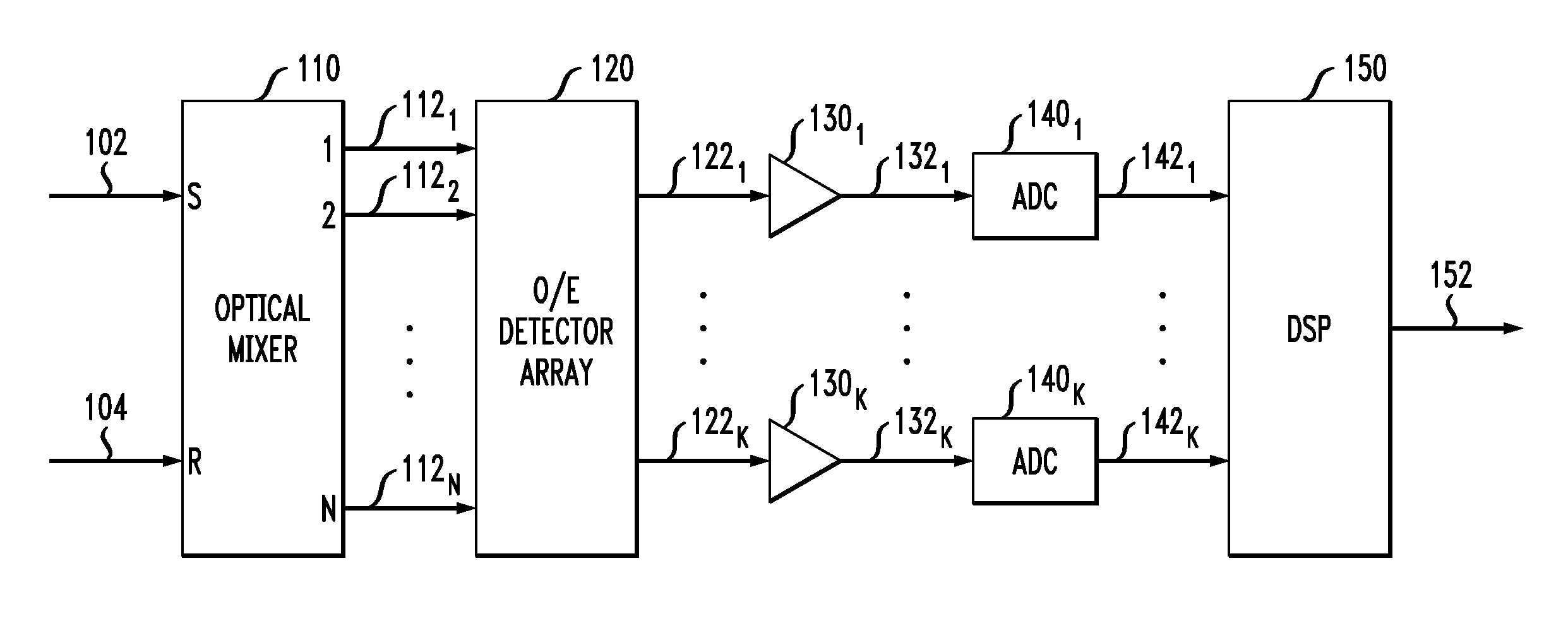
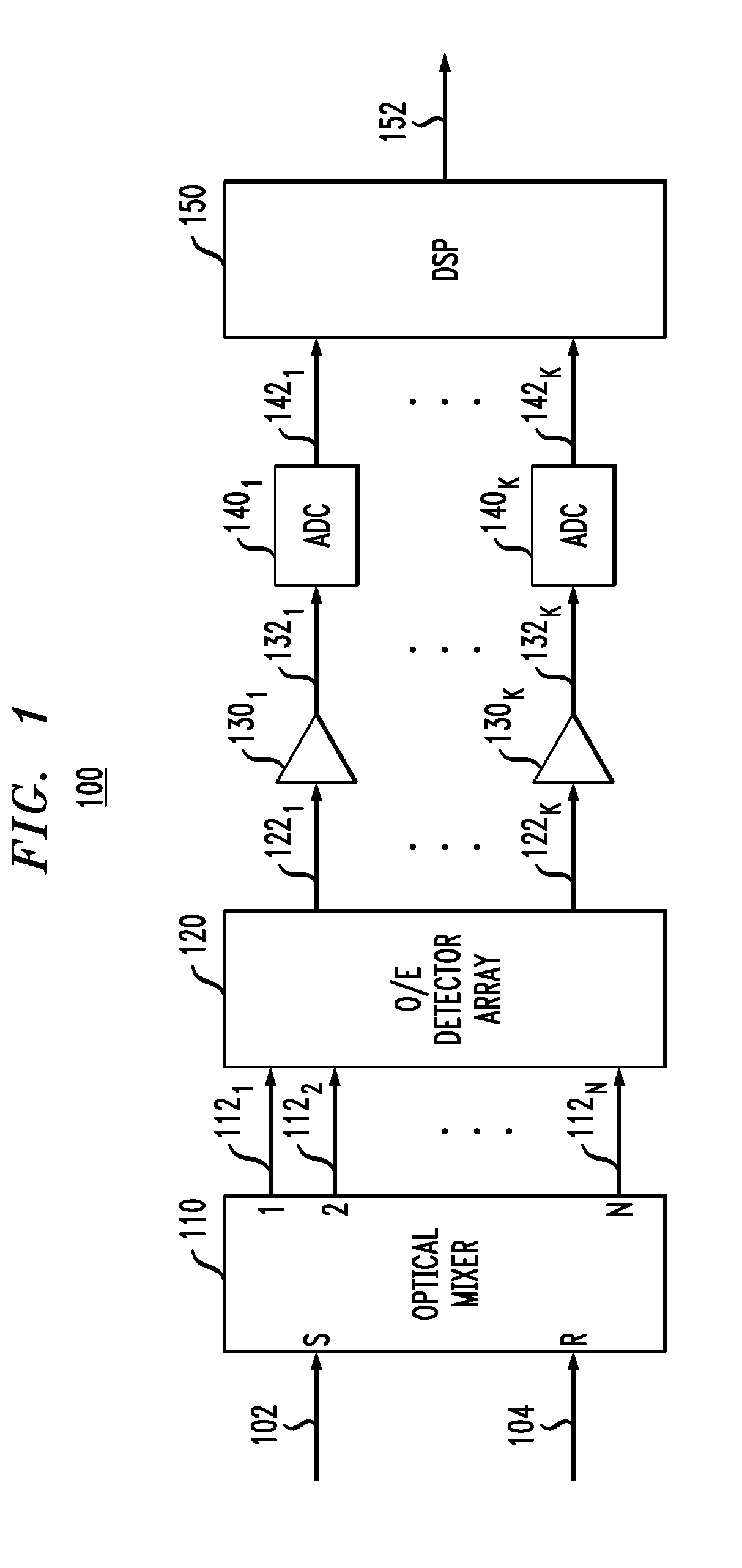
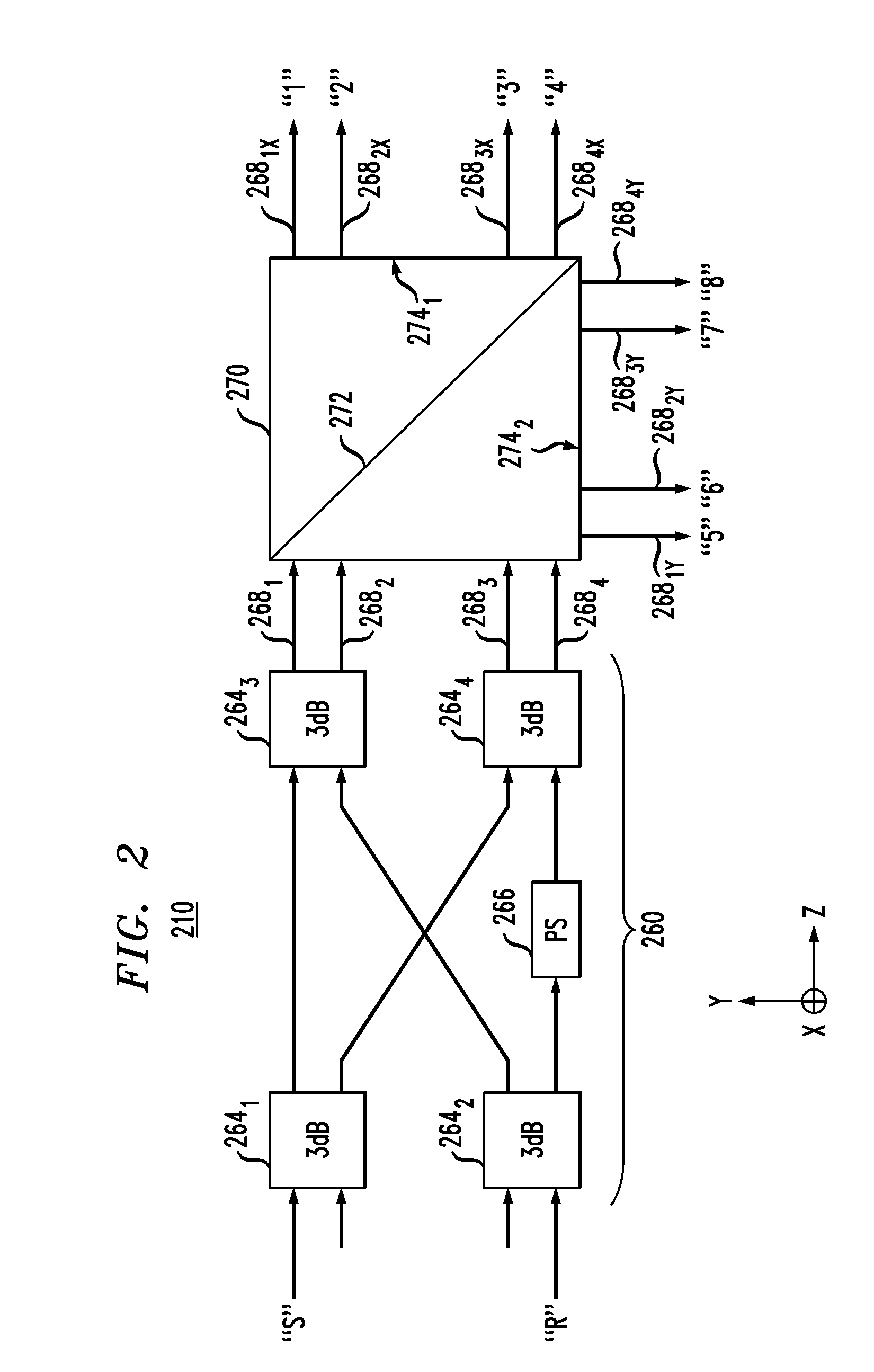
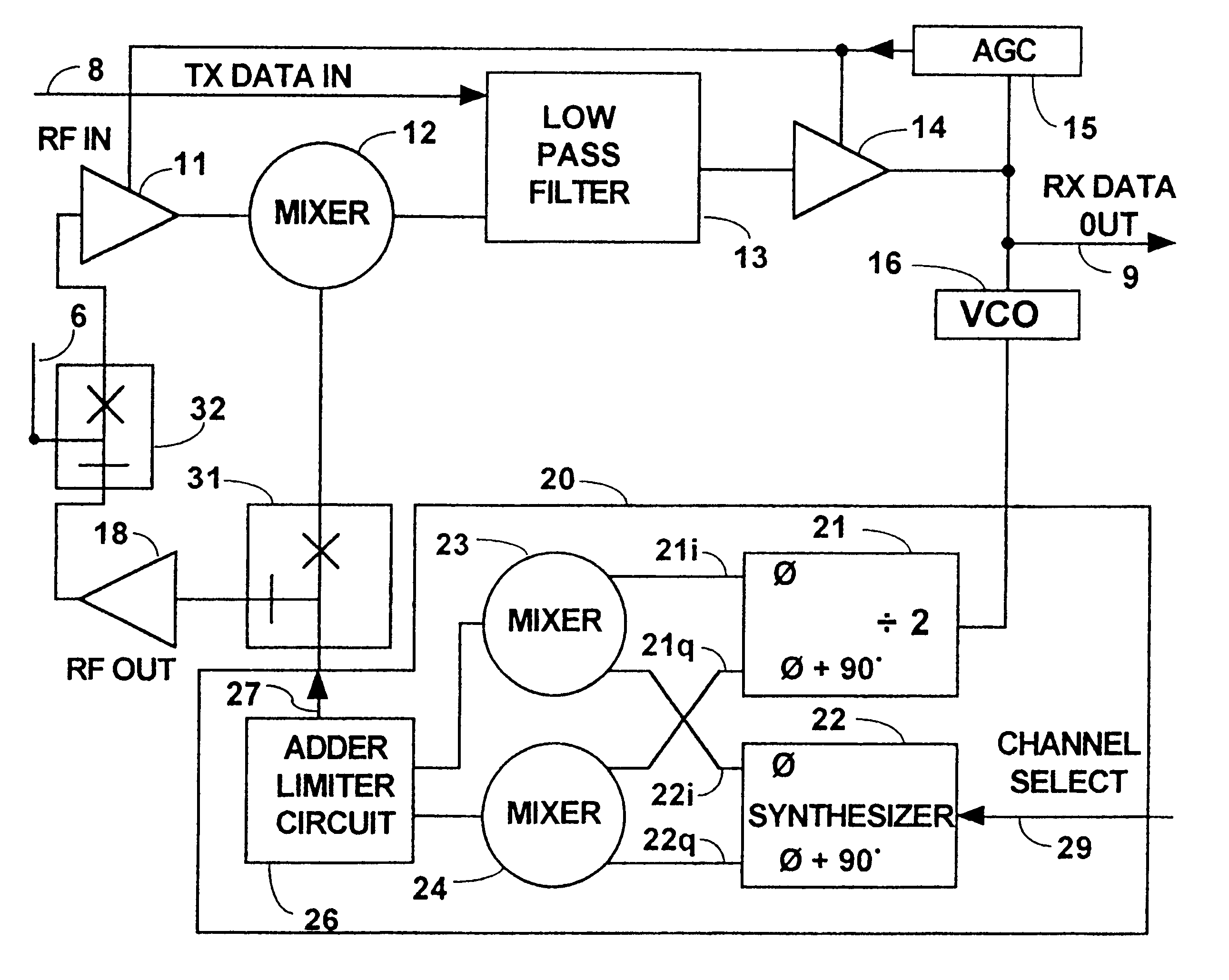
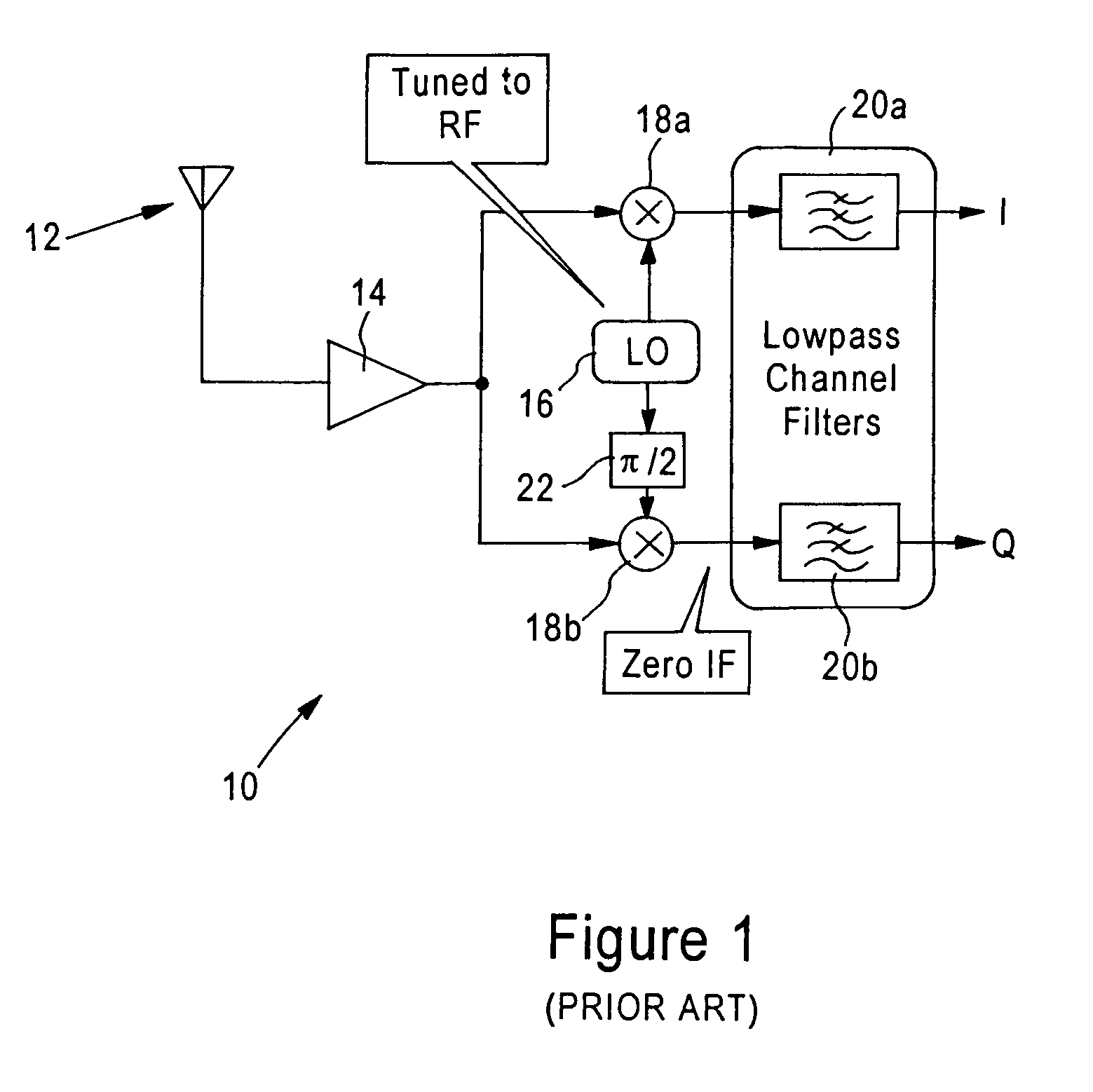
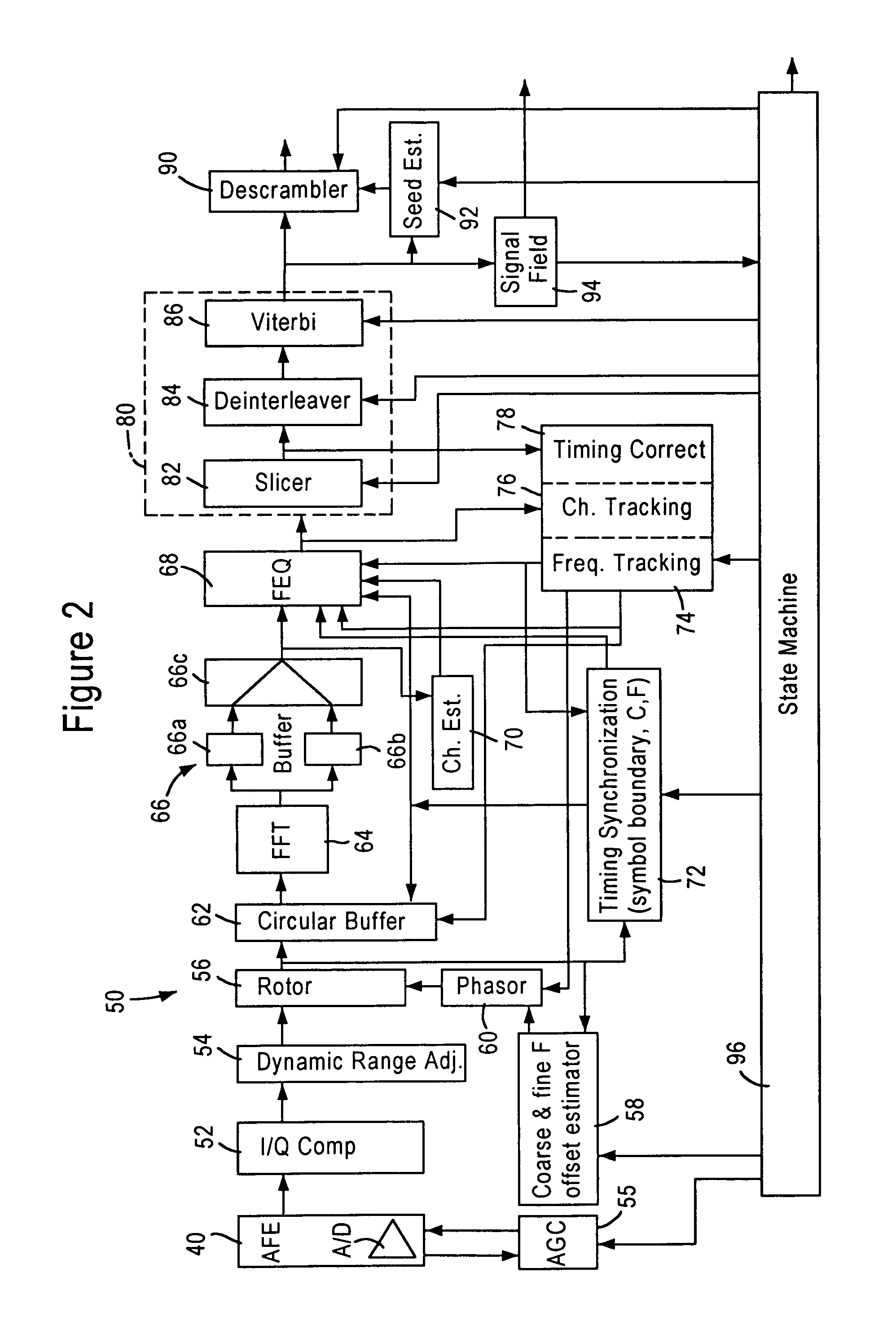
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1745 results about "Local oscillator signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
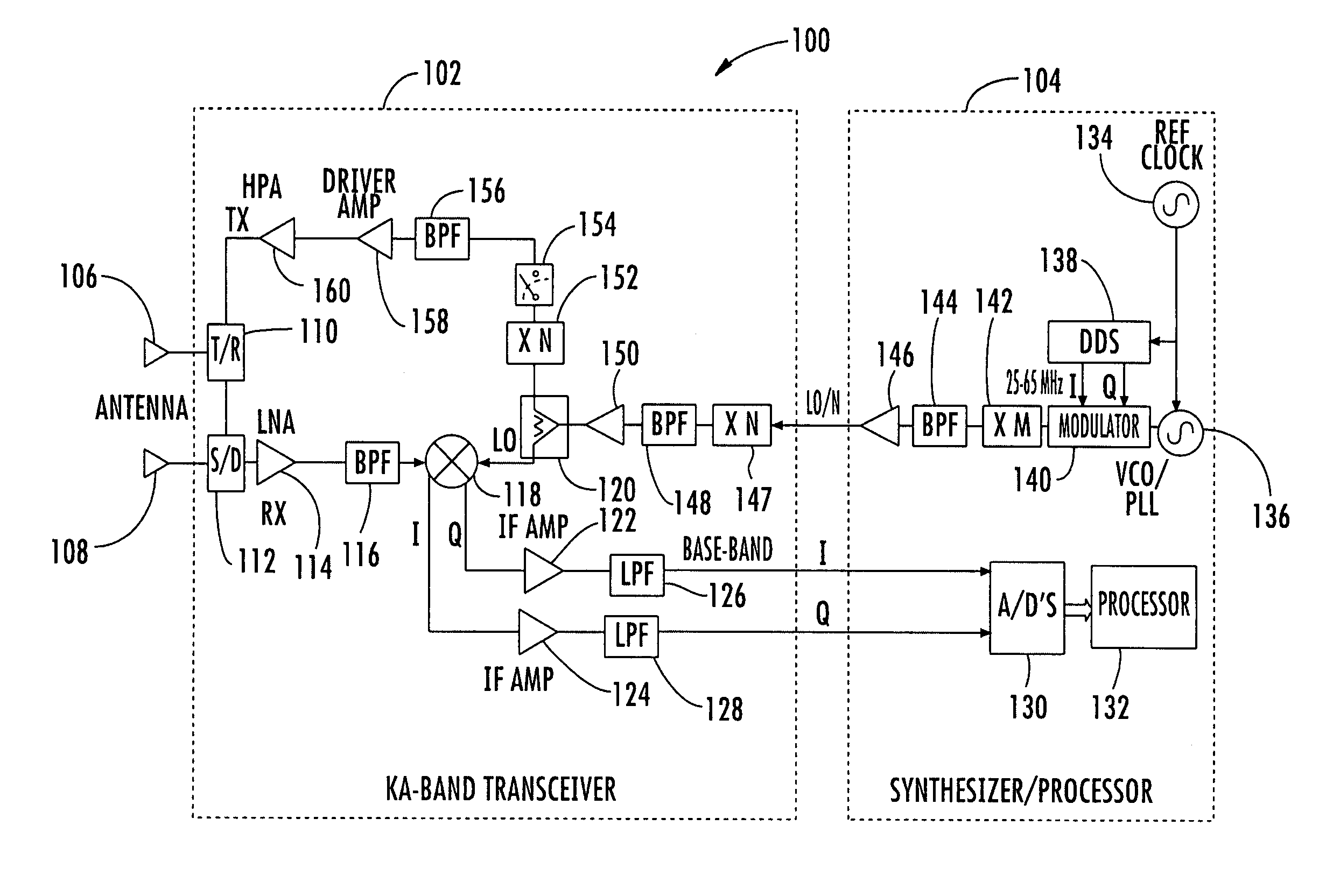
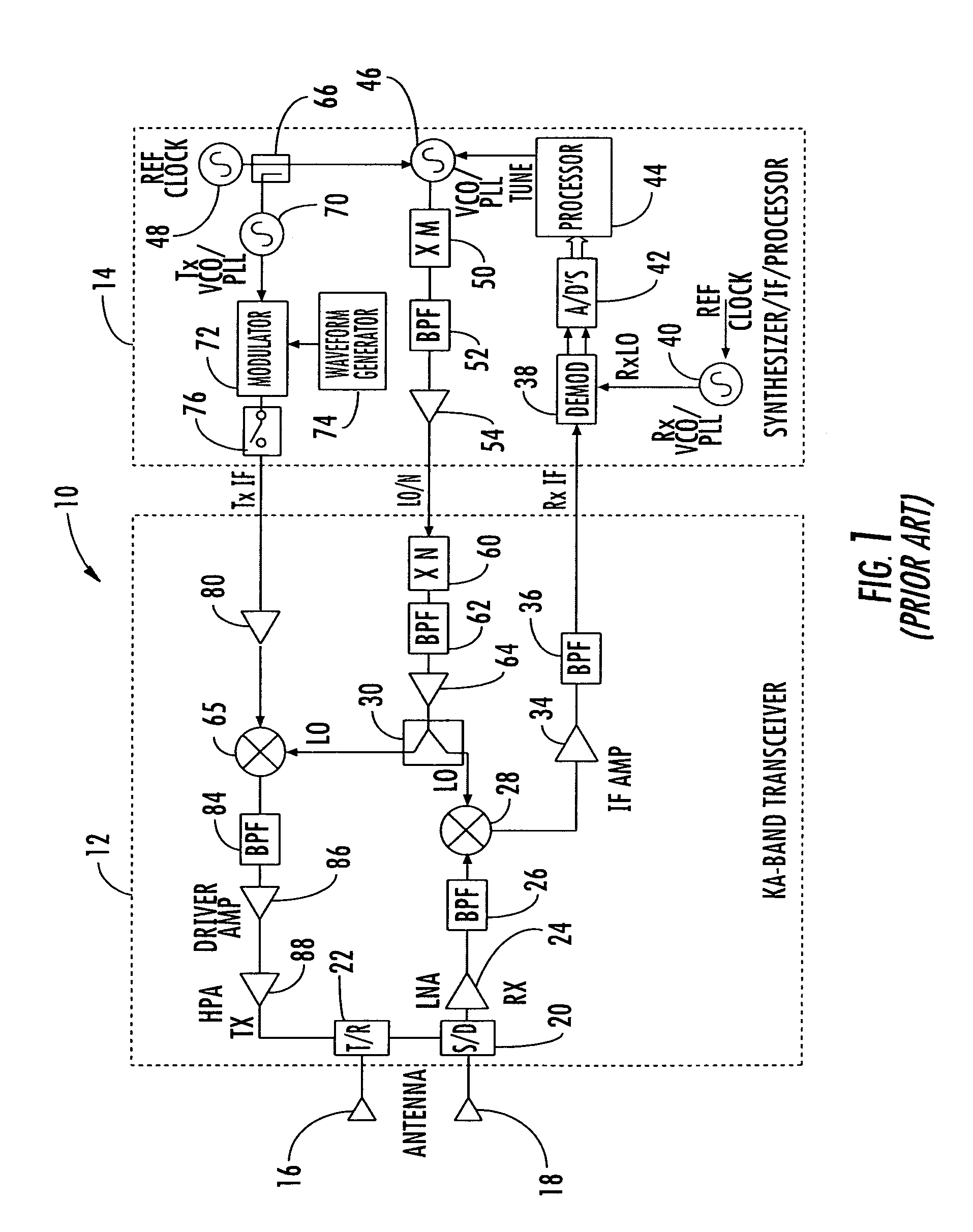
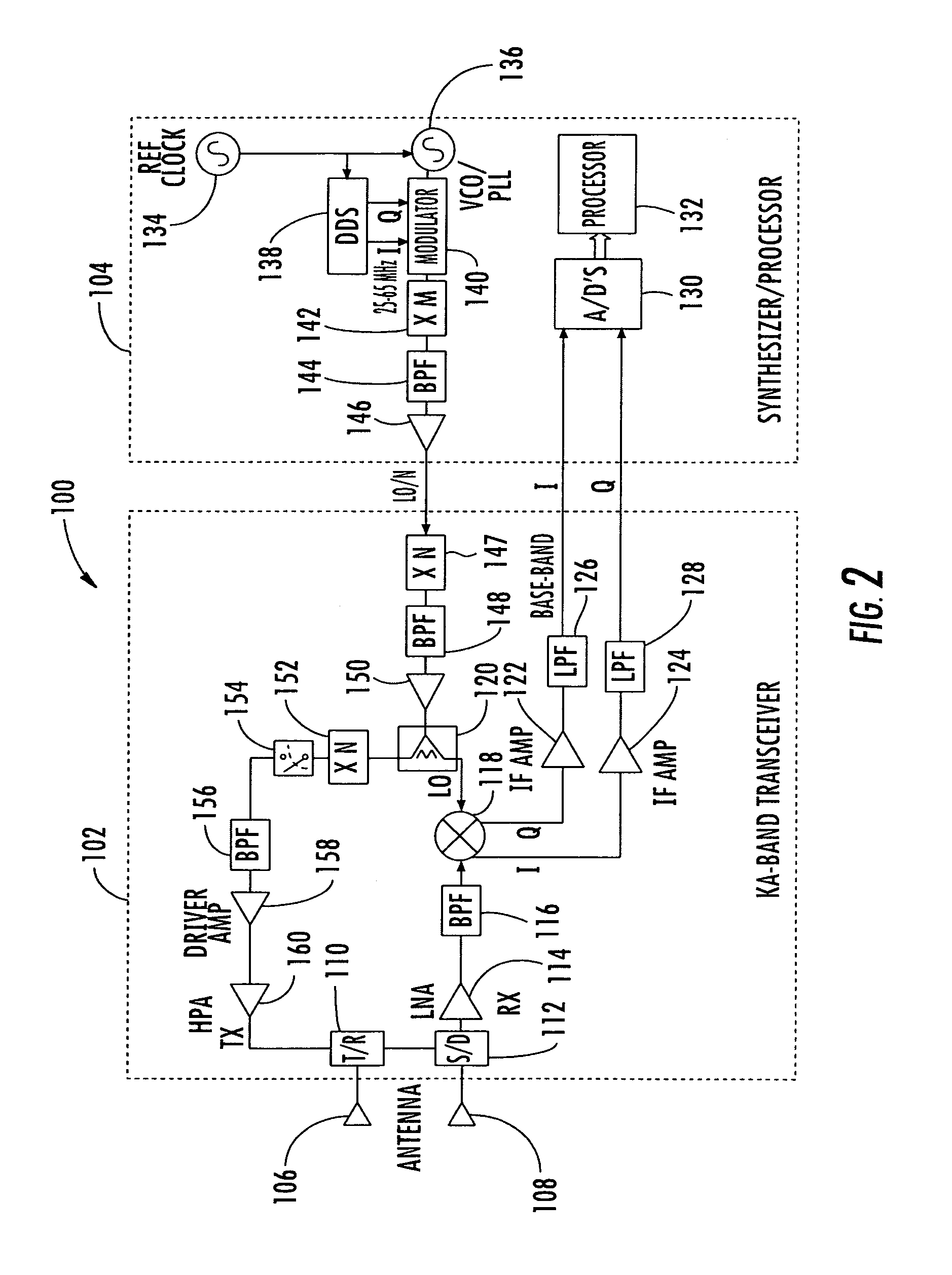
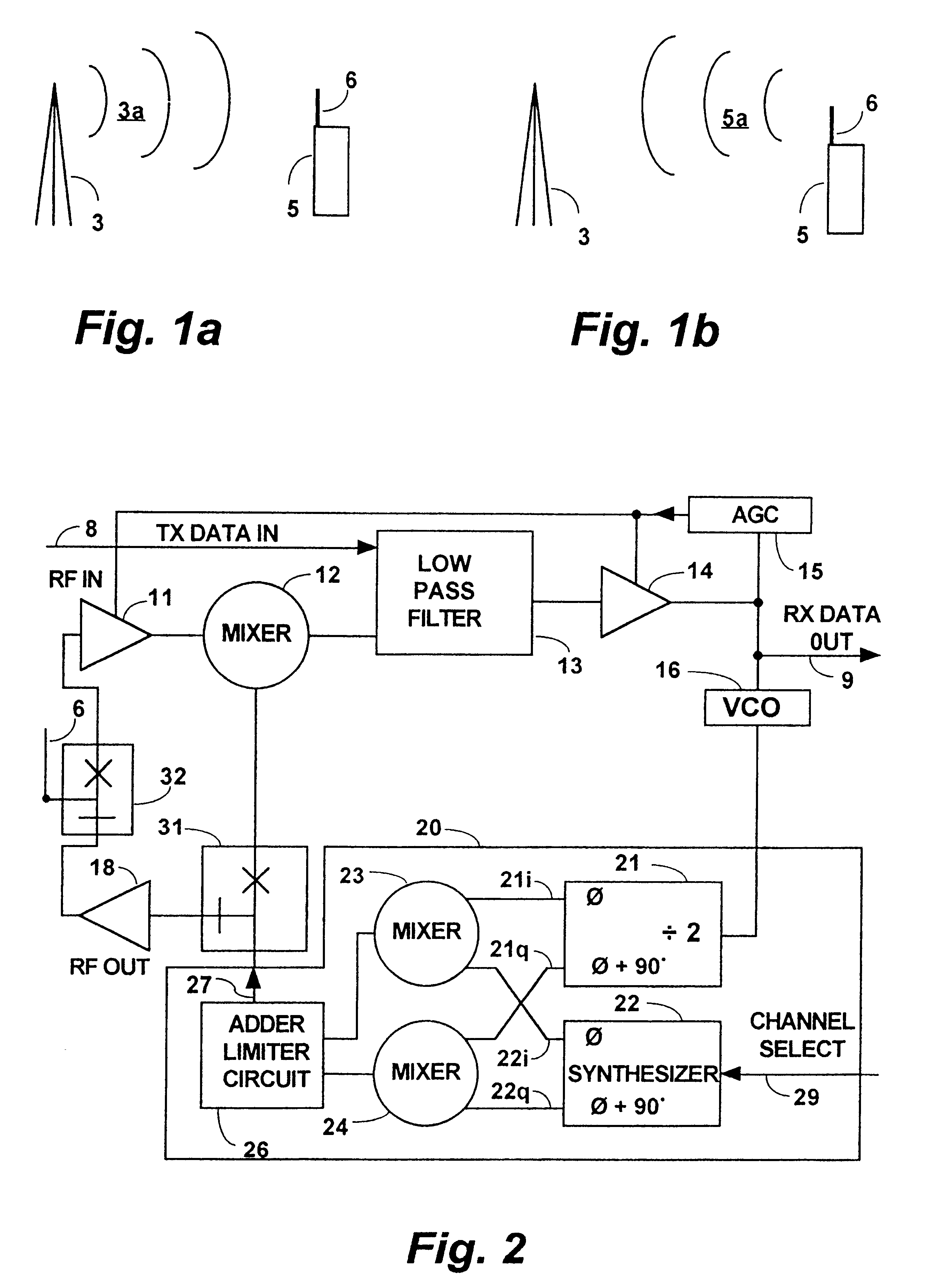
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
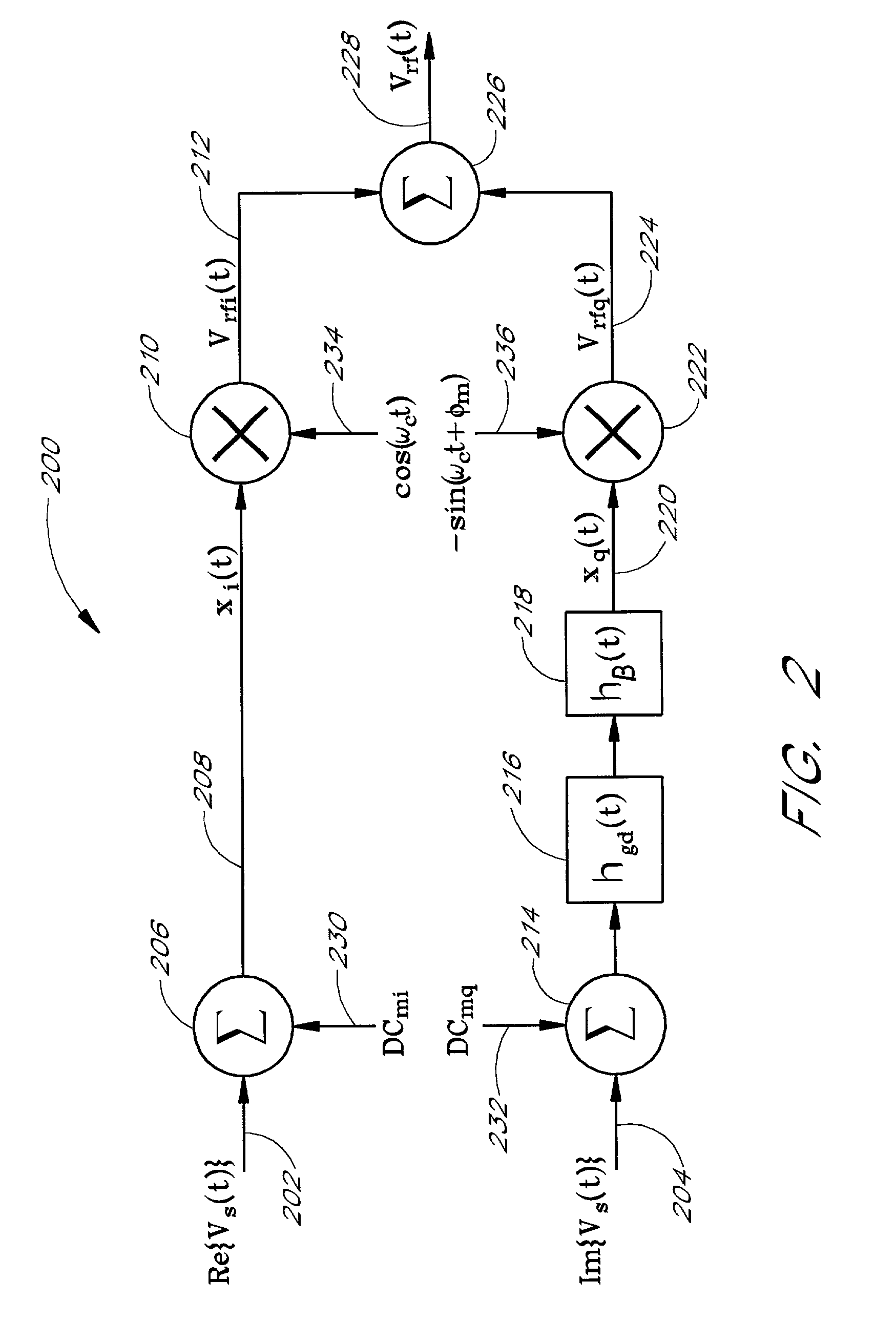
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
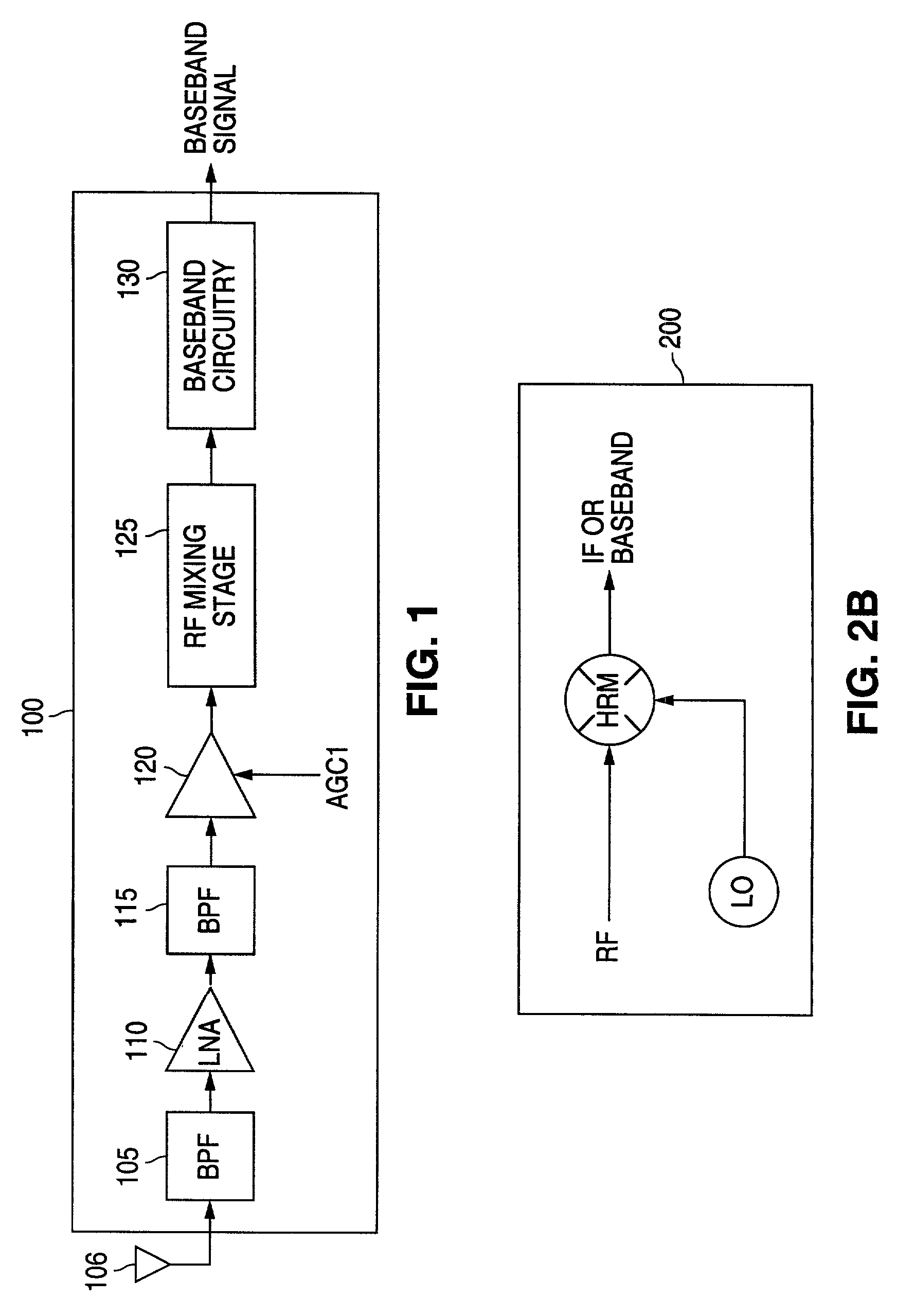
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
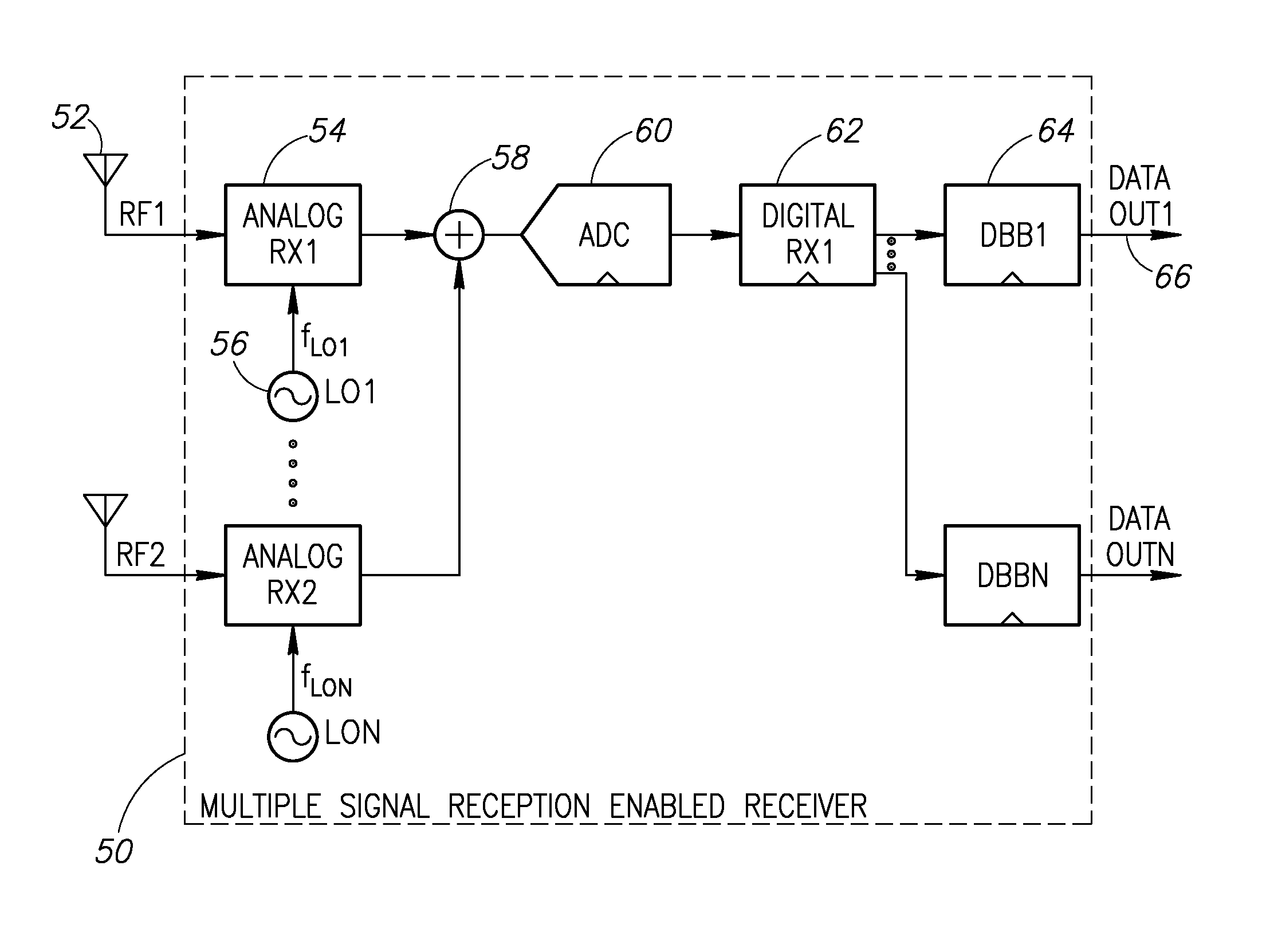
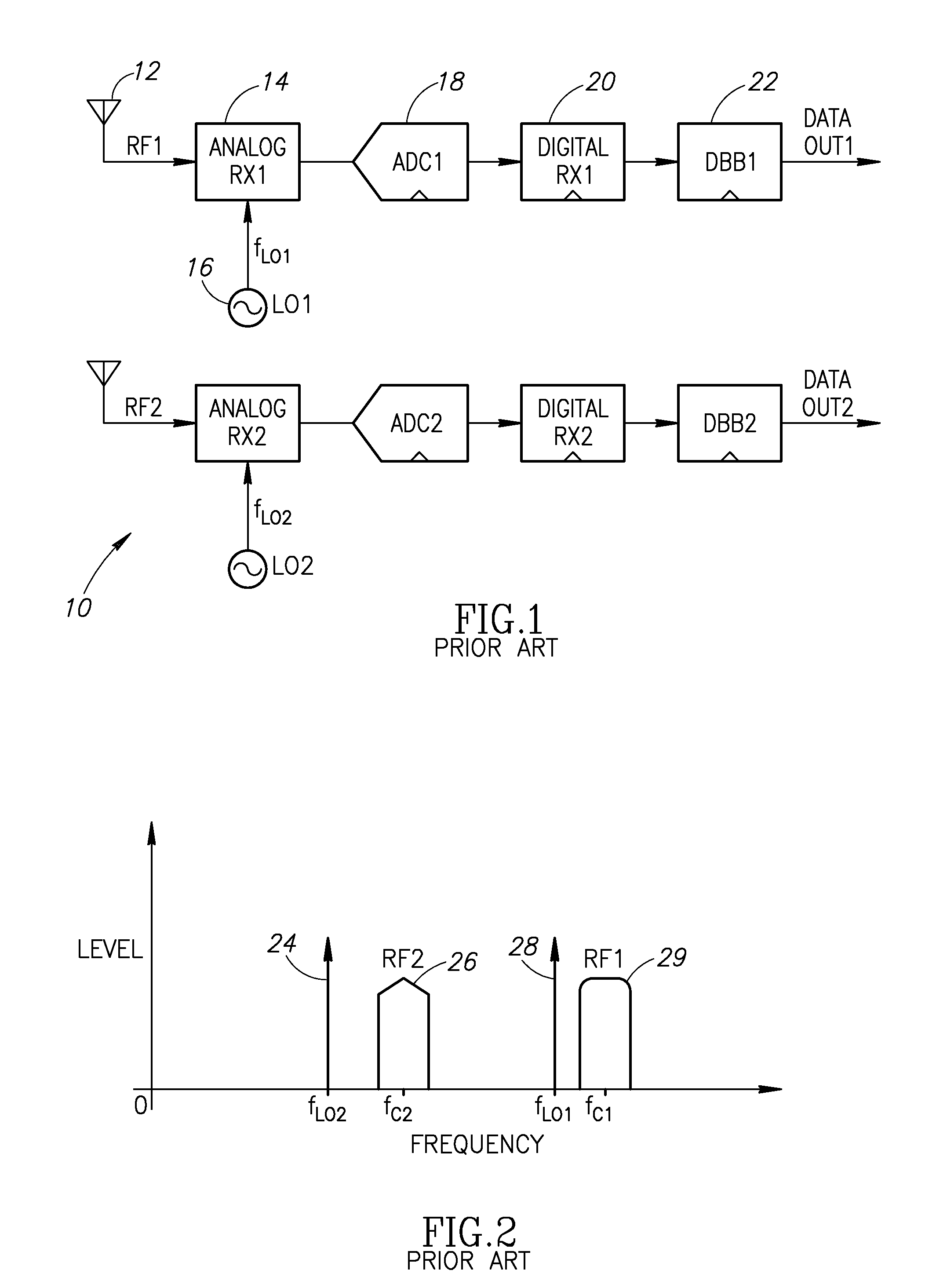
Simultaneous multiple signal reception and transmission using frequency multiplexing and shared processing
ActiveUS20100091688A1Reduce total powerReduce spacingModulation transferenceModulated-carrier systemsDigital signal processingMultiplexing
A novel mechanism for simultaneous multiple signal reception and transmission using frequency multiplexing and shared processing. Multiple RF signals, which may be of various wireless standards, are received using one or more shared processing blocks thereby significantly reducing chip space and power requirements. Shared components include local oscillators, analog to digital converters, digital RX processing and digital baseband processing. In operation, multiple RX front end circuits, one for each desired wireless signal, generate a plurality of IF signals that are frequency multiplexed and combined to create a single combined IF signal. The combined IF signal is processed by a shared processing block. Digital baseband processing is performed on each receive signal to generate respective data outputs. Further, simultaneous full-duplex transmission and reception is performed using a single local oscillator. The phase / frequency modulation of the frequency synthesizer used in the TX is removed from the local oscillator signal for use in the receiver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
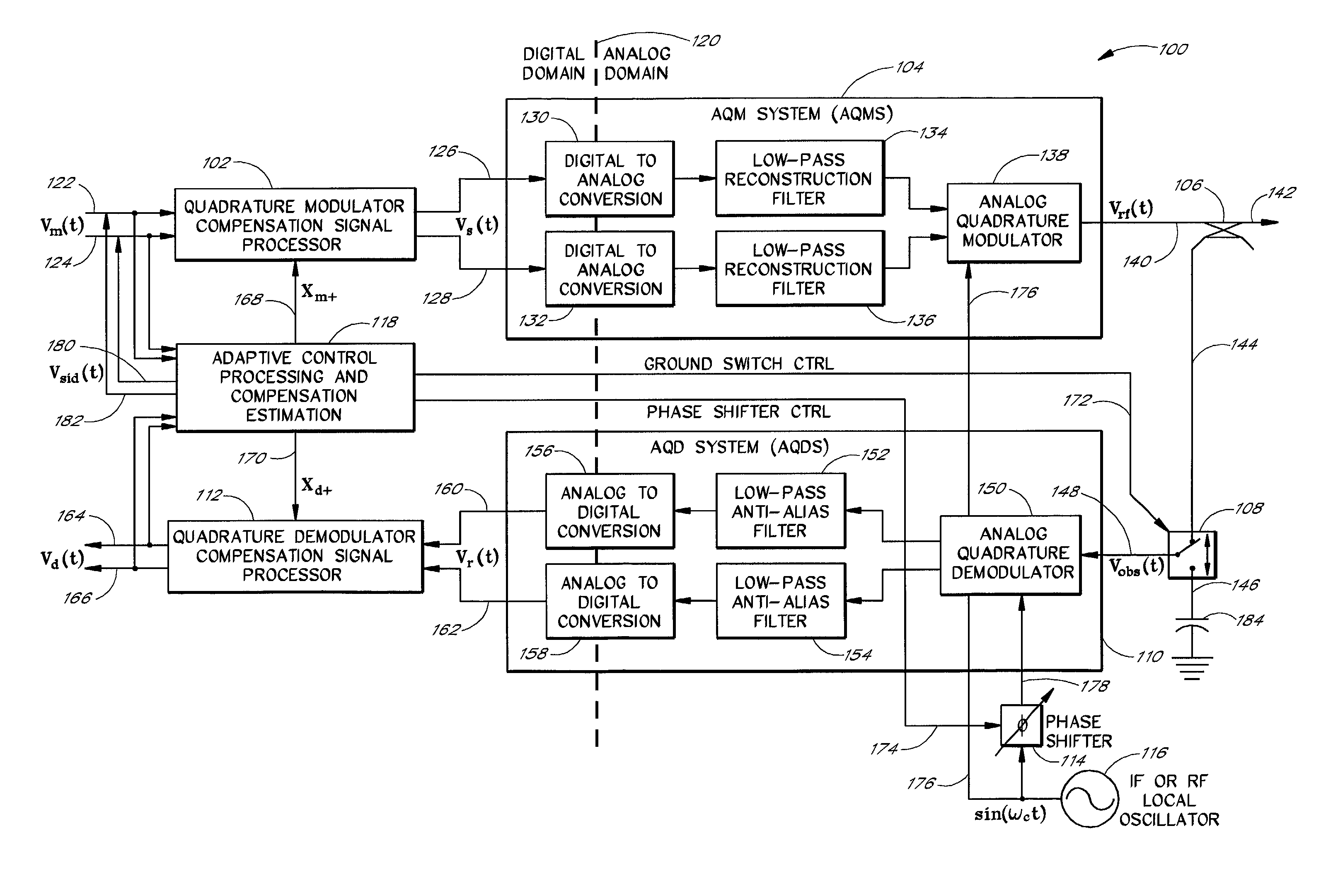
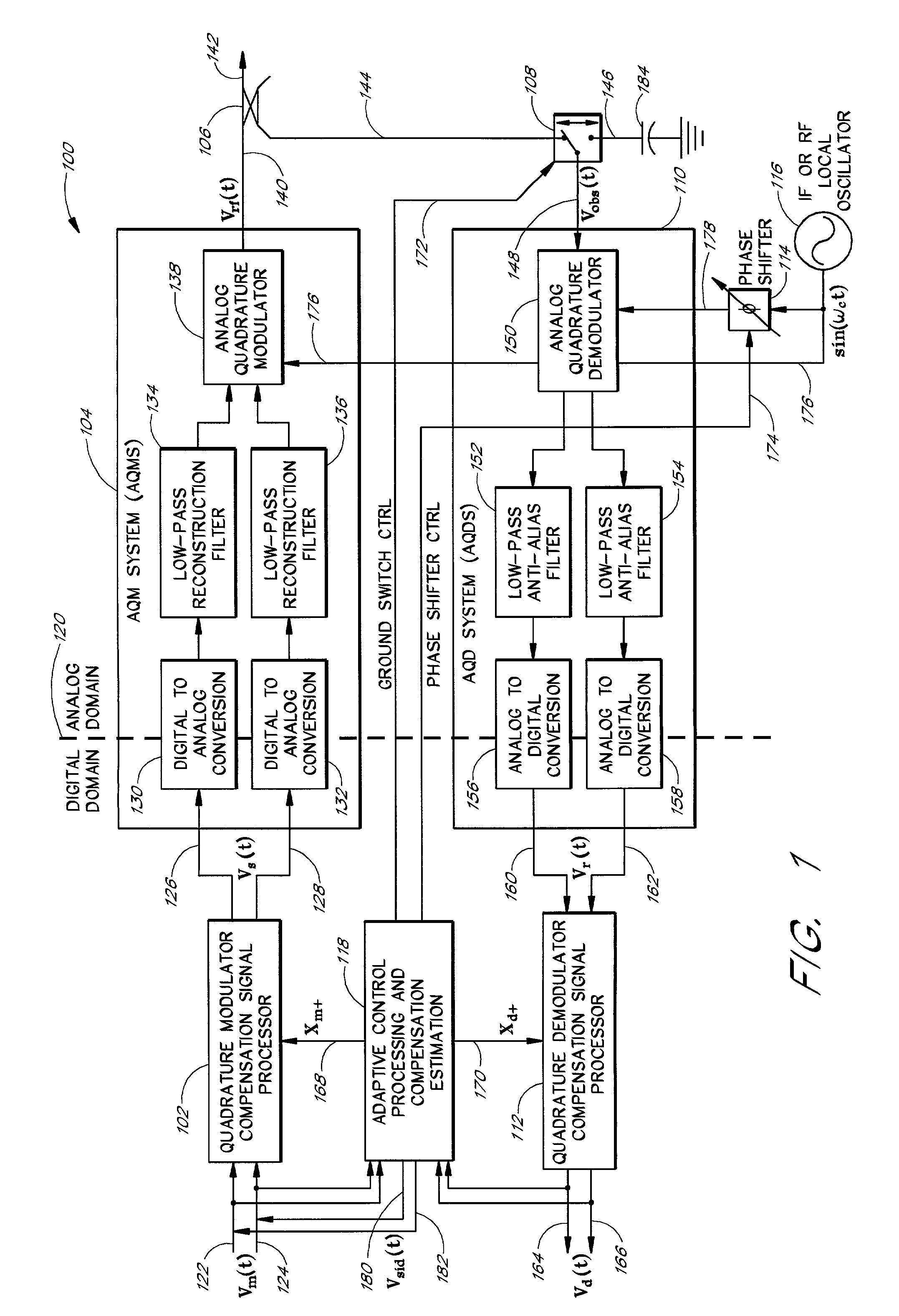
Wideband analog quadrature modulator/demodulator with pre-compensation/post-compensation correction
