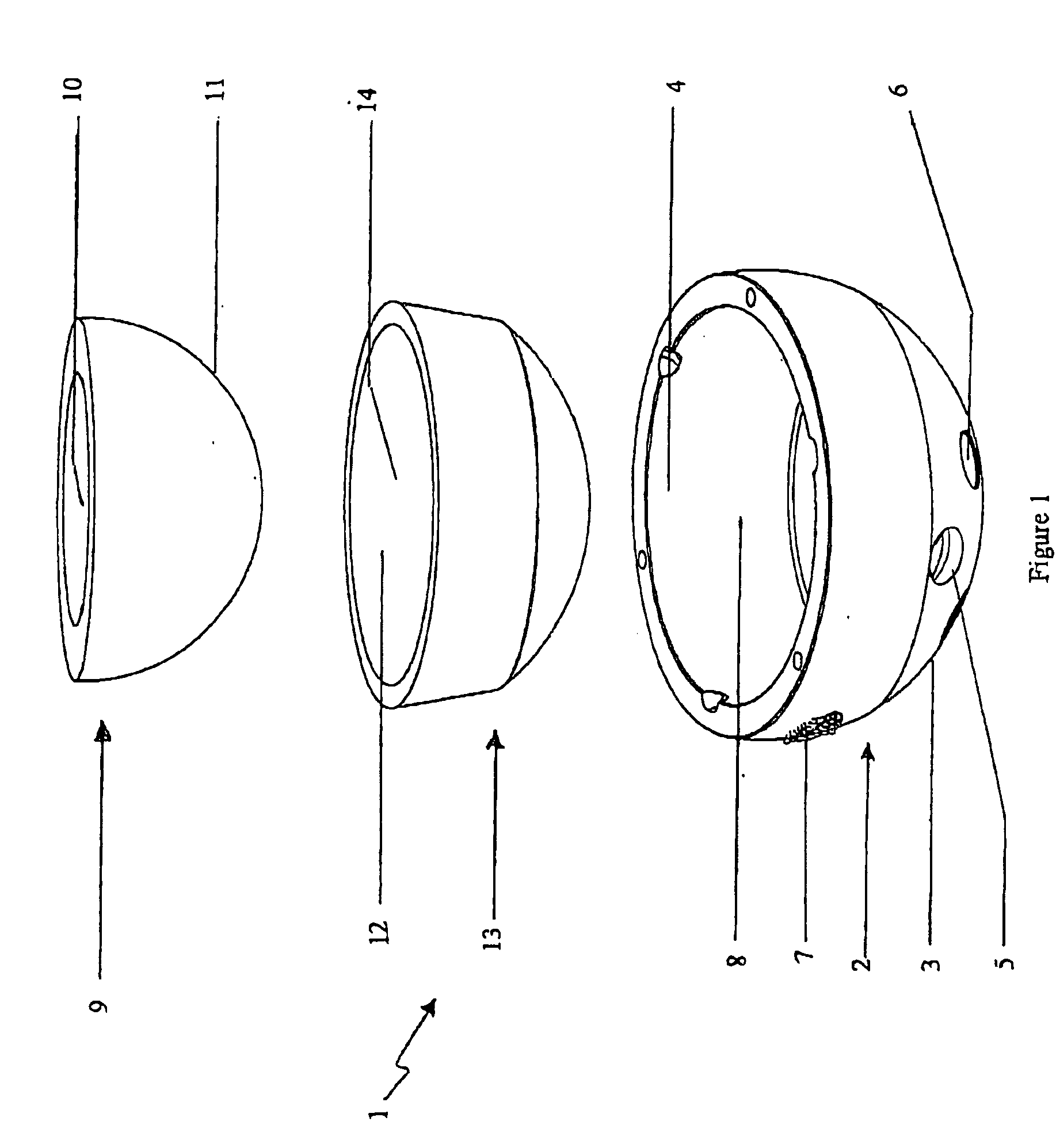Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
976 results about "Cotyloid Cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
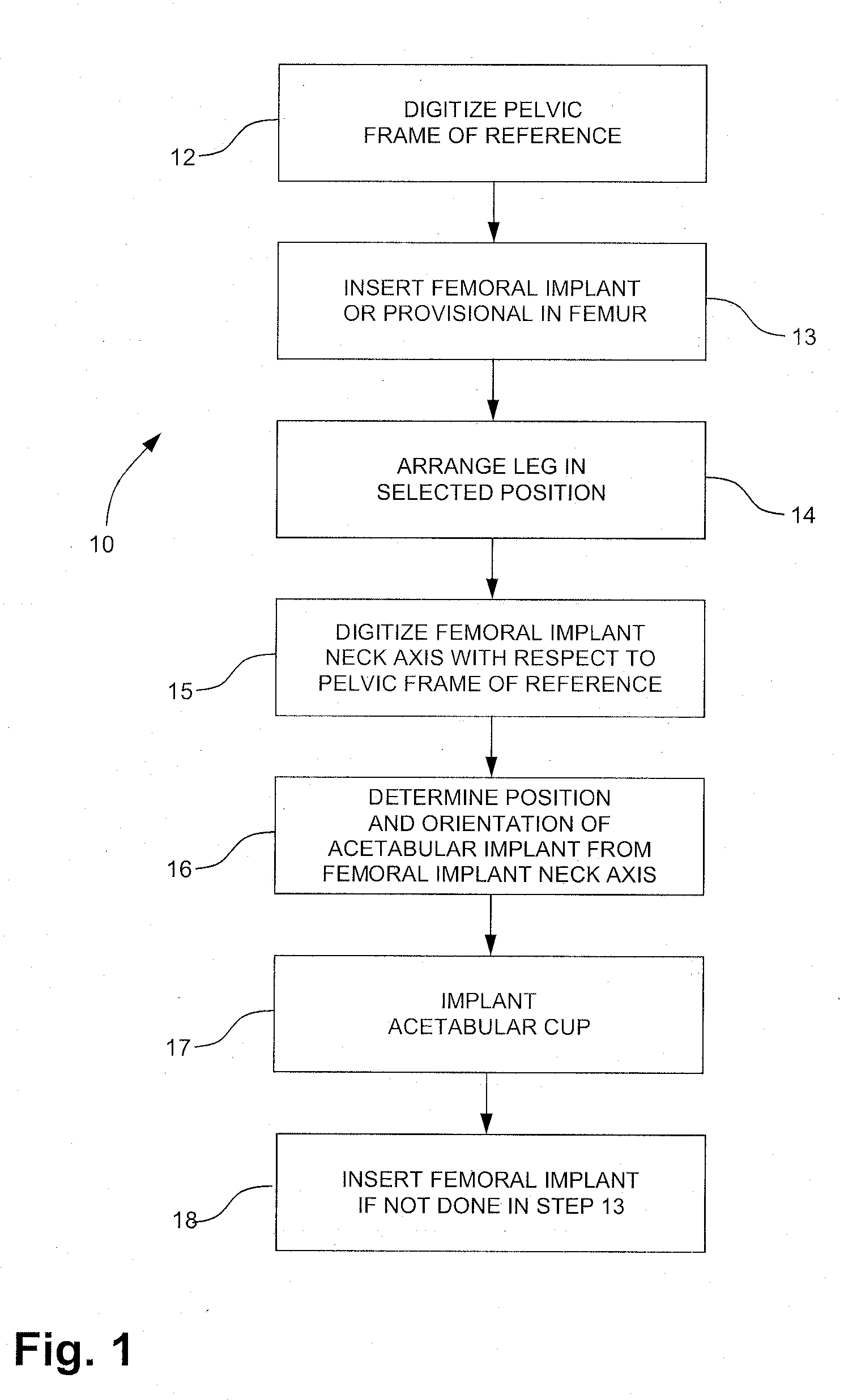
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
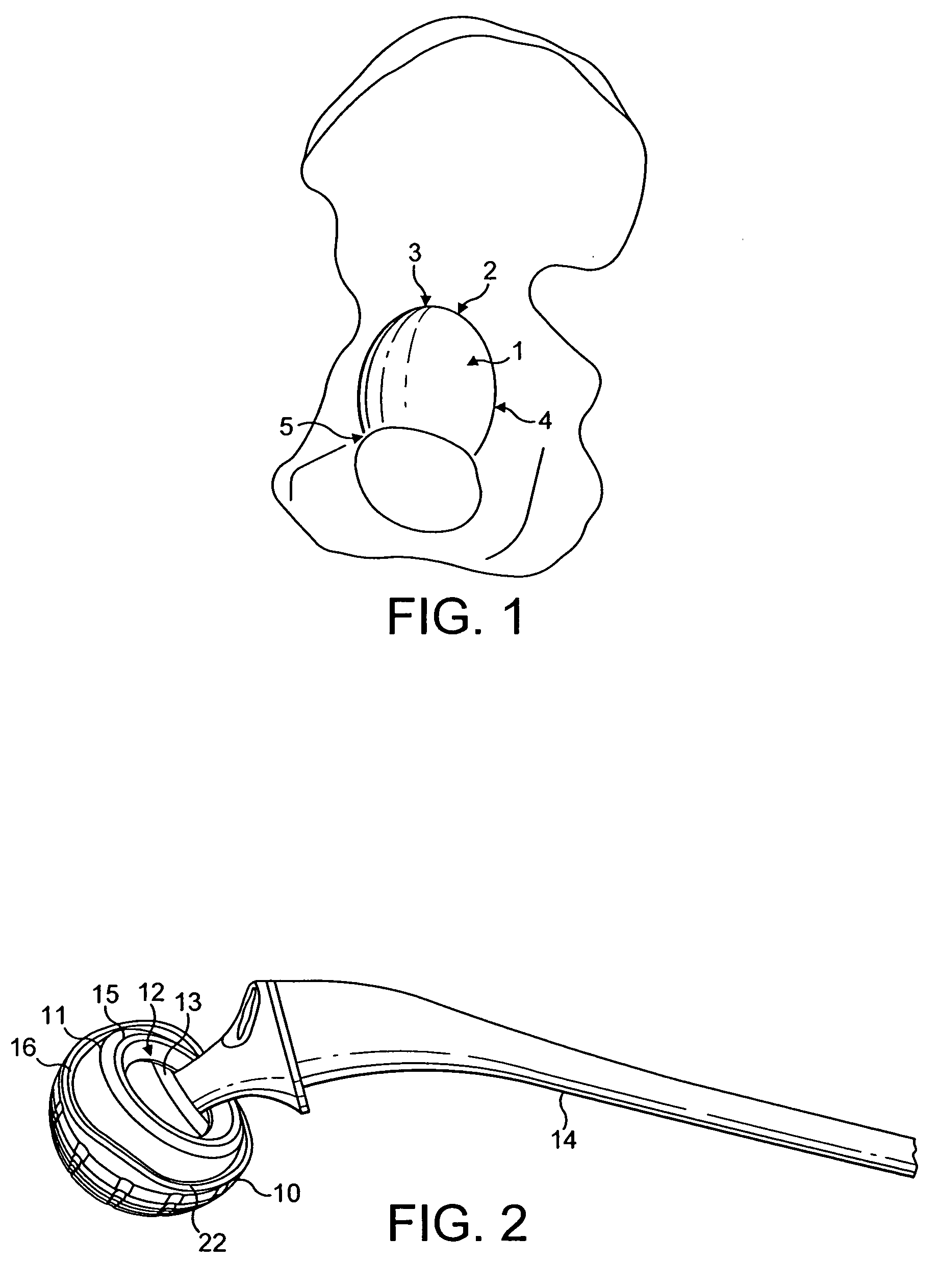
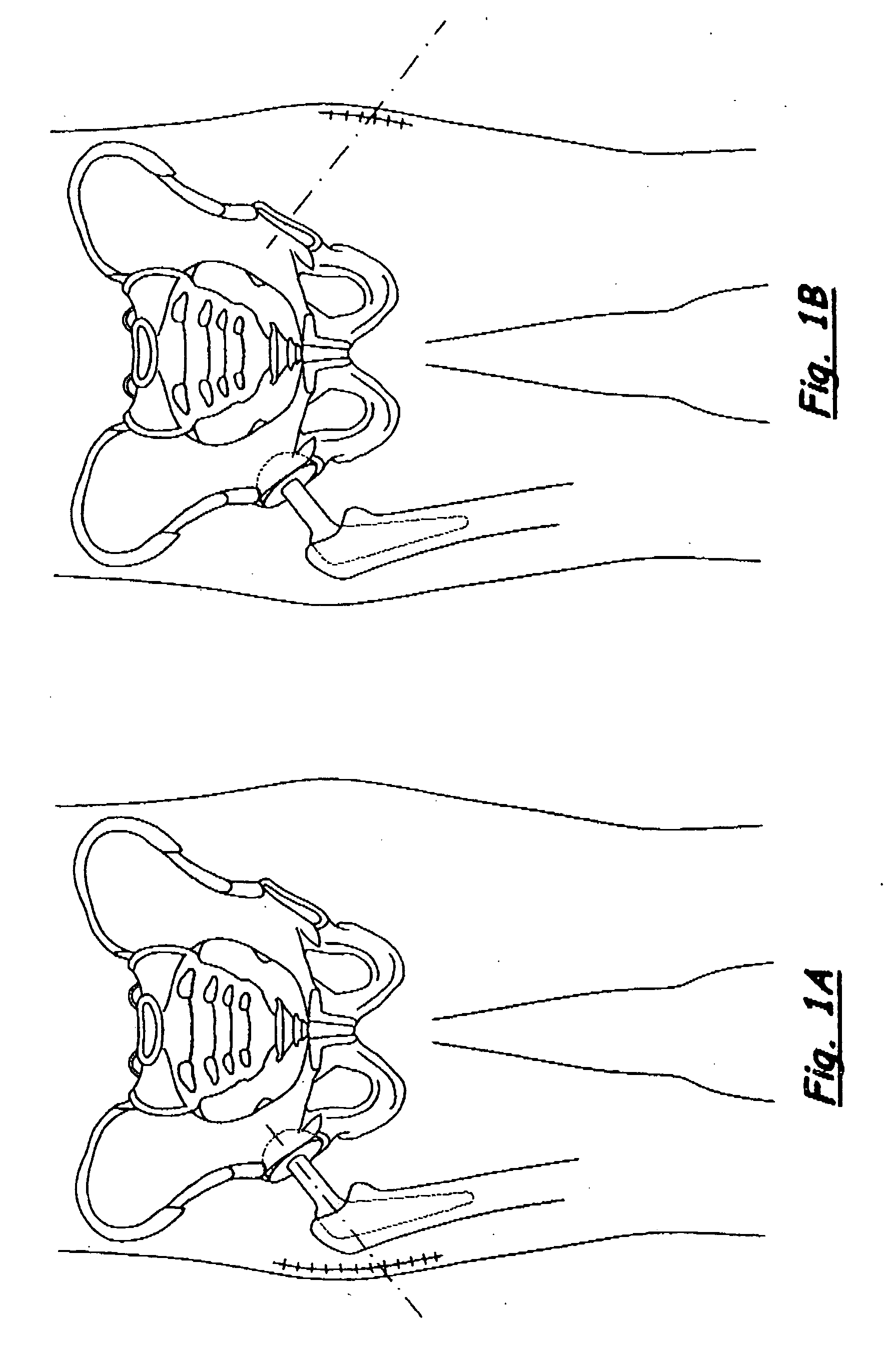
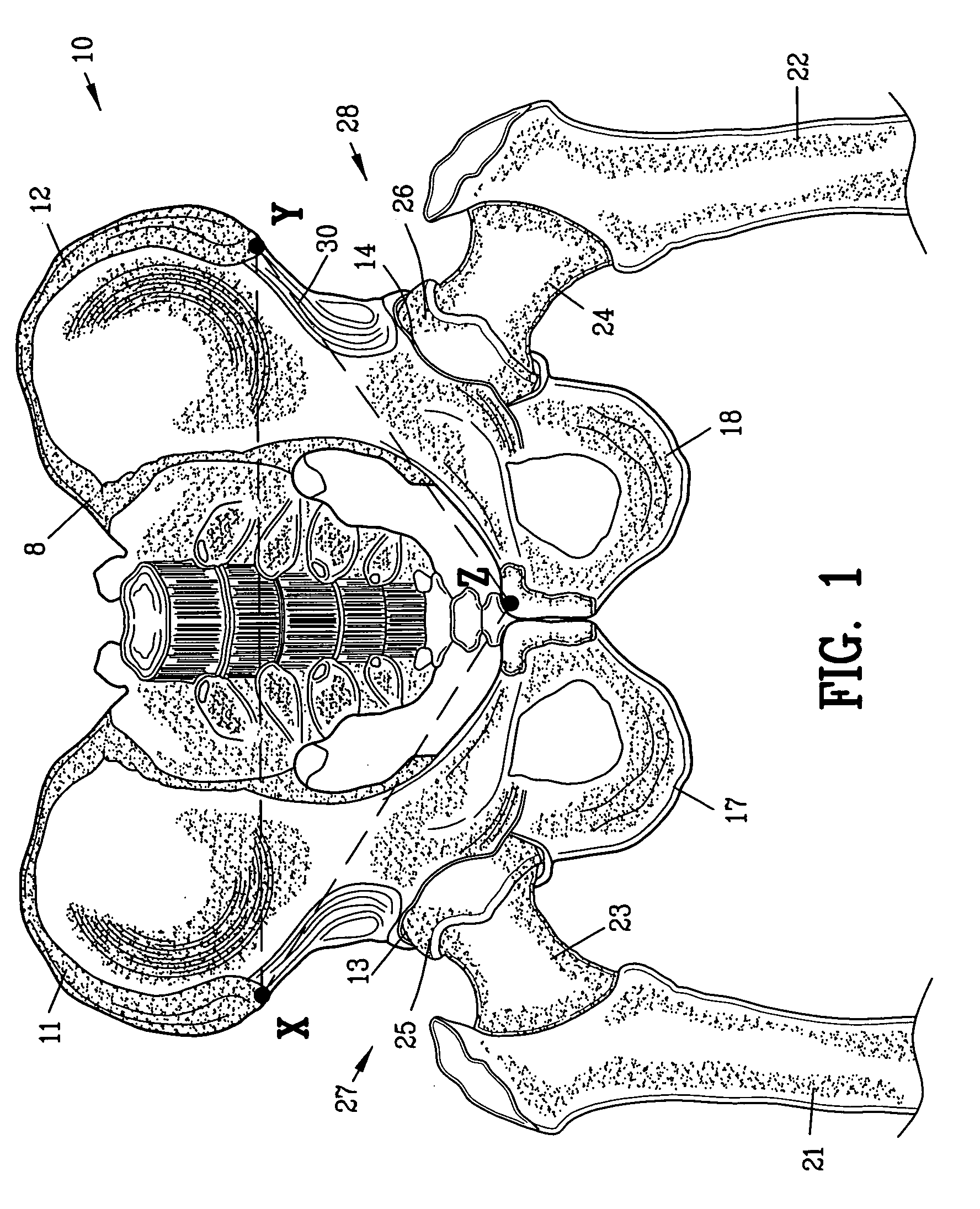
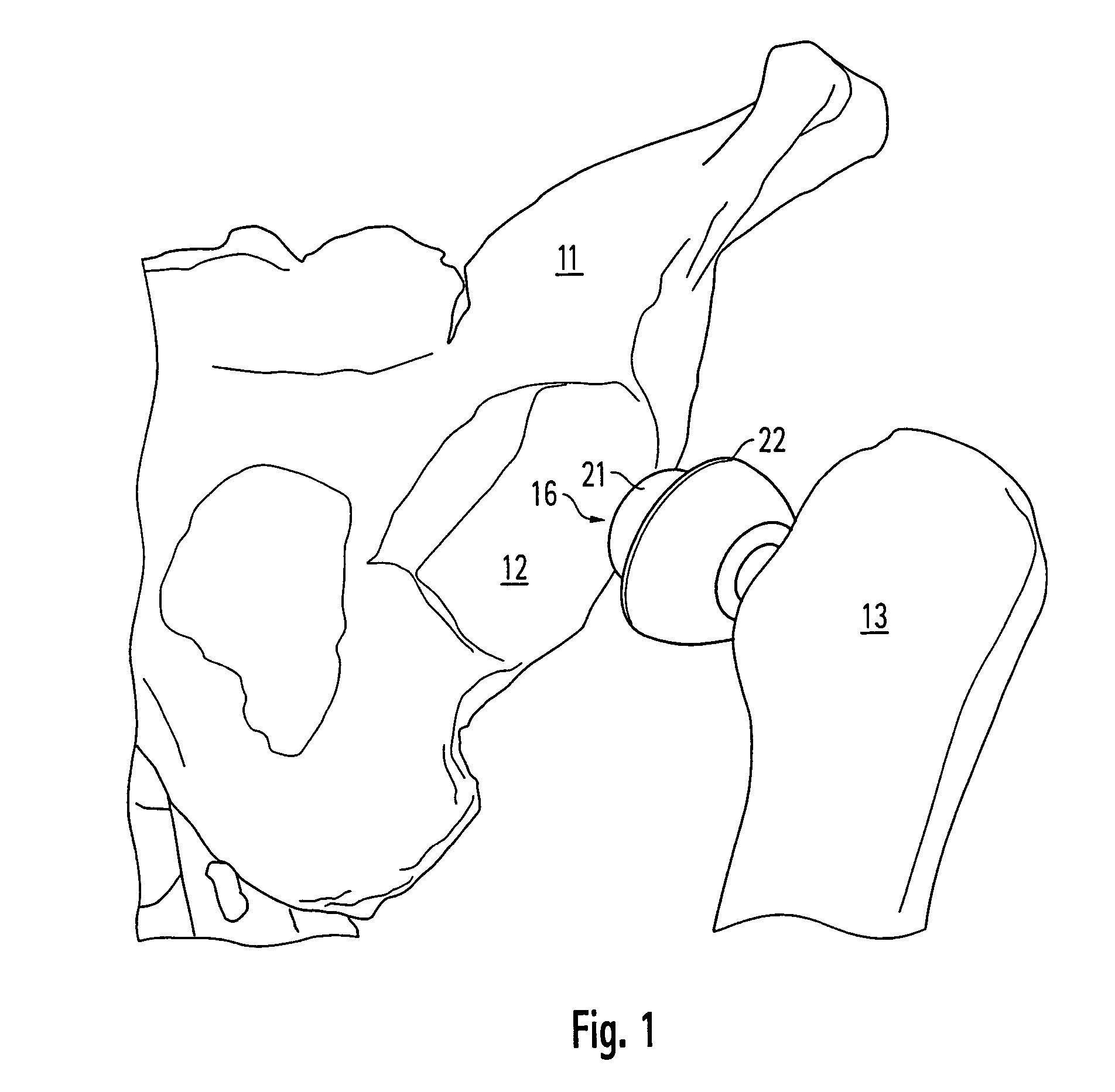
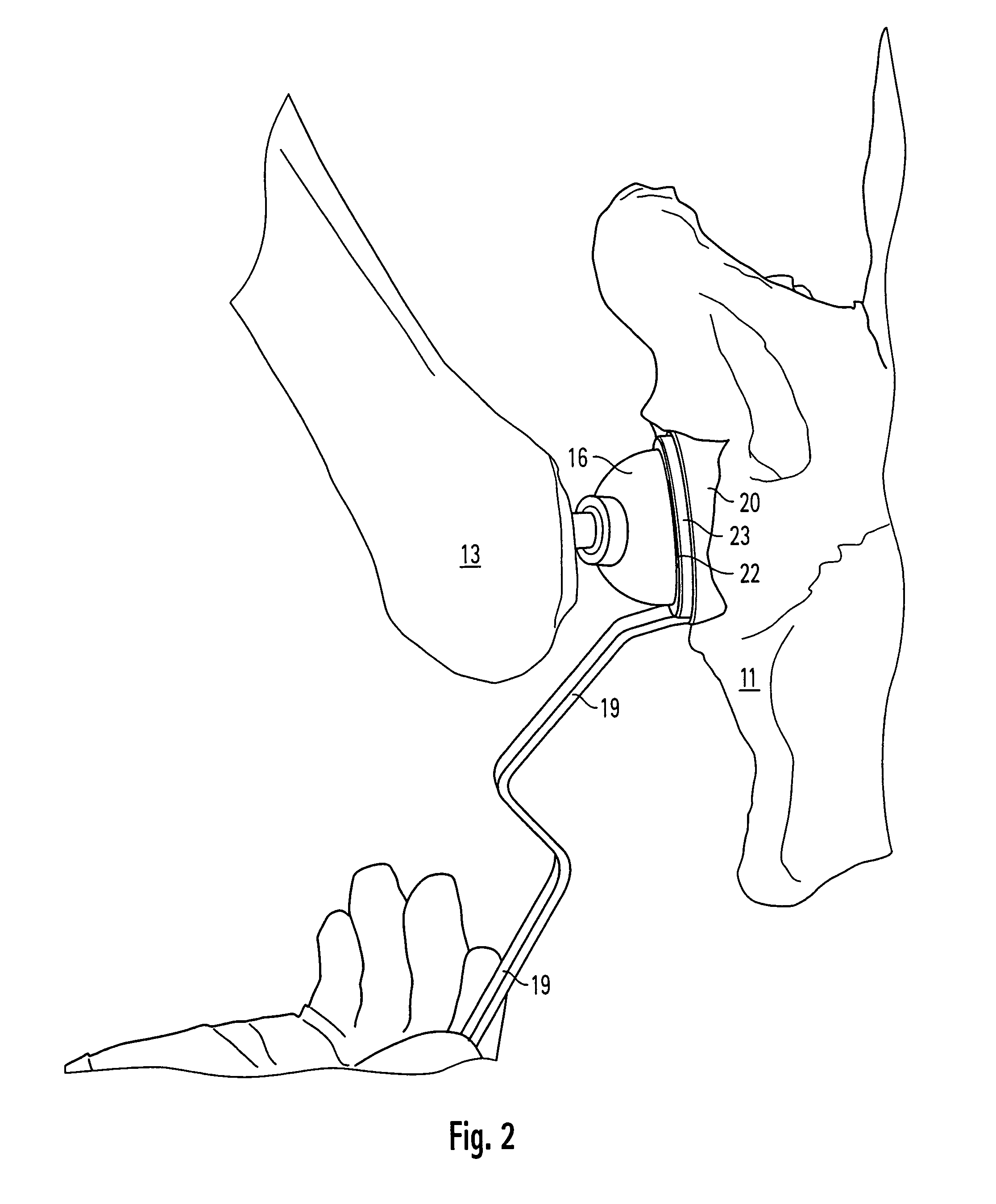
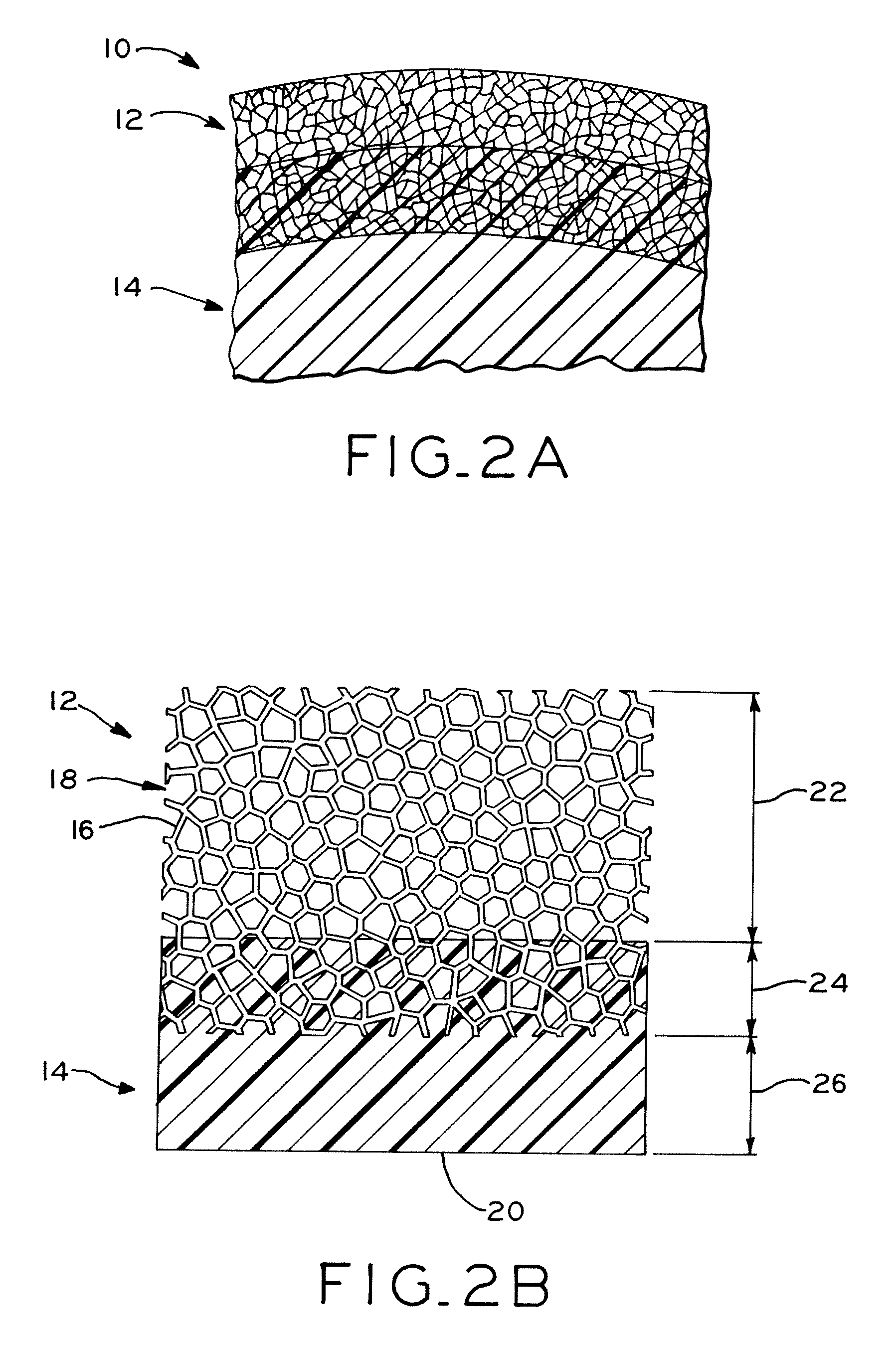
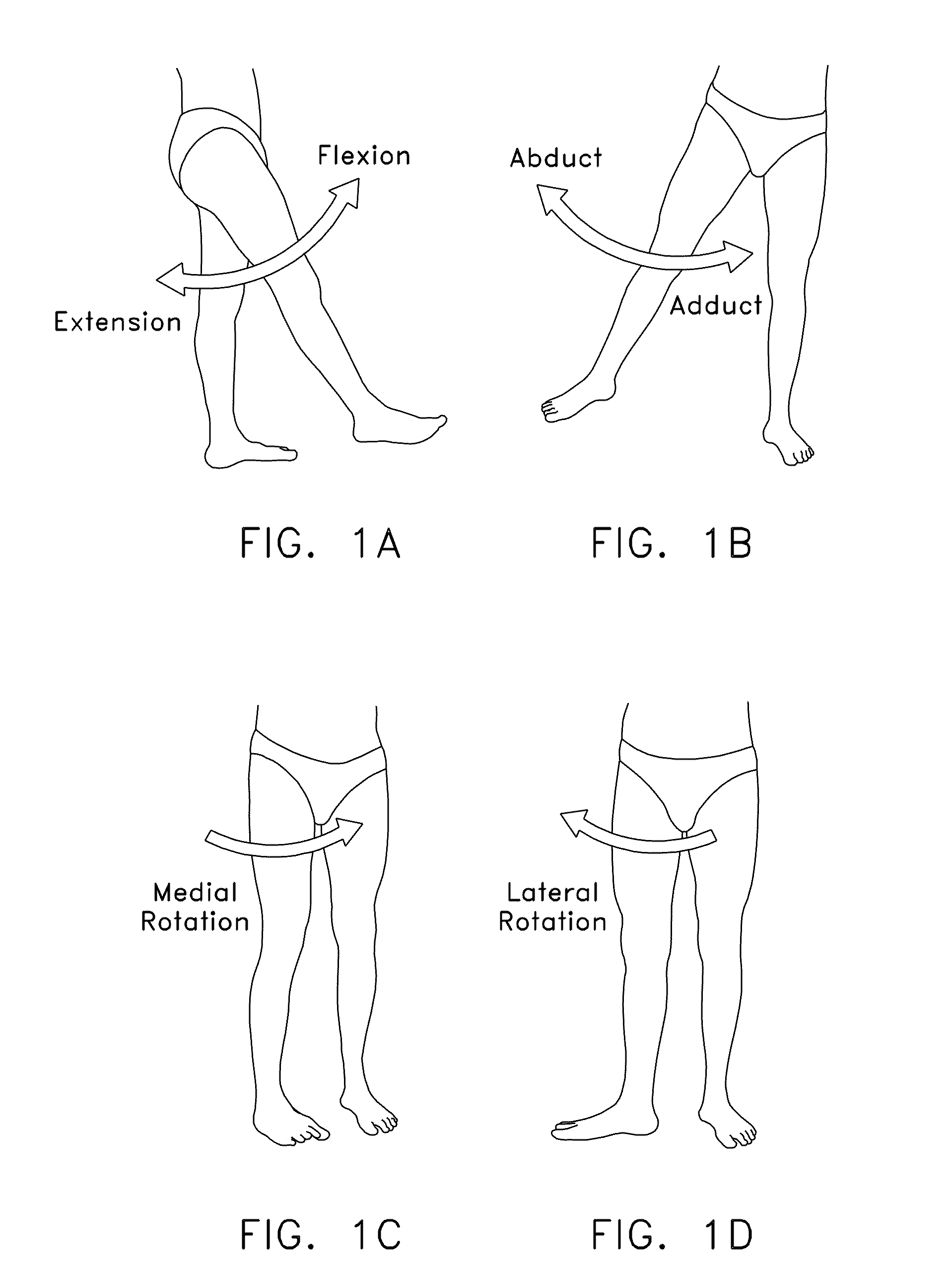
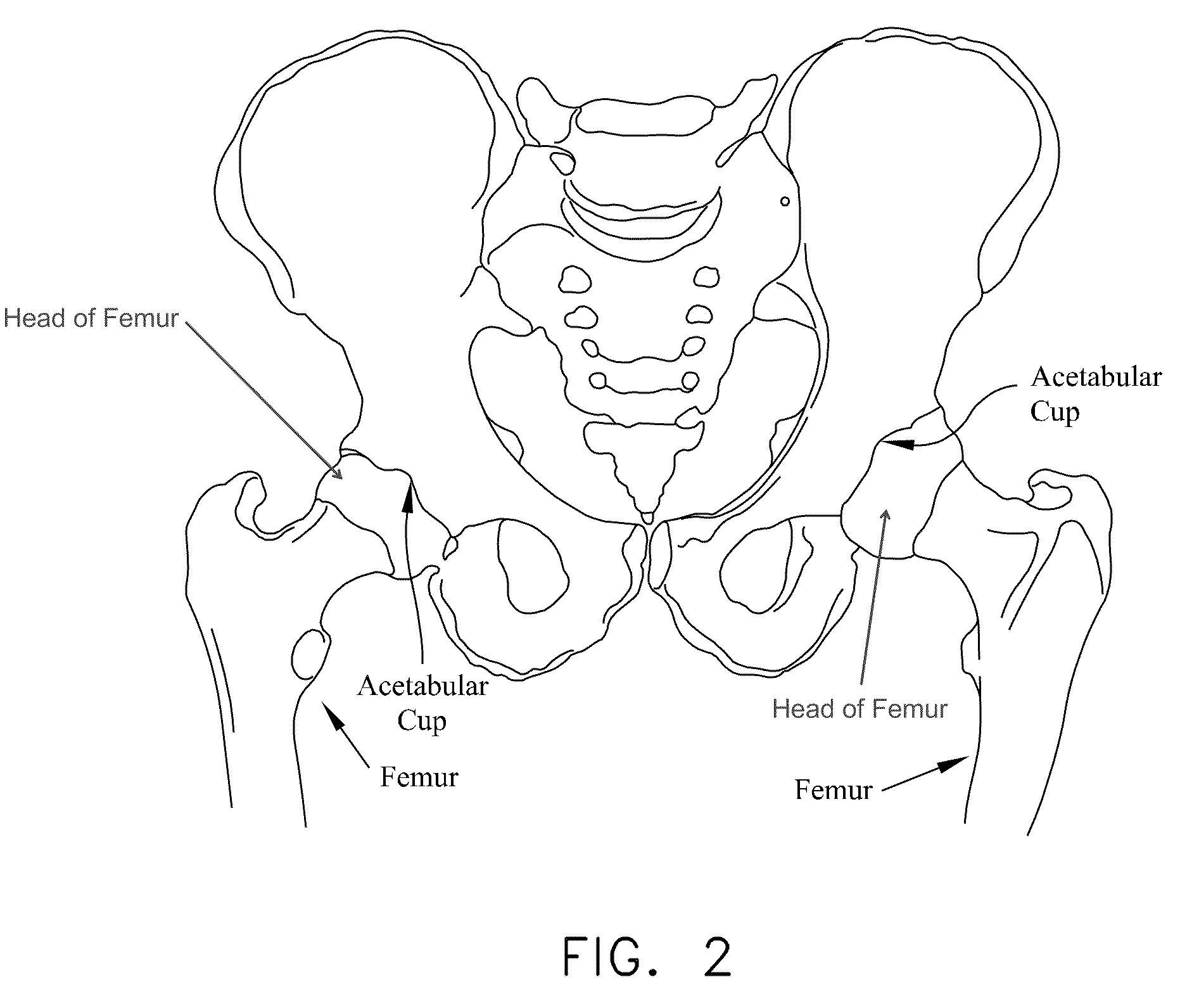
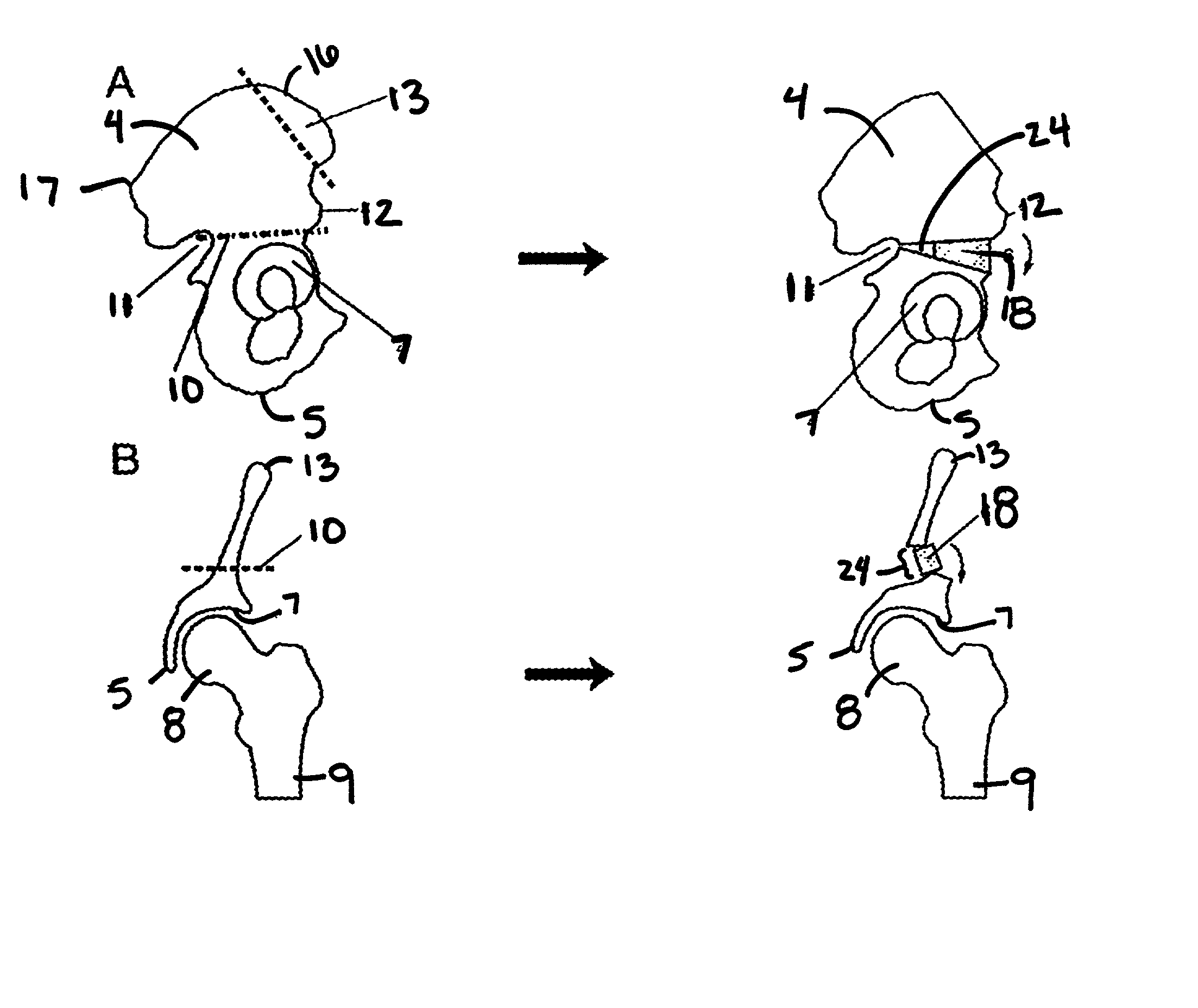
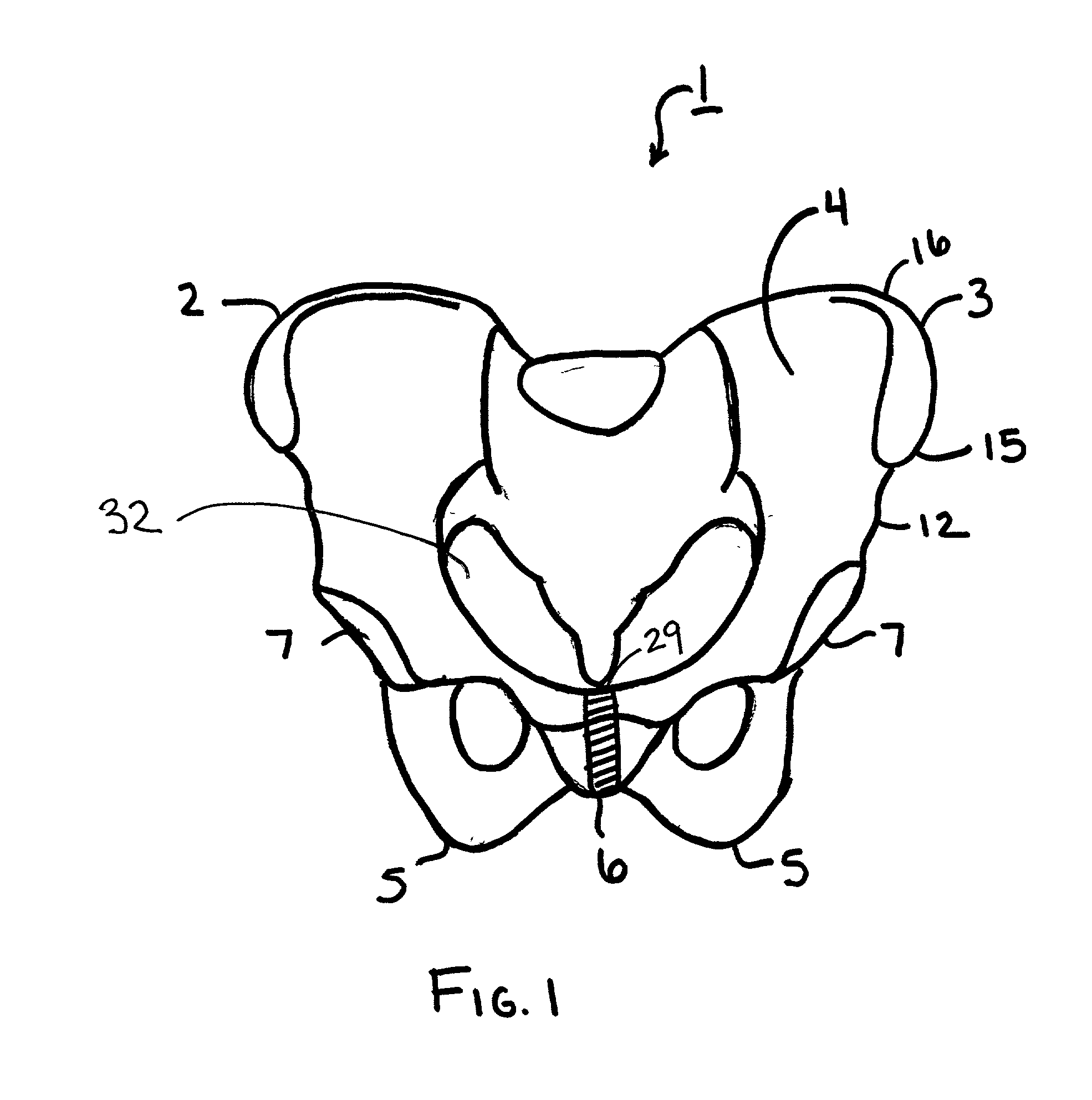
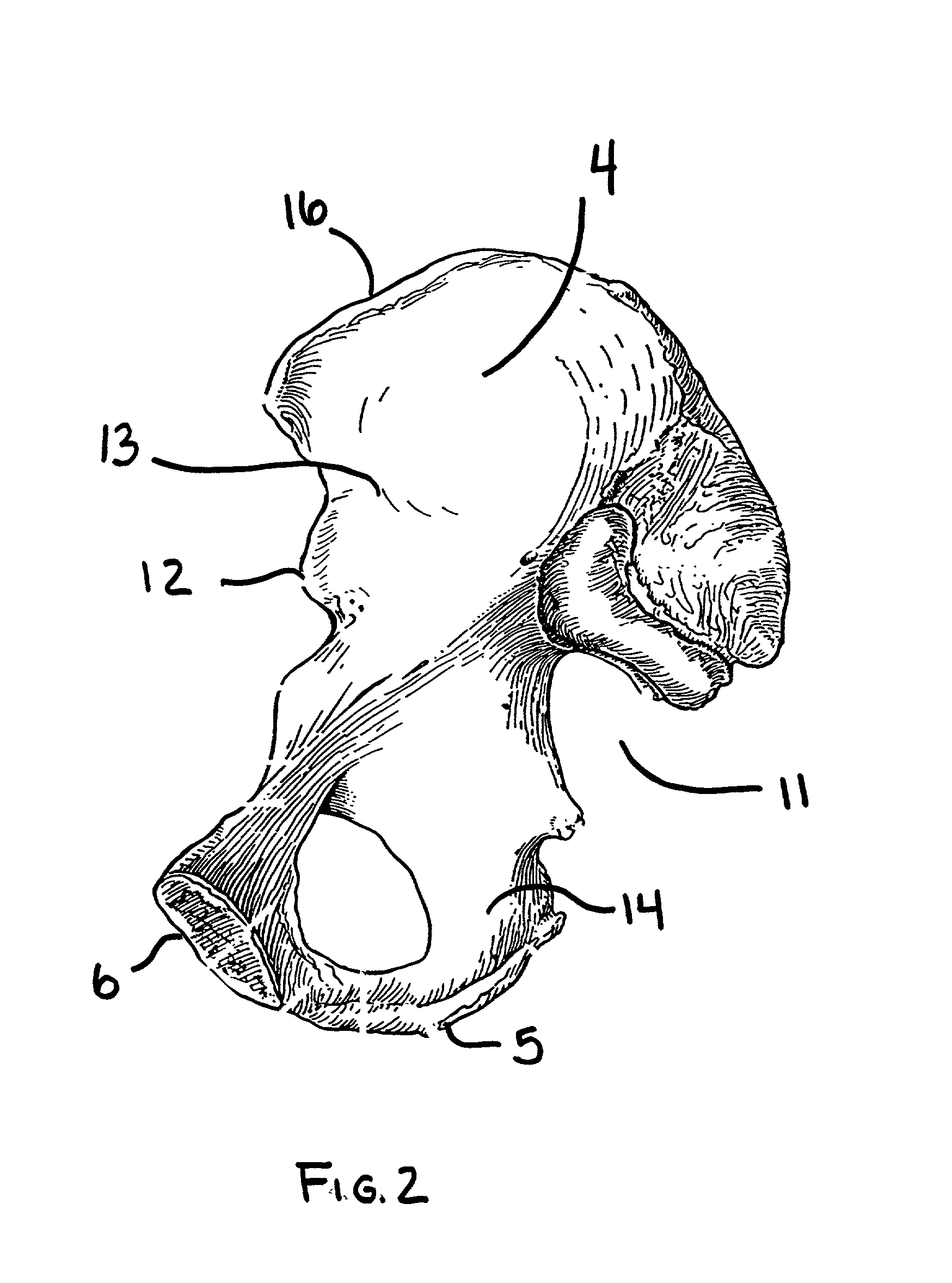
The acetabulum /æsəˈtæbjʊləm/ (cotyloid cavity) is a concave surface of a pelvis. The head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint.
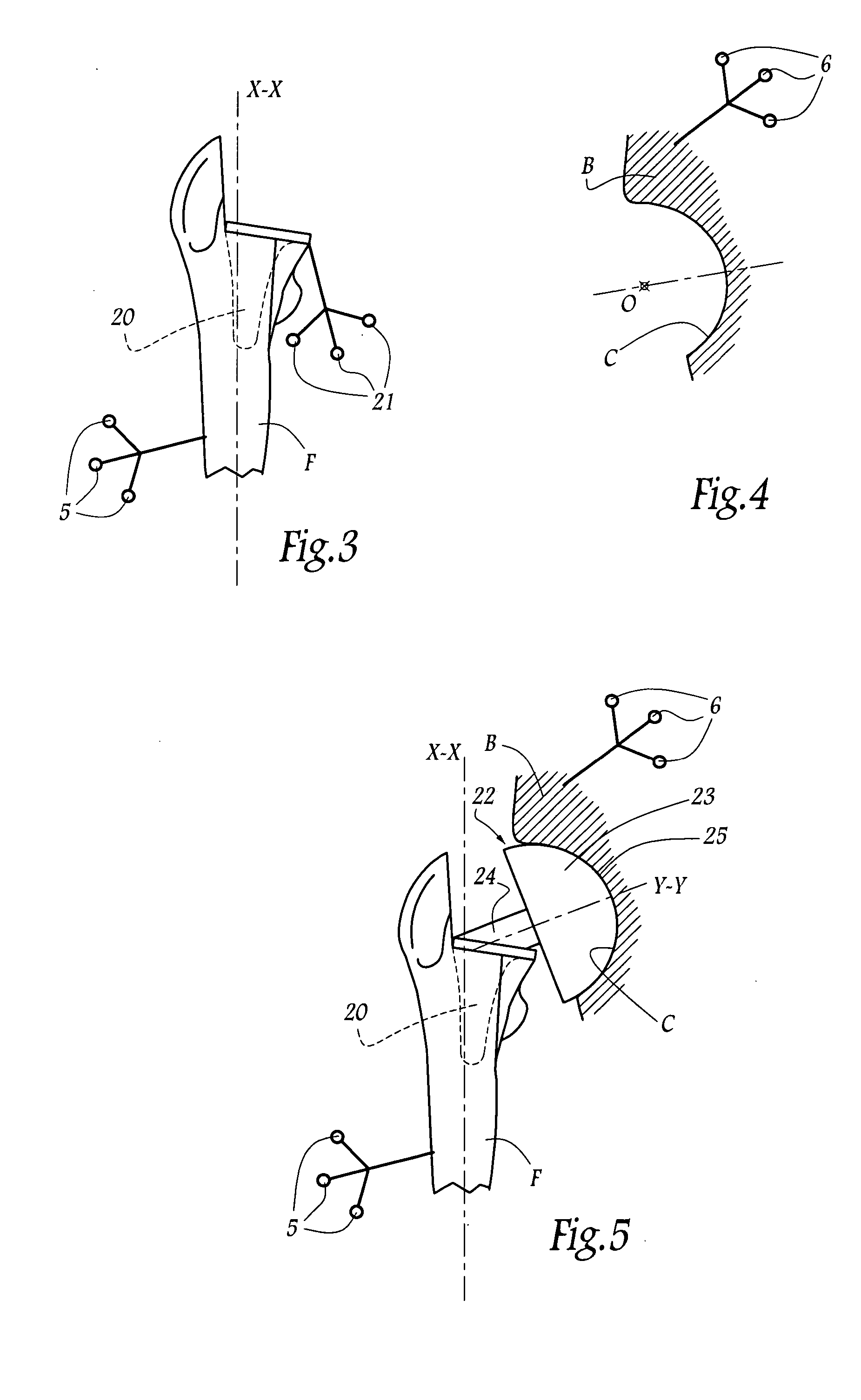
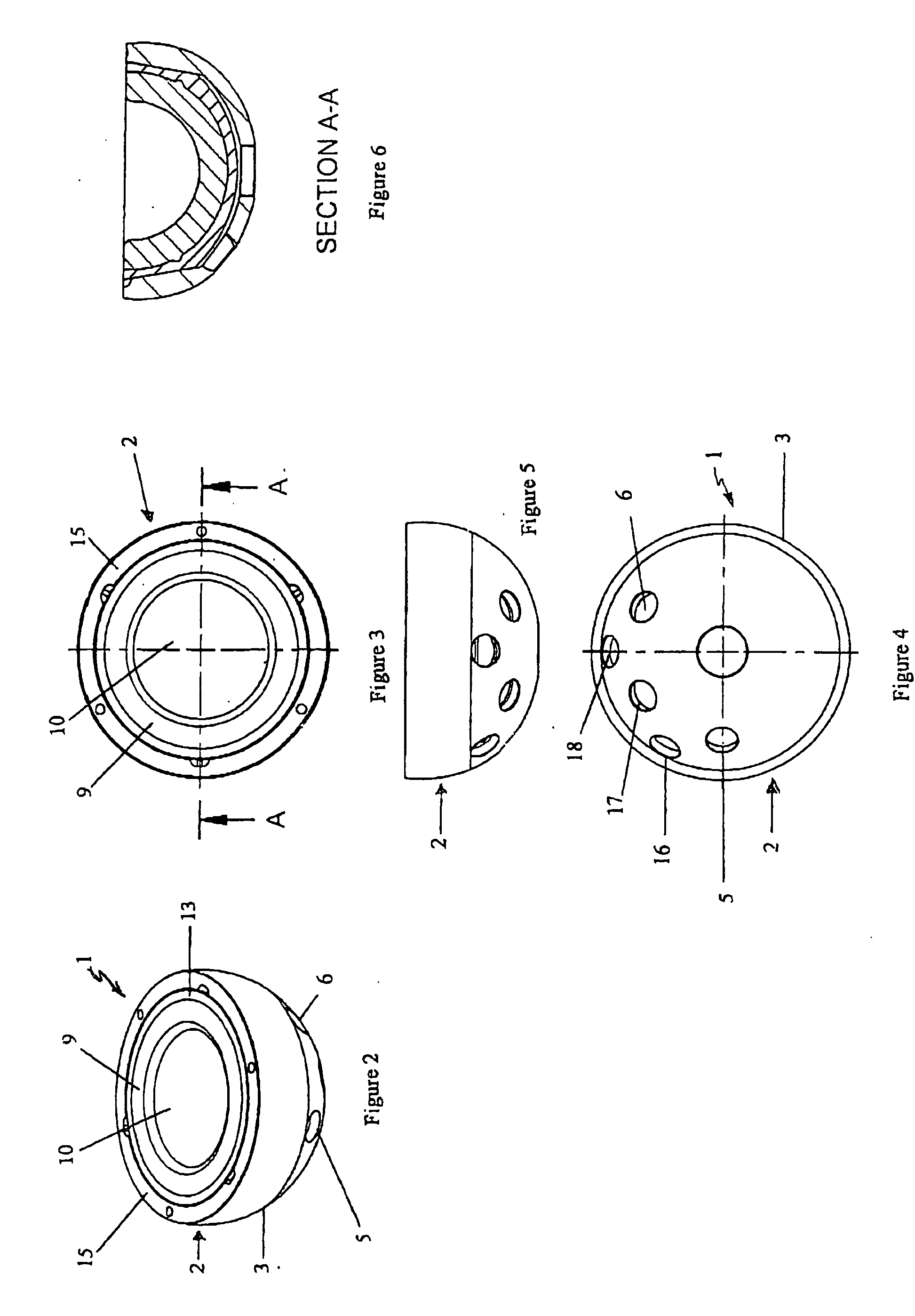
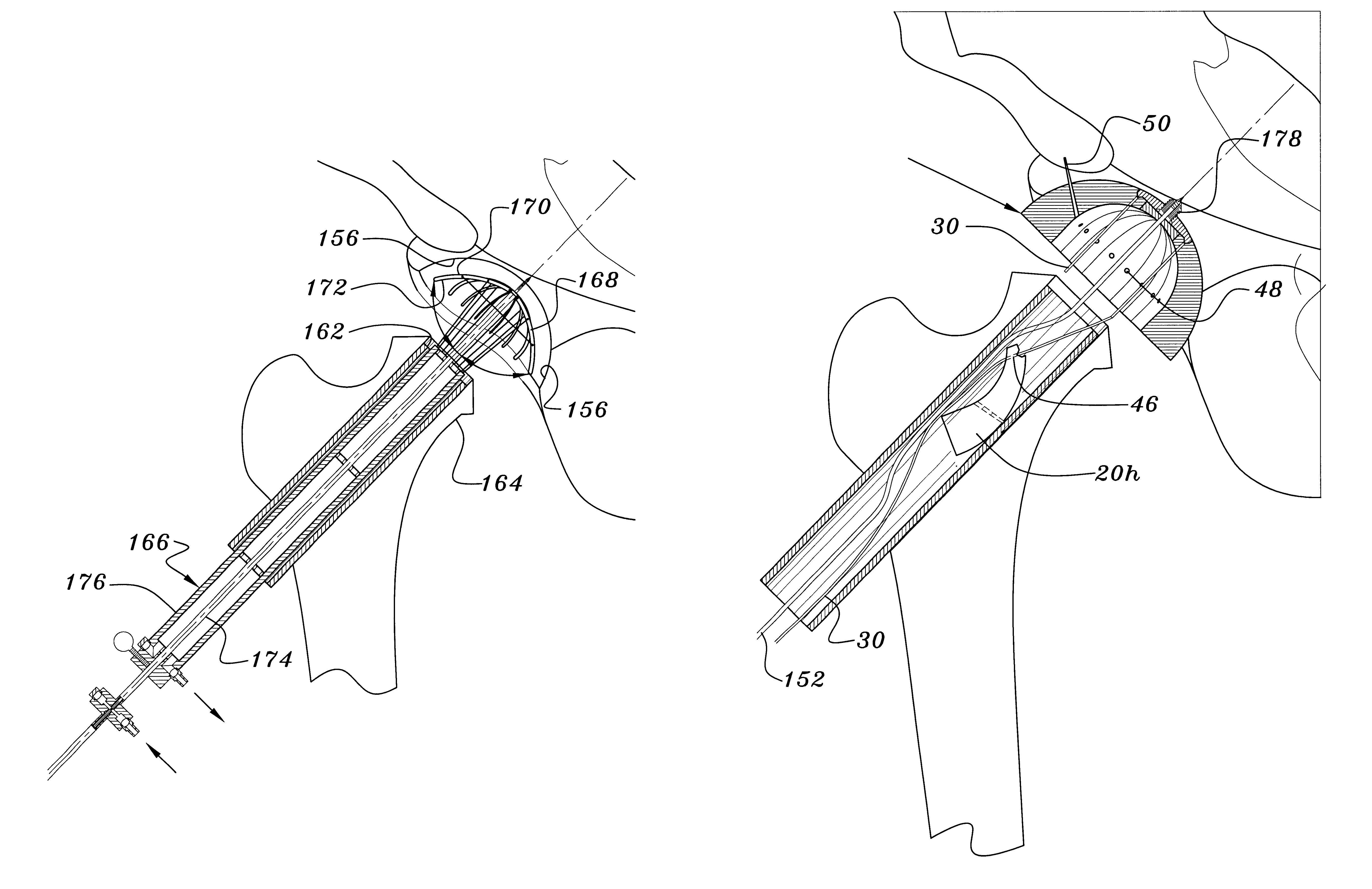
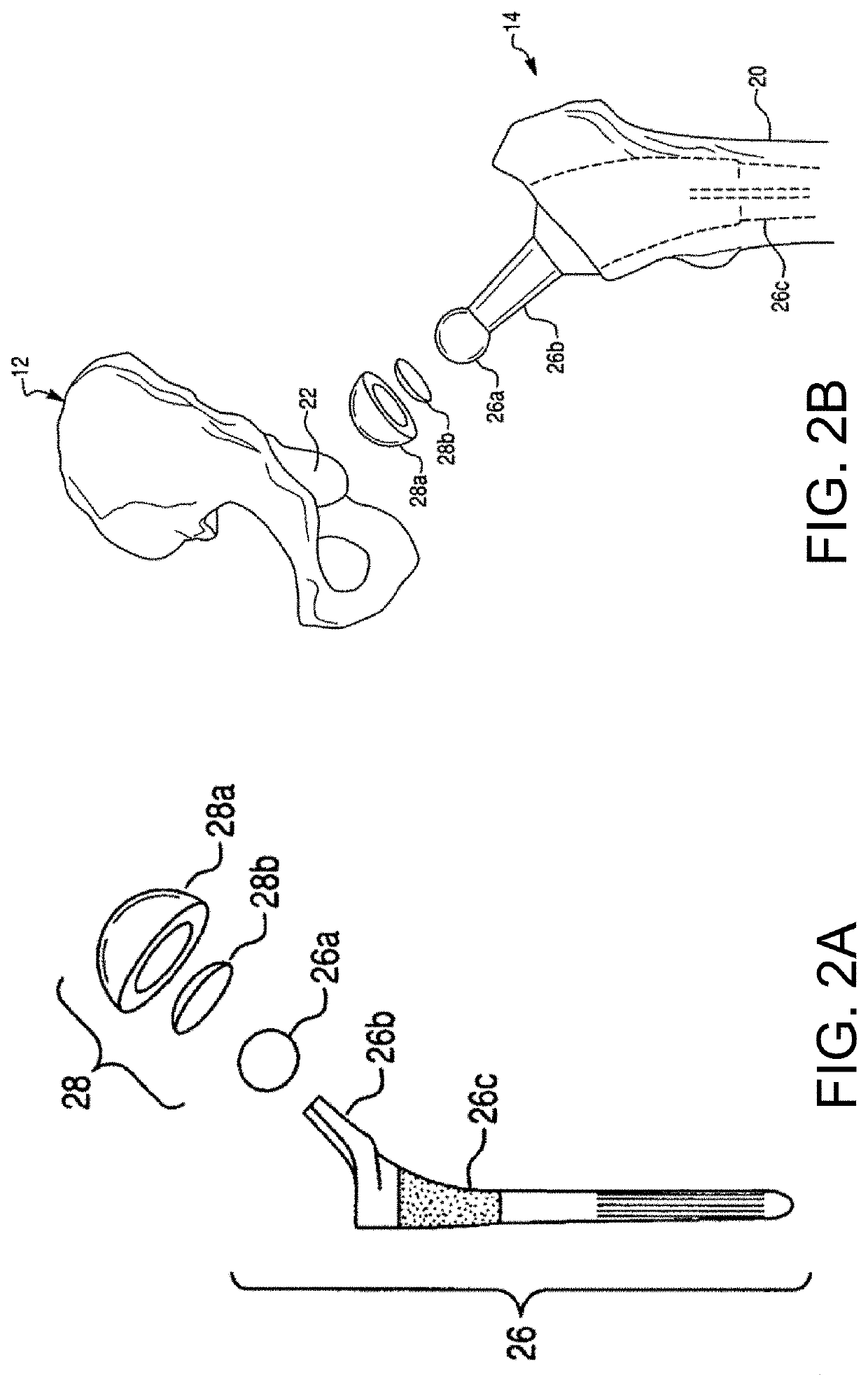
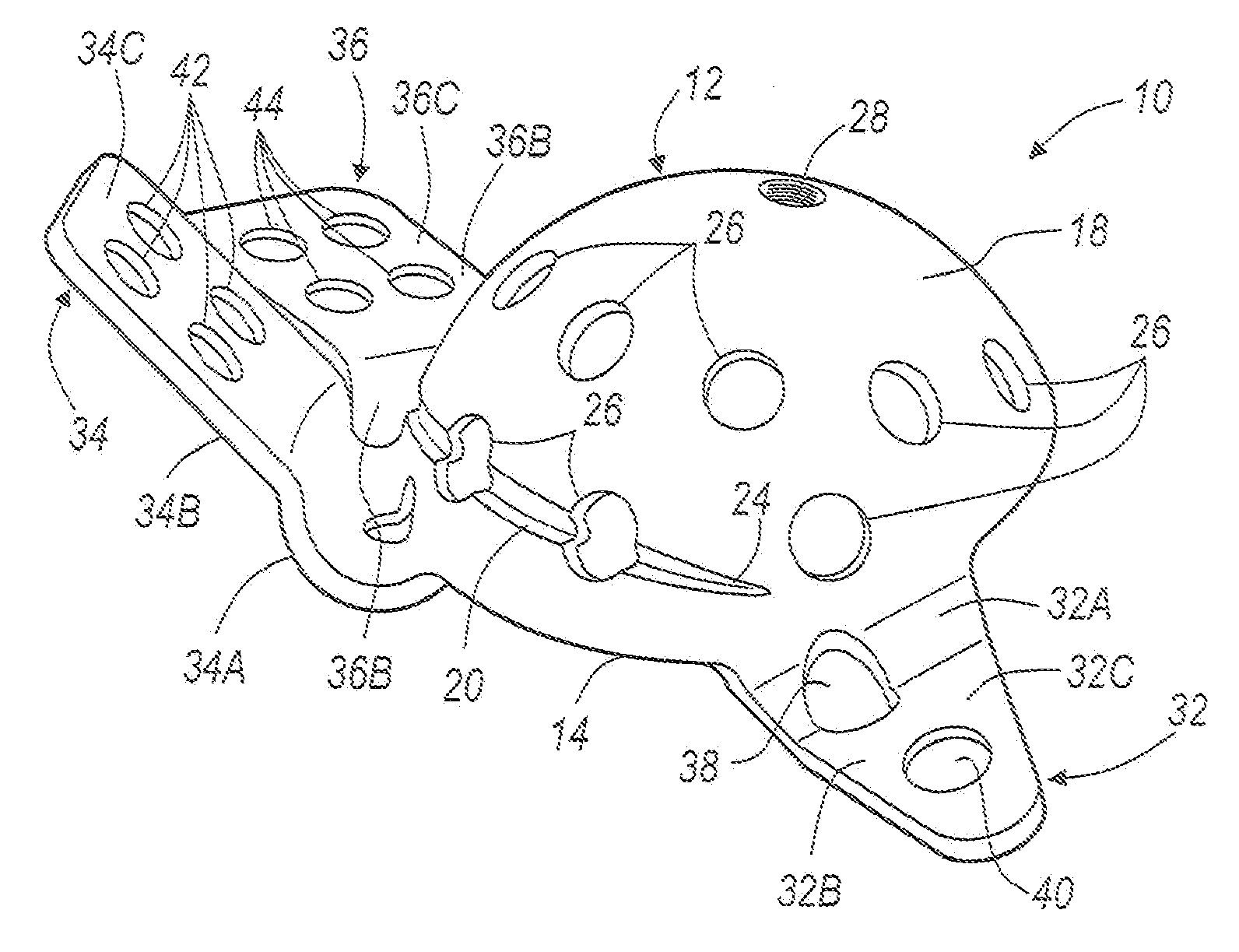
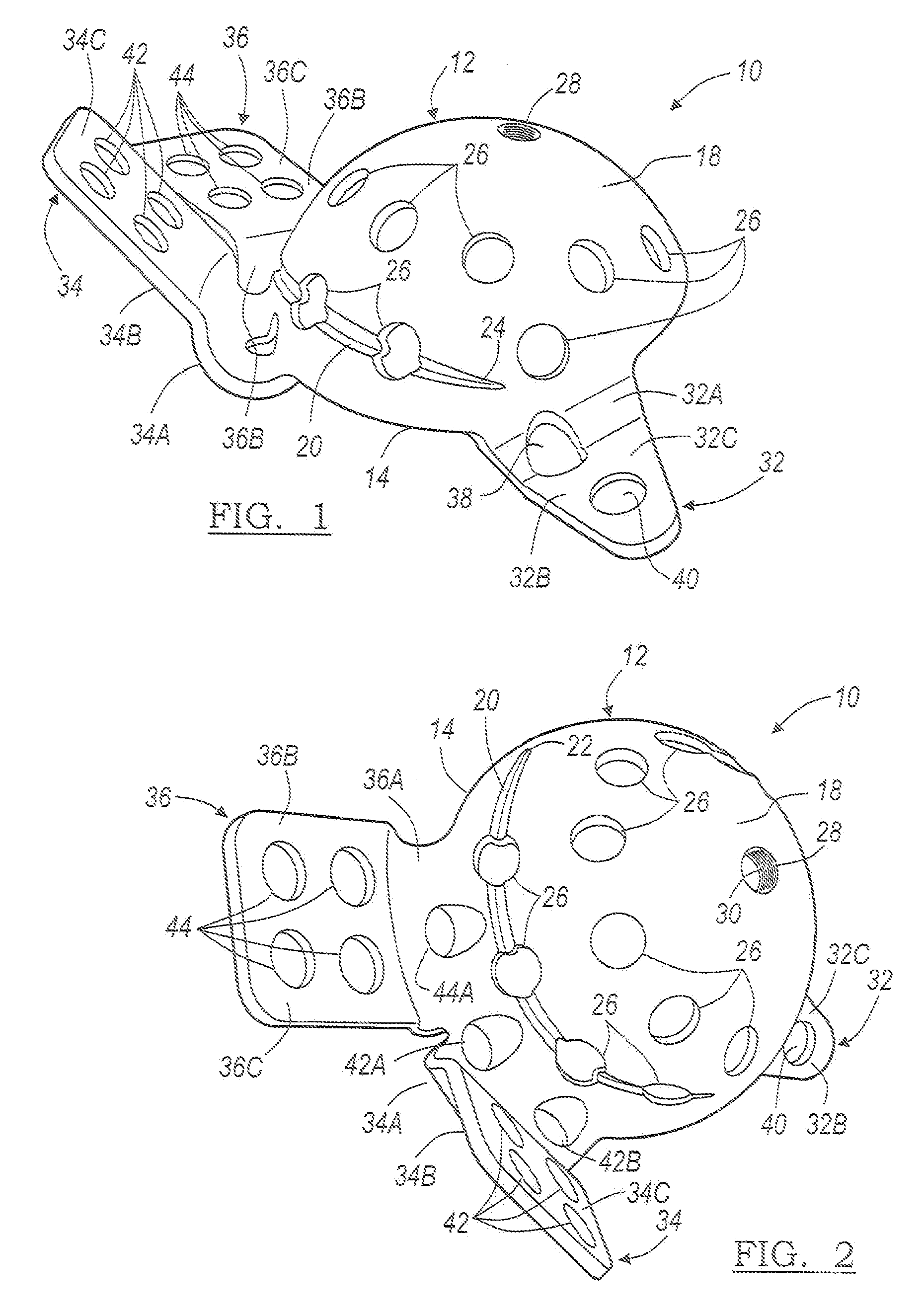
