Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
278 results about "Phakic intraocular lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
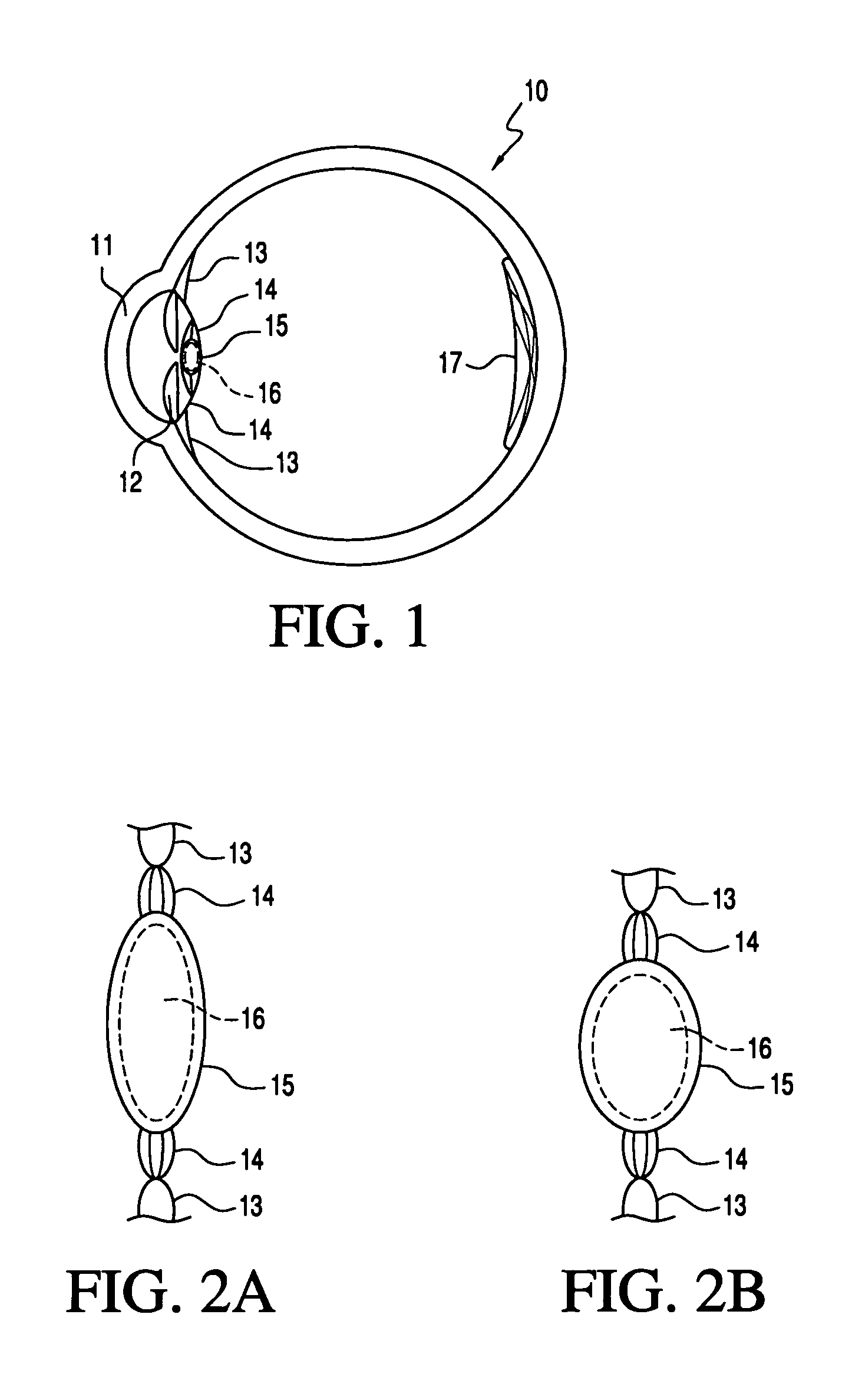
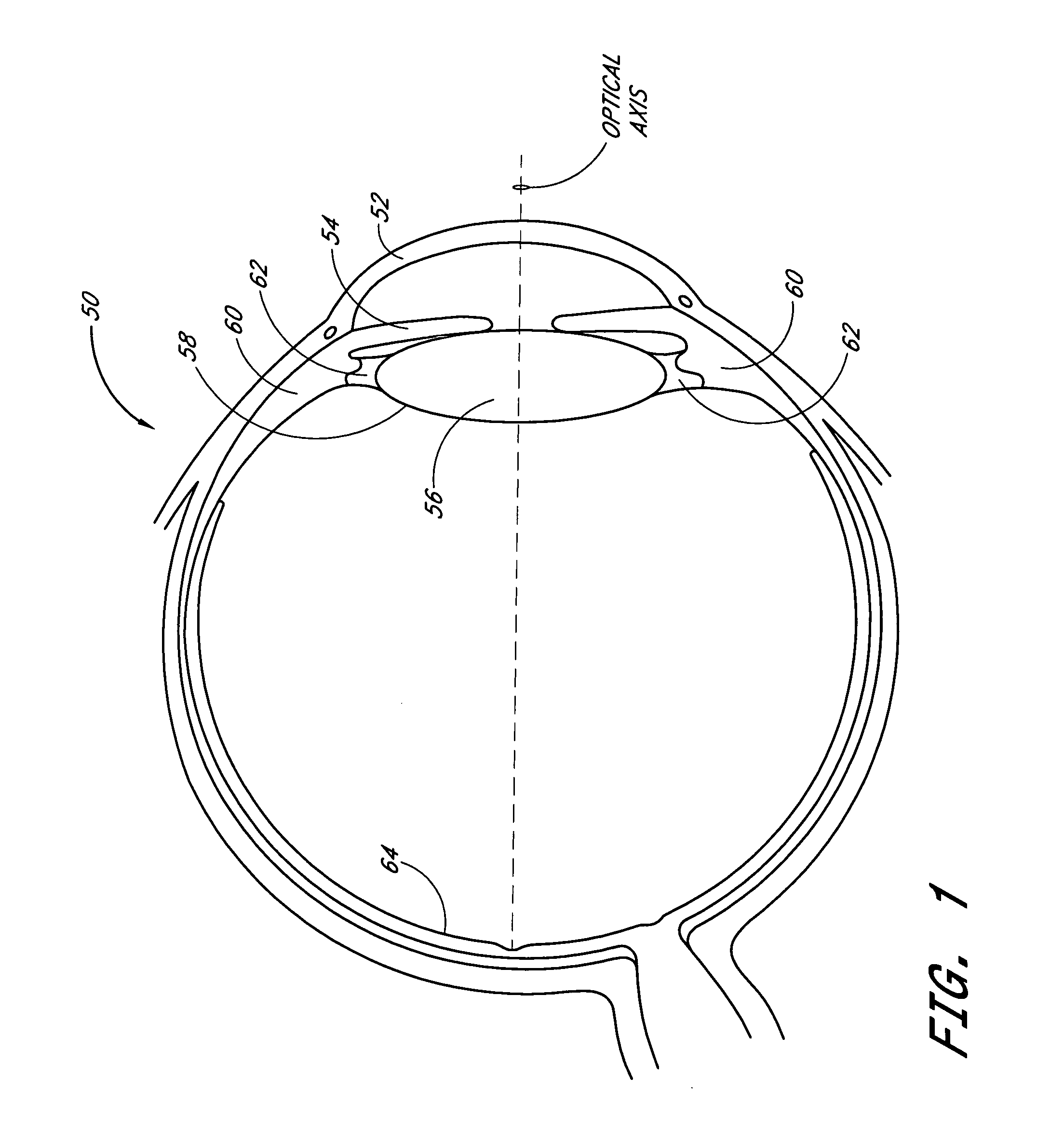
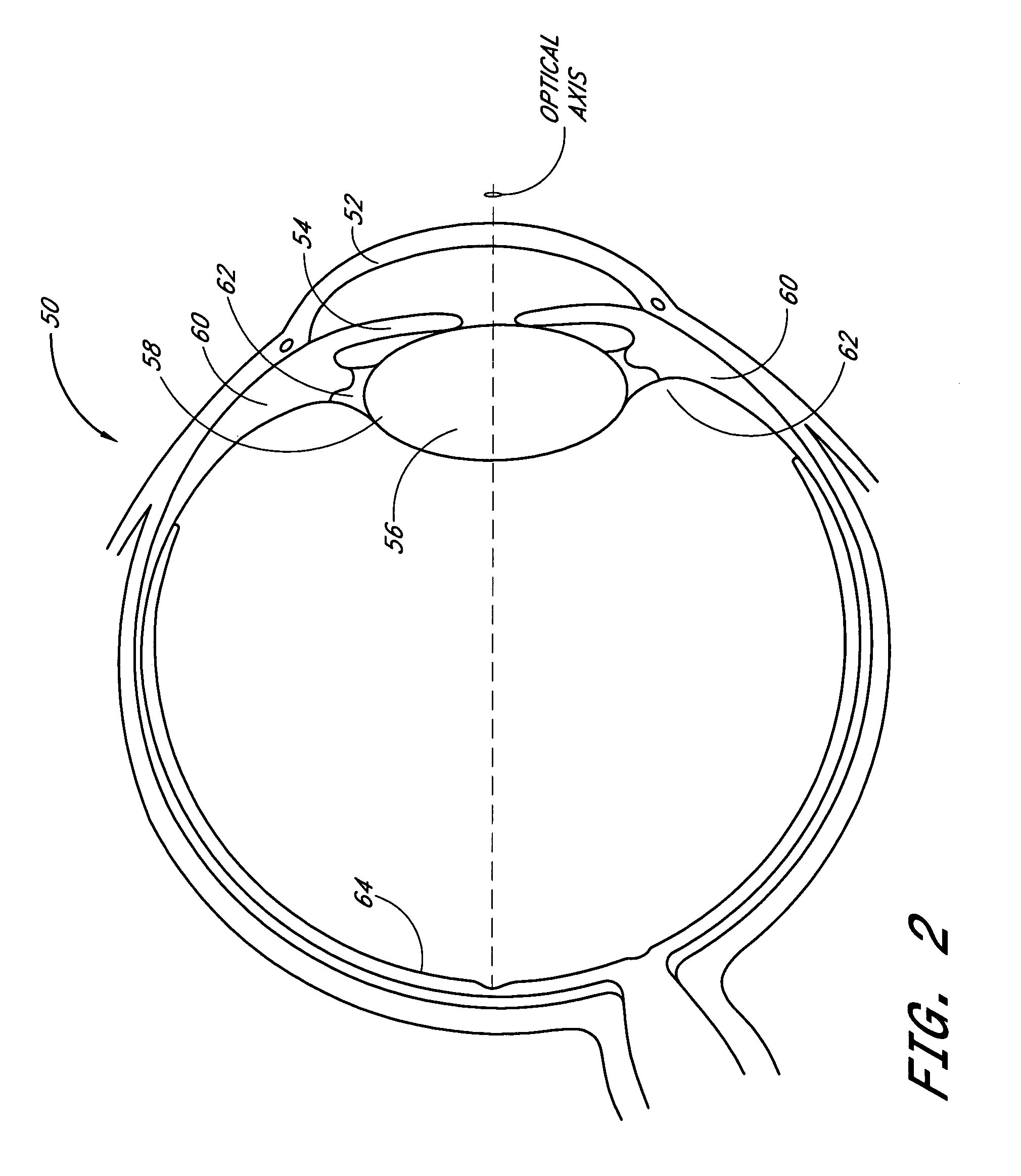
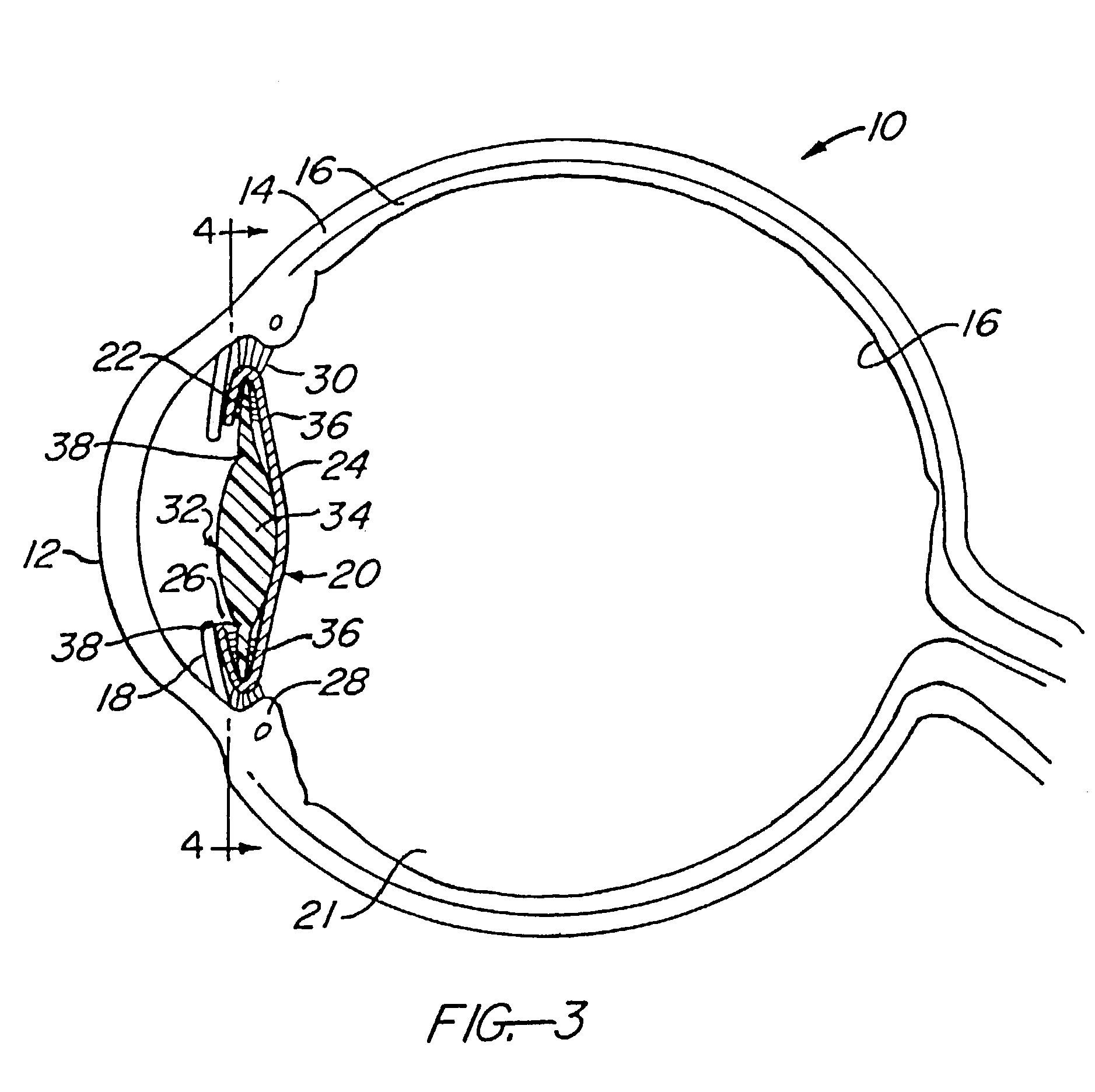
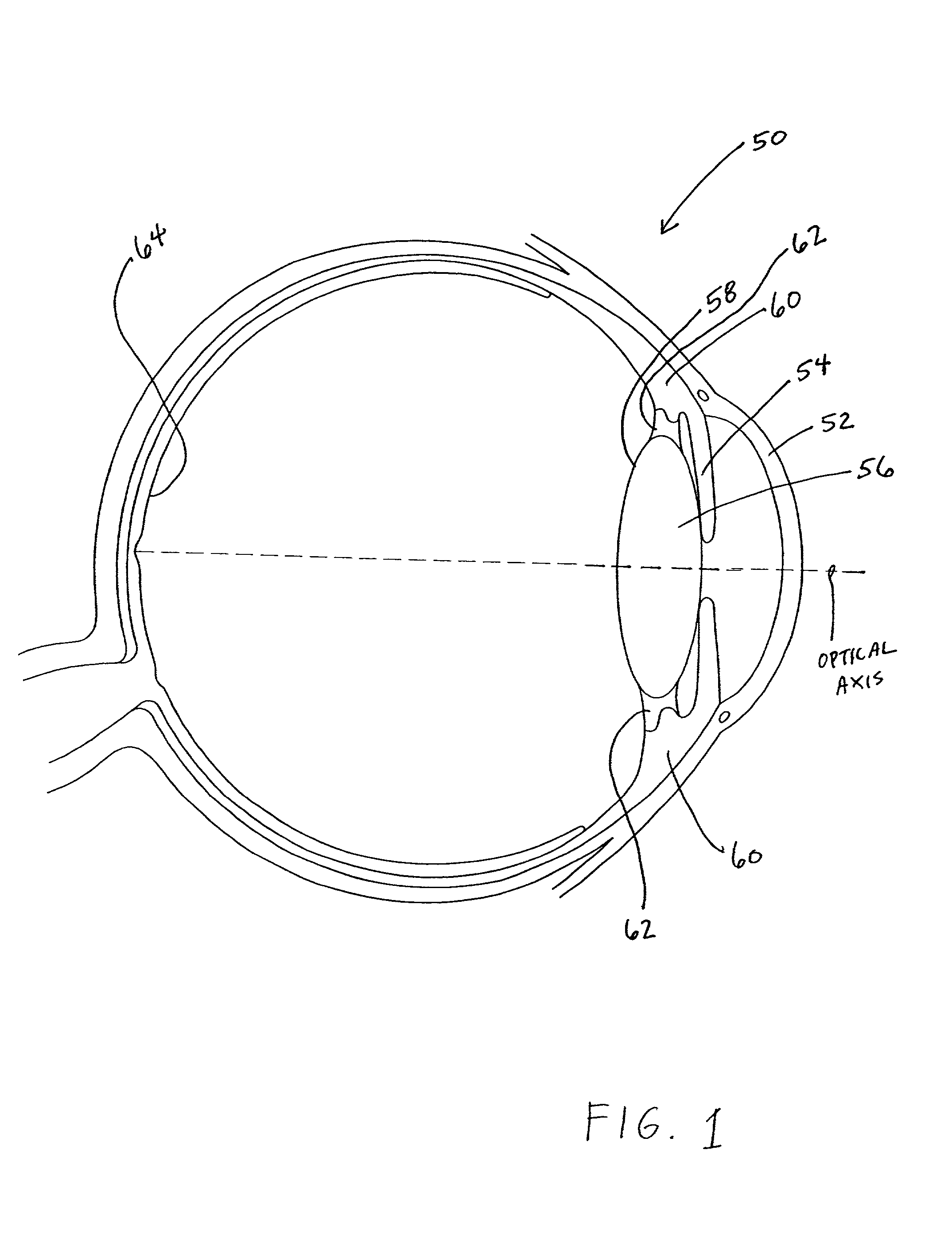
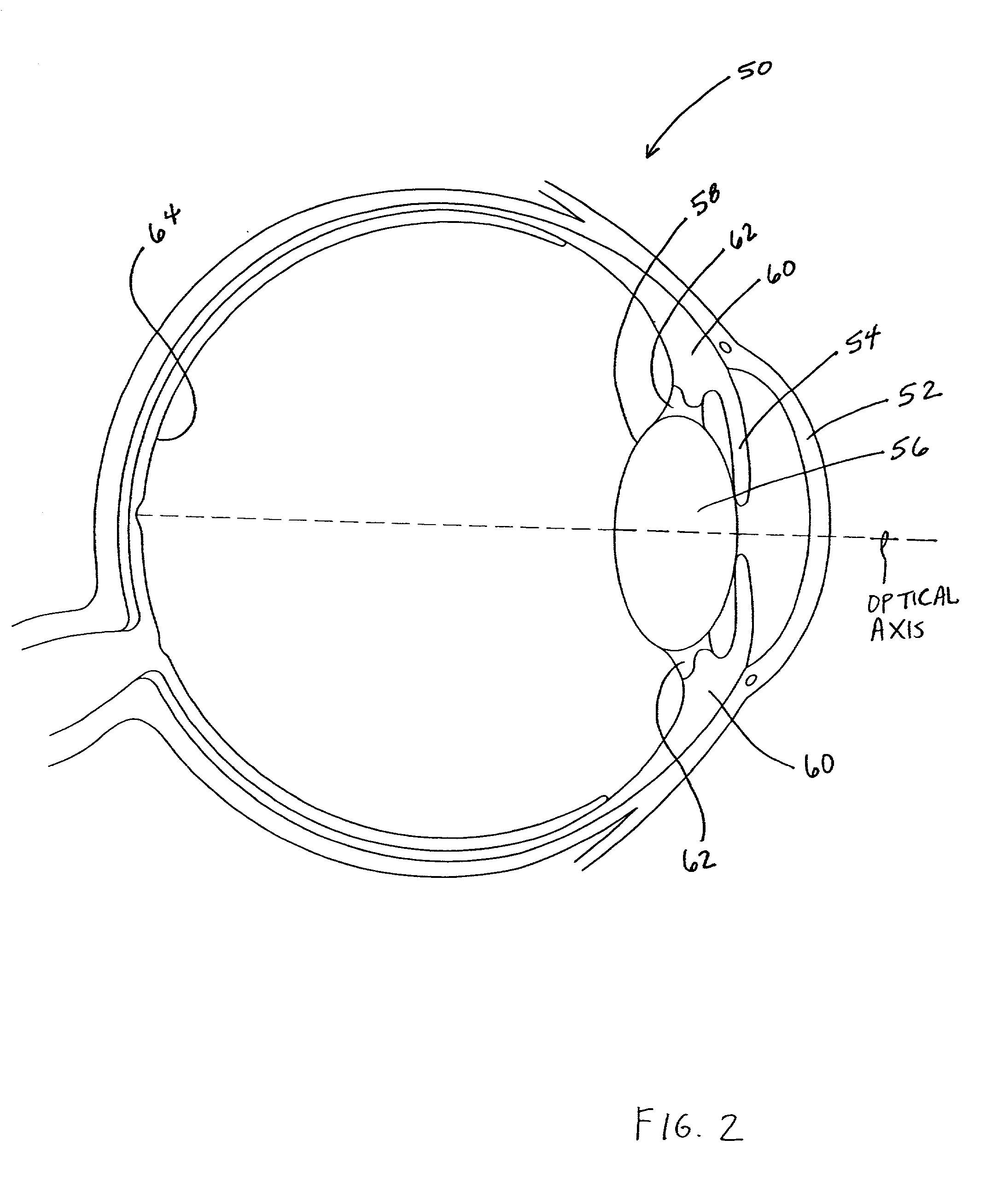
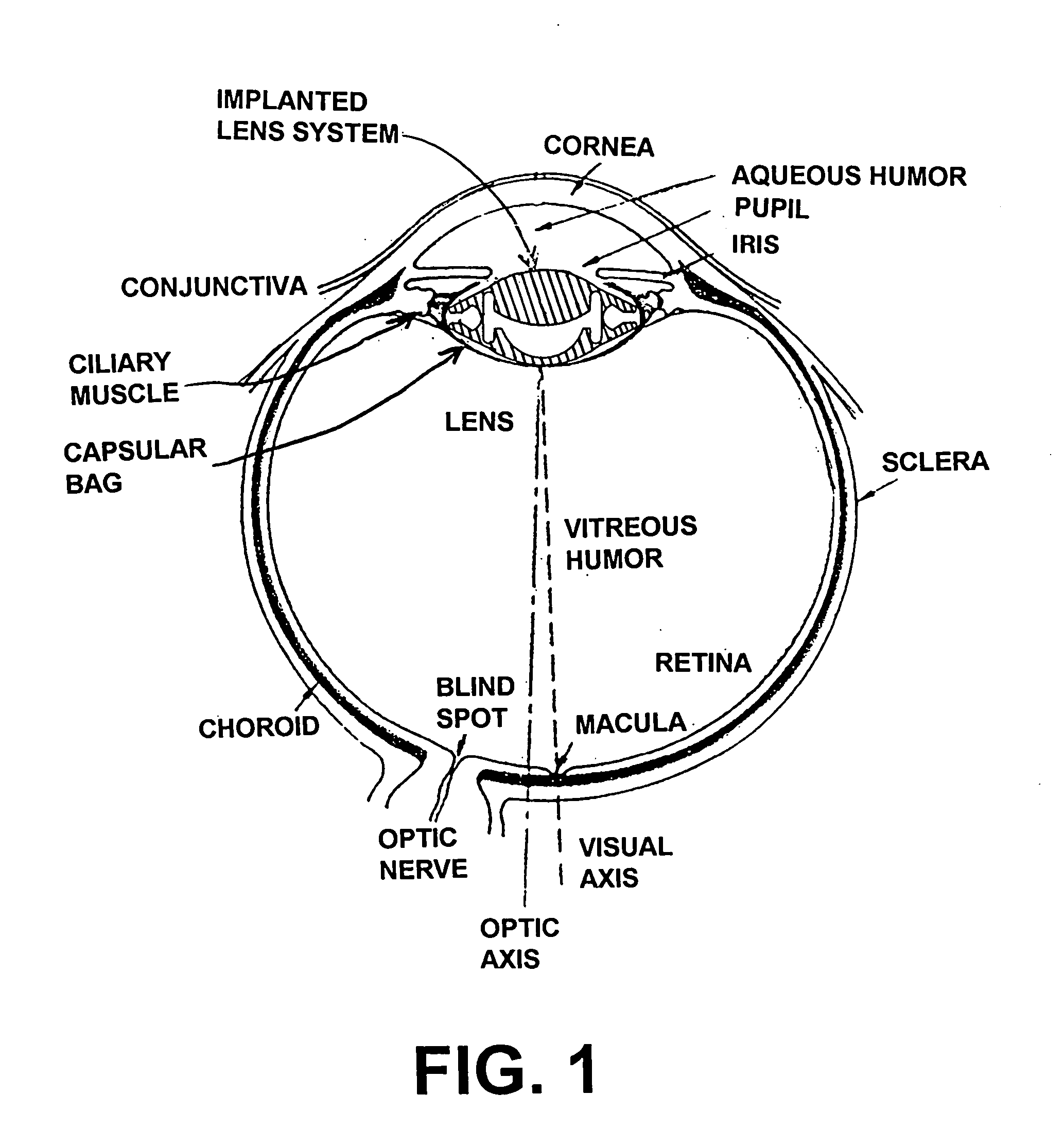
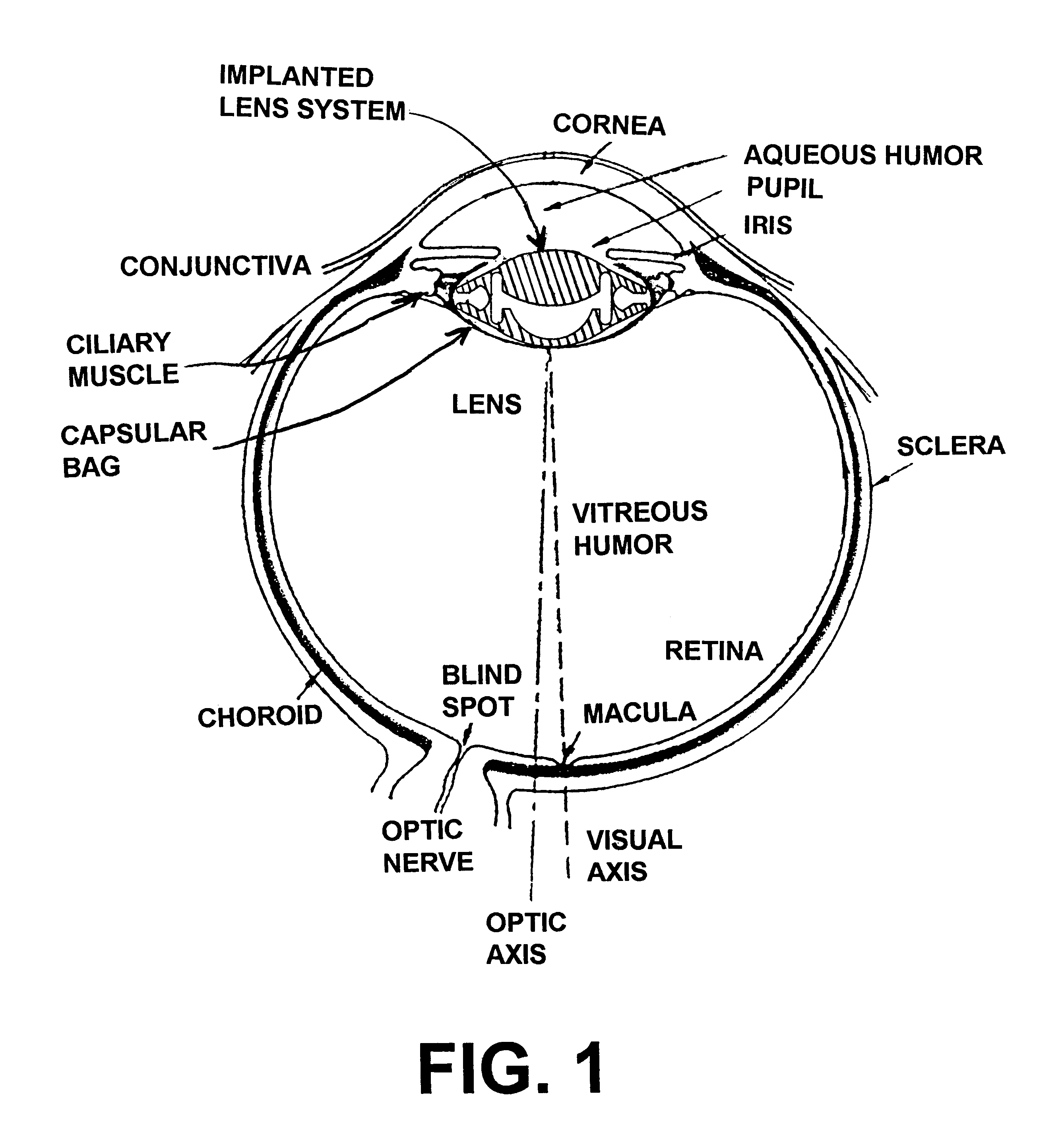
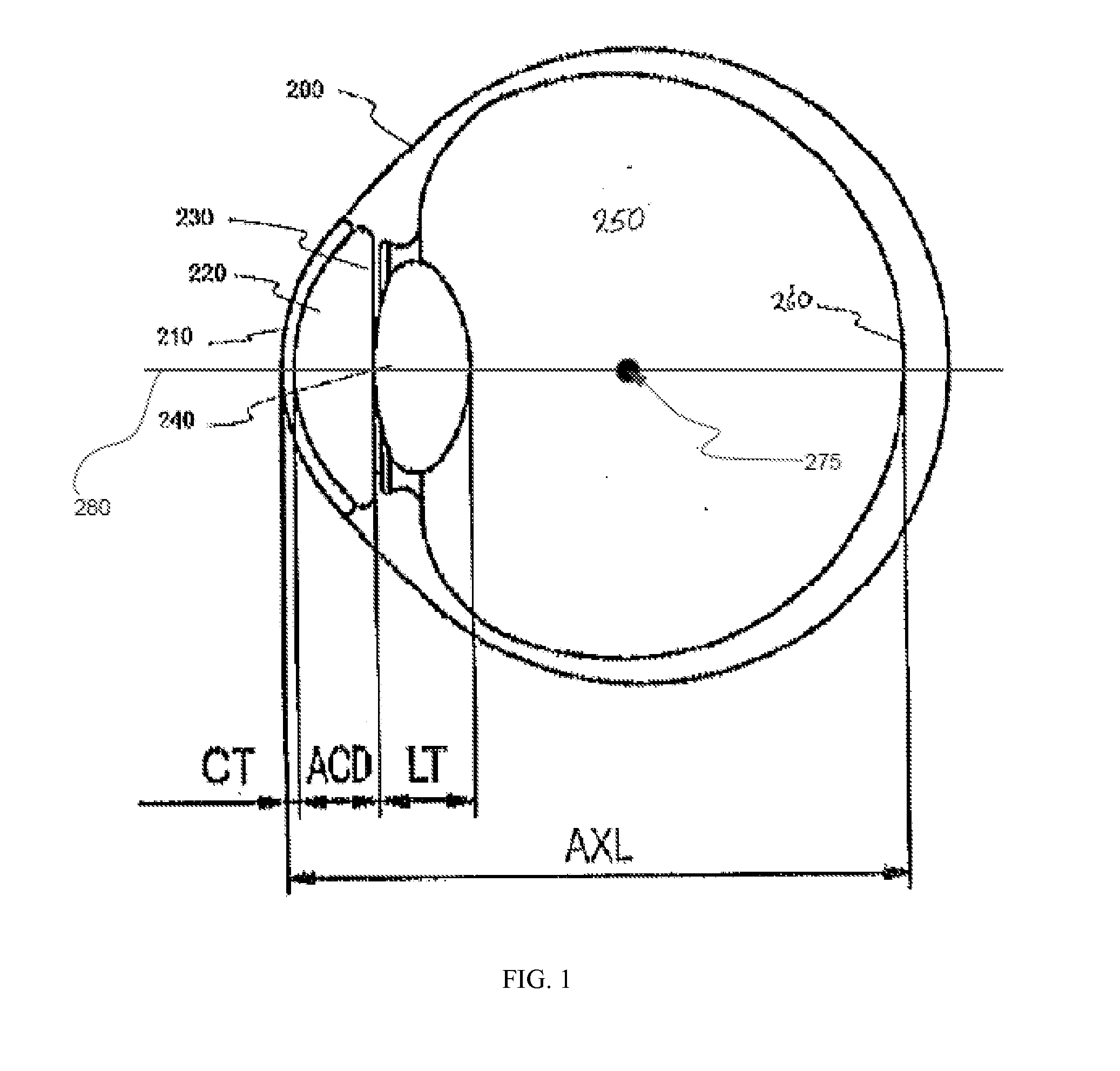
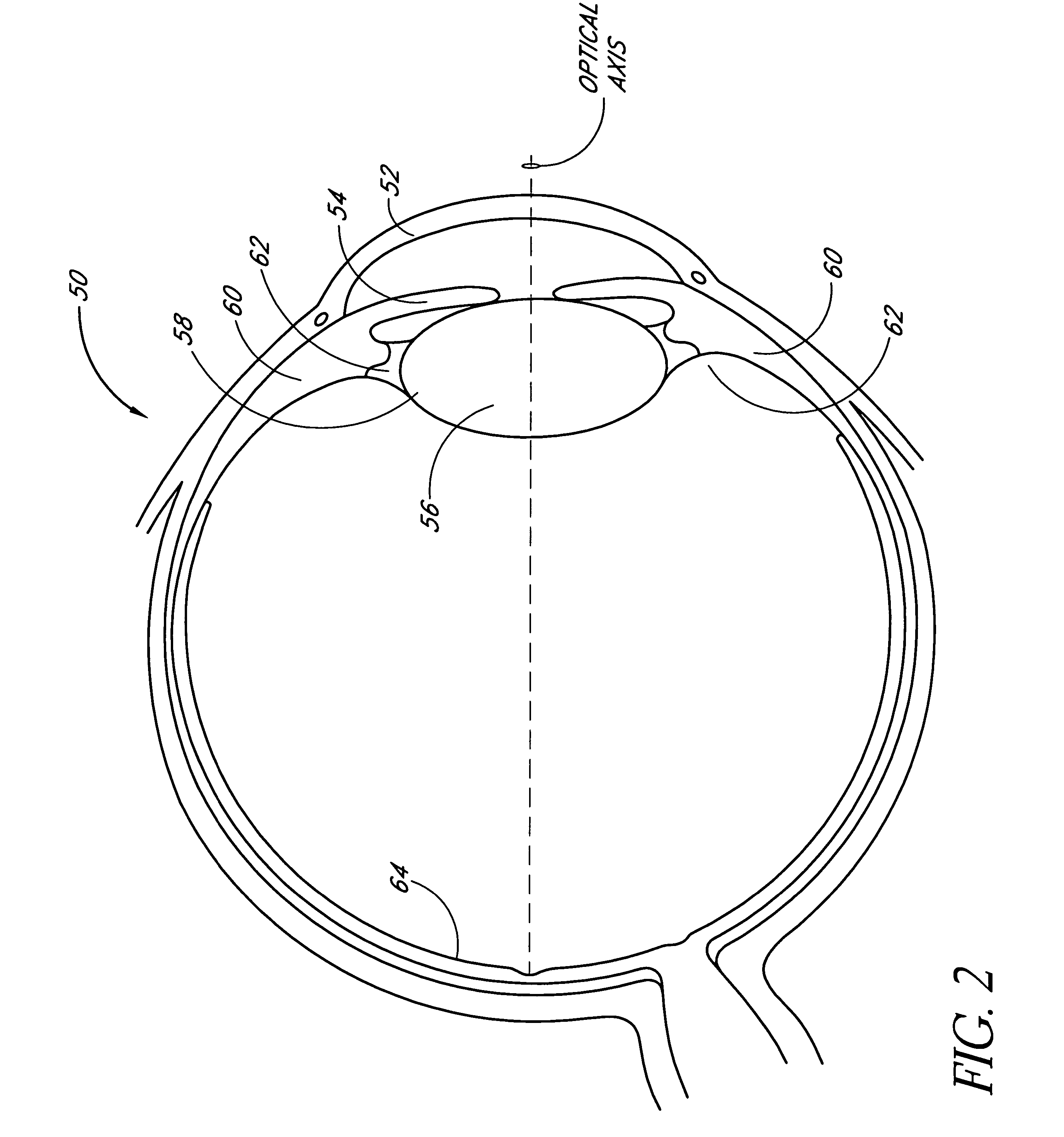
