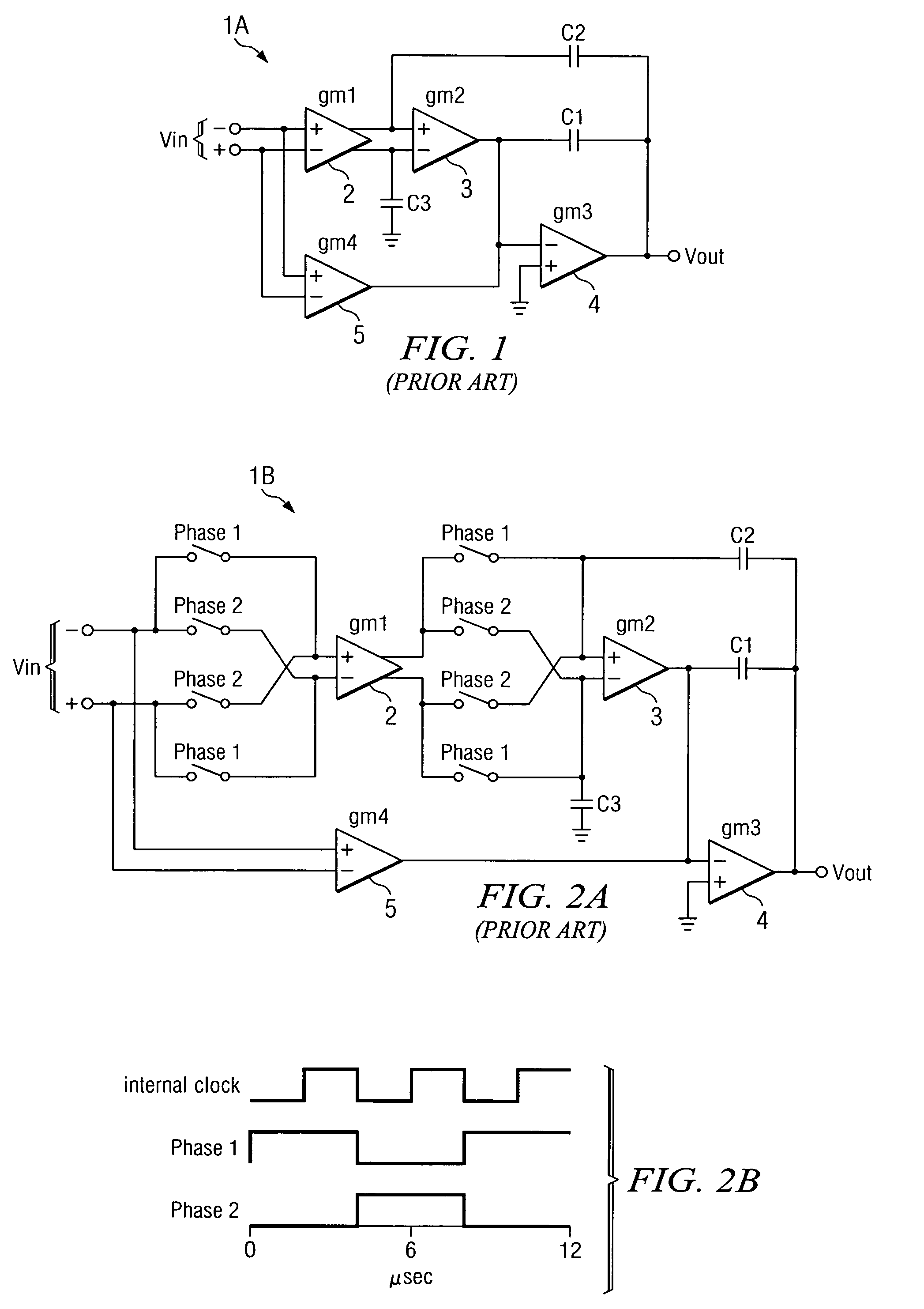
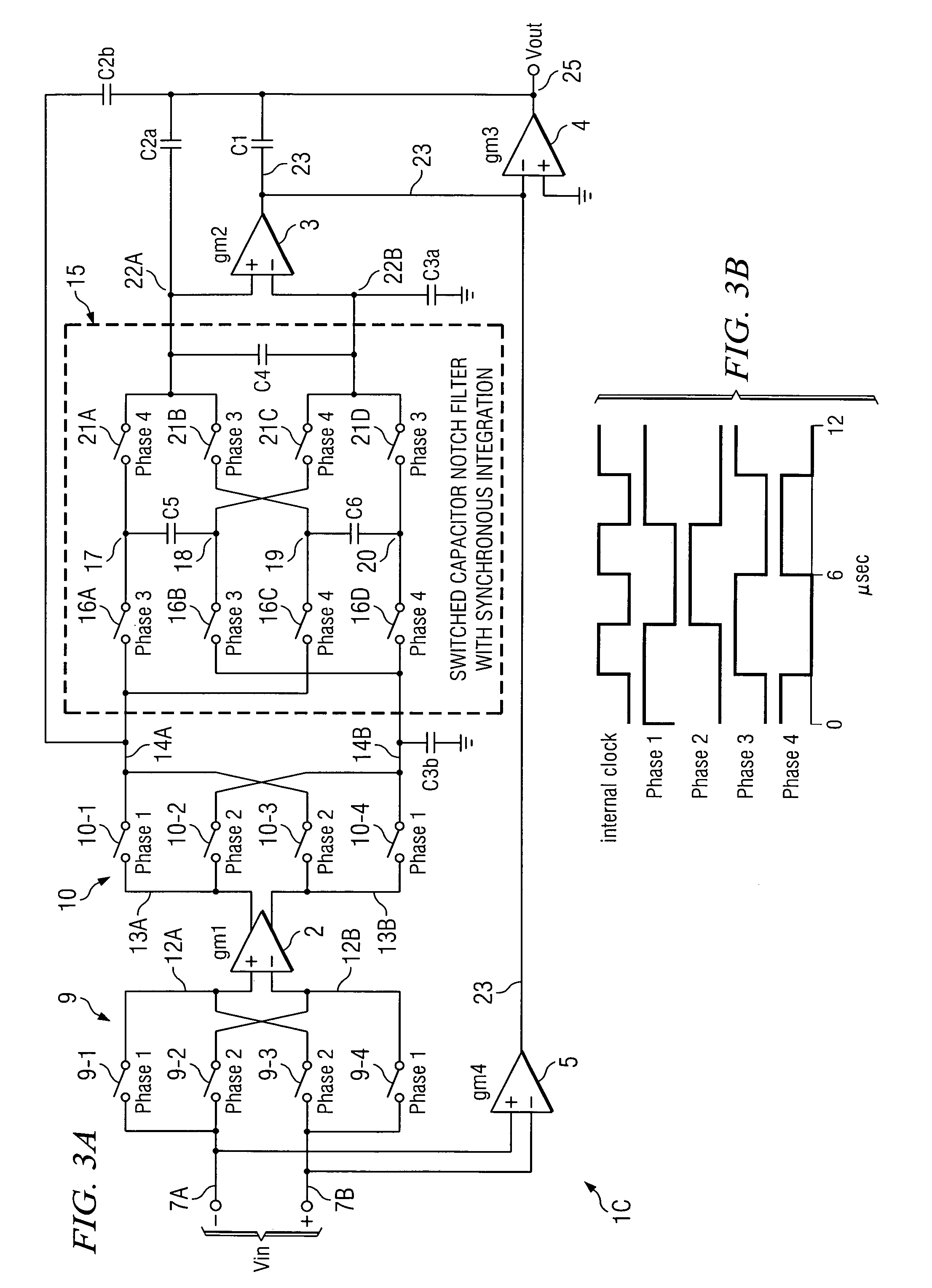
A chopper-stabilized amplifier receiving an input signal includes a first operational transconductance amplifier having an input chopper and an output chopper for chopping an output signal produced by the first operational transconductance amplifier. A switched capacitor notch filter filters the chopped output signal by operating synchronously with the chopping frequency of output chopper to filter ripple voltages that otherwise would be produced by the output chopper. In one embodiment, a second operational transconductance amplifier amplifies the notch filter output. The input signal is fed forward, summed with the output of the second operational transconductance amplifier, and applied to the input of a fourth operational transconductance amplifier. Ripple noise and offset are substantially reduced.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
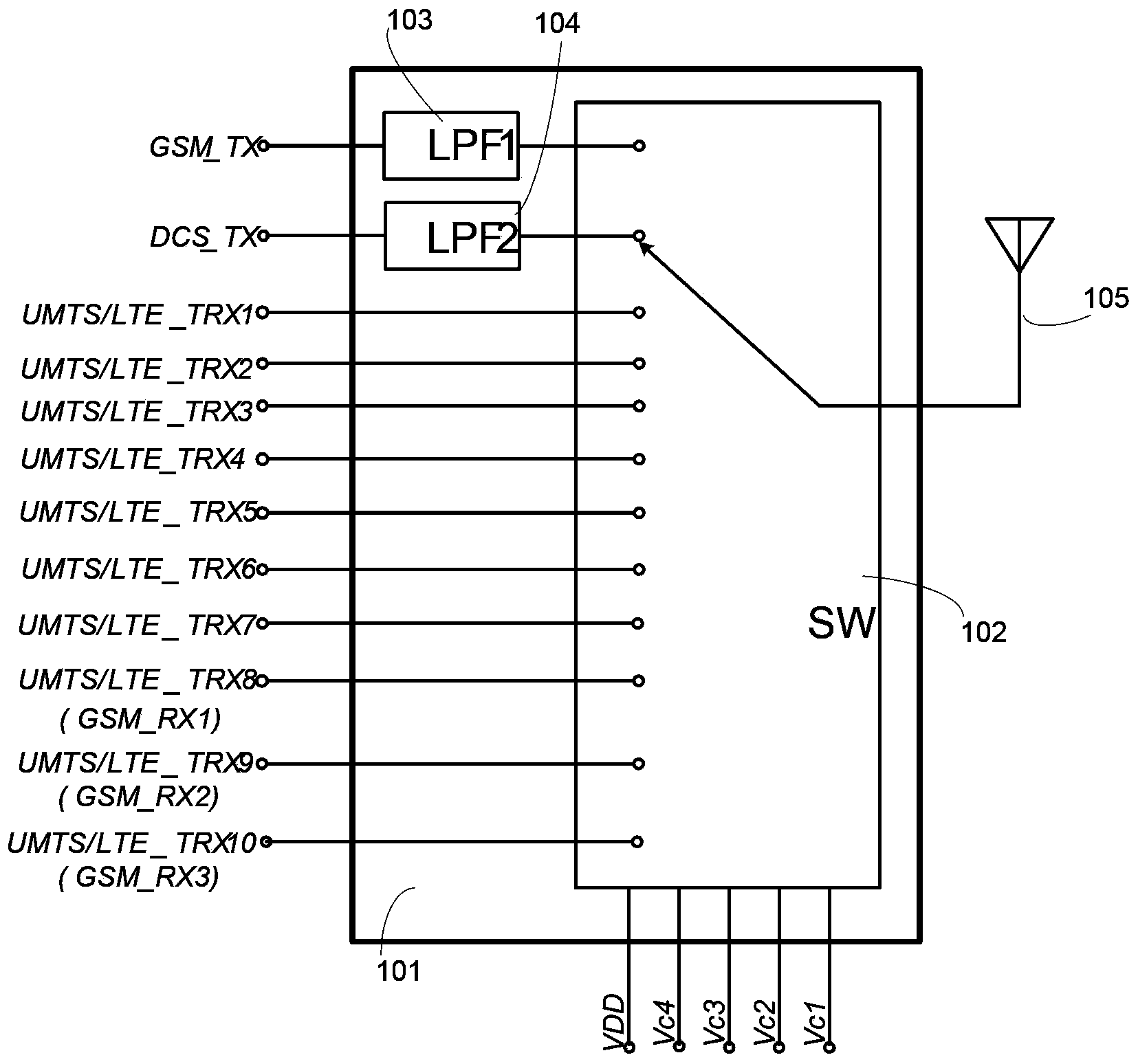
High-frequency switching circuit, high-frequency module, and wireless communications device
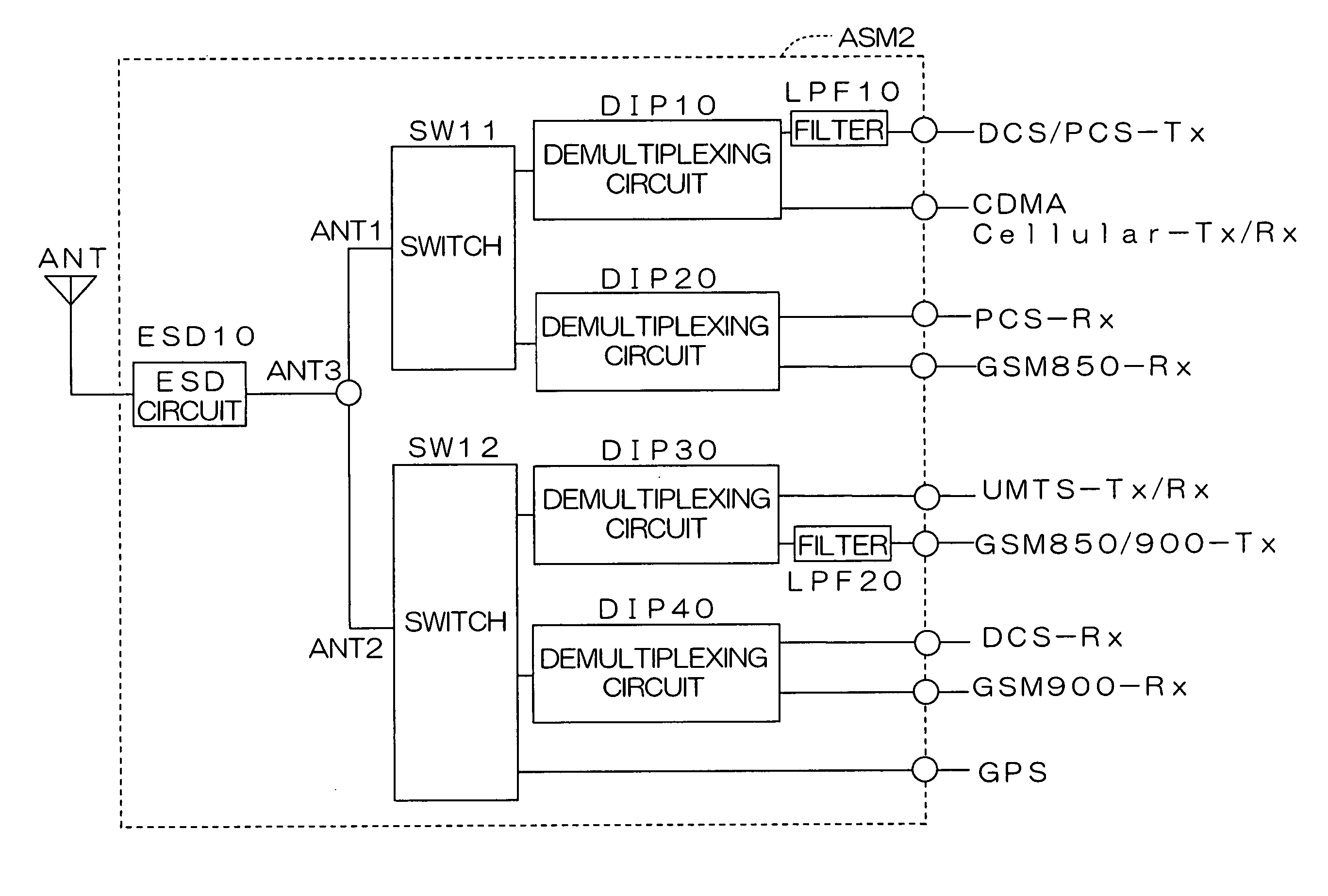
InactiveUS7596357B2Low costReduce designActive element networkTelephonic communicationCommunications systemEngineering
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Frequency agile filter using a digital filter and bandstop filtering
InactiveUS8385871B2Large dynamic rangeHigh transmission powerTransmission control/equlisationDigital technique networkBandpass filteringFrequency changer
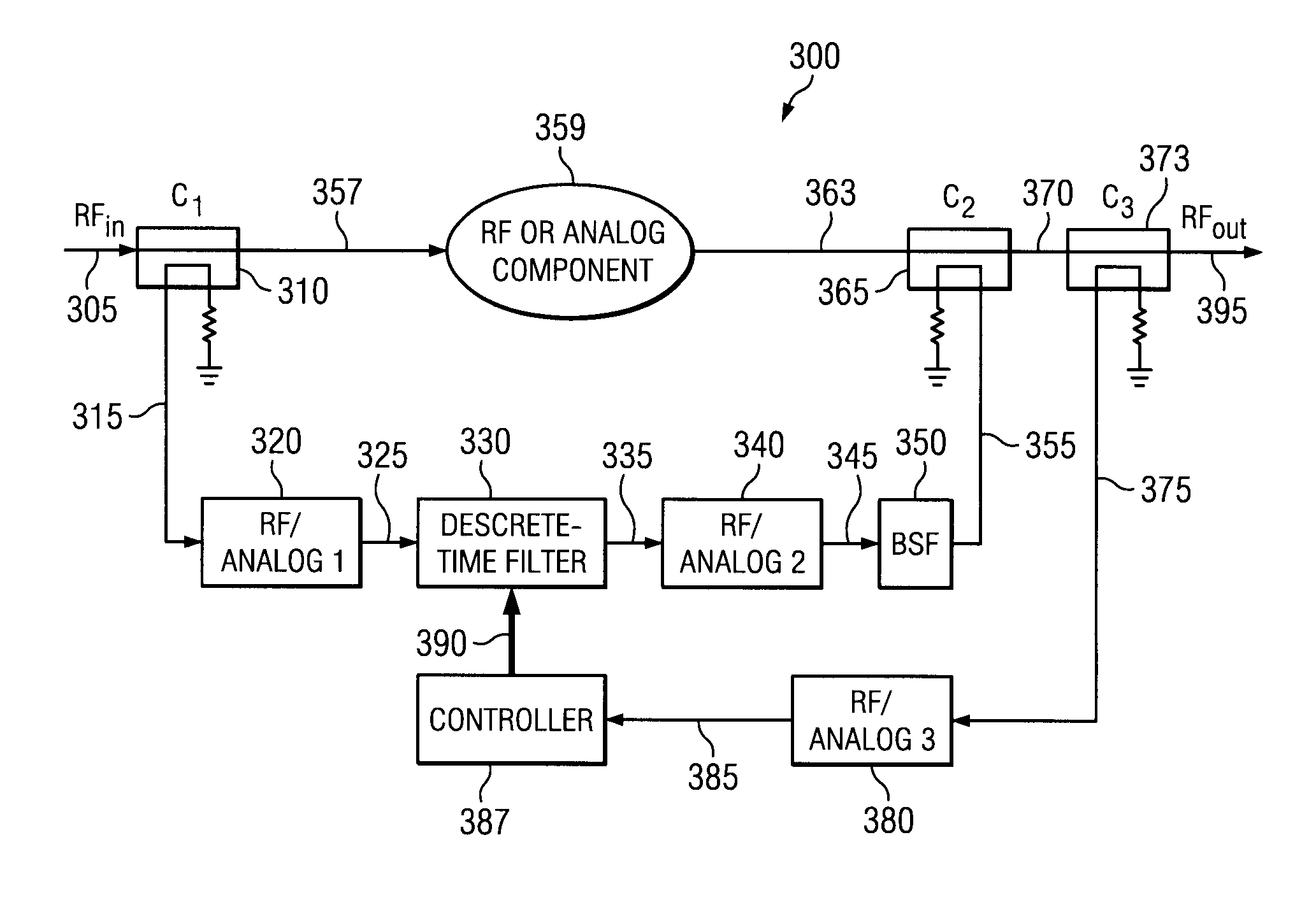
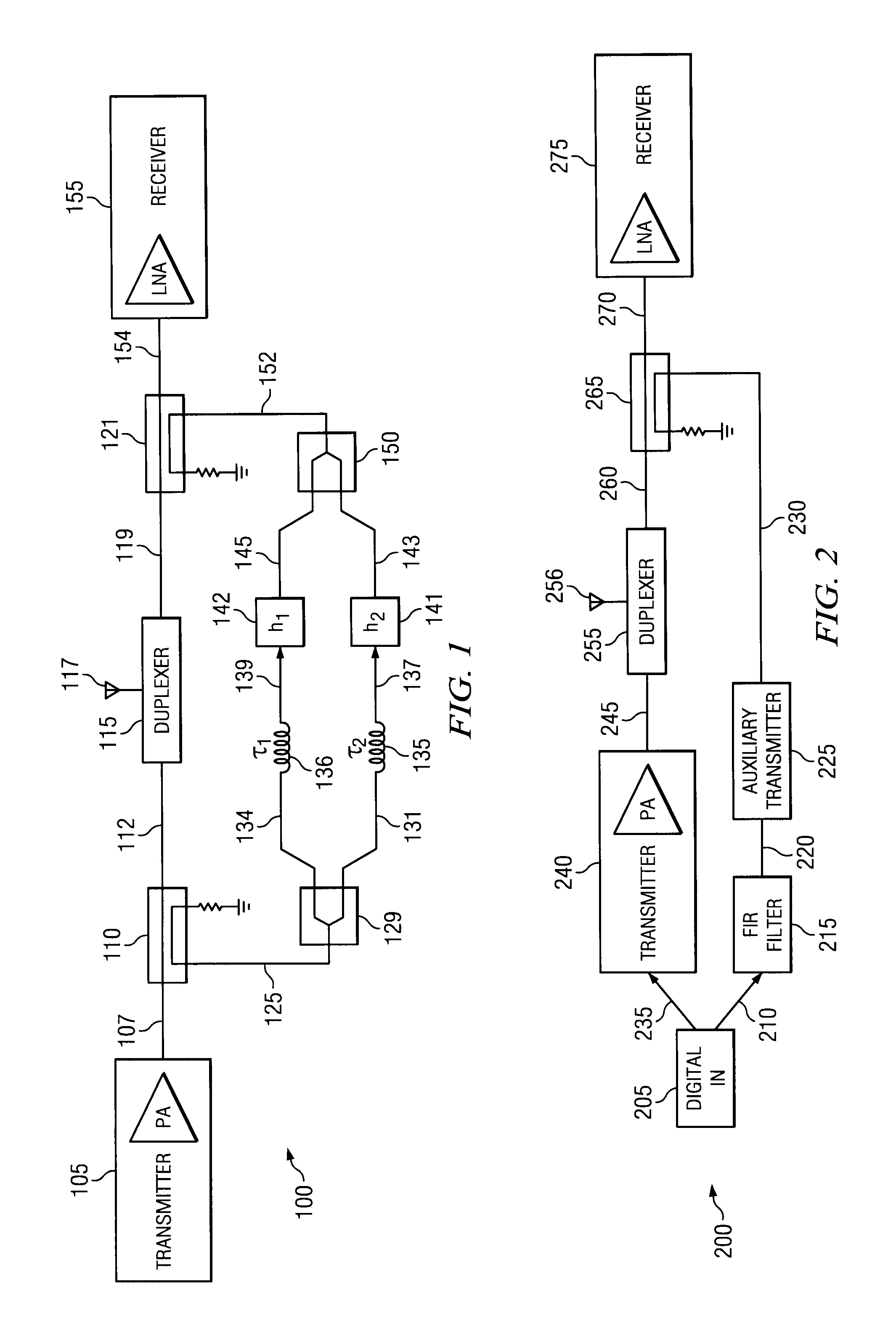
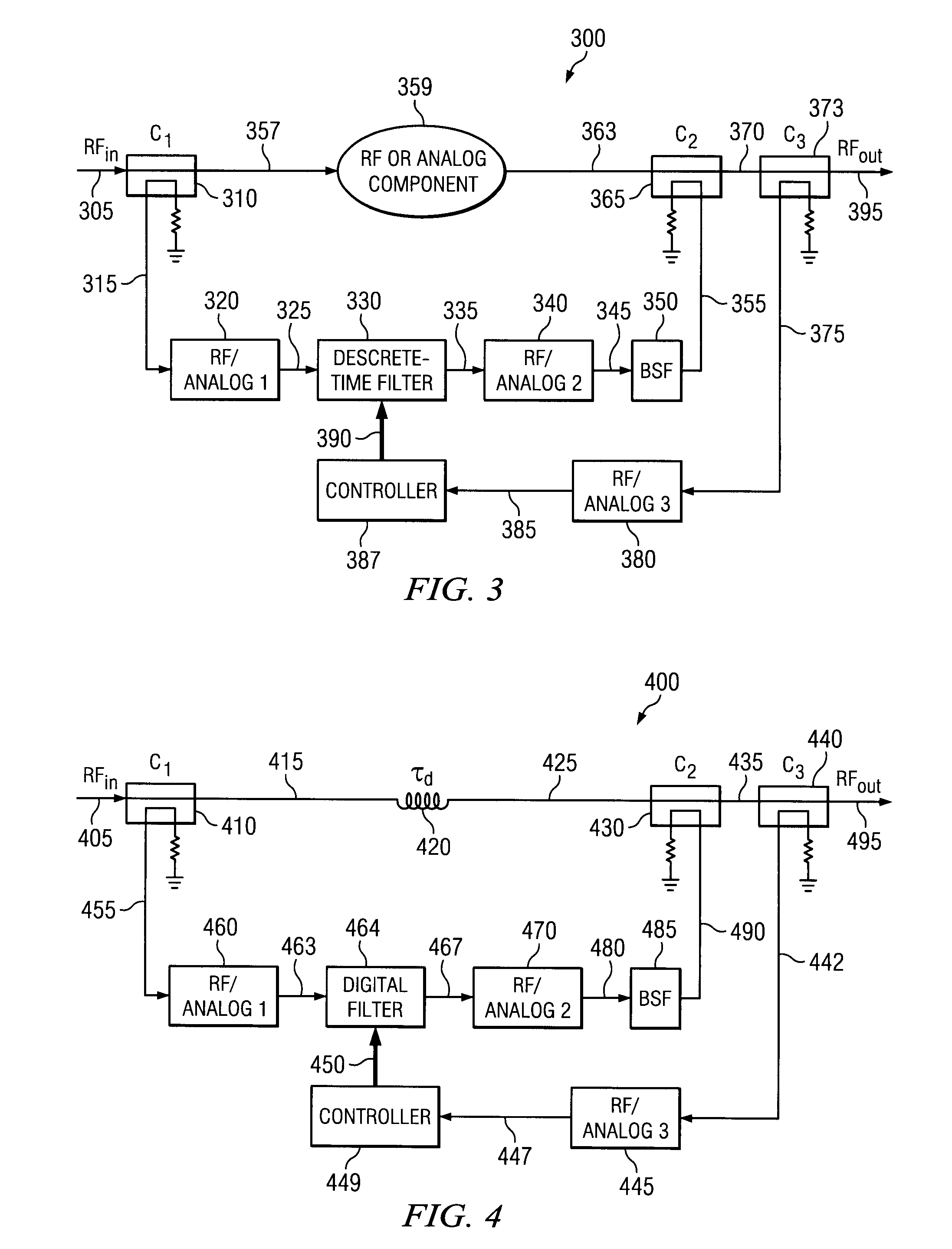
The present invention is a hybrid RF-digital signal processor-based filter for multiband radio architectures systems capable of spectrum re-farming and software defined radios. It performs low-loss frequency agile multiple notch filtering at RF where a large dynamic range exists at a filter input between signals in a stopband and passband. It is a frequency dependent signal attenuation apparatus having two paths connected together by directional couplers. The first path comprising a component such as a delay component or duplexer. The second path comprising a bandstop filter connected to a down converter, a digital filter, and an up converter. At the output of a power amplifier, the invention can be used to attenuate spurs, or noise within bands with strict emission constraints. At the input of a low noise amplifier, the invention can be used to attenuate blockers and transmitter noise outside of the receiver passband.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