ActiveUS6940916B1Reduce errorsImproved performance characteristicsCarrier regulationMultiple carrier systemsQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
The present invention is related to methods and apparatus that compensate for quadrature impairments of an analog quadrature modulator and / or demodulator over a relatively wide signal bandwidth. One embodiment pre-distorts baseband signals in a quadrature modulator compensation signal processor (QMCSP) to negate the quadrature impairment of an analog quadrature modulator and corrects a received baseband signal in a quadrature demodulator compensation signal processor (QDCSP) to cancel the quadrature impairment of an analog quadrature demodulator. The QMCSP and the QDCSP contain adaptive digital filter correction structures that pre-compensate and post-compensate, respectively, for the quadrature impairments introduced by the analog quadrature modulator and the analog quadrature demodulator over a relatively wide bandwidth. A phase shifter advantageously shifts the phase of a local oscillator signal to the analog quadrature demodulator to distinguish quadrature impairments introduced by the modulation path from quadrature impairments introduced by the demodulation path.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
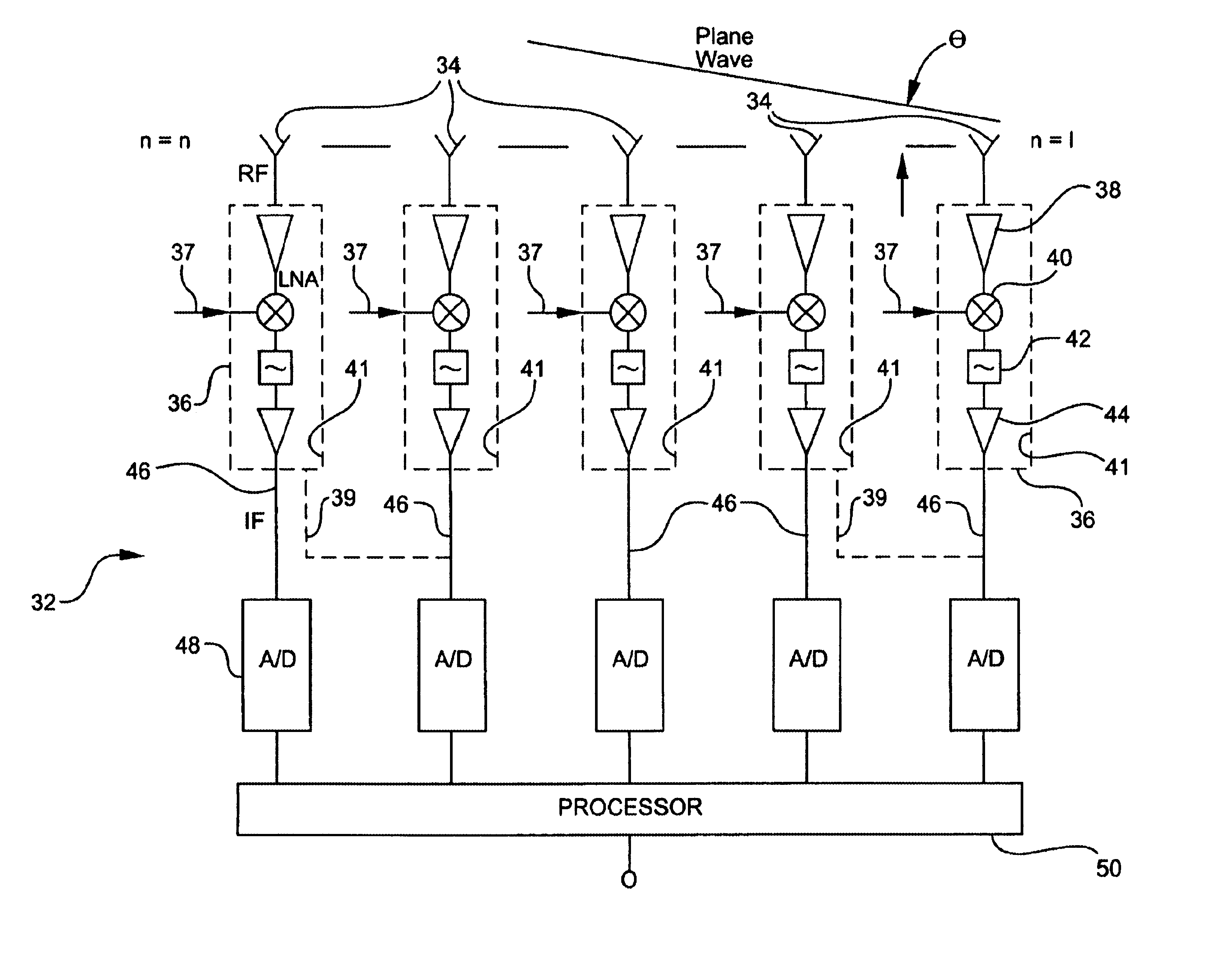
Digital beamforming radar system
InactiveUS6882311B2Less spaceEasy to manufactureModular arraysTransmissionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
A receiver for a digital beamforming radar system includes a plurality of antenna elements, low-noise block converters, one or more analog-to-digital converters, and a processor. The antenna elements receive a radar signal and output a received signal. The low-noise block converters are modified commercially available components used in satellite television systems, respond to the received signal from a corresponding antenna element, and output an intermediate frequency signal. The low-noise block converters include at least one amplifier, a mixer, and a local oscillator input. The local oscillator input enables an external local oscillator signal to be inputted to the mixer. The analog-to-digital converters are responsive to the intermediate frequency signal of a corresponding low-noise block converter. The processor is responsive to the digital signals output by the analog-to-digital converters.
