Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Central vision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
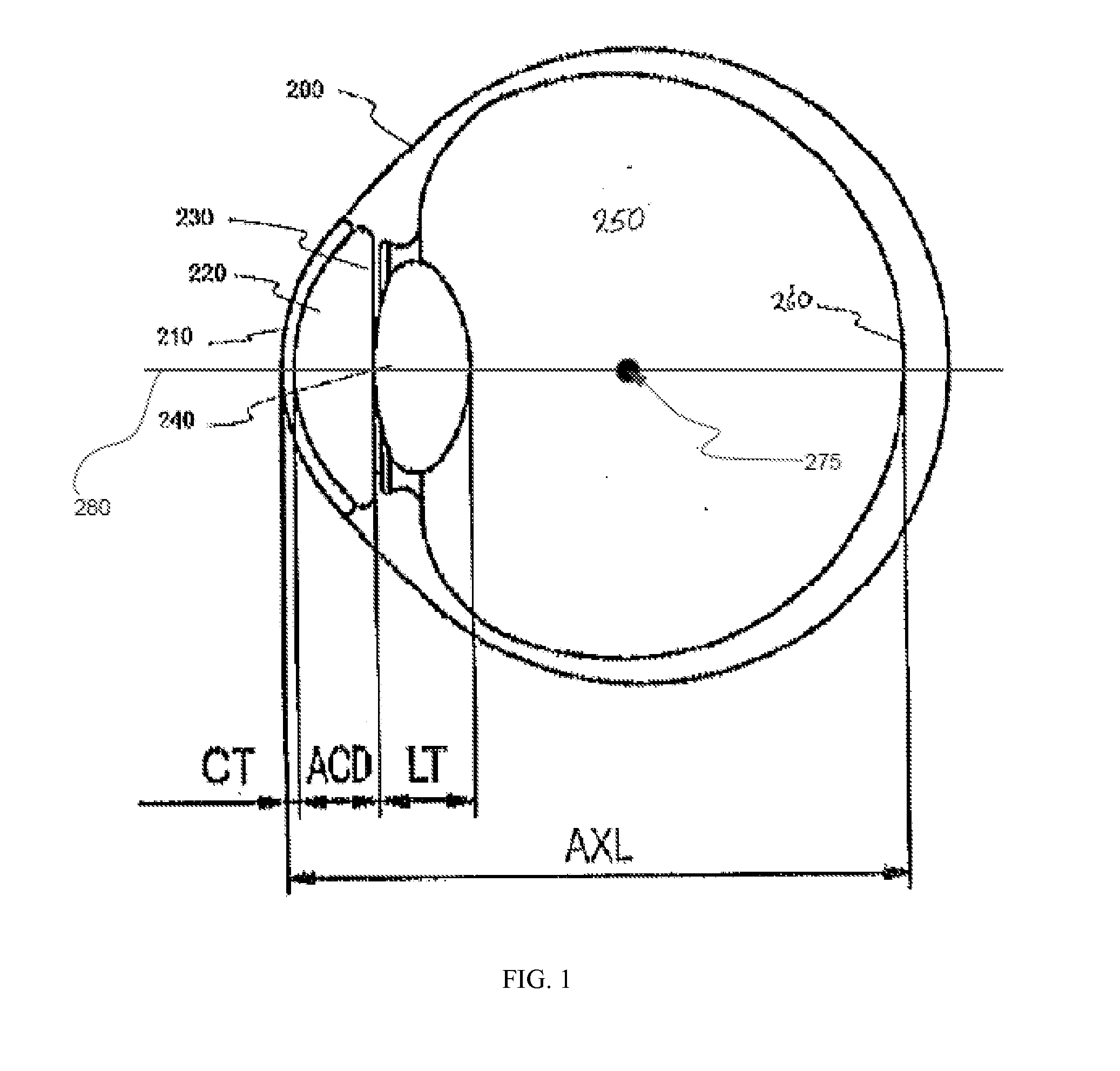
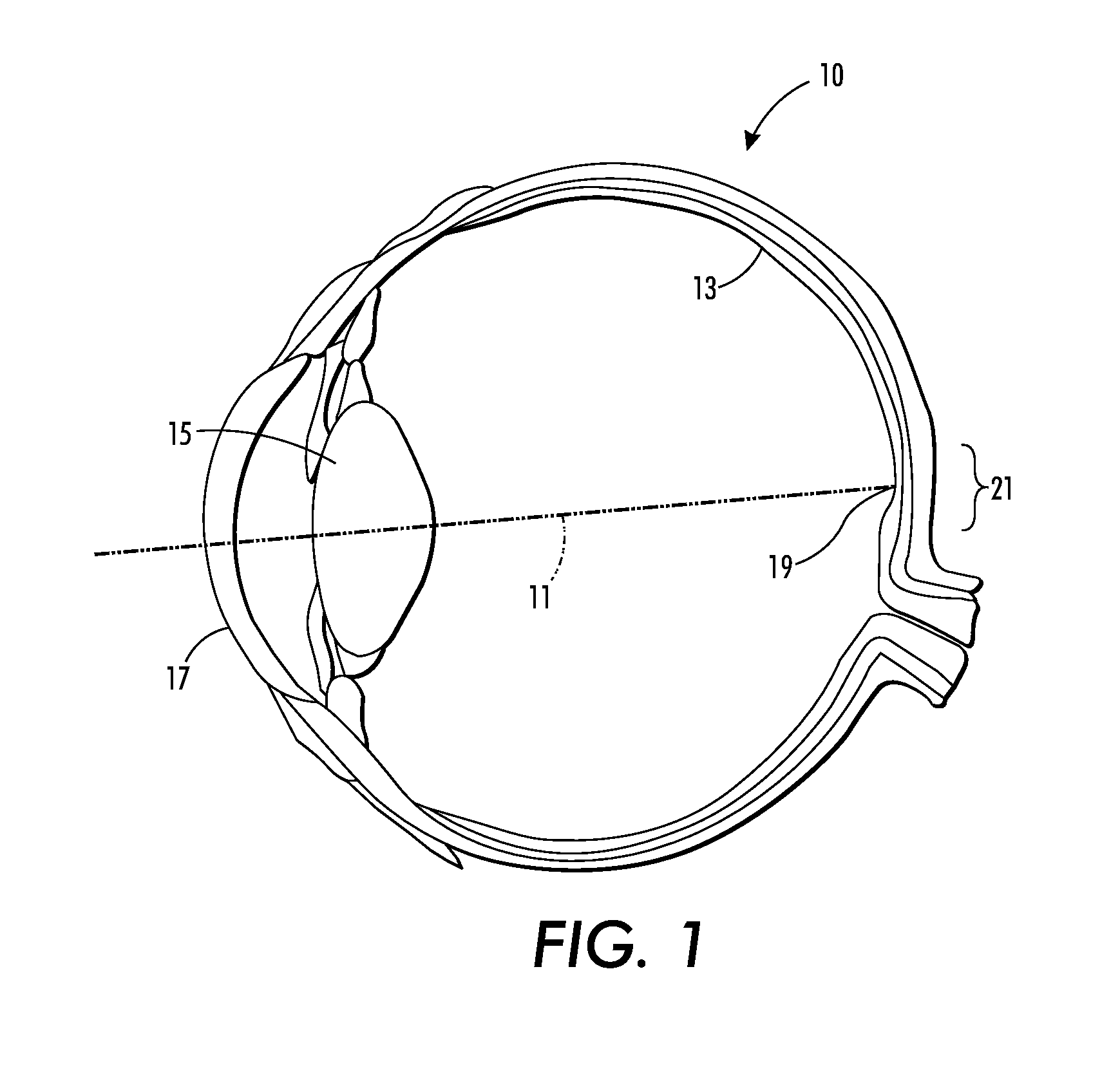
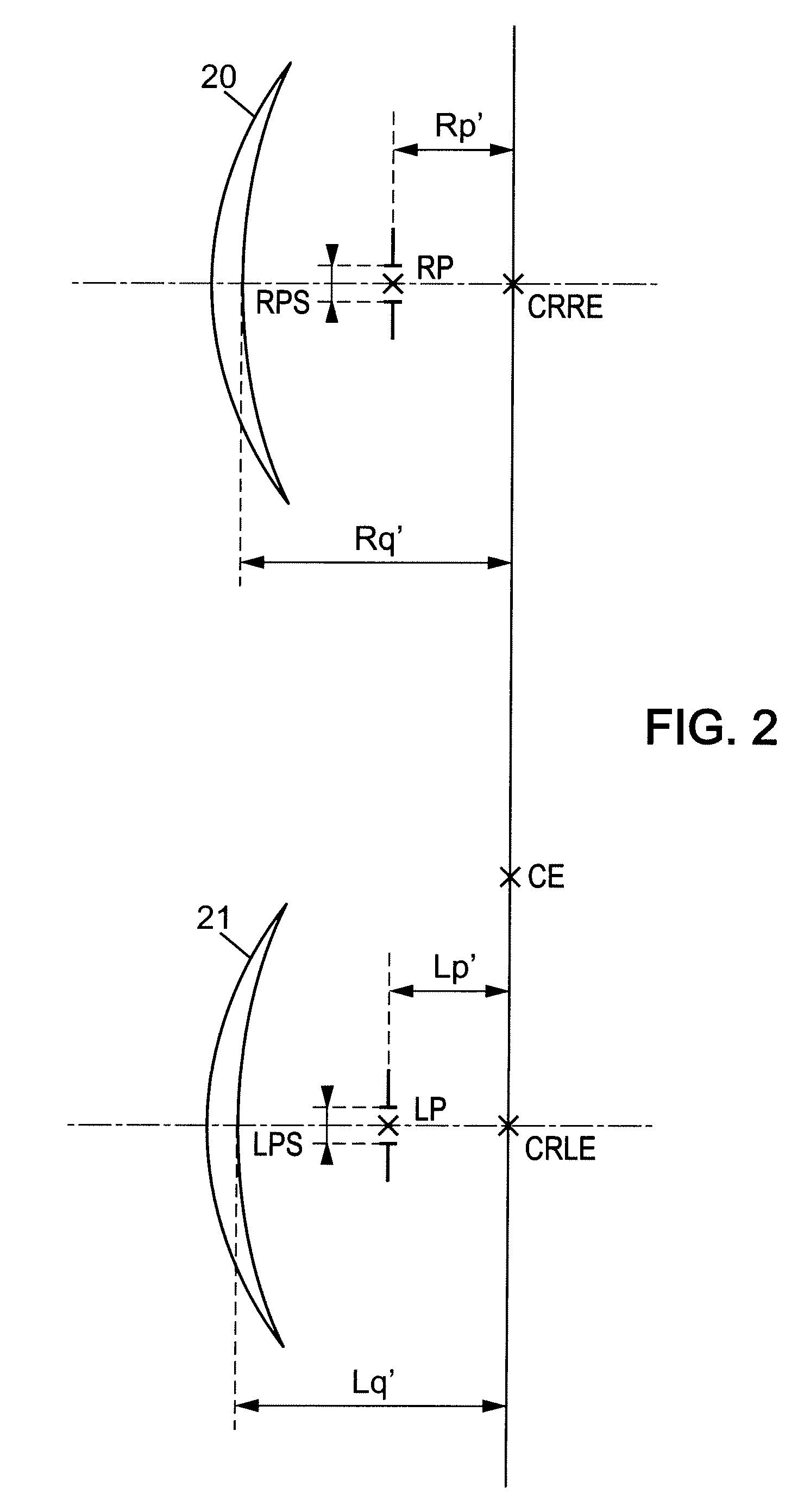
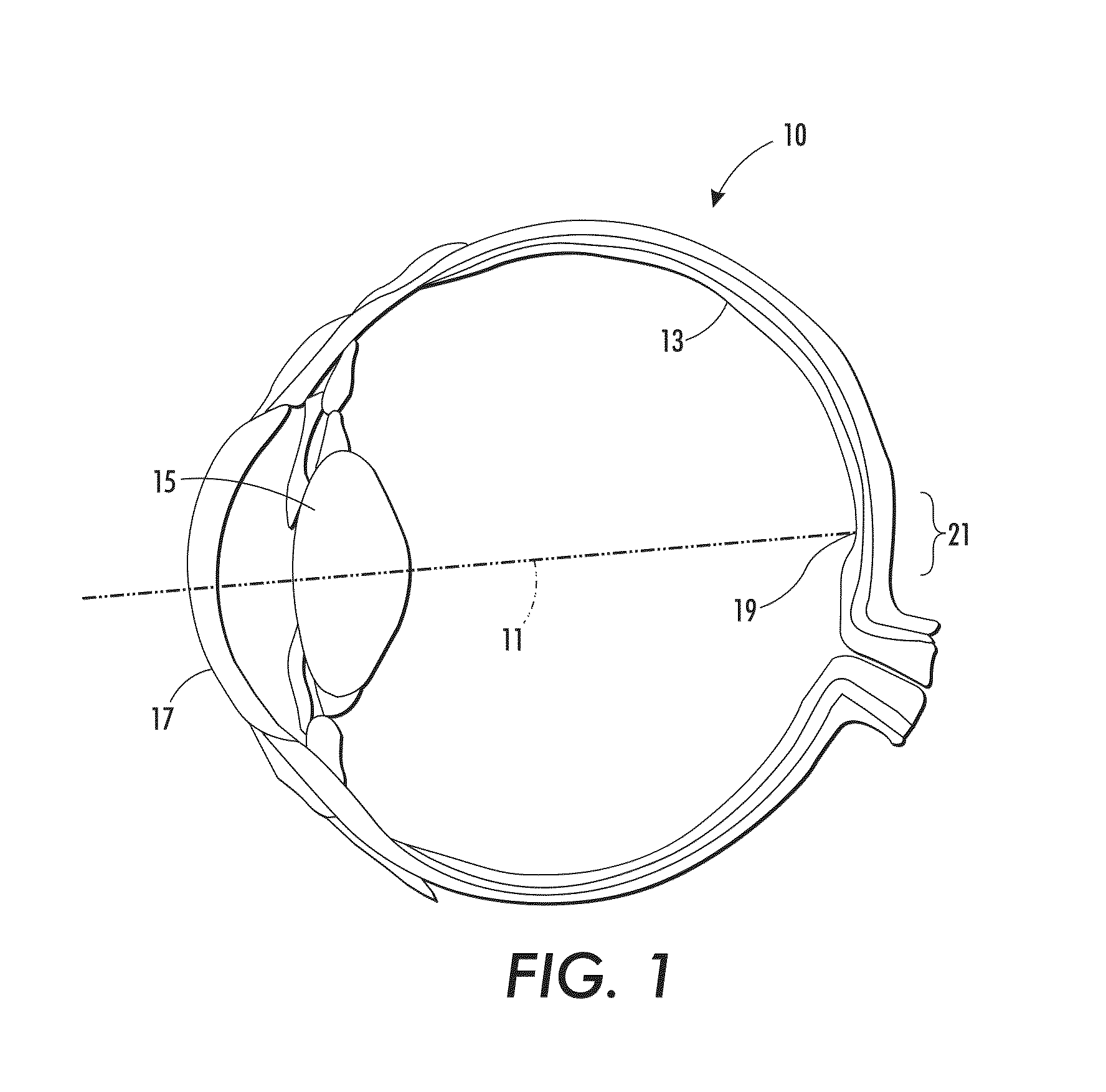
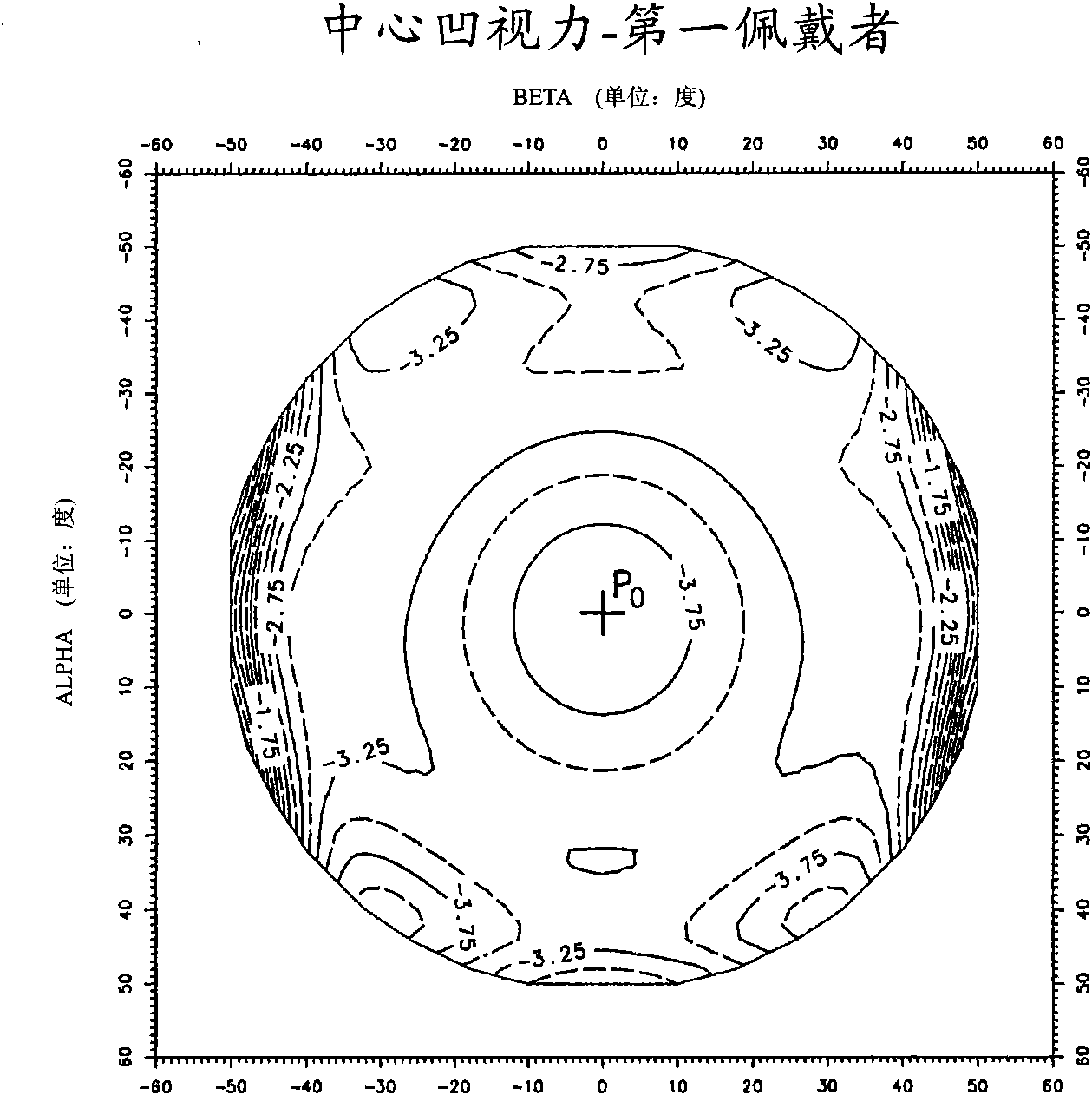
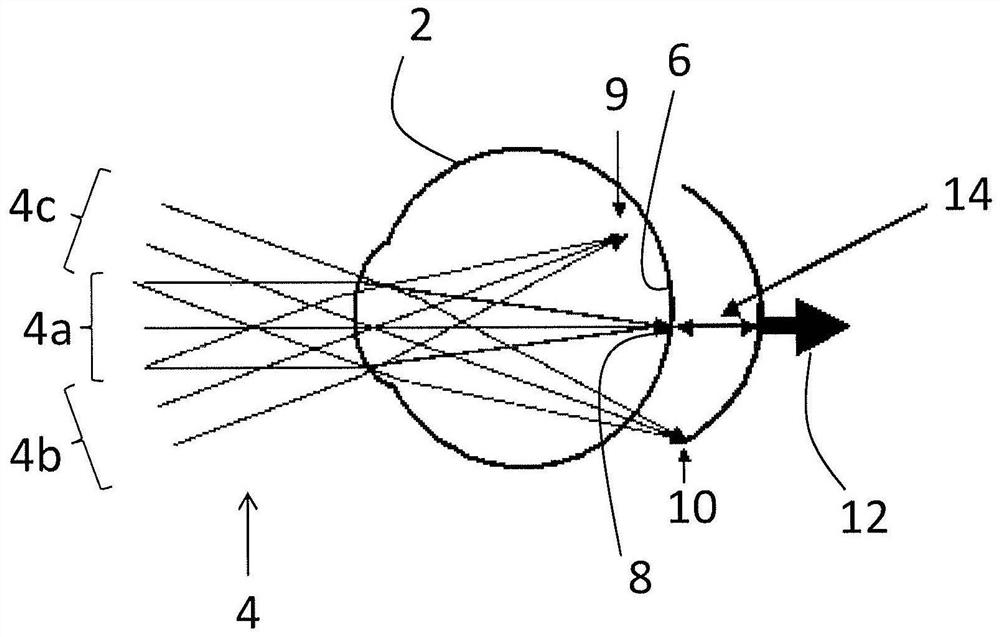
The central vision is the most commonly used part of human vision. It allows people to read, see objects in front of them, and perform other daily tasks and routines. The central vision picks out details of objects, providing the brain with feedback and creating a crisp, clear picture in front of the viewer's eyes.