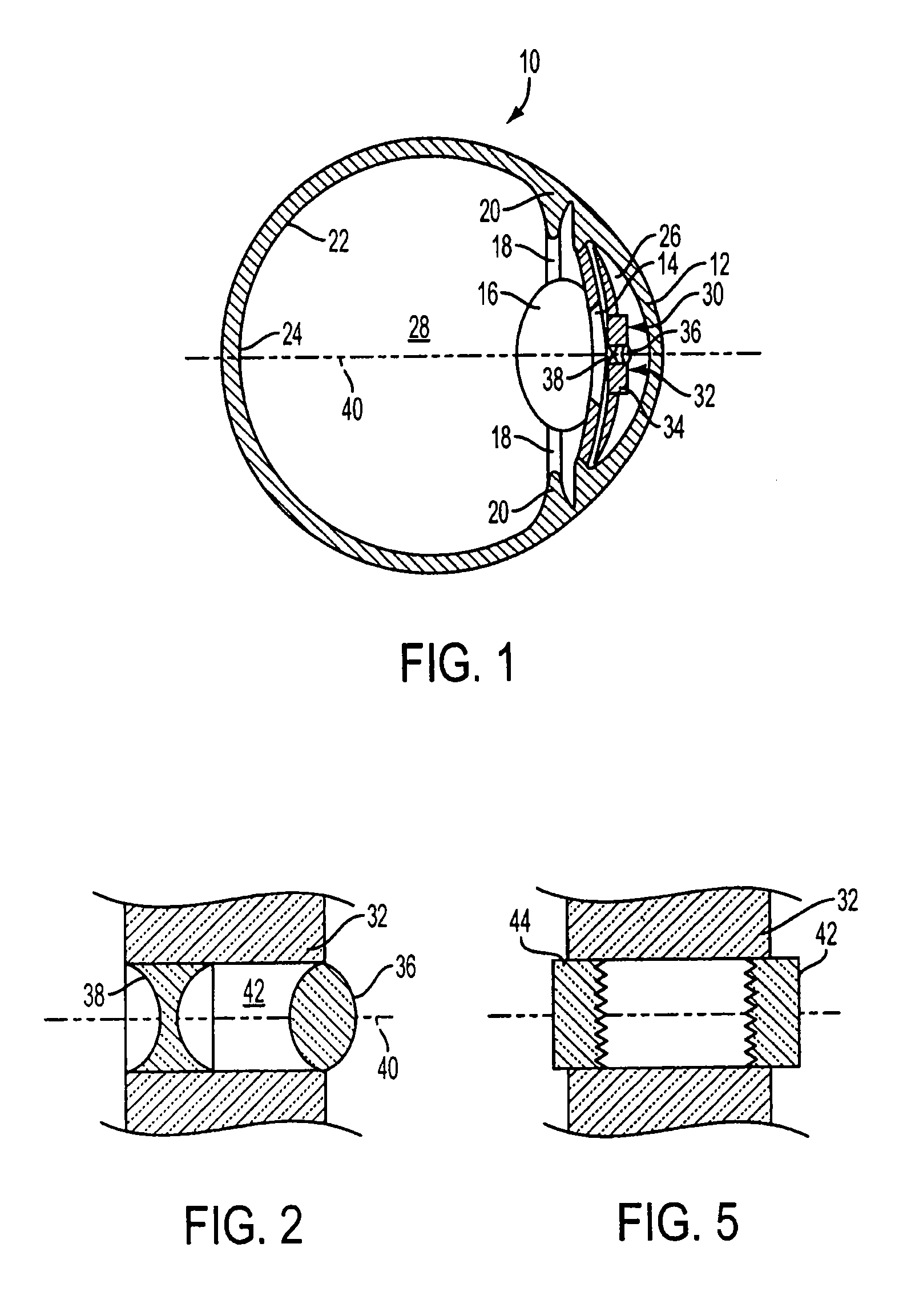
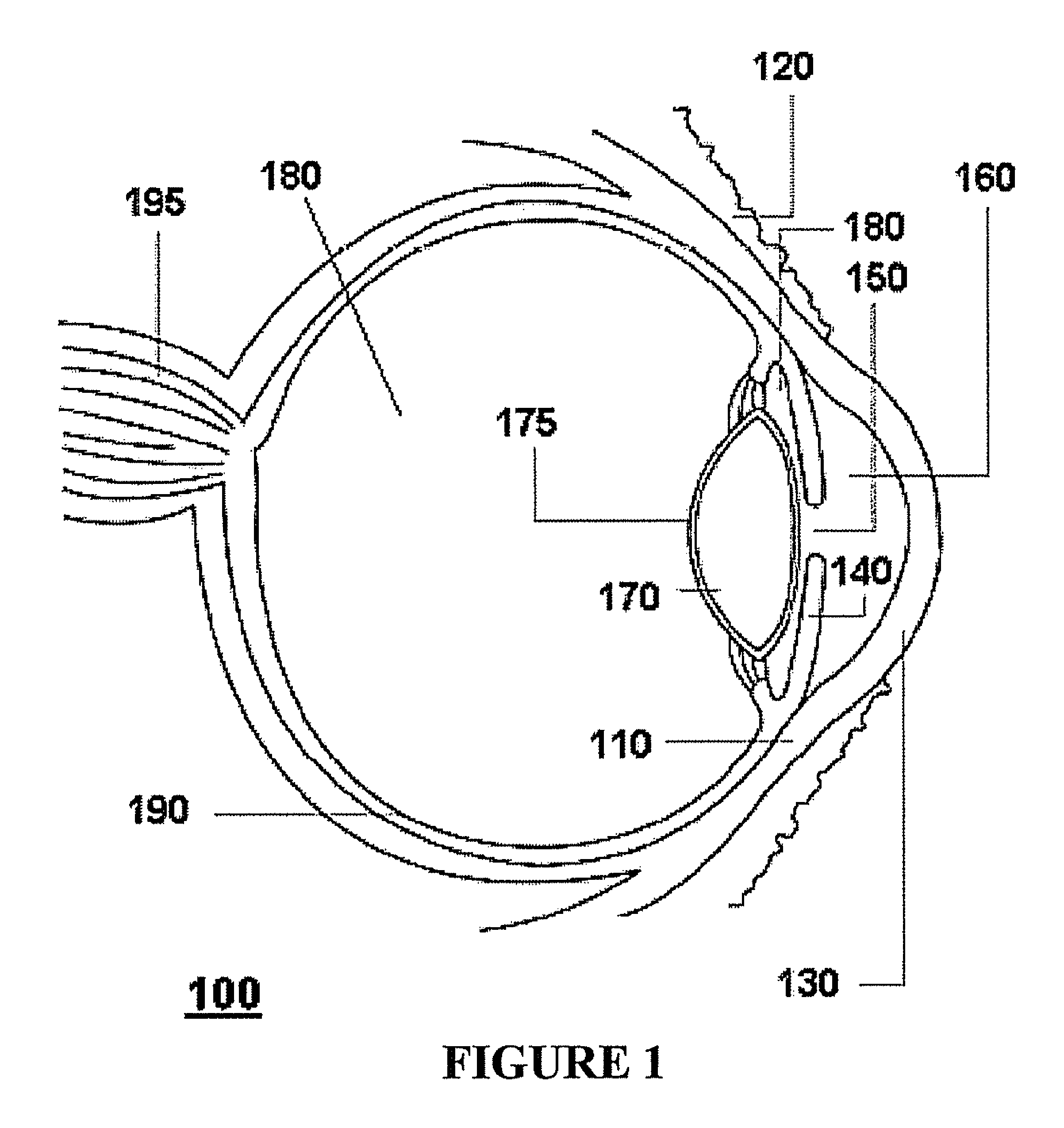
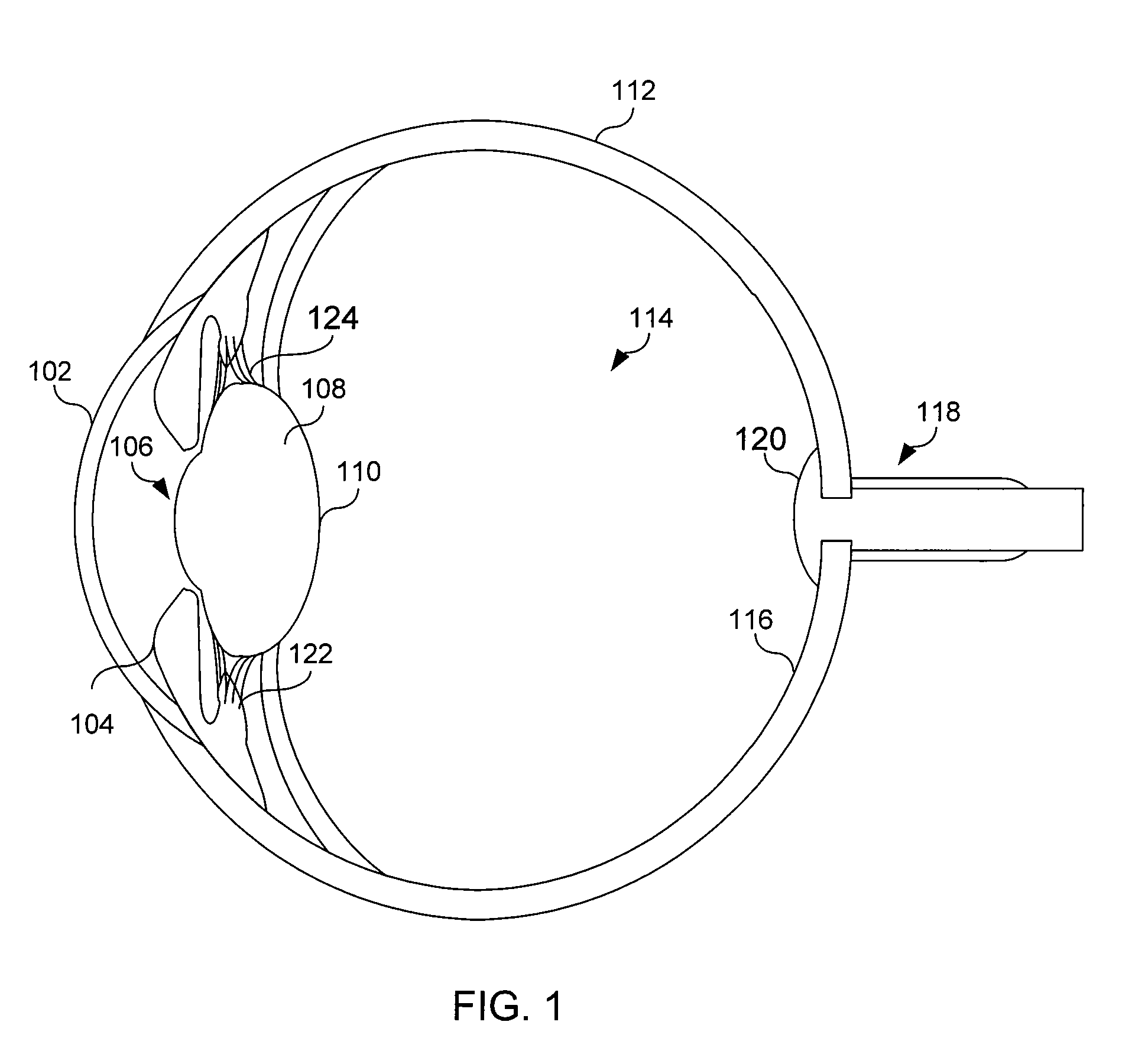
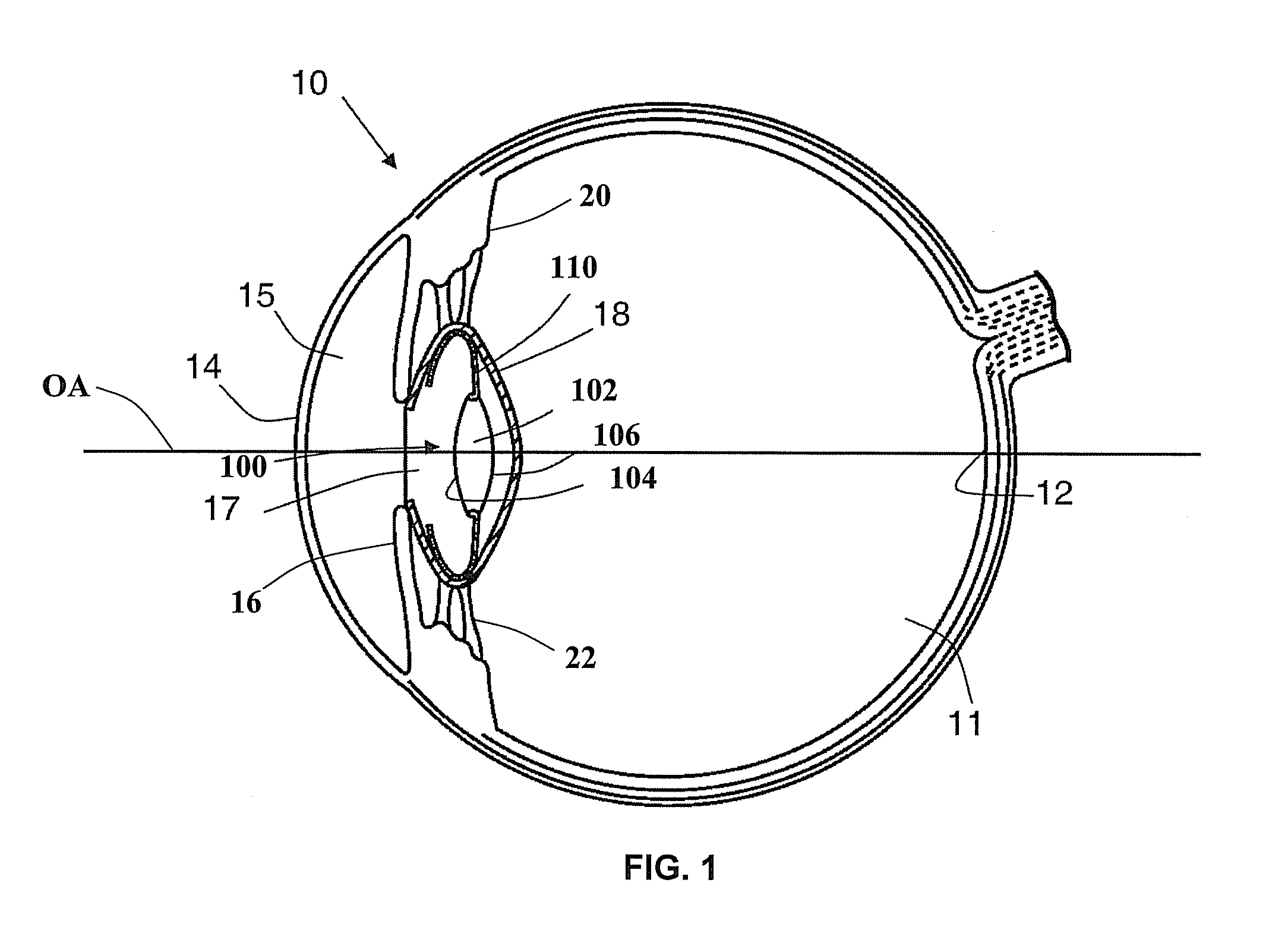
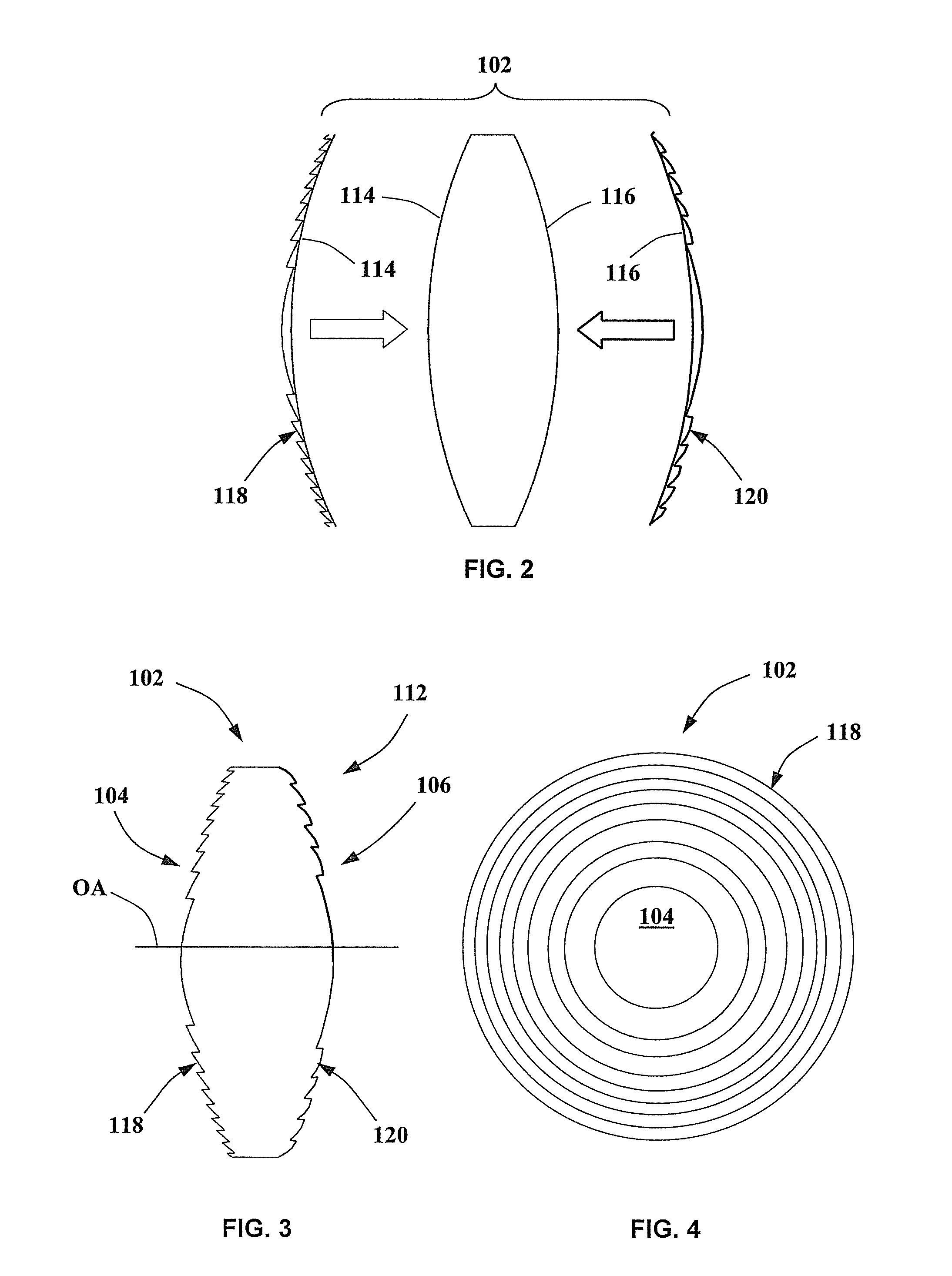
A phakic intraocular lens (PIOL) is a special kind of intraocular lens that is implanted surgically into the eye to correct myopia (nearsightedness). It is called "phakic" (meaning "having a lens") because the eye's natural lens is left untouched. Intraocular lenses that are implanted into eyes after the eye's natural lens has been removed during cataract surgery are known as pseudophakic.
