Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "Patient Motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
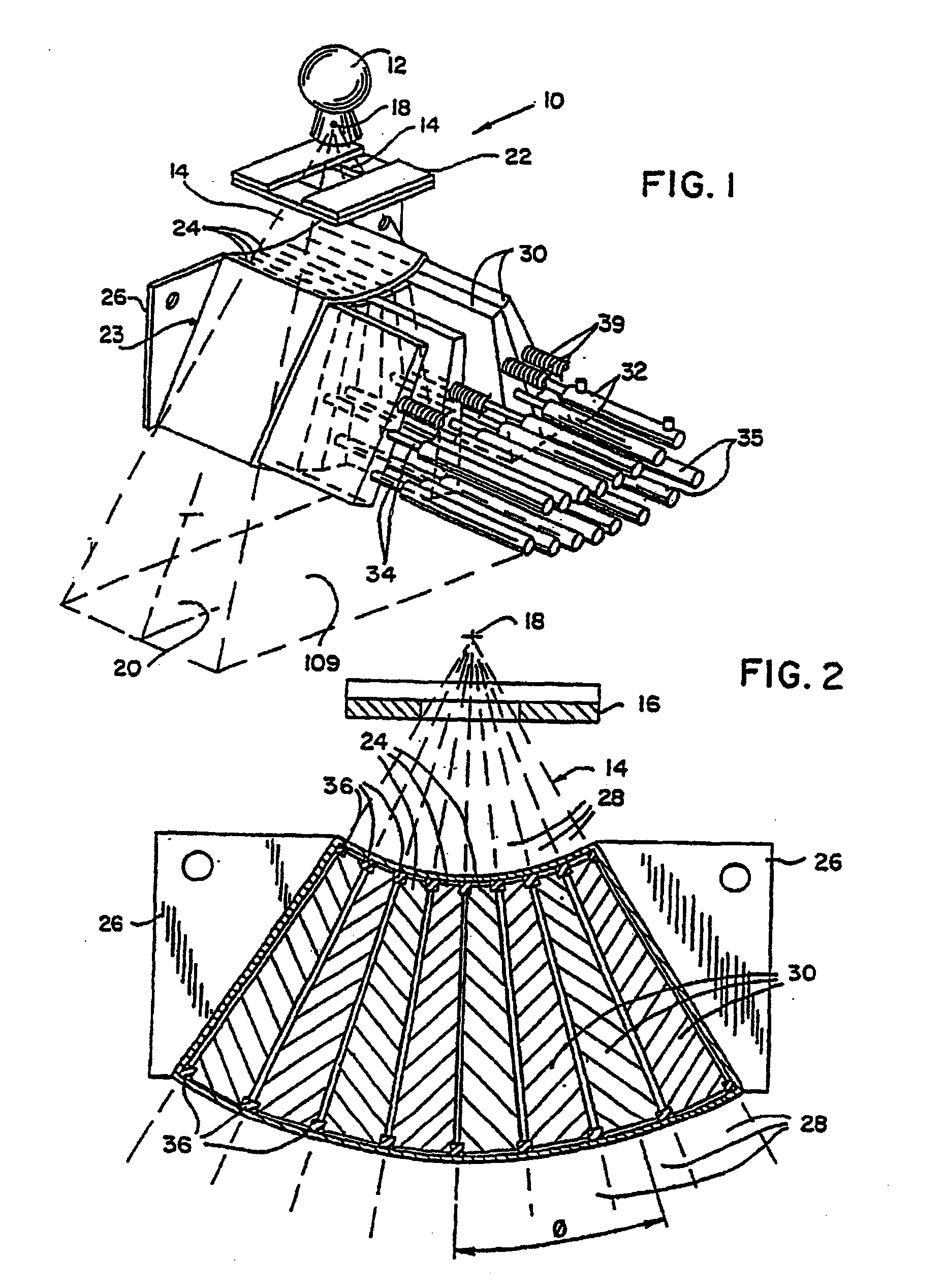
Apparatus and method for compensating for respiratory and patient motion during treatment
An apparatus and method for performing treatment on an internal target region while compensating for breathing and other motion of the patient is provided in which the apparatus comprises a first imaging device for periodically generating positional data about the internal target region and a second imaging device for continuously generating positional data about one or more external markers attached to the patient's body or any external sensor such as a device for measuring air flow. The apparatus further comprises a processor that receives the positional data about the internal target region and the external markers in order to generate a correspondence between the position of the internal target region and the external markers and a treatment device that directs the treatment towards the position of the target region of the patient based on the positional data of the external markers.
Owner:ACCURAY
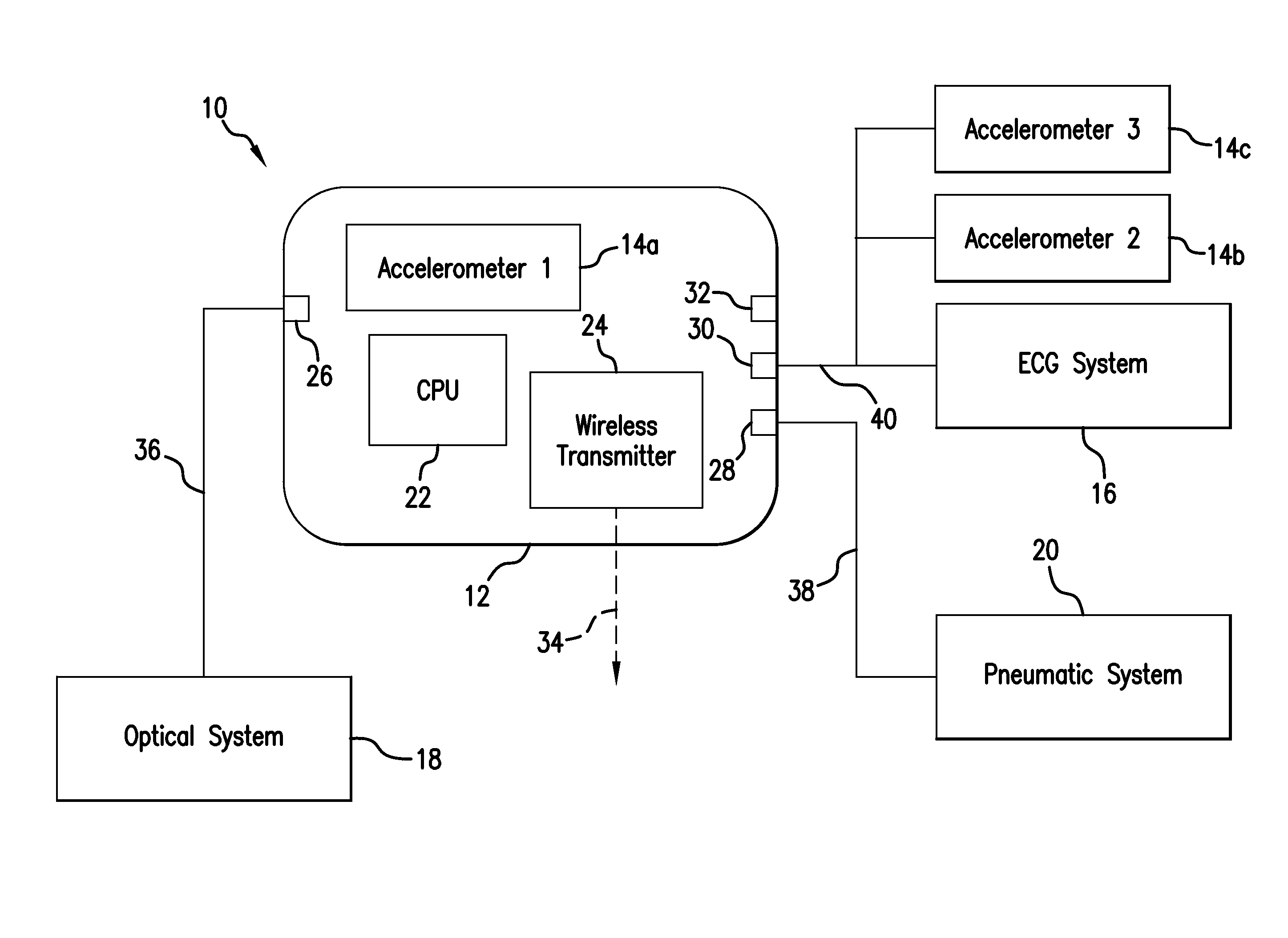
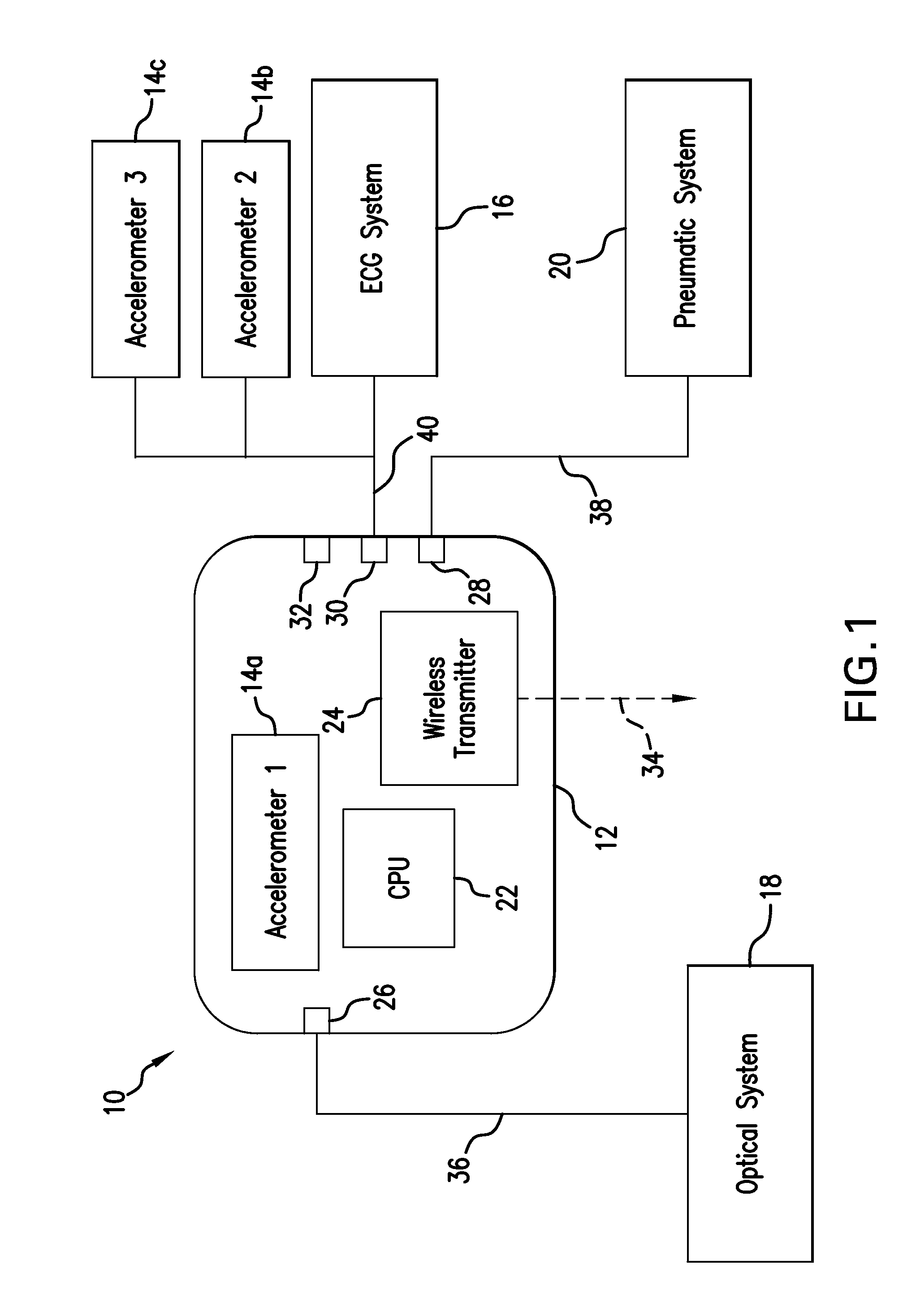
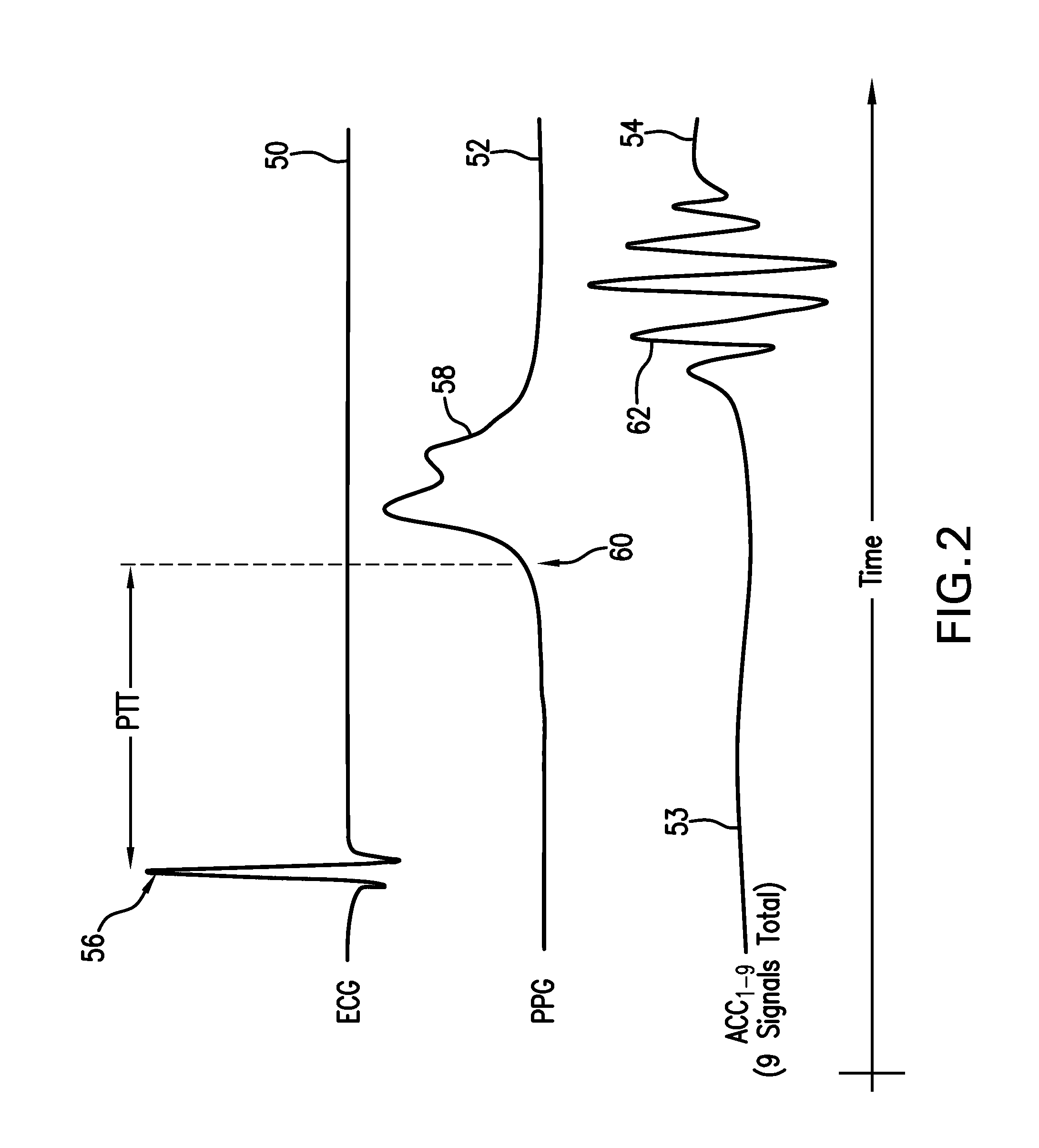
Method for measuring patient motion, activity level, and posture along with ptt-based blood pressure
ActiveUS20100298653A1Useful characteristicElectrocardiographyPerson identificationMotion parameterActivity level
The invention provides a system and method for measuring vital signs (e.g. SYS, DIA, SpO2, heart rate, and respiratory rate) and motion (e.g. activity level, posture, degree of motion, and arm height) from a patient. The system features: (i) first and second sensors configured to independently generate time-dependent waveforms indicative of one or more contractile properties of the patient's heart; and (ii) at least three motion-detecting sensors positioned on the forearm, upper arm, and a body location other than the forearm or upper arm of the patient. Each motion-detecting sensor generates at least one time-dependent motion waveform indicative of motion of the location on the patient's body to which it is affixed. A processing component, typically worn on the patient's body and featuring a microprocessor, receives the time-dependent waveforms generated by the different sensors and processes them to determine: (i) a pulse transit time calculated using a time difference between features in two separate time-dependent waveforms, (ii) a blood pressure value calculated from the time difference, and (iii) a motion parameter calculated from at least one motion waveform.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Biomedical positioning and stabilization system
InactiveUS20070129634A1Minimal effortGood flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresPrimary operation
This invention provides a support device that allows the adjustable, yet rigid placement of a probe or other medical instrument against a region of interest / treatment on a patient. The system and method of rigid fixation, positioning, and adjustment contemplated herein is useful for a broad array of medical procedures including, but not limited to, ultrasound-guided anesthetic delivery. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a flexible armature is attached to a rigid stand placed upon the floor, or attached to another stable surface such as a bed rail, wall, ceiling or piece of equipment. A joint connects the armature to an instrument holder able to accommodate and rigidly attach an ultrasound sensing probe or other medical device. The medical device then remains rigidly attached to the described invention during the procedure. Furthermore, this set position is resistant to minor patient motion or other disturbances. If required, small alterations can be made by the operator during the procedure with minimal effort. Such adjustment may be desirable, for example, if access to a new anatomical structure is needed. In this manner, the primary operator is able to maintain a ‘hands-free’ approach.
