Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1464 results about "Pelvis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
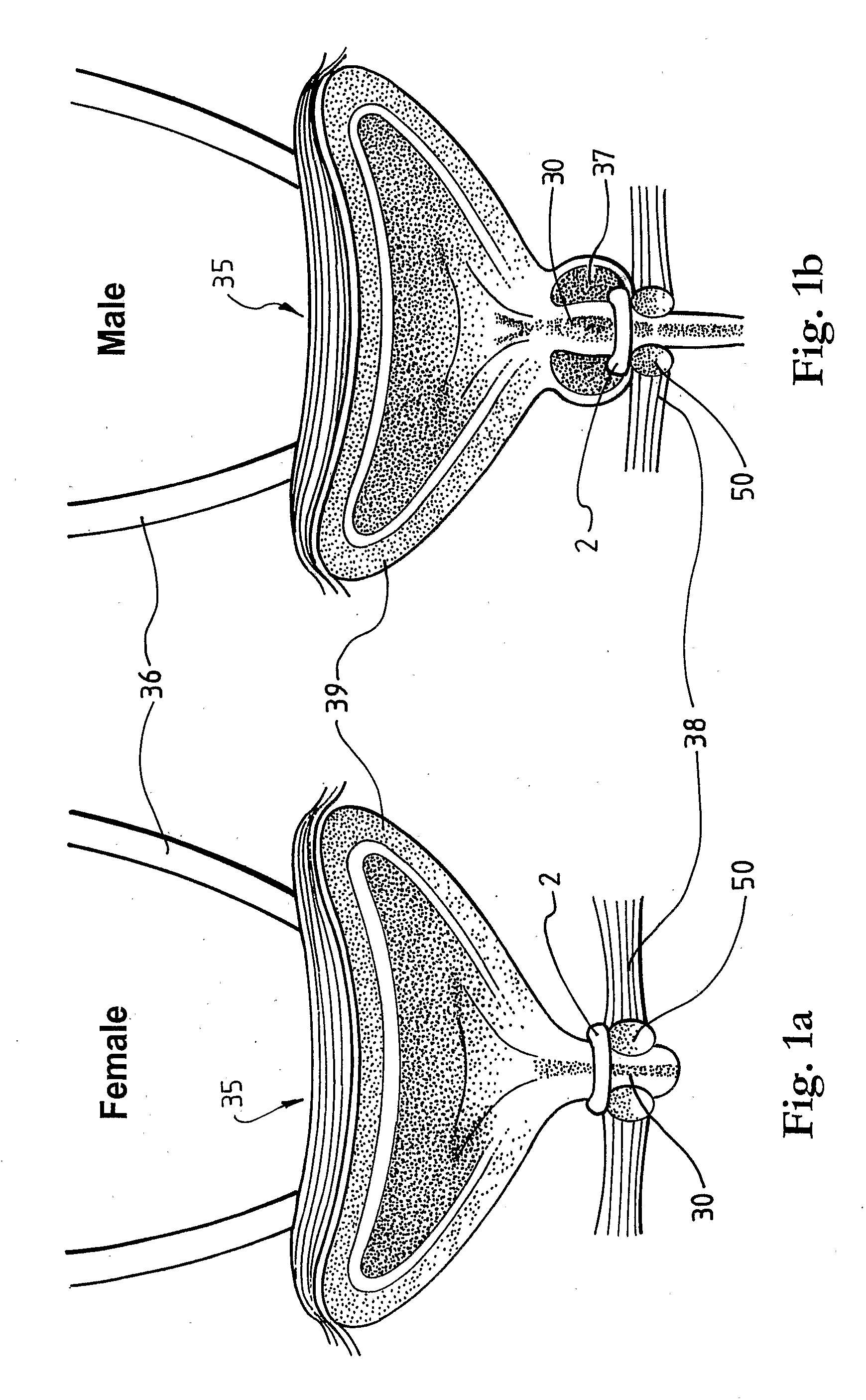
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is either the lower part of the trunk of the human body between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region of the trunk) or the skeleton embedded in it (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
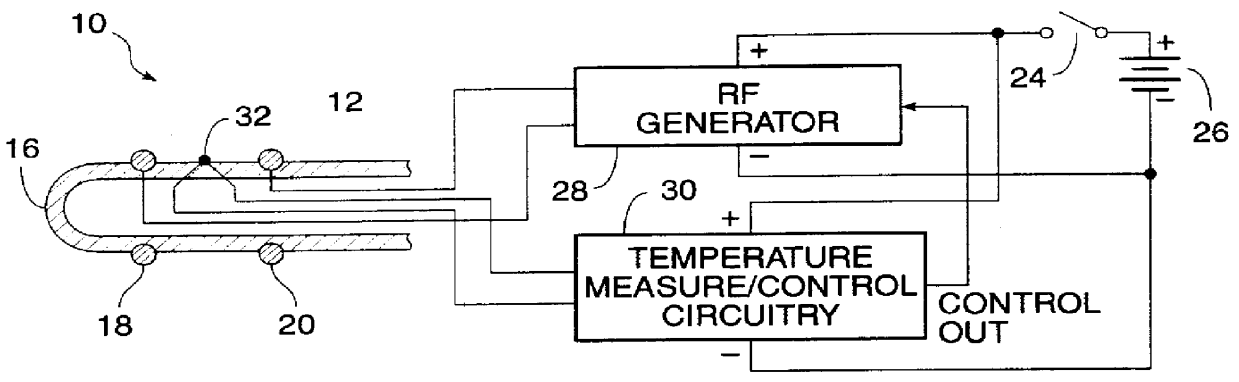
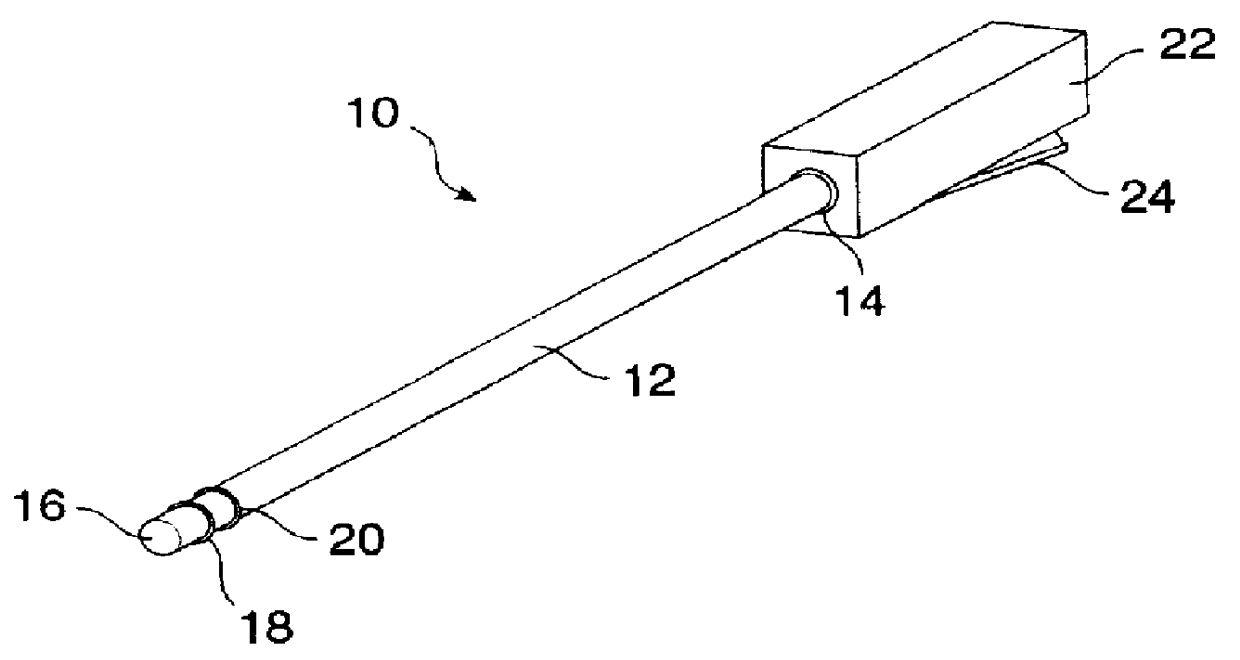
Devices, methods, and systems for shrinking tissues
InactiveUS6091995AReduce power levelControl depthSurgical needlesInternal electrodesSphincterPelvic supports
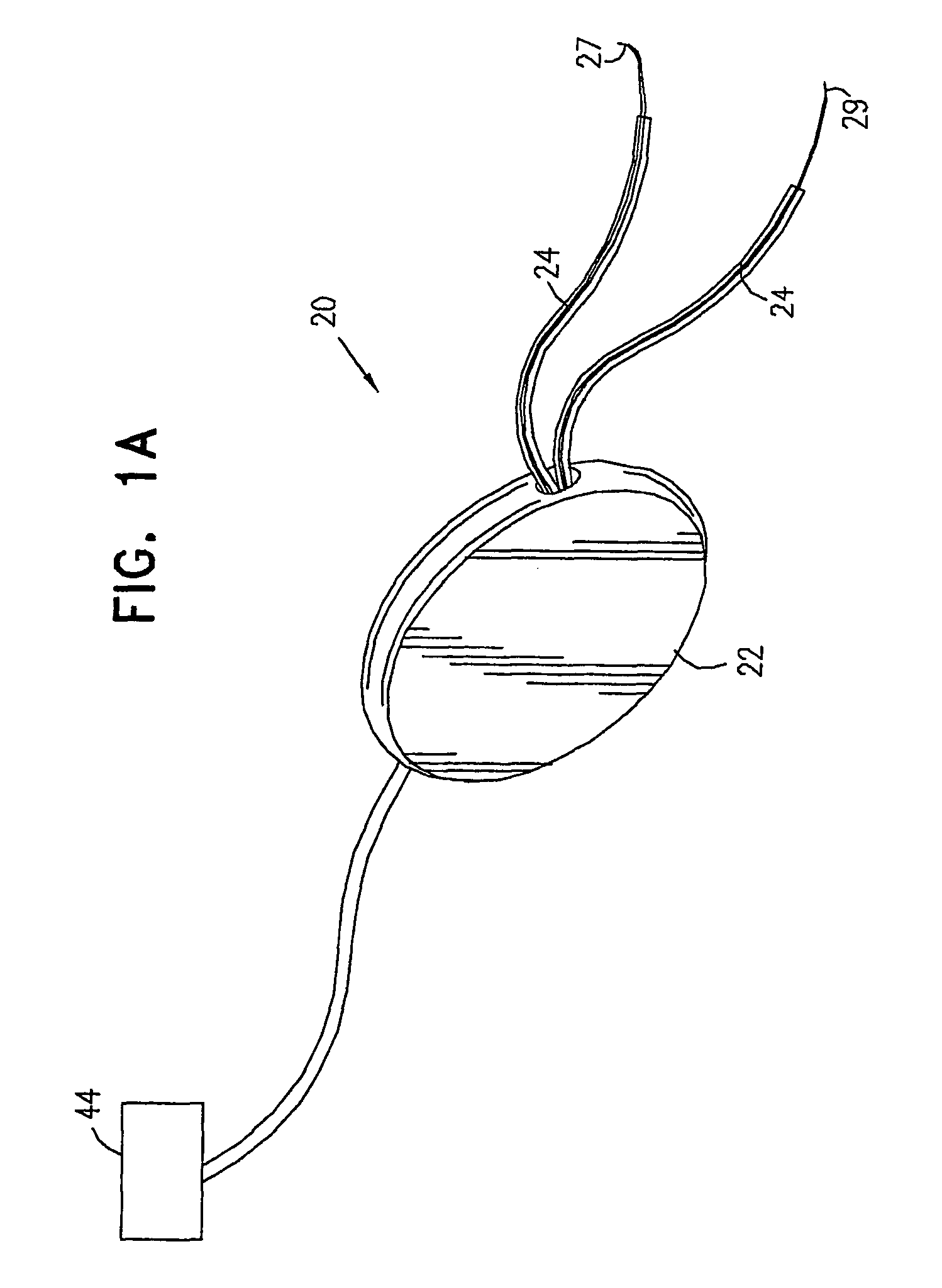
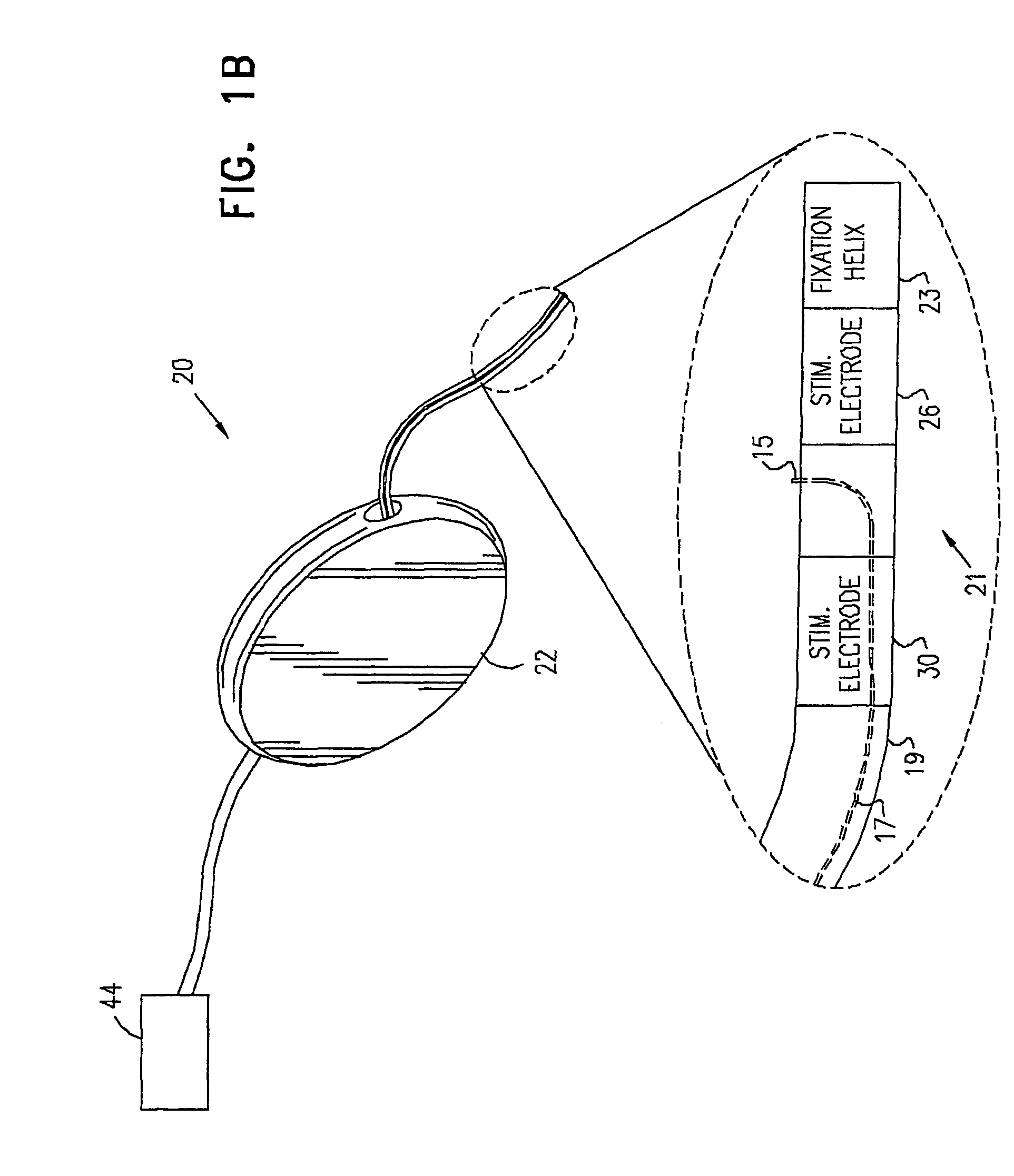
Devices, systems, and method for treating urinary incontinence generally rely on energy delivered to a patient's own pelvic support tissue to selectively contract or shrink at least a portion of that pelvic support tissue so as to reposition the bladder. The energy will preferably be applied to the endopelvic fascia and / or an arcus tendineus fascia pelvis. The invention provides a variety of devices and methods for applying gentle resistive heating of these and other tissues to cause them to contract without imposing significant injury on the surrounding tissue structures. Alternatively, heat-applying probes are configured to heat tissue structures which comprise or support a patient's urethra. By applying sufficient energy over a predetermined time, the tissue can be raised to a temperature which results in contraction without significant necrosis or other tissue damage. By selectively contracting the support tissues, the bladder neck, sphincter, and other components of the urinary tract responsible for the control of urinary flow can be reconfigured or supported in a manner which reduces urinary leakage.
