Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
351 results about "Intramedullary rod" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
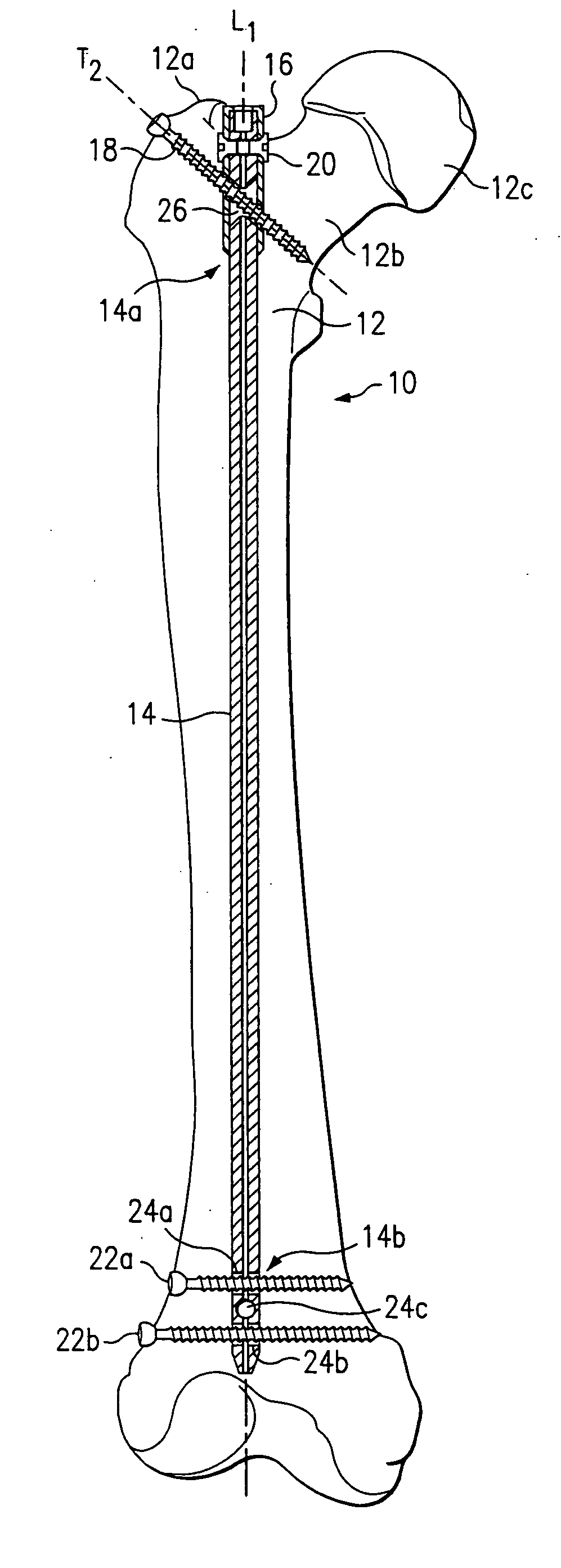
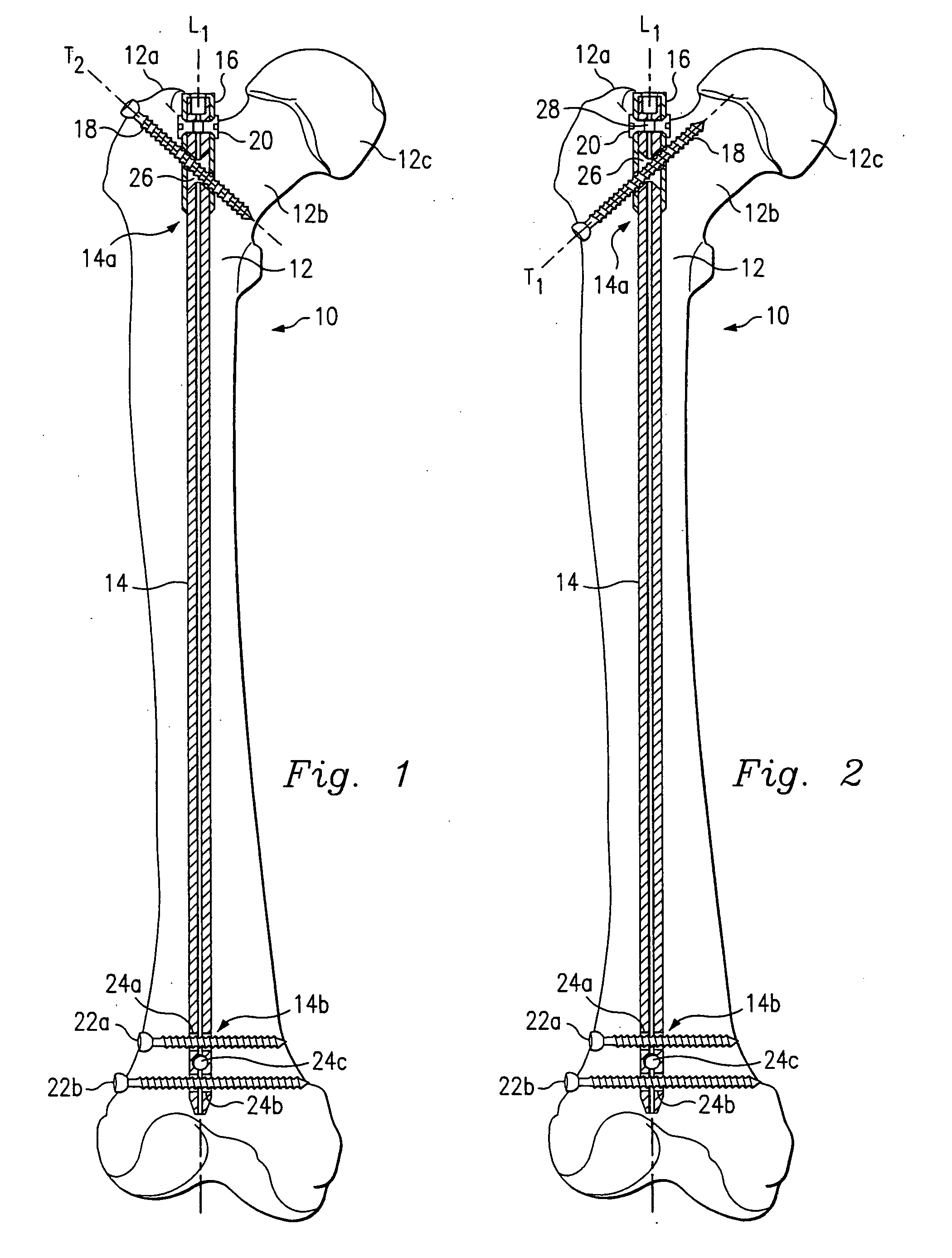
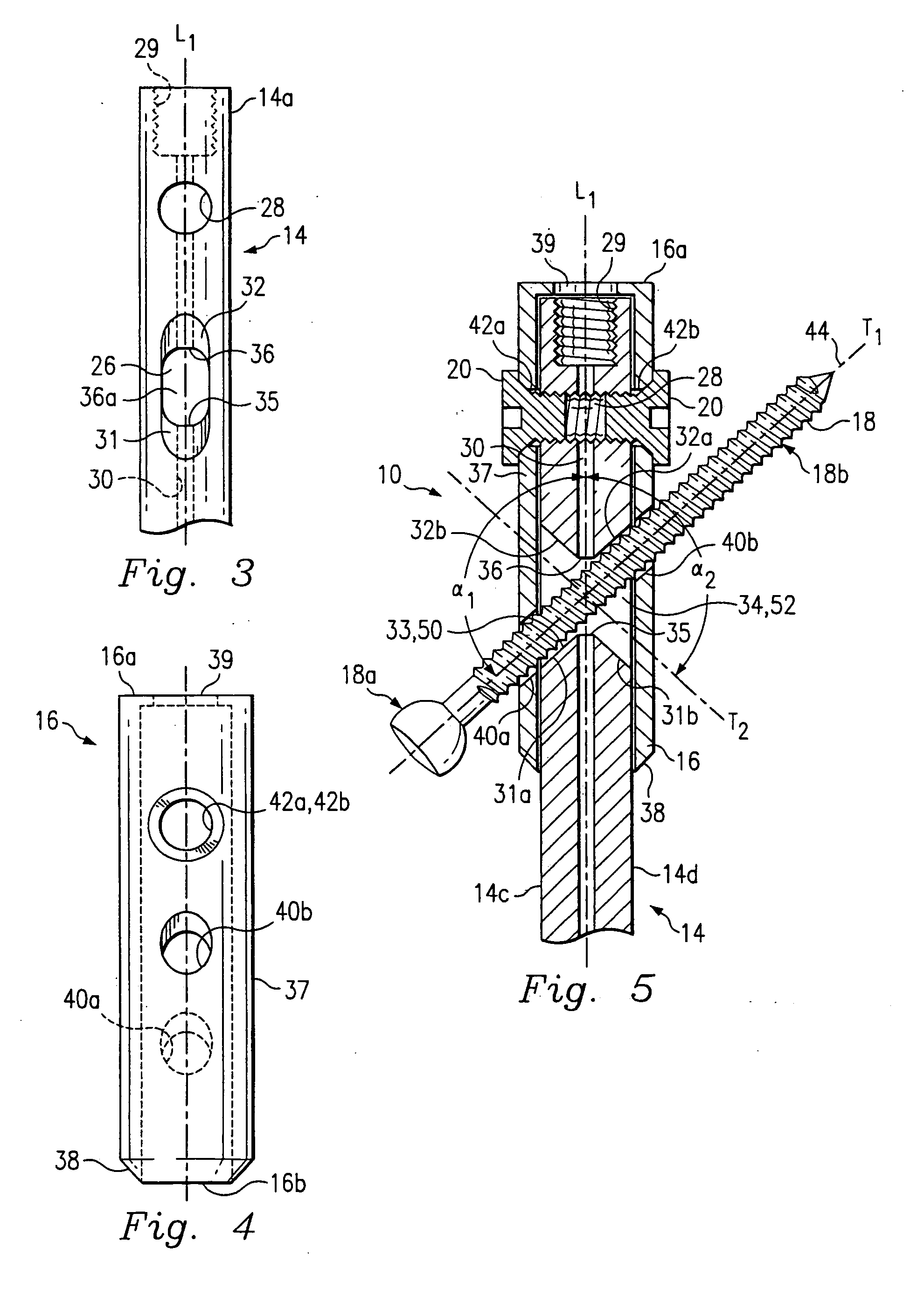
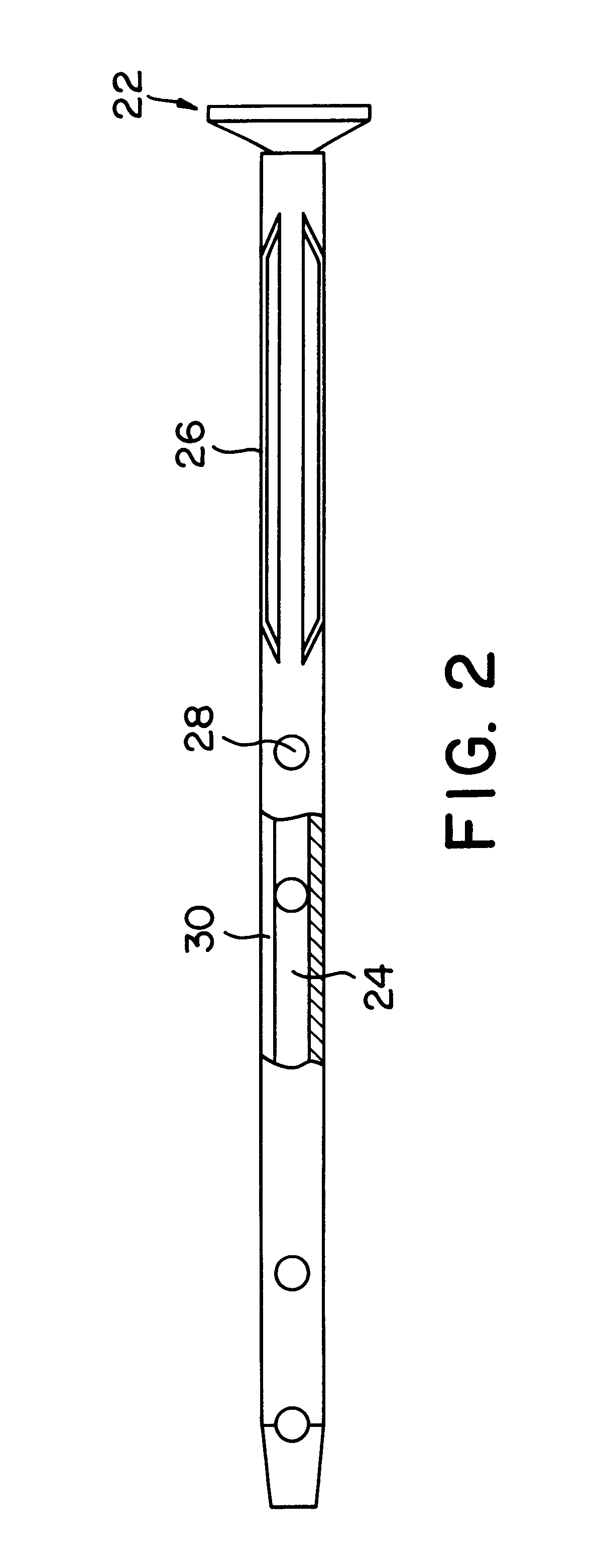
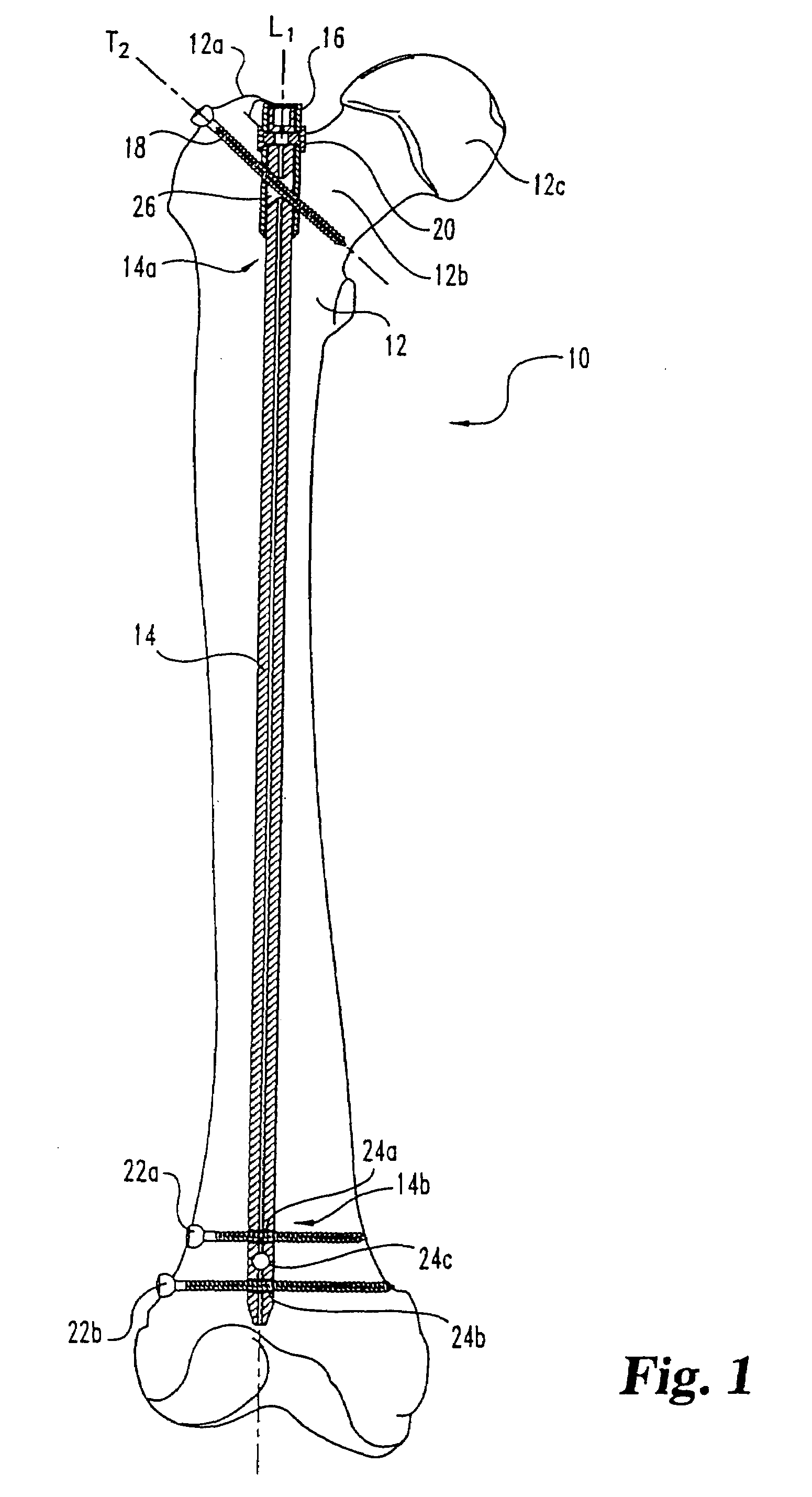
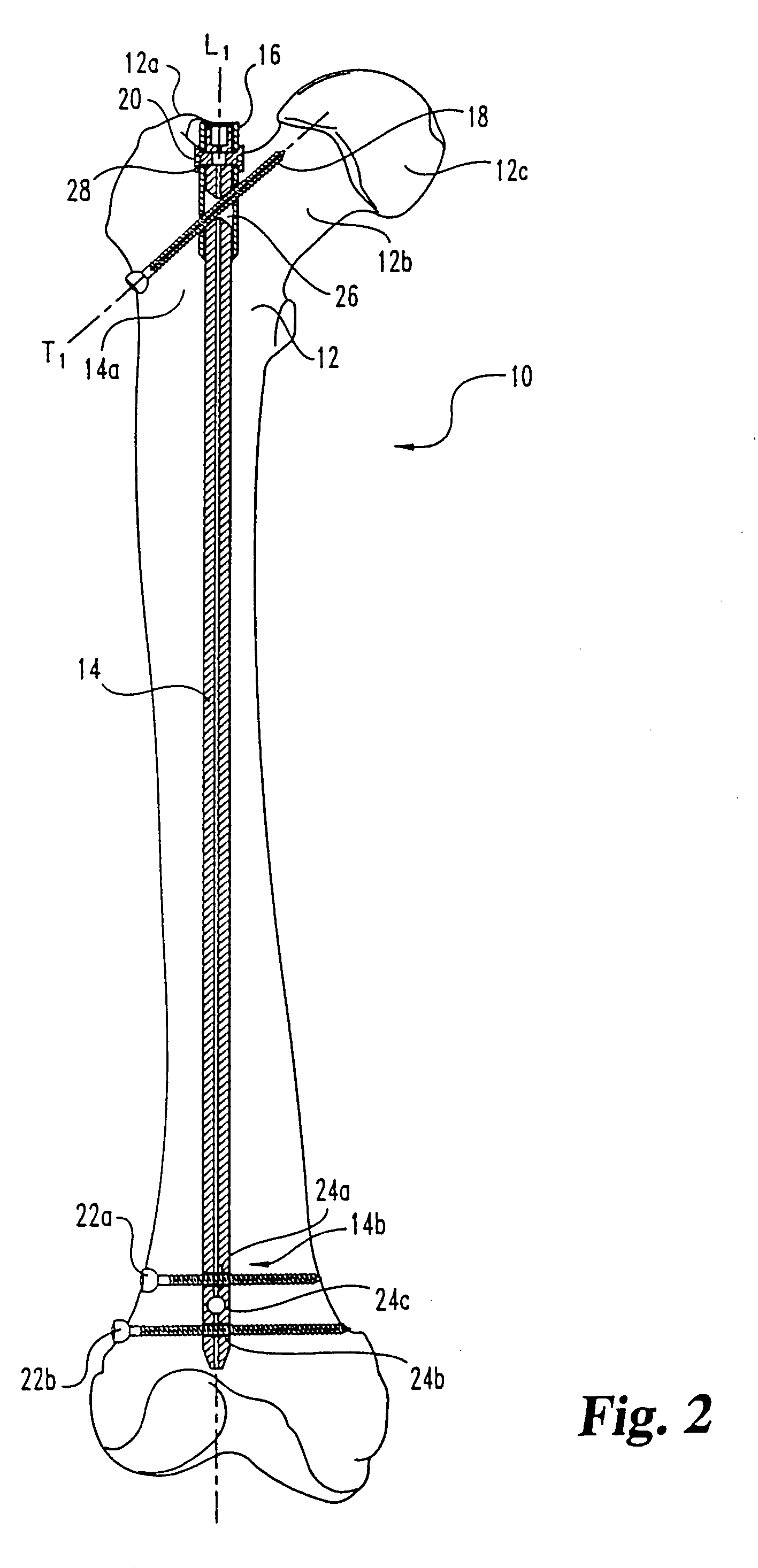
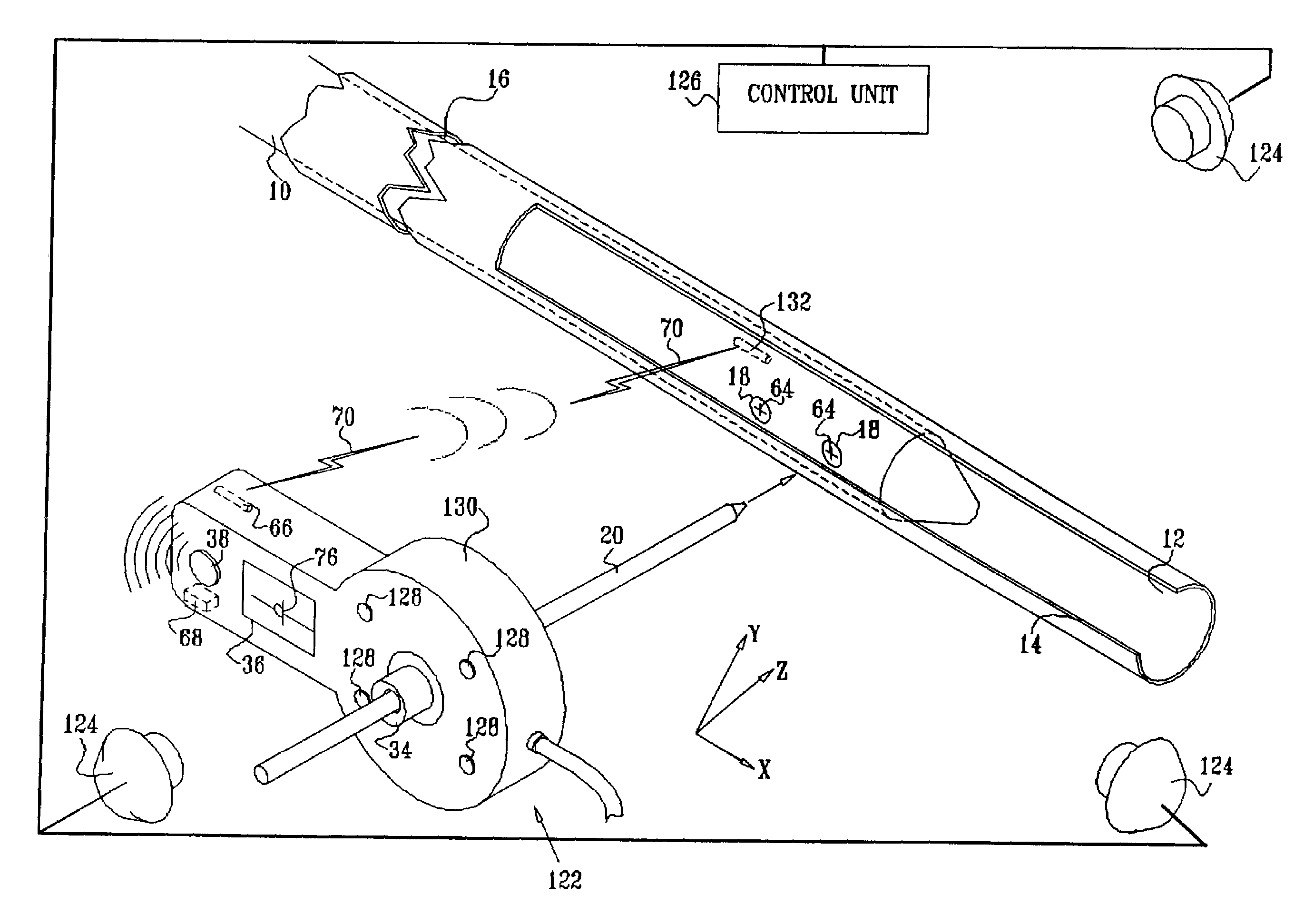
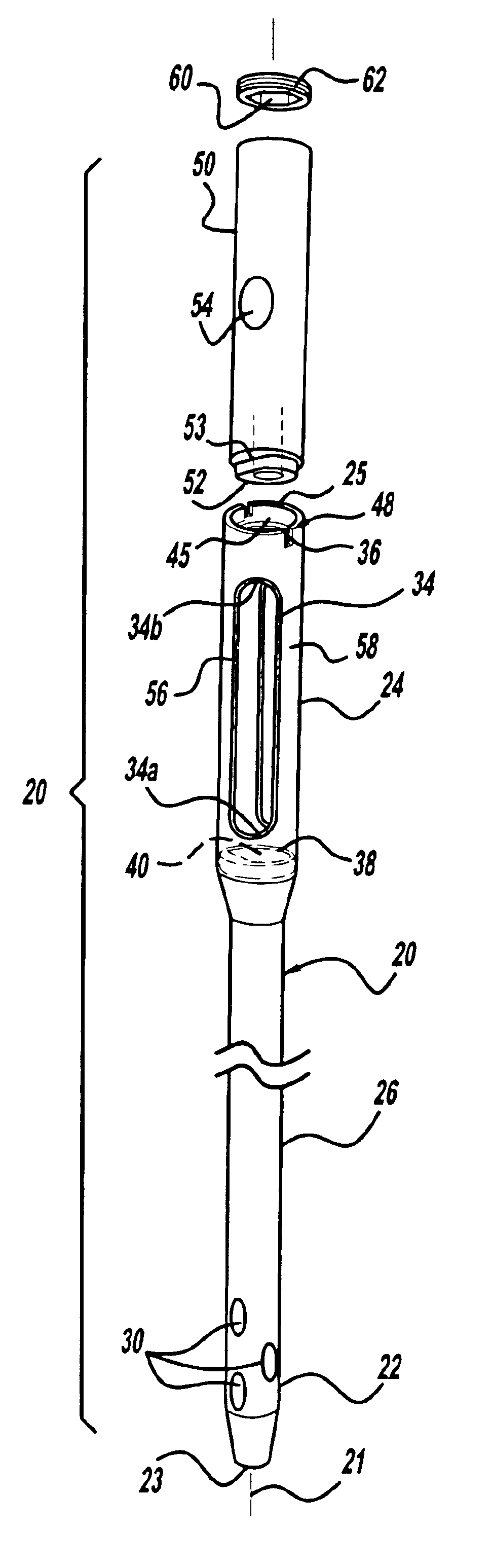
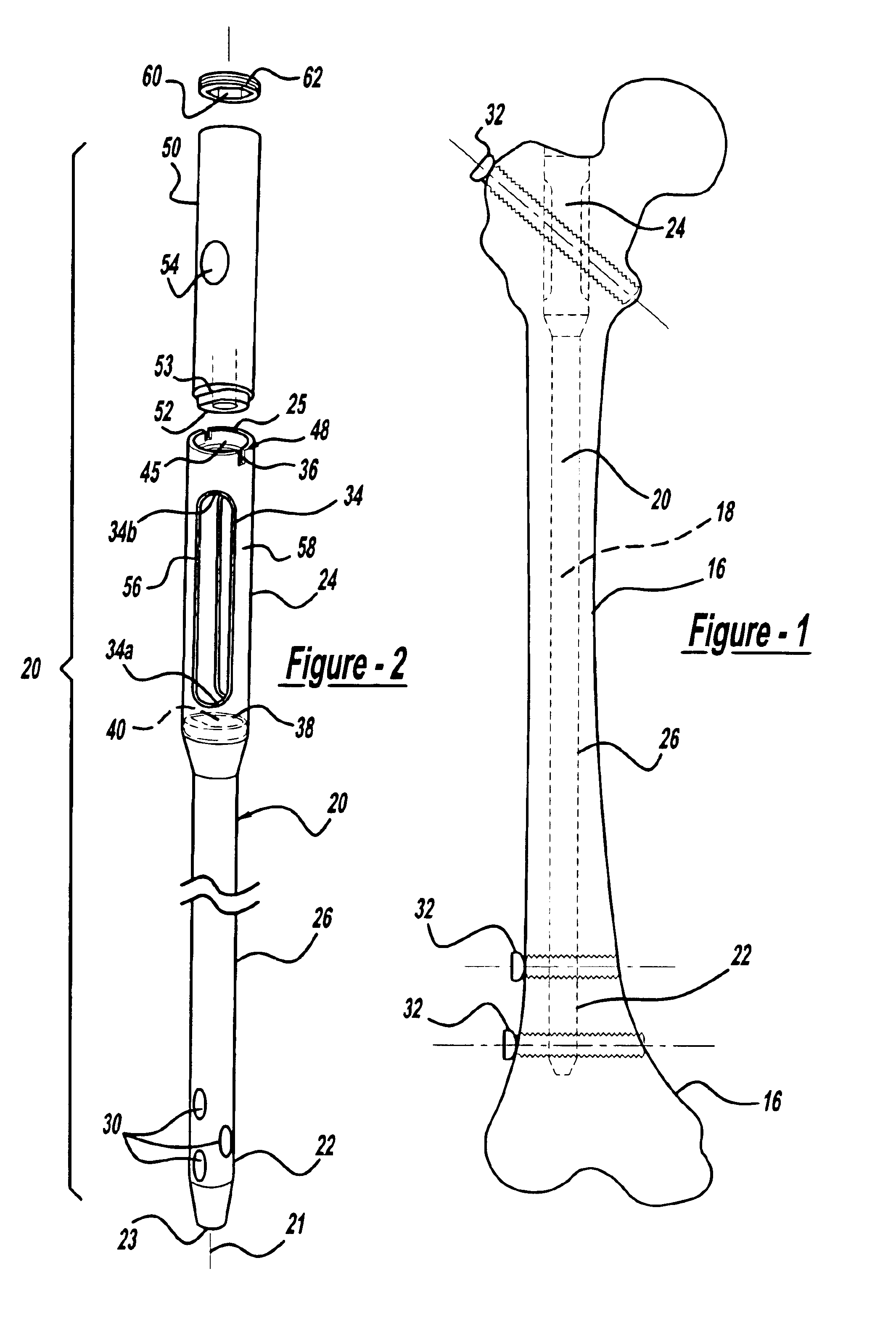
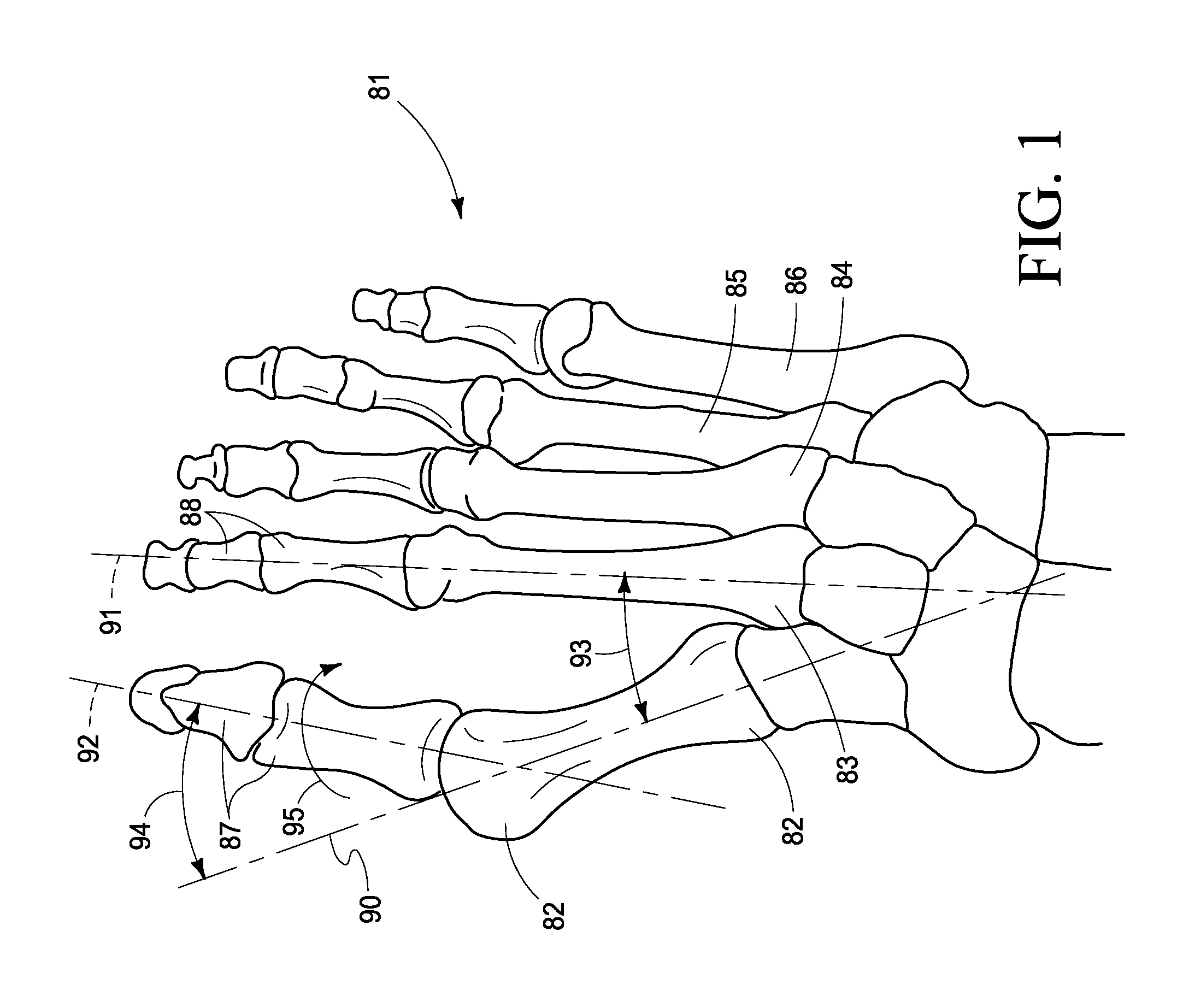
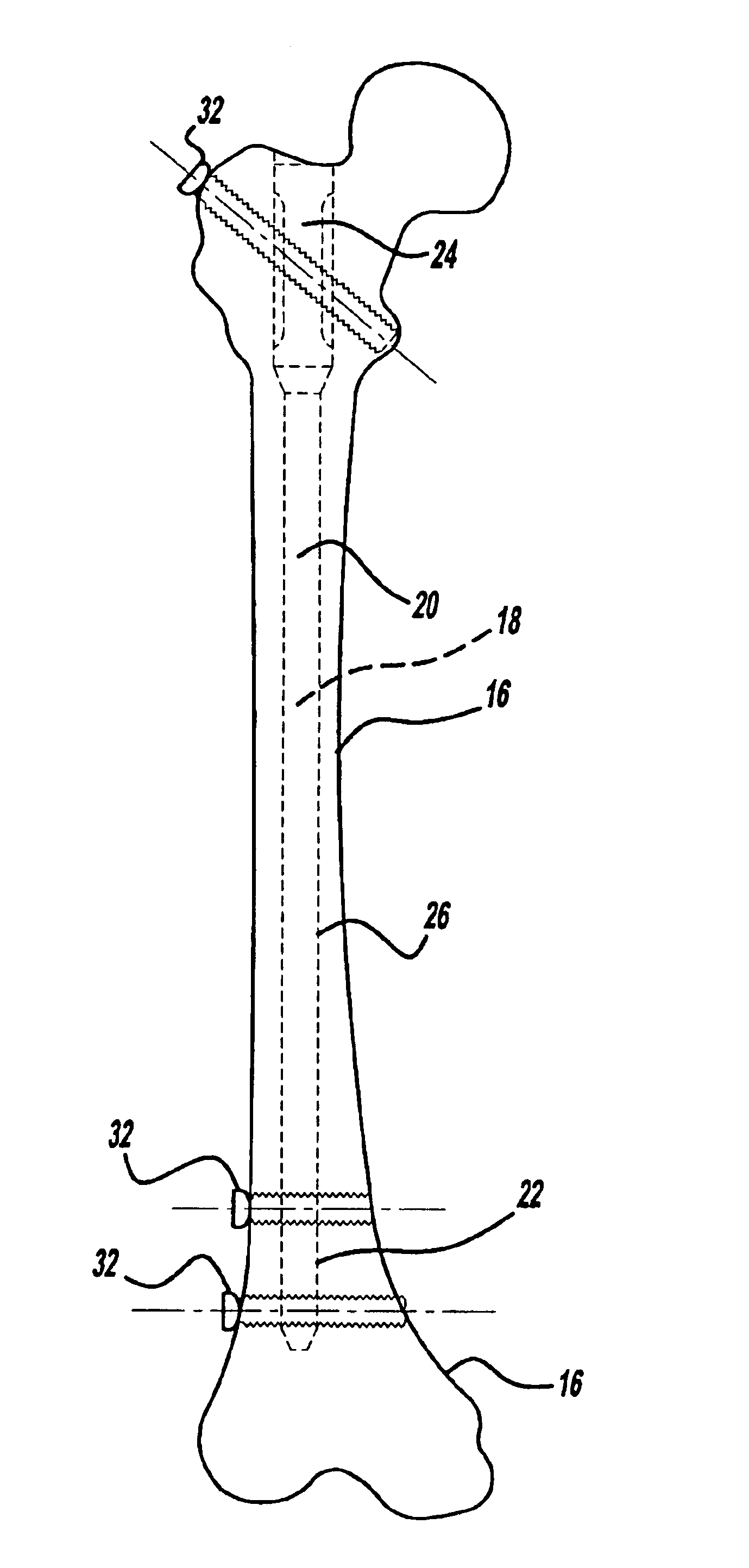
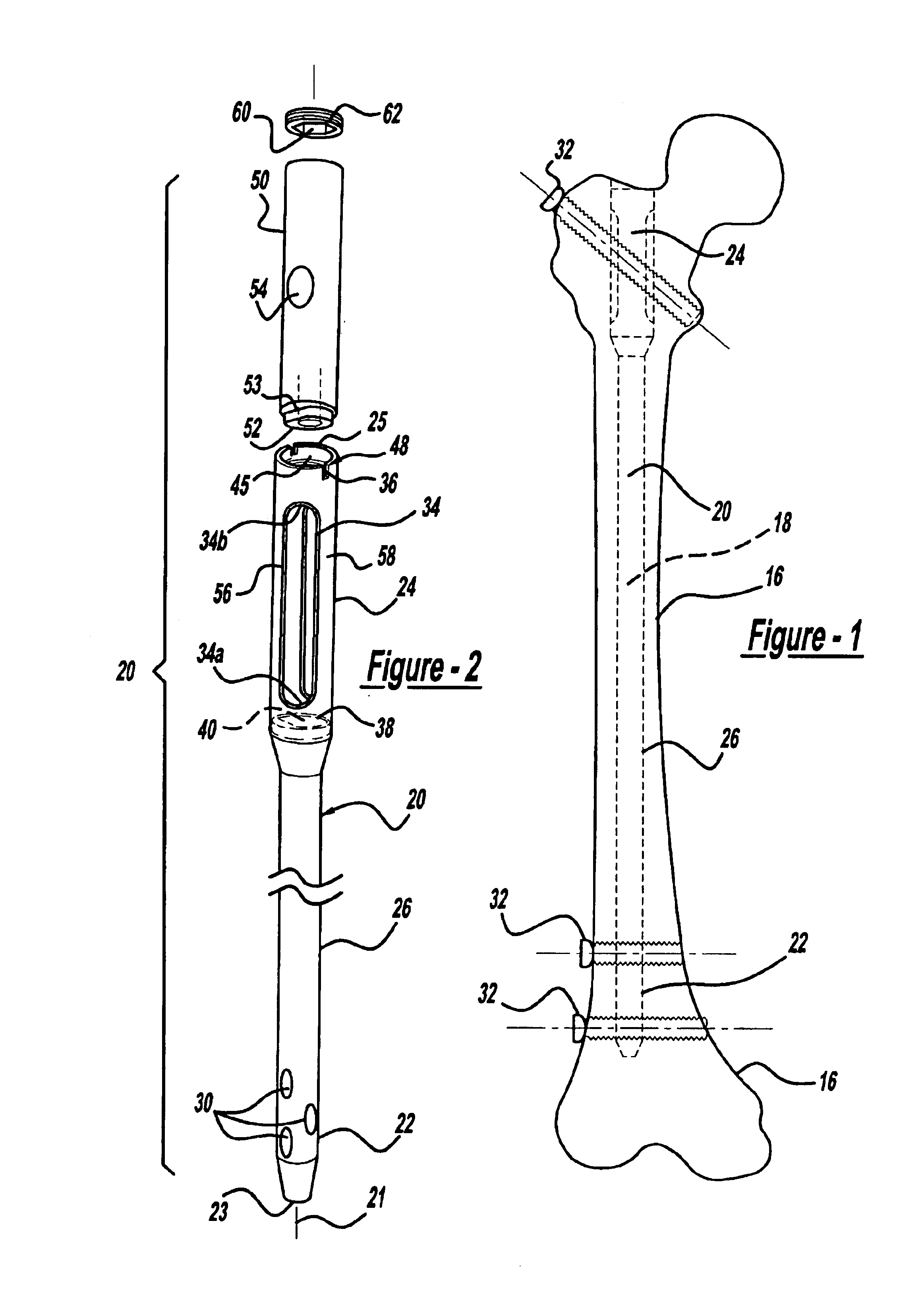
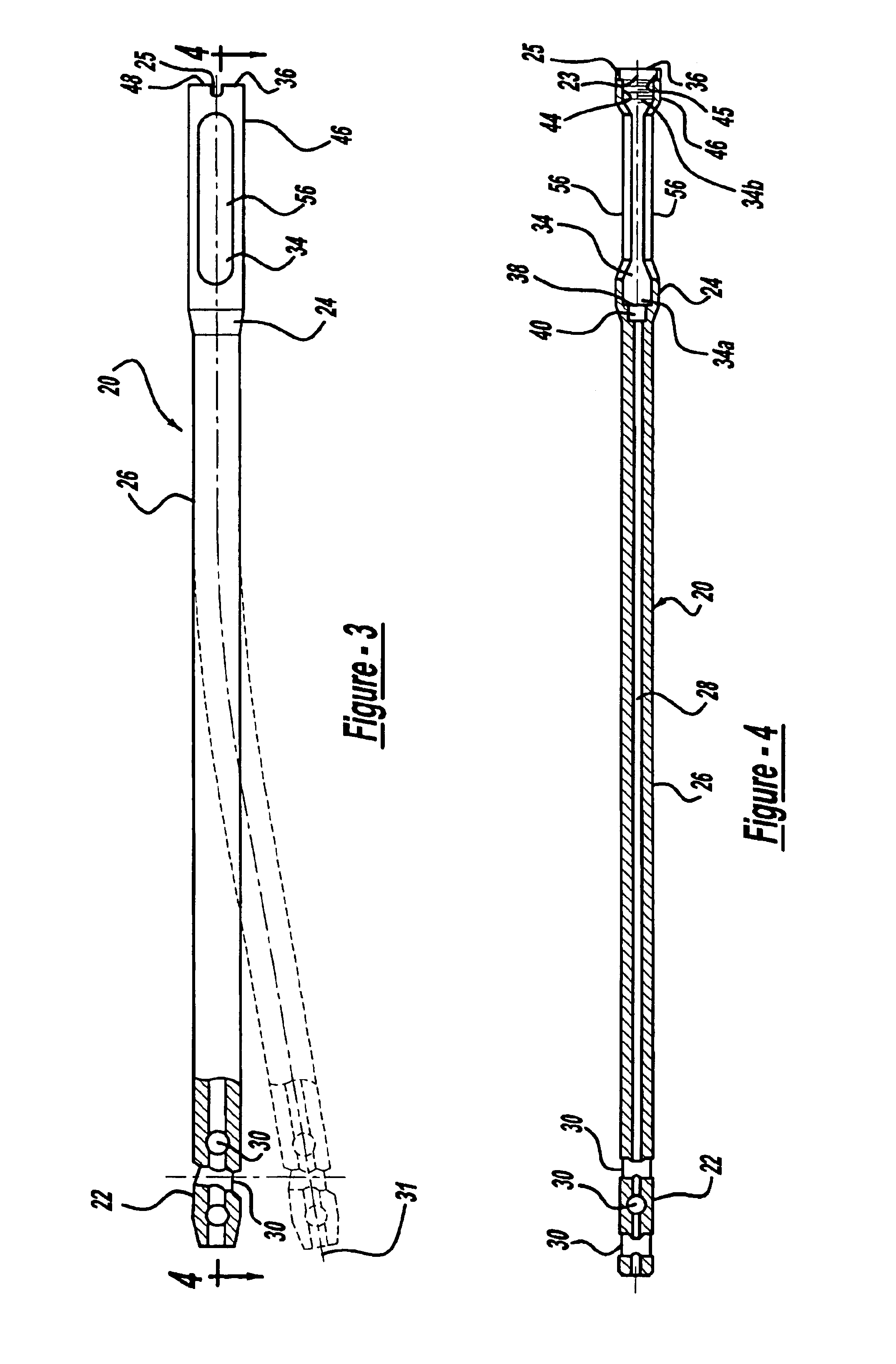
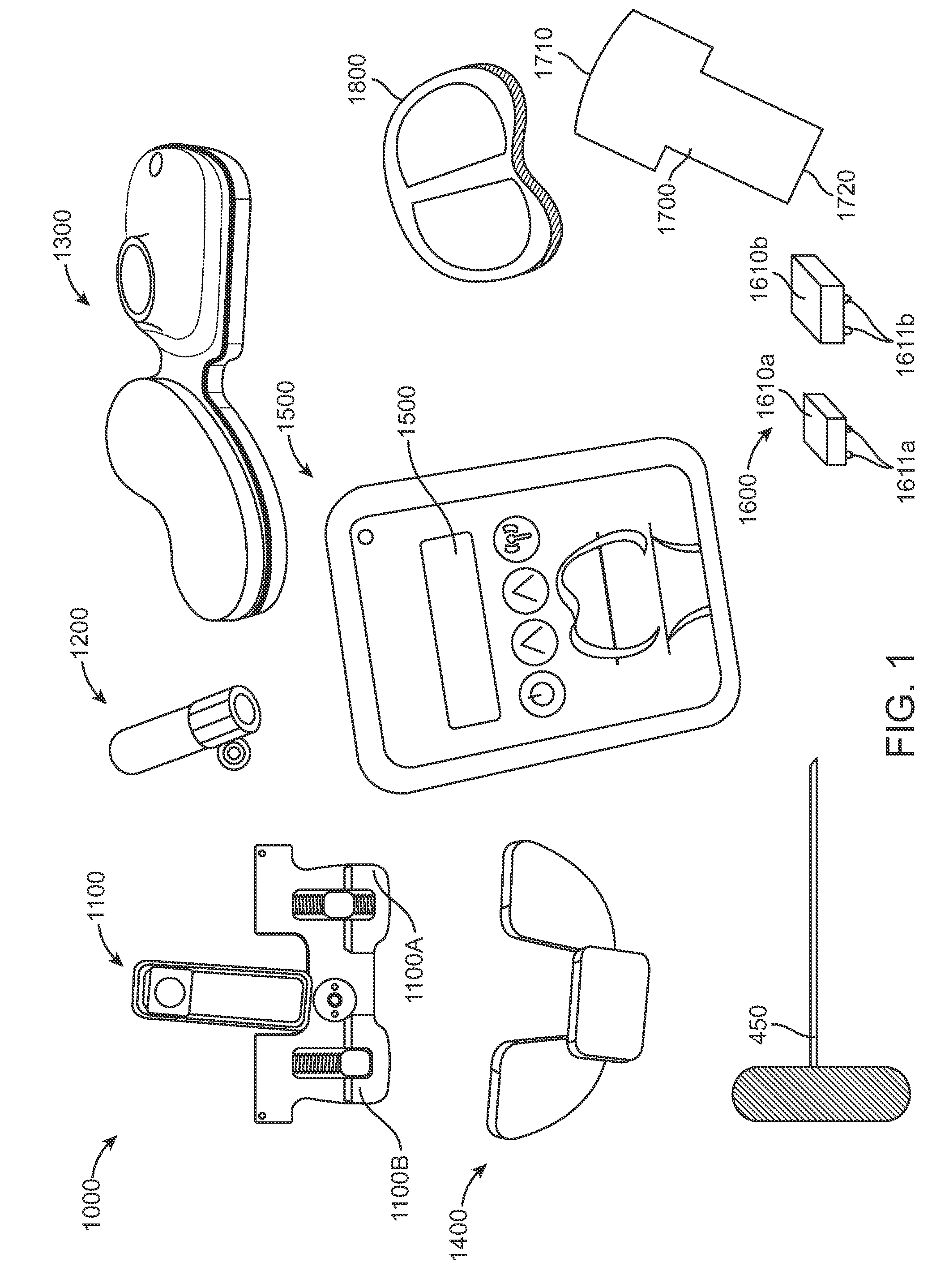
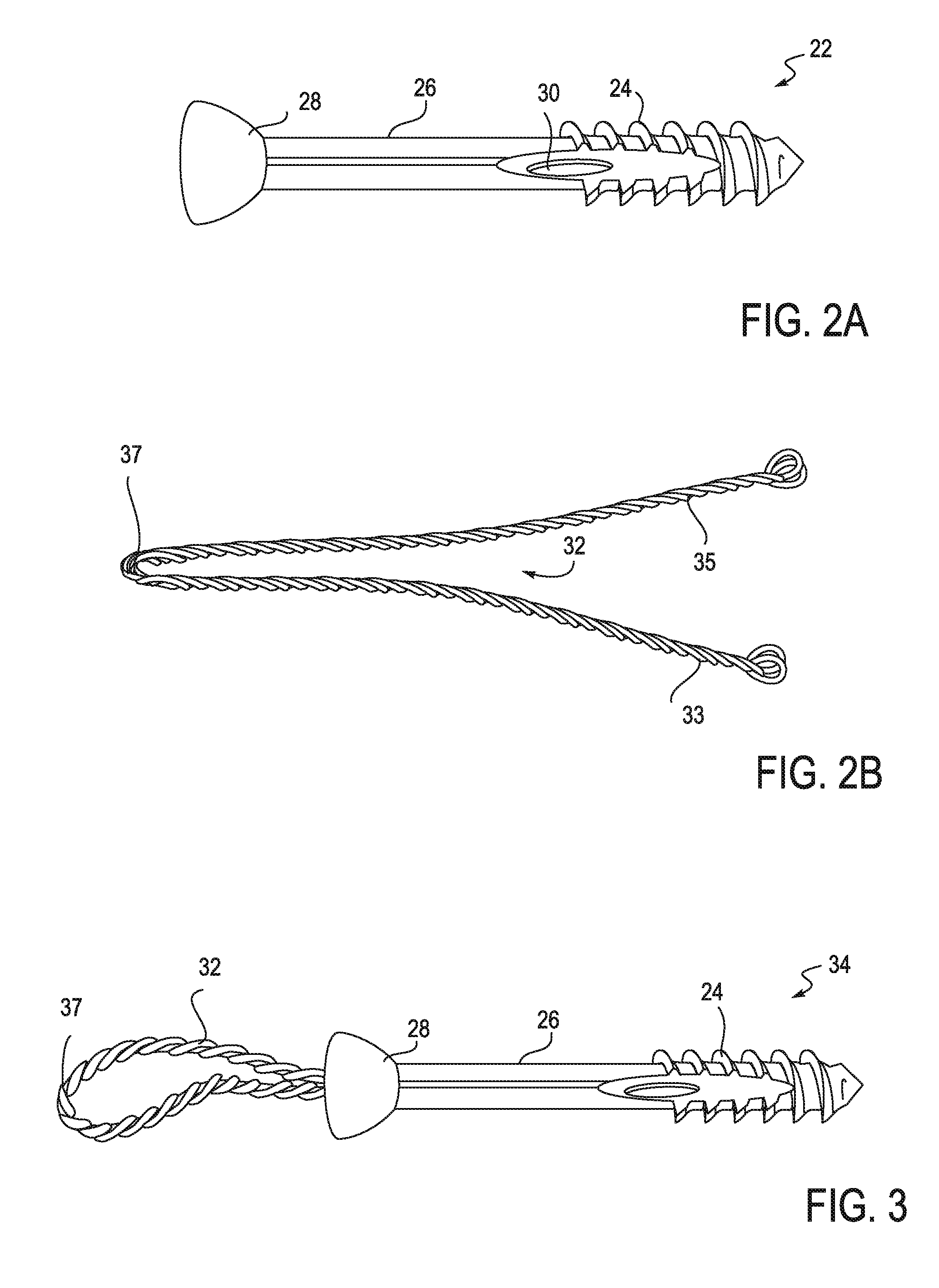
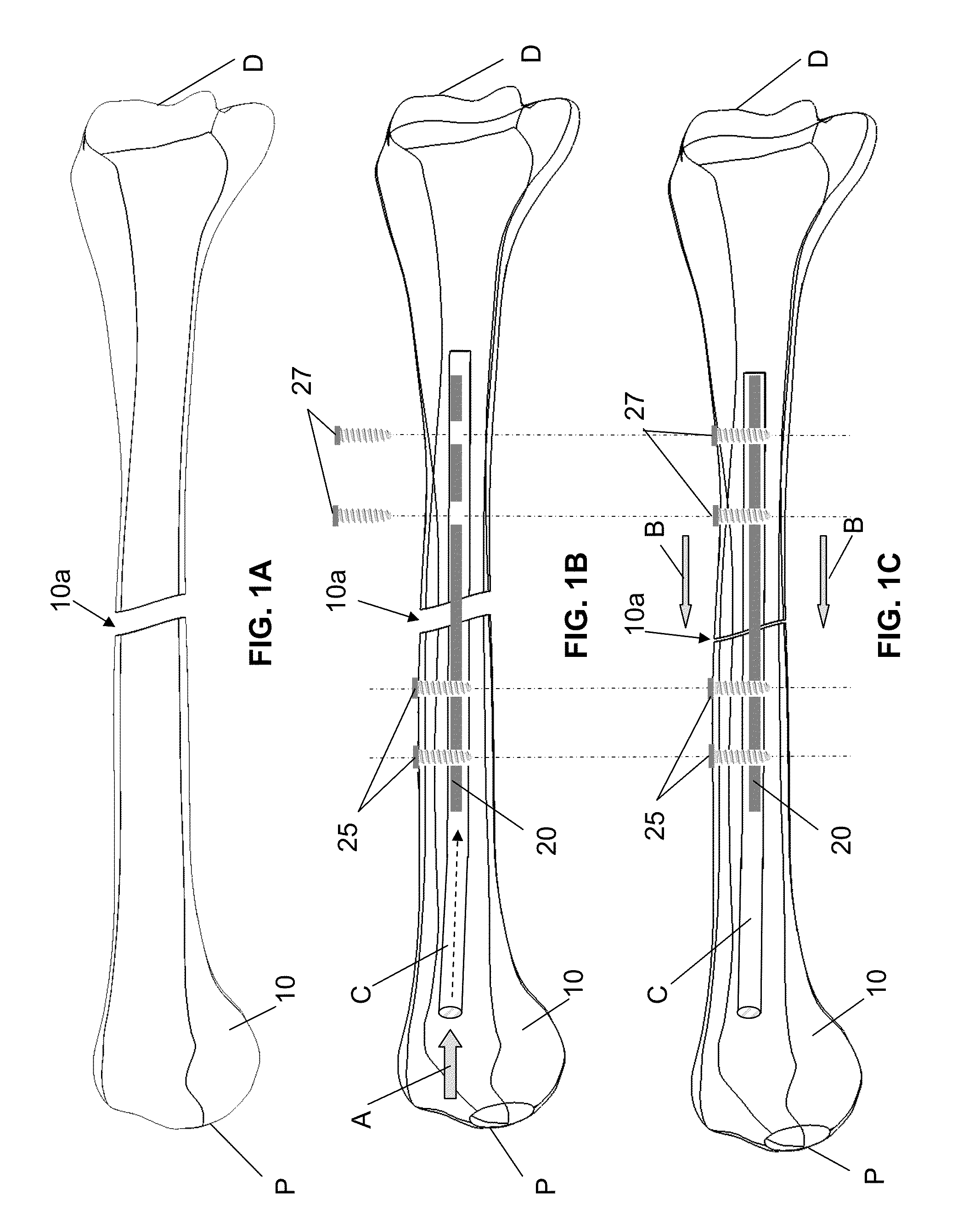
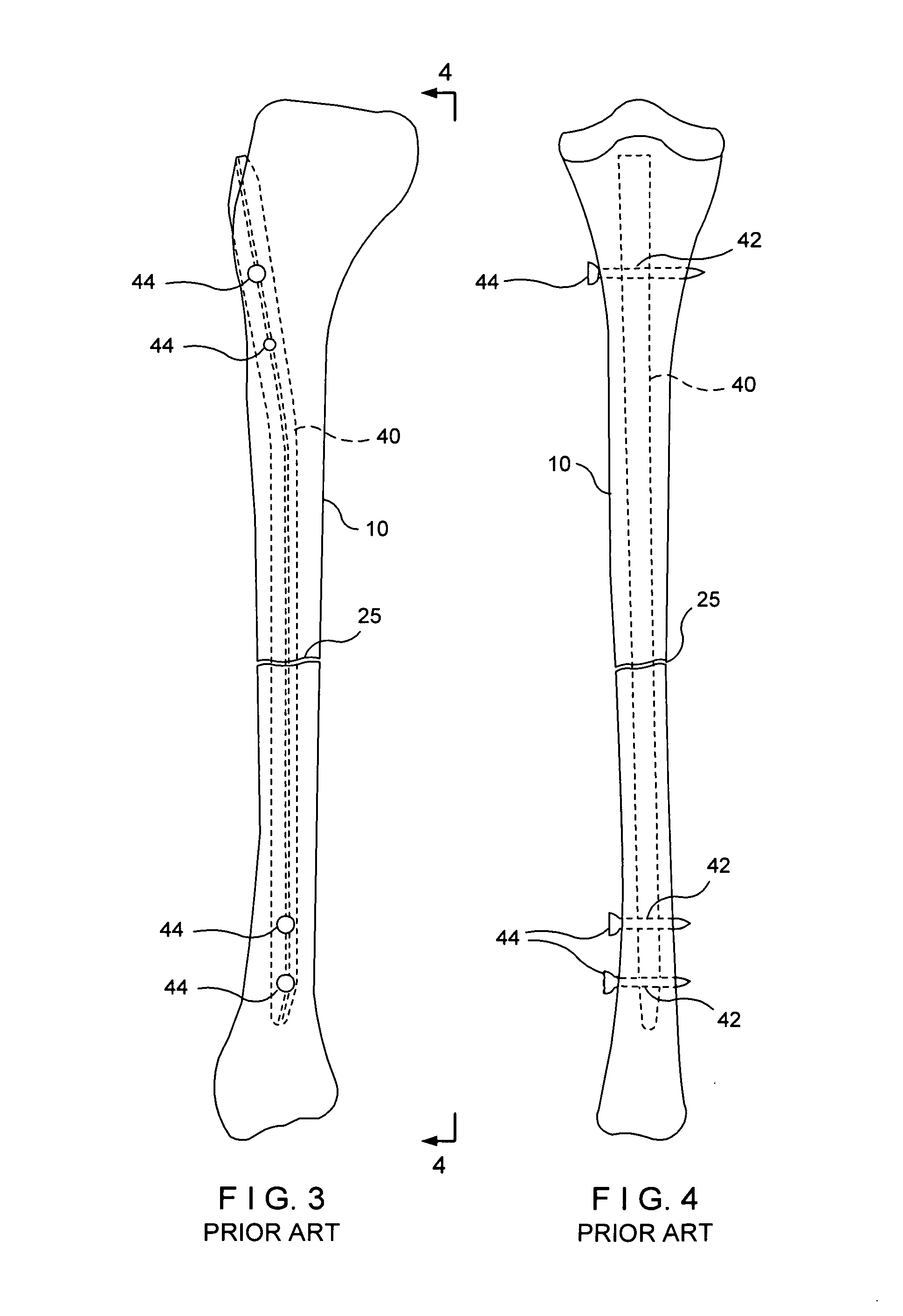
