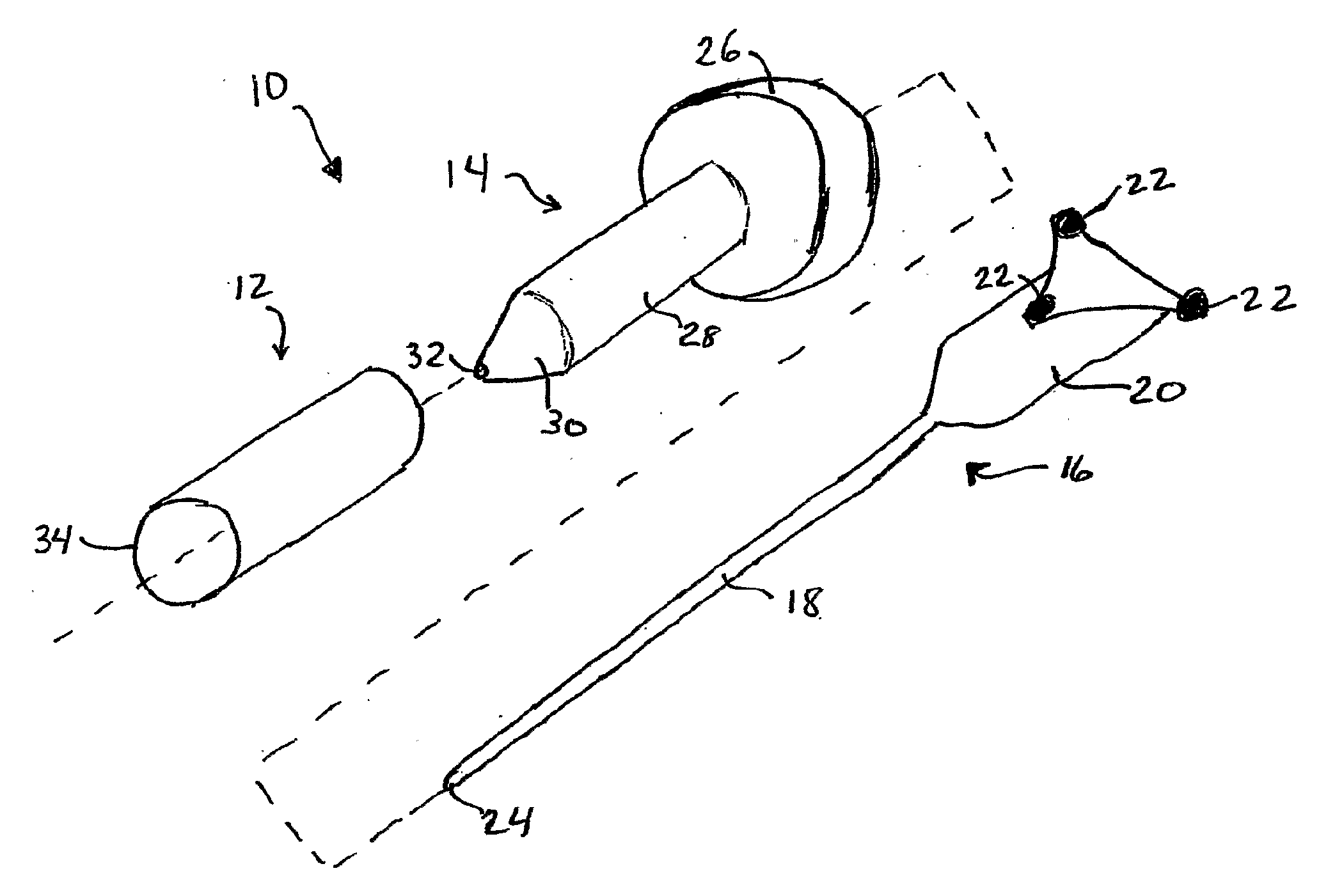
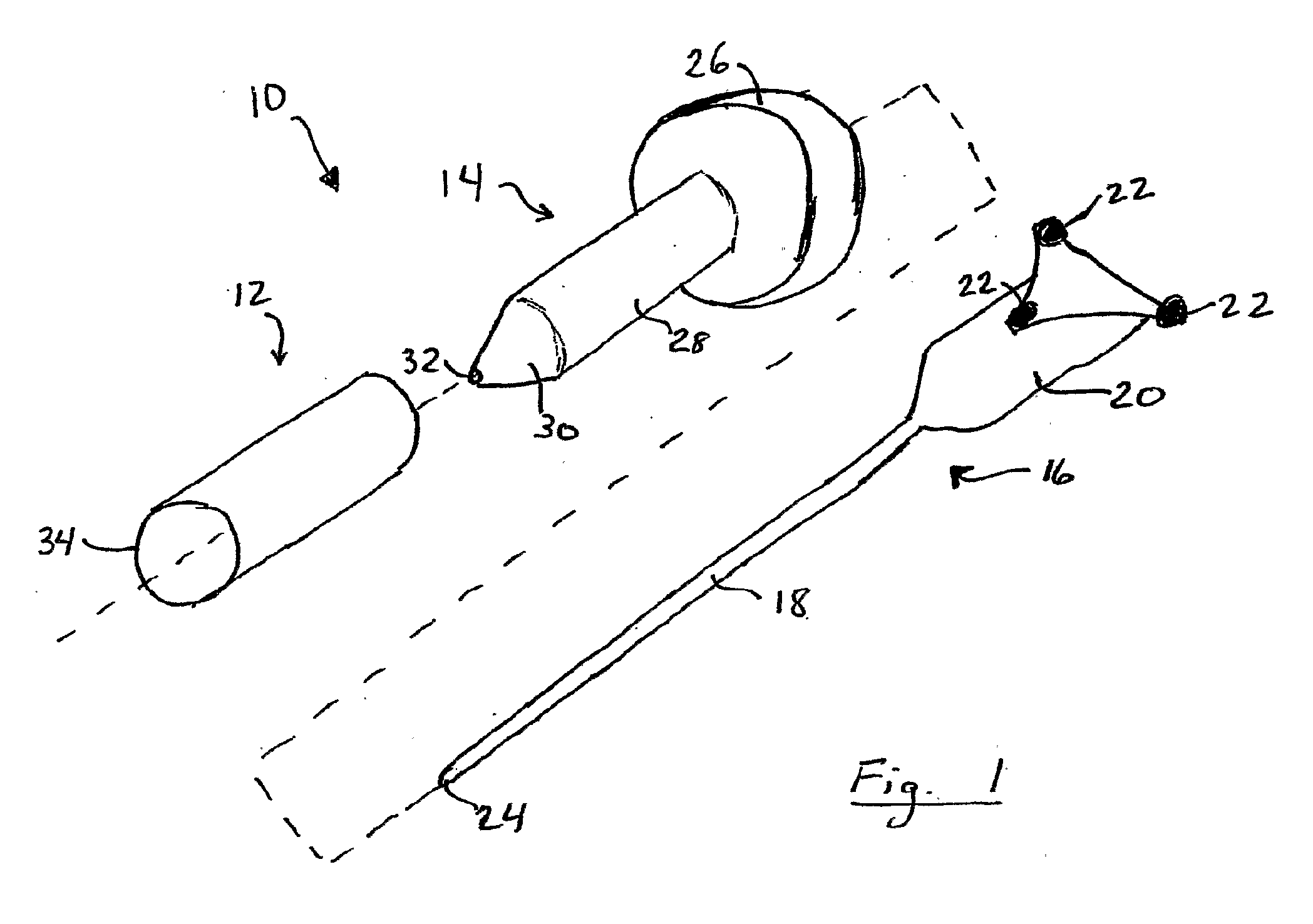
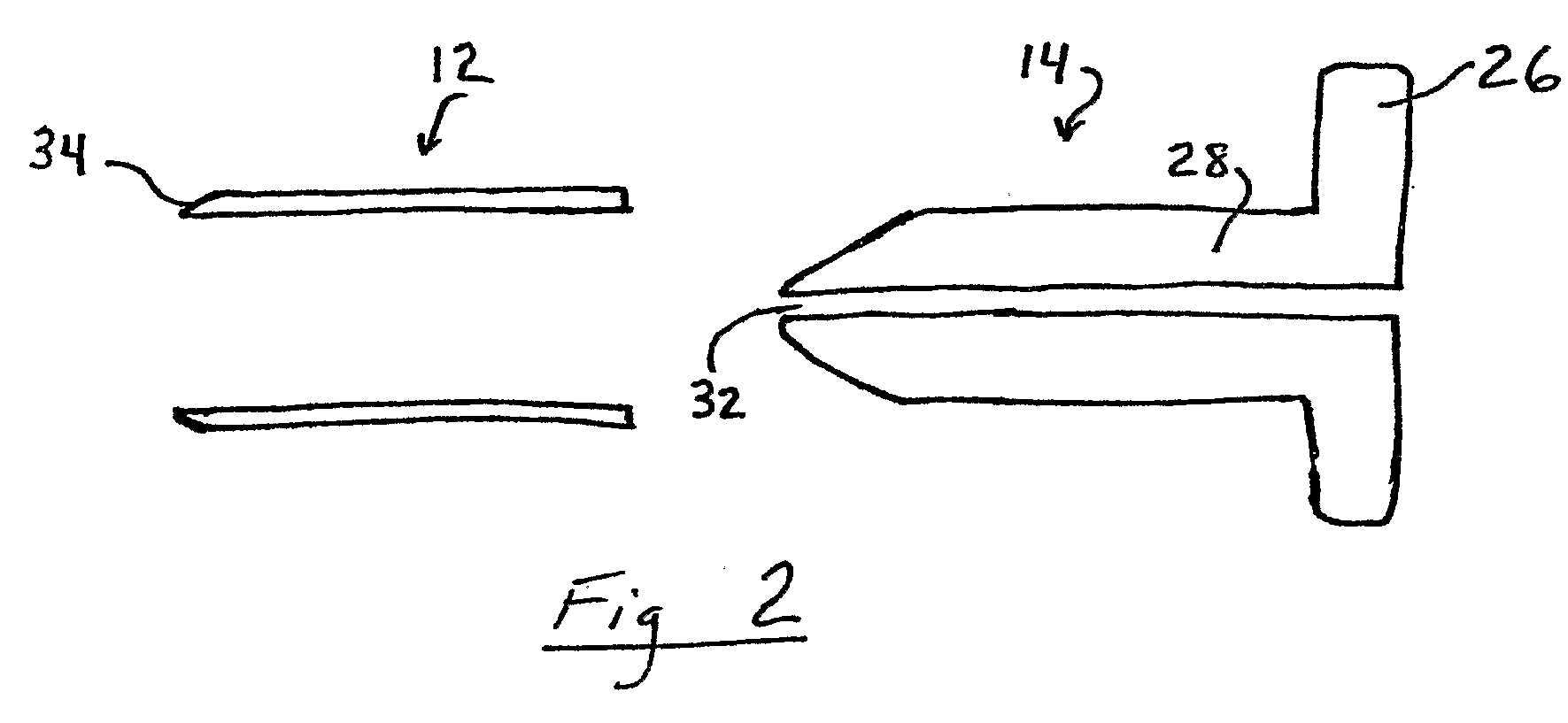
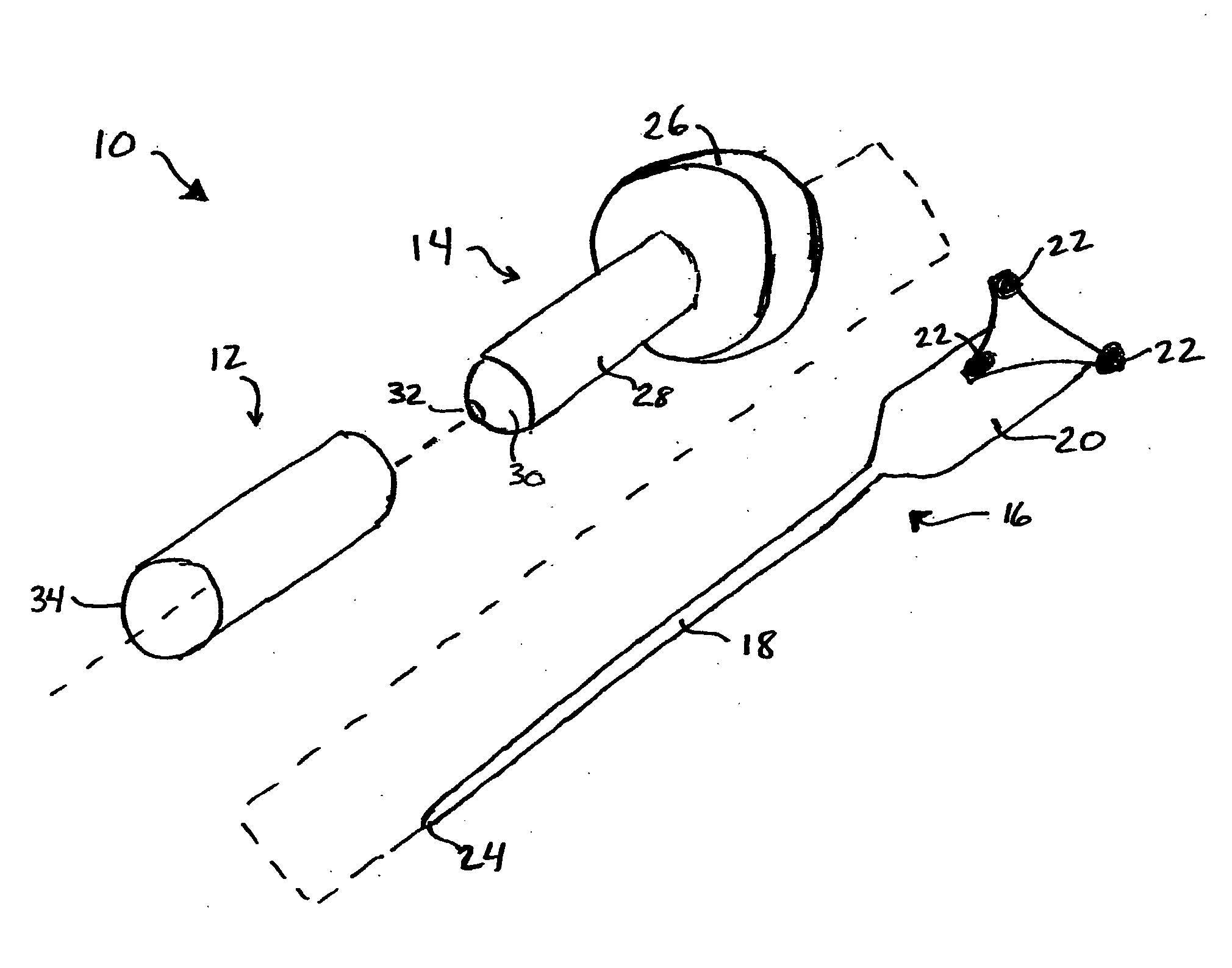
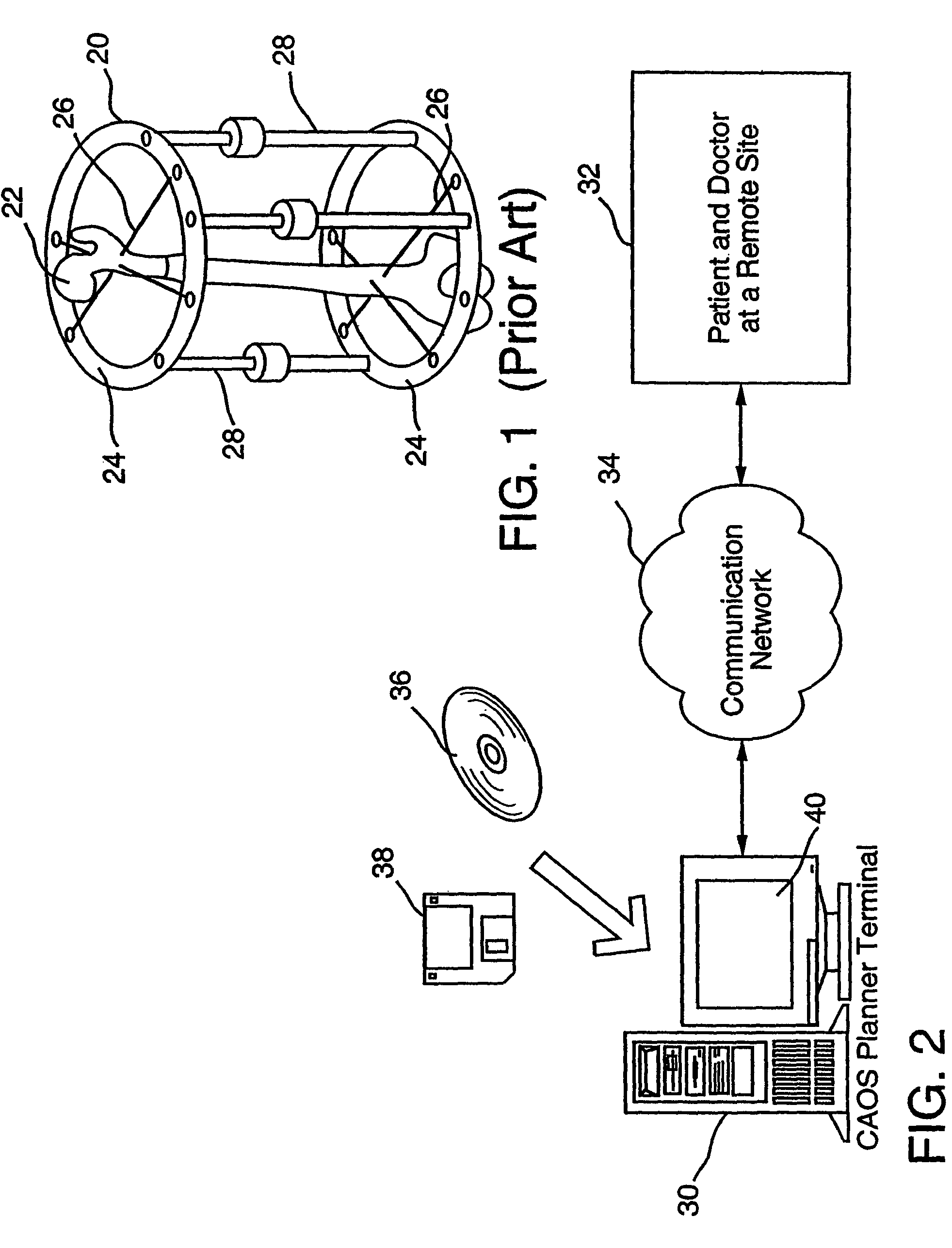
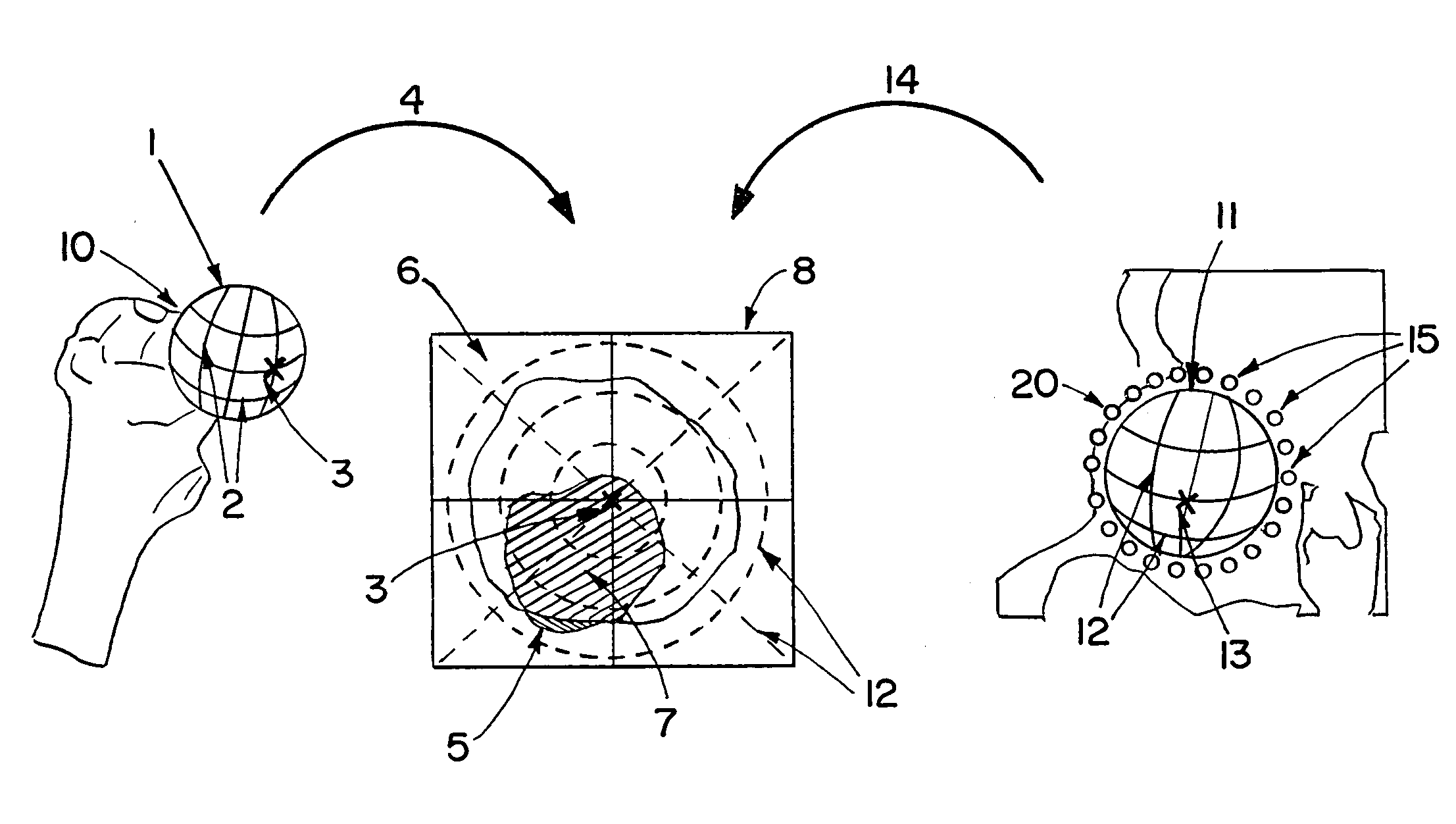
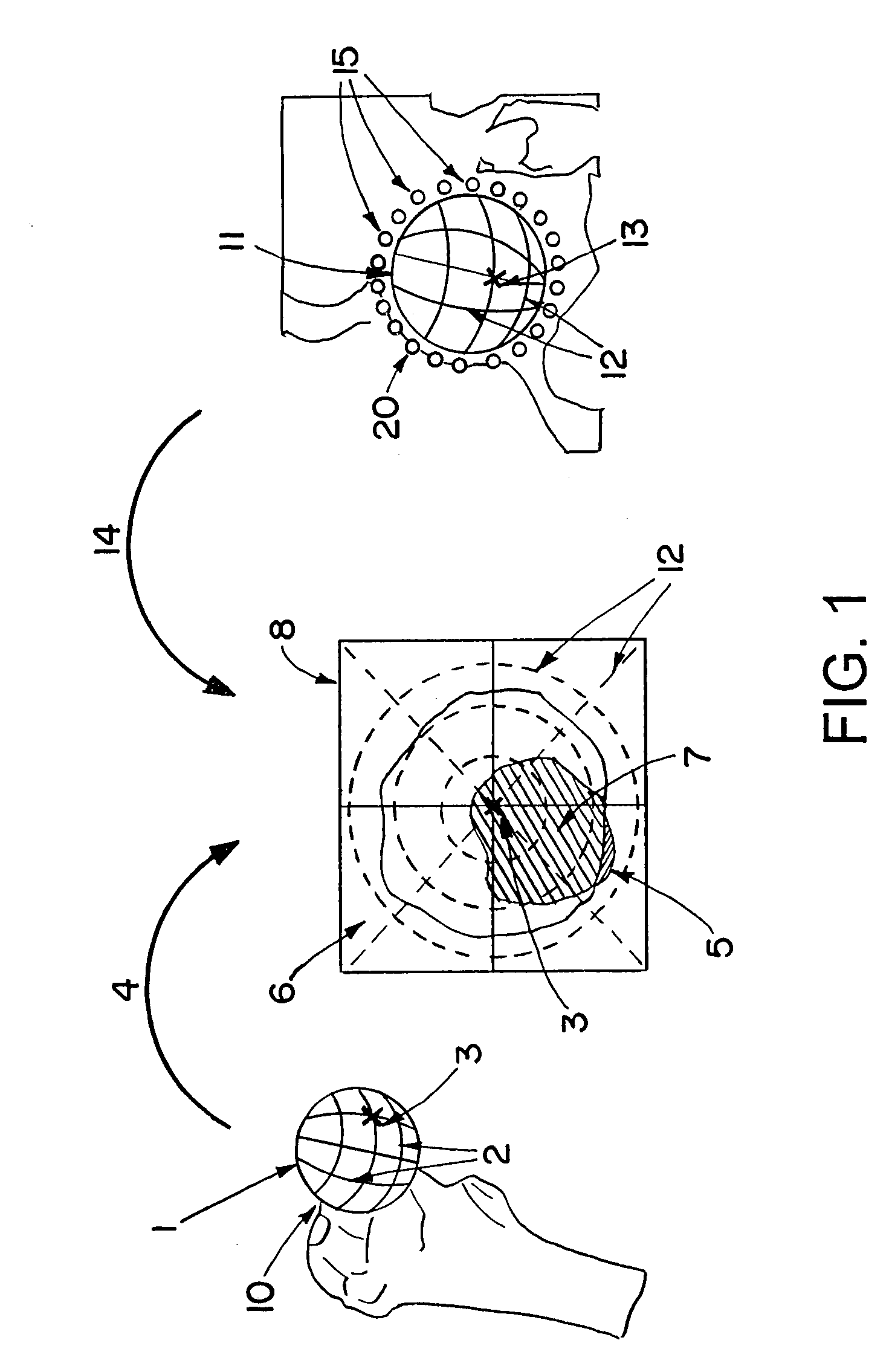
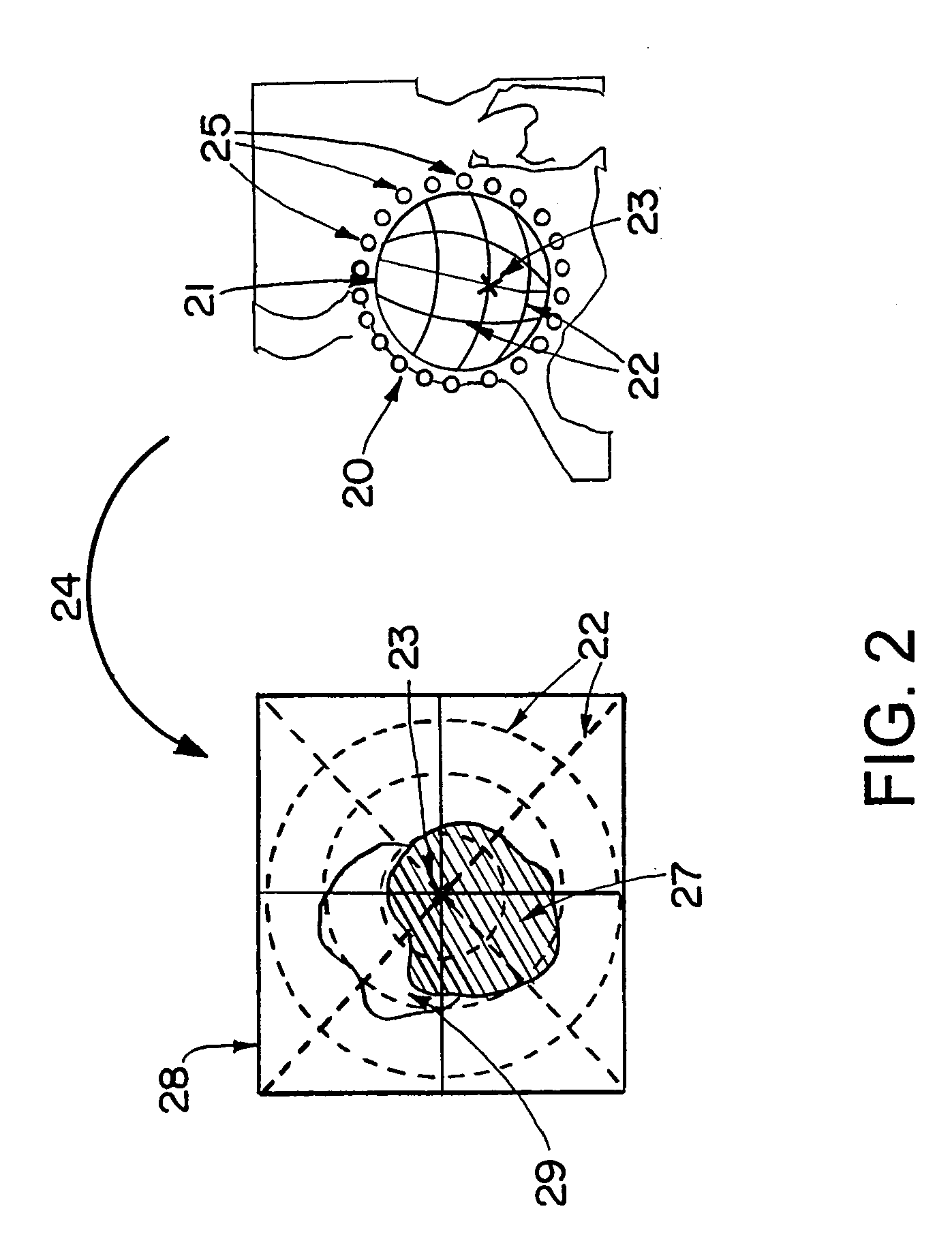
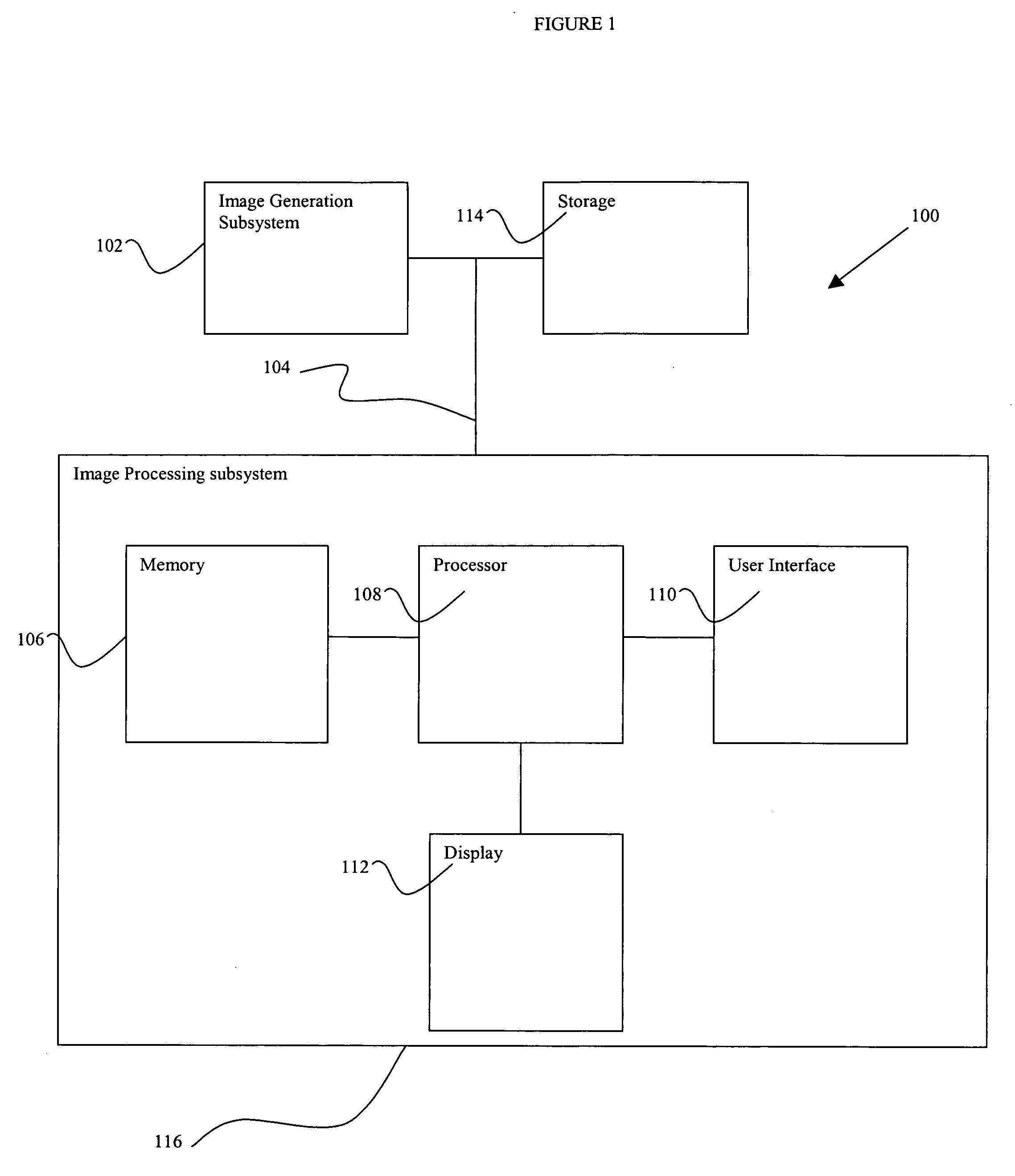
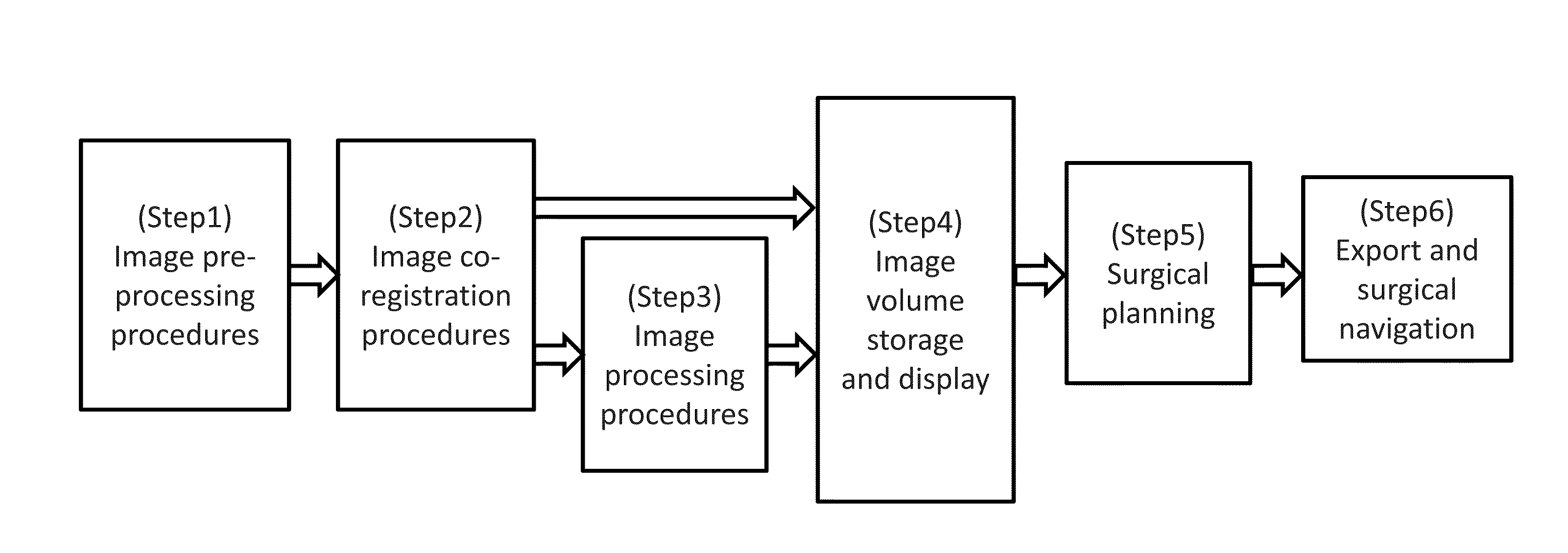
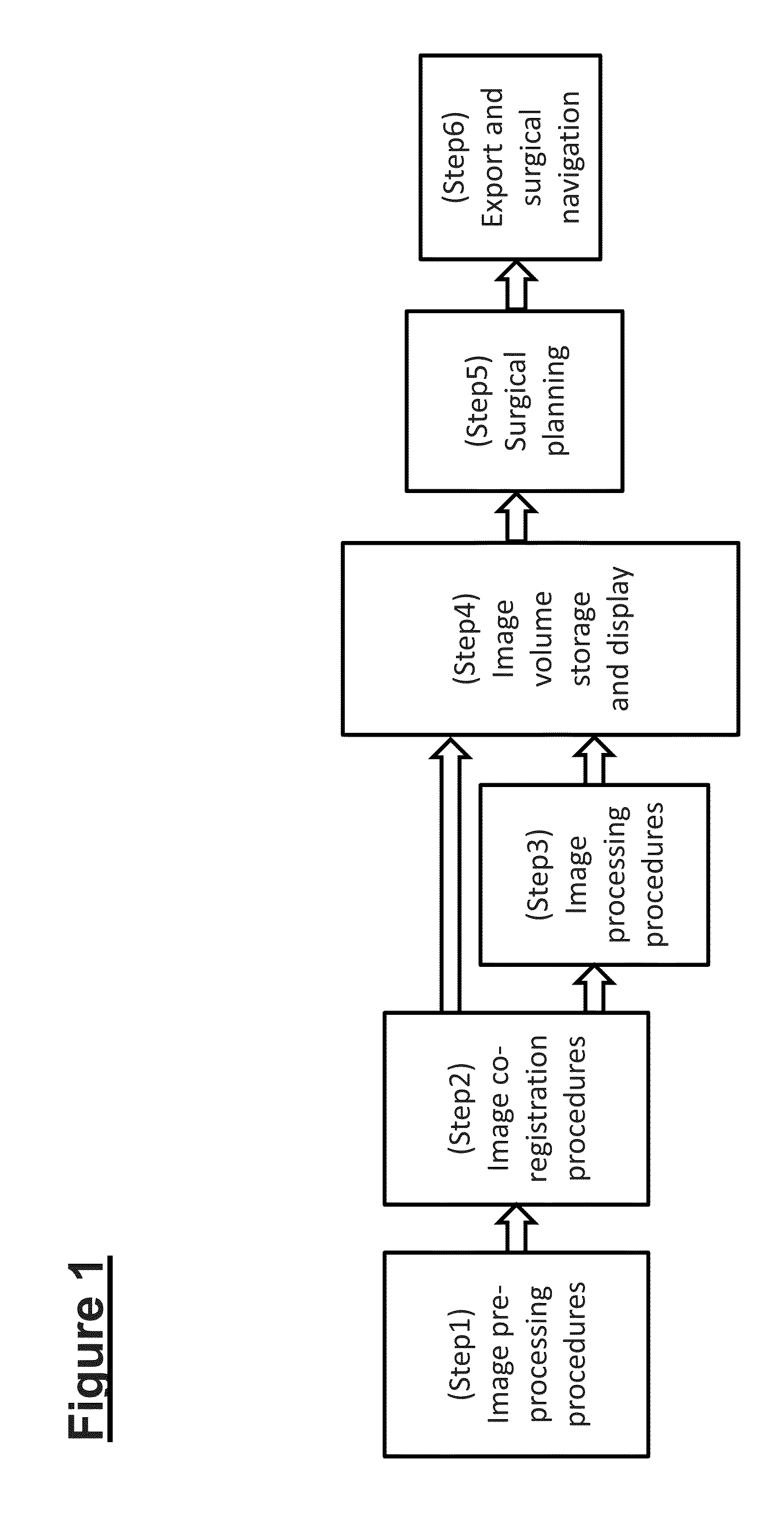
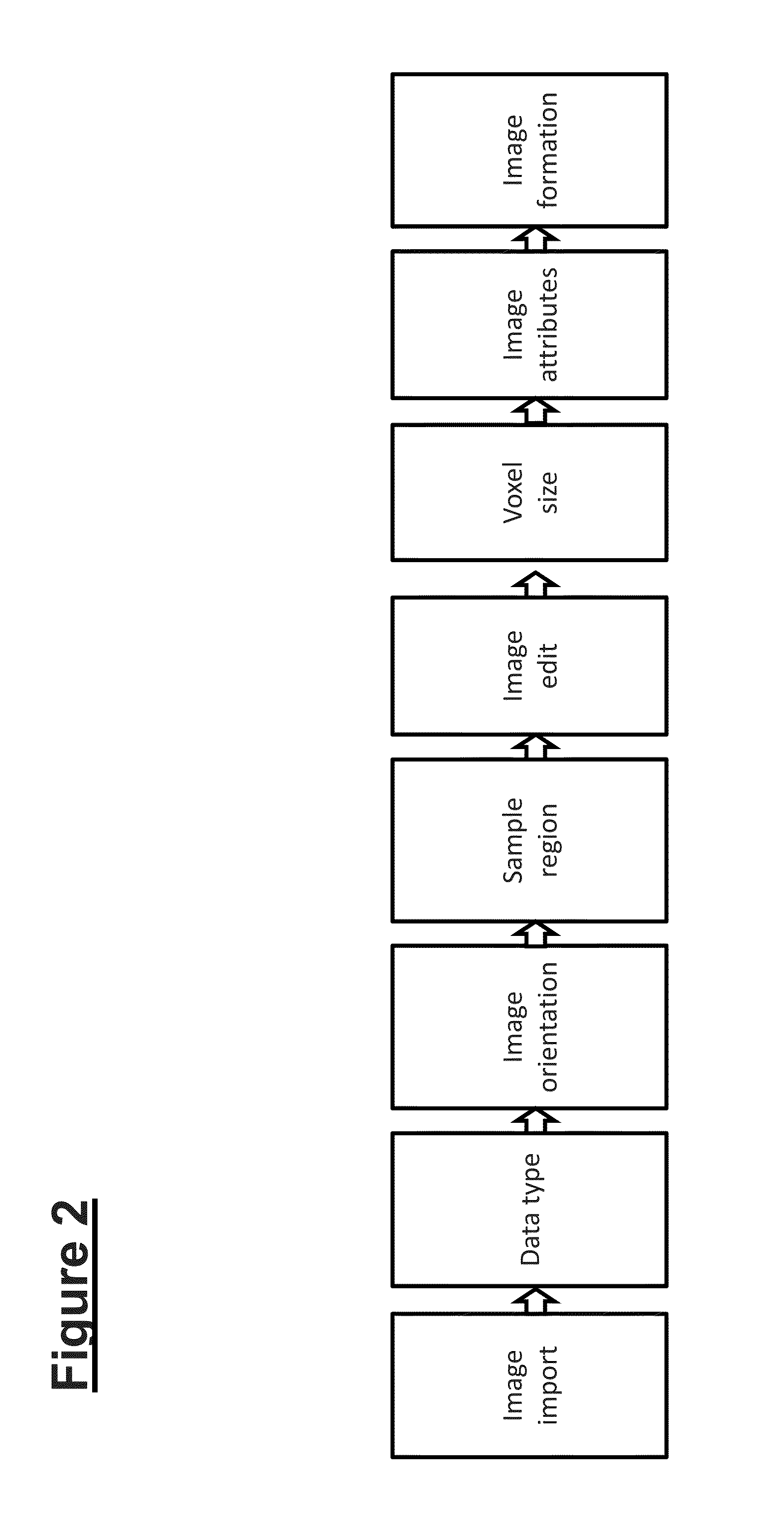
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
225 results about "Surgical planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The surgical planning is the preoperative method of pre-visualising a surgical intervention, in order to predefine the surgical steps and furthermore the bone segment navigation in the context of computer-assisted surgery. The surgical planning is most important in neurosurgery and oral and maxillofacial surgery. The transfer of the surgical planning to the patient is generally made using a medical navigation system.
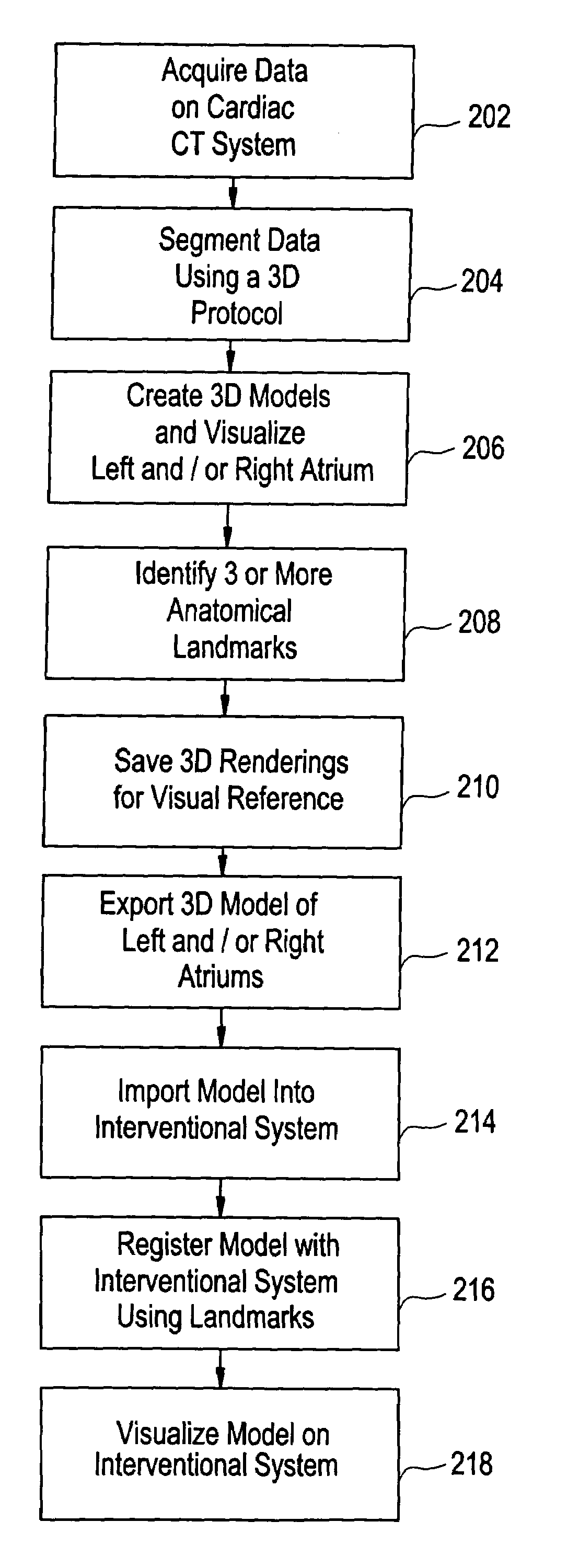
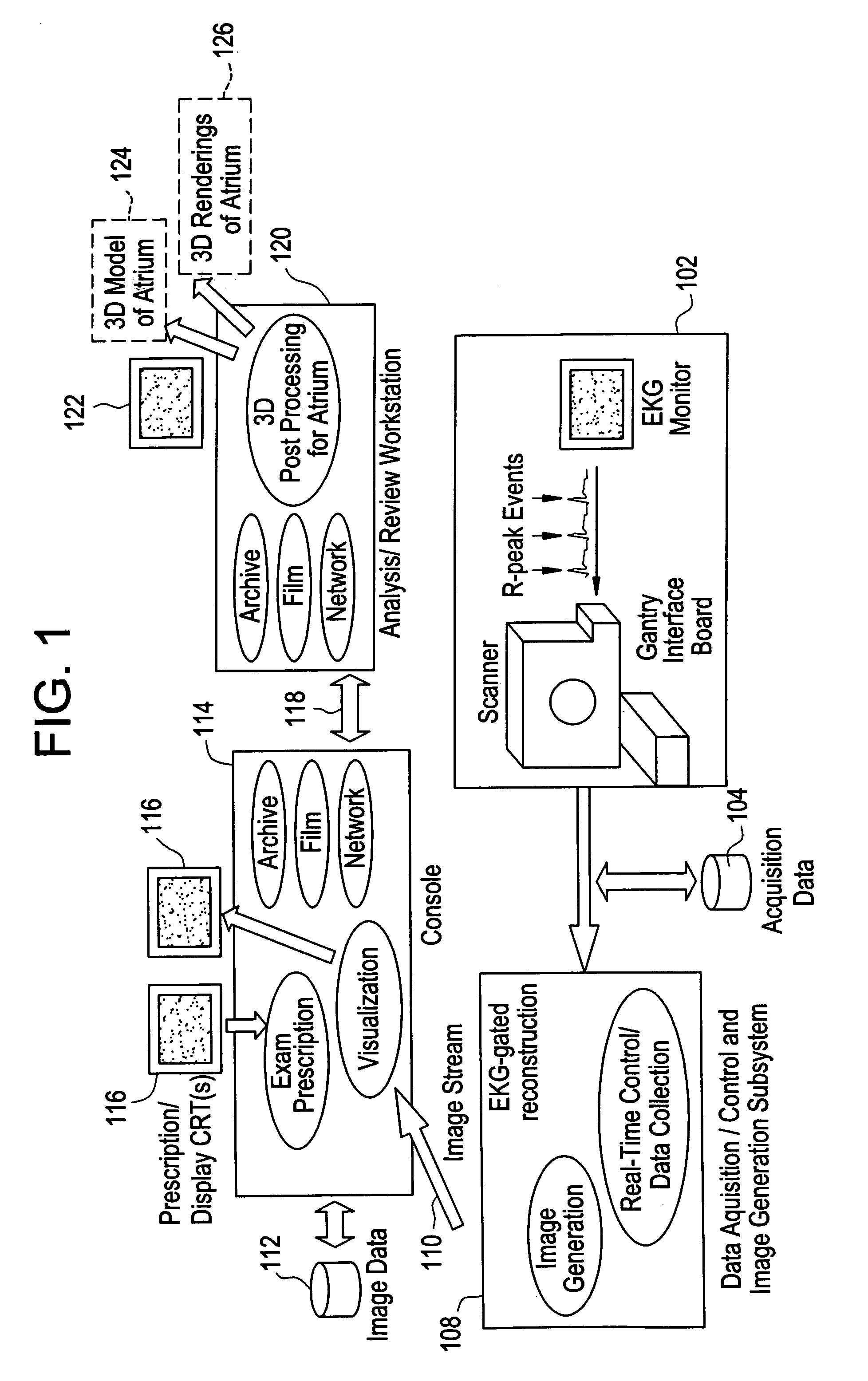
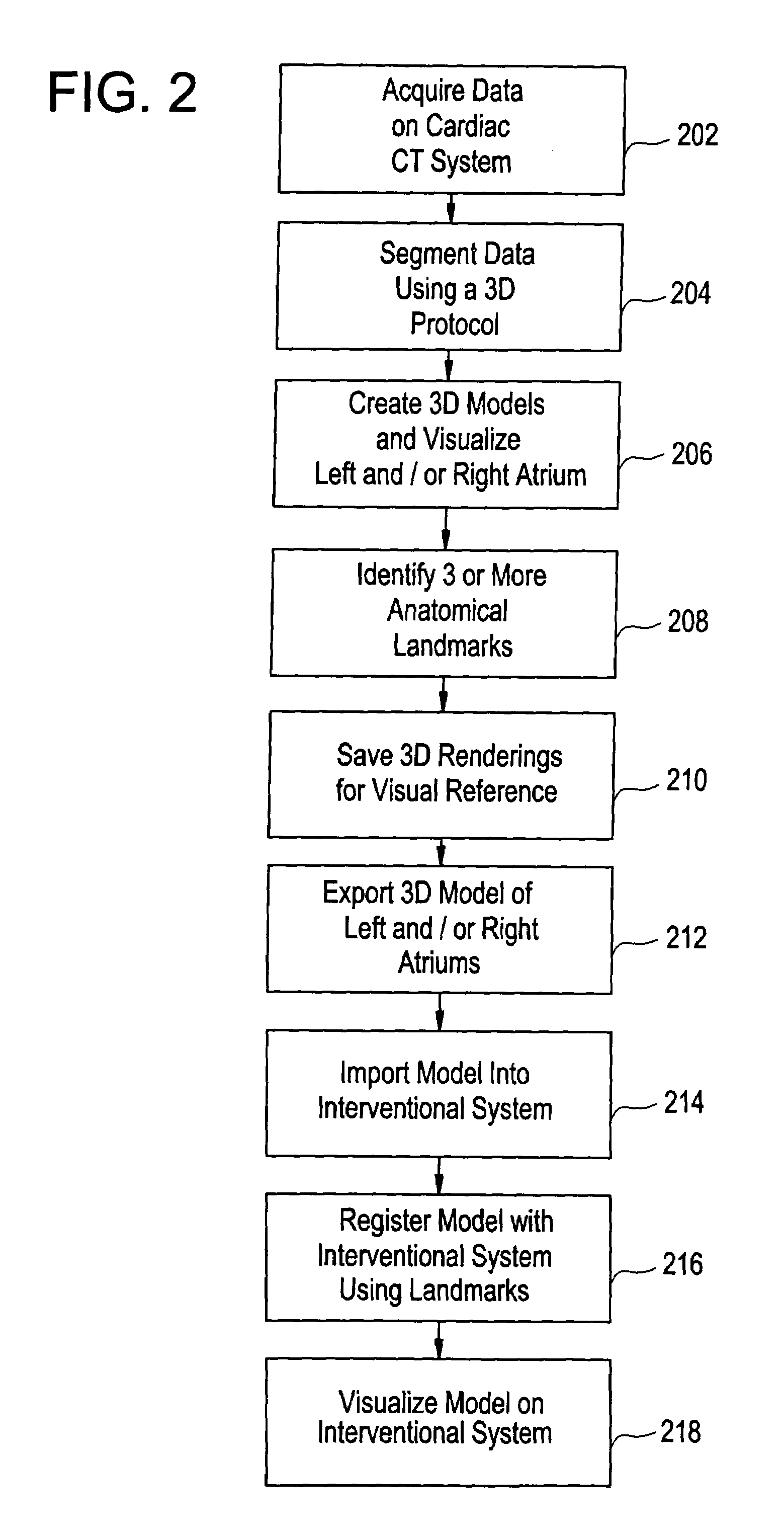
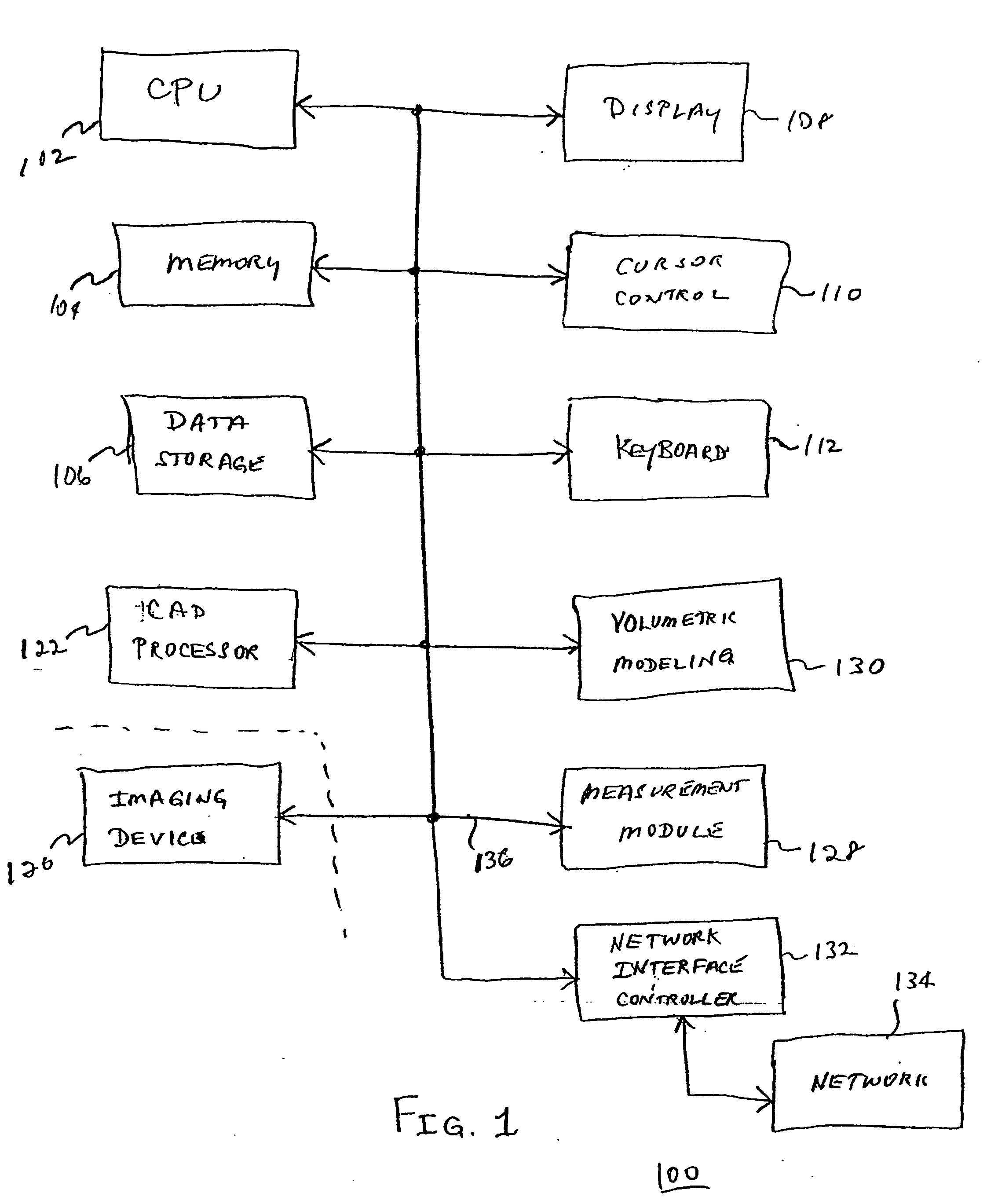
Method, system and computer product for cardiac interventional procedure planning
InactiveUS7286866B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTherapiesAnatomical landmarkProgram planning
A method of creating 3D models to be used for cardiac interventional procedure planning. Acquisition data is obtained from a medical imaging system and cardiac image data is created in response to the acquisition data. A 3D model is created in response to the cardiac image data and three anatomical landmarks are identified on the 3D model. The 3D model is sent to an interventional system where the 3D model is in a format that can be imported and registered with the interventional system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
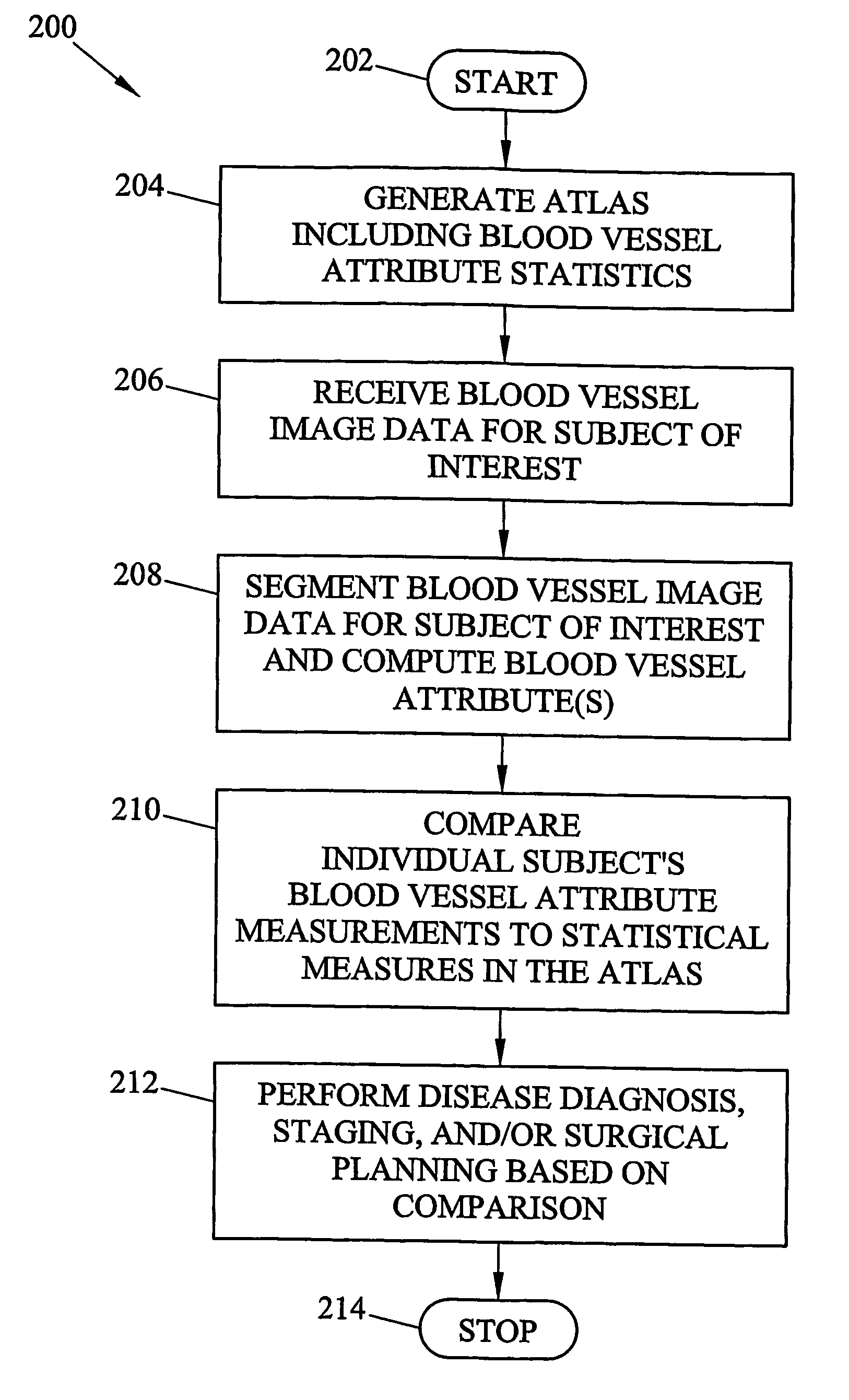
Systems, methods, and computer program products for analysis of vessel attributes for diagnosis, disease staging, and surfical planning
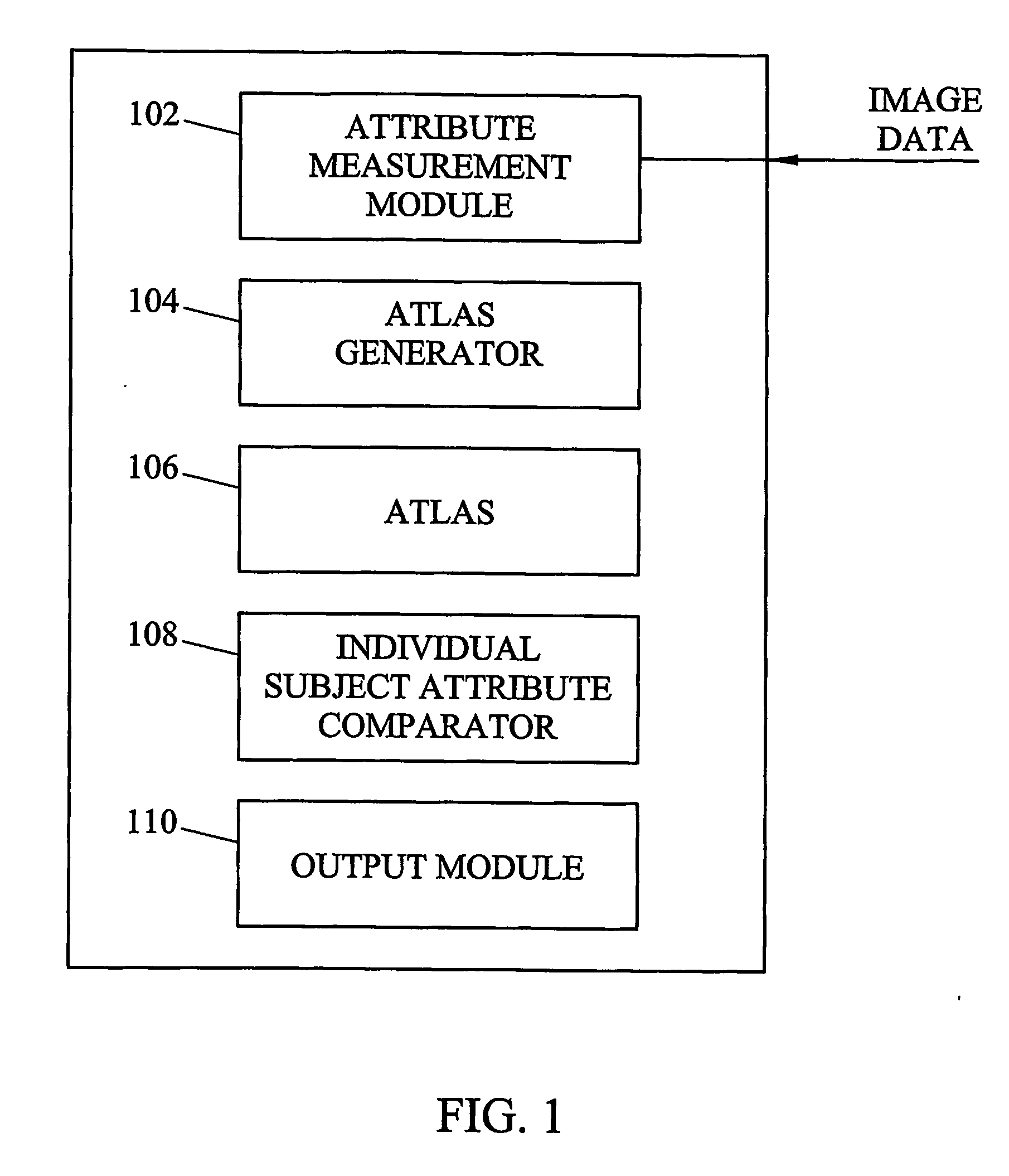
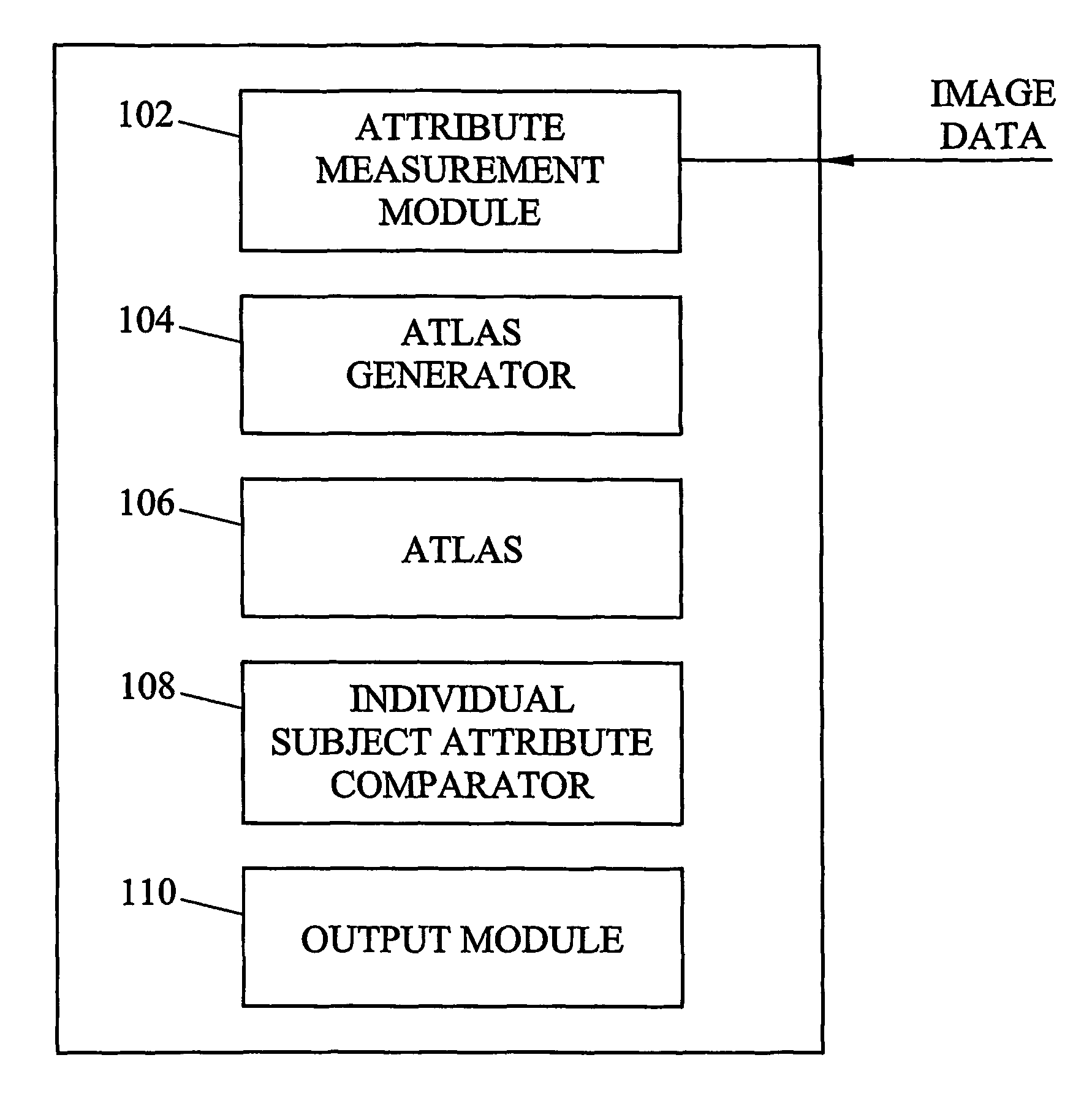
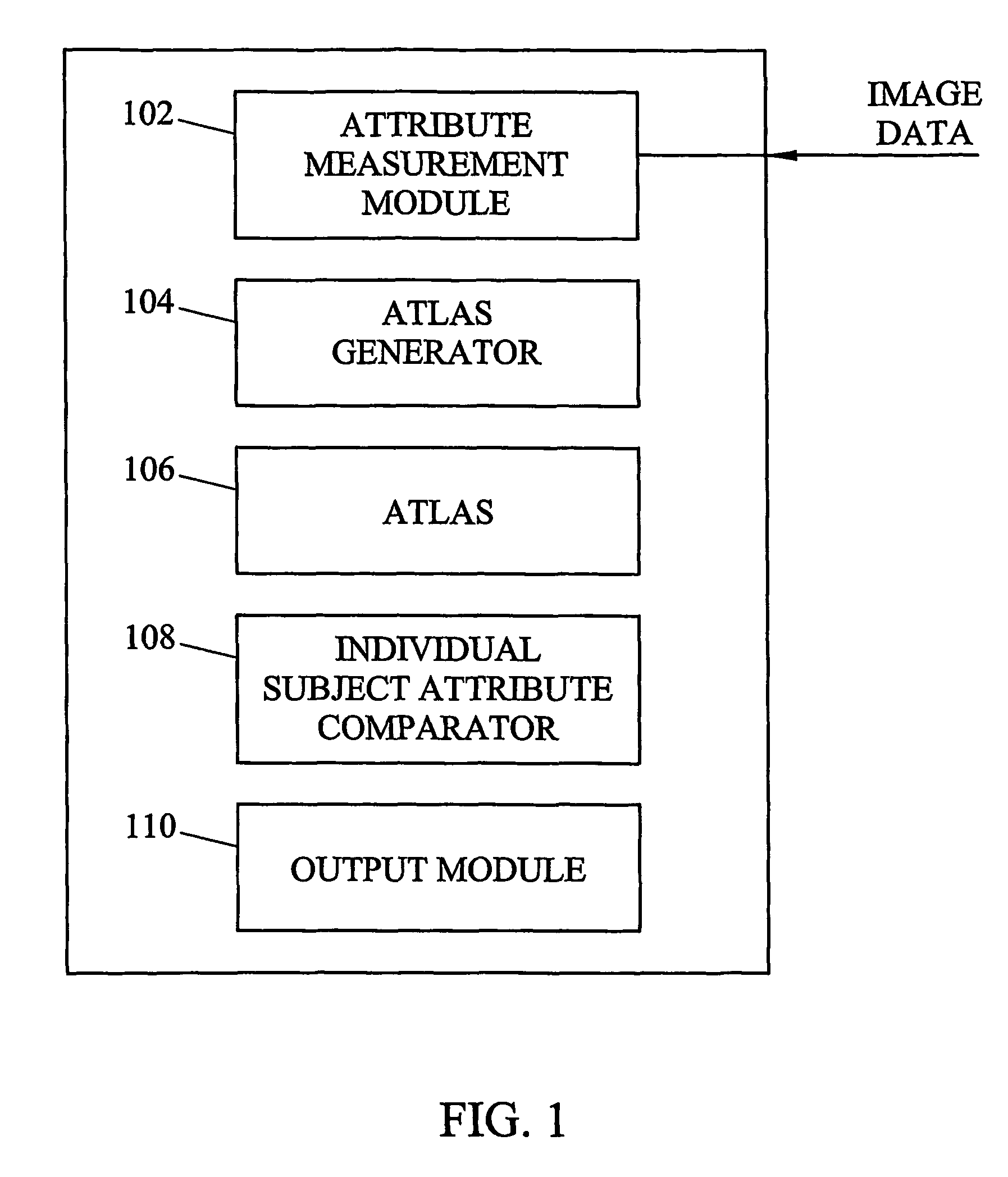