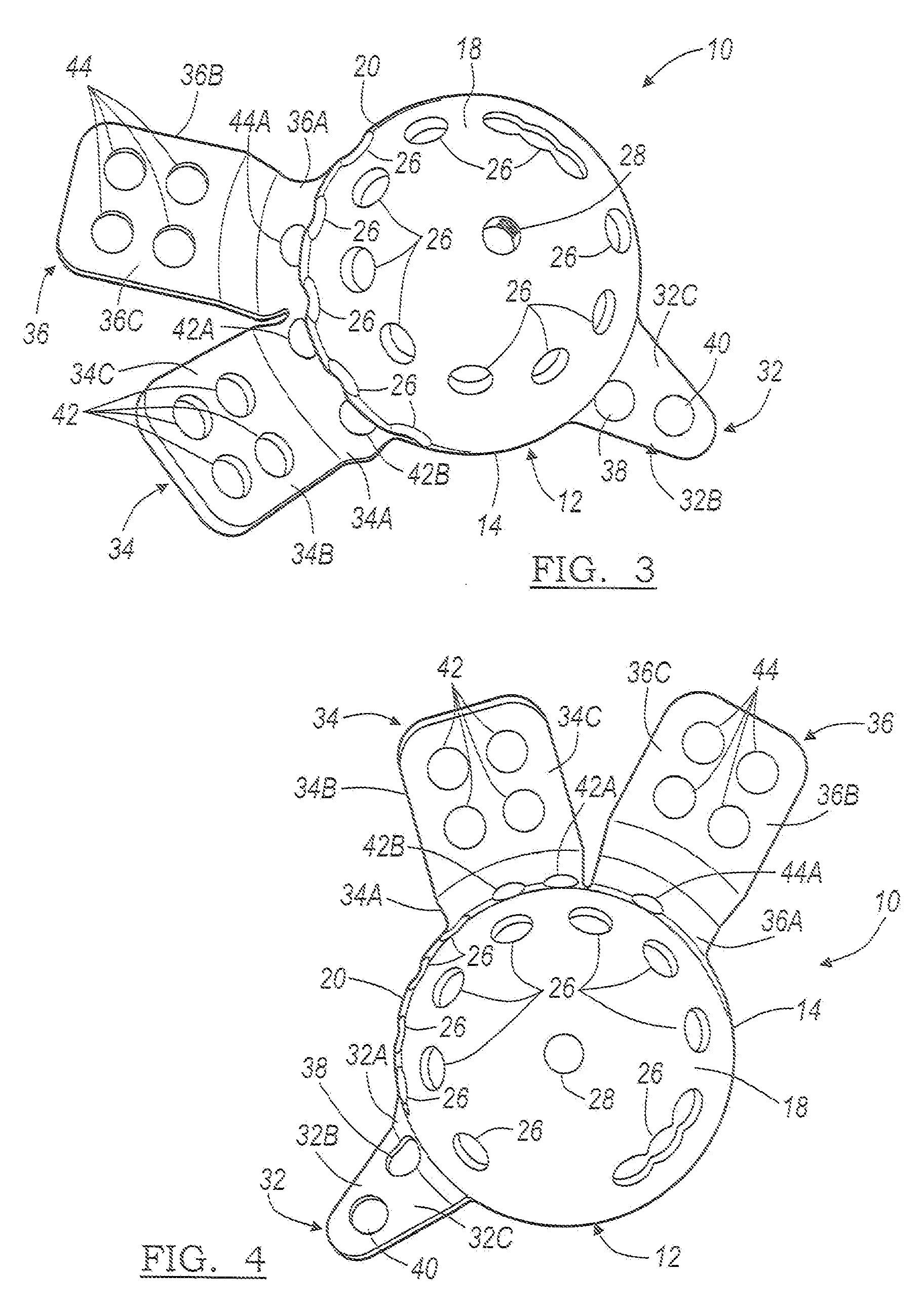
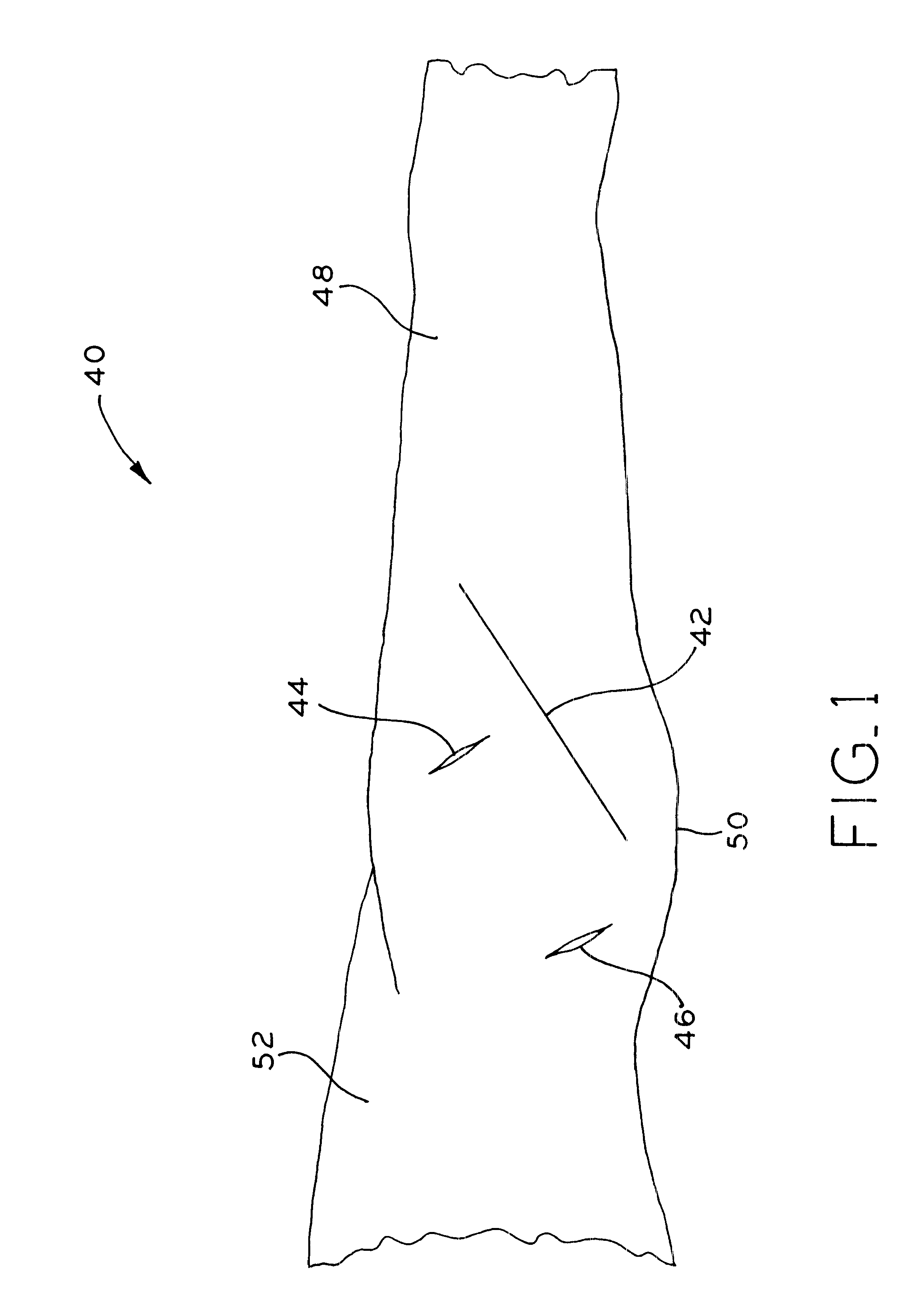
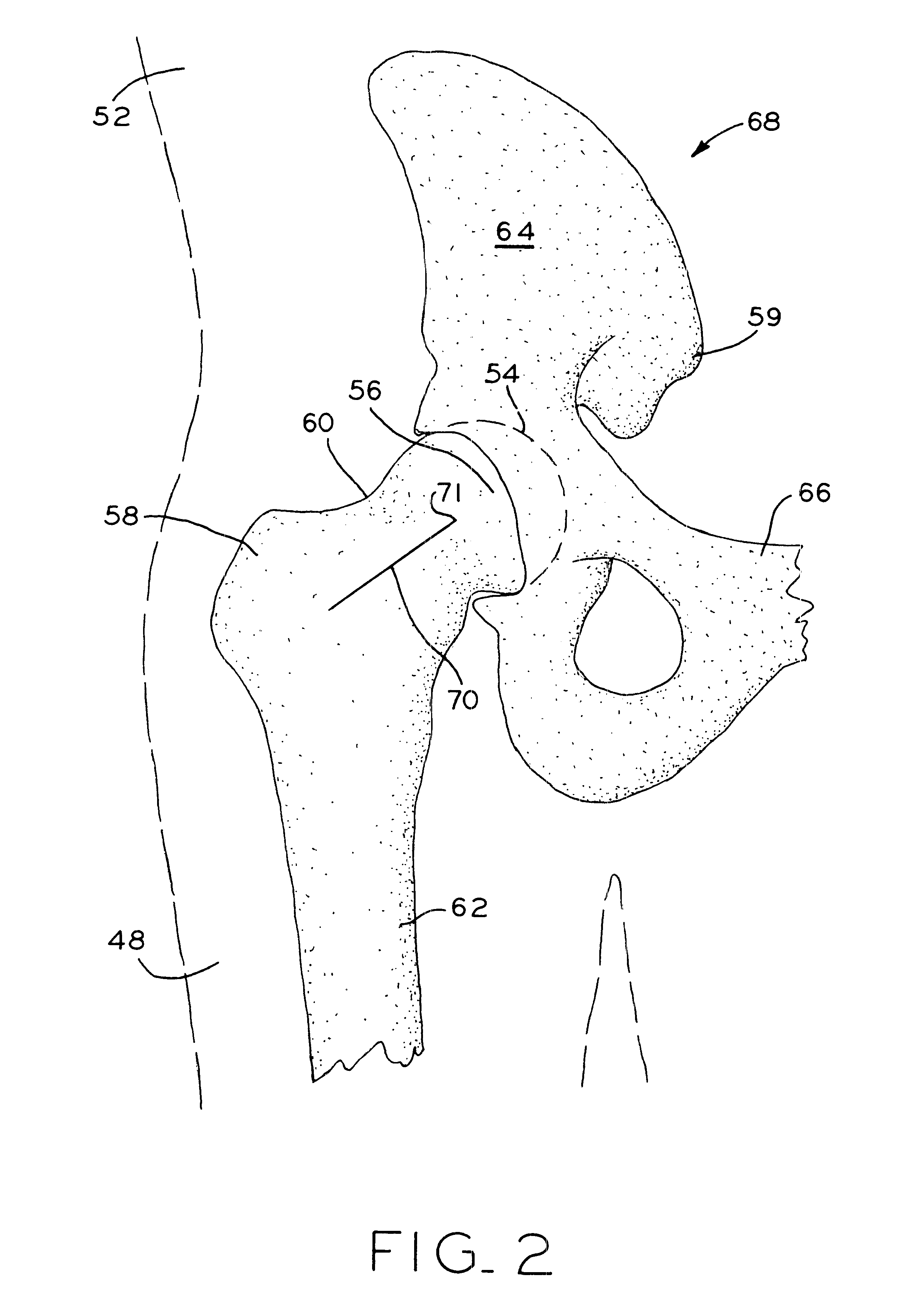
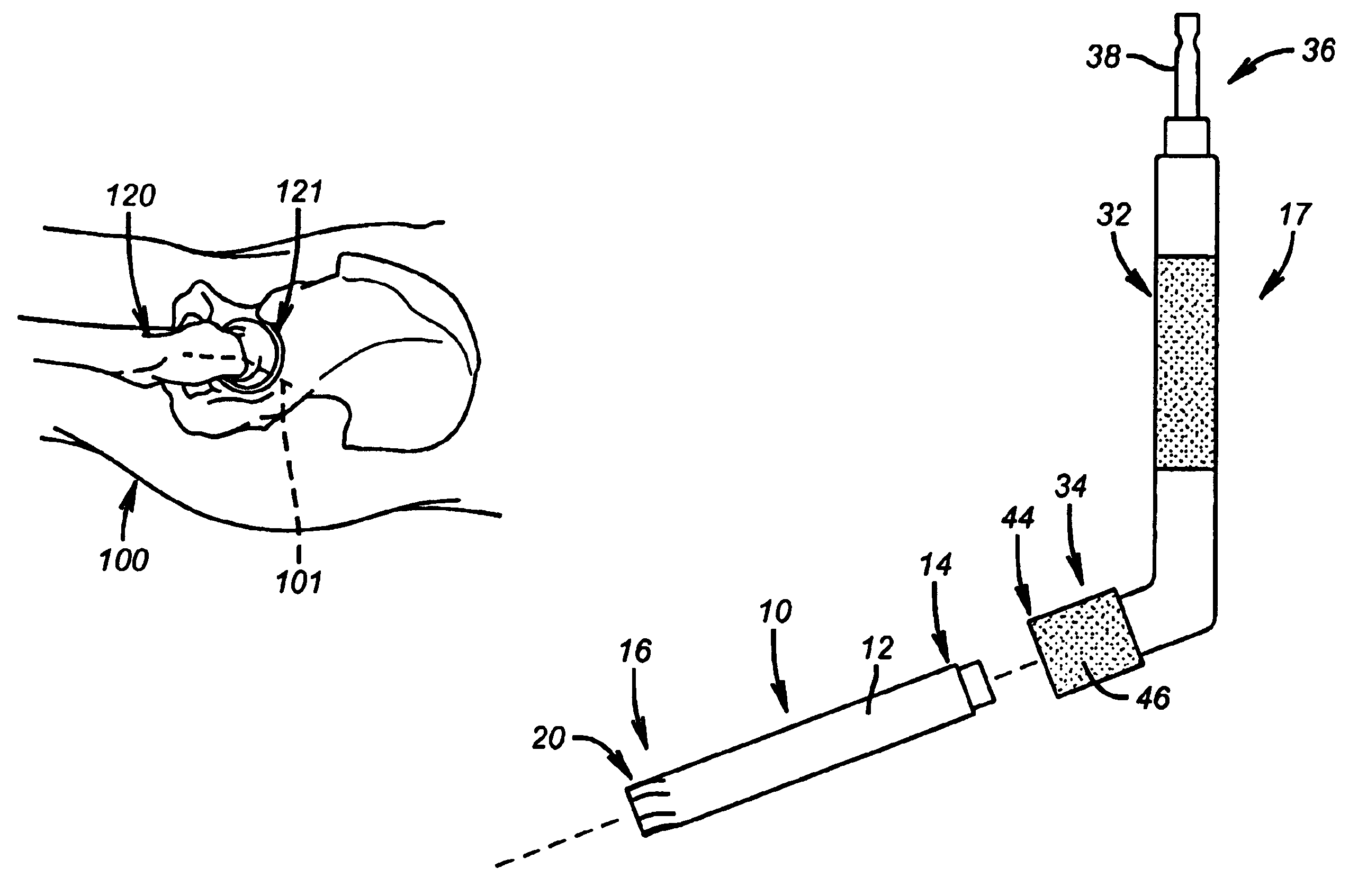
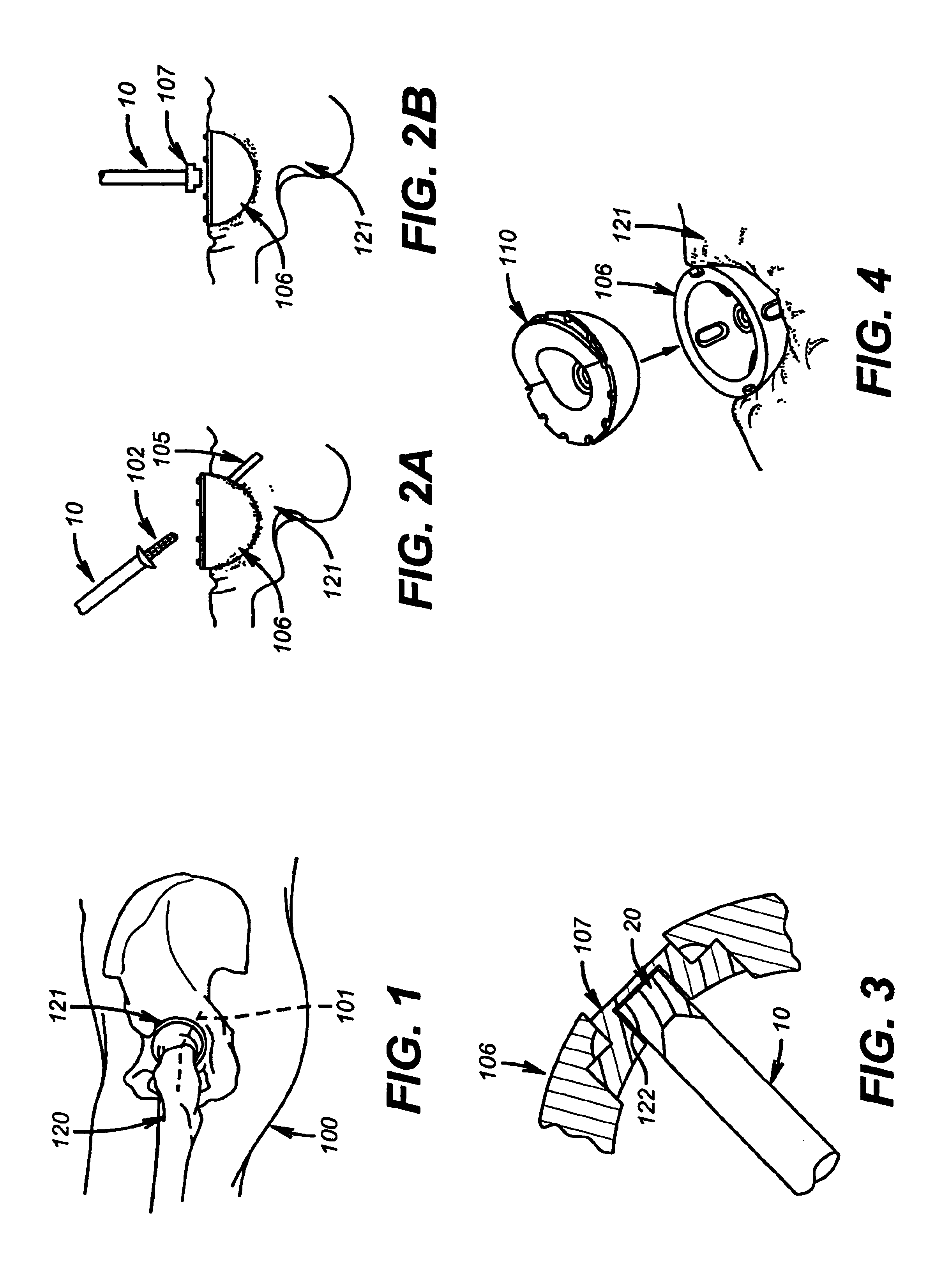
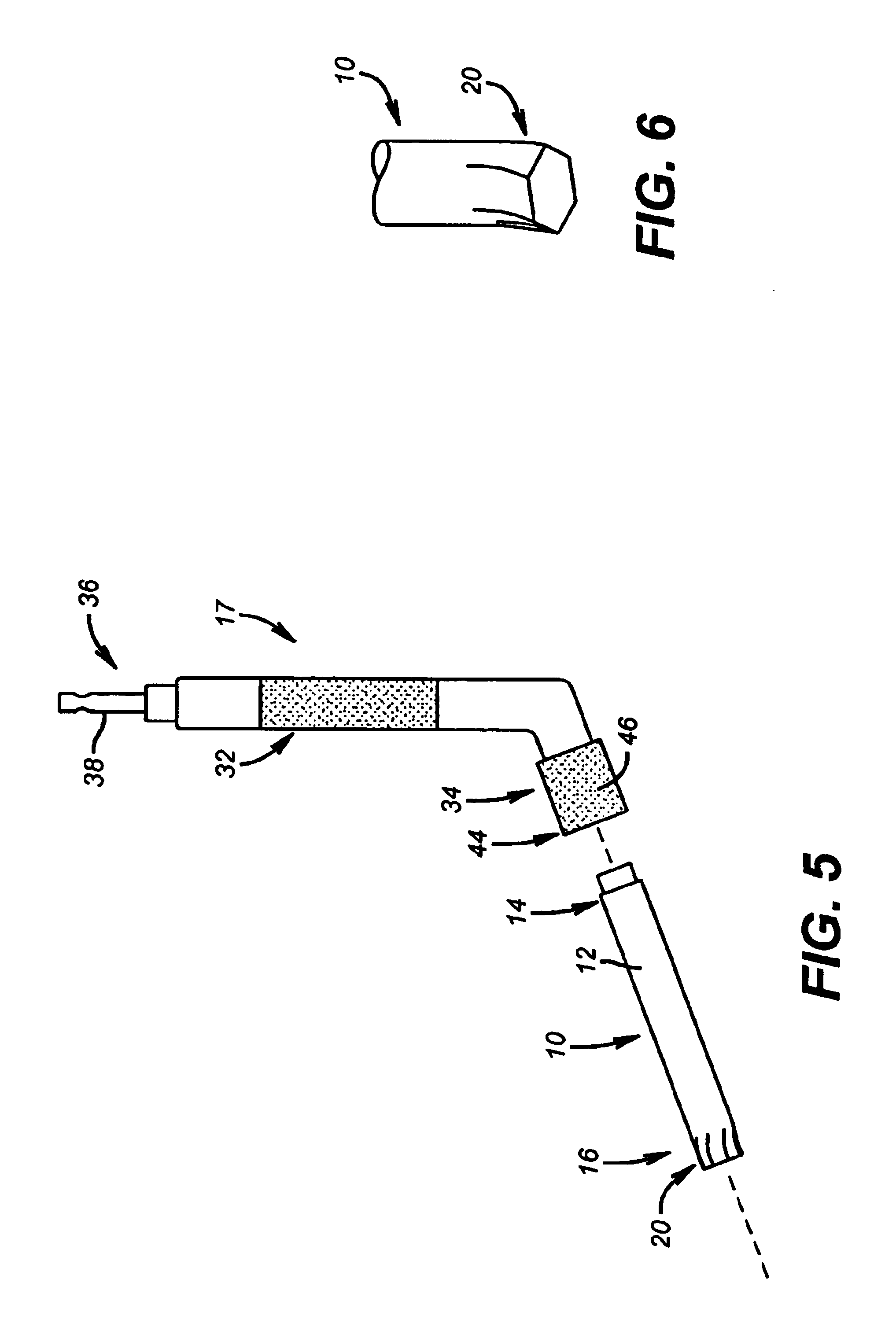
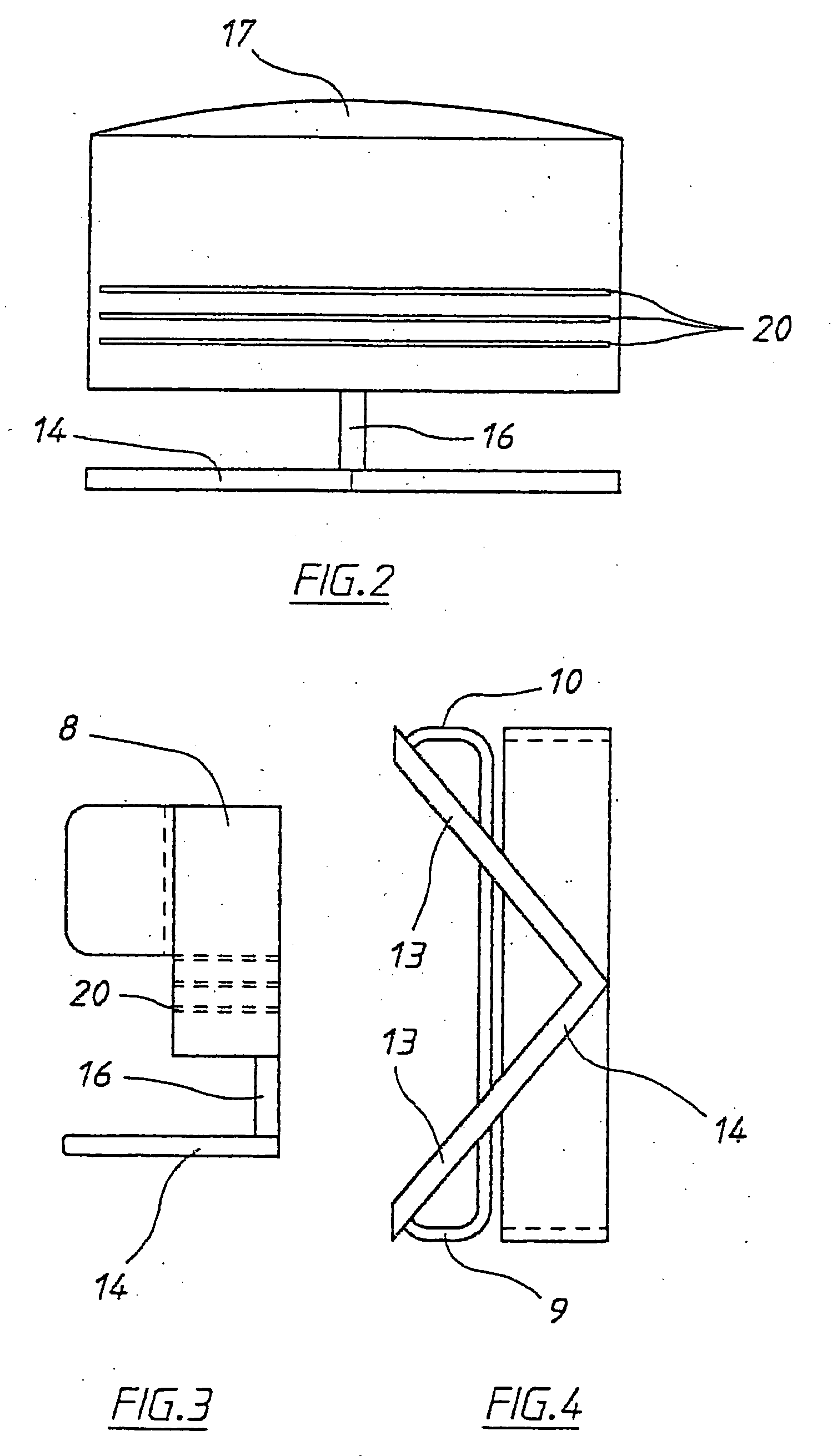
Instruments and method for minimally invasive surgery for total hips
InactiveUS7601155B2Precise cuttingHigh cutting precisionSurgical sawsProsthesisLess invasive surgeryRight femoral head
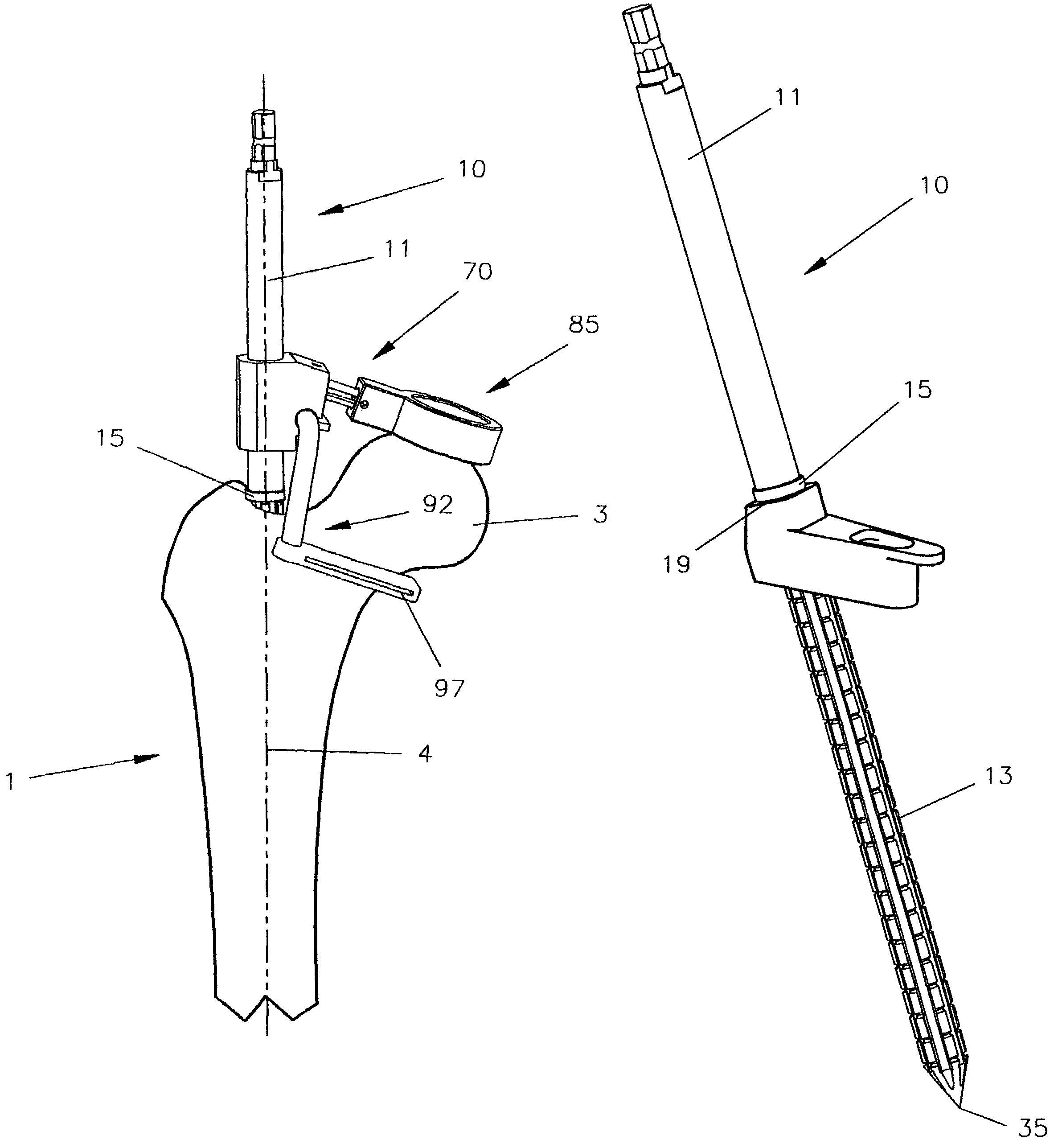
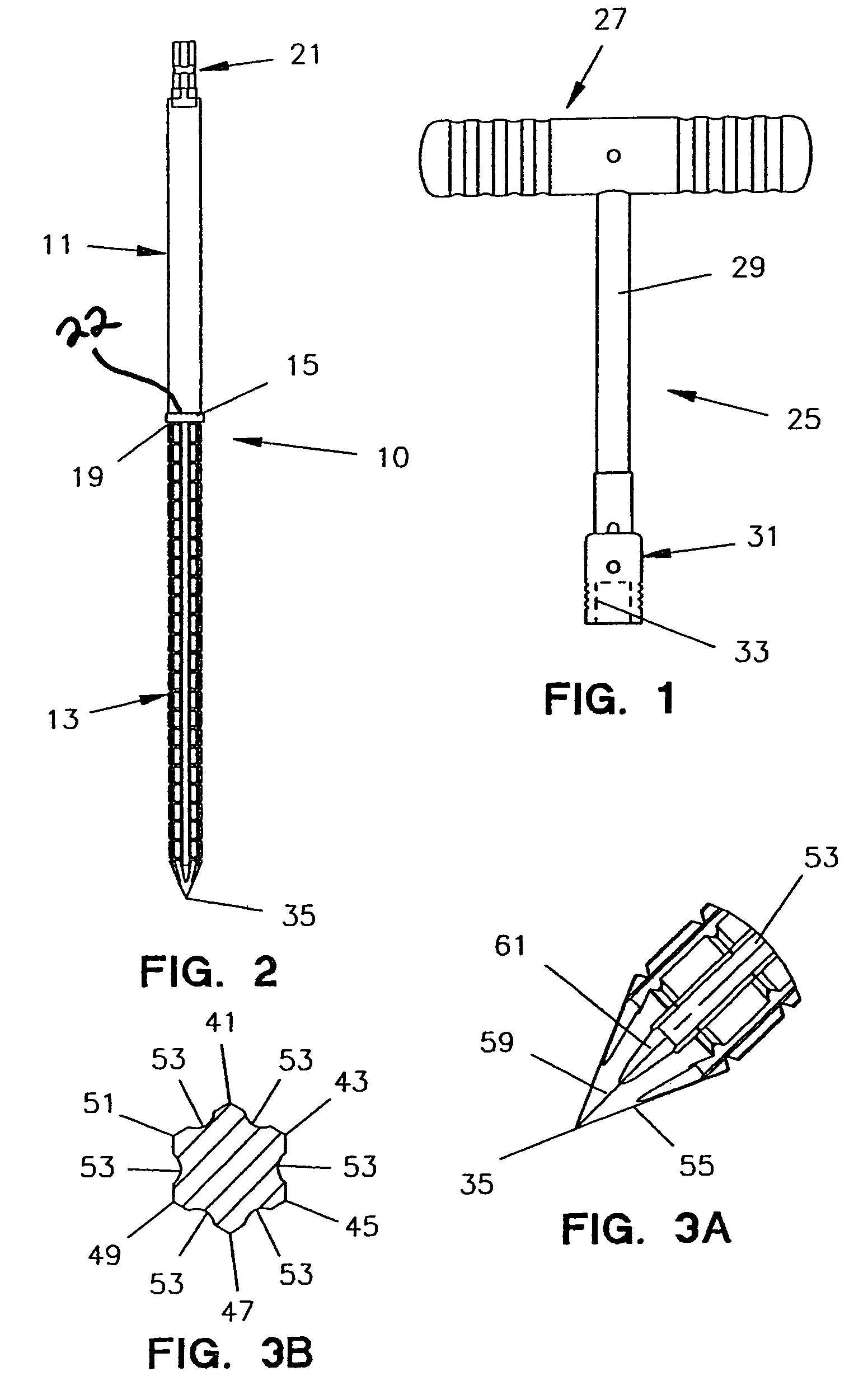
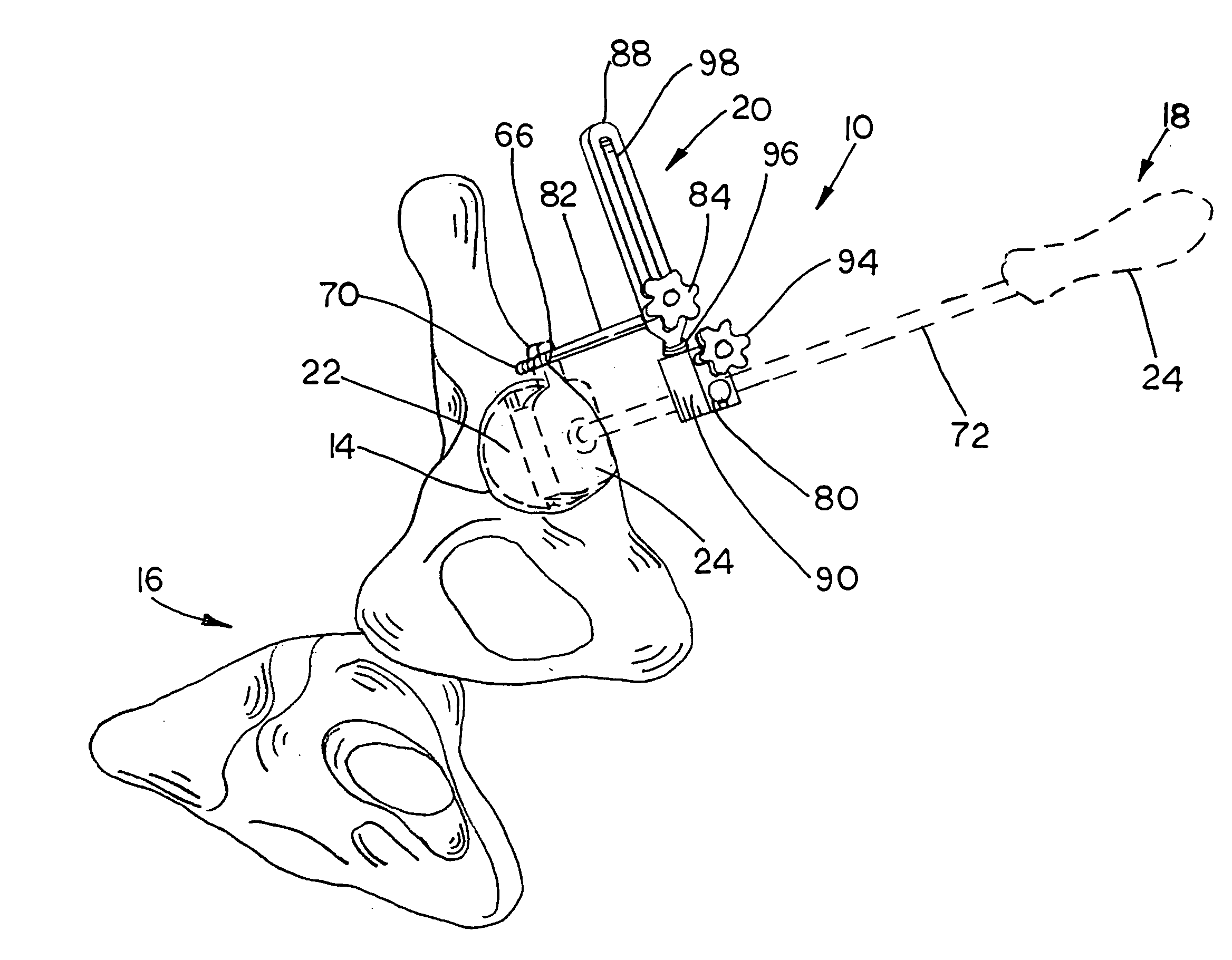
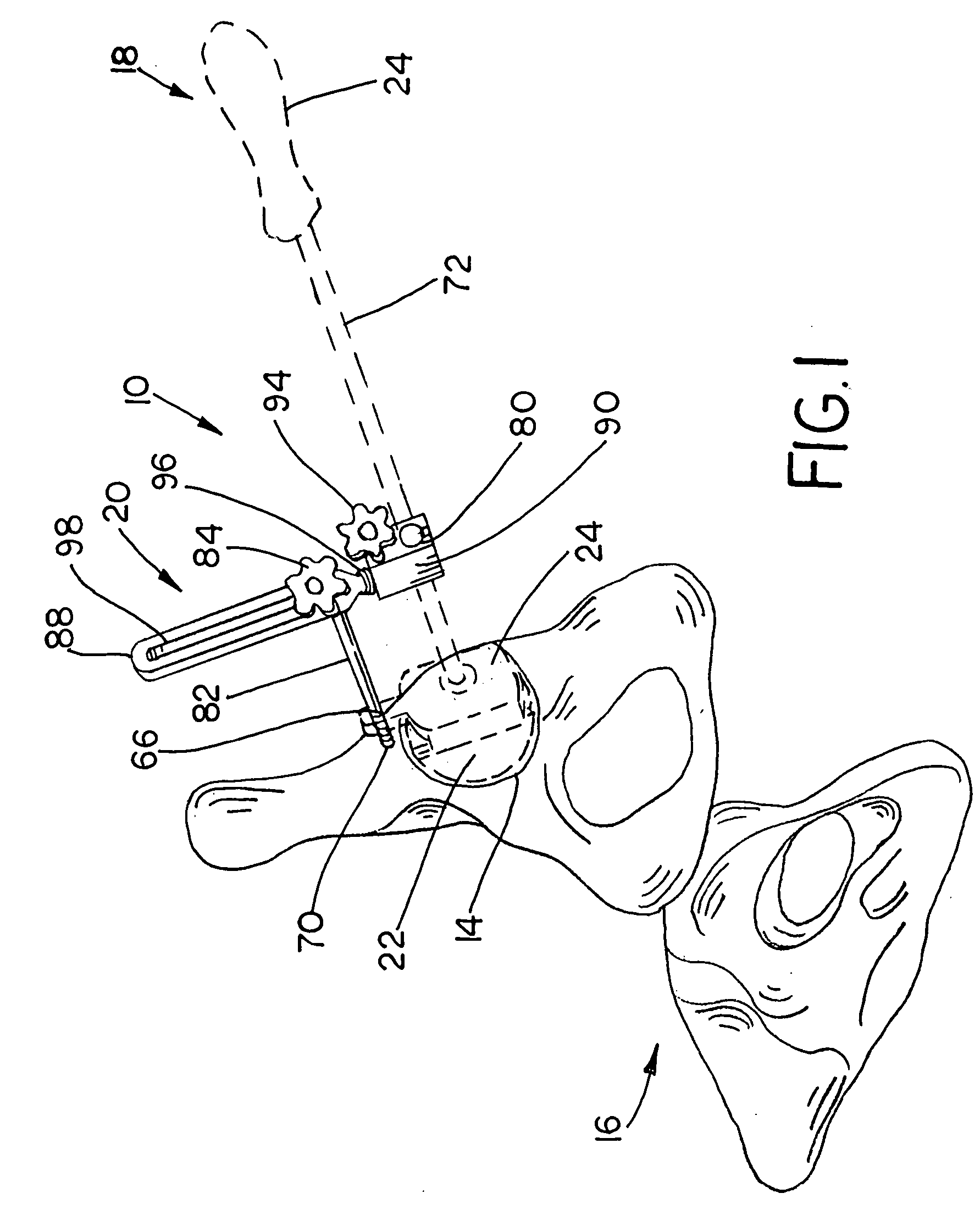
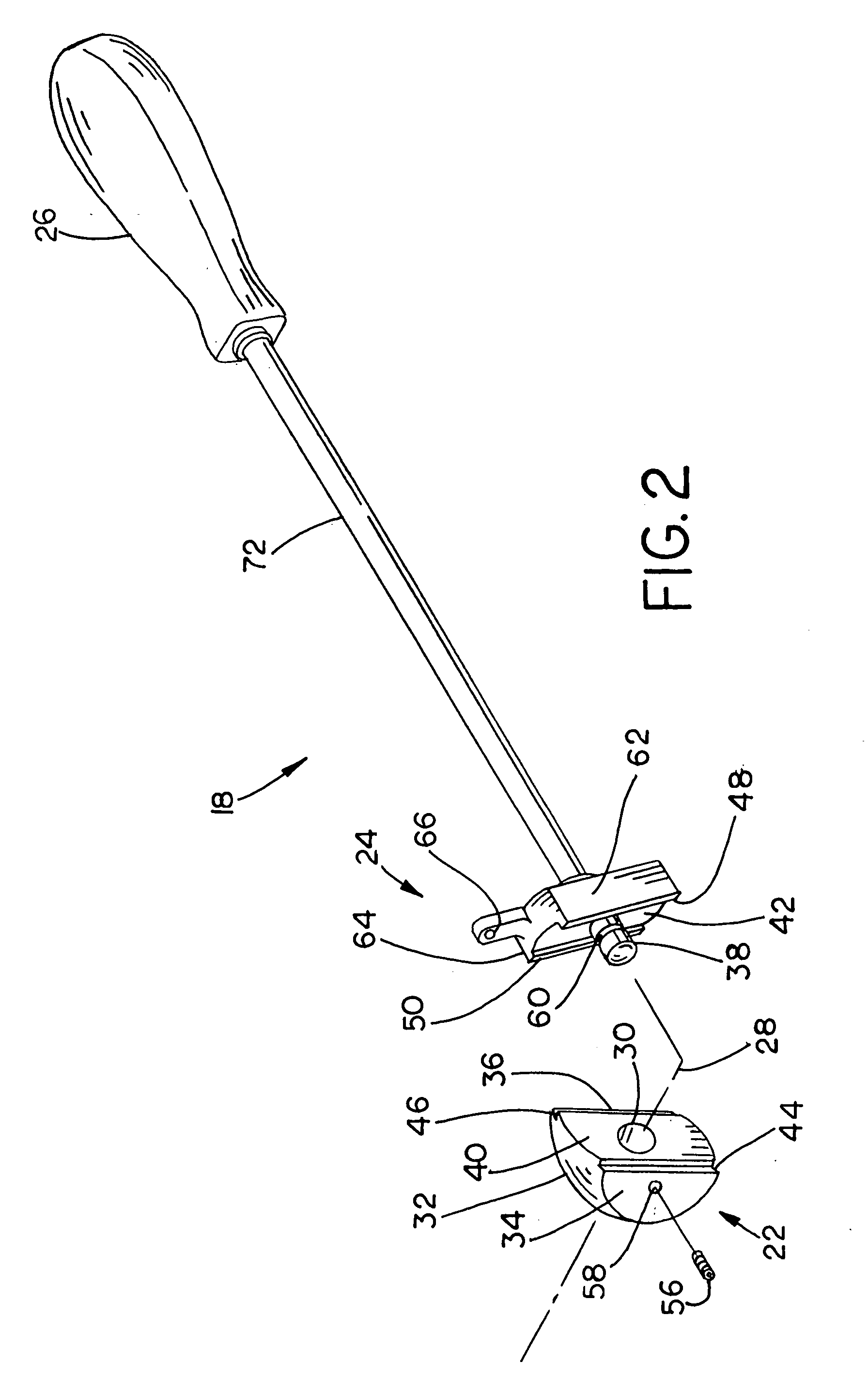
An intramedullary femoral broach aligns two instruments. A femoral neck resector guide slides over the broach and centers on the patient's femoral head to determine the height and angular rotation of resection. A circular ring of the head and cutting arms assure the system will fit any femur. A template is applied to the femoral broach and seats itself against the buttress of the broach locking