Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
260 results about "Apodization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
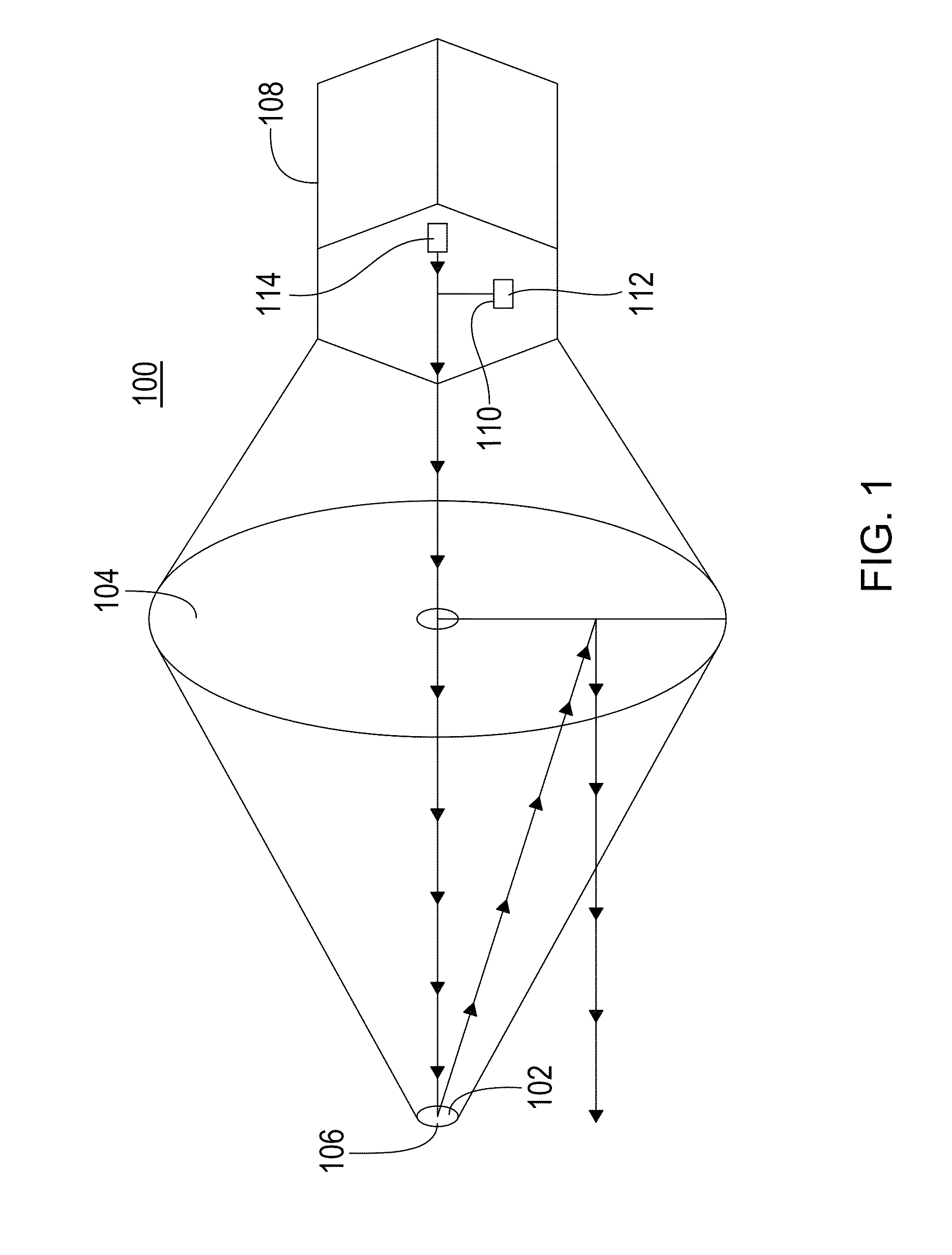
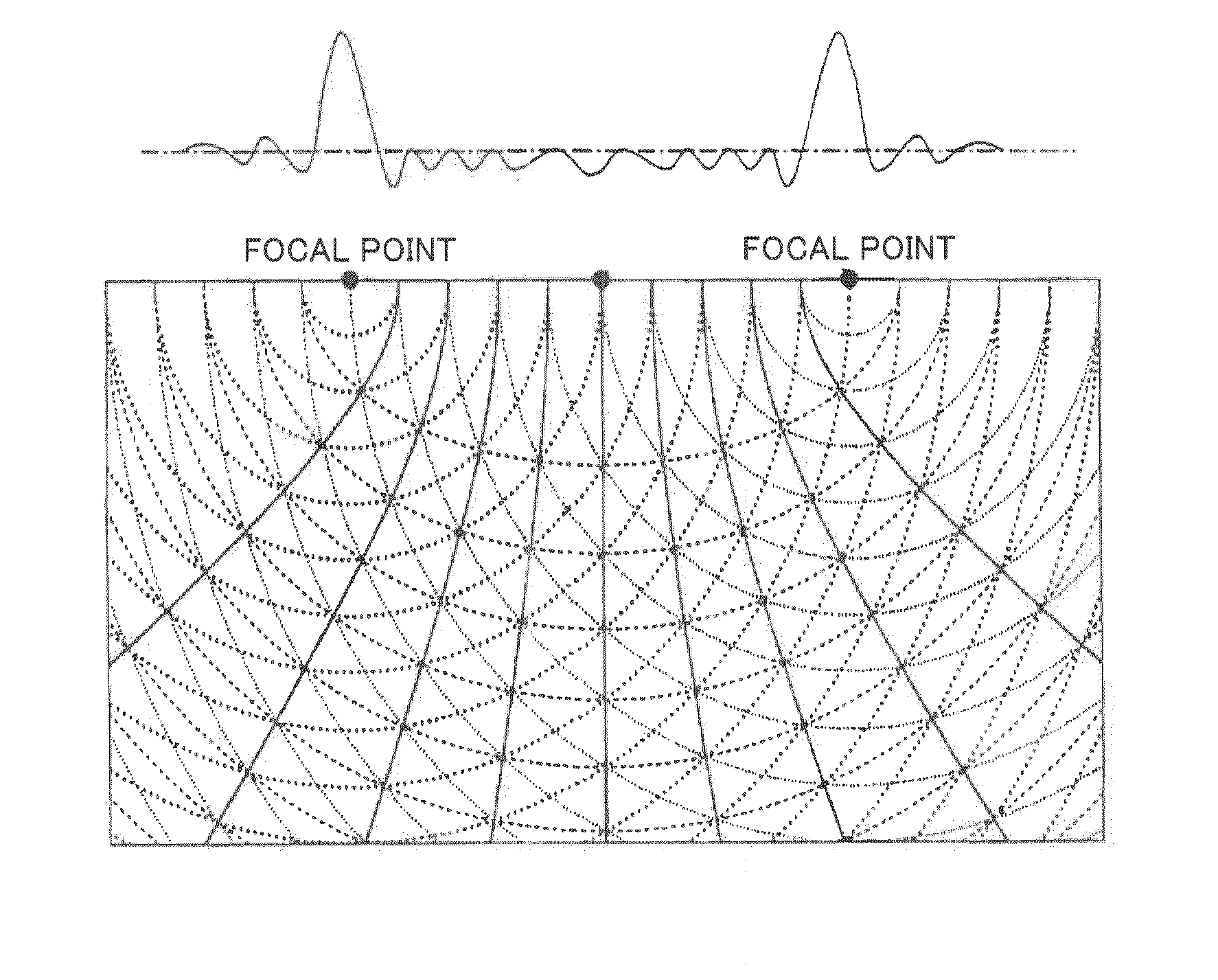
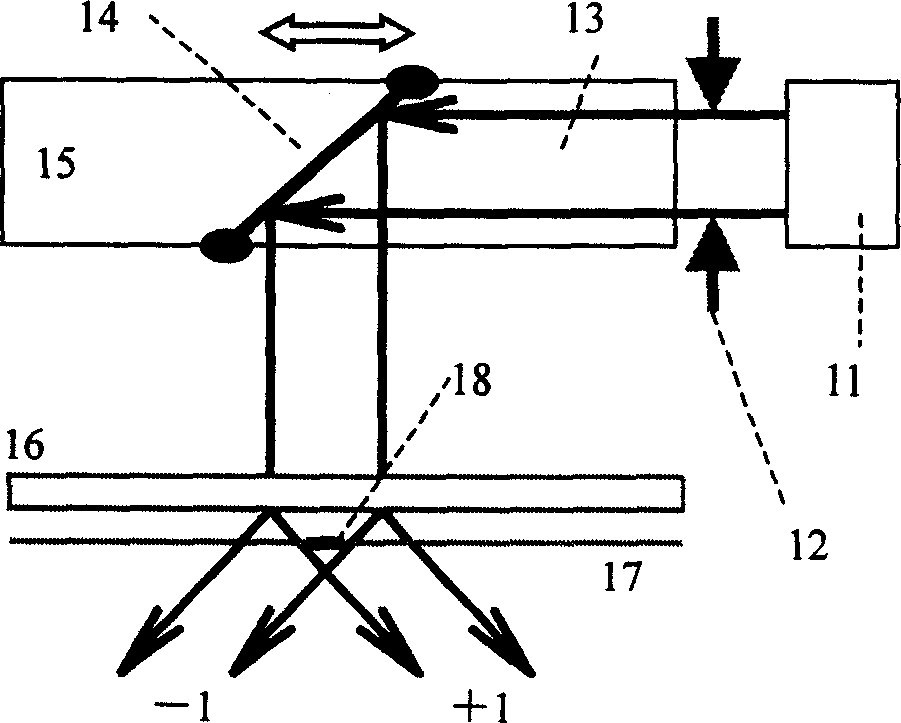
Apodization is an optical filtering technique. Its literal translation is "removing the foot". It is the technical term for changing the shape of a mathematical function, an electrical signal, an optical transmission or a mechanical structure. In optics, it is primarily used to remove Airy disks caused by diffraction around an intensity peak, improving the focus.
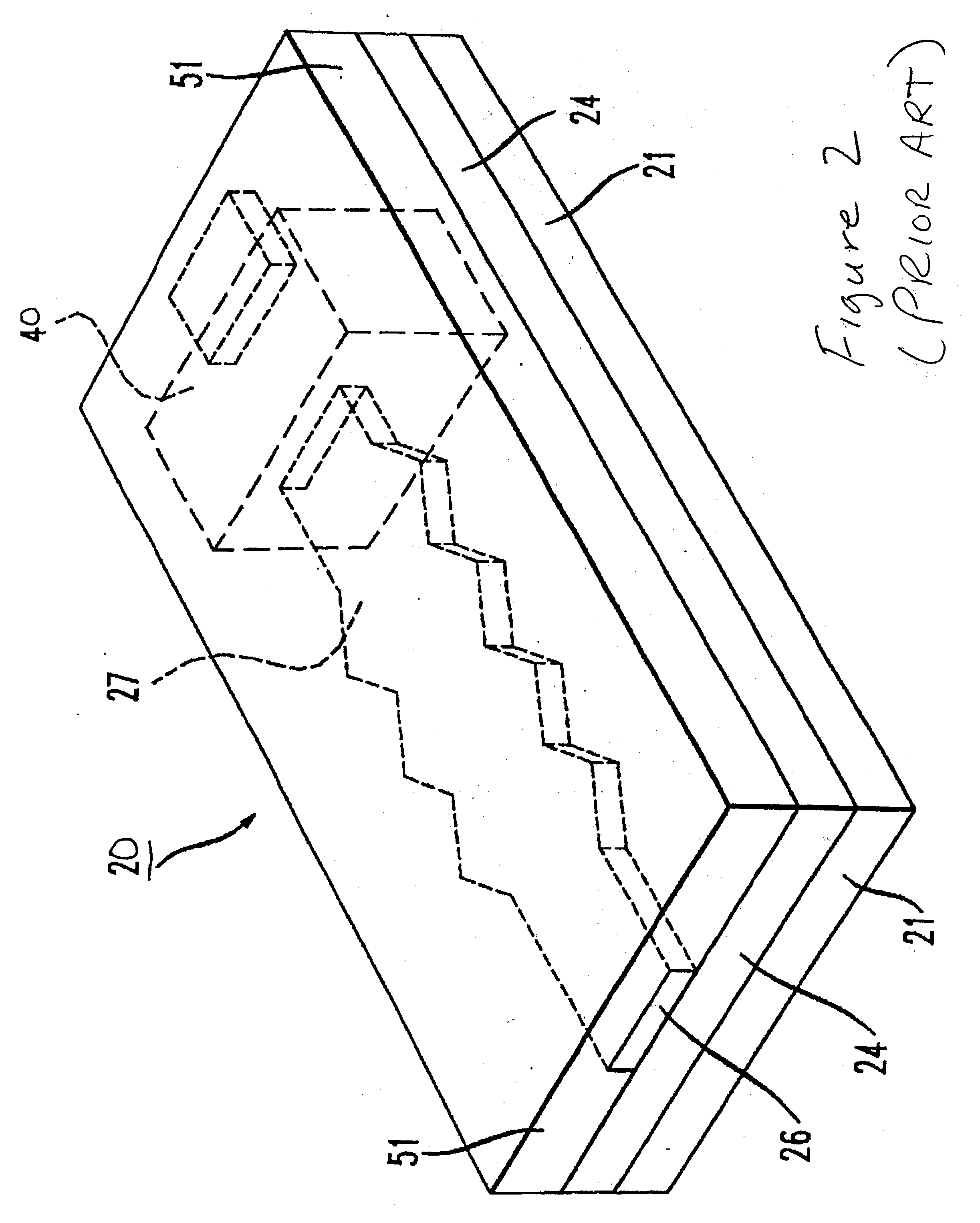
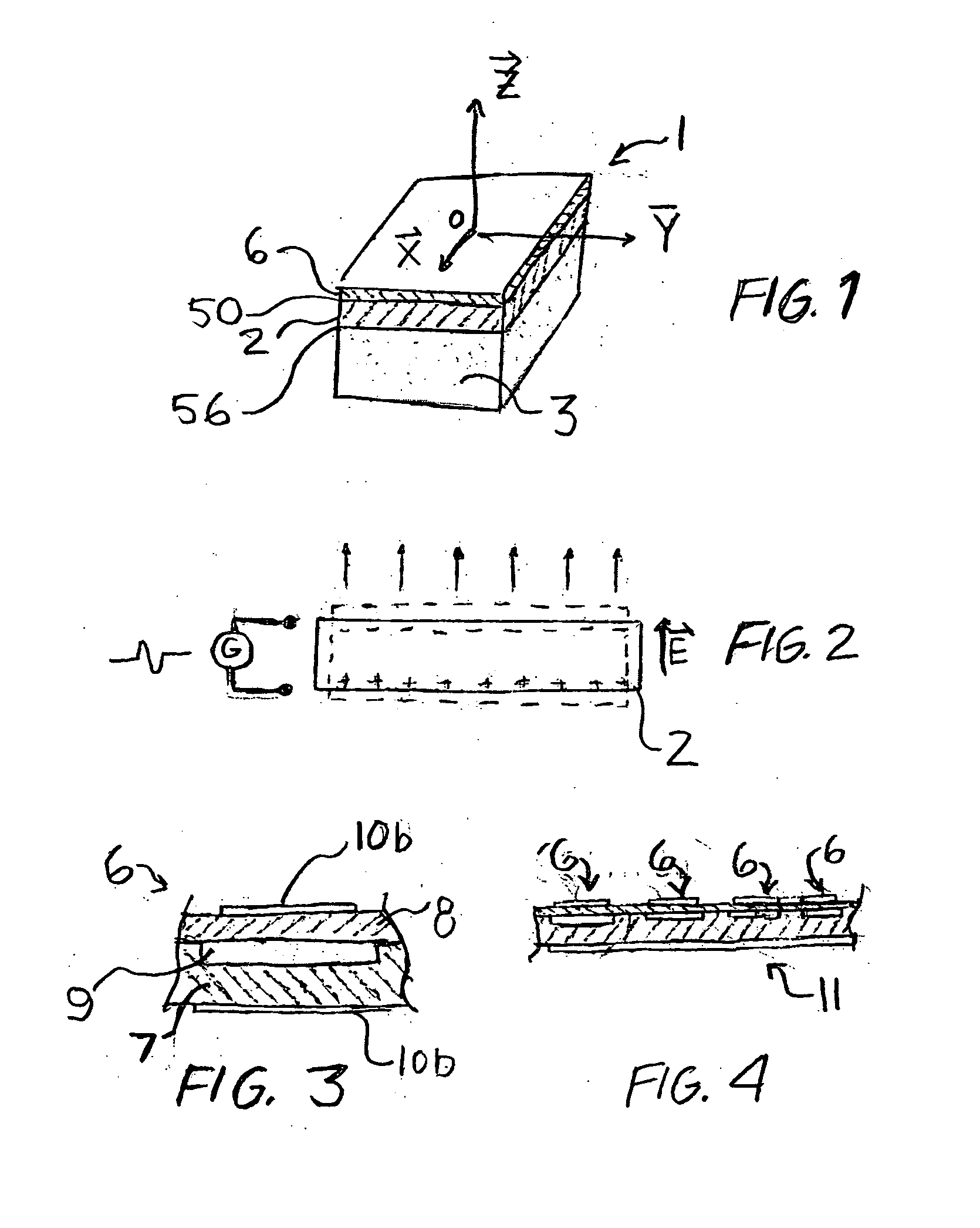
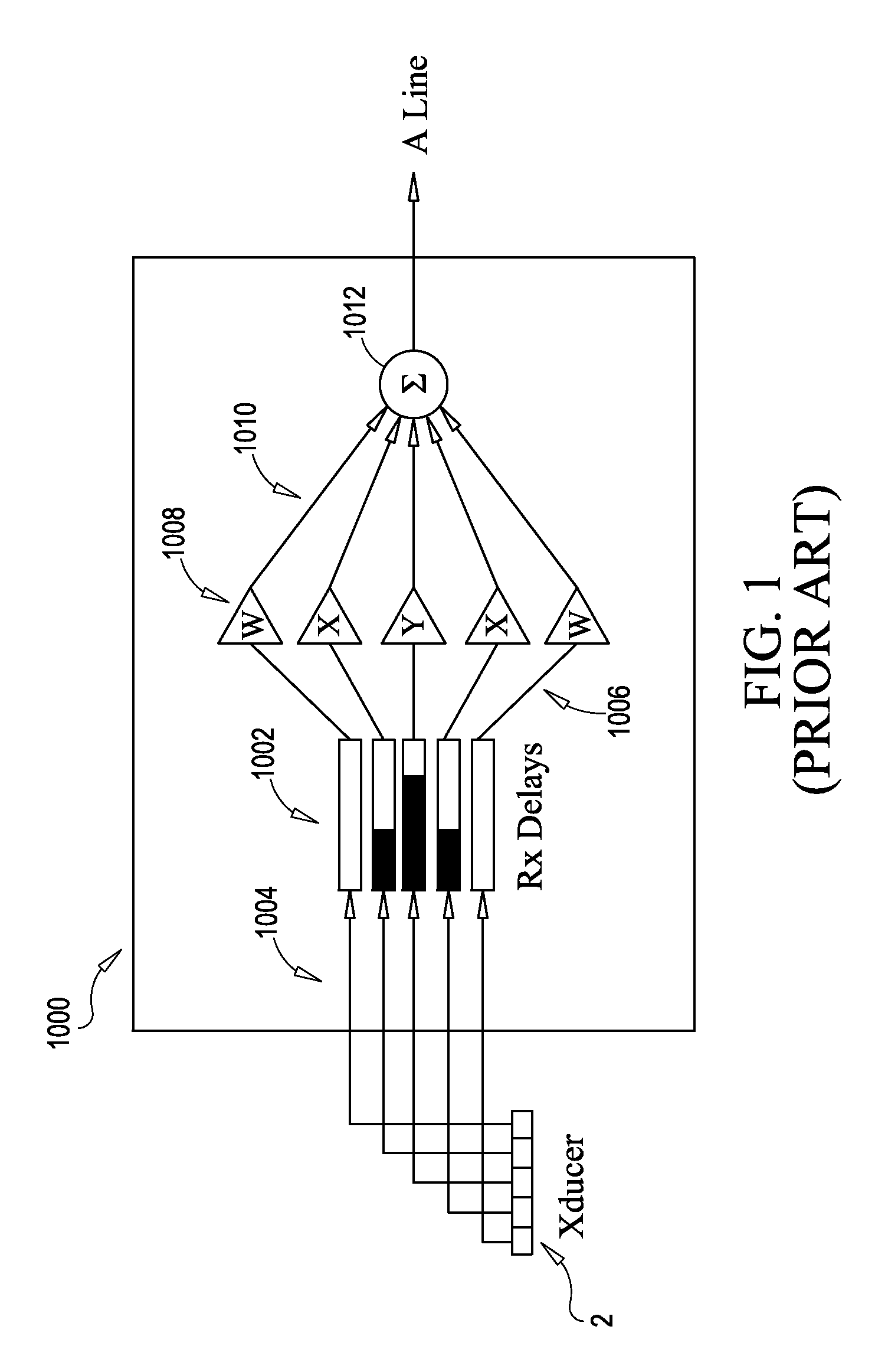
Apodization methods and apparatus for acoustic phased array aperture for diagnostic medical ultrasound transducer
InactiveUS6258034B1Reduce side lobe side lobe image artifactLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyUltrasonographyAzimuth direction
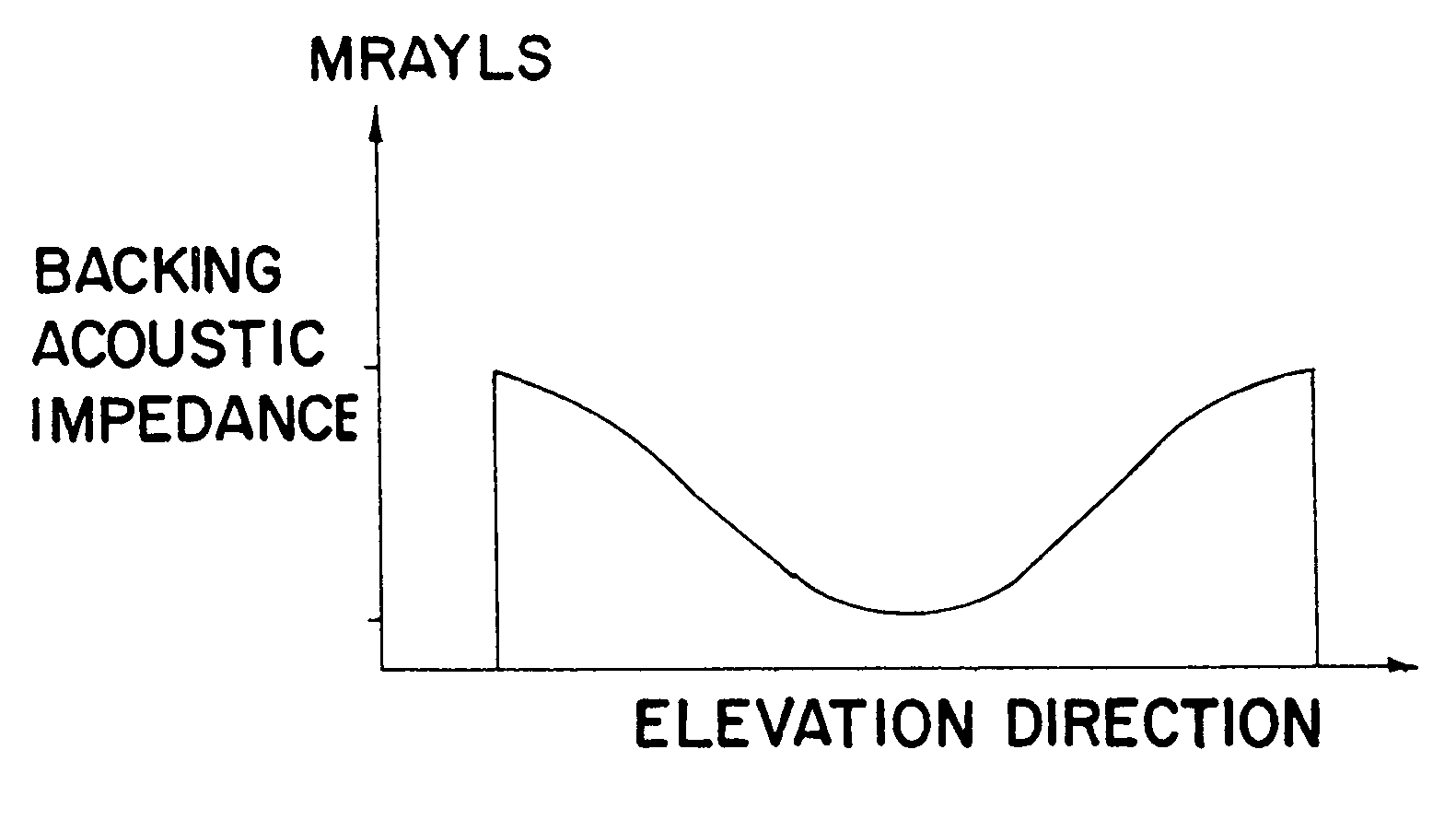
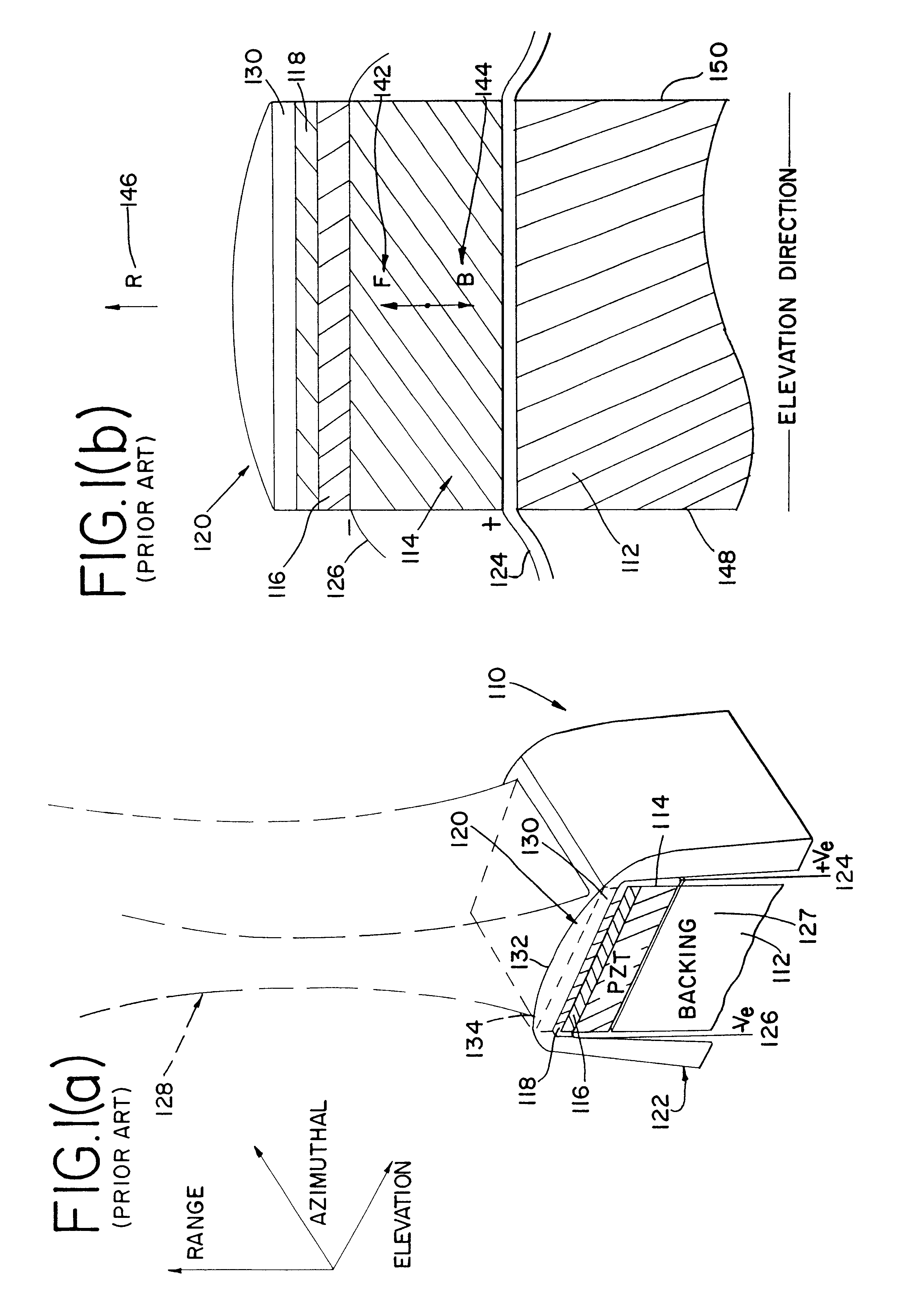
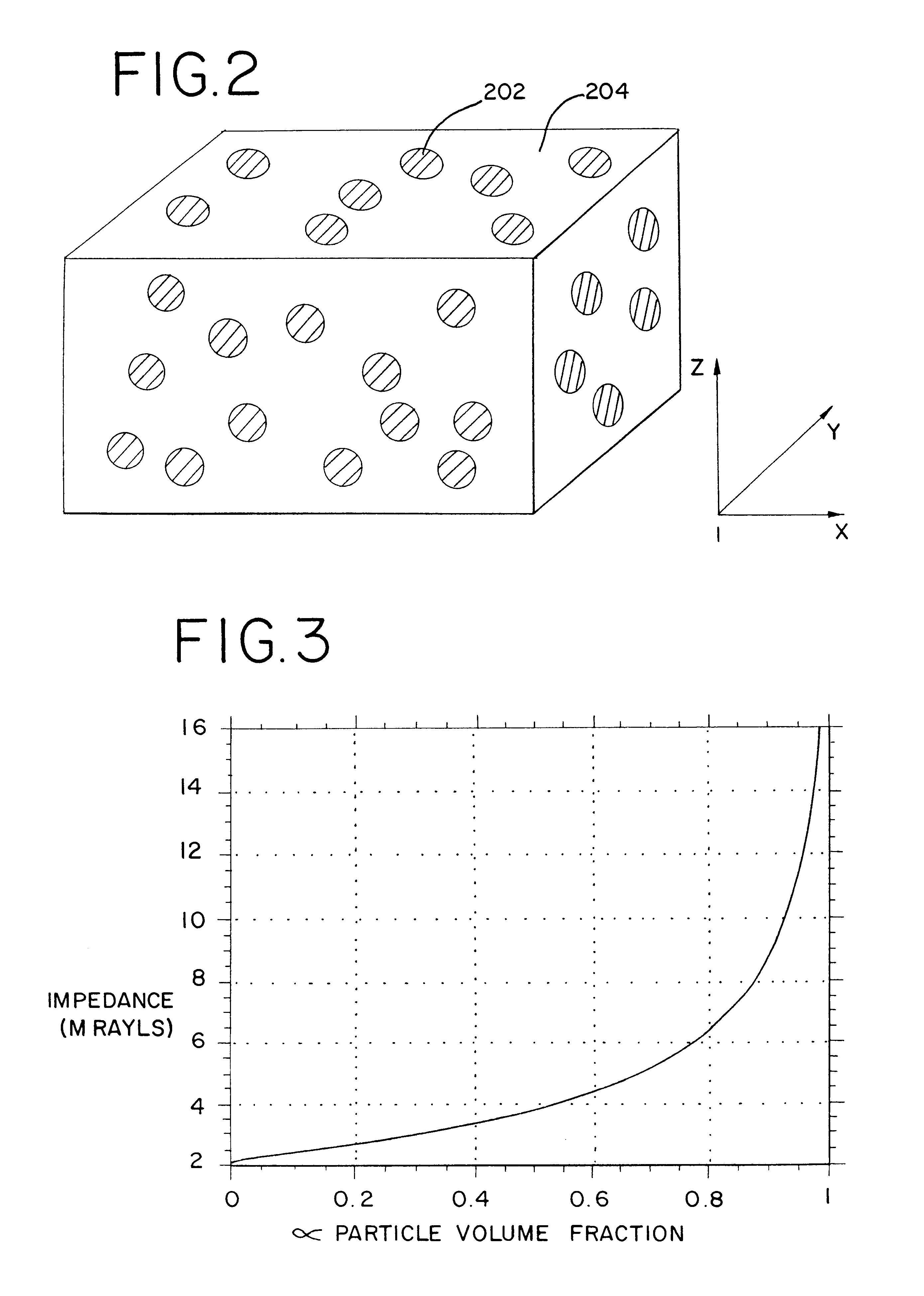
An apparatus and method using a backing block having a variable acoustic impedance as a function of elevation or azimuth, to achieve a desirable apodization of the aperture of an ultrasound transducer stacked with the backing block. The backing block has a gradient profile in acoustic impedance that changes from a minimum value to a maximum value along the elevation direction and / or azimuthal direction of the stacked ultrasound transducer. Typically, the backing block has an elevation gradient profile in acoustic impedance that increases from a minimum value of acoustic impedance near the center of the backing block to a maximum value of acoustic impedance at opposing lateral faces of the backing block. The backing block can be discretely segmented in acoustic impedance, with as many segments as are practically manufacturable. An individual segment can have a uniform or variable acoustic impedance. The backing block can be continuous in acoustic impedance, with a minimum acoustic impedance in the center and a maximum acoustic impedance at two or more planar lateral faces.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