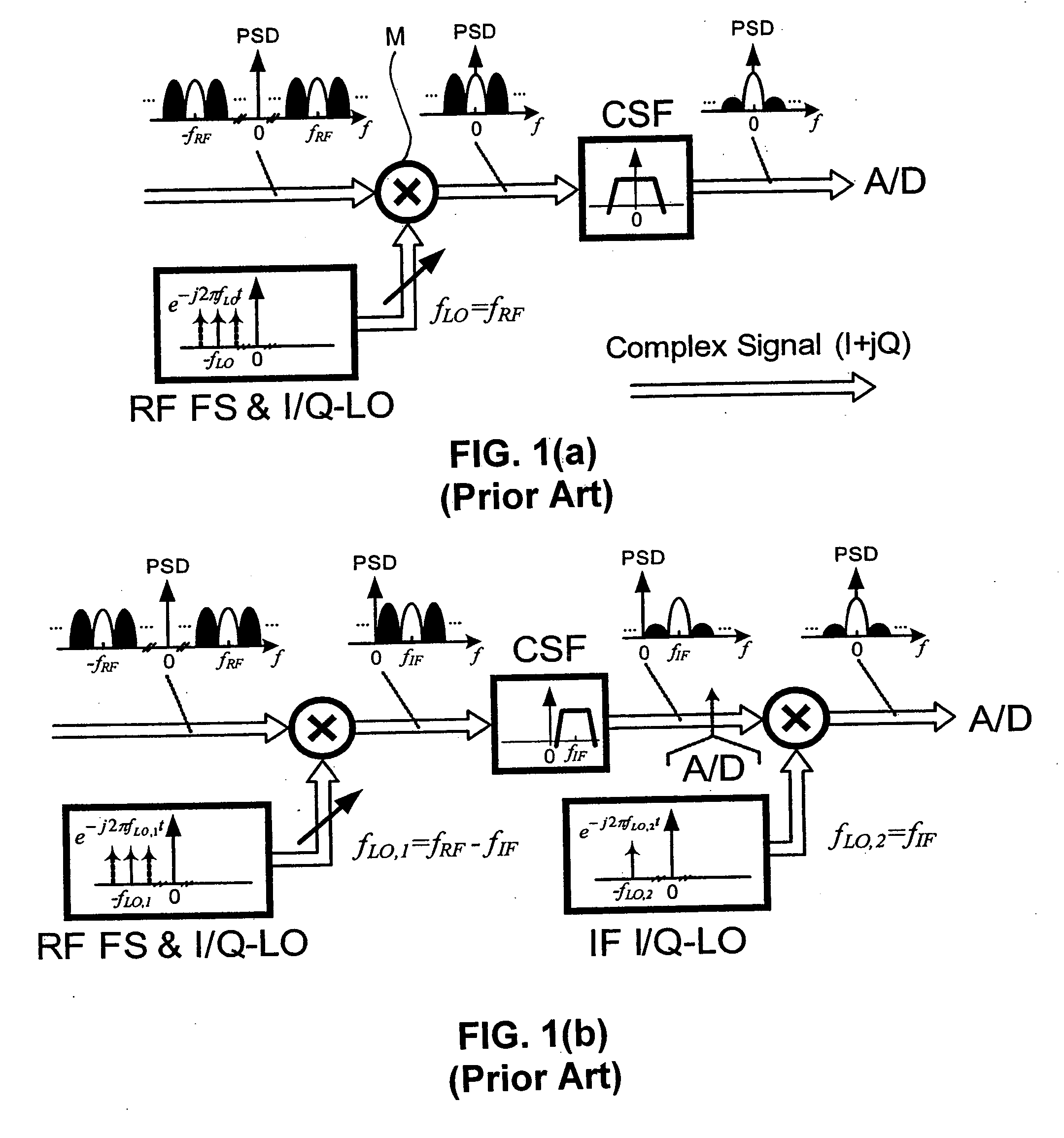
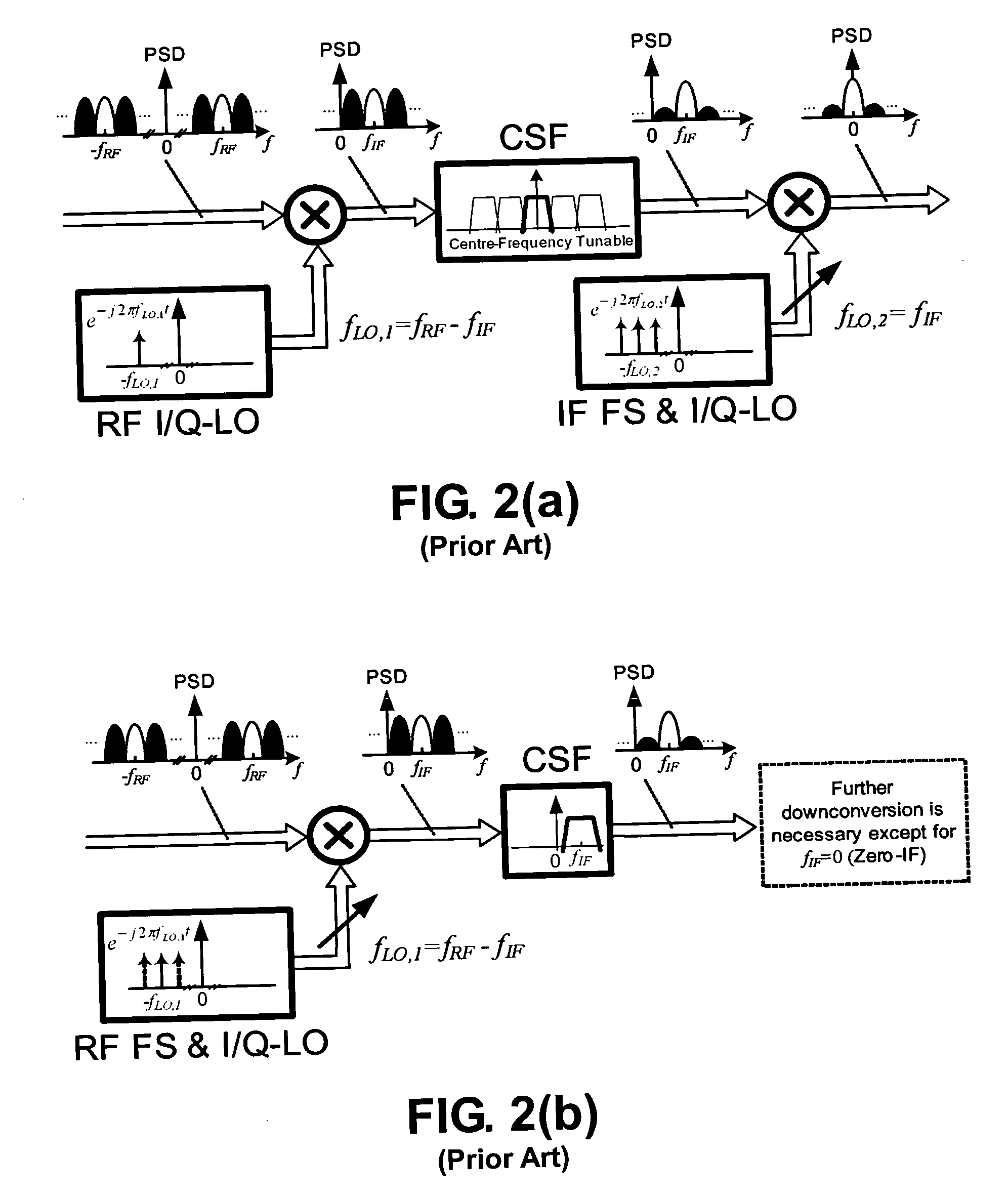
Two-step channel selection for wireless receiver and transmitter front-ends
ActiveUS20070047669A1Easy to implementActive element networkAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverIntermediate frequency
A reconfigurable receiver, a reconfigurable transmitter and a multimode receiver are disclosed, operating in accordance with a two-step channel selection. In the receiver, the first step provides for a coarse radio frequency (RF) channel selection, to downconvert a desired channel and an image channel of the desired channel to IF. The second step provides for a fine intermediate frequency (IF) channel selection to select either the desired channel or the image channel. In the transmitter, the first step provides for a fine channel selection and upconversion of a desired channel to either positive or negative IF. The second step is a coarse channel selection and upconversion of a desired channel to the RF. The receiver and transmitter can be used in a transceiver.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF
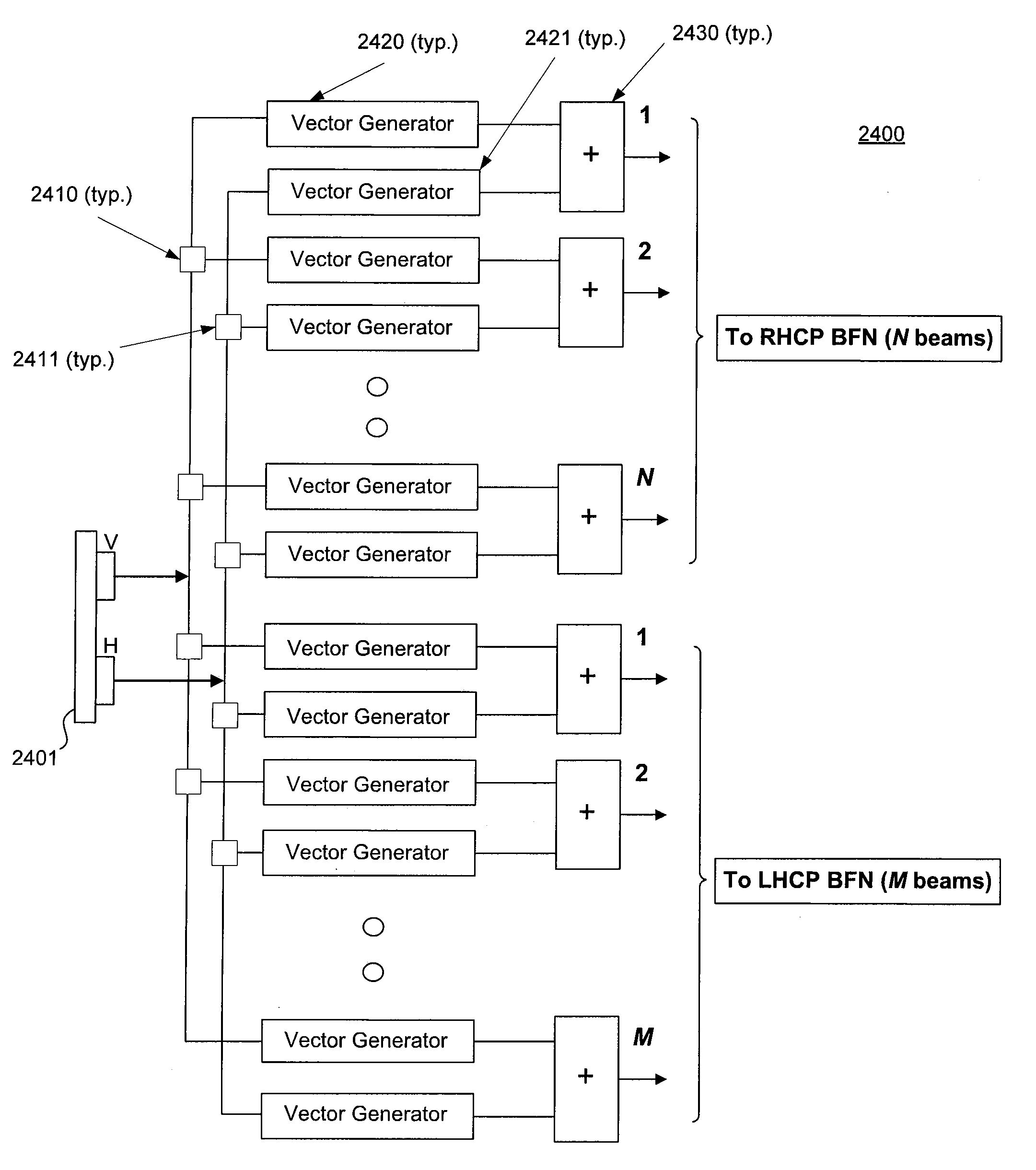
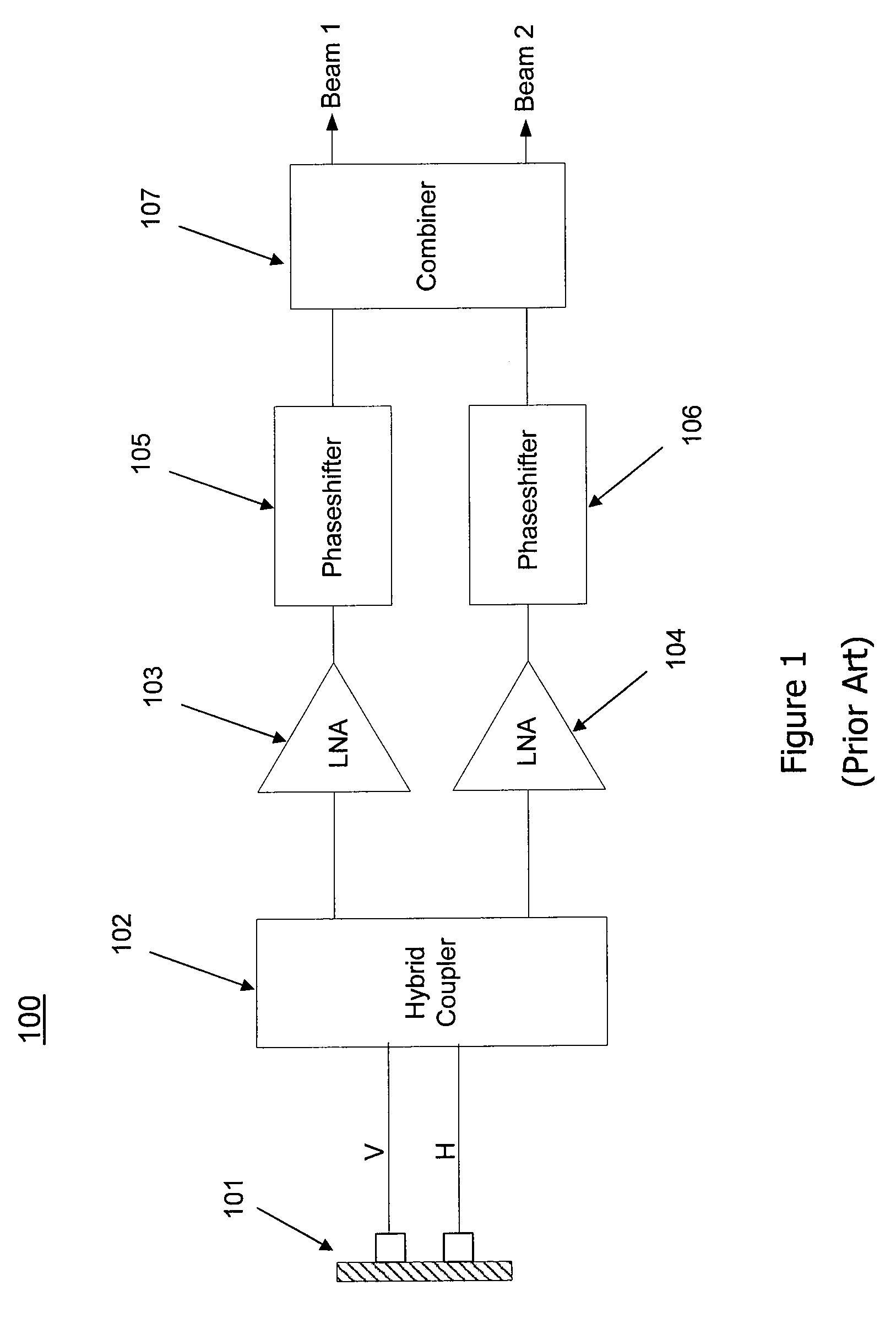
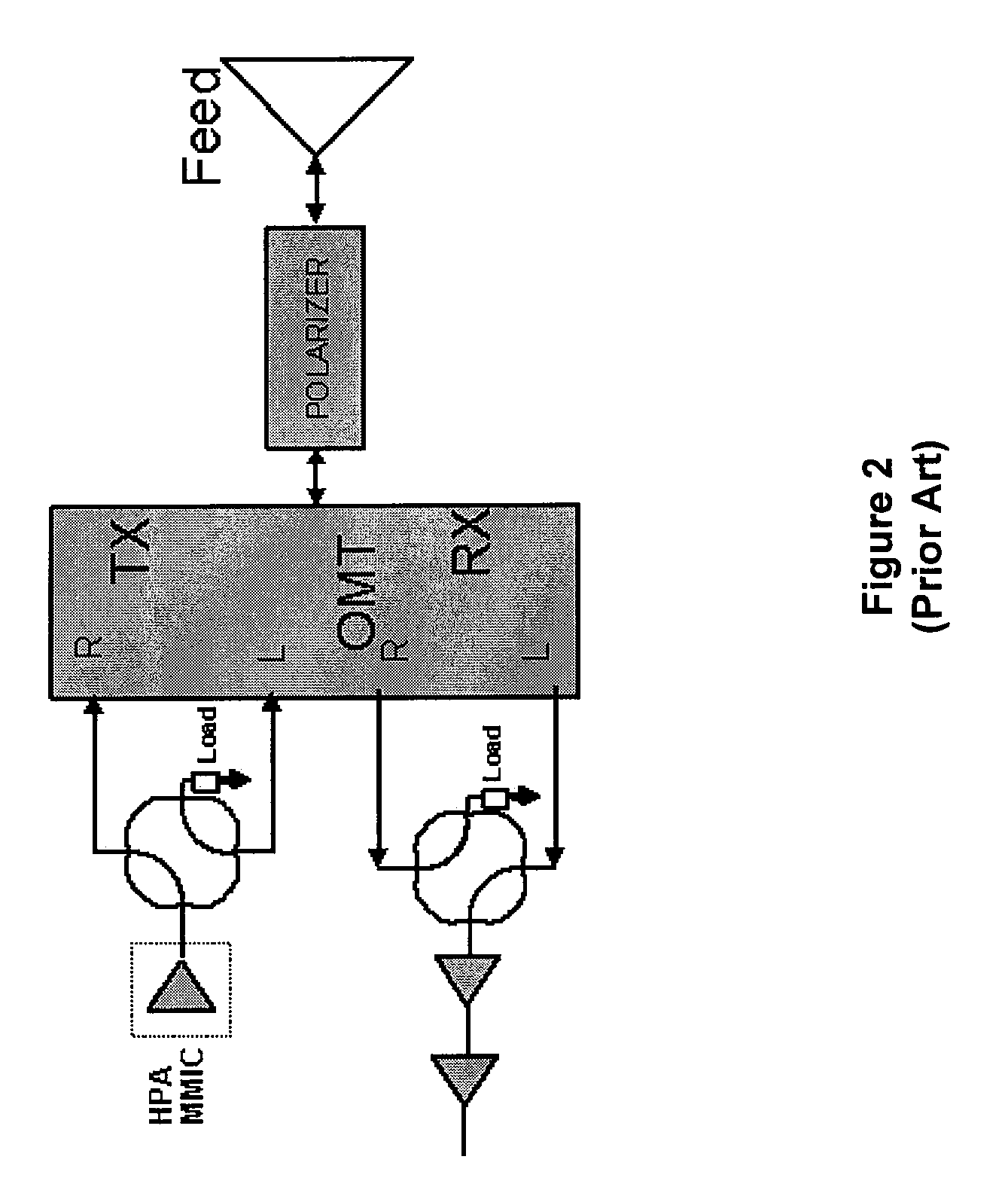
Multi-beam active phased array architecture
ActiveUS20100261440A1Increase flexibilityIncrease system capacityActive element networkComputing operation arrangementsAntenna polarizationBeam steering
In an exemplary embodiment, a phased array antenna comprises multiple subcircuits in communication with multiple radiating elements. The radio frequency signals are adjusted for both polarization control and beam steering. In a receive embodiment, multiple RF signals are received and combined into at least one receive beam output. In a transmit embodiment, at least one transmit beam input is divided and transmitted through multiple radiating elements. In an exemplary embodiment, the phased array antenna provides multi-beam formation over multiple operating frequency bands. The wideband nature of the active components allows for operation over multiple frequency bands simultaneously. Furthermore, the antenna polarization may be static or dynamically controlled at the subarray or radiating element level.
