Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
270 results about "Distal femur" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
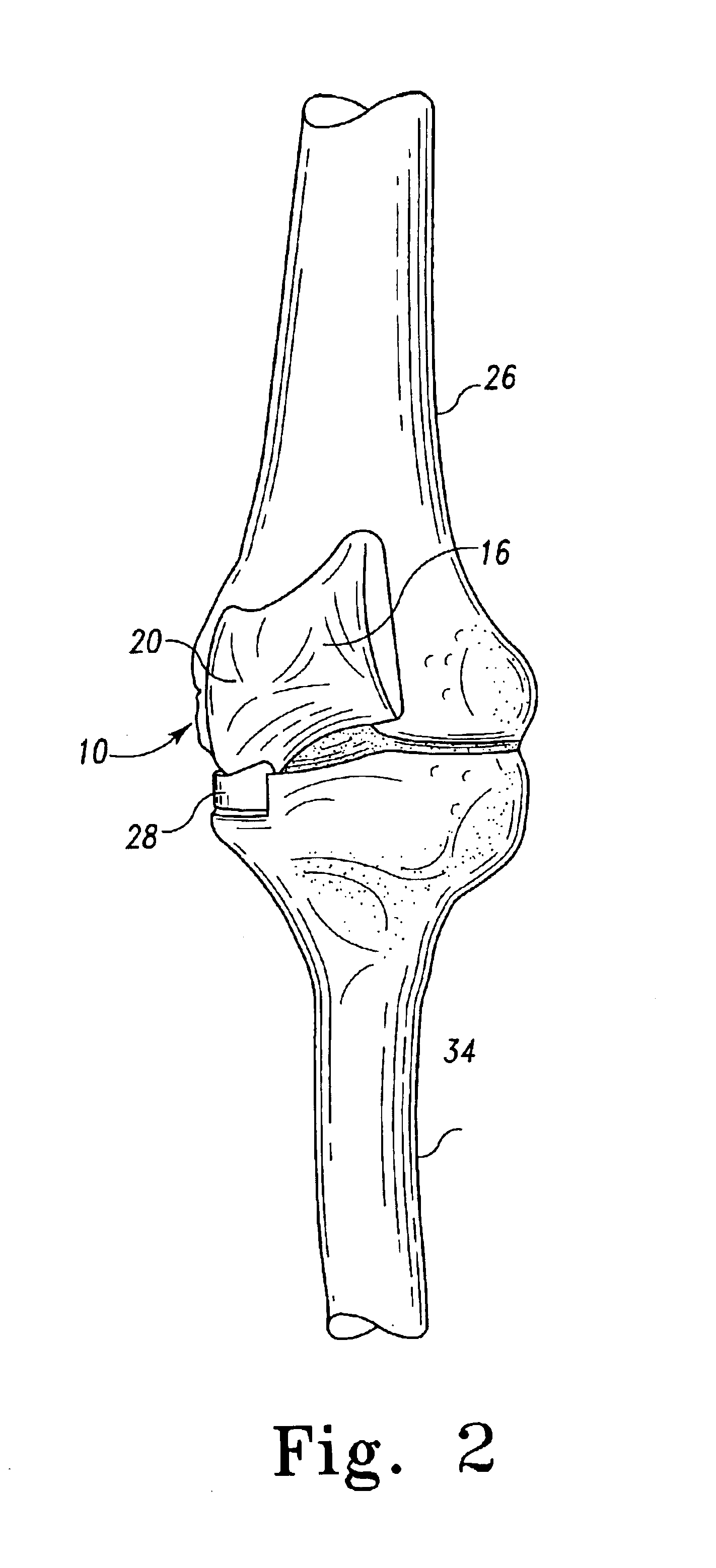
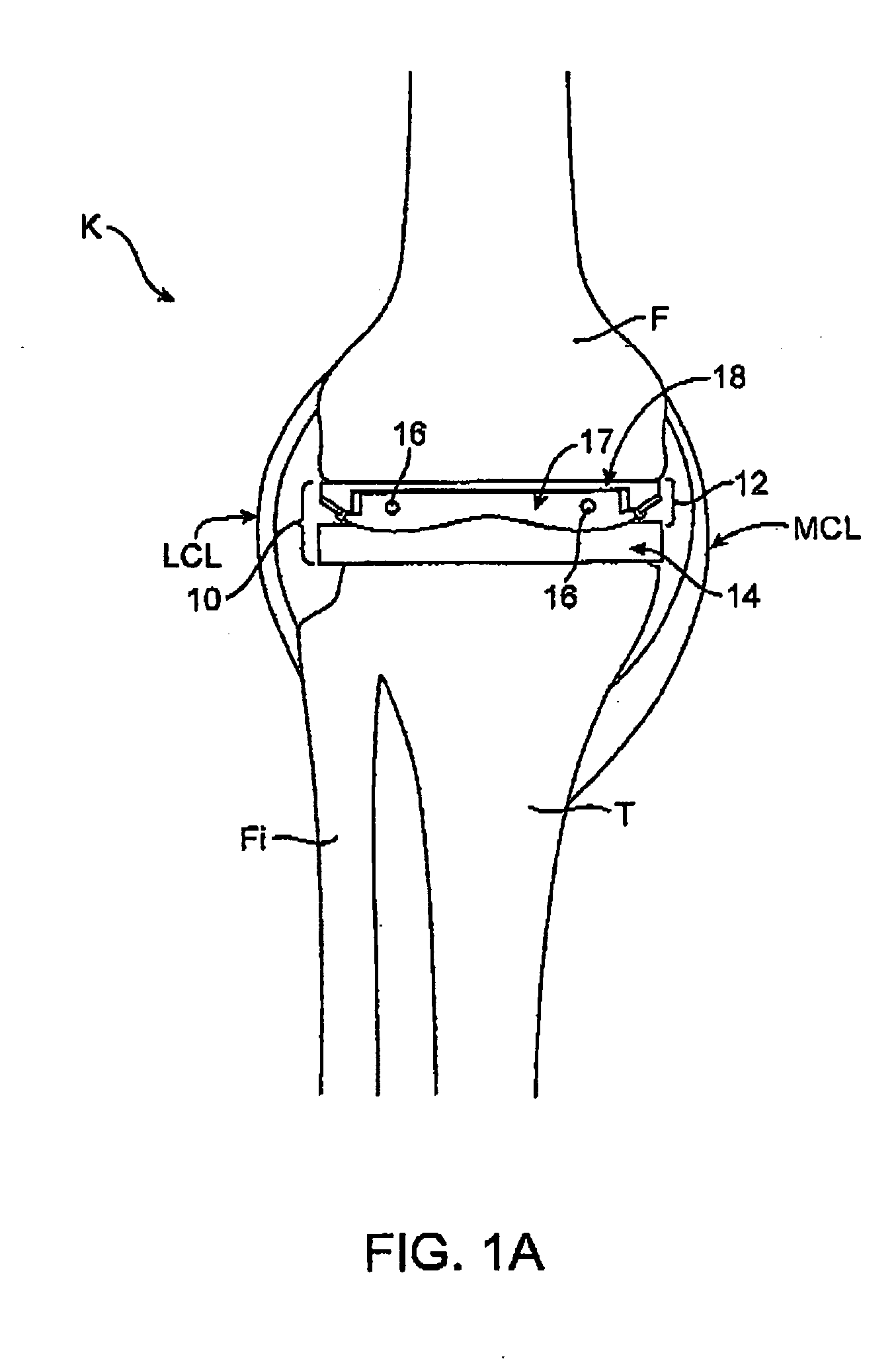
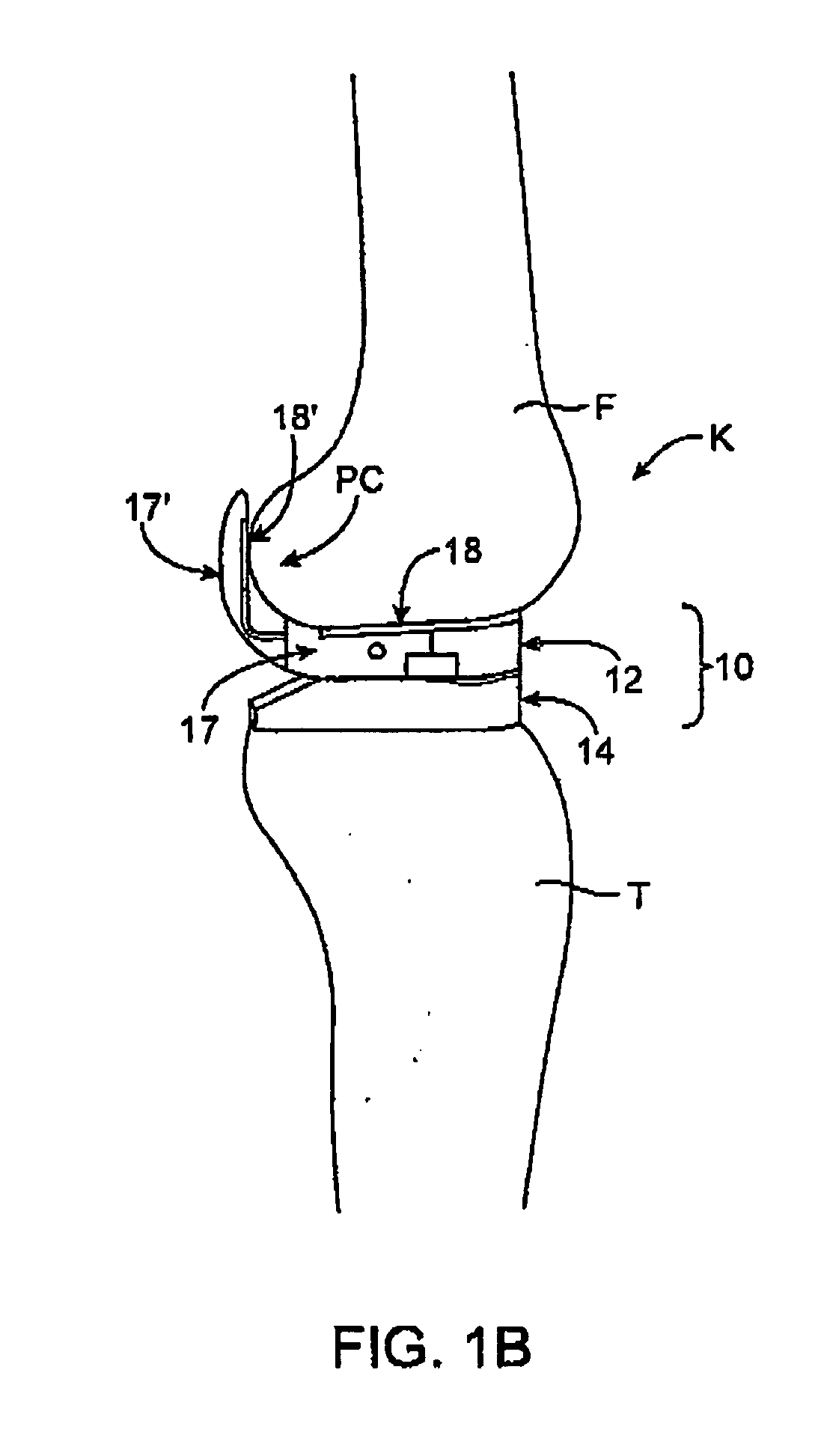
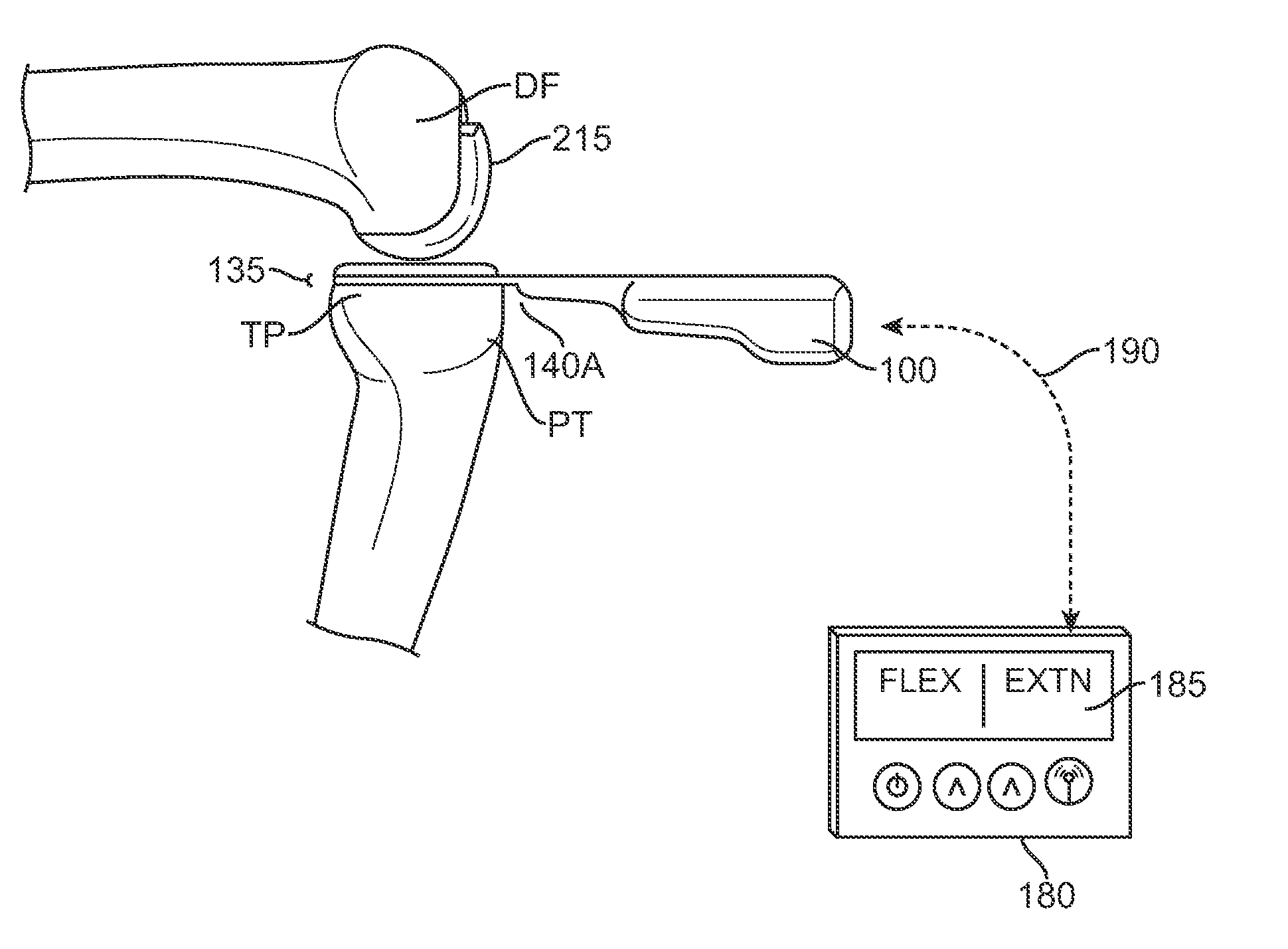
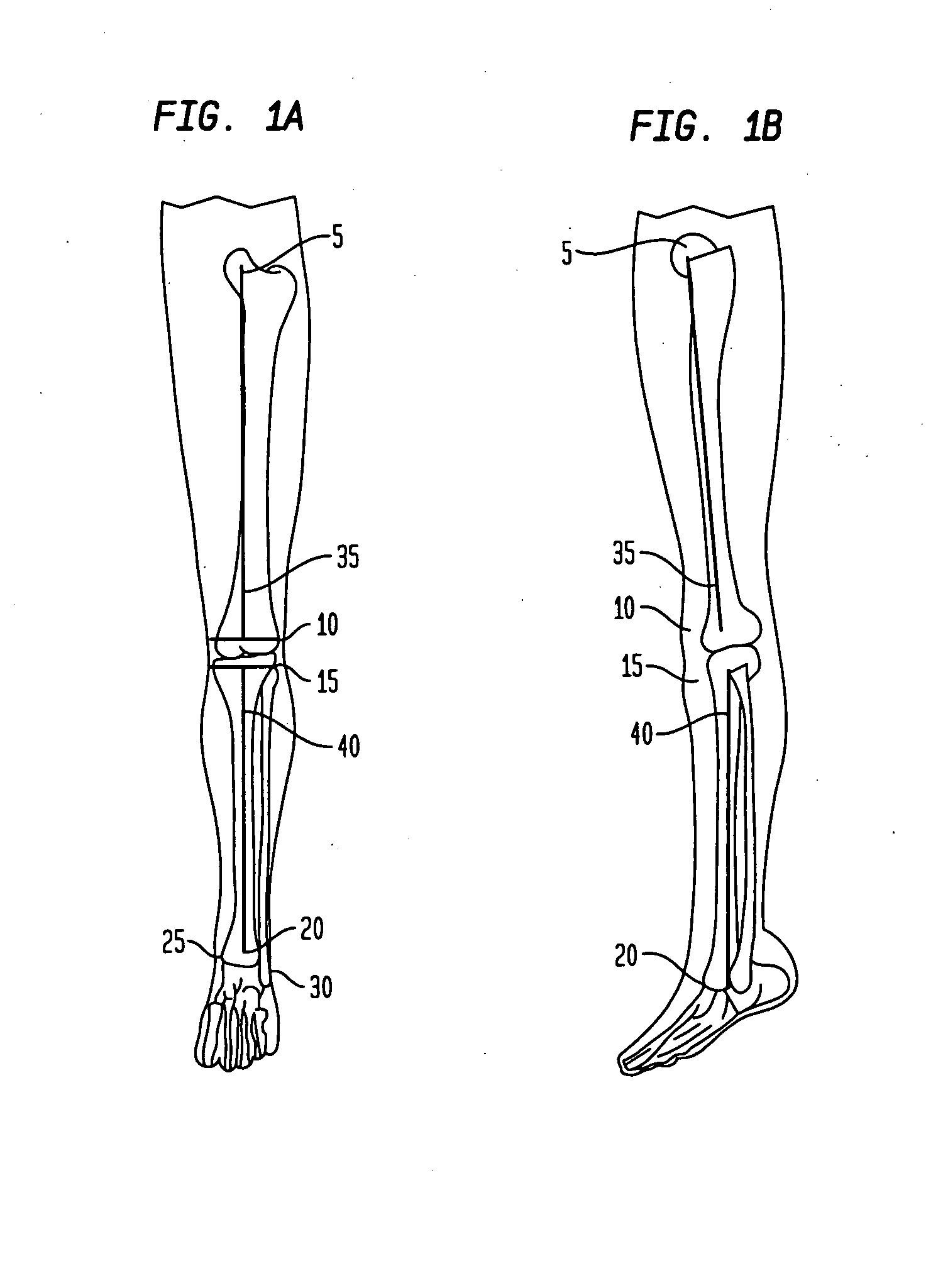
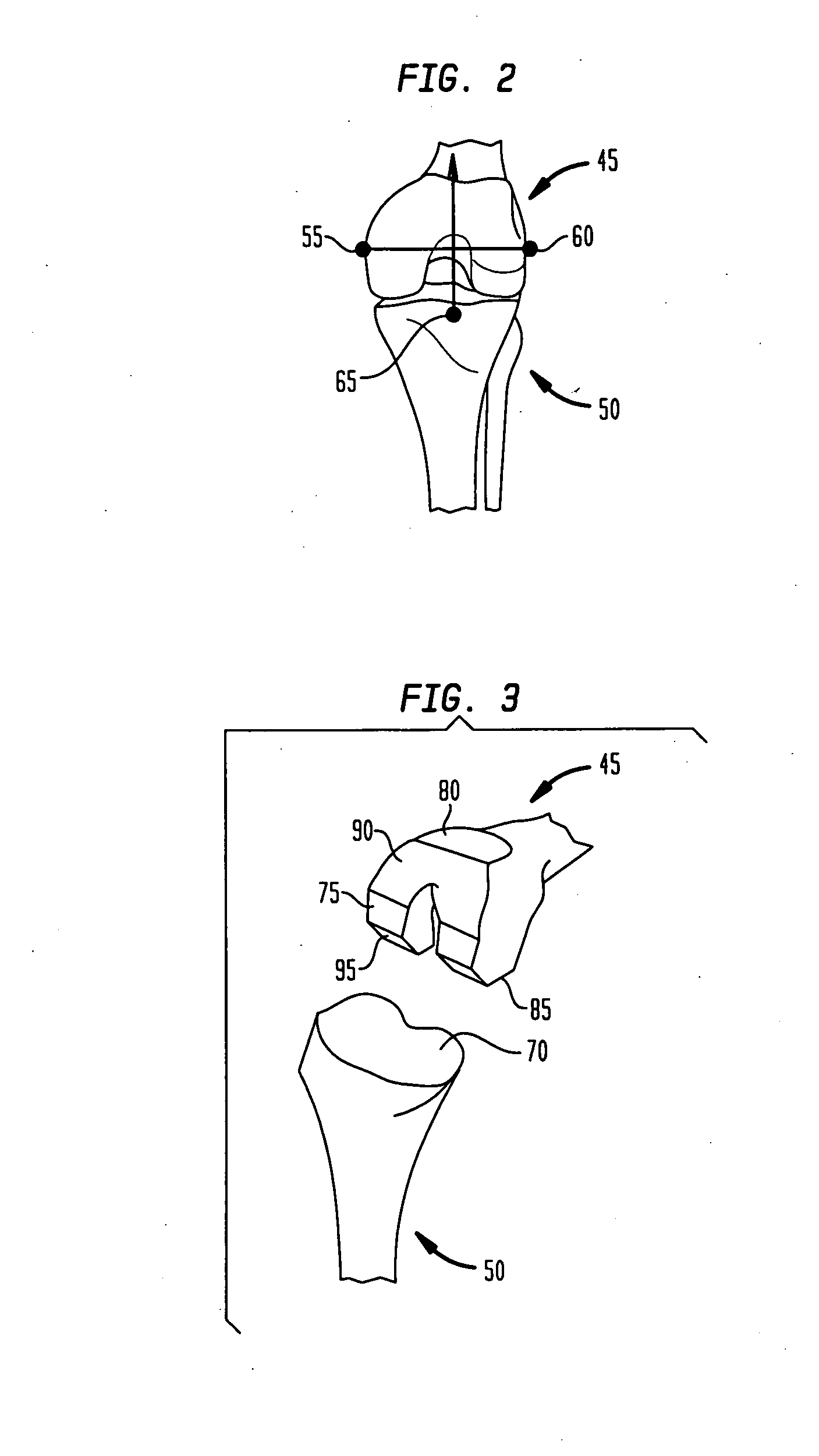
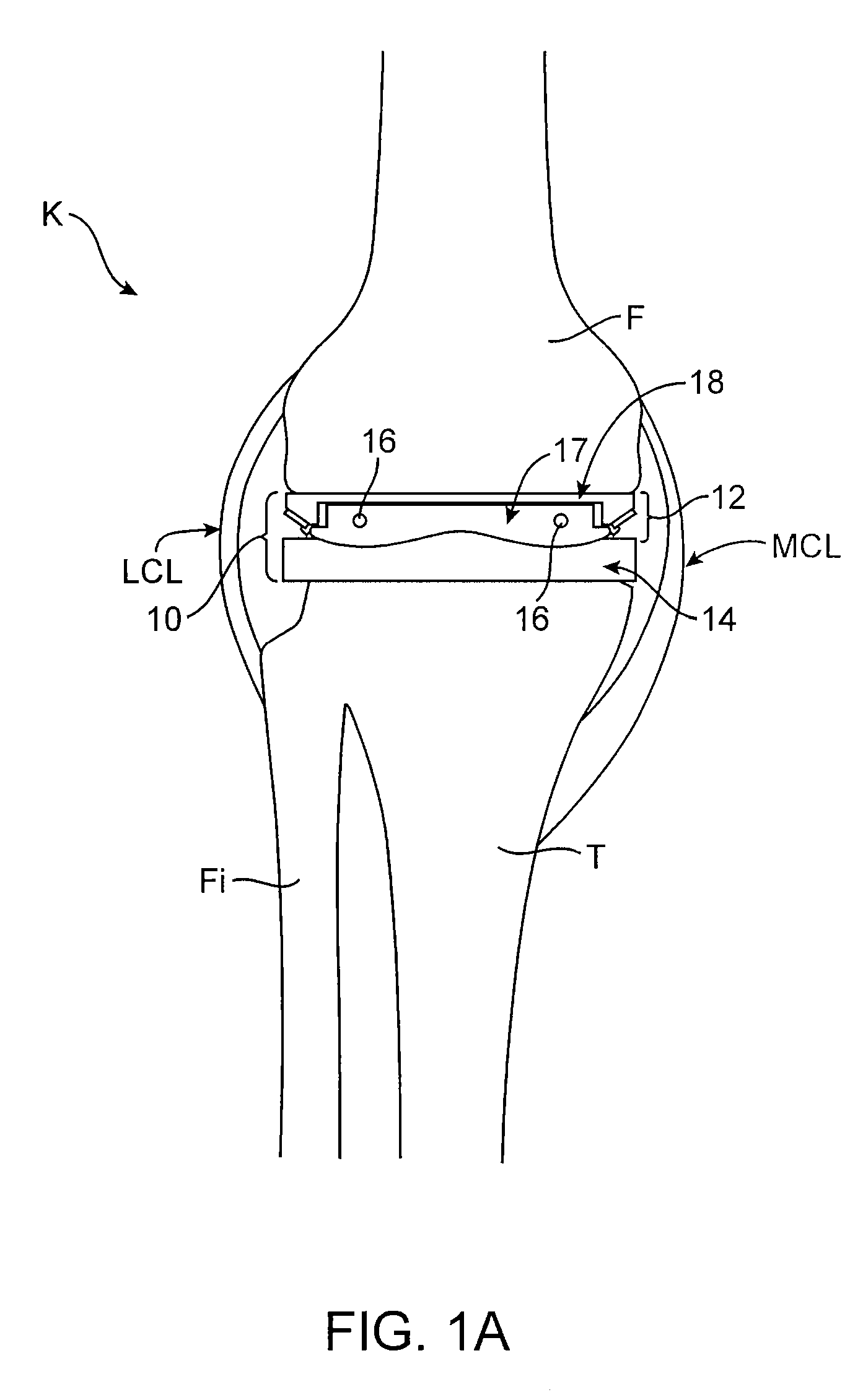
The femur is the thigh bone. Distal femur indicates the part of the thigh bone just above the knee. A Fracture of the Distal Femur is a break or crack that occurs anywhere within the lower region of the femur (near the knee)
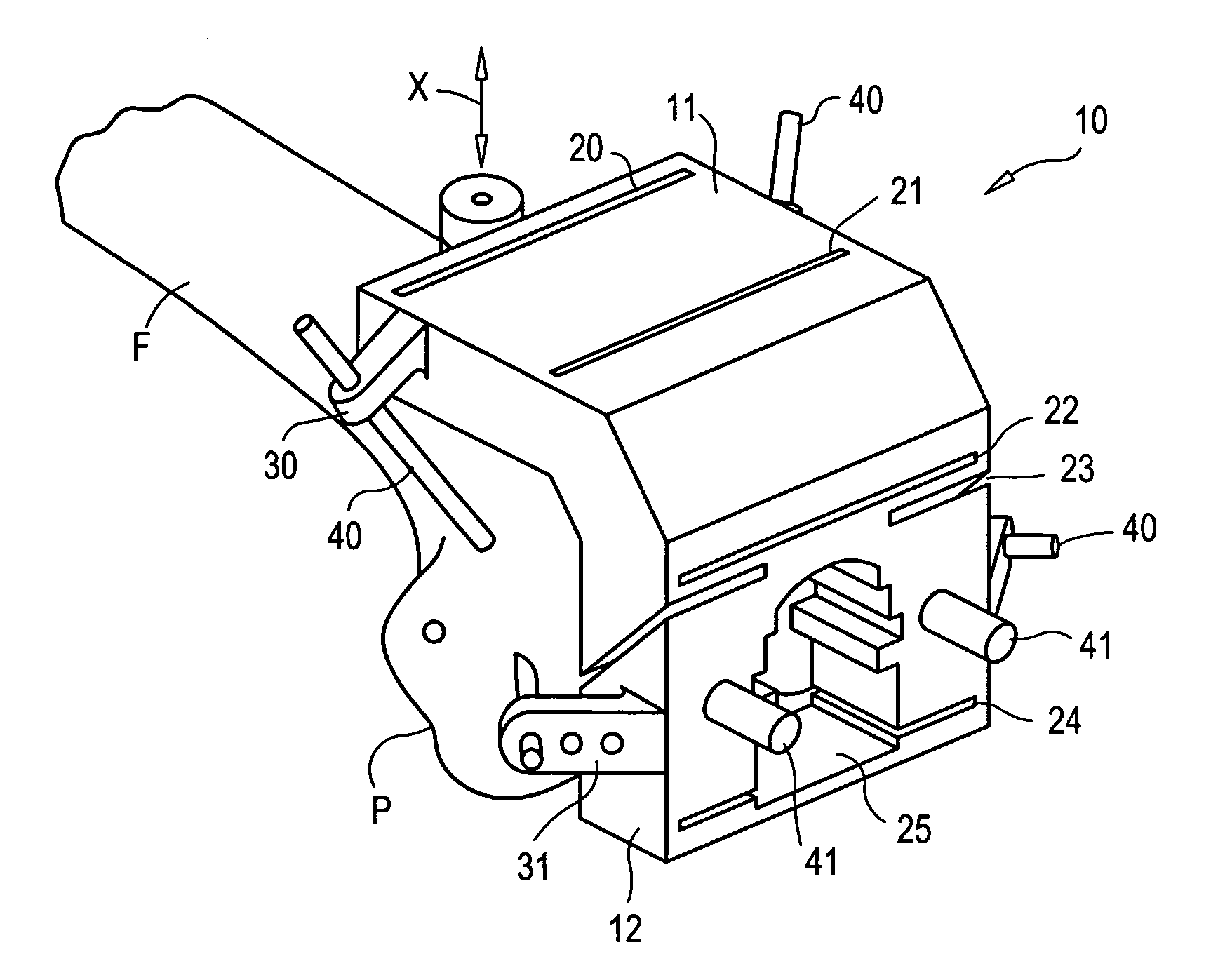
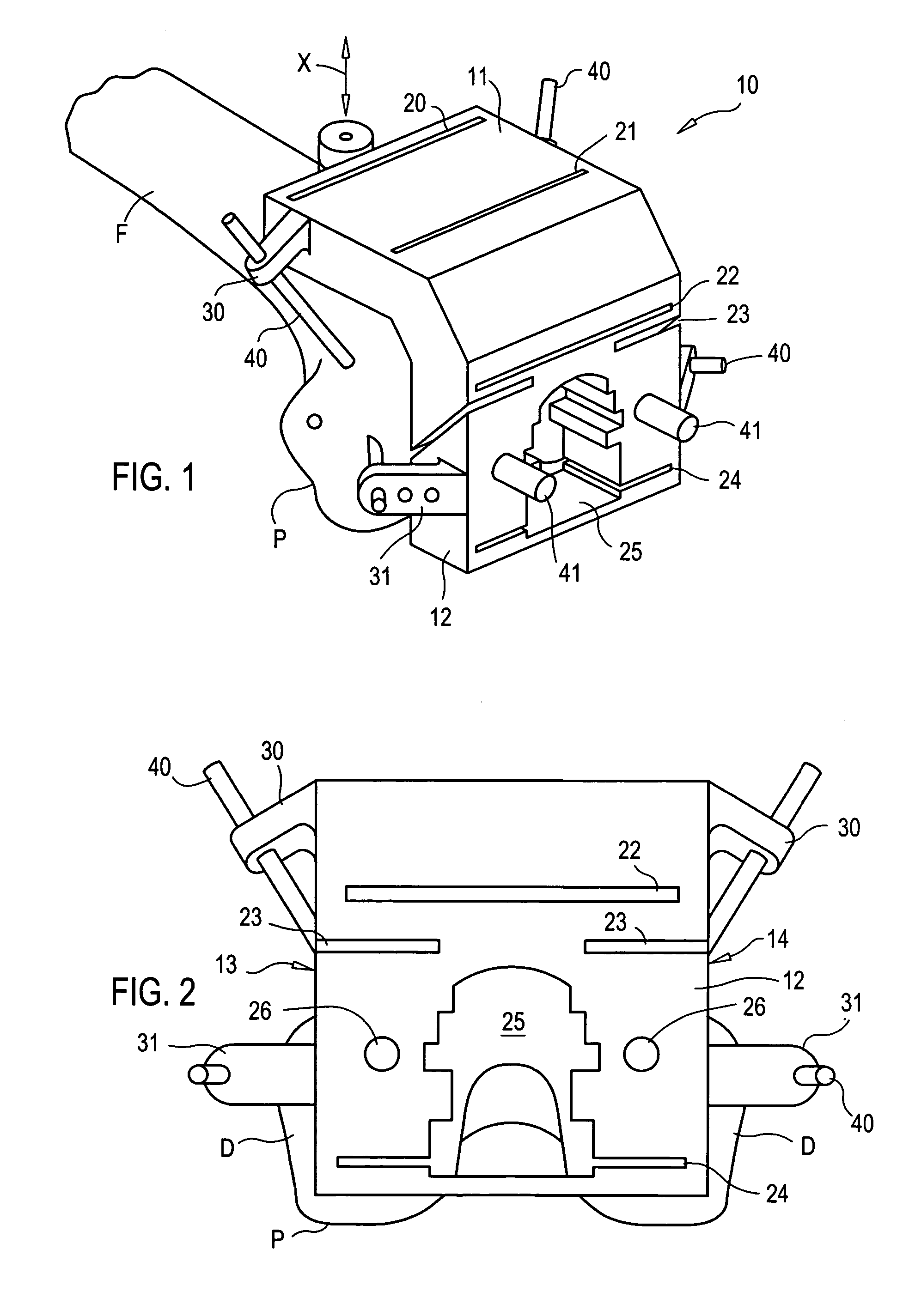
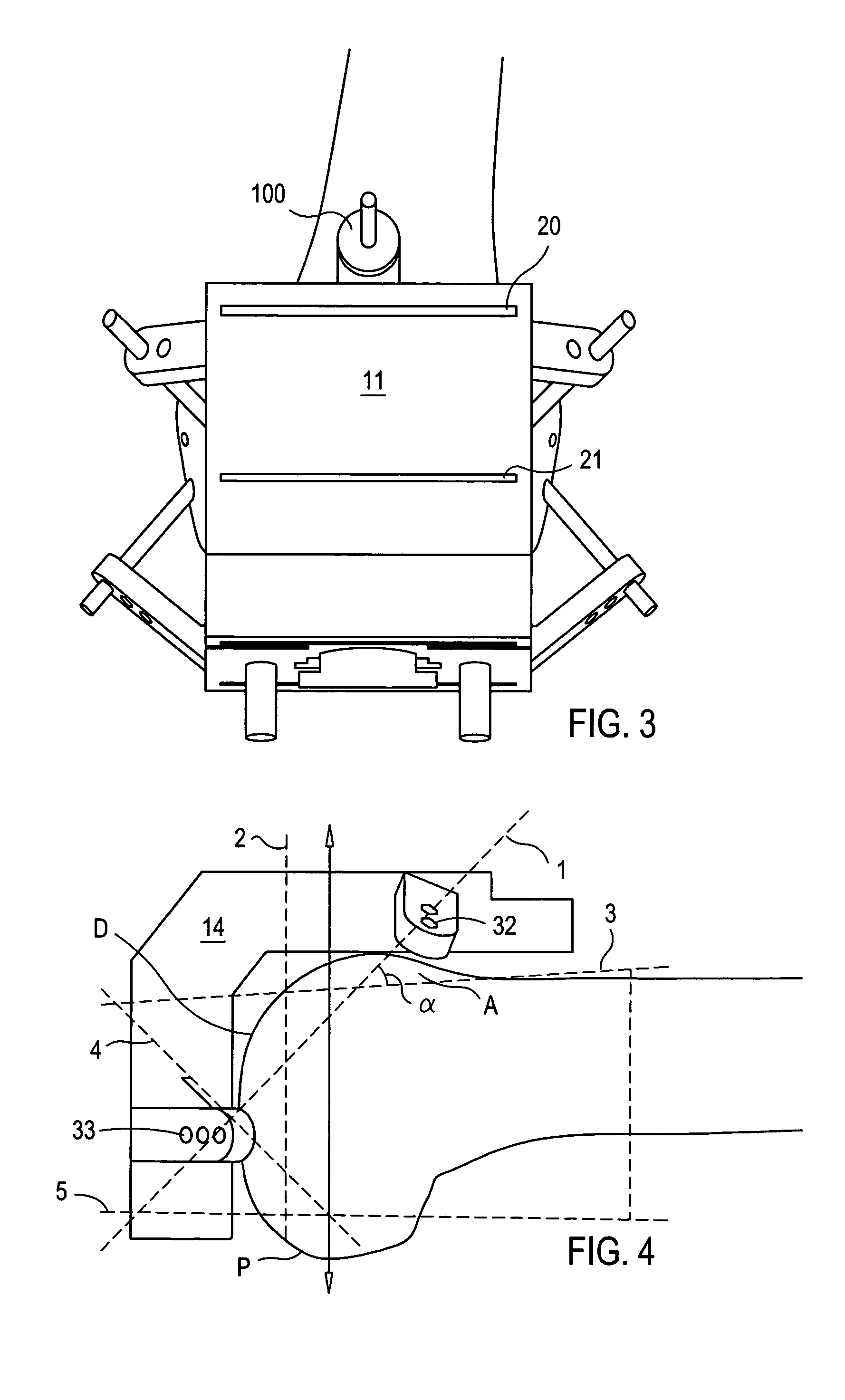
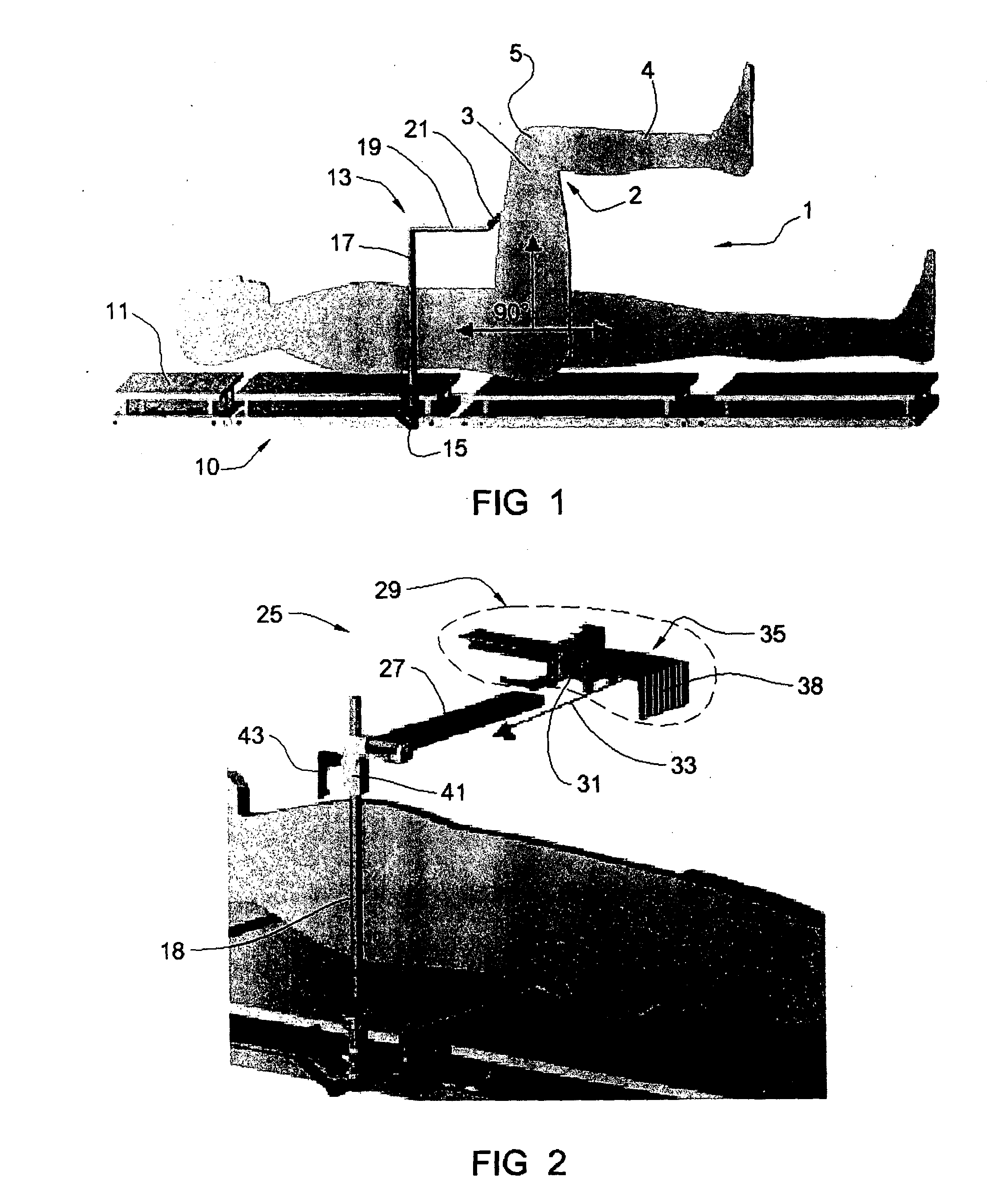
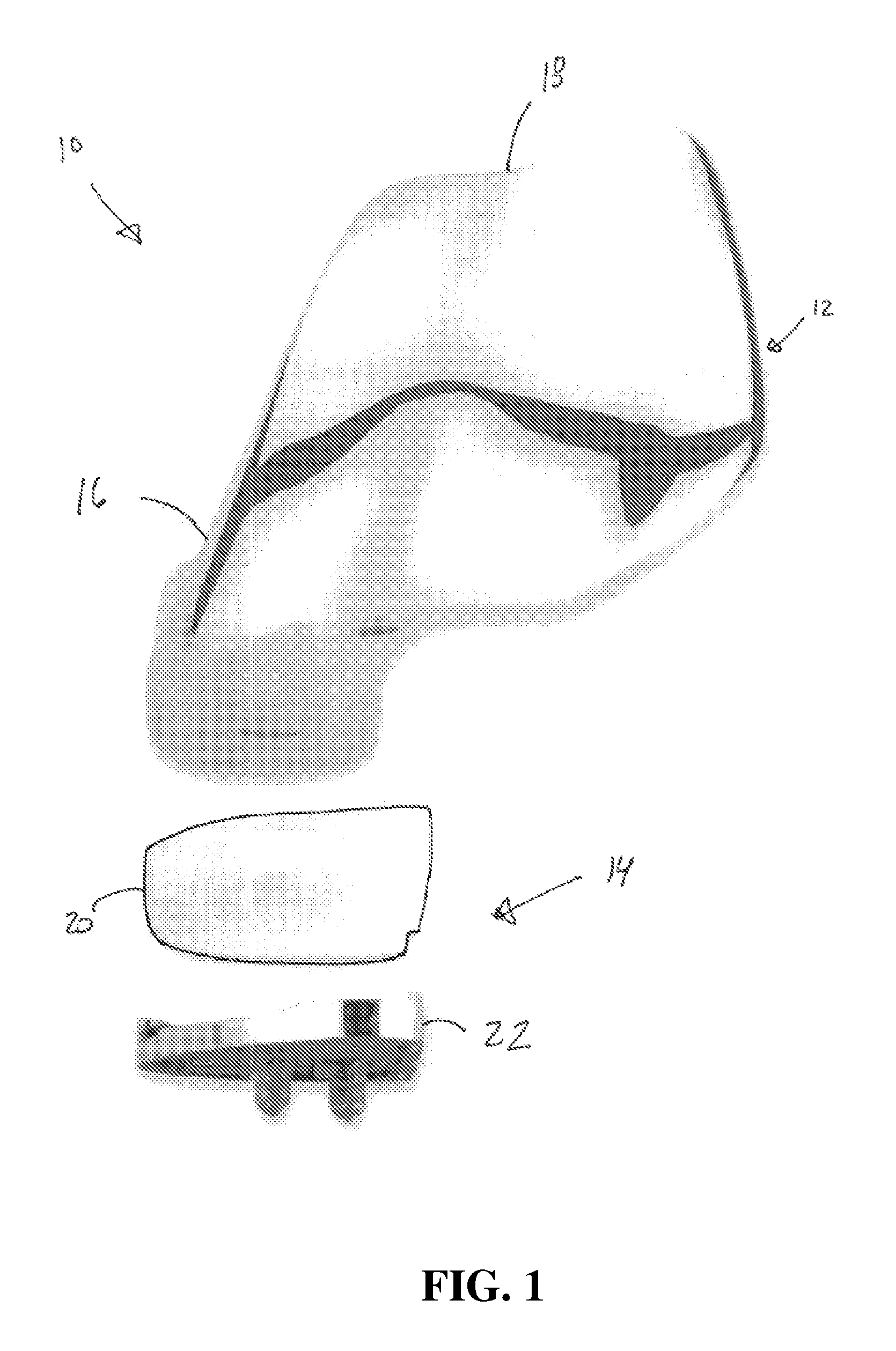
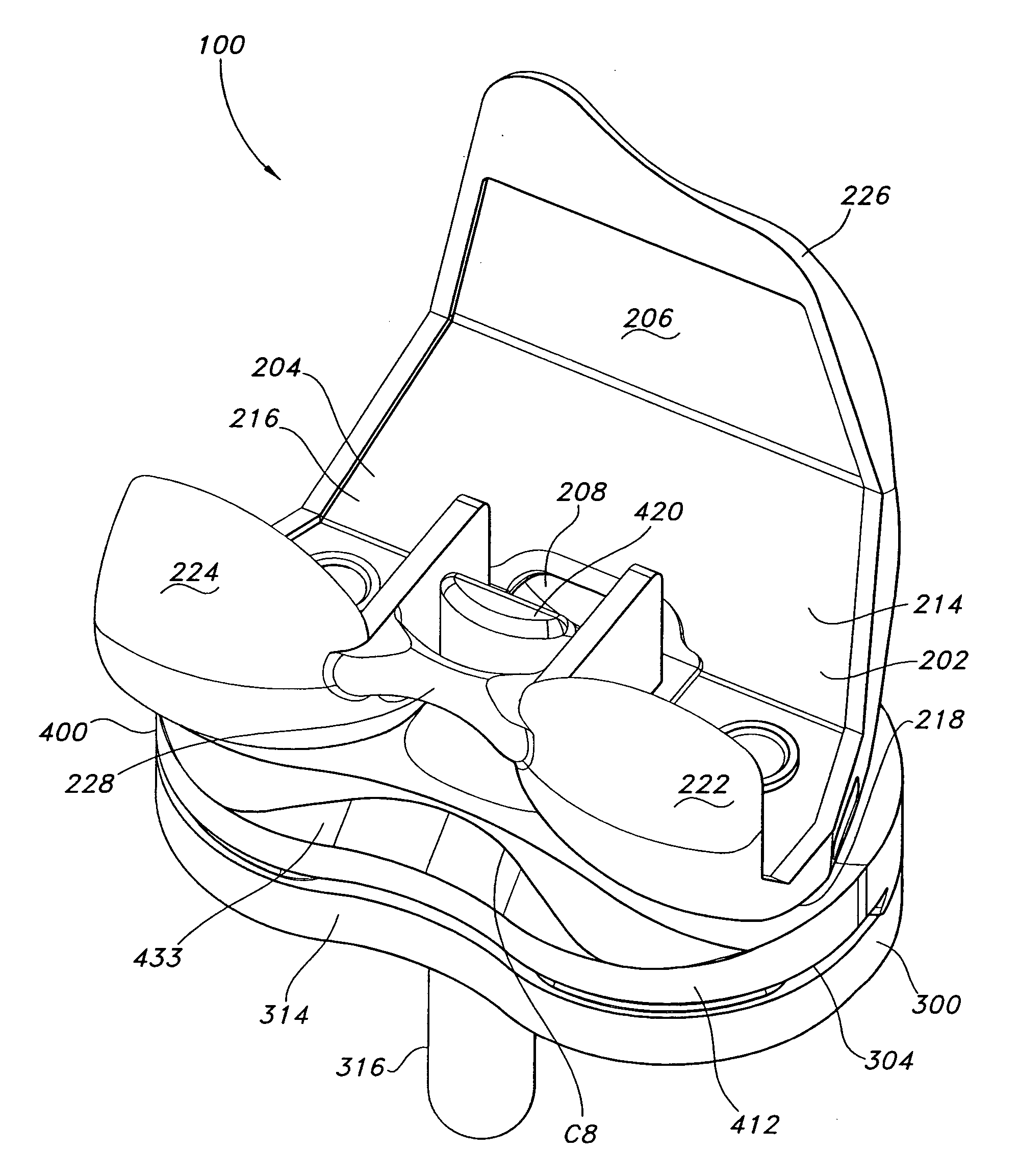
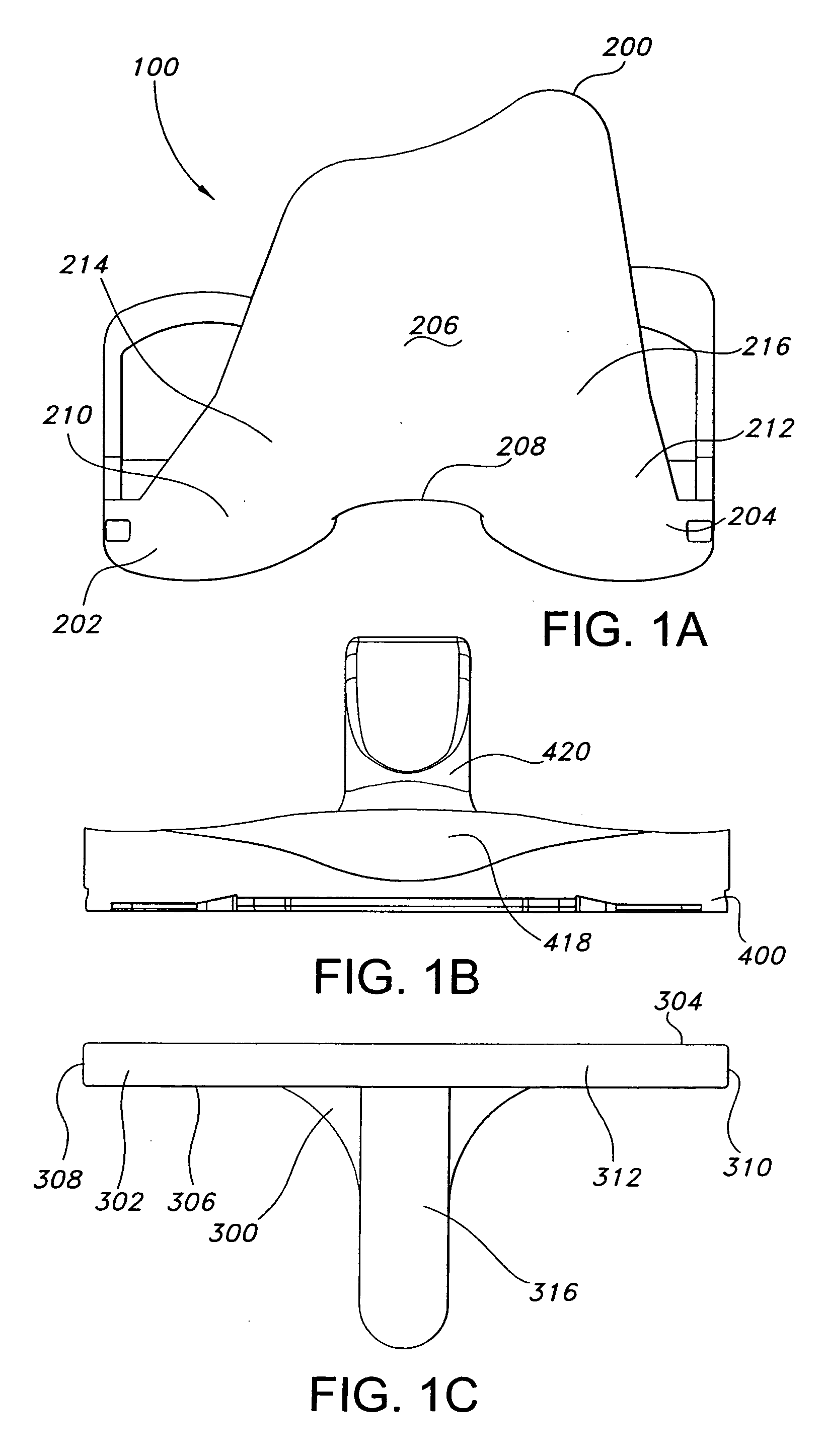
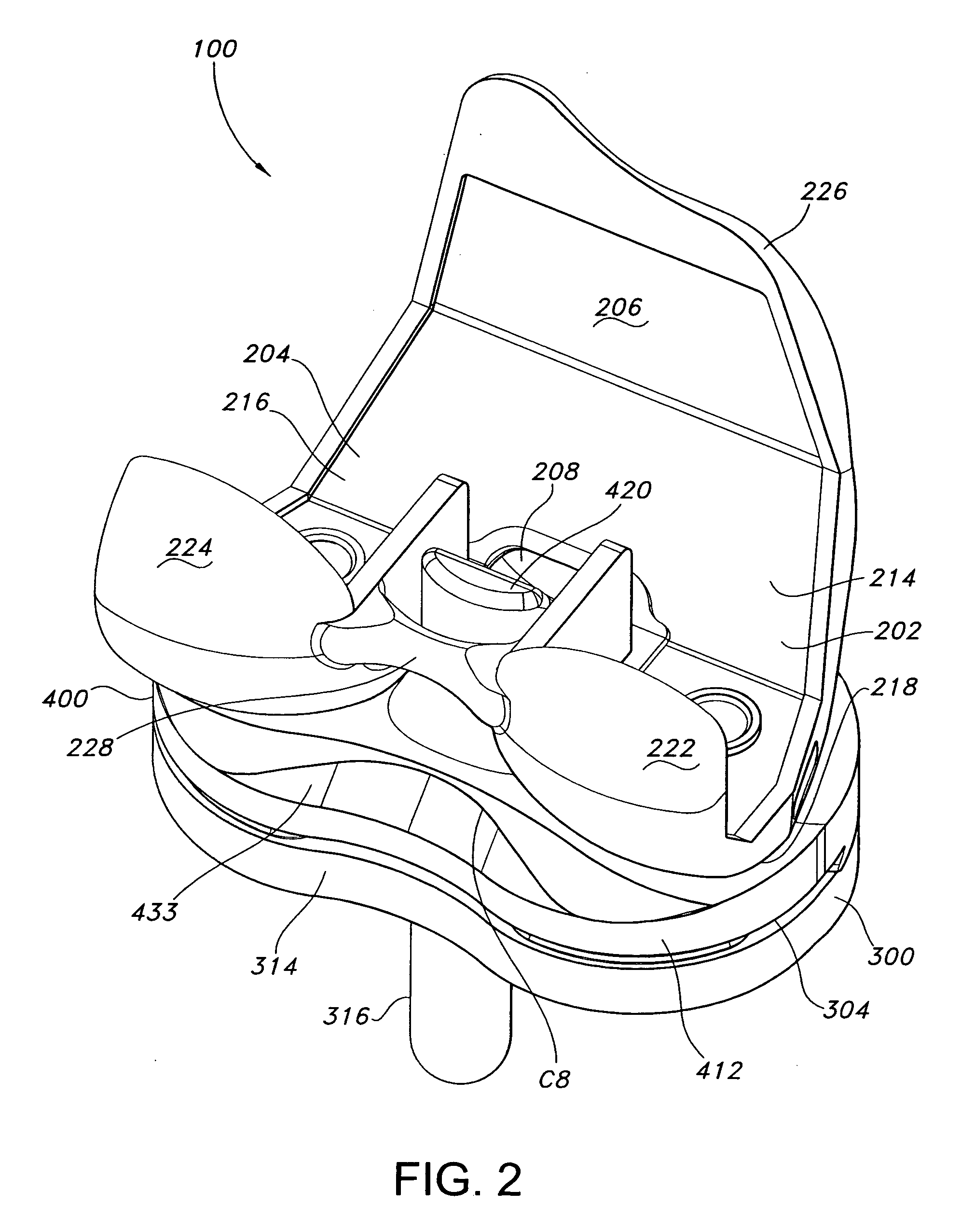
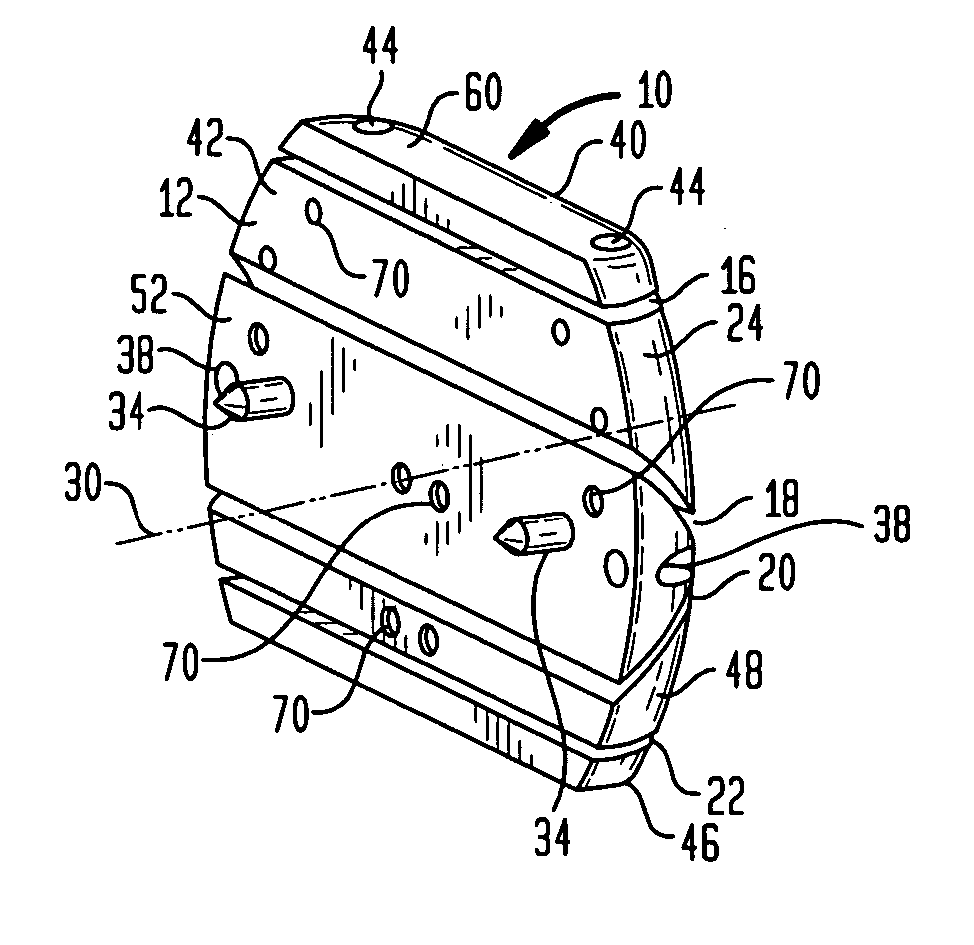
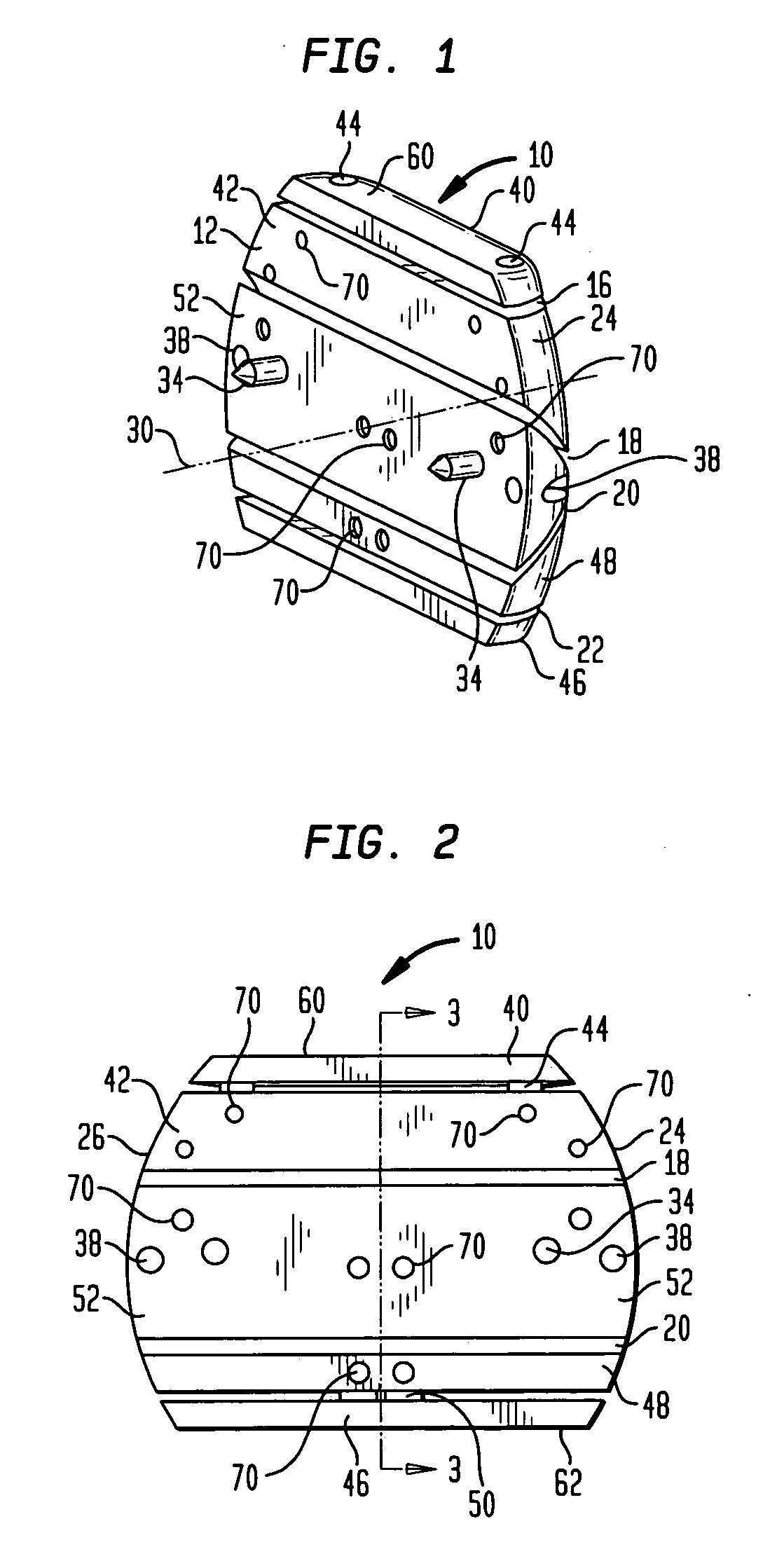
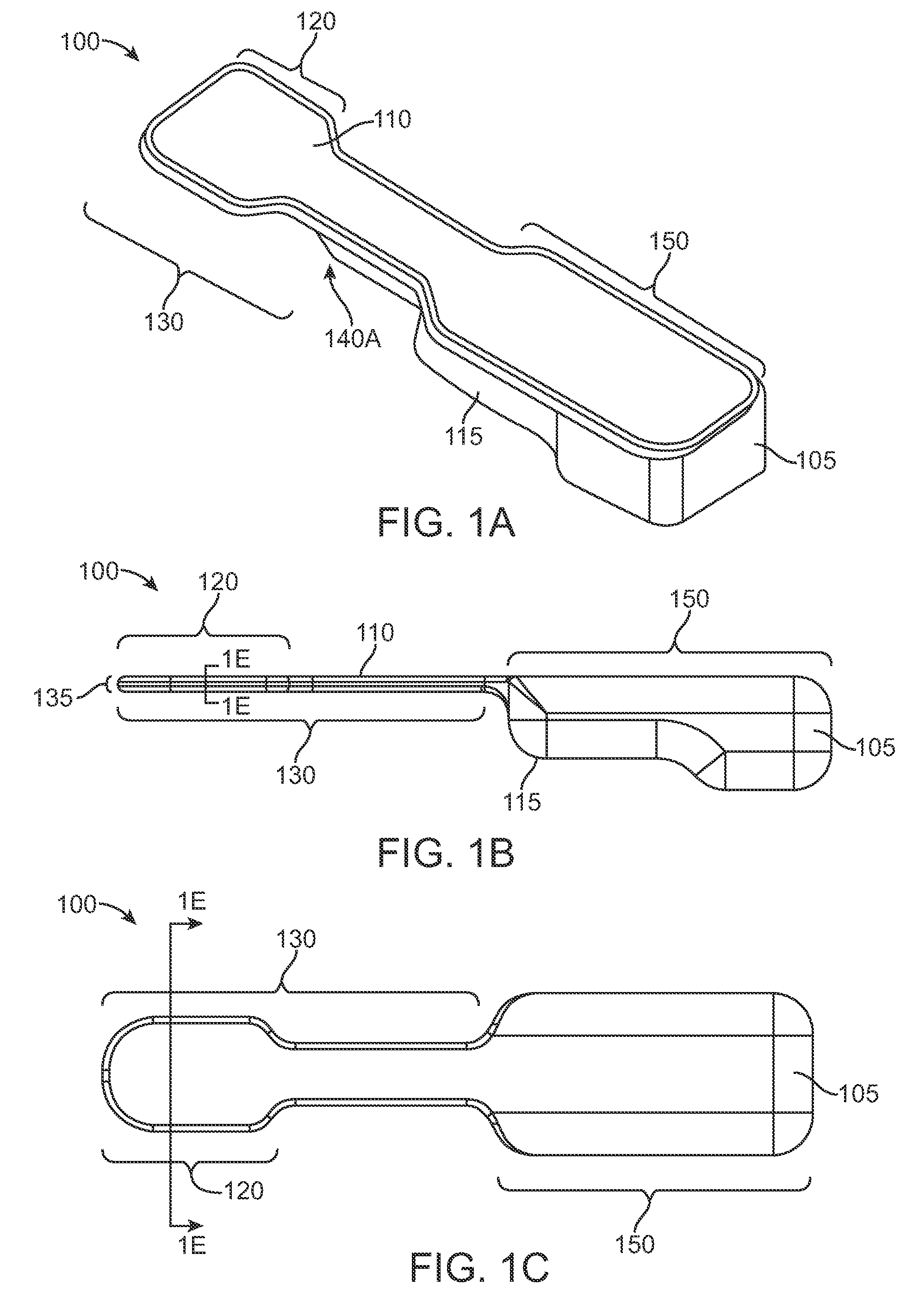
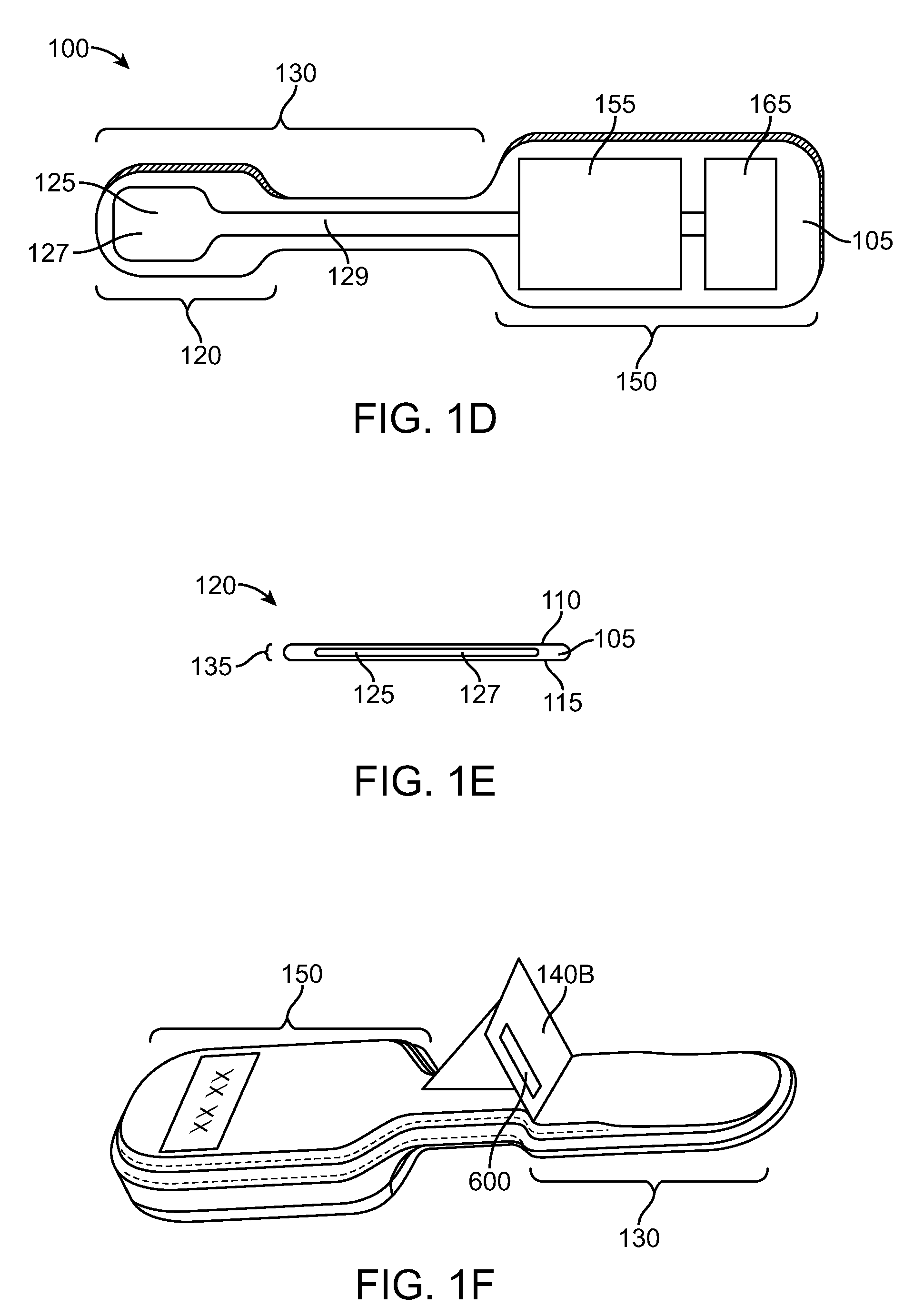
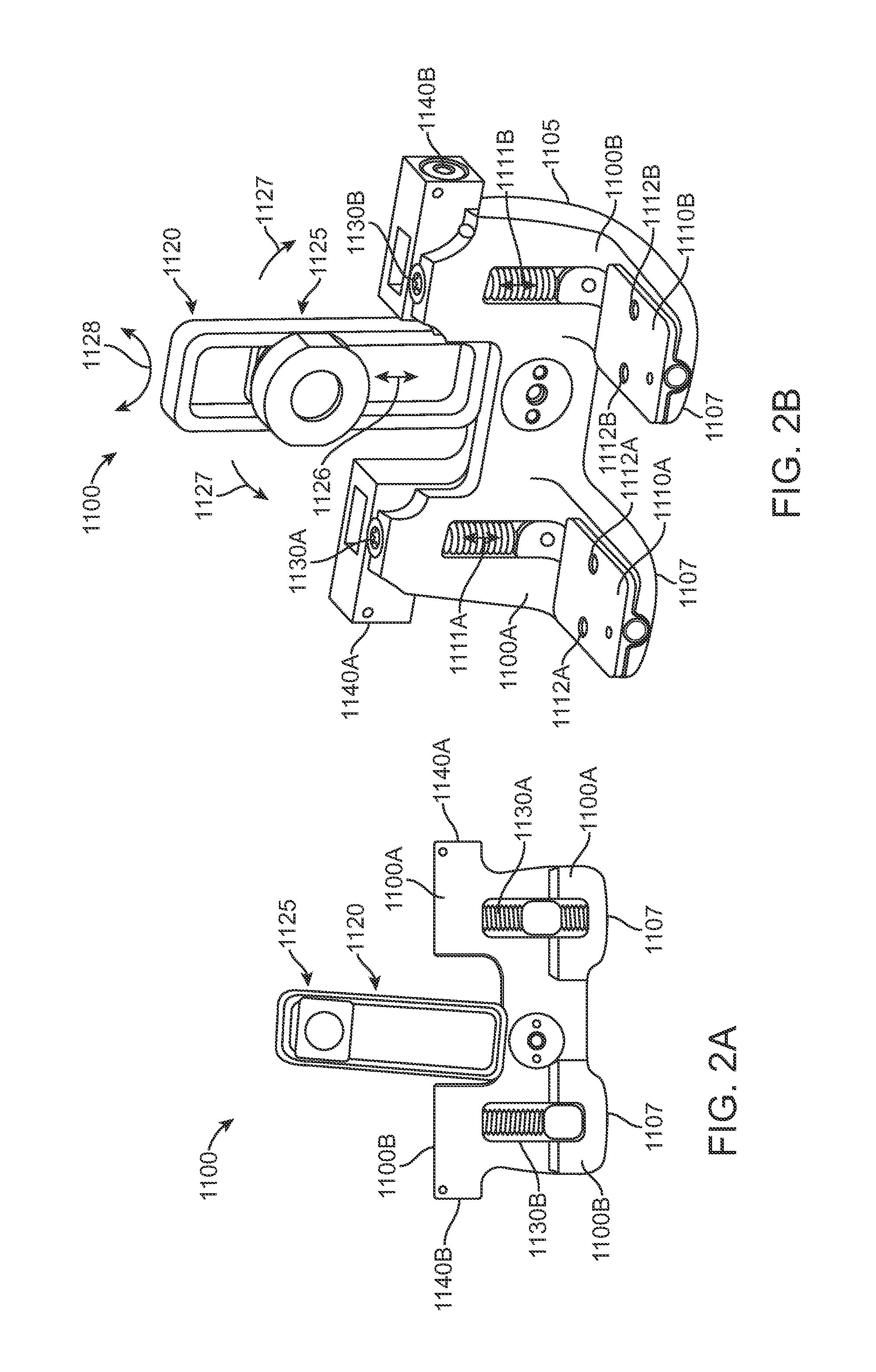
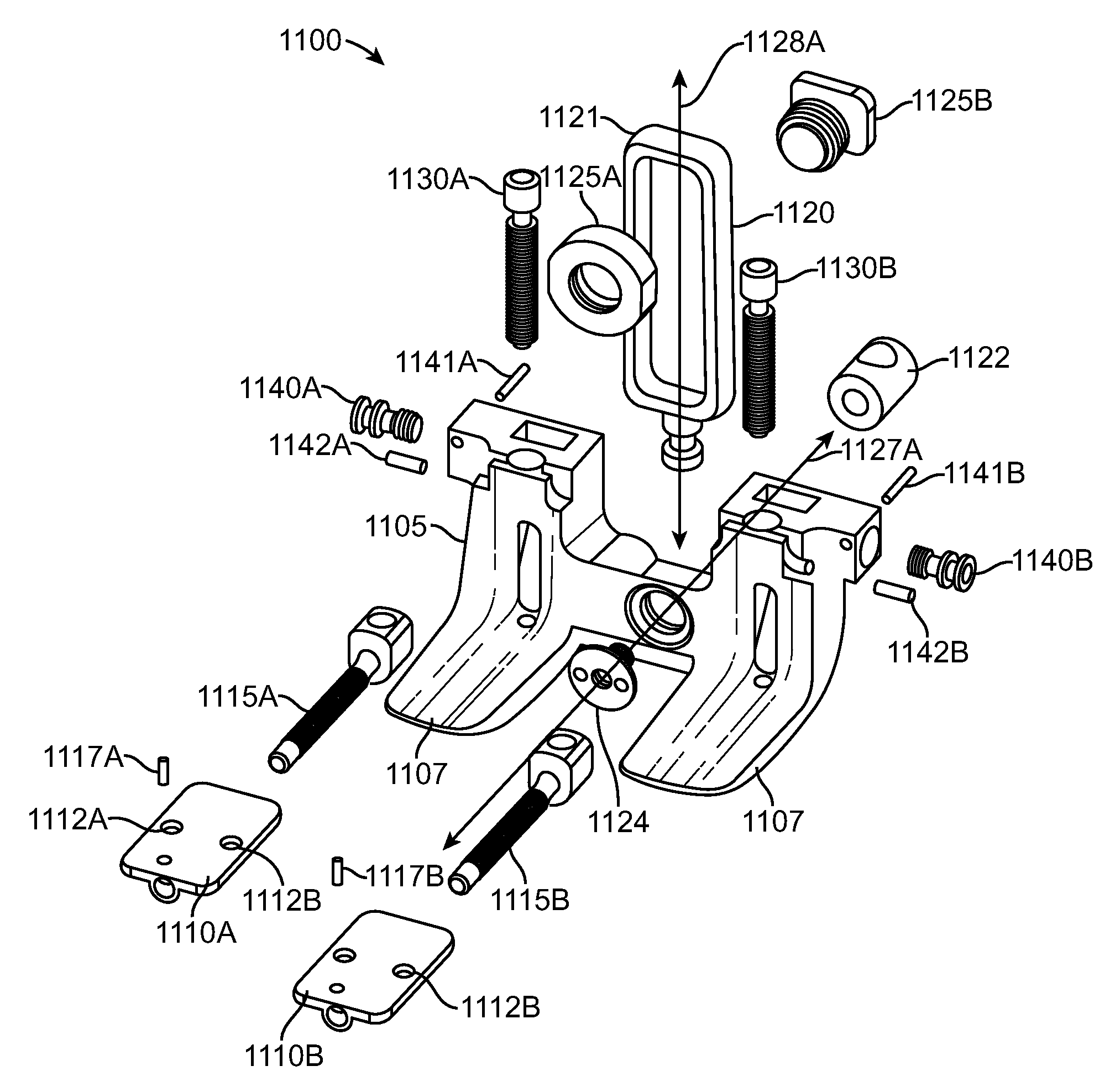
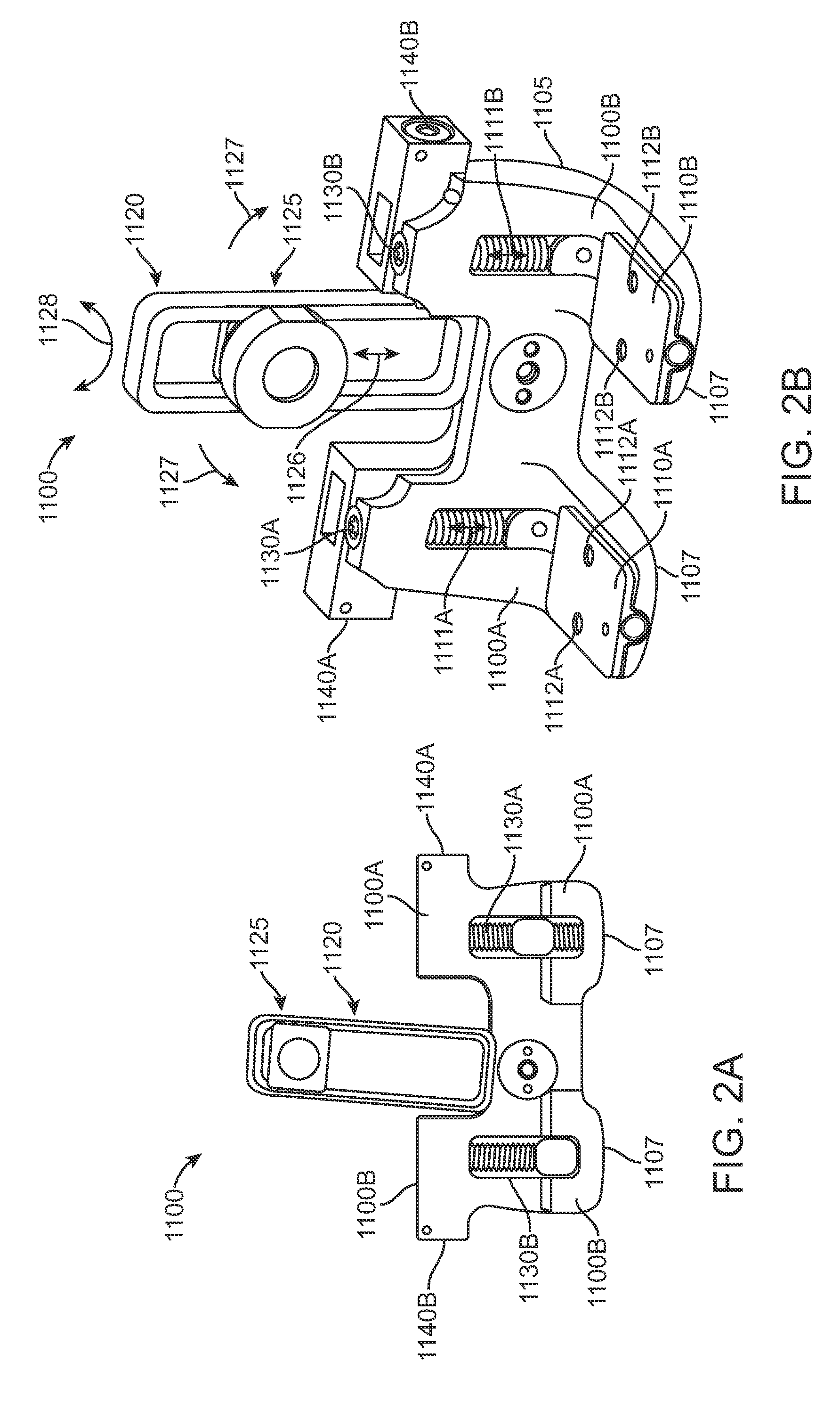
Cutting guide apparatus and surgical method for use in knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7104997B2Avoiding minimizing errorPrecise alignmentSurgical sawsProsthesisSurgical approachSurgical incision