it into place. The broach is then reinserted into the intramedullary canal. When the template reaches the greater trochanter the sizer is adjusted to the rotational anteversion of the canal. The handle of the femoral broach is struck with a mallet until the template is imbedded into the proximal femoral neck intramedullary bone. A retractor facilitates reaming of the acetabulum through a small anterior incision. A proximal portion digs into the bone of the superior acetabulum to allow for retraction of soft tissues.
Owner:PETERSEN THOMAS D
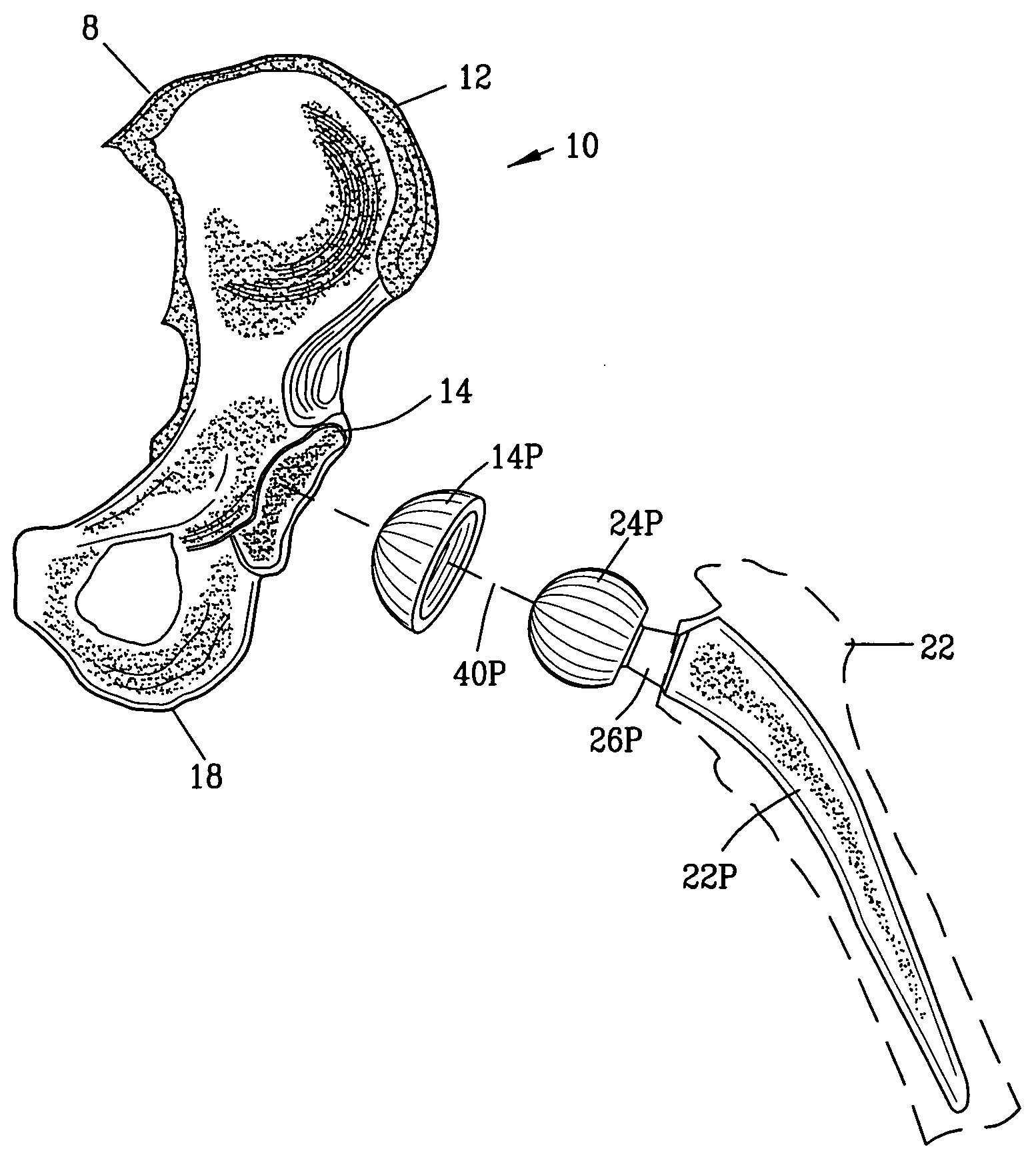
Prosthetic acetabular cup and prosthetic femoral joint incorporating such a cup
ActiveUS20050060040A1Natural angular movementReduce the possibility of misalignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpherical bearingProsthesis
An acetabular prosthesis having an outer member for engaging the acetabulum. The outer member has a part-spherical bearing surface terminating in a distal rim. The rim has a contour such that the portion thereof to be located between the ischium and the pubis extends distally further from an equator of the bearing surface than the contour to be implanted between the pubis and the illium and between the ischium and the illium.