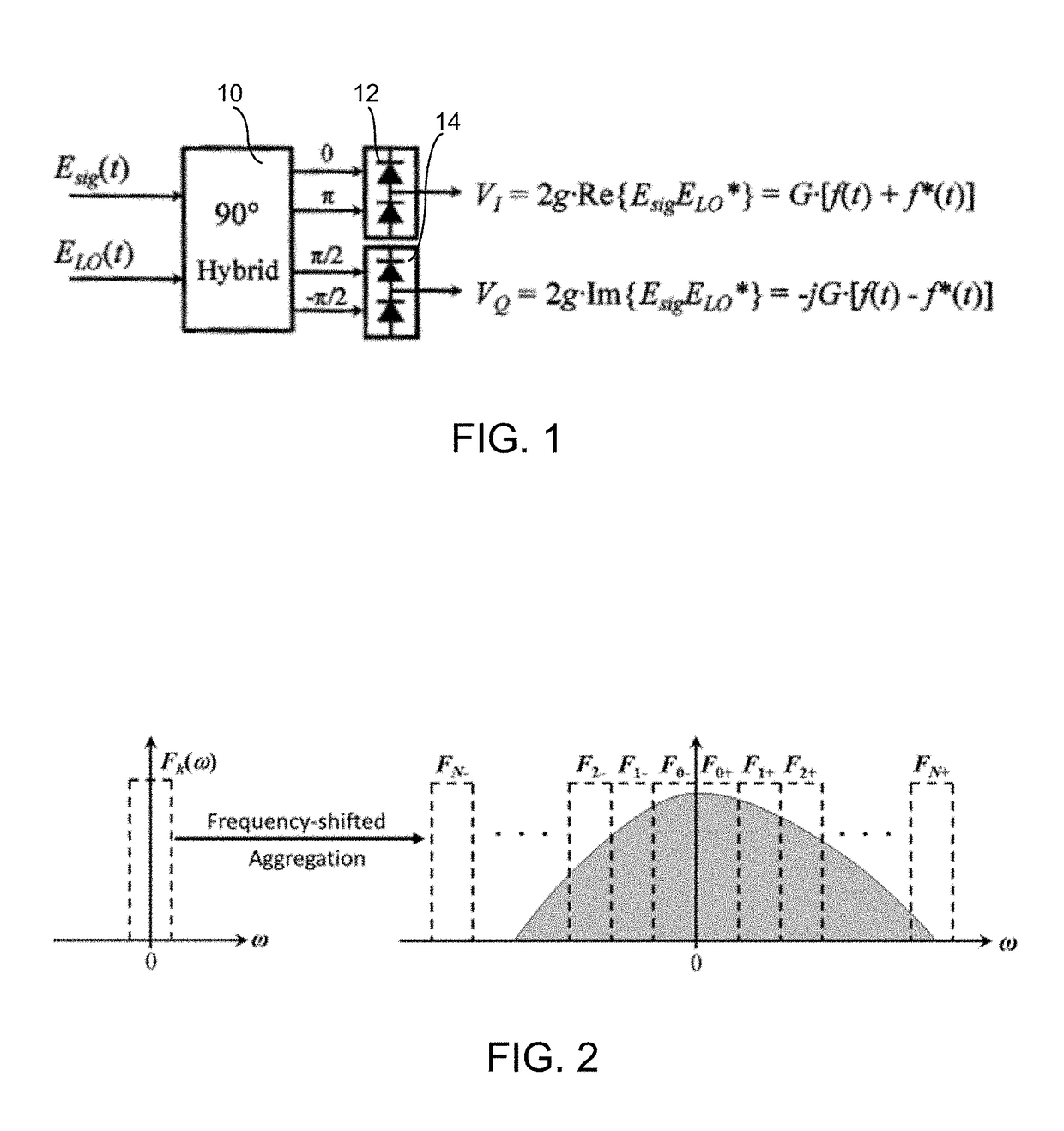
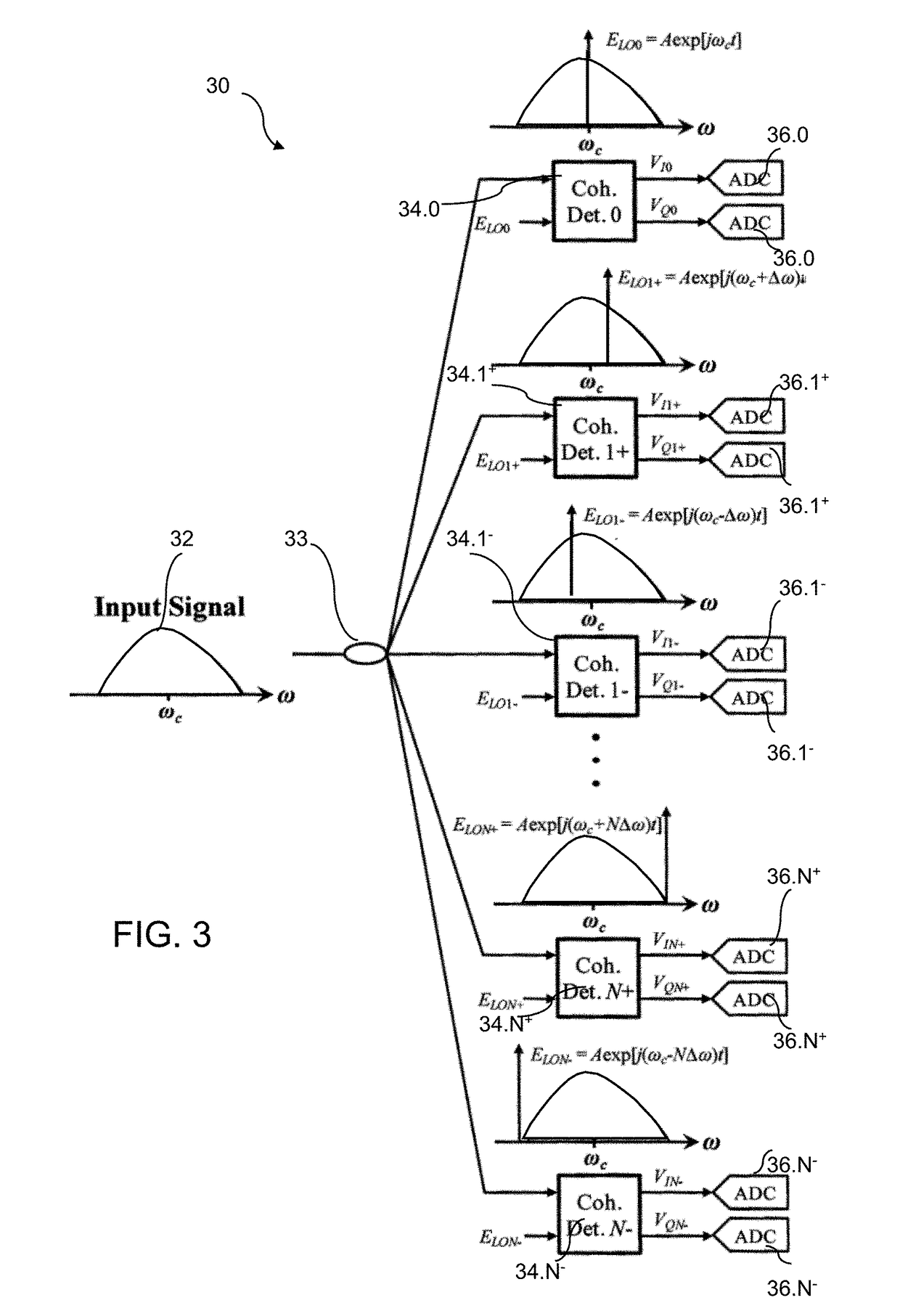
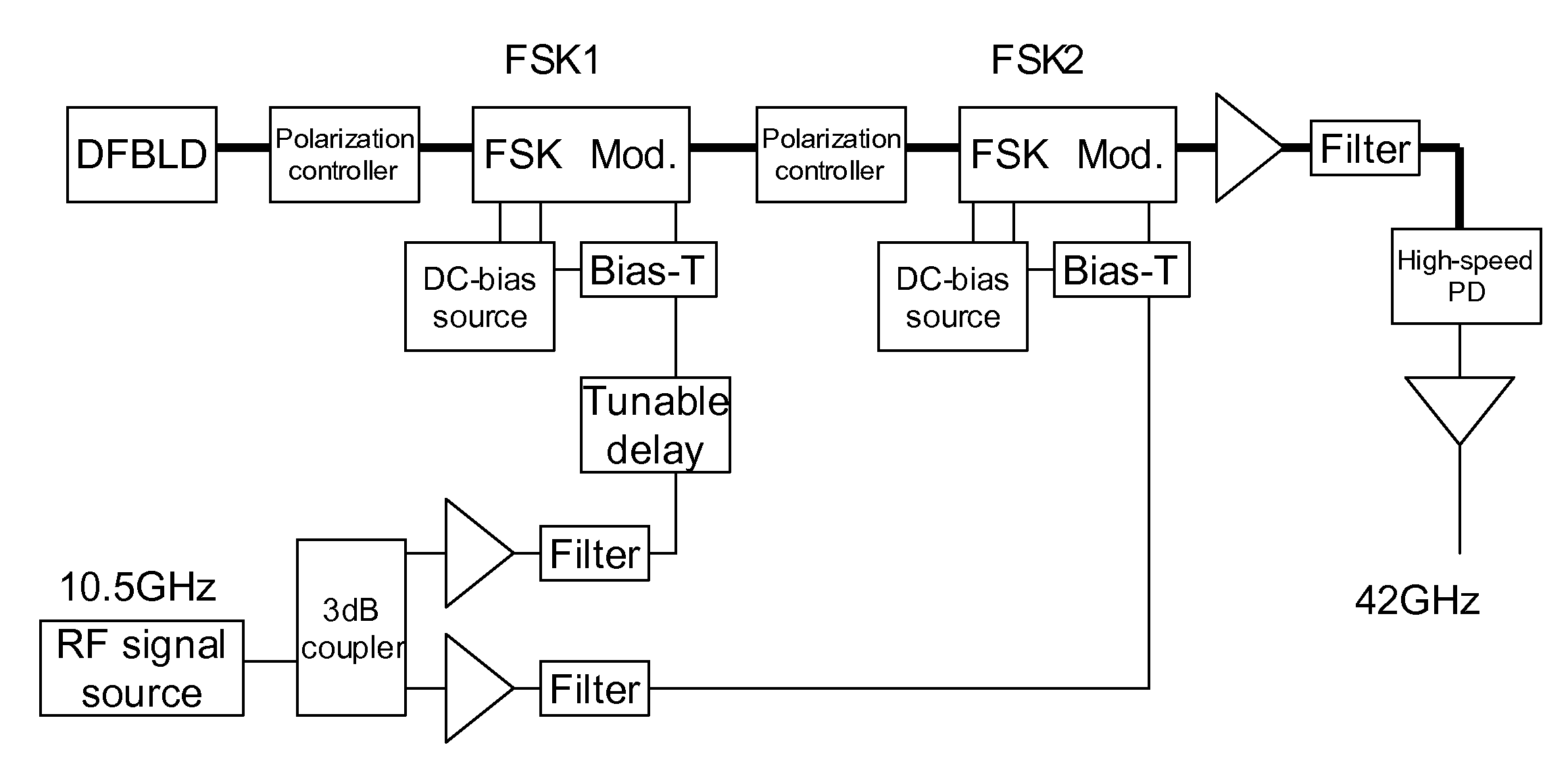
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
248results about "Optical transmission for RF signal generation/processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
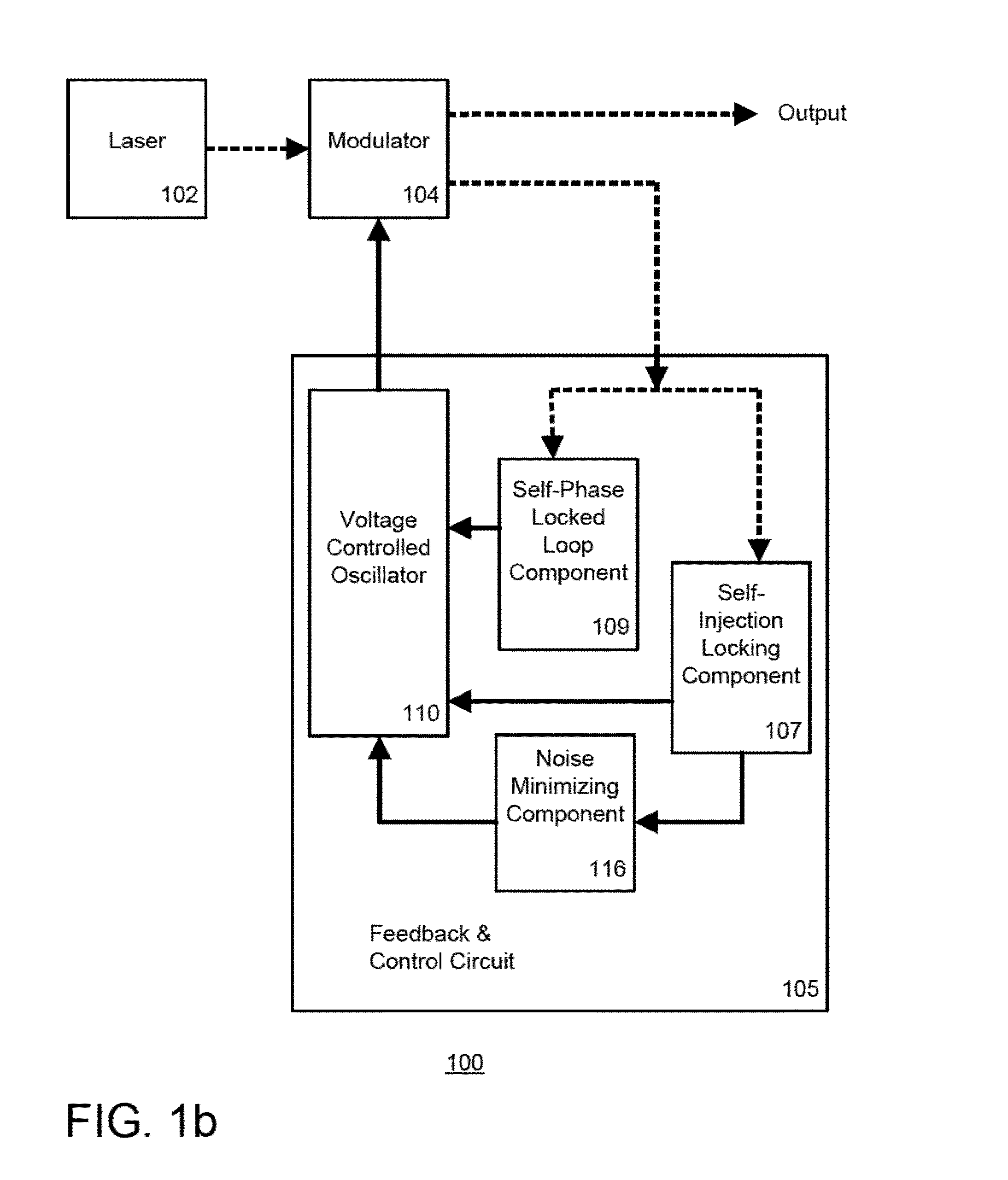
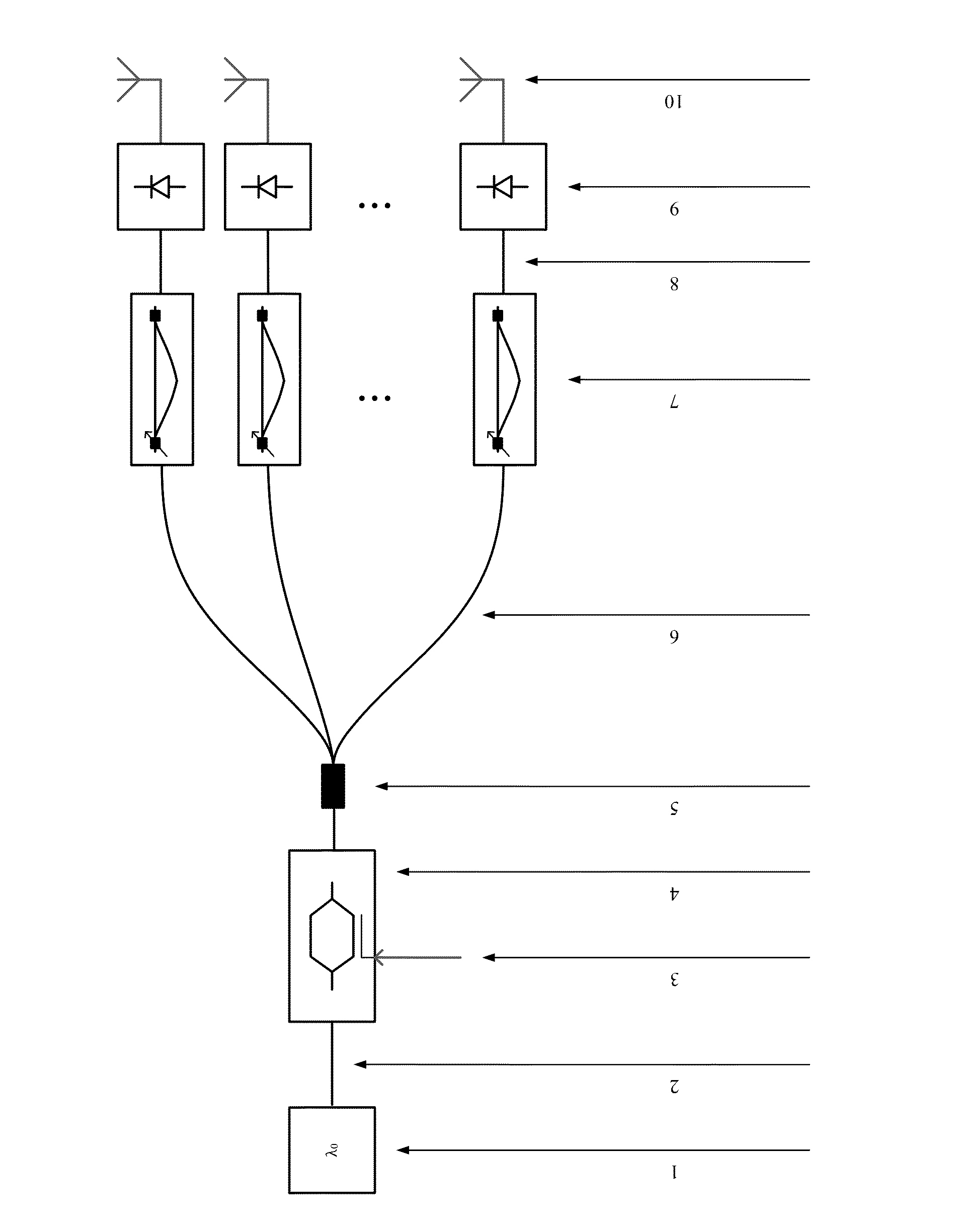
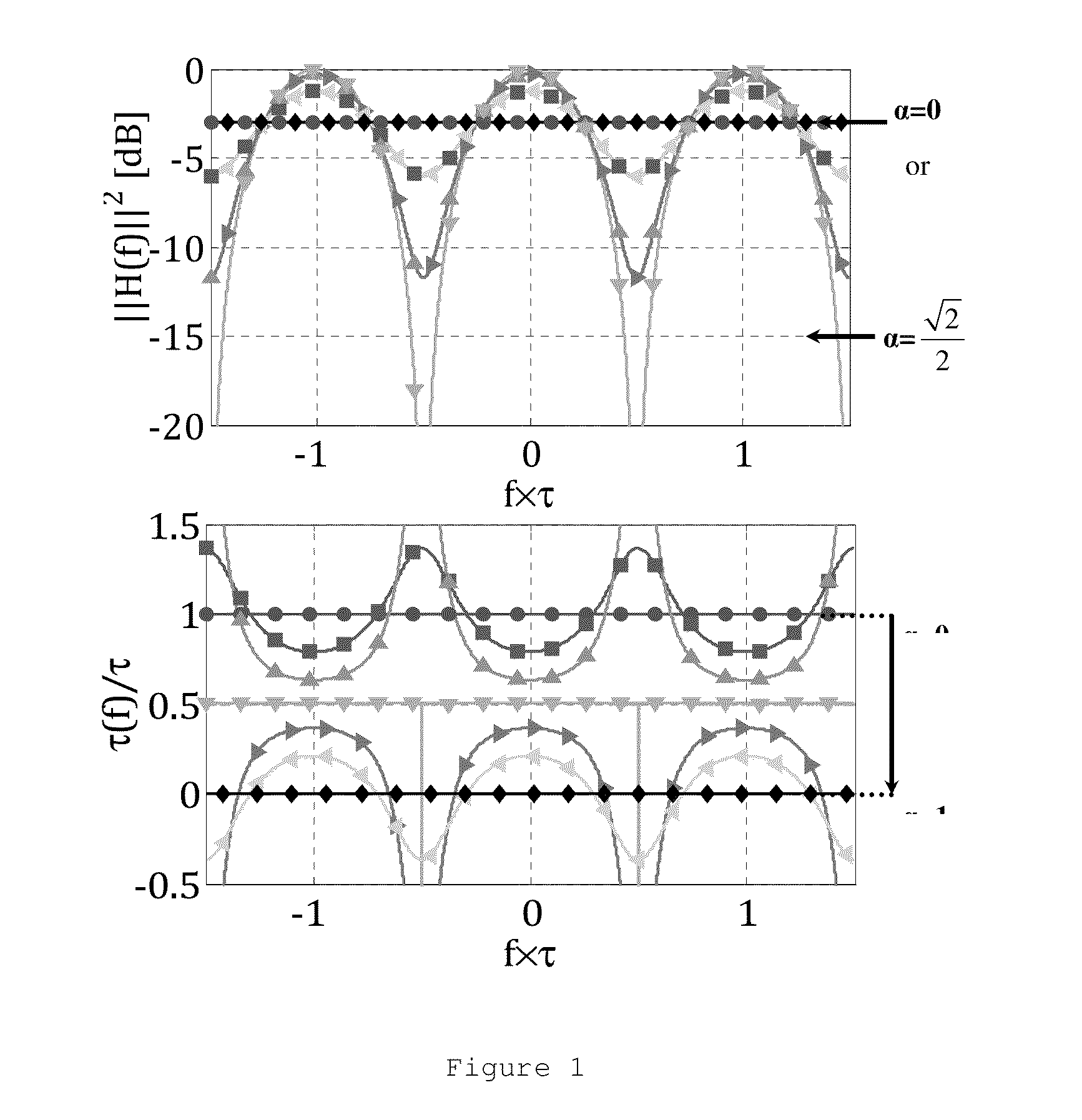
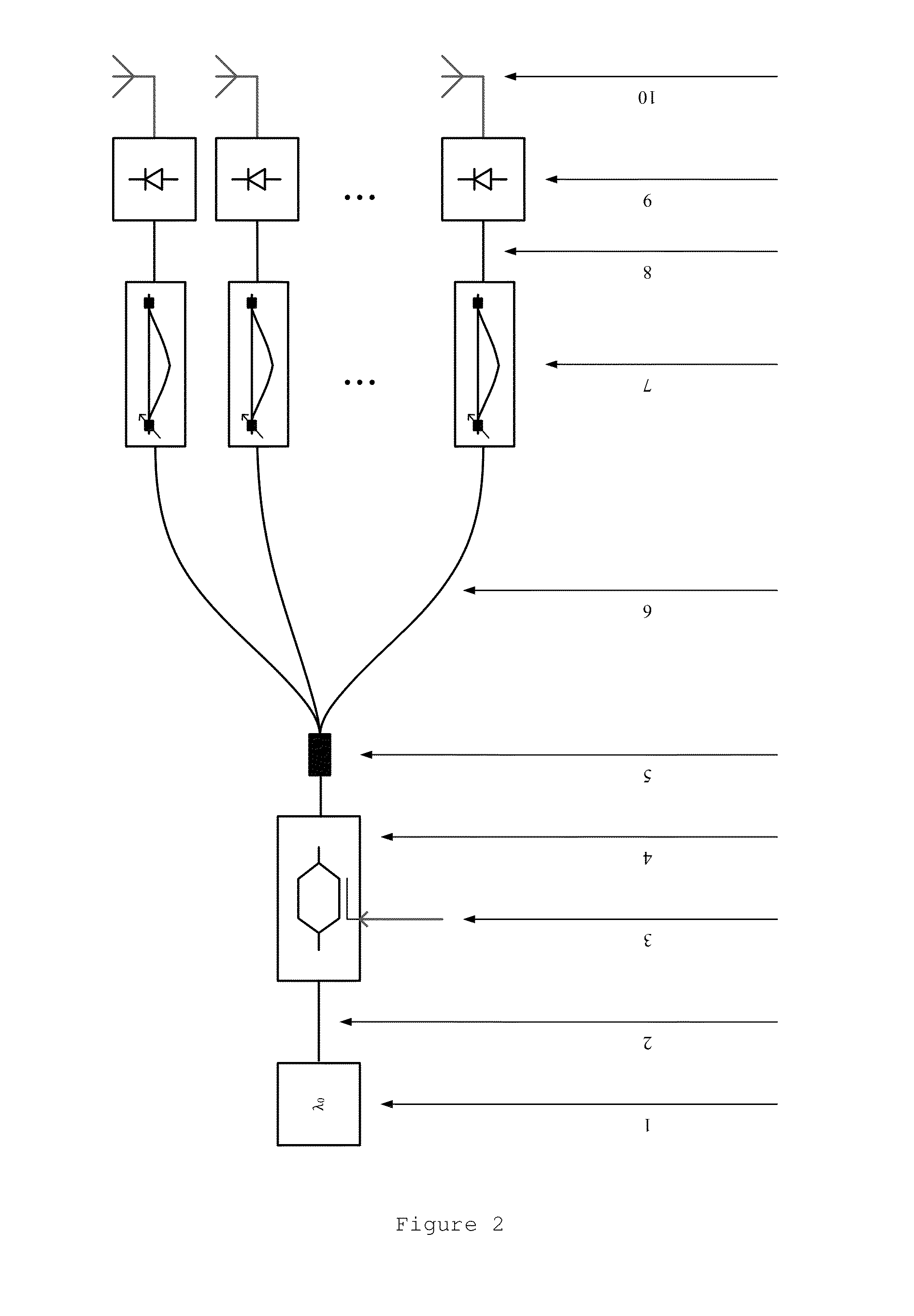
Self injection locked phase locked looped optoelectronic oscillator
Aspects of the disclosure relate generally to a circuit for sustaining an radio frequency (RF) modulated optical signal. The circuit may comprise a self injection locking component having a fiber optic delay line over which a portion of the optical signal propagates. The circuit may also comprise a self phase locked loop component having at least two fiber optic cables having different lengths and over which another portion of the optical signal propagates and a phase detector coupled to the at least two fiber optic cables and configured to determine a phase difference between the signals propagating over one of the respective fiber optic cables. The circuit may further comprise a voltage controlled oscillator configured to generate a stable oscillating signal in response to signals generated by each of the self injection locking and self phase locked loop components, the stable oscillating signal being configured to sustain the optical signal.