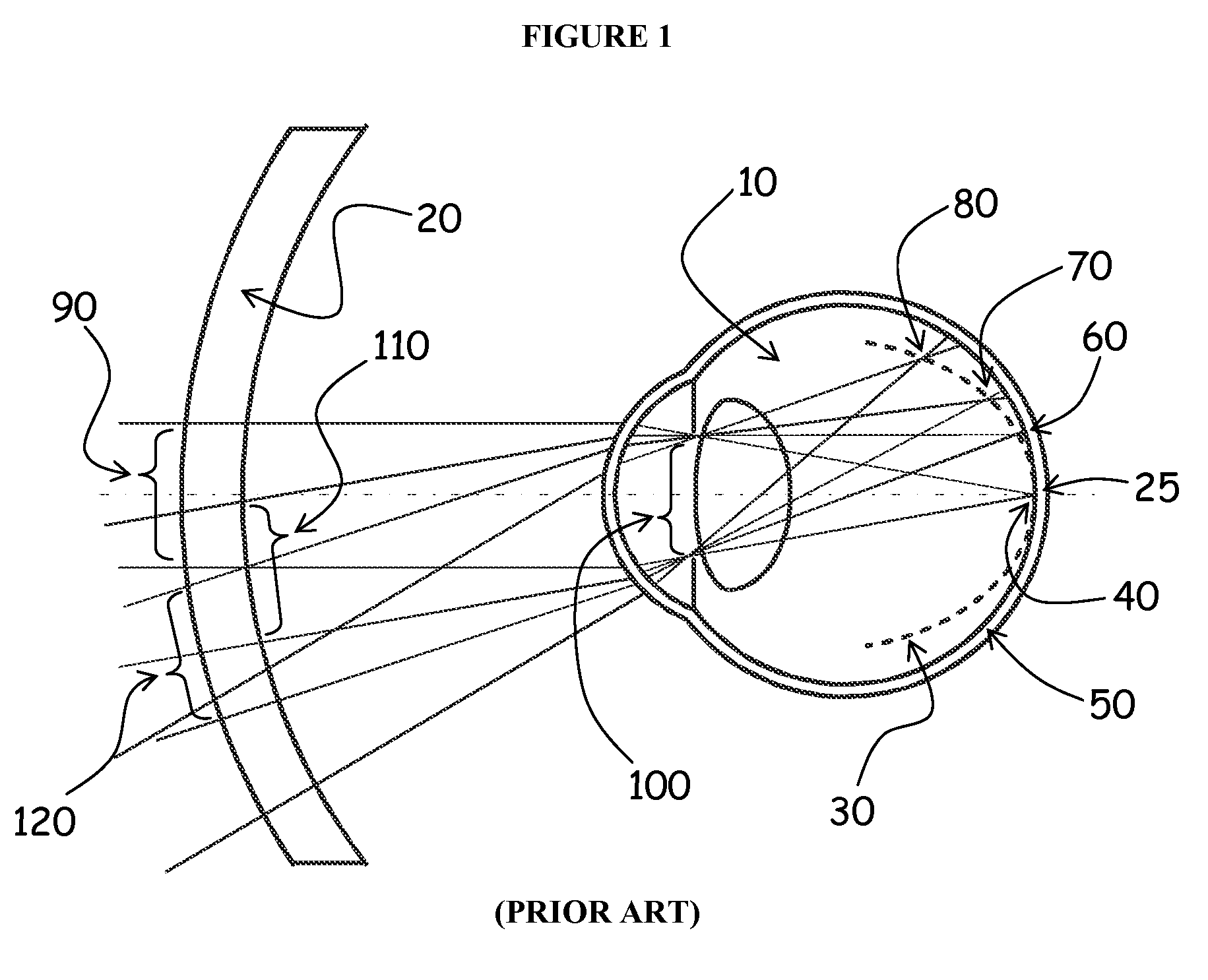
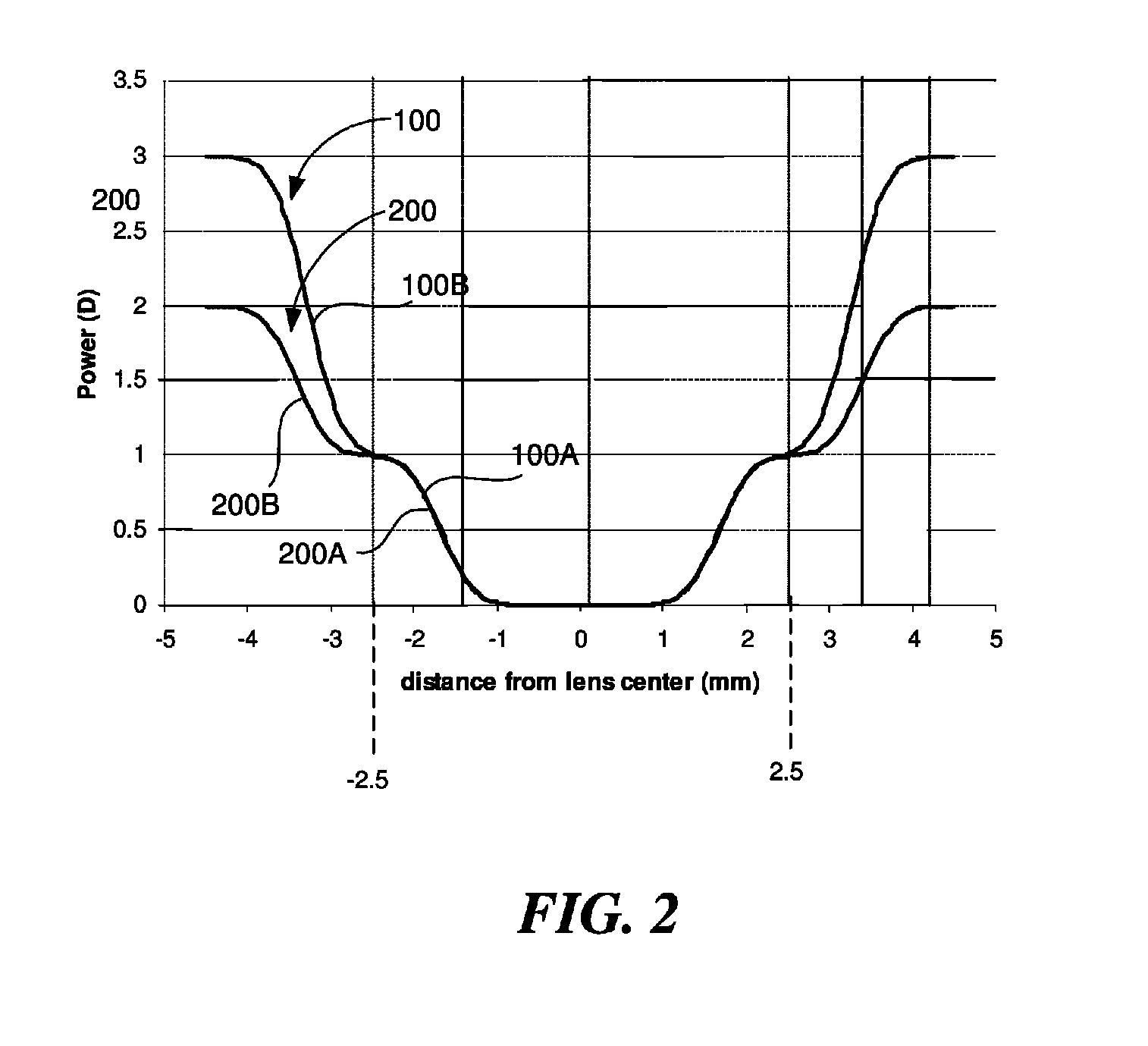
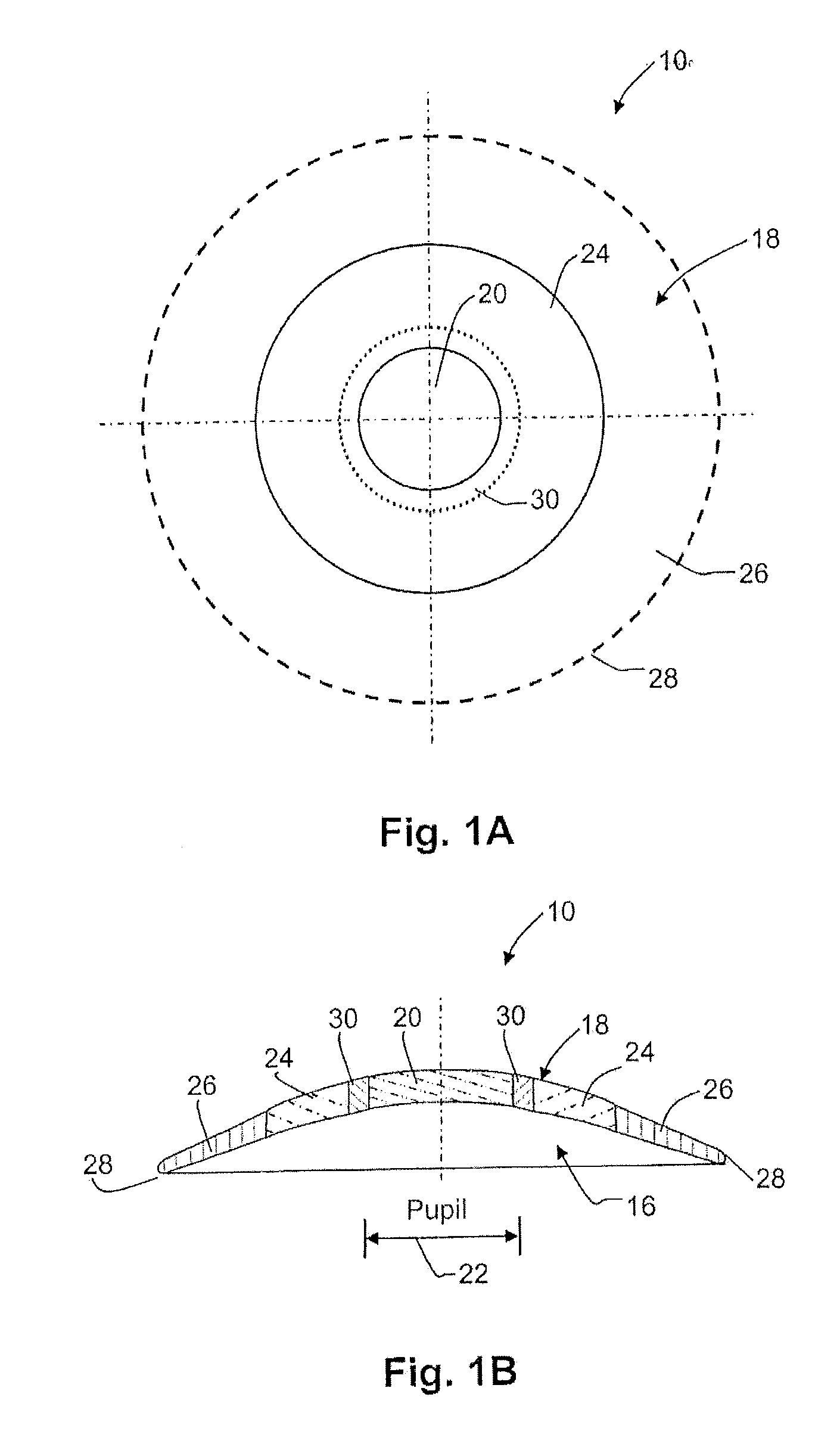
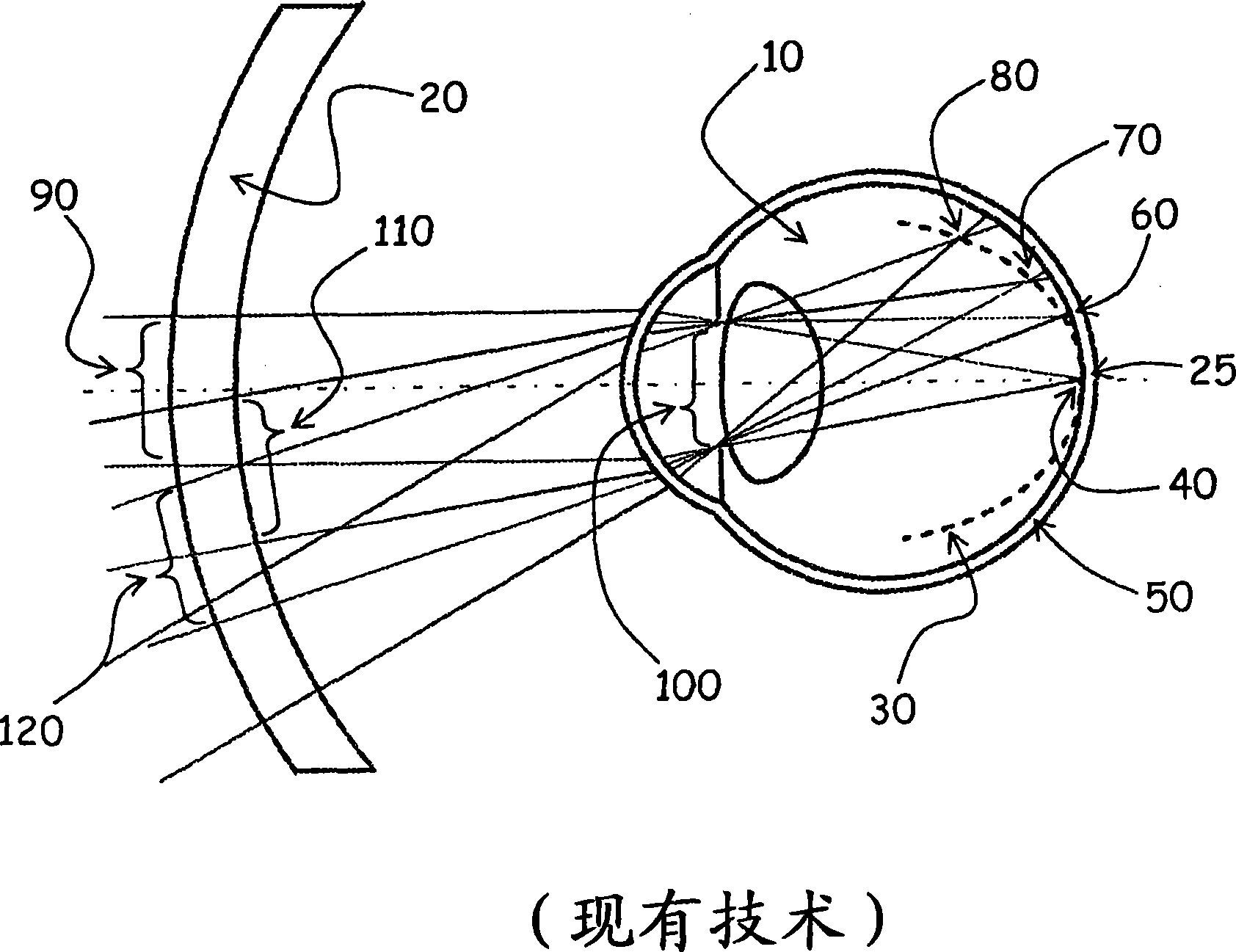
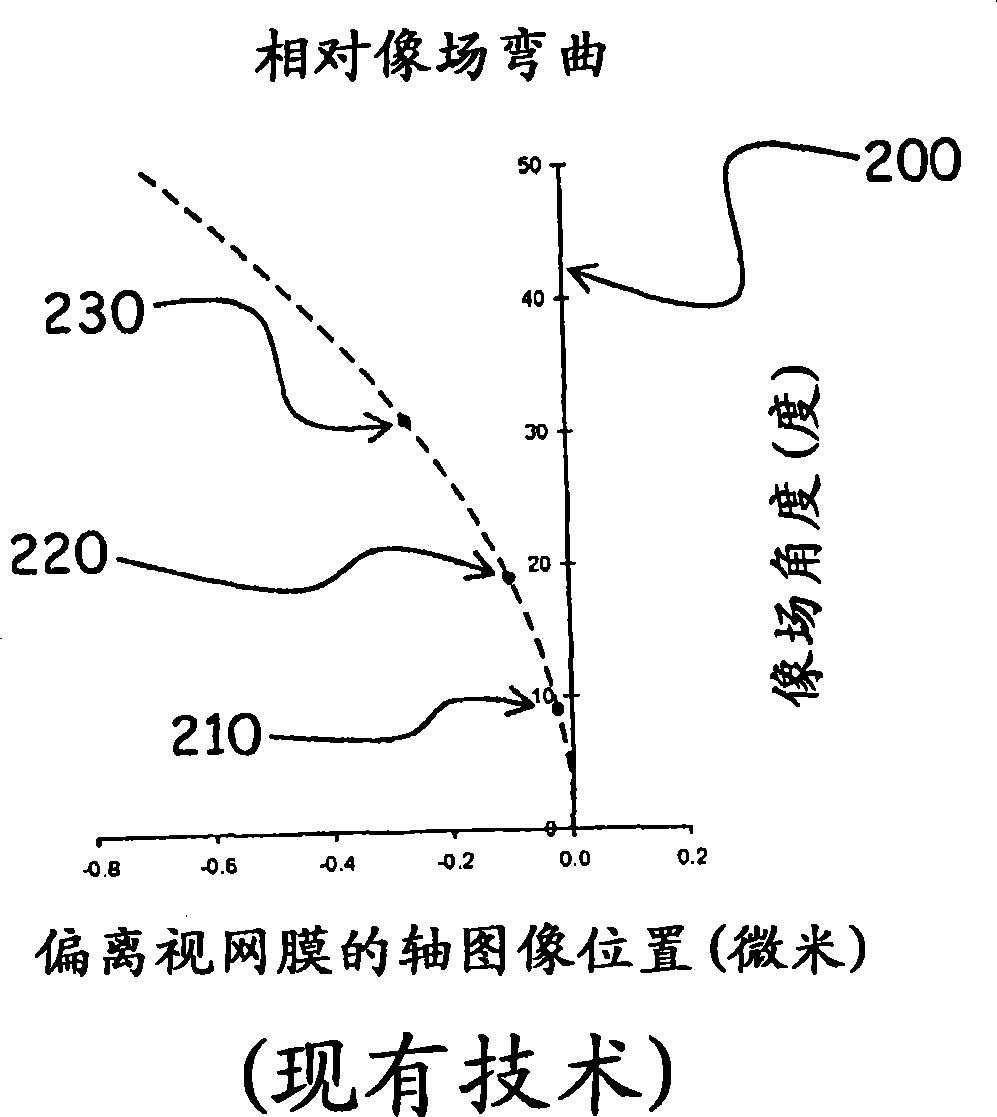
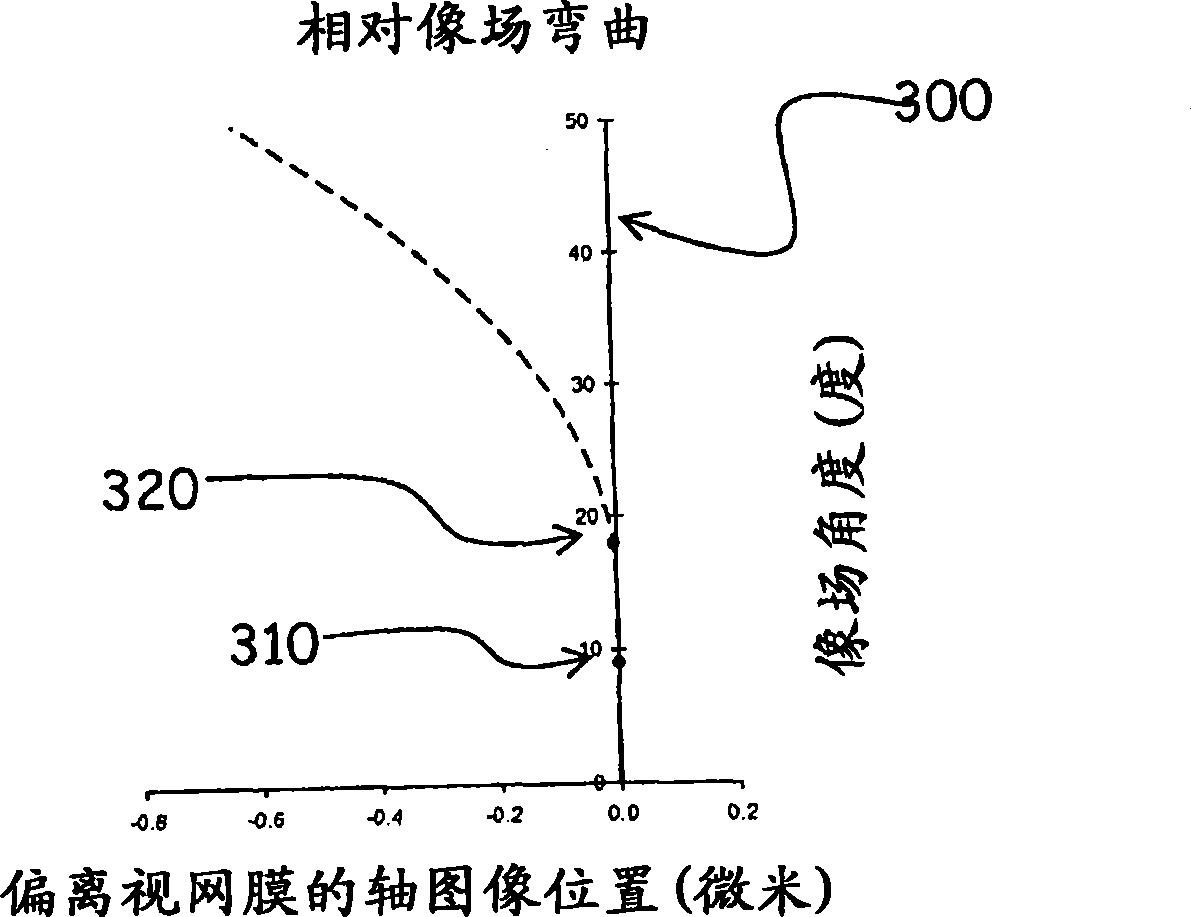
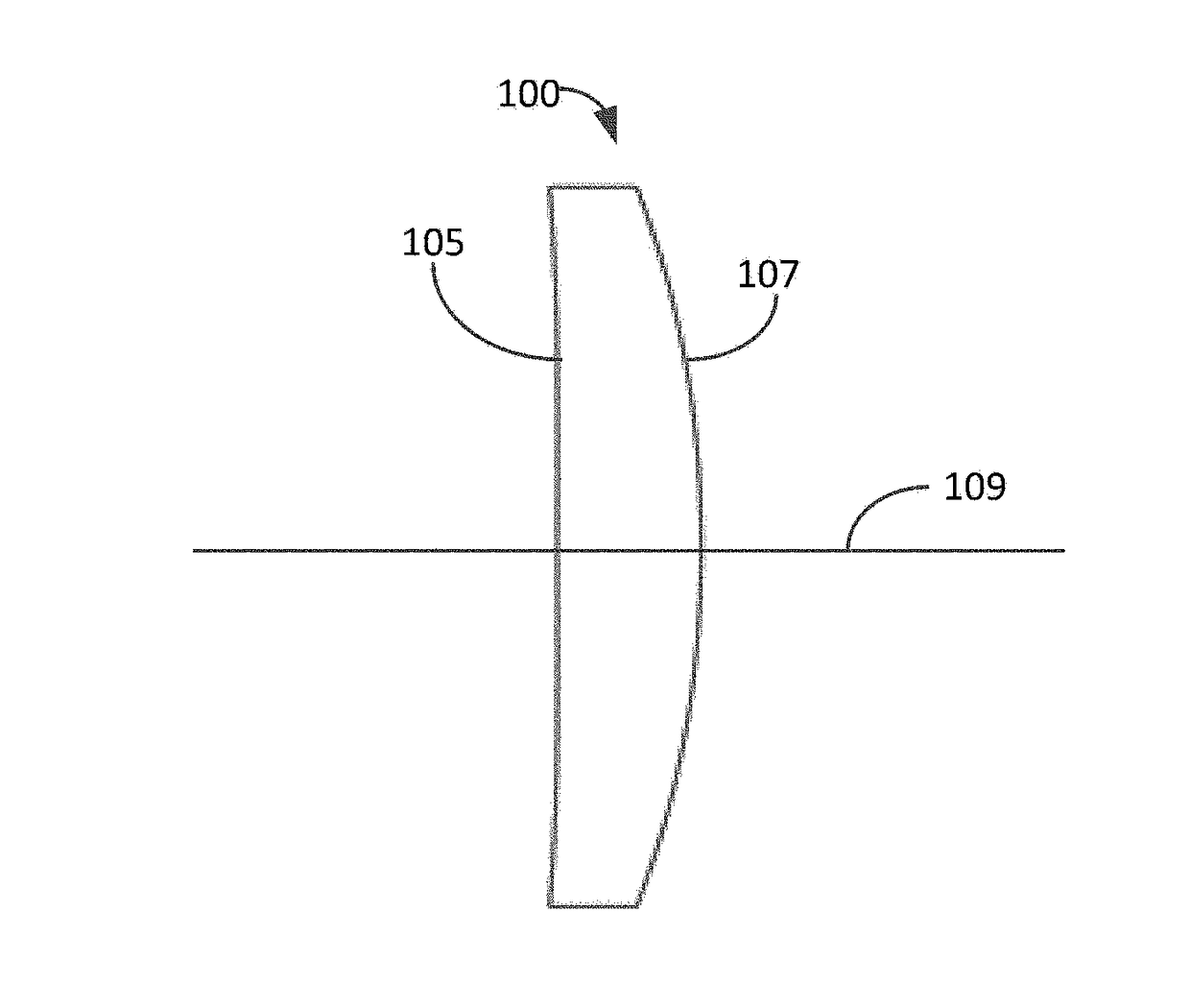
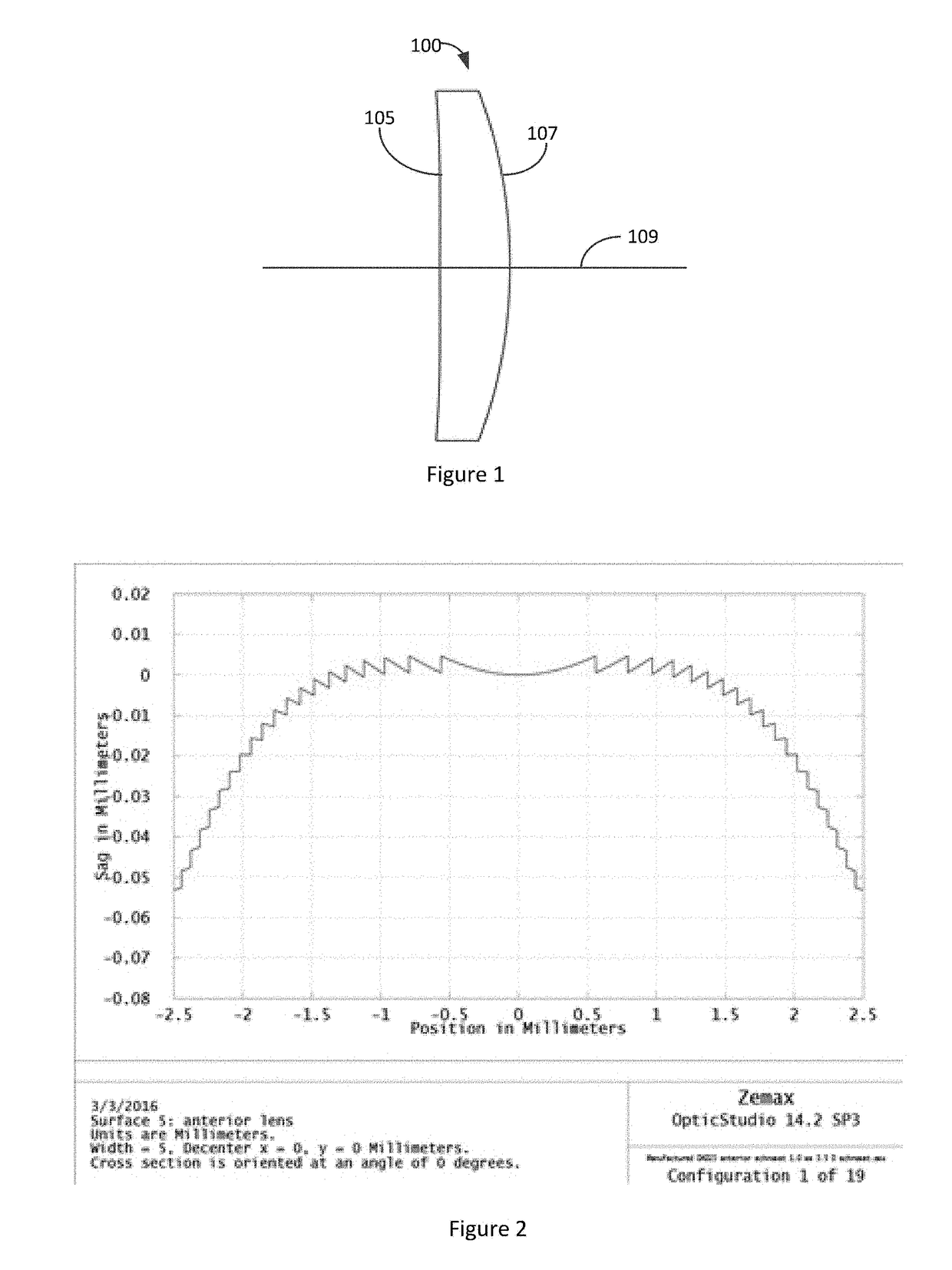
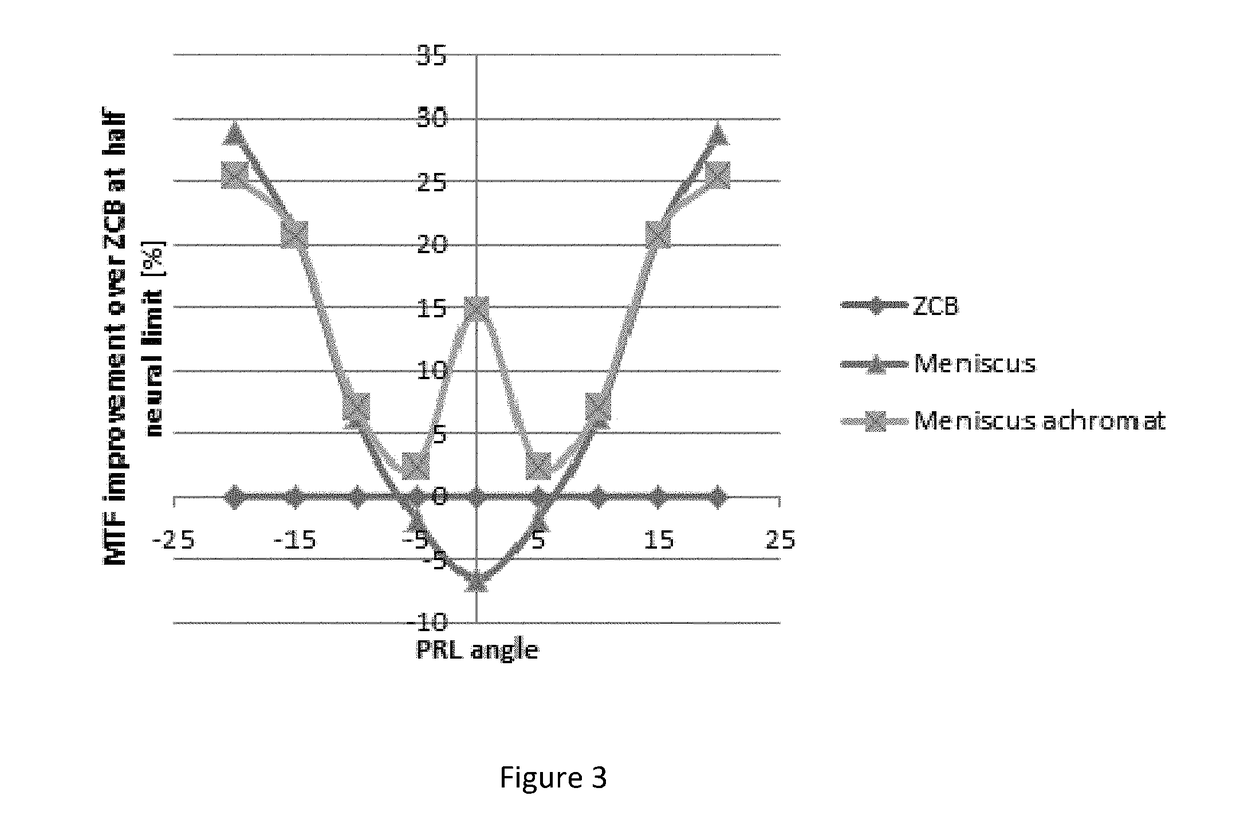
Lens design and method for preventing or slowing the progression of myopia
ActiveUS20100036489A1Prevent myopiaShorten the progressSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensCamera lensCentral vision
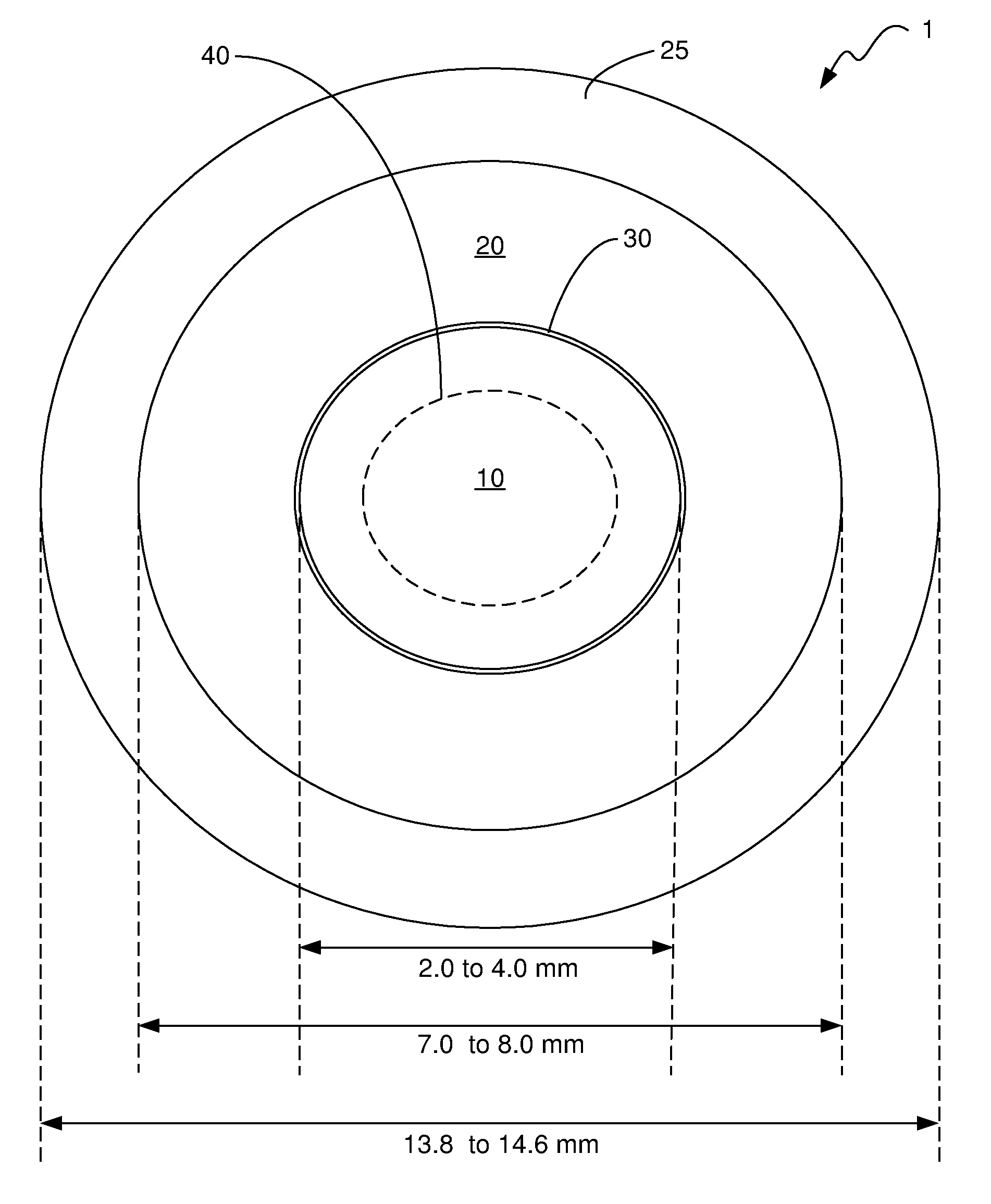
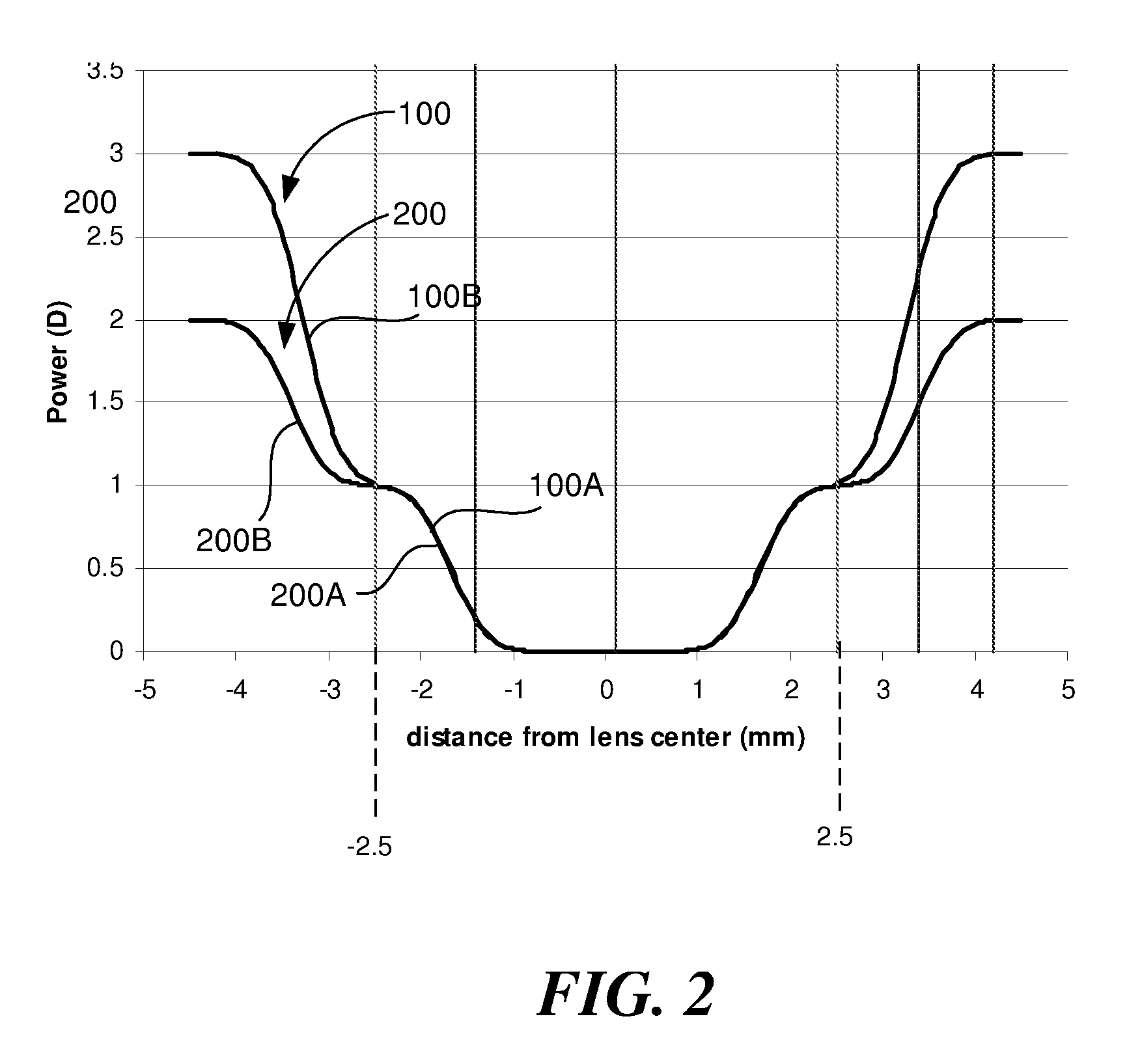
A lens is provided that is capable of preventing or slowing the progression of myopia when worn by a person. The lens has a power profile that reduces on-axis and off-axis hyperopic defocus created by the optics of the eye by creating on-axis and off-axis myopic defocus. The on-axis and off-axis myopic defocus is created by providing light rays that pass through a central vision region of the optical portion and light rays that pass through a peripheral region of the optical portion an increase in positive (plus) power. The overall effect is to prevent or slow the progression of myopia without any perceptible degradation in the person's central vision.
Owner:ALCON INC
Intraocular lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
ActiveUS20150250583A1Improve eyesightReduce sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesOptical propertyPeripheral retina
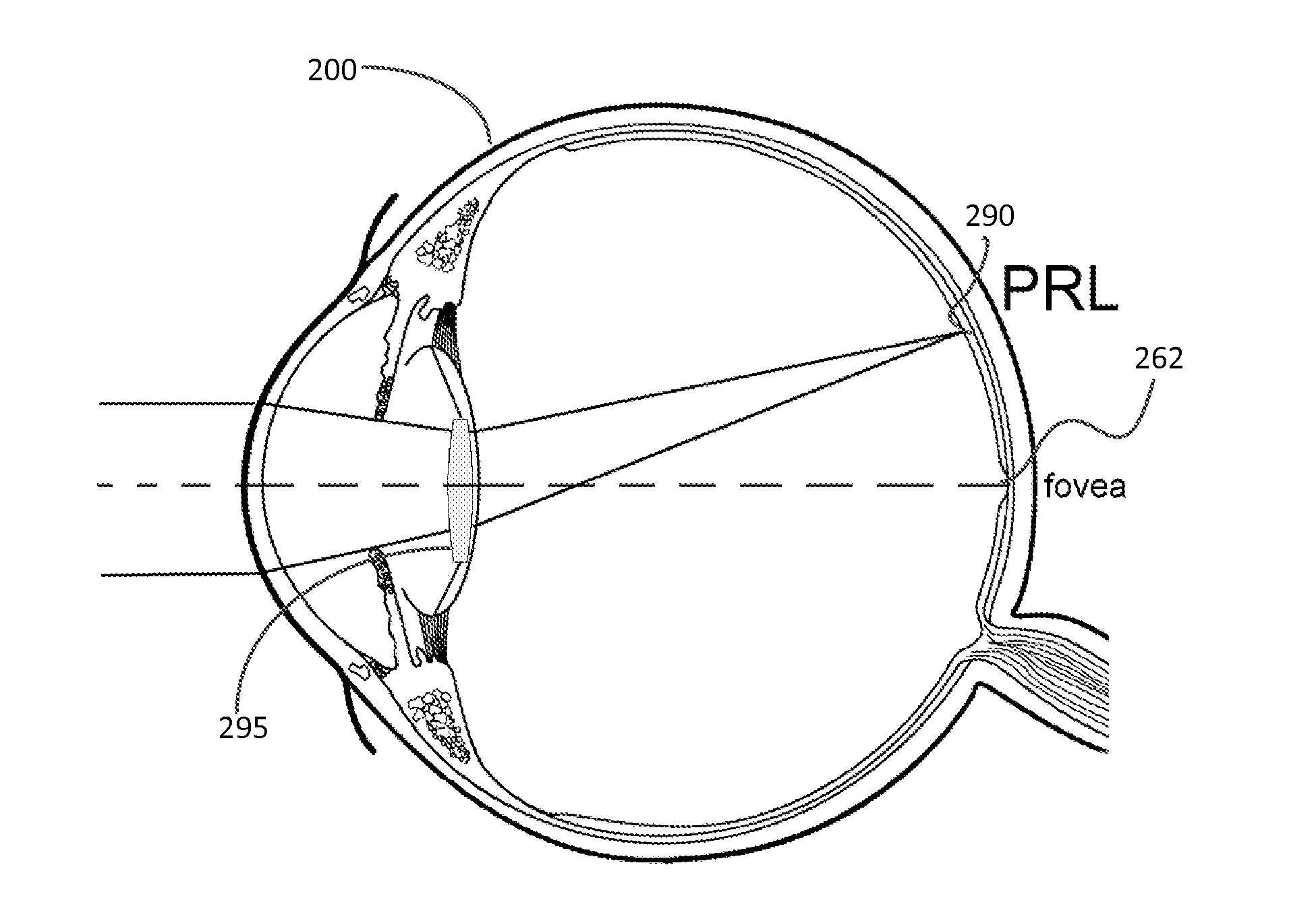
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing symmetric or asymmetric optic with aspheric surface which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
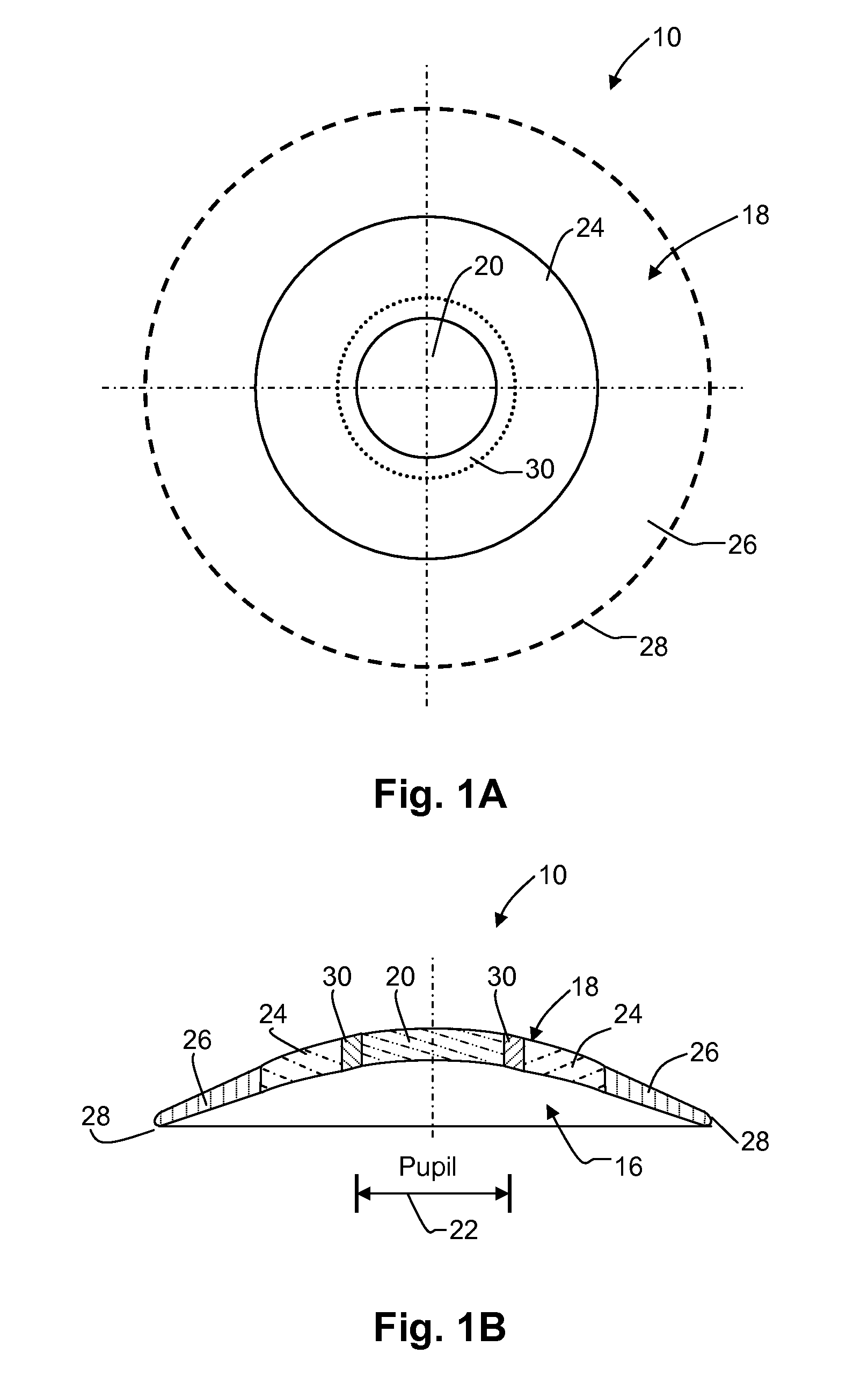
Means for controlling the progression of myopia
ActiveUS20070296916A1Low elongationInhibit progressSpectales/gogglesOptical partsOptical propertyCentral vision
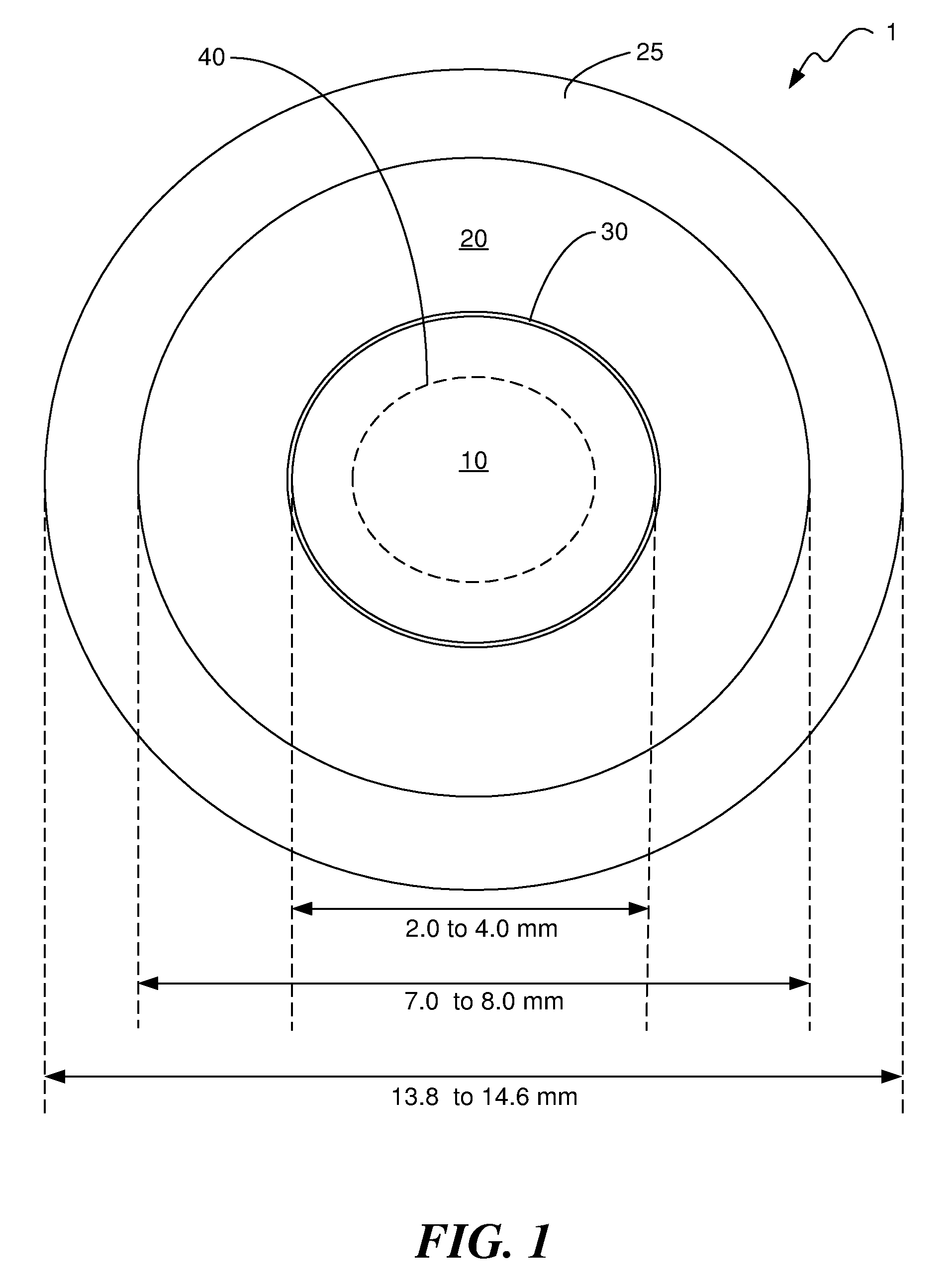
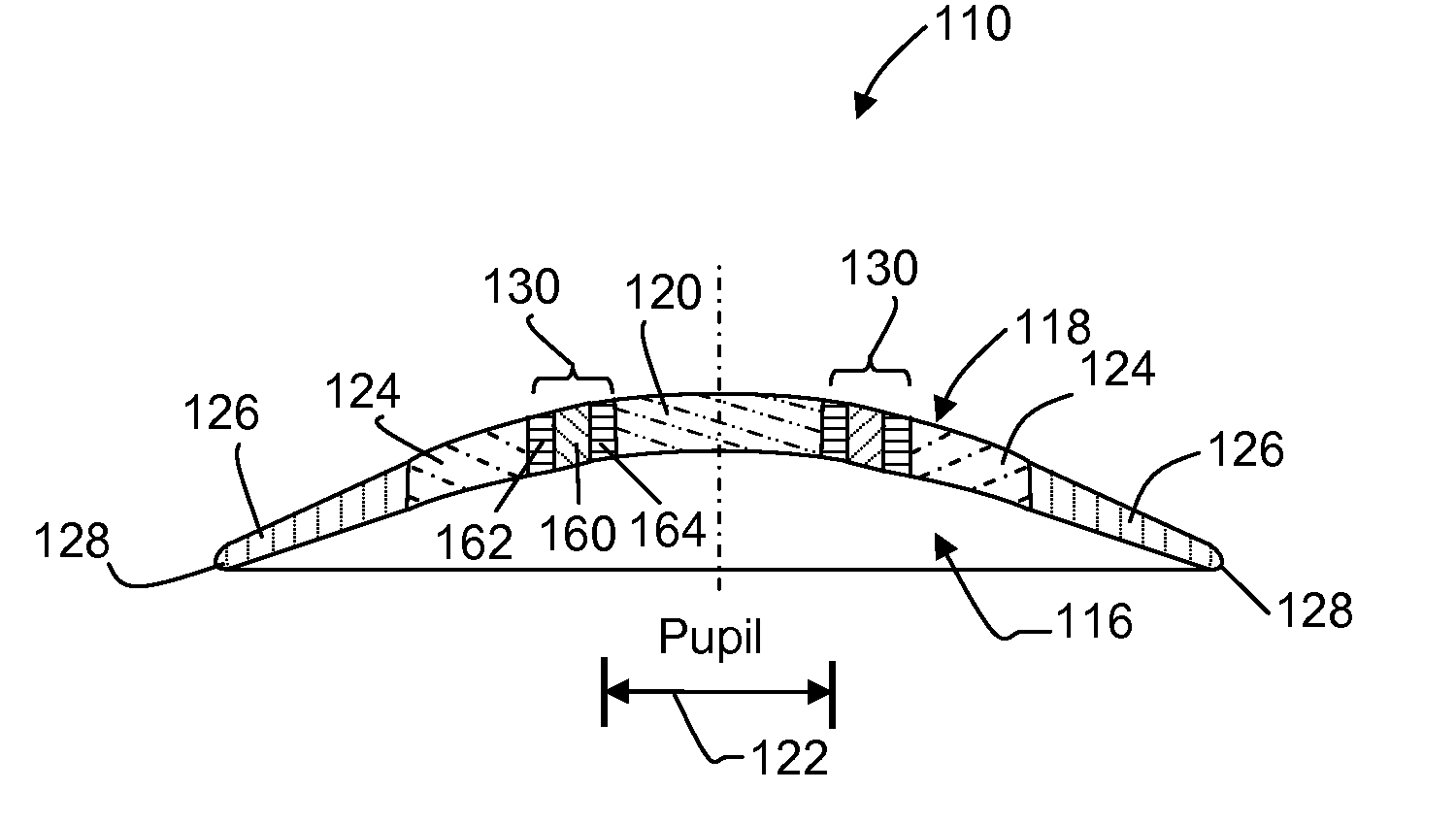
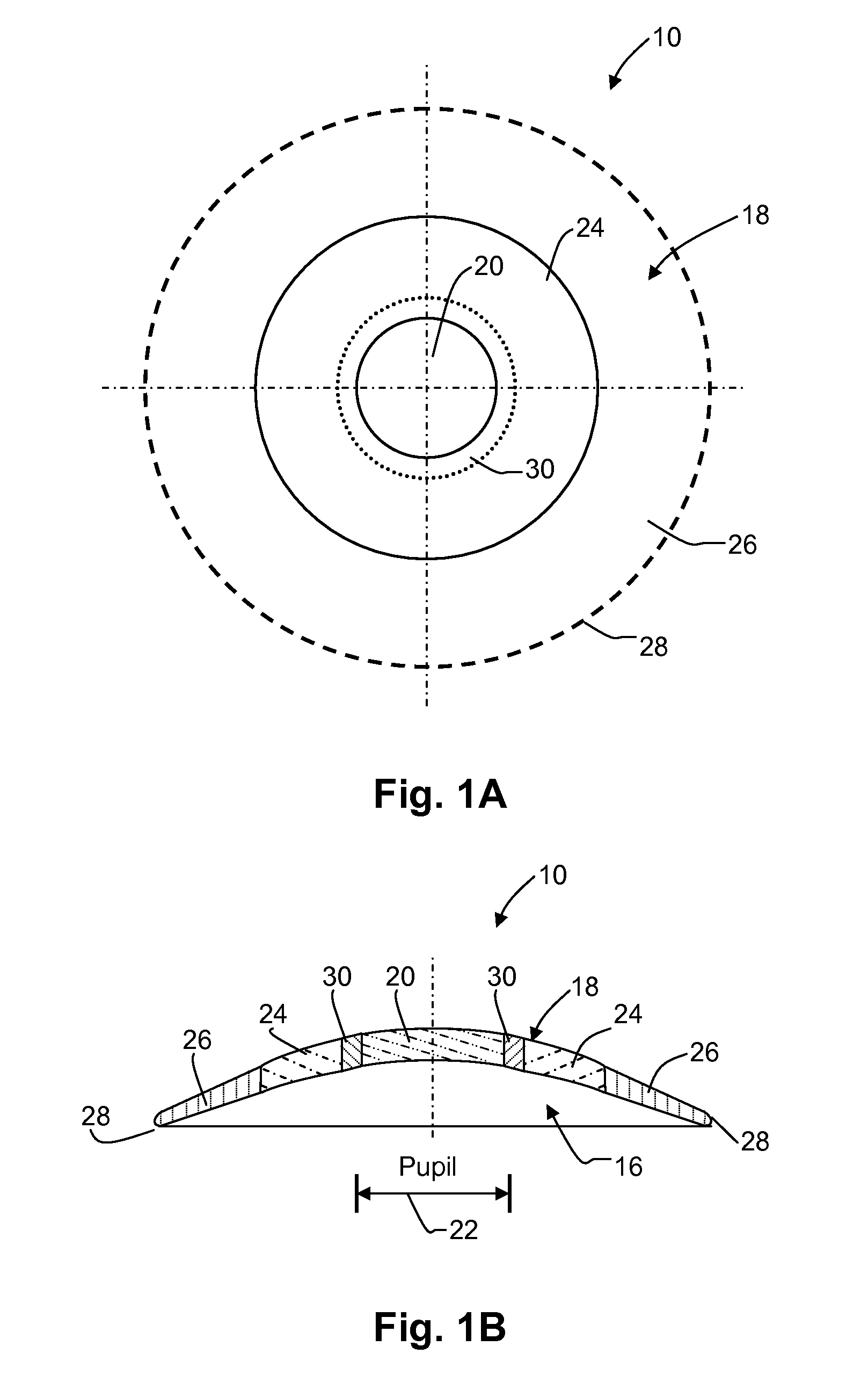
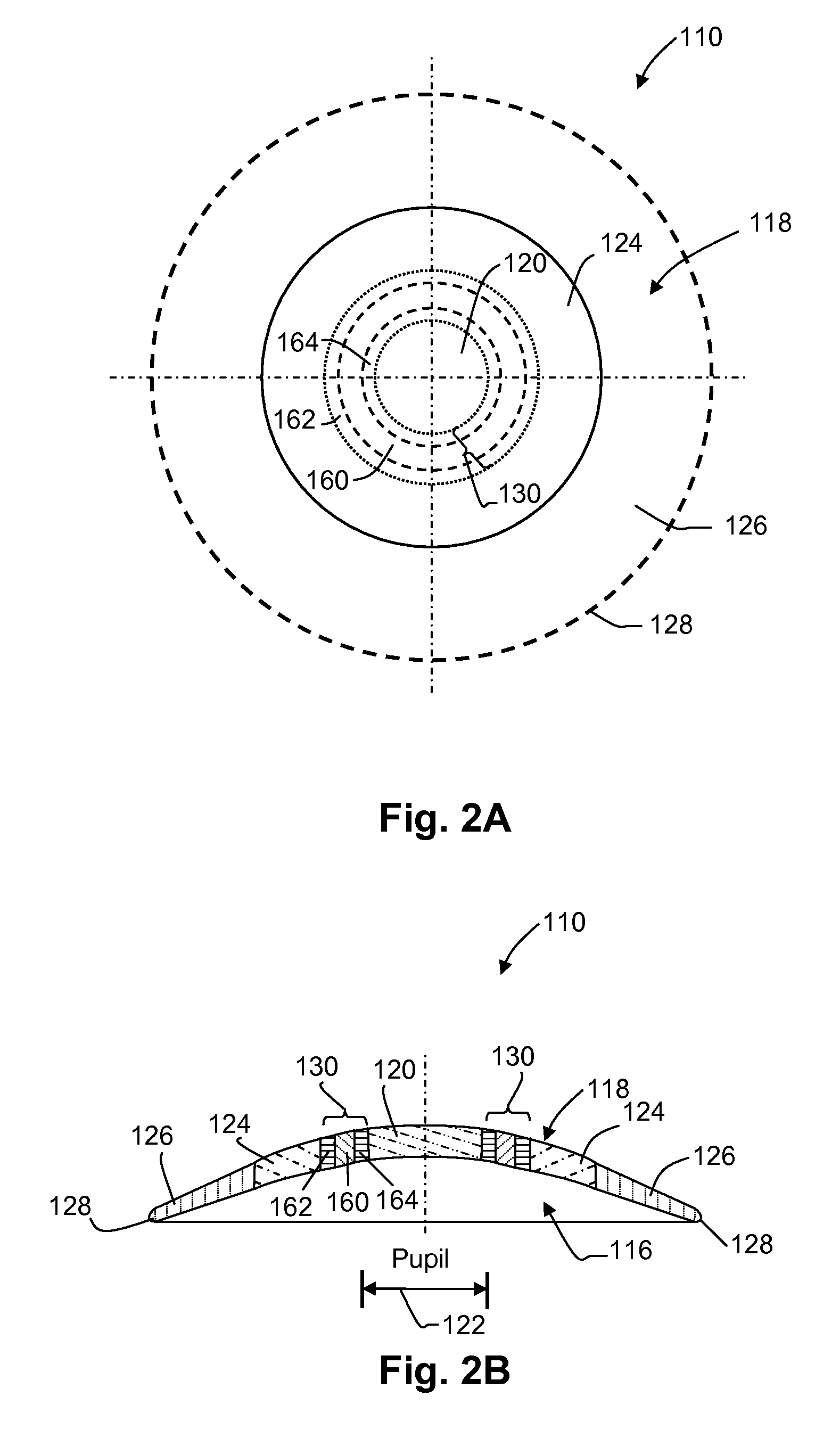