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Surgical device for implanting a total hip prosthesis
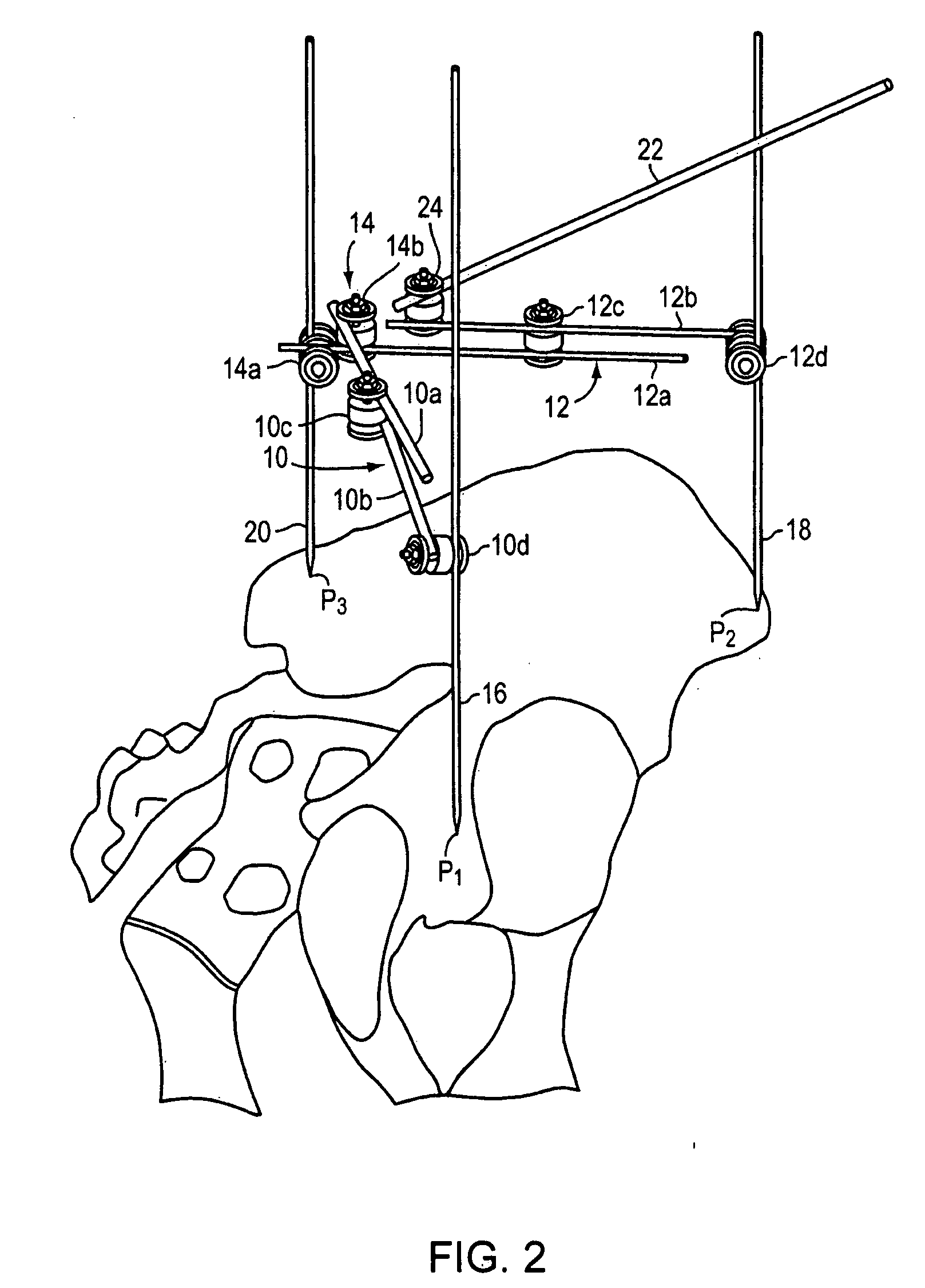
The surgical device according to the invention comprises both means for per-operative measurement and for memorization of a plurality of positions of a given femoral prosthetic direction and means for per-operative comparison of these positions with the cone of mobility of the prosthesis to be implanted, the position of the axis of revolution of this cone being, during the implantation of the prosthesis, adjustable with respect to the zone of the pelvis where the implantation of an acetabulum of the prosthesis is provided. By using this device, the surgeon can easily and rapidly determine, in the course of the surgical operation, a preferential direction for implanting the prosthetic acetabulum in order to reduce the subsequent risks of dislocations of the implanted prosthesis.