Owner:SYNERGY MICROWAVE CORP
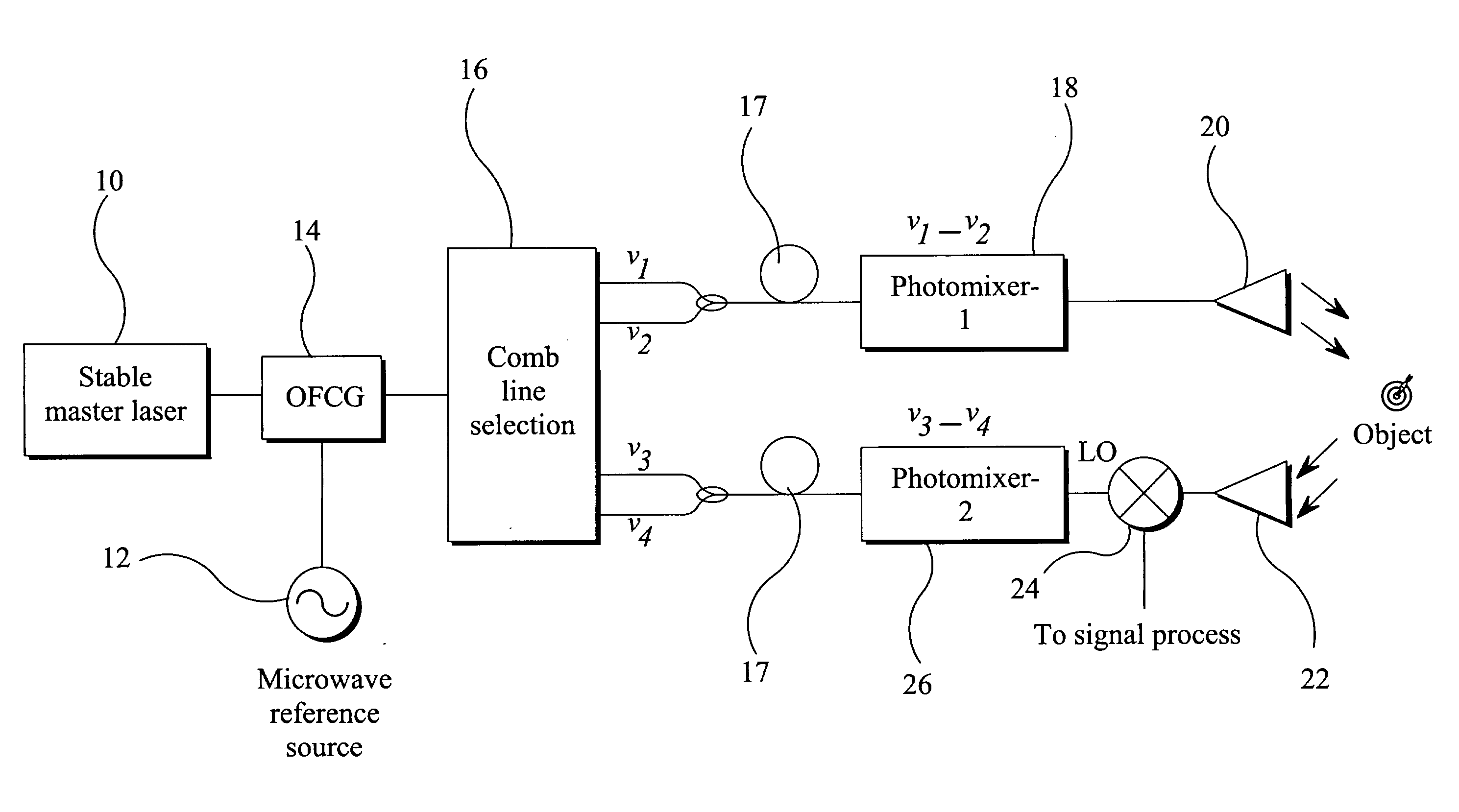
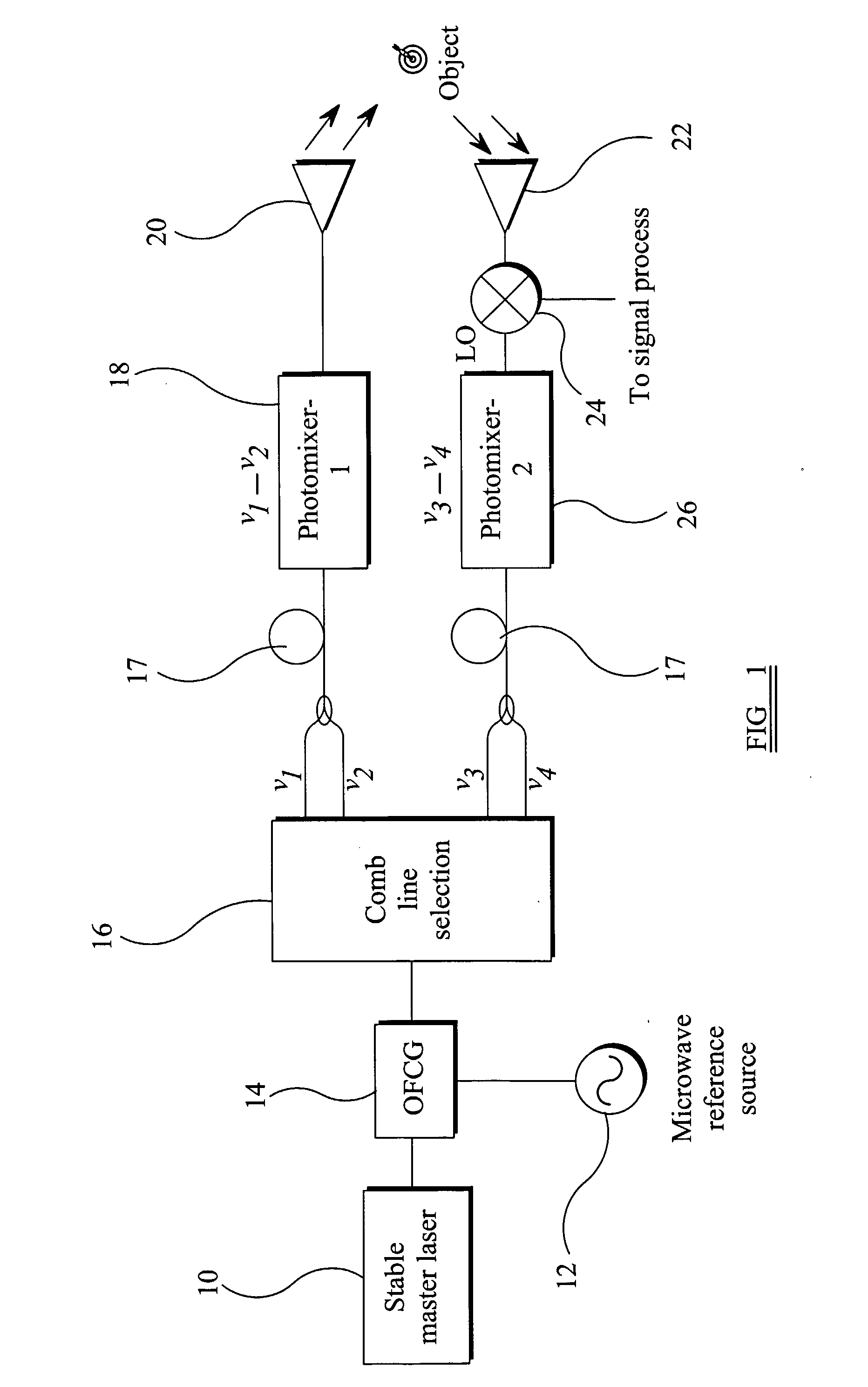
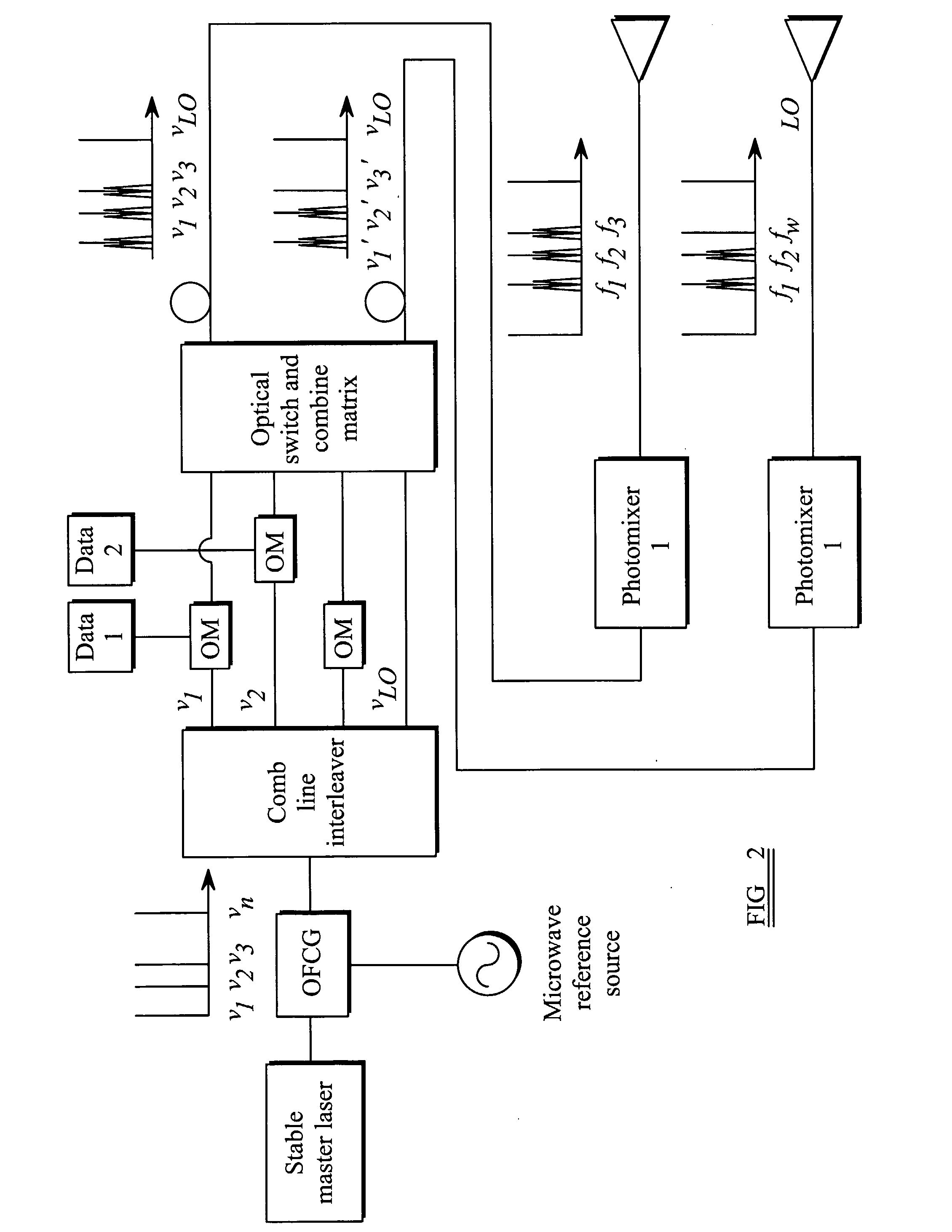
Electromagnetic Transmission/Reception System
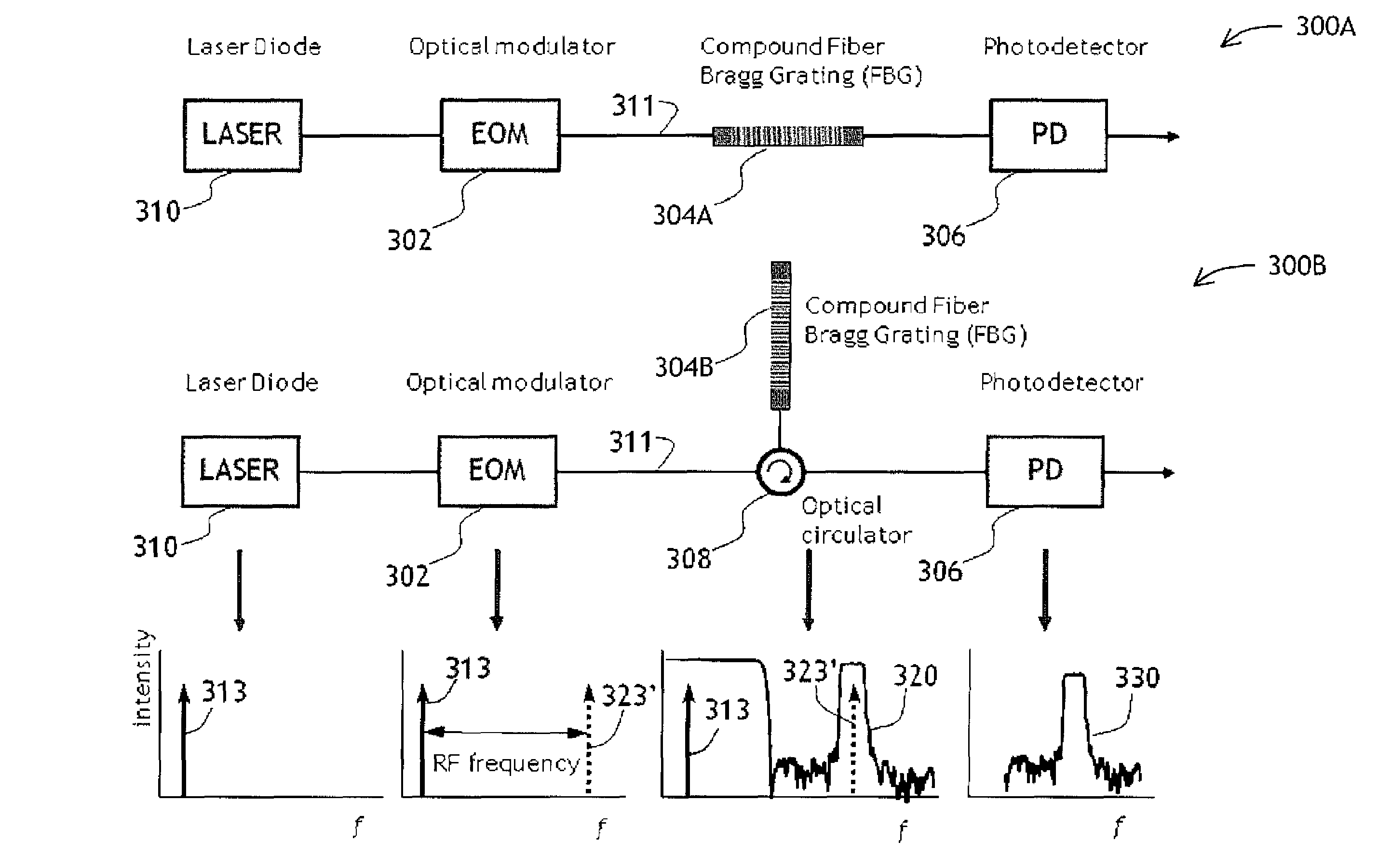
InactiveUS20080212974A1Promote generationStable coherent detectionOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
An electromagnetic transmission and reception system comprises a transmitter section and a receiver section. The transmitter section has a first signal source, a second signal source at a lower frequency than the first signal source, and means for generating from the first and second signal sources a plurality of signals with fixed frequency spacing derived from the second signal source frequency. One or more pairs of the plurality of signals are selected, and for the or each pair, the signals of the pair are combined to derive an output signal having a frequency derived from the difference between the frequencies of the signals of the pair. The receiver section combines a received signal, which comprises a received version of the output signal, with a local oscillator signal for frequency down-conversion of the received signal. This local oscillator signal is generated by the transmitter section. This provides a system in which the generation of signals of the desired frequency is achieved by mixing signals of specific frequencies. The reception uses frequency down-conversion using the same signal sources as used for the transmission. This enables a low noise system to be implemented.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KENT
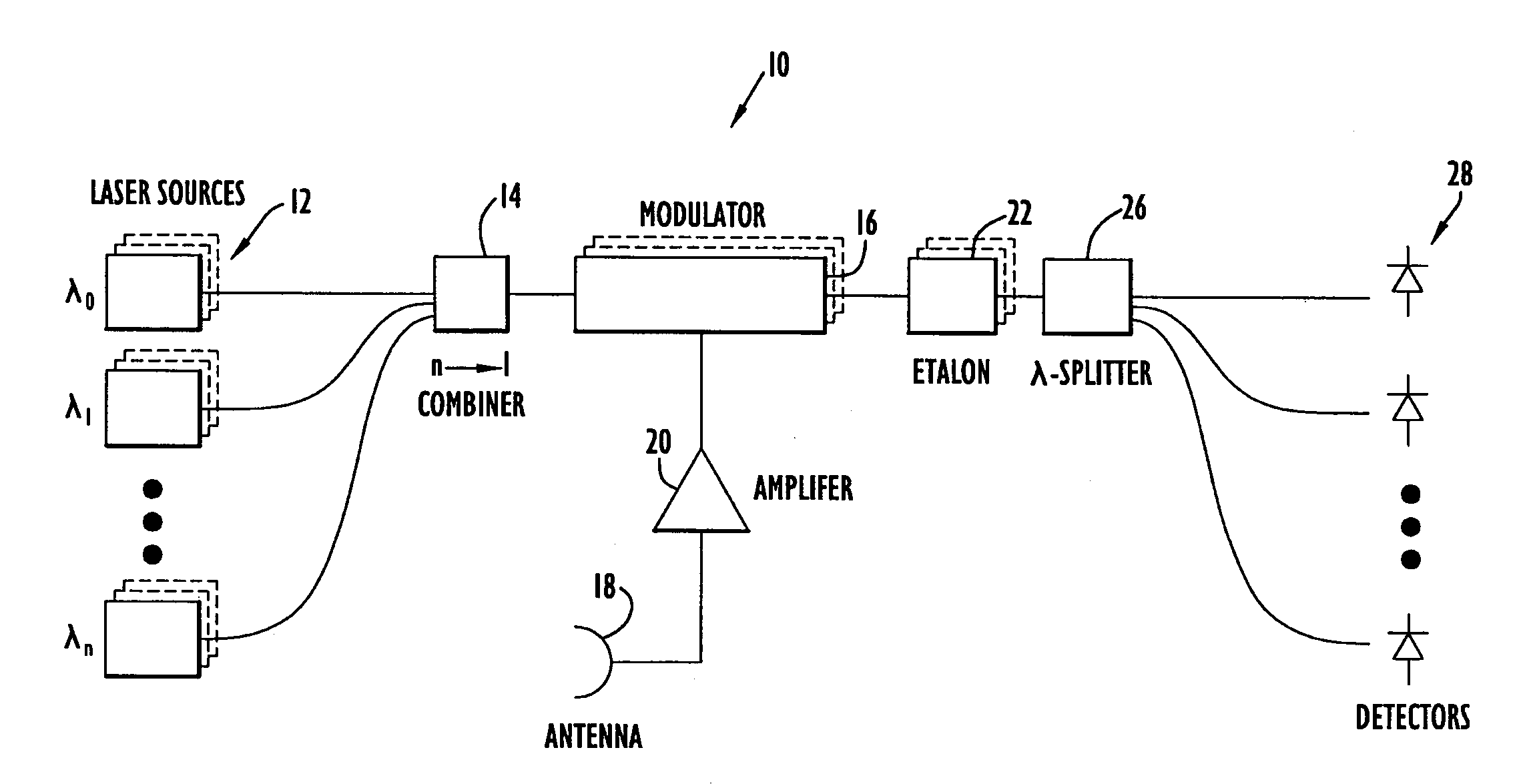
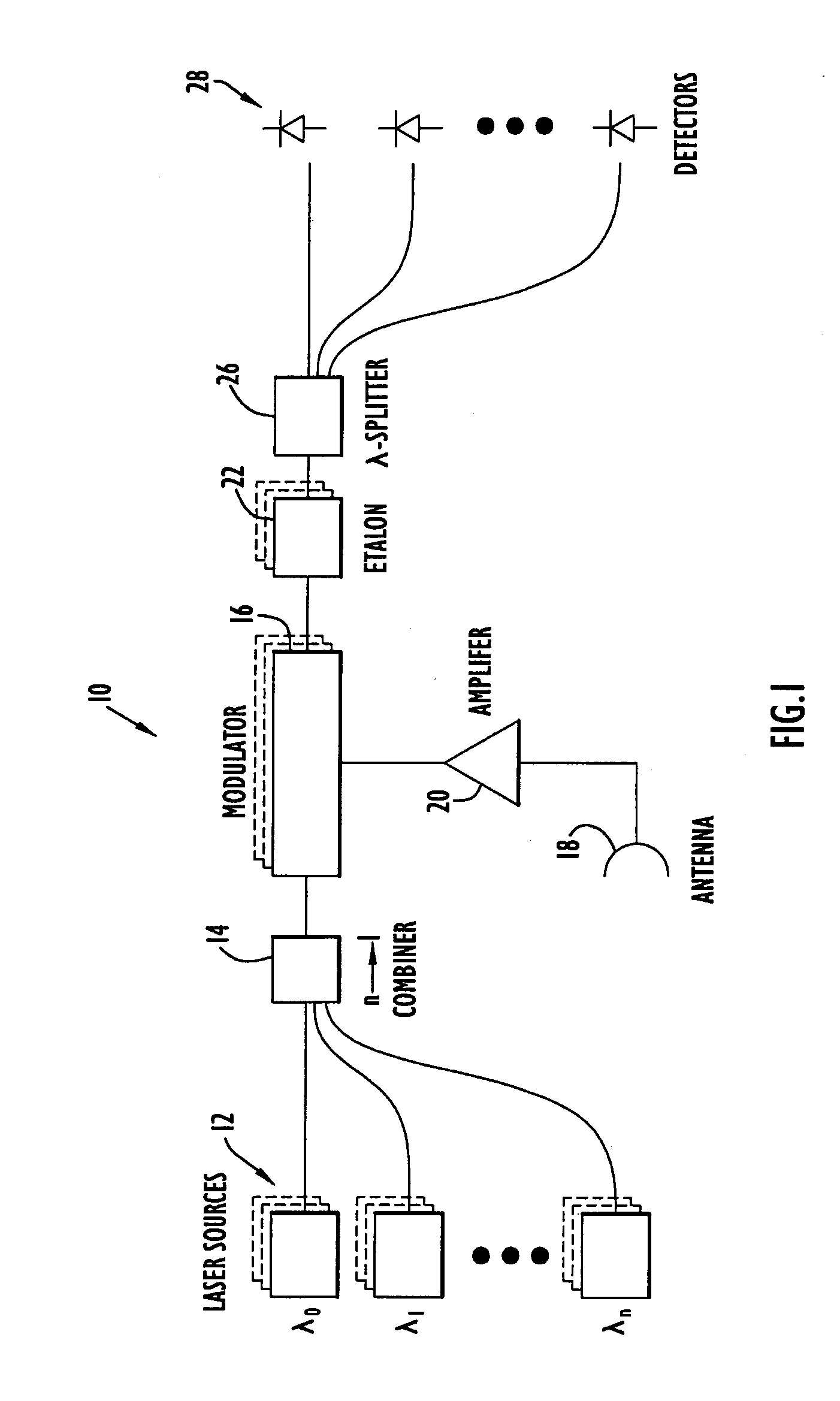
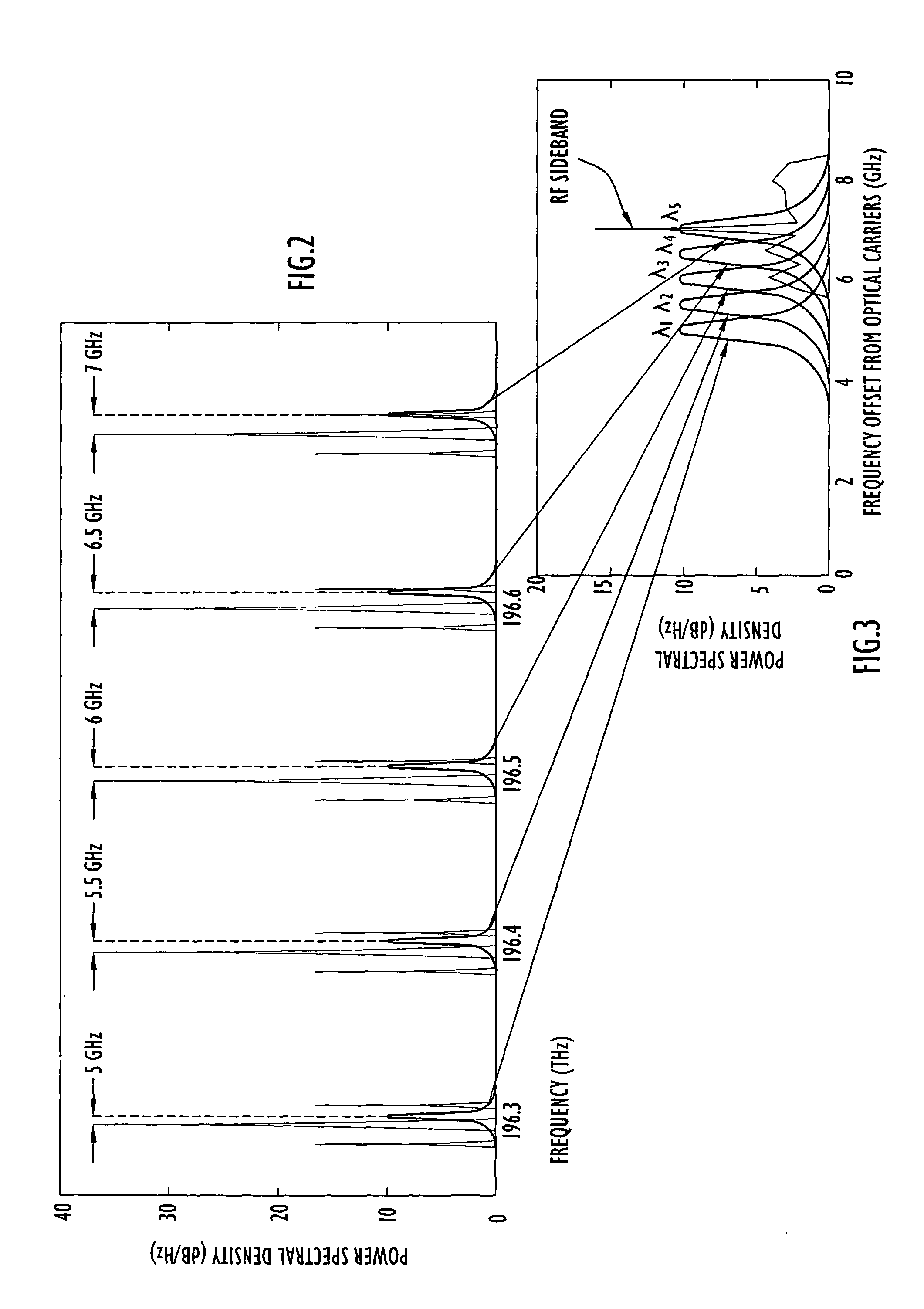
Photonic channelized RF receiver employing dense wavelength division multiplexing
ActiveUS7245833B1Reliable detectionHigh sensitivity and reliabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingLight beamPhotonics
A photonic channelized receiver includes: an optical source, an optical combiner, an electro-optical modulator, an etalon, a wavelength splitter, and a set of detectors. The optical source produces a set of optical signals at spaced wavelengths, and the optical combiner combines the optical signals into a common beam. The electro-optical modulator modulates the common beam with an RF signal to produce sidebands offset from frequencies of the optical signals by the RF signal frequency. The etalon has a periodic transfer function that filters the modulated common beam such that the signals in the filtered, modulated common beam function as receiver channels corresponding to respective RF frequencies. The wavelength splitter separates the common beam into channel output signals whose intensities are a function of the frequency of the RF signal. The detectors measure the intensities of the channel output signals to determine the frequency of the RF signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
RF channelizer based on parametrically generated combs derived from a single master seed
ActiveUS9287993B1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingLight beamCenter frequency
An RF channelizer comprising: a master laser for generating a reference beam; a splitter for splitting the reference beam into first and second beams; first and second modulator modules for converting the first and second beams into first and second modulated beams; first and second seed tone generators for deriving first and second seed tones; first and second parametric mixers for converting the first and second seed tones into first and second combs; a signal modulator for modulating a received RF signal onto the first comb; first and second optical filters for separating the first and second combs into pluralities of first and second filtered beams with center frequencies corresponding to the second comb lines; and a coherent detection array for selecting, combining, and detecting corresponding pairs from first and second filtered beams providing at the output a contiguous bank of channelized signals covering the bandwidth of the RF signal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Modulated light signal processing method and apparatus