Intraocular lens
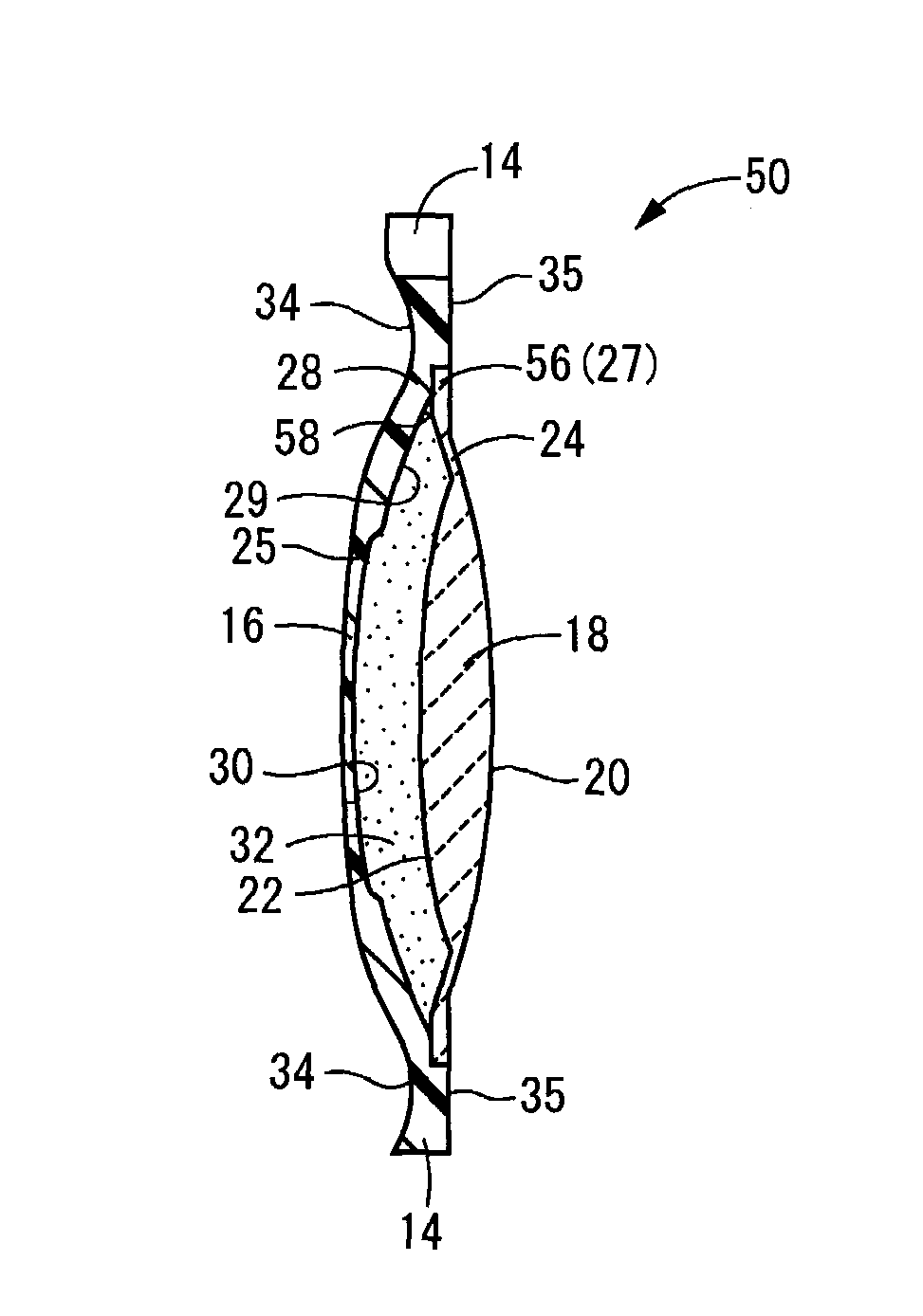
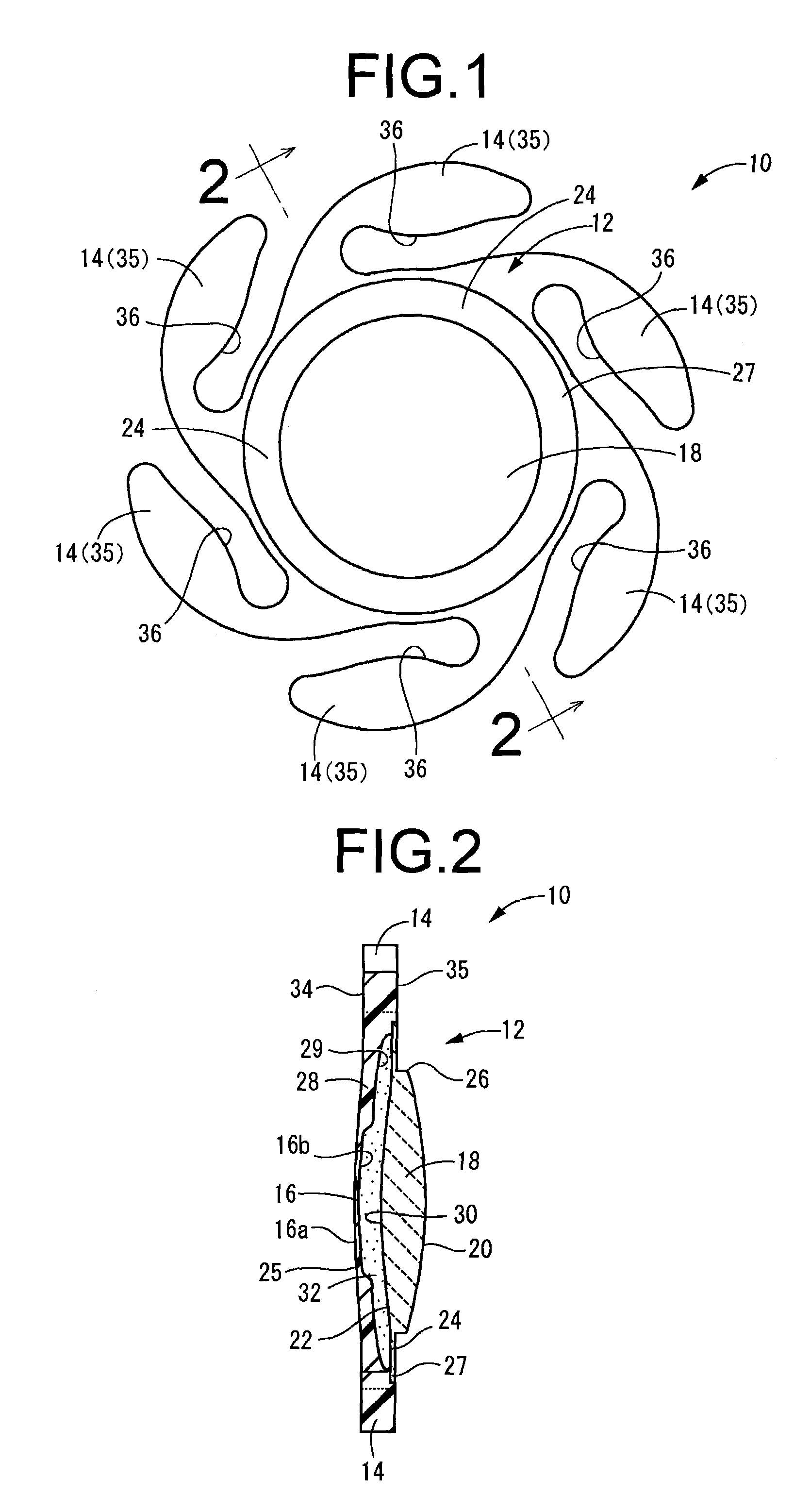
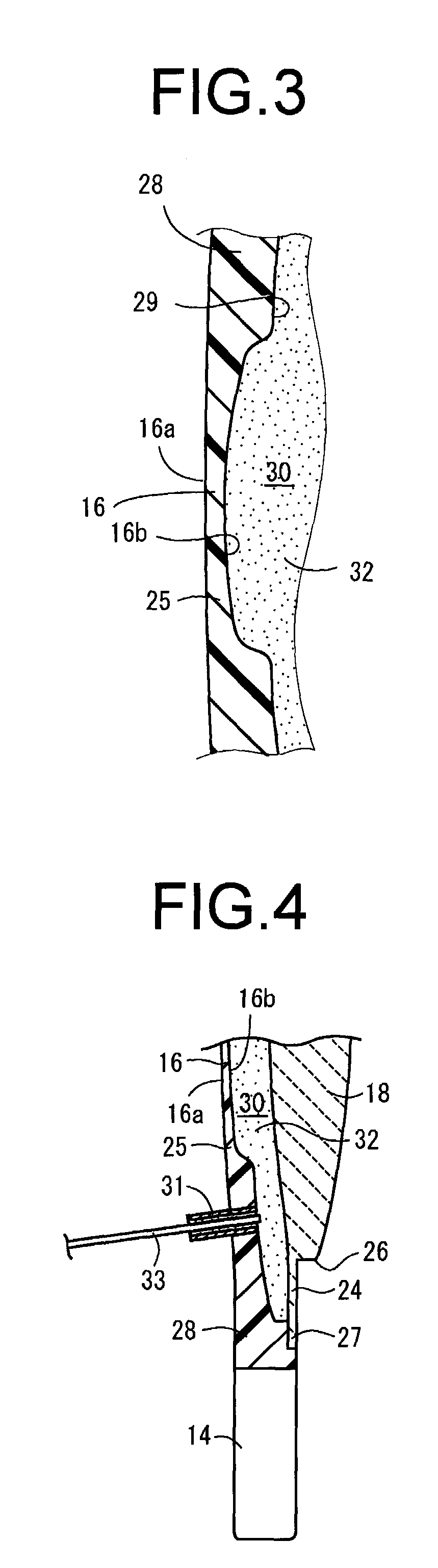
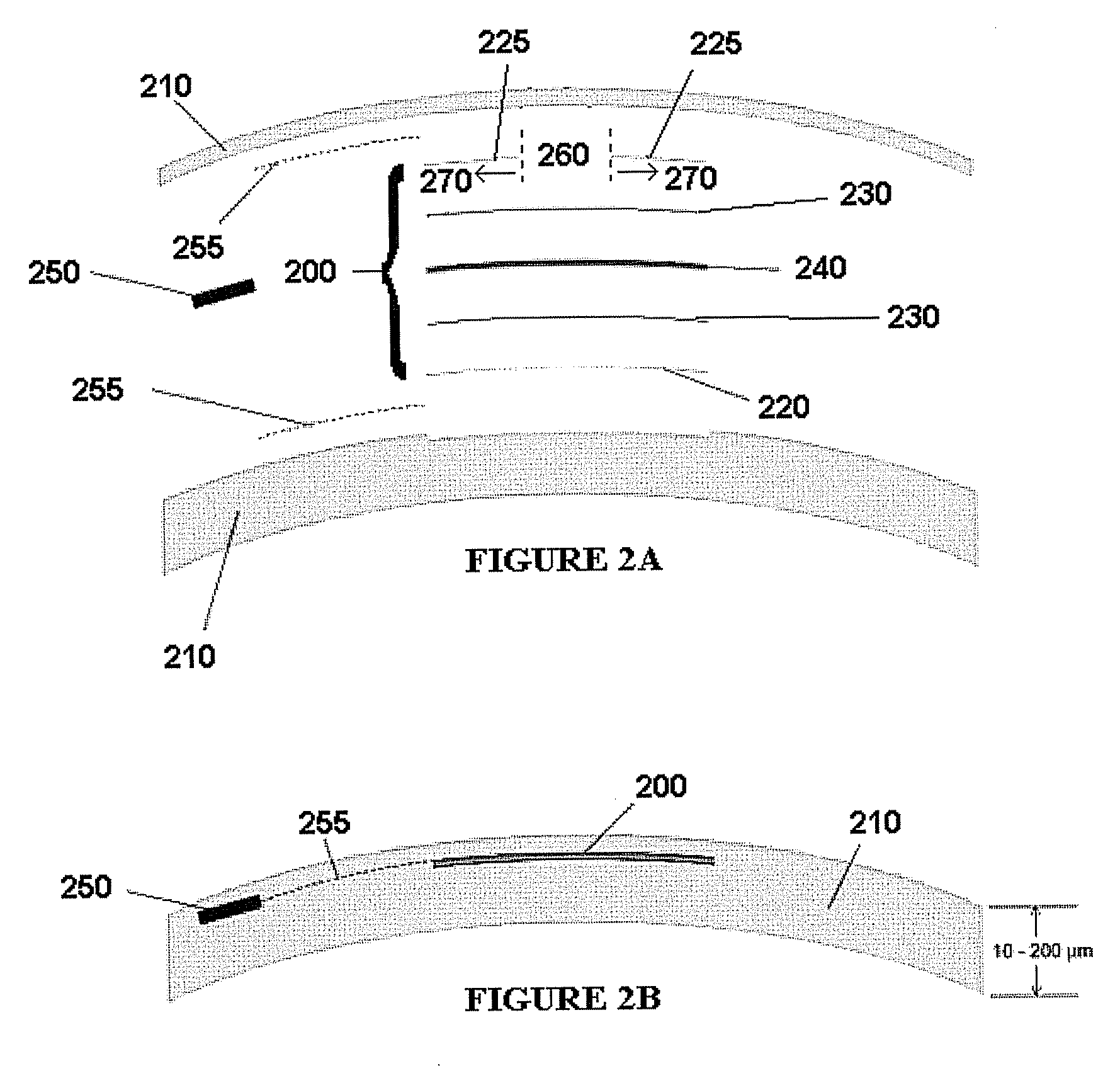
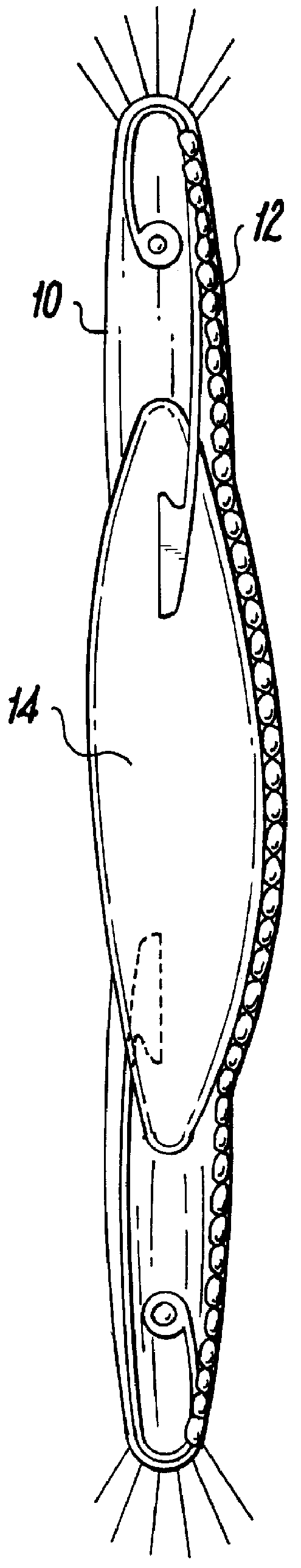
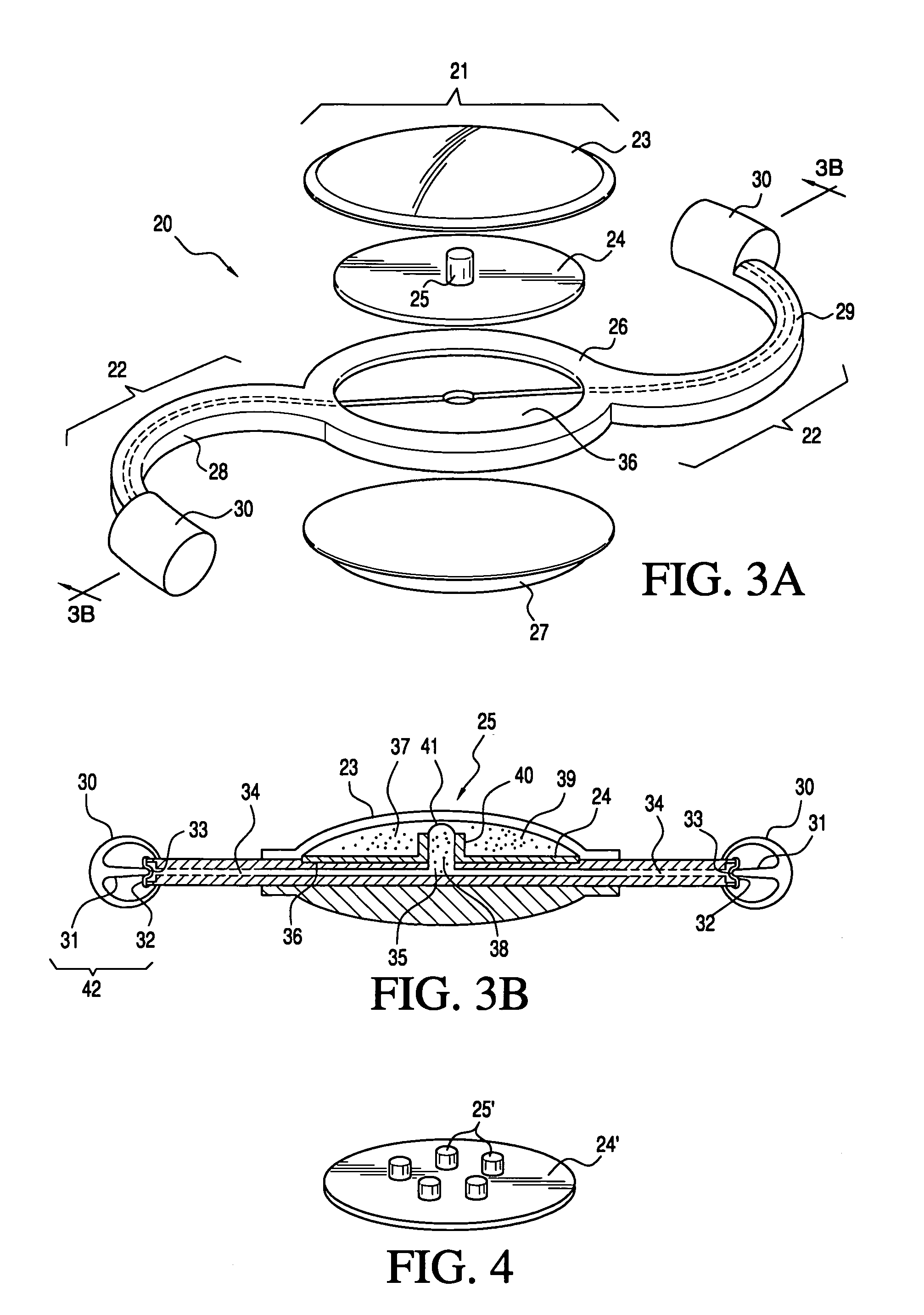
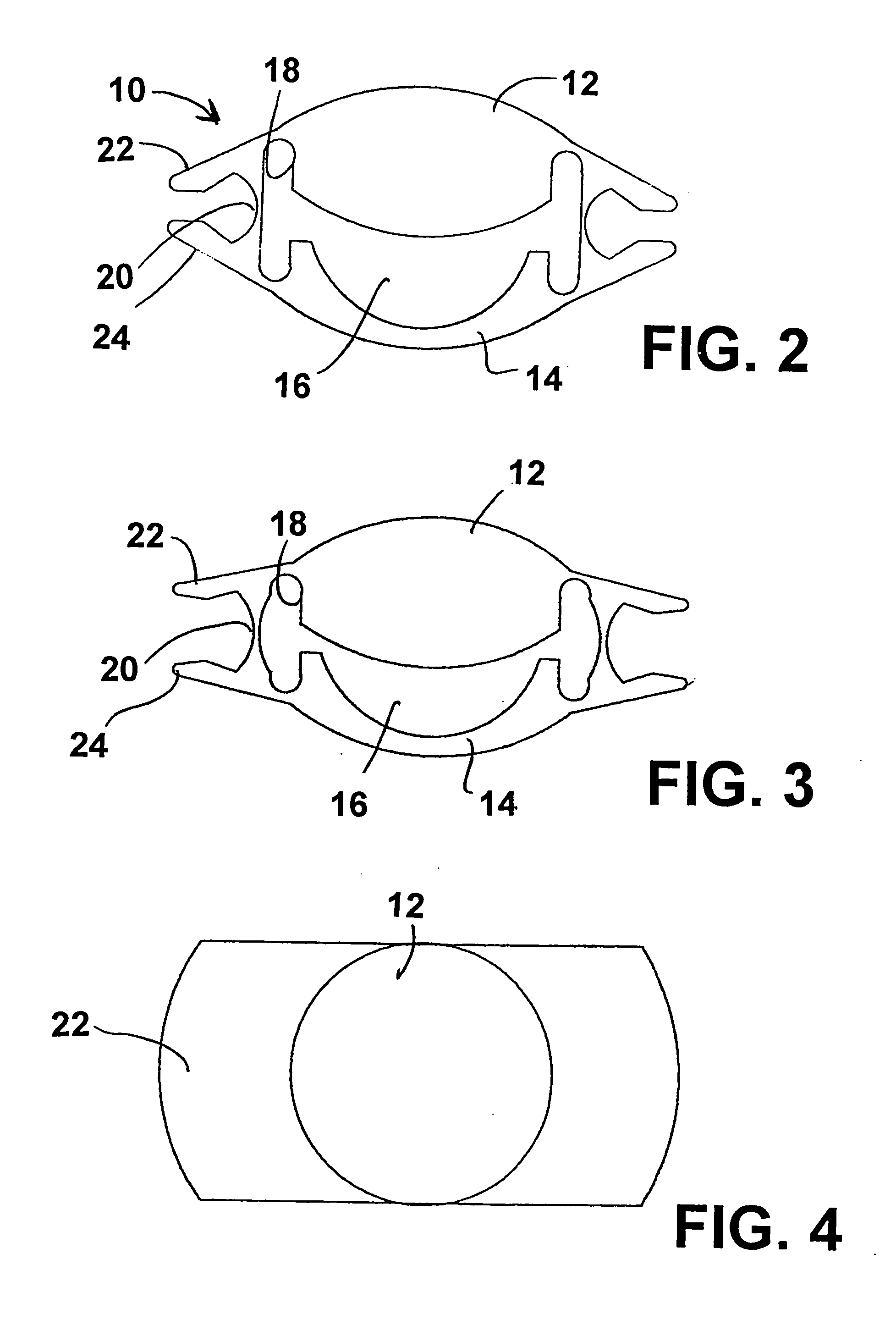
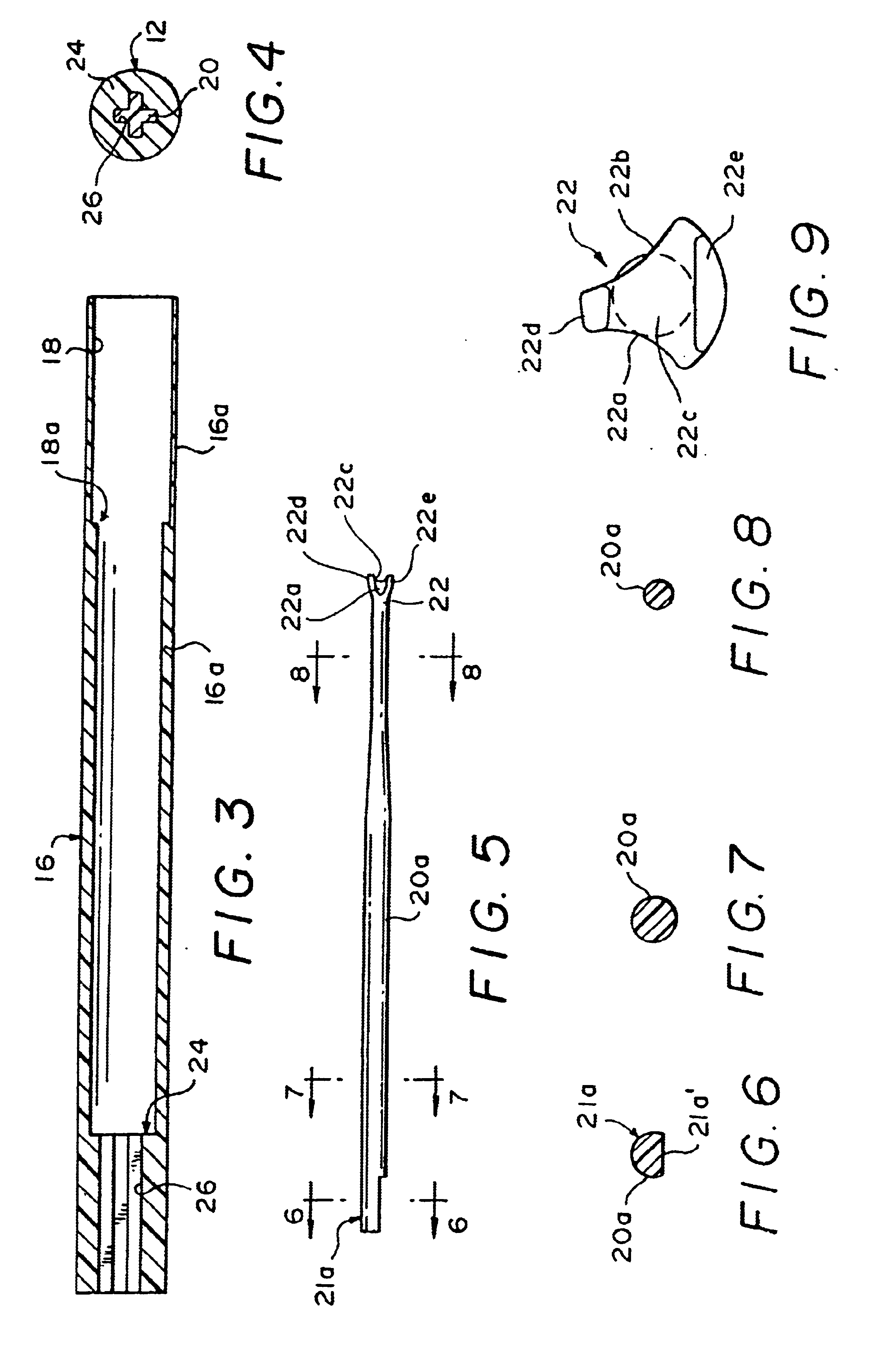
An intraocular lens of novel structure exhibiting an excellent focus adjusting power. A hollow capsule structure is filled with a transparent liquid-like or gel-like filler (32). A front wall of the capsule structure is composed of a flexible lens front film (16), and a rear wall of the capsule structure is composed of an optical lens (18) having a diameter larger than that of the flexible lens front film (16). Under a state inserted into and attached to a capsula lentis, pressure variation of a corpus vitreum acts on the optical lens (18) to enable focal refraction power to be adjusted by utilizing swelling deformation of the lens front film (16).
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Dynamic Changeable Focus Contact And Intraocular Lens
InactiveUS20120140167A1Small sizeIncrease powerEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensIntraocular lensEngineering
In some embodiments, a first device may be provided. The first device may include a first lens that comprises a contact lens or an intraocular lens. The first lens may include an electronic component and a dynamic optic, where the dynamic optic is configured to provide a first optical add power and a second optical add power, where the first and the second optical add powers are different. The dynamic optic may comprise a fluid lens.
Owner:HPO ASSETS
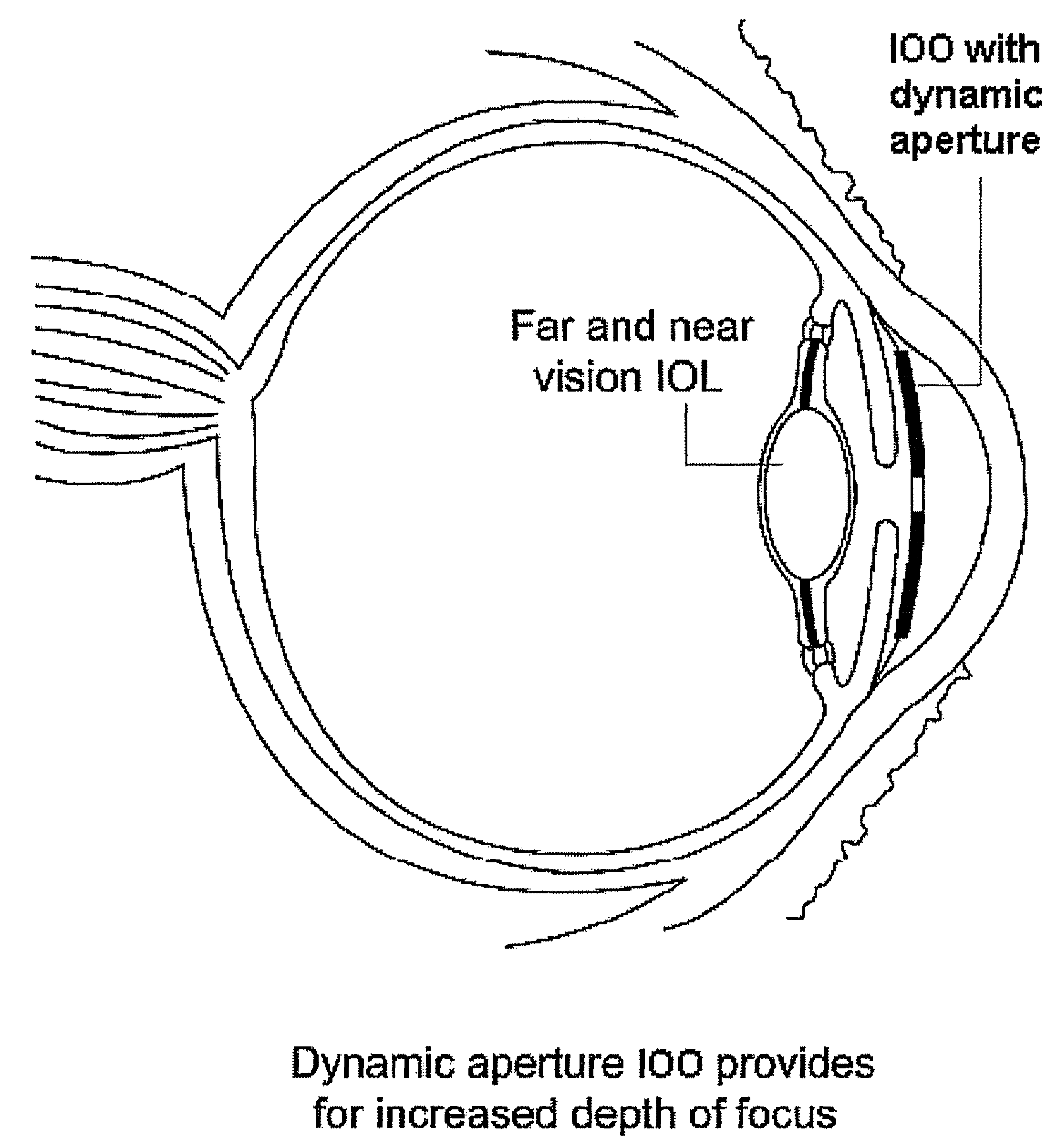
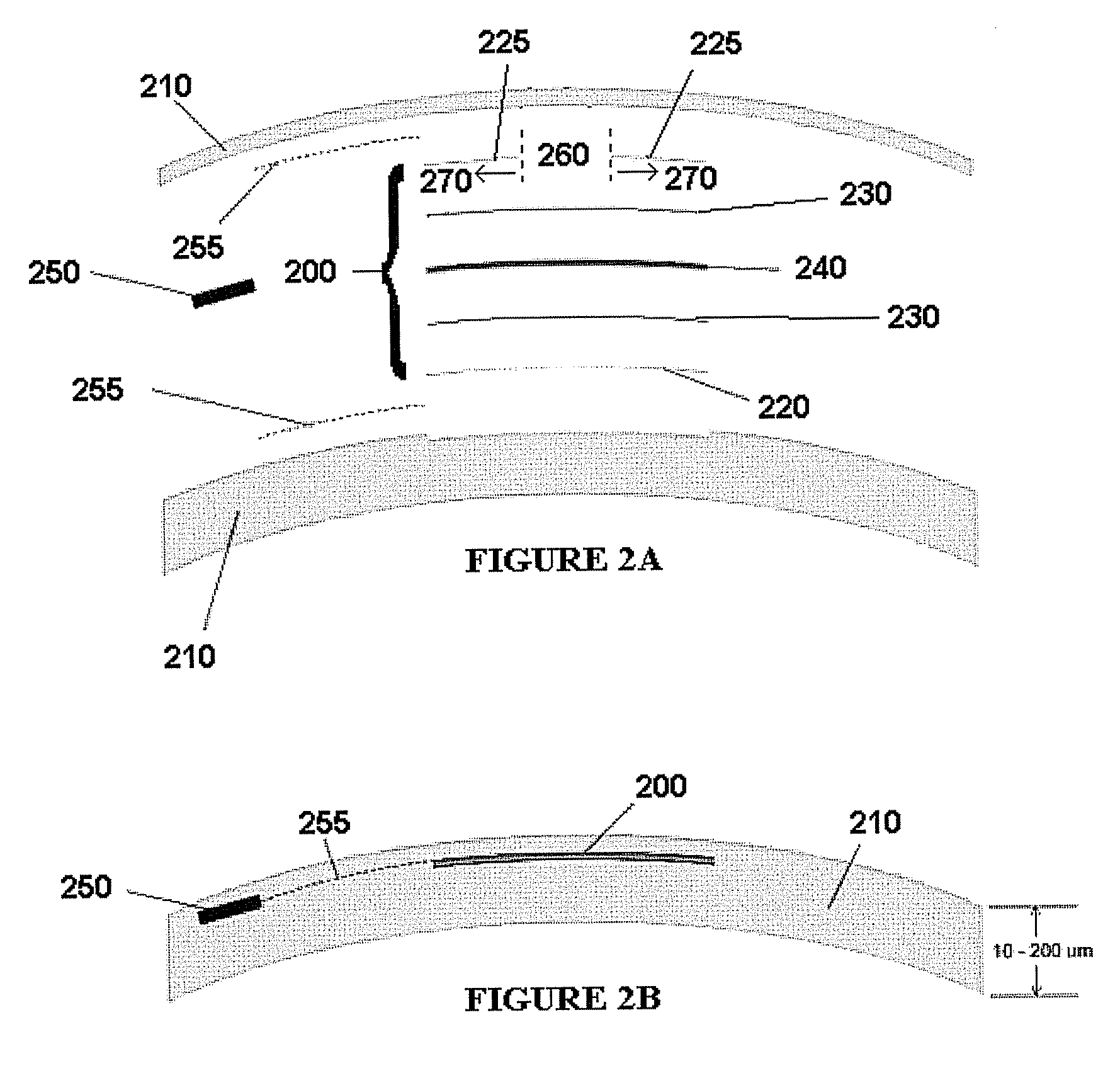
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
ActiveUS20090033863A1Increase heightAdd depthSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCorneal inlayDynamic aperture
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
Intraocular lens with accommodative properties
InactiveUS6200342B1Focus assistPrevent excessive lateral movement and luxationIntraocular lensPupil diameterIntraocular lens
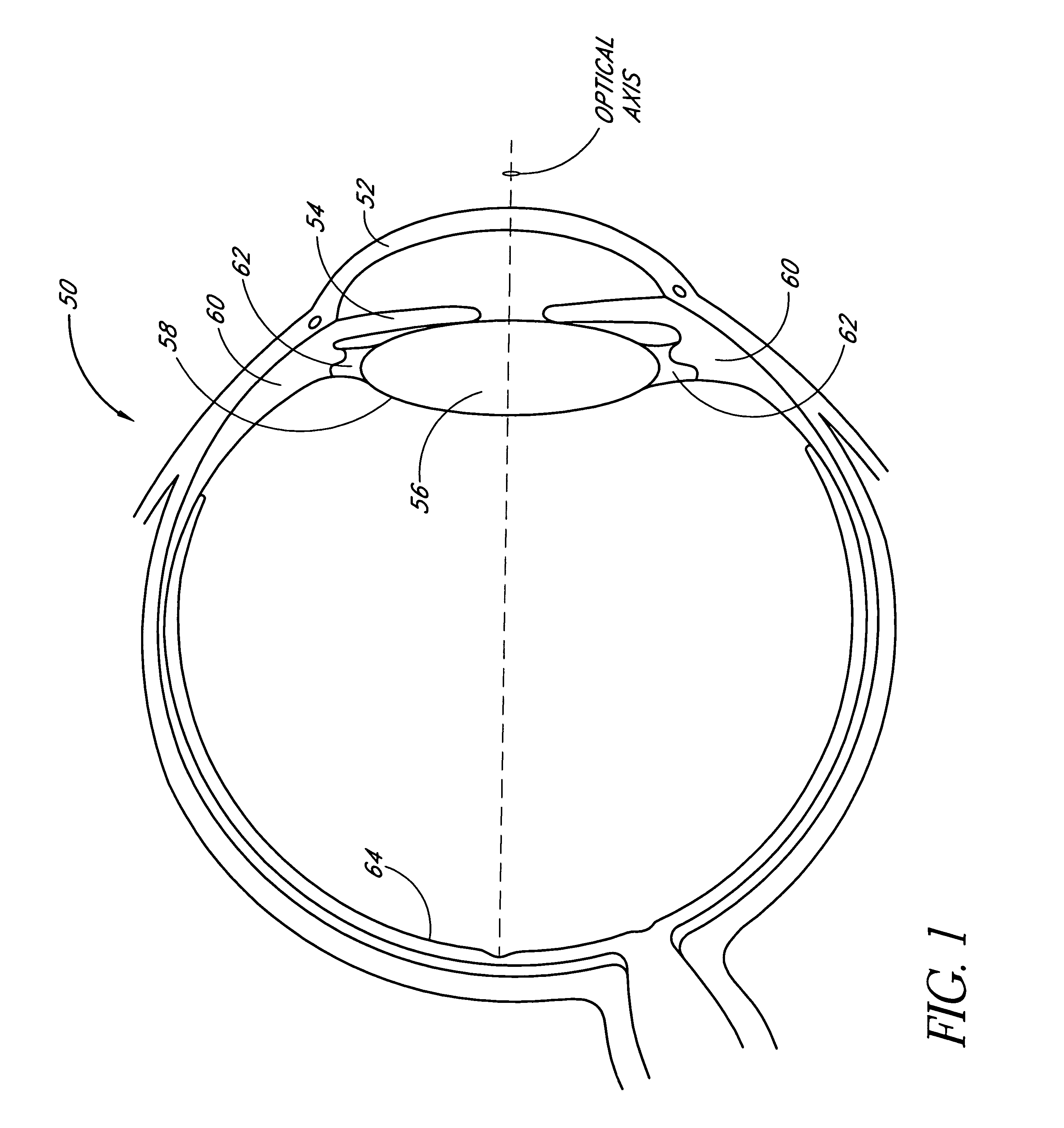
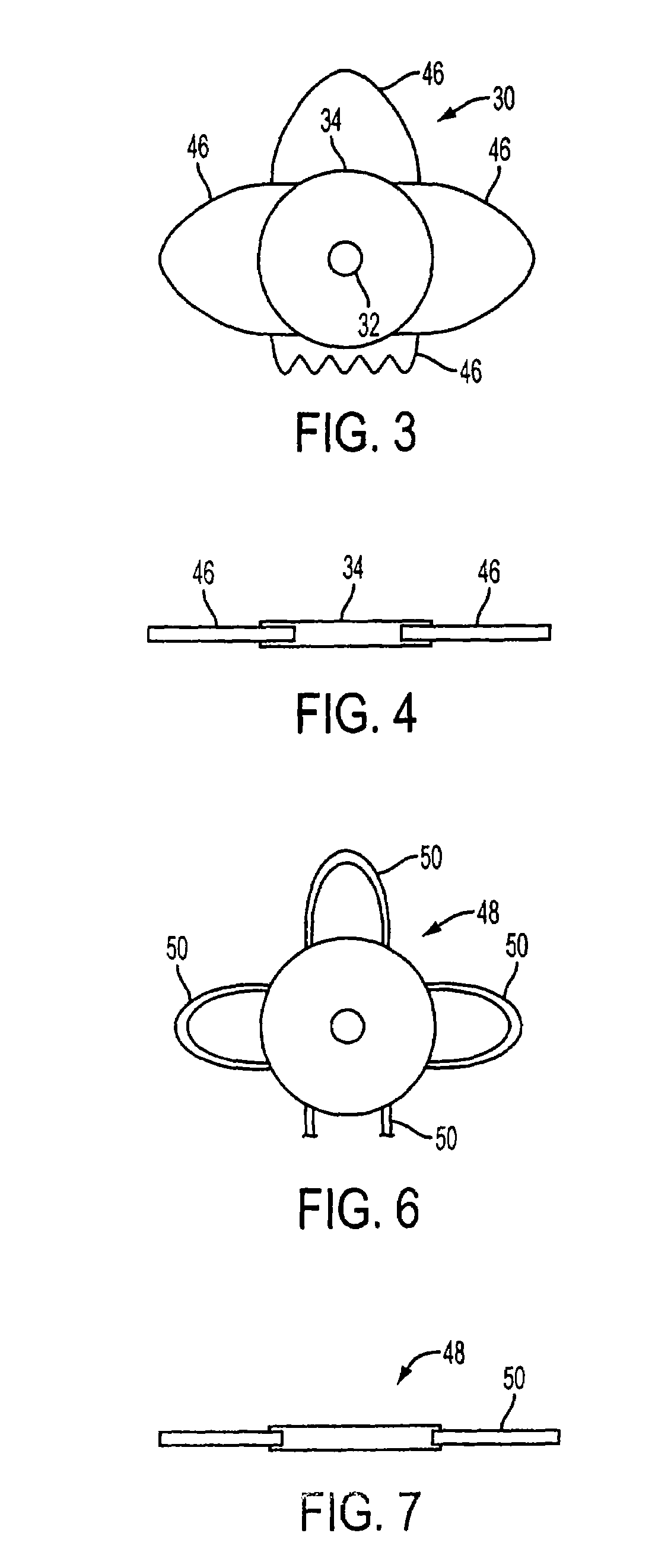
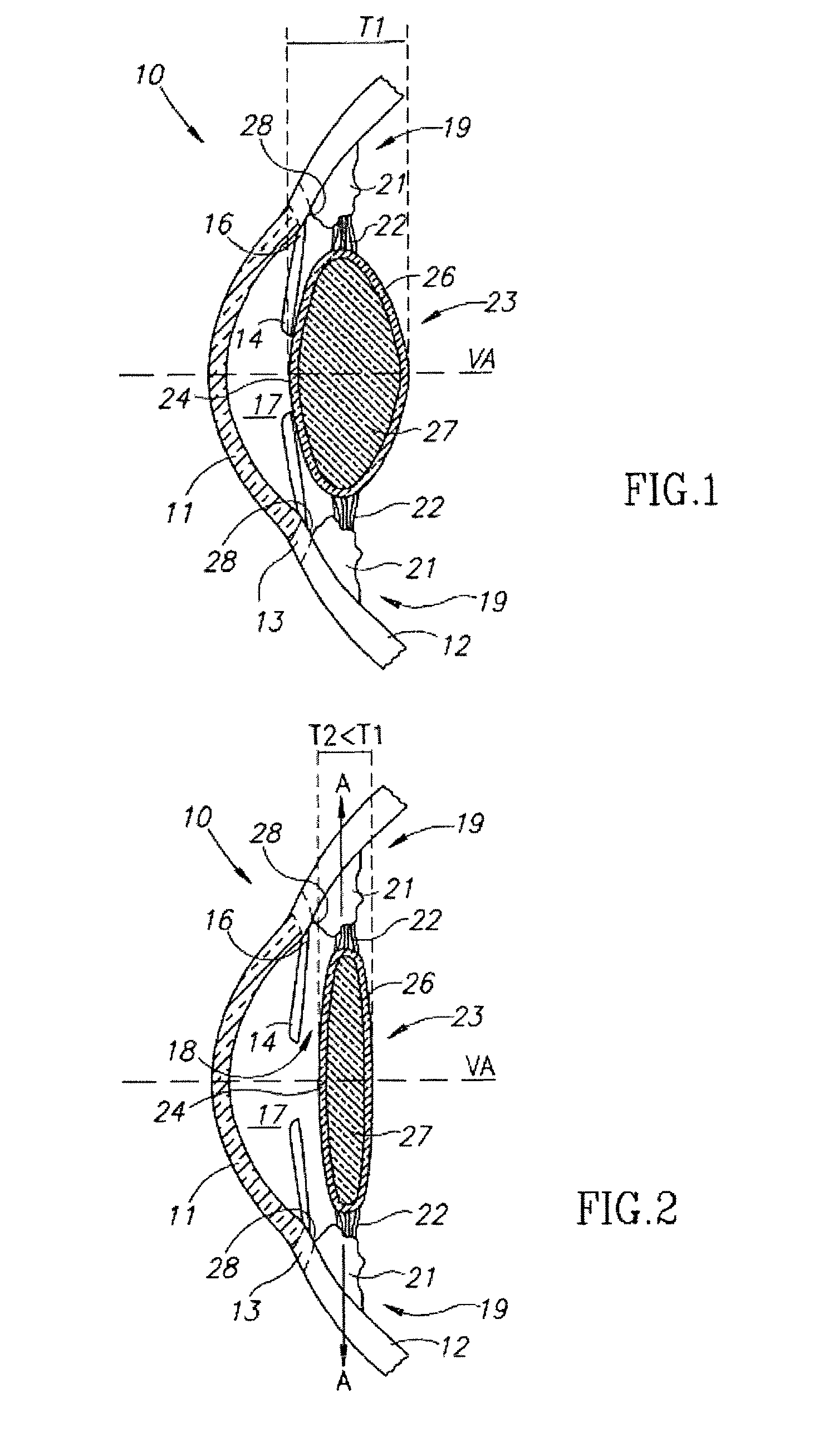
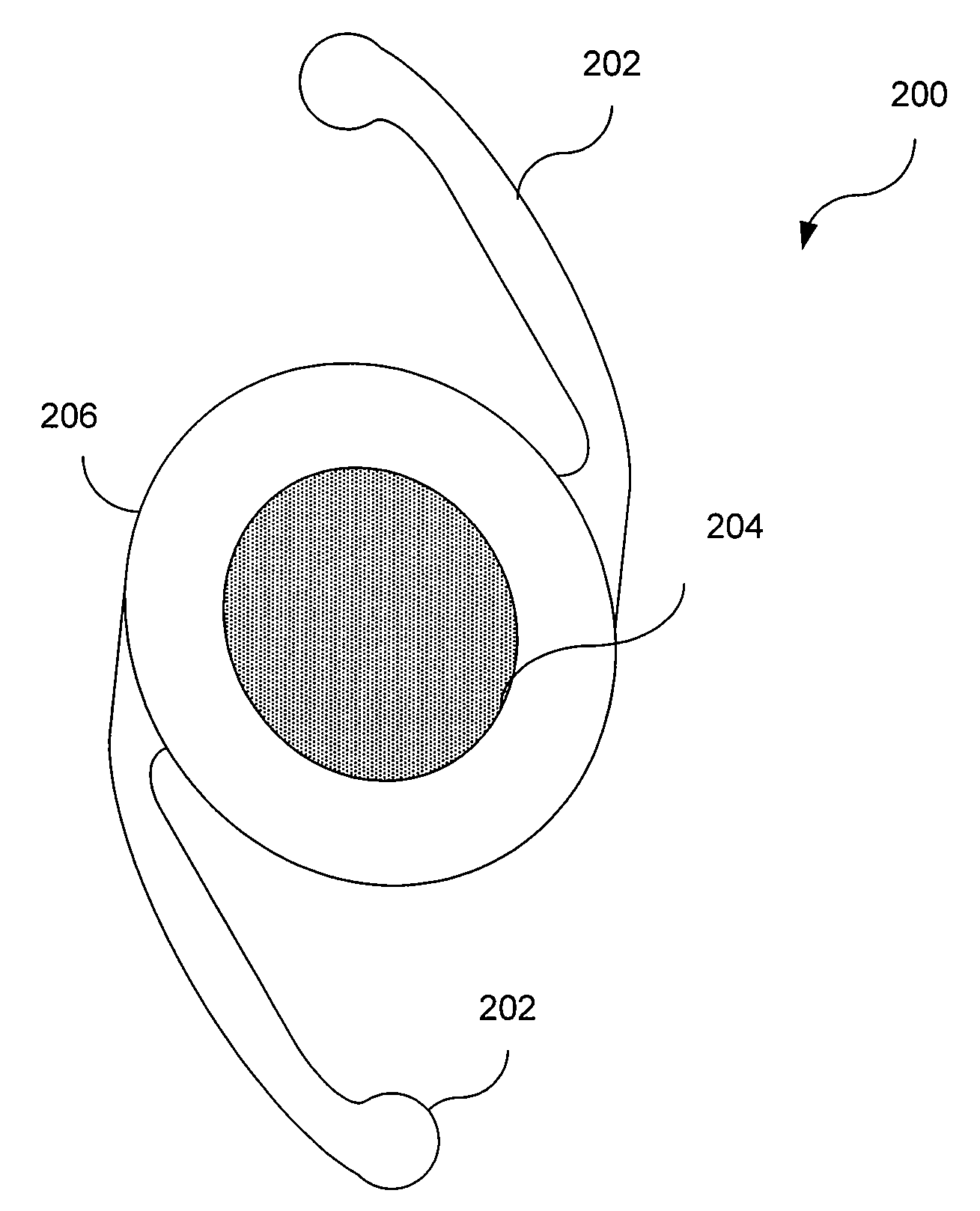
A new lens design and method of implantation uses the change in pupil diameter of the eye concurrent with the changes induced by a contraction of the ciliary muscle during the accommodative reflex, in order to assist in focusing of nearby objects. This new intraocular lens consists of two parts. The posterior part or haptic part is inserted behind the iris and in front of the natural lens or artificial implant. Its main