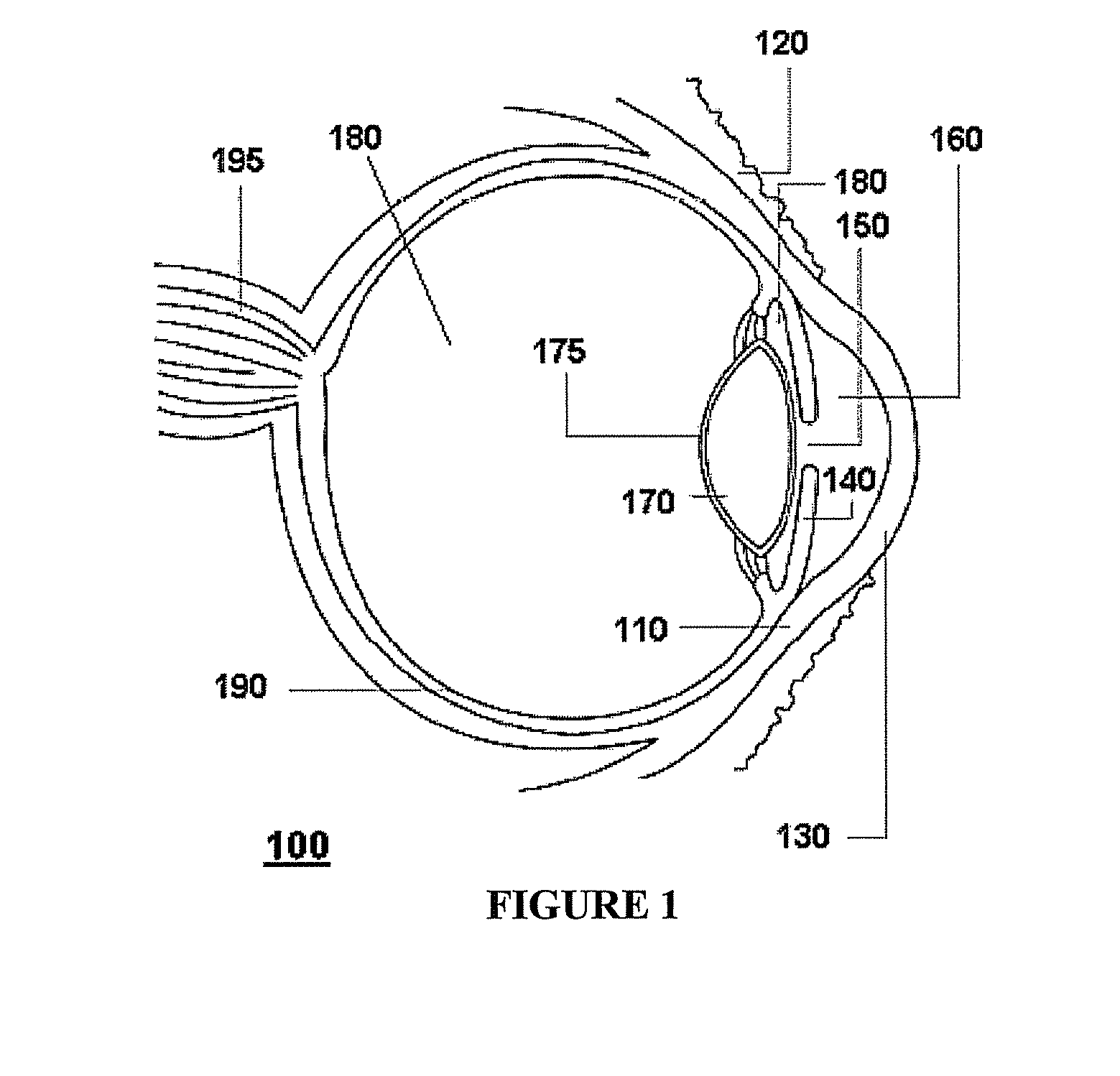
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC +1
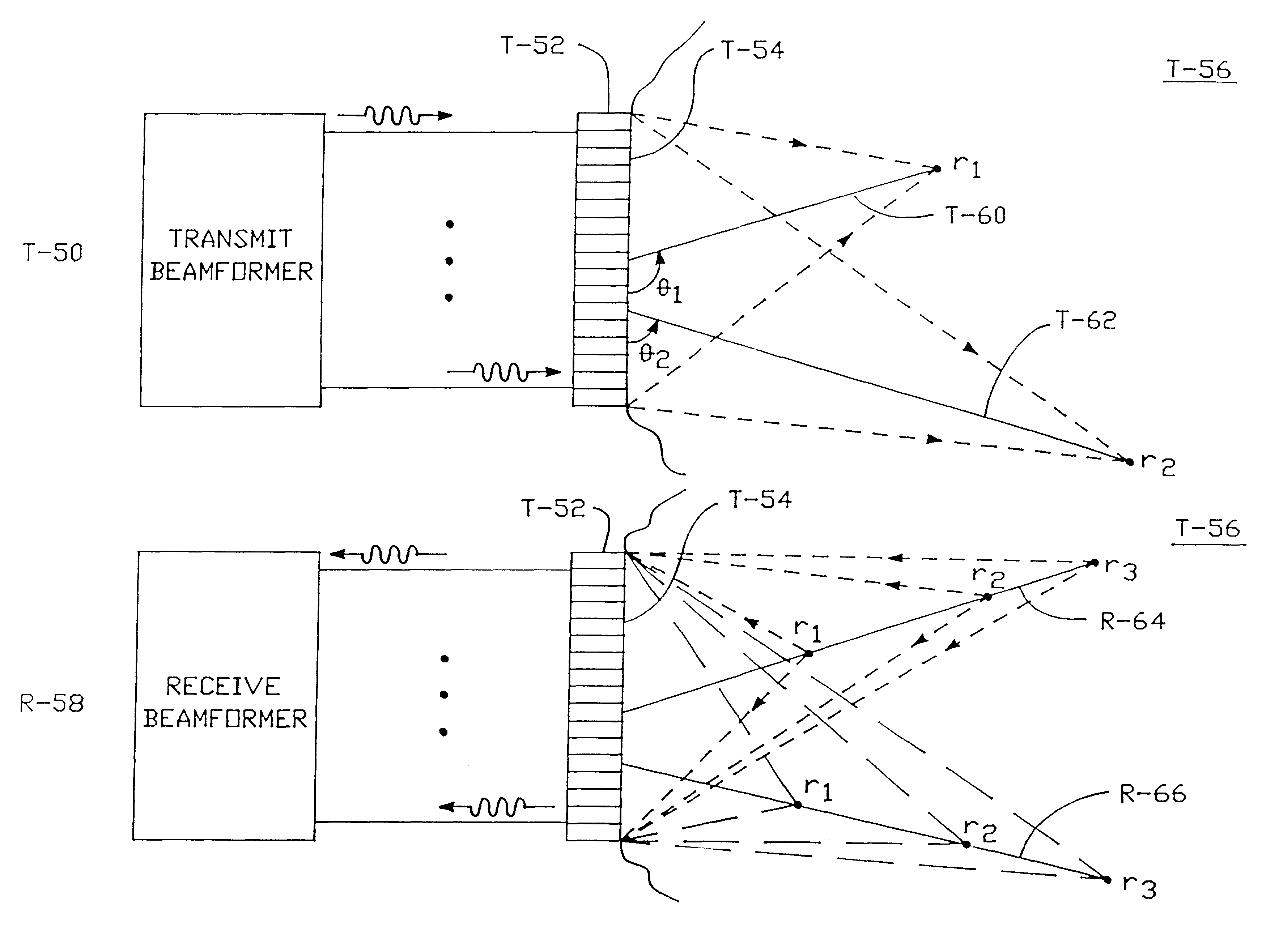
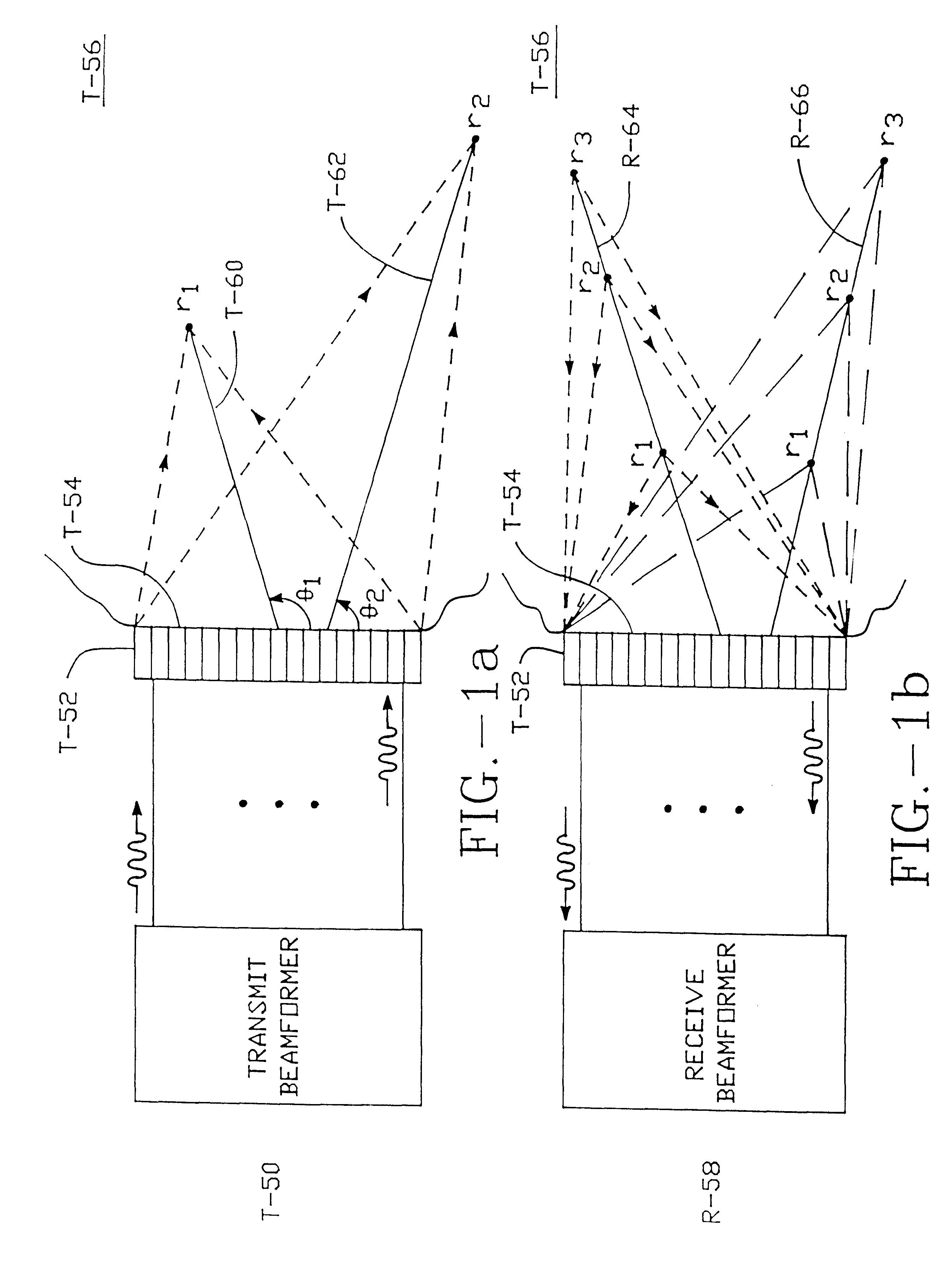
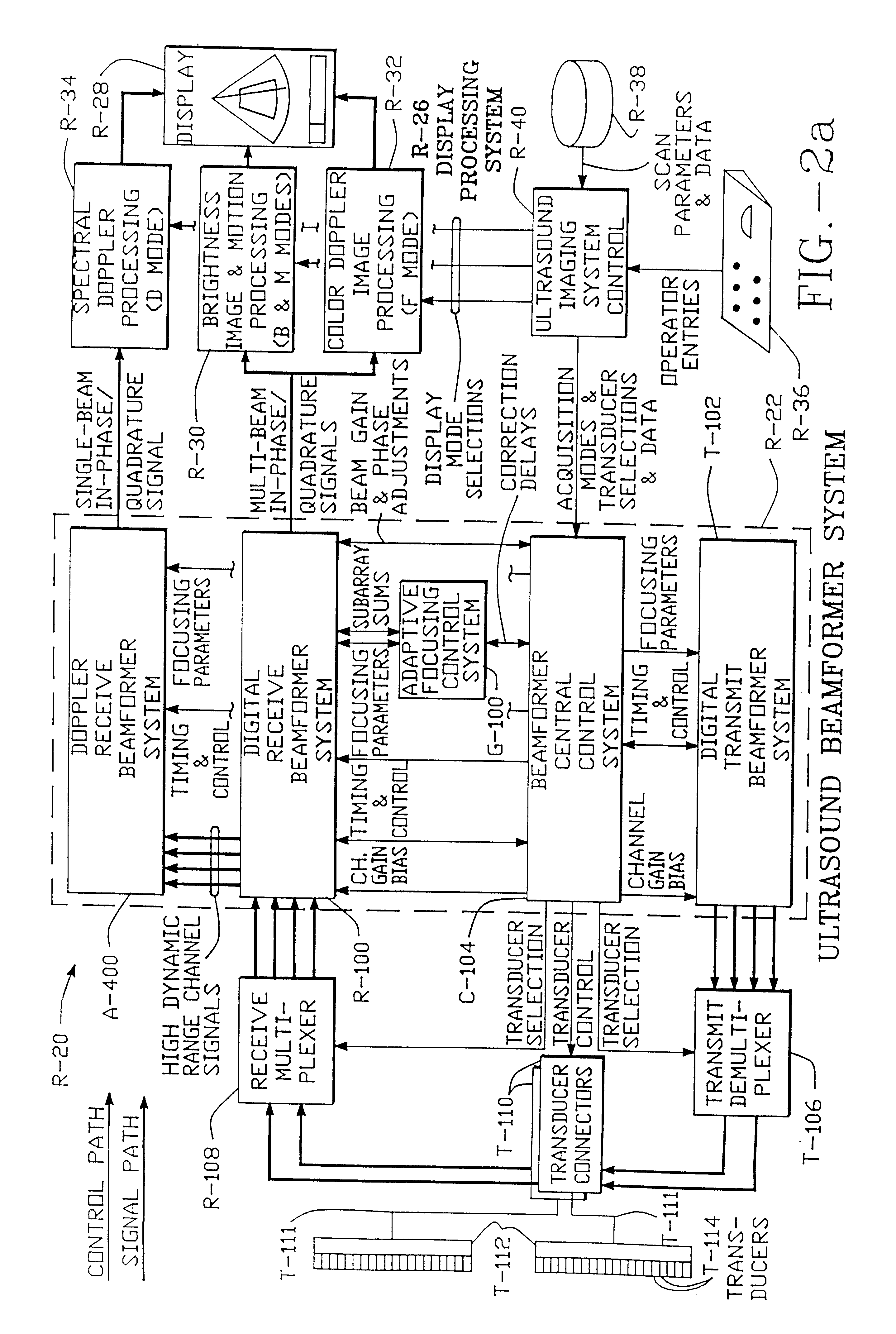
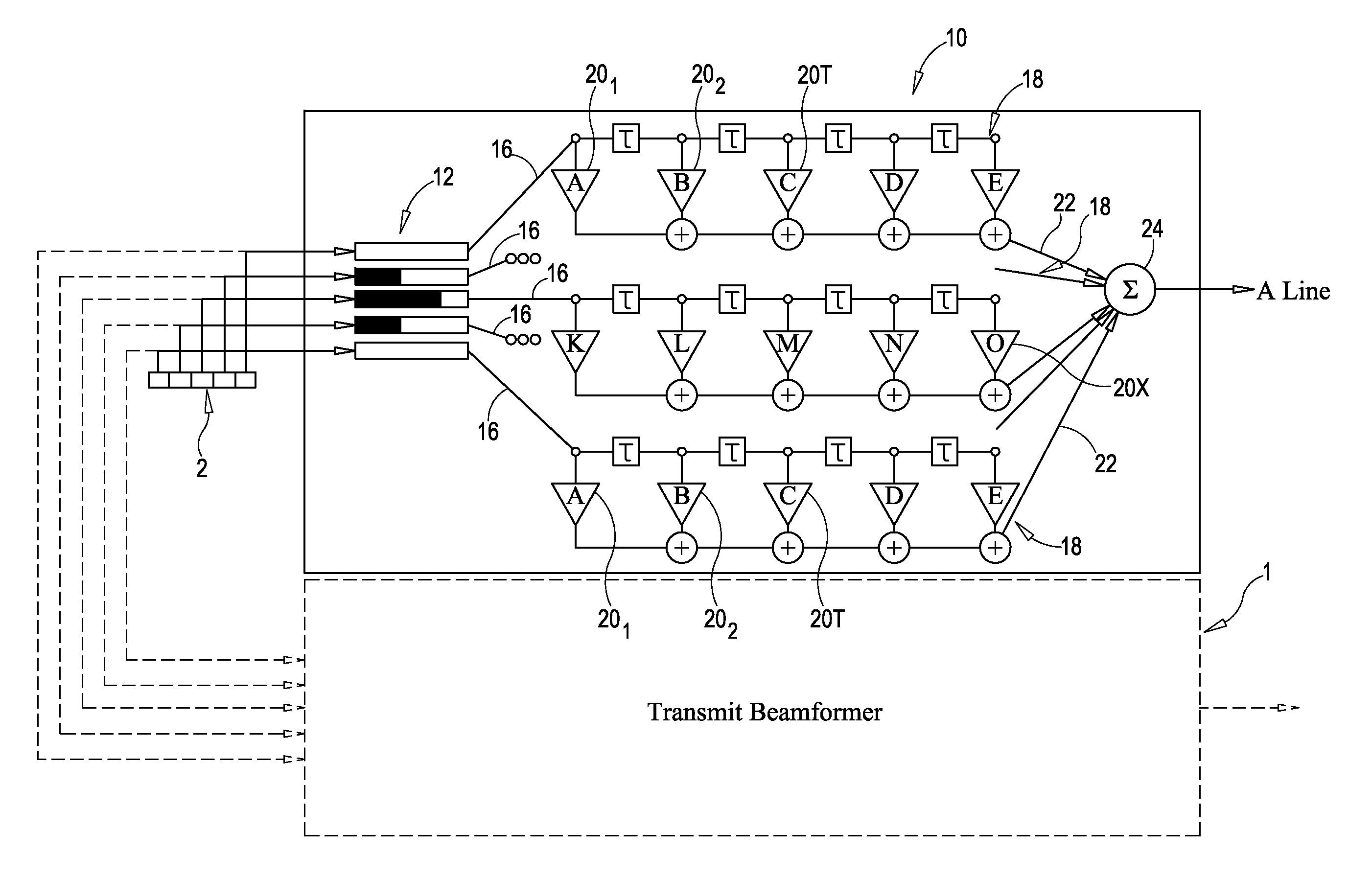
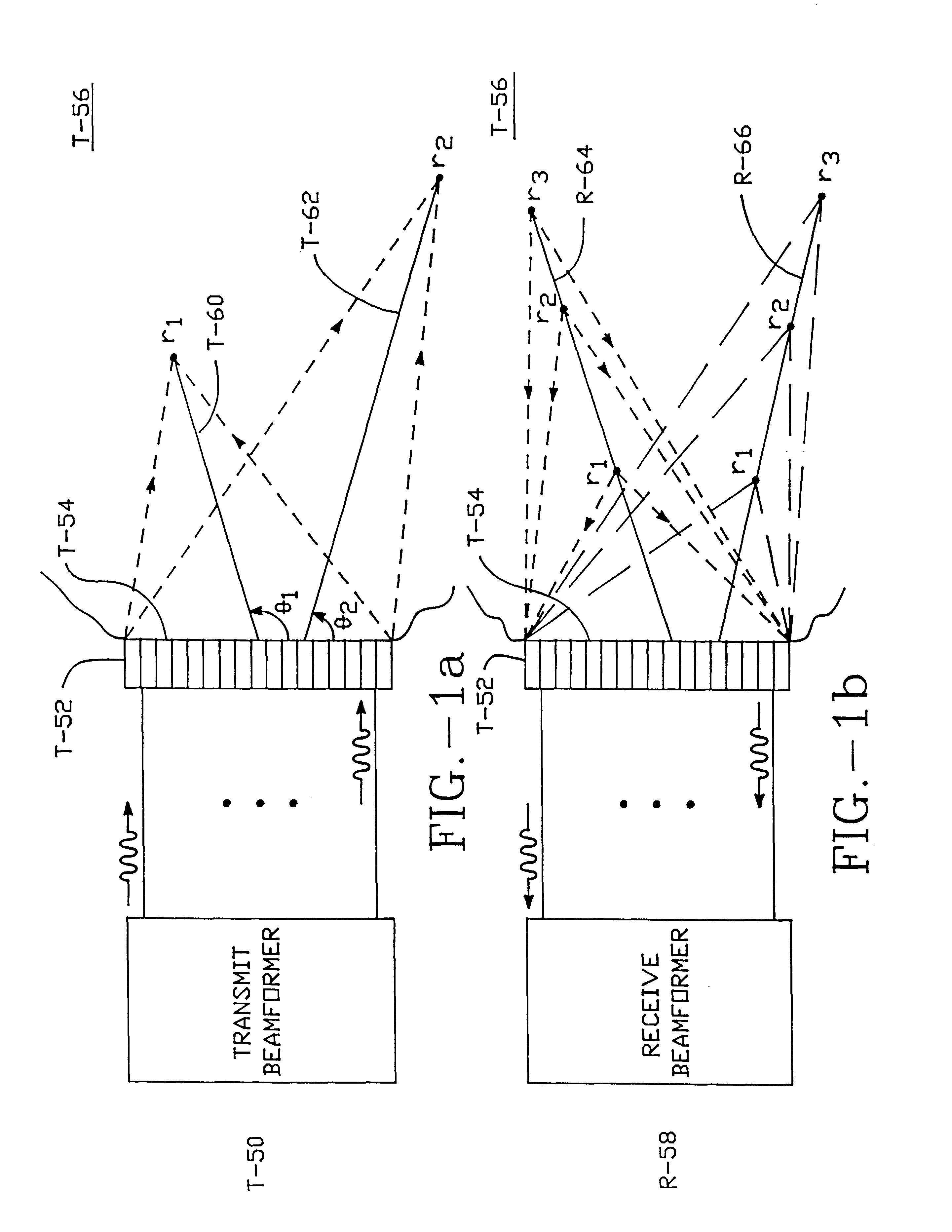
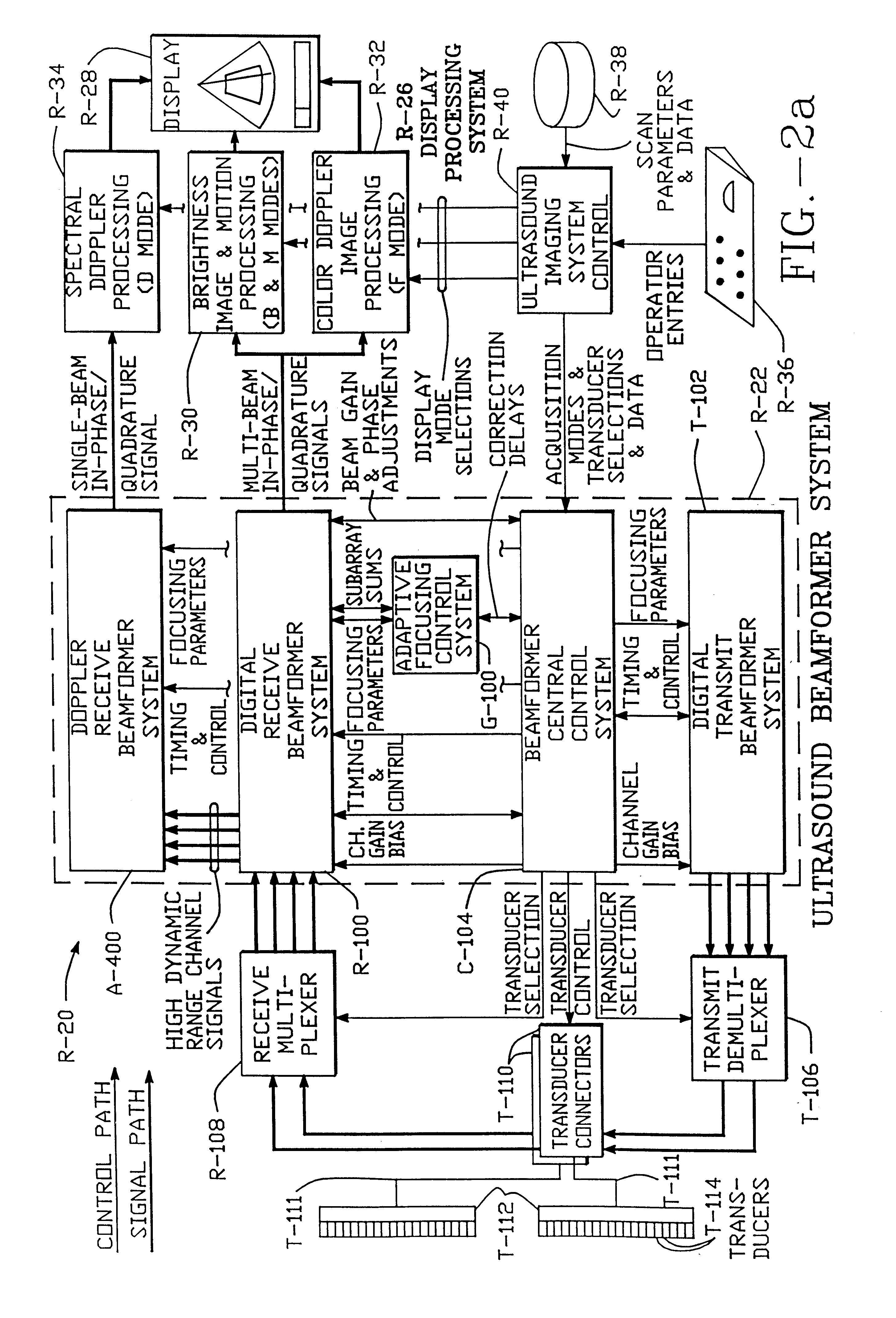
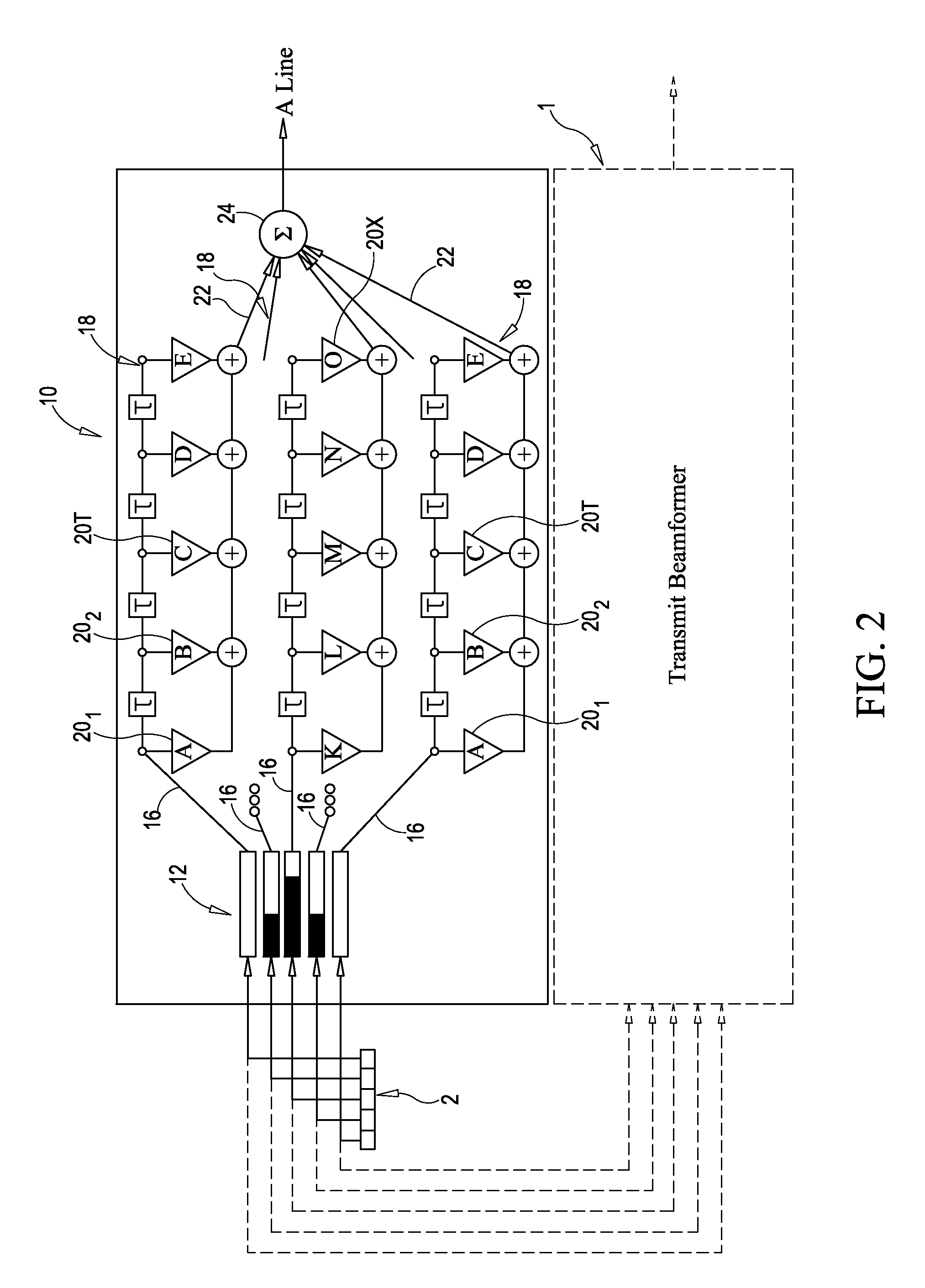
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6363033B1Improve programmabilityMaximum flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalTrade offsApodization
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values, For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
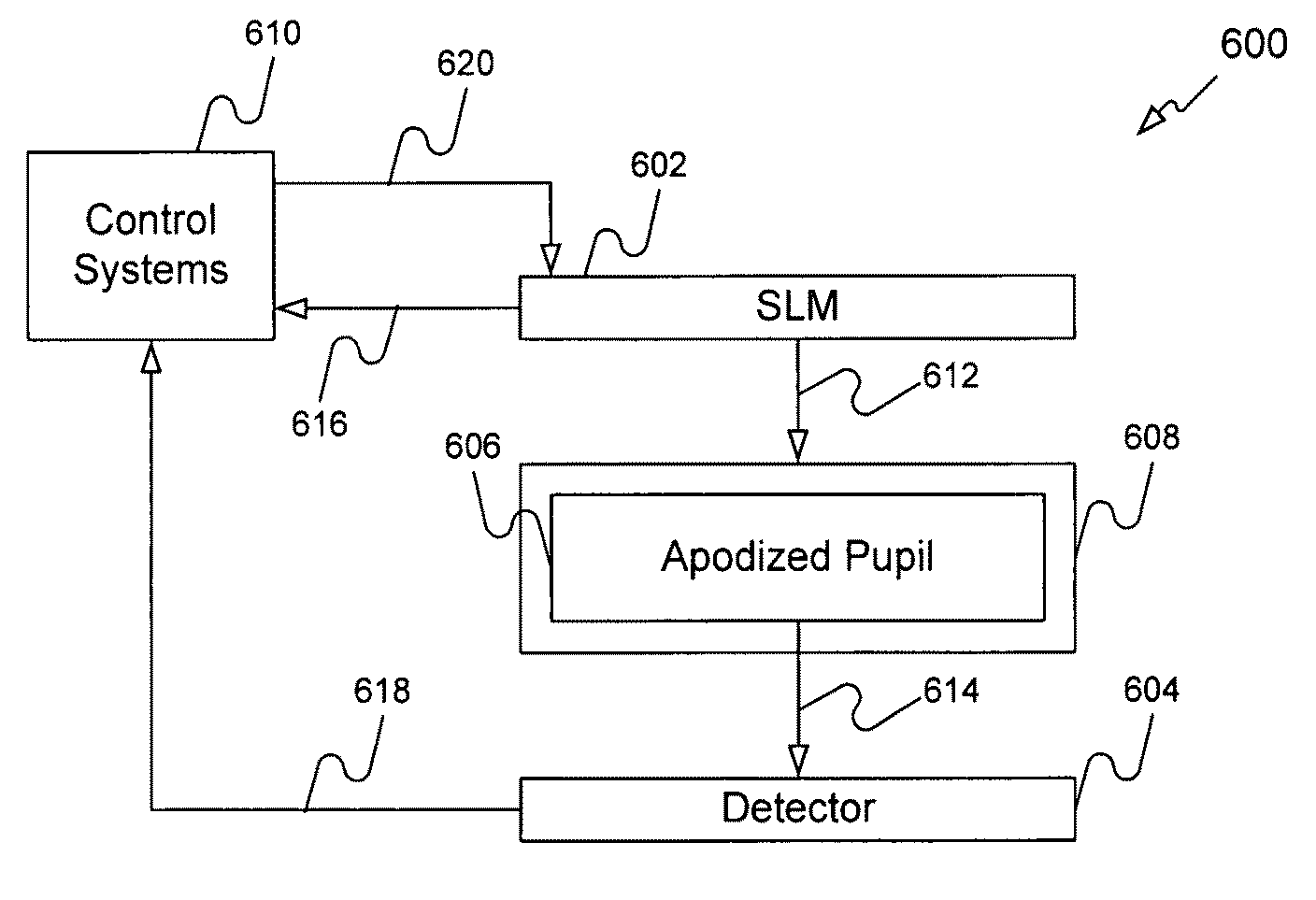
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator
InactiveUS20050168790A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
A method and system as used to calibrate a reflective SLM. The system can include a reflective SLM having an array of pixels (e.g., moving, tilting, rotating, pivoting, etc. pixels) and a projection optical system resolving individual pixels and having an apodized pupil. During a calibration operation, the pixels of the SLM receive varying voltage values to either continuously or incrementally move them through various angles. Light reflecting from each of the pixels during these movements forms individual images for each pixel at each angle. The light passes through the apodized pupil and is received on one or more sections (e.g., pixels) of a detector (e.g., a CCD array). The pupil apodization pattern is selected so that individual pixels remain well resolved and their resolved images have strong sensitivity to the pixel mirror tilt. The light intensity received for each pixel at each angle is correlated to the voltage value received at the pixel to tilt the pixel to that angle. The correlation produces a result signal. The result signal is used by a control device before and during normal operation of the SLM to calibrate the SLM one or more times.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Microfabricated ultrasonic transducers with bias polarity beam profile control and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7087023B2Increased complexityIncrease expensesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceSlice thickness
A capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducer with control of elevation phase through alternating bias polarity is disclosed. Such control of elevation phase results in simple ultrasonic probes with excellent slice thickness attributes. Furthermore, tight spatial variation of phase results in an effective way to achieve transmit aperture and apodization control. Further still, such capacitive microfabricated ultrasonic transducers can achieve elevation focus without the need of a lossy mechanical lens.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
System and method for nanostructure apodization mask for transmitter signal suppression in a duplex telescope
Disclosed herein is a system for an apodization mask composed of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) for absorbing unwanted stray light. An apodization mask is a precise pattern or shape that is mathematically derived using light scattering measurement techniques to achieve optimal light absorption.Also disclosed herein is an apparatus for a duplex telescope with stray light suppressing capabilities comprising: a primary mirror for transmitting and receiving light; a secondary mirror for defocusing transmitted light onto the primary mirror and for focusing received light; a photodetector which receives light; a laser transmitter which transmits light; and an apodization mask for absorbing stray transmitted light.
