Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
906results about How to "Reduce phase noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
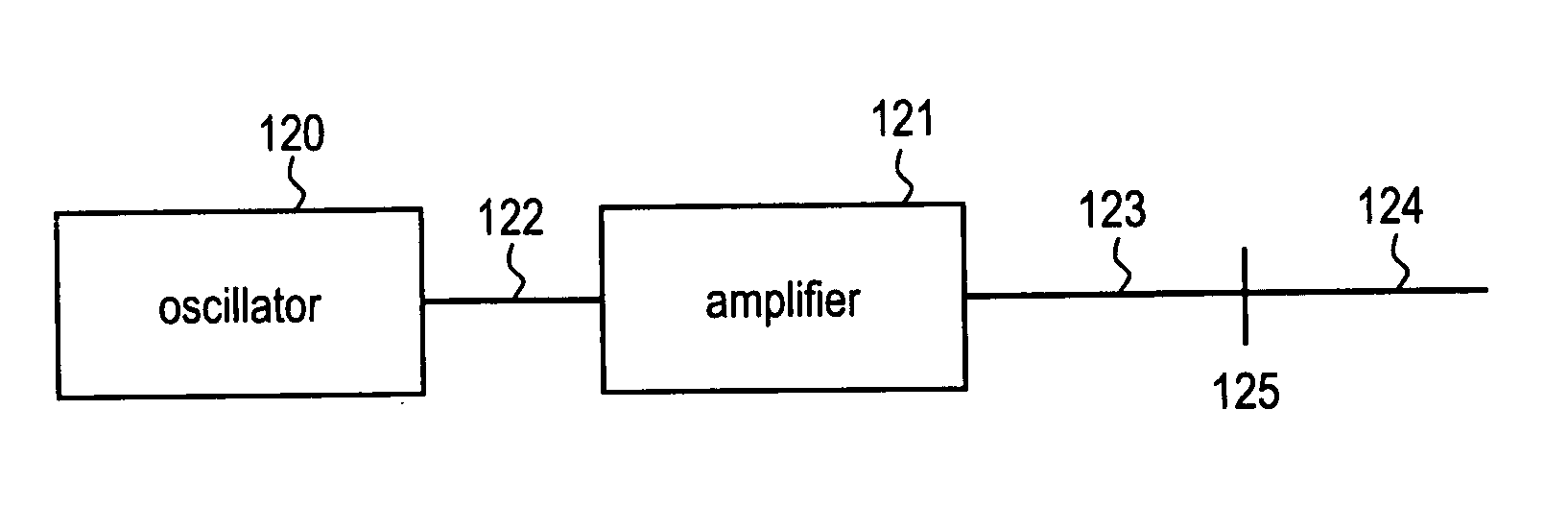
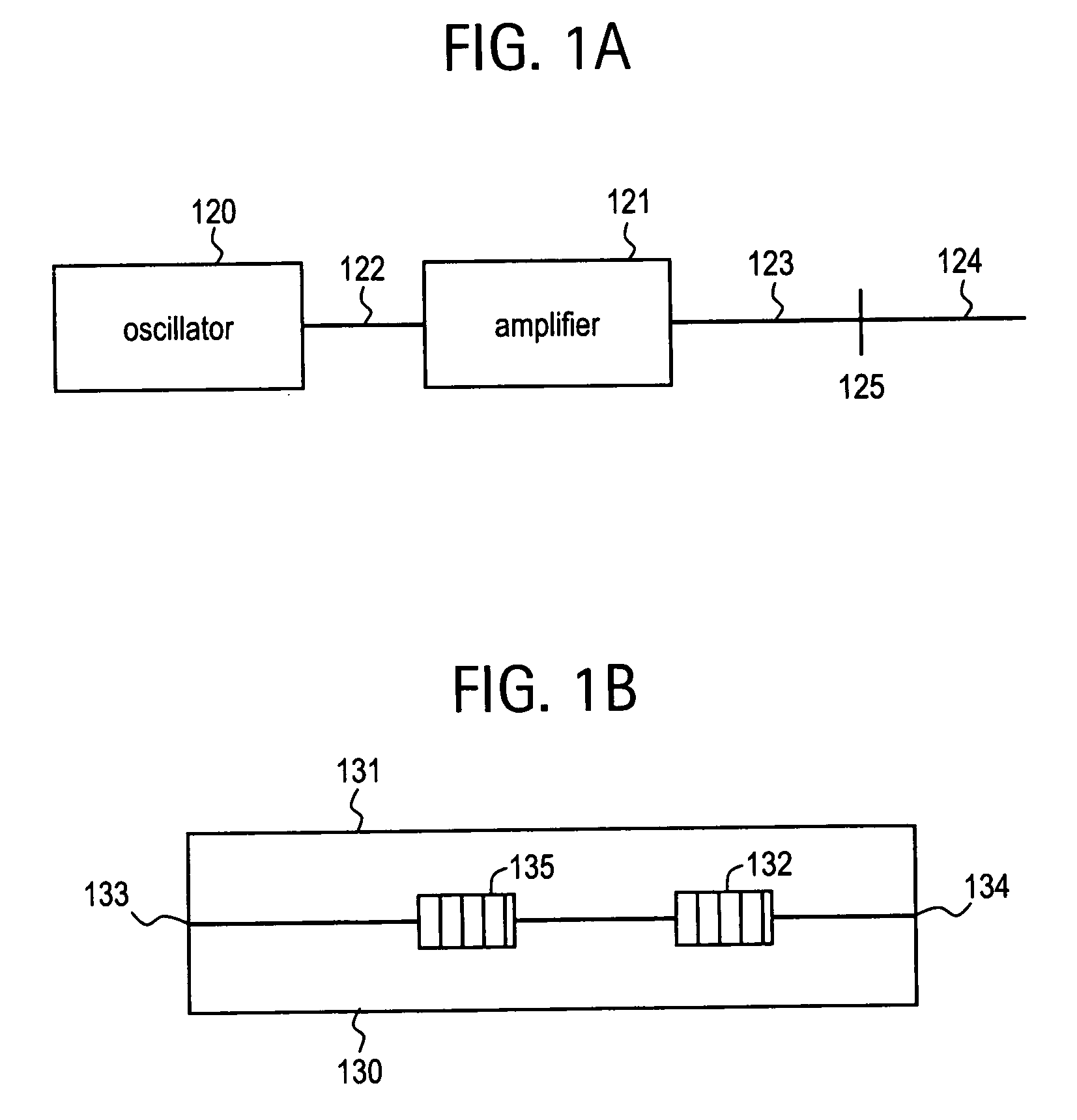
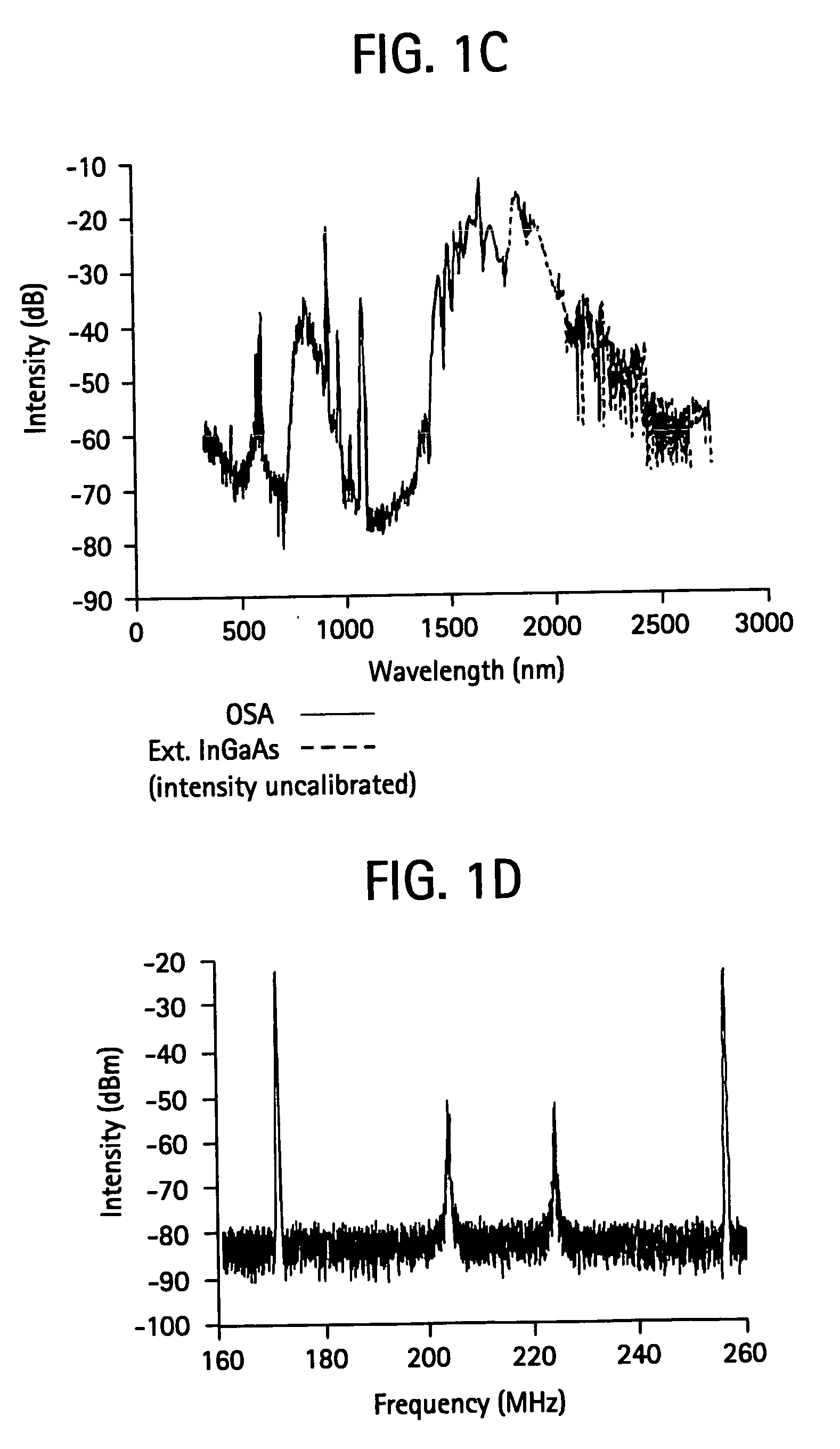
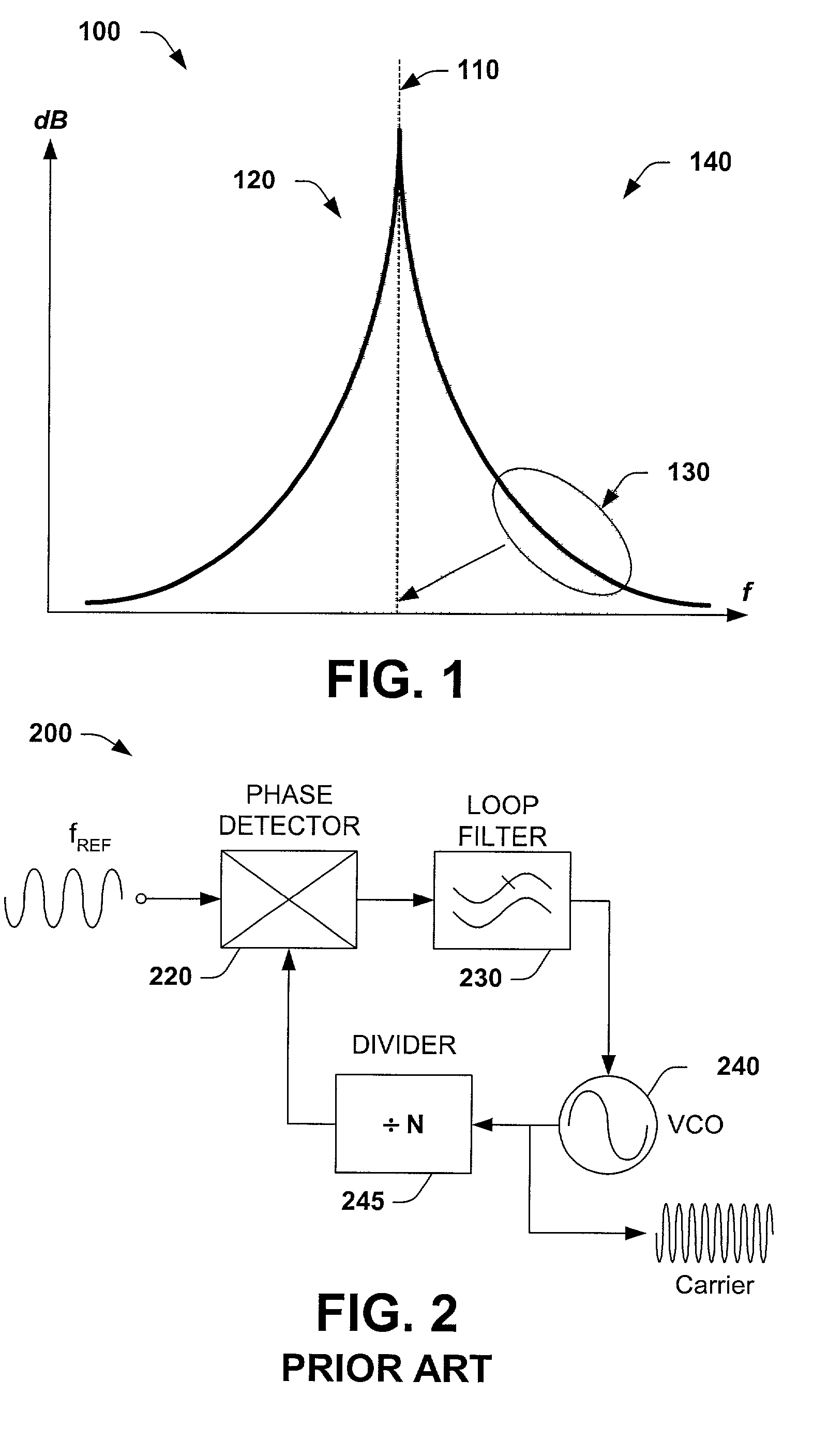
Laser based frequency standards and their applications
InactiveUS20070086713A1Minimize lossLow phase noiseLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFrequency standardLight source
Frequency standards based on mode-locked fiber lasers, fiber amplifiers and fiber-based ultra-broad bandwidth light sources, and applications of the same.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
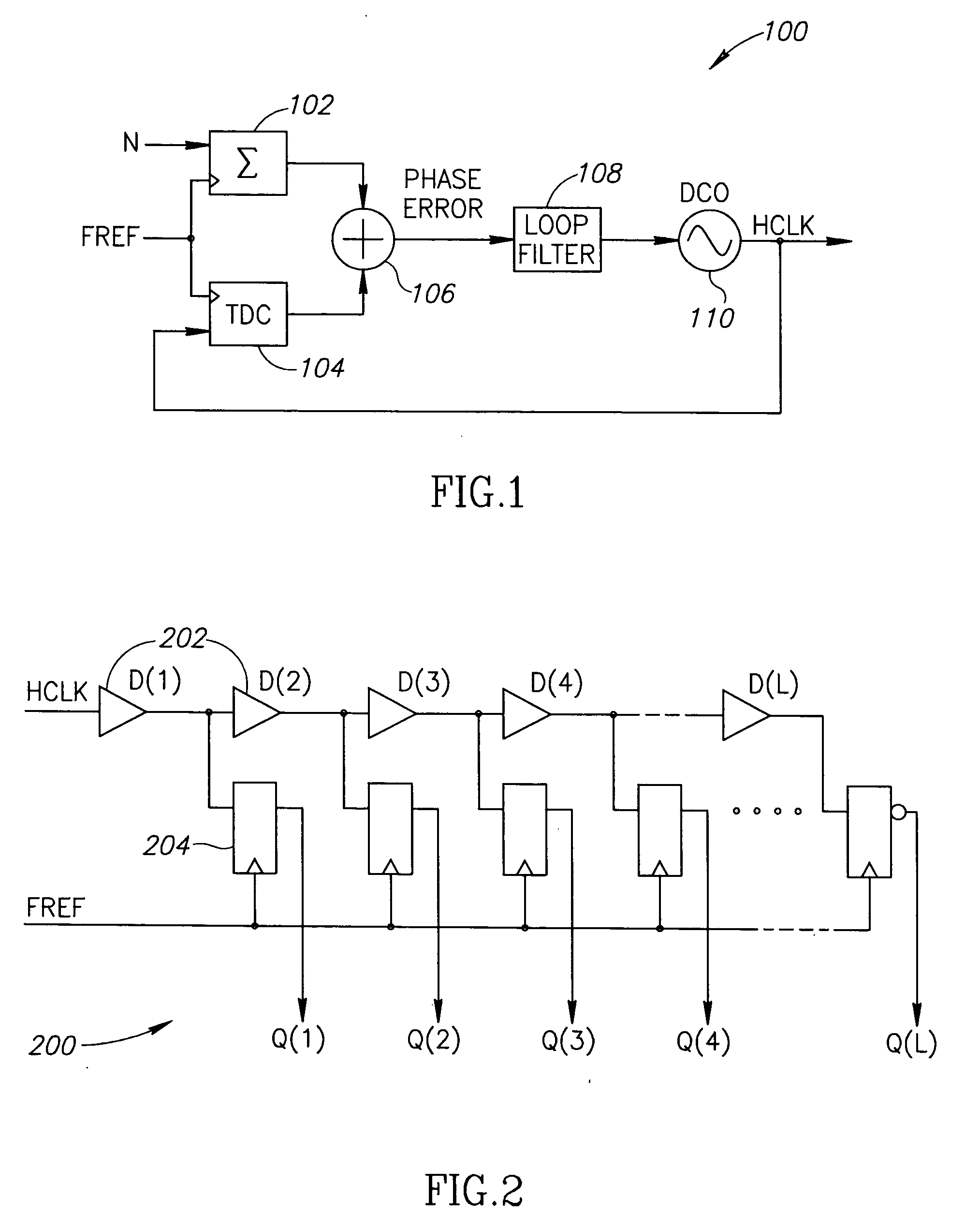
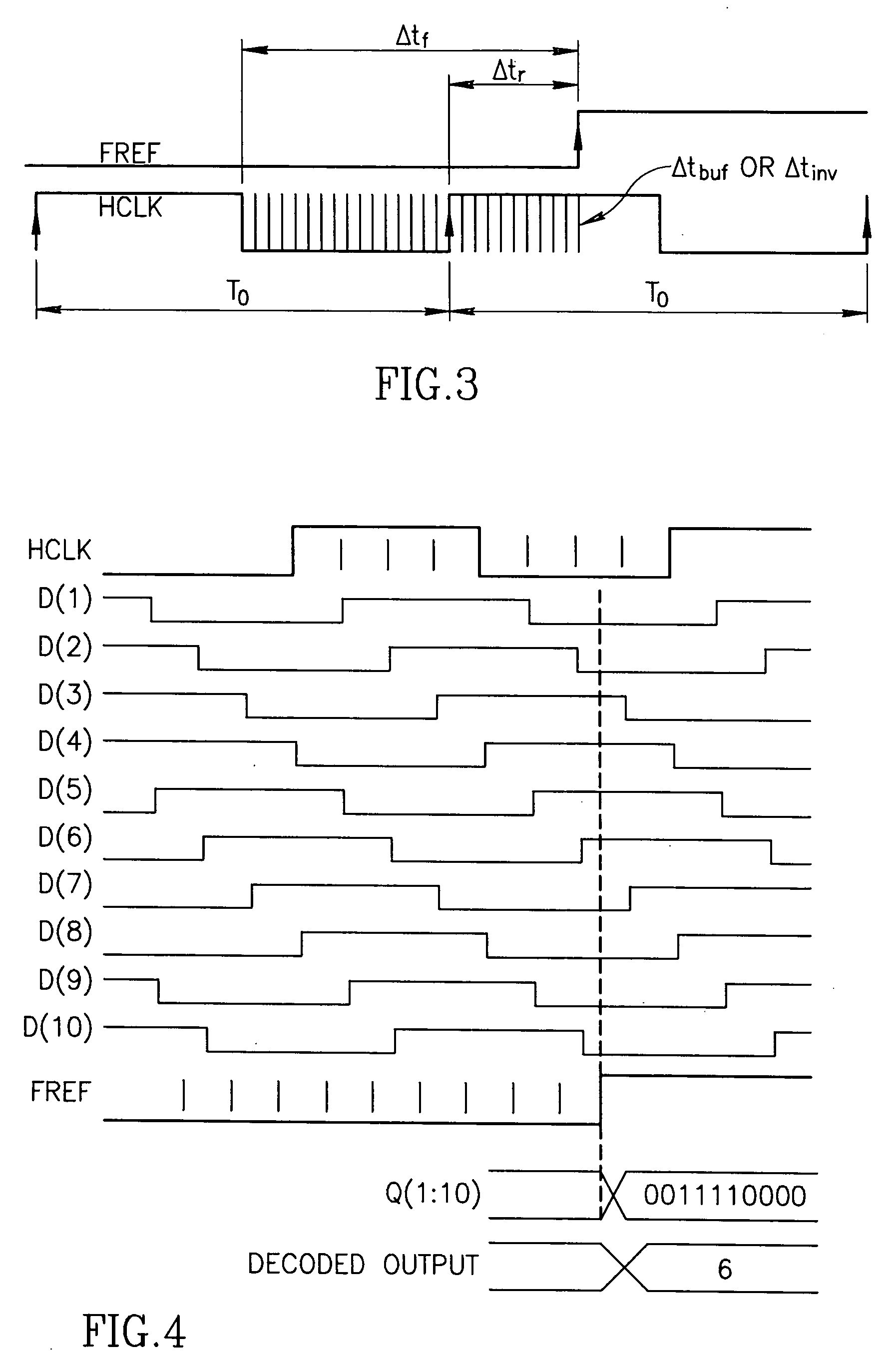
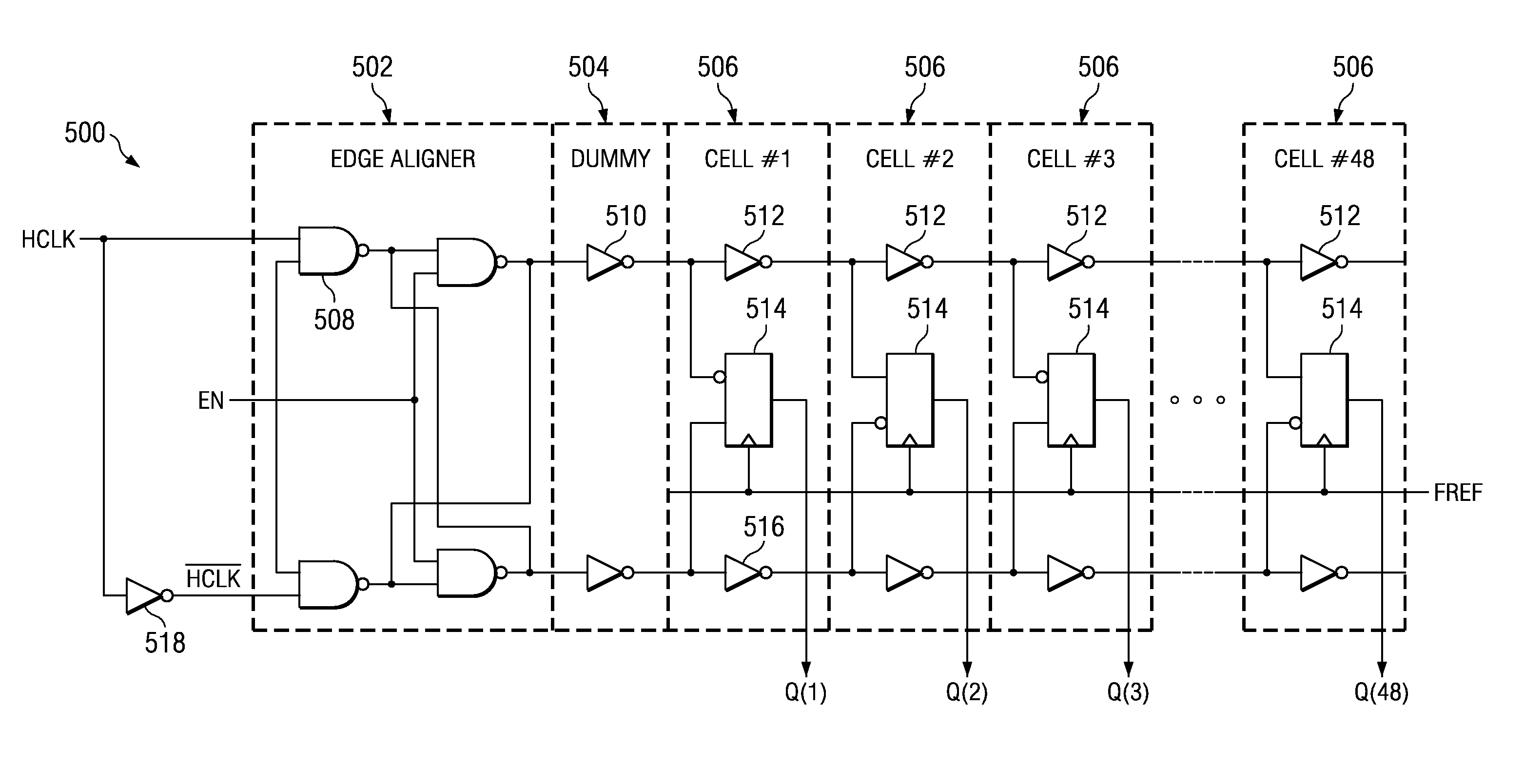
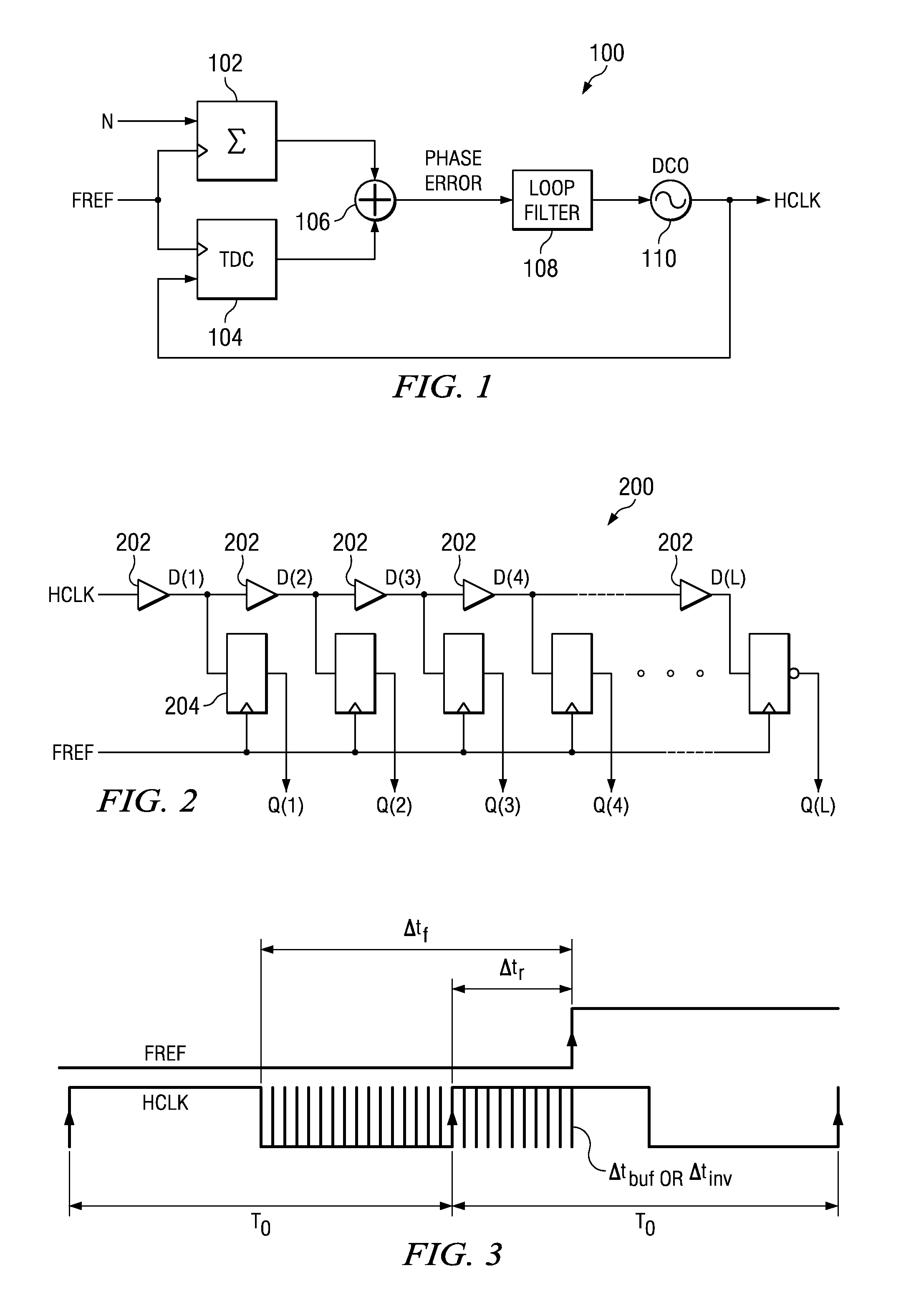
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS20060103566A1Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlEngineeringDigital converter
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
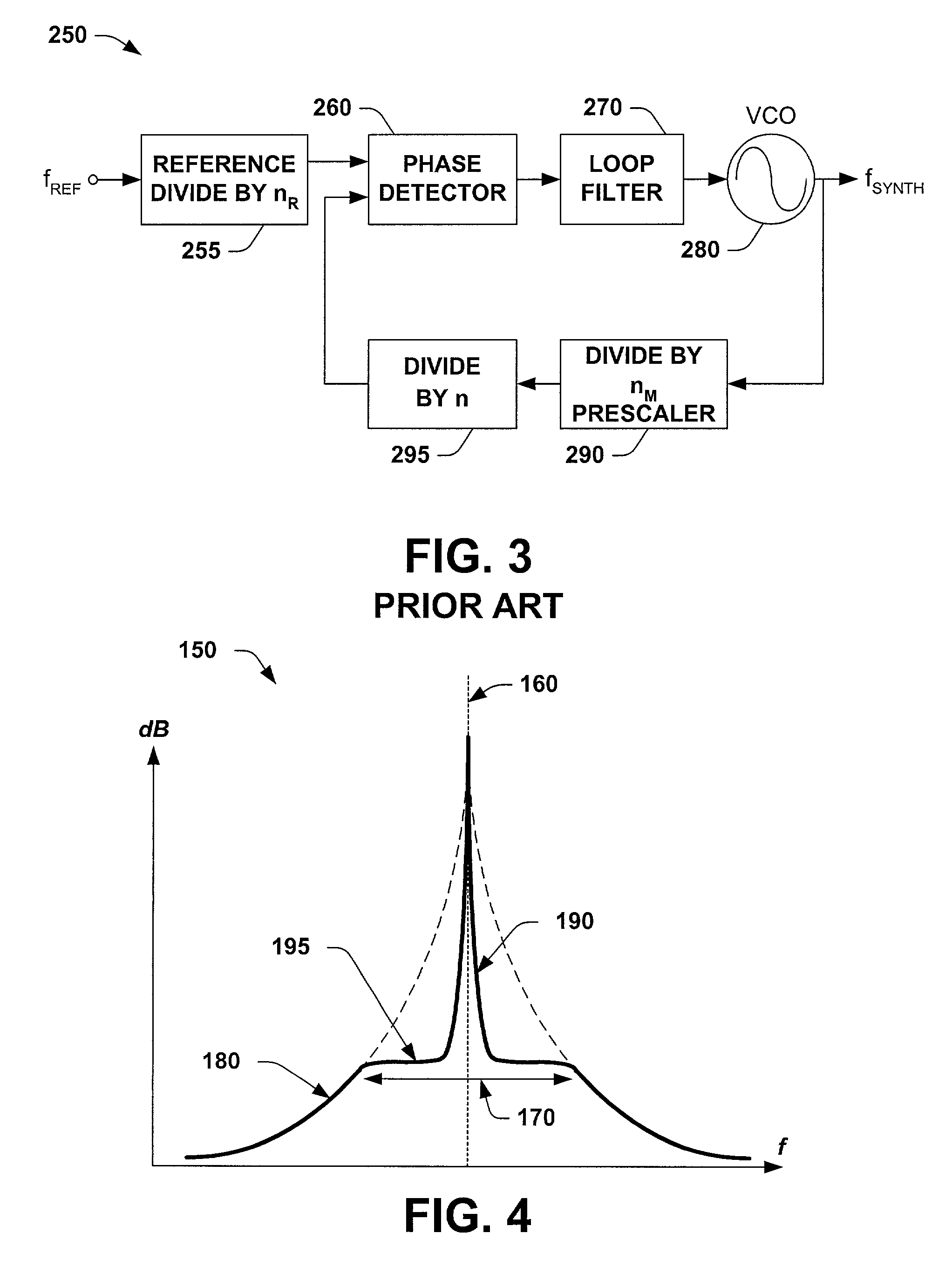
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS7205924B2Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsDigital converterCmos process
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
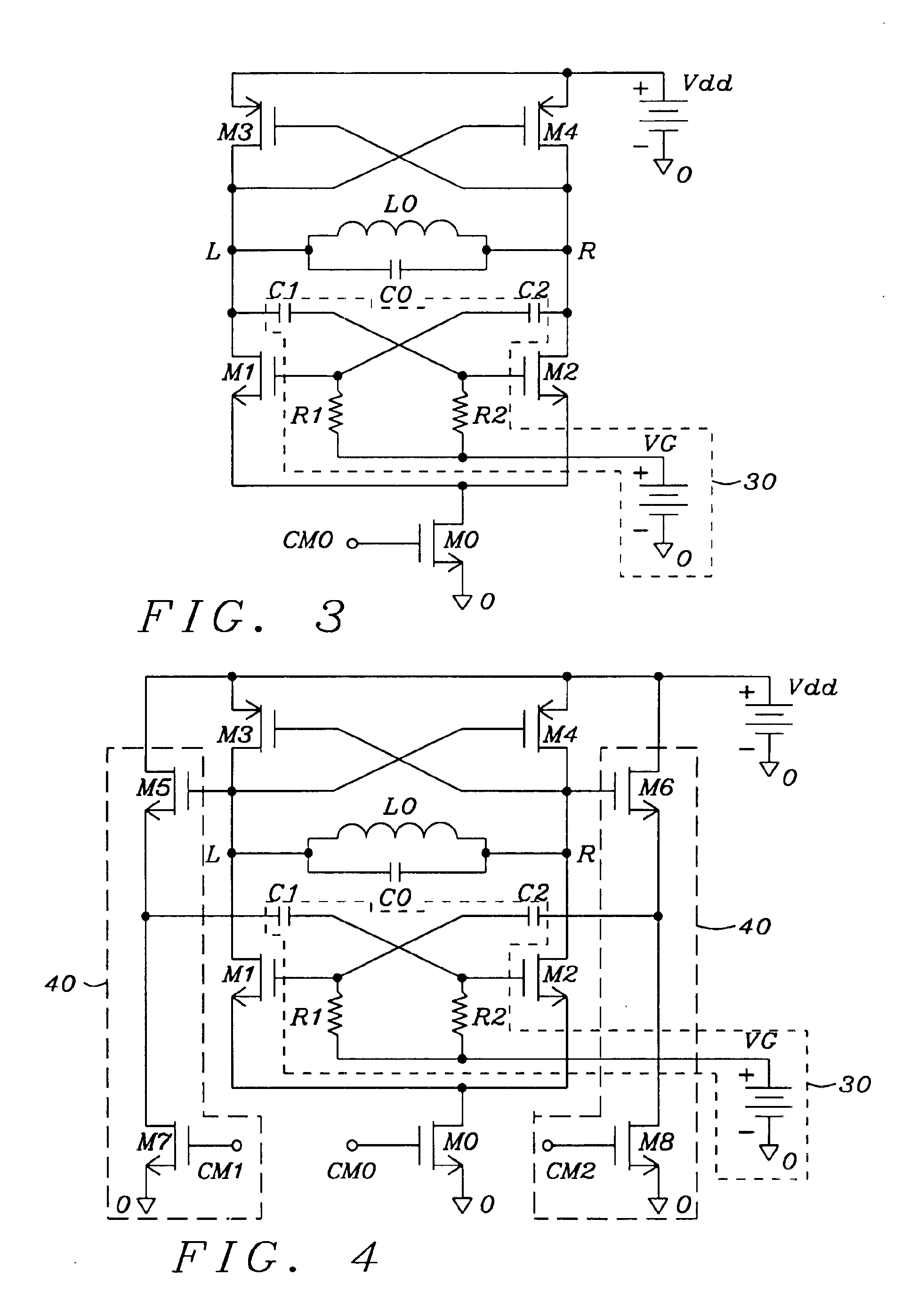
MEMS-based, computer systems, clock generation and oscillator circuits and LC-tank apparatus for use therein
InactiveUS6972635B2Reduce flicker noiseReduce phase noiseAngle modulation by variable impedenceMultiple-port networksEngineeringVaricap
MEMS-based, computer system, clock generation and oscillator circuits and LC-tank apparatus for use therein are provided and which are fabricated using a CMOS-compatible process. A micromachined inductor (L) and a pair of varactors (C) are developed in metal layers on a silicon substrate to realize the high quality factor LC-tank apparatus. This micromachined LC-tank apparatus is incorporated with CMOS transistor circuitry in order to realize a digital, tunable, low phase jitter, and low power clock, or time base, for synchronous integrated circuits. The synthesized clock signal can be divided down with digital circuitry from several GHz to tens of MHz—a systemic approach that substantially improves stability as compared to the state of the art. Advanced circuit design techniques have been utilized to minimize power consumption and mitigate transistor flicker noise upconversion, thus enhancing clock stability.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
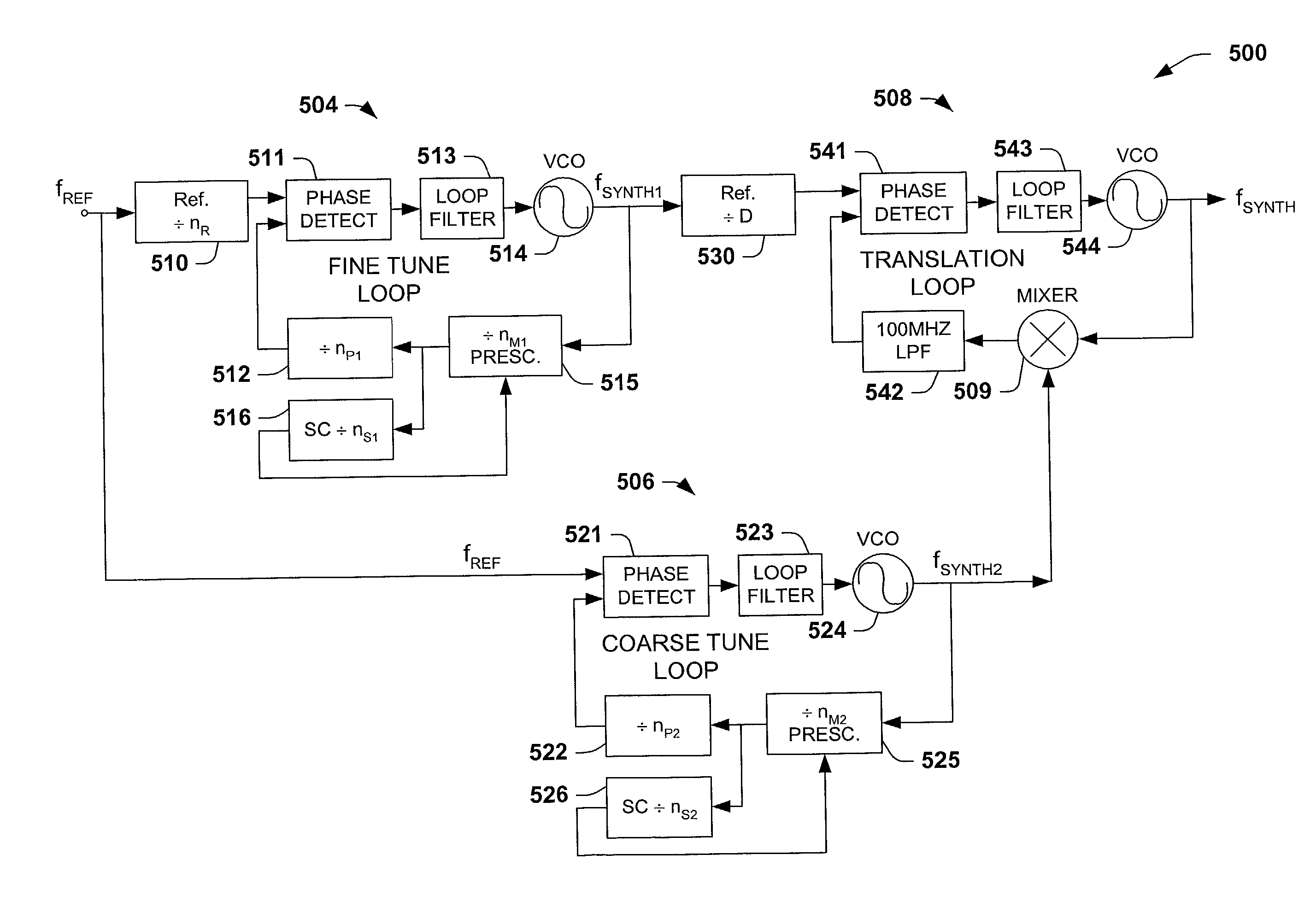
Fully integrated low noise multi-loop synthesizer with fine frequency resolution for HDD read channel and RF wireless local oscillator applications