Owner:VERATHON
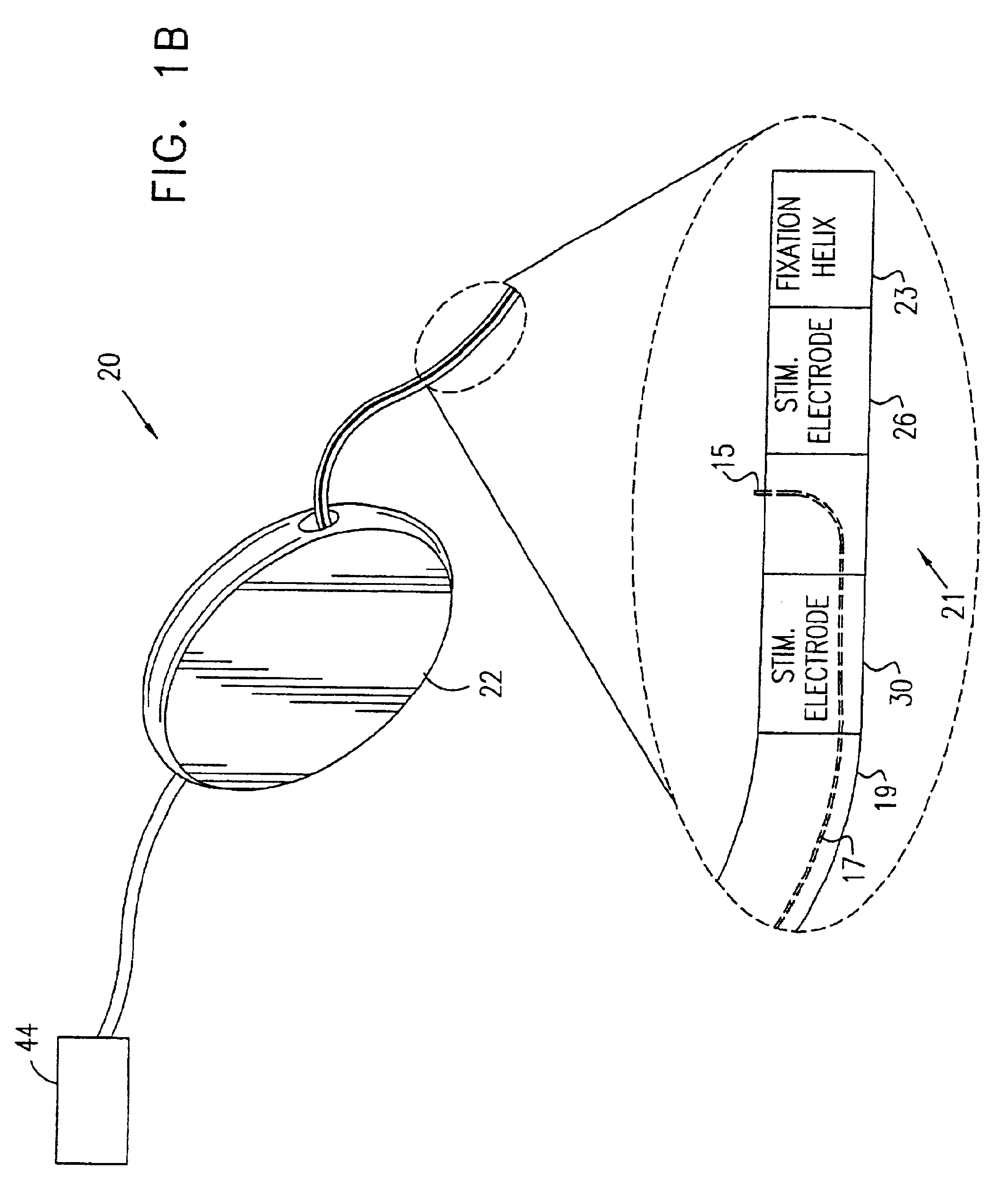
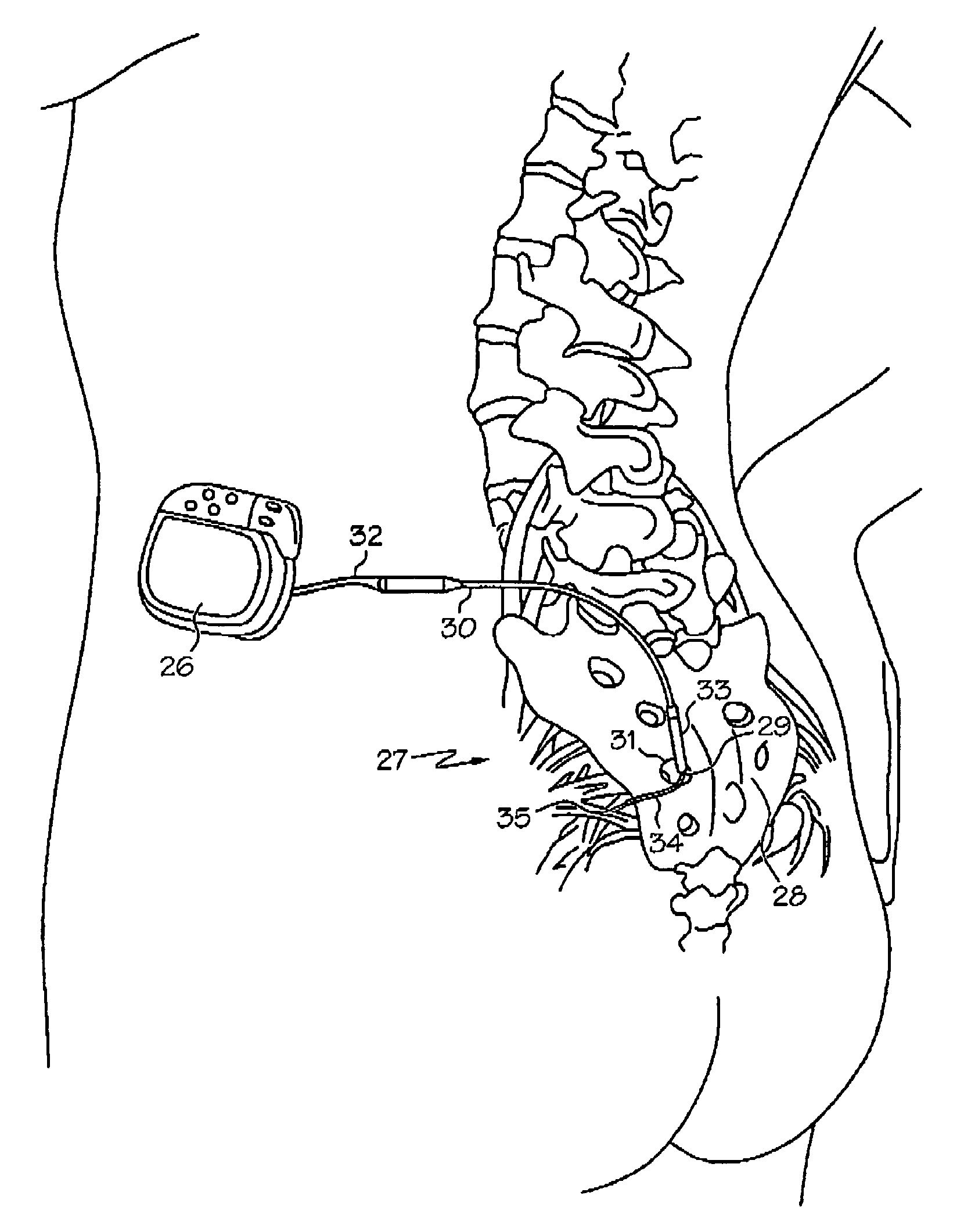
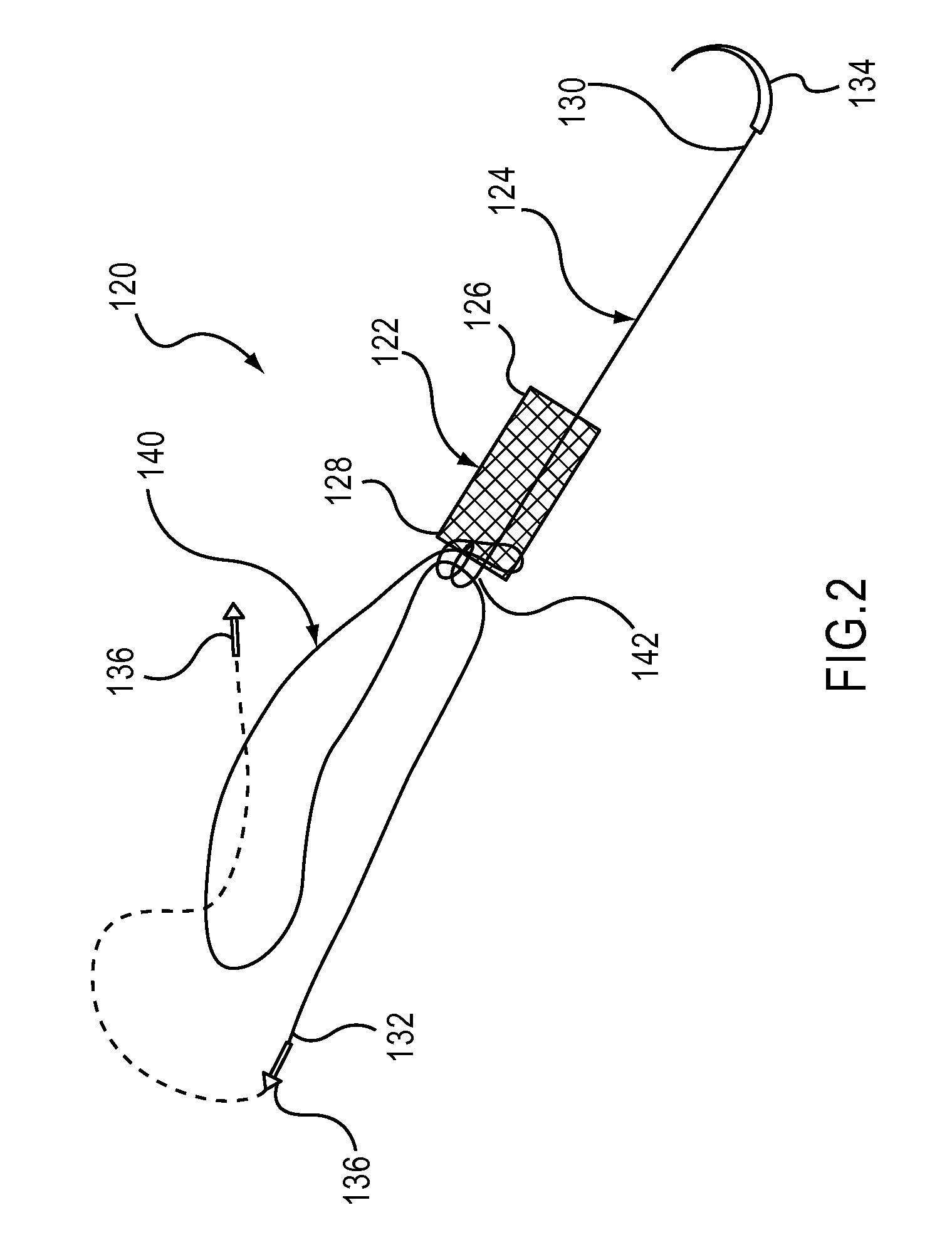
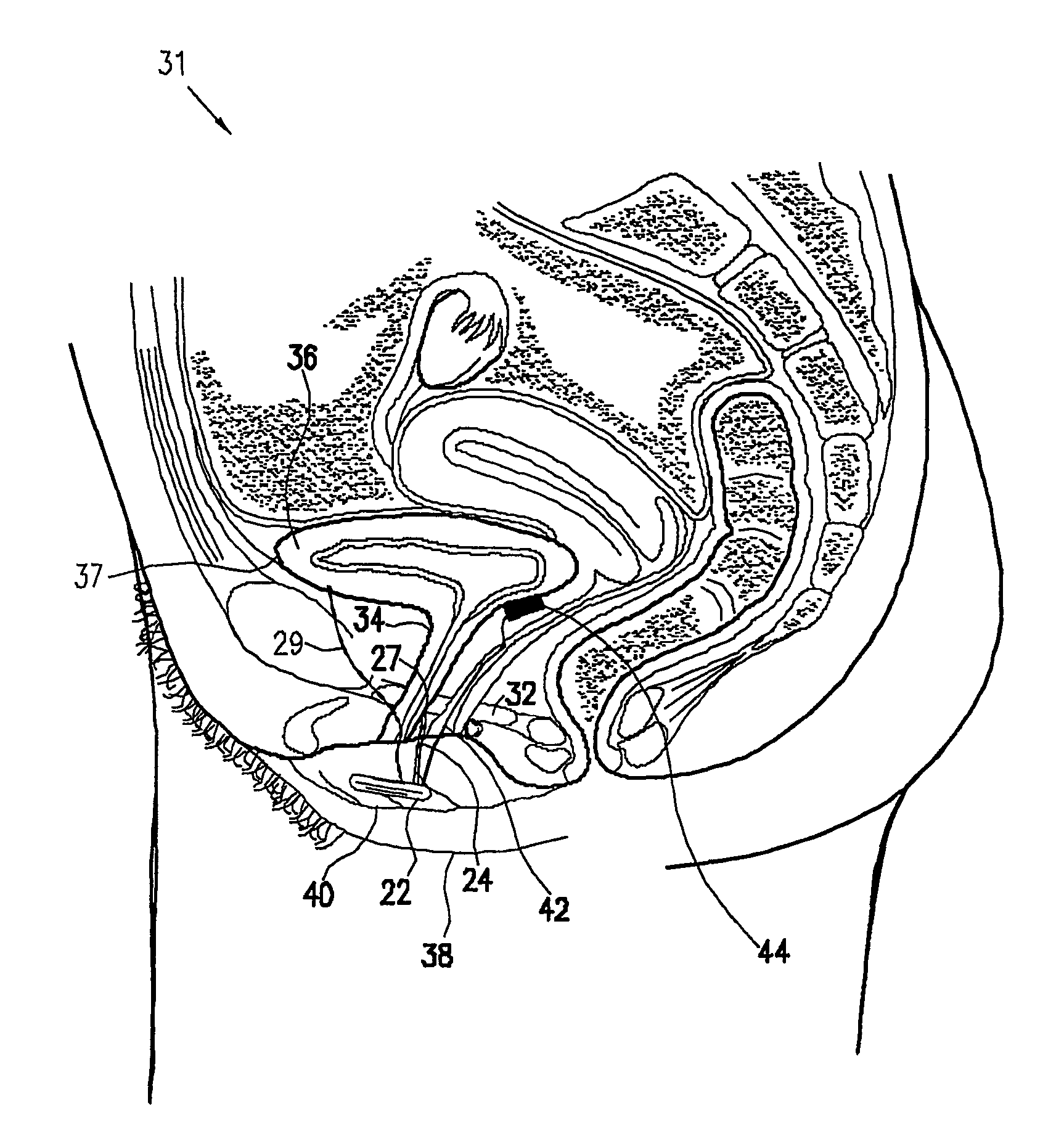
Minimally invasive apparatus for implanting a sacral stimulation lead
Methods and apparatus for implanting a stimulation lead in a patient's sacrum to deliver neurostimulation therapy that can reduce patient surgical complications, reduce patient recovery time, and reduce healthcare costs. A surgical instrumentation kit for minimally invasive implantation of a sacral stimulation lead through a foramen of the sacrum in a patient to electrically stimulate a sacral nerve comprises a needle and a dilator and optionally includes a guide wire. The needle is adapted to be inserted posterior to the sacrum through an entry point and guided into a foramen along an insertion path to a desired location. In one variation, a guide wire is inserted through a needle lumen, and the needle is withdrawn. The insertion path is dilated with a dilator inserted over the needle or over the guide wire to a diameter sufficient for inserting a stimulation lead, and the needle or guide wire is removed from the insertion path. The dilator optionally includes a dilator body and a dilator sheath fitted over the dilator body. The stimulation lead is inserted to the desired location through the dilator body lumen or the dilator sheath lumen after removal of the dilator body, and the dilator sheath or body is removed from the insertion path. If the clinician desires to separately anchor the stimulation lead, an incision is created through the entry point from an epidermis to a fascia layer, and the stimulation lead is anchored to the fascia layer. The stimulation lead can be connected to the neurostimulator to delivery therapies to treat pelvic floor disorders such as urinary control disorders, fecal control disorders, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic pain.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
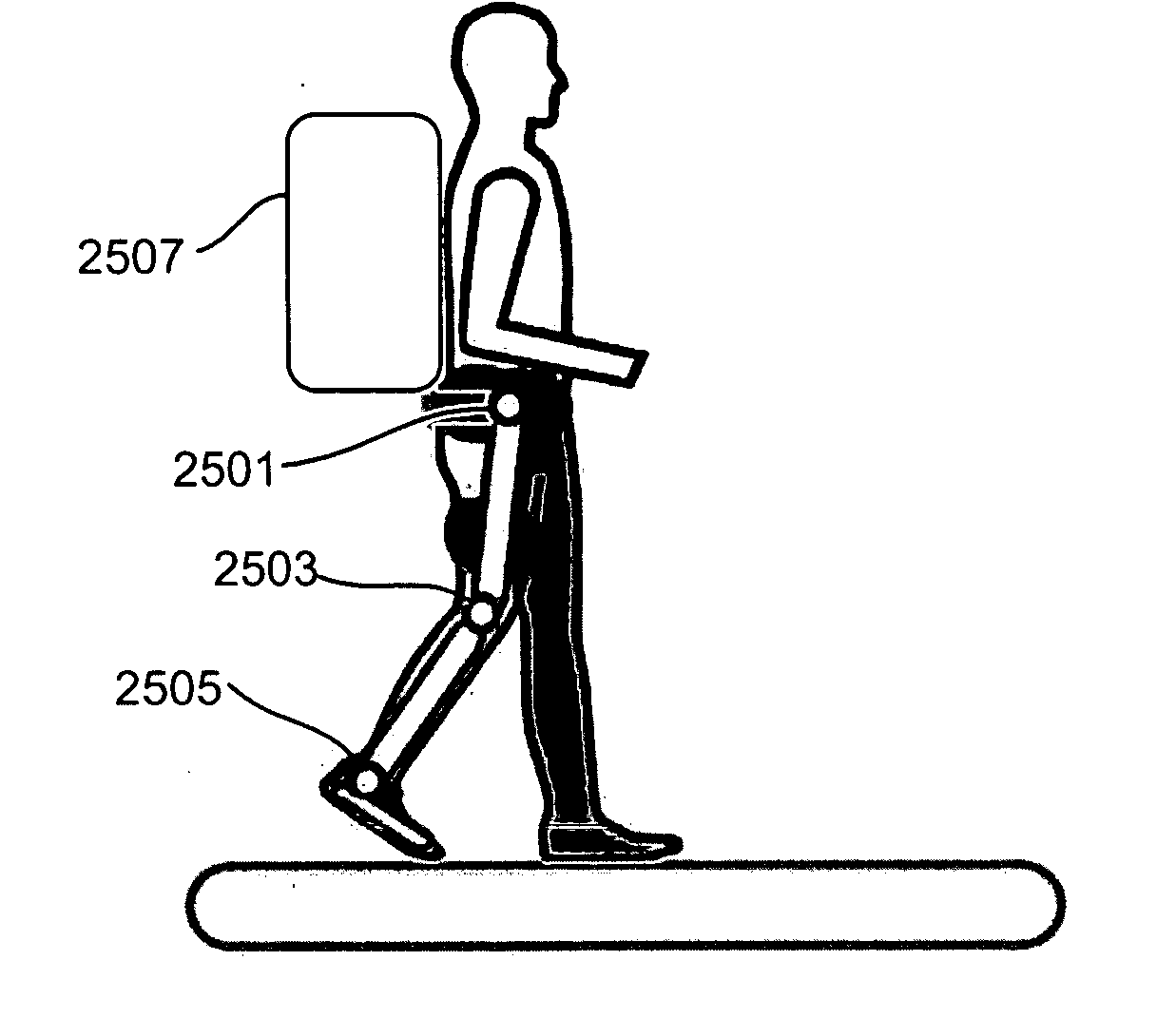
Exoskeletons for running and walking
InactiveUS20070123997A1Augment leg extensionDestabilizeProgramme-controlled manipulatorNon-surgical orthopedic devicesExoskeletonPelvis
An exoskeleton worn by a human user consisting of a rigid pelvic harness worn about the waist of the user and exoskeleton leg structures each of which extends downwardly alongside one of the human user's legs. The leg structures include hip, knee and ankle joints connected by adjustable length thigh and shin members. The hip joint that attaches the thigh structure to the pelvic harness includes a passive spring or an active actuator to assist in lifting the exoskeleton and said human user with respect to the ground surface upon which the user is walking and to propel the exoskeleton and human user forward. A controllable damper operatively arresting the movement of the knee joint at controllable times during the walking cycle, and spring located at the ankle and foot member stores and releases energy during walking.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for evaluating the urethra and the periurethral tissues
InactiveUS6898454B2Reduce thermal effectsImprove performanceGastroscopesOesophagoscopesDiseaseUrethra
The present invention provides systems and methods for the evaluation of the urethra and periurethral tissues using an MRI coil adapted for insertion into the male, female or pediatric urethra. The MRI coil may be in electrical communication with an interface circuit made up of a tuning-matching circuit, a decoupling circuit and a balun circuit. The interface circuit may also be in electrical communication with a MRI machine. In certain practices, the present invention provides methods for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions involving the urethra and periurethral tissues, including disorders of the female pelvic floor, conditions of the prostate and anomalies of the pediatric pelvis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