Owner:NASA
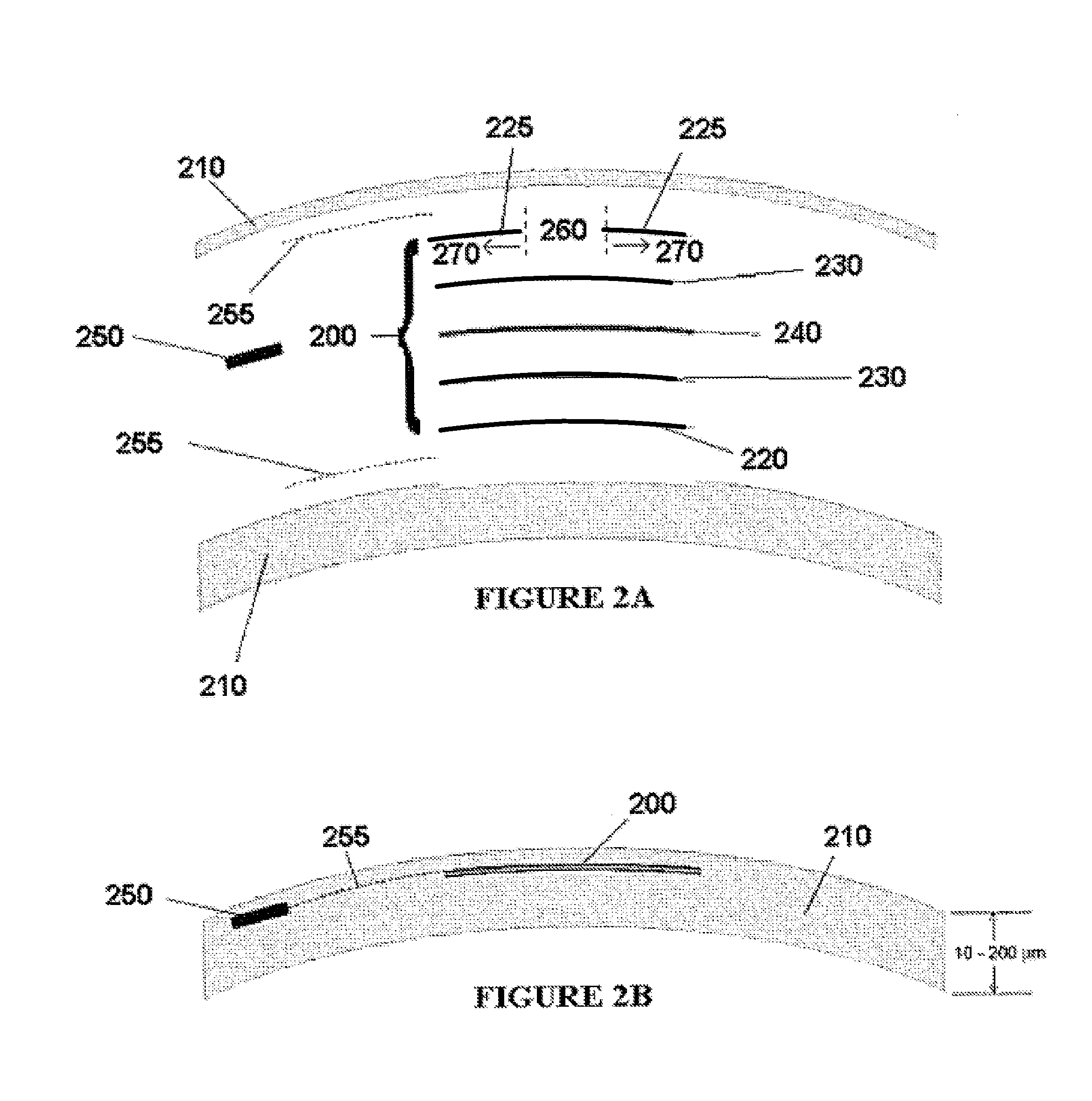
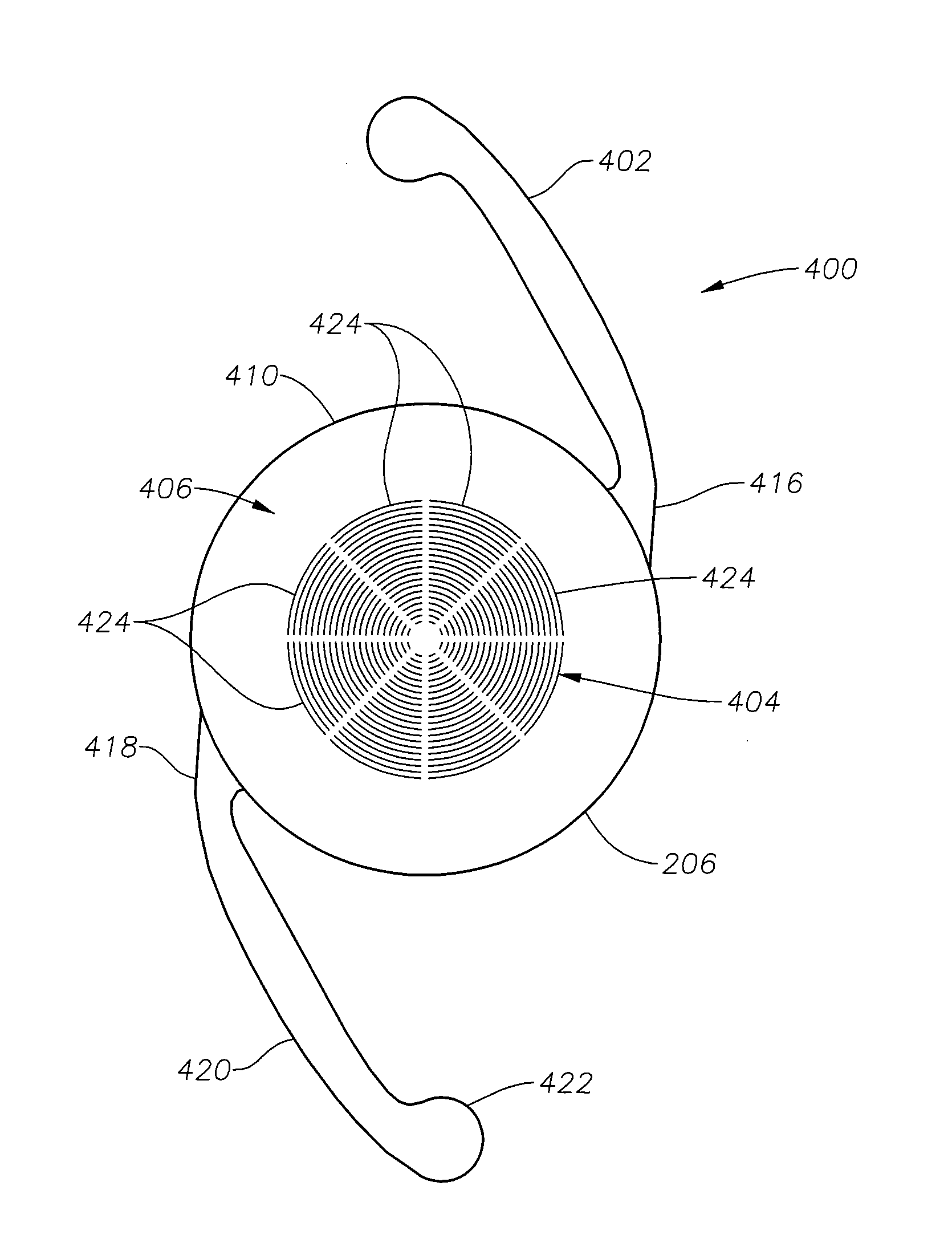
Radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal design for ocular implant
ActiveUS20100161048A1Reduce step heightIncrease depth of focusIntraocular lensMedicineOptical energy
A radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL for ocular implant is provided. The ocular implant can comprise a radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal intraocular lens optic and a number of haptics. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may pass optical energy in both photopic and mesopic conditions. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL includes a number of radially segmented apodization zones, each radially segmented apodization zones having a unique focal length. The haptics mechanically couple to the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL optic in order to position and secure the apodized diffractive multifocal IOL within the eye. The radially segmented apodized diffractive multifocal IOL may include both a diffractive region and a refractive region.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multifocal contact lens designs utilizing pupil apodization
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Optical waveguide with non-uniform sidewall gratings
A diffraction grating of non-uniform strength is introduced into an optical waveguide by modulating its width. The waveguide may be fabricated using one of several planar processing techniques. Varying the size, position, and / or thickness of the grating teeth provides the desired variation of grating strength. Certain functional variations of grating strength suppress side-lobe levels in the grating reflection and transmission spectra. This process, termed apodization, is necessary for precise wavelength filtering and dispersion compensation. If desired, different periodicity gratings can be introduced in each side of the waveguide, multiple periodicities can be superimposed, the grating can be angled with respect to the waveguide, and the grating period and phase can be varied.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Imaging or communications system utilizing multisample apodization and method
ActiveUS20090299184A1Easy to optimizeMinimizing ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFinite impulse responseCommunications system
Methods systems and system components for optimizing contrast resolution of an imaging or sensing system utilizing multiple channels of broadband data associated with an array of transducers. Channels or data are filtered by passing the channels of data through finite impulse response (FIR) filters on each channel. The filters each have multiple taps having tap weights pre-calculated as a function of distance of the array from an object that energy is being transmitted to or reflected from. The weights are pre-computed through a deterministic equation based on an a priori system model.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Capacitive micro-machined ultrasonic transducer for element transducer apertures
ActiveUS20070193354A1Enhance electrical impedance characteristicImproving impedanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
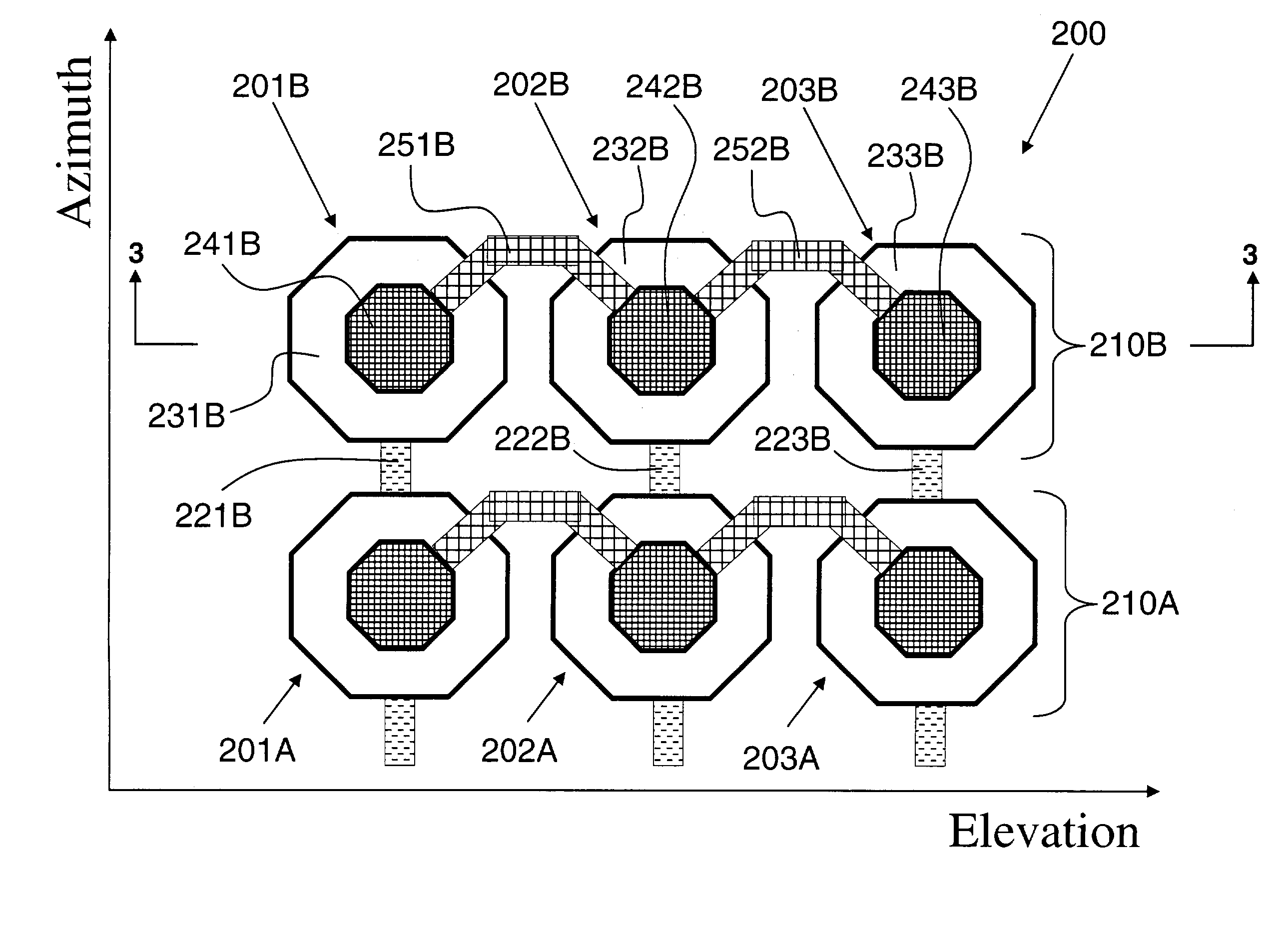
A capacitive micro-machined ultrasonic transducer (CMUT) array includes an improved elementary aperture for imaging operations. The transducer can be of a linear, curved linear, annular, matrix or even single surface configuration. The elementary apertures thereof are formed by a specific arrangement of capacitive micromachined membranes (CMM) so as to exhibit ideal acoustical and electrical behavior when operated with imaging systems. The CMM arrangements can be either conventional where the element transducers of the array are uniformly shaped by predefined CMMs in a manner such as to exhibit acoustic behavior similar to a piezoelectric transducer, or can be more sophisticated, wherein each element transducer is formed by a specific combination of different CMMs (i.e., of a different size and / or shape) so as to provide the transducer with built-in acoustic apodization that can be implemented in the azimuth and / or elevation dimension of the device.
Owner:VERMON
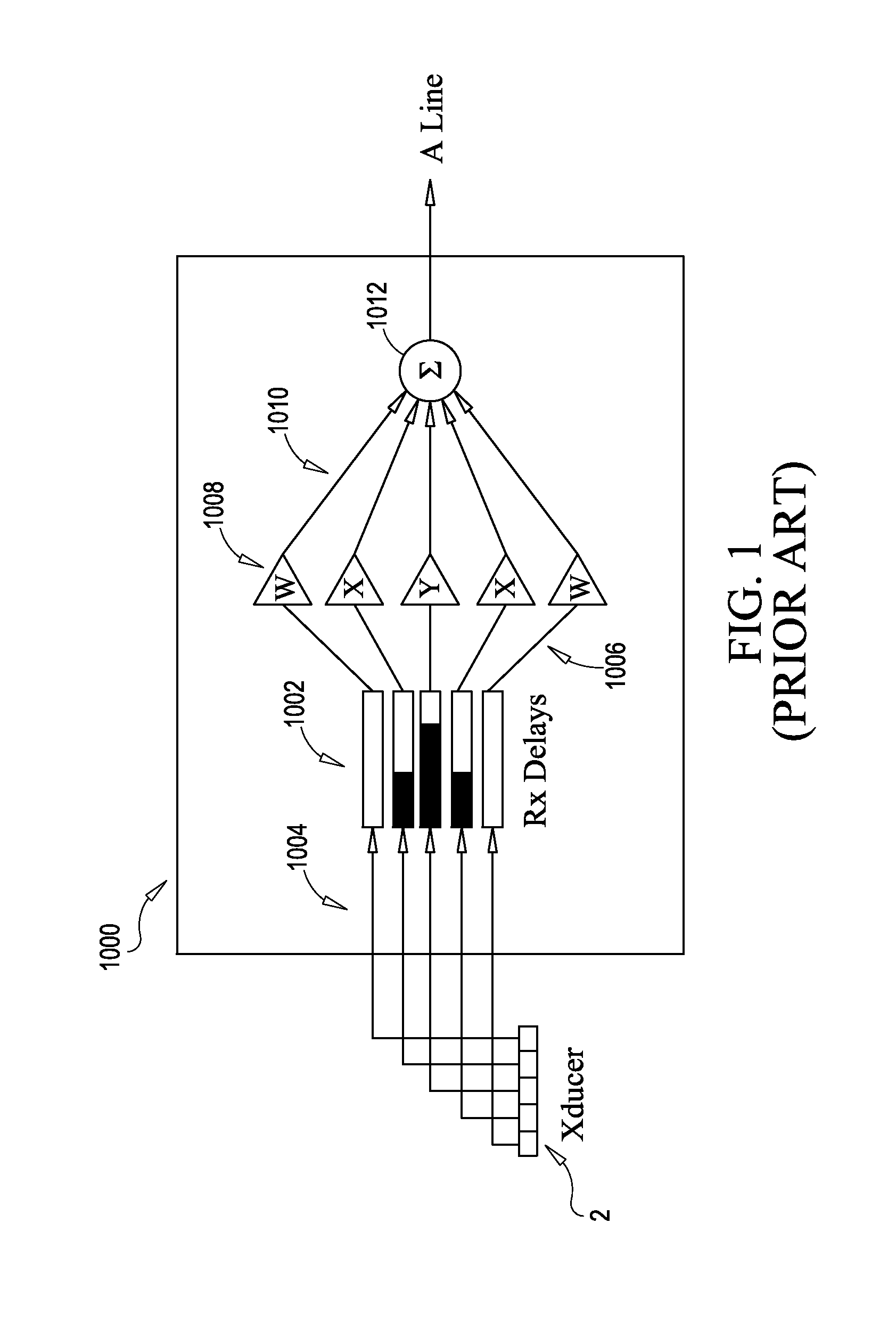
Method and apparatus for transmit beamformer system
InactiveUS6172939B1Improve abilitiesImprove programmabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProcessing detected response signalEngineeringTrade offs
A digital transmit beamformer system with multiple beam transmit capability has a plurality of multi-channel transmitters, each channel with a source of sampled, complex-valued initial waveform information representative of the ultimate desired waveform to be applied to one or more corresponding transducer elements for each beam. Each multi-channel transmitter applies beamformation delays and apodization to each channel's respective initial waveform information digitally, digitally modulates the information by a carrier frequency, and interpolates the information to the DAC sample rate for conversion to an analog signal and application to the associated transducer element(s). The beamformer transmitters can be programmed per channel and per beam with carrier frequency, delay, apodization and calibration values. For pulsed wave operation, pulse waveform parameters can be specified to the beamformer transmitters on a per firing basis, without degrading the scan frame rate to non-useful diagnostic levels. Waveform parameters can be specified to the transmitters by an external central control system which is responsible for higher level flexibility, such as scan formats, focusing depths and fields of view. The transmit pulse delay specified per-channel to each transmitter is applied in at least two components: a focusing time delay component and a focusing phase component. The carrier frequency can be specified for each transmit beam, to any desired frequency within a substantially continuous predefined range of frequencies, and a beam-interleaved signal processing path permits operation in any of several predefined processing modes, which define different parameter sets in a trade-off among (1) the number of beams produced; (2) per-beam initial waveform sample interval; and (3) transmit frequency.