A contact lens (10) for use in controlling or retarding the progression of myopia in an eye has a central optical zone (20) approximating the normal diameter of the pupil of the eye (22) that gives clear central vision at distance for the wearer. An annular peripheral optical zone 24 that is substantially outside the diameter of the pupil is formed around the central optical zone (20) with greater refractive power than that of the central zone (22) so that oblique rays entering the eye through the peripheral optical zone (24) will be brought to focus at a focal plane that is substantially on or anterior to the peripheral region of the retina. Preferably, the rear surface (16) of the lens is shaped to conform to the cornea of the eye and the front surface (18) of the lens (10) is shaped to provide—in conjunction with the rear surface (16)—the desired optical properties of the central and peripheral optical zones. The front surface (18) is also preferably contoured to form a smooth transition (30) between the junction of the central optical zone (20) and the peripheral optical zone (24), with or without designed optical properties such as progressive power.
Owner:THE VISION CRC LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling peripheral image position for reducing progression of myopia
ActiveUS7665842B2Improve visual effectsGood and useful visionSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryRefractive errorCentral vision
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Lens design and method for preventing or slowing the progression of myopia
ActiveUS8684520B2Prevent myopiaShorten the progressSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsCentral visionVisual perception
A lens is provided that is capable of preventing or slowing the progression of myopia when worn by a person. The lens has a power profile that reduces on-axis and off-axis hyperopic defocus created by the optics of the eye by creating on-axis and off-axis myopic defocus. The on-axis and off-axis myopic defocus is created by providing light rays that pass through a central vision region of the optical portion and light rays that pass through a peripheral region of the optical portion an increase in positive (plus) power. The overall effect is to prevent or slow the progression of myopia without any perceptible degradation in the person's central vision.