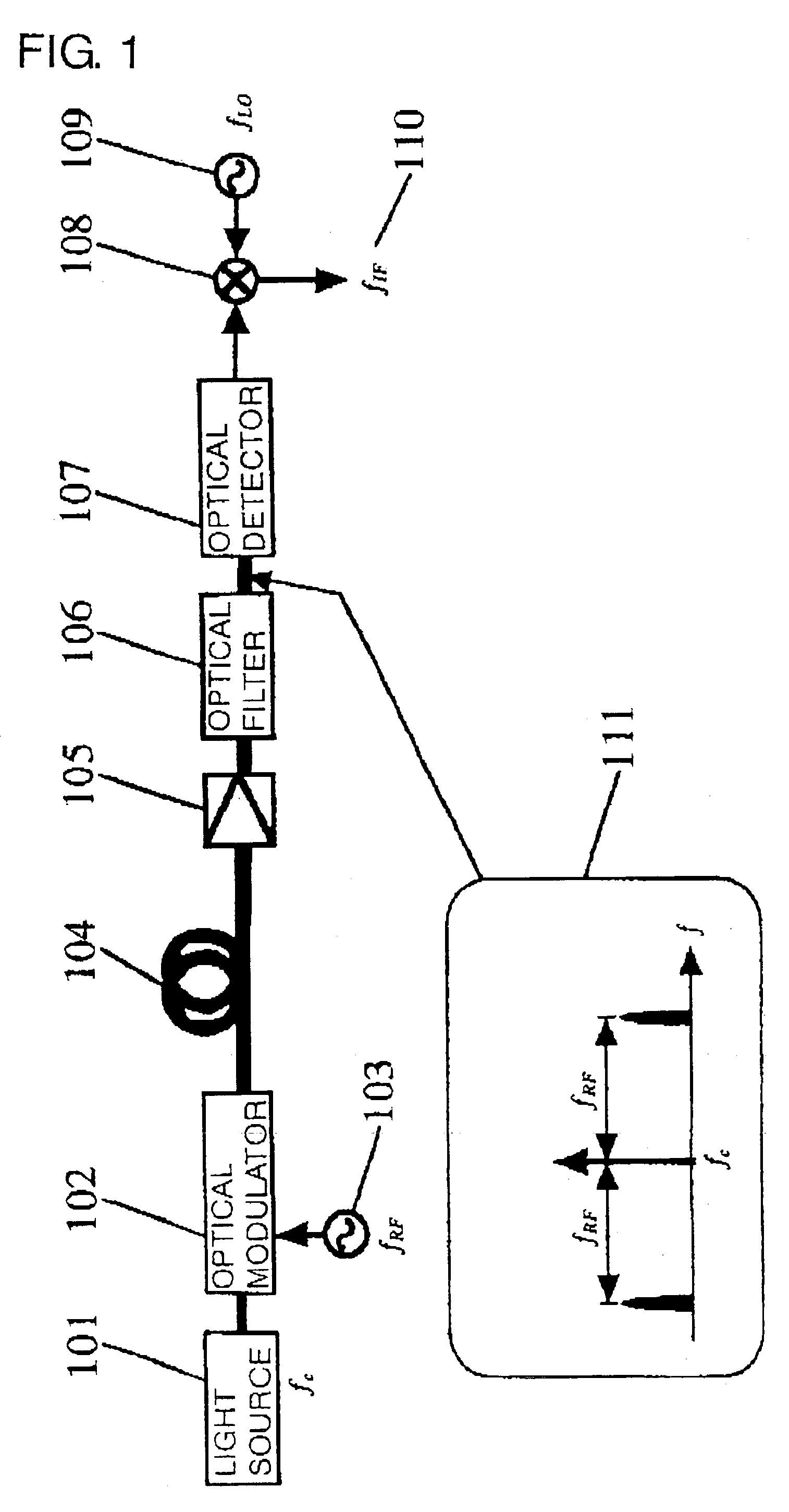
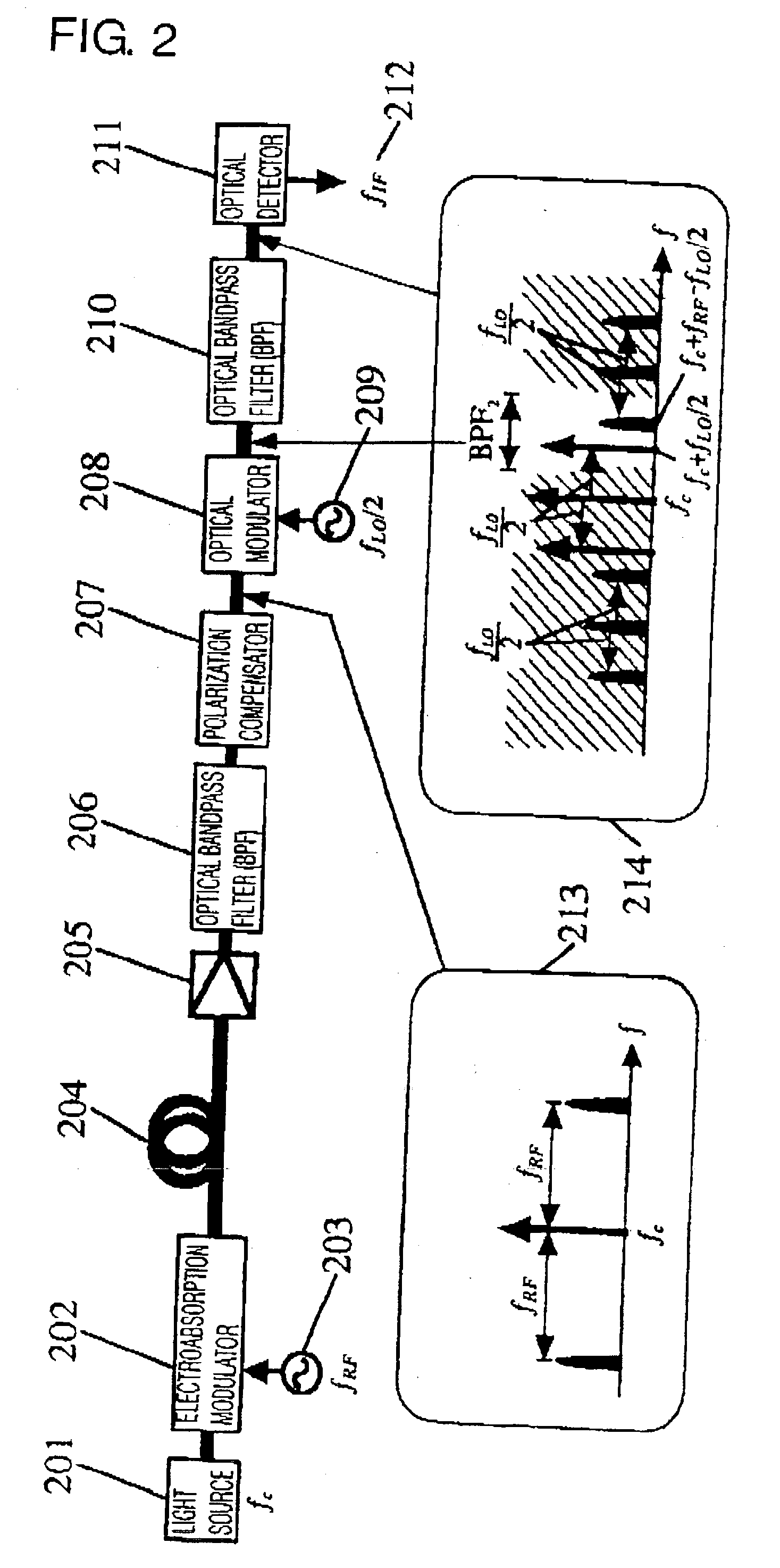
InactiveUS20030198477A1Optical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreElectricityIntermediate frequency
A modulated optical signal processing method and apparatus optically convert an optical signal to an intermediate frequency band that simplifies electrical processing after optical detection, thereby increasing the optical reception sensitivity. Either single-mode light is modulated with a first radio wave overlaid with data, or a modulated optical signal is directly generated, and the optical carrier and optical sideband contained in that modulated optical signal are transmitted, the transmitted optical carrier and optical sideband are input and the input optical carrier and optical sideband are mixed with a radio wave of a predetermined frequency and a combination of an adjacent optical carrier and optical sideband that are closer together than the frequency of the first radiofrequency electrical signal is optically selected from among a frequency-converted or frequency-unconverted optical carrier and optical sideband thus obtained and an electrical signal is detected from this selected optical signal.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Frequency tunable terahertz continuous wave generator
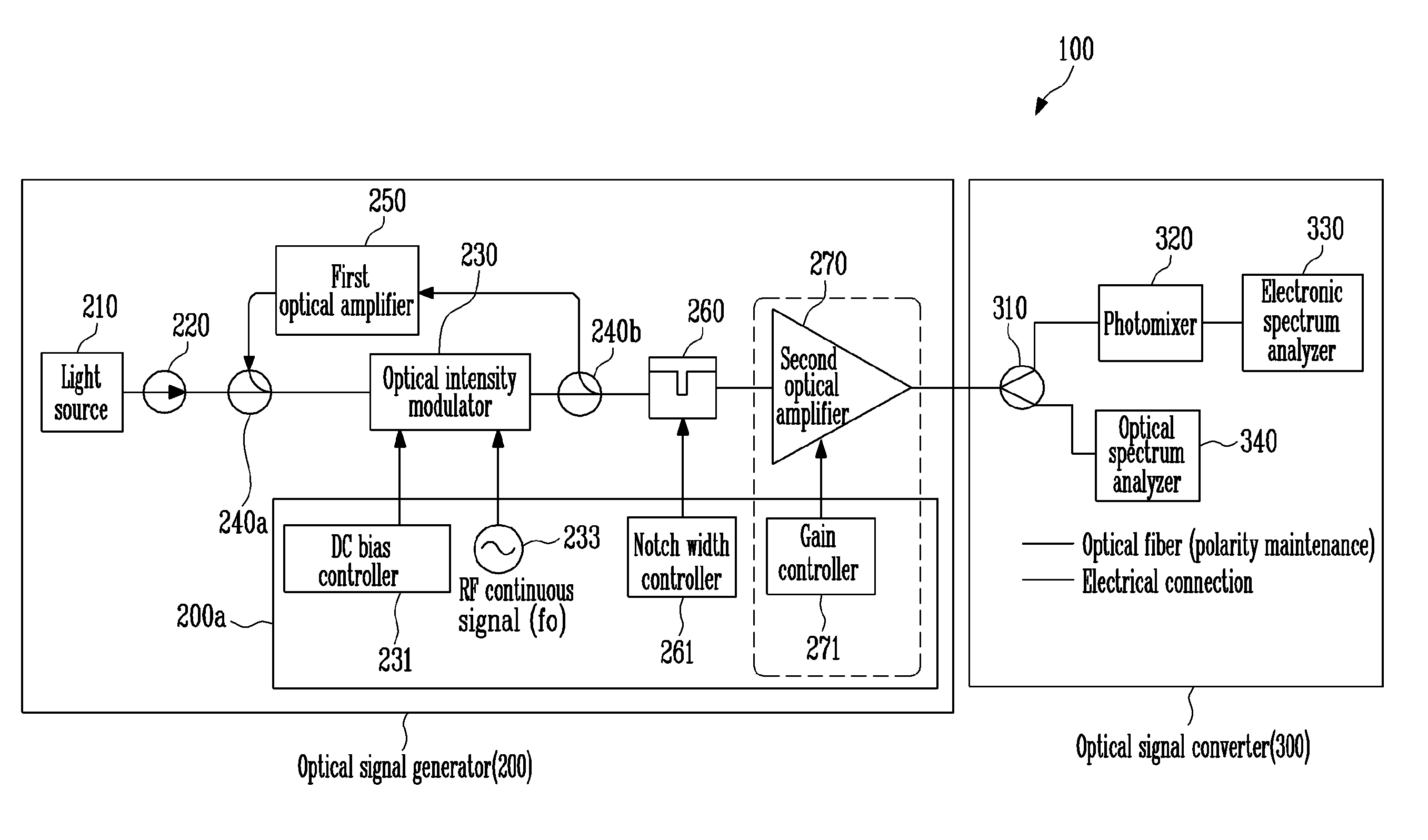
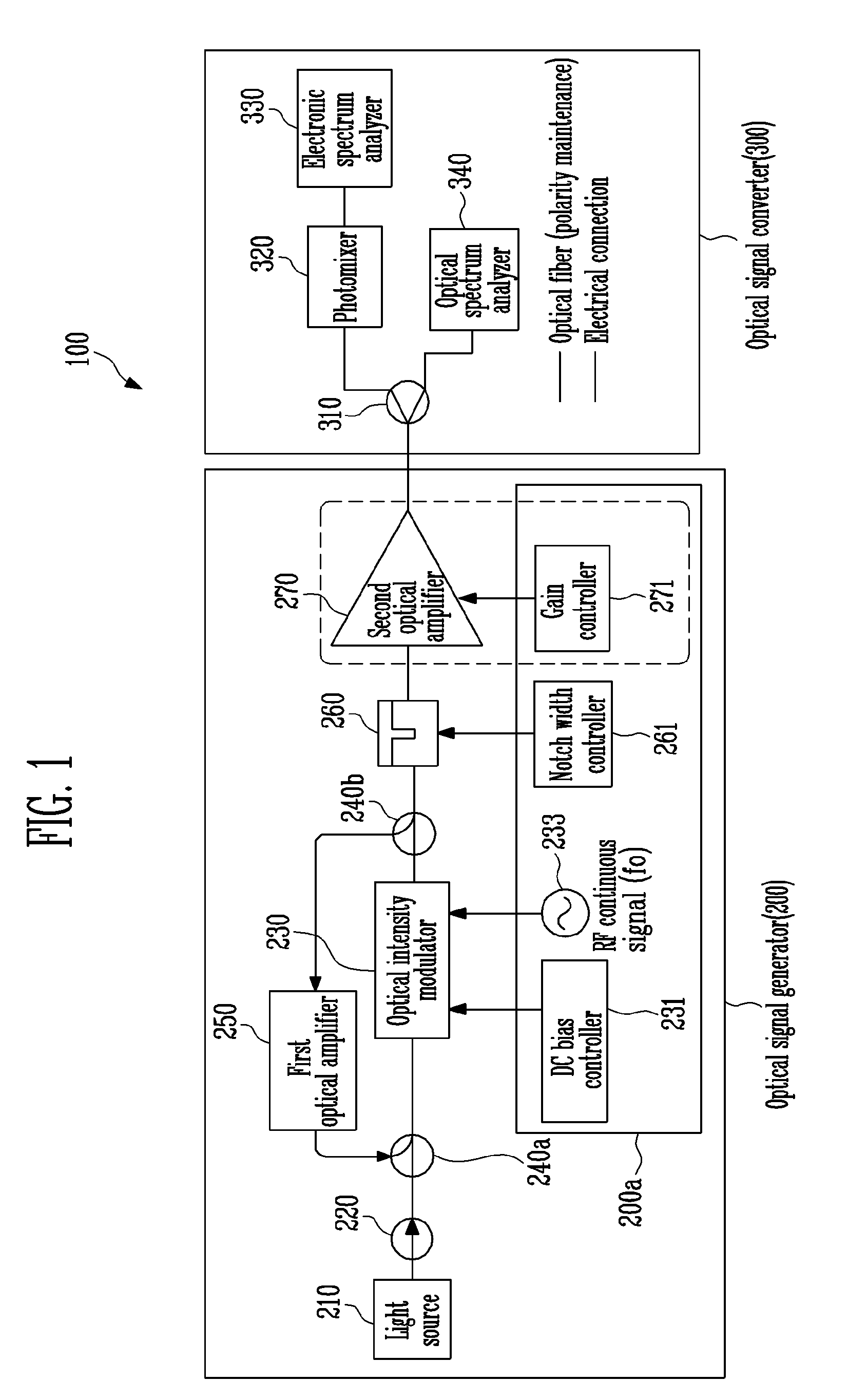
InactiveUS20100092183A1Easy to adjustReduce phase noiseOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreContinuous waveOptical intensity
A frequency tunable terahertz continuous wave generator controls the number of feedbacks of an optical signal output from an optical intensity modulator by adding a feedback loop between input and output terminals of the optical intensity modulator, thereby simply tuning a frequency of a terahertz continuous wave.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
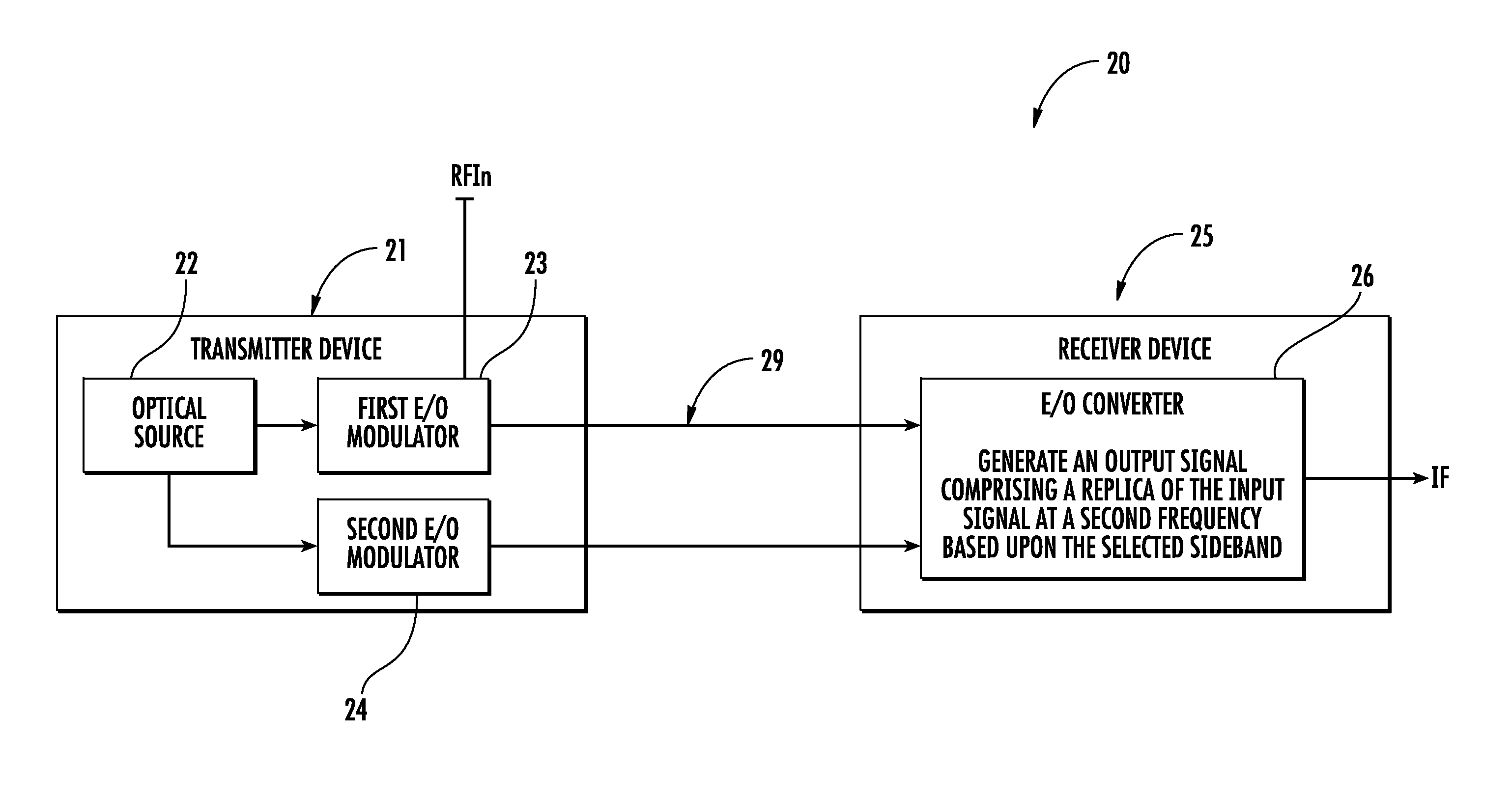
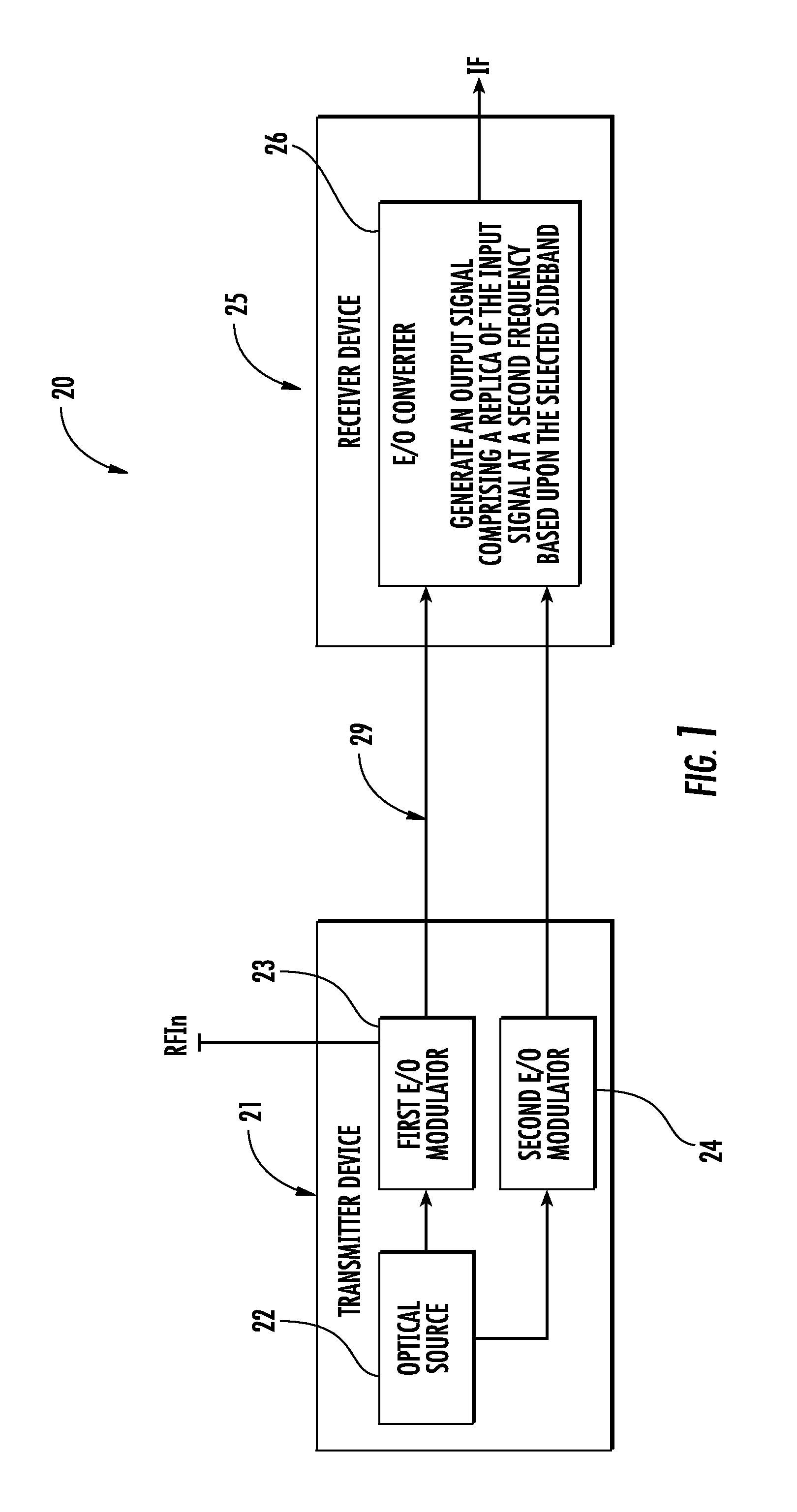
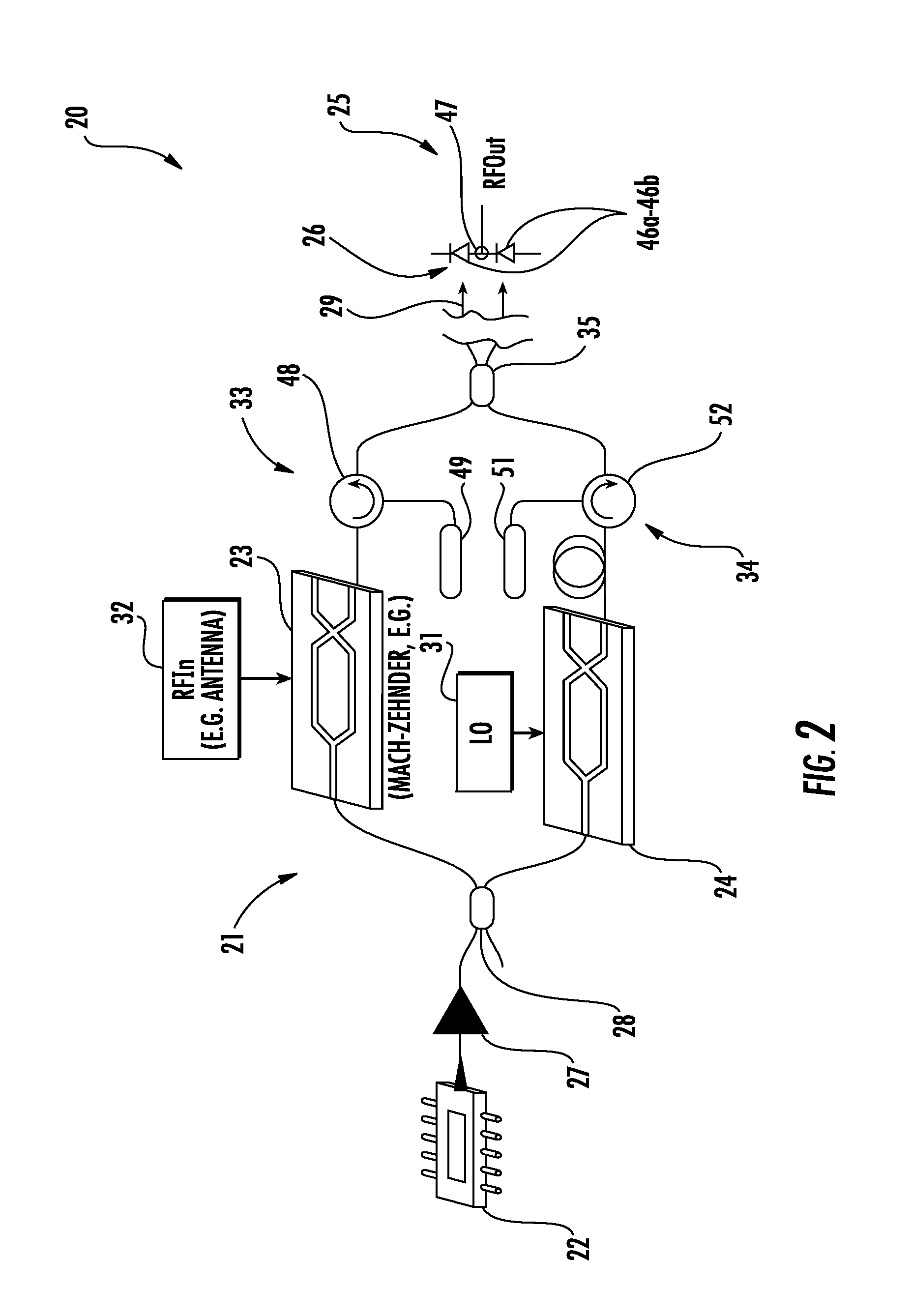
Electro-optic communications device with frequency conversion and related methods
ActiveUS20130236187A1Easy to operateImprove dynamic rangeOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency conversionCarrier signal
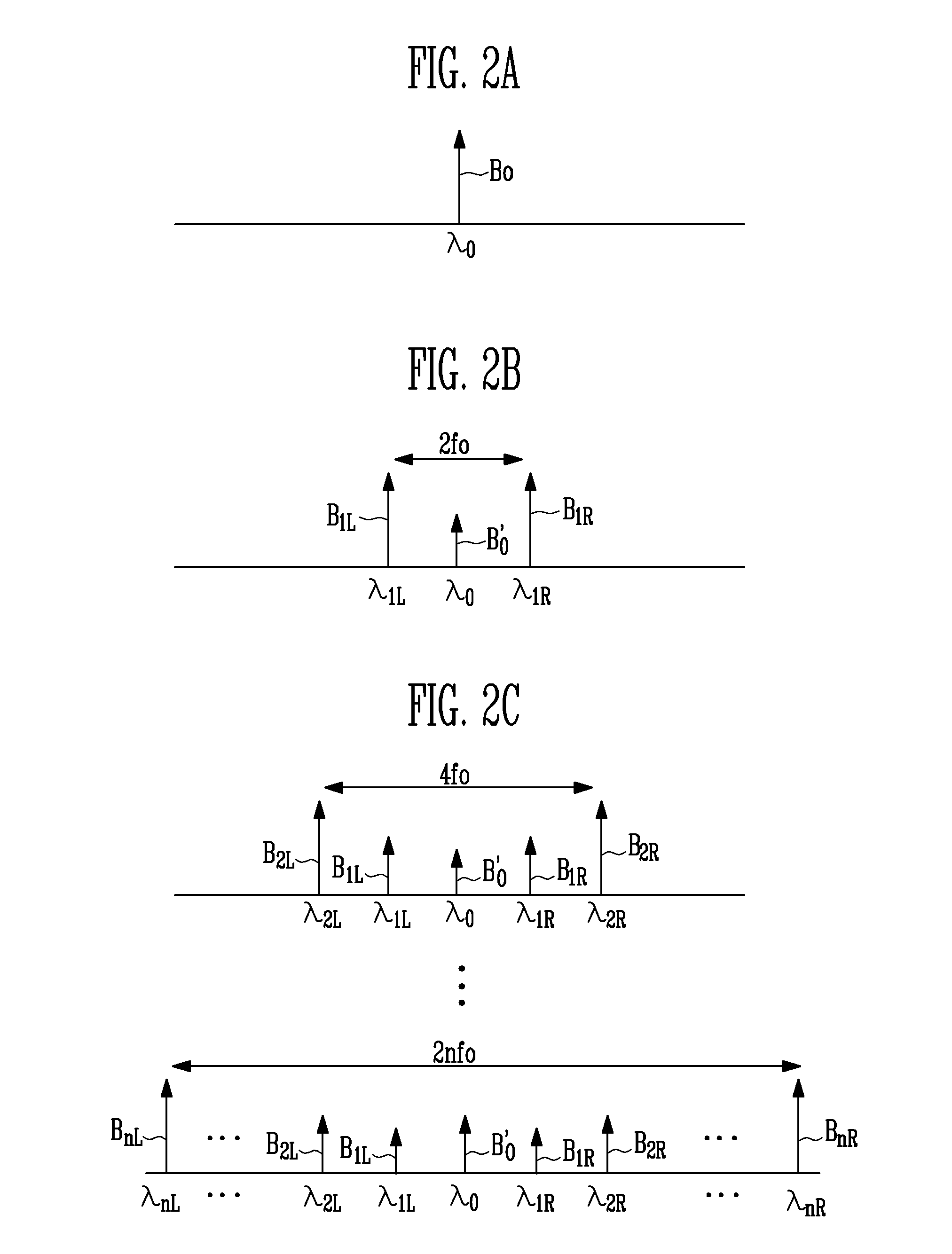
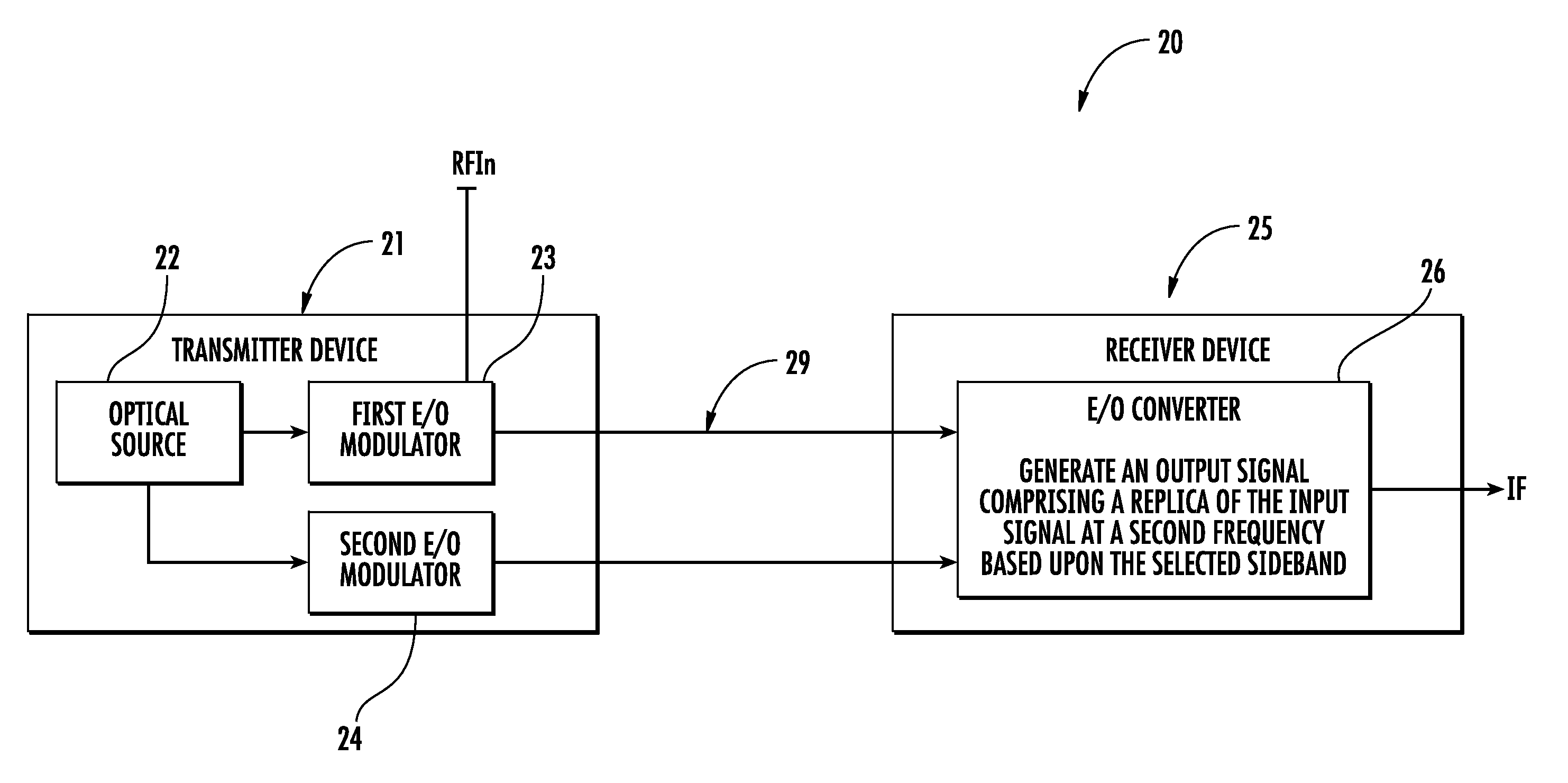
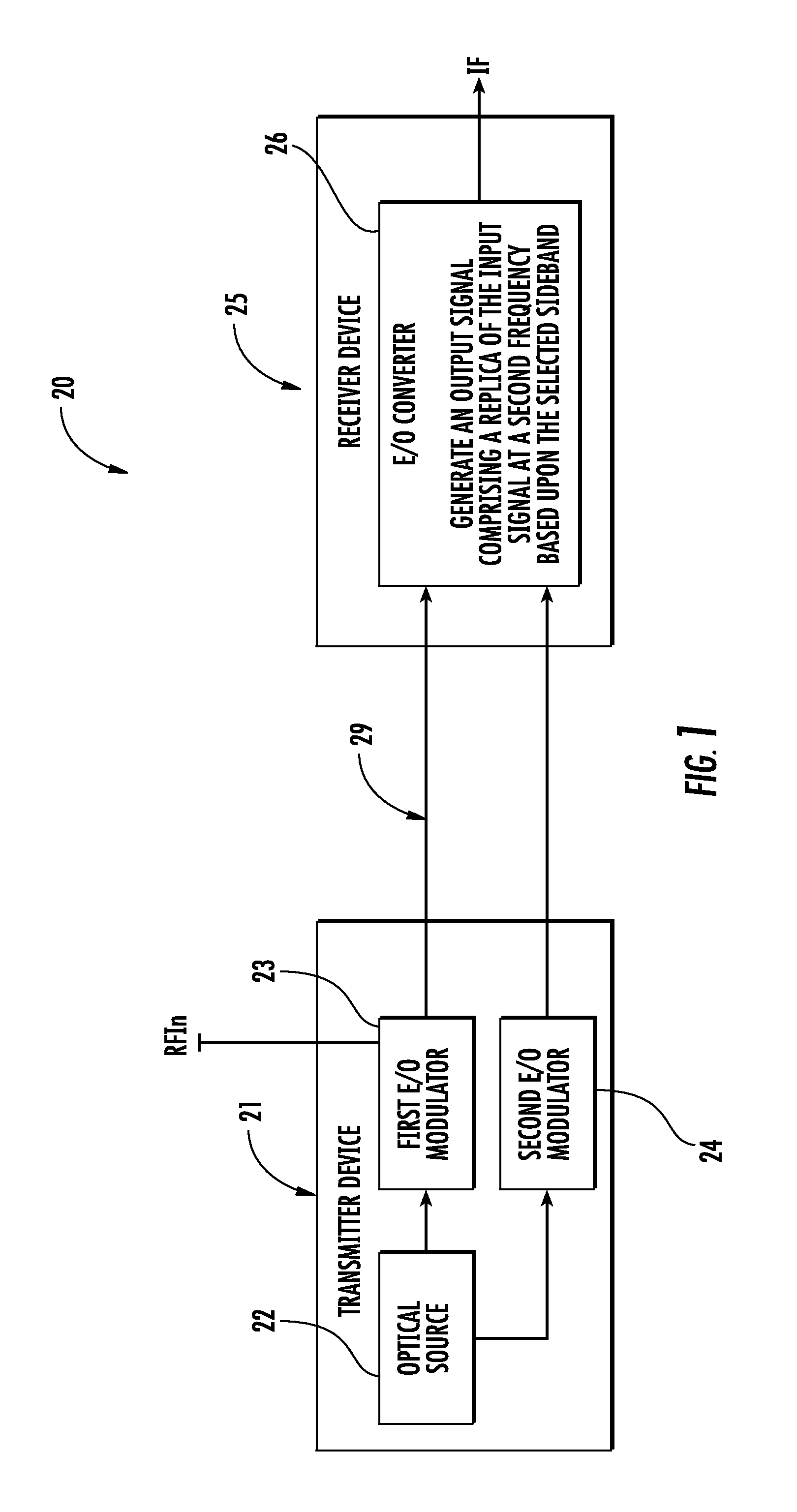
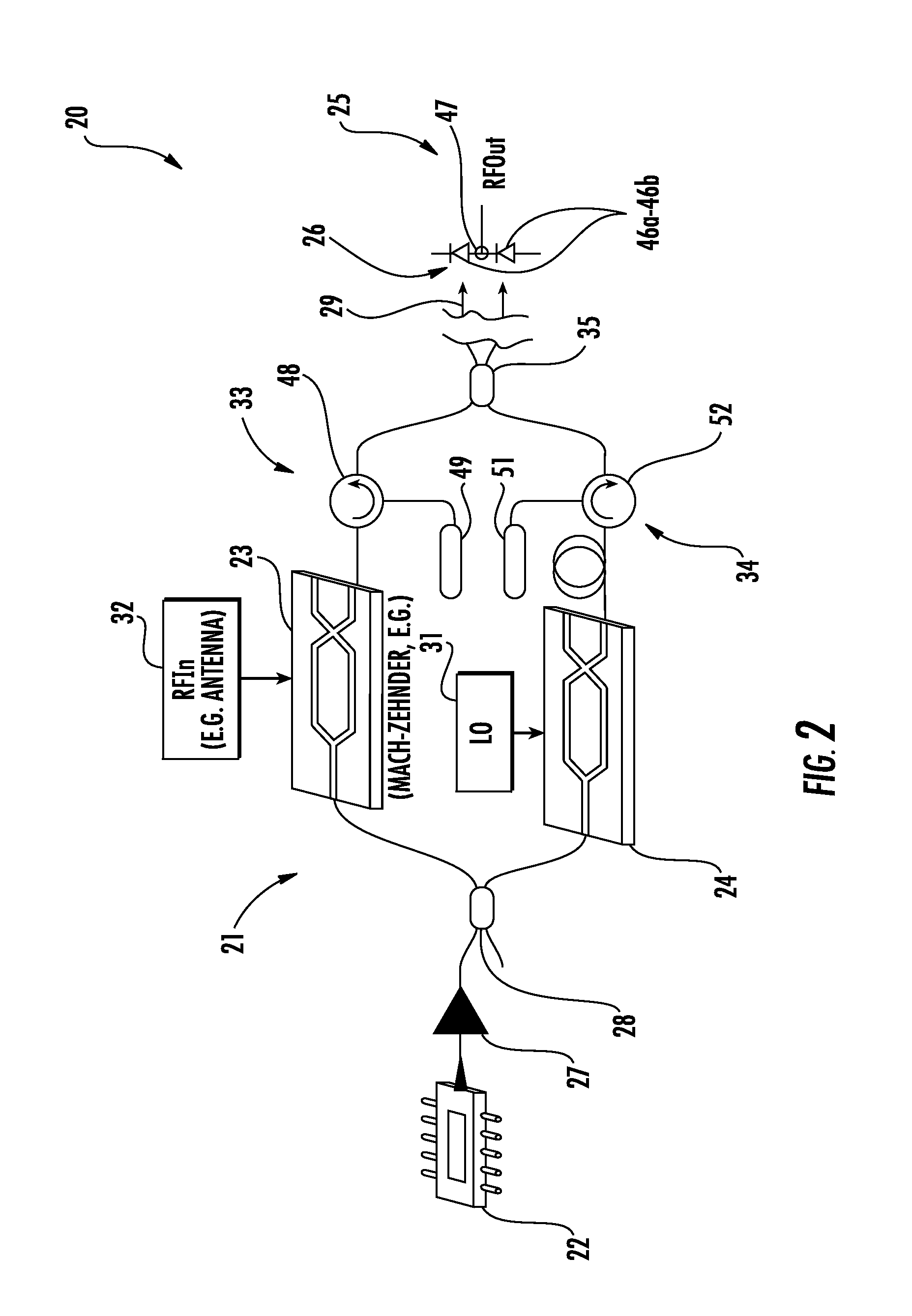
A communications device includes a transmitter device having an optical source configured to generate an optical carrier signal, a first E / O modulator coupled to the optical source and configured to modulate the optical carrier signal with an input signal having a first frequency, and a second E / O modulator coupled to the optical source and configured to modulate the optical carrier signal with a reference signal. The communications device includes an optical waveguide coupled to the transmitter device, and a receiver device coupled to the optical waveguide and including an O / E converter coupled to the optical waveguide and configured to generate an output signal comprising a replica of the input signal at a second frequency based upon the reference signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Ultra-low noise photonic phase noise measurement system for microwave signals
InactiveUS20180180655A1Reduce the noise floorHigh sensitivitySpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow noisePhase noise
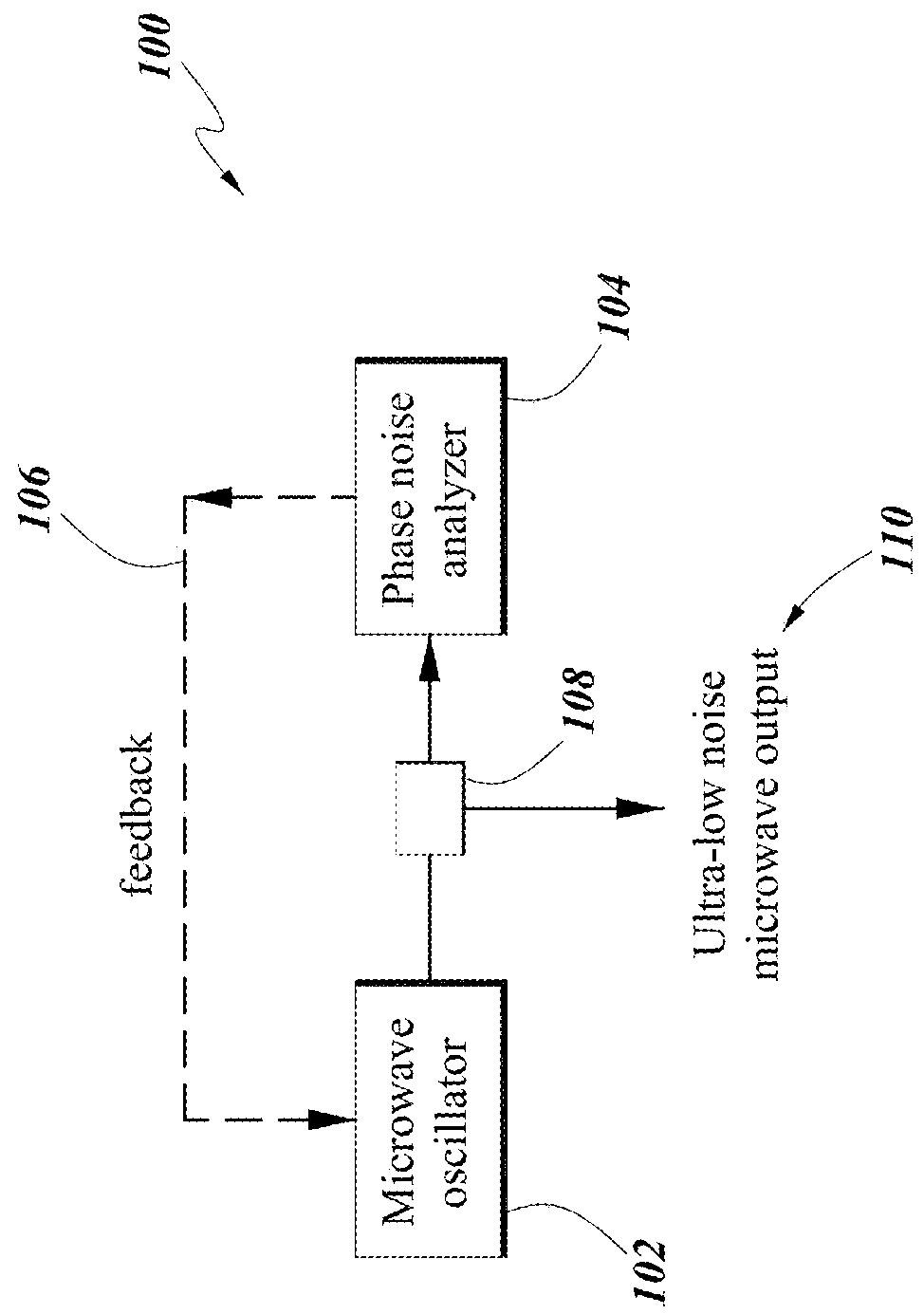
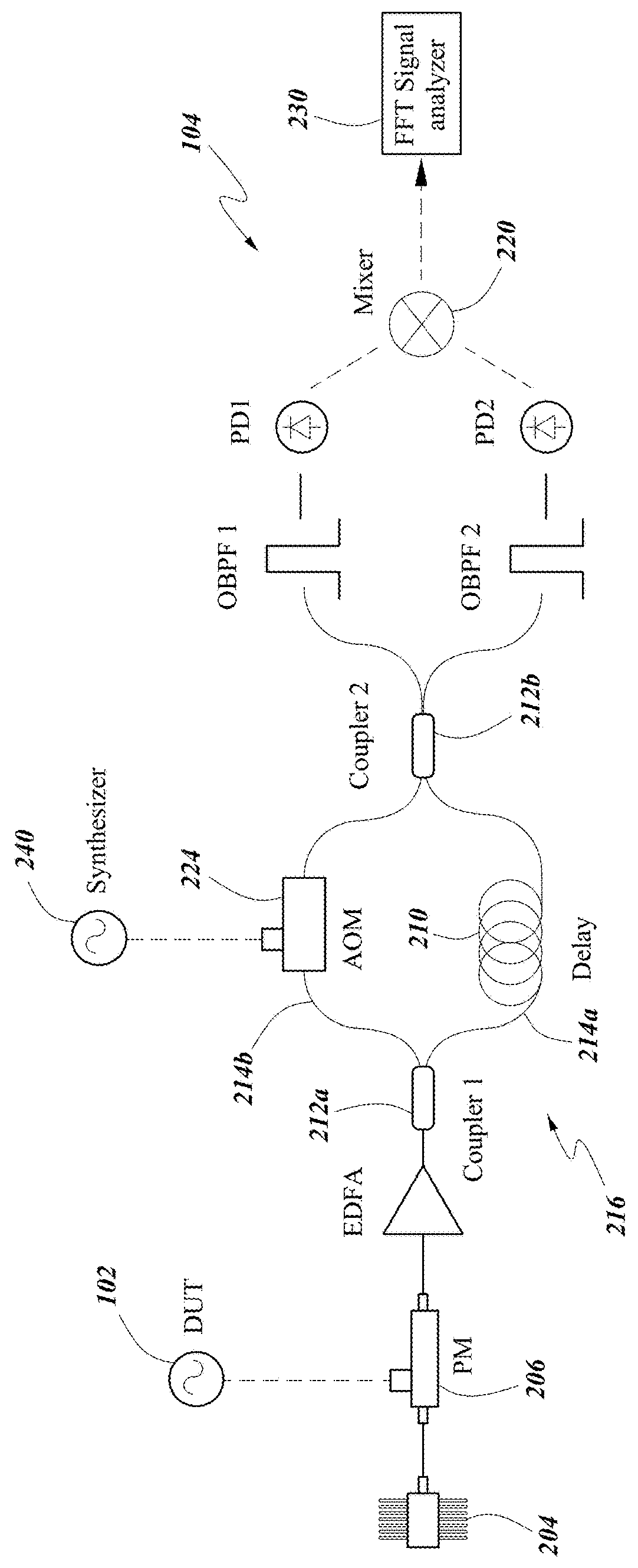
Systems and methods for precision phase noise measurements of radio frequency (RF) oscillators are provided. An RF signal under test can be modulated on a continuous wave (cw) laser carrier frequency via generation of modulation sidebands using an appropriate modulator. A photonic delay line can be implemented as a self-heterodyne detection system for the phase noise, allowing for photonic down-conversion of the phase noise measurement to direct current (DC). The self-heterodyne detection system allows detection outside of any 1 / f noise issues. Ultra-low phase noise detection for RF frequencies in a range from below 1 GHz to beyond 100 GHz is enabled with a low noise floor in the whole frequency range. Higher-order modulation sidebands can further reduce the noise floor of the system. Ultra-low noise RF (microwave) output can be generated. The RF signal under test can be generated by a dielectric resonance oscillator or opto-electronic oscillator.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Receiver with mutually coherent optical frequency combs