Novel cutting guides and surgical methods for use in knee arthroplasty are described. Embodiments of the inventive cutting guide apparatus include fixed and adjustable cutting guide blocks having a series of slots designed to accommodate a cutting saw. The cutting guides and surgical method are designed to allow for the provision of all desired surgical cuts upon the distal end of the femur, for subsequent implantation of a prosthesis thereto, without having to remove the cutting guide block.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID +1
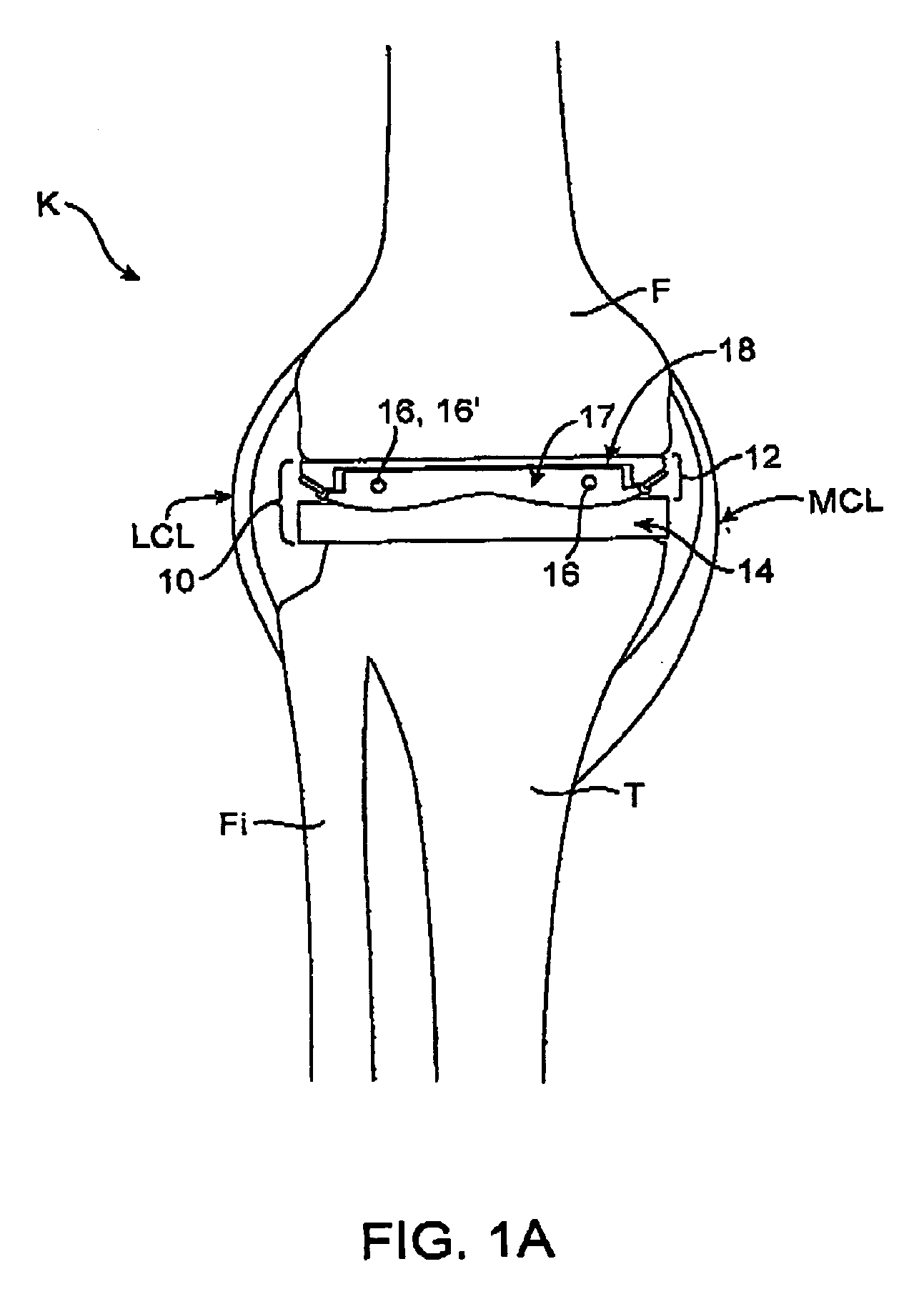
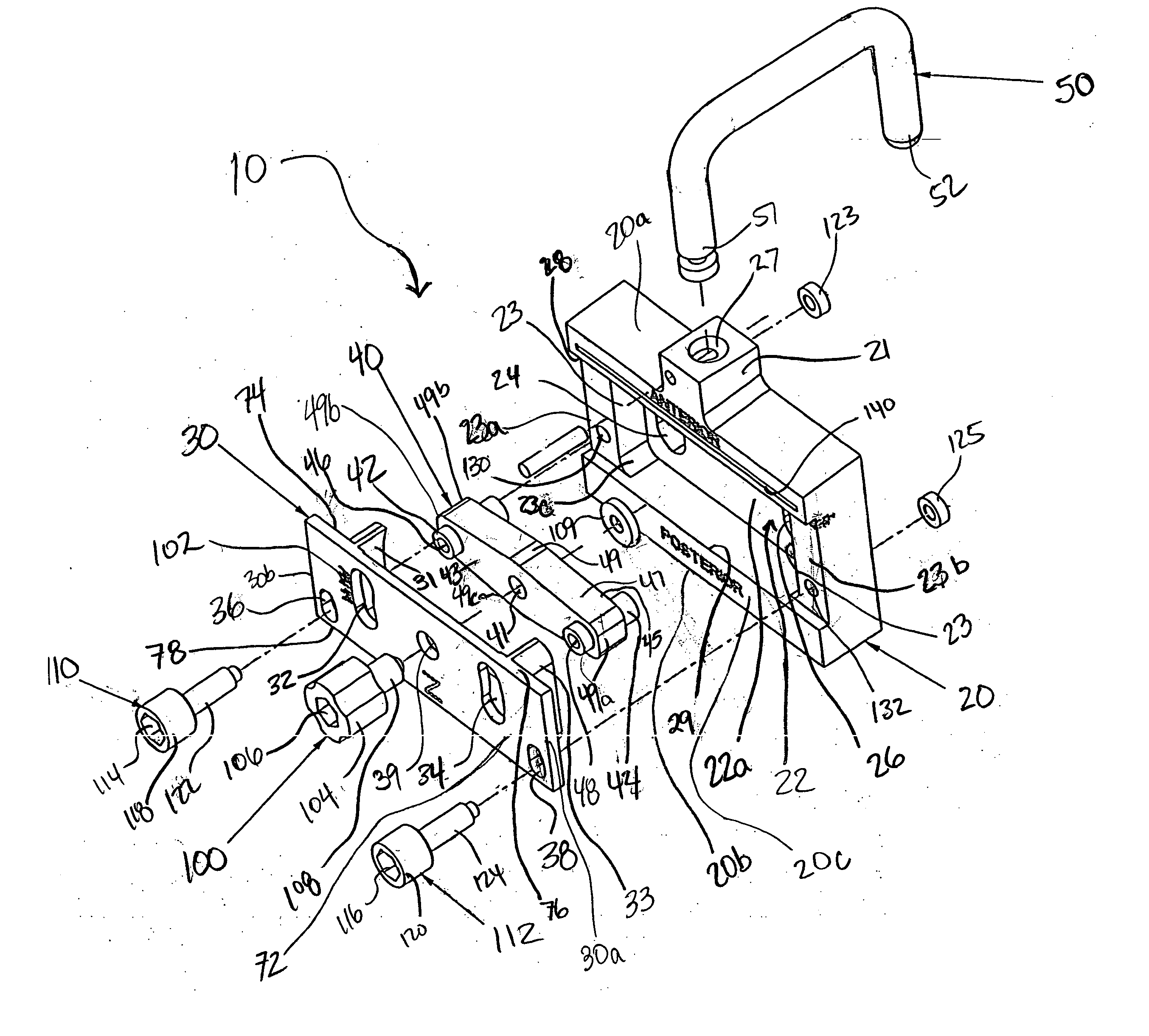
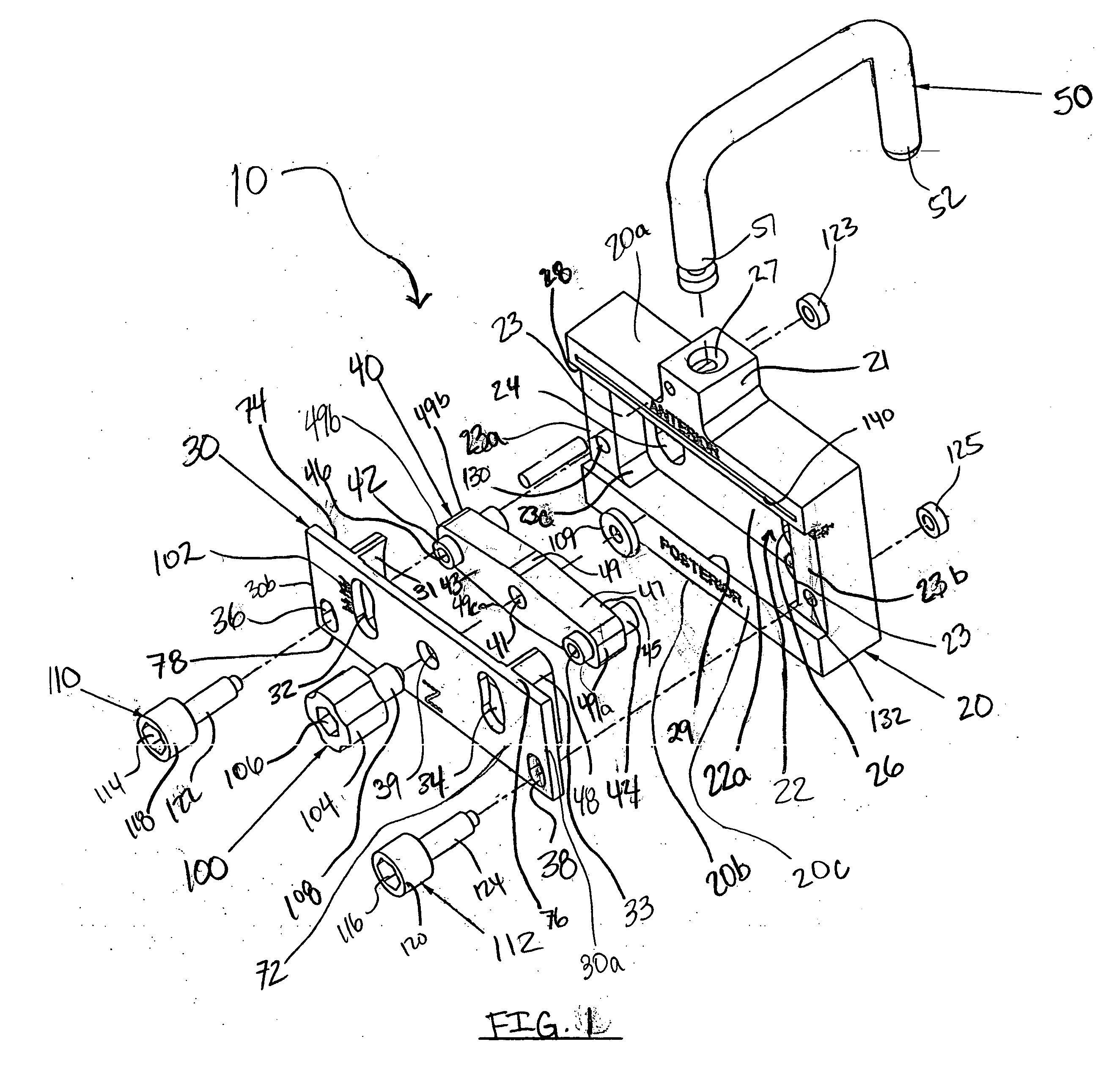
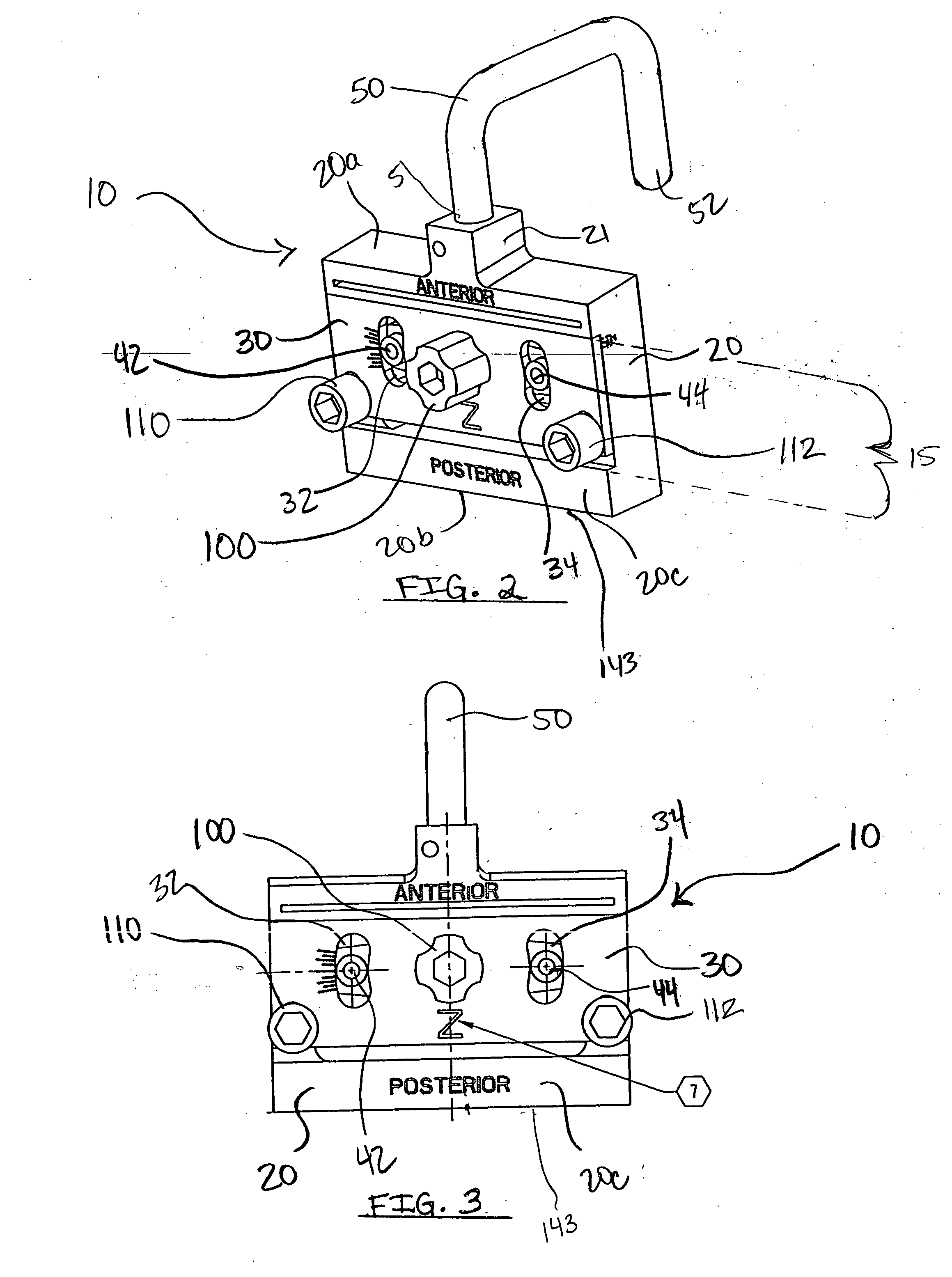
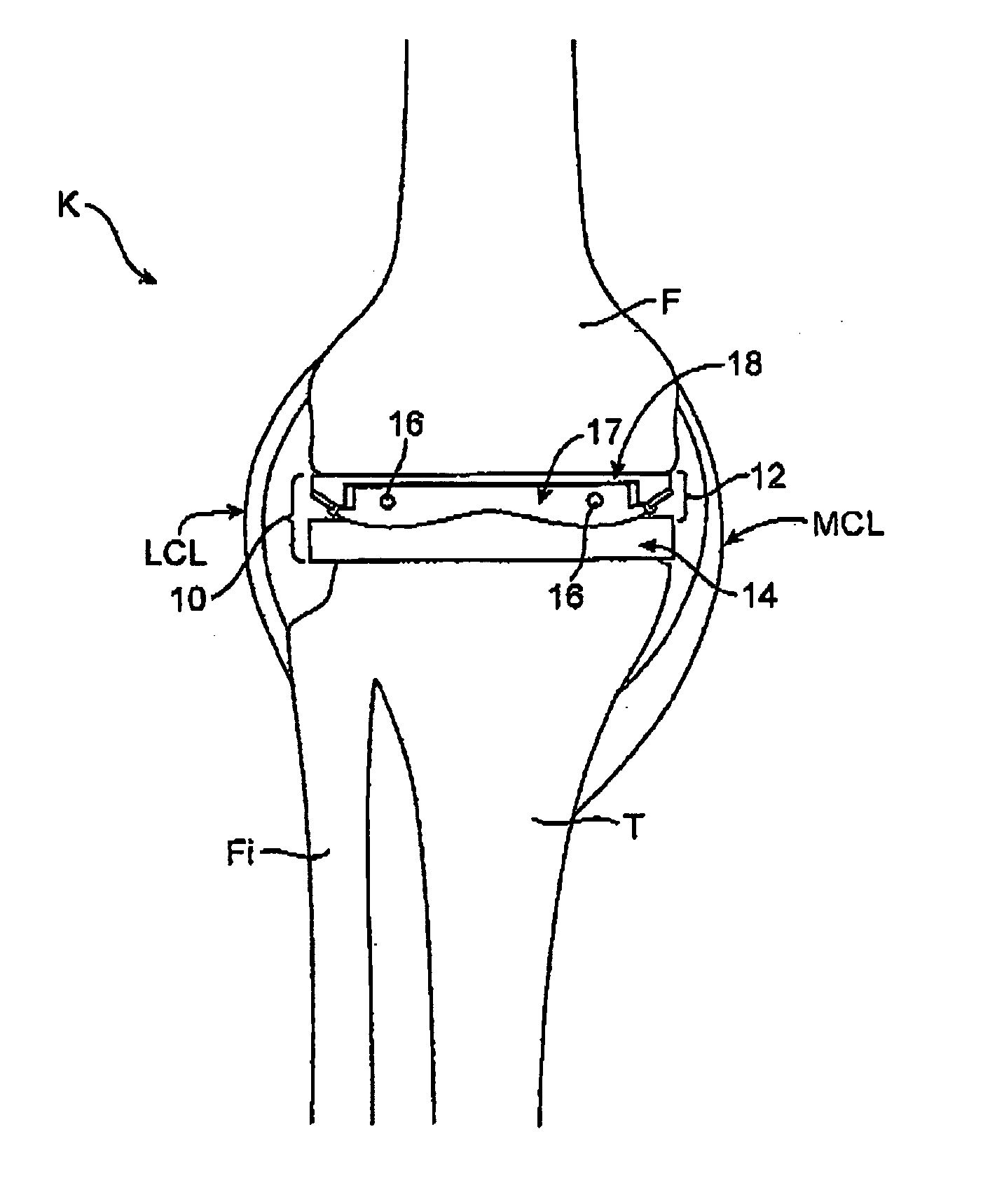
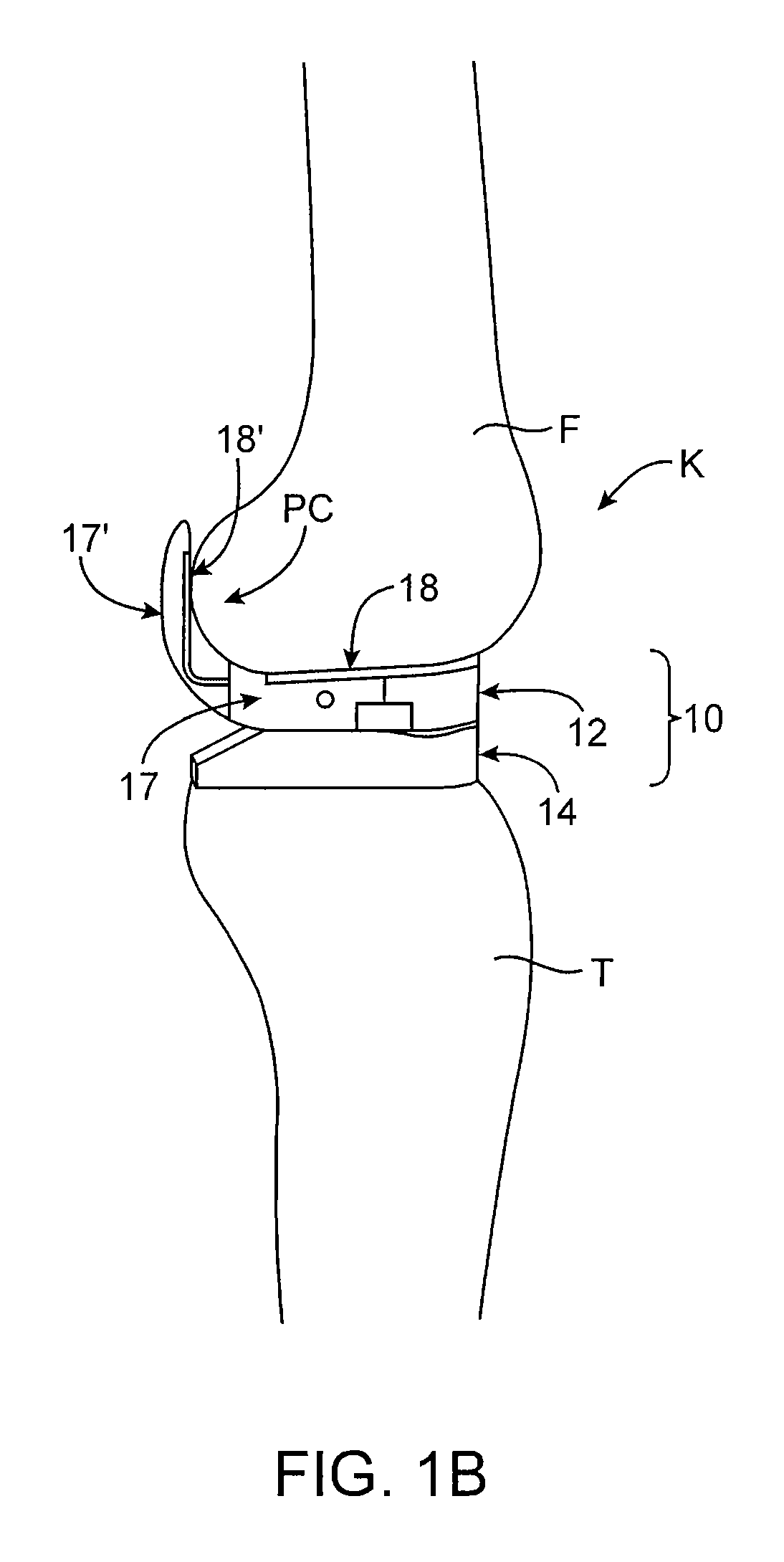
Dynamic knee balancer with opposing adjustment mechanism
ActiveUS20050267485A1Accelerated programImproved surgical outcomeDiagnosticsJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRange of motion
A device for performing a surgical procedure on a knee comprises a femoral assembly comprising a stationary femoral member attachable to the distal femur, an adjustable femoral member movably coupled with the stationary member to adjust tension in at least one ligament of or adjacent the knee and an adjustment mechanism coupled to the assembly. The adjustable member