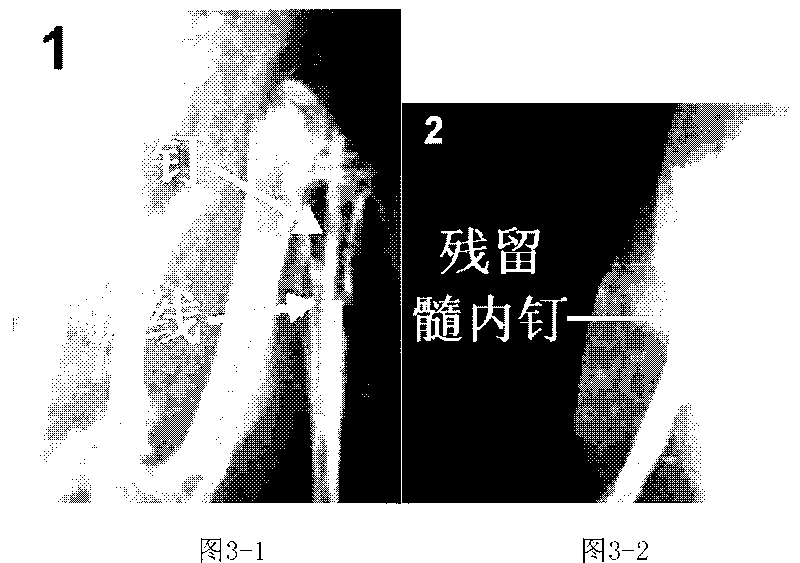
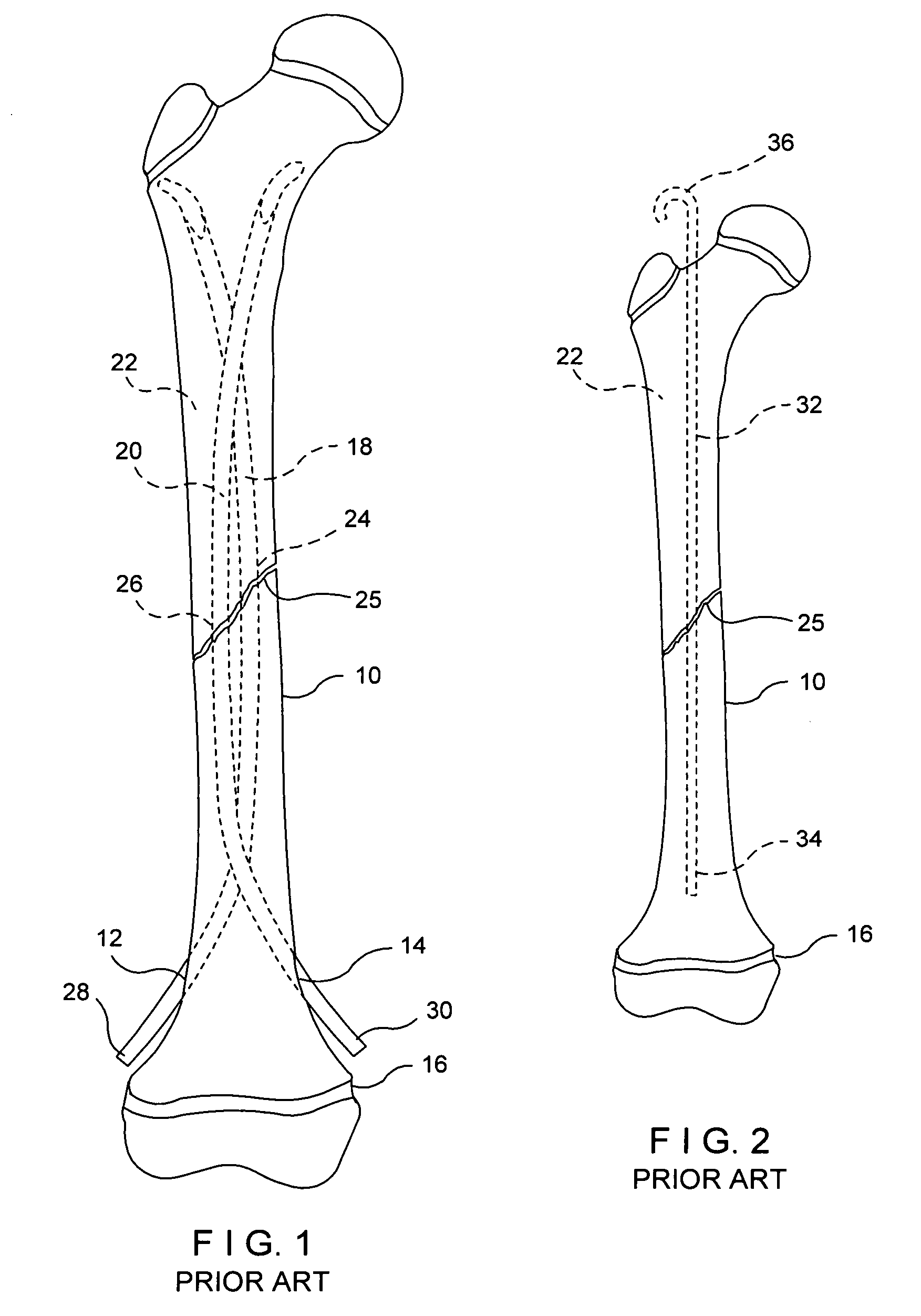
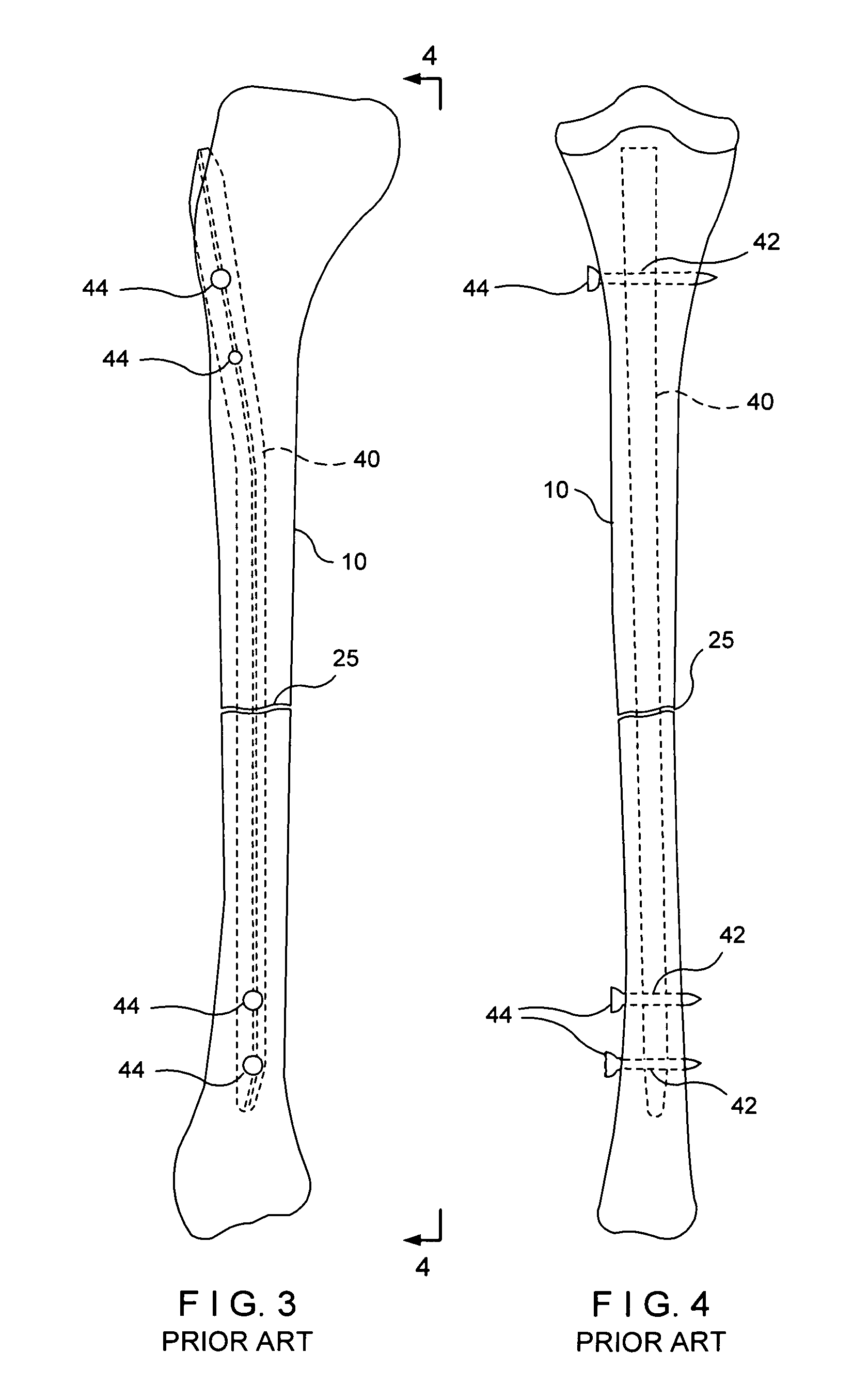
An intramedullary rod, also known as an intramedullary nail (IM nail) or inter-locking nail or Küntscher nail (without proximal or distal fixation), is a metal rod forced into the medullary cavity of a bone. IM nails have long been used to treat fractures of long bones of the body. Gerhard Küntscher is credited with the first use of this device in 1939, during World War II, for soldiers with fractures of the femur. Prior to that, treatment of such fractures was limited to traction or plaster, both of which required long periods of inactivity. IM nails resulted in earlier return to activity for the soldiers, sometimes even within a span of a few weeks, since they share the load with the bone, rather than entirely supporting the bone.