InactiveUS20030119466A1Avoid discontinuitiesLower performance requirementsPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionLow noiseHard disc drive
A low noise multi-loop radio frequency synthesizer is disclosed for the read channel in a hard disk drive, and for RF wireless communications local oscillator applications. The frequency synthesizer receives an input reference signal having a frequency fR, into a fine tune phase locked loop and into a coarse tune phase locked loop. Driven by the input reference signal, the fine tune PLL outputs a fine tune signal with a frequency fR.P, where P is an integer, while the coarse tune PLL, also driven by the same input reference signal, outputs a coarse tune signal with a frequency fR.A, where A is an integer. A translation phase locked loop has a unity multiplication factor and is driven by the fine tune signal output. The frequency synthesizer finally has a Gilbert cell double balanced mixer coupled between the coarse tune and the translation phase locked loops, wherein the Gilbert cell mixer combines the coarse tune signal and the output signal of the translation phase locked loop and couples the mixed signal into the translation phase locked loop. The translation loop outputs a signal with a frequency which is proportional to the linear sum of the coarse tune signal and the fine tune signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
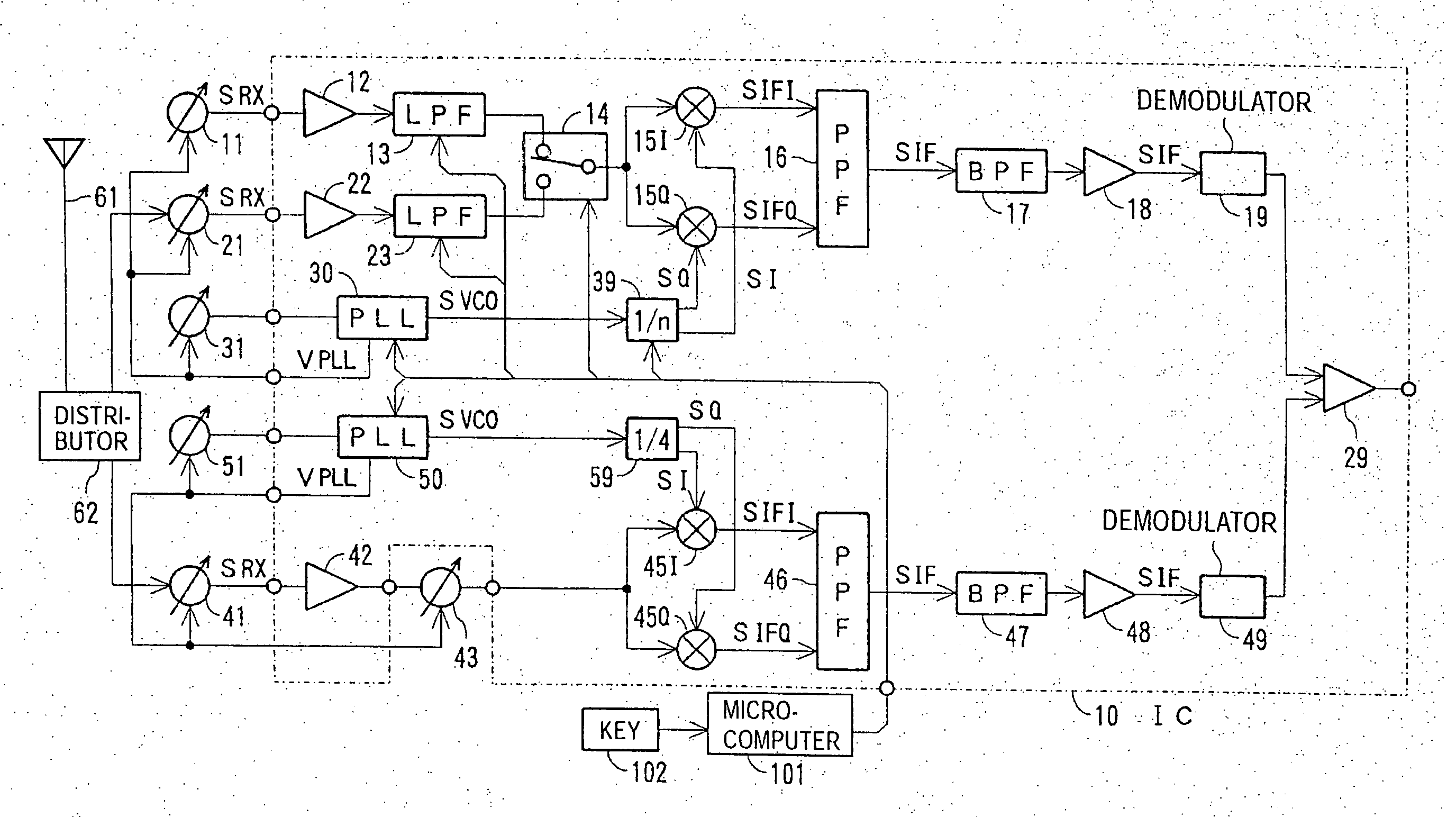
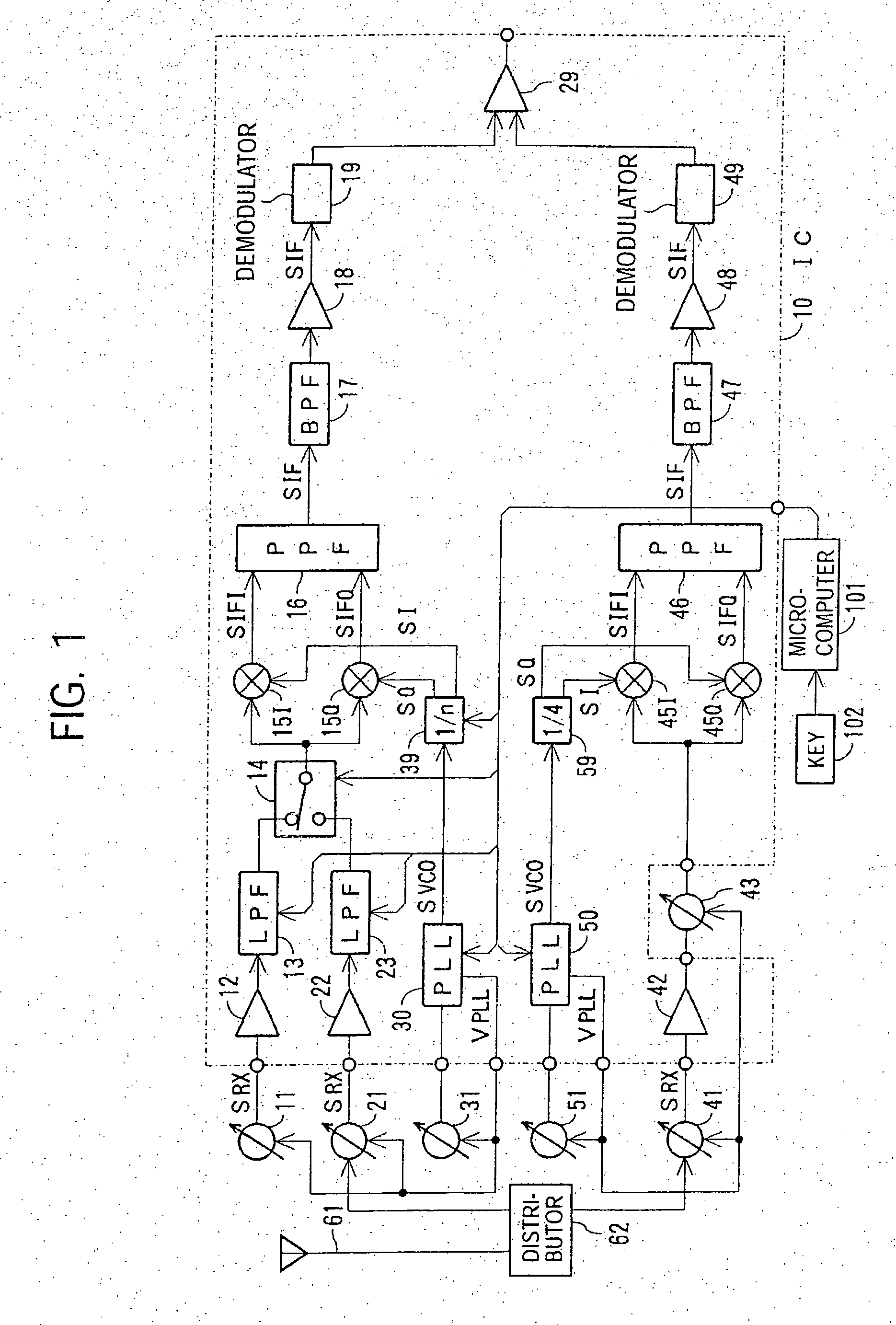
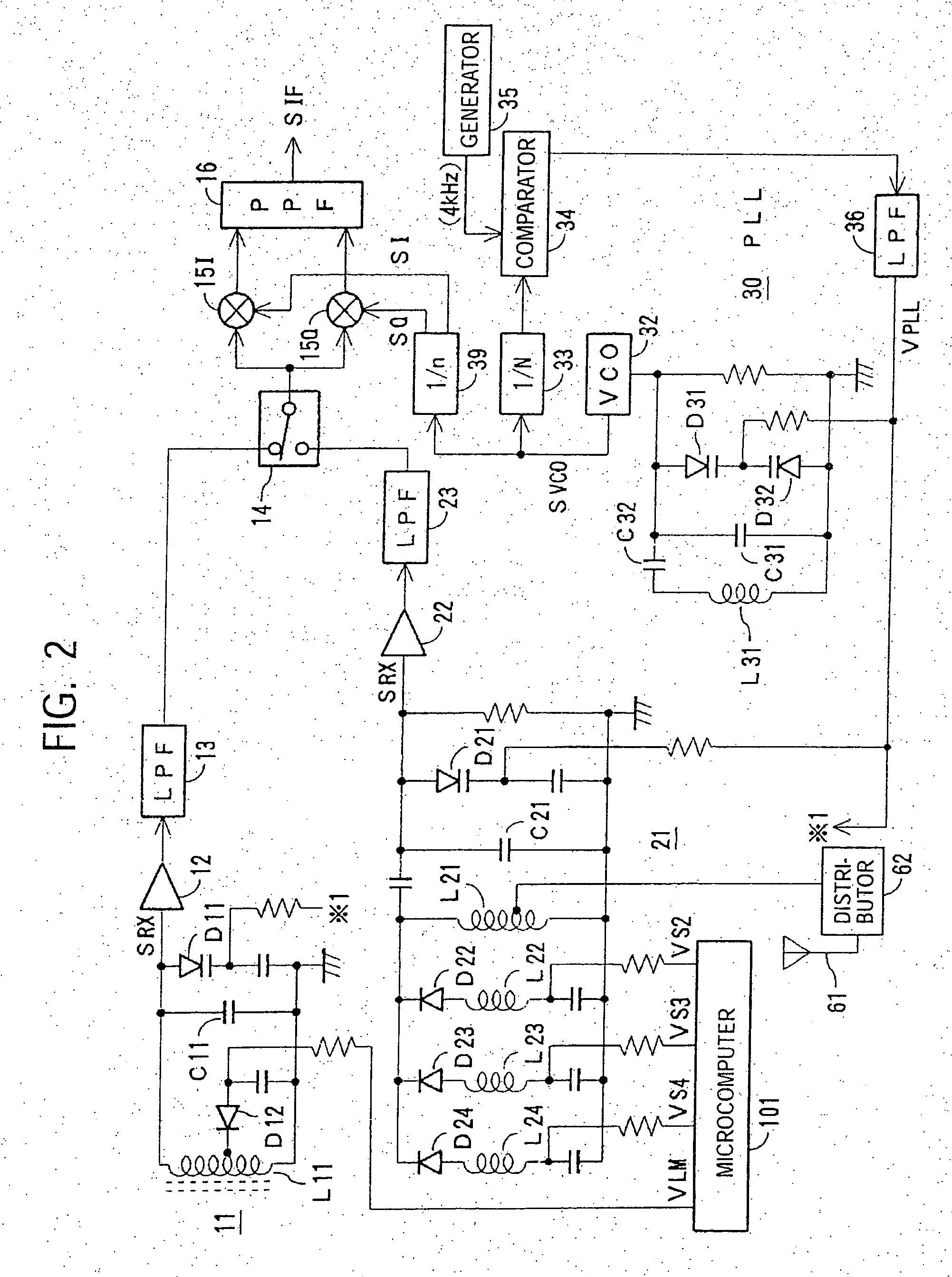
IC receiver to minimize tracking error
InactiveUS20070004371A1Low costReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlSinusoidal oscillation interference reductionMulti bandFrequency conversion
A multi-band receiver in which characteristics including a tracking error are improved is provided with a variable frequency oscillator circuit, a variable divider circuit (39) for dividing an oscillation signal (SVCO) of the variable frequency oscillator circuit, and mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q) for subjecting a received signal SRX to frequency conversion into an intermediate frequency signal (SIF) by a local oscillation signal (SLO). A divided output of the variable divider circuit (39) is supplied as the local oscillation signal (SLO) to each of the mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q). When a signal in a first frequency band is received, the division ratio n of the variable divider circuit (39) and the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator are changed to change the reception frequency in the first frequency band. When a signal in a second frequency band is received, at least the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator circuit is changed to change the reception frequency in the second frequency band.