ActiveUS20180006730A1Limited tone countPrevent frequency reconfigurabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsOpticsFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
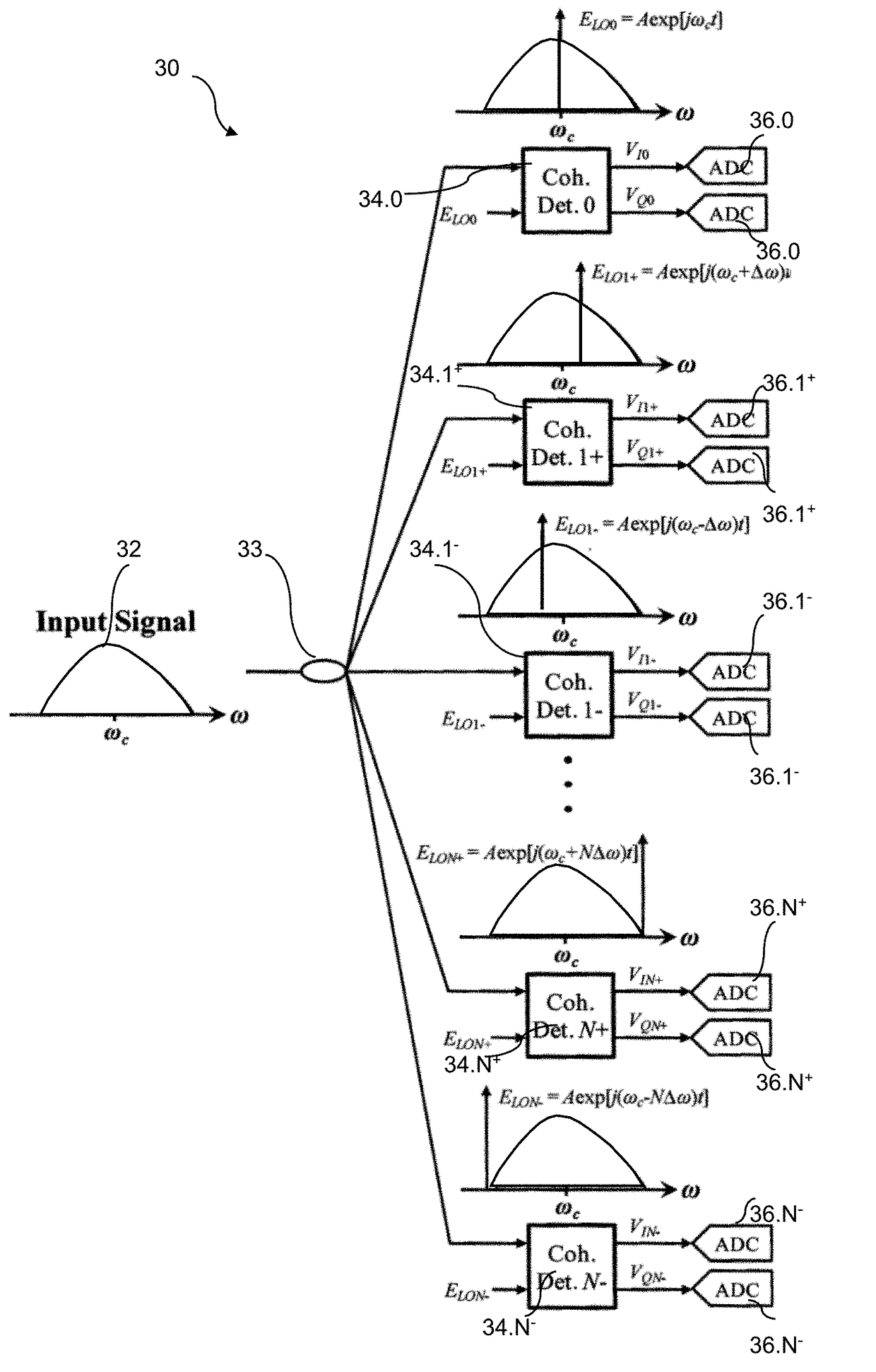
A receiver architecture for physically-assisted computing of transforms, such as discrete Fourier transforms (DFT) and discrete Hilbert transforms (DHT), employs mutually-coherent optical frequency combs for detection of the coherent beating between an optical signal and a reference optical tone generated by a local oscillator (LO). A signal replication mixer generates a plurality of signal optical tones having a frequency pitch with an input signal mapped thereon. A reference mixer (local oscillator) generates a plurality of reference optical tones having an offset frequency pitch relative to the signal tones. A receiver backplane detects coherent beating between the signal optical tones and the reference optical tones. The input signal may be in the optical domain or in the radio-frequency domain.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fourth harmonic generating system using optical double side-band suppressed carrier modulator
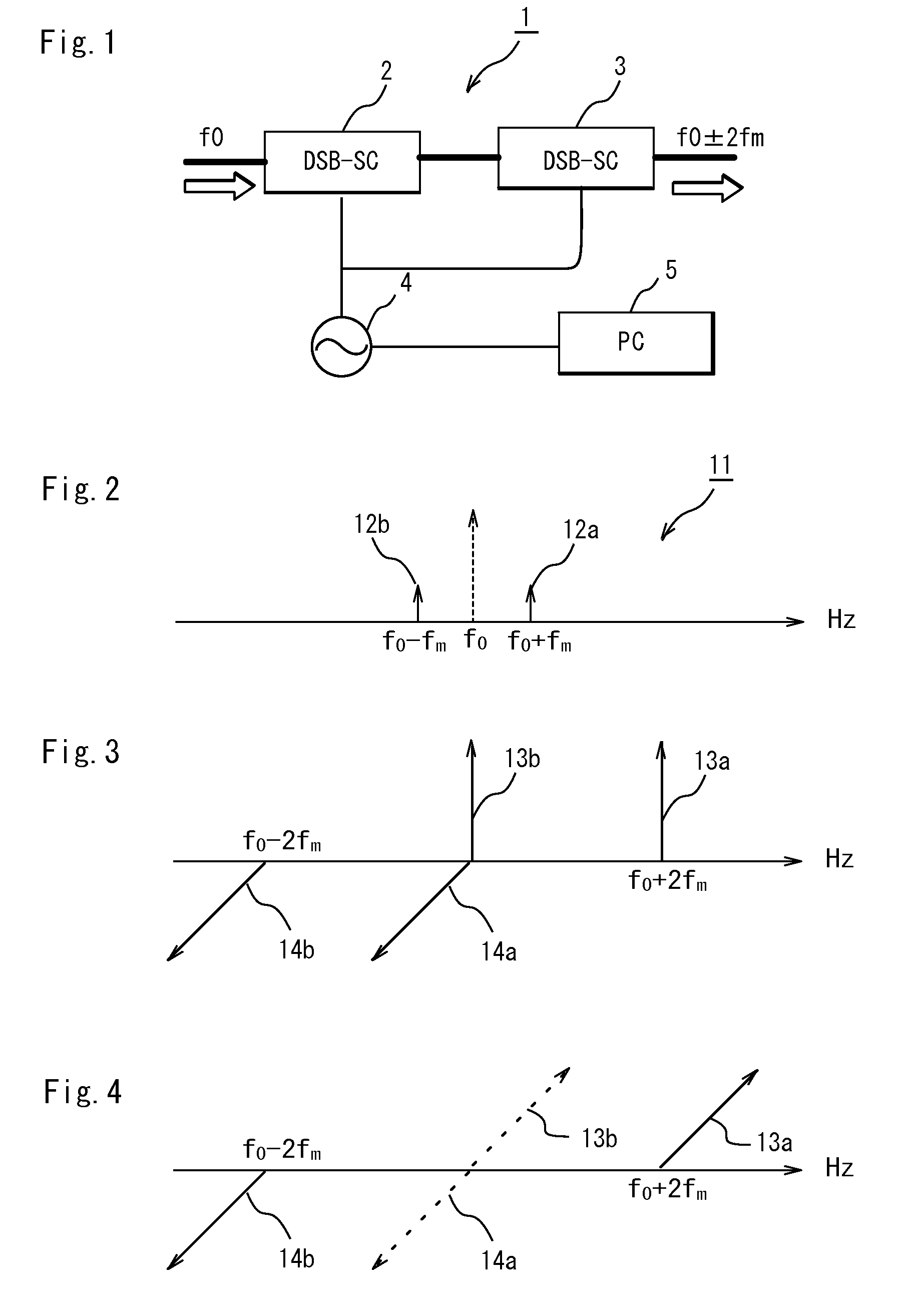
InactiveUS20090103924A1Promote generationOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFourth harmonic generationFourth harmonic
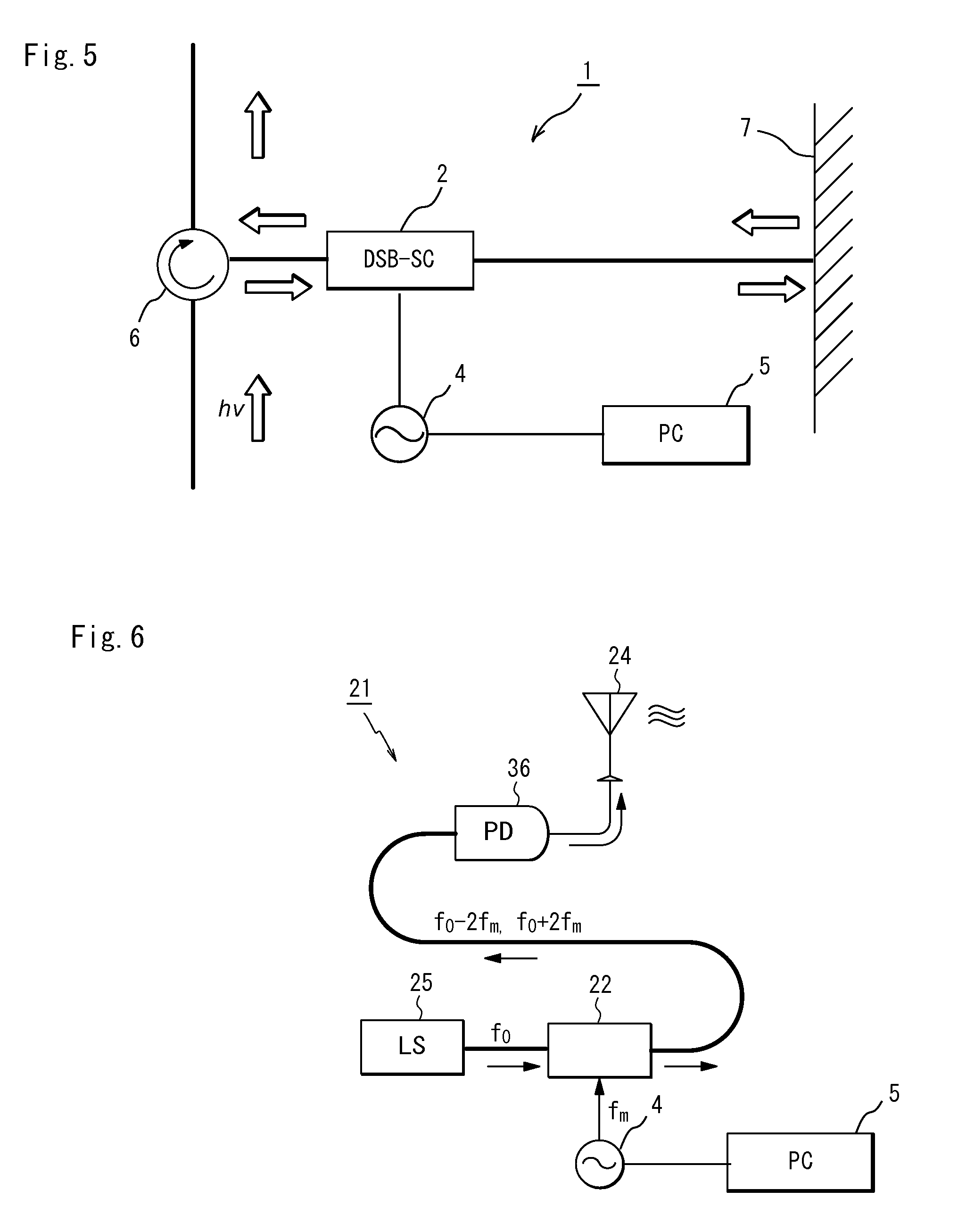
The present invention is to provide an optical modulating system for generating a signal of a frequency (f0+2fm) and a signal of a frequency (f0−2fm) and suppressing a signal of a frequency (f0) by a DSB-SC modulator.A fourth harmonic generating system for solving the above problem comprises a first DSB-SC modulator (2) a second DSB-SC modulator (3) and a signal control section (5) for controlling a modulating signal from a signal source (4) for generating modulating signals applied to the first and second DSB-SC modulators (2,3) so that a lower side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the upper side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) and an upper side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the lower side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) cancel each other.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Radio oscillating and radar systems
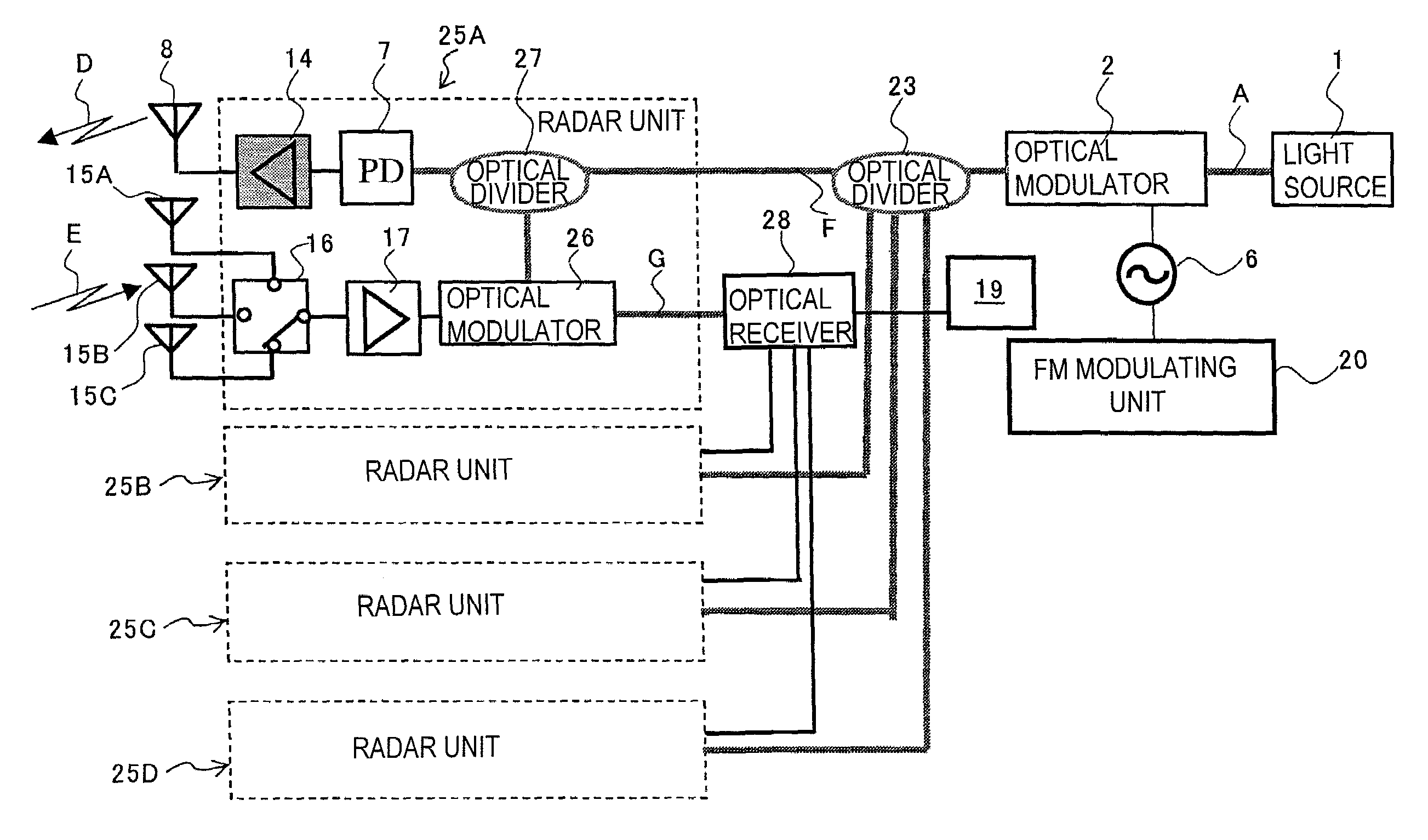
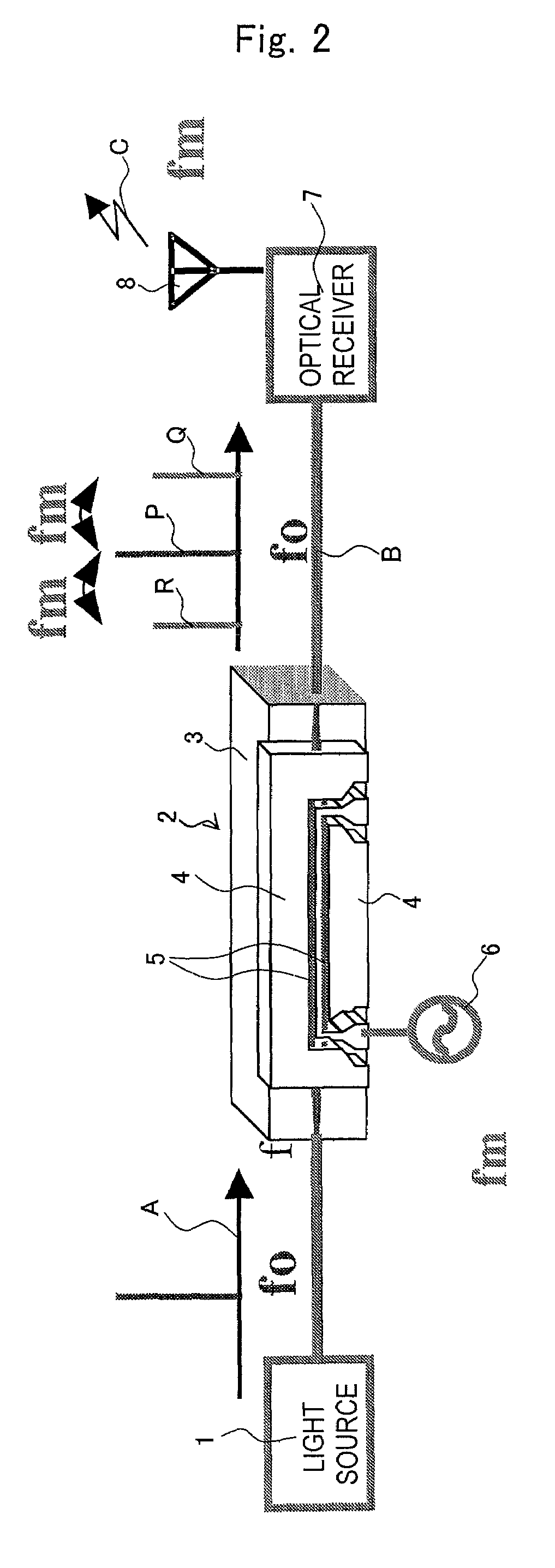
ActiveUS7446696B2Excessive signalingEnhancing practice useAutomatic initiationsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadar systemsCarrier signal
The present invention provides a radio signal radiation system that alleviates the necessity of a highly specified pass band reception filter and a high performance / reliability amplifier. The radio signal radiation system includes an optical modulator; a light source for inputting an optical carrier wave into the optical modulator; a power source for applying a modulating signal having a frequency Fm on the optical modulator to superimpose a sideband wave onto the carrier wave, the modulating signal having an amplitude of N-times the drive voltage of the optical modulator; a light receiver to receive and convert the outgoing light into an electrical signal; and a radiating means for radiating a radio signal based on the electrical signal, wherein the sideband wave is superimposed at a position shifted by n×fm.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
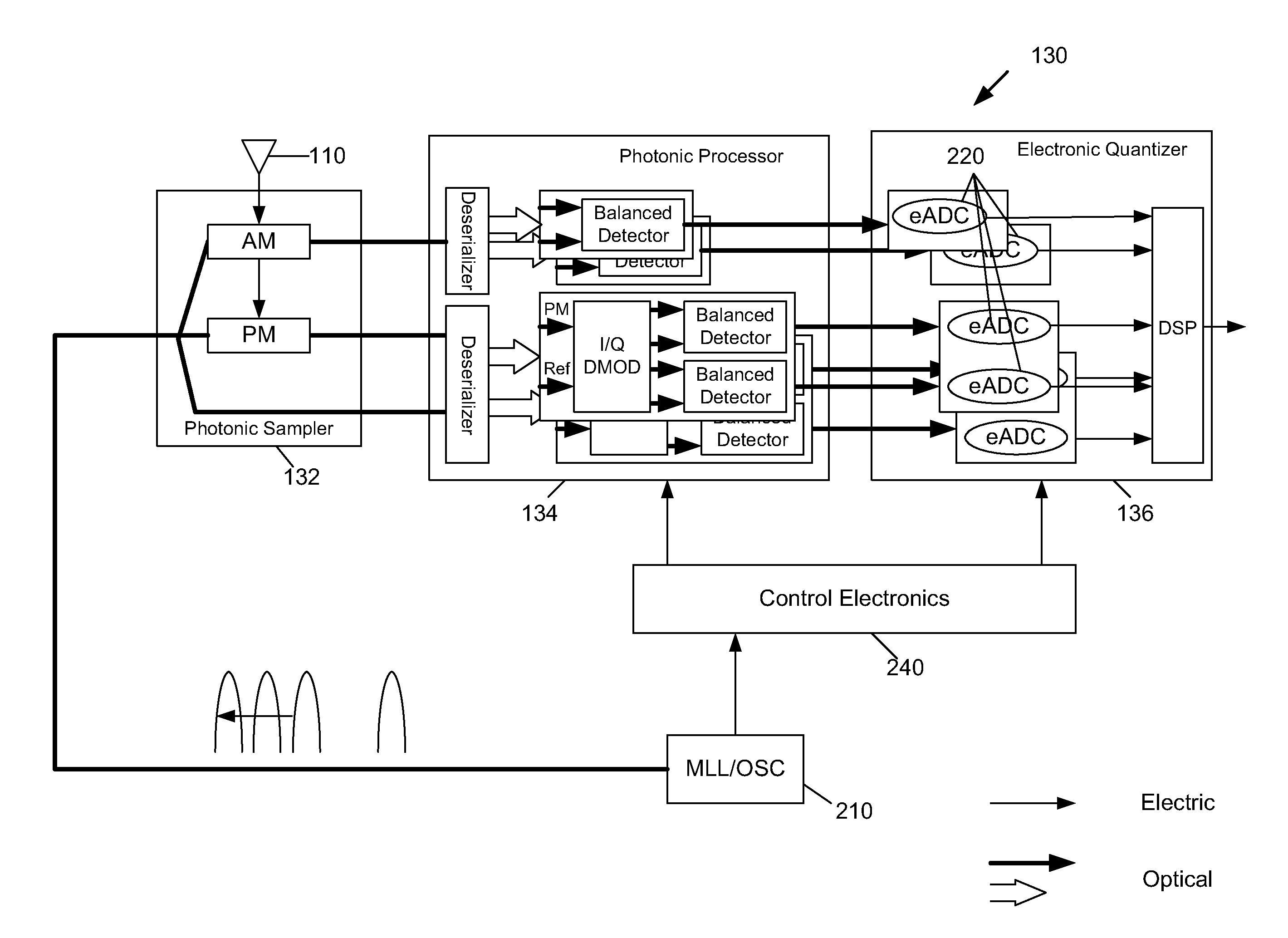
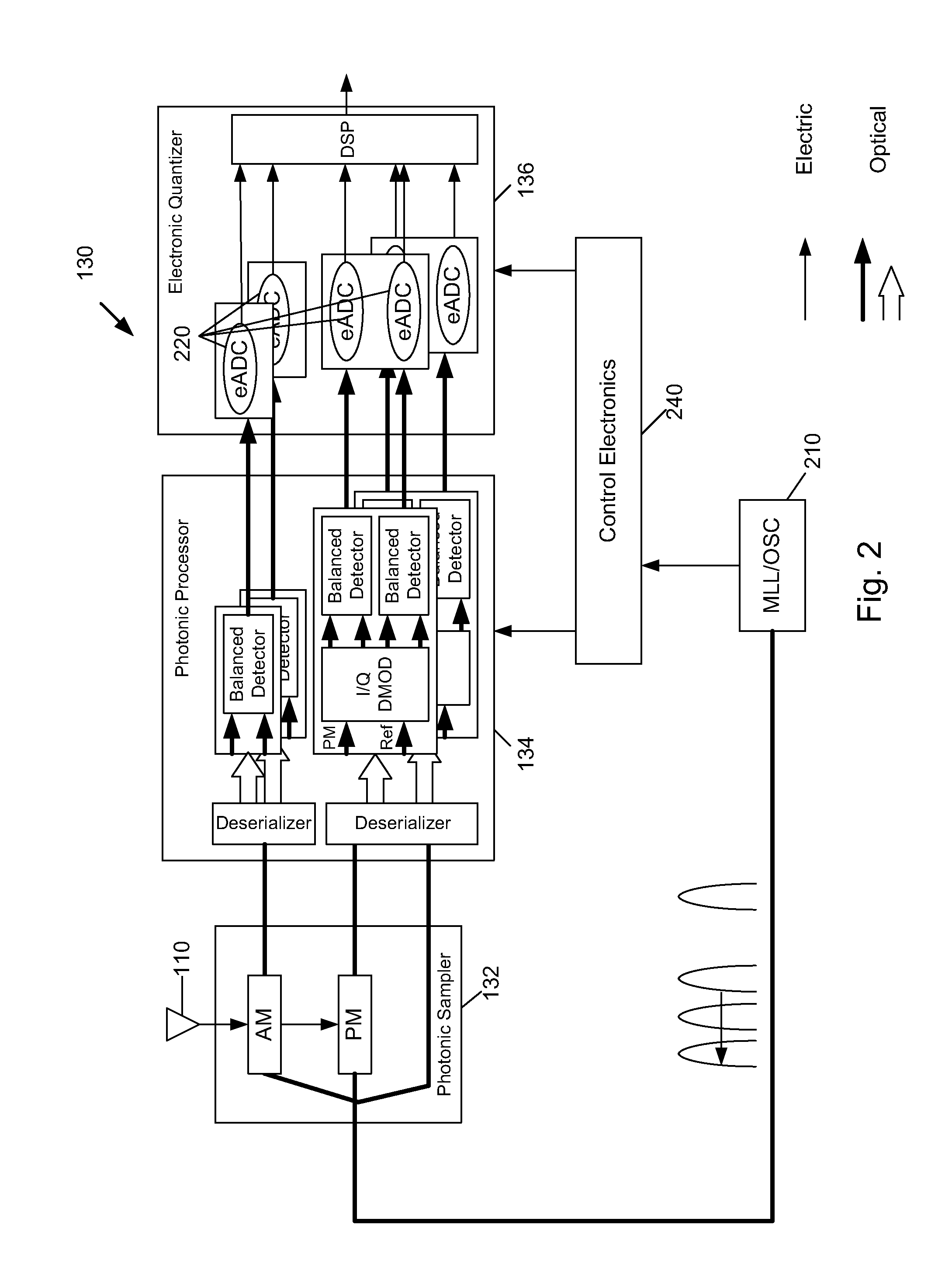
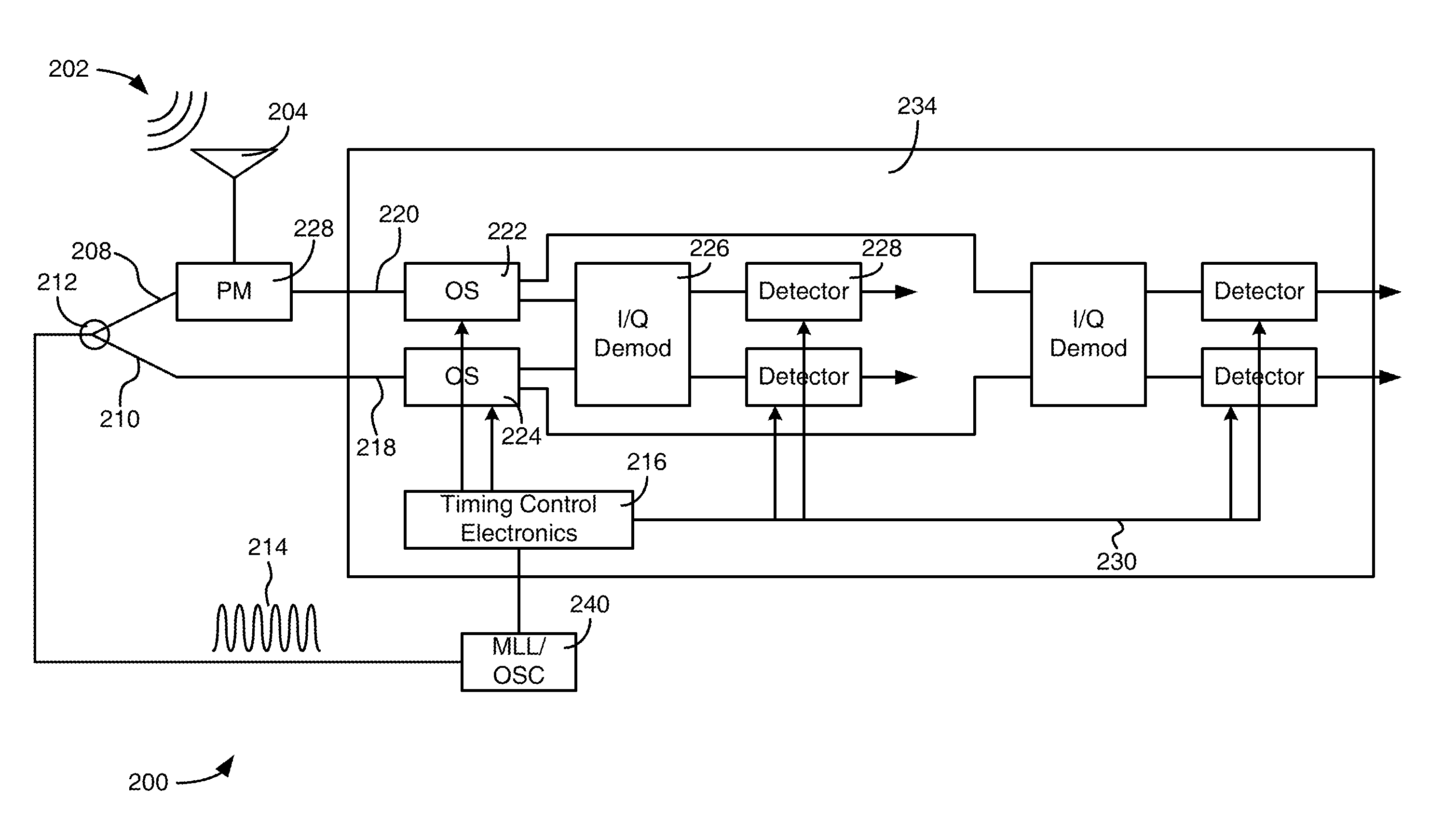
Optically interleaved electronic analog to digital converters
ActiveUS8548331B1Electromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingDigital down converterPhotonics