Owner:VIASAT INC
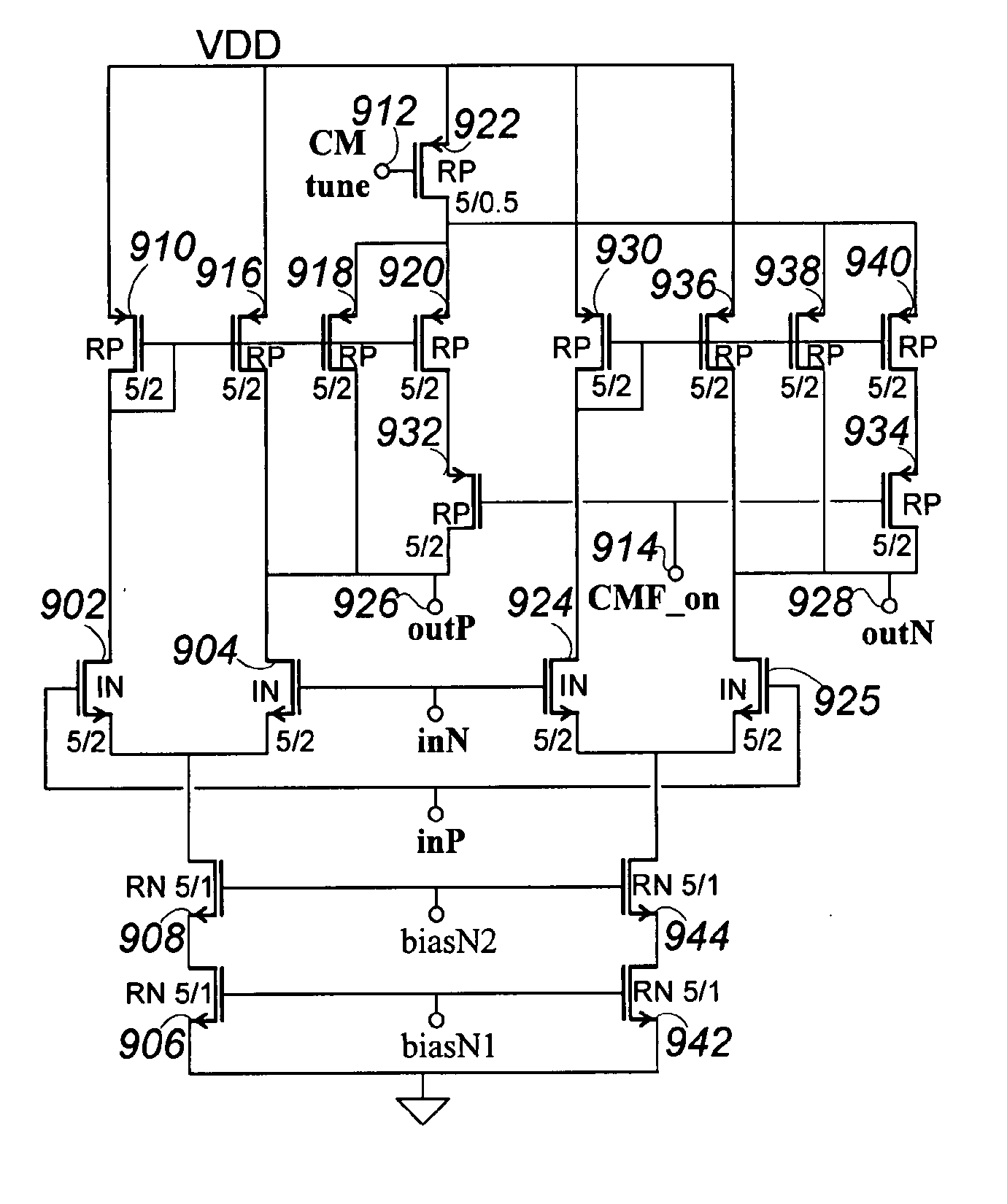
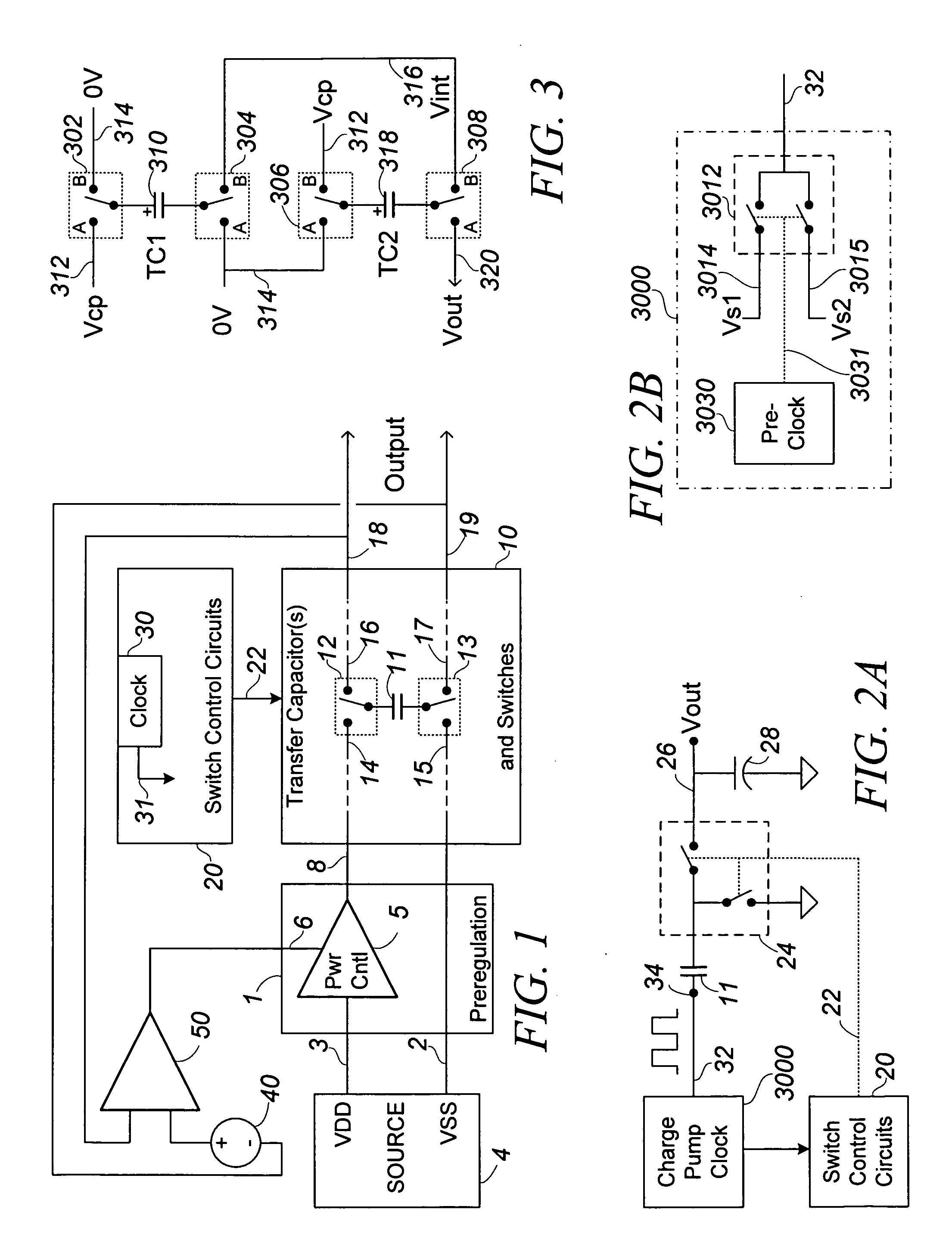
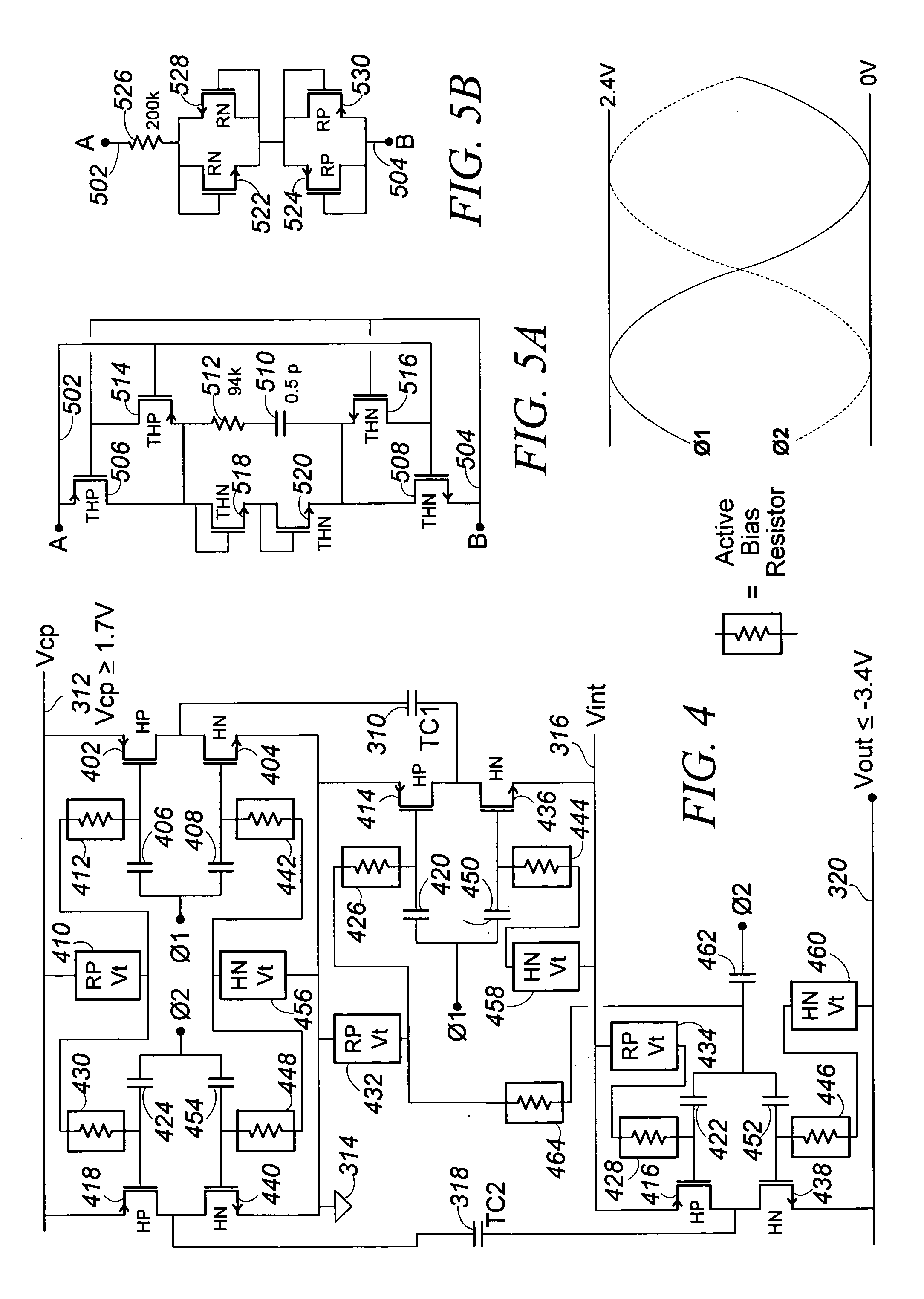
Low-Noise High Efficiency Bias Generation Circuits and Method
ActiveUS20110156819A1Reduce voltageAvoid problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceActive element networkLow noiseCapacitance
A bias generation method or apparatus defined by any one or any practical combination of numerous features that contribute to low noise and / or high efficiency biasing, including: having a charge pump control clock output with a waveform having limited harmonic content or distortion compared to a sine wave; having a ring oscillator to generating a charge pump clock that includes inverters current limited by cascode devices and achieves substantially rail-to-rail output amplitude; having a differential ring oscillator with optional startup and / or phase locking features to produce two phase outputs suitably matched and in adequate phase opposition; having a ring oscillator of less than five stages generating a charge pump clock; capacitively coupling the clock output(s) to some or all of the charge transfer capacitor switches; biasing an FET, which is capacitively coupled to a drive signal, to a bias voltage via an “active bias resistor” circuit that conducts between output terminals only during portions of a waveform appearing between the terminals, and / or wherein the bias voltage is generated by switching a small capacitance at cycles of said waveform. A charge pump for the bias generation may include a regulating feed back loop including an OTA that is also suitable for other uses, the OTA having a ratio-control input that controls a current mirror ratio in a differential amplifier over a continuous range, and optionally has differential outputs including an inverting output produced by a second differential amplifier that optionally includes a variable ratio current mirror controlled by the same ratio-control input. The ratio-control input may therefore control a common mode voltage of the differential outputs of the OTA. A control loop around the OTA may be configured to control the ratio of one or more variable ratio current mirrors, which may particularly control the output common mode voltage, and may control it such that the inverting output level tracks the non-inverting output level to cause the amplifier to function as a high-gain integrator.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
High-frequency circuit and high-frequency device
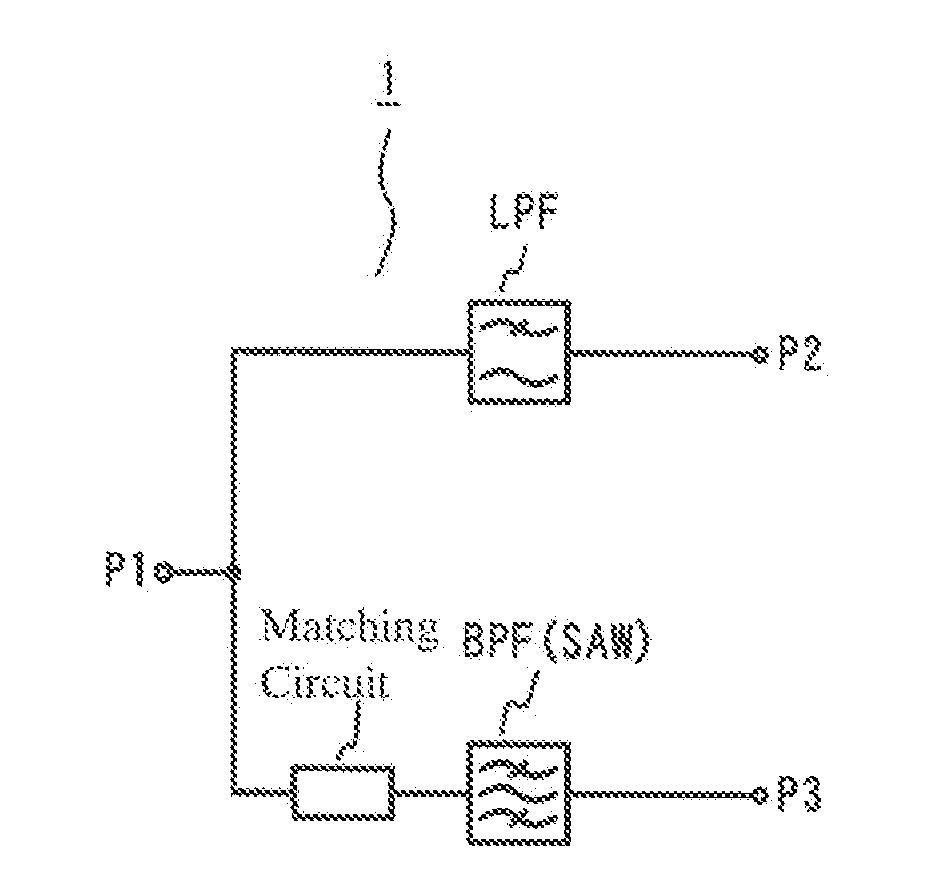
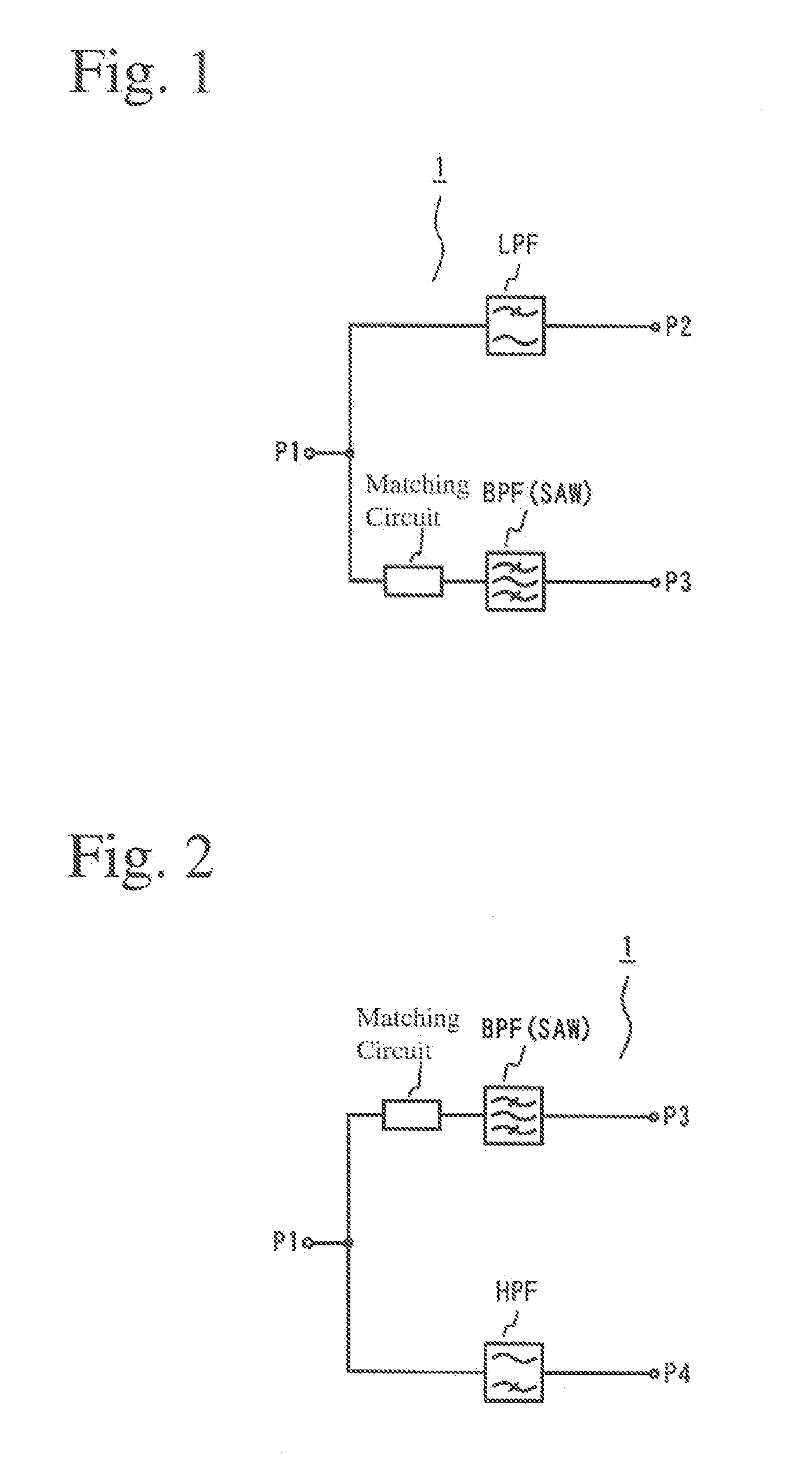
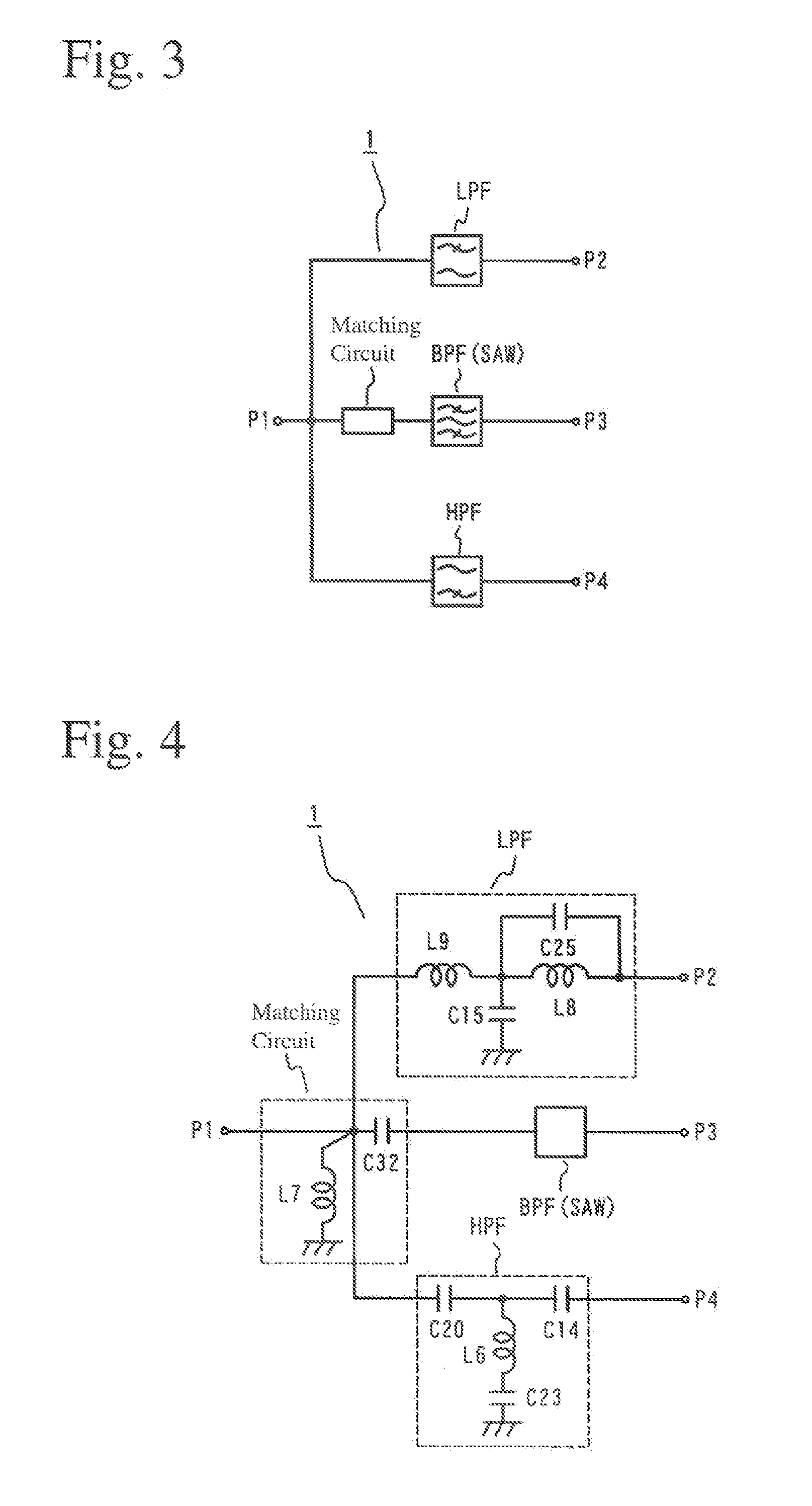
ActiveUS20070190954A1Excellent electrical propertiesAvoid interferenceMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityBandpass filteringCapacitance
A high-frequency circuit for branching high-frequency signals for pluralities of communications systems of different frequencies, which comprises a lowpass filter circuit disposed between first and second ports and / or a highpass filter circuit disposed between the first port and a fourth port; and a matching circuit and a bandpass filter circuit disposed between the first port and a third port; the lowpass filter circuit, the highpass filter circuit and the matching circuit comprising capacitance elements and inductance elements; the bandpass filter circuit being a SAW filter; and the passband f1 of the lowpass filter circuit, the passband f2 of the bandpass filter circuit, and the passband f3 of the highpass filter circuit meeting the condition of f1<f2<f3.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