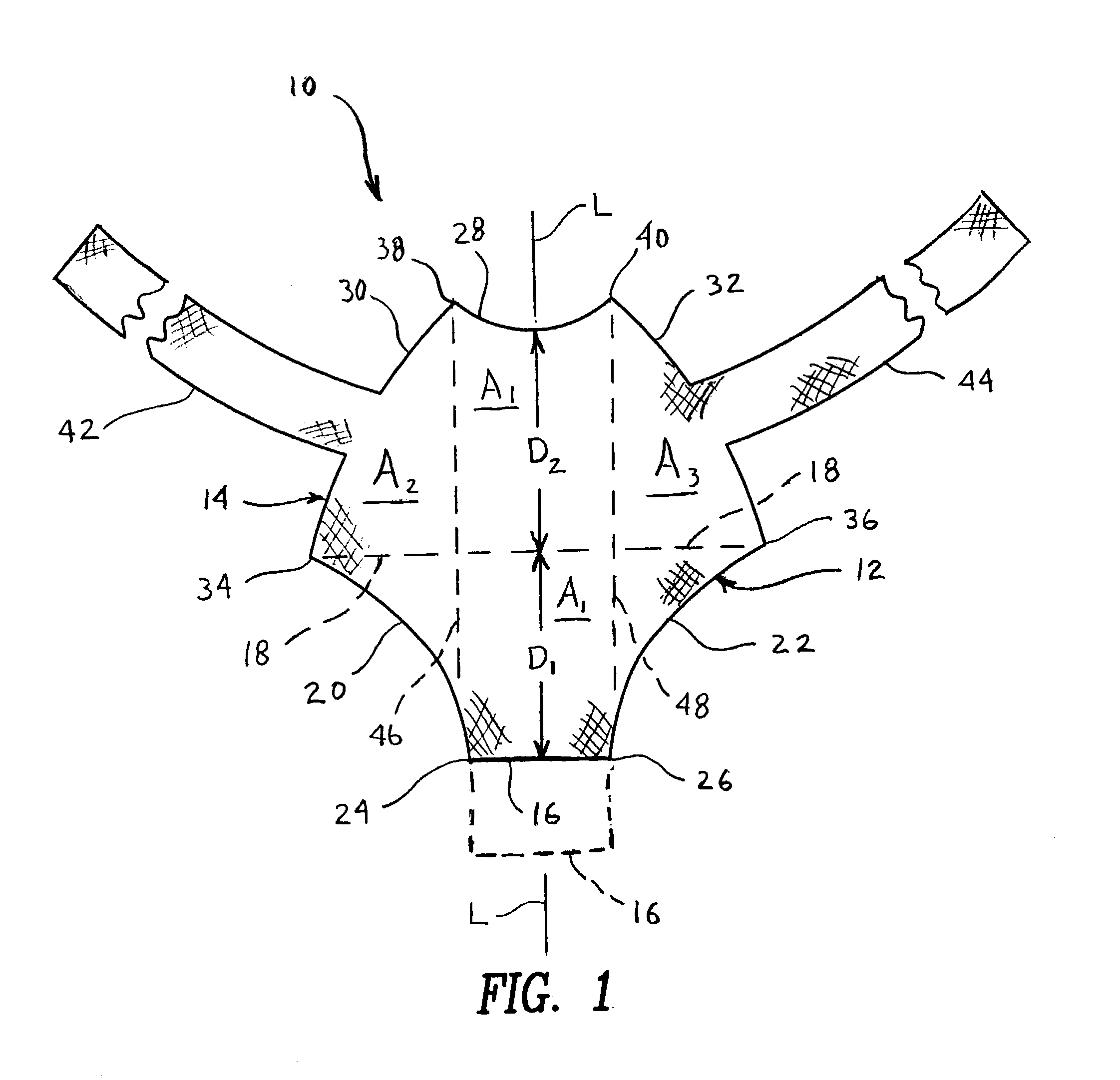
Mesh for pelvic floor repair
InactiveUS7087065B2Reduce vaginal prolapseIncrease heightSuture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesPelvisPelvic floor repair
A woven mesh is provided for supporting tissue or an organ within a female patient's pelvis, and a method for using the same. The mesh includes a central portion having a width, a length, first and second ends, and first and second side edges, and first and second wing portions extending from the first and second ends of the central portion respectively. The first and second wing portions each have a width, a length, and first and second peripheral edges. The width of the wing portions are each greater than the width of the central portion, and when positioned within the female patient, the central portion is positioned below and supports the tissue or organ. A mesh is also provided having woven fibers with voids therebetween, and having a central portion and first and second ends. The average size of the voids at least in the central portion is at least 25–50 mm2, and when positioned within the patient, the central portion is positioned below and supports the tissue or organ.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS20080051910A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceLocalization systemCoxal joint
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system to position the femoral component of a prosthetic hip during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. Optionally, a second point on the femur that is not on the first line is palpated. The system can calculate the position and length of a second line that is perpendicular to the first line and that runs from the first line to the second palpated point on the femur. The prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. While the tool is fixed to the femur, the surgeon re-palpates the same point(s) on the femur that were previously palpated. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. If a second point on the femur was re-palpated, the navigation system also calculates the position and length of a perpendicular line between the first line and the second point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery, such as change in the patient's leg length and / or medialization / lateralization of the joint.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Pelvic disorder treatment device
InactiveUS6862480B2Reduce decreaseRelieving pelvic painUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyInterstitial cystitisFecal incontinence
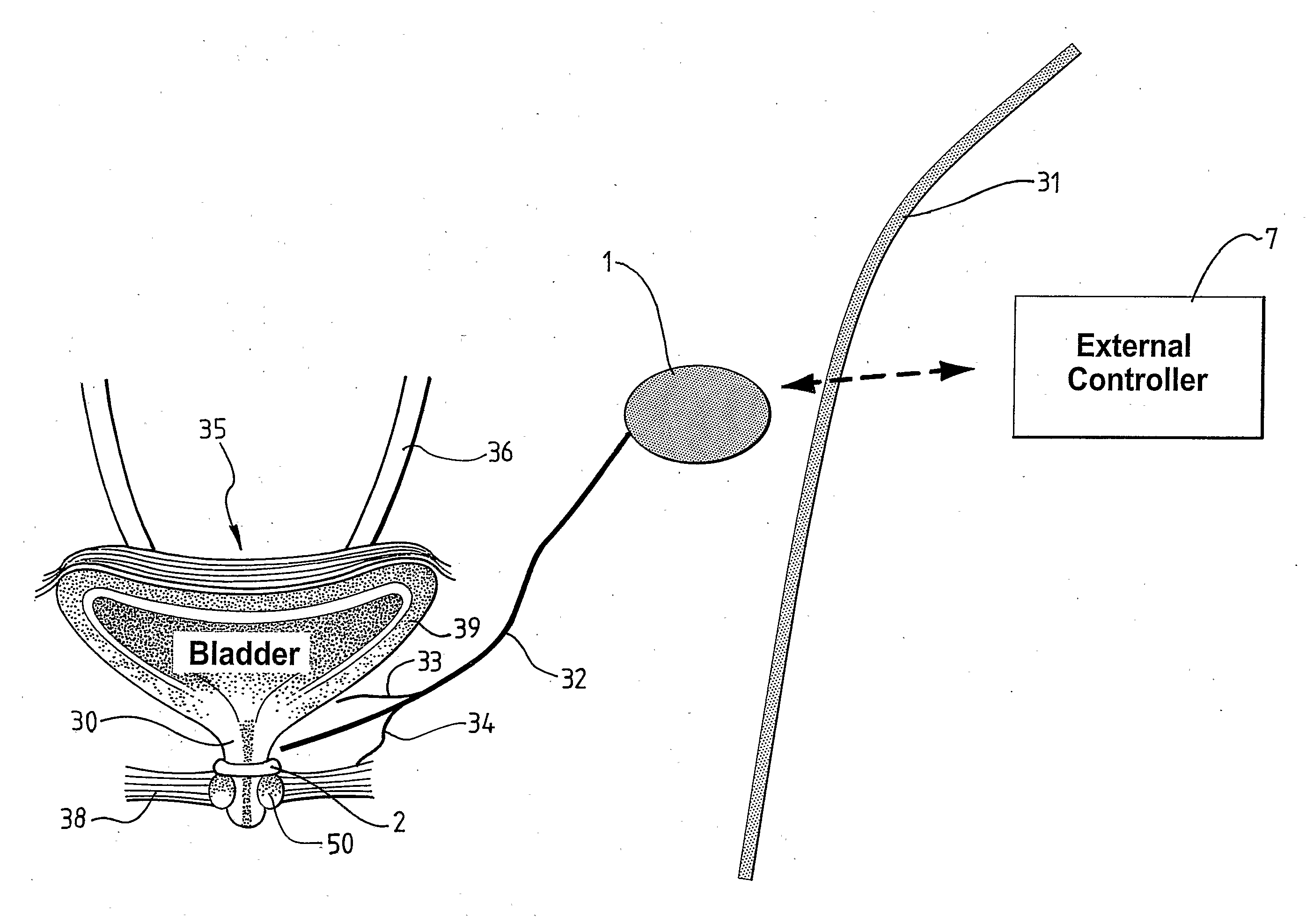
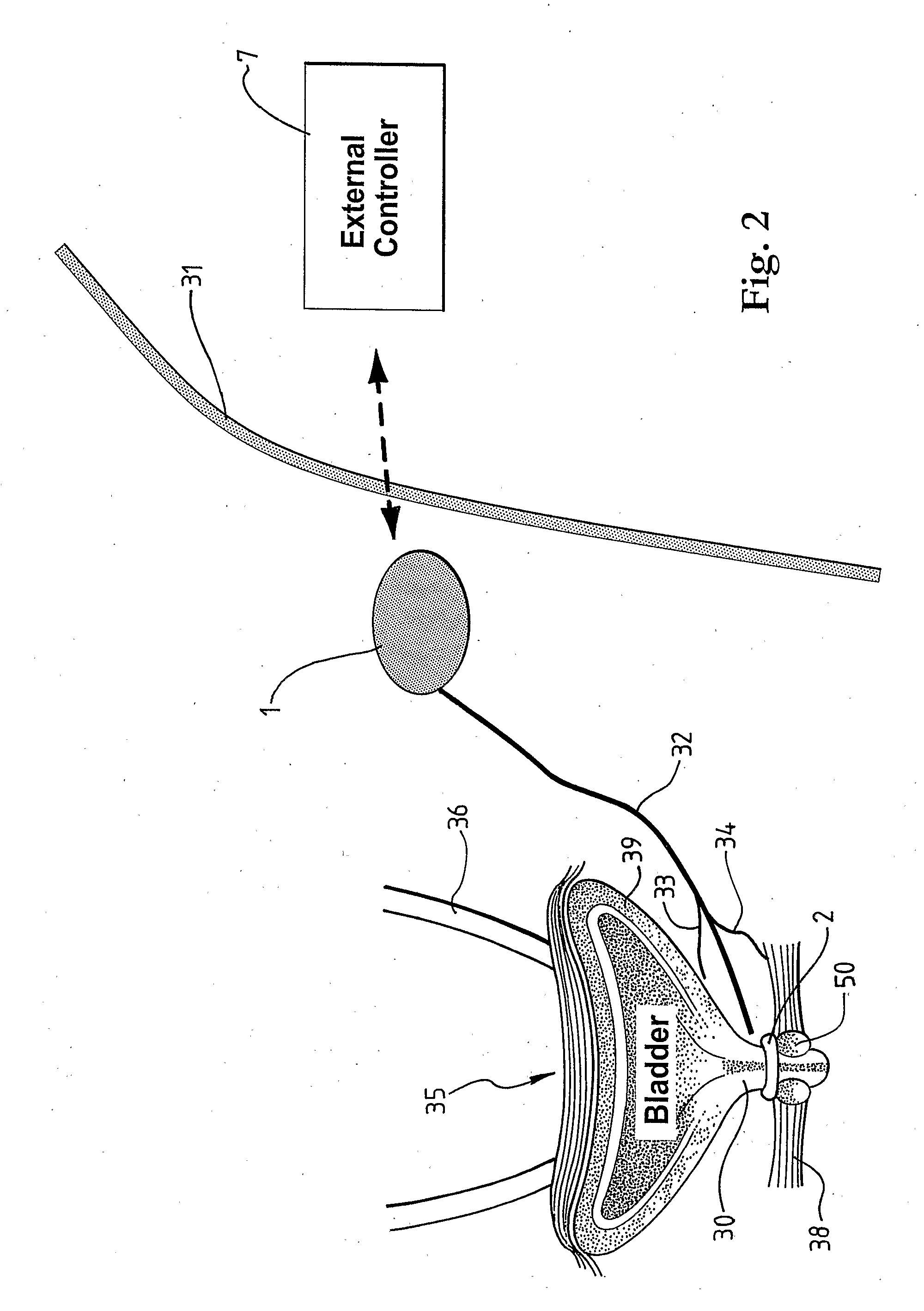
A device for treating a medical condition is provided, and a surgical procedure for implanting the device is disclosed. The device includes a sensor, which is adapted to generate a signal responsive to a state of a patient, and at least one electrode, which is adapted to be coupled to a pelvic site of the patient. A control unit is adapted to receive the signal, to analyze the signal so as to distinguish between an imminent stress incontinence event and an imminent urge event, and, responsive to analyzing the signal, to apply an electrical waveform to the at least one electrode. In various configurations, the device may be used alternatively or additionally to treat fecal incontinence, interstitial cystitis, chronic pelvic pain, or urine retention.
