Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Toric lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
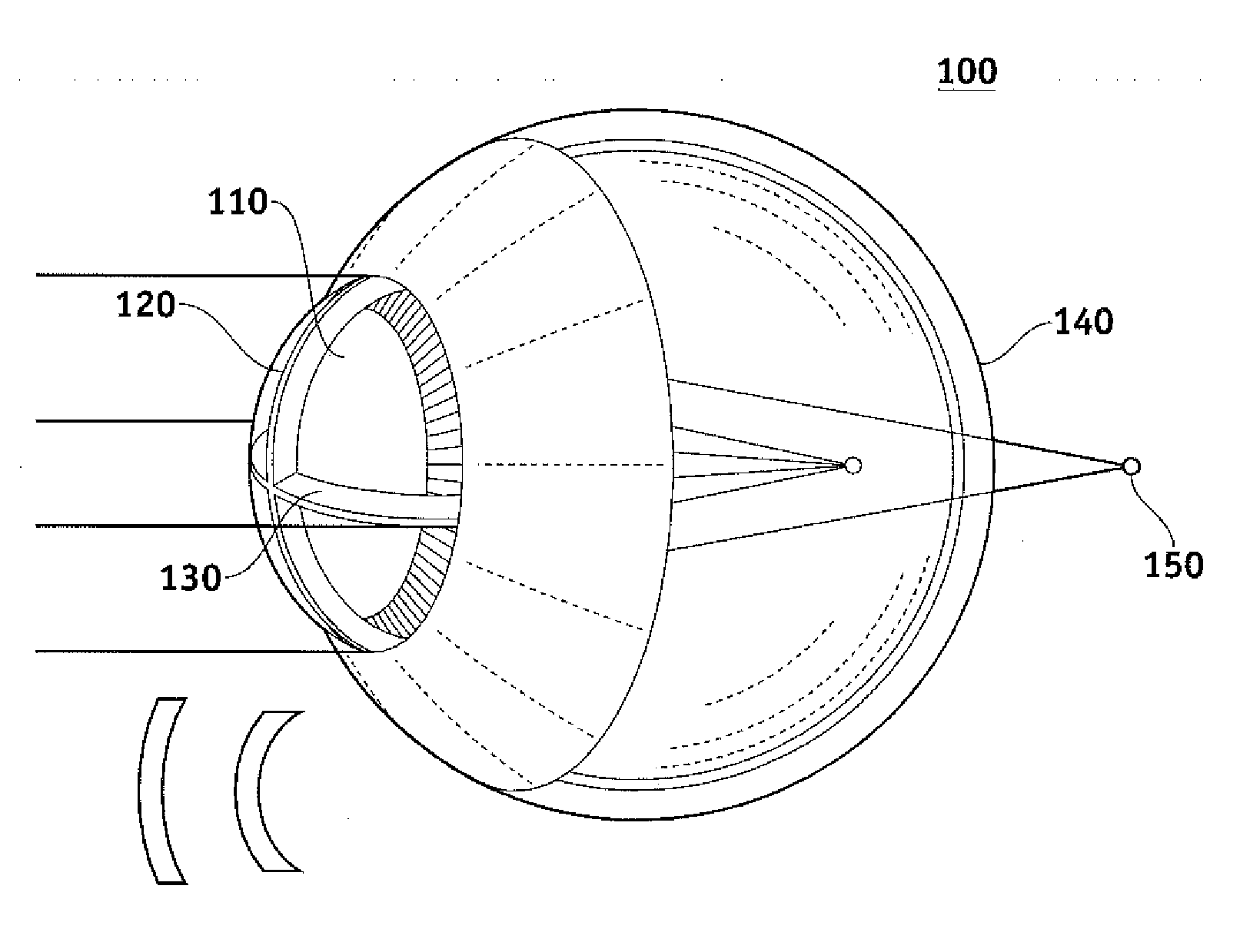
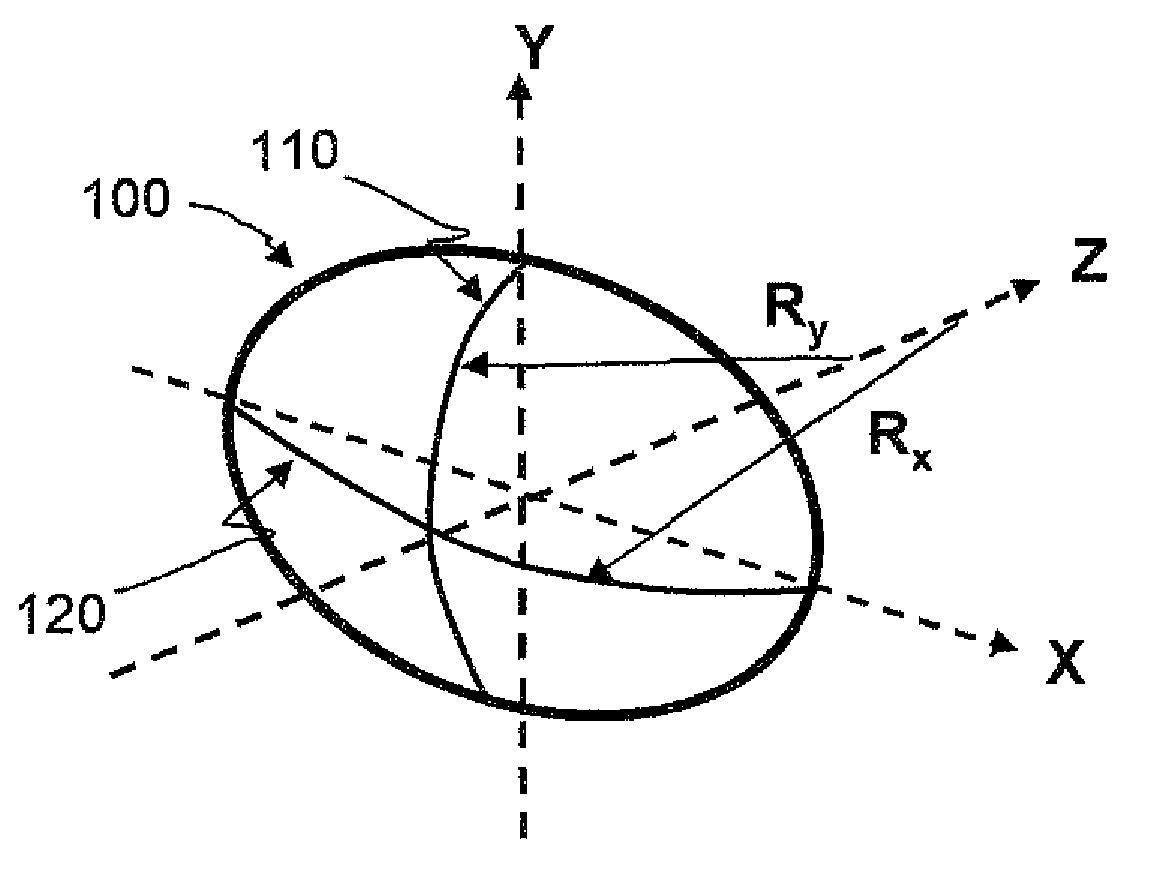
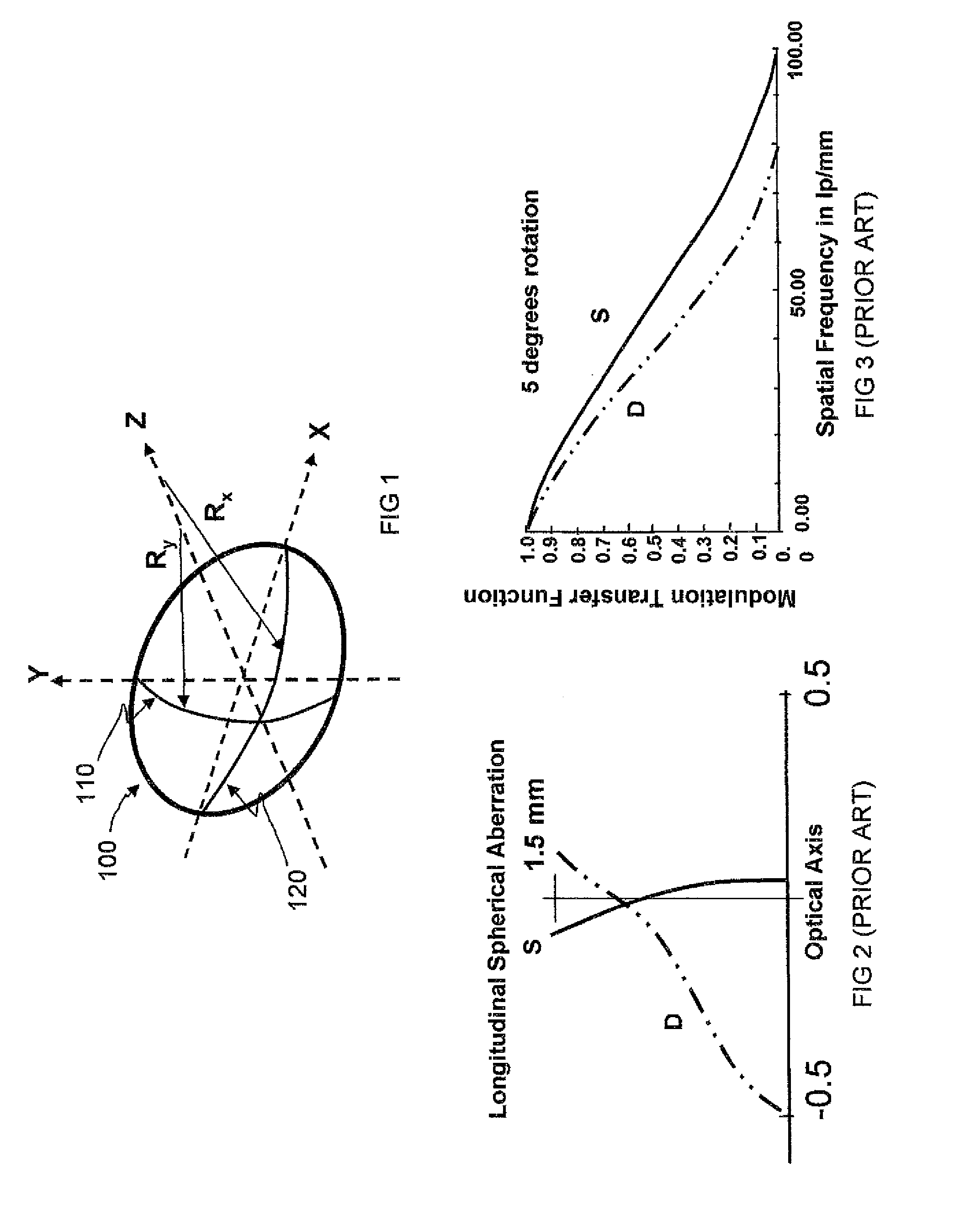
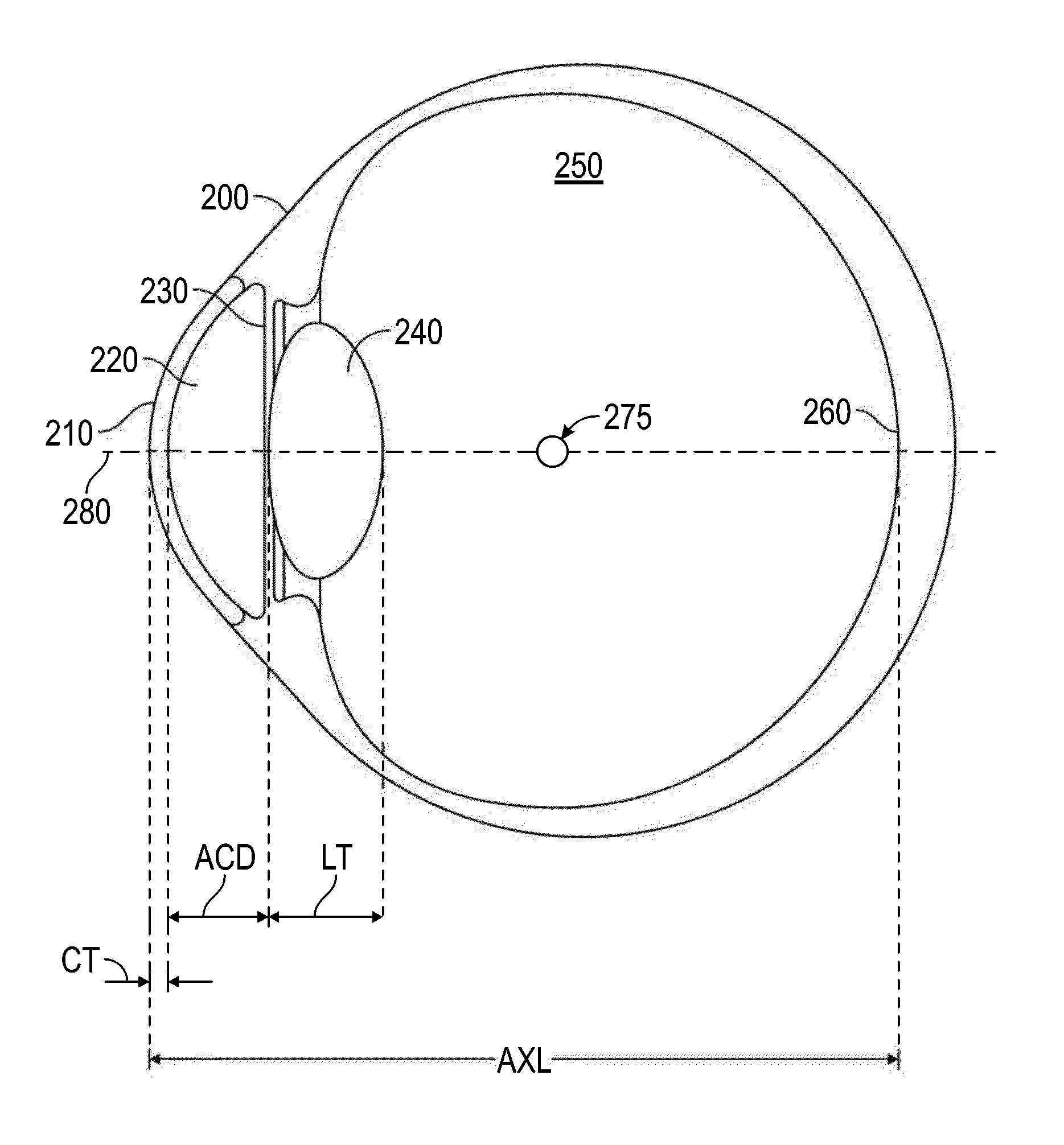
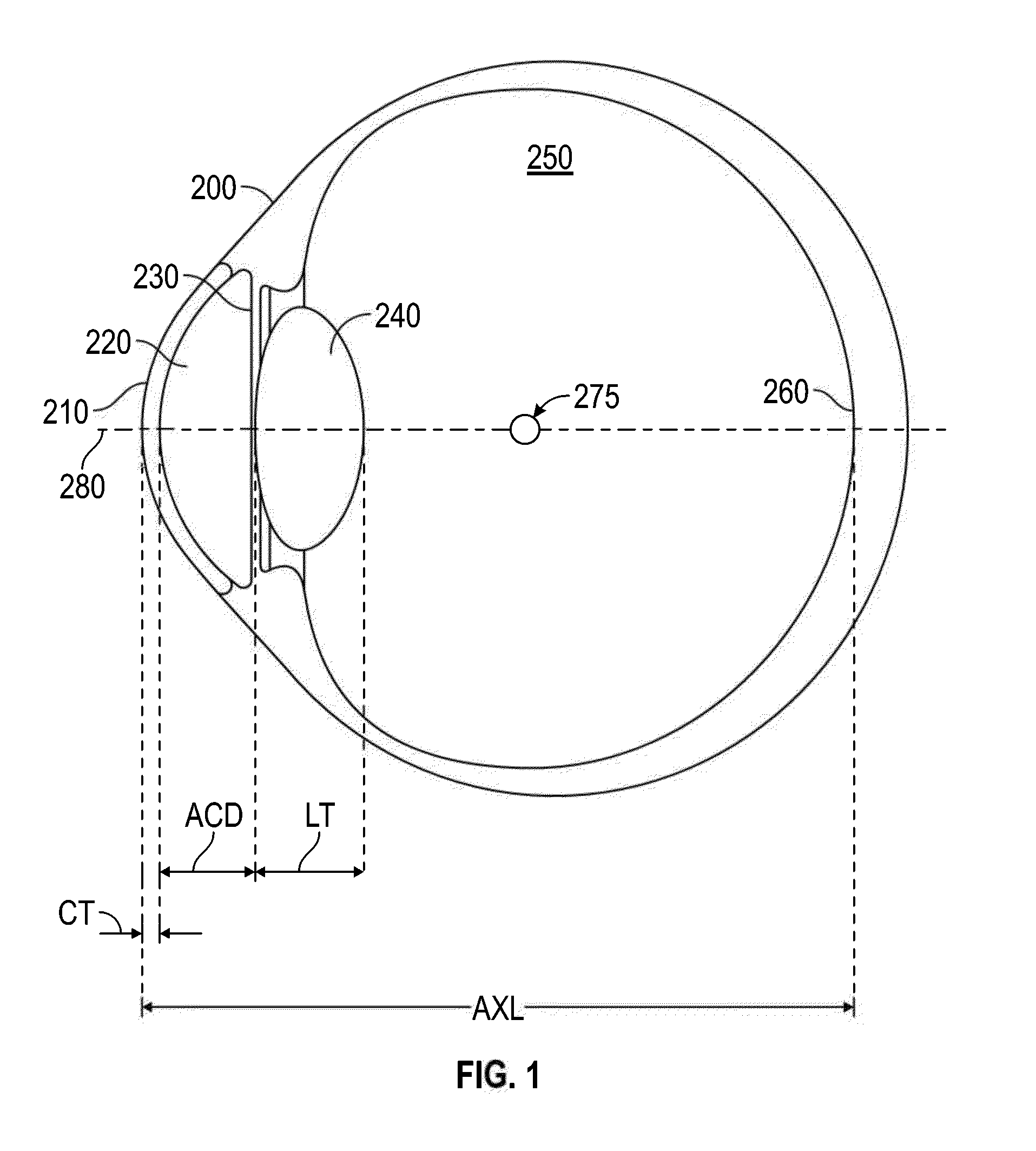
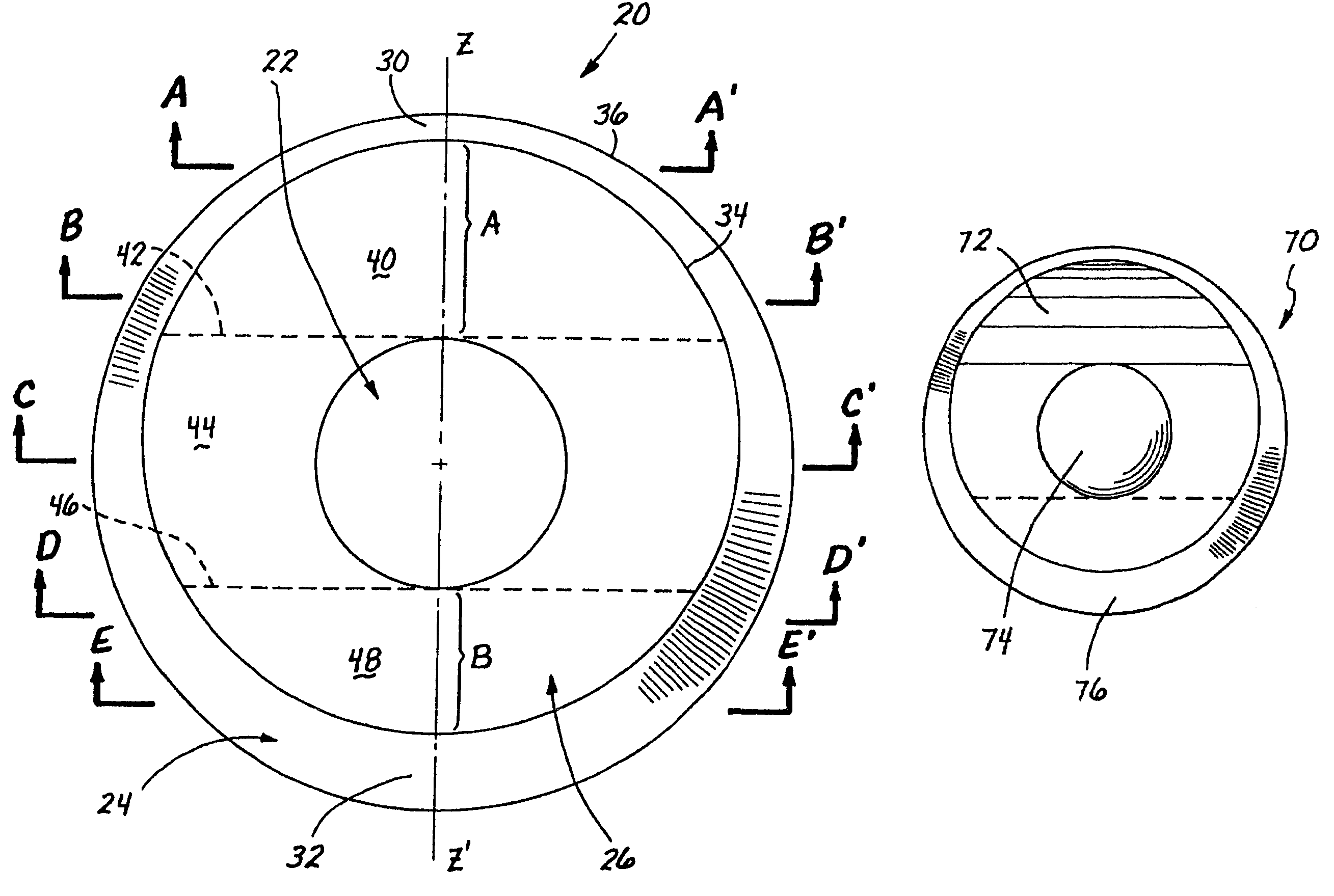
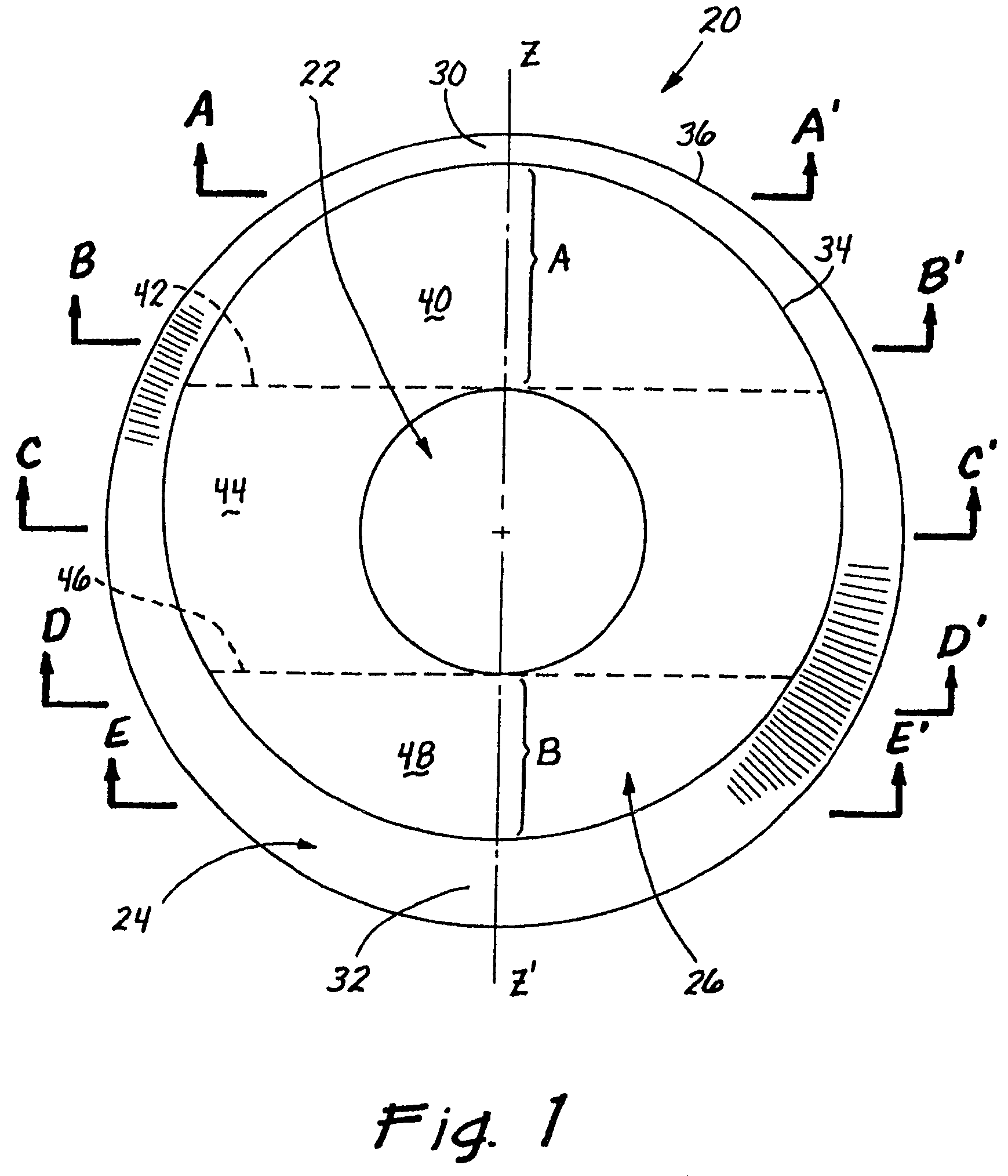
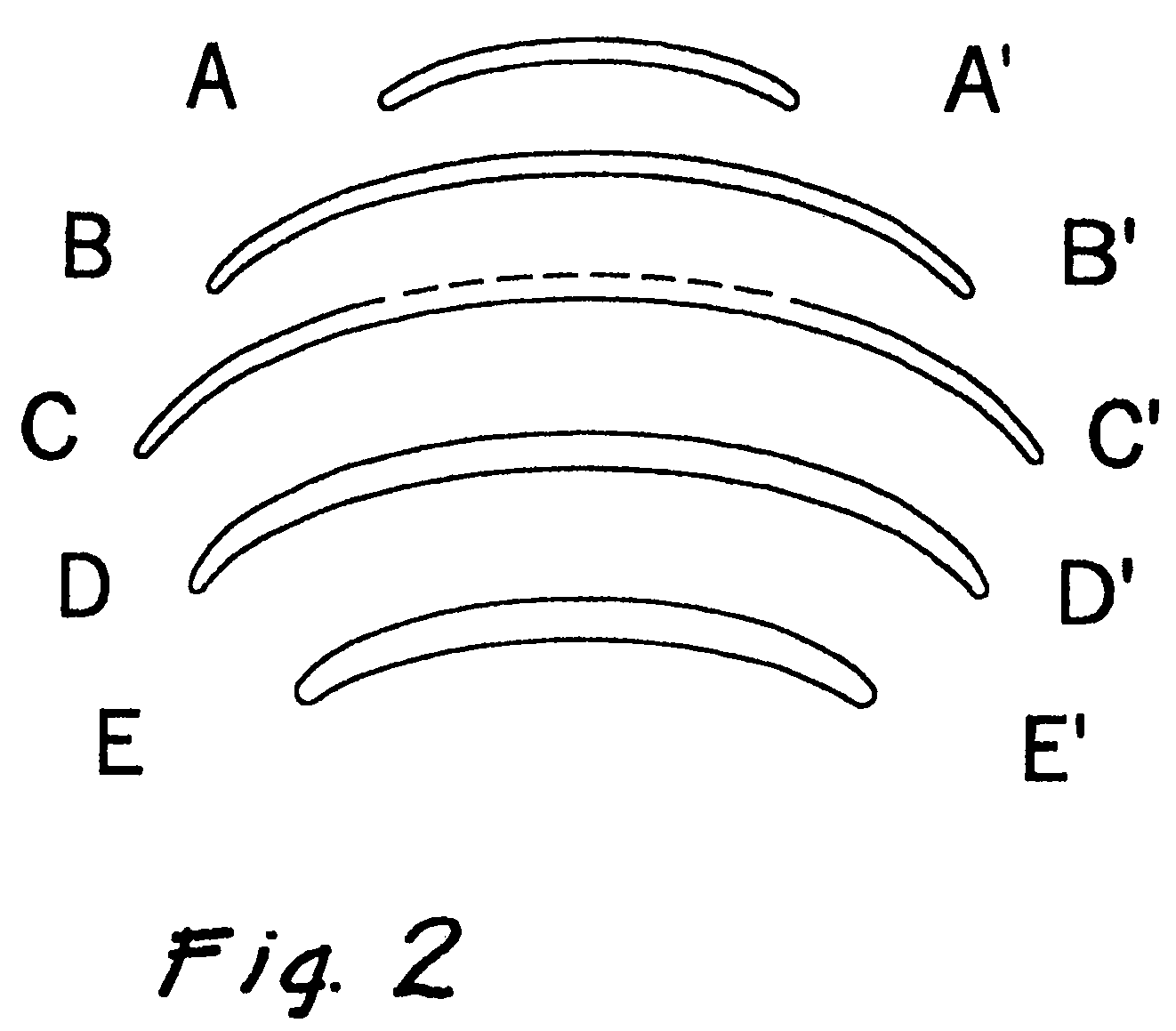
A toric lens is a lens with different optical power and focal length in two orientations perpendicular to each other. One of the lens surfaces is shaped like a "cap" from a torus (see figure at right), and the other one is usually spherical. Such a lens behaves like a combination of a spherical lens and a cylindrical lens. Toric lenses are used primarily in eyeglasses, contact lenses and intraocular lenses to correct astigmatism.