includes at least one positioning feature that moves relative to the distal femur as the adjustable member is adjusted and identifies at least one position on the distal femur. The adjustable member is movably couplable with a tibial member engaged with a proximal tibia to allow the knee to be moved through a range of motion without removing the femoral and tibial members. The mechanism includes an actuator positioned proximate a medial or lateral portion of the adjustable member. The actuator is configured to adjust an opposite portion of the adjustable member.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
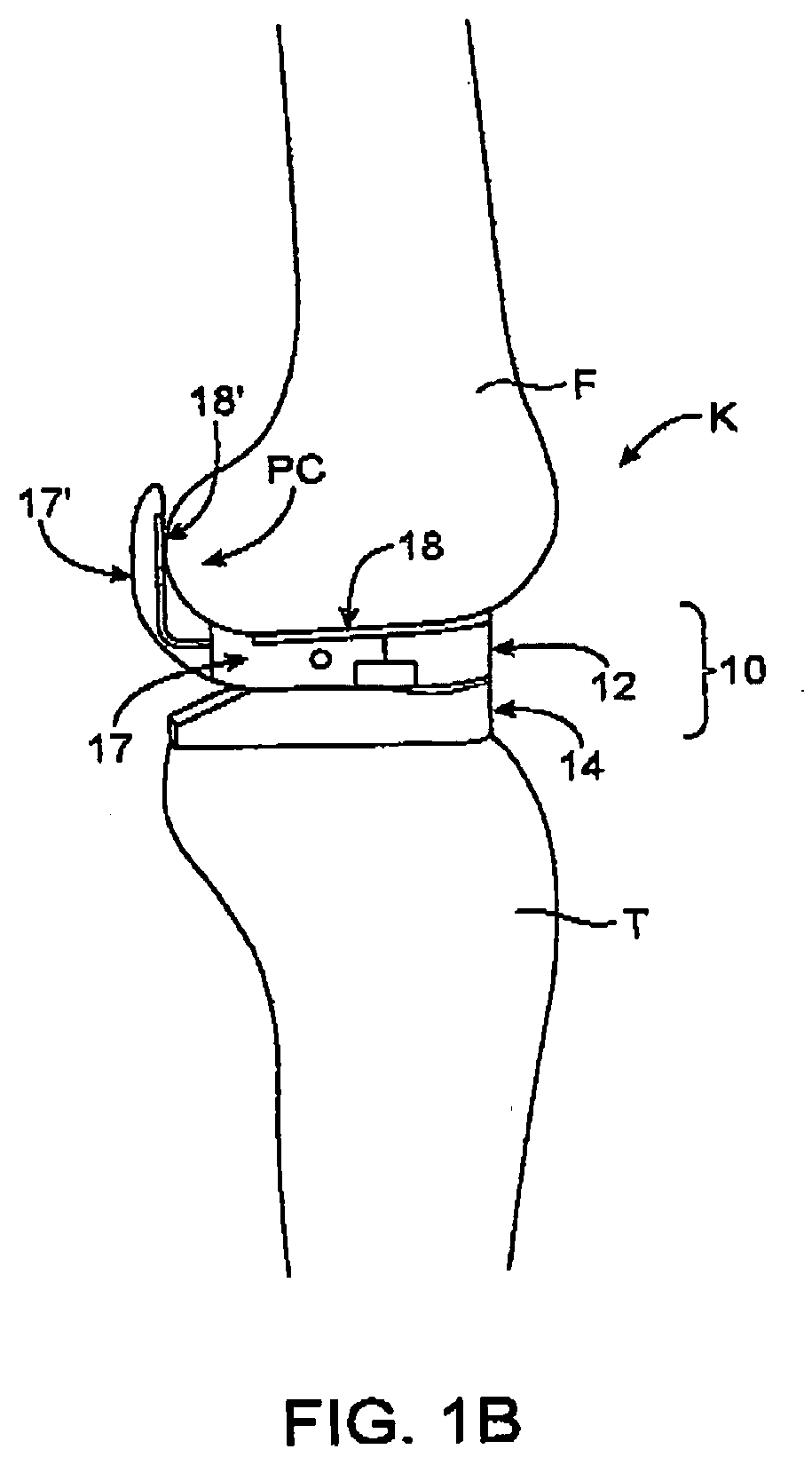
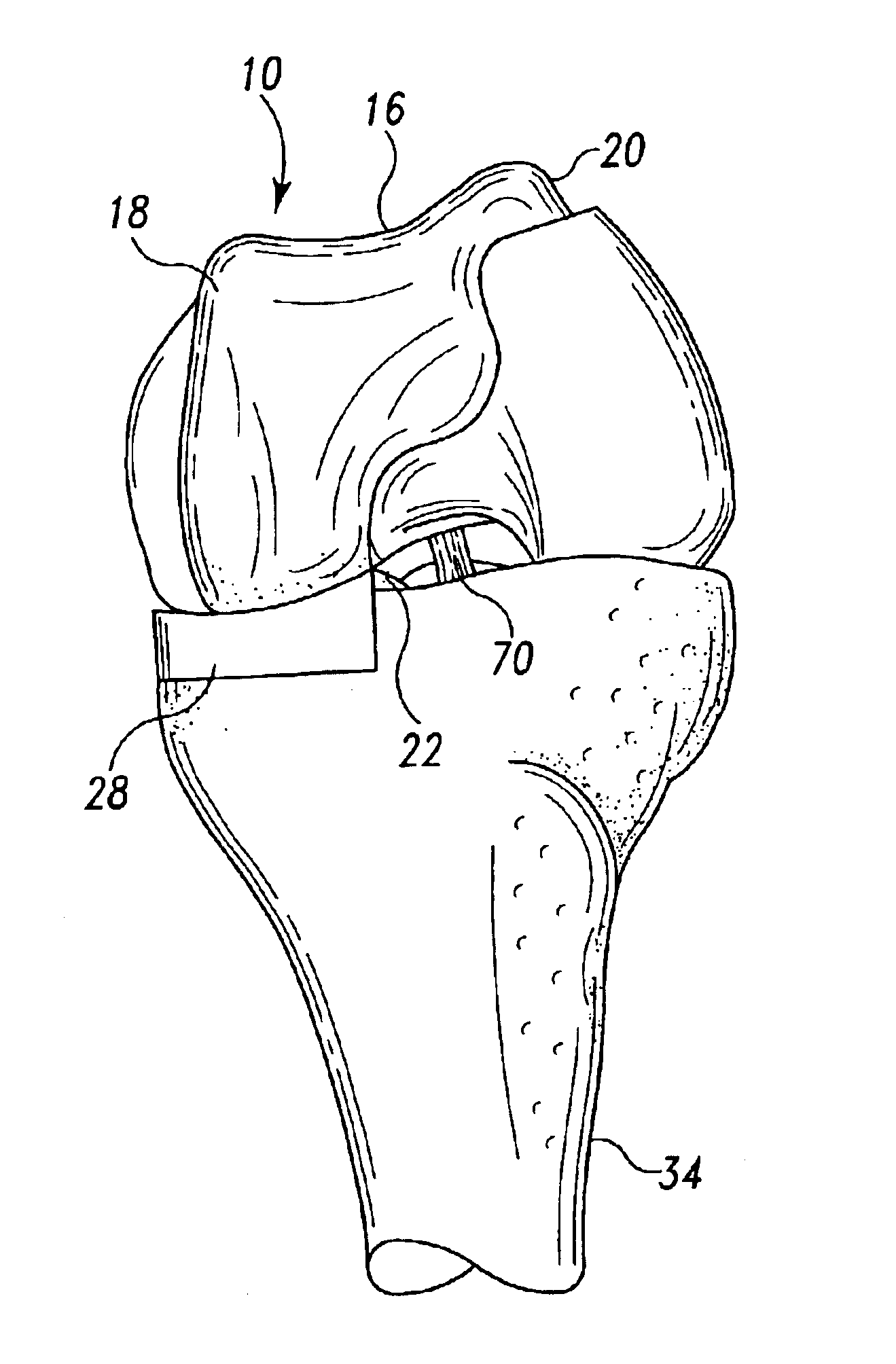
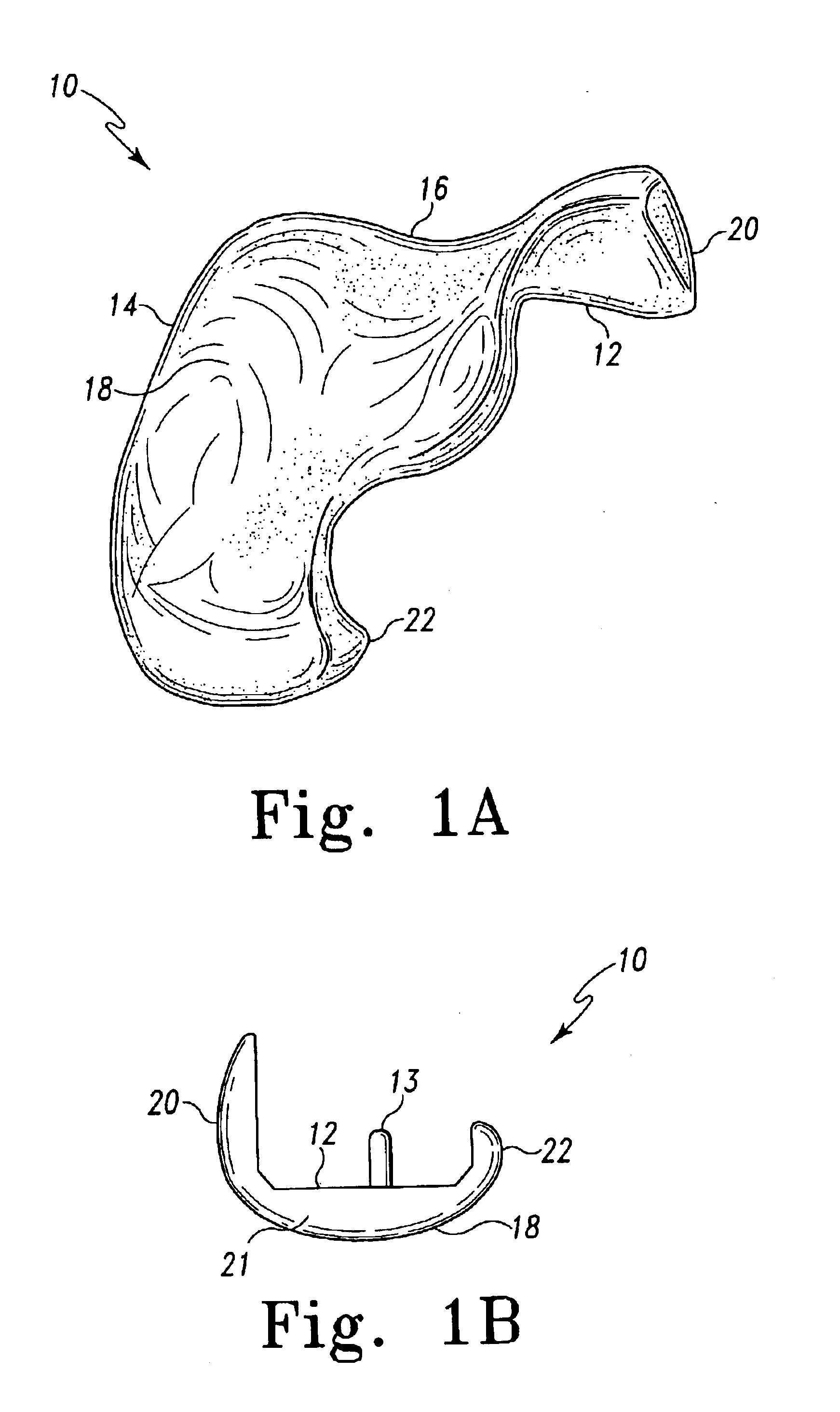
Device and method for bicompartmental arthroplasty
Disclosed is a device and method of bicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. The device permits arthroplasty of the medial or lateral and patellofemoral compartments of the knee while leaving the opposite compartments and the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments intact. The device provides a femoral prosthesis component that includes a trochlear surface and a tibial prosthesis component which can be secured to the tibia. The femoral component is essentially “u” shaped having an anterior leg upon which the trochlear surface is positioned and a posterior leg which engages the posterior