Owner:SONY CORP
Laser based frequency standards and their applications
InactiveUS7809222B2Increase powerReduced Power RequirementsLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFiberMode locked fiber laser
Frequency standards based on mode-locked fiber lasers, fiber amplifiers and fiber-based ultra-broad bandwidth light sources, and applications of the same.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
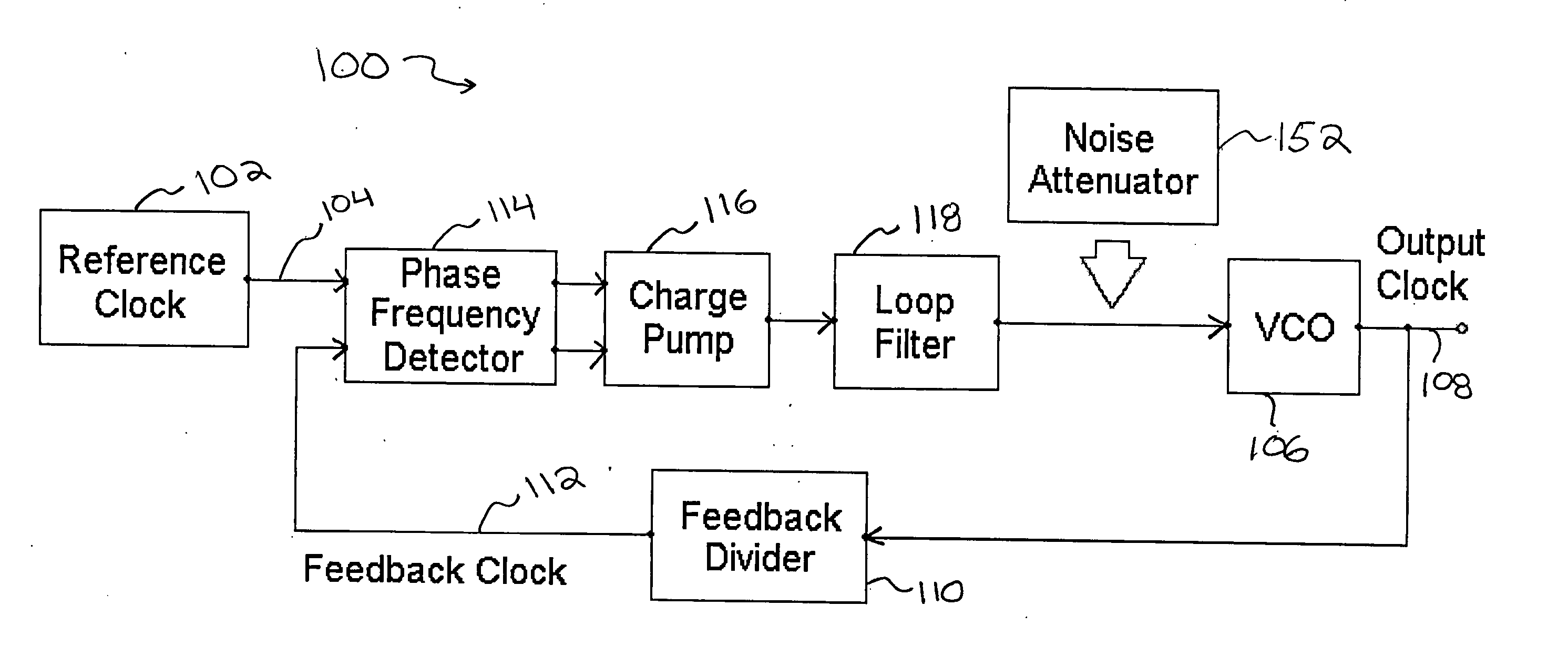
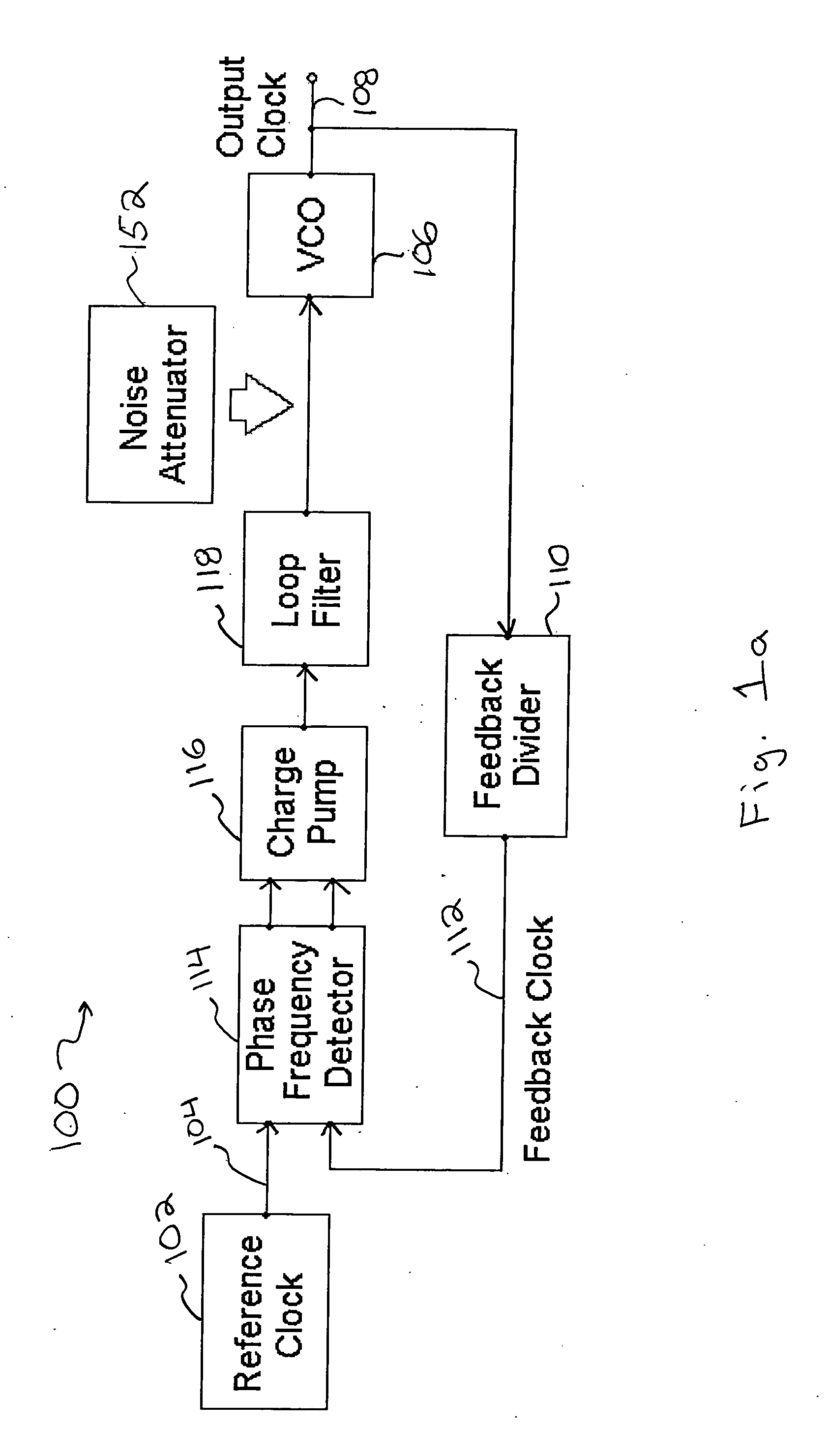
Method and apparatus to reduce the jitter in wideband PLL frequency synthesizers using noise attenuation
InactiveUS20060141963A1Reduce noise contributionReduce phase noisePulse automatic controlTransmissionMOSFETCapacitance
A noise attenuator loop filter for PLL applications that allows a full on-chip integration of the loop filter capacitors, while ensuring a low output clock phase noise (jitter) is disclosed. A voltage attenuator (A) is inserted between the loop filter (passive or active) and the controlled oscillator. The attenuator attenuates the noise coming from the loop filter. In case of a passive RC filter, the series resistor noise power is attenuated by A2 times, allowing the usage of a resistor that is A2 times larger and therefore the loop filter capacitors result A2 times smaller (easy to integrate on-chip). The relatively low value capacitor allows the usage of thick-oxide accumulation-mode MOSFET capacitors that take a reasonable low area, have a good linearity, are isolated from the substrate by the grounded N-well, and have negligible gate leakage current. Several embodiments of the noise attenuator are proposed for different practical applications: clock generation for digital circuits, frequency translation, low or high supply voltage, narrow or wide frequency range, processes with or without isolated well devices, processes with or without polysilicon resistors, and medium or high reference spurs rejection.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Method and device for carrying out frequency synthesis in a distance measuring device
InactiveUS6859744B2Reduce phase noiseReduce energy consumptionDigital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsMultiplexerElectromagnetic radiation
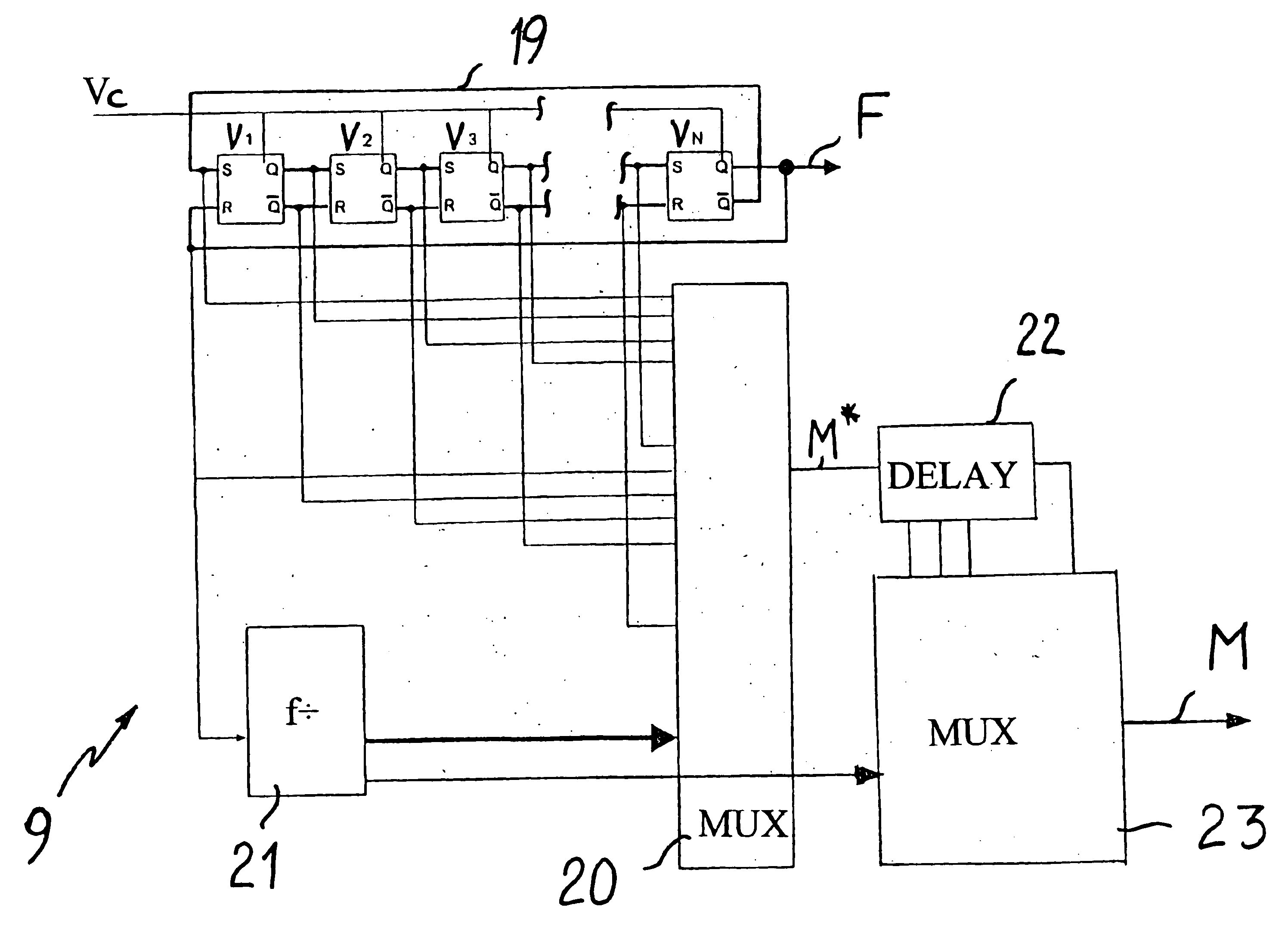
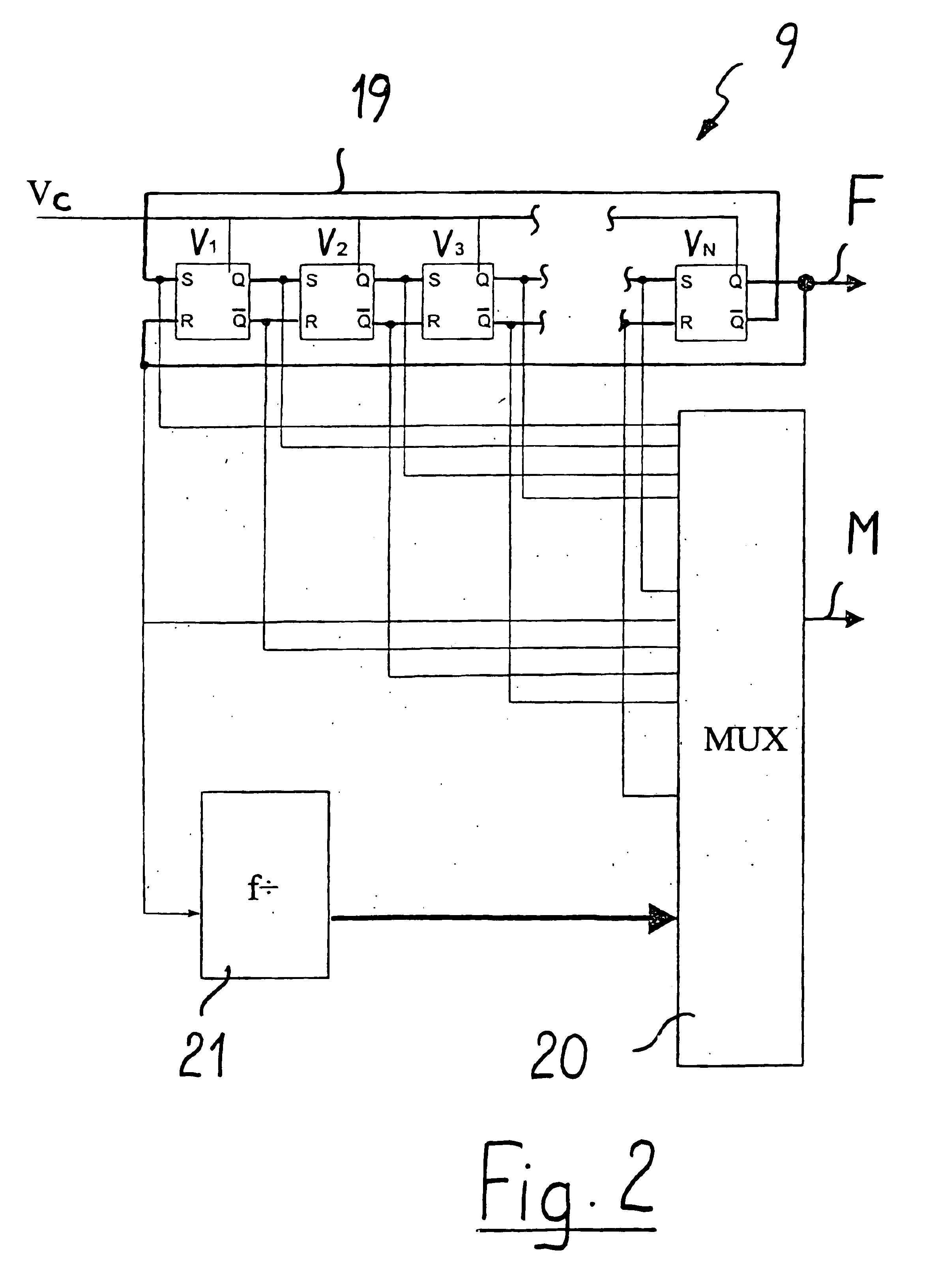
In a method and a device for carrying frequency synthesis, in particular in a distance measuring device based on the principle of evaluating the change over time in the phase of an electromagnetic radiation emitted by a radiation source and remitted by an object aimed at, a frequency, which is preferably furnished by a quartz oscillator, is regulated in a ring oscillator with N delay elements (V1, V2, V3, . . . , VN) to a desired first high frequency (F), which is used as a mixer frequency or as a modulation frequency. The signals at the N delay elements (V1, V2, V3, . . . , VN) are delivered to a multiplexer, which is switched over with a cadence that is equivalent to 2*N times the frequency of the low-frequency measurement signal to be evaluated to produce a modulation frequency or mixer frequency.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
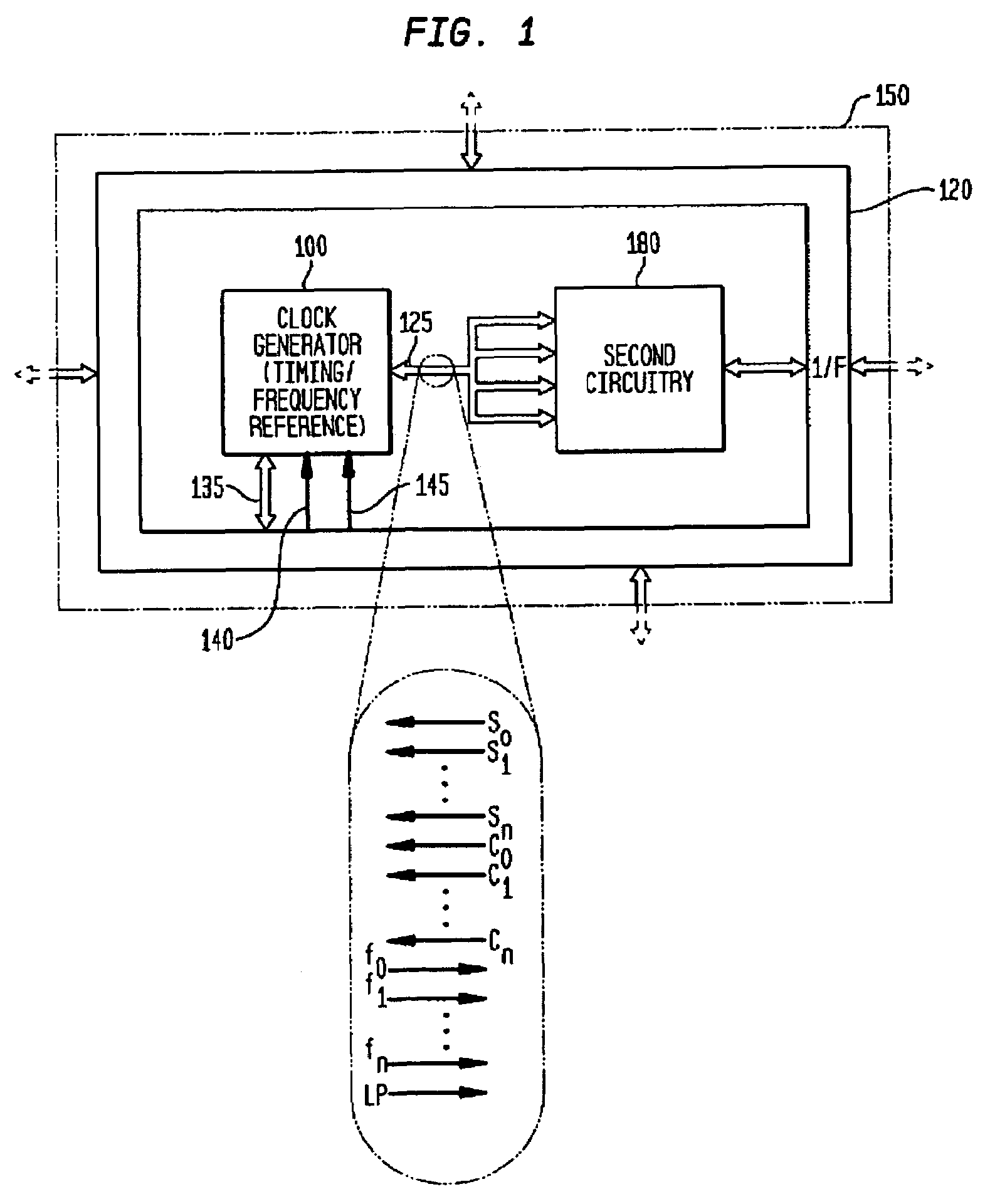
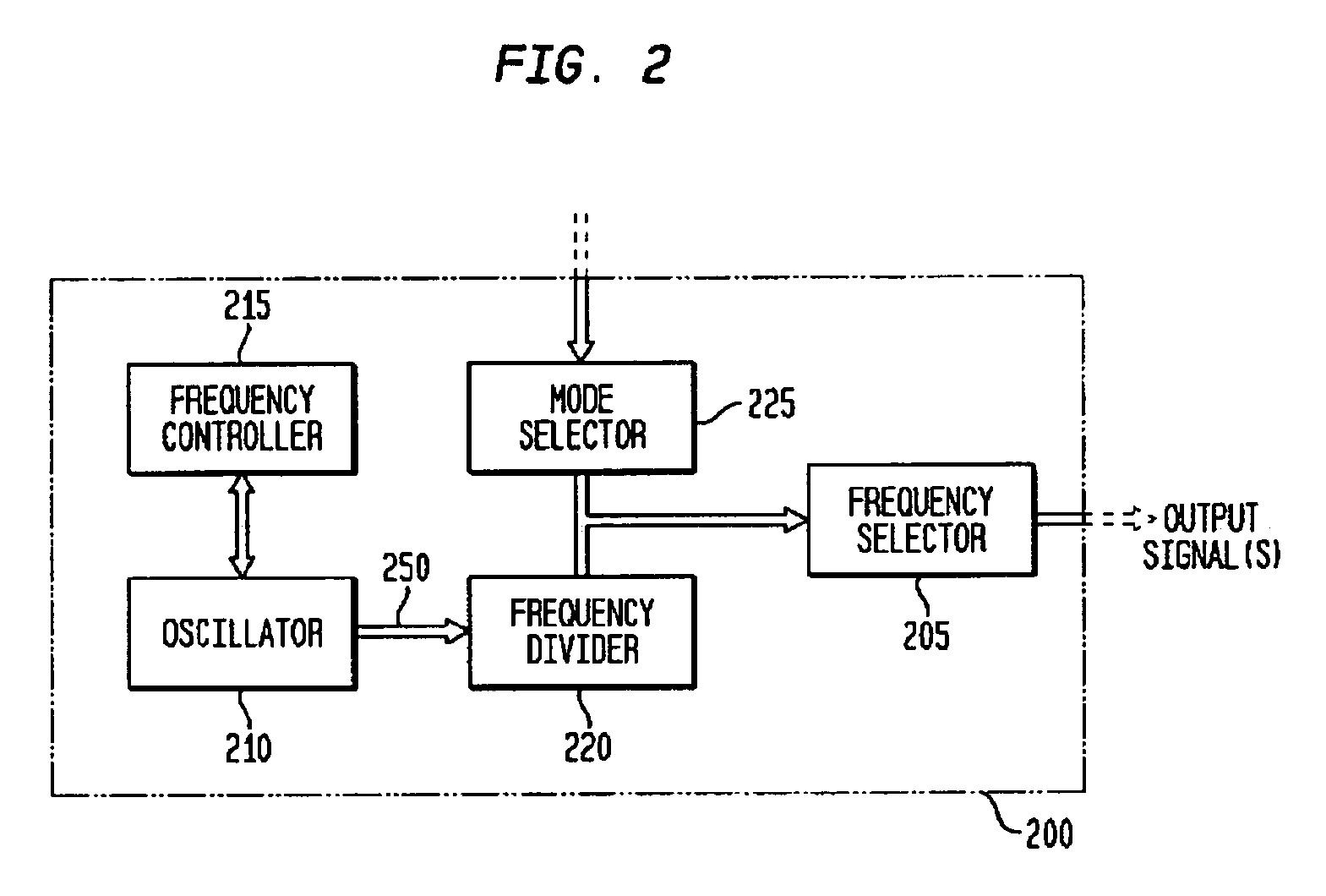
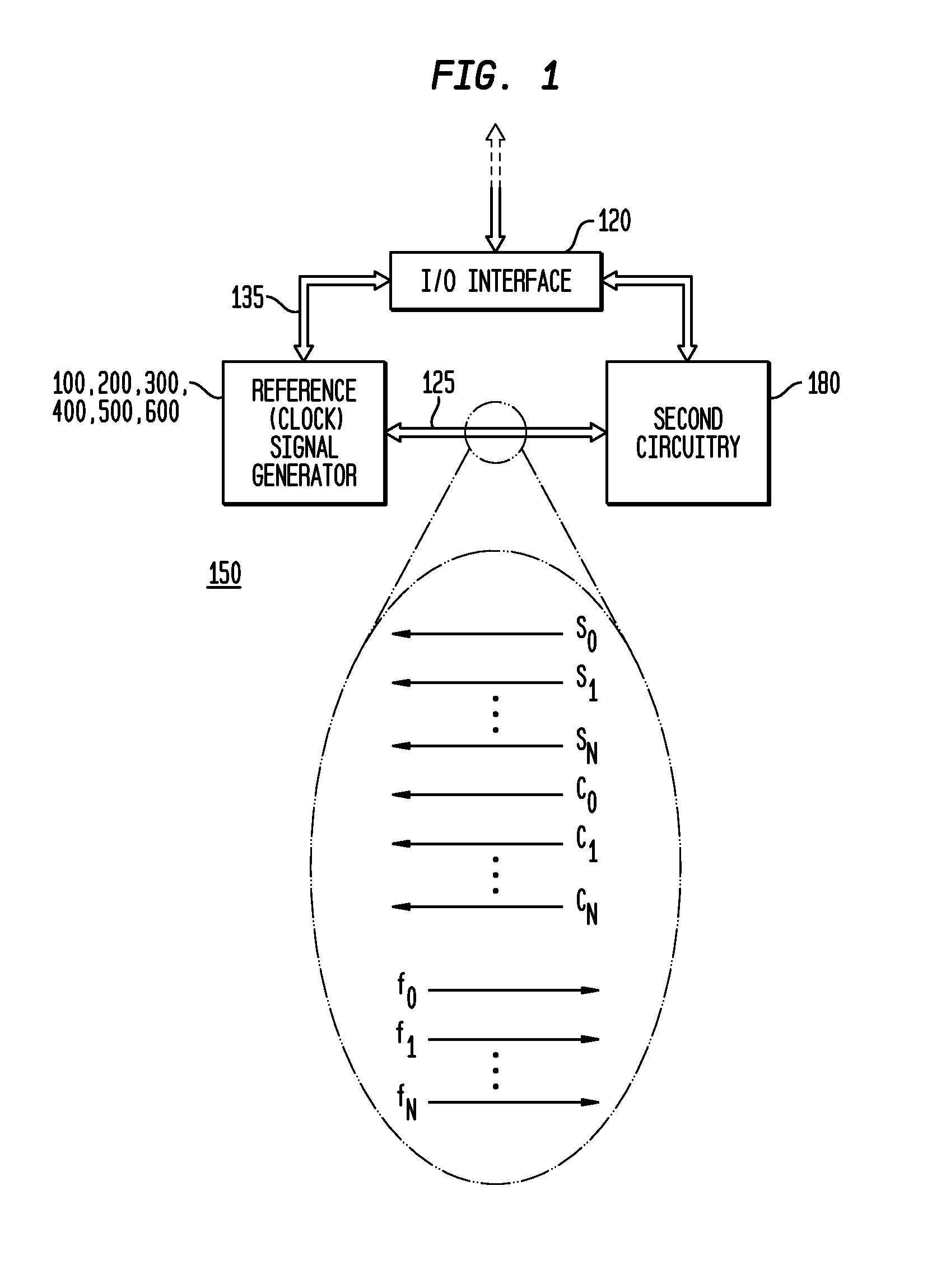
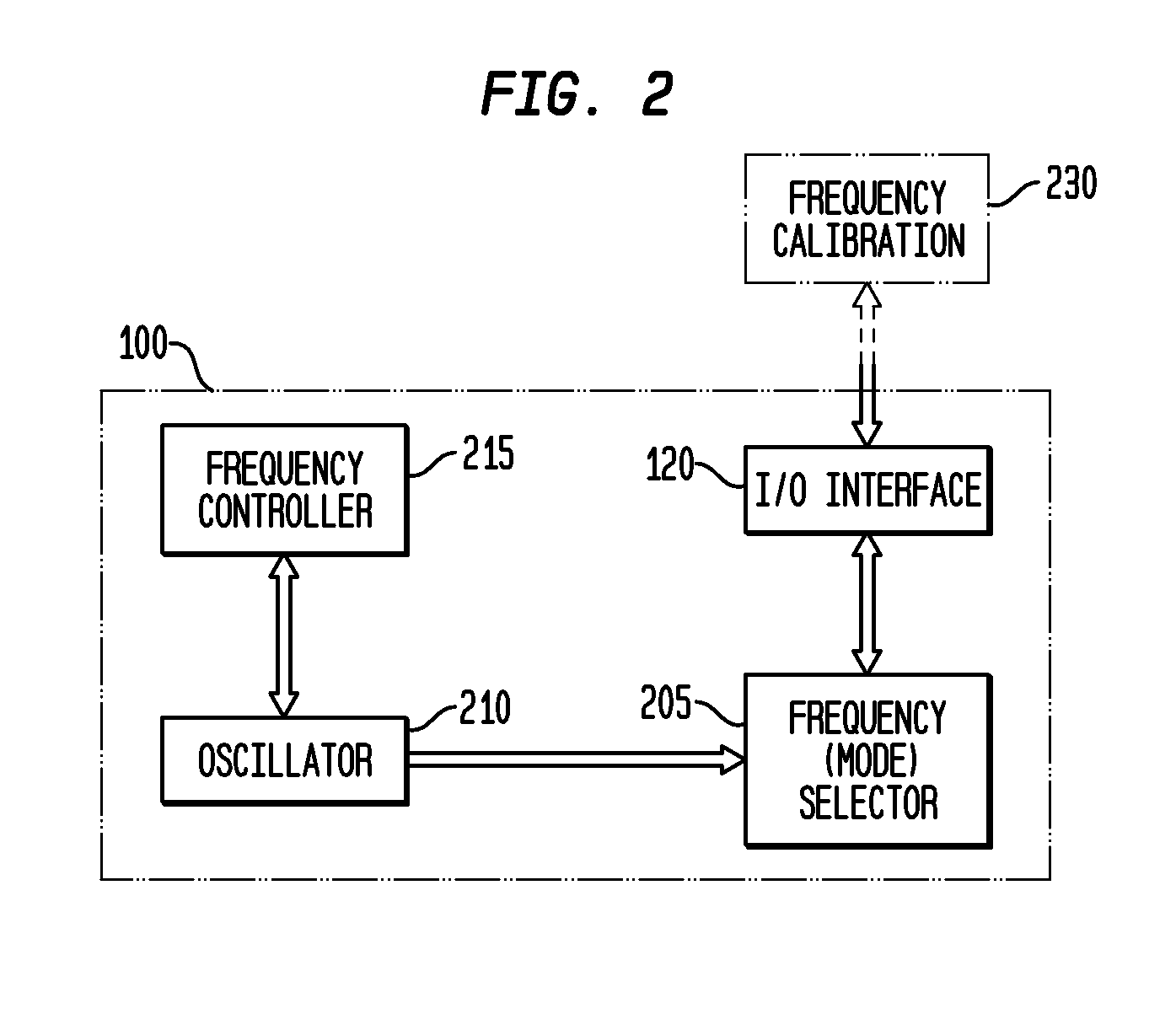
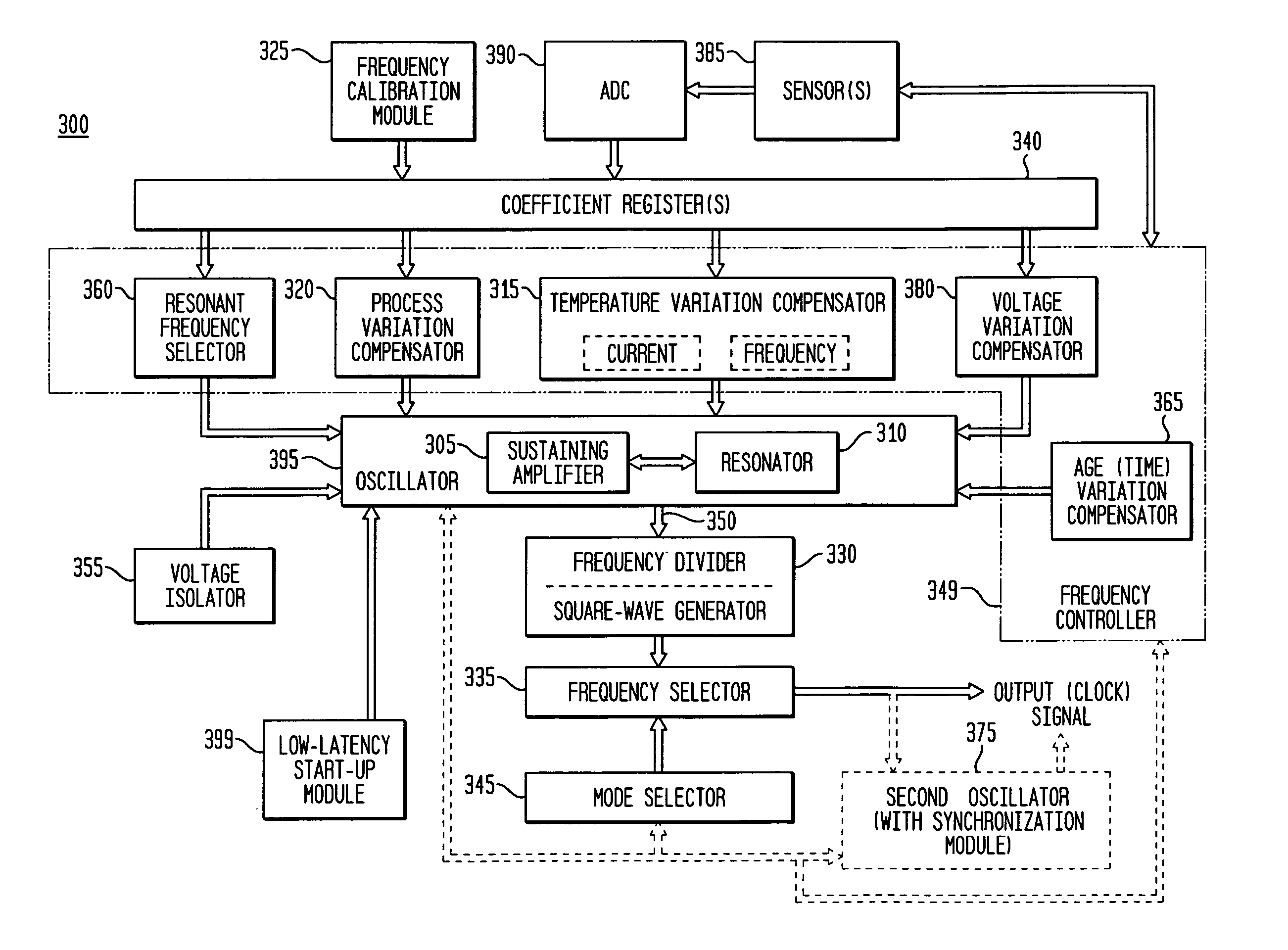
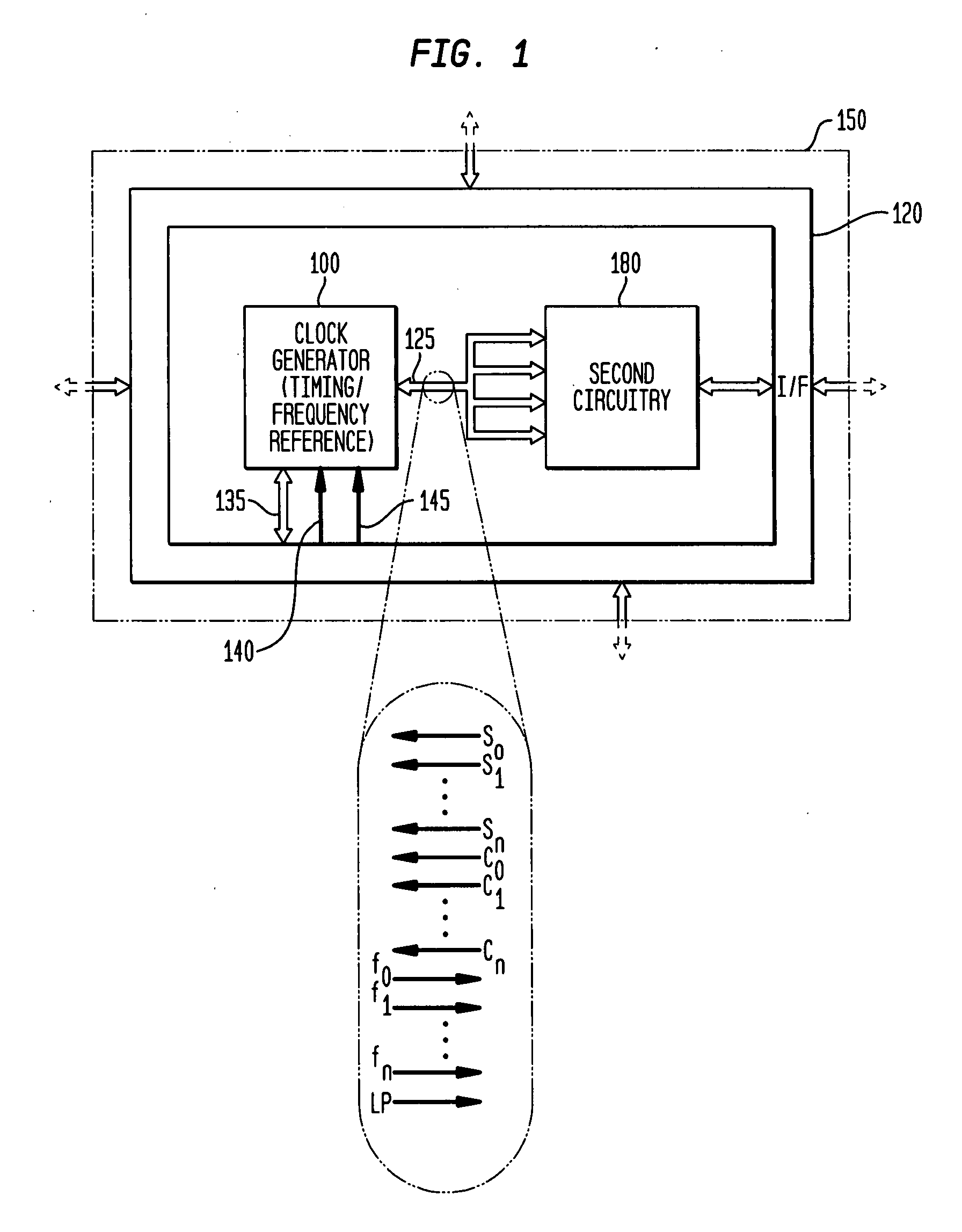
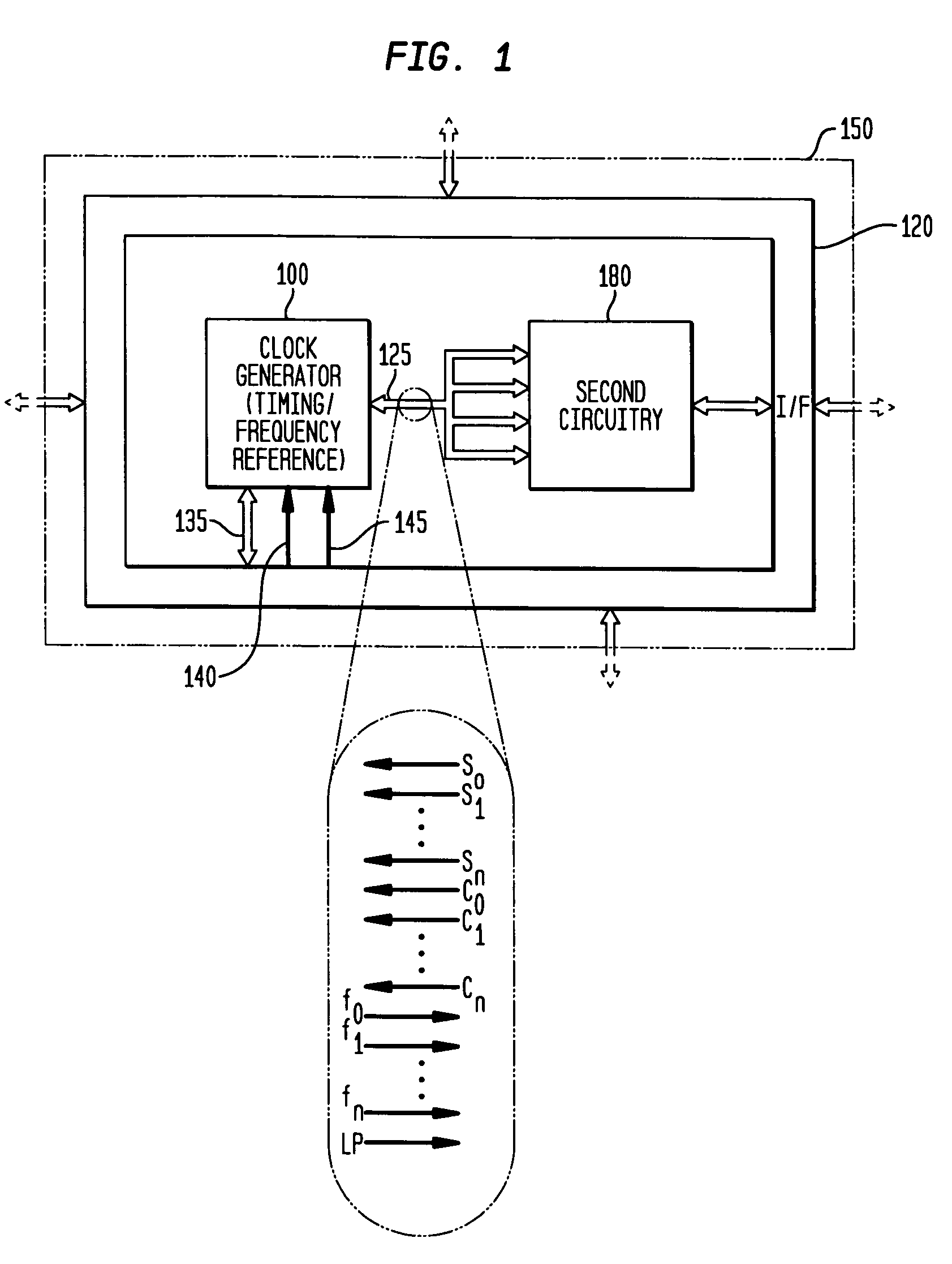
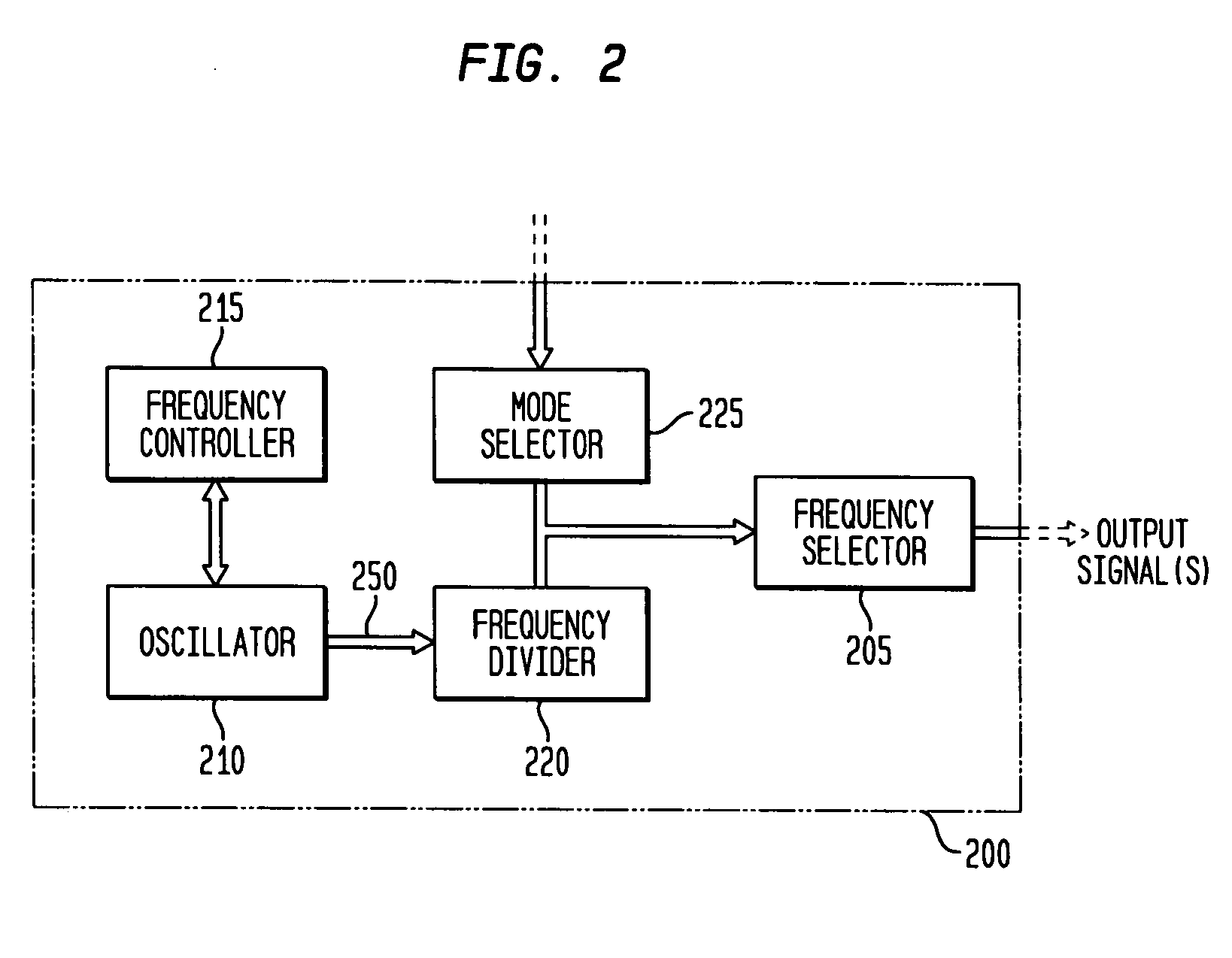
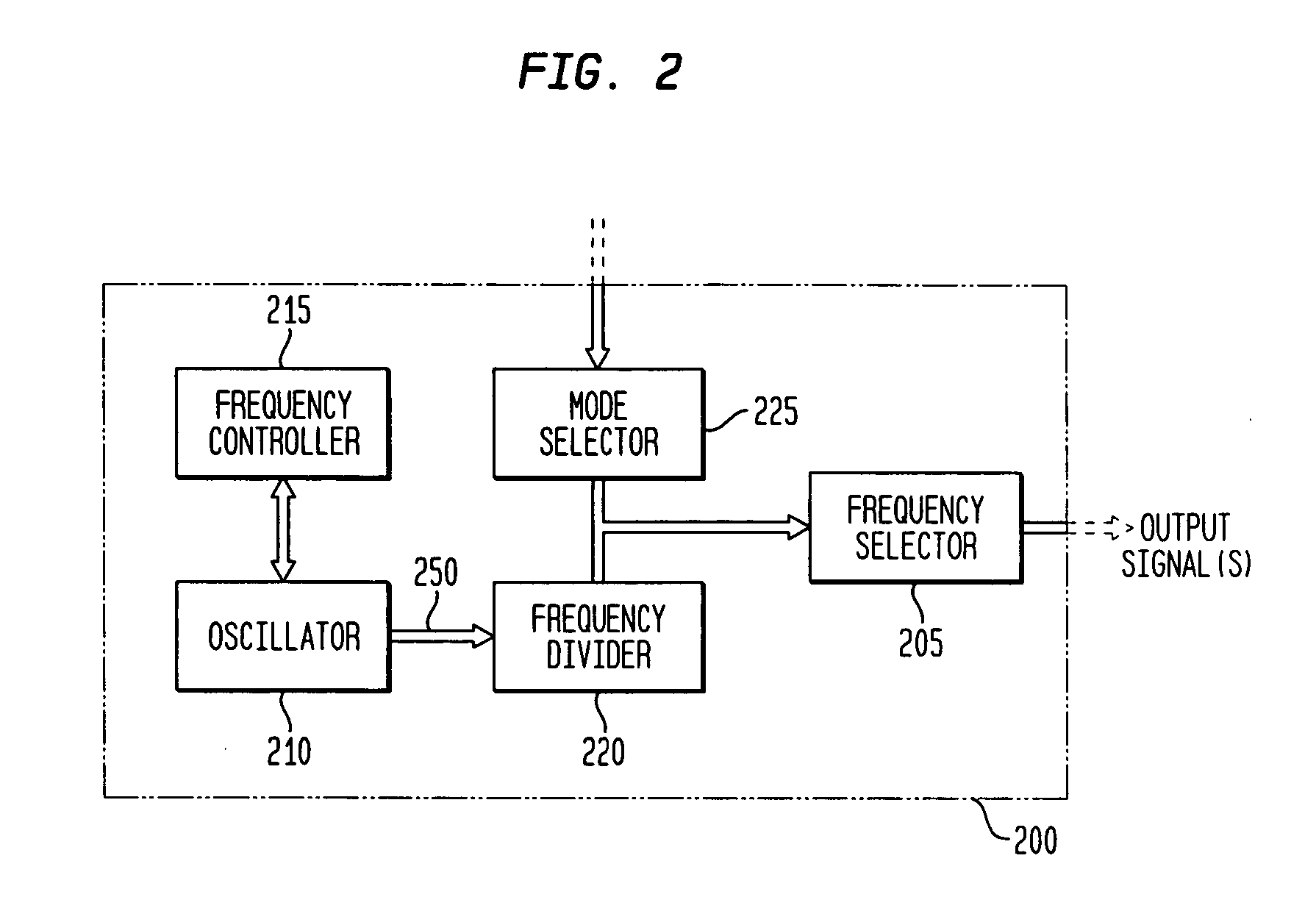
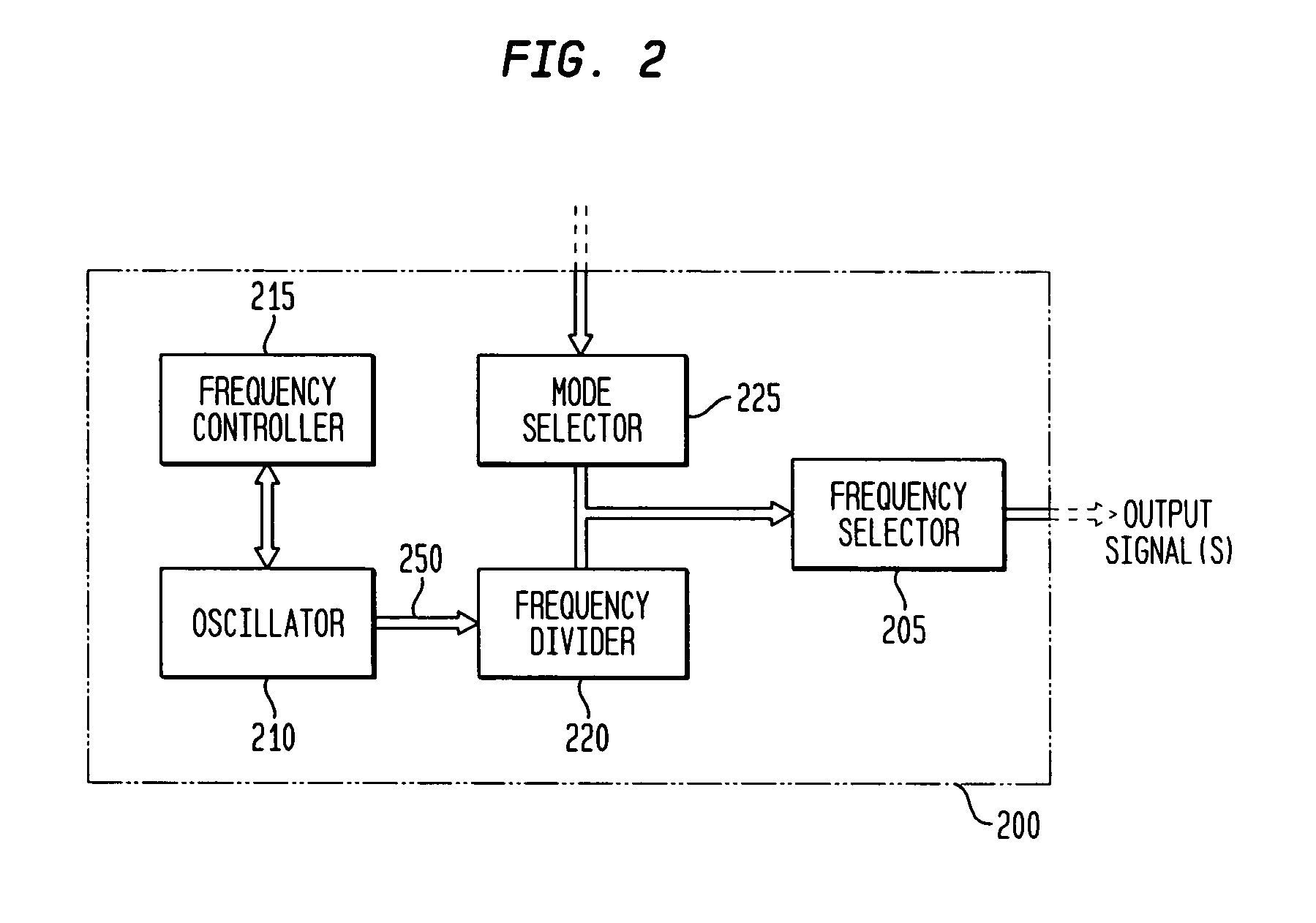
Monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7227423B2High frequencyLoud noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlAudio power amplifierPulsed mode
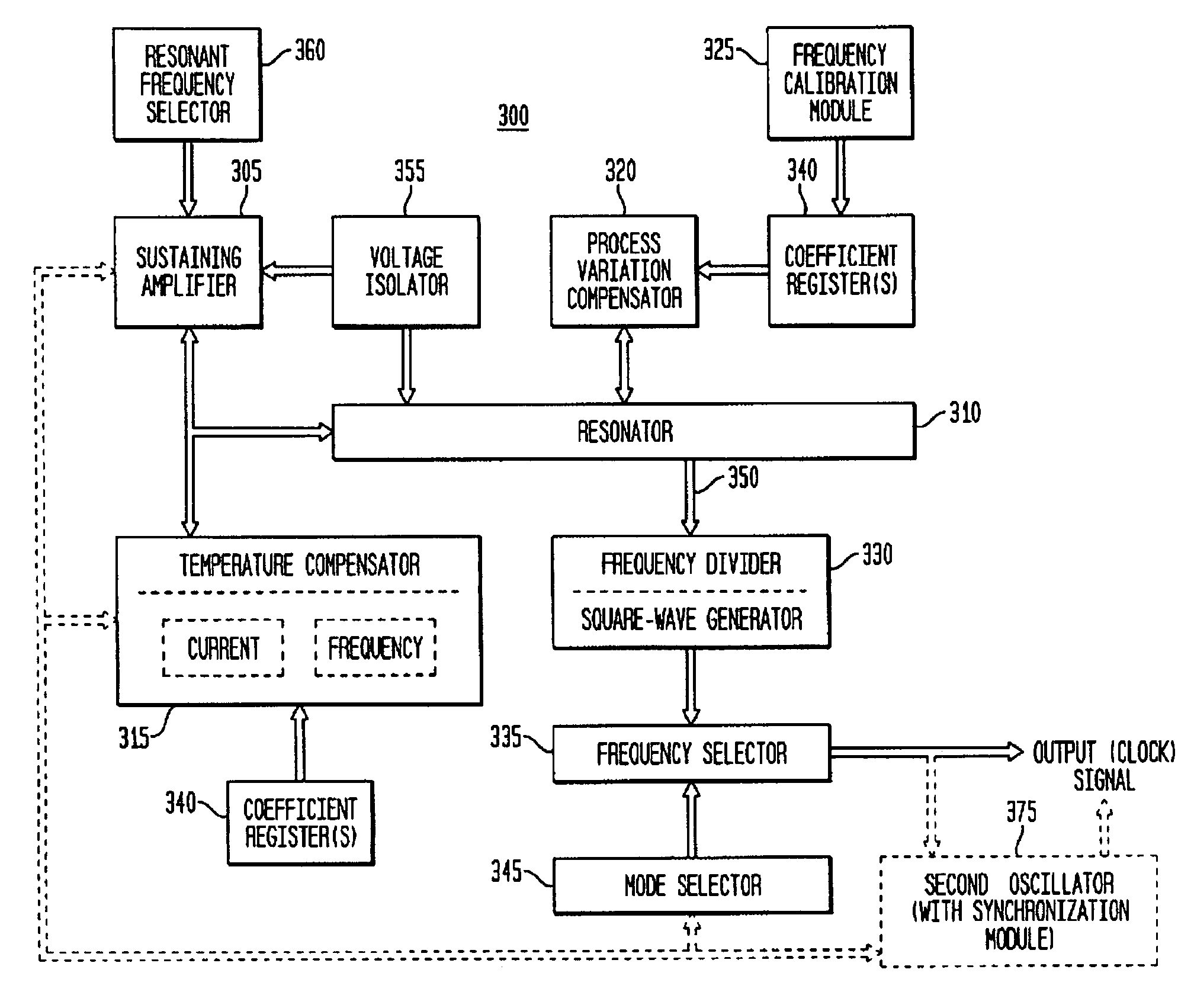
In various embodiments, the invention provides a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference, with multiple operating modes, such power conservation, clock, reference, and pulsed modes. The various apparatus embodiments include a resonator adapted to provide a first signal having a resonant frequency; an amplifier; a temperature compensator adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to temperature; and a process variation compensator adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to fabrication process variation. In addition, the various embodiments may also include a frequency divider adapted to divide the first signal having the resonant frequency into a plurality of second signals having a corresponding plurality of frequencies substantially equal to or lower than the resonant frequency; and a frequency selector adapted to provide an output signal from the plurality of second signals. The output signal may be provided in any of various forms, such as differential or single-ended, and substantially square-wave or sinusoidal.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