Systems, methods, and computer program products for analysis of vessel attributes for diagnosis, disease staging, and surgical planning are disclosed. A method for analyzing blood vessel attributes may include developing an atlas including statistical measures for at least one blood vessel attribute. The statistical measures can be developed from blood vessel image data from different individuals. Blood vessel attribute measurements can be obtained from an individual subject. The individual subject's blood vessel attribute measurements can be compared to the statistical measures in the atlas. Output may be produced indicative of a physical characteristic of the individual based on results from the comparison.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Methods and apparatus for surgical planning
ActiveUS7607440B2Easy to planPrecise positioningProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical siteEngineering
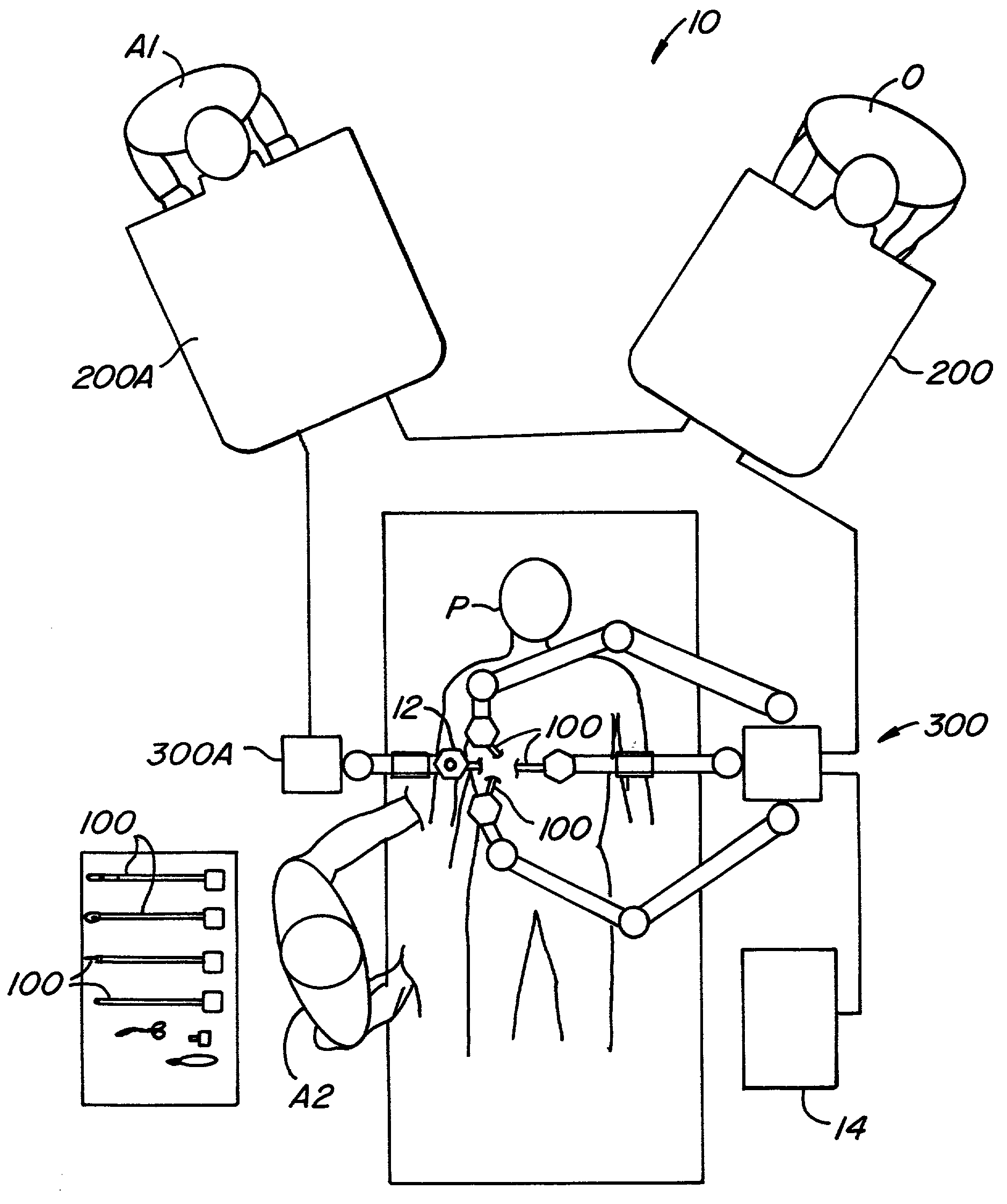
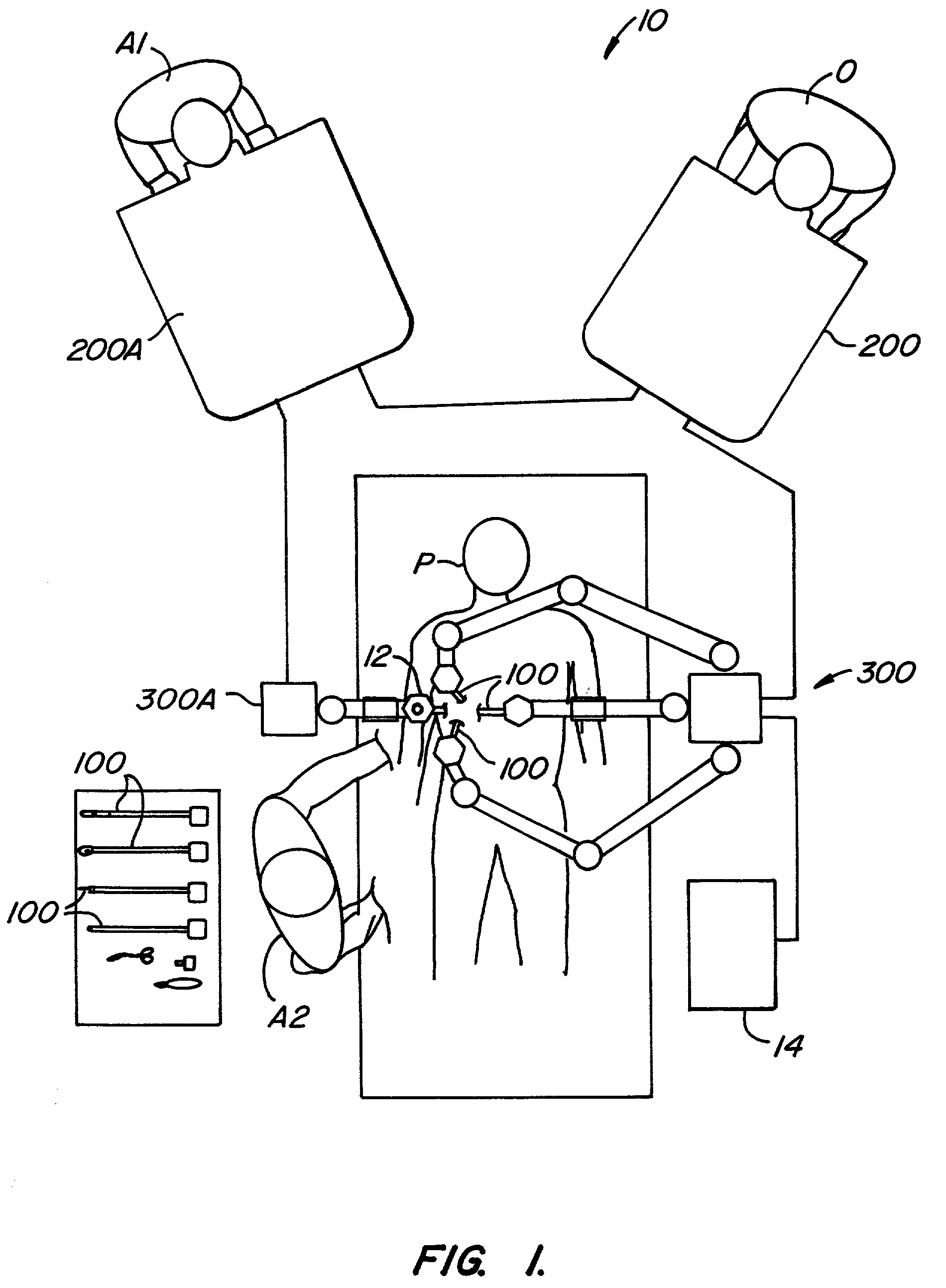
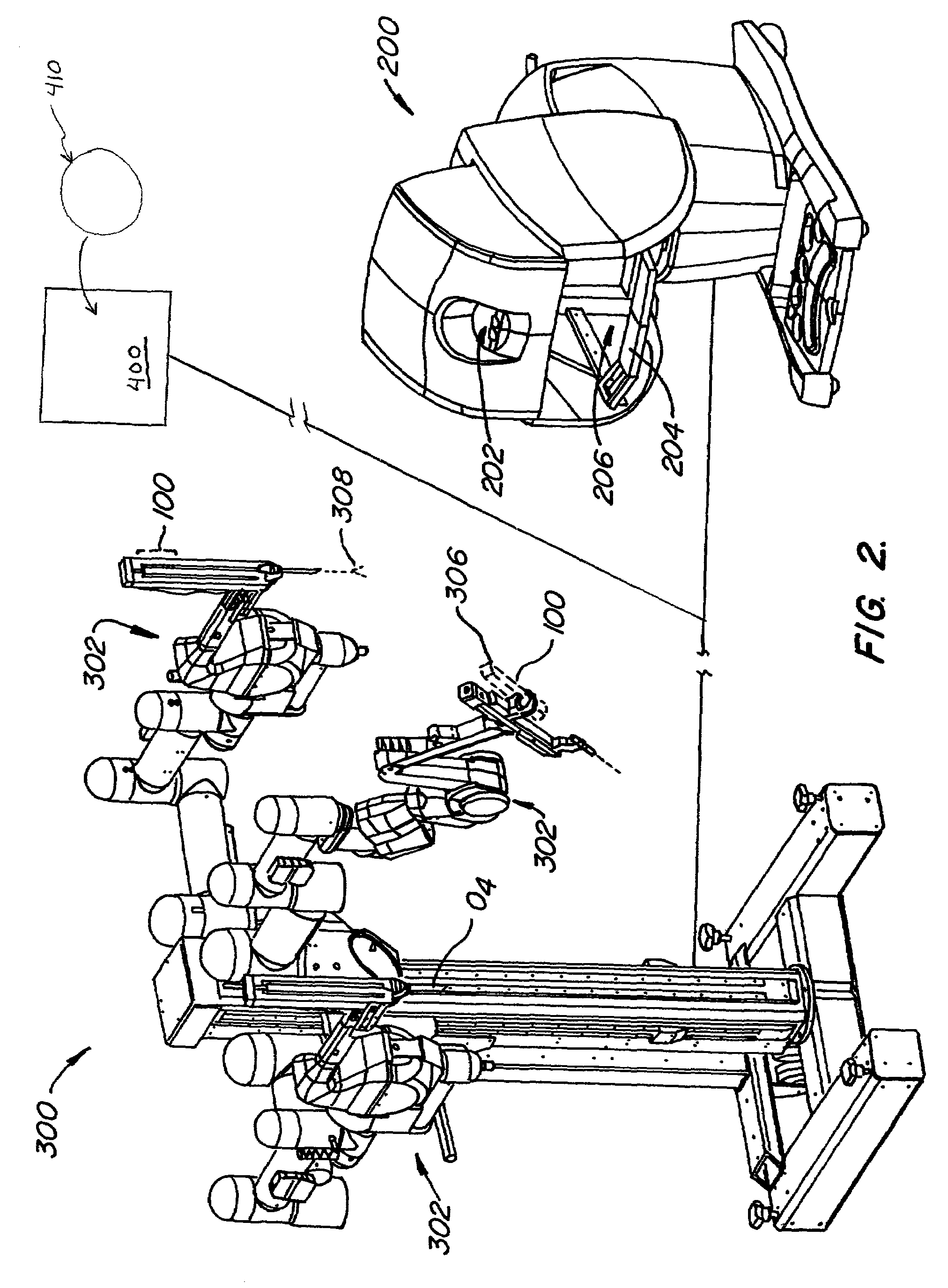
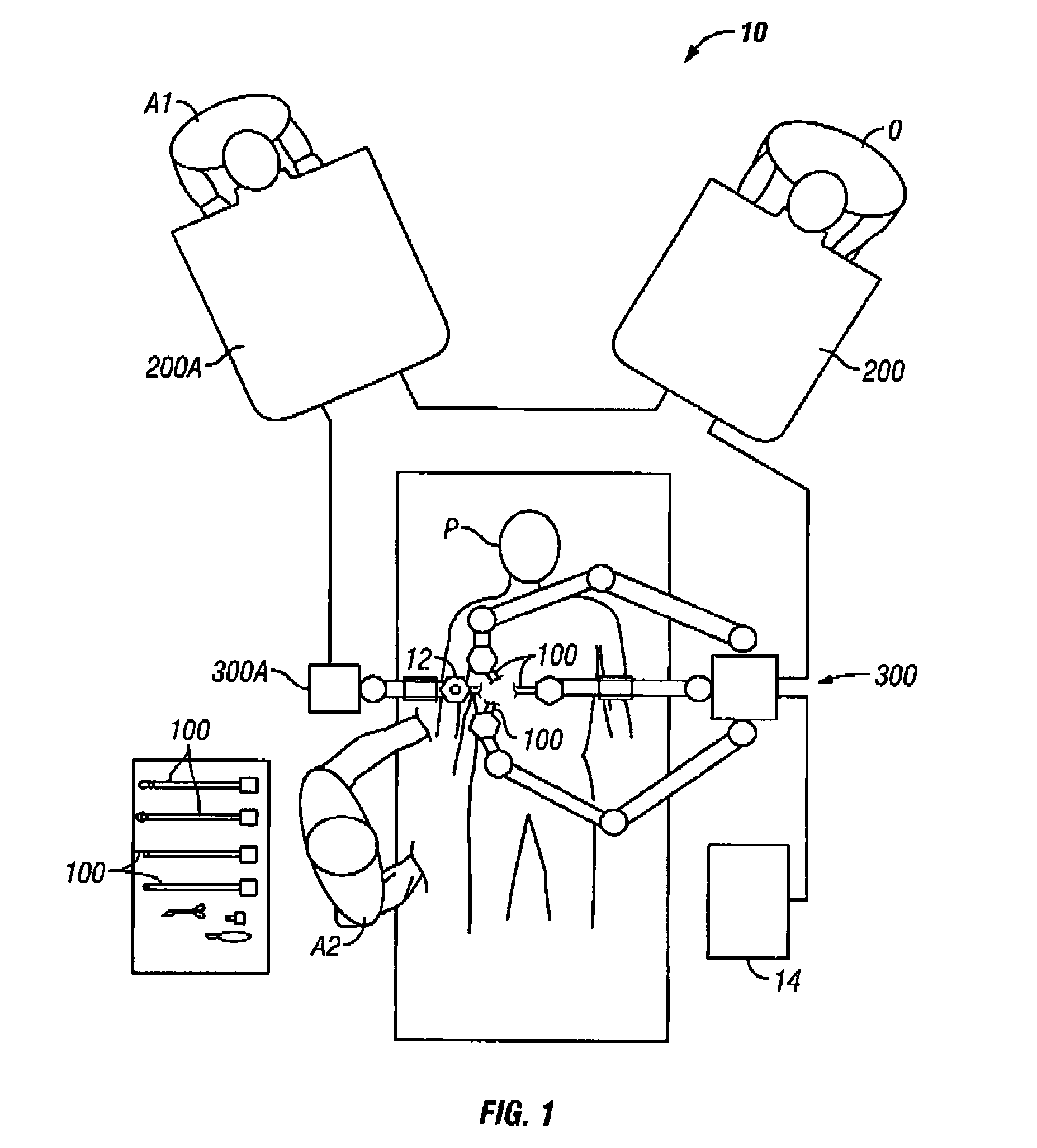
Methods and apparatus for enhancing surgical planning provide enhanced planning of entry port placement and / or robot position for laparoscopic, robotic, and other minimally invasive surgery. Various embodiments may be used in robotic surgery systems to identify advantageous entry ports for multiple robotic surgical tools into a patient to access a surgical site. Generally, data such as imaging data is processed and used to create a model of a surgical site, which can then be used to select advantageous entry port sites for two or more surgical tools based on multiple criteria. Advantageous robot positioning may also be determined, based on the entry port locations and other factors. Validation and simulation may then be provided to ensure feasibility of the selected port placements and / or robot positions. Such methods, apparatus, and systems may also be used in non-surgical contexts, such as for robotic port placement in munitions diffusion or hazardous waste handling.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
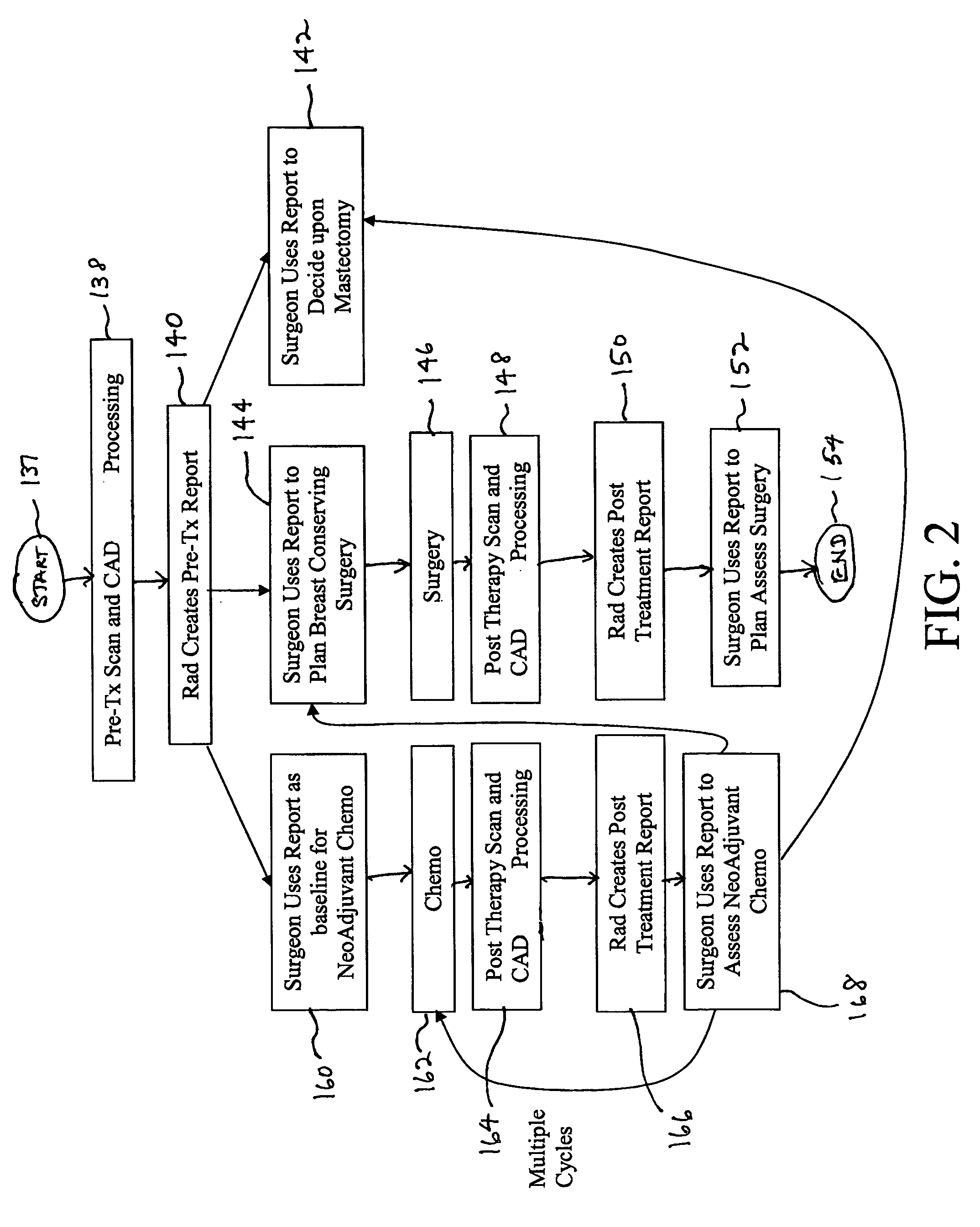
Apparatus and method for surgical planning and treatment monitoring
A system for surgical planning and therapeutic monitoring utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection (CAD) technology to identify cancerous tumors. A pre-treatment report identifies all volumes of interest (VOIs) and provides data regarding the size and location of each VOI as well as volumetric data for use in surgical planning. The system can be used to monitor the progress of adjuvant chemotherapy or other non-surgical treatment and measures changes in tumor size and location. Post-treatment reports provide data regarding changes in tumor size and location as well as trend data to provide guidance to the physician.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP +1