Owner:COMM & POWER IND
Harmonic rejection mixer and method of operation
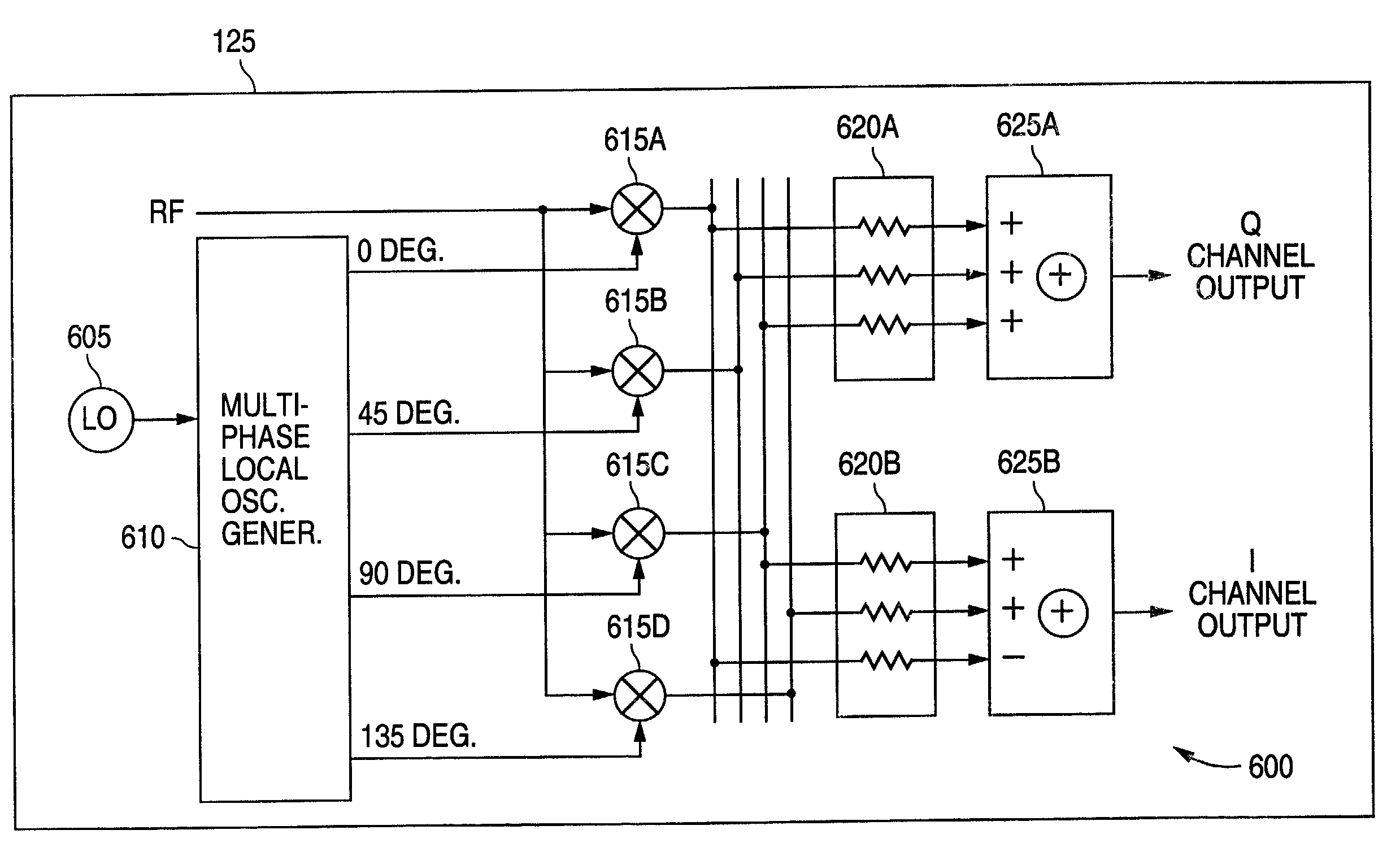
InactiveUS7130604B1Suppress unwanted responseSuperb suppressionModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesTransmissionPhase shiftedLocal oscillator signal
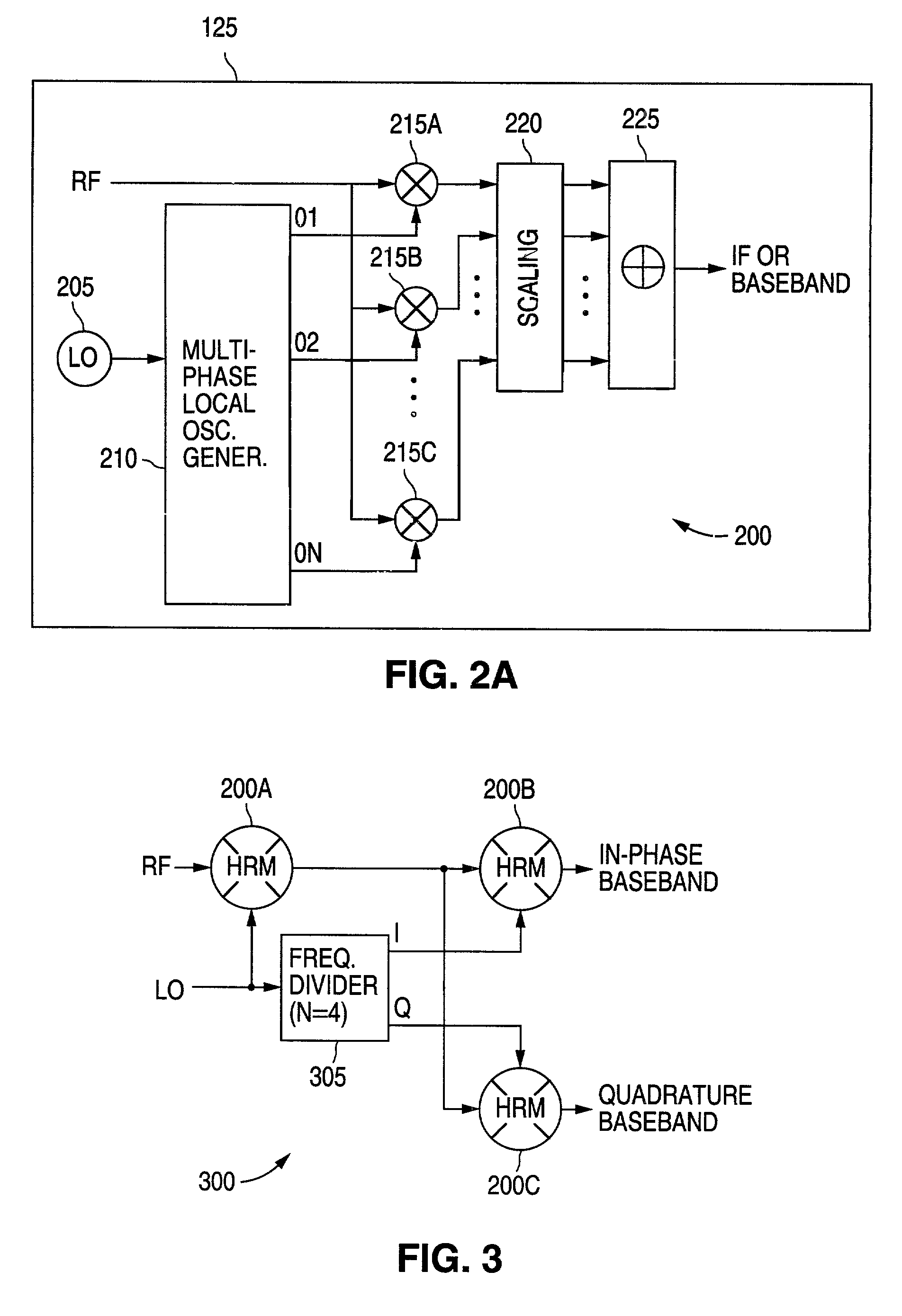
A radio frequency (RF) demodulation circuit comprising a harmonic rejection mixing stage capable of receiving and mixing an incoming radio frequency (RF) signal having a frequency RF and a reference local oscillator (LO) signal having a frequency LO and generating an output signal in which out-of-band harmonic signals are suppressed. The harmonic rejection mixing stage comprises 1) a multiphase local oscillator (LO) generator for receiving the reference LO signal and generating M phase-shifted local oscillator signals having frequencies LO and 2) M mixers, each of the M mixers receiving the incoming radio frequency signal and one of the M phase-shifted local oscillator signals. Each of the M mixers generates a subcomponent signal. The subcomponent signals are then scaled and combined to produce the output signal.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Radio system including mixer device and switching circuit and method having switching signal feedback control for enhanced dynamic range and performance
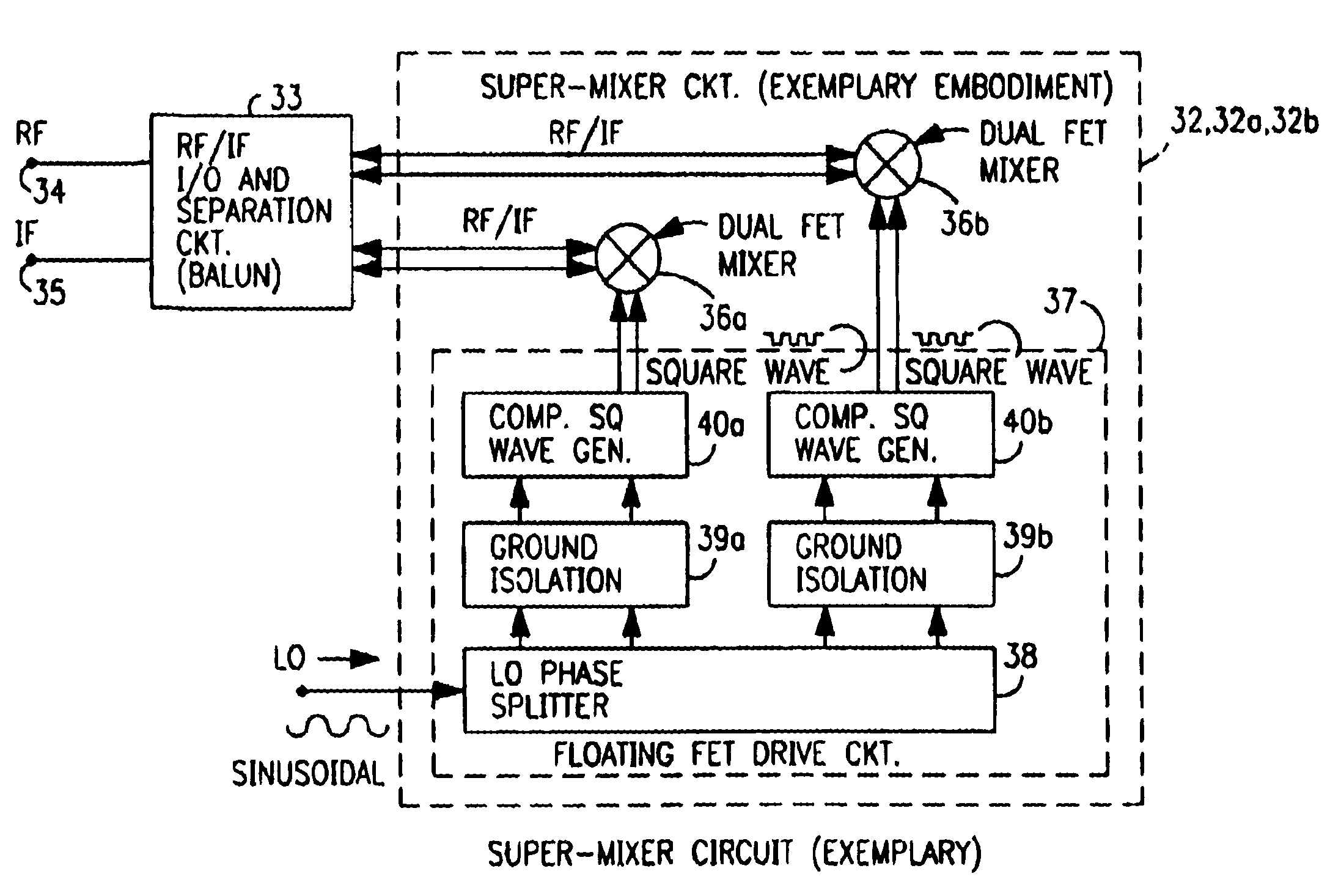
InactiveUS6654595B1Modulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsFrequency changerLocal oscillator signal
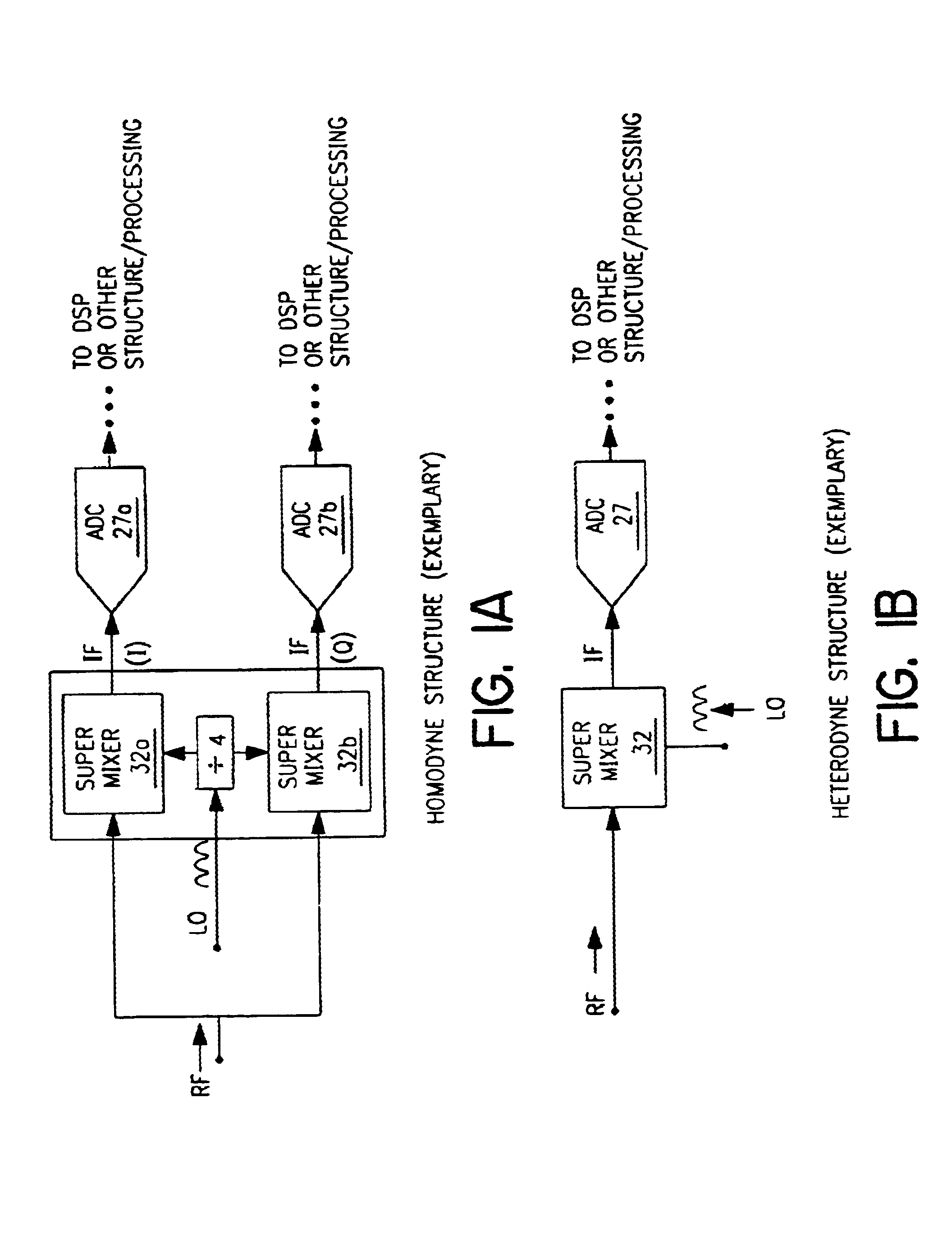
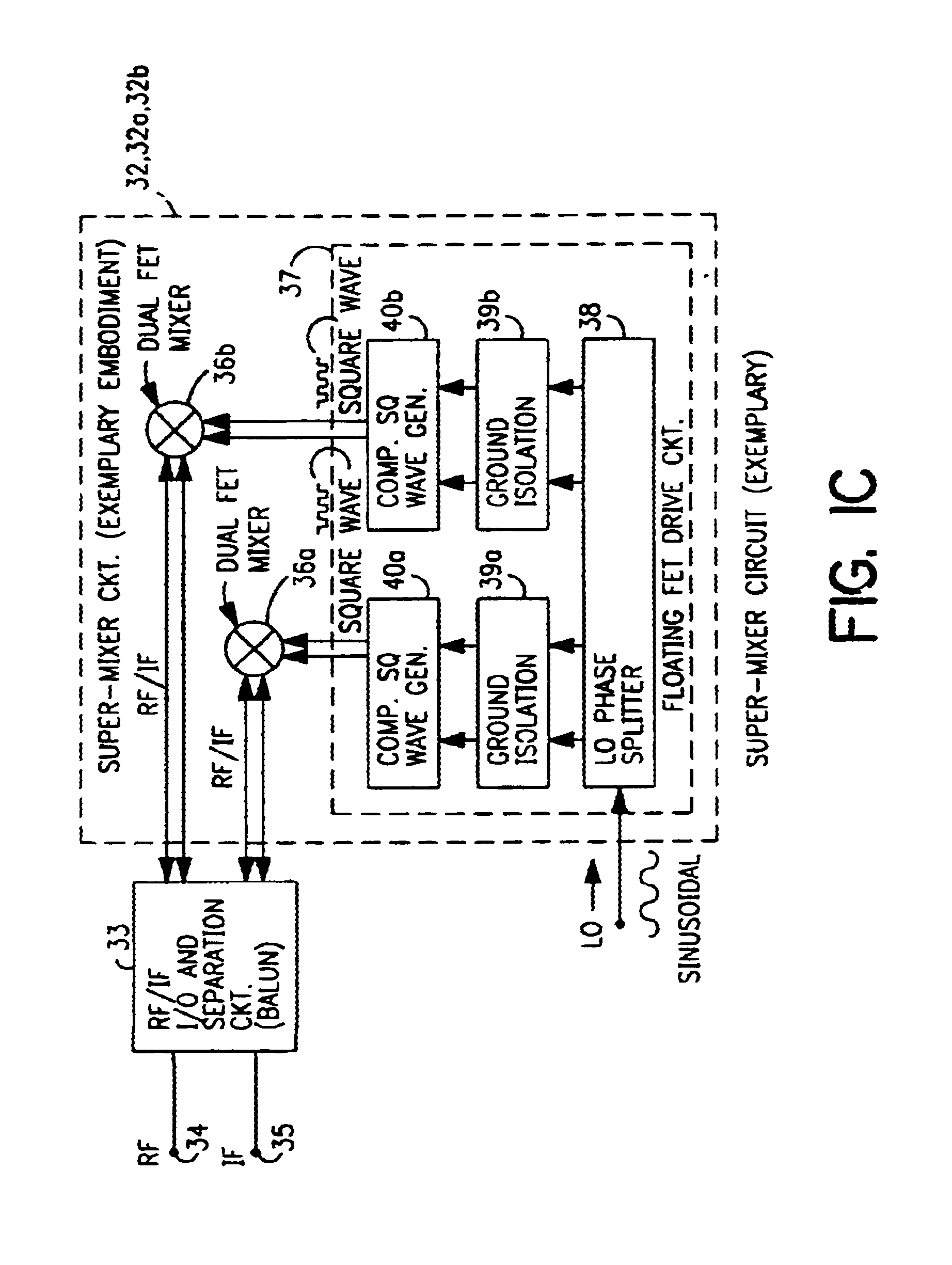
Radio system including mixer device and switching circuit and method having switching signal feedback control for enhanced dynamic range and performance. Radio apparatus including: local oscillator input port for receiving periodic sinusoidal local oscillator signal; drive circuit for generating a substantially square-wave two-voltage level switching signal including: phase splitter circuit, voltage potential isolation circuit, and square wave signal generation circuit; FET mixing device; input / output signal separation circuit; analog-to-digital converter; and feedback control circuit. Radio tuner apparatus including low-band signal processing circuit; high-band signal processing circuit including first mixer circuit operating as an up-frequency converter, amplifier circuit, second mixer circuit operating as a down-frequency converter, and feedback control circuit for adjusting a duty cycle of a mixer switching device; signal combining circuit and output processing circuit. Method for operating radio system, apparatus, and tuner. Method of operating switching circuit.