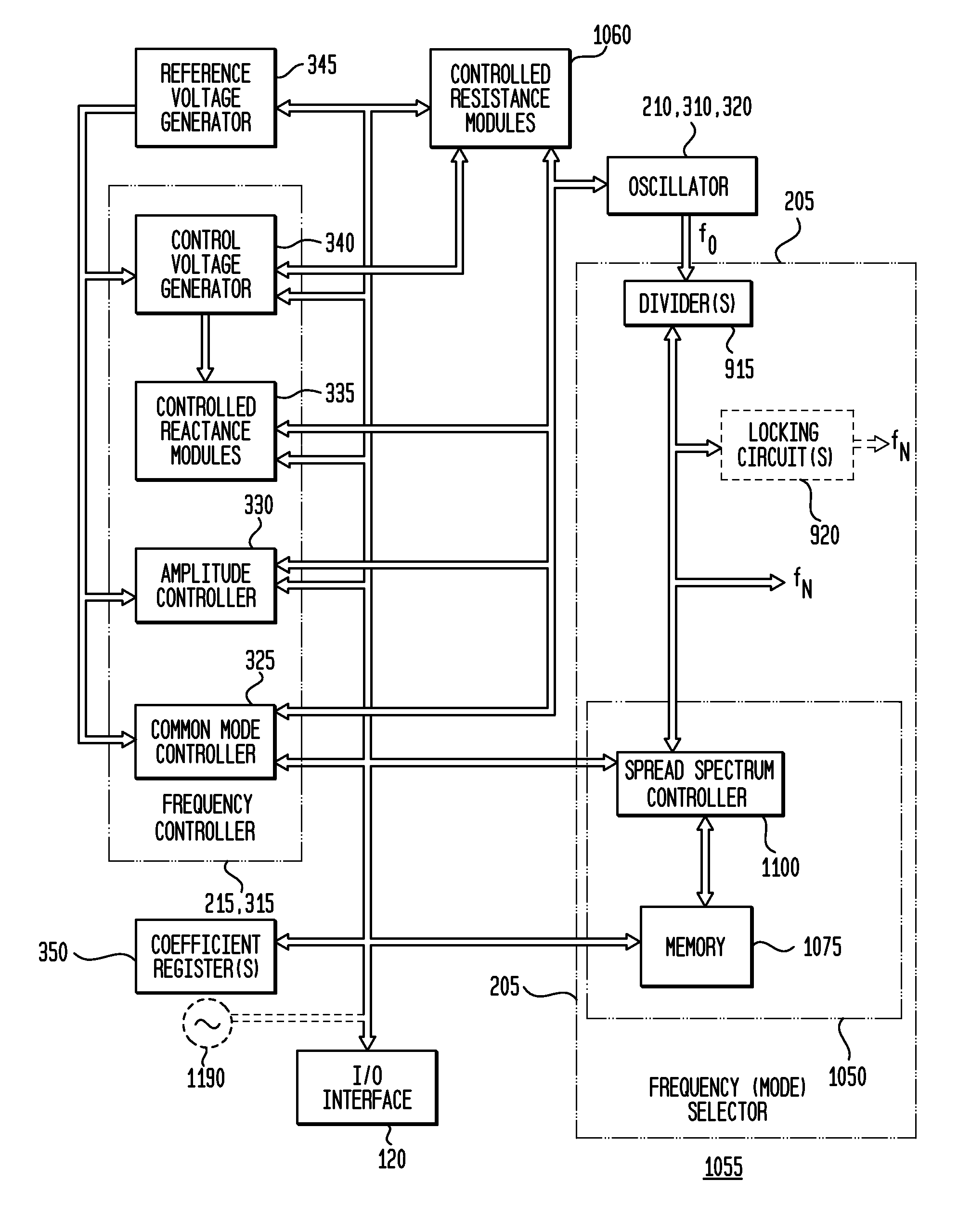
Spread Spectrum Clock and Reference Signal Generator
InactiveUS20080100350A1Reduce mistakesFast fall timeAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlEngineeringSignal generator
Exemplary embodiments of the invention provide a system, method and apparatus for spread spectrum functionality for a free-running, reference harmonic oscillator. In an exemplary embodiment, an apparatus comprises a reference oscillator adapted to provide a reference signal having a reference frequency; and a spread spectrum controller adapted to control the reference oscillator to generate a spread-spectrum reference signal at a plurality of different reference frequencies during a predetermined or selected time period. An exemplary apparatus may also include a coefficient register adapted to store a plurality of coefficients and a plurality of controlled reactance modules responsive to a corresponding coefficient of the plurality of coefficients to modify an amount of reactance effectively coupled to the reference oscillator. An exemplary spread spectrum controller is further adapted to sequentially modify the plurality of coefficients during the predetermined time period to provide the spread spectrum reference signal.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Multi-band RF transceiver with passive reuse in organic substrates
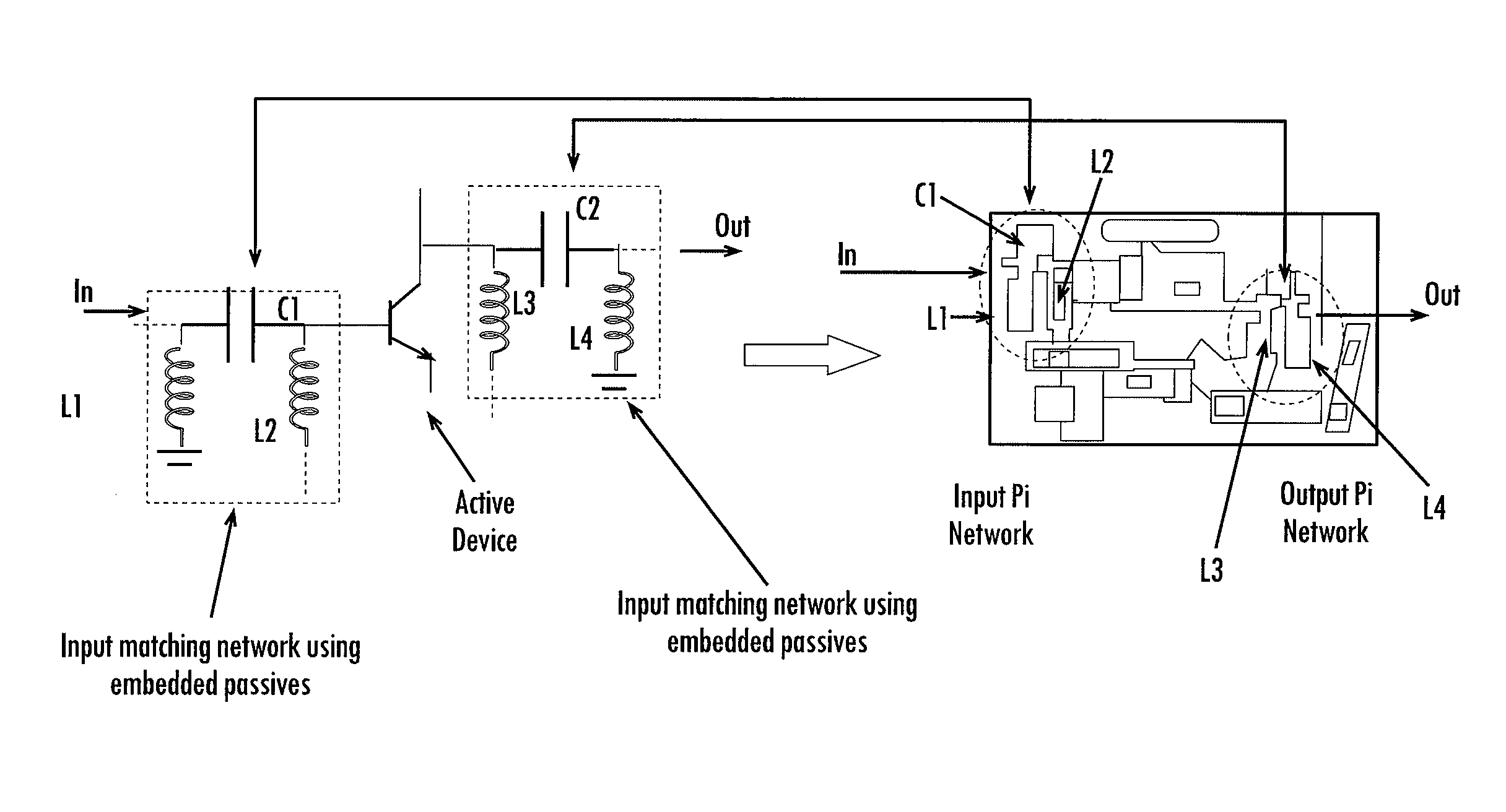
ActiveUS20050248418A1Reduce in quantityReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMulti bandLow noise
The present invention allows for the use of chip-package co-design of RF transceivers and their components by using discrete active devices in conjunction with passive components. Two particular components are described, including voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) and low noise amplifiers (LNAs). The high quality passive components for use in the VCOs and LNAs may be obtained by the use of embedded passives in organic substrates. Further, the embedded passives may have multi-band characteristics, thereby allowing multi-band VCOs and LNAs to be implemented with fewer components. In situations where size is a concern, the active devices and passive components utilized in an RF transceiver may be implemented in a low form factor module of less than 1.1 mm thick according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
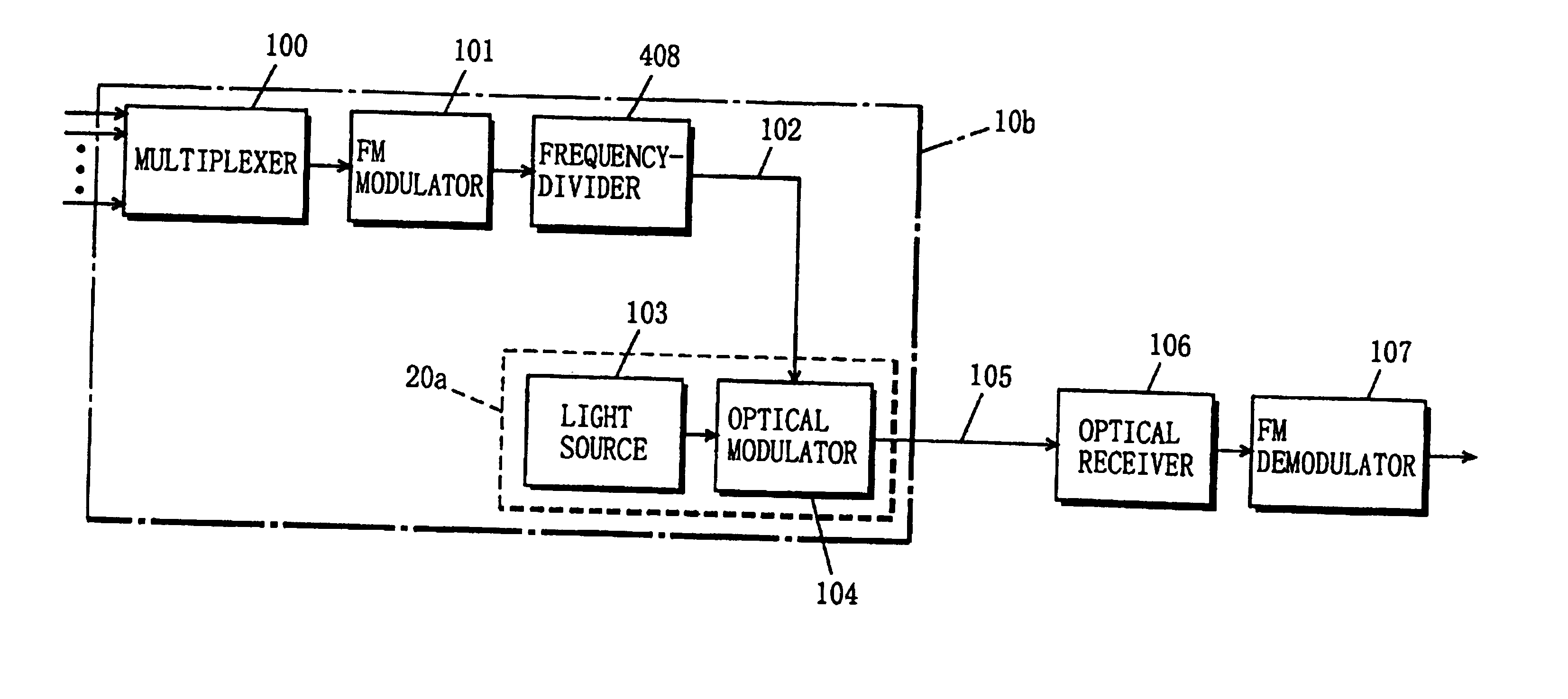
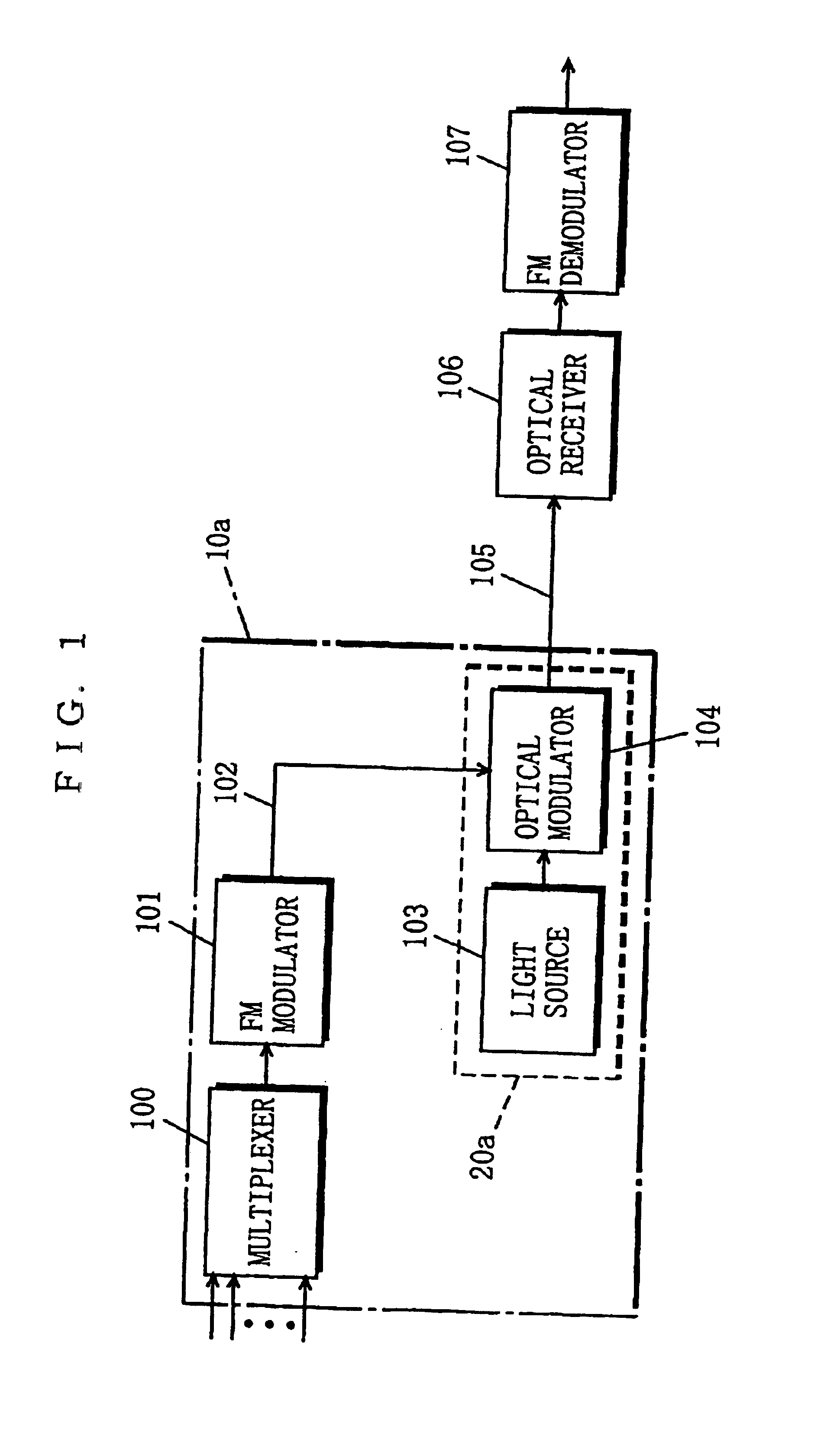
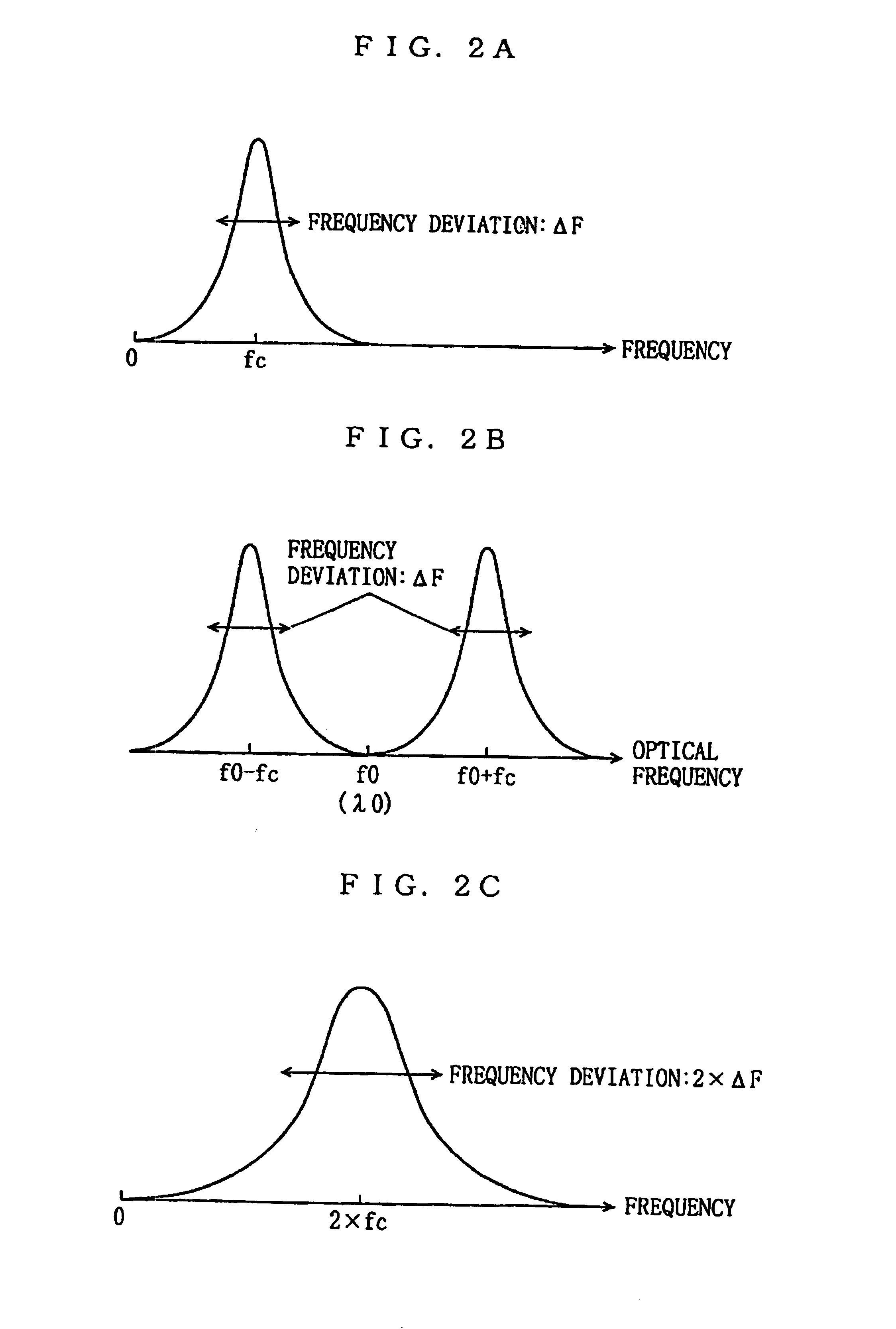
System for optically transmitting frequency-division-multiplexed signal and transmitter therefor
InactiveUSRE39785E1Attenuation bandwidthSufficient FM gainWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringFrequency modulation
In an optical transmission system, a multiplexer frequency-division-multiplexes a plurality of signals, and outputs the resultant signal to an FM modulator. The FM modulator converts the frequency-division-multiplexed signal into an FM modulated signal through frequency modulation using the frequency-division-multiplexed signal as an original signal. A frequency-divider converts the FM modulated signal into a frequency-divided FM modulated signal whose frequency is ½n (n is an integer of not less than 1) the frequency of the FM modulated signal. An optical modulator has a predetermined input-voltage vs. output-optical-power characteristic, and is biased at the minimum point (voltage) about the output optical power. The optical modulator modulates an unmodulated light fed from a light source with the applied frequency-divided FM modulated signal to produce an optical signal whose optical carrier component is suppressed, and sends the optical signal to an optical transmission line. An optical receiver receives the optical signal, and square-law detects the signal to convert into an FM modulated signal. A FM demodulator demodulates the FM modulated signal to reproduce the original frequency-division-multiplexed signal. This configuration makes it possible to narrow the bandwidth of an FM modulated signal while increasing the frequency deviation thereof, and realize high-quality signal transmission as a result.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multi-terminal harmonic oscillator integrated circuit with frequency calibration and frequency configuration
InactiveUS20070222528A1High frequencyLoud noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlHarmonicSpread spectrum