Owner:WELLAN MEDICAL SOLUTIONS +1
Adjusting acquisition protocols for dynamic medical imaging using dynamic models
ActiveUS20100183206A1More standardizedBetter quantifiableImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic modelsHemodynamics
The invention relates to automatically adjusting an acquisition protocol for dynamic medical imaging, such as dynamic CT, MRI or PET imaging. The protocols are adjusted based on anatomic and dynamic models (10, 12, 14) which are individualized or fitted to each patient based on a scout scan (6, 8). The adjustment can compensate for changes in the patient due to patient motion (e.g. breathing or heartbeat) or flow of contrast or tracing agent during the sequence. This ensures that changes in the reconstructed images are indicative of pathological changes in the patient and not caused by patient motion or changes in scanning parameters or timing. The dynamic model can be a motion model (12) used to predict the motion of anatomic / physiologic features, typically organs, during scanning, or a haemodynamic model (14) used to predict flow of the contrast agent allowing for precise timing of the scanning sequence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Versatile stereotactic device and methods of use
InactiveUS6684098B2Easy to checkEasily and repeatedly examinedDiagnostic markersComputer-aided planning/modellingFollow up examinationResonance
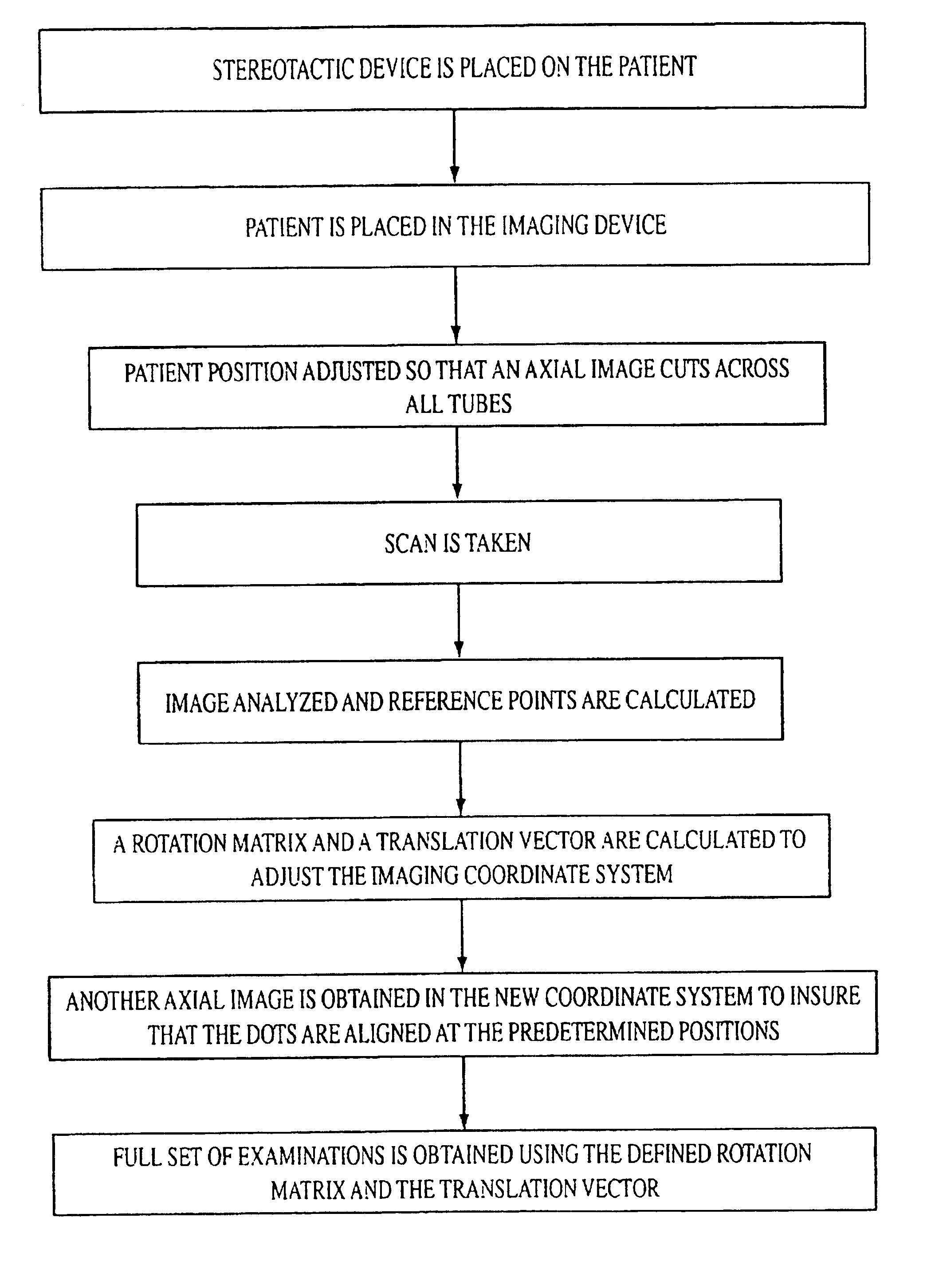
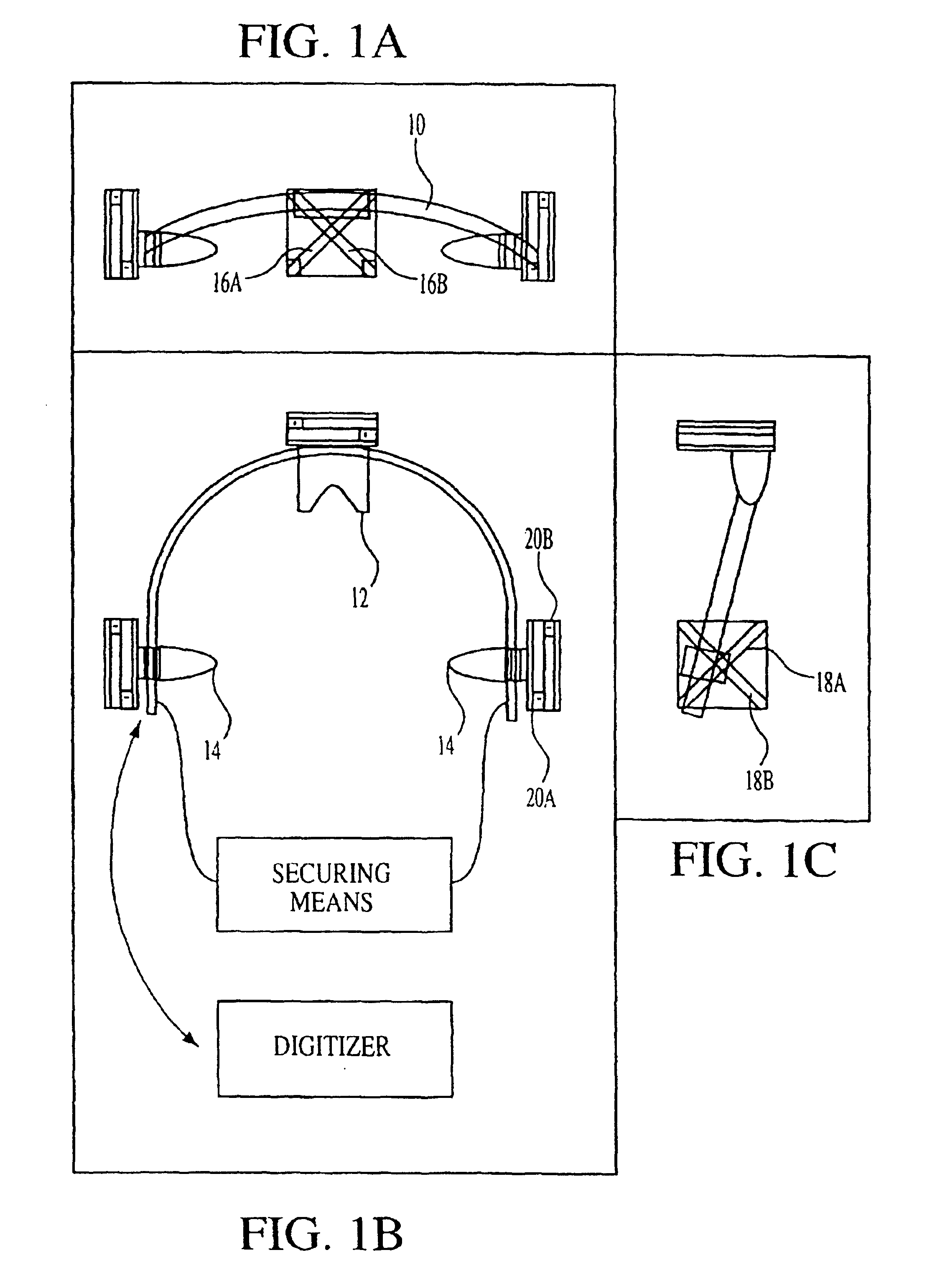
A stereotactic device for use with an imager such as a magnetic resonance imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation. Markers on a stereotactic device can be tracked during an MRI scan to compensate for patient motion during the scan.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Medical sensor and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to provide output to indicate when the sensor experiences abnormal forces or pressure. The forces may be outside forces, or the forces may be generated by patient motion. A sensor system as provided may also be adapted to correct for such forces when calculating measurements related to a physiological characteristic.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Blood pressure-monitoring system with alarm/alert system that accounts for patient motion
ActiveUS20100298654A1Useful characteristicElectrocardiographyPerson identificationRespiratory rateMicroprocessor
The invention provides a system and method for measuring vital signs (e.g. SYS, DIA, SpO2, heart rate, and respiratory rate) and motion (e.g. activity level, posture, degree of motion, and arm height) from a patient. The system features: (i) first and second sensors configured to independently generate time-dependent waveforms indicative of one or more contractile properties of the patient's heart; and (ii) at least three motion-detecting sensors positioned on the forearm, upper arm, and a body location other than the forearm or upper arm of the patient. Each motion-detecting sensor generates at least one time-dependent motion waveform indicative of motion of the location on the patient's body to which it is affixed. A processing component, typically worn on the patient's body and featuring a microprocessor, receives the time-dependent waveforms generated by the different sensors and processes them to determine: (i) a pulse transit time calculated using a time difference between features in two separate time-dependent waveforms, (ii) a blood pressure value calculated from the time difference, and (iii) a motion parameter calculated from at least one motion waveform.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
