Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Hip implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
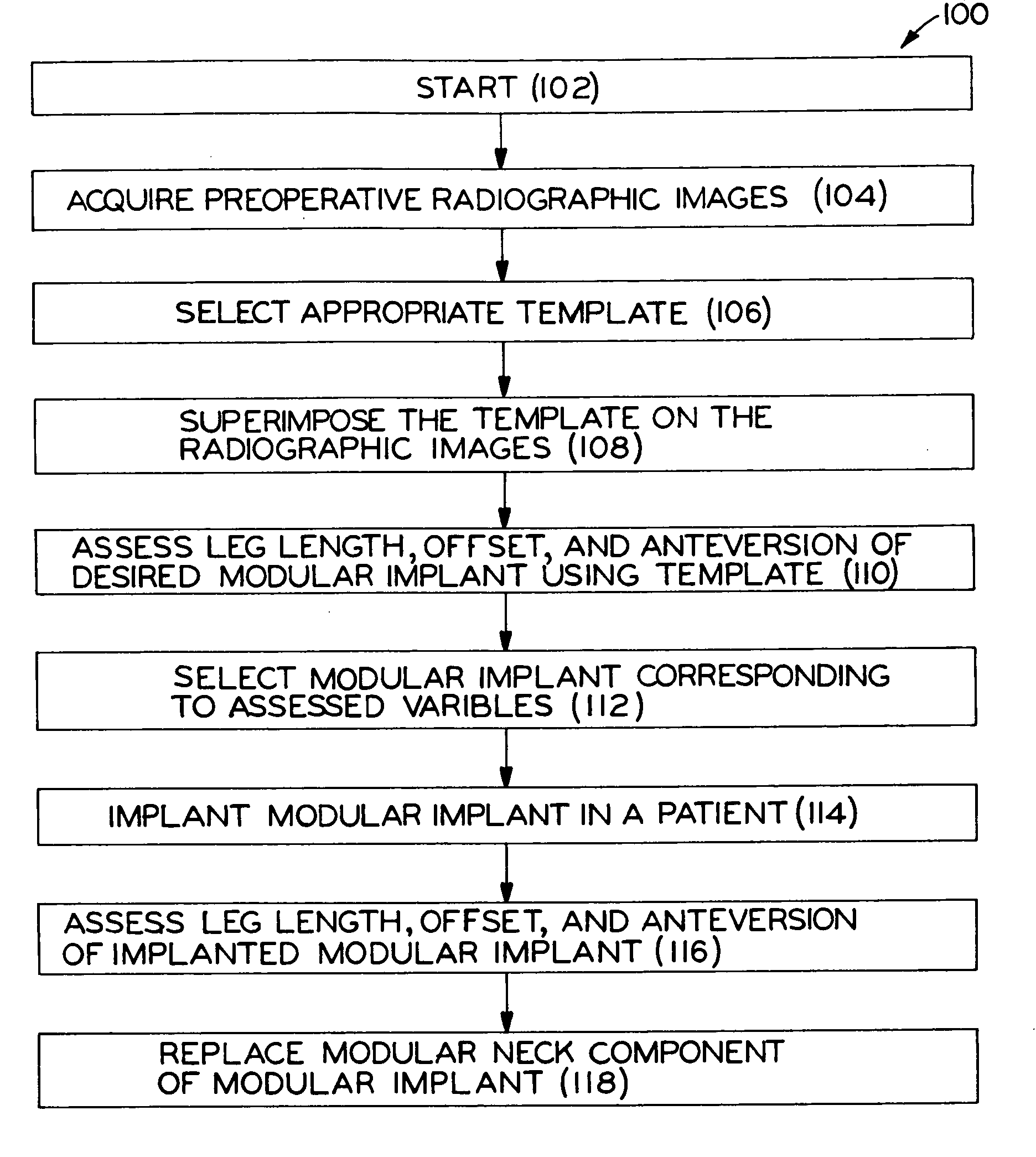
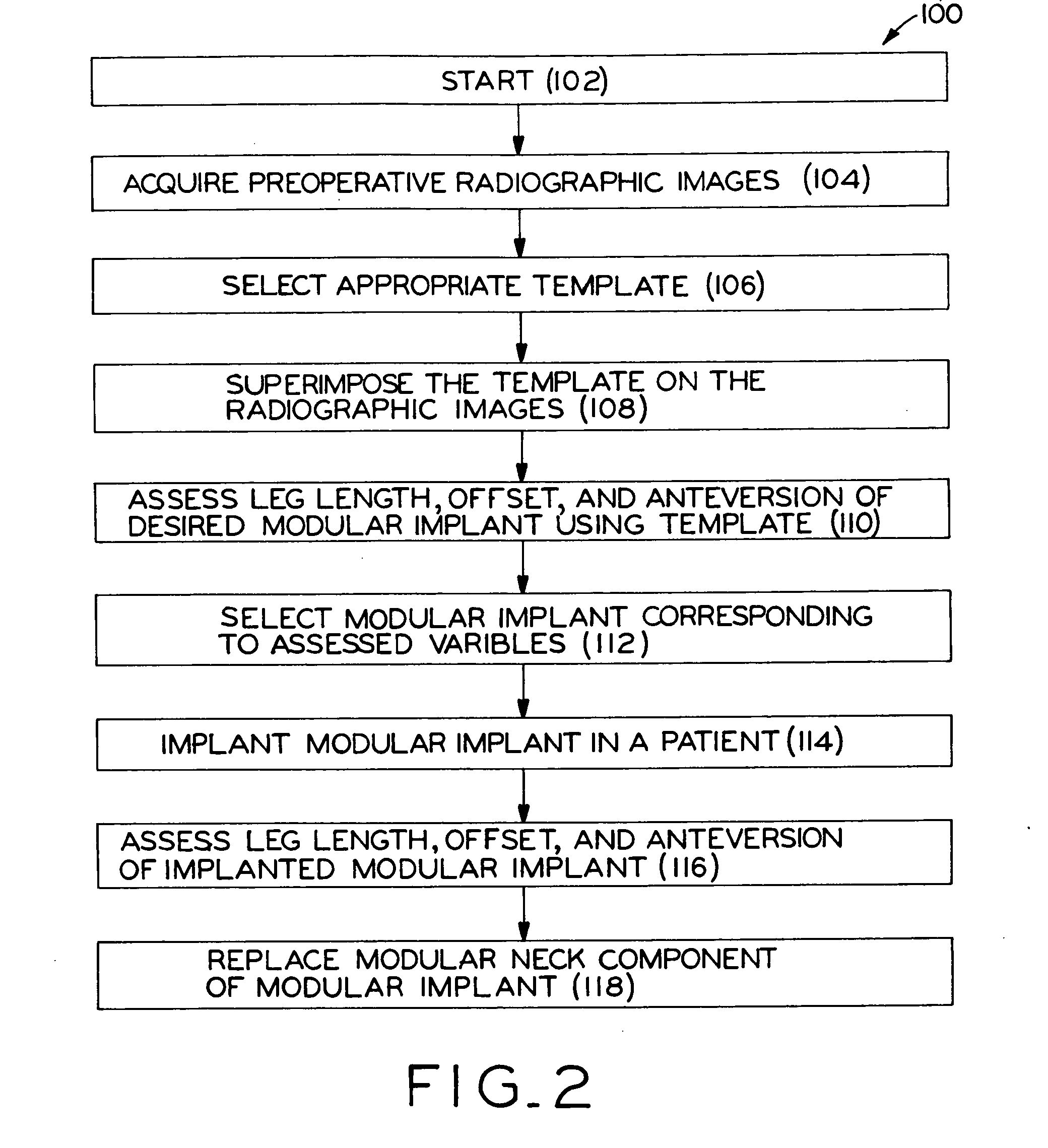
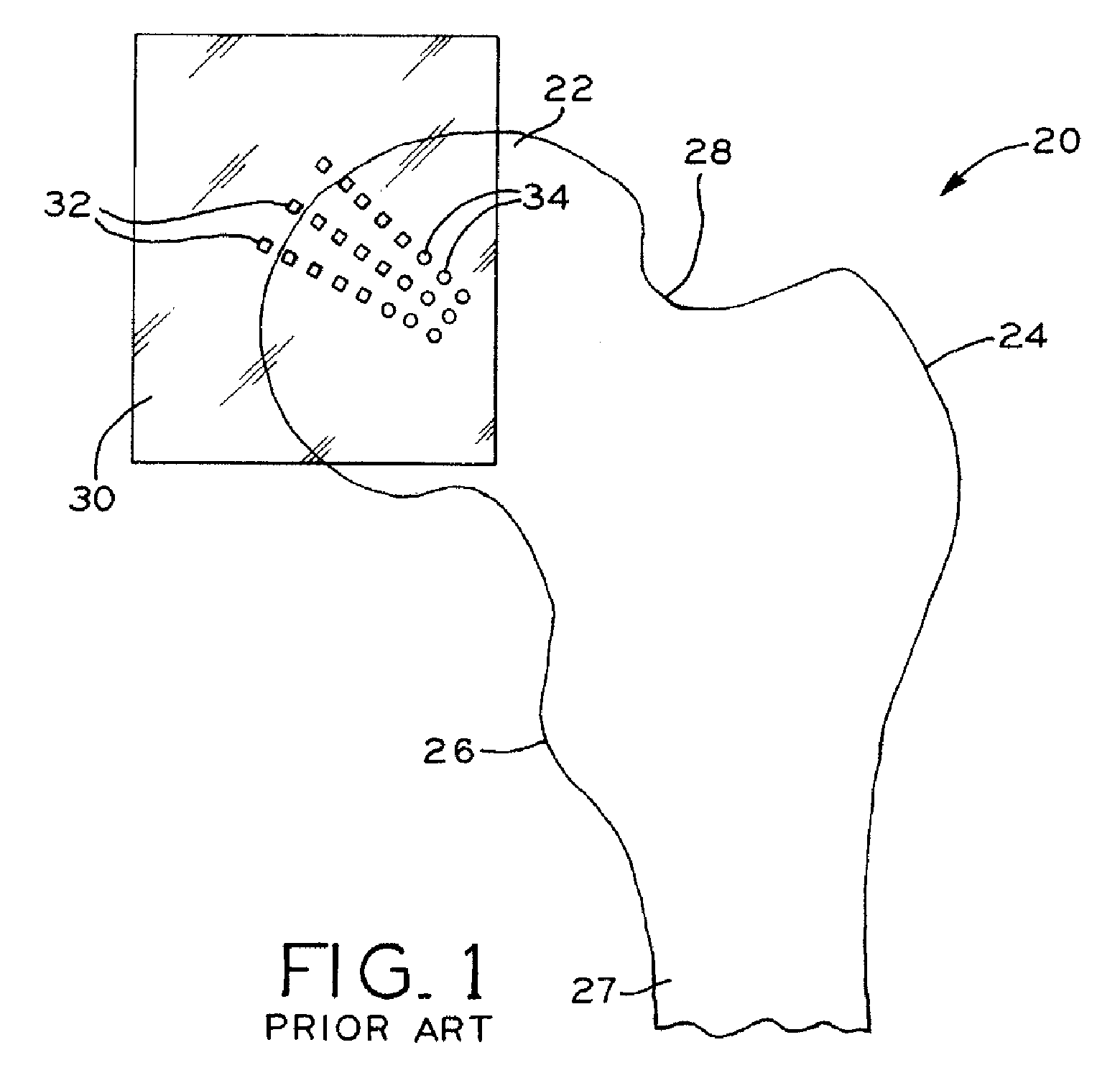
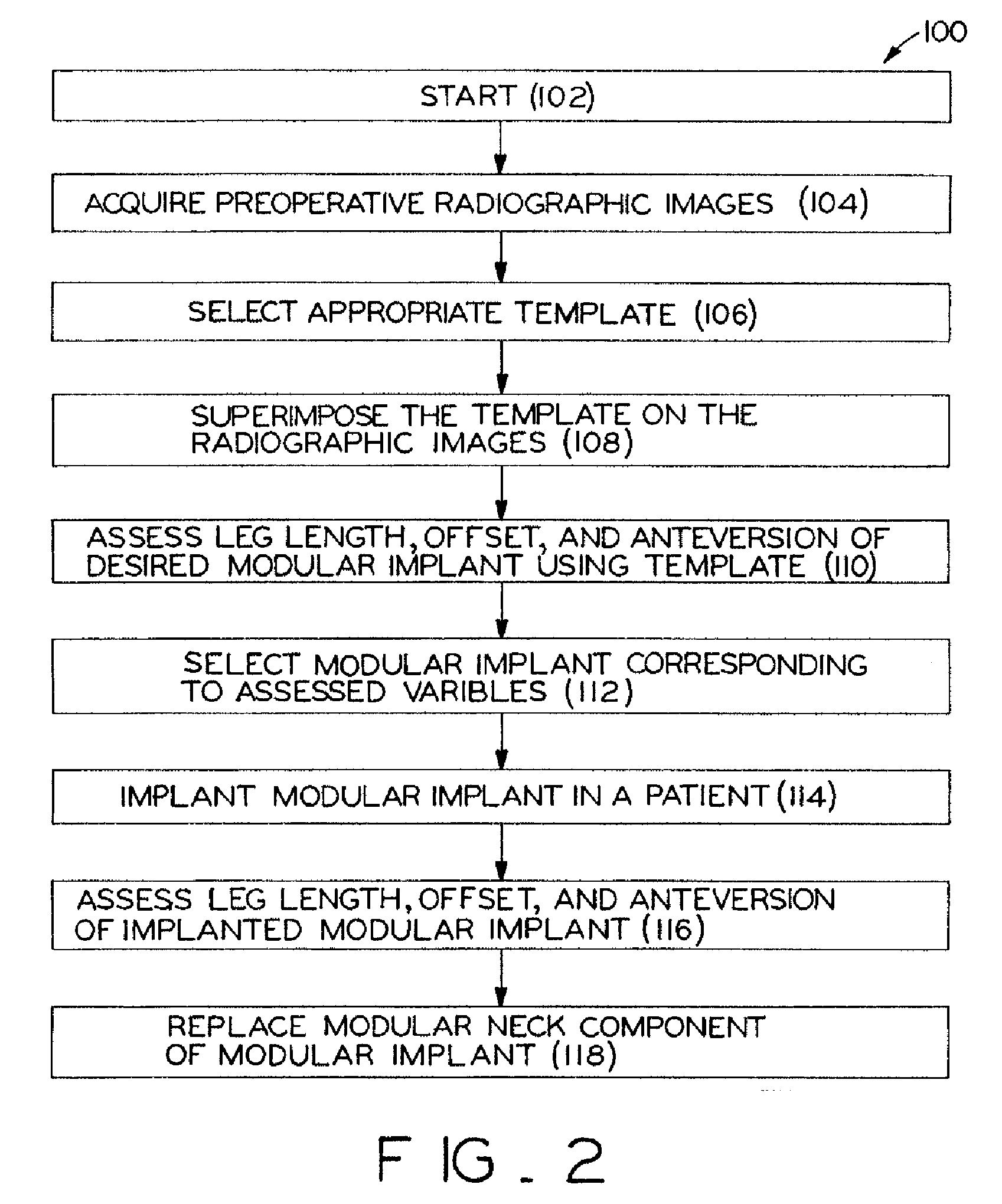
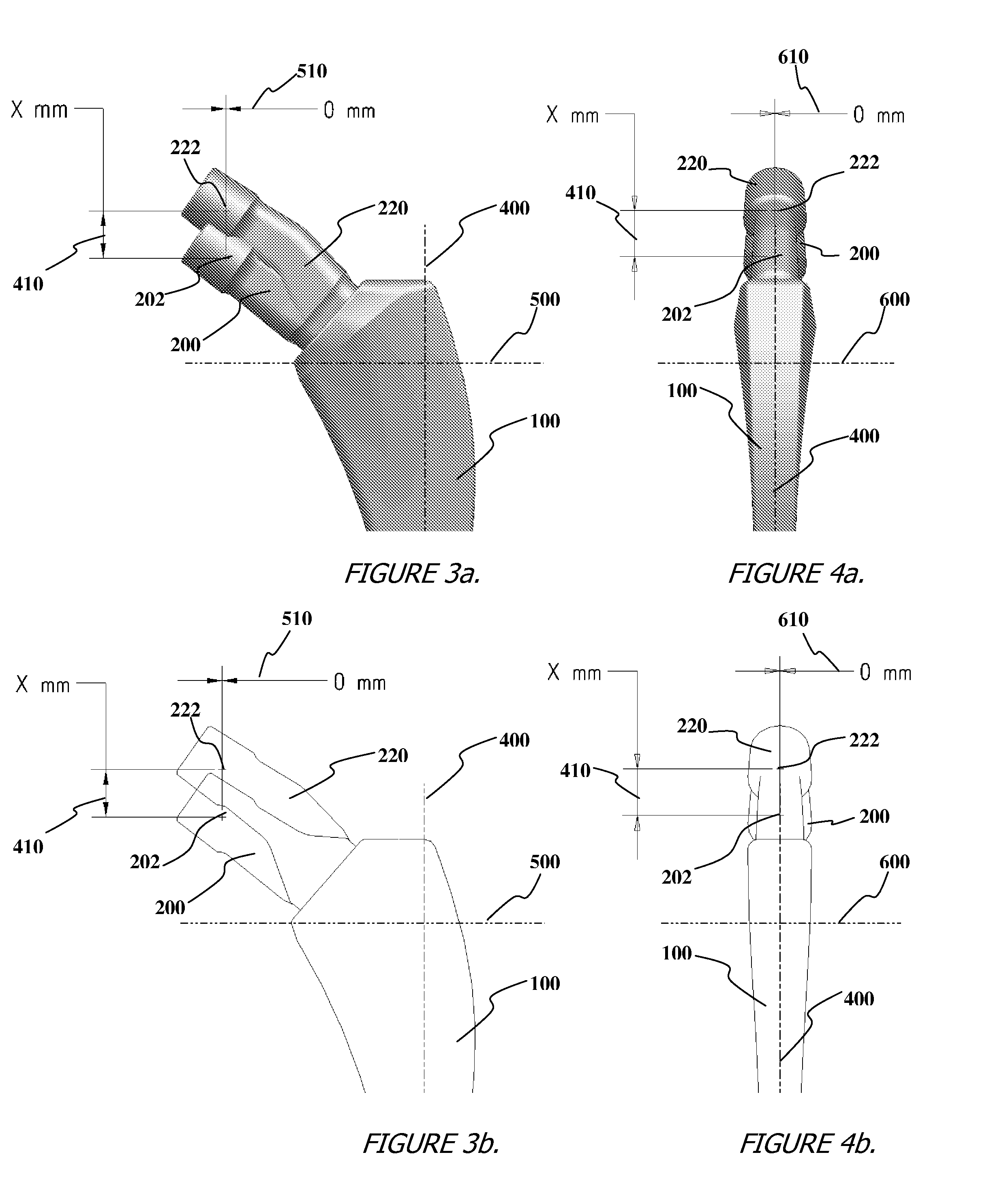
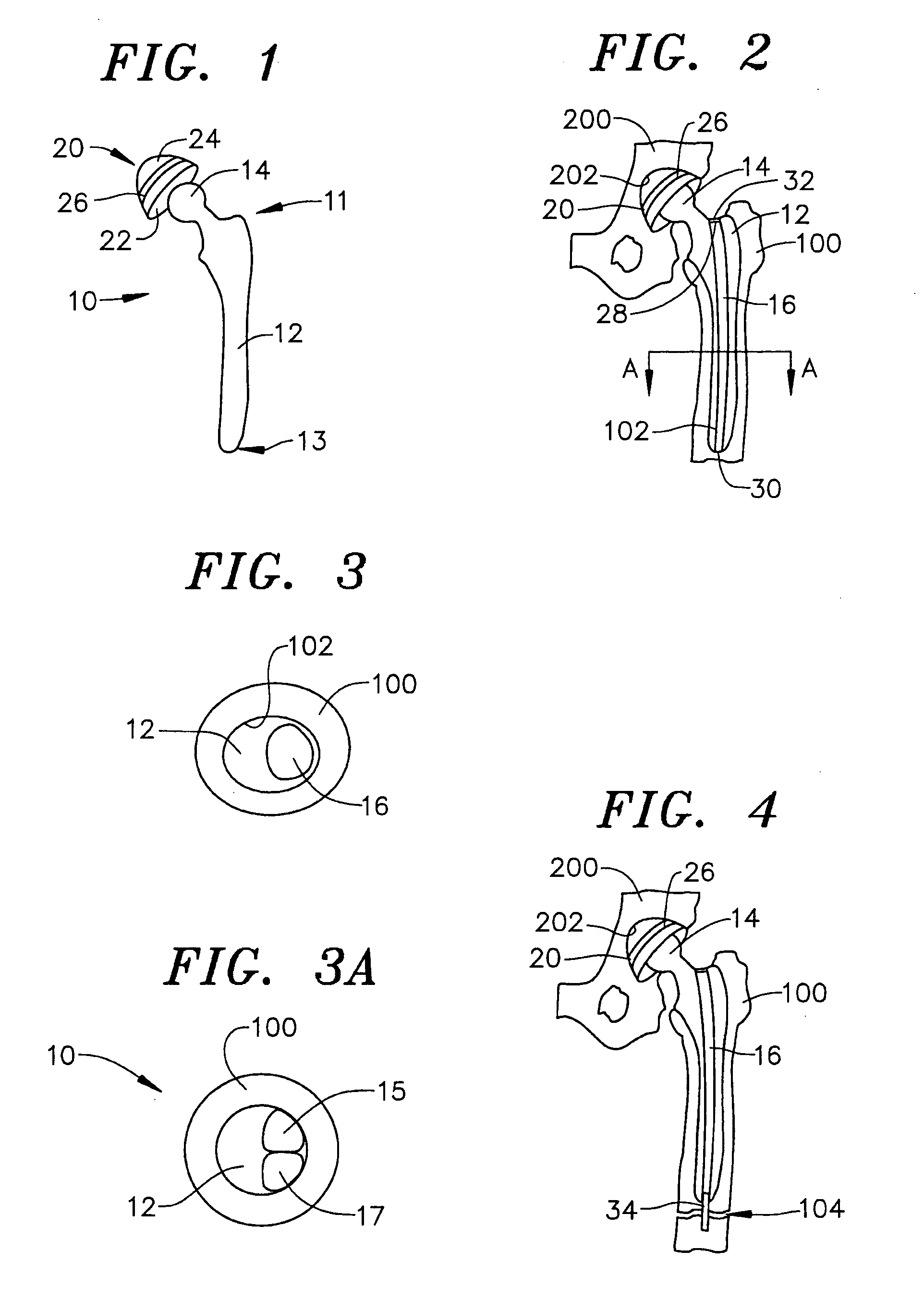
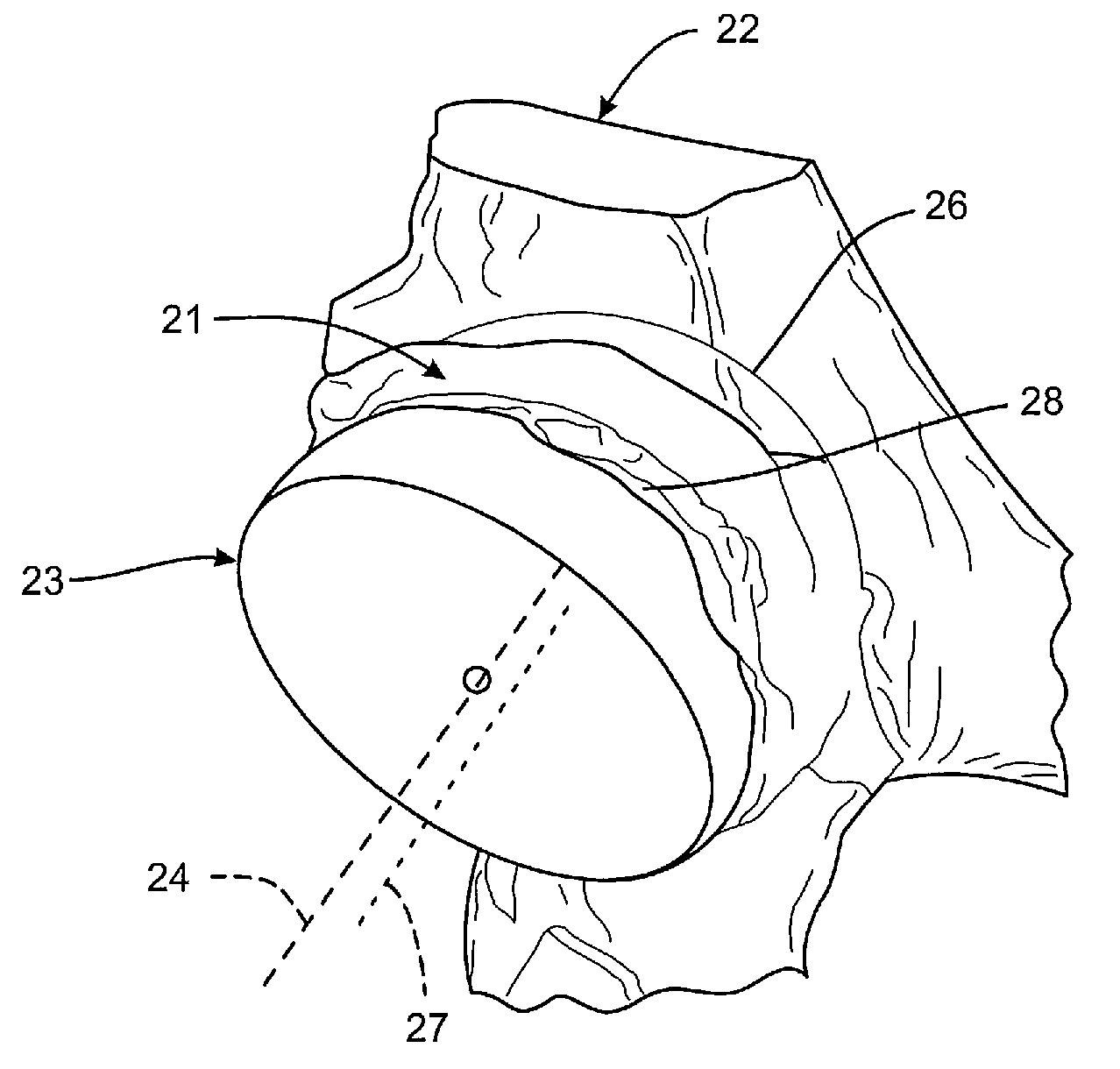
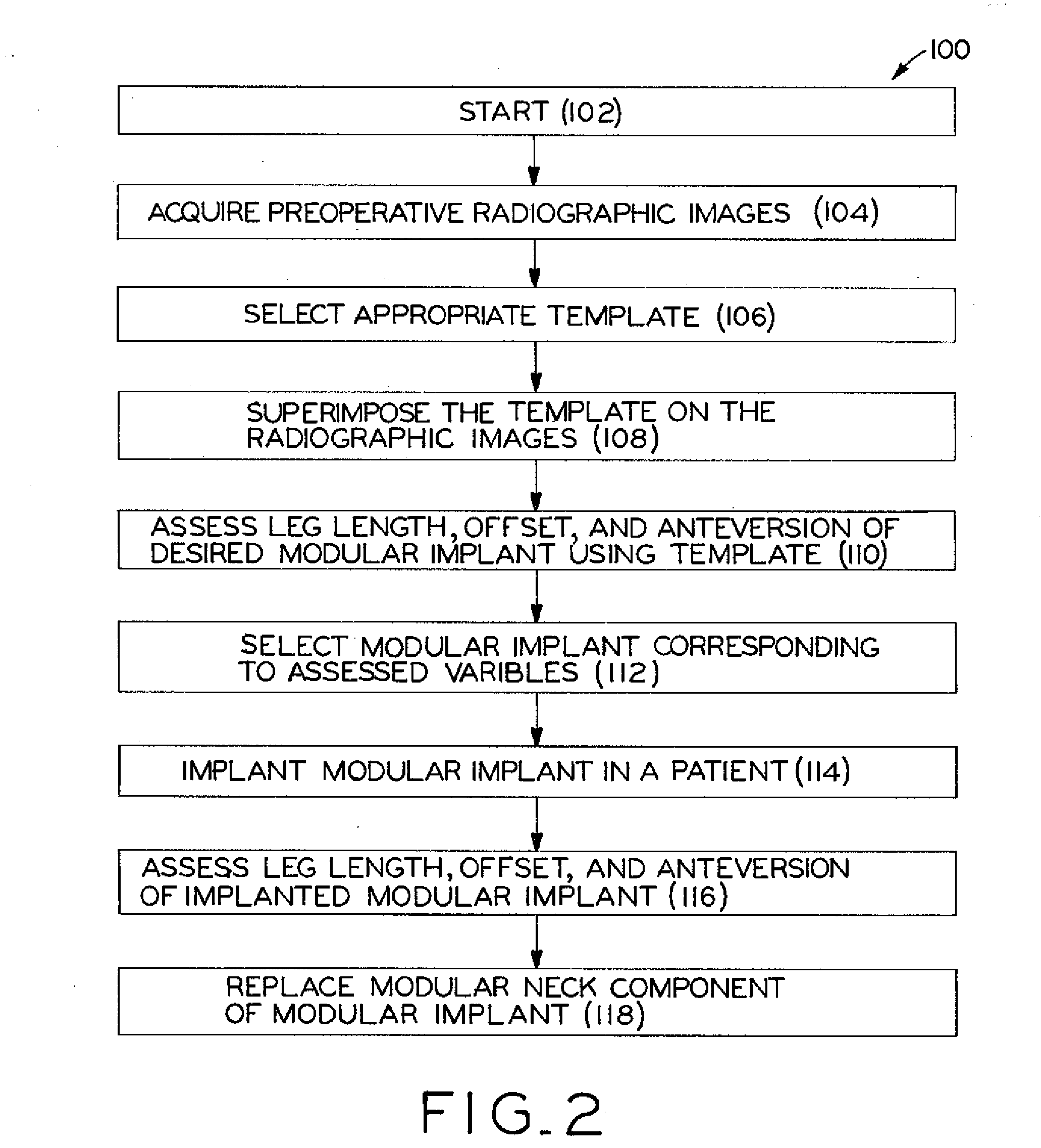
Method for selecting modular implant components
InactiveUS20080021299A1Easy and quick selectionProvide goodSurgical furnitureJoint implantsPresent methodModularity
A method for selecting modular neck components for hip implants based on independent variables associated with physical characteristics of the implant, including leg length, offset, and anteversion. During surgery, the surgeon may be confronted with a need to change a preoperatively-chosen modular neck. For example, the surgeon may desire a change in at least one of the variables, e.g., leg length, offset, and / or anteversion. The present method allows the surgeon to quickly and easily select a different modular neck based on an evaluation of one of the variables without requiring reevaluation of the other variables. The method may include preoperative planning in which a template including a grid coordinate system is used.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
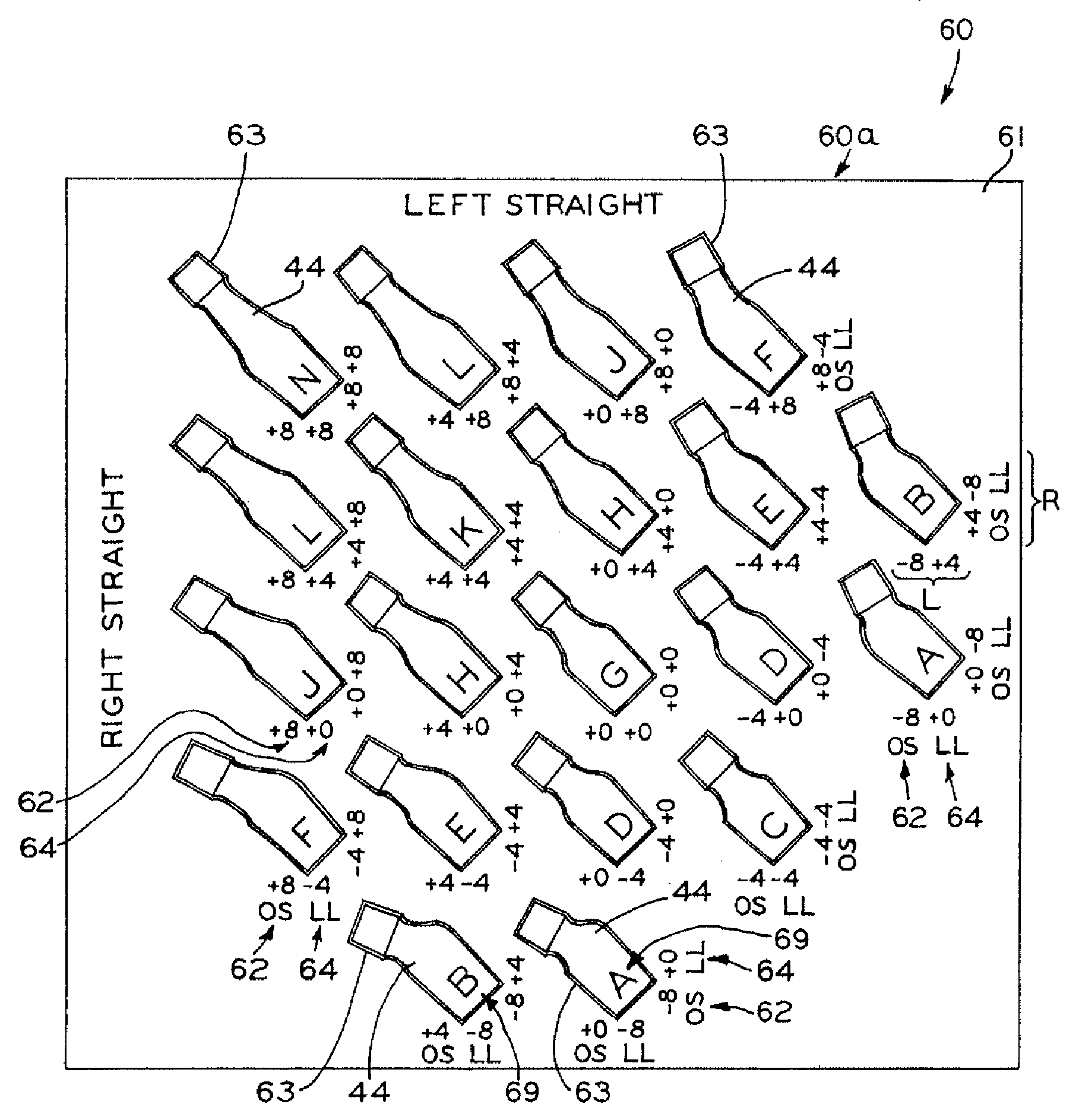
Modular orthopaedic component case
InactiveUS20080021567A1Easy and quick selectionProvide goodSurgical furnitureJoint implantsCoxal jointModularity
A case for modular neck components for hip implants. The case may include indicators based on independent variables associated with physical characteristics of the implant, including leg length, offset, and anteversion. During surgery, the surgeon may be confronted with a need to change a preoperatively-chosen modular neck. For example, the surgeon may desire a change in at least one of the variables, e.g., leg length, offset, and / or anteversion. The case allows the surgeon to quickly and easily select a different modular neck based on an evaluation of one of the variables without requiring reevaluation of the other variables. A method described herein may include preoperative planning in which a template including a grid coordinate system is used, which advantageously provides an intuitive system for the surgeon both preoperatively and during surgery.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Expandable hip implant