Femoral intramedullary rod system
InactiveUS20060122600A1Easy to compressFacilitate distractionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFemoral boneIntramedullary rod
Owner:ORTHODYNE
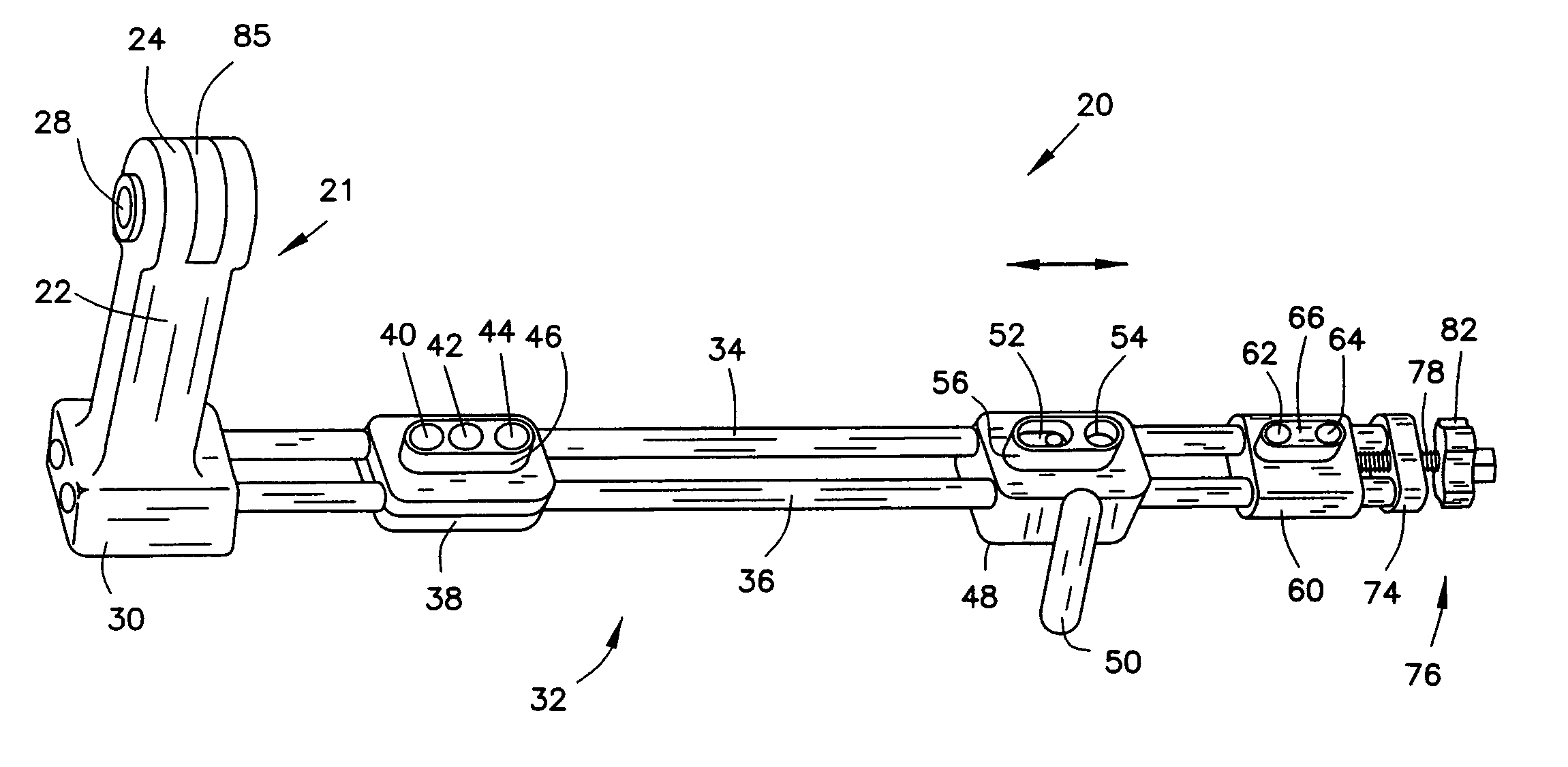
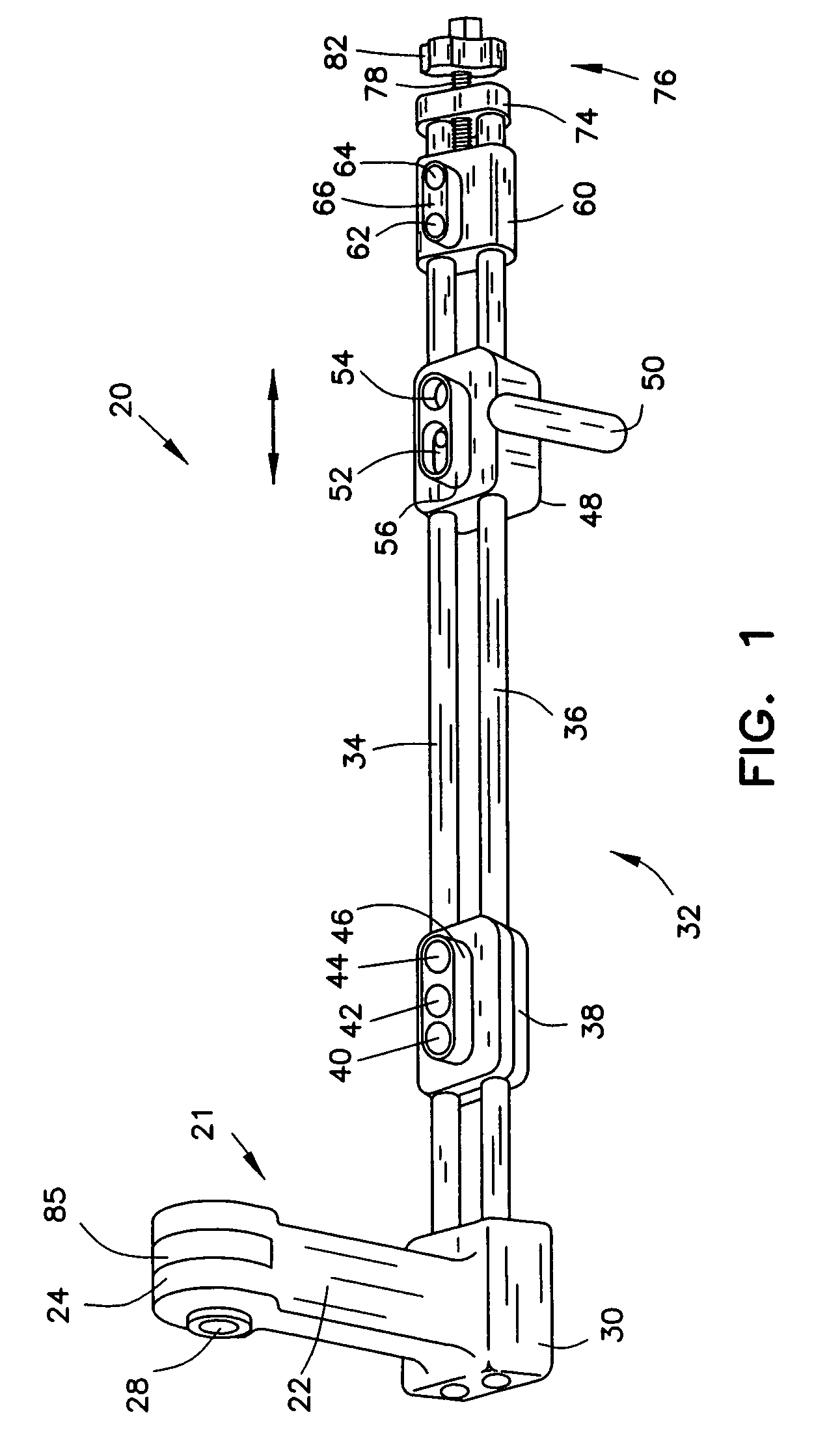
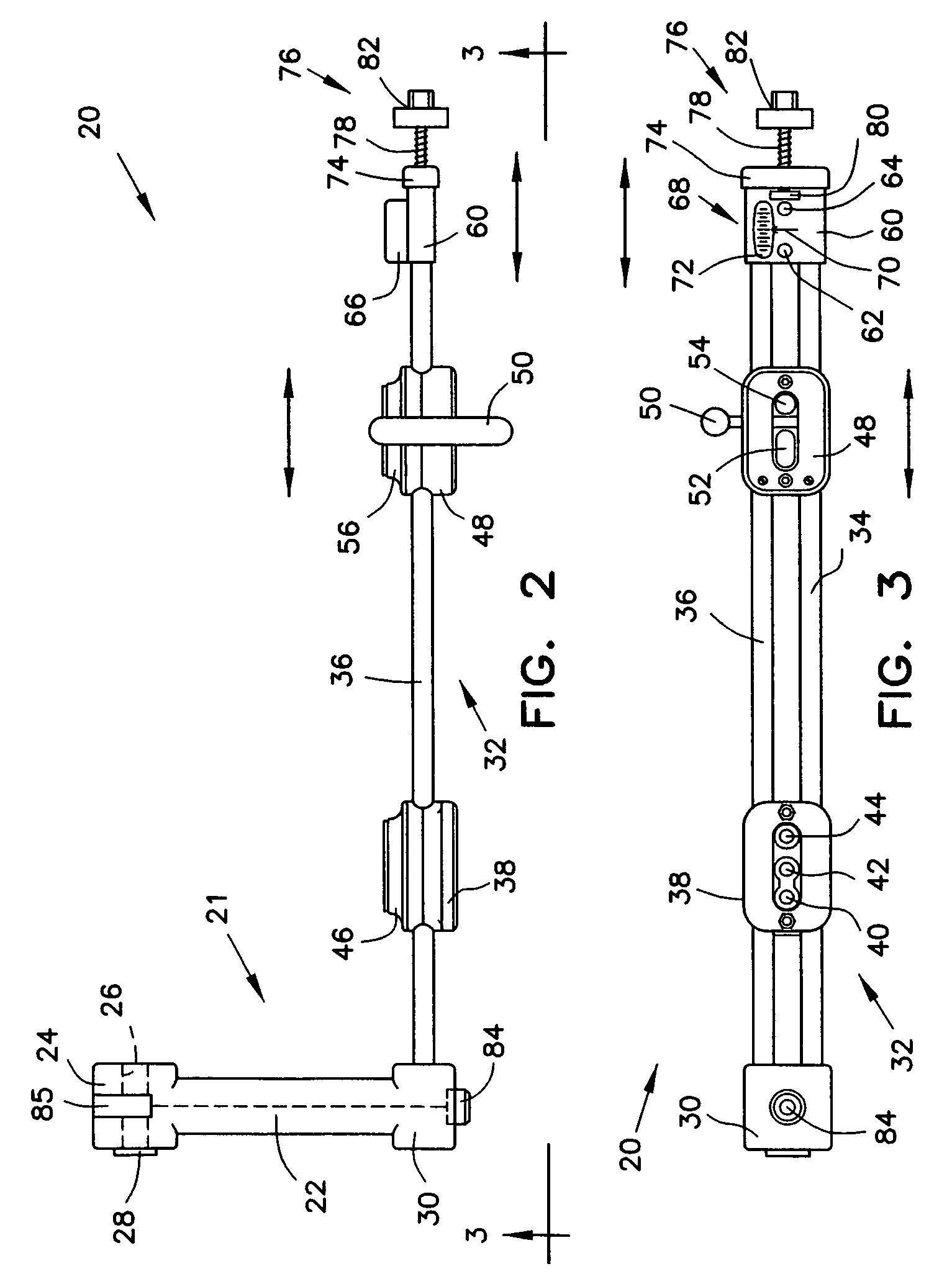
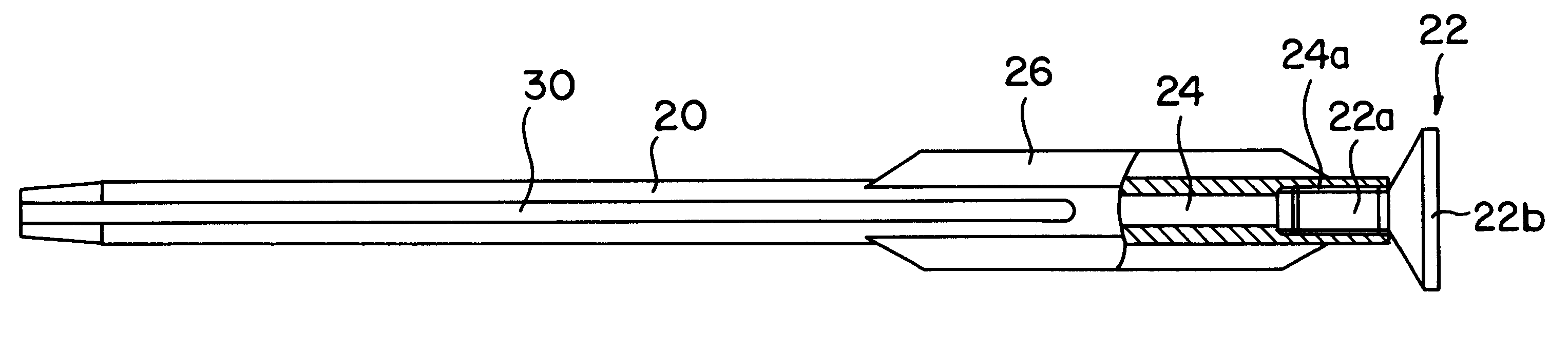
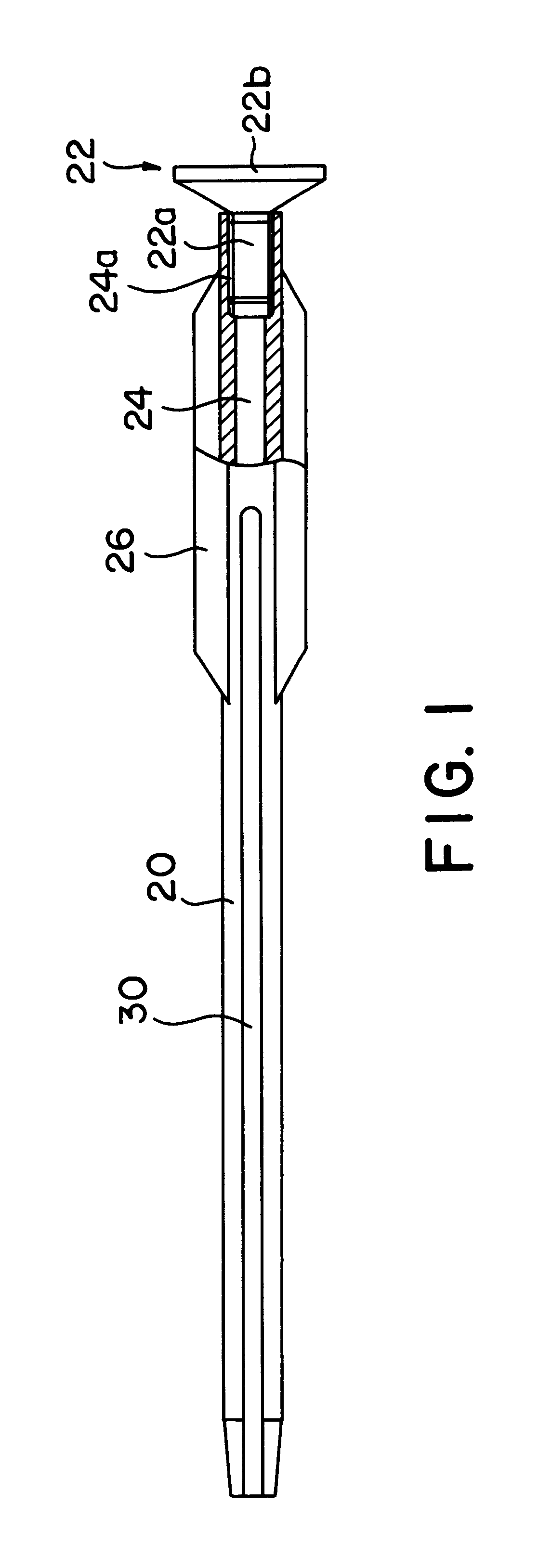
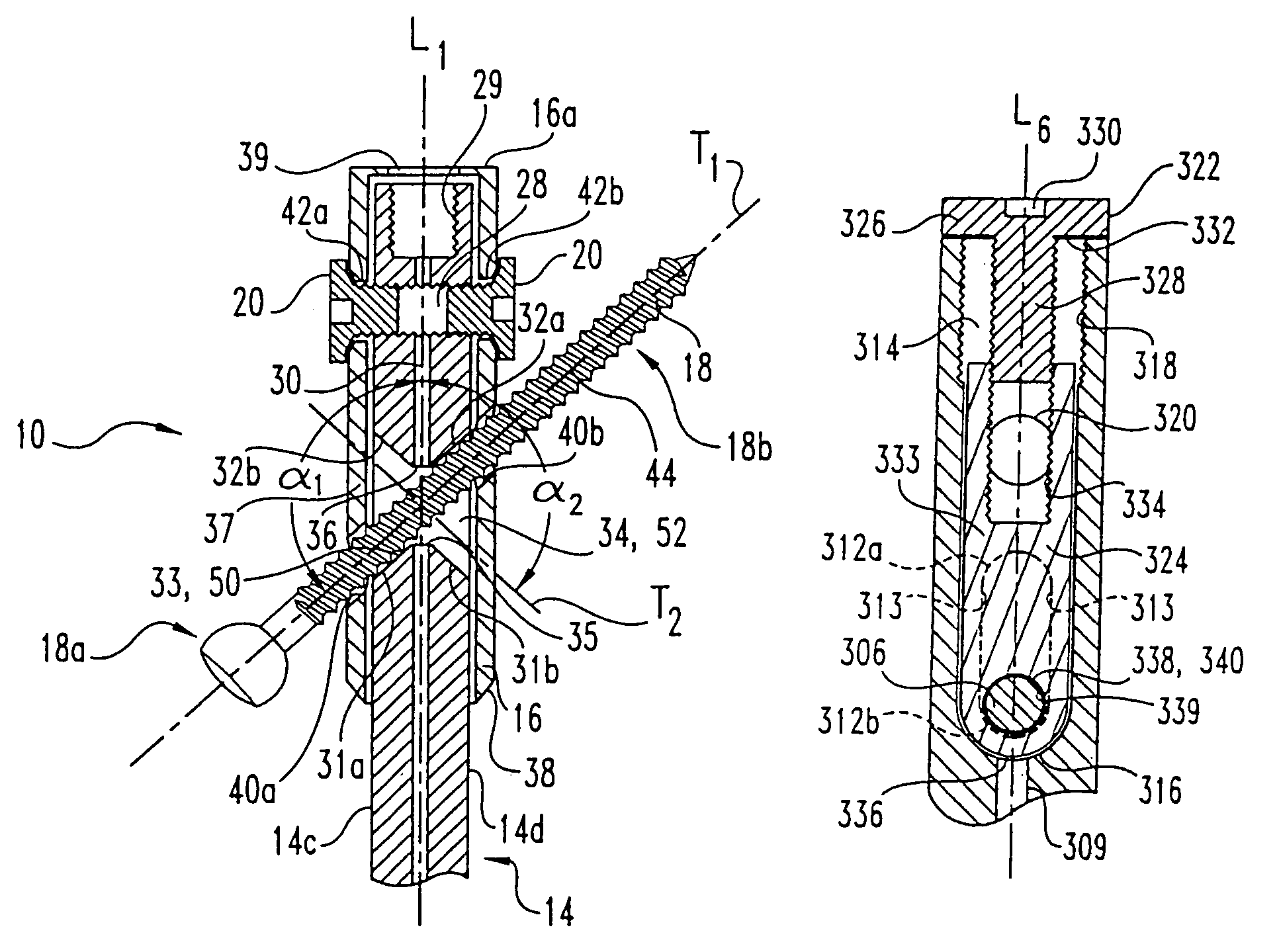
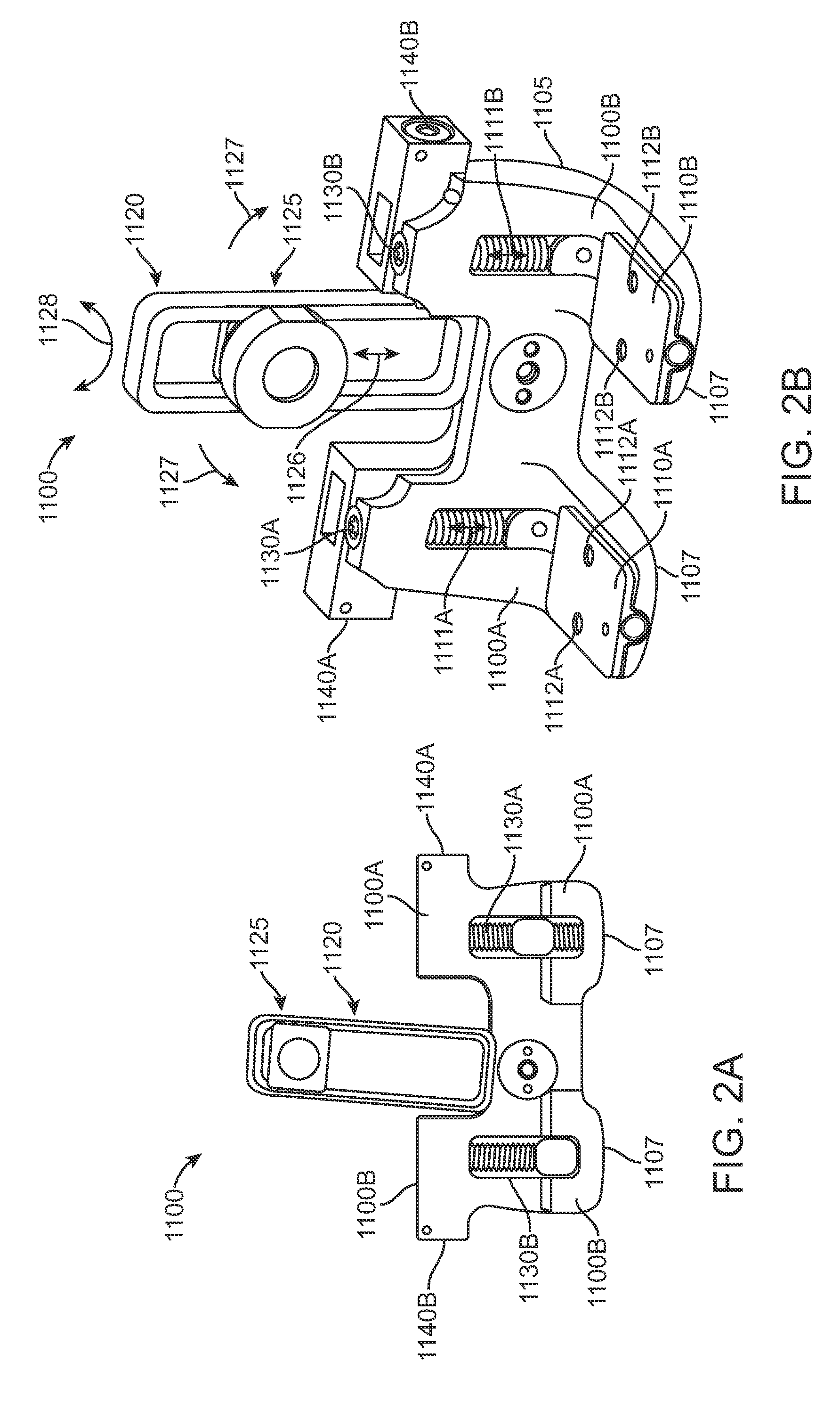
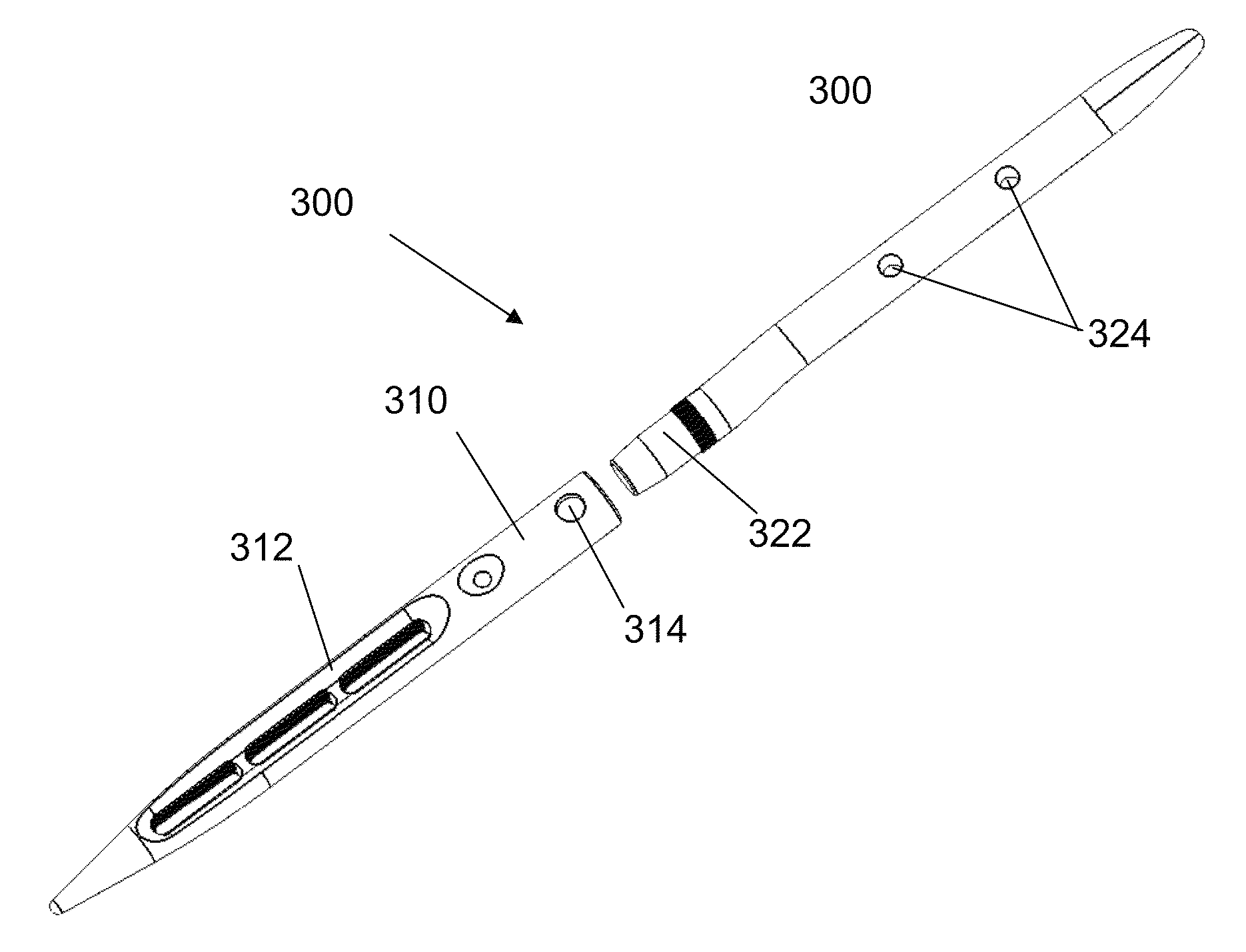
Bone fastener targeting and compression/distraction device for an intramedullary nail and method of use
An intramedullary nail fastener targeting and bone compression / distraction device provides bone fastener alignment and compression or distraction of the bone. The intramedullary nail fastener targeting and bone compression / distraction device has a nail carrier portion, a bone fastener alignment and drill jig portion, and a compression / distraction mechanism. Various sizes of intramedullary nails are retained by the device while alignment carriages provides for proper drilling of the bone and placement of bone fasteners such as screws. The compression / distraction mechanism provides measured compression or distraction of the bone prior to final bone fastener placement.
Owner:BIOMET CV
Intramedullary nail
An intramedullary nail in which a plurality of fins (26) which protrude radially are formed on the outer circumference of the nail, providing firm internal fixation which makes the nail easy to operate.
Owner:FUJIMORI JUHRO +2
Femoral intramedullary rod system
InactiveUS7041104B1Convenient treatmentReduce complexityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFemoral boneIntramedullary rod
A femoral intramedullary rod system capable of treating a variety of femoral bone fractures using a uniform intramedullary rod design. The system generally comprising an intramedullary rod defining an opening having an upper surface and a transverse member including a bone engaging portion and a connection portion defining a thru-hole with the nail sized to pass therethrough. A pin is selectively coupled to the transverse member to rigidly assemble the transverse member to the nail when the nail is passed through the thru-hole and the pin is received within the opening.