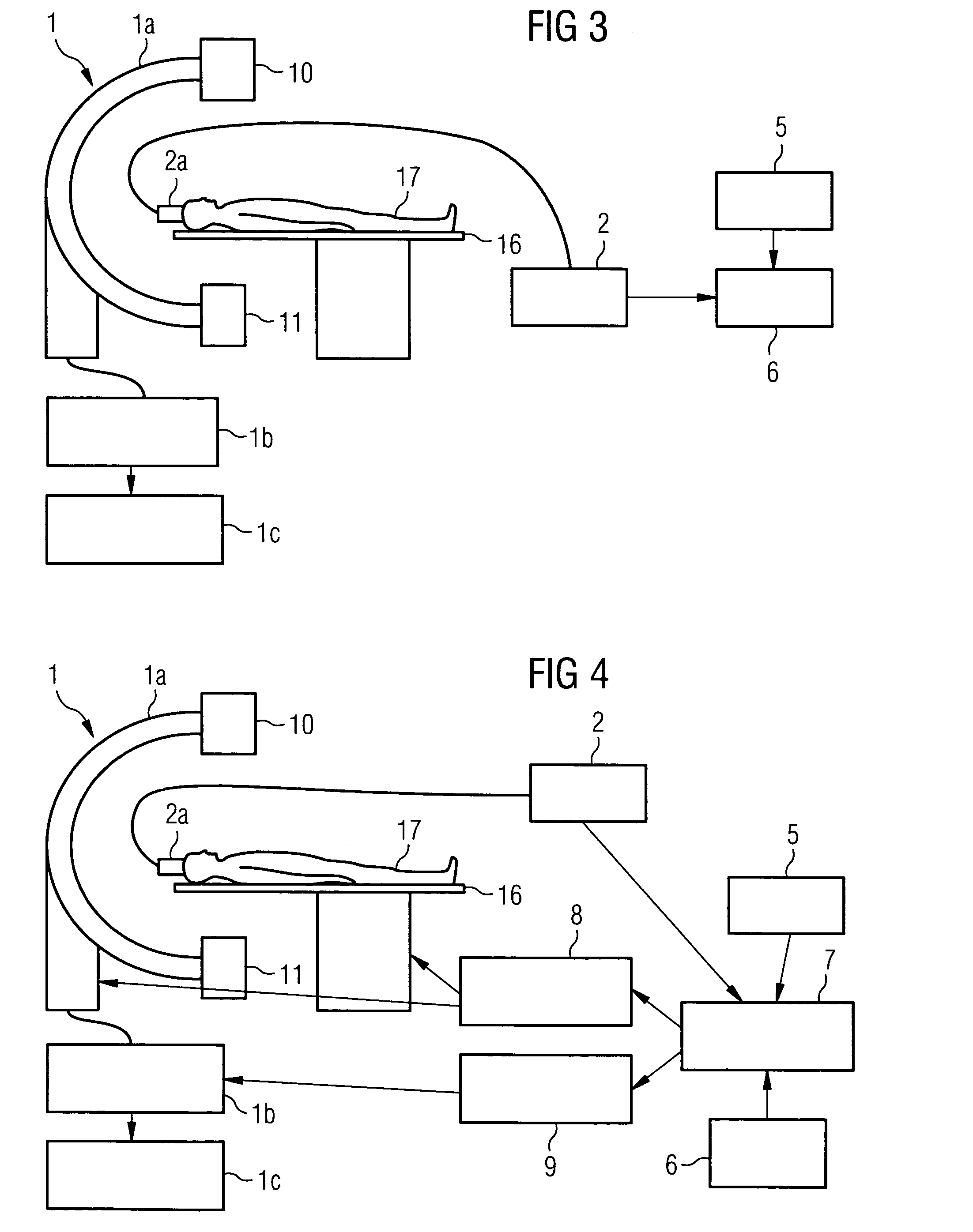
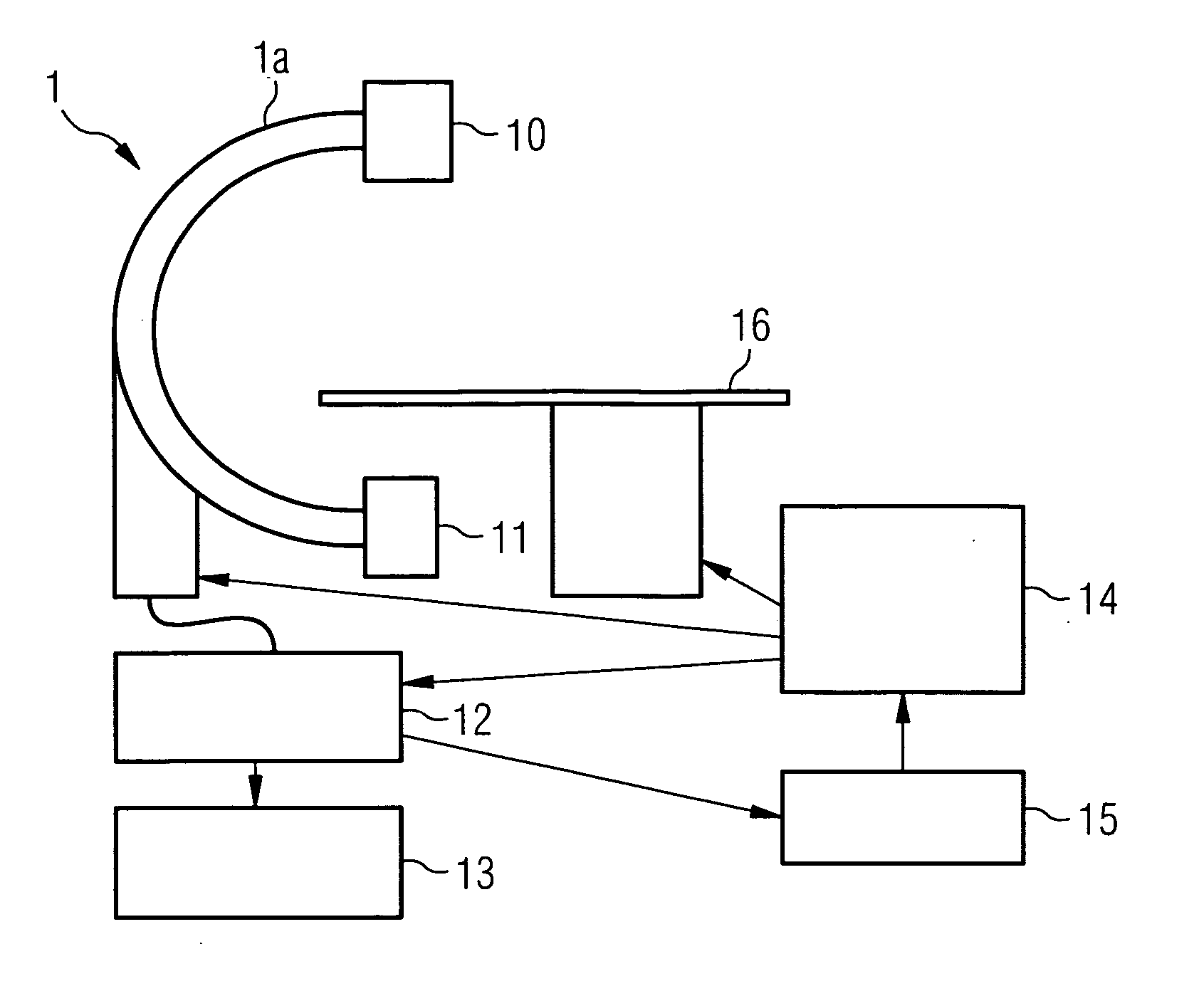
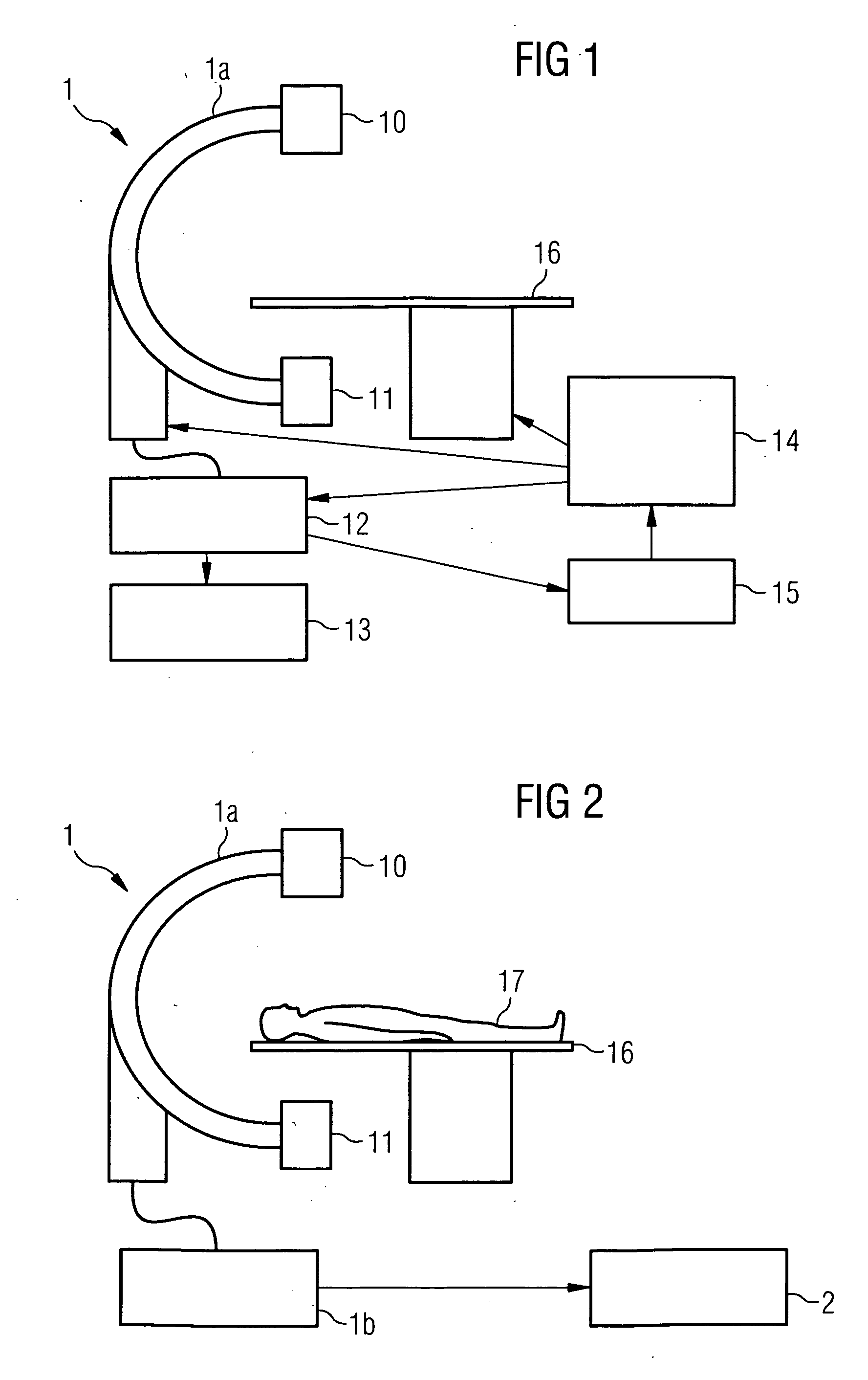
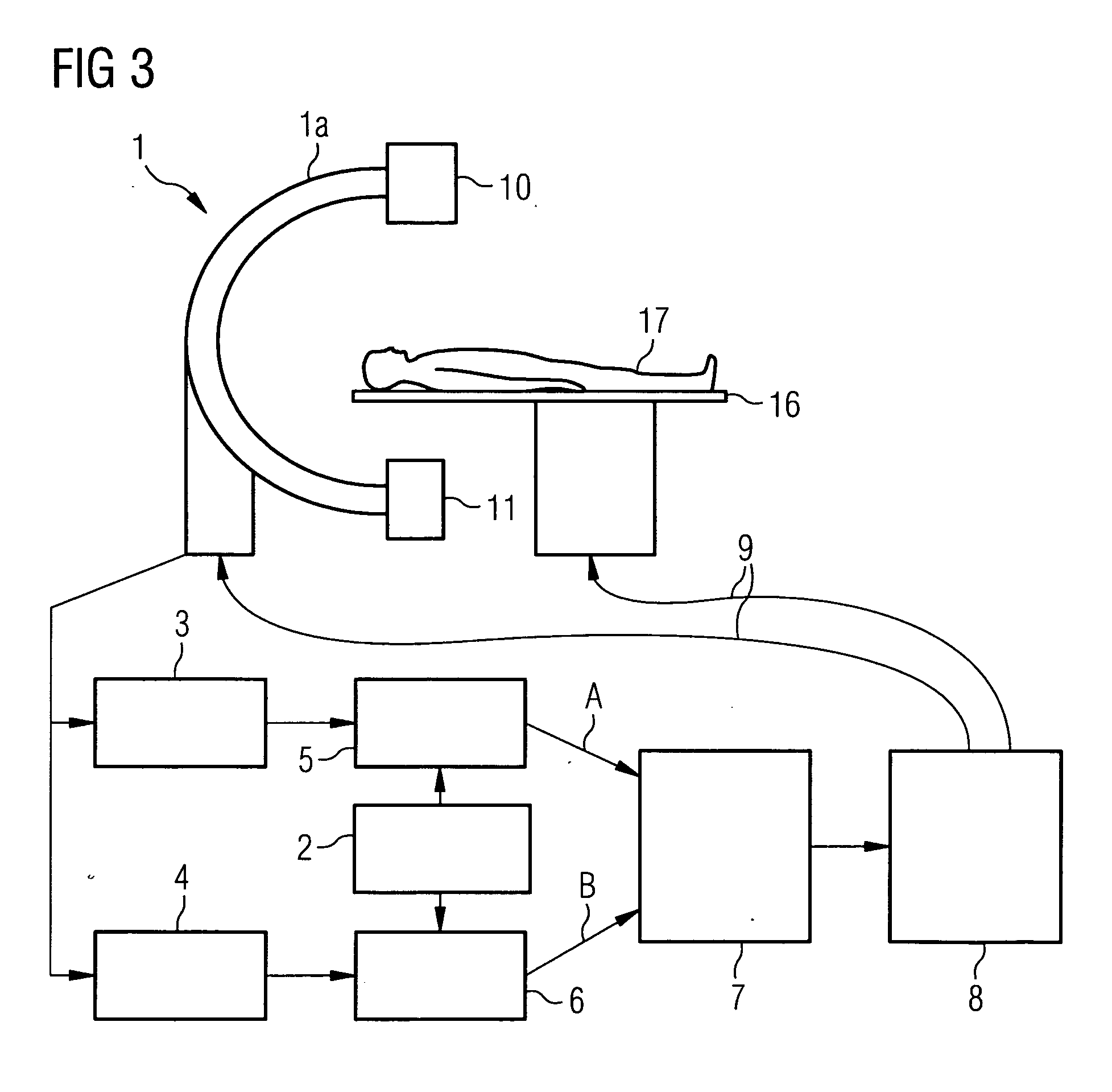
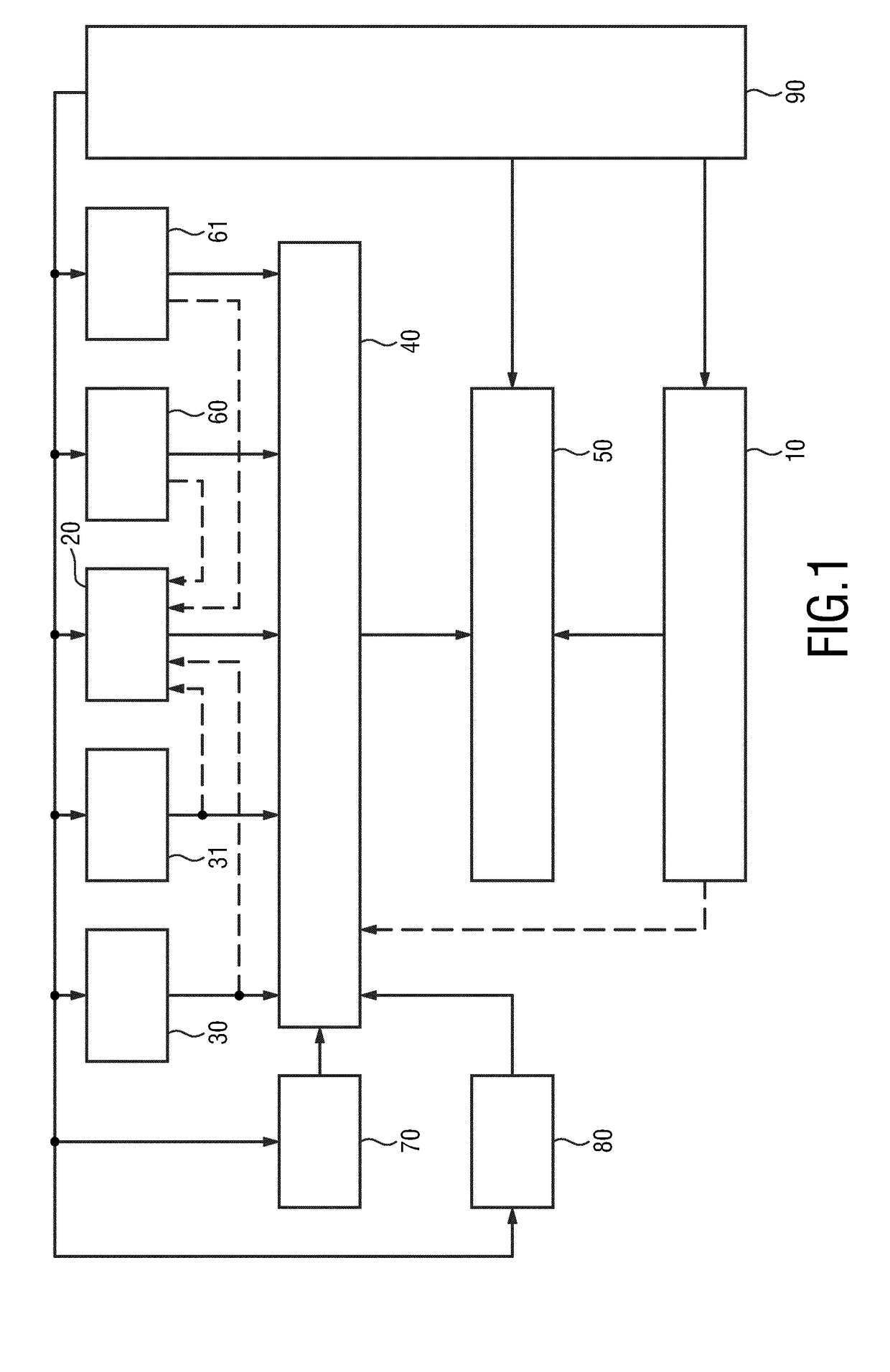
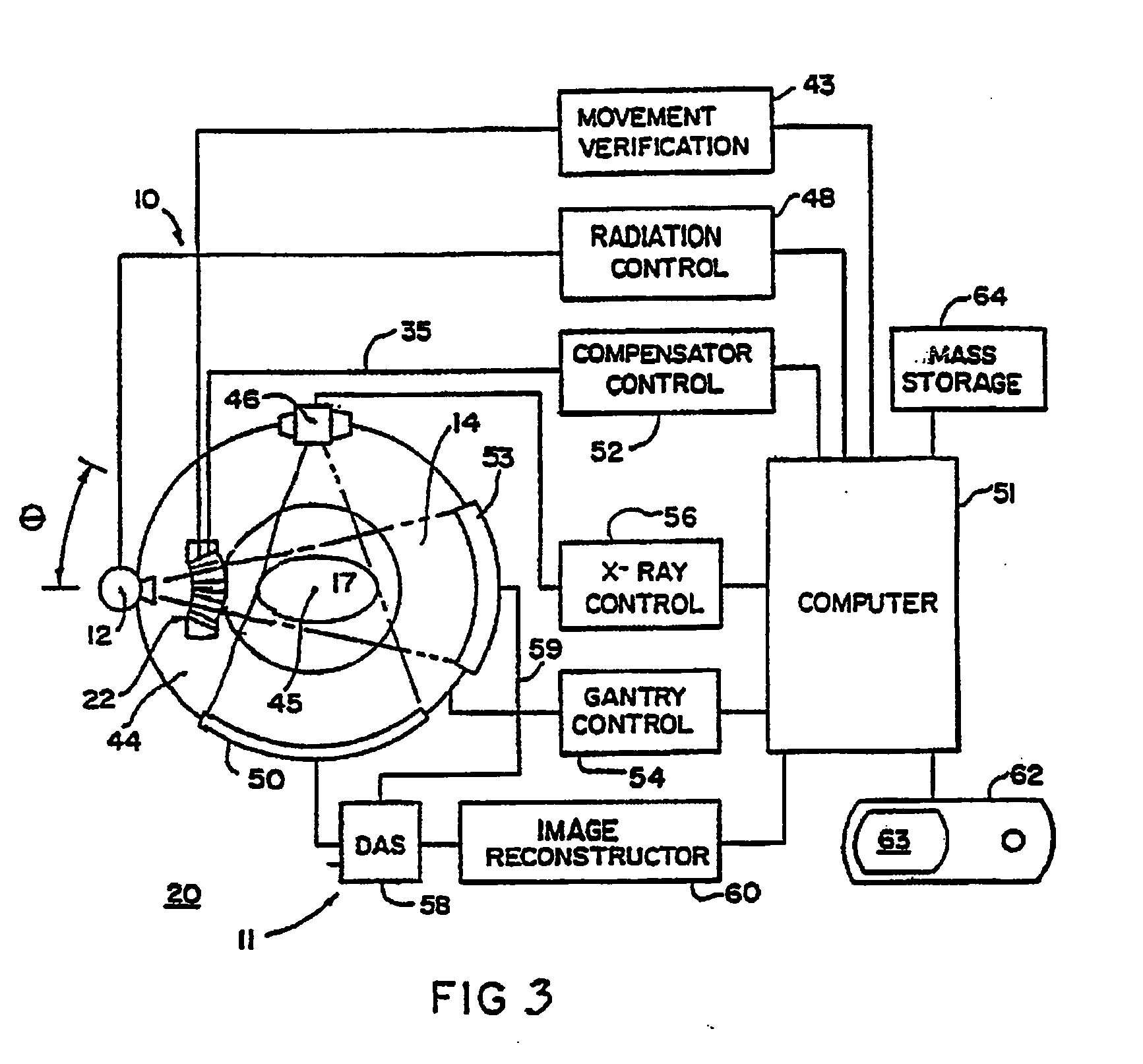
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS7421061B2Improving Imaging ResultsMotion compensationPatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringLocalization systemMedical imaging
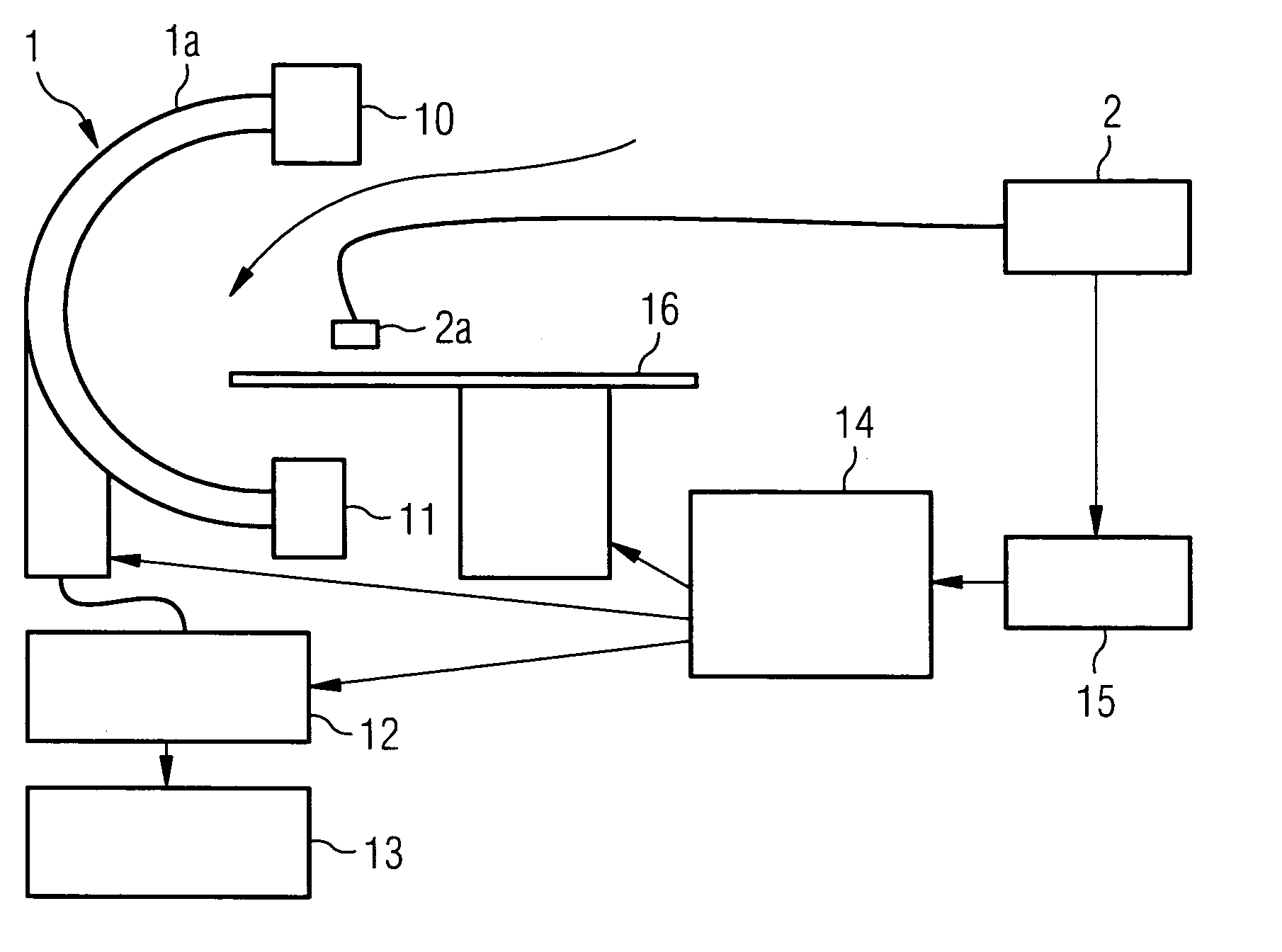
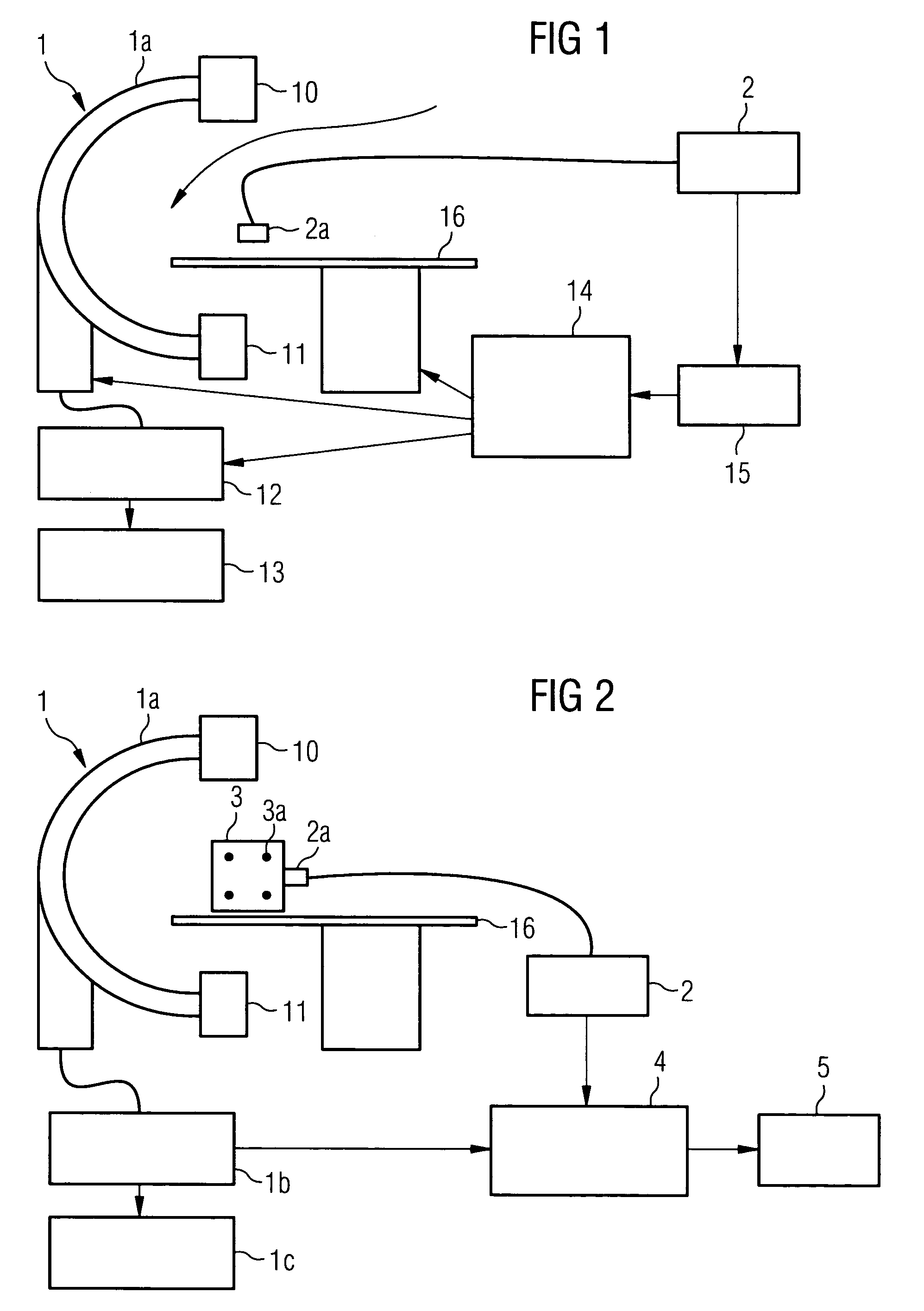
The present invention relates to a method and also an imaging system to compensate for patient motion when recording a series of images in medical imaging, in which a number of images of an area under examination of a patient (17) are recorded at intervals with an imaging system (1) and are related to one another. With the method a localization system (2) is used as the series of images are being recorded to permanently or at a time close to the recording of the individual images, record a momentary spatial location of the area under examination in a reference system permanently linked to the imaging system (1), a first spatial location of the area under examination recorded close to the time of recording of a first image is stored, and a deviation of the images recorded momentarily in each case of the first spatial location is determined and by changing the geometrical circumstances of the imaging system (1) at a time to close the recording of the spatial location and / or through geometrical adaptation of an image content of an image just recorded, is at least approximately commentated for, so that the images show the area under examination in the same position and orientation. The method does not require any time-consuming interaction with the operator and is also suitable for compensating for larger movements of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
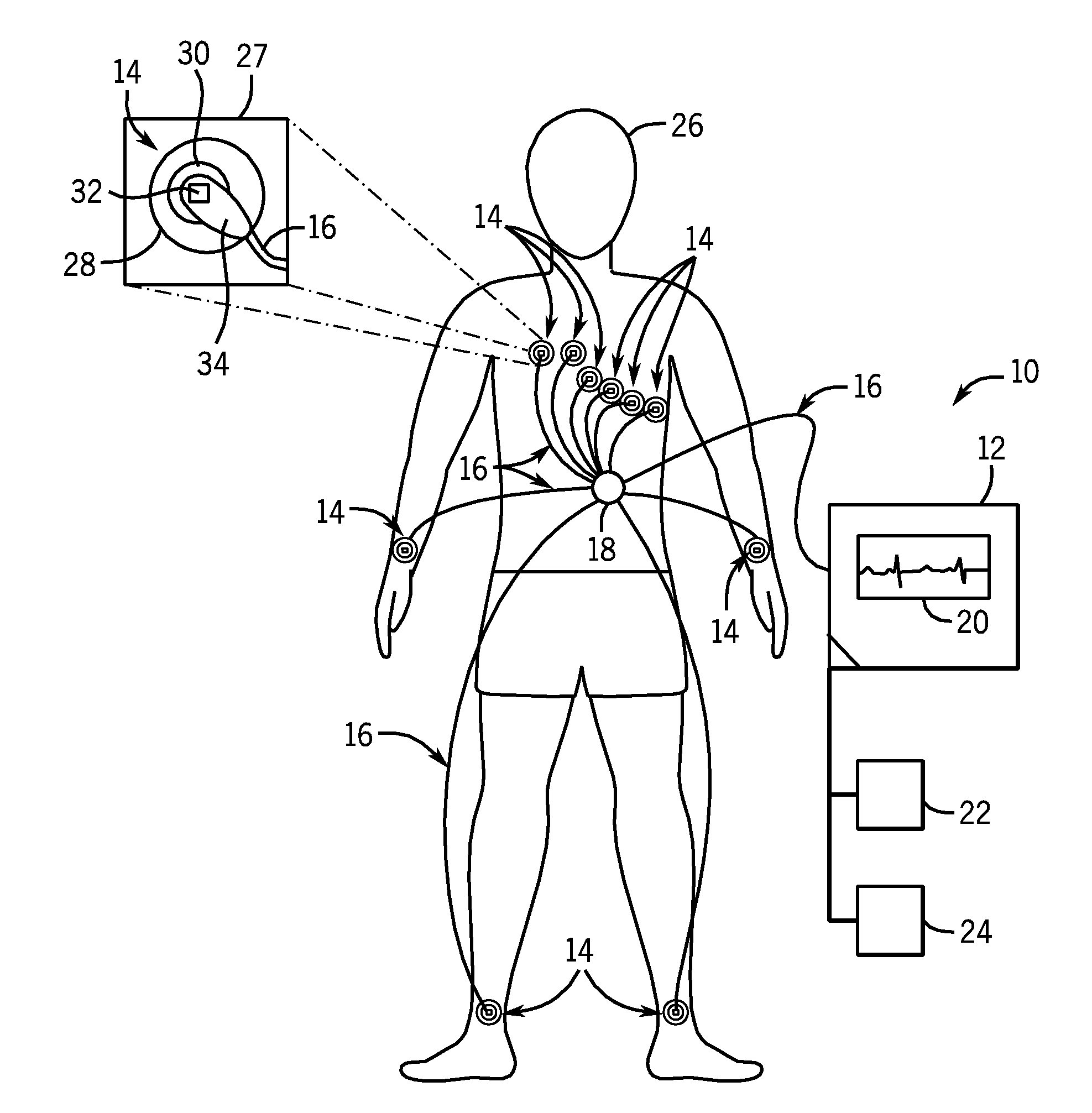
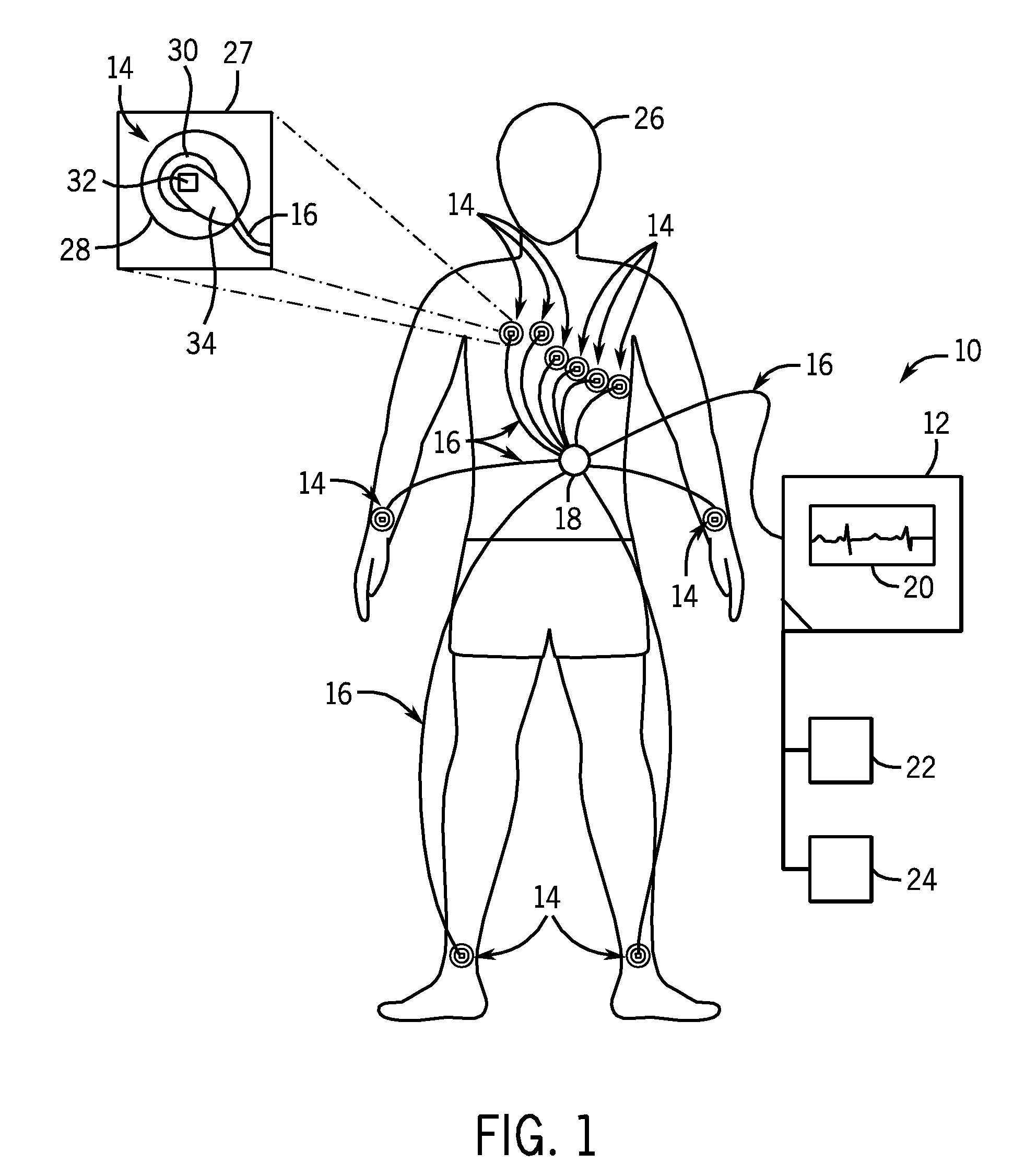
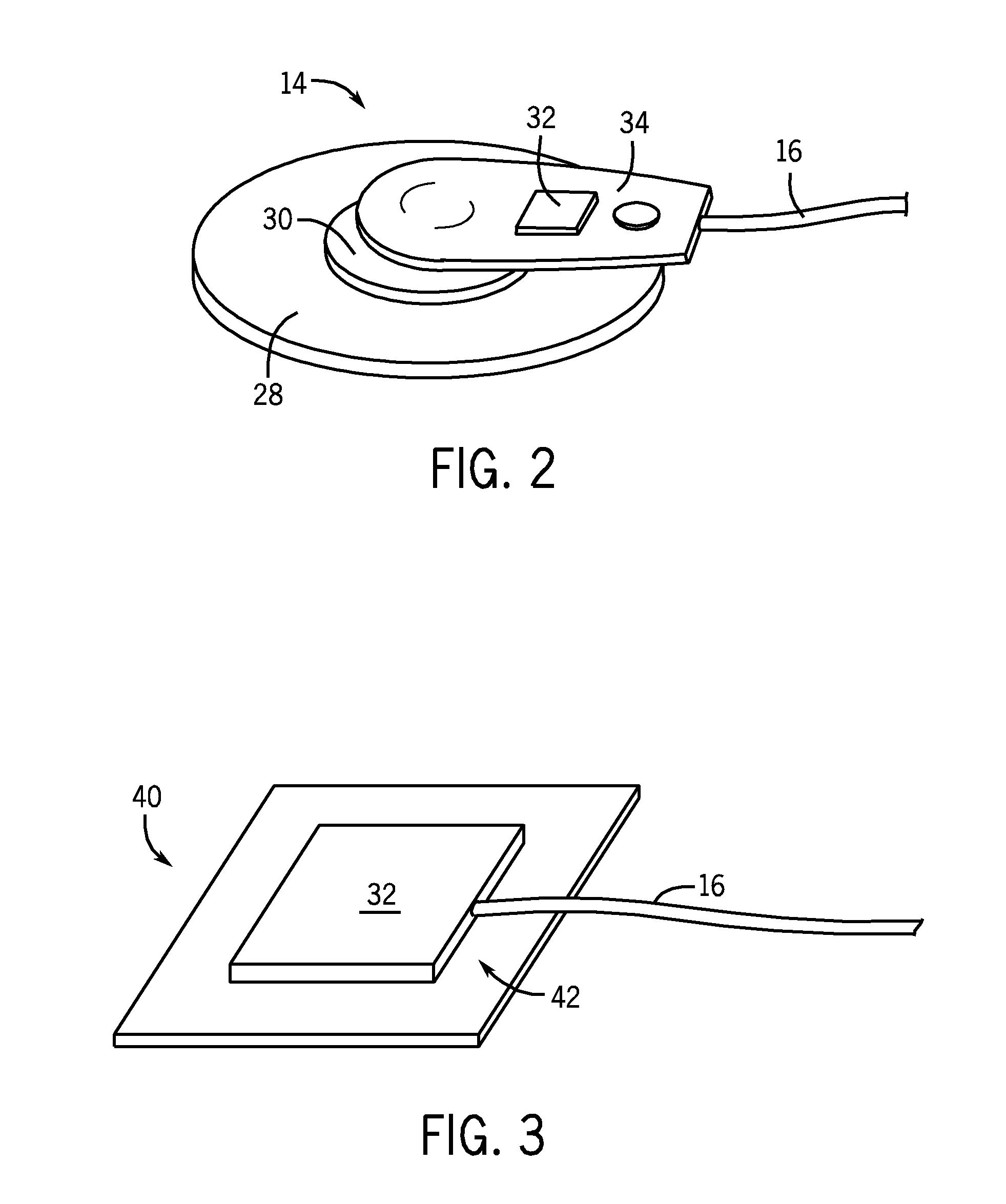
System and method of performing electrocardiography with motion detection
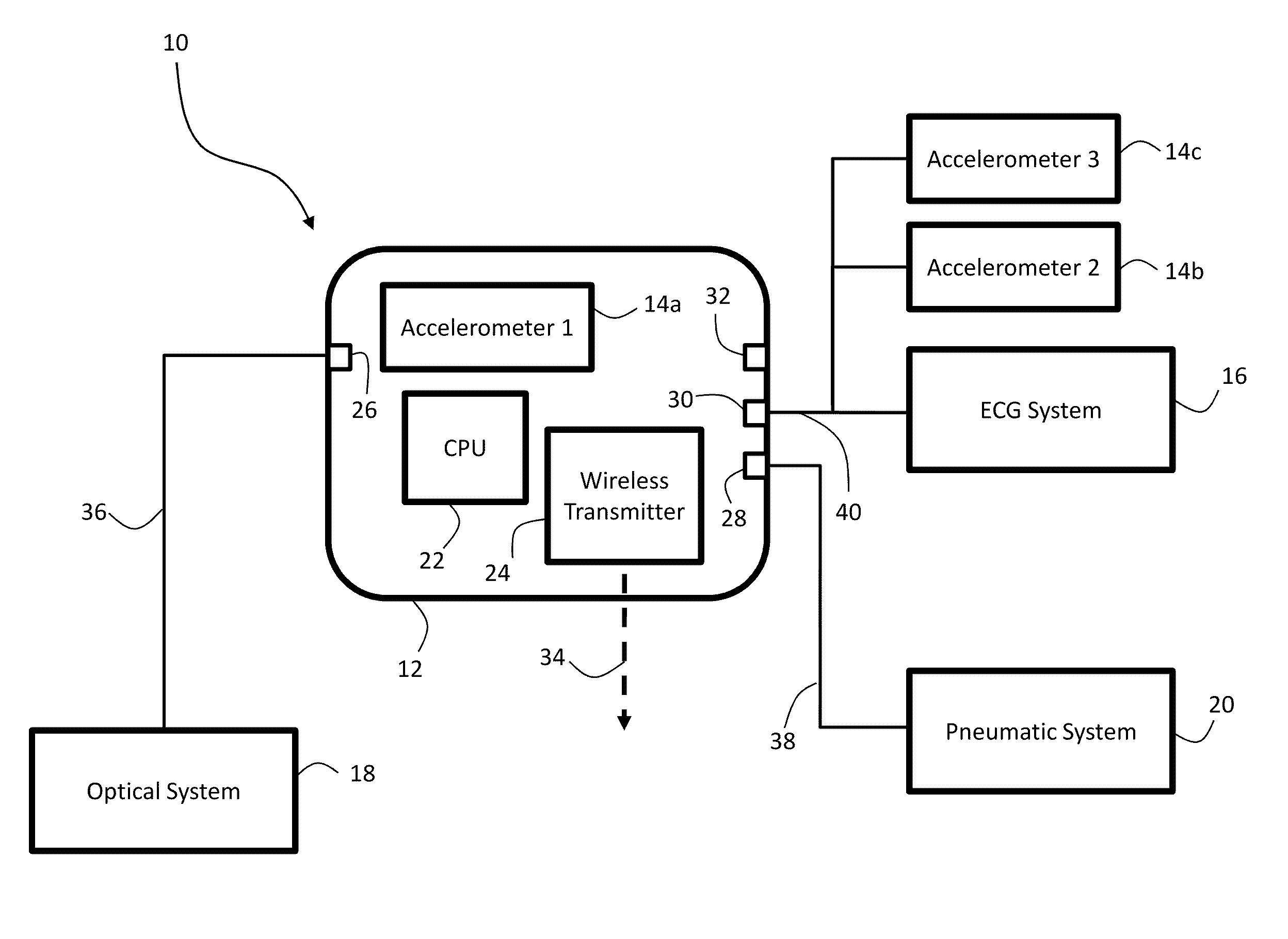
A system in accordance with present embodiments includes an electrocardiograph, a plurality of sensors communicatively coupled with the electrocardiograph, wherein each of the plurality of sensors comprises an electrode capable of detecting electrical impulses generated by a patient's body and transmitting signals indicative of detected electrical impulses to the electrocardiograph. In one embodiment, the system also includes a motion detection feature communicatively coupled with the electrocardiograph, wherein the motion detection feature is capable of detecting movement of the patient's body and providing signals indicative of detected movement to the electrocardiograph, and wherein the electrocardiograph is capable of detecting a particular type of patient motion and / or patient position based on the signals indicative of the detected motion, capable of providing output based on the signals indicative of the detected electrical impulses, and capable of providing output based on the signals indicative of the detected movement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