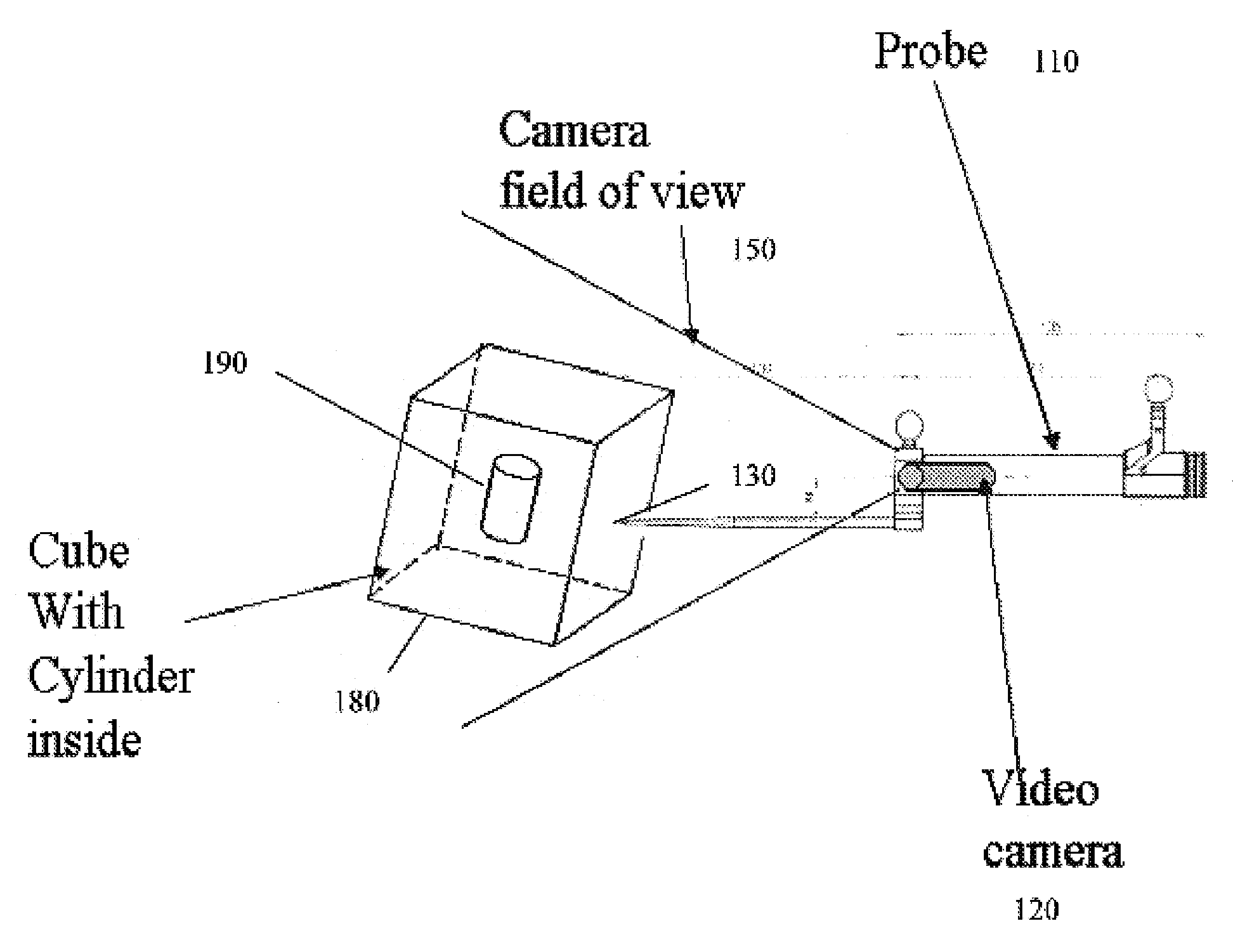
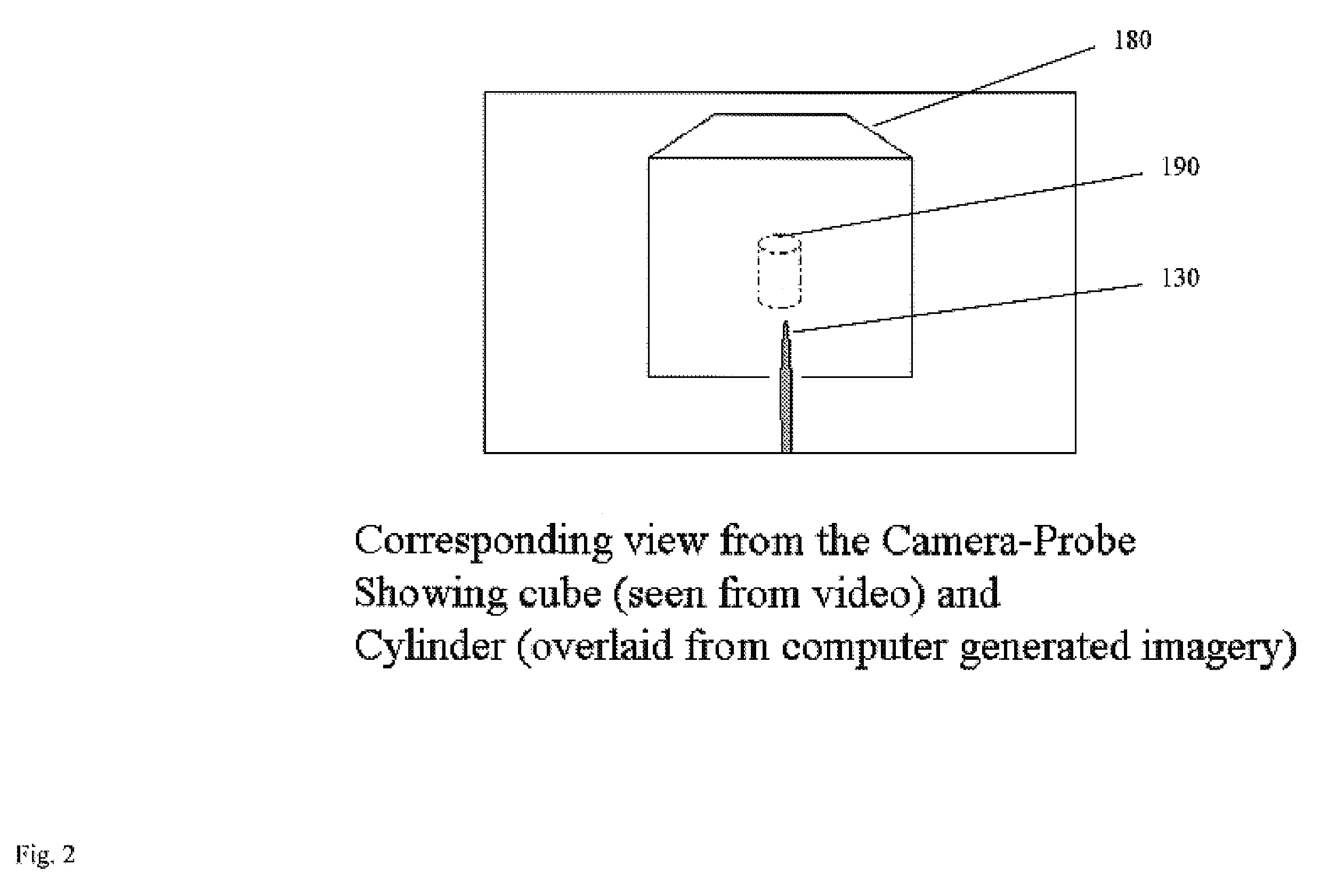
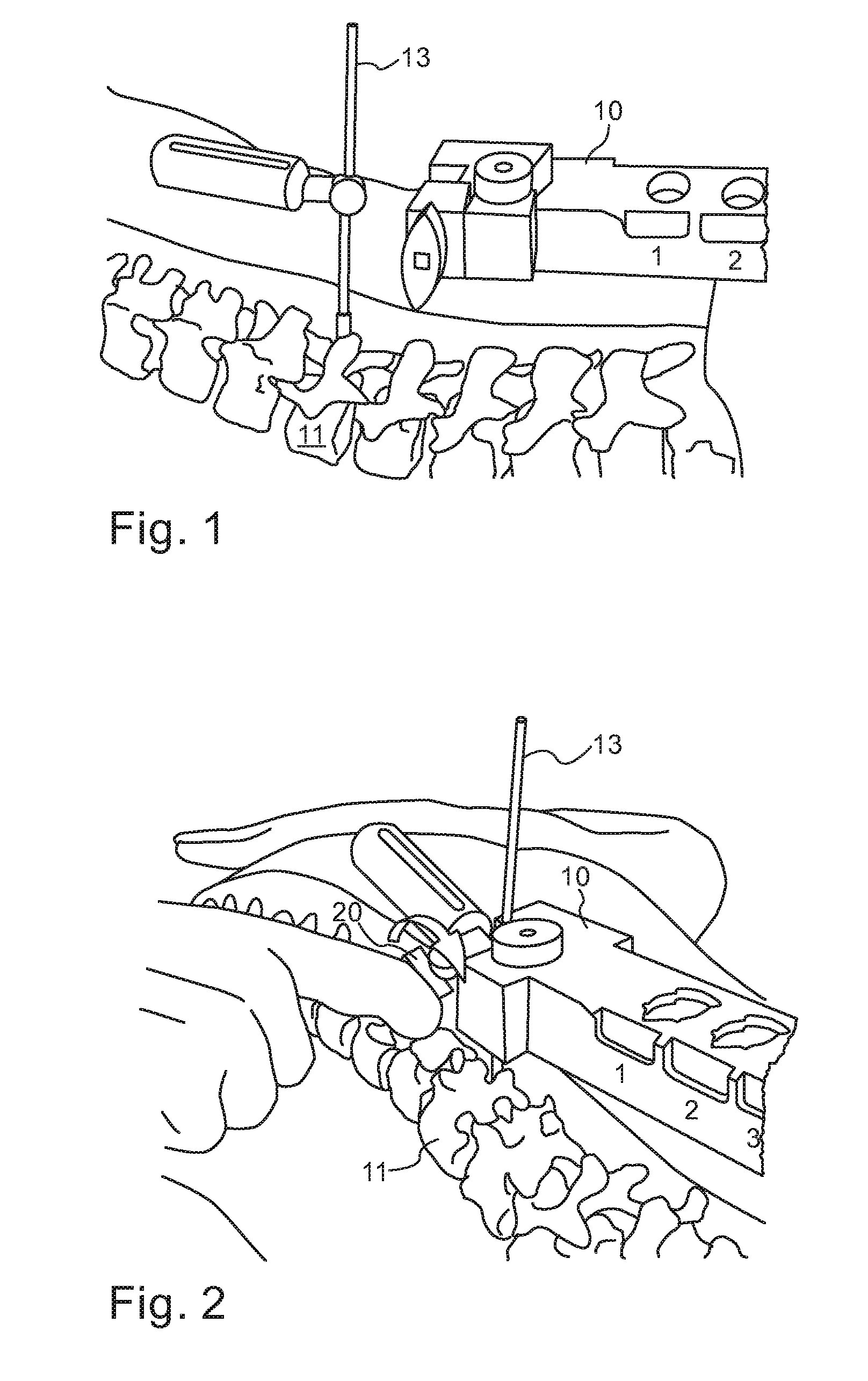
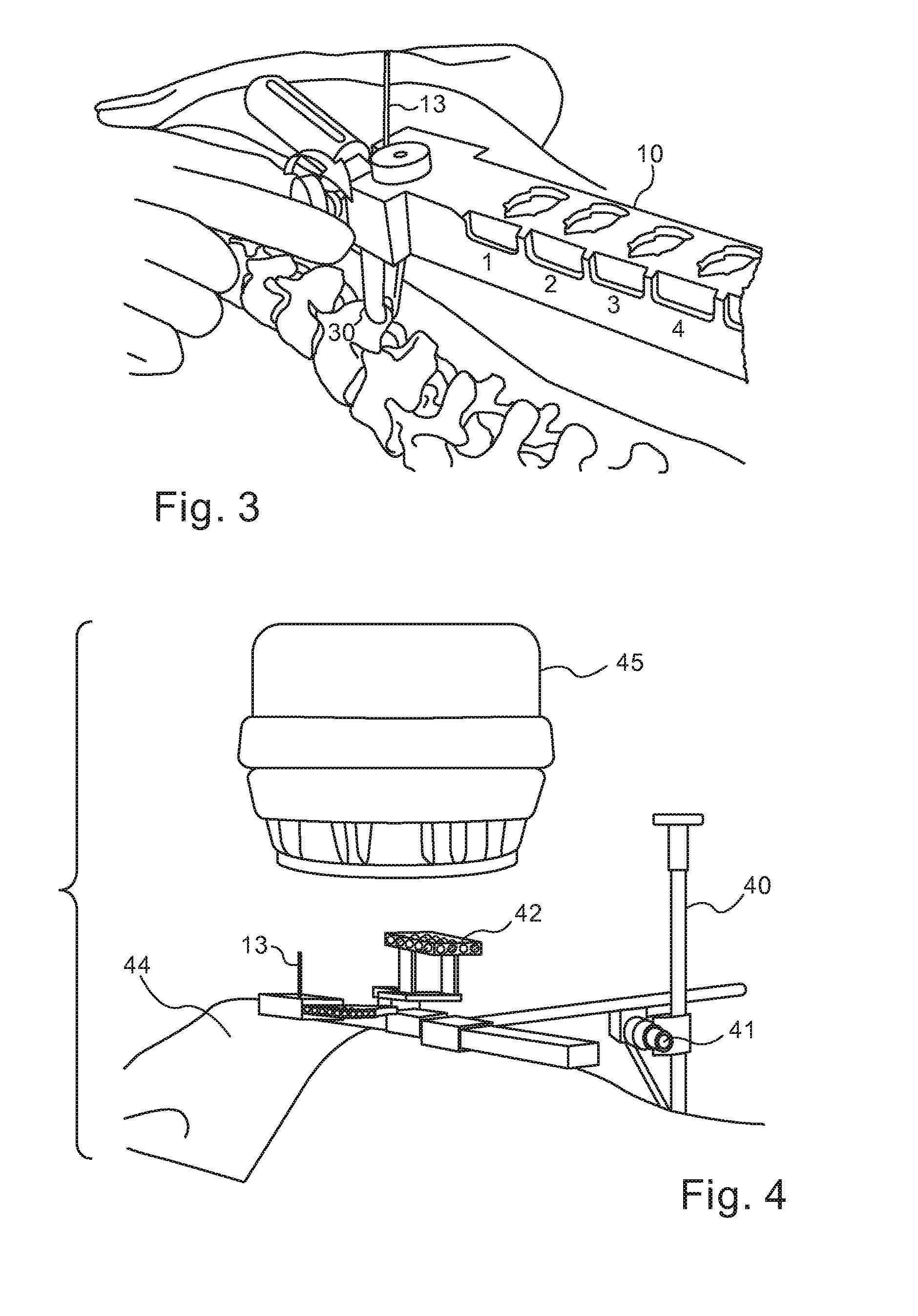
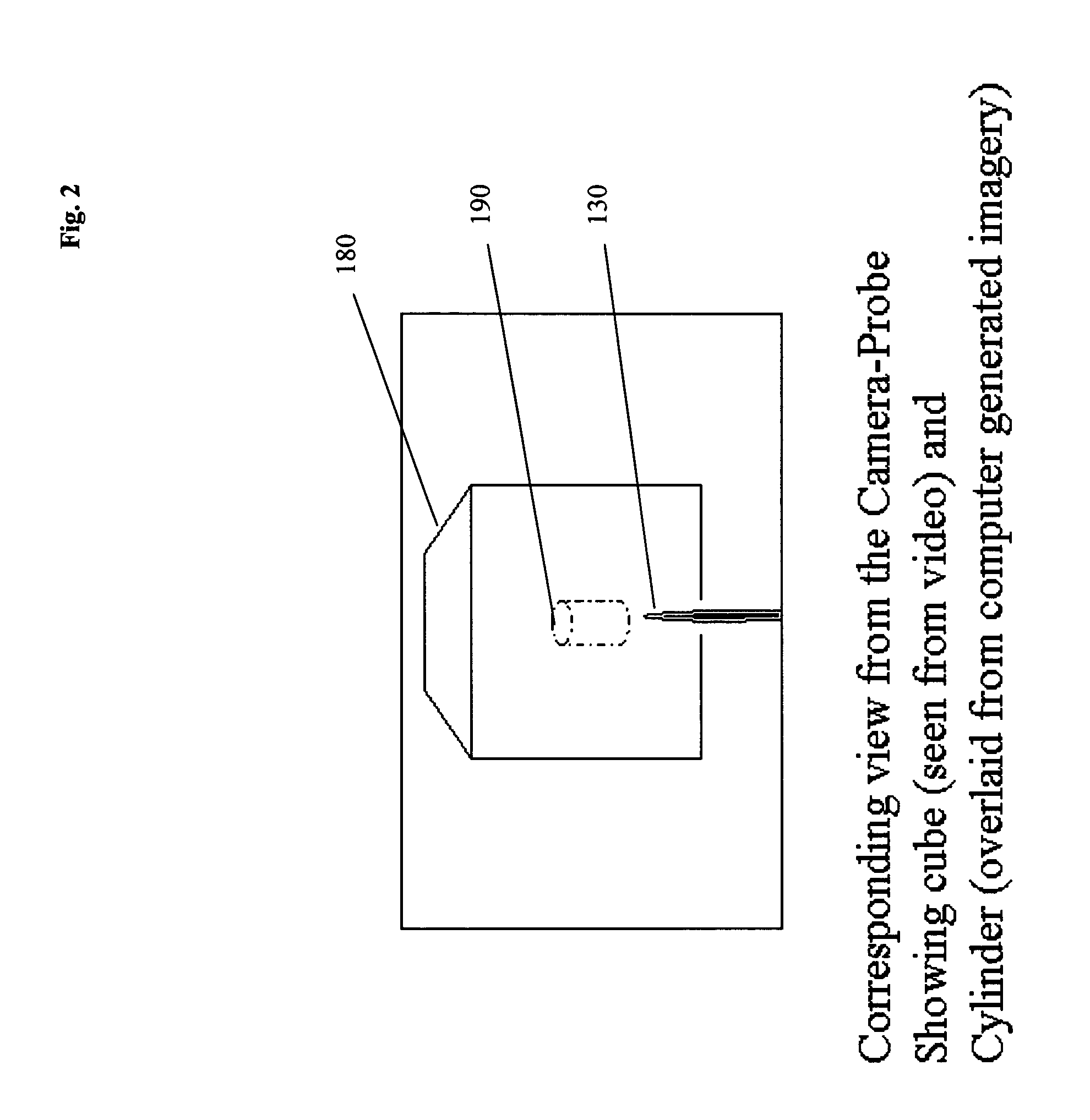
Computer enhanced surgical navigation imaging system (camera probe)
ActiveUS7491198B2Enhanced interactionEasy to navigateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesViewpointsSurgical approach
A system and method for navigation within a surgical field are presented. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention a micro-camera can be provided in a hand-held navigation probe tracked by a tracking system. This enables navigation within an operative scene by viewing real-time images from the viewpoint of the micro-camera within the navigation probe, which are overlaid with computer generated 3D graphics depicting structures of interest generated from pre-operative scans. Various transparency settings of the camera image and the superimposed 3D graphics can enhance the depth perception, and distances between a tip of the probe and any of the superimposed 3D structures along a virtual ray extending from the probe tip can be dynamically displayed in the combined image. In exemplary embodiments of the invention a virtual interface can be displayed adjacent to the combined image on a system display, thus facilitating interaction with various navigation related functions. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention virtual reality systems can be used to plan surgical approaches with multi-modal CT and MRI data. This allows for generating 3D structures as well as marking ideal surgical paths. The system and method presented thus enable transfer of a surgical planning scenario to a real-time view of an actual surgical field, thus enhancing navigation.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
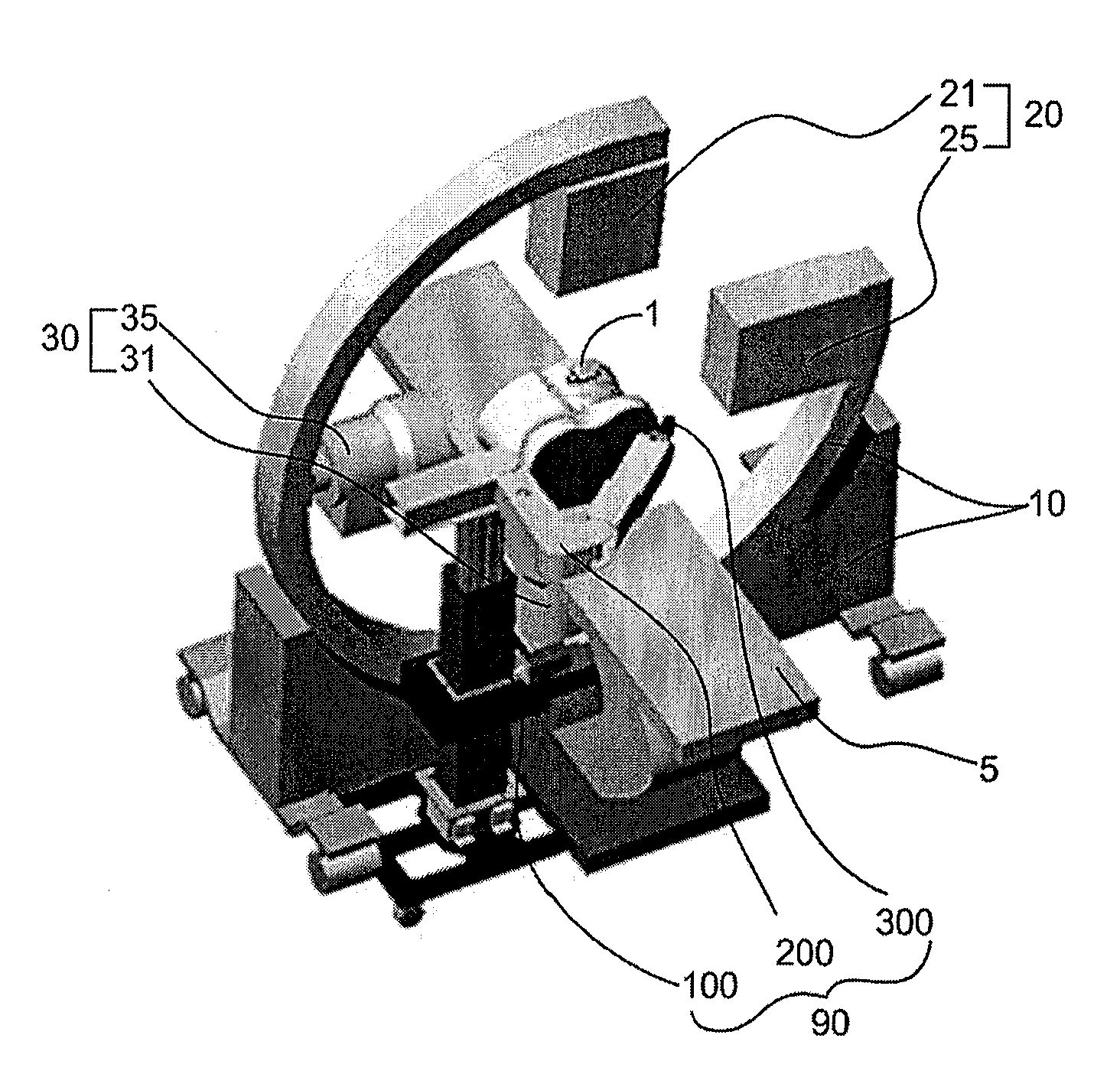
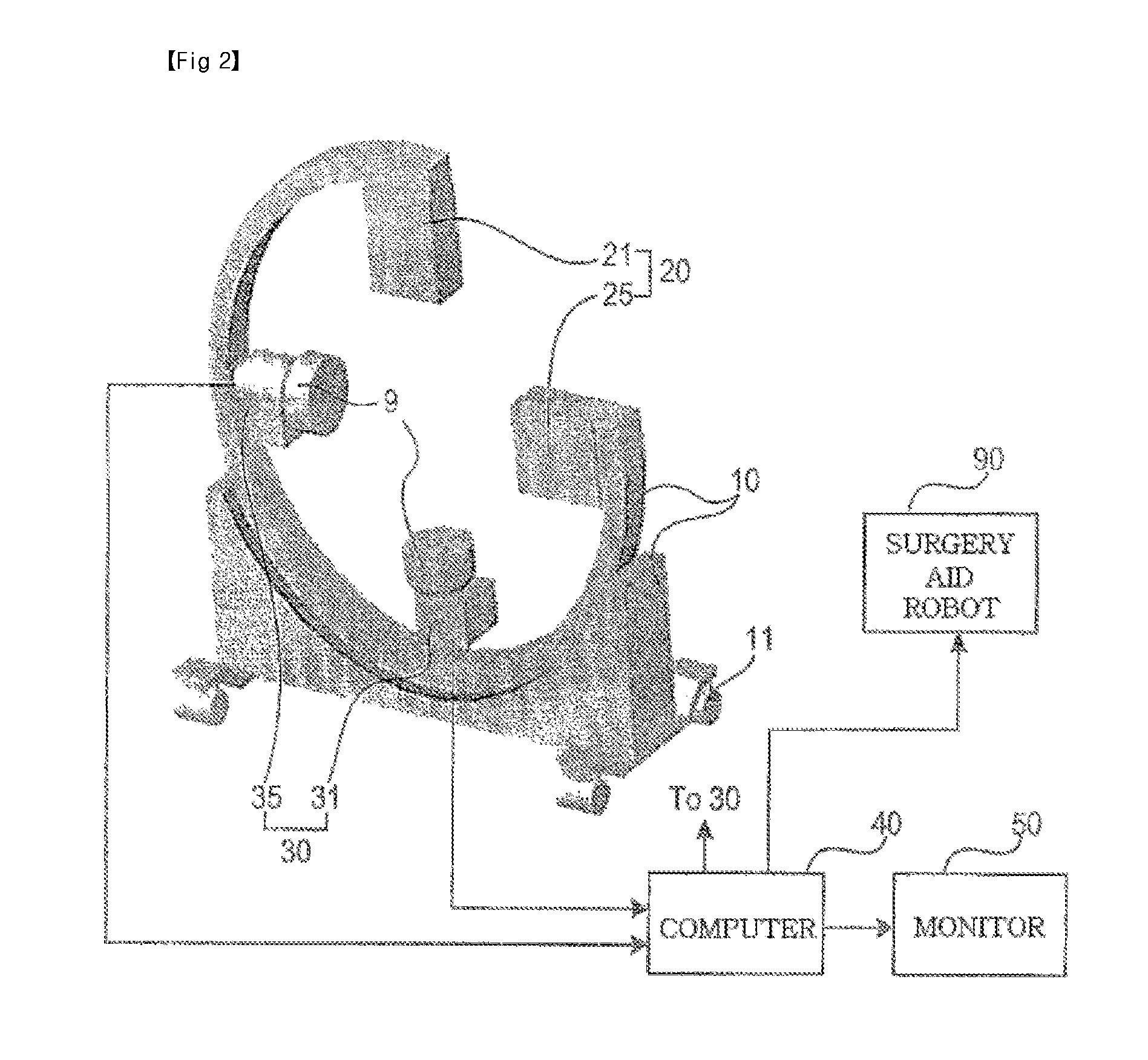
Bi-planar fluoroscopy guided robot system for minimally invasive surgery and the control method thereof
InactiveUS8046054B2Accurate three-dimensional surgery planAccurate surgery planMasksUmbrellasLess invasive surgeryProgram planning
Disclosed is a computer-integrated surgery aid system for minimally invasive surgery and a method for controlling the same. The system includes a surgery planning system for creating three-dimensional information from two-dimensional images obtained by means of biplanar fluoroscopy so that spinal surgery can be planned according to the image information and a scalar-type 6 degree-of-freedom surgery aid robot adapted to be either driven automatically or operated manually.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Robotic guided endoscope