Exemplary embodiments of the invention provide a reference harmonic oscillator integrated circuit having three or more terminals, with systems and methods for calibrating the harmonic oscillator to a selected first frequency using a limited number of terminals. An exemplary apparatus comprises: a reference harmonic oscillator, a first terminal to receive a supply voltage, a second terminal to receive a ground potential, a third terminal to provide an output signal having an output frequency, and may also include a fourth terminal. One of the first, second, third or fourth terminals is further adapted for input of a calibration of the first frequency. The exemplary apparatus may enter calibration and testing modes in response to various commands such as a calibration mode signal, and may also be configured through one of the terminals for output frequency selection, spread-spectrum output, and output voltage levels.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
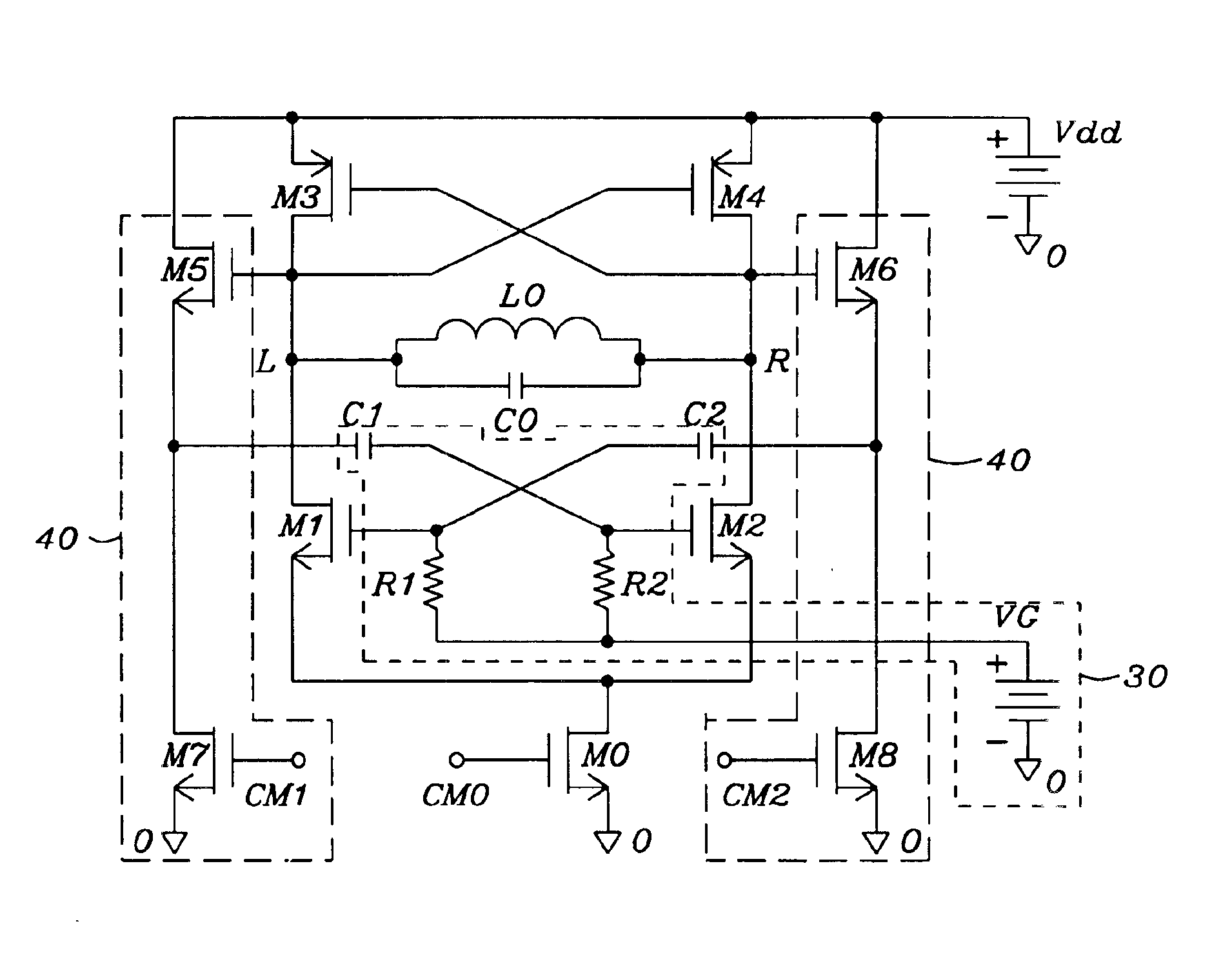
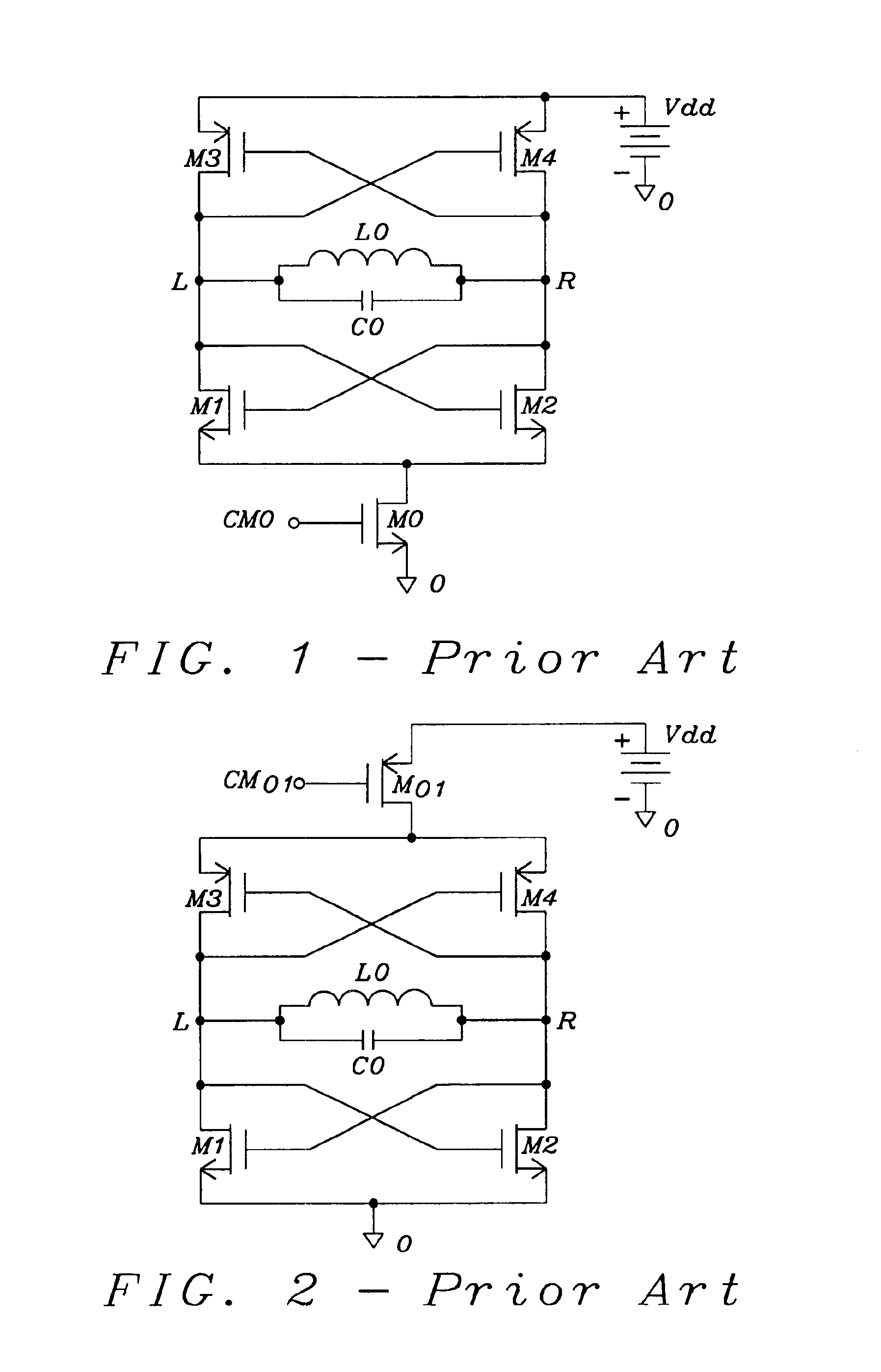
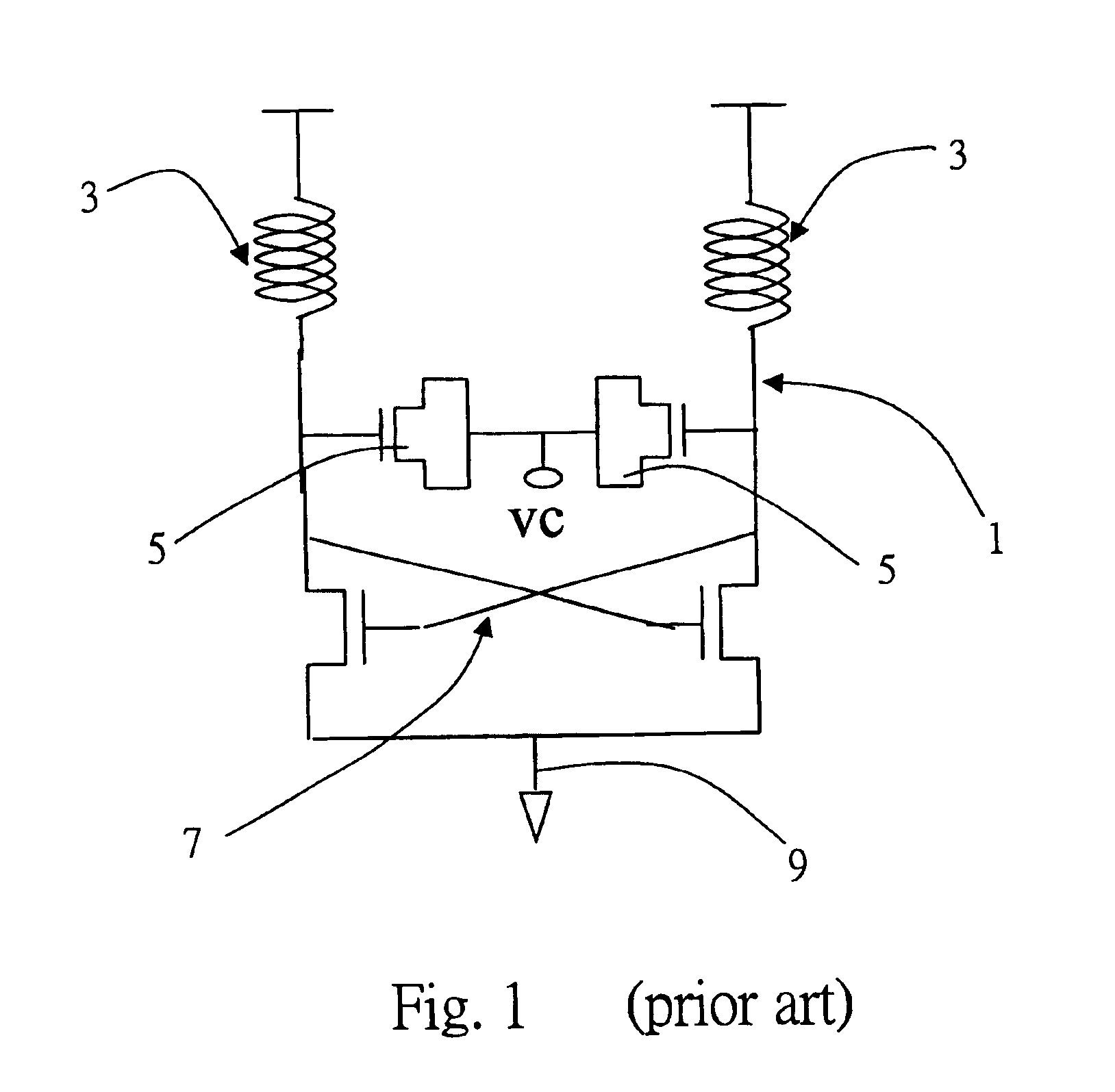
Enhanced architectures of voltage-controlled oscillators with single inductor (VCO-1L)
InactiveUS6867658B1Reduce phase noiseReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlPhase noiseEngineering
Five circuit topologies of Voltage-Controlled Oscillators with Single Inductor (VCO-1L) are proposed. They offer lower power consumption, higher output amplitude, broader tuning range, cleaner s-rum and higher frequency stability seen as lower phase-noise. Most of the achievements are based on the development of active pull-down control circuitries of the timing and active charge dissipation in the transistors. The applications of the present invention are of critical importance for wireless communication systems not allowing any limitations in the frequency range. Among them are base stations and mobile terminals mobile phones, GSM, PCS / DCS, W-CDMA etc., as well BlueTooth, Wireless LAN, Automotive and ISM band etc. The advanced performance of the circuits is based on important architectural specifics and proven by simulation on advanced CMOS process. The architectures are not limited to use on CMOS; they can be efficiently used in any semiconductor process where complimentary polarity transistors are available, for example BiCMOS, SiGe / BiCMOS, GaAs etc.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
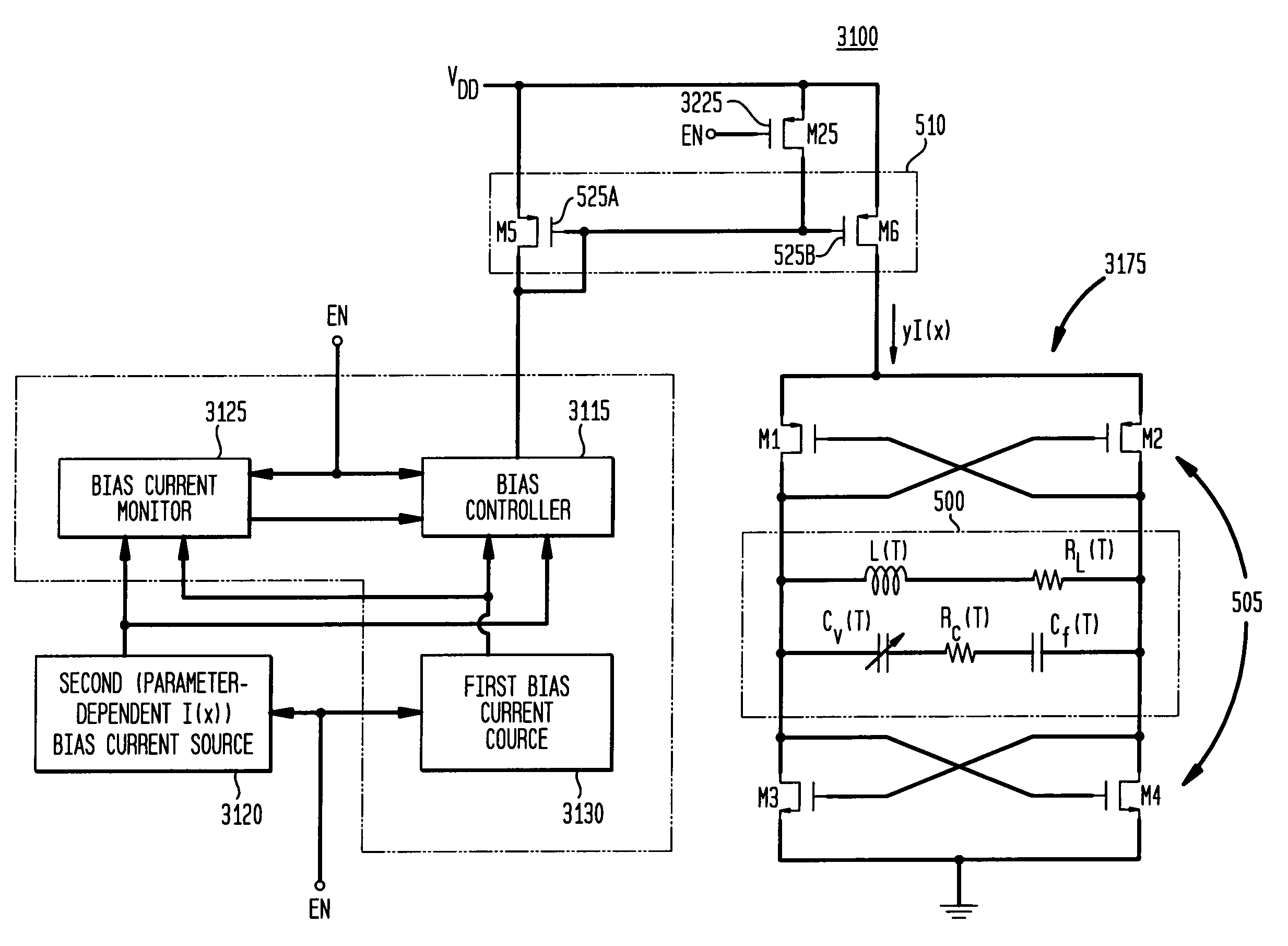
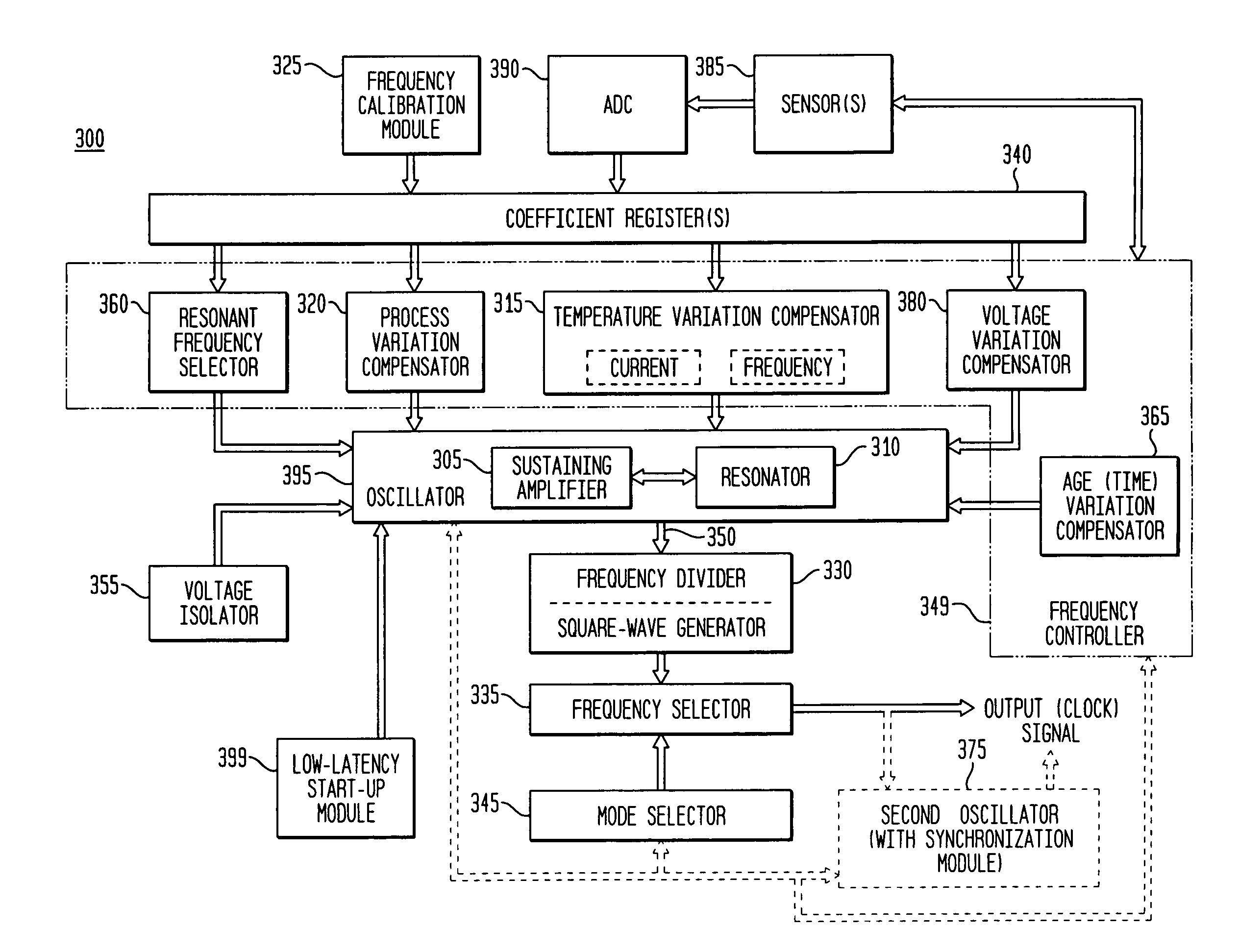
Low-latency start-up for a monolithic clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7307486B2High frequencyLoud noiseAngle modulation by variable impedenceResonant circuit tuningMicrocontrollerVoltage generator
An apparatus, system and method are provided for low-latency start-up of a free-running harmonic oscillator. The exemplary apparatus embodiment comprises a first and second current sources to generate first and second currents; a bias current monitor adapted to detect a magnitude of the second current and to provide a control signal when the magnitude of the second current is equal to or greater than a predetermined magnitude; and a bias controller adapted to switch the first current from the oscillator and to switch the second current to the oscillator in response to the control signal. a reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller. Exemplary embodiments include reference voltage generator, a comparator, and a bias controller.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Phase noise compensation for MIMO WLAN systems
InactiveUS20060262868A1Reduce time vary componentReduce phase noiseError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionDecompositionTransceiver
The present invention provides a method for reducing phase noise in OFDM systems by analyzing a time-dependent representation of the phase noise that changes in real time according to received data. The analysis of real time signals is based on processing statistical properties of phase noise and received data. The statistical properties of phase noise are represented by a covariance matrix Rψψ. The basis of the multiplicative phase noise decomposition which represents the varying in time phase noise component, is selected from the eigenvectors of Rψψ. The present invention suggests replacing the fixed representation of the phase noise as suggested by prior art with a system and time-dependent representation that changes in real time according to received data. The method according to the present invention is implemented within An OFDM transceiver.
Owner:LANTIQ ISRAEL +1
Method of producing micromachined air-cavity resonator, micromachined air-cavity resonator, band-pass filter and oscillator using the method
InactiveUS20100308925A1Easy to manufactureEasy to integrateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow-pass filterBand-pass filter
