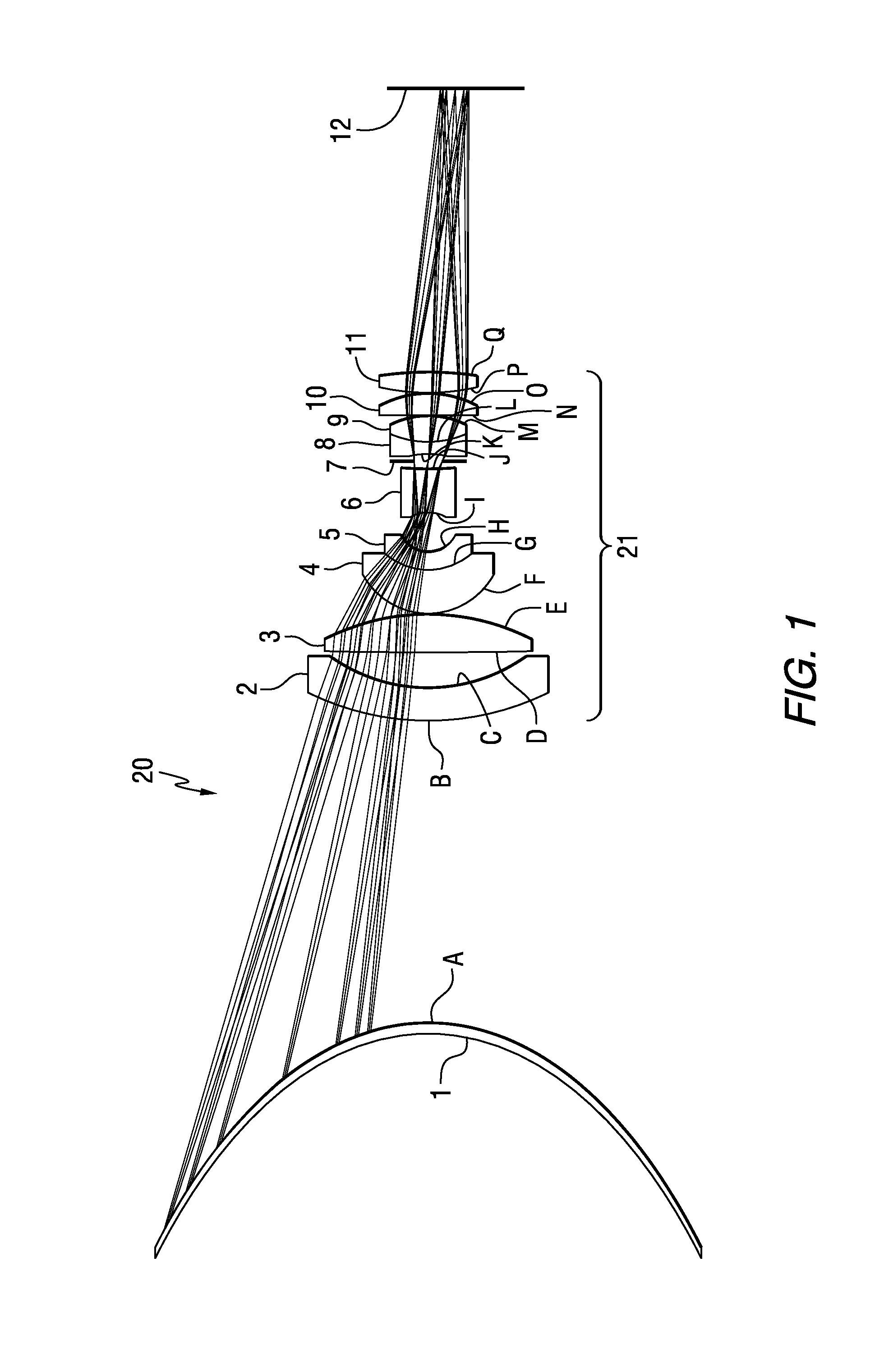
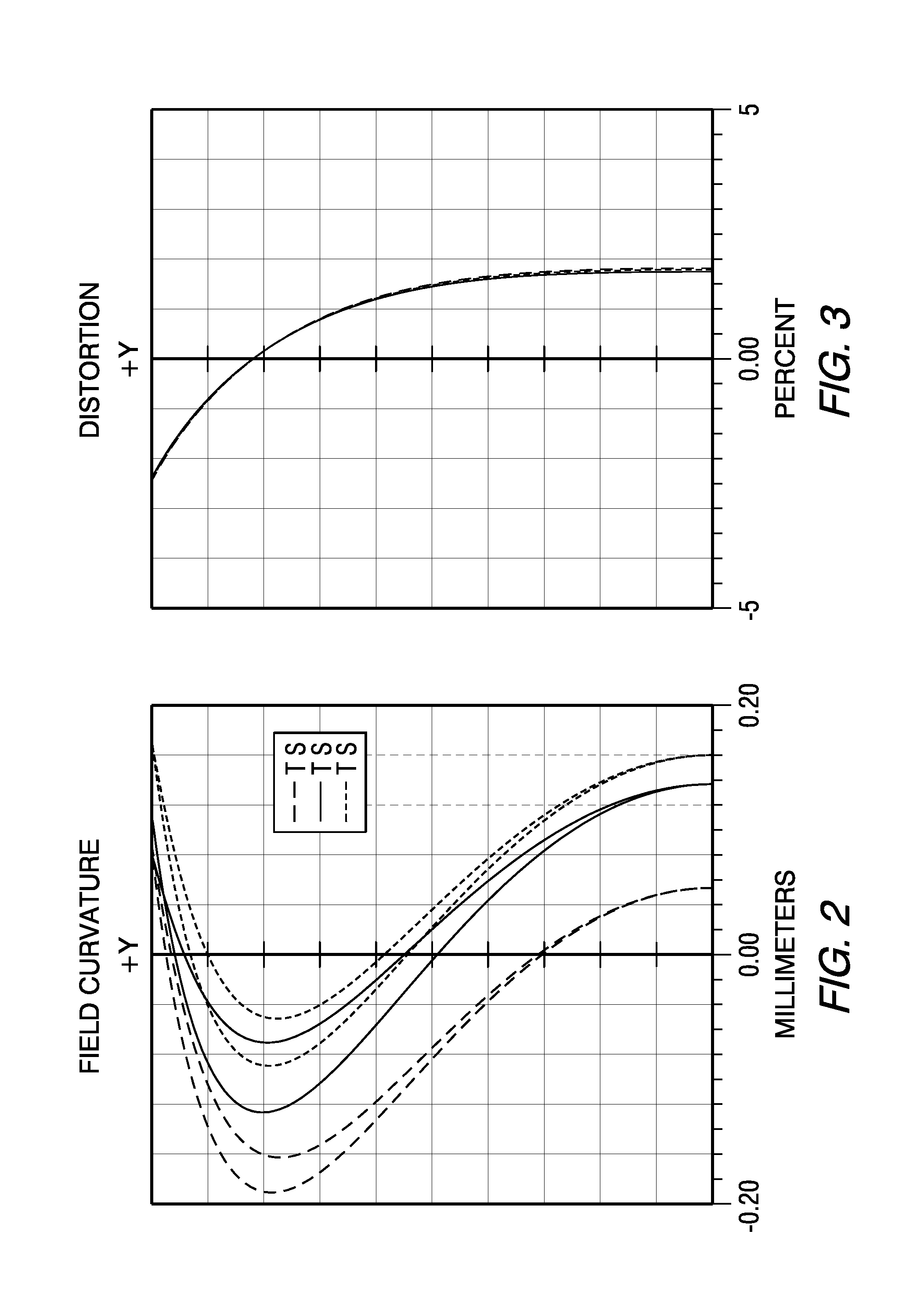
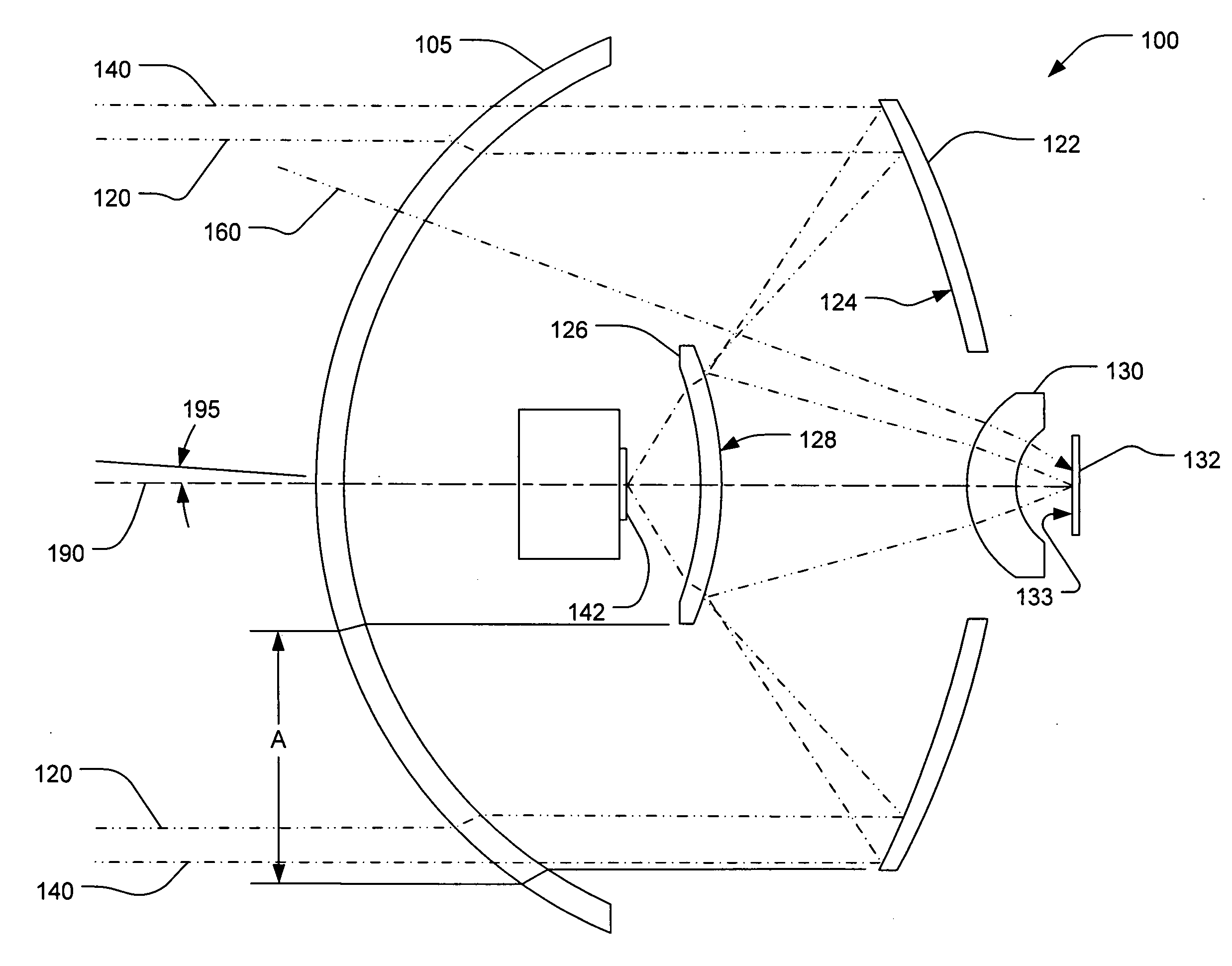
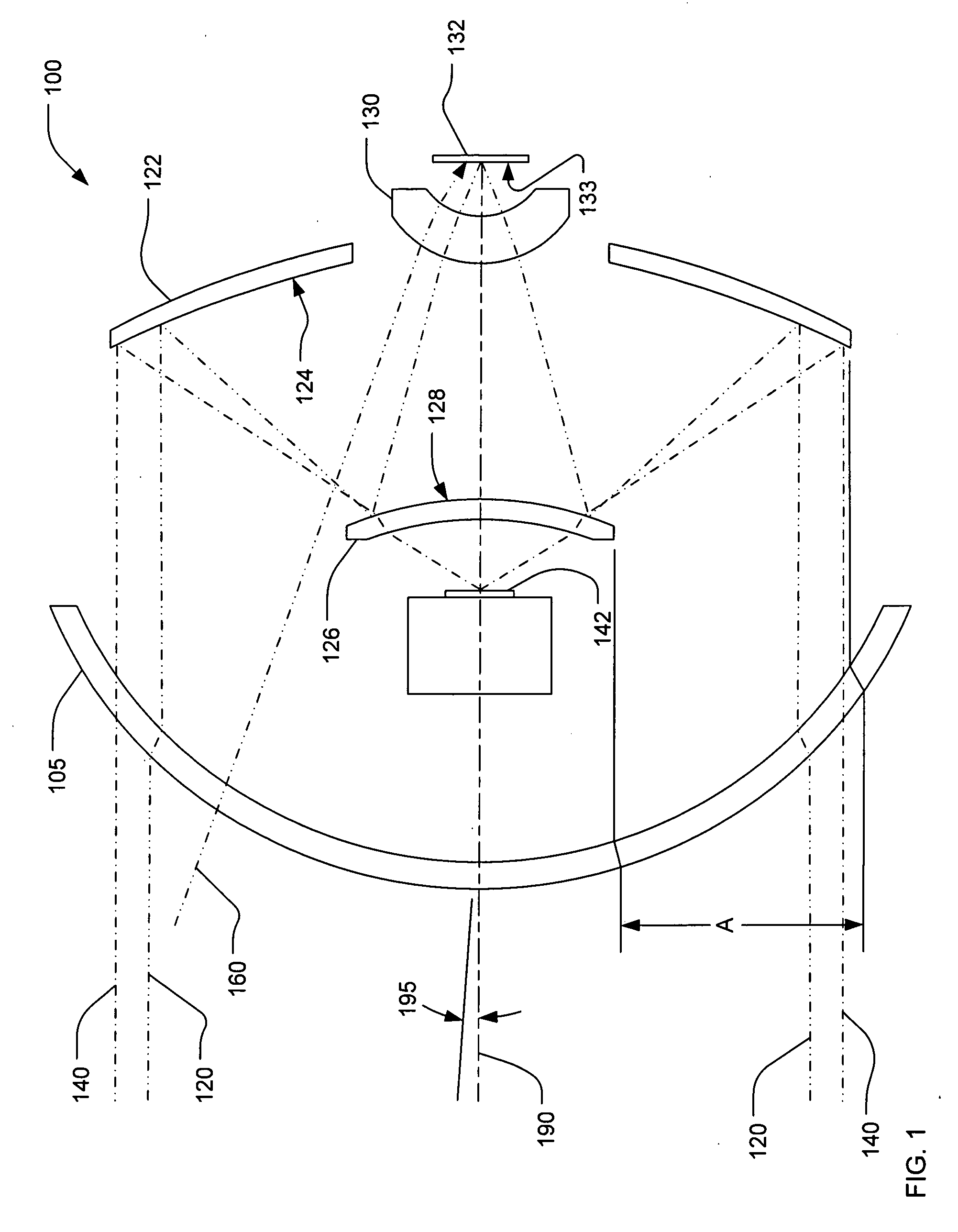
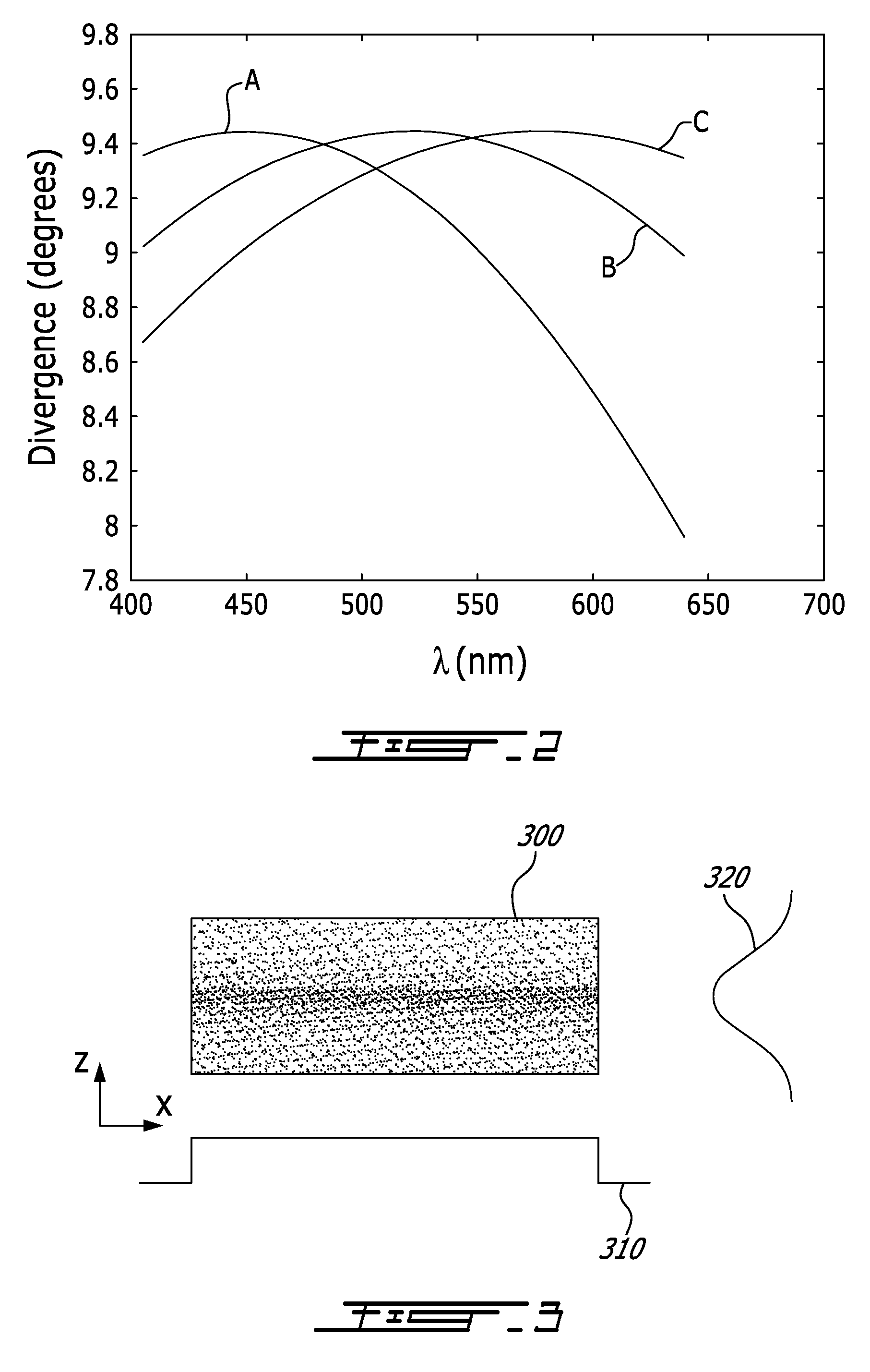
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
349 results about "Stigmatism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
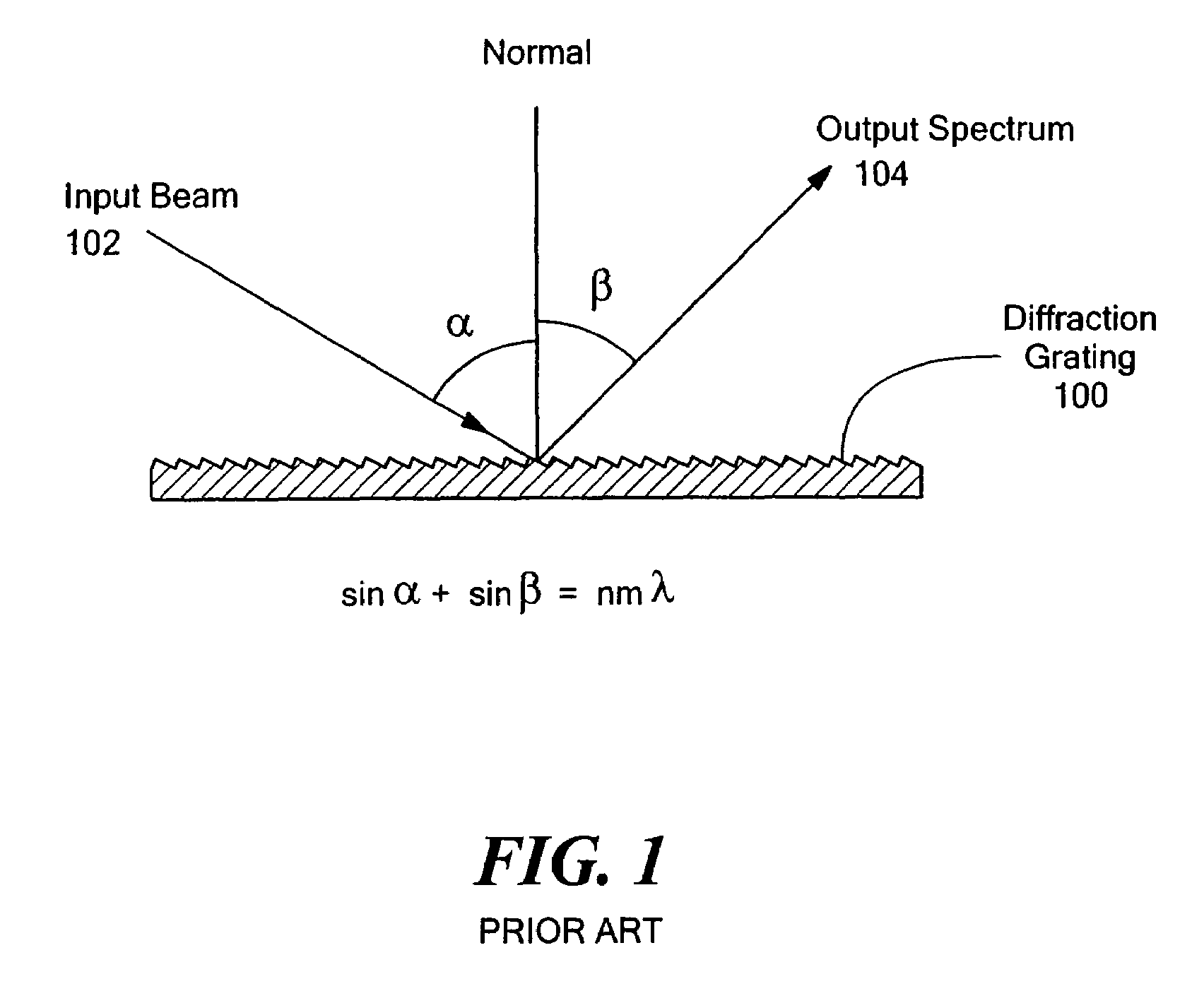
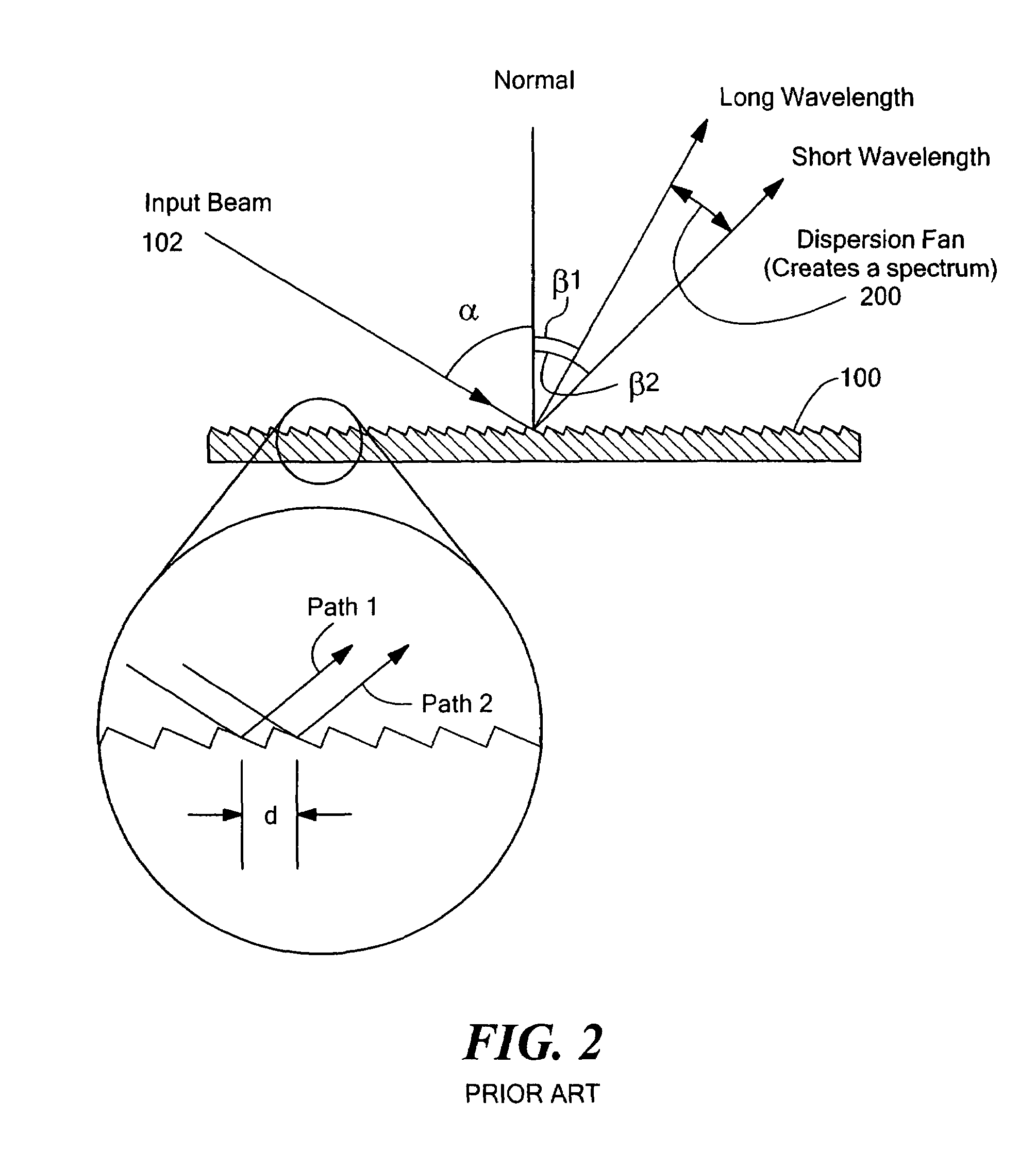
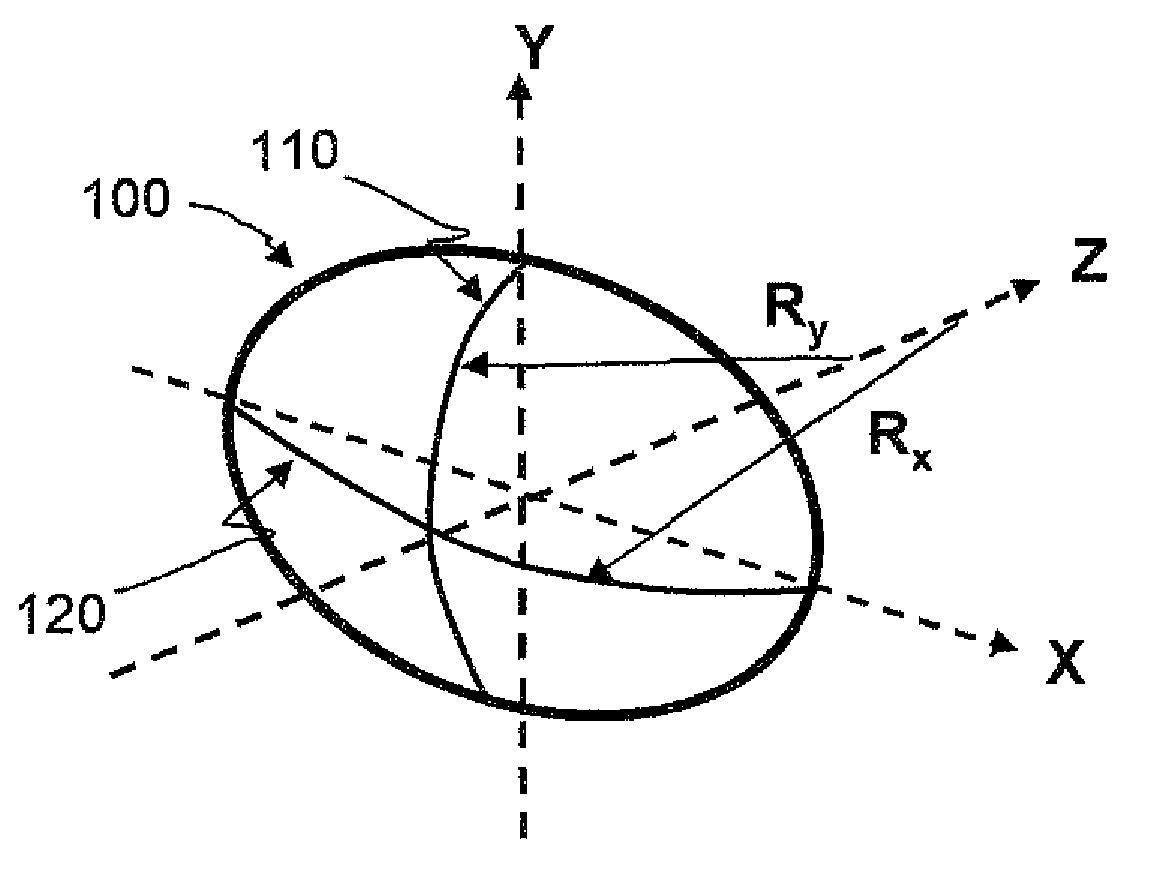
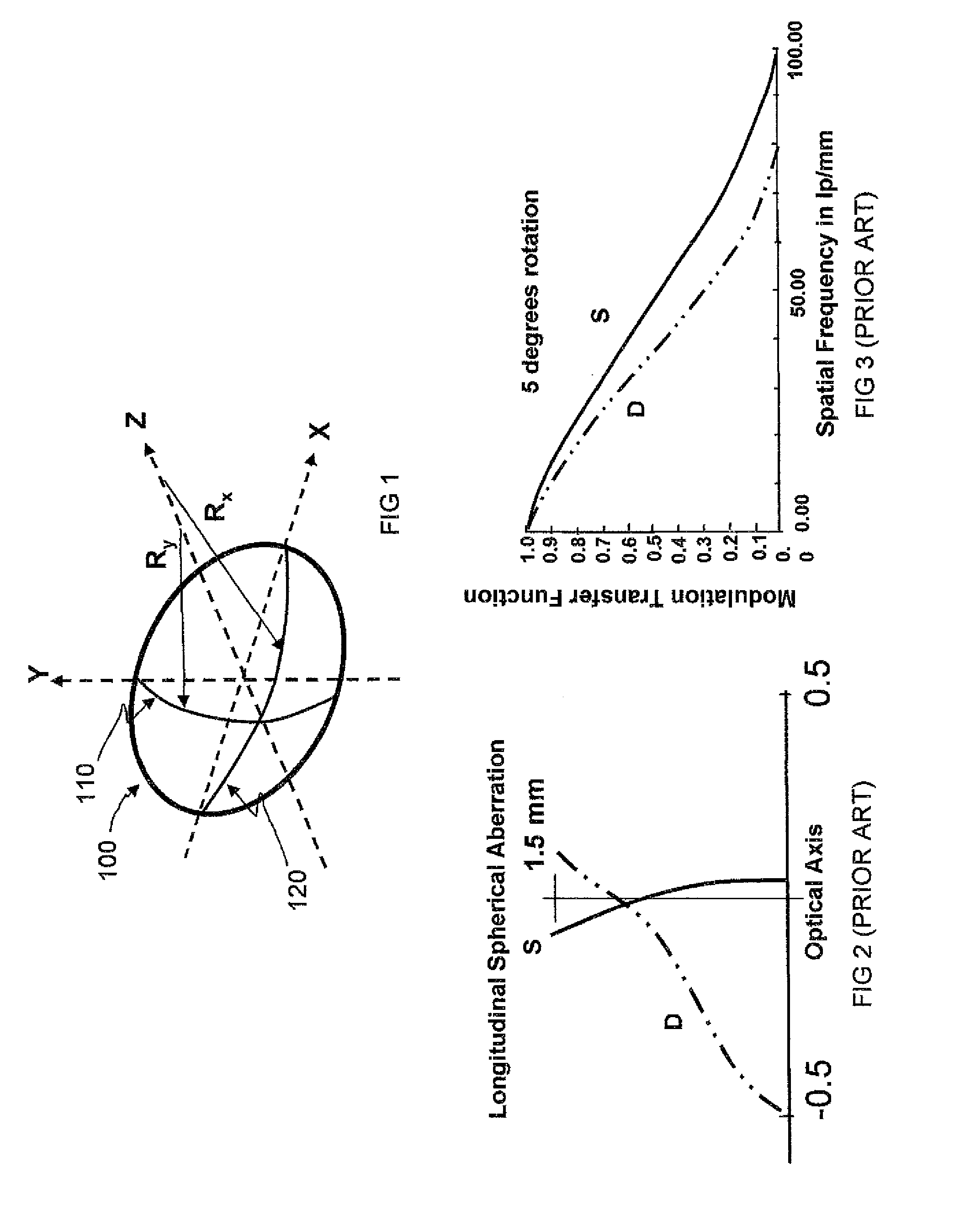
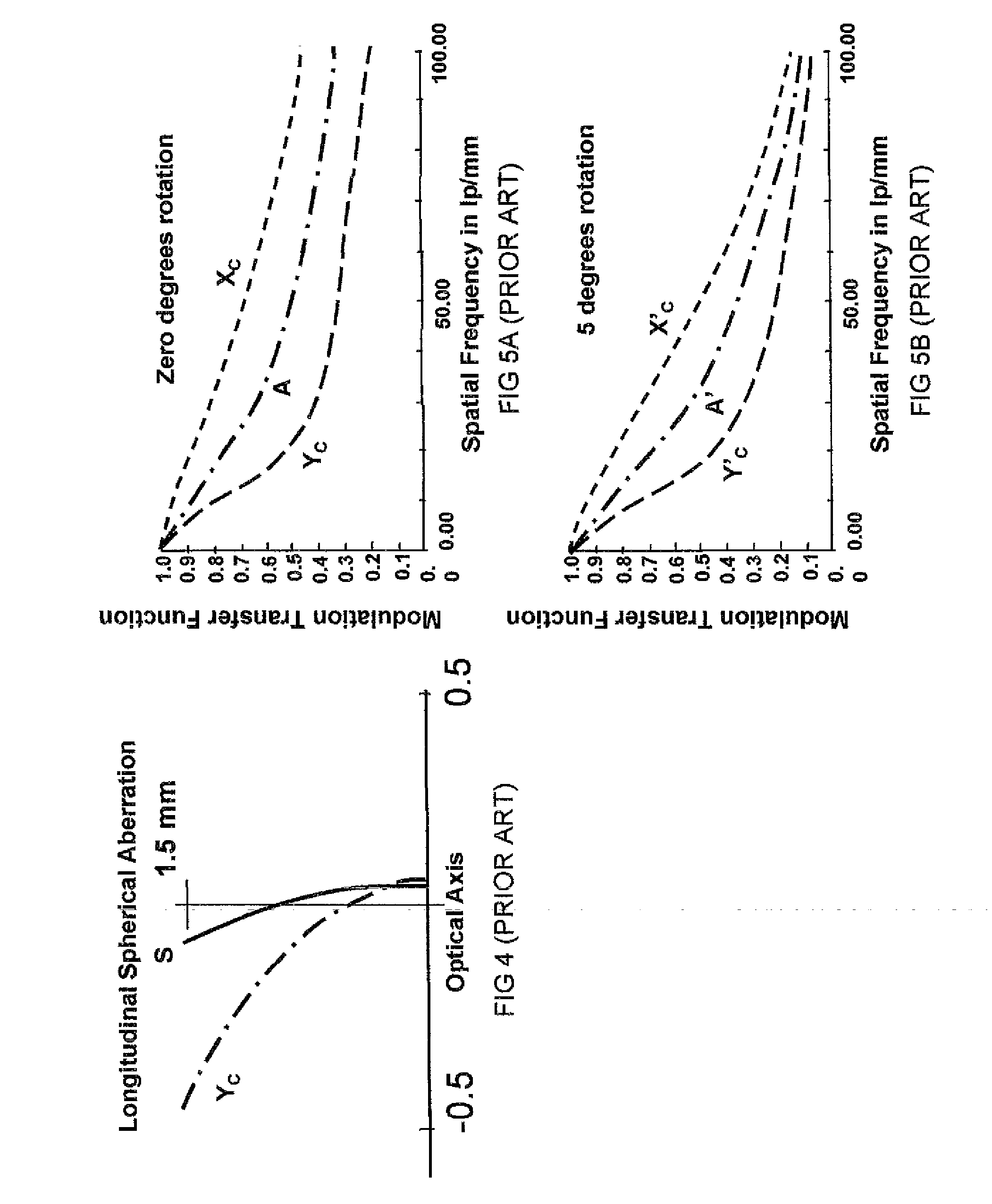
In geometric optics, stigmatism refers to the image-formation property of an optical system which focuses a single point source in object space into a single point in image space. Two such points are called a stigmatic pair of the optical system. Many optical systems, even those exhibiting optical aberrations including astigmatism, have at least one stigmatic pair. Stigmatism is applicable only in the approximation provided by geometric optics. In reality, image formation is at best diffraction limited and point-like images are not possible.
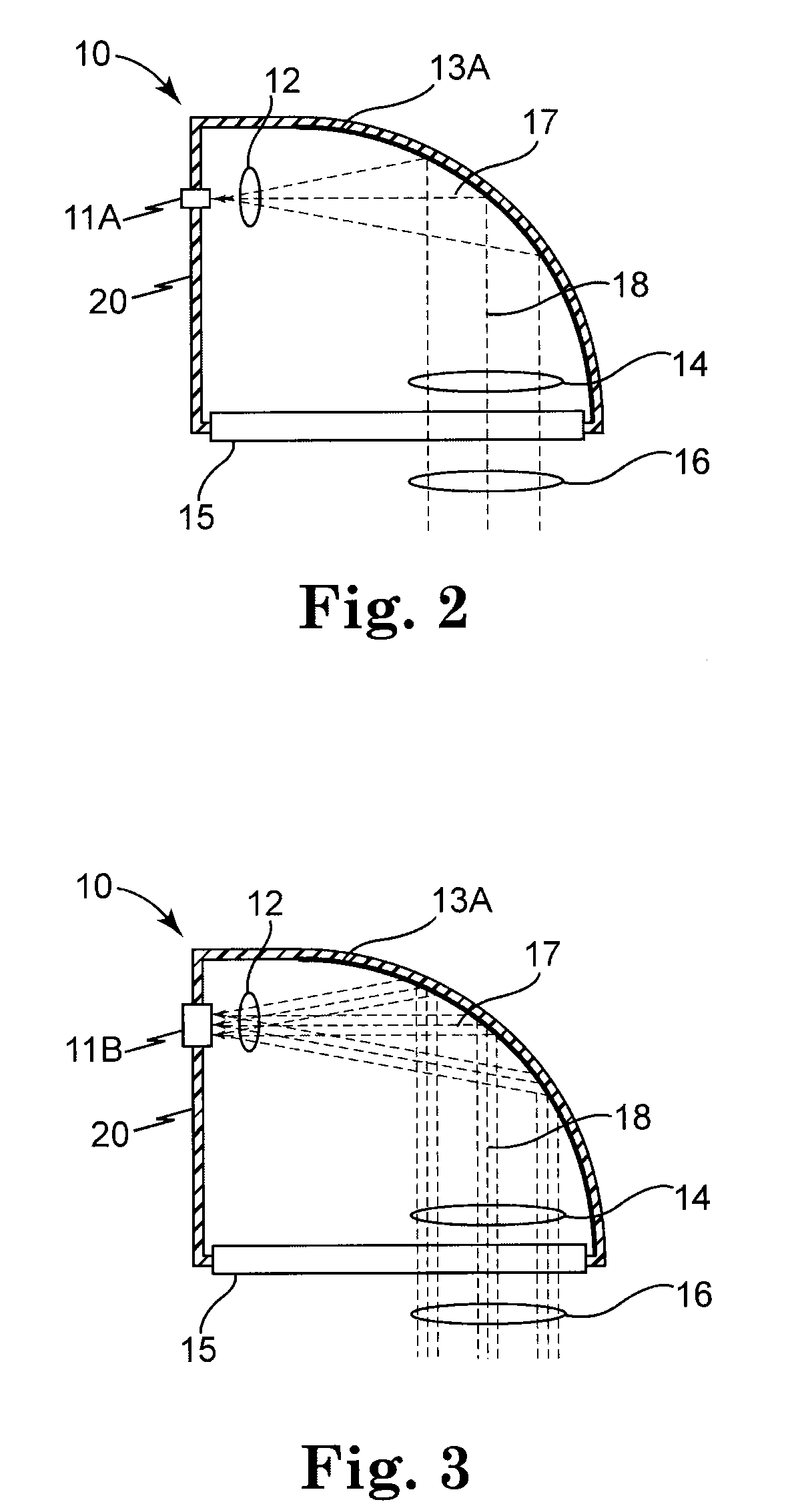
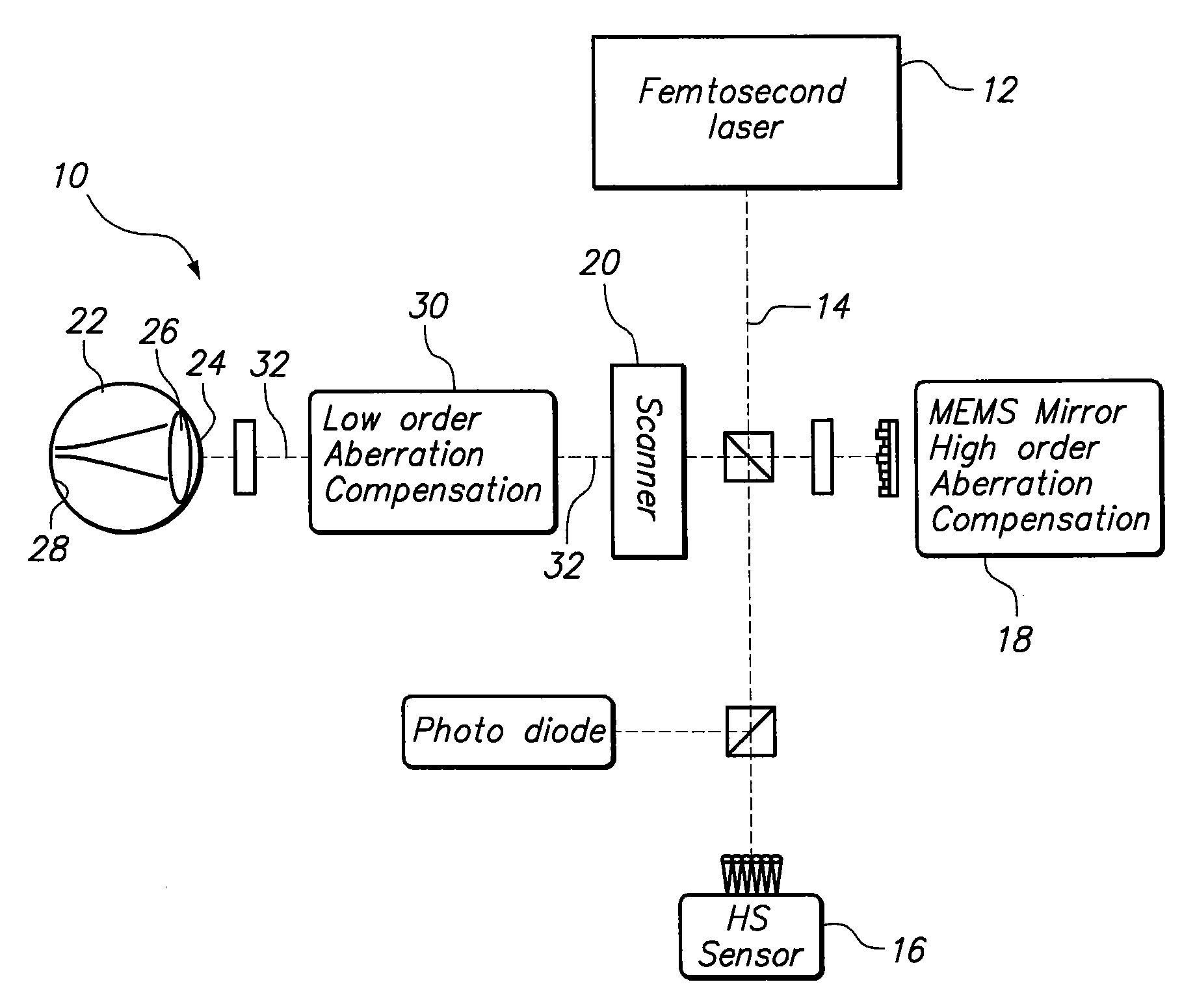
Methods and devices to design and fabricate surfaces on contact lenses and on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations
Methods and devices are described that are needed to design and fabricate modified surfaces on contact lenses or on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism. The invention provides the means for: 1) measuring the eye's optical aberrations either with or without a contact lens in place on the cornea, 2) performing a mathematical analysis on the eye's optical aberrations in order to design a modified surface shape for the original contact lens or cornea that will correct the optical aberrations, 3) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a contact lens by diamond point turning, three dimensional contour cutting, laser ablation, thermal molding, photolithography, thin film deposition, or surface chemistry alteration, and 4) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a cornea by laser ablation.
Owner:BROOKFIELD OPTICAL SYST
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors by active composite artificial muscle implants
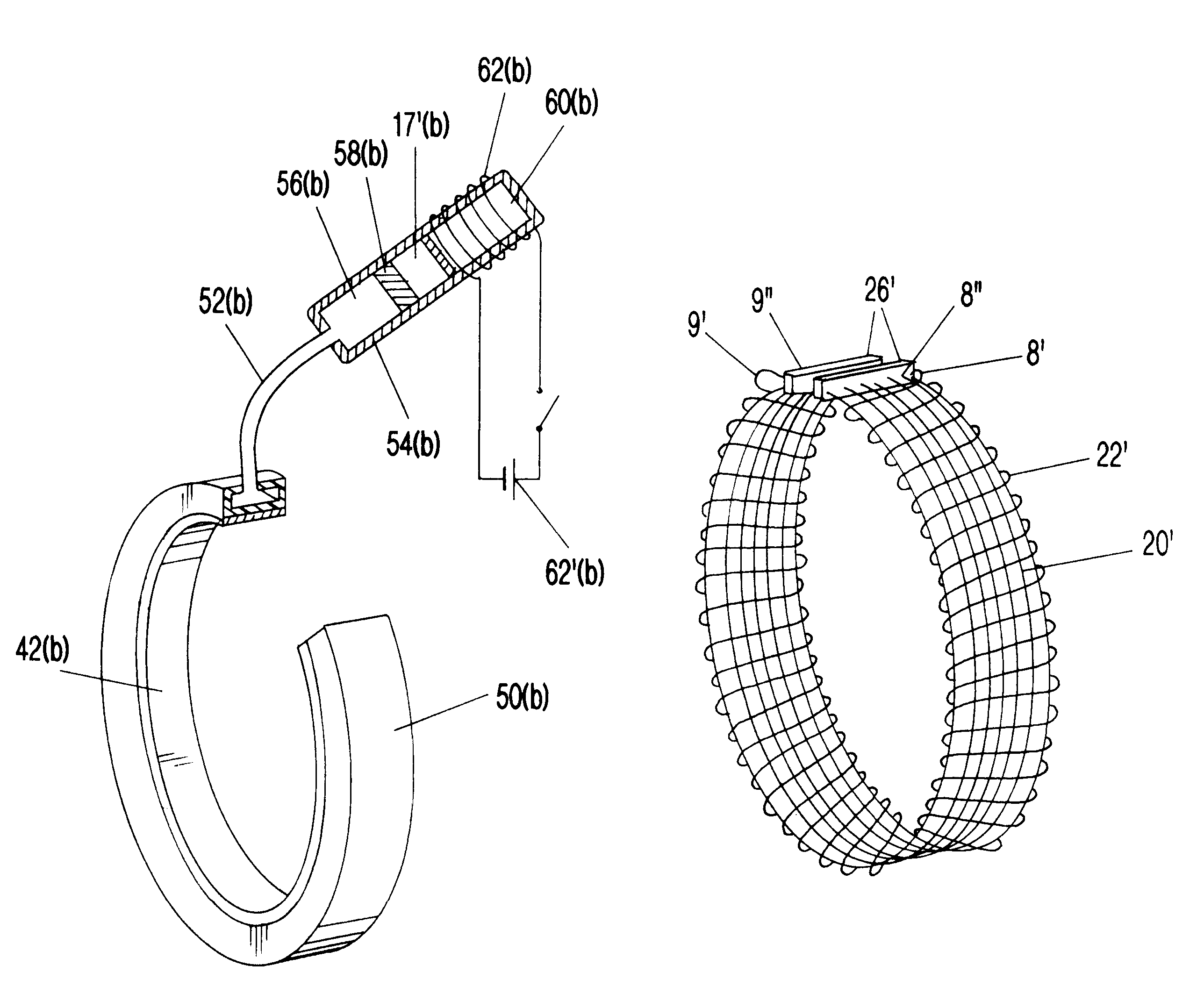
Surgical correction of human eye refractive errors such as presbyopia, hyperopia, myopia, and stigmatism by using transcutaneously inductively energized artificial muscle implants to either actively change the axial length and the anterior curvatures of the eye globe. This brings the retina / macula region to coincide with the focal point. The implants use transcutaneously inductively energized scleral constrictor bands equipped with composite artificial muscle structures. The implants can induce enough accommodation of a few diopters, to correct presbyopia, hyperopia, and