Owner:ASTORA WOMENS HEALTH
Surgical device for implanting a total hip prosthesis
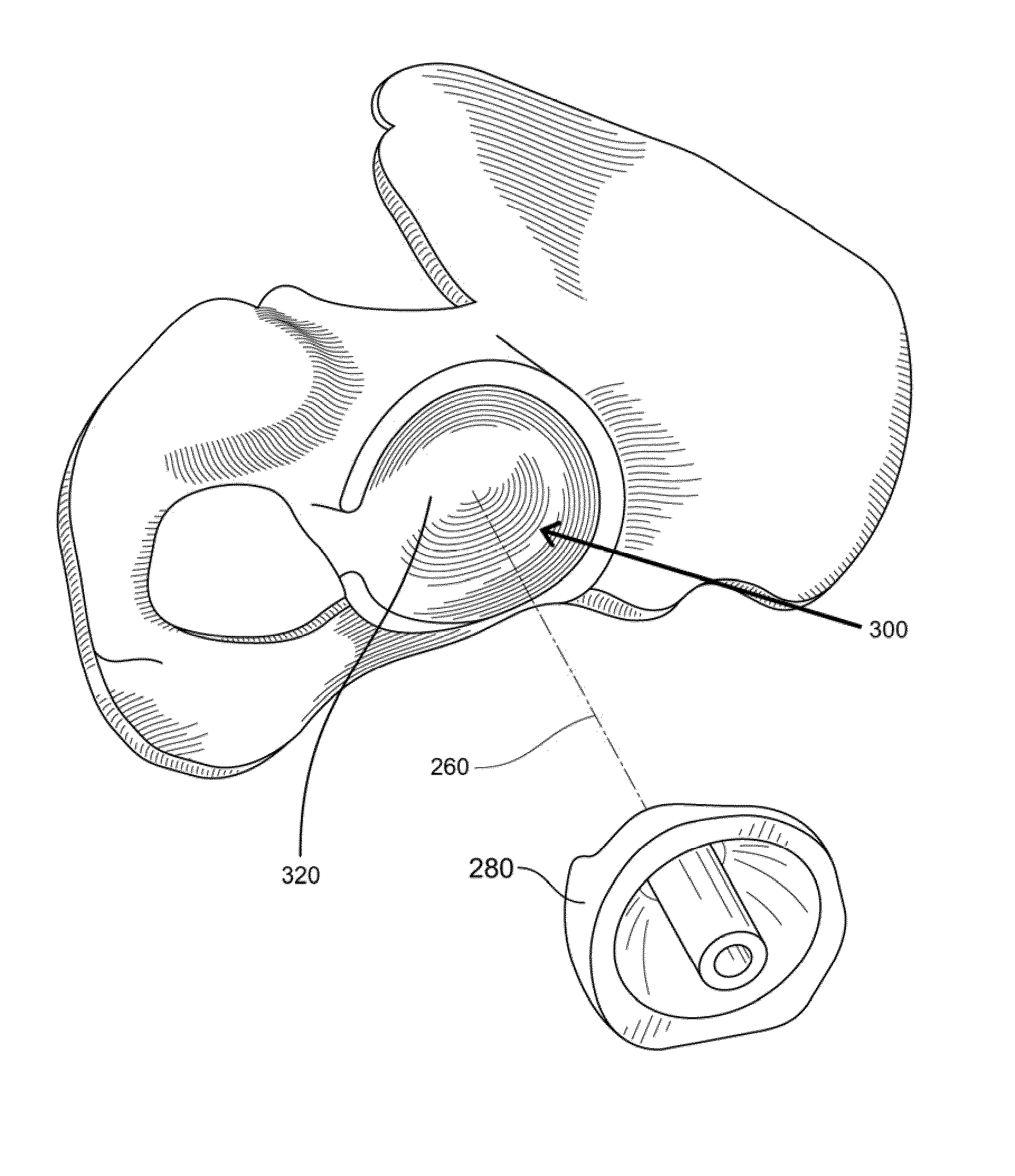
The surgical device according to the invention comprises both means for per-operative measurement and for memorization of a plurality of positions of a given femoral prosthetic direction and means for per-operative comparison of these positions with the cone of mobility of the prosthesis to be implanted, the position of the axis of revolution of this cone being, during the implantation of the prosthesis, adjustable with respect to the zone of the pelvis where the implantation of an acetabulum of the prosthesis is provided. By using this device, the surgeon can easily and rapidly determine, in the course of the surgical operation, a preferential direction for implanting the prosthetic acetabulum in order to reduce the subsequent risks of dislocations of the implanted prosthesis.
Owner:CORIN
Orientation device for surgical implement
InactiveUS20060184177A1Improve objectivityFacilitates and improves trainingDiagnosticsJoint implantsSurgical operationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
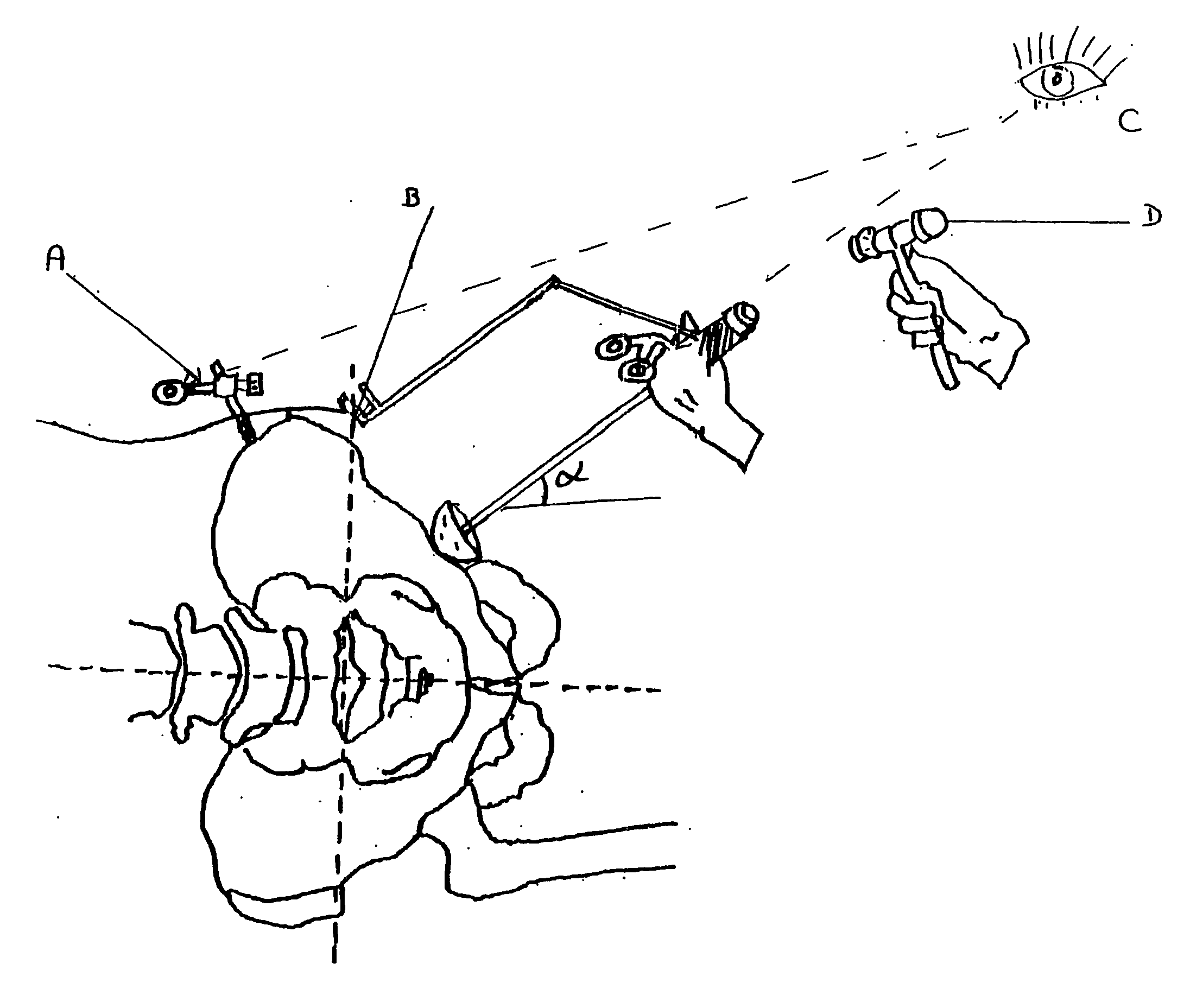
Orientation device for surgical use includes a frame and a level device attached to the frame. The feature may be oriented with a reference such as the Antero Superior Iliac Spine, the acetabulum or the operating table to position the pelvis or the device. The level device is adapted to define a reference plane. The device thus allows precise orientation with respect to the pelvis through use of a reference plane.