ActiveUS9125556B2Level accuracyReduce traumaEndoscopesComputerised tomographsSurgical robotEngineering
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
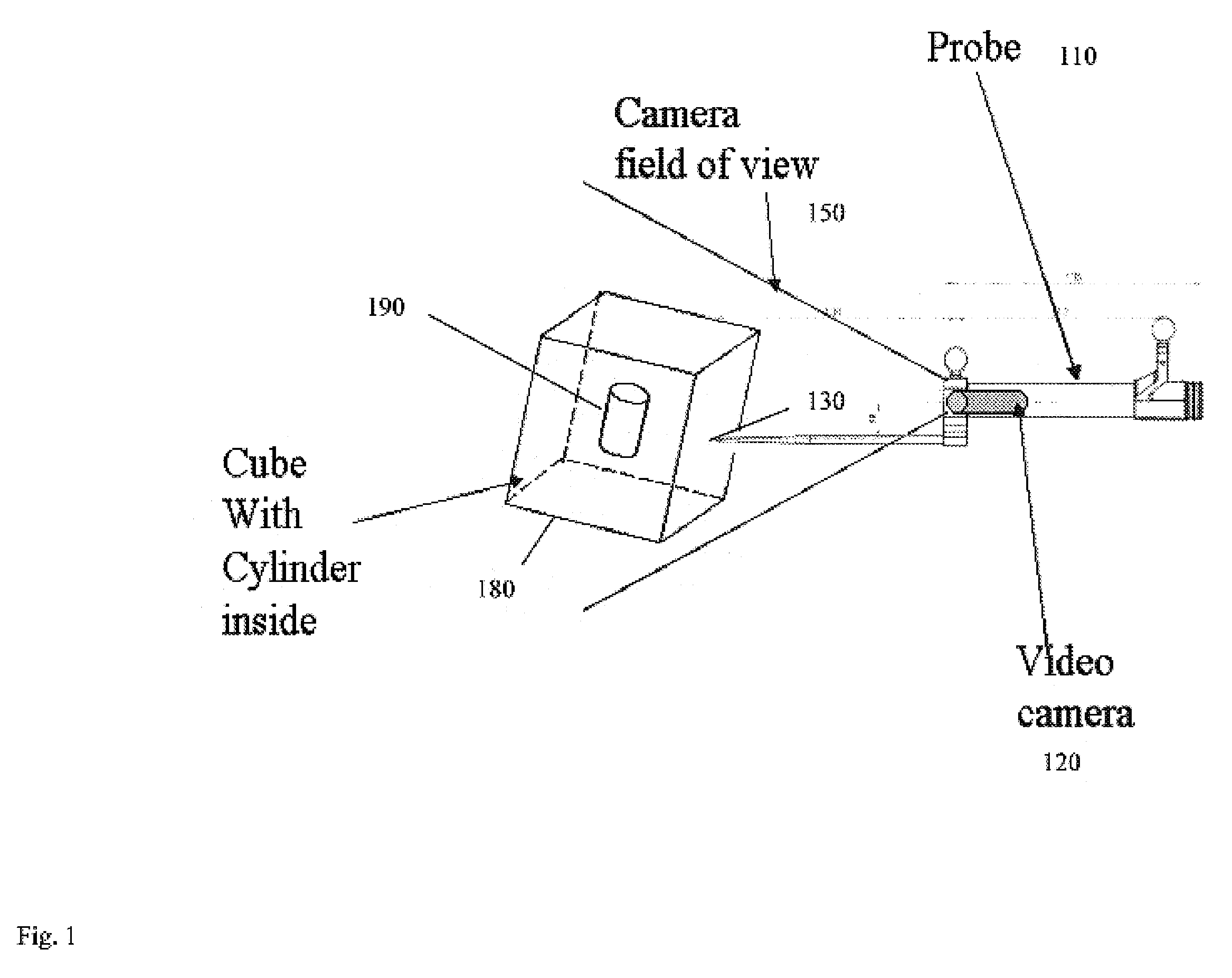
Computer enhanced surgical navigation imaging system (camera probe)
ActiveUS20050015005A1Enhanced interactionEasy to navigateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesViewpointsSurgical approach
A system and method for navigation within a surgical field are presented. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention a micro-camera can be provided in a hand-held navigation probe tracked by a tracking system. This enables navigation within an operative scene by viewing real-time images from the viewpoint of the micro-camera within the navigation probe, which are overlaid with computer generated 3D graphics depicting structures of interest generated from pre-operative scans. Various transparency settings of the camera image and the superimposed 3D graphics can enhance the depth perception, and distances between a tip of the probe and any of the superimposed 3D structures along a virtual ray extending from the probe tip can be dynamically displayed in the combined image. In exemplary embodiments of the invention a virtual interface can be displayed adjacent to the combined image on a system display, thus facilitating interaction with various navigation related functions. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention virtual reality systems can be used to plan surgical approaches with multi-modal CT and MRI data. This allows for generating 3D structures as well as marking ideal surgical paths. The system and method presented thus enable transfer of a surgical planning scenario to a real-time view of an actual surgical field, thus enhancing navigation.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
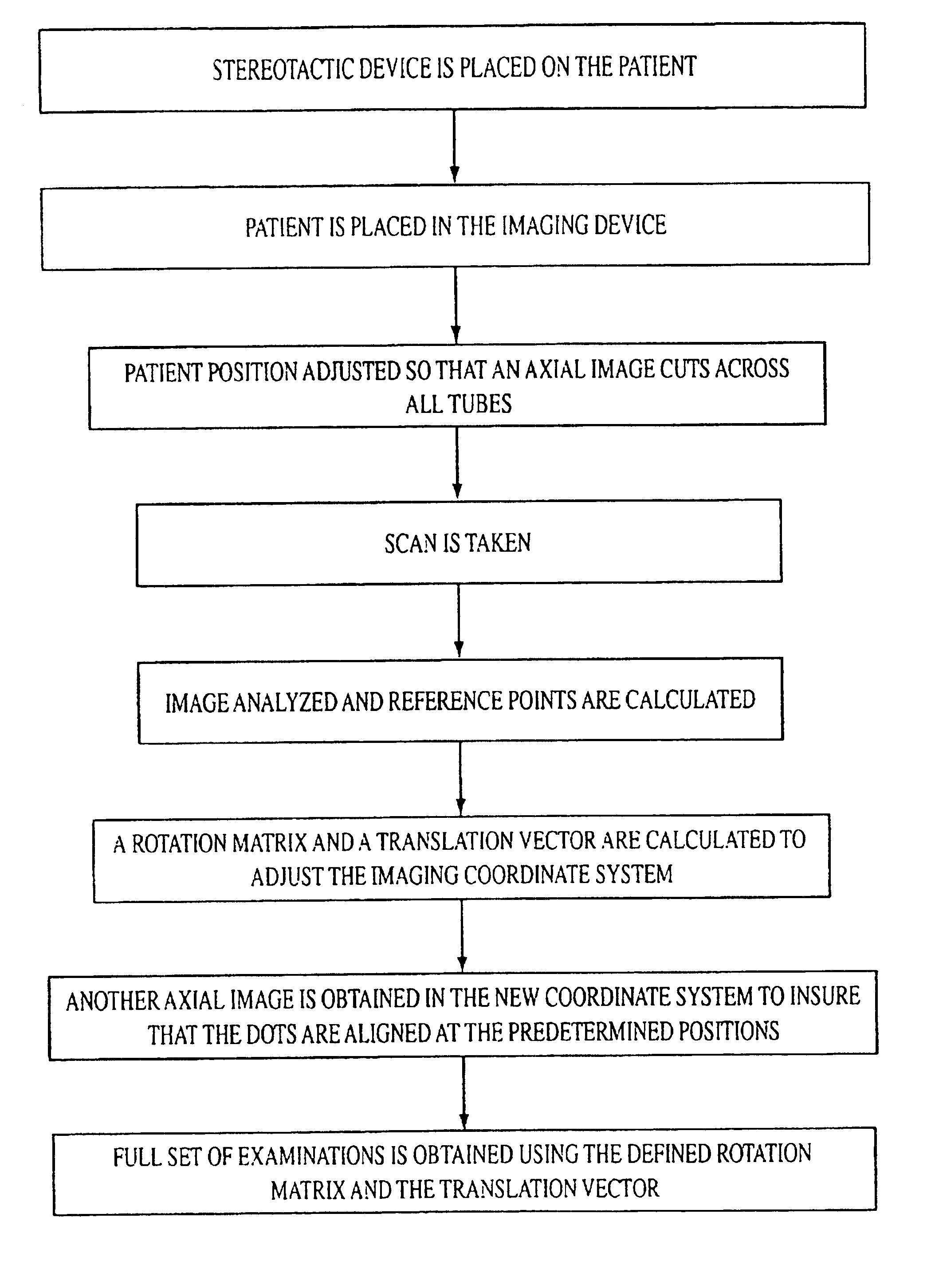
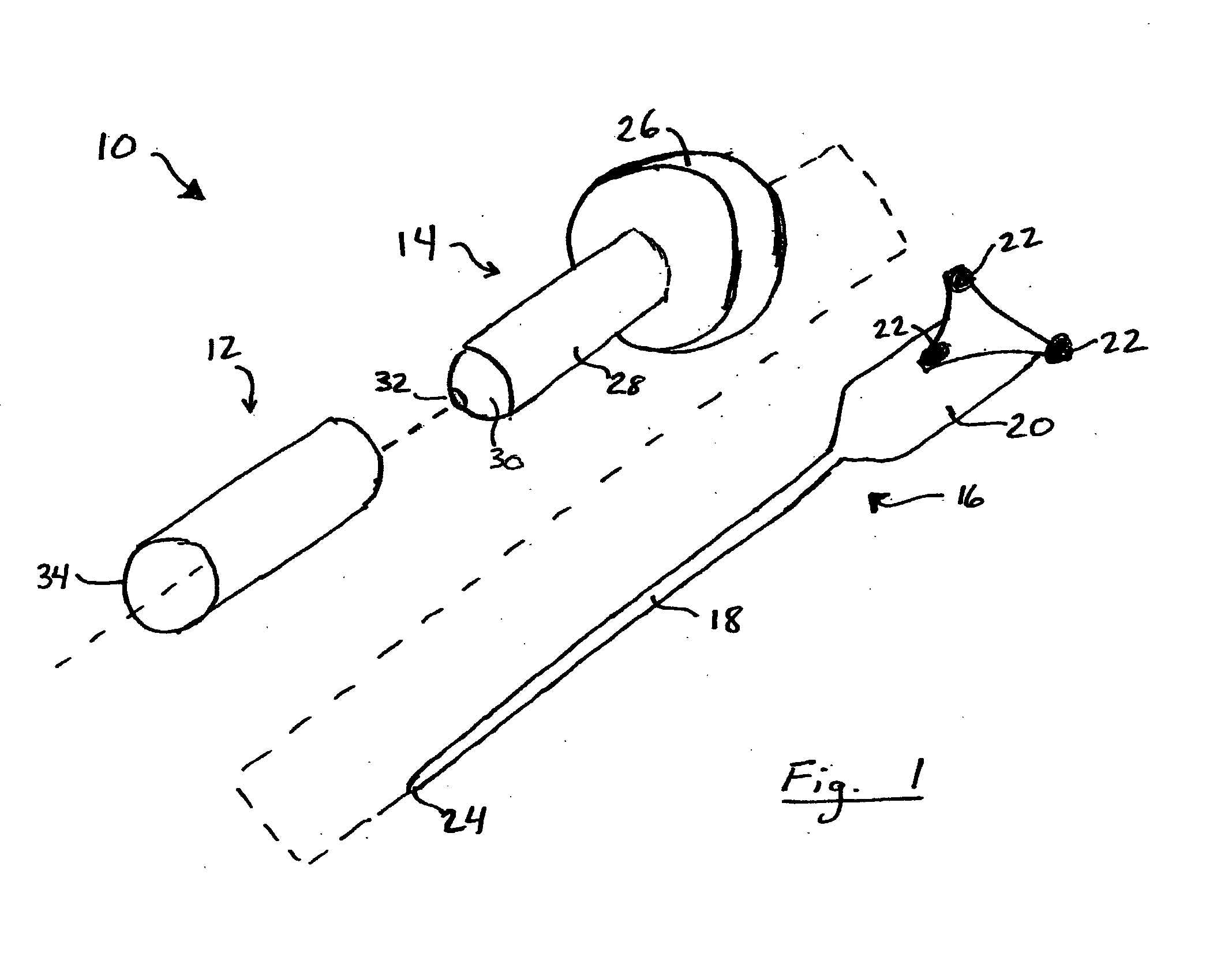
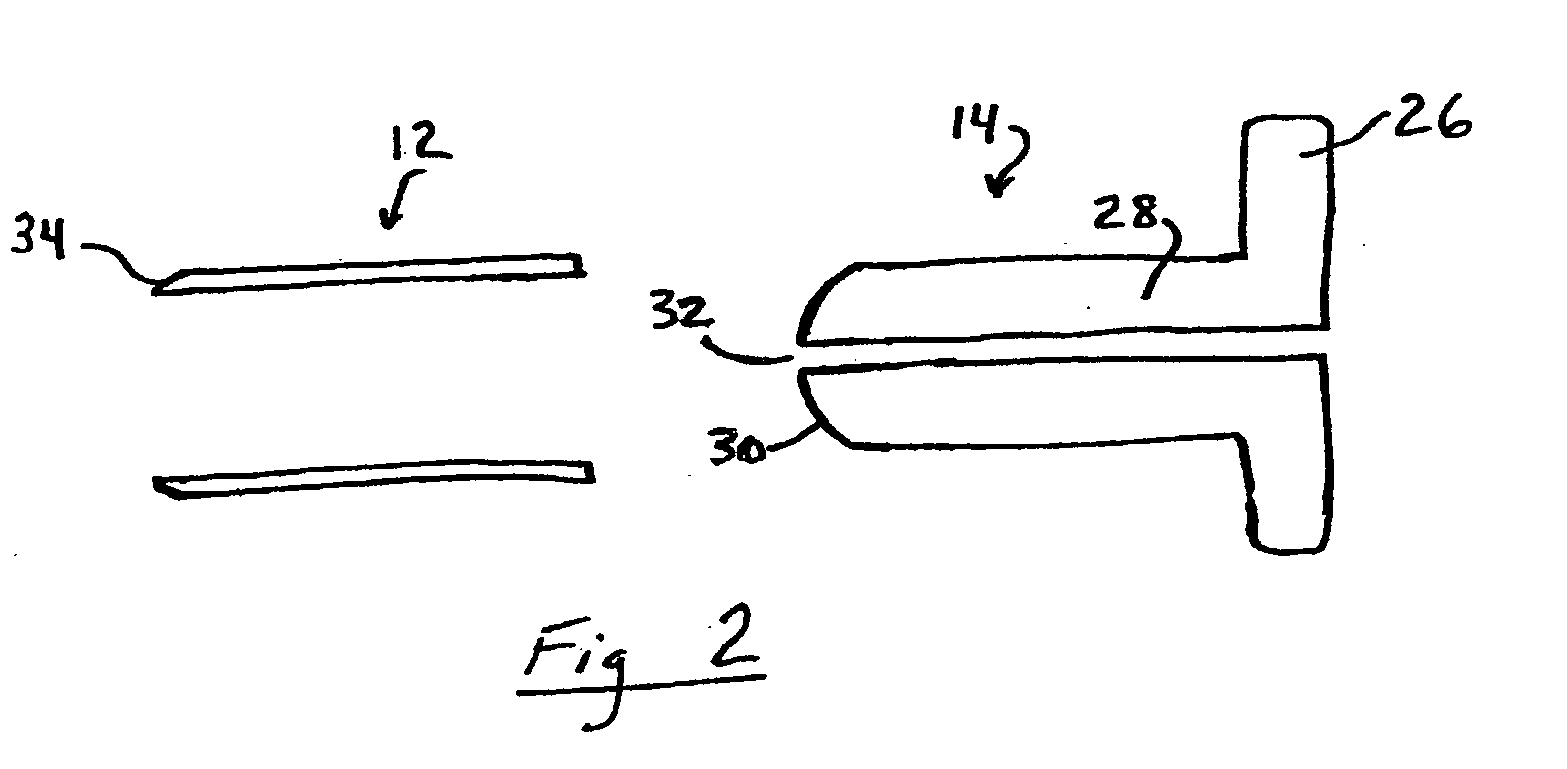
Versatile stereotactic device and methods of use
InactiveUS6684098B2Easy to checkEasily and repeatedly examinedDiagnostic markersComputer-aided planning/modellingFollow up examinationResonance
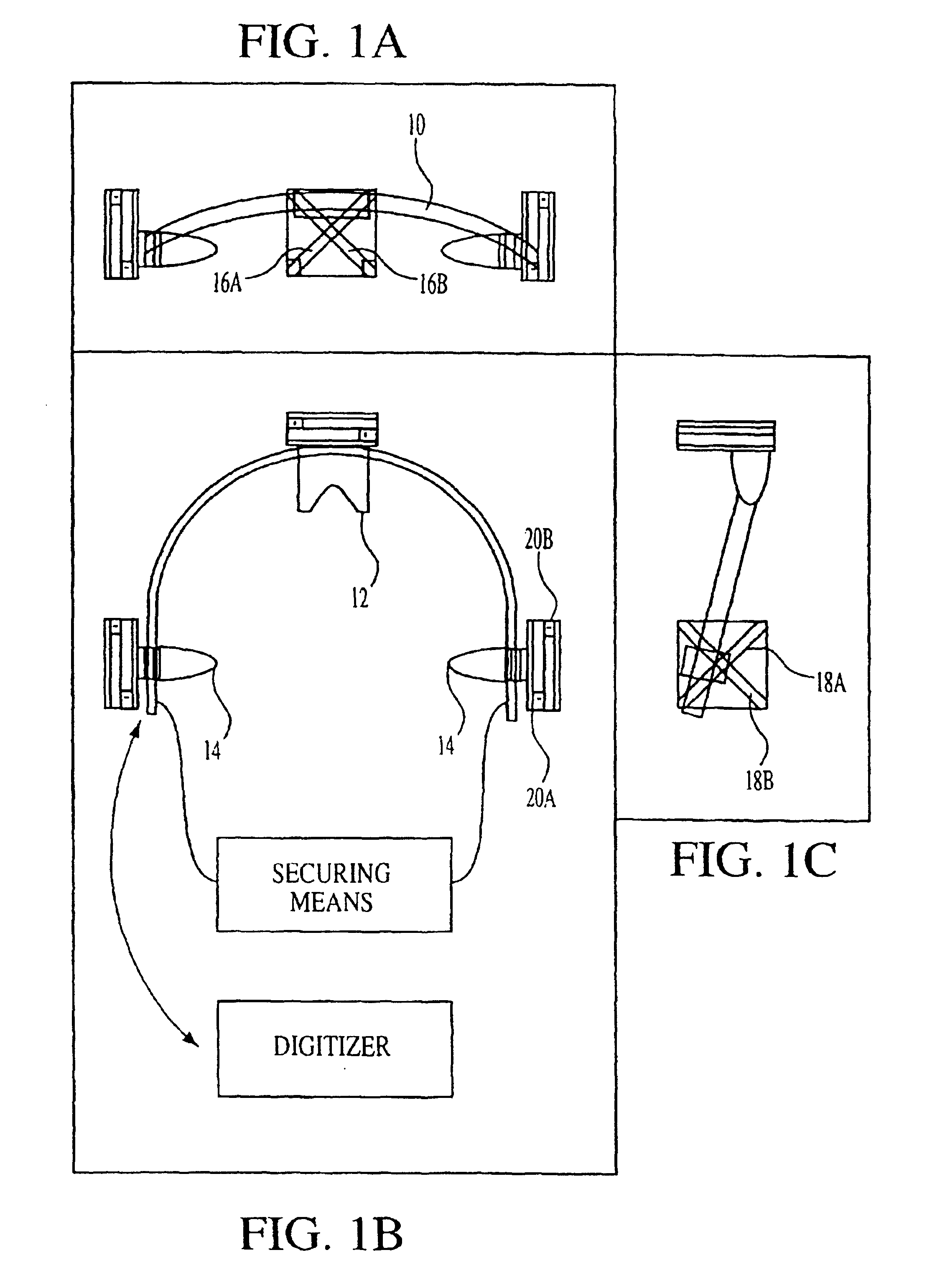
A stereotactic device for use with an imager such as a magnetic resonance imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation. Markers on a stereotactic device can be tracked during an MRI scan to compensate for patient motion during the scan.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Methods and apparatus for surgical planning