myopia on demand. In the preferred embodiment, the implant comprises an active sphinctering smart band to encircle the sclera, preferably implanted under the conjunctiva and under the extraocular muscles to uniformly constrict the eye globe, similar to a scleral buckle band for surgical correction of retinal detachment, to induce active temporary myopia (hyperopia) by increasing (decreasing) the active length of the globe. In another embodiment, multiple and specially designed constrictor bands can be used to enable surgeons to correct stigmatism. The composite artificial muscles are either resilient composite shaped memory alloy-silicone rubber implants in the form of endless active scleral bands, electroactive ionic polymeric artificial muscle structures, electrochemically contractile endless bands of ionic polymers such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN), thermally contractile liquid crystal elastomer artificial muscle structures, magnetically deployable structures or solenoids or other deployable structures equipped with smart materials such as preferably piezocerams, piezopolymers, electroactive and eletrostrictive polymers, magnetostrictive materials, and electro or magnetorheological materials.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ROBOTS
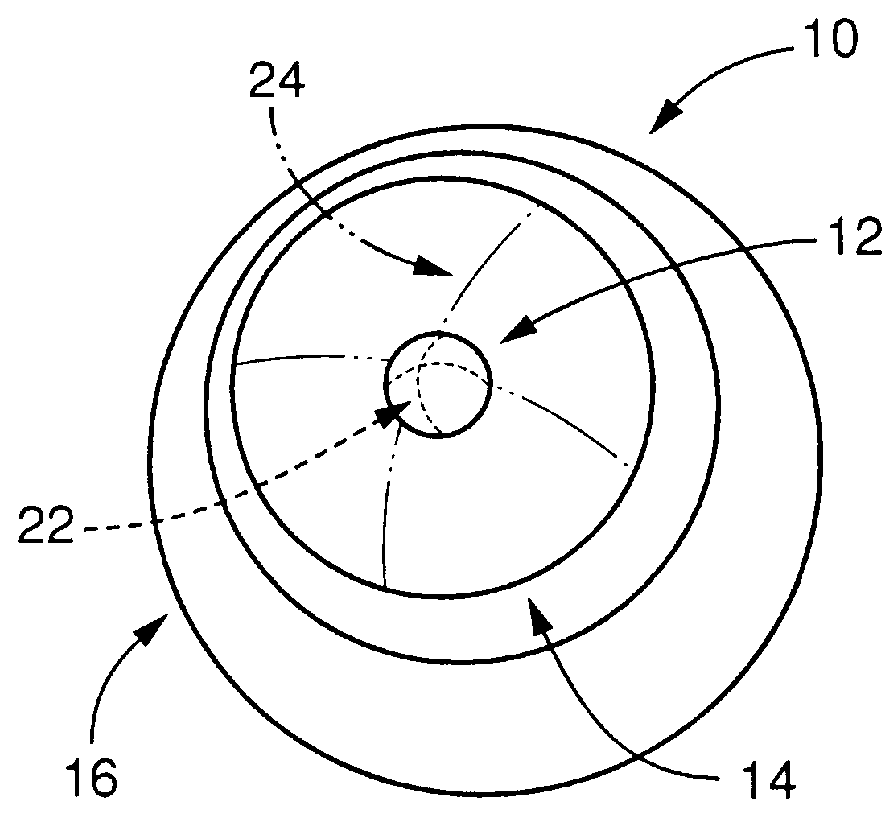
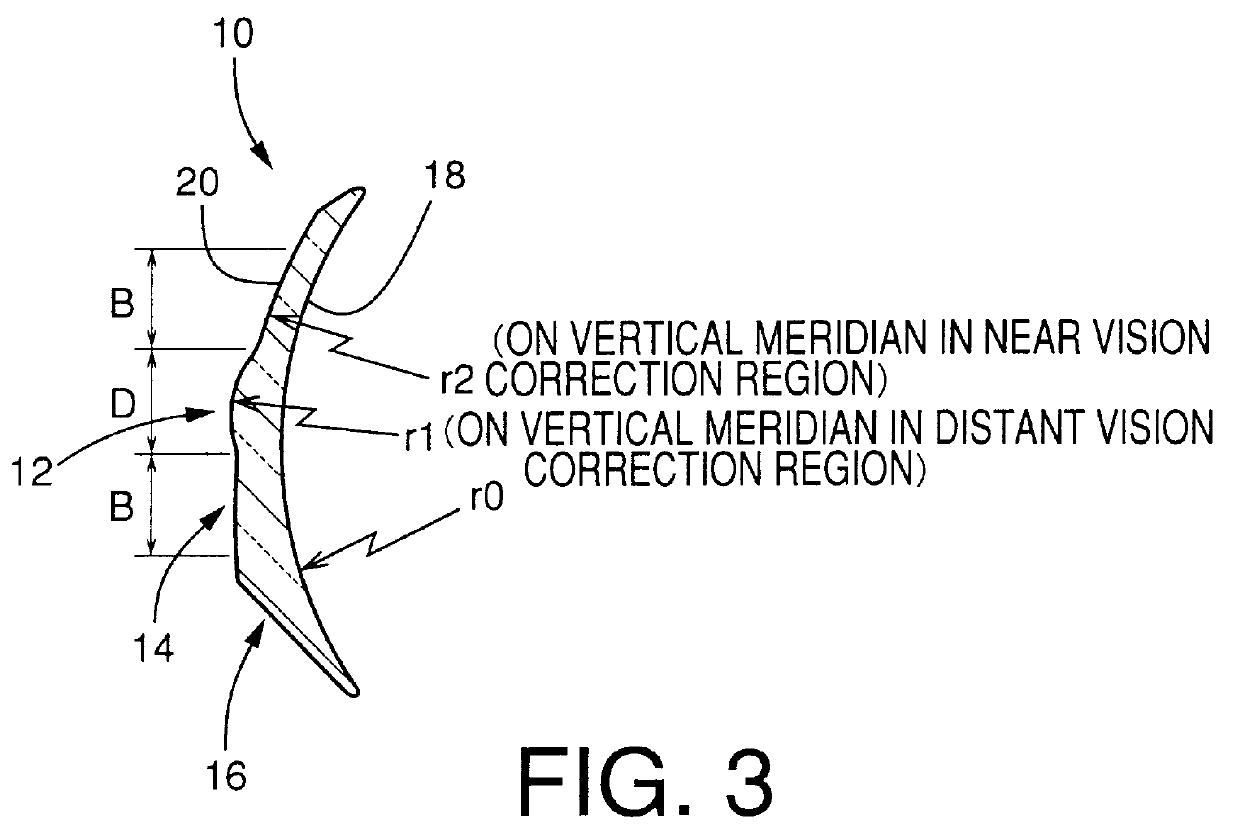
Toric multifocal lens having different astigmatism corrective optical powers in respective vision correction regions, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6142625AEasy to produceImprove stabilitySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical powerStigmatism
A toric multifocal lens including a plurality of vision correction regions having centers on a common optical center axis, the plurality of vision correction regions providing respective different values of a spherical optical power, each of the plurality of vision correction regions having an optical power for correction of astigmatism, wherein the improvement comprises: at least one of a cylindrical optical power and a cylindrical axis orientation which determine the optical power for correction of astigmatism being different in at least two different vision correction regions of the plurality of vision correction regions, so that the at least two different vision correction regions have respective different values of the optical power for correction of astigmatism.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Toric intraocular lens with modified power characteristics