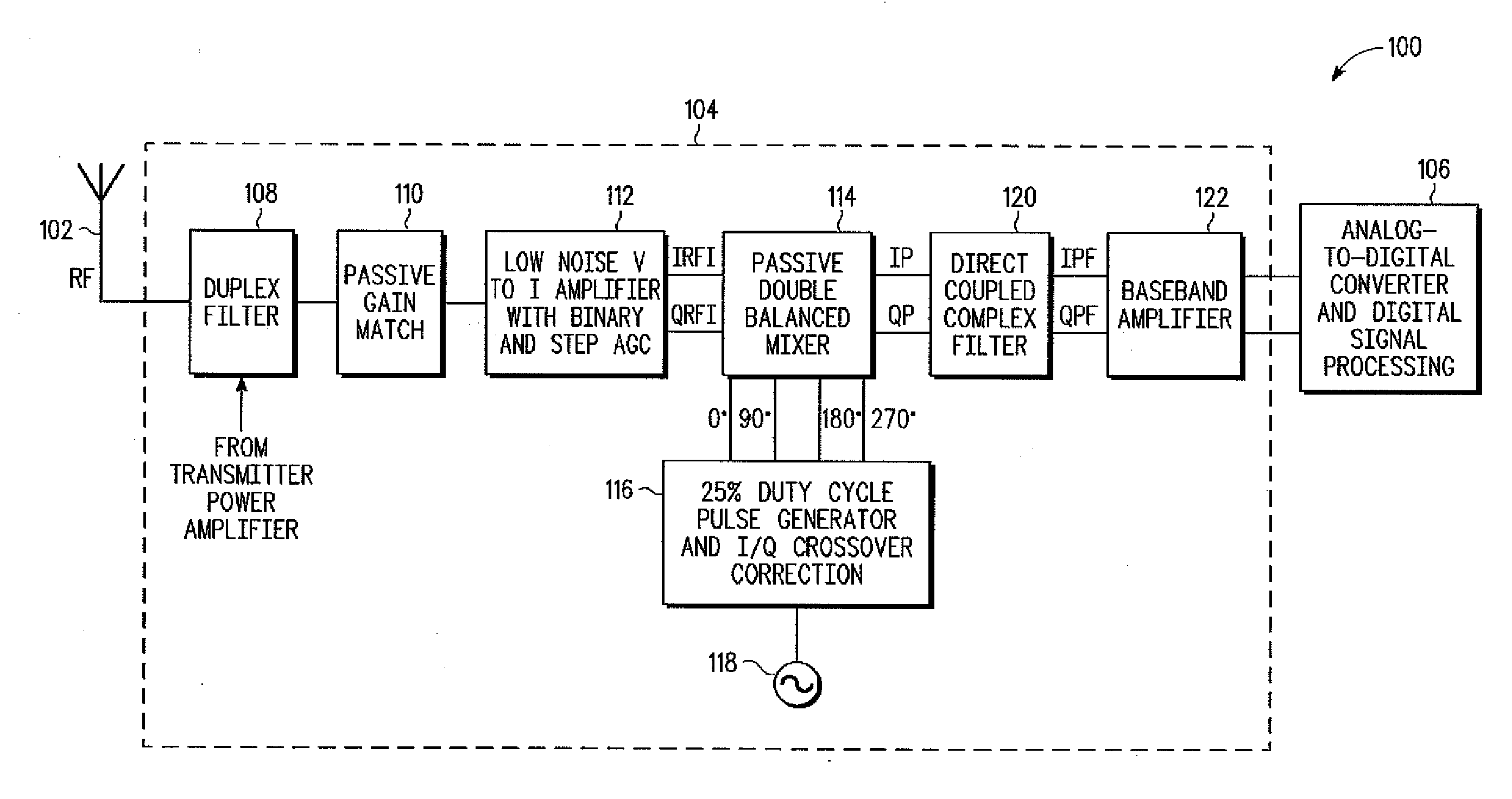
High performance CMOS radio frequency receiver
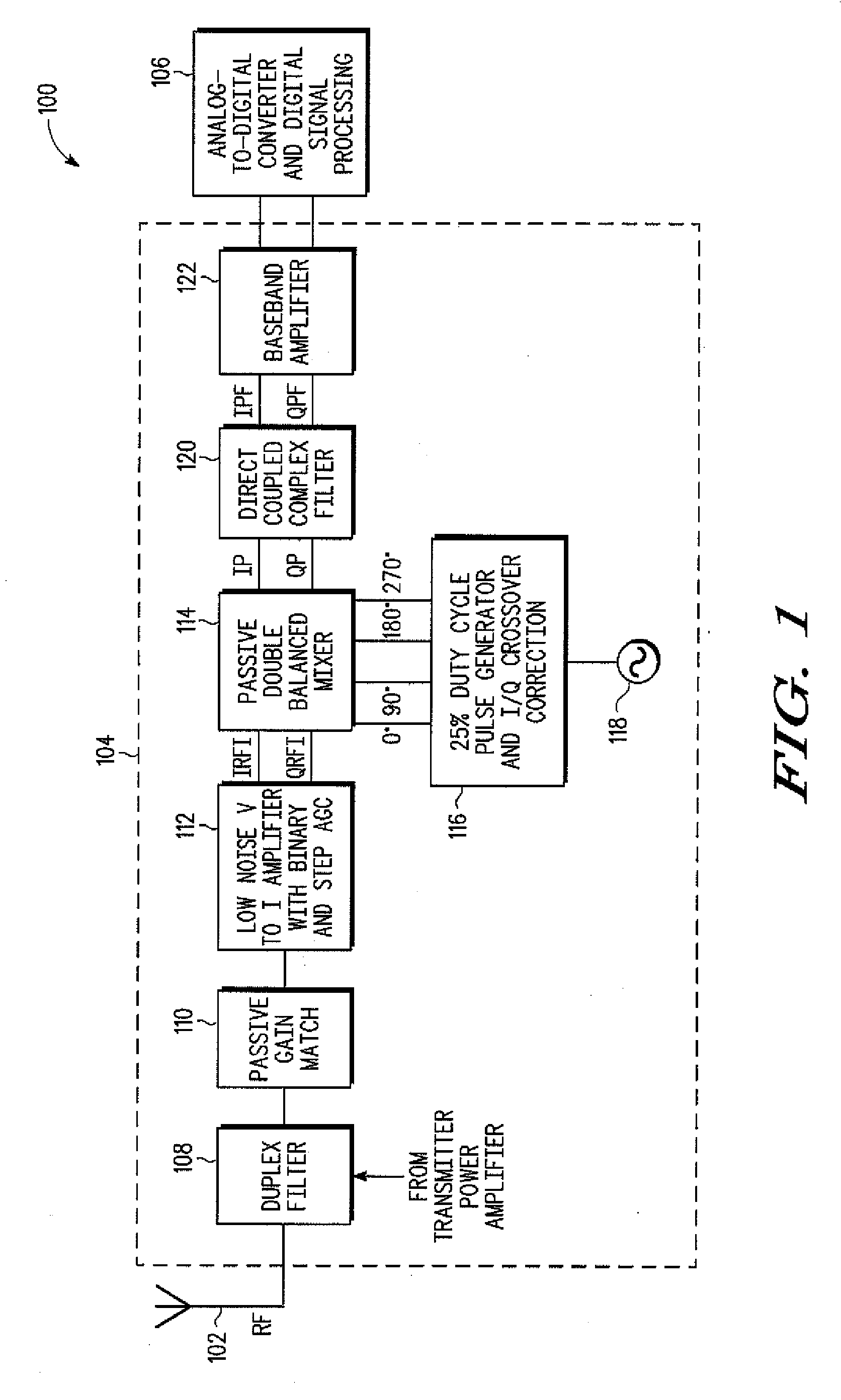
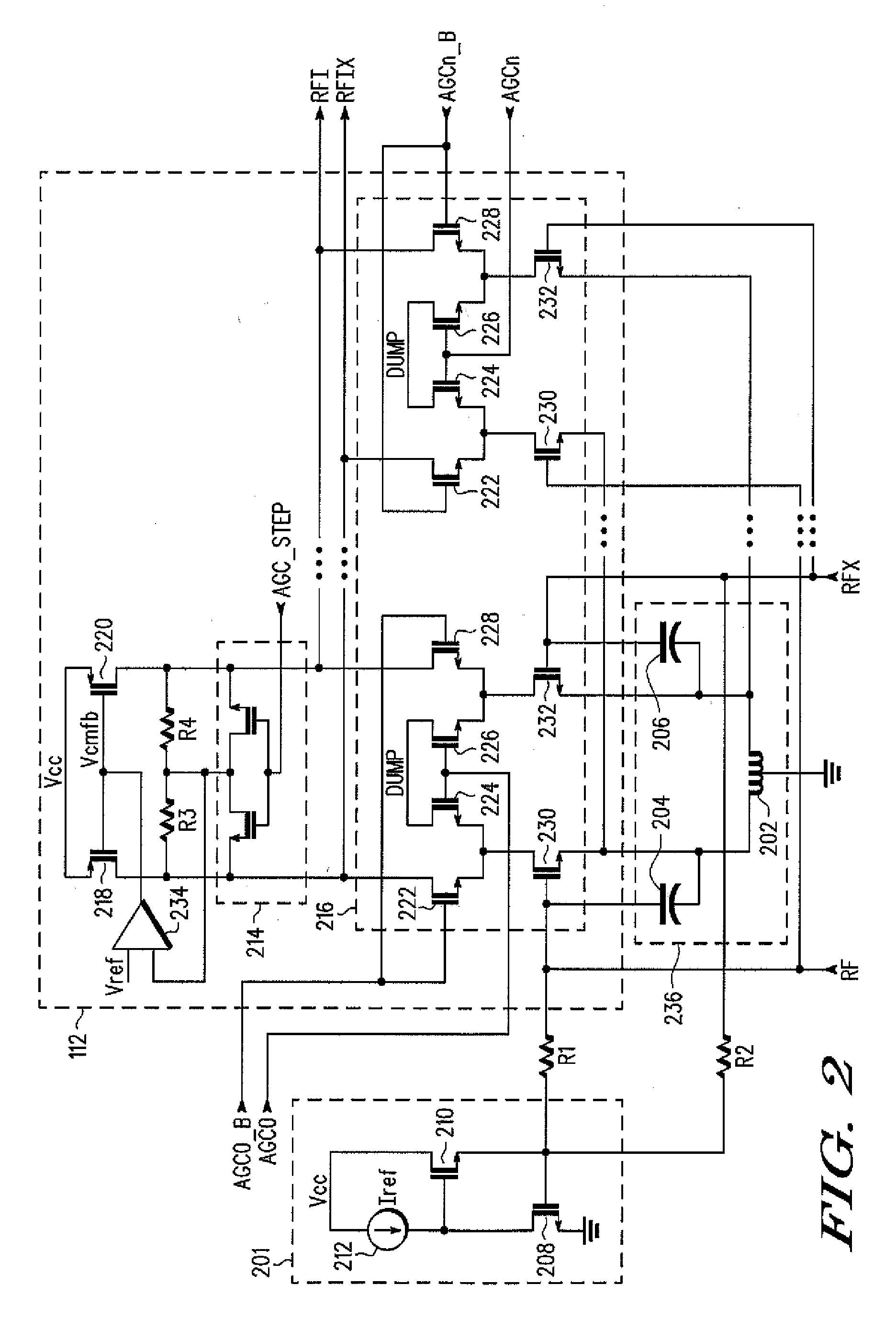
InactiveUS20090191833A1Modulation transferenceActive element networkTuned radio frequency receiverLow-pass filter
A high performance radio frequency receiver includes a low noise amplifier with large binary and stepped gain control range, controlled impedance, and enhanced blocker immunity, for amplifying and converting a radio frequency signal to a current; a pulse generator for generating in-phase and quadrature pulses; a crossover correction circuit and pulse shaper for controlling a crossover threshold of the pulses and interaction between in-phase and quadrature mixers; and a double balanced mixer for combining the RF signal with the pulses to generate an intermediate frequency or baseband zero intermediate frequency current-mode signal. The in-phase and quadrature pulses have a duty cycle of 20-35%. The intermediate frequency signal and second order harmonics may be filtered with a high frequency low pass filter and a current injected complex direct-coupled filter. Decreased die size, current drain, cost, and complexity, as well as improvements in gain, 1 / f noise, noise figure, sensitivity, and linearity may result.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
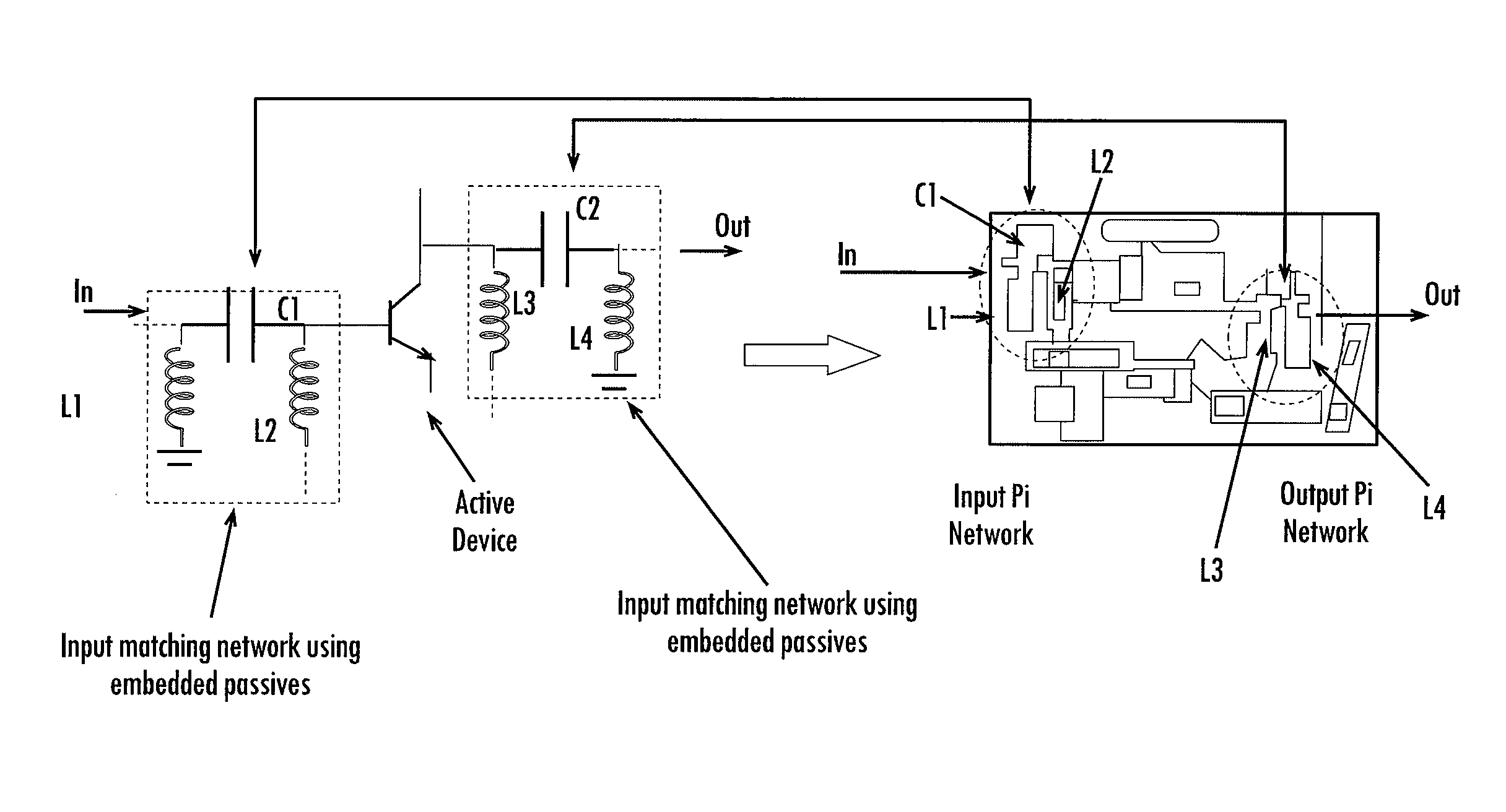
Multi-band RF transceiver with passive reuse in organic substrates
ActiveUS20050248418A1Reduce in quantityReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMulti bandLow noise
The present invention allows for the use of chip-package co-design of RF transceivers and their components by using discrete active devices in conjunction with passive components. Two particular components are described, including voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) and low noise amplifiers (LNAs). The high quality passive components for use in the VCOs and LNAs may be obtained by the use of embedded passives in organic substrates. Further, the embedded passives may have multi-band characteristics, thereby allowing multi-band VCOs and LNAs to be implemented with fewer components. In situations where size is a concern, the active devices and passive components utilized in an RF transceiver may be implemented in a low form factor module of less than 1.1 mm thick according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
High-frequency switching circuit, high-frequency module, and wireless communications device
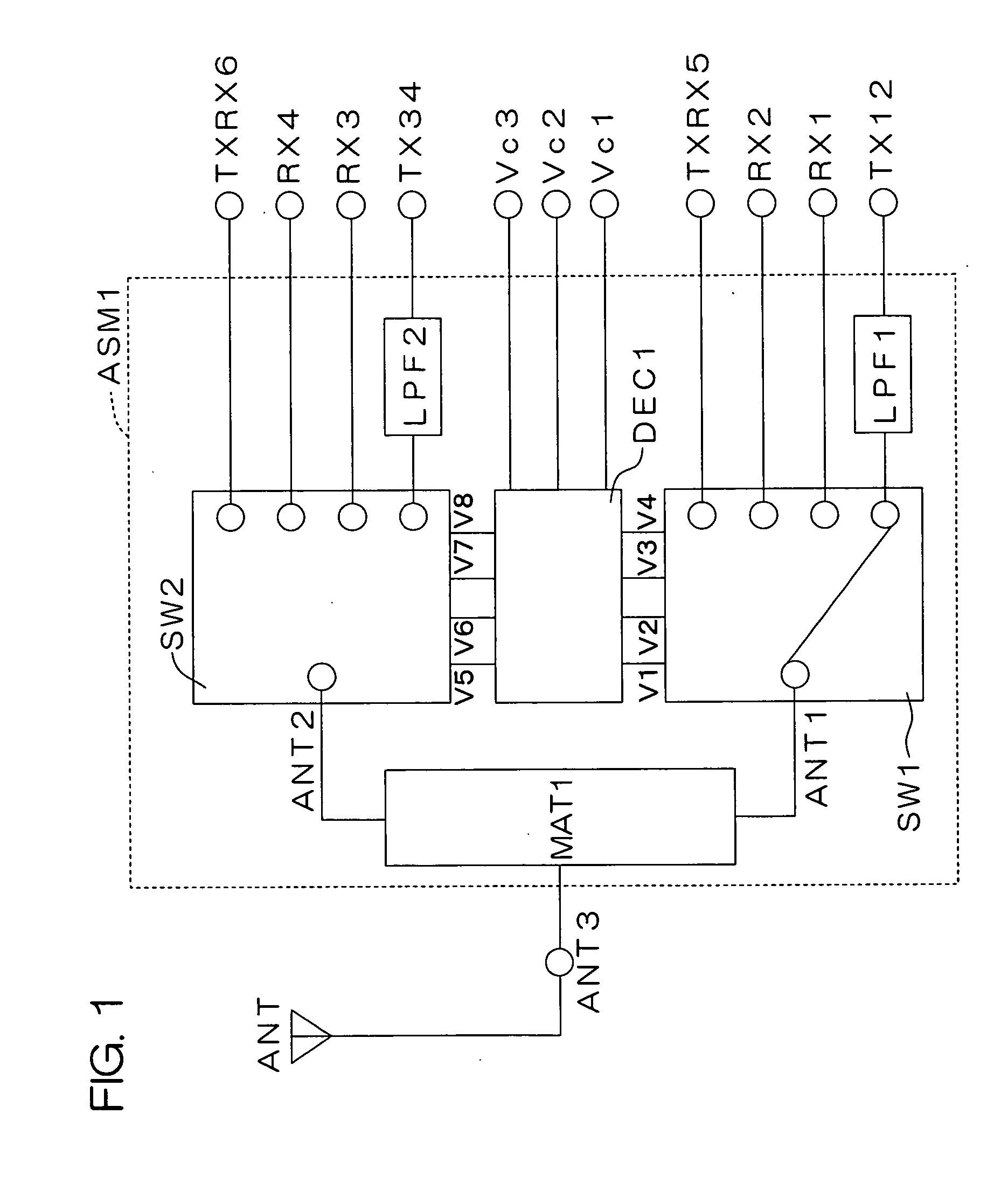
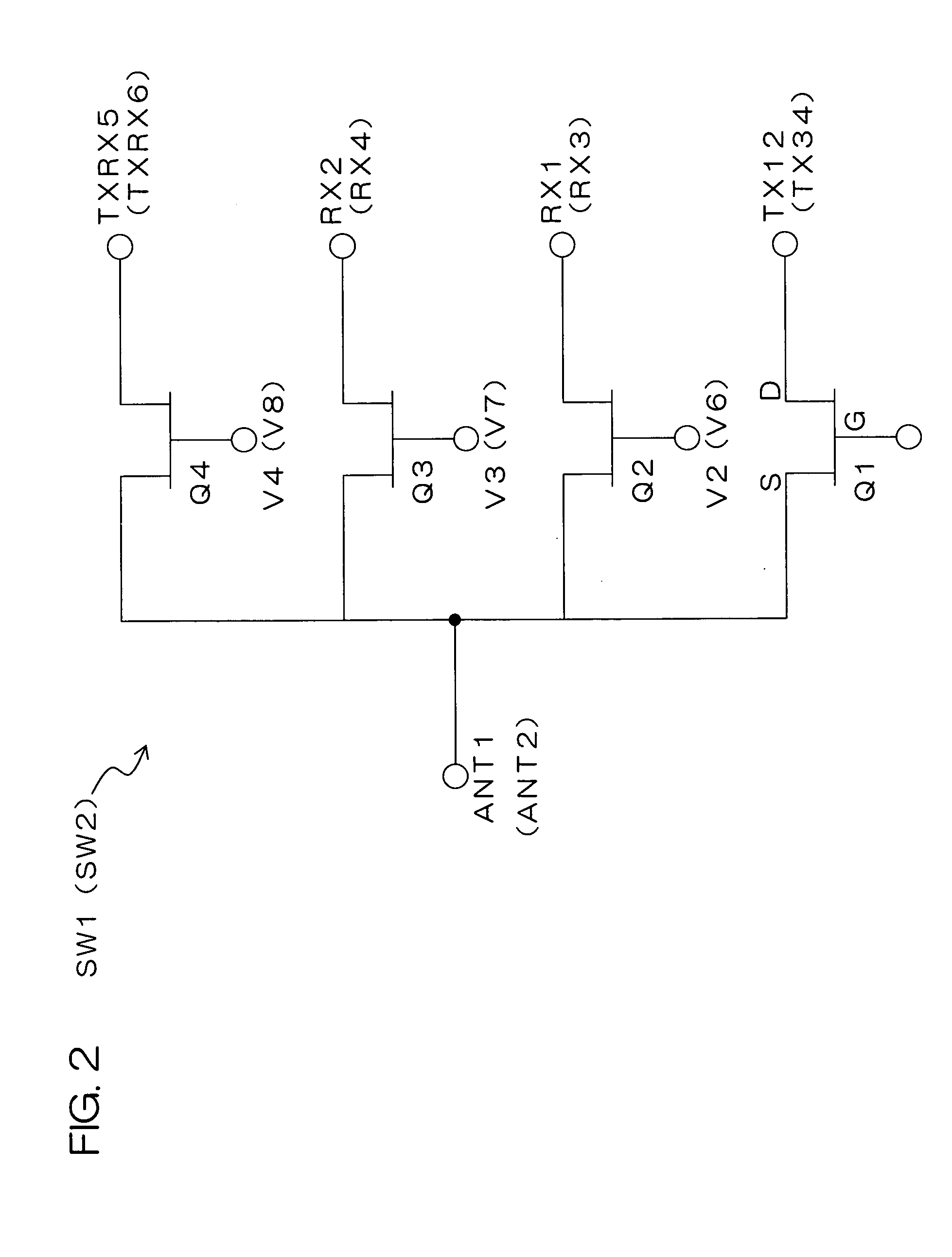
InactiveUS20050197095A1Low costReduce designActive element networkTelephonic communicationCommunications systemEngineering
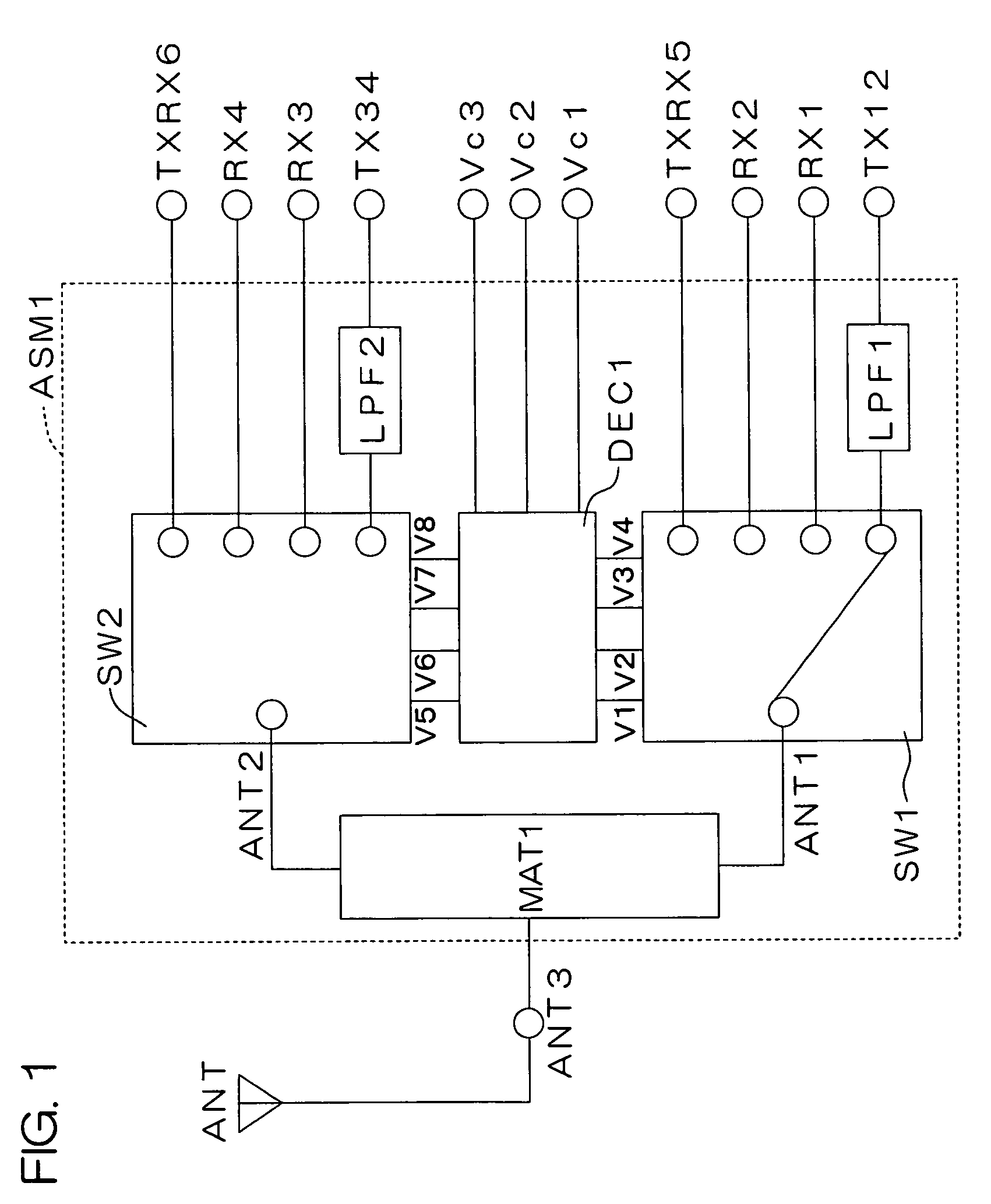
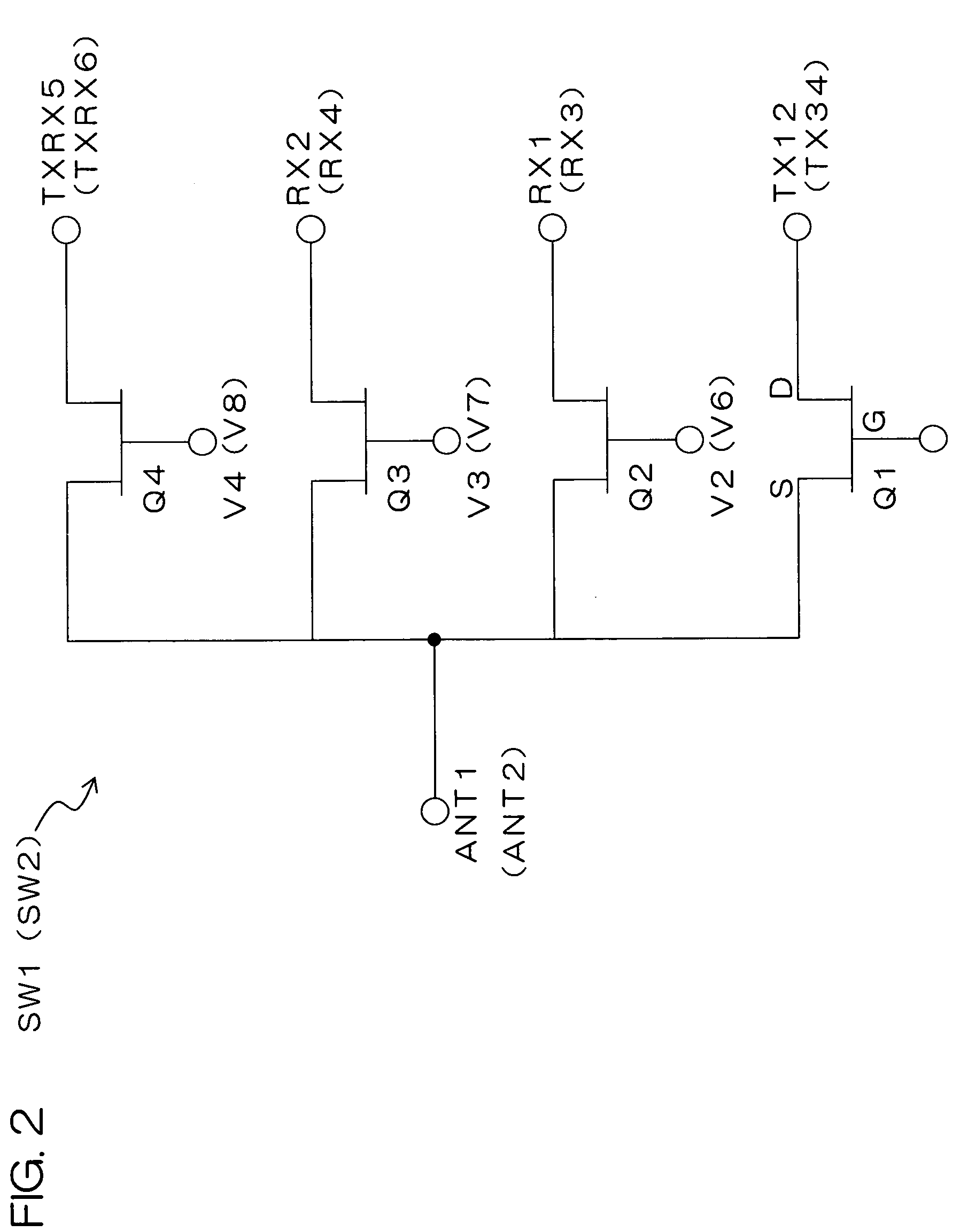
The present invention provides a high-frequency switching circuit comprising: two or more high-frequency switches SW1 and SW2 provided correspondingly to a plurality of communication systems having mutually different frequency bands; and a control circuit DEC1 adapted to control the switching of the two or more high-frequency switches SW1 and SW2, in which a common antenna terminal ANT3 and common terminals ANT1 and ANT2 of the respective high-frequency switches SW1 and SW2 are connected via a matching circuit MAT1 having a filtering function capable of allowing passage of direct current. When one path of the high-frequency switch SW1 is turned on, the other paths of the high-frequency switch SW1 and all paths of the high-frequency switch SW2 can be turned off.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Modulized wave filter