ActiveUS8170716B2Easy to planPrecise positioningProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical siteEngineering
Methods and apparatus for enhancing surgical planning provide enhanced planning of entry port placement and / or robot position for laparoscopic, robotic, and other minimally invasive surgery. Various embodiments may be used in robotic surgery systems to identify advantageous entry ports for multiple robotic surgical tools into a patient to access a surgical site. Generally, data such as imaging data is processed and used to create a model of a surgical site, which can then be used to select advantageous entry port sites for two or more surgical tools based on multiple criteria. Advantageous robot positioning may also be determined, based on the entry port locations and other factors. Validation and simulation may then be provided to ensure feasibility of the selected port placements and / or robot positions. Such methods, apparatus and systems may also be used in non-surgical contexts, such as for robotic port placement in munitions diffusion or hazardous waste handling.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC +1
Systems, methods, and computer program products for analysis of vessel attributes for diagnosis, disease staging, and surgical planning
Systems, methods, and computer program products for analysis of vessel attributes for diagnosis, disease staging, and surgical planning are disclosed. A method for analyzing blood vessel attributes may include developing an atlas including statistical measures for at least one blood vessel attribute. The statistical measures can be developed from blood vessel image data from different individuals. Blood vessel attribute measurements can be obtained from an individual subject. The individual subject's blood vessel attribute measurements can be compared to the statistical measures in the atlas. Output may be produced indicative of a physical characteristic of the individual based on results from the comparison.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Apparatus and Methods for Performing Brain Surgery
InactiveUS20080109026A1Easy to installAssisting understandingCannulasInfusion syringesLess invasive surgeryMedicine
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may he inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferable is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor.