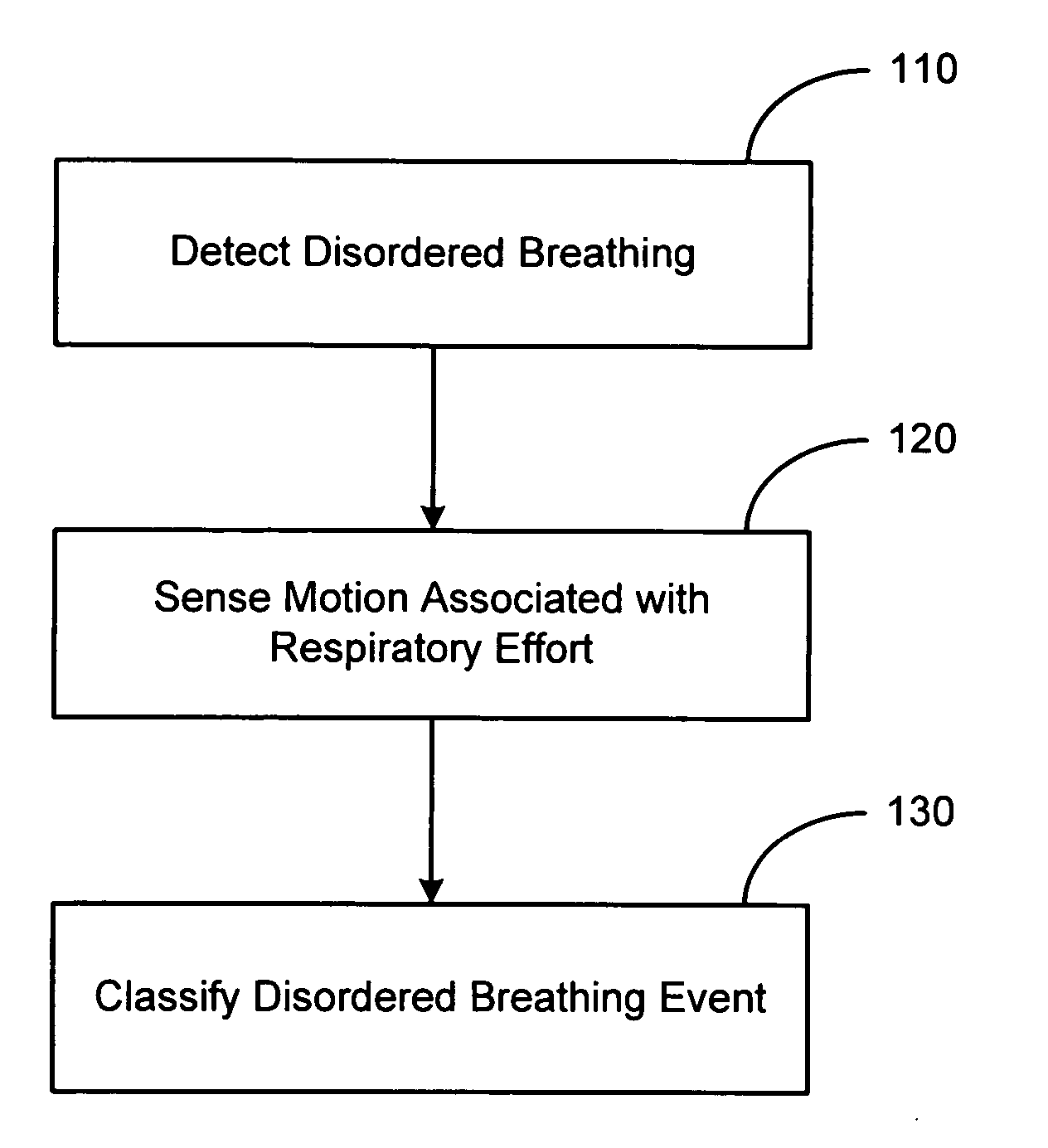
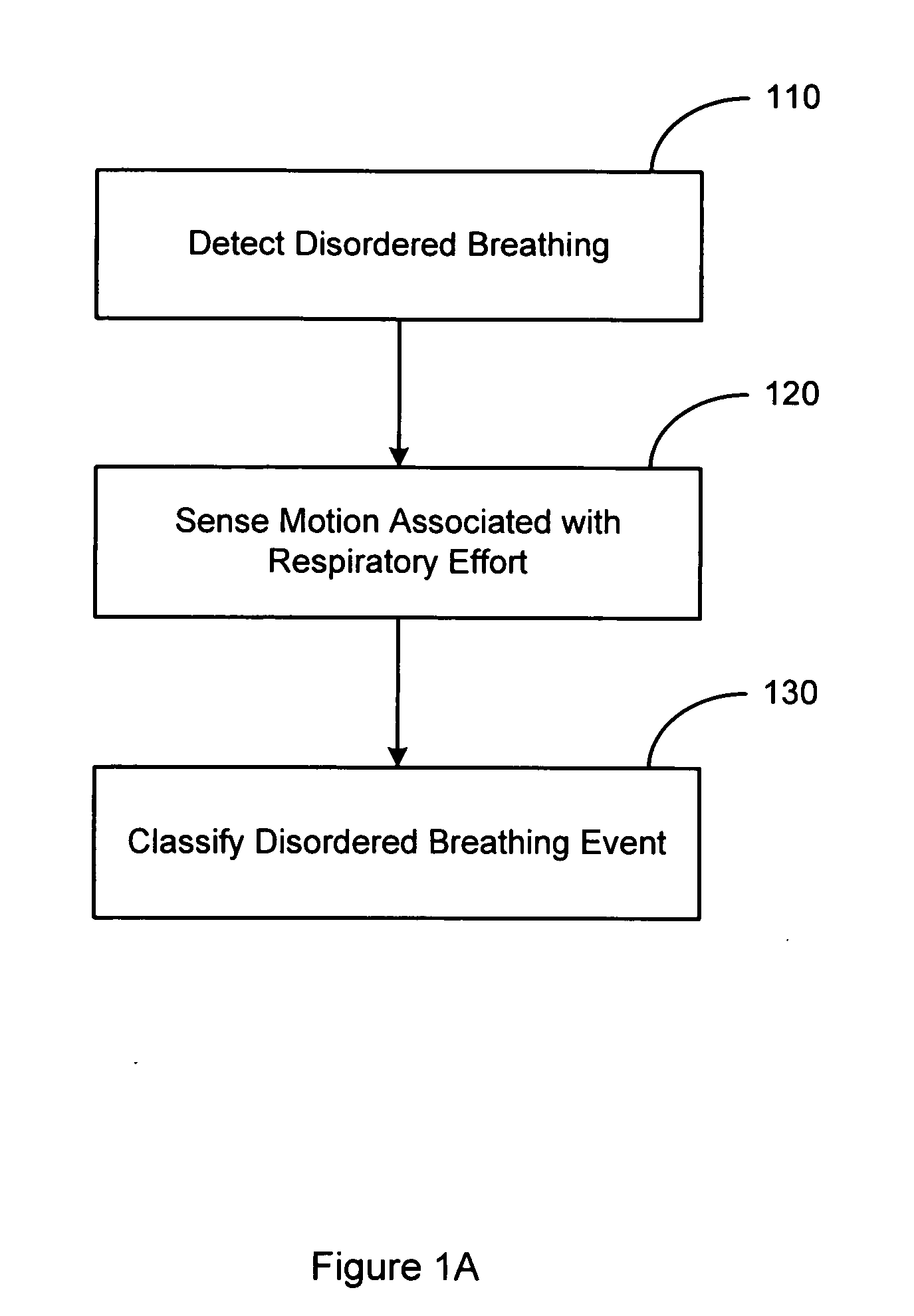
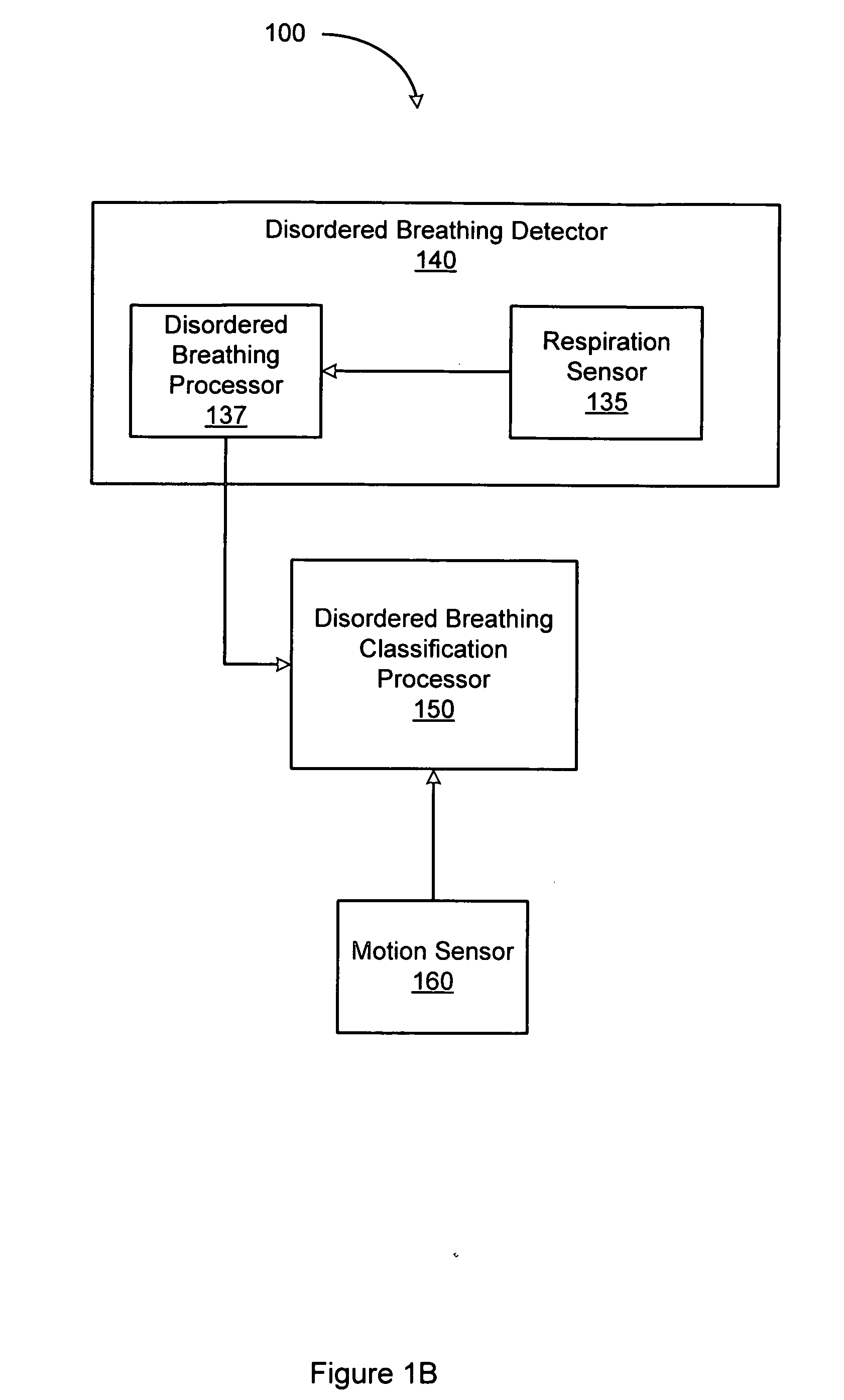
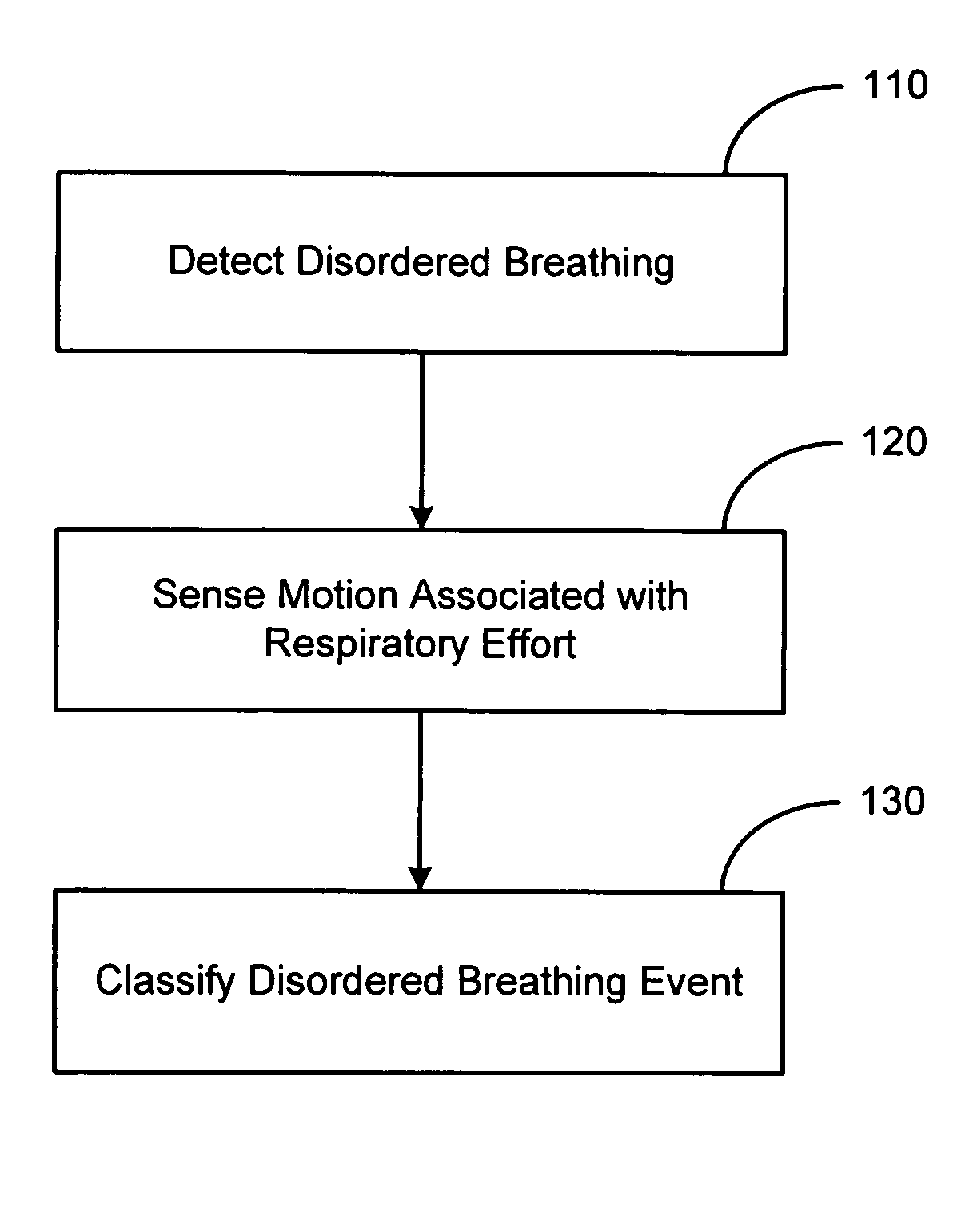
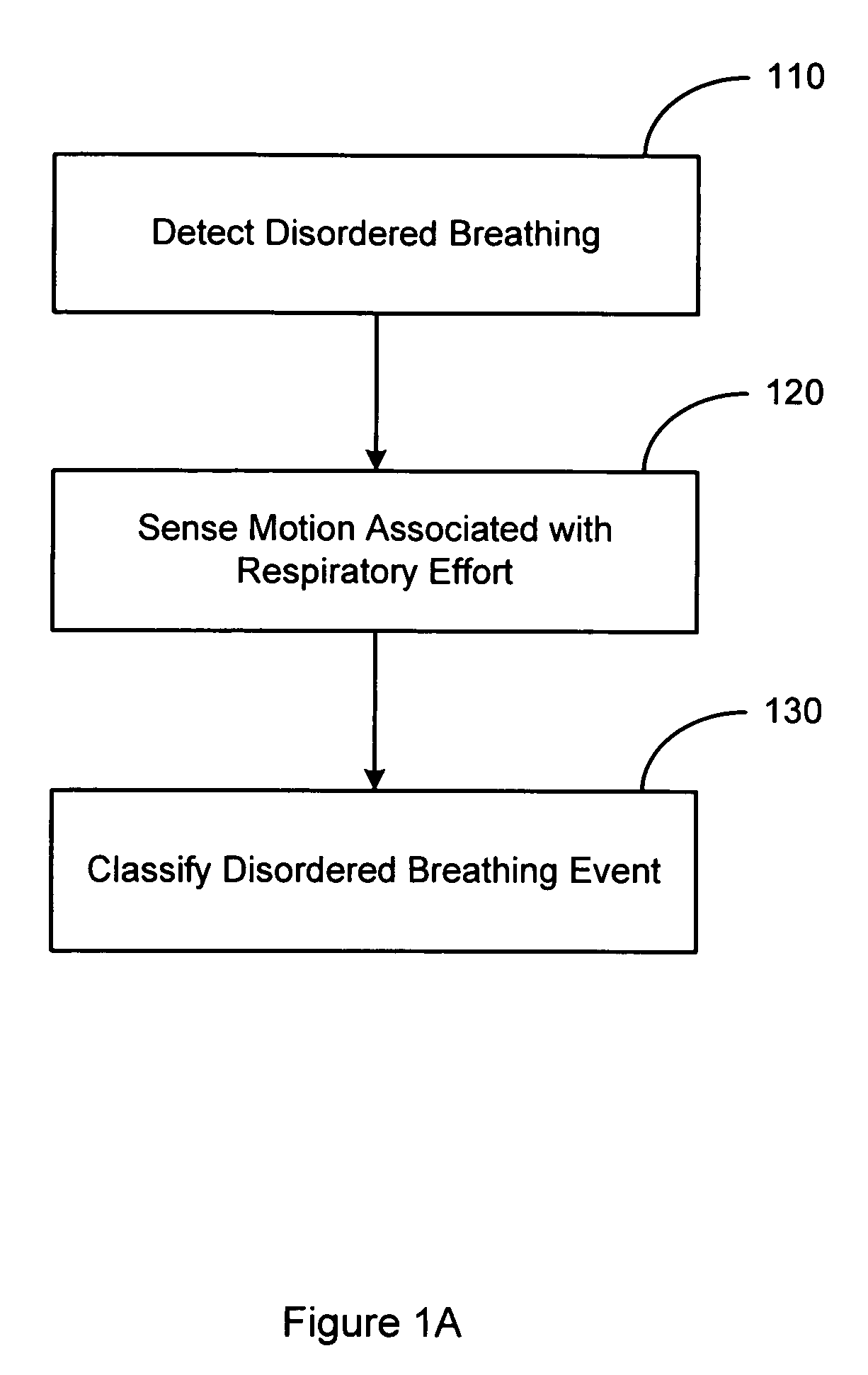
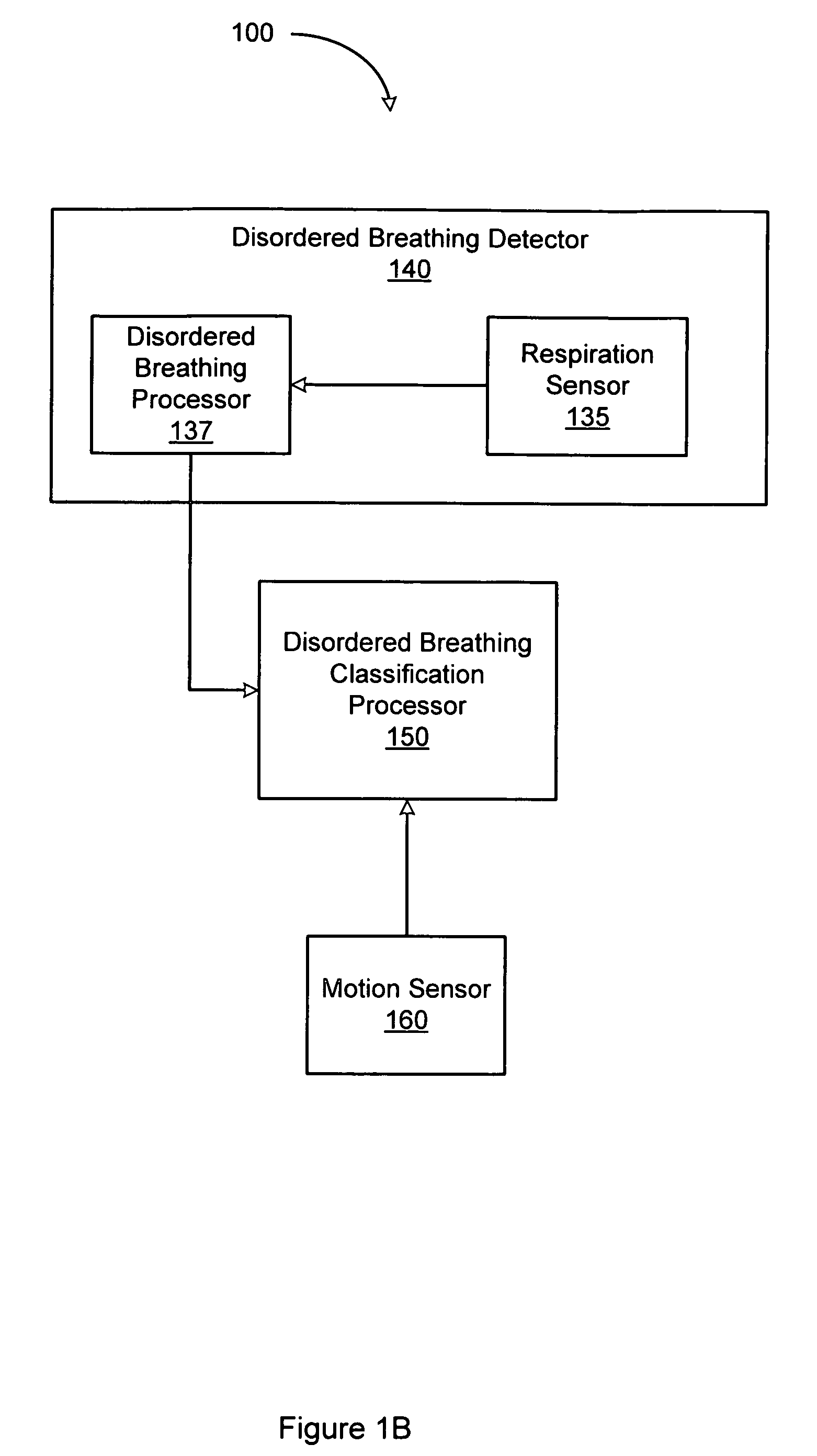
System and method for discrimination of central and obstructive disordered breathing events
Disordered breathing events may be classified as central, obstructive or a combination of central an obstructive in origin based on patient motion associated with respiratory effort. Central disordered breathing is associated with disrupted respiration with reduced respiratory effort. Obstructive disordered breathing is associated with disrupted respiration accompanied by respiratory effort. A disordered breathing classification system includes a disordered breathing detector and a respiratory effort motion sensor. Components of the disordered breathing classification system may be fully or partially implantable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Medical sensor for reducing signal artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by mitigating the effects of the tissue moving within the sensor. A sensor is provided with an elastomeric sensor body adapted to accommodate patient motion. Further, a sensor is provided in which the sensor cable is arranged to mitigate its pressure on a patient's tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Methods and systems for assessing patient movement in diagnostic imaging
ActiveUS20090003655A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionStatistical correlationMedical imaging
Methods and systems for automatically detecting gross patient motion using a diagnostic medical imaging system are provided. The method provides for acquiring a plurality of frames of image data, positioning a first time window and a second time window over overlapping frames of image data, calculating a statistical correlation value based on the first time window and the second time window, and comparing a first derivative of the statistical correlation value to a threshold value to determine patient motion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
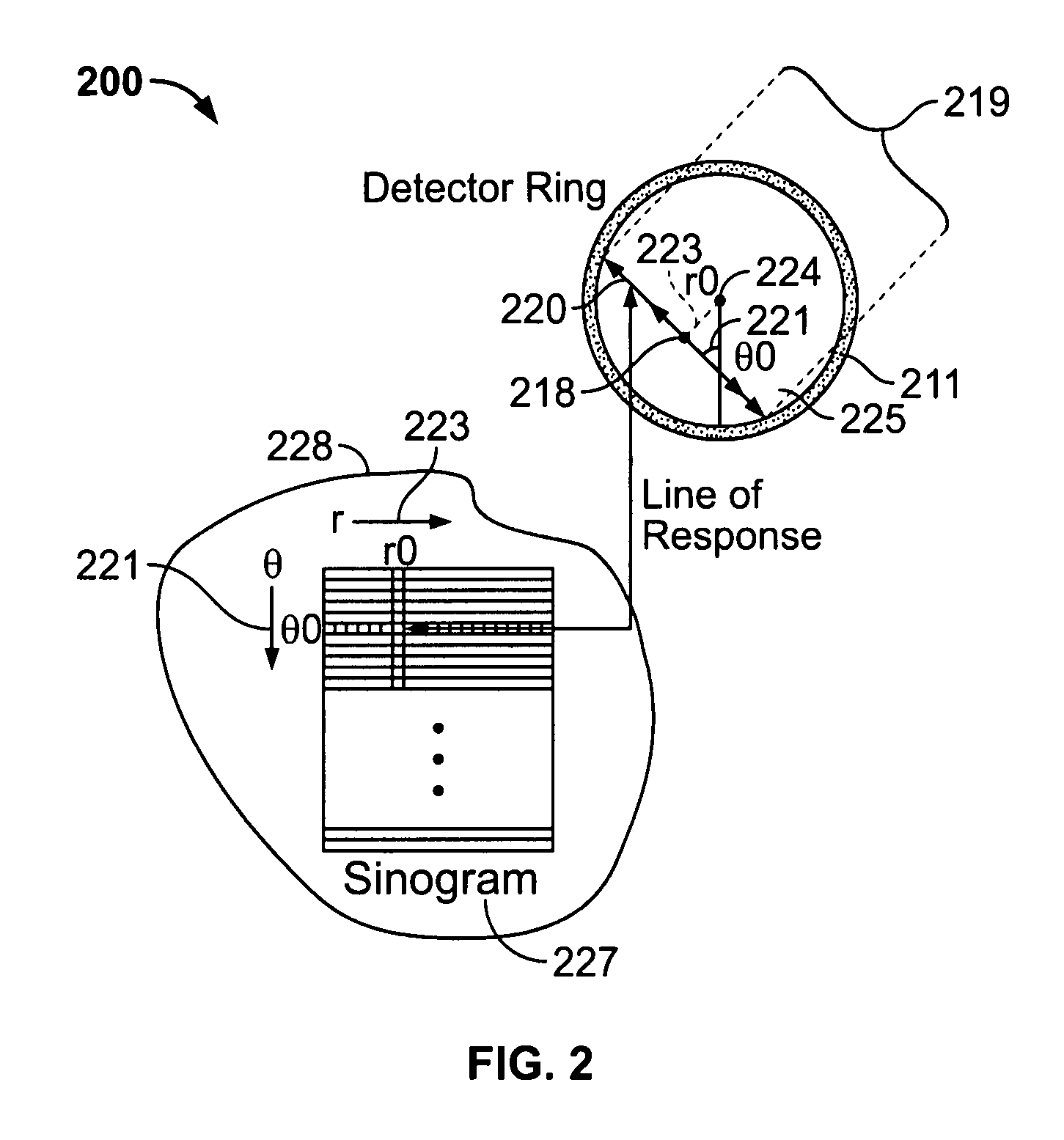
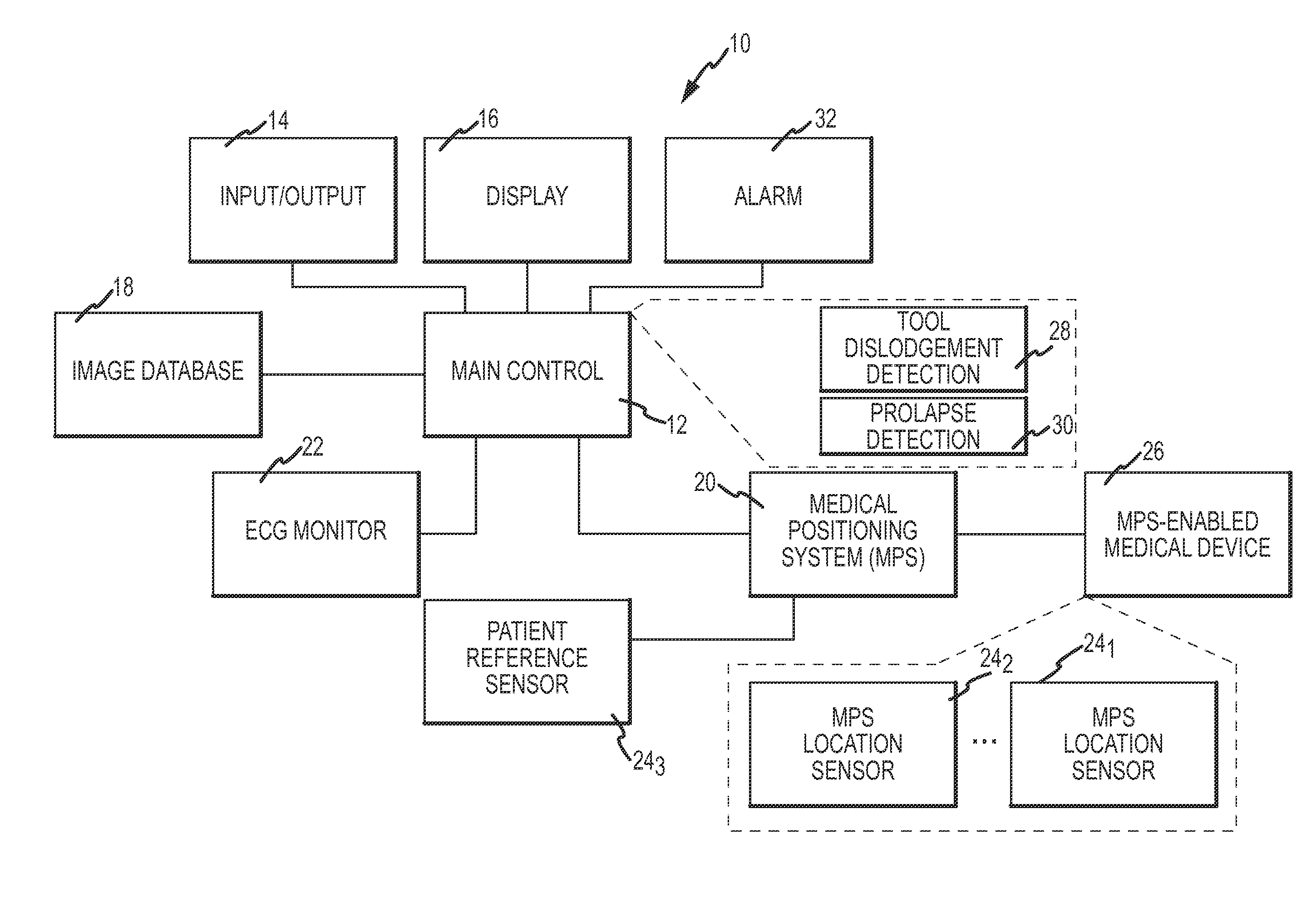
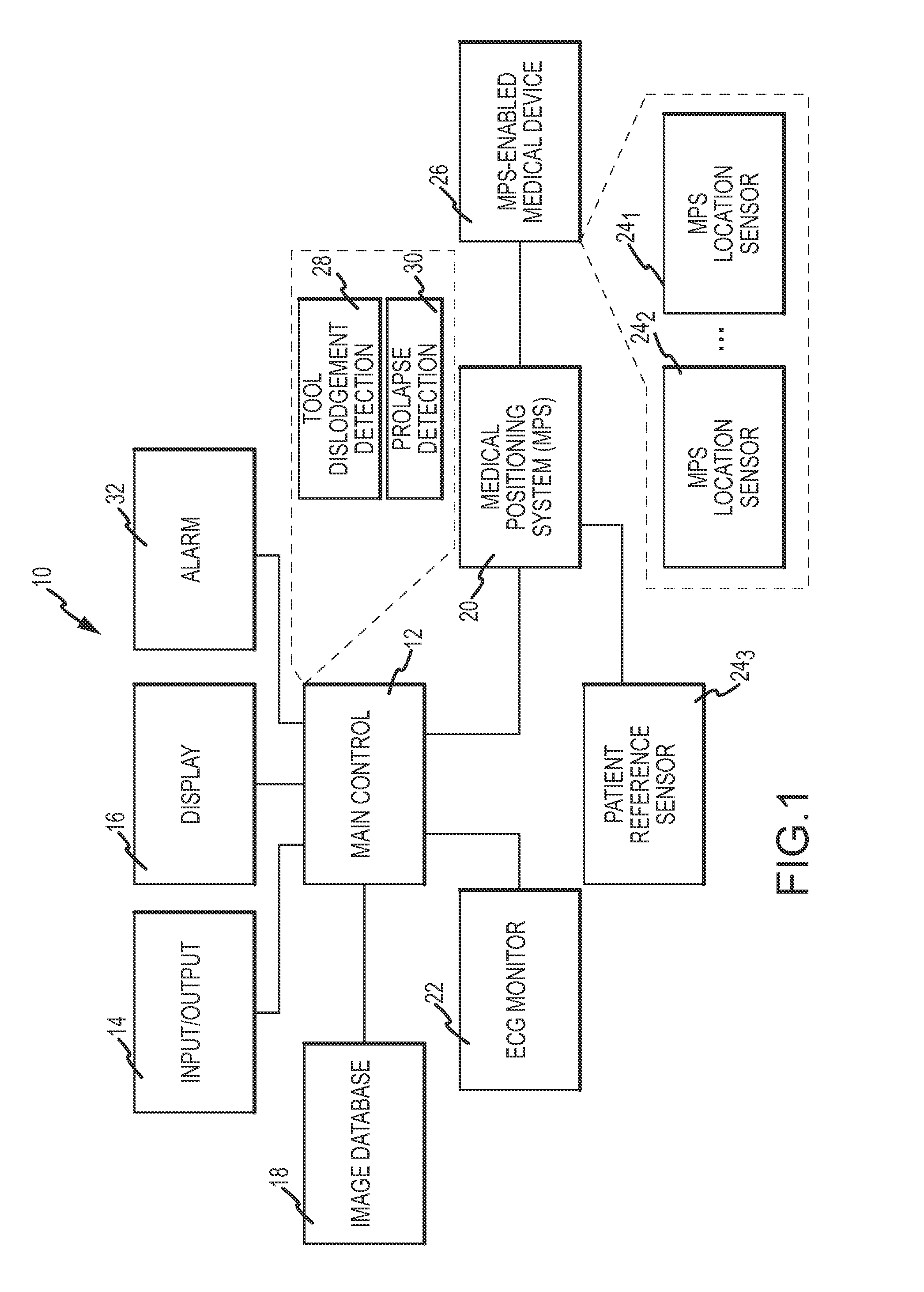
Prolapse detection and tool dislodgement detection
ActiveUS20110160570A1Little and no exposure to X-raysQuick identificationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsPatient characteristicsMotion vector