Owner:ALCON INC
Means for controlling the progression of myopia
ActiveUS8240847B2Inhibit progressLow elongationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical propertyCentral vision
A contact lens (10) for use in controlling or retarding the progression of myopia in an eye has a central optical zone (20) approximating the normal diameter of the pupil of the eye (22) that gives clear central vision at distance for the wearer. An annular peripheral optical zone 24 that is substantially outside the diameter of the pupil is formed around the central optical zone (20) with greater refractive power than that of the central zone (22) so that oblique rays entering the eye through the peripheral optical zone (24) will be brought to focus at a focal plane that is substantially on or anterior to the peripheral region of the retina. Preferably, the rear surface (16) of the lens is shaped to conform to the cornea of the eye and the front surface (18) of the lens (10) is shaped to provide—in conjunction with the rear surface (16)—the desired optical properties of the central and peripheral optical zones. The front surface (18) is also preferably contoured to form a smooth transition (30) between the junction of the central optical zone (20) and the peripheral optical zone (24), with or without designed optical properties such as progressive power.
Owner:THE VISION CRC LTD
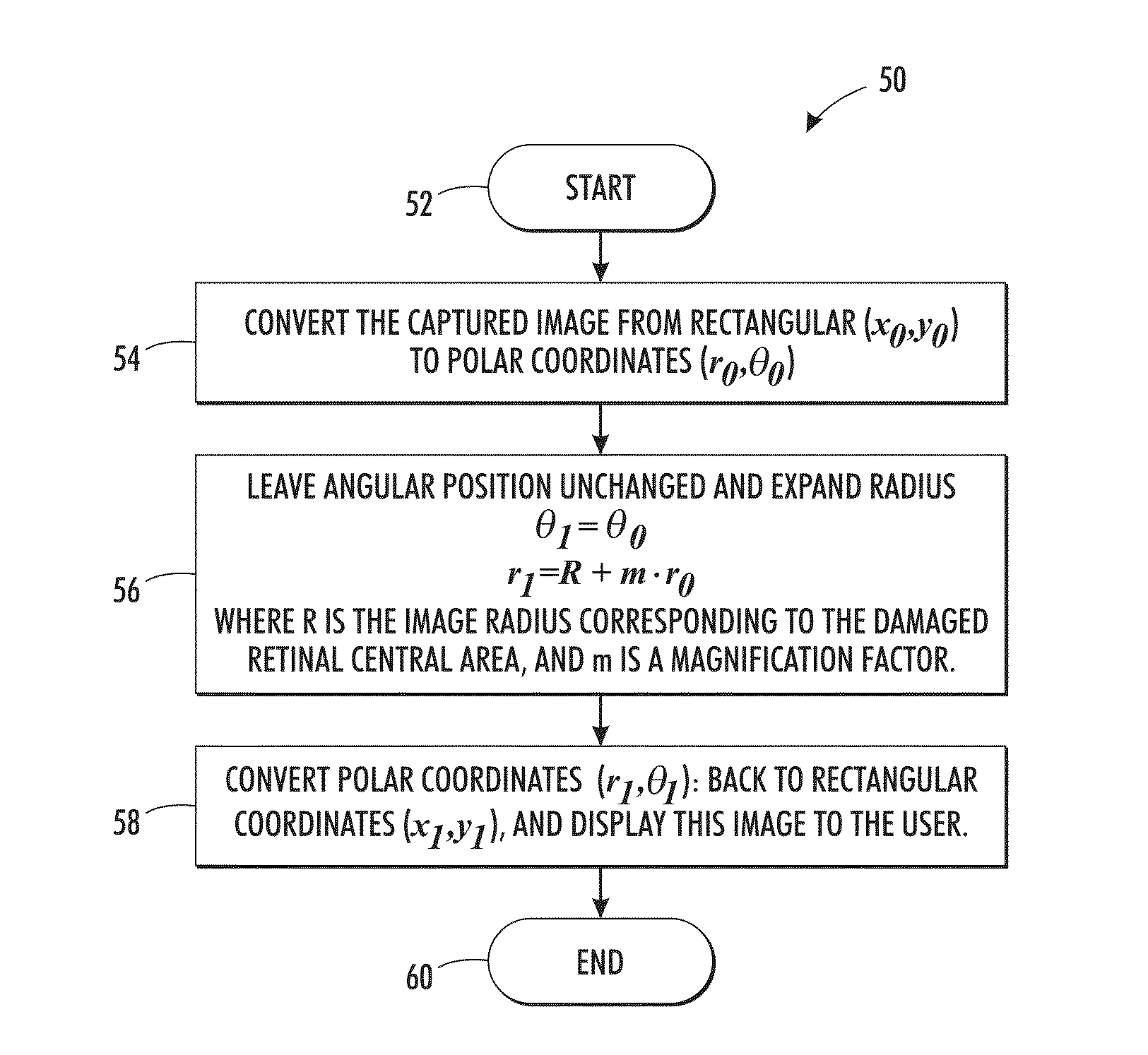
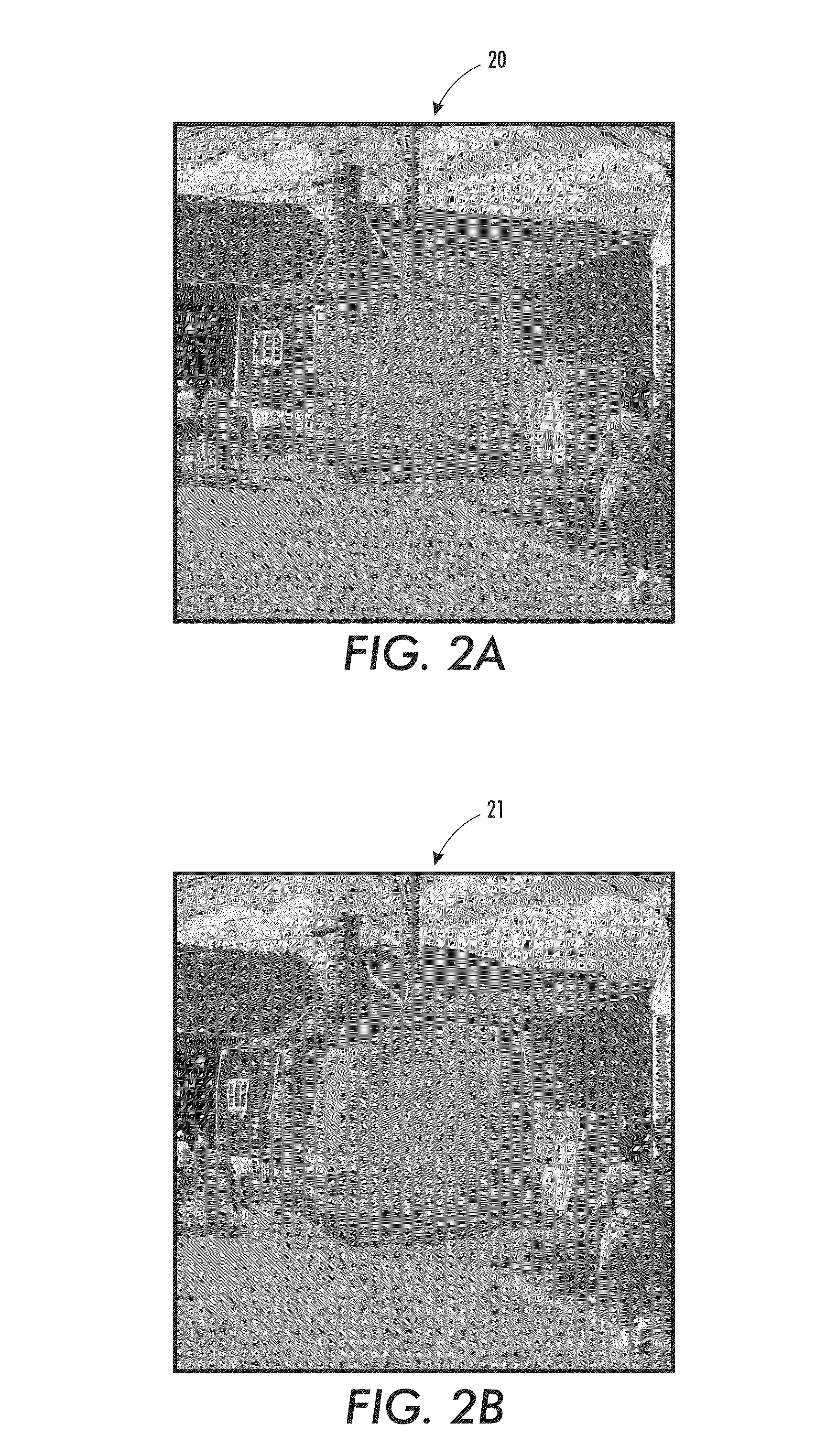
Central vision impairment compensation
ActiveUS20140210970A1Easy to understandColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsCentral visionDigital image
A method, system, and processor-readable medium for non-invasive visual compensation for a person suffering from central vision impairment. Digital images of a target field of view can he obtained and processed to generate processed images thereof, wherein central regions of the digital images that normally would reach an impaired portion of a retina of the person are moved to other regions of the target field of view. The processed images can be presented to the person such that the central regions are now directed at an unimpaired peripheral portion of the retina of the person.