Owner:ACUSON
Ultrasound transmit beamformer integrated circuit and method
ActiveUS20050033168A1Compact implementationLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsPulse envelopeSonification
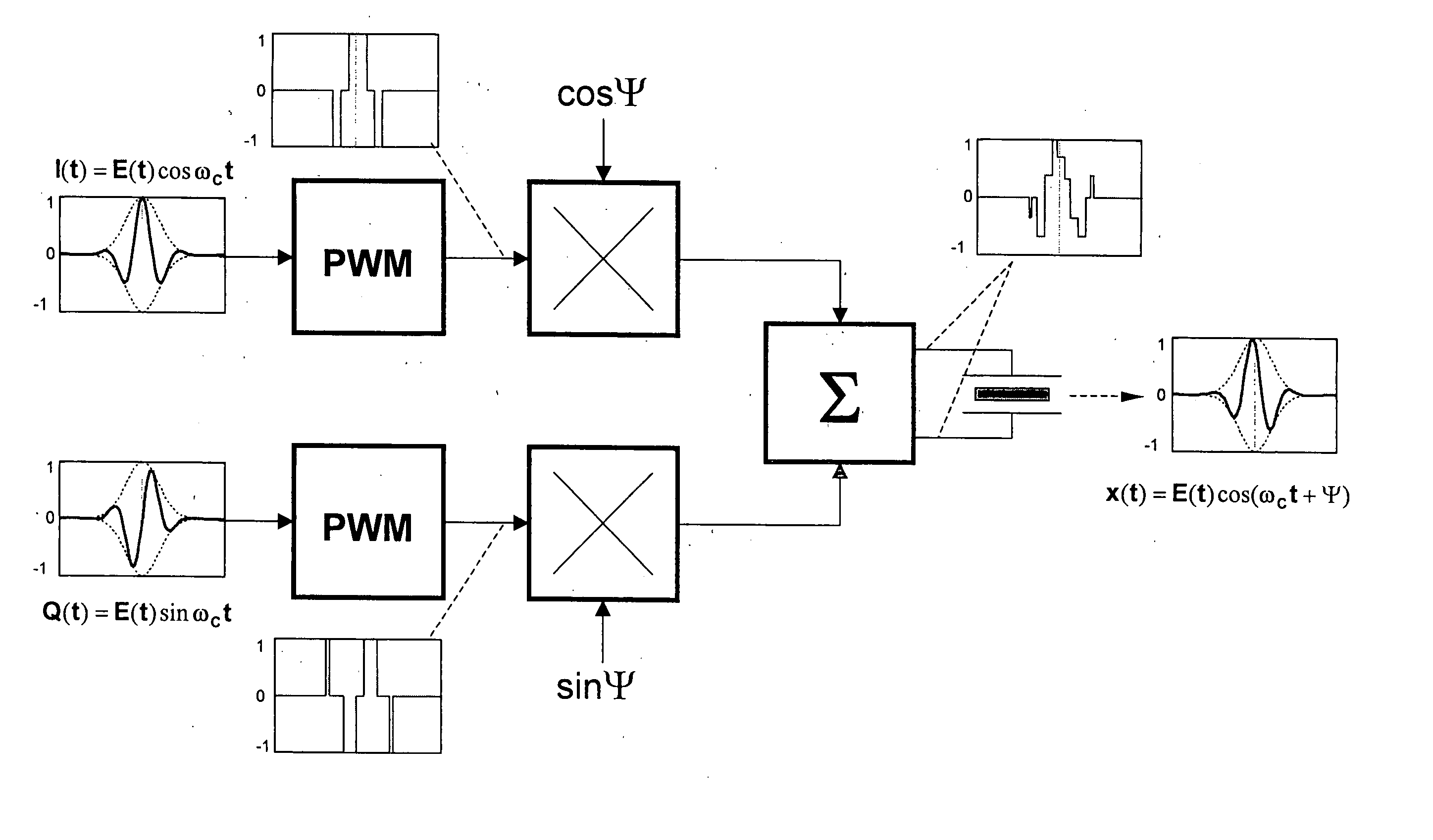
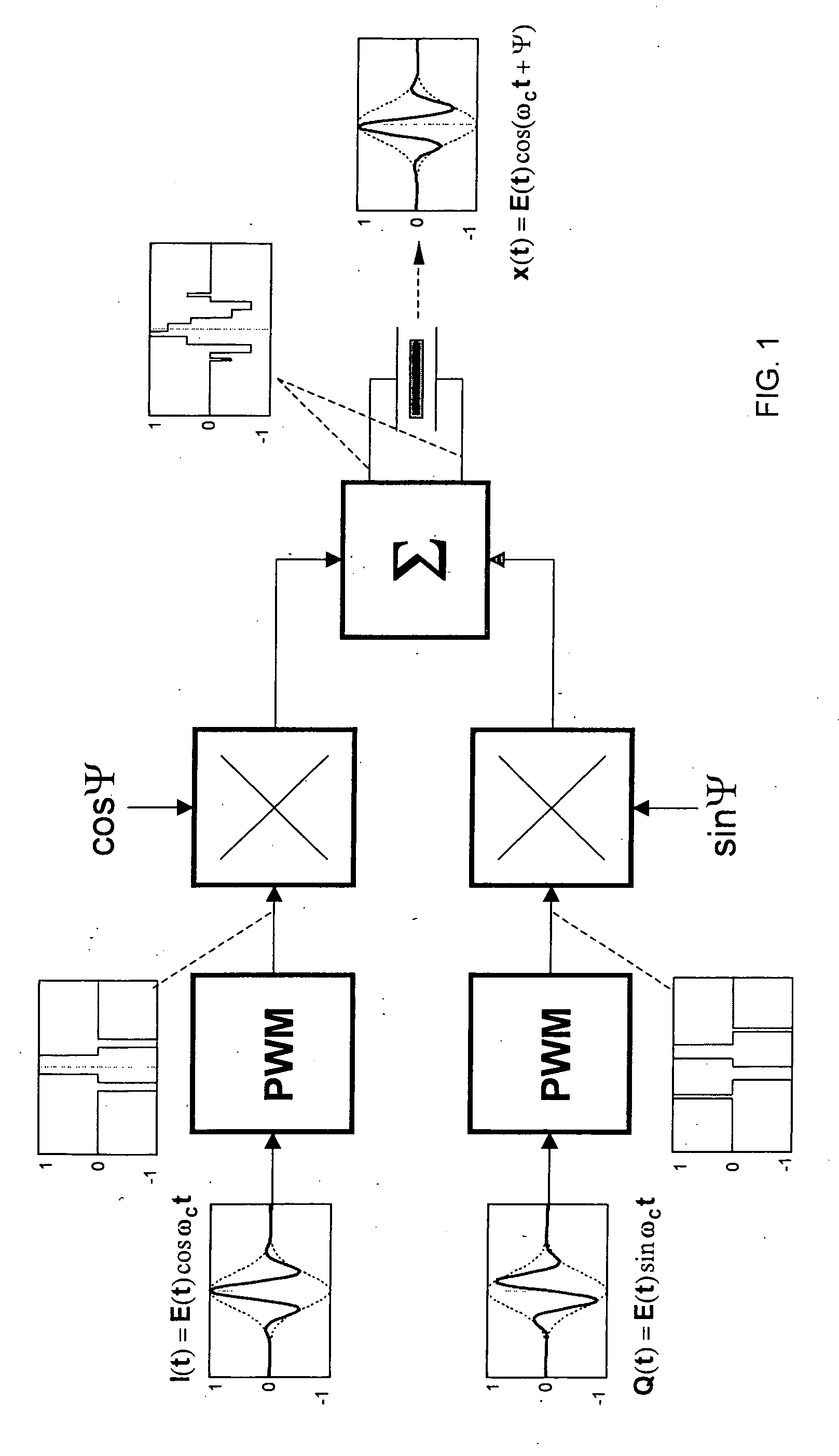
The invention provides a novel method of transmit beamforming, which allows compact analog implementation of complex digital algorithms without compromising their features. It is aimed to support envelope shaping, apodization, and phase rotation per channel and per firing. Each of three embodiments represents a complete transmit channel driven by pulse-width modulated (PWM) waveforms stored in a conventional sequence memory. PWM signals controls the transmit pulse envelope (shape) by changing the duty cycle of the carrier. Beamformation data are loaded prior to a firing via serial interface. Under the direction of a controller, the circuitry allows high precision (beyond sampling rate) phase rotation of the carrier. It also provides transmit apodization (aperture weighting), which maintains an optimal trade-off among low sidelobe level and widening of the mainlobe. Implementing such an IC, the manufacturing cost of a high-end ultrasound system can be reduced. Equally, the proposed solution makes the benefits of digital transmit beamformers available to midrange and entry-level machines since it merely requires a modified programming of the sequence memory.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:PIXELOPTICS
Beam unitized real-time computing technique for receiving apodized parameters and the device thereof
ActiveCN101116622ASave resourcesHigh speedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDigital data processing detailsSonificationUltrasonic imaging
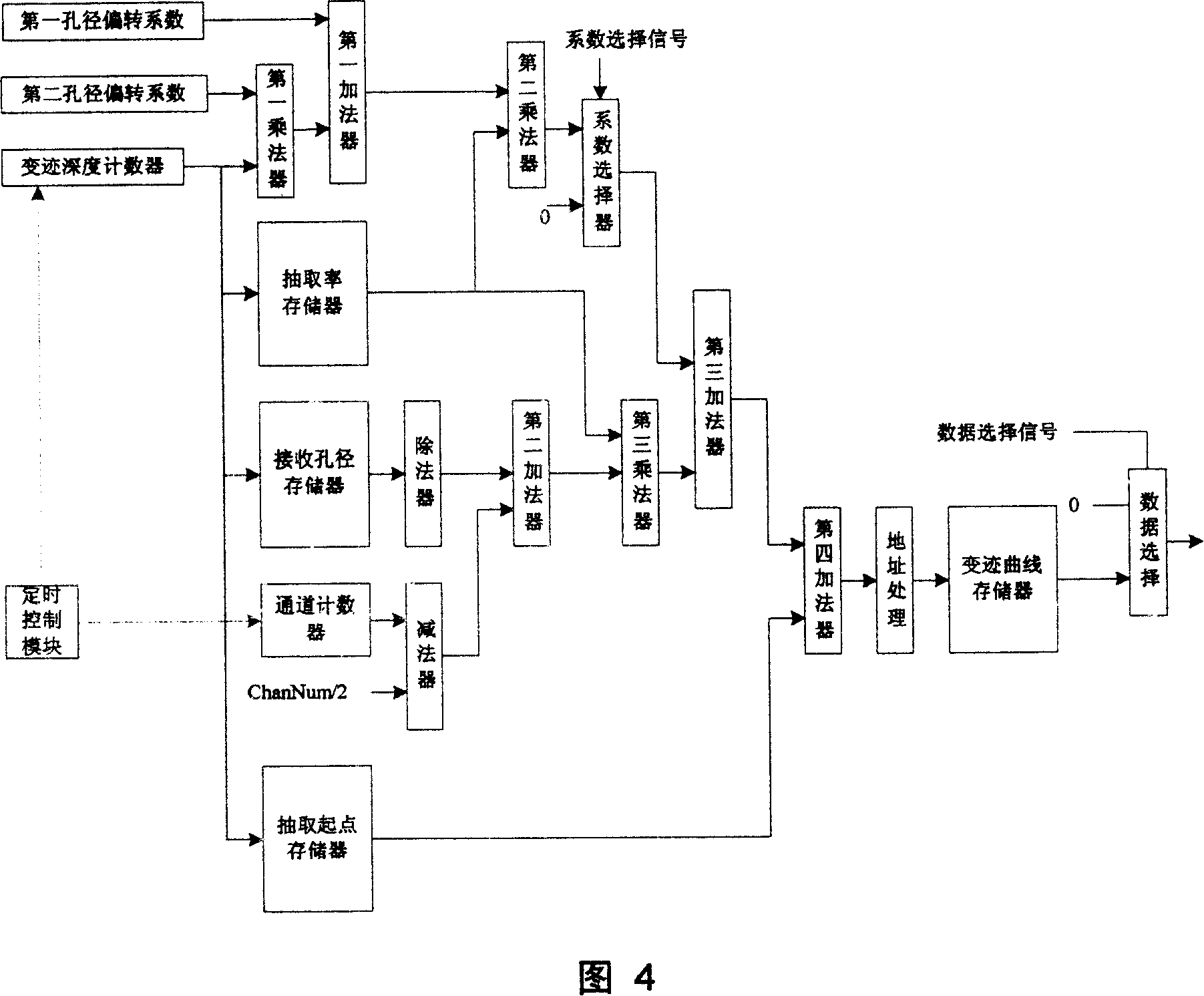
The invention relates to a beam composition realtime computation method and device receiving apodization parameter, wherein the device which is connected to the signal input end of the beam composition receiving module of an ultrasonic imaging system as an independent accessory comprises a first, second and third multipliers, a first, second, third and fourth adders, a subtracter, a divider, an extraction ratio memory, a receiving aperture memory, an extraction starting point memory, a preset apodization curve memory, an apodization depth counter, a channel counter, a coefficient selector, a data selector, an address processor and a timing control module. The realtime computation of apodization parameter comprises the following procedures: an apodization reference curve with the length being N is preset inside the system; the preset apodization reference curve is extracted at different start and extraction ratio according to depth with the extraction results being used as apodization curves of different depth of each signal receiving and processing channel. Adopting the technical proposal of the invention can save memory resource of the system and obtains faster parameter loading speed during switching prove of the system.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Ultrasonic transducer system
ActiveUS20080156577A1Improve featuresEfficient productionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesApodizationAcoustic lens
An improved acoustic lens and an improved ultrasonic transducer system comprising an improved acoustic lens and related methods are provided. The improved acoustic lens may have a uniform loss along an elevation axis or may have a loss along the elevation axis that provides for an apodization of an acoustic signal. The improved acoustic lens may be a multi-component lens. In a two-component lens embodiment, the inner lens component, for interfacing with a transducer, may have a concave outer surface and the outer lens component may have a flat or convex outer surface. In a three-component lens embodiment, the inner lens component, for interfacing with a transducer, may have a concave outer surface, the middle lens component may have a concave outer surface and the outer lens component may have a flat or convex outer surface.
Owner:SOUND TECH
Planar waveguide Bragg grating and laser thereof based on reconstruction-equivalent chirp and equivalent apodization
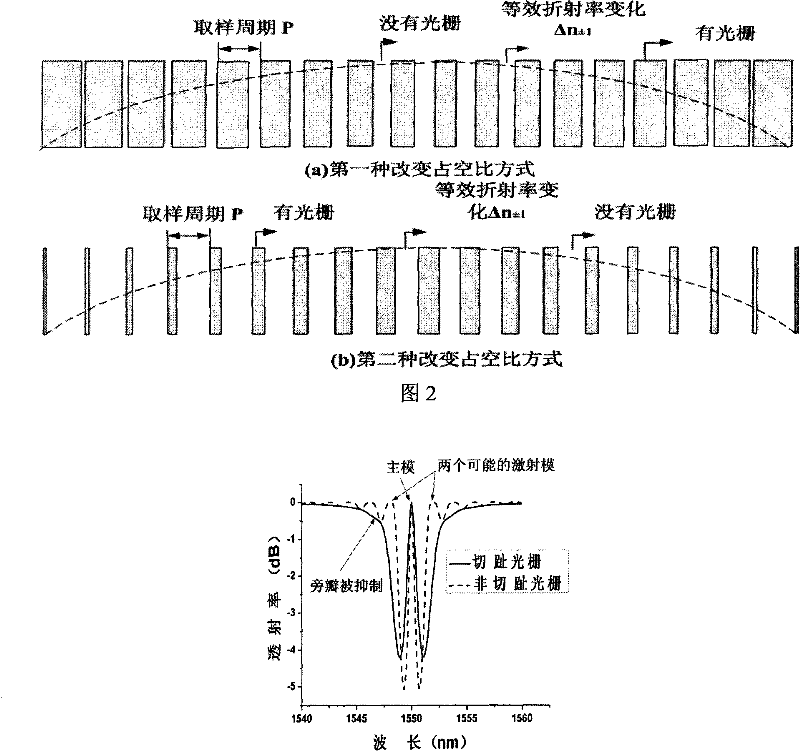
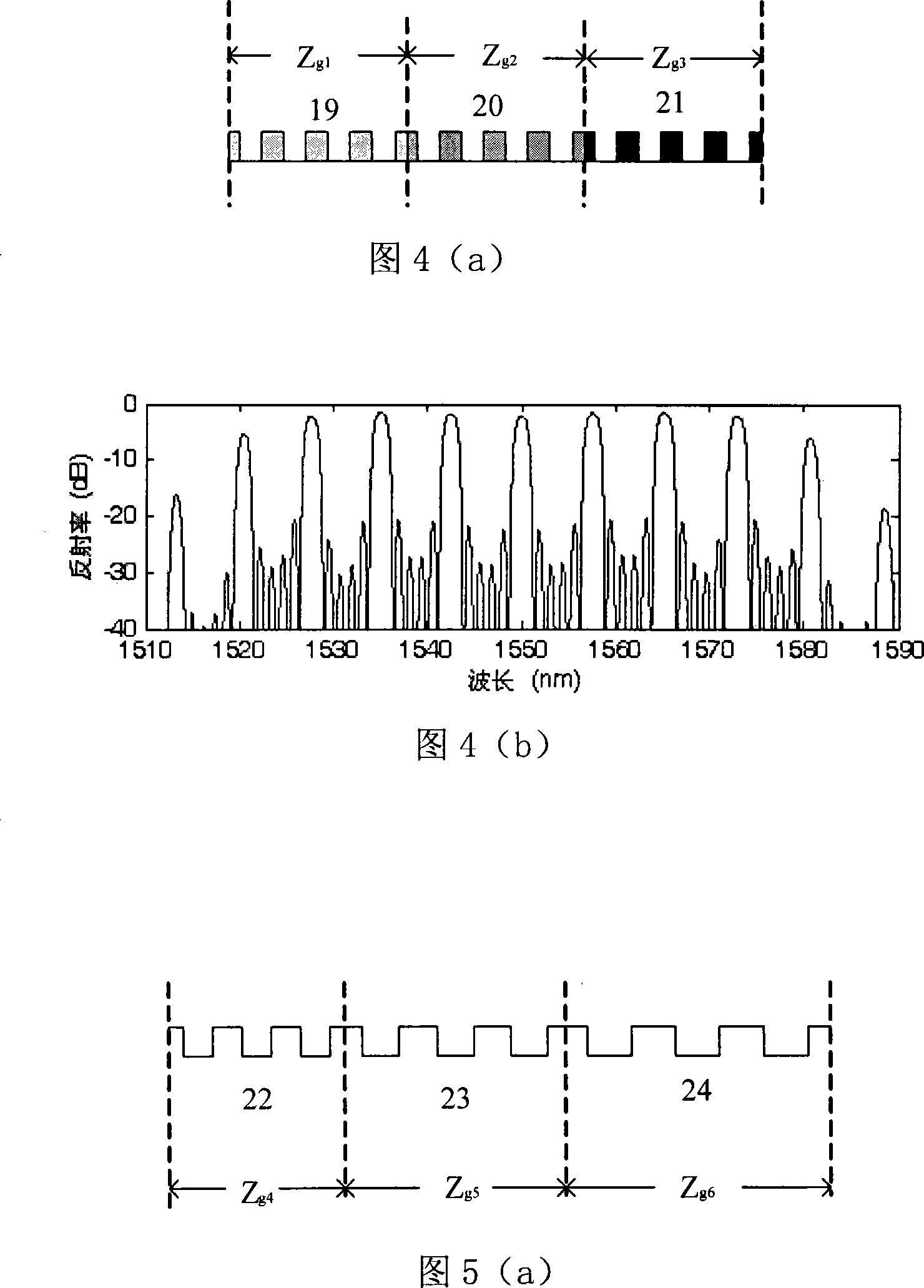
InactiveCN101750671AImprove single modelImprove stabilityLaser detailsCladded optical fibrePhase shiftedApodization
Disclosed are a planar waveguide Bragg grating and a laser thereof based on reconstruction-equivalent chirp and equivalent apodization; the grating adopts sampling structure, the real phase shift or real chirp of the grating is fabricated through reconstruction-equivalent chirp technology; meanwhile, the equivalent apodization is also introduced to the sampling structure to change the sampling duty cycle Gamma along the cavity length direction to realize apodization. The invention combines the equivalent apodization technology in FBG design with the reconstruction-equivalent chirp technology to design a planar waveguide Bragg grating device and a high-performance DFB semiconductor laser. The invention maintains the cycle and refractive index modulation of a seed grating constant, utilizes the sampling structure of gradient duty cycle to effectively introduce the apodization to the planar waveguide Bragg grating, accordingly eliminates the sidelobe of the transmission spectrum of the planar waveguide Bragg grating and ensures the time delay spectrum to be smooth so that planar waveguide Bragg grating devices with high performance are designed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
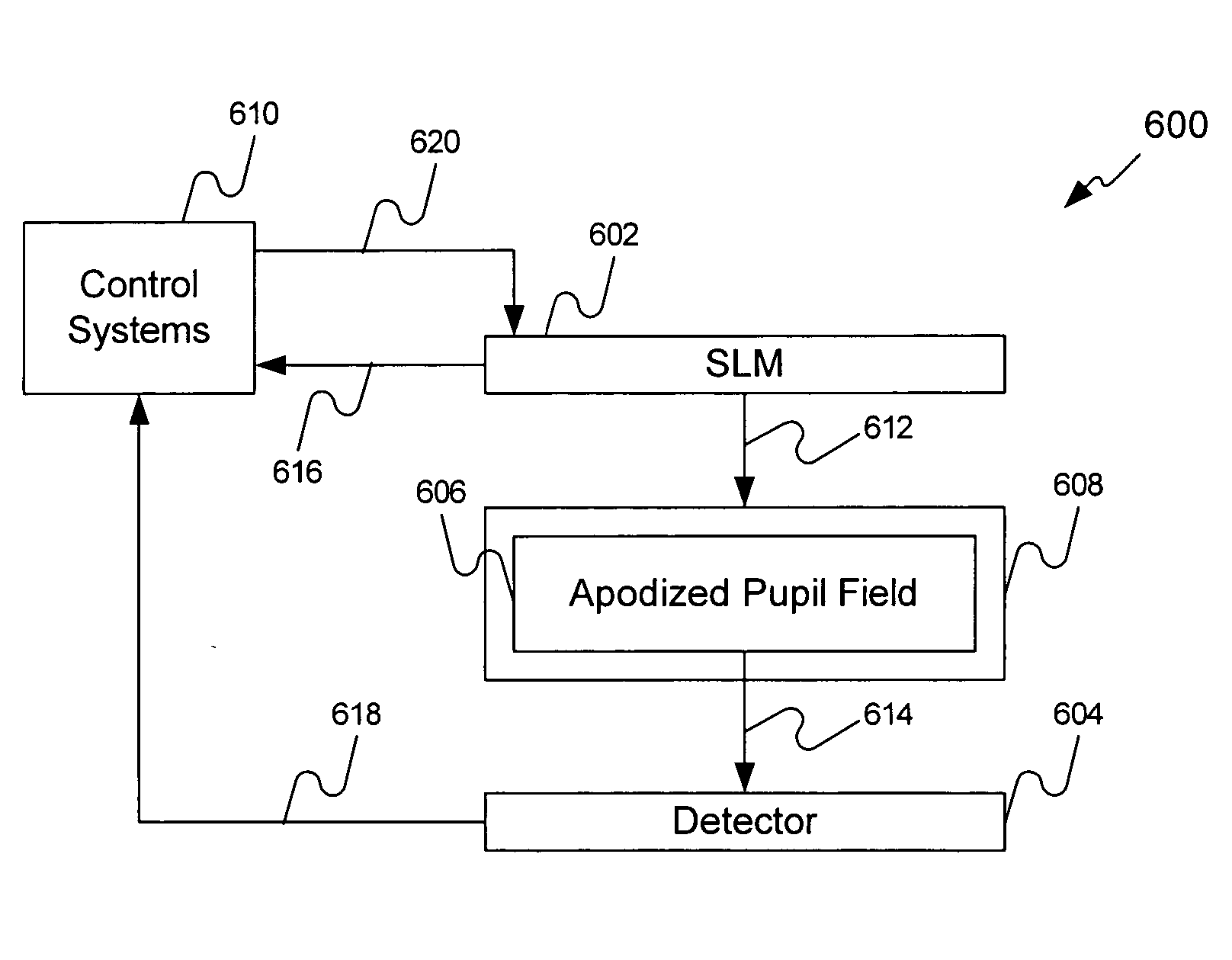
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator
InactiveUS7580559B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorPupil
A method and system as used to calibrate a reflective SLM. The system can include the SLM having an array of pixels and a projection optical system resolving individual pixels and having an apodized pupil. During a calibration operation, the pixels of the SLM receive varying voltage values to move them through various angles. Light reflecting from the pixels during these movements forms individual images for each pixel at each angle. The light passes through the apodized pupil and is received on one or more sections of a detector. The apodization pattern is selected so that individual pixels remain well resolved with strong sensitivity to the pixel mirror tilt. The light intensity received for each pixel at each angle is correlated to the voltage value received at the pixel to tilt the pixel to that angle producing a result signal used by a control device to calibrate the SLM.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Ultrasonographic diagnostic system and ultrasonic diagnostic device
ActiveUS20110270088A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationScan line
An ultrasonic probe is constituted by ultrasonic transducer elements arranged in a direction. A beam forming unit forms acoustic field sensitivity modulated in a direction substantially orthogonal to scan lines in a subject by focusing an ultrasonic wave on a sequence of sampling points existing along the scan lines, and applying delay and apodization on a transmission / reception signal of each of the ultrasonic transducer elements. A detecting unit detects displacements at each sampling point in a direction tangential to the scan lines and in a direction tangential to curves substantially orthogonal to the scan lines by arithmetic between reception signals for the sampling point at different time points. Each curve of the curves substantially orthogonal to the scan lines is constituted by a sequence of points for which a total of times taken for ultrasonic pulses to reach from two points fixed to the ultrasonic probe is substantially the same.