A tool dislodgement detection apparatus includes an MPS outputting position and orientation (P&O) readings for determining tool motion. A control generates an alarm based on the tool motion and dislodgement criteria. The criteria includes whether the tool motion meets a condition based on the type of medical procedure or tool, the tool parking position, a patient characteristic (e.g., age, weight, gender) or a physician preference. The criteria includes when the correlation between the tool motion and the cardiac, respiration and patient motion changes abruptly. In a prolapse detection apparatus, guidewire tip P&O readings determine a tip motion vector. The control generates an alarm using the motion vector and predetermined criteria. The criteria include a substantial change in the tip orientation not accompanied by a corresponding position change and a change in the motion vector by about 180° accompanied by a corresponding position change no greater than a threshold.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
System and method for discrimination of central and obstructive disordered breathing events
InactiveUS7510531B2ElectroencephalographyElectro-oculographyRespiratory effortIntensive care medicine
Disordered breathing events may be classified as central, obstructive or a combination of central an obstructive in origin based on patient motion associated with respiratory effort. Central disordered breathing is associated with disrupted respiration with reduced respiratory effort. Obstructive disordered breathing is associated with disrupted respiration accompanied by respiratory effort. A disordered breathing classification system includes a disordered breathing detector and a respiratory effort motion sensor. Components of the disordered breathing classification system may be fully or partially implantable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Medical sensor for reducing signal artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by mitigating the effects of the tissue moving within the sensor. A sensor is provided with an elastomeric sensor body adapted to accommodate patient motion. Further, a sensor is provided in which the sensor cable is arranged to mitigate its pressure on a patient's tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical sensor for reducing signal artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by mitigating the effects of the tissue moving within the sensor. A sensor is provided with an elastic sensor body adapted to accommodate patient motion. Further, a sensor is provided in which the sensor cable is arranged to mitigate its pressure on a patient's tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Medical sensor and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to provide output to indicate when the sensor experiences abnormal forces or pressure. The forces may be outside forces, or the forces may be generated by patient motion. A sensor system as provided may also be adapted to correct for such forces when calculating measurements related to a physiological characteristic.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
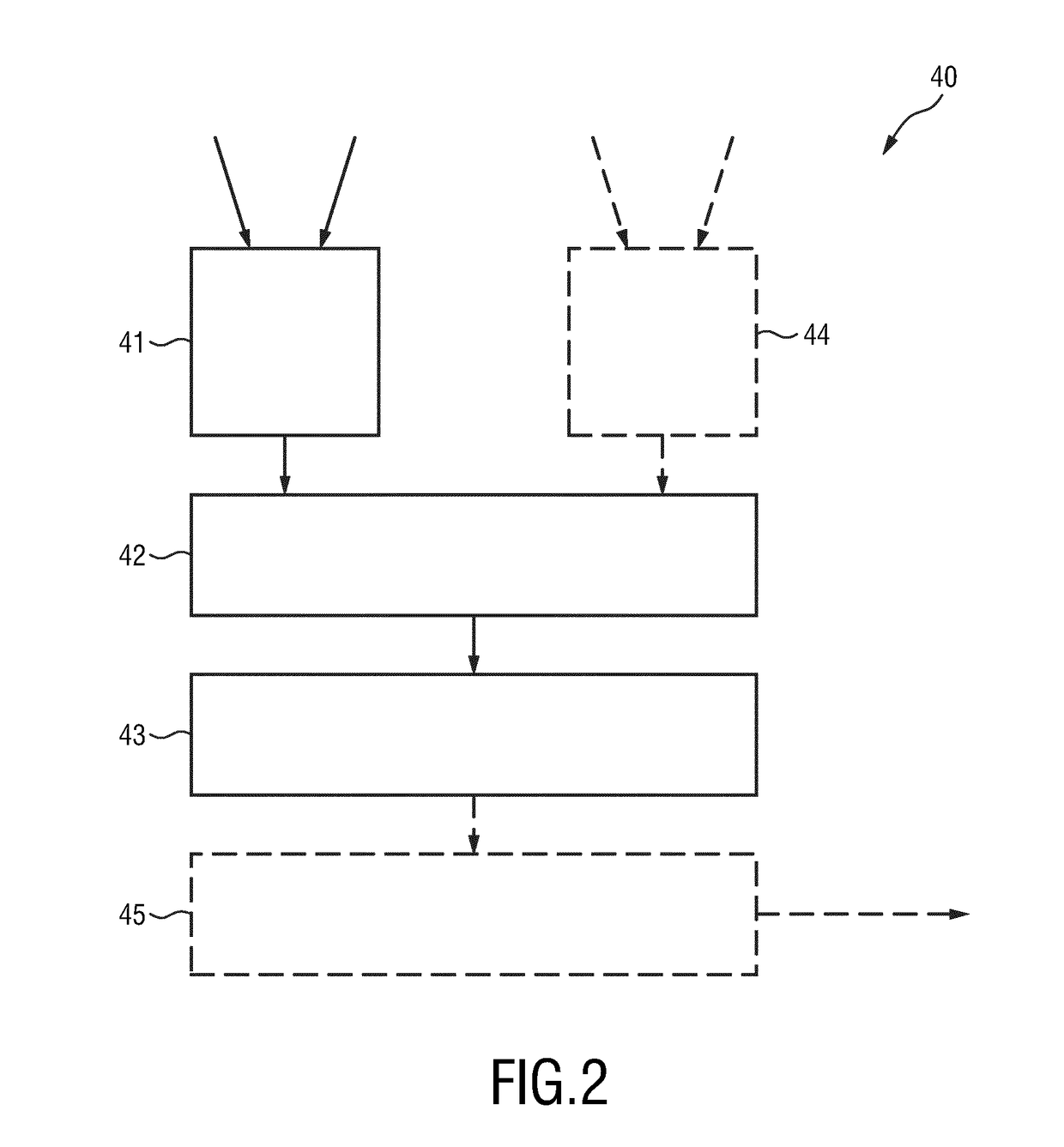
Method and medical imaging system for compensating for patient motion
InactiveUS20050203373A1Improving Imaging ResultsSmall possible time outlayImage enhancementImage analysisData set3d image