Owner:XEROX CORP
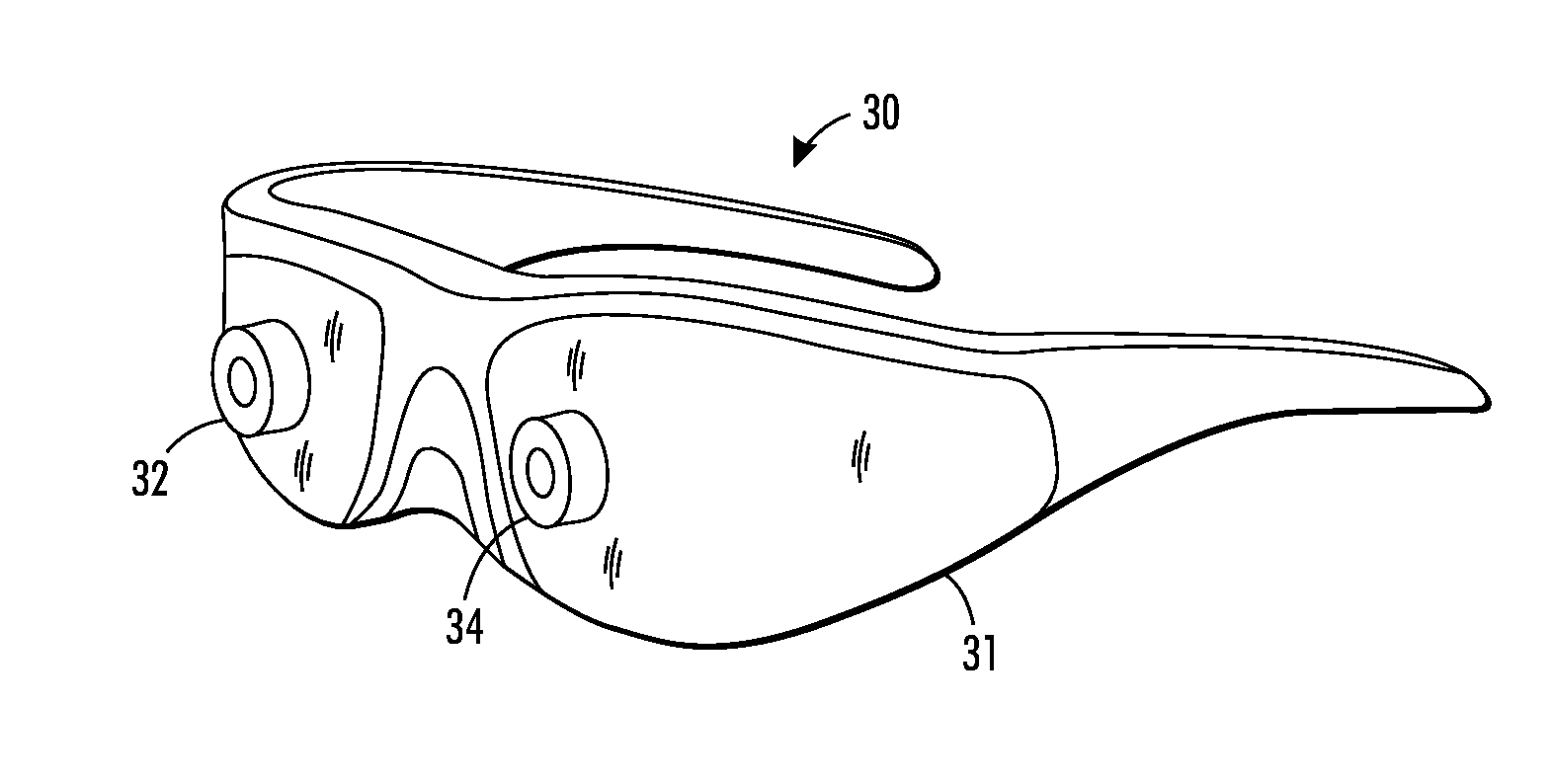
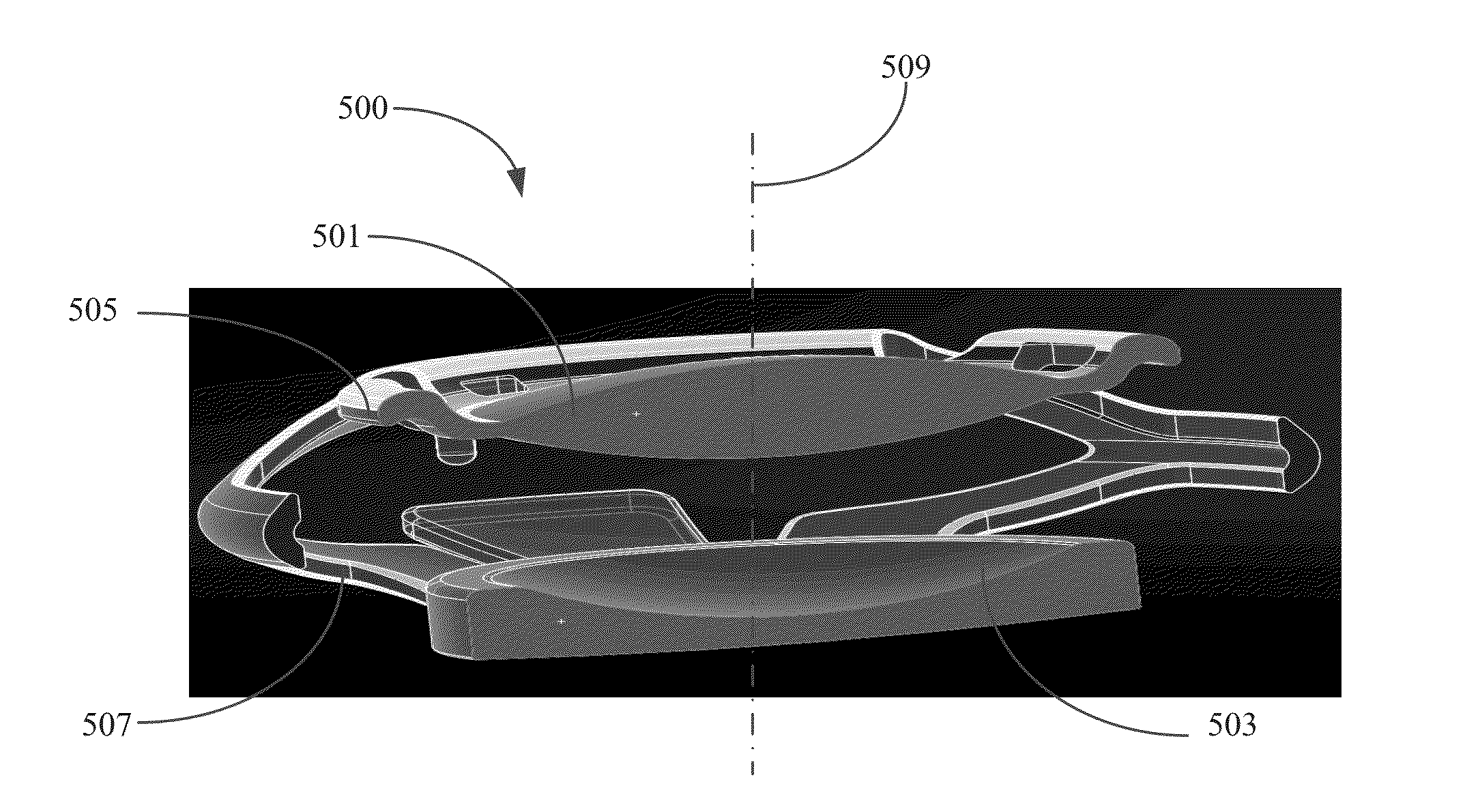
Hybrid lens system for head wearable display
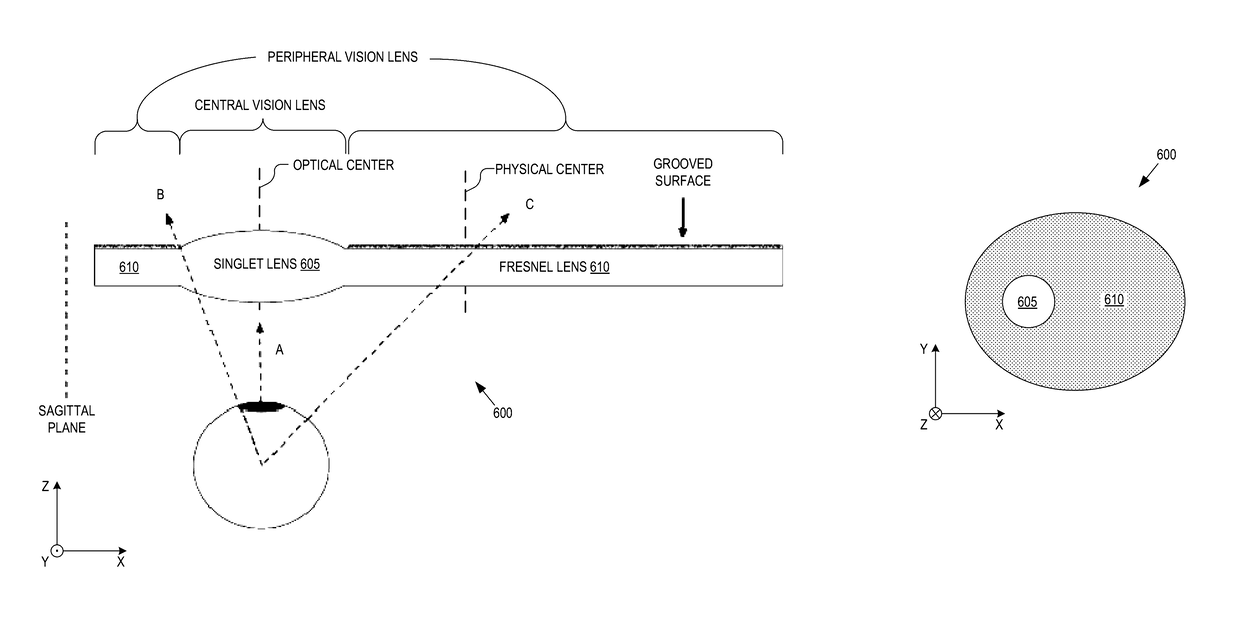
A hybrid optical system for a head wearable display includes a central vision lens and a peripheral vision lens. The central vision lens approximately aligns with a cornea of a user to provide lensing to a central vision of the user when the user is looking straight forward. The peripheral vision lens, different than the central vision lens, provides lensing to an extended field of view that extends angularly beyond the central vision lensed by the central vision lens when the user is looking straight forward. The peripheral vision lens is disposed around the central vision lens. The peripheral vision lens has a co-incident optical center with the central vision lens but the central vision lens is offset from a physical center of the peripheral vision lens.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
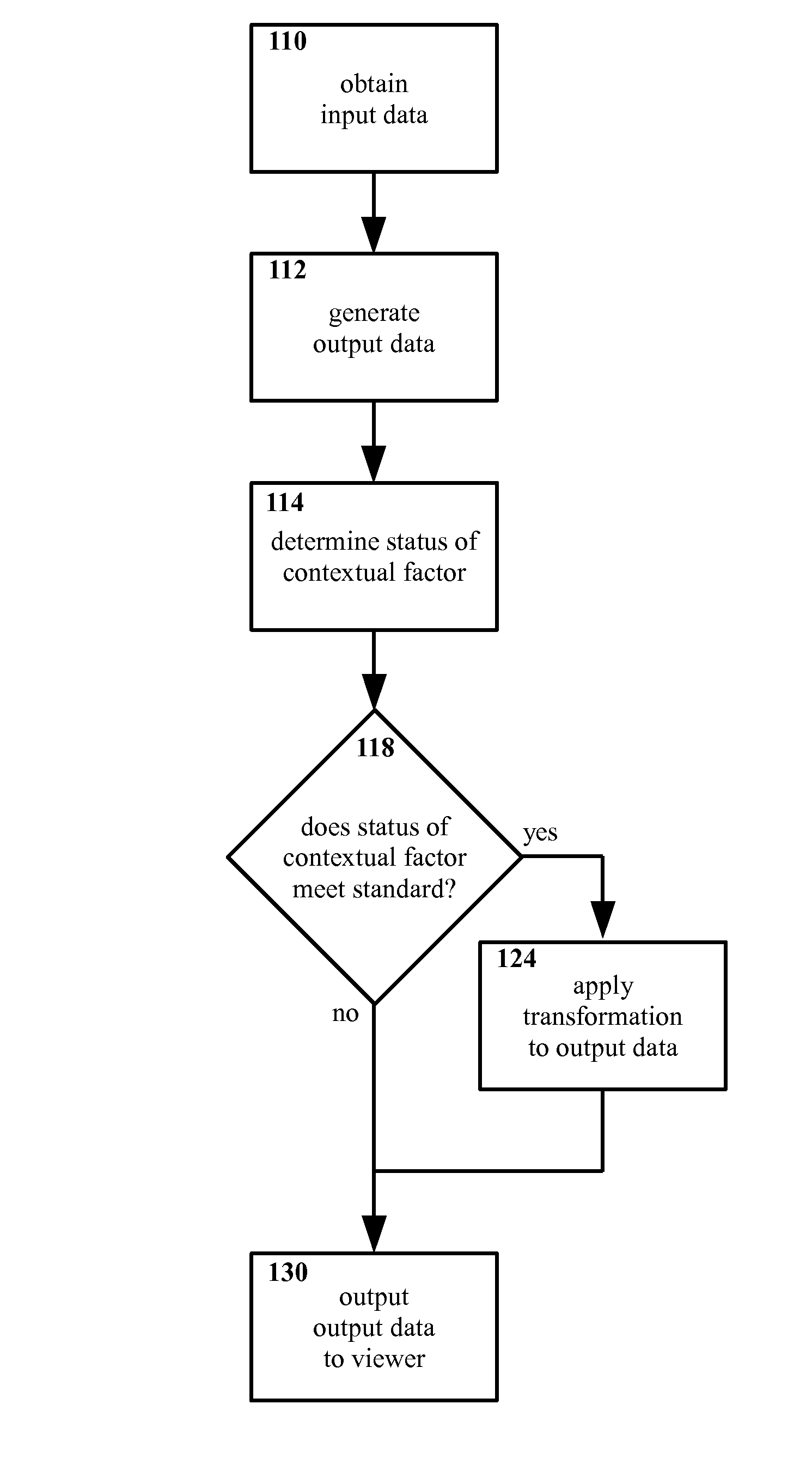
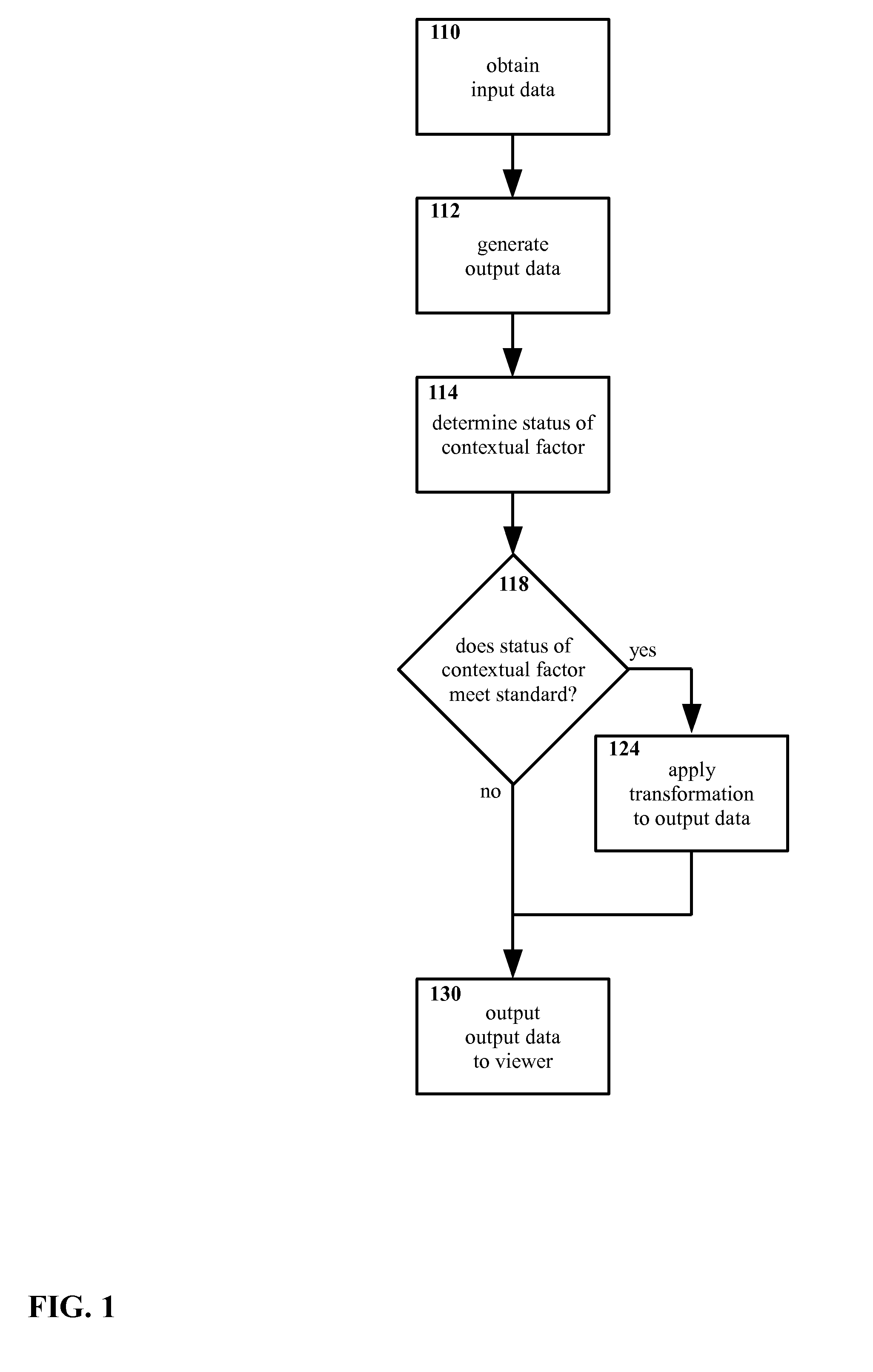
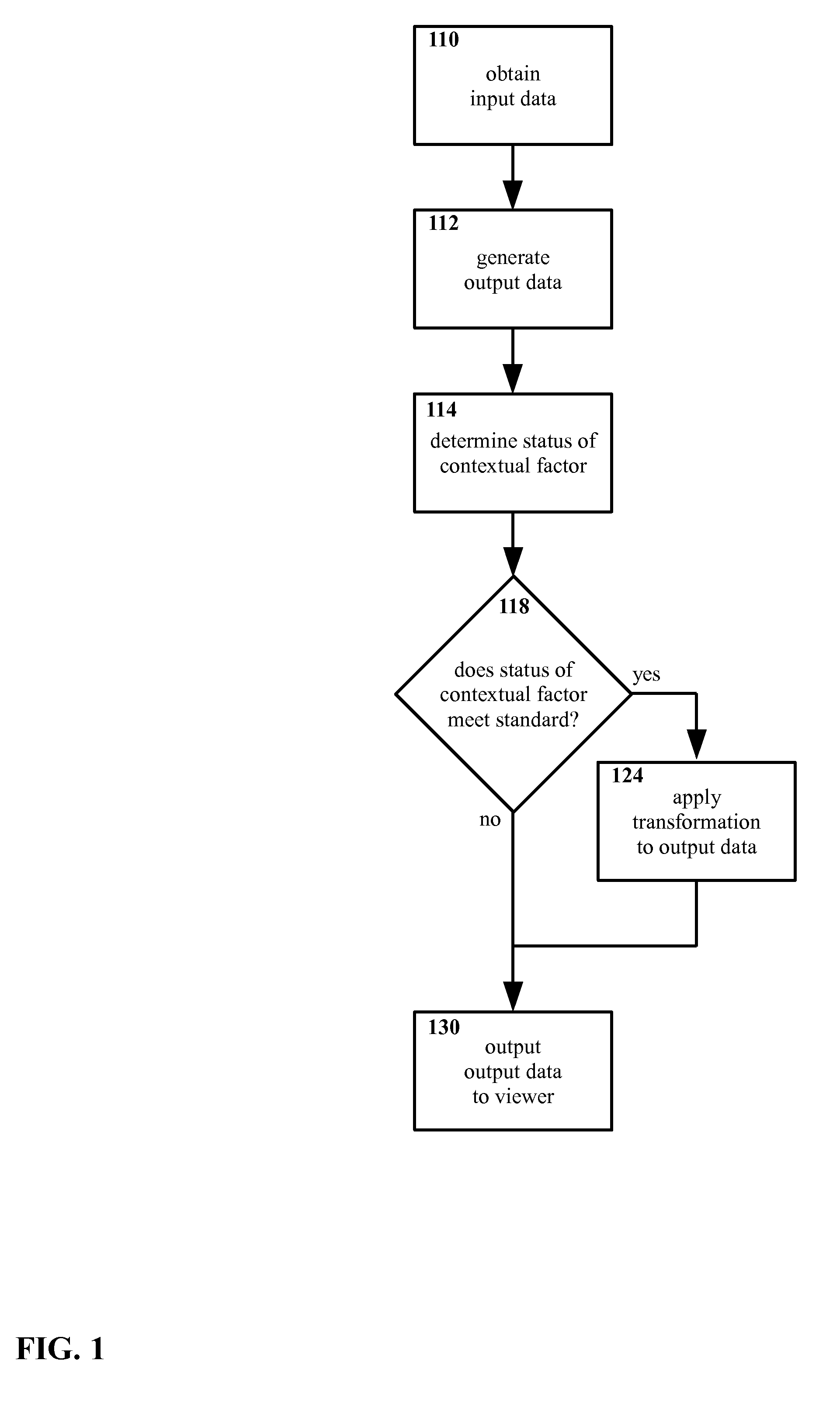
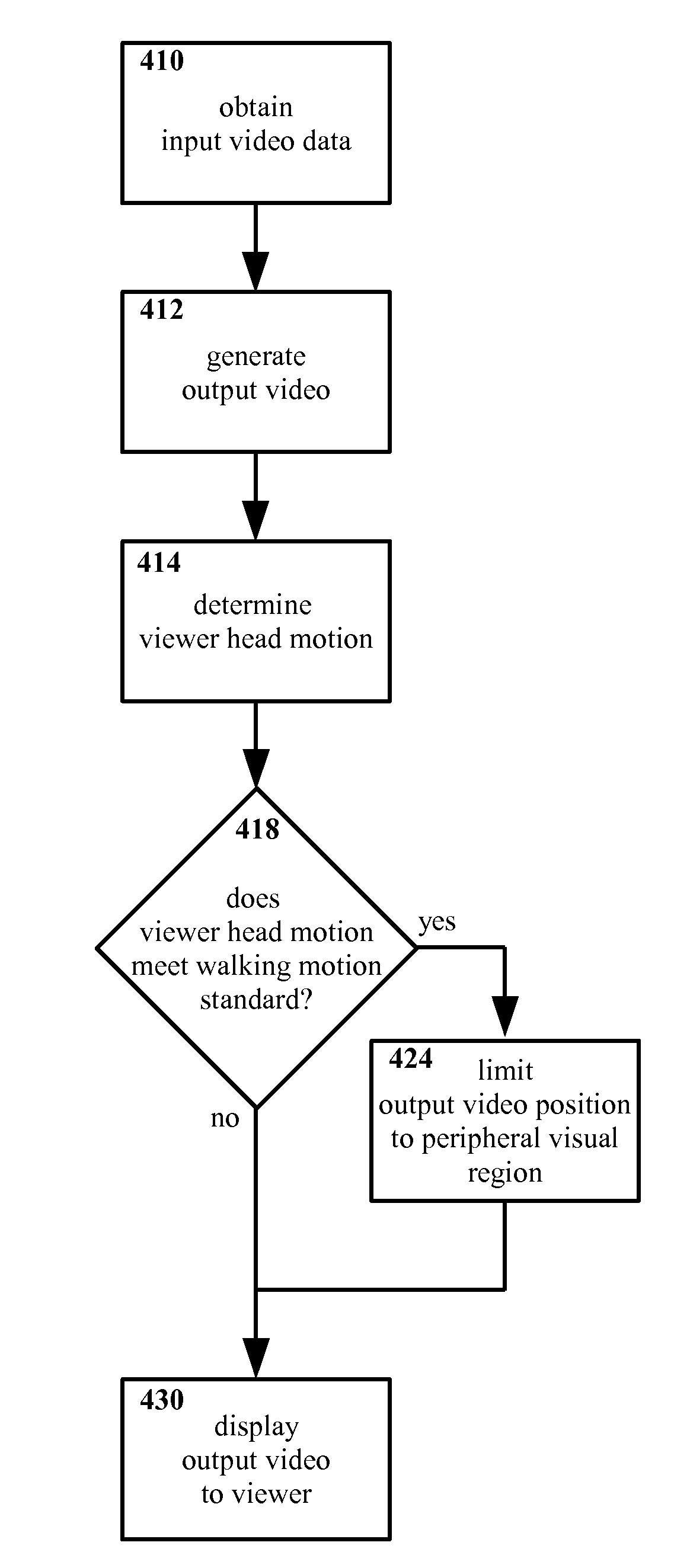
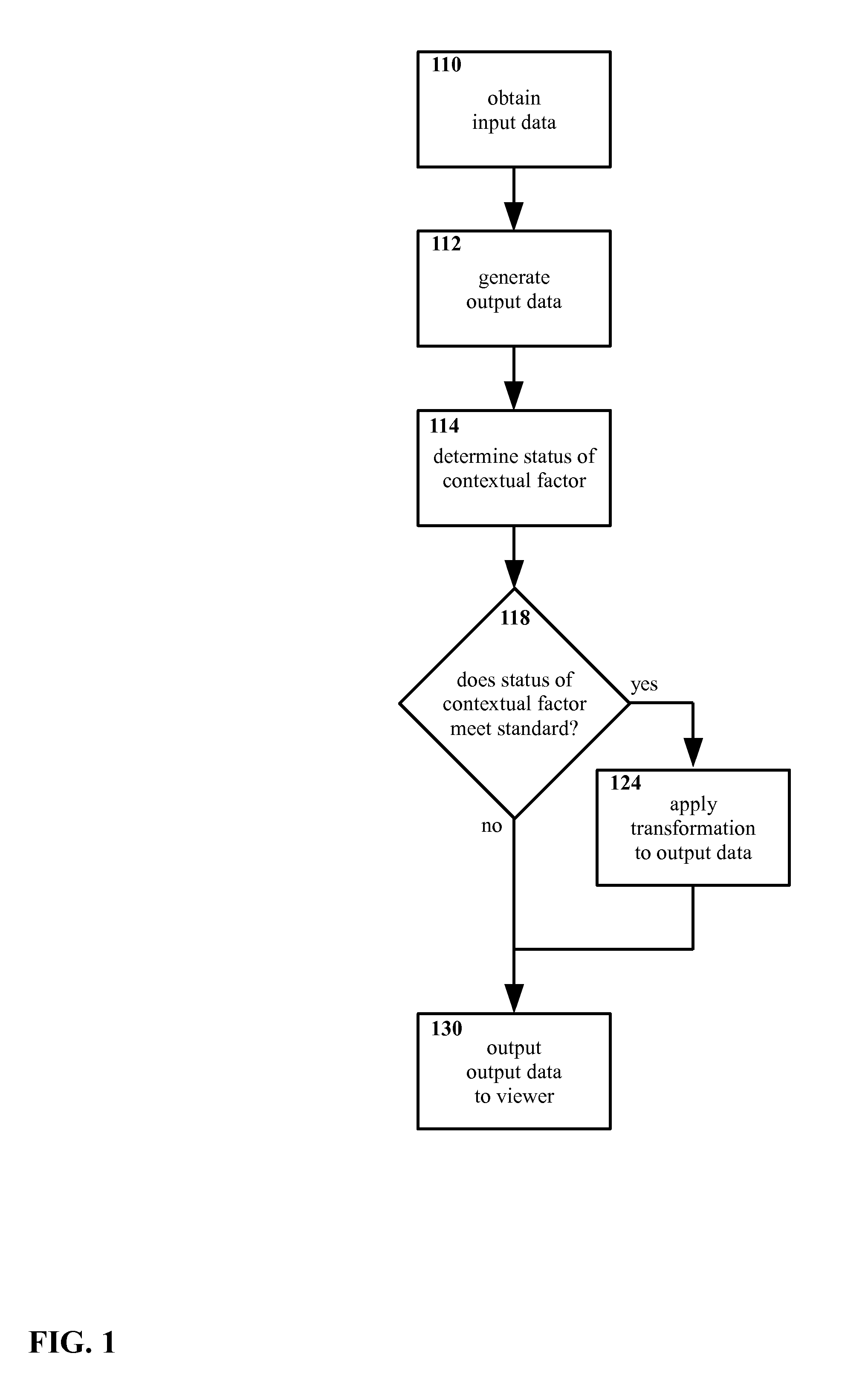
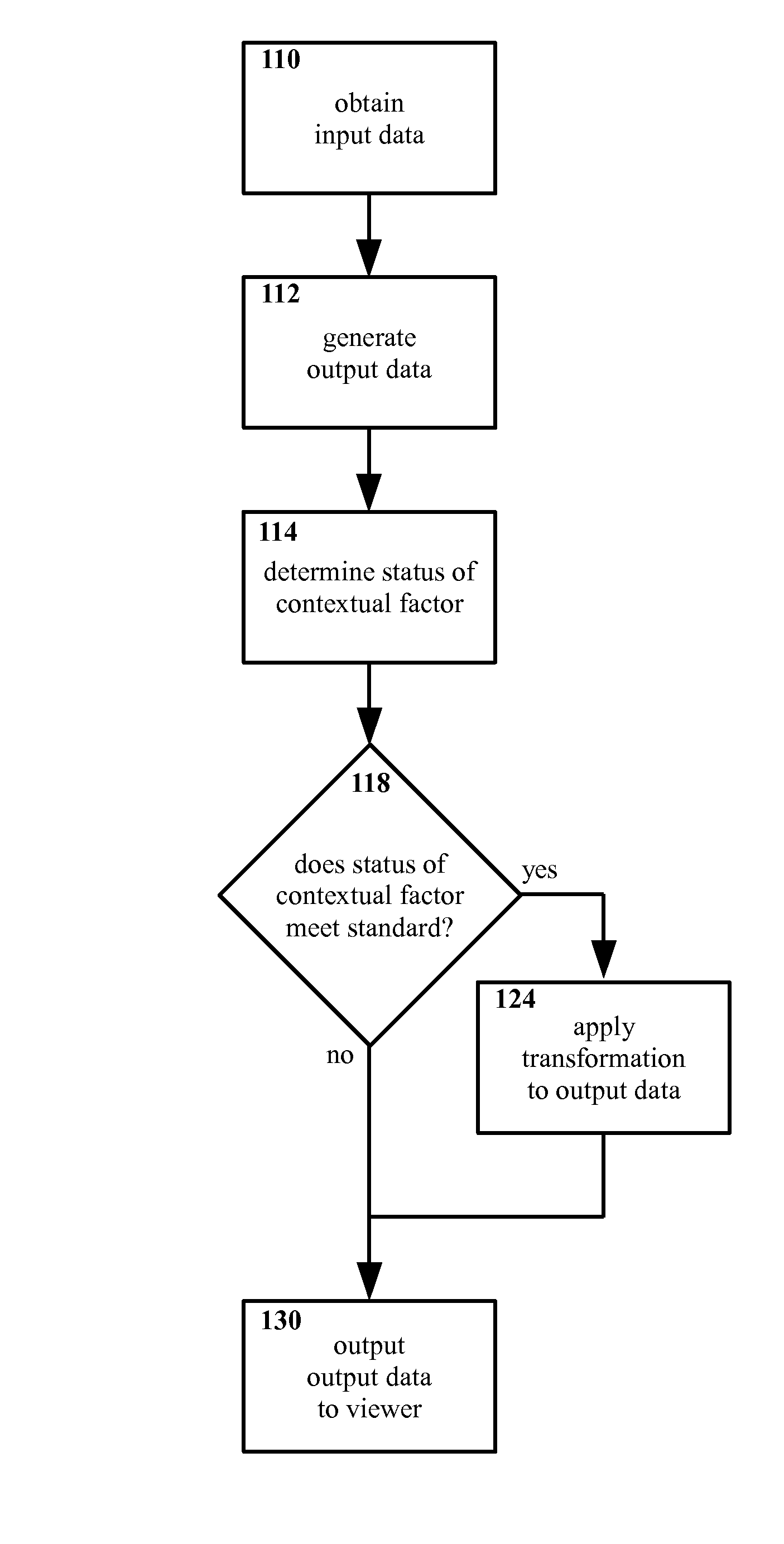
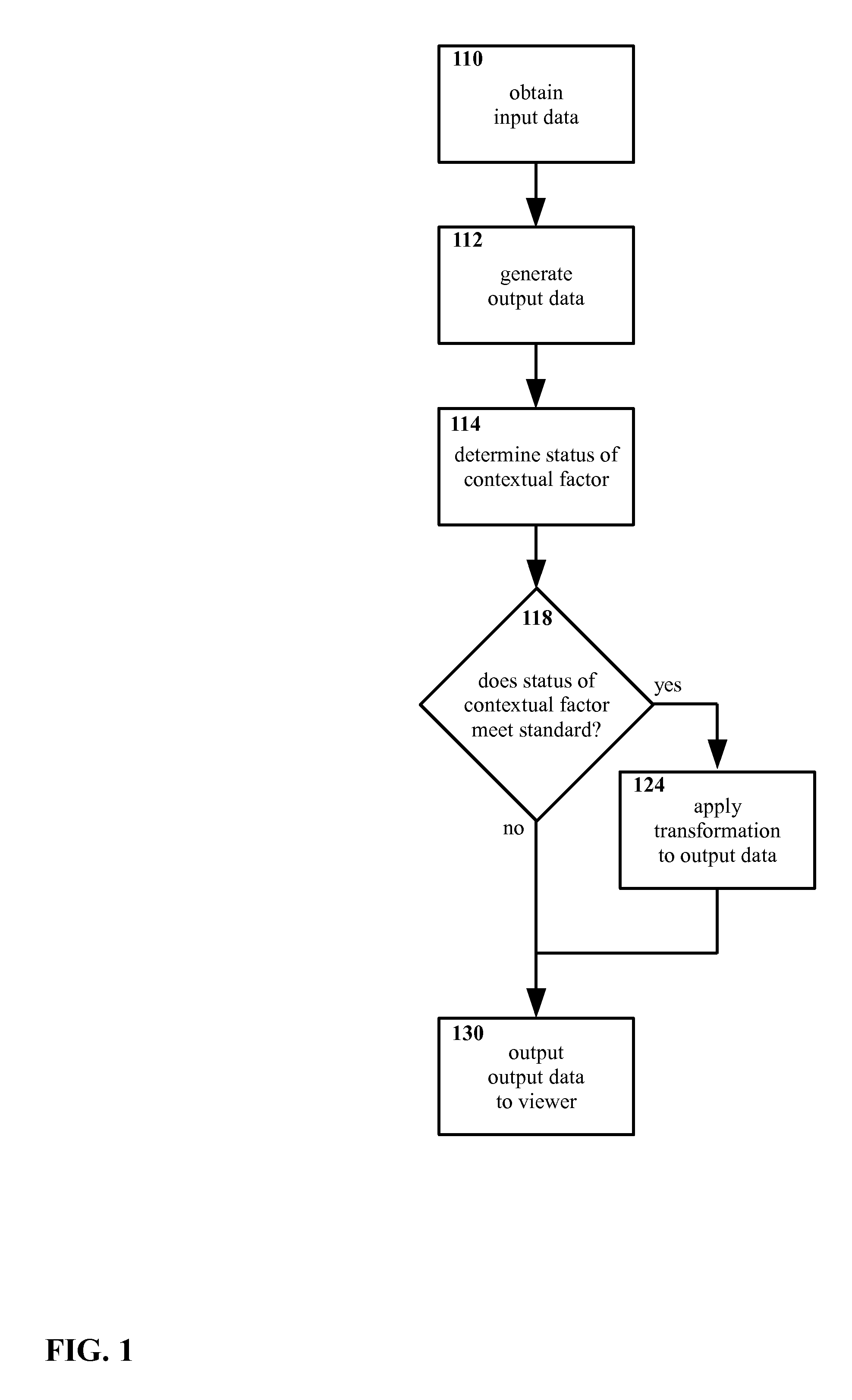
Method and apparatus for selectively presenting content
A machine-implemented method includes obtaining input data and generating output data. The status of at least one contextual factor is determined and compared with a standard. If the status meets the standard, a transformation is applied to the output data. The output data is then outputted to the viewer. Through design and / or selection of contextual factors, standards, and transformations, output data may be selectively outputted to viewers in a context-suitable fashion, e.g. on a head mounted display the viewer's central vision may be left unobstructed while the viewer walks, drives, etc. An apparatus includes at least one sensor that senses a contextual factor. A processor determines the status of the contextual factor, determines if the status meets a standard, generates output data, and applies a transformation to the output data if the status meets the standard. A display outputs the output data to the viewer.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
Method and apparatus for selectively presenting content
A machine-implemented method includes obtaining input data and generating output data. The status of at least one contextual factor is determined and compared with a standard. If the status meets the standard, a transformation is applied to the output data. The output data is then outputted to the viewer. Through design and / or selection of contextual factors, standards, and transformations, output data may be selectively outputted to viewers in a context-suitable fashion, e.g. on a head mounted display the viewer's central vision may be left unobstructed while the viewer walks, drives, etc. An apparatus includes at least one sensor that senses a contextual factor. A processor determines the status of the contextual factor, determines if the status meets a standard, generates output data, and applies a transformation to the output data if the status meets the standard. A display outputs the output data to the viewer.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
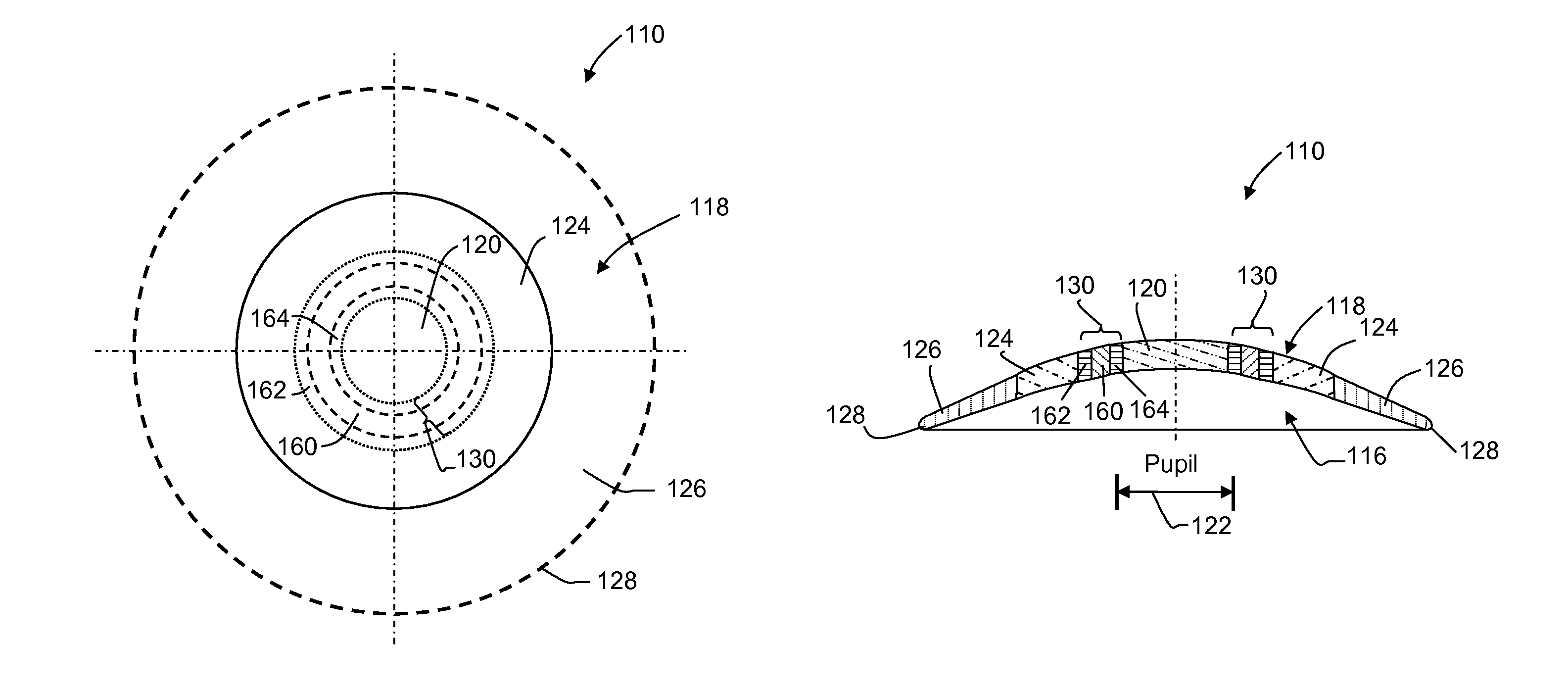
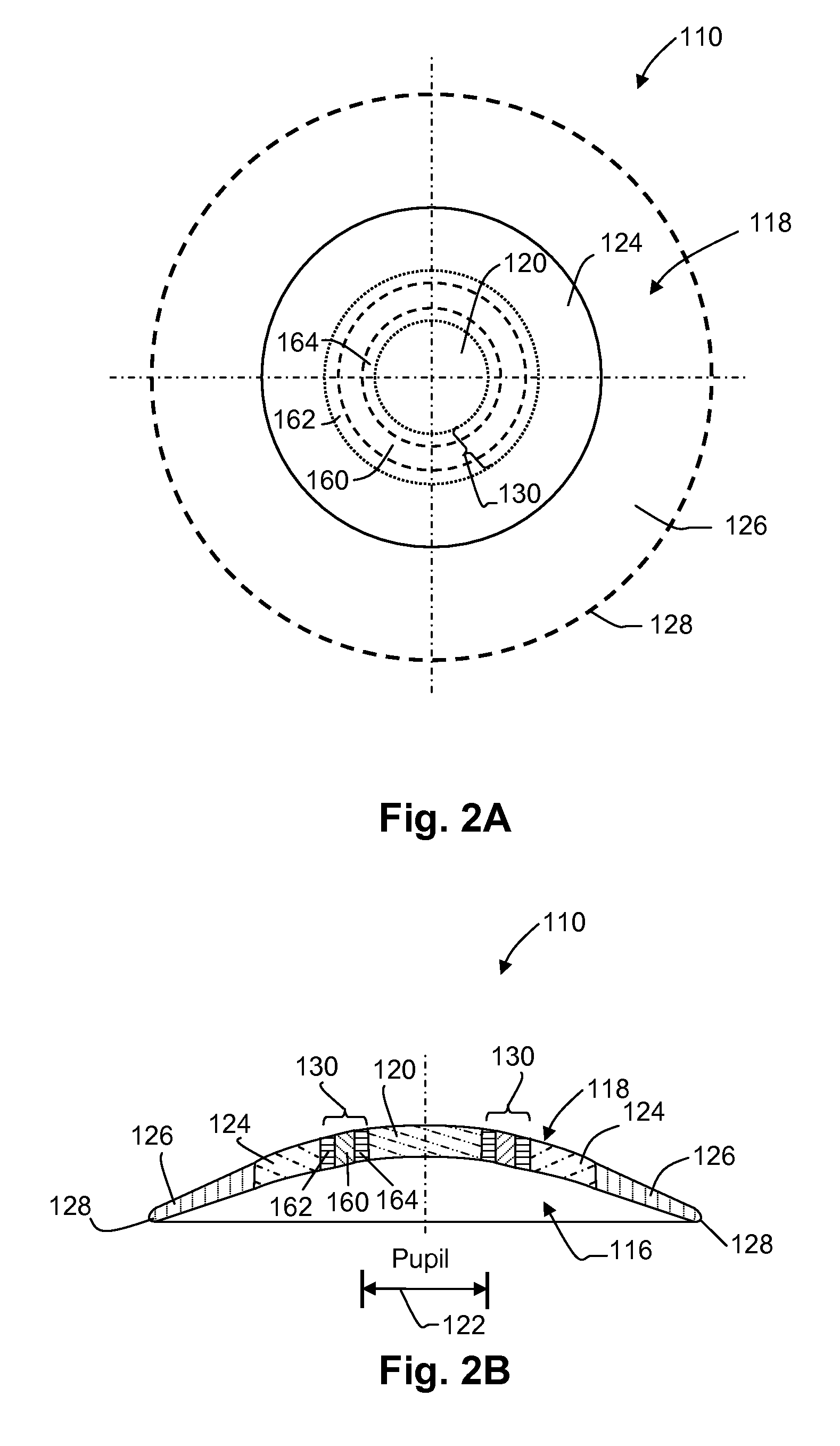
Enhanced toric lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
ActiveUS20150250585A1Improve acuityImproves contrast sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesOptical propertyCentral vision
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing an enhanced toric lens which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Dual-optic intraocular lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
ActiveUS20150265399A1Improve eyesightReduce sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesCentral visionPeripheral retina
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing a dual optic intraocular lens which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Method and apparatus for selectively presenting content