Owner:ORTHODYNE
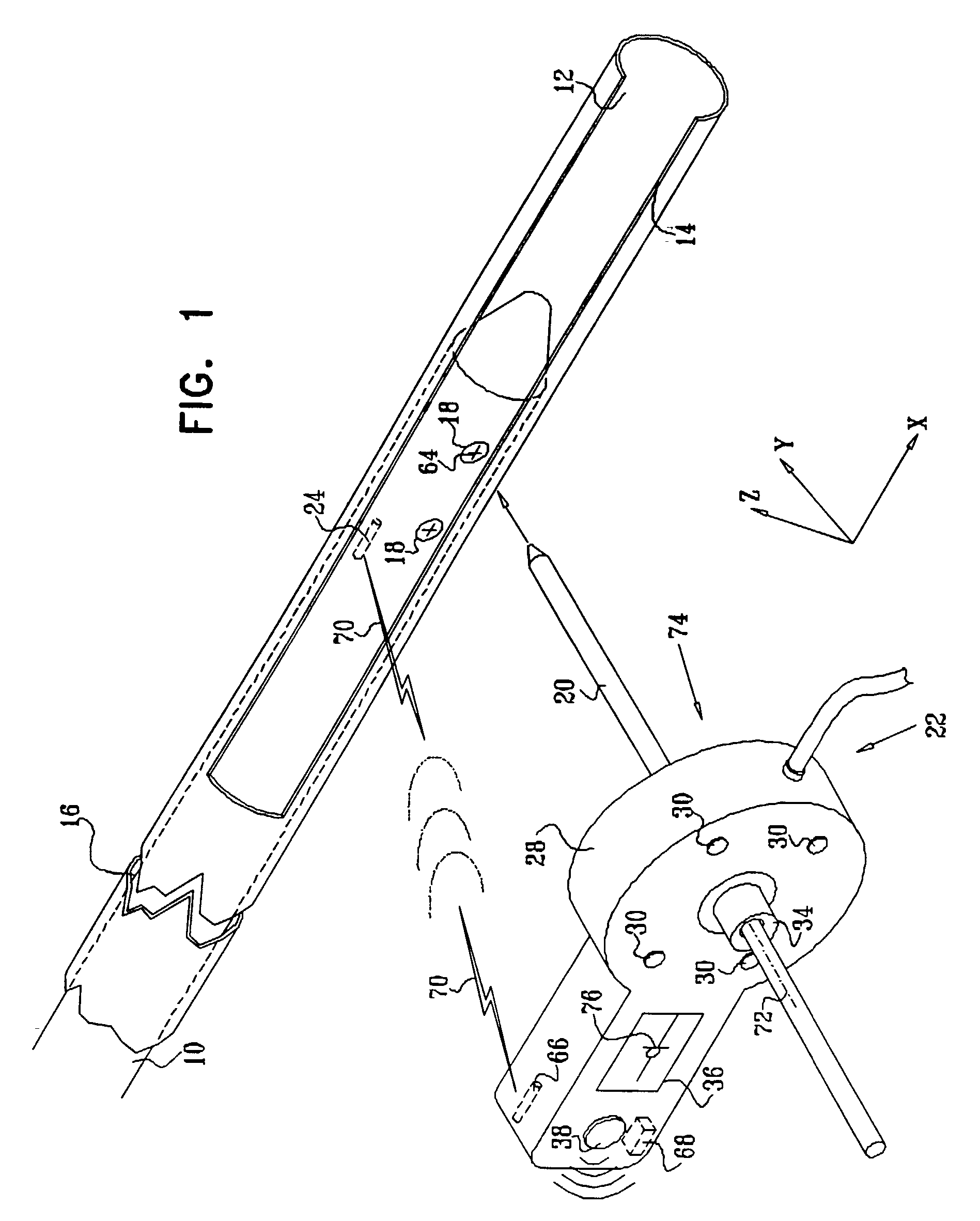
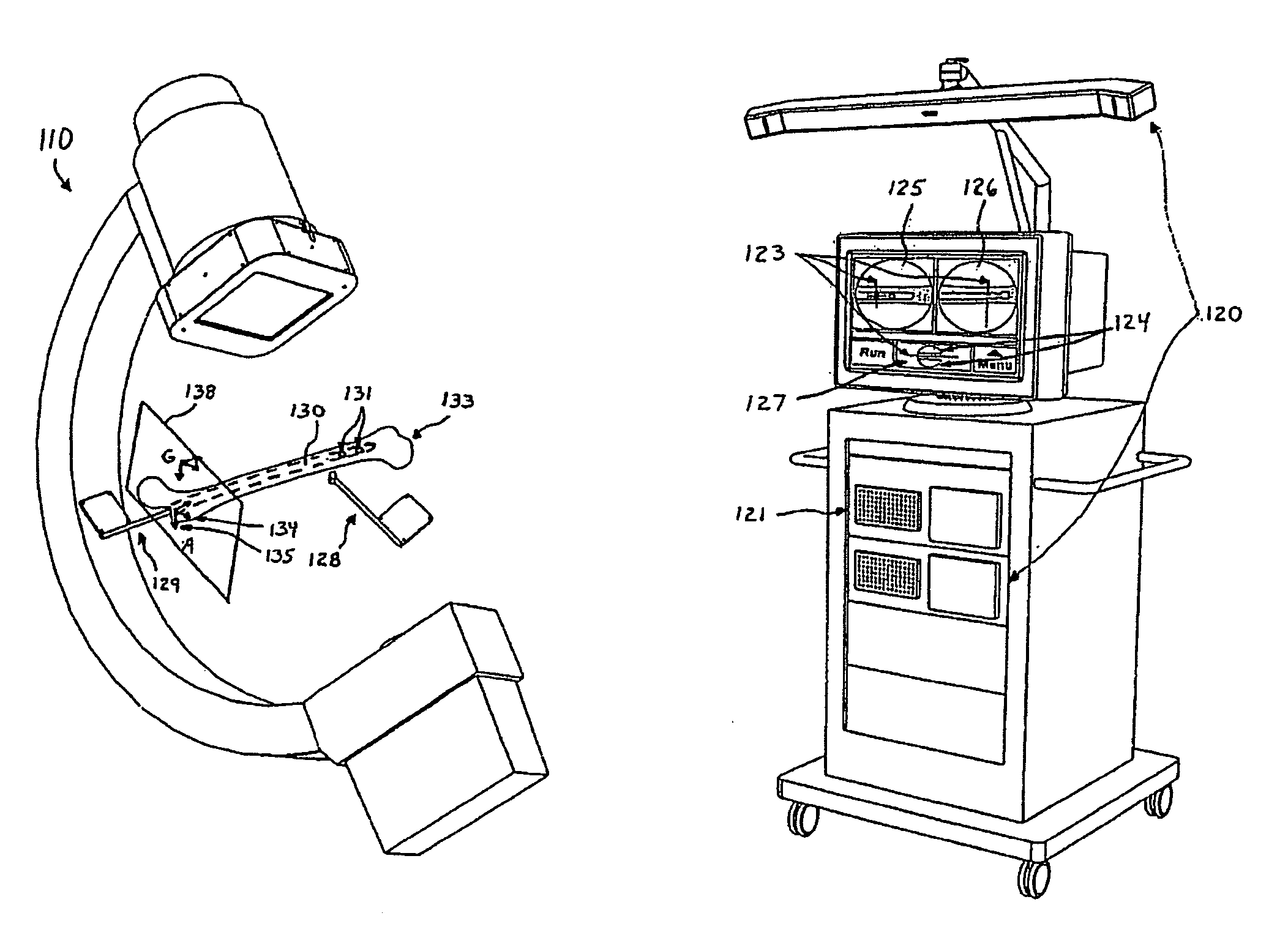
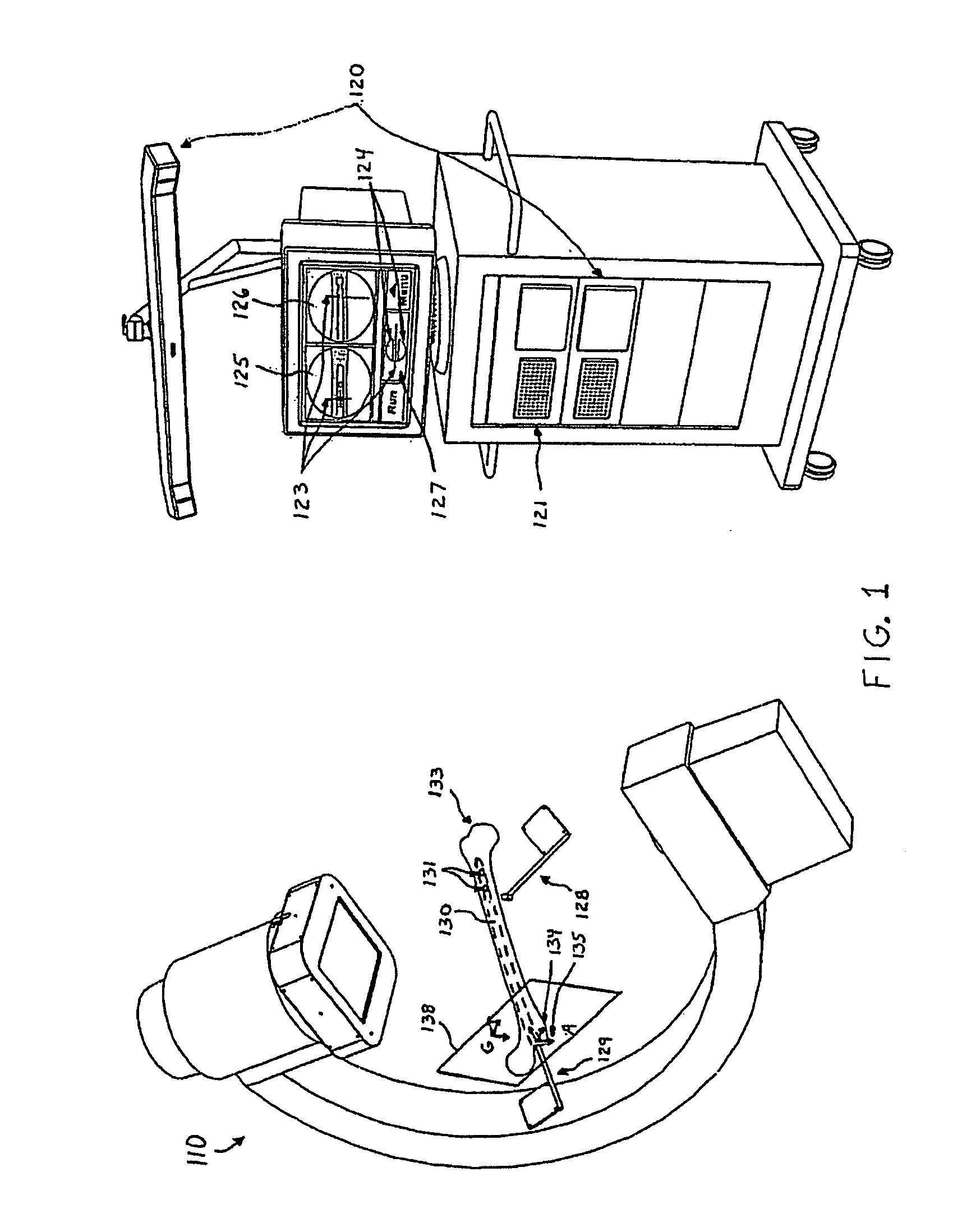
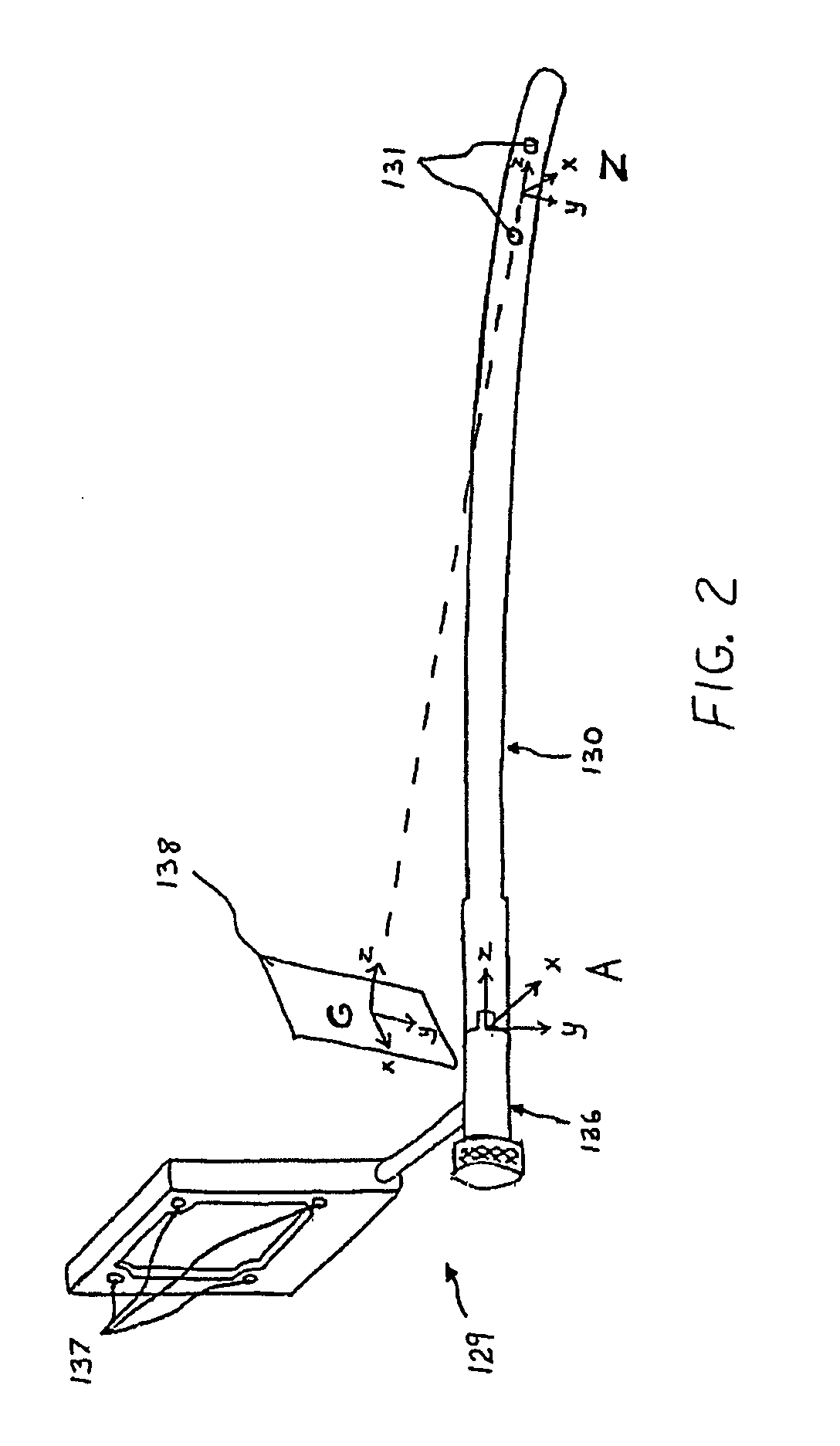
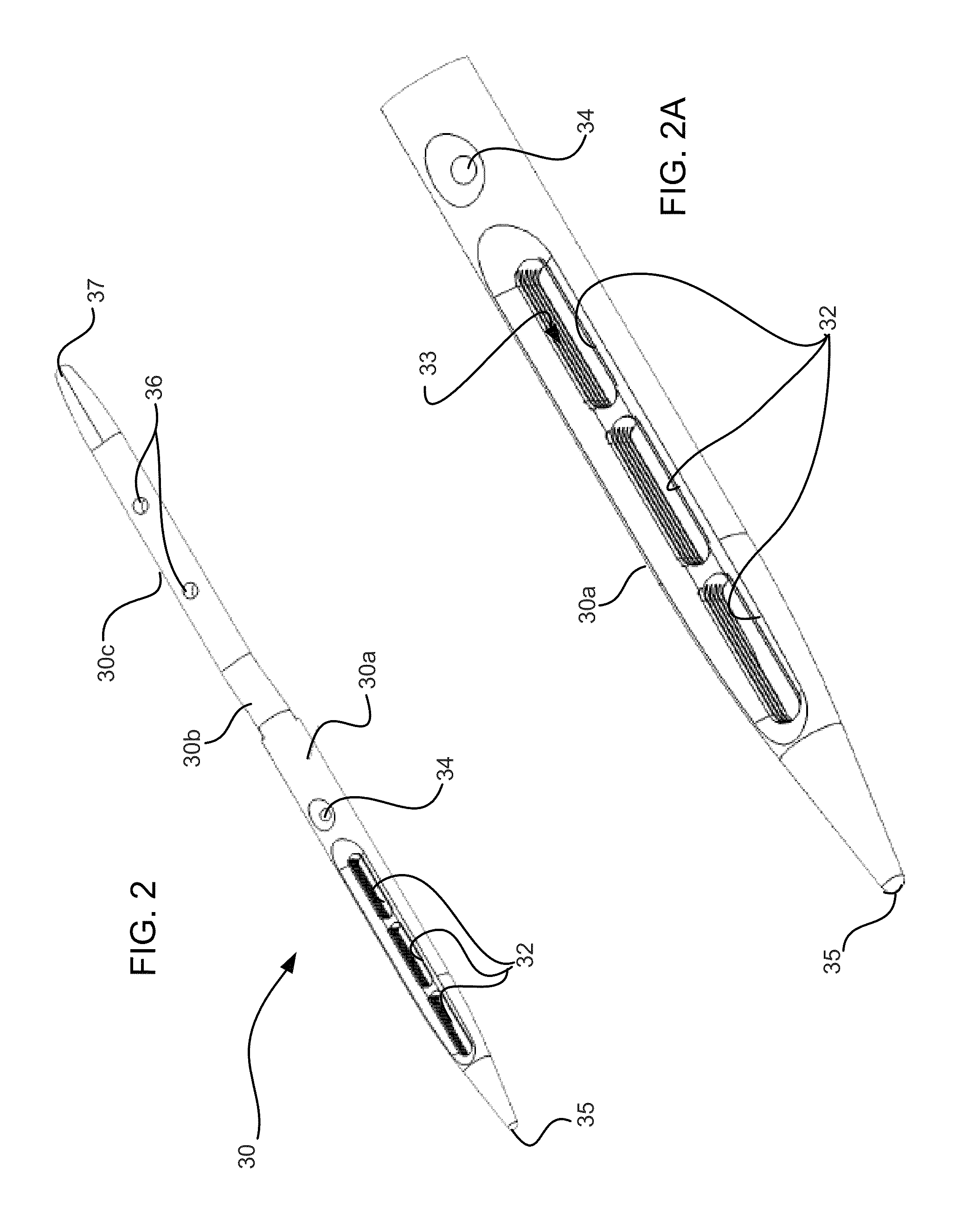
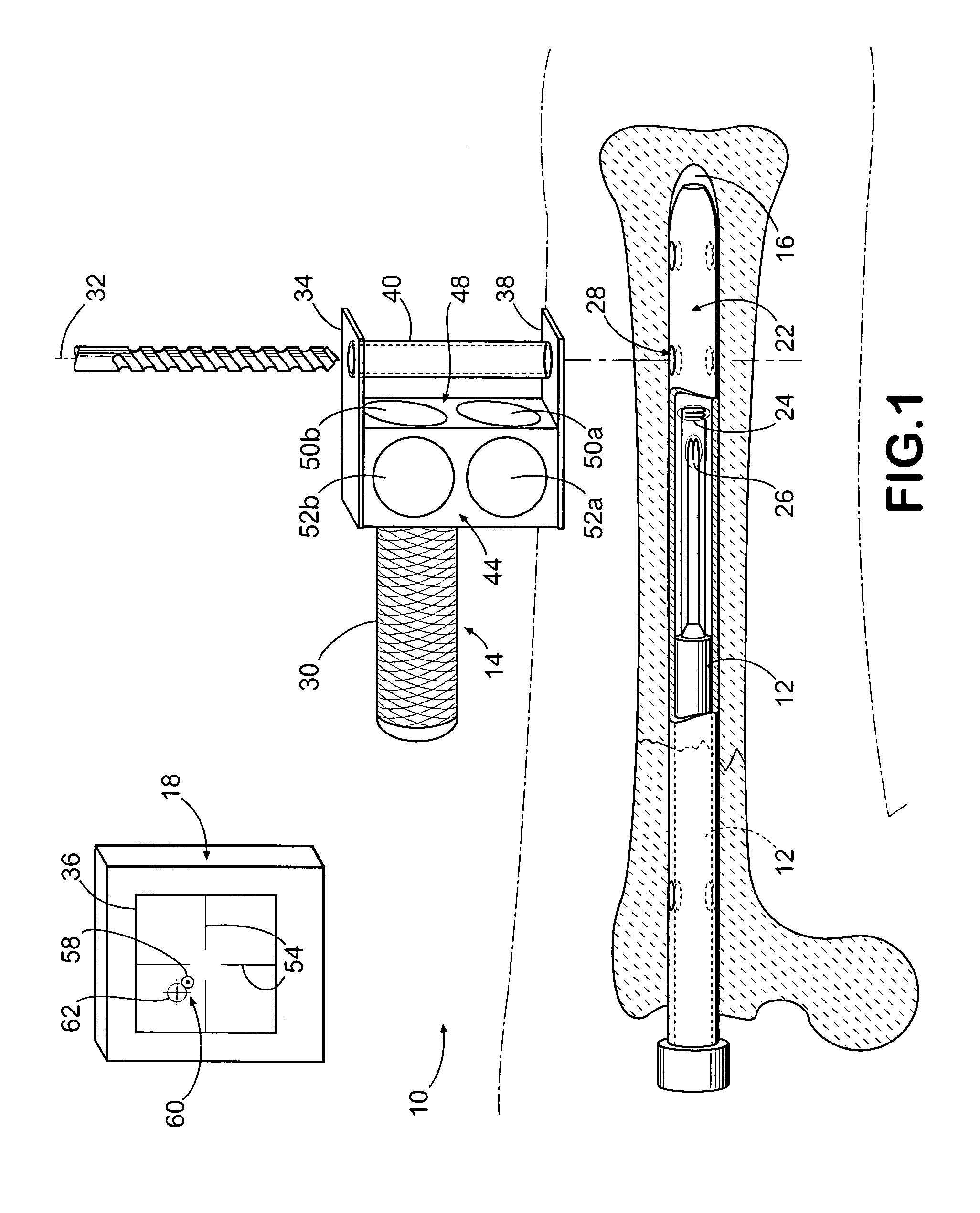
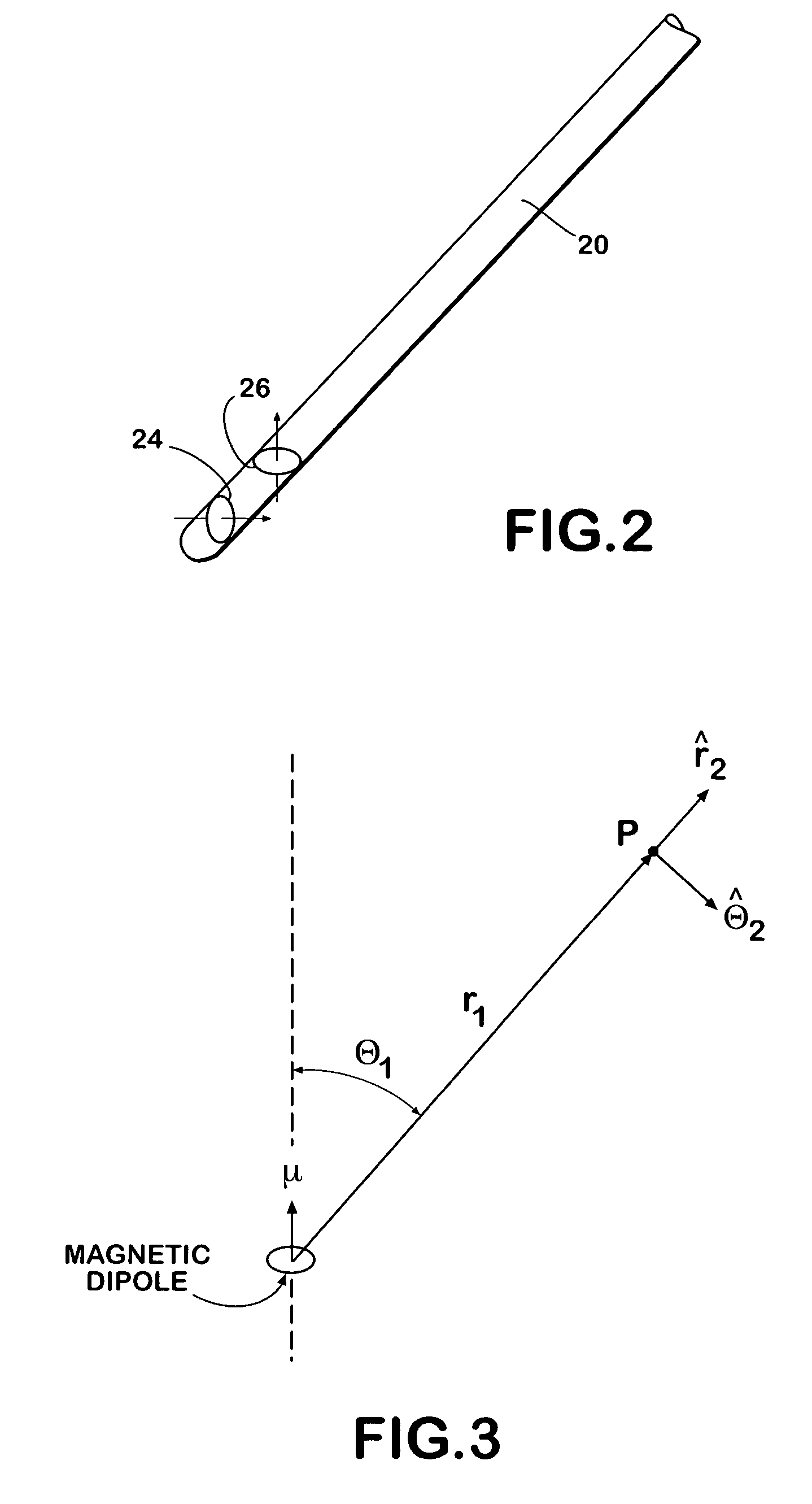
Distal targeting of locking screws in intramedullary nails
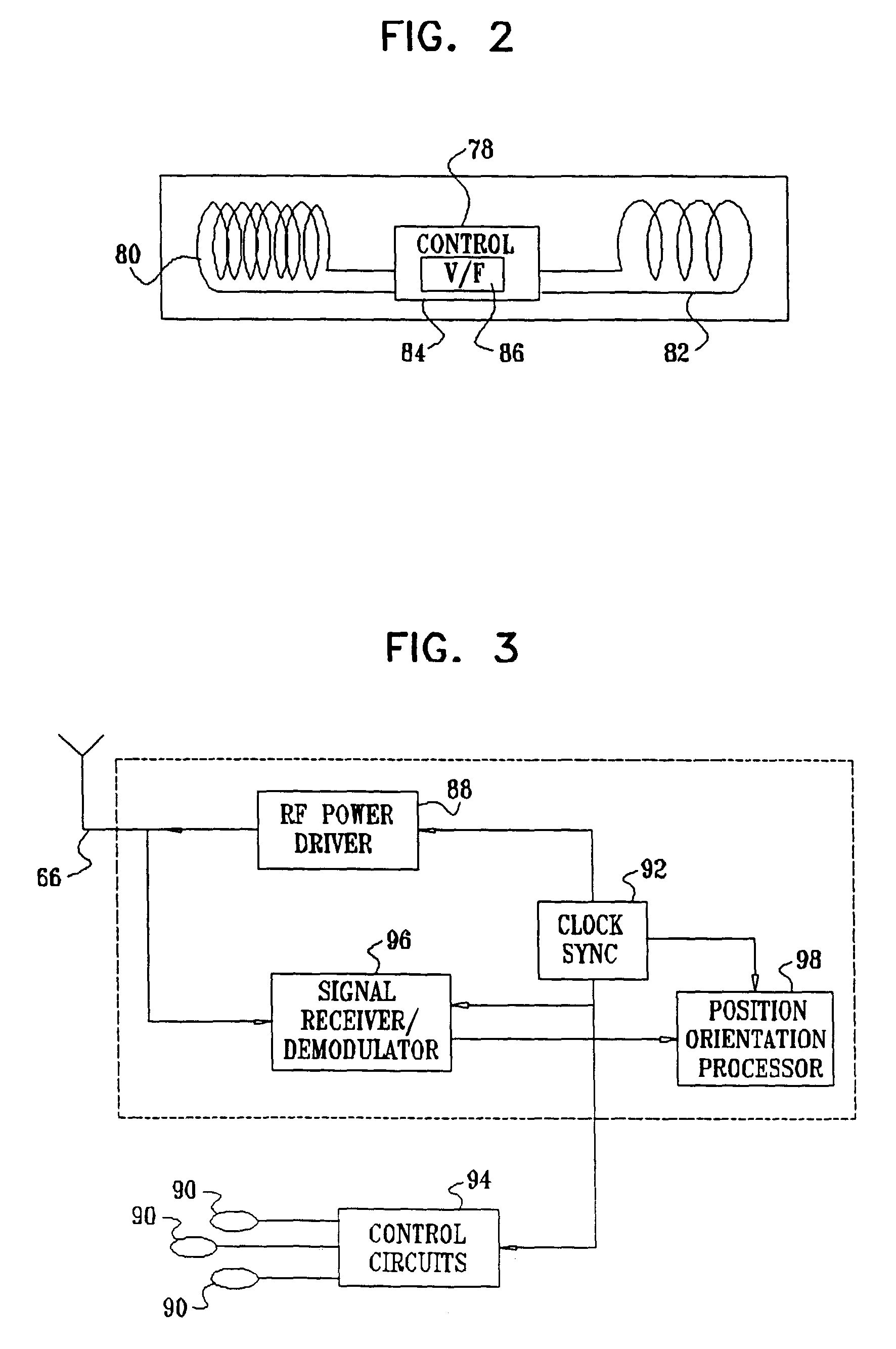
In a distal targeting system a hand-held location pad is integral with a guide section for a drill or similar surgical instrument, and has a plurality of magnetic field generators. A sensor, such as a wireless sensor, having a plurality of field transponders, is disposed in an orthopedic appliance, such as an intramedullary nail. The sensor is capable of detecting and discriminating the strength and direction of the different fields generated by the field generators. Control circuitry, preferably located in the location pad is responsive to a signal of the sensor, and determines the displacement and relative directions of an axis of the guide section, and a bore in the orthopedic appliance. A screen display and optional speaker in the location pad provide an operator-perceptible indication that enables the operator to adjust the position of the guide section so as to align its position and direction with the bore.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Instruments for minimally invasive surgery total knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20060241634A1Improve easeImprove accuracyDiagnosticsJoint implantsLess invasive surgeryIntramedullary rod
An anti-backout stylus comprising a stylus and a locking stylus holder. The locking stylus holder engages the stylus at a series of discrete positions during insertion of the stylus into the holder. The locking stylus holder prevents inadvertent backing out of the stylus by preventing the stylus from being withdrawn to a previous one of the discrete positions. The locking stylus holder can preferably be selectively disengaged from the stylus to allow for selective withdrawal of the stylus. Each engagement of one of the discrete positions by the locking stylus holder preferably indicates a femoral size. The discrete positions are preferably defmed by detents formed on the stylus and a stop member on the locking stylus holder. The locking stylus holder can be provided on an anterior rough cut guide, with the anterior rough cut guide preferably mountable on an intramedullary rod.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Bone screw system and method for the fixation of bone fractures
InactiveUS20100312245A1Facilitate stabilization and fixationReduce MechanismsSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
An bone screw with comprising a sleeve, a shaft reciprocally received within the sleeve, and a compressive device is disclosed. The bone screw may be extended, placing a fracture in tension, after insertion into a bone and then retained in place by a setscrew that is retained by an intramedullary rod. The shaft of the bone screw may have a blade thread that allows the bone screw to be installed into a bone by tapping the bone screw with a hammer.