The present invention relates to a method to compensate for patient motion in series recordings in medical imaging, in which a plurality of images of an examination area of a patient (17) are recorded at time intervals with an imaging system (1) and related to each other. The invention also relates to an imaging system (1) for implementing the method. With the method, before the start of the series recordings a 3D image data set is recorded by a 3D recording of the examination area, which establishes a reference system. A first spatial position of the examination area in the reference system is then either obtained by recording a first image of the series recordings and registering it with the 3D image data set or by calculating it from a known calibration of the imaging system (1). Each further image of the series recordings is registered immediately after recording with the 3D image data set, to obtain the current spatial position of the examination area in the reference system. Finally a difference in respect of the first spatial position is determined and at least some of the difference is compensated for at least approximately by changing geometric relationships of the imaging system (1) in temporal proximity to registration. The method allows patient motion to be compensated for without interaction by the user of the imaging system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Device and method for suv determination in emission tomography
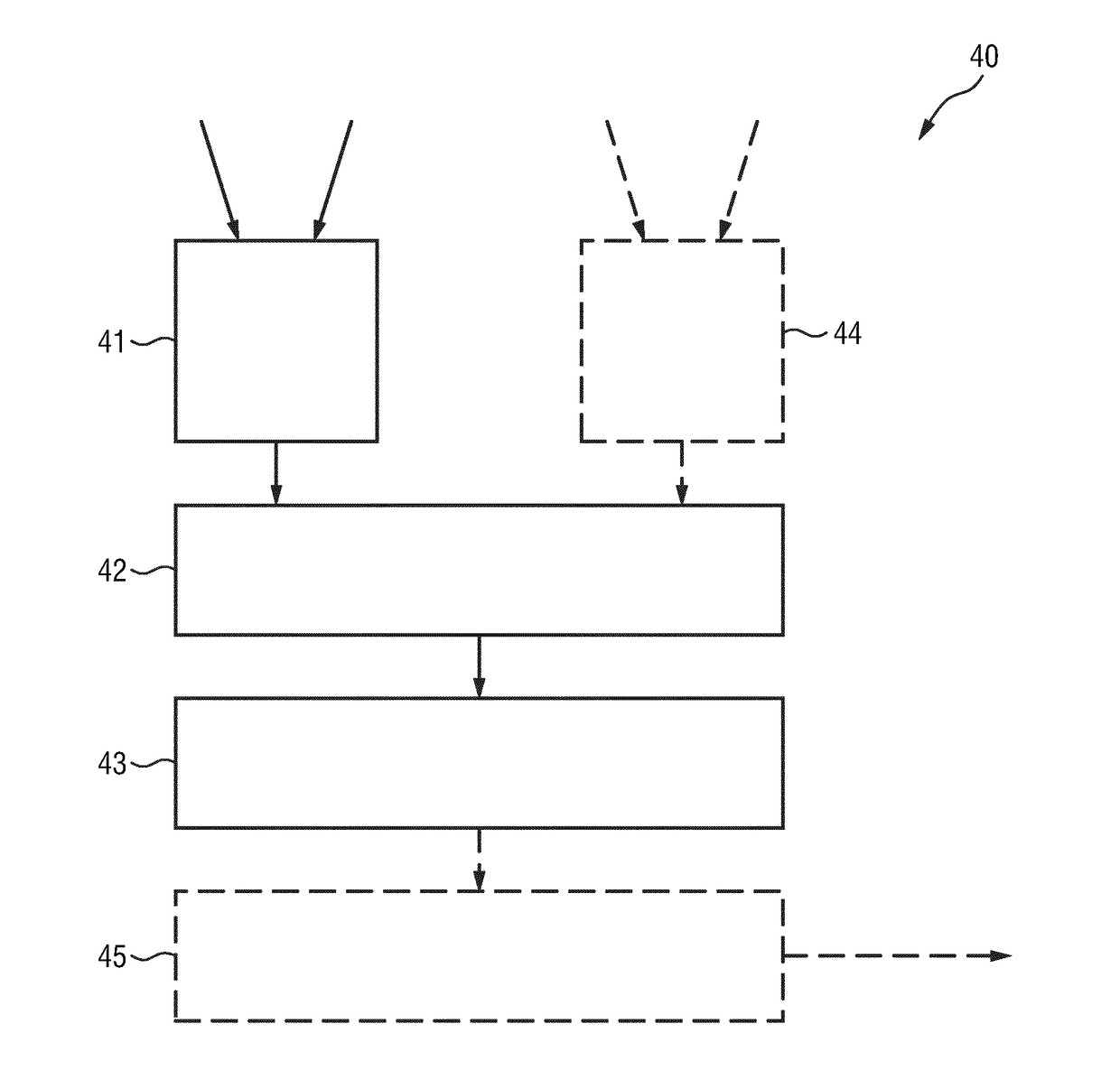
ActiveUS20180289340A1Less cumbersomeMore comfortable for the patientRadiation diagnosis data transmissionComputerised tomographsRadioactive tracerSize determination
The invention relates to a device (40) for standard uptake value, SUV, determination during an emission tomography imaging procedure of a patient. The device receives SUV-related data required for SUV determination, and event data relating to one or more events that may affect the SUV determination. The SUV-related data includes a time of administration of the radiotracer dose to the patient. The event data includes at least one of: a time at which an emission tomography imaging procedure of the patient is performed, patient motion data, patient position data, and patient vital signs data. An anomalous event determination unit (42) determines, based on the event data, anomalous event information indicative of one or more anomalous events that affect the SUV determination. An SUV determination unit (43) determines the SUV based on said SUV-related data taking into account the anomalous event information.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Integrated infusion management system
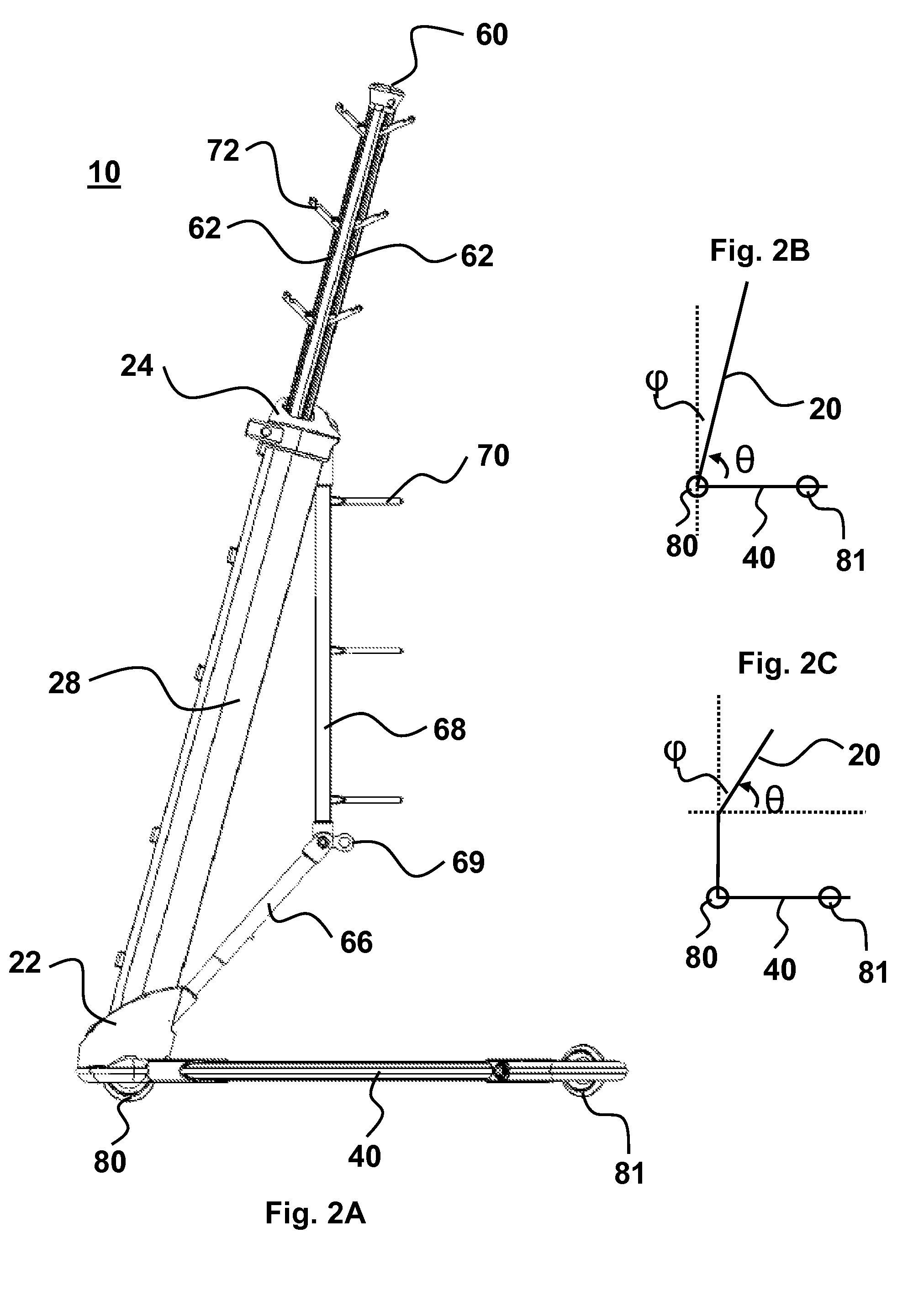
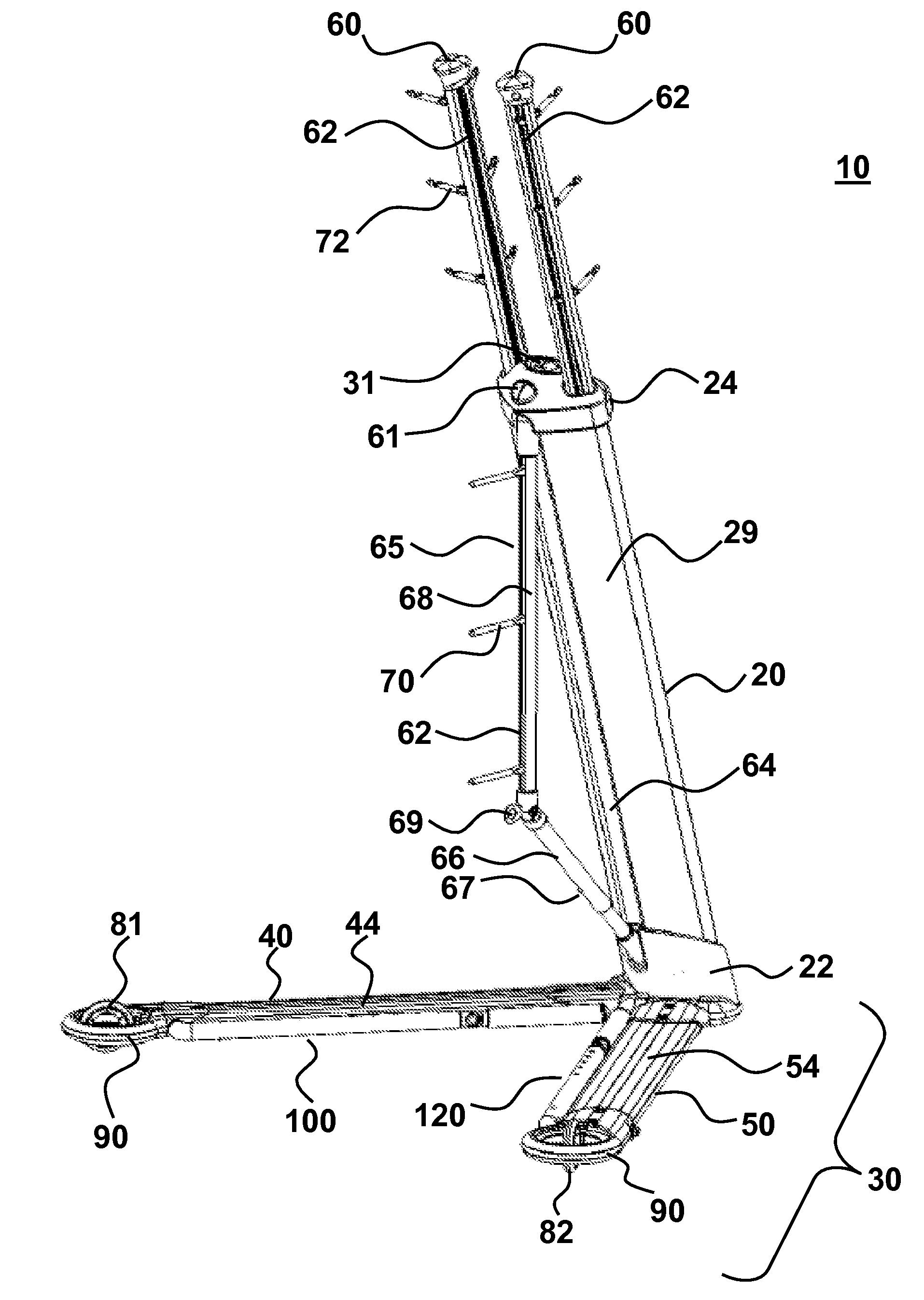
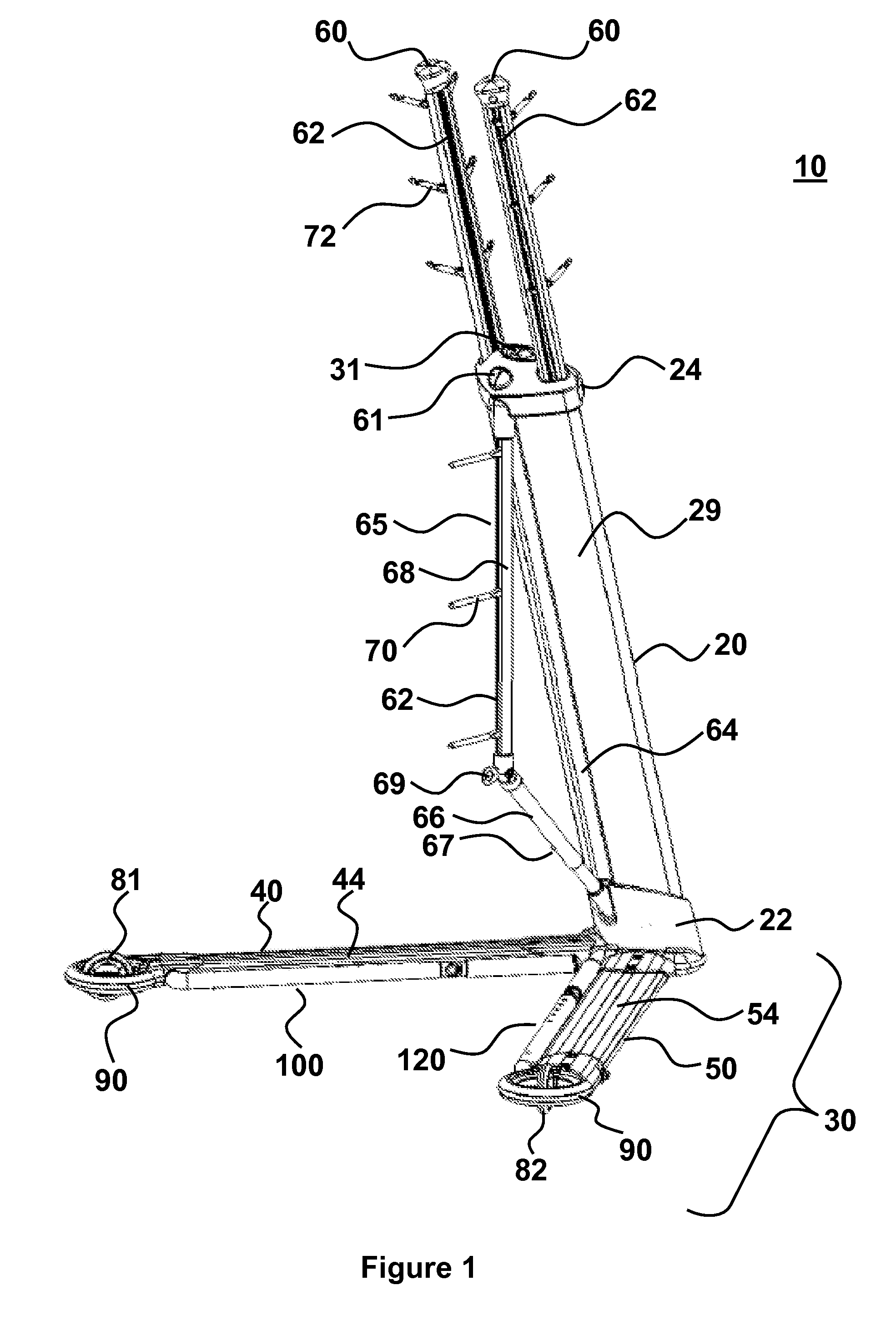
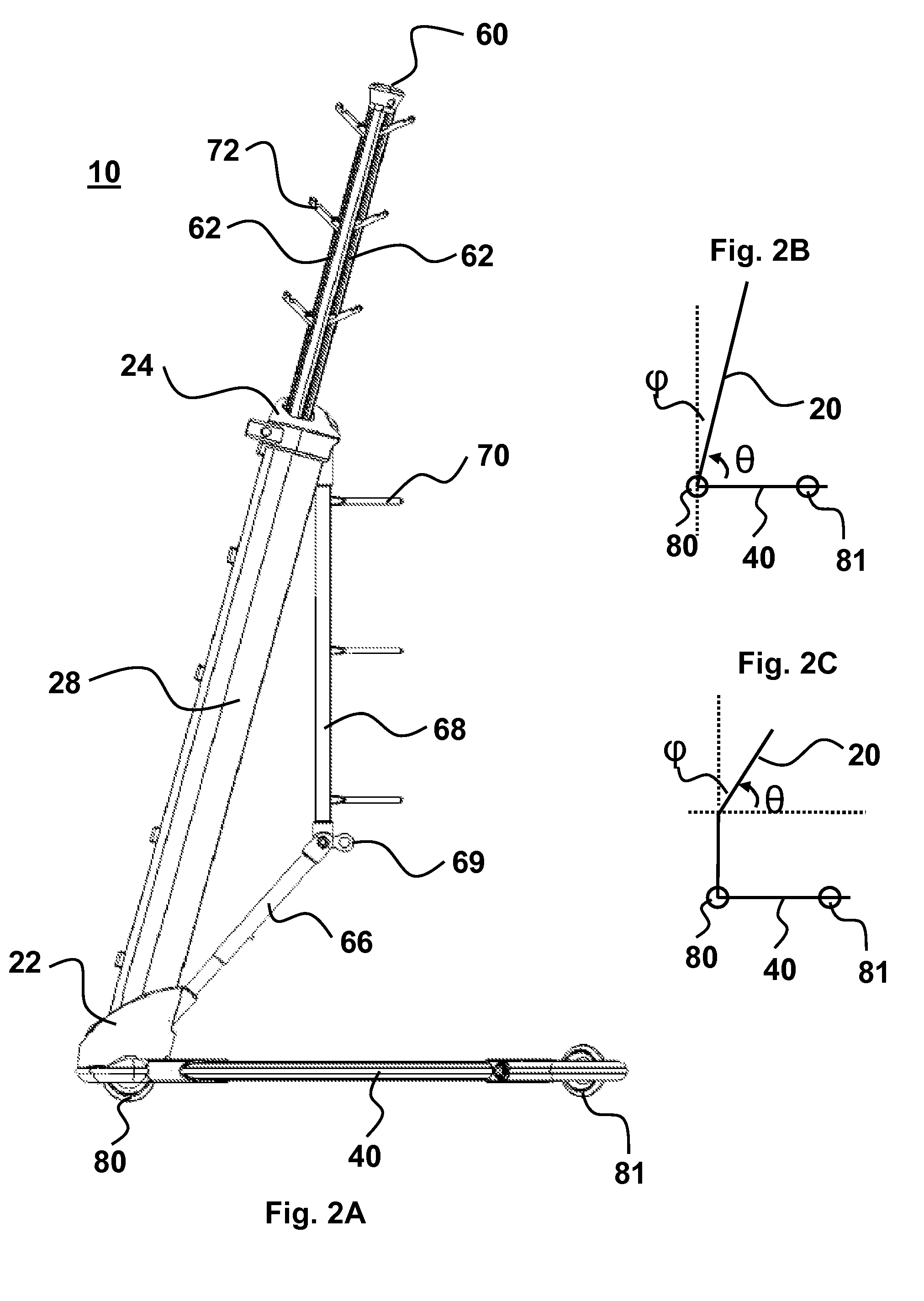