An intraocular lens for correcting or reducing the astigmatism of a cornea includes an optical element that has optical properties and characteristics that make it tolerant of rotational misalignment, when compared to a comparable lens having a uniform astigmatism orientation across its entire optical element, leading to more relaxed tolerances for a surgeon that implants the lens. The optical element of the toric ophthalmic lens has meridians associated therewith, including a high power meridian and a low power meridian orthogonal to the high power meridian. The optical element has at least one radially modulated meridian along which power monotonically varies with increasing radial position.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
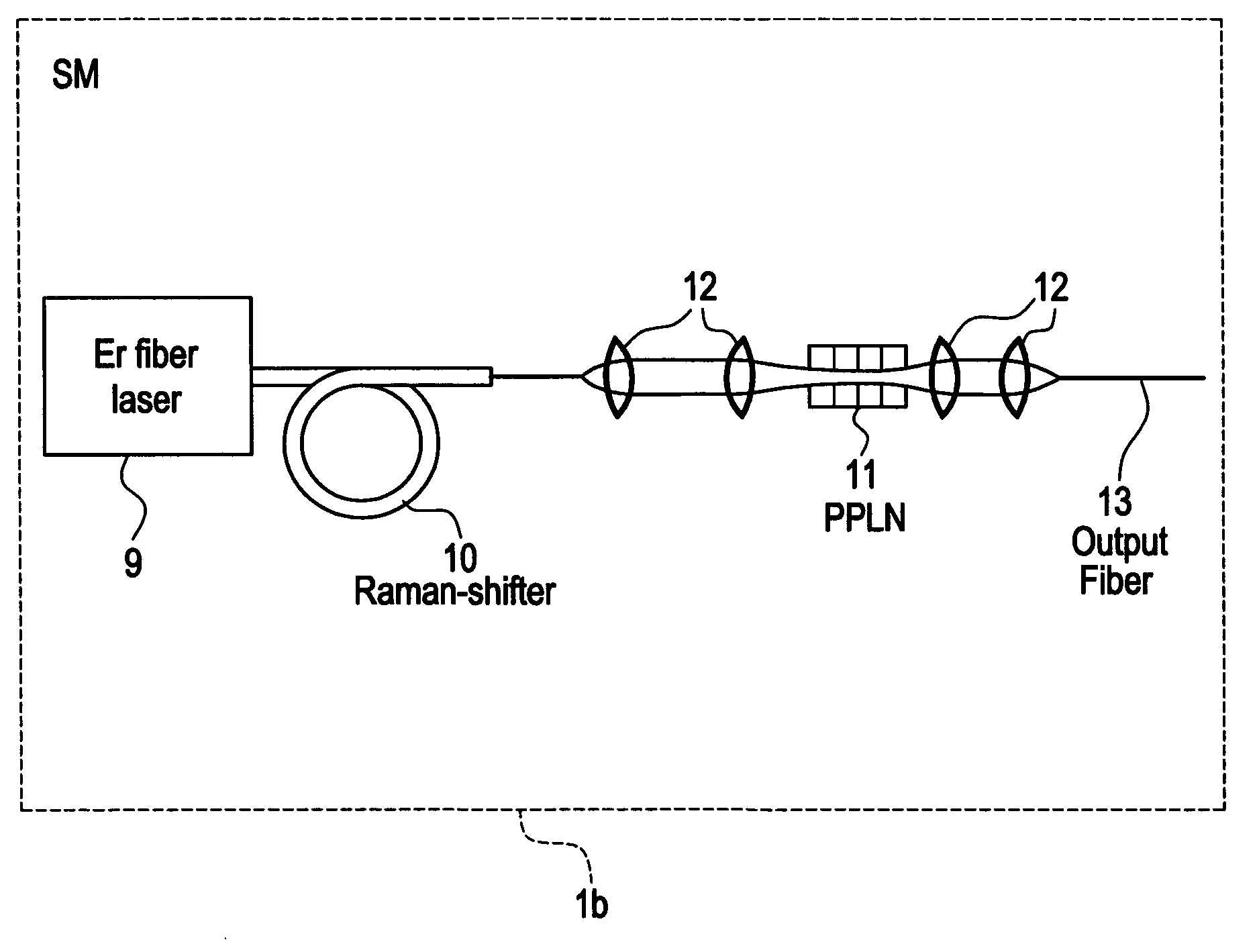
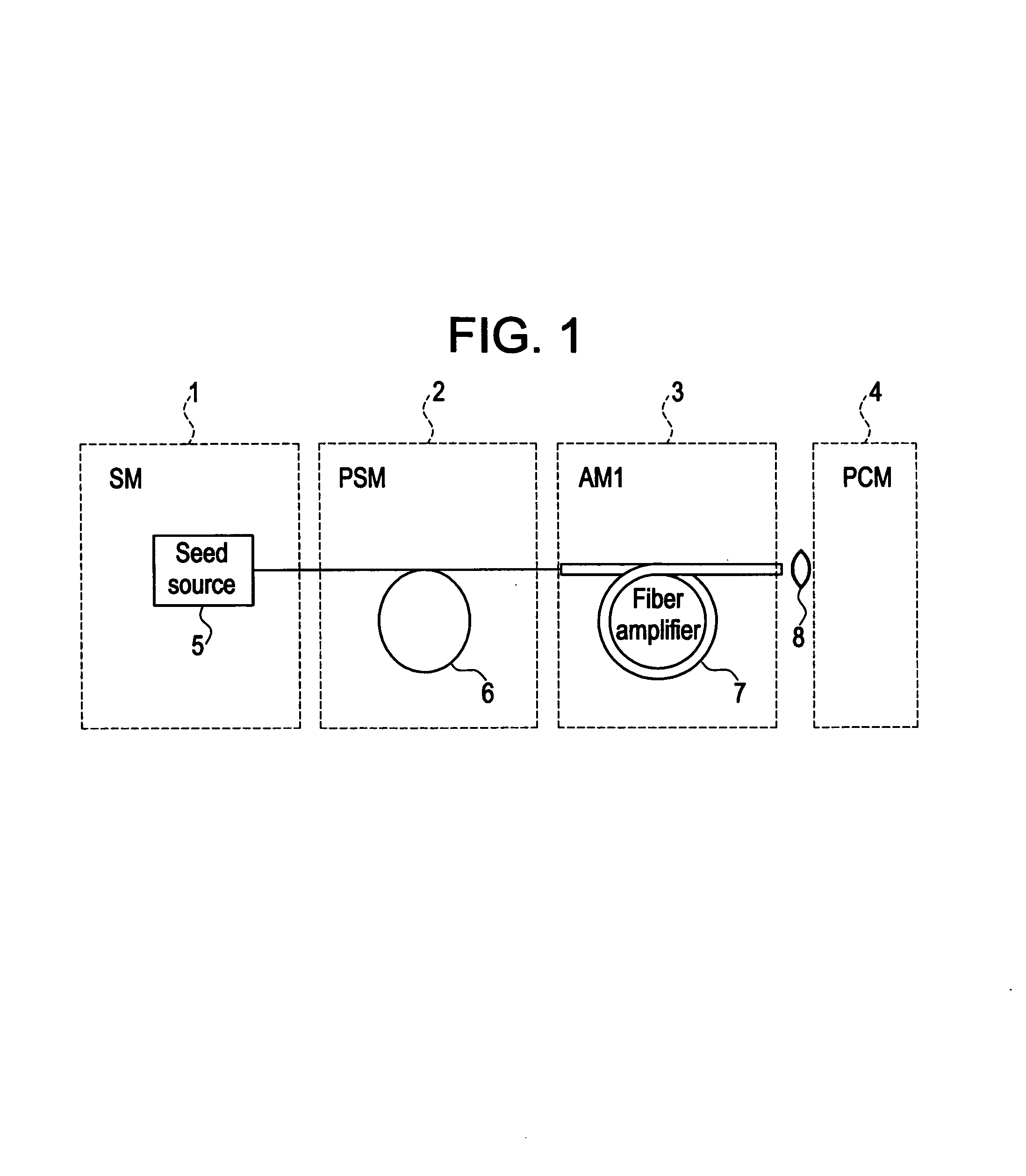
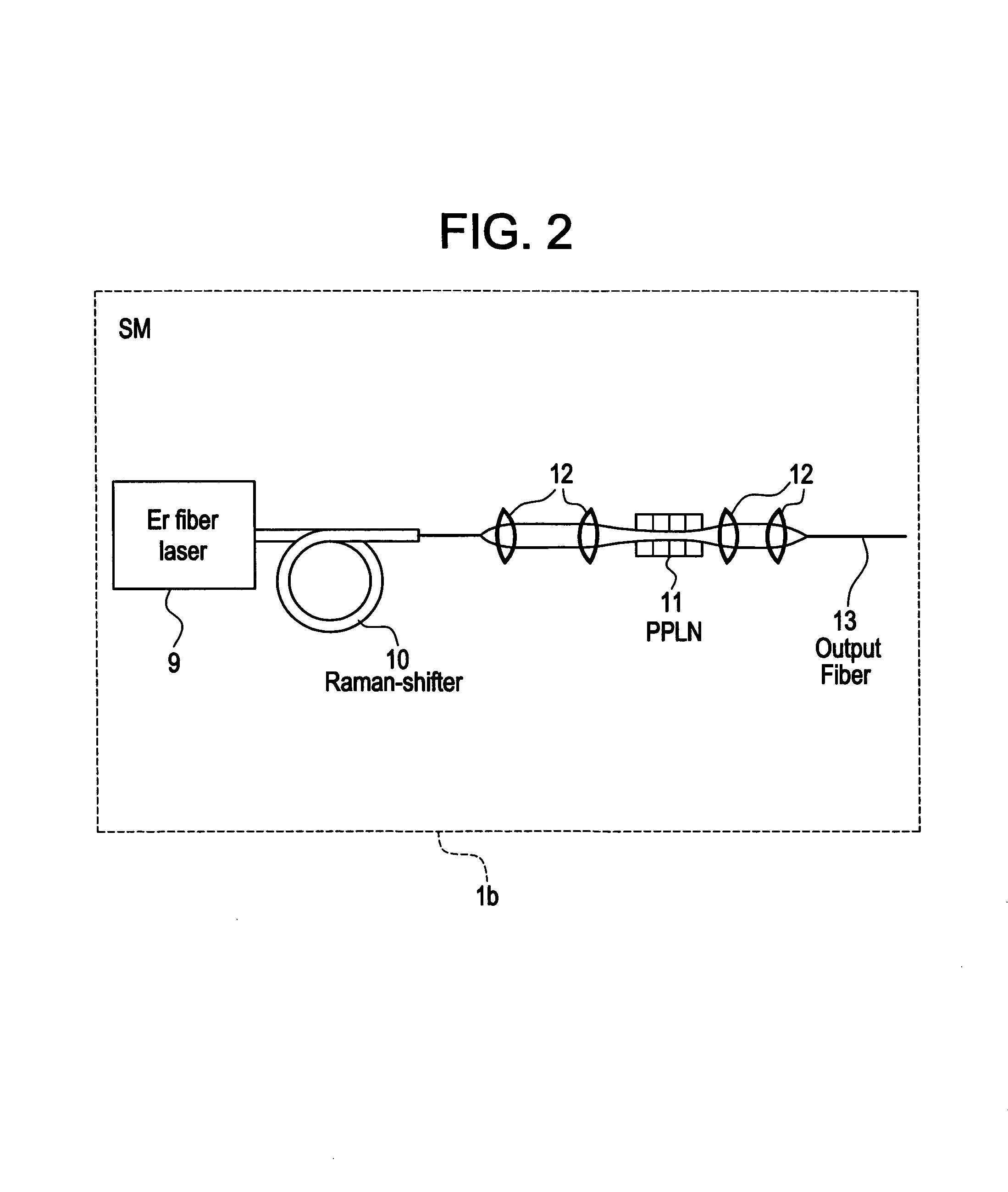
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS7167300B2High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
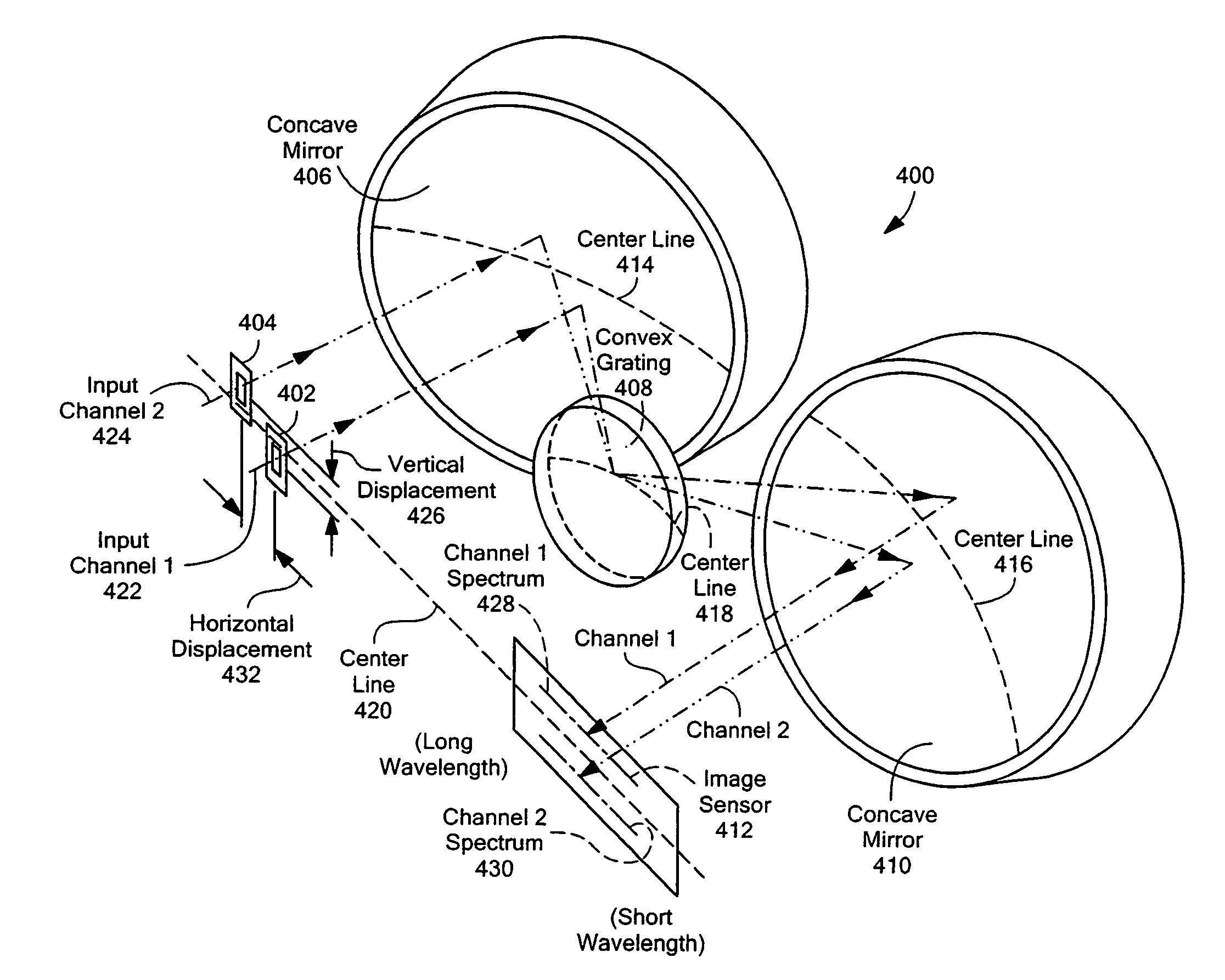
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
Method and Device for Cornea Reshaping by Intrastromal Tissue Removal
A method and device for flapless, intrastromal keratomileusis for the correction of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism, i.e., for vision correction by corneal reshaping without creating a flap. Ultra-short laser pulses are used to create a temporary micro-channel extending to an end point located within the cornea. A second series of ultra-short laser pulses are then delivered to photo-ablate material in the vicinity of the micro-channel end-point. The photo-ablated material may exit through the micro-channel used to deliver the laser pulses, or via a separate micro-channel. With the micro-channel oriented substantially normal to the optical axis of the cornea, and by continuing to supply the ultra-short laser pulses in the appropriate number while moving the point of ablation along the micro-channel, the photo-ablation of the intrastromal tissue may continue in a controlled fashion and the cornea reshaped in a predetermined manner without creating a flap.
Owner:FEMTO VISION LTD
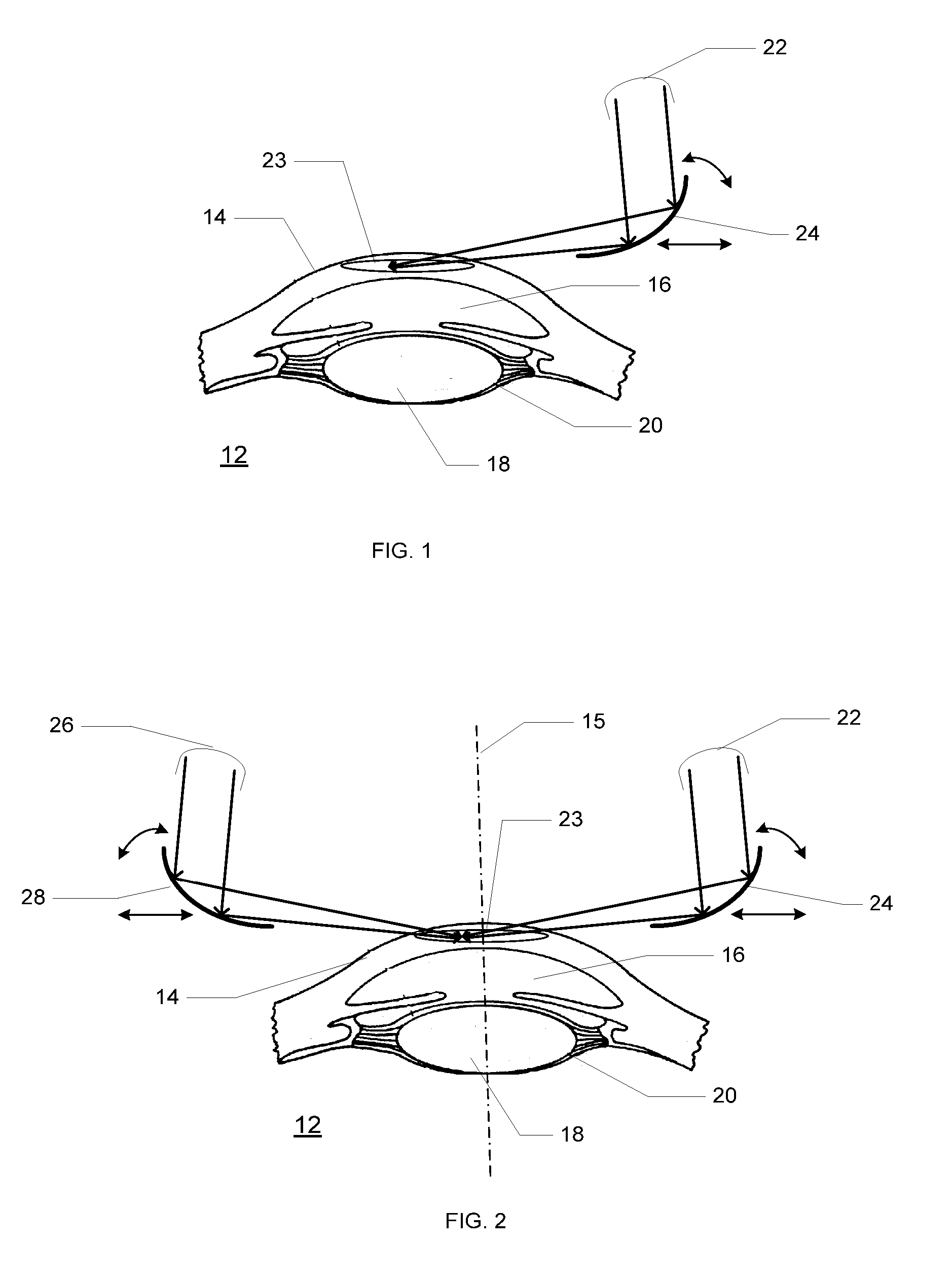
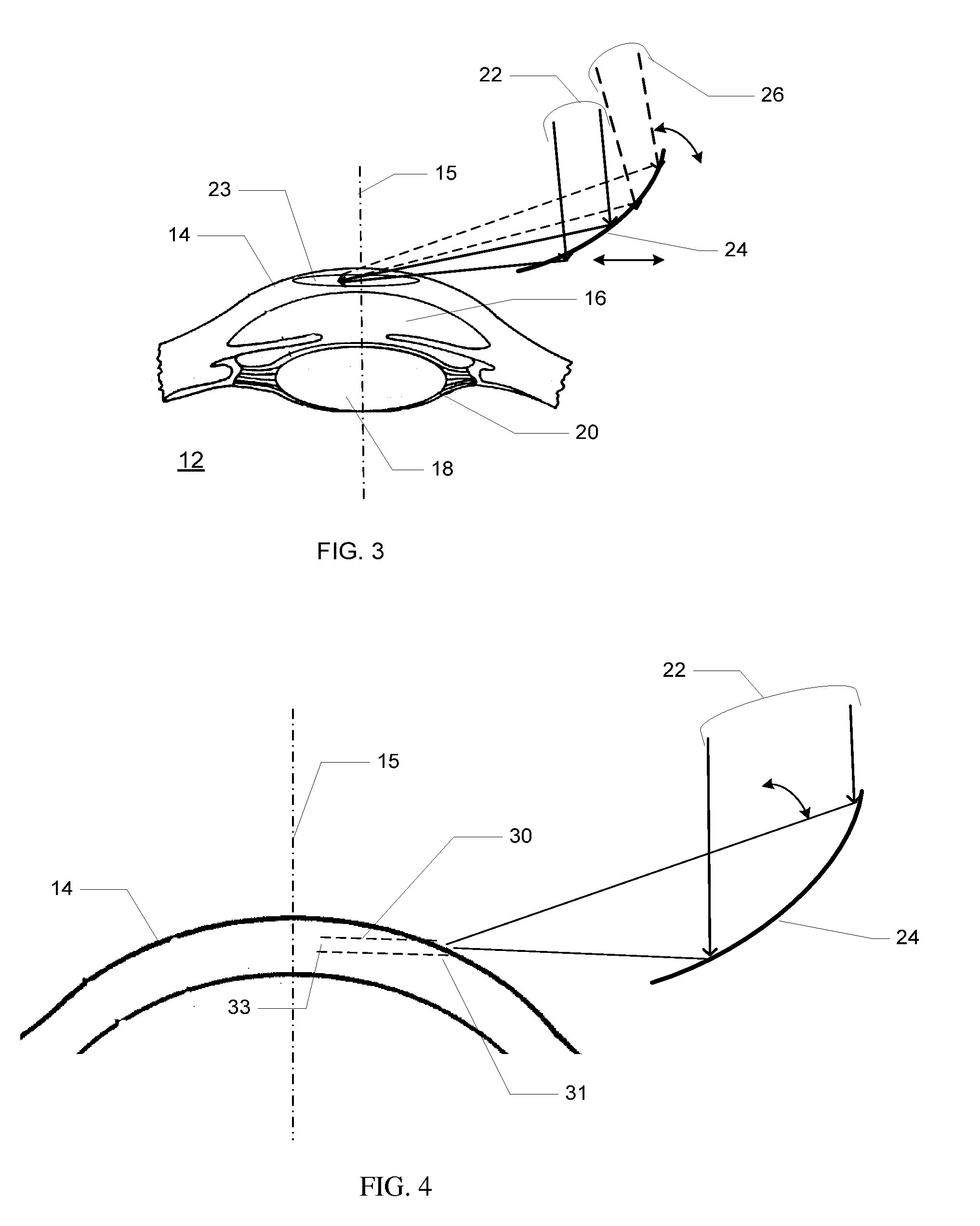
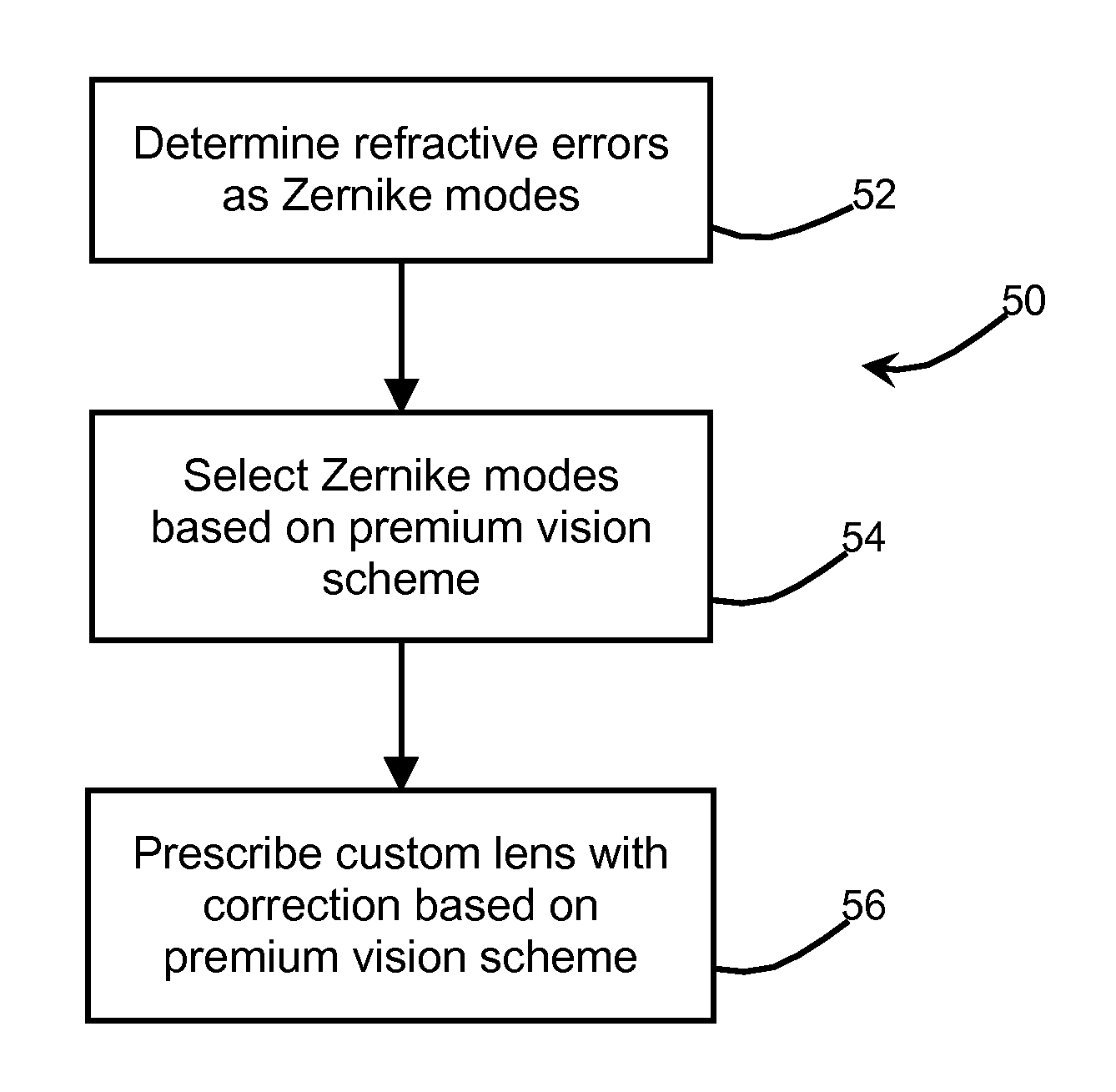
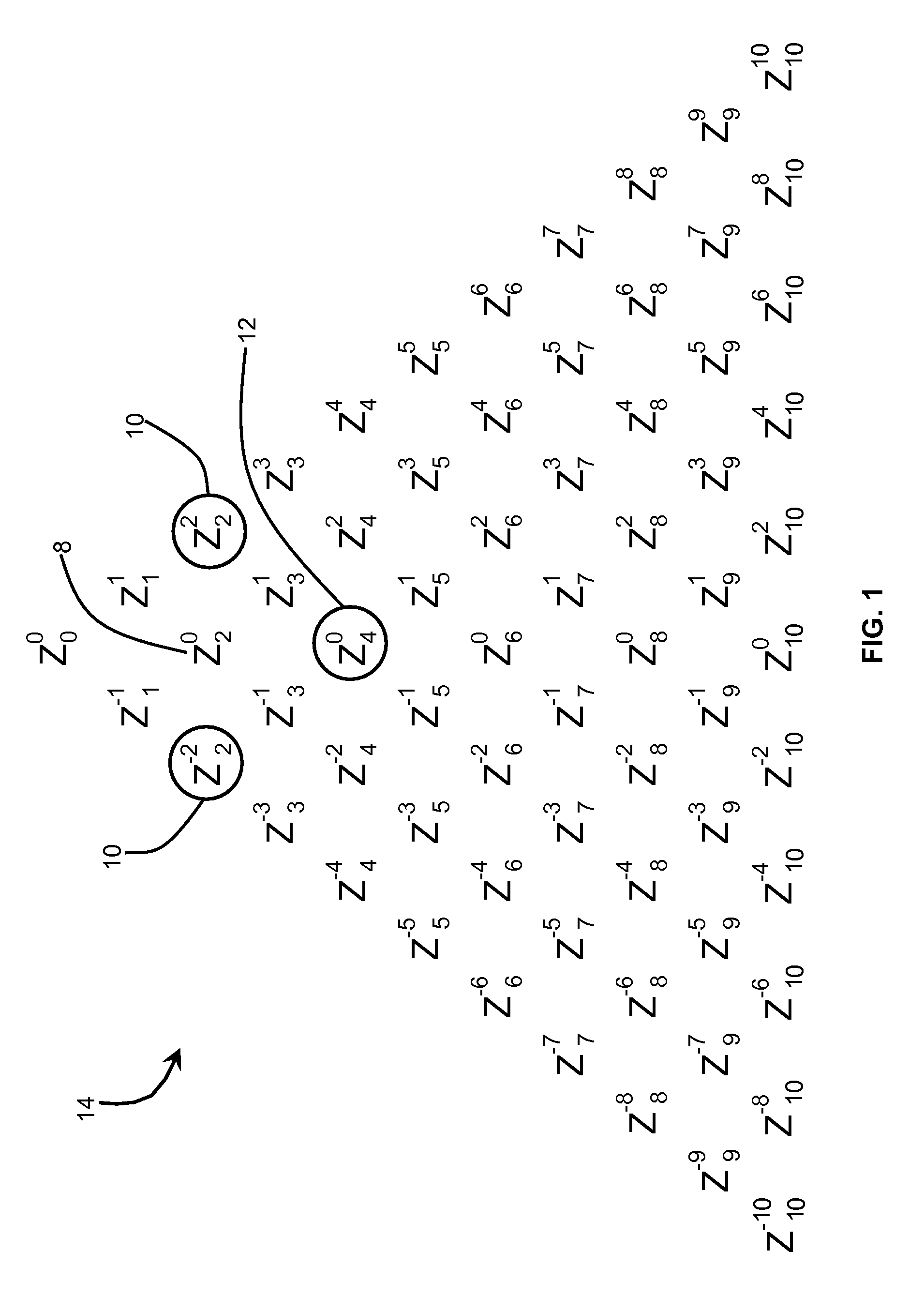
Premium vision ophthalmic lenses
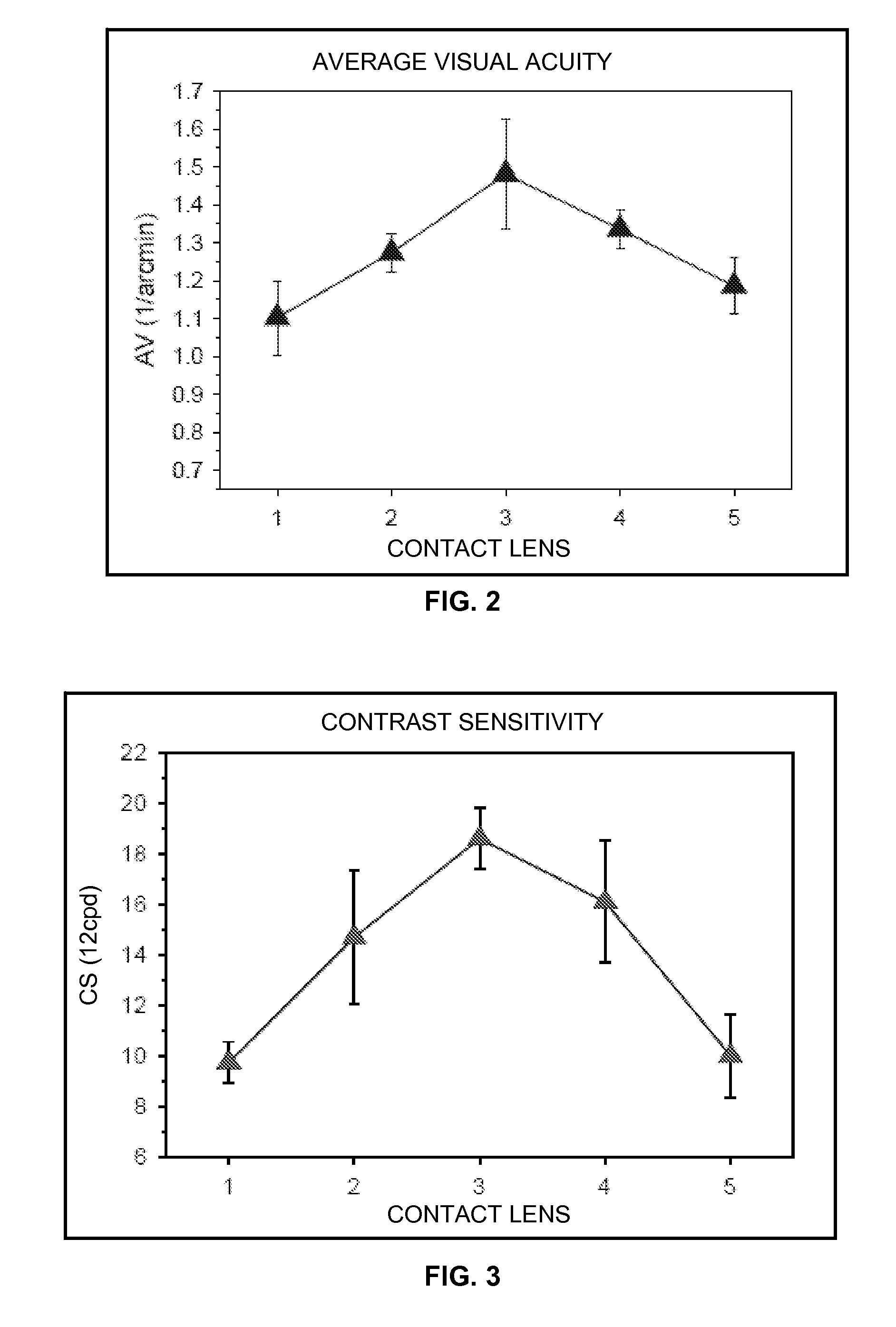
ActiveUS20080143963A1Accurately cancel outImprove visual acuitySpectales/gogglesRefractometersMass customizationStigmatism
An ophthalmic lens with premium vision corrections provides significantly improved visual acuity and contrast sensitivity. The premium vision corrections include precisely correcting for two aberration mode sets simultaneously, second-order astigmatism and fourth-order spherical aberration, instead of correcting for only second-order astigmatism or simultaneously correcting for all aberrations present. Fourth-order astigmatism, sixth-order spherical aberration, and third-order coma are additionally corrected in other premium vision correction schemes. In addition, methods are provided for prescribing and fabricating the premium vision lenses to permit mass customization.