ActiveUS9142185B2Input/output for user-computer interactionDrawing from basic elementsCentral visionDisplay device
A machine-implemented method includes obtaining input data and generating output data. The status of at least one contextual factor is determined and compared with a standard. If the status meets the standard, a transformation is applied to the output data. The output data is then outputted to the viewer. Through design and / or selection of contextual factors, standards, and transformations, output data may be selectively outputted to viewers in a context-suitable fashion, e.g. on a head mounted display the viewer's central vision may be left unobstructed while the viewer walks, drives, etc. An apparatus includes at least one sensor that senses a contextual factor. A processor determines the status of the contextual factor, determines if the status meets a standard, generates output data, and applies a transformation to the output data if the status meets the standard. A display outputs the output data to the viewer.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
Optical System Determination According to Advanced Criteria
ActiveUS20110202286A1Optical system calculationEasy to calculateBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsCentral visionMagnification
A method implemented by computer means for calculating by optimization an optical system for example an ophthalmic lens according to at least one criterion among the following list consisting of: ocular deviation, object visual angular field in central vision, image visual angular field in central vision, pupil field ray deviation, object visual angular field in peripheral vision, image visual angular field in peripheral vision, prismatic deviation in peripheral vision, magnification in peripheral vision, lens volume, magnification of the eyes, temple shift, or a variation of preceding criteria.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Means for Controlling the Progression of Myopia
ActiveUS20130010255A1Inhibit progressLow elongationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical propertyCentral vision
A contact lens (10) for use in controlling or retarding the progression of myopia in an eye has a central optical zone (20) approximating the normal diameter of the pupil of the eye (22) that gives clear central vision at distance for the wearer. An annular peripheral optical zone 24 that is substantially outside the diameter of the pupil is formed around the central optical zone (20) with greater refractive power than that of the central zone (22) so that oblique rays entering the eye through the peripheral optical zone (24) will be brought to focus at a focal plane that is substantially on or anterior to the peripheral region of the retina. Preferably, the rear surface (16) of the lens is shaped to conform to the cornea of the eye and the front surface (18) of the lens (10) is shaped to provide—in conjunction with the rear surface (16)—the desired optical properties of the central and peripheral optical zones. The front surface (18) is also preferably contoured to form a smooth transition (30) between the junction of the central optical zone (20) and the peripheral optical zone (24), with or without designed optical properties such as progressive power.
Owner:THE VISION CRC LTD
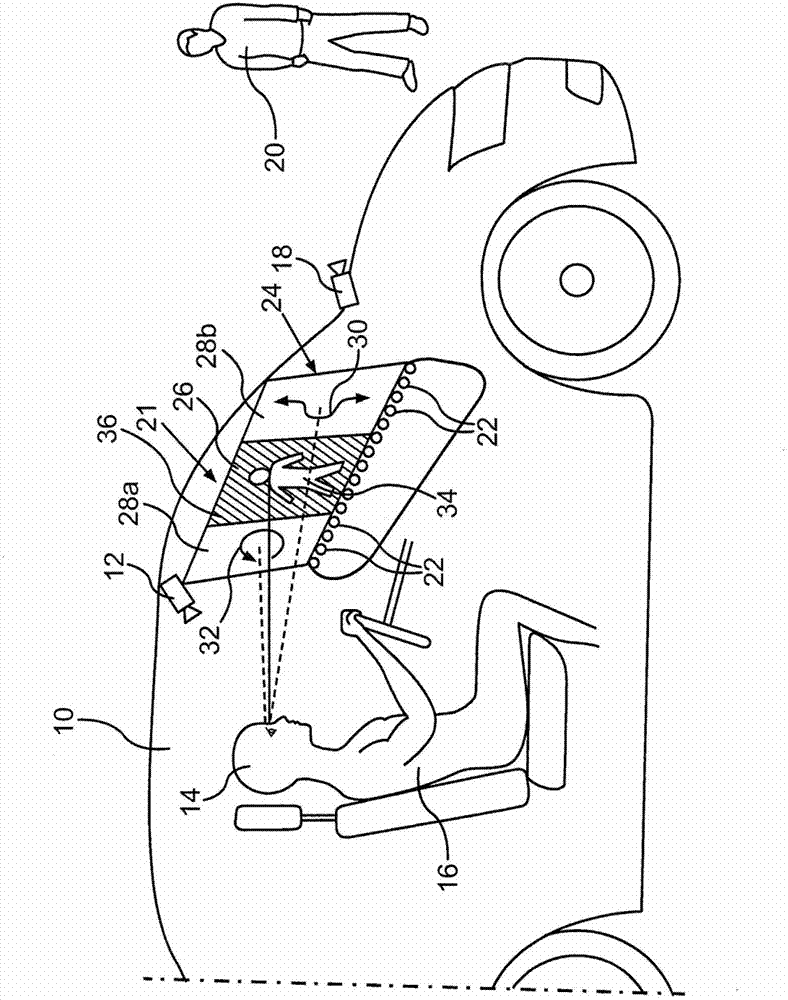
Method used for providing display in motor vehicle according to visual direction of vehicle driver
The present invention relates to a method used for providing display on at least one display position in a motor vehicle, through the method, physiological conditions of eyes can be well taken into account. In the method, the display is selected from at least two kinds of display types on the basis that the corresponding display position is located in a central vision field (26) of the vehicle driver or is located in peripheral vision fields (28a, 28b) of the vehicle driver. In the central vision field (26) of the vehicle driver (16), contrast between intense colors is preferredly selected, while in the peripheral vision fields (28a, 28b), the display changes over time is selected.