Owner:BAE SYST AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS
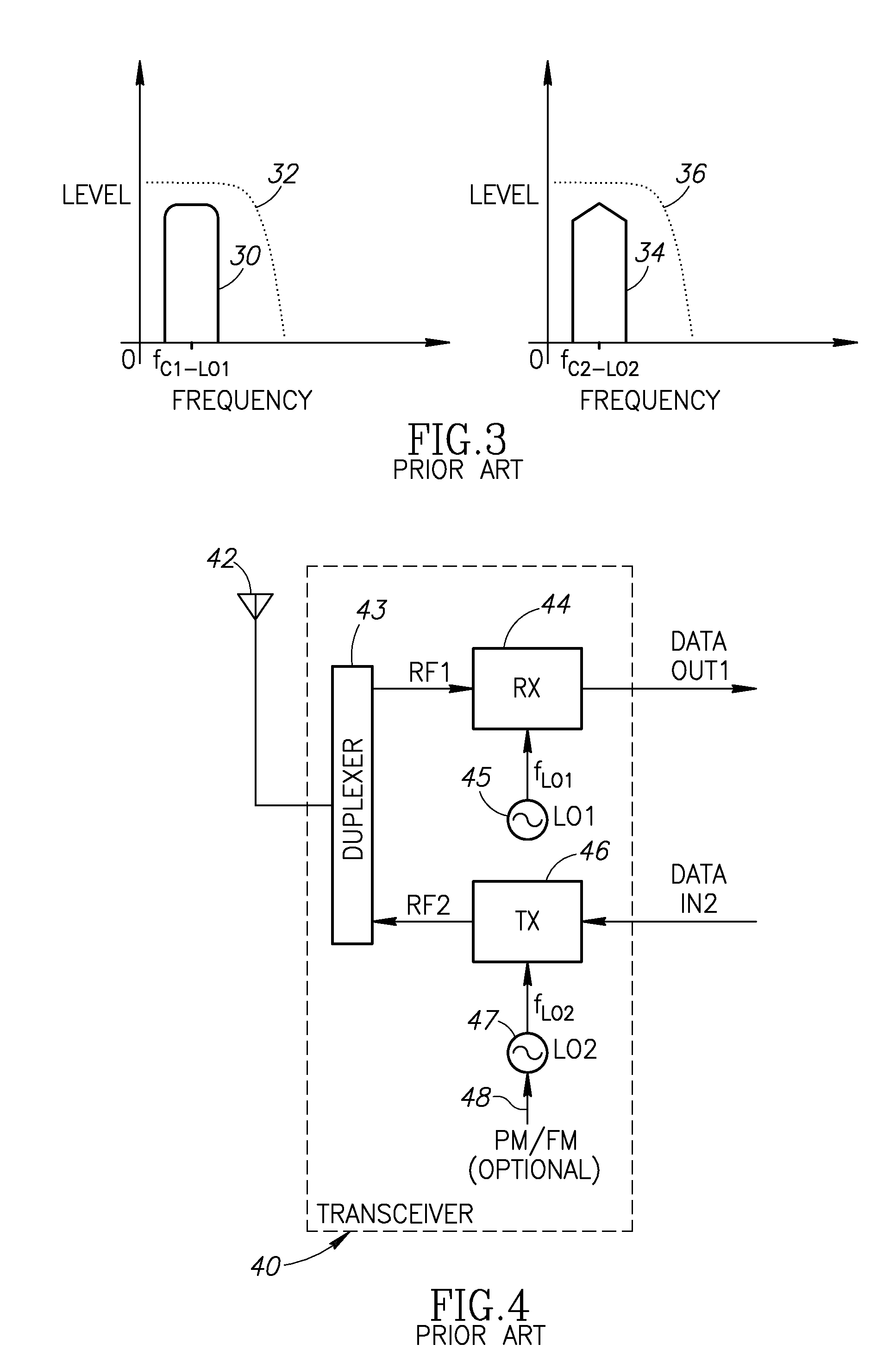
Radio frequency control for communication systems
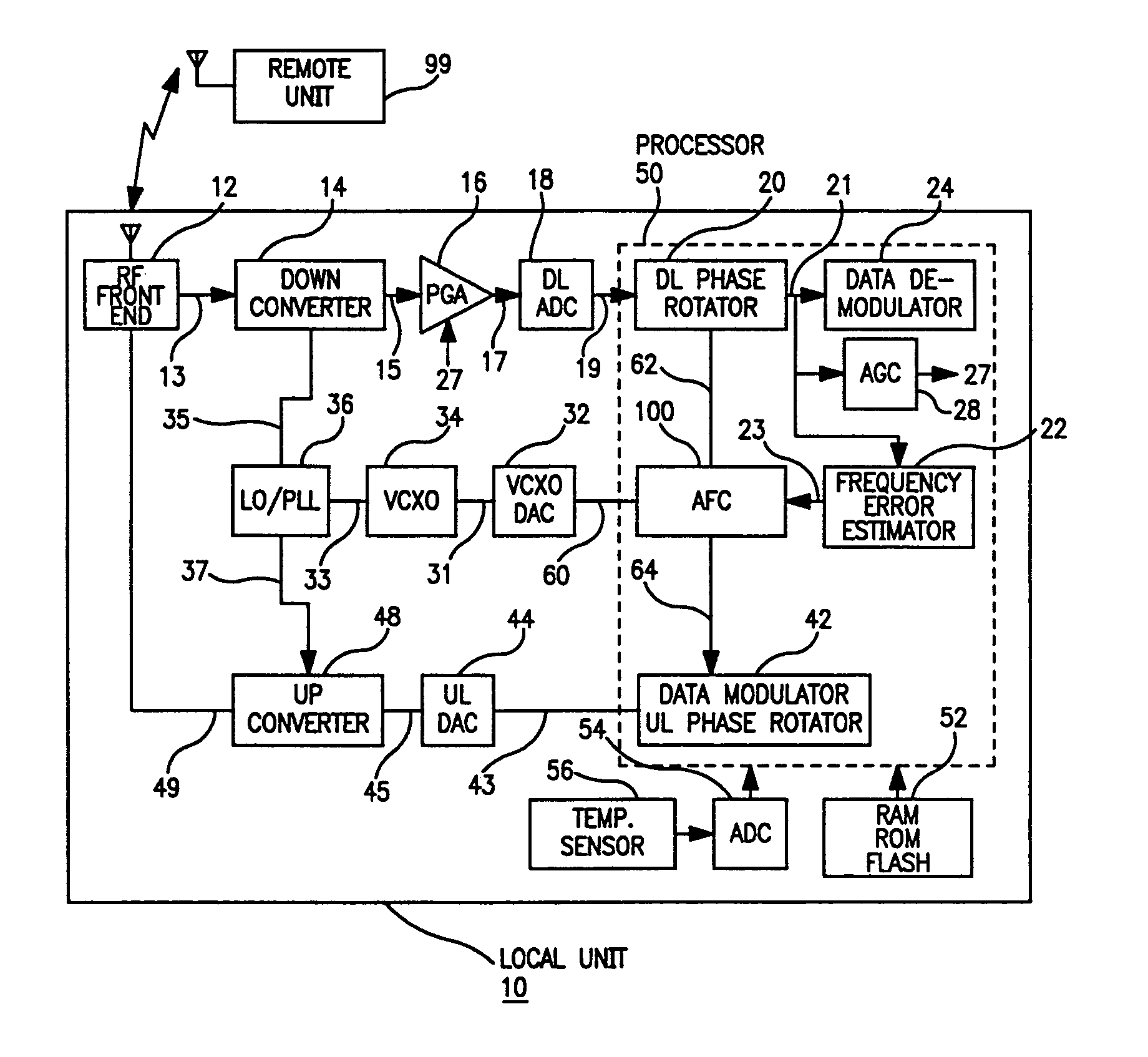
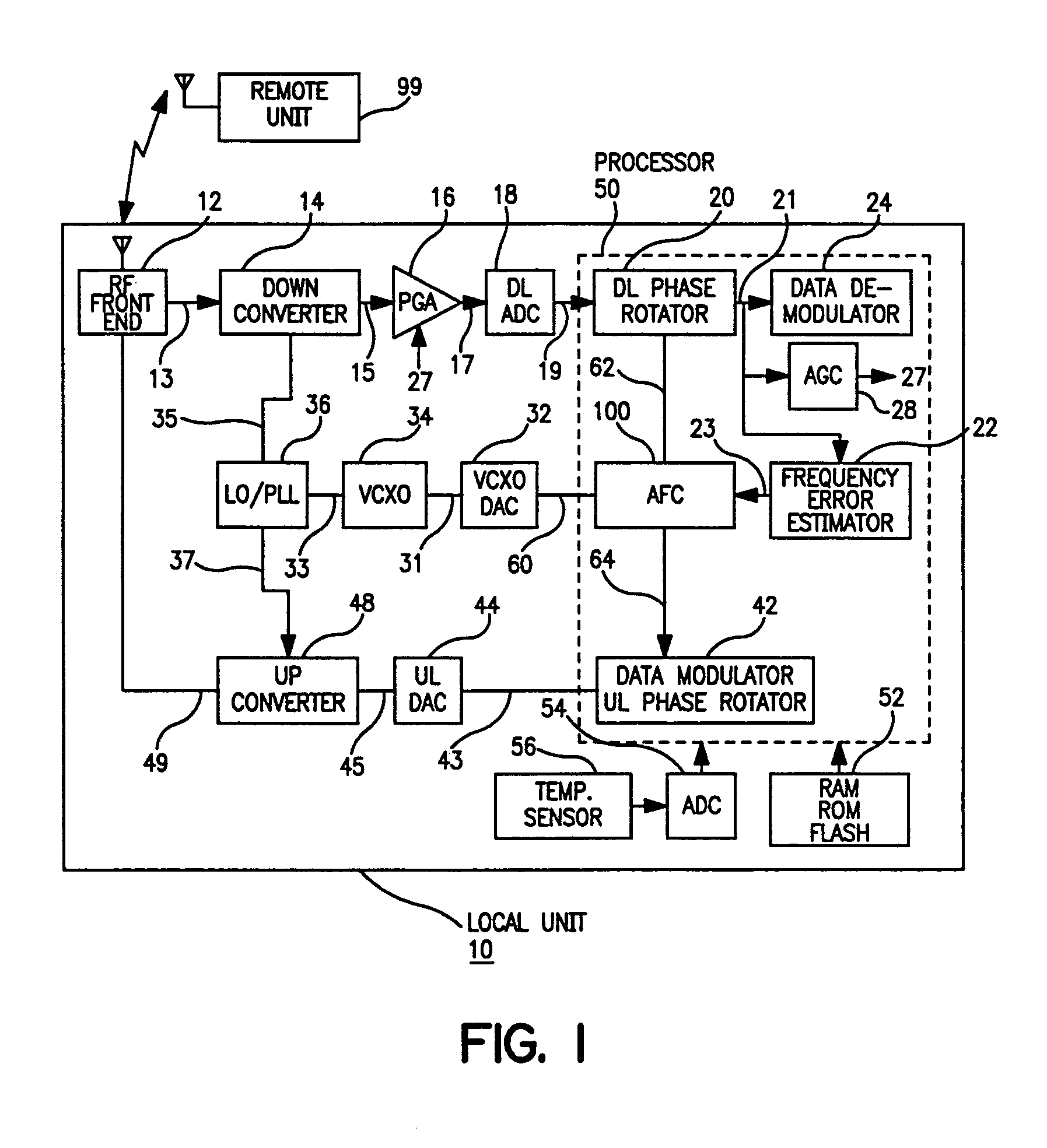
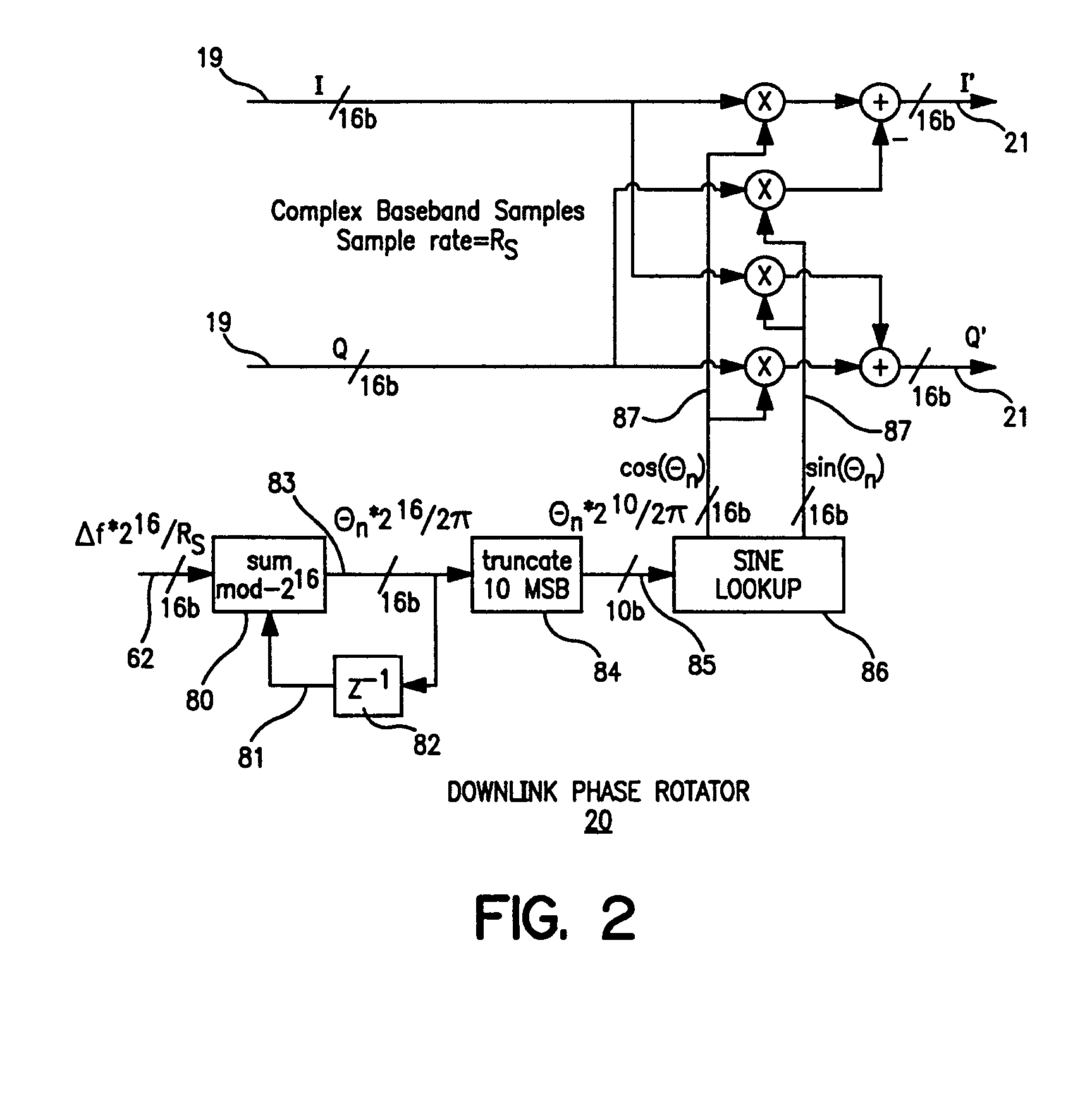
InactiveUS20050078743A1Low costHigh resolutionModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionDigital dataLocal oscillator signal
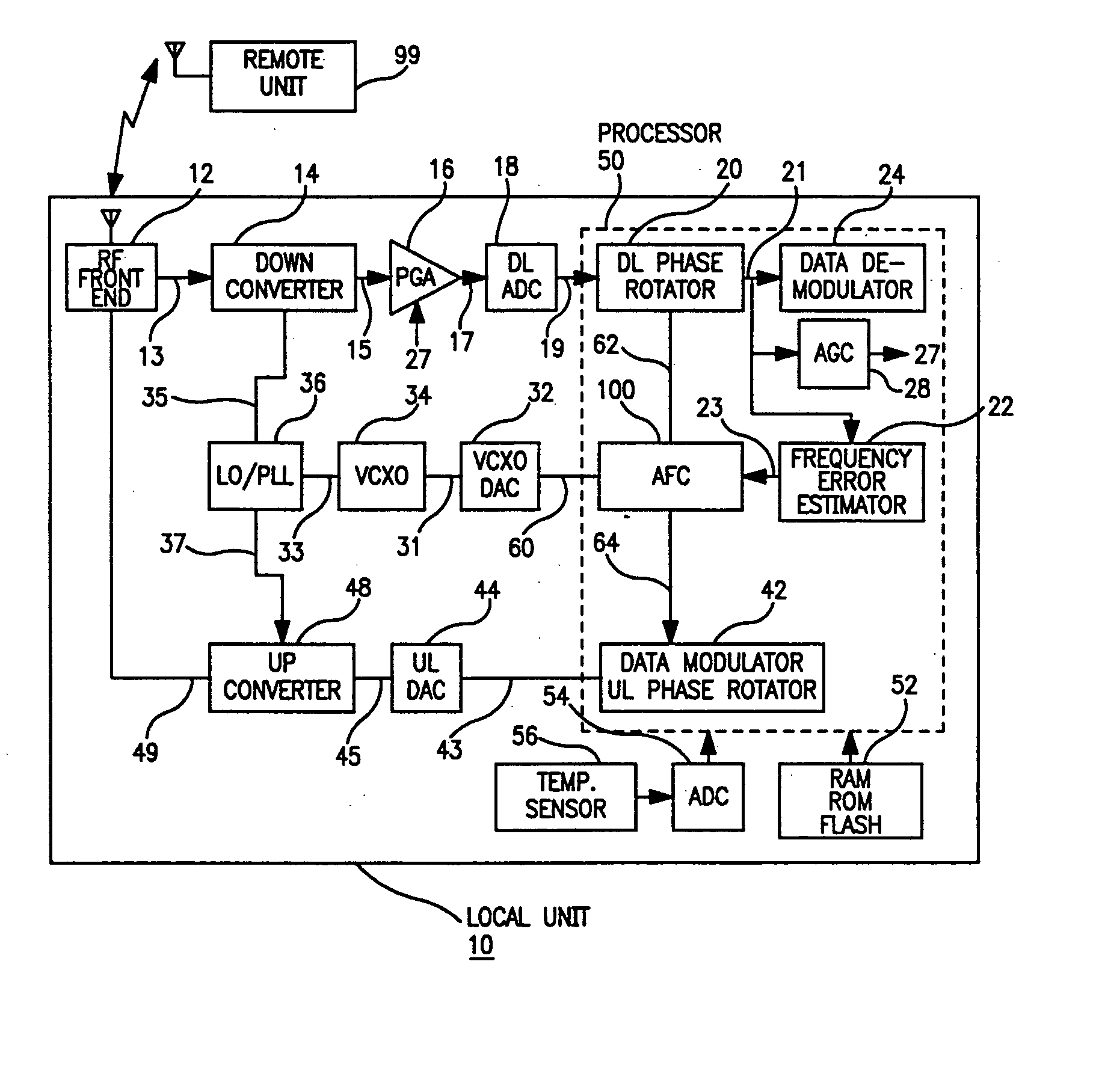
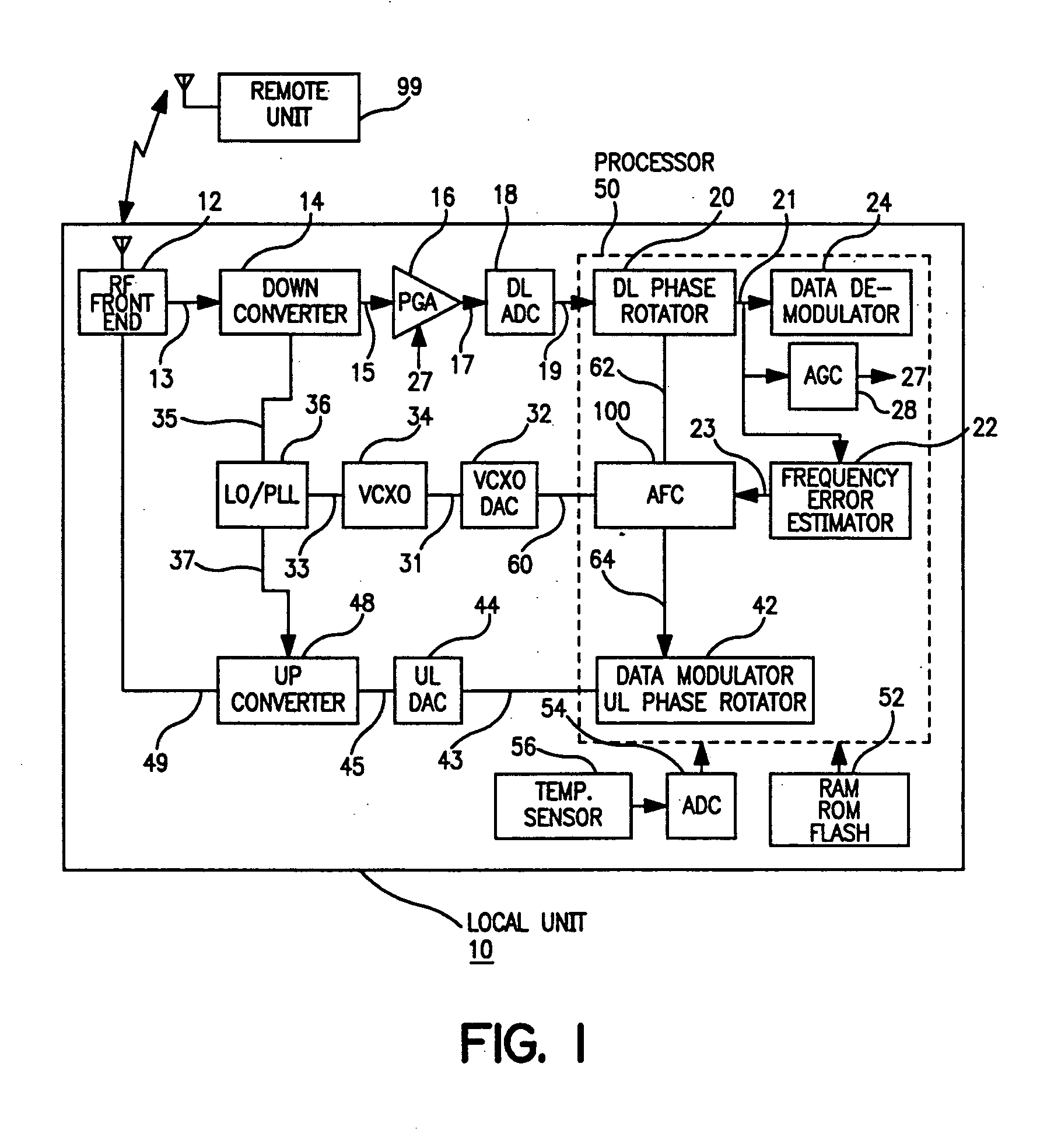
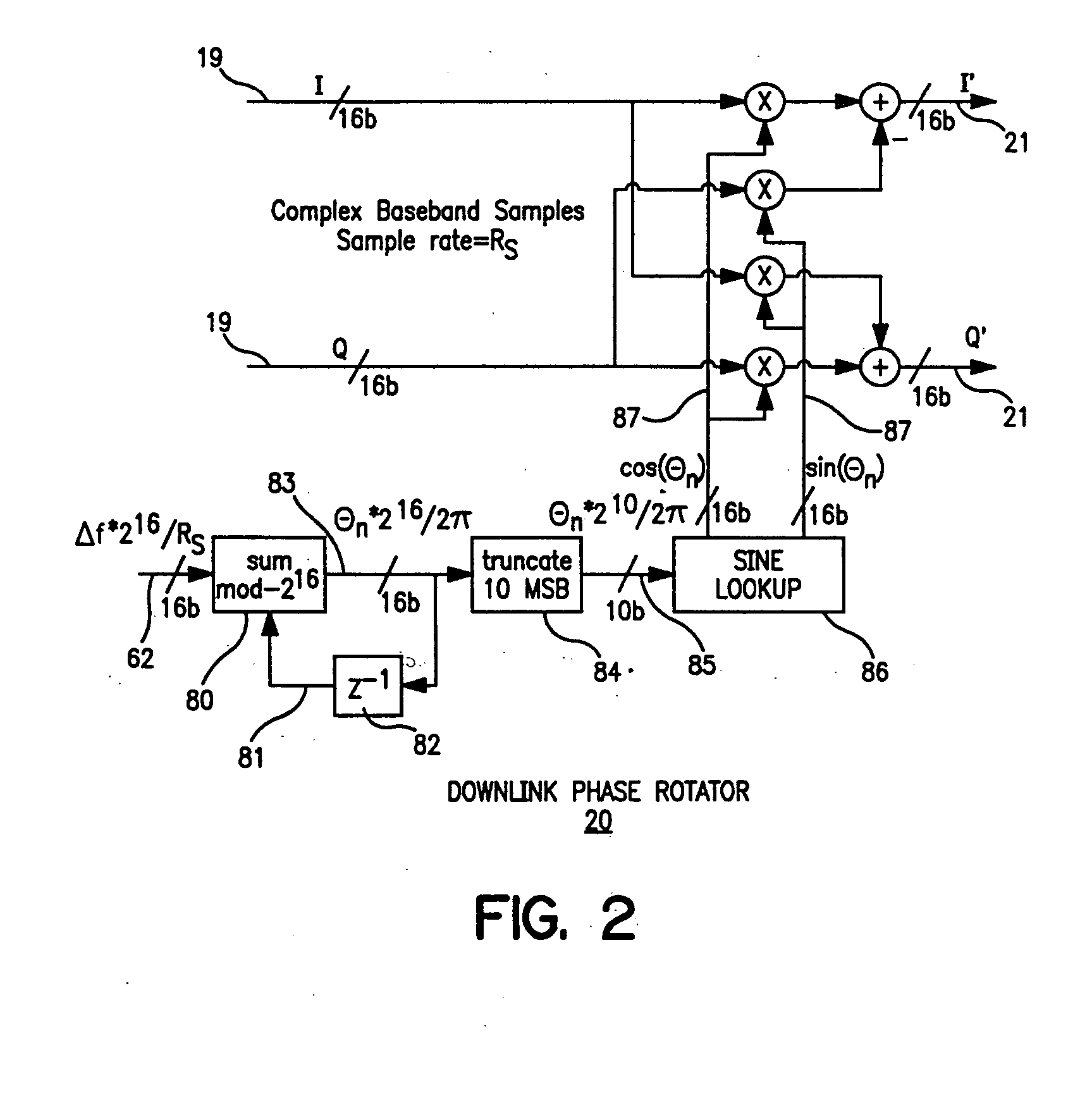
The present invention provides for a system and method for improvement of radio transmitter and receiver frequency accuracy for a local radio communication unit that communicates digital data with a remote communication unit. In the local unit the received radio signal is down-converted, and converted to complex baseband digital samples by an analog-to-digital converter. A downlink digital phase rotator applies a fine frequency shift to the samples in accordance with a receiver frequency offset command. The resultant baseband signal is used by the data demodulator and by a receiver frequency error estimator to obtain receiver frequency errors. A data modulator generates baseband complex samples which are shifted in carrier frequency by an integrated uplink digital phase rotator in accordance with a transmitter frequency offset command. The modulated samples are then converted by a digital-to-analog converter and upconverted in frequency for radio transmission to the remote unit. The local oscillator signals for both upconverter and downconverter are phase locked to a reference frequency generated by a VCXO. An automatic frequency control (AFC) function nulls the transmitter and receiver frequency error by the frequency adjustment commands to the uplink and downlink phase rotators or to the VCXO digital-to-analog converter (VCXO DAC) by feedback control principals based on measured receiver frequency error. During frequency track mode when communications between local and remote units are possible, the AFC only adjusts radio frequency via phase rotator commands and the VCXO command remains fixed, thereby avoiding communications performance degradation by VCXO frequency quantization error due to the VCXO DAC. The AFC adjusts VCXO frequency only during a preliminary acquisition mode prior to data communications, or to back out excessively large frequency offsets accumulated in the downlink and uplink phase rotators during track mode. When a VCXO adjustment is made in track mode, phase rotator adjustments are simultaneously applied to cancel the errors in transmitter and receiver radio frequencies caused by the step change due to VCXO frequency quantization thereby mitigating VCXO frequency quantization noise.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
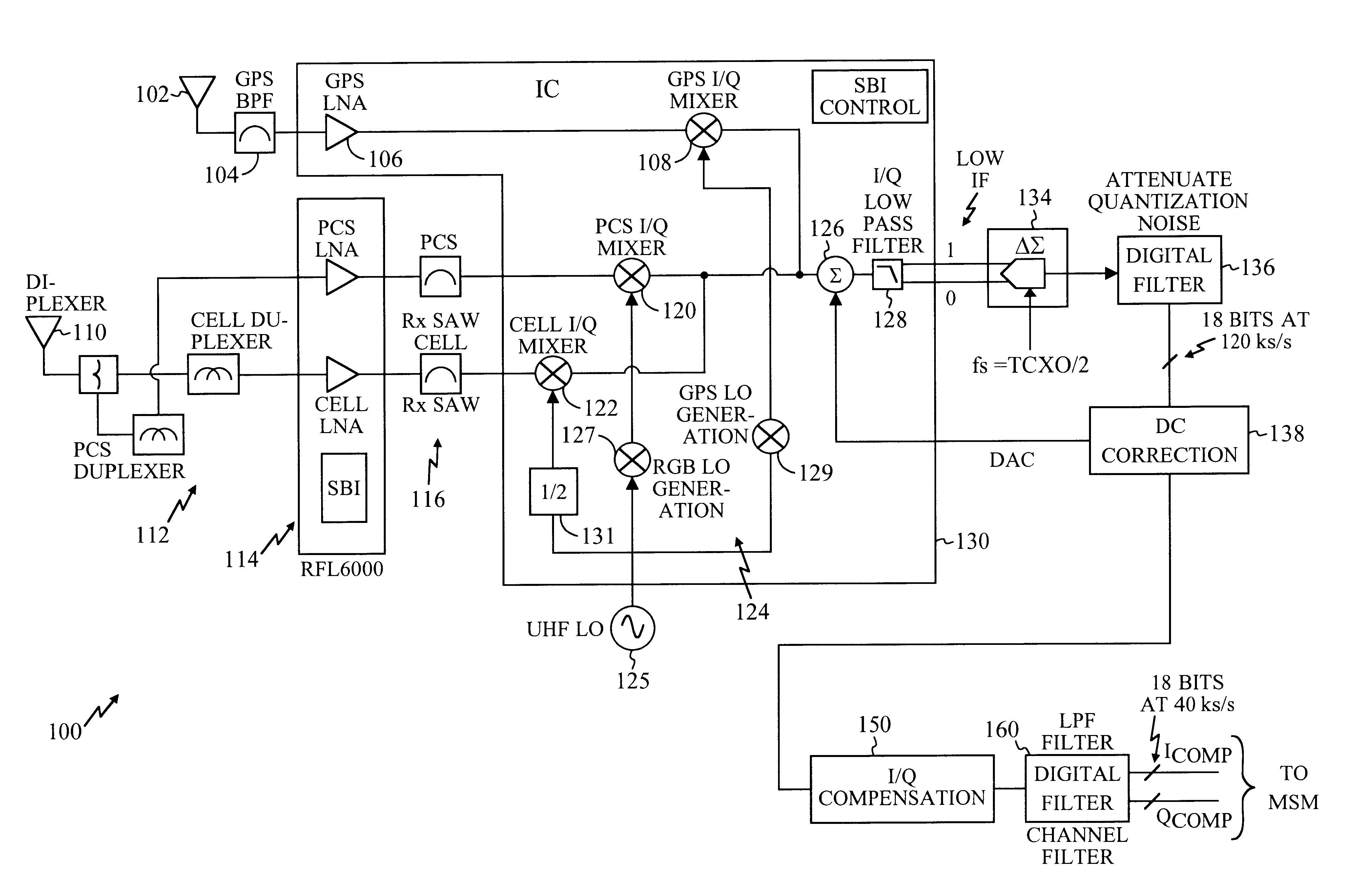
System and method for I-Q mismatch compensation in a low IF or zero IF receiver
InactiveUS6785529B2Modulated-carrier systemsAngle demodulation by oscillations conversionLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Optical mixer for coherent detection of polarization-multiplexed signals
InactiveUS20100158521A1Data recoveryPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversLocal oscillator signalBeam splitter
An optical mixer that, in one embodiment, has a single optical hybrid optically coupled to a single polarization beam splitter. The optical hybrid mixes a polarization-multiplexed optical communication signal and a local-oscillator signal to generate four mixed signals, each corresponding to a different relative phase shift between the communication and local-oscillator signals. The polarization beam splitter separates each of the mixed signals into two polarization components, subsequent processing of which enables an optical receiver employing the optical mixer to recover the data carried by the communication signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Direct conversion receiver
In a frequency modulation radio receiver with direct conversion, a local oscillator signal is generated having a frequency within a preselected frequency range and the frequency is varied in response to a variable low frequency signal; the local oscillator signal is mixed with a received signal to provide a baseband signal. The variable low frequency signal is generated by a controlled oscillator in inverse relationship to a direct current component in said baseband signal. In a frequency modulation radio transceiver a broadcast function is provided by varying the low frequency signal with an information signal with the resulting local oscillator frequency being varied accordingly and amplified for broadcast. The transceiver is controlled to operate alternately in either a receive mode and a broadcast mode at substantially the same frequency. While in the receive mode the controlled oscillator causes the local oscillator signal to be drawn toward the carrier frequency of a received signal yielding preferred direct conversion of modulating information into the base band.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
Radio frequency control for communication systems
InactiveUS6985705B2Low costHigh resolutionPulse automatic controlModulated-carrier systemsDigital dataLocal oscillator signal