InactiveUS6361565B1Reduce retentionReduce capacitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisProsthesisBody fluid
An implant is formed of an expandable material. An opening is formed in a bone in a patient's body. At least a portion of the implant is positioned in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant is retained against movement relative to the bone in the patient's body by absorbing body fluid with the implant and expanding the implant while the implant is disposed in the opening in the bone in the patient's body. The implant may be a hip replacement member.
Owner:BONUTTI 2003 TRUST A THE +1
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A trial shell is provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
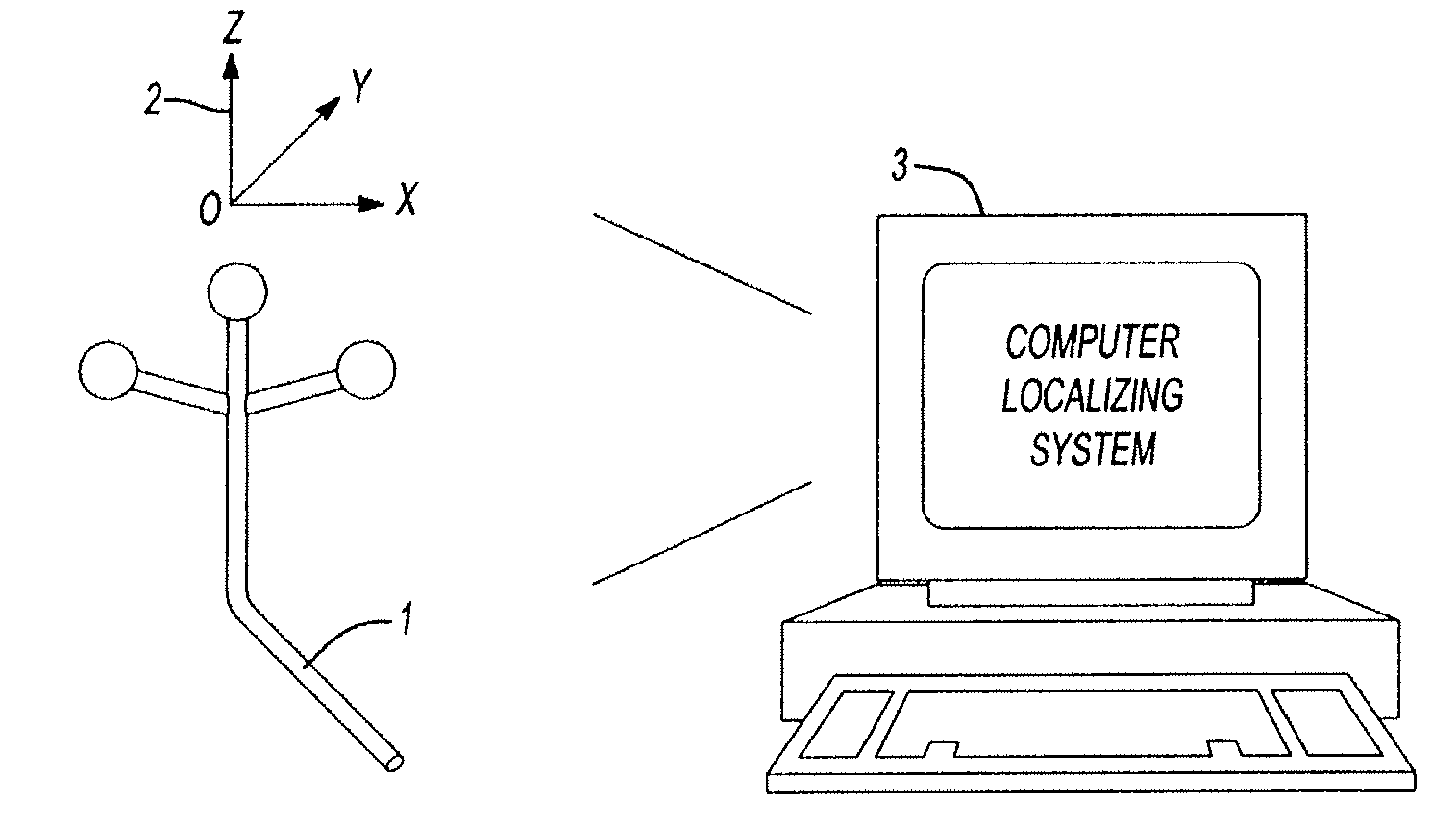
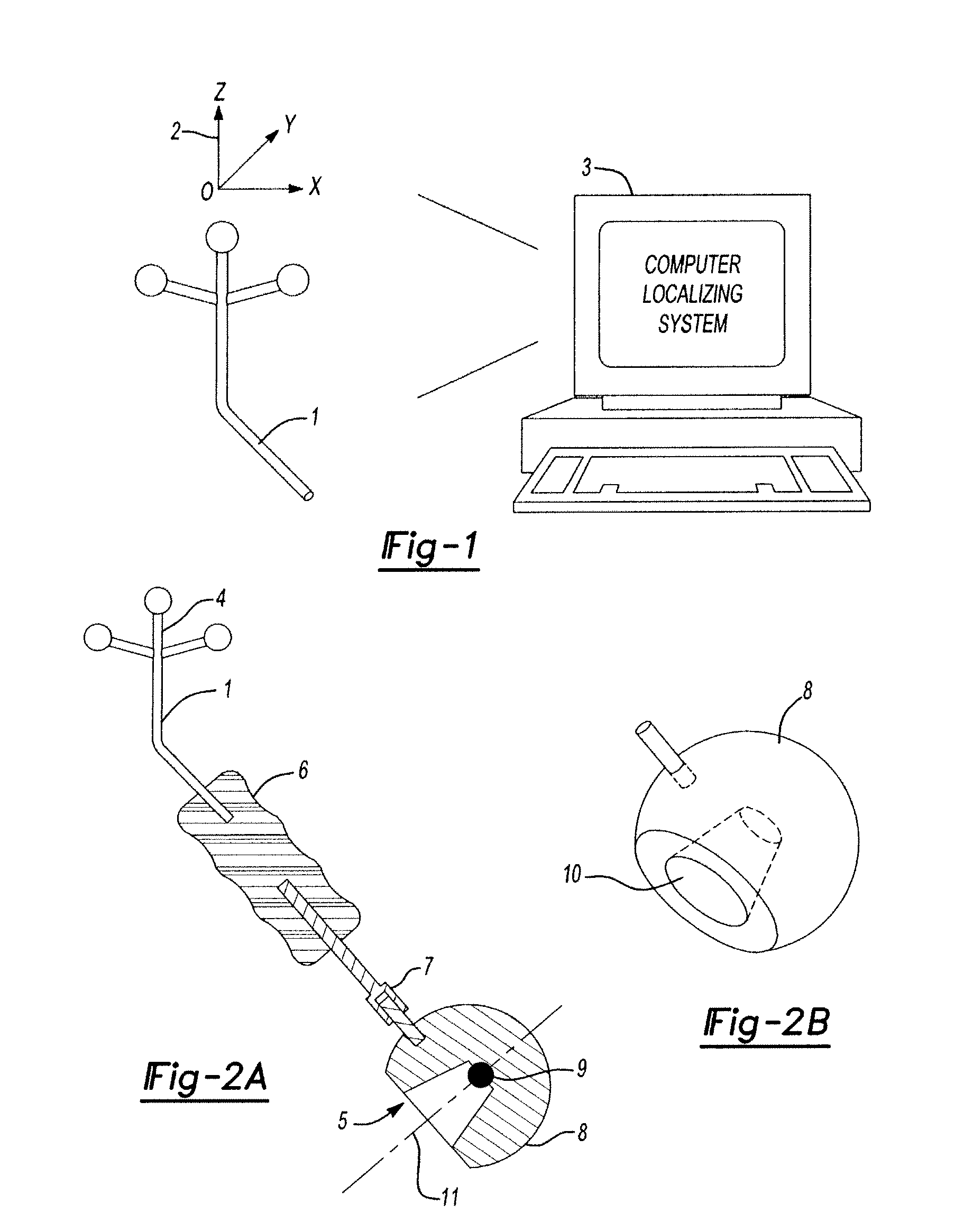
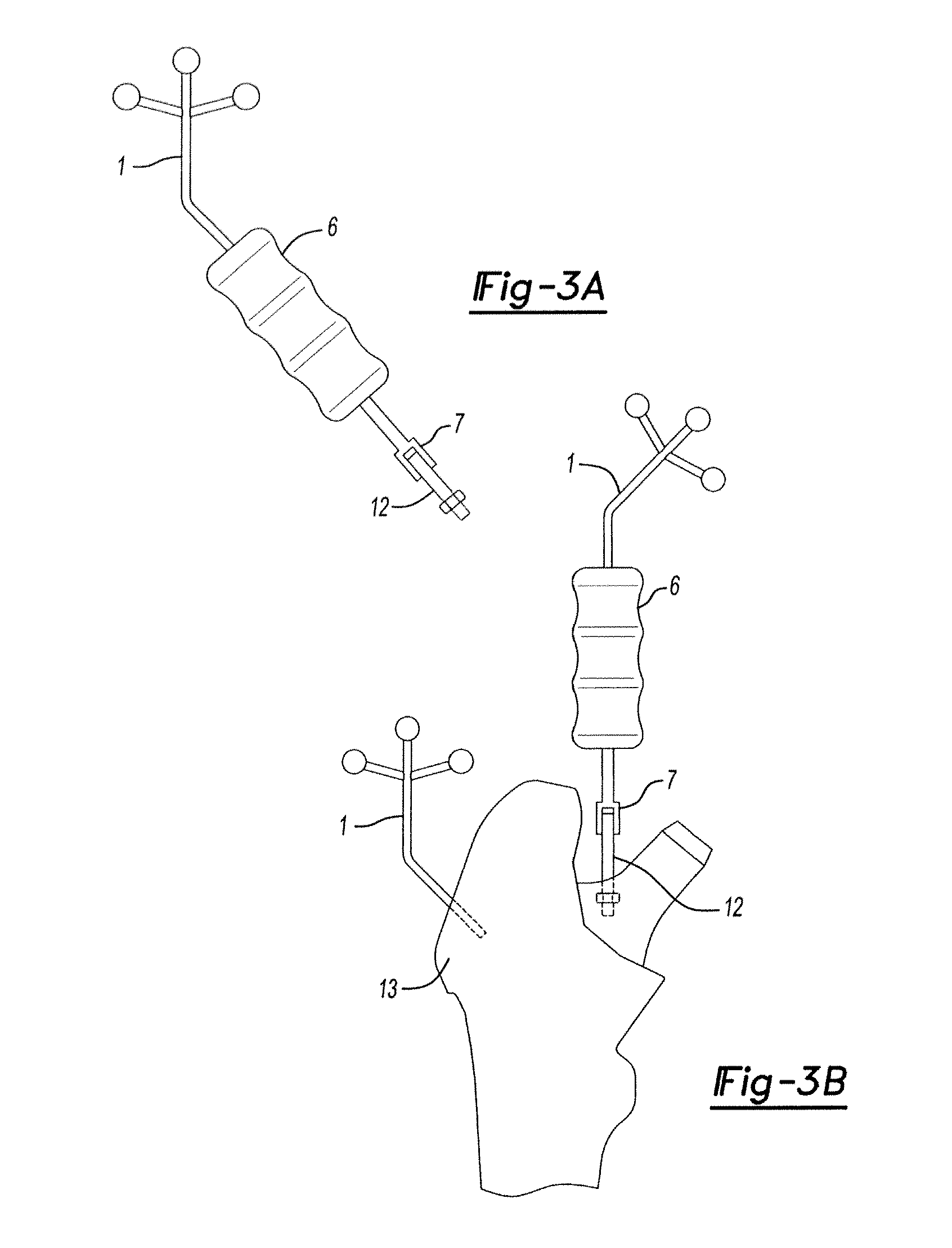
Hip implant registration in computer assisted surgery
ActiveUS20100261998A1Shorten the time to eliminateHigh precisionSurgical navigation systemsJoint implantsArray data structureCoxal joint
A computer assisted surgical navigation system and method is disclosed for registering the position of prosthetic hip joint components. Elements are applied to the pelvis and femur, generating a three-dimensional array. These two arrays combine to derive a reference point representing the native joint. A tracking device with a pre-determined shape and dimensions that precisely articulate with an acetabular cup component generates a third three-dimensional array. The device has a further shape and dimensions that independently articulate precisely with a neck portion of a femoral component, which represents a prosthetic joint center that is independently registered in the system. The tracking device concurrently registers the three dimensional positions of the femoral and acetabular prosthetic components, along with the prosthetic joint center and the native joint center, respectively enabling alterations in three dimensional location of the leg length and offset prior to reduction of the prosthetic joint.