InactiveUS7675381B2Practical and convenientMultiple-port networksActive element networkBandpass filteringEngineering
A wave filter is installed in a multimedia wideband router, and includes a circuit board having a first low-pass wave-filtering circuit, and a band-pass wave-filtering circuit; the band-pass wave-filtering circuit consists of a high-pass wave-filtering circuit and a second low-pass wave-filtering circuit; the first low-pass wave-filtering circuit is connected to the high-pass wave-filtering circuit; the circuit board further includes an input terminal, and a first switching component, which is movable to such a position as to electrically connect the input terminal and a joint between the first low-pass wave-filtering circuit and the high-pass wave-filtering circuit; the circuit board further includes two output terminals, which are connected to the first and the second low-pass wave-filtering circuits respectively; a second switching component is provided on the circuit board, which is movable to such a position as to electrically connect the high-pass wave-filtering circuit and the second low-pass wave-filtering circuit.
Owner:SOONTAI TECH
Reconfigurable baseband filter
ActiveUS20040209591A1Reduce switching noiseSimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationActive element networkCommunications systemEngineering
A reconfigurable baseband filter for use in a multimode communication system is disclosed. One or more filter elements can each be configured as a plurality of sub-elements. The value of each of the filter elements can be varied by switching between at least two of the plurality of sub-elements. Switching noise within a desired passband can be reduced by switching at a rate that is greater than the desired passband. The switching noise in the passband can be further reduced by pseudo-randomly switching between the sub-elements. The filter can use a delta-sigma modulator to generate a pseudo-random switching signal.
Owner:SPREADTRUM
Modulized wave filter
InactiveUS20090153263A1Practical and convenientMultiple-port networksActive element networkBandpass filteringWide band
A wave filter is installed in a multimedia wideband router, and includes a circuit board having a first low-pass wave-filtering circuit, and a band-pass wave-filtering circuit; the band-pass wave-filtering circuit consists of a high-pass wave-filtering circuit and a second low-pass wave-filtering circuit; the first low-pass wave-filtering circuit is connected to the high-pass wave-filtering circuit; the circuit board further includes an input terminal, and a first switching component, which is movable to such a position as to electrically connect the input terminal and a joint between the first low-pass wave-filtering circuit and the high-pass wave-filtering circuit; the circuit board further includes two output terminals, which are connected to the first and the second low-pass wave-filtering circuits respectively; a second switching component is provided on the circuit board, which is movable to such a position as to electrically connect the high-pass wave-filtering circuit and the second low-pass wave-filtering circuit.