Owner:NICO CORP
Apparatus and methods for performing brain surgery
ActiveUS20090048622A1Many of techniqueEasy to installCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryLess invasive
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent to the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may be inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferably is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor. Dilating obturator structures having a rounded or semi-spherical tip and / or an optical window for visualizing brain tissue during expansion are contemplated.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL INC
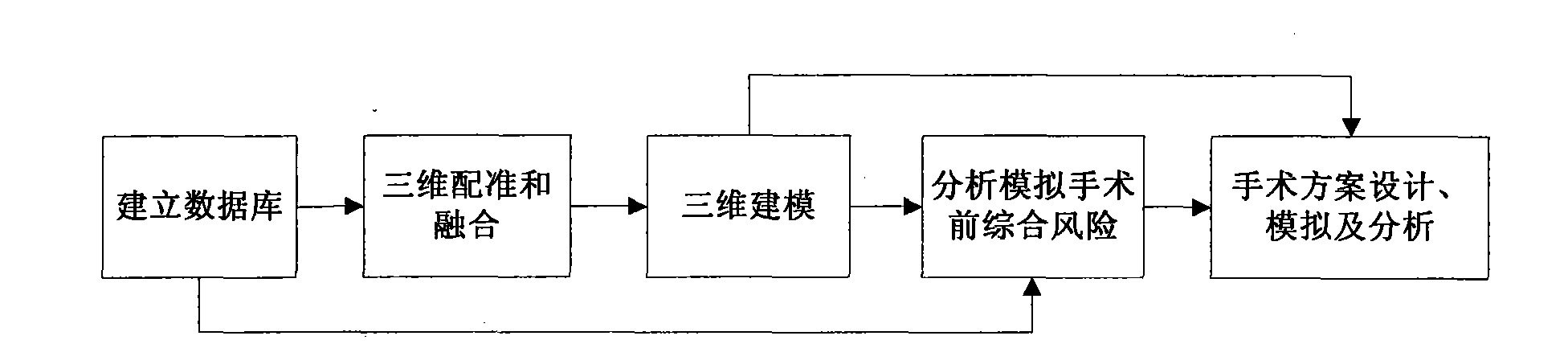
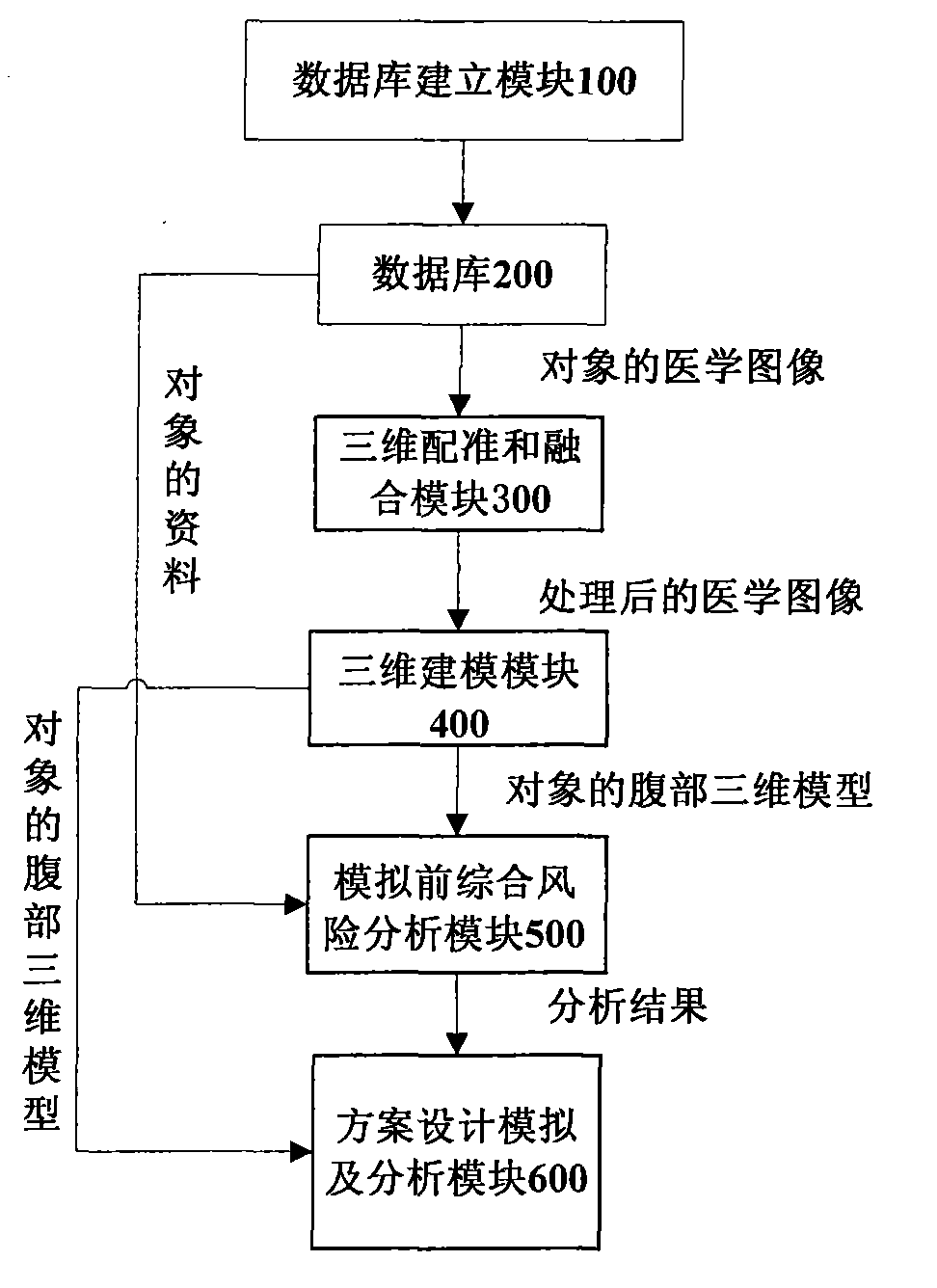
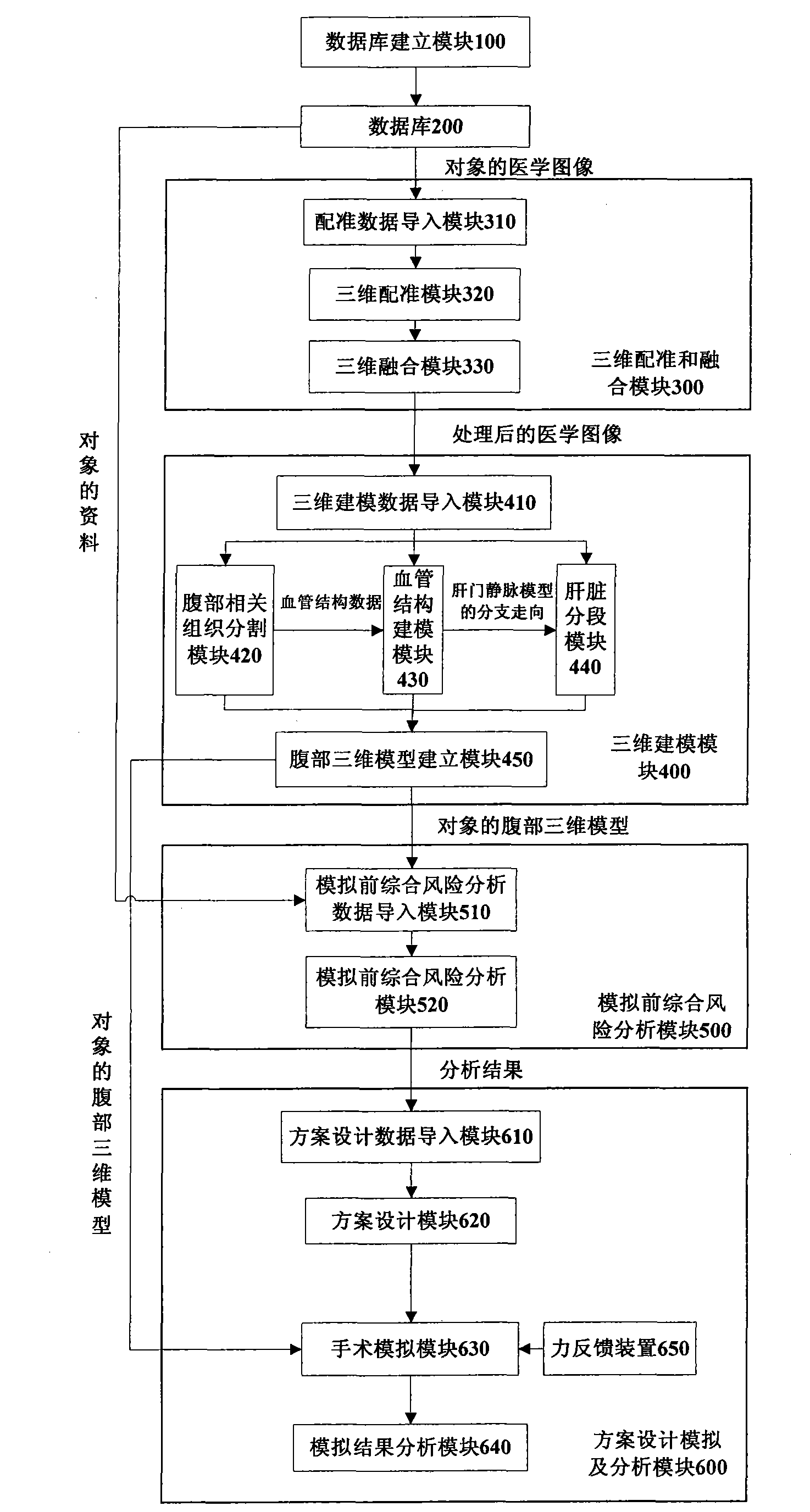
Hepatic tumor comprehensive surgical planning analogy method and system thereof based on three-dimensional multimode images
ActiveCN102117378AImprove proficiencySpecial data processing applications3D modellingSurgical skillsReoperative surgery
The invention discloses a hepatic tumor comprehensive surgical planning analogy method and a system thereof based on three-dimensional multimode images. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a data base containing the data of an object is constructed; secondly, three-dimensional registration and fusion are conducted on the medical images, having different modes or single mode and different periods, of the object; thirdly, a specific tissue is divided by the automatic and semi-automatic modes, and the three-dimensional modeling of important tissues in and around the liver is realized by the three-dimensional reconstruction technology so as to reconstruct an abdominal three-dimensional model having the immersion and interaction features; fourthly, before-simulation comprehensive risk analysis is conducted based on the modeling result, referred to the practice guidelines and combined with the object information; and finally, all kinds of simulation surgical plans are designed according to the result of the comprehensive risk analysis, surgical simulation with strong sense of reality is conducted, a surgical route is planned, and risk and prognosis analysis is conducted on the planning simulation result. Through repeated surgical simulations, the surgical skills and the mastery of a user can be improved, and medical teaching can be conducted through the method and the system.
Owner:RAYCAN TECH CO LTD SU ZHOU +1
Apparatus and method for customized report viewer
InactiveUS20050096530A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical report generationAbnormal tissue growthBI-RADS
A system for the automatic generation of custom report viewing utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection technology to identify cancerous tumors. A typical collection of data from a patent's scan may include hundreds of images and associated data. The custom report viewer allows one physician, such as a radiologist, to analyze the data and prepare a report. The generated report may contain images, computed measurements, classifications based on a standard (such as the ACR BI-RADS for Breast MR), and locations relative to landmarks. Different physicians, such as an oncologist or a surgeon, may have need of differing images and supporting data for their own purposes. Each physician may select, in advance, custom selection criteria that are stored in association with that physician. A report generator module uses the stored selection criteria and report filtering to extract the images and supporting data specified by the particular physician. The system allows a surgeon to alter the selection criteria and obtain further images if necessary and permits the generation of multiple selection criteria by one physician for different purposes, such as surgical planning, therapy reporting, and the like.
Owner:MERGE CAD
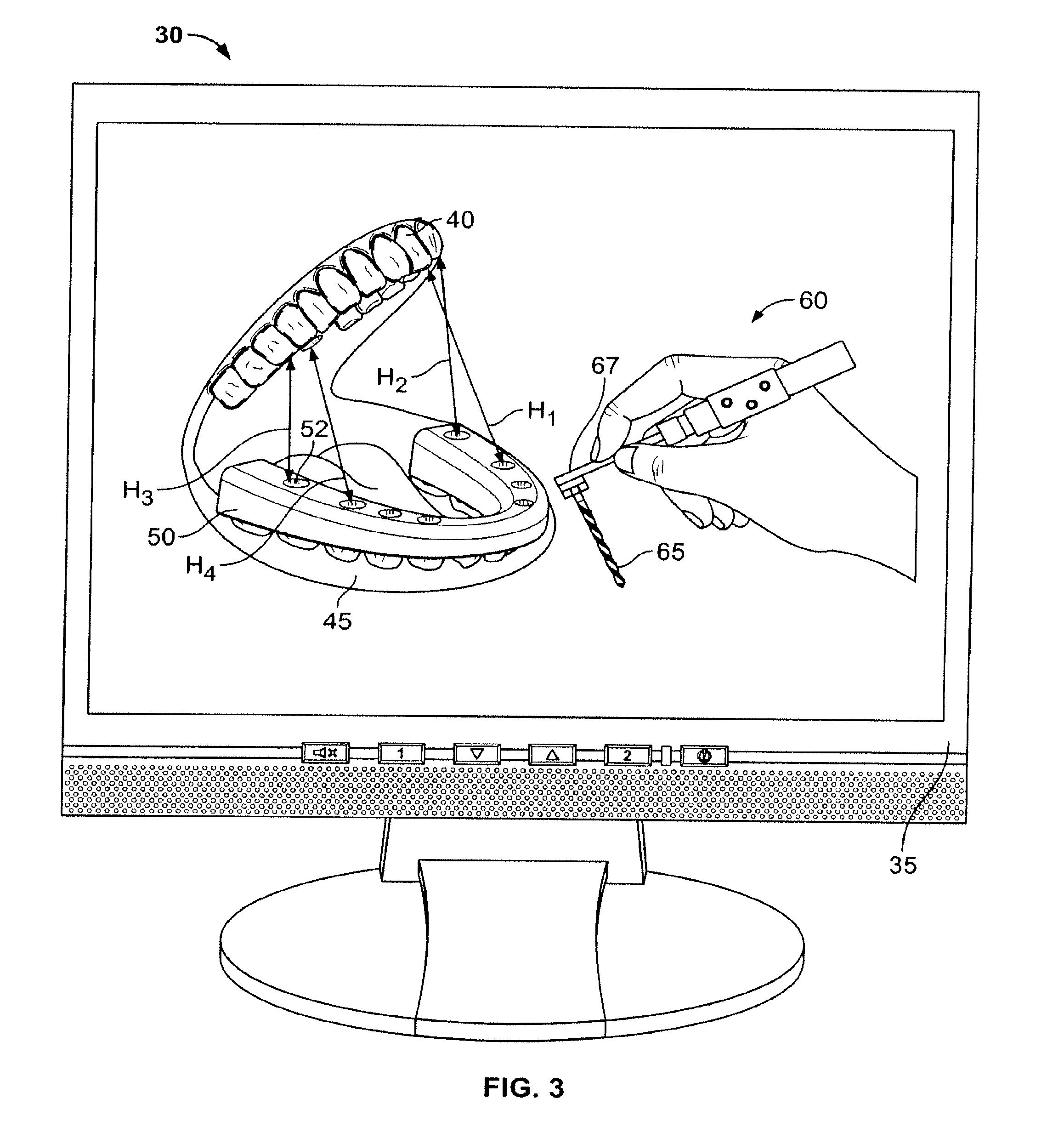
Method for pre-operative visualization of instrumentation used with a surgical guide for dental implant placement
The invention relates to manufacturing a surgical guide to be placed in a patient's mouth. The patient's mouth is scanned to obtain surgical-region scan data at a region where an implant is to be located. The patient's mouth is also scanned in the opened position to acquire dental conditions opposite from the surgical region so as to obtain opposing-condition scan data. A virtual model is developed using the surgical-region scan data and the opposing-condition scan data. Using the virtual model, a surgical plan is developed that includes the location of the implant to be installed in the patient. A virtual surgical guide is also developed based on the surgical plan. The dimensions of instrumentation to be used with the surgical guide are checked to ensure they will fit within the mouth by use of the opposing-condition scan data. After checking, final surgical-guide manufacturing information is obtained for manufacturing the surgical guide.
Owner:BIOMET 3I LLC
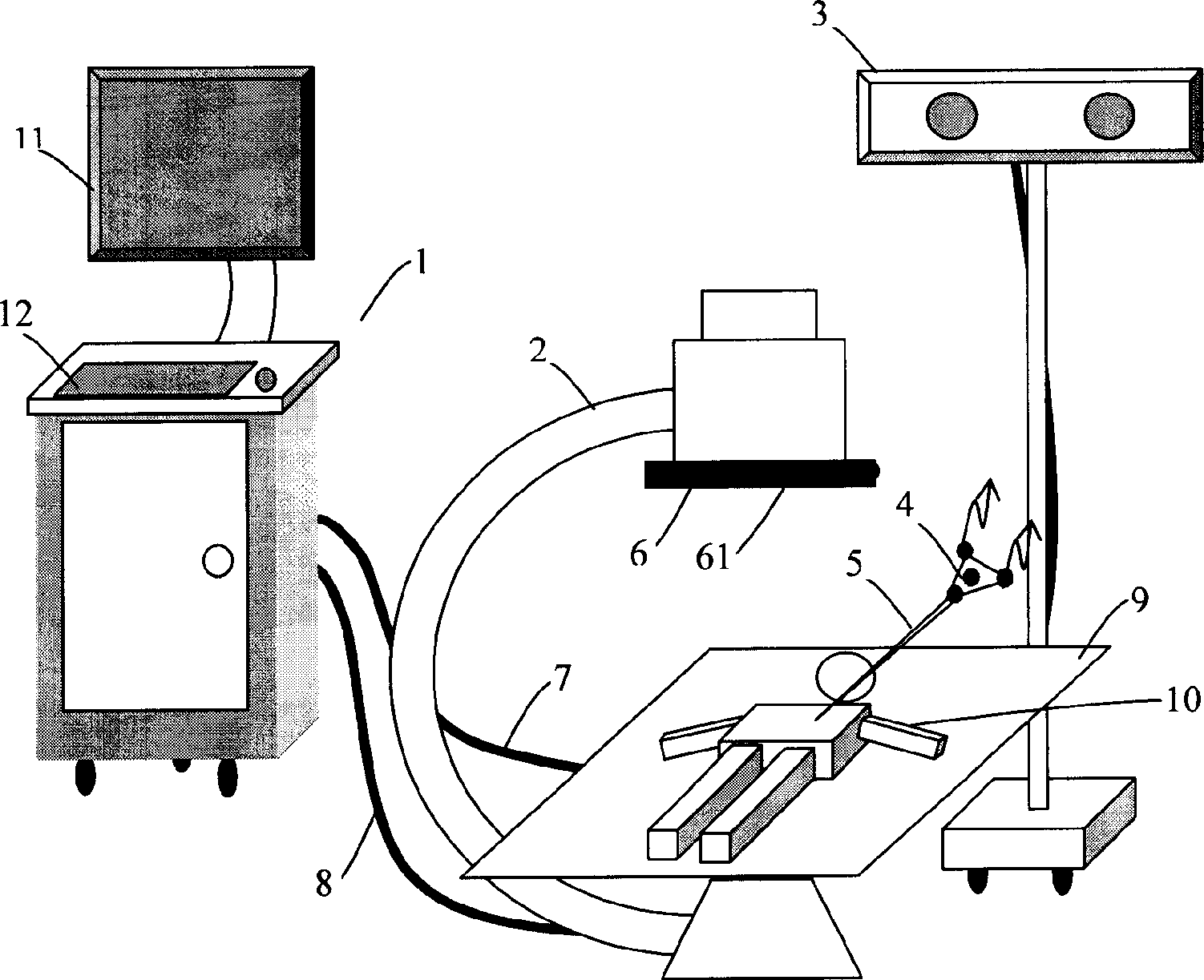
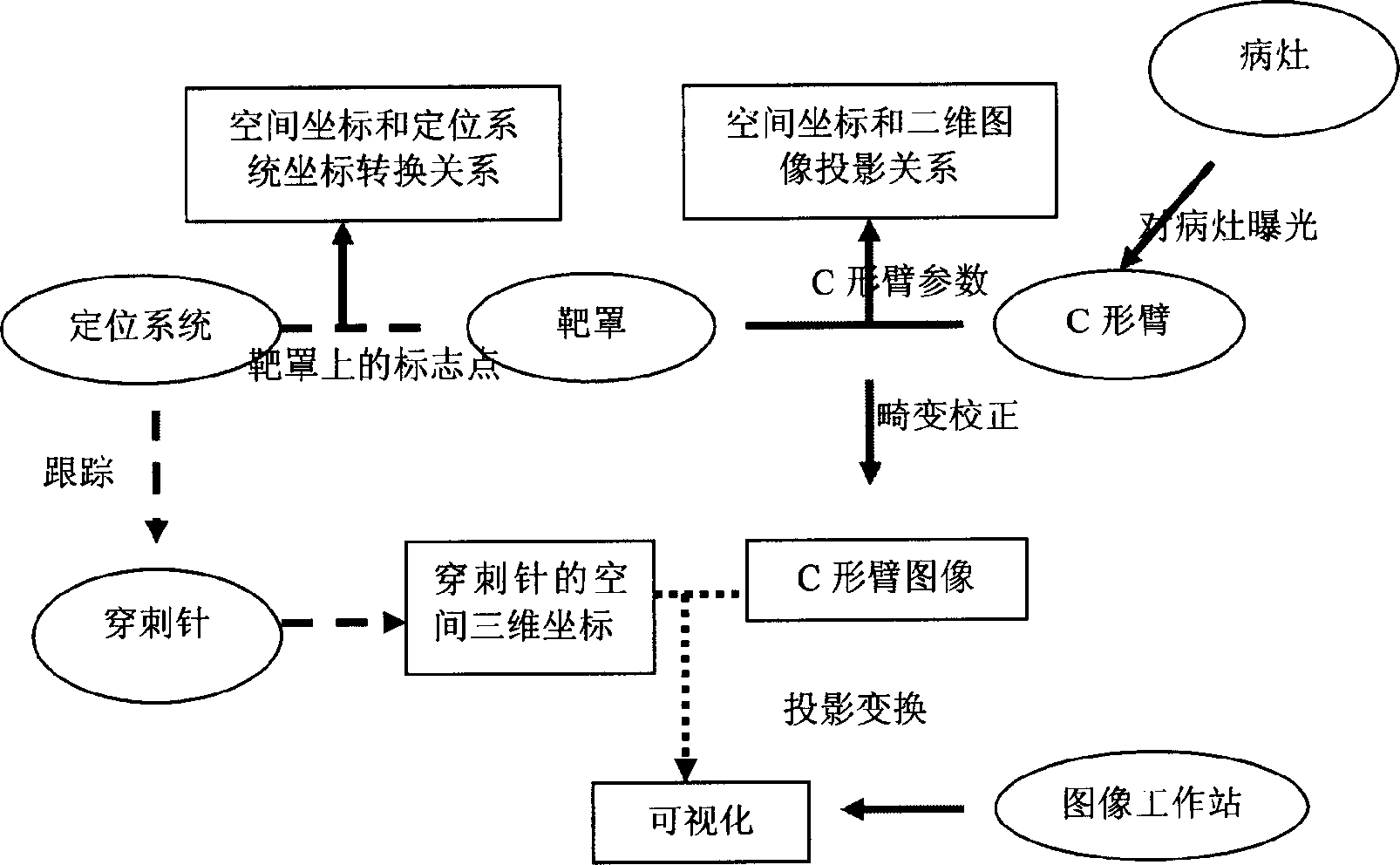
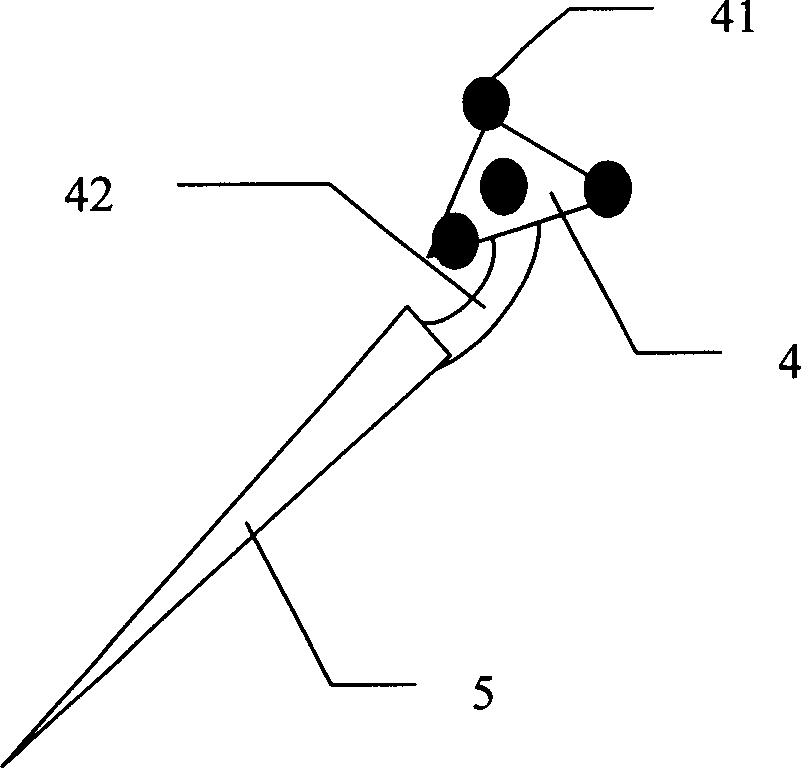
Puncture guiding system and method in computer aided percutaneous nephrostolithotomy
InactiveCN1806771AReduce the number of X-ray exposuresAccurate spatial positioningSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsNeedle positionComputer-aided
A computer assistant piercing leading system for dermal nephrocentesis, comprising: a brachial in C shape and its mating image taking device, a positioning system and its mating tracker, a target cover, an image working station, and a mating software treating image leading. The invention employs tracking for space target and image treating technology with computer to track the position and direction of puncture needle in real time, which helps doctor choose proper position for puncture needle and make detail operation plan. The choice of needle position can be decided by taking only one or two images, which can reduce the X exposition time for doctor and patient.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Computer-aided bone distraction
InactiveUS7837621B2Easy to installLow costAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputerised tomographsDistractionMedicine
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Computer-assisted joint analysis using surface projection
InactiveUS20080312663A1Improve visualizationReduce decreaseImage enhancementImage analysisData setJoint analysis
A system and method for computer-assisted joint analysis, wherein the joint elements in a three-dimensional imaging data set are segmented and then projected onto a two-dimensional or three-dimensional reference area for interference analysis and surgical planning.