surface of the distal end of the femur. The femoral component also has a convex articulating surface which engages a concave articulating surface of the tibial prosthesis component to approximate the articulation of a healthy knee.
Owner:ROLSTON LINDSEY R
Knee balancing block
ActiveUS20050049603A1Non-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsBiomedical engineeringCutting guide
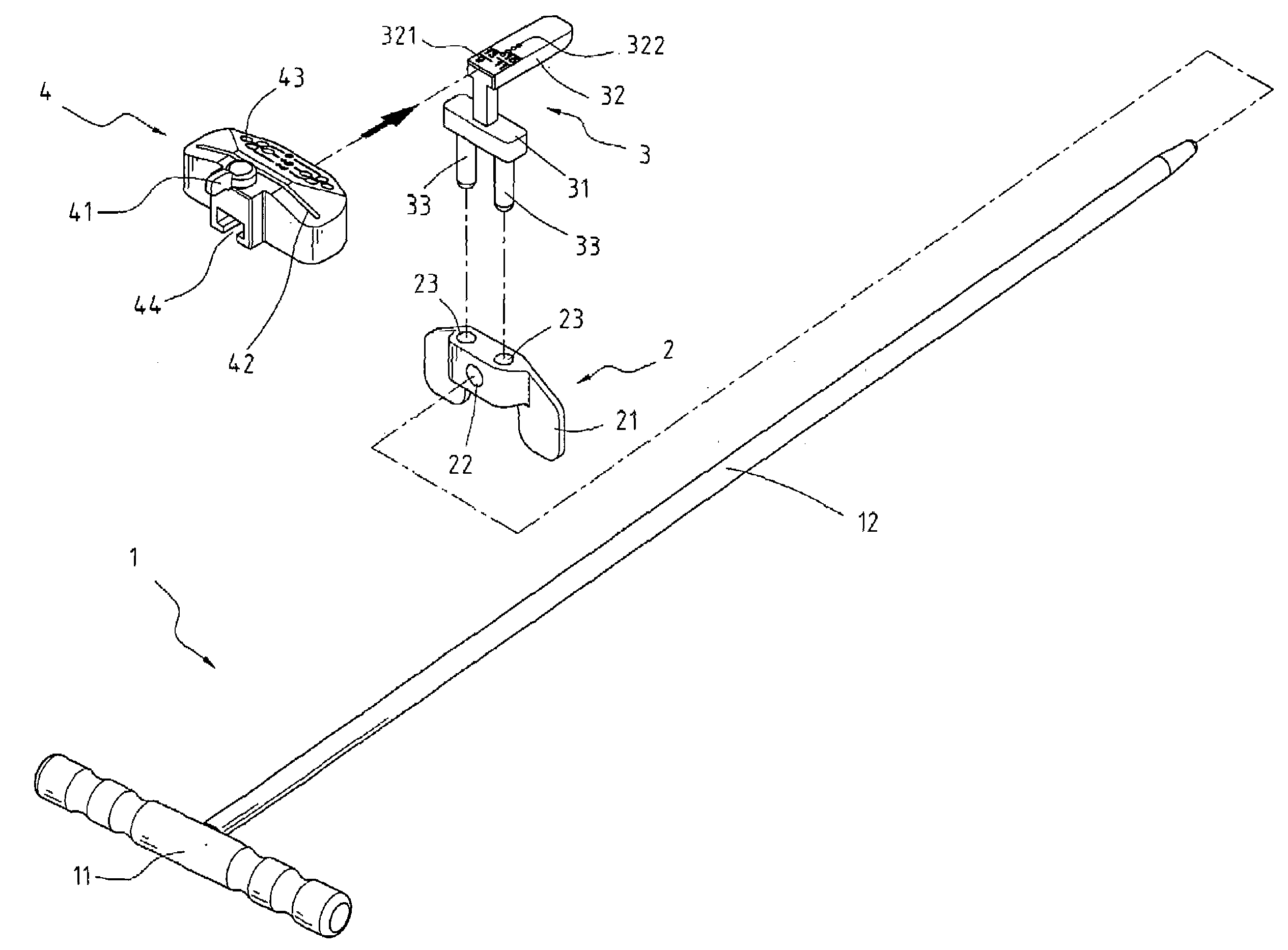
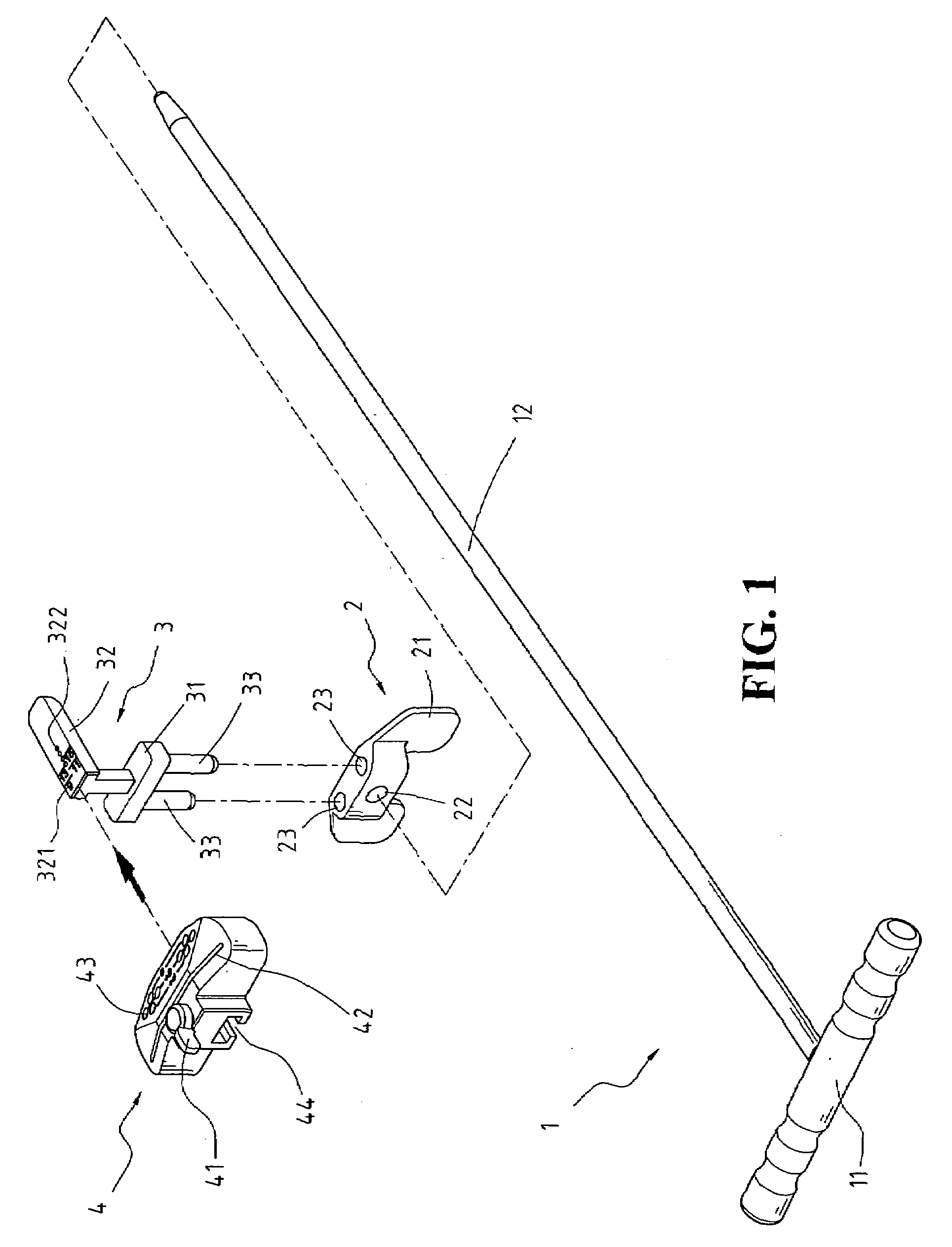
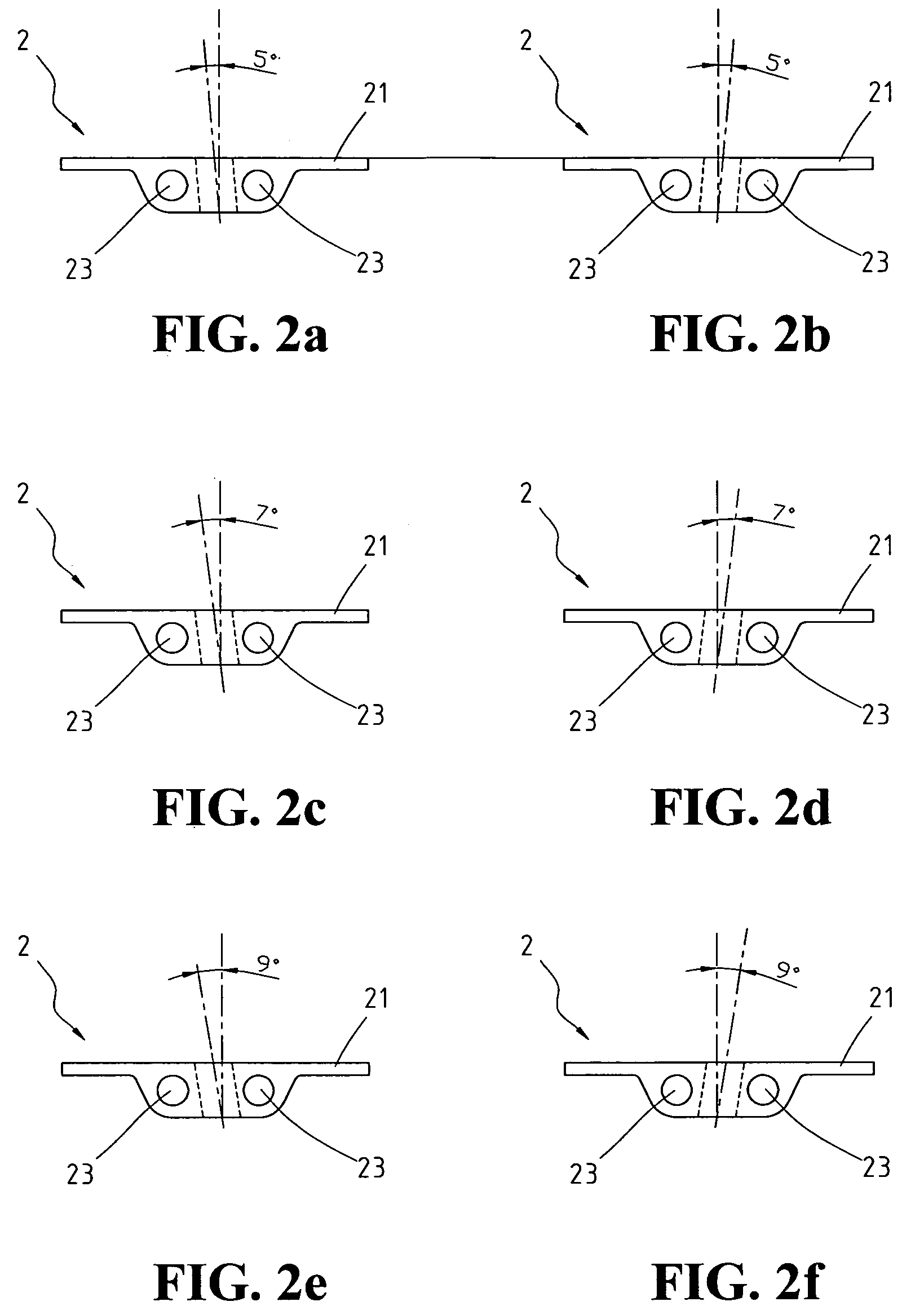
An orthopedic A / P cutting guide device, including a cut guide member, a support member and a positioning member for permitting both (i) rotational, and (ii) translational movement after the A / P cutting guide device has been attached to the distal femur by quick pins or other securing devices, is disclosed. Rotational movement may occur by loosening a knob thereby releasing the positioning member and the cut guide member from the support member, which may be fixed in position by the quick pins, and rotating the positioning member and the cut guide member together. Translational movement may occur by loosening a plurality of knobs thereby releasing the cut guide member from the support member and the positioning member, and moving the cut guide member anteriorly or posteriorly. After the device has been rotated and translated, the knobs may be tightened, thus securing the device from further movement.