An analog signal receiver includes photonic sampling and electronic quantization. The receiver includes timing control circuitry configured to receive a series of optical pulses and output a plurality of timing signals based on the series of optical pulses to synchronize optical switches that receive a sampled optical signal to time deinterleave the optically sampled signal. The time deinterleaved signals are then sent to a plurality of demodulators wherein each demodulator receives at least one time deinterleaved optically sampled signal and at least one time deinterleaved optical reference signal to produce electrical signals based on the demodulated optical signals.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Interference cancellation methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20180063745A1Network traffic/resource managementOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingInterference cancelationEngineering
Methods and apparatus for reducing and / or canceling signal interference between receiver and transmitter components of a wireless communications device are described. The methods and apparatus are well suited for use in a wide range of devices including user equipment devices such as cell phones as well as in network equipment such a base stations. Opto-mechanical devices are used in some embodiments as part of an apparatus which performs interference cancelation on RF (Radio Frequency) signals.
Owner:GENXCOMM INC
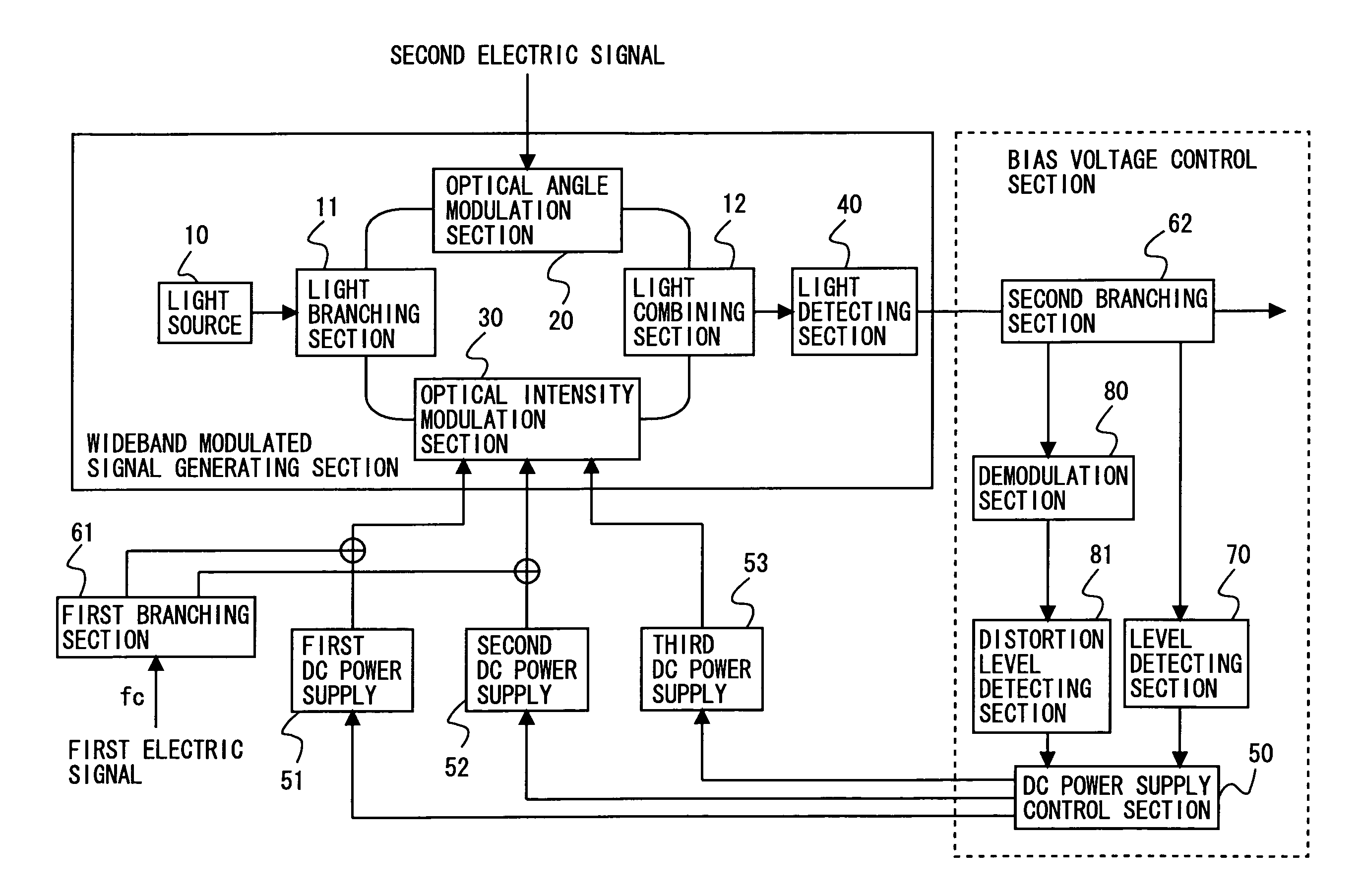
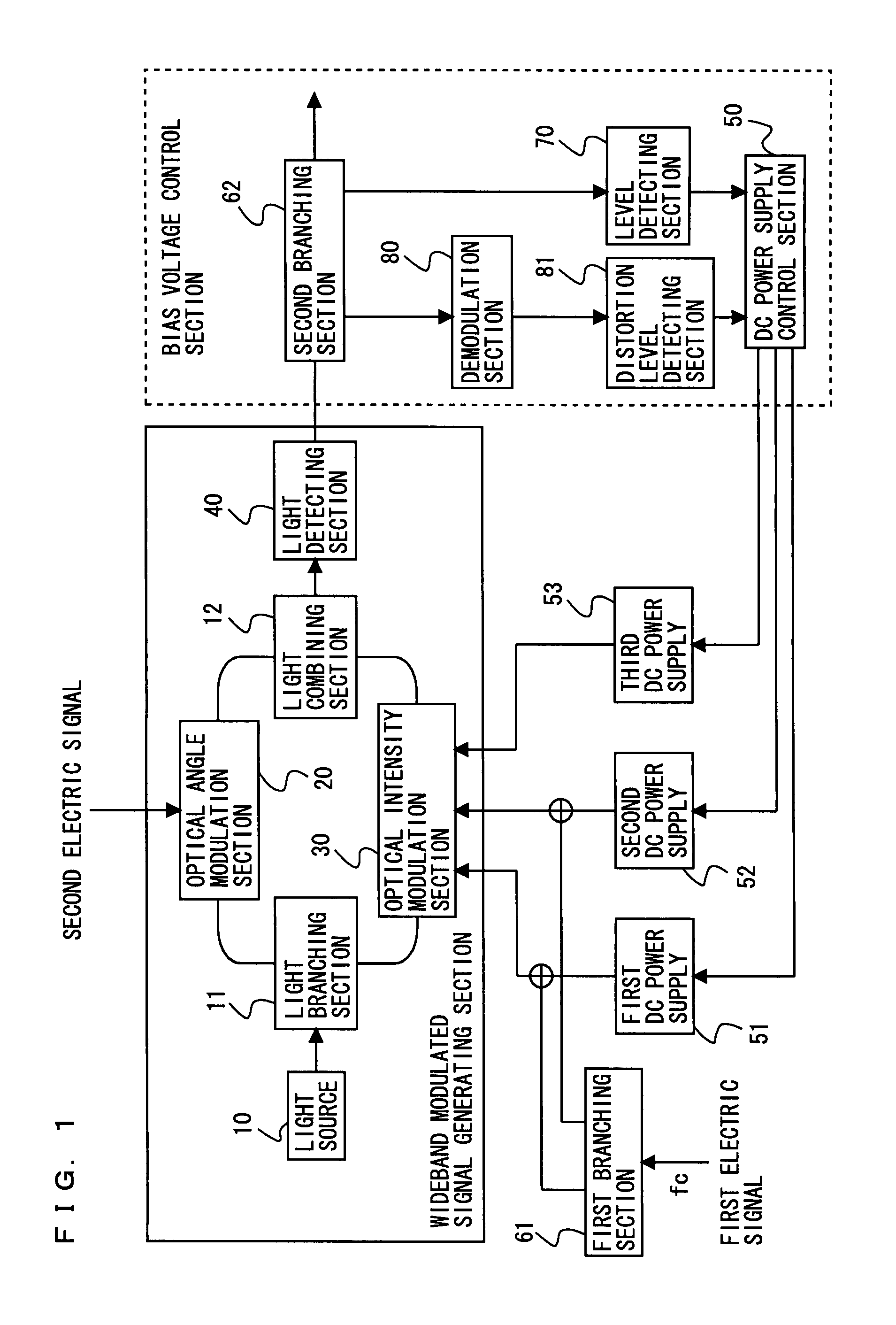
Wideband modulated signal generating device
InactiveUS20080037999A1Easy to controlDesirable modulation characteristicOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingElectromagnetic transmittersEngineeringWideband
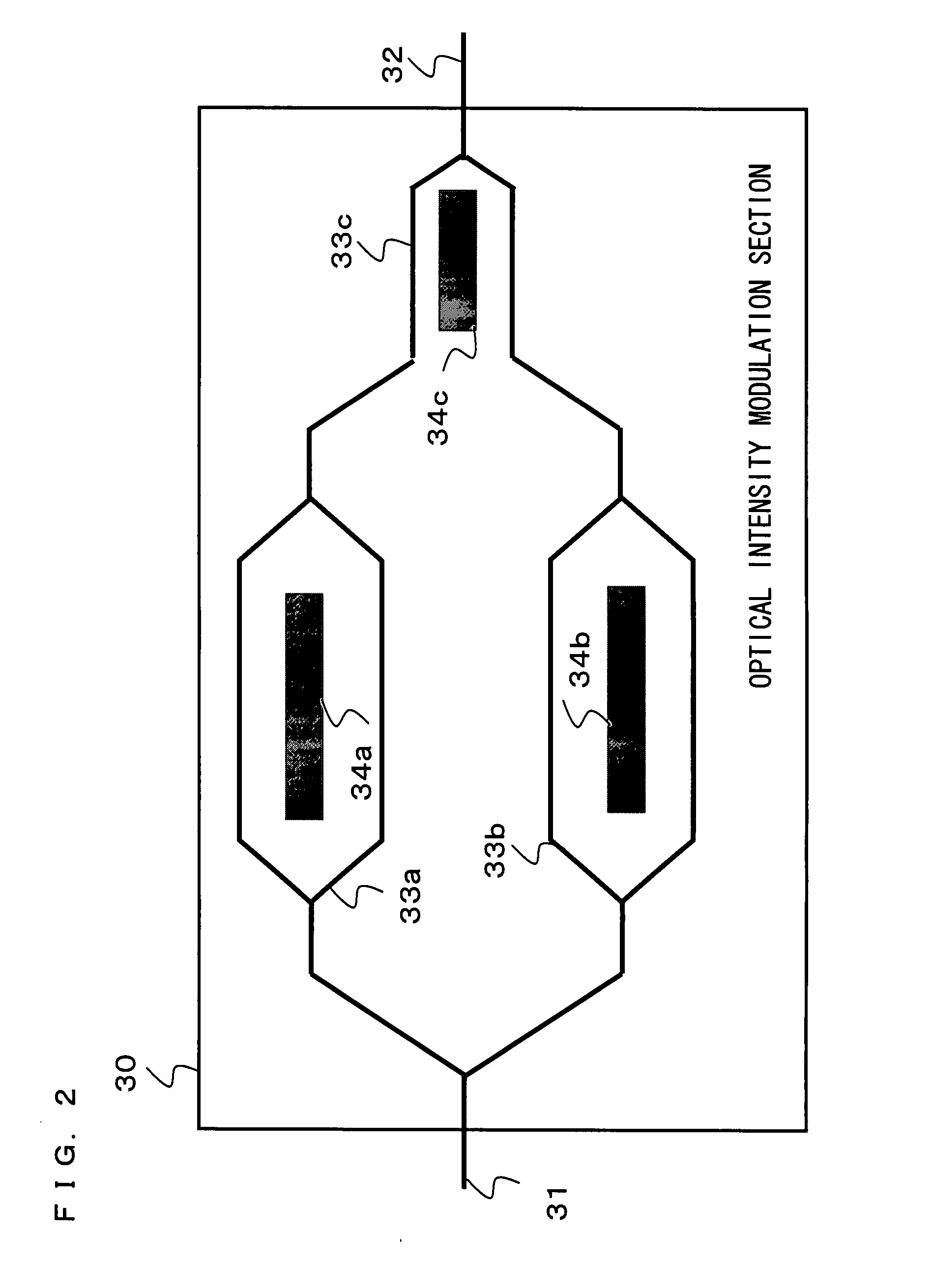
The present invention provides a wideband modulated signal generating device capable of realizing an always stable operation and obtaining an intended wideband modulated signal in spite of a shift in the optimal bias voltage due to DC drift occurring in an optical intensity modulation section. In the wideband modulated signal generating device, a DC power supply control section 50 controls a first DC power supply 51 and a second DC power supply 52 for applying first and second bias voltages to an optical intensity modulation section 30 based on a signal level detected by a level detecting section 70, and controls a third DC power supply 53 for applying a third bias voltage to an optical intensity modulation section 30 based on a distortion level detected by a distortion level detecting section 81, thus compensating for a shift in the optimal bias voltage occurring due to DC drift.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and Apparatus for Analyzing the Spectrum of Radio-Frequency Signals Using Unamplified Fiber Optic Recirculation Loops
ActiveUS20130315590A1High strengthMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingMultiplexingFiber
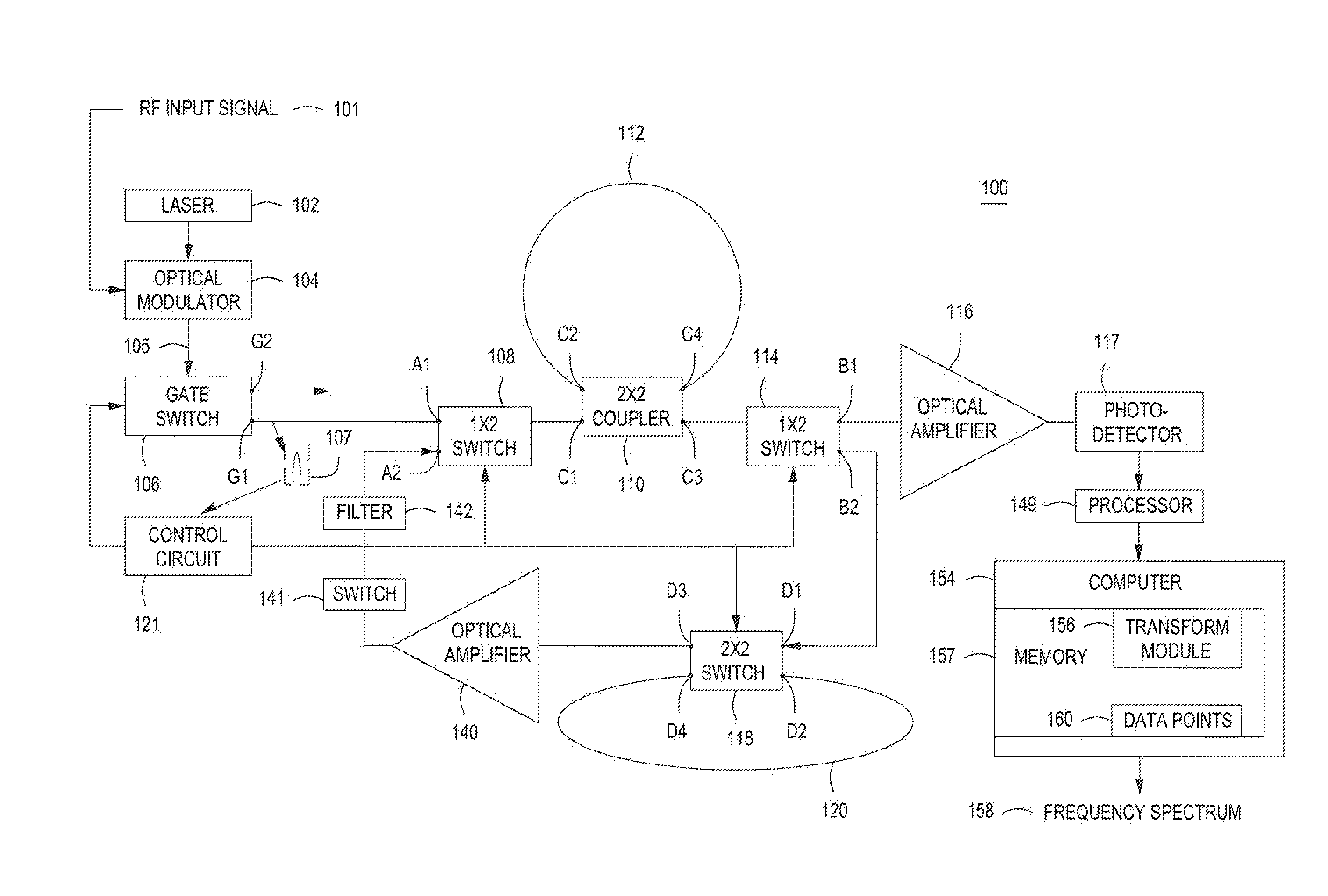
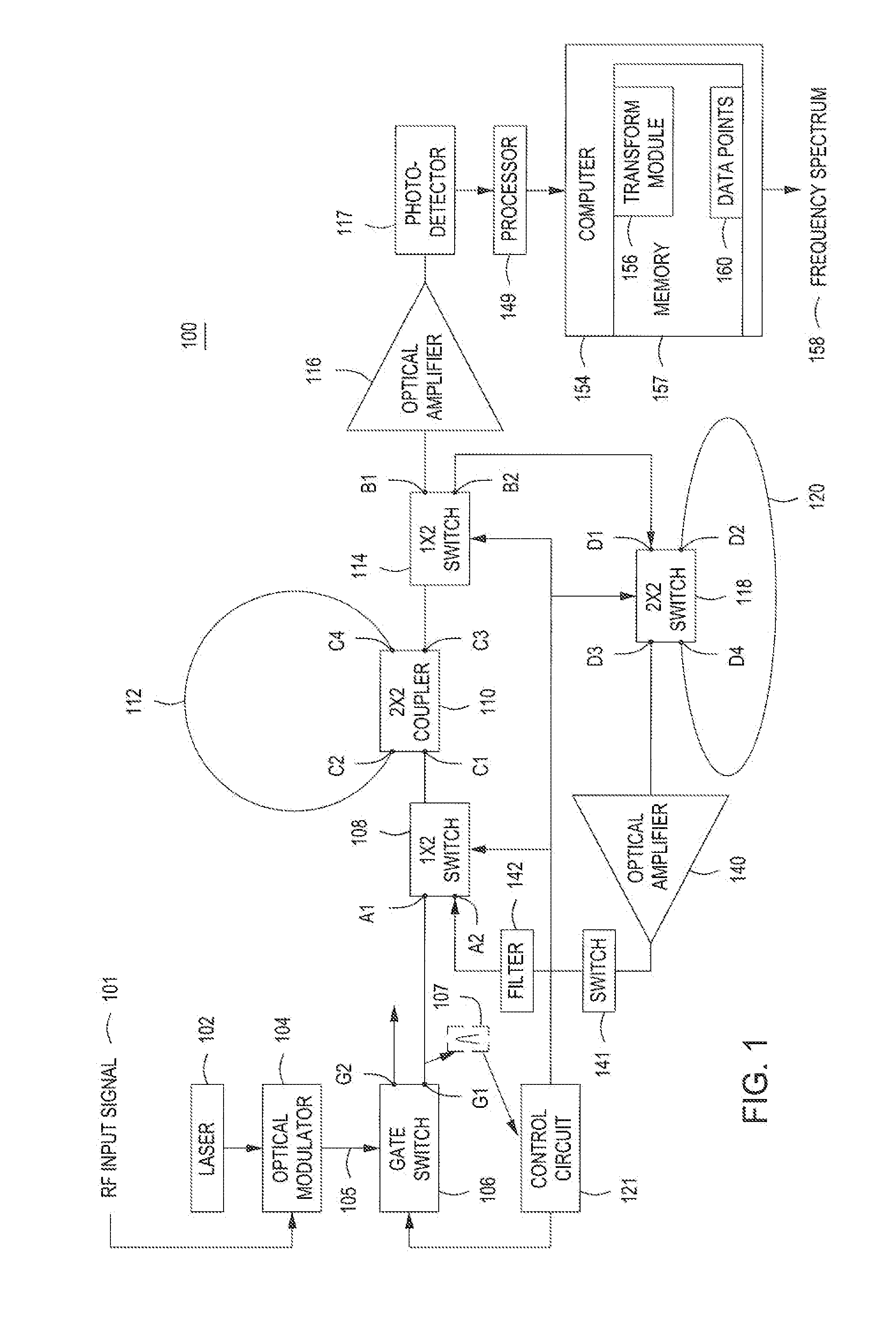
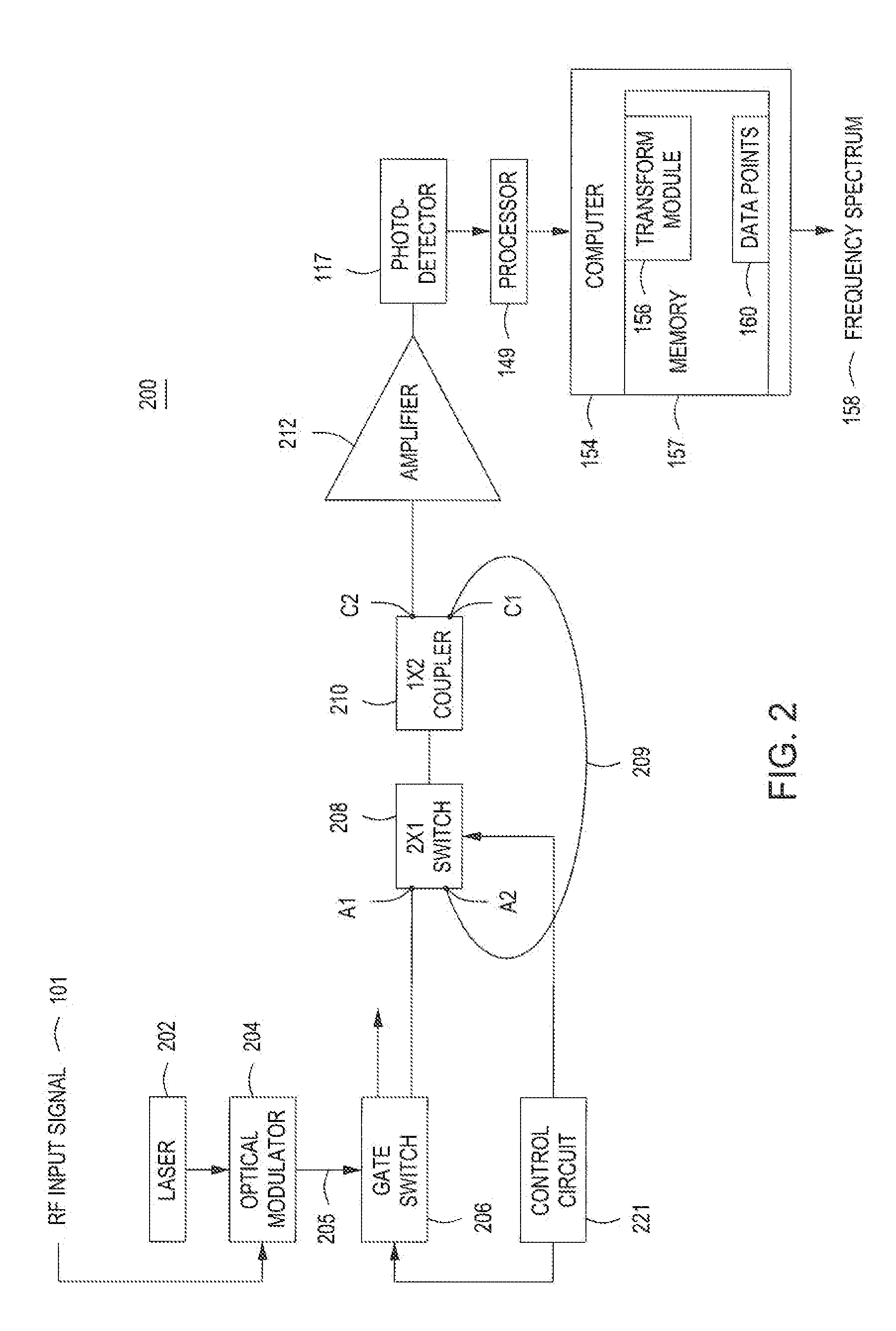
An apparatus for generating a frequency spectrum of an RF signal comprising a gate switch for generating a series of pulses from a laser of wavelength lambda modulated by an input RE signal, a first fiber optical loop for circulating a first percentage of a first pulse of the series of pulses from the gate switch, for a predetermined number of cycles n where each cycle takes time t1, a second fiber optical loop for conducting a second percentage of the first pulse for predetermined number of cycles “k”, where each cycle takes time t2, where t2*k=t1*n, a first switch with a first state for coupling the first pulse from the gate switch to a coupler, the coupler coupling the first pulse into the first fiber optical loop and tapping replicas of the pulse from the first fiber optical loop, and a second state for coupling the second percentage of the first pulse to the coupler to increase intensity of the tapped replica pulses, a processor for correlating the replicas of the pulse with each other to produce a set of data points comprising a plurality of multiplexed correlated pulses and transforming the data points into a channelized frequency spectrum of the input RF signal.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Photon microwave down conversion device and method