Owner:CORIN
Orientation device for surgical implement
InactiveUS20060184177A1Improve objectivityFacilitates and improves trainingDiagnosticsJoint implantsSurgical operationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Orientation device for surgical use includes a frame and a level device attached to the frame. The feature may be oriented with a reference such as the Antero Superior Iliac Spine, the acetabulum or the operating table to position the pelvis or the device. The level device is adapted to define a reference plane. The device thus allows precise orientation with respect to the pelvis through use of a reference plane.
Owner:SAN TECH SURGICAL
Acetabular instrument alignment guide
InactiveUS20060161167A1Eliminate needSave surgical timeDiagnosticsJoint implantsEngineeringPlastic surgery
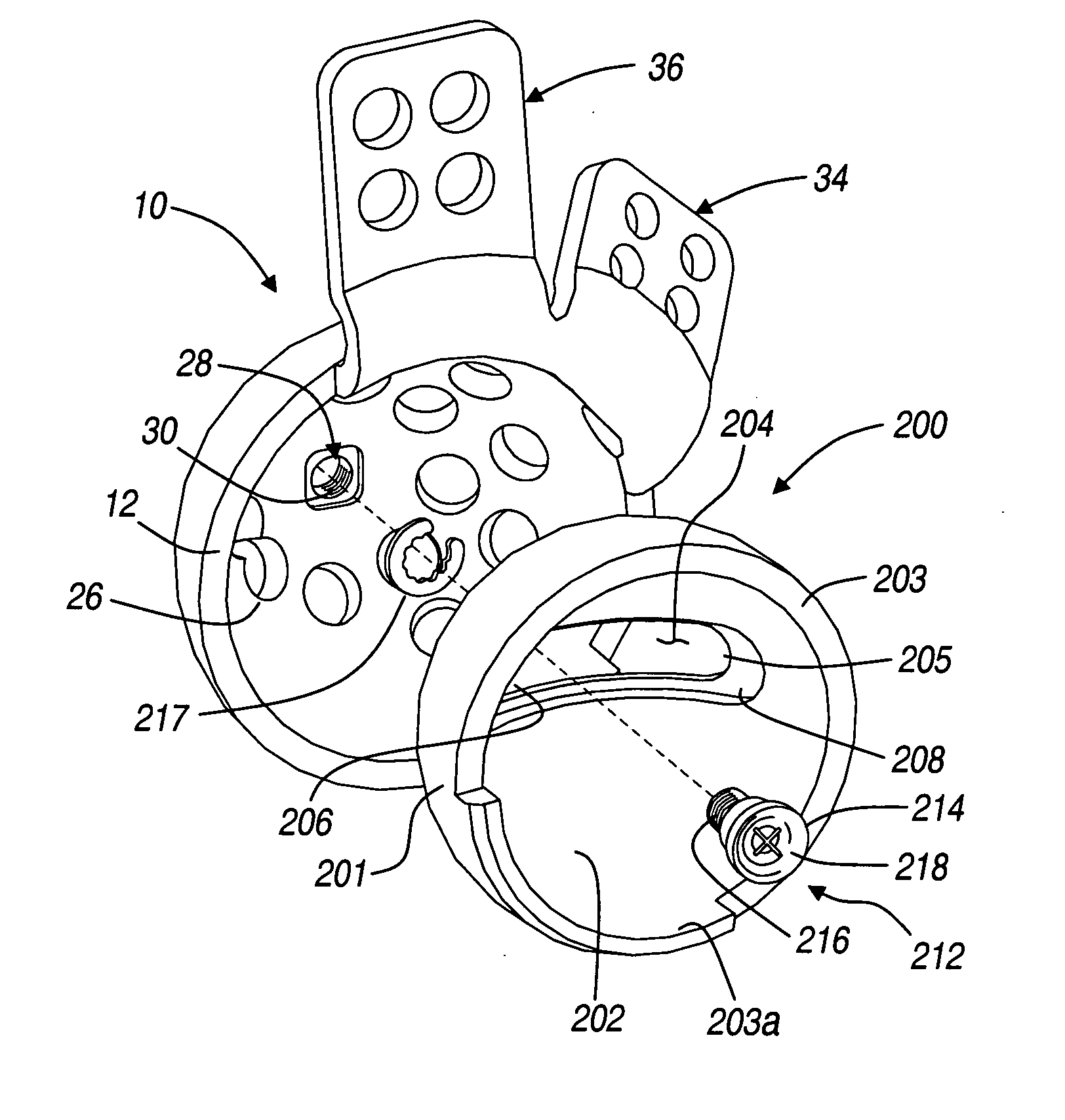
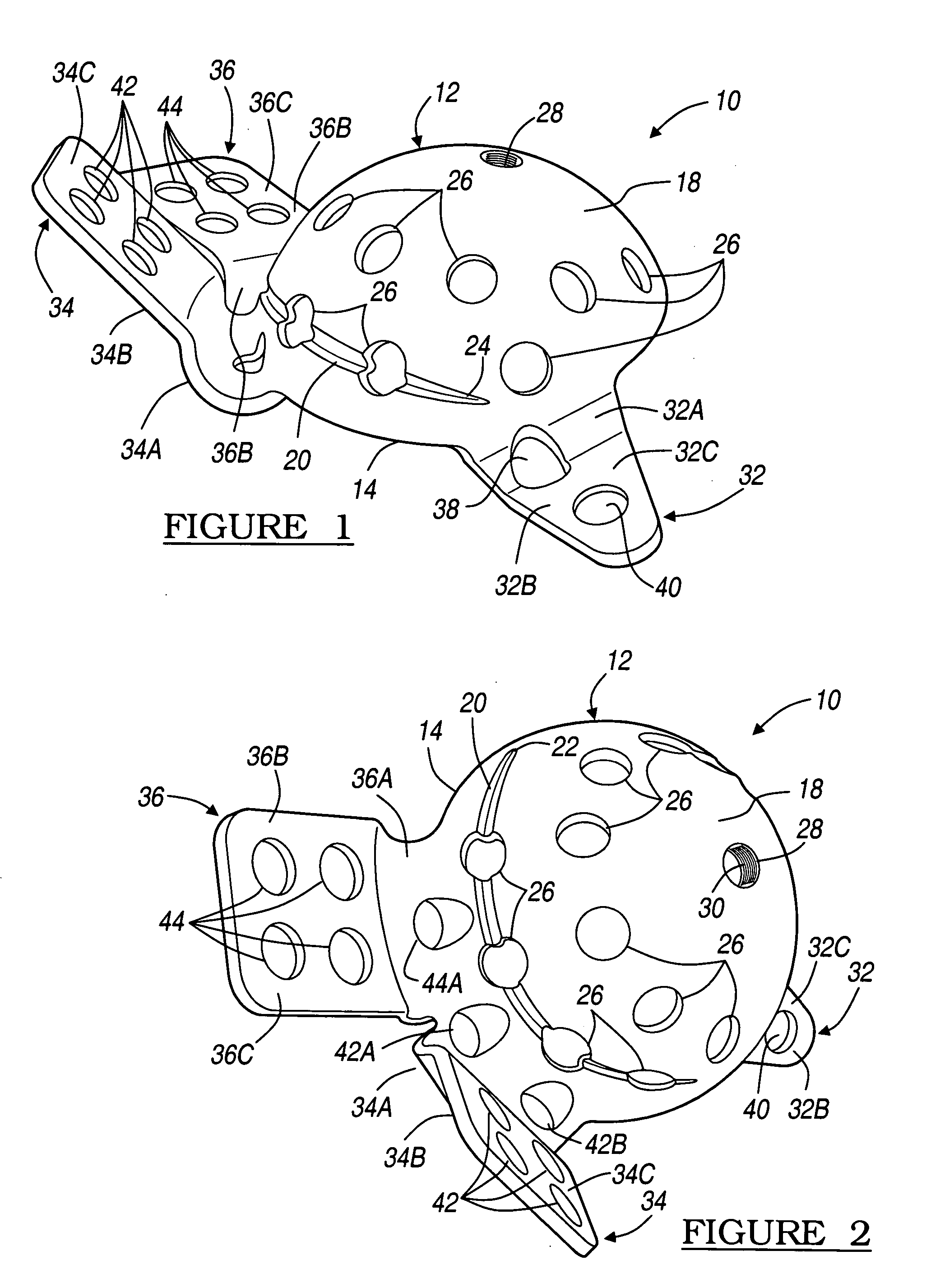
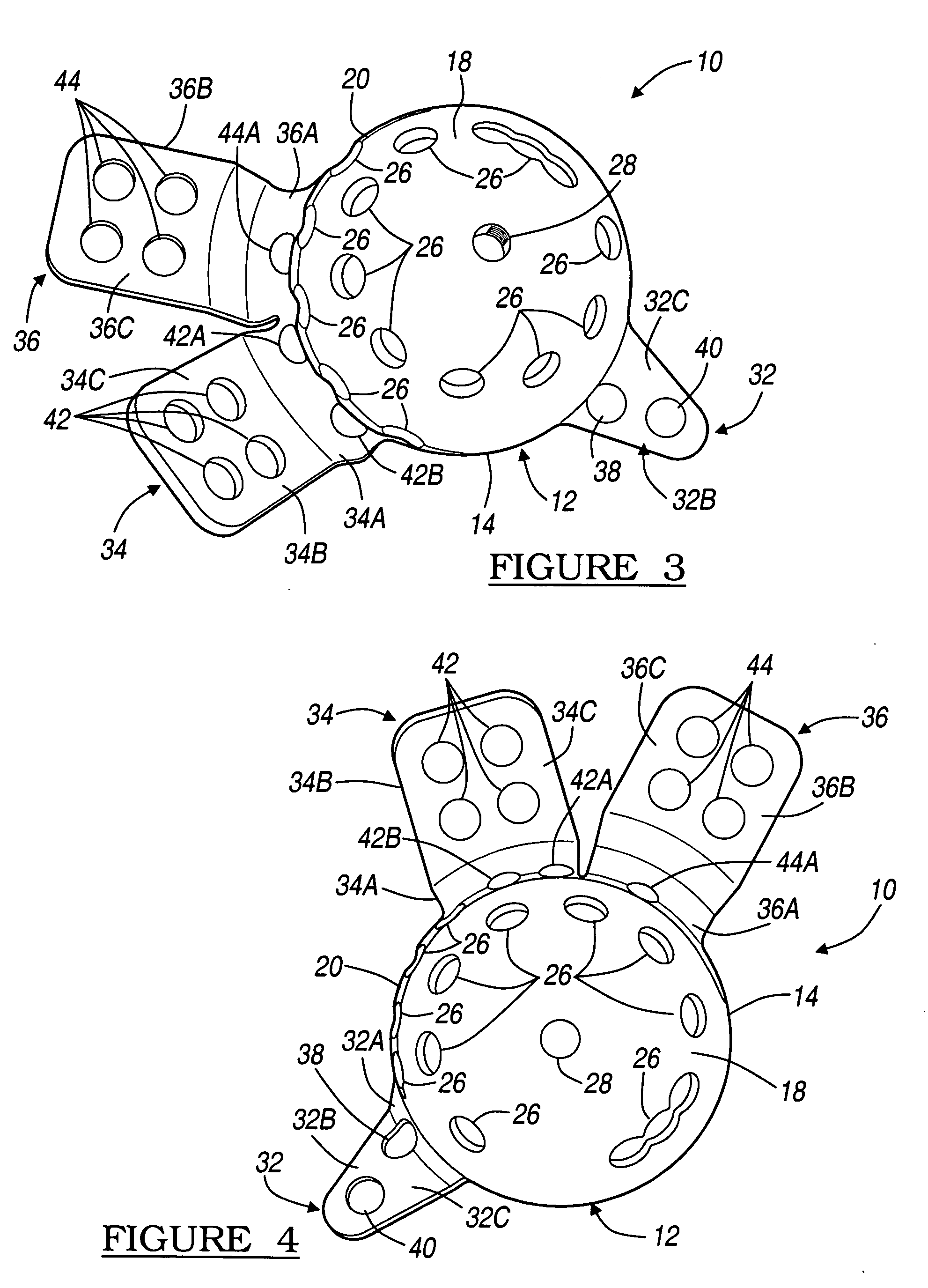
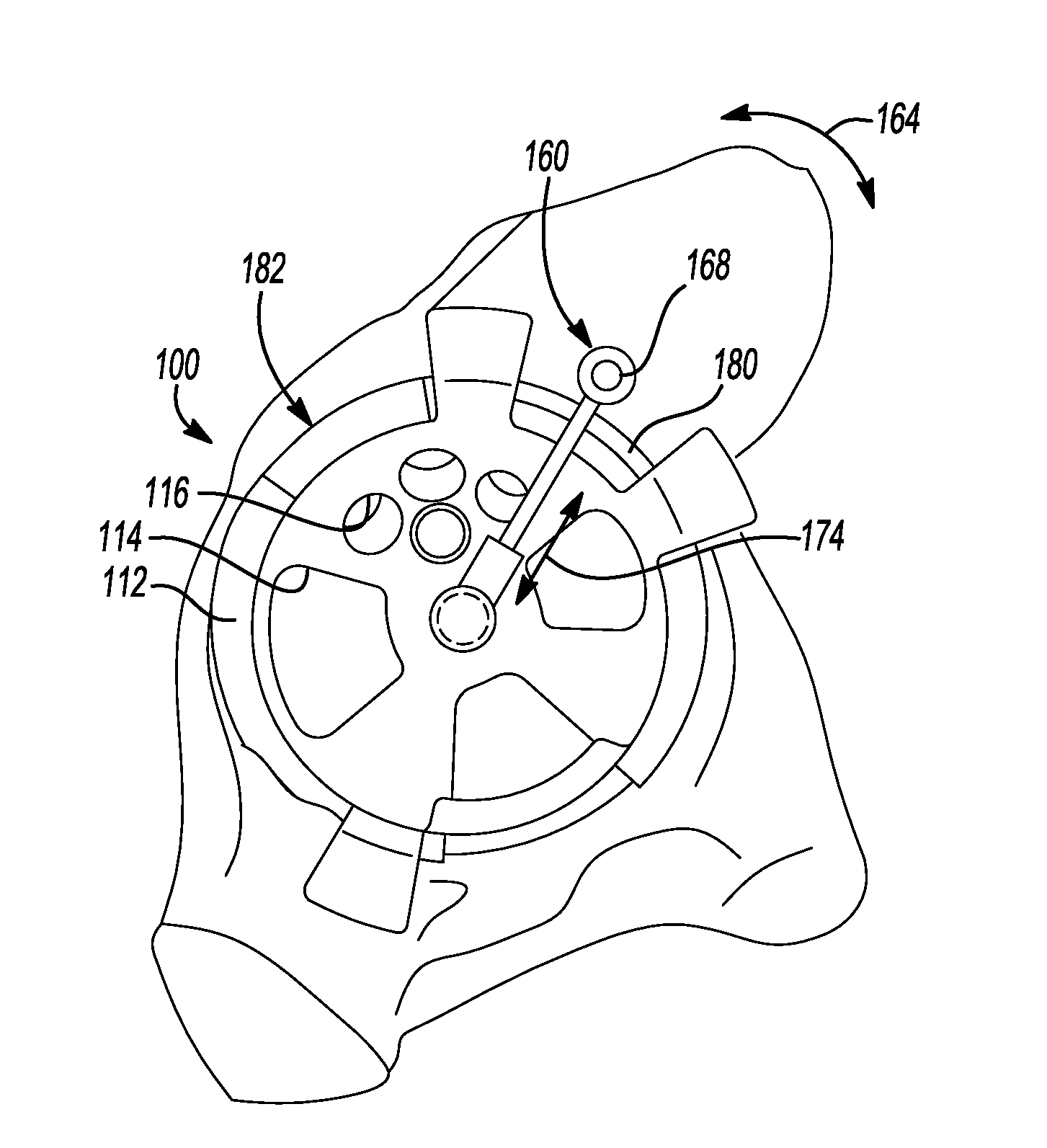
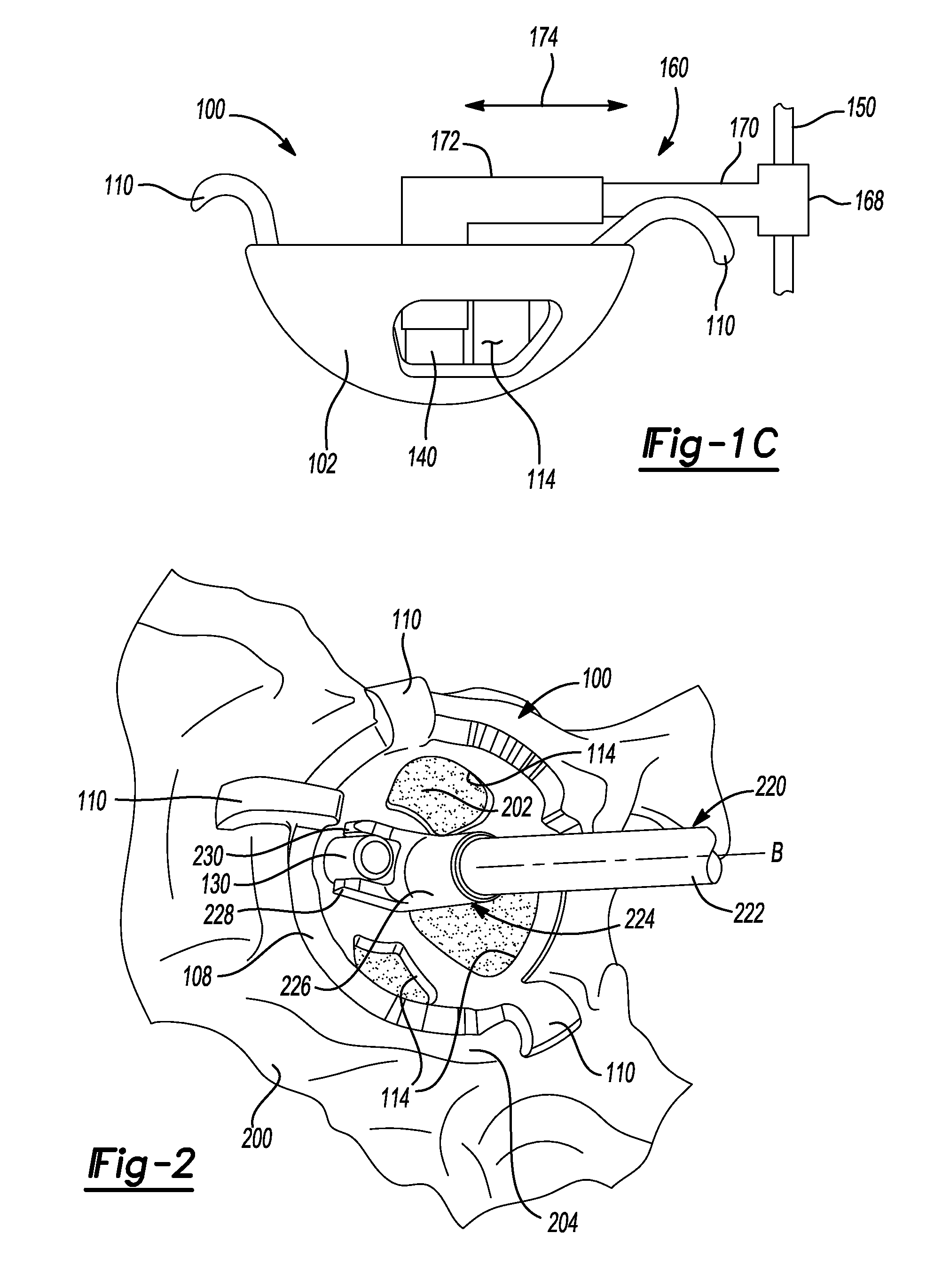
An acetabular instrument alignment guide for aligning at least one orthopaedic instrument relative to an acetabulum in a pelvis. The acetabular instrument alignment guide includes an interchangeable head configured for positioning within the acetabulum where the interchangeable head has a primary axis. A drill guide is releasably connected to the interchangeable head. The drill guide includes a drill bore offset from the primary axis, and the drill bore is configured for aligning a drill relative to the pelvis. The acetabular instrument alignment guide further includes at least one reference pin and an instrument guide connected to the at least one reference pin, the instrument guide being both rotatable and translatable relative to the at least one reference pin. The reference pin is configured for placement in at least one hole in the pelvis produced by the drill.