Owner:AUDI AG
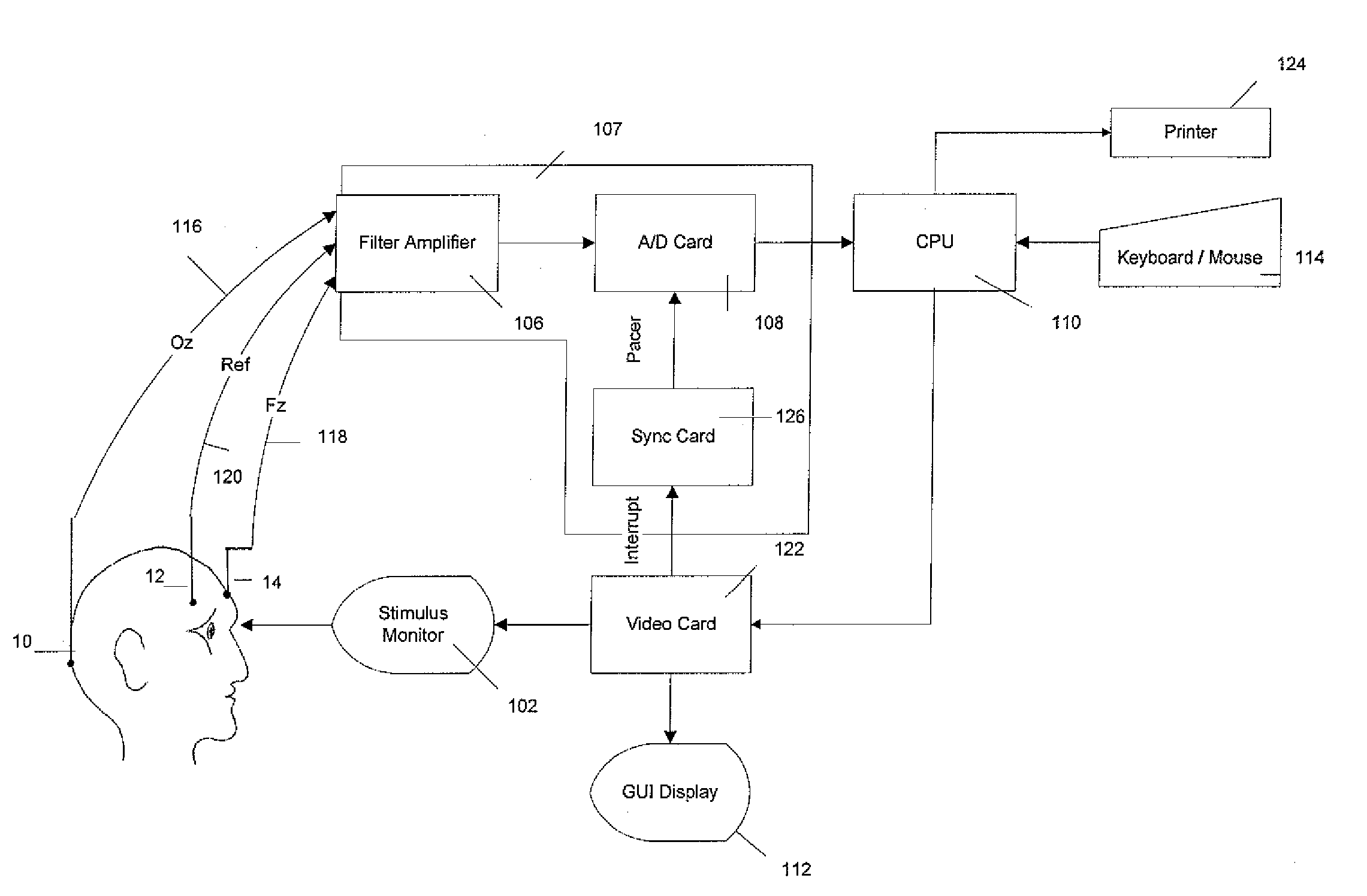
Apparatus and method for screening for glaucoma using visually evoked potentials
ActiveUS20100283973A1Rapid objective screeningEasy-to-interpret resultEye diagnosticsDiseaseData modeling
A pattern VEP system for screening for glaucoma and other optic nerve related diseases / deficiencies. The system combines high contrast and low contrast testing. The low contrast testing allows for highly sensitive glaucoma testing and the high contrast allows for a sensitive test of the central vision. The system also includes a narrowly tailored method of rejecting corrupted data allowing the system to selectively salvage useful portions of a signal. The system also provides a method of data modeling to locate the N75-P100-N135 complex in a waveform and determine if it falls within the normal range
Owner:DIOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for selectively presenting content
A machine-implemented method includes obtaining input data and generating output data. The status of at least one contextual factor is determined and compared with a standard. If the status meets the standard, a transformation is applied to the output data. The output data is then outputted to the viewer. Through design and / or selection of contextual factors, standards, and transformations, output data may be selectively outputted to viewers in a context-suitable fashion, e.g. on a head mounted display the viewer's central vision may be left unobstructed while the viewer walks, drives, etc. An apparatus includes at least one sensor that senses a contextual factor. A processor determines the status of the contextual factor, determines if the status meets a standard, generates output data, and applies a transformation to the output data if the status meets the standard. A display outputs the output data to the viewer.
Owner:WEST TEXAS TECH PARTNERS LLC
Hybrid lens system for head wearable display
A hybrid optical system for a head wearable display includes a central vision lens and a peripheral vision lens. The central vision lens approximately aligns with a cornea of a user to provide lensing to a central vision of the user when the user is looking straight forward. The peripheral vision lens, different than the central vision lens, provides lensing to an extended field of view that extends angularly beyond the central vision lensed by the central vision lens when the user is looking straight forward. The peripheral vision lens is disposed around the central vision lens. The peripheral vision lens has a co-incident optical center with the central vision lens but the central vision lens is offset from a physical center of the peripheral vision lens.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for Determining Binocular Performance of a Pair of Spectacle Lenses
A method of determining binocular performance of a pair of spectacle lenses comprises: a eyes characteristics providing step, a pair of spectacle lenses providing step, a environment providing step, a binocular performance criteria selecting step, and a binocular performance criteria determining step, wherein the at least one binocular performance criterion is selected among one or a combination of the following criteria groups consisting of central vision criteria group and / or peripheral vision criteria group.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method for determining binocular performance of a pair of spectacle lenses
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Central vision impairment compensation
Owner:XEROX CORP
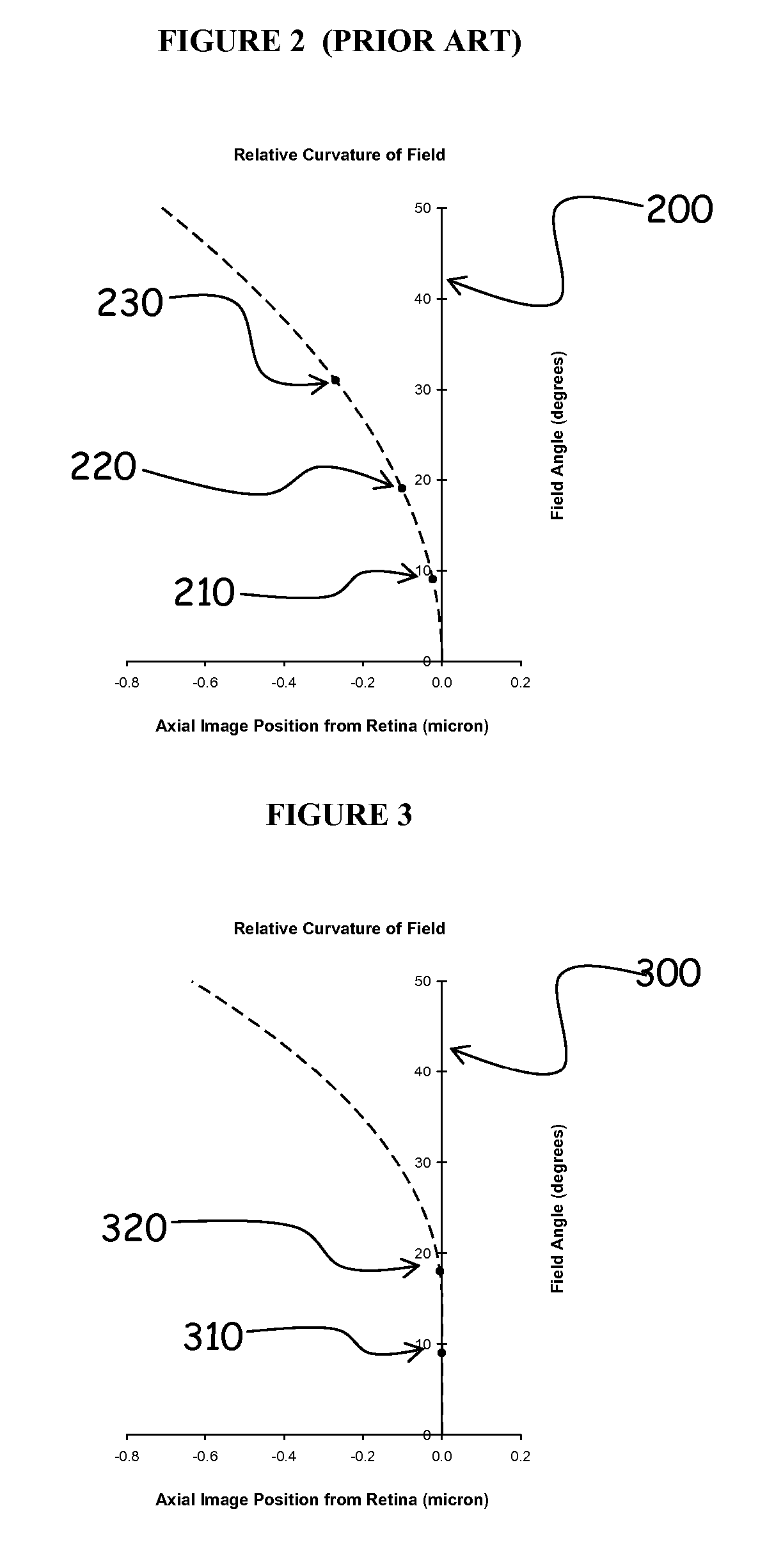
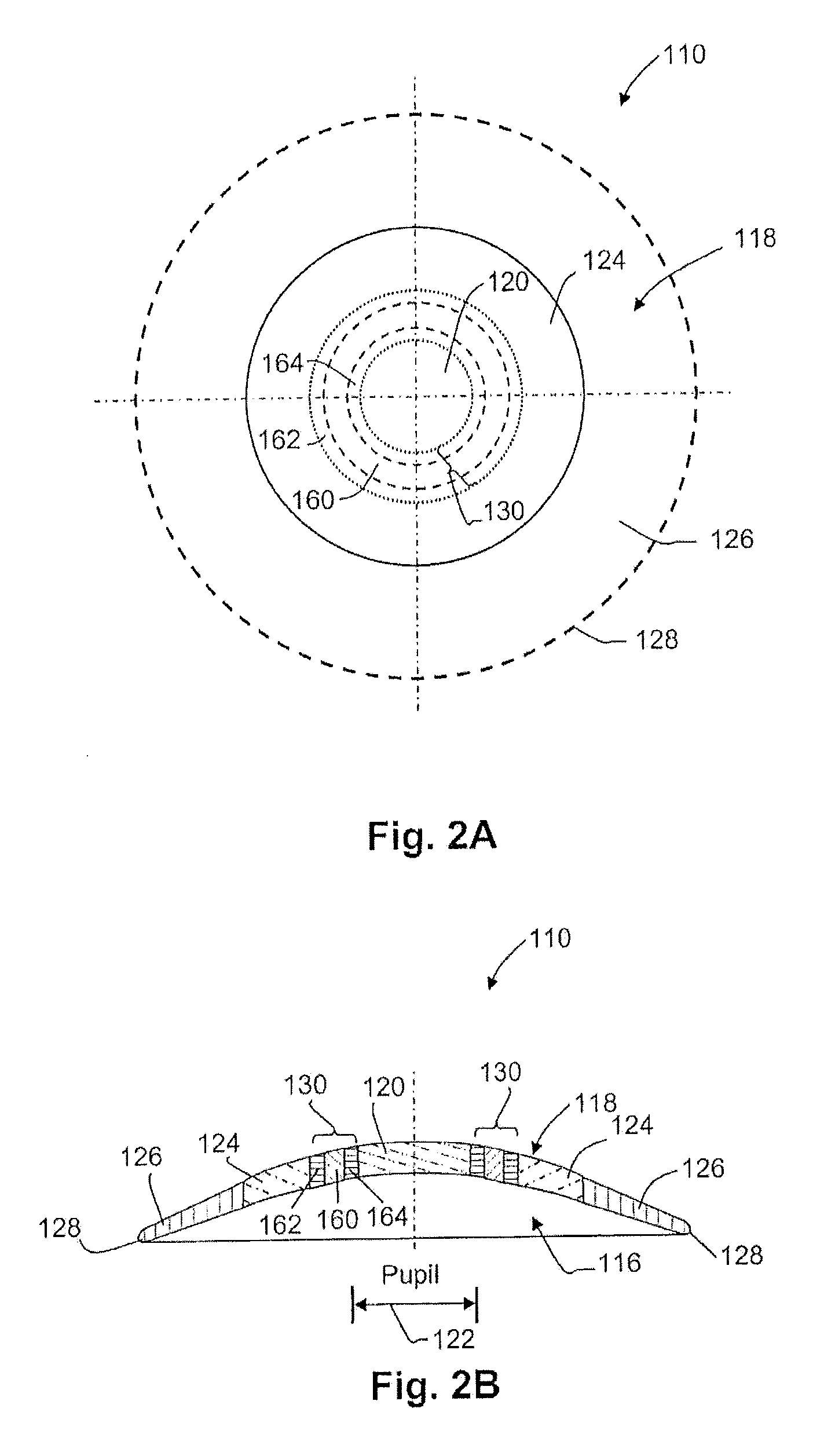
Method and apparatus for controlling peripheral image position for reducing progression of myopia
A method and apparatus are disclosed for controlling optical aberrations to alter relative curvature of field by providing optical devices and methods comprising the repositioning of peripheral off-axis focal points relative to the retina to produce stimulus for influencing the progression of refractive error while simultaneously controlling the position of the central focal point near to the retina to provide clear central vision and simultaneously providing zones of controlled peripheral defocus and other optical aberrations to improve peripheral vision for select directions of gaze.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Intraocular lenses that improve peripheral vision
ActiveUS20170258578A1Improve eyesightImprove Optical Imaging QualityIntraocular lensRefractive errorIntraocular pressure
Lenses and methods are provided for improving peripheral and / or central vision for patients who suffer from certain retinal conditions that reduce central vision or patients who have undergone cataract surgery. The lens is configured to improve vision by having an optic configured to focus light incident along a direction parallel to an optical axis at the fovea in order to produce a functional foveal image. The optic is configured to focus light incident on the patient's eye at an oblique angle with respect to the optical axis at a peripheral retinal location disposed at a distance from the fovea, the peripheral retinal location having an eccentricity between −30 degrees and 30 degrees. The image quality at the peripheral retinal location is improved by reducing at least one optical aberration at the peripheral retinal location. The method for improving vision utilizes ocular measurements to iteratively adjust the shape factor of the lens to reduce peripheral refractive errors.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
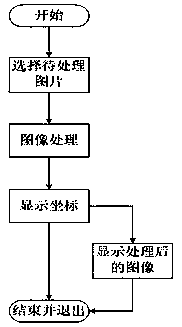
Recognition method for automatically detecting position of lifting lug
InactiveCN108921858AReduce wasteImprove work efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisMaximum errorComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a recognition method for automatically detecting the position of a lifting lug. The method comprises the steps of carrying out OpenCV-based camera calibration on a camera for an imaging model of the camera and carrying out distortion correction on a collected image; through taking Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 as an algorithmic compilation platform and combining an OpenCV2.4.9 open source image library, developing a detection and recognition algorithm for the mounting position of the lifting lug of a pressure vessel; processing an image of the lifting ear to obtain the contour of the lifting lug and the coordinate of the center point of the lifting lug; and analyzing and processing the data. The method has the advantages that according to the design algorithm, the maximum error of the coordinate point is 2.5mm and the minimum error can be up to 0.1mm; by analyzing the relationship between the data and the image, when the position coordinate of the lifting lug atthe central vision field of the camera is more inaccurate and is more deviated from the center position, the obtained coordinate error is larger; and through the method disclosed by the invention, theposition coordinate of the lifting lug can be found.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Amblyopia vision increasing treatment method and system thereof
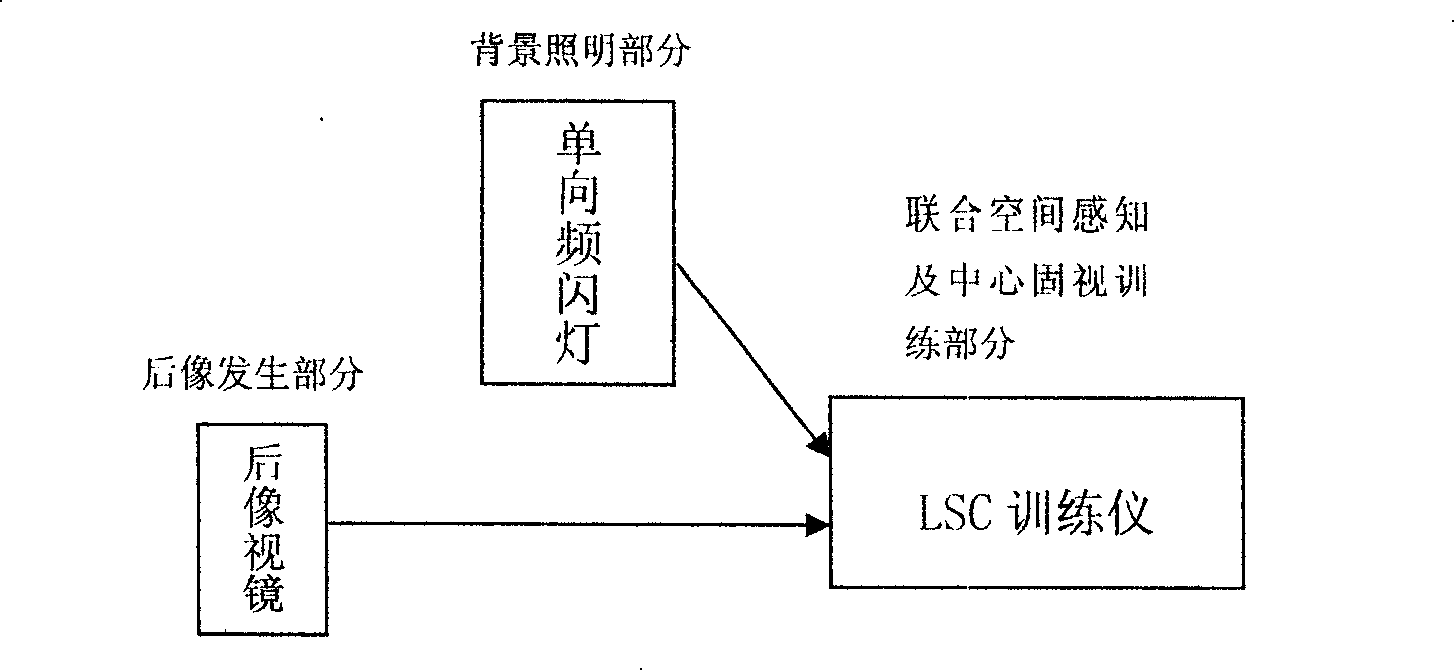
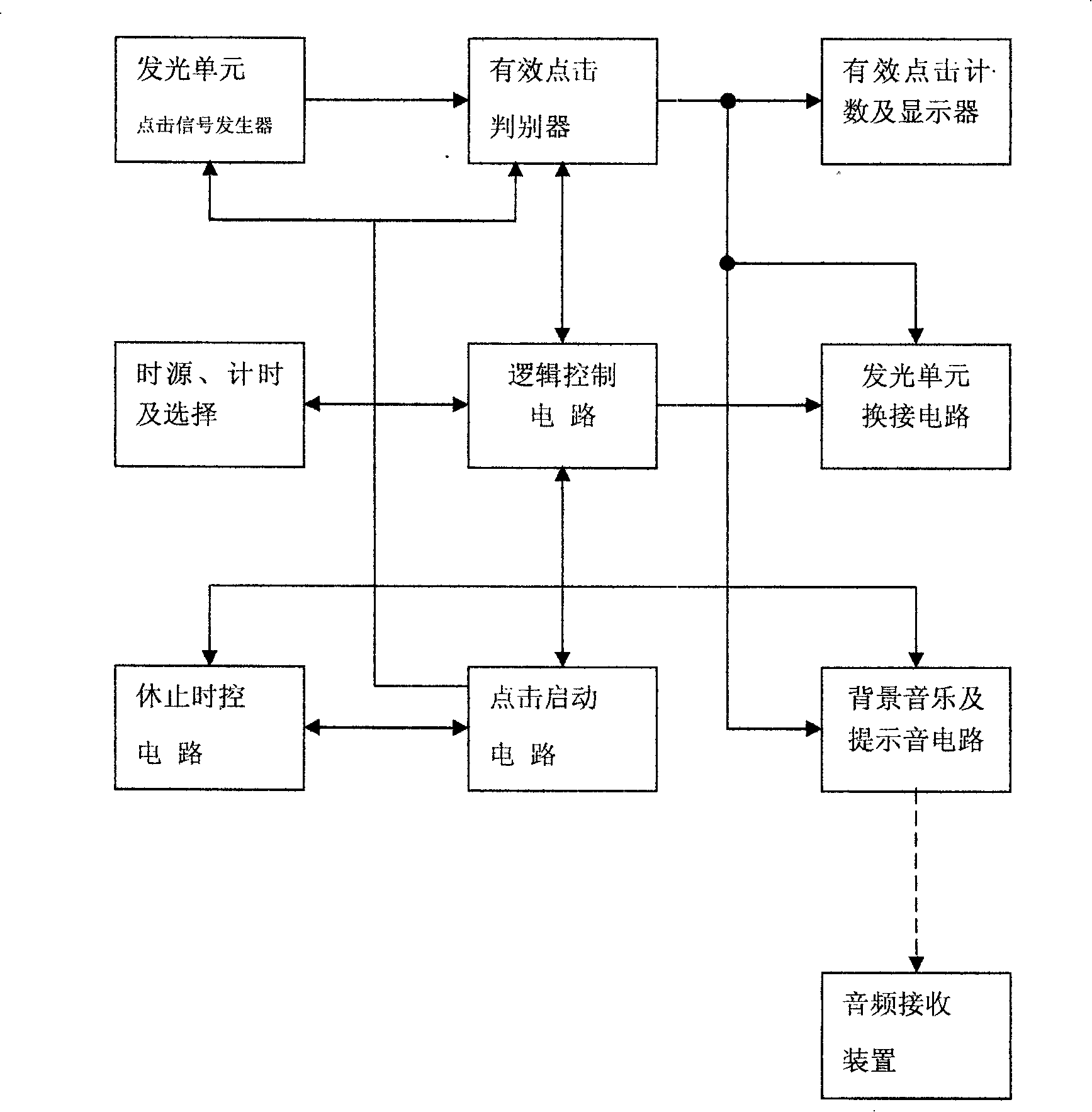
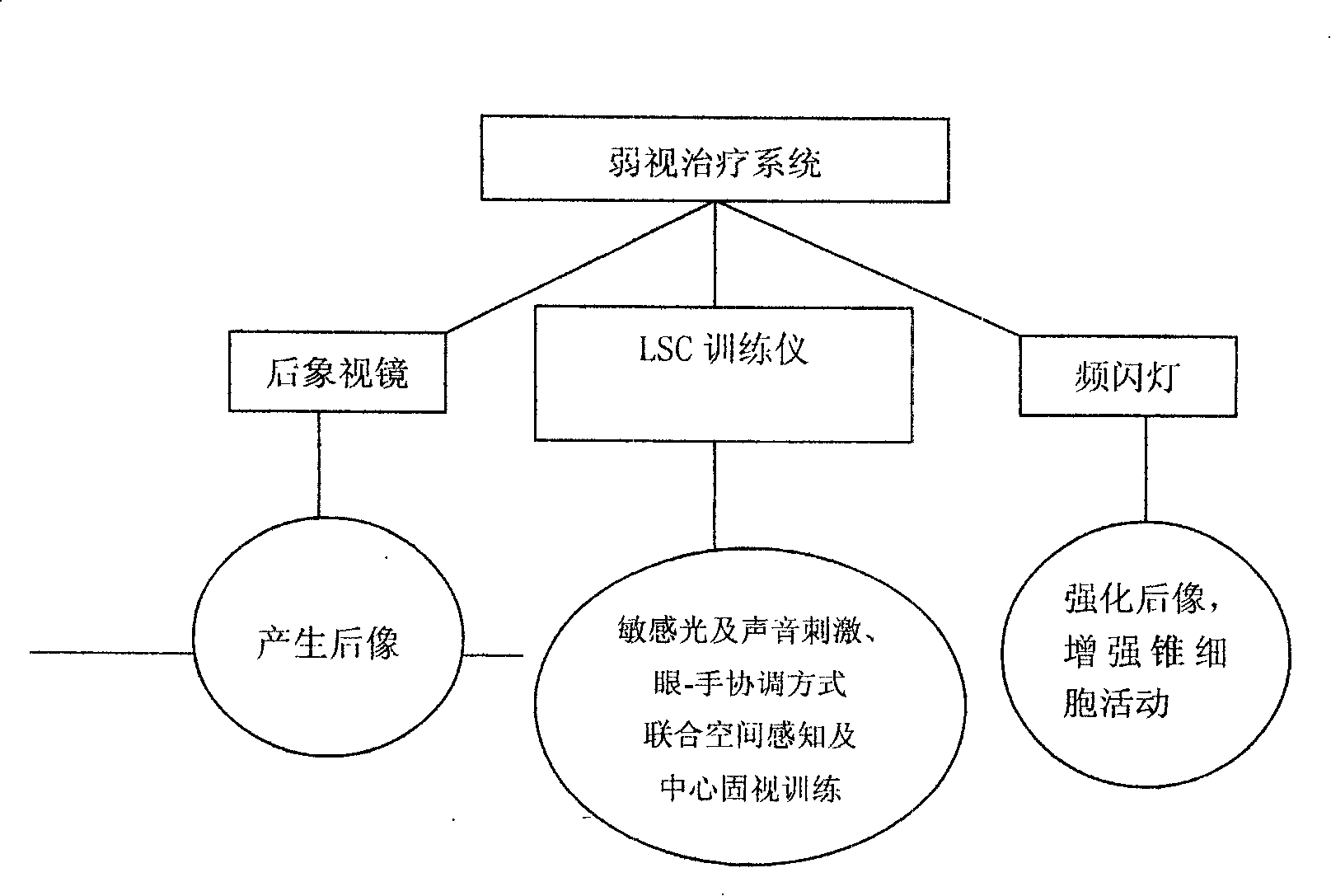
InactiveCN101224151ADisinhibitionEnhanced synchronization activitiesEye exercisersEye treatmentVisual cortexTraining - action
The invention relates to an amblyopia vision increase treatment method and the system, which combines the modern visual physiology research results on the basis of the traditional after-image vision increase therapy, the invention can allow patients to organically integrate the direct stimulation of a characteristic light source on the vision and the indirect stimulation of the sound signal on the visual cortex by the eyes-hands-brain cortex combined space perception and the central vision fixation training actions on the light, sound, electric and data controlled technical lever, so as to strengthen the synchronous activities of the input cortex cells of the amblyopia eye, further to relieve the suppression of the vision on the brain cortex level, promote vision development and finally realize the effective treatment of amblyopia. The clinical observations of 2 years show that the improved after-image vision increase therapy is an amblyopia treatment method which is safe, reliable and good in efficacy, and the invention especially has the treatment effect which is significantly better than other methods for the non-center watch type and other refractory amblyopia. The system can not only greatly improve efficacy, but also improve the working conditions of the medical staff and enhance working efficiency.