purpose is to participate in the accommodative mechanism and to prevent excessive lateral movement and luxation of the lens. An anterior or optical part is made of flexible material and is placed before the iris. Its diameter is variable but should be large enough to cover the pupillary margins to some degree under various conditions of natural dilation. The anterior and posterior part of the lens are separated by a compressible circular groove in which the iris will settle. The diameter of this groove is slightly larger than the pupillary diameter measured under normal photopic daylight conditions and for distance vision. Since the pupil becomes smaller in near vision, the iris will exert a slight pressure at the level of the groove of the lens which will cause a progressive and evenly distributed flexing of the anterior part of the intraocular lens, as the diameter of the compressible circular groove slightly decreases. This flexing will induce an increase in refractive power which corresponds to a variable part of the amount necessary for focusing nearby objects.
Owner:TASSIGNON MARIE JOSE B
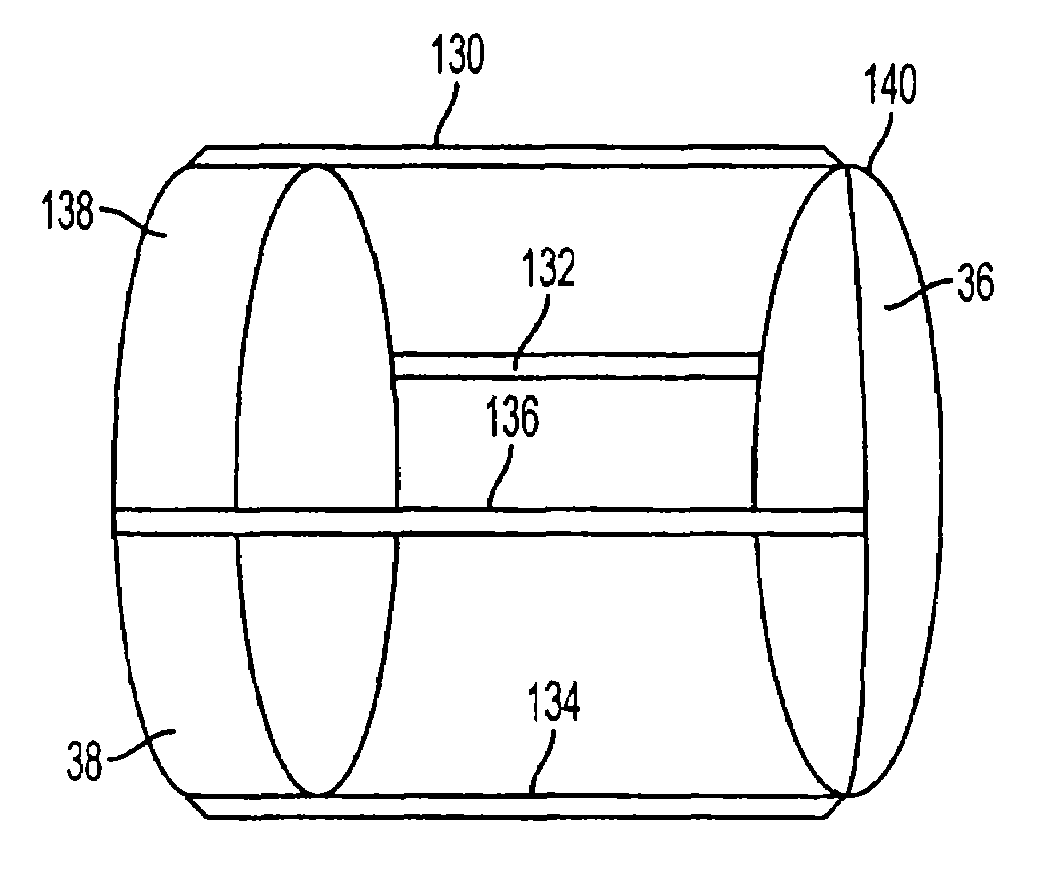
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7122053B2Great motionEfficiently manipulatedIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensRelative Volume
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided that having optical parameters that are altered in-situ using forces applied by the ciliary muscles, in which a lens body carries an actuator separating two fluid-filled chambers having either the same index of diffraction or different indices of refraction, actuation of the actuator changing the relative volumes of fluid within an optic element of the lens and altering the optical power of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
Intraocular lens and method for preventing secondary opacification
InactiveUS6027531APrevent proliferationImprove stabilityDiagnosticsSurgeryCataract extractionPosterior capsulorhexis
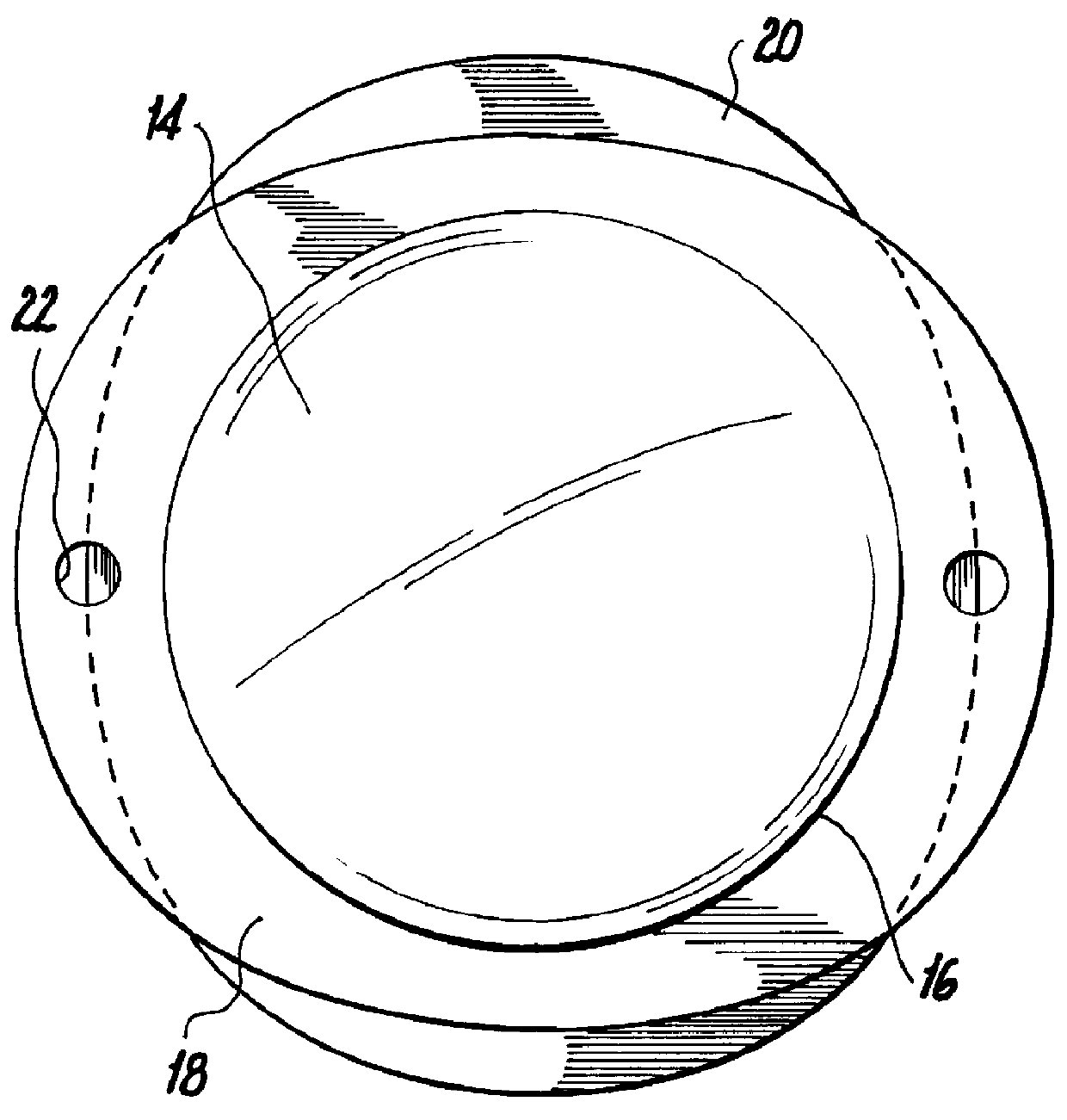
An intraocular lens for use in extracapsular cataract extraction has a haptic pat that surrounds the optical pat of the lens and further contains a groove of such shape to accommodate the anterior and posterior capsules of the lens bag after anterior capsulorhexis, extracapsular cataract extraction and posterior capsulorhexis. The lens is preferably inserted in a calibrated, circular and continuous combined anterior and posterior capsulorhexis, slightly smaller than the inner circumference of the groove as to induce a stretching of the rims of the capsular openings. This new approach is believed to prevent the appearance of secondary opacification of the capsules, allows a very stable fixation of the intraocular lens and ensures a tight separation between the anterior and posterior segment of the eye. This new principle of insertion is called the bag-in-the-lens technique, in contrast with the classical lens in-the-bag technique.