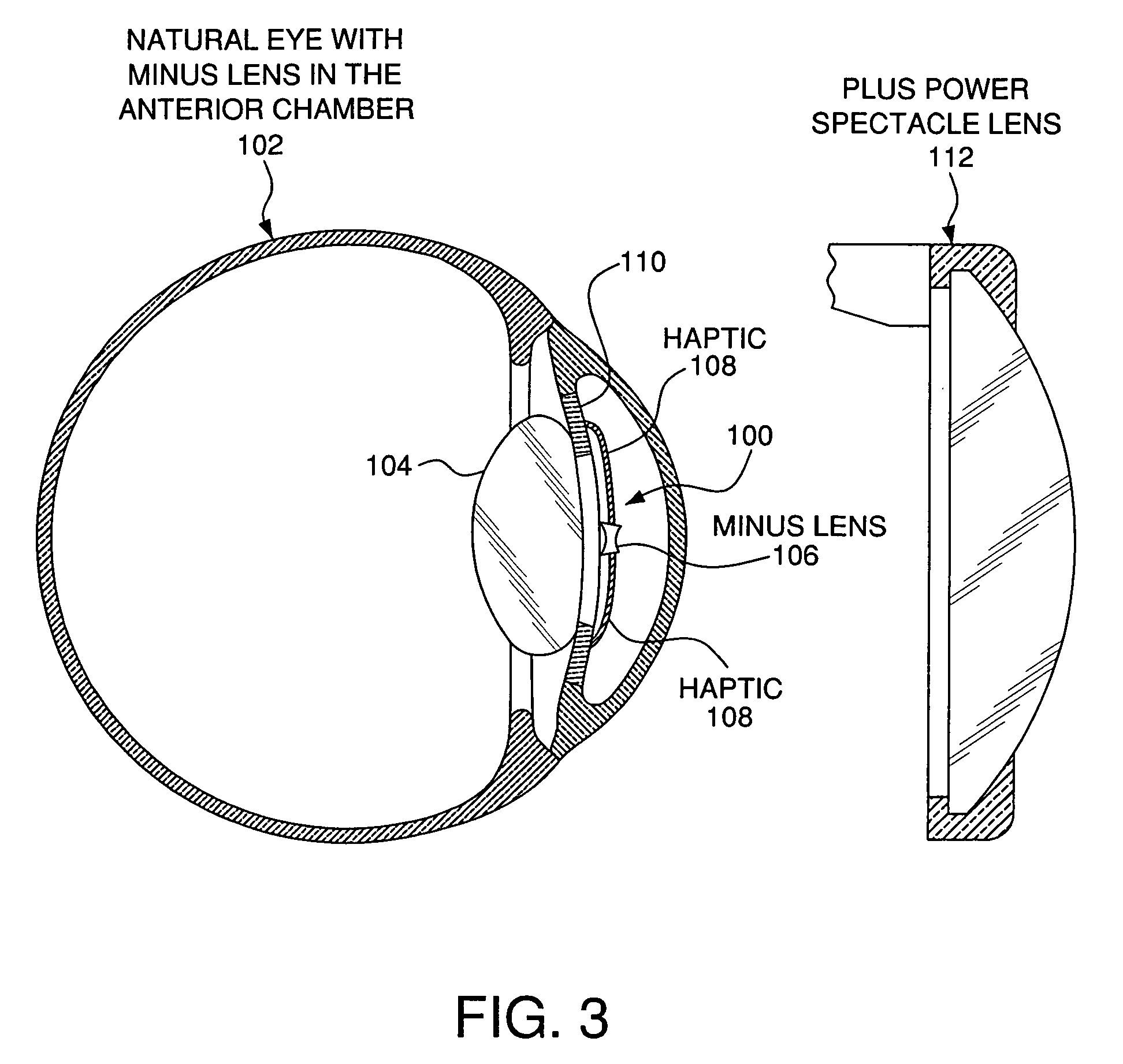
Toric lens with decreased sensitivity to cylinder power and rotation and method of using the same
ActiveUS20110166652A1Reduce sensitivityCorrected astigmatismSpectales/gogglesEye surgeryVisual acuityDecreased Sensitivity
A method, system and apparatus for vision correction are disclosed. The method, system and apparatus include a toric intraocular element for correcting astigmatism and having a cylinder power, and a depth of focus extender coupled to the toric intraocular element, the depth of focus extender extending a depth of focus. The extended depth of focus may reduce sensitivity of the toric intraocular element to at least one of rotation and selected cylinder power.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Contact lens with high-order compensation for non-axisymmetric structure
ActiveUS7172285B1Improve imaging effectAberration compensationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsPrismWavefront aberration
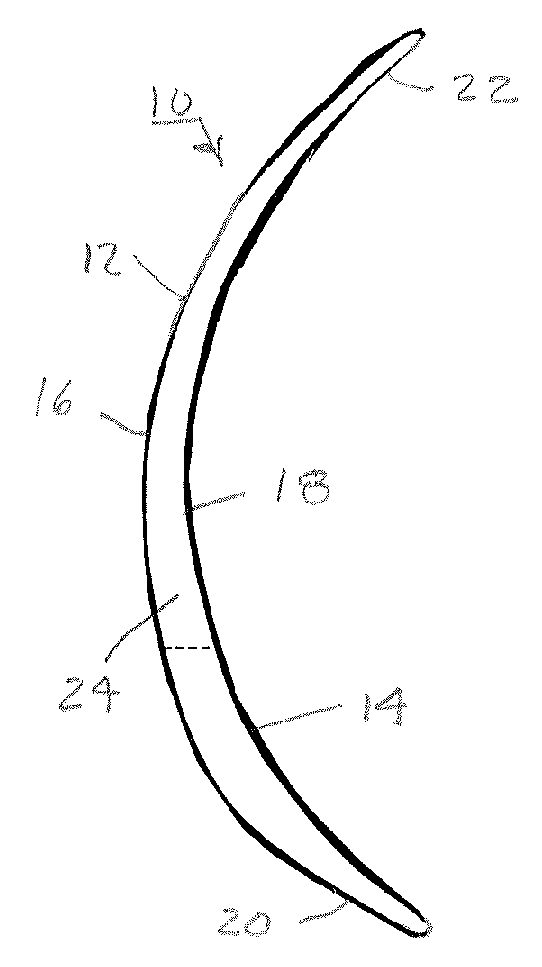
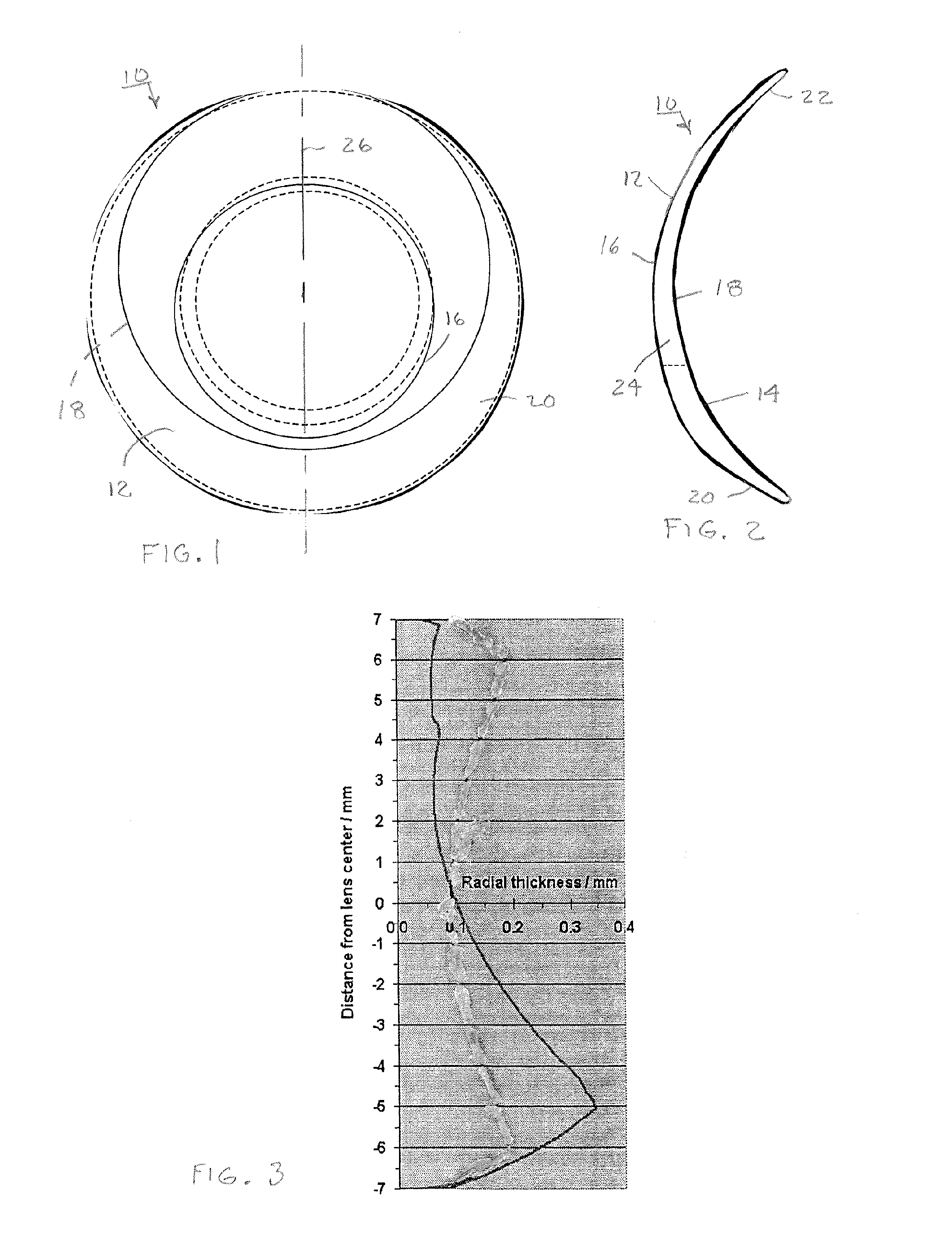
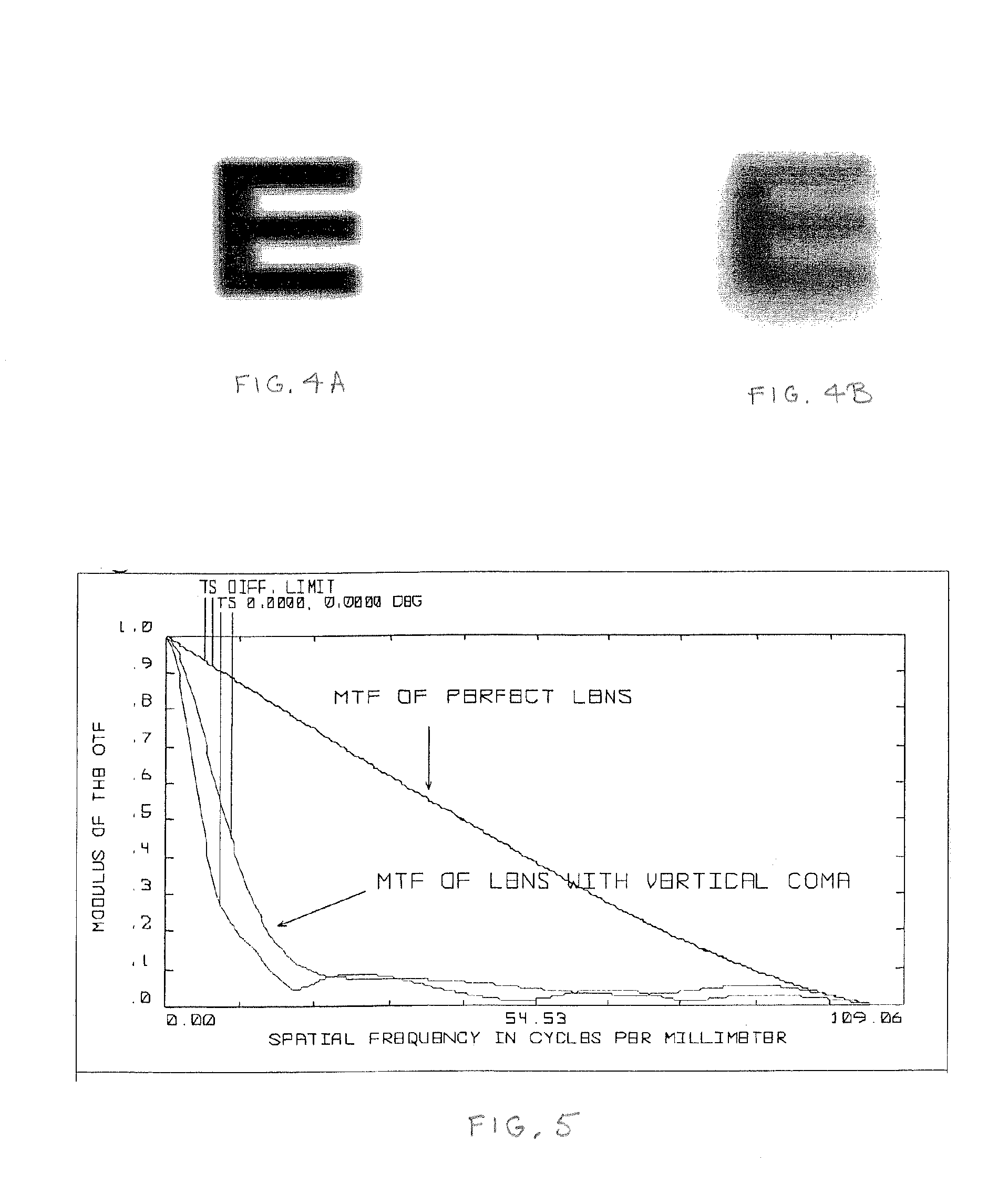
Contact lenses, such as prism ballasted toric lenses, having anterior and posterior surfaces related by way of non-axisymmetric thickness variation can exhibit a third-order aberration, particularly vertical coma. A wavefront modifier, such as an aspheric surface modification, is incorporated into the lenses to at least partially compensate for the wavefront aberration associated with the non-axisymmetric thickness variation. A magnitude of the modifications can be adjusted to set a target value for any remaining wavefront aberration of the lenses based on a population-wide goal.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Toric ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20100315589A1Image quality is preservedSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensStigmatismLens plate
An ophthalmic lens for placement on the human eye or implanted into an eye is described. The lens has a cylinder power for eye astigmatism refraction error correction and incorporates aspherization of at least one of the surfaces to reduce vision quality reduction with toric ophthalmic lens rotation that creates meridional misalignment as compared with the equivalent toric lens with non-aspherized surface.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Teledioptic lens system and method for using the same
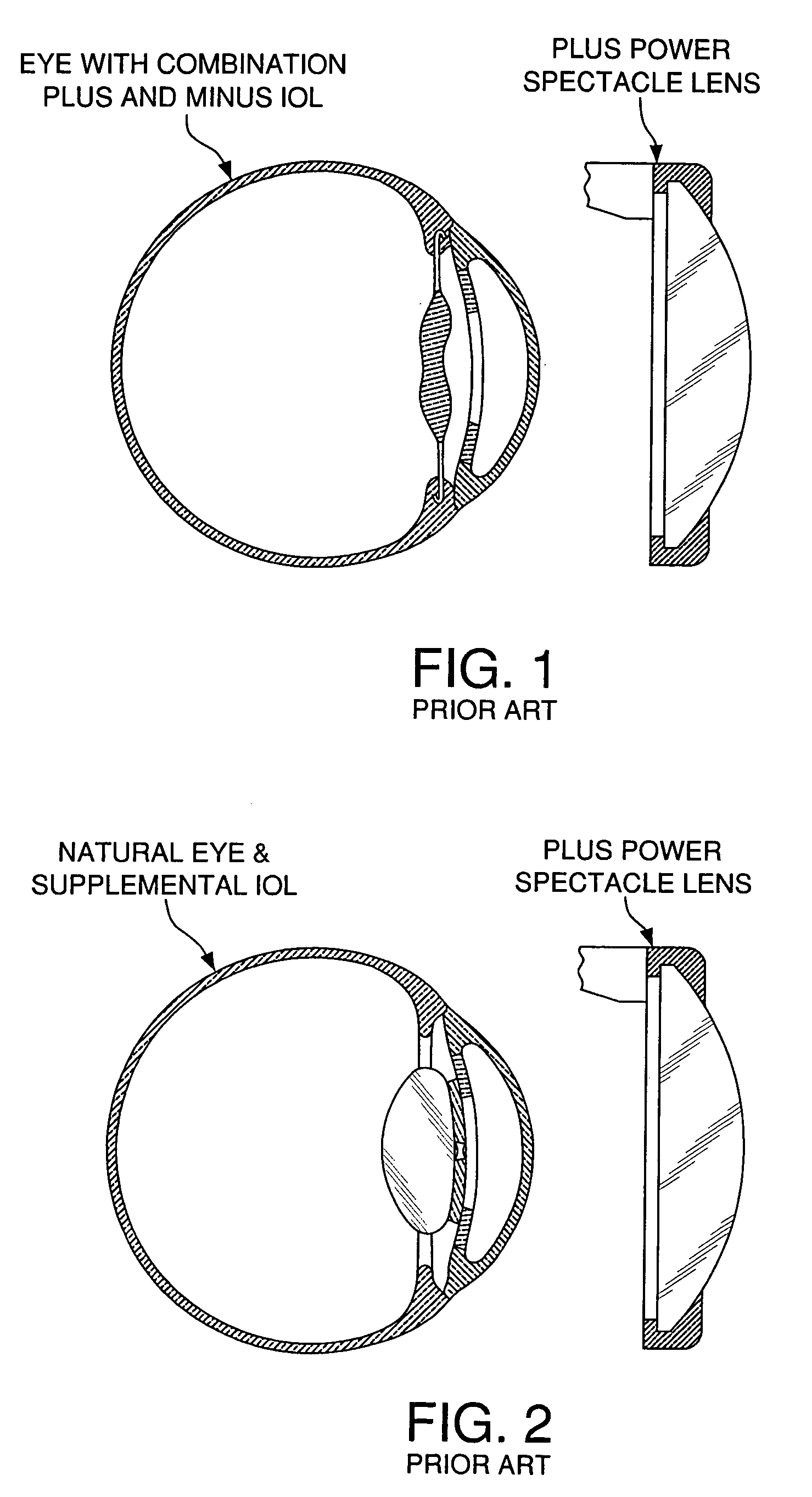
An intraocular lens system for implantation in the eye to modify the lens system of the eye comprising the cornea and the natural or existing artificial lens in the eye, and a method for using the same. The system and method comprises a lens having a high minus portion, adapted to be implanted in the eye to create a lens system that functions as a teledioptic lens system which, when used without an external lens, provides unmagnified and peripherally unrestricted vision and which, when used with an external lens, provides magnified and peripherally restricted vision to correct for macular degeneration. The lens can be attached to the iris, to a portion of the iris that was removed by iridectomy, or can be implanted in the cornea. The lens can also include a plus portion that is surrounded by the high minus portion. The high minus portion is preferably about one to about three millimeters in diameter, and can have an outer perimeter with no surrounding material or can be surrounded by a plus, minus or toric lens.
Owner:TELEDIOPTIC LENS SYST
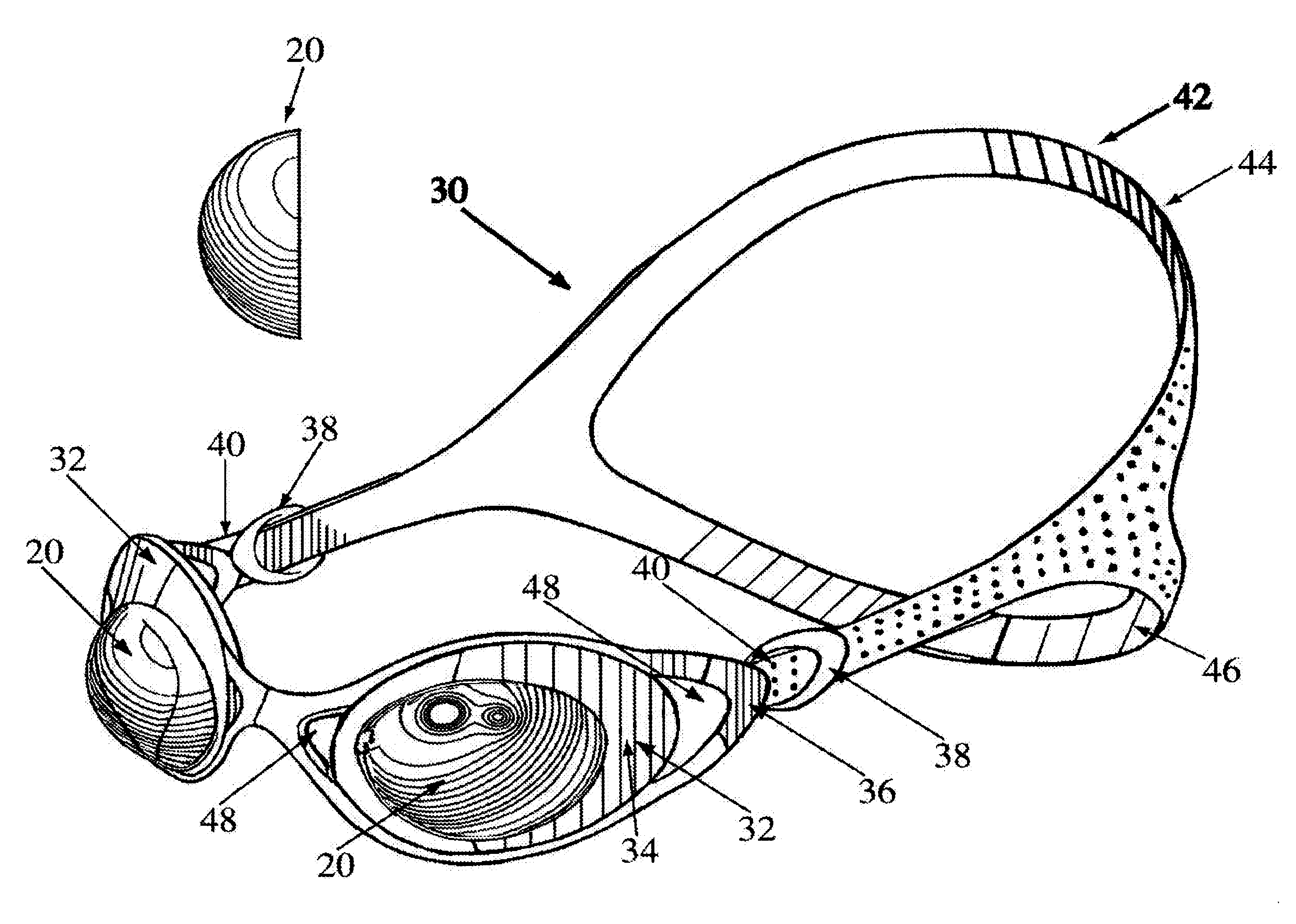
Toric-shaped lenses and goggle assembly
The present invention relates to toric-shaped see through lenses used in eyewear. The lenses have a substantially constant thickness and having base curve with a substantially constant radius of curvature of at least 15 mm and preferably in the range of 19-23 mm. The toric lenses may be supported in a frame formed of either rigid or flexible material and attached to a strap assembly adaptable to be worn by the user. Optionally, each of the lenses may be supported by a flanged member and ventilation passages preferably extending through the frame and / or the lenses to allow air to circulate around the lenses.