A micromachined air-cavity resonator, a method for fabricating the micromachined air-cavity resonator, and a band-pass filter and an oscillator using the same are provided. In particular, a micromachined air-cavity resonator including a current probe fabricated together when the air-cavity resonator is fabricated, and a groove structure for rejecting detuning effect when an external circuit of a package substrate is coupled to the current probe, a millimeter-wave band-pass filter using the same, and a millimeter-wave oscillator using the same are provided. The micromachined air-cavity resonator includes a cavity structure which comprises a current probe simultaneously formed through a fabrication process, and a groove structure; and a package substrate integrated with the cavity structure. Thus, the micromachined air-cavity resonator can be easily fabricated by etching a silicon substrate and easily integrated to the package substrate using the flip-chip bonding.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
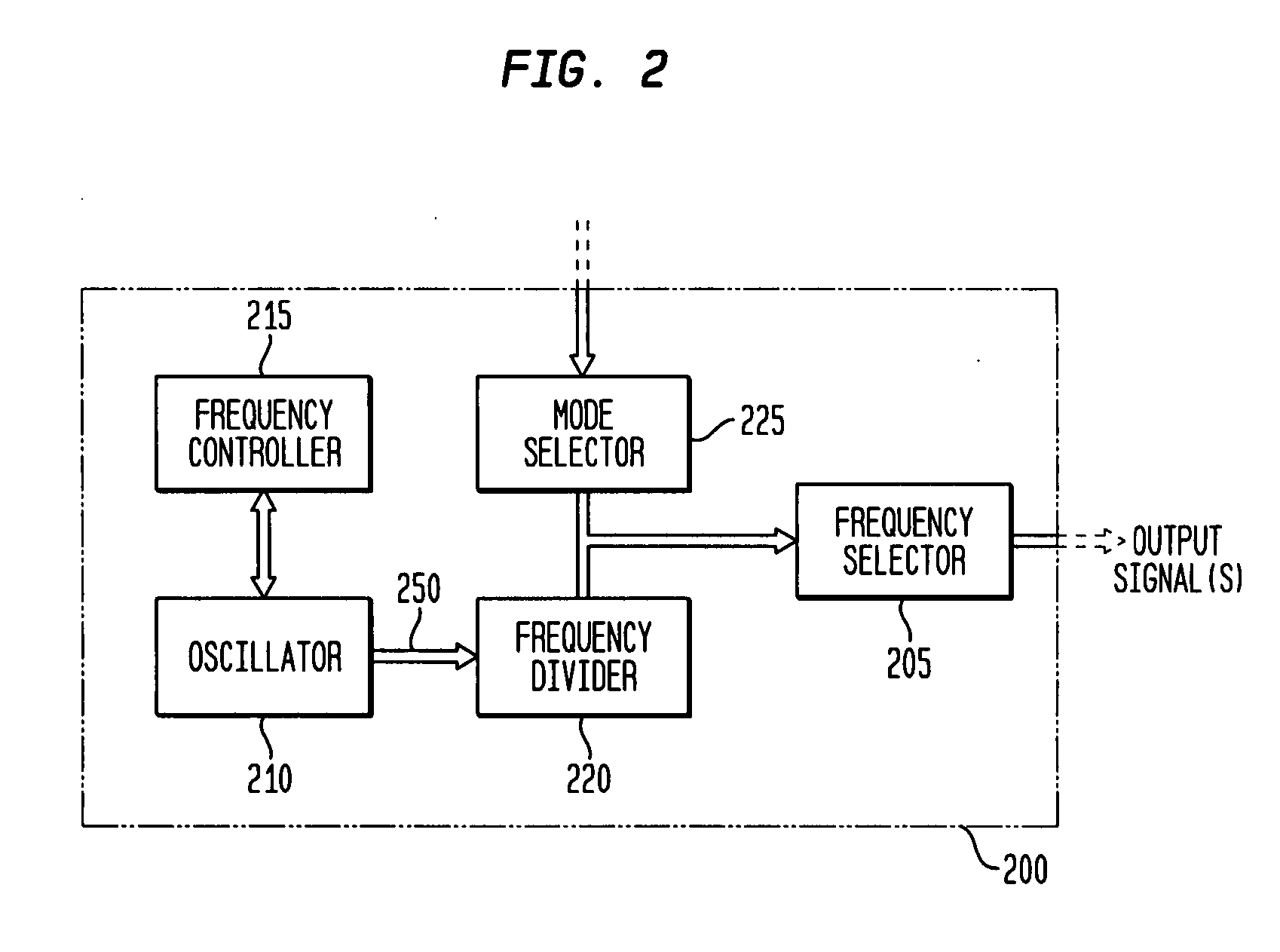
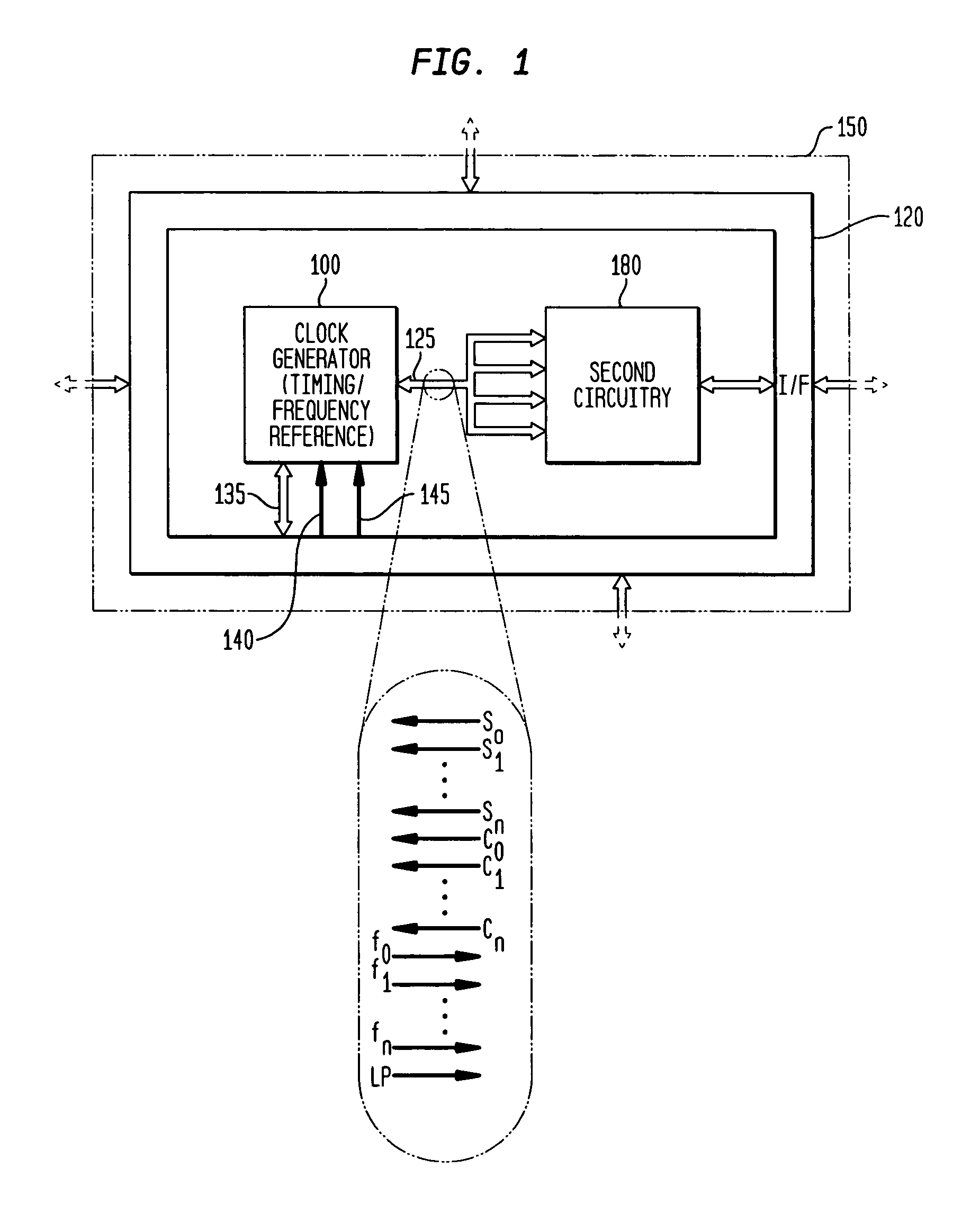
Discrete clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS20060158268A1High frequencyLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceFrequency stabilization
In various embodiments, the invention provides a discrete clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which may then be provided to other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Integrated clock generator and timing/frequency reference
ActiveUS7365614B2High frequencyLoud noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
In various embodiments, the invention provides a clock generator and / or a timing and frequency reference using an LC-oscillator topology, having a frequency controller to control and provide a stable resonant frequency, which is integrated with other, second circuitry such as a processor or controller. Frequency stability is provided over variations in a selected parameter such as temperature and fabrication process variations. The various apparatus embodiments include a sensor adapted to provide a signal in response to at least one parameter of a plurality of parameters; and a frequency controller adapted to modify the resonant frequency in response to the second signal. In exemplary embodiments, the sensor is implemented as a current source responsive to temperature fluctuations, and the frequency controller is implemented as a plurality of controlled reactance modules which are selectively couplable to the resonator or to one or more control voltages. The controlled reactance modules may include fixed or variable capacitances or inductances, and may be binary weighted. Arrays of resistive modules are also provided, to generate one or more control voltages.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Multi-band RF transceiver with passive reuse in organic substrates
ActiveUS7489914B2Reduce in quantityReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMulti bandLow noise
The present invention allows for the use of chip-package co-design of RF transceivers and their components by using discrete active devices in conjunction with passive components. Two particular components are described, including voltage controlled oscillators (VCOs) and low noise amplifiers (LNAs). The high quality passive components for use in the VCOs and LNAs may be obtained by the use of embedded passives in organic substrates. Further, the embedded passives may have multi-band characteristics, thereby allowing multi-band VCOs and LNAs to be implemented with fewer components. In situations where size is a concern, the active devices and passive components utilized in an RF transceiver may be implemented in a low form factor module of less than 1.1 mm thick according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
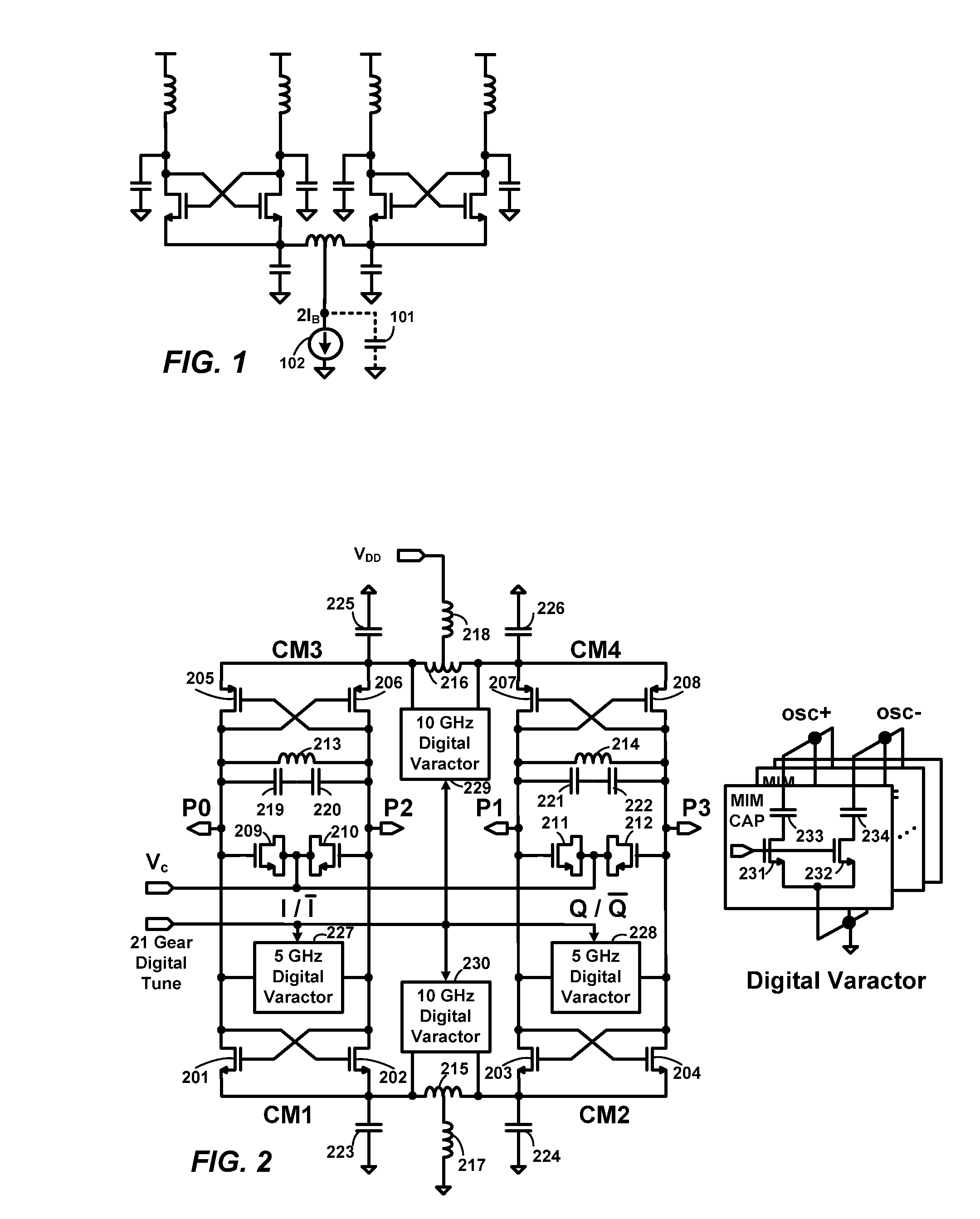
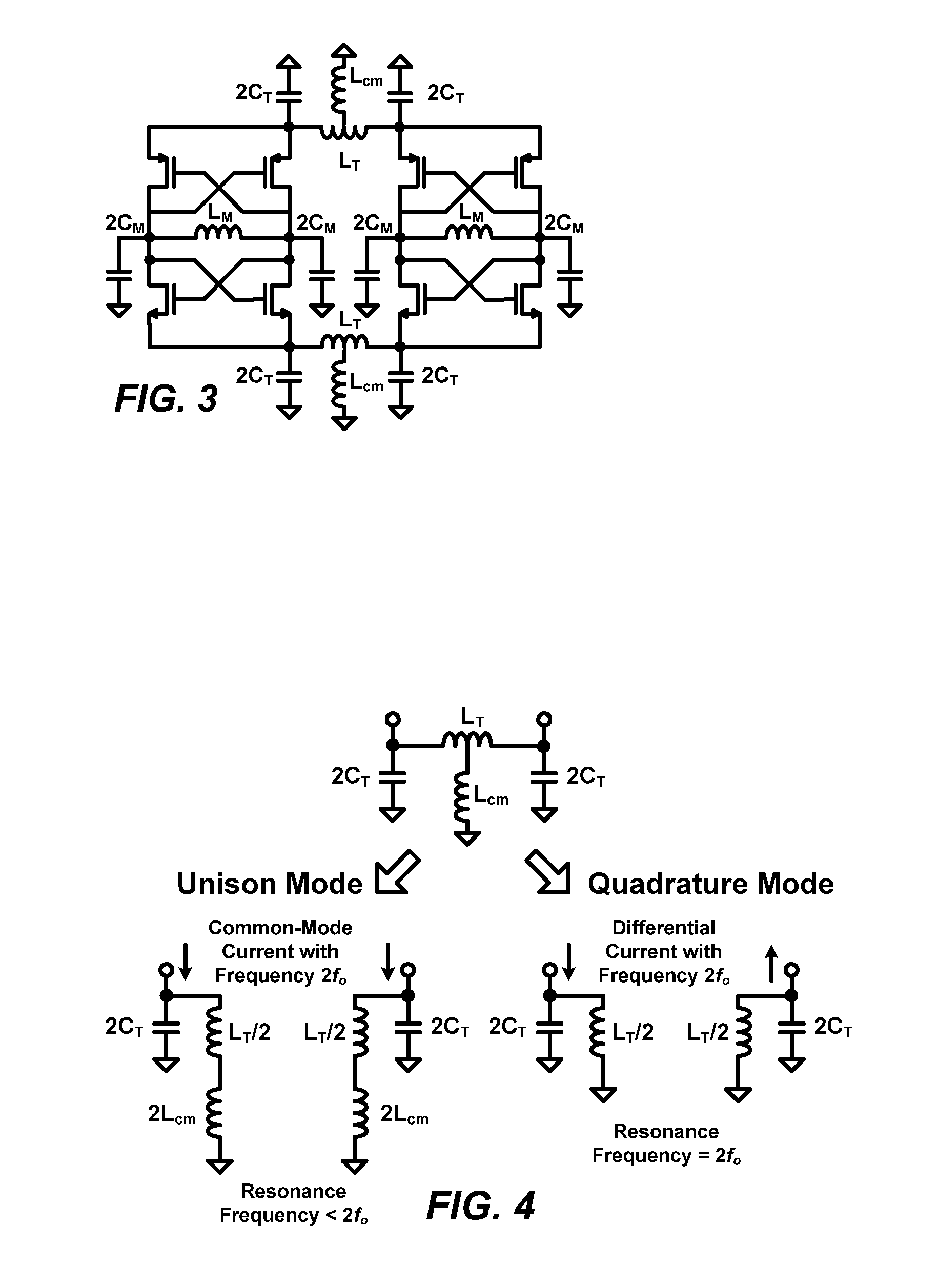
Low Phase-Noise Oscillator
InactiveUS20080143446A1Reduce impactTotal current dropPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorPhase noiseCoupling
A tail-tank coupling technique combines two complementary differential LC-VCOs to form a quadrature LC-VCO. The technique reduces phase noise by providing additional energy storage for noise redistribution and by cancelling noise injected by transistors when they operate in the triode region. The resulting noise factor is close to the theoretical minimum 1+γ, similar to a differential LC-VCO driven by an ideal noiseless current source. However, its figure-of-merit is higher, due to the absence of voltage head-room being consumed by a current source. The optimal ratio of tail-tank capacitor to main-tank capacitor for minimizing phase noise is approximately 0.5. The method can be extended to combine any even number of LC tanks resonating at fo and 2fo to form an integrated oscillator producing quadrature phase at frequency fosc and differential output at 2fosc.