The present invention provides for a system and method for improvement of radio transmitter and receiver frequency accuracy for a local radio communication unit that communicates digital data with a remote communication unit. In the local unit the received radio signal is down-converted, and converted to complex baseband digital samples by an analog-to-digital converter. A downlink digital phase rotator applies a fine frequency shift to the samples in accordance with a receiver frequency offset command. The resultant baseband signal is used by the data demodulator and by a receiver frequency error estimator to obtain receiver frequency errors. A data modulator generates baseband complex samples which are shifted in carrier frequency by an integrated uplink digital phase rotator in accordance with a transmitter frequency offset command. The modulated samples are then converted by a digital-to-analog converter and upconverted in frequency for radio transmission to the remote unit. The local oscillator signals for both upconverter and downconverter are phase locked to a reference frequency generated by a VCXO. An automatic frequency control (AFC) function nulls the transmitter and receiver frequency error by the frequency adjustment commands to the uplink and downlink phase rotators or to the VCXO digital-to-analog converter (VCXO DAC) by feedback control principals based on measured receiver frequency error. During frequency track mode when communications between local and remote units are possible, the AFC only adjusts radio frequency via phase rotator commands and the VCXO command remains fixed, thereby avoiding communications performance degradation by VCXO frequency quantization error due to the VCXO DAC. The AFC adjusts VCXO frequency only during a preliminary acquisition mode prior to data communications, or to back out excessively large frequency offsets accumulated in the downlink and uplink phase rotators during track mode. When a VCXO adjustment is made in track mode, phase rotator adjustments are simultaneously applied to cancel the errors in transmitter and receiver radio frequencies caused by the step change due to VCXO frequency quantization thereby mitigating VCXO frequency quantization noise.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
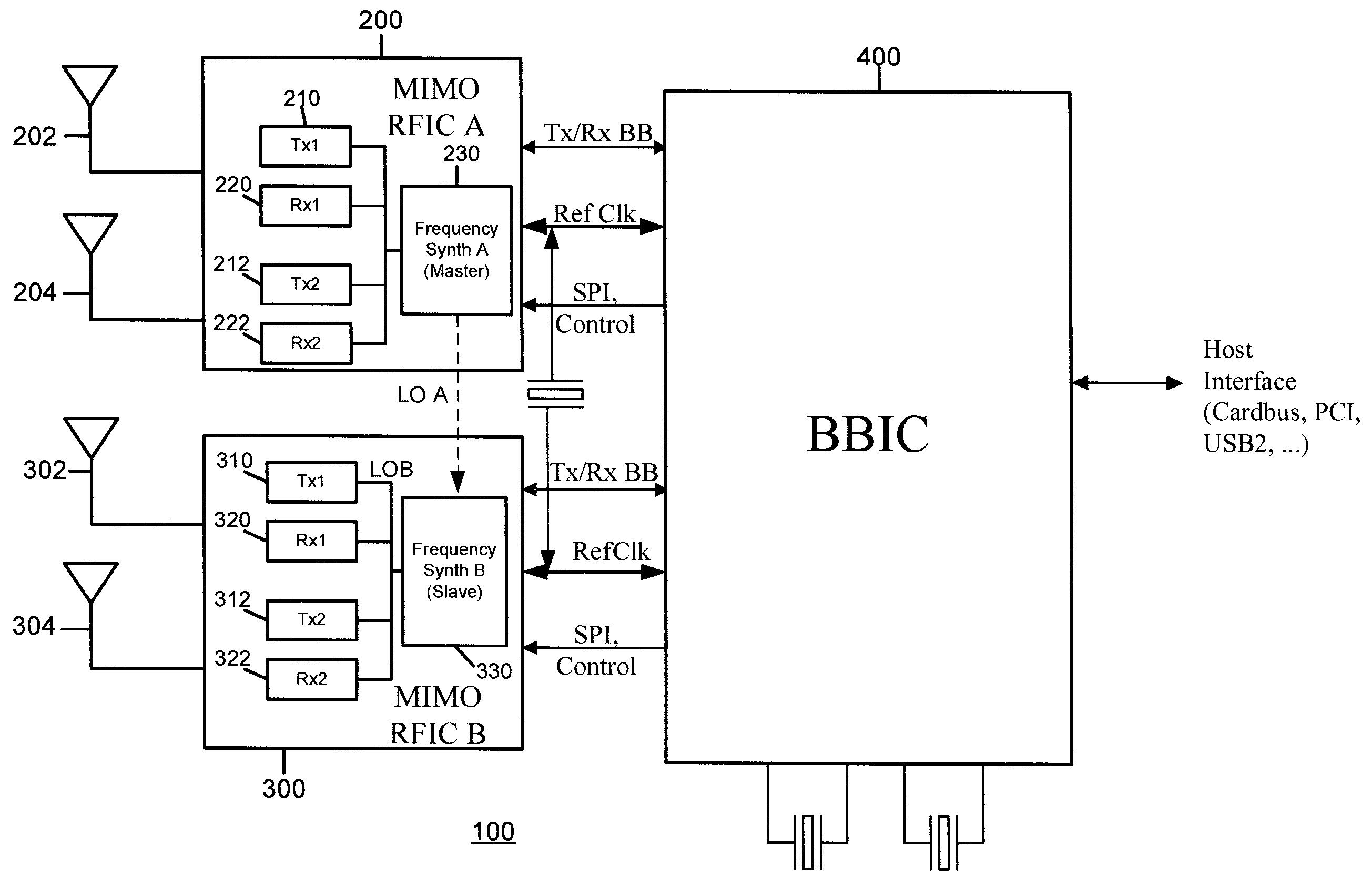
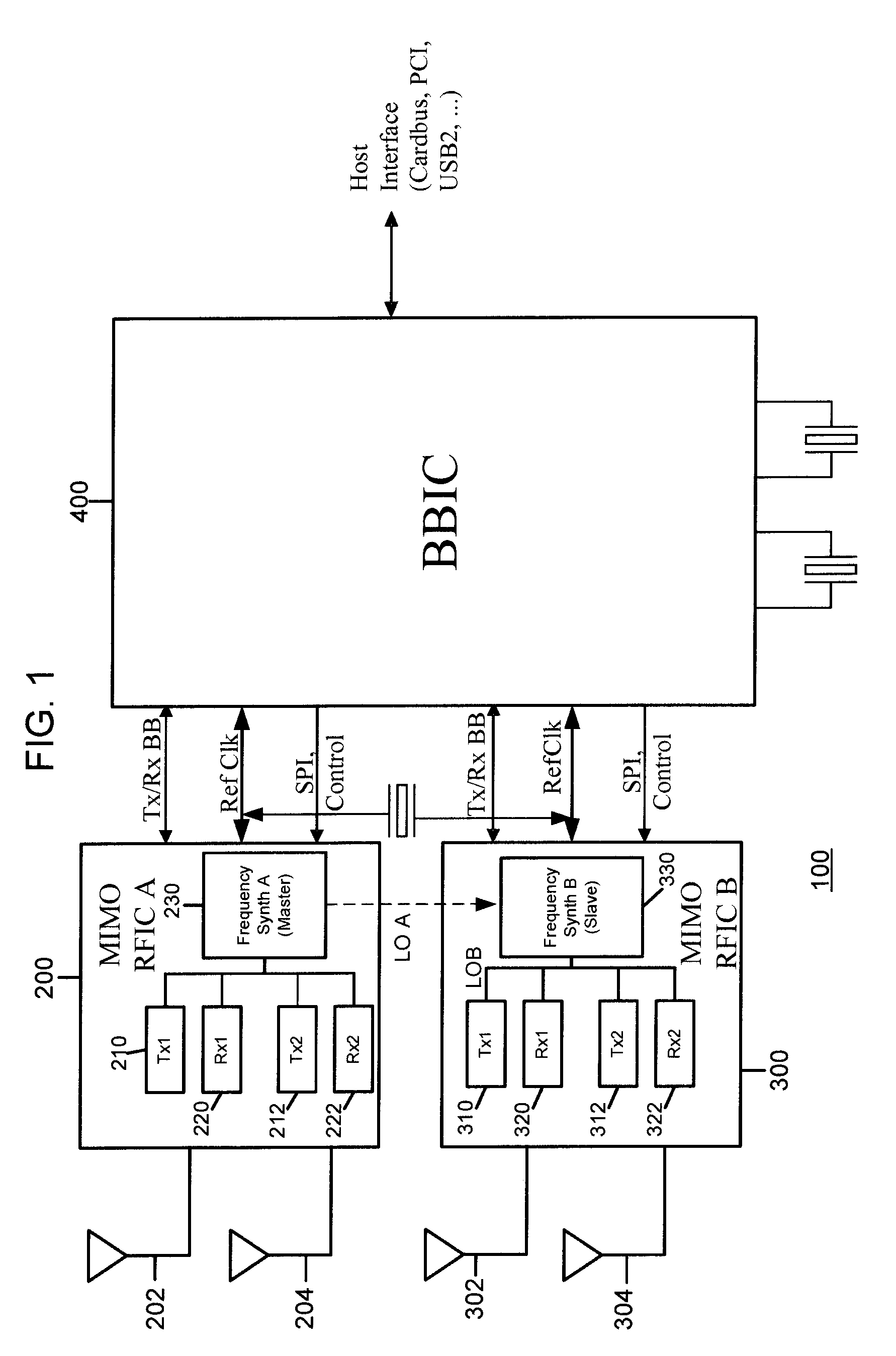
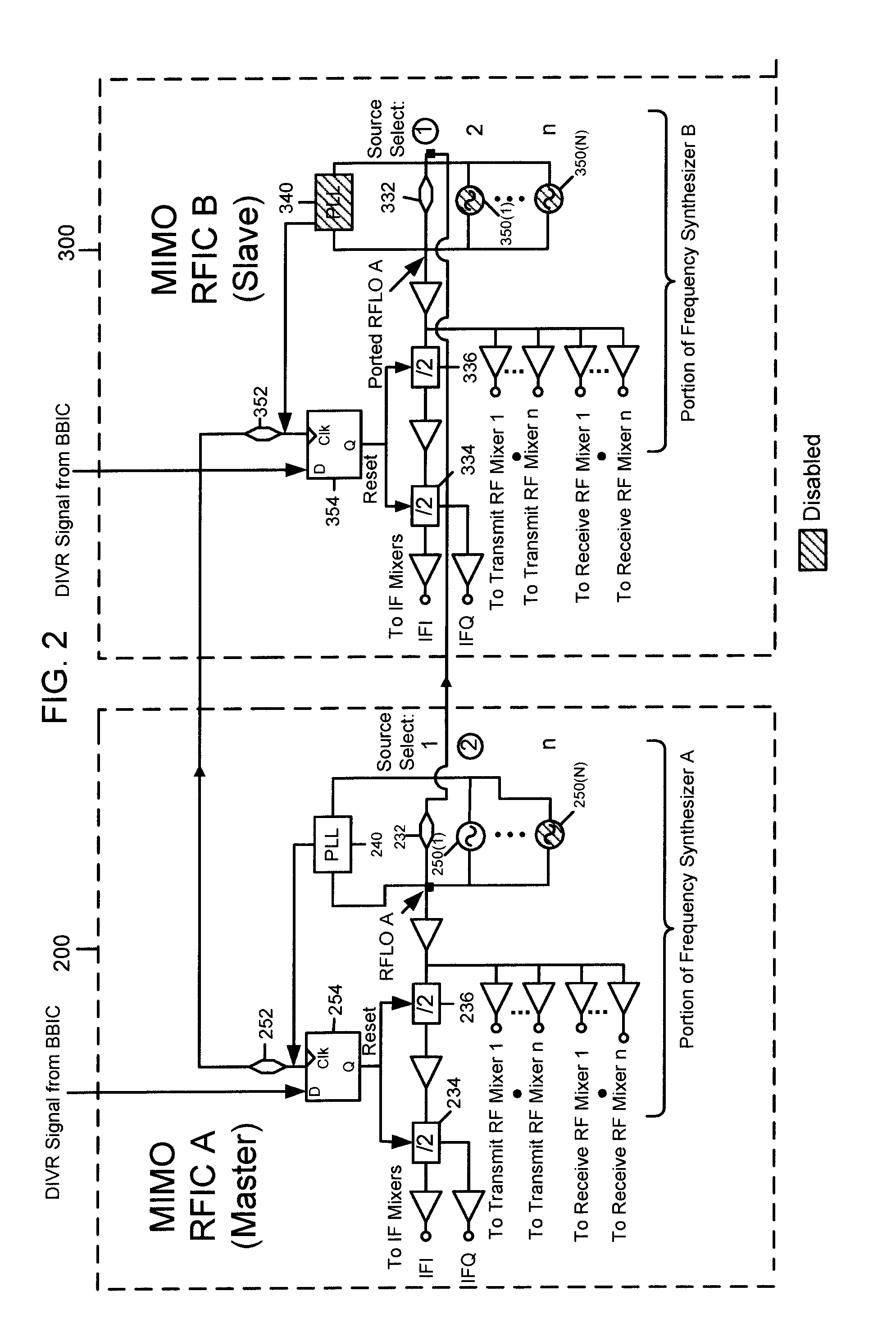
Master-Slave Local Oscillator Porting Between Radio Integrated Circuits
ActiveUS20050064892A1Improve performanceAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayPulse automatic controlLocal oscillator signalRFIC
A technique to share a local oscillator signal between two radio frequency integrated circuits (RFICs). The local oscillator signal generated internally by one RFIC is ported to the other RFIC for use in transmit and / or receive operation. The local oscillator signal that is ported may be an RF local oscillator signal. Each RFIC may include a bi-directional port circuit that can be operated to make the RFIC a master, slave or may be totally disabled to disable the porting feature. This is particularly useful in RFICs that are used to communicate using MIMO radio algorithms which rely for optimum performance on phase and frequency coherency among a plurality of transmitters and a plurality of receivers.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Radio-Receiver Front-End and A Method For Frequency Converting An Input Signal
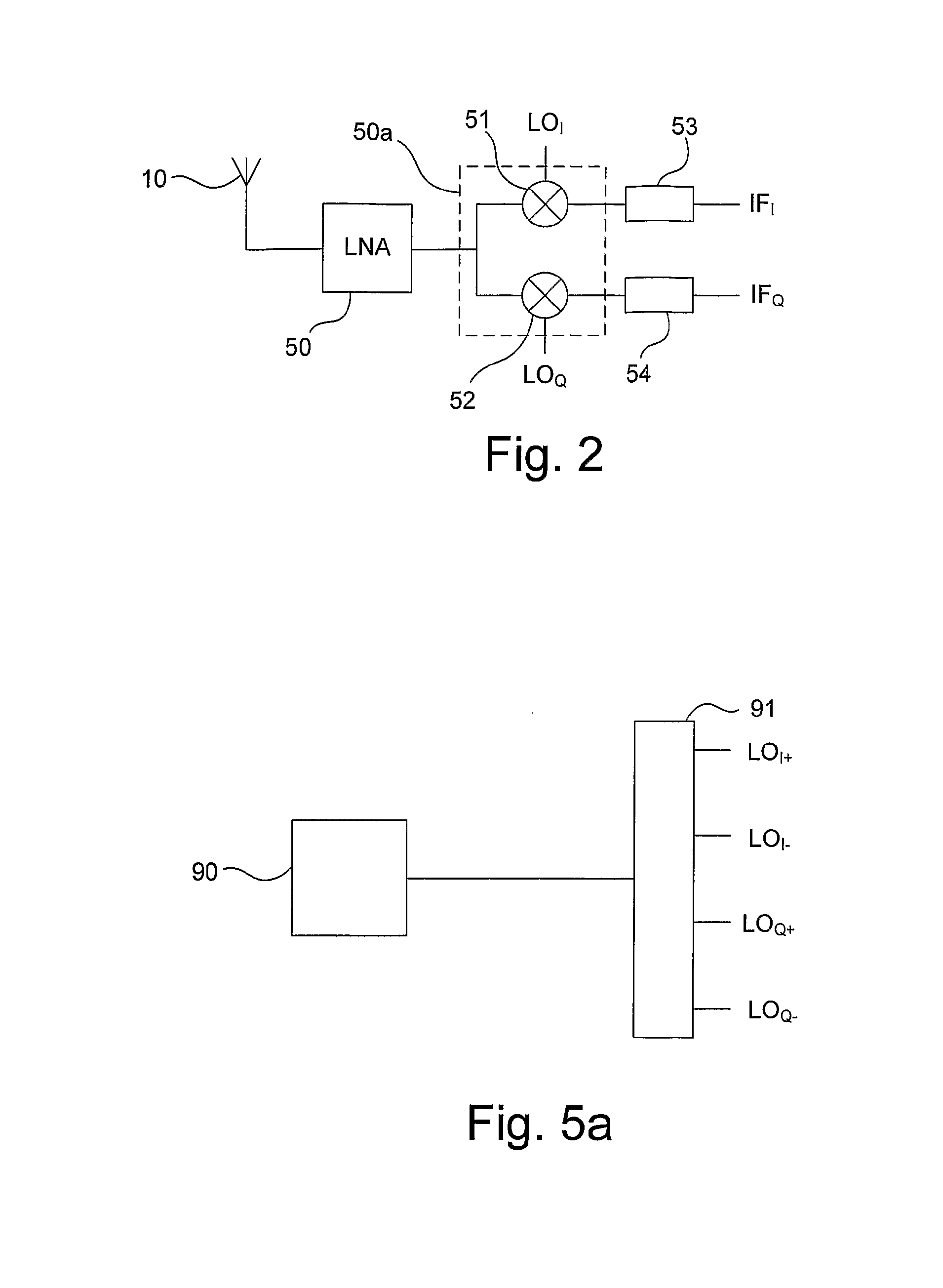
InactiveUS20070287403A1Reduce complexitySmall sizeModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
An N-phase radio receiver front-end for converting an input signal having a first frequency to output signals having a second frequency, and a method for converting an input signal in an N-phase radio receiver front-end. An input port of the N-phase radio receiver front-end is directly connected to an input port of a low noise amplifier (50). A mixer arrangement (50a) is a current mode mixer arrangement. An output port of the low-noise amplifier is directly connected to an input port of the mixer arrangement. A signal generator operatively connected to the mixer arrangement is adapted to generate N phase shifted local oscillator signals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Integrated switchless programmable attenuator and low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6879816B2Multiple-port active networksSwitched capacitor networksCapacitanceLocal oscillator signal
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
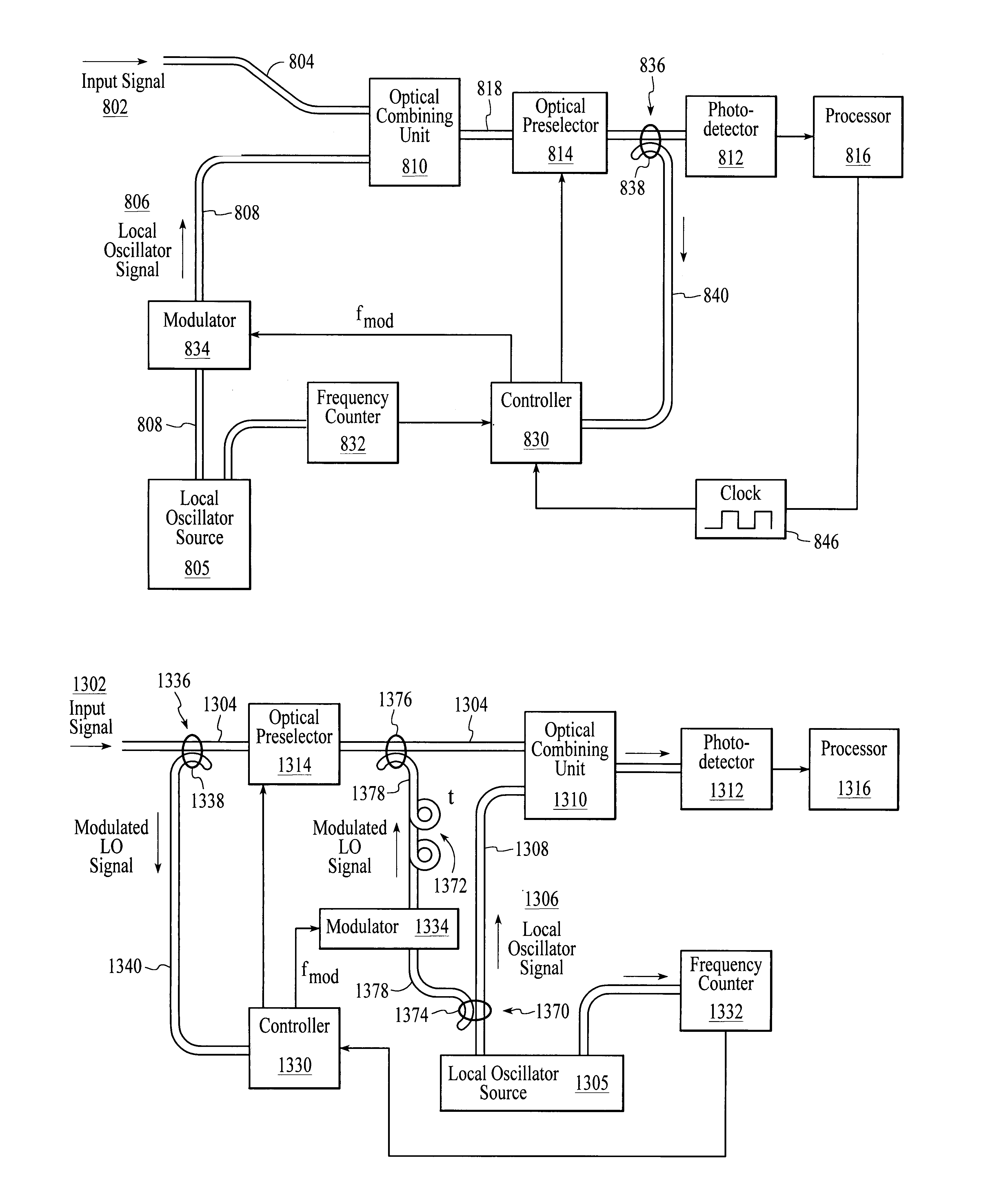
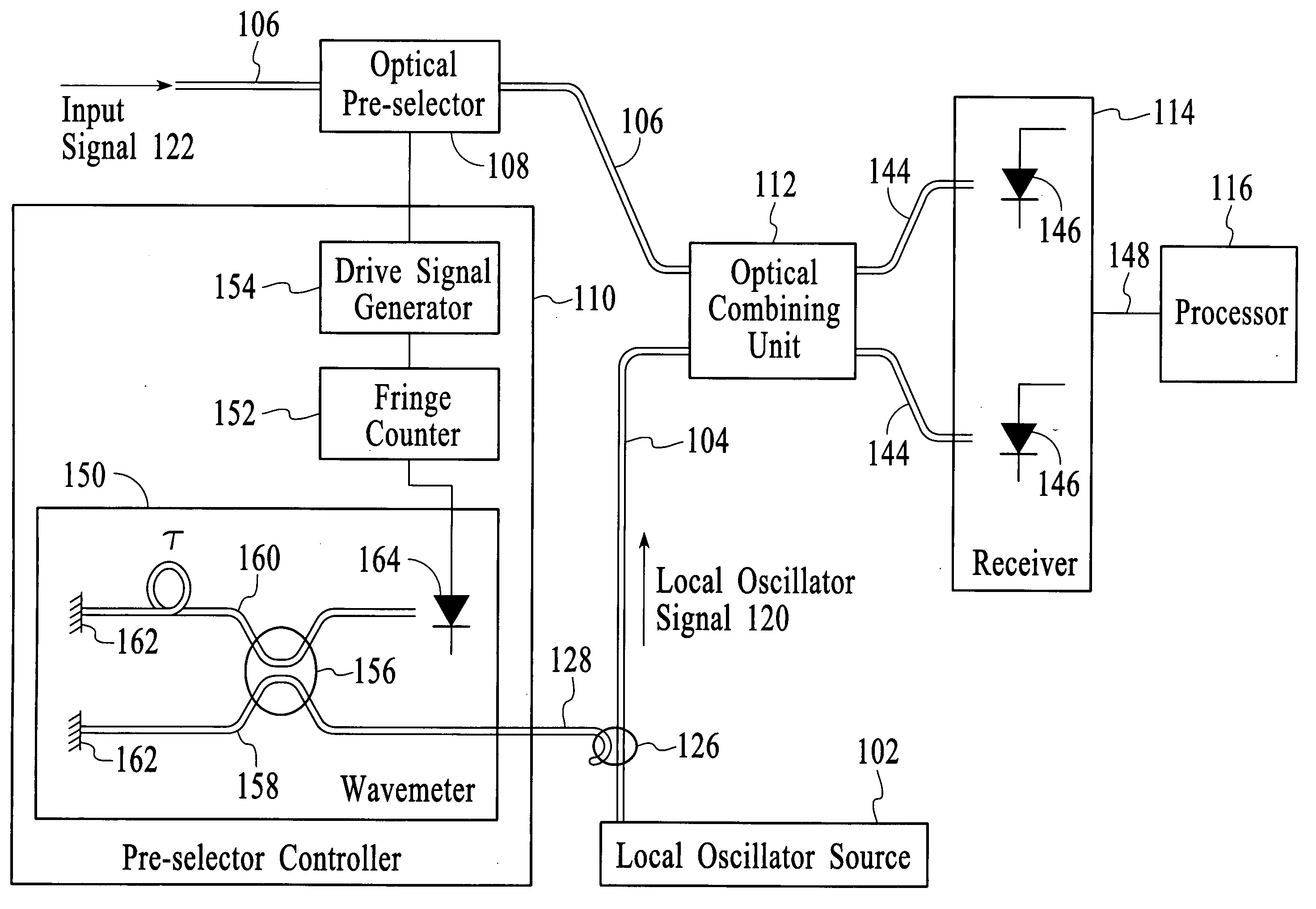
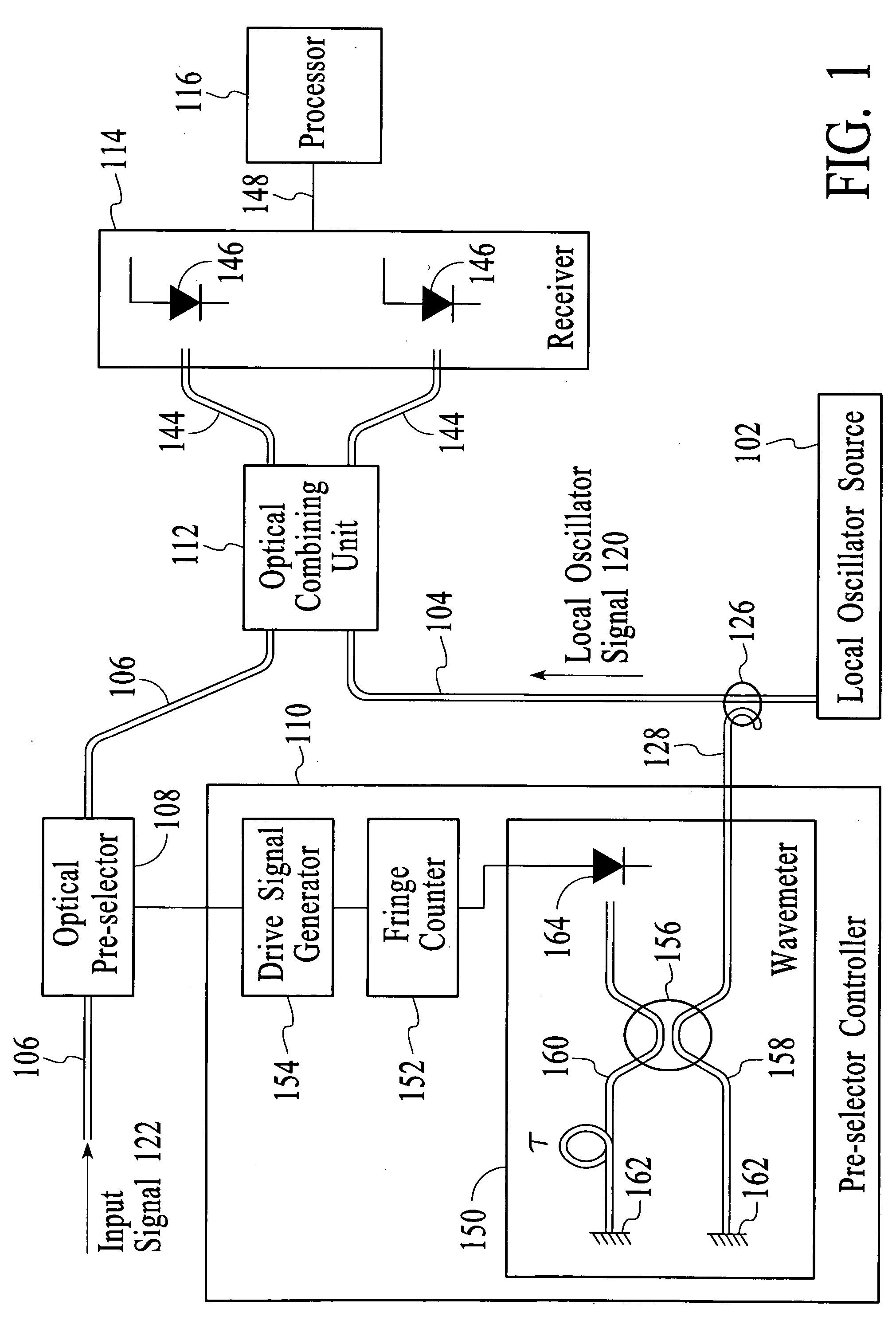
System and method for optical heterodyne detection of an optical signal including optical pre-selection that is adjusted to accurately track a local oscillator signal
InactiveUS7027743B1Reduce noiseImprove dynamic rangeOptical measurementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLocal oscillator signalControl signal
An optical heterodyne detection system includes a tunable optical pre-selector that is adjusted to track the frequency of a swept local oscillator signal. The tunable optical pre-selector is adjusted in response to a measure of the frequency of the swept local oscillator signal and in response to a measure of a portion of the swept local oscillator signal after the portion of the swept local oscillator signal has optically interacted with the optical pre-selector. In an embodiment, at least some portion of the swept local oscillator signal is modulated before it interacts with the optical pre-selector. In an embodiment, the portion of the swept local oscillator signal that interacts with the pre-selector is detected and used in a feedback control circuit to generate a control signal which causes the error between the center frequency of the pre-selector and the frequency of the swept local oscillator signal to be small.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
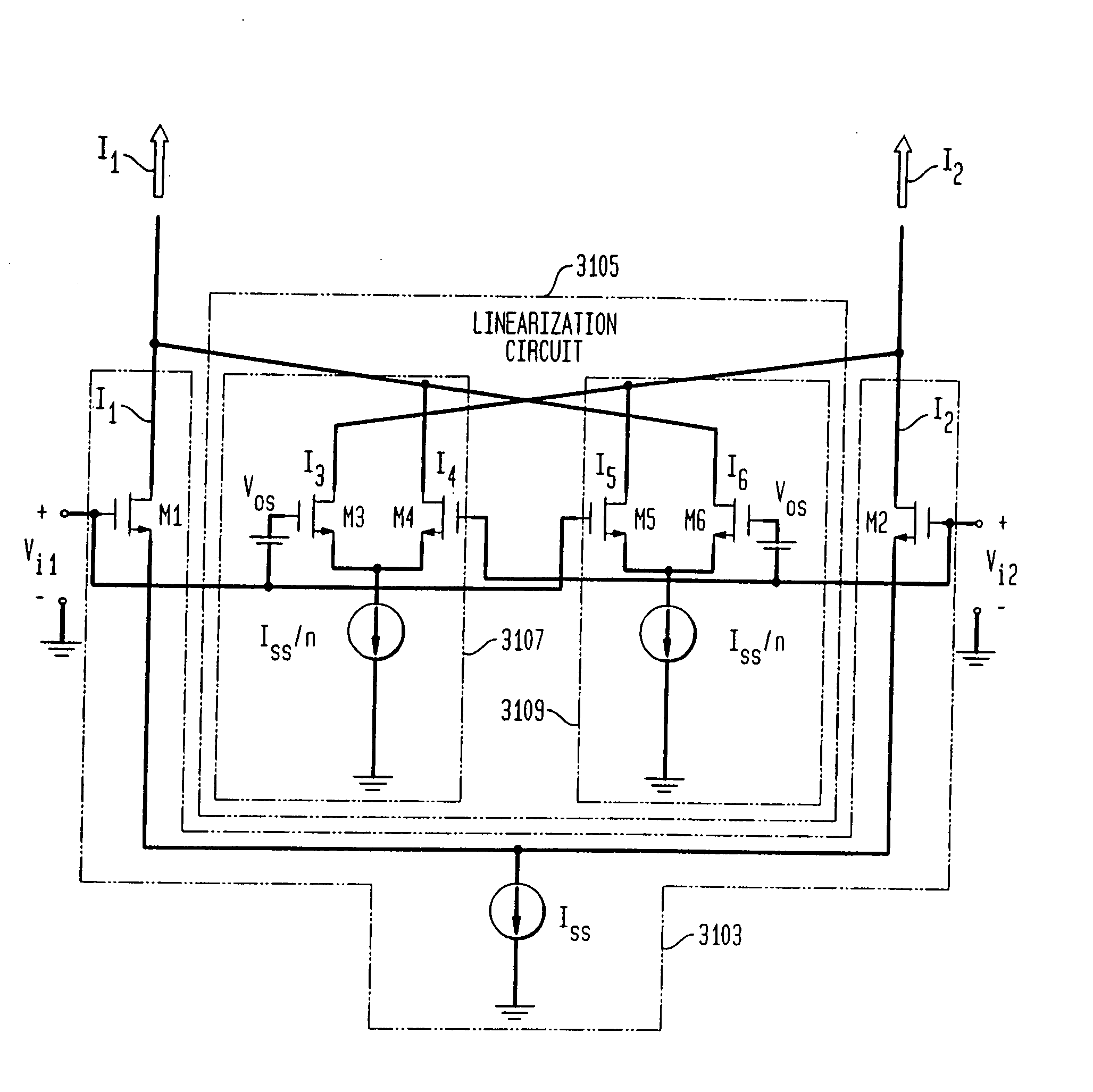
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS20080036536A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiphase receiver and oscillator
InactiveUS6385442B1Single output arrangementsPulse generation by logic circuitsLocal oscillator signalEngineering