Owner:ORTHO DEV CORP
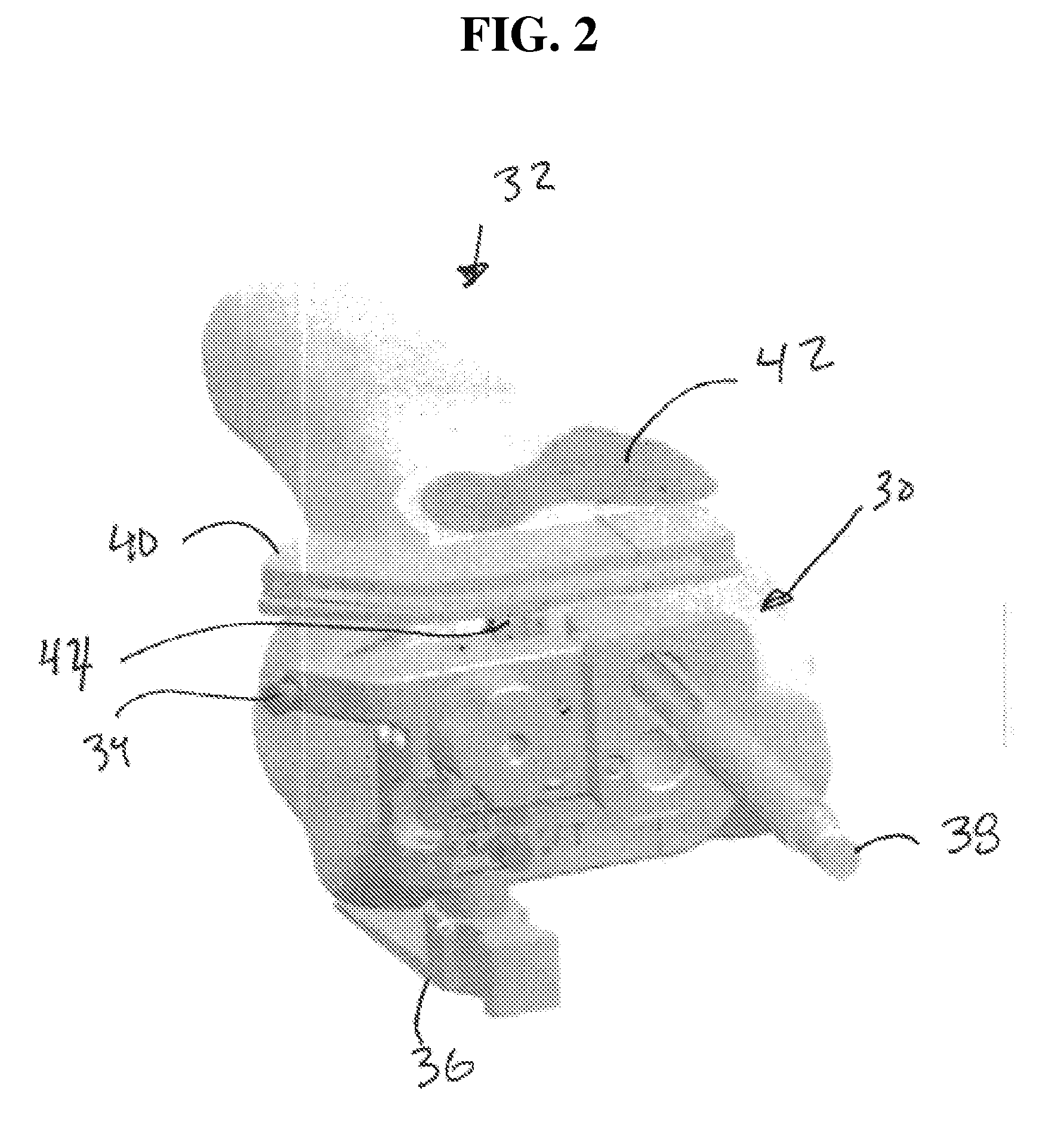
Cutting guide apparatus and surgical method for use in knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20070073305A1Avoiding minimizing errorPrecise alignmentNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsKnee JointProsthesis
Novel cutting guides and surgical methods for use in knee arthroplasty are described. Embodiments of the inventive cutting guide apparatus include fixed and adjustable cutting guide blocks having a series of slots designed to accommodate a cutting saw. The cutting guides and surgical method are designed to allow for the provision of all desired surgical cuts upon the distal end of the femur, for subsequent implantation of a prosthesis thereto, without having to remove the cutting guide block.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID R +1
Laser triangulation of the femoral head for total knee arthroplasty alignment instruments and surgical method
InactiveUS20050070897A1Improve accuracyConsiderable morbidityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArticular surfacesArticular surface
An Extramedullary system of alignment for total knee arthroplasties uses a small diode laser at the center of the knee adjustable to the longitudinal axis of the femur to triangulate the center of the femoral head. It utilizes a V-Frame positioning device that fits into the distal femoral intercondylar notch and is tangent to the articular surfaces of the notch. It is also parallel to the anterior femoral cortex by using a removal tongue flange that sits flat on the filed surface of the anterior cortex. This prepositions the Distal Femoral Resector Guide within a few degrees of the center of the femoral head. An adjustment knob on the V-Frame pivots the distal femoral resector guide to the exact center of the femoral head for that particular patient accomplishing fine adjustment of the longitudinal axis of the femur. There is only one position where the laser beam will go through the center of the target no matter where you position the leg and that is when the target's bulls-eye is exactly over the rotational center of the femoral head. Since the laser confirms this position, the surgeon is assured that the alignment is accurate. The Distal Femoral Resector Guide is then fixed to bone with fixation pins and the resection made with a power saw. The laser is moved to the target mount to act as a longitudinal “laser ruler” for the remainder of the operation.
Owner:PETERSEN THOMAS D
Device and method for bicompartmental arthroplasty
Disclosed is a device and method of bicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. The device permits arthroplasty of the medial or lateral and patellofemoral compartments of the knee while leaving the opposite compartments and the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments intact. The device provides a femoral prosthesis component that includes a trochlear surface and a tibial prosthesis component which can be secured to the tibia. The femoral component is essentially “u” shaped having an anterior leg upon which the trochlear surface is positioned and a posterior leg which engages the posterior surface of the distal end of the femur. The femoral component also has a convex articulating surface which engages a concave articulating surface of the tibial prosthesis component to approximate the articulation of a healthy knee. The patellar prosthesis is applied to the posterior surface of the patella and articulates with the trochlear exterior surface of the femur.
Owner:ROLSTON LINDSEY R
Dynamic knee balancer
ActiveUS20050177169A1Enhancing knee surgery procedureAccelerated programBone implantDiagnosticsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRange of motion
Dynamic knee balancing devices, systems and methods provide for enhanced total knee arthroplasty (“TKA”) procedures. Devices generally include a stationary femoral member for removably attaching to a distal femur and an adjustable femoral member coupled with the stationary member for adjusting ligament tension of the knee. The adjustable femoral member includes at least one positioning feature for providing positional and / or orientation information for facilitating the TKA procedure. Additionally, the adjustable femoral member is movably couplable with a tibial member engaged with the proximal tibia to allow movement of the knee through a range of motion without removing the device from the joint space. When the adjustable femoral member is adjusted, the positional feature(s) move relative to the distal femur to provide positional information.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Method and system for computer assisted surgery for bicompartmental knee replacement
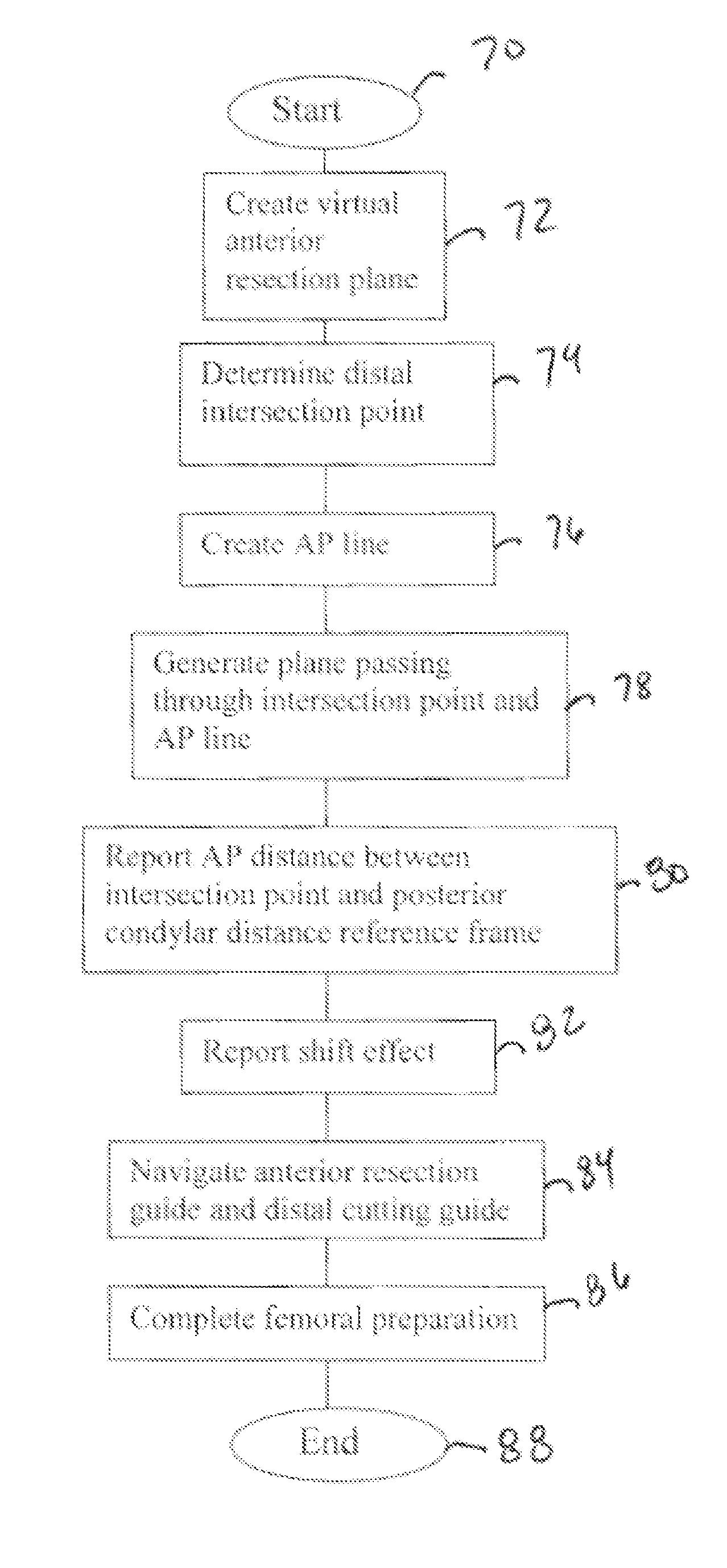
A method of resecting distal and anterior portions of a distal portion of a femur for a bicompartmental prosthesis is provided. The method includes generating a geometric representation of the distal portion of the femur. A virtual anterior resection plane is calculated at a predetermined depth and is oriented at a predetermined angle relative to the femur. The method identifies a distal-most point of a lateral portion of the virtual anterior resection plane and an AP line. A varus / valgus angle and an anterior-posterior distance are calculated. Anterior and distal resection guides are navigated according to the parameters calculated from the method.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS RECON
Instruments and methods for use in performing knee surgery
InactiveUS20050085920A1Avoid excessive bone removalJoint implantsKnee jointsKnee surgeryPatellar luxation