Owner:ALCON INC
Multi-primary LED collimation optic assemblies
ActiveUS20090168414A1High strengthImprove uniformityMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceFree formStigmatism
The present invention relates to an optical assembly which improves color uniformity and improved collimation of light produced by multiple LED light sources in a light engine. The optical assembly is specifically tailored to match the placement of the solid-state emitters making up the light engine or light producing element. Specifically, a shaped free-form spline patch inner collimation lens having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse light; multi-lobe TIR collimation lens having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse and redistribute phase as well as provide collimation; primary mixing lenslet array having an optimized surface is used to disperse light from the light emitter; a spline profile reflector further mixes and collimates the light; a secondary lenslet array further mixes the light; and a secondary collimation lens further collimates the light.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Toric ophthalmic lens
InactiveUS20100315589A1Image quality is preservedSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensStigmatismLens plate
An ophthalmic lens for placement on the human eye or implanted into an eye is described. The lens has a cylinder power for eye astigmatism refraction error correction and incorporates aspherization of at least one of the surfaces to reduce vision quality reduction with toric ophthalmic lens rotation that creates meridional misalignment as compared with the equivalent toric lens with non-aspherized surface.
Owner:PORTNEY VALDEMAR
Light emitting diode retrofit module for traffic signal lights
InactiveUS6905227B2Easy to installNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesFresnel lensTraffic signal
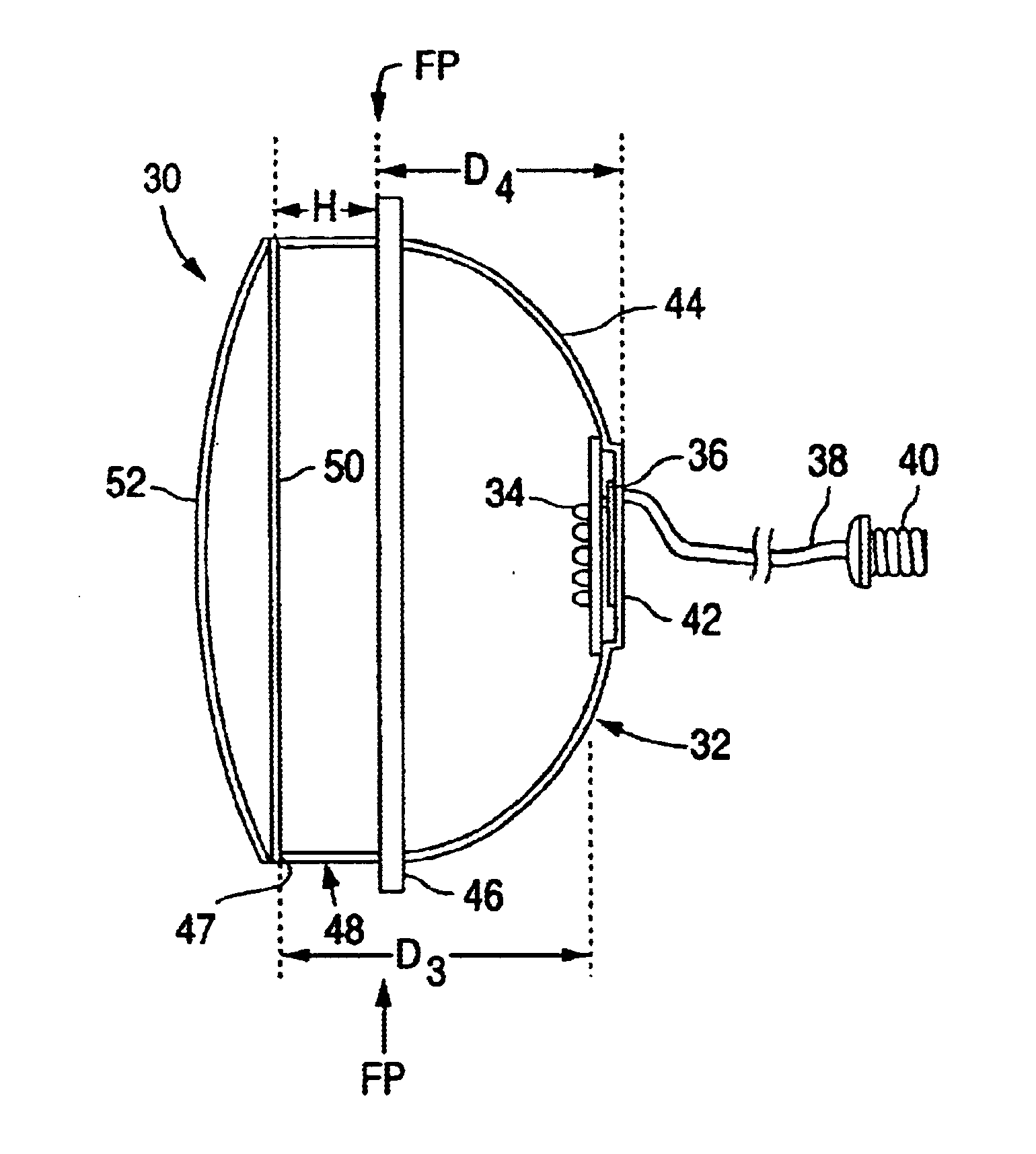
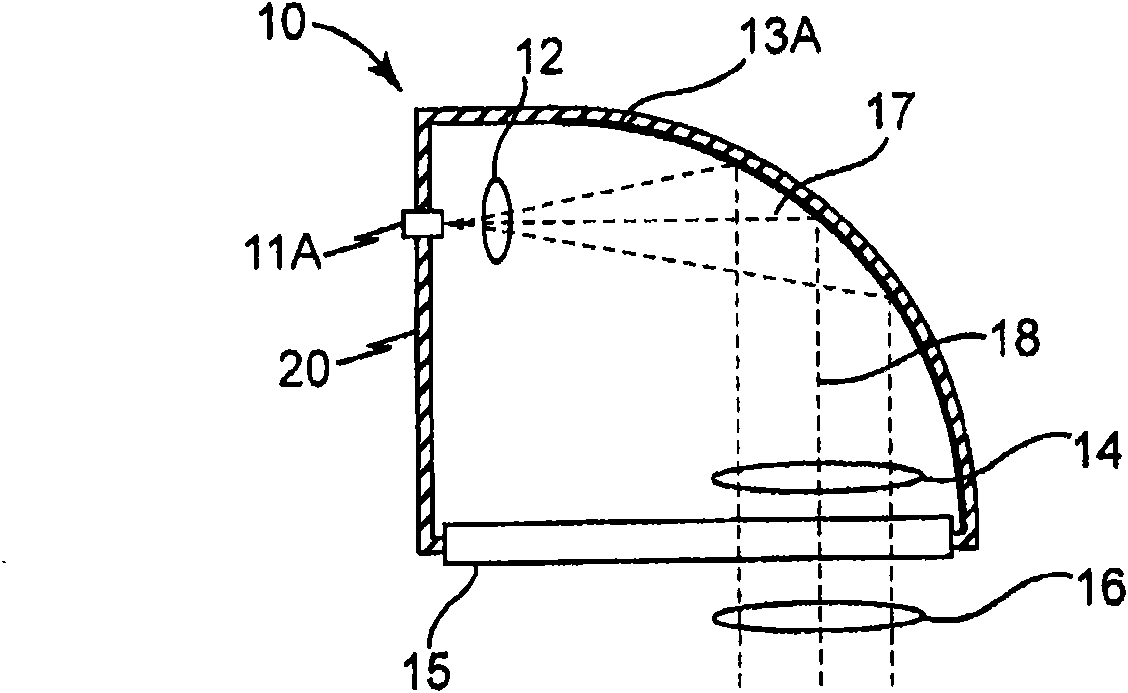
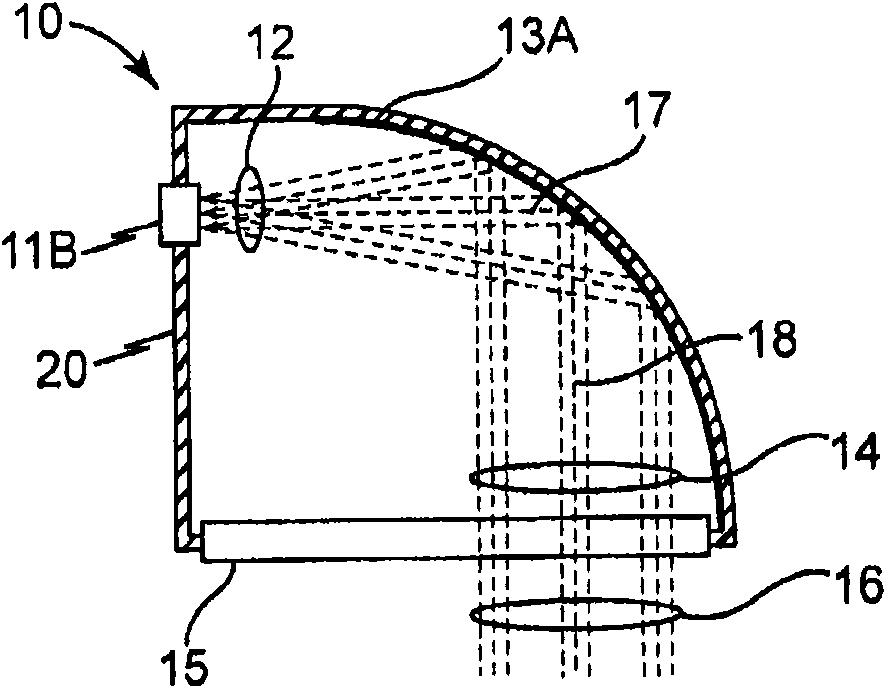
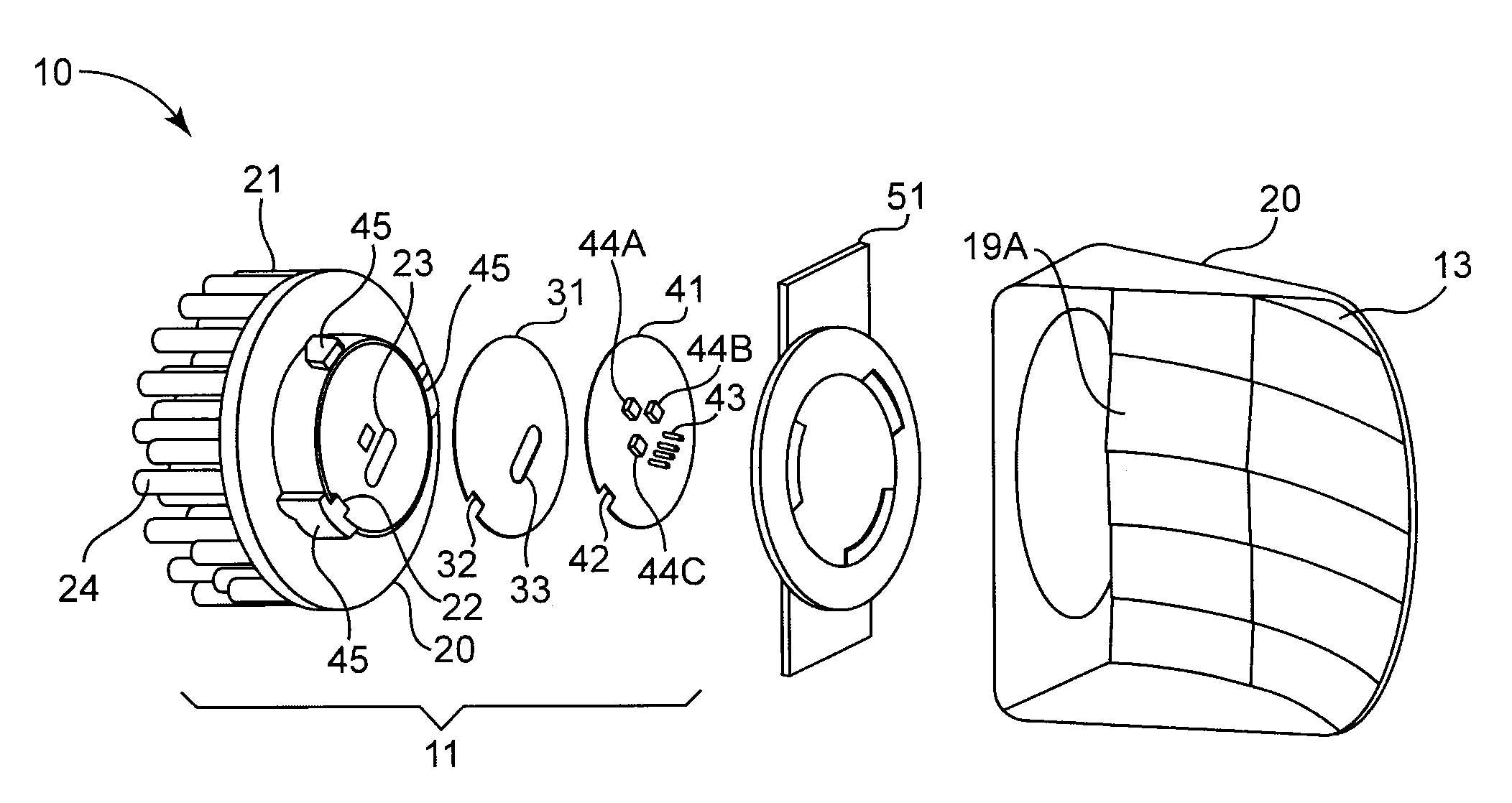
A high power LED lamp module for installation in conventional traffic signal lamps includes a housing with a side flange and a spacer ring extending therefrom, a plurality of LEDs disposed inside the housing for producing diverging light, a power supply disposed in the housing between the LEDs and the housing rear wall, a threaded electrical connector extending therefrom, and Fresnel / outer lenses extending across the open end of the spacer ring for collimating the diverging light from the LEDs. The Fresnel lens is disposed a first distance from the light emitting diodes wherein the light collimated thereby just fills and illuminates the entire outer lens. The flange is separated from the rear wall portion by a second distance that does not exceed about 100 mm or about 70mm for a 12 or 8 inch diameter lamp module respectively, to ensure the lamp module fits inside conventional traffic signal lamps.
Owner:LEOTEK ELECTRONICS
Methods and devices to design and fabricate surfaces on contact lenses and on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations
Methods and devices are described that are needed to design and fabricate modified surfaces on contact lenses or on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism. The invention provides the means for: 1) measuring the eye's optical aberrations either with or without a contact lens in place on the cornea, 2) performing a mathematical analysis on the eye's optical aberrations in order to design a modified surface shape for the original contact lens or cornea that will correct the optical aberrations, 3) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a contact lens by diamond point turning, three dimensional contour cutting, laser ablation, thermal molding, photolithography, thin film deposition, or surface chemistry alteration, and 4) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a cornea by laser ablation.
Owner:MAGNANTE PETER C
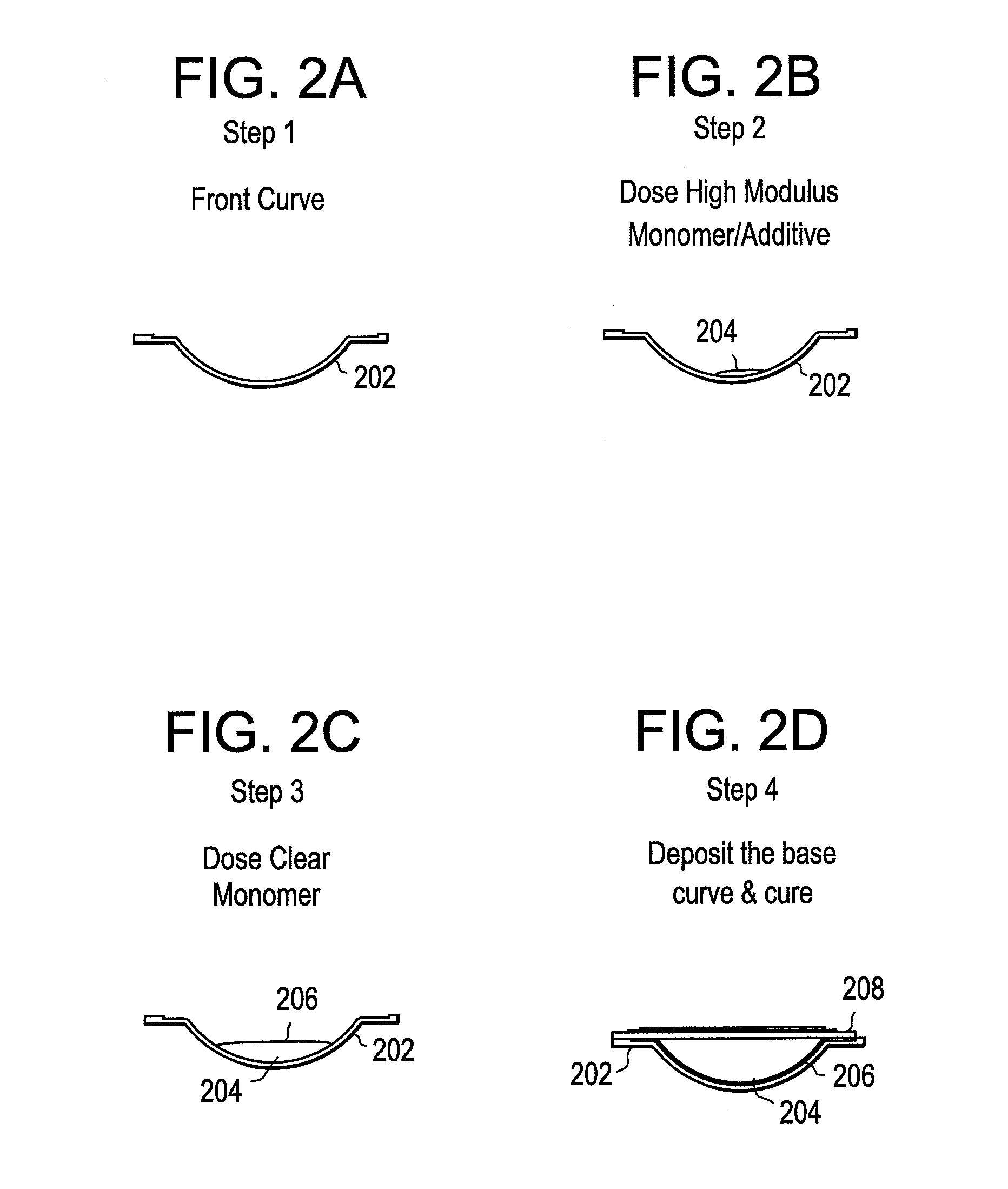
Increased stiffness center optic in soft contact lenses for astigmatism correction
InactiveUS20130258276A1Increase stiffnessHigh modulusOptical articlesOptical partsRefractive errorStigmatism
A molded contact lens comprising a stiffer optic zone relative to the peripheral zone of the contact lens provides an optical element for correcting astigmatism without the need for or substantially minimizing the need for the correction of rotational misalignment. The higher elastic modulus optic zone vaults over the cornea thereby allowing a tear lens to form. The tear lens follows or assumes the shape of the back surface of the contact lens. The combination of the tear lens and the optical zone provide an optical element for correction of refractive error.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Catadioptric lens system for collecting and directing light from large aperture luminescent light illuminating fixtures
A projection illumination fixture includes luminescent light tubes lined with an emulsion coating of titanium dioxide and phosphors for producing an appropriate mixture of highly scattered red, blue and green wavelengths of sustained luminescent light emission, a reflector housing for reflecting scattered rays of emitted luminescent light toward an aperture, a catadioptric lens for collecting and redirecting luminescent light rays reaching the aperture into and through a light snoot or barrel and a large area projection (magnifying) Fresnel lens at the end of the light snoot or barrel for directing and spreading the emitted light to fill an illumination field with directional divergent light ideal for dimensionally "painting' talent and objects positioned and moving within the illumination field.
Owner:COSTA PAUL D
Panoramic optical systems
Panoramic optical systems are disclosed comprising an ellipsoidal mirror and a lens system that reduces astigmatism. The lens systems are capable of operating at fast speeds. Simple and highly manufacturable lens systems are provided for capturing and / or projecting high quality 360-degree panoramic scenes.