Owner:SAN TECH SURGICAL
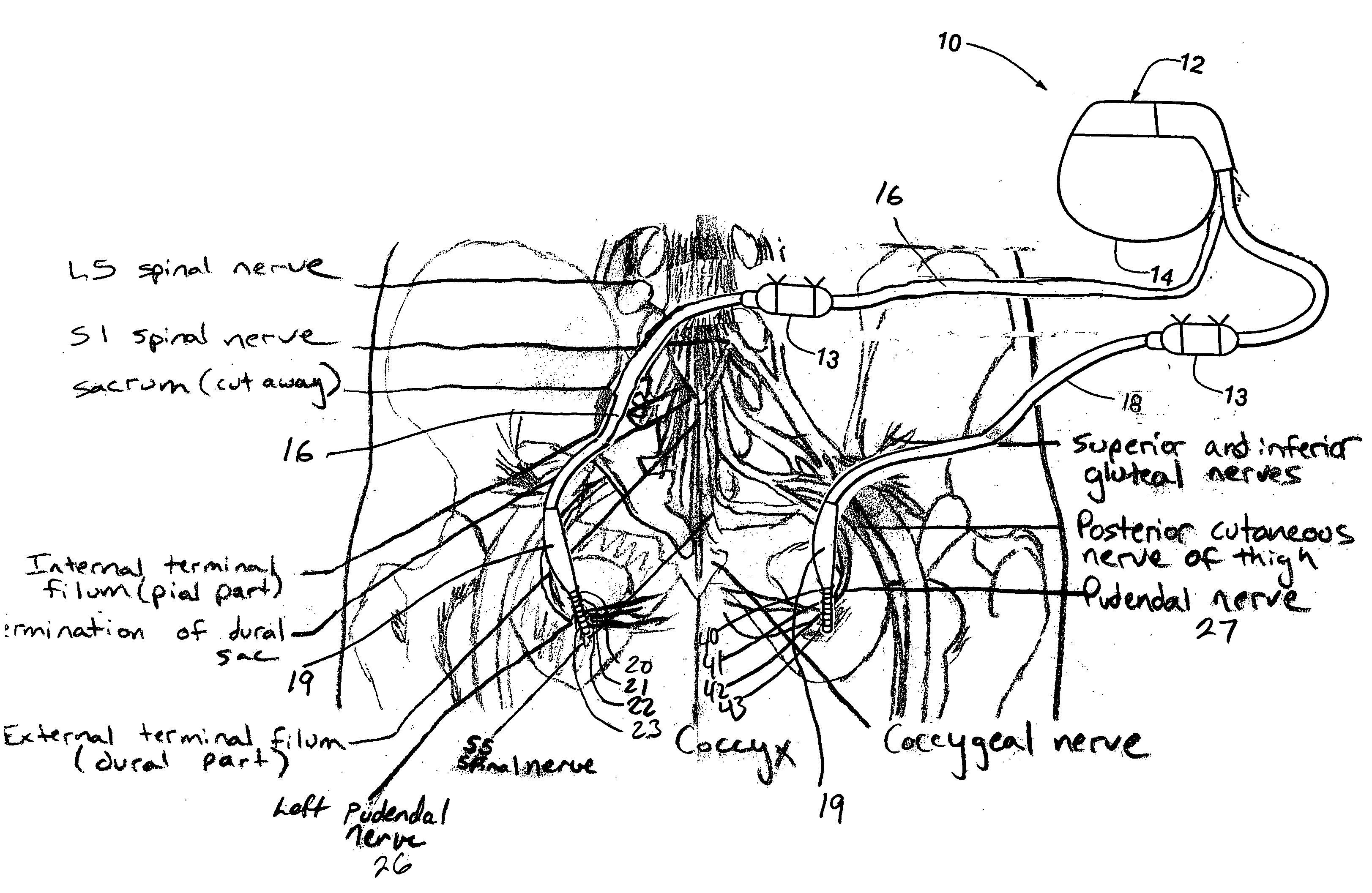
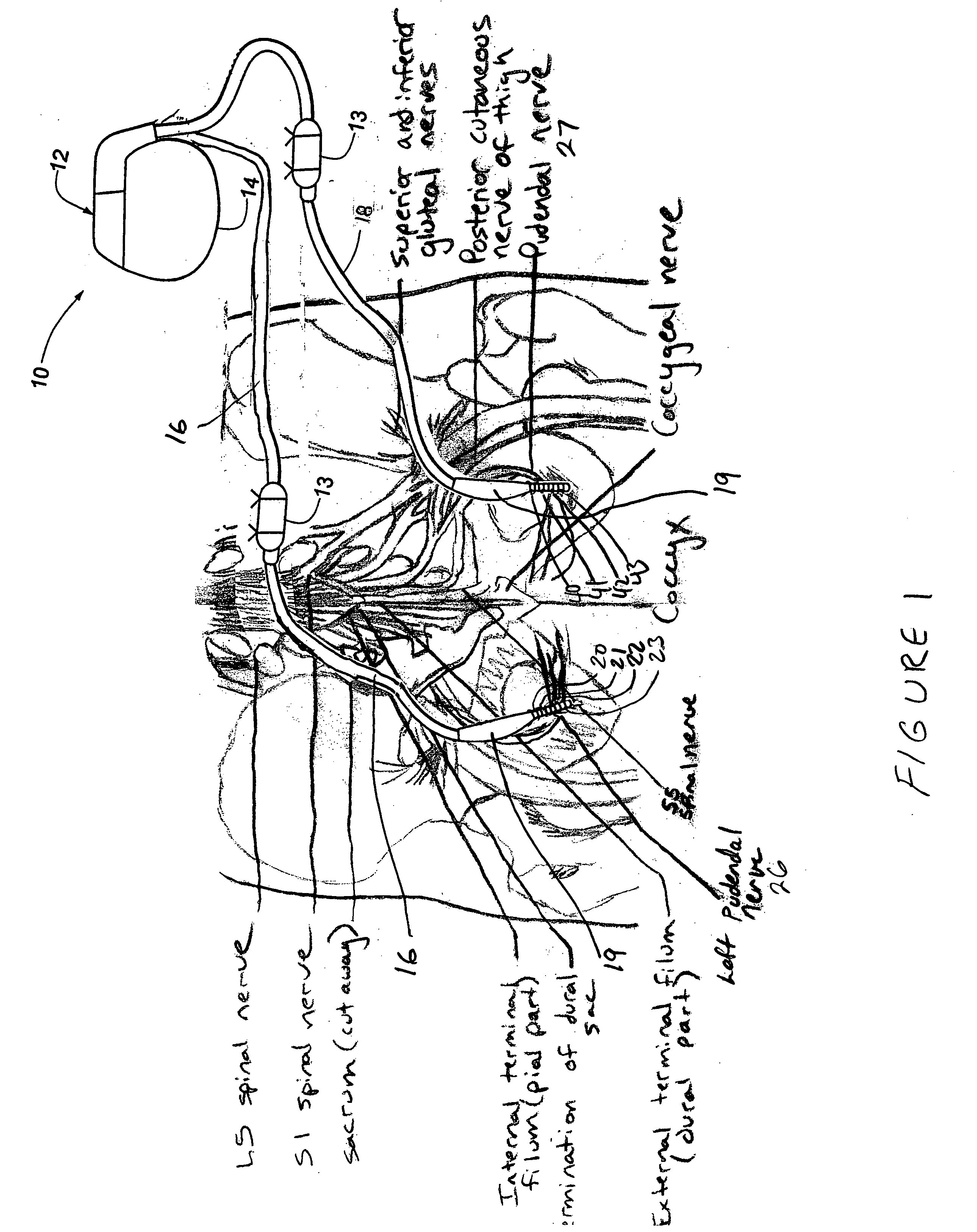
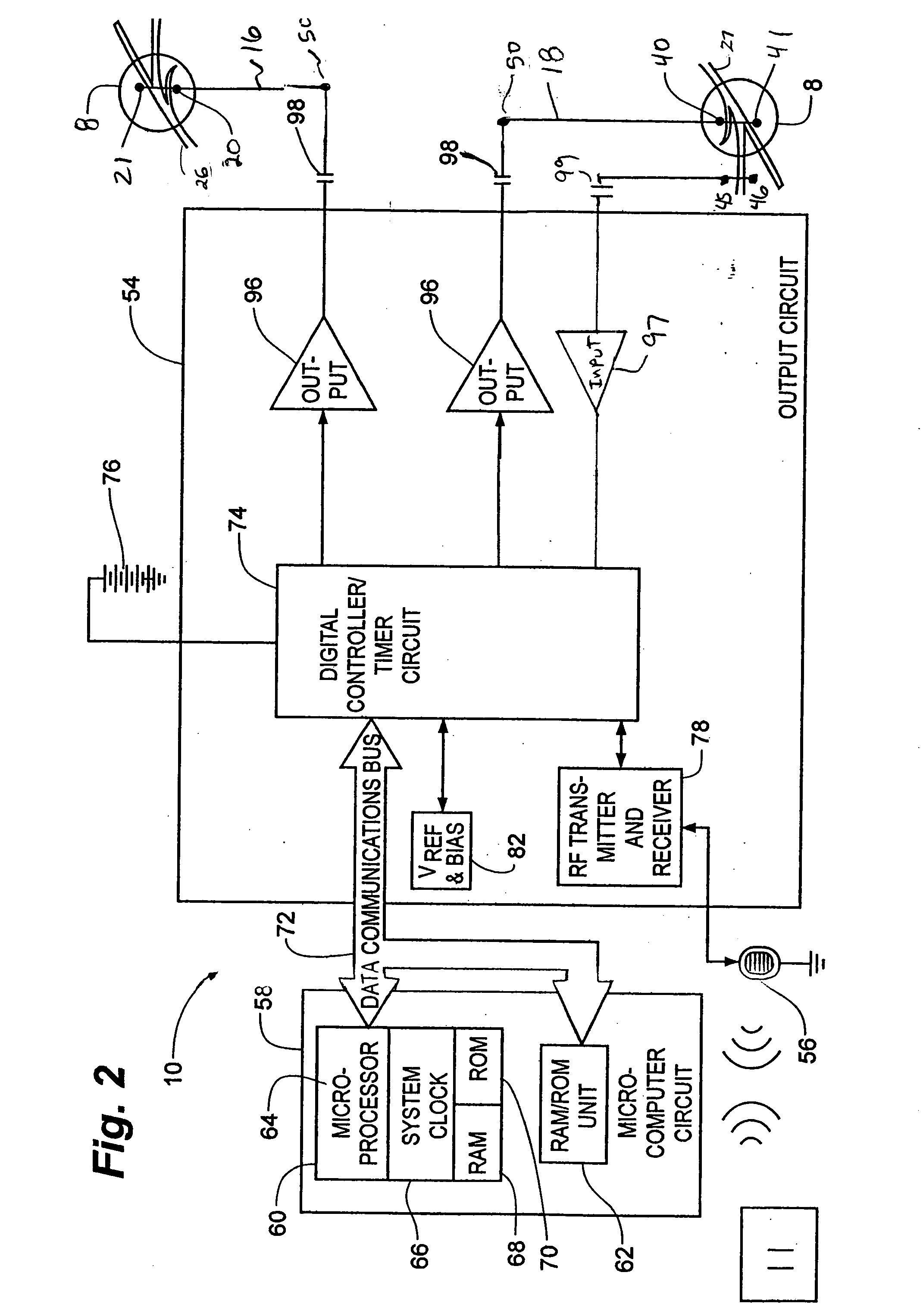
Method, system and device for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by electrical stimulation of the left and right pudendal nerves
InactiveUS20040193228A1Directly and effectively stimulatingUndesirable side effects of sacral nerve stimulation may be avoided or minimizedElectrotherapyDiseaseProstatalgia
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by means of electrical stimulation of the pudendal and sacral nerves, or portions thereof, and optional means for delivering drugs in association therewith. Two or more electrical stimulation regimes are applied on a continuous, alternating, intermittent or other basis to the sacral and pudendal nerves, and optionally one or more drugs are infused, injected or otherwise administered, to appropriate portions of a patient's pelvic floor and pudendal nerve and / or sacral nerve, or portions thereof, in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:GERBER MARTIN T
Acetabular instrument alignment guide
InactiveUS20060161167A1Eliminate needSave surgical timeDiagnosticsJoint implantsEngineeringPlastic surgery
An acetabular instrument alignment guide for aligning at least one orthopaedic instrument relative to an acetabulum in a pelvis. The acetabular instrument alignment guide includes an interchangeable head configured for positioning within the acetabulum where the interchangeable head has a primary axis. A drill guide is releasably connected to the interchangeable head. The drill guide includes a drill bore offset from the primary axis, and the drill bore is configured for aligning a drill relative to the pelvis. The acetabular instrument alignment guide further includes at least one reference pin and an instrument guide connected to the at least one reference pin, the instrument guide being both rotatable and translatable relative to the at least one reference pin. The reference pin is configured for placement in at least one hole in the pelvis produced by the drill.
Owner:SYMMETERY MEDICAL
Tool
An alignment trial system for a hip prosthesis comprising: (a) a trial femoral prosthesis comprising a head component, a neck component and a stem component; and (b) a trial acetabular cup prosthesis wherein the head component of the trial femoral prosthesis and the trial acetabular cup prosthesis include interlocking engagement formations and wherein the trial acetabular cup prosthesis includes means to facilitate the formation of a bore in the pelvis. The invention also relates to a method of inserting an acetabular cup prosthesis comprising the steps of: (I) preparing the femur and pelvis for insertion of a femoral prosthesis and an acetabular cup prosthesis; (ii) inserting the alignment trial apparatus of the above first aspect such that the trial femoral prosthesis is located in the prepared femur; (iii) locating the patient's hip such that the trial cup prosthesis is seated in the prepared portion of the pelvis; (v) drilling a bore in the pelvis; (vi) removing the alignment trial apparatus; (vii)inserting the acetabular cup prosthesis into the pelvis using the mark as a guide.