Owner:GREENHOUSE GROWN PRODS
Enhanced toric lens that improves overall vision where there is a local loss of retinal function
ActiveUS20150250585A1Improve acuityImproves contrast sensitivityRefractometersSkiascopesOptical propertyCentral vision
Systems and methods are provided for improving overall vision in patients suffering from a loss of vision in a portion of the retina (e.g., loss of central vision) by providing an enhanced toric lens which redirects and / or focuses light incident on the eye at oblique angles onto a peripheral retinal location. The intraocular lens can include a redirection element (e.g., a prism, a diffractive element, or an optical component with a decentered GRIN profile) configured to direct incident light along a deflected optical axis and to focus an image at a location on the peripheral retina. Optical properties of the intraocular lens can be configured to improve or reduce peripheral errors at the location on the peripheral retina. One or more surfaces of the intraocular lens can be a toric surface, a higher order aspheric surface, an aspheric Zernike surface or a Biconic Zernike surface to reduce optical errors in an image produced at a peripheral retinal location by light incident at oblique angles.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Toric lens design
This invention is related to contact lenses. In particular, the present invention is related to a toric contact lens design with thickness zones in the carrier portion of the lens for increased rotational stability.
Owner:ALCON INC
Toric lens with decreased sensitivity to cylinder power and rotation and method of using the same
ActiveUS20160100938A1Reduce sensitivitySpectales/gogglesEye surgeryVisual acuityDecreased Sensitivity
A method, system and apparatus for vision correction are disclosed. The method, system and apparatus include a toric intraocular element for correcting astigmatism and having a cylinder power, and a depth of focus extender coupled to the toric intraocular element, the depth of focus extender extending a depth of focus. The extended depth of focus may reduce sensitivity of the toric intraocular element to at least one of rotation and selected cylinder power.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Non-corrective lenses with improved peripheral vision