Owner:360AI SOLUTIONS LLC
Multimode Seeker System With RF Transparent Stray Light Baffles
There is disclosed a multimode seeker including an imaging infrared seeker and a radio frequency seeker. The imaging infrared seeker and the radio frequency seeker may share an optical system adapted to form an infrared image of an outside scene on a focal plane array image detector and to collimate radio frequency radiation transmitted from a radio frequency transceiver and focus millimeter ware radiation received from the outside scene onto the radio frequency transceiver. The shared optical system may include a plurality of baffles to block sunlight from reaching the focal plane array image detector, each baffle comprising a material that is opaque to infrared radiation and transparent to radio frequency radiation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
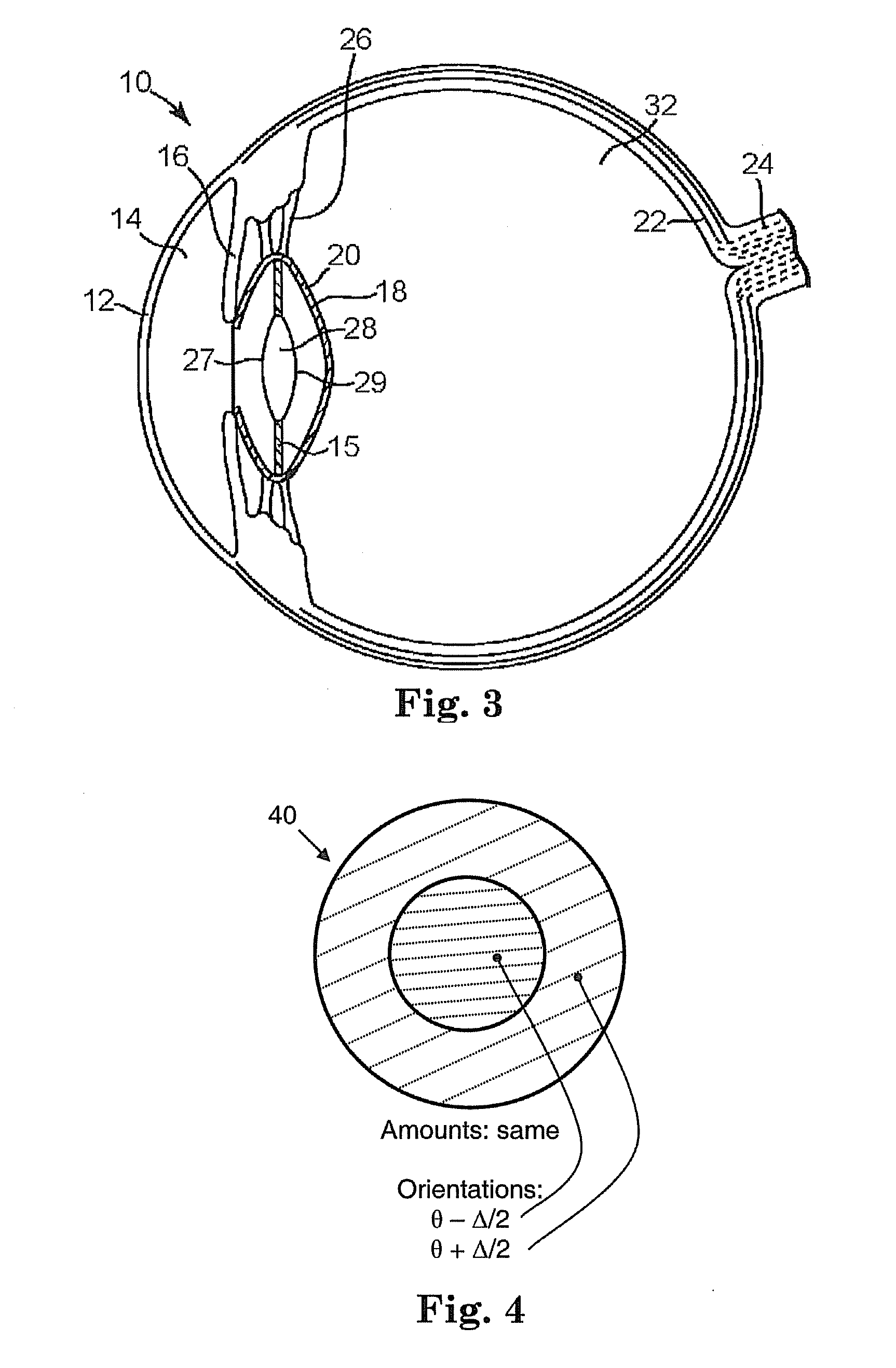
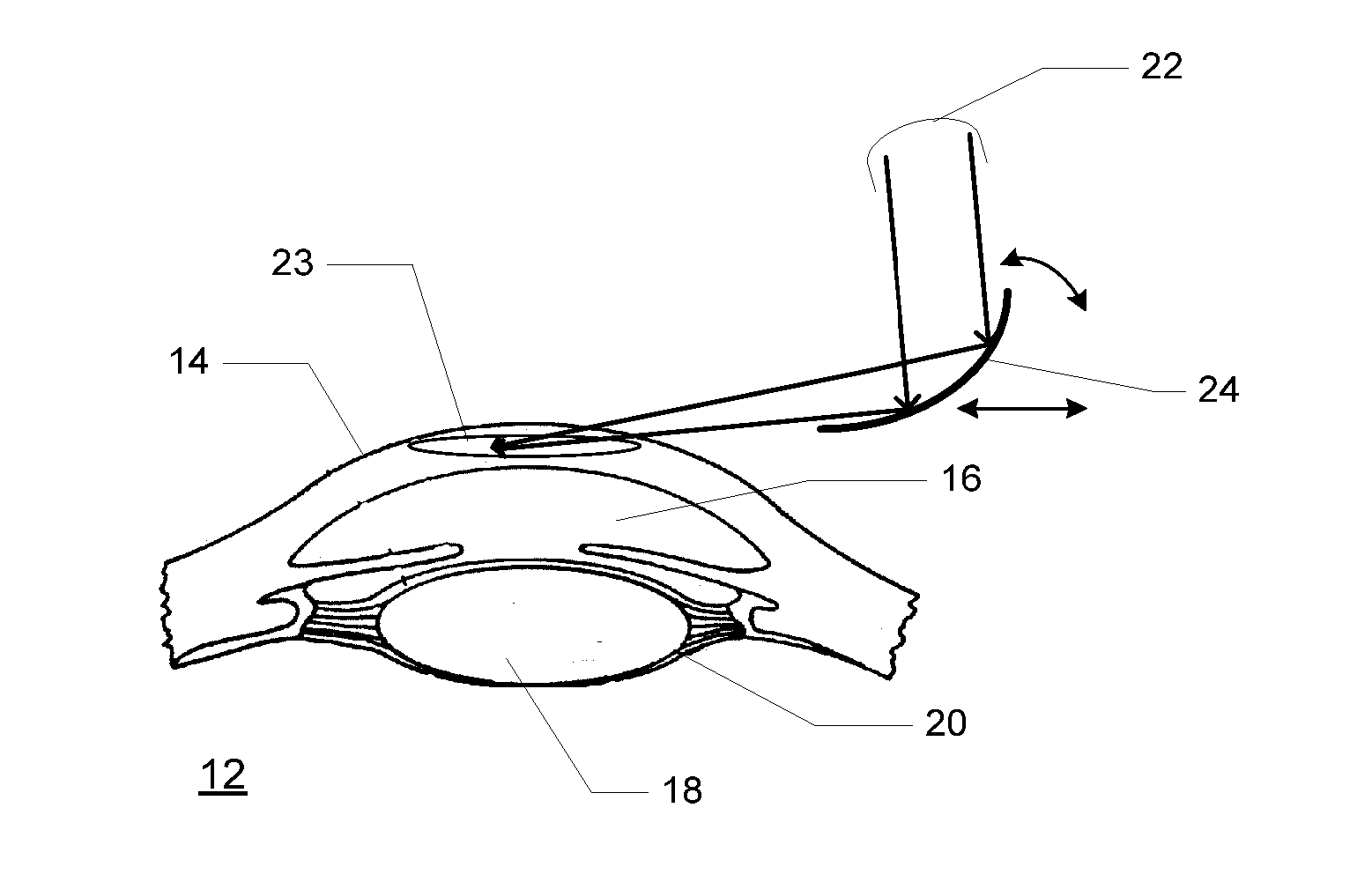
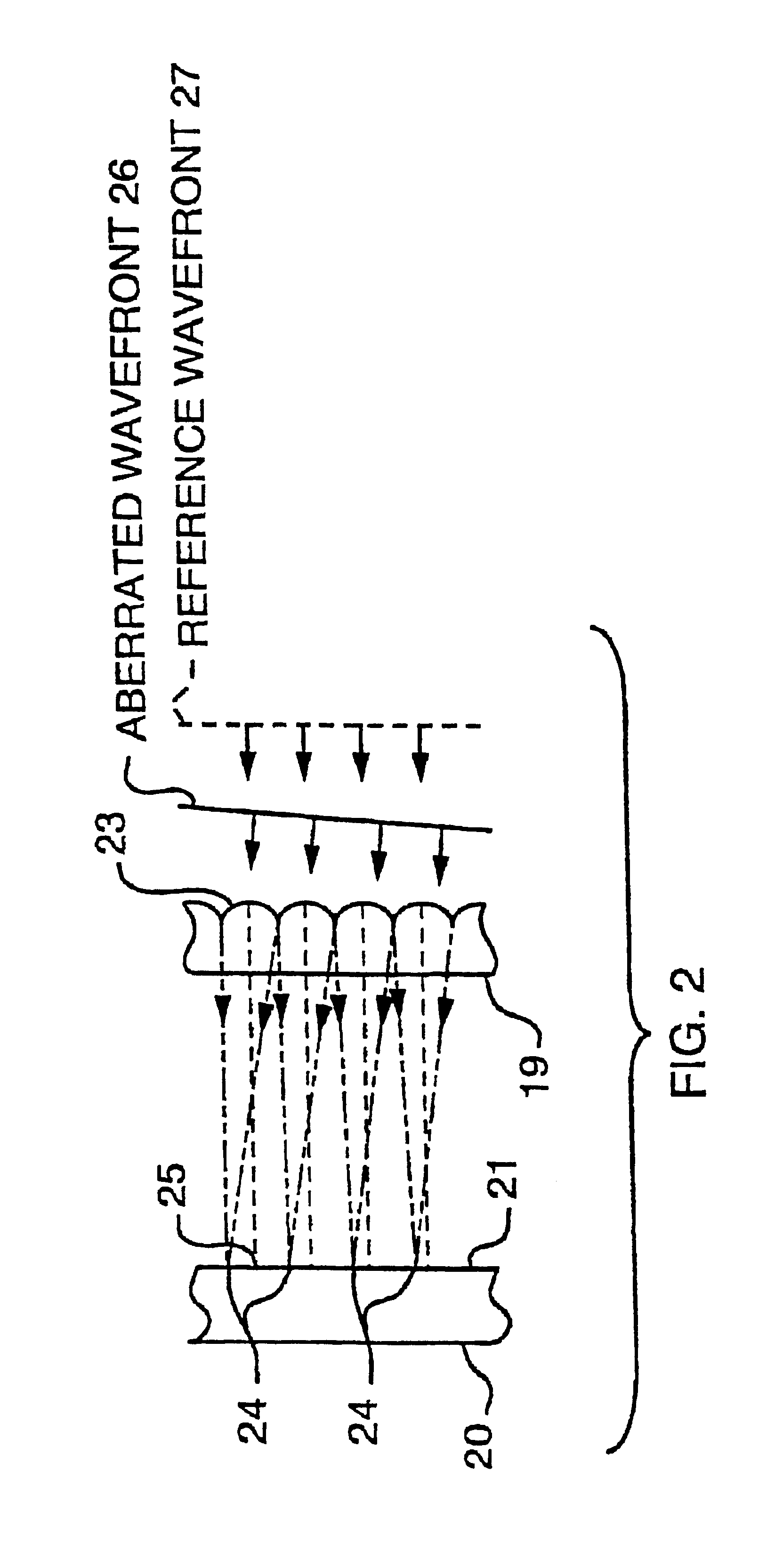
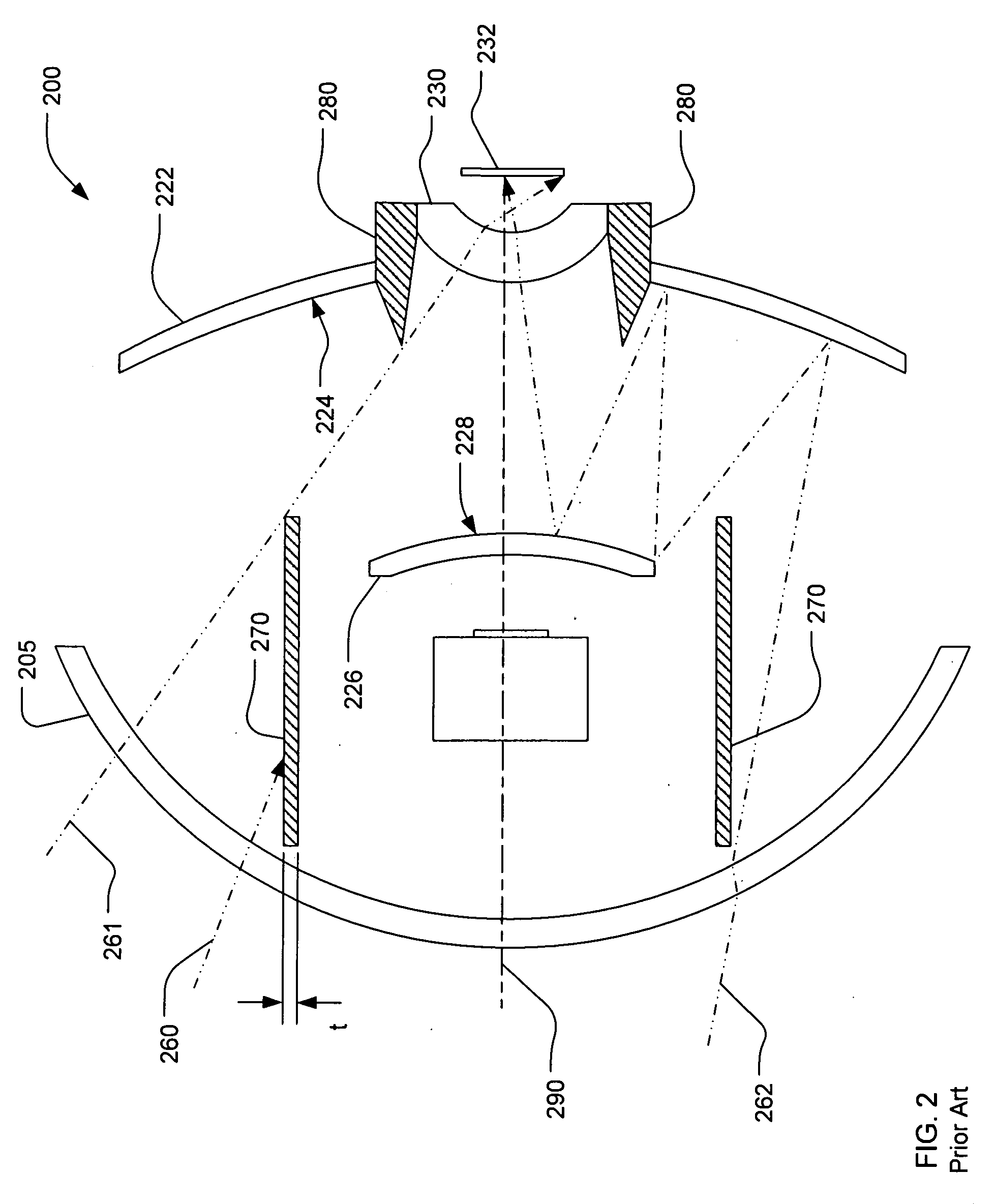
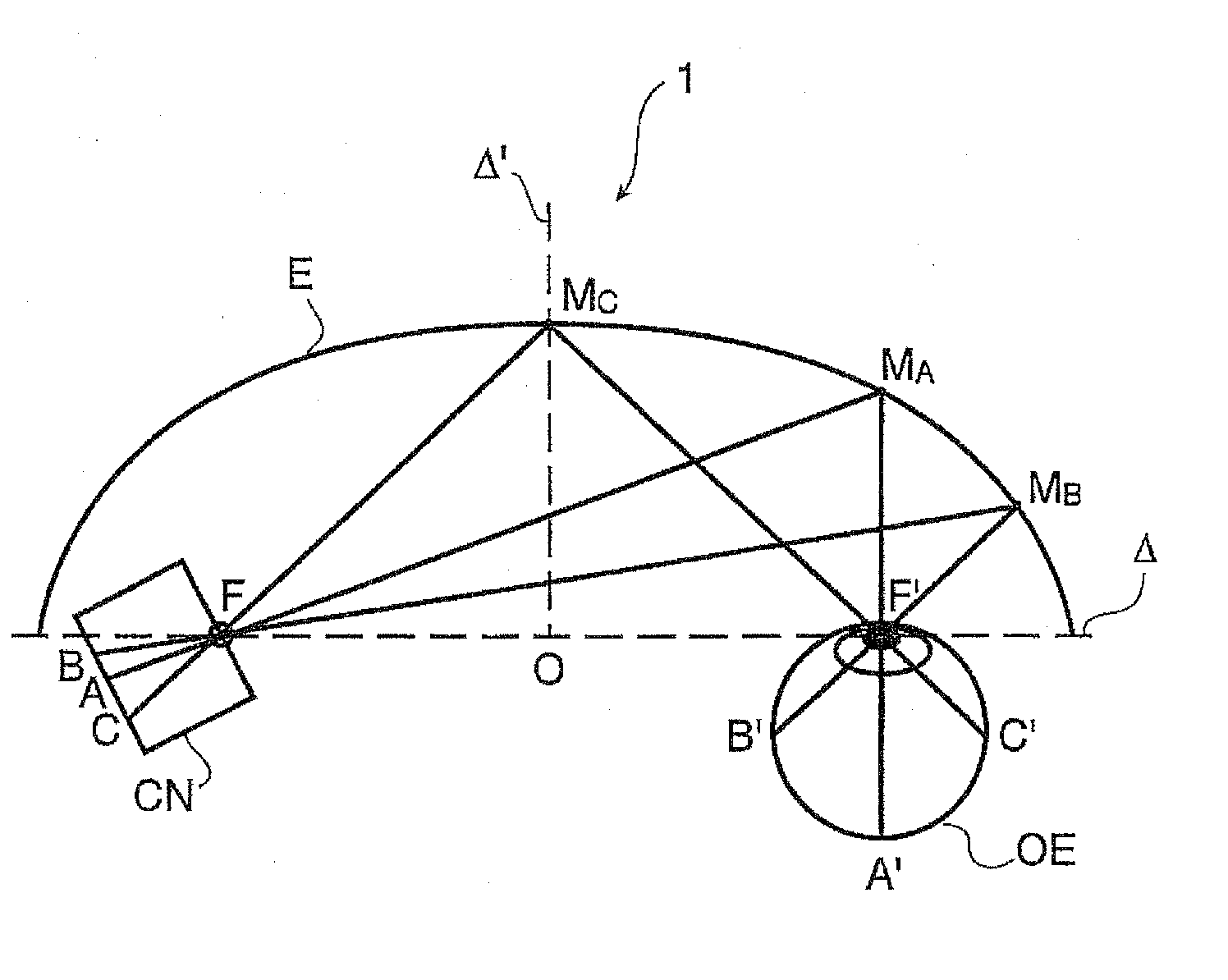
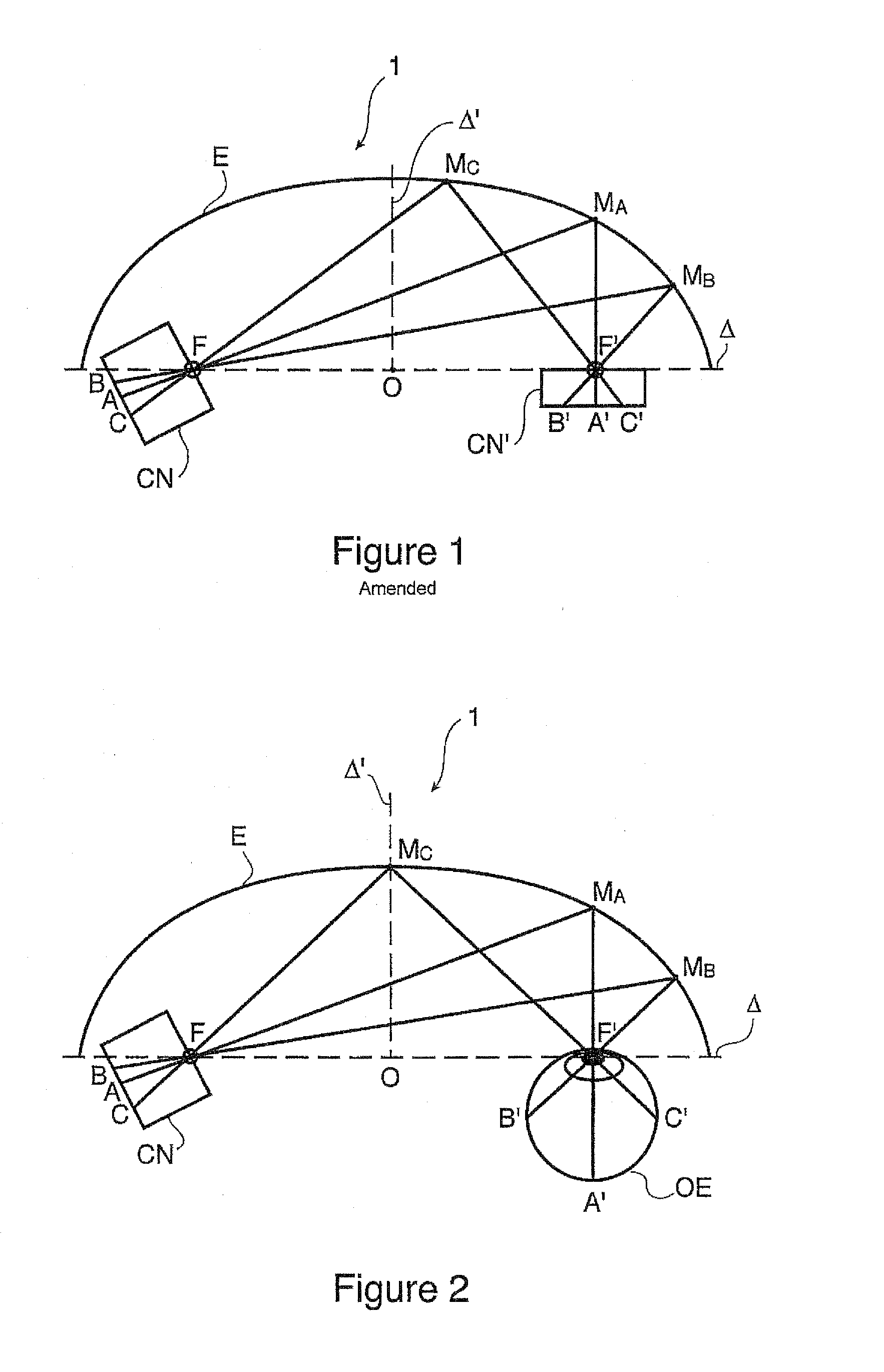
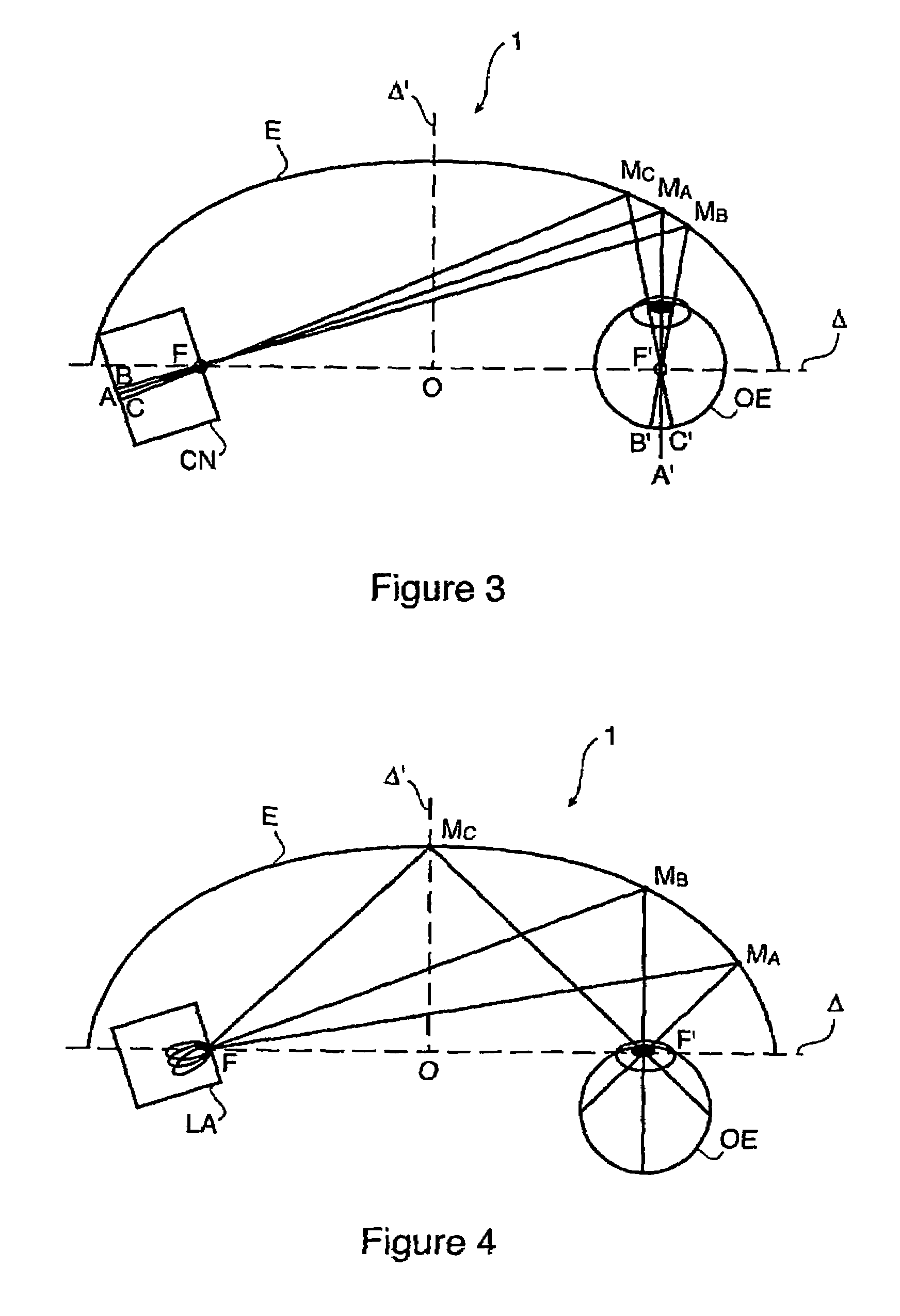
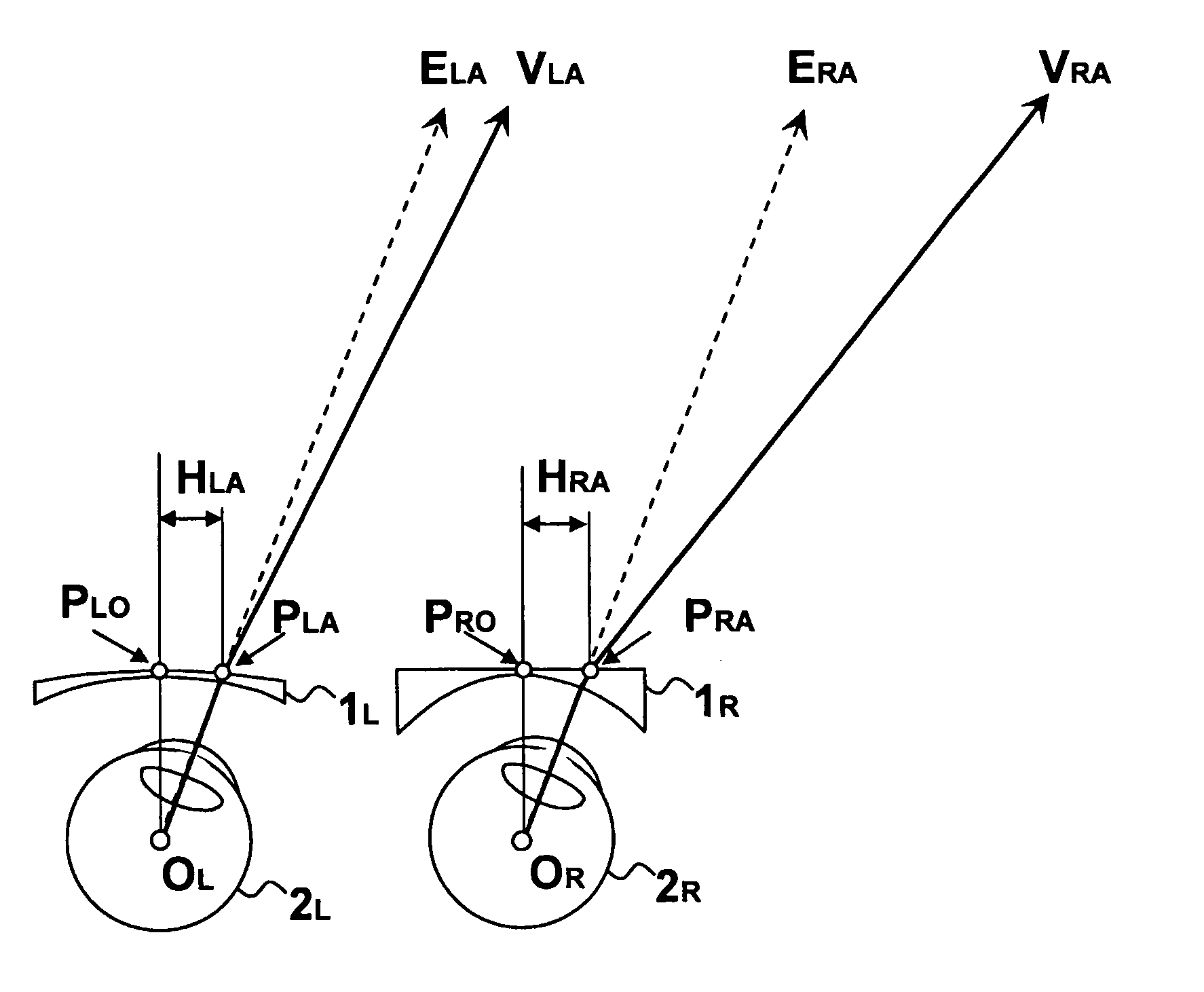
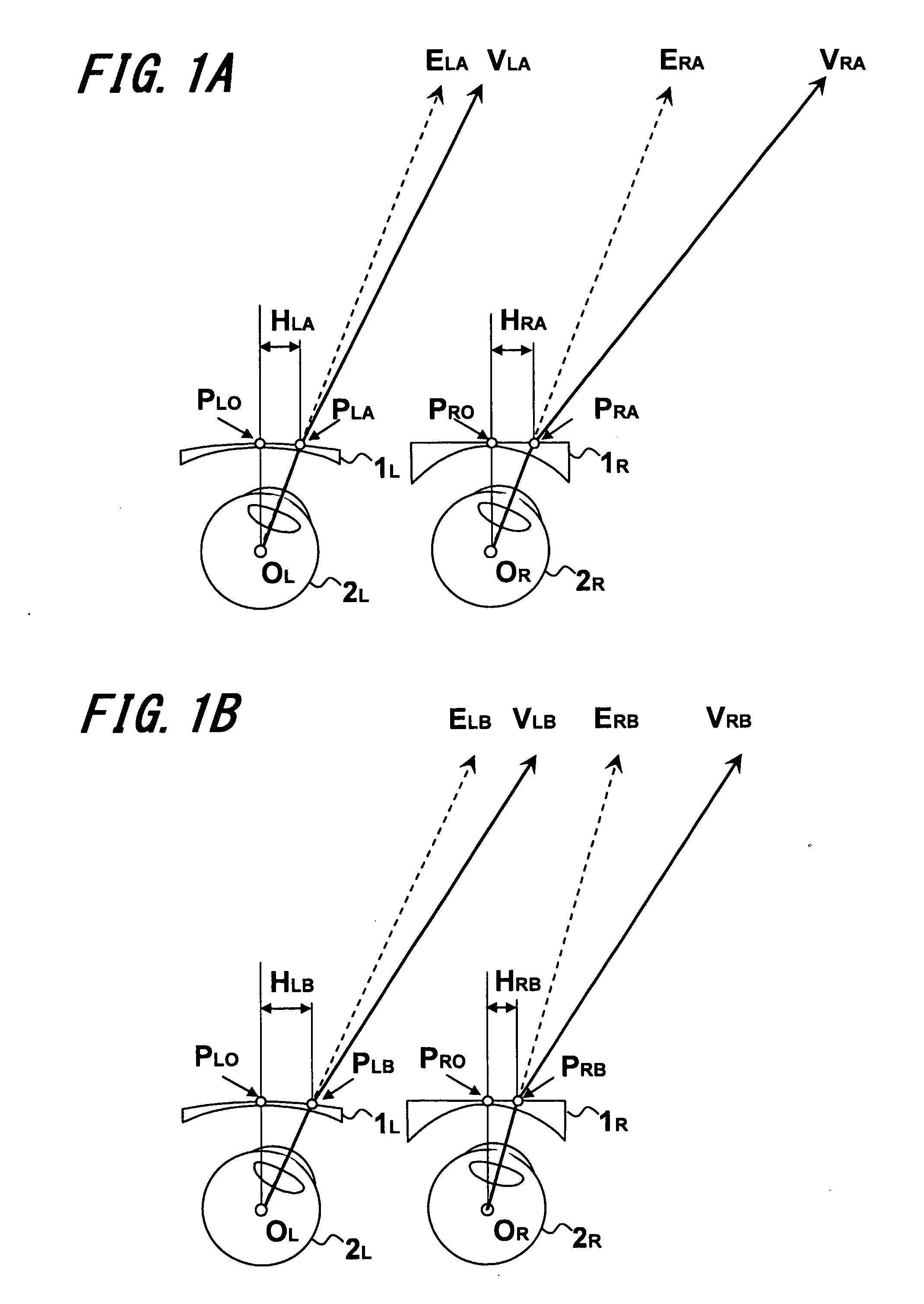
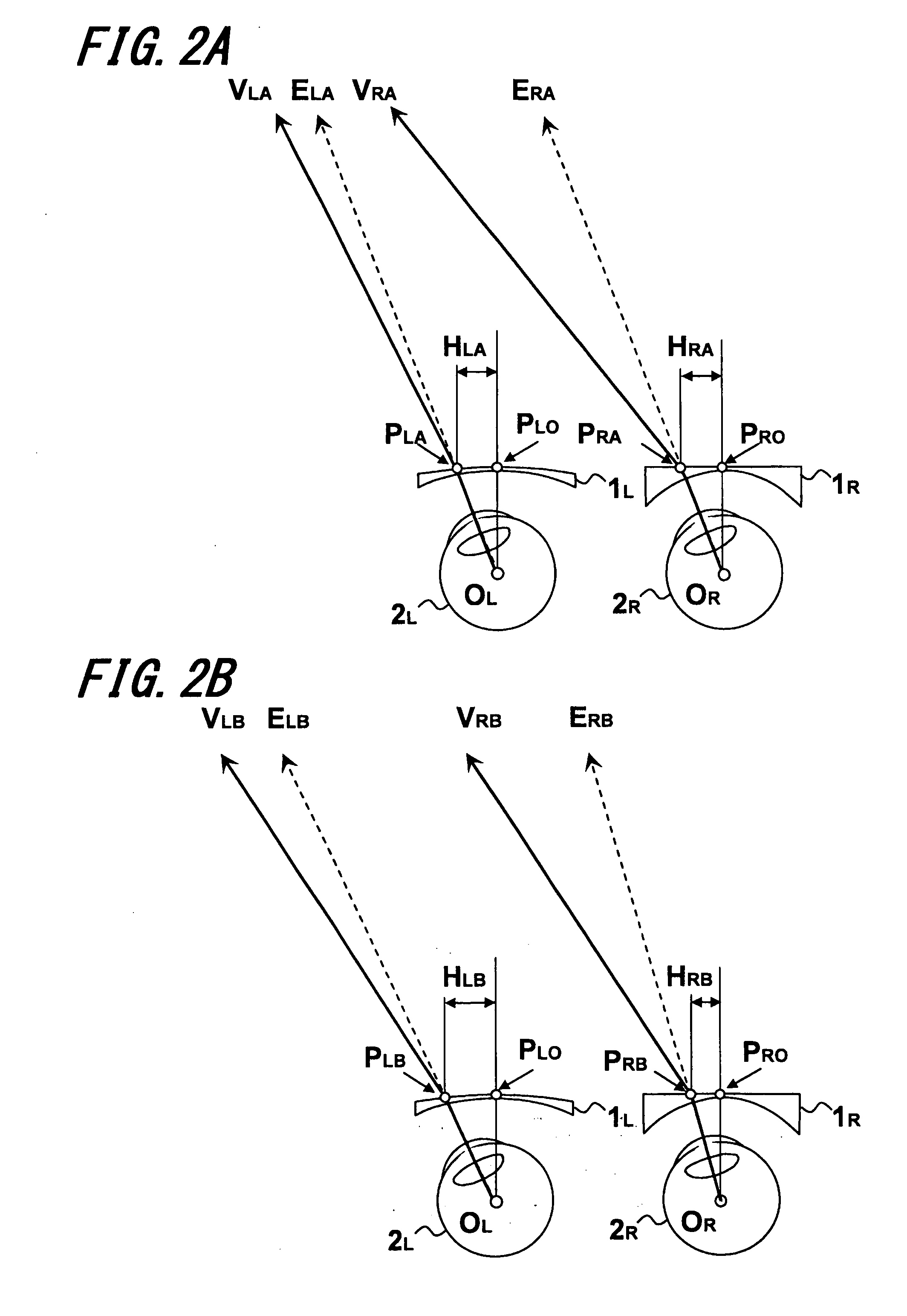