Owner:BLUE ORTHO
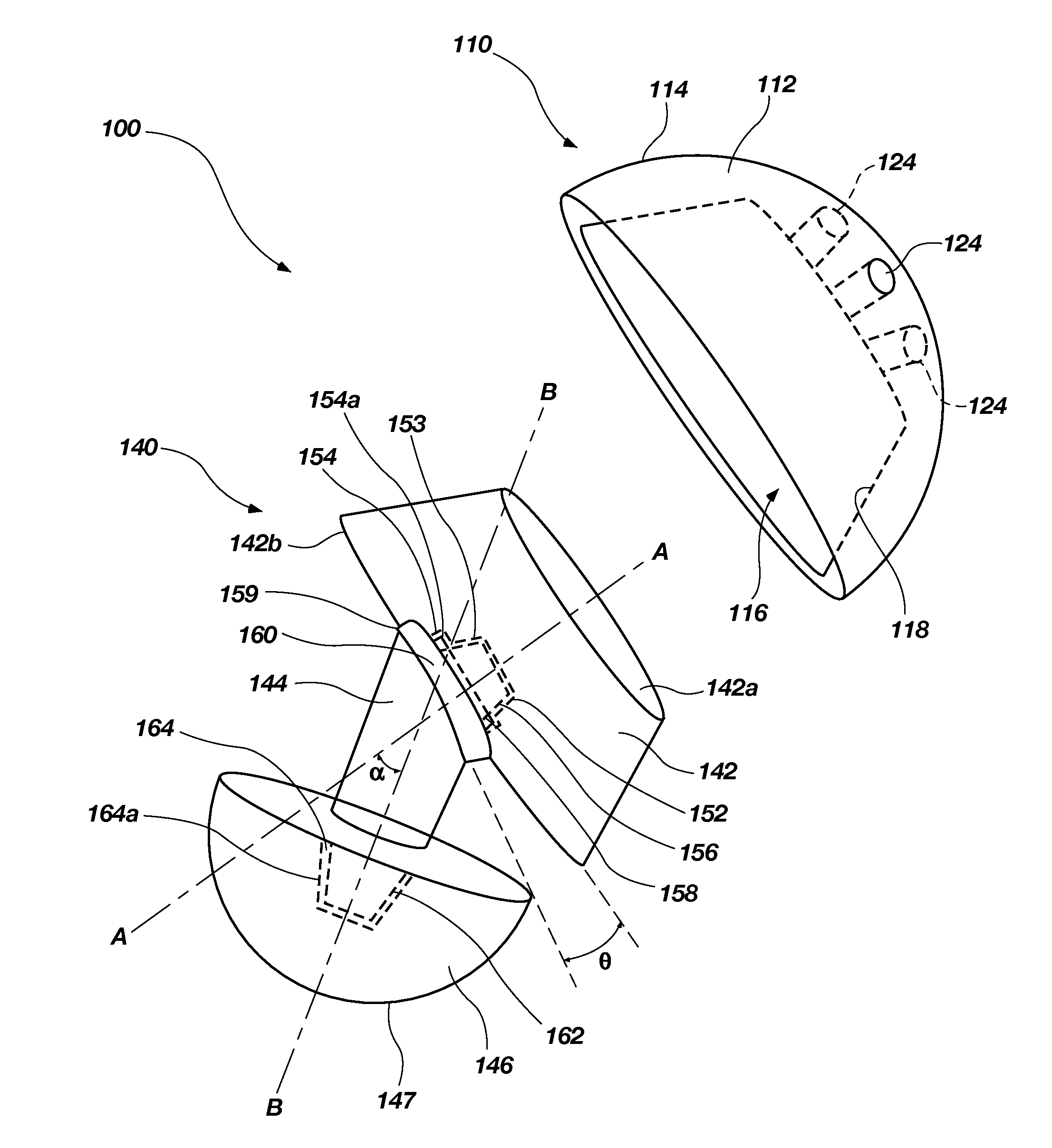
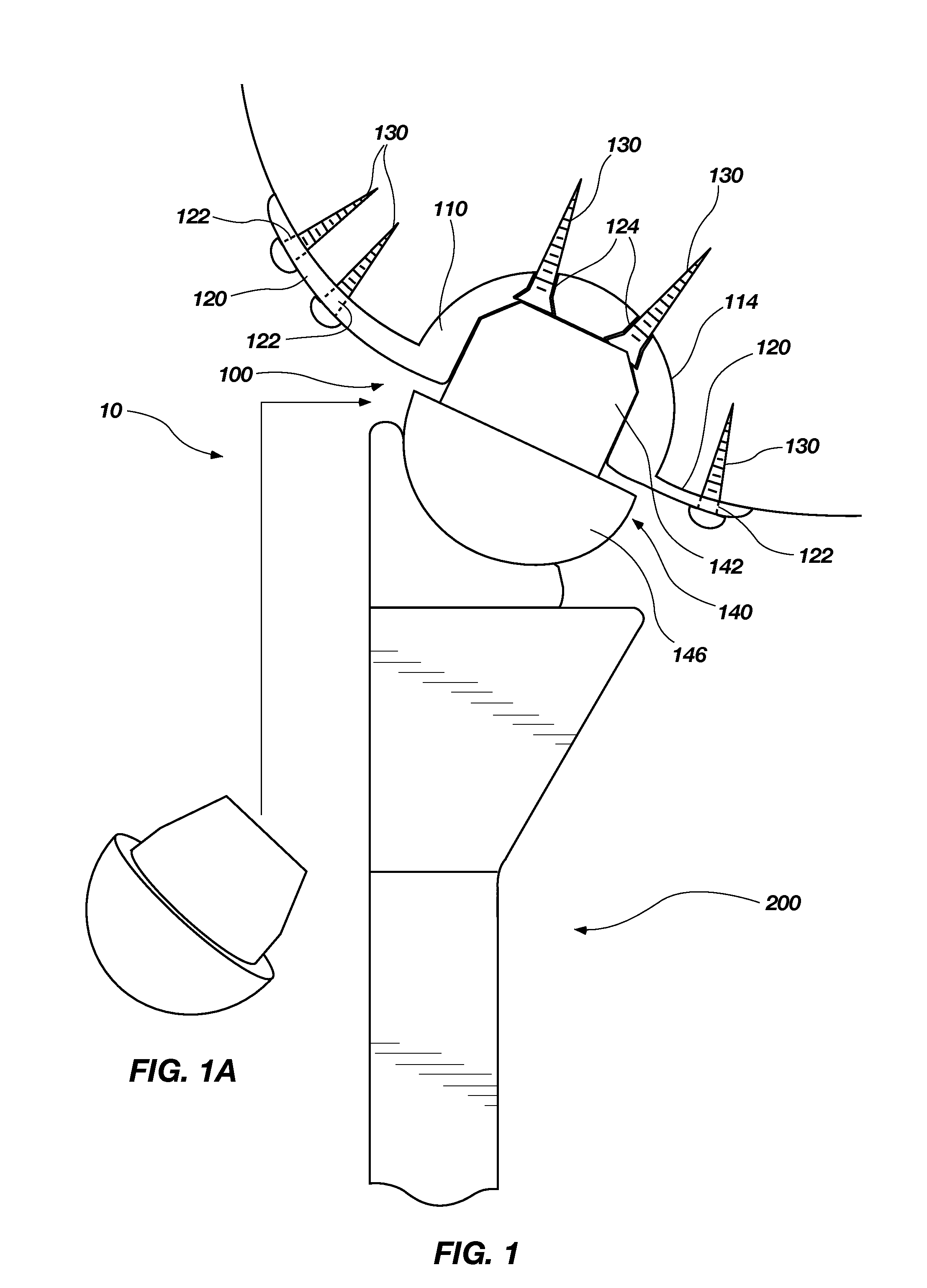
Reflex fixation geometry revision and reconstruction system reverse articulation
An orthopedic device is disclosed for restoring the normal or natural joint mechanics in, for example, a hip joint. The device includes a first component, such as an acetabular component in a hip implant, that includes a convex articulation surface and a second component, such as a femoral component in a hip implant, that includes a concave articulation surface. It will be appreciated that the convex articulation surface of the device disclosed herein articulates with the concave articulation surface in a mating engagement that may be reversed with respect to the traditional hip implant, in which the concave articulation surface is part of the acetabular component and the convex articulation surface is part of the femoral component.
Owner:GLOBAL ORTHOPAEDIC TECH
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
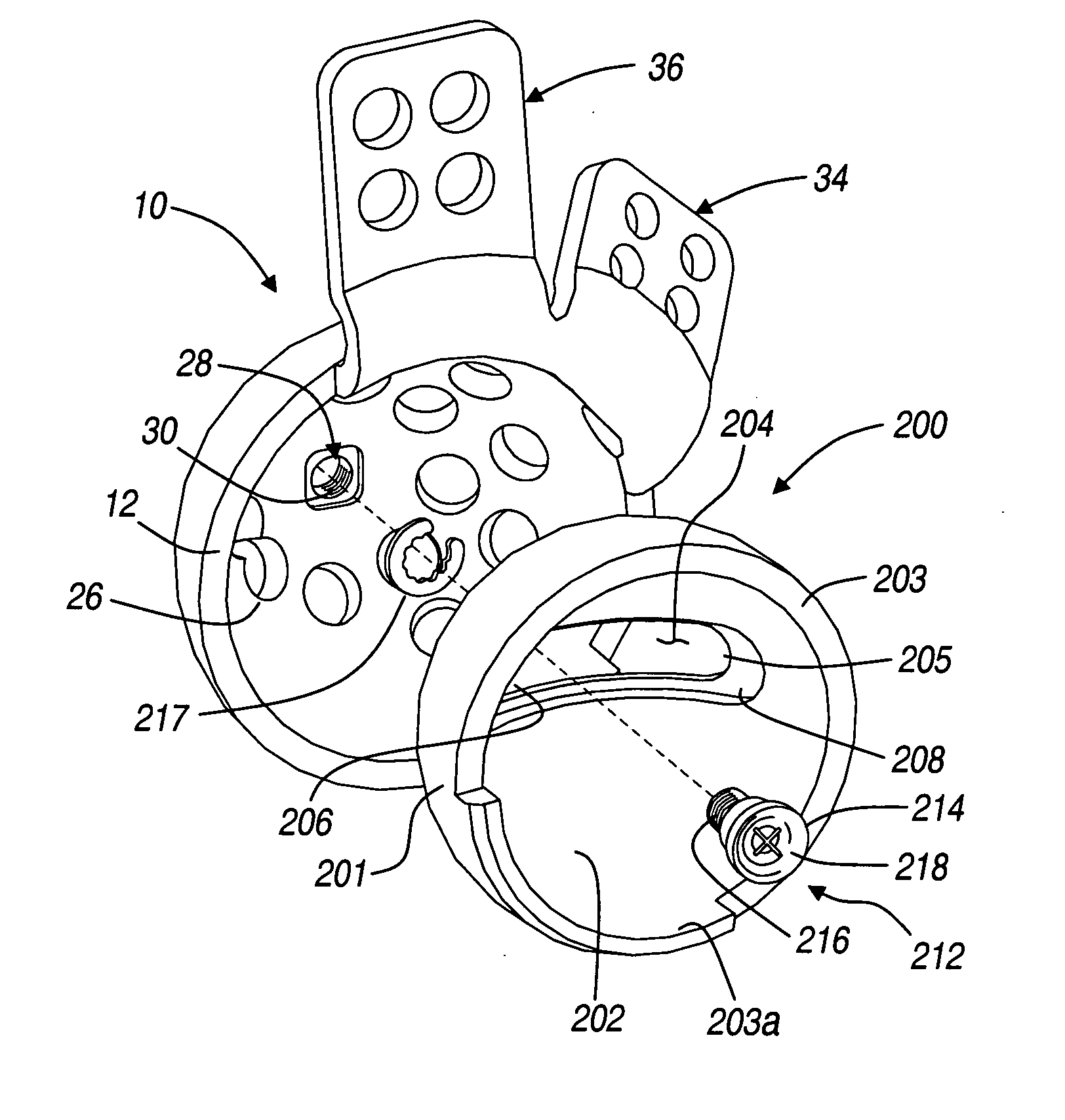
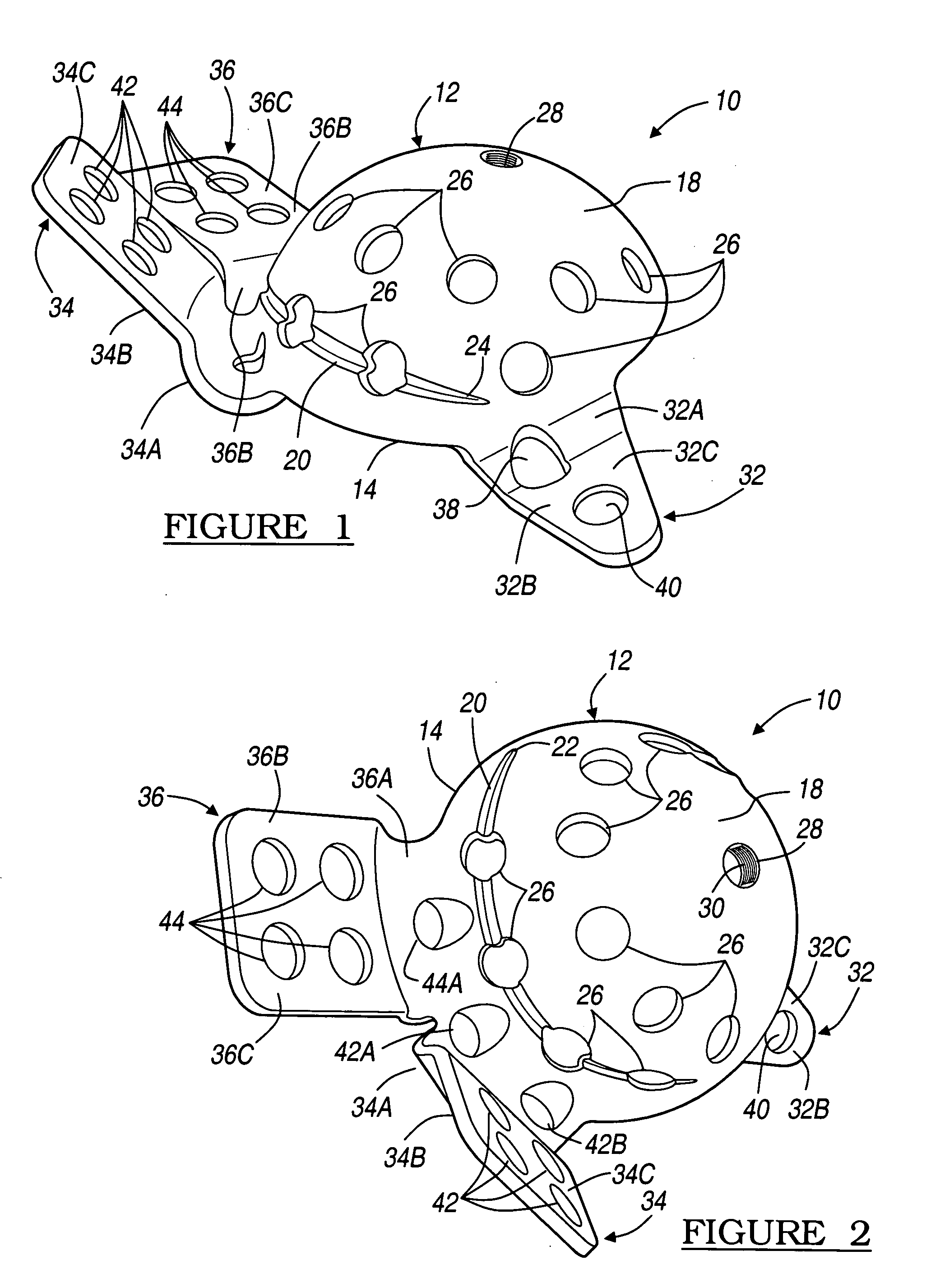
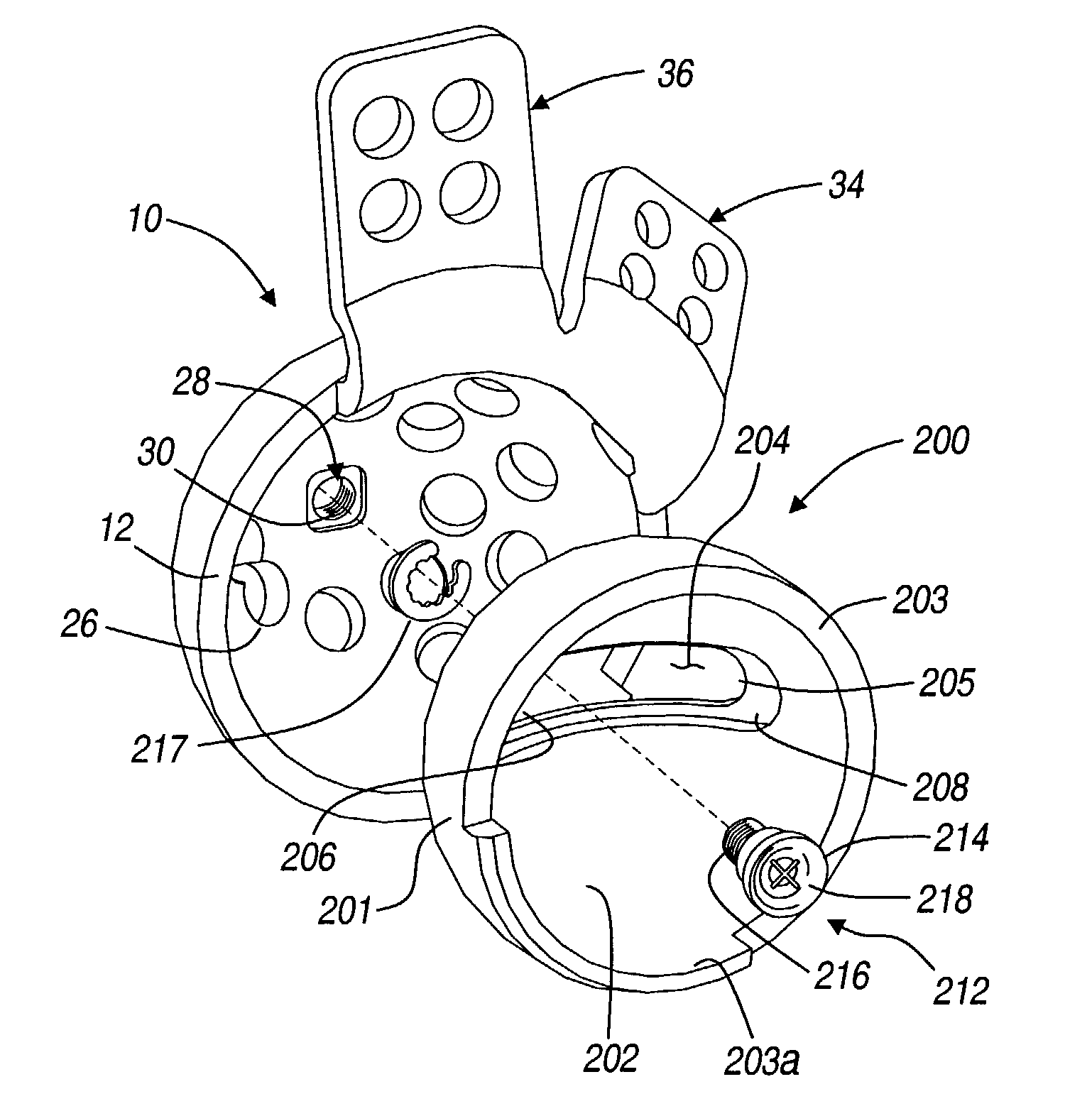
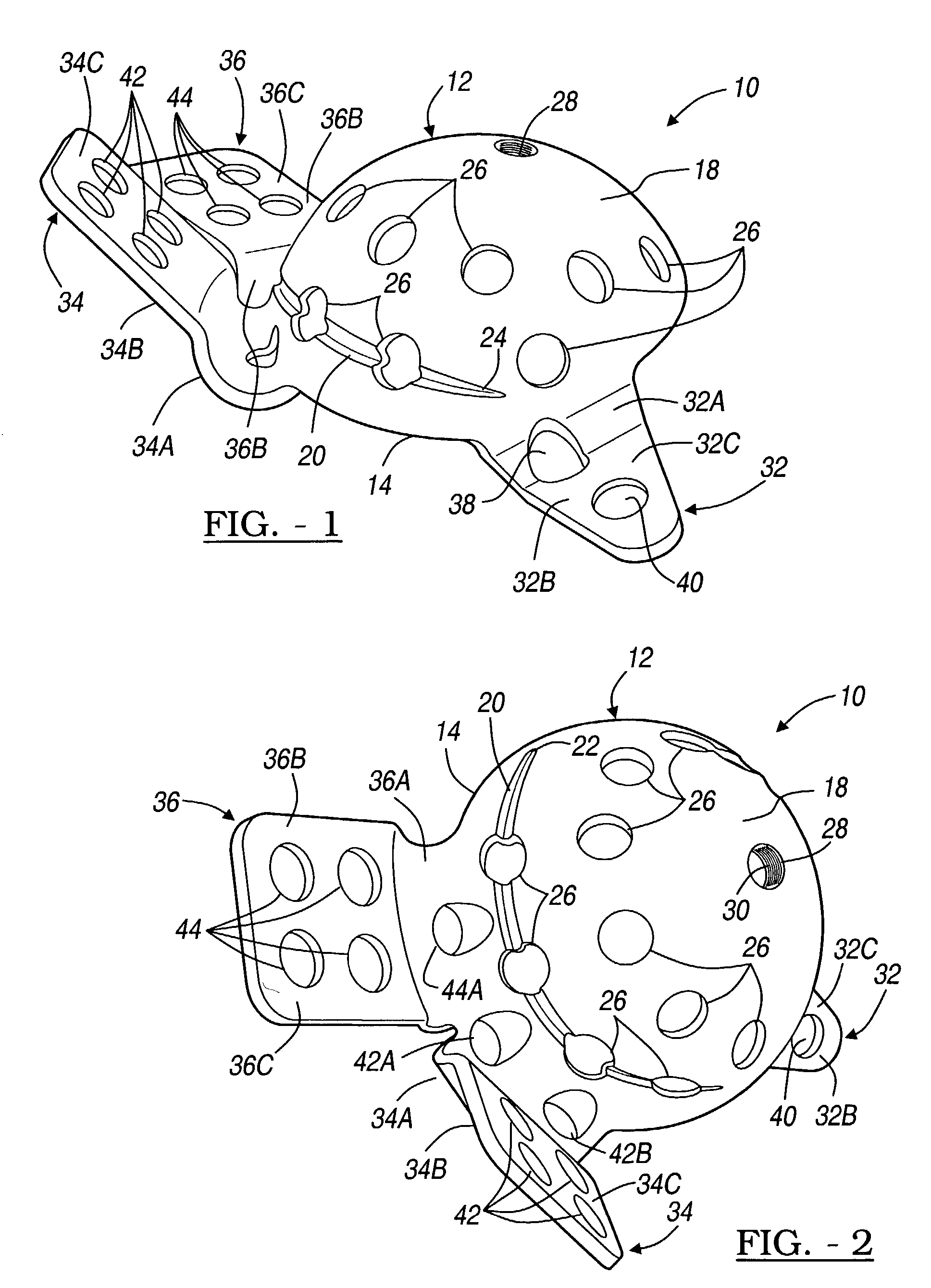
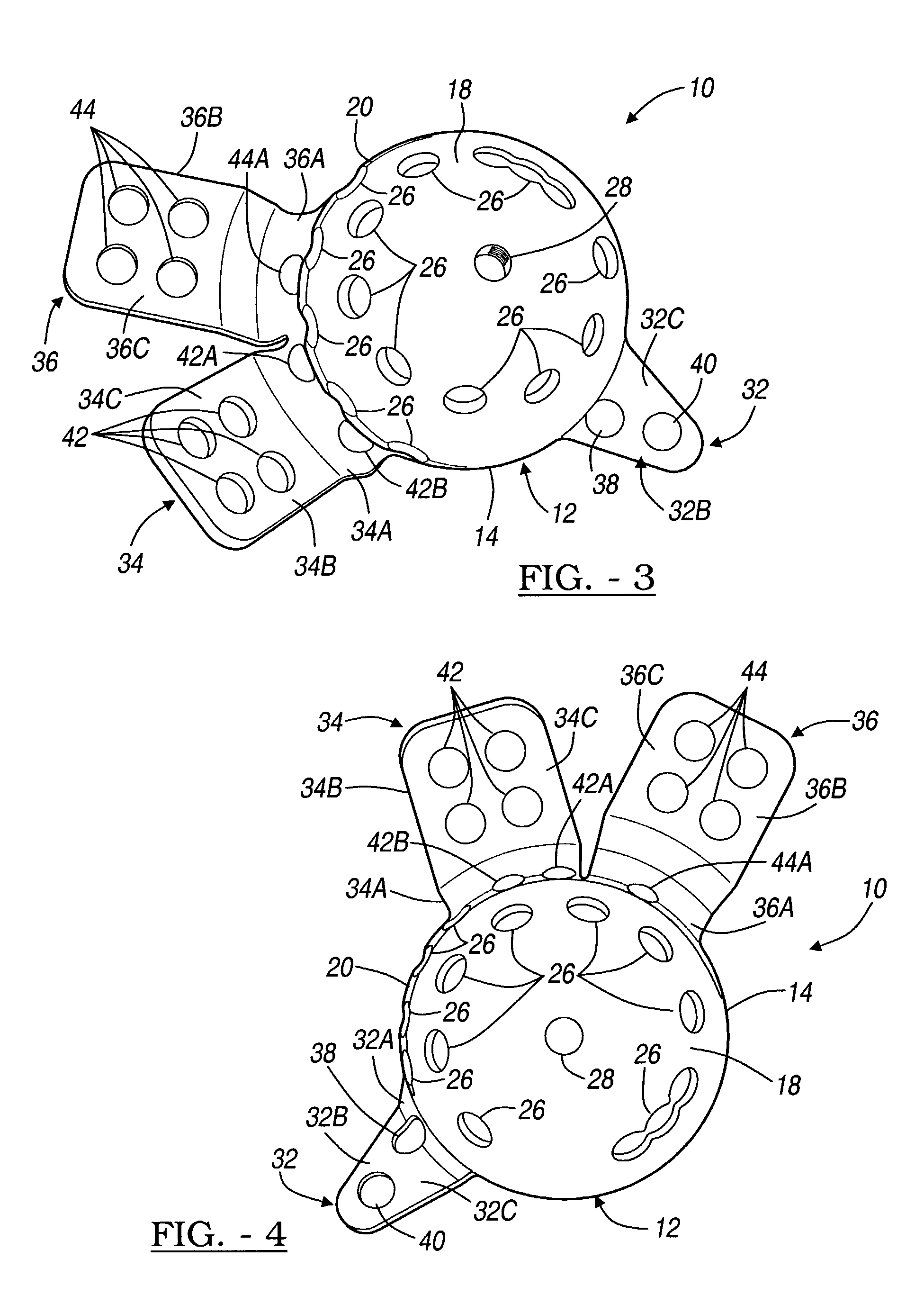
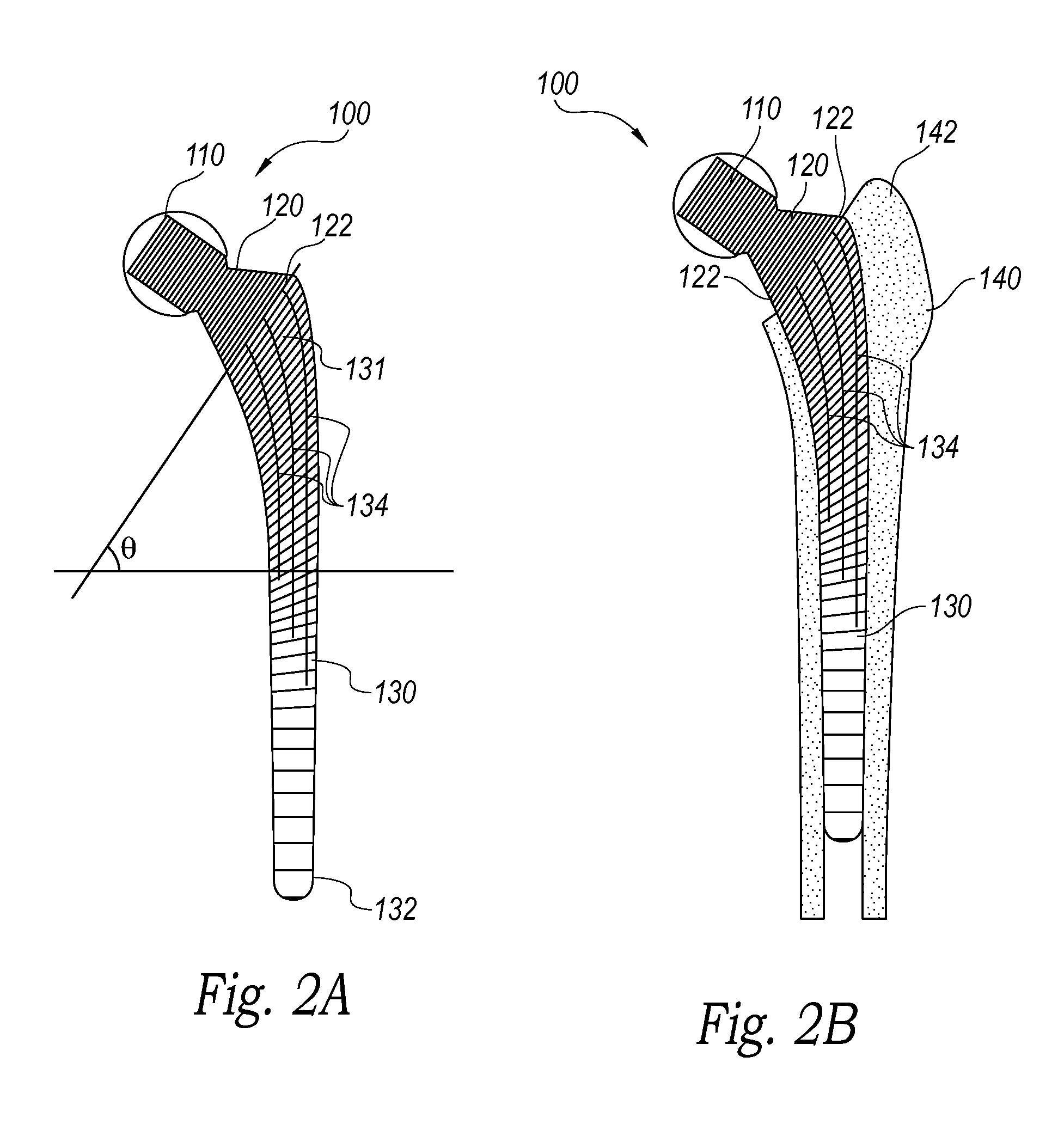
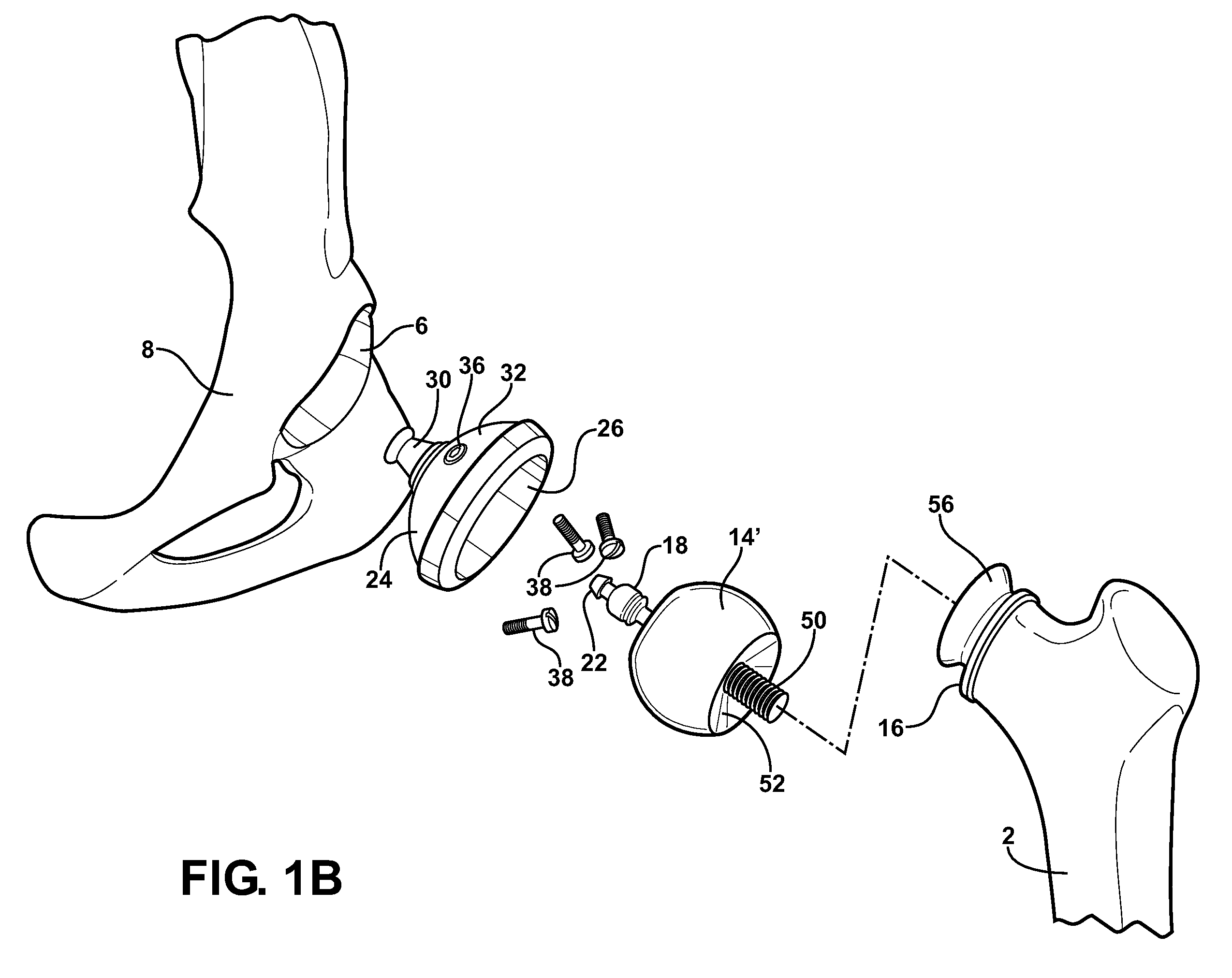
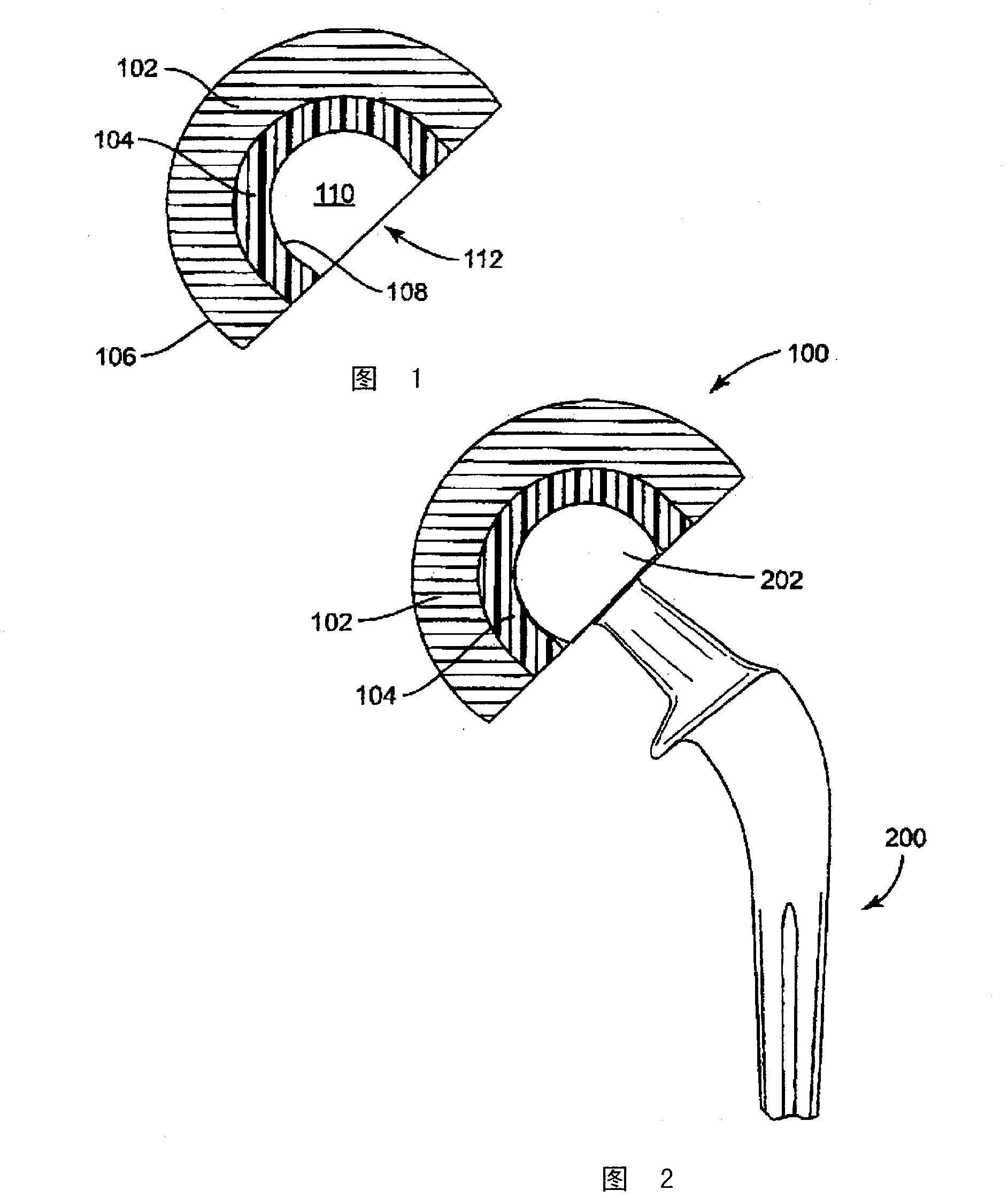
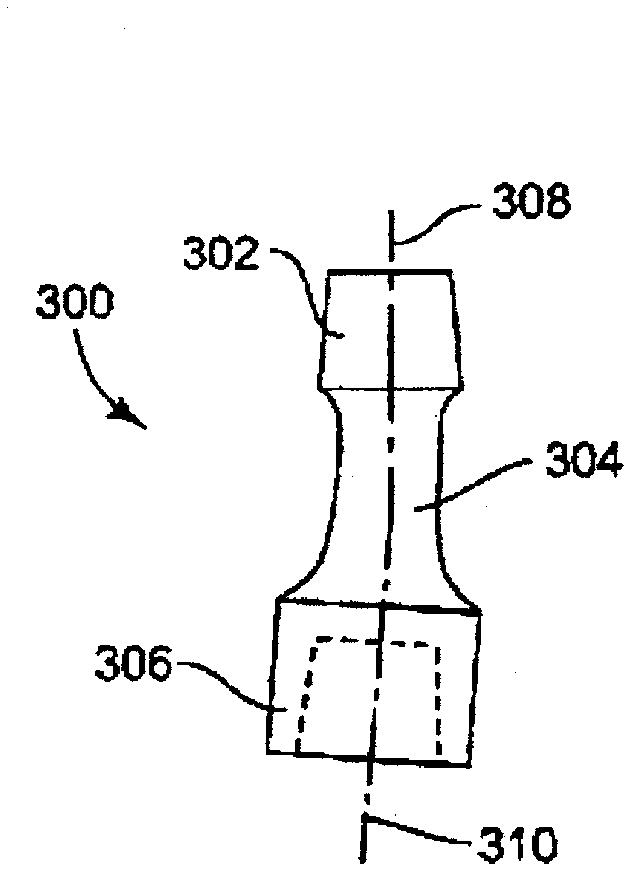
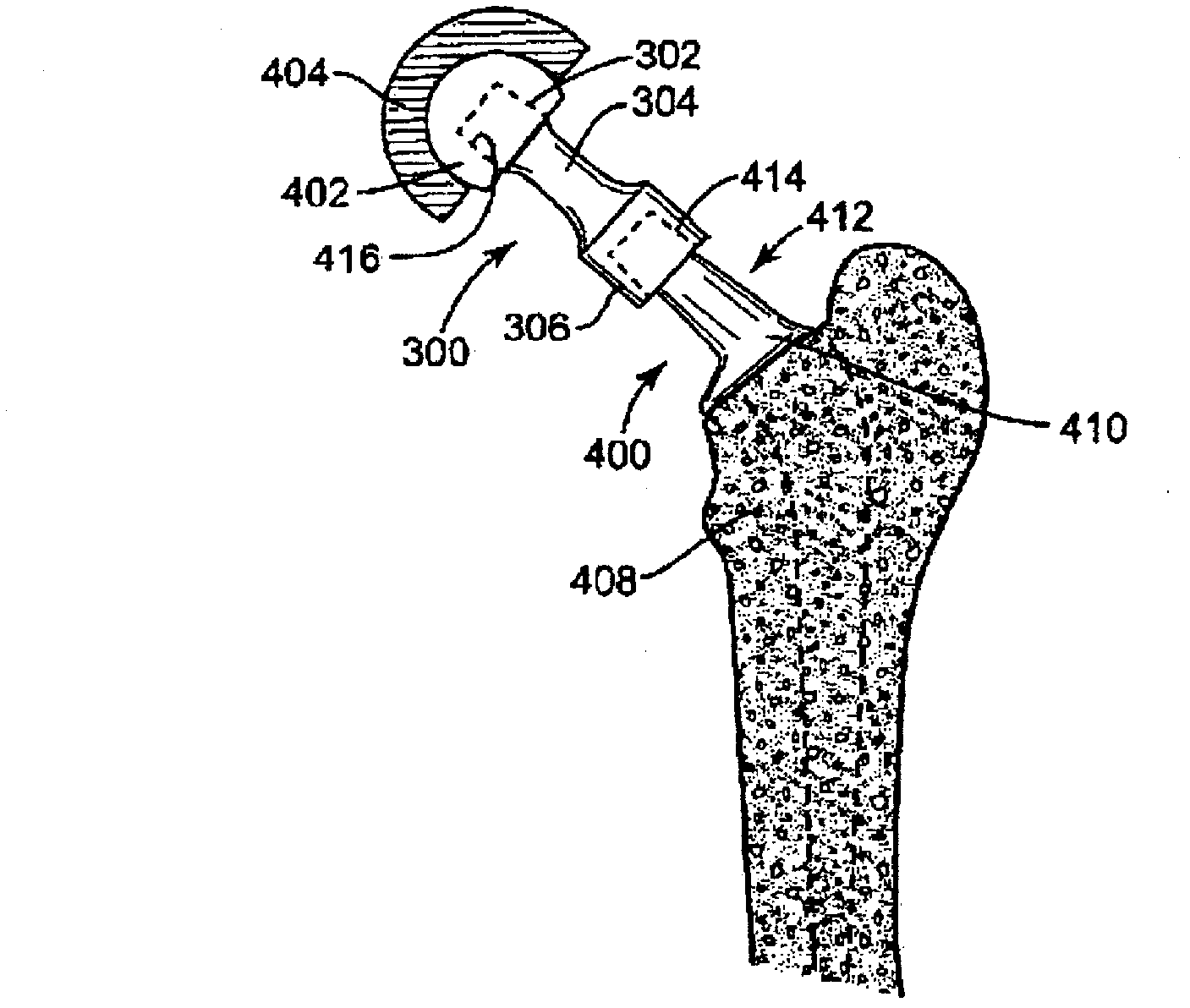
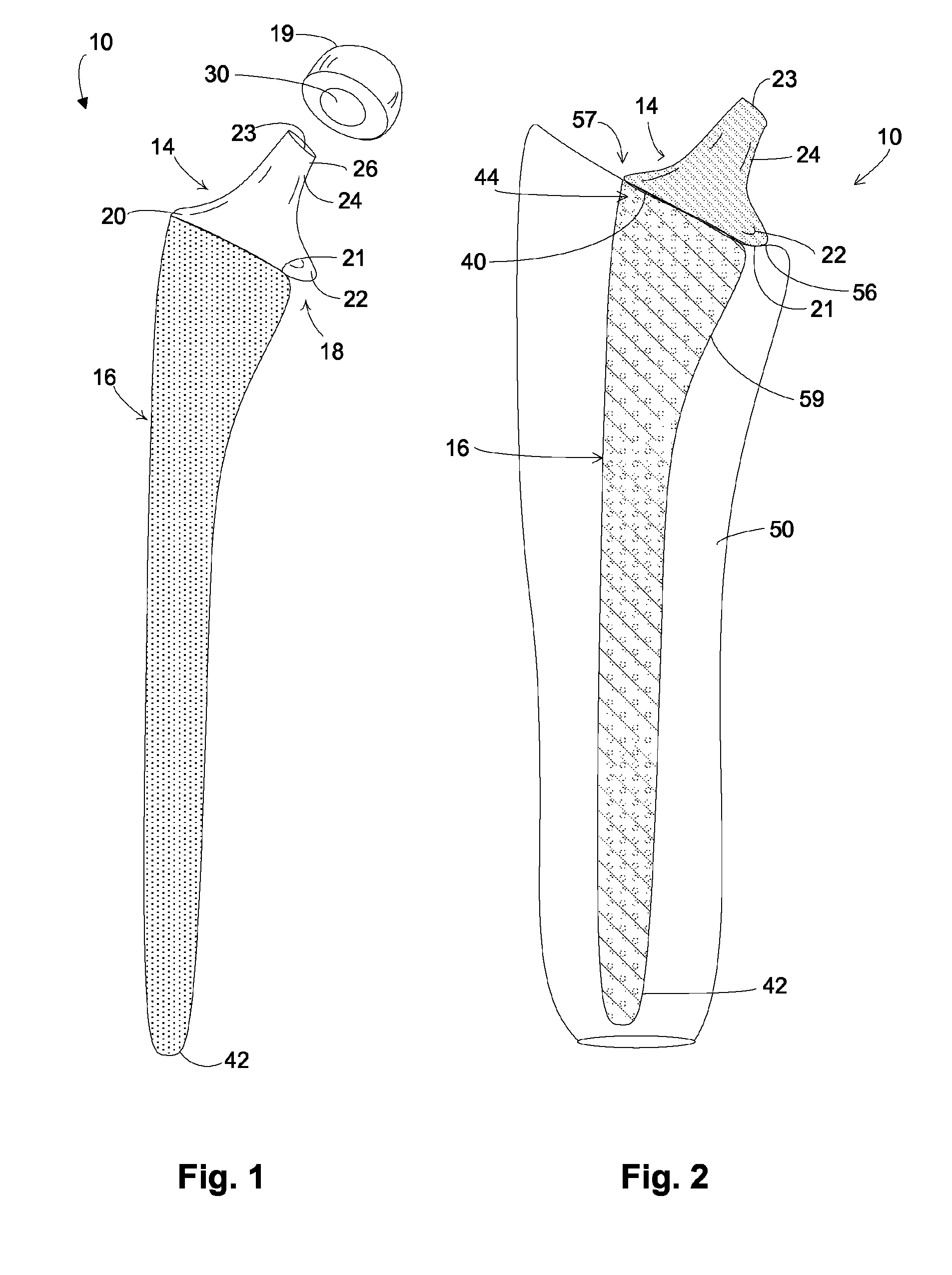
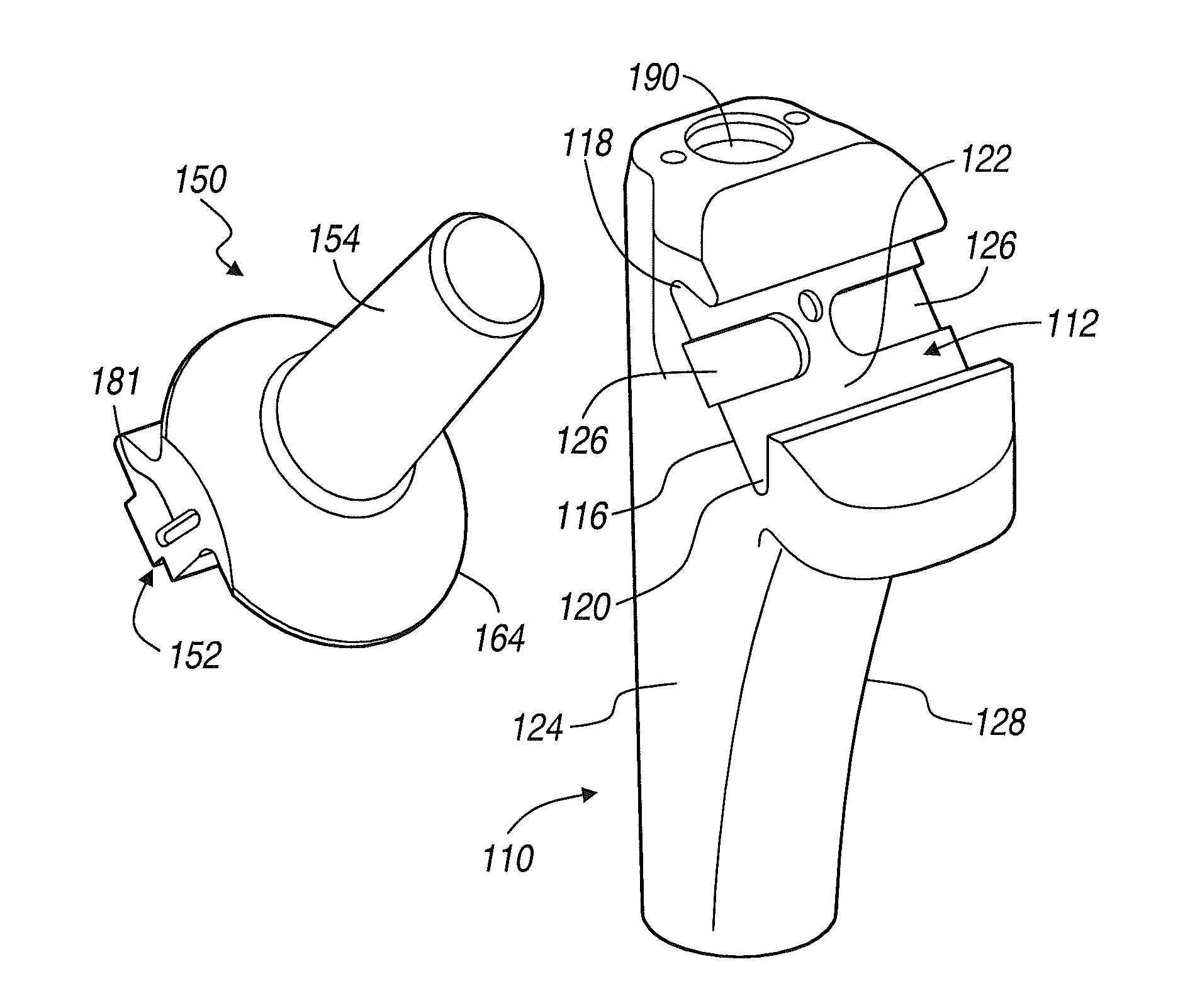
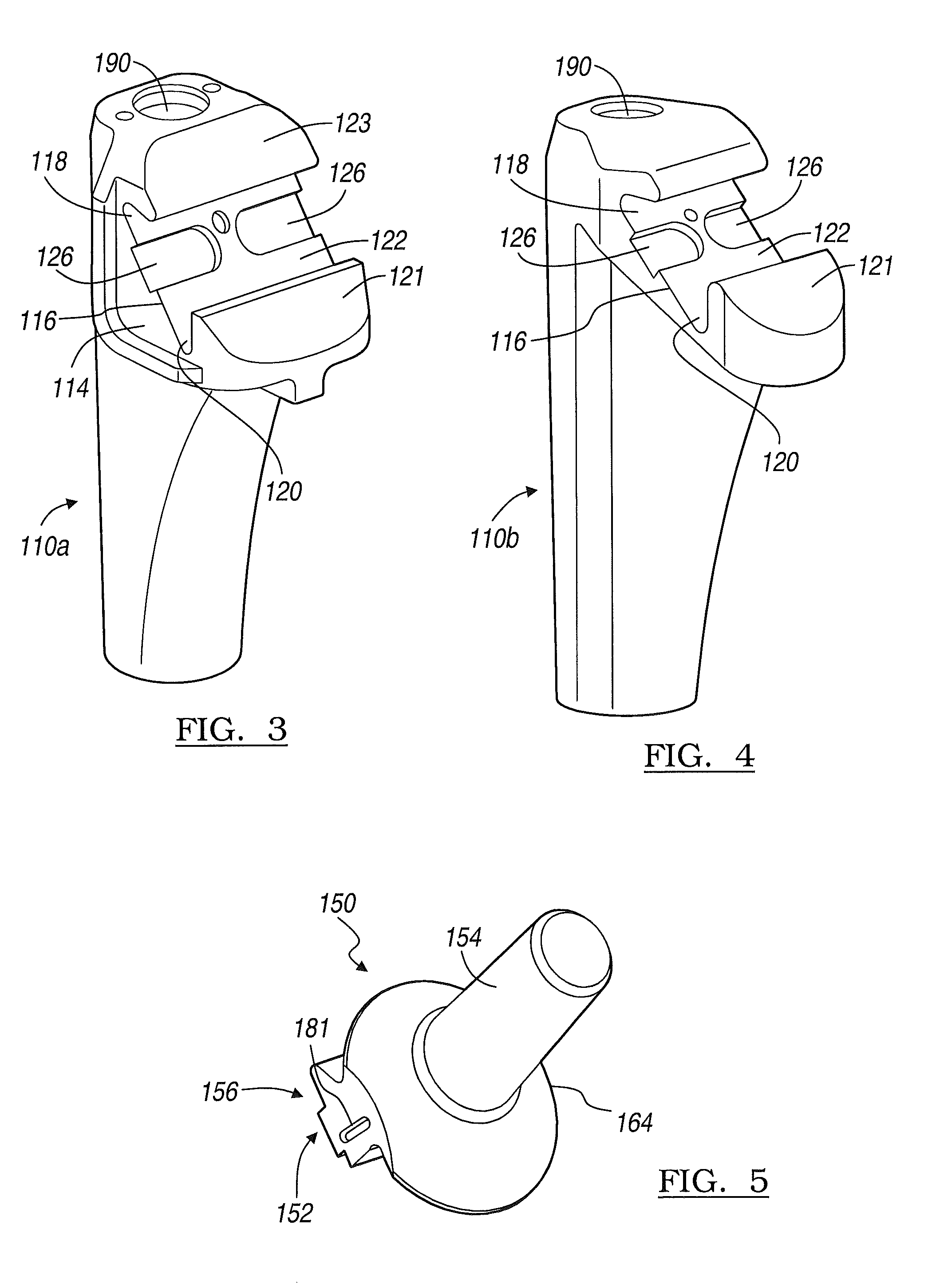
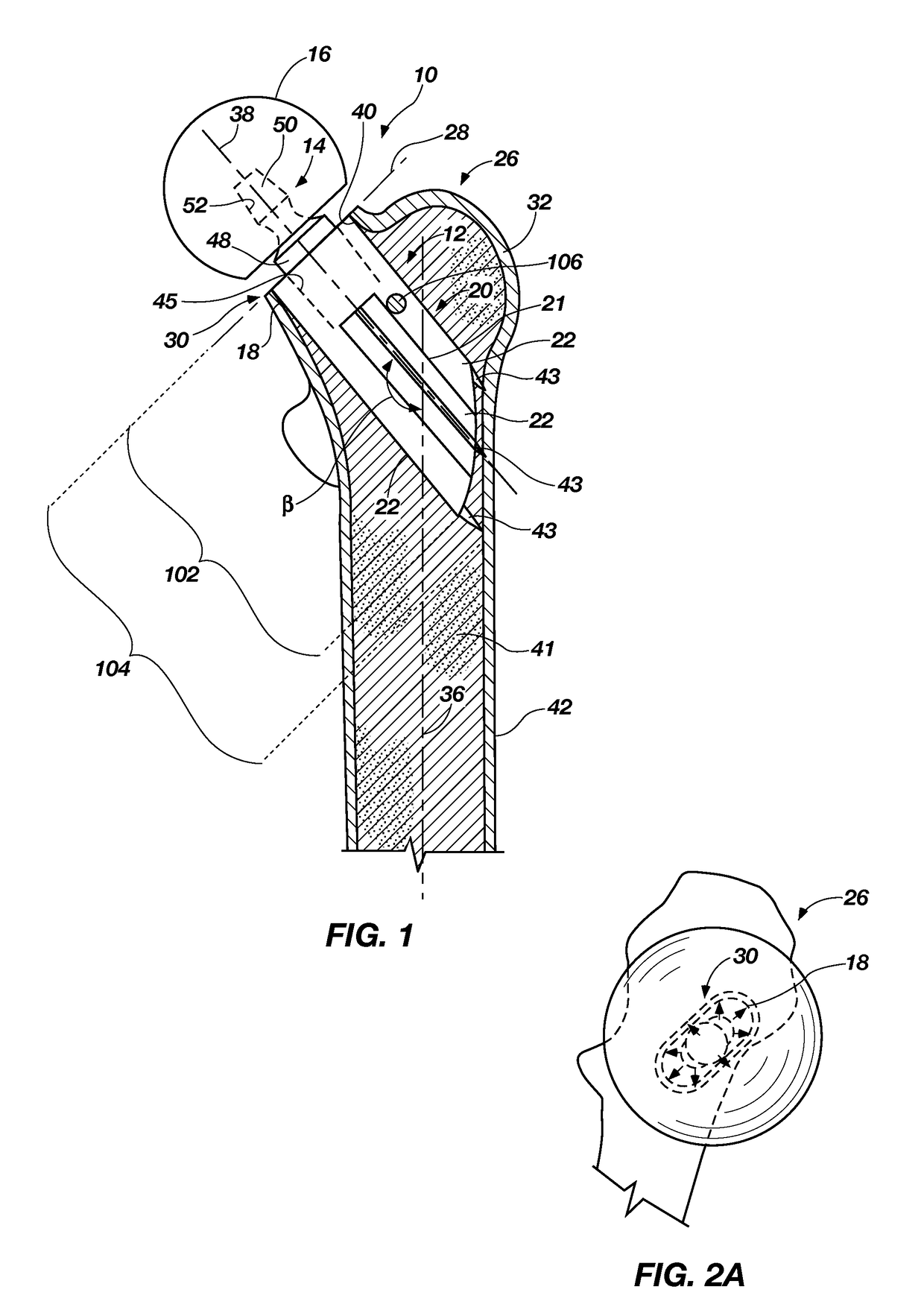
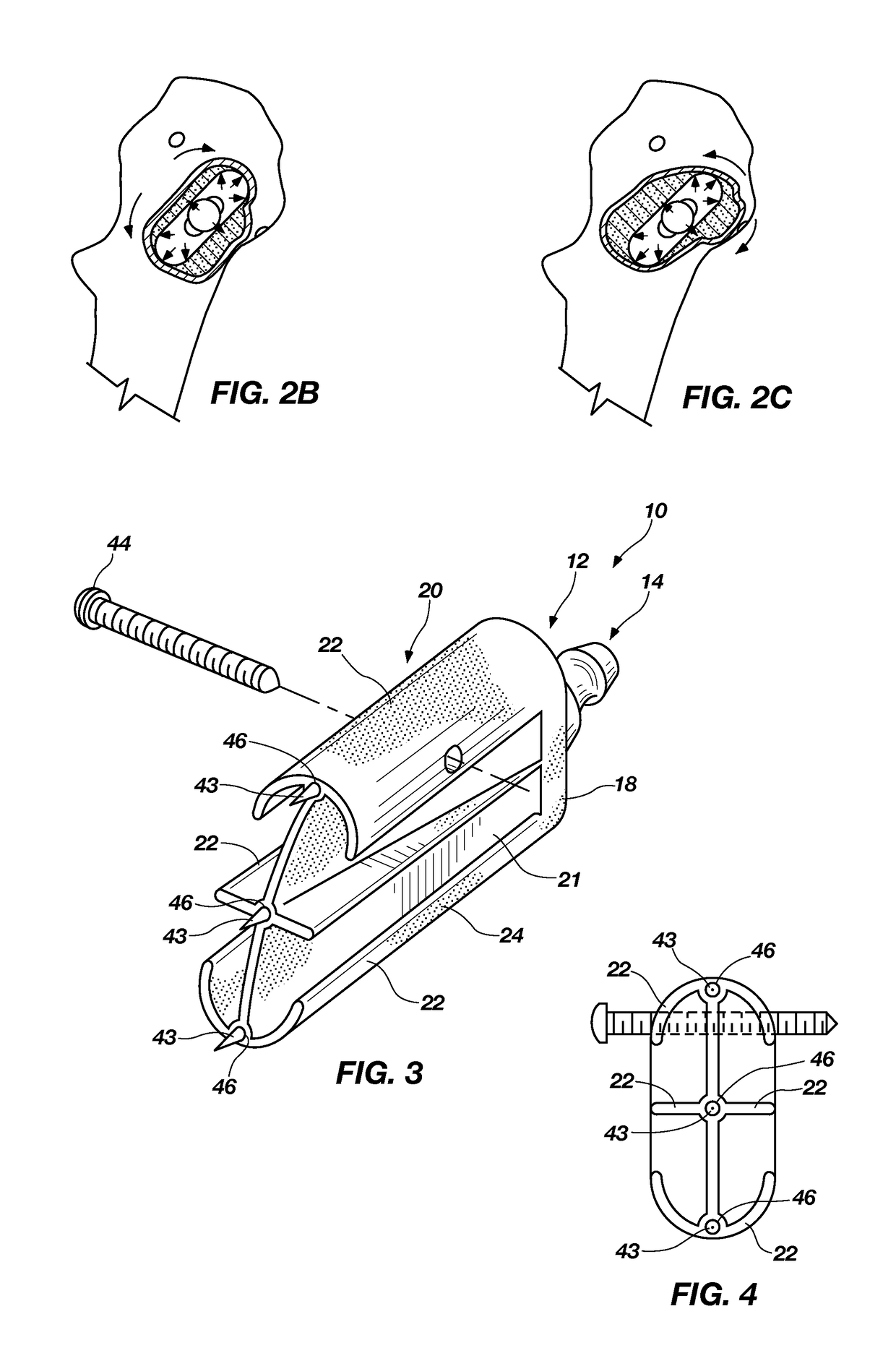
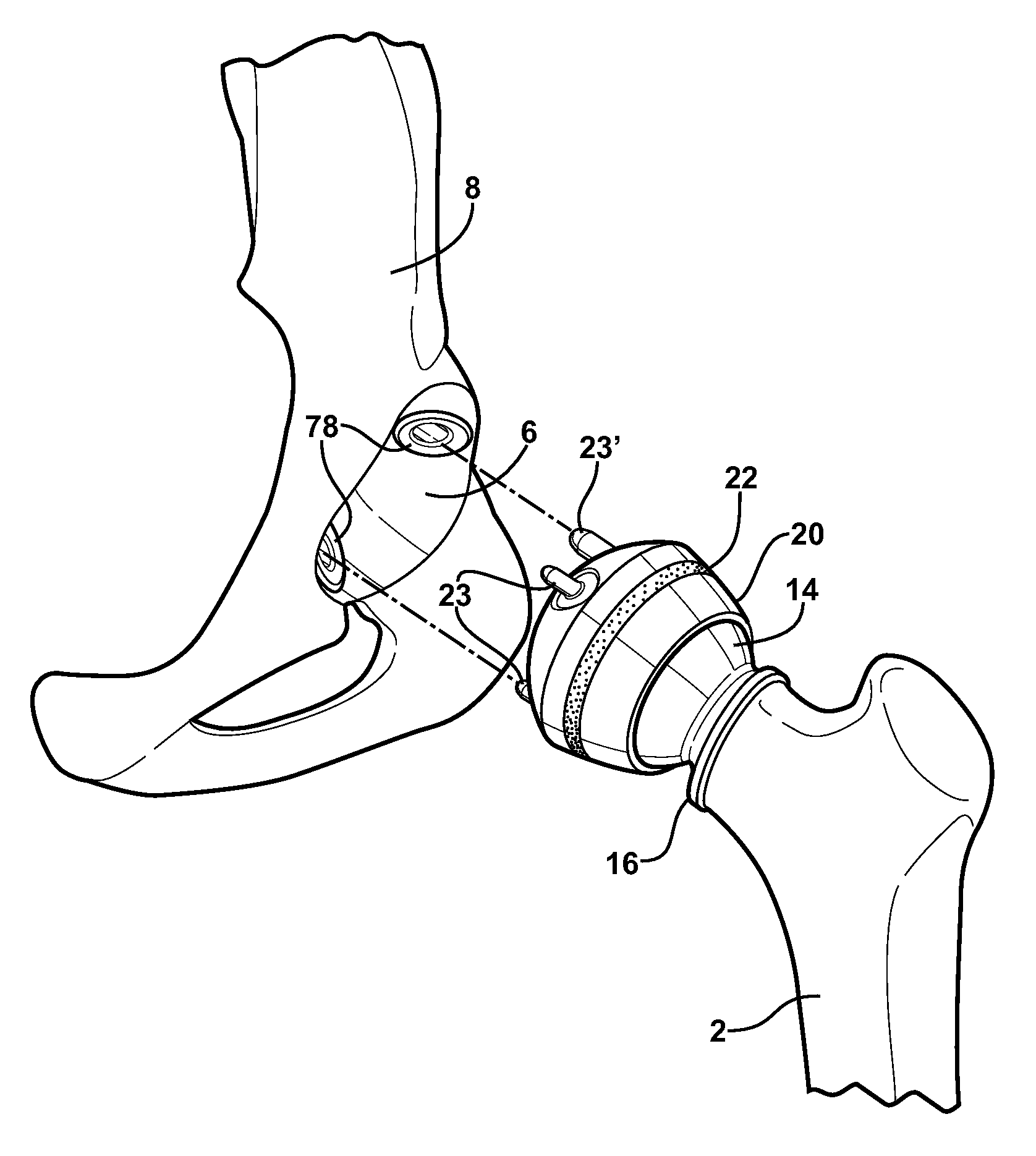
Modular hip implants