A system and method for aligning a patient's leg, for establishing the ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making a horizontal femoral cut or a horizontal tibial cut, for preparing the distal femur for receiving a femoral implant, and for making the horizontal, femoral and tibial cuts. The system and method incorporate a spacer, a cutting guide, and a template. The spacer is insertable between a distal femur and a proximal tibia to rotate the tibia with respect to the femur into the desired alignment. The cutting guide is engageable with the spacer, and can be fixed to the proximal tibia and the distal femur. The cutting guide has openings sized and shaped to guide a surgical saw to make the horizontal femoral cut and the horizontal tibial cut. The template is shaped to closely conform with the distal femur to allow the leg to be extended and to allow the procedure to be performed without dislocating a patella. Through one method of the present invention, the practitioner can select the desired ultimate alignment of the leg prior to making the horizontal, tibial and femoral cuts. As a result, when a replacement knee is implanted, the leg will be in the desired alignment.
Owner:WILLIAMSON RICHARD V
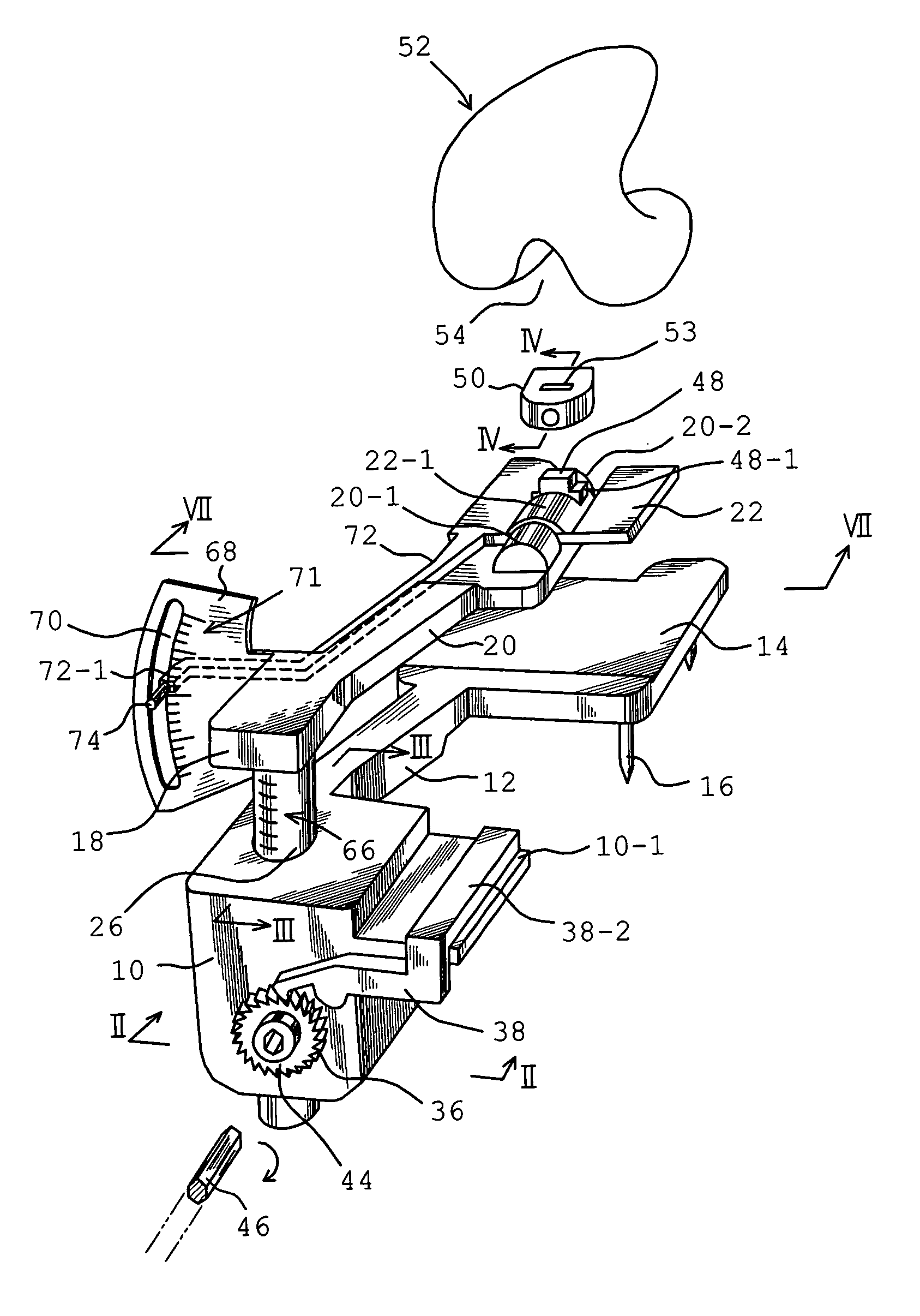
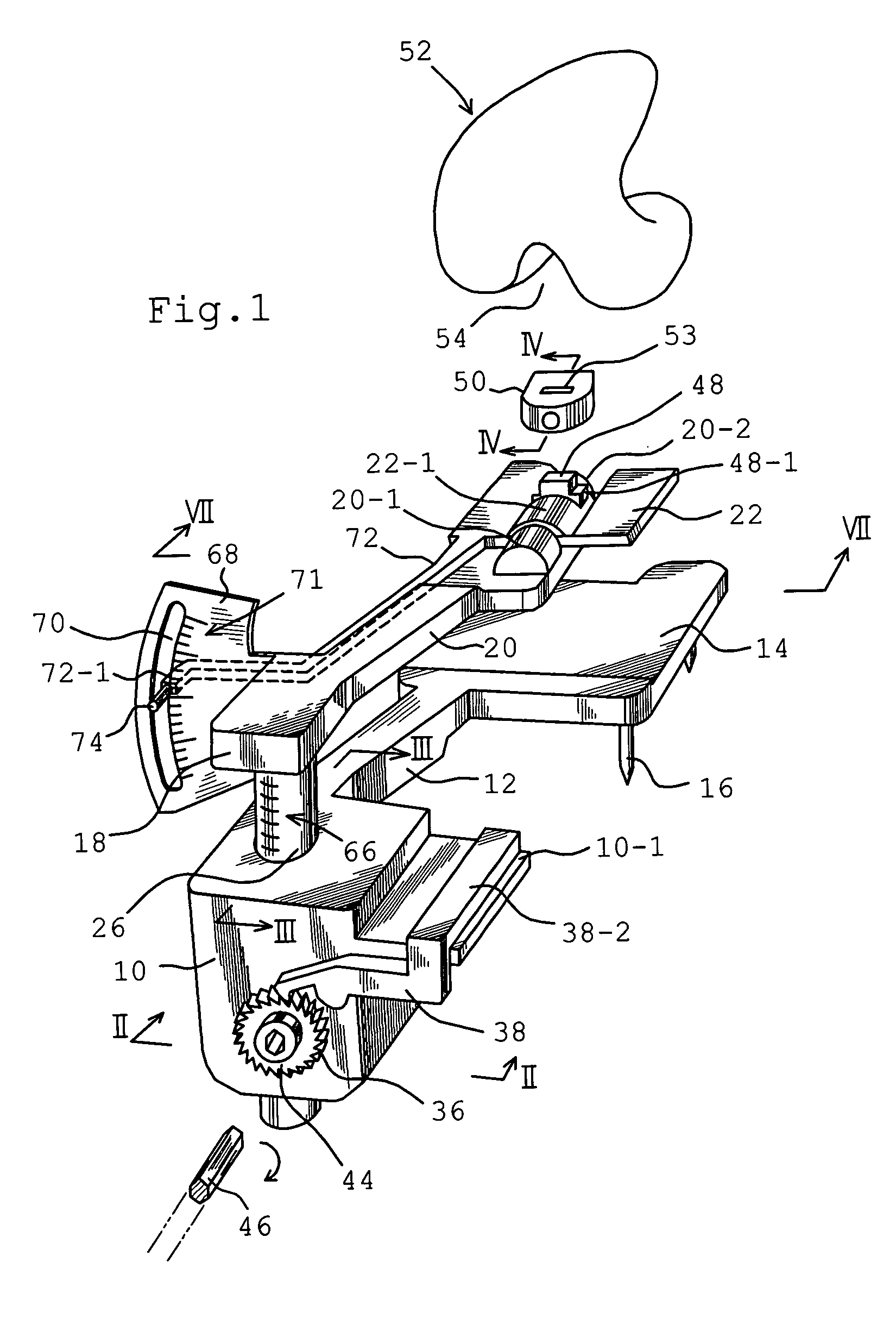
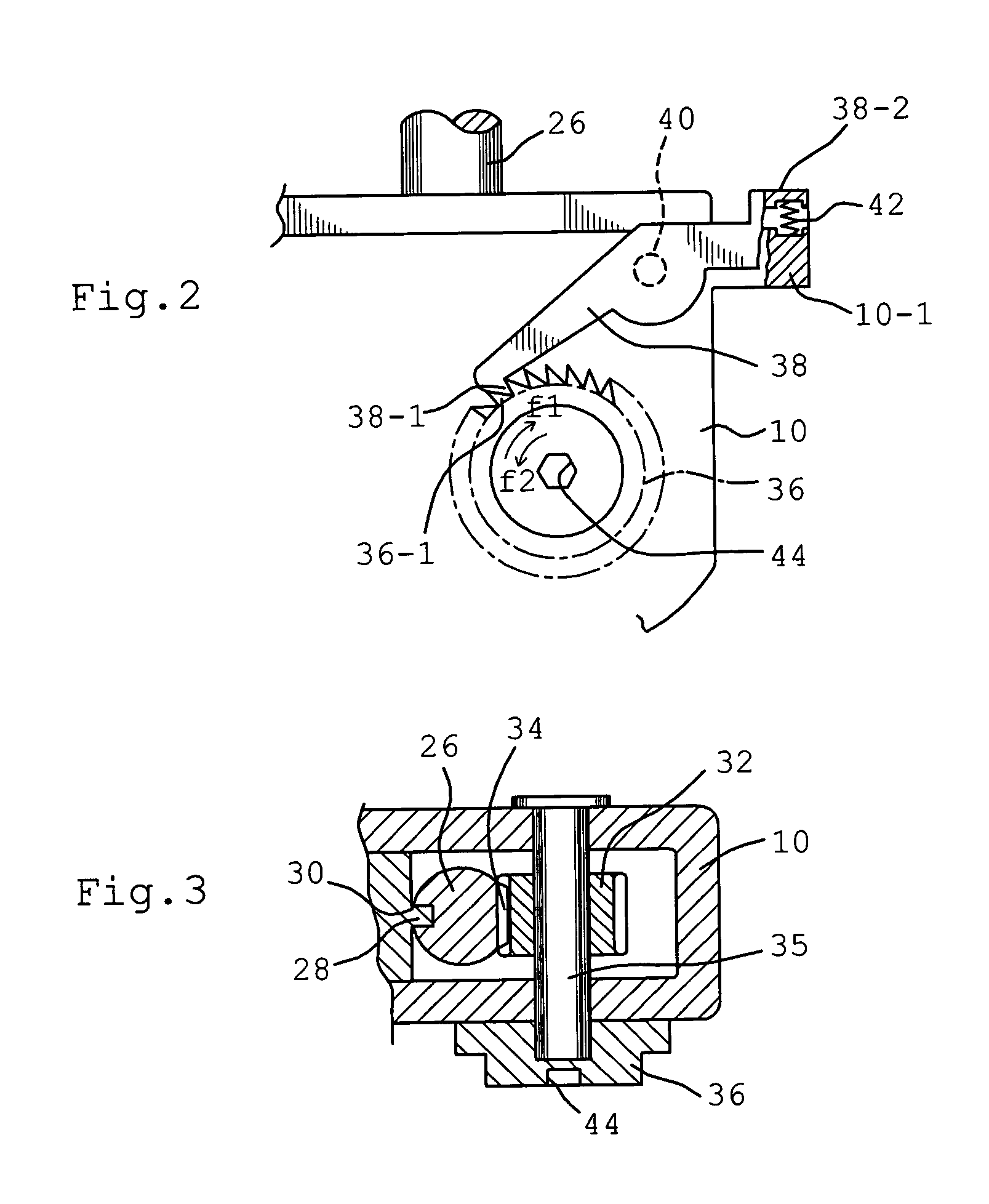
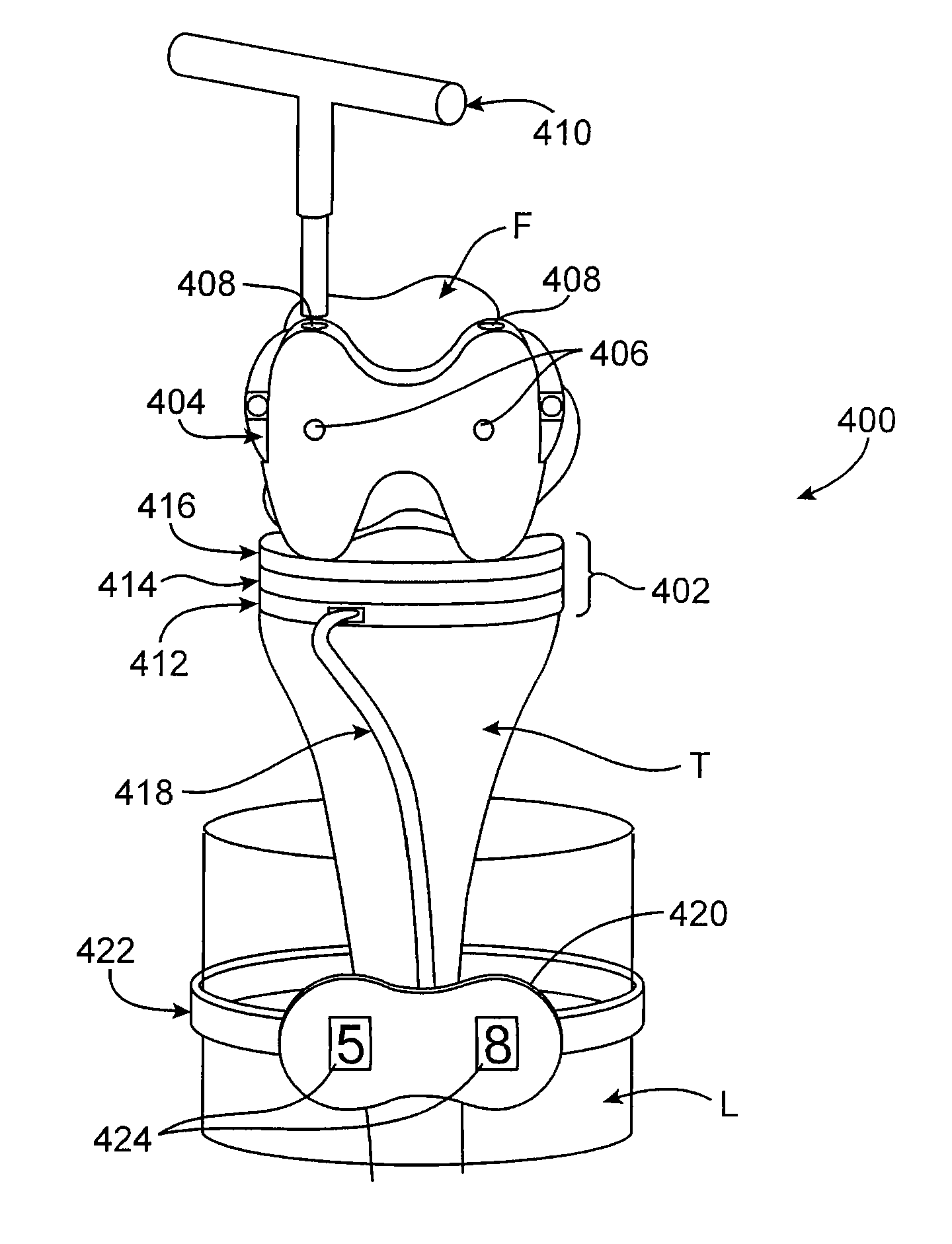
Measuring apparatus for total knee replacement operation
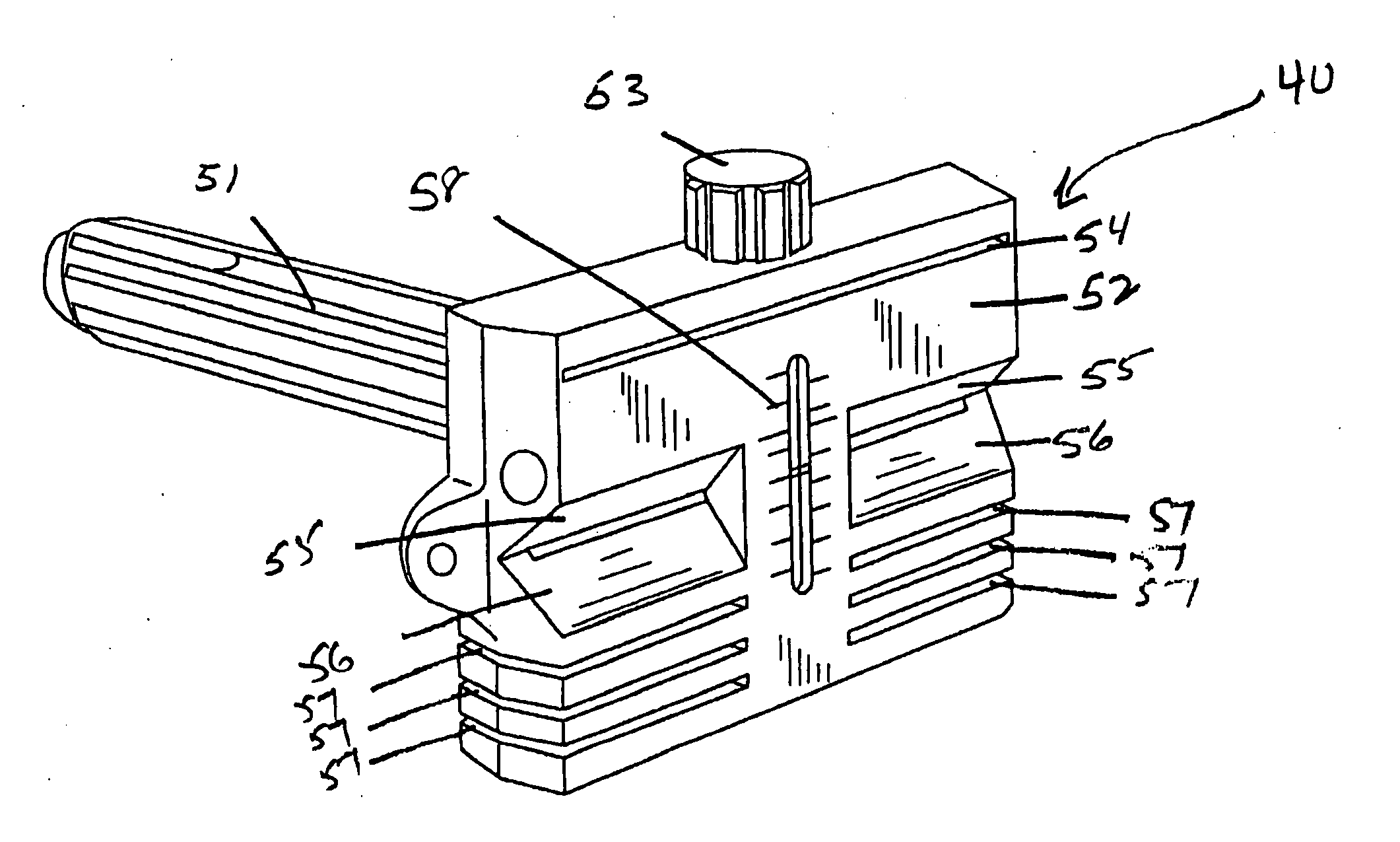
ActiveUS20040122441A1Smooth movementEasy to disassembleJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement devicePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
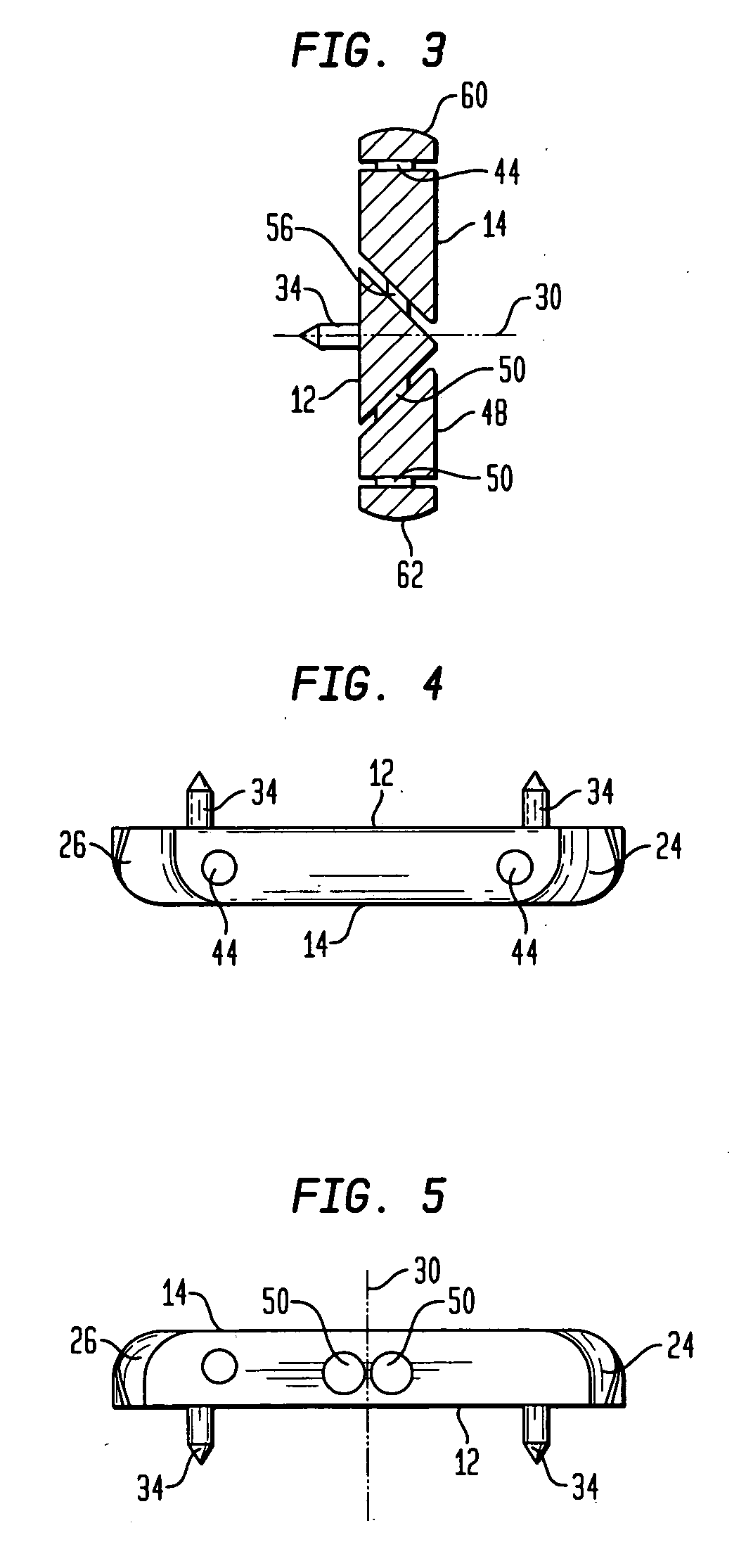
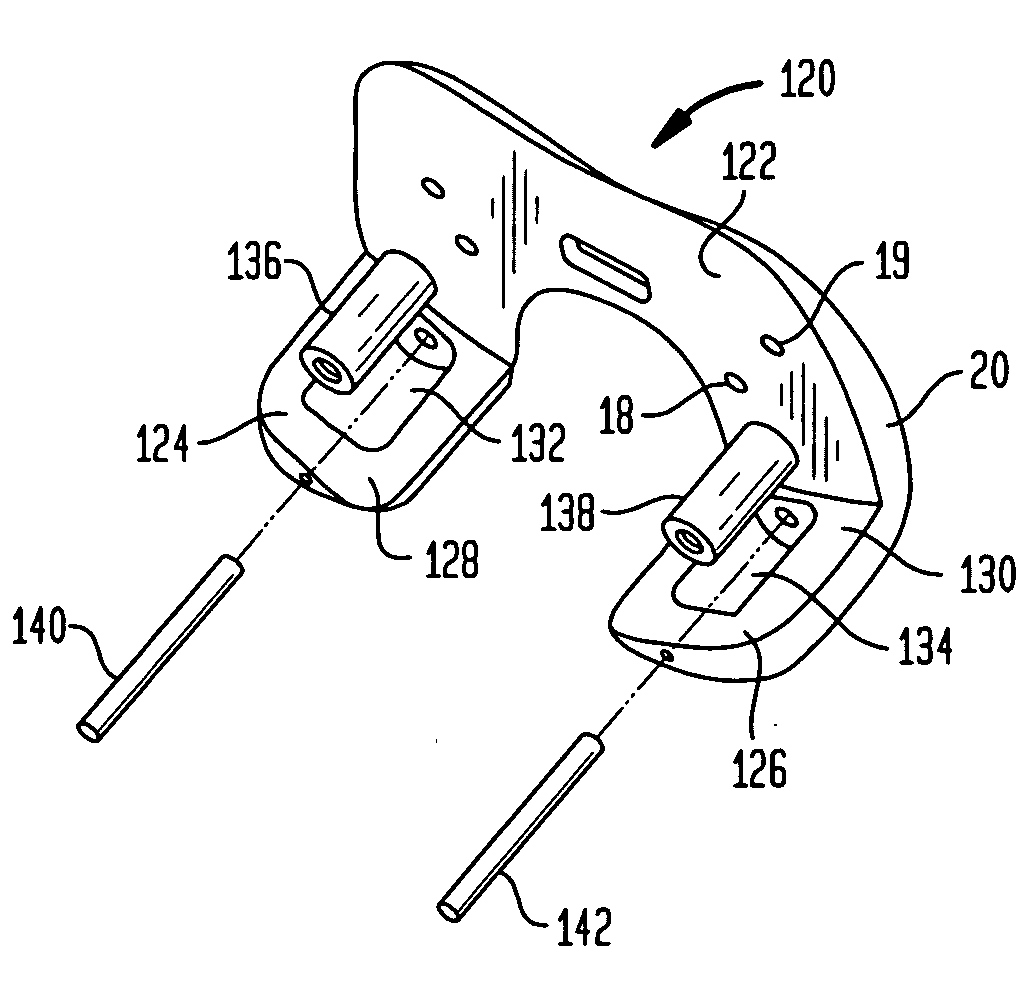
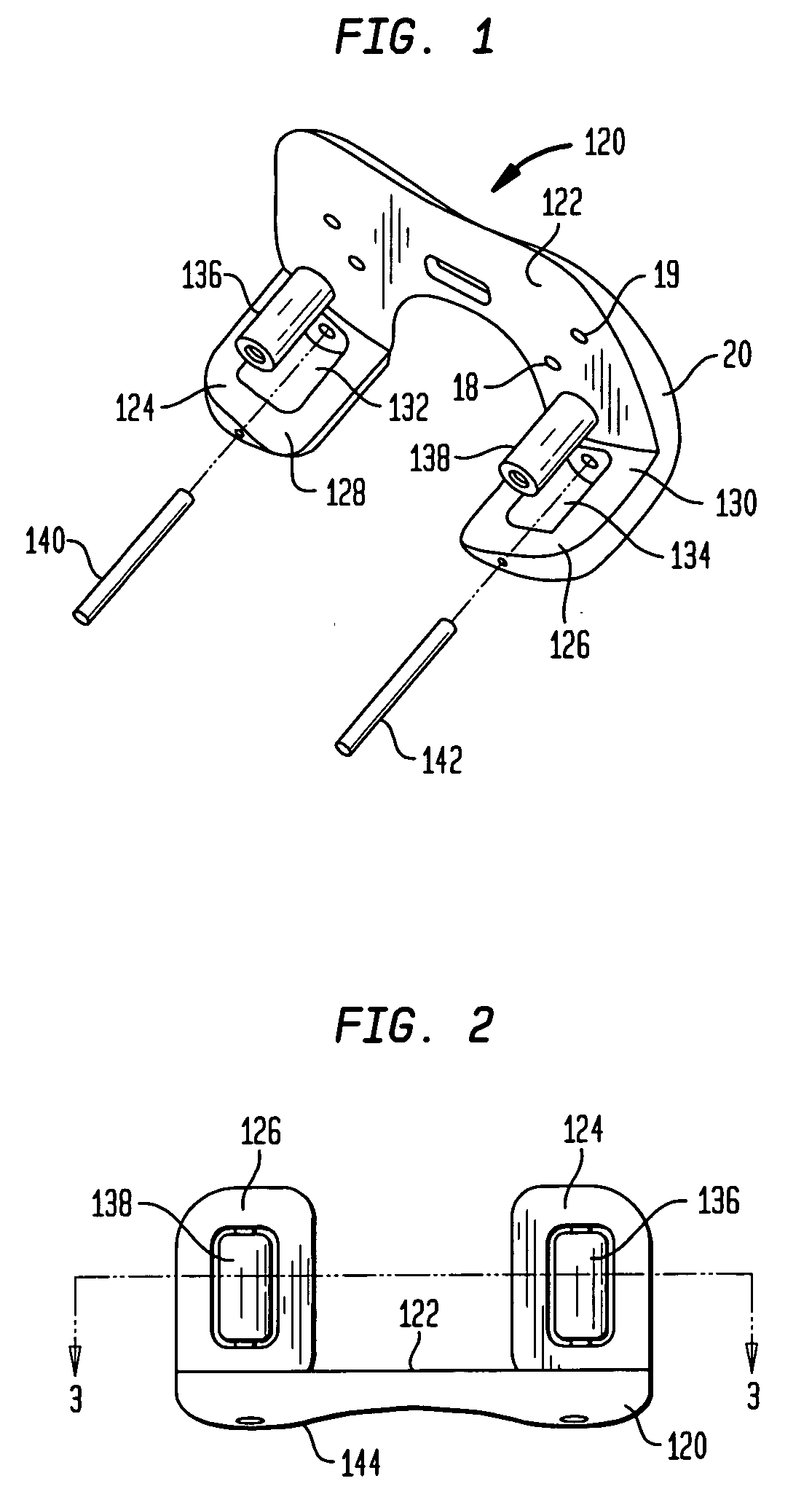
An apparatus in a total knee replacement and arthroplasty operation for measuring a joint gap and ligament balance between a osteotomized surface at a femoral distal end and a osteotomized surface at a tibial proximal end. The apparatus is provided with a base 10, from which an engaging plate 14 extends by way of an arm, so that the engaging plate 14 contacts with the osteotomized surface at the tibial proximal end. A moving body 18 is vertically movably connected to the base 10, from which moving body 18 an arm 20 extends, to which arm a supporting plate 22 is rotatably mounted about a central axis. The supporting plate 22 has, at its top surface, a projected portion 48. to which an auxiliary guiding piece 50 is connected under a snap like fitted manner. A femoral component 52 is mounted, at its groove portion 54, to the osteotomized surface at the femoral distal end. The engaging plate 14 as well as the supporting plate 22 are under an offset arrangement with respect to the base and moving body, respectively.
Owner:ZIMMER KK
High flexion articular insert
A knee prosthesis is provided that allows for increased flexion. The knee prosthesis includes (a) a femoral component adapted to fit on a distal end of the femur which includes a lateral condylar structure and a medial condylar structure and (b) an intermediate structure configured to cooperate with a femoral component of a knee prosthesis. The intermediate structure includes at least one surface for contacting the femoral component and a transition of a sagittal curvature of the at least one contact surface from a concave surface into a convex surface at the contact interface of the femoral component and the intermediate structure when the knee is flexed at approximately 120° to 140°. The knee prosthesis minimizes impingement on the femoral posterior cortex in deep flexion, increases the dislocation safety factor and allows for easier reengagement of the articular surface should the femoral component externally rotate off of the tibial plateau.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Dynamic knee balancer with pressure sensing
ActiveUS20050177170A1Enhancing knee surgery procedureAccelerated programPerson identificationJoint implantsTibiaRelative pressure
A device for performing a surgical procedure on a knee includes an adjustable femoral portion, a tibial portion and at least one sensor coupled with the femoral and / or tibial portions to sense pressure exerted by the femoral and tibial portions against one another. The femoral portion is adapted for removably coupling with a distal end of a femur to adjust tension in soft tissue adjacent the knee and has at least one positioning feature adapted to move relative to the distal end of the femur as the femoral portion is adjusted, thus helping position a femoral prosthetic on the distal end of the femur. The sensor(s) may be adapted to sense pressure at medial and lateral sides of the knee, and relative pressures may be displayed as data on a visual display. Adjustments to the femoral member may be made to balance pressure at flexion and extension of the knee.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
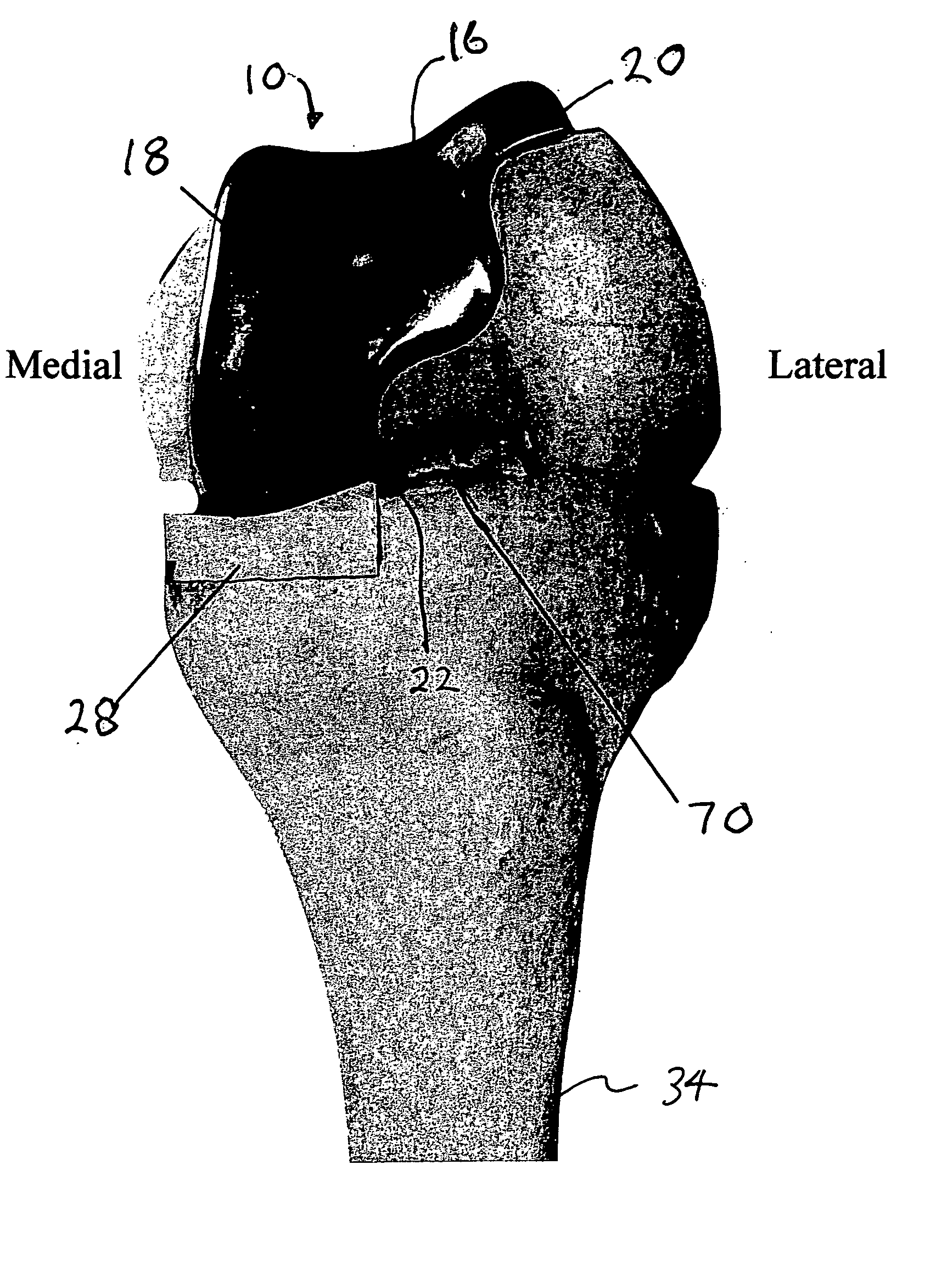
Bone shaped cutting block
ActiveUS20050240195A1Potential damageMaintaining amountNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsBone shapeBiomedical engineering
A cutting block for resecting a bone, particularly the distal femur, has a body with a first generally planar bone contacting surface to contact the resected distal surface of the femur. The body has a second surface spaced from the bone contacting surface along an axis perpendicular to said generally planar bone contacting surface. The body has a perimeter surface extending between the first and second surfaces, wherein the perimeter surface is at least partially curved with respect to the axis in both a direction generally perpendicular thereto and generally parallel thereto. The perimeter surface may be polished.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Surgical tool assembly for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080097451A1More convenienceMinimize damageJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTotal hip arthroplastyCutting guide
A surgical tool assembly for Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) including a femoral intra-medullary (IM) rod, a femoral intra-medullary (IM) alignment guide, a distal femoral alignment guide, and a distal femoral cutting guide. After the femoral IM alignment guide is selected to fit the valgus angle and utilized with the femoral IM rod with respect to the distal femur, the distal femoral alignment guide is integrated to the complex. Then, the distal femoral cutting guide is slid to the distal femoral alignment guide in the orientation from distal to proximal through the sliding concave integrated with the sliding track.