Owner:ORTHOIP
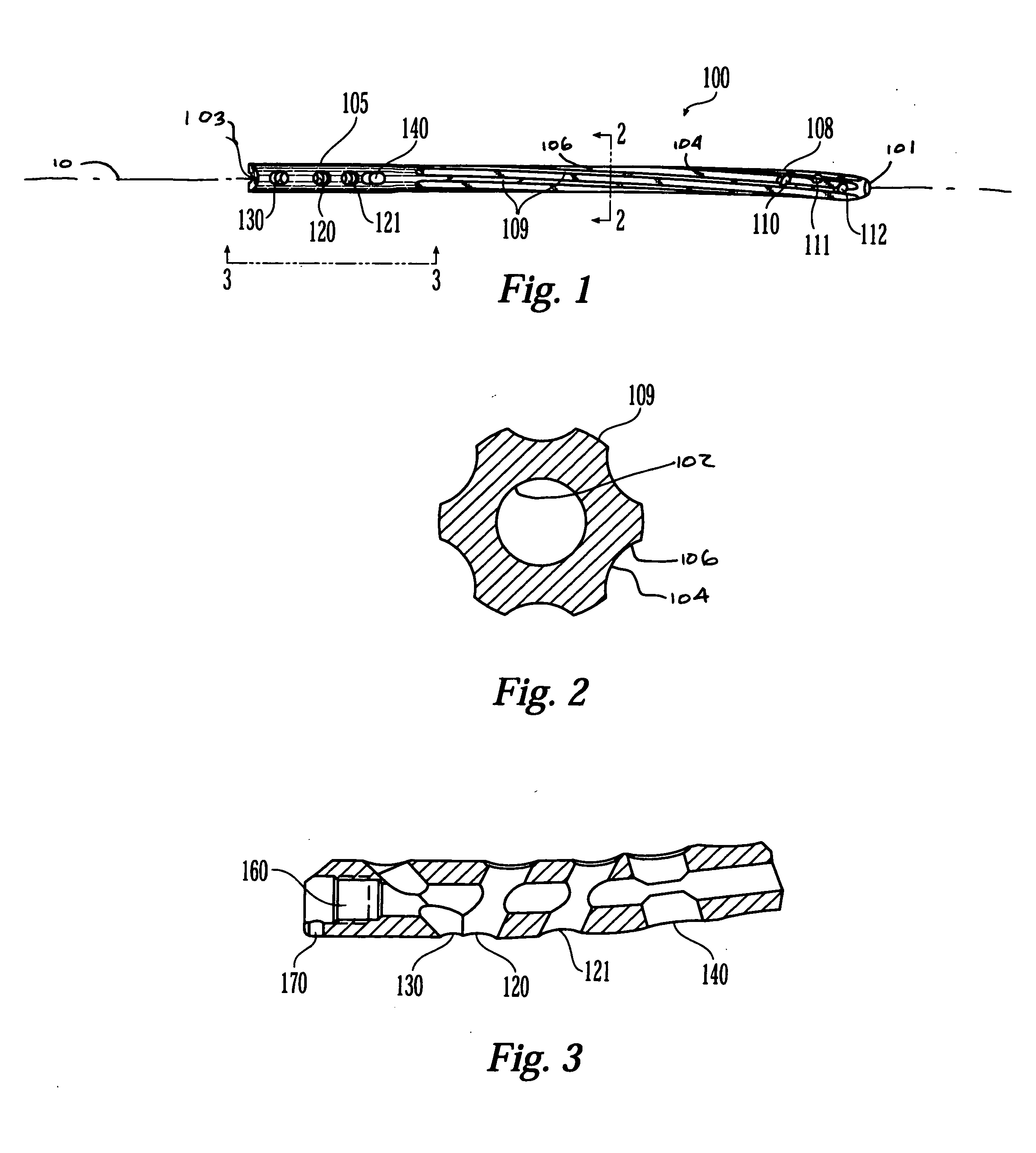
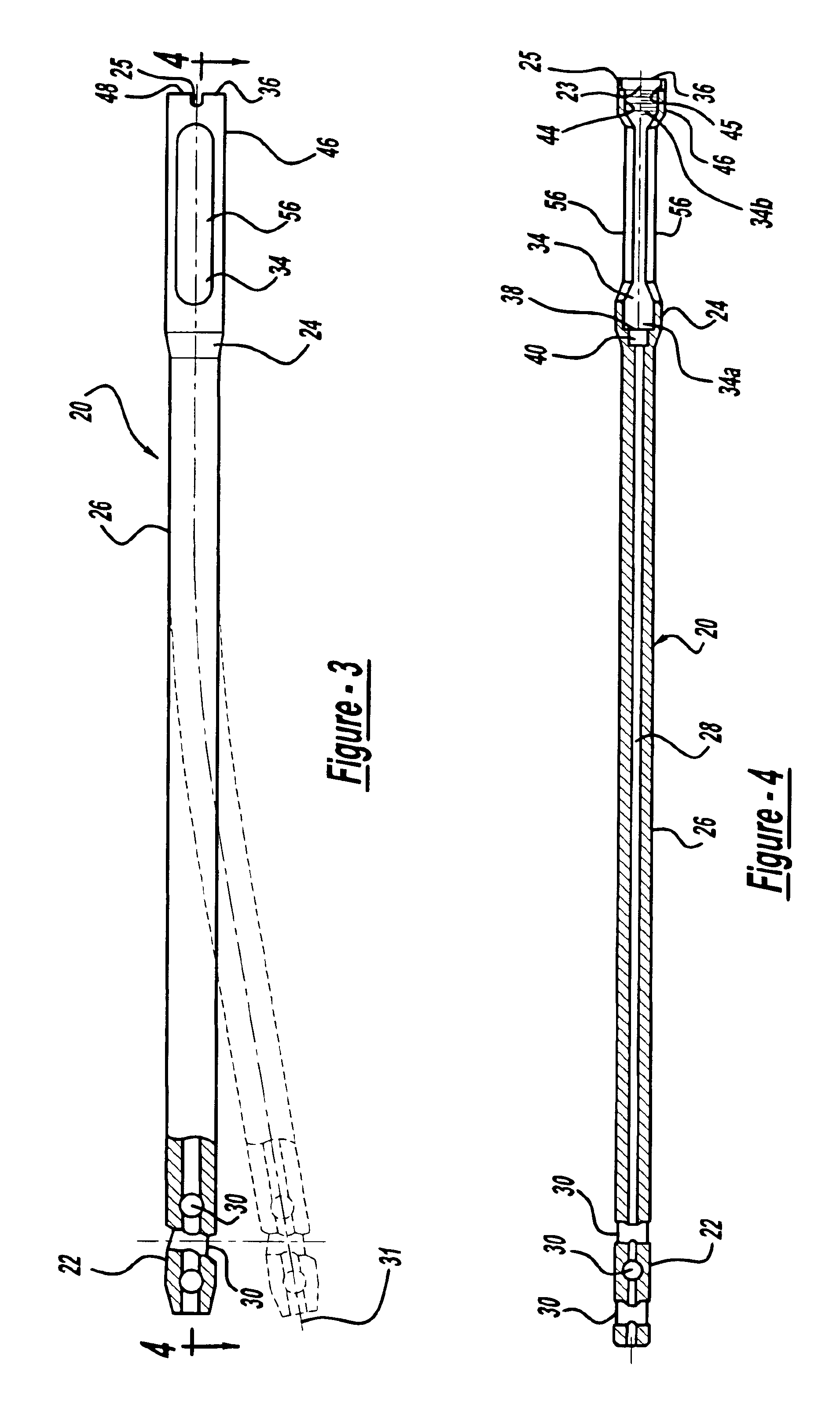
Intramedullary rod with spiraling flutes
ActiveUS20050277936A1Reduce usageLower potentialInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFluteIntramedullary rod
This invention relates generally to devices, systems and methods for the internal fixation of bone fractures, and particularly, to intramedullary fracture fixation devices such as those used in, for example, the treatment of long bone fractures. An IM rod preferably is provided with multiple curved sections in different planes preferably designed to conform with the long bones of a patient, both during insertion and in the rod's final position in the long bone. In addition, the overlap of portions of the curved sections results in a co-planar curvature of portions of the IM rod which assist in the insertion process by guiding the proper rotation of the IM rod as it is inserted into the bone. Spiraling flutes extending down the distal portion of the rod also assist in properly guiding and orienting the rod about its longitudinal axis during insertion such that the appropriate segment of the curved rod conforms with the appropriate portion of the long bone at the appropriate place.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
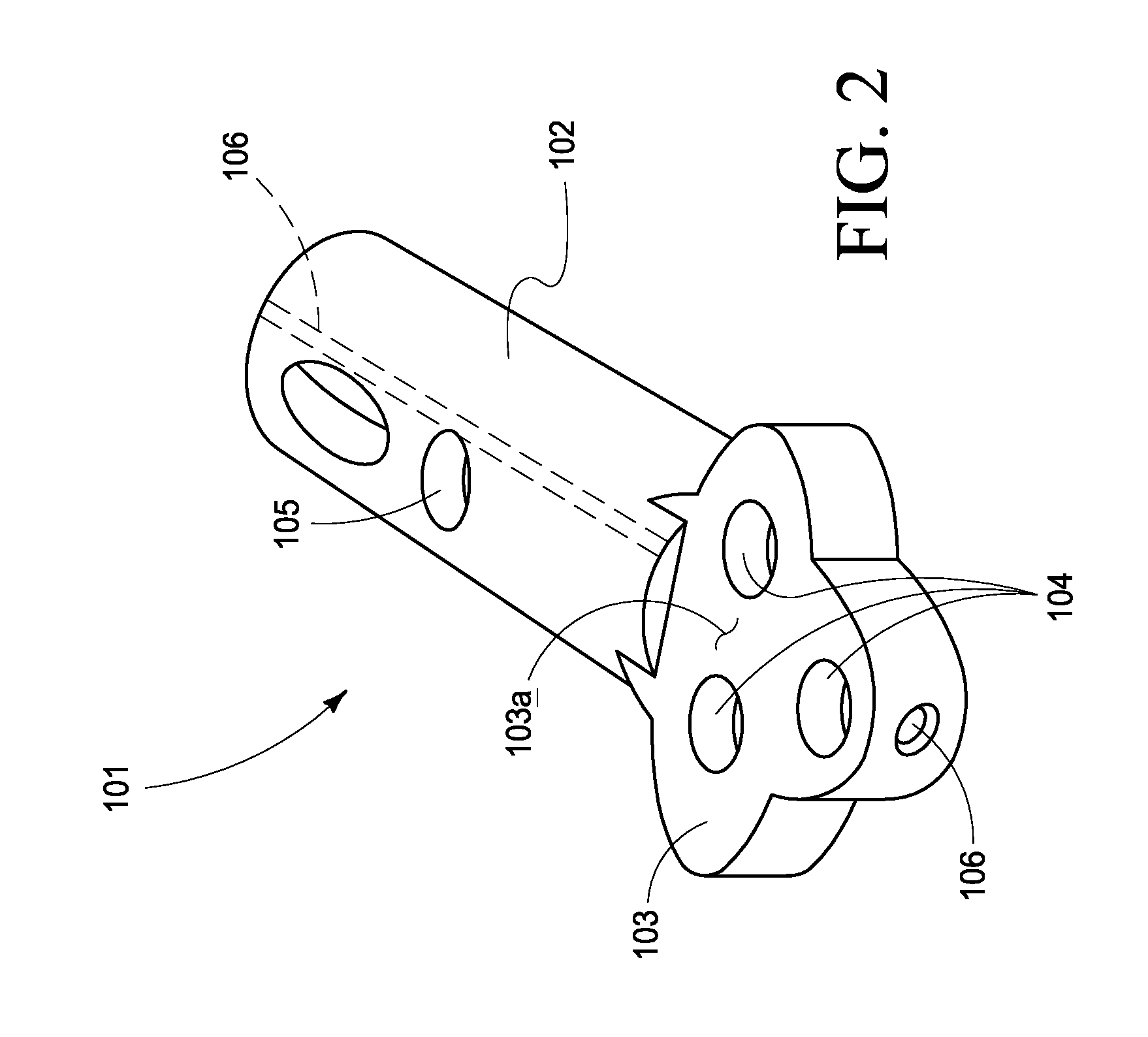
Modular intramedullary nail
An intramedullary nail for repair of bone fractures. The intramedullary nail is of a modular configuration including a nail member having a chamber formed on the proximal end thereof. An insert having at least one opening therein for receiving a bone screw or fastener is disposed within the chamber and is secured therein by a locking ring. Accordingly, various inserts may be used to achieve selected bone screw or fastener configurations.
Owner:SOHNGEN GARY W
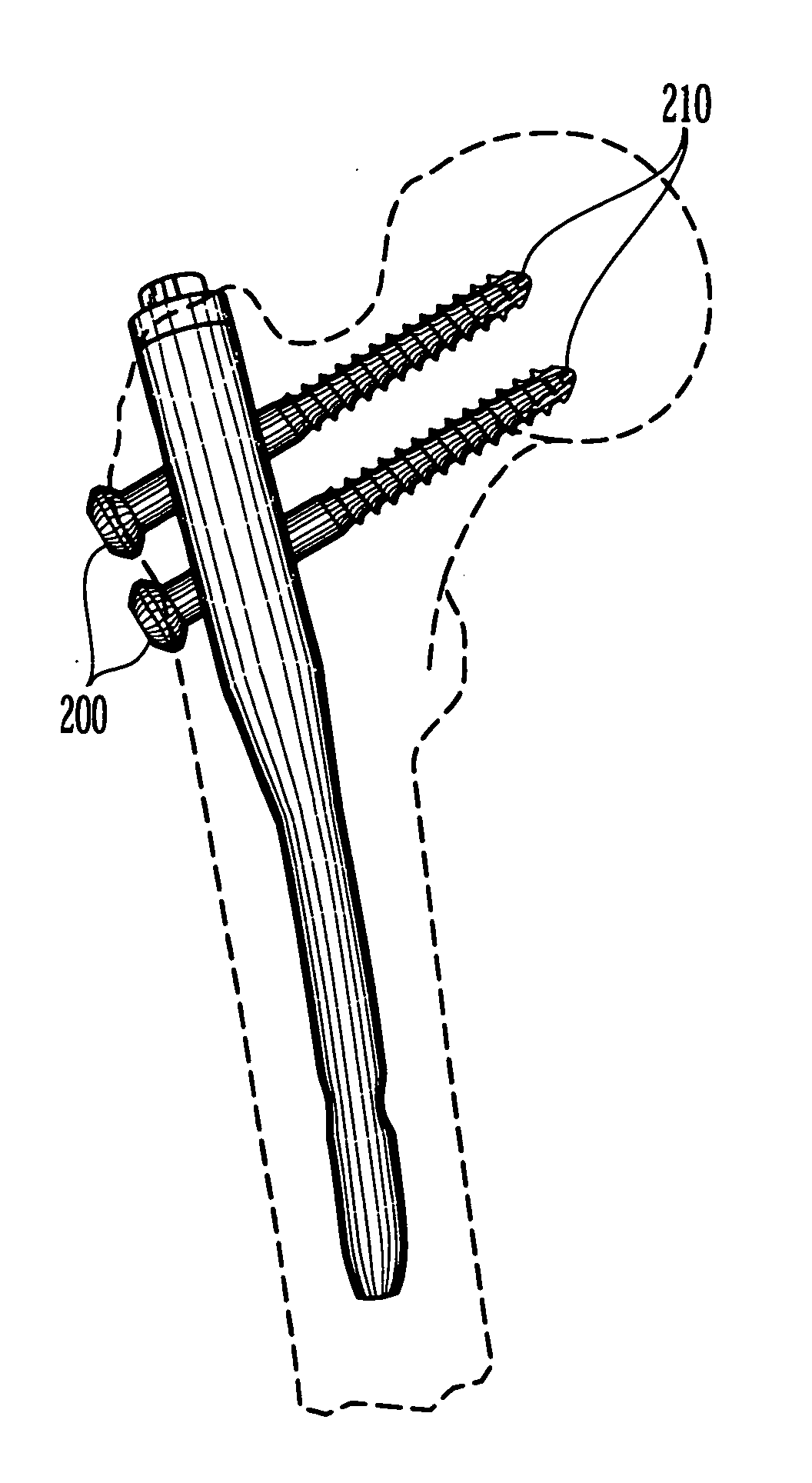
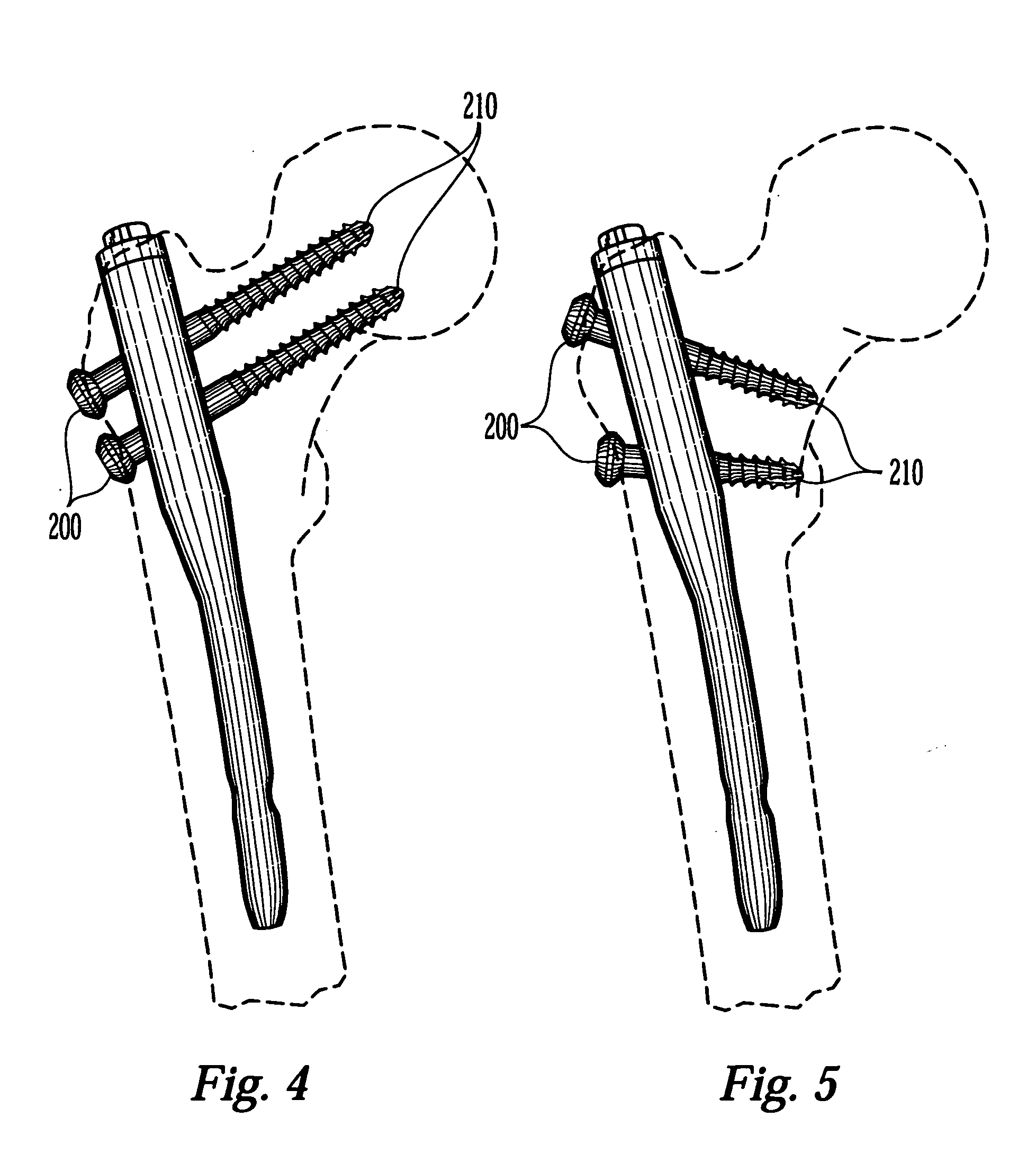
Combined Intramedullary - Extramedullary Bone Stabilization and Alignment System
Disclosed is a combined intramedullary and extramedullary bone stabilization and alignment system, which includes both methods and apparatuses for the alignment and stabilization of a first bone or piece of bone to a second bone or piece of bone. Embodiments of the system may include an implant device which has an elongated framework within intramedullary portion and an extramedullary portion which are cannulated. The cannulated aspect of the framework includes a wire aperture through both the intramedullary portion and the extramedullary portion.
Owner:LUNDQUIST ANDREW +1
Modular intramedullary nail
An intramedullary nail for repair of bone fractures. The intramedullary nail is of a modular configuration including a nail member having a chamber formed on the proximal end thereof. An insert having at least one opening therein for receiving a bone screw or fastener is disposed within the chamber and is secured therein by a locking ring. Accordingly, various inserts may be used to achieve selected bone screw or fastener configurations.
Owner:SOHNGEN GARY W +1
Computer assisted intramedullary rod surgery system with enhanced features
InactiveUS20050251113A1Accurate displayAccurately determineDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsComputer-assisted surgeryIntramedullary rod
A computer assisted surgery system for positioning a surgical implant within a patient's body that includes a localizing device configured to measure a pose of the surgical implant, an imaging device adapted for acquiring images of the surgical implant, and a computer adapted for calculating an adjusted pose for the surgical implant based on information developed from the images so as to compensate for deformation of the surgical implant or inaccuracies in localization.
Owner:KIENZLE THOMAS C III
Articulated intramedullary nail
InactiveUS20130325006A1Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
System, including methods, apparatus, and kits, for bone fixation with an articulated nail. The nail may have a first segment and a second segment that extend from respective opposite ends of the nail to a joint region that connects the segments. Each segment may define one or more transverse apertures configured to receive a fastener that attaches the segment to bone. The joint region may have a movable configuration that permits pivotal rearrangement of the segments relative to each other and a locked configuration that fixes the segments relative to each other.
Owner:MICHELINIE JAMES W +2
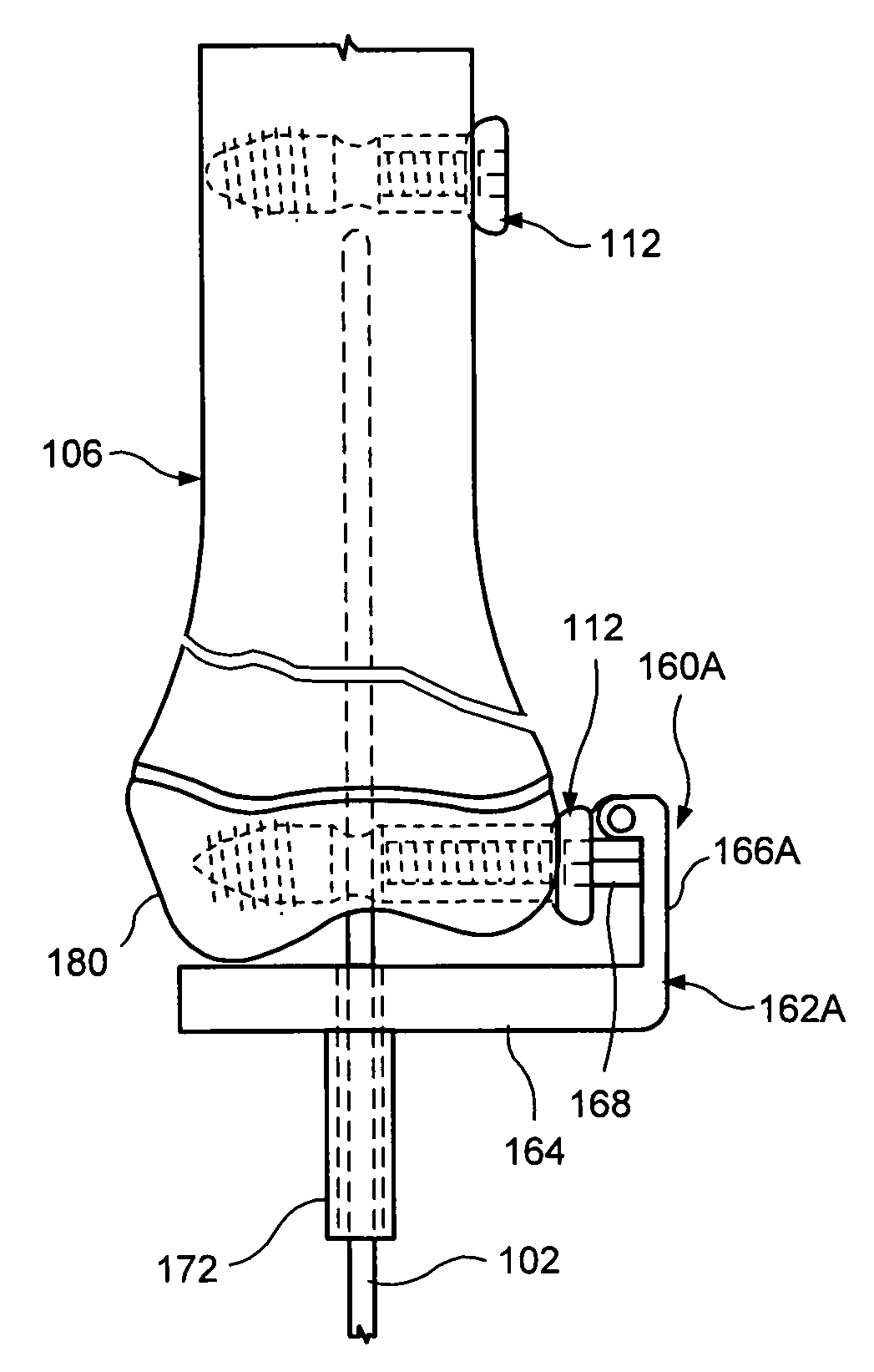
Intramedullary nail targeting device
InactiveUS20100249782A1Precise positioningMinimize degree of freedomInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSensor arrayIntramedullary rod
An intramedullary nail targeting apparatus for targeting and drilling screw openings in the intramedullay nail is provided herein. A preferred version of the targeting apparatus includes a magnetic targeting device, a nail extension for connecting to an intramedullary nail, and a magnet member, preferably in a “bucking configuration,” for affixing to the intramedullary nail at a defined position relative to the screw openings in the nail. The nail extension includes a targeting arm with one or more bores which align with the screw openings in the nail when the targeting arm is aligned with the intramedullary nail. The magnetic targeting device includes a support member with a sensor array that extends through one of the bores on the targeting arm to target the magnet member, thereby aligning the targeting arm with the intramedullary nail. A second bore on the targeting arm can then be used for drilling through the bone at the position of an aligned screw opening. Methods for using the targeting apparatus for targeting and drilling screw openings in intramedullary nails or openings in bone plates are also described herein.
Owner:DURHAM ALFRED A
Knee balancing for revision procedures
ActiveUS8506571B2Promote balance between supply and demandImprove balanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaIntramedullary rod
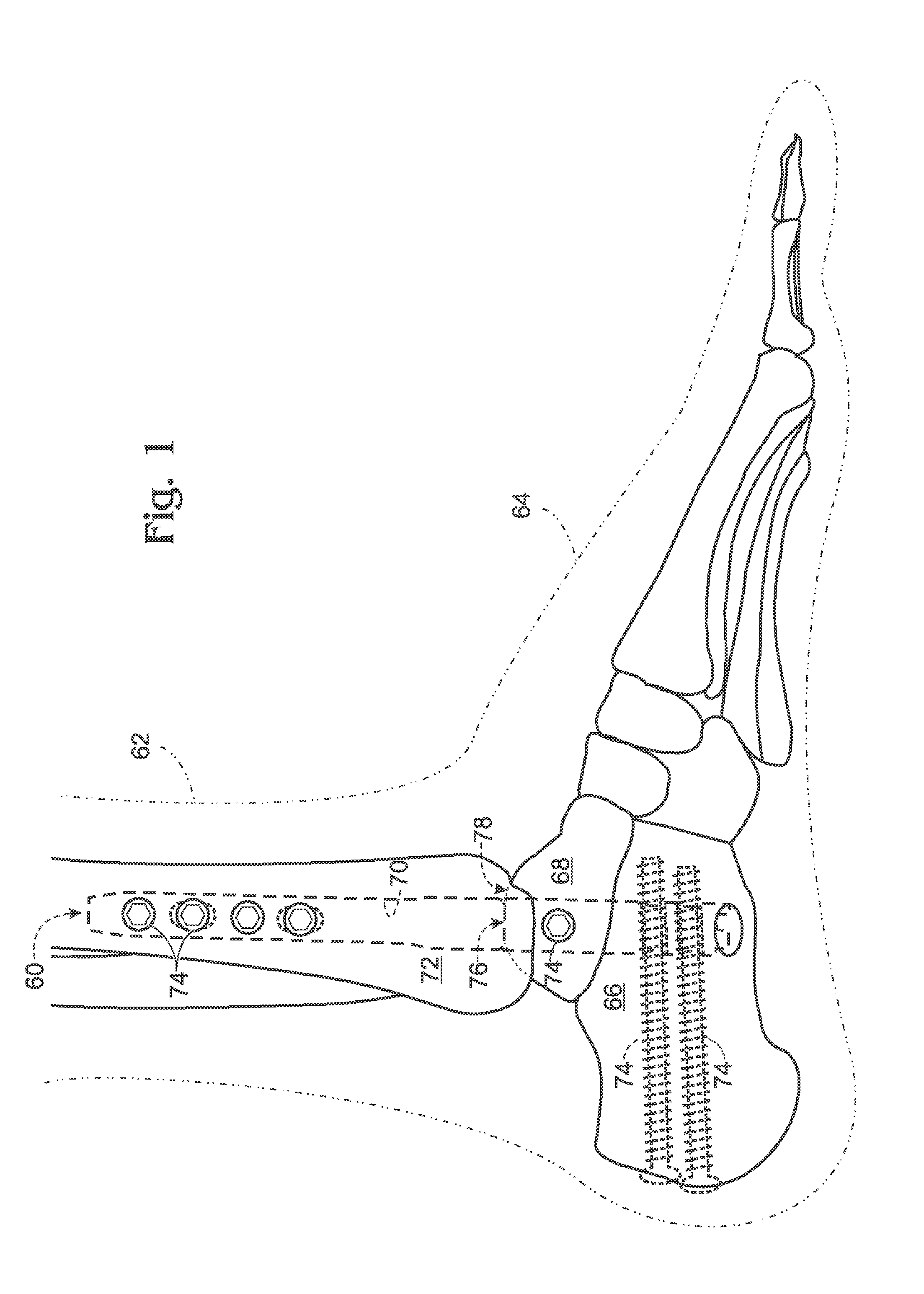