An implant for improved engagement between modular components is provided. The implant includes a body member for insertion, in use, in a natural femoral neck; and a rod for insertion, in use, in the intramedullary canal of a femur. The body member has a first engagement surface and the rod has a second engagement surface such that the first and second engagement surfaces are configured for complementary engagement with each other. One of the first or second engagement surfaces may be a protrusion while the other of the first or second engagement surfaces may be a recess for receiving the protrusion. The implant may further include a locking member, a stabilizing member and a guide means. A domed head portion is provided for attachment to a medial end of the body member and insertion, in use, in a natural or prosthetic acetabulum.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Tissue sparing implant
A femoral component of a hip implant is disclosed. The femoral component may be used specifically in a neck sparing resection (i.e., any process or device that avoids removing the femoral neck) and may include a shortened stem (with respect to a conventional stem) having a terminal flare portion for internally contacting a medial calcar portion of the proximal femur, and a significant curvature on its medial side. Other features of the femoral component include, flat side portions on the anterior and posterior sides of the stem, a lateral fin or a wing or T-back to aid in resisting torsional forces. The femoral component may also include a sagittal slot for proper fitting and placement in the femoral canal. The femoral component may also include a neck component that is modular with respect to the stem component. A head component, whether monoblock or modular with respect to the neck component, may also be utilized as part of the femoral component.