Owner:SYMMETERY MEDICAL
Patient-specific total hip arthroplasty
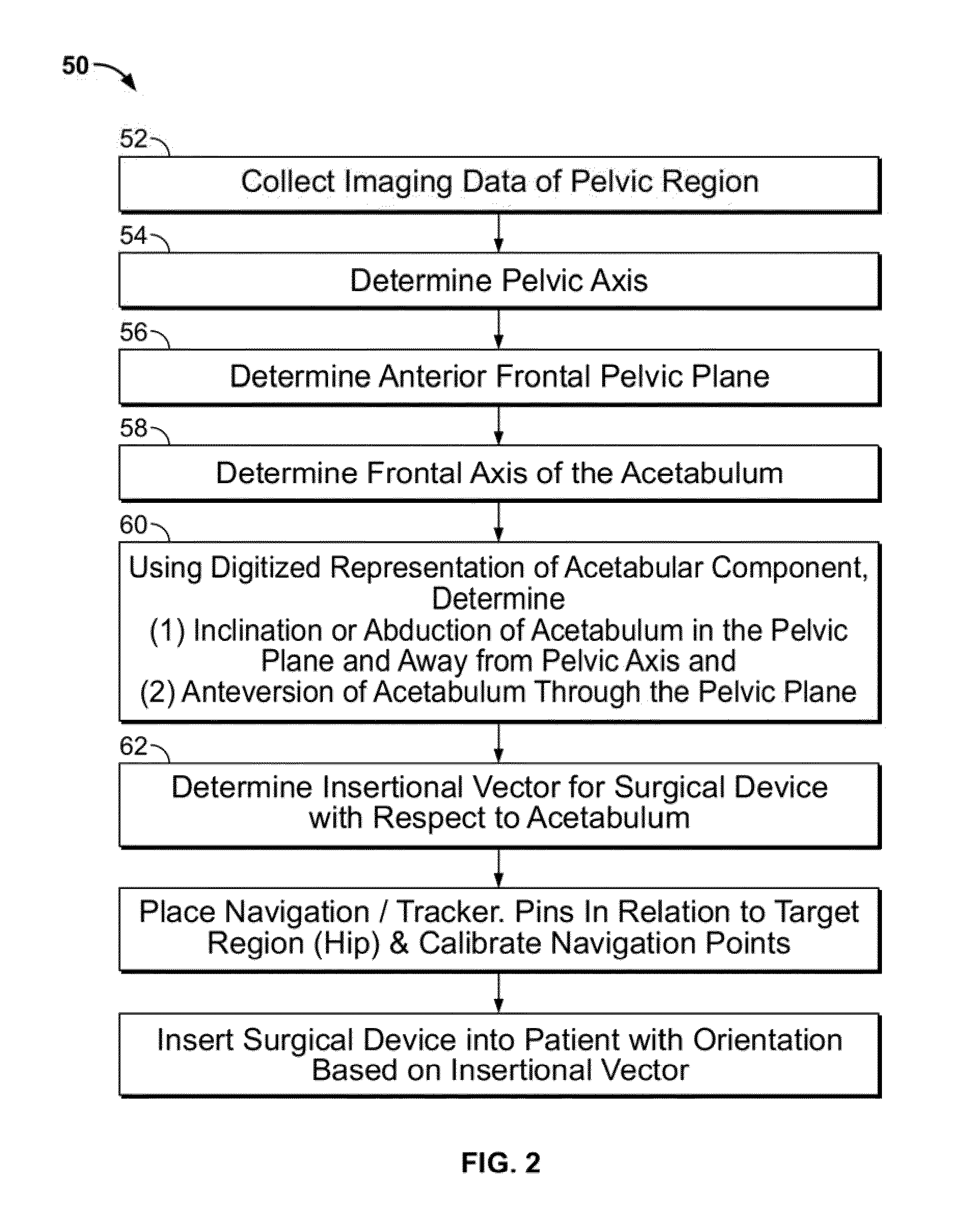
ActiveUS20110313424A1Large range of motionMinimizing reaction forceMedical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesPelvic regionAcetabular component
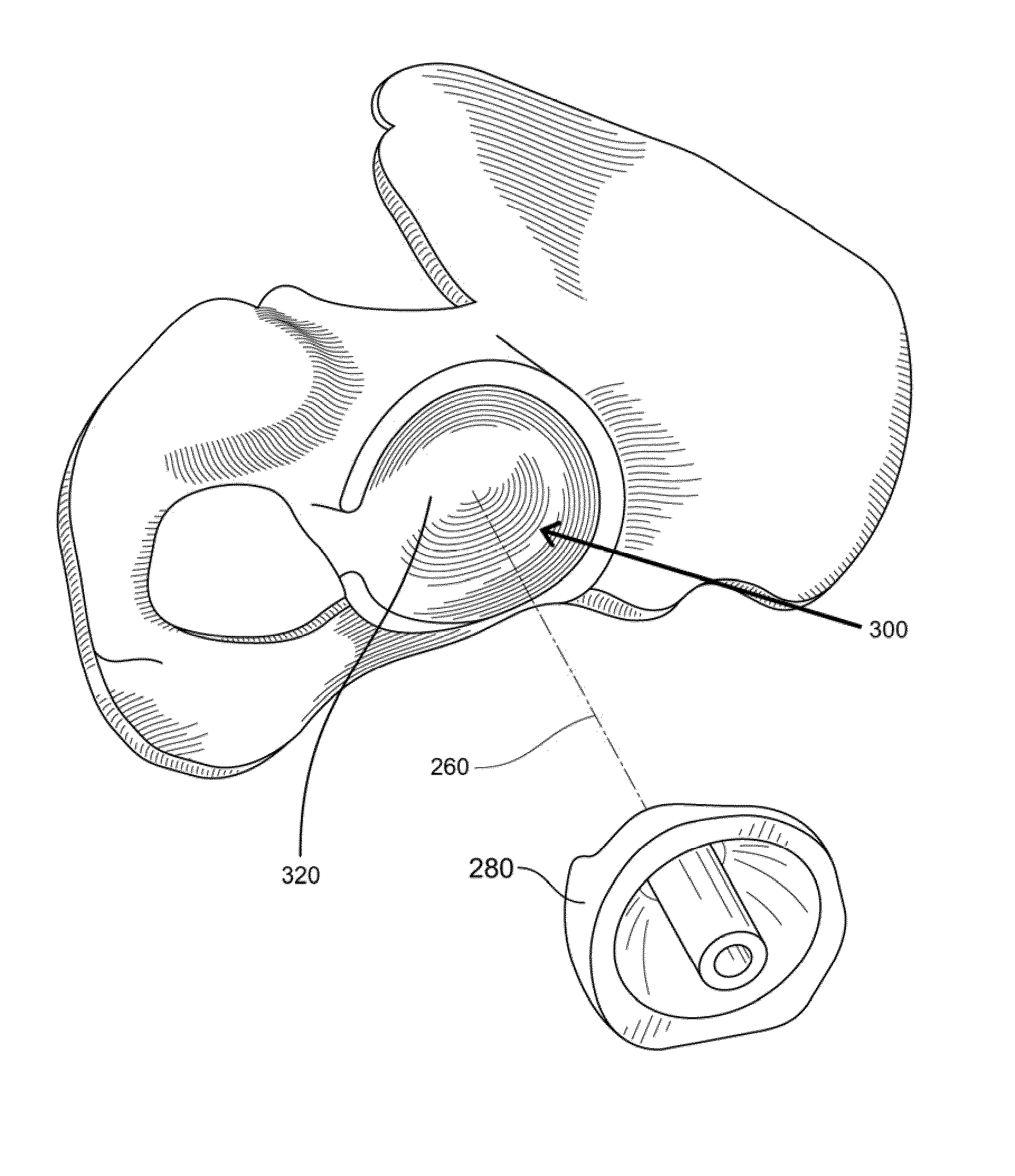
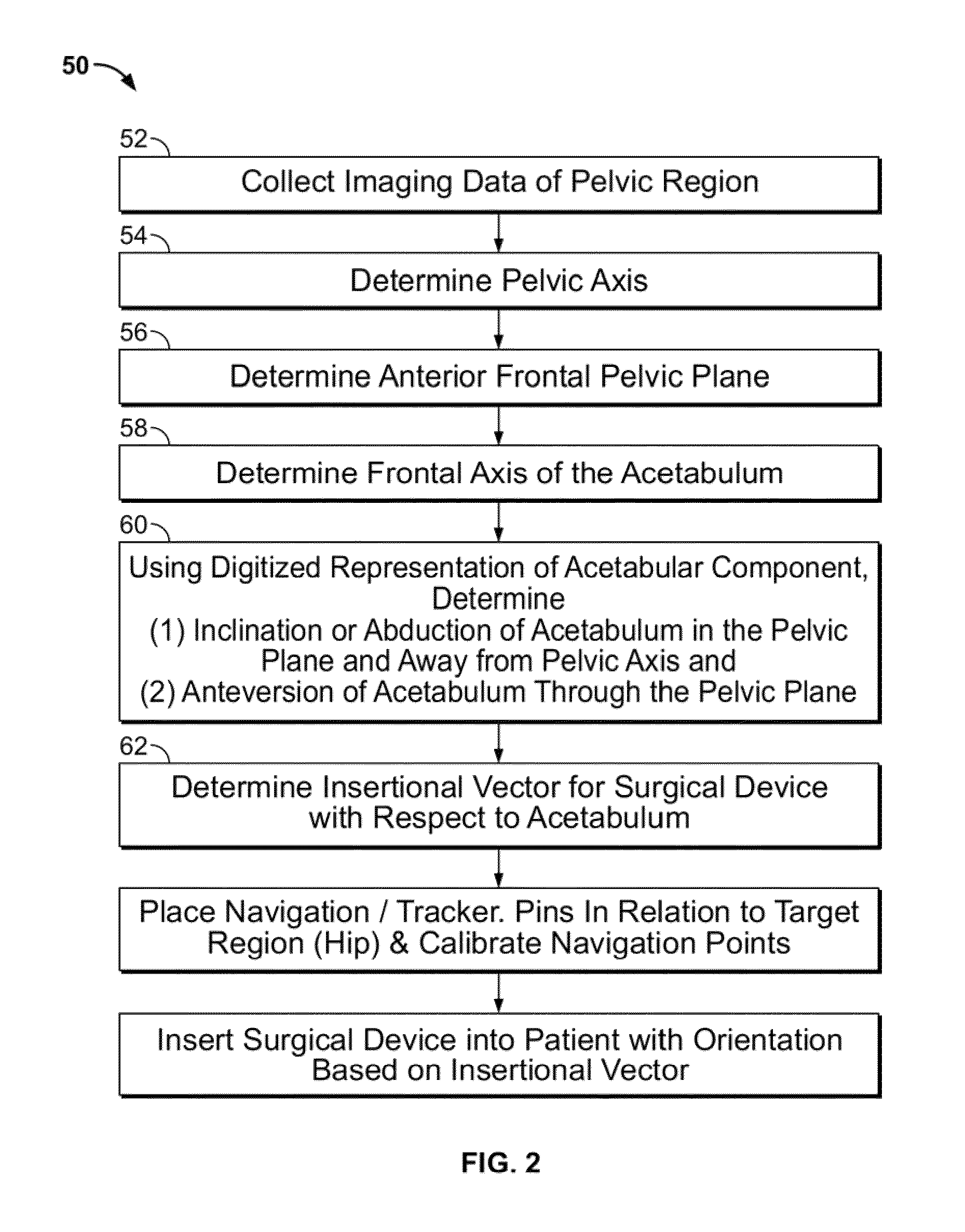
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for performing total hip arthroplasty with patient-specific guides Pre-operative images of a pelvic region of a patient are taken in order to predefine the structure of the guides and corresponding implants. From the obtained image data an insertional vector for implanting an acetabular implant or component into an acetabulum of the patient is determined, wherein the insertional vector is coaxial with a polar axis of the acetabular component. Also from the obtained image data, a superior surface of the guides and implants can be shaped to match the acetabulum of the patient. A nub portion extending outwardly from the superior surface of the guides and implants is shaped to substantially match the shape of a fovea of the acetabulum. A guide portion of the guides forming a slot has a longitudinal axis coaxial with the determined insertional vector of a corresponding acetabular component.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
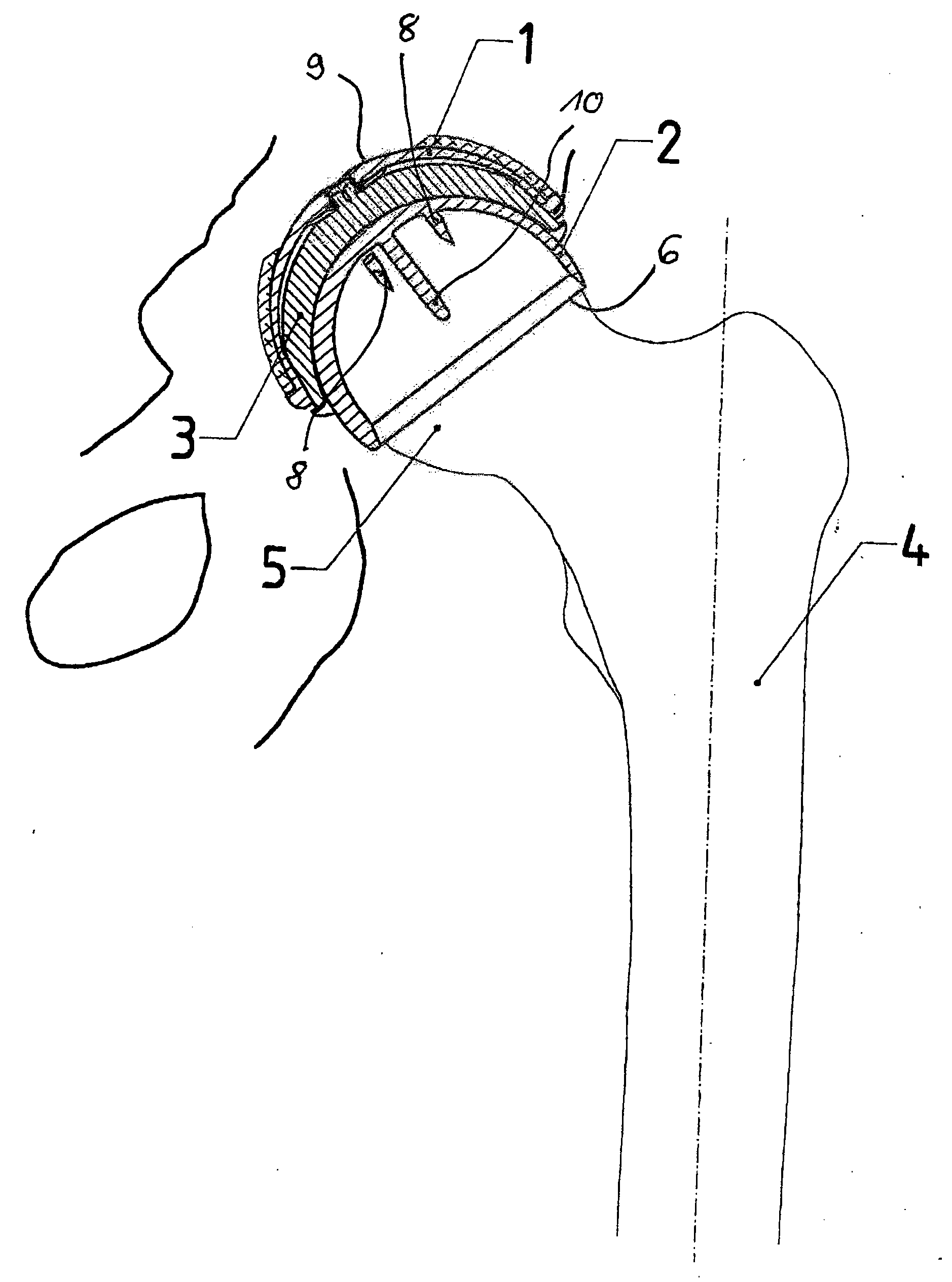
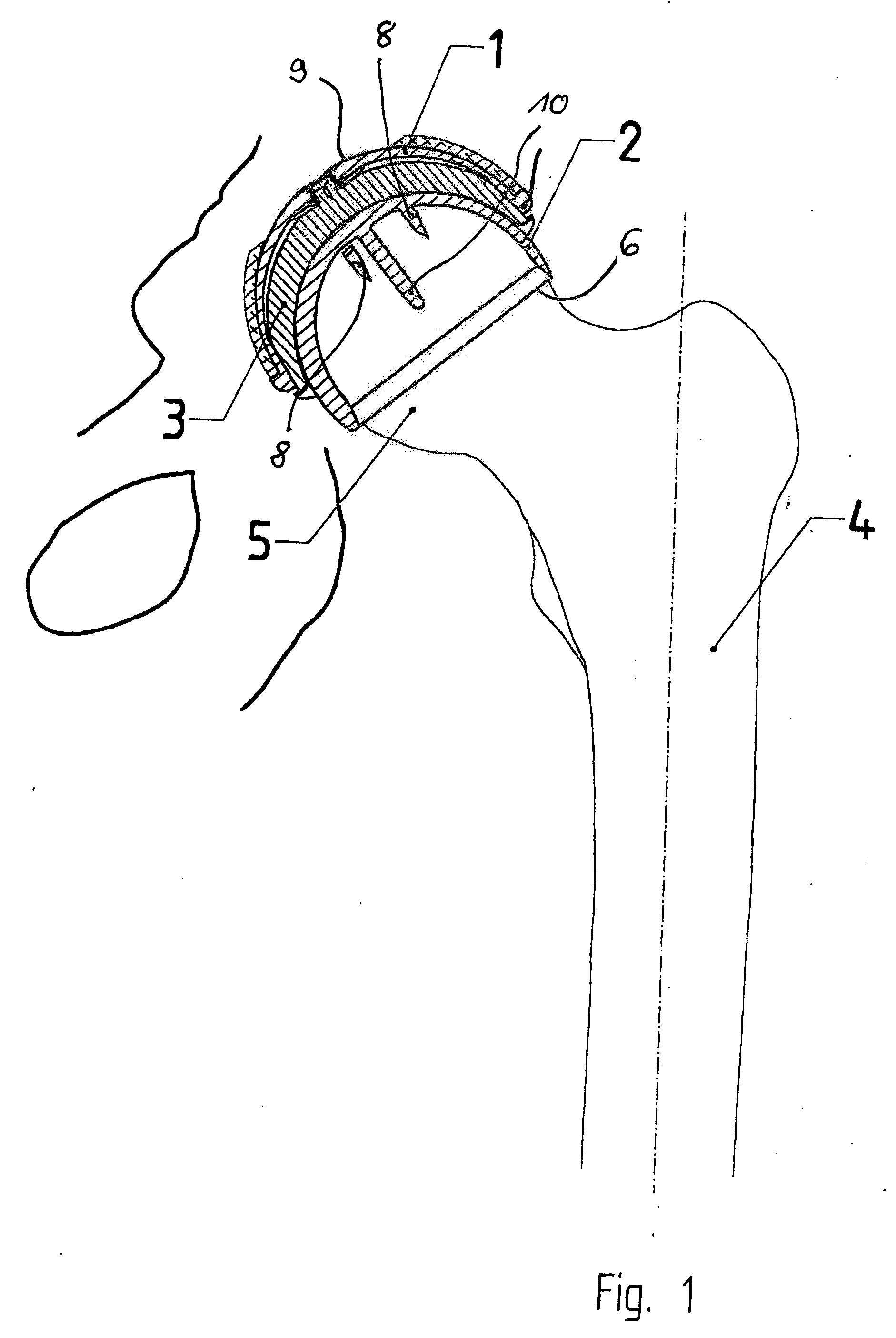
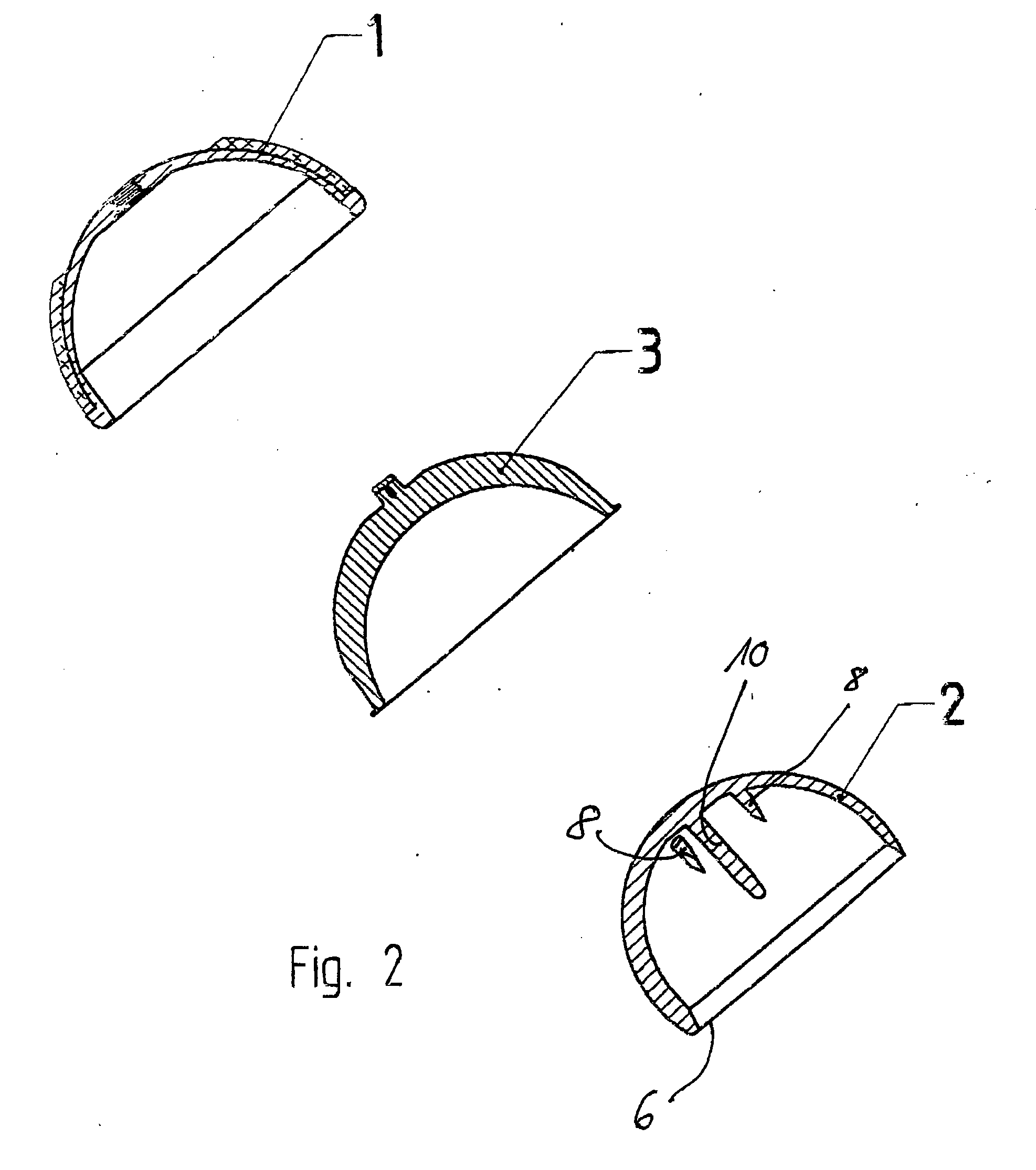
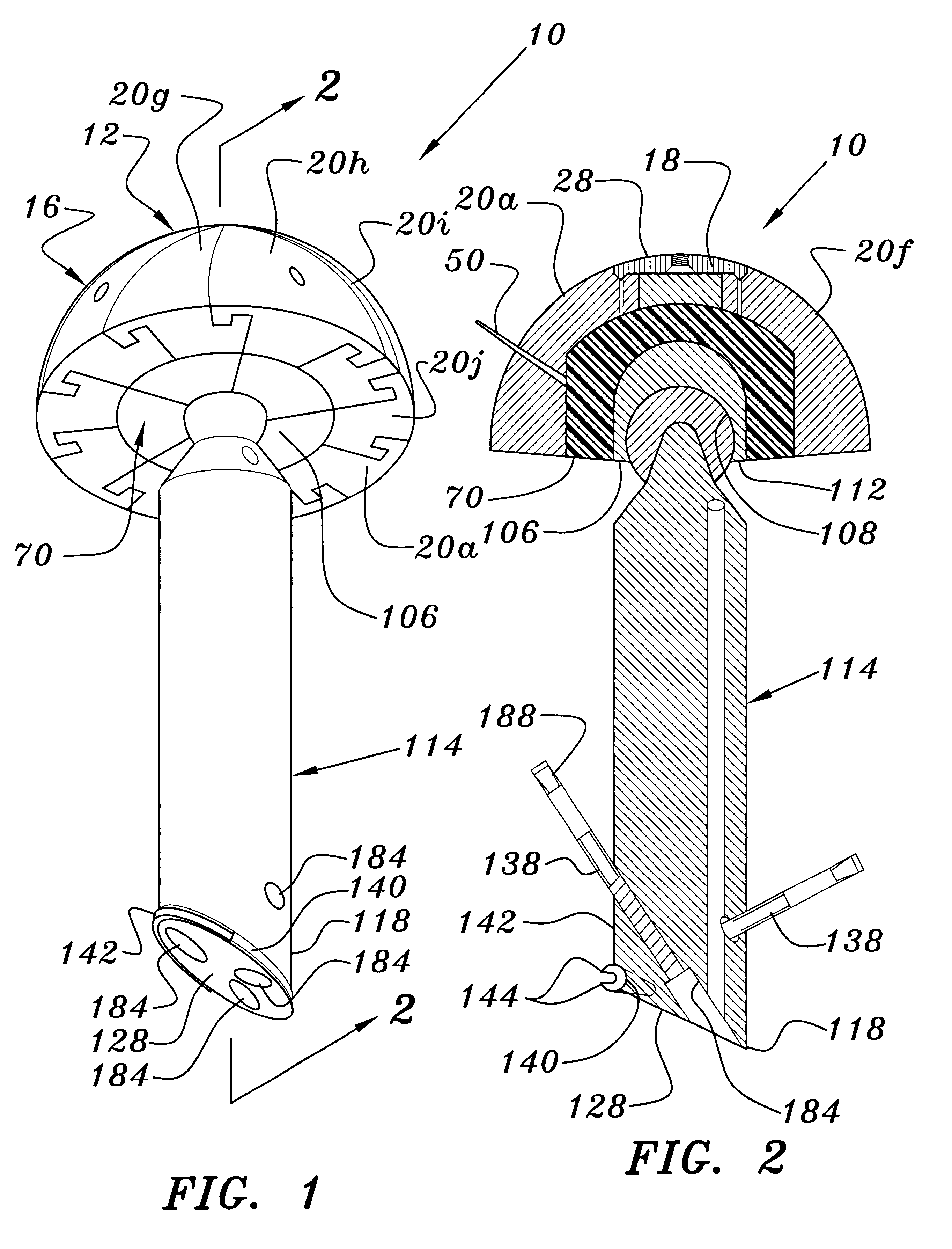
Set For Creating An Offset-Resurfacing Hip-Joint Implant
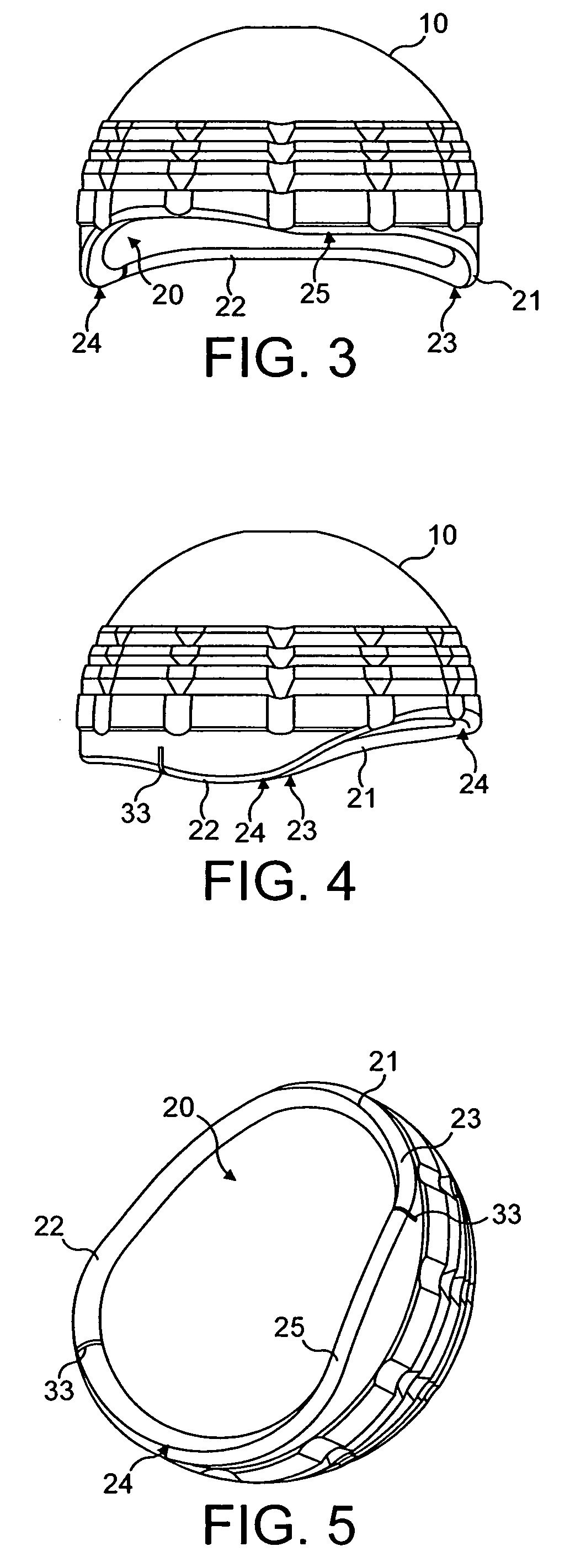
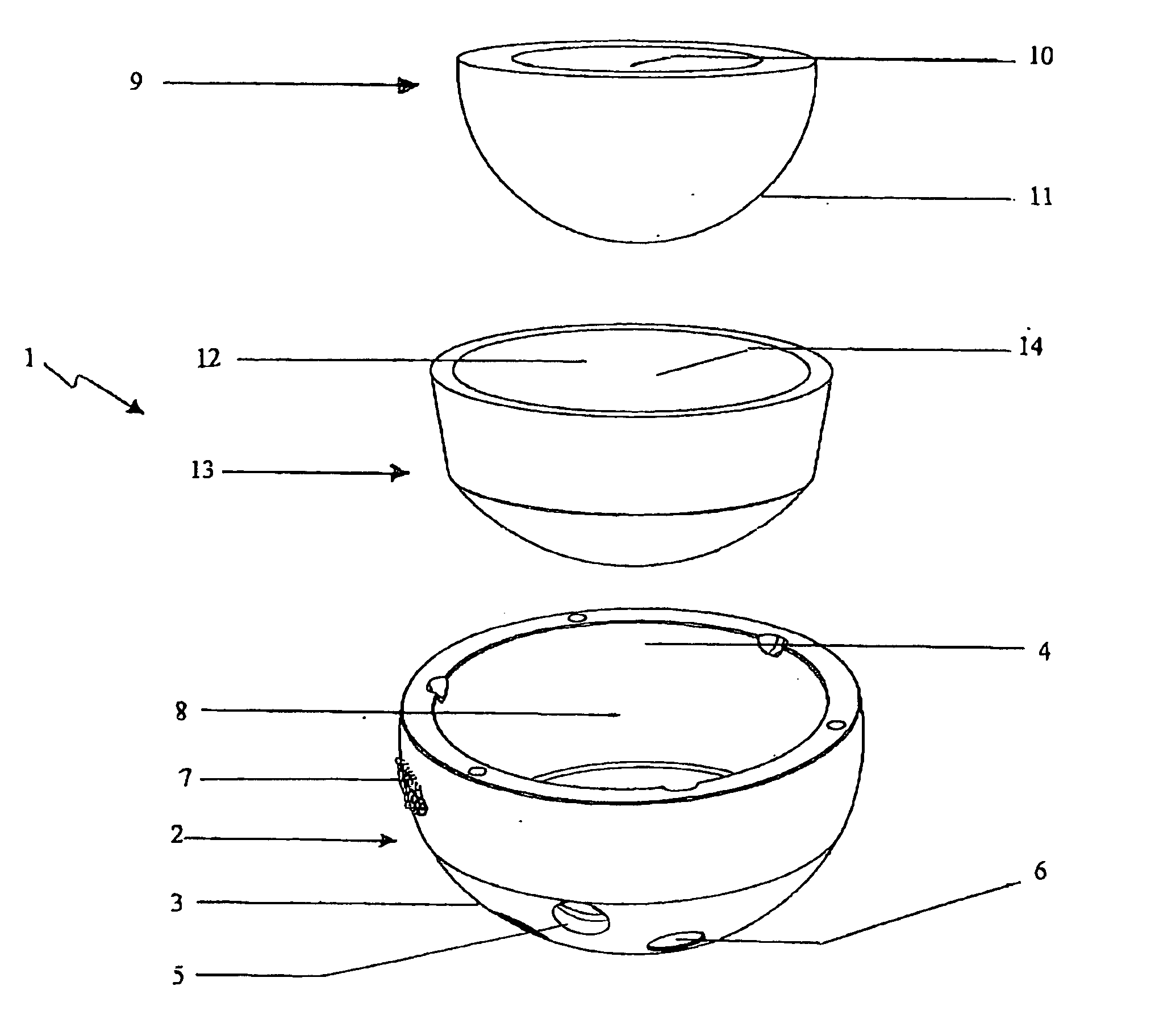
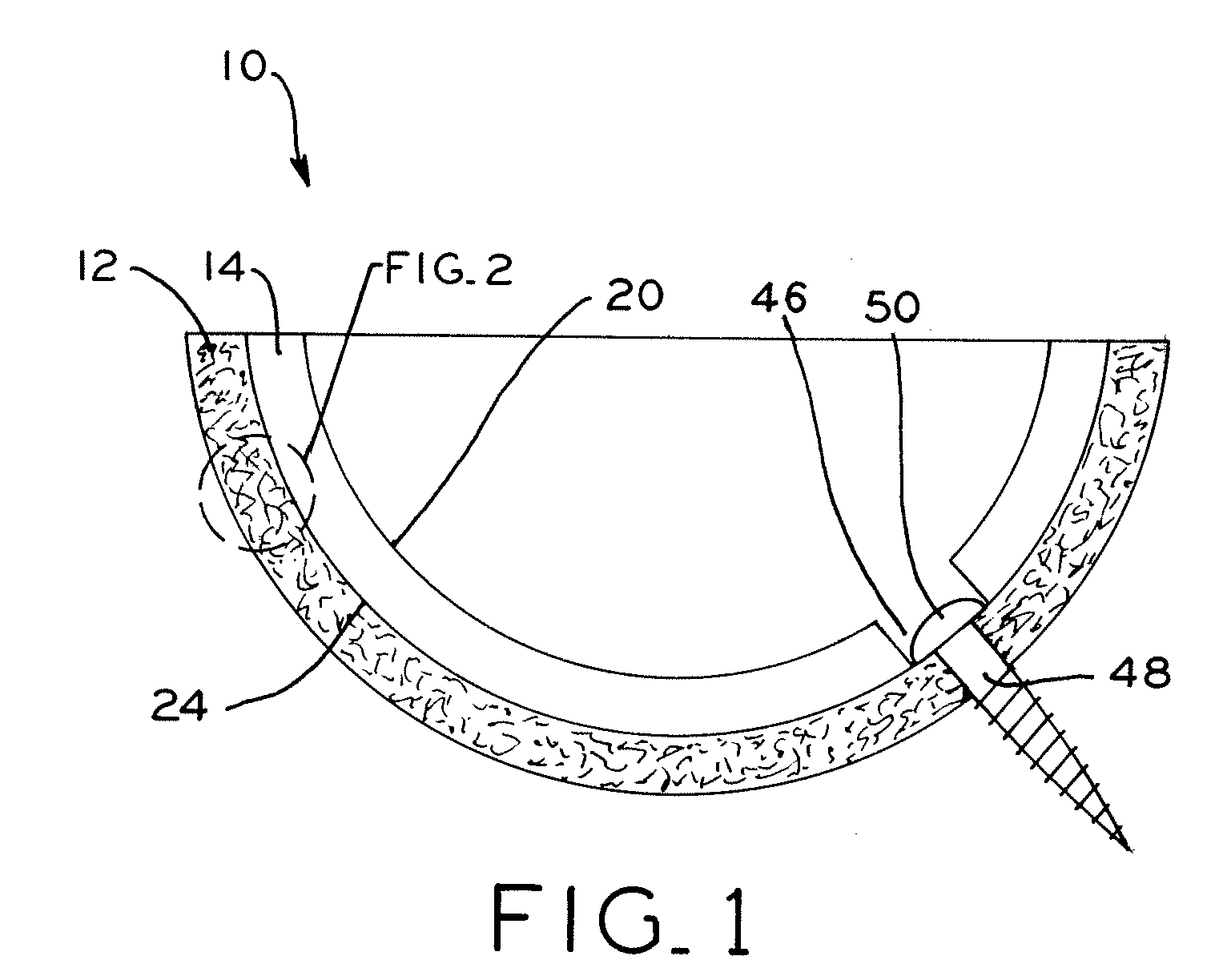
A set is provided for creating an offset-resurfacing hip-joint implant. The set includes a 1 to 1.5 mm thick metallic acetabulum shell (1) for insertion into the natural acetabulum, from which only cartilage has been removed, a metallic head cap (2) for placement on the natural hip-joint head, from which only cartilage has been removed, and an inlay (3) for insertion into the acetabulum shell (1) as a sliding partner for the head cap (2). The inlay has a material thickness of 2 to 5 mm. The head cap (2) has a wall thickness which increases constantly from a thickness of 2 mm to 6 mm viewed in cross section in the region of the base edge (6) of the head cap, so that an eccentricity is produced in its outer shape
Owner:ORTHODYNAMICS GMBH
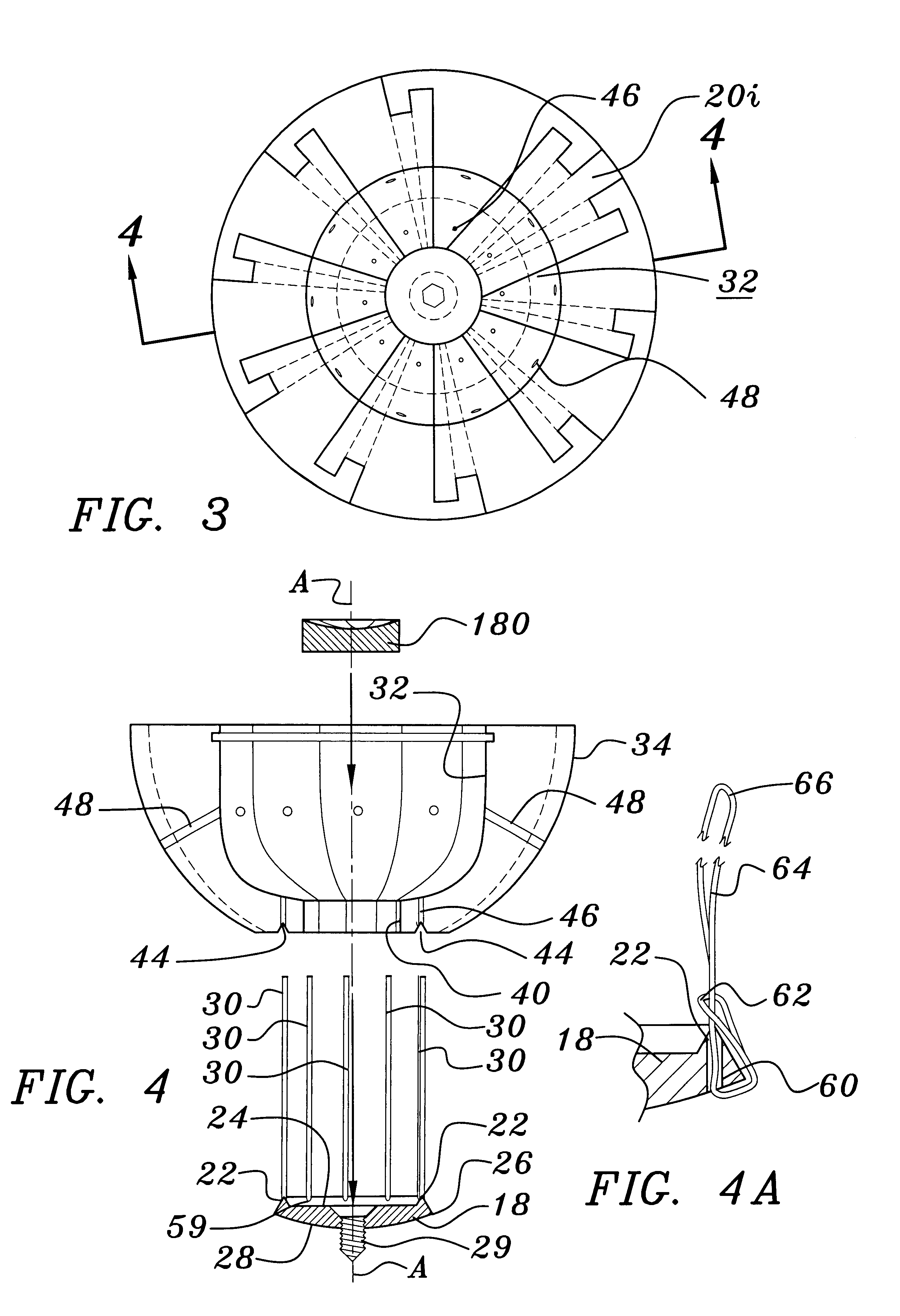
Expandable reaming device
InactiveUS20060276797A1Increase the effective diameterGood flexibilitySurgerySurgical drillProsthesis
An expanding reamer for reaming or cutting a concave surface, for example, for reaming an acetabulum in preparation for implanting a prosthetic component, such as an acetabular cup or socket, during a hip arthroplasty. The reamer includes a rotating shaft cooperating with a surgical drill or other power source at one end and rotating a reamer head at the other end, and a system adapted to expand one or more blades on the reamer head. In a preferred version, the reamer head comprises a plurality of generally circular, preferably substantially flat and parallel blades, the outer blades of which are radially expandable as segments of a cutting sphere to enlarge the effective diameter of the reamer head. A transverse blade may guide expansion of the blades to move upwards as well as outward to maintain a nearly perfect cutting sphere across a range of diameters. Upon rotation of the reamer head, the blades form a portion of an effective cutting sphere that is preferably greater-than-180-degrees in order to allow greater flexibility in placement of the shaft of the reamer relative to the surface being reamed, for example, relative to the center of axis of the acetabulum.