Owner:UNITED ORTHOPEDIC CORP +1
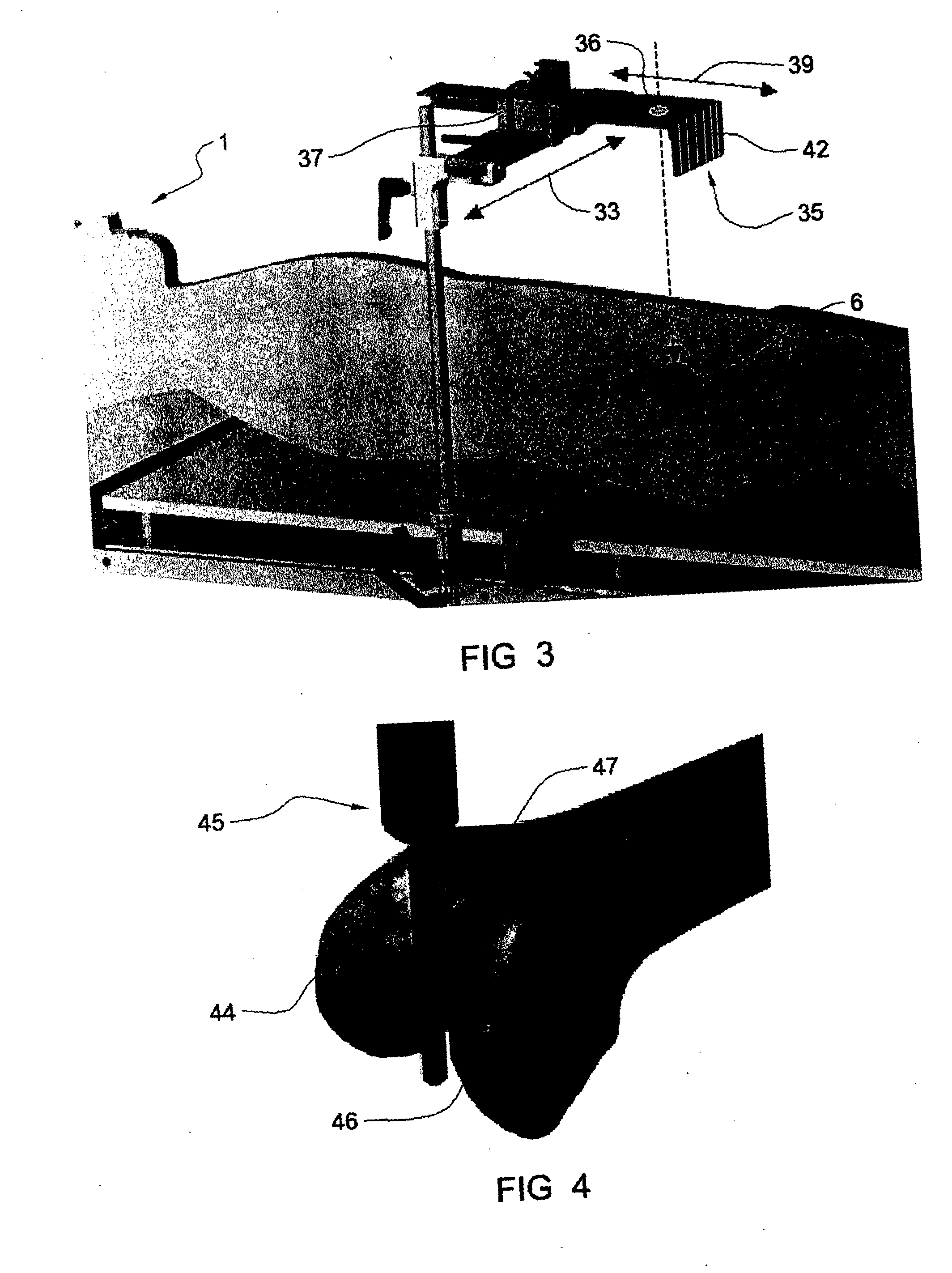
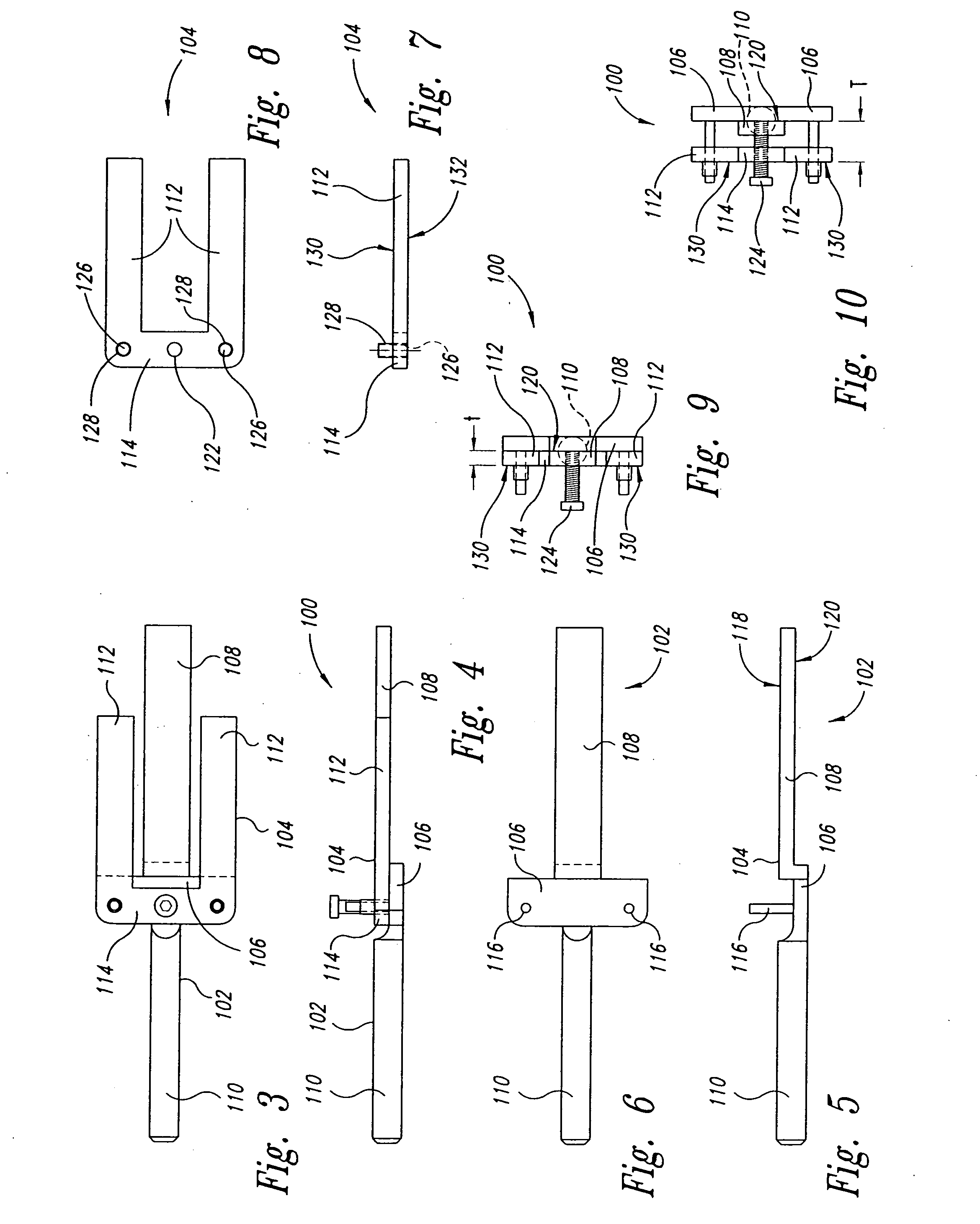
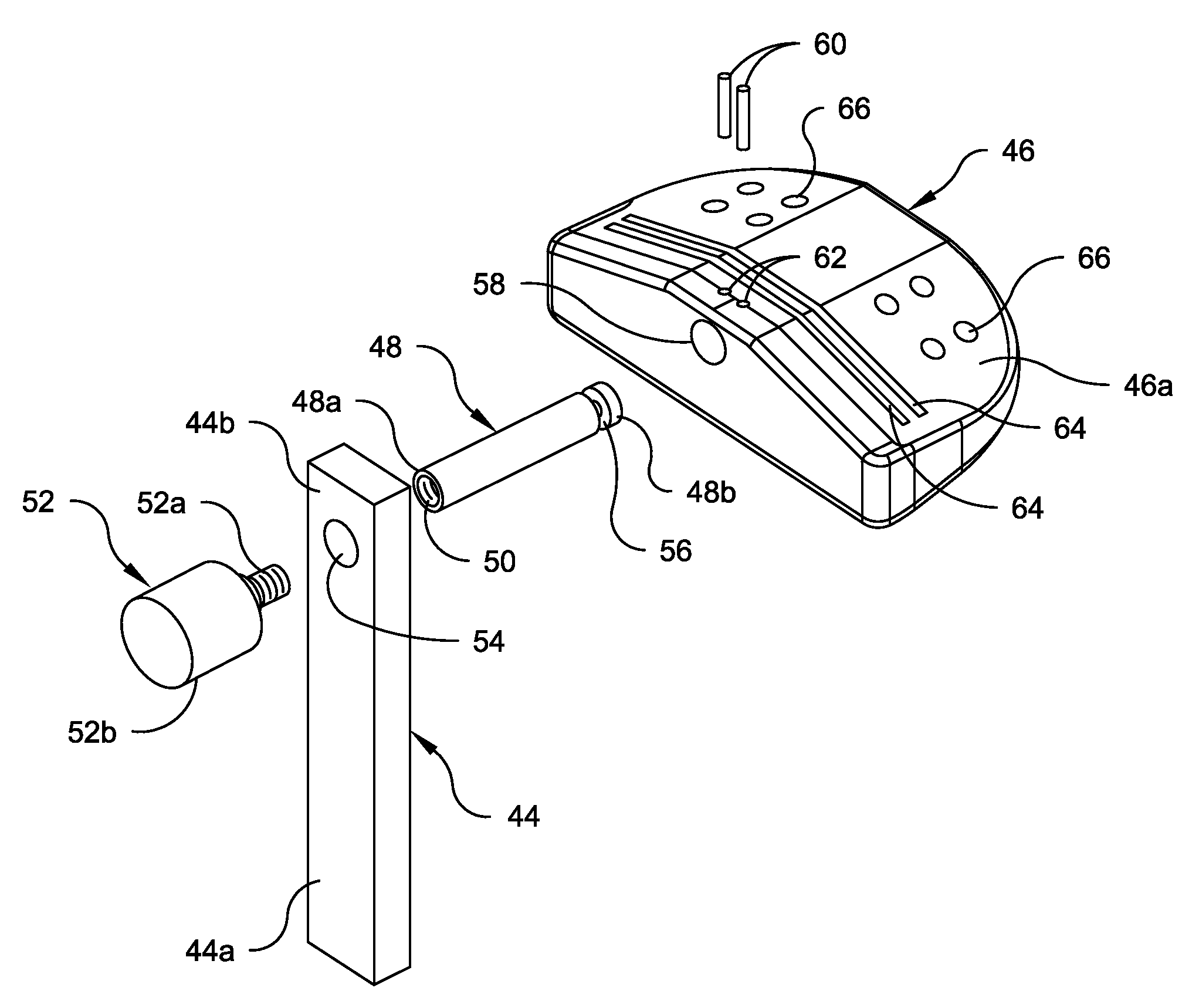
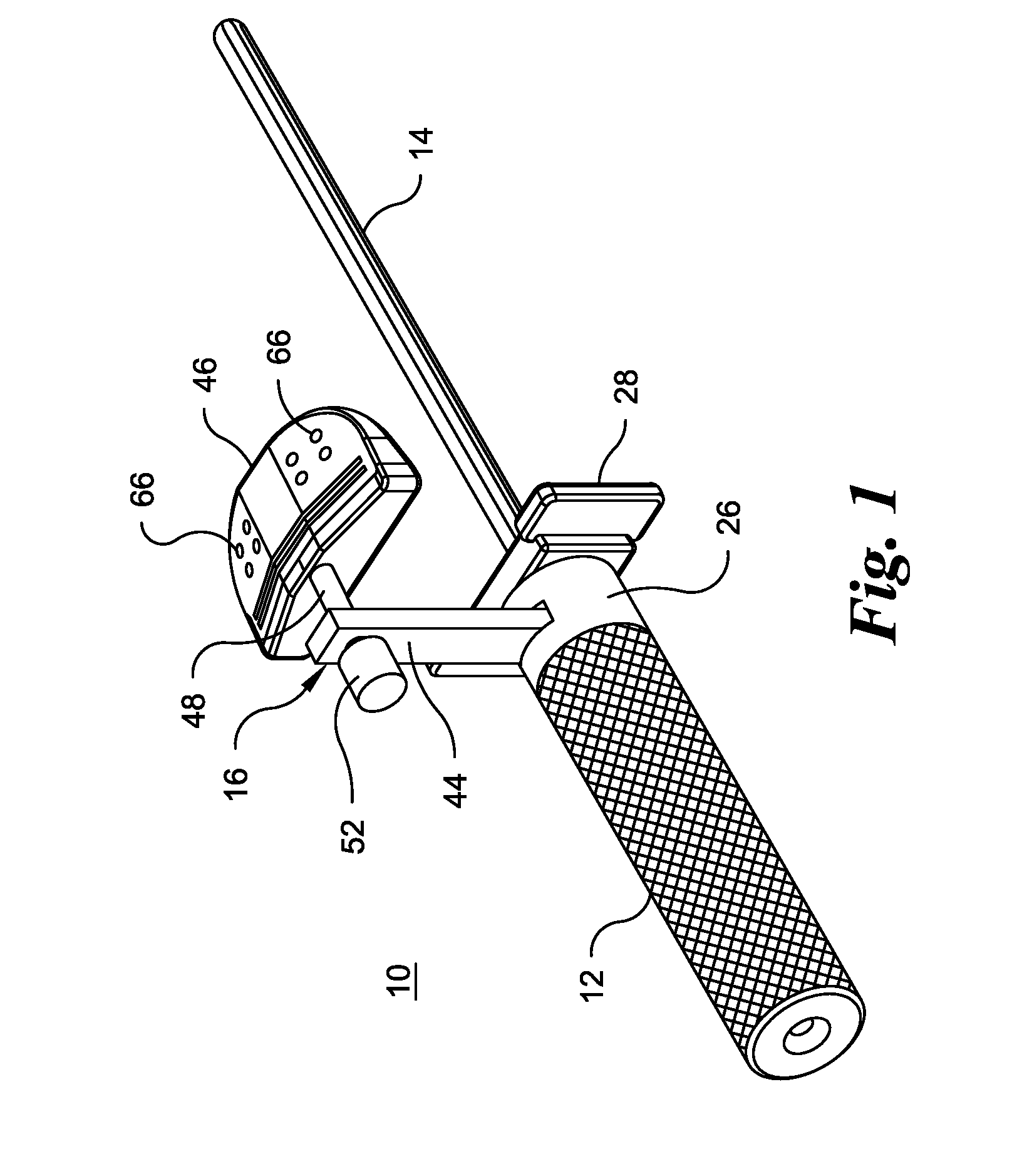
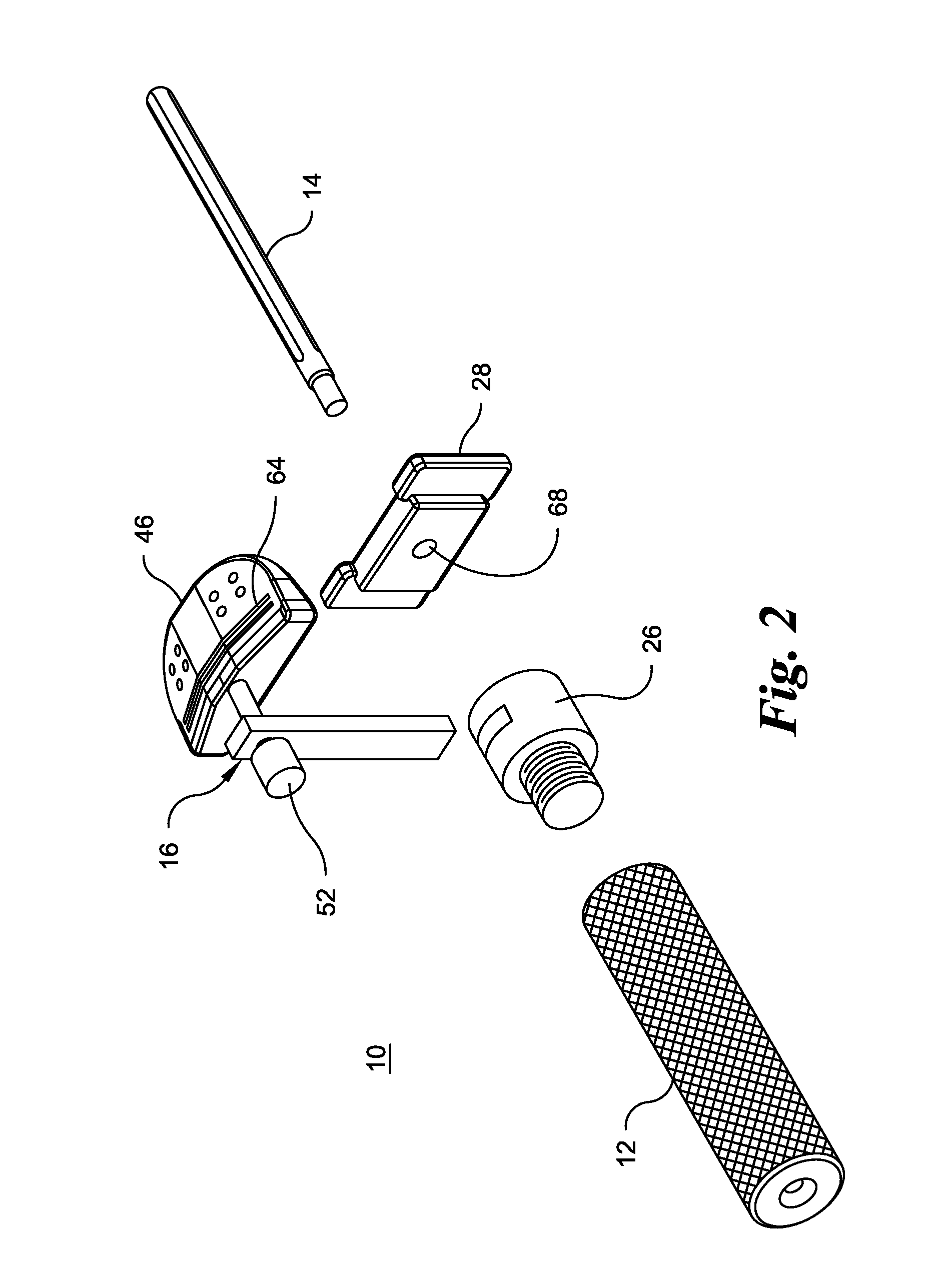
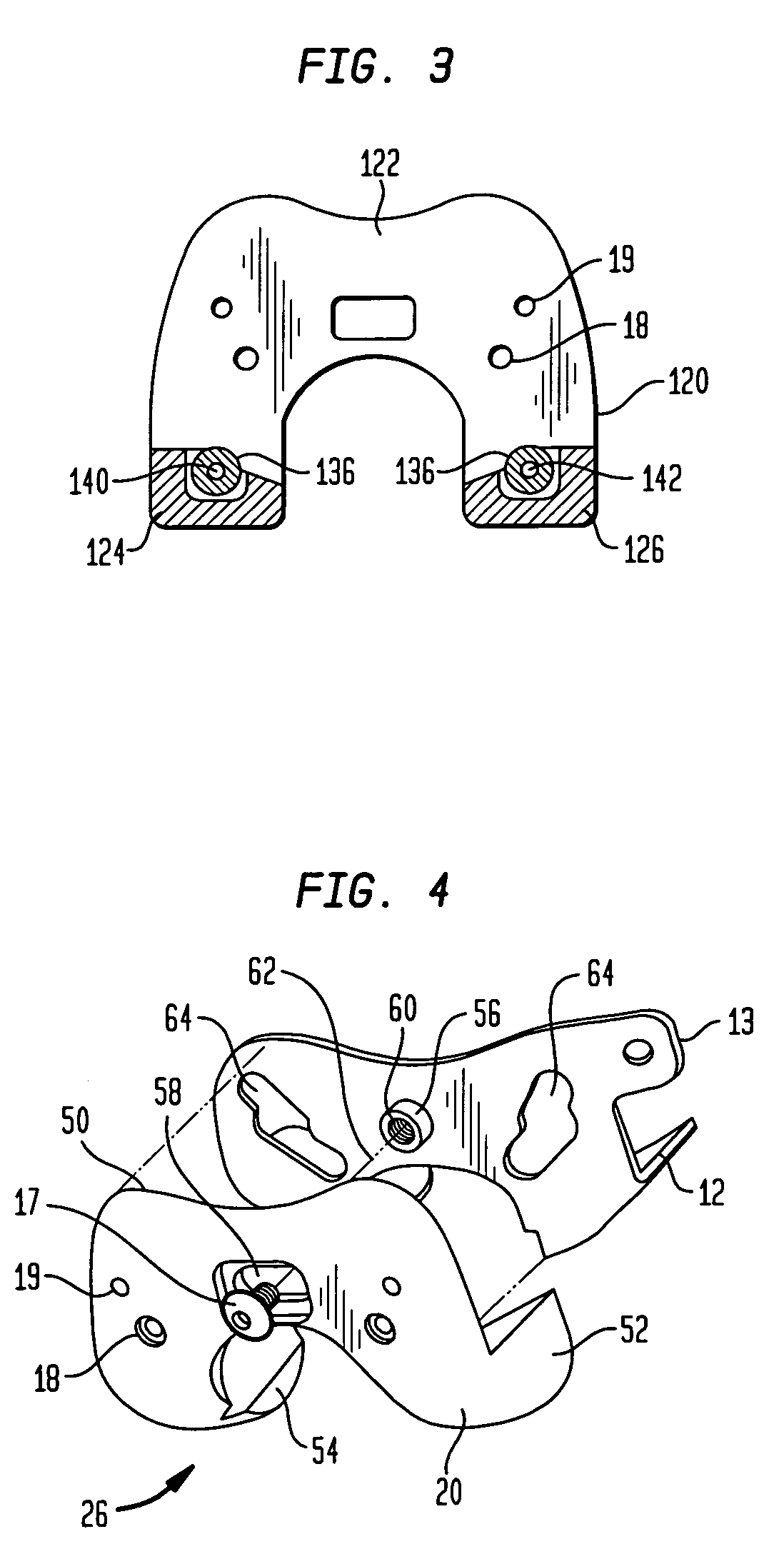
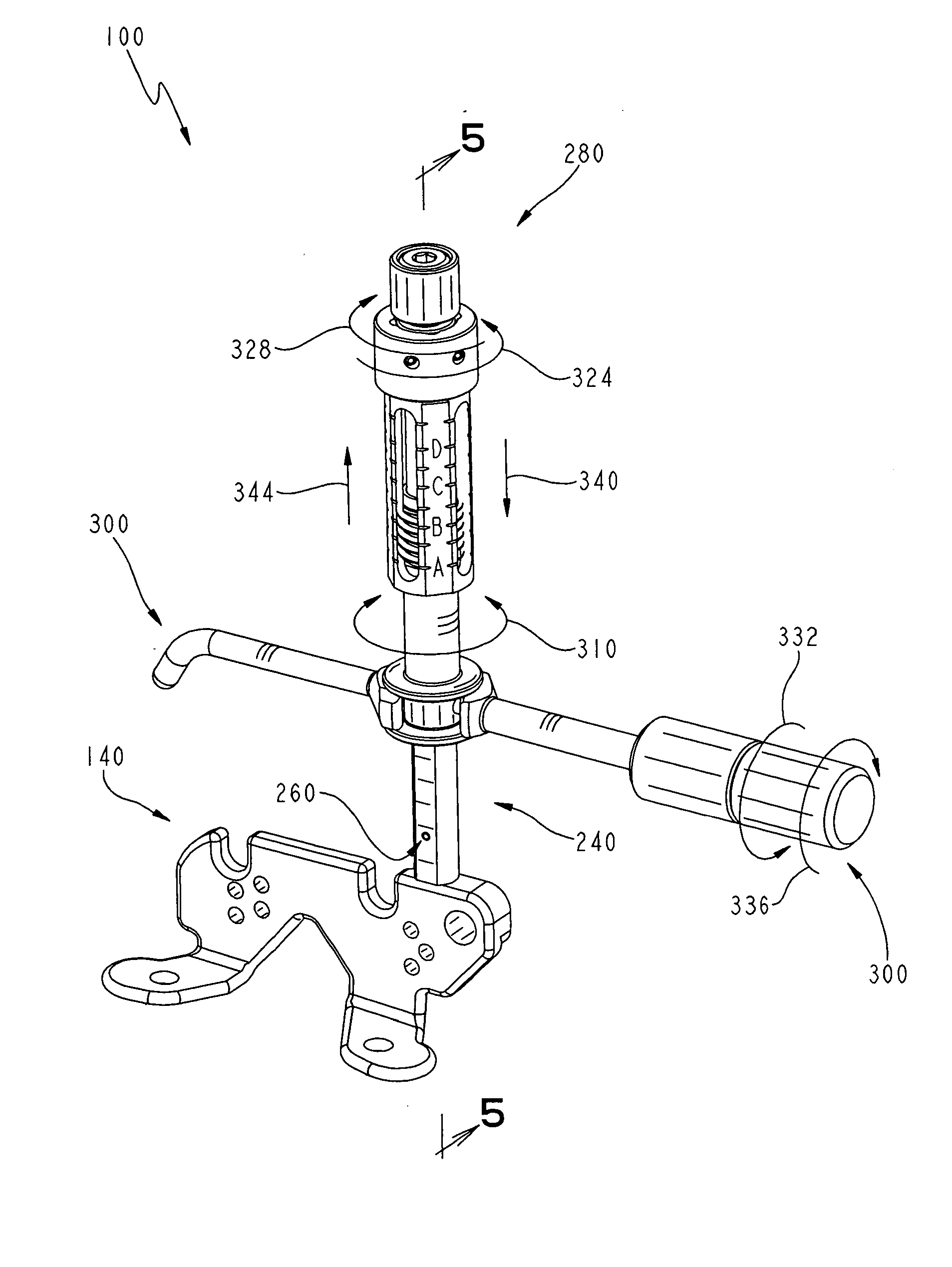
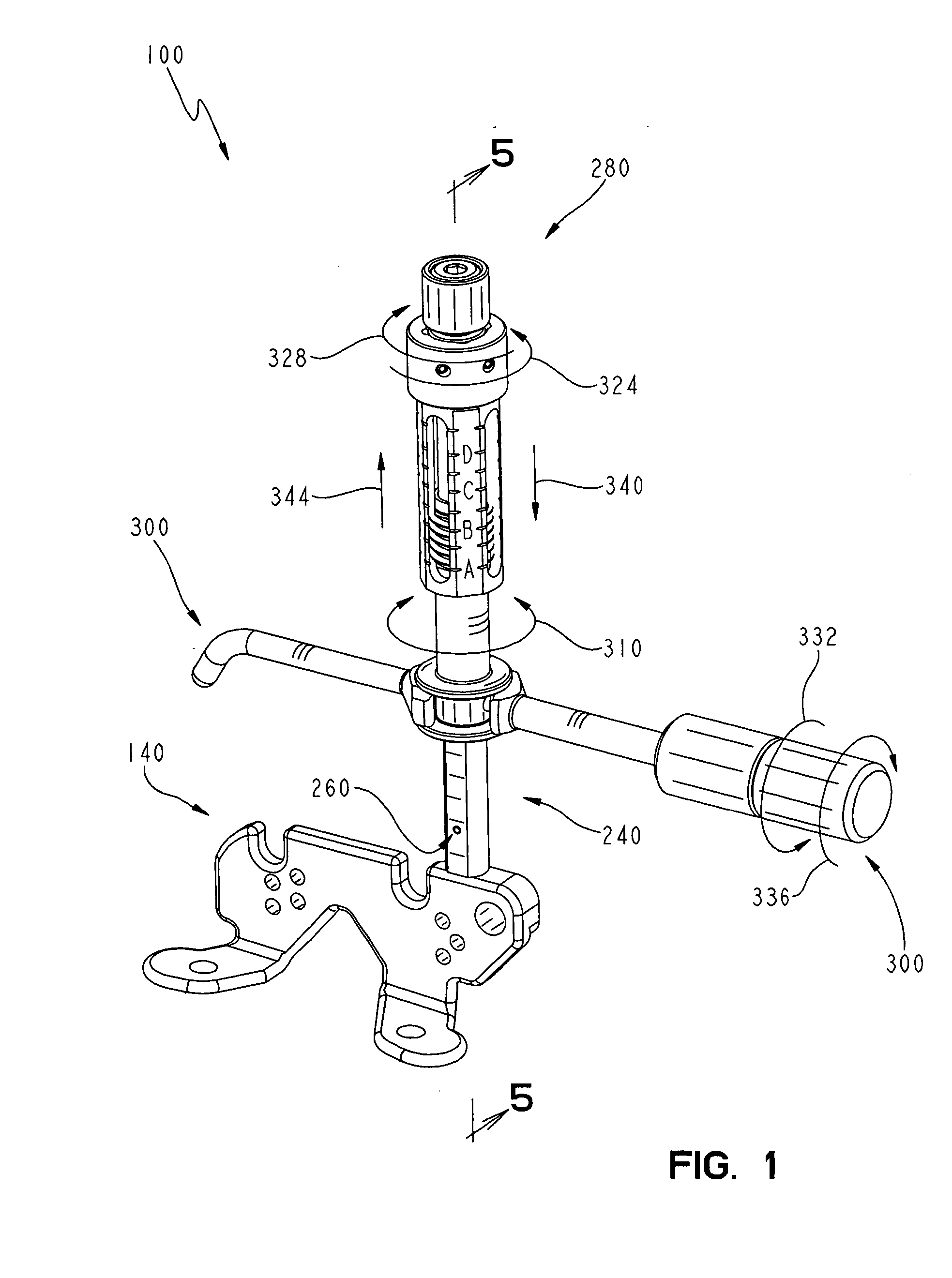
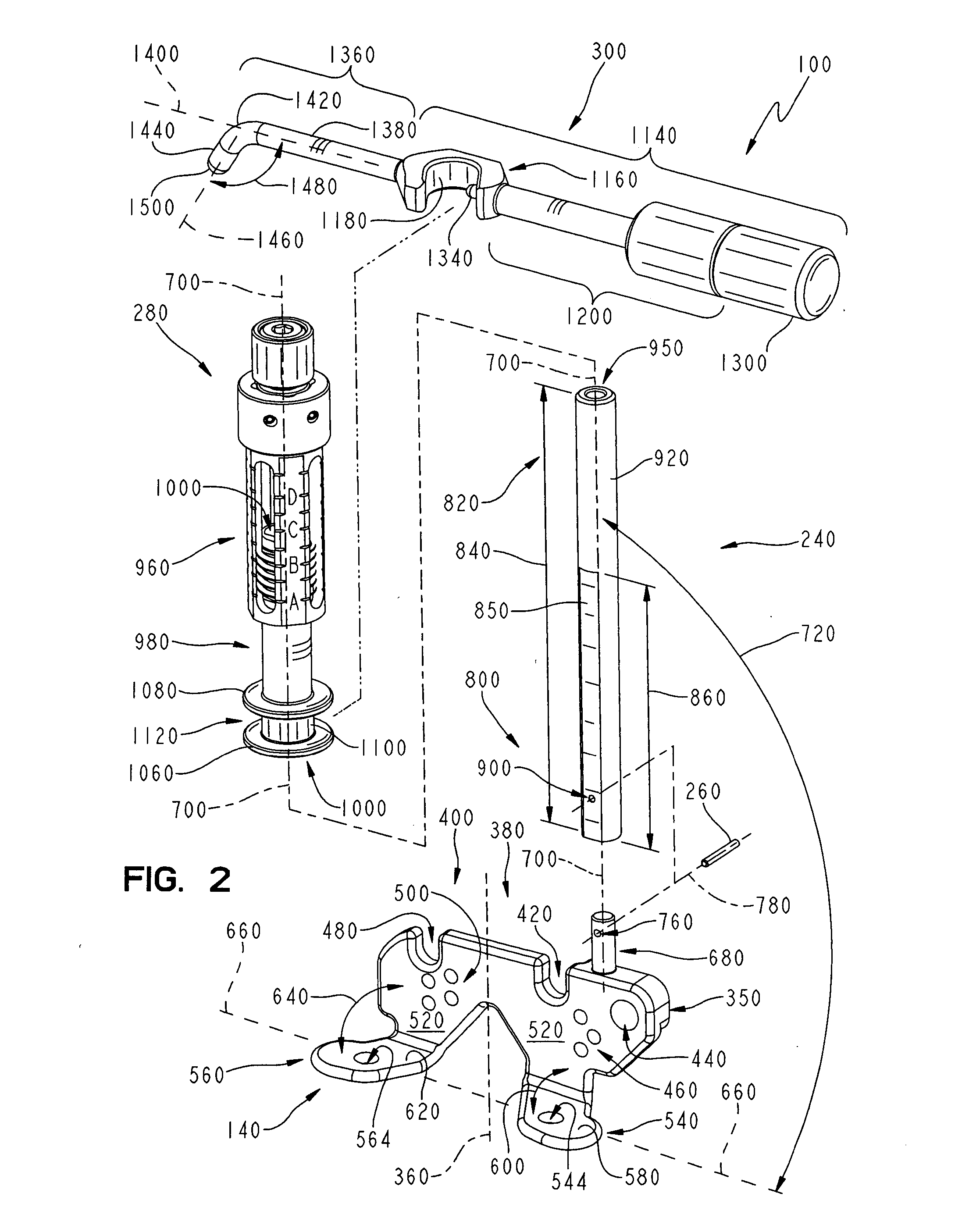
Distal Femoral Cutting Guide
An apparatus for resecting the distal face of either the left or right femur at a predetermined valgus angle relative to the patient's intramedullary canal prior to implanting the femoral component of a total knee prosthesis. The apparatus has a distal elongate sword having a longitudinal axis and being adapted for insertion into the intramedullary canal of the femur. A proximal handle is connected to and has a longitudinal axis coaxial with the sword. A base cartridge is fixed intermediate the sword and handle and has an axial passage extending therethrough. A face plate is fixed at the distal end of the base cartridge and is adapted to abut the face of the natural distal femur. The face plate is oriented at the predetermined valgus angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the sword. A cutting jig connects to the base cartridge. The cutting jig has a guide plate with at least one blade slot adapted to receive and guide a cutting blade, and a bracket that supports the guide plate and detachably engages the axial passage and orients the at least one blade slot at the predetermined valgus angle relative to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Prosthetic revision knee system
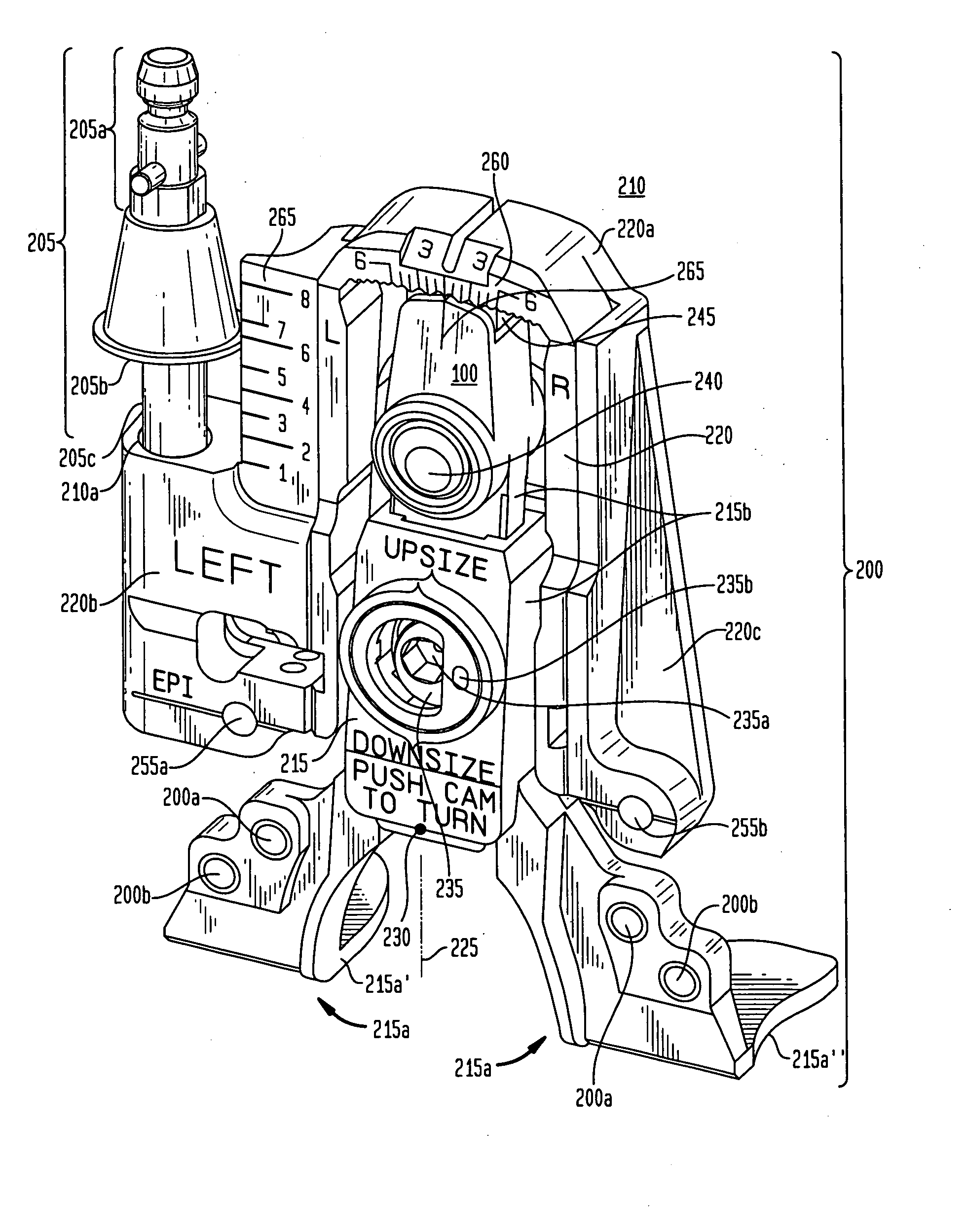
The present invention provides a femoral component, and a method for surgical implantation of a femoral prosthesis, comprised of a revision knee implant and corresponding cutting block system. In particular, the revision knee implant, comprised of a femoral component having incremental markings thereon and a femoral stem, and corresponding cutting block system having corresponding incremental markings thereon, enables a surgeon maximally to position the cutting block adjacent as much area as possible of a distal femur of a patient and to infinitely position the femoral component in the exact position indicated by the cutting block.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
High flexion articular insert
A knee prosthesis is provided that allows for increased flexion. The knee prosthesis includes (a) a femoral component adapted to fit on a distal end of the femur which includes a lateral condylar structure and a medial condylar structure and (b) an intermediate structure configured to cooperate with a femoral component of a knee prosthesis. The intermediate structure includes at least one surface for contacting the femoral component and a transition of a sagittal curvature of the at least one contact surface from a concave surface into a convex surface at the contact interface of the femoral component and the intermediate structure when the knee is flexed at approximately 120° to 140°. The knee prosthesis minimizes impingement on the femoral posterior cortex in deep flexion, increases the dislocation safety factor and allows for easier reengagement of the articular surface should the femoral component externally rotate off of the tibial plateau.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
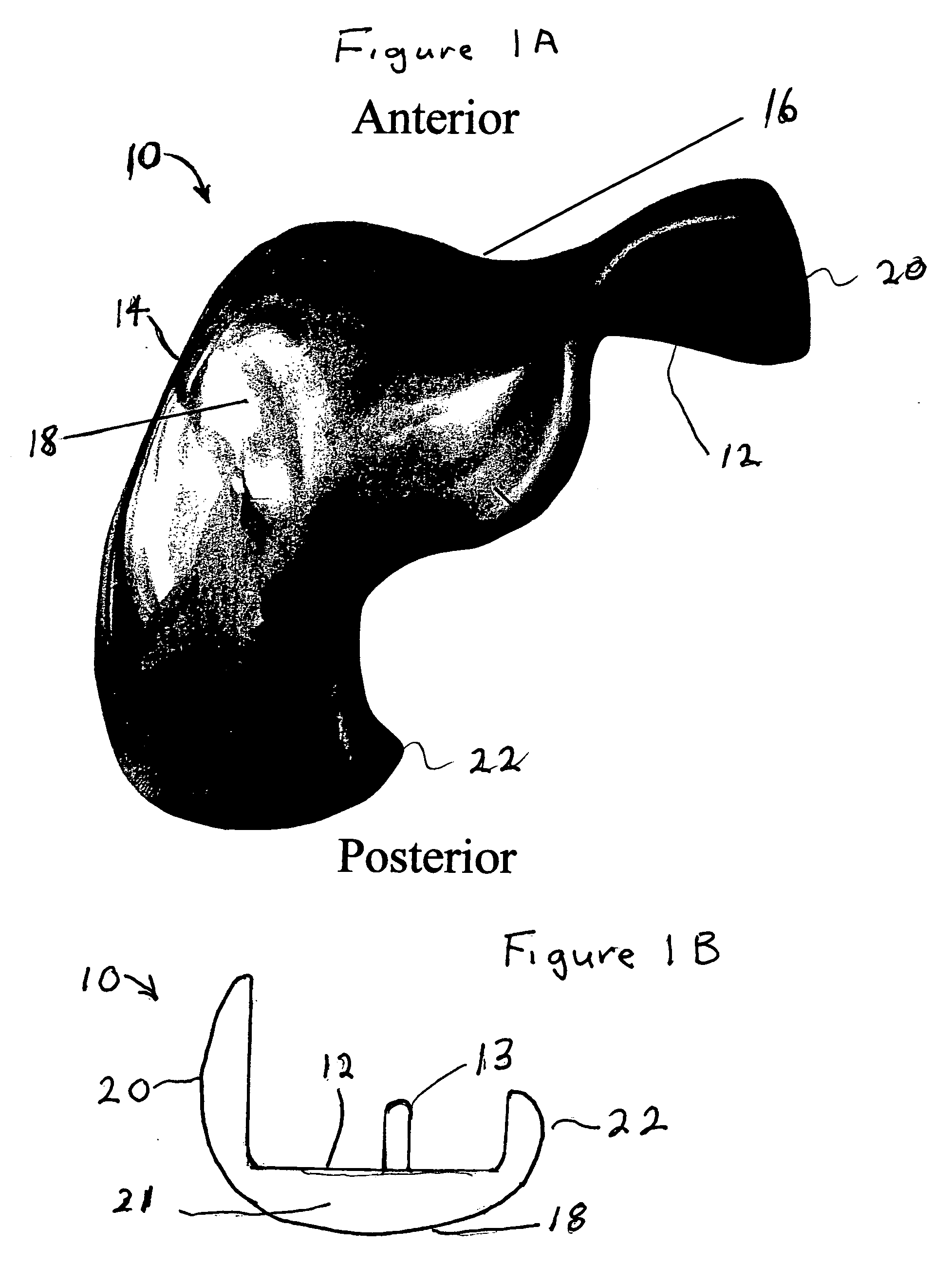
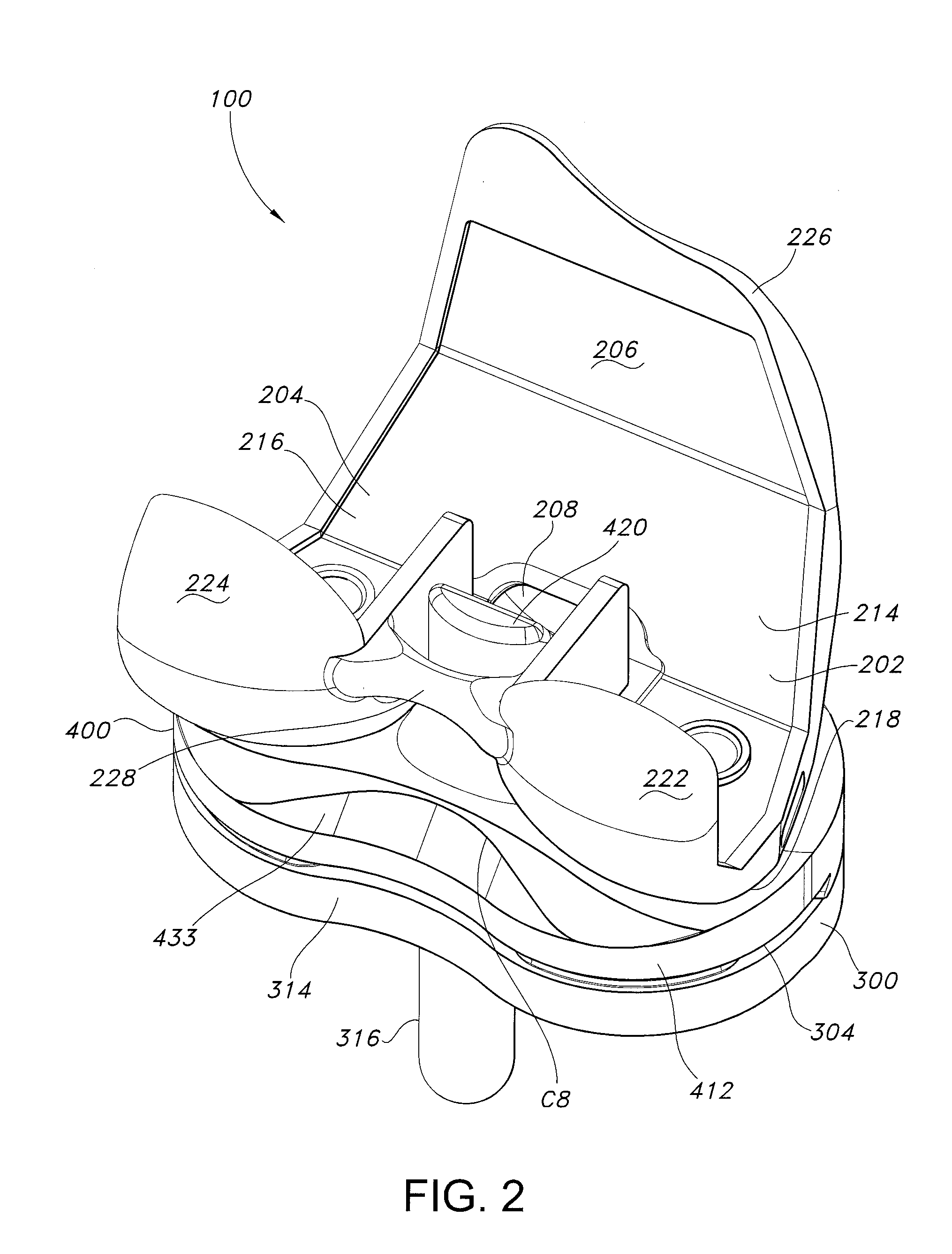
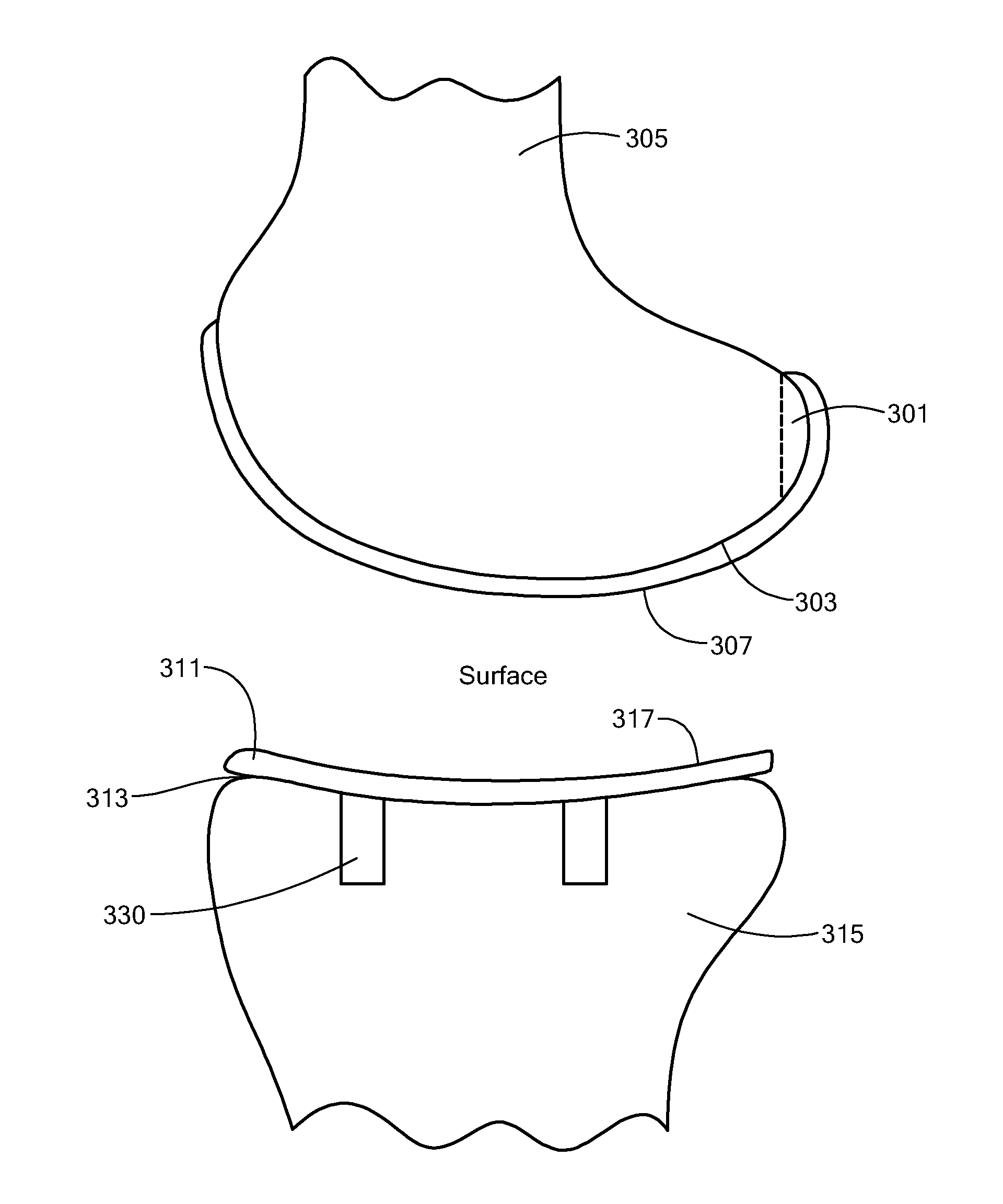
Ethnic-Specific Orthopaedic Implants and Custom Cutting Jigs
An orthopedic implant comprising: (a) a distal femoral component comprising a first condyle bearing surface having a first profile comprising at least three consecutive arcs of curvature; and (b) a proximal tibial component comprising a first condyle bearing surface having a second profile comprising at least three parallel arcs of curvature. The disclosure also includes a method of designing and fabricating an orthopedic implant, the method comprising: (a) evaluating images of distal femurs of a particular ethnicity to extract common shape features exhibited across an ethnicity that are unique to the ethnicity to create an ethnic specific template; (b) designing a distal femoral component comprising a first condyle surface using the ethnic specific template; and, (c) fabricating a distal femoral component embodying the first condyle surface.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Implant device and method for manufacture
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Femoral component and instrumentation
A method for setting the internal-external rotational position of a prosthetic femoral component with respect to the tibial comprising: forming a cylindrical surface on the posterior femoral condyles, said cylindrical surface formed about an axis extending in a proximal distal direction with respect to the femur; placing a template having a cylindrical guide surface for engaging said posterior femoral condyles against a planar resected surface of the distal femur with said guide surfaces in contact with said cylindrically shaped posterior condyles; and rotating said template on said cylindrical guide surface as the knee joint is moved from flexion to extension until the template cylindrical guide surfaces are in a position with respect to the tibial condyle surfaces to properly balance the knee ligaments.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
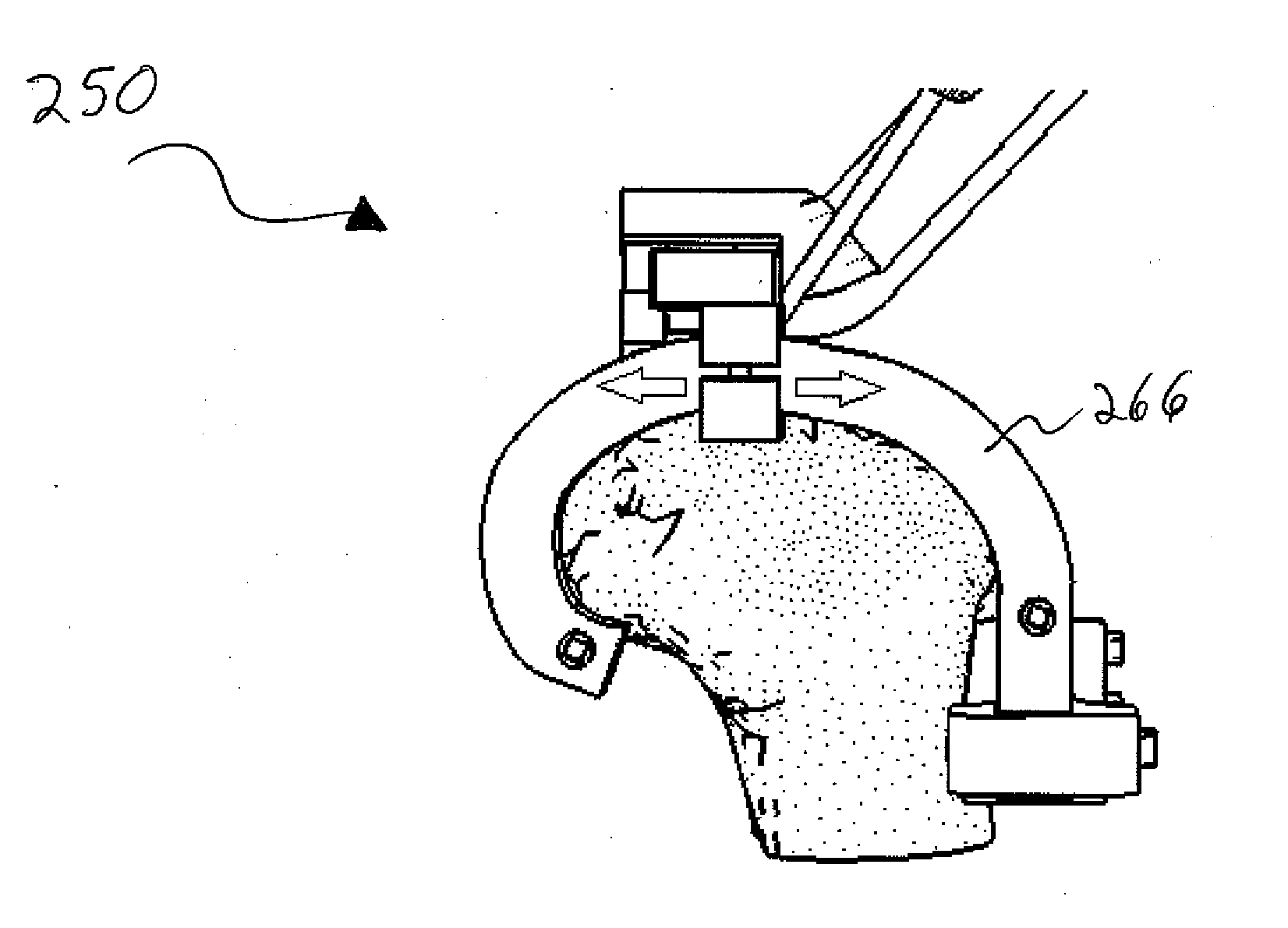
System and method for performing femoral sizing through navigation
An apparatus, method, and system for sizing a distal portion of a patient's femur during knee arthroplasty. The femur is sized by positioning the patient such that the distal femur portion of the patient is in a field of view of a sensor array; attaching a femoral sizer to the distal femur portion, the femoral sizer including a tracker that is operable to provide signals to the sensor array; manipulating the sizer while observing a display that displays an image based on the signals provided by the tracker to the sensor array; and determining the size of the distal portion of the femur by observing the sizer in response to an indication provided on the display.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Apparatus and method for sizing a distal femur