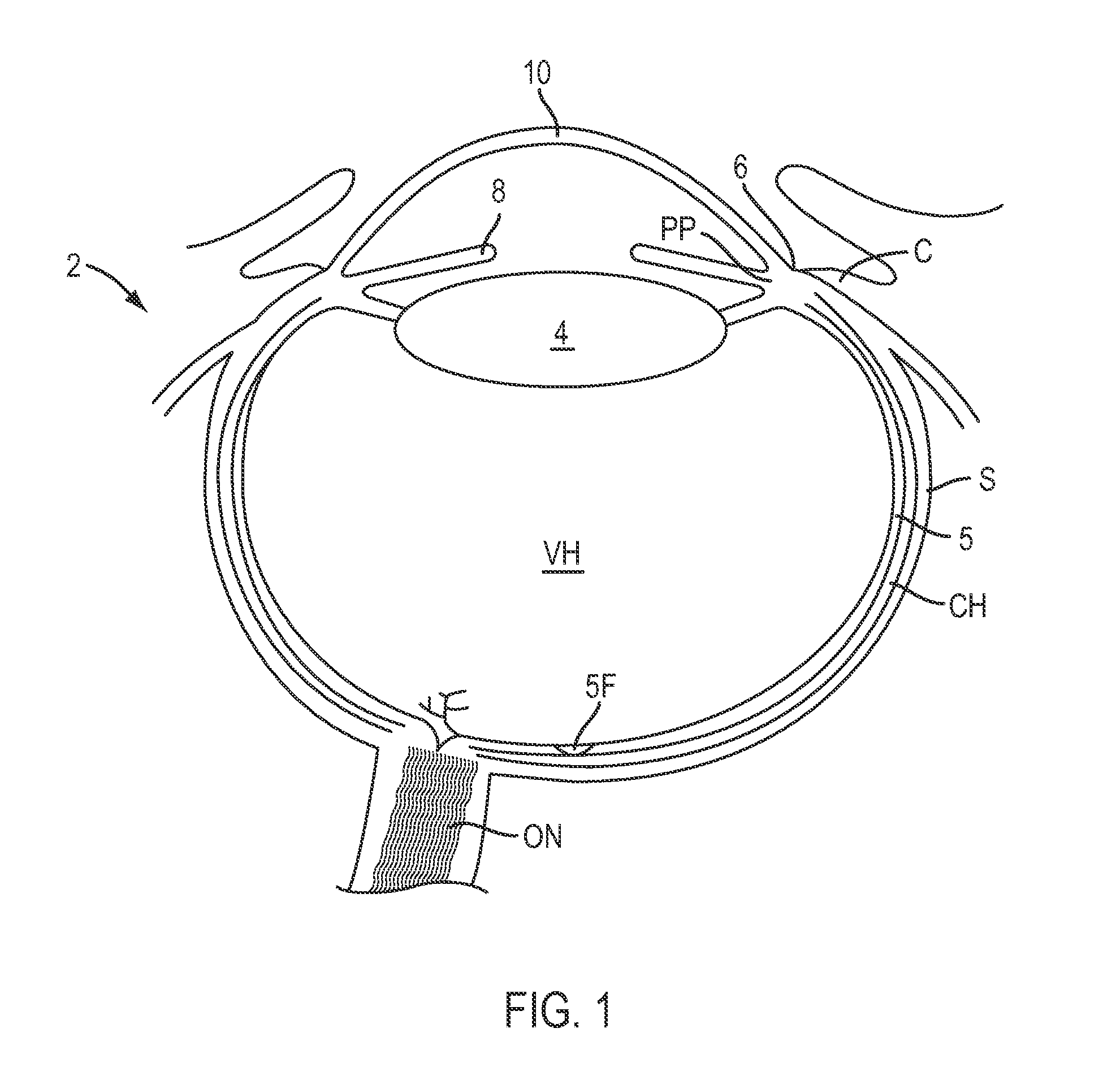
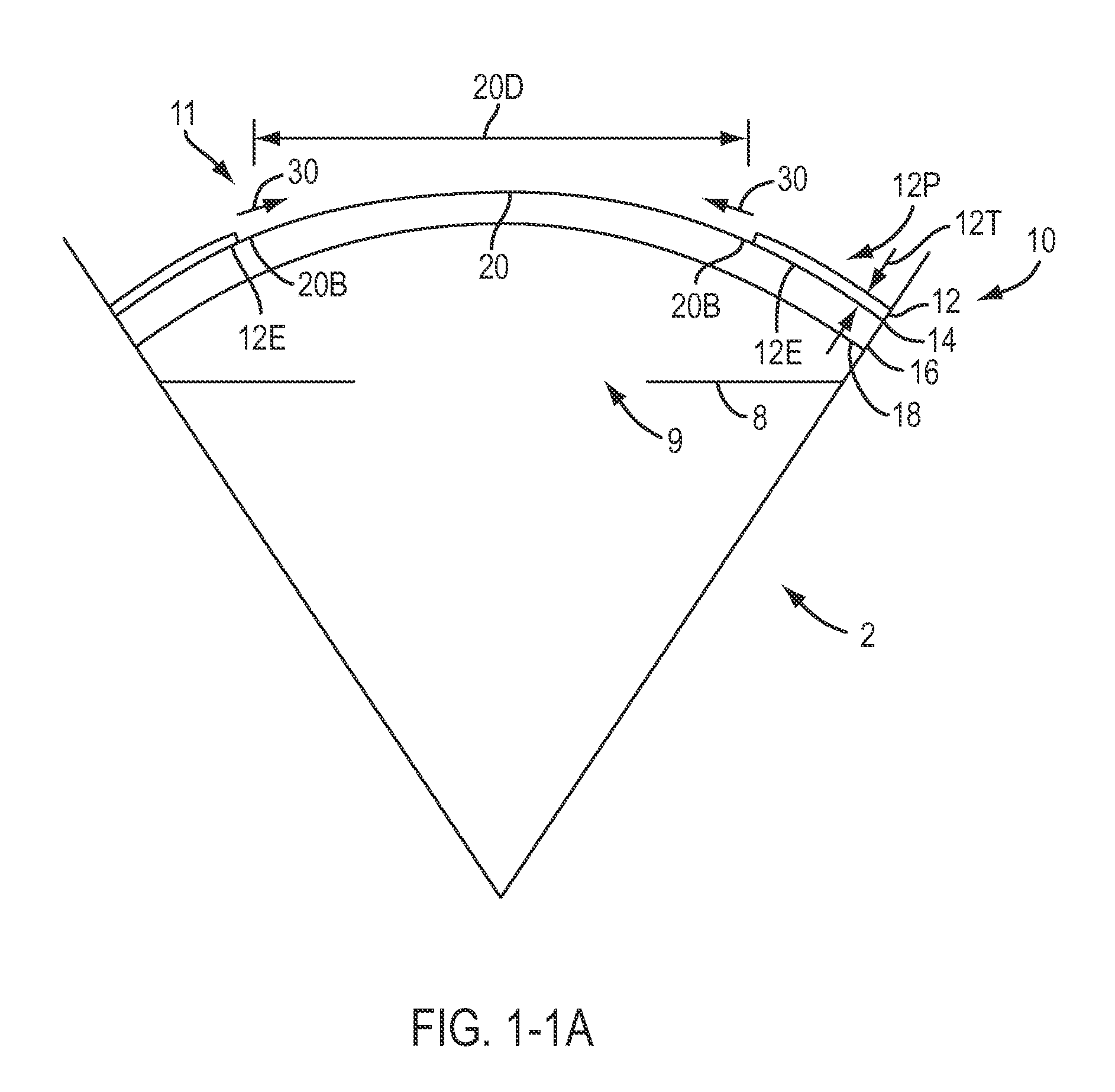
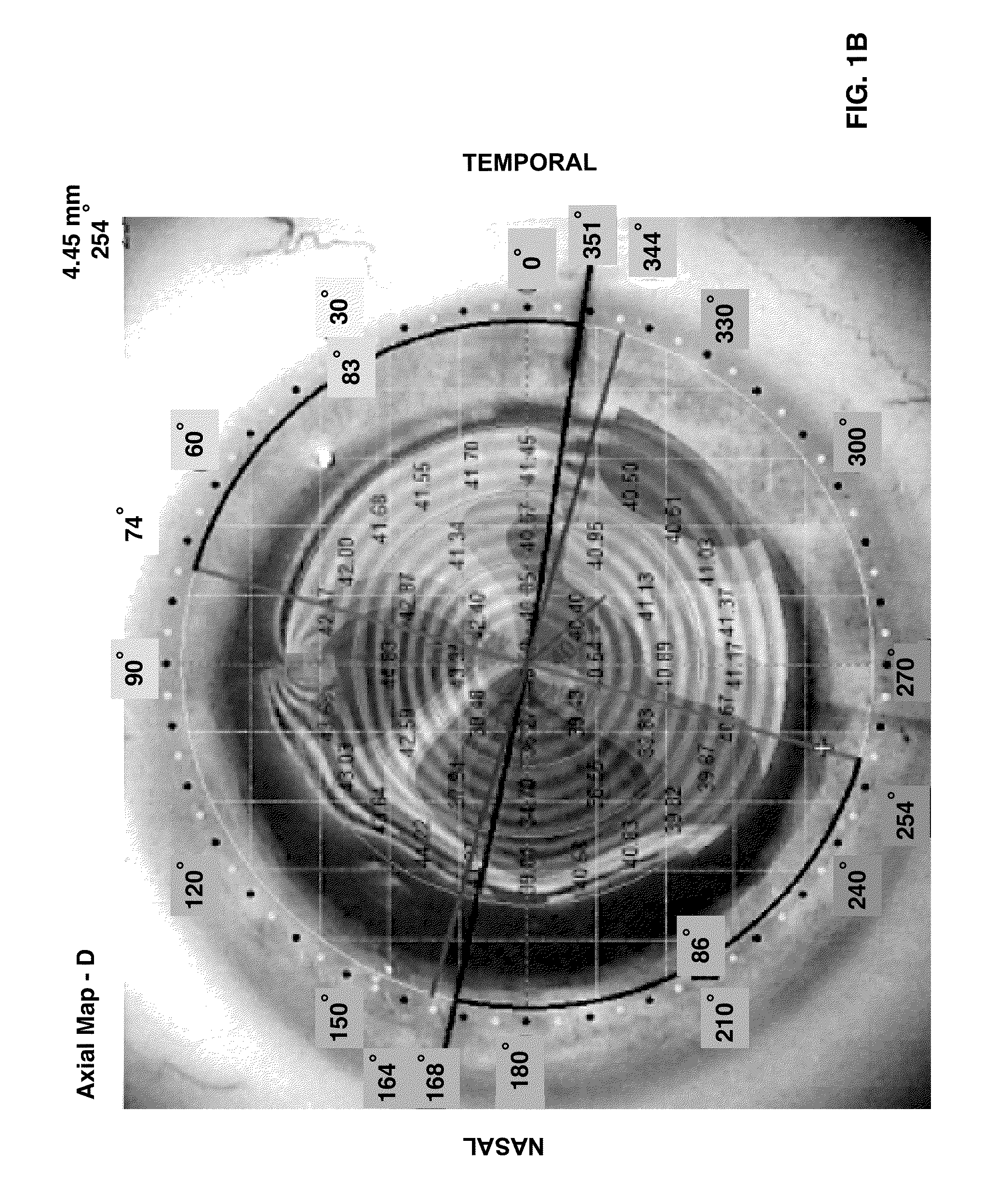
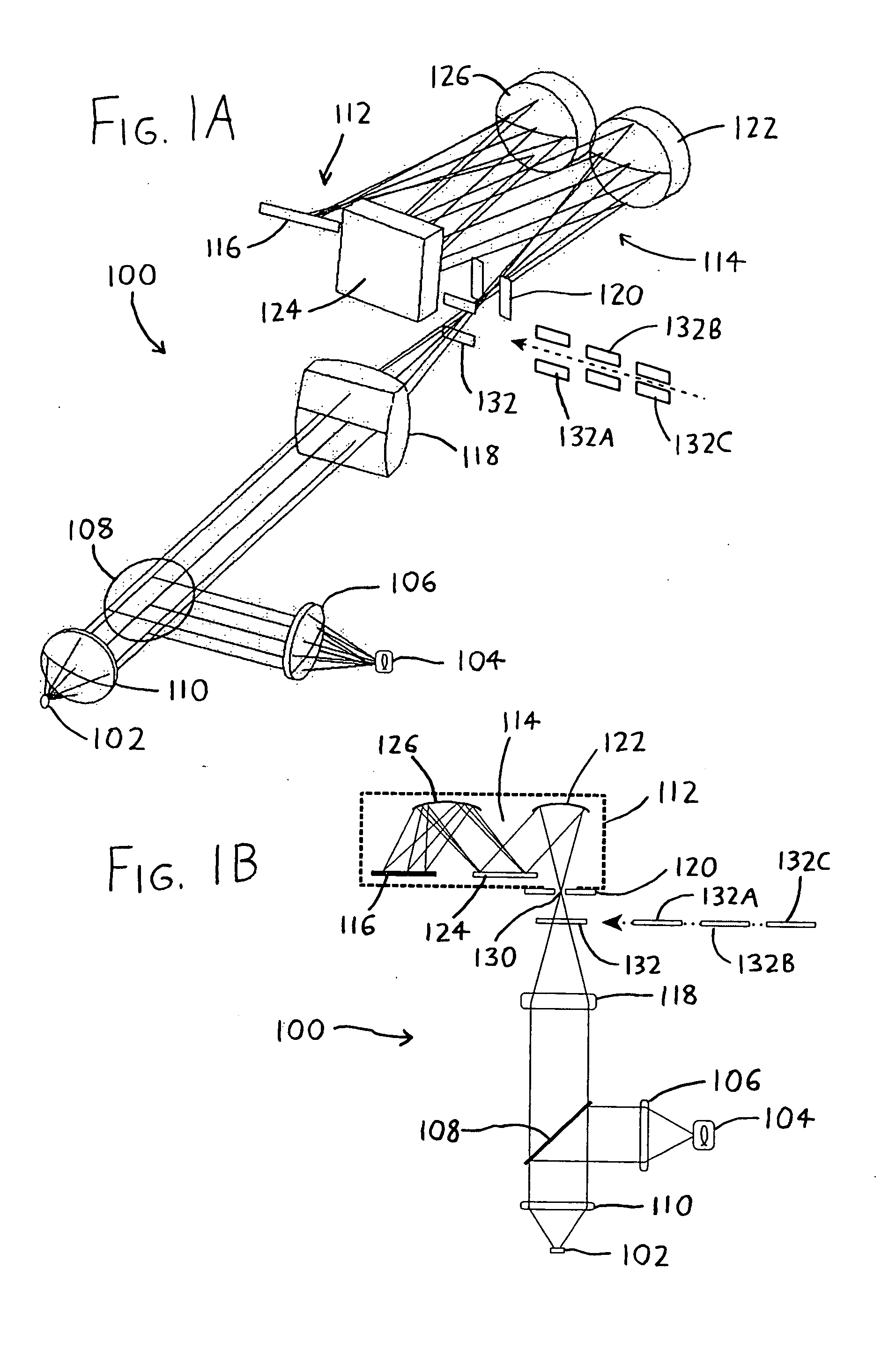
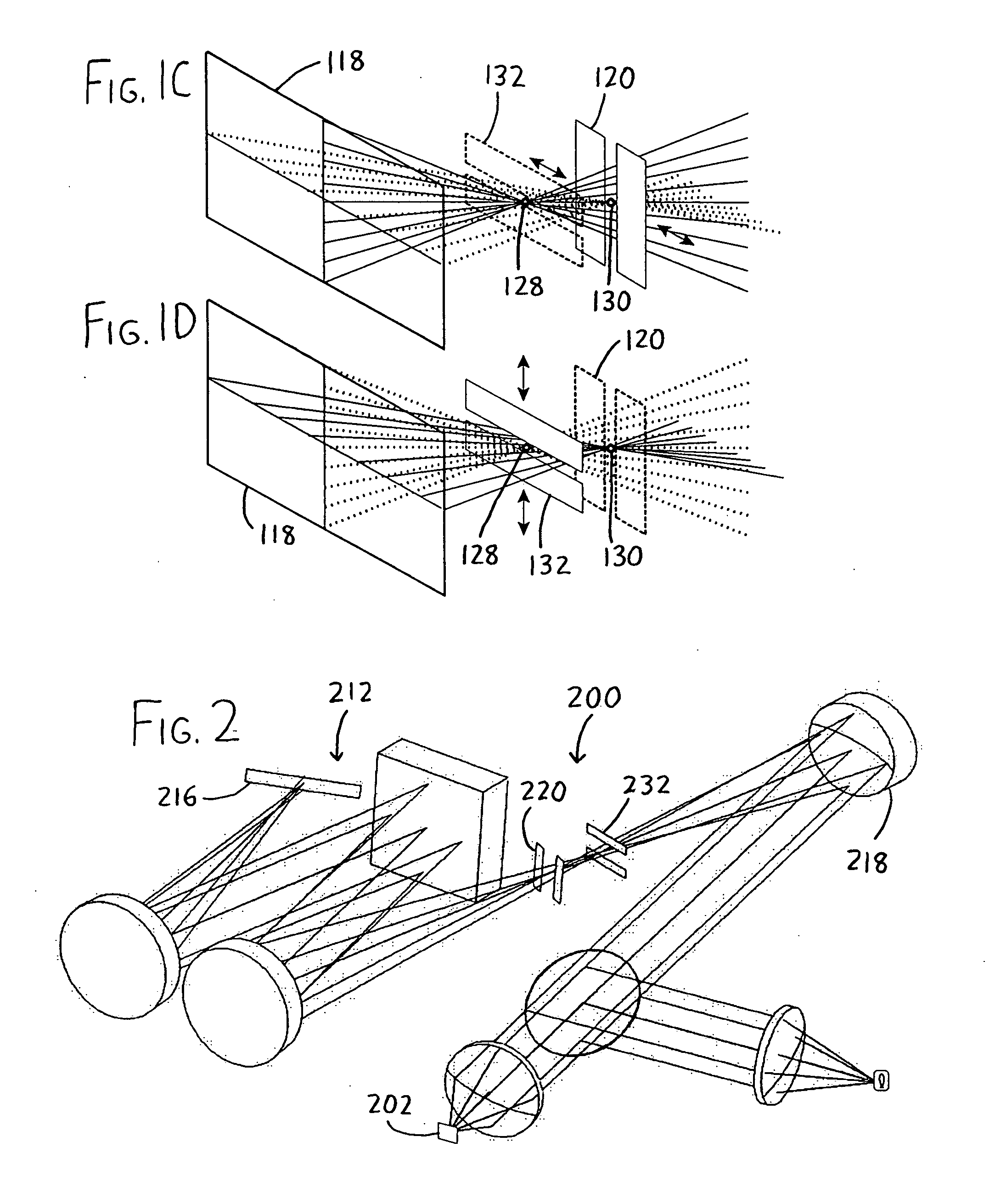
Method and device for generating retinal images using the stigmatism of the two foci of a substantially elliptical sight
InactiveUS7637617B2Reduce the overall diameterMirrorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceStigmatism
A method for generating retinal images using the stigmatism of the two foci (F, F′) of a substantially elliptical sight (E) with a semi-reflective surface, wherein a so-called object focus consisting of the diaphragm of a pinhole disc forming the convergence point of an image generated by a light-emitting display or a collimated light source is positioned adjacent to the first focus (F) of the substantially elliptical sight (E), a so-called image focus consisting of the pupil or the centre of the user's eye (OE) is positioned adjacent to the second focus (F′) of said substantially elliptical sight (E), and the image generated by said light-emitting display or said collimated light source and reflected by the semi-reflective surface of the substantially elliptical sight (E) is projected adjacent to the retina of the user's eye.