Owner:SOONTAI TECH
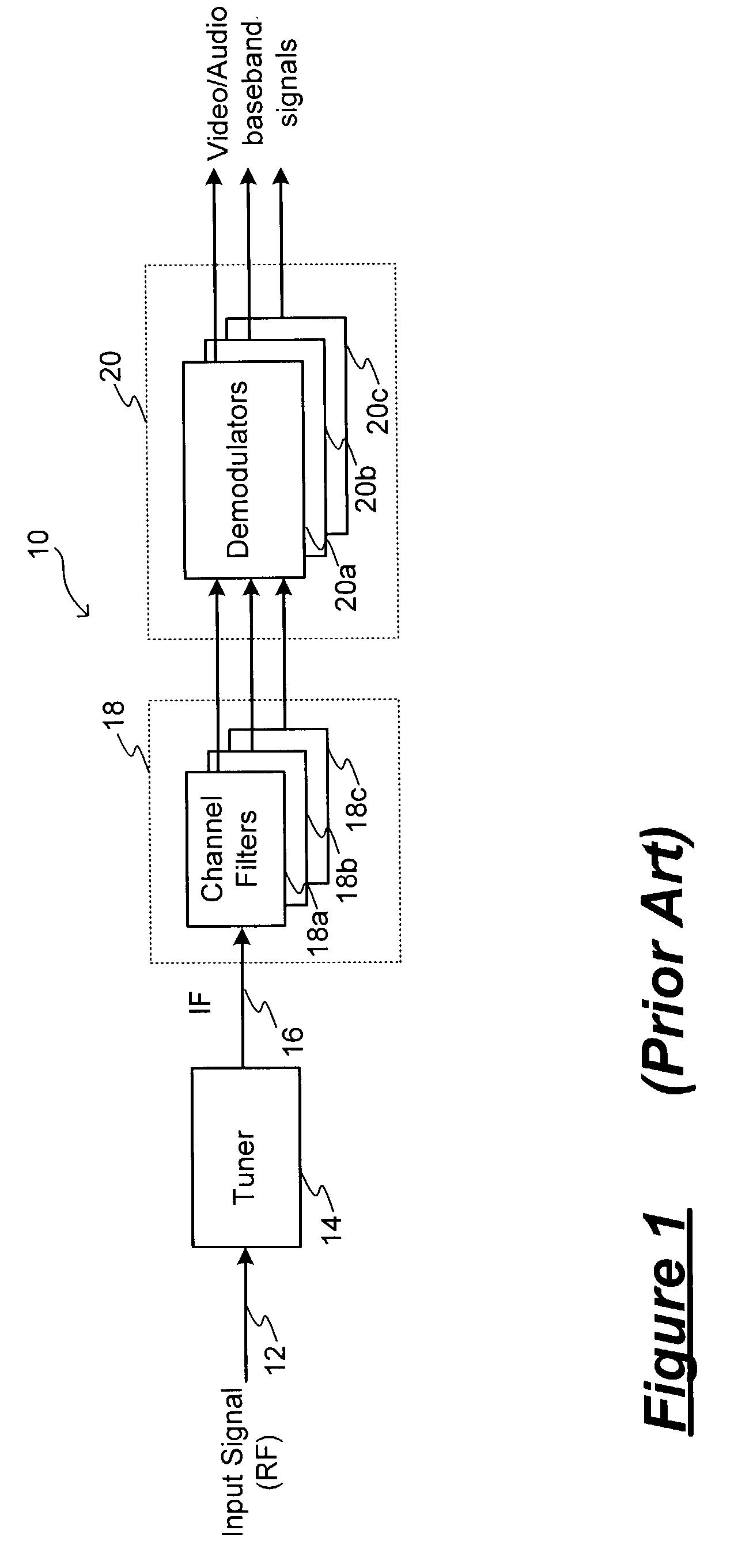
Broadband receiver having a multistandard channel filter
A television (TV) receiver includes a multi-standard channel filter with a programmable intermediate frequency adapted to receive television signals in a variety of television standards and formats. In one embodiment, a receiver includes a tuner and a channel filter. The tuner receives input RF signals encoding information in one of a number of formats and converts the input RF signals to intermediate signals having an intermediate frequency (IF). The intermediate signals are coupled to the channel filter. The channel filter includes an anti-aliasing filter for filtering the intermediate signals, an analog-to-digital converter for sampling the filtered intermediate signals and generating a digital representation thereof, and a signal processor for processing the digital representation of the intermediate signals in accordance with the format of the input RF signal. The signal processor generates digital output signals indicative of information encoded in the input RF signal.
Owner:CR CRESPE LLC +1
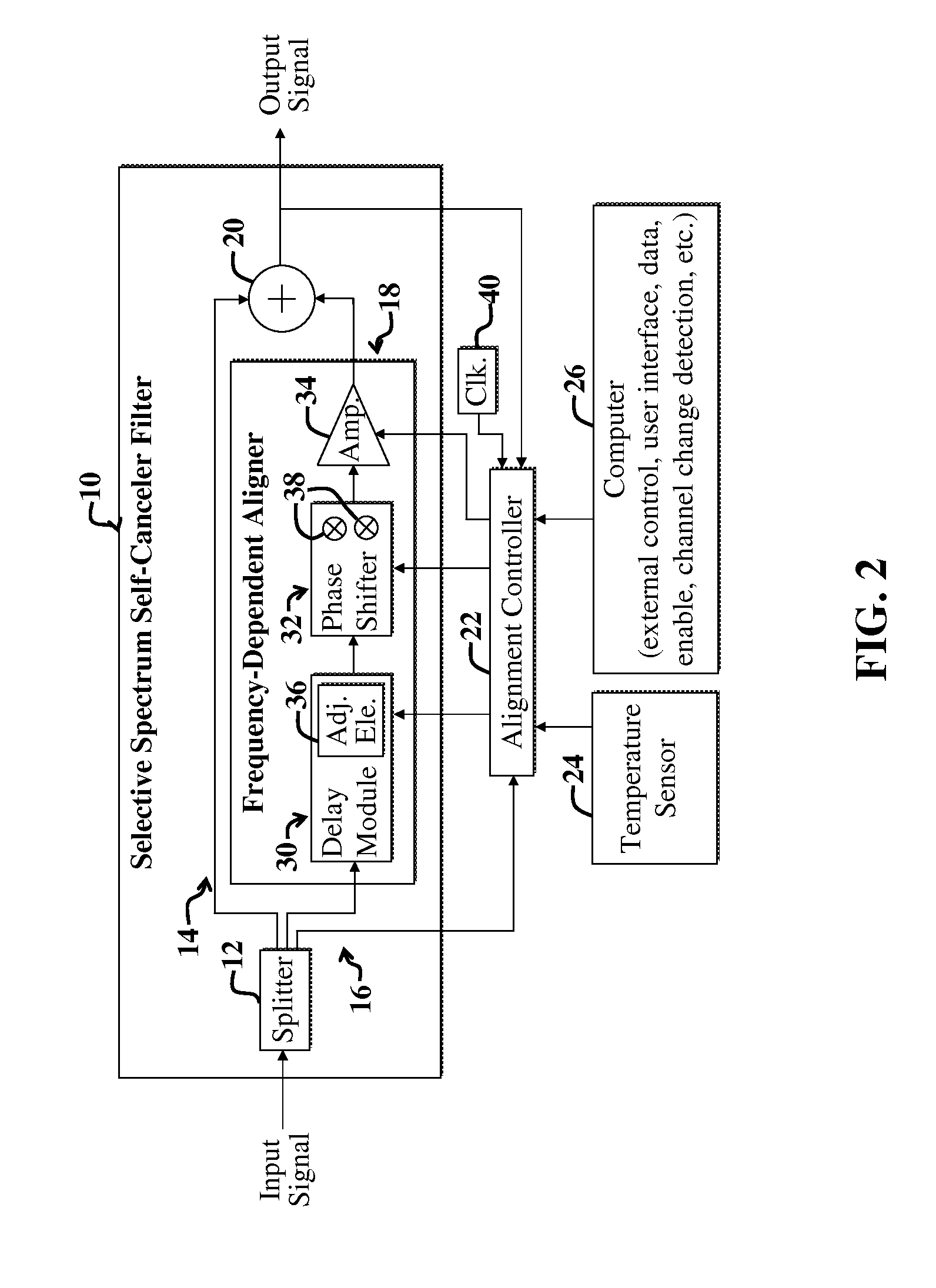
Filter shaping using a signal cancellation function
InactiveUS20100244943A1Active element networkPulse descriminationAudio power amplifierSignal cancellation
A signal filter and accompanying methods. In one embodiment, the filter includes a first mechanism for receiving a first signal. A second mechanism employs one or more modified representations of the first signal to cancel one or more frequency components of the first signal, yielding an output signal in response thereto. In a more specific embodiment, the first mechanism includes a splitter for receiving the first signal and splitting the first signal onto a first path and a second path. The second mechanism further includes one or more delay modules and one or more phase shifters in the first path and / or the second path. One or more controllable amplifiers are optionally included in the first path and / or the second path. The one or more delay modules, phase shifters, or amplifiers are responsive to one or more control signals from a controller. The controller is adapted to modify behavior of the second mechanism so that the filter is characterized by a desired frequency response.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Multi-band RF transceiver with passive reuse in organic substrates
ActiveUS7489914B2Reduce in quantityReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMulti bandLow noise
The present invention allows for the use of chip-package co-design of RF transceivers and their components by using discrete active devices in conjunction with passive components. Two particular components are described, including voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) and low noise amplifiers (LNAs). The high quality passive components for use in the VCOs and LNAs may be obtained by the use of embedded passives in organic substrates. Further, the embedded passives may have multi-band characteristics, thereby allowing multi-band VCOs and LNAs to be implemented with fewer components. In situations where size is a concern, the active devices and passive components utilized in an RF transceiver may be implemented in a low form factor module of less than 1.1 mm thick according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
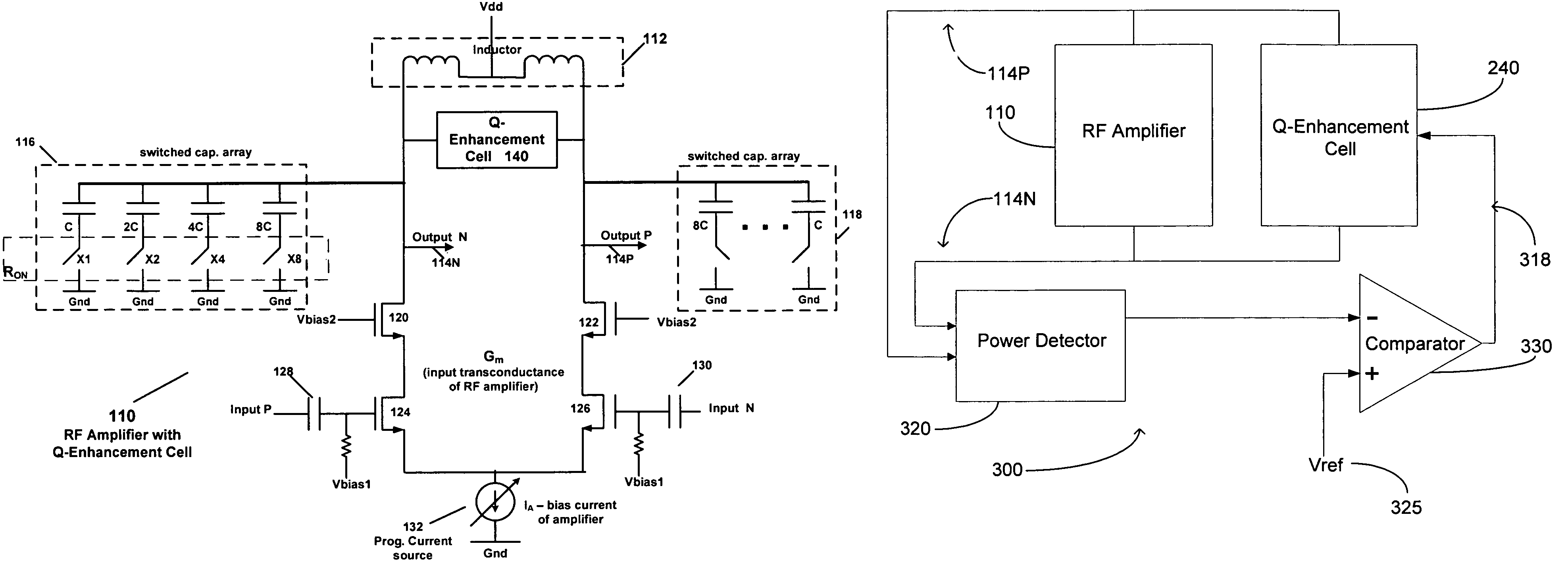
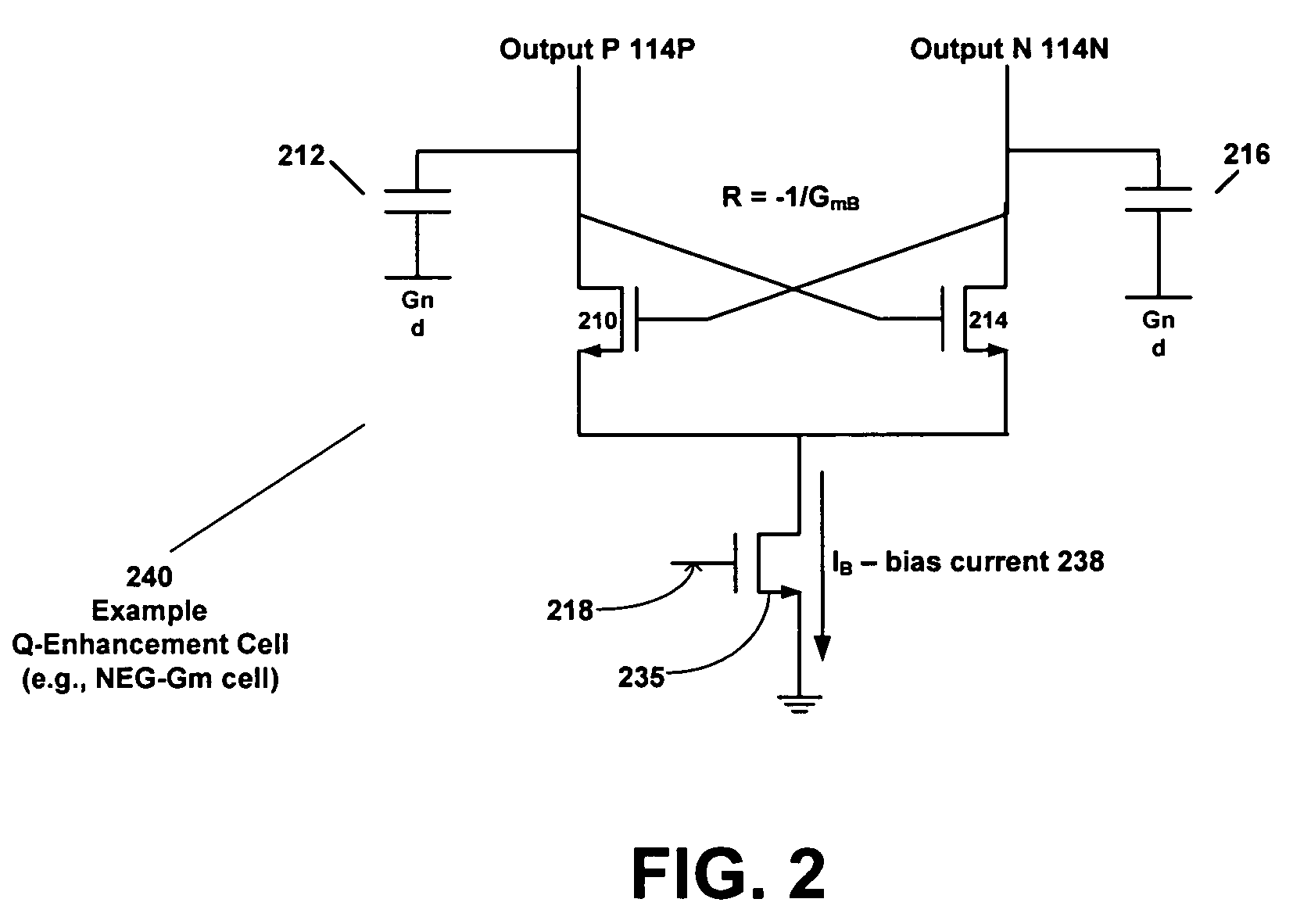
Circuit with Q-enhancement cell having feedback loop
According to an example embodiment, an amplitude feedback loop may include an RF amplifier, a detector, a comparator, and a Q-enhancement cell. In an example embodiment, the RF amplifier has an output signal, and the detector has an input coupled to the output signal of the RF amplifier and is configured to detect a level of the output signal of the RF amplifier. The comparator circuit may receive as inputs a reference voltage and the output of the detector. Also, the comparator circuit is configured to output a control signal based on a difference between the reference voltage and the output signal of the power detector. The Q-enhancement cell may be coupled to the RF amplifier and have an input coupled to an output of the comparator circuit. A bias current of the Q-enhancement cell may be adjusted based on the control signal output by the comparator circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
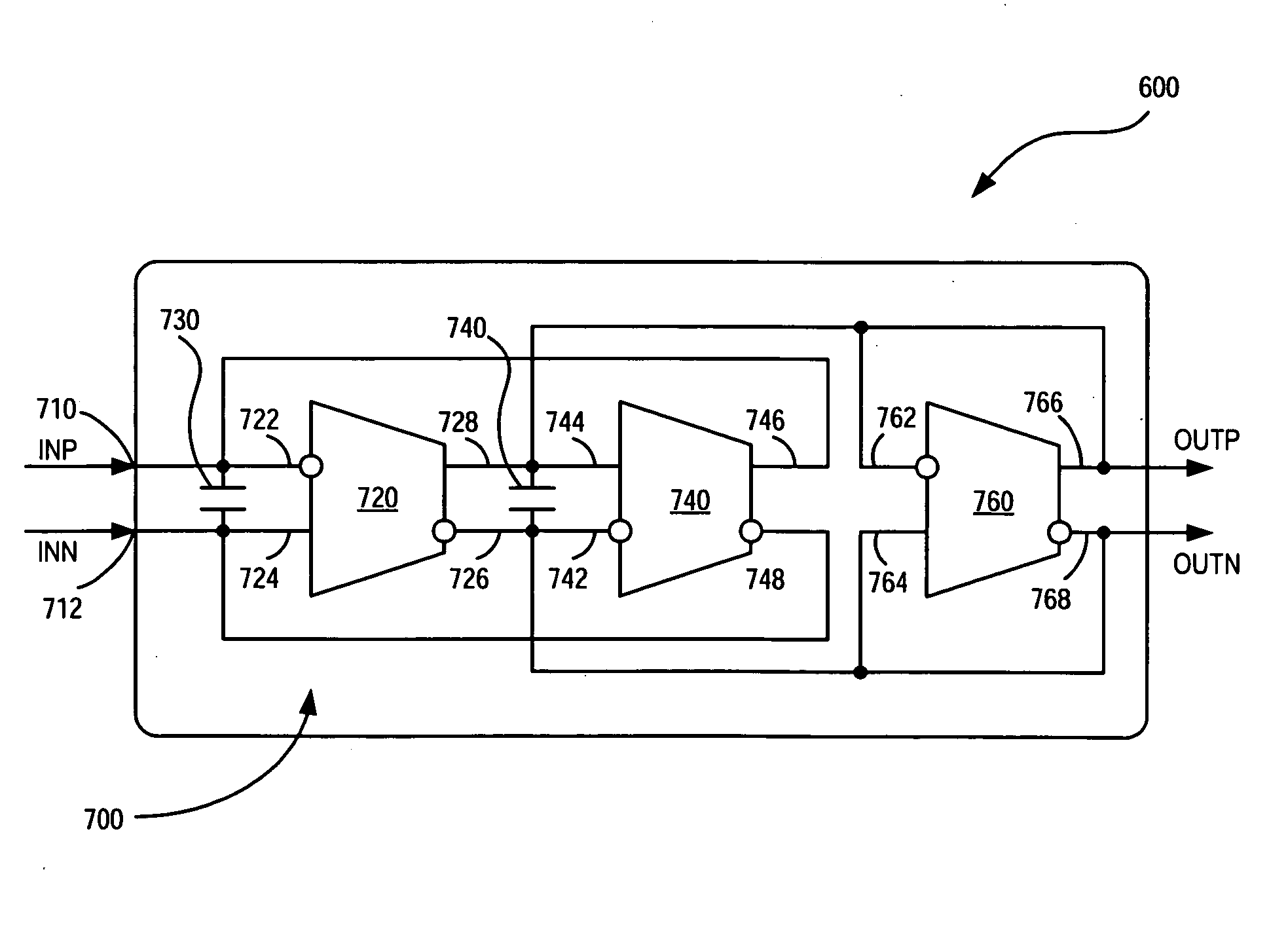
Nth Order Tunable Low-Pass Continuous Time Filter for Fiber Optic Receivers
ActiveUS20100052778A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsActive element networkNegative feedbackSoftware engineering
According to one embodiment of the invention, a circuit comprising a plurality of operational transconductance amplifiers (OTAS) is described. The first OTA has differential input and differential output. The second OTA also has differential input, where a first output of the first OTA is coupled to the first differential input of the second OTA, which is an inverting input. A second output of the first OTA is coupled to the second input of the second OTA, which is a non-inverting input. The first differential output being coupled to a first input of the first OTA and the second differential output being coupled to a second input of the first OTA for negative feedback and current biasing.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Switched-capacitor band-pass filter of a discrete-time type, in particular for cancelling offset and low-frequency noise of switched-capacitor stages
ActiveUS8497746B2Eliminate offsetReduce flicker noiseComputing operations for integral formationMultiple-port networksCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A band-pass filter made up by an operational amplifier and by an input circuit. The input circuit is formed by a capacitive filtering element, connected to the input of the operational amplifier; a coupling switch, coupled between an input node and the capacitive filtering element; a capacitive sampling element, coupled between the input of the filter and the input node; and a sampling switch, coupled between the input node and a reference-potential line. The coupling switch and the input sampling switch close in phase opposition according to a succession of undesired components sampling and sensing steps, so that the capacitive sampling element forms a sampler for sampling the undesired component in the undesired components sampling step, in the absence of the component of interest, and forms a subtractor of the undesired components from the input signal in the sensing step.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