Owner:BRAINLAB
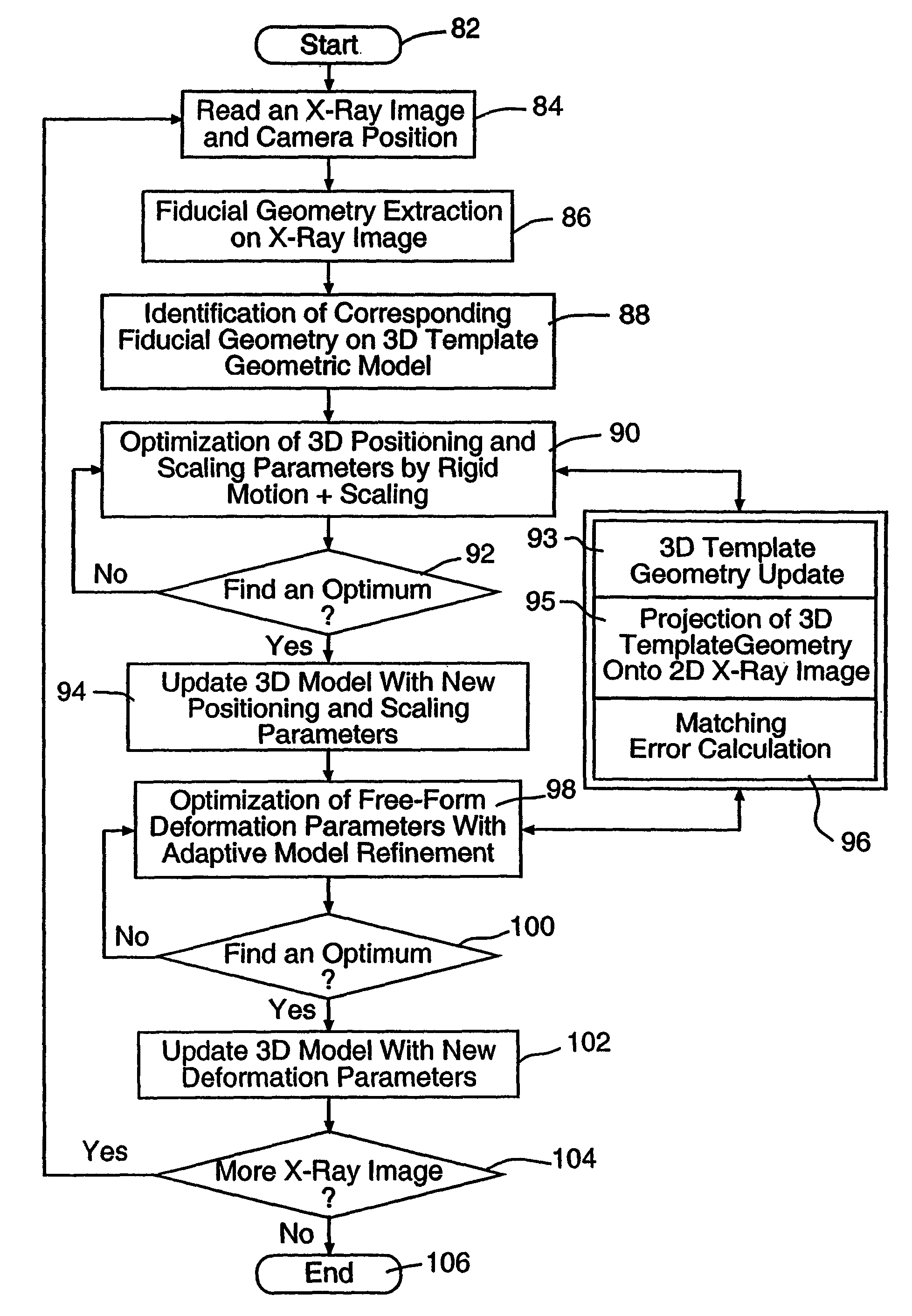
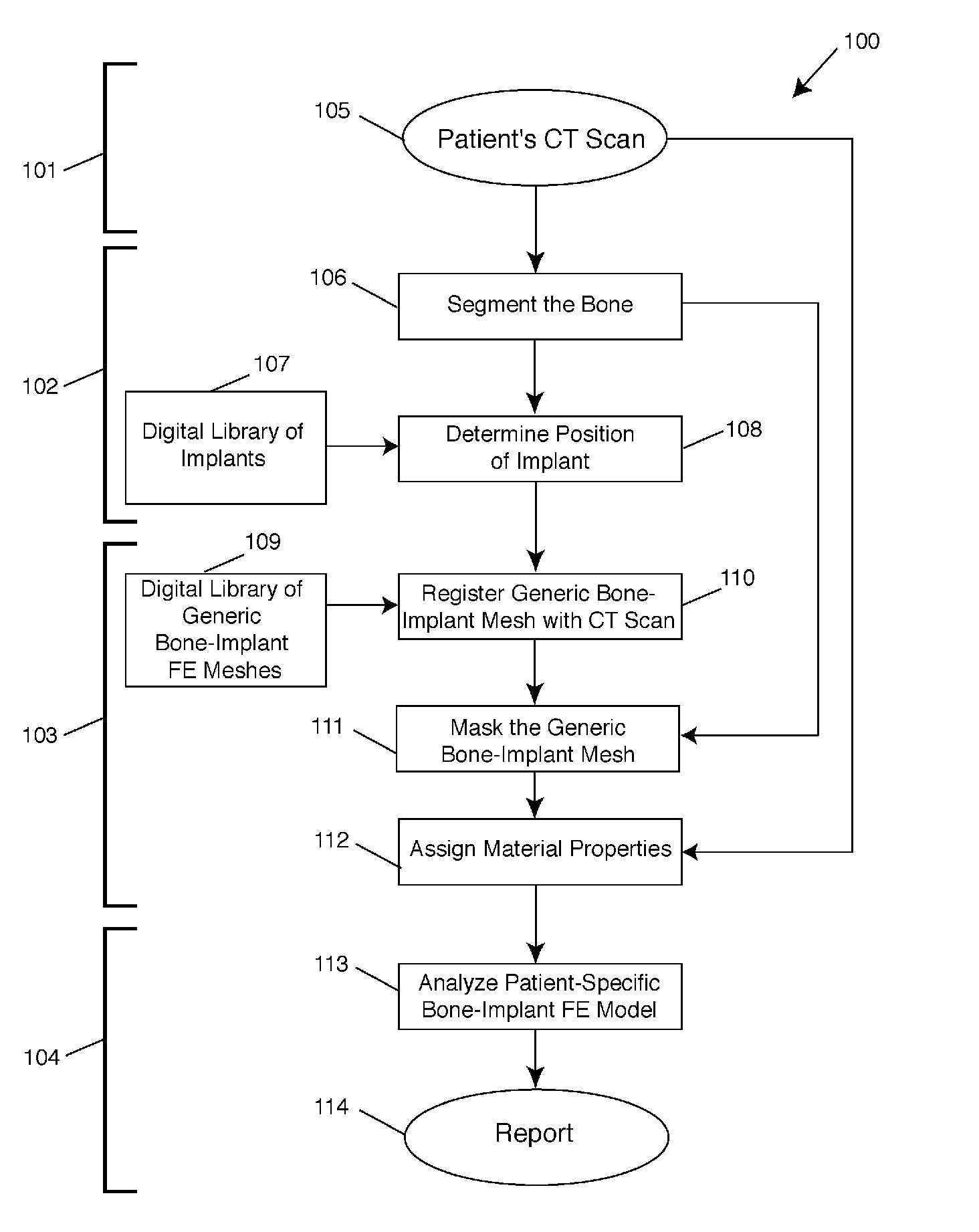
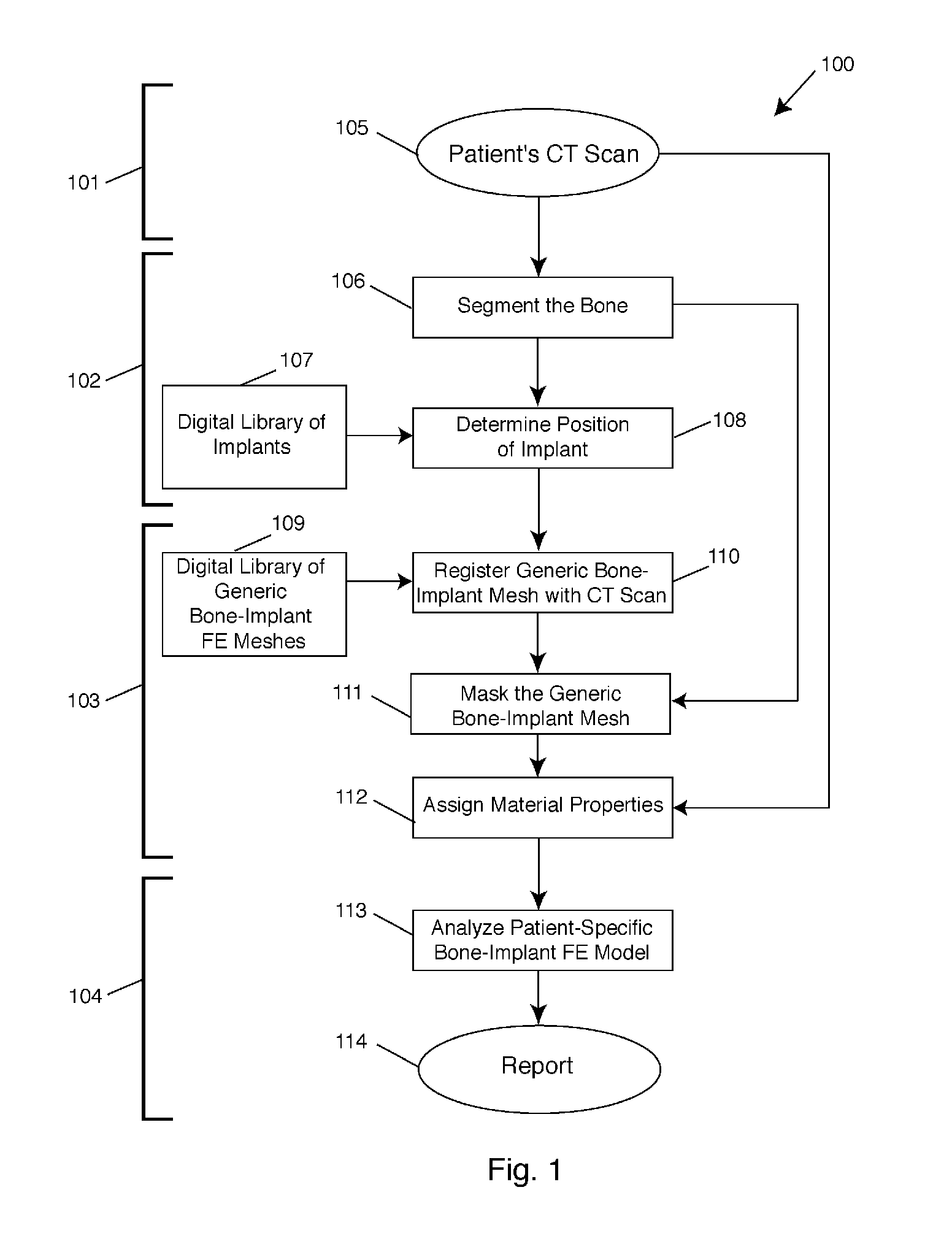
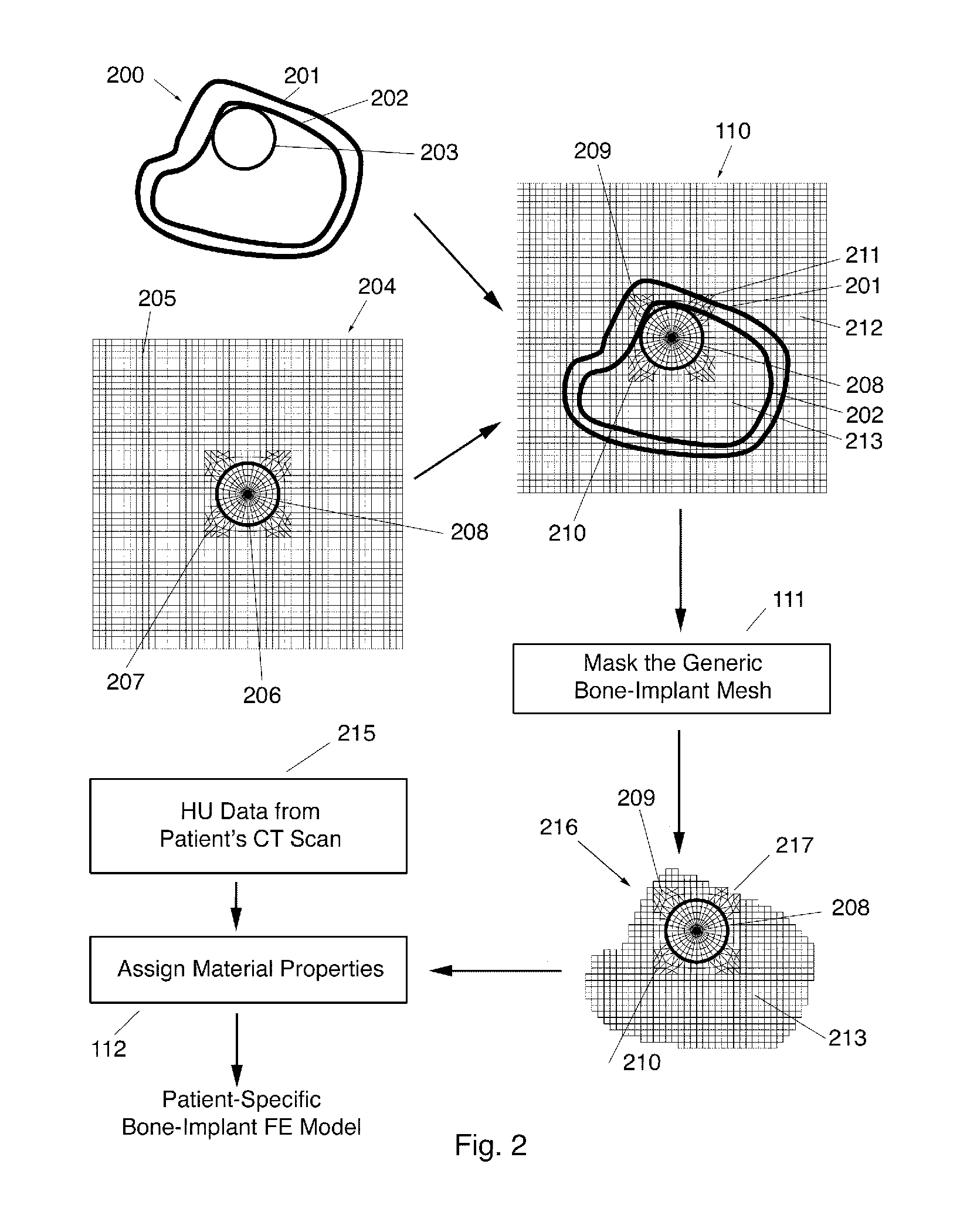
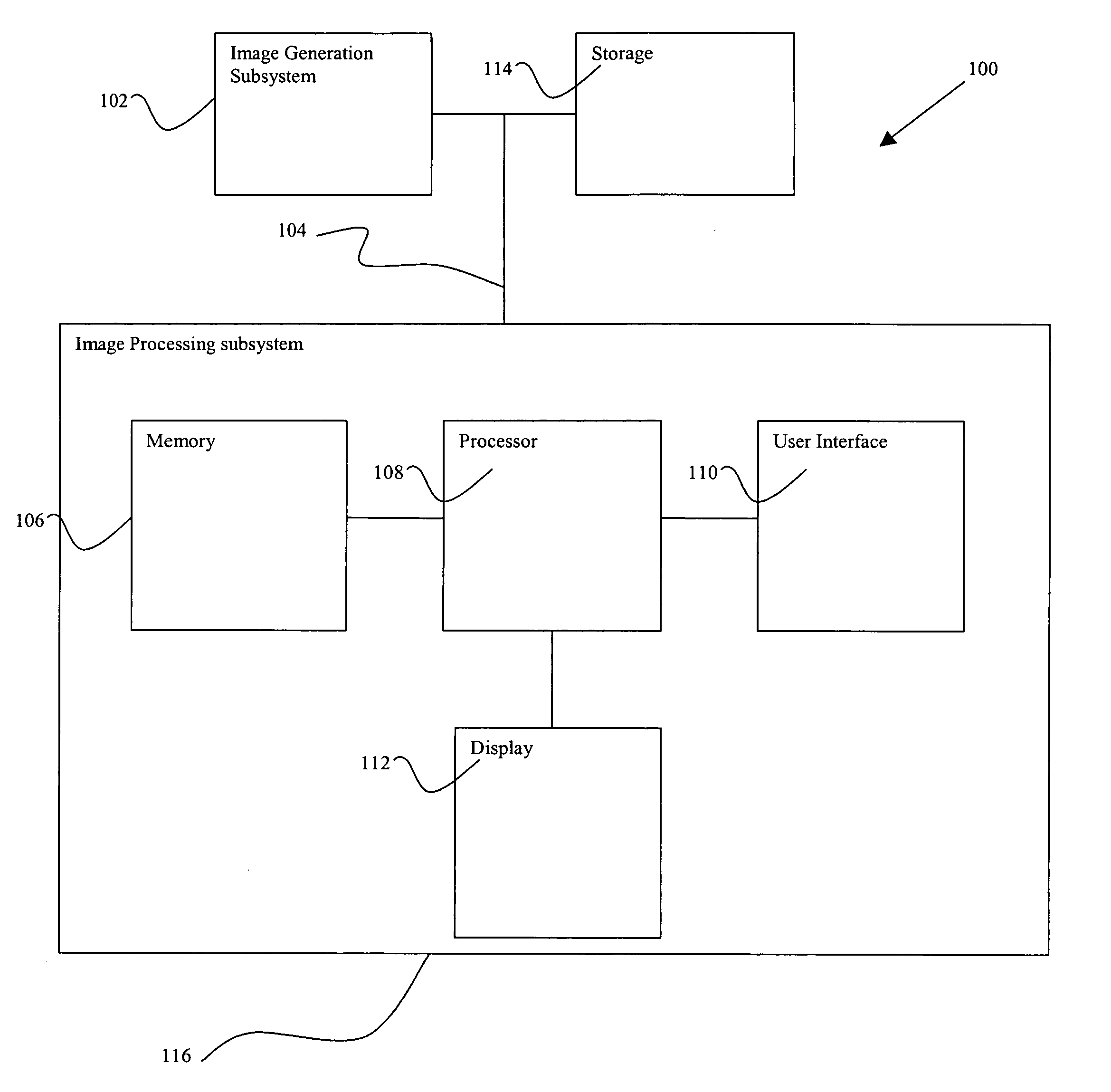
Automated patient-specific bone-implant biomechanical analysis
ActiveUS8855389B1Eliminate needRule out the possibilityMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBiomechanicsElement analysis
Owner:O N DIAGNOSTICS
Methods and systems for facilitating surgical procedures
InactiveUS20070129626A1Facilitate surgeryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic markersAuditory feedbackSurgery procedure
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a method for facilitating surgery including: tracking a position of at least a portion of a surgical implement in a volume of interest; recognizing a surgical plan corresponding to at least a portion of the volume of interest; and providing feedback based on a correspondence between the position of the at least a portion of the surgical implement and the surgical plan. In an embodiment, the feedback is provided in real-time. In an embodiment, the feedback includes at least one of: haptic feedback, thermal feedback, optical feedback, and auditory feedback. In an embodiment, the surgical plan includes a previously generated radiological image. In an embodiment, the surgical plan includes at least one trajectory for the at least a portion of the surgical implement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Surgical Navigation Planning System and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20140303486A1Simplifying display settingConvenient reviewSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingMedical imagingImage conversion
The present disclosure provides a surgical planning and navigation system imports multiple medical imaging sources of the same body part for integrated display in the same coordinate. Images are converted into 3D volumes, spatially co-registering each image volume to a base anatomical image.
Owner:ADVENTIST HEALTH SYSTSUNBELT
Method For Pre-Operative Visualization Of Instrumentation Used With A Surgical Guide For Dental Implant Placement
The invention relates to manufacturing a surgical guide to be placed in a patient's mouth. The patient's mouth is scanned to obtain surgical-region scan data at a region where an implant is to be located. The patient's mouth is also scanned in the opened position to acquire dental conditions opposite from the surgical region so as to obtain opposing-condition scan data. A virtual model is developed using the surgical-region scan data and the opposing-condition scan data. Using the virtual model, a surgical plan is developed that includes the location of the implant to be installed in the patient. A virtual surgical guide is also developed based on the surgical plan. The dimensions of instrumentation to be used with the surgical guide are checked to ensure they will fit within the mouth by use of the opposing-condition scan data. After checking, final surgical-guide manufacturing information is obtained for manufacturing the surgical guide.
Owner:BIOMET 3I LLC
Surgical planning method and system for percutaneous puncture
ActiveCN102961187AReduce riskLow implementation costDiagnosticsComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical operationMedicine
The invention is suitable for the mechanical technology field, and provides a surgical planning method and system for the percutaneous puncture. In order to realize the above purpose, the invention provides a surgical planning method for the percutaneous puncture. The method comprises the following steps of: A) obtaining the mechanical image data of a patient; B) according to the mechanical image data, reconstructing the three-dimensional model of the relevant organ and / or tissue and / or focus of the patient; and C) determining the surgical operation process of the percutaneous puncture on the three-dimensional model by a virtual puncture device. Therefore, according to the invention, a user can repeatedly carry out the skin puncture operation by the virtual puncture device so as to accurately obtain the skin puncture point, the angle and the puncture path of the patient.
Owner:SHENZHEN YORATAL DMIT
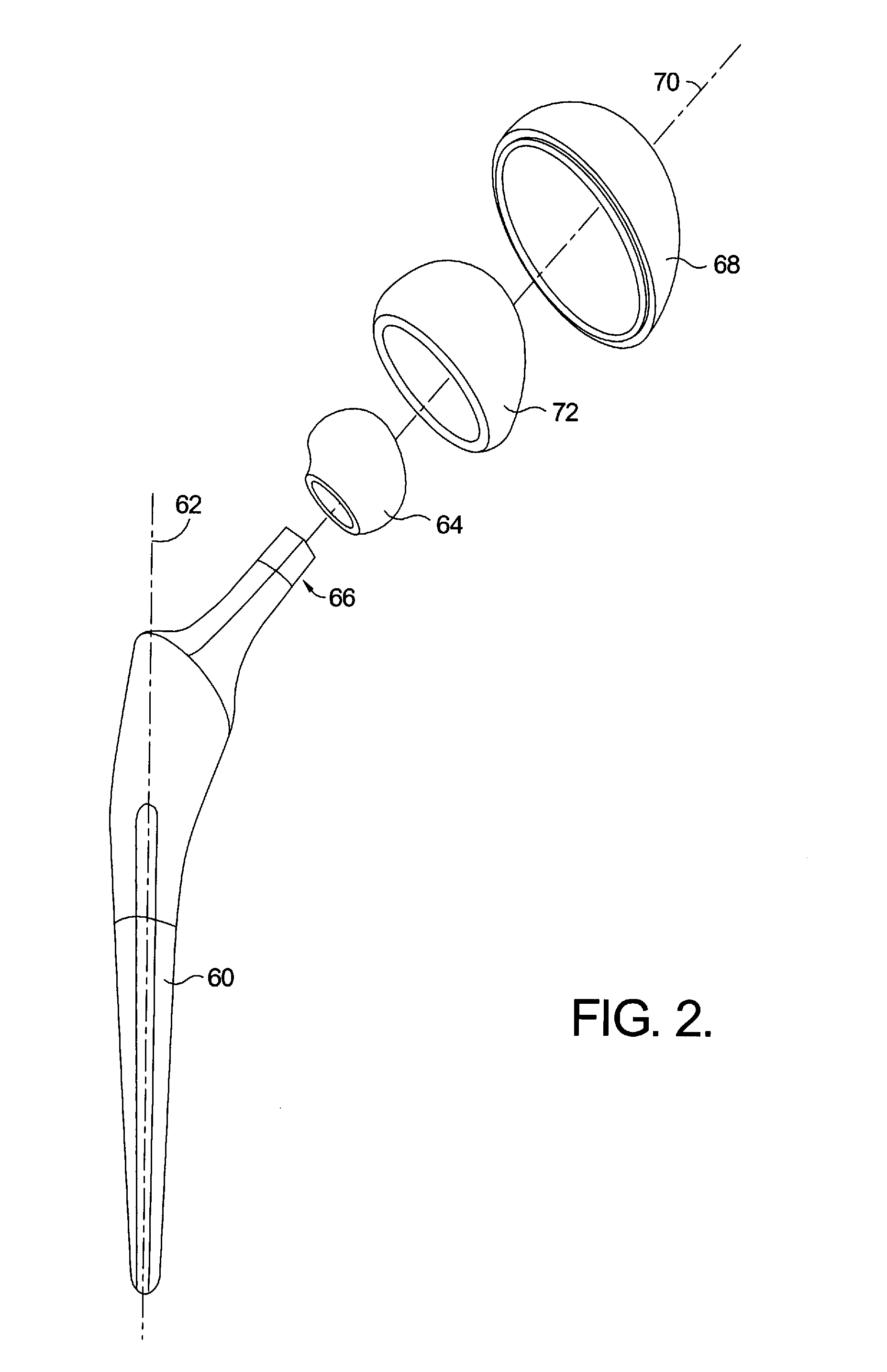
Accurate analogs for prostheses using computer generated anatomical models
Pre-surgical planning for cranial and facial reconstruction includes preparing a computer generated jaw or skull model for determining a locational position for a dental implant, a surgical bone implant to repair missing bone in the cranium, install ear prostheses, and / or install nose prostheses. The computer generated jaw or skull model is made from medical imagery and computer aided design. A surgical guide is prepared with oversize holes in registration with analogs for the dental or surgical bone implants to be inserted at the locational positions determined by a dentist or surgeon in the jaw or cranial skull model. The surgical guide is fitted atop each analog, and the surgical guide is bonded to the jaw or skull model at a predetermined angle of the analog in the jaw or skull. The surgical guide is removed from the model attached to the law or skull of a patient for accurate drilling during the dental or surgical procedure for insertion of the implants into the jaw or skull of the patient.