Owner:LASTER SA
Pair of progressive power lens and method for designing same
ActiveUS20100271590A1Reduce and eliminate inconvenienceAvoid visionOptical partsUses eyeglassesMultifocal lenses
An object is to reduce the inconvenience given to the binocular vision function when wearing and using spectacles making use of a pair of progressive power lenses having different distance dioptric power for right and left. For this reason, the present invention associates, in a pair of progressive power lenses corresponding to the right and left eyes, an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of one of the progressive power lenses with an average dioptric power distribution and an astigmatism distribution determined from prescribed dioptric power and a wear state of the other progressive power lens, and thereby average dioptric power distributions and astigmatism distributions of the respective progressive power lenses are changed.6
Owner:HOYA CORP
Contact lenses for refractive correction
Ophthalmic lenses for correcting refractive error of an eye are disclosed. Ophthalmic lenses include a deformable inner portion and a deformable peripheral portion. When disposed over the optical region of an eye, the inner portion is configured so that engagement of the posterior surface against the eye deforms the posterior surface so that the posterior surface has a shape diverging form the refractive shape of the epithelium when viewing with the eye through the ophthalmic lens. The rigidity of the inner portion is greater than the rigidity of the peripheral portion and the ophthalmic lenses are configured to allow movement relative to the eye upon blinking of the eye and to be substantially centered on the optical region of the cornea following the blinking of the eye. Methods of correcting refractive errors of an eye such as astigmatism or spherical aberration using the ophthalmic lenses are also disclosed.
Owner:JOURNEY1 INC
Tools and methods for the surgical placement of intraocular implants
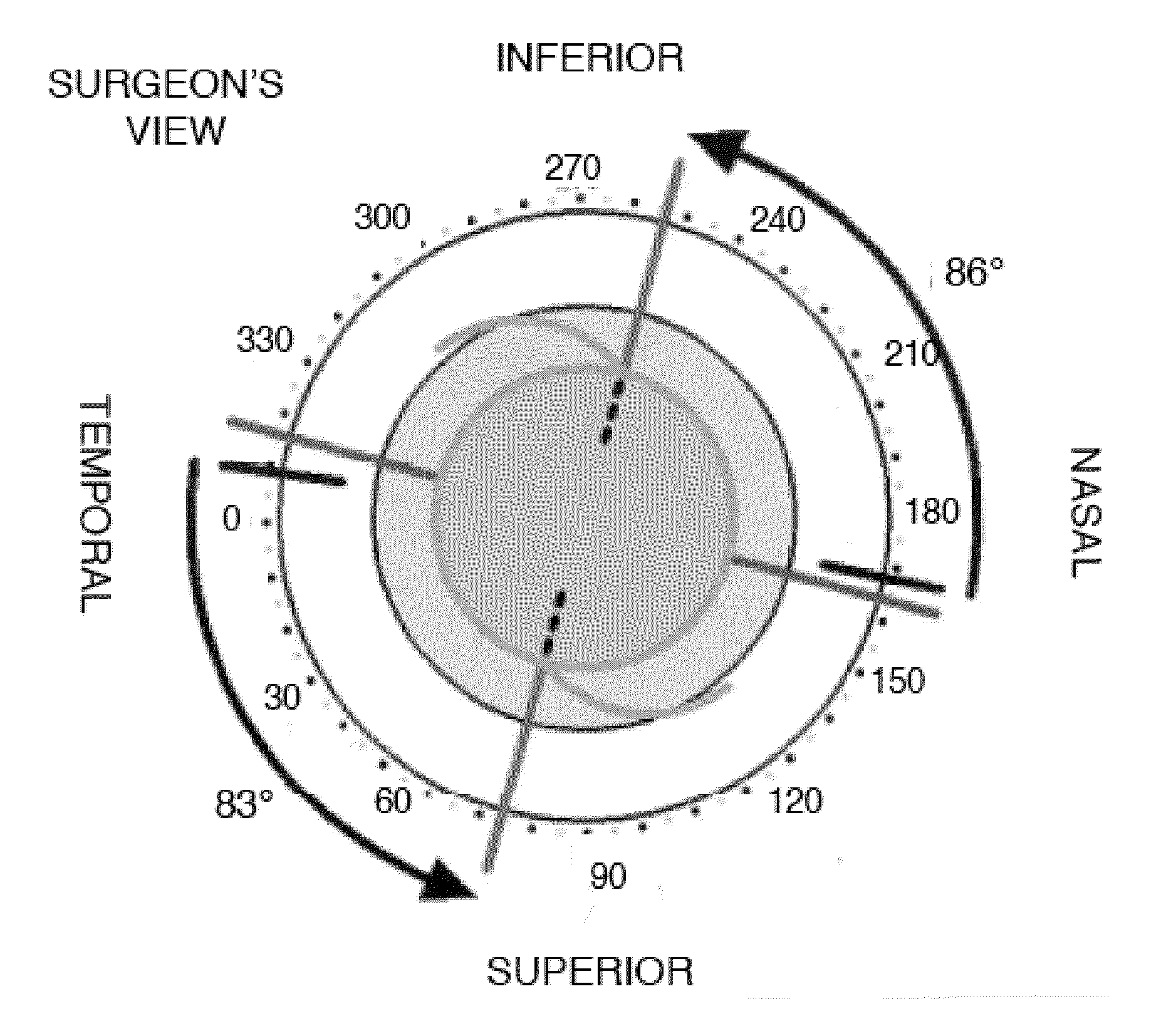
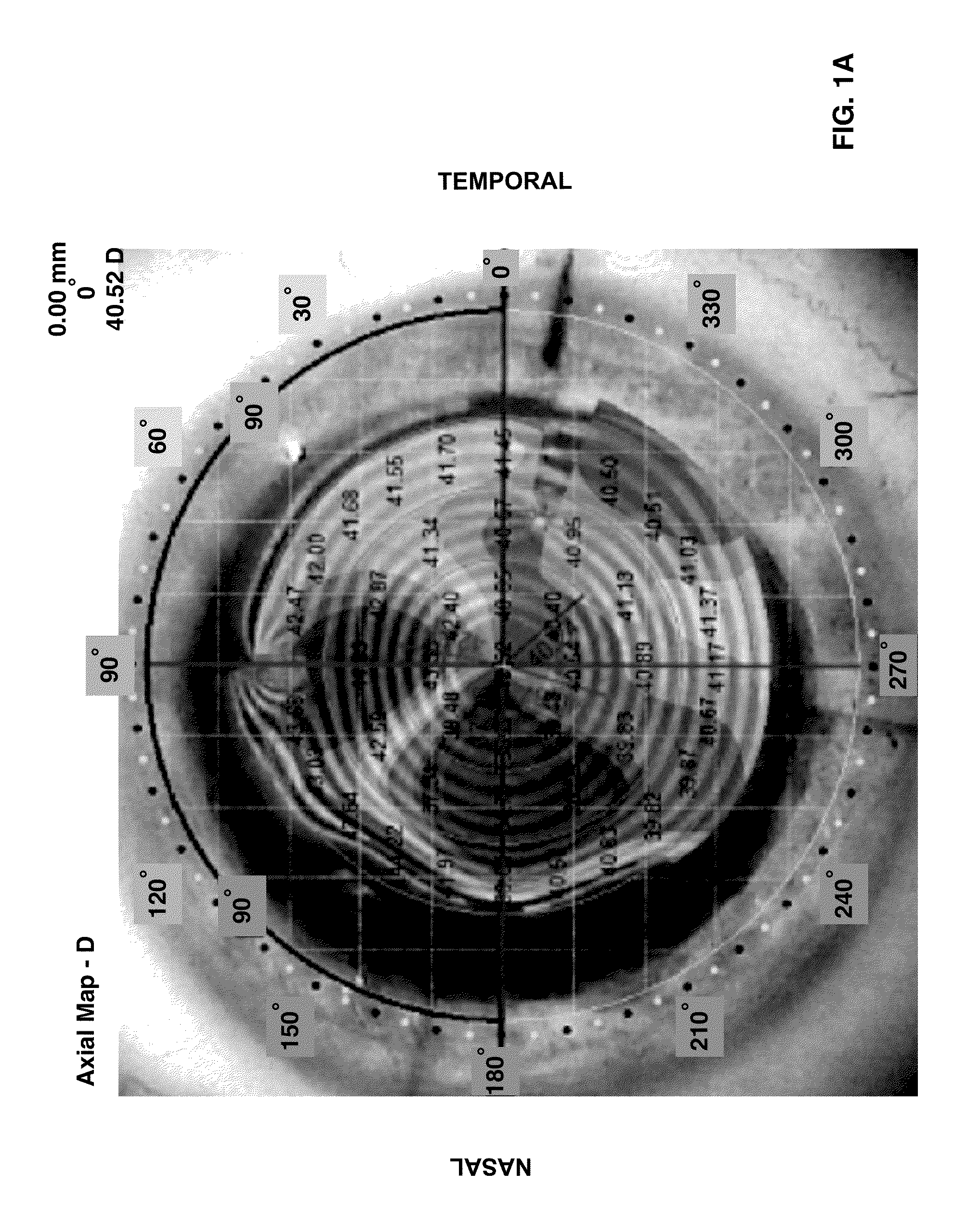
InactiveUS20130018276A1Optimal astigmatic correctionMinimize and eliminate post-operative residual astigmatismDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVisual acuityCataract surgery
Provided herein is a measurement tool for implantable non-spherical asymmetric optics comprising a viewable, rotatable angular caliper superimposable over an image of an eye. Also provided are methods for optimally placing non-spherical asymmetric optics in an eye of a patient and for correcting post-operative astigmatism in a patient having cataract surgery. The measurement tool is useful to plan the optimal correct surgical placement of a non-spherical asymmetric optic, e.g., a toric intraocular implant or a toric intraocular contact lens, in the eye. By superimposing the measurement tool over a corneal topographic image, an optimal positioning of the non-spherical asymmetric optic can be effected in an optical zone of interest. Correct placement or re-placement at least minimizes astigmatism in post-operative vision. Also provided are computer program products and computer readable media comprising modules and methods for data entry, lens selection and surgical planning utilized to practice the methods provided herein.
Owner:ZALDIVAR ROBERTO +2
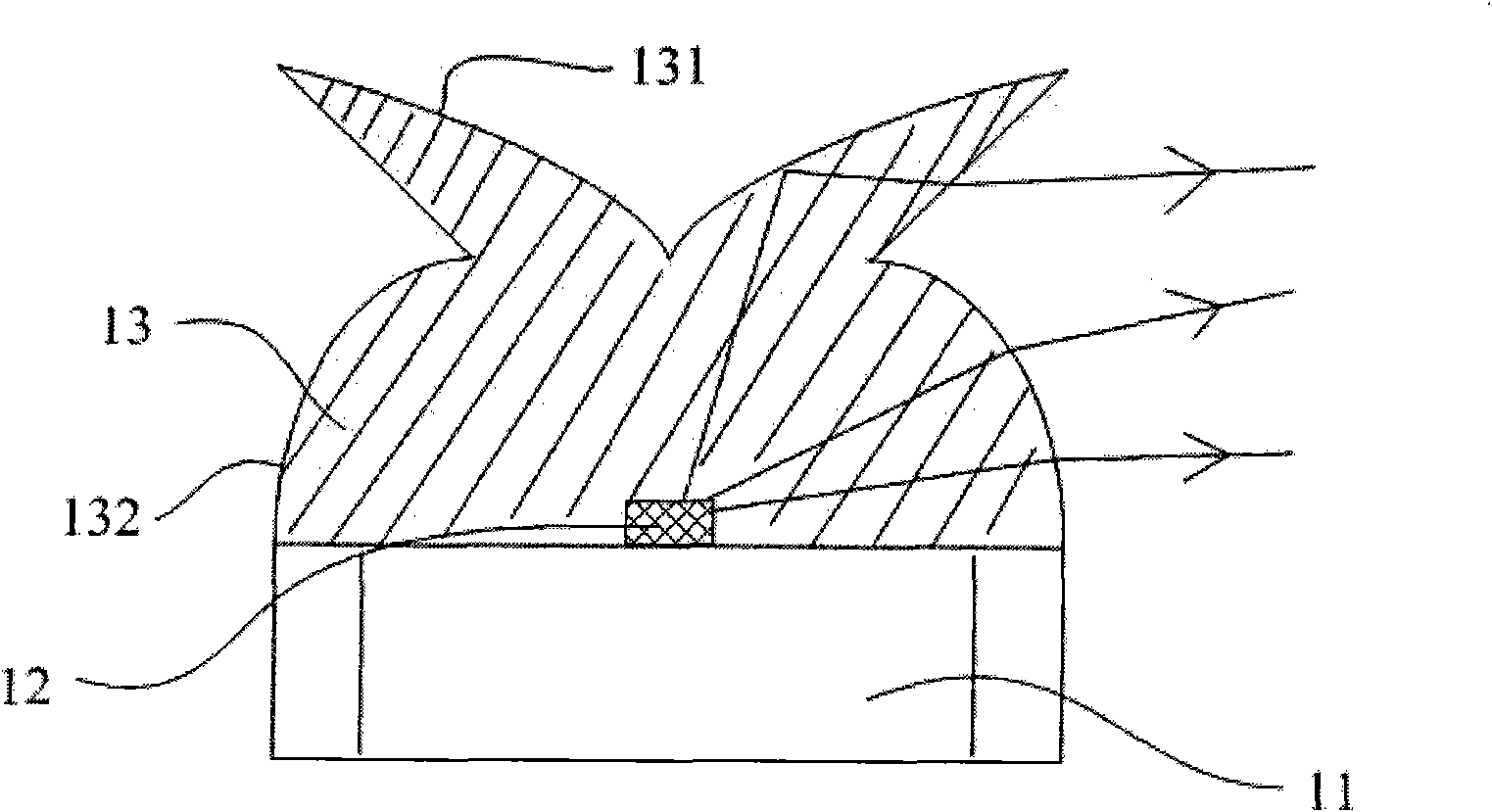
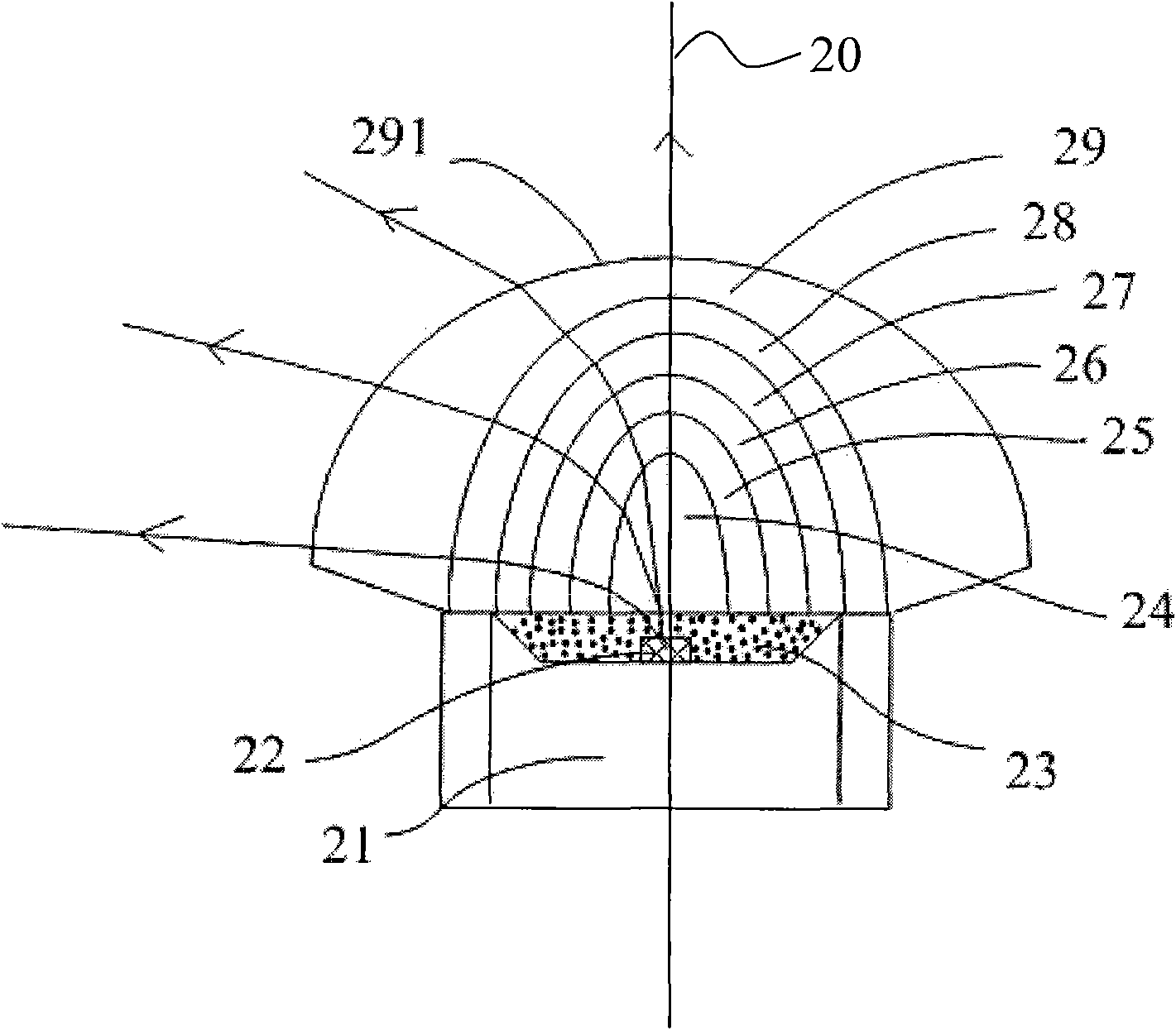
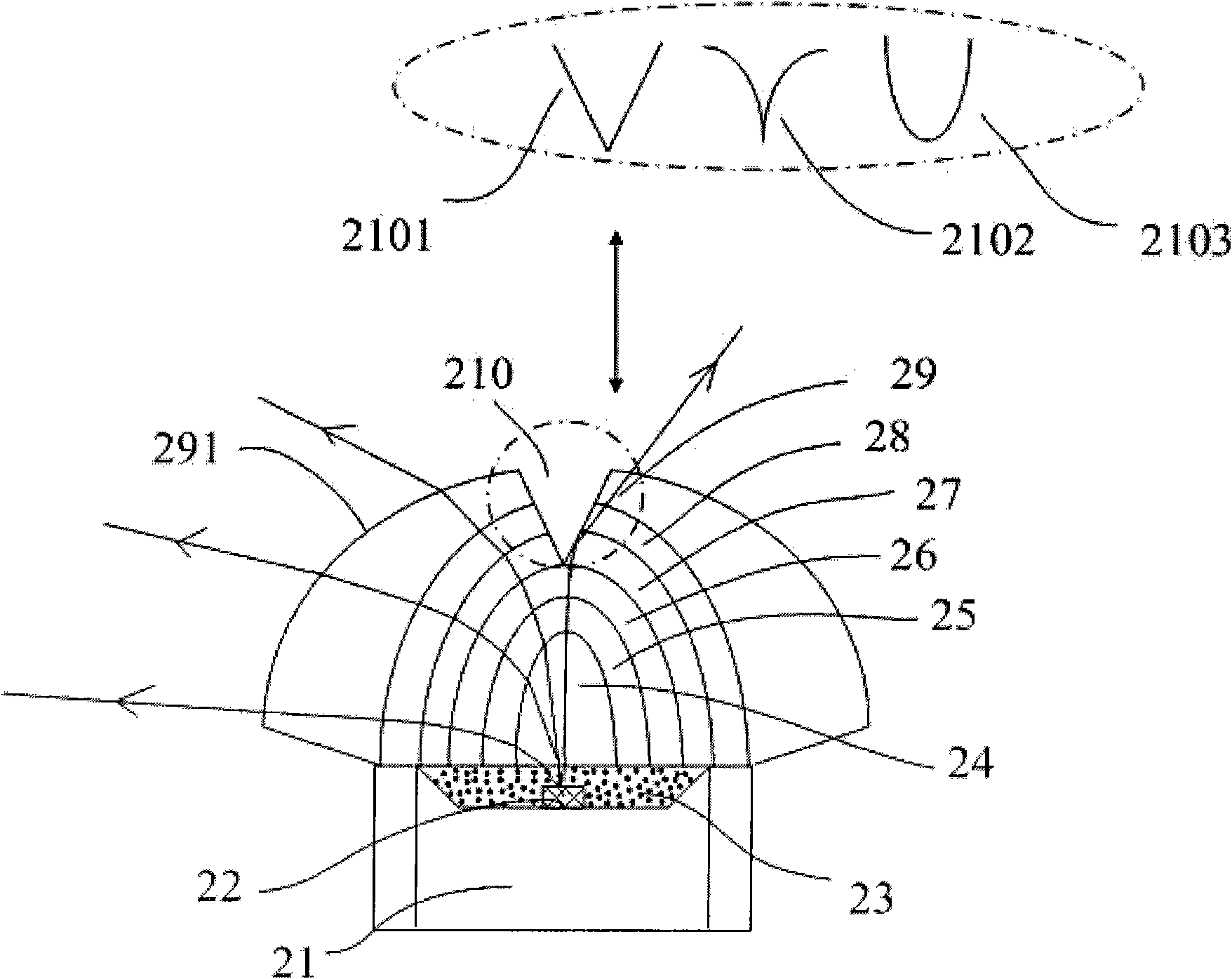
LED light source with wide-angle lens
InactiveCN101556023AImprove refraction effectImprove light utilizationPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor devices for light sourcesRefractive indexStigmatism
The invention relates to an LED light source with a wide-angle lens, comprises a base, an LED luminescence chip and a lens; the LED luminescence chip and the lens have same central axis; wherein the lens is made of a plurality of layers of mediums which have same central axis; and the index of refraction of the plurality of layers of mediums increases sequentially and outward along the central axis. The LED light source with a wide-angle lens has a plurality of layers of mediums with the gradually changing index of refraction, effectively widens the angle of diffused light, reduces the distance of mixed light and realizes thinning of the backlight module.