Owner:CANON KK
System for rebuilding spectrum of high spectrum intervention data and method thereof
ActiveCN101598798AUniform lightAvoid demandElectromagnetic wave reradiationApodizationImaging spectrometer
The invention relates to a system for rebuilding spectrum of high spectrum intervention data and a method thereof. Based on the interference imaging mechanism of an HJ-1A high spectrum camera, the system adopts a particular data processing method to rebuild intervention data into spectrum data, which solves the practical engineering problems in processing ground system building data. The system comprises a relative radiation correction unit, an interference data de-noising unit, an apodization processing unit, a spectrum recovering unit and a spectrum checking unit; wherein, the spectrum recovering unit converts an interference data cube into a spectrum image data cube by the symmetrization processing of interference data; the spectrum checking unit carries out wavelength positioning to a real object spectrum image cube by checking the position of the characteristic spectral line of an imaging spectrometer. The technical scheme of the invention fills the blank of data processing of satellite-bone interference imaging spectrometers in China, and satisfies user demand for the data of satellite-bone interference imaging spectrometers.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Edge ringing artifact suppression methods and apparatuses
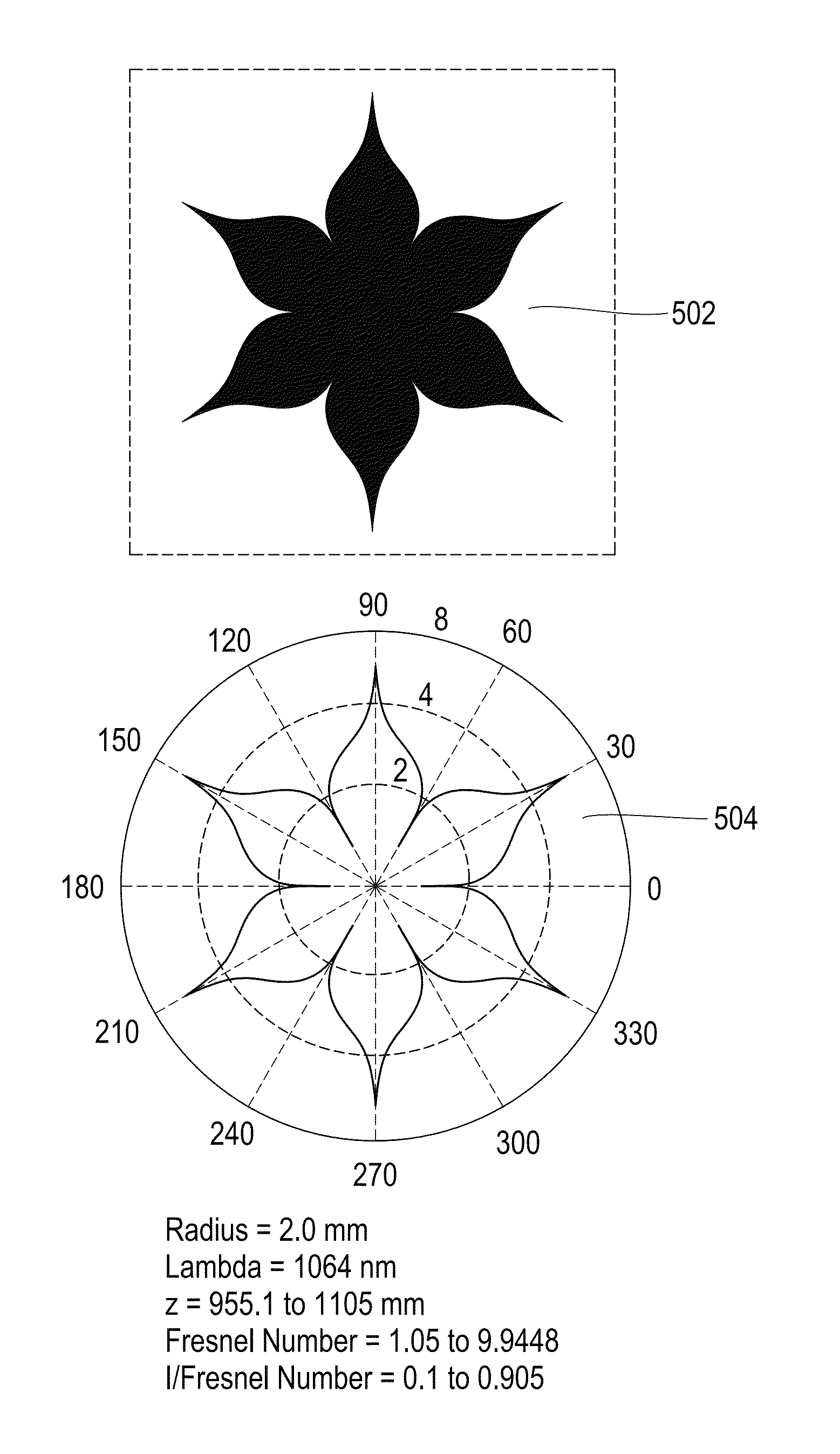
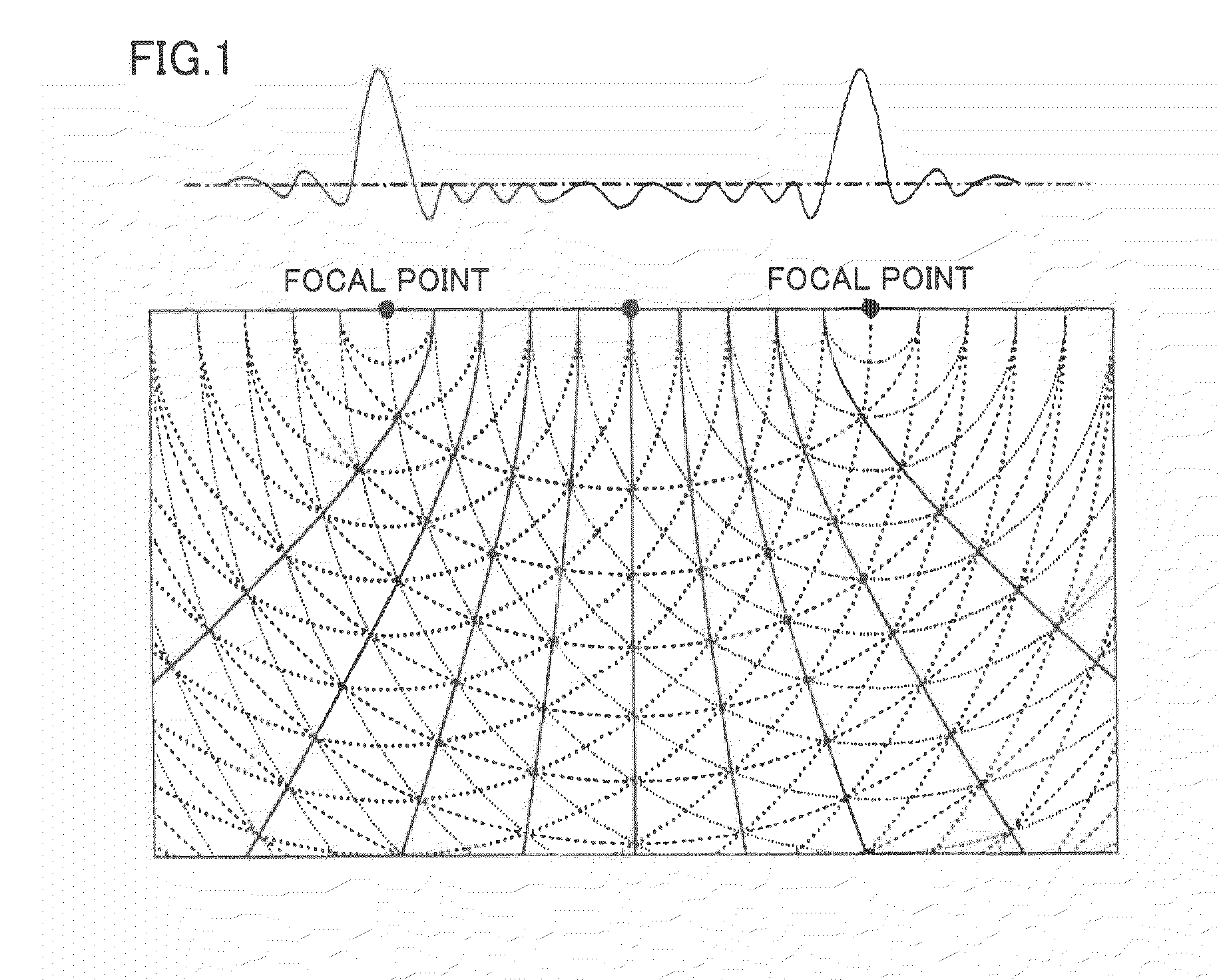
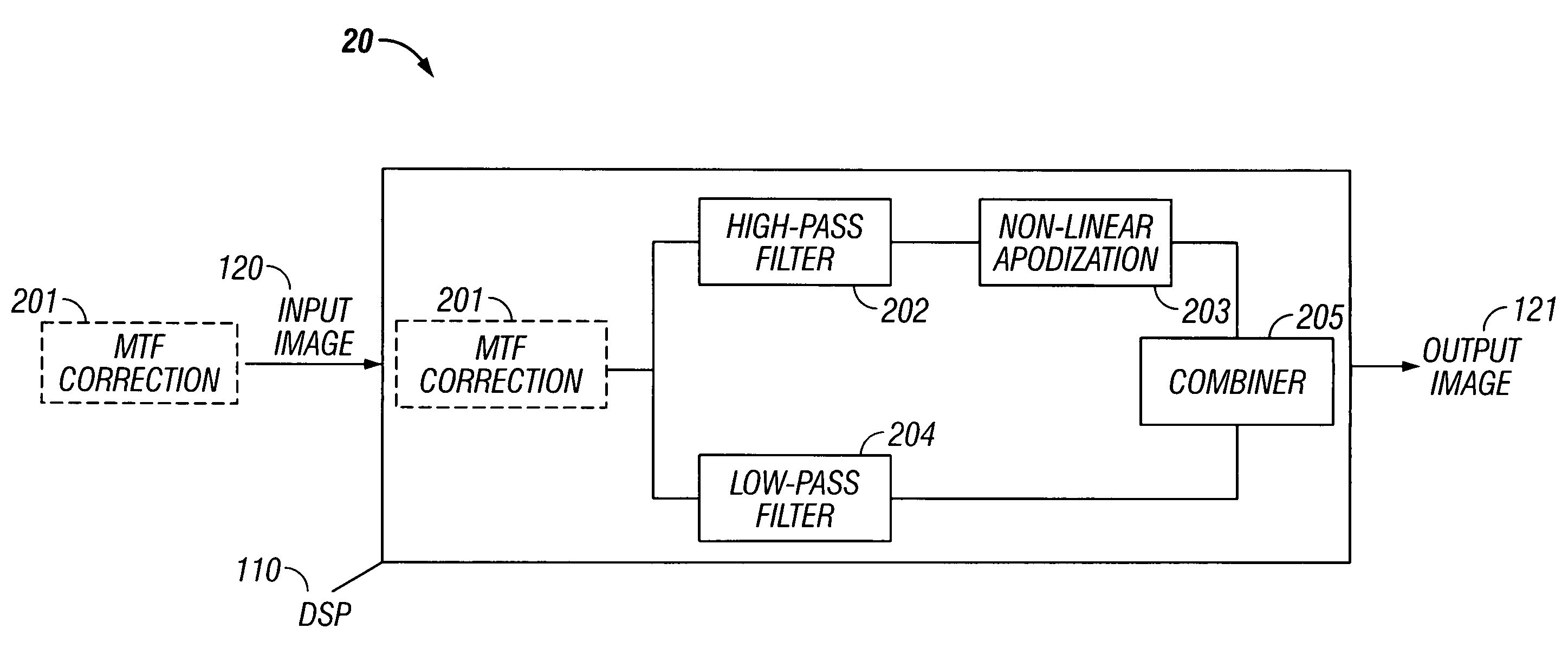
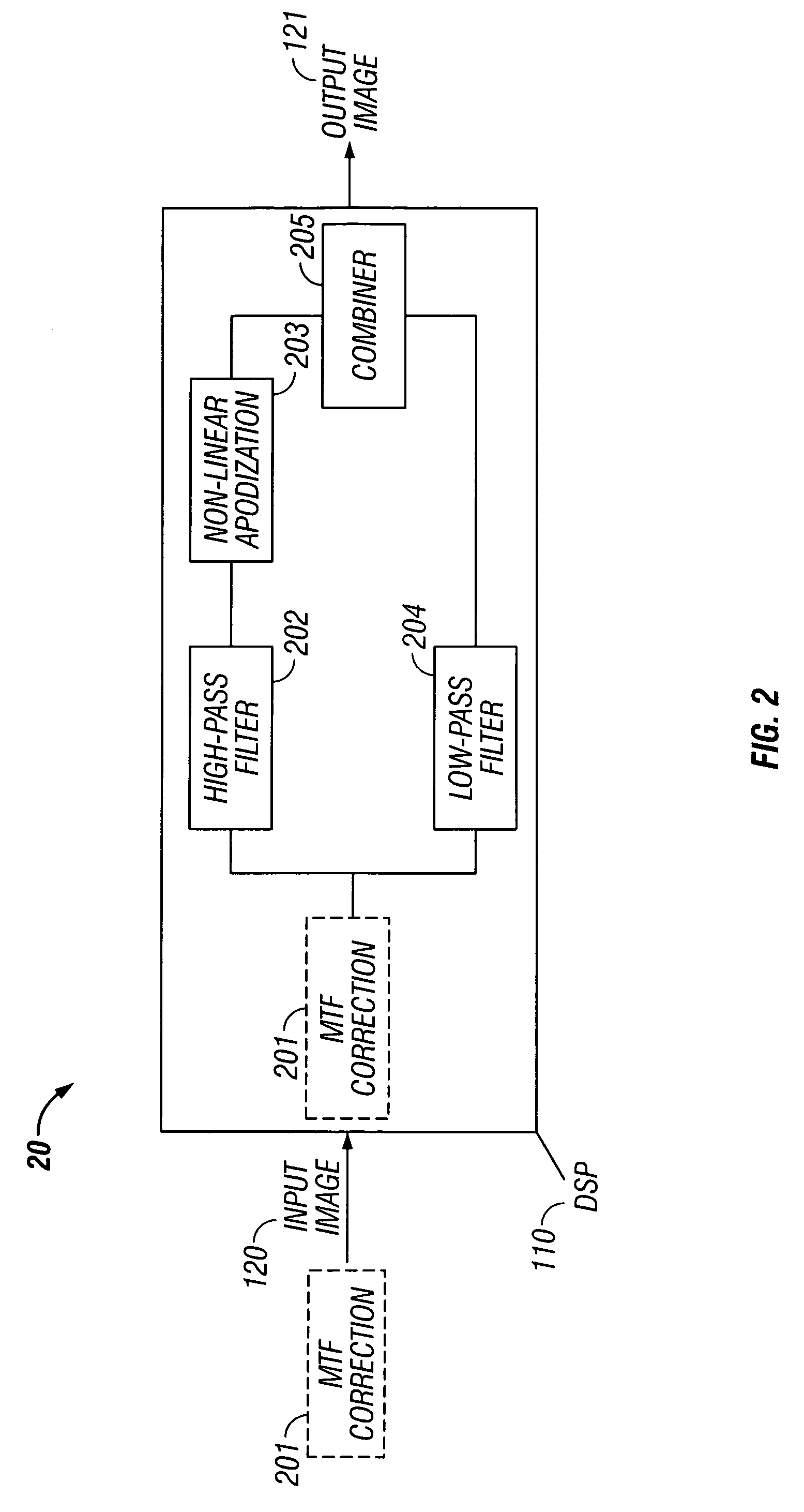
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to methods or suppressing edge ringing in images. For example, in some embodiments a method of processing an image to suppress ringing and broadened edges induced by image correction processing, includes high-pass filtering a first image to obtain a second image, processing said second image including applying non-linear apodization to said second image to obtain a third image, low-pass filtering said first image to obtain a fourth image, and combining the third image and the fourth image to obtain an output image, wherein the output image is characterized by having reduced edge-response sidelobes as compared to the first images. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to devices comprising means and / or modules to suppress edge ringing in images.