Owner:TASSIGNON MARIE JOSE B R
Accommodating intraocular lens system and method
ActiveUS7261737B2Efficiently manipulatedAltering the optical parametersIntraocular lensOptical partsIntraocular lensOptical power
An accommodating intraocular lens is provided having optical parameters that are altered in-situ, wherein an optic portion of the lens includes a lens piston that alters the shape of a lens element of the lens to alter the optical power of the lens, responsive to forces applied to a haptic portion to the lens by contraction of the ciliary muscles. Forces applied to the haptic portion are concentrated by the lens piston to provide a greater dynamic range, and may be further augmented by the use of haptic pistons disposed in the haptic portion of the lens.
Owner:ALCON INC
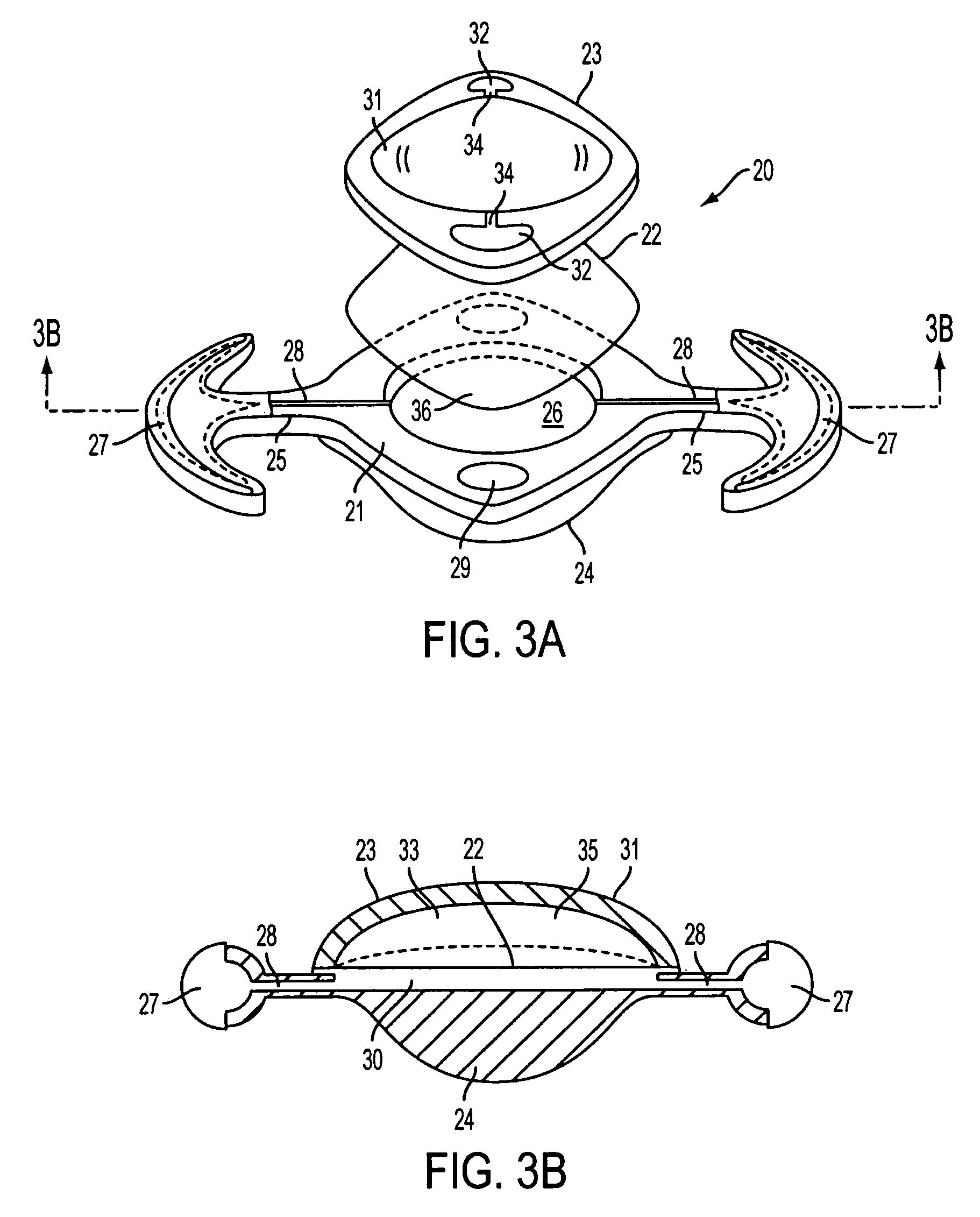
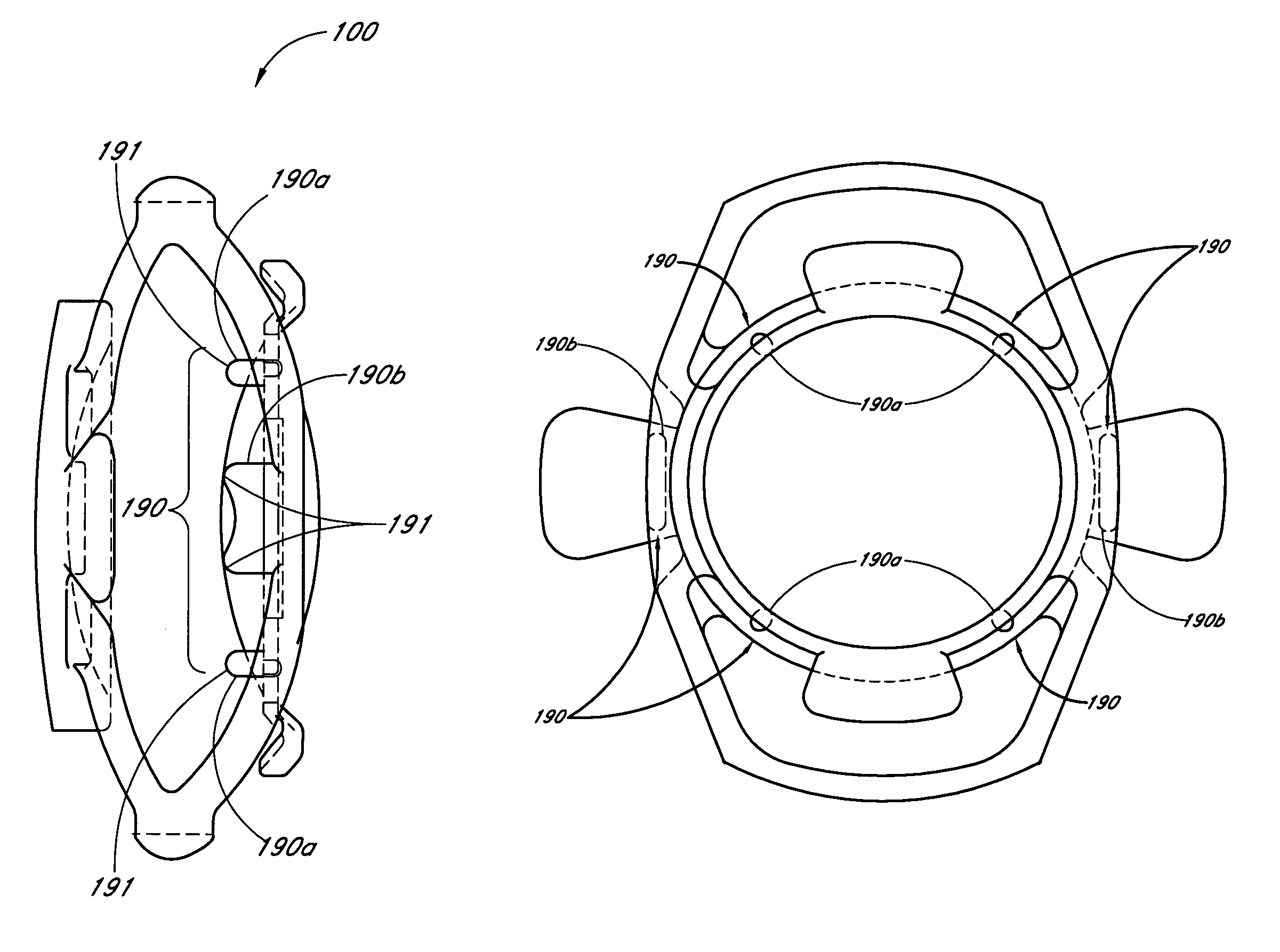
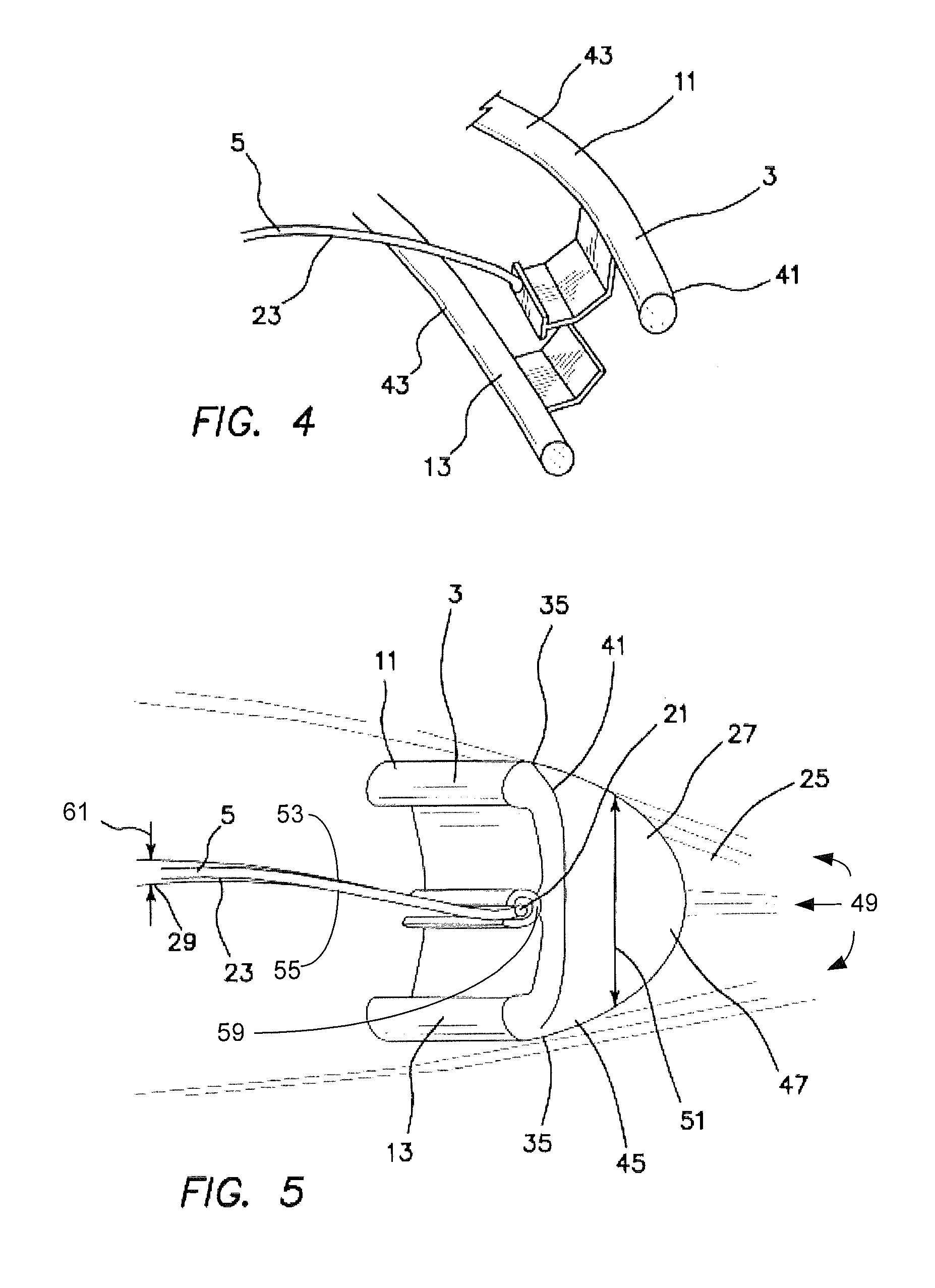
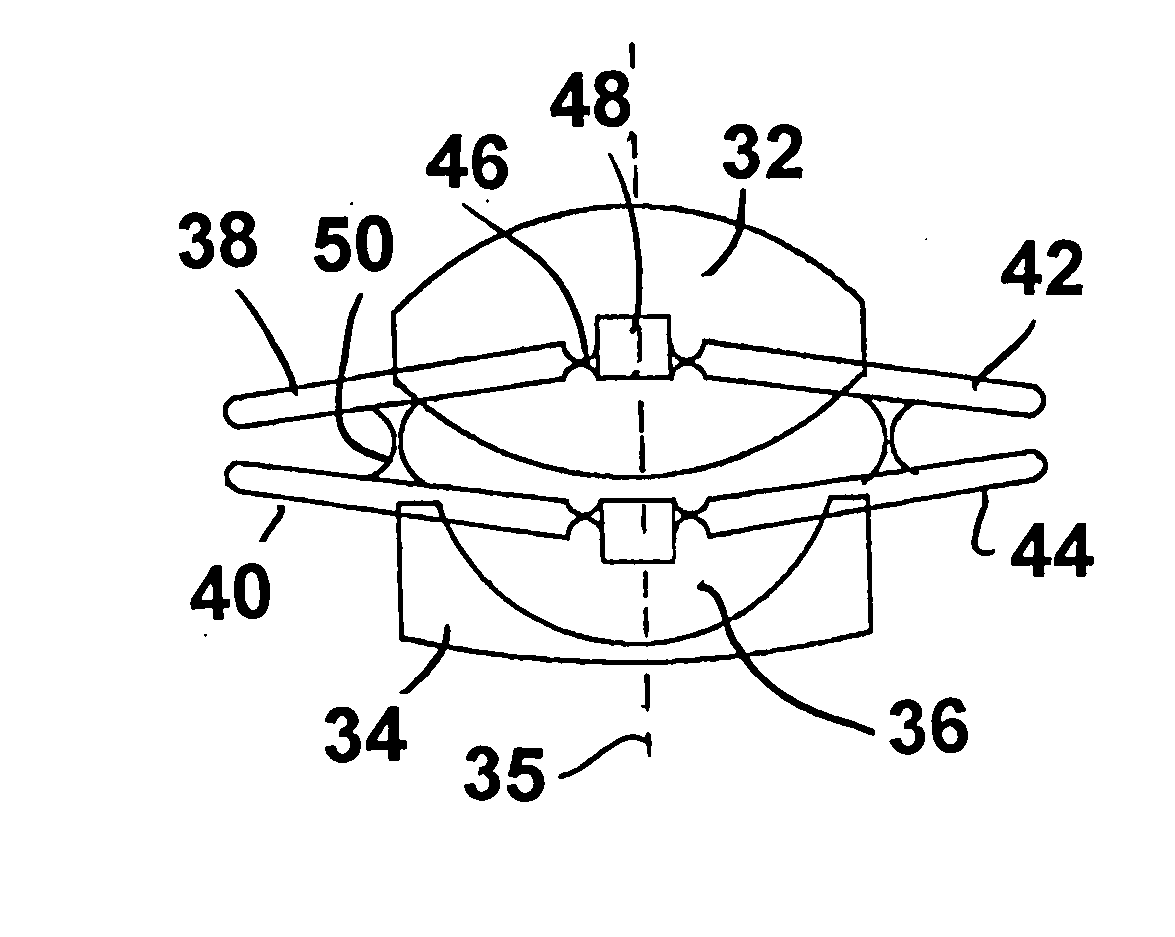
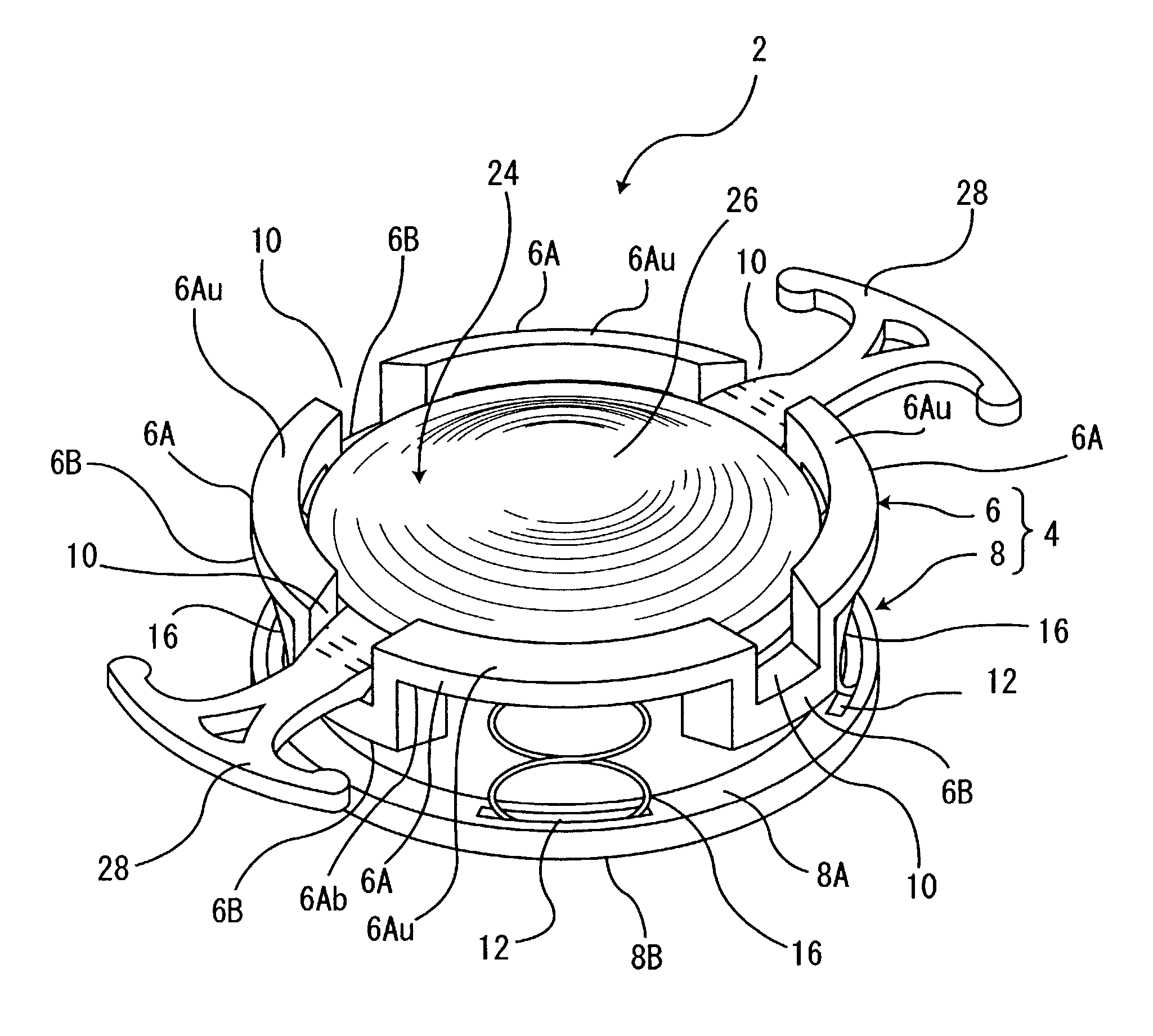
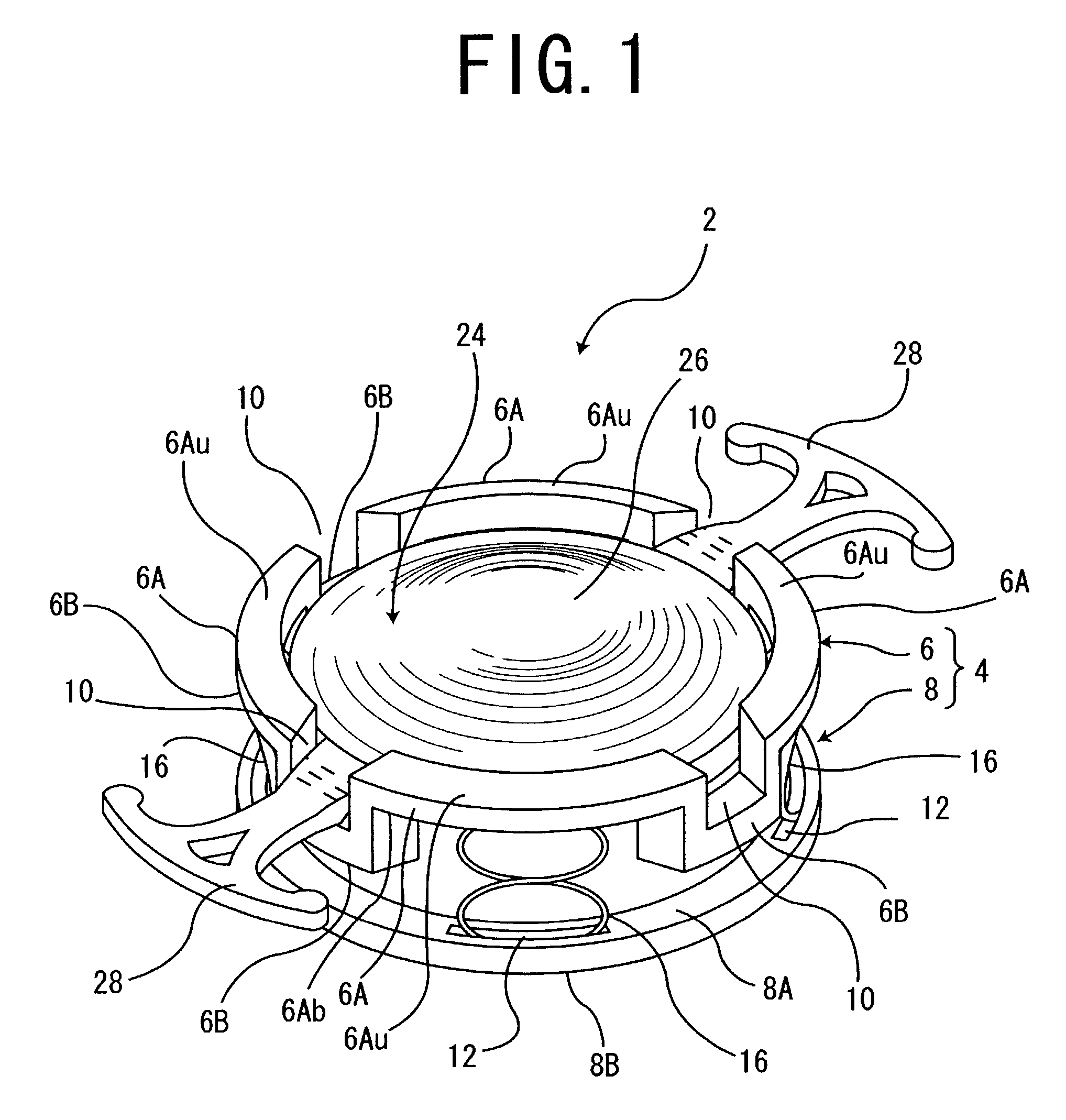
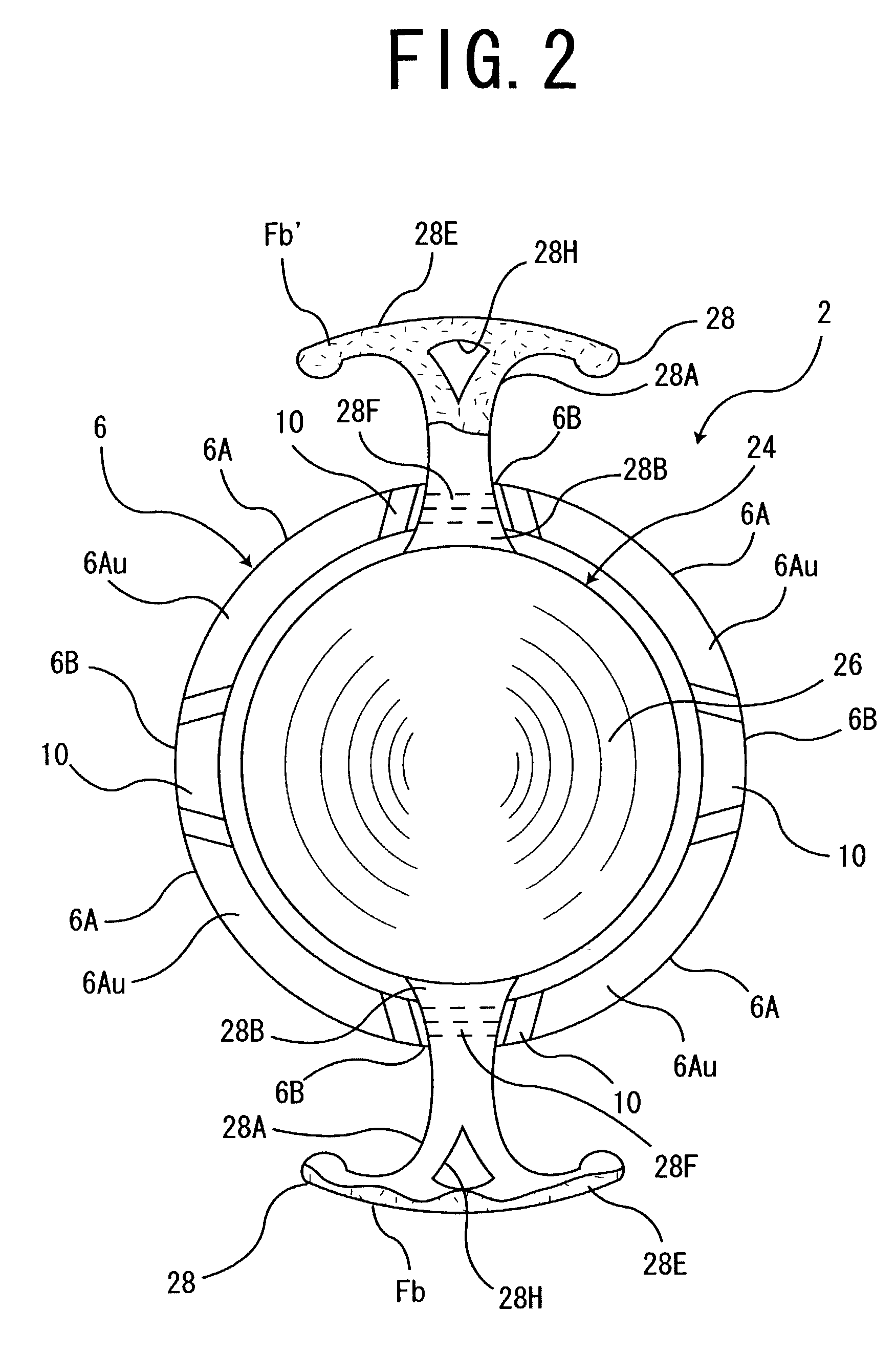
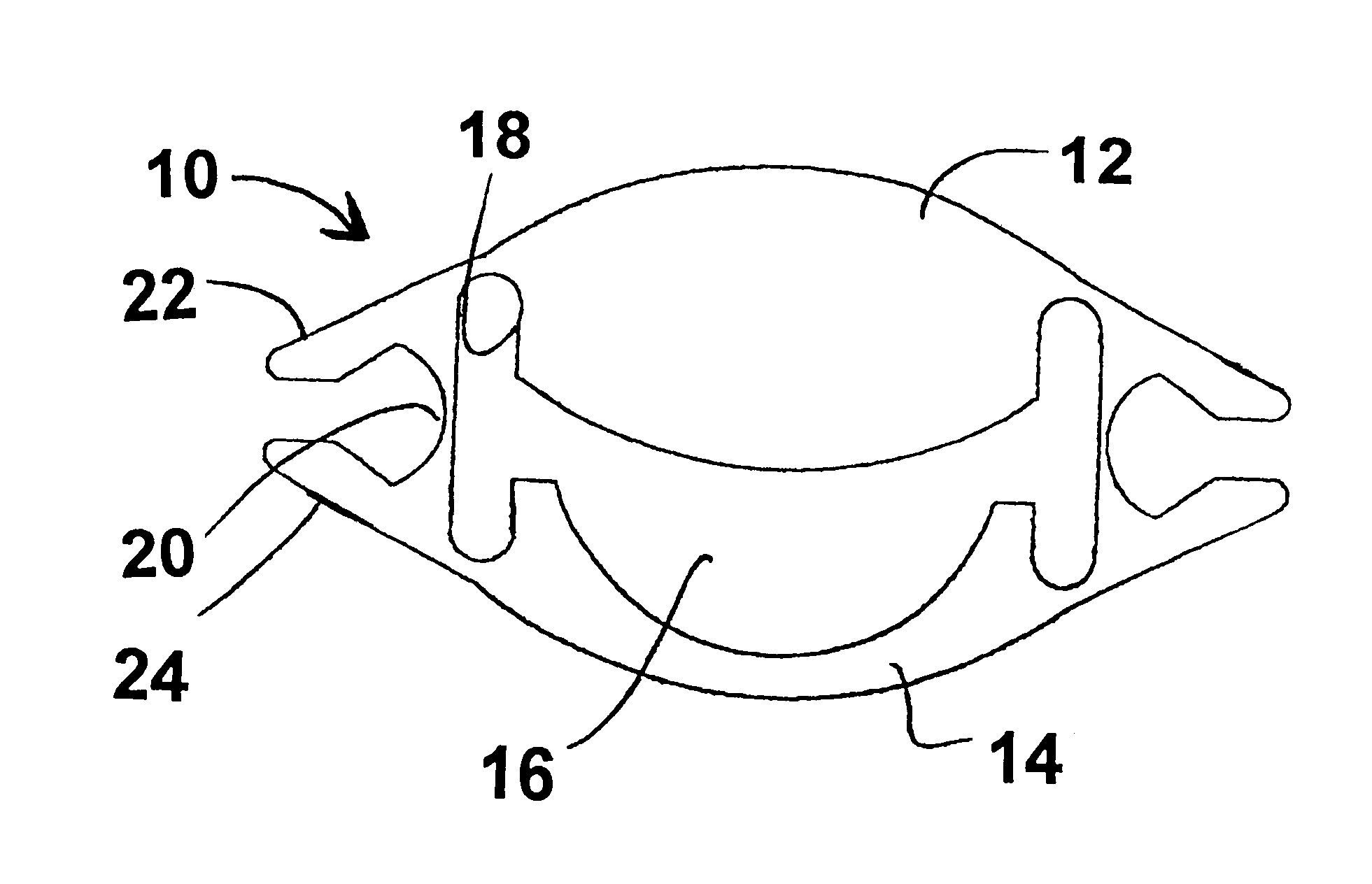
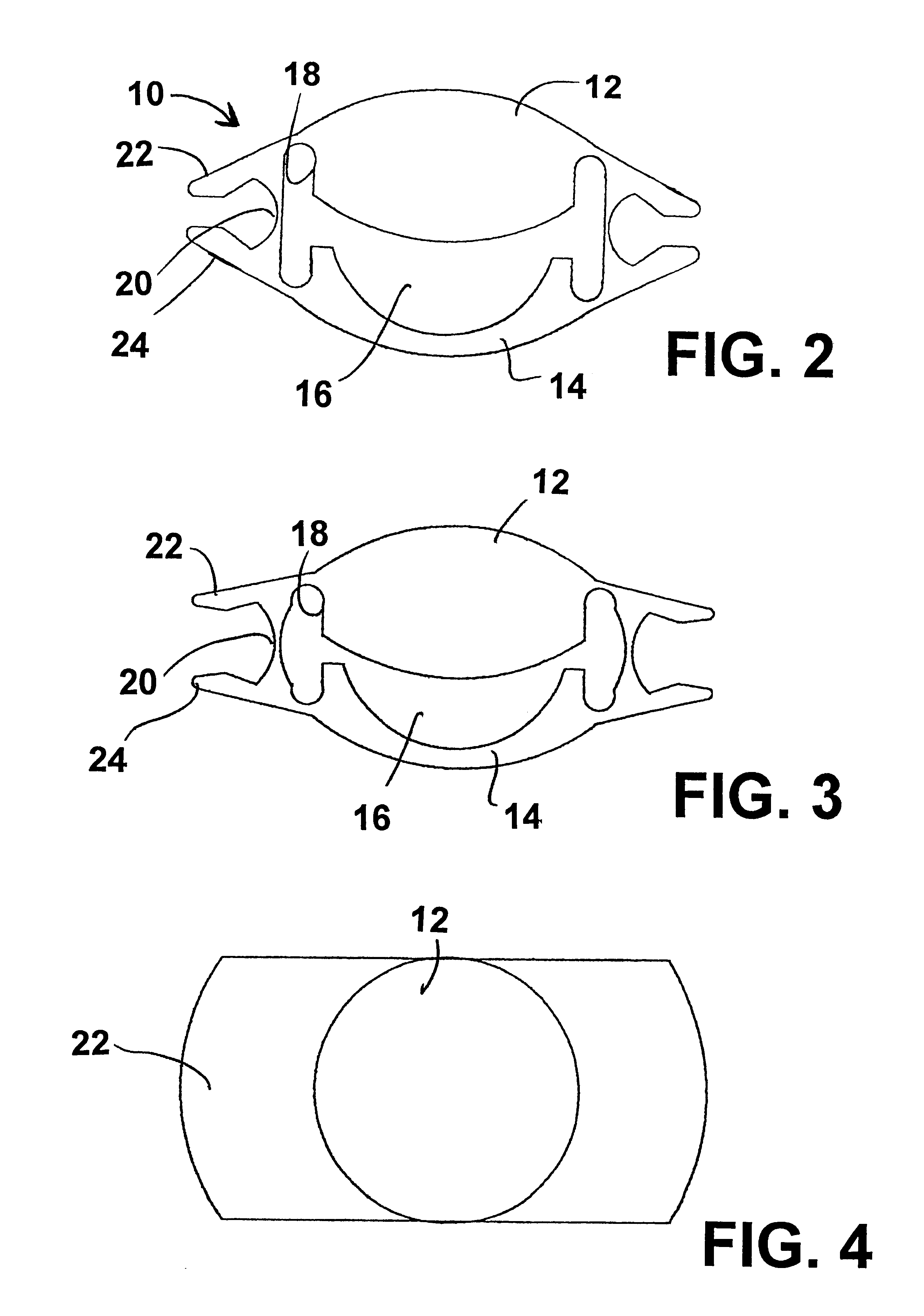
Accommodating intraocular lens system with separation member
InactiveUS7198640B2SeparationEasy to separateOptical articlesIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
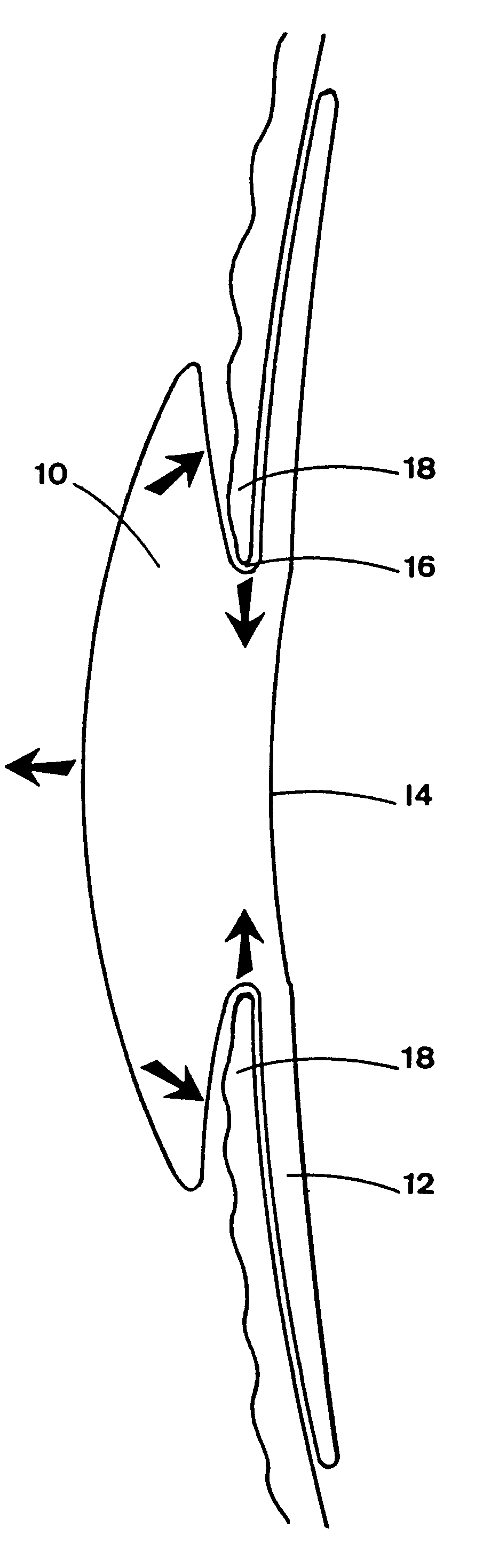
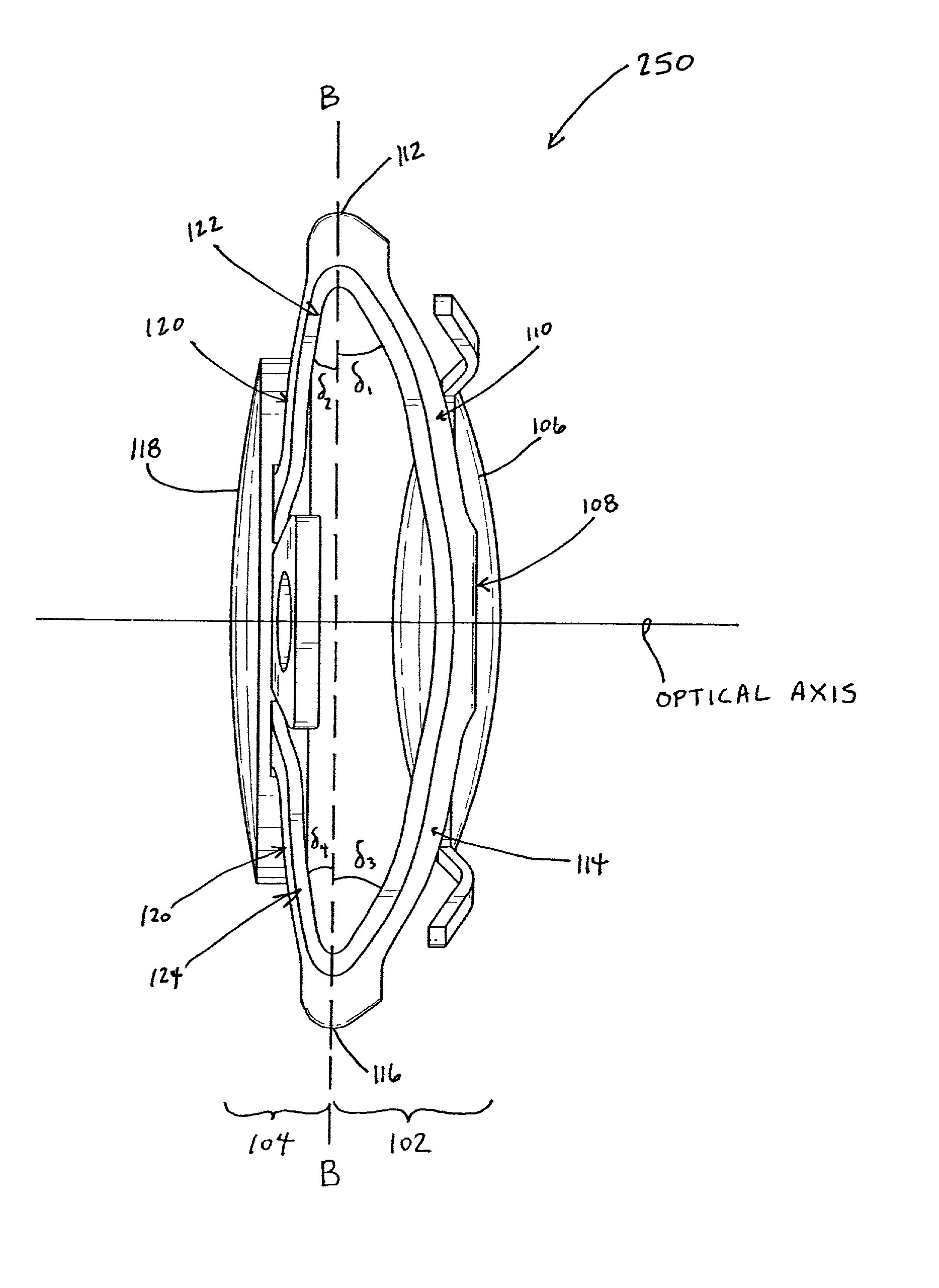
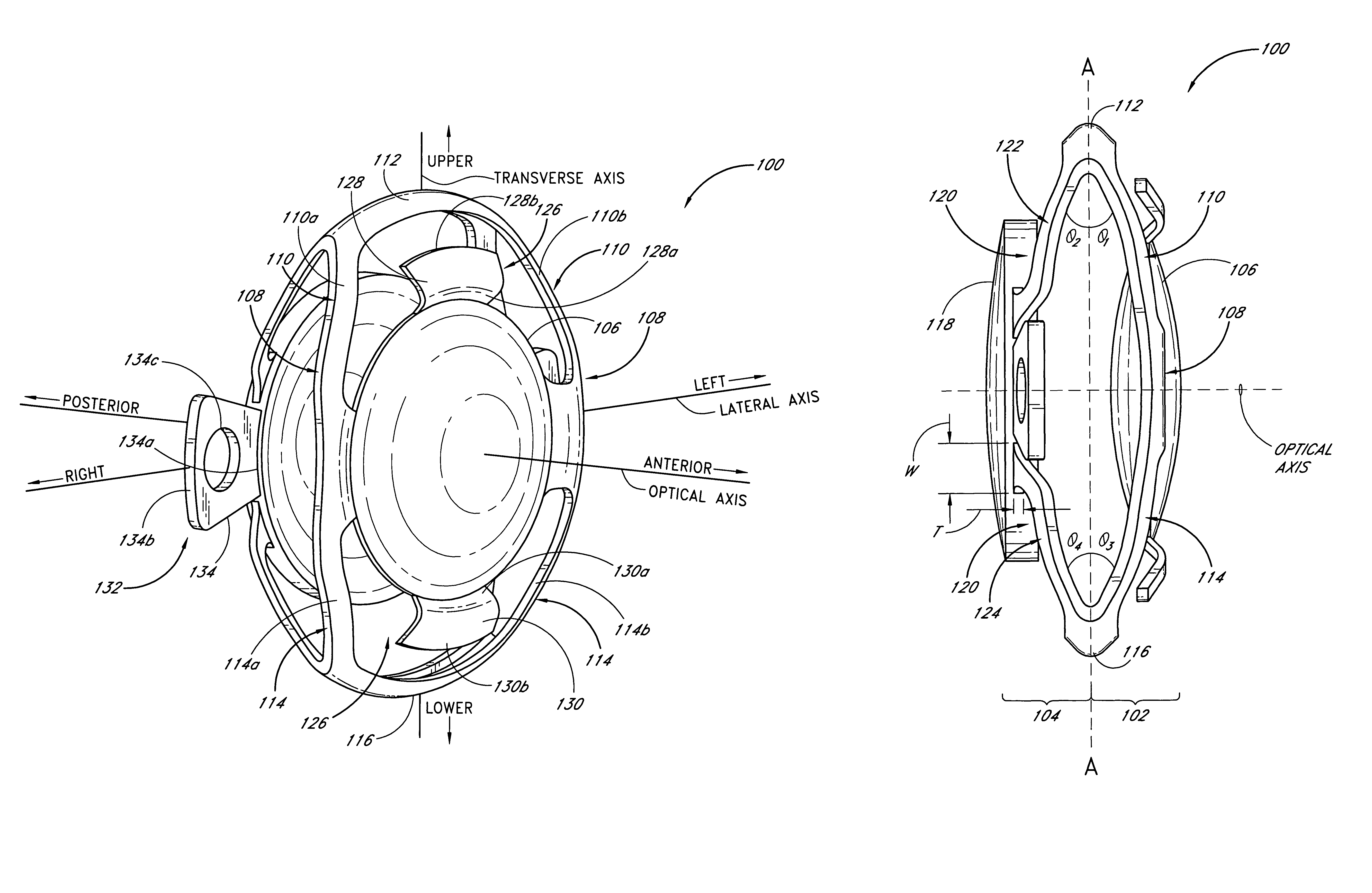
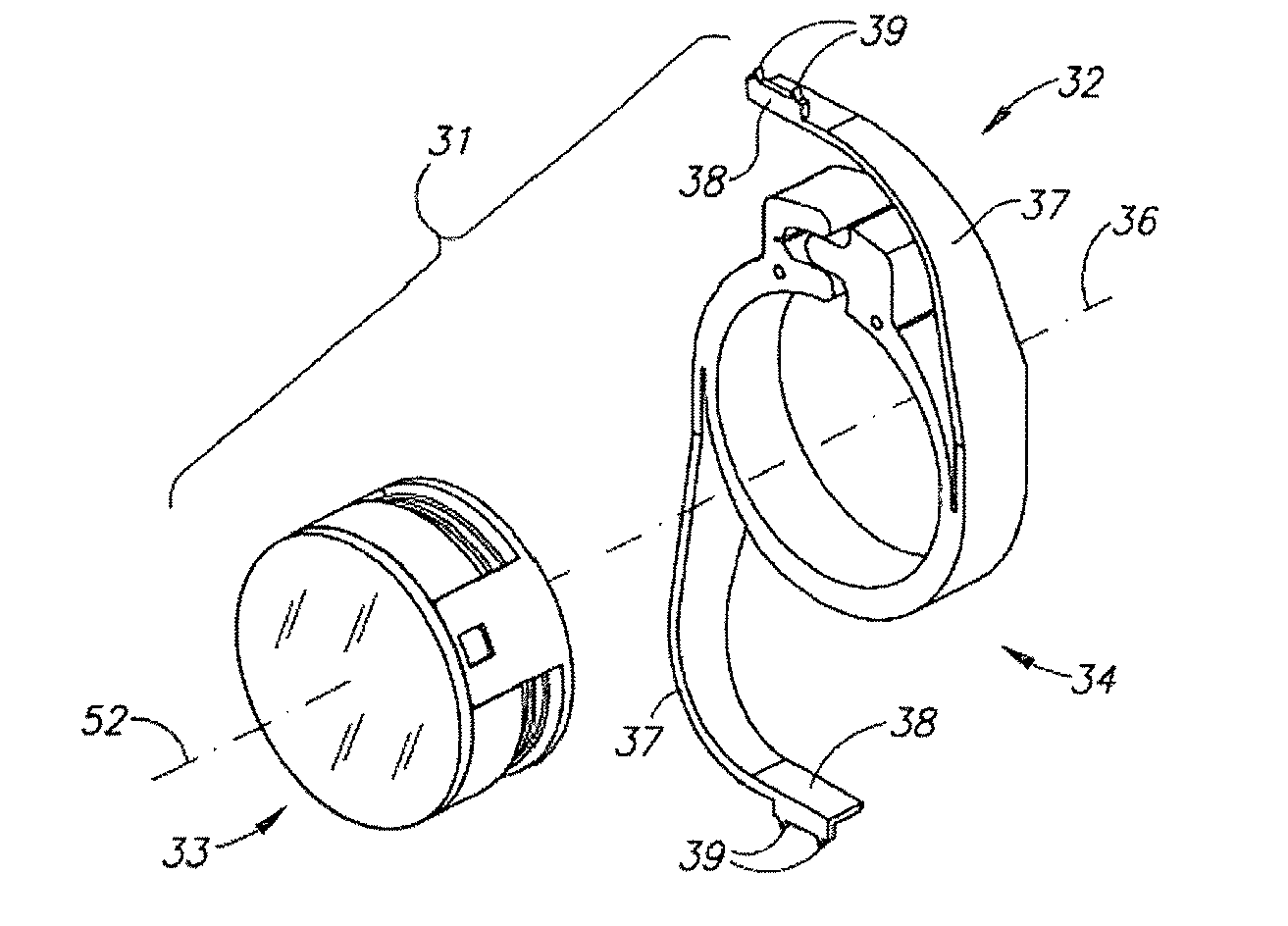
There is disclosed an accommodating intraocular lens for implantation in an eye having an optical axis. The lens comprises an anterior portion which in turn comprises an anterior viewing element and an anterior biasing element. The lens further comprises a posterior portion which in turn comprises a posterior viewing element in spaced relationship to the anterior viewing element and a posterior biasing element. The anterior portion and posterior portion meet at first and second apices of the intraocular lens. The anterior portion and the posterior portion and / or the apices are responsive to force thereon to cause the separation between the viewing elements to change. Additional embodiments and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VISIOGEN
Advanced electro-active optic device
Optical devices having a dynamic aperture and / or an apodization mask are provided. The aperture and / or mask may be provided by one or more electro-active elements, and may be used in an ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power.