Owner:上海广电光电子有限公司
Method for designing spectacle lens, spectacle lens, and spectacles
ActiveUS20080024719A1The effect is accurateEye diagnosticsNon-optical partsUses eyeglassesPower added
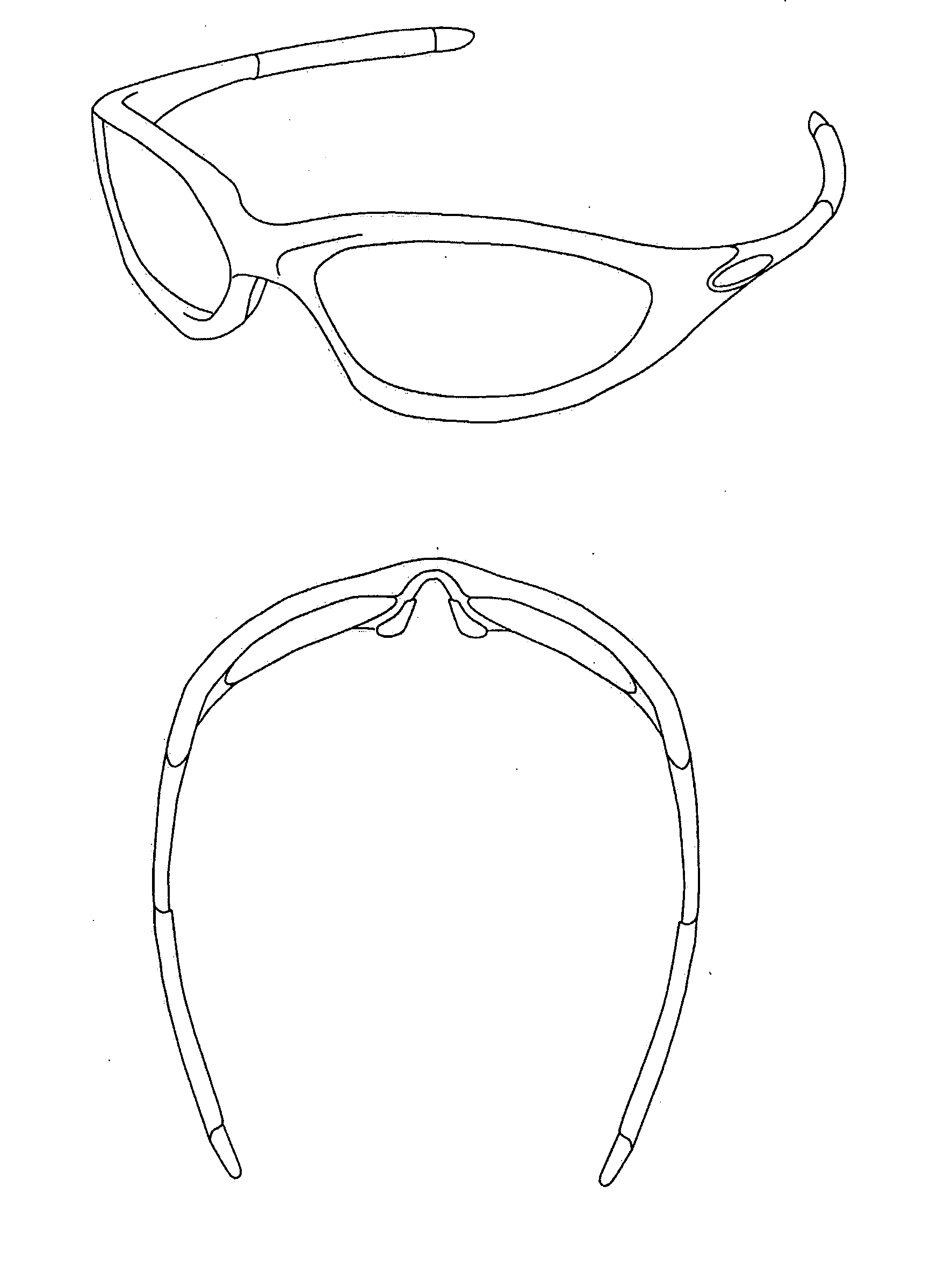
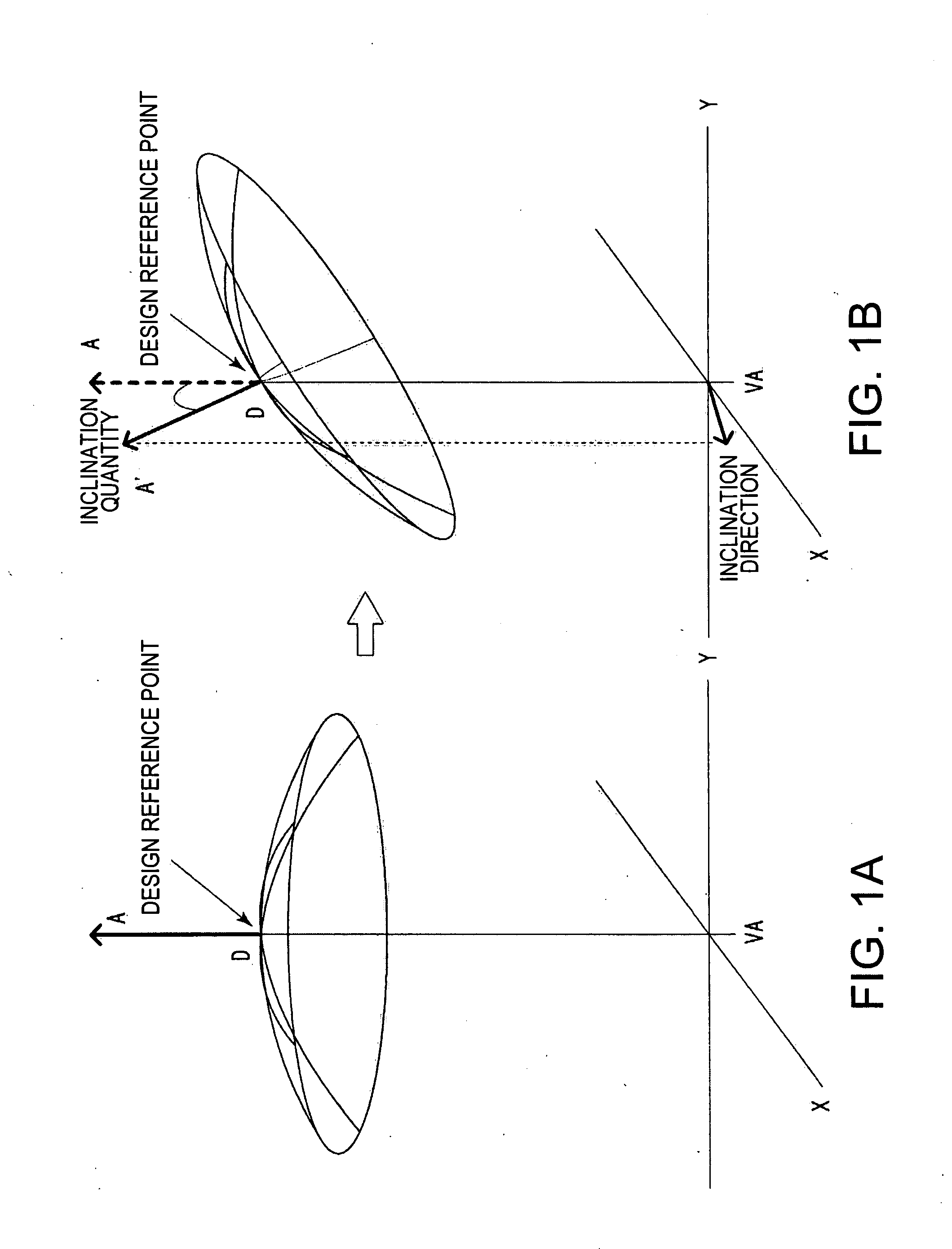
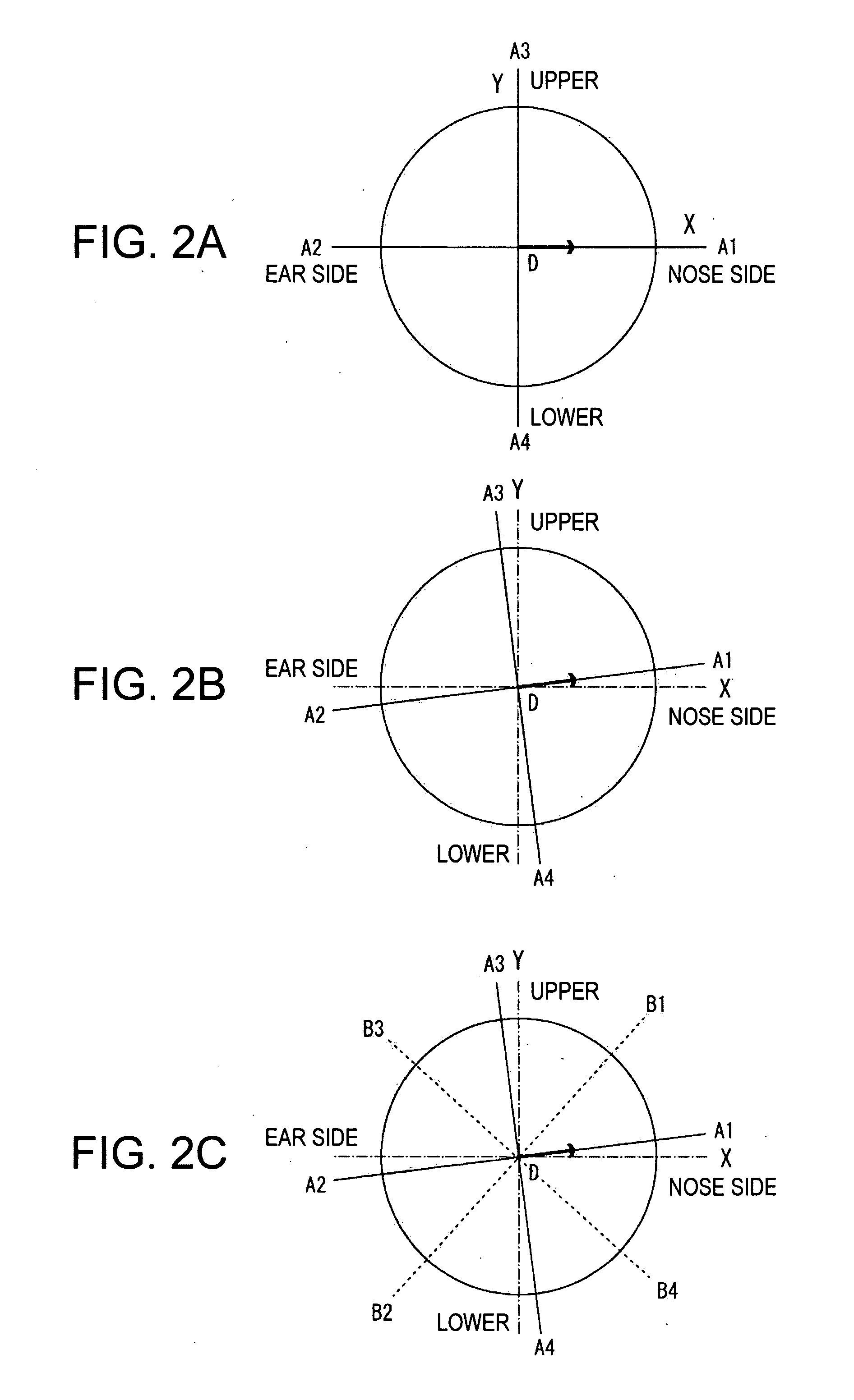
A method of correcting the effects of a bend angle of 200 degrees or larger of spectacle frames, and astigmatism correcting characteristics in such spectacle frames. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes a design method for a spectacle lens mounted in a spectacle frame having a bend angle of 200 degrees or larger including an astigmatic power adding step, on the object side refractive surface or eyeball side refractive surface of the spectacle lens, for canceling astigmatic aberration caused by the bend angle of the spectacle frame, at a design reference point of the spectacle lens, and a step setting prismatic power by tilting the refractive surface, which is on an object side or an eyeball side, of the spectacle lens for canceling prismatic power caused by the bend angle of the spectacle frame, at the design reference point of the spectacle lens.
Owner:HOYA LENS MFG PHILIPPINES
Side loading LED module for motor vehicle rear assembled lamp
InactiveCN101592301AEasy to assembleReduce in quantityPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLight beamStigmatism
The invention discloses a side loading LED module for rear assembled lamp mounted of assembled lamp mounted on the rear part of a motor vehicle. One or more LED are mounted on remote side of a printed circuit board with a circuit that drives the one or more LED. A circuit board and a heat yielding pad are fixed onto a heat radiator by screw thread or rivets, then the heat radiator is mounted on lateral face of an outer housing. The LED emits astigmatism in the outer housing. One surface of the outer housing is multi-faceted parabolic reflector, which receives divergent light from the LED, and reflects the collimated light beam to foreside of the outer housing vertically, and there ejaculated from the lamp through a transparent cover. Each facet on the parabolic reflector makes part of the reflected light beam off set angularly, and reflected light is collimating with angle wider than single collimated light beam.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Side-loaded light emitting diode module for automotive rear combination lamps
A side-loading LED module for a rear combination lamp is disclosed. One or more LEDs are mounted on a distal side of a printed circuit board, which also includes the circuitry that drives the one or more LEDs. The circuit board and a thermal pad are screwed / riveted to a heat sink, then the heat sink is mounted to a lateral face of a housing. The LEDs emit diverging light laterally inside the housing. One face of the housing is a faceted parabolic reflector, which receives the diverging light from the LEDs and reflects a collimated beam longitudinally to the front of the housing, where it passes through a clear cover and exits the lamp. The facets on the parabolic reflector angularly deviate portions of the reflected beam, so that the reflected light is collimated, and is angularly broader than a single collimated beam.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Adaptive optics for compensating for optical aberrations in an imaging process
Owner:HEIDELBERG ENGINEERING GMBH
Lens stray light detection device and lens stray light detection method
InactiveCN102235939AImprove accuracyAccurate analysisTesting optical propertiesOptical axisOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a lens stray light detection device for detecting stray light of a lens. The lens stray light detection device comprises a workbench, a lens bearing seat arranged on the surface of the workbench, a light source bearing seat arranged on the surface of the workbench, a rail formed on the surface of the workbench, a light source arranged at the top of the light source bearing seat, and an image acquisition unit. The lens bearing seat is used for bearing the lens. The light source bearing seat is glidingly connected with the rail. When the light source bearing seat glides along the rail, rays emitted by the light source face the lens all the time. The image acquisition unit receives the rays from the lens to form images. The workbench is provided with a plurality of scale lines for indicating the angles of the rays emitted by the light source relative to the optic axis of the lens. The invention also relates to a lens stray light detection method.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Confocal spectrometer with astigmatic aperturing
A confocal spectrometer provides astigmatic optics which supply a monochromator or spectrograph with the image of a sample, with the astigmatic optics thereby providing separate first and second (tangential and sagittal) focal planes for the image. The monochromator / spectrograph has an entrance slit oriented along one of the focal planes, and this slit defines the spectral resolution of the monochromator / spectrograph and the field of view of the sample in one direction (in one focal plane). A supplemental slit is situated outside the monochromator / spectrograph adjacent the entrance slit, with the supplemental slit being oriented along the other focal plane. The supplemental slit therefore defines the field of view of the sample in a perpendicular direction (in the other focal plane). By varying the width of the supplemental and / or entrance slits, one may easily achieve the desired field of view.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRONICS SCI INSTR LLC
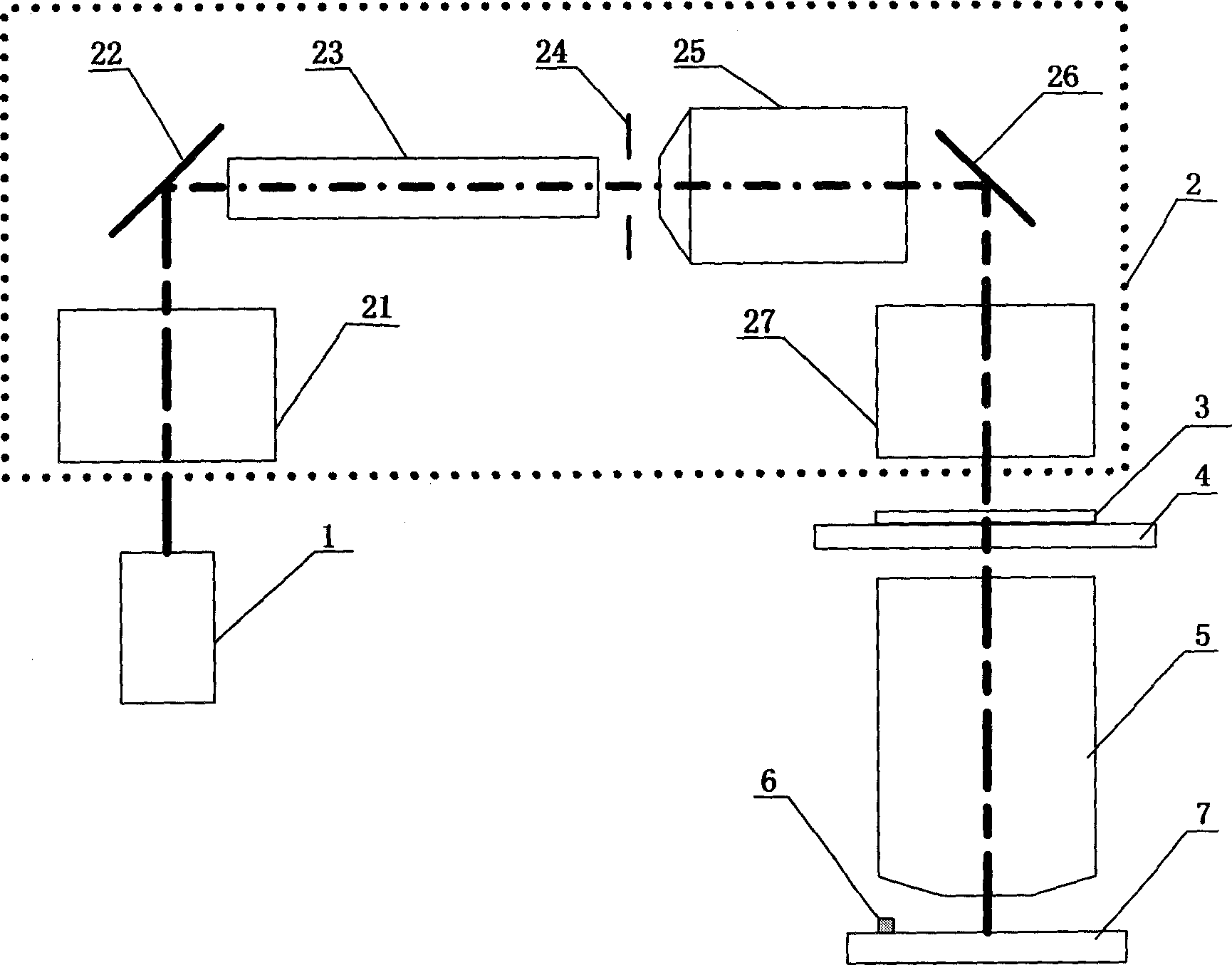
In-situ detection method for stray light in step scan projection mask aligner
ActiveCN1655064AQuick measurementImprove measurement efficiencyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPoint lightMeasurement point
This invention relates to an in-situ test method for stray light in a step scan projection aligner, which limits a spot on an object face by accurately positioning four slit blades and images on a working platform by a projecting object lens. An energy sensor tests that the light intensity at the spot photo center is Lo and finishes testing to MXN spots then to open the slit, the light intensity of above mentioned point light intensity is measured to be l, the stray light coefficient is computed by formula (1, -10) / 10, if the stray light exceeds the required target of the exposure system, it analyses source of stray light. A special mask and two slit blades limit a spot imaged by projection object lens, an energy sensor tests light intensity distribution in the image spot to analyze if the stray light is from the illumination system or the project object lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Achromatic flat top beam shaping
ActiveUS20100208356A1Reduce deviation from uniformityUniform strengthLensRefractorsShaped beamLight beam
There is provided an optical system and method for shaping a polychromatic light into a substantially uniform profile beam along a first axis. A polychromatic divergent light with having multiple wavelength components is provided with a dispersion of divergence. A collimation optic collimates the polychromatic divergent light. A shaping lens shapes the collimated beam into a shaped beam with a nearly uniform profile along the first axis, the dispersion of divergence causing a deviation from uniformity of the nearly uniform profile. A focusing optic focuses the shaped beam. A combination of the collimation and focusing optics shows a chromatic focal shift that compensates for said dispersion of divergence, so as to reduce the deviation from uniformity to obtain a profile with a substantially uniform intensity along the first axis, for all of said multiple wavelength components.
Owner:COHERENT INC
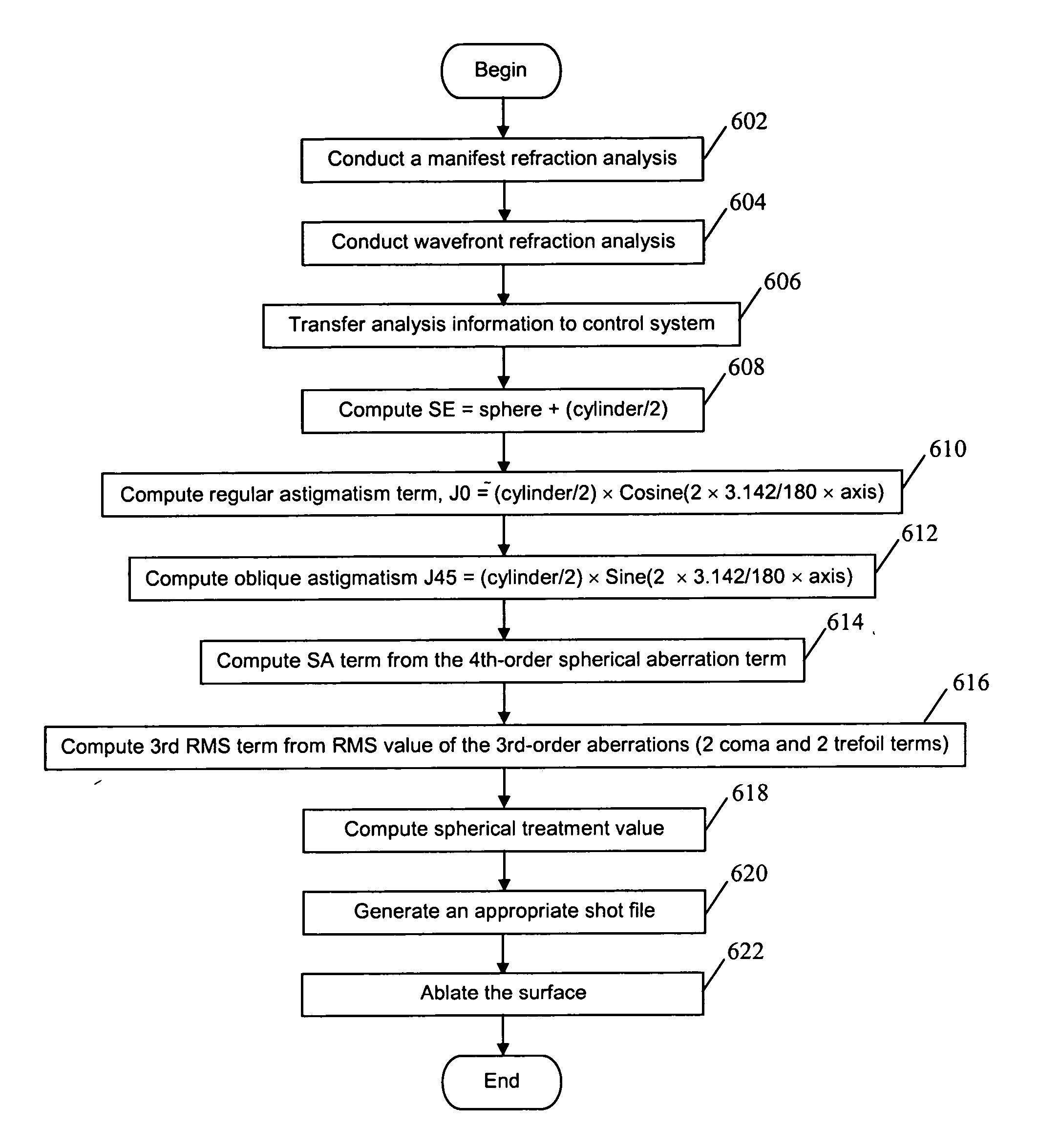
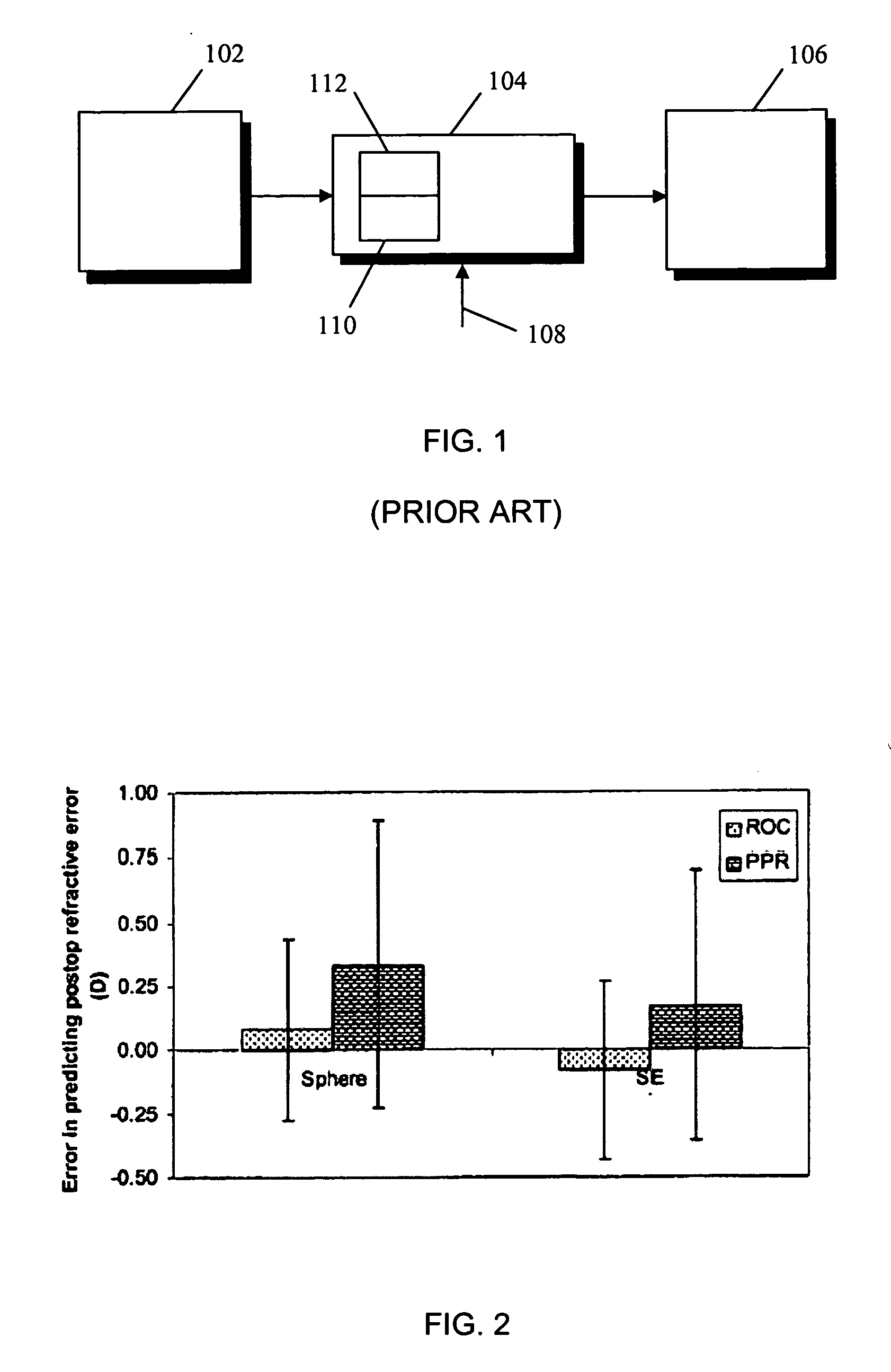
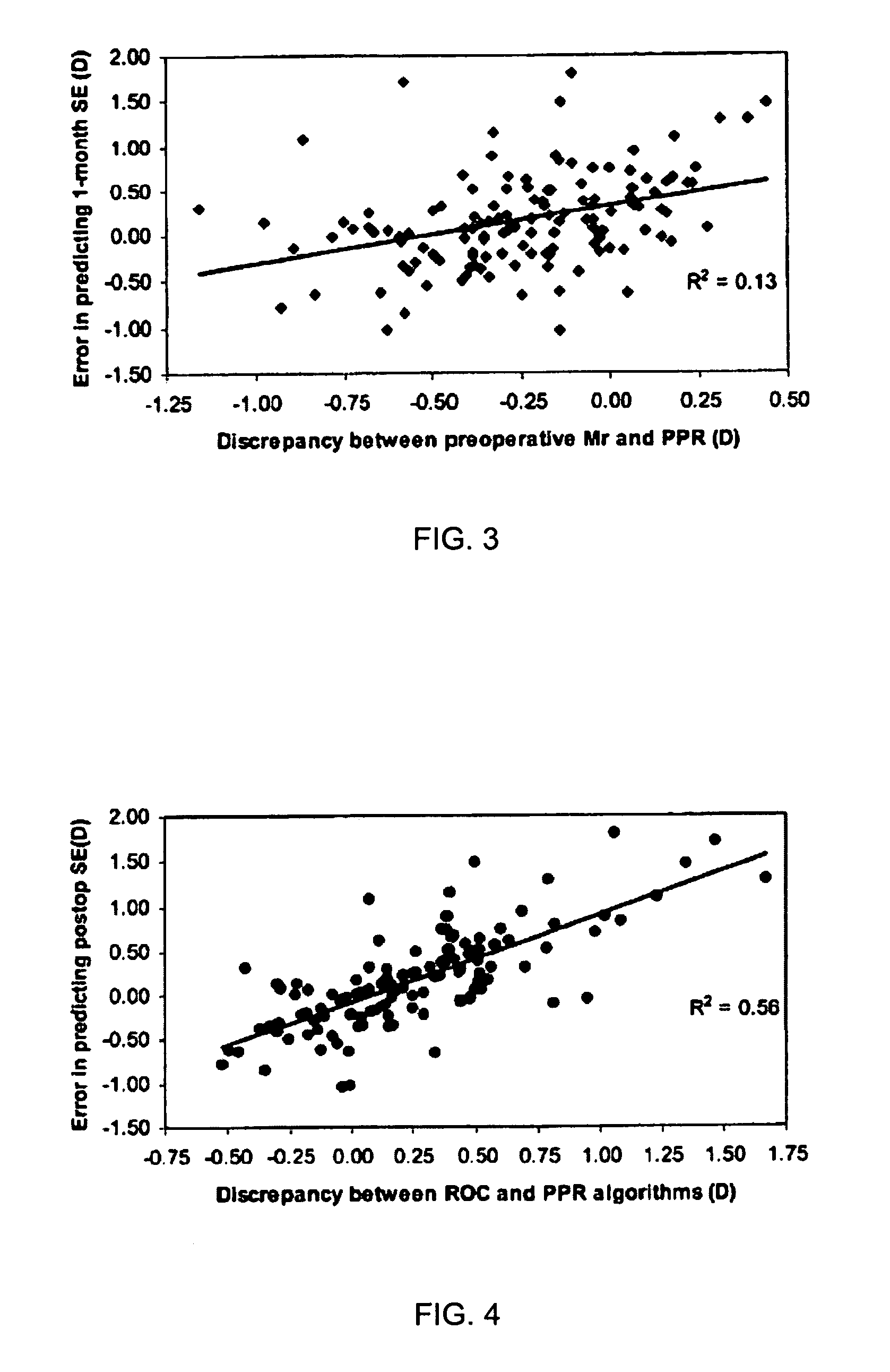
System and method for treating vision refractive errors
ActiveUS20060235369A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove postoperative refractive outcomeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsTherapy visionLuminosity
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method for correcting refractive errors in a living eye using a laser vision correction system that involves first calculating an amount of sphere based on preoperative manifest refraction and higher order aberrations data associated with the eye, and then correcting for the calculated amount of sphere by ablating at least a portion of the eye. The preoperative manifest refraction may include preoperative manifest sphere, preoperative spherical equivalent, regular astigmatism, and oblique astigmatism, and the preoperative higher-order aberrations may include 4th-order spherical and 3rd root mean square. Other factors may also be used to adjust the calculated amount of sphere. A device readable medium for storing the calculation and instructions for operating a laser vision correction system for practicing the method is also disclosed, as is a method of treating refractive errors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com