An integrated infusion management system provides for stable support of components attached to the system, even when the system is mobile. The system is optionally a mobility assist or walker for a patient who is attached to any number of medical components. A central trunk connects to a two-sided base that does not interfere with patient motion. The trunk may be angled with respect to vertical and oriented to support medical components in a configuration that is tip-resistant. The system is optionally deployable to facilitate conversion between a compact storage configuration and a stable deployed configuration. In an embodiment, additional deployable features include holding arms for holding various medical components, wheels, mobility arms and handles. Also provided is a novel wheel system with deployable wheels and methods associated with providing compact storage of any one or more of the systems presented herein.
Owner:FIREFLY MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for detecting artifact signals in the electrocardiogram of a patient caused by CPR and/or patient motion using patient impedance
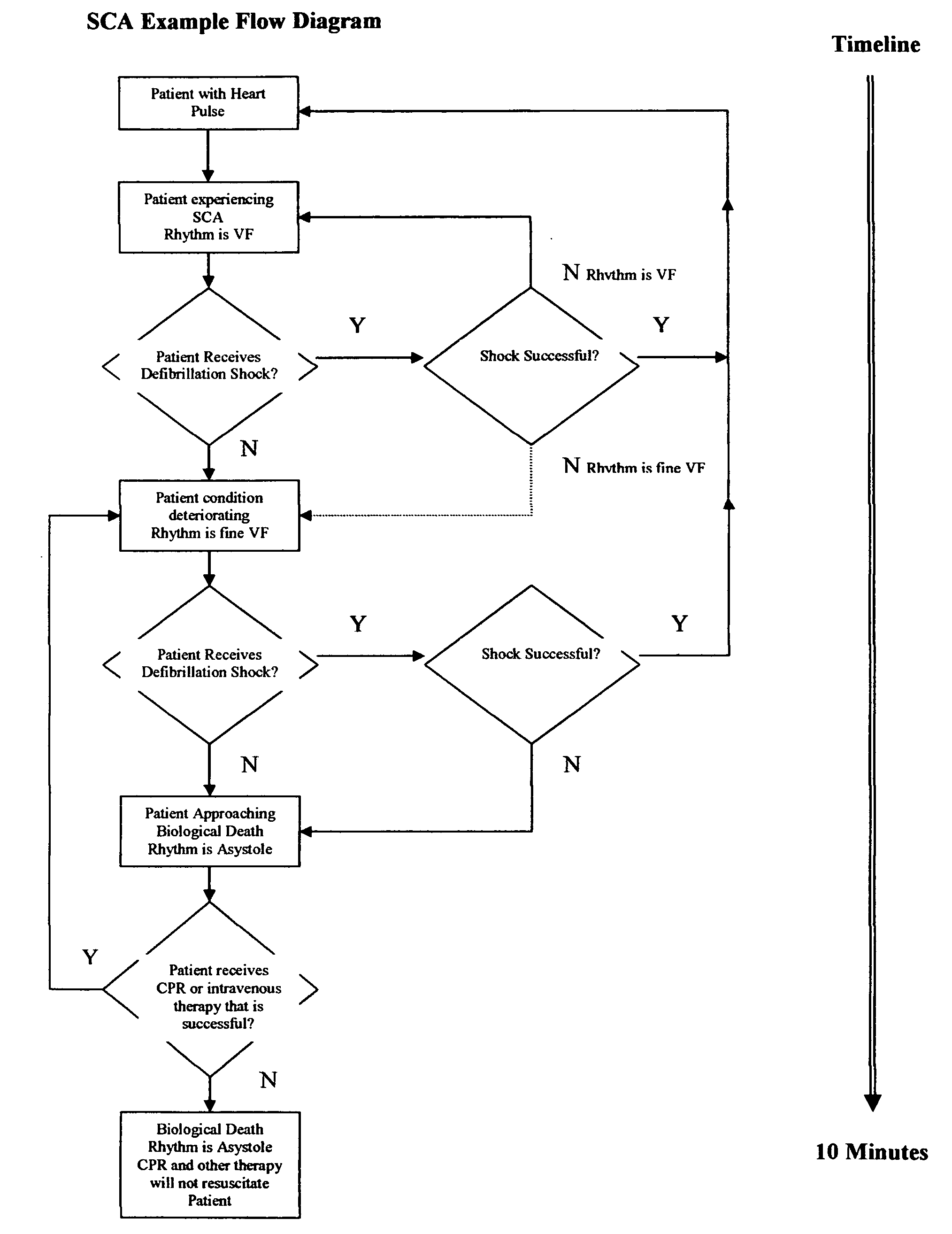
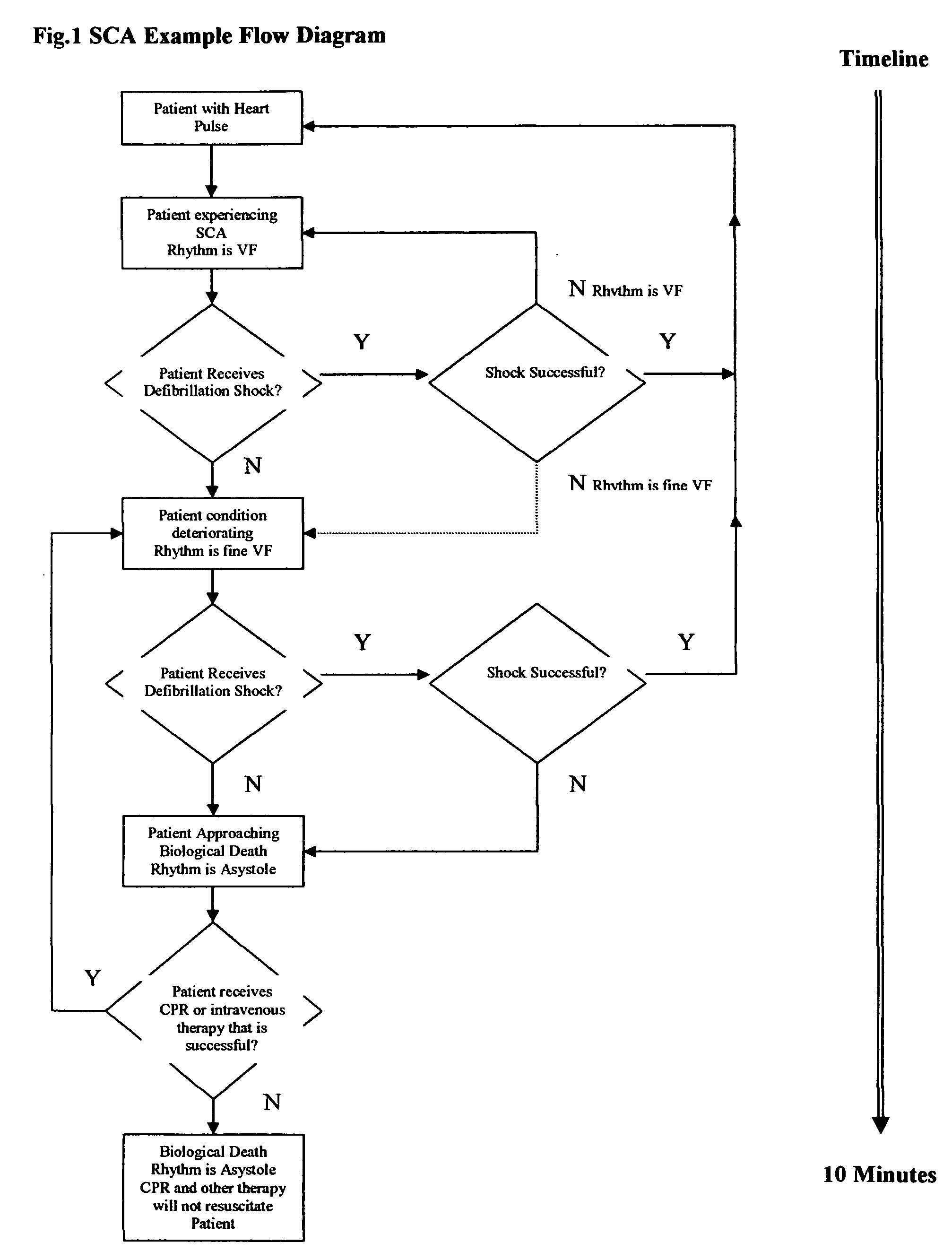
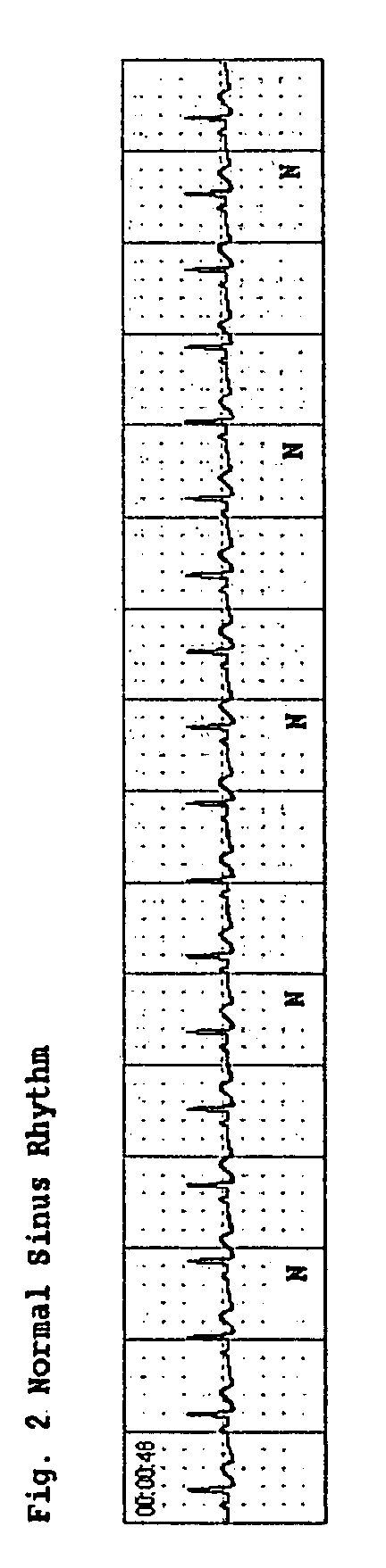
Medical apparatus for detecting the presence of artifact signals generated in the electrocardiogram of a patient by CPR and / or other patient motion. The presence of artifact signals is determined by analyzing variations in a measured electrical signal that represents the patient's transthoracic impedance. Such detection is important because the presence of CPR and / or motion artifacts can disrupt a patient's electrocardiogram (ECG) signal. The patient's impedance signal data is stored in the apparatus and analyzed to determine if the characteristics are indicative of the presence of CPR and / or motion artifacts. This analysis is performed independently of ECG data and may be used as an indicator of the underlying ECG rhythm classification. In essence, if the impedance exceeds some threshold amount, so as to indicate the presence of CPR or patient motion which can render the ECG data unreliable, the normal interpretation of the ECG data is interrupted. Applications of the invention include, but are not limited to, advising or not advising, defibrillation therapy, CPR or intravenous medicinal therapy.
Owner:SCION MEDICAL
Integrated infusion management system
ActiveUS20080156946A1Improve stabilityIncrease resistanceWash-standsWalking aidsEngineeringManagement system
Owner:FIREFLY MEDICAL
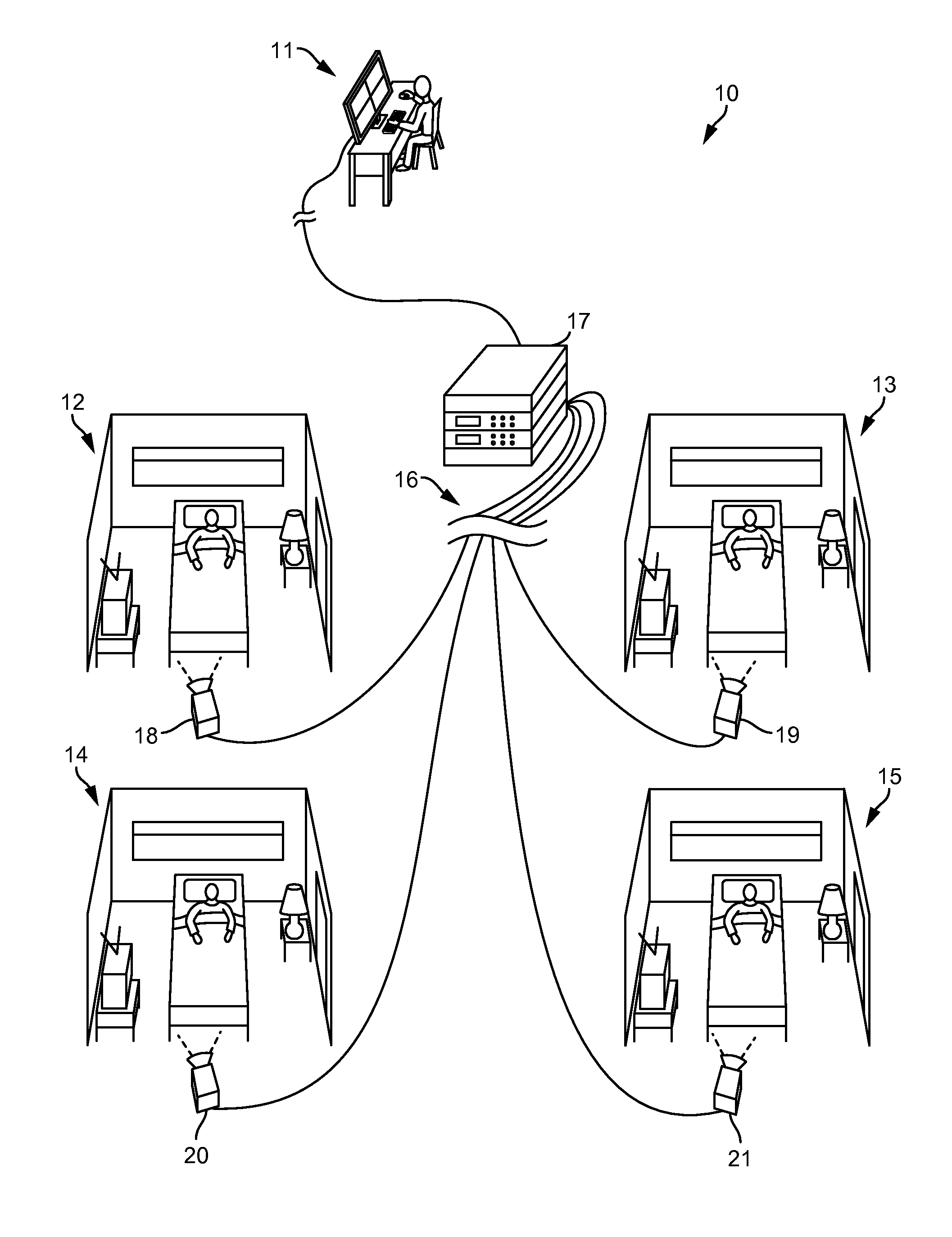
Patient video monitoring systems and methods having detection algorithm recovery from changes in illumination
ActiveUS20140204207A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringMonitoring system
Various embodiments concern video patient monitoring with detection zones. Various embodiments can comprise a camera, a user interface, and a computing system. The computing system can be configured to perform various steps based on reception of a frame from the camera, including: calculate a background luminance of the frame; monitor for a luminance change of a zone as compared to one or more previous frames, the luminance change indicative of patient motion in the zone; and compare the background luminance to an aggregate background luminance, the aggregate background luminance based on the plurality of frames. If the background luminance changed by more than a predetermined amount, then the aggregate background luminance can be set to the background luminance, luminance information of the previous frames can be disregarded, and motion detection can be disregarded.