InactiveUS20060098161A1Improve eyesightImprove deviationEye diagnosticsNon-optical partsCorrective contact lensConvex side
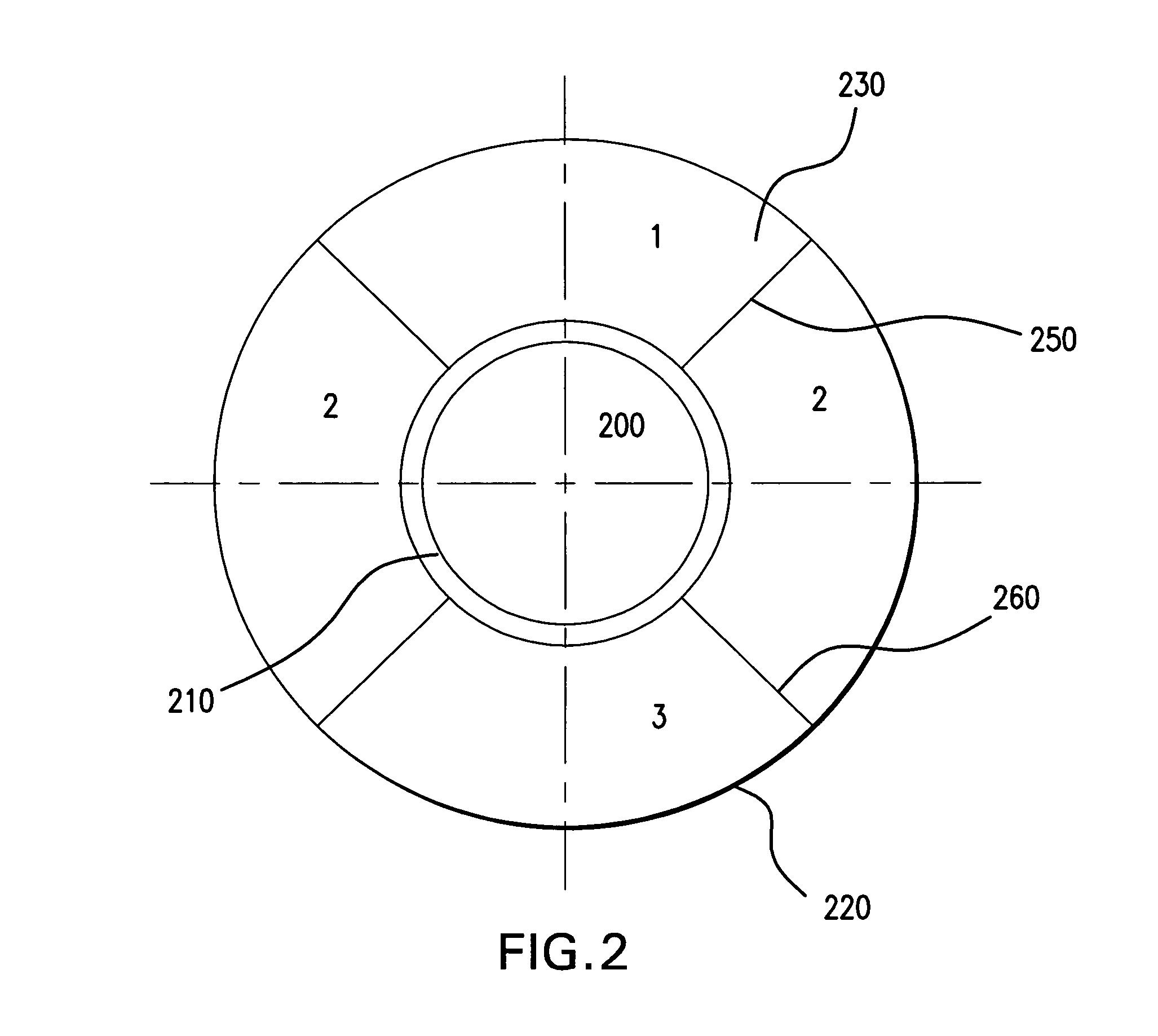
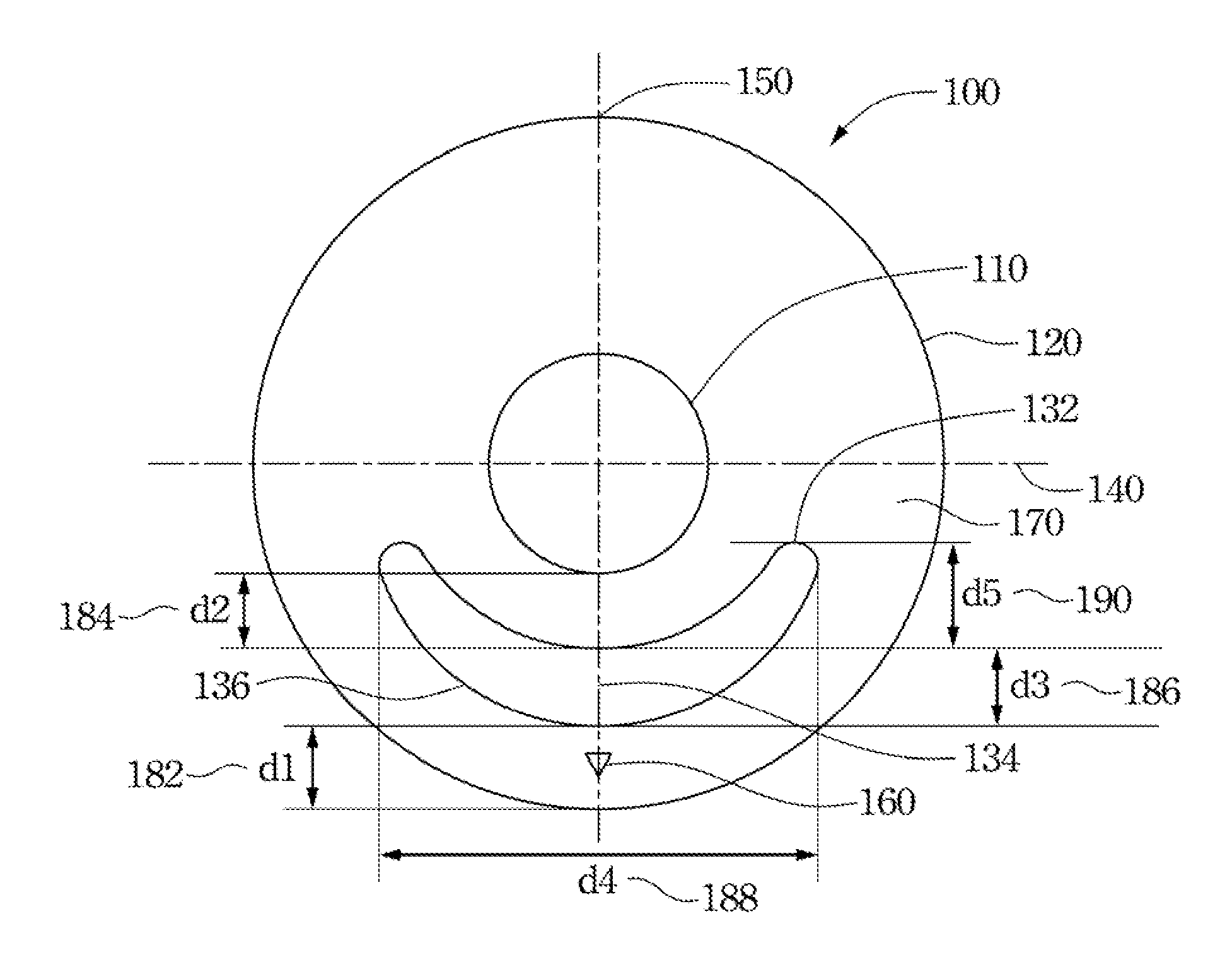
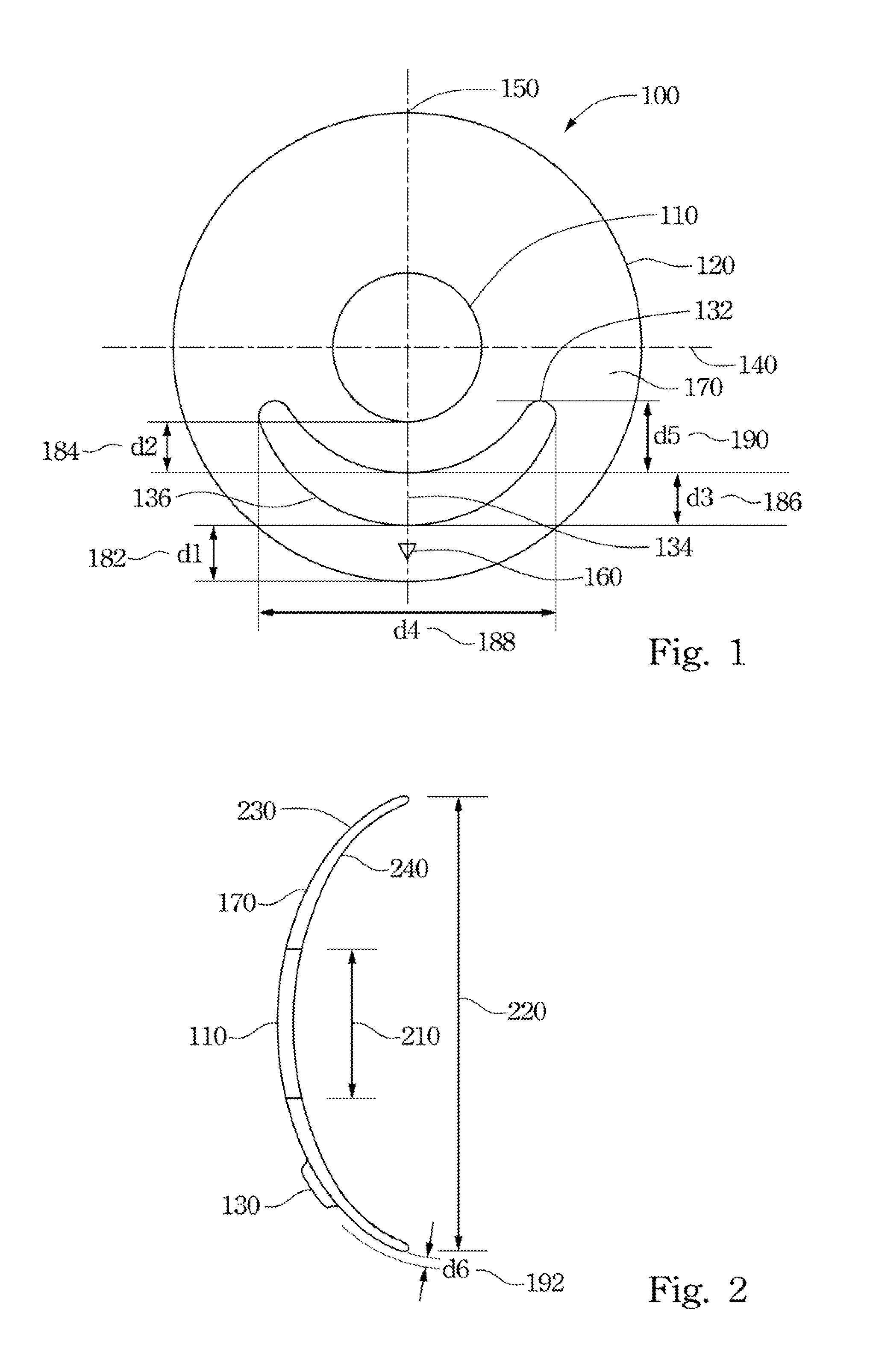
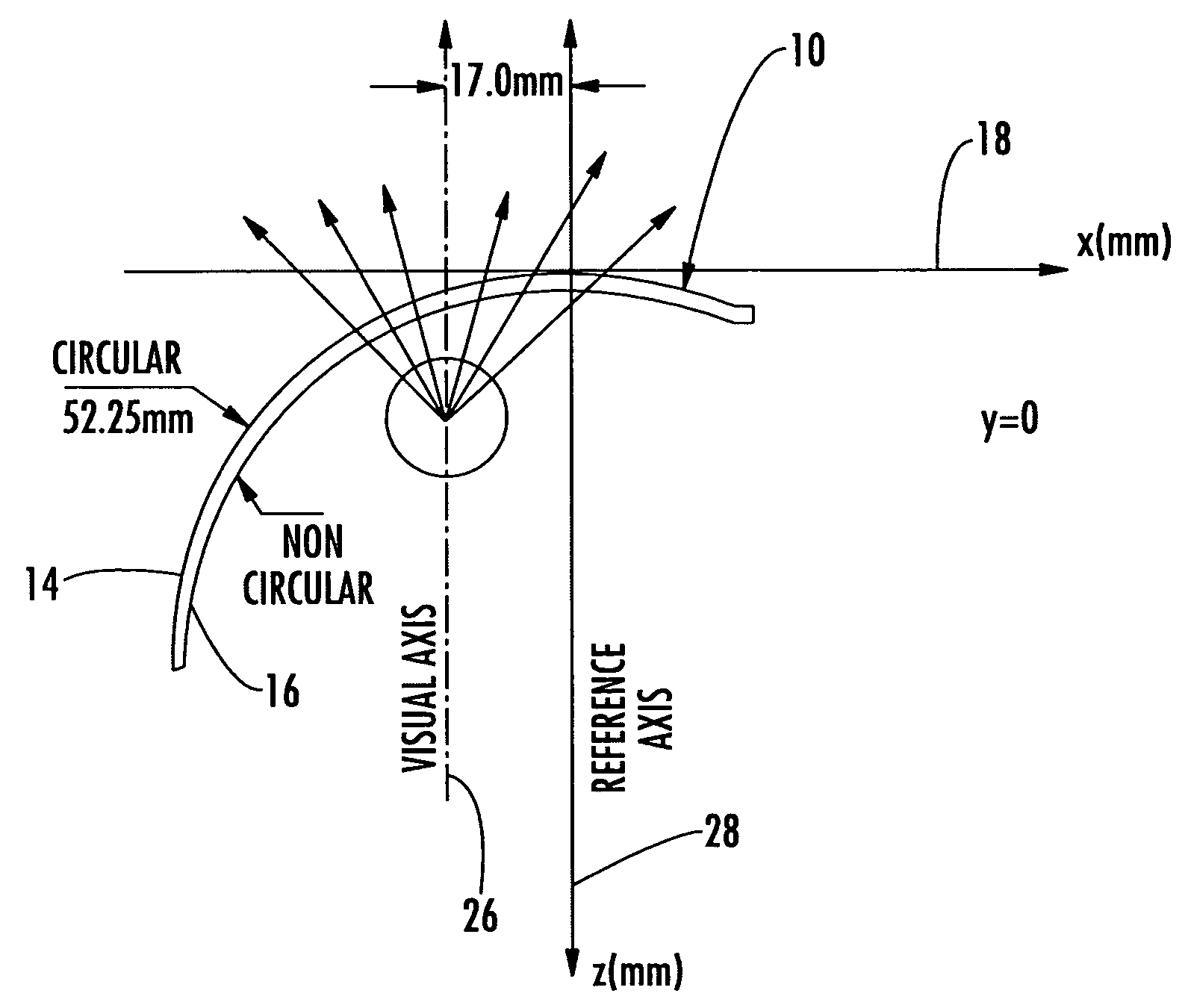
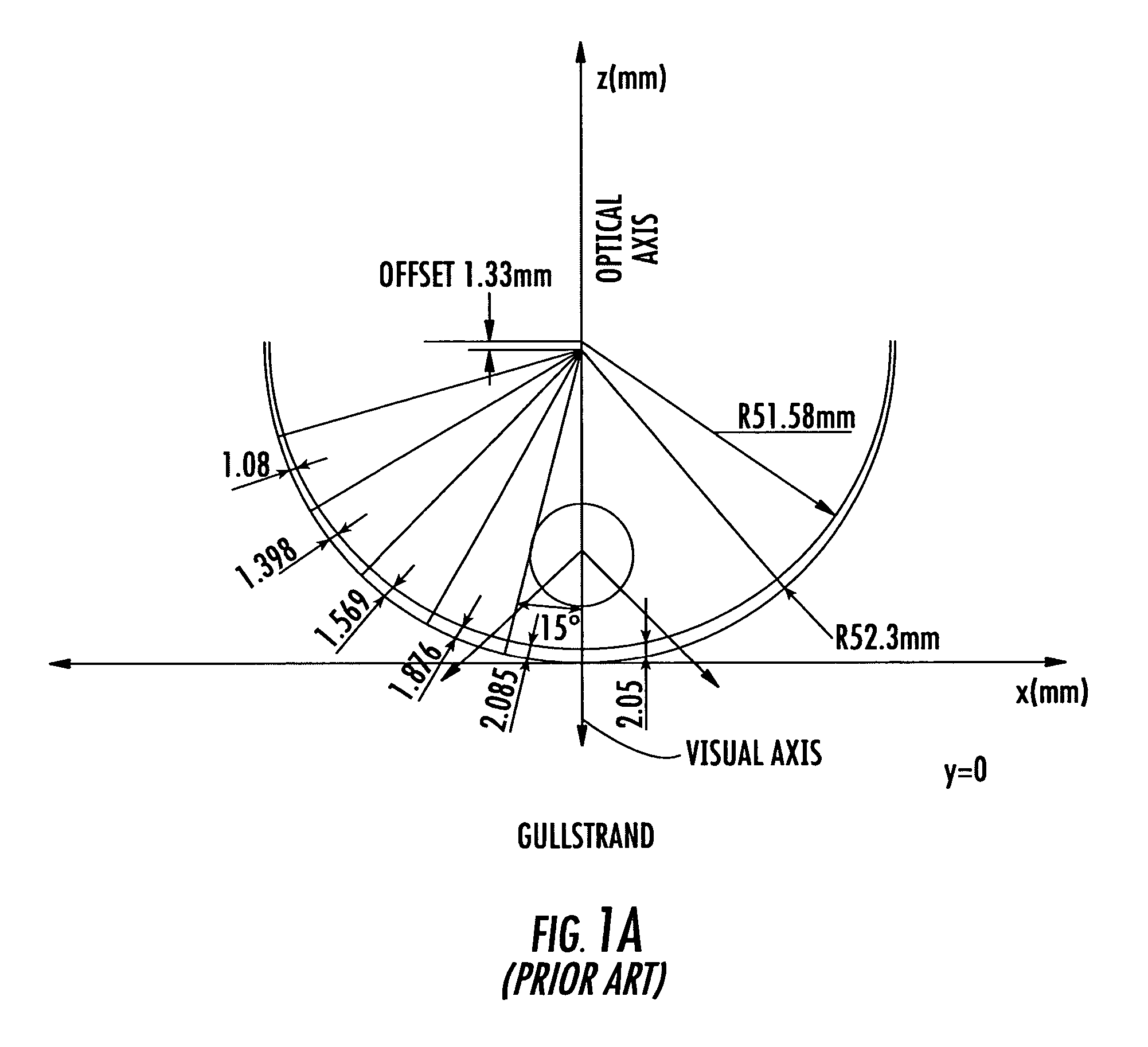
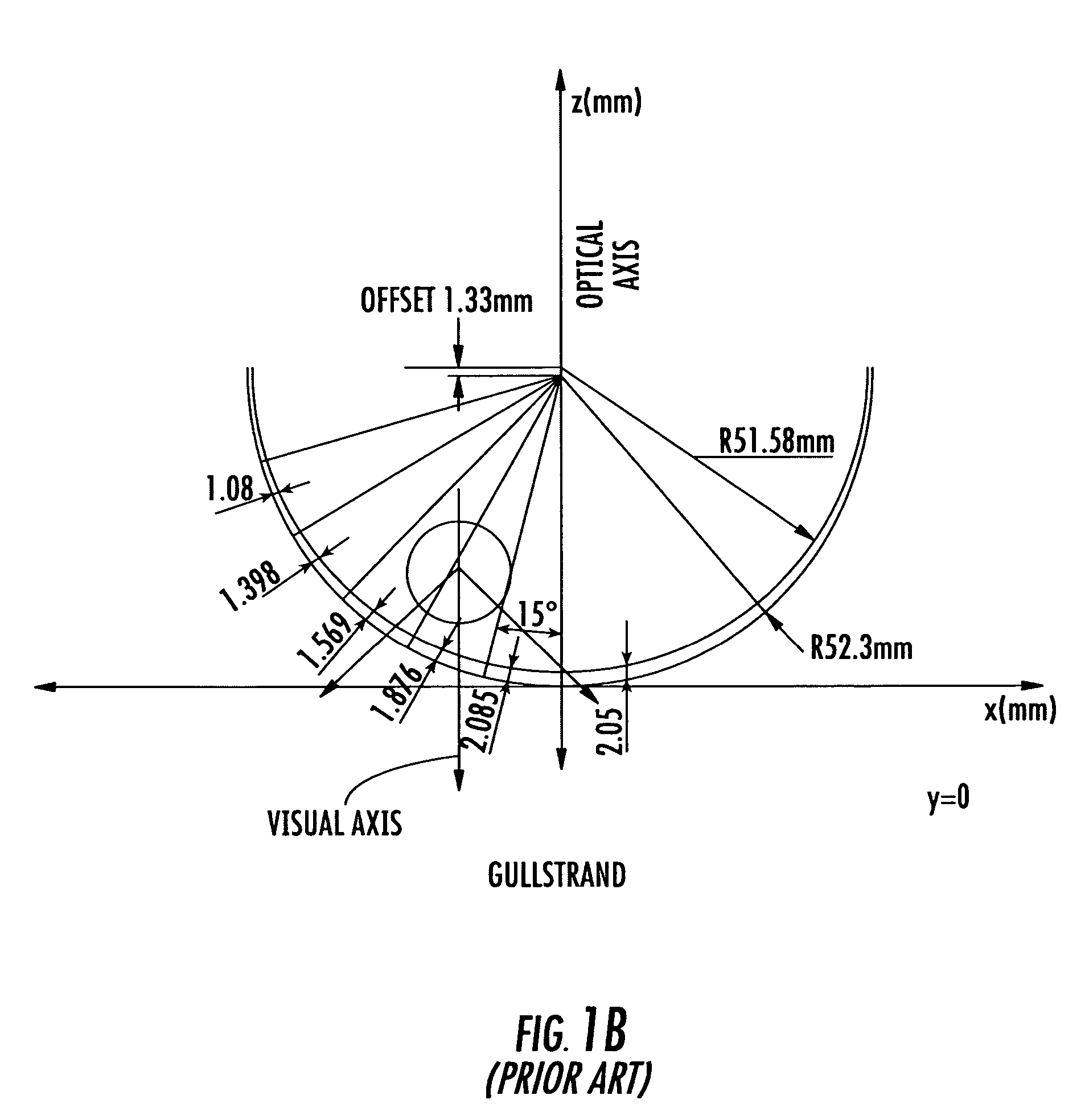
A method for modifying the shape of a spheric or toric non-corrective lens blank such that astigmatic and peripheral defects are reduced. The outer convex and inner concave sides of the lens are initially designed according to the Gullstrand Formula. Thereafter, a visual axis of the lens is defined relative to a reference axis of the lens blank. In the preferred toric lens, the visual axis of the lens is offset from the reference axis. Once the visual axis is defined, the inner concave surface of the lens is modified so as to improve optical quality in a visual center surrounding the visual axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL SAFETY PROD USA INC
Toric lens
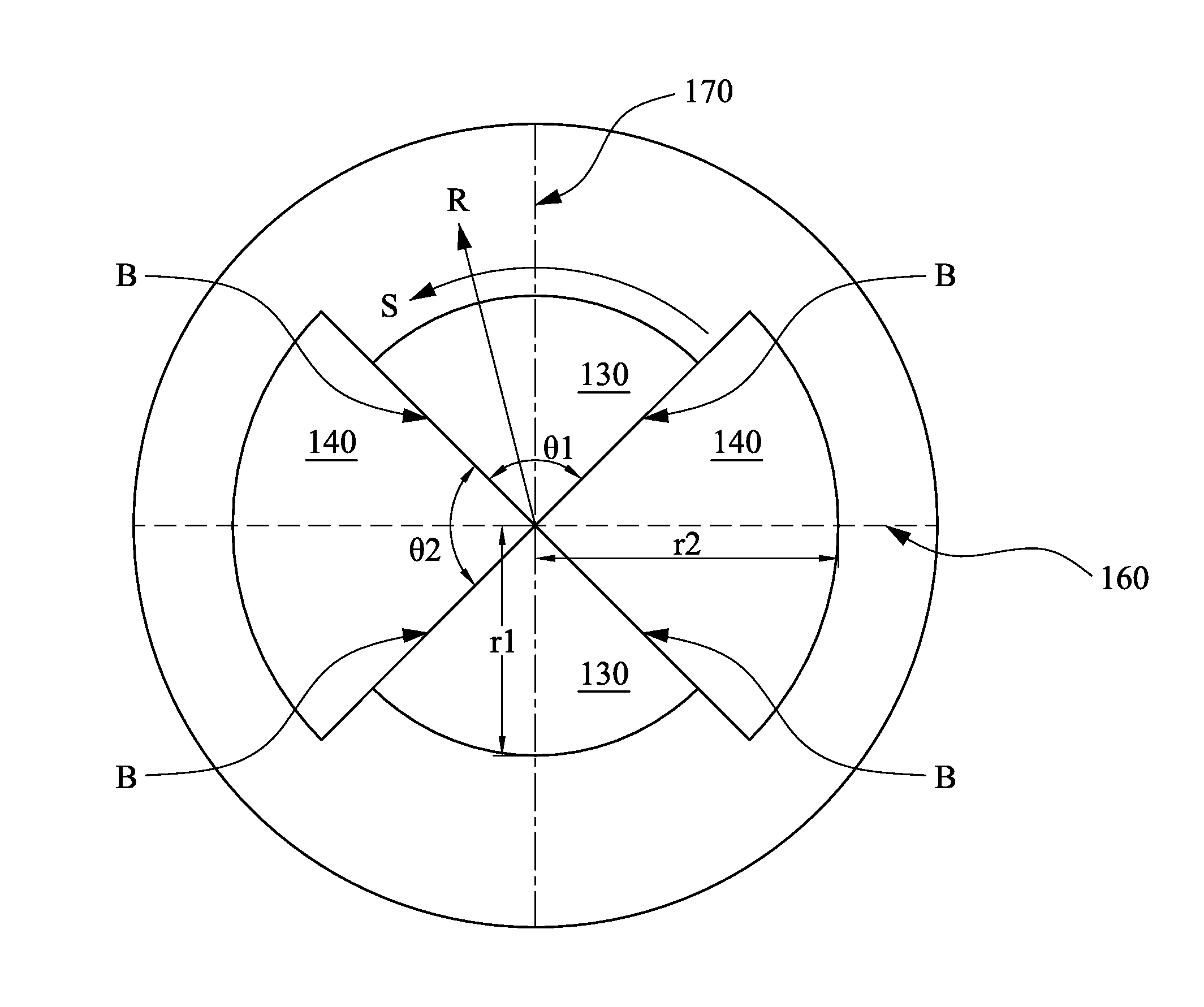
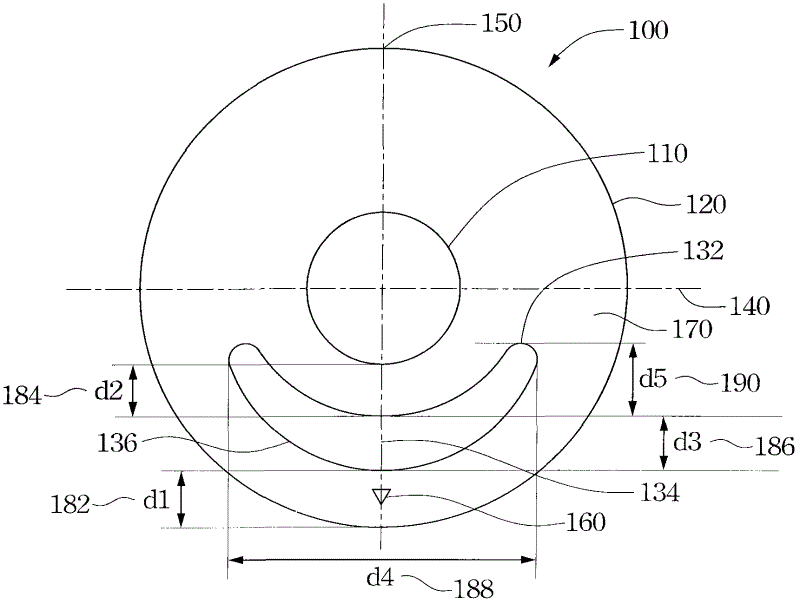
A toric lens includes a first surface, a second surface, two first sector zones, and two second sector zones. The first surface and the second surface are opposite to each other. Each of the first sector zones has a first curvature on the first surface along a radial direction of the toric lens, and the first curvature is constant along an arc direction of the toric lens. The two second sector zones are alternately arranged with the two first sector zones. Each of the second sector zones has a second curvature on the first surface along the radial direction, and the second curvature is constant along the arc direction. The first curvature is steeper than the second curvature.