Methods, systems and devices are provided for facilitating a surgical procedure on a knee, particularly, a revision total knee replacement procedure. Prior femoral and tibial prostheses are removed. A cut end of a distal femur is engaged with a femoral adjustment member, which will typically center itself about an intramedullary rod placed into the femur. The lateral and medial forces exerted by lateral and medial sides of the femoral adjustment member and the cut tibial plateau against each other are measured. The femoral adjustment member is adjusted to apply and / or adjust tension to the lateral collateral ligament and / or the medial collateral ligament based on the measured forces, for example, such that the measured lateral force and the measured medial force are matched. Based on the position of the adjusted femoral member, guided clean-up cuts for placement of a new femoral prostheses are made on the cut end of the distal femur.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
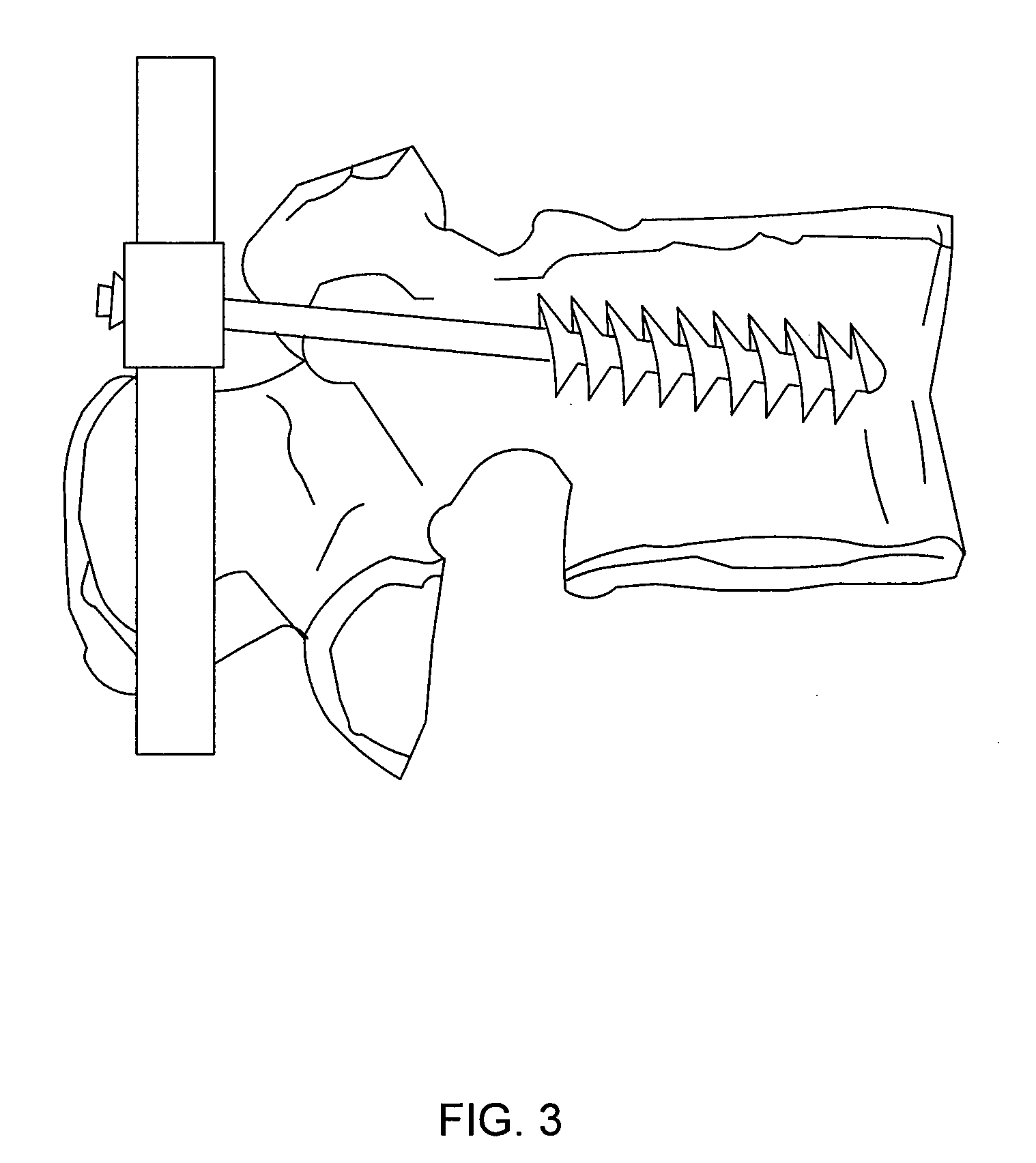
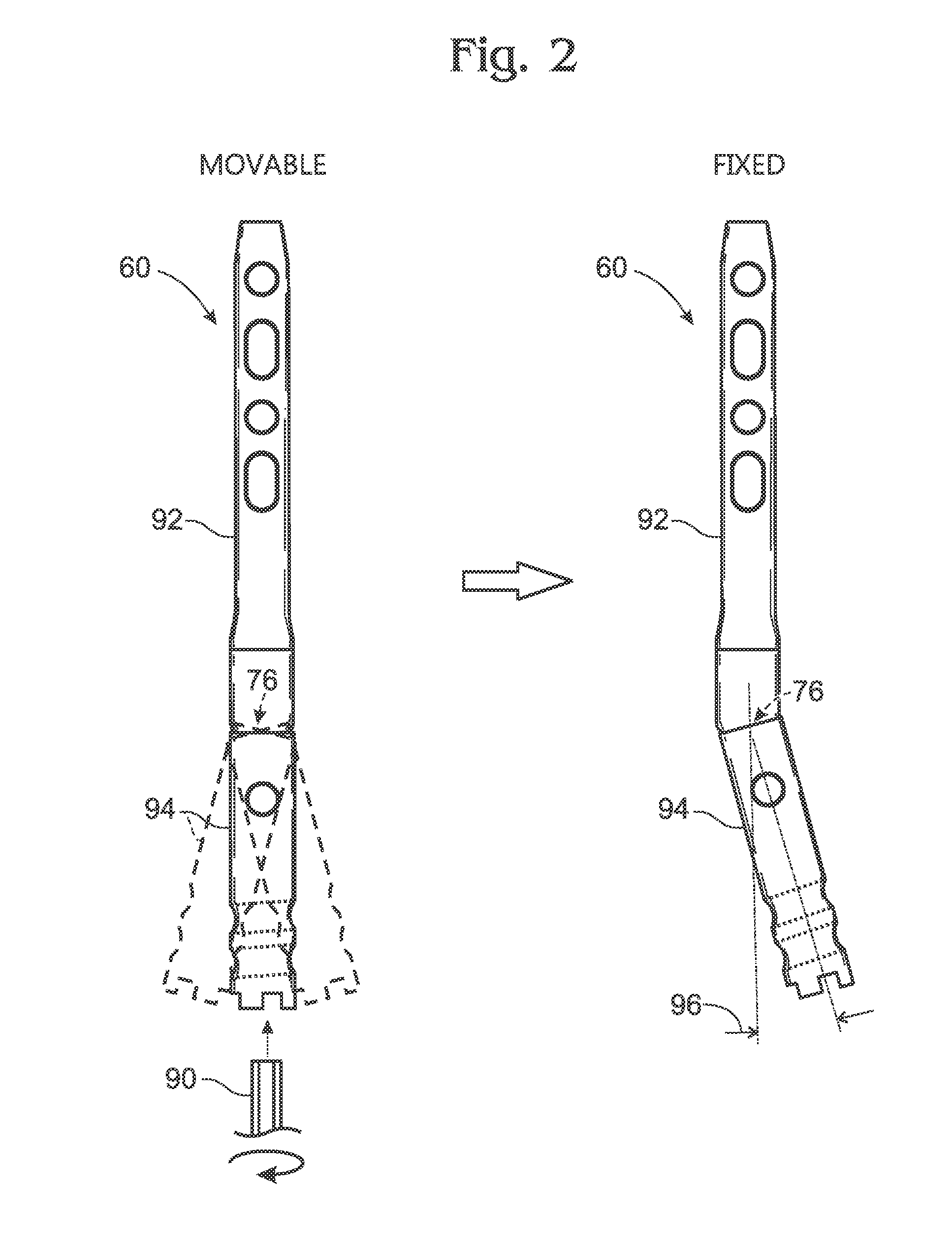
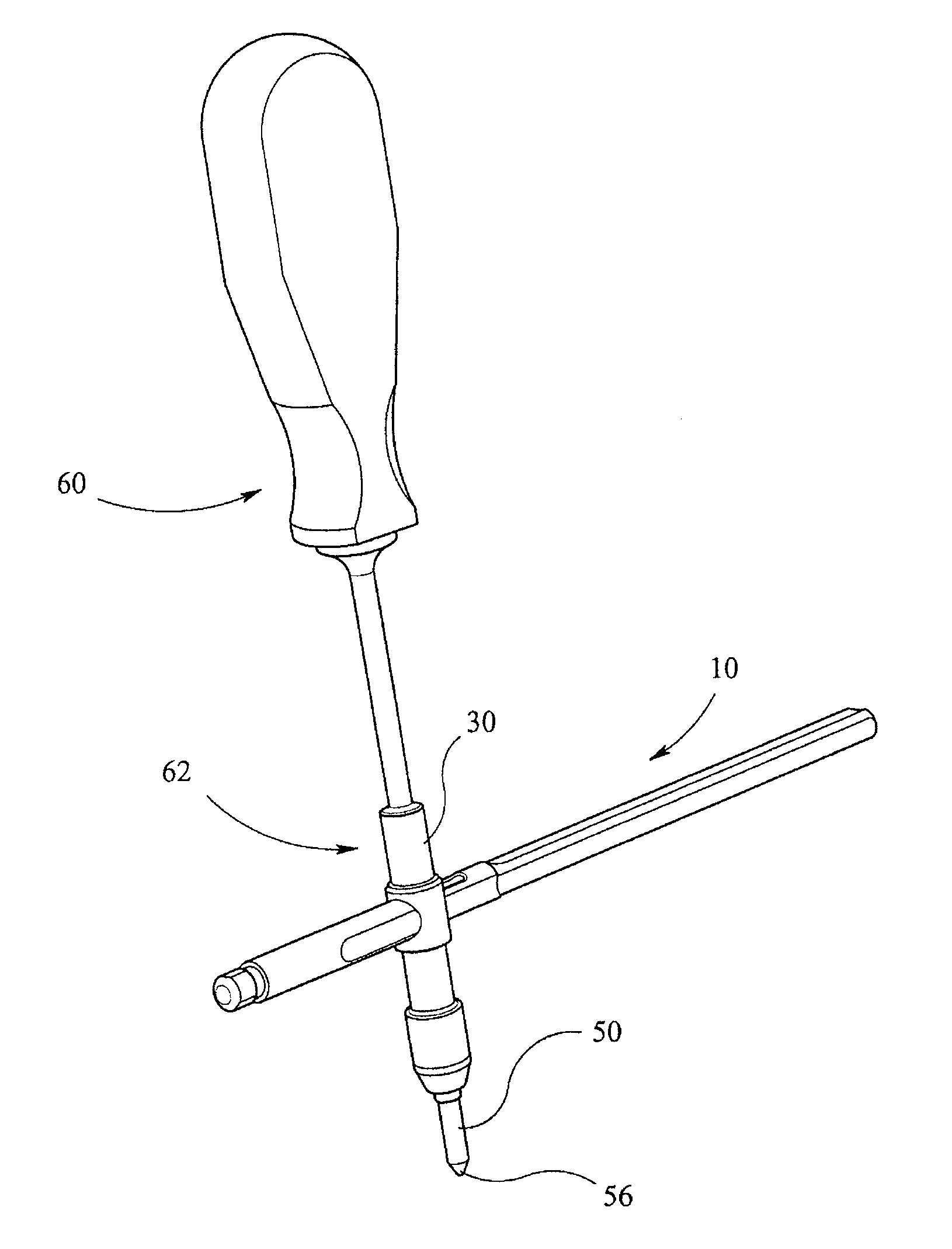
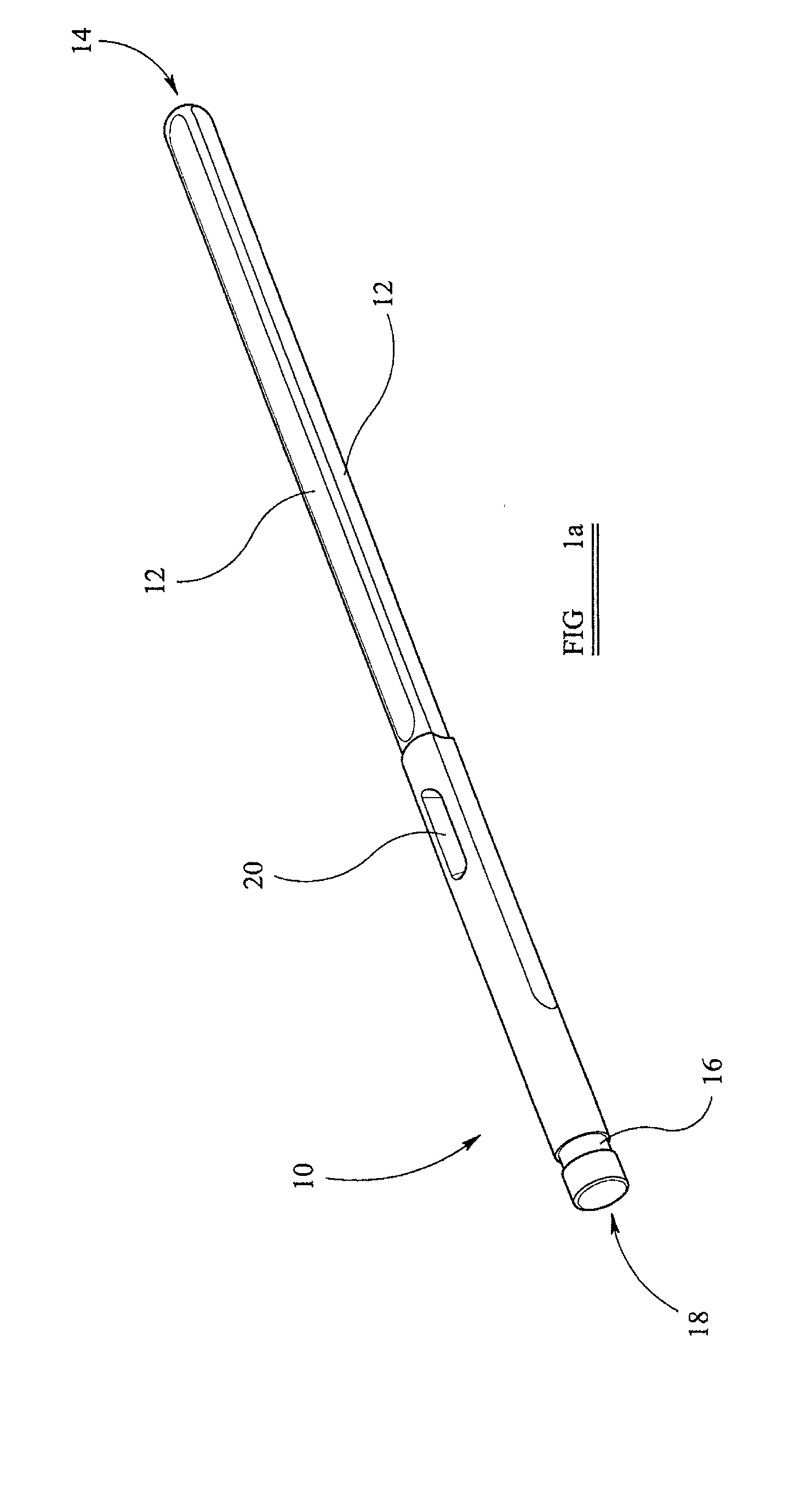
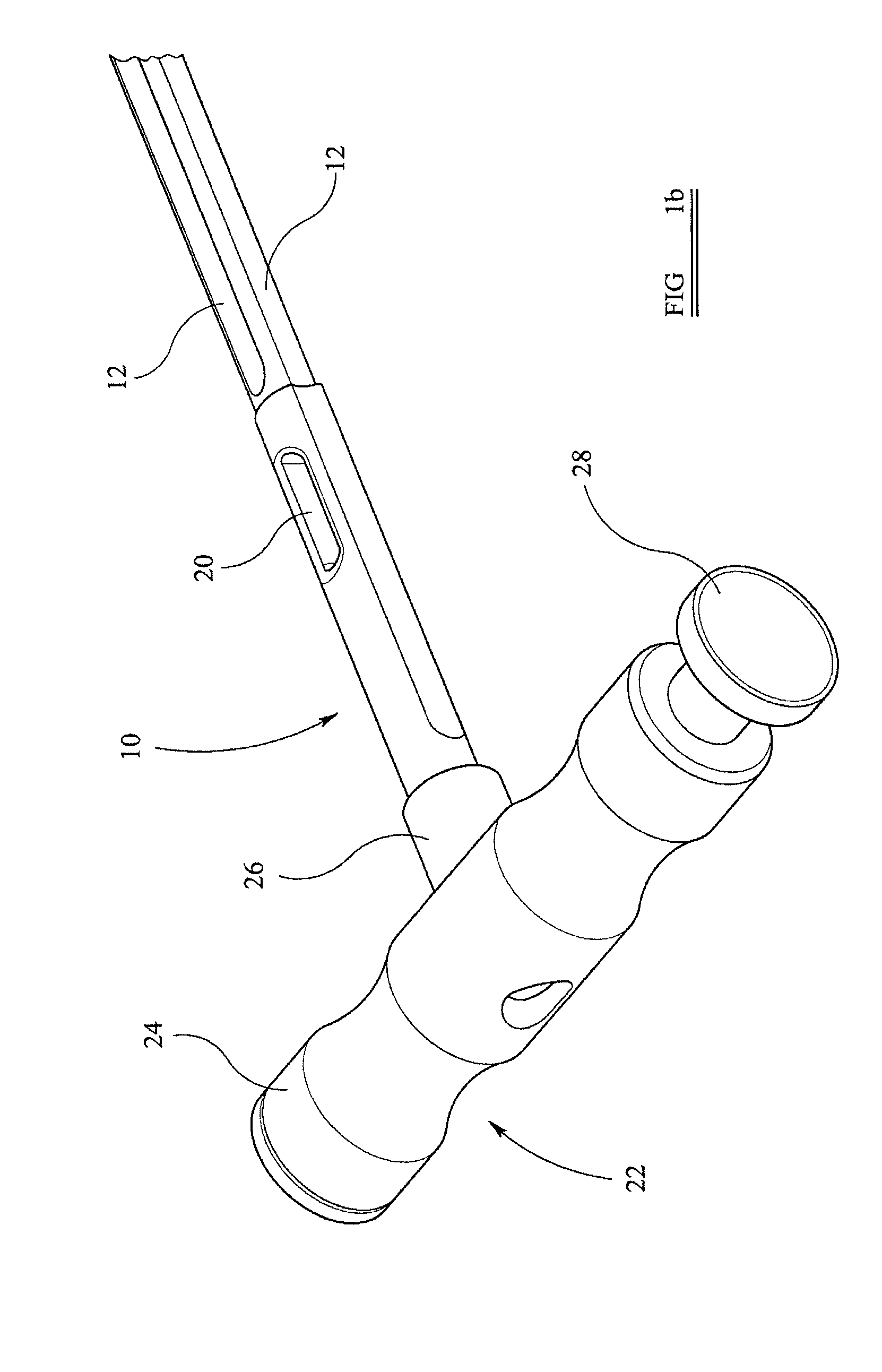
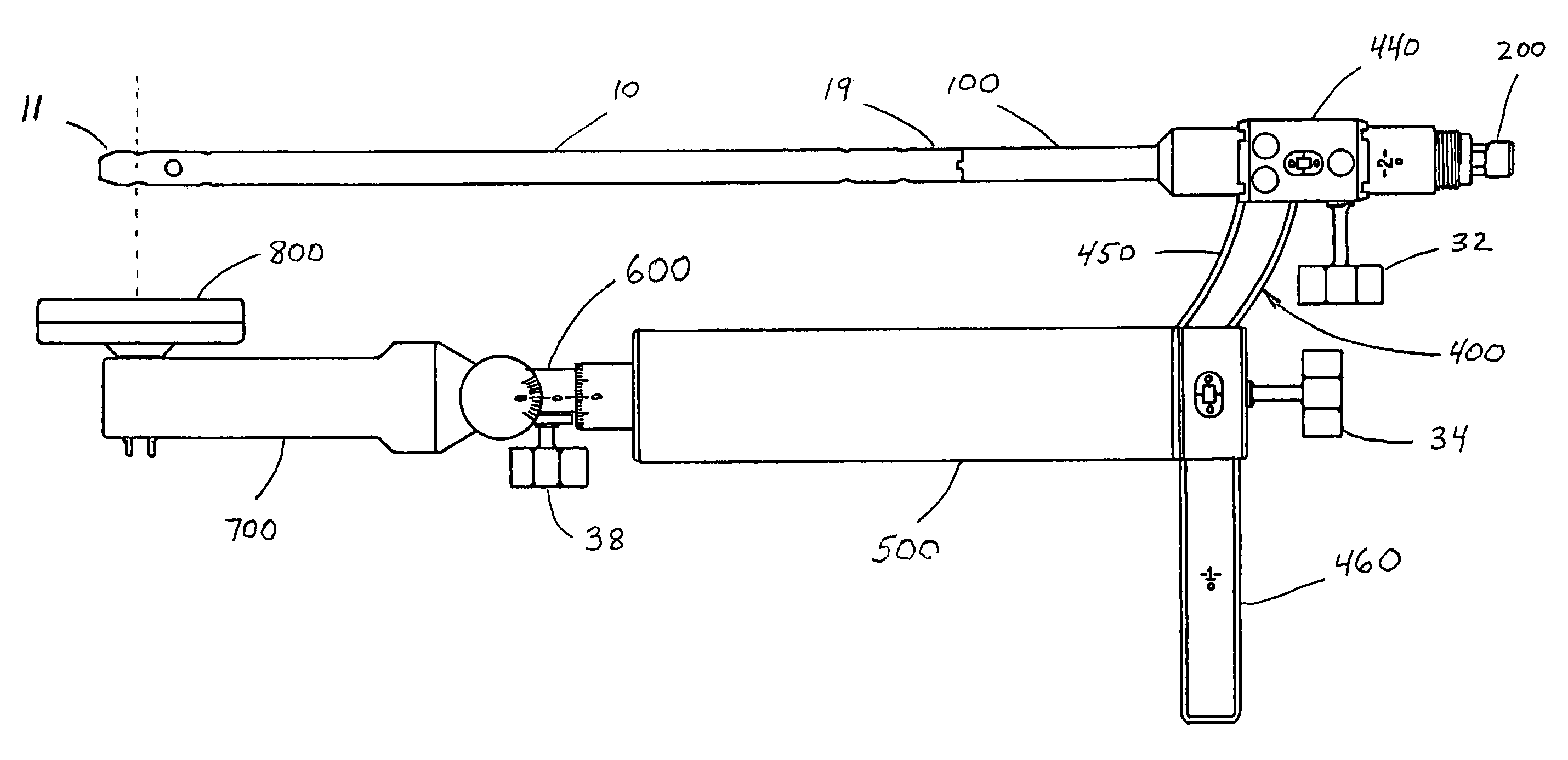
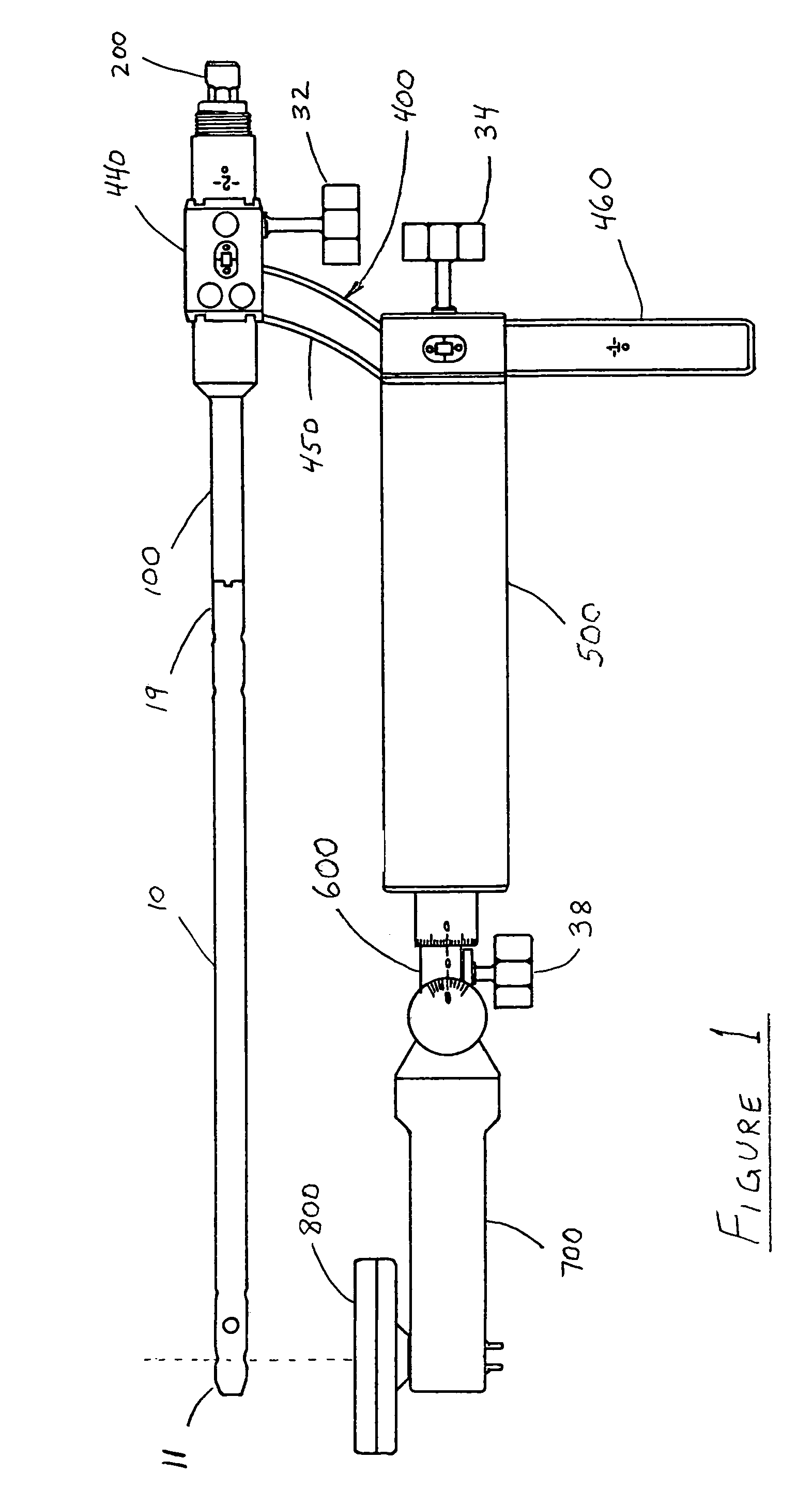
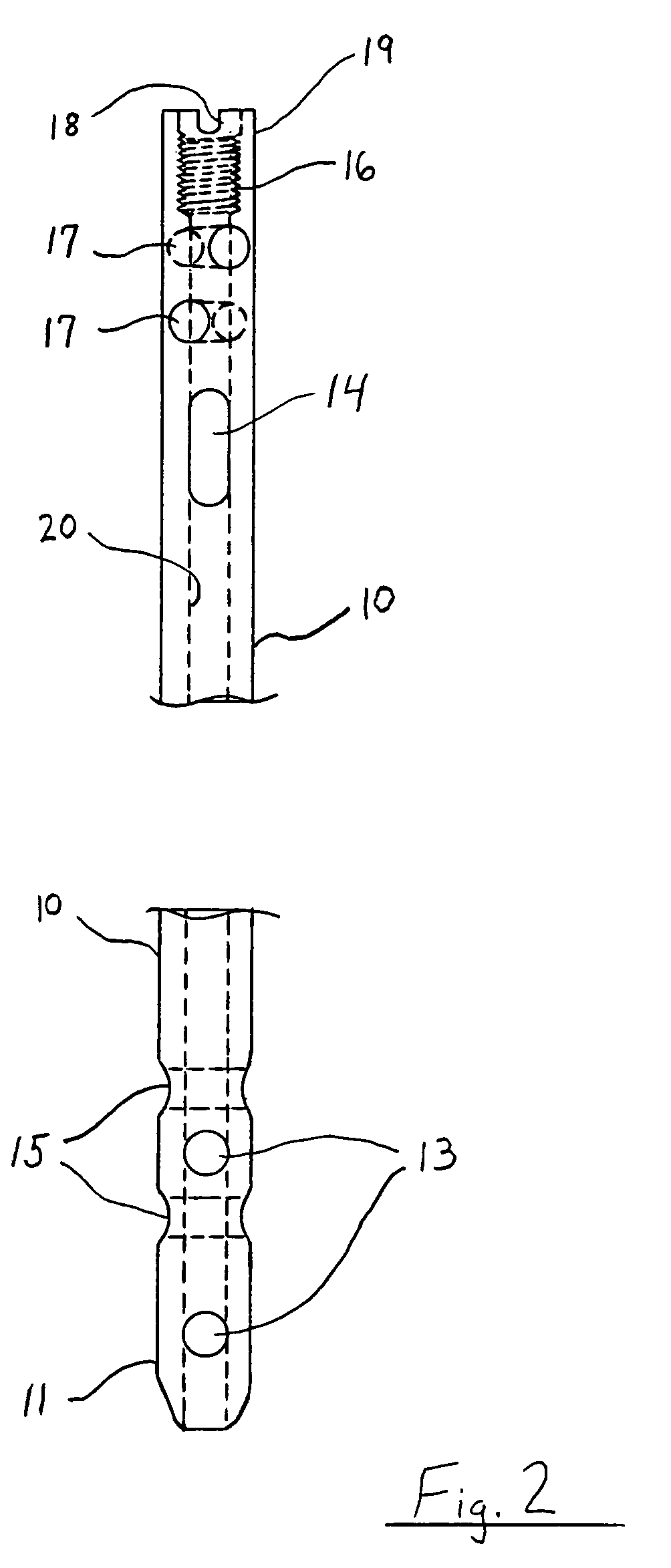
Instrumentation for knee surgery
Instrumentation for use in knee surgery comprises an intramedullary rod (10) for insertion into an end of a femur (100) and a distraction device (62) coupleable to the intramedullary rod (10) and operable between the intramedullary rod (10) and the tibia for adjusting the tension of the collateral ligaments on either side of the knee. A cutting guide (70) is configured to locate over an intramedullary rod (10) that has been inserted into an end of a femur (100), such that the position of the cutting guide (70) relative to the intramedullary rod (10), and therefore the femur (100), is adjustable in at least the anterior-posterior direction. A kit for use in knee surgery is provided and a method of adjusting the tension of the collateral ligaments on either side of a knee is taught.
Owner:MCMINN DEREK JAMES WALLACE
Intramedullary rod with spiraling flutes
ActiveUS7771428B2Lower potentialReduce usageInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFluteIntramedullary rod
This invention relates generally to devices, systems and methods for the internal fixation of bone fractures, and particularly, to intramedullary fracture fixation devices such as those used in, for example, the treatment of long bone fractures. An IM rod preferably is provided with multiple curved sections in different planes preferably designed to conform with the long bones of a patient, both during insertion and in the rod's final position in the long bone. In addition, the overlap of portions of the curved sections results in a co-planar curvature of portions of the IM rod which assist in the insertion process by guiding the proper rotation of the IM rod as it is inserted into the bone. Spiraling flutes extending down the distal portion of the rod also assist in properly guiding and orienting the rod about its longitudinal axis during insertion such that the appropriate segment of the curved rod conforms with the appropriate portion of the long bone at the appropriate place.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Intramedullary nail, system, and method with dynamic compression
The present invention describes an intramedullary nail for use in orthopedic surgery for the fixation of bone fractures and fusion sites. The nail employs one or more internal loaded springs, biocompatible elastic or rubber bands, or other mechanism that provides continuous dynamic compression across the healing site throughout the healing process. By altering the size, tension and / or number of the internal compression devices, the amount of compression may be customized on a case-by-case basis. Further, the slots within the nail for its attachment can be utilized to create a torsional force when desired. The nail can have a cross-sectional shape that prevents its rotation. A system and method of use is also described.
Owner:AFCN
Intramedullary nail
InactiveUS6855146B2Eliminates angular rigidityPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headIntramedullary rod
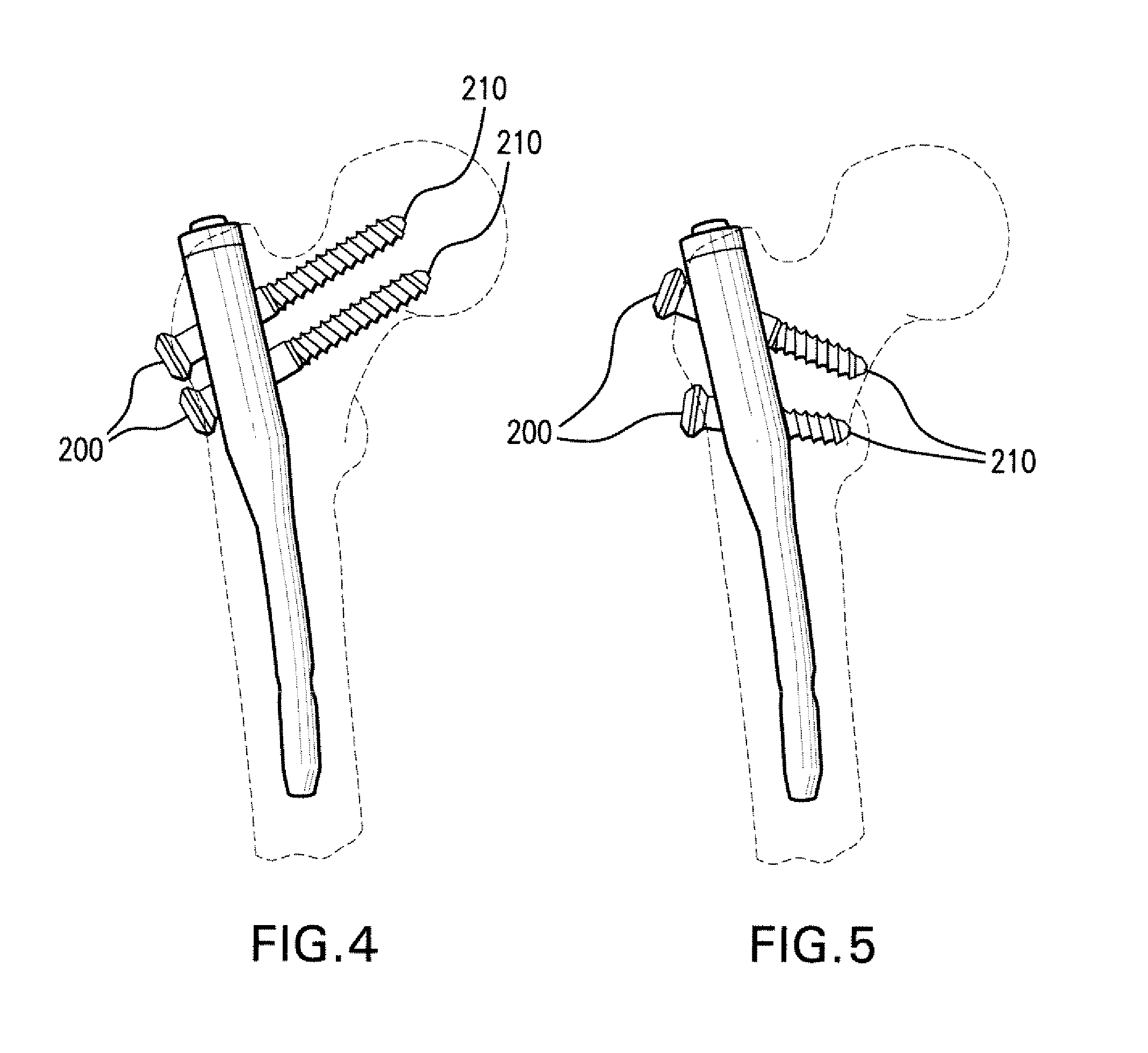
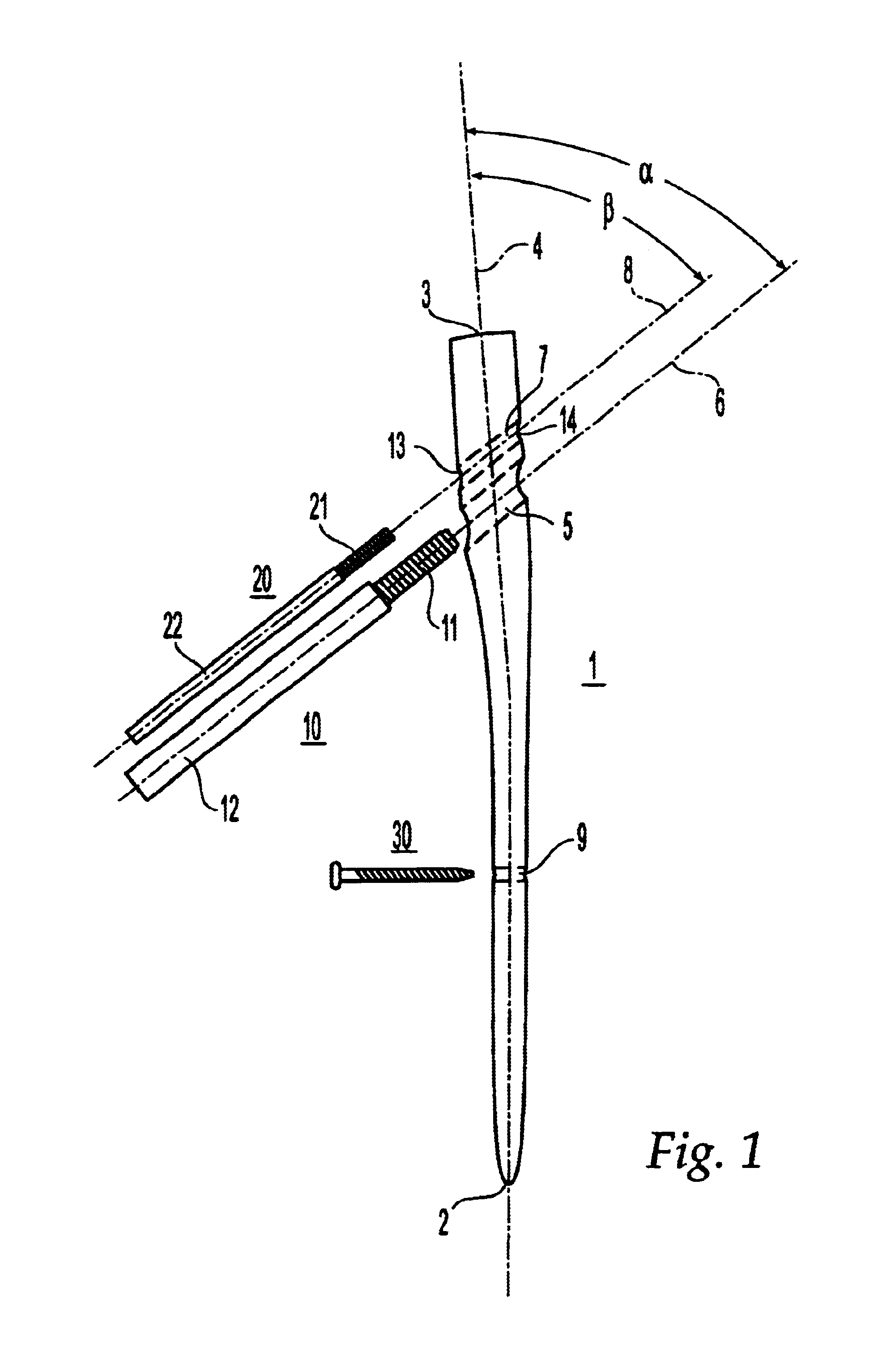
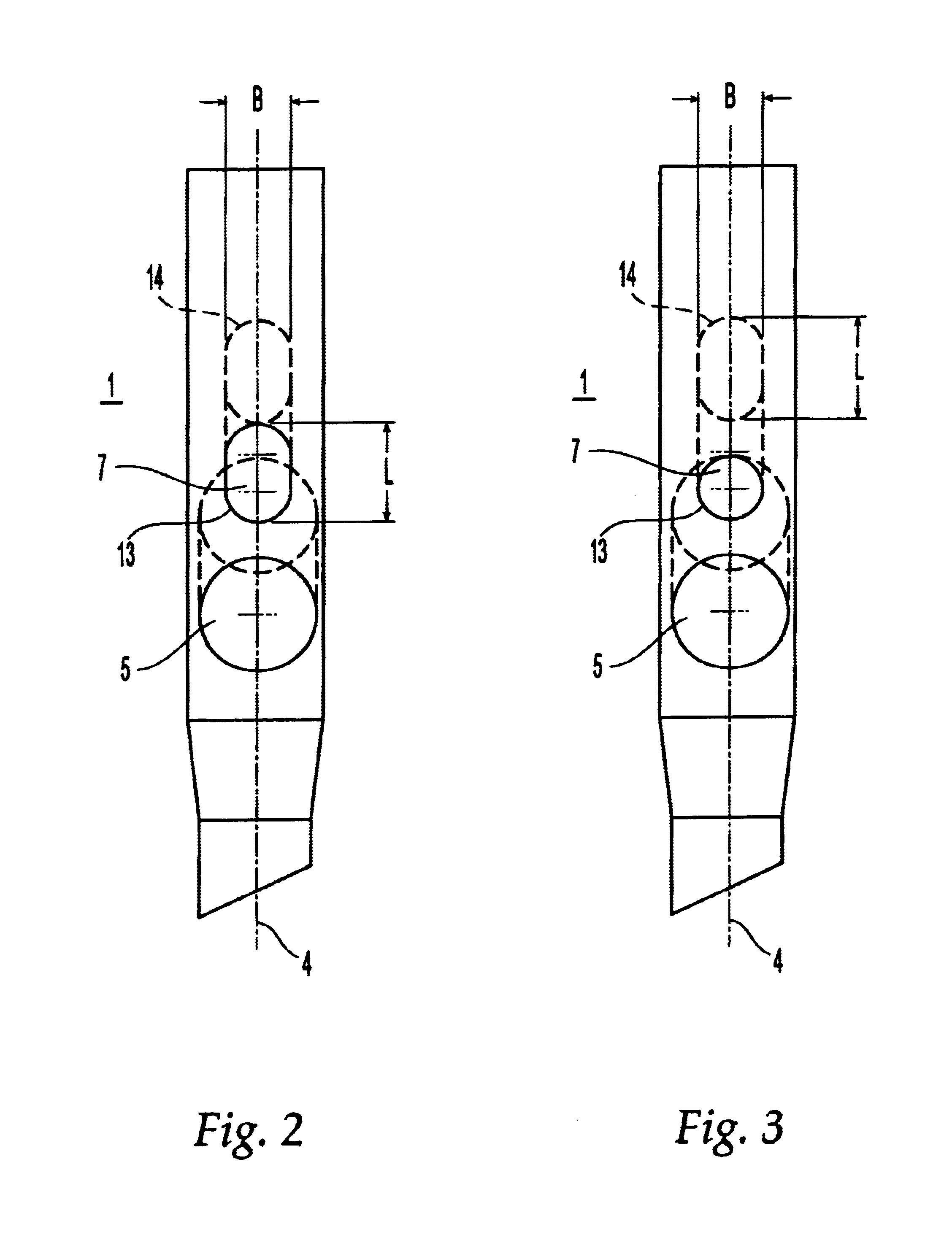
The invention relates to an intramedullary nail used for treating fractures of the femur. It comprises a distal end, which is appointed for insertion into the marrow cavity channel, a proximal end, and a longitudinal axis. A first bore is located adjacent the proximal end and extends through the proximal end and transversely intersects the longitudinal axis, and serves to accommodate a femoral head screw. The center axis of the first bore forms an angle with the longitudinal axis that ranges from 110° to 150°. A second bore is located between the first bore and the proximal end and extends through the proximal end and transversely intersects the longitudinal axis, and serves to accommodate a hip pin. The second bore is at least partially shaped as an oblong hole or slot with a width B and a length L>B, and the length L of the oblong hole extends in the direction of the longitudinal axis.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Bone implant and systems that controllably releases silver
ActiveUS20120123485A1Help with stability of devicePromote tissue growthSuture equipmentsDental implantsIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
Silver and / or zinc ion releasing implants, systems and method of operating, inserting and activating / inactivating them are described. In some variations the implant is configured as a bone implant that includes a bone-screw or intramedullary rod like body configured to receive a treatment cartridge having a plurality of ion-releasing members configured as an anode that can controllably engage with a catheter to turn galvanic release of ions on / off as desired. These devices may be configured to release silver ions (and / or zinc ions) above a predetermined level for a predetermined period of time and may maintain a concentration of ions over a relatively large volume of tissue. The ion-releasing members may be configured to reduce or prevent implant movement.