Owner:WILLSON ALAN N JR
Clock recovery circuit through NFC active load modulation based on digital phase-locked loop
InactiveCN103269220AReduce frequency differenceSave bandwidthPulse automatic controlCarrier signalClock recovery
Owner:SHANGHAI QUANRAY ELECTRONICS
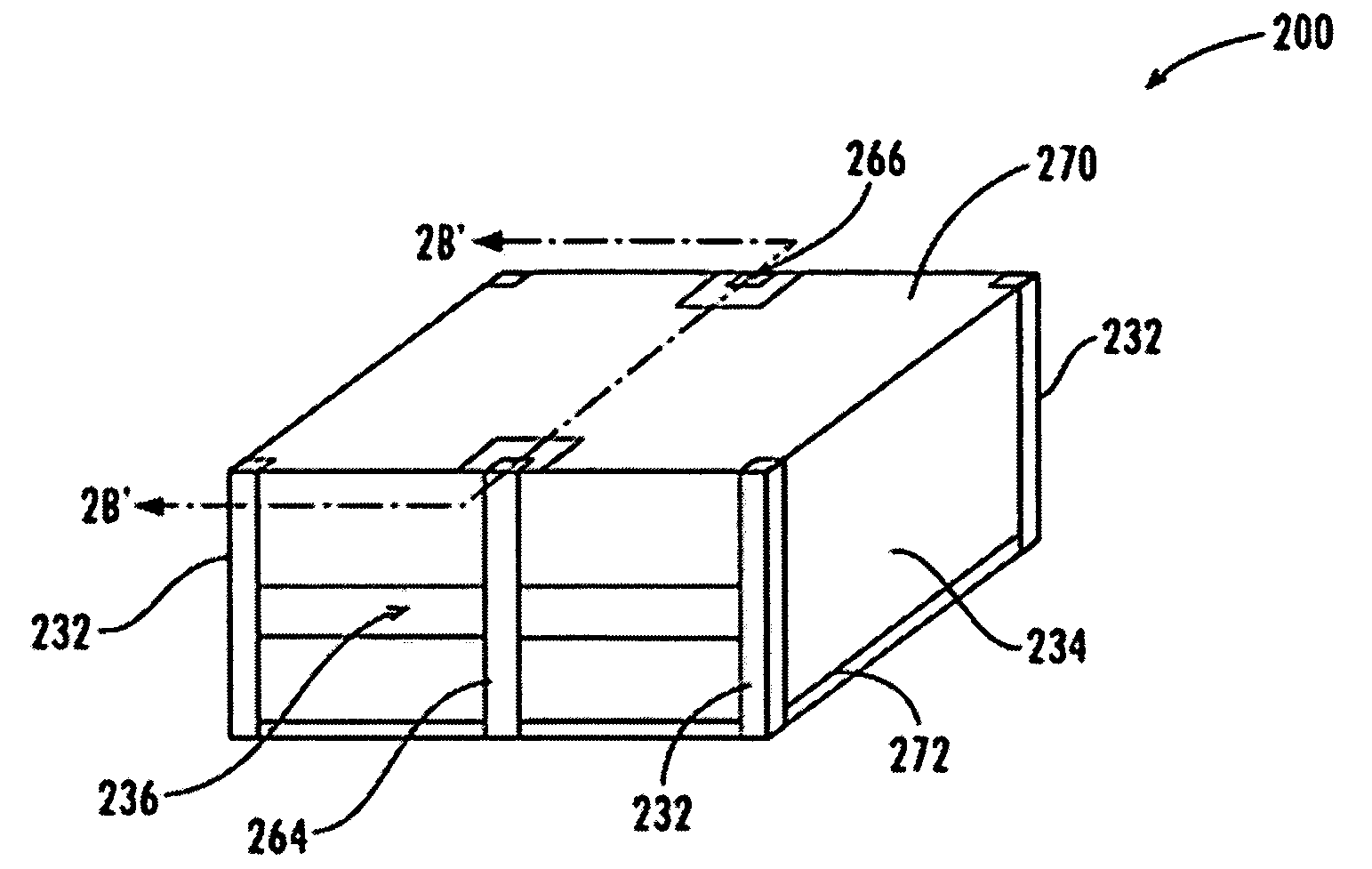
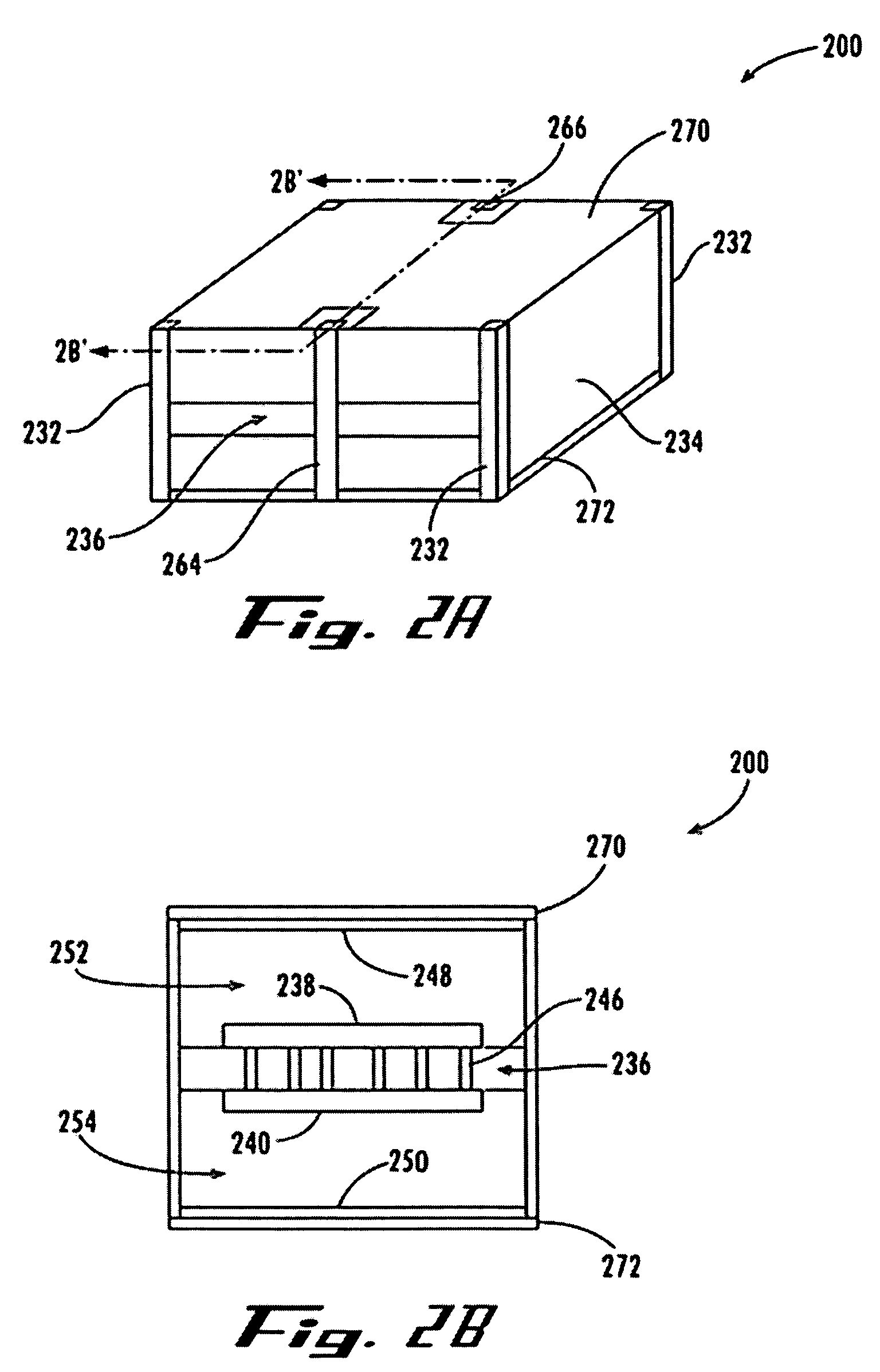
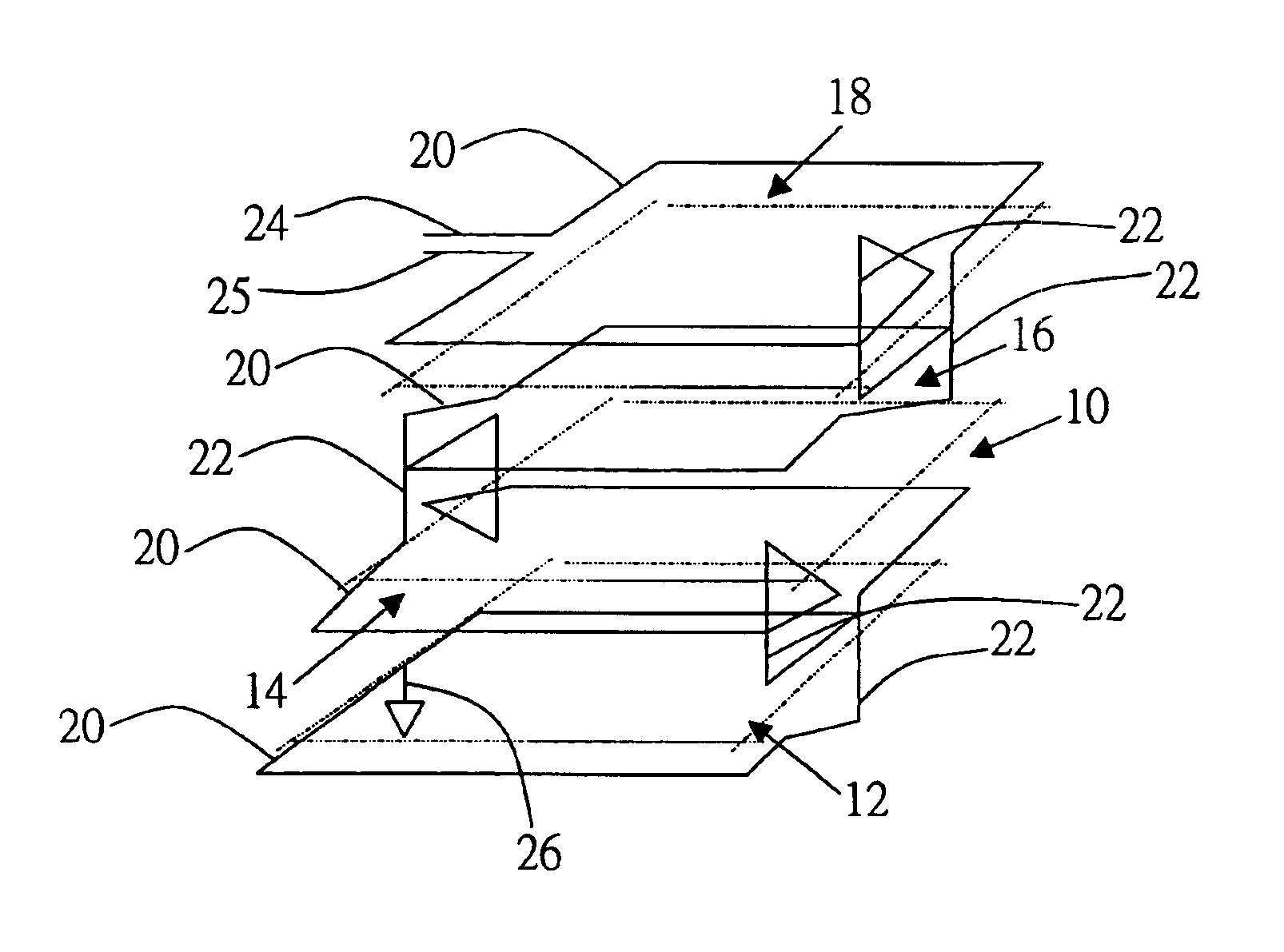
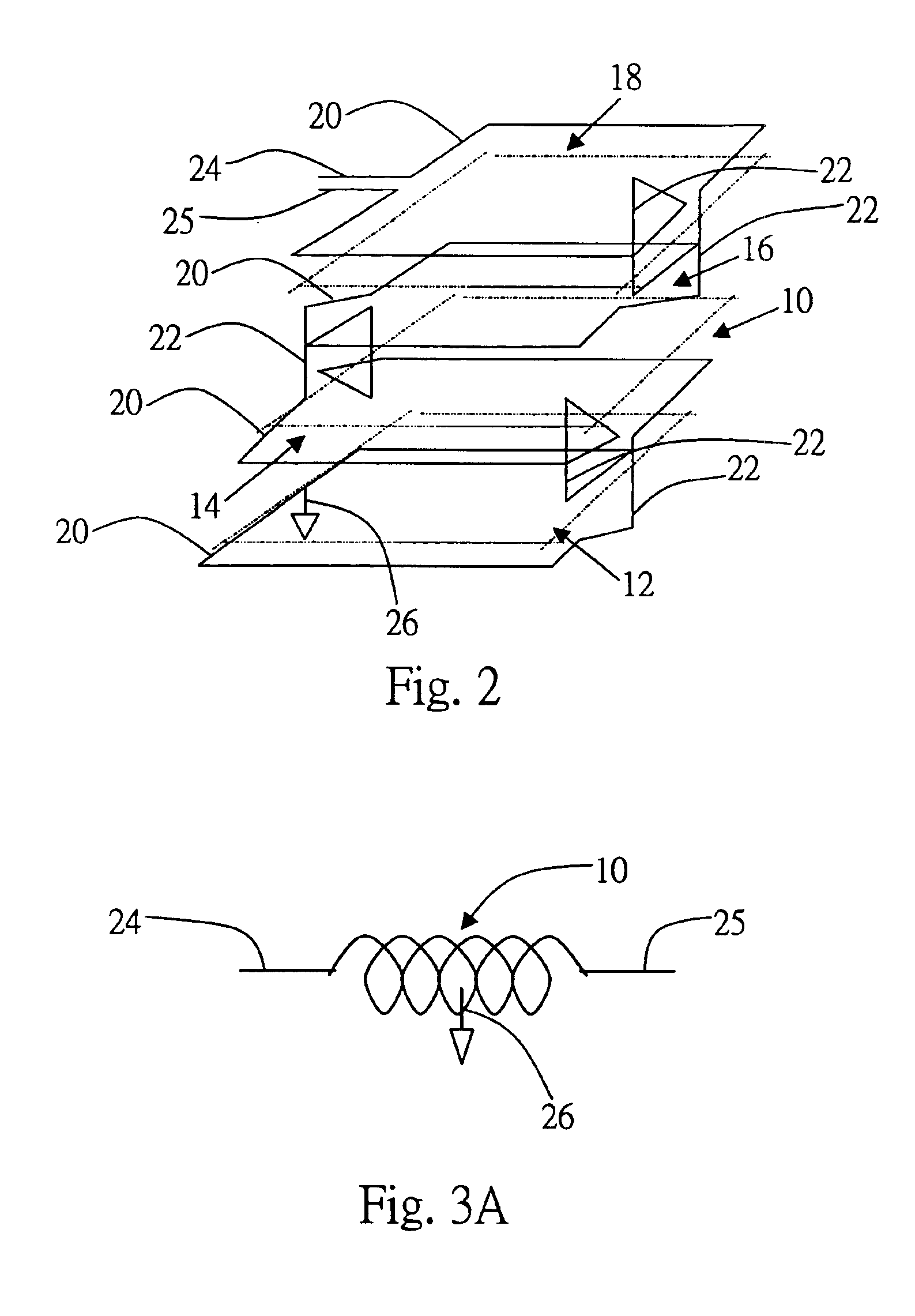
Symmetrical stacked inductor
InactiveUS6870457B2Reduce in quantityHigh quality factorTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances casingsEngineeringInductor
A symmetrical stacked inductor comprising a plurality of conductive layers using at least one conductive line formed out of a symmetrical and geometric conductive layer and having at least one inter-metal dielectric layer for isolating each conductive layer, and wherein the conductive line does not intersect; and a plurality of vias placed between the inter-metal dielectric layers for electrical conduction.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
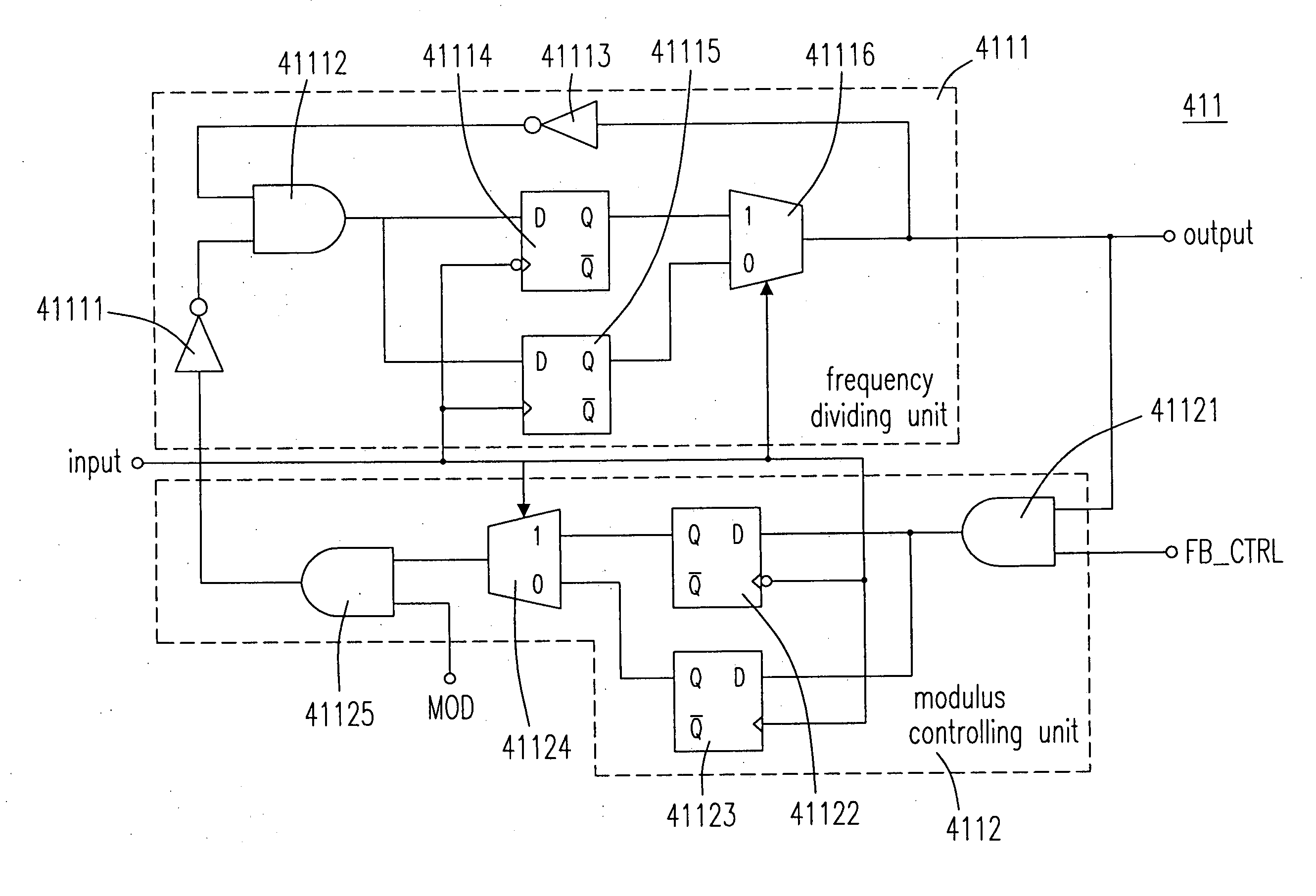
Configuration and controlling method of Fractional-N PLL having fractional frequency divider
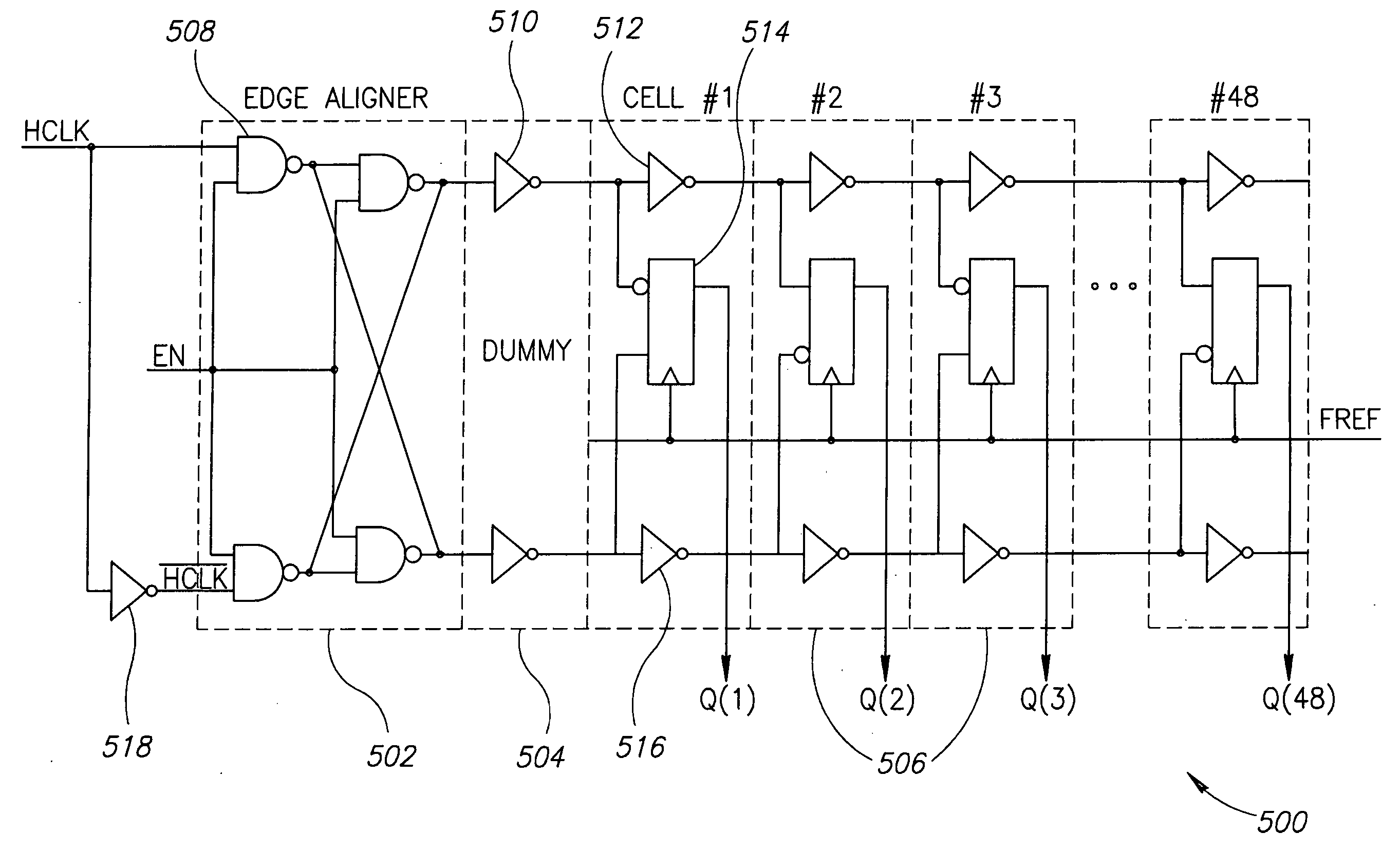
InactiveUS20070147571A1Modulus resolutionReduce mistakesCounting chain pulse countersControl unitFrequency divider
The provided fractional frequency divider includes a divider controlling unit for generating a divider selection signal in response to a dual-edge triggering of an input signal and a frequency dividing unit coupled to the divider controlling unit for dividing the frequency of the input signal by one of an integer and a fractional dividers in response to the dual-edge triggering and the divider selection signal to generate the output signal of the fractional frequency divider. An operation of the frequency dividing unit is not suppressed when the integer divider is employed, the operation of the frequency dividing unit is not suppressed for a period of the input signal and is suppressed for half of that period, and this cycle is kept on recurring when the fractional divider is employed. The fractional-n PLL having the fractional frequency divider is also provided.
