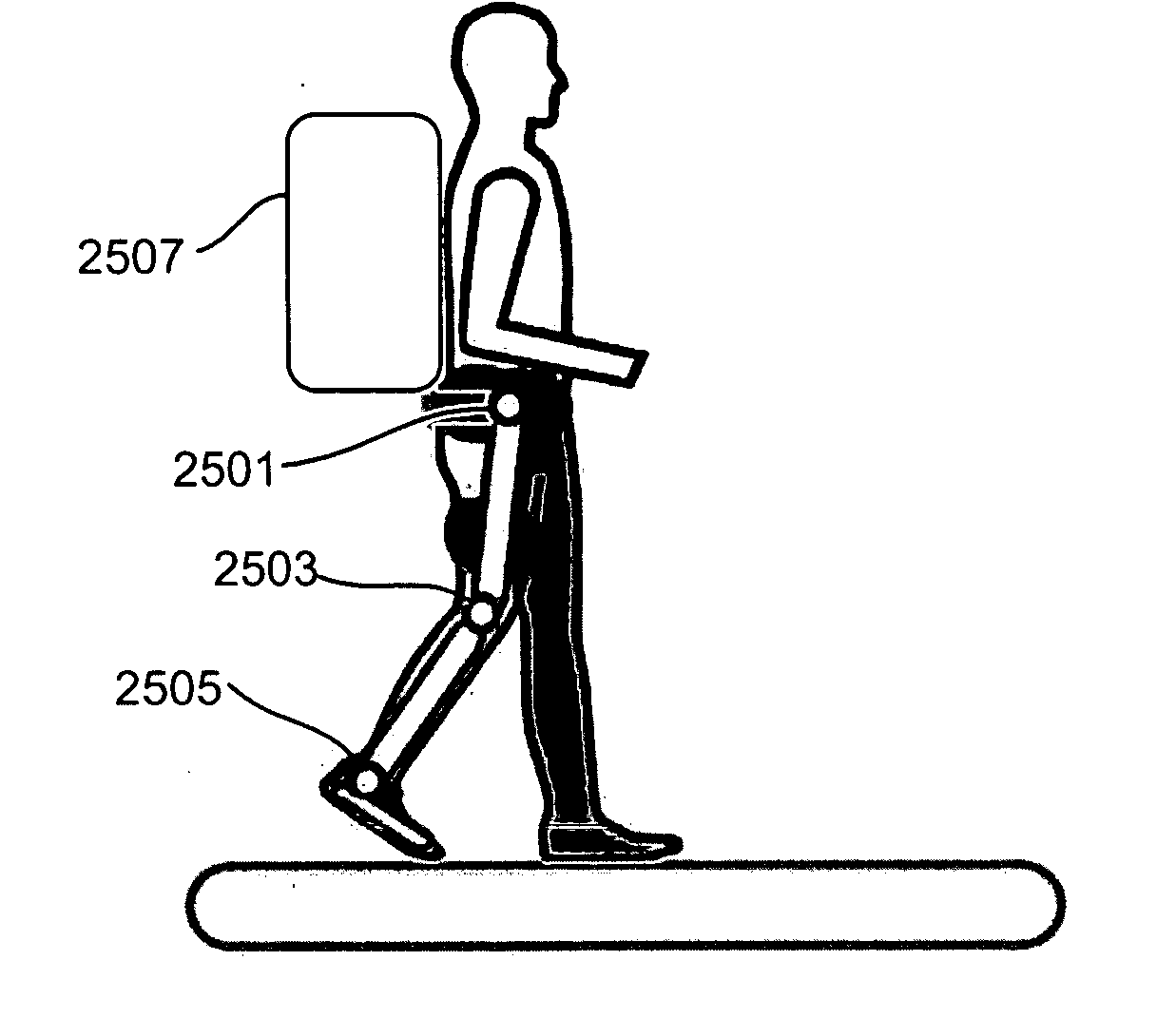
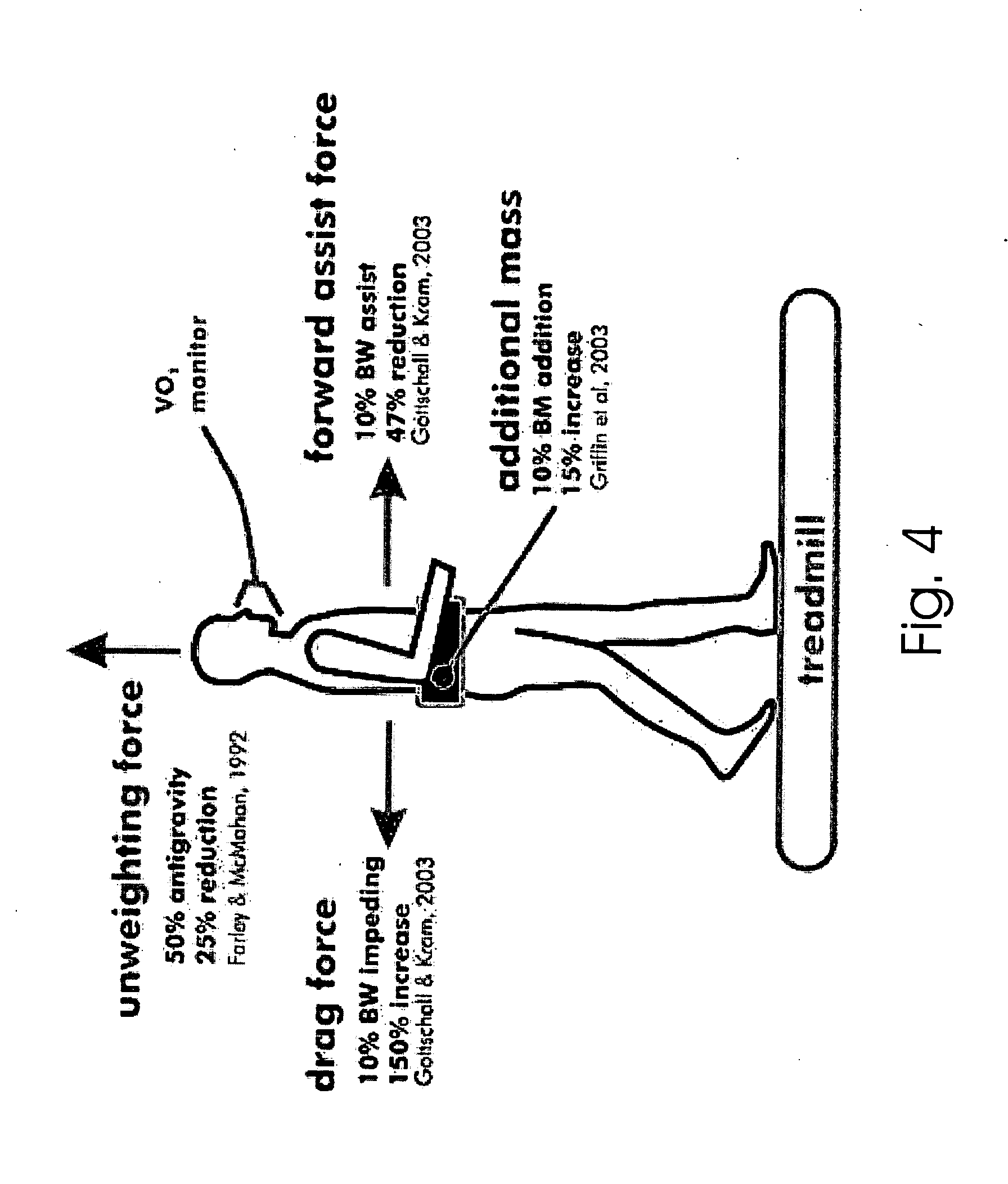
Exoskeletons for running and walking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
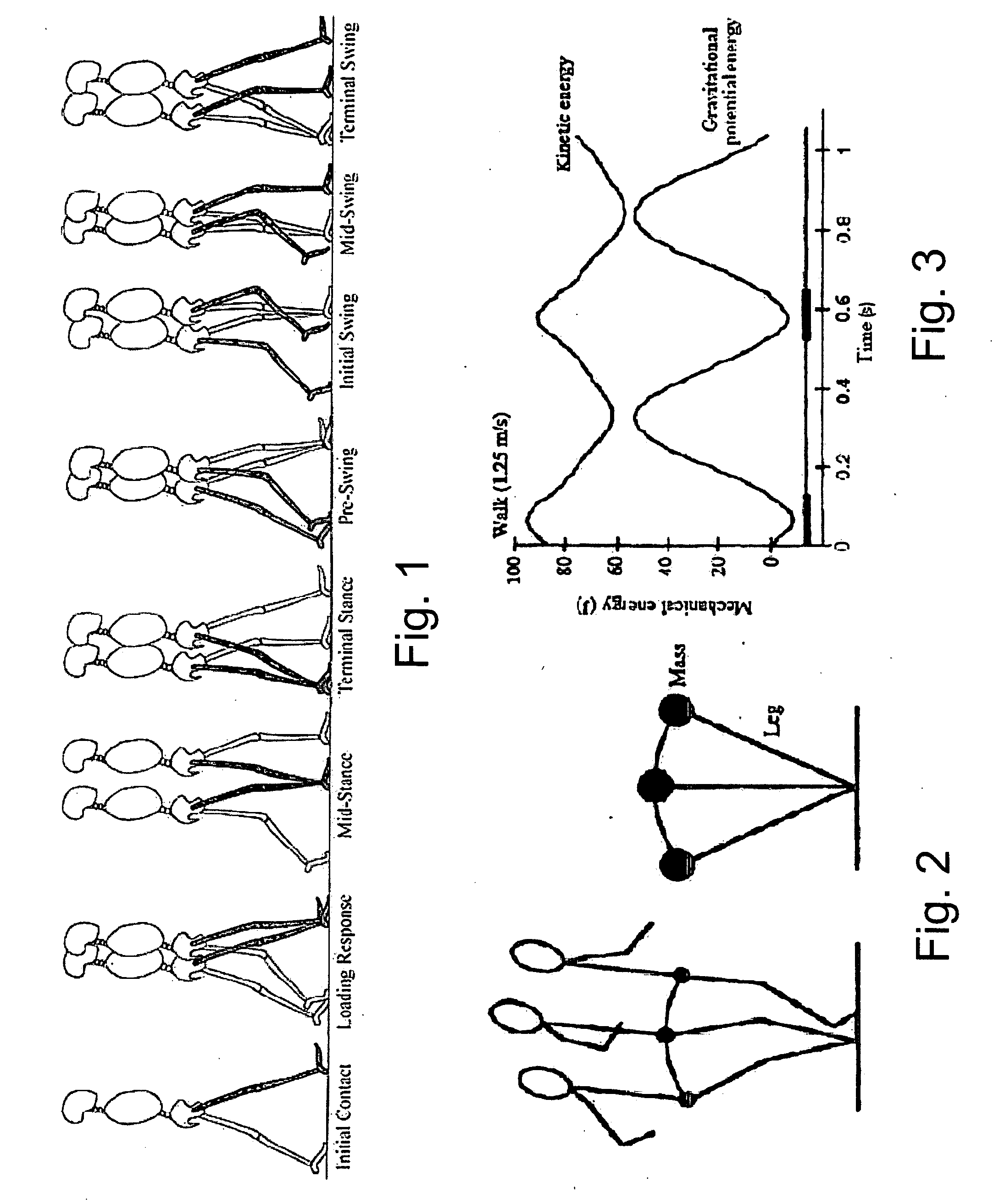
[0084] Biomechanics of Walking and Running In this section the biomechanics of human walking and running are examined. In later sections, these biomechanics will motivate the design of the exoskeleton system described herein.
[0085] Walking
[0086] Walking consists of two phases, a stance phase and a swing phase. During the early stance phase, the muscles at the hip, knee and ankle generally act to decelerate and stabilize the body. At the end of stance, the ankle undergoes powered plantar flexion where it provides the energy to power the body forward and upwards. Additionally, at the start of the swing phase, the hip gives a burst of energy to raise the lower leg from the ground surface. FIG. 1 outlines eight phases of the walking cycle.
[0087] The kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy of the center of mass are approximately 180 degrees out of phase in walking. At mid-stance in walking, the gravitational potential energy is at its maximum and the kinetic energy is at its...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com