Owner:SILVER BULLET THERAPEUTICS
Rotary-rigid orthopaedic rod
InactiveUS20110178520A1Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
Apparatus and method for repairing a fractured bone. The apparatus and methods may involve an intramedullary rod. The rod may include a first elongated member and a second elongated member. Each of the first and second elongated members may be configured to bend in a first direction and to resist bending in a second direction. The first and second elongated members may be arranged such that: (1) the rod is bendable when the first direction of the first elongated member is aligned with the first direction of the second elongated member; and (2) the rod is rigid when the first direction of the first elongated member is aligned with the second direction of the second elongated member. Some embodiments may include rods that have sections that may be configured to be curved and rigid.
Owner:CONVENTUS ORTHOPAEDICS INC
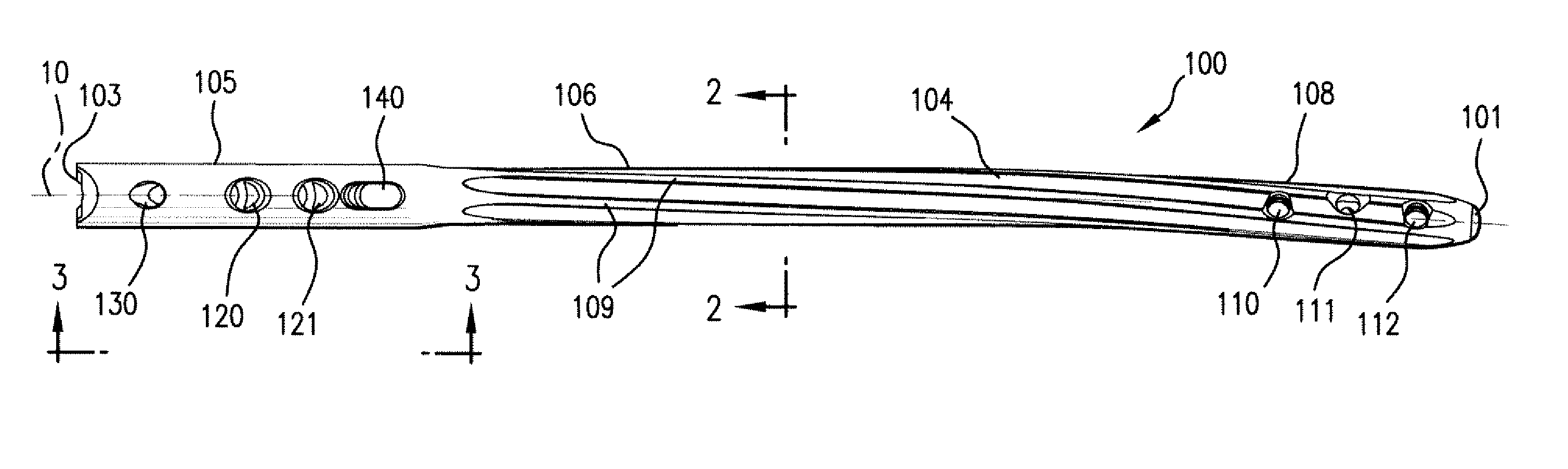
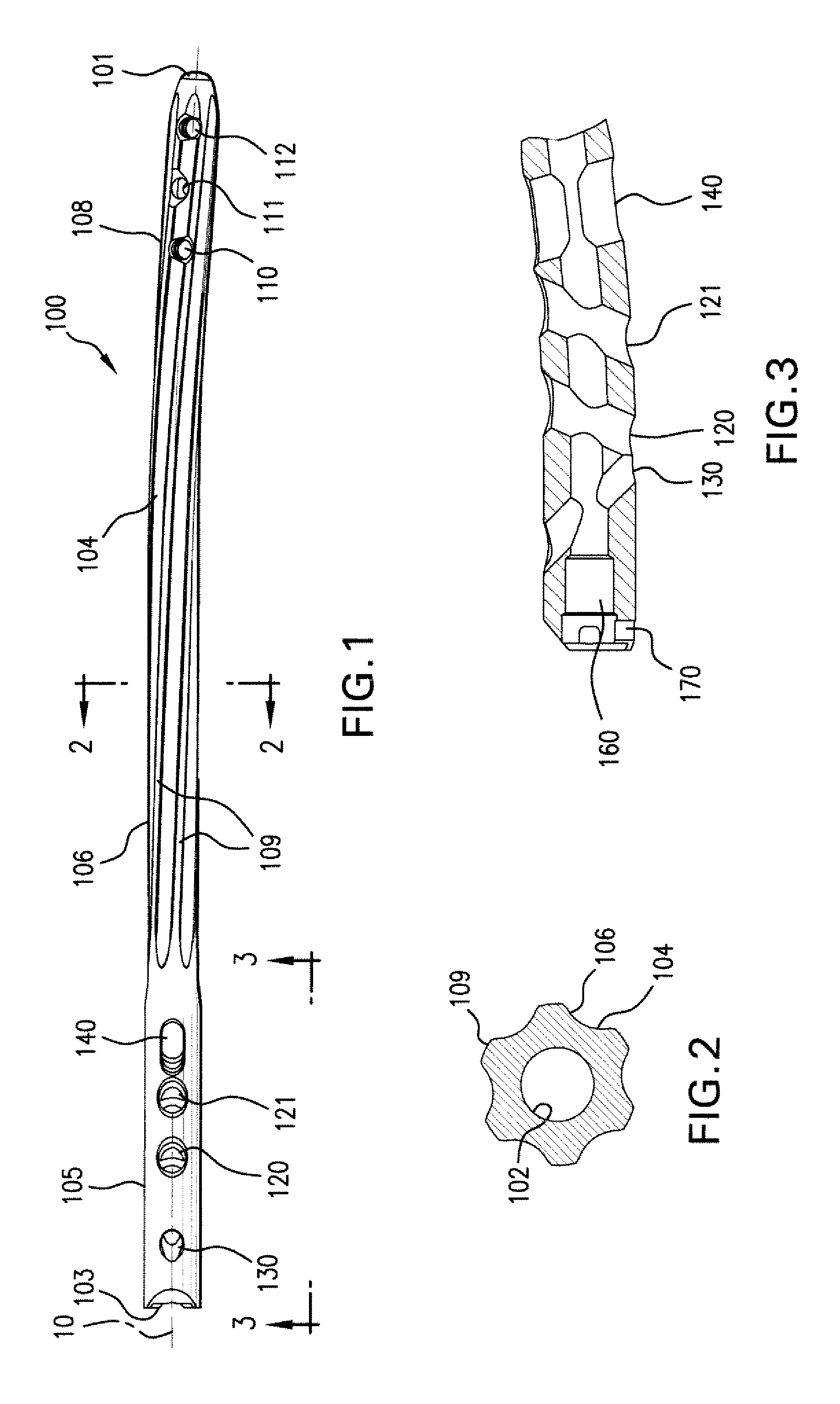
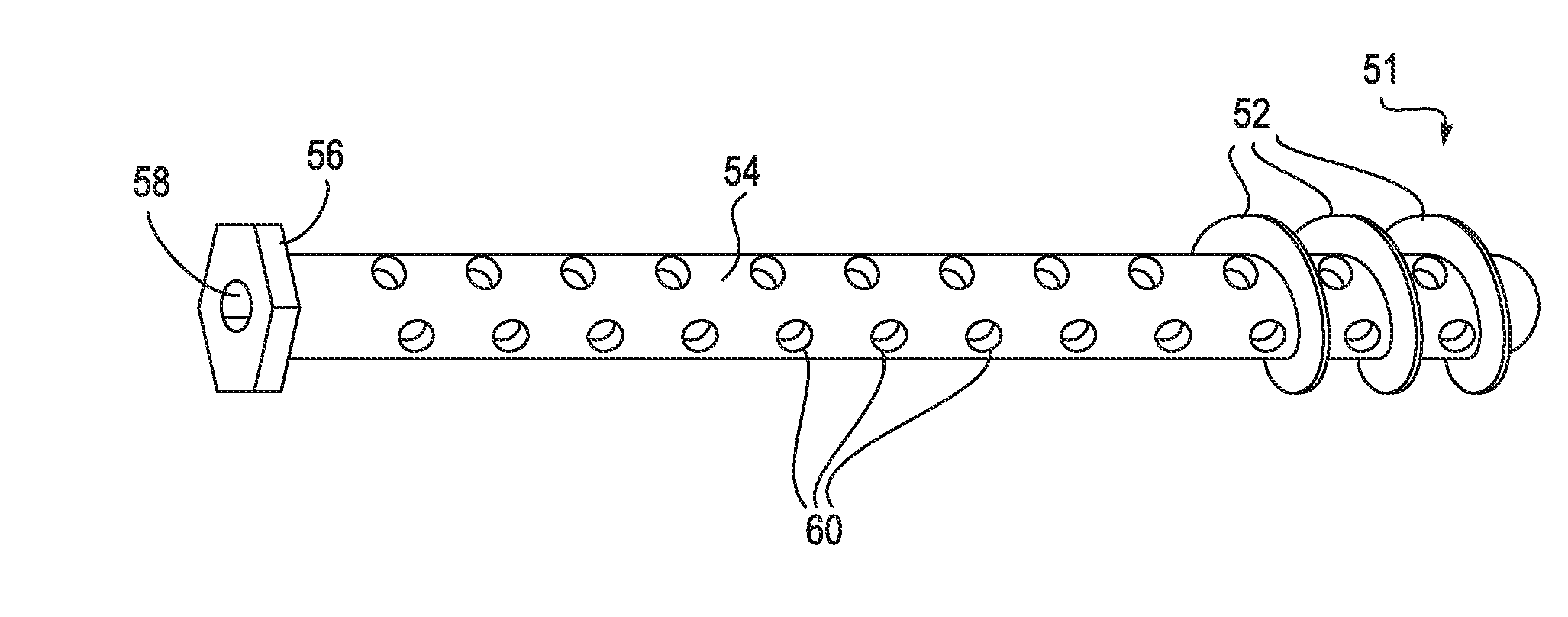
Endosteal nail plate for fixing bone segments
An endosteal nail plate for fixing bone segments is provided. More particularly, there is provided an endosteal nail plate that can be made up of a single piece, or of multiple pieces, as desired. Additionally, the intramedullary nail utilizes a threaded slot on the body thereof, for engaging locking screws for fixation of the intramedullary nail within a bone of a patient.
Owner:SKELETAL DYNAMICS INC
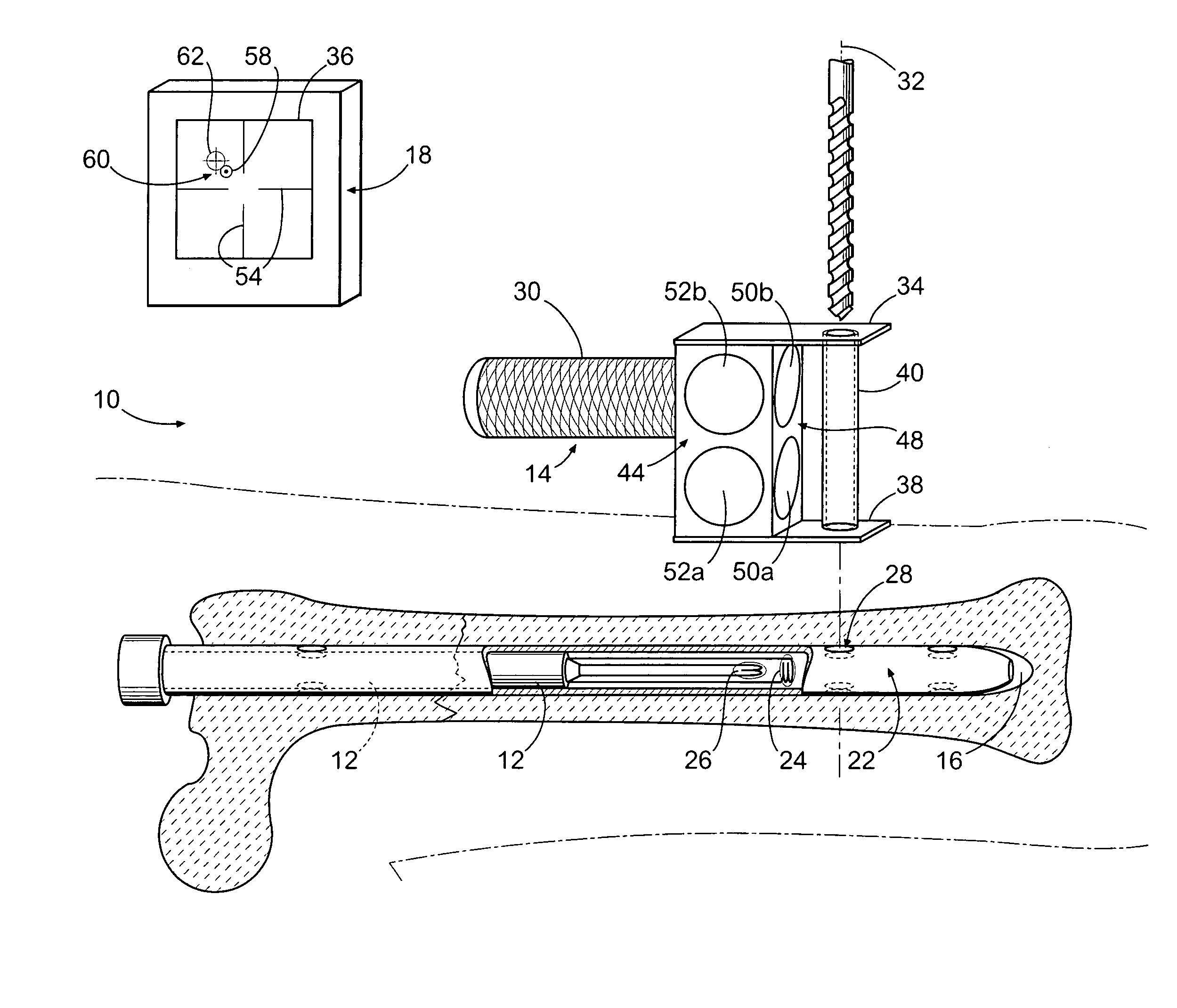
Method and apparatus for distal targeting of locking screws in intramedullary nails
InactiveUS7029478B2Simple formatHigh mechanical strengthProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesIntramedullary rodDisplay device
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
System for intramedullary rod fixation and method therefor
ActiveUS20070100342A1Suture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
A system and method for securing an intramedullary rod in a medullary canal of a long bone is provided. The system includes an intramedullary rod and a screw assembly for receiving the rod. The screw assembly has a transverse receiving bore for receiving the intramedullary rod and a securing member movable toward the bore for securing the rod to the screw assembly. An alignment jig may also be provided for aligning the rod with the receiving bore during installation.
Owner:PEGA MEDICAL
Method and system for securing an intramedullary nail
InactiveUS7727240B1Simple designSimple and efficient procedureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntramedullary rodEngineering
A device, method and system adapted to determine a targeting position on a surgically implantable nail adapted to be used in internal fixation of a bone, the nail comprising a distal end and a proximal end, the device including an extension rod comprising a longitudinal axis and adapted to be detachably coupled to the proximal end of the nail, a bridge member adjustably secured to the extension rod and extending radially from the longitudinal axis of the extension rod, a position of the bridge member on the extension rod being rotationally and longitudinally adjustable with respect to the longitudinal axis of the extension rod, and a targeting arm adjustably coupled to the bridge member and extending from the bridge member toward the distal end of the locking nail, the targeting arm comprising a drill guide.
Owner:BENTON BLAKE
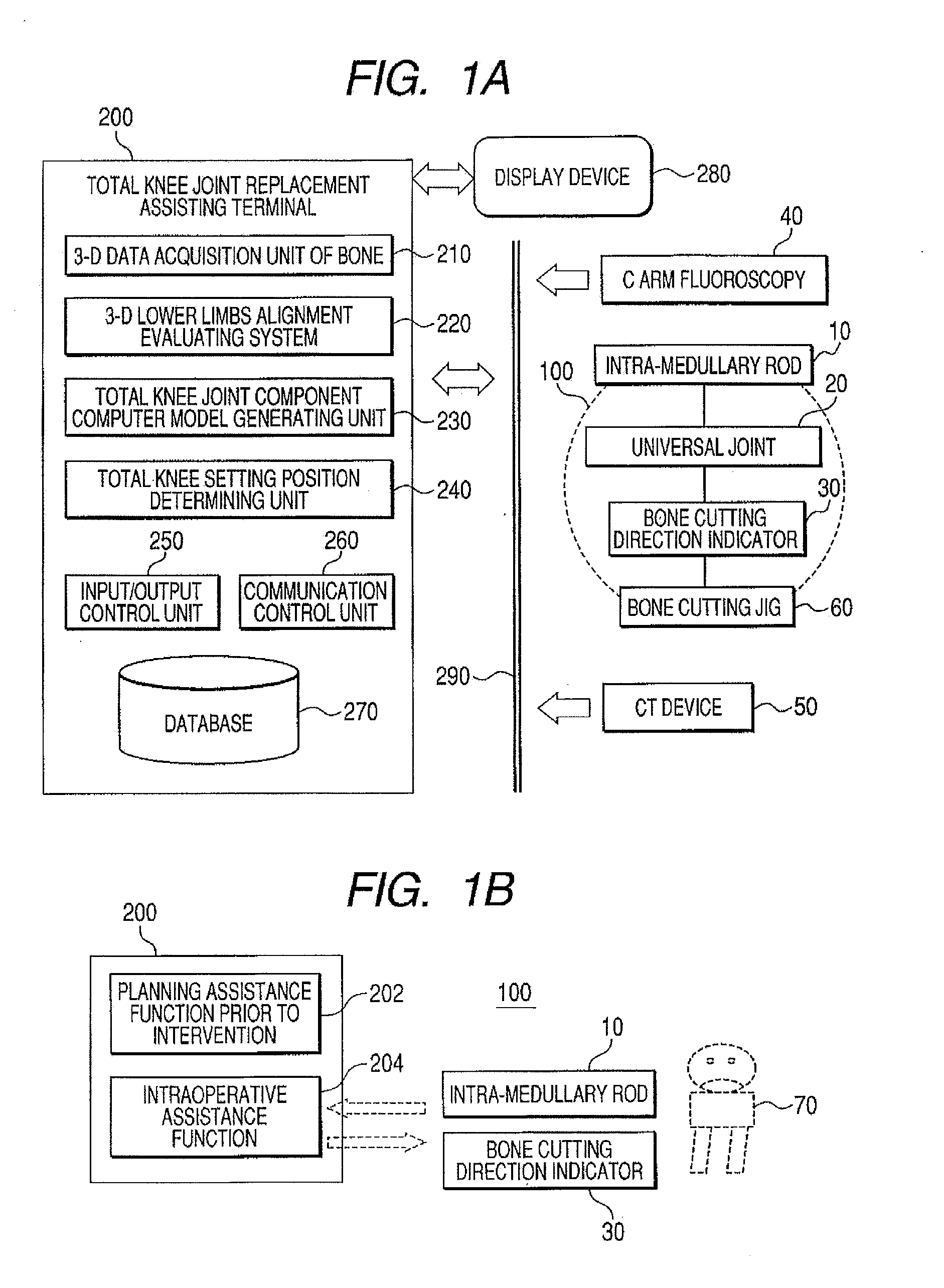
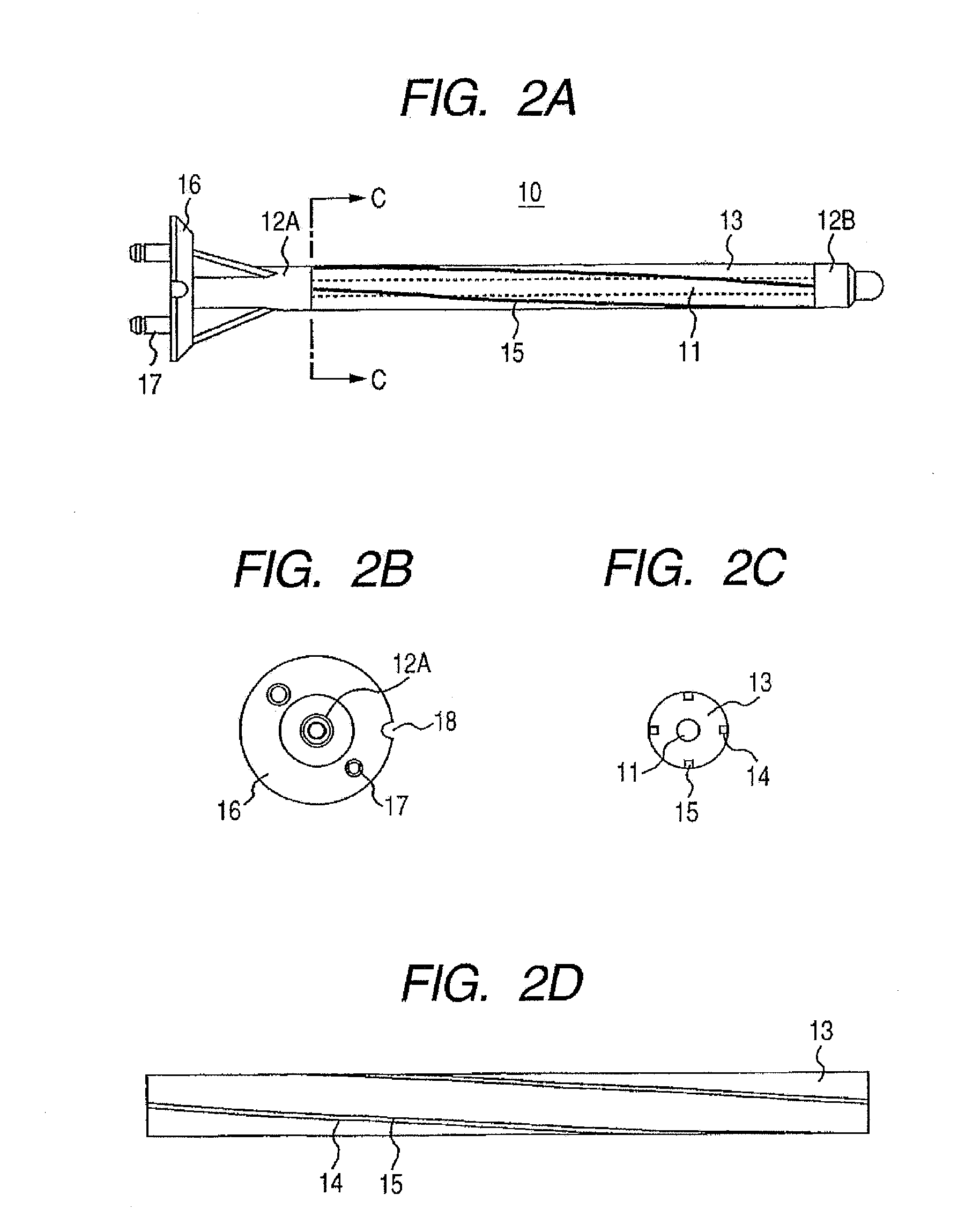
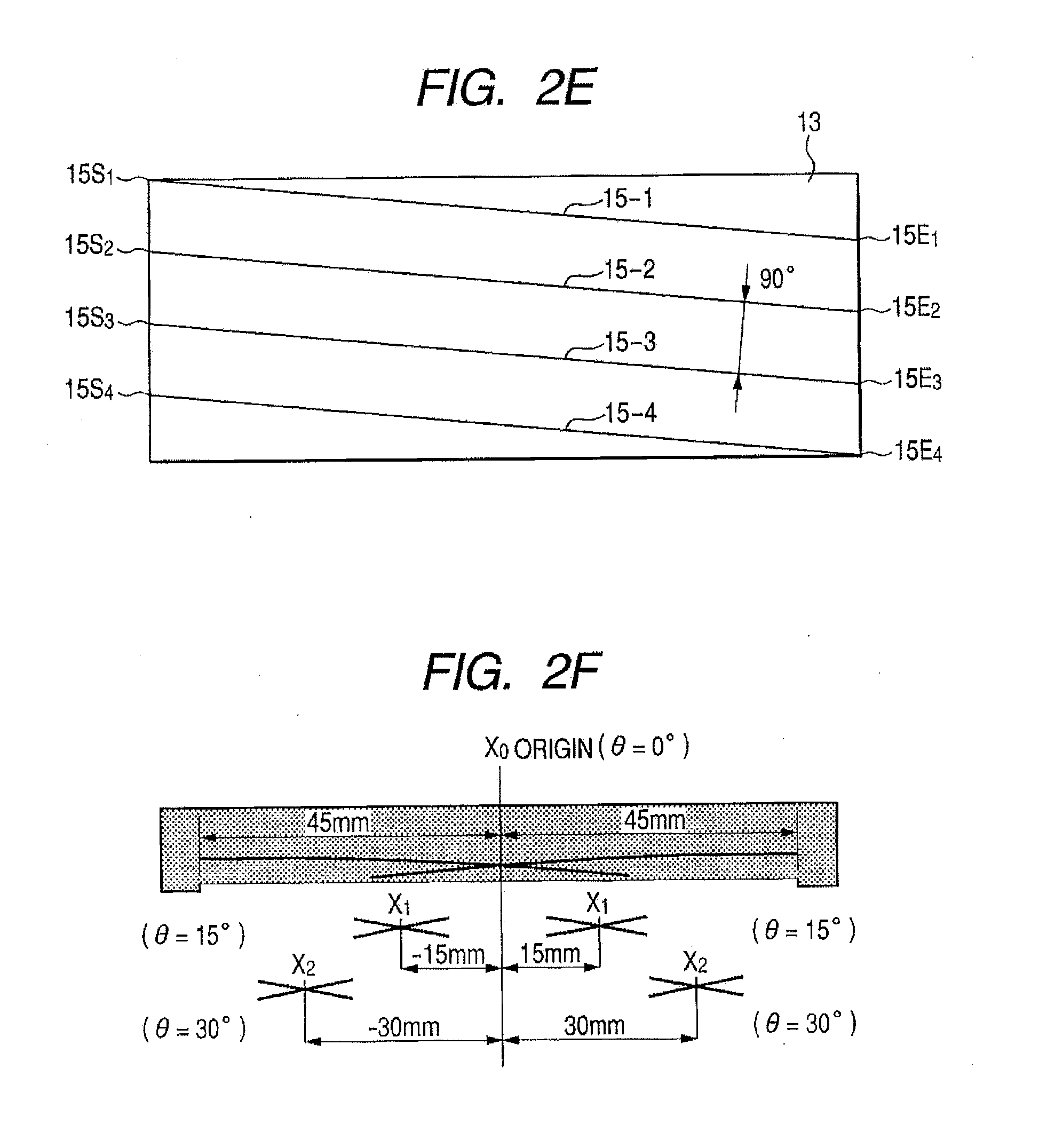
Intramedullary Rod for Assisting Total Knee Joint Replacing Operation and Method for Controle Operation Using the Rod
InactiveUS20110071537A1Accurate identificationShorten operation timeDiagnostic markersJoint implantsIntramedullary rodFluoroscopic image
Disclosed is an intra-medullary rod, including: a cylindrical body made of an X-ray transmitting material; a plurality of wires, which are made of a material that does not transmit X-ray and are deposited at regular intervals along a surface of the cylindrical body in the circumferential direction, being extended in an axial direction in a spiral shape, wherein each of the wires is made in a way that a starting end and a terminating end of the cylindrical body are connected by the shortest distance along the outer surface thereof. In a fluoroscopic image of the cylindrical body, a distance from a reference position to an intersection location of a pair of the wires corresponds to an amount of rotational angle of the intra-medullary rod. By digitizing the intersection location, the rotational angle of the intra-medullary rod is measured.
Owner:NLLGATA TLO LNC
Absorbable metal intramedullary nail and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101690676AAvoid or reduce stress shielding effectsPromotes fracture healingInternal osteosythesisCoatingsAlloyVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses an absorbable metal intramedullary nail and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of medical appliance. The intramedullary nail is a straight nail or a radian nail and is characterized in that the intramedullary nail comprises the follow components in percentage by mass: 0.01 to 10 percent of Zn, 0.01 to 5 percent of Ca, 0.001 to 5 percent of Fe, 0.01 to 5 percent of Mn and the balance of Mg; and the outer surface of the intramedullary nail is provided with a compound coating. The elastic modulus and the density of the intramedullary nail are close to those of a human body, which avoids or reduces stress shielding effect and promotes fracture union; and simultaneously, the intramedullary nail has higher intensity so as to make up the shortage of a degradable polymeric material. The intramedullary nail can be absorbed continuously in the human body and can generate a phosphate layer of Ca and Mg during the absorption and degradation, which contributes to bone conduction. The degradation rate can be regulated effectively by changing components and a structure of alloy, and components and a structure of a coated coating.
Owner:CHANGSHU MICROTUBE TECH
System for intramedullary rod fixation and method therefor
ActiveUS7785326B2Suture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisIntramedullary rodFemur intramedullary nailing
A system and method for securing an intramedullary rod in a medullary canal of a long bone is provided. The system includes an intramedullary rod and a screw assembly for receiving the rod. The screw assembly has a transverse receiving bore for receiving the intramedullary rod and a securing member movable toward the bore for securing the rod to the screw assembly. An alignment jig may also be provided for aligning the rod with the receiving bore during installation.