Owner:MEMETICS TECH +1
System and method for frequency tunable microwave phase shifting
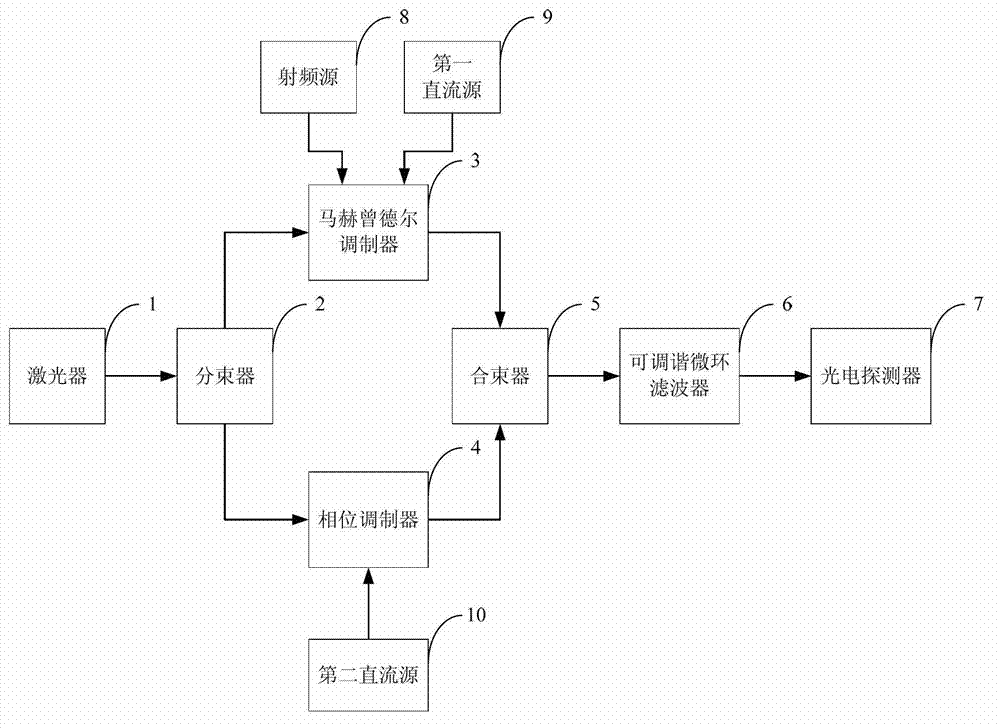
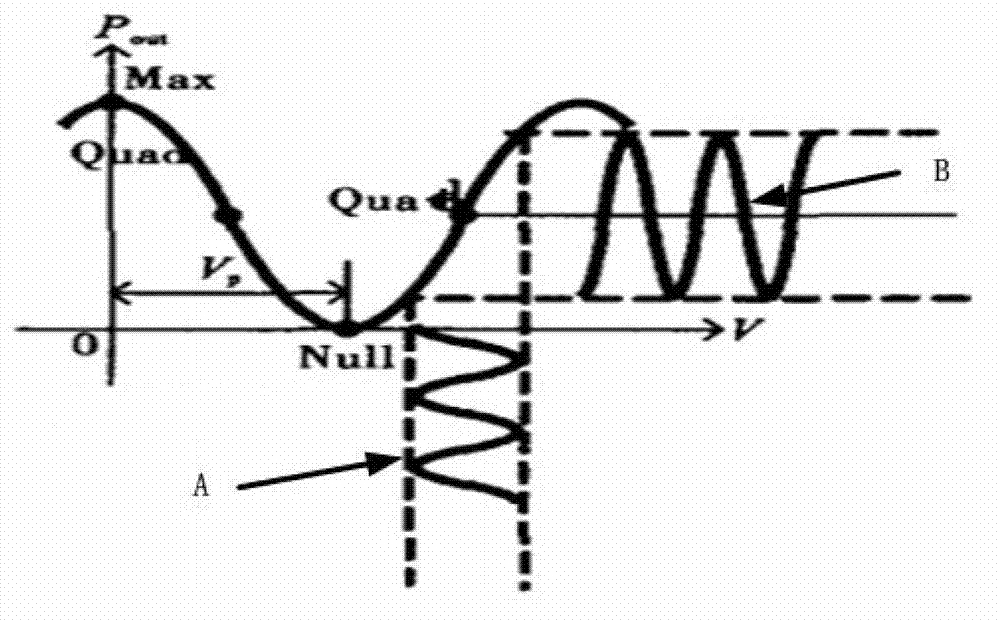
ActiveCN103326789AReduce phase noiseSmall amplitude fluctuationPhotonic quantum communicationContinuous lightCarrier signal
The invention belongs to the field of microwave photonics, and discloses a system and method for frequency tunable microwave phase shifting. The method comprises the following steps that after a continuous light carrier is splitted, one beam of the continuous light carrier is processed by a MZ Mach-zehnder, and double-sideband optical signals restrained by the carrier are produced; the other beam of the continuous light carrier is processed by a phase modulator, and phase-shifted light carrier signals are produced; two beams of light signals are combined in a wave mode, one one-step sideband is removed through a tunable micro-ring filter in a filtering mode, a frequency-moved carrier signal and a phase-shifted carrier signal are obtained, photovoltaic conversion is carried out through a photoelectric detector, and a phase shift microwave electrical signal is produced; the resonant frequency of the tunable micro-ring filter is equal to any one-step sideband of the two one-step sidebands output by the MZ Mach-zehnder by changing the frequency of an input voltage drive signal and the resonant wavelength of the tunable micro-ring filter, and the frequency of the phase shift microwave signal is changed. The system and method for the frequency tunable microwave phase shifting is stable in output performance, fast in phase shift adjusting response, small in output microwave range fluctuation and continuously adjustable in wide frequency range.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
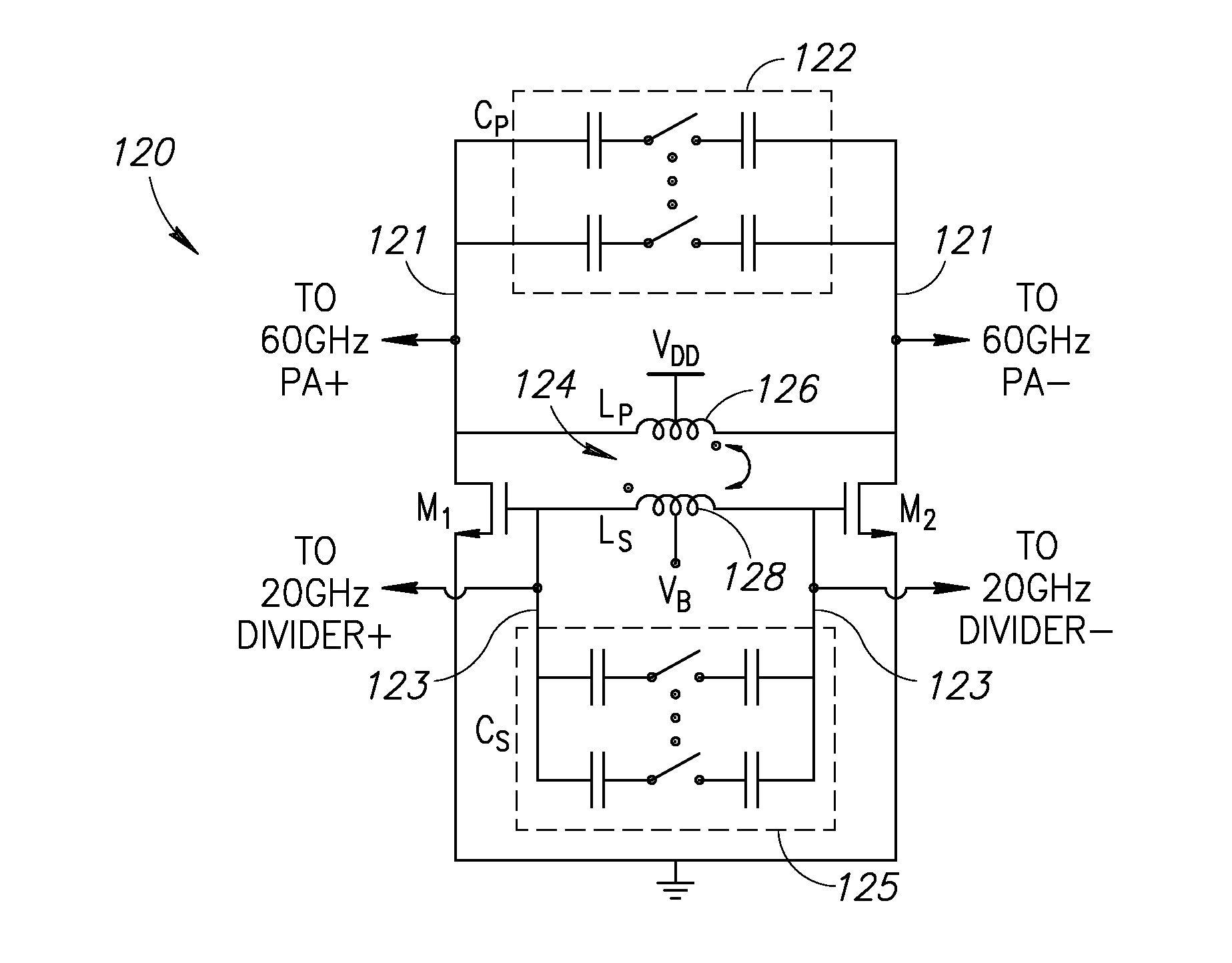
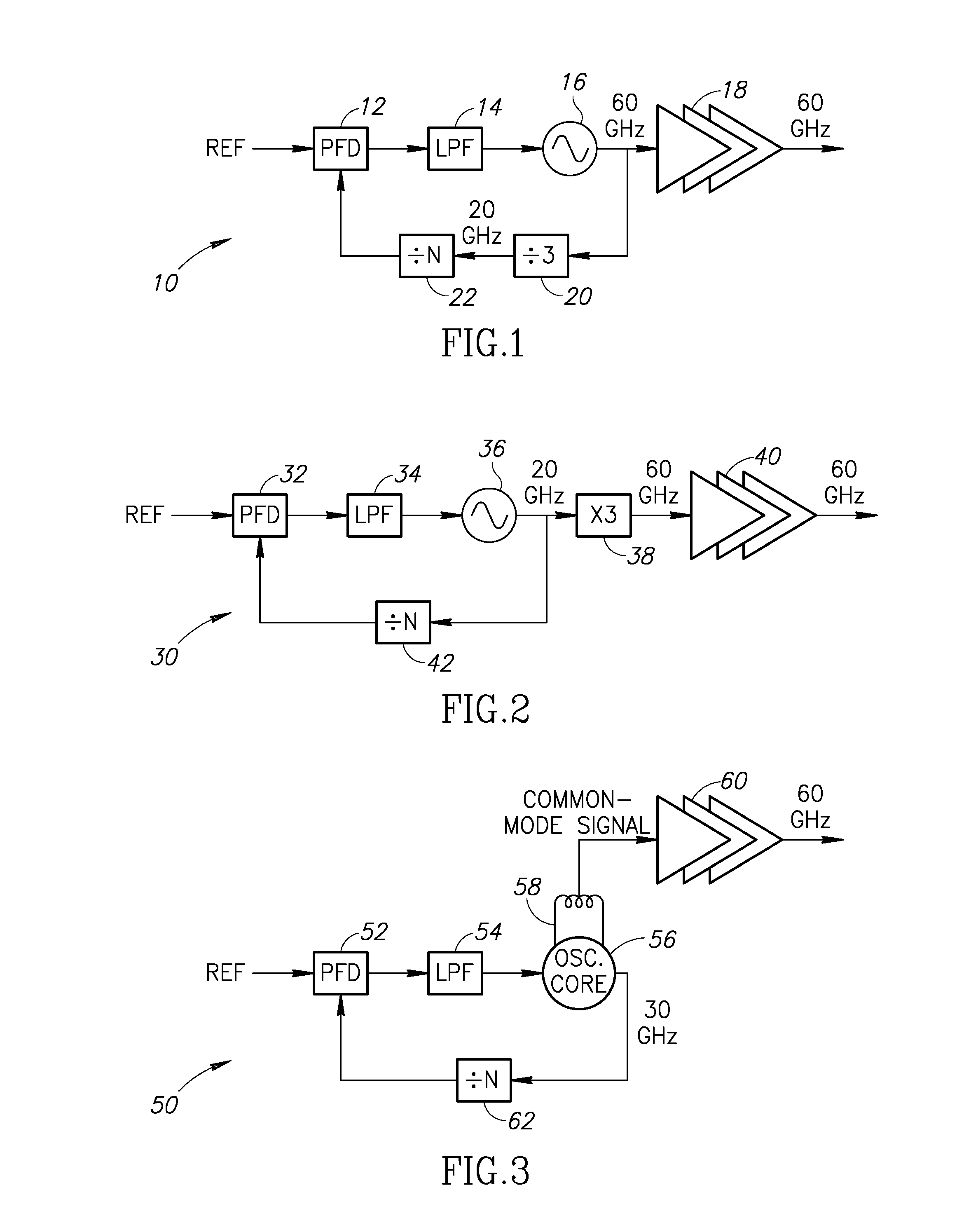
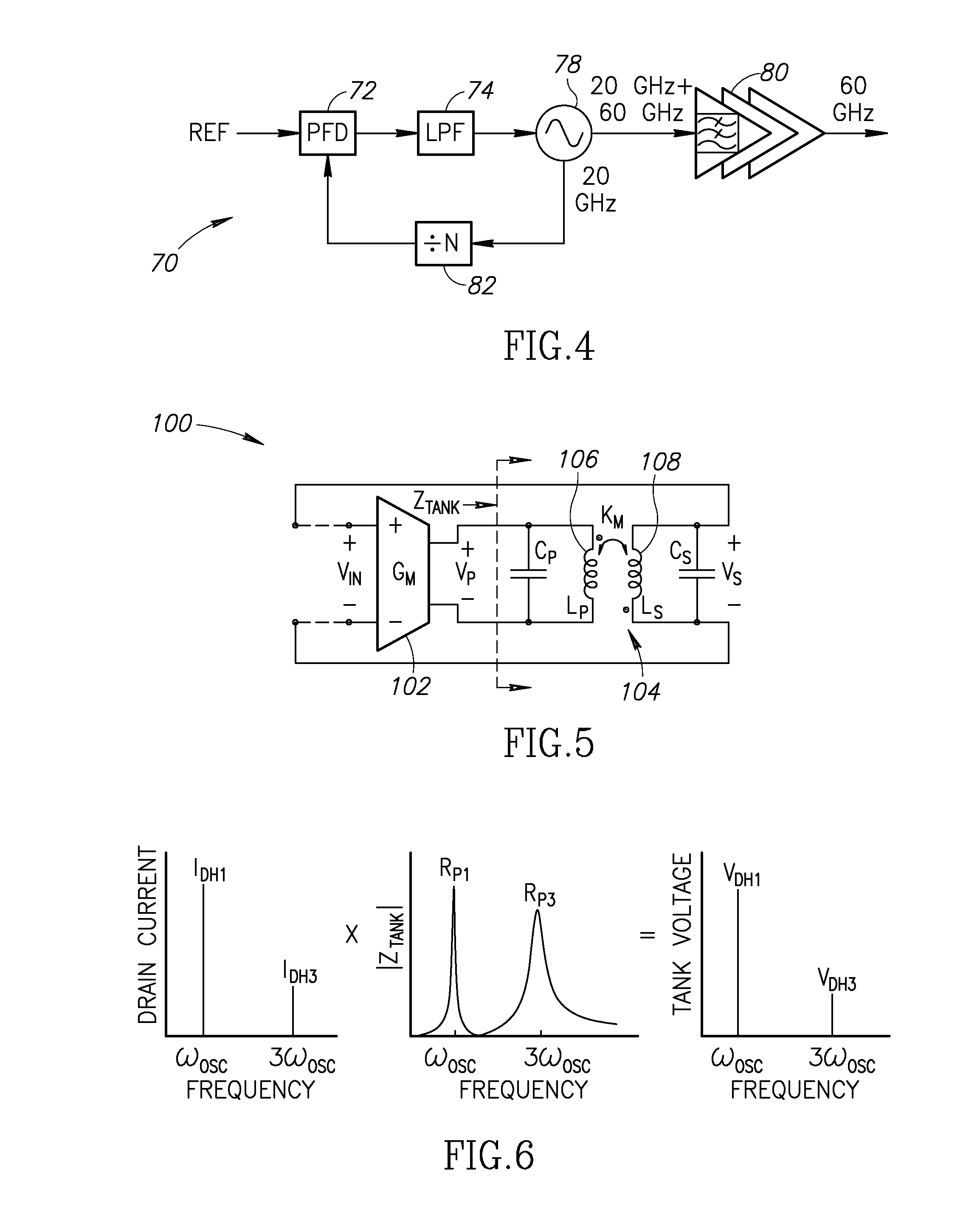
60 GHz Frequency Generator Incorporating Third Harmonic Boost And Extraction
ActiveUS20160099681A1Improve efficiencyImprove noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCMOSDBc
A novel and useful 60 GHz frequency generator based on a third harmonic extraction technique which improves system level efficiency and performance. The frequency generator employs a third harmonic boosting technique to increase the third harmonic at the output of the oscillator. The oscillator generates both ˜20 GHz fundamental and a significant amount of the third harmonic at ˜60 GHz and avoids the need for a frequency divider operating at 60 GHz. The undesired fundamental harmonic at ˜20 GHz is rejected by the good fundamental HRR inherent in the oscillator buffer stage while the ˜60 GHz component is amplified to the output. The fundamental harmonic is further suppressed by an active cancellation by properly combining the two outputs. The oscillator fabricated in 40 nm CMOS exhibits a phase noise of −100 dBc / Hz at 1 MHz offset from a 60 GHz carrier and have a tuning range of 25%.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
Simplified high frequency tuner and tuning method
InactiveUS7116963B2Reduce frequencyLow processing rateFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTransmission noise suppressionLocal oscillator signalFrequency spectrum
A disclosed method tunes a signal from a channelized spectrum having a predetermined channel spacing. A signal of interest having a predetermined maximum bandwidth is mixed with a local oscillator signal, which has a frequency that is an integer multiple of the channel spacing or one-half of a channel spacing displaced from an integer multiple of the channel spacing. The local oscillator signal is selected to frequency translate the signal of interest to within a near-baseband passband whose lower edge is spaced from DC by at least about the maximum bandwidth of the signal of interest. Problems associated with 1 / f noise, DC offsets, and self-mixing products are avoided or substantially diminished. Other methods and systems are also disclosed.
Owner:WASHINGTON RES FOUND
Frequency-locked loop calibration of a phase-locked loop gain
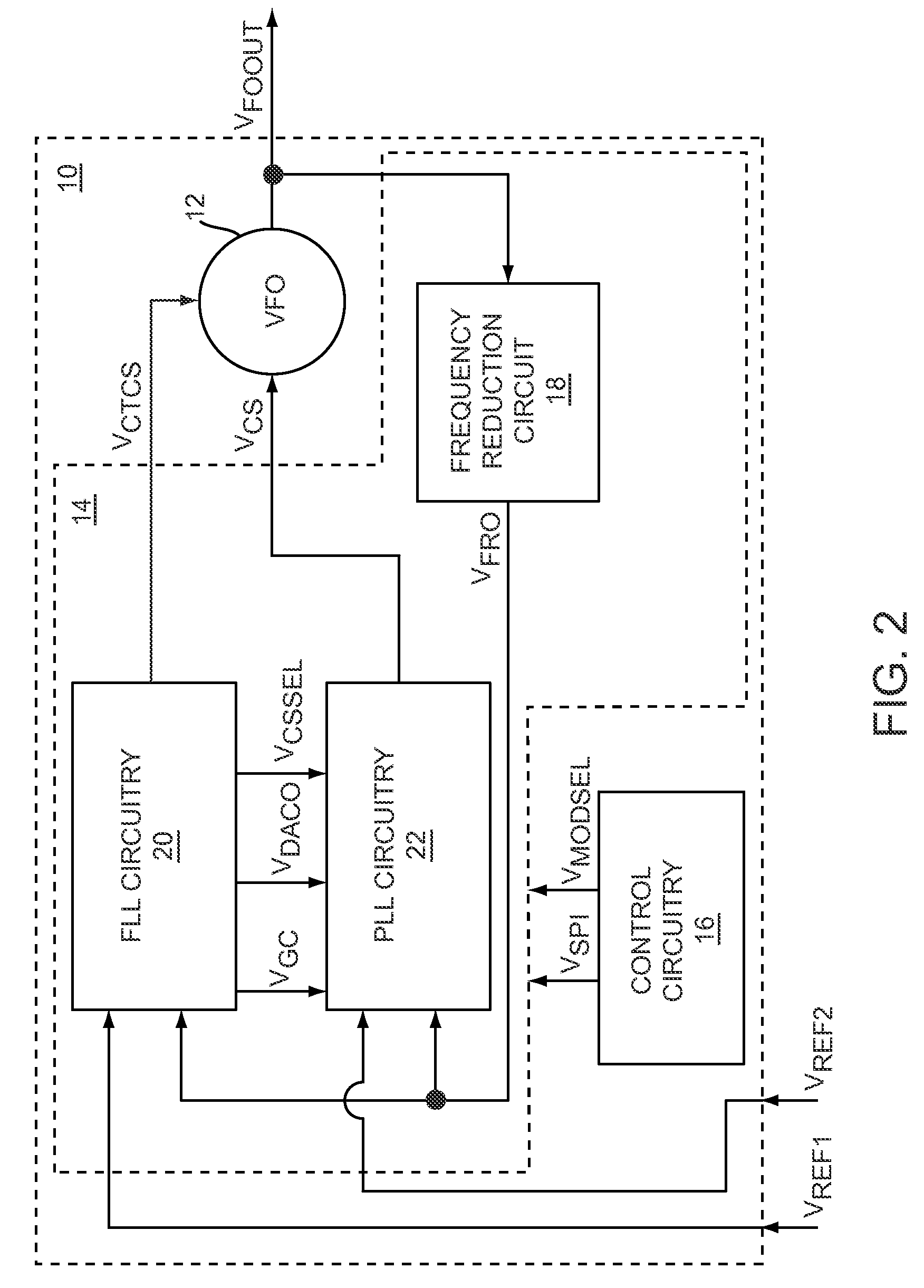
InactiveUS7898343B1Reduce locking timeHigh frequency accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisNoise spectrumVariable-frequency oscillator
The present invention relates to a calibrated phase-locked loop (PLL), which has a calibration mode for measuring a tuning gain of a variable frequency oscillator (VFO) and a PLL mode for normal operation. Calibration information based on the tuning gain is used during the PLL mode to regulate a PLL loop gain. During the calibration mode, the calibrated PLL operates as a frequency-locked loop (FLL) for low frequency lock times, and during the PLL mode the calibrated PLL operates as a PLL for high frequency accuracy and low noise. By regulating the PLL loop gain, the desired noise spectrum and dynamic behavior of the PLL may be maintained in spite of variations in the operating characteristics or in the characteristics of the PLL components.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Interference cancellation for reconfigurable direct RF bandpass sampling interference cancellation
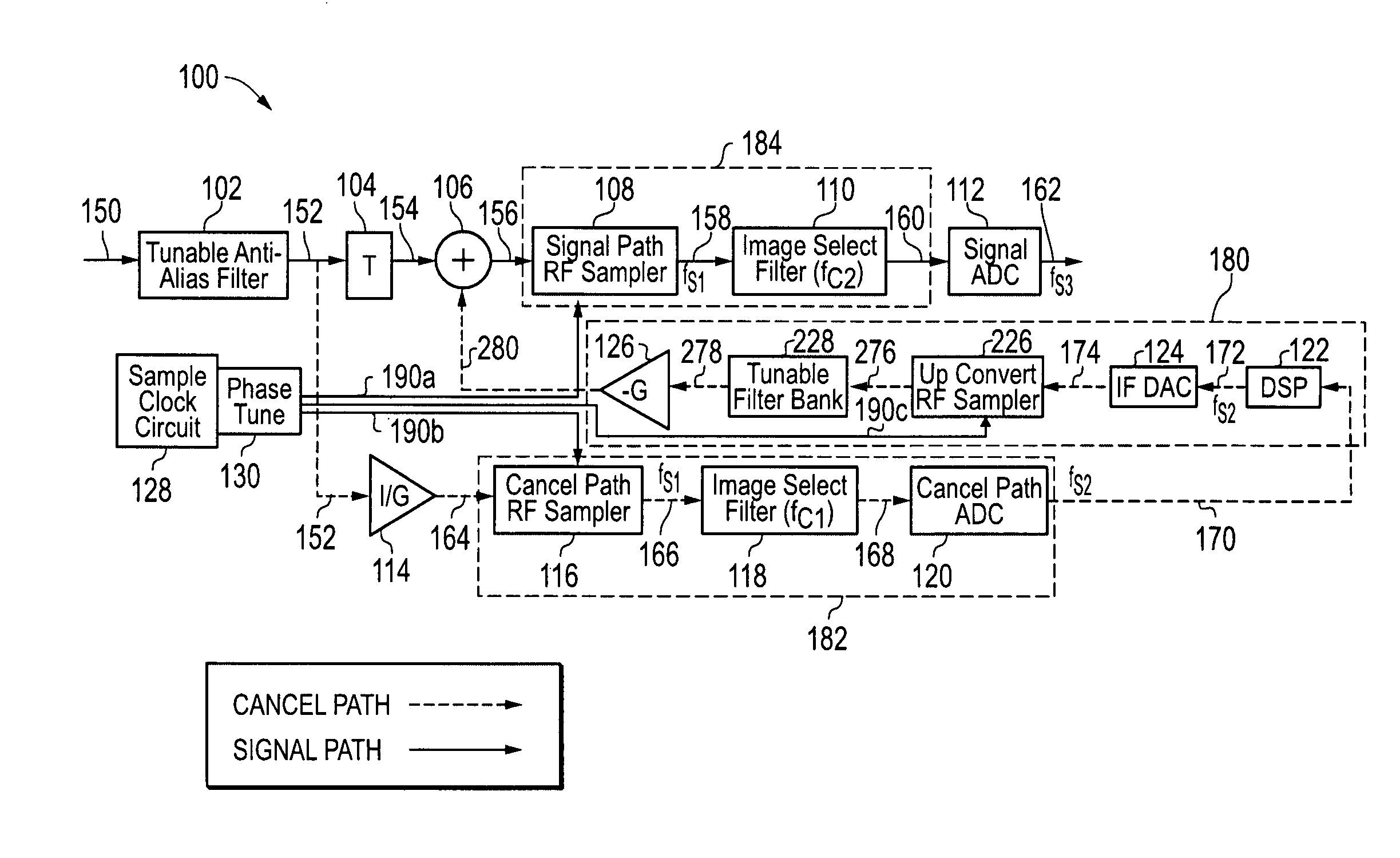
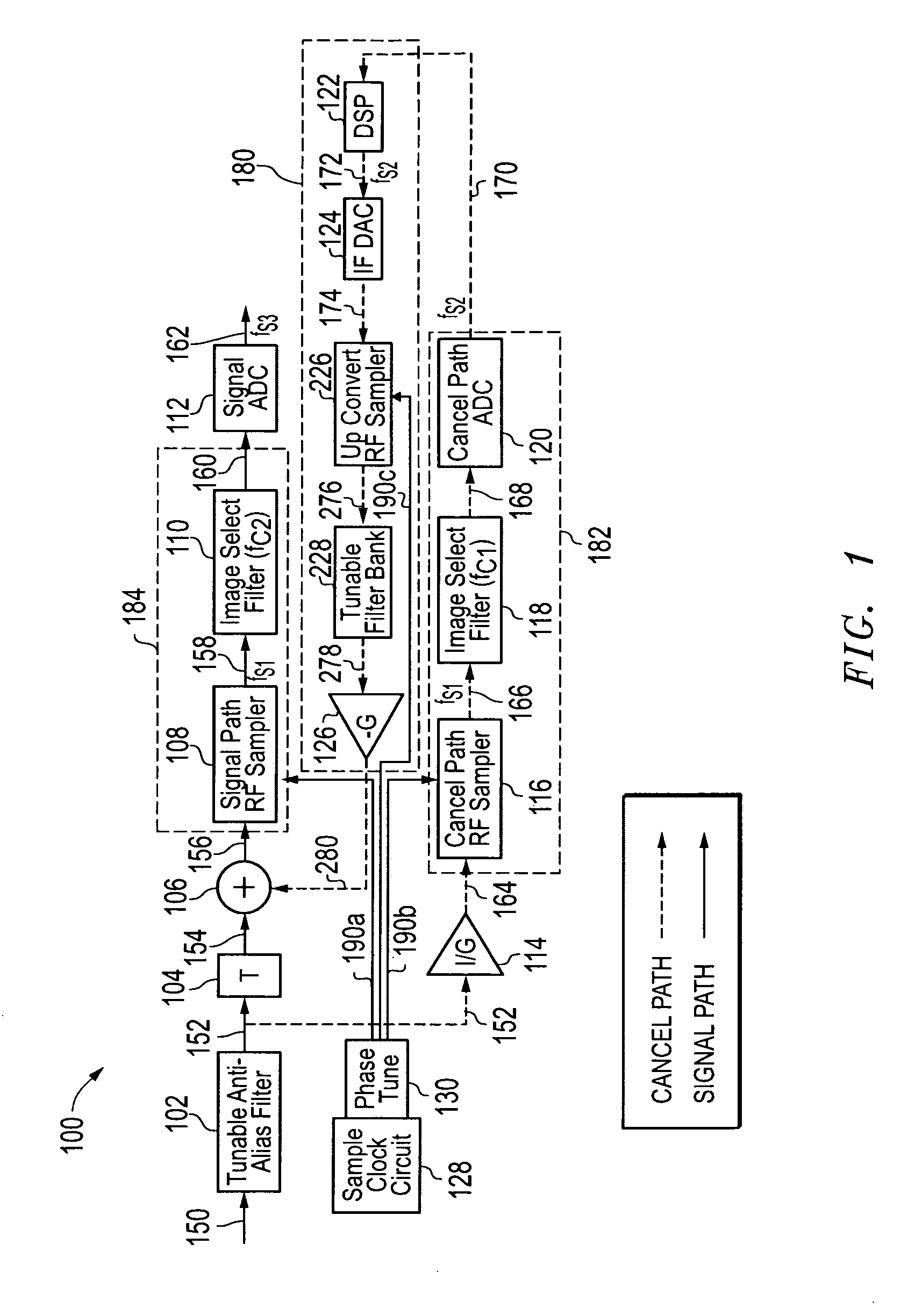
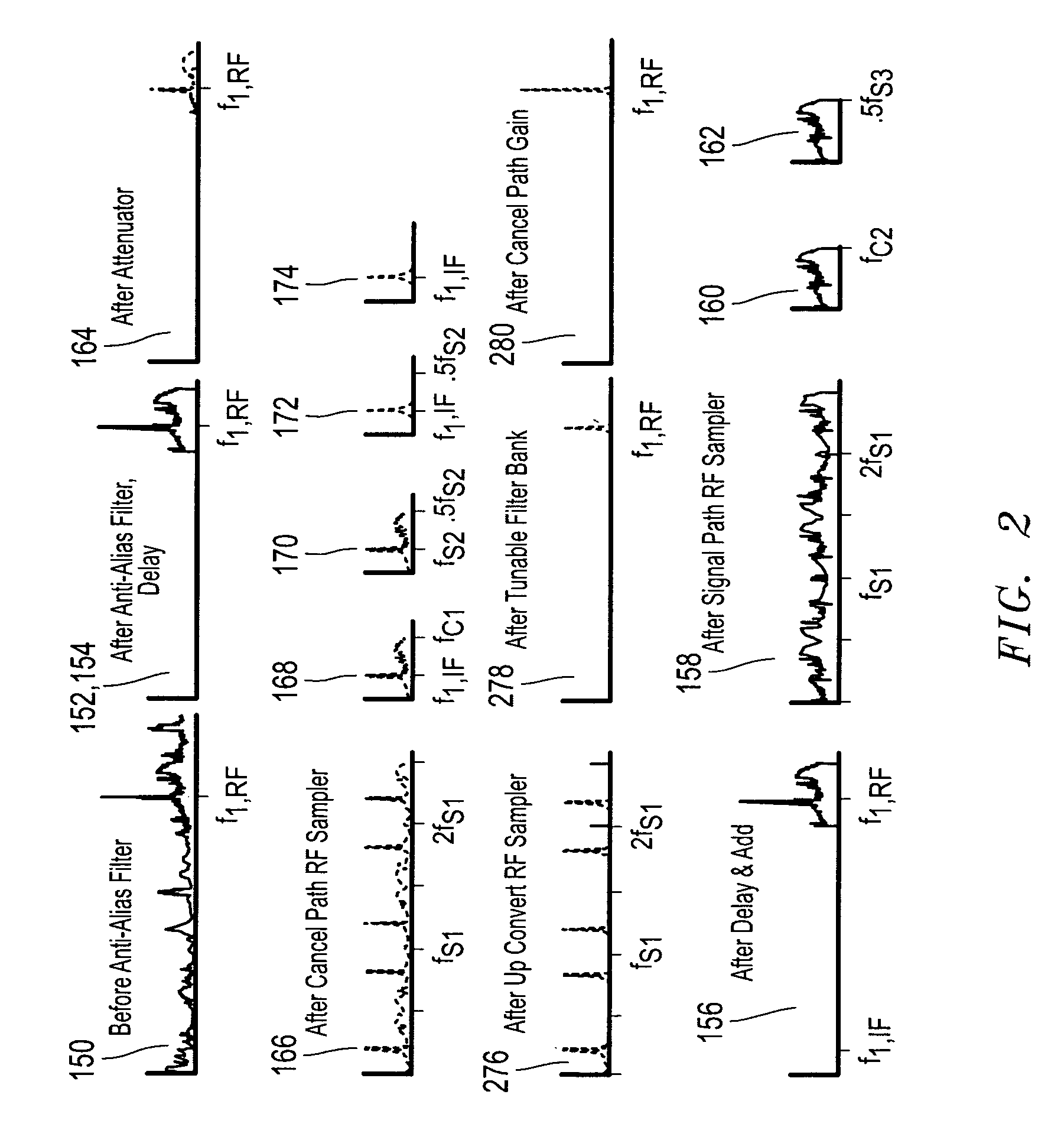
InactiveUS8081946B2Avoid badReduce impactElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersRadio frequencyVIT signals
Sampling may be employed to cancel an analog input radio frequency (RF) signal by using an upconverted analog cancellation RF signal to cancel the analog input RF signal at the sample instances. At least two sampling paths may be employed, a signal path and a cancel path, and direct RF bandpass sampling may be included in both the signal and cancel paths.
Owner:L 3 COMM INTEGRATED SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com