Owner:EA3TECH LLC +1
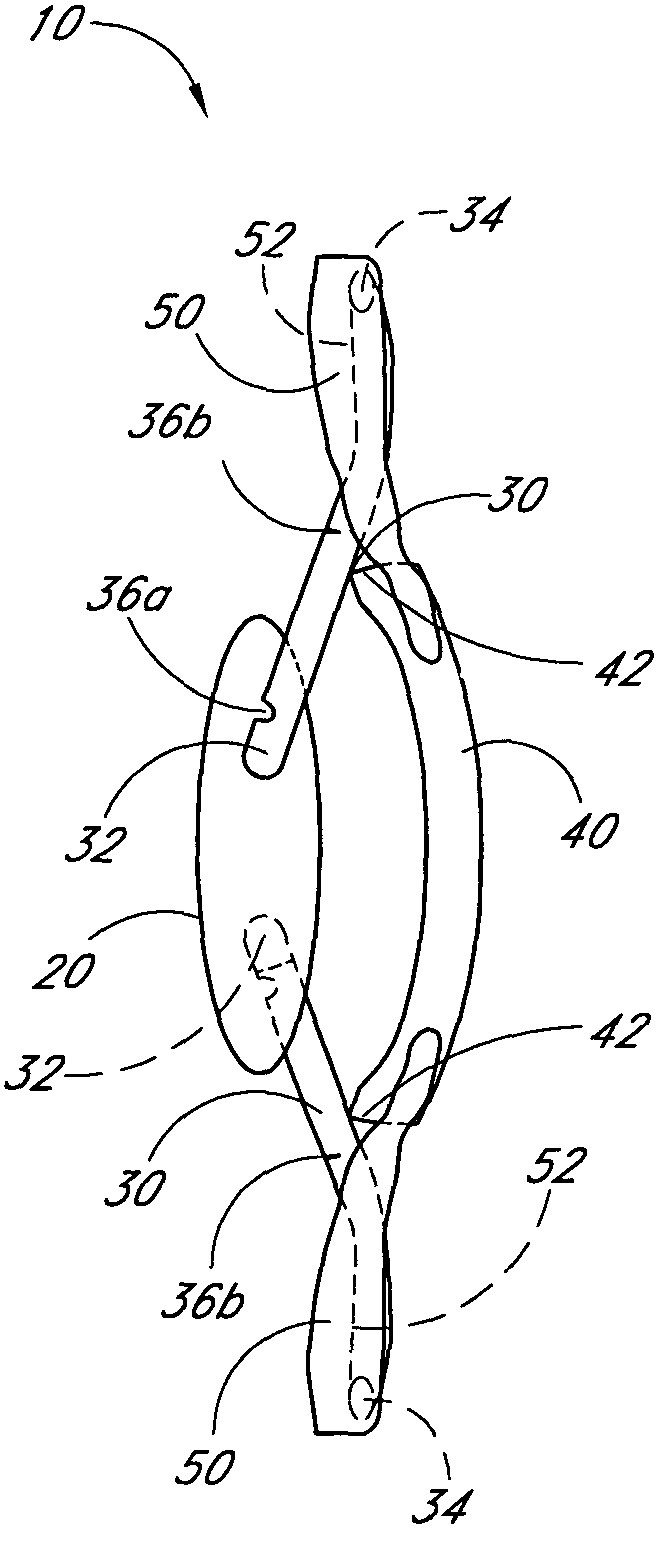
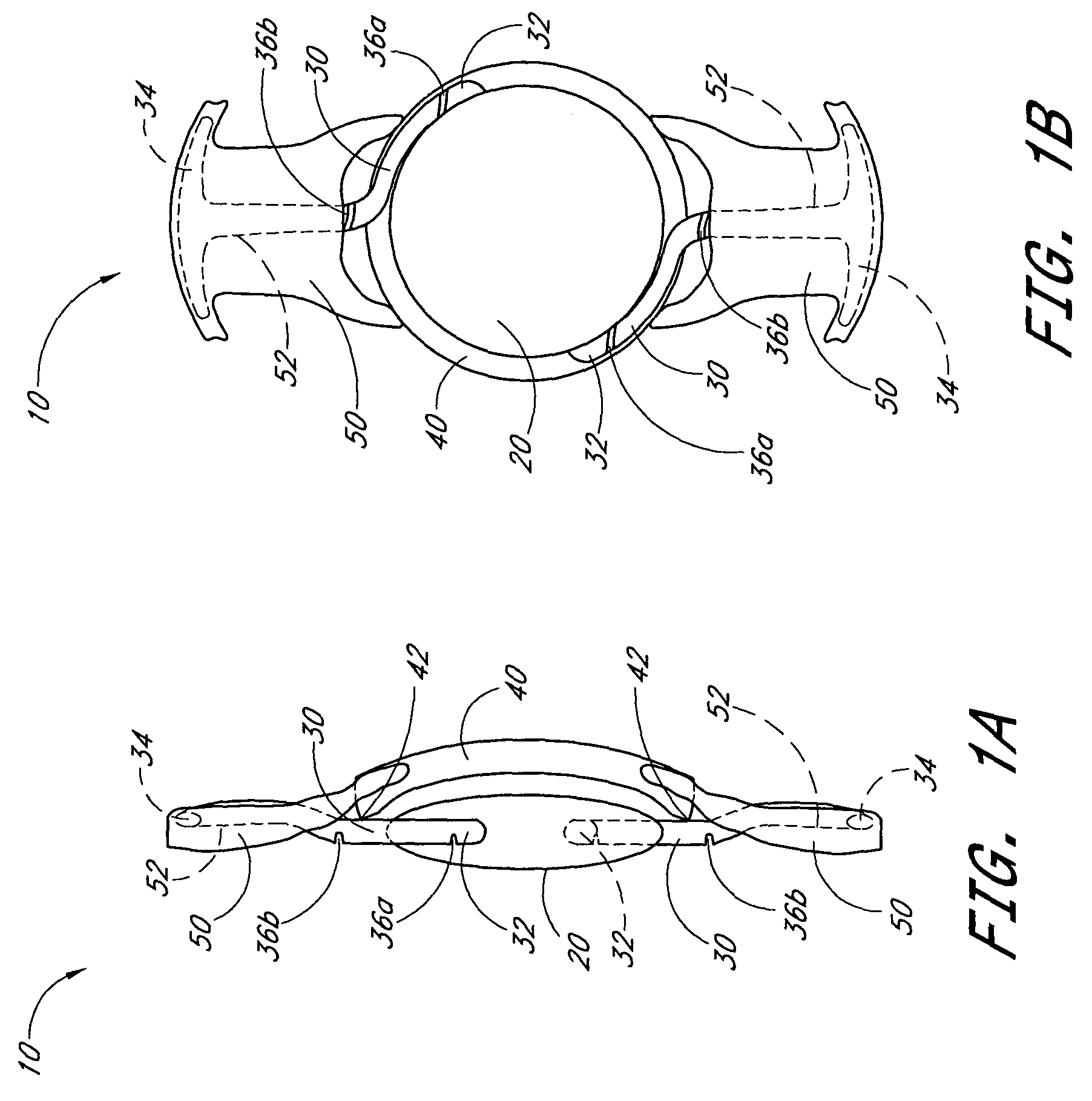
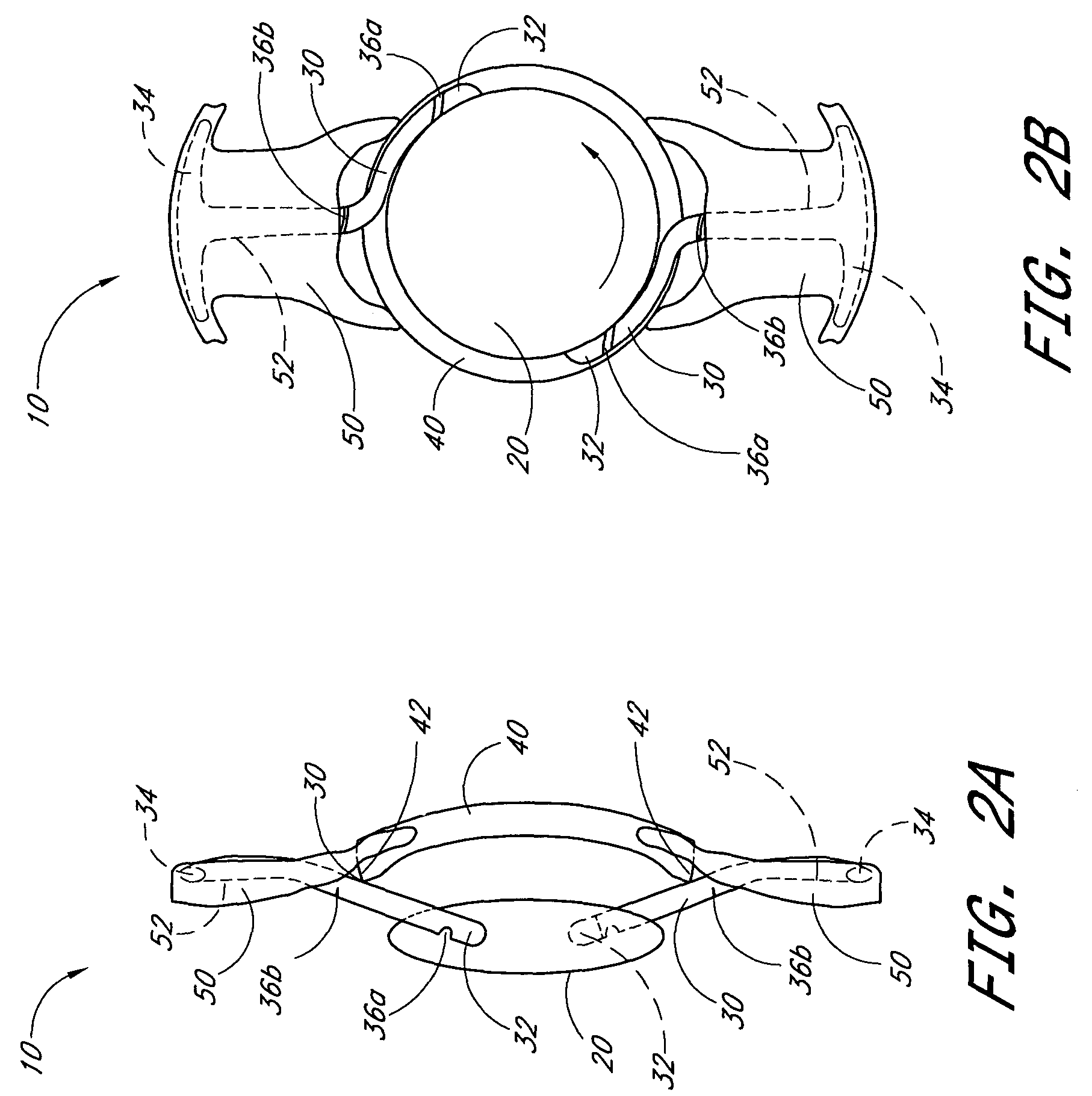
Accommodating intraocular lens having T-shaped haptics
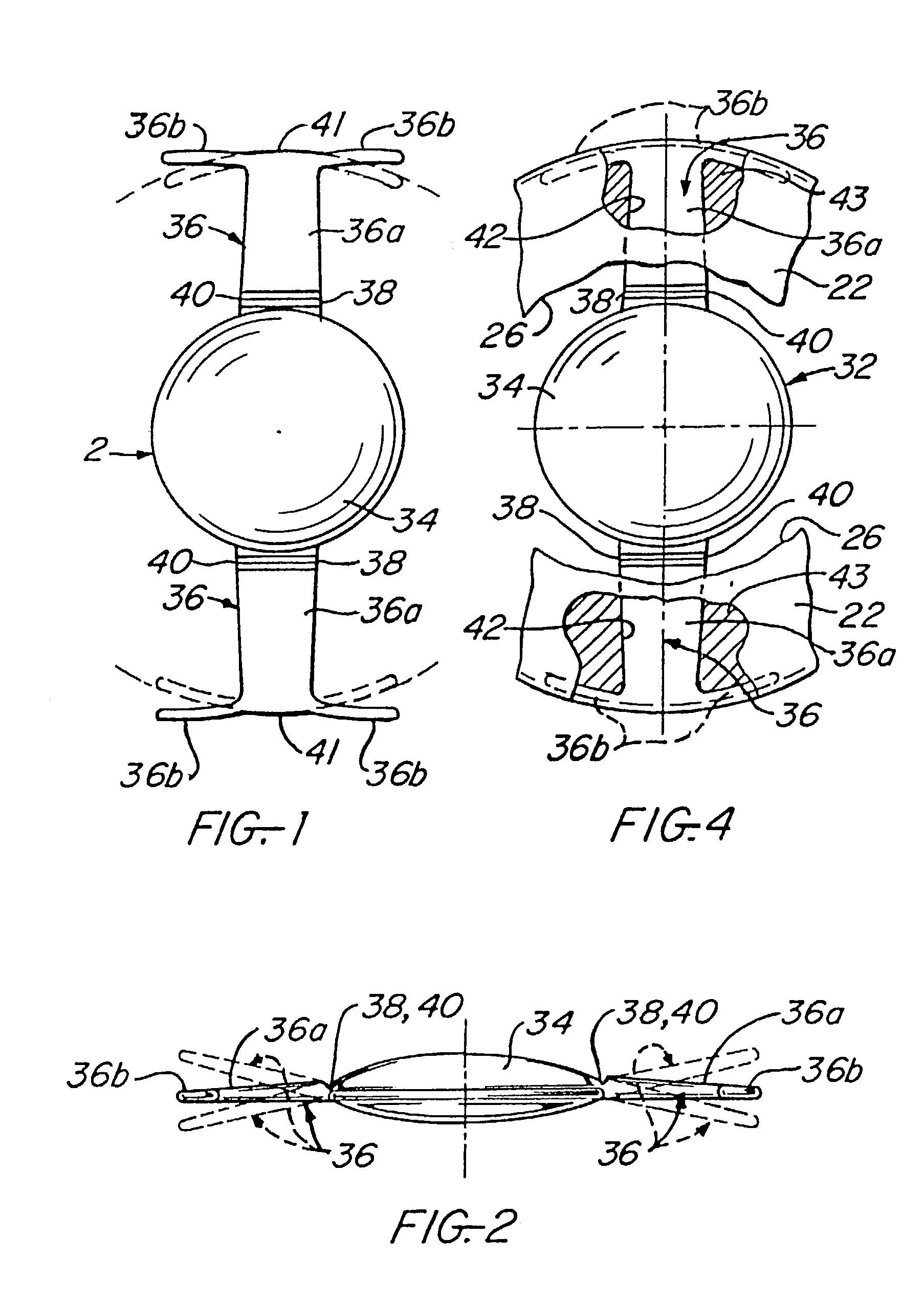
An accommodating intraocular lens having anteriorly and posteriorly movable extended portions, such as T-shaped haptics, extending from a central optic to be implanted within a natural capsular bag of a human eye with the extended portions positioned between an anterior capsular rim and a posterior capsule of the bag, whereby during a post-operative healing period, fibrosis occurs about the extended portions to fixate the lens in the bag in a manner such that subsequent natural contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscle moves the optic to provide vision accommodation of increased accommodation amplitude and diopters of accommodation.
Owner:THE NICE TRUST
Materials for making hydrophobic intraocular lens
Owner:BENZ RES & DEV
Accommodating intraocular lens system with enhanced range of motion
An intraocular lens system adapted to be implanted within an eye includes an anterior optic movable in a forward direction within the eye. The intraocular lens system further includes at least two anterior haptic arms, each anterior haptic arm having a first end coupled to the anterior optic and a second end adapted to be coupled to the eye. The intraocular lens system further includes a posterior optic movable in the forward direction within the eye and coupled to the anterior haptic arms. The intraocular lens system further includes at least one posterior haptic member adapted to be coupled to the eye and coupled to the posterior optic. The anterior haptic arms are responsive to a first forward movement of the posterior optic by actuating a second forward movement of the anterior optic substantially larger than the first forward movement.
Owner:VISIOGEN
Connection geometry for intraocular lens system
There is disclosed an accommodating intraocular lens for implantation in an eye having an optical axis. The lens comprises an anterior portion which in turn comprises an anterior viewing element and an anterior biasing element. The lens further comprises a posterior portion which in turn comprises a posterior viewing element in spaced relationship to the anterior viewing element and a posterior biasing element. The anterior portion and posterior portion meet at first and second apices of the intraocular lens. The anterior portion and the posterior portion and / or the apices are responsive to force thereon to cause the separation between the viewing elements to change. Additional embodiments and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:VISIOGEN
Accommodating intraocular lens
An Accommodating Intraocular Lens (AIOL) is disclosed herein, that is comprised of a flexible optic and a flexible haptic rim that conforms to the human eye capsule. The spherical or custom shape of the optic is engineered to be maintained during accommodation through the mechanical / optic design of the implant and the interaction between the implant and the naturally occurring position and actuating forces applied through ciliary muscle / zonules / and capsule as the brain senses the need to increase the diopter change or magnification when an object of fixation approaches the eye. The axial relocation or position of the AIOL may also be further adjusted anatomically to further improve the affect needed to achieve improved accommodation. Optionally, the accommodating intraocular lens is foldable or injectable for delivery of the lens into the eye.
Owner:STENGER DONALD C
High gain wide range accommodating intraocular lens for implant into the capsular bag
InactiveUS20040148023A1Large range adjustable focal lengthHigh optical gainIntraocular lensFar distanceMuscle contraction
A high gain lens system for implant into the capsular bag after removal of the natural crystalline lens. A preferred embodiment of the invention comprises a combination of a positive or convex lens and a negative or concave lens. These two lenses are spaced from one another and their relative spacing and respective focal lengths determine their combined focal length. When the lens system is inserted into the capsular bag, two opposed haptic flanges on each side, extend toward the inner radial edge of the bag adjacent the ciliary muscles. When the muscles contract, the bag is stretched thereby compressing the haptic flanges together or at least toward one another. This action cause the two lenses to separate further from each other and the increased spacing between the positive and negative lenses shortens the focal length to permit focusing of objects at near distances. On the other hand, when the muscles relax, the bag relaxes also, the haptic flanges separate and the lenses come closer together. The reduced spacing between the positive and negative lenses, increases the focal length to permit focusing of objects at far distances.
Owner:SHU STEPHEN K
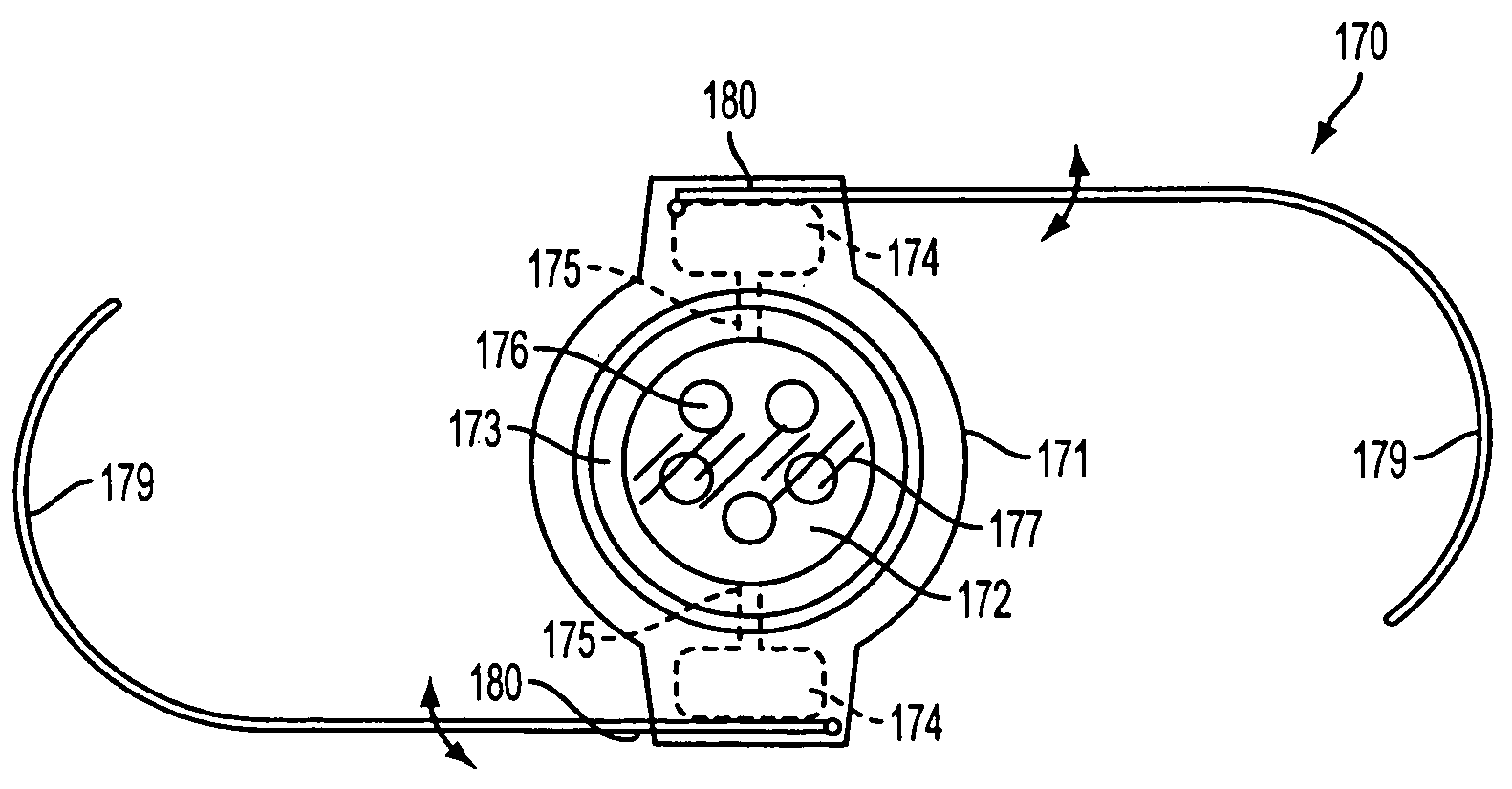
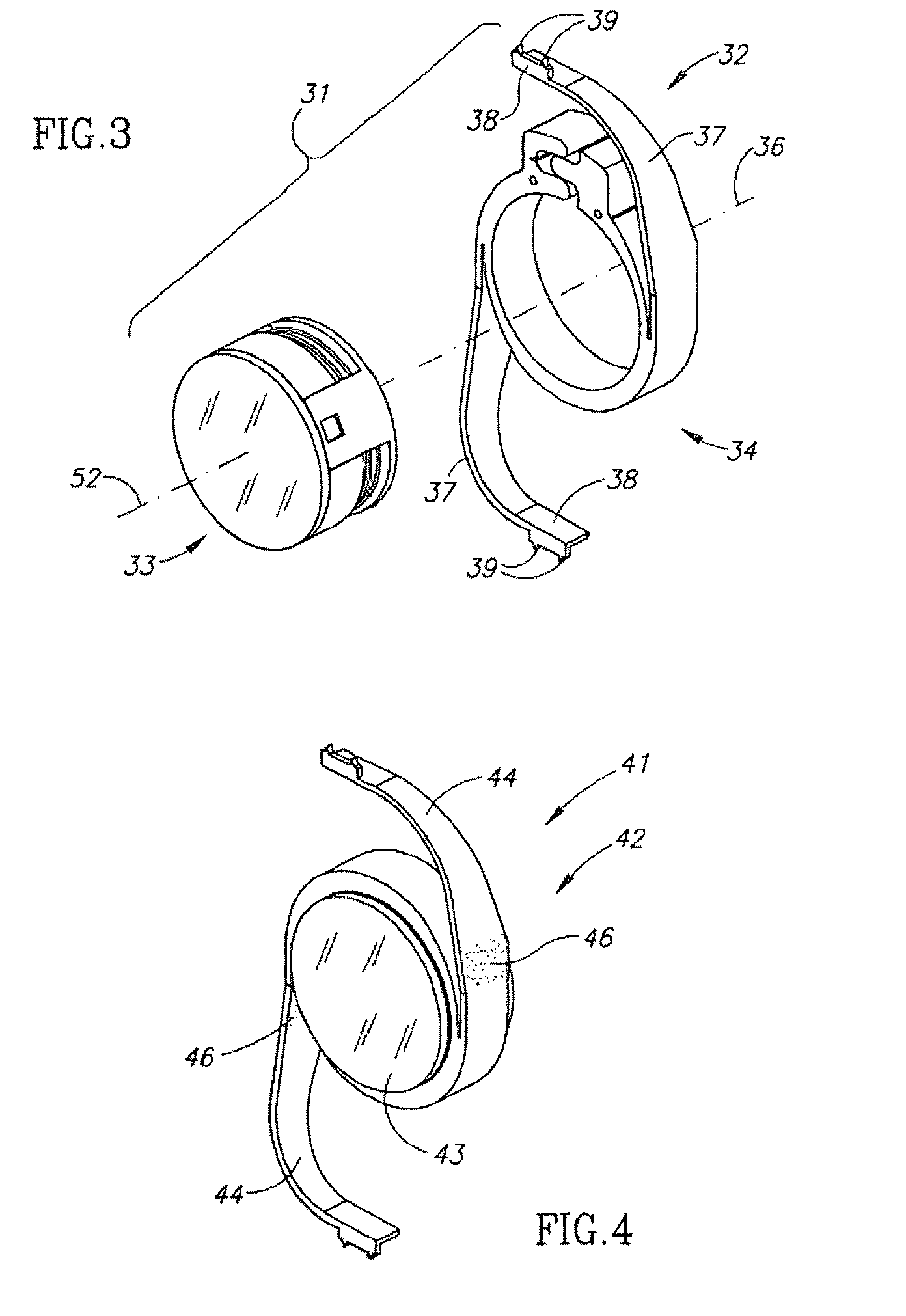
Intraocular ring assembly and artificial lens kit
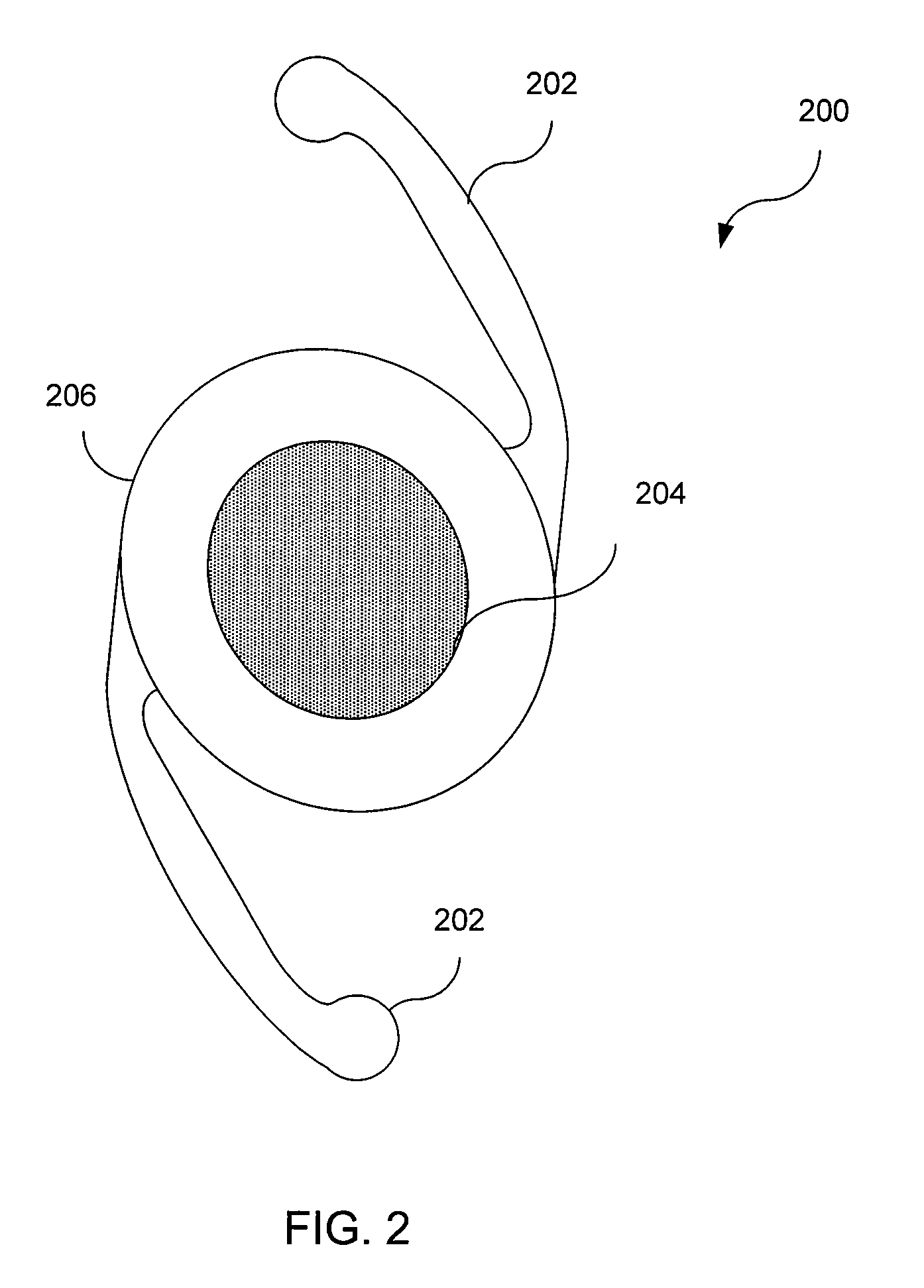
InactiveUS20030114927A1Convenient to accommodateHigh sensitivityIntraocular lensIntraocular lensPhakic intraocular lens
An intraocular ring assembly and an artificial lens kit, both of which are usable for implantation in a lens capsule or capsular bag of natural eye. The intraocular ring assembly includes a first ring element having recessions therein, a second ring element, and a biasing element provided between the first and second ring elements. The artificial lens kit comprises such intraocular ring assembly and an intraocular lens to be movably supported in the recessions of the ring assembly in a coaxial relation therewith. A guide element may be provided to assist in rectilinear coaxial movement of the first and second ring elements.