Owner:BOTIMER GARY
Acetabular prosthesis assembly
InactiveUS20050071015A1Reduce wearEliminate wear and tearJoint implantsFemoral headsRight femoral headEngineering
An acetabular prosthesis assembly (1) comprising an acetabular cup (3) with a generally convex outer surface for engaging acetabular bone and a generally concave inner surface, an insert (10) capable of insertion in the cup (3) for receiving a femoral head component, wherein a wear liner (13) is disposed between the cup (3) and the insert (10), the liner (13) providing a wear inhibiting surface (4a).
Owner:PORTLAND ORTHOPAEDICS
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A trial shell is provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Joint prosthesis and method for placement
A prosthesis for replacement of a ball and socket joint in the human body. The prosthetic components comprise a plurality of separate parts which may be inserted through a hole in the femur of the patient and assembled and attached to the prepared acetabulum of the hip bone to form a cup-shaped first shell. A cup is also passed through the hole in the femur and attached to the first shell to form the socket portion of the joint. A shaft having a first end with a ball formed thereon is inserted in the hole through the femur so that the ball engages the cup for movement therein.
Owner:TARABISHY IMAD ED
Systems and methods for intra-operative pelvic registration
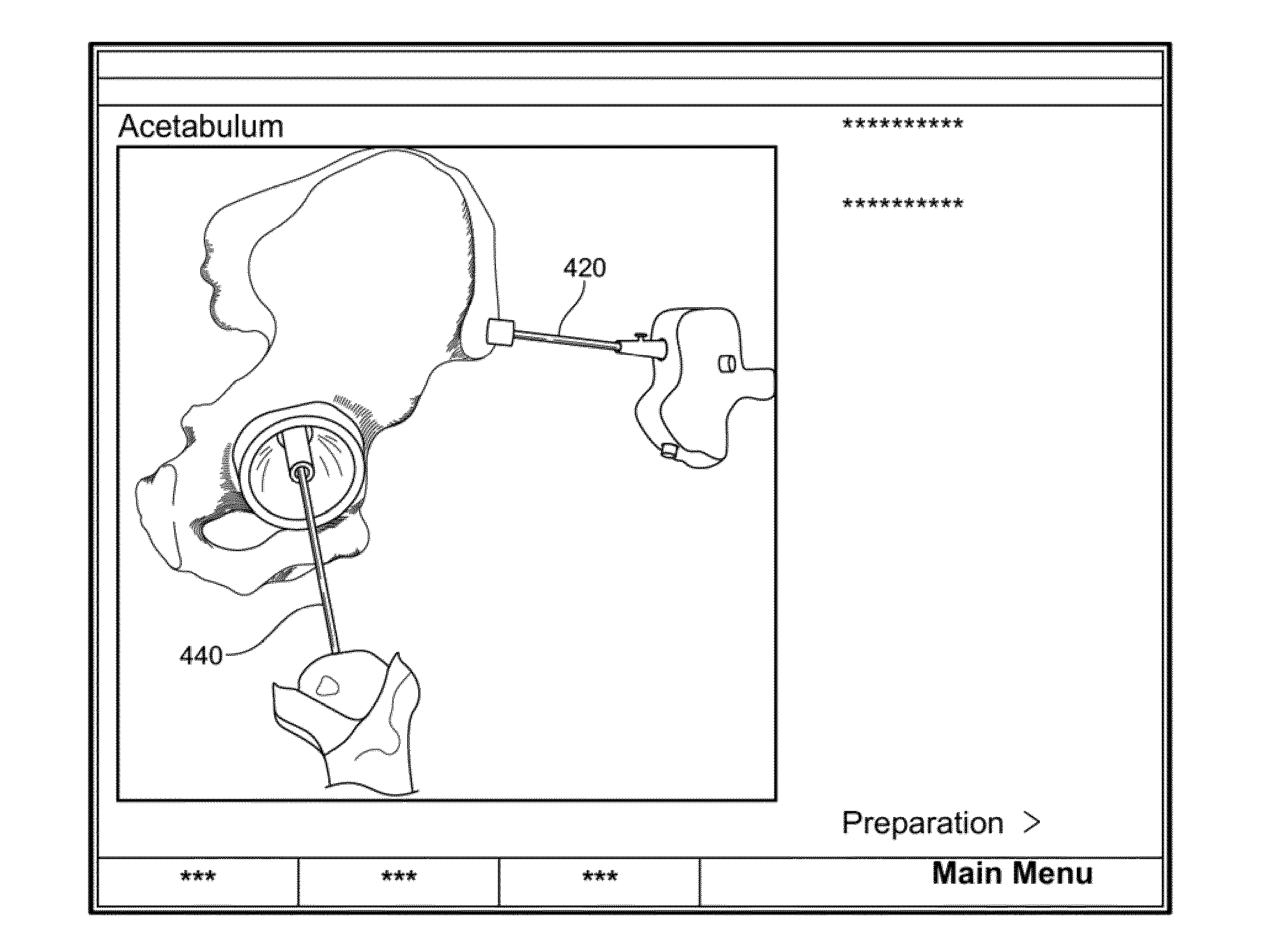
A system for intra-operatively registering a pelvis comprising an acetabulum with a computer model of the pelvis in a coordinate system. The system may include: a) a surgical navigation system including a tracking device; and b) at least one computing device in communication with the surgical navigation system. The at least one computing device: i) receiving first data points from first intra-operatively collected points on an articular surface of the acetabulum, the first data points collected with the tracking device; ii) receiving a second data point from a second intra-operatively collected point on the pelvis, the second data point collected with the tracking device, the second data point corresponding in location to a second virtual data point on the computer model; and iii) determining an intra-operative center of rotation of the femur relative to the pelvis from the first data points.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Apparatus and method of determining acetabular center axis
ActiveUS20080306558A1DiagnosticsSurgical systems user interfaceAcetabular componentBiomedical engineering
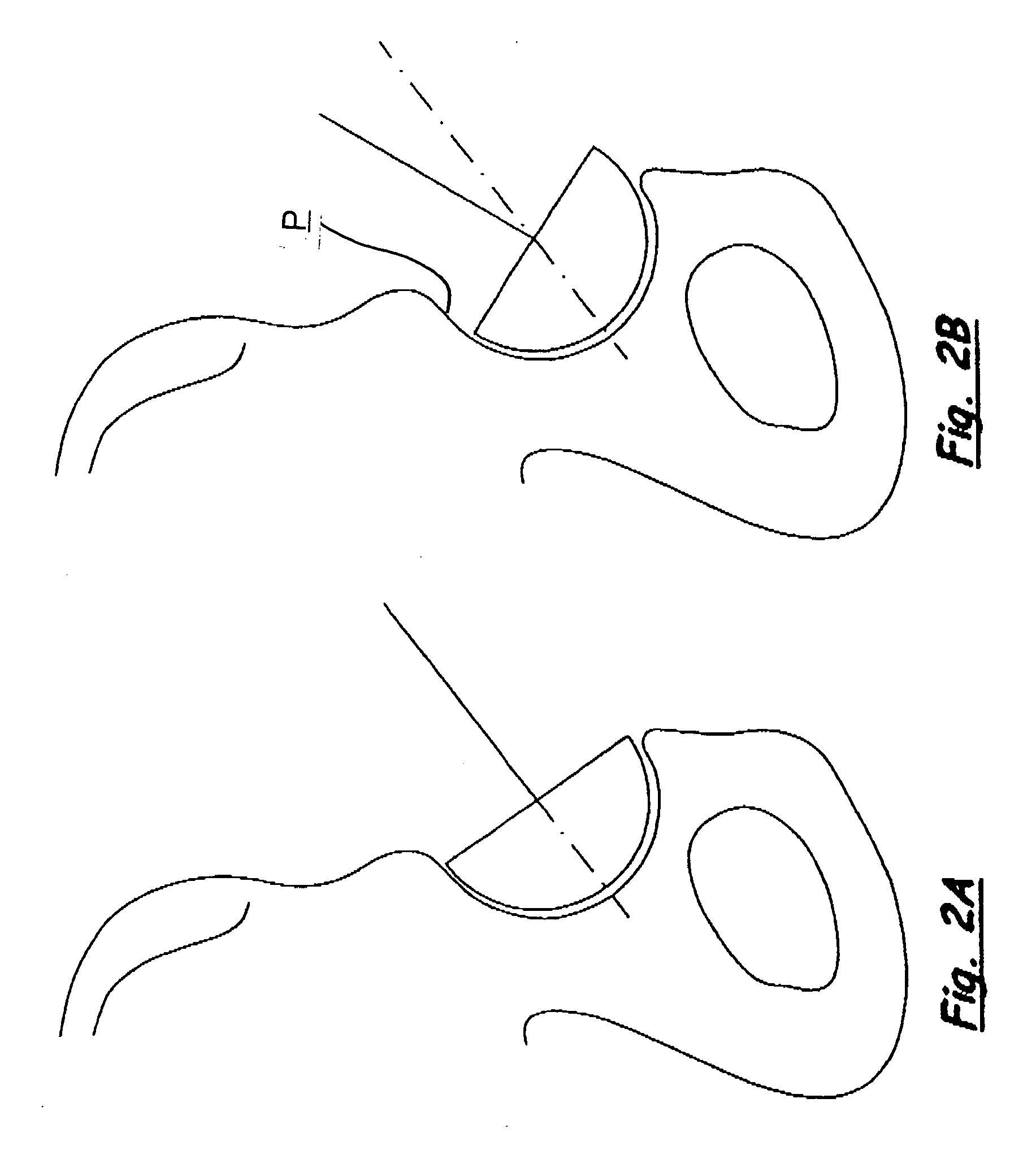
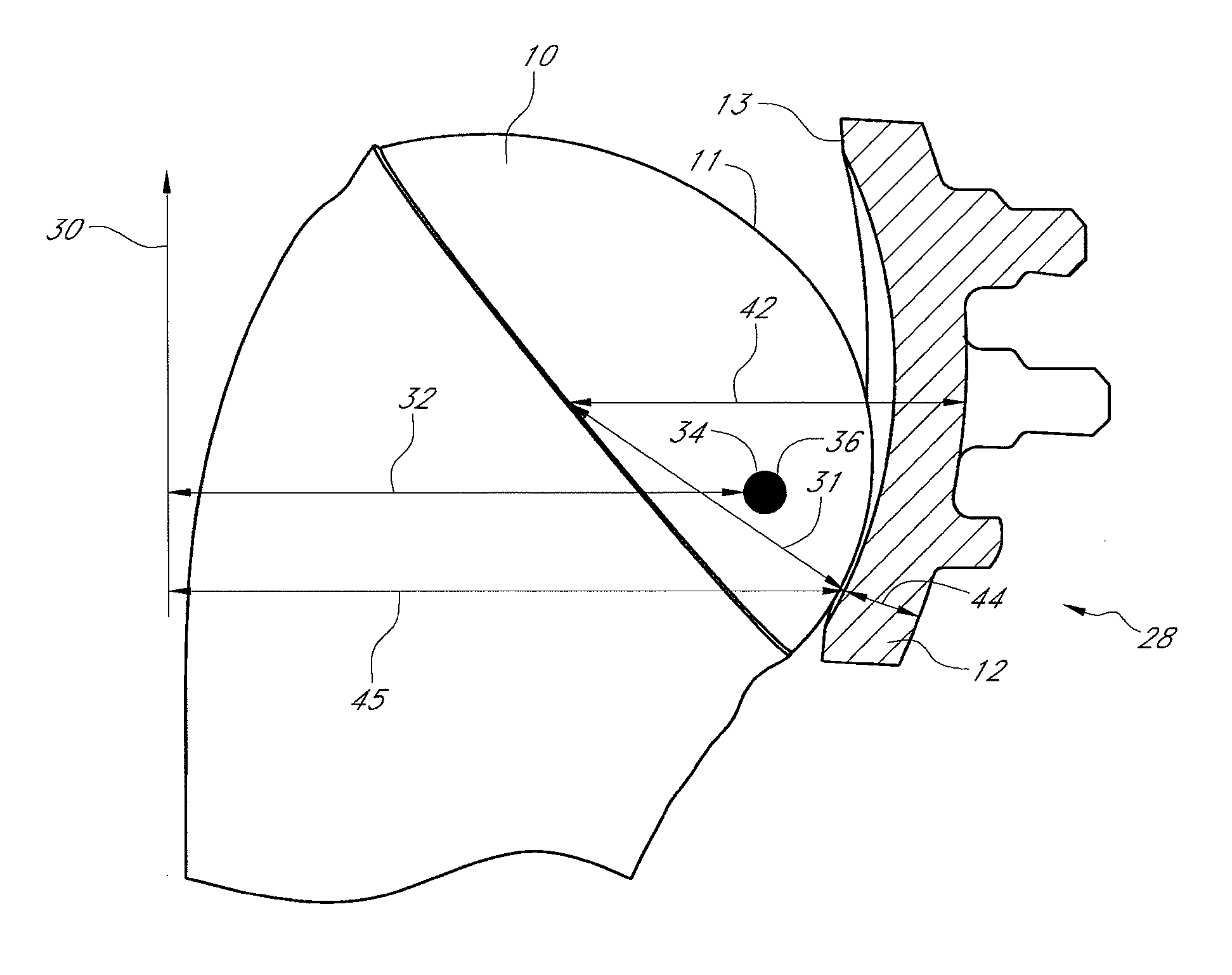
An apparatus and method is disclosed for aligning the anteversion and the inclination of an acetabular prosthetic cup within an acetabulum of a patient. The apparatus and method comprises calculating the orientation of acetabulum center axis. The acetabular prosthetic cup is aligned relative to the calculated acetabulum center axis. The acetabulum center axis is calculated from selecting rim points located about the acetabulum of the patient.
Owner:HAKKI SAM
Method And Appartus For Acetabular Reconstruction
A trial system for a prosthesis is described. The prosthesis can include an acetabular prosthesis generally for implantation in an acetabulum and the surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. One trial shell or a collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a shell prosthesis into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
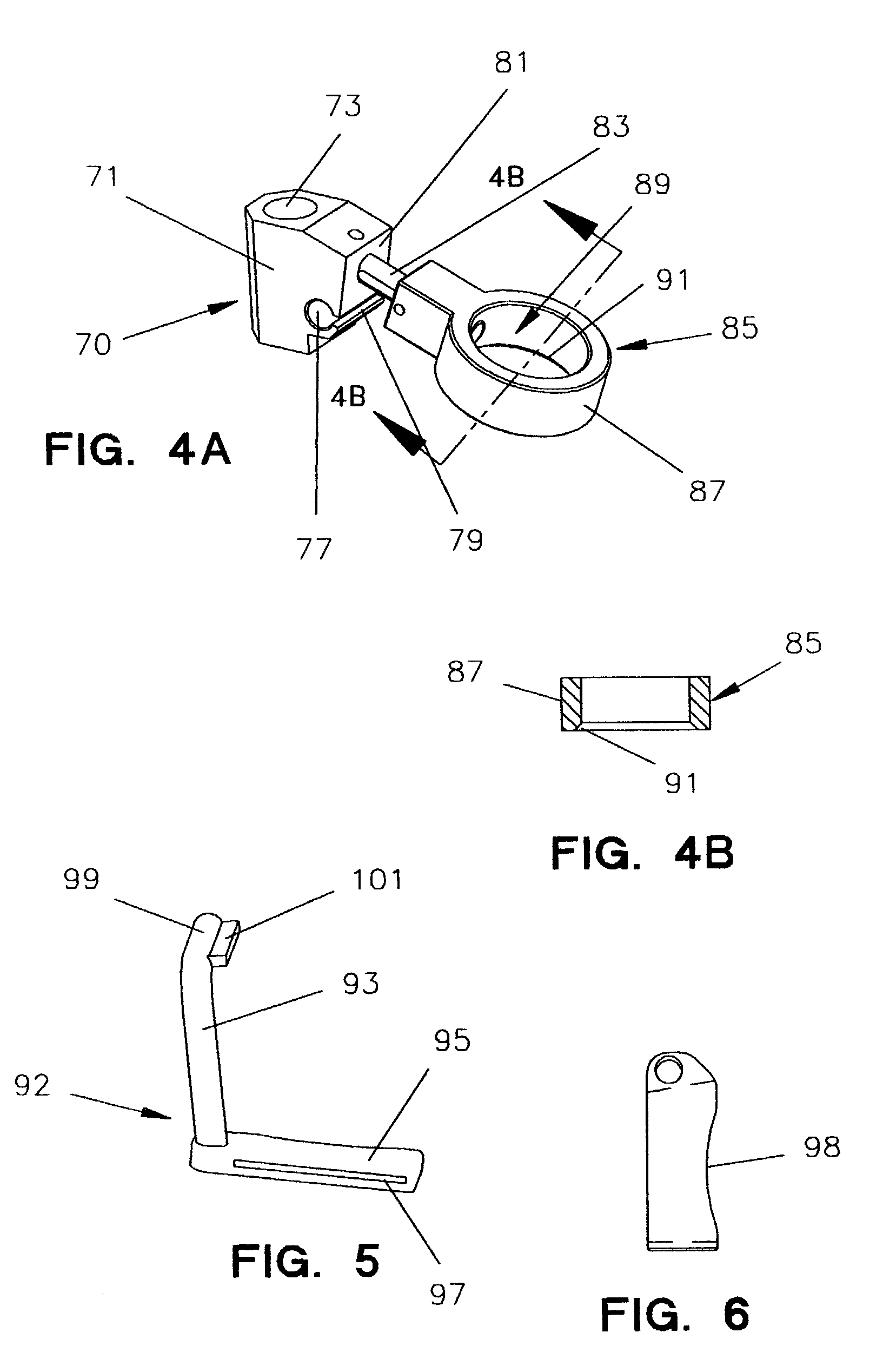
Method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
A method and apparatus for performing a minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. An approximately 3.75-5 centimeter (1.5-2 inch) anterior incision is made in line with the femoral neck. The femoral neck is severed from the femoral shaft and removed through the anterior incision. The acetabulum is prepared for receiving an acetabular cup through the anterior incision, and the acetabular cup is placed into the acetabulum through the anterior incision. A posterior incision of approximately 2.5-3.75 centimeters (1-1.5 inches) is generally aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft and provides access to the femoral shaft. Preparation of the femoral shaft including the reaming and rasping thereof is performed through the posterior incision, and the femoral stem is inserted through the posterior incision for implantation in the femur. A variety of novel instruments including an osteotomy guide; an awl for locating a posterior incision aligned with the axis of the femoral shaft; a tubular posterior retractor; a selectively lockable rasp handle with an engagement guide; and a selectively lockable provisional neck are utilized to perform the total hip arthroplasty of the current invention.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Patient-Specific Guide for Acetabular Cup Placement
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
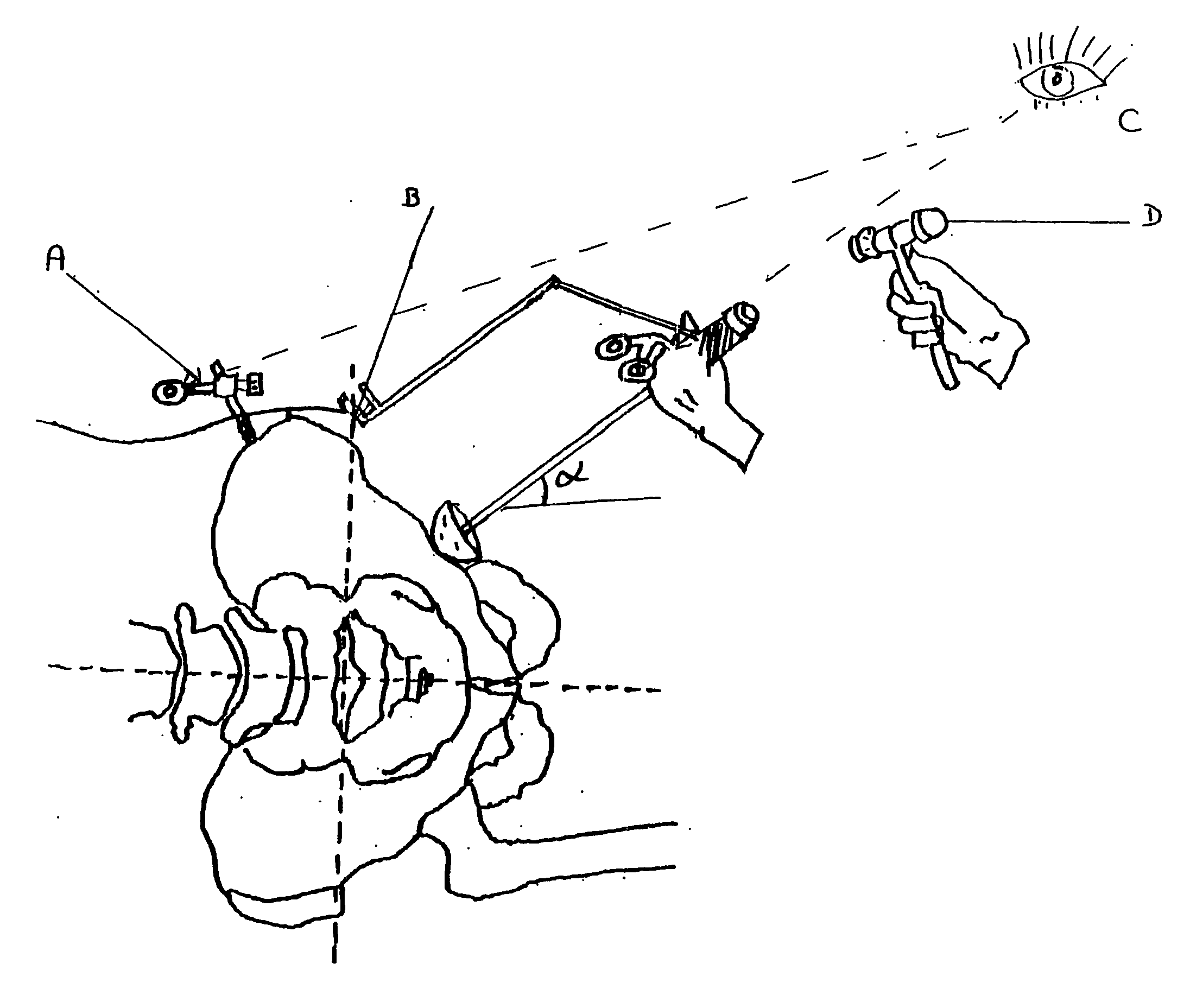
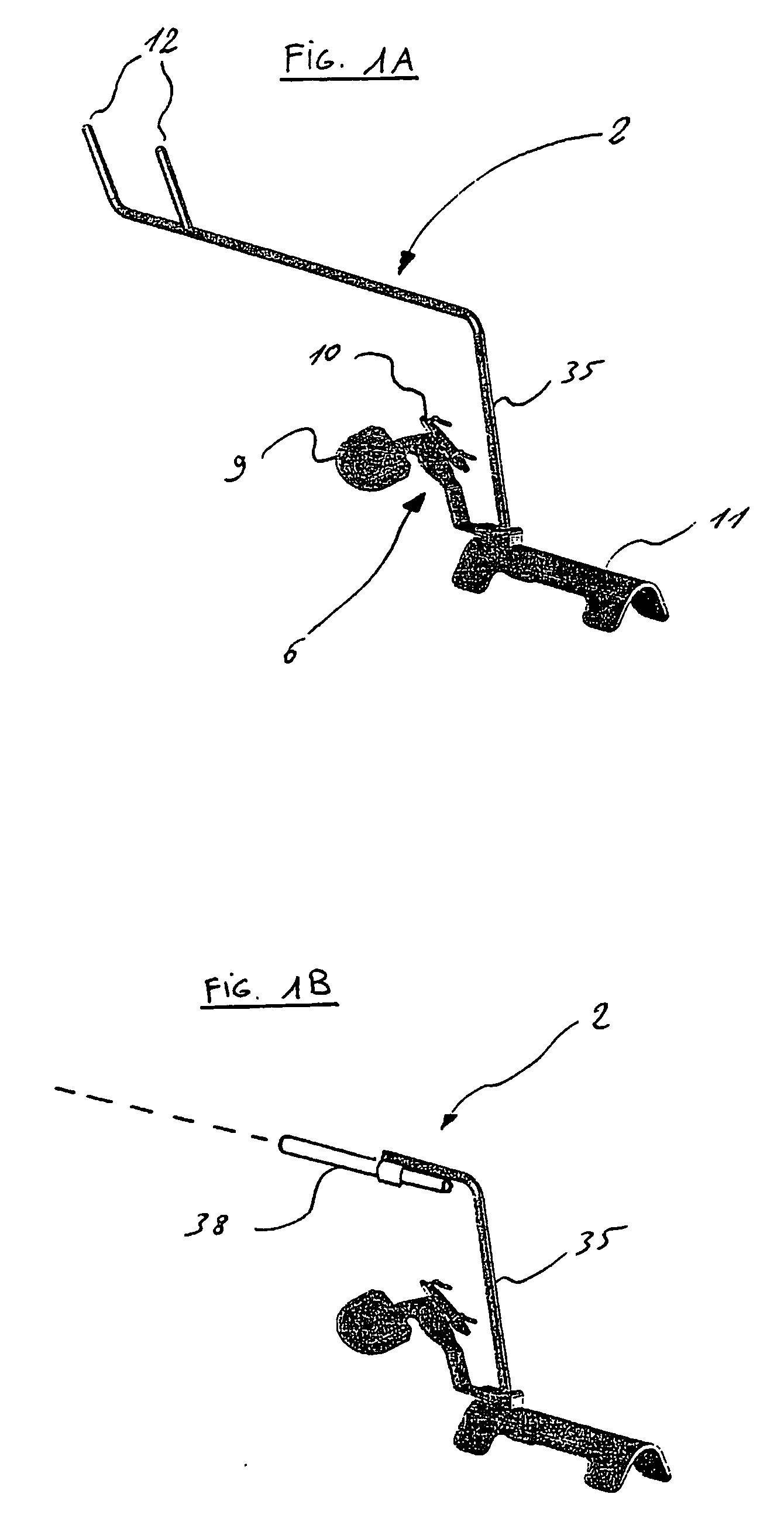
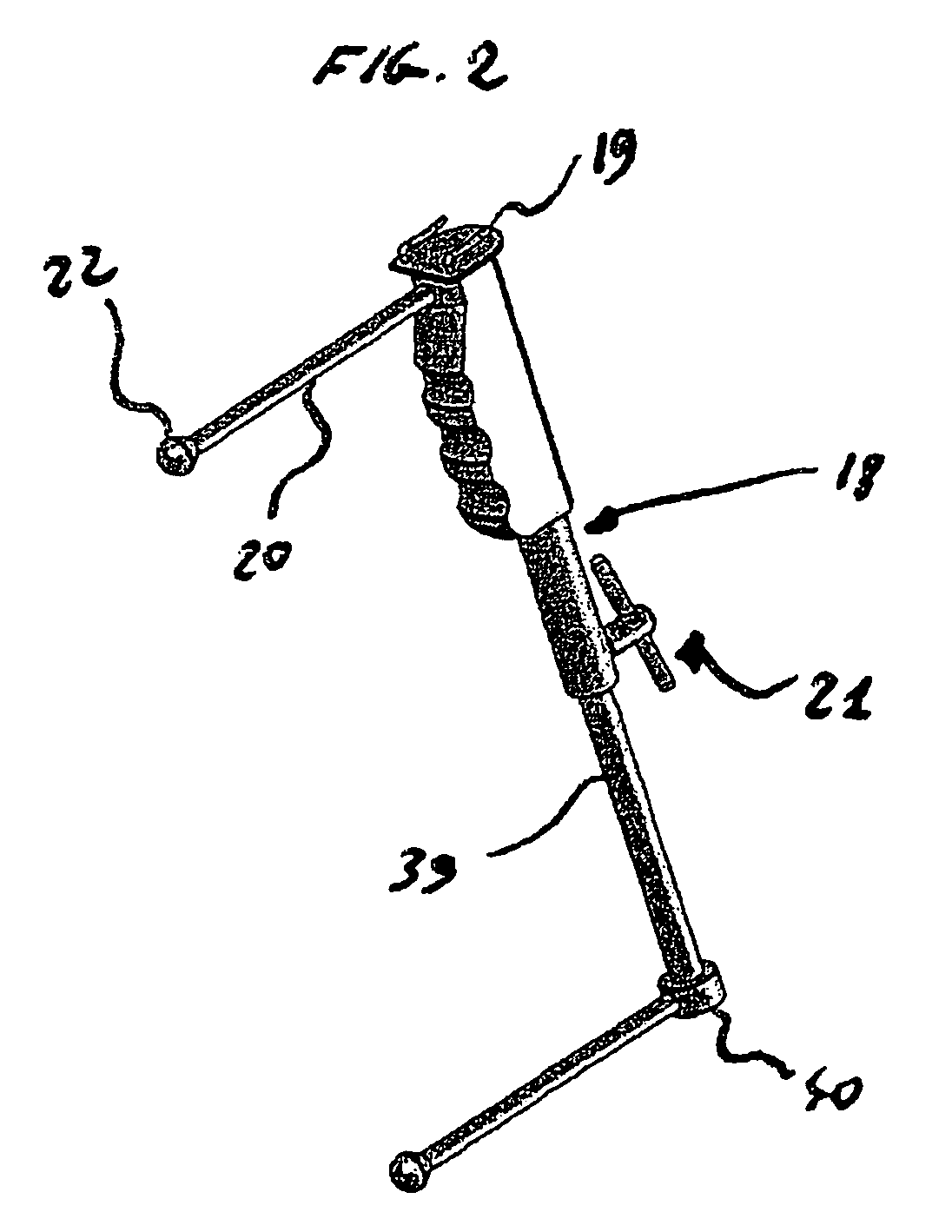
Accessory for implanting a hip endoprosthesis, and method for manipulating the same
Accessory for implantation of a hip joint endoprosthesis, with a manipulation cup, a manipulation joint head with means for orienting the manipulation cup in the acetabulum, and with a device to represent the correctly oriented position of the manipulation cup such that by means of this device a bone-milling cutter and an impact instrument can then oriented appropriately for placement of the prosthesis cup.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Methods, Systems, and Apparatus for Implanting Prosthetic Devices Into Cartilage
ActiveUS20080294266A1Dissipate bone stressDissipate strainJoint implantsAcetabular cupsProsthesisSacroiliac joint
A method of implanting a prosthetic acetabular cup into a patient is disclosed. The method comprises gaining access to an acetabulum of the patient, where the acetabulum includes an inner portion formed of bone and an outer portion formed of articular cartilage. The method also comprises creating a recess within the articular cartilage of the outer portion of the acetabulum without removing any portion of bone from the inner portion of the acetabulum. The recess is shaped to mate with a snap-fit structure of the prosthetic acetabular cup. Finally, the method comprises securely engaging the prosthetic acetabular cup with the acetabulum by snap-fitting the snap-fit structure of the prosthetic acetabular cup with the recess in the articular cartilage of the outer portion of the acetabulum.