Owner:CAREVIEW COMM INC
Contactless non-invasive analyzer of breathing sounds
InactiveUS20130060100A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStethoscopeMotion detectorAbnormal breathing
A device and method for monitoring and analyzing breathing sounds, the device including at least one microphone adapted and configured for placement adjacent a body to be monitored for contactless recording of breathing sounds, a motion detector using an ultrasound distance sensor to detect the patient body motions, and a processor coupled to the microphones and the motion detector for receiving and processing the breathing sounds and patient motions to detect abnormal breathing events.
Owner:SENSEWISER
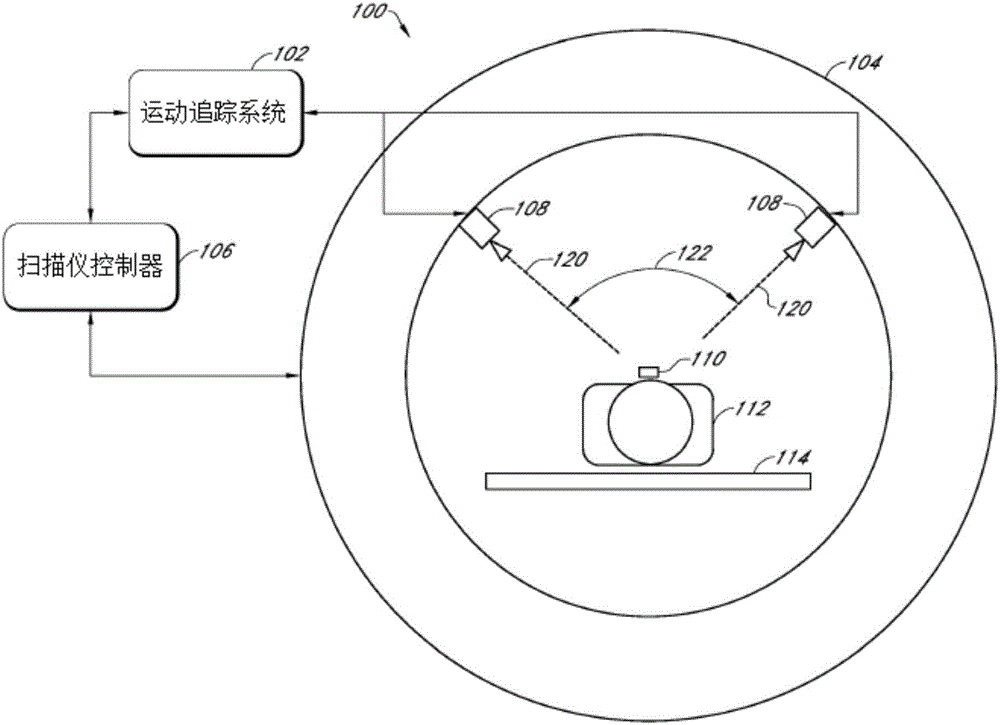
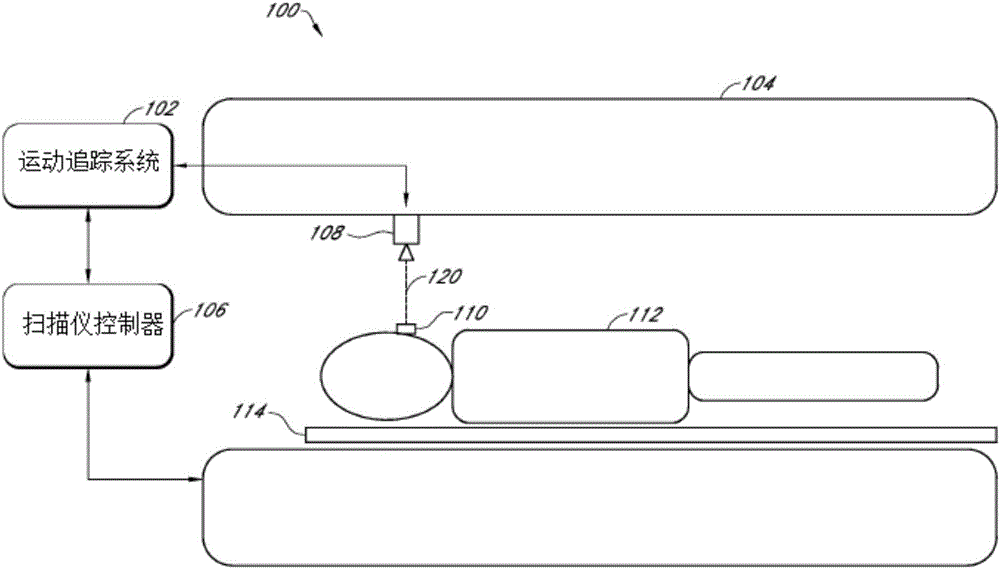
Systems, devices, and methods for tracking and compensating for patient motion during a medical imaging scan
A motion tracking system for dynamic tracking of and compensation for motion of a patient during a magnetic resonance scan comprises a first camera positioned to view an optical marker along a first line of sight; a second camera positioned to view the optical marker along a second line of sight; and a computer system configured to analyze images generated by the first and second cameras to determine changes in position of the optical marker, and to generate tracking data for use by a magnetic resonance scanner to dynamically adjust scans to compensate for the changes in position of the optical marker, wherein the computer system is configured to dynamically adapt its image analysis to utilize images from all cameras that are currently viewing the optical marker.
Owner:KINETICOR
Medical sensor for reducing signal artifacts and technique for using the same
A sensor may be adapted to reduce motion artifacts by mitigating the effects of the tissue moving within the sensor. A sensor is provided with an elastic sensor body adapted to accommodate patient motion. Further, a sensor is provided in which the sensor cable is arranged to mitigate its pressure on a patient's tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Socket and prosthesis for joint replacement
InactiveUS7909882B2Preventing bone lossAvoid introducingInternal osteosythesisLigamentsRight femoral headBone structure
A joint replacement prosthesis and procedure reduce the number of steps to complete a joint replacement. The joint replacement prosthesis comprises a ball and socket unit that fixes the ball in the socket prior to surgery. The unit is coupled to a bone structure in the patient and is coupled with a prosthesis that is fixed to another bone of the patient, such as a femoral implant fixed in a femur and providing a coupling at the end of a neck portion that is easily fit into a femoral head and acetabulum unit. A tether may be used to retain the ball in the socket and / or the ball may be retained by extension in the socket that do not restrict patient motion.
Owner:STINNETTE ALBERT
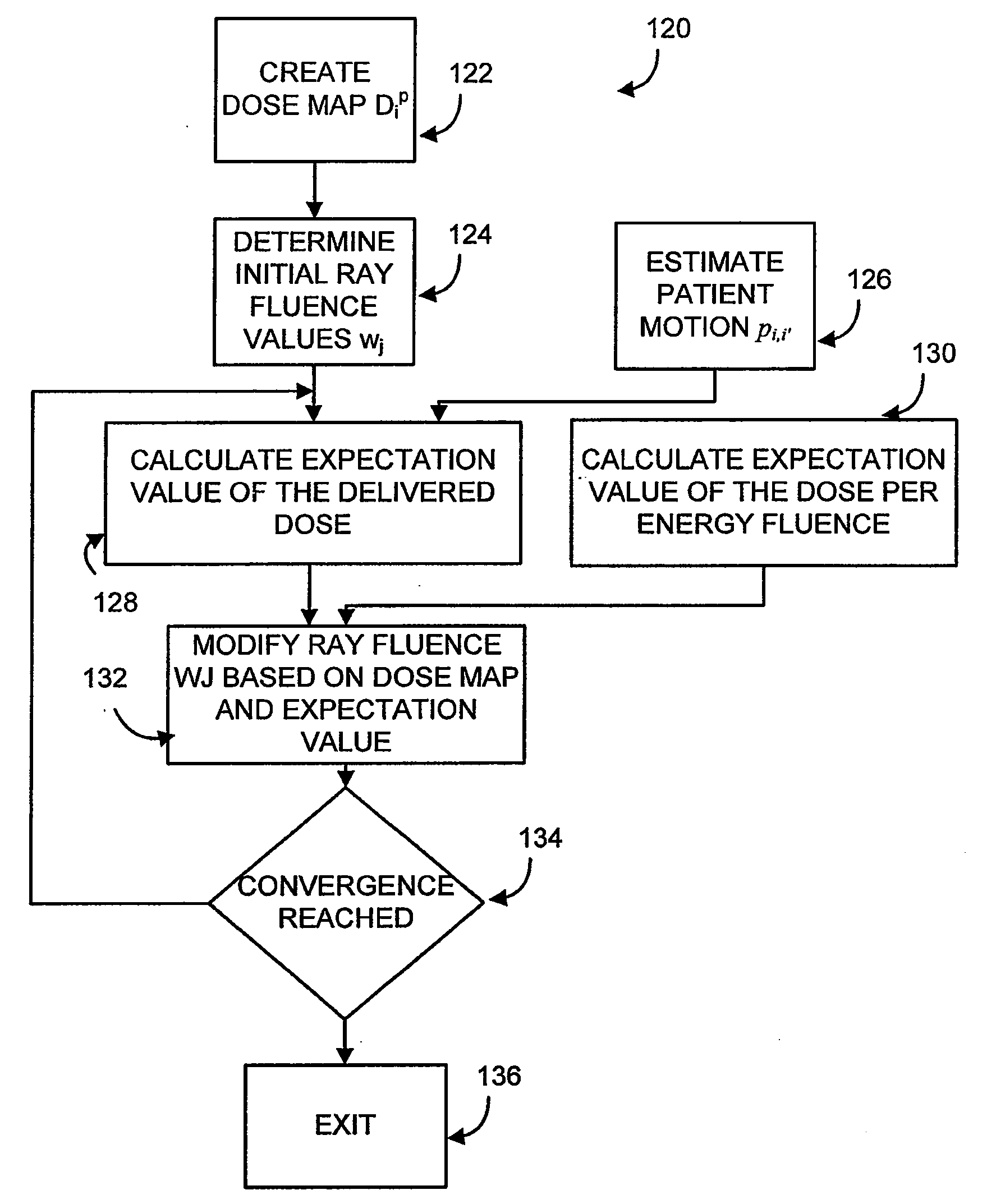
System and method for optimization of a radiation therapy plan in the presence of motion
A computer-implemented method for optimizing a radiation treatment plan for a radiotherapy machine providing independently controlled radiation along a plurality of rays j directed toward a patient and configured to account for the effects of patient motion. The method includes generating a probability distribution function quantitatively expressing patient motion, identifying a prescribed total dose Dip at the voxels i in a treatment area, assigning a fluence value wj for each ray j based on an iterative function, calculating an actual total dose Did produced each voxel i within the assigned fluence values and calculating an expectation value of the dose per energy fluence, dij based on the actual total dose Did and the probability distribution function.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Versatile stereotactic device and methods of use
InactiveUS20010020127A1Accurate and reproducible resultEasy to useDiagnostic markersSurgical instrument detailsFollow up examinationResonance
A stereotactic device for use with an imager such as a magnetic resonance imager is disclosed, which permits an imaging scan to be taken with reference to a personal coordinate system (or PCS) that is independent of a machine coordinate system (or MCS). Methods using the device to obtain imaging scans are described such that the imaging scans are superimposable even if taken at different time periods using the same or a different imager. The device comprises a frame that can be reproducibly positioned on a subject and which is equipped with non-invasive affixing means and localizing means that provide the PCS. The device and methods of the invention are particularly well suited for routine initial or follow-up examinations, pre-surgical planning and post-surgical evaluation. Markers on a stereotactic device can be tracked during an MRI scan to compensate for patient motion during the scan.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
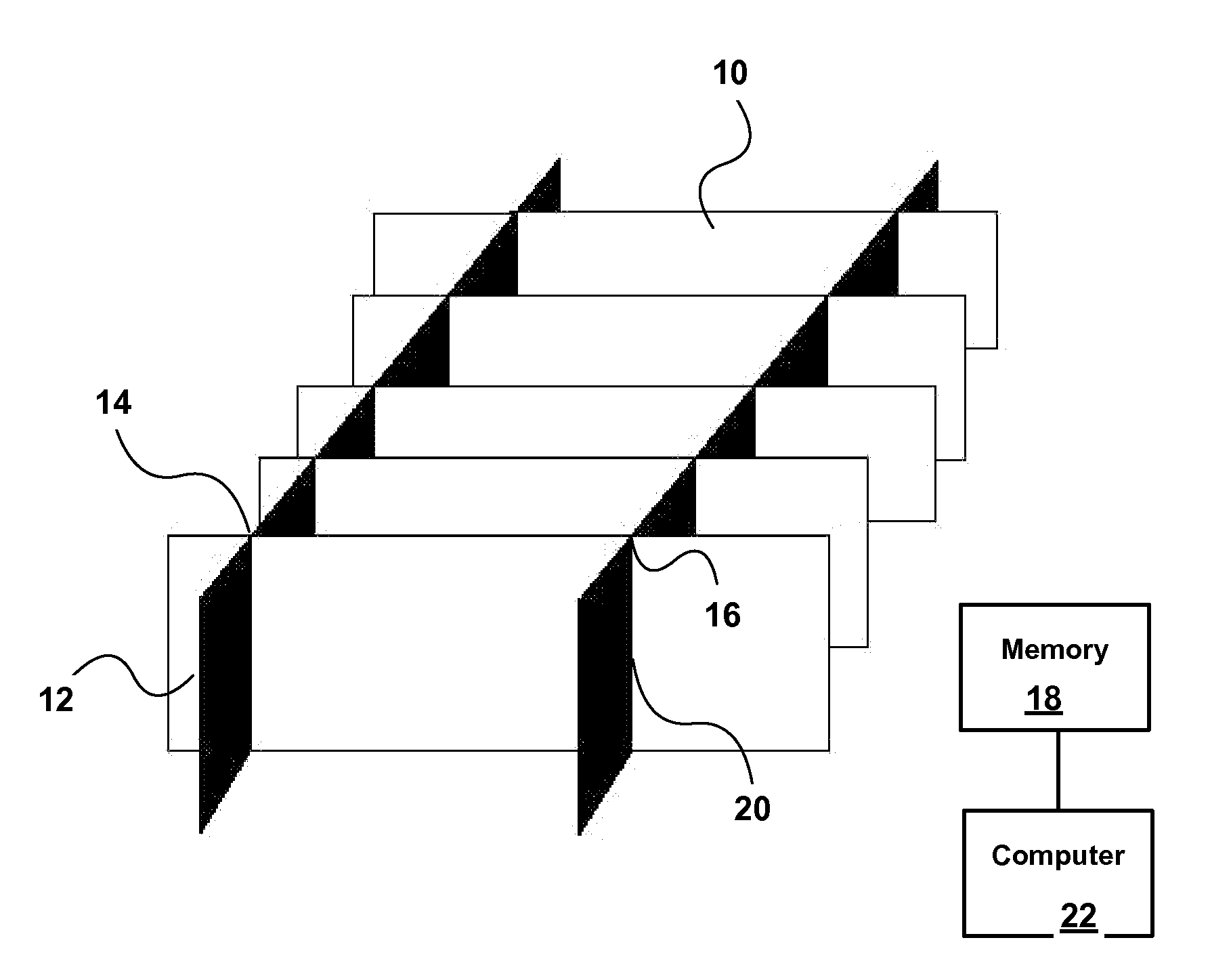
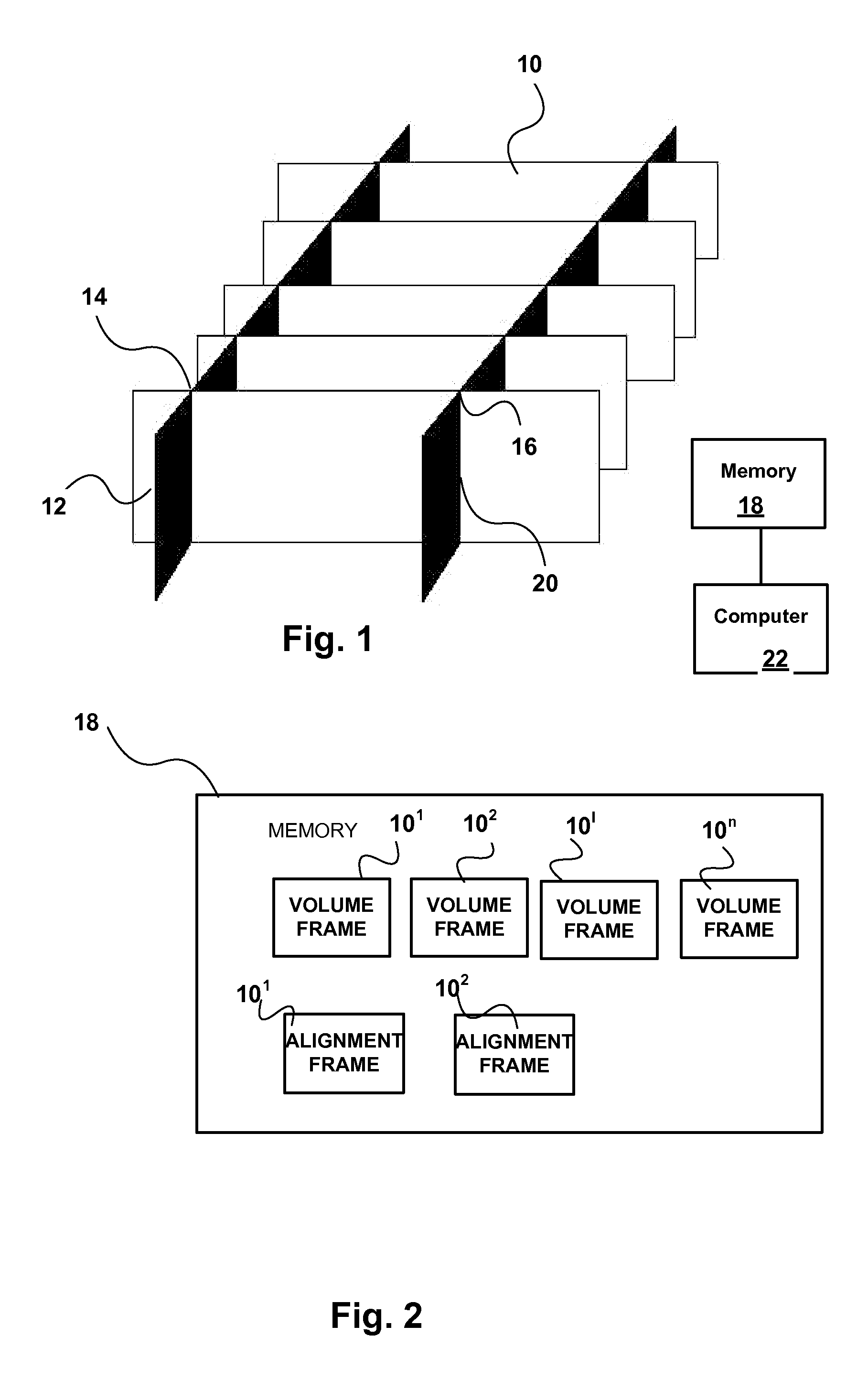
Method for correcting patient motion when obtaining retina volume using optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20090103049A1Remove Motion ArtifactsImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeRelative displacement
A computer-implemented method of correcting for motion of a sample during OCT imaging obtains a series of cross-sectional volume scans through the sample at different positions on a first coordinate axis, obtains at least two cross-sectional alignment scans in planes intersecting said volume scans at an angle, and stores the alignment scans and the volume scans in memory. The alignment scans are matched to the volume scans at lines of intersection thereof to determine the relative displacement of the volume scans to the sample due to sample motion. The relative displacement is used to correct for motion of the sample between successive volume scans.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com