Owner:NAGAMOTO TOSHIYUKI
High gain wide range accommodating intraocular lens for implant into the capsular bag
InactiveUS6818017B1Large range adjustable focal lengthHigh optical gainIntraocular lensFar distanceMuscle contraction
A high gain lens system for implant into the capsular bag after removal of the natural crystalline lens. A preferred embodiment of the invention comprises a combination of a positive or convex lens and a negative or concave lens. These two lenses are spaced from one another and their relative spacing and respective focal lengths determine their combined focal length. When the lens system is inserted into the capsular bag, two opposed haptic flanges on each side, extend toward the inner radial edge of the bag adjacent the ciliary muscles. When the muscles contract, the bag is stretched thereby compressing the haptic flanges together or at least toward one another. This action cause the two lenses to separate further from each other and the increased spacing between the positive and negative lenses shortens the focal length to permit focusing of objects at near distances. On the other hand, when the muscles relax, the bag relaxes also, the haptic flanges separate and the lenses come closer together. The reduced spacing between the positive and negative lenses, increases the focal length to permit focusing of objects at far distances.
Owner:SHU STEPHEN K
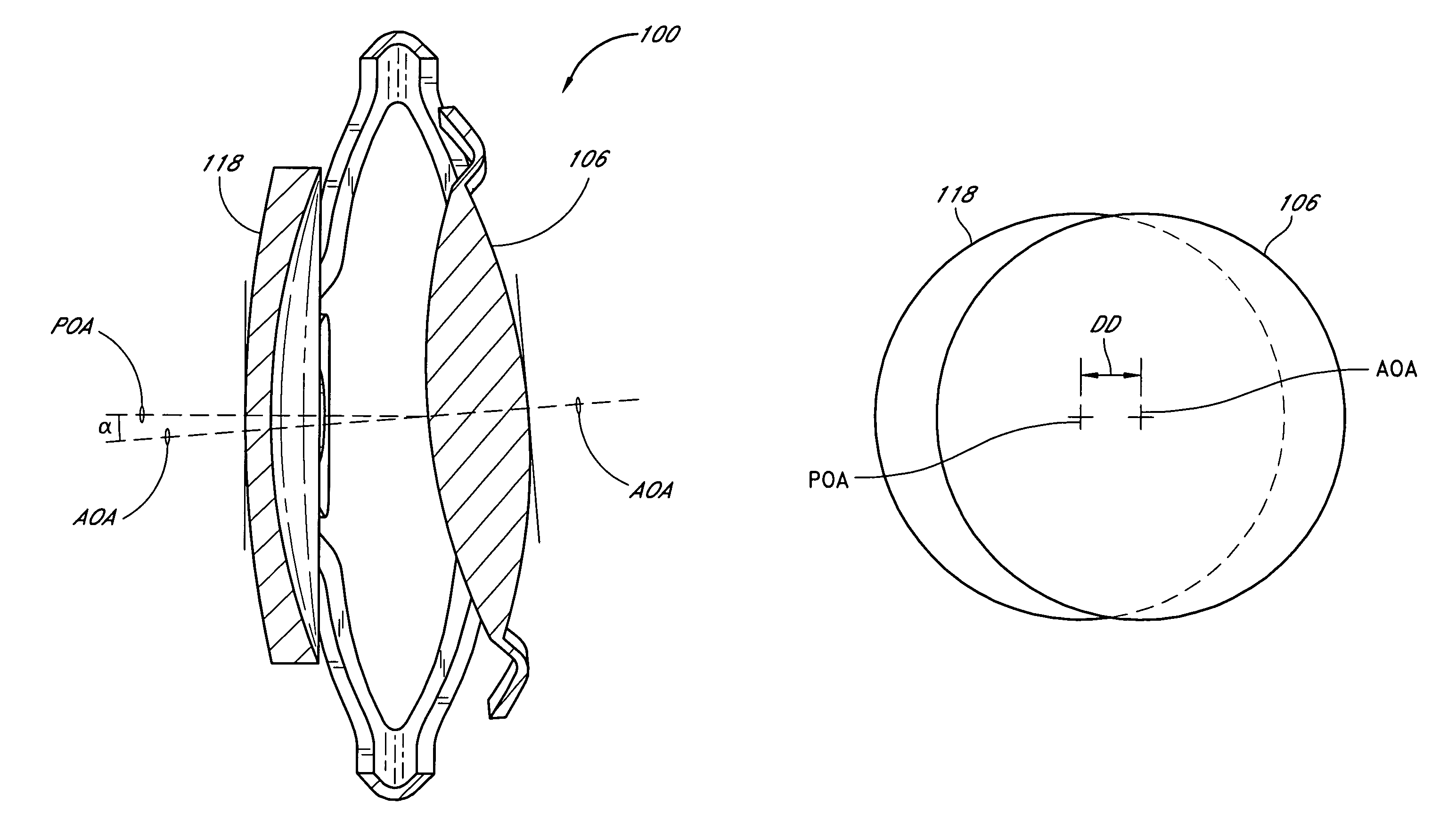
Intraocular lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
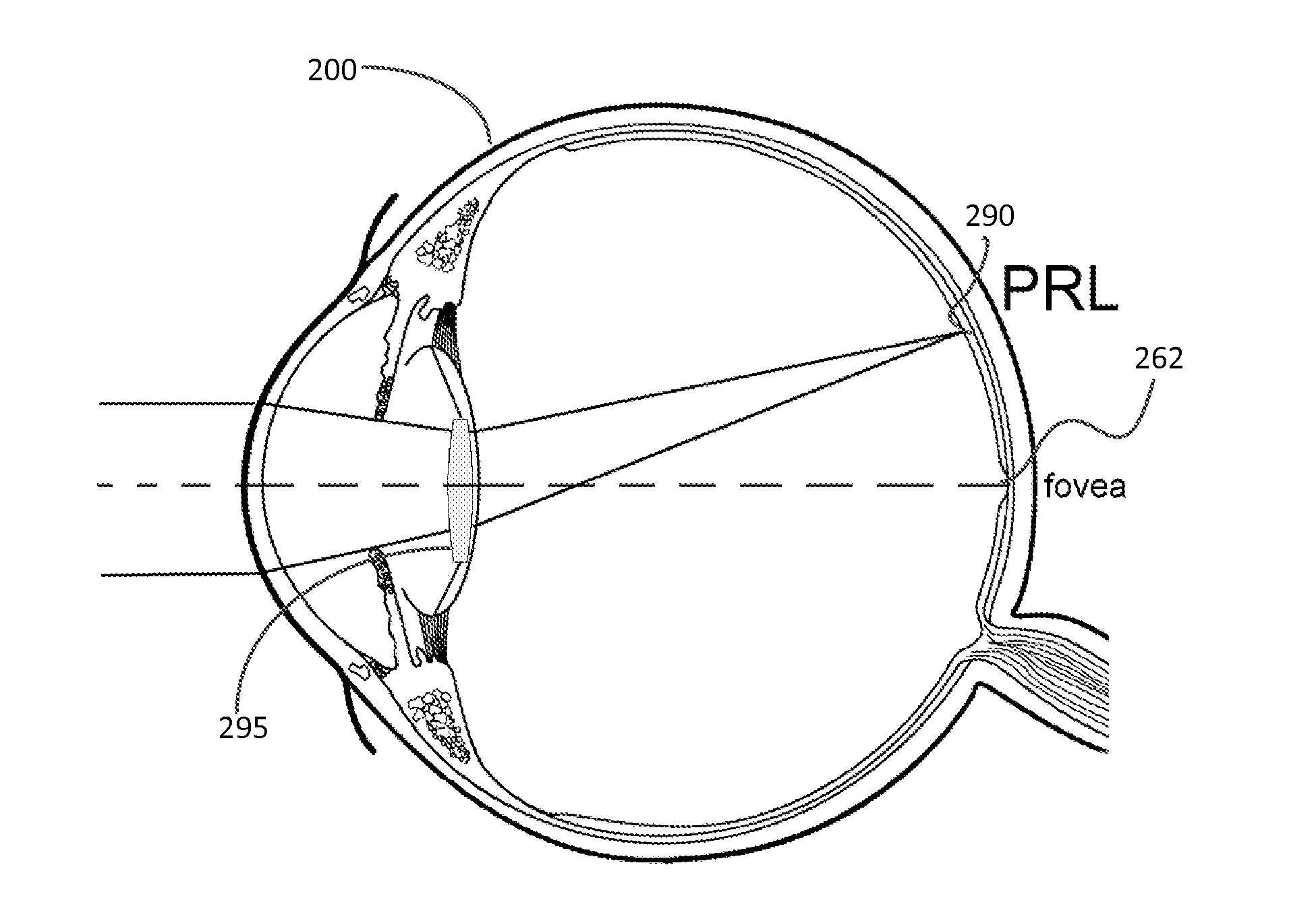
ActiveUS20150250583A1Improve eyesightReduce sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesOptical propertyPeripheral retina
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing symmetric or asymmetric optic with aspheric surface which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Materials for use in accommodating intraocular lens system
InactiveUS8187325B2SeparationEasy to separateOptical articlesIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
Owner:VISIOGEN
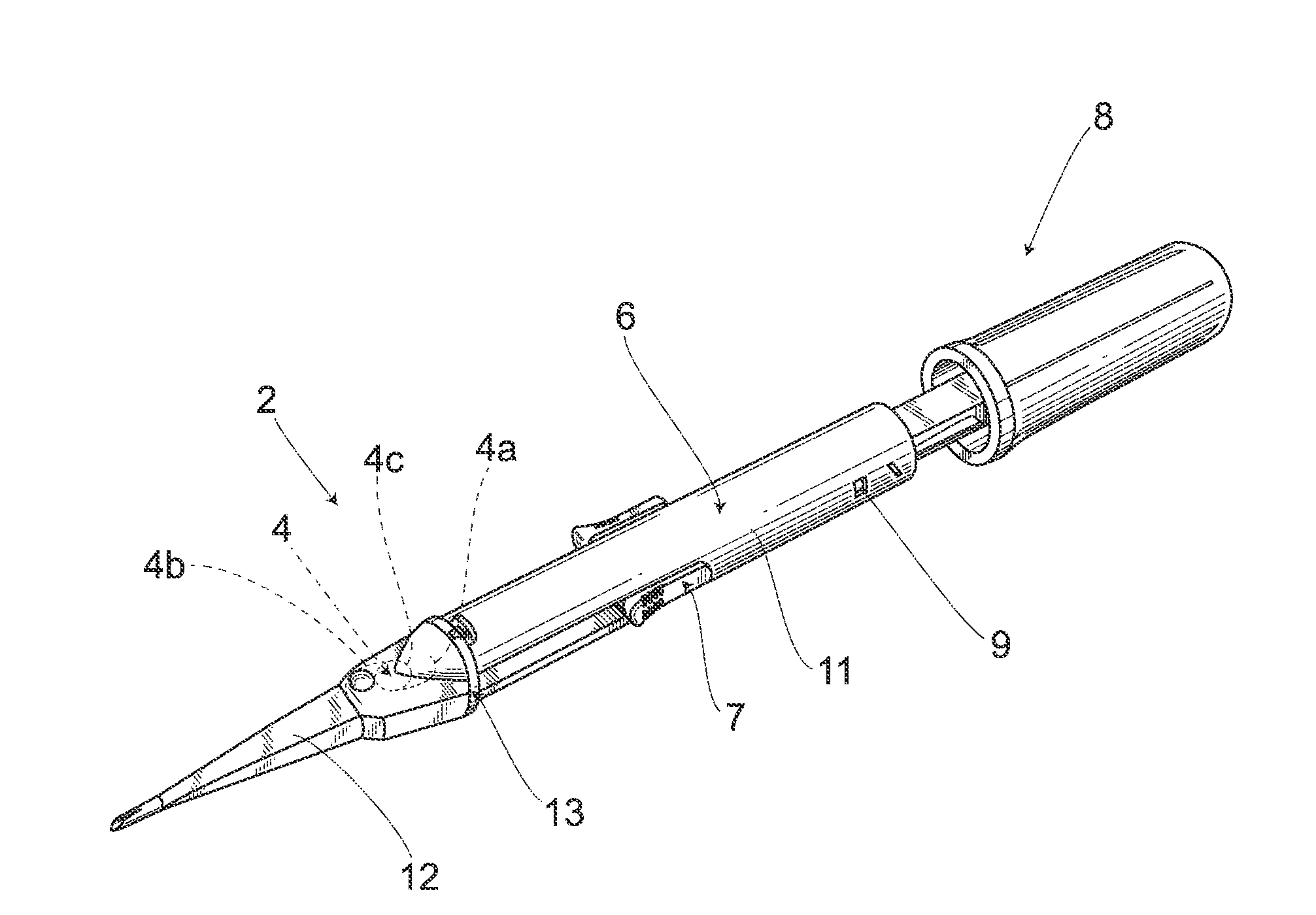
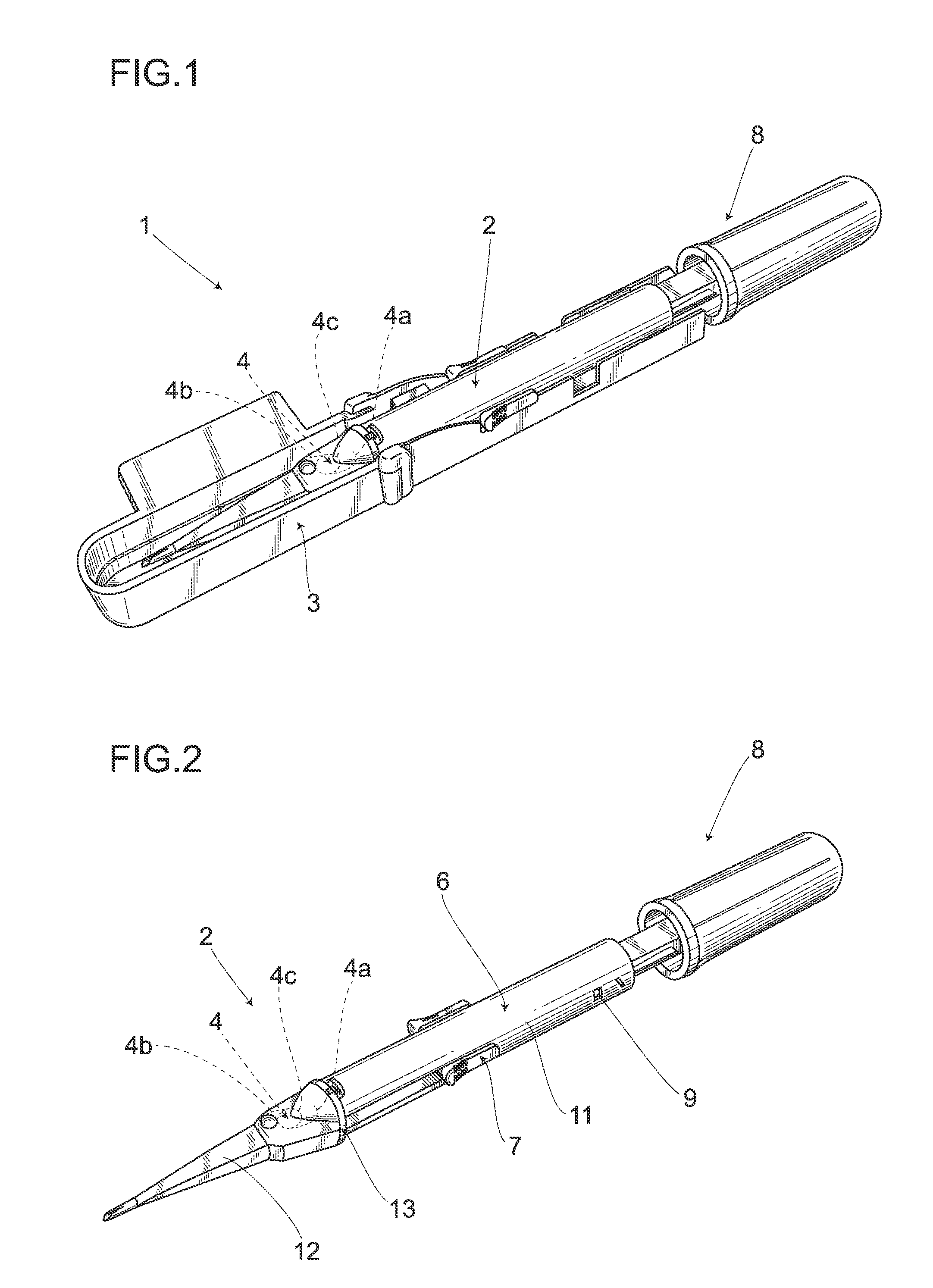
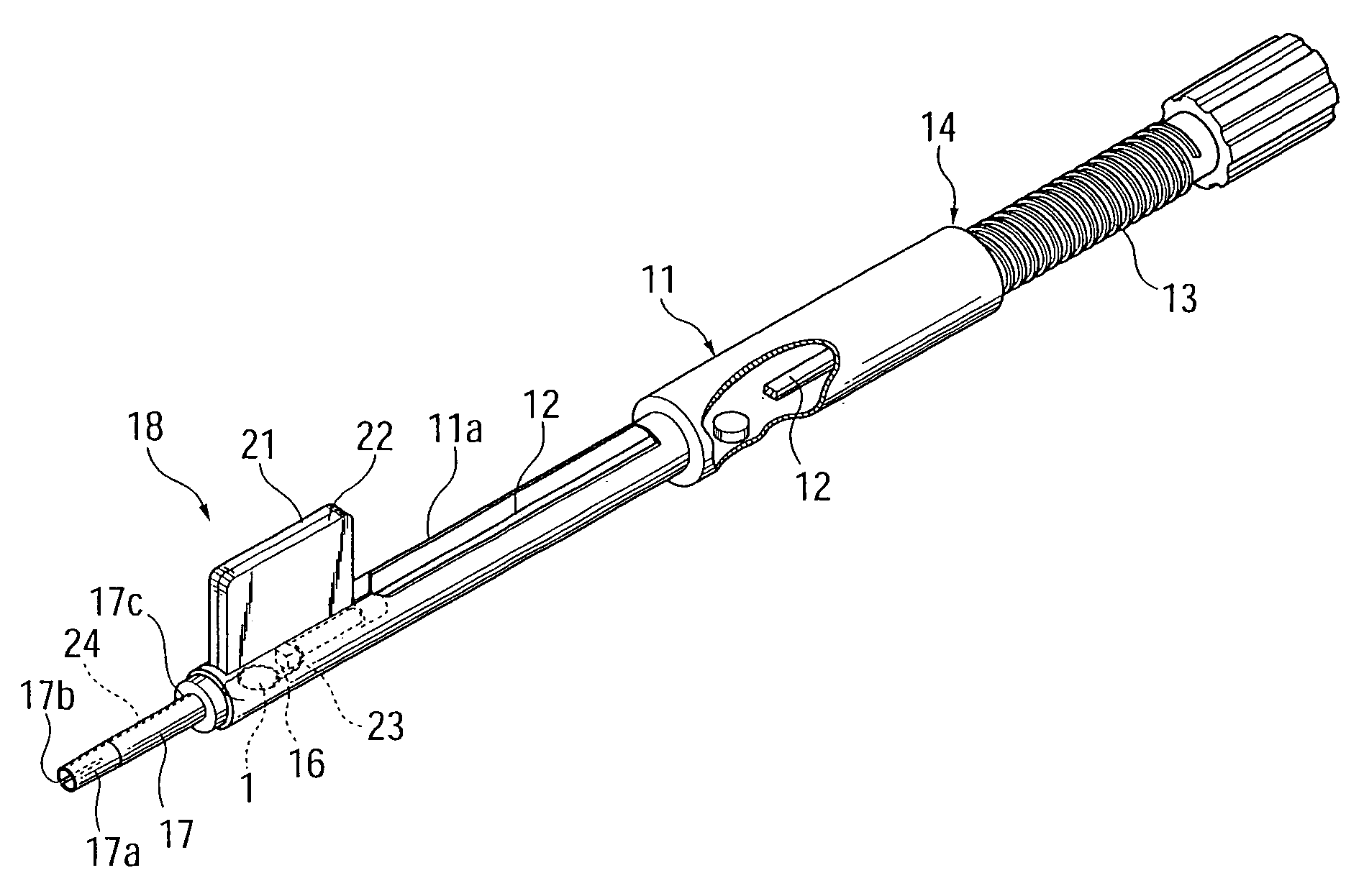
Intraocular Lens Insertion Device
ActiveUS20100217273A1Reduce harmReduce the possibilityEye surgeryIntraocular lensMedicineIntraocular lens insertion
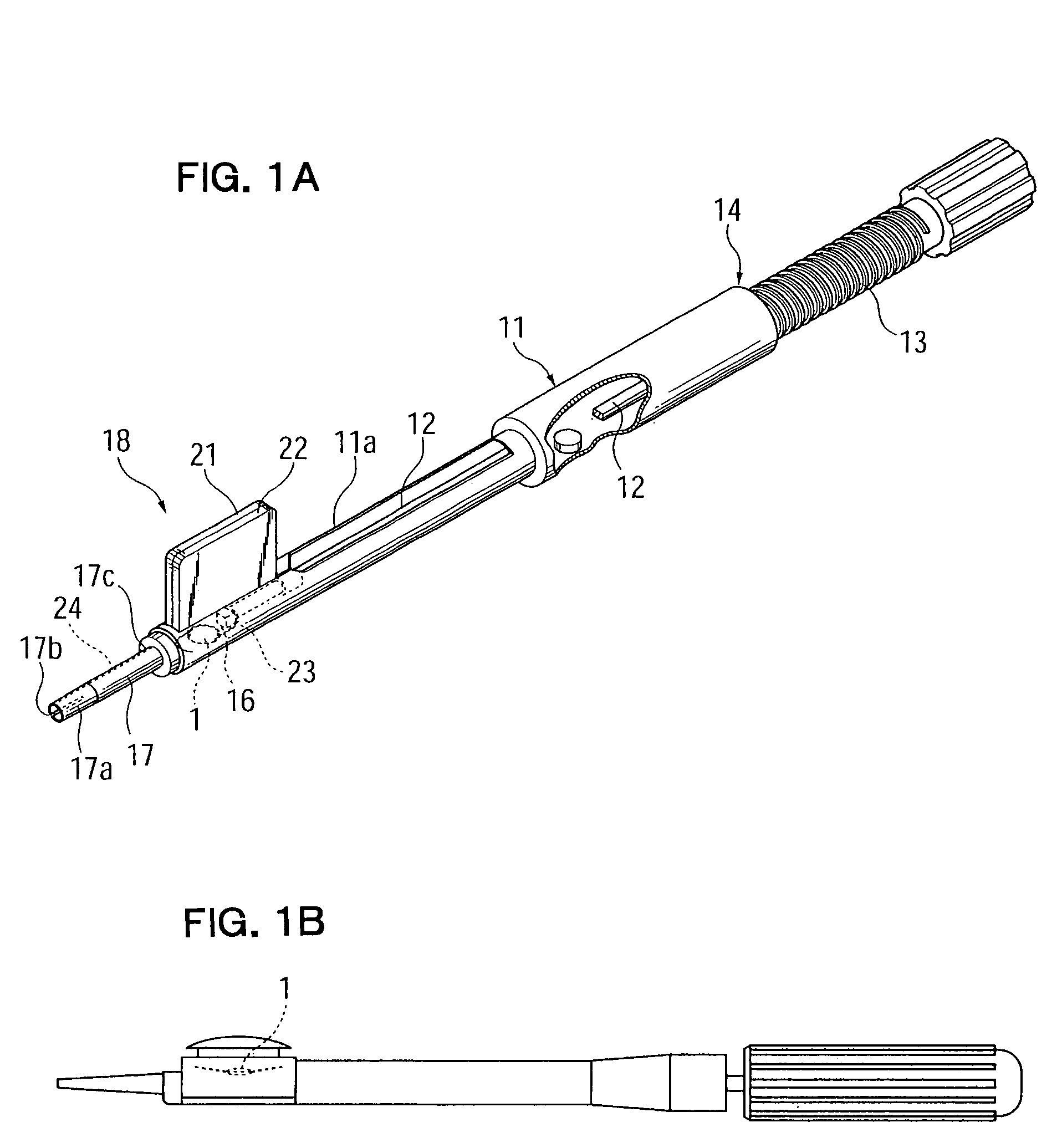
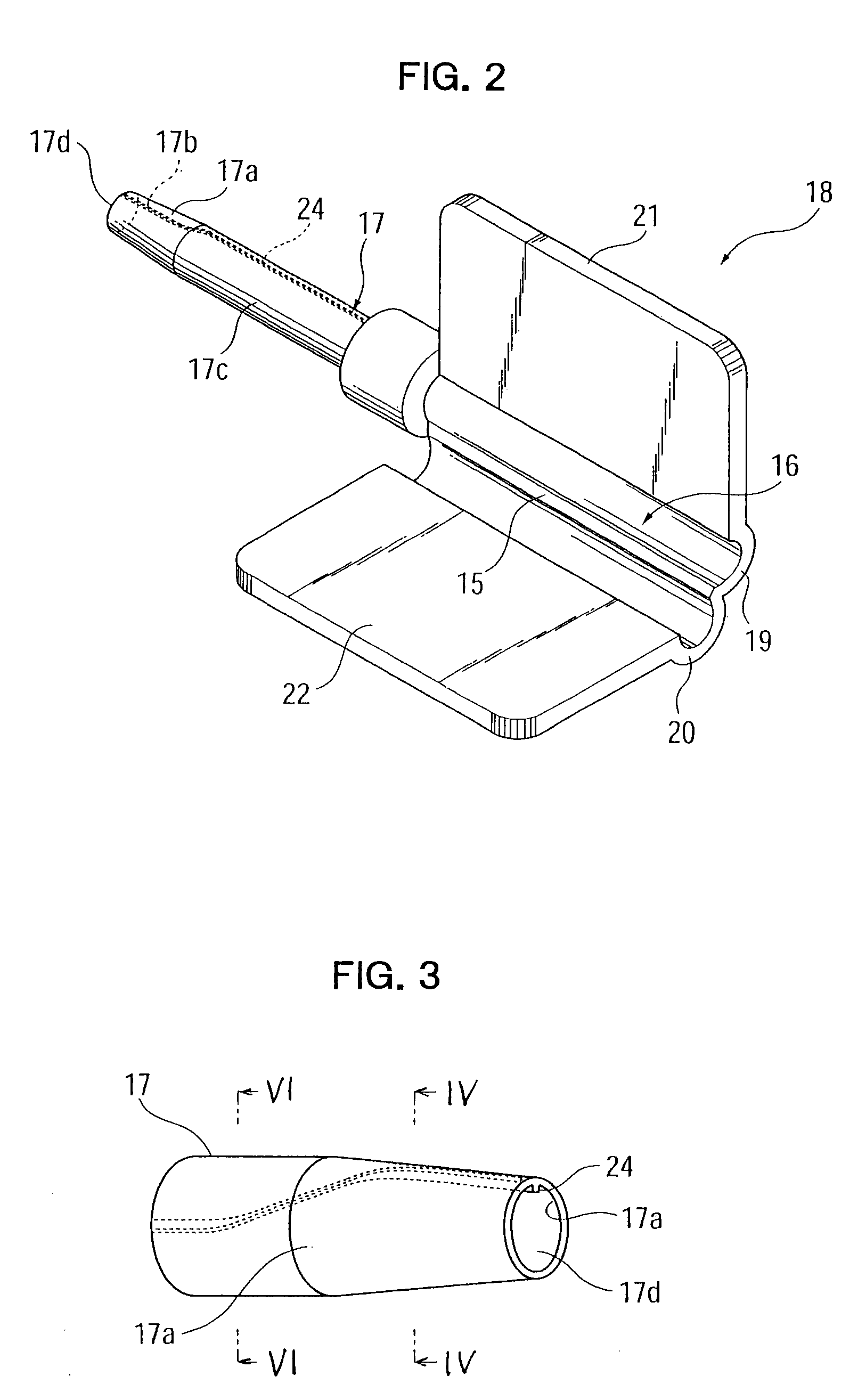
An intraocular lens insertion device which dramatically reduces the possibility that a plunger damages an intraocular lens, and which can safely and surely insert an intraocular lens into an eye is provided. An intraocular lens insertion unit comprises a lens disposing part for disposing an intraocular lens, a plunger for pushing out the intraocular lens disposed at the lens disposing part, a transition part for deforming the intraocular lens pushed out by the plunger, and a nozzle for ejecting the deformed intraocular lens. The plunger has a lens contact part for contacting the outer edge of the intraocular lens, and a protrusive part for pushing the lens contact part downward the intraocular lens by the deformation of the intraocular lens, both lens contact part and protrusive part are provided at the leading end of the plunger.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Bifocal intraocular telescope for low vision correction
InactiveUS7186266B2Provide bifocal correction to the eyeIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
Owner:TELEDIOPTIC LENS SYST
Accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL), and AIOL assemblies including same
InactiveUS7815678B2Natural positive diopter strengthFacilitate accommodationIntraocular lensIntraocular lensCiliary body
An accommodating intraocular lens (AIOL) including a biasing mechanism for elastically deforming an elastically deformable shape memory disk-like optical element for affording the AIOL a natural positive diopter strength for near vision. The AIOL is intended to be implanted in a human eye such that relaxation of its ciliary body causes its capsular diaphragm to apply an accommodation force for overcoming the biasing mechanism to reduce the AIOL's natural positive diopter strength for distance vision.