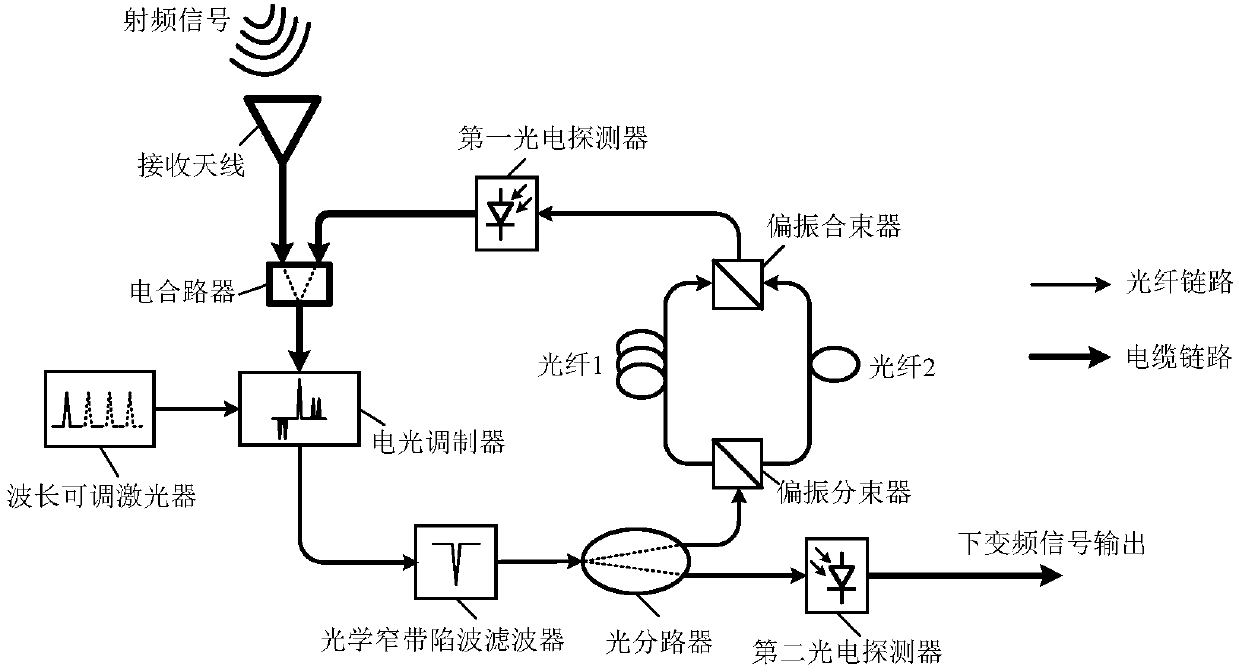
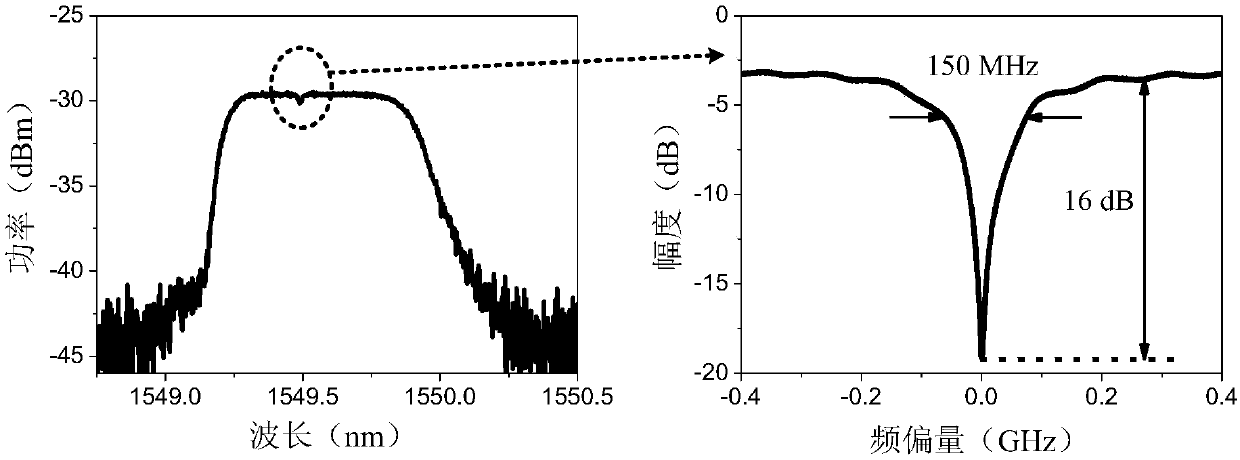
ActiveCN107947864AComplete RF Isolation BenefitsAdvantages of flexible regulationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingPhotovoltaic detectorsIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a photon microwave down conversion device and method, and belongs to the technical field of microwave signal processing. In the device, an electro-optic modulator, an optical narrow band notch filter, a photoelectric detector and an electric mixer form an oscillating loop, the device has a function of generating microwave local oscillation, and the frequency of a local oscillation signal can be flexibly adjusted by changing the frequency of output optical waves of a variable length adjustable laser. Due to a phase modulation function of the electro-optic modulator, a radio frequency signal is output from an output end of the down conversion photoelectric detector, thus having complete radio frequency isolation advantages. The down conversion device has flexible regulation and control ability, can not only perform down conversion on the radio frequency signals with different frequency to intermediate frequency signals with the same frequency, but also can performdown conversion on the same radio frequency signal to the intermediate frequency signals with different frequency. The photon microwave down conversion device solves the problems of complex structure, poor radio frequency isolation, flexible tuning difficulty and the like of microwave down conversion in the prior art.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
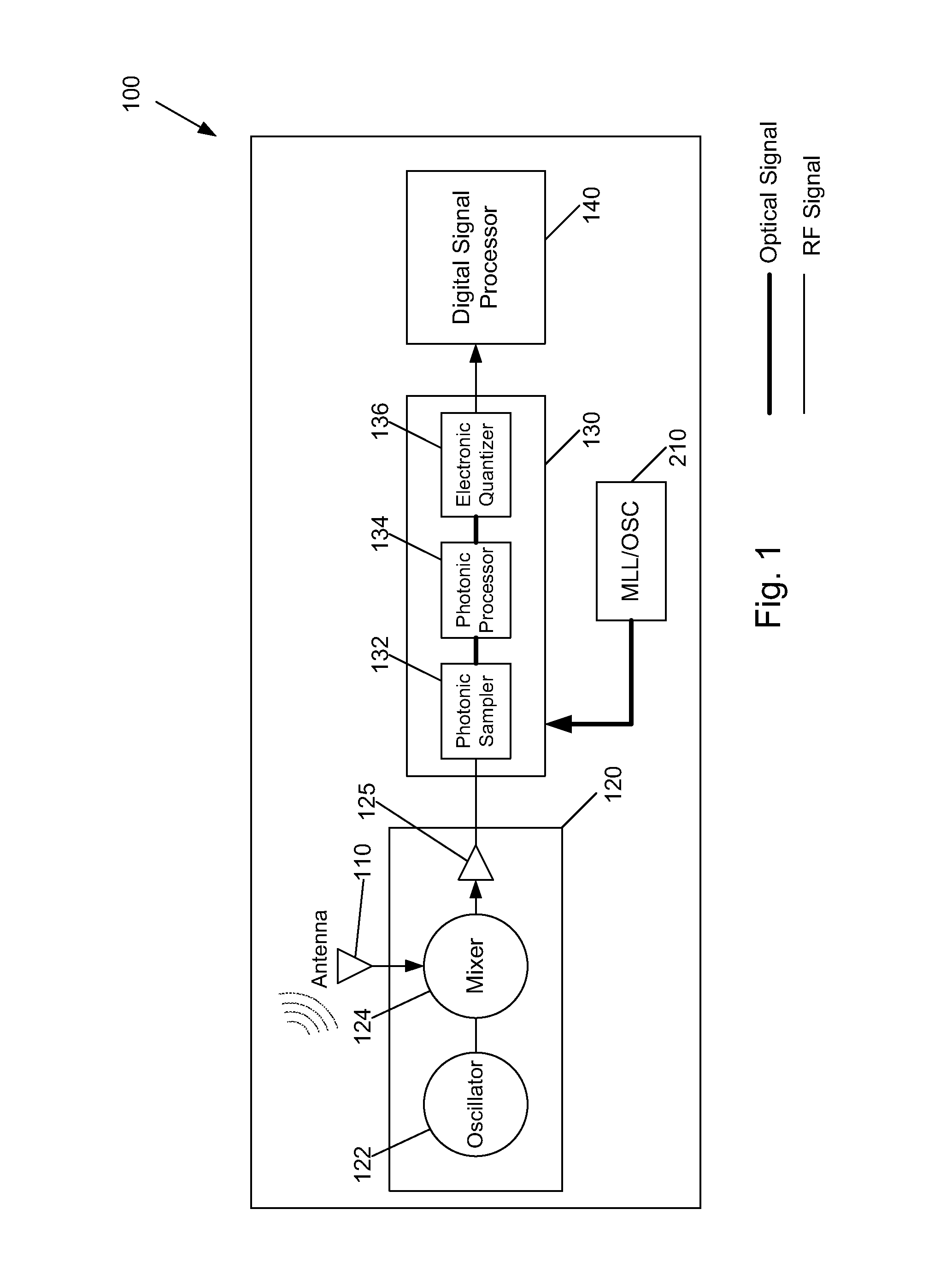
Wide band digital receiver: system and method
ActiveUS8442402B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsRF front endPhotonics
A wide band digital RF receiver includes an RF front end configured to convert a RF signal into an IF signal. A wide band digital receiver also includes a photonic Analog-to-Digital Converter (pADC), and a digital processor. The pADC includes a photonic sampler that phase-encodes a stream of optical pulses with the IF signal to obtain phase-encoded optical pulses, and that amplitude-encodes an identical stream of optical pulses with the IF signal to obtain amplitude-encoded optical pulses. The pADC also includes a photonic processor and an electronic quantizer. The photonic processor processes the phase-encoded optical pulses by way of an I channel and a Q channel, and processes the amplitude-encoded optical pulses by way of an amplitude channel.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
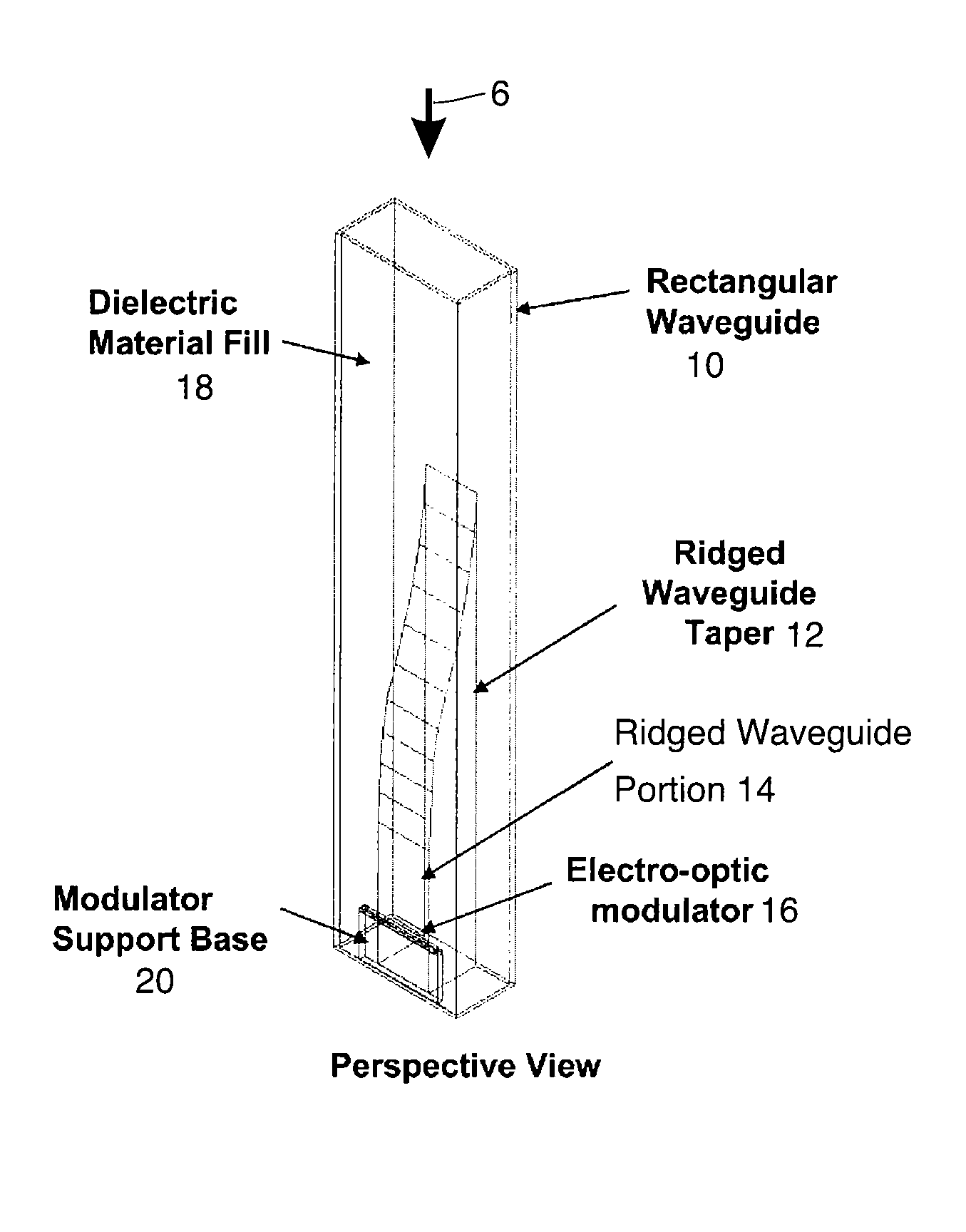
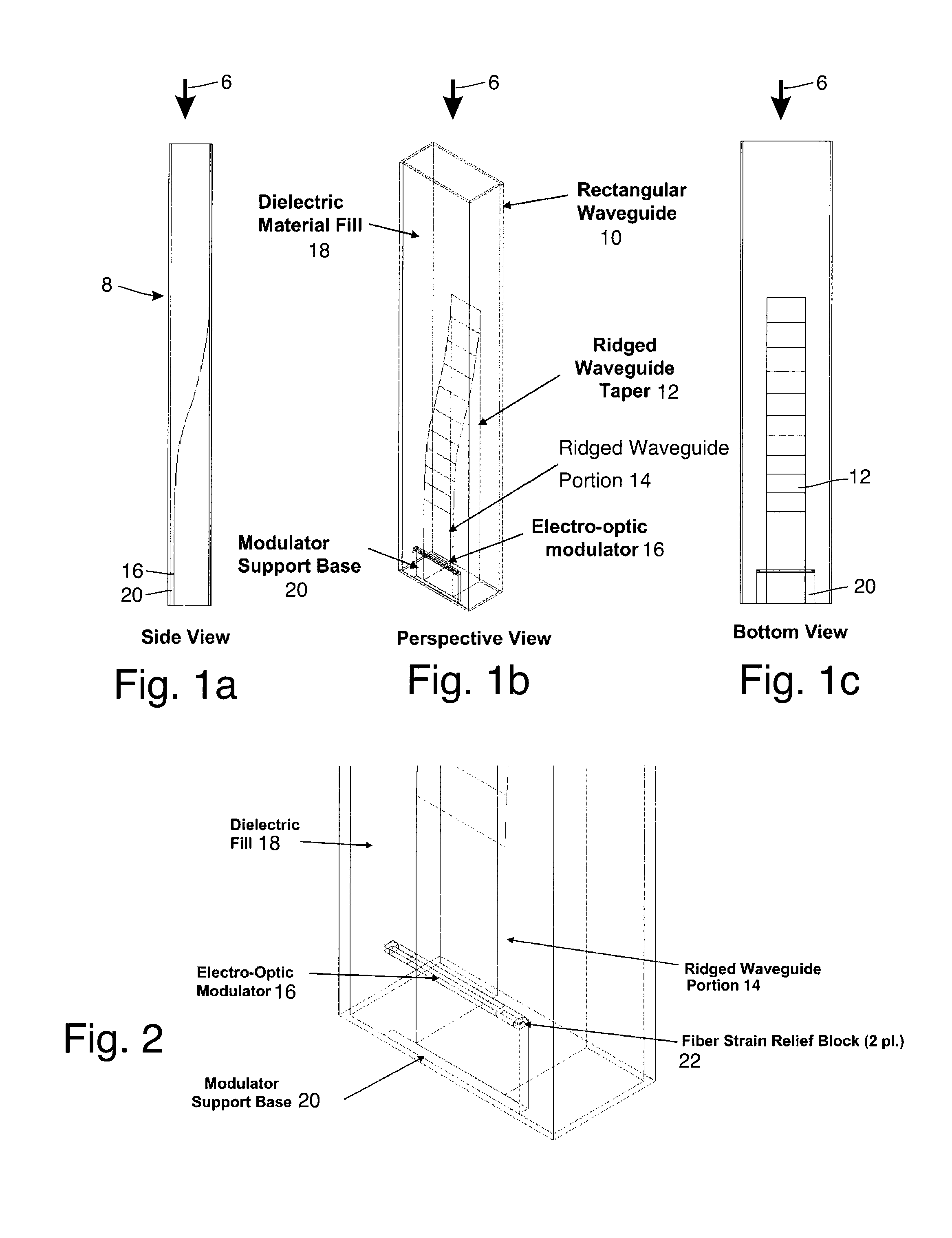
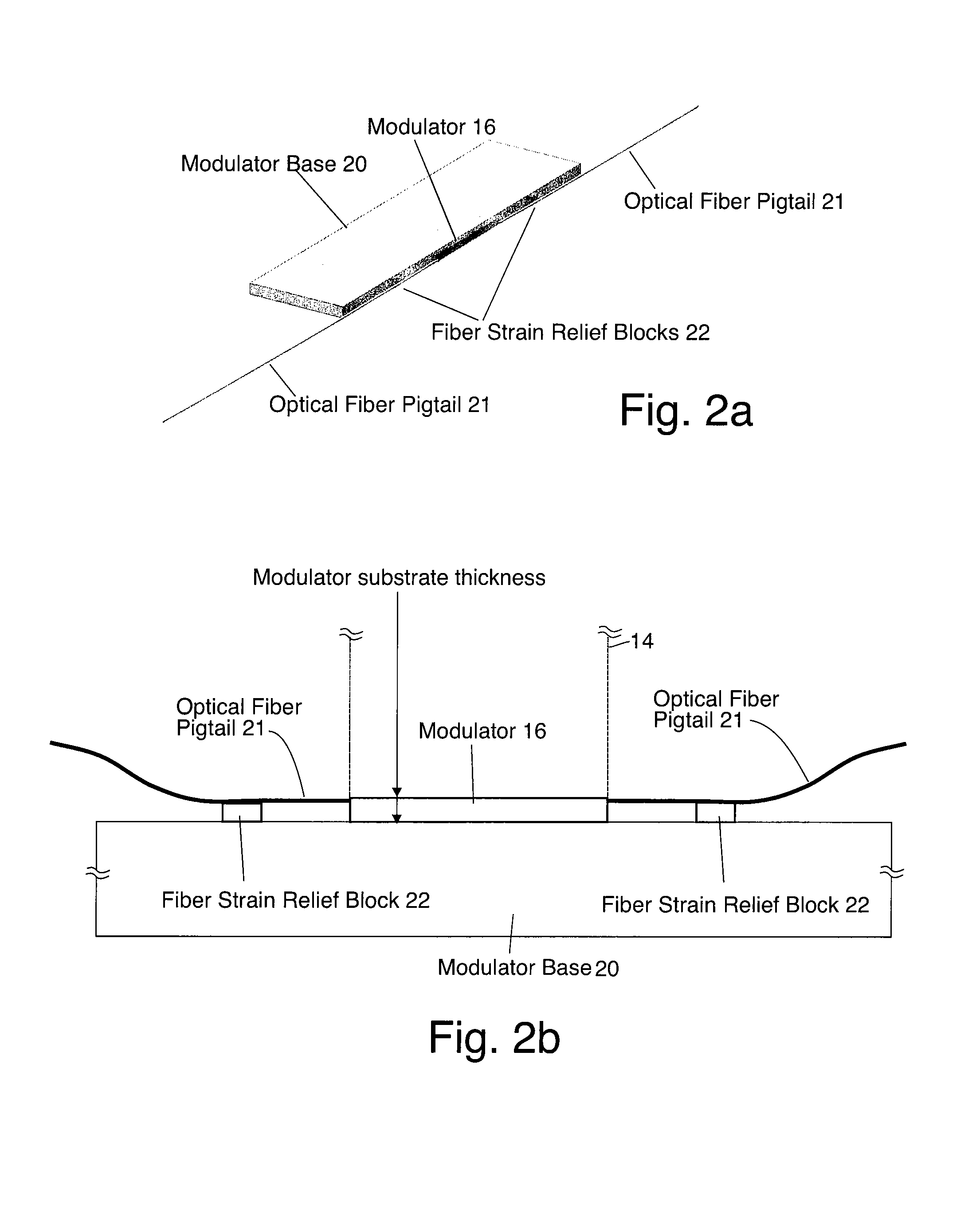
Waveguide assembly for a microwave receiver with electro-optic modulator
InactiveUS8995838B1Efficient ConcentrationPrevent electric field breakdownWaveguide hornsElectromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsMicrowaveDielectric substrate
A waveguide assembly for a use with, for example, a microwave receiver. The waveguide assembly includes: a waveguide; a tapered structure disposed within the waveguide, the tapered structure tapering in thickness from a first end with a zero height to a second end where the tapered structure has a height which nearly fills, but does not completely fill, the waveguide, to thereby define a modulator receiving space between the tapered structure and an adjacent wall of said waveguide. The second end of the tapered structure is preferably disposed adjacent an open circuited end of the waveguide. An electro-optic modulator is disposed on a dielectric substrate, the dielectric substrate being disposed at least partially within the modulator receiving space and the electro-optic modulator being disposed so that it is located, in use, at an antinode of a standing wave of the waveguide assembly.
