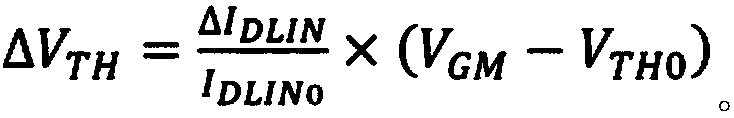Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
224 results about "Total dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
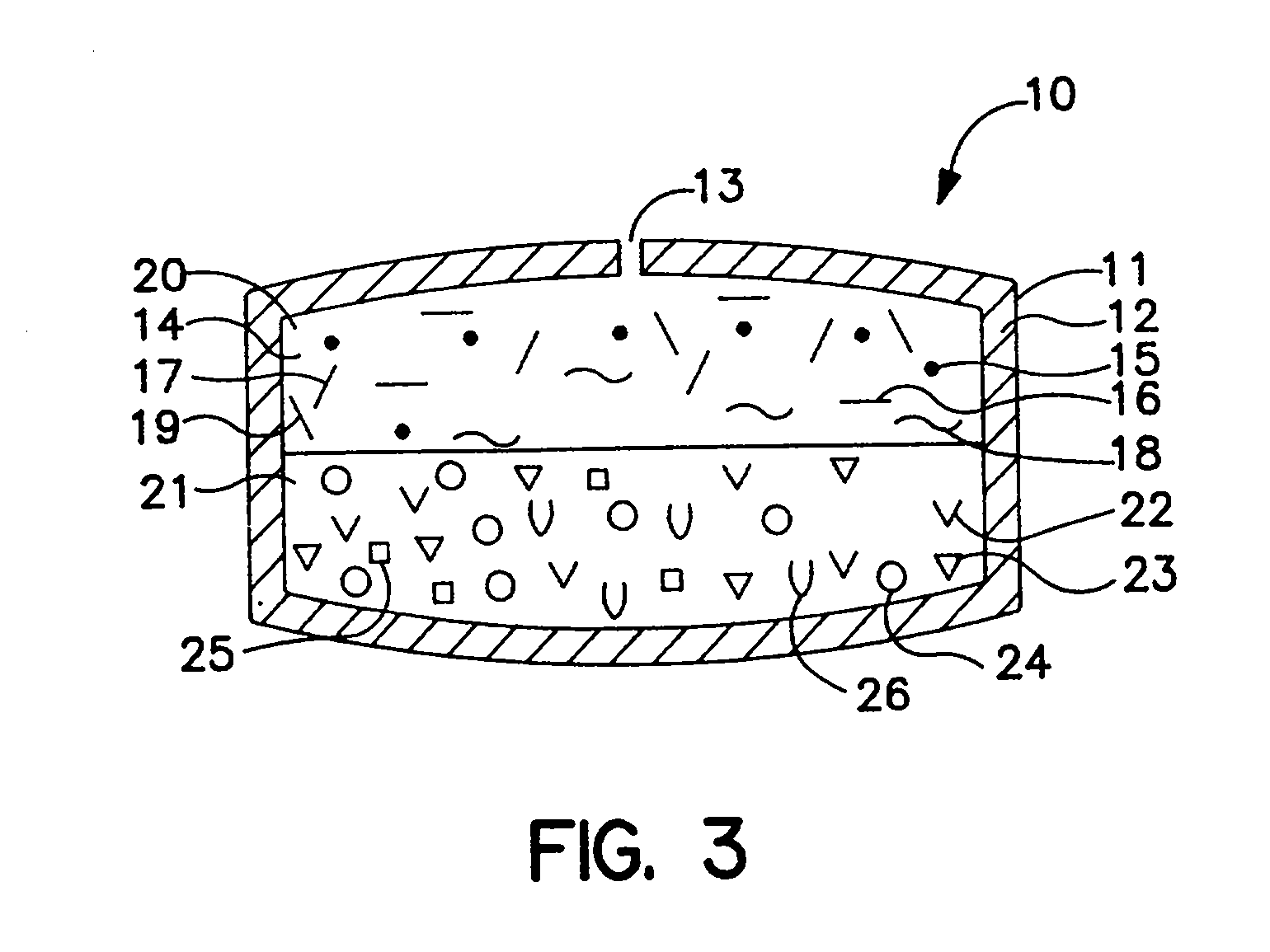
The total daily dose is calculated from the dose and the number of times per day the dose is taken. The dosage form is the physical form of a dose of drug. Common dosage forms include tablets, capsules, creams, ointments, aerosols and patches. Each dosage form may also have a number of specialized forms such as...
Generic multi-step therapeutic treatment protocol
InactiveUS7008413B2Improve versatilityOvercomes shortcomingPhysical therapies and activitiesDrug and medicationsDosage adjustmentTherapeutic treatment