Owner:PEGAVISION CORP
Contact lens having a uniform horizontal thickness profile
A contact lens having a rotational stabilization mechanism thereon, such as prism ballast, and a thickness profile that reduces the torque imparted on the lens by the action of the eyelids, especially for stabilizing toric lenses. The prism ballast is provided on one or more portions of the anterior face of the lens such that the lens body has a uniform thickness of within 10% along horizontal cross-sections. The anterior face of the lens may be segregated into a peripheral zone, an inner zone circumscribed by the peripheral zone, and a central optic zone. The prism ballast portion is provided within the inner zone, which may be further subdivided into a superior portion, an intermediate portion proximate the optic zone, and an inferior portion. The ballast portion increases in thickness along a superior-inferior line parallel to a vertical meridian, and has a substantially uniform thickness perpendicular thereto. The peripheral zone may be tapered, and have a rounded edge. The rate of thickness change across any portion of the peripheral zone is less than about 250 μm / mm.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Systems and methods for providing astigmatism correction
ActiveUS20150062529A1Promote resultsImprove selection accuracyEye diagnosticsAnterior corneaAstigmatism correction
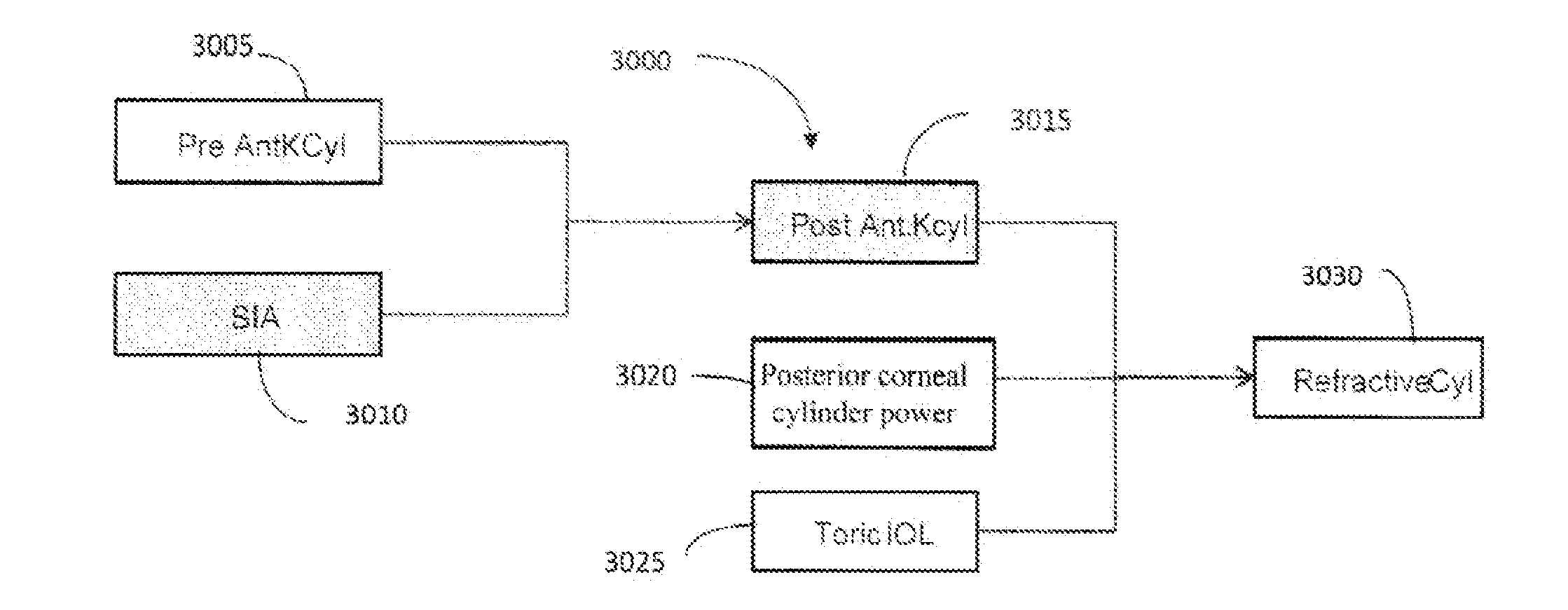
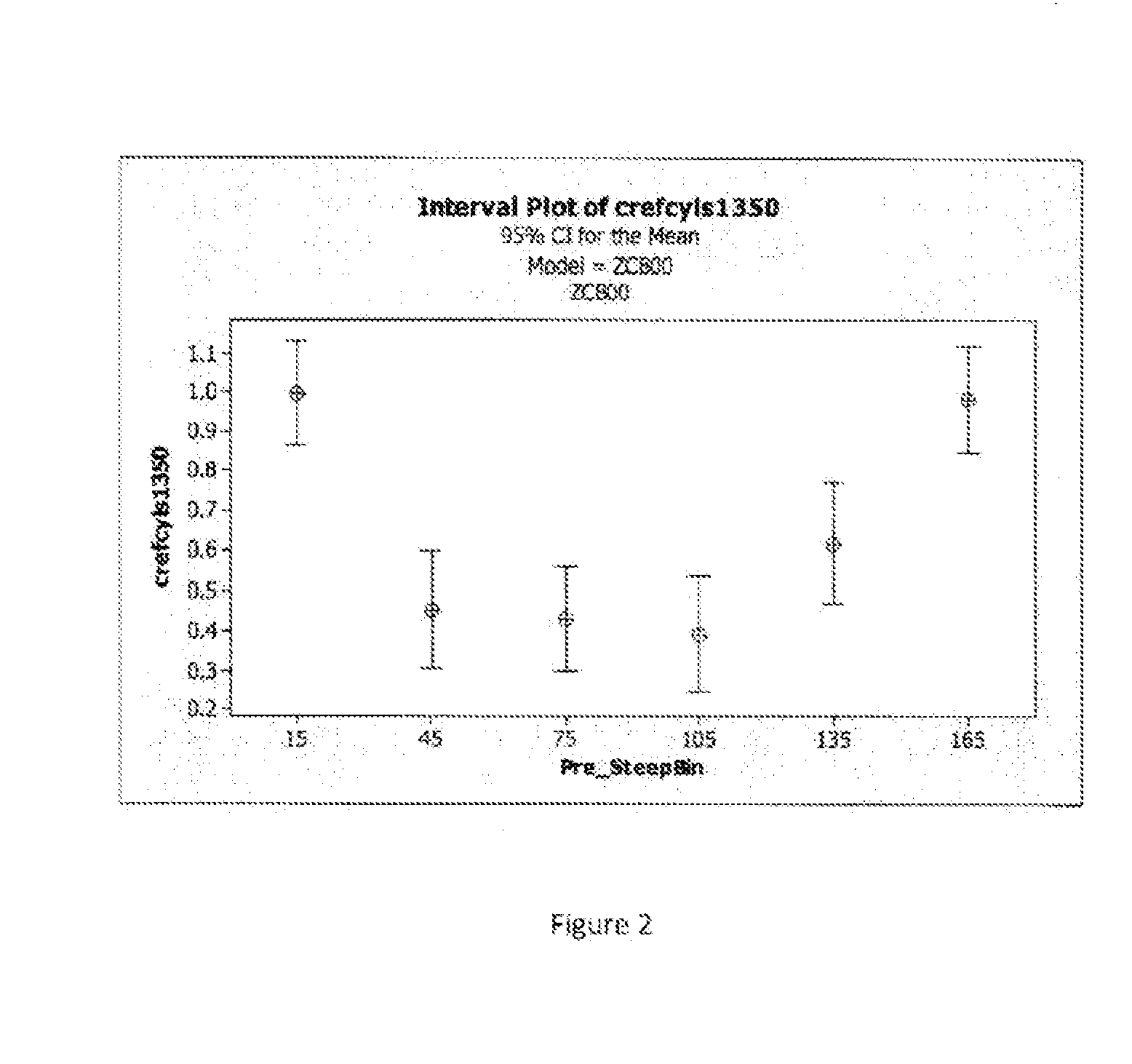
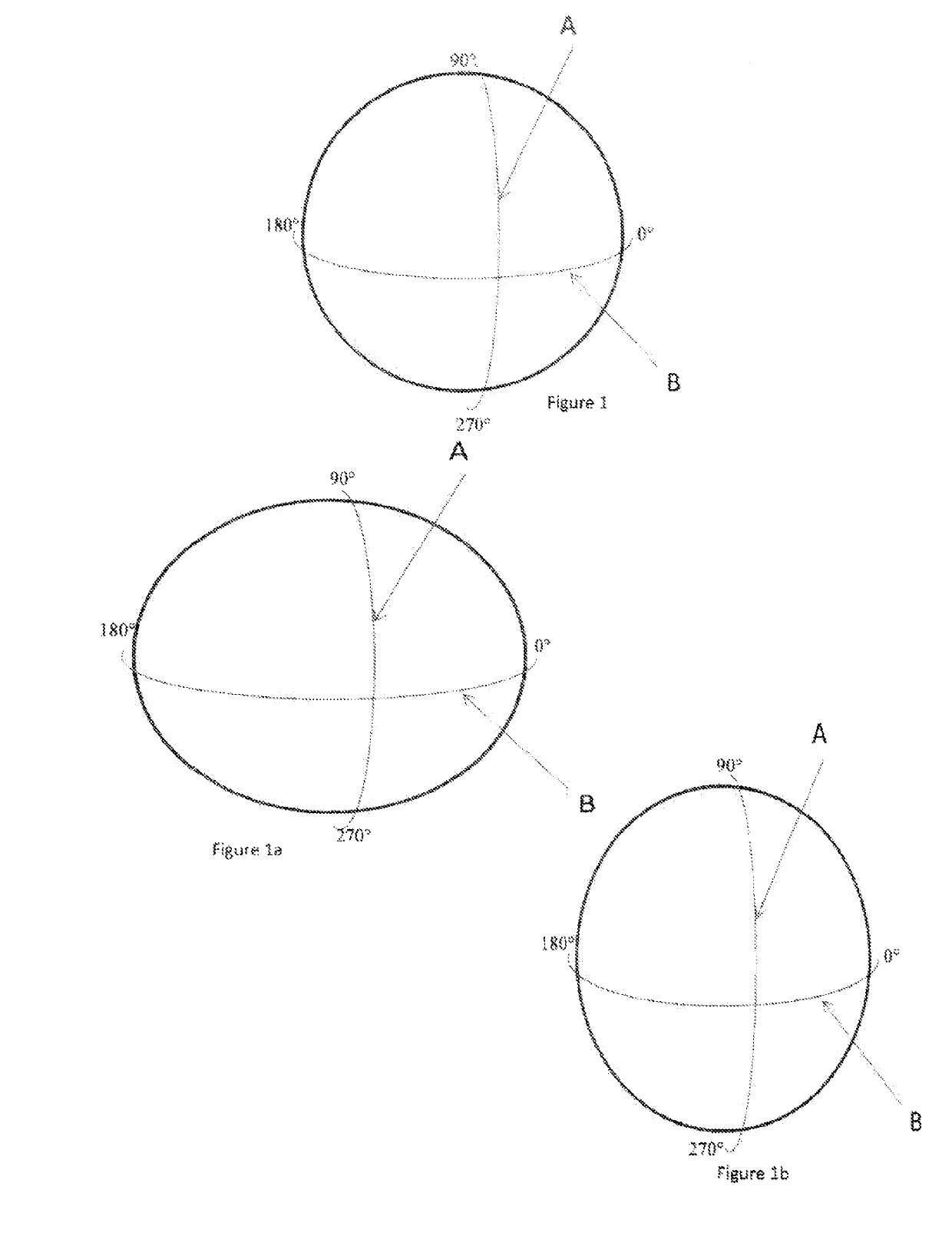
A method of selecting a toric lens by taking into consideration the magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea and / or the location of the incision axis is described. The magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea can be calculated as a function of the measured pre-operative orientation of the steep meridian of the anterior cornea.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Contra-Aspheric Toric Ophthalmic Lens
ActiveUS20120147321A1Increase in sizeReduce image qualitySpectales/gogglesUsing optical meansOphthalmologyEye lens
An ophthalmic toric lens to be worn on an eye or implanted inside of an eye, the lens includes an anterior surface, a posterior surface, and a toric shape formed into one of the anterior and posterior surfaces, the toric shape comprising two non-spherical principle meridians each having a region within an annular area of optical zone and the region of one principle meridian being configured for producing a longitudinal ray aberration of a different sign than a longitudinal ray aberration sign from the region of another principle meridian.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Segmented delta toric lens
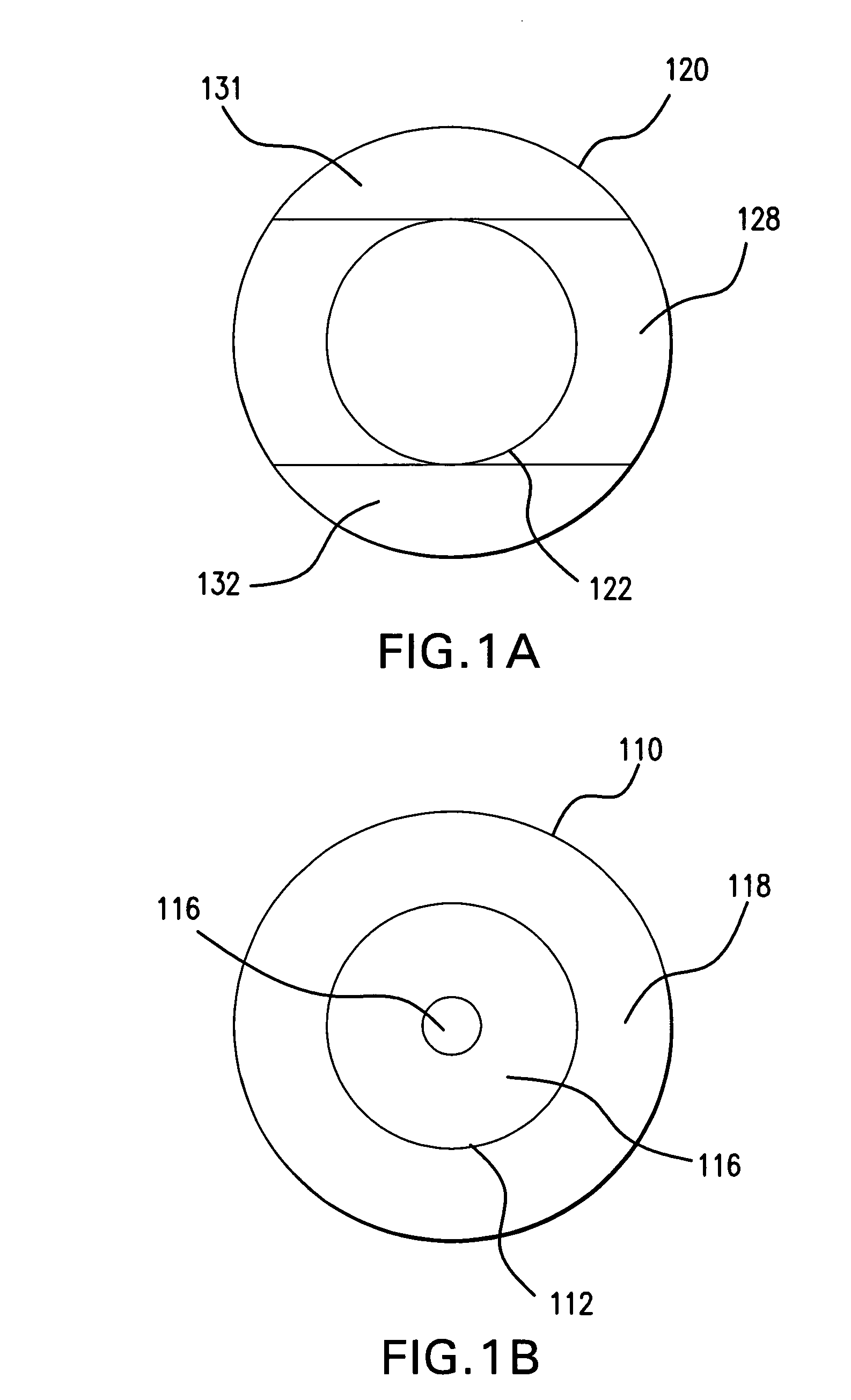
A segmented delta toric lens is described. The segmented delta toric lens includes an optical area, a circumference area surrounding the optical area and a segmented delta protrusion formed on the circumference area. The segmented delta protrusion is located apart from the optical area and the edge of the circumference area. The segmented delta toric lens can further include a mark to indicate a direction of the segmented delta toric lens.