Owner:HRL LAB
Photonic filtering of electrical signals
InactiveUS20100230621A1Reliable and simple and widely tunable filterMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingPhotodetectorCarrier signal
A filter and a method of filtering a high frequency electrical signal using photonic components is disclosed. The filter has a serially fiber-coupled laser source, a modulator, a filter, and a photodetector. The electrical signal is applied to the modulator. The modulated light propagates through the filter which is constructed to pass not only a modulated sideband, but also at least a fraction of light at the carrier frequency of the laser. The photodetector detects a signal at the beat frequency between the carrier and sideband signals, after both signals have propagated through the filter. As a result, a separate optical branch for light at the carrier frequency is not required, which considerably simplifies the filter construction and makes it more stable and reliable.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Electro-optic communications device with frequency conversion and related methods
ActiveUS8842992B2Easy to operateImprove dynamic rangeOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreFrequency conversionCarrier signal
Owner:HARRIS CORP
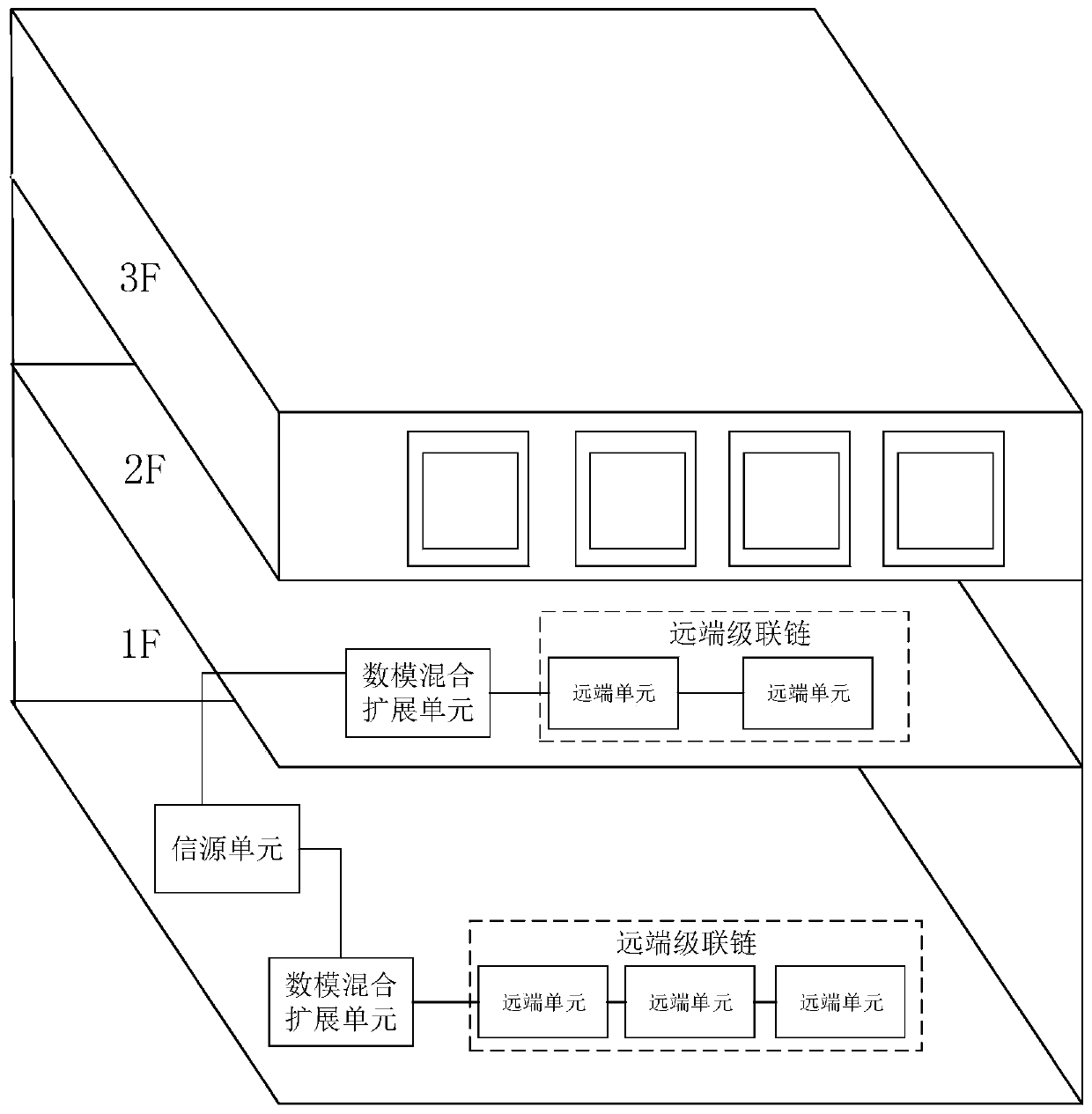
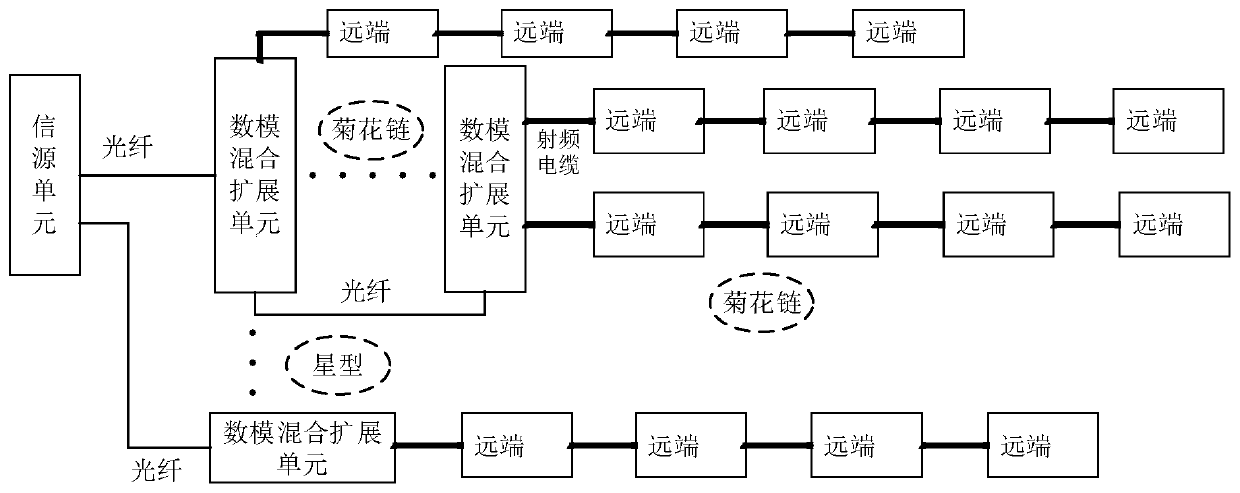
Distributed antenna system, method and device
ActiveCN110278011ALow costReduce performanceSite diversityOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingDistributed antenna systemDigital radio
The invention relates to a distributed antenna system, method and device. The distributed antenna system comprises a digital-to-analog expansion unit and a far-end cascade chain. The far-end cascade chain comprises a plurality of far-end units which are in cascade connection through radio frequency cables, and the head-stage far-end unit of the far-end cascade chain is connected with the digital-to-analog expansion unit through the radio frequency cables. And the digital-to-analog expansion unit is used for carrying out baseband processing operation on the received external signal and carrying out mutual conversion operation on the analog radio frequency signal and the digital radio frequency signal. Based on this, the digital-to-analog expansion unit and the remote unit adopt a daisy chain topological structure based on cable connection, so that the cost of a transmission link can be effectively reduced while the transmission bandwidth is improved. Moreover, the digital-to-analog expansion unit executes baseband processing, and the far-end unit does not need baseband processing equipment, so that the device cost and the operation power consumption of the system can be effectively reduced. The system has the characteristics of supporting multi-mode and multi-frequency, cell splitting and the like, and is easy to expand the capacity and low in construction difficulty.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
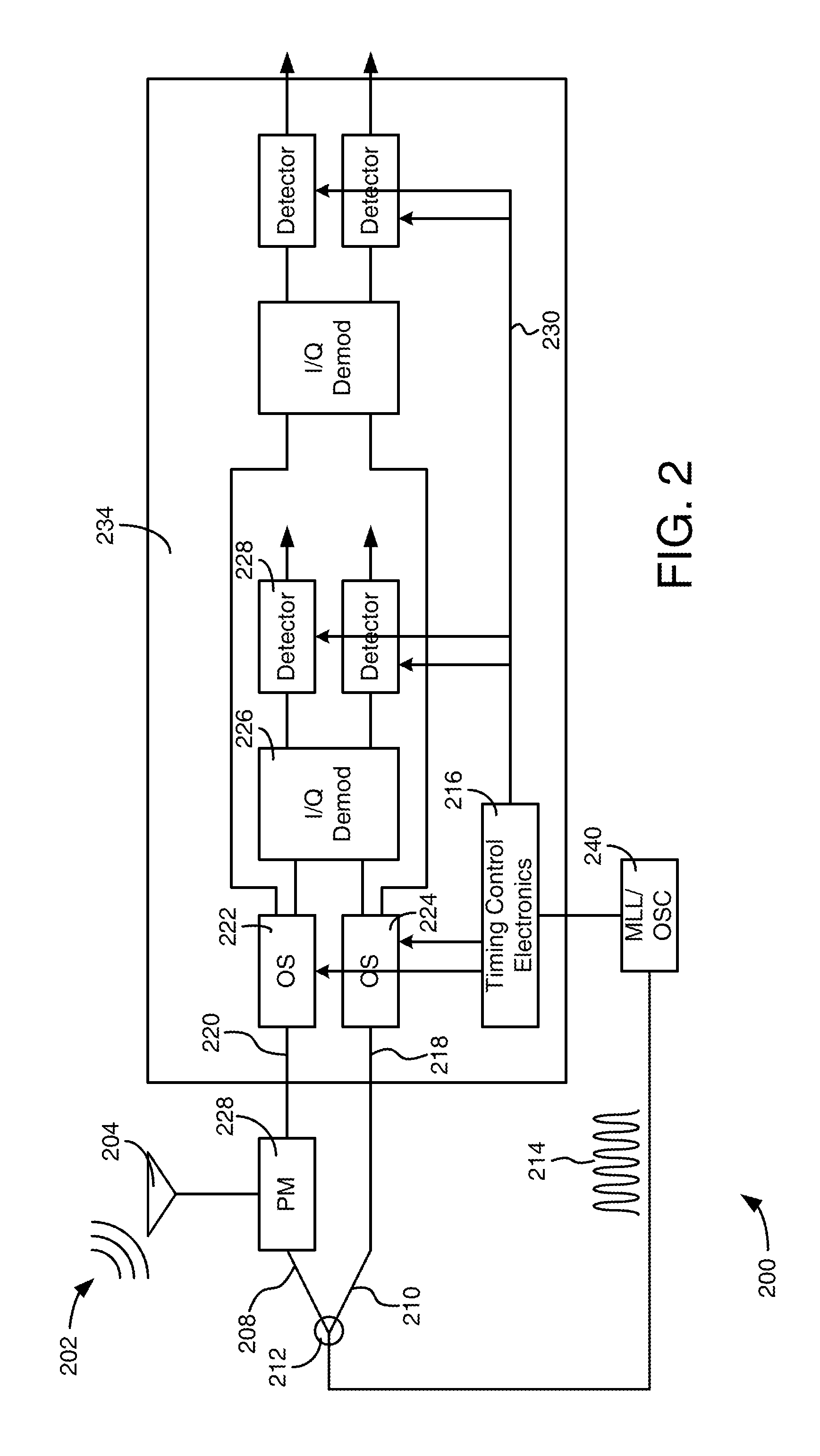
Optically interleaved photonic analog to digital converters
ActiveUS9197471B1Electromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingAudio power amplifierPhotonics
A method of and system of processing a phase-modulated optical signal includes performing, by demodulators, demodulation of the phase-modulated optical signal and outputting optical demodulated signals. The processing further includes performing, by pairs of gated photo detectors respectively connected to the I / Q demodulators, photo detection of the demodulated signals. The processing further tracks and holds electronicversions of the demodulated signals with a track and hold amplifier.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
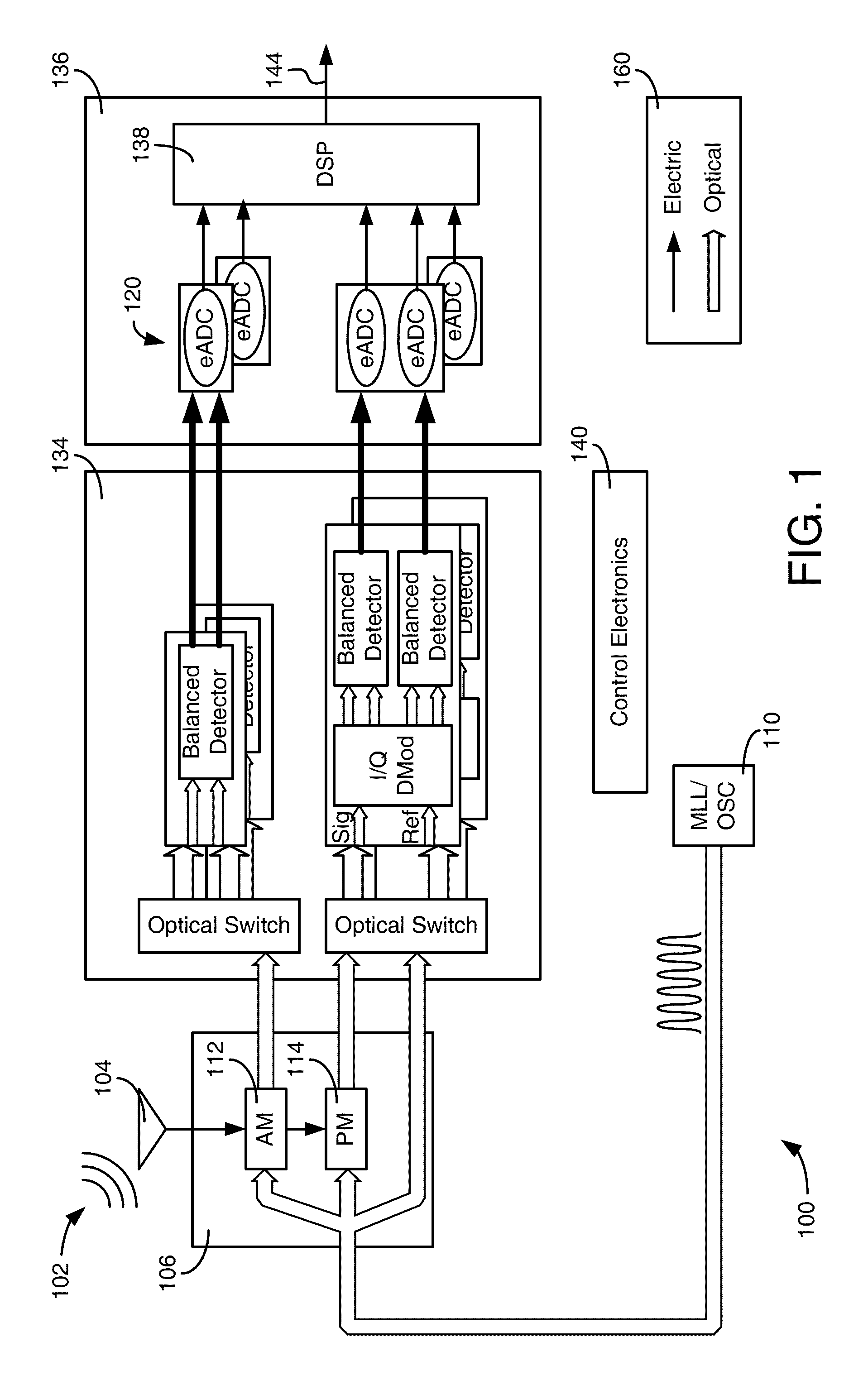
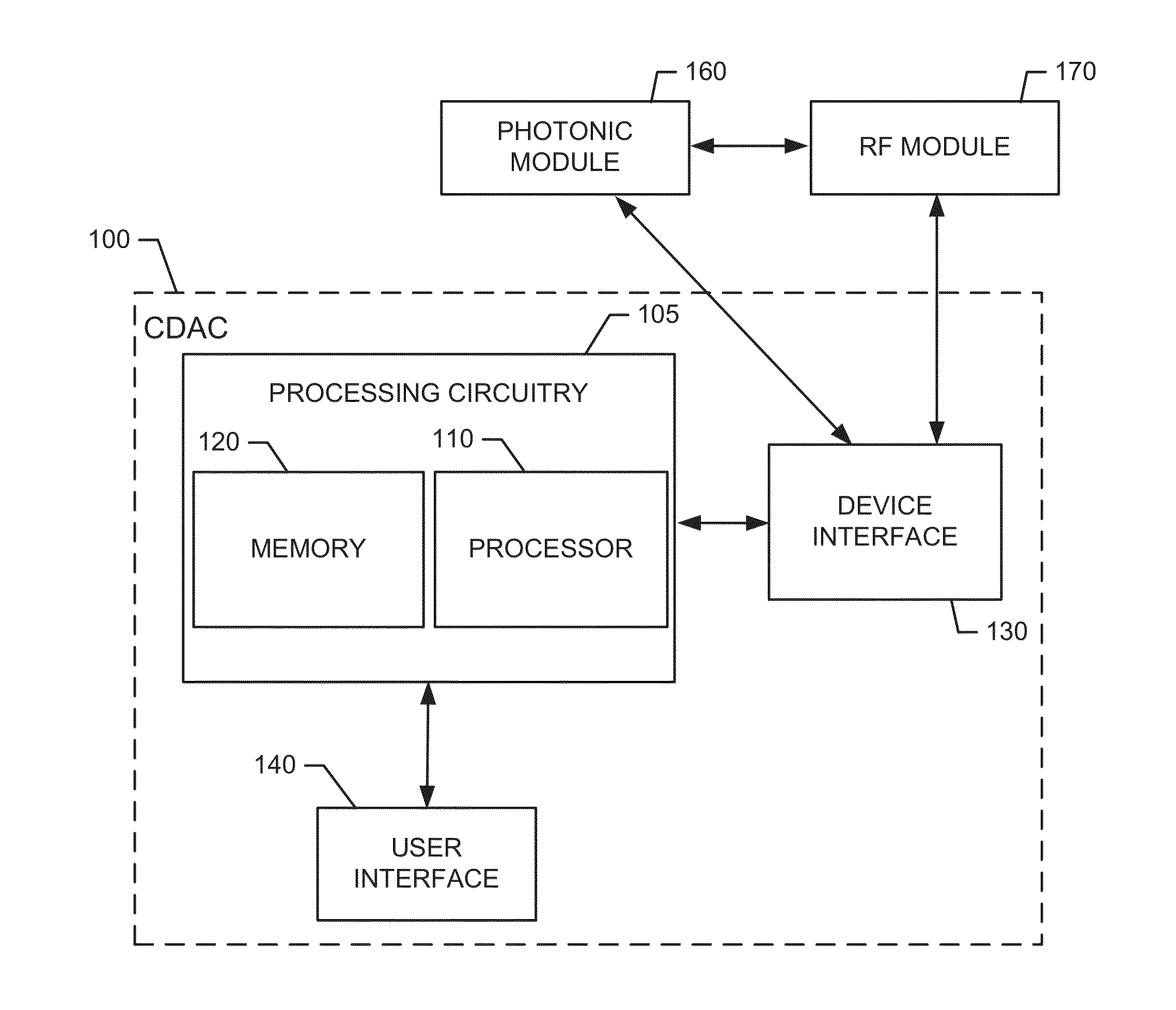
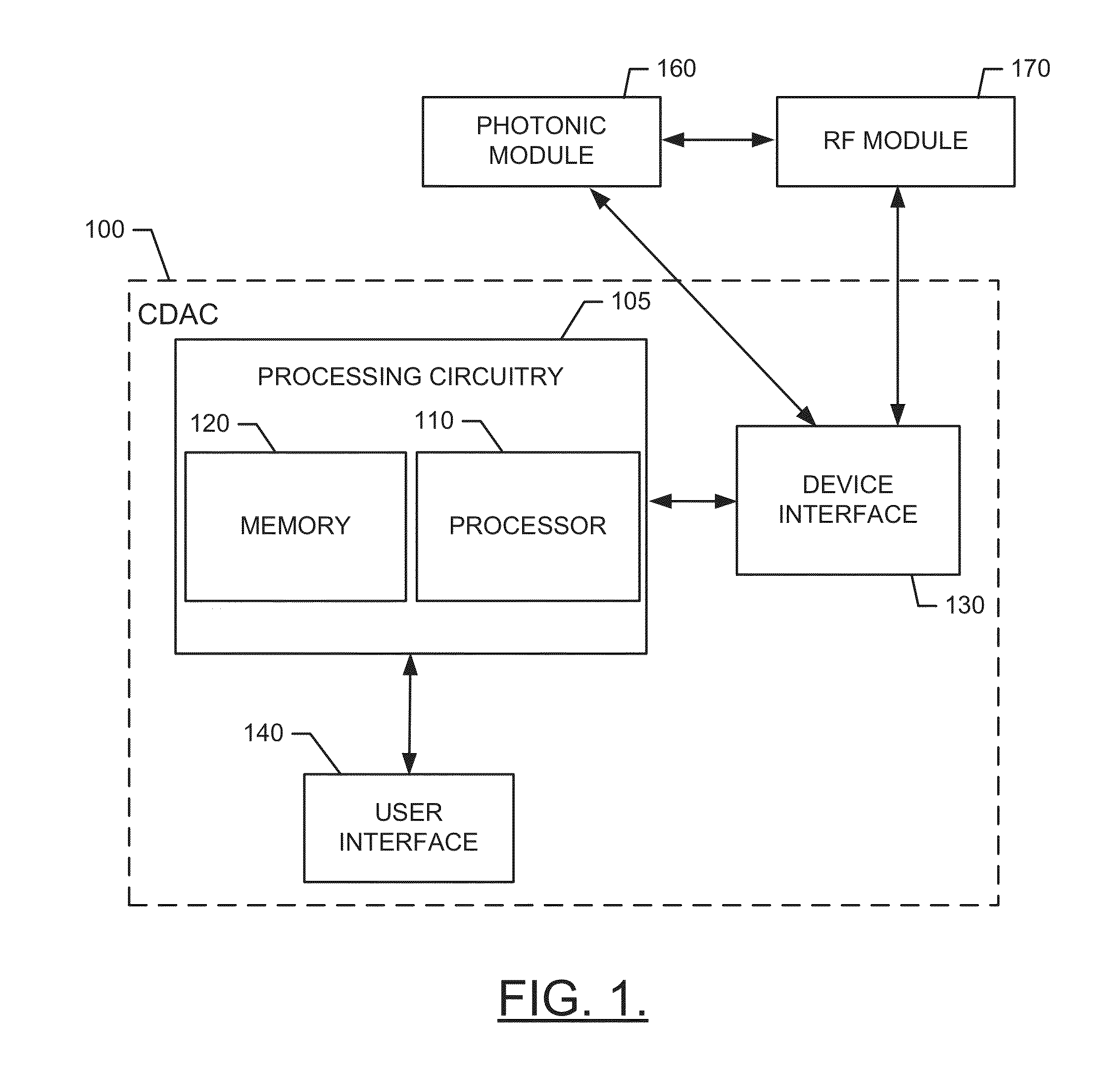
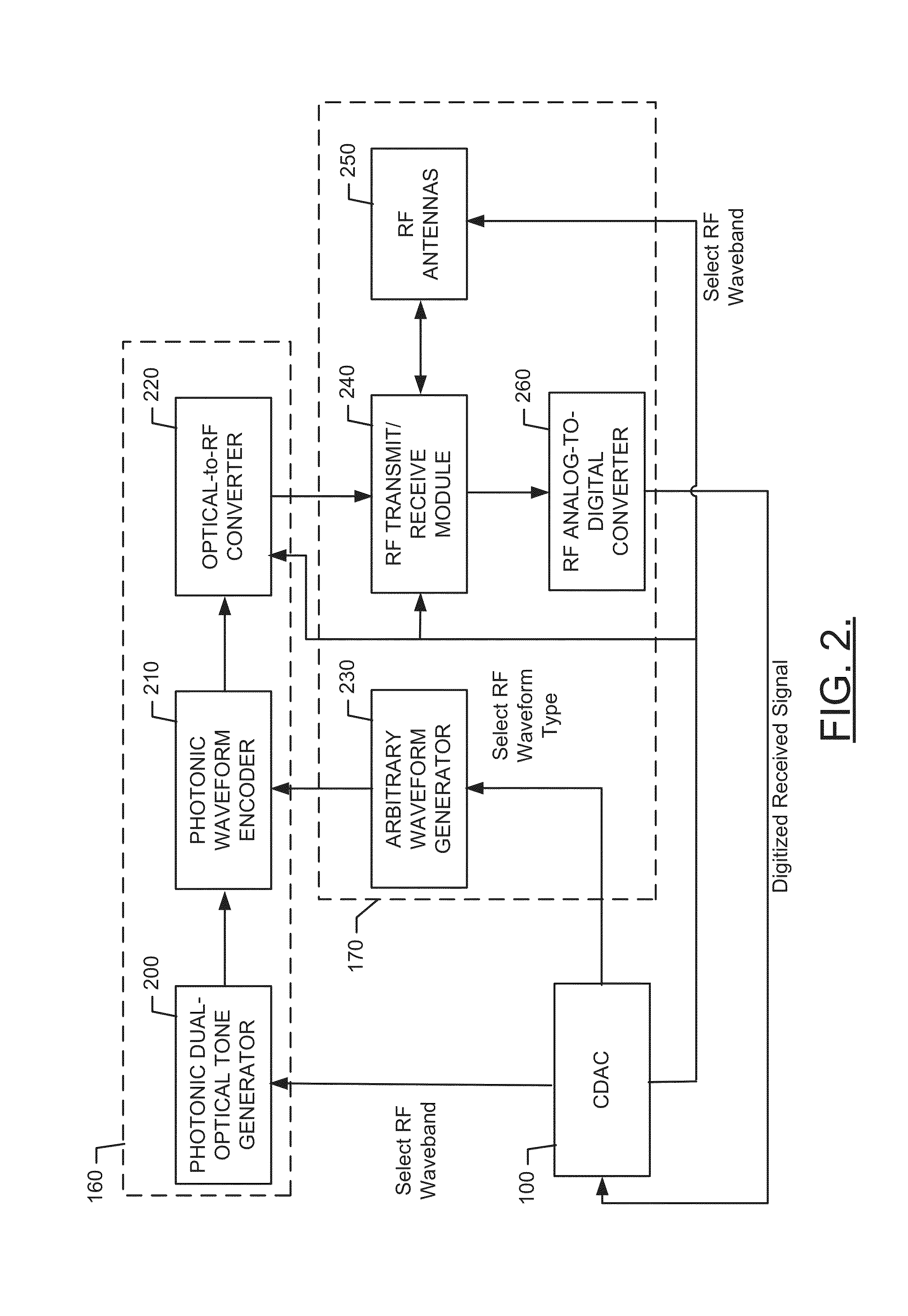
Photonically Enabled RF Transmitter/Receiver
ActiveUS20140022119A1Wide rangeRapid fashionElectromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingPhotonicsComputer module
A detection system includes a photonic module, a radio frequency (RF) module and processing circuitry. The photonic module may be configured to generate an optical tone for modulation in an optical domain prior to conversion to the RF domain. The RF module may be configured to interface with the photonic module to receive a transmission signal converted from the optical domain. The processing circuitry may be configured to interface with the photonic module and RF module to enable an operator to control of the photonic module and the RF module at least with respect to selectively determining a carrier frequency of the optical tone and a modulation technique to be employed with respect to the transmission signal converted from the optical domain.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Beamforming (BF) weight assigning method and device
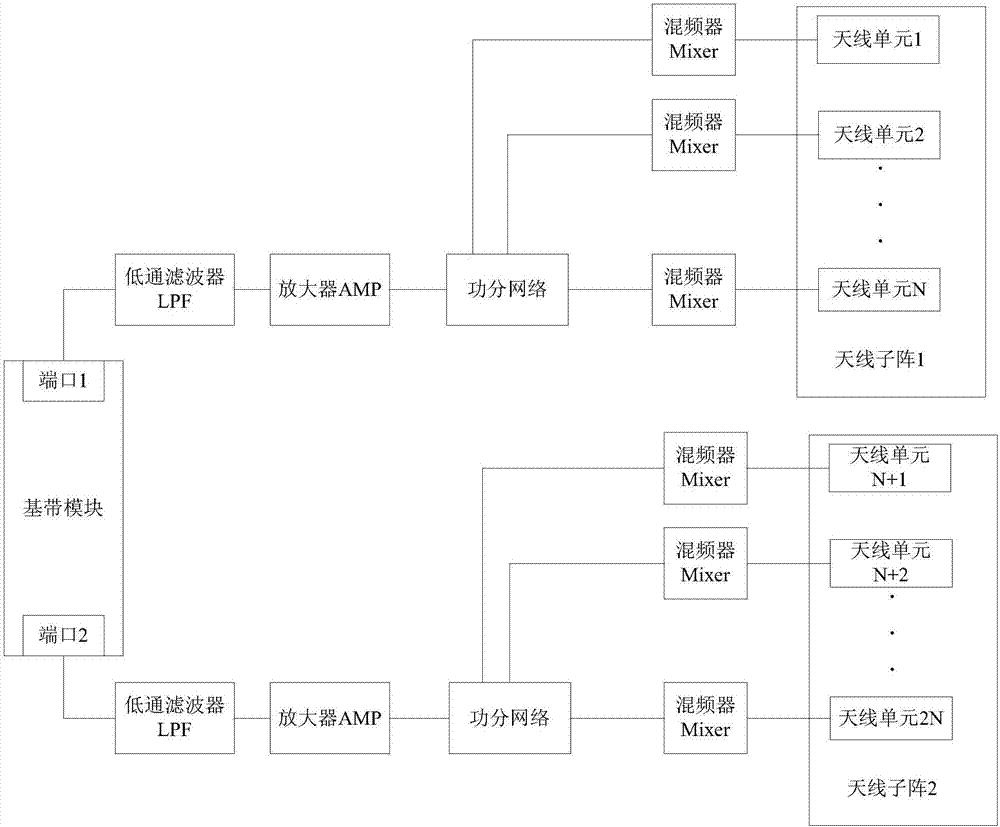
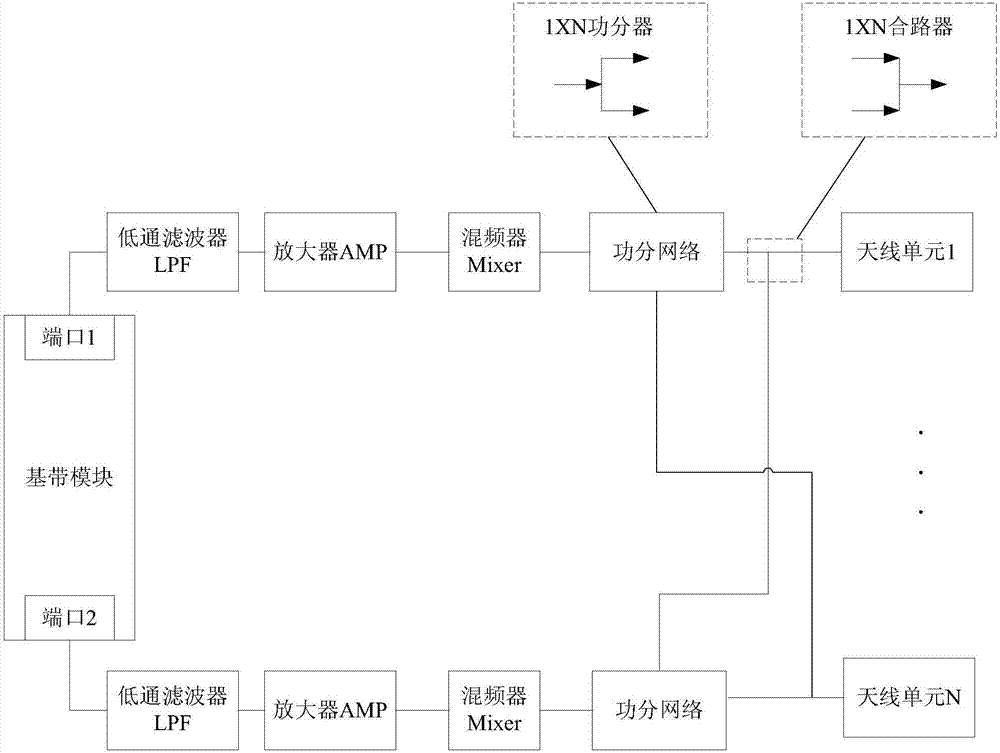
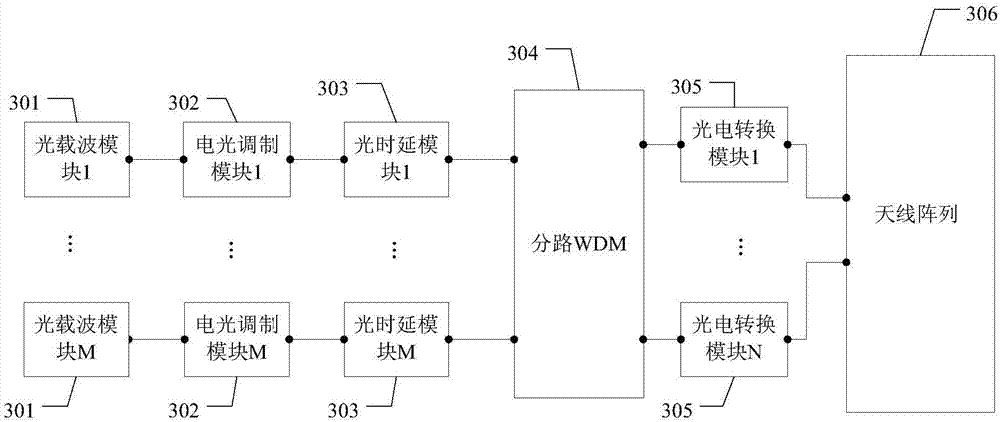
ActiveCN106972881AMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpatial transmit diversityRadio frequencyBeamforming
The invention provides a beamforming (BF) weight assigning method and a BF weight assigning device, used for reducing power dividing insertion loss of the BF, and avoiding electromagnetic interference between a power dividing network and each base band port-antenna unit channel. The device provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises M optical carrier modules, M electro-optical modulation modules, M optical delay modules, a branch wavelength division multiplexer (WDM), N photovoltaic conversion modules, and an antenna array with a k*N antenna unit, wherein M and N are integers more than or equal to 1; the optical carrier modules are used for generating N optical carriers with different wavelengths; the electro-optical modulation modules are used for modulating electrical signals to the optical carriers to acquire a modulated optical signal; the optical delay modules are used for adjusting delay of the modulated optical signal; the branch WDM is used for shunting according to the wavelength of the modulated optical signal after the delay is adjusted to acquire N optical sub-signals; the photovoltaic conversion modules are used for converting the N optical sub-signals into N electric sub-signals; and the antenna array is used for forming a plurality of beams with adjustable direction according to N radio frequency electric signals.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Radio-over-fibre beamforming device based on array waveguide grating (AWG) and method thereof
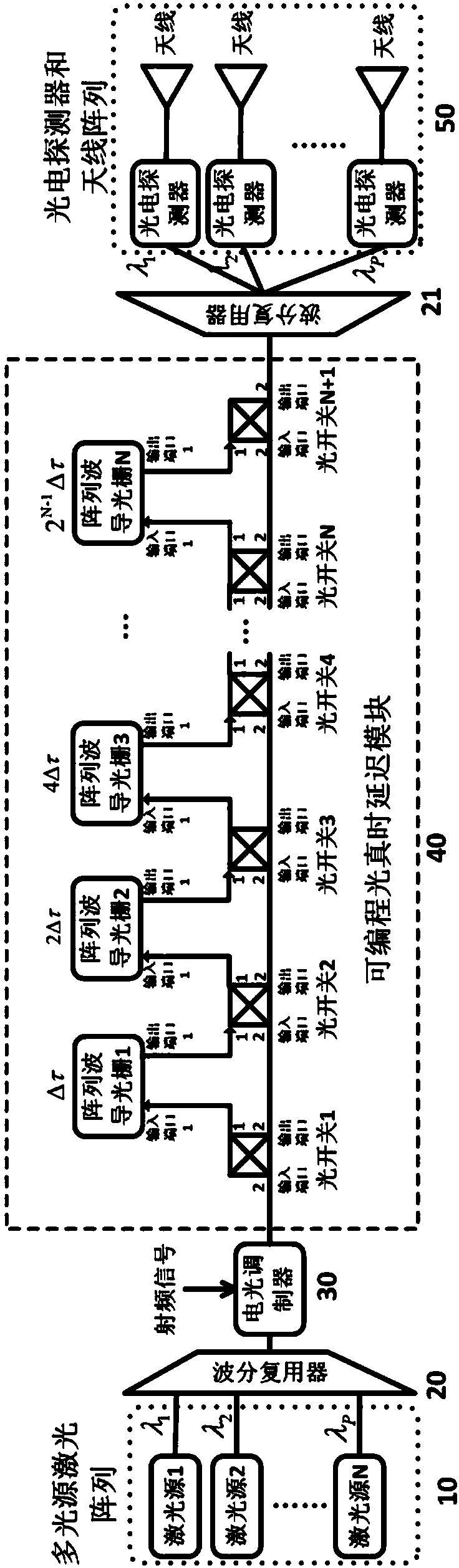
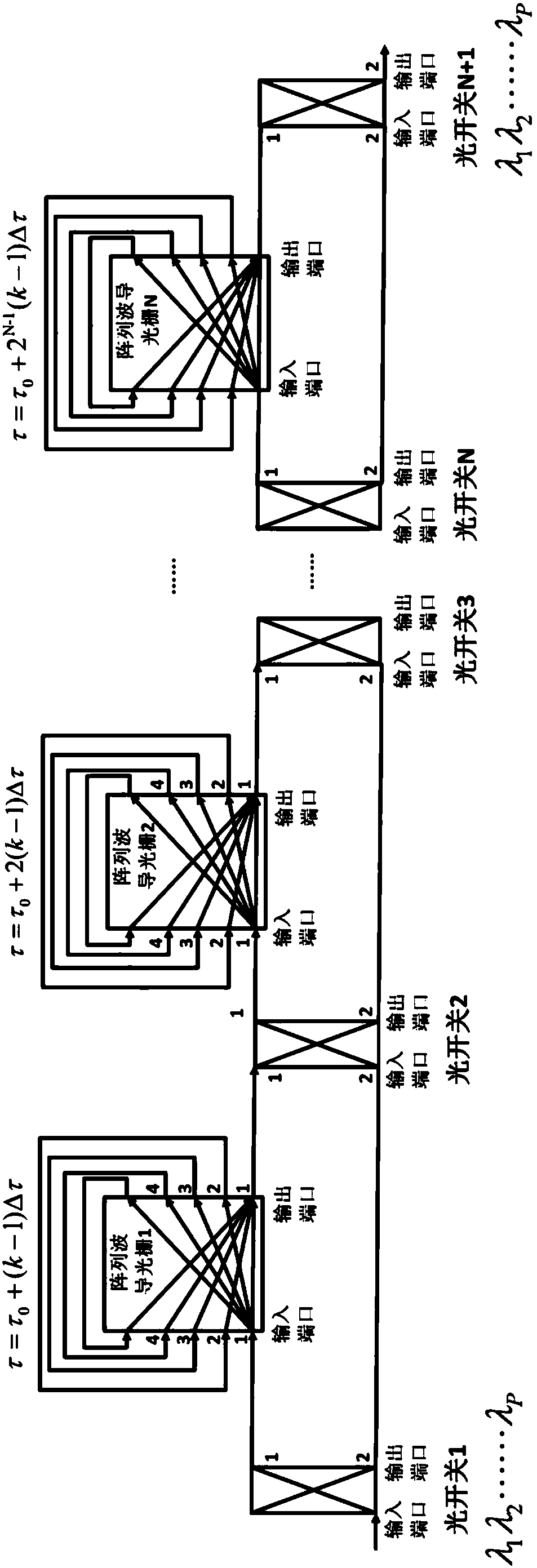
ActiveCN107911189ASimple structureHigh bandwidthSpatial transmit diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingCarrier signal