A differential ring oscillator is provided with three differential amplifiers and provides three-phase output signals which can be used for synchronous detection of a received multi-phase modulated signal in a multi-phase receiver, wherein the phase of the local oscillator signals may be in other-than-quadrature relation. Two of the phase outputs of the local oscillator can be combined to provide a signal that is in quadrature with the remaining output. The oscillator is preferably controlled in coarse frequency control steps and using a fine voltage control signal responsive to a phase-locked loop to reduce frequency modulation of the oscillator signal arising out of leakage signals.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Electromagnetic Transmission/Reception System
InactiveUS20080212974A1Promote generationStable coherent detectionOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
An electromagnetic transmission and reception system comprises a transmitter section and a receiver section. The transmitter section has a first signal source, a second signal source at a lower frequency than the first signal source, and means for generating from the first and second signal sources a plurality of signals with fixed frequency spacing derived from the second signal source frequency. One or more pairs of the plurality of signals are selected, and for the or each pair, the signals of the pair are combined to derive an output signal having a frequency derived from the difference between the frequencies of the signals of the pair. The receiver section combines a received signal, which comprises a received version of the output signal, with a local oscillator signal for frequency down-conversion of the received signal. This local oscillator signal is generated by the transmitter section. This provides a system in which the generation of signals of the desired frequency is achieved by mixing signals of specific frequencies. The reception uses frequency down-conversion using the same signal sources as used for the transmission. This enables a low noise system to be implemented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
Receiver including an oscillation circuit for generating an image rejection calibration tone
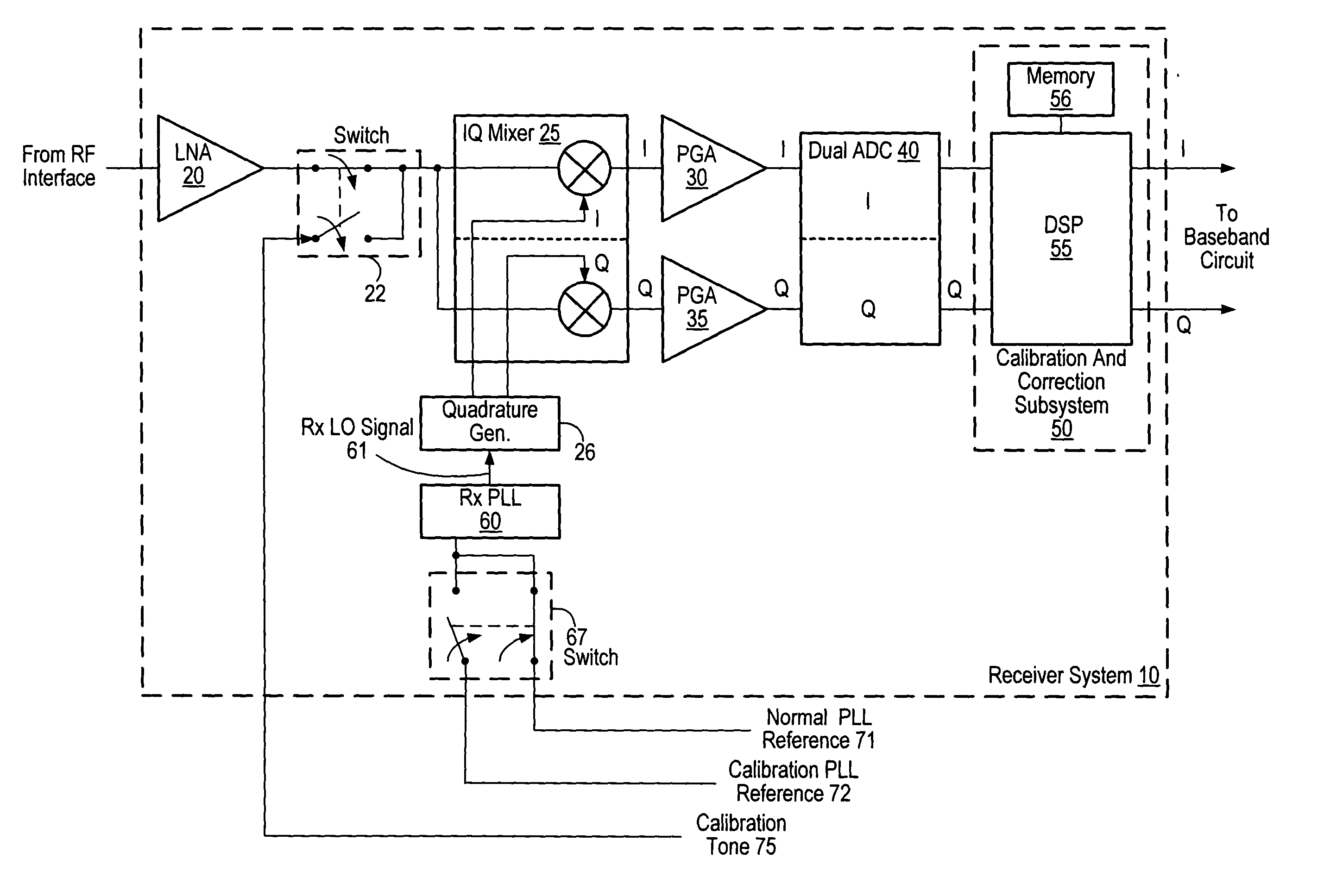
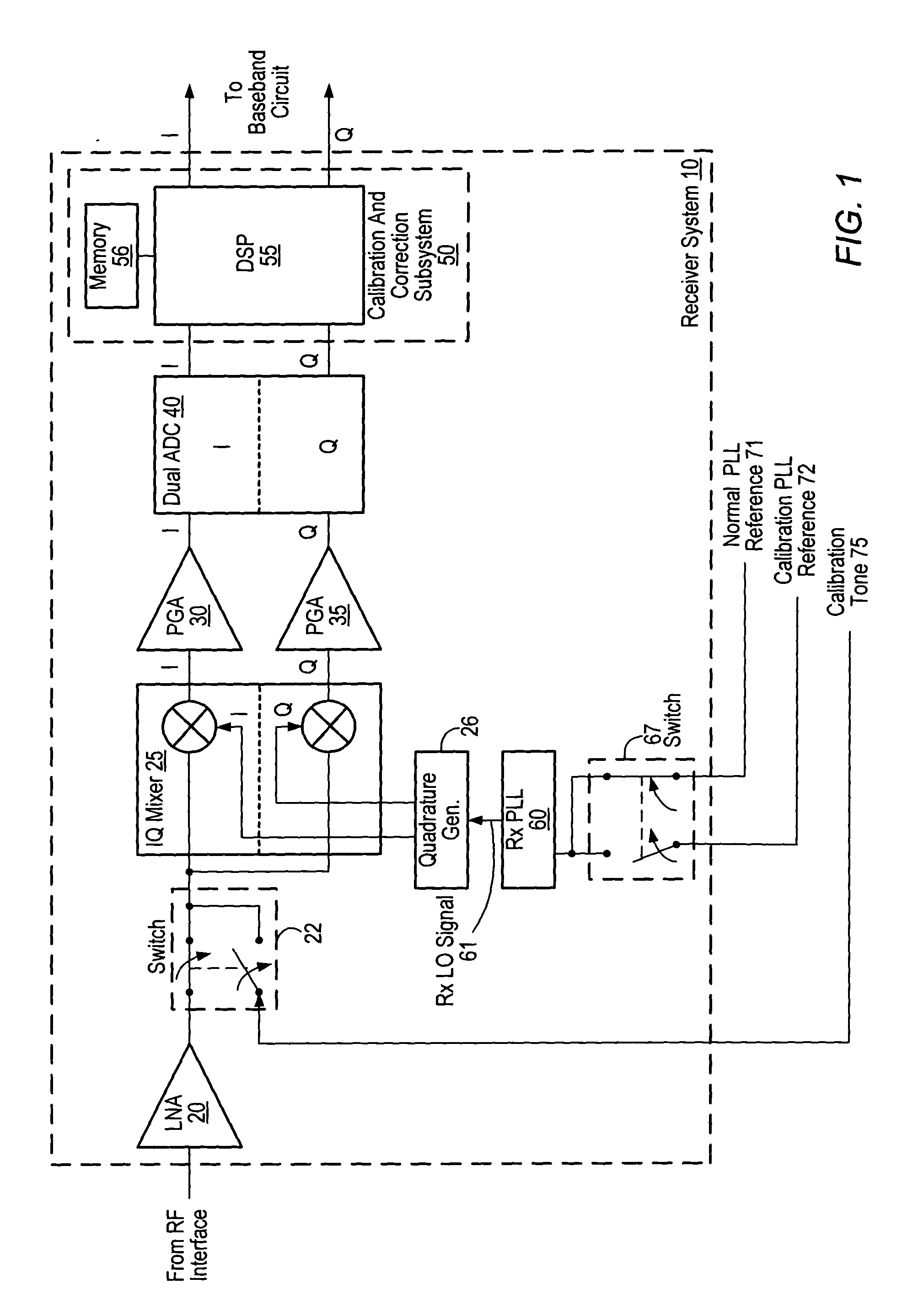
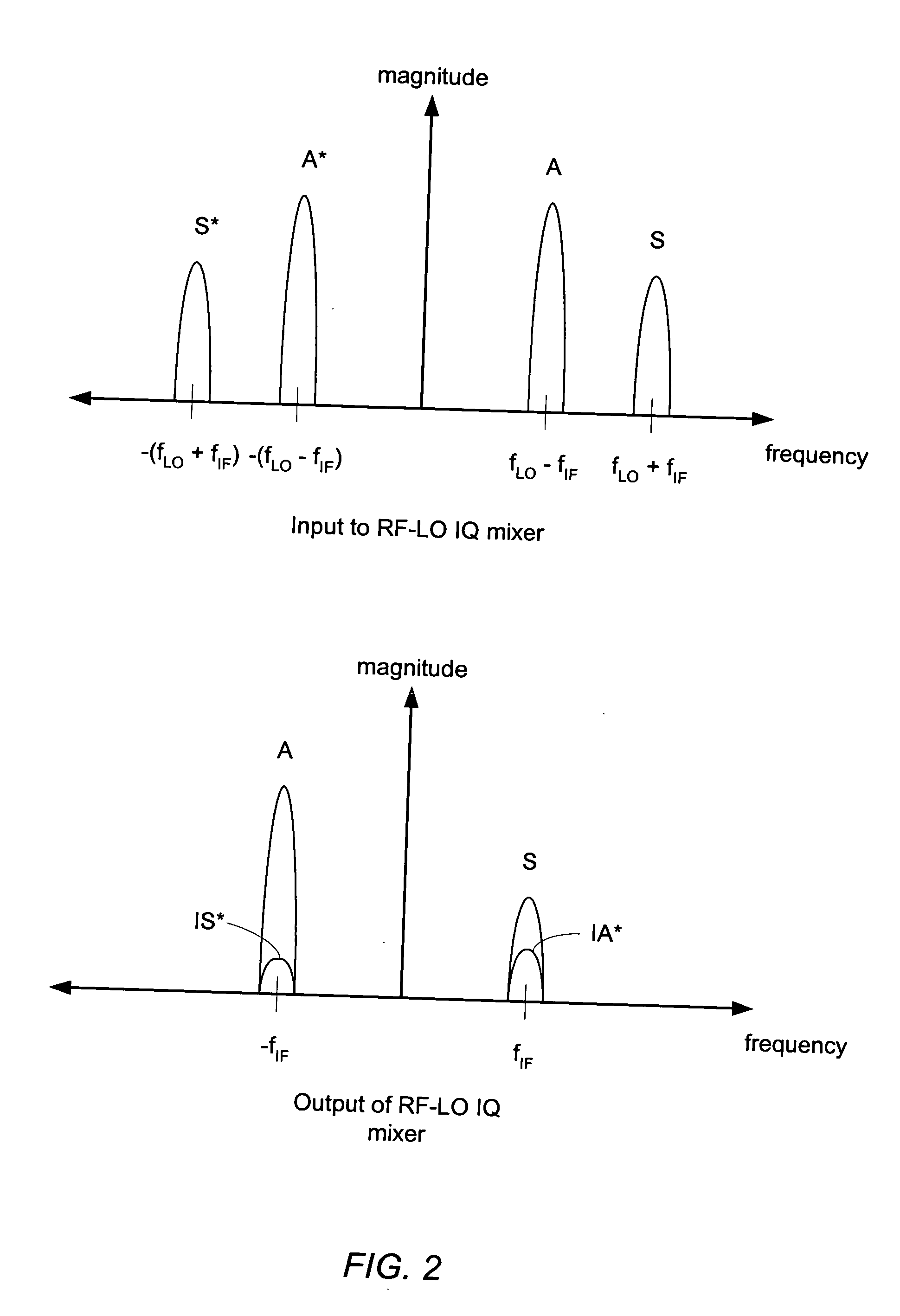
ActiveUS20050069056A1Receivers monitoringPulse automatic controlLocal oscillator signalQuadrature mixer
A receiver circuit includes an oscillator circuit configured to generate a calibration tone and a phase locked loop (PLL) reference signal. An output frequency of the VCO may be divided by respective amounts to derive a desired calibration tone frequency and a desired PLL reference signal frequency. In addition to the oscillator circuit, the receiver circuit may further include a phase locked circuit configured to generate a PLL output signal that is phase locked in relation to the PLL reference signal. During a calibration mode, a quadrature generator may be used to generate quadrature mixer local oscillator signals dependent upon the PLL output signal, and an in-phase / quadrature mixer may be used to mix the calibration tone with the quadrature mixer LO signals.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Highly integrated microwave outdoor unit (ODU)
InactiveUS7050765B2Fast disconnectionUse minimizedActive radio relay systemsRadiating element housingsLocal oscillator signalTransceiver
A lightweight millimeter wave outdoor unit includes a lightweight housing with a heat sink and mounting member configured for mounting on the antenna to form a wireless link. A millimeter wave transceiver board is formed of ceramic material and mounted within the housing. It includes a millimeter wave transceiver circuit that has microwave monolithic integrated circuit (MMIC) chips and operable with the transmit and receive boards. An intermediate frequency (IF) board has components forming an intermediate frequency circuit operable with the millimeter wave transceiver circuit. A frequency synthesizer board has a signal generating circuit for generating local oscillator signals to the transceiver circuit. A controller board has surface mounted DC and low frequency discrete devices thereon forming power and control circuits that supply respective power and control signals to other circuits on other boards. A quick connect / disconnect assembly is operative with the housing for allowing the housing to be rapidly connected and disconnected to the antenna circuit contact members interconnect circuits between boards.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
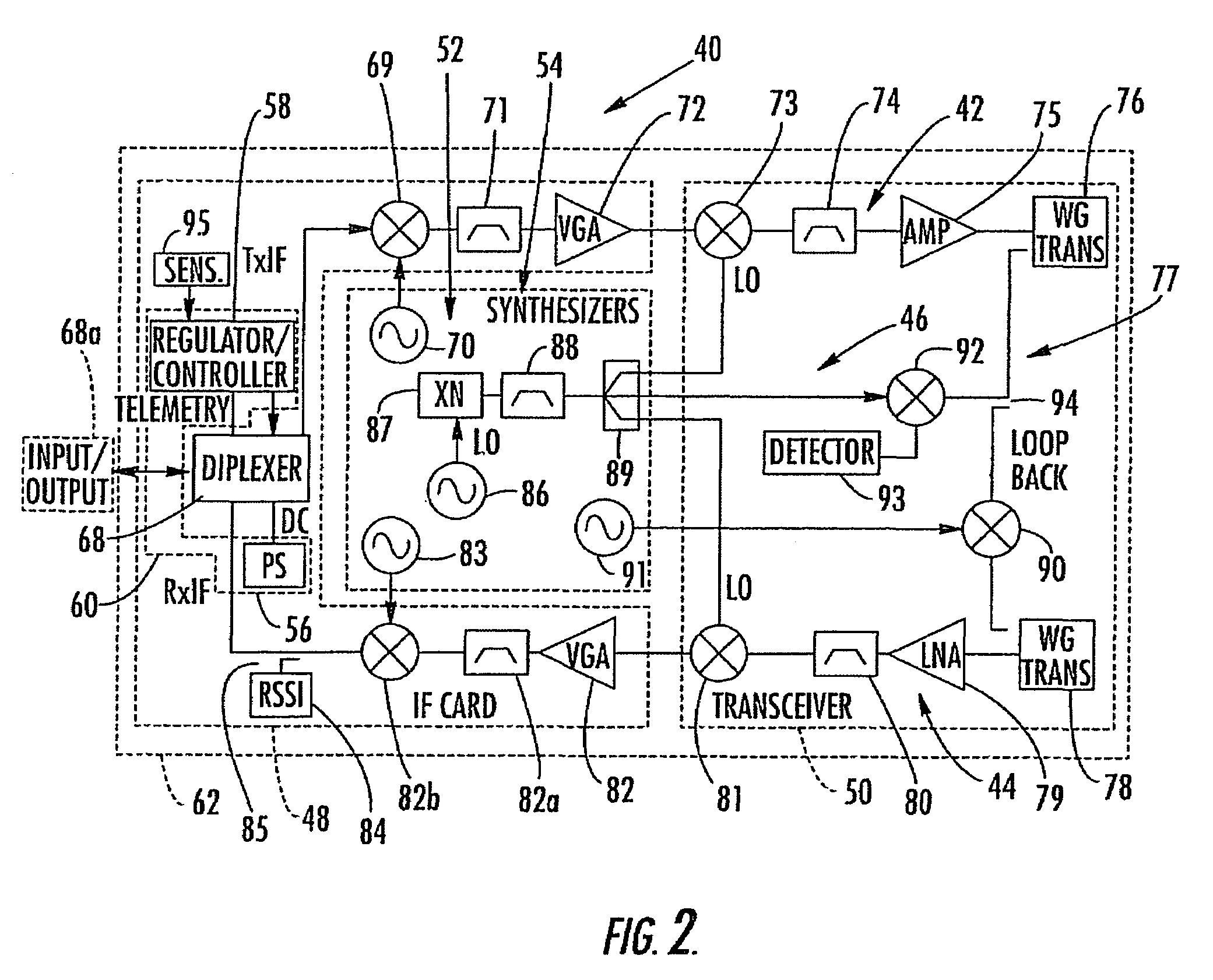
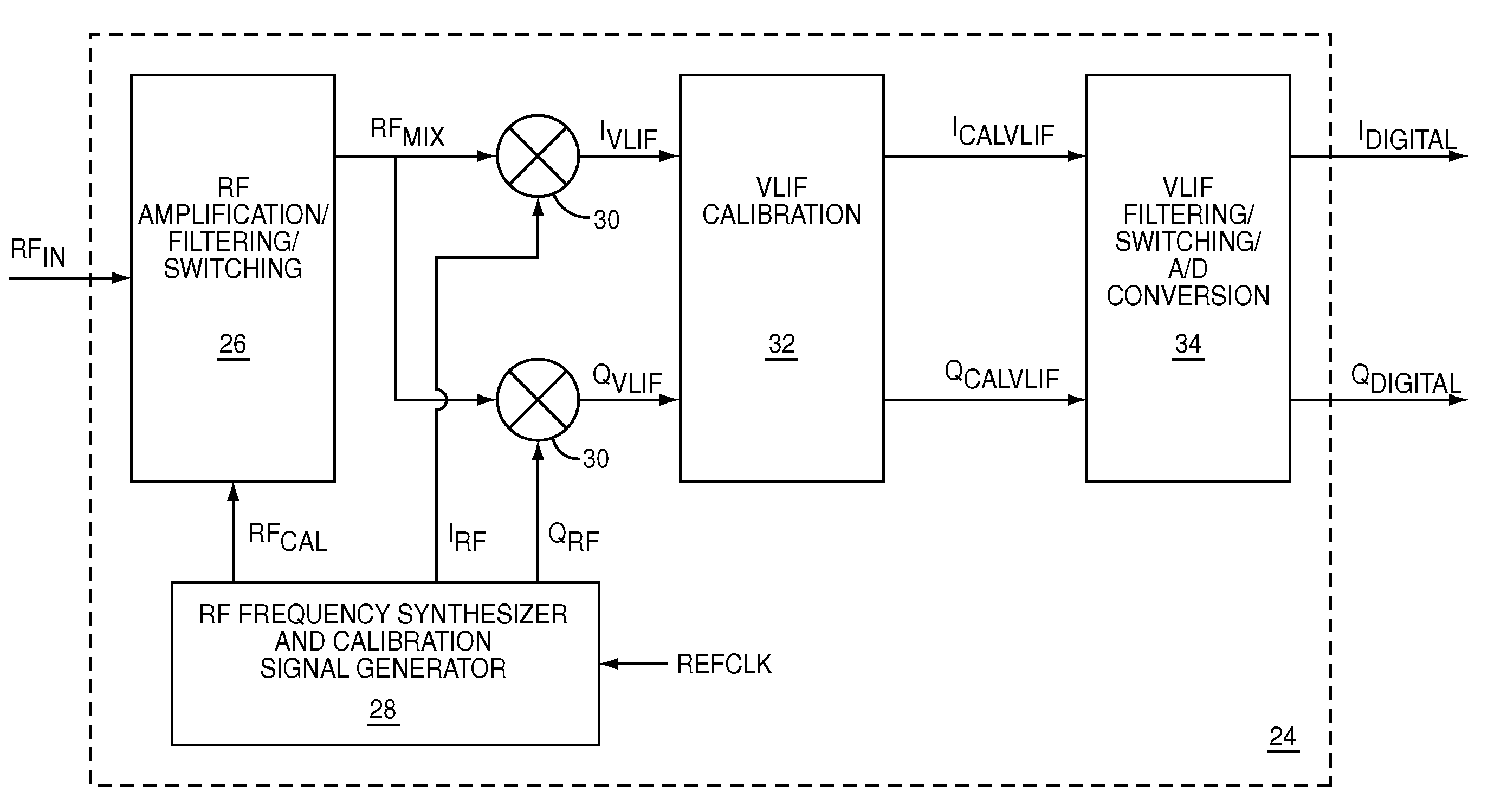
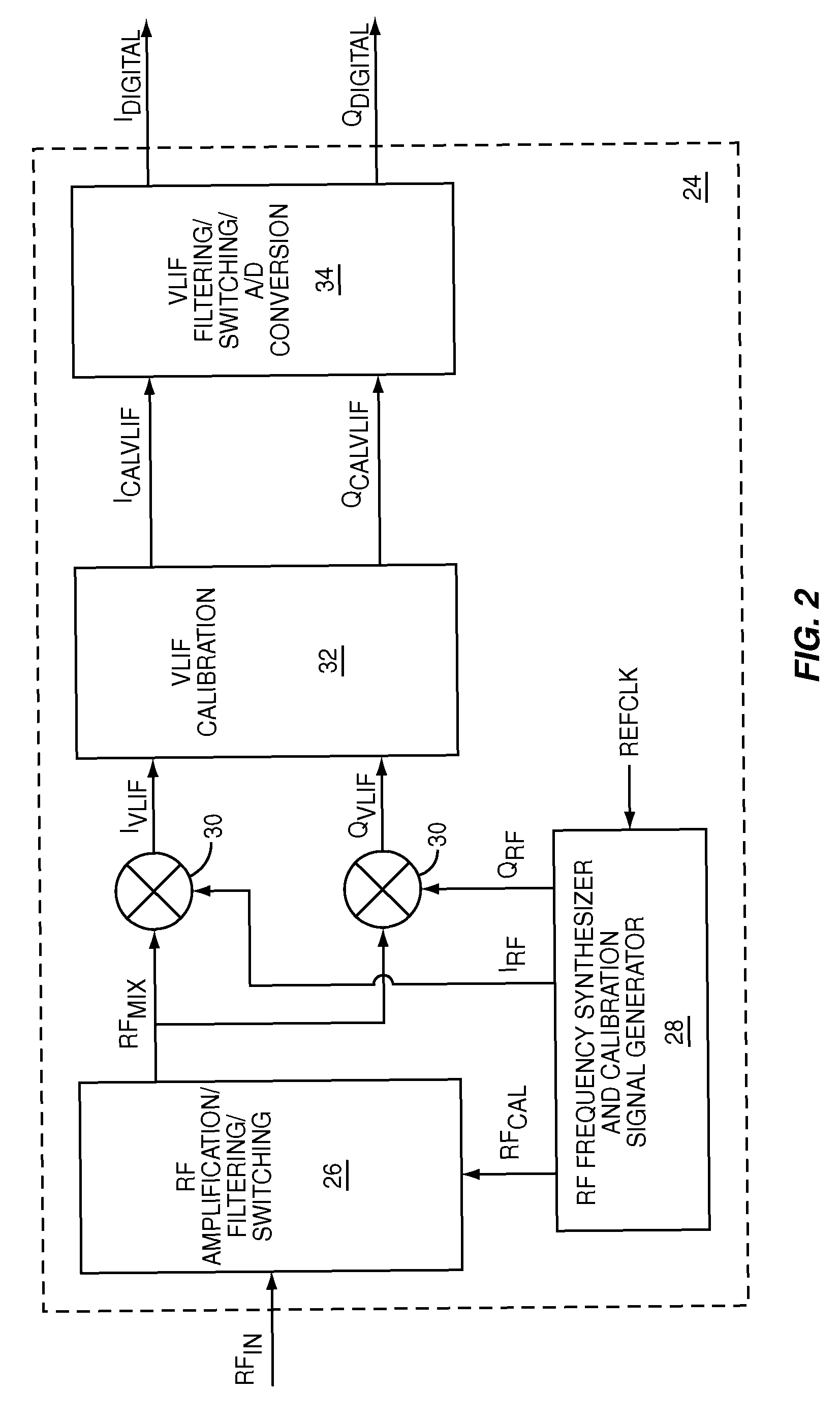
Calibrated quadrature very low intermediate frequency receiver
ActiveUS7773965B1Optimize VLIF image rejectionSimplifies calibration measurementTransmission monitoringAmplitude demodulationVariable-gain amplifierLocal oscillator signal
The present invention is a quadrature VLIF receiver, including calibration circuitry, and methods to closely match signal processing of an in-phase signal path and a quadrature-phase signal path to optimize VLIF image rejection. The calibration circuitry includes a variable gain variable-phase calibration signal generator, a variable gain amplifier for each signal path, phase adjustment circuitry for each signal path, and switching circuitry to support calibration steps. The calibration signal generator supplies a calibration signal at the same frequency as mixer local oscillator signals; therefore, during calibration, all signals downstream of the VLIF mixer are at DC, which simplifies calibration measurements, thereby minimizing calibration times.