Owner:CLM ANALOGS LLC
Method and system for surgical planning
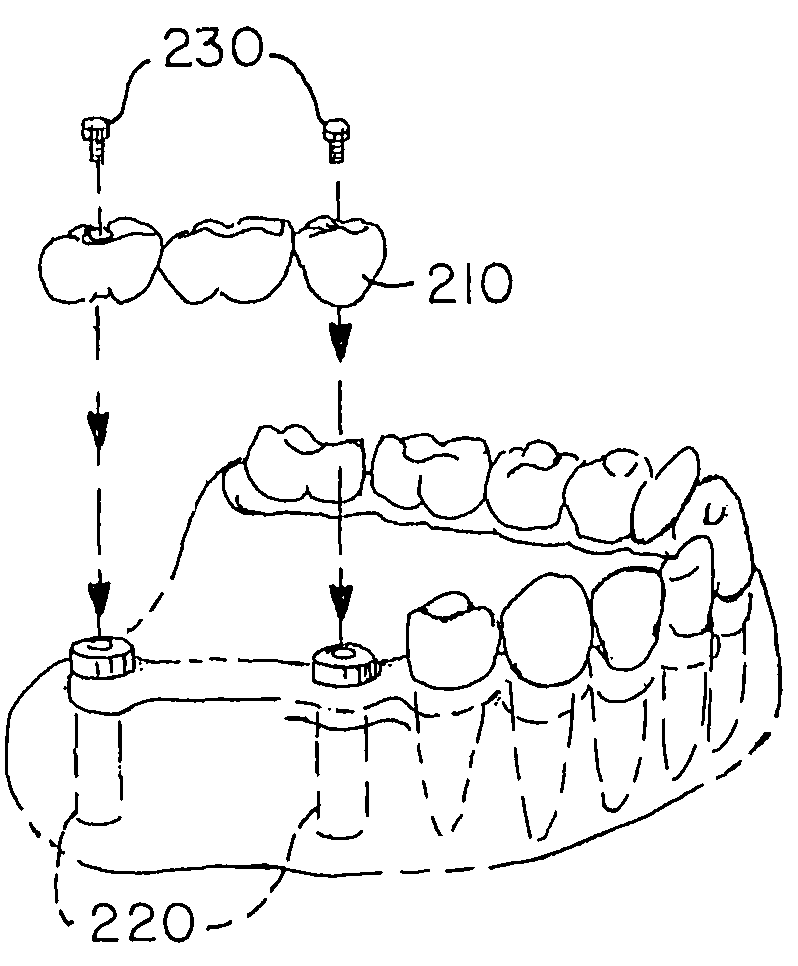
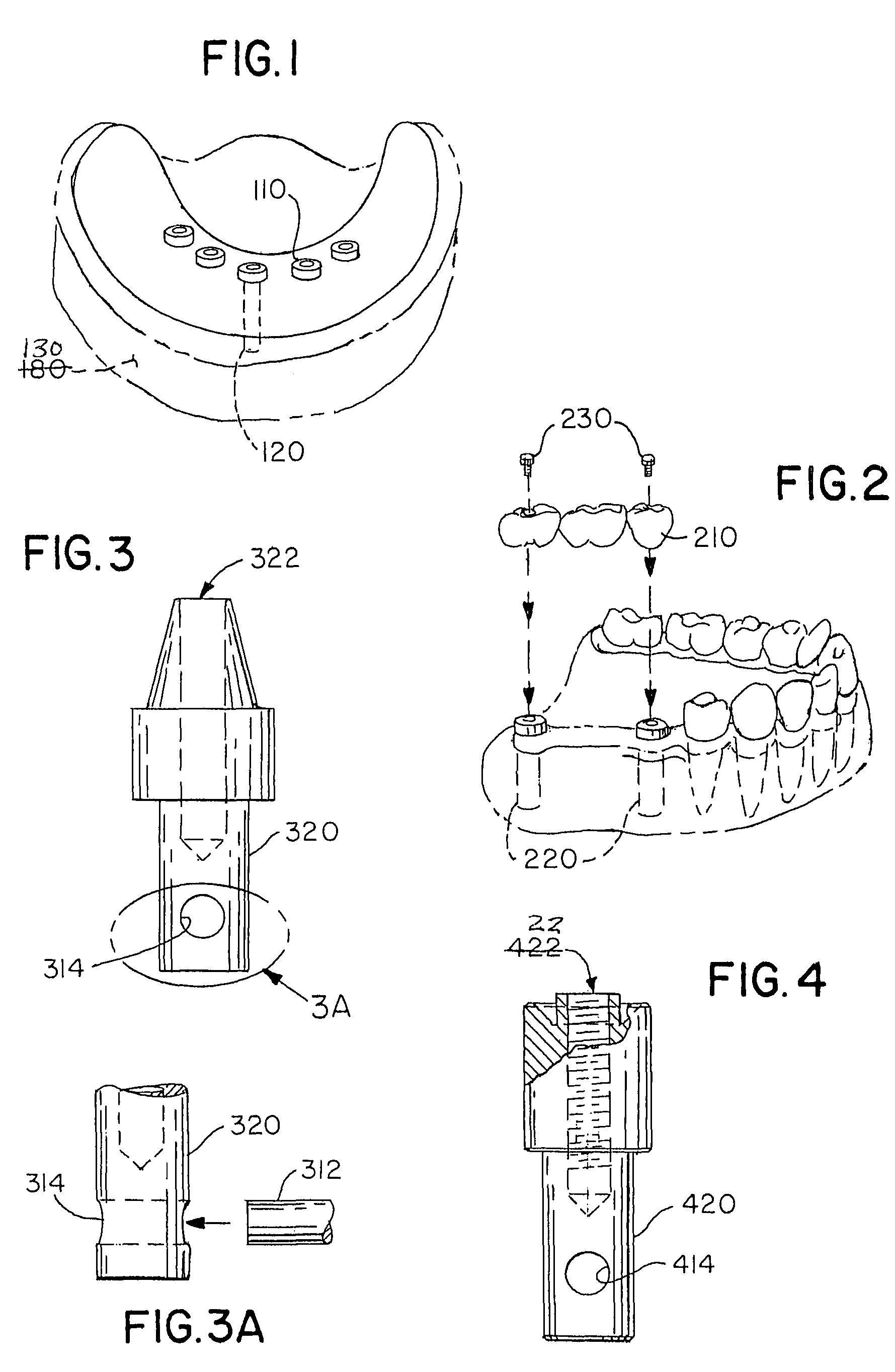
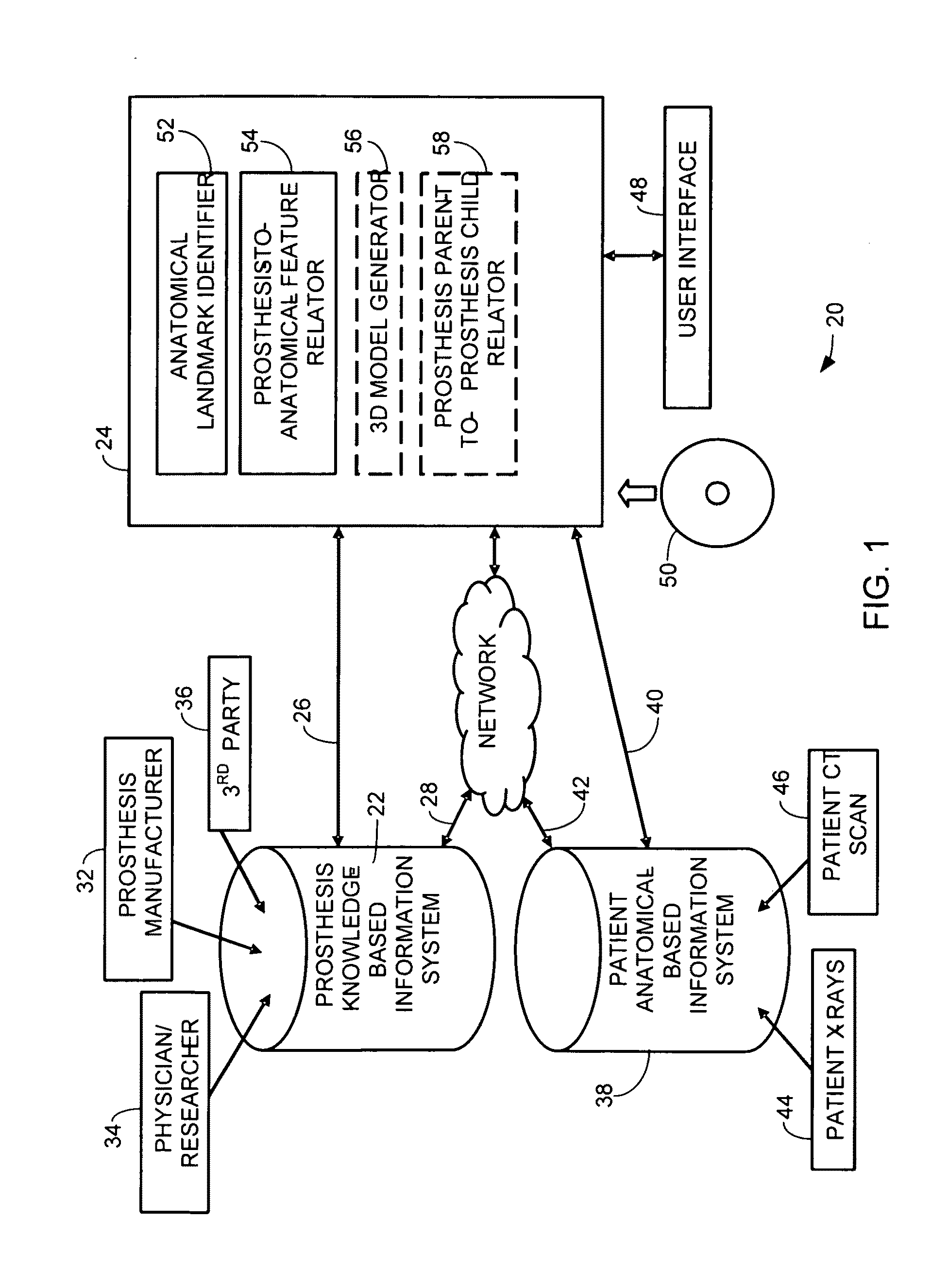
ActiveUS20100086186A1Analogue computers for chemical processesJoint implantsAnatomical structuresAnatomical landmark
A method for surgical planning is disclosed. A set of related two-dimensional (2D) anatomical images or 3D images is displayed. A plurality of anatomical landmarks are identified on the set of anatomical images. A three-dimensional (3D) representation of a parent prosthesis is scaled to match a scale of the 2D anatomical images based at least in part on a relationship between the anatomical landmarks. A 2D representation of the scaled 3D parent prosthesis is displayed on at least one of the 2D anatomical images. A system for surgical planning is also disclosed. The system has a prosthesis knowledge-based information system, a patient anatomical-based information system, a user interface, and a controller. The controller has an anatomical landmark identifier. The controller also has a prosthesis-to-anatomical-feature relator. The controller is configured to display a set of related two-dimensional (2D) anatomical images from the patient anatomical-based information system on the user interface.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Opposed orthogonal fusion system and method for generating color segmented MRI voxel matrices
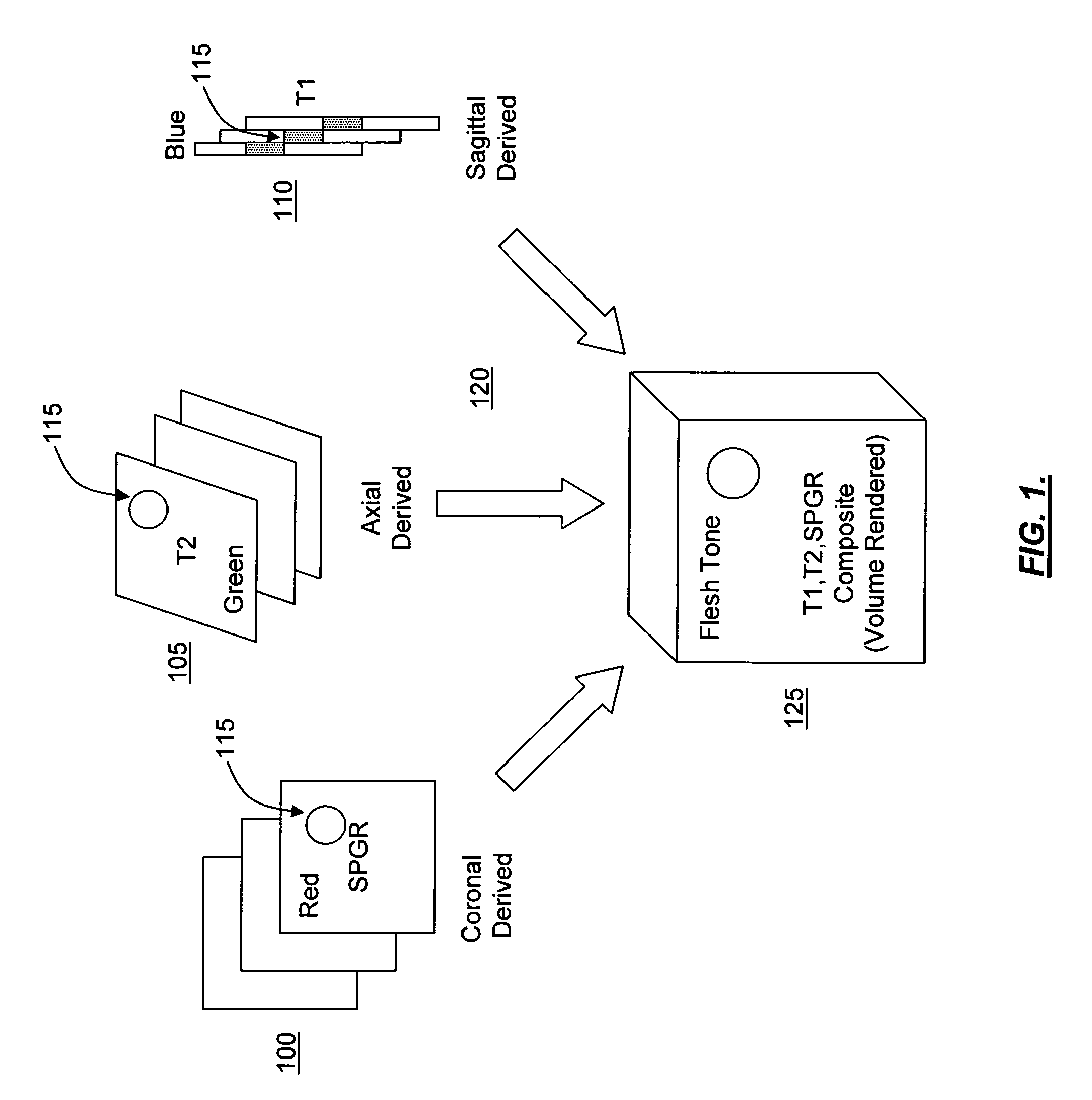
InactiveUS6956373B1Easy to understandCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelTissue characterization
Systems and methods for producing multi-dimensional tissue characterization images are described. By combining colorized MRI images composited from multiple gray tone MRI images, riffle stacks can be formed and combined to render multidimensional reconstruction of anatomical, physiological and pathological features. Biophysical parameters are therefore automatically segmented, characterized, tagged, mapped and otherwise labeled. In another embodiment, gray tone images are collected by acquiring orthogonally opposed pulse sequences, the images of which are color masked and uniquely rendered in three dimensions to obtain voxels in which the color is determined by the summative color masks applied to original gray tone pixels. This method can be embodied as specific applications designed for the brain, abdomen, breast, pelvis, musculoskeletal and other organs and biophysical systems to facilitate diagnosis, surgical planning and virtual exploration.
Owner:BROWN HUGH KEITH +1
Apparatus and methods for performing brain surgery
ActiveUS9216015B2Easy to installAssisting understandingCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryLess invasive
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent to the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may be inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferably is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor. Dilating obturator structures having a rounded or semi-spherical tip and / or an optical window for visualizing brain tissue during expansion are contemplated.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL INC
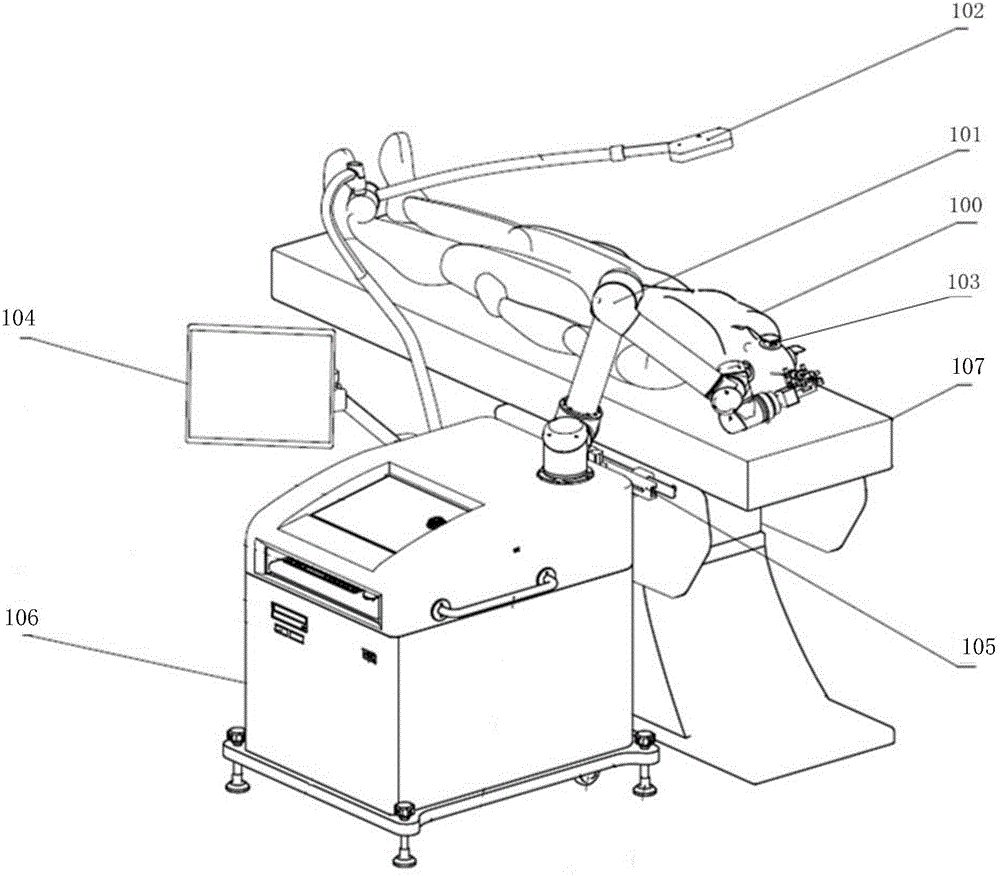
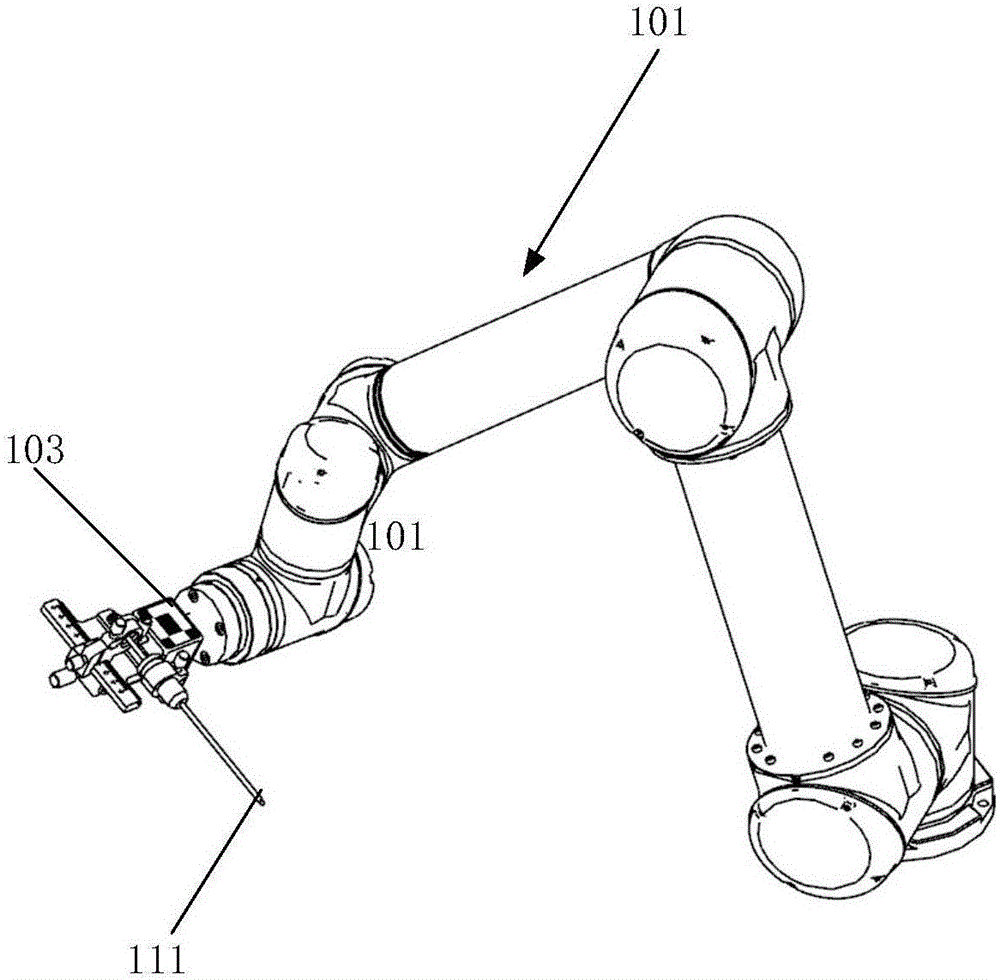
Navigation and location system and method adopting neurosurgical robot
An embodiment of the invention provides a navigation and location system and method adopting a neurosurgical robot. The navigation and location system comprises motion execution equipment, a spatial position sensor, a matched position marking unit and a host, wherein the host is connected with the motion execution equipment and the spatial position sensor and used for creating surgical planning on a digital graphic image, and the surgical planning contains a position positioned to a lesion part independently and precisely as well as a motion path; the spatial position sensor is used for capturing the matched position marking unit, so that the position mapping of different space coordinates systems can be finished by the host; the motion execution equipment carries surgical instruments, is used for performing independent and precise positioning on the lesion part according to a specific motion scheme generated on the basis of the position positioned to the lesion part, the motion path and the position mapping of the different space coordinates systems, and is further used for stabilizing and locking the surgical instruments and then supporting surgery.
Owner:BEIJING BAIHUI WEIKANG SCI & TECH CO LTD
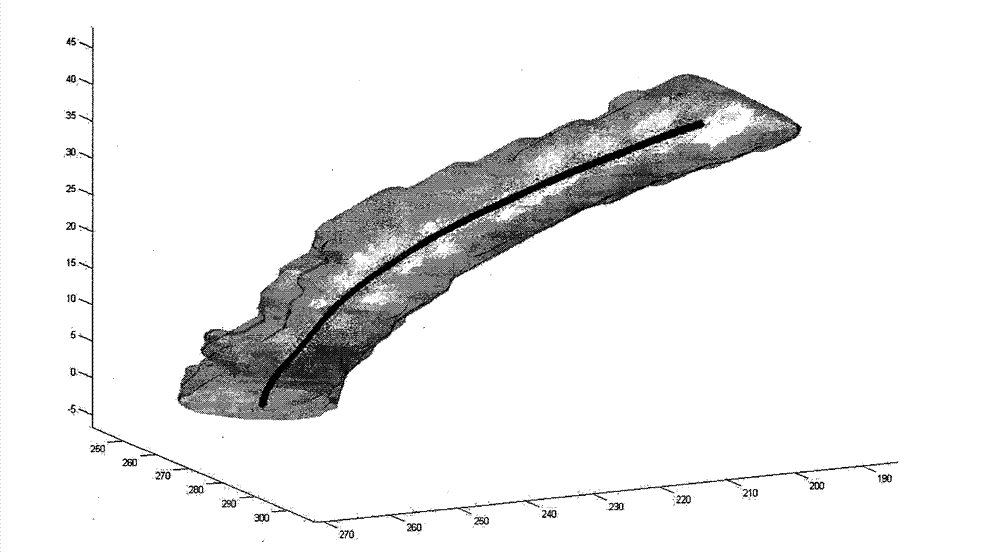
Image simulation method for intracranial aneurysm interventional therapy stent implantation
InactiveCN103198202AFacilitated releaseGuaranteed continuous smoothnessSpecial data processing applicationsWeight adjustmentTomographic image
The invention provides a visualization calculation method for a whole intracranial aneurysm interventional therapy stent implantation process, establishes a stent release expansion model, provides an effective numerical simulation method for the intracranial aneurysm interventional therapy stent implantation, and provides a visualization method used for detection, calculation and analysis of the surgical planning of intracranial aneurysm interventional therapy. The adopted technical scheme is as follows: firstly, a blood vessel centerline is utilized to implant a numerical simulation stent into the blood vessel, and an active contour model is utilized to perform stent expansion, then the distance of each two nodes of the stent is changeless through optimization, and finally hemodynamics calculation and analysis are performed, and optimal configuration for stent implantation is simulated and calculated. The image simulation method can be directly applied to three-dimensional vascular angiography tomographic images, enables the stent to keep own geometric morphological characters through optimization, and can utilize weight adjustment to enable the stent to be clung to the blood vessel wall as far as possible. The simulation process can control the stent implantation position conveniently, and better clinical application value is achieved in the surgical planning of interventional therapy.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com