Owner:FINSBURY DEV
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Robotic total/partial knee arthroplastics
ActiveUS20070100258A1Improve accuracyReduce responsibilityPerson identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansTibiaSurgical robot
A system and method for knee arthroplasty procedures, using a novel leg rotation fixture to enable the leg mechanical axis, the tibia and the femur to be mutually disposed such that the load bearing, mechanical axis of the leg runs through the center of the knee joint. A measurement gauge is provided for mounting on the tibia and for aligning a baseplate in a known position on the tibia. This baseplate supports an X-ray target plate in a known position relative to the tibia, used in determining the mechanical axis, and an optional surgical robot, used to perform tibial and femoral cuts. The position of the femur relative to the robot may be determined from X-ray imaging of the pelvic region after attachment to the baseplate of an additional target extending to the pelvic region. The system enables improvement in the accuracy of knee arthroplasty procedures.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A trial shell is provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Systems and methods for intra-operative pelvic registration
A system for intra-operatively registering a pelvis comprising an acetabulum with a computer model of the pelvis in a coordinate system. The system may include: a) a surgical navigation system including a tracking device; and b) at least one computing device in communication with the surgical navigation system. The at least one computing device: i) receiving first data points from first intra-operatively collected points on an articular surface of the acetabulum, the first data points collected with the tracking device; ii) receiving a second data point from a second intra-operatively collected point on the pelvis, the second data point collected with the tracking device, the second data point corresponding in location to a second virtual data point on the computer model; and iii) determining an intra-operative center of rotation of the femur relative to the pelvis from the first data points.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Systems and methods for evaluating the urethra and the periurethral tissues
InactiveUS20020040185A1Accurate diagnosisImprove clinical outcomesGastroscopesOesophagoscopesDiseaseUrethra
The present invention provides systems and methods for the evaluation of the urethra and periurethral tissues using an MRI coil adapted for insertion into the male, female or pediatric urethra. The MRI coil may be in electrical communication with an interface circuit made up of a tuning-matching circuit, a decoupling circuit and a balun circuit. The interface circuit may also be in electrical communication with a MRI machine. In certain practices, the present invention provides methods for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions involving the urethra and periurethral tissues, including disorders of the female pelvic floor, conditions of the prostate and anomalies of the pediatric pelvis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method And Appartus For Acetabular Reconstruction
A trial system for a prosthesis is described. The prosthesis can include an acetabular prosthesis generally for implantation in an acetabulum and the surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. One trial shell or a collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a shell prosthesis into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Pelvic waypoint clamp assembly and method
InactiveUS20050027303A1Accuracy can be to newBrevity can be to newDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsRight femoral headComputer-aided
A pelvic waypoint clamp assembly designed for external attachment to a patient's hips. The clamp assembly serves as a foundation for a fixation mount (i.e. a passive or active tracker) that, when in communication with conventional computer-assisted orientation systems, is used to determine, non-invasively, the center of the femoral head prior to or during knee arthroscopy.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID R +1
System and method for treating tissue wall prolapse
The invention disclosed herein includes an apparatus and a method for treatment of vaginal prolapse conditions. The apparatus is a graft having a central body portion with at least one strap extending from it. The strap has a bullet needle attached to its end portion and is anchorable to anchoring tissue in the body of a patient. The invention makes use of a delivery device adapted to deploy the graft in a patient. The inventive method includes the steps of making an incision in the vaginal wall of a patient, opening the incision to gain access inside the vagina and pelvic floor area, inserting the inventive apparatus through the incision, and attaching the straps of the apparatus to anchoring tissue in the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
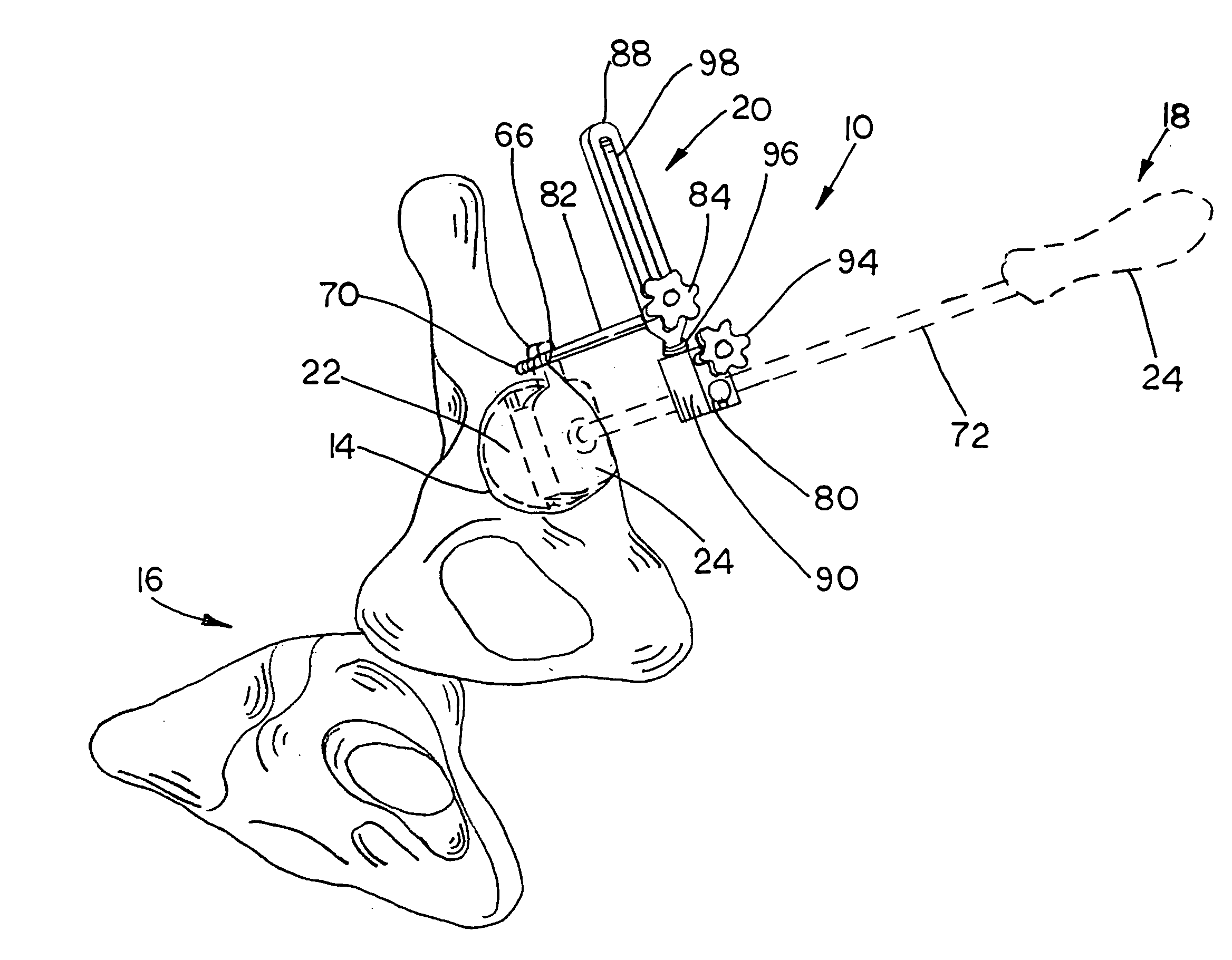
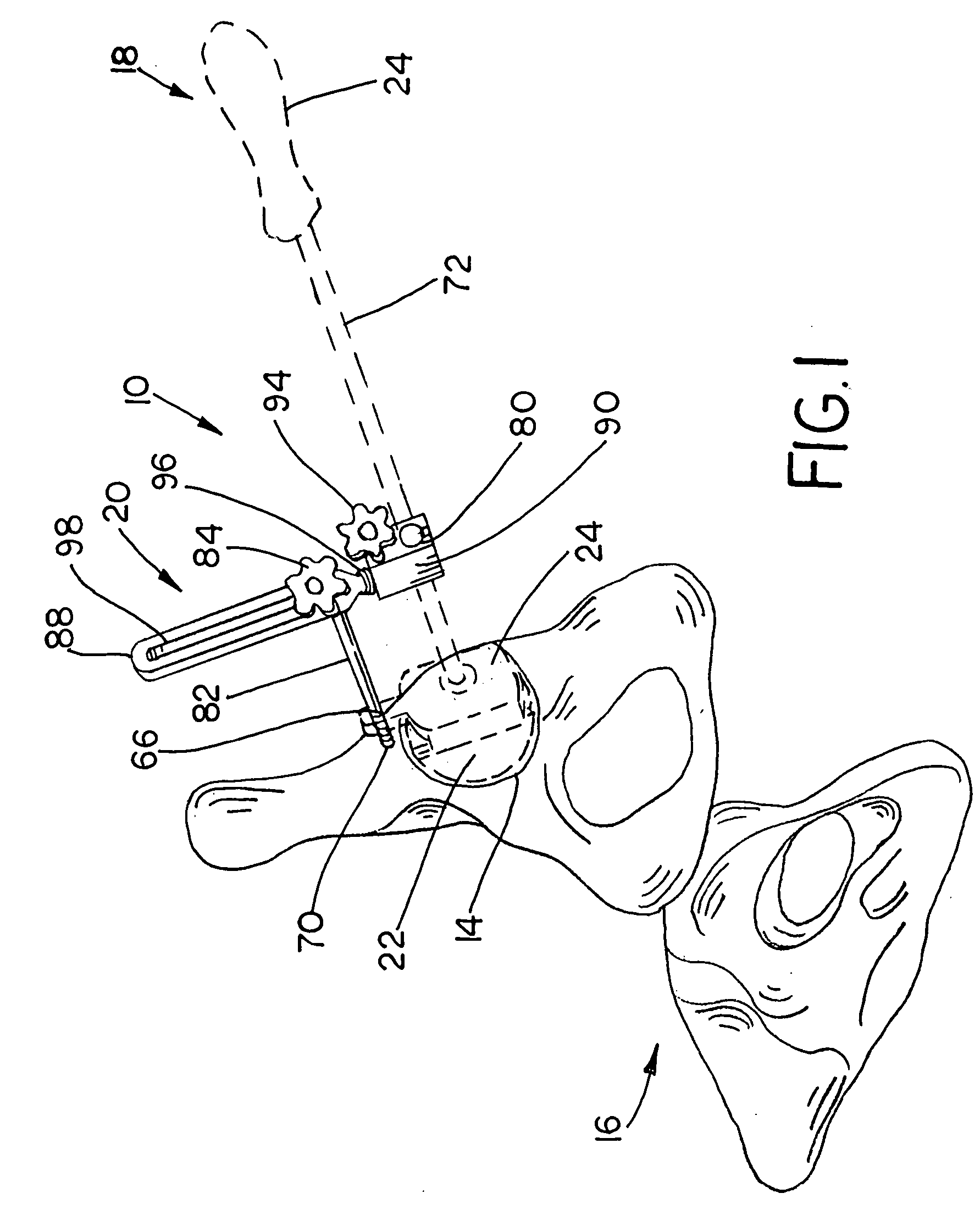
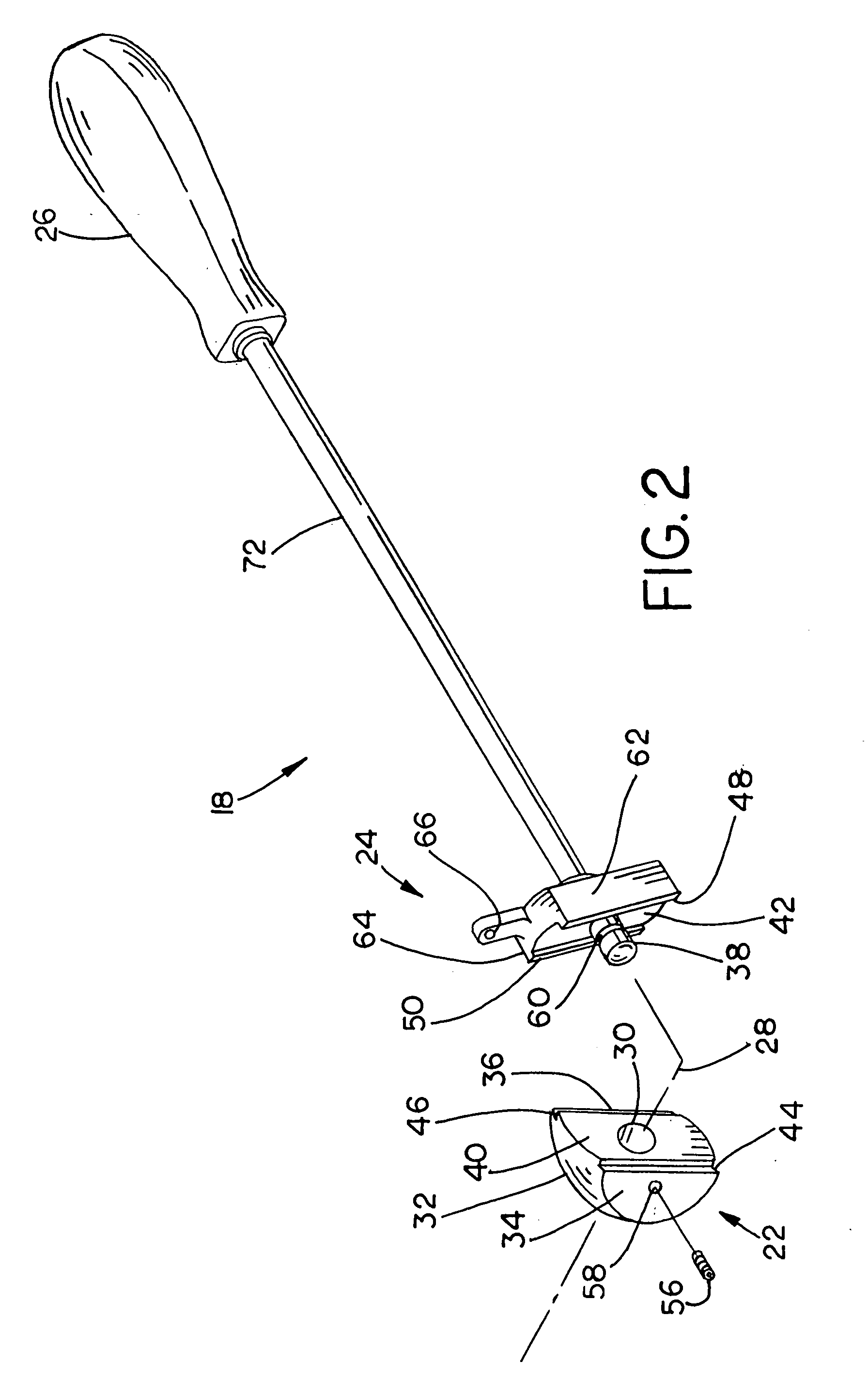
Pelvis level