Owner:CONCEPT DESIGN & DEV
Modular necks for orthopaedic devices
There is provided a system of modular orthopaedic devices. The system comprises one or more hip implants or trials, each hip implant or trial having a femoral stem and one of at least two neck segments having different geometries. Each neck segment comprises a proximal end configured to receive a femoral head portion and a distal end configured to be operably received by a proximal portion of the femoral stem. Each proximal end comprises a central portion generally representative of a femoral head center. When each of the at least two neck segments are joined with the femoral stem, the central portion is displaced a predetermined distance in a single direction relative to the femoral stem. The neck segments provided, therefore, advantageously allow a user to independently adjust any one of a height, an offset, or a version angle of an orthopaedic device for best performance and fit.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Modular implant assembly tool
InactiveUS20060027027A1Material strength using tensile/compressive forcesJoint implantsModularityAxial force
This invention provides for a tool that produces, and directly and accurately measures, an axial force used to assemble two members of a modular implant, specifically, a modular hip implant.
Owner:SERRA MICHAEL A +1
Load bearing implants with engineered gradient stiffness and associated systems and methods
Implants are made of materials having asymmetric modulus gradients. For example, an implant, such as a hip implant, is made of a material having a stiffness gradient between a proximal portion near a hip joint and a distal portion extending downward into the marrow of the femur. Among other benefits, the asymmetric modulus gradient mitigates problems associated with stress shielding and does not excessively wear or deteriorate the proximal portion of the implant.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
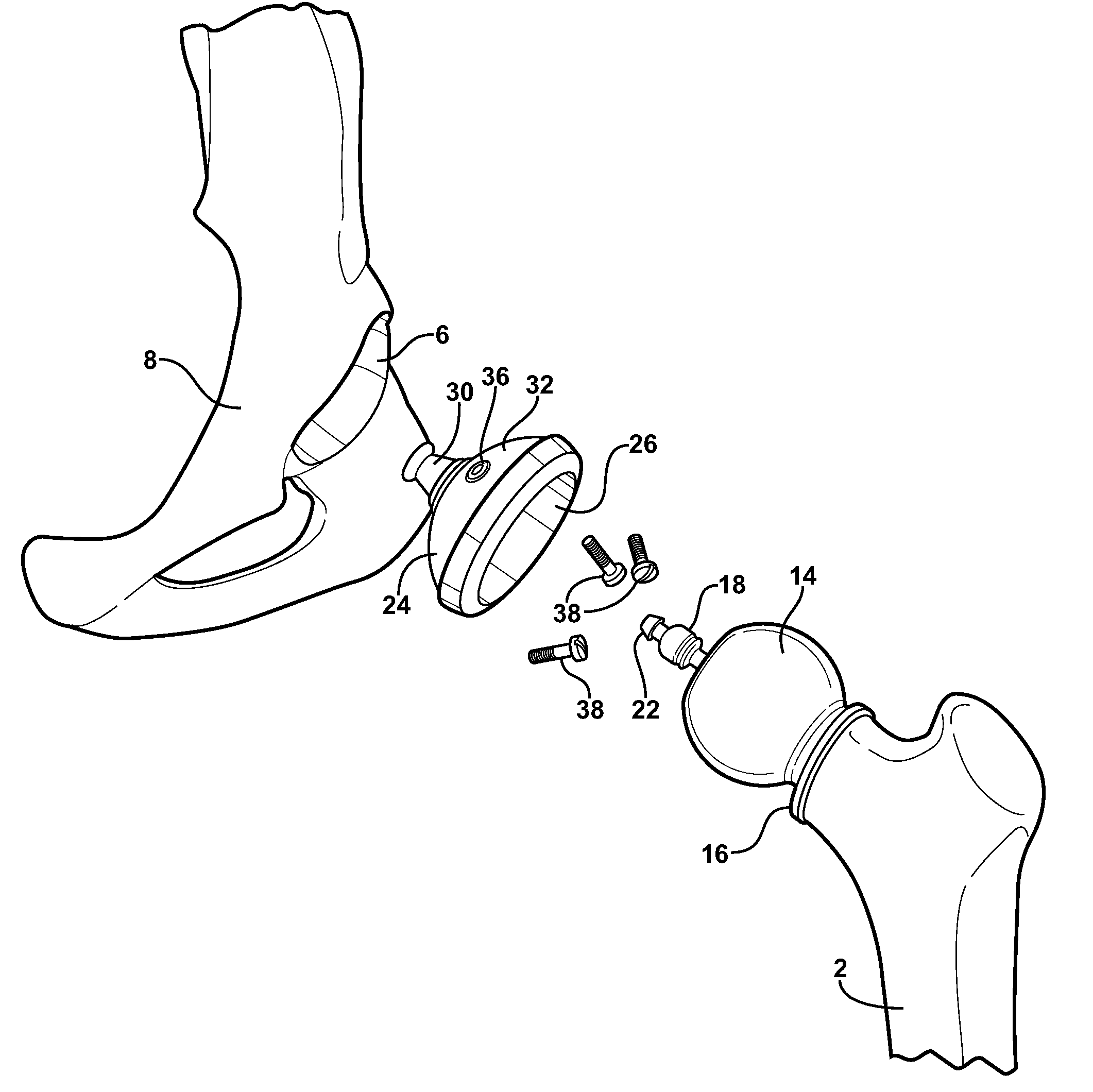
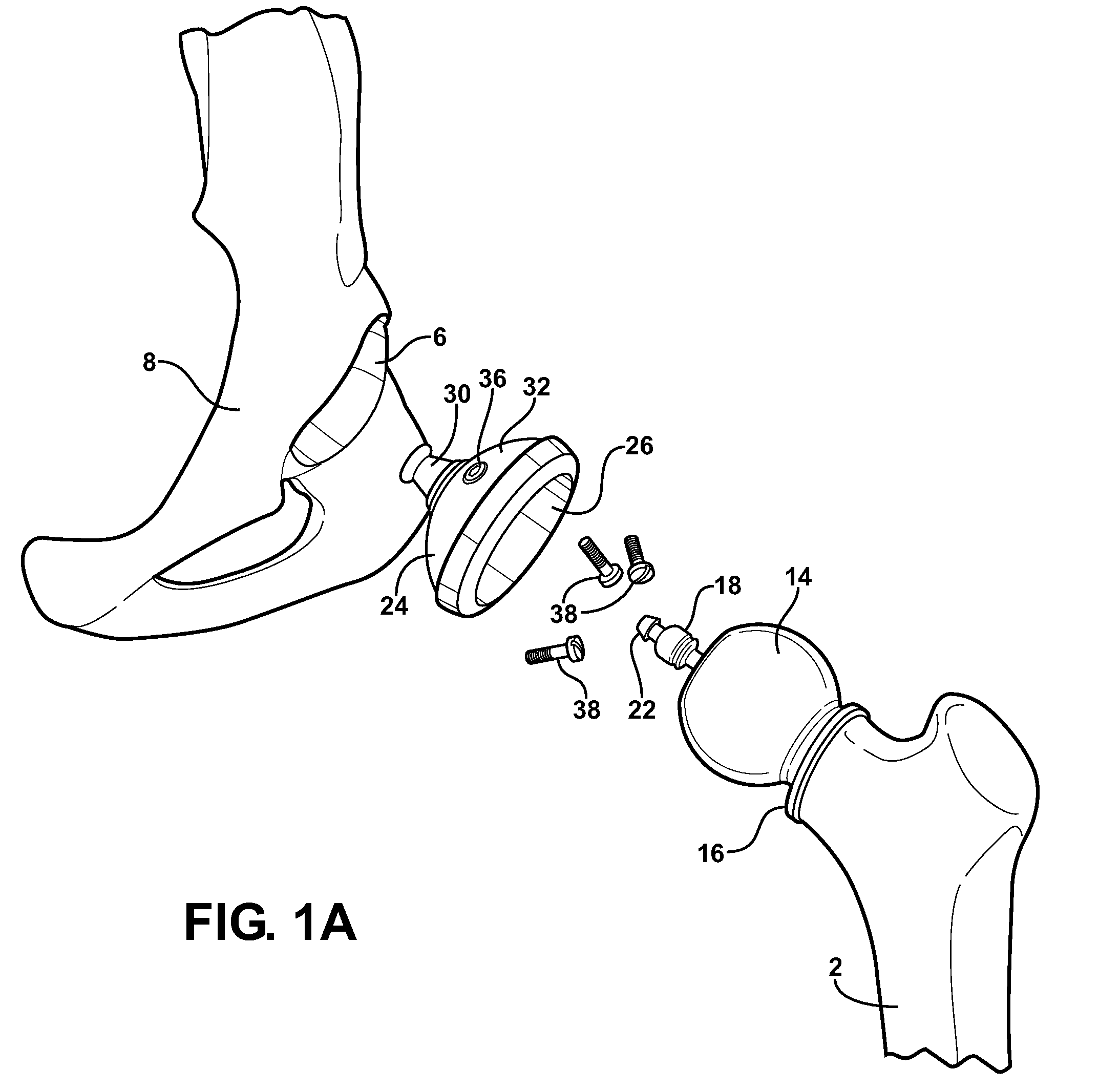
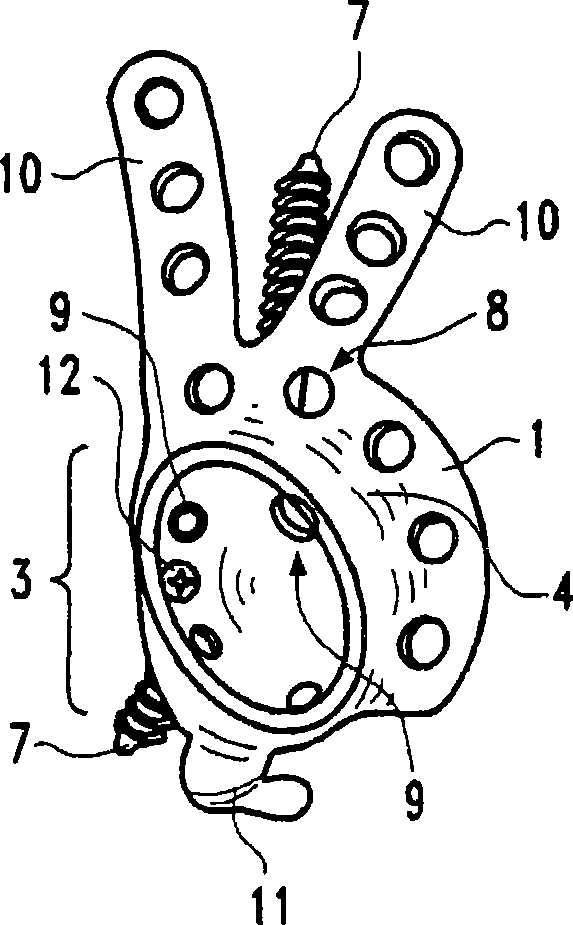
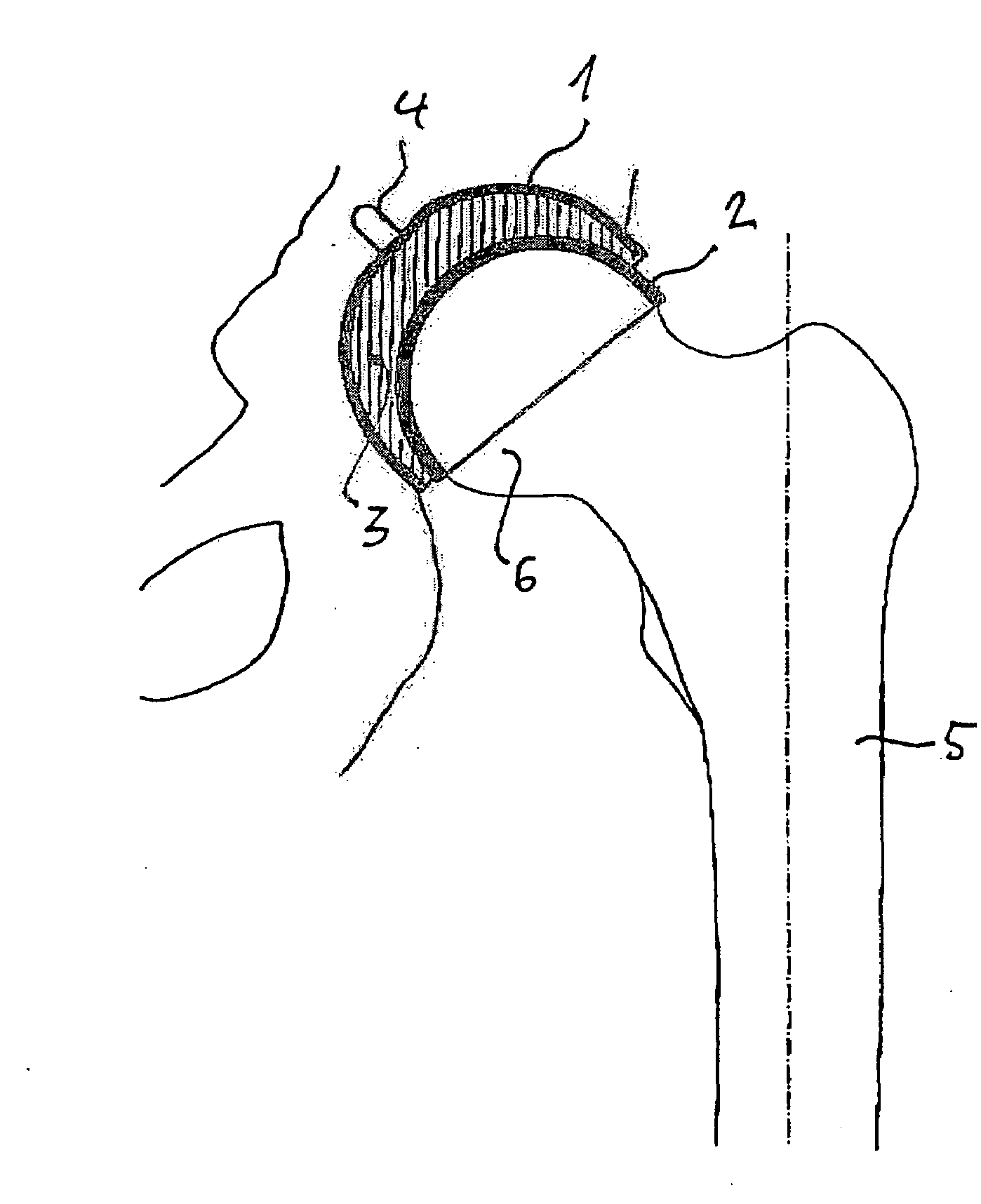
Hip socket with assembleable male ball shape having integrally formed ligament and female receiver and installation kit
A hip implant assembly including a spherical shaped ball and an elongated stem. An annular defining rim separates the ball from the stem and abuts, in a maximum inserting condition, over an exterior reconditioned surface of the femur and upon inserting the stem within an interior passageway formed within the femur. A cup shaped support seats the ball in a universally articulating permitting fashion via a flexible and resilient ligament which extends from the ball and is received within a recess passageway of the cup. The cup also includes a mounting surface with a central projecting portion which is in turn resistively fitted within an undercut defined recess formed in the ilium bone in communication with a base surface of the reconditioned acetabulum socket. A corresponding installation kit assists the preparation of the femur and ilium bones defining the hip joint, as well as the installation of the implant body into the upper conditioned femur end and the cup shaped and outer socket support to a reconditioned acetabulum defined in the ilium bone.