Owner:ACTIVE IMPLANTS LLC
Universal Acetabular Guide And Associated Hardware
An orthopedic device includes a patient-specific acetabular guide that may be used for preparing an acetabulum of a patient to receive an acetabular implant. The acetabular guide has a body with an outer three-dimensional surface configured to match an acetabulum of a specific patient's hip joint designed from data of the patient's hip joint. The acetabular guide may further include a peripheral annular rim.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Orthopedic component of low stiffness
ActiveUS20090192610A1Component can be removedReduce the impactBone implantSynthetic resin layered productsAcetabular linerPlastic surgery
An orthopedic component having multiple layers that are selected to provide an overall modulus that is substantially lower than the modulus of known orthopedic components to more closely approximate the modulus of the bone into which the orthopedic component is implanted. In one exemplary embodiment, the orthopedic component is an acetabular shell. For example, the acetabular shell may include an outer layer configured for securement to the natural acetabulum of a patient and an inner layer configured to receive an acetabular liner. The head of a femoral prosthesis articulates against the acetabular liner to replicate the function of a natural hip joint. Alternatively, the inner layer of the acetabular shell may act as an integral acetabular liner against which the head of the femoral prosthesis articulates.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Patient-specific total hip arthroplasty
ActiveUS8932299B2Large range of motionMinimizing reaction forcePhysical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationAcetabular componentPre operative
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for performing total hip arthroplasty with patient-specific guides Pre-operative images of a pelvic region of a patient are taken in order to predefine the structure of the guides and corresponding implants. From the obtained image data an insertional vector for implanting an acetabular implant or component into an acetabulum of the patient is determined, wherein the insertional vector is coaxial with a polar axis of the acetabular component. Also from the obtained image data, a superior surface of the guides and implants can be shaped to match the acetabulum of the patient. A nub portion extending outwardly from the superior surface of the guides and implants is shaped to substantially match the shape of a fovea of the acetabulum. A guide portion of the guides forming a slot has a longitudinal axis coaxial with the determined insertional vector of a corresponding acetabular component.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Non-spherical articulating surfaces in shoulder and hip replacement
An orthopedic device and method of use are provided that incorporate complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces to allow a greater available range of motion compared with existing artificial shoulder joint and artificial hip joints. According to some embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on a humeral head and / or glenoid of a shoulder prosthesis. In other embodiments, complex, non-spherical articulating surfaces can be incorporated on the acetabulum and / or femoral head of a hip prosthesis. These non-spherical surfaces can be used to adjust constraint, joint thickness, soft tissue tension, moment and arc of motion, and in doing so, influence motion.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for passing suture through the labrum of a hip joint in order to secure the labrum to the acetabulum
A suture passer comprising:a handle;a shaft extending distally from the handle;first and second jaw members mounted to the distal end of the shaft, the first jaw member having a suture support for supporting a length of suture;a pitch adjustment mechanism for adjusting the pitch of the first and second jaw members relative to the shaft;a lever mechanism for opening and closing the first and second jaw members relative to one another; anda needle mechanism for selectively urging a needle having a groove therein so that the groove in the needle can engage a length of suture supported by the suture support.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Method and apparatus for determining acetabular component positioning
ActiveUS20090306679A1Solve precise positioningError componentJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringAcetabular componentMedicine
An instrument for establishing orientation of a pelvic prosthesis comprises a tri-pod having an angularly adjustable guide rod on it. The tips of the legs define a plane, and the guide rod is set by the surgeon to a defined orientation with respect to this plane on the basis of preoperative studies. In use, two of the legs of the instrument are positioned by the surgeon at defined anatomical locations on the pelvis (e.g., a point in the region of the posterior / inferior acetabulum and a point on the anterior superior iliac spine). The third leg then lands on the pelvis at a point determined by the position of the first two points, as well as by the separations between the third leg and the other two legs. The separations are adjustable, but are preferably fixed percentages of the separation between the first and second legs. The position of the guide rod then defines with respect to the actual pelvis the direction for insertion of a prosthesis.
Owner:MURPHY STEPHEN B
Innominate osteotomy
InactiveUS20020092532A1Expand coverageConcentric reductionDiagnosticsOsteosynthesis devicesThalamusCoxal joint
This invention provides a surgical method to treat hip diseases, including Legg-Calve-Perthes disease or developmental hip dysplasia. This method includes several surgical techniques: a transverse osteotomy of the posterior portion of supraacetabular portion, an oblique and inclined osteotomy of the anterior portion of the supraacetabulum, detachment of a bone block from iliac crest, anterolateral displacement of the distal fragment, and insertion of the bone block into the distracted space of the osteotomy site.
Owner:YOON TAEK RIM
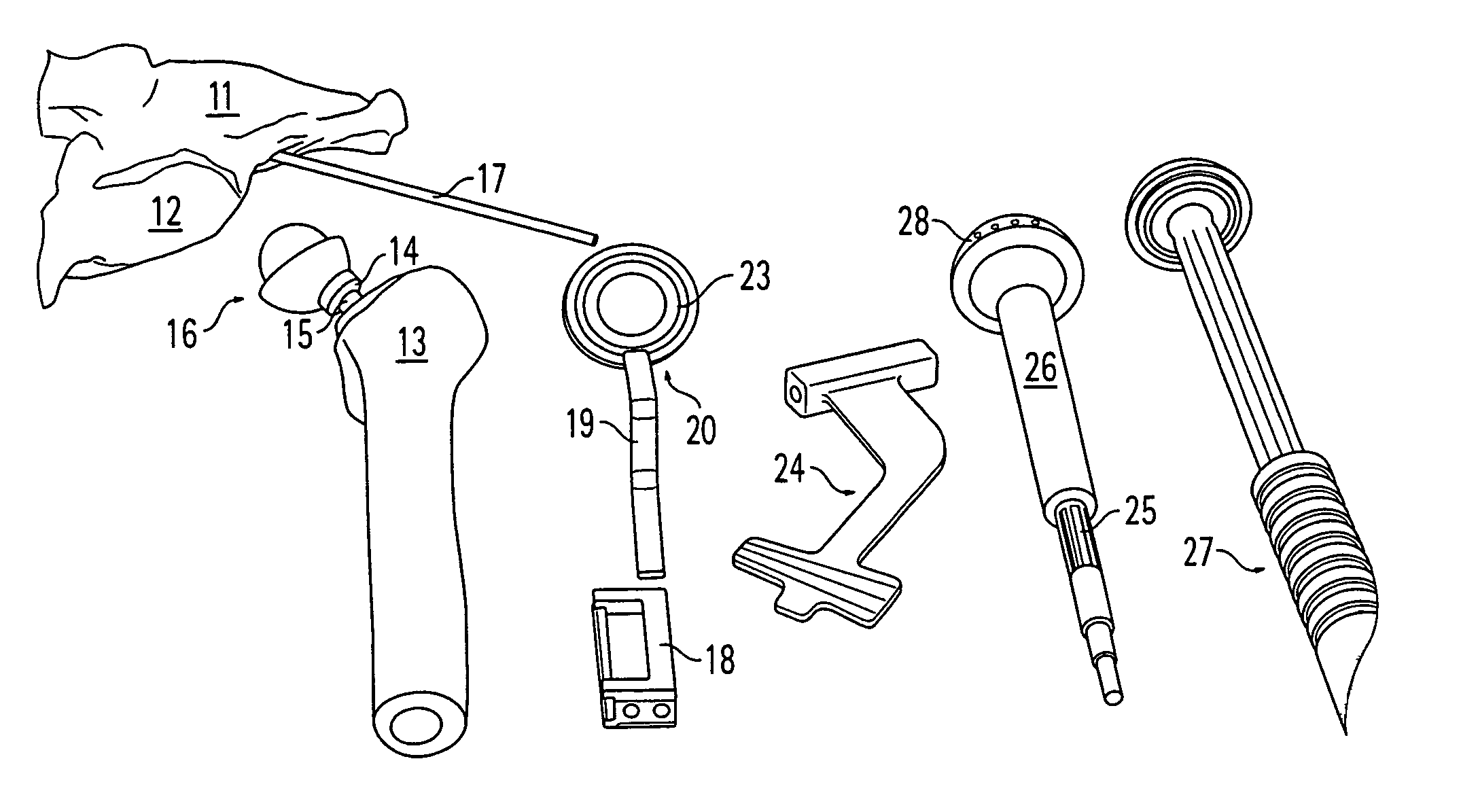
Elongated driving bit attachable to a driving instrument and method of use for minimally invasive hip surgery
InactiveUS6875218B2Short incisionLow costInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsAcetabular componentProsthesis
A method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive hip surgery for implanting a prosthetic acetabular component into a natural acetabulum. The method and apparatus include a driving bit having one end connectable to an angled driving instrument and another end connectable to a screw-hole plug, dome plug, or bone screw. The driving bit has an elongated body with a length adapted for use in minimally invasive acetabular surgery.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
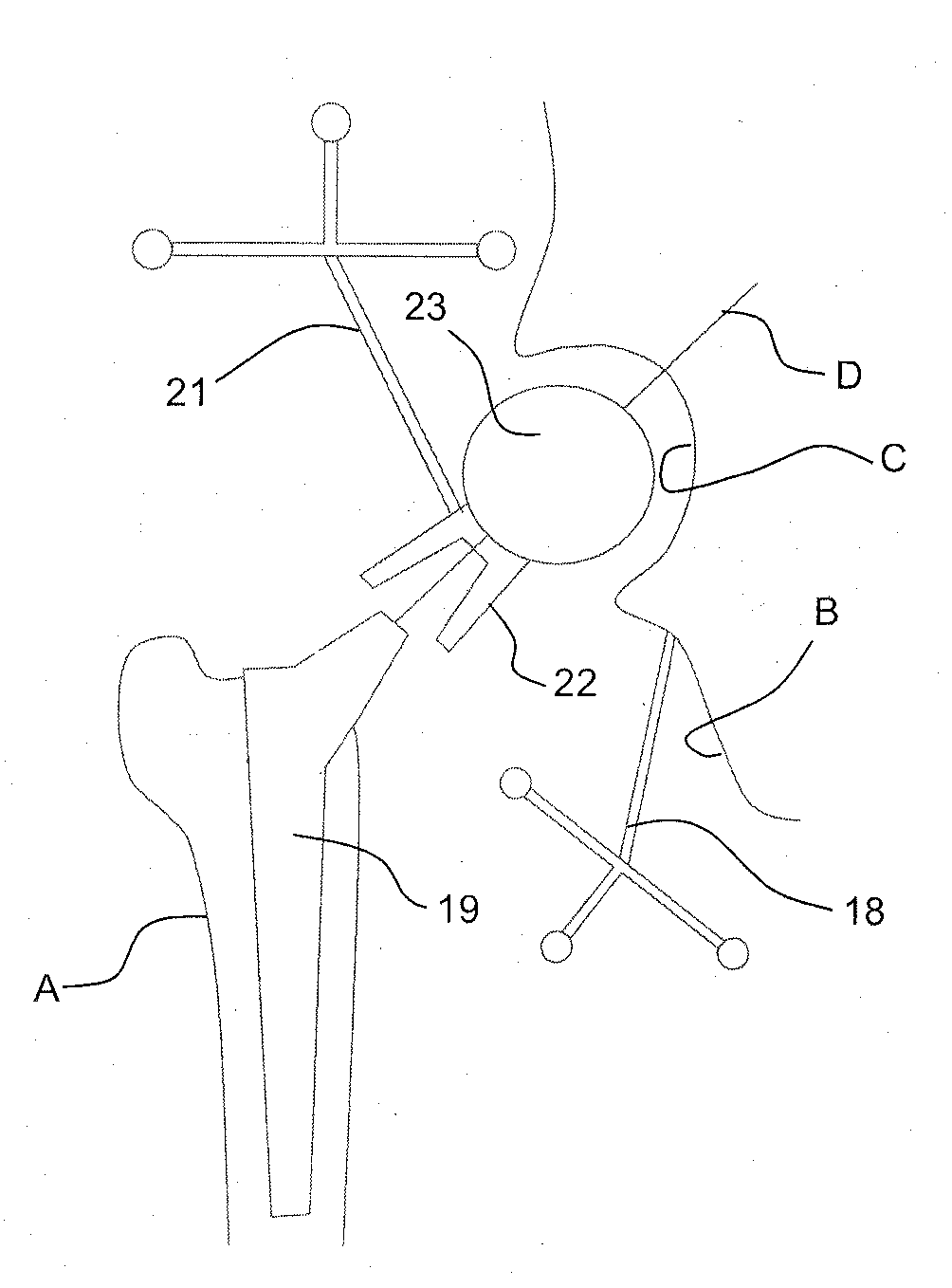
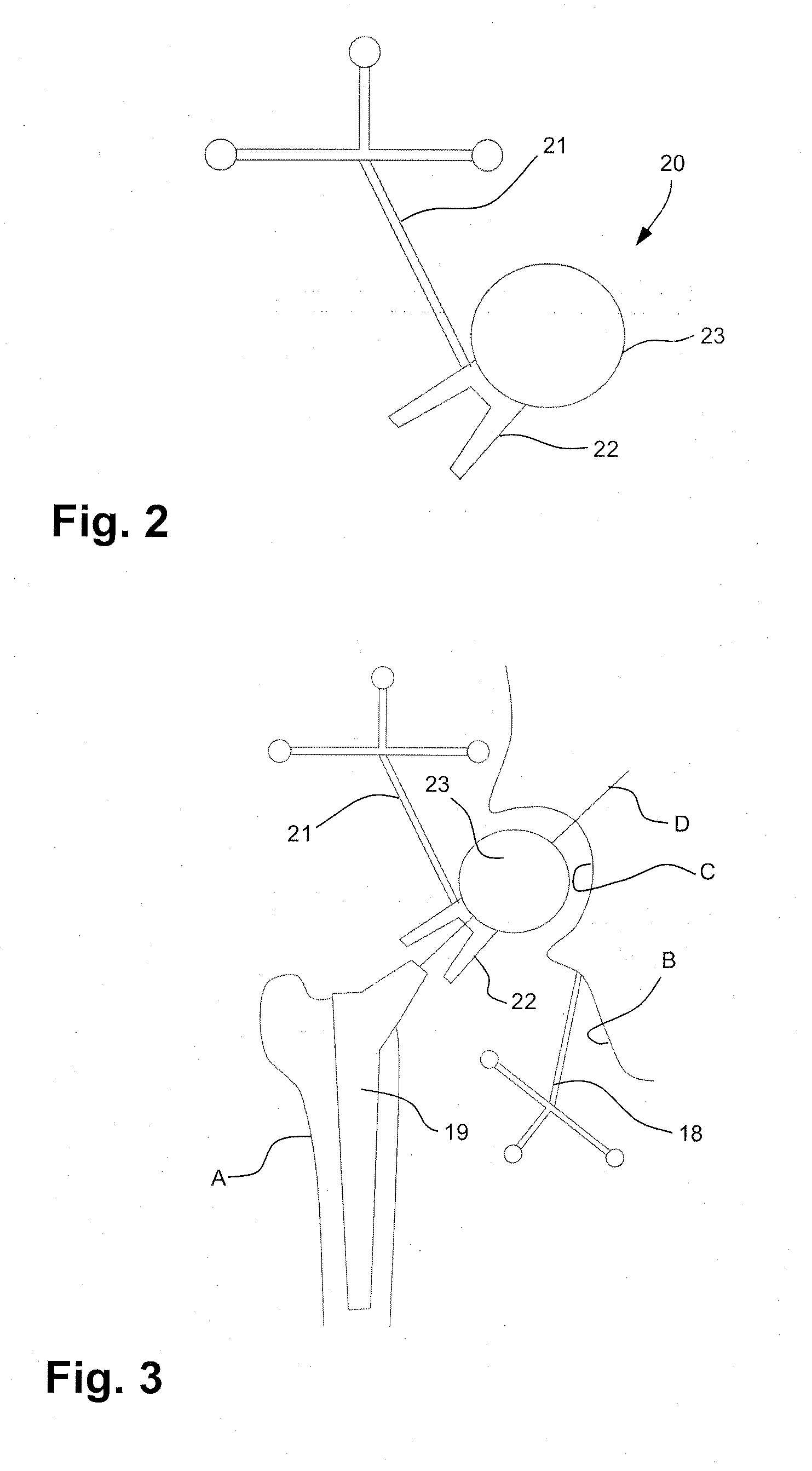
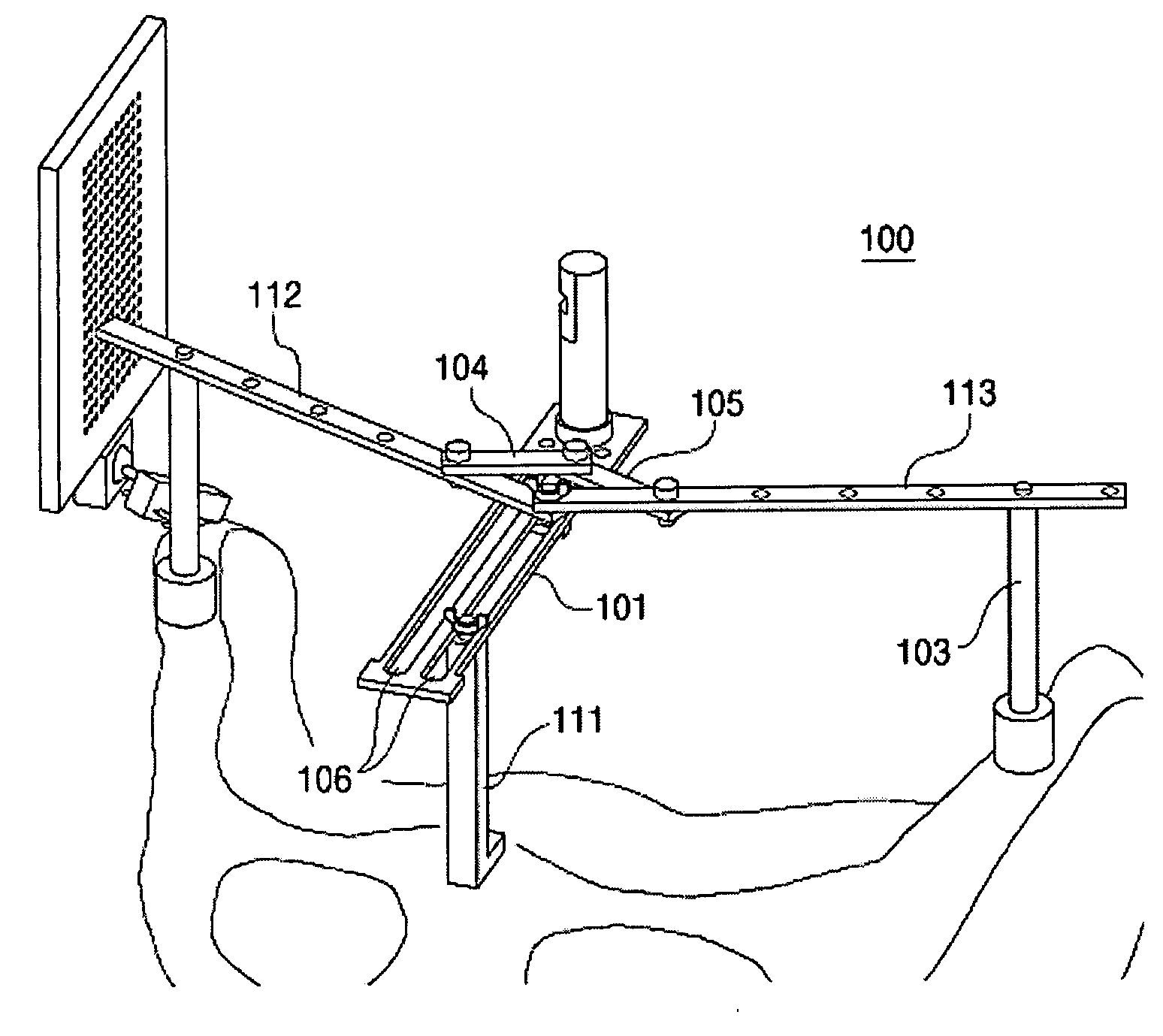
Hip replacement in computer-assisted surgery
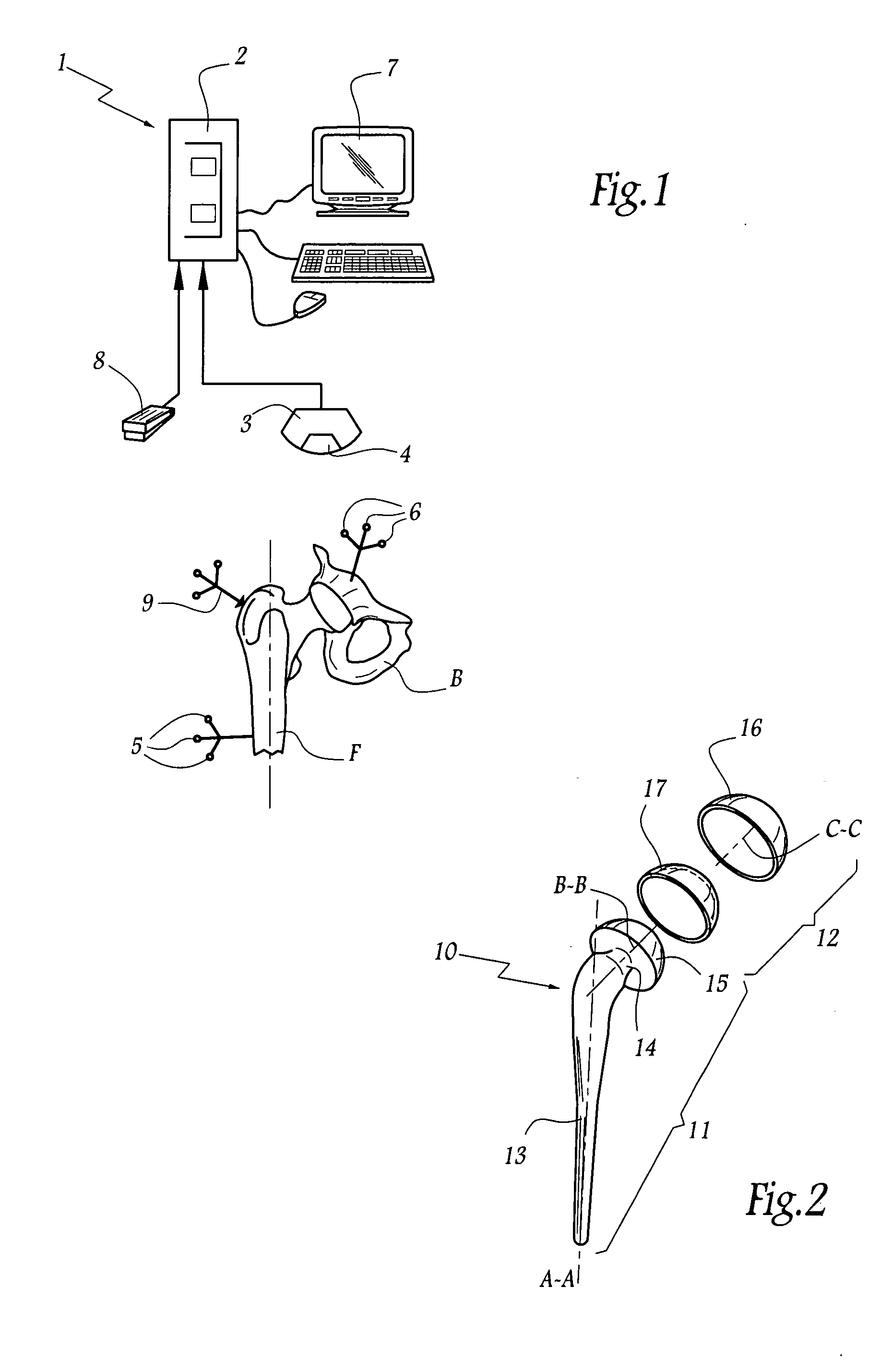
A system for calculating a position and orientation of an acetabular cup in computer-assisted surgery comprises a first trackable reference secured to a pelvis, with a frame of reference being associated with the first trackable reference. A device is positionable between a femoral neck and the acetabulum of the pelvis in a known relation, the device having a second trackable reference. Sensors track the trackable references for position and orientation. A position / orientation calculator calculates a position and orientation of the frame of reference and of the device and for determining an orientation of the neck axis with respect to the frame of reference from the known relation at a desired position of the femur. An implant position / orientation calculator provides cup implanting information with respect to the orientation of said neck axis as a function of the tracking for position and orientation of at least the first trackable reference.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Apparatus and methods for bone surgery
InactiveUS20050059978A1Joint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRight femoral headLeft femoral head
The surgeon grasps the jig by its handle and manipulates the head of the jig through the patient wound and onto the femoral neck. The head of the jig includes jig location means in the form of an elongate rod which acts as a spacer. The spacer has an end which abuts the trochanteric fossa so as to position the slot of the jig at the required position, which is between 5 mm and 25 mm, and most preferably 15 mm, from the trochantic fossa. Additional jig location means are provided by a surface adapted to receive a bone formation. This surface is provided by contours on the base of the head which are adapted to mate with contours of the femur. The slot is oriented generally perpendicularly to the elongate dimension of the rod. The slot functions as a surgical tool guide means which is positioned by the jig at the correct position for osteotomisation of the neck. Advantageously, osteotomisation takes place while the femoral head is still disposed within the acetabulum.
Owner:INT PATENT OWNERS CAYMAN
Navigation System for Hip Replacement Surgery Having Reference Mechanism and Method Using the Same
InactiveUS20090171370A1Simple structureDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsAirplaneAnterior pelvic plane
A navigation system for an acetabular cup, which guides an insertion orientation of the acetabular cup inserted into a pelvis during a total hip replacement surgery, includes: a pelvis position tracer which includes probes in contact with three particular points of the pelvis placed on an anterior pelvic plane and a first reference mechanism disposed to indicate a specific reference plane when the probes come in contact with the particular points; and a pelvis position indicator which is fixed to the pelvis, and includes a second reference mechanism that is adjustable to indicate a plane parallel to the specific reference plane indicated by the first reference mechanism, or to indicate a plane perpendicular thereto, or to indicate the both planes. Accordingly, an insertion orientation of an acetabular cup can be guided by using a reference mechanism having a simple structure, and the acetabular cup can be accurately guided regardless of changes in the patient's pelvic position during surgery, because a plane used in the insertion of the acetabular cup can be indicated continuously.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com