Instrumentation and method for determining the orientation of the pelvic bone during hip-replacement surgery. Instrumentation includes a pelvis frame and a pelvis level. The pelvis frame is used for performing an operation which provides preliminary information for determining the position of the pelvic bone, and includes pads which are specifically contoured for contact with the pelvic bone. The pelvis level is used in combination with the pelvis frame to determine the exact position of the patient's pelvic bone, and includes a ball level which is capable of withstanding steam sterilization.
Owner:BROYLES JOSEPH E
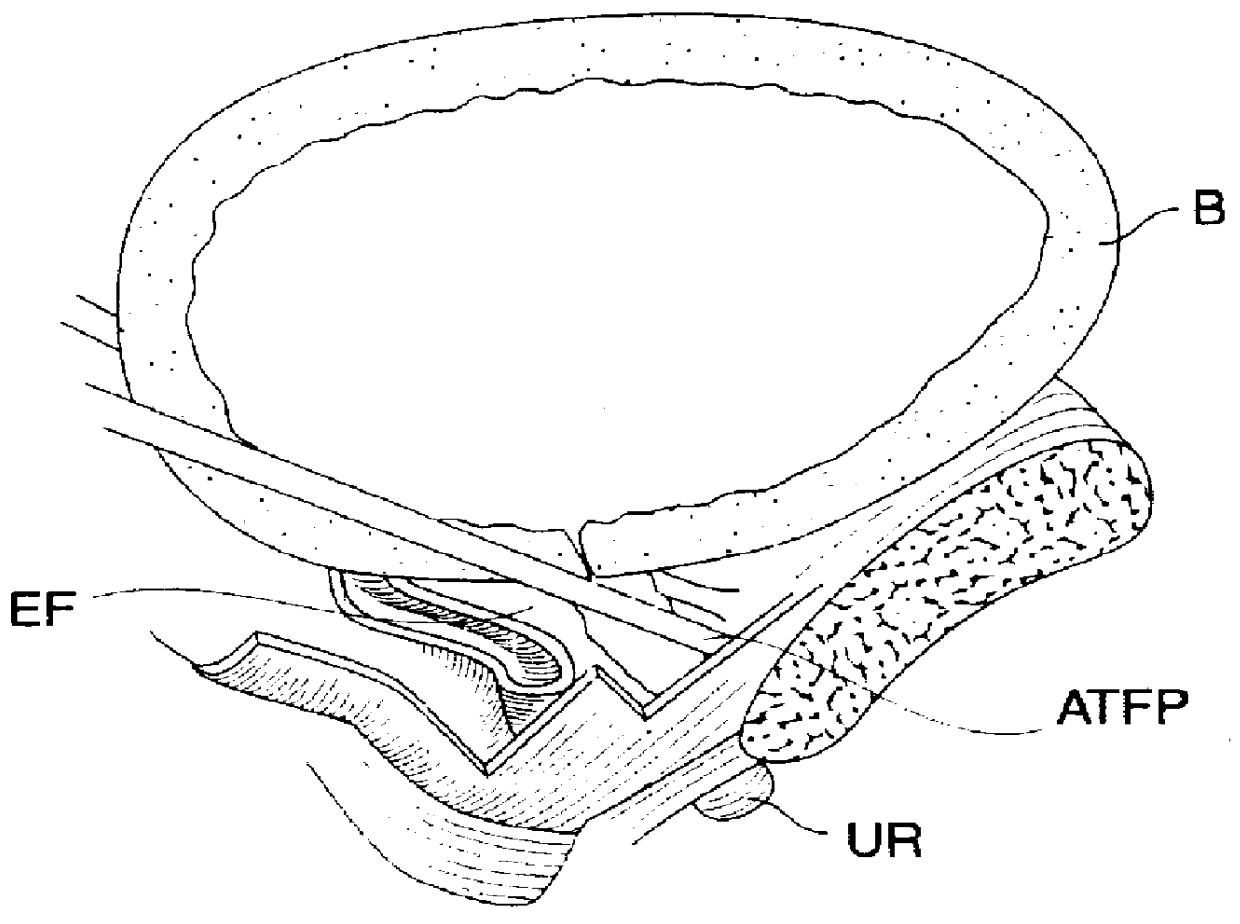
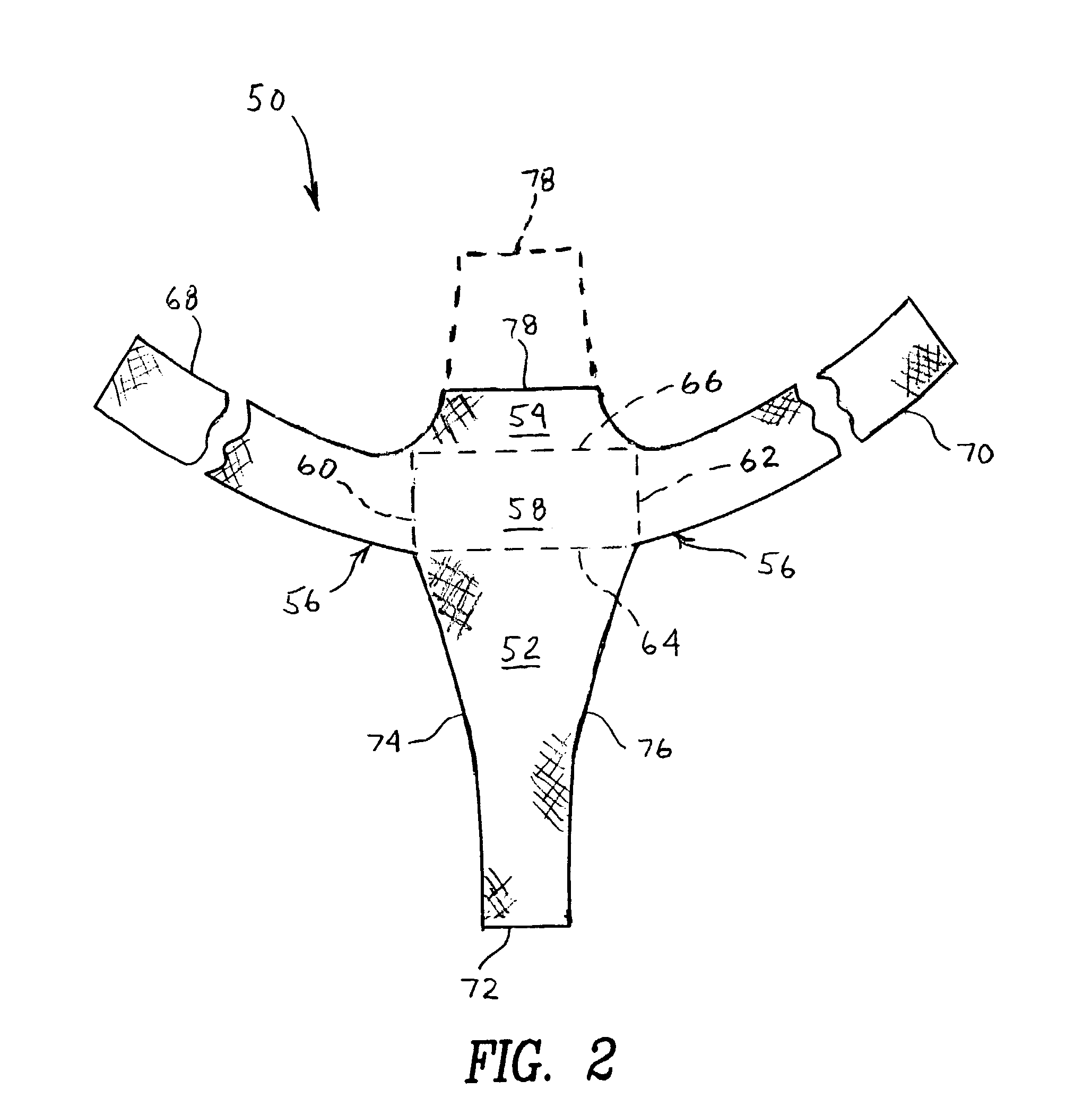
Method and apparatus for treating pelvic organ prolapses in female patients
An anterior implant adapted to treat central and lateral cystoceles present in a female patient includes laterally extending stabilizing straps for supporting the implant between the patient's bladder and vagina independently of the patient's arcus tendineous fascia pelvis. Rectocele and hysterocele repairs can be carried out using a single posterior implant which, like the anterior implant, is provided with laterally extending stabilizing straps for supporting the implant between the patient's rectum and vagina.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Apparatus and method for incision-free vaginal prolapse repair
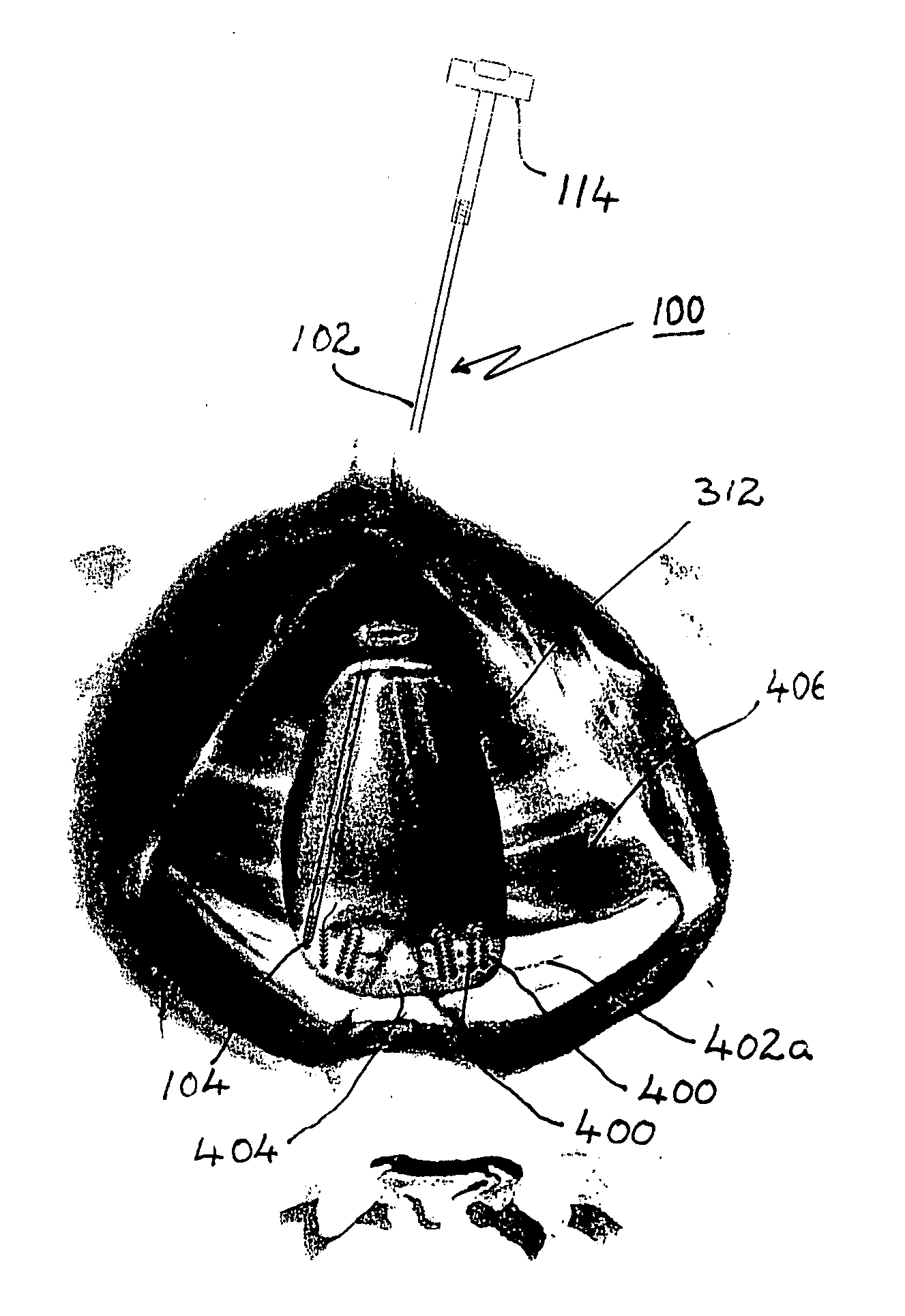
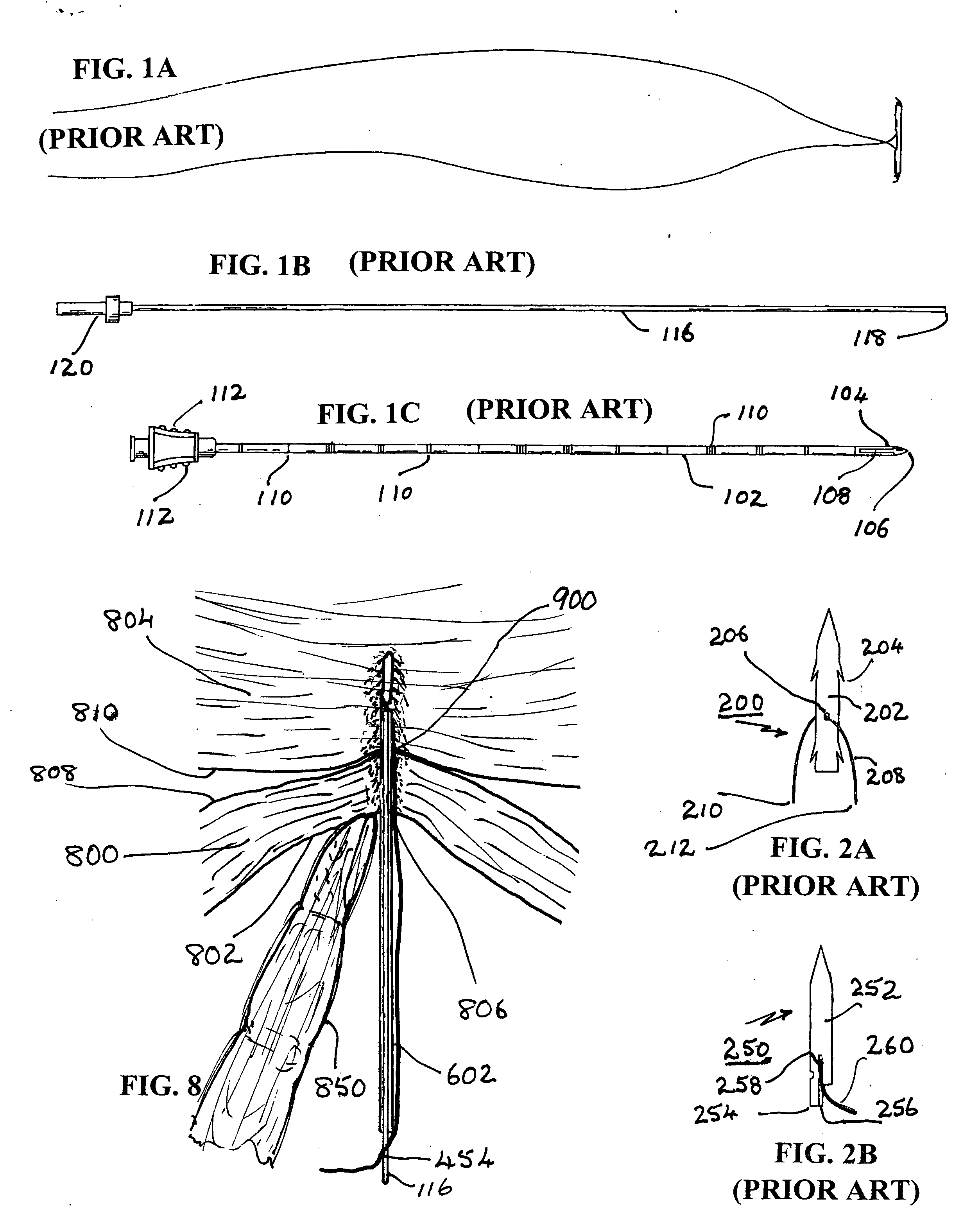
InactiveUS20050199249A1Simple, minimally invasive and inexpensiveQuick fixSuture equipmentsBed wetting preventionVaginal ProlapsesDistressing
In a preferred application, e.g., the repair of vaginal prolapse after relocation of the vagina and any organs displaced by the prolapse, corrective surgery is initiated by applying a hollow tubular element, formed to forcibly insert a barbed anchor attached to a distal end of a first length of suture, without any incision, from the inside of the vagina through the vaginal wall (the supported tissue) into selected support tissue within a patient's pelvis. This involves puncturing and thus locally severe physical distressing of both the supported tissue and the support tissue. The barbed anchor is left in the support tissue as the tubular element is then withdrawn from the support tissue and out of the vagina, leaving the proximate end portion of the suture extending through the vaginal wall into the vagina. A second such anchor, with a second length of suture attached thereto, is similarly inserted adjacent to the first anchor. The proximate end portions of the sutures are tied to each other inside the vagina, to thereby secure the vaginal wall to the support tissue with corresponding punctures formed in each by the insertions of the two anchors being thereby held in respective, precisely aligned, intimate contact during healing. This results in a pair of fused scars that cooperate to permanently bond the vaginal wall locally to the support tissue. If the sutures and / or the anchors are made of absorbable material they will all eventually disappear and the fused scars will provide the permanent bonding. If the anchors are made of non-absorbable material they may remain where located. A plurality of such paired fused-scar bonds may be generated, at the surgeon's discretion, to ensure adequate support for the repaired vagina. The apparatus and method can be readily adapted to similarly effect deliberate, local, beneficial bonding between other adjacent living tissues in a patient.
Owner:KARRAM MICKEY M
Gynecological ablation procedure and system using an ablation needle
InactiveUS6840935B2Efficient ablationFast recovery timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesProximateMedicine
A method for treating pelvic tumors, such as uterine leiomyomata, includes inserting an ablation apparatus into a pelvic region and positioning the ablation apparatus either proximate or into a pelvic tumor. The method further includes using a laparoscope and an imaging device, such as an ultrasound machine, to confirm the location of the pelvic tumor and placement of the ablation apparatus. Various ablation apparatuses may be used, including those with multiple needles or deployable arms that are inserted into the pelvic tumor and those without arms. The method further includes delivering electromagnetic energy or other energy through the ablation apparatus to the pelvic tumor to ablate the tumor. A surgical system for ablating pelvic tumors is also provided.
Owner:ACESSA HEALTH INC +1
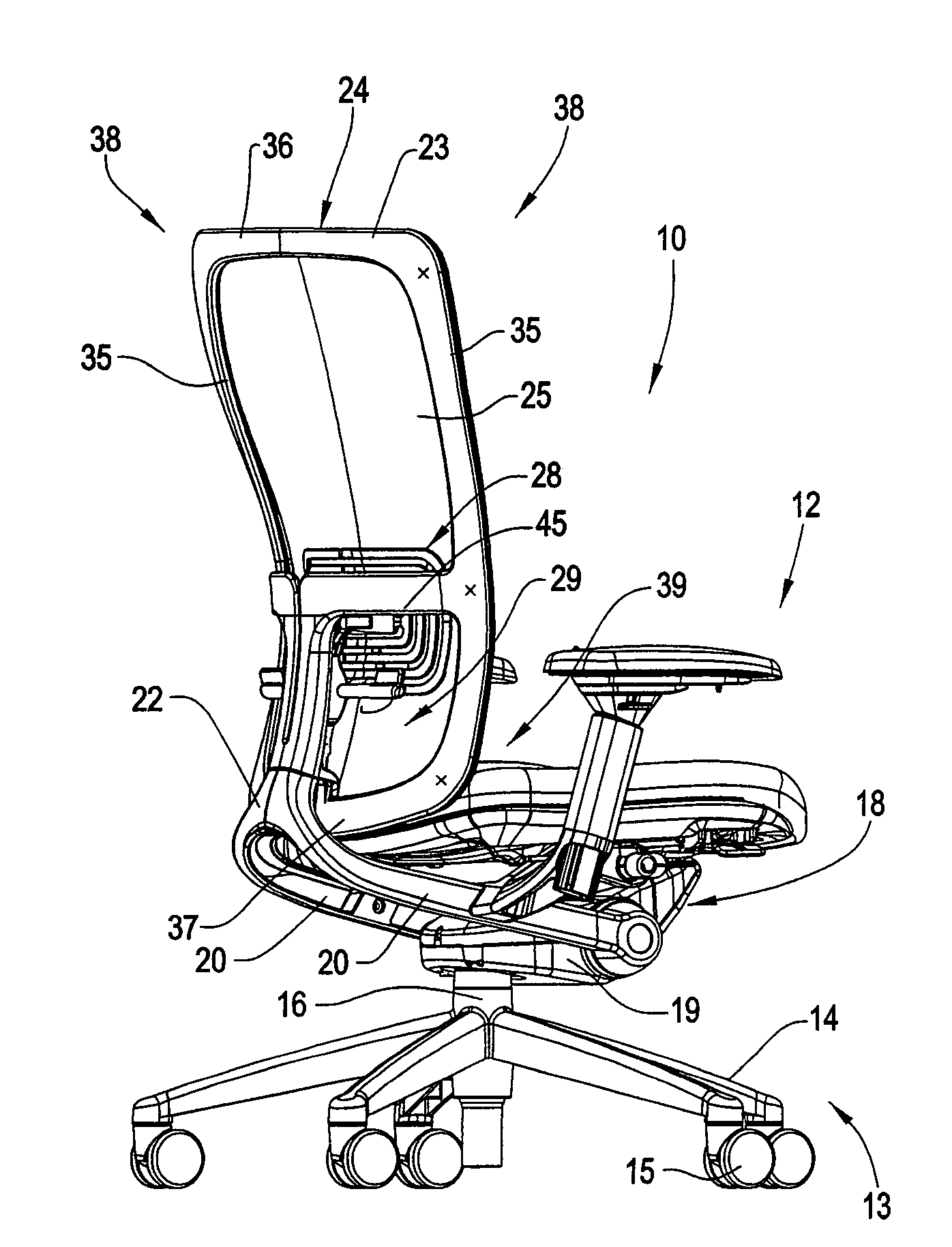
Chair back with lumbar and pelvic supports
ActiveUS7347495B2Readily feltGreat variation in pressureStoolsAdjustable chairsOffice chairLumbar vertebrae
An office chair is provided having a back assembly which is configured to provide supplemental support to the back of a chair occupant in addition to the support provided by the primary support surface of the chair back. The chair back includes a lumbar support unit having a lumbar support pad wherein asymmetric support is provided to the left and right halves of the lumbar pad. As such, the asymmetric support loads are independently adjustable to more comfortably support a chair occupant. The chair back also includes a pelvic support pad which is disposed vertically adjacent to the lumbar support.