Owner:PEGAVISION CORP
Illuminating module for a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20140078768A1Improve transmission efficiencyImprove efficiencyVehicle headlampsWave amplification devicesLight beamComputer module
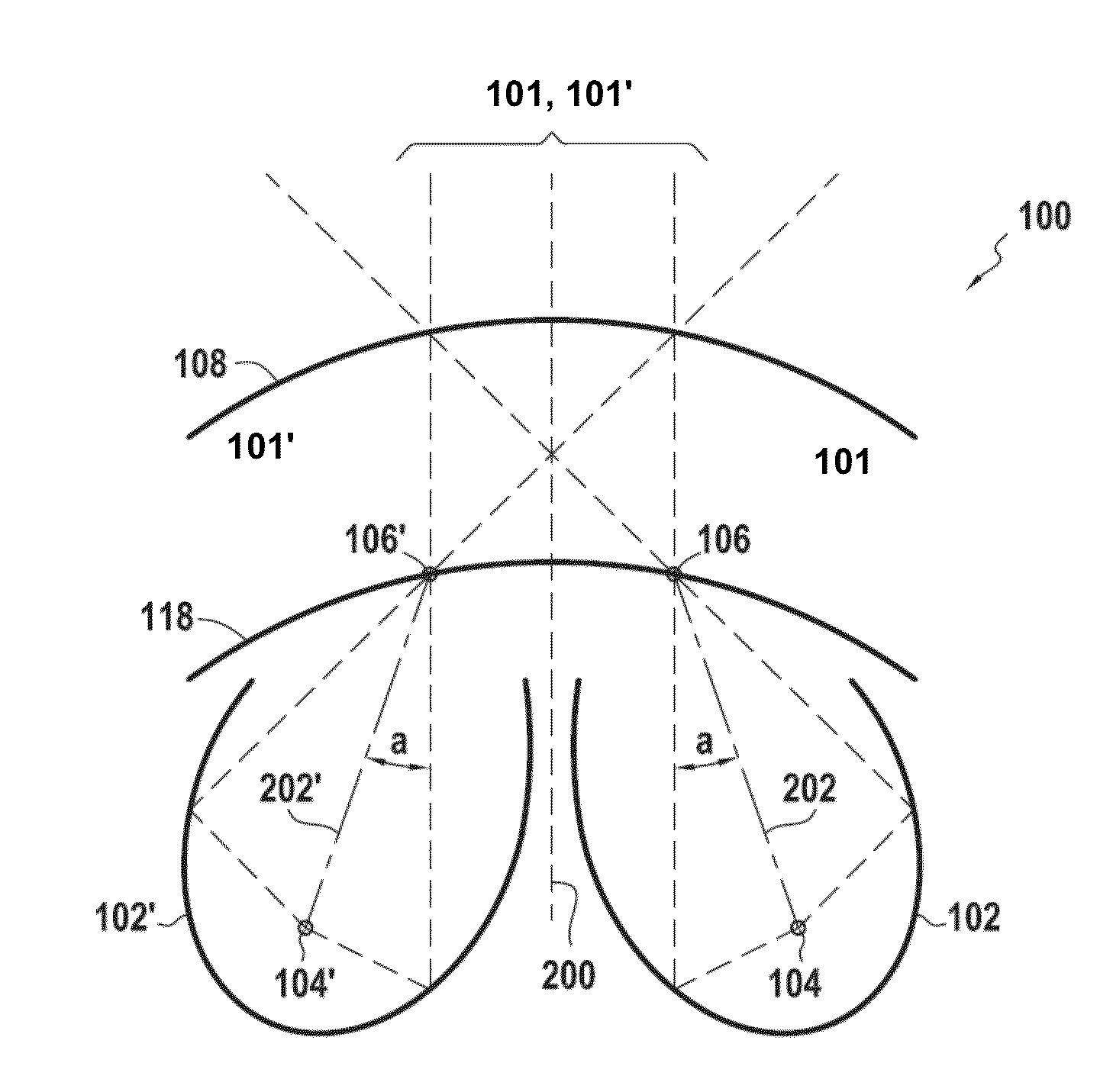
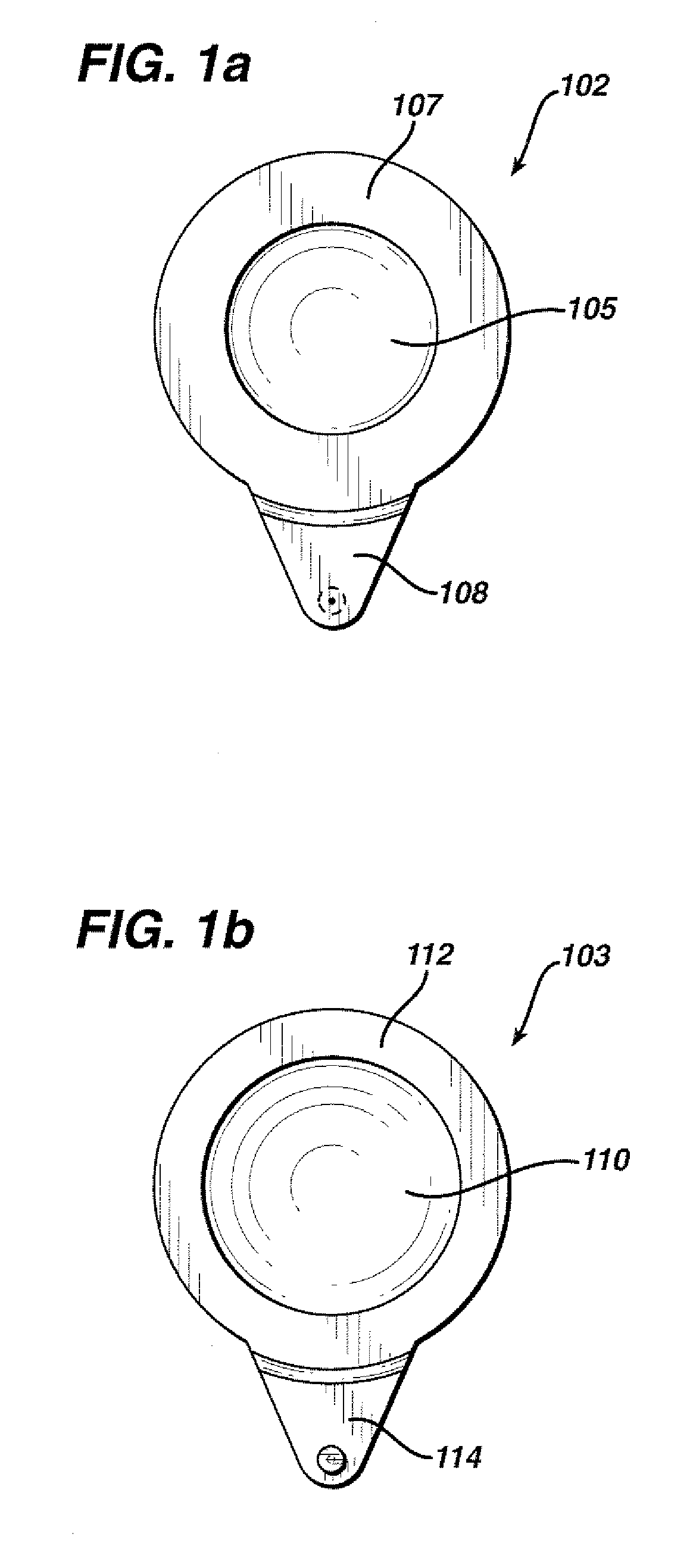
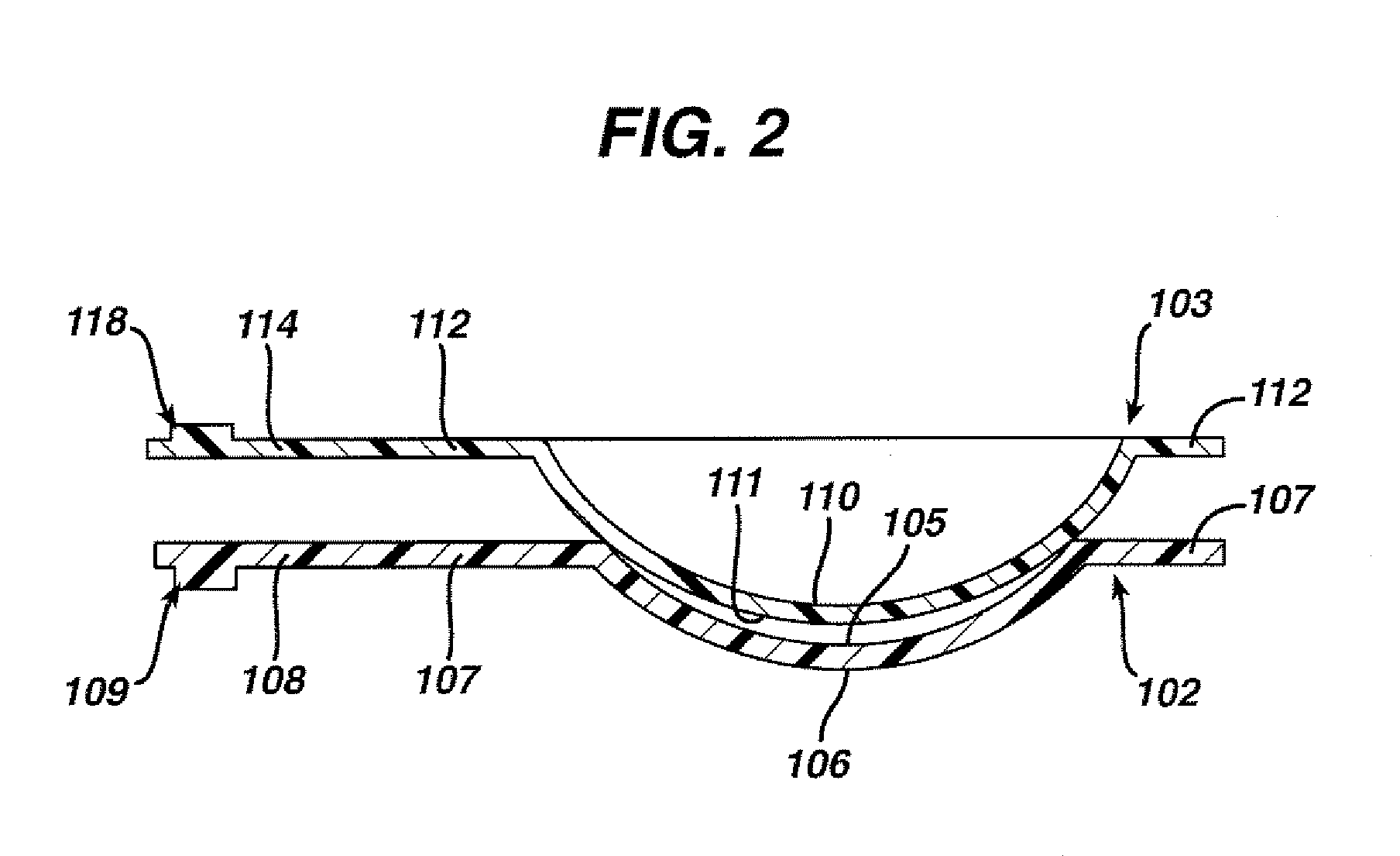
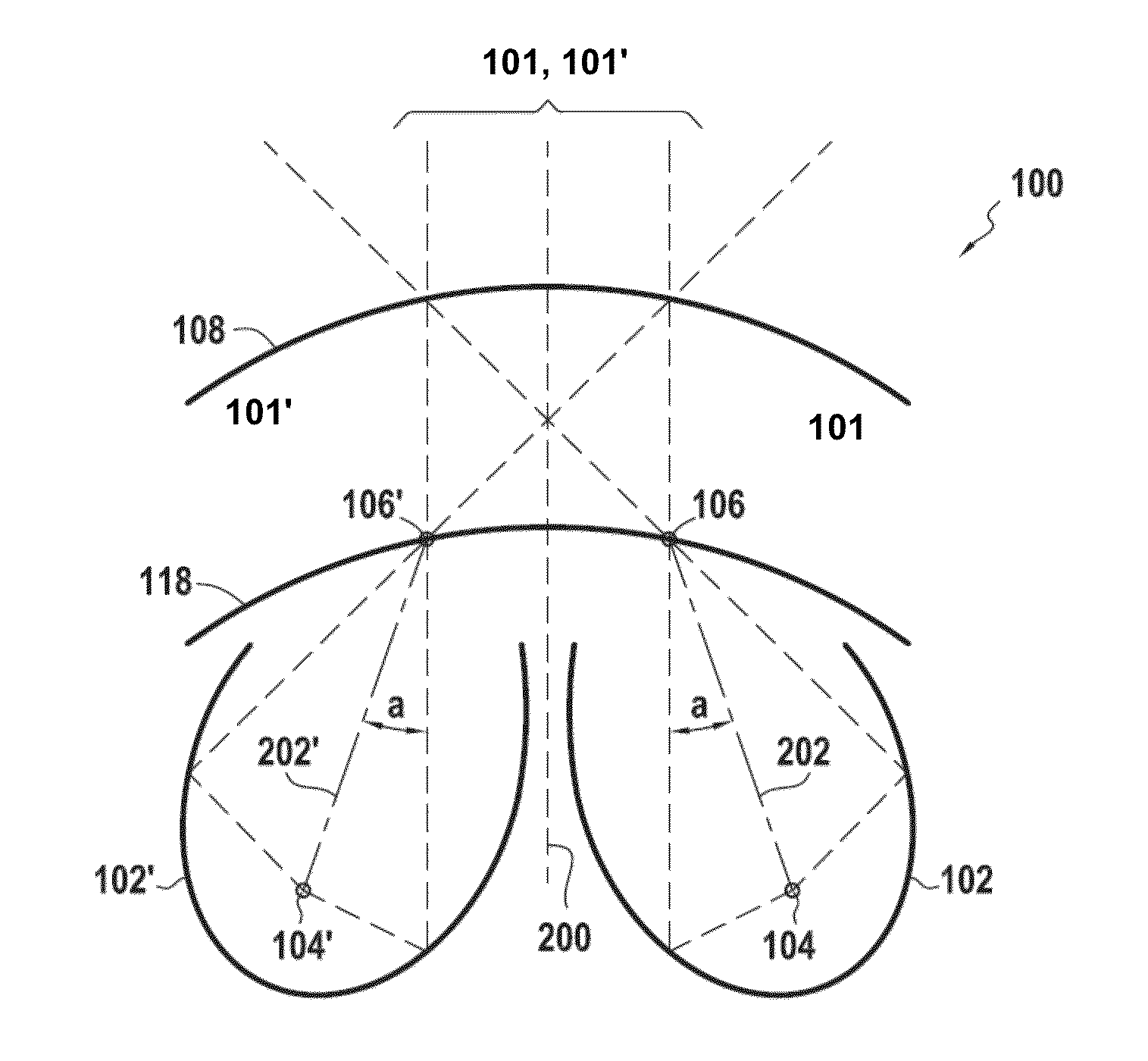
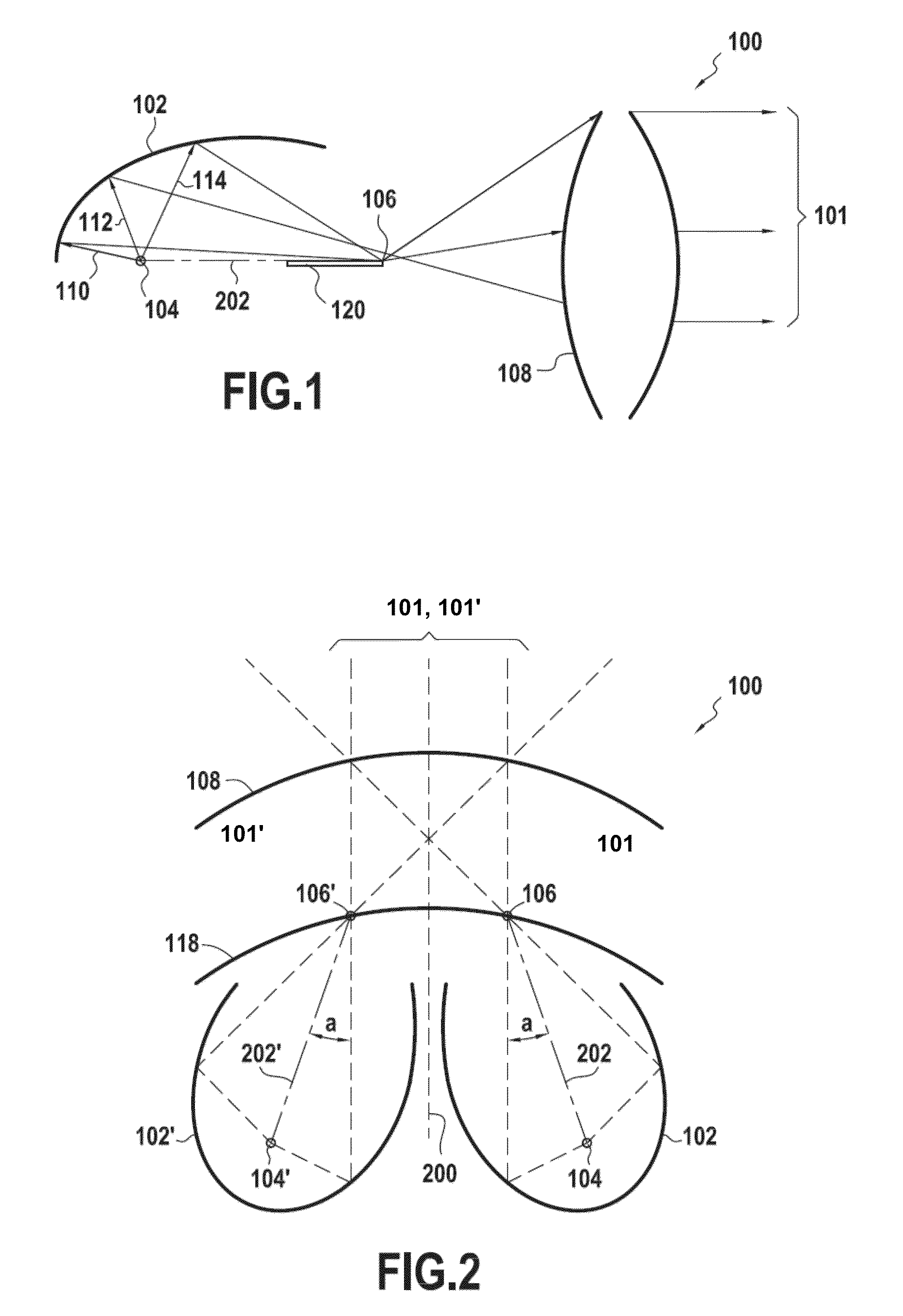
An illuminating module for a motor vehicle lamp able to form a wide light beam containing a cutoff, which module is equipped with optical elements comprising an output lens and a plurality of concave reflectors associated with a deflector having a reflective face intended to deflect light beams generated by light sources located in the concavities of the reflectors. The output lens is a toric lens, and these optical elements are arranged in order to make the light beams generated by said light sources converge on points of focus before these light beams are transmitted through the output lens.The module comprises two reflectors (102, 102′) oriented toward each other.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Toric lens design
ActiveUS20060244903A1Improve rotational stabilityOptical partsRotational stabilityComputational physics
This invention is related to contact lenses. In particular, the present invention is related to a toric contact lens design with thickness zones in the carrier portion of the lens for increased rotational stability.
Owner:ALCON INC
Segmented delta toric lens
A segmented delta toric lens is described. The segmented delta toric lens includes an optical area, a circumference area surrounding the optical area and a segmented delta protrusion formed on the circumference area. The segmented delta protrusion is located apart from the optical area and the edge of the circumference area. The segmented delta toric lens can further include a mark to indicate a direction of the segmented delta toric lens.
Owner:PEGAVISION CORP
Non-corrective lenses with improved peripheral vision
InactiveUS7419261B2Promote resultsVisual comfortEye diagnosticsNon-optical partsCorrective contact lensSpherical shaped
A method for modifying the shape of a spheric or toric non-corrective lens blank such that astigmatic and peripheral defects are reduced. The outer convex and inner concave sides of the lens are initially designed according to the Gullstrand Formula. Thereafter, a visual axis of the lens is defined relative to a reference axis of the lens blank. In the preferred toric lens, the visual axis of the lens is offset from the reference axis. Once the visual axis is defined, the inner concave surface of the lens is modified so as to improve optical quality in a visual center surrounding the visual axis.
Owner:HONEYWELL SAFETY PROD USA INC
Method for manufacturing toric contact lenses
A method of manufacturing of an astigmatic contact lens having a toric portion and a ballast portion such that said ballast portion causes the toric portion of the contact lens to properly orient in the eye of the wearer. The toric lenses are manufactured by an effective process control method for cylinder axis angle in toric lens production by modifying the target cylinder angle for mold rotation by eliminating the accumulative cylinder axis error from all previous steps including tool making, tool assembly, and molding. The amount modifying the target angle is determined by accurately determine the true cylinder axis on the corresponding mold by using a high-resolution interferometer, such as FISBA FS10M or equivalent models from Trioptics μShape® vertical series.