An apparatus for sizing a distal femur includes a base configured to concurrently abut a distal surface and a posterior surface of the distal femur, and further includes an axial distance scale. The scale includes a first sleeve axially fixedly coupled to the base and further includes a second sleeve spirally movably coupled to the first sleeve. A method for sizing a distal femur includes concurrently abutting a base against a distal surface and a posterior surface of the distal femur, and further includes measuring a distance relative to the base. The measuring step includes spirally moving a first sleeve relative to a second sleeve.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Dynamic knee balancer with pressure sensing
InactiveUS8758355B2Accelerated programDesired stability and range of motion and patellar trackingJoint implantsSurgical robotsTibiaRelative pressure
A device for performing a surgical procedure on a knee includes an adjustable femoral portion, a tibial portion and at least one sensor coupled with the femoral and / or tibial portions to sense pressure exerted by the a moral and tibial portions against one another. The femoral portion is adapted for removably coupling with a distal end of a femur to adjust tension in soft tissue adjacent the knee and has at least one positioning feature adapted to move relative to the distal end of the femur as the femoral portion is adjusted, thus helping position a femoral prosthetic on the distal end of the femur. The sensor(s) may be adapted to sense pressure at medial and lateral sides of the knee, and relative pressures may be displayed as data on a visual display. Adjustments to the femoral member may be made to balance pressure at flexion and extension of the knee.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Knee balancing for revision procedures
ActiveUS20110093081A1Promote balance between supply and demandImprove balanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibial Collateral LigamentsTotal knee replacement
Methods, systems and devices are provided for facilitating a surgical procedure on a knee, particularly, a revision total knee replacement procedure. Prior femoral and tibial prostheses are removed. A cut end of a distal femur is engaged with a femoral adjustment member, which will typically center itself about an intermedullary rod placed into the femur. The lateral and medial forces exerted by lateral and medial sides of the femoral adjustment member and the cut tibial plateau against each other are measured. The femoral adjustment member is adjusted to apply and / or adjust tension to the lateral collateral ligament and / or the medial collateral ligament based on the measured forces, for example, such that the measured lateral force and the measured medial force are matched. Based on the position of the adjusted femoral member, guided clean-up cuts for placement of a new femoral prostheses are made on the cut end of the distal femur.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Hybrid femoral implant
ActiveUS8070821B2Implantation possiblePossible removalAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantPinna structureMedicine
A hybrid prosthetic femoral component has an outer bearing surface for engaging a tibial bearing and an inner surface for engaging a prepared distal femur. The inner surface having a distal surface, an anterior surface and a posterior surface, wherein said posterior surface has a first surface structure for allowing tissue ingrowth and the anterior and distal surfaces having a second surface structure for contacting bone cement. The first and second structure have different surface characteristics with different properties wherein the first surface structure is a porous surface and the second surface is a non-porous textured surface. The hybrid prosthetic femoral component further comprises an anterior chamfered surface and a posterior chamfered surface wherein the posterior chamfered surface includes the first surface structure and the anterior chamfered surface includes the second surface structure.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Knee balancing for revision procedures
ActiveUS8506571B2Promote balance between supply and demandImprove balanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaIntramedullary rod
Methods, systems and devices are provided for facilitating a surgical procedure on a knee, particularly, a revision total knee replacement procedure. Prior femoral and tibial prostheses are removed. A cut end of a distal femur is engaged with a femoral adjustment member, which will typically center itself about an intramedullary rod placed into the femur. The lateral and medial forces exerted by lateral and medial sides of the femoral adjustment member and the cut tibial plateau against each other are measured. The femoral adjustment member is adjusted to apply and / or adjust tension to the lateral collateral ligament and / or the medial collateral ligament based on the measured forces, for example, such that the measured lateral force and the measured medial force are matched. Based on the position of the adjusted femoral member, guided clean-up cuts for placement of a new femoral prostheses are made on the cut end of the distal femur.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Natural alignment knee instruments
A method for aligning an orthopedic implant in a joint replacement includes determining the bone and cartilage deficiency from an undegenerated state caused by wear of a joint. Then a resection of a bone in the joint is made based on the deficiency of bone and cartilage from the undegenerated state and the size of a joint implant so as to locate the joint surface of the implant in the undegenerated cartilage location. The condylar wear from the undegenerated states may be assessed at a distal and posterior location on each of a medial and a lateral femoral condyle. A distal cut is made on the femur at a location adjusting for the condylar wear from the undegenerated state. The distal cut varus-valgus angle is oriented parallel to a plane across the distal femur after adjusting for wear in the distal location on the medial and lateral condyle.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
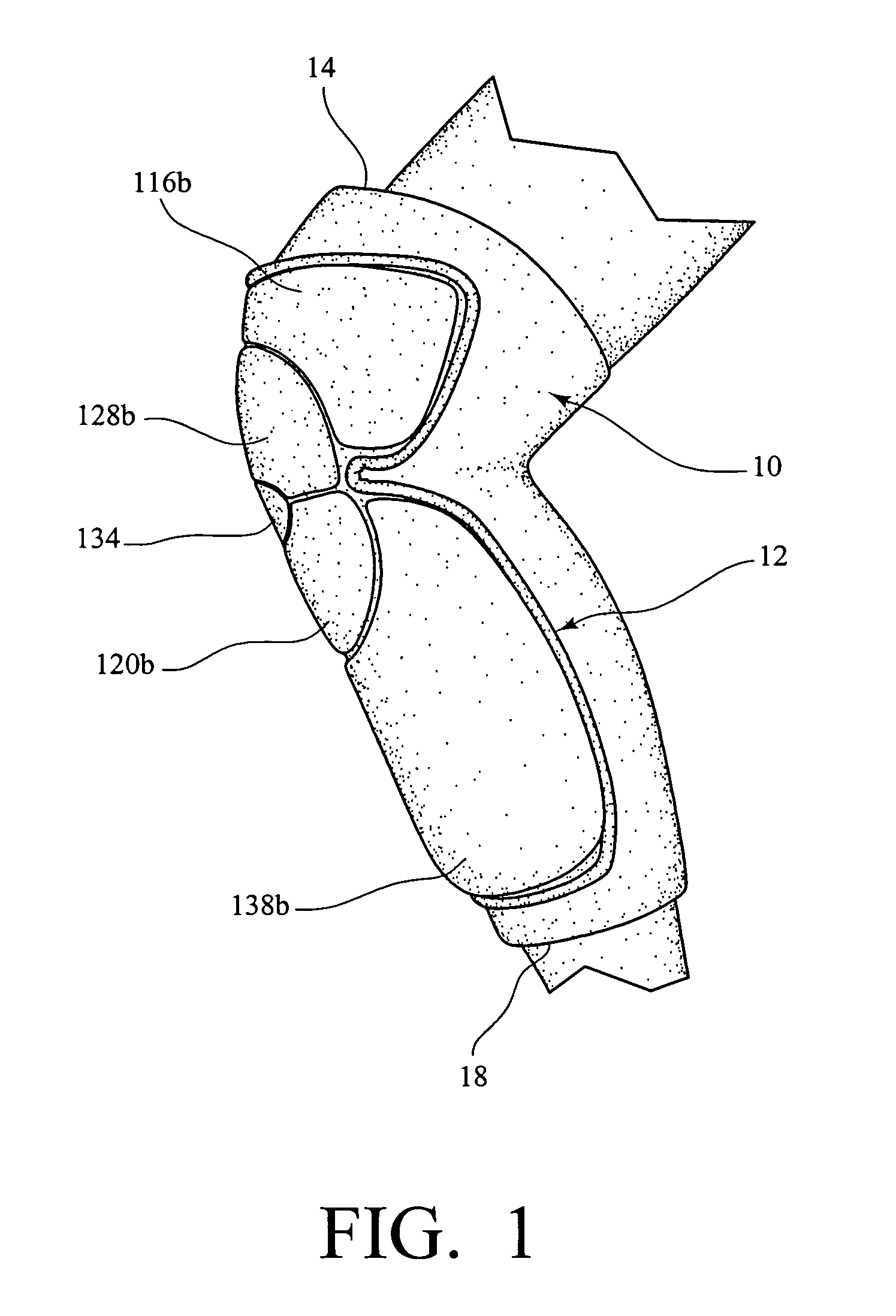
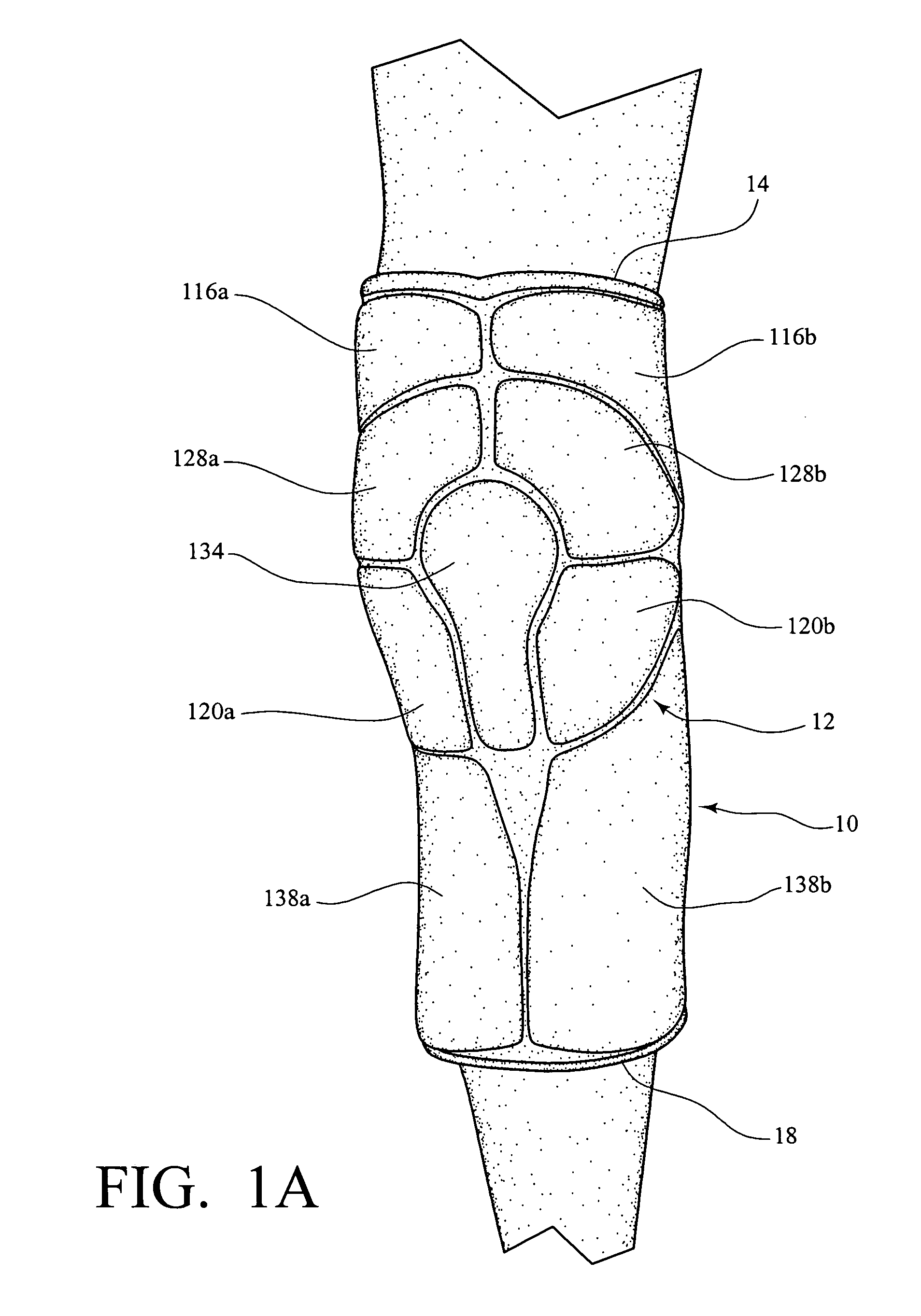
Knee protector
ActiveUS7114189B1Improve protectionProtective garmentPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee protector
A knee protector includes a plurality of pads positioned to cover a patella, a lower portion of the distal femur, the femoral condyles, the upper end of the fibula and an upper end of the proximal tibia with spacings between said pads to accommodate the flexion and extension of the knee when in use from a standing to a squatting position by a wearer.
Owner:HILLERICH & BRADSBY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com