Owner:LINARES MEDICAL DEVICES
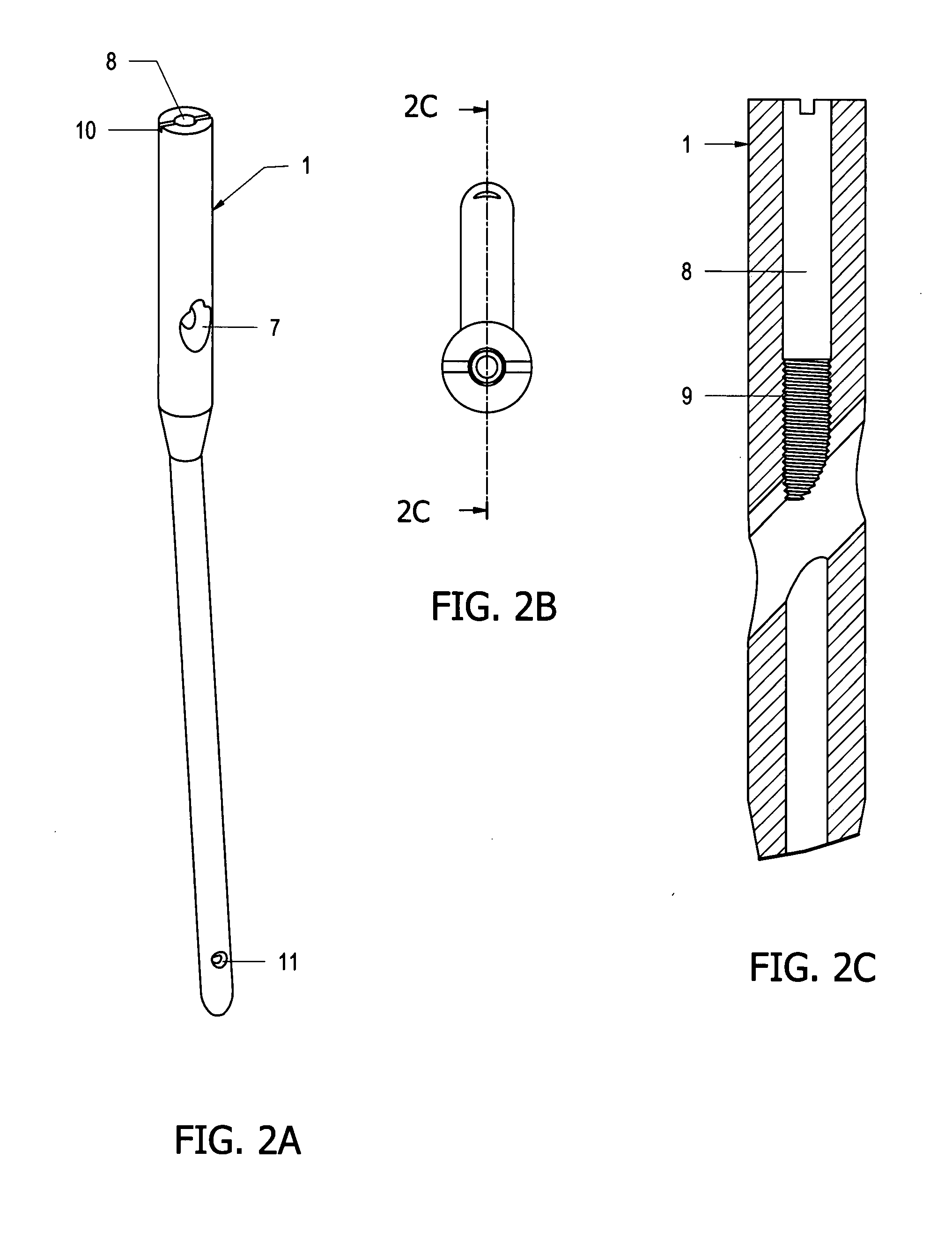
Cannulated femoral hip implant apparatus
The femoral hip implant is defined by a femoral ball and a femoral stem. The femoral stem has a proximal end, a distal end and a length. The femoral stem extends from the femoral ball and terminates at the distal end. The femoral stem is arranged and configured to be received by a femur bone. A method of use is also provided.
Owner:CHAPPUIS JAMES L
Revision hip implants and prosthesis systems
Revision hip implants and prosthesis systems include femoral heads, cups, screws, bridges, and segmental prostheses for revision surgeries.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
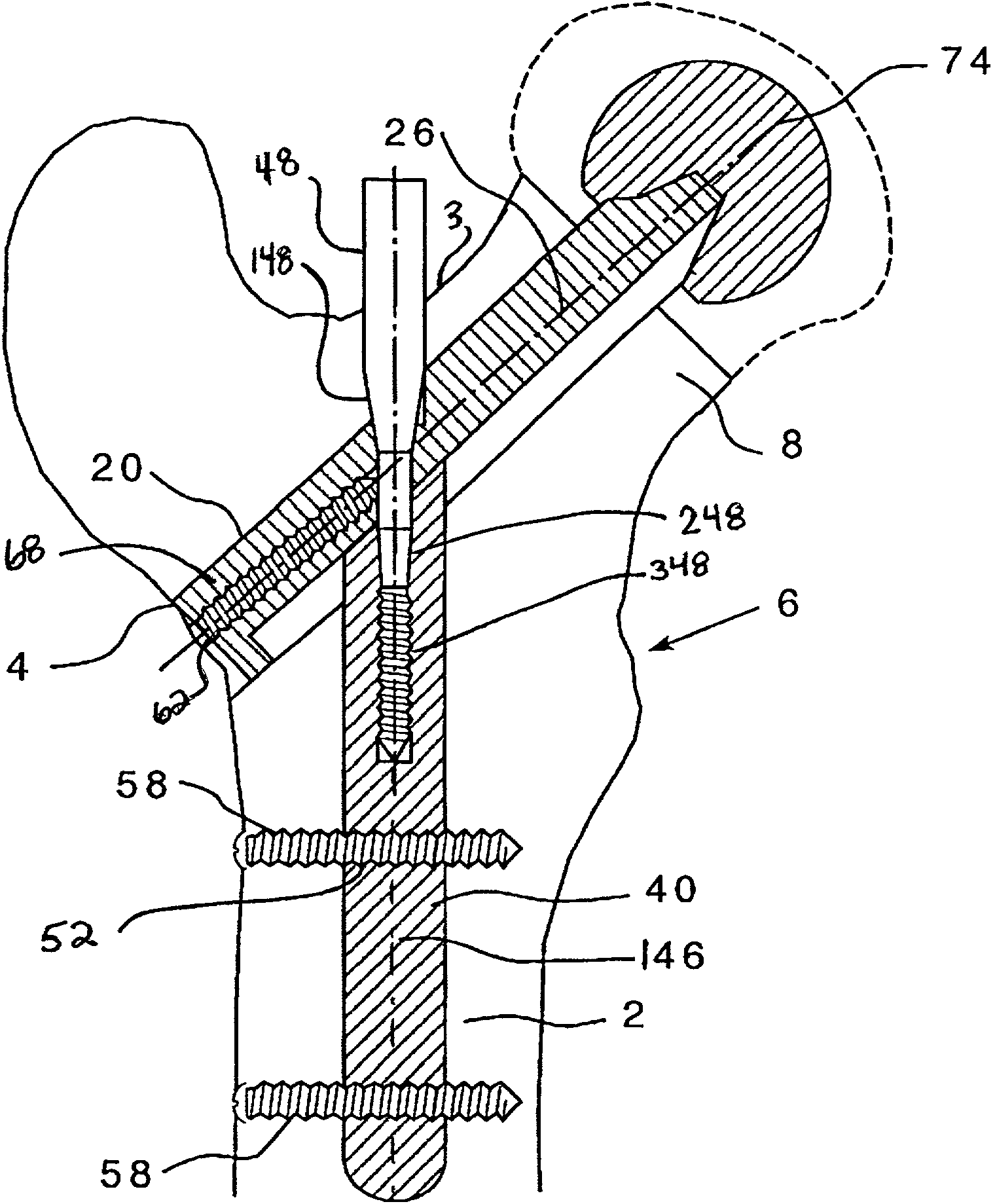
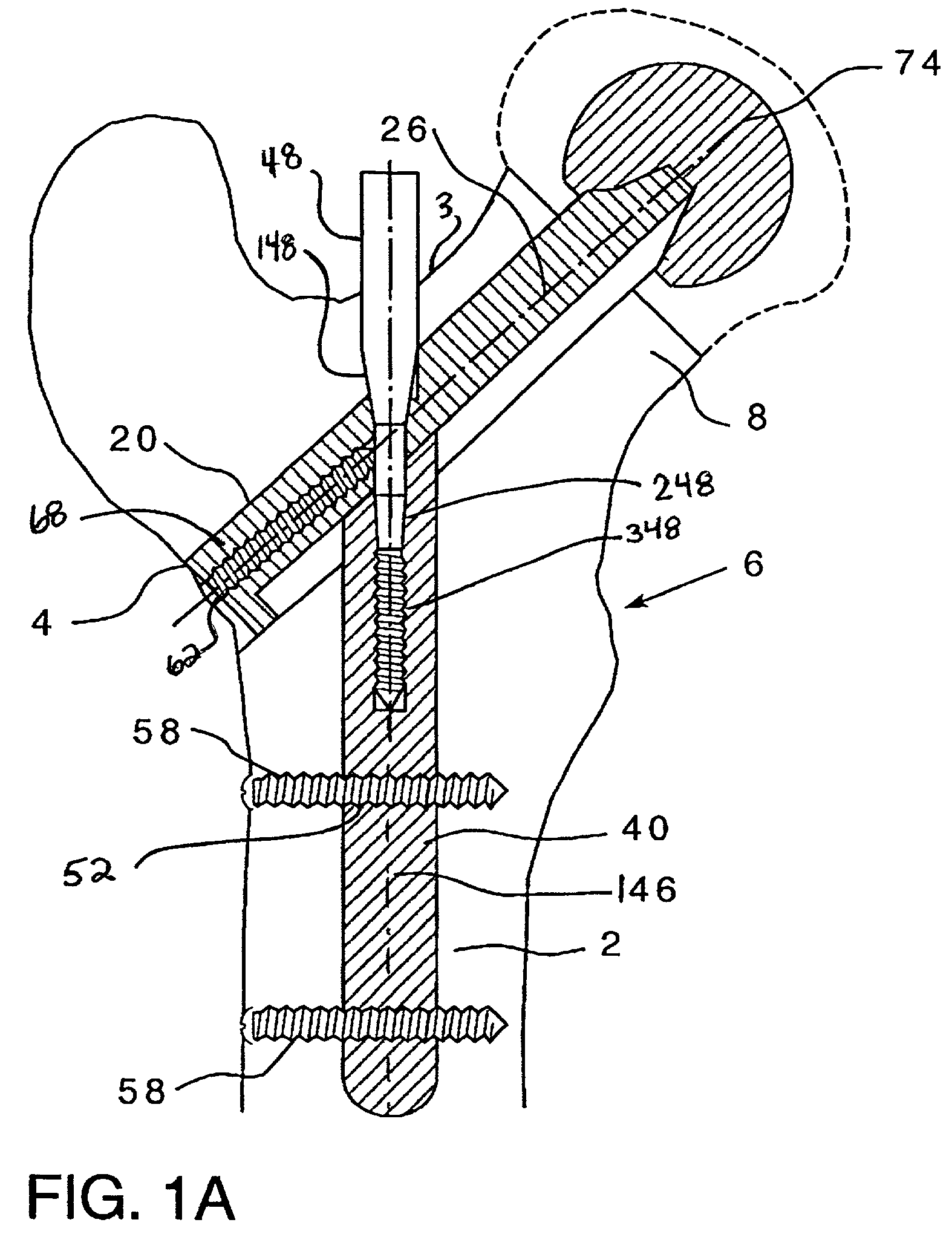
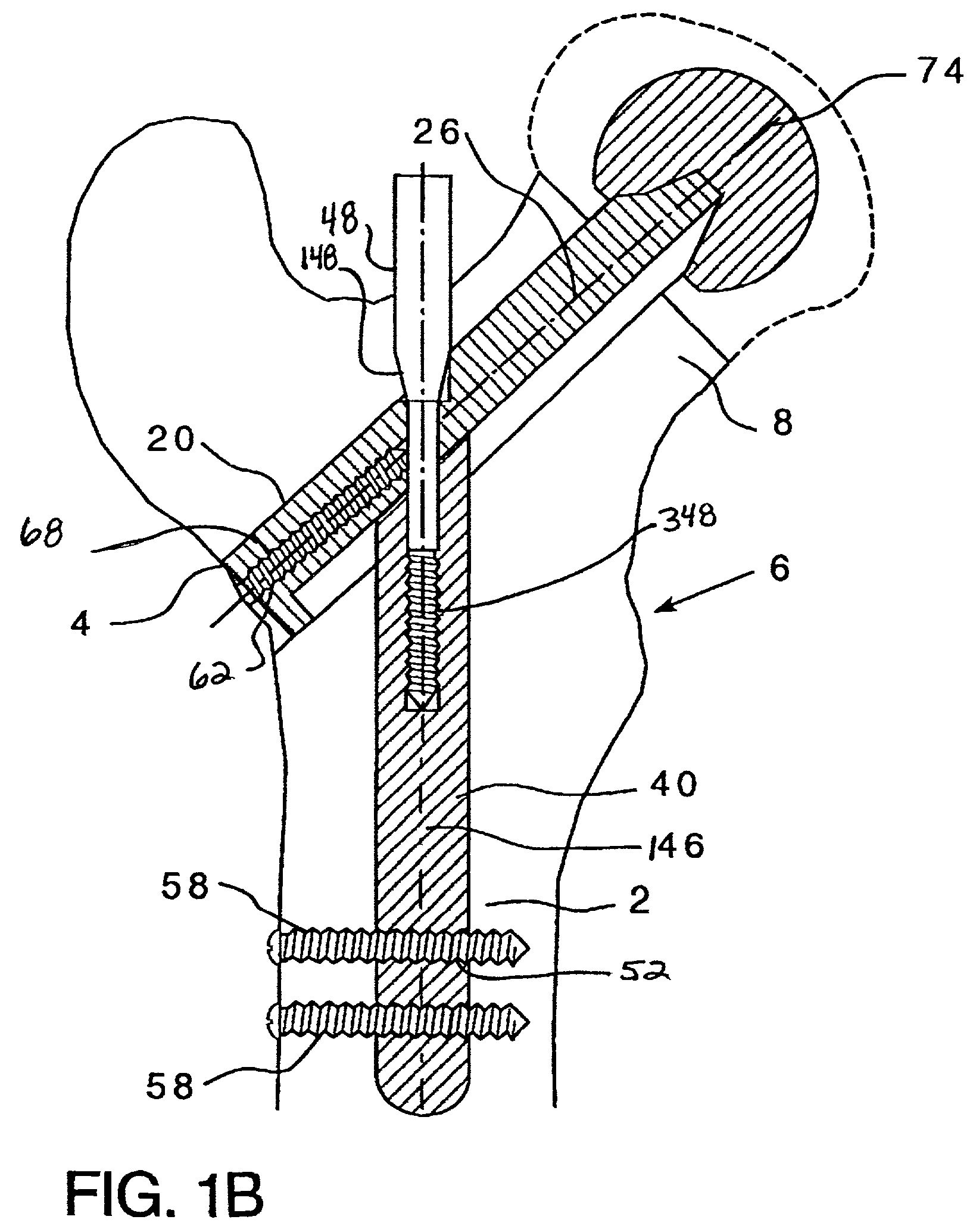
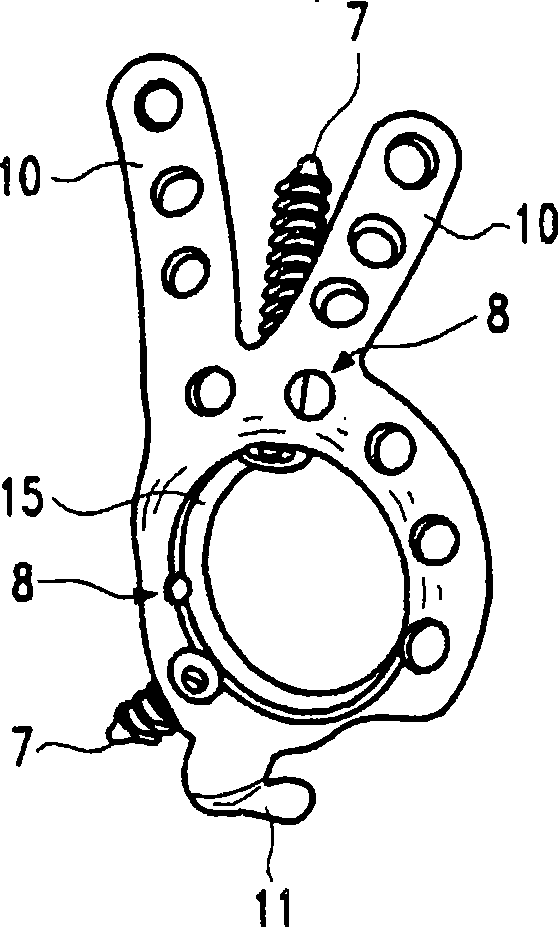
Double locked hip implant
InactiveUS20080262498A1Less surgical timeBone fixation of simple and fastInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headIntramedullary rod
A novel apparatus for treating fractures of the femur is disclosed. The assembly includes two hip implants positioned into the head and neck of the femur. The hip implants solidly lock into each other, while retaining the possibility of being slided together through either the oblique bore of an intramedullary nail or through the barrel of a side plate. This novel apparatus allows the surgeon to achieve sliding rotational control of the femoral head, while avoiding independent rotation of each screw around its own axis. This novel apparatus also avoids independent sliding of each screw.
Owner:FERNANDEZ DELLOCA ALBERTO ANGEL
Dual mobility hip replacement system
InactiveUS20150025647A1Improve stabilityReduce morbidityJoint implantsFemoral headsSpherical bearingFemoral component
A total hip implant system comprising: a prosthetic femoral component having a head with a part-spherical bearing surface; and a dual mobility acetabular cup system comprising a first bearing component made of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene mounted on the head, the first bearing component having a part-spherical inner bearing surface rotatably engaging the part-spherical bearing surface of the head, and having a part-spherical outer bearing surface, a second bearing component made of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) having an inner part-spherical bearing surface rotatably engaging the part-spherical outer bearing surface of the first bearing surface.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Femoral hip stem explant system and methods of using the same
A system for facilitating the removal of a prosthetic hip implant from a femur. The explant system has at least one blade coupled to a handle. The shape of the blade conforms to a portion of the implant so that a cutting tip of the blade can be positioned in a desired position relative to the implant and the femur. A plurality of blades can be provided, each blade configured to conform to a different portion of the implant. Force is applied to the handle so that the cutting tip of the blade cuts through bone growth from the femur into the implant, thereby facilitating removal of the implant.