Owner:北京同仁验光配镜有限责任公司
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating central serous chorioretinopathy
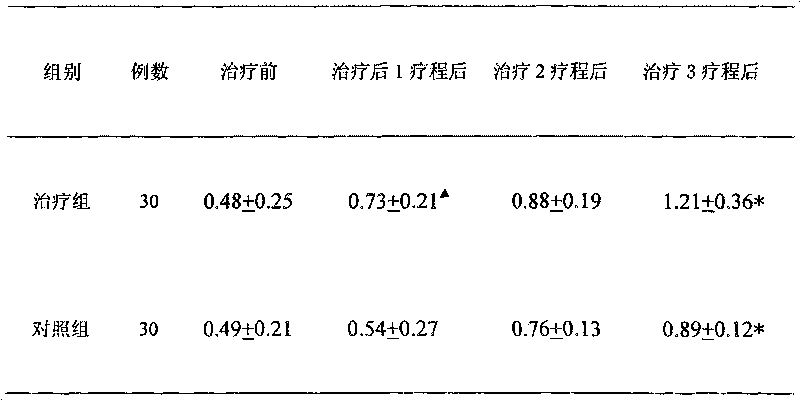
InactiveCN101700379AShorten the course of the diseaseImprove central visionSenses disorderPlant ingredientsCentral visionDisease course
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating central serous chorioretinopathy, which is prepared from 17 traditional Chinese drugs of atractylodes macrocephaia, peach kernel, carthamus tinctorius linne, radix astragali, apricot seed, roud cardamon seed, tuber pinellia, magnolia officinalis, common dodder, wolfberry fruit, prepared rhizome of rehmannia, raw semen coicis, tuckahoe, umbellate pore furgus, salvia miltiorrhiza, radix bupleuri and liquorice. Due to the pathogenesis of the central serous chorioretinopathy, such as complicated phlegm, dampness, deficiency, stagnancy and the like, the central serous chorioretinopathy needs to be treated in both the superficiality and the origin. The clinical screening and the control observation indicate that the traditional Chinese medicine preparation organically combines the comprehensive curative principles of removing dampness to reduce phlegm, invigorating spleen to eliminate dampness, replenishing kidney and promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis; and the observation on clinical symptoms, physical signs, fundus fluorescein angiography and other indexes indicates that the total effective rate of the treatment group is 93.33%, and the recurrence rate is 4%. The treatment group is obviously better than the control group in the aspects of shortening the disease course of central serous chorioretinopathy, enhancing the central vision of patients with central serous chorioretinopathy, and obviously improving the eye symptoms and fundus symptoms of edema, exudation and effusion.
Owner:李军
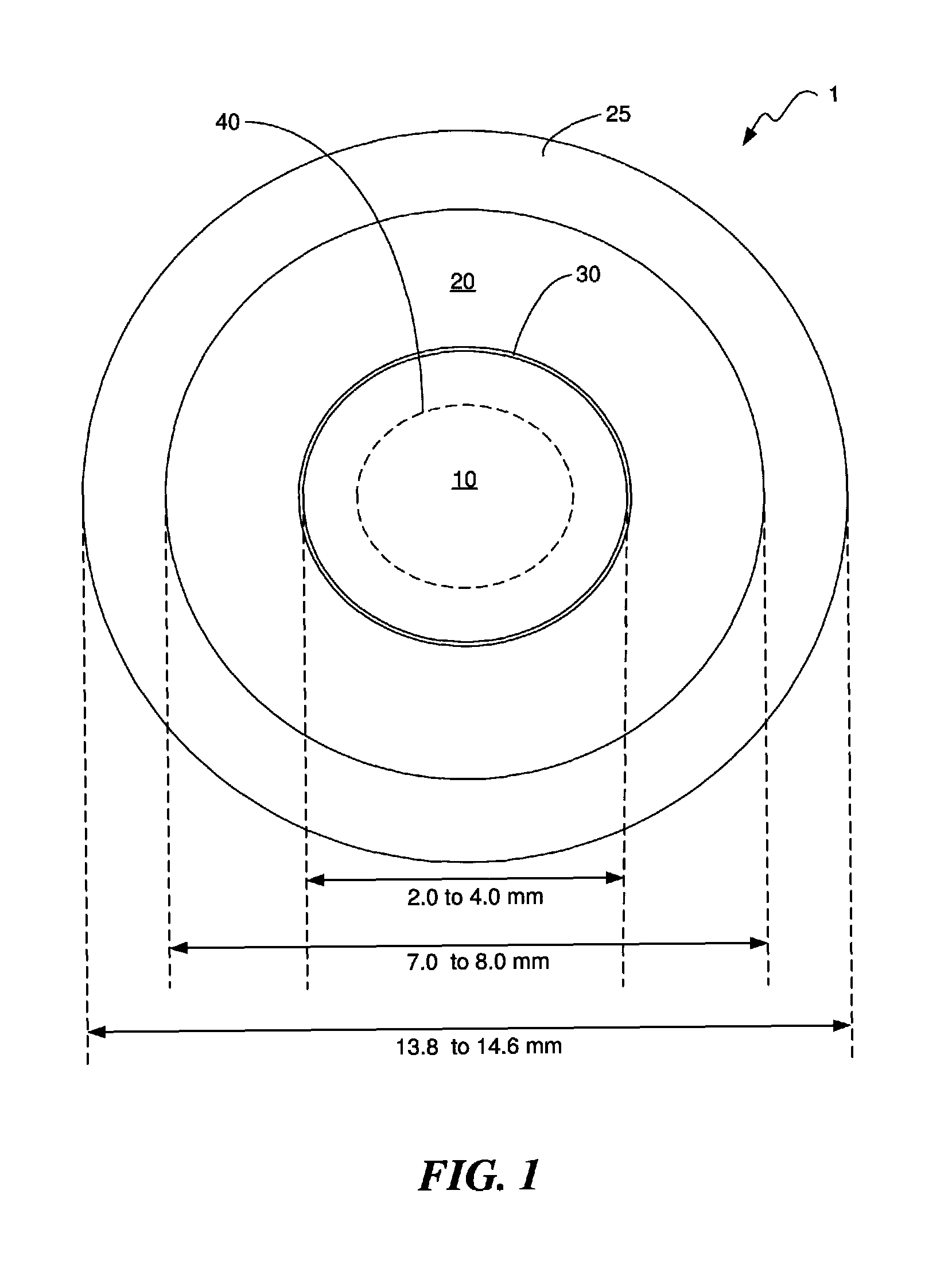
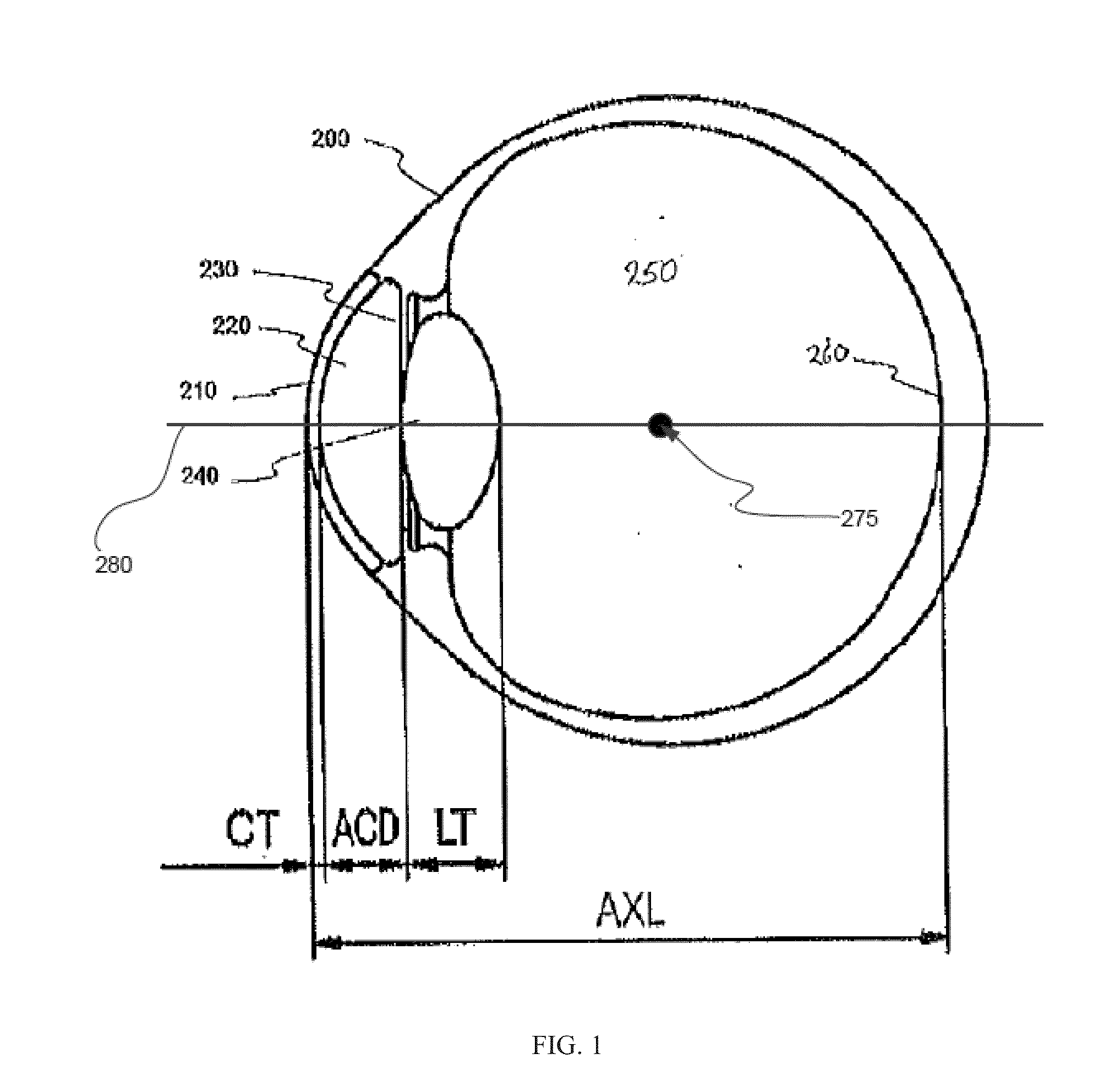
Production of an ophthalmic member adapted for central and peripheral vision
ActiveCN101663609AAccurate imagingAdapt to Peripheral VisionOptical partsRefractive errorHead movements
The invention relates to a method for making an ophthalmic member for correcting ametropia, that is adapted for correcting the central and peripheral vision of a wearer and takes into account the amplitudes of the movements of the wearer's eyes and head. A central area of the member, in which the central vision is corrected, is sized based on the amplitude of the eyes' movements in order to provide good visual comfort. The peripheral vision is corrected in a peripheral area of the ophthalmic member in order to prevent an increase of the wearer's ametropia in the long run.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
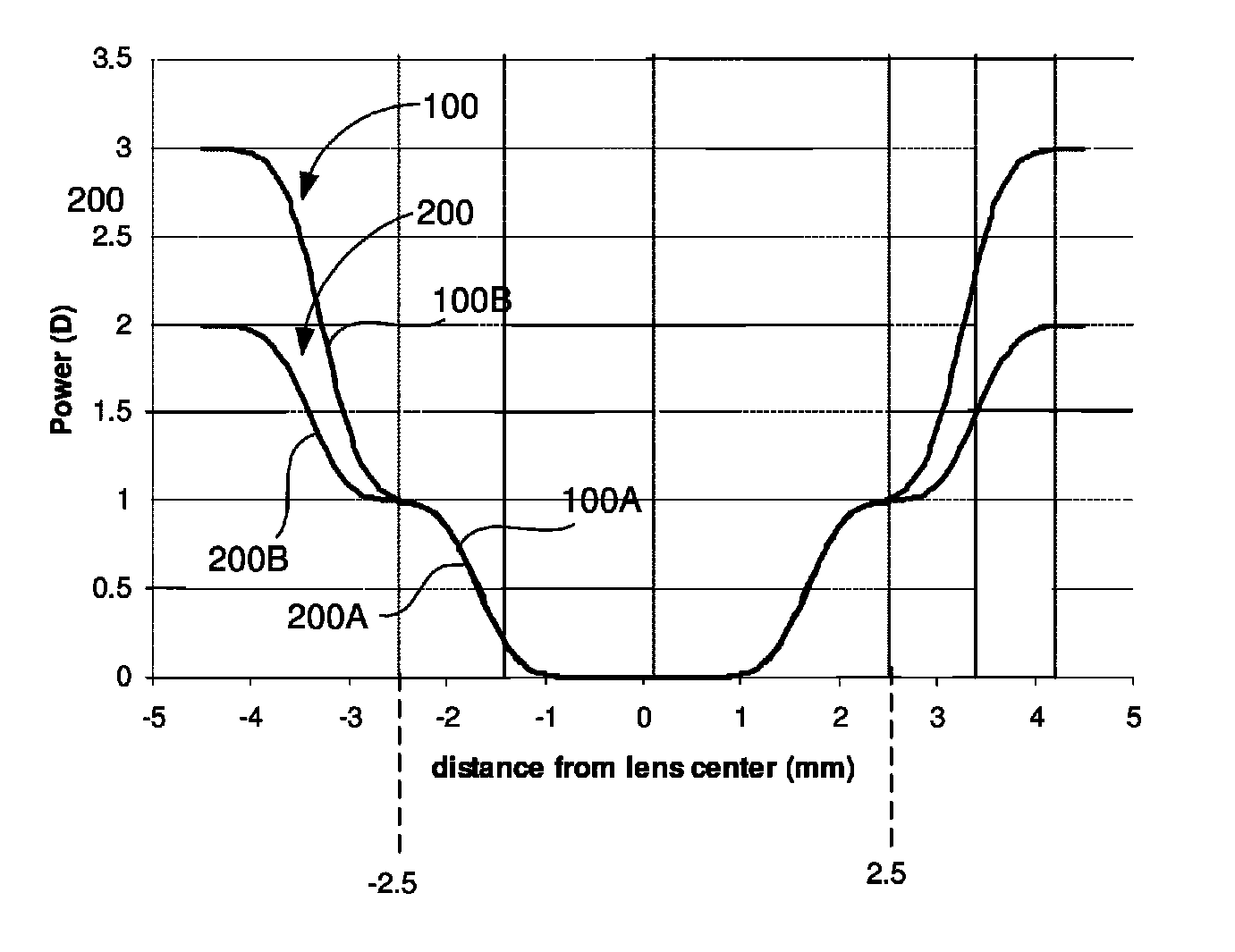
Multi-area contact lens with property of controlling progression of myopia and application method of multi-area contact lens
InactiveCN109407342ALarge peripheral myopic defocusFlexible adjustment of surface parametersOptical partsUses eyeglassesCentral vision
The invention provides a multi-area contact lens with a property of controlling progression of myopia and an application method of the multi-area contact lens. The multi-area contact lens comprises alens body, wherein the lens body comprises a myopia correction area, a myopia treatment area and a connection area for fixing wearing of the contact lens, the myopia correction area is an area capableof completely correcting myopia vision, and the myopia treatment area is an area capable of generating myopic defocusing along the peripheral retina. The multi-area contact lens with the property ofcontrolling the progression of the myopia and the application method of the multi-area contact lens have the advantages that the front surface of the lens body is provided with rotationally symmetrical multi-area aspheric surface / spherical surface profiles so that the use of the aspheric surface can be avoided, thereby reducing the processing difficulty, surface profile parameters of all areas onthe front surface of the lens body can be adjusted flexibly, and by adjusting the size of the area and size of additional refractive power of all the areas of the lens body, the correction ability ofthe central vision and the size of provided peripheral myopic defocusing can be effectively adjusted, thereby being capable of providing personalized customization according to different individual needs.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
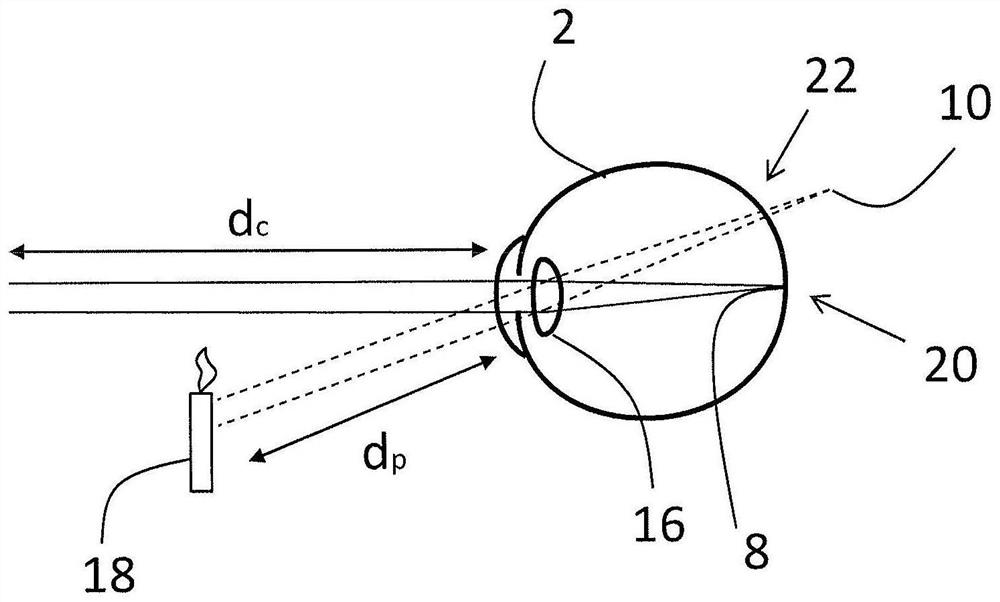
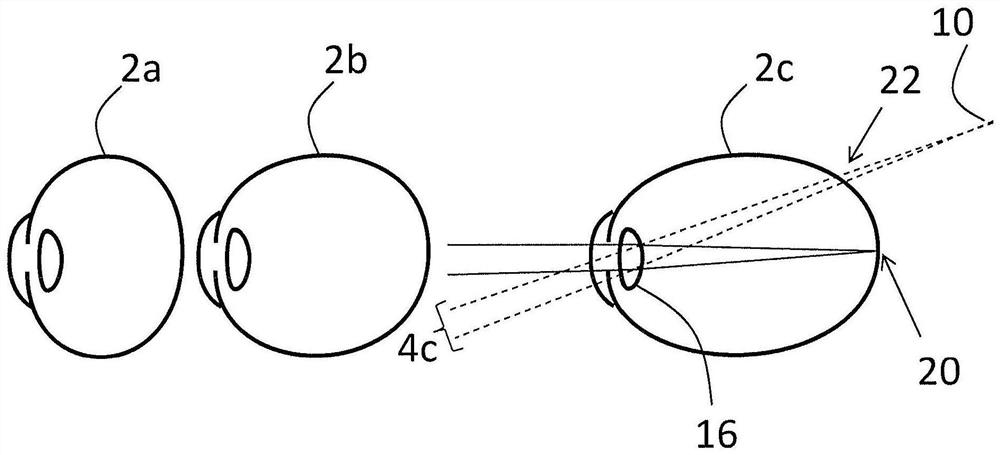
Technique for determining a risk indicator for myopia
A system is provided for determining a risk indicator for myopia. The system comprises a wearable device configured to be attached to a body of a user. The wearable device comprises at least one distance sensor configured to determine at least a first distance value indicative of a distance between the wearable device and an object located in a central vision zone of the user and a second distance value indicative of a distance between the wearable device and an object located in a peripheral vision zone of the user. The system further comprises a control unit configured to determine, based on the first distance value and the second distance value, a risk indicator for myopia. Further, a method and a computer program product are provided.
Owner:VIVIOR AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com