Owner:PEGA MEDICAL
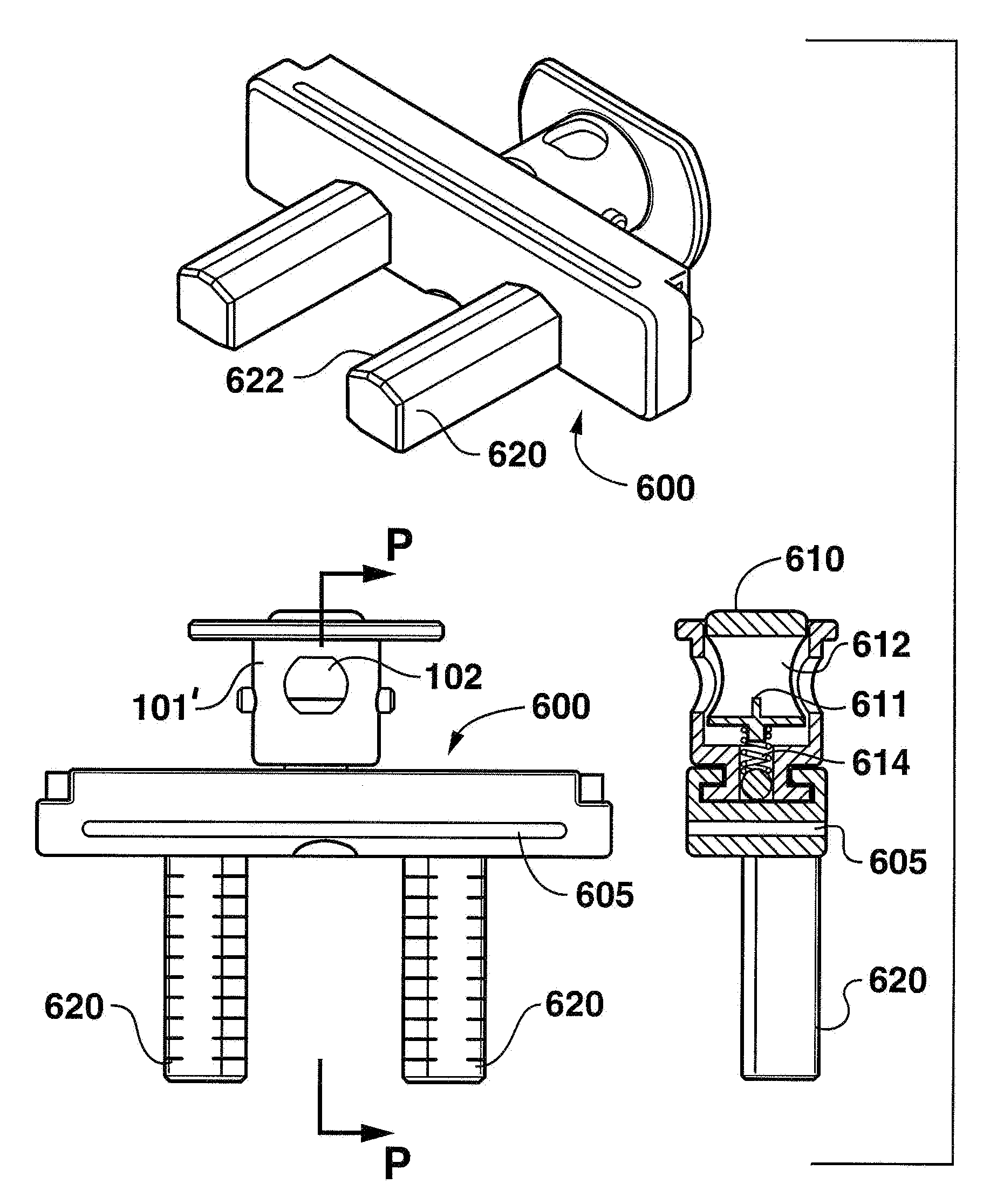
Device and method for distal resections of a knee prosthetic
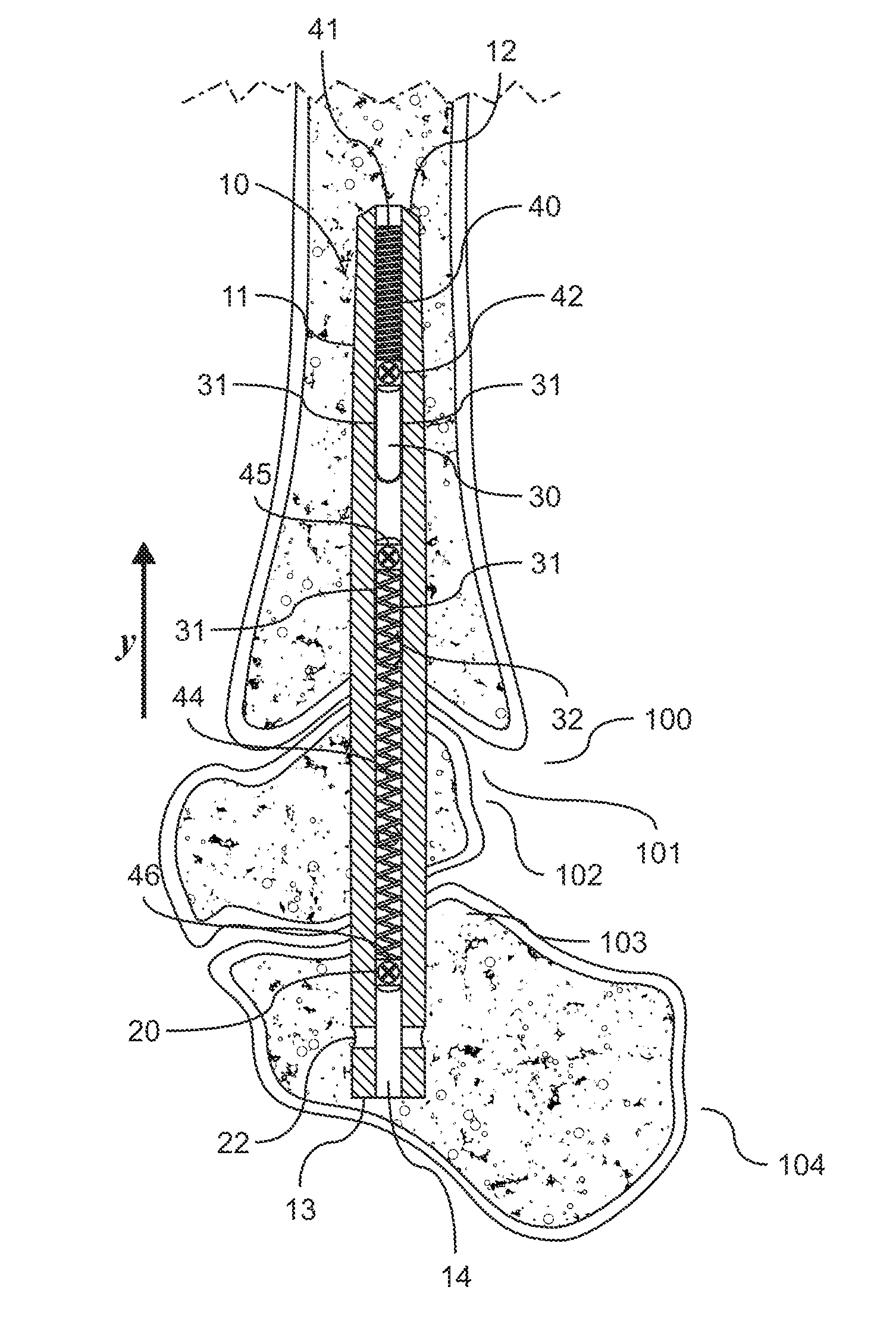
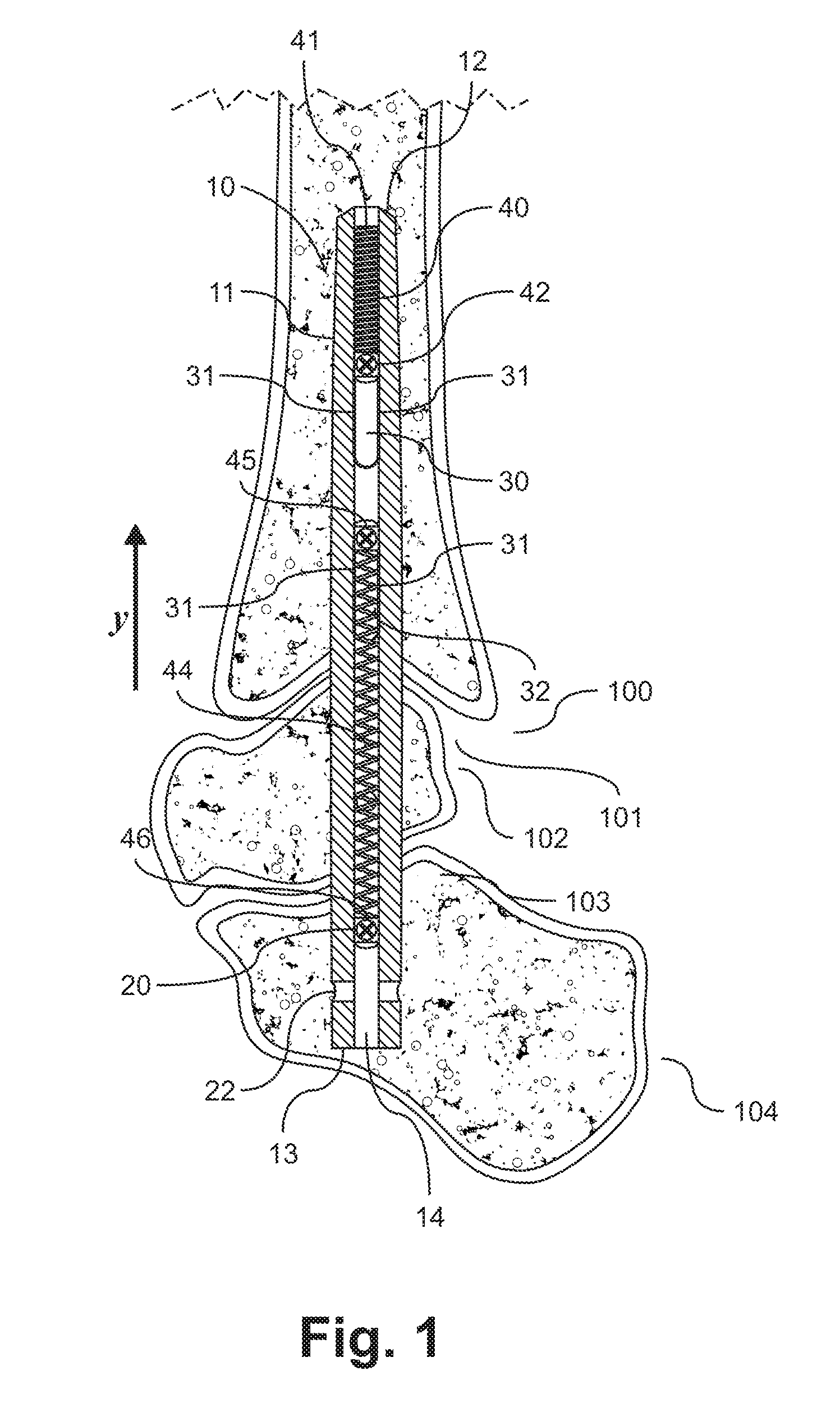
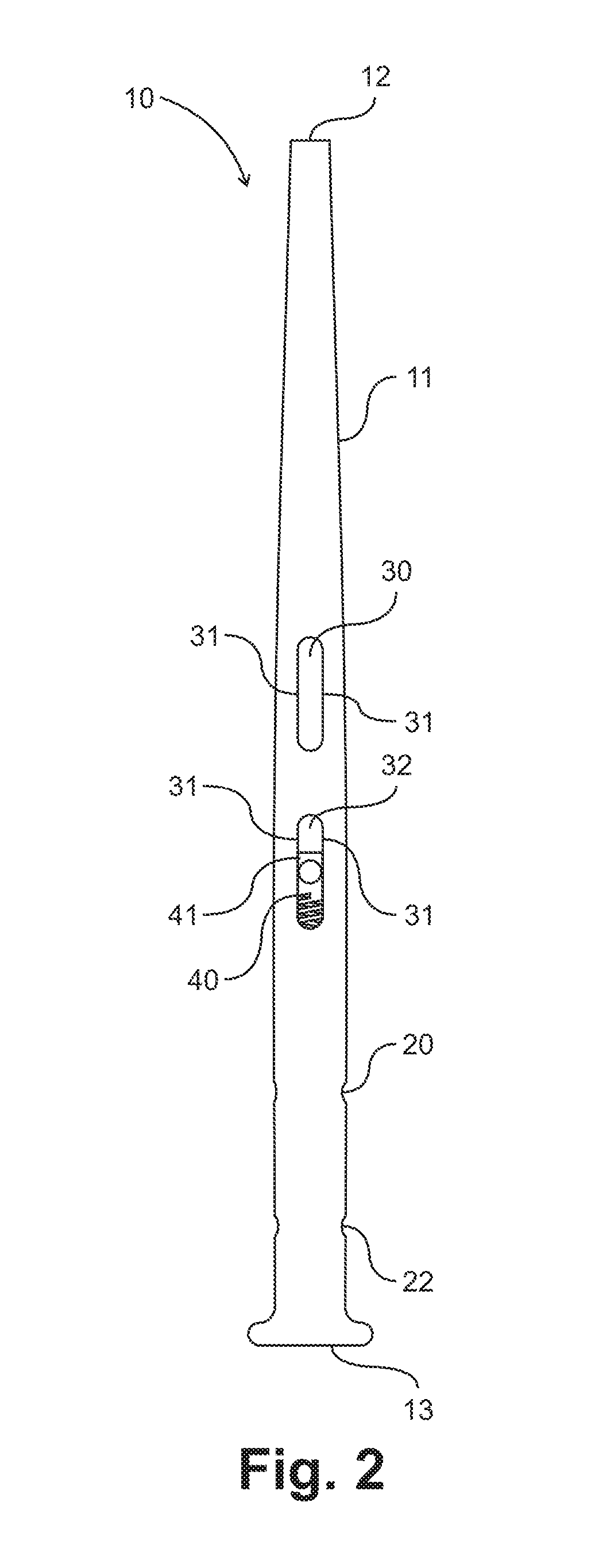
ActiveUS20100094301A1Accurate placementImprove performanceSurgical sawsProsthesisIntramedullary rodMedicine
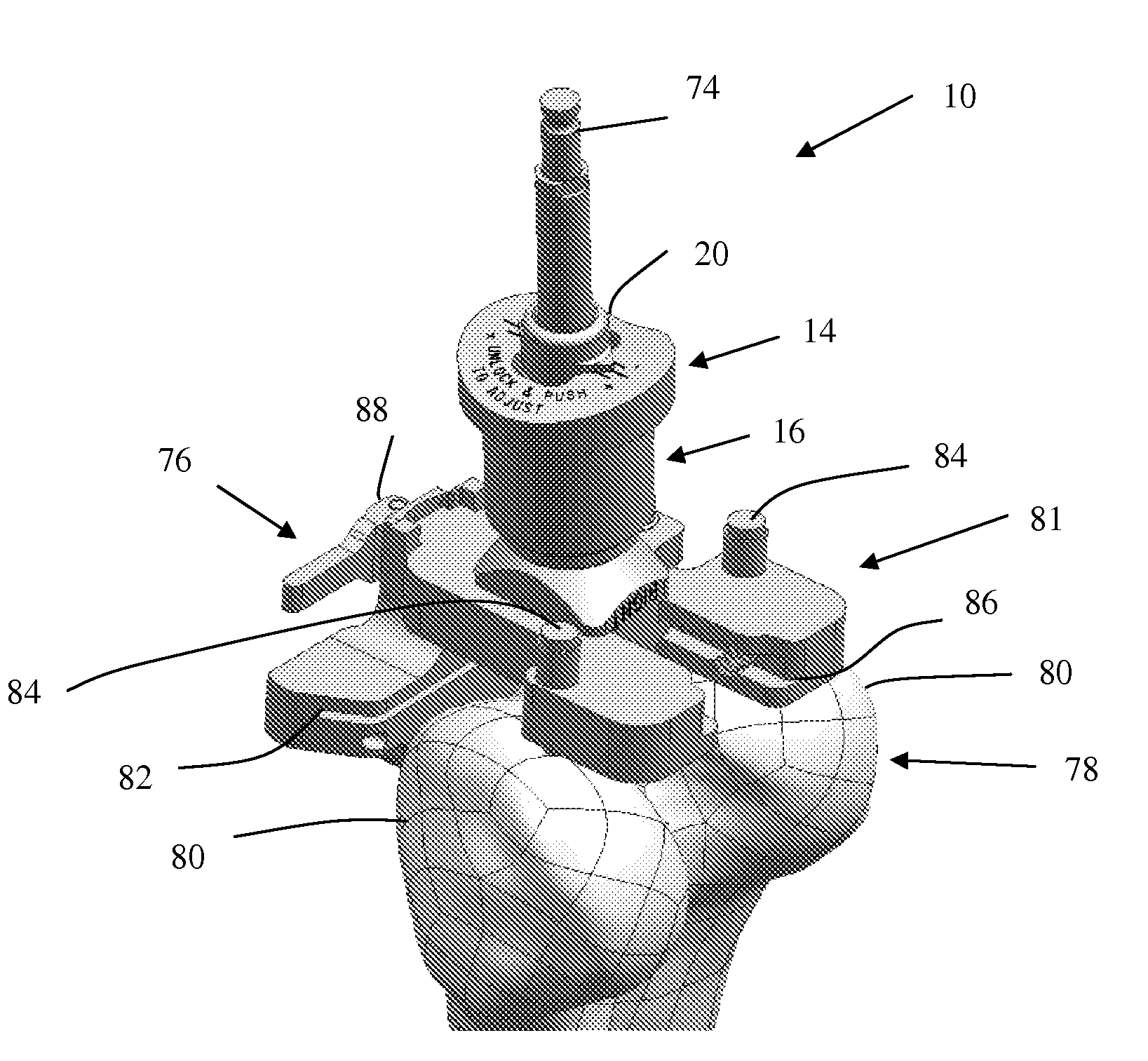
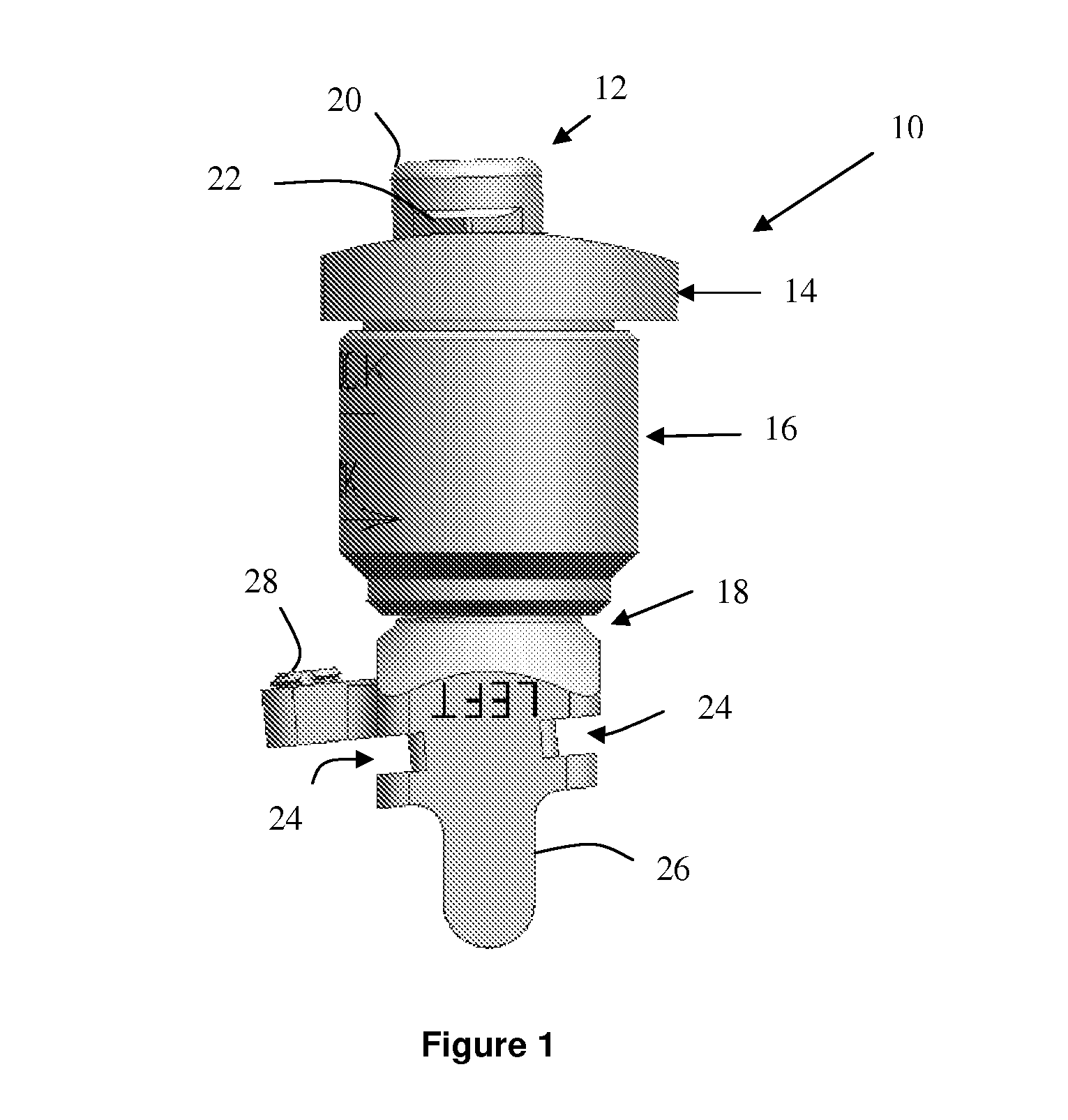
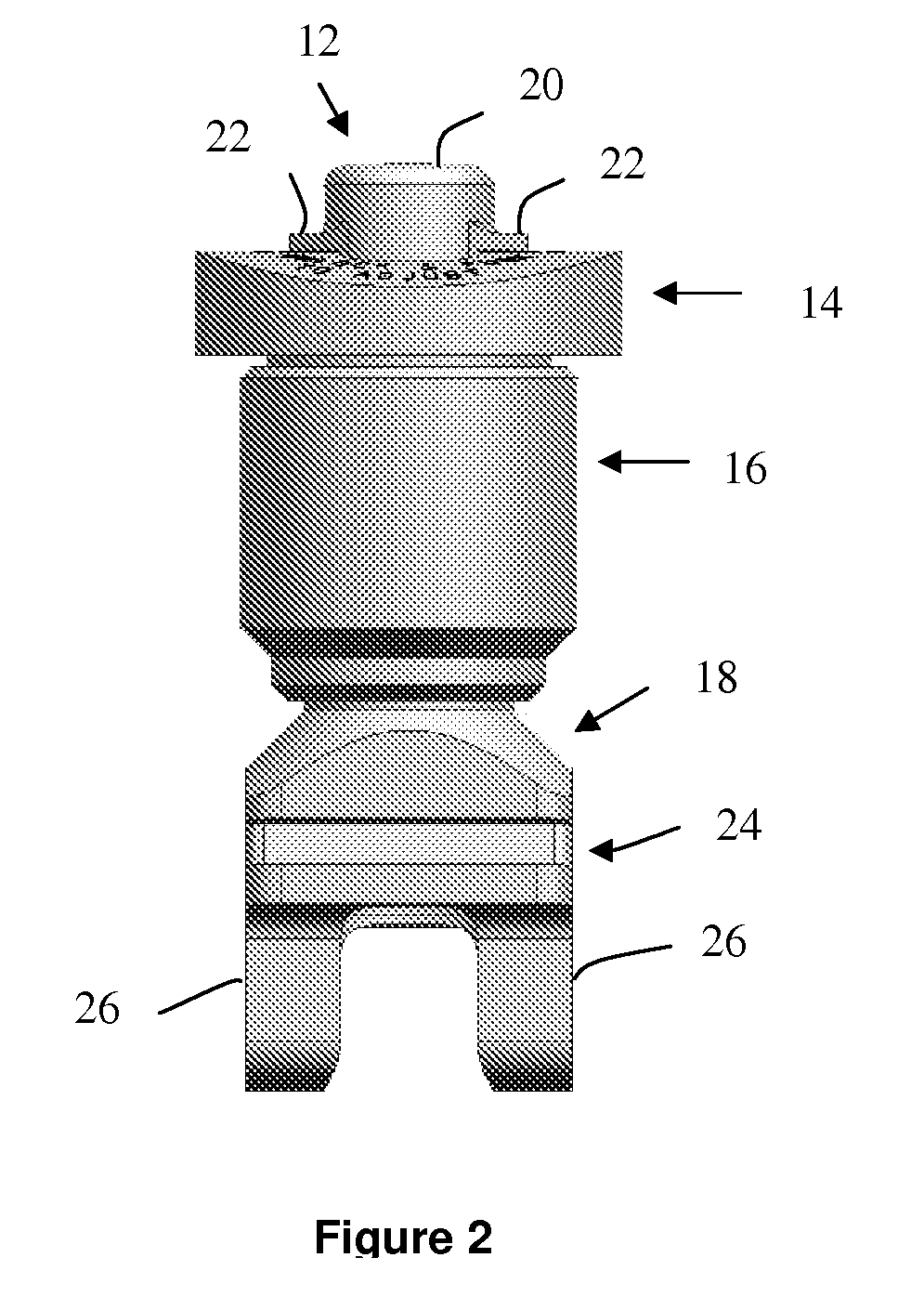
A device and method for resecting a distal portion of a femur comprises a distal cutting guide [98], a valgus guide [102], and a variable collet [10]. The distal cutting guide [98] is configured to overlie an anterior portion of the femur and comprises a slot for guiding a cutting tool across a distal portion of the femur. The valgus guide [102] is configured to connect to the distal cutting guide [98]. The valgus guide [102] is configured to align the slot of the distal cutting guide[98] at the proper varus / valgus angle. The variable collet [10] is configured to attach to an intramedullary rod and the valgus guide [102]. The variable collet [10] comprises a port [30] for receiving the intramedullary rod. The port [30] is angularly adjustable with respect to the valgus guide [102] such that adjusting the port [30] adjusts the varus / valgus angle of the distal cutting guide [98].
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
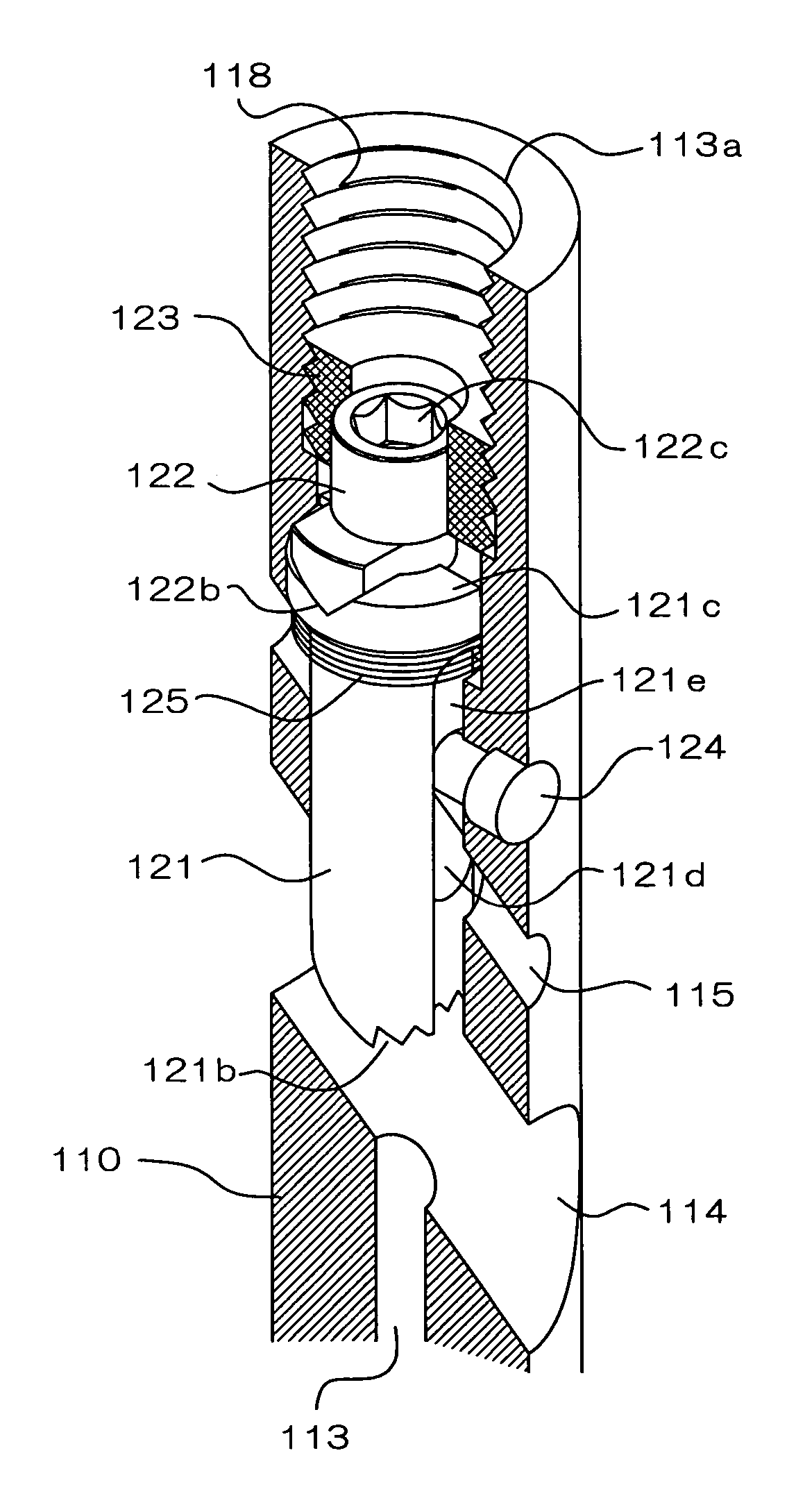
Intramedullary nail
InactiveUS7601153B2Easily and securely and accuratelyAccurate settingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntramedullary rodBiomedical engineering
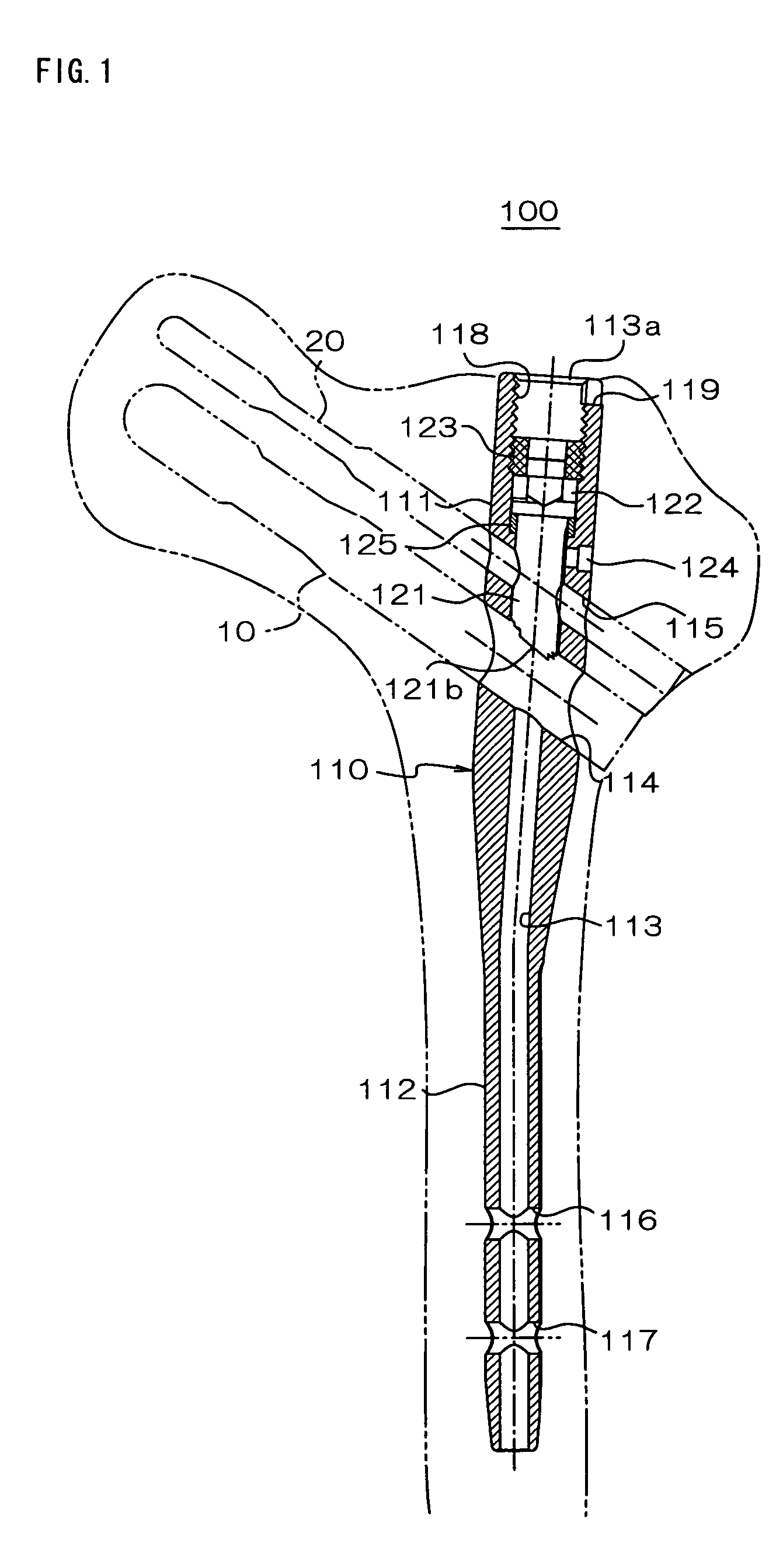
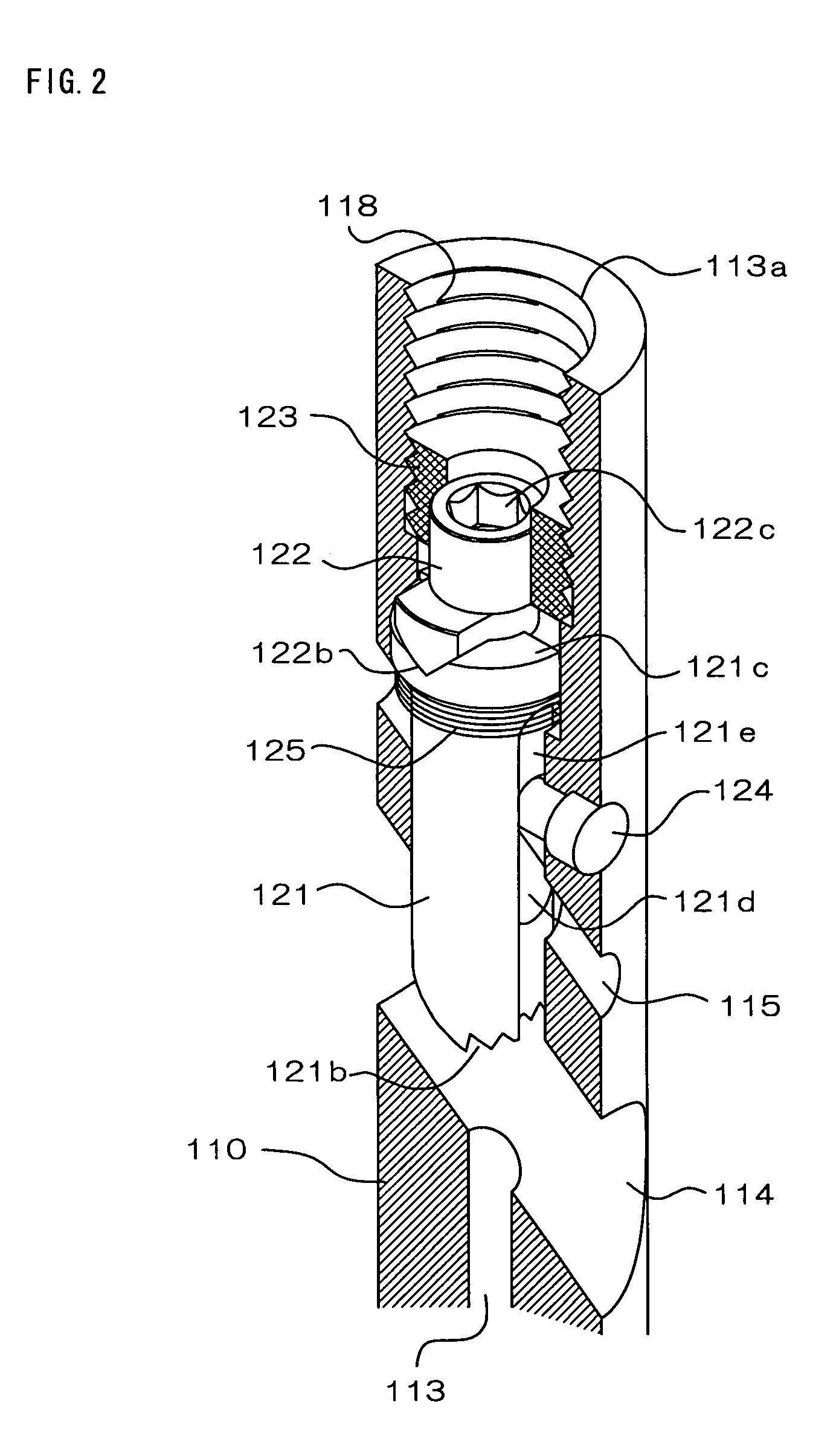
The present invention is an intramedullary nail (100) to be used by being intramedullarily inserted into a bone, having a nail body (110) comprising an axial hole (113) extending from an opening formed at a proximal end portion toward a distal end portion along an axis line and a transverse hole (114) intersecting with the axis line, and having: an engaging member (221) comprising an engaging portion (221b) at distal end thereof engageable with a bone fastener inserted through the transverse hole and arranged so as to be shiftable in the axial hole in a manner where the distal end portion is engageable and disengageable with the bone fastener (10); an adjusting member (222) controlling the position of the engaging member; and an elastic member (125) for charging, against the nail body, the engaging member in a direction opposite the controlling direction by the adjusting member.
Owner:HOMS ENG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com