Owner:KBR WYLE SERVICES LLC
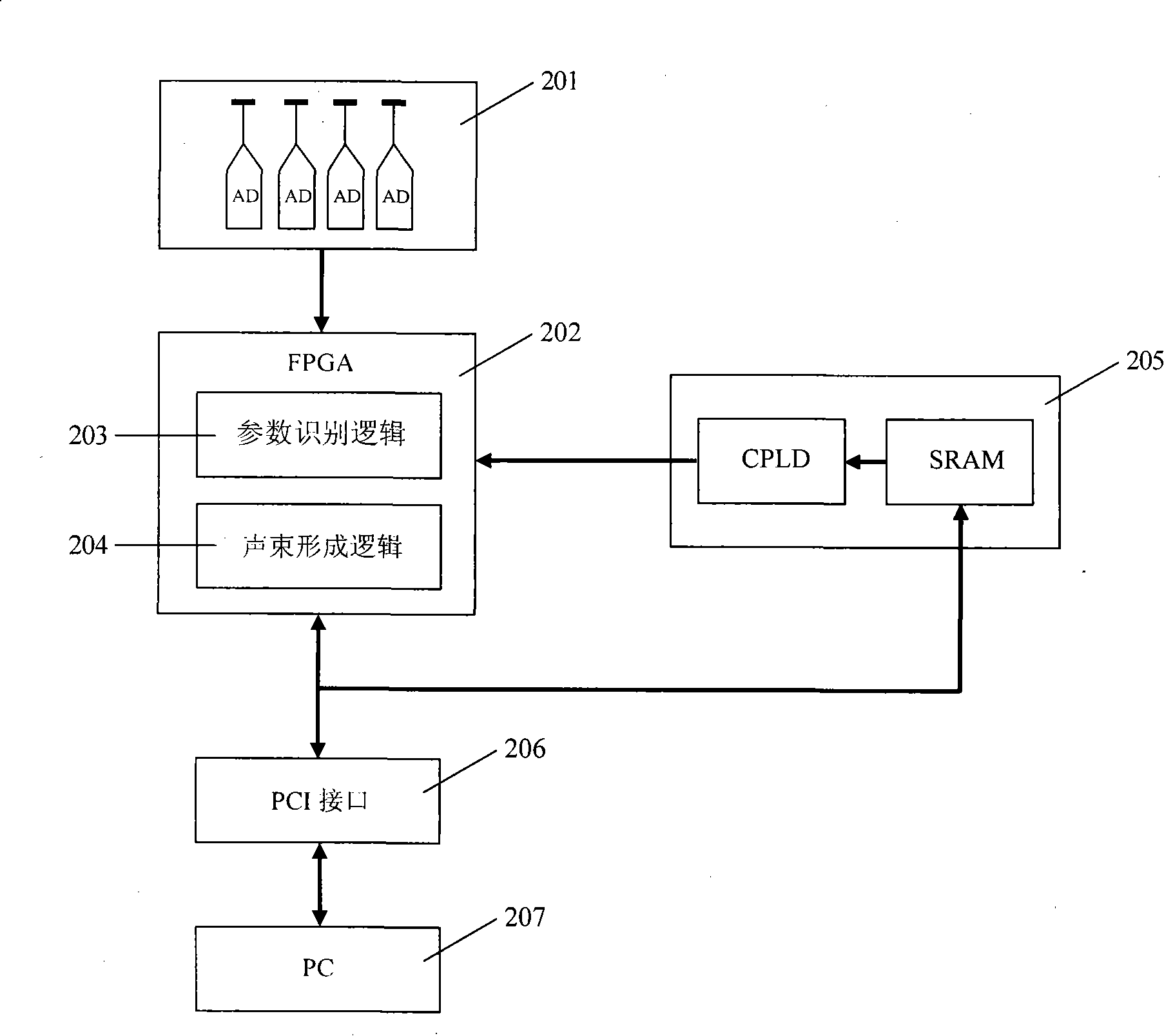
Medical B-ultrasound front-end excitation device and excitation method thereof
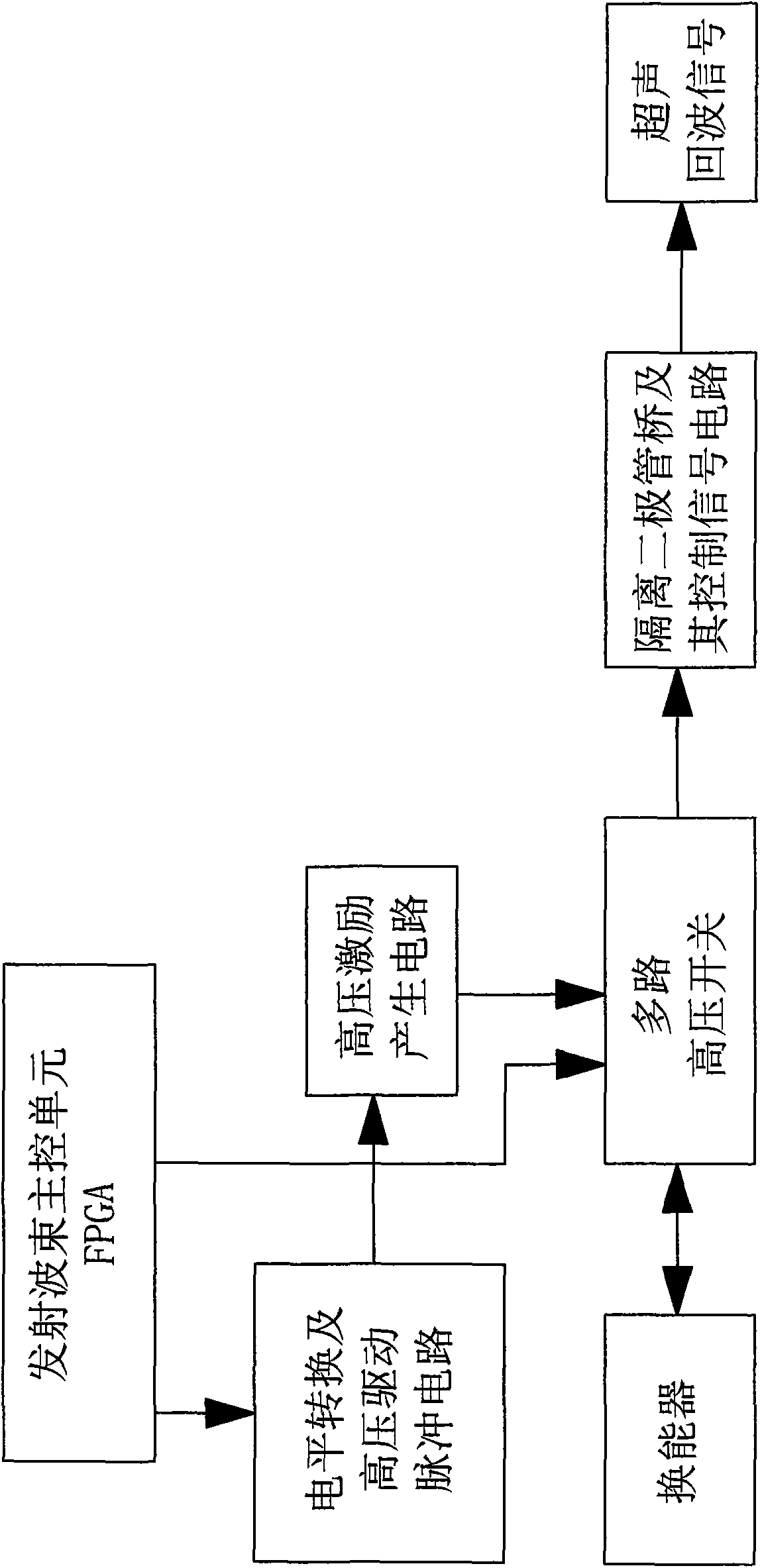
The invention discloses a medical B-ultrasound front-end excitation device, comprising a FPGA-based transmitted beam main control unit, a multi-channel high-voltage switch circuit, a level conversion and high-voltage driving pulse circuit, a high-voltage excitation generating circuit, an isolation diode bridge and the control signal circuit thereof. In the invention, an apodization bipolar transmission circuit is adopted, thereby overcoming the characteristics of the beam and the limitation of the spectrum transmitted by the traditional B-ultrasound front-end system which uses unipolar high-voltage pulse. By using a energy distribution apodization excitation technology which is near Gaussian shape, the characteristics and side lobe suppression of the transmitted beam are effectively improved; thereby not only improving the utilization of transmission energy, but also effectively improving the detection penetration when the transmission high-pressure is unchanged. The excitation device can obtain obvious variable frequency effect, and improve the image resolution, so that the image is more uniform and finer, and the overall performance of the system is enhanced.
Owner:SHANTOU INST OF UITRASONIC INSTR CO LTD
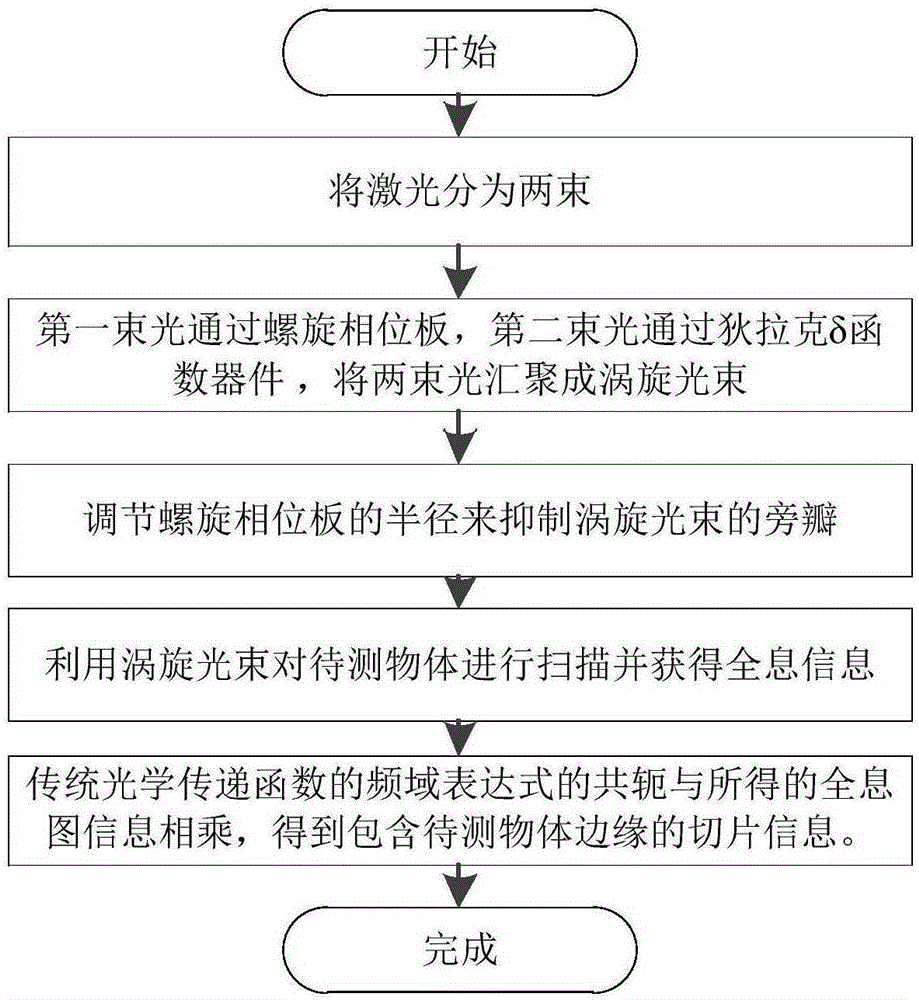
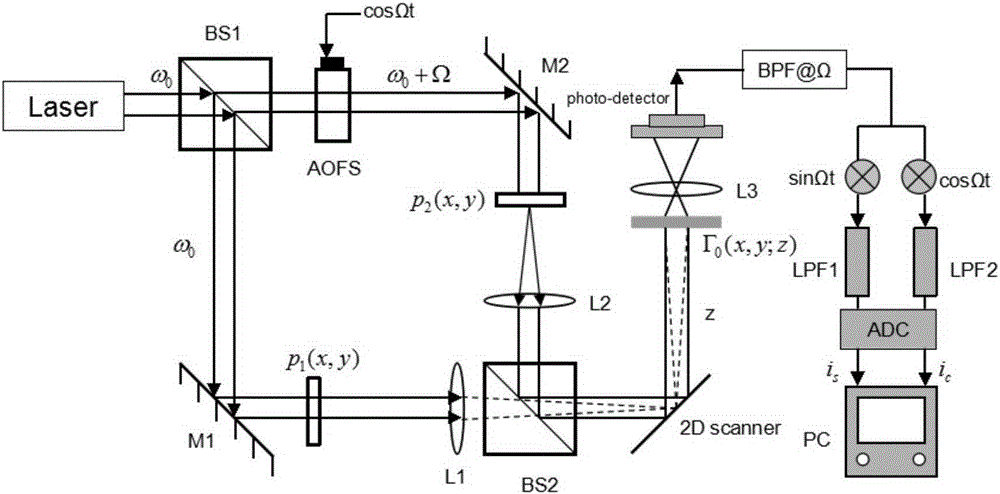
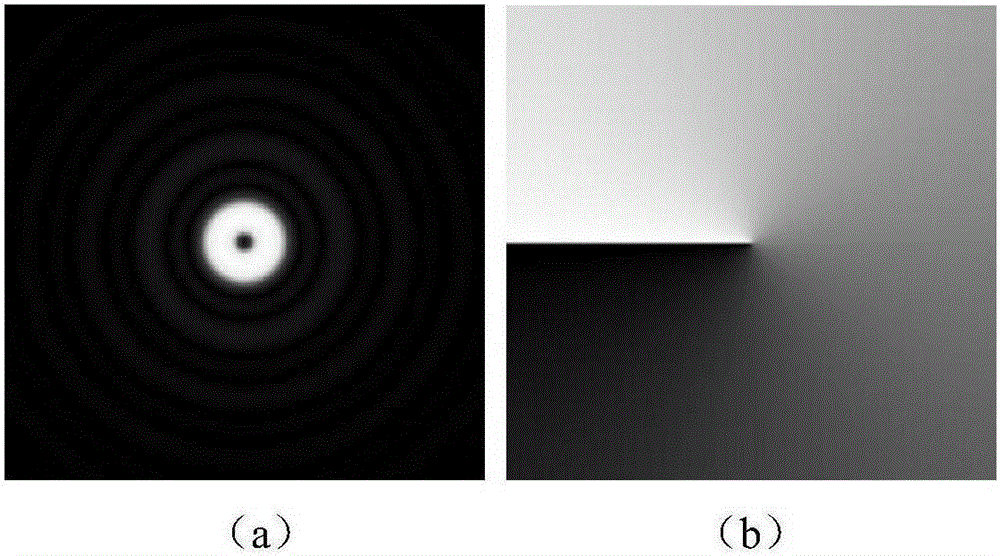
Gaussian apodization based optical scanning holographic edge detection method
InactiveCN105204311AAchieve inhibitionImprove the extraction effectInstrumentsOptical scanning holographyImage resolution
The invention provides an improved method which adopts a spiral phase plate to generate vortex beams so as to carry out edge extraction, belongs to the field of optical scanning and image reconstruction, and mainly solves a problem of suppressing the spiral phase plate to diffract side lobes. In an optical scanning holographic system which carries out edge extraction by adopting the spiral phase plate, suppression for the side lobes is realized through reducing the radius of the spiral phase plate, and a frequency domain expression of the corrected vortex beams is provided, thereby improving the resolution of edge extraction. The method provided by the invention effectively improves the resolution of edge extraction, and the side lobe suppressing method is applicable to various fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Imaging or communications system utilizing multisample apodization and method
ActiveUS8744155B2Minimizing ratioOptimization of contrast resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementFinite impulse responseContrast resolution
Methods, systems and system components for optimizing contrast resolution of an imaging or sensing system utilizing multiple channels of broadband data associated with an array of transducers. Channels or data are filtered by passing the channels of data through finite impulse response (FIR) filters on each channel. The filters each have multiple taps having tap weights pre-calculated as a function of distance of the array from an object that energy is being transmitted to or reflected from. The weights are pre-computed through a deterministic equation based on an a priori system model.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Fibre-optical raster of implementing arbitrary target response
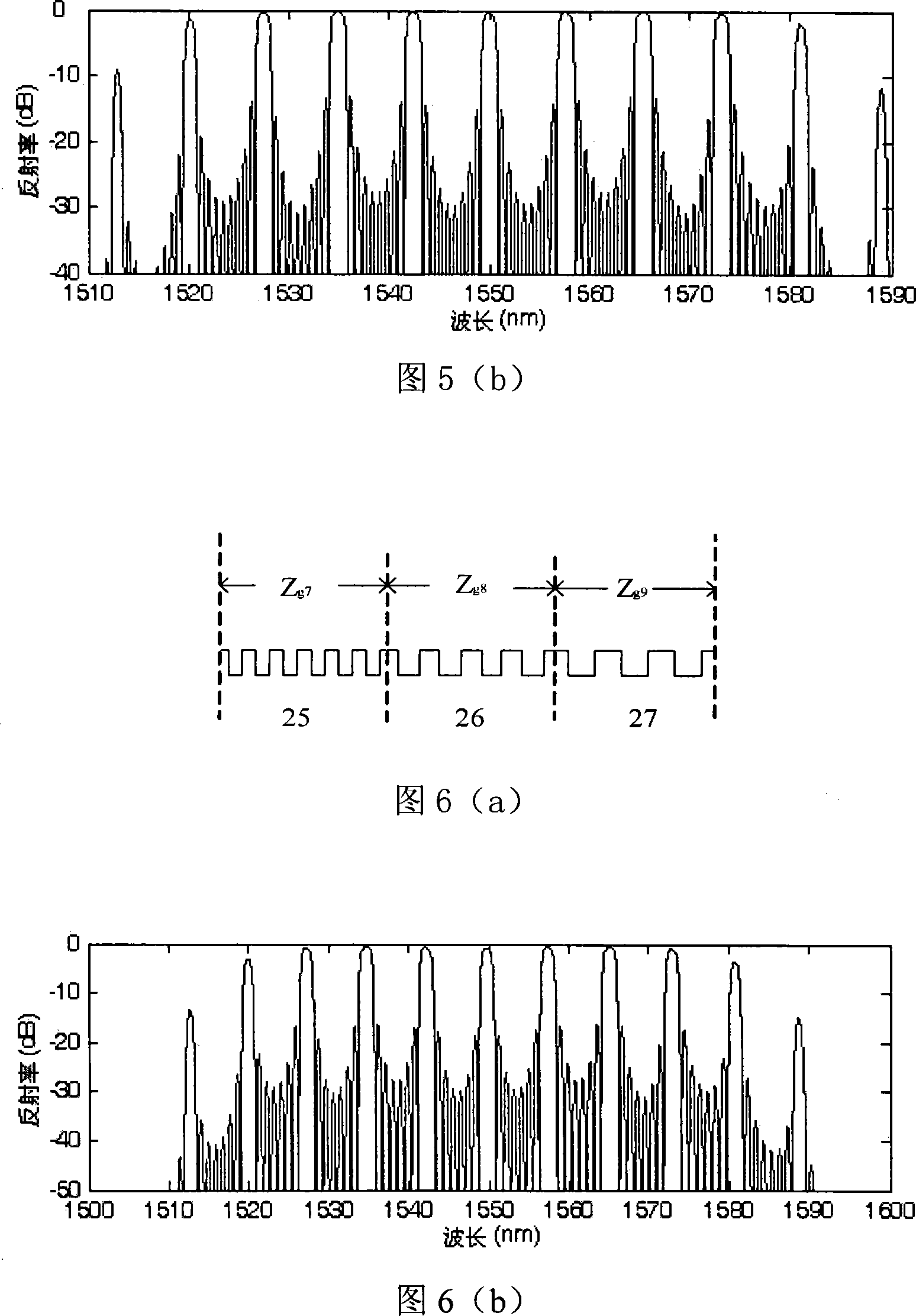
InactiveCN1560656AReduce manufacturing costExpand the range of reflex responsesElectromagnetic transmissionOptical light guidesFiberRate modulation
The invention relates to a fiber grating which can realize any target response, which belongs to fiber communication, optical sensor and other relative light signal processing fields. The product is a fiber grating of sampling structure realized with phase model scanning method; the period and phase function of the initial end of the fiber grating, As, Phi s (z) and A s (z) are period, phase function and apodization function of any given fiber grating initial end. And it can acquires distance Zk from the K ultraviolet exposure position to the sample fiber grating initial end and the amplitude Ak of refraction rate modulation leaded in at the Zk. The character of the invention is: its reflection spectrum has multi-channel type, and some special reflection peak in them has the demanded target reflection response, or has the character of target phase shift.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Coherent Image Formation for Dynamic Transmit Beamformation
ActiveUS20090306512A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasonographyData set
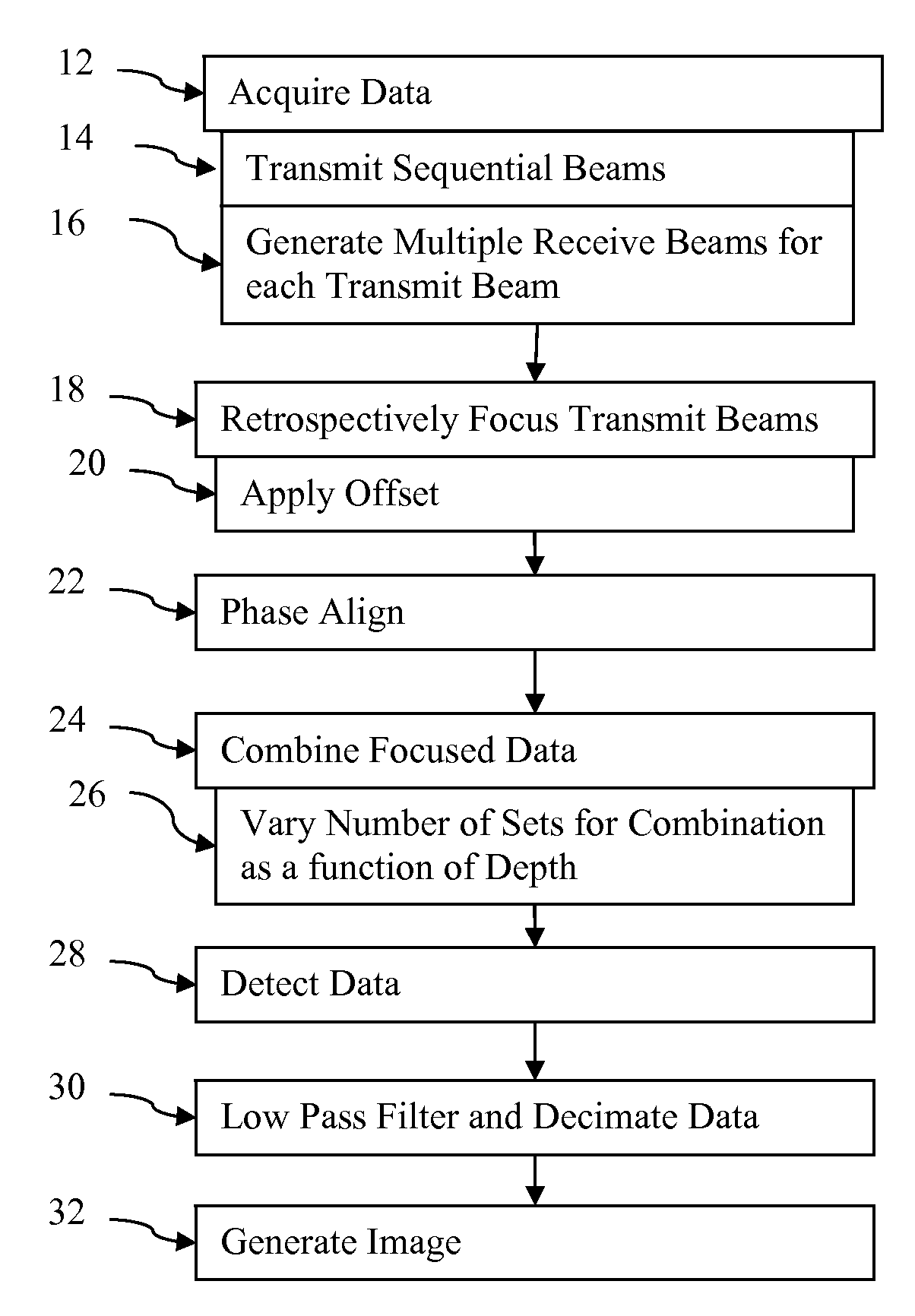
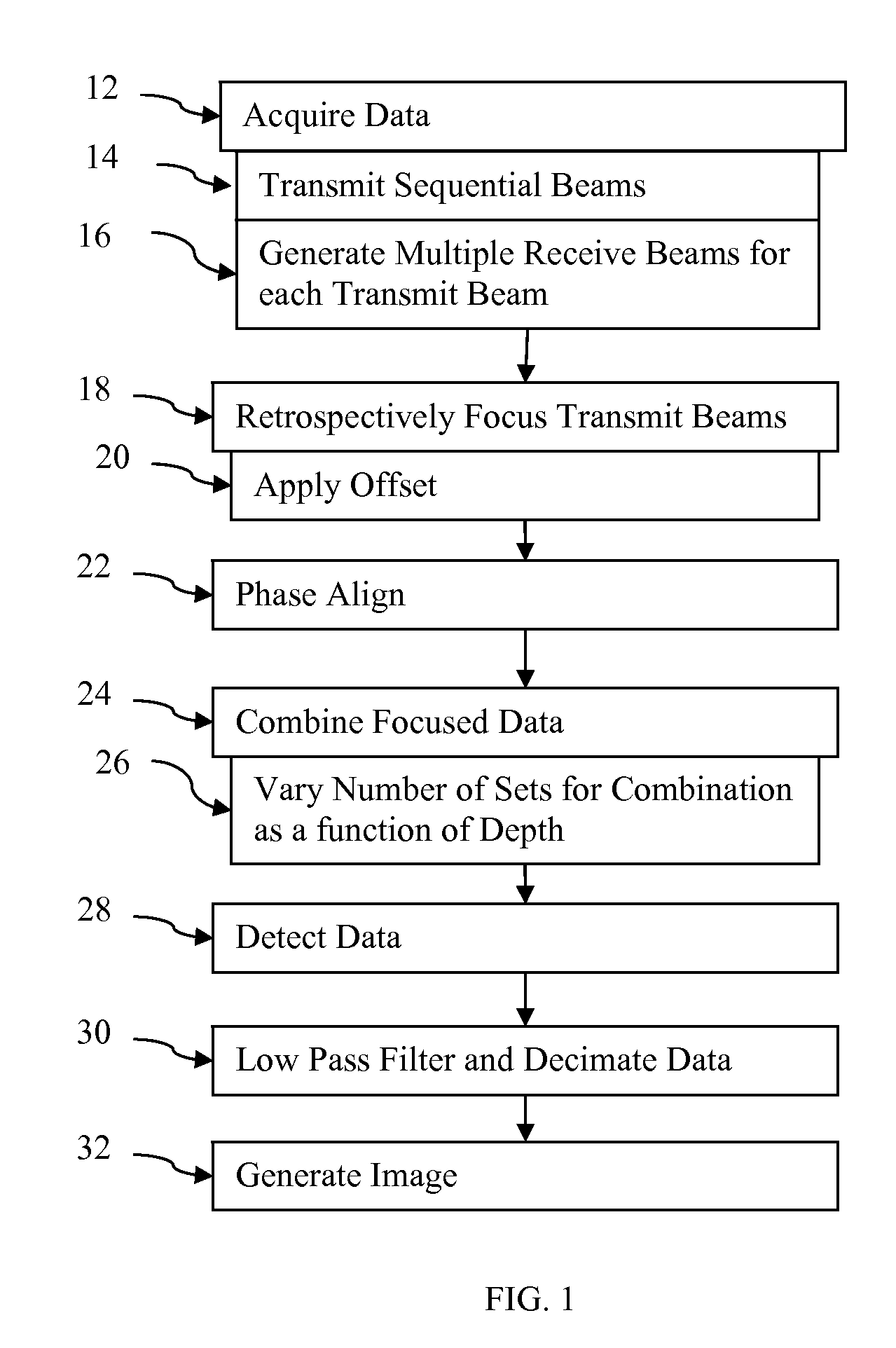
Retrospective dynamic transmit beamformation is provided in medical ultrasound imaging. Using parallel receive beamformation, sets of data representing locations in at least a common field of view are obtained, each set in response to a transmit with a spatially distinct phase front. The common field of view receive data are time aligned and amplitude weighted for retrospective transmit focusing and retrospective transmit apodization, respectively. A time offset, such as of a cycle or more in some cases, is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit focusing. The offset is selected to emulate shifting the transmit delay profile to be tangentially intersecting with the dynamic receive delay profile for each location which is the desired transmit delay profile. A weight is applied to the receive data for retrospective transmit apodization. The weight is selected based on the desired transmit apodization profile. The offset and weighted data representing a same location from different transmit events is coherently combined. The number of sets of data offset, weighted and combined may vary as a function of depth for dynamic transmit beamformation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Tunable semiconductor laser