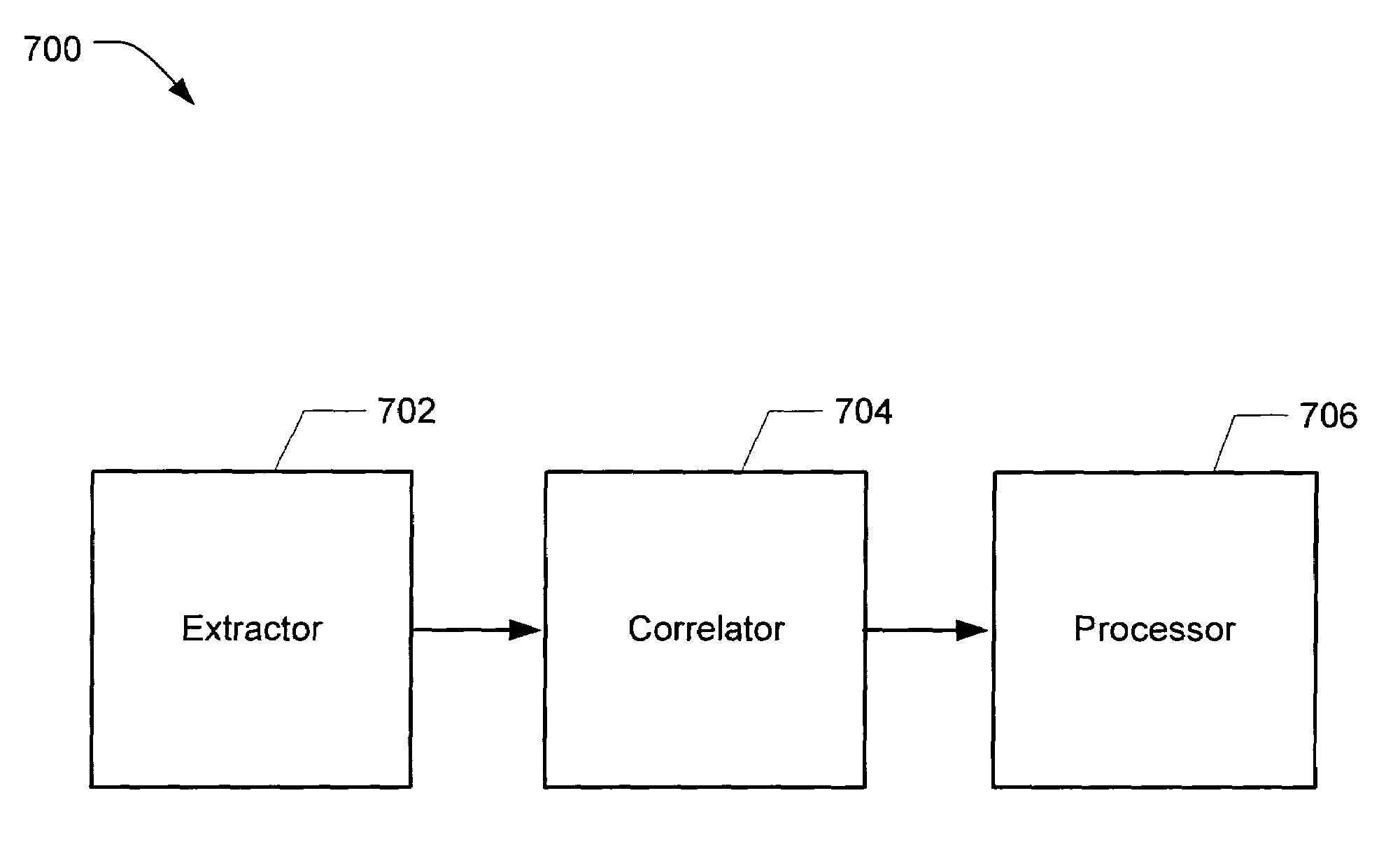
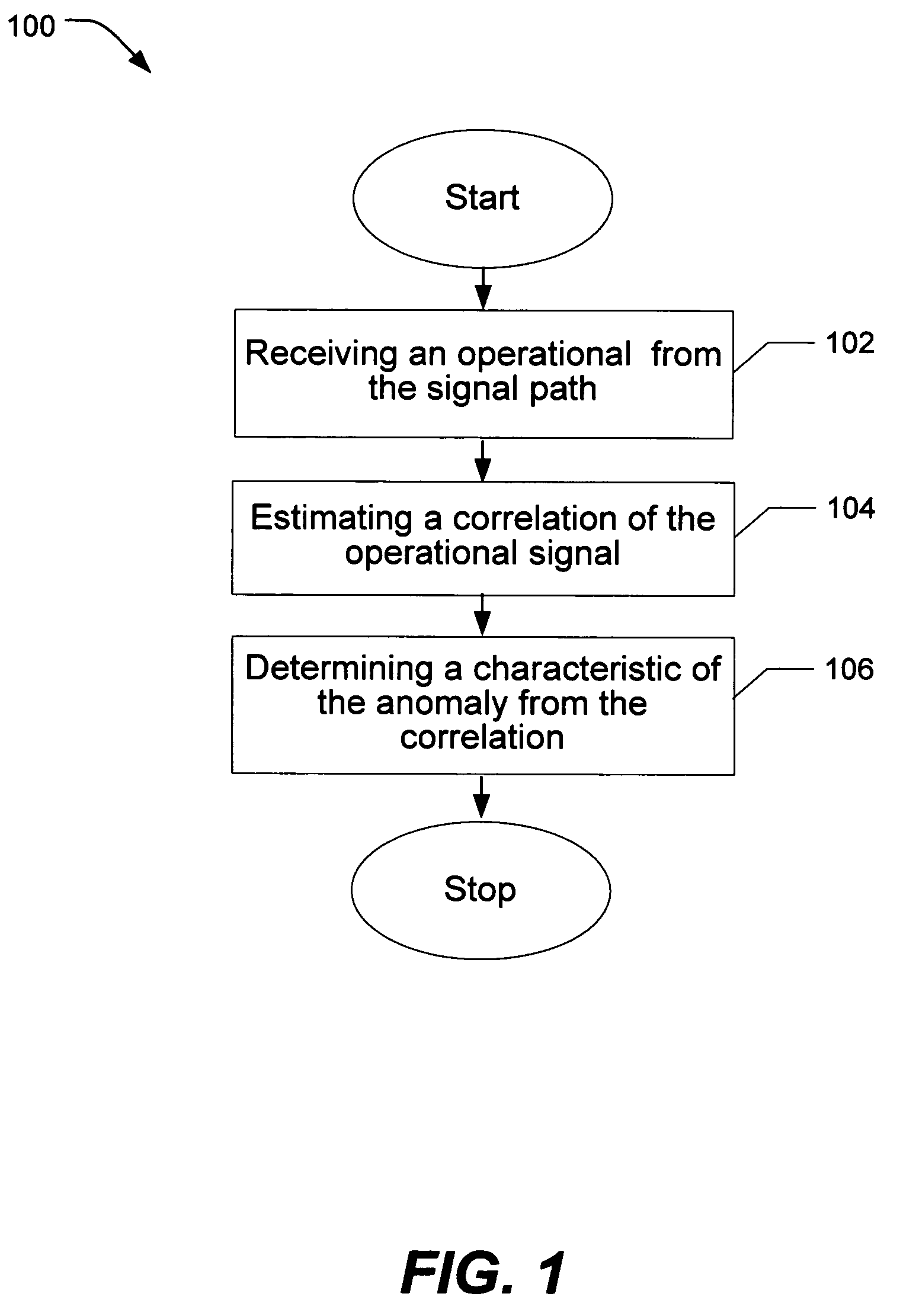
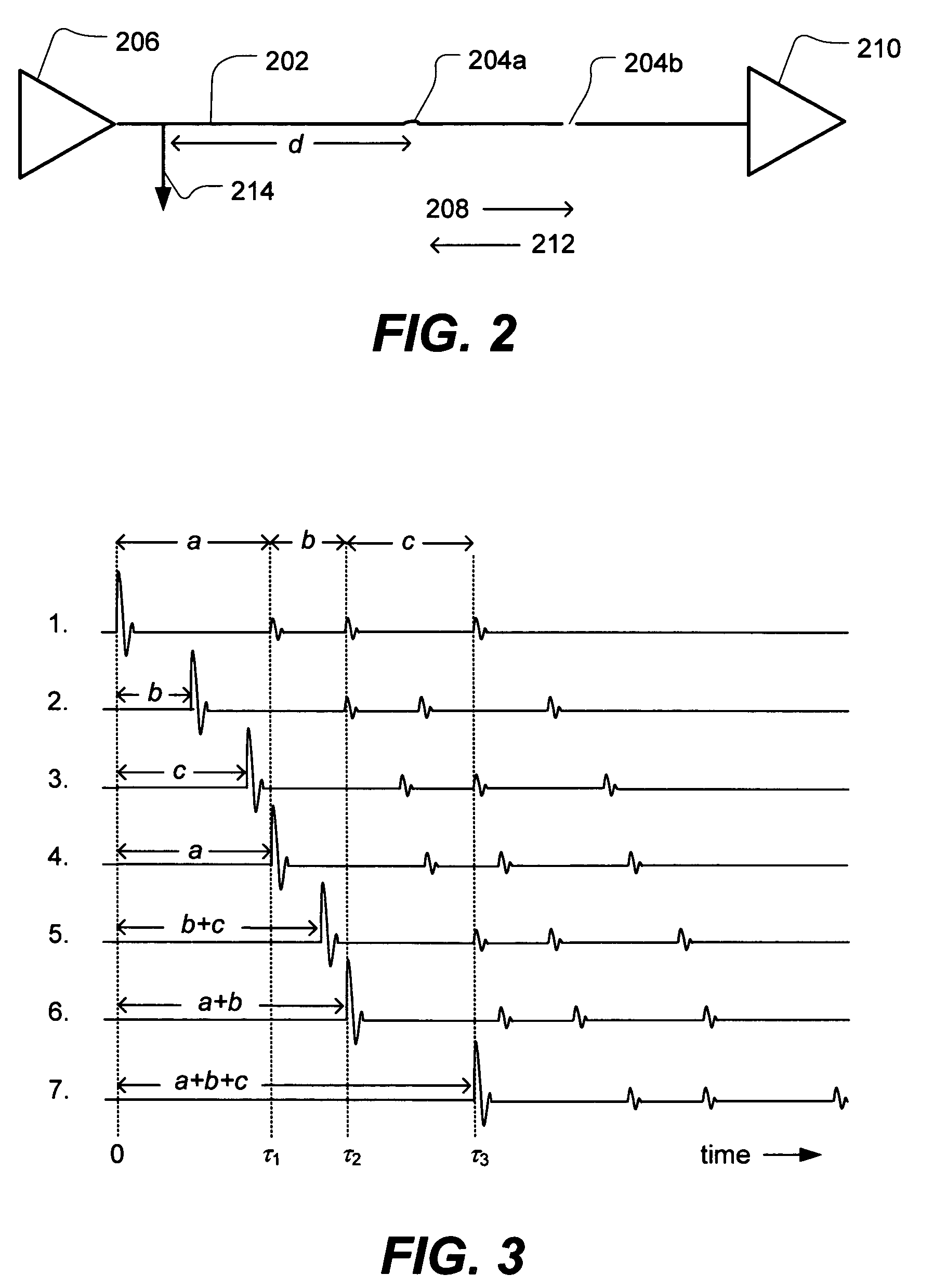
Method and system for testing a signal path having an operational signal
ActiveUS7271596B2Reduce distractionsEasy to detectActive element networkFault location by pulse reflection methodsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A technique for testing a signal path while an operational signal is present is disclosed. The technique may be performed without injecting a test signal into the signal path by using an operational signal already present in the signal path. A method of testing a signal path includes receiving an operational signal from the signal path and estimating a correlation of the operational signal. A system for testing a signal path includes an extractor configured to extract a sample of the operational signal when coupled to a signal path and a correlator configured to estimate a correlation of the operational signal. Various properties of the signal path may be determined using the technique.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Multi-mode radio frequency antenna switch
ActiveCN103401531ASmall sizeReduce layoutSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsActive element networkParasitic capacitanceTree shaped
The invention relates to the field of wireless communication technology and discloses a multi-mode radio frequency antenna switch. The multi-mode radio frequency antenna switch comprises a main switch element, at least one branch switch element, at least one node switch element and at least one branch circuit formed by connecting at least two node switch elements in parallel, wherein all the switch elements form a tree-shaped topological structure, and each node switch element is connected with an emitting / receiving port; each branch circuit is provided with a branch switch element; one end of the main switch element is connected with a radio frequency antenna, and the other end is connected with the branch switch elements in a single-pole multi-throw manner. The multi-mode radio frequency antenna switch adopts the tree-shaped topological structure, not only has a wider frequency band range, but also can effectively reduce parasitic capacitance of the radio frequency antenna to the ground and improve the isolation between the ports, and can achieve a more remarkable parasitic capacitance reduction effect along with increase of the wireless communication working frequency, effectively improve the degree of circuit linearity and reduce insertion loss.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
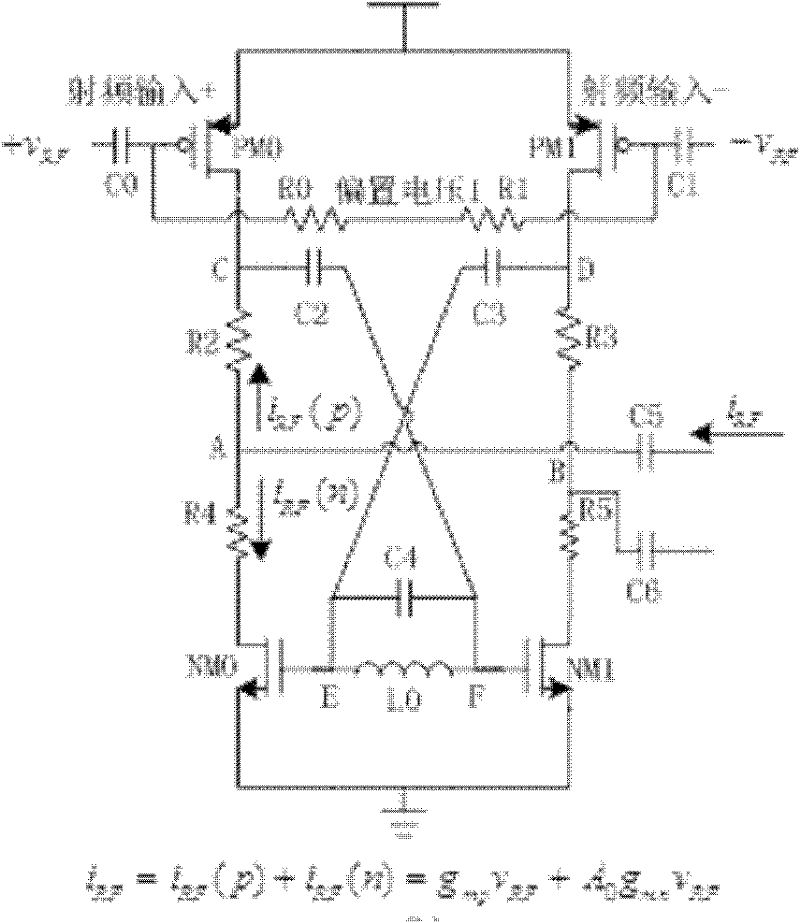
Transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer
InactiveCN102412786AImprove linearityReduce power consumptionActive element networkMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceFrequency mixerHemt circuits
The invention discloses a transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer, which comprises a mixing stage and a biasing circuit, and further comprises a transconductance stage with a transconductance-enhancing function, a passive mixing switch pair and an enhanced load output stage, wherein the transconductance stage with a transconductance-enhancing function transforms an input radio-frequency voltage into a radio-frequency current; and frequency mixing of the radio-frequency current is achieved through the double-balance mixing switch pair, and the current after frequency mixing is transformed into a mid-frequency voltage for output through the transconductance-enhanced load output stage. As the transconductance stage uses a pre-amplifying transconductance-enhancing structure, transconductance is greatly enhanced, thus the same transconductance value can be achieved at a lower bias current, and an output mid-frequency current signal is generated after the radio-frequency current is modulated through the mixing stage. Voltage output is generated through a transresistance amplifier, and finally the mid-frequency voltage signal is obtained. As the transresistance amplifier uses a transconductance-enhancing structure, input impedance is reduced, and current utilization efficiency and port isolation are improved. The transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer provided by the invention has the characteristics of low power consumption, high conversion gain, good port isolation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV WUXI CAMPUS
Filter circuit arrangement
InactiveUS20080136473A1Not impairing transmission behaviorExpand the capture rangePulse automatic controlActive element networkUltrasound attenuationLocal oscillator signal
A filter circuit arrangement for filtering of a radio-frequency signal has a first tunable filter and a phase regulation loop in order to hold the first tunable filter to a transmission phase constant relative to the frequency of the radio-frequency signal. The filter circuit arrangement has a second tunable filter arranged parallel to the first tunable filter in the phase regulation loop. The first tunable filter and the second tunable filter exhibit different attenuation characteristics and are fashioned and connected within the phase regulation loop so that: a capture range of the filter circuit arrangement, in which a tuning of the phase regulation loop to a radio-frequency signal to be filtered is possible is dominated by the attenuation characteristic of the second tunable filter, and so that the transmission behavior of the filter circuit arrangement in operation is dominated by the attenuation characteristic of the first tunable filter, given a tuned phase regulation loop. A circuit arrangement for generation of a local oscillator signal has an oscillation generator and a filter circuit arrangement as described above arranged downstream of the oscillation generator.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