Owner:FORSIGHT VISION5 INC
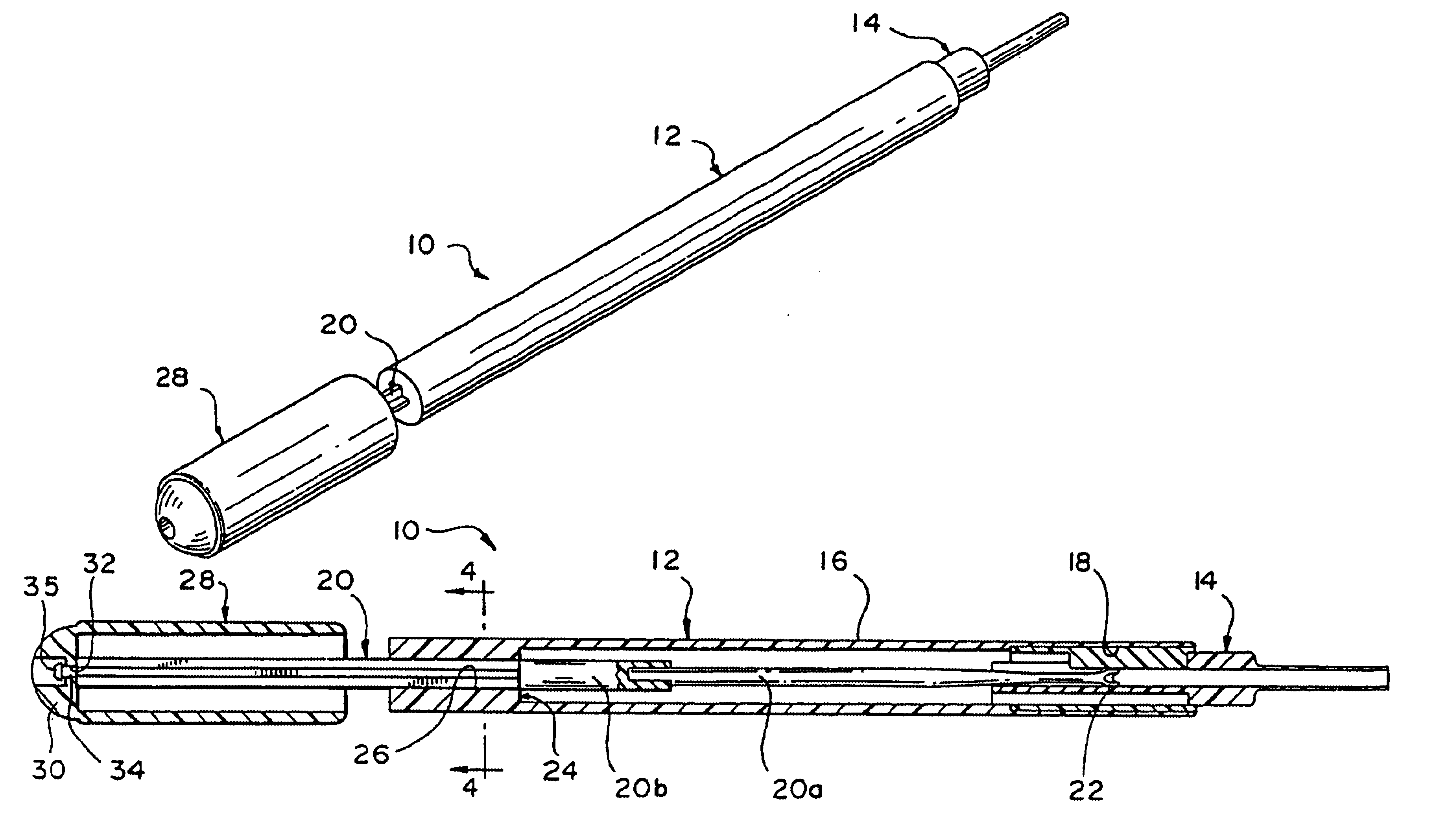
Disposable intraocular lens insertion system
InactiveUS6921405B2Reduce the amount requiredRemove loadEye surgeryIntraocular lensMedicineIntraocular lens insertion
An intraocular lens injection system comprising an injecting device and cartridge. The cartridge comprises a lens holding portion and an outer sleeve portion. The invention includes a method of pre-loading the injecting system, particularly the cartridge, to reduce the amount of packaging, prevent damage to the intraocular lens during packaging and shipping, allow the pre-loaded injecting cartridge to be autoclaved as a unit, and eliminate the step of loading the cartridge with the intraocular lens by the end user to prevent potential damage during this step.
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
Intraocular lens system with injectable accommodation material
ActiveUS9005282B2Modulus of accommodationModifies its propertyIntraocular lensIntraocular lensLens placode
The invention relates to a intraocular lens system having a flexible anterior lens accommodation material behind the lens. The accommodation material may comprise of one or more macromers, which, when polymerized, adjust the properties of the accommodation material. The anterior lens is flexible such that the curvature of the lens changes during accommodation. The anterior lens may be used alone or in combination with a posterior lens.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Ophthalmic dynamic aperture
Embodiments of the present invention relate to an electro-active element having a dynamic aperture. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may be used in a non-focusing ophthalmic device that that is spaced apart from but in optical communication with an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, a contact lens, or a spectacle lens that provide an optical power. The electro-active element provides increased depth of field and may also be used in a focusing or non-focusing device such as an intraocular optic, an intraocular lens, a corneal inlay, a corneal onlay, or a contact lens which may or may not have an optical power. By changing the diameter of dynamic aperture either increased depth of field or increased light reaching the retina may be achieved.
Owner:E VISION LLC +1
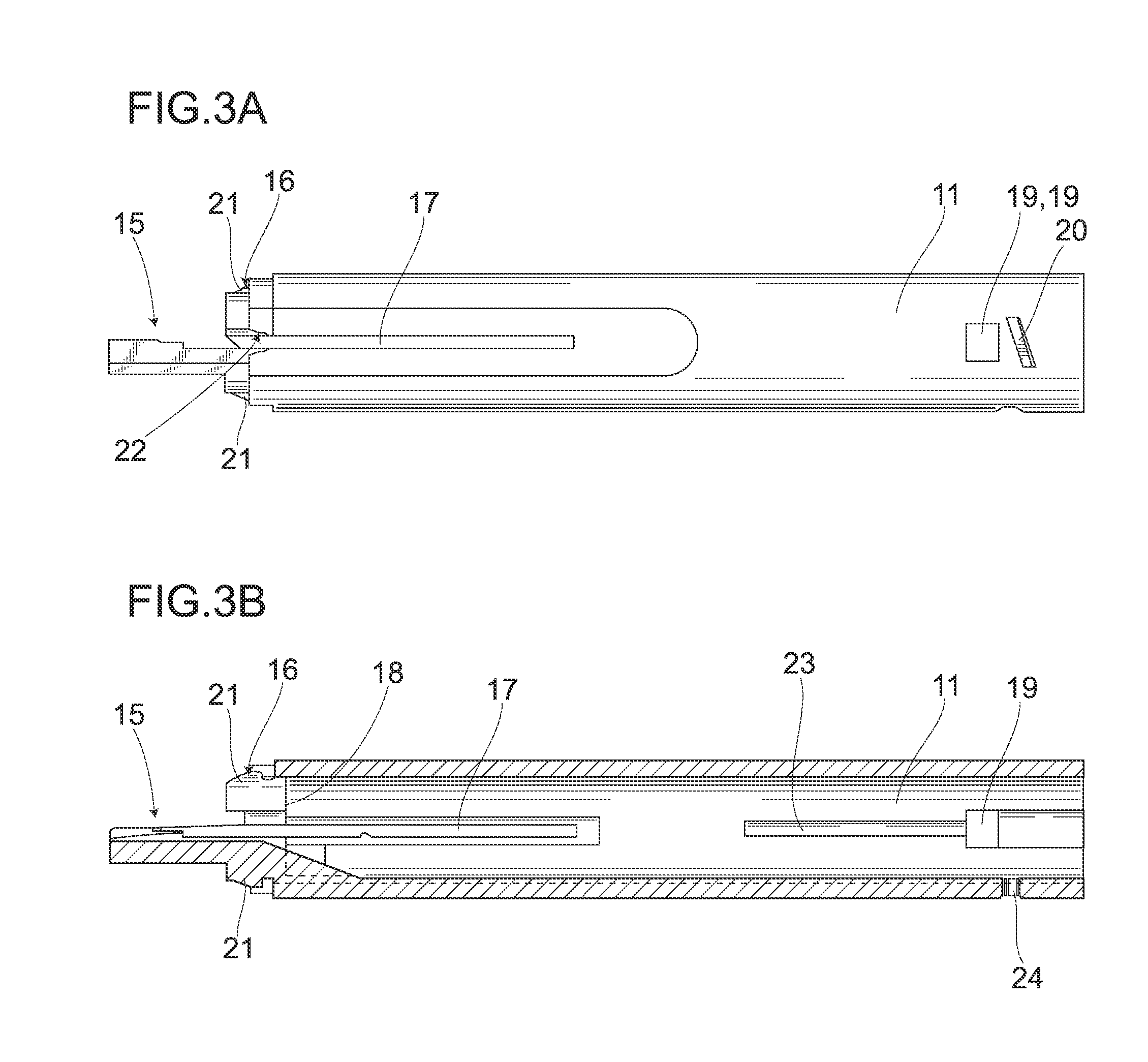
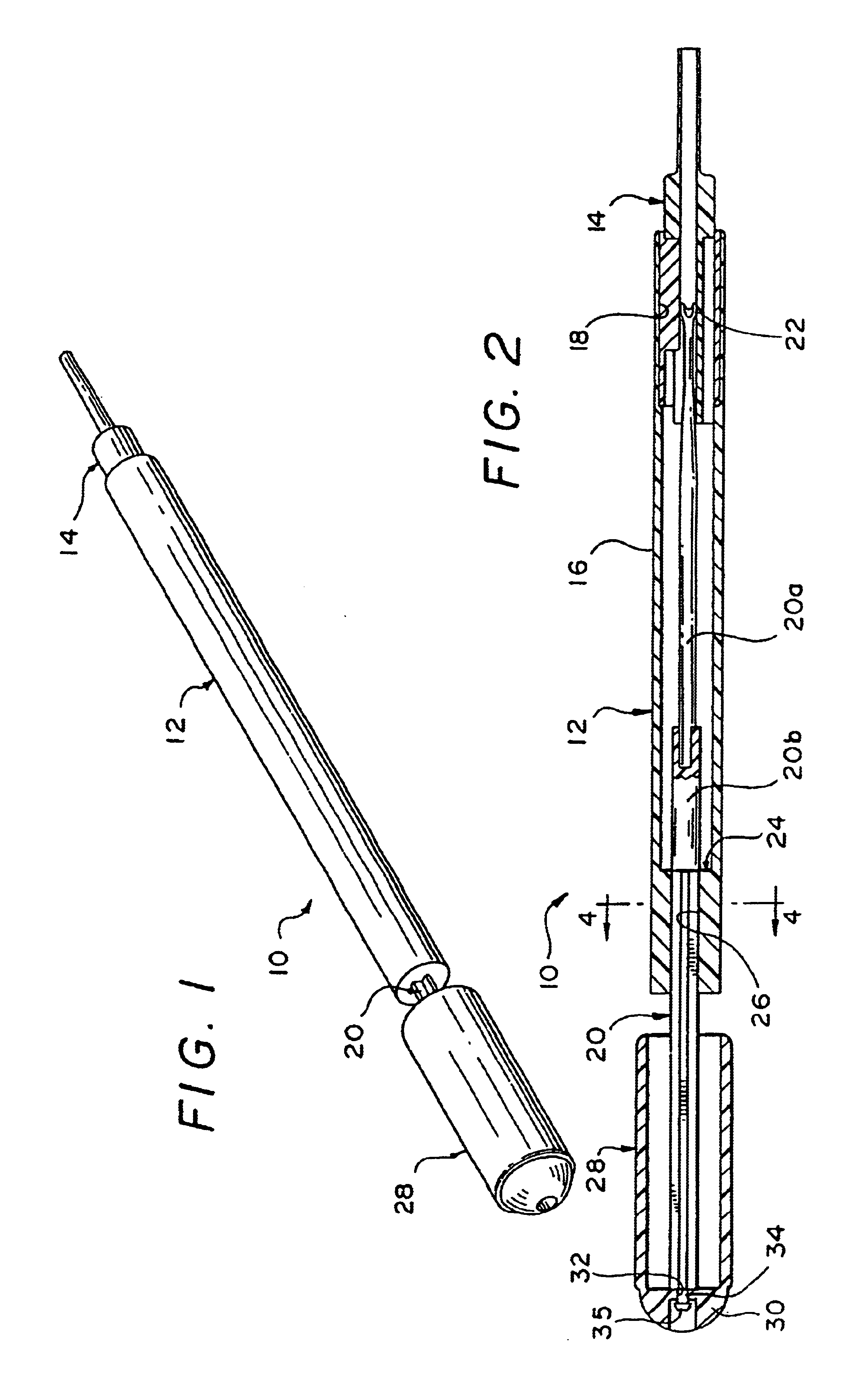
Insertion device for an intraocular lens
ActiveUS7476230B2Guaranteed stable insertionStable supportEye surgeryIntraocular lensMedicineIntraocular lens insertion
In an intraocular-lens insertion device for deforming a deformable intraocular lens to a smaller size and inserting the intraocular lens into an eye via an insertion tube, the insertion tube has such an inner wall shape as to cause the deformable intraocular lens to move rotationally about an insertion tube axis by a predetermined angle in the course of axial movement.
Owner:STAAR JAPAN
Accommodating intraocular lens
InactiveUS20100094412A1Correct visual impairmentImproved ocular implantEye surgeryIntraocular lensLiquid ChangeHigh surface
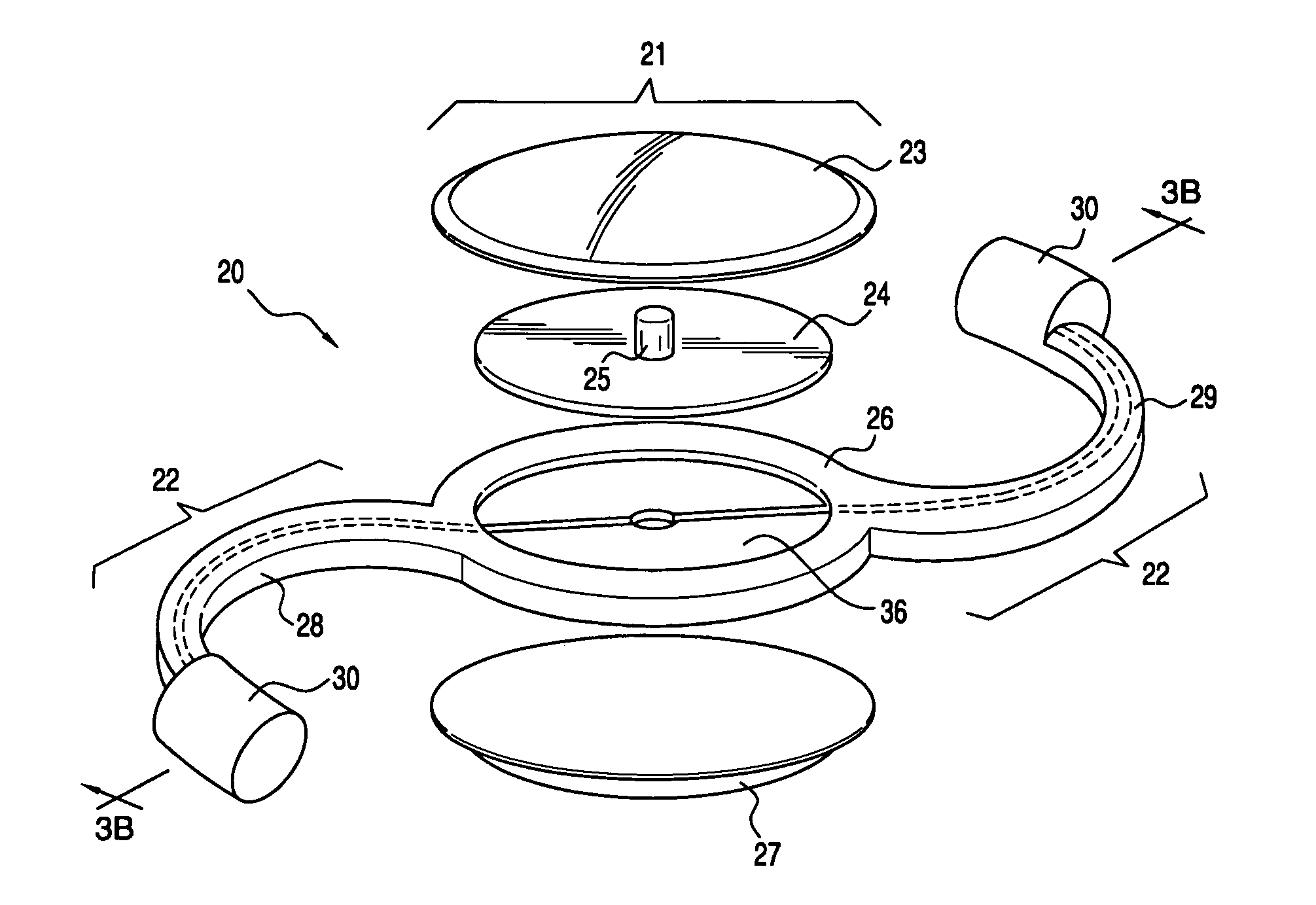
An improved multifocal design for an ocular implant is provided. This ocular implant can include an accommodating intraocular lens (IOL) and a number of haptics. The accommodating IOL includes a liquid suspended between two optically transparent plates or membranes to form a pressure lens that passes optical energy. The haptics mechanically couple to the IOL in order to position and secure the IOL within the eye. The IOL achieves accommodation by using the eye's ciliary muscles to vary the surface curvature of the liquid. The liquid may have a high surface tension and be surrounded by phobic liquid. Pressure from the ciliary muscles causes fluid to be added from or withdrawn to a reservoir. Increasing / decreasing the internal pressure of the liquid changes the angle (curvature) of the surface thus changing the optical properties of the lens. When the pressure is released the liquid returns to the reservoir. The whole system may be sealed off from the interior of the eye by a membrane / transparent lens.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Intraocular lens having extended depth of focus
Owner:AMO REGIONAL HLDG
Intraocular Lens Insertion Device
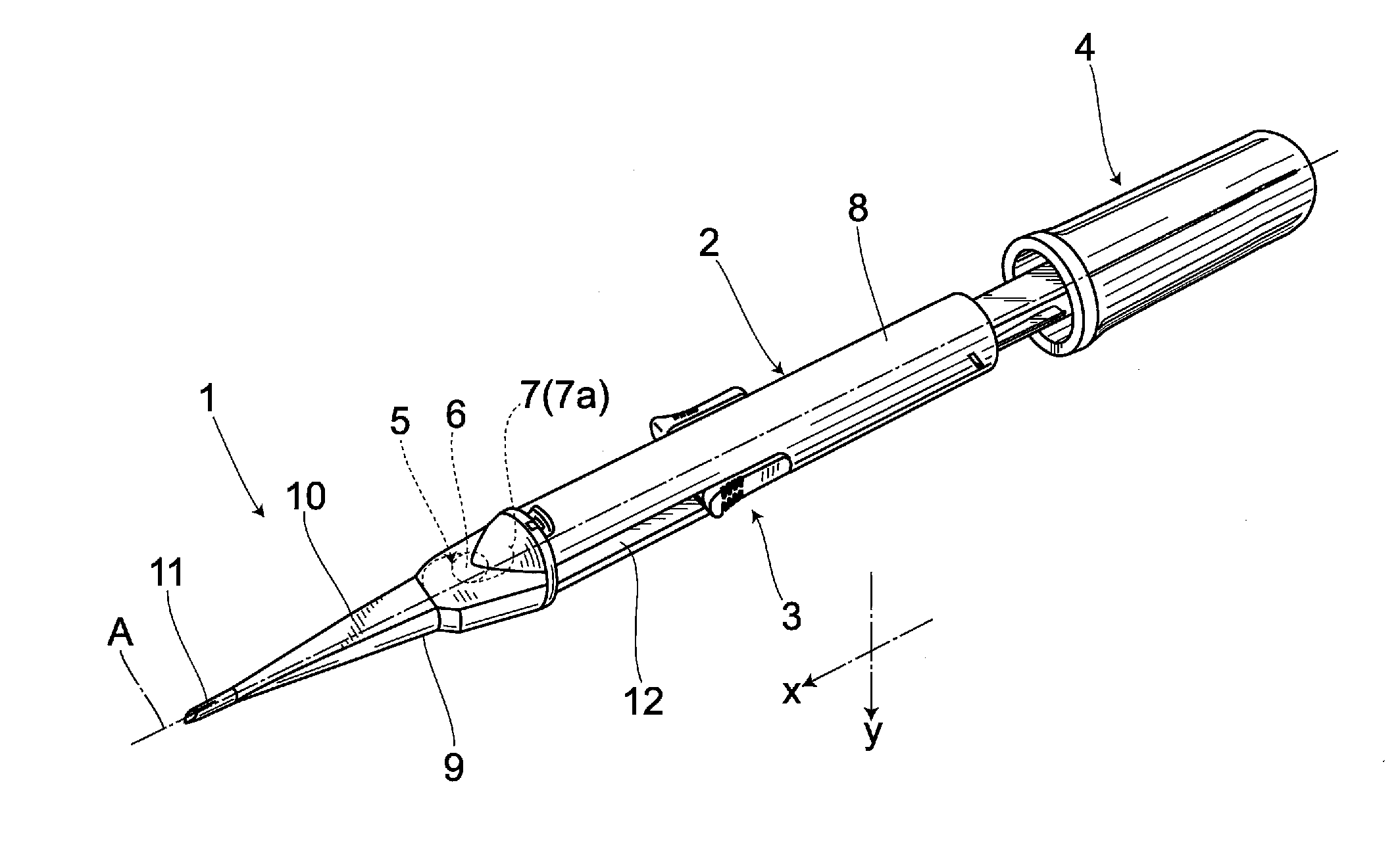
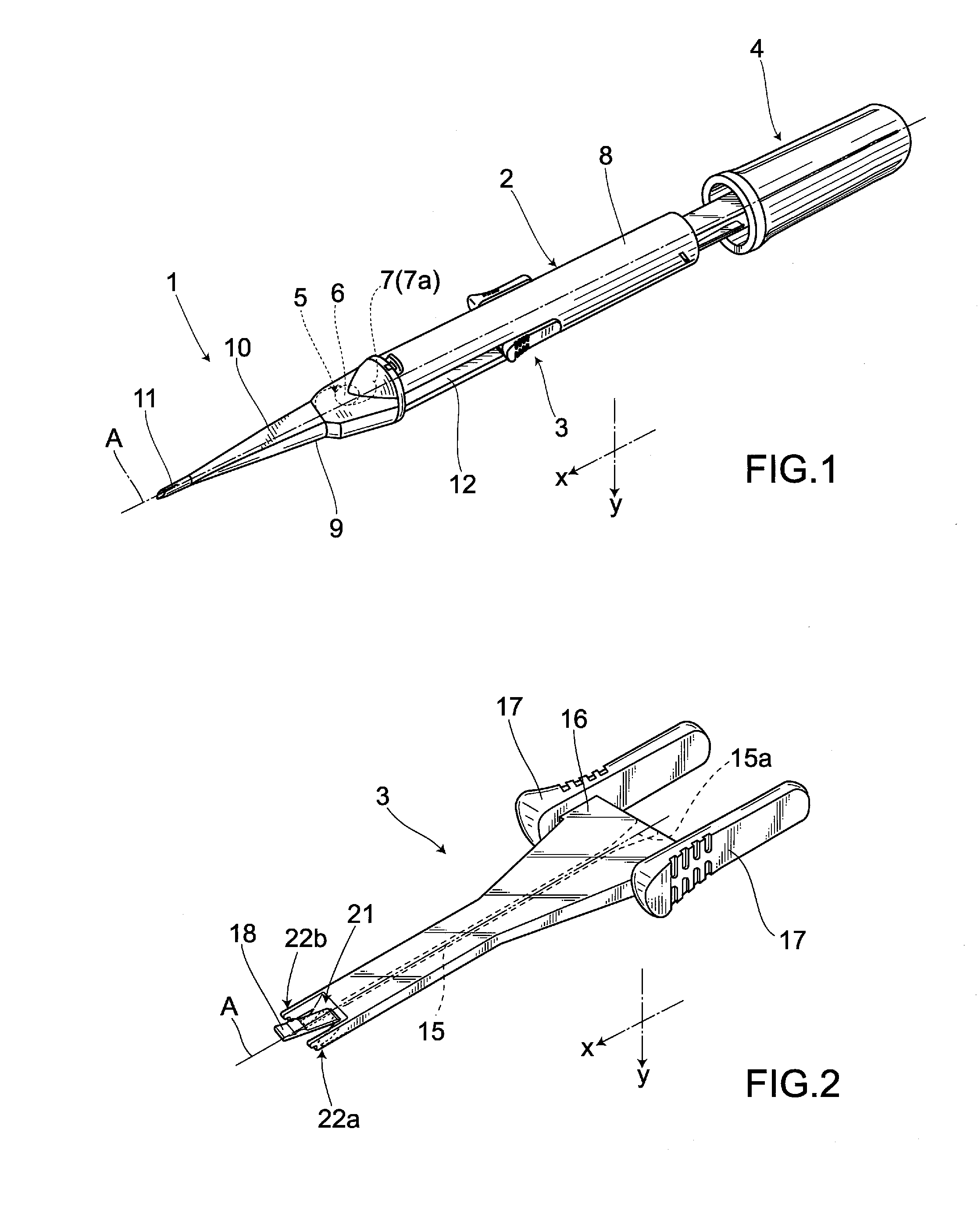
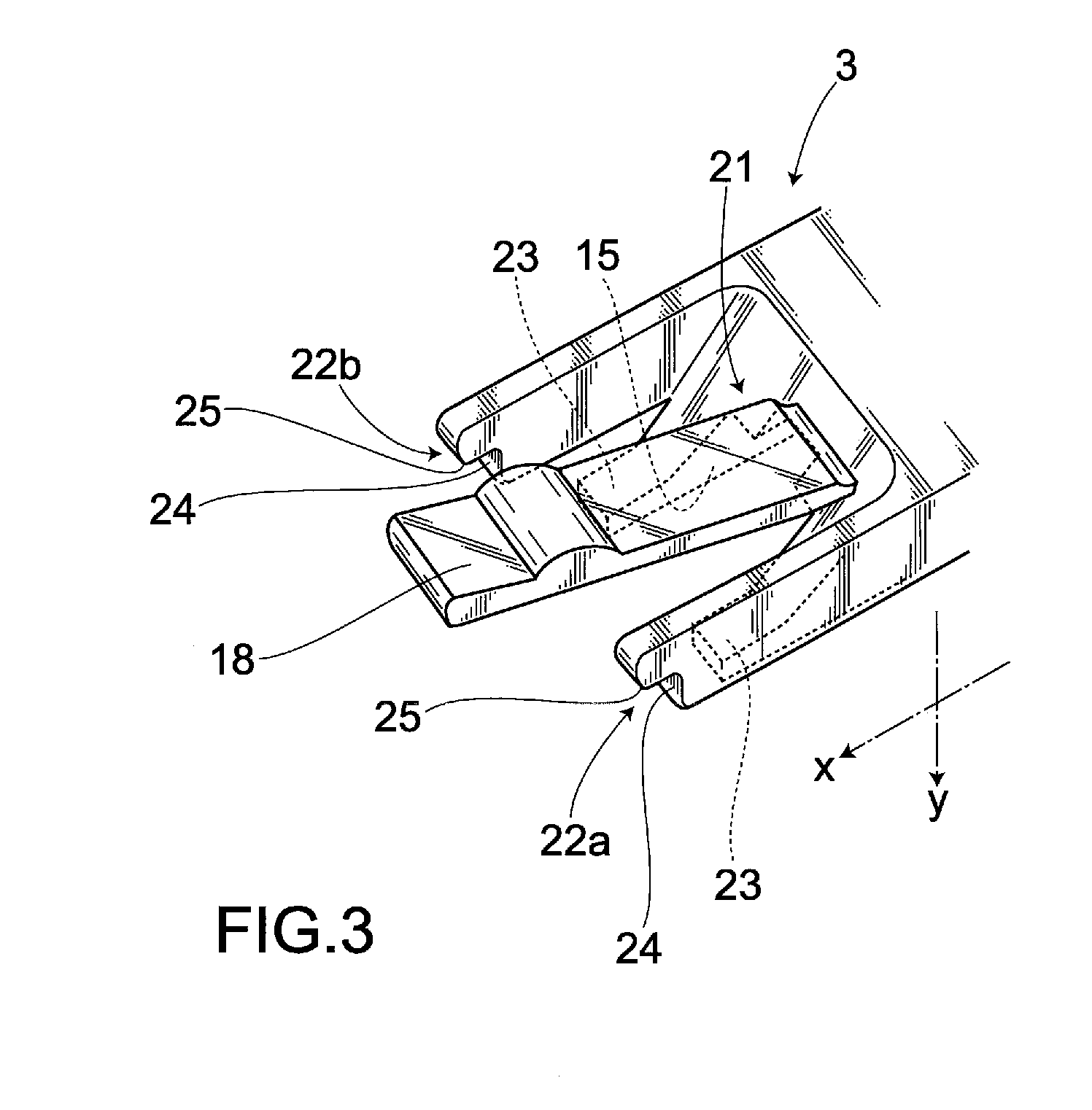
ActiveUS20110288557A1Reduce the possibilityEye surgeryIntraocular lensMedicineIntraocular lens insertion
There is provided an intraocular lens insertion device capable of appropriately regulating the motion of a rear supporting portion during a process of moving an intraocular lens, and reducing the possibility of reoperation being required after the intraocular lens is inserted into an eye. An intraocular lens insertion device 1 comprises a main body 2, and a slider 3 and a plunger 4 that are attached to the main body 2. Further, the intraocular lens insertion device 1 is of a preset type in which an intraocular lens 5 is placed inside the main body 2 in advance. The slider 3 includes a first abutting portion 21 for pushing up a supporting portion 7 (rear supporting portion 7a) arranged on a rear side of an optical part 6 with respect to a lens advancement axis A, and second abutting portions 22a, 22b abutting against an outer edge of a rear portion of the optical part 6.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com