Owner:HAWORTH SPA
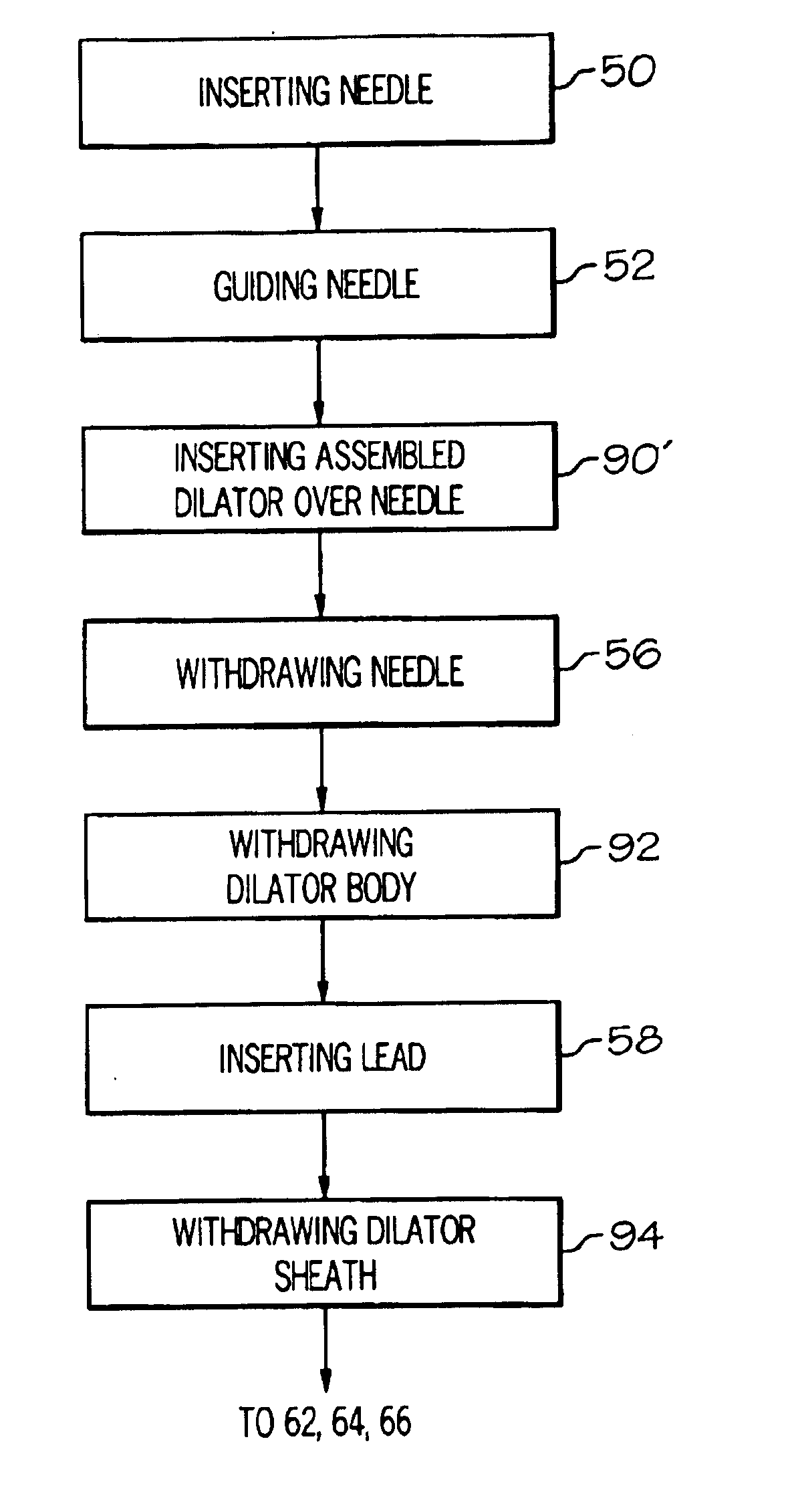
Minimally invasive method for implanting a sacral stimulation lead
Method embodiments to implant a stimulation lead in a patient's sacrum to deliver neurostimulation therapy can reduce patient surgical complications, reduce patient recovery time, and reduce healthcare costs. A method embodiment begins by inserting a needle posterior to the sacrum through an entry point. The needle is guided into a foramen along an insertion path to a desired location. The insertion path is dilated with a dilator to a diameter sufficient for inserting a stimulation lead. The needle is removed from the insertion path. The stimulation lead is inserted to the desired location. The dilator is removed from the insertion path. Additionally if the clinician desires to separately anchor the stimulation lead, an incision is created through the entry point from an epidermis to a fascia layer. The stimulation lead is anchored to the fascia layer. After the stimulation lead has been anchored, the incision can be closed, or the stimulation lead proximal end can be tunneled to where an implantable neurostimulator is located and then the incision can be closed. A implanted sacral stimulation lead can be connected to the neurostimulator to delivery therapies to treat pelvic floor disorders such as urinary control disorders, fecal control disorders, sexual dysfunction, and pelvic pain.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Devices and method for treating pelvic dysfunctions
ActiveUS20090171143A1Prevent movementSuture equipmentsSurgical furnitureFunctional disturbanceUterus
In one embodiment, a method includes securing an implant that includes a pre-formed loop to a vaginal apex. An end of the suture is inserted through a selected portion of a pelvic tissue to dispose at least a portion of the implant within a pelvic region of the patient. The end of the suture is drawn through the loop while simultaneously advancing a uterus to approximate the vaginal apex to the selected portion of pelvic tissue. An apparatus includes an implant and a suture coupled to the implant having a pre-formed loop. configured to receive a portion of a delivery device therethrough. A trocar is coupled to an end of the suture that can be releasably coupled to an end of the delivery device. The trocar can be inserted through a pelvic tissue and drawn through the loop forming a knot to secure the implant to the pelvic tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Pelvic disorder treatment device
ActiveUS7613516B2Relieving pelvic painReliable controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyInterstitial cystitisFecal incontinence
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Method and Apparatus for Treating Incontinence
InactiveUS20090054950A1Alleviate and avoid symptomDigestive electrodesProsthesisSmooth muscleUrethra
A medical condition is treated using electrical stimulation of contractile tissue, such as a sphineter, as well as electrical stimulation of afferent nerves to illicite a neuron-modulation response. The device (1) and method is particular useful for treating urge incontinence where the tissue is a smooth muscle neo-sphineter (2) about the urethra and the nerves are in the pelvic region.
Owner:CONTINENCE CONTROL SYST INT
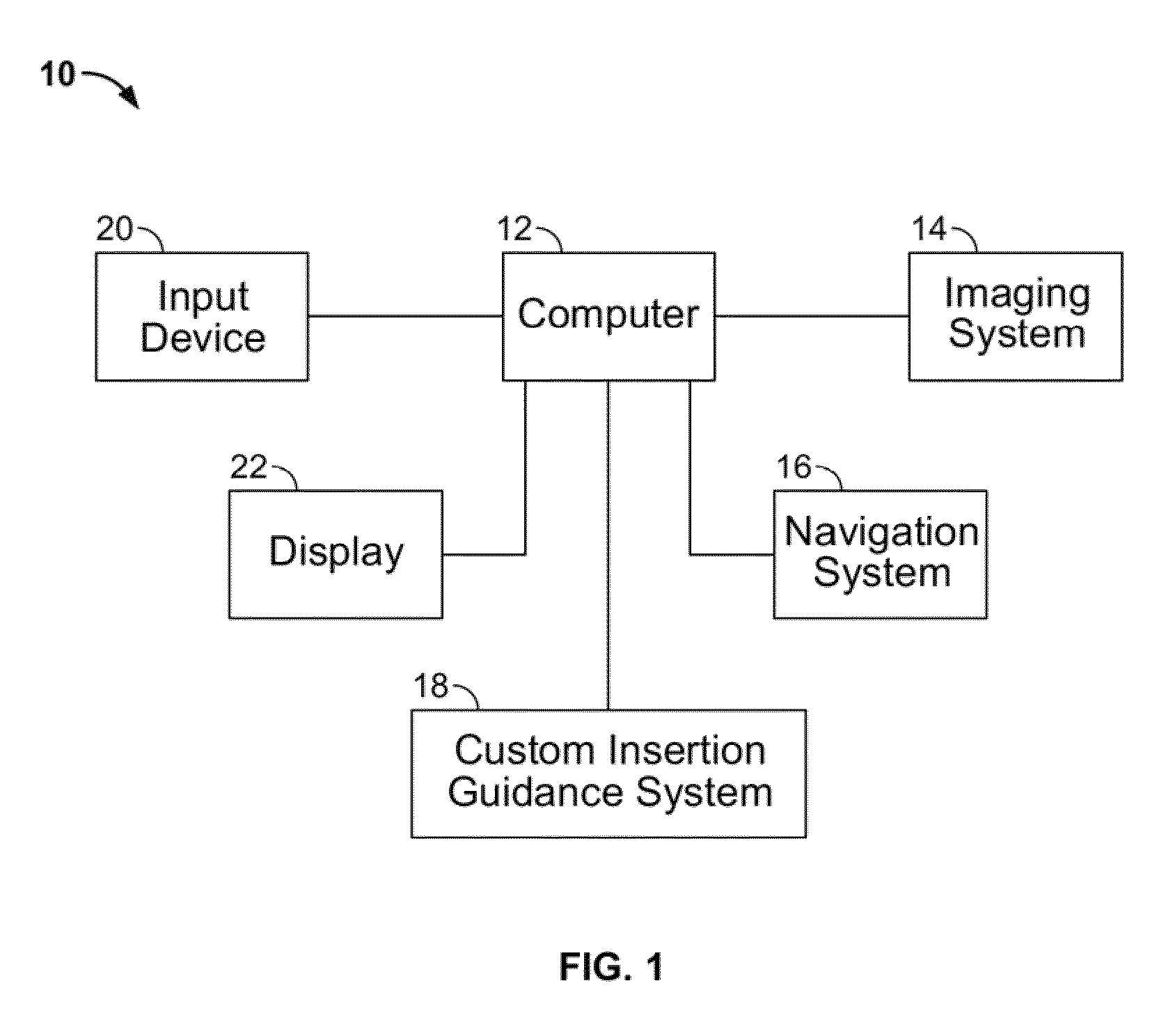
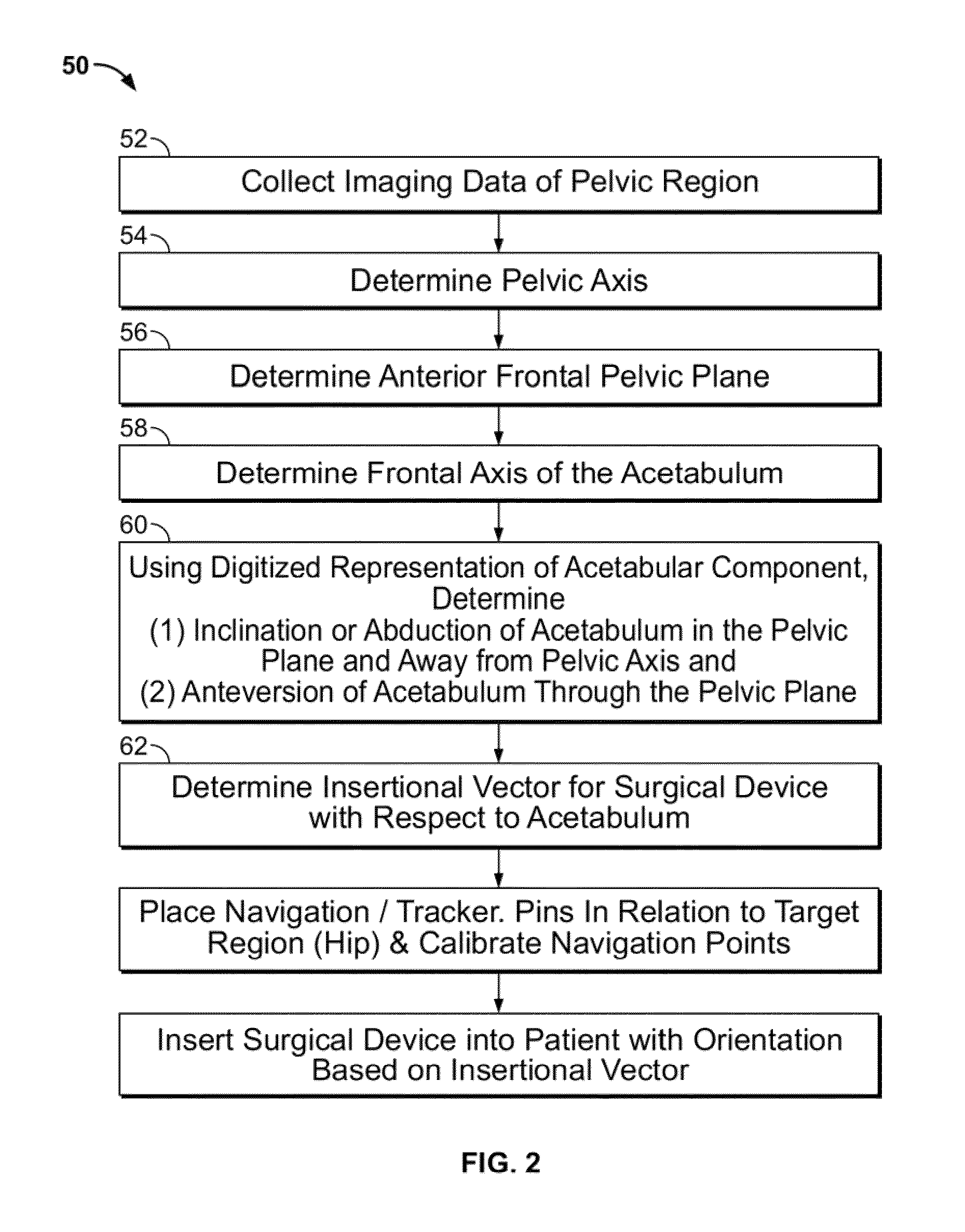
Patient-specific total hip arthroplasty
ActiveUS8932299B2Large range of motionMinimizing reaction forcePhysical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationAcetabular componentPre operative
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for performing total hip arthroplasty with patient-specific guides Pre-operative images of a pelvic region of a patient are taken in order to predefine the structure of the guides and corresponding implants. From the obtained image data an insertional vector for implanting an acetabular implant or component into an acetabulum of the patient is determined, wherein the insertional vector is coaxial with a polar axis of the acetabular component. Also from the obtained image data, a superior surface of the guides and implants can be shaped to match the acetabulum of the patient. A nub portion extending outwardly from the superior surface of the guides and implants is shaped to substantially match the shape of a fovea of the acetabulum. A guide portion of the guides forming a slot has a longitudinal axis coaxial with the determined insertional vector of a corresponding acetabular component.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com