Owner:SHENZHEN RIDER THINKING TECH CO LTD +1
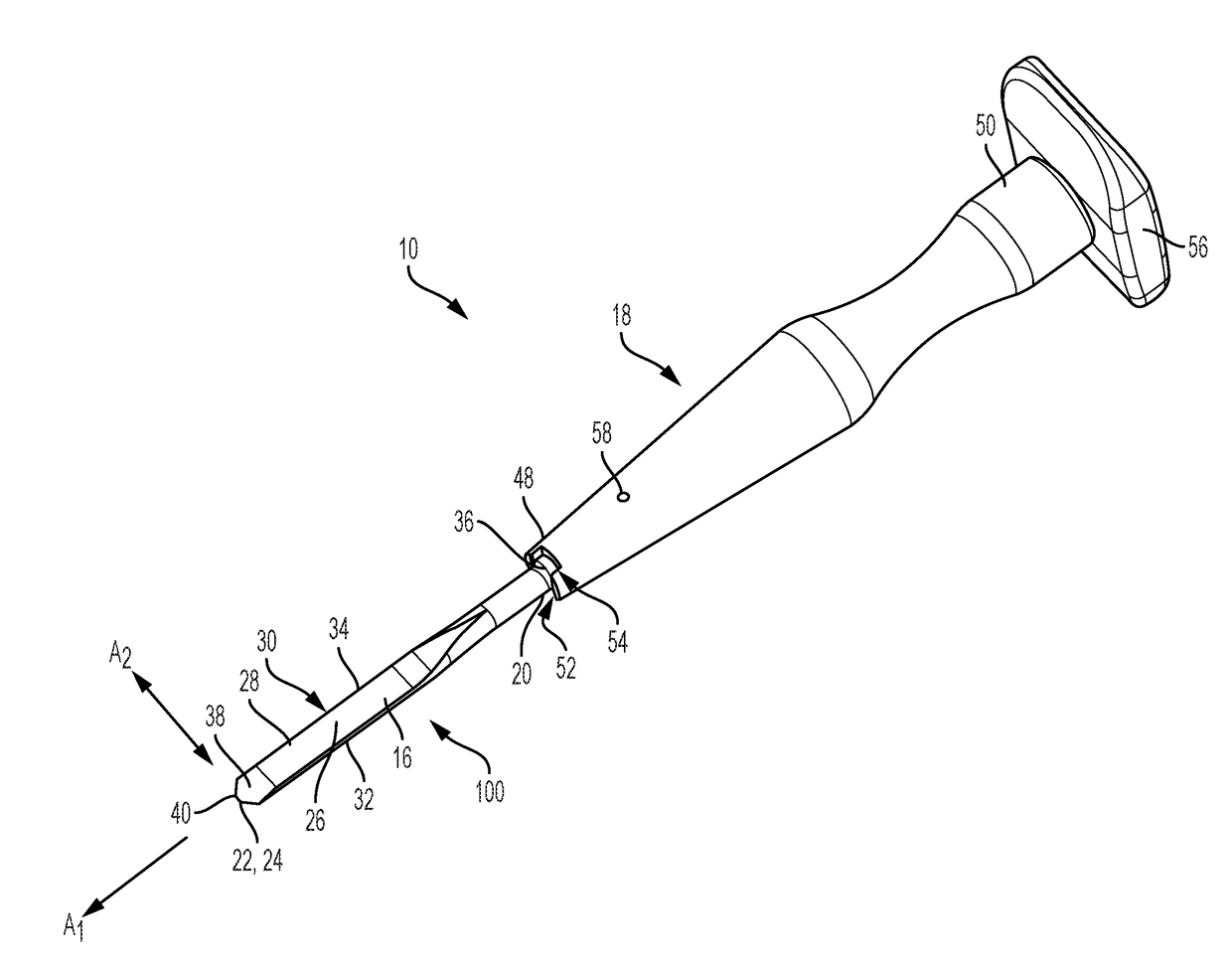
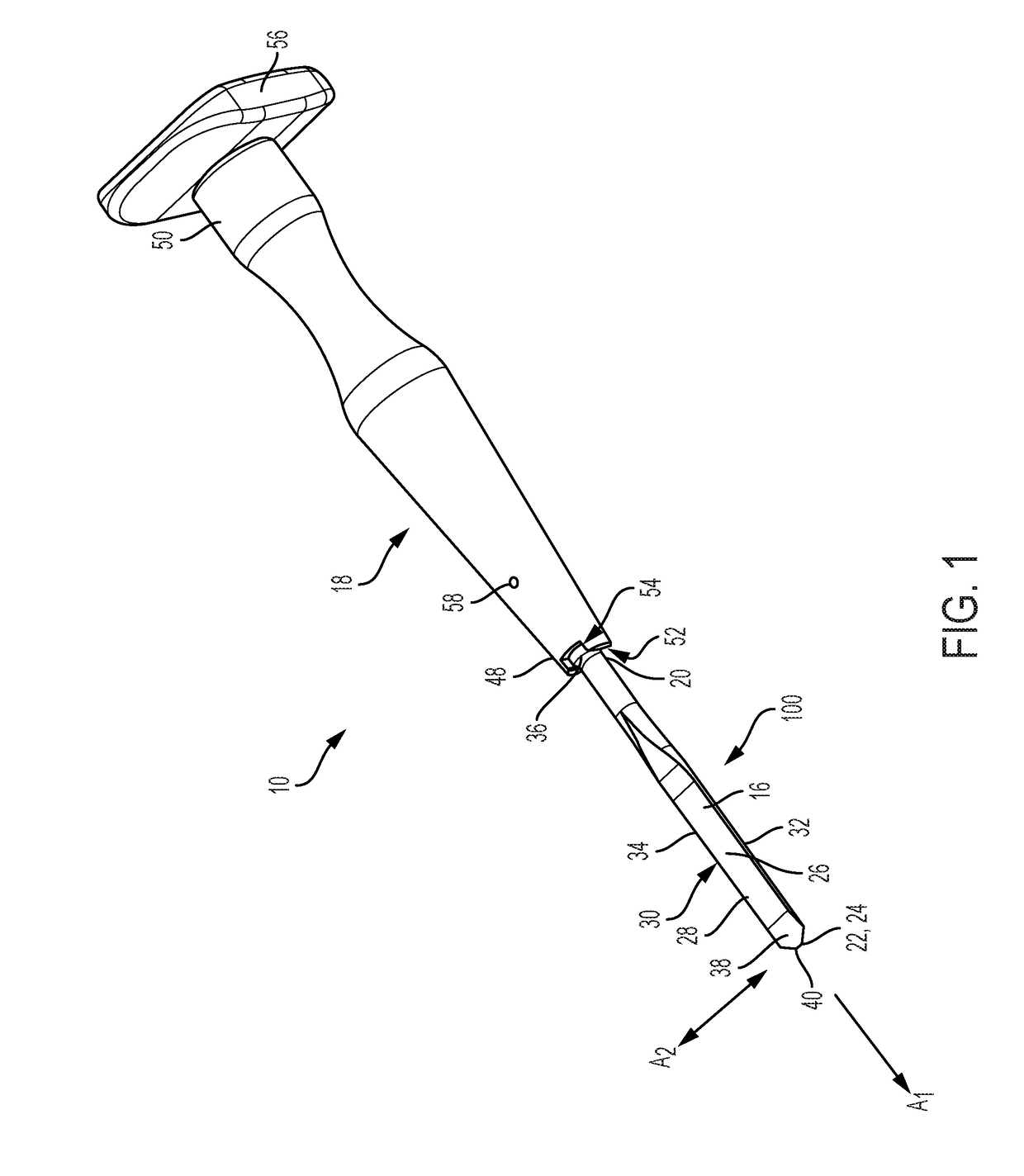
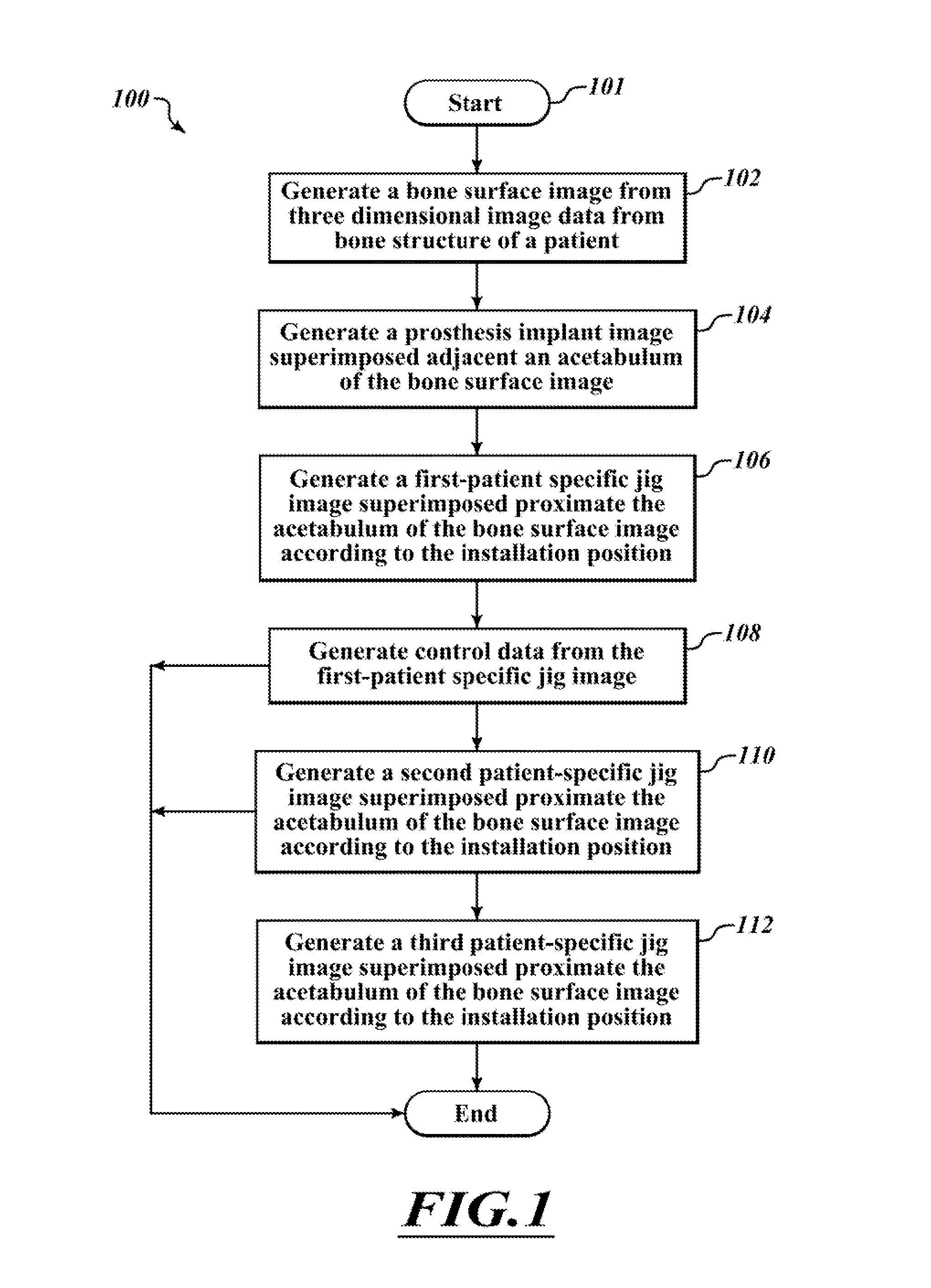
Devices and methods for hip replacement
InactiveUS9211128B2Precise alignmentPrecise positioningJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHip joint replacement operationBone structures
Devices and methods for use in hip replacement surgery can incorporate computer models of a patient's acetabulum and surrounding bone structure, a first patient-specific jig designed from the computer model and configured to correspond to a final installation position and orientation of a prosthetic hip implant, a second patient-specific jig, also designed from the computer model, configured to refine the procedure, if necessary, following use of the first patient-specific jig, and / or a third patient specific jig, designed from the computer model, configured to refine the procedure, if necessary, following use of the first and second patient-specific jigs, allowing the surgeon to properly position and orient the hip prosthesis. Also shown and described are novel devices for implanting an acetabular cup.
Owner:BULLSEYE HIP REPLACEMENT
Hip implant with porous body
A hip implant has a neck body that connects to a bone fixation body. The bone fixation body has a porous structure with an elongated shape. An internal cavity is formed in the bone fixation body and includes a substance to stimulate bone growth.
Owner:FOUR MILE BAY
Short stem femoral prosthesis
InactiveUS20080119942A1Improve rotational stabilityRaise the potentialJoint implantsFemoral headsShort stemMedial side
A prosthetic hip implant comprising: a neck portion including a prosthetic head mounted thereon; and a stem portion coupled to the neck portion having a generally u-shaped cross-section, the stem curving towards a medial side of a femur on moving in a proximal to distal direction when the stem is implanted, a base portion of the u-shaped cross-section extending between first and second legs of the u-shaped cross-section, the base portion decreasing in thickness while moving in a proximal to distal direction and a length of the first and second legs of the u-shaped cross-section decreasing on moving in a proximal to distal direction.
Owner:BENOIST GIRARD & CIE
Modular hip joint implant
ActiveUS8066779B2Increase choiceIncrease flexibilityJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral stemHip implant
A modular hip joint implant and associated method. The modular hip implant includes a femoral stem having a proximal surface defining a dovetail groove having first and second female wings, and a neck component having a distal surface defining a semi-dovetail projection engaging the dovetail groove. The projection includes a single male wing mating with the first femoral wing.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Modular hip implant
InactiveCN101478933AImprove stabilityAchieve stabilityJoint implantsAcetabular cupsModularitySacroiliac joint
The invention relates to a modular hip implant comprising a base that is to be attached to a hipbone, and a socket for accommodating a hip joint prosthesis. The base is provided with fastening means for mounting the base on the hipbone as well as a concave receiving area for the socket. The socket has a convex outer form which is complementary to the receiving area such that the radii of curvature determining the concave receiving area and the convex outer form essentially correspond to each other. The socket can be fastened within the base. The inventive hip implant is characterized in that the base and / or the socket encompass / es means for adjusting the position of the socket relative to the base. The invention allows the inclination and anteversion to be adjusted by arranging the socketinside the base.
Owner:彼得布雷姆控股两合公司
Neck sparing total hip implant system
A femoral prosthesis. The femoral prosthesis includes an implant body having a proximal end and a distal end and a shoulder at the proximal end, the shoulder being structured and dimensioned for a tight press fit into the neck of a femur. The implant body includes a trunk at the distal end, the trunk having a wedge formed by a tapered portion extending in the direction of the distal end of the implant body. The implant body also includes a medial column extending from the shoulder toward the distal end and a lateral column extending from the shoulder toward the distal end. The wedge, the medial column, and the lateral column to provide multi-planar stability for the implant body and surface area for fixation of the implant body.
Owner:CONCEPT DESIGN & DEV
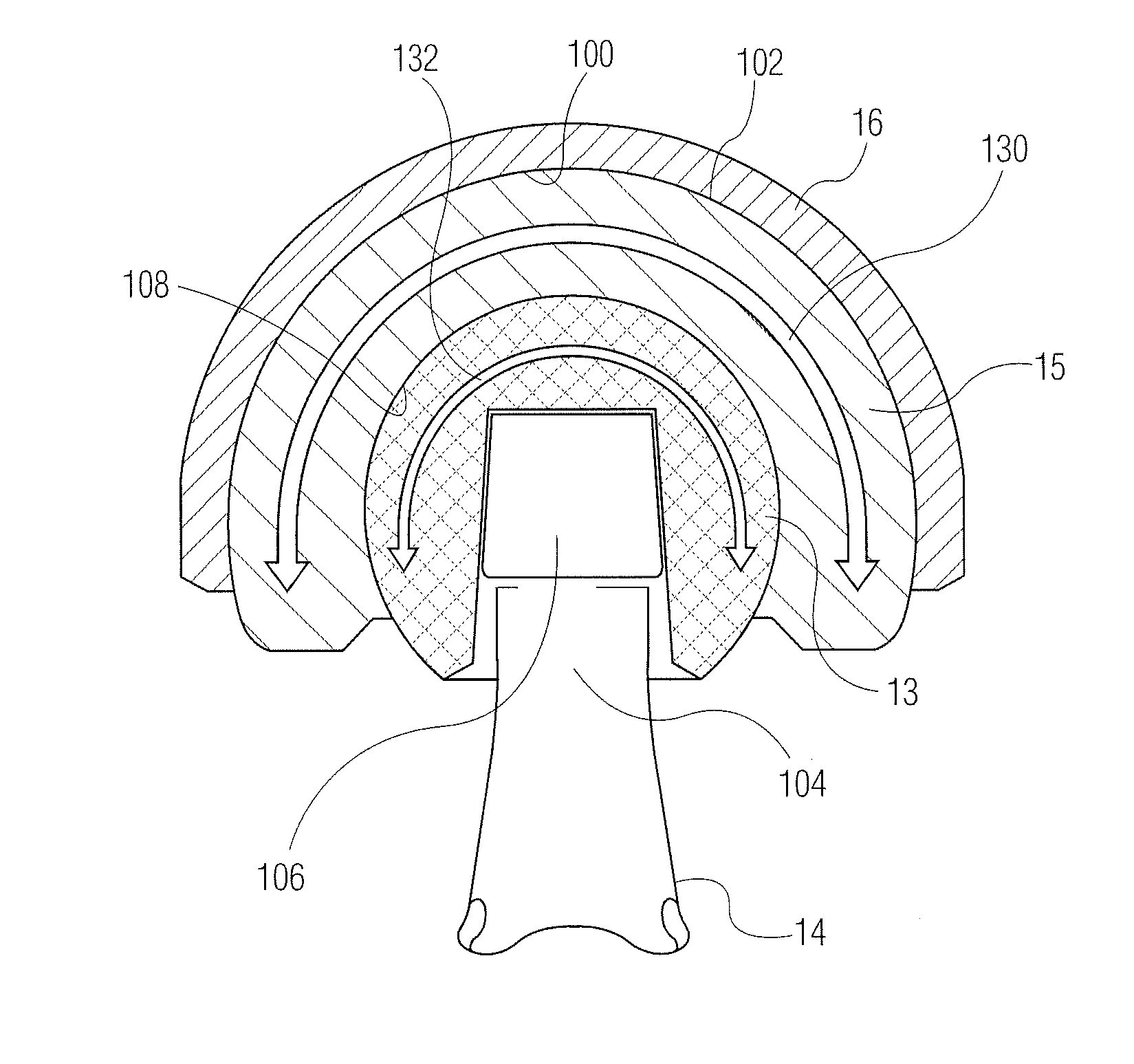
Resurfacing-Hip Implant Construction Set
InactiveUS20080215160A1Precise positioningImprove stabilityJoint implantsFemoral headsThin metalRight femoral head
Described here is a set for the construction of a resurfacing hip implant. It comprises a thin metal cup for cemented insertion into the natural acetabulum, a thin metal cap for cemented placement upon the natural femoral head, and an inlay which can be placed in the cup of the acetabulum as a sliding partner for the cap for the femoral head.
Owner:ESKA IMPLANTS GMBH & CO
Haptic volumes for reaming during arthroplasty
A haptic robotic system for reaming an acetabulum prior to inserting an acetabular cup is more accurate than conventional instruments and may reduce the risk of dislocation and improve durability of a hip implant. Disclosed is a three-dimensional tool path, referred to as a haptic volume. Once the haptic volume is implemented into the software of a haptically constrained surgical robotic system, the cutting tool or reamer can only be utilized within the haptic volume. The haptic volume guides the surgeon in preparing the final reamed bone surface with a greatly reduced chance of the reaming unintended bone and greatly increases the chance that the reaming procedure may be carried out using one reaming tool, or using a single-stage reaming process.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Modular orthopaedic components
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Combination male/female hip joint and installation kit
A hip implant assembly including body exhibiting a substantially spherical shaped ball and an elongated stem. An annular defining rim separates the ball from the stem and abuts, in a maximum inserting condition, an exterior surface of a reconditioned femur upon inserting the stem within an interior passageway associated with the femur. A three dimensional and interior volume defining support secures around the ball in a universally articulating permitting fashion, the support being fixed to a reconditioned acetabulum socket associated with an ilium bone by interconnecting posts and anchors established between the fixed support and the reconditioned surface of the acetabulum. A corresponding installation kit assists the preparation of the femur and ilium bones defining the hip joint, as well as the installation of the implant body into the upper conditioned femur end and the outer socket support to a reconditioned acetabulum defined in the ilium bone.
Owner:LINARES MEDICAL DEVICES
Objective, Real-Time Acoustic Measurement and Feedback for Proper Fit and Fill of Hip Implants
The present invention relates to a system and method for objective, real-time acoustic measurement and feedback for proper fit and fill of hip implants during total hip replacement surgery, or other bone implant surgical procedures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com