InactiveCN101022206AGood peak balanceImprove consistencyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersGratingRefractive index
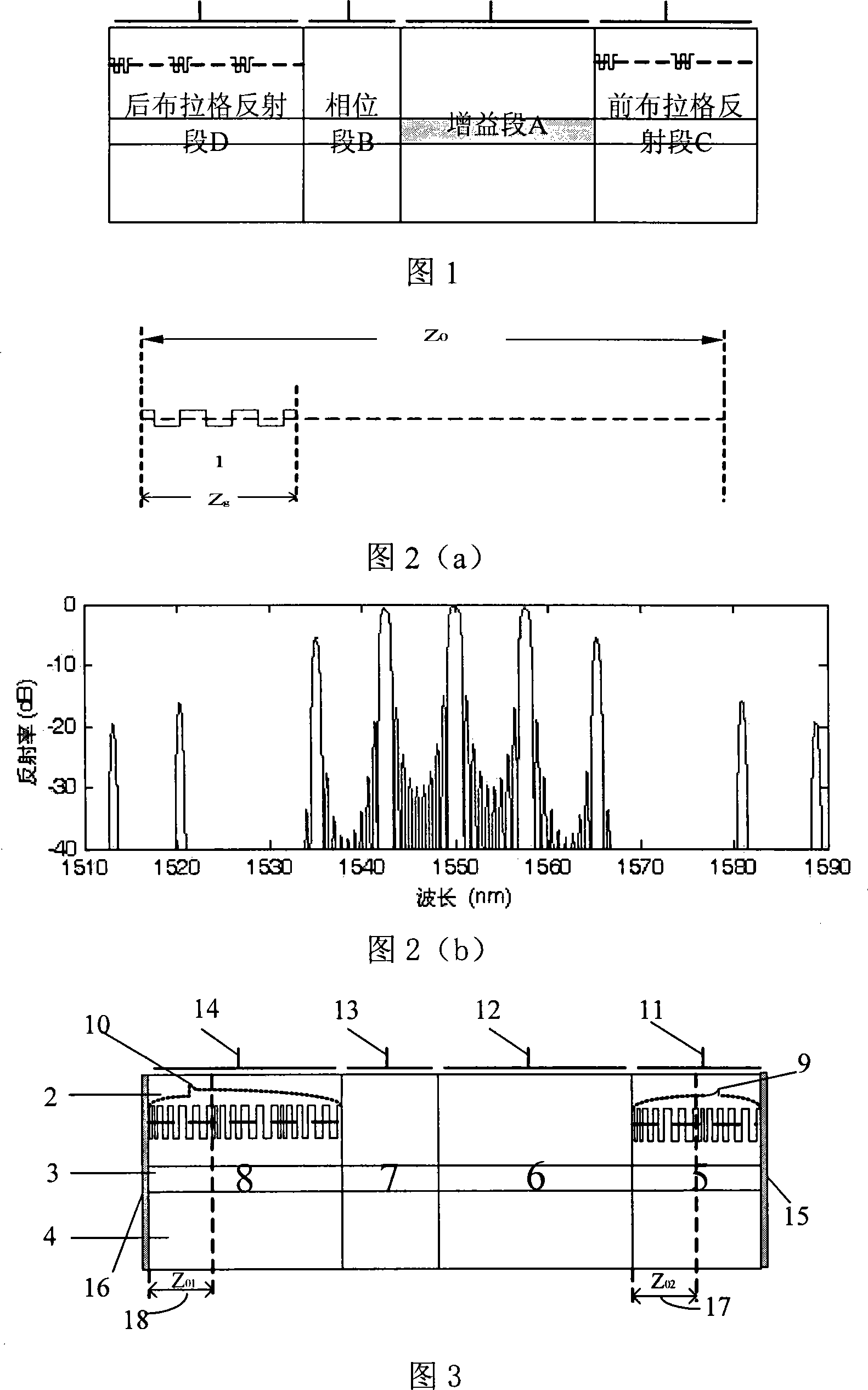
This invention discloses a tunable semiconductor laser, in which, two Prague reflection secions limit borders of a gain section at both ends, reflection sections of the front and back ends can be designed to Prague grating suitable for generating comb reflection peaks with even peak values in form, two Prague reflection sections of a laser can be designed to the form of various traces, phase shift and chirp of Prague grating and the theory of vernier caliper is used to change the refraction rate of the two reflection sections of the laser to realize quasi-continuous tune of broad spectrum.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ultrasonic imaging system self-adaption beam former based on correlation analysis
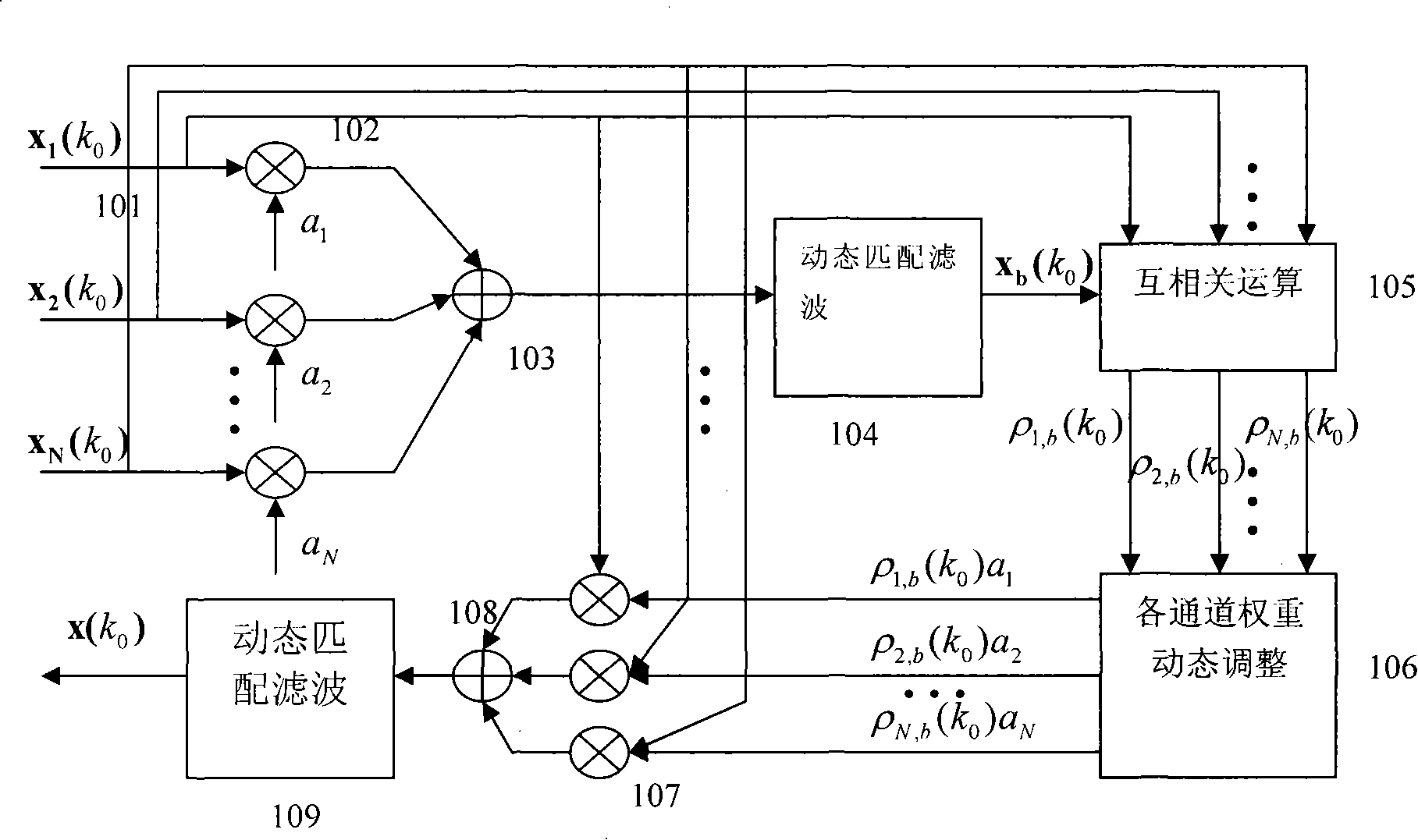
InactiveCN101238992AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationCorrelation analysis
An adaptive beamforming device belongs to medicine ultrasound imaging field. The invention provides an adaptive beamforming technique based on correlativity analysis, directing towards the difficulty that the traditional beamforming device can not completely restrain sidelobe effect resulted from interchannel random phase error and not affect the focusing effect along with the dynamic alignment of detection position. The technique divides the echo signal obtained from each channel into several segments, direct towards each segment, firstly the reference signal is obtained by a classical beam forming method, and then the signal of each channel is mutually correlated with the reference signal, furthermore weight of channel in each segment is dynamically adjusted using correlation coefficient, finally signals of each channel are synthesized to obtain final beam output using adjusted weight. The adaptive beamforming device adaptively detects the variance of enviroment using dynamic apodization and restrains the sidelobe effect resulted from interchannel random phase error. The adaptive beamforming device has wide application prospect in ultrasound imaging field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
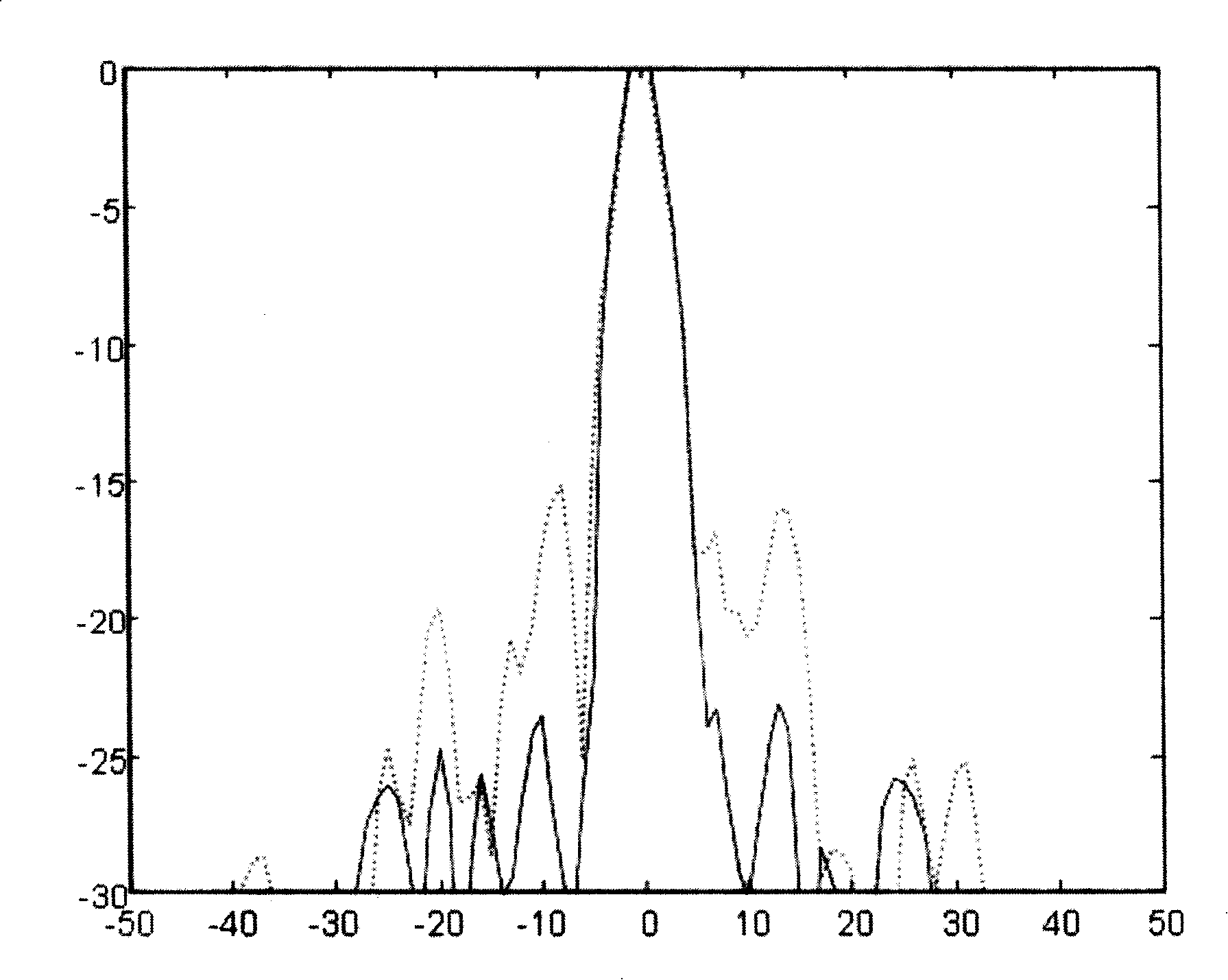
Optical component, optical system including such an optical component, lithographic apparatus, method of correcting apodization in an optical system, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20060091324A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPupilComputational physics
A method of correcting apodization in an optical system includes determining effects of apodization on an intensity distribution of a beam of radiation in a predetermined plane of the optical system; determining a more desirable intensity distribution of the beam of radiation in the predetermined plane such that apodization is corrected for; and absorbing portions of the beam of radiation in the predetermined plane as a function of location such that downstream from the predetermined plane the beam of radiation shows the more desirable intensity distribution. An optical component includes one or more absorbing layers designed to perform the absorption as a function of the location. The optical component may located in the pupil plane of the optical system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Filter based on axial direction apodized grating
ActiveCN106896446ARealize downloadLarge toleranceOptical waveguide light guideSingle mode waveguidesSideband
The present invention discloses a filter based on axial direction apodized grating. Input single mode waveguide is connected with the upper end port of the left end of an asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler through input gradual changing waveguide, and the lower end port of the left end of the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler is connected with bending waveguide to realize reflection signal download; and the upper end port of the right end of the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler is connected with the left end of an antisymmetrical multimode waveguide grating, and the right end of the antisymmetrical multimode waveguide grating is connected with the output single mode waveguide through output gradual changing waveguide. The separation of grating reflection signals employs the asymmetrical gradual changing directional coupler with large tolerance and small insertion loss to realize download of the grating signals; based on a grating filter, the filter based on axial direction apodized grating is large in tolerance and wide in bandwidth regulation range and cannot be limited by the FSR so as to realize filters with various different bandwidth demands; and moreover, the axial direction position regulation of grating teeth realizes apodization so as to realize a grating filter with large sideband suppression ratio and greatly improve the performance of the grating filter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com