Owner:ALCON INC
Toric lens with decreased sensitivity to cylinder power and rotation and method of using the same
A method, system and apparatus for vision correction are disclosed. The method, system and apparatus include a toric intraocular element for correcting astigmatism and having a cylinder power, and a depth of focus extender coupled to the toric intraocular element, the depth of focus extender extending a depth of focus. The extended depth of focus may reduce sensitivity of the toric intraocular element to at least one of rotation and selected cylinder power.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
Axis control in toric contact lens production
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Illuminating module for a motor vehicle
ActiveUS9134000B2Improve transmission efficiencyImprove efficiencyVehicle headlampsVehicle lighting systemsMobile vehicleLight beam
An illuminating module for a motor vehicle lamp able to form a wide light beam containing a cutoff, which module is equipped with optical elements comprising an output lens and a plurality of concave reflectors associated with a deflector having a reflective face intended to deflect light beams generated by light sources located in the concavities of the reflectors. The output lens is a toric lens, and these optical elements are arranged in order to make the light beams generated by said light sources converge on points of focus before these light beams are transmitted through the output lens. The module comprises two reflectors (102, 102′) oriented toward each other.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Method and System of Measuring Toric Lens Axis Angle
ActiveUS20110266703A1Cost efficientShorten cycle timeOptical articlesAuxillary shaping apparatusAxis–angle representationBallast
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
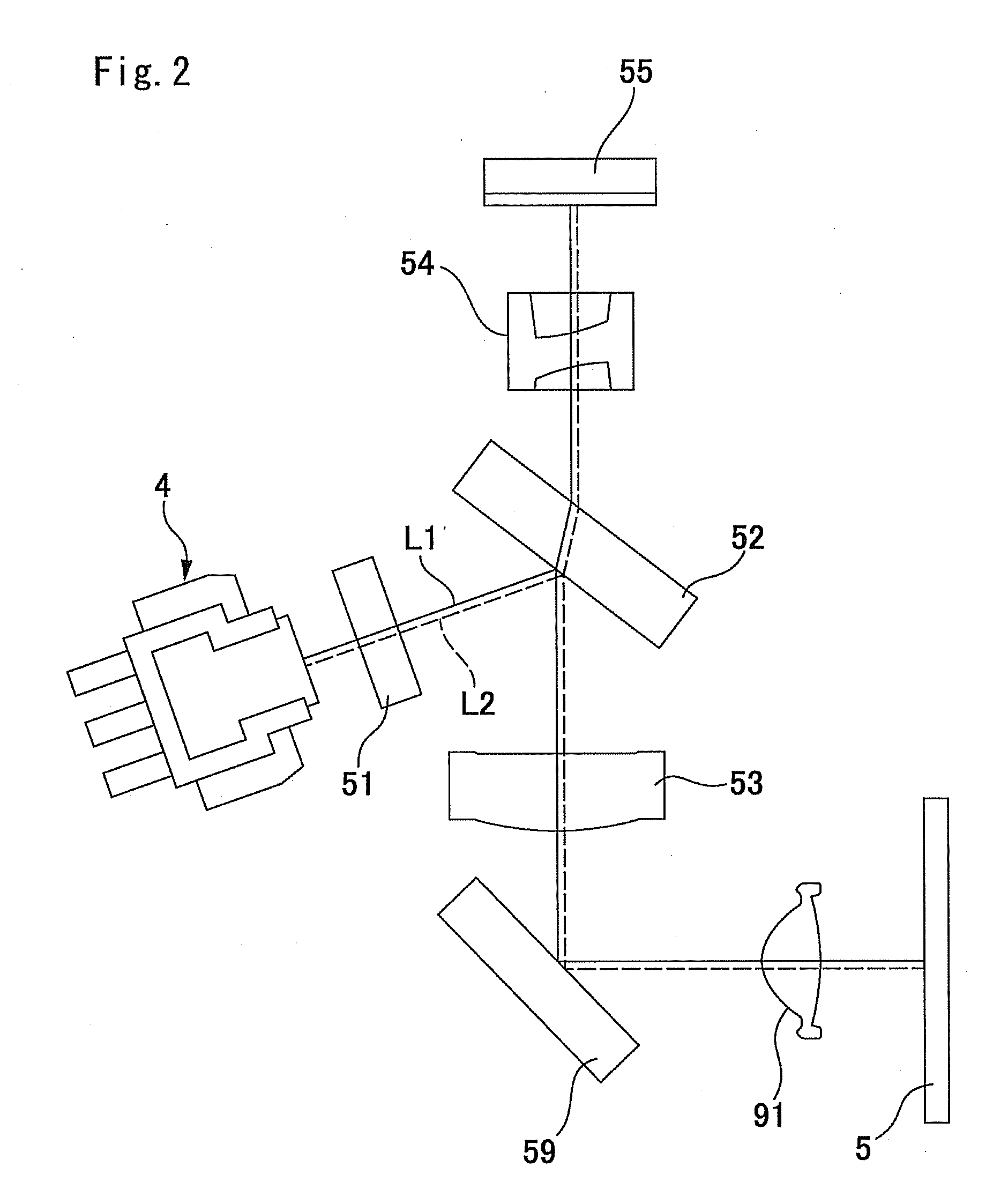
Optical scanning apparatus and image-forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060268381A1Deterioration correctingInking apparatusOptical elementsImage formationLight beam
An optical scanning apparatus includes a light-source unit, an incident optical system for directing light beams emitted from the light-source unit to a deflecting unit, and an imaging optical system for guiding the light beams deflected from the deflecting unit to a surface to be scanned. The imaging optical system includes a toric lens whose power in the main scanning direction is different from that in the sub-scanning direction; the toric lens having the curvature centers of the meridians of a first toric surface connected to form a curved line located in a common plane Ha, and the curvature centers of the meridians of a second toric surface connected to form a curved line not located in a common plane.
Owner:CANON KK
Intelligent control vision correction spectacles
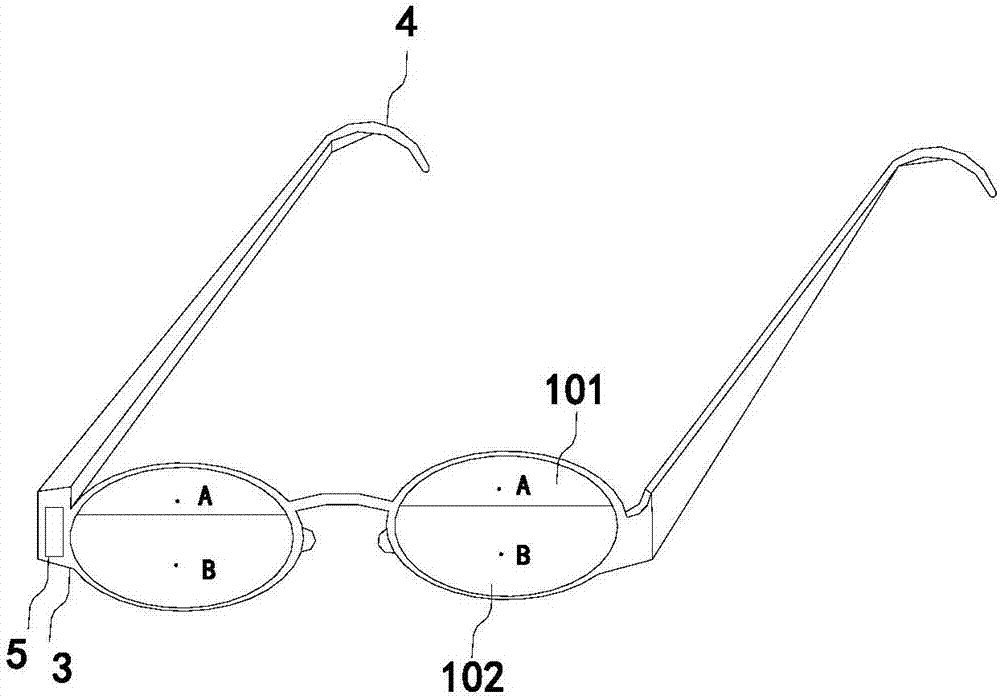
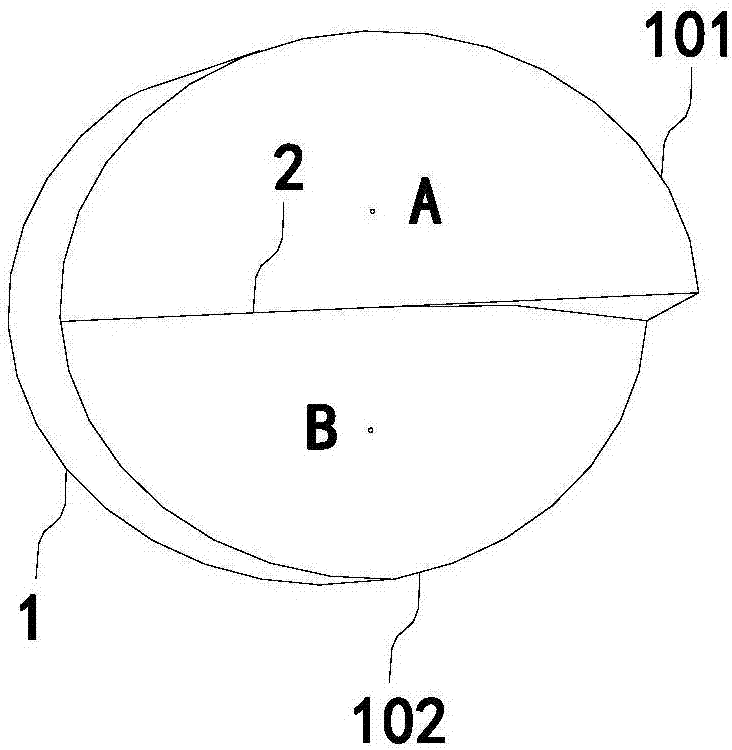
The invention belongs to the field of vision correction spectacles, and particularly relates to intelligent control vision correction spectacles. The intelligent control vision correction spectacles comprise a spectacle frame (3) and spectacle legs (4); integrated eye position myoporthosis lenses are arranged in the spectacle frame (3); each integrated eye position myoporthosis lens comprises a round lens body (1); each round lens body (1) is divided into an upper functional region and a lower functional region; each upper functional region is a distant vision region (101); each lower functional region is a near vision region (102); the distant vision regions (101) are concave lenses; each lower functional region is a composite toric lens formed by compounding a curved prism with a thick end and a thin end with a convex lens; a control module (5) is arranged on the spectacle frame (3). The intelligent control vision correction spectacles disclosed by the invention are convenient in design accuracy control, effectively relieve ciliaris spasm of a myopic patient, can provide an alarm when a user is at an informal reading-writing gesture, can effectively prevent and treat pseudomyopia, and also can correct eisophoria and exophoria.
Owner:永康视光科技集团有限公司
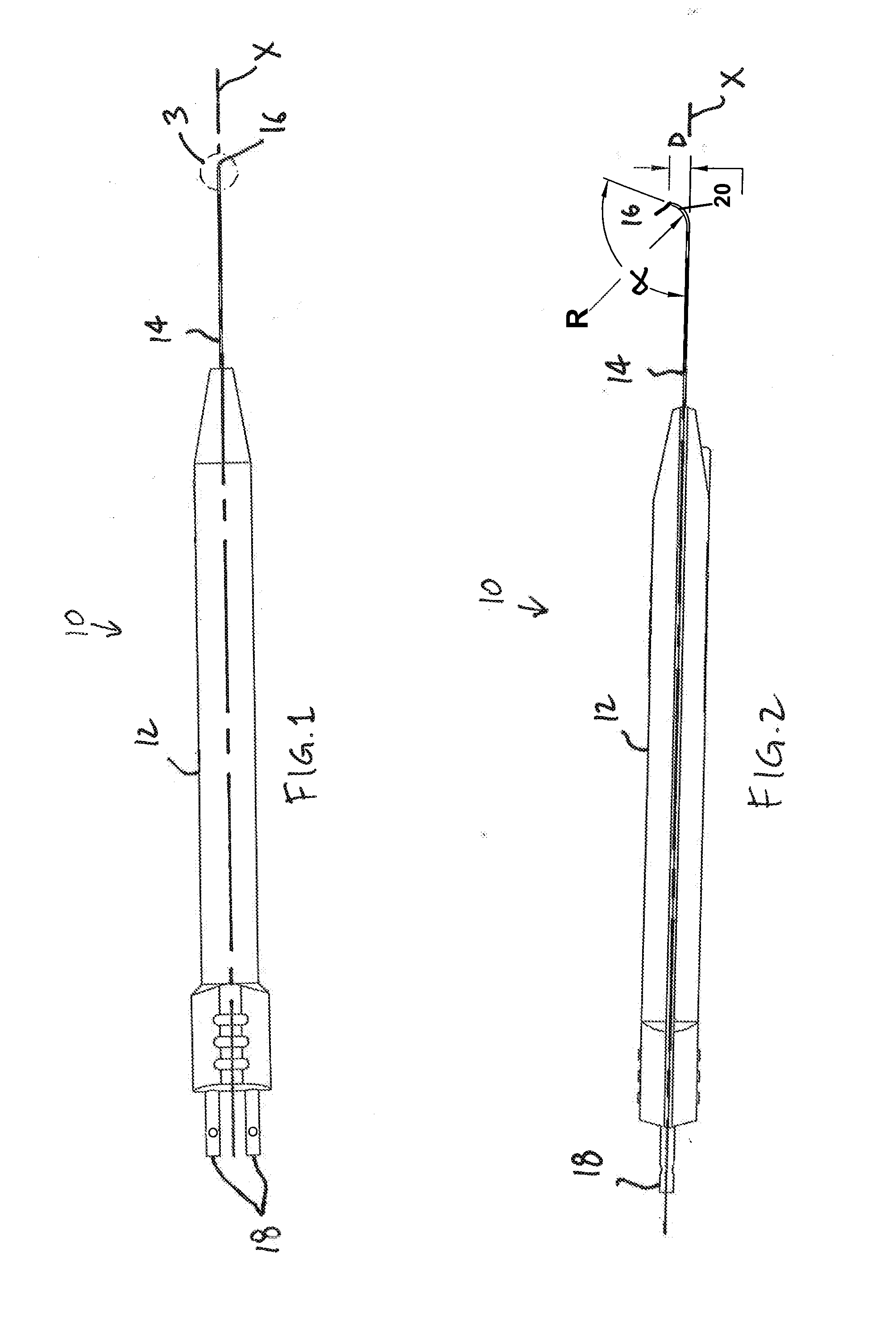
Method of, and device for, marking a patient's eye for reference during a toric lens implantation procedure
ActiveUS20130096547A1Smaller, minimally eccentric reference marksEye surgerySurgical needlesOptometryToric lens
In one aspect, a method is provided herein of marking a patient's eye for reference during a tonic lens implantation procedure. The method includes providing an electrocautery device having a handle, a shaft extending from the handle, and a tip defined at the terminus of the shaft. The handle is elongated and extends along a longitudinal axis with the shaft being bent or curved such that the tip is spaced from, and not aligned with, the longitudinal axis. The method further includes using the electrocautery device to cauterize one or more points on the patient's eye, the points being located as reference marks for placement of the toric lens. Advantageously, with the subject invention, a device is used having a bent or curved shaft Which may better accommodate the curvature of a patient's eye While marking.
Owner:BEAVER VISITEC INT US
Optical head device
An optical head device may include a twin laser light source which is integrally provided with a first laser beam emitting element and a second laser beam emitting element, a light receiving element, and an optical system including an objective lens for converging a laser beam on an optical recording medium. The optical system is provided with a detection lens structured of a toric lens. The toric lens applies an astigmatic difference caused by a toric face to the one of the return light beams, and the toric lens applies the other of the return light beams an astigmatic difference caused by a toric face and astigmatism composed of astigmatism and curvature of image field caused by passing off-axis position to coincide a focusing position of the first laser beam with that of the second laser beam.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Contact lens having a uniform horizontal thickness profile
A contact lens having a rotational stabilization mechanism thereon, such as prism ballast, and a thickness profile that reduces the torque imparted on the lens by the action of the eyelids, especially for stabilizing toric lenses. The prism ballast is provided on one or more portions of the anterior face of the lens such that the lens body has a uniform thickness of within 10% along horizontal cross-sections. The anterior face of the lens may be segregated into a peripheral zone, an inner zone circumscribed by the peripheral zone, and a central optic zone. The prism ballast portion is provided within the inner zone, which may be further subdivided into a superior portion, an intermediate portion proximate the optic zone, and an inferior portion. The ballast portion increases in thickness along a superior-inferior line parallel to a vertical meridian, and has a substantially uniform thickness perpendicular thereto. The peripheral zone may be tapered, and have a rounded edge. The rate of thickness change across any portion of the peripheral zone is less than about 250 μm / mm.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Systems and methods for providing astigmatism correction
ActiveUS10357154B2Promote resultsImprove selection accuracyEye diagnosticsAnterior corneaAstigmatism correction
A method of selecting a toric lens by taking into consideration the magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea and / or the location of the incision axis is described. The magnitude and orientation of the posterior cornea can be calculated as a function of the measured pre-operative orientation of the steep meridian of the anterior cornea.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Optical head device
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com