Owner:QORVO US INC
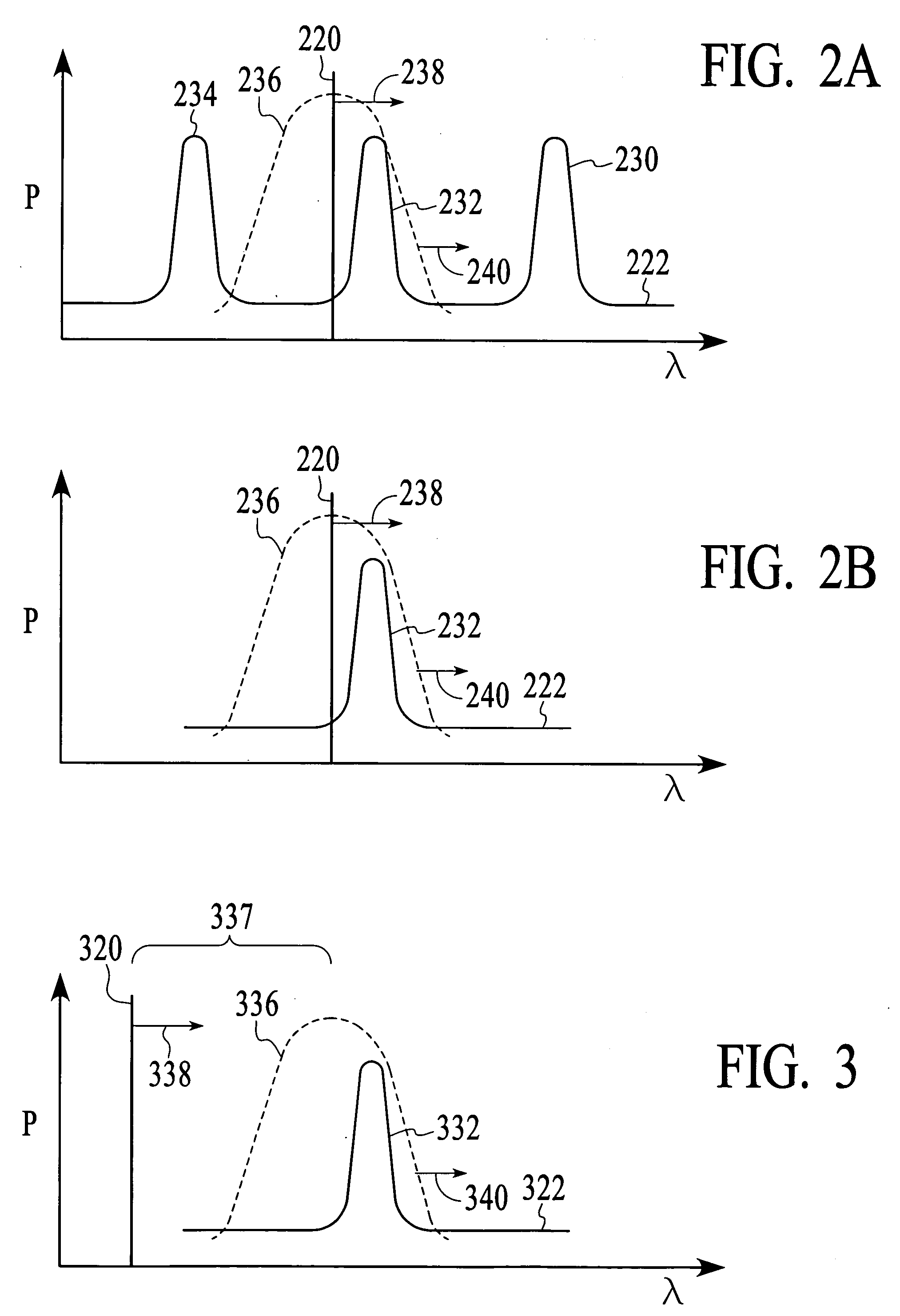
Synchronizing the filter wavelength of an optical filter with the wavelength of a swept local oscillator signal
InactiveUS20050078317A1Accurate trackingOptical measurementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLocal oscillator signalWavelength
Ensuring that a tunable device, such as a tunable optical filter, accurately tracks the wavelength of a local oscillator signal involves generating at least one synchronization signal as the local oscillator signal is swept across a range of wavelengths and adjusting an operating characteristic of the tunable device in response to the at least one synchronization signal. Before the local oscillator signal is swept across the range of wavelengths, the operating characteristic of the tunable device and the wavelength of the local oscillator signal are initially set to matching values.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
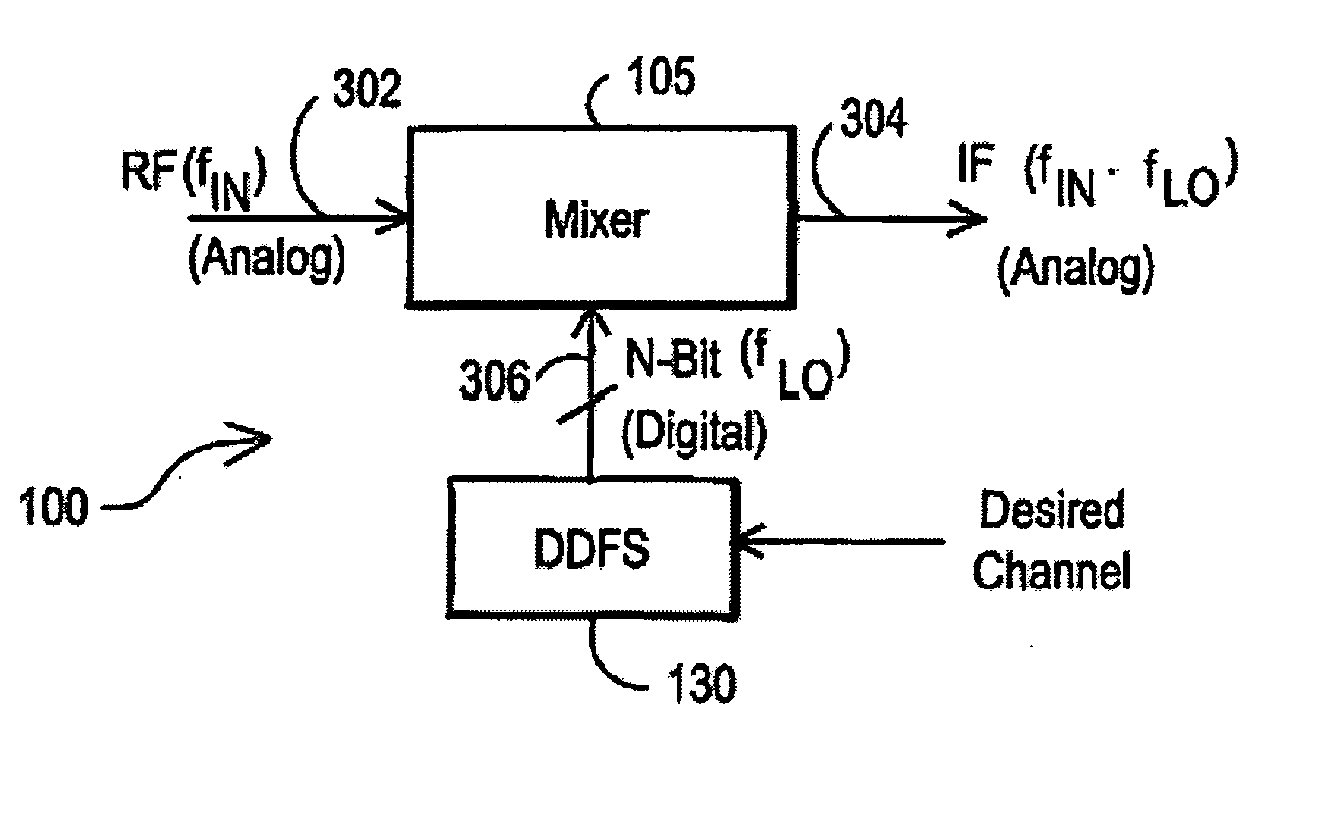
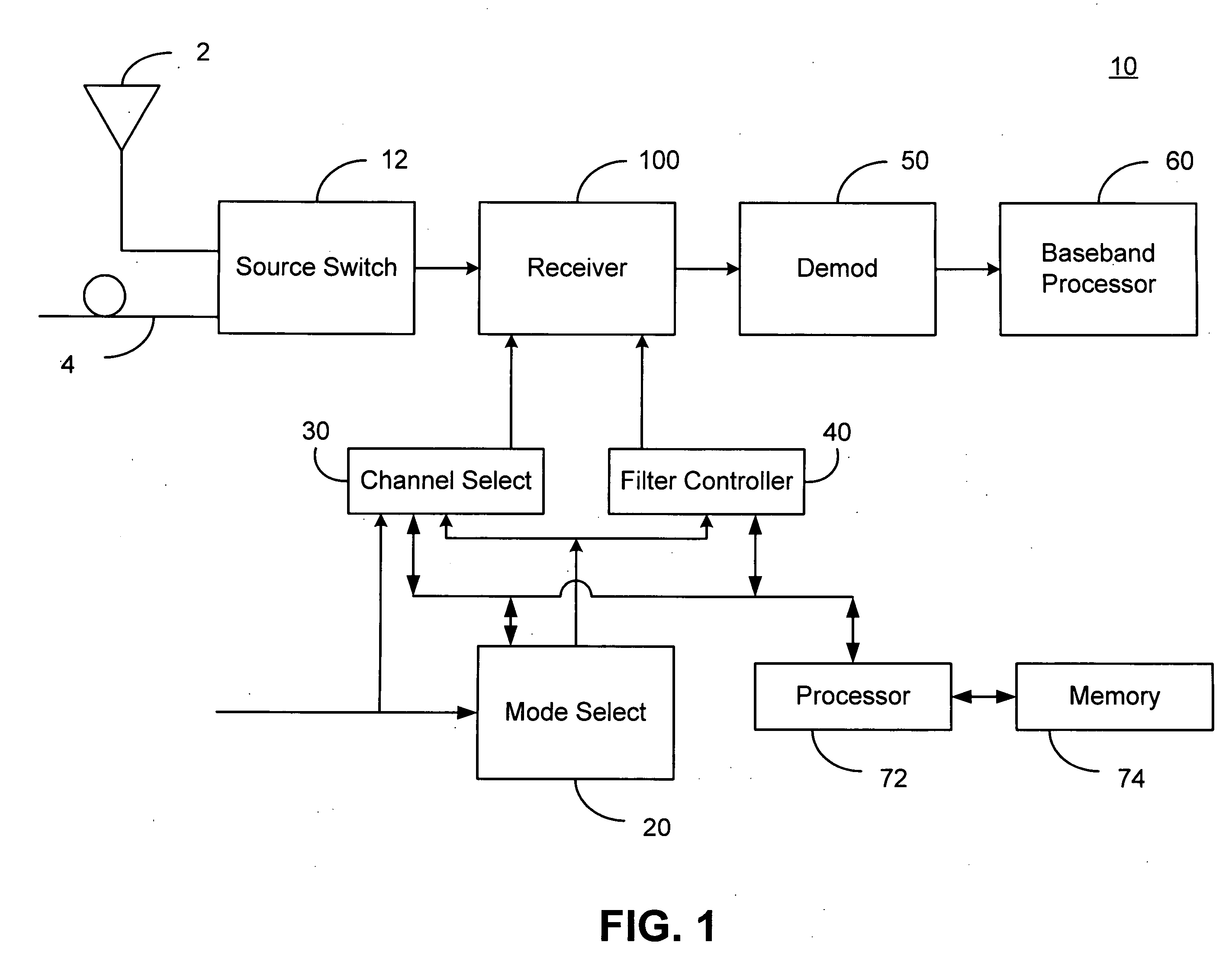
Television receiver suitable for multi-standard operation and method therefor
ActiveUS20050266818A1Television system detailsModulation transferenceFrequency spectrumLocal oscillator signal
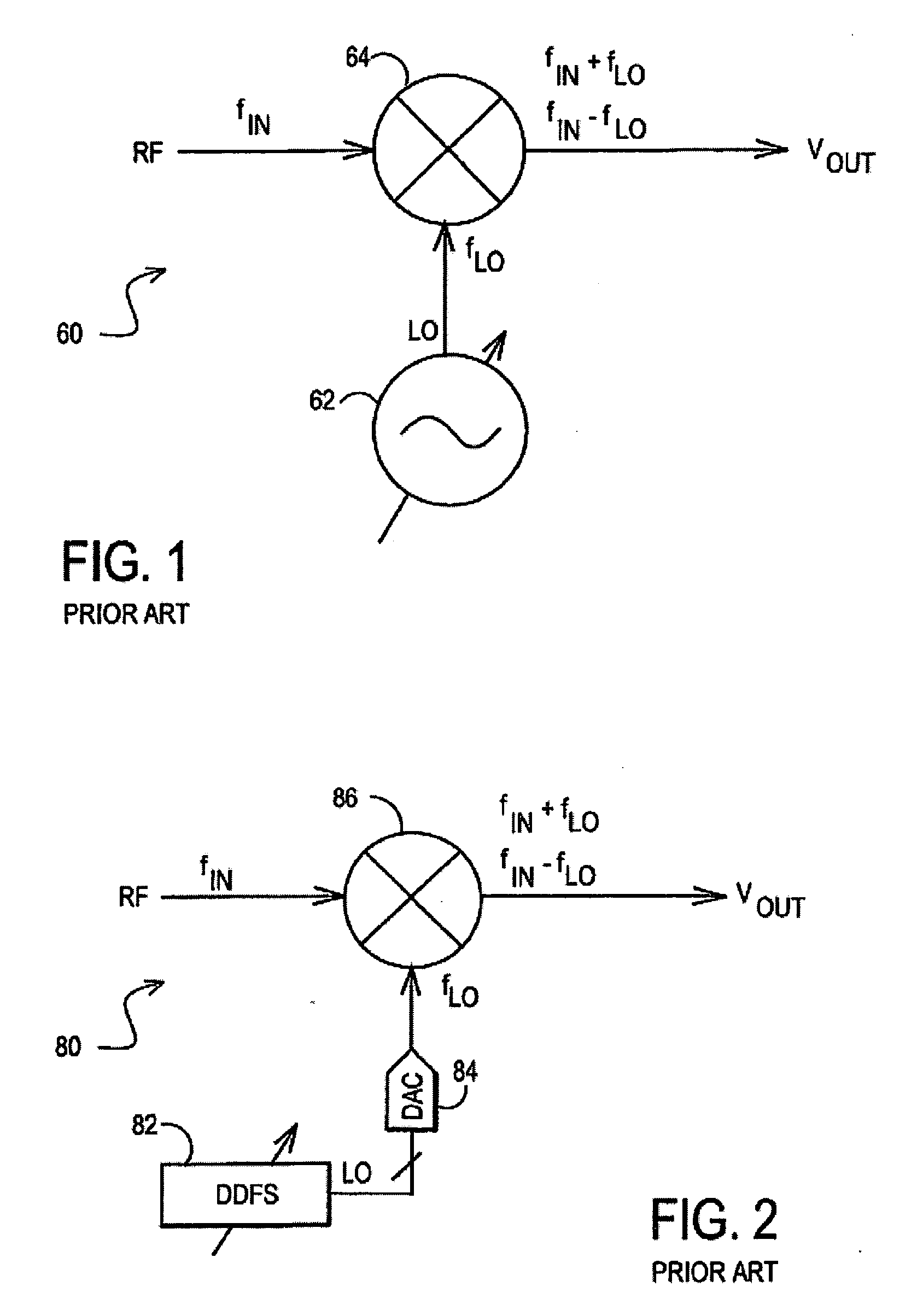
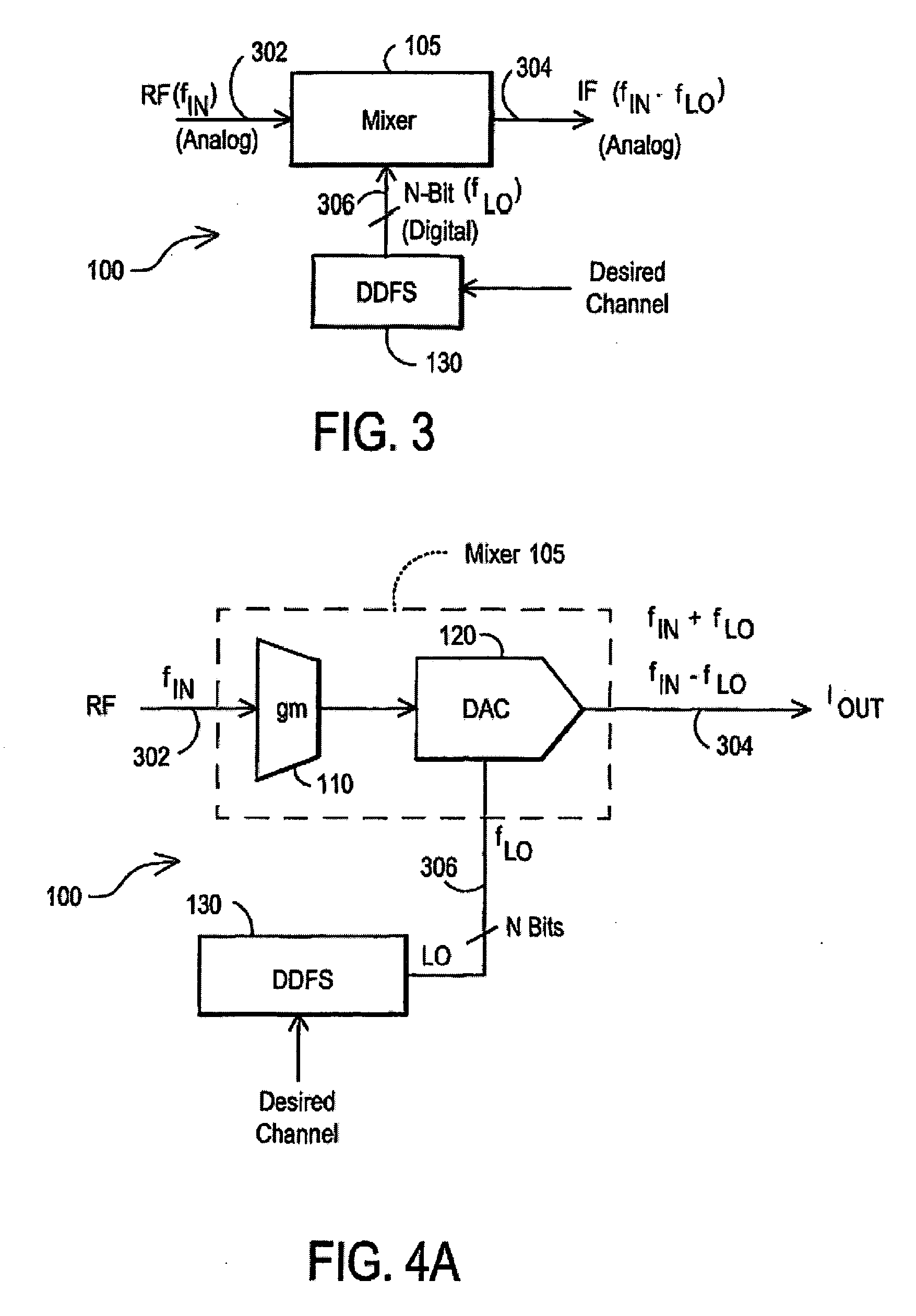
A receiver (1100) includes a direct digital frequency synthesizer (130), a mixer (105), and a clock source (1110, 1130). The direct digital frequency synthesizer has an input terminal for receiving a first clock signal at a first frequency, and an output terminal for providing a digital local oscillator signal synchronously with the first clock signal. The mixer (105) has a first input terminal for receiving a radio frequency (RF) signal, a second input terminal coupled to the output terminal of the direct digital frequency synthesizer (130), and an output terminal for providing an IF signal having a spectrum centered about a selectable one of a plurality of center frequencies. The clock source (1110, 1130) has an output terminal for providing the first clock signal without using any harmonic frequency that overlaps the spectrum for any of the plurality of center frequencies.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Harmonic reject receiver architecture and mixer
InactiveUS20060160518A1Reducing mixer responseReduced responseModulation transference balanced arrangementsMultiplex with amplitude-modulated carrierLocal oscillator signalFrequency mixer
Receiver architectures and methods of processing harmonic rich input signals employing harmonic suppression mixers are disclosed herein. The disclosed receivers, mixers, and methods enable a receiver to achieve the advantages of switching mixers while greatly reducing the mixer response to the undesired harmonics. A harmonic mixer can include a plurality of mixers coupled to an input signal. A plurality of phases of a local oscillator signal can be generated from a single local oscillator output. Each of the phases can be used to drive an input of one of the mixers. The mixer outputs can be combined to generate a frequency converted output that has harmonic rejection.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
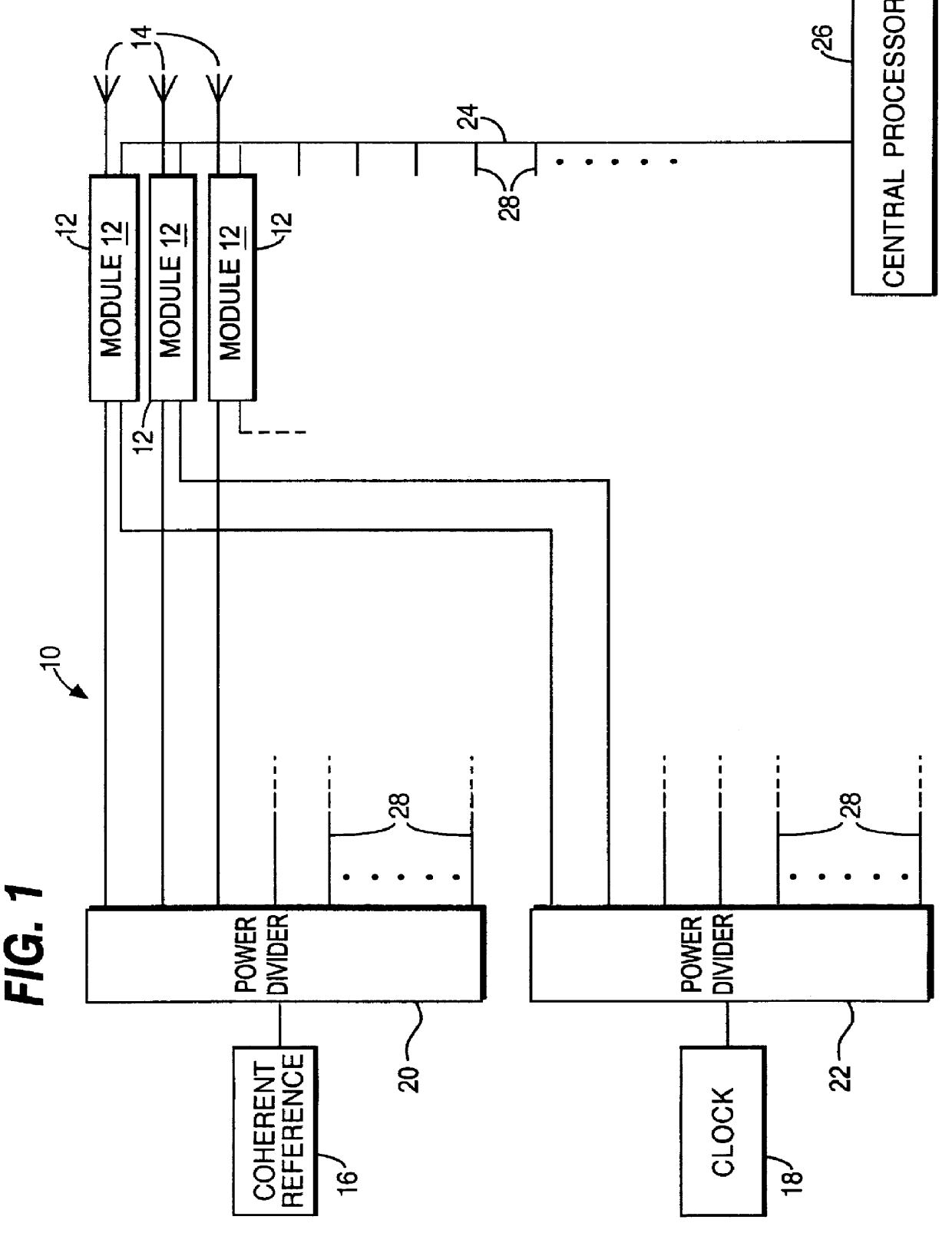
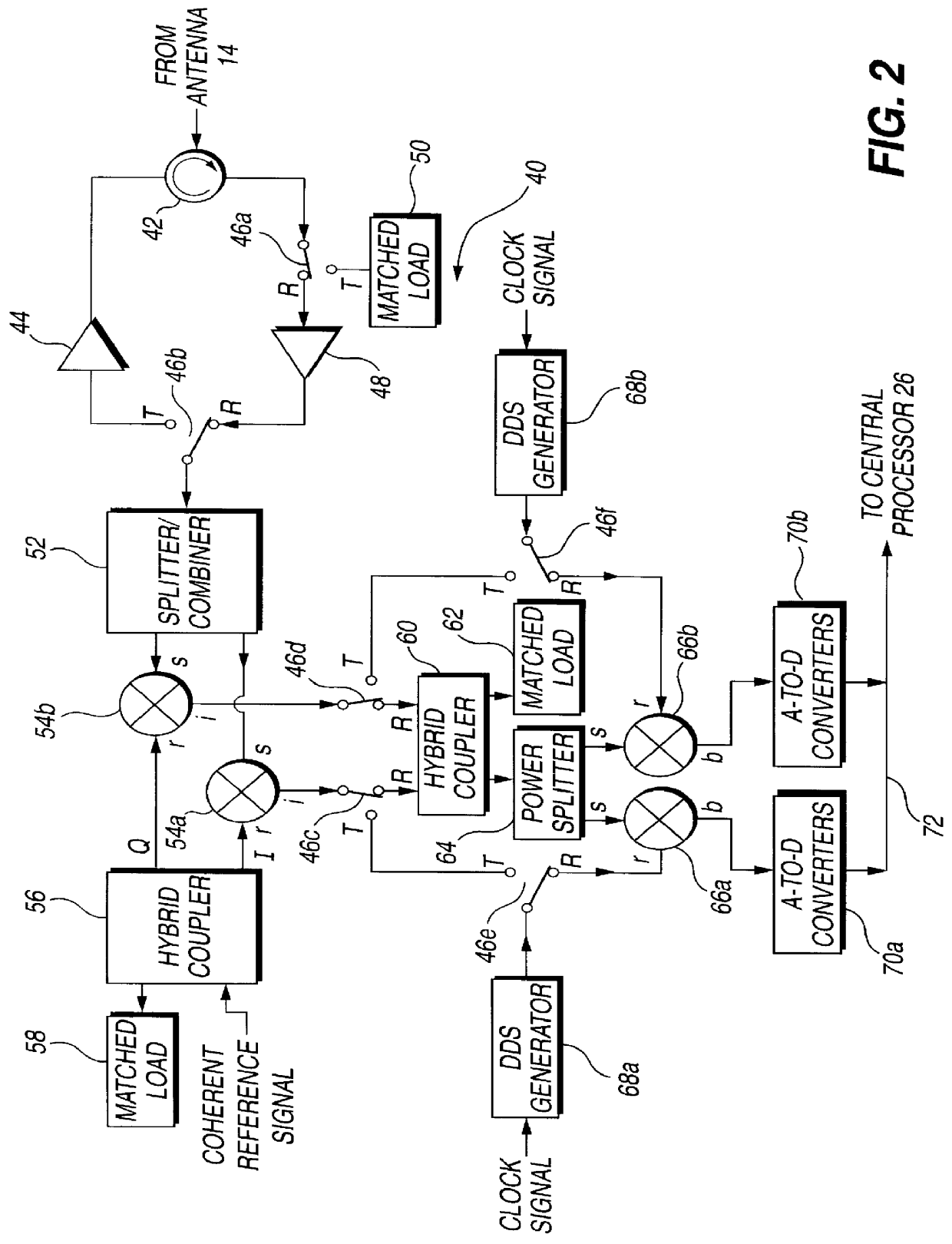
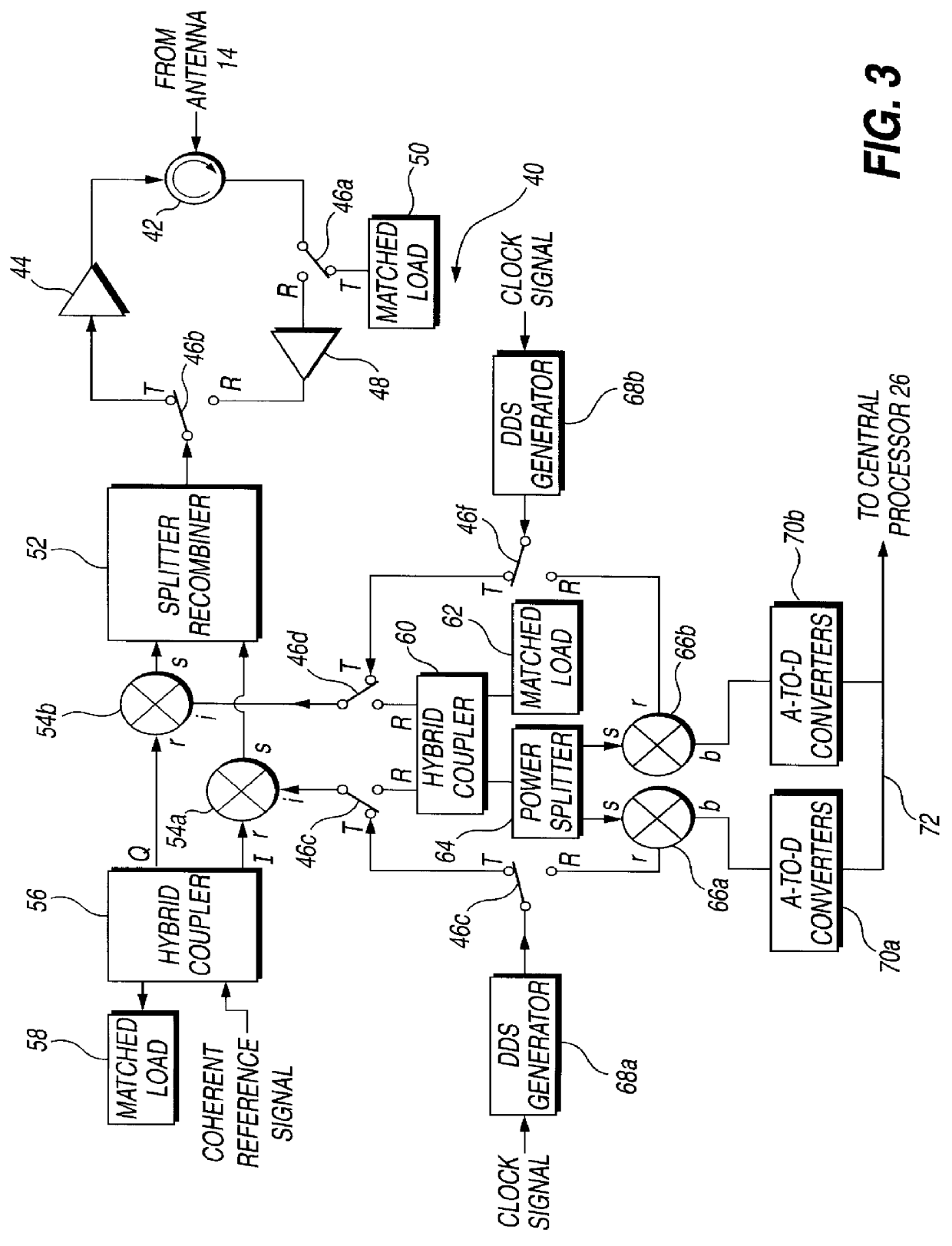
Circuit module for a phased array
InactiveUS6441783B1Low costReduce the amount requiredMultiplex system selection arrangementsAntennasLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
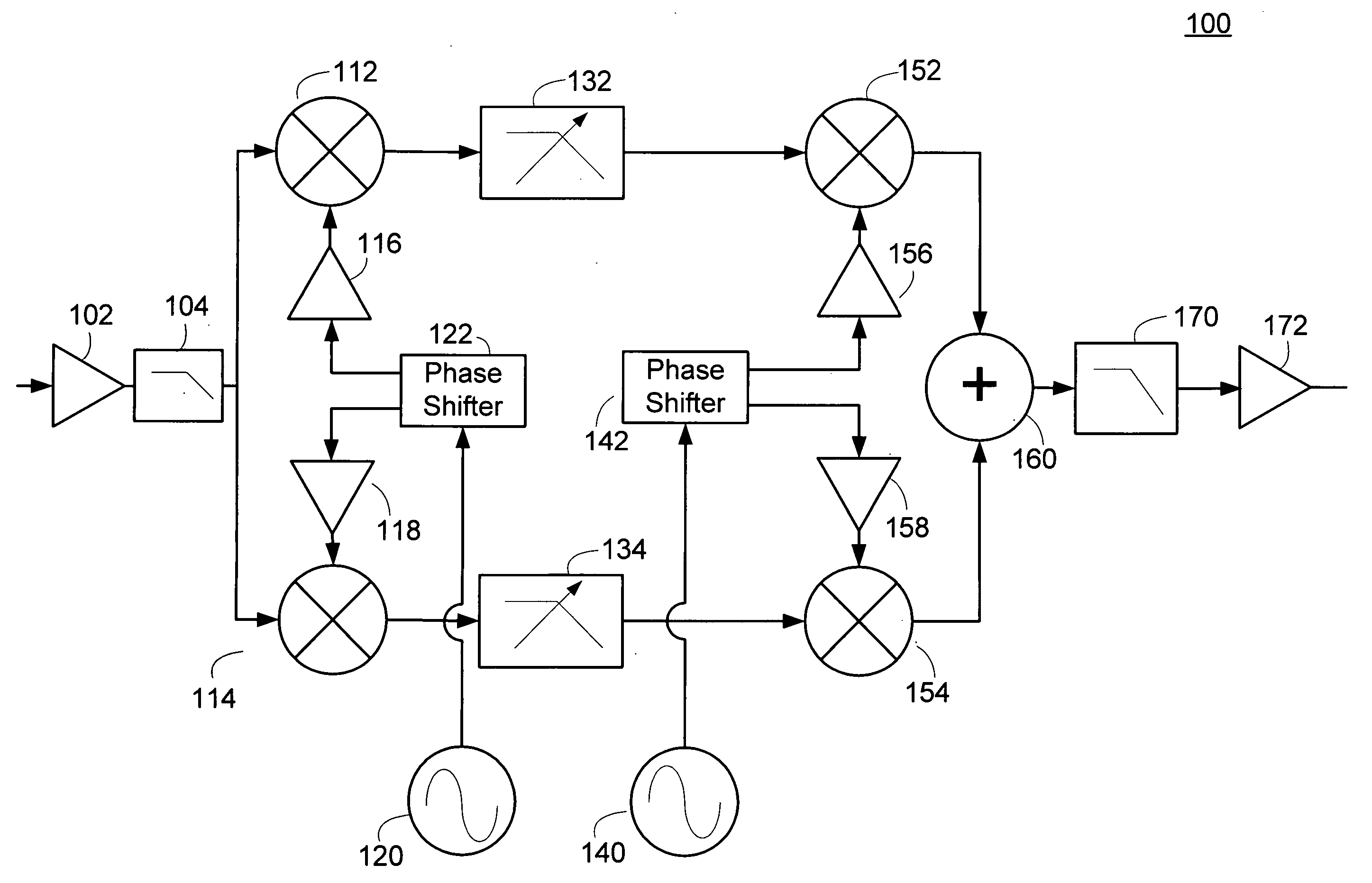
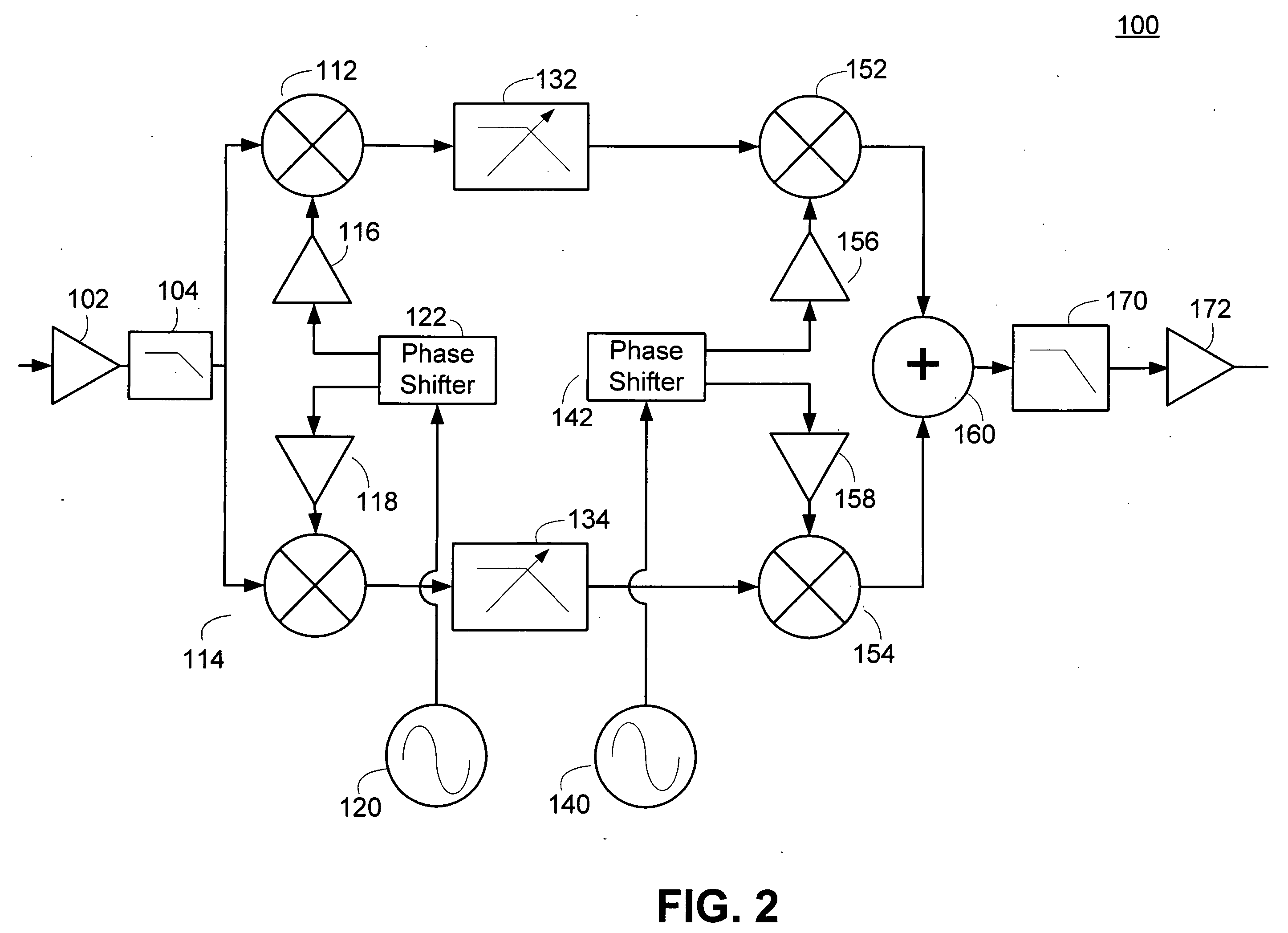
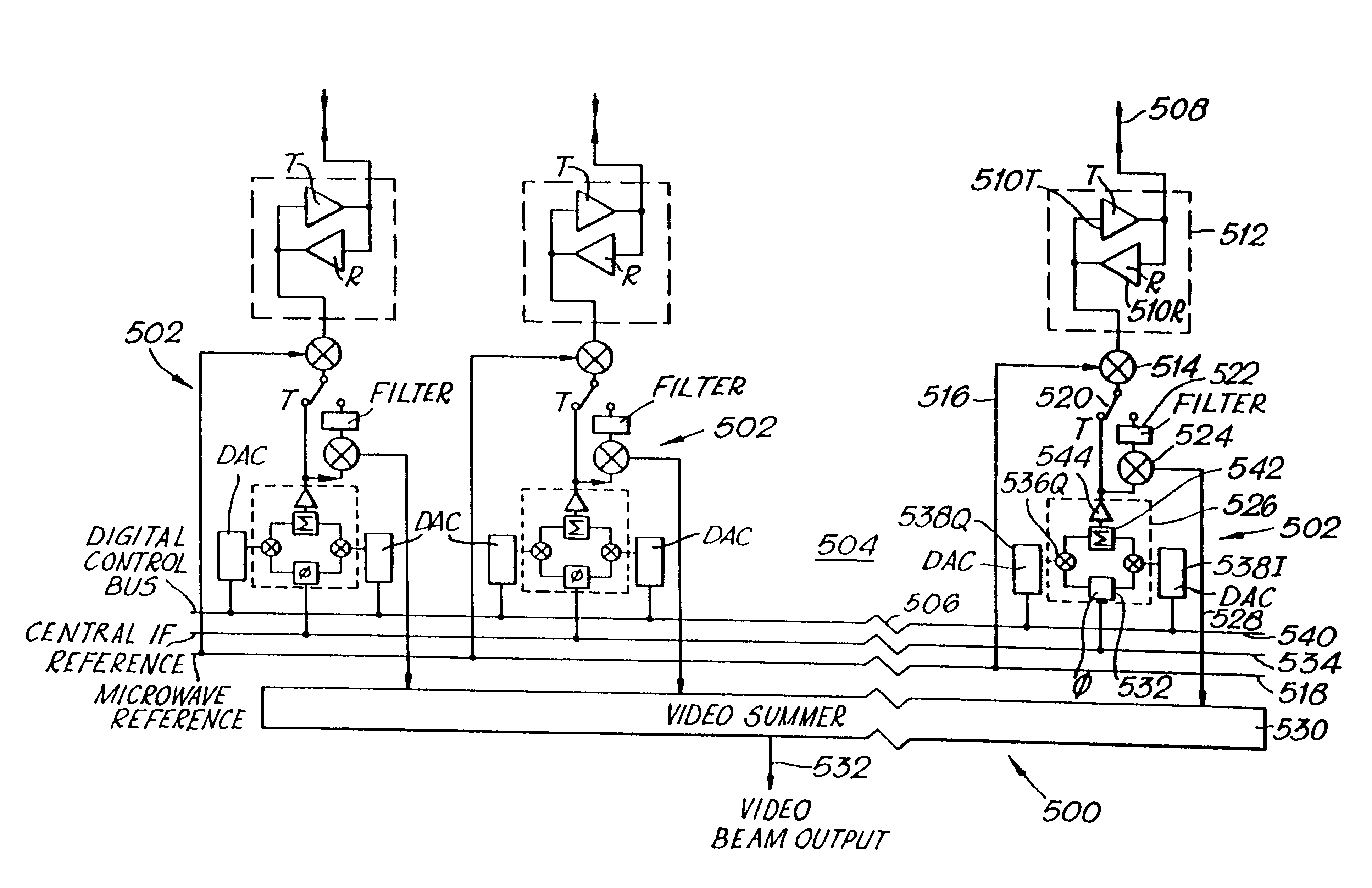
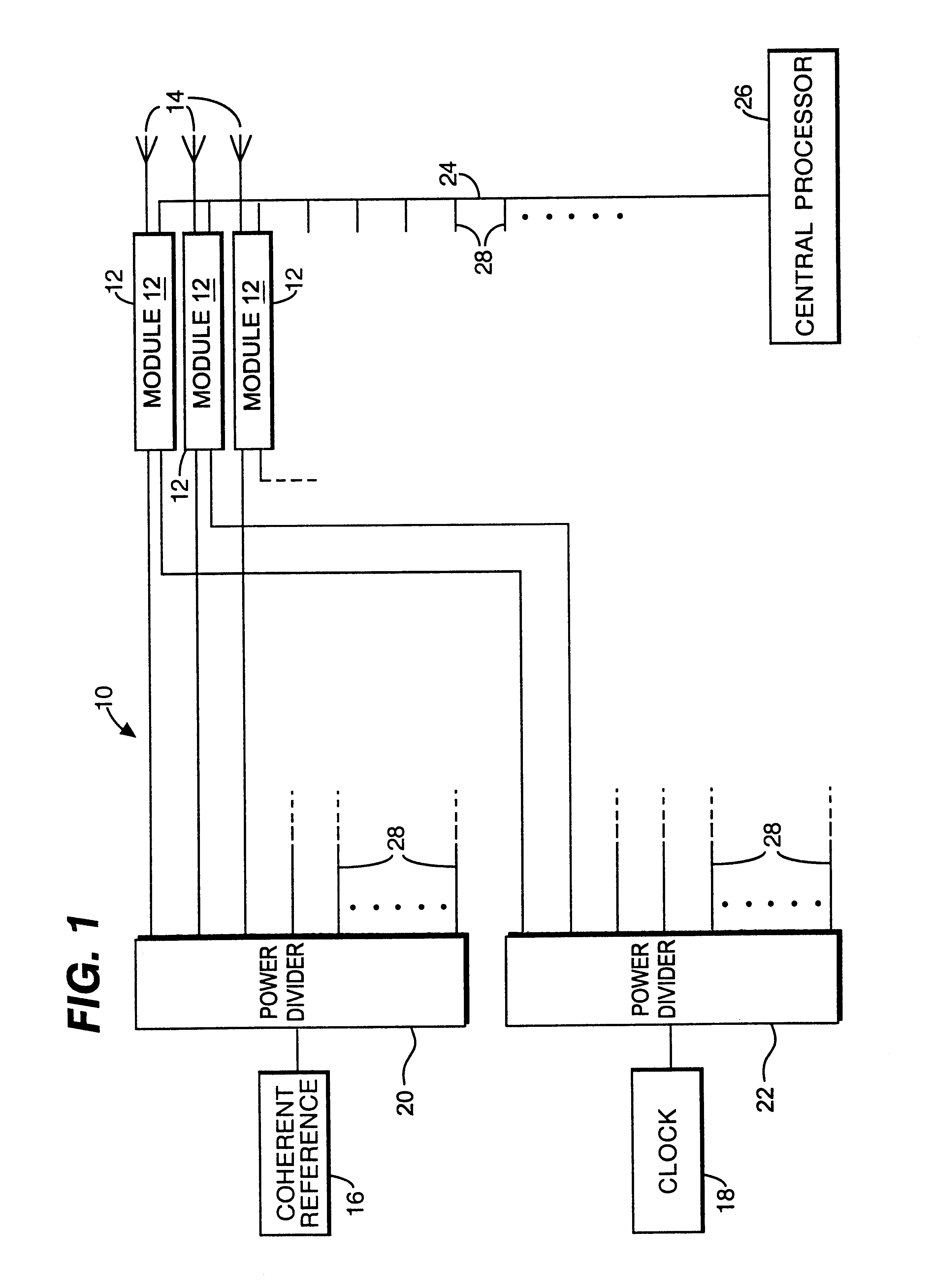
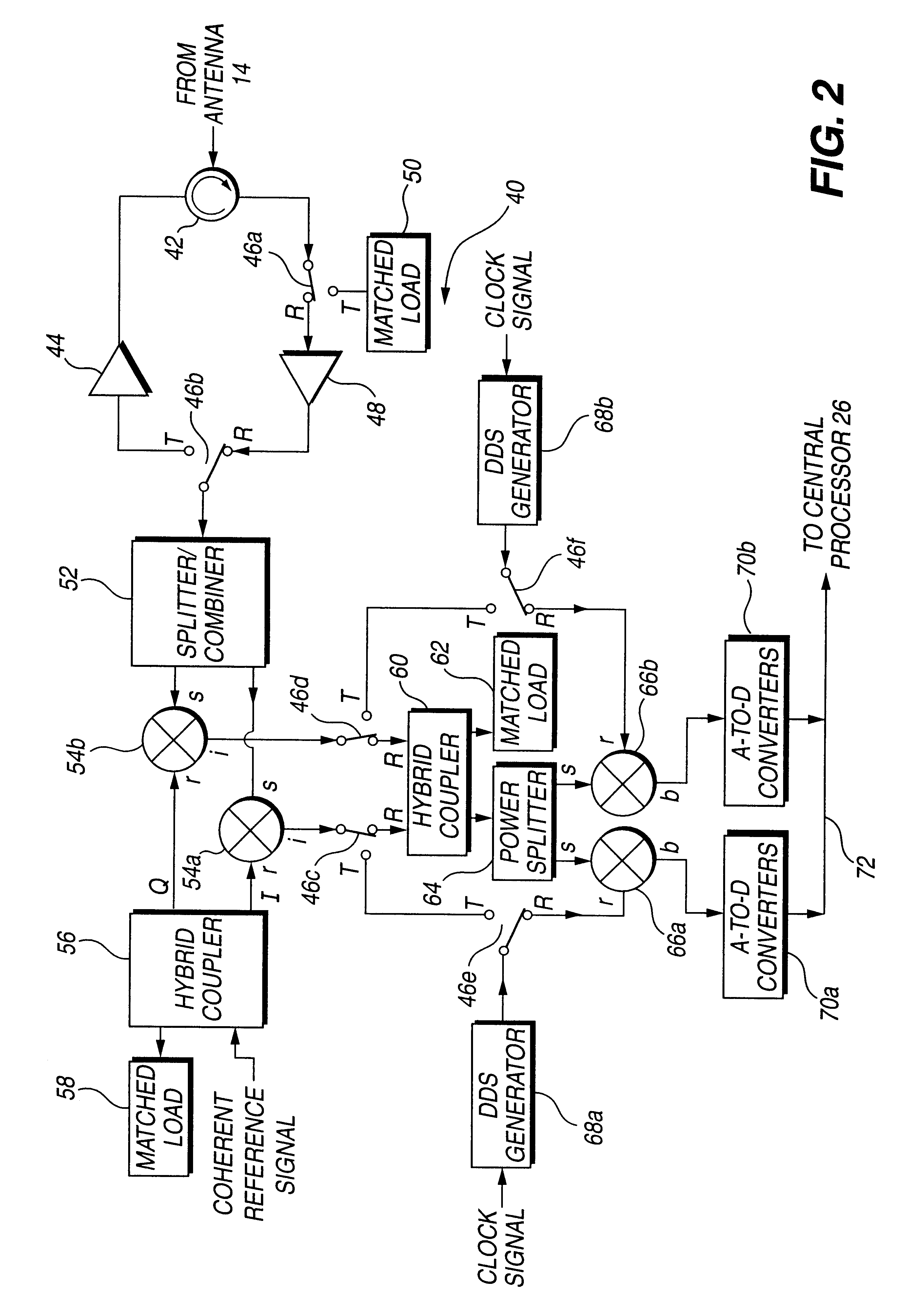
A circuit module for a phased array (10) incorporates radio frequency (RF) mixers (54a, 54b) connected to an RF splitter / combiner (52) and to in-phase and quadrature RF reference signals. The RF mixers (54a, 54b) are also connected to intermediate frequency (IF) processing circuitry (60 to 68) providing for phase control of RF signals and IF reference signals. In transmission mode, the RF mixer (54a, 54b) receive phase-controlled, digitally synthesised IF signals from clock-activated generators (68a, 68b). Their outputs are combined at the RF splitter / combiner (52) to provide single sideband upconversion of the phase-controlled IF signals. In reception mode, the RF splitter / combiner (52) and the RF mixers (54a, 54b) act as an image rejection mixer circuit in which the phase-controlled IF signals are local oscillator signals. Beamforming is carried out by computer control of the IF phase together with, in the case of reception, analogue or digital summation of output signals from an array of modules (12).
Owner:FLIR BELGIUM BVBA
Circuit module for a phased array radar
InactiveUS6054948ALow costReduce the amount requiredMultiplex system selection arrangementsModular arraysLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