The invention relates to a radio-over-fibre beamforming device based on an array waveguide grating (AWG) and a method thereof. Radio-frequency signals are modulated onto carriers of multiple wavelengths, and processed by a programmable optical true time delay module in an optical domain; the module is composed of an optical switch and multiple cascade AWGs capable of providing different basic delays between adjacent wavelength channels; the basic delay amounts of different-level AWGs are in geometric distribution by taking 2 as the common ratio; optical carriers different in wavelength enter different branches to perform photoelectric conversion, so that radio-frequency signals different in delay (phase) are recovered; and thus, a far-field beam directional radiation mode is realized. Theradio-over-fibre beamforming device based on the AWG and the method thereof disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of being wide in band, adjustable, flexible, small in volume, easy to integrate and the like, and are very importantly applied in dynamic scenes, such as next generation mobile communication and high-speed railways.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
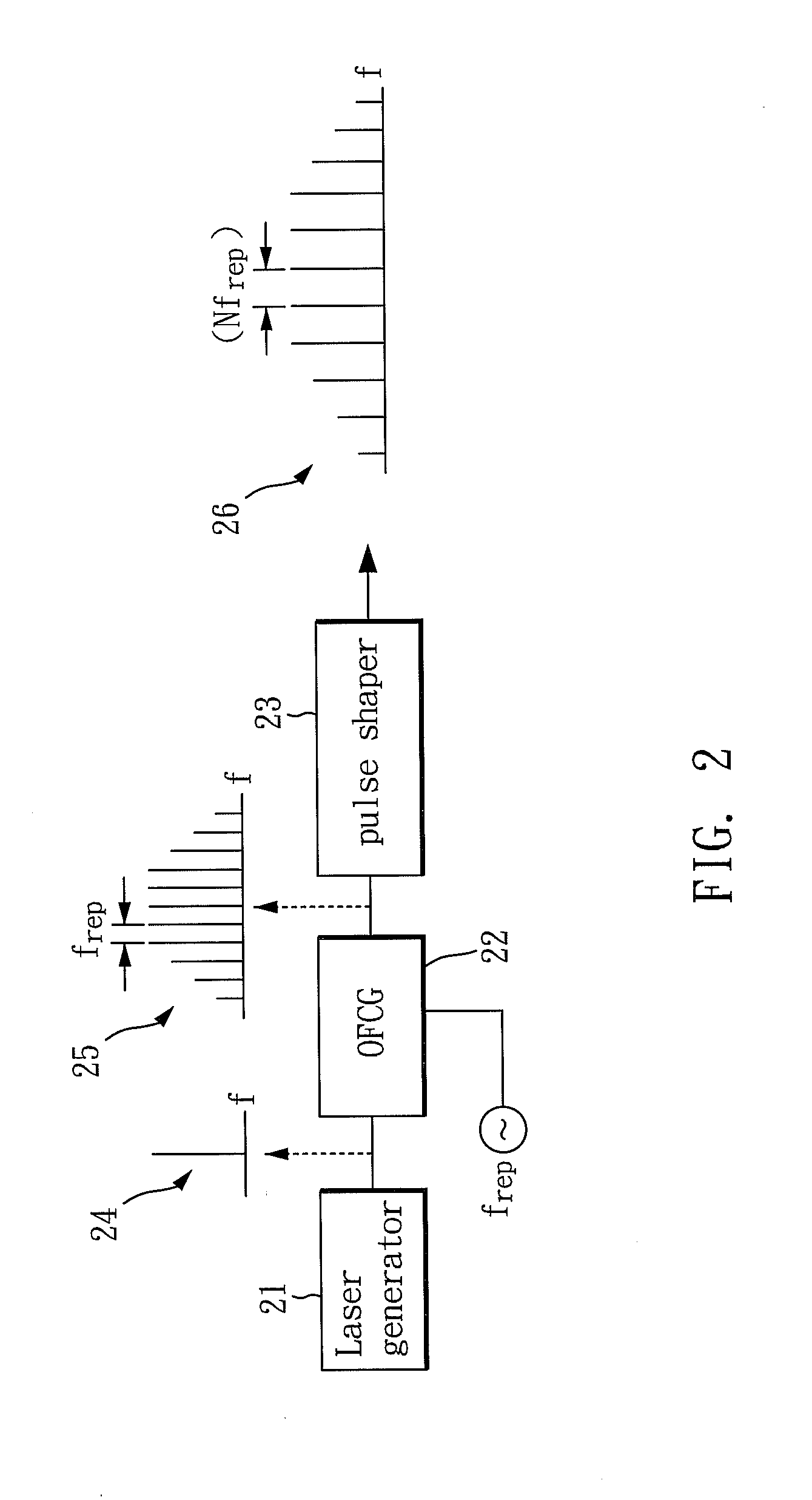
Photonic millimeter-wave generator
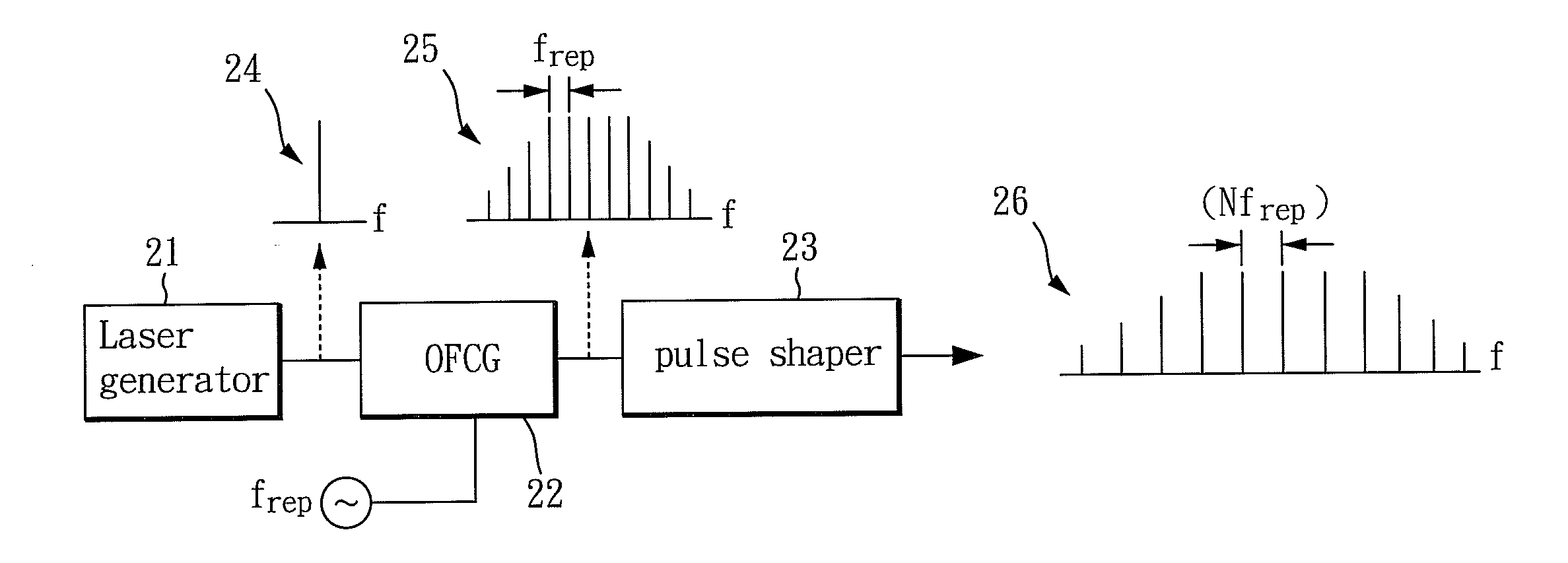
InactiveUS20130051807A1Ultra-high repetition-rateOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingElectromagnetic transmittersPhotonicsPulse shaper
A photonic millimeter-wave generator capable of combining wired and wireless communication facilities to further elongate the transmission distance comprises a laser generator for generating a first optical signal; an optical frequency comb generator coupled with the laser generator; and a pulse shaper coupled with the optical frequency comb generator. The optical frequency comb generator receives the first optical signal generated by the laser generator and outputs a second optical signal. The second optical signal contains multiple frequency components and is sent to the pulse shaper. The pulse shaper adjusts the amplitude and phase of the second optical signal and then outputs the signal as a third optical signal.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
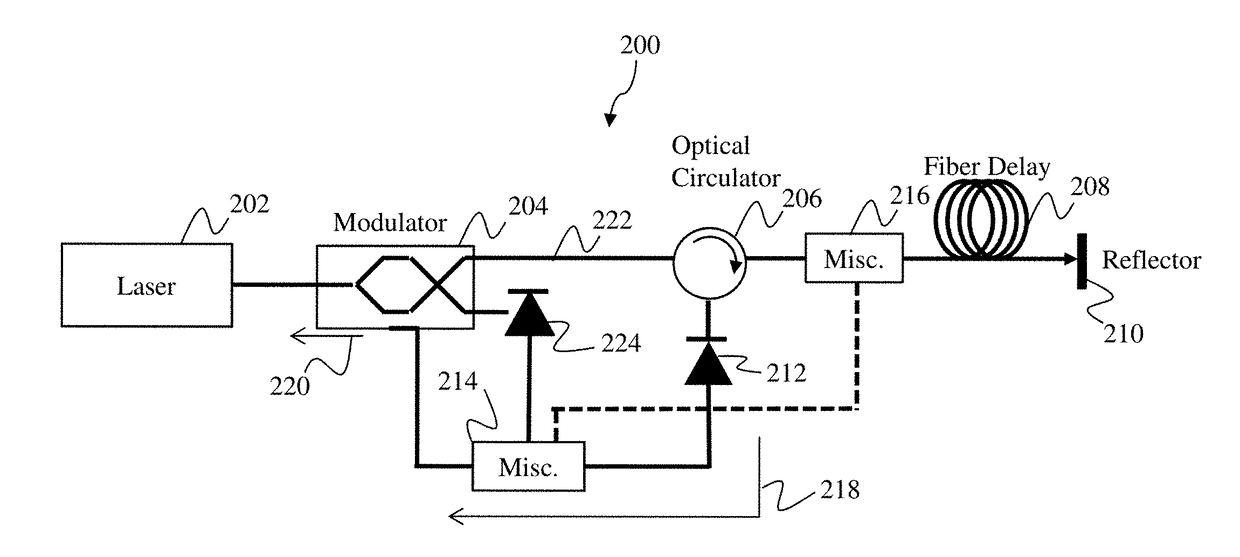
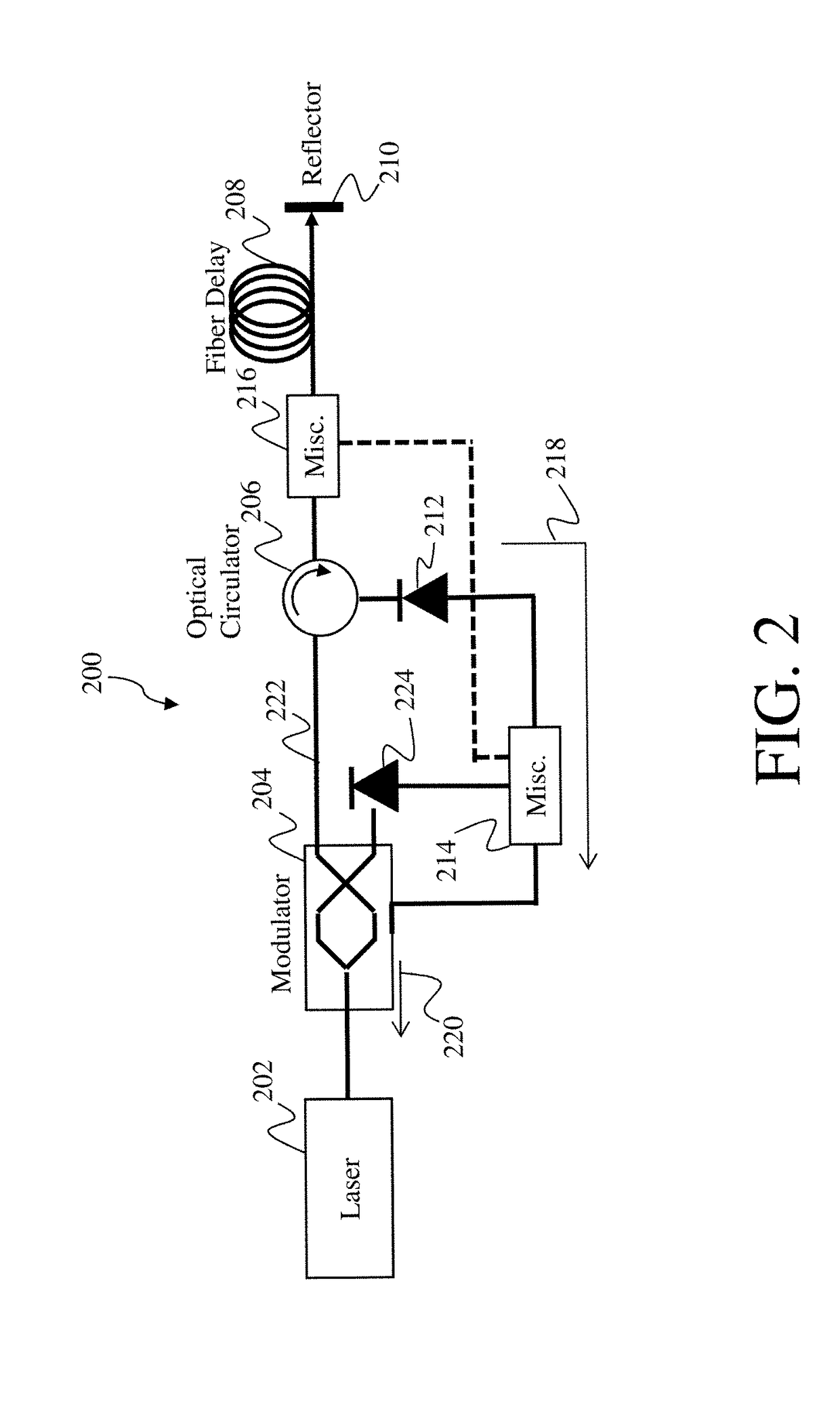
Methods and systems for reducing noise in optoelectronic oscillators
ActiveUS9887779B2Reduce noiseInherent noiseOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingElectromagnetic transmittersFiberPhotovoltaic detectors
Optoelectronic oscillator systems and an optoelectronic oscillator noise reduction method. One example of an optoelectronic oscillator system includes an optical source positioned at a first end of a fiber-optic path, the optical source being configured to transmit an optical signal along the fiber-optic path, an optical modulator positioned to receive and modulate the optical signal based on at least a reference signal, a retro-reflector positioned at a second end of the fiber-optic path, the retro-reflector being configured to receive and retro-reflect the optical signal, the retro-reflected optical signal having at least a frequency range of inherent fiber noise canceled, and an optical circulator positioned along the fiber-optic path between the optical modulator and the retro-reflector, the optical circulator being configured to direct the optical signal to the retro-reflector and direct the retro-reflected optical signal along a feedback path to a first photodetector to generate the reference signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Photonic system and method for tunable beamforming of the electric field radiated by a phased array antenna
ActiveUS20130169483A1Optical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreTime delaysCoupling ratio
This invention discloses a photonic system to beamform the electric field yield by a phased array antenna. The system function relies on a photonic tunable delay line, which consists on an optical Mach-Zehnder interferometer with a predefined time delay difference between arms. The time delay is tuned by adjusting the coupling ratio between the power applied to each one of the interferometer's delay lines. Three embodiments are proposed, wherein one of them just uses a single delay line and a single monchromatic light source, independently of the quantity of the array elementary antennas.
Owner:INST DE TELECOMUNICACOES
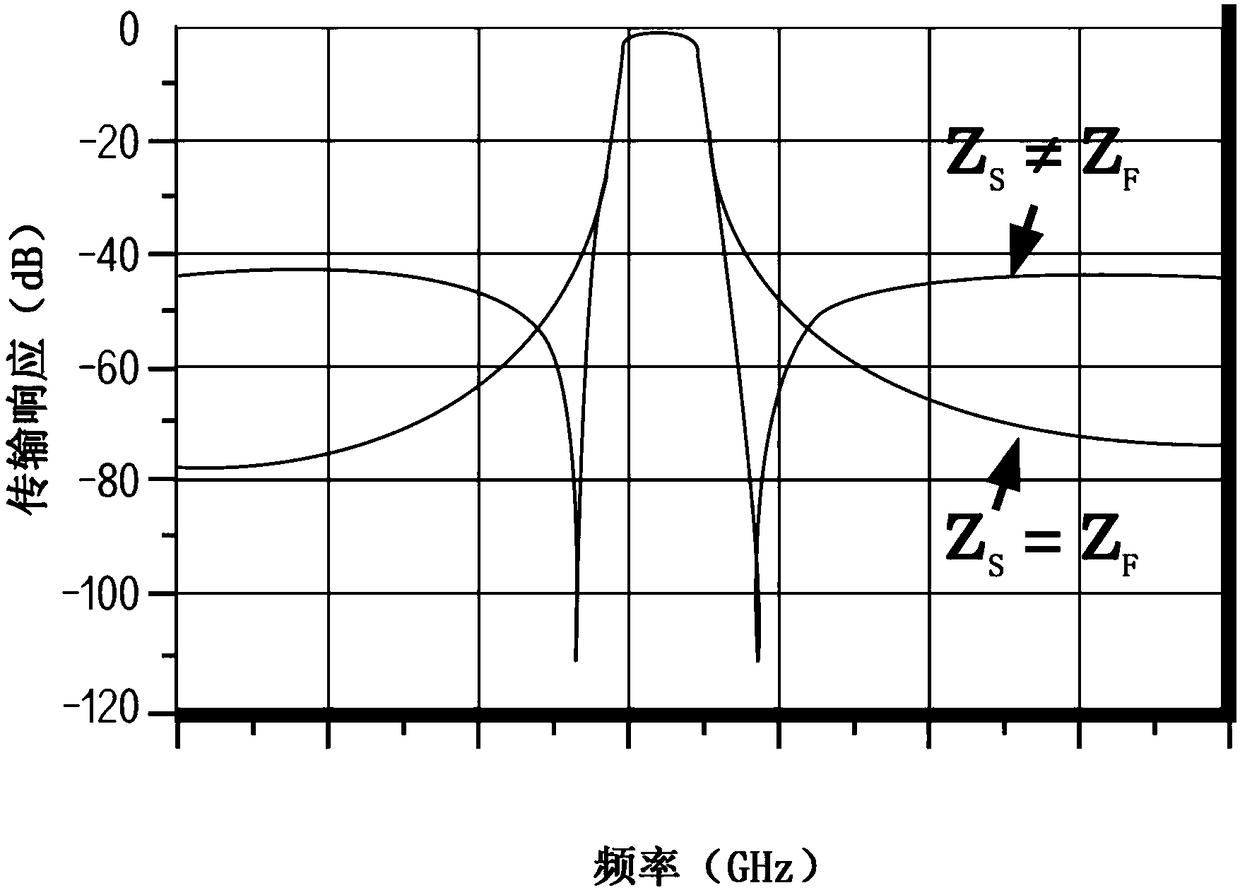
Method for manufacturing filter containing single-crystal piezoelectric radio-frequency resonators
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a filter containing single-crystal piezoelectric radio-frequency (RF) resonators. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring one removablecarrier with a releasing layer; manufacturing a piezoelectric film on the releasing layer; depositing a first electrode layer on the piezoelectric film; manufacturing a back film on a silicon cover; attaching a wafer back film onto an electrode; separating the removable carrier; necessarily measuring piezoelectricity and modification; selectively corroding the piezoelectric film to form an island;corroding a coating and a silicon crystal film in order to form SiO2; coating a passivation layer above a corrosive groove and around and above a piezoelectric island; applying a top electrode; adding a coupler used for connecting an adapter plate; selectively removing electrode material in order to leave out coupled resonators; manufacturing a gasket; peeling the silicon cover; manufacturing a cavity in SOI (otherwise using the SOI having the cavity); cutting; acquiring the adapter plate; manufacturing an epoxy resin dam structure; and connecting the resonators onto a substrate of the adapter plate (a flip-chip); encapsulation and separation.
Owner:ZHUHAI CRYSTAL RESONANCE TECH CO LTD
Rf-photonic transversal filter method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100028012A1Significant changeHigh SLSRTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingPhotonics
A method and apparatus for implementing an RF photonic transversal filter that utilizes tap apodization and wavelength reuse to obtain a high side lobe suppression together with narrow and configurable passbands. Several taps are obtained from one wavelength by using dispersive optical delay lines such as chirped fiber gratings that introduce a delay between successive wavelengths. A selected subset of the input wavelengths is utilized to generate multiple taps per wavelength. Some of the taps are apodized to generate various filter transfer functions that yield a high side lobe suppression ratio.
Owner:HRL LAB
Popular searches
Synchronisation by photonic/optical means Oscillations generators Transmission monitoring Electromagnetic receivers Transmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systems Light demodulation Multimode transmission Radiofrequency circuit testing Phase-modulated carrier systems Distortion/dispersion elimination
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com