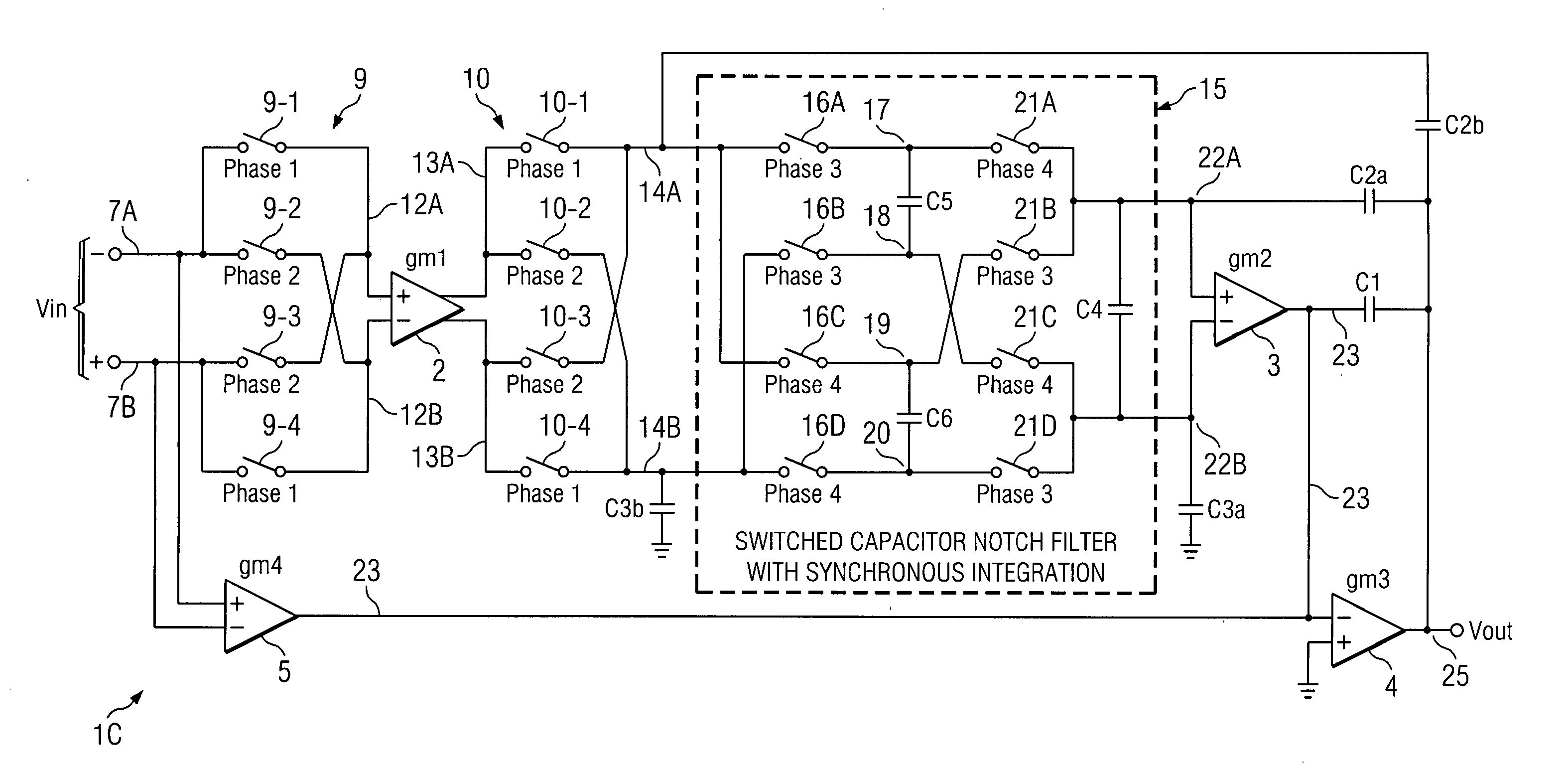
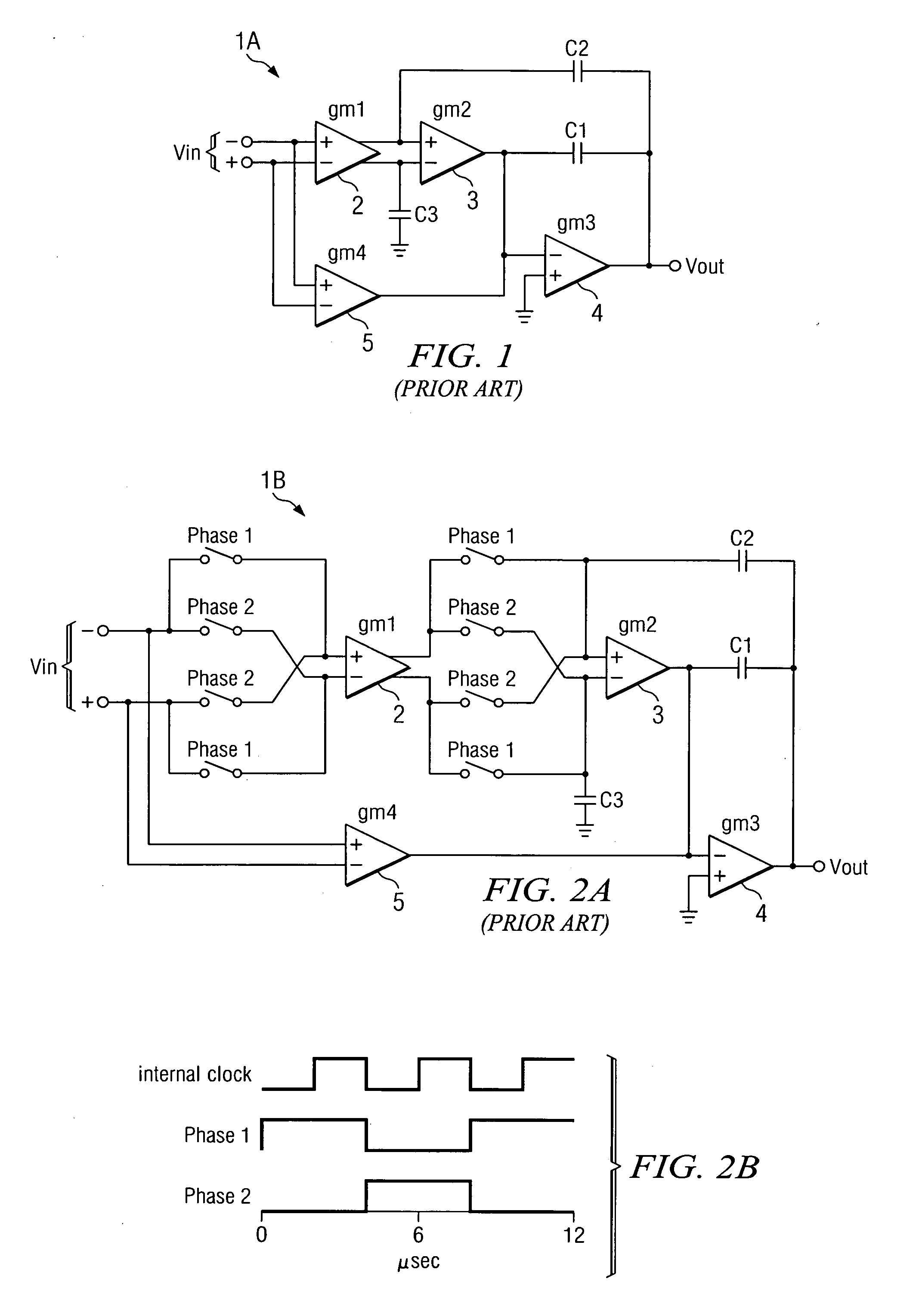
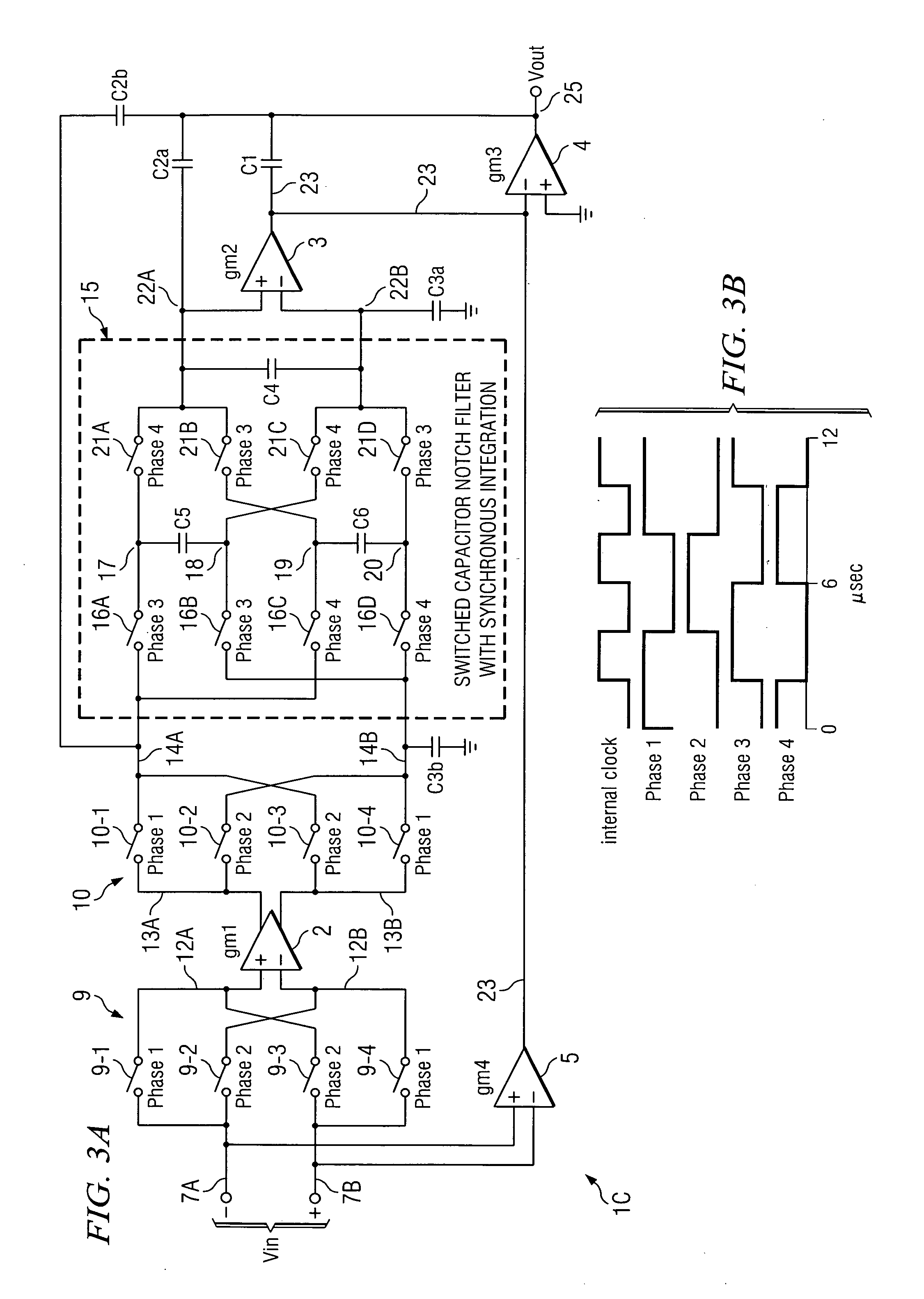
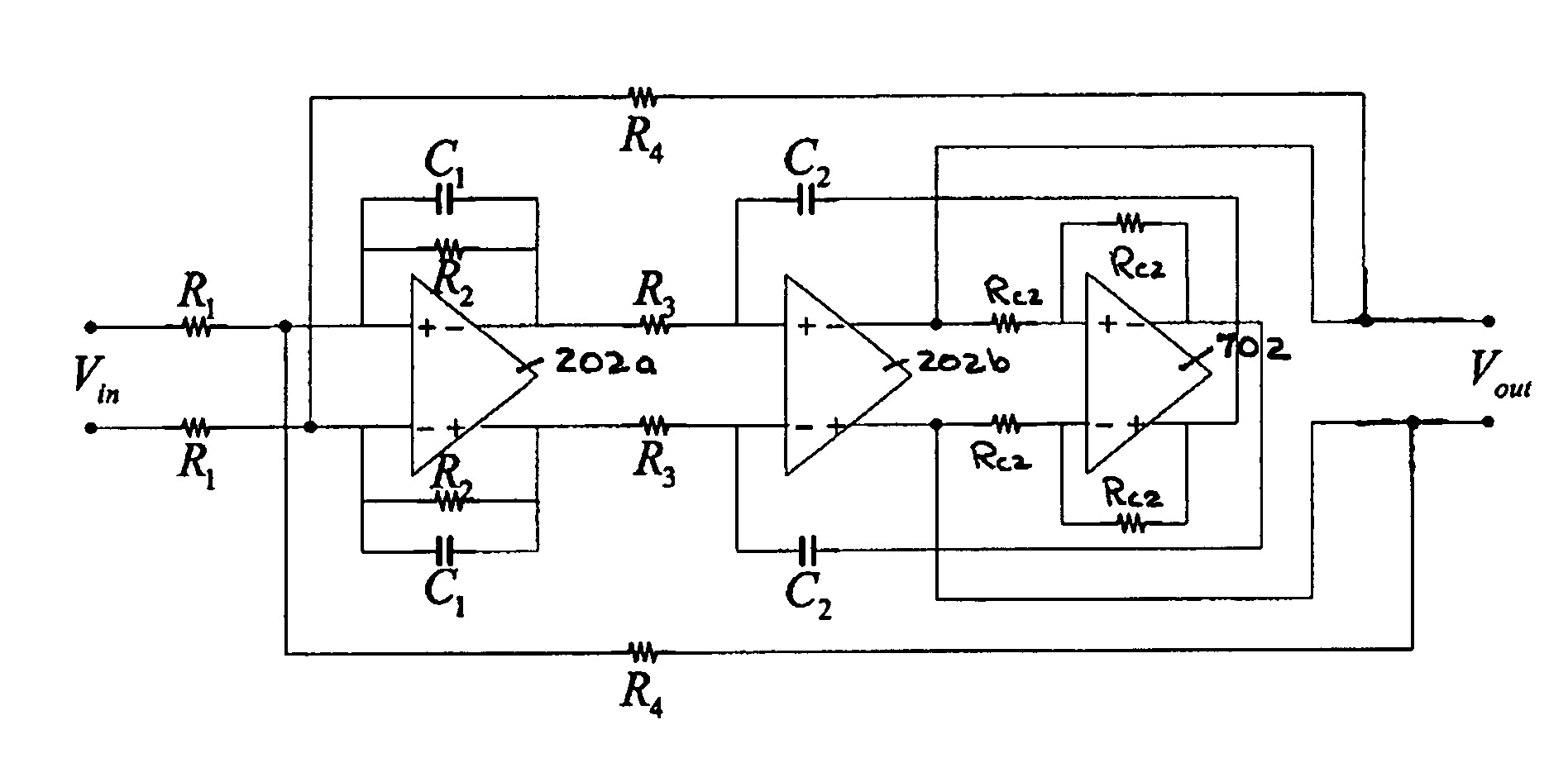
Notch filter for ripple reduction in chopper stabilized amplifiers
ActiveUS20070170981A1Reduce ripple noiseFast signalAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
A chopper-stabilized amplifier receiving an input signal includes a first operational transconductance amplifier having an input chopper and an output chopper for chopping an output signal produced by the first operational transconductance amplifier. A switched capacitor notch filter filters the chopped output signal by operating synchronously with the chopping frequency of output chopper to filter ripple voltages that otherwise would be produced by the output chopper. In one embodiment, a second operational transconductance amplifier amplifies the notch filter output. The input signal is fed forward, summed with the output of the second operational transconductance amplifier, and applied to the input of a fourth operational transconductance amplifier. Ripple noise and offset are substantially reduced.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Active-RC filter with compensation to reduce Q enhancement
InactiveUS7075364B2Active element networkOscillations generatorsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
An active filter with compensation to reduce Q-enhancement is disclosed. The filter may include a first amplifier and a second amplifier coupled to the first amplifier. The second amplifier having a negative feedback loop including a buffer having a plurality of compensation resistors. The compensation resistors may each have a value that results in the biquad filter having substantially zero Q-enhancement. The biquads may cascaded to form higher order filters.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Electrically tunable filters with dielectric varactors
InactiveUS7145415B2Increase powerReduce distortion problemsMultiple-port networksActive element networkEngineeringBand-stop filter
Owner:NXP USA INC
Integrated digital television tuner
InactiveUS20070132889A1Television system detailsMultiple-port networksIntermediate frequencyRf filters
A highly integrated terrestrial and cable tuner for receiving digital television signals is disclosed. It achieves high performances in sensitivity, image rejection, dynamic range, channel selectivity and power consumption. The tuner first converts an RF input signal into a high-frequency first intermediate frequency (IF) using a single quadrature image rejection converter. Consequently, it significantly relaxes RF filter design. A second converter downconverts the first IF signal into either a baseband signal or a low-IF signal. The tuner can interface with a demodulator having the baseband and / or low-IF input interface. The tuner is integrated by using standard processes, with minimal off-chip components excluding SAW and LC filters. Small tuner modules cost less than discrete (can) tuners. They can be used in digital TV sets and portable / handheld TV devices.
Owner:PAN JIANPING
High q monolithic inductors for use in differential circuits
ActiveUS20060220737A1High quality factorActive element networkVariable inductances/transformersPhase shiftedEngineering
The present invention provides a differentially driven monolithic inductor circuit having a shield differentially driven by phase shift buffers and a single-ended monolithic inductor circuit having single-ended shields driven by phase shift buffers, both inductor circuit types providing high Quality factor (Q) at operating frequencies in the multi-GHz range and circuits incorporating the same.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
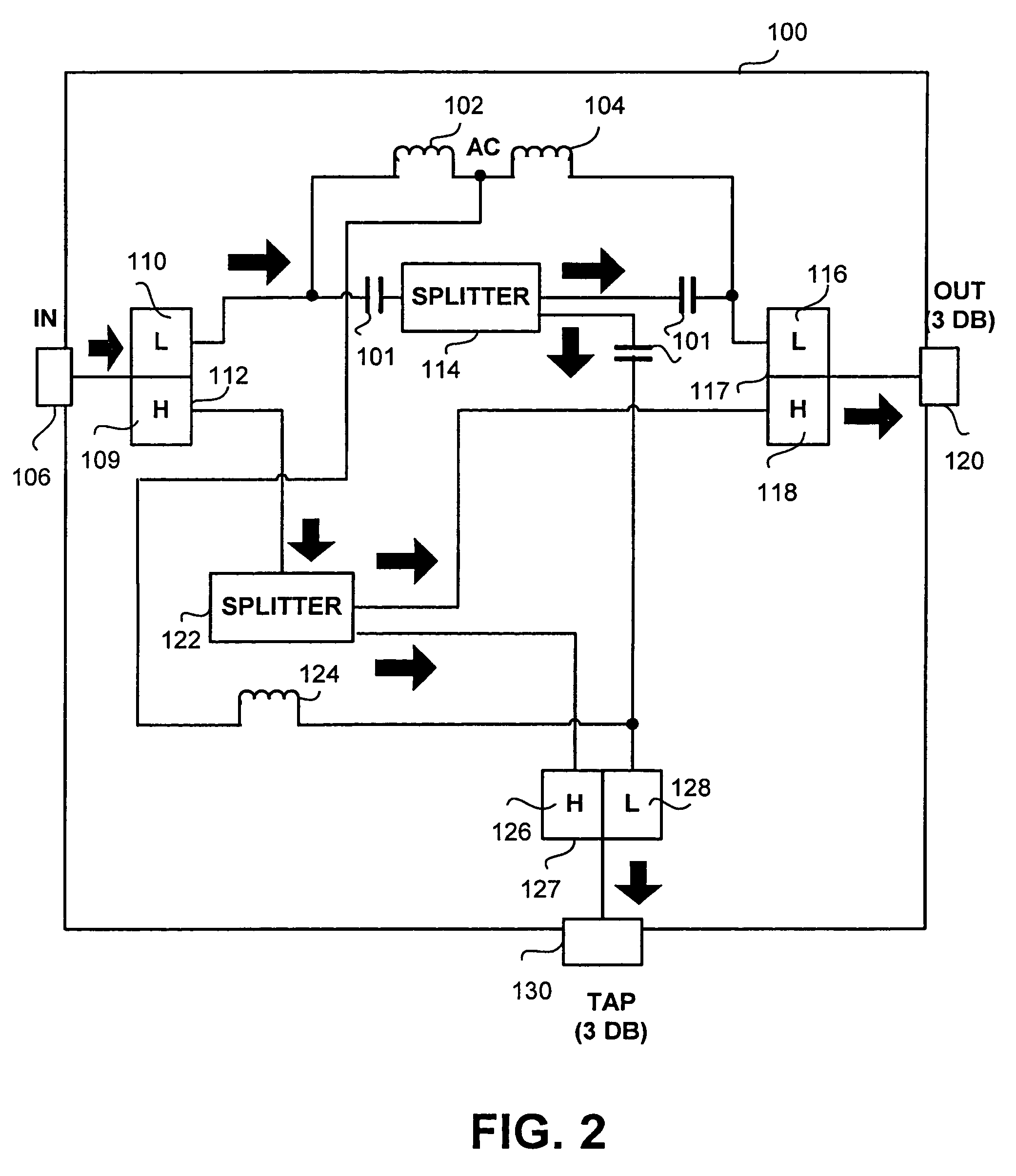
Wideband CATV signal splitter device
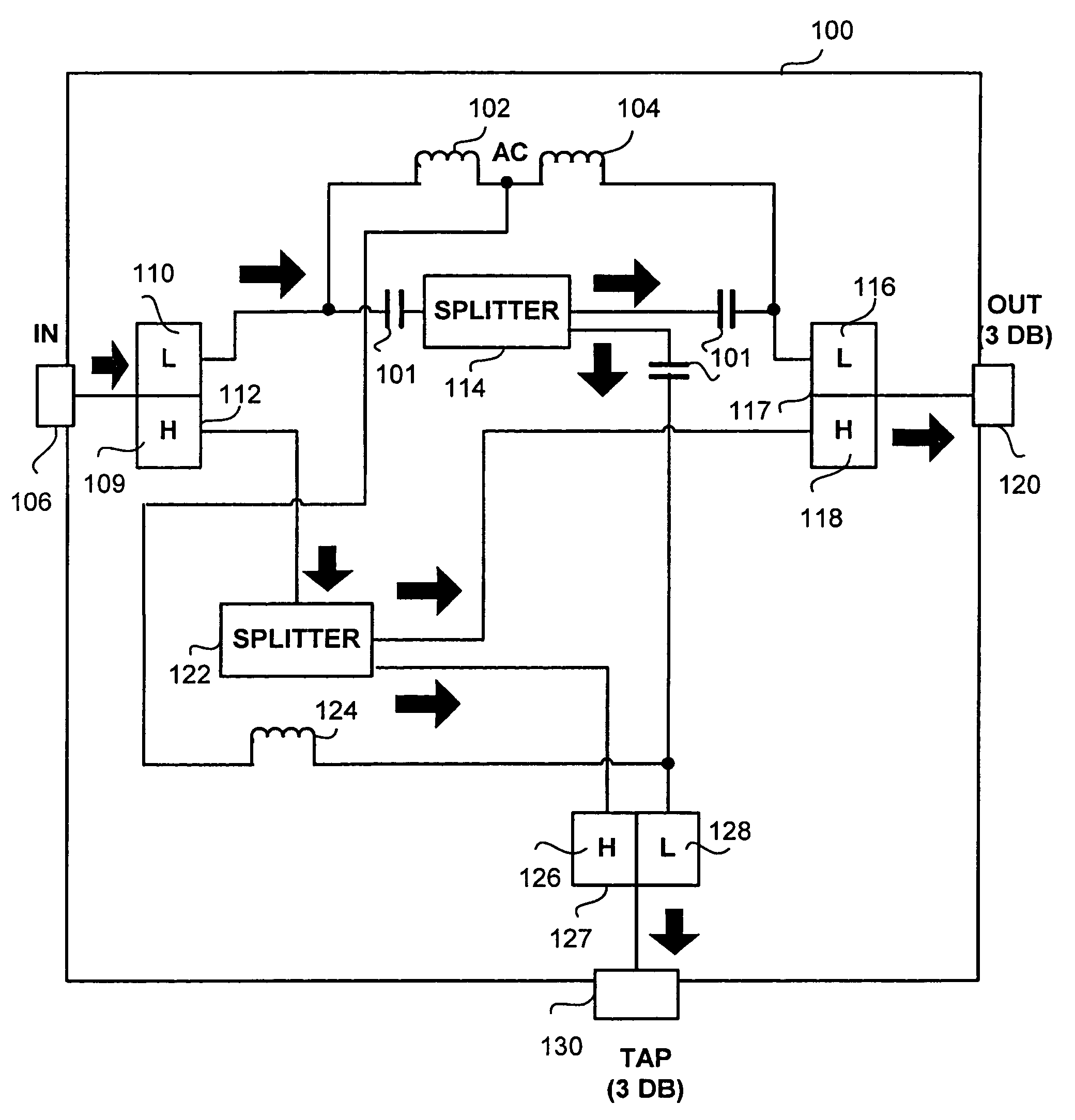
A wideband high frequency signal splitter device utilized in a signal distribution network is disclosed. An input signal having a substantially extended frequency bandwidth is applied to an input port of the proposed signal splitter from the upstream portion of a signal distribution network. Within the signal splitter the signal is suitably divided into its constituent components. The constituent components include a low frequency component, a high frequency component and an AC current power component. The components are divided separately and re-routed to combiner units associated with suitable output ports. The separate components are combined and fed through the output ports to the downstream portion of the signal distribution network. The signal splitter device is also functional as a signal combiner device by combining separate signals received from the downstream portion of the network via the output ports and transmitting the combined signals to the upstream portion of the signal distribution network.
Owner:ATX NETWORKS (TORONTO) CORP
Filter circuit with variable capacitance for use with implantable medical devices
An implantable medical device (IMD) as described herein includes an input filter circuit having variable capacitor elements that can be electronically adjusted based upon current operating conditions (such as electromagnetic conditions, noise conditions, and / or environmental conditions). The variable capacitor elements can be adjusted to accommodate pre-designated operating modes of the IMD and / or dynamically in response to changing operating conditions. In one embodiment, the variable capacitor elements are realized using digitally programmable switched capacitor arrangements.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Popular searches
Switched capacitor networks Differential amplifiers Amplifiers using switched capacitors Dc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stages Radio/inductive link selection arrangements Transmission Line-faulsts/interference reduction Radio transmission Signal/carrier strength dependant limiting amplitude Amplifier details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com