PCT No. PCT / GB95 / 01607 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 10, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 10, 1997 PCT Filed Jul. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 03367 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 30, 1997A circuit module for a phased array radar (10) incorporates radar frequency (RF) mixers (54a, 54b) connected to an RF splitter / combiner (52) and to in-phase and quadrature RF reference signals. The RF mixers (54a, 54b) are also connected to intermediate frequency (IF) processing circuitry (60 to 68) providing for phase control of RF signals and IF reference signals. In transmission mode, the RF mixer (54a, 54b) receive phase-controlled, digitally synthesised IF signals from clock-activated generators (68a, 68b). Their outputs are combined at the RF splitter / combiner (52) to provide single sideband upconversion of the phase-controlled IF signals. In reception mode, the RF splitter / combiner (52) and the RF mixers (54a, 54b) act as an image rejection mixer circuit in which the phase-controlled IF signals are local oscillator signals. Beamforming is carried out by computer control of the IF phase together with, in the case of reception, analogue or digital summation of output signals from an array of modules (12).
Owner:RAYMARINE BELGIUM
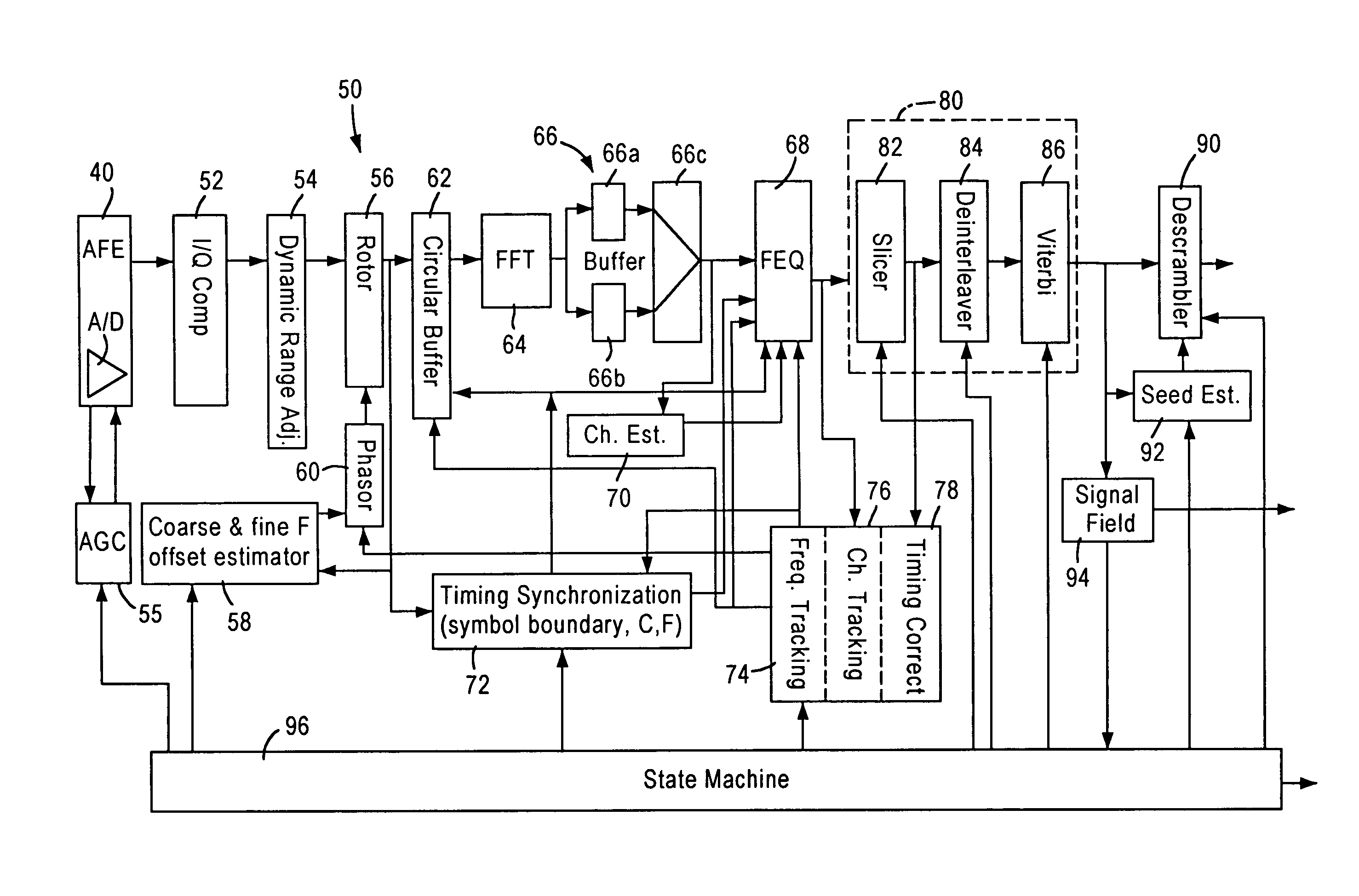
Frequency domain estimation of IQ imbalance in a wireless OFDM direct conversion receiver using loopback connection
ActiveUS7184714B1Accurate estimateAccurate amplitudeModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationLocal oscillator signalPhase imbalance
An OFDM transceiver has a transmitter, a receiver, and a loopback switch. The loopback switch configured is for selectively establishing a physical connection between an output terminal of the transmitter and an input terminal of the receiver. The transmitter is configured for outputting to the output terminal an OFDM signal generated based on a local oscillator signal. The receiver is configured for demodulating the OFDM signal, received via the physical connection, using the local oscillator signal and determining amplitude and phase imbalance parameters based on performing frequency-domain estimation of amplitude and phase imbalances. Hence, the receiver is configured for performing imbalance compensation on a received wireless OFDM signal based on the determined amplitude and phase imbalance parameters. Hence, amplitude and phase imbalances can be estimated accurately despite channel fading and frequency variations encountered between the transmitter of the wireless OFDM signal and the receiver.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
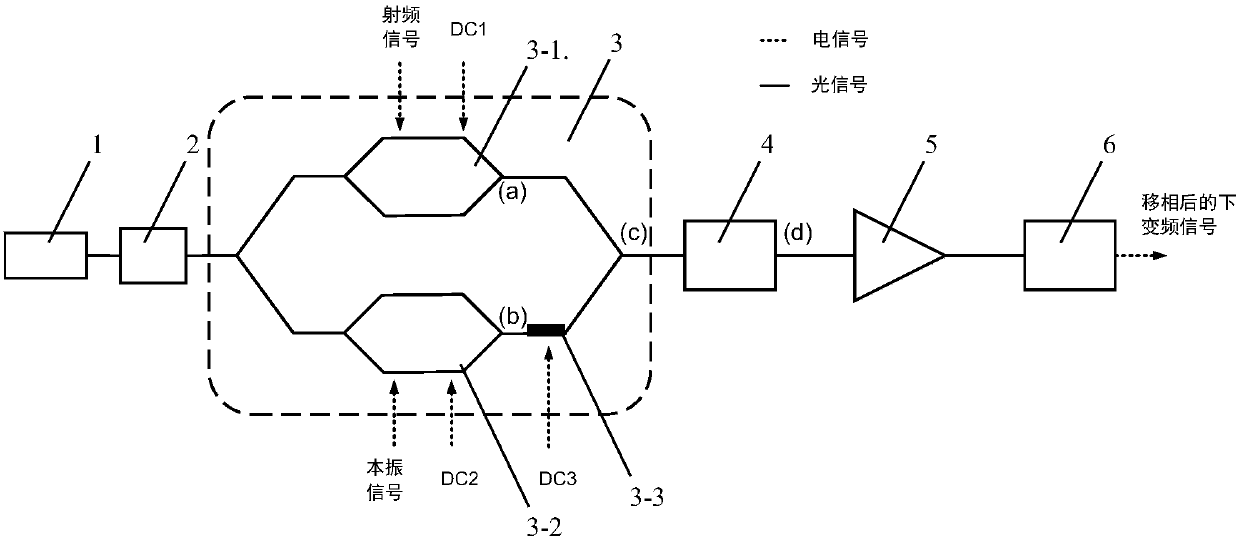
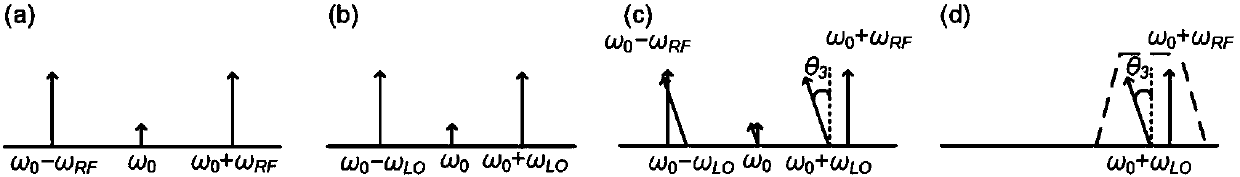
Photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices
ActiveCN107846254AImprove performanceRealize functionPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmittersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a photon method and system for realizing microwave down-conversion and phase shift by using integrated devices, and belongs to the field of microwave photonics. Firstly, opticalcarriers generated by a laser are input to a double-parallel Mach-Zehnder modulator after passing through a polarization controller, a radio frequency signal is modulated by an upper arm sub-modulator, and carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by DC bias; a local oscillator signal is modulated by a lower arm sub-modulator, and the carrier suppression double-sideband modulation is realized by the DC bias; the DC bias of a main intensity modulator is used for changing the phase difference between the radio frequency optical signal and the local oscillator optical signal. A-1 order optical sideband is filtered from an output carrier suppression double-sideband modulation optical signal by an optical bandpass filter, a +1 order optical sideband is retained, and the useless optical sideband is suppressed below the noise floor. Then, power amplification is performed on the optical signal to compensate the insertion loss of modulator and the filter. At last, a down-conversion signal subjected to phase shift is obtained by performing beat frequency by using a photodetector. A very pure frequency spectrum signal is output, and the performance of an integrated functionlink of down-conversion and phase shift is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +1
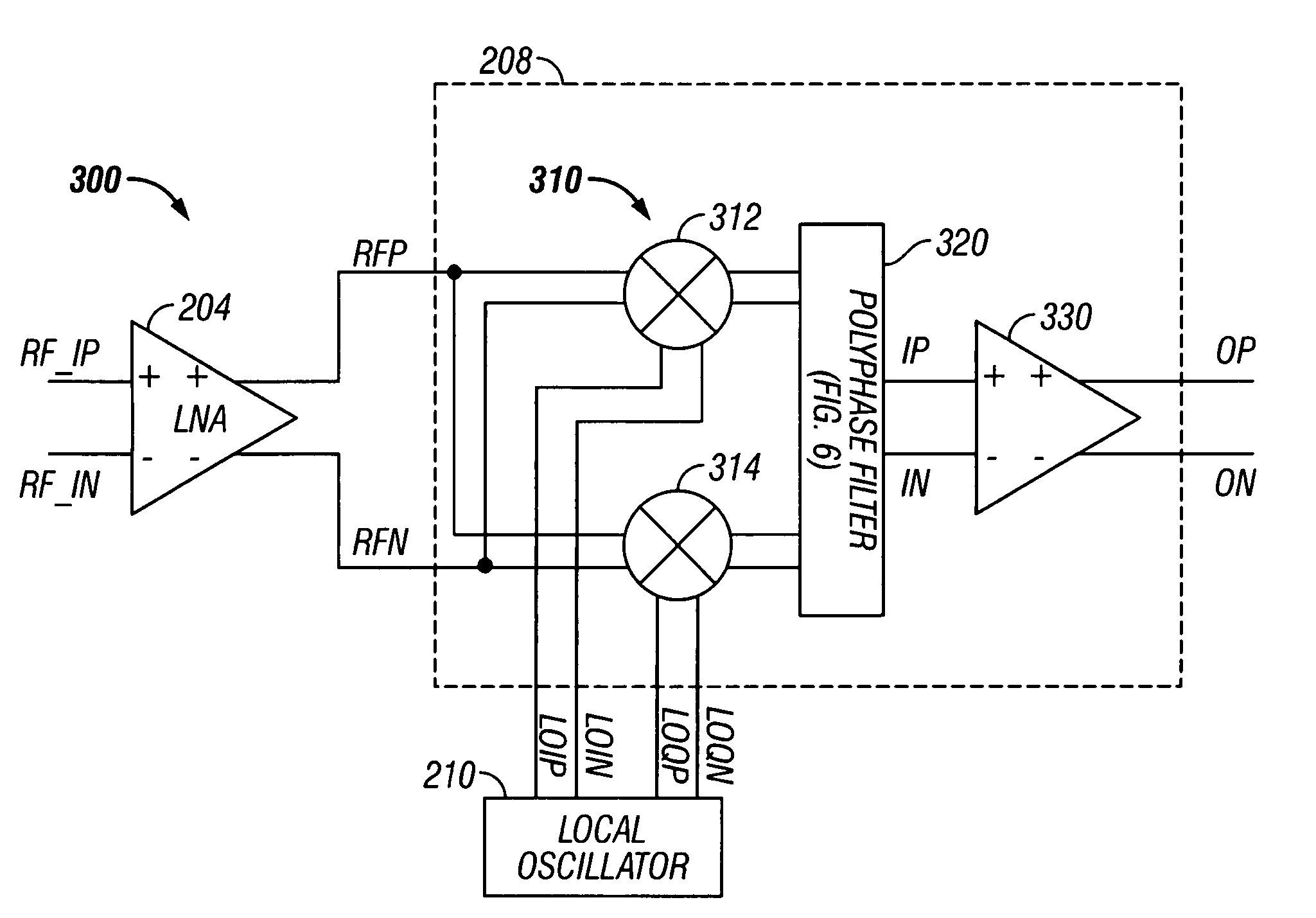
Low noise image reject mixer and method therefor
A receiver (200) includes a transconductance mixer (310), a polyphase filter (320), and a transimpedance amplifier (330). The transconductance mixer (310) mixes a radio frequency (RF) voltage signal into a current signal having a plurality of phases using a local oscillator signal. The polyphase filter (320) filters the current signal to provide a filtered current signal. The transimpedance amplifier (330) converts the filtered current signal into an output voltage signal.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Radio frequency filter using intermediate frequency impedance translation
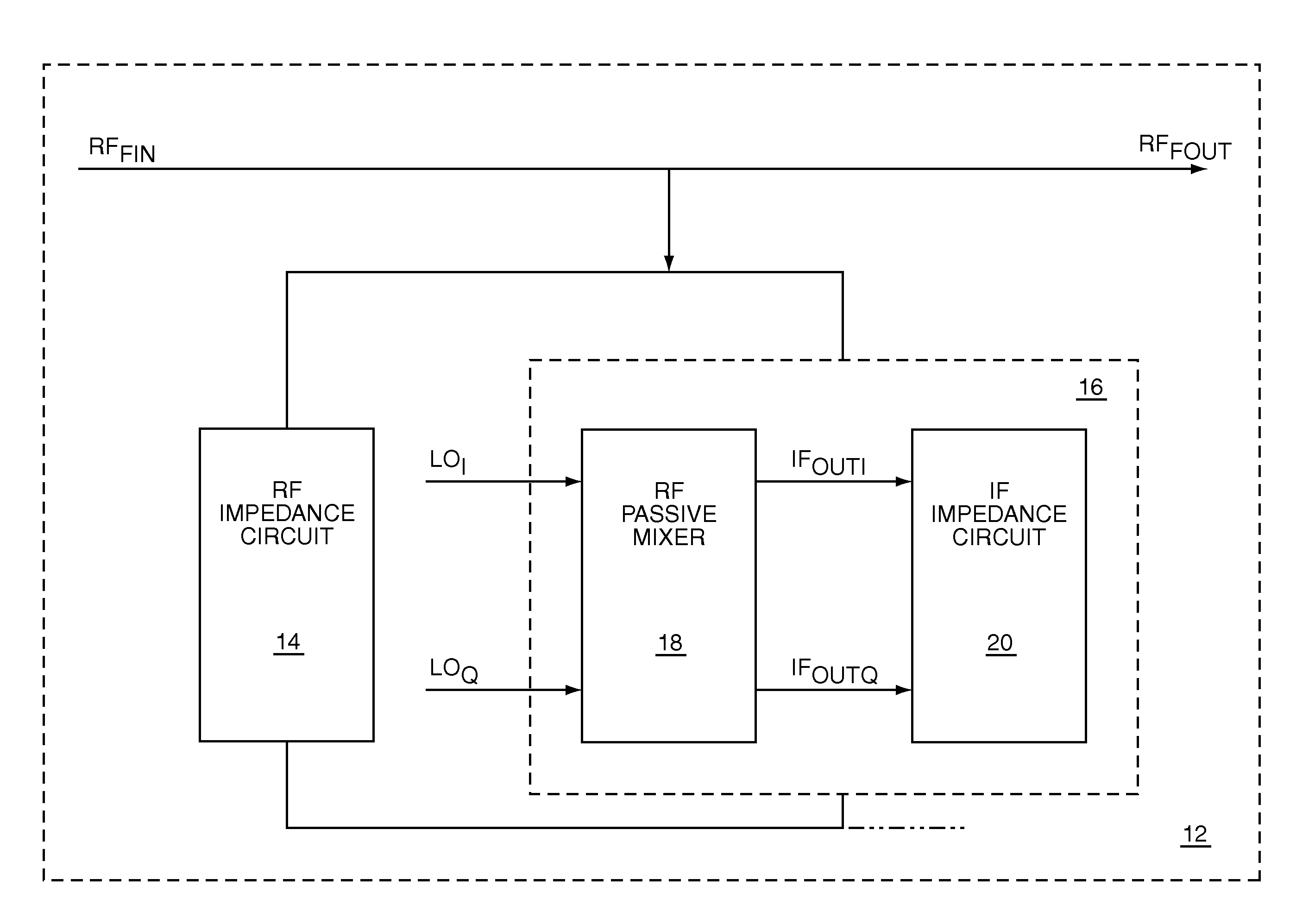
The present invention is an RF filter that translates impedances of an IF circuit to create a filter with an RF center frequency having the high Q roll-off characteristics of an IF filter. The RF filter is self-aligned with the frequency of an RF local oscillator. The RF filter has an impedance divider, which is formed by coupling an RF impedance circuit to a translated IF impedance circuit. The translated IF impedance circuit includes an RF passive mixer and an IF impedance circuit. The mixer translates the impedance of the IF impedance circuit by mixing an RF input signal with an RF local oscillator signal, which determines the RF center frequency. Filtered RF signals may be provided by the impedance divider. Filtered IF signals may be provided by the IF impedance circuit. To effectively translate and preserve the IF impedance characteristics, the IF impedance circuit presents a high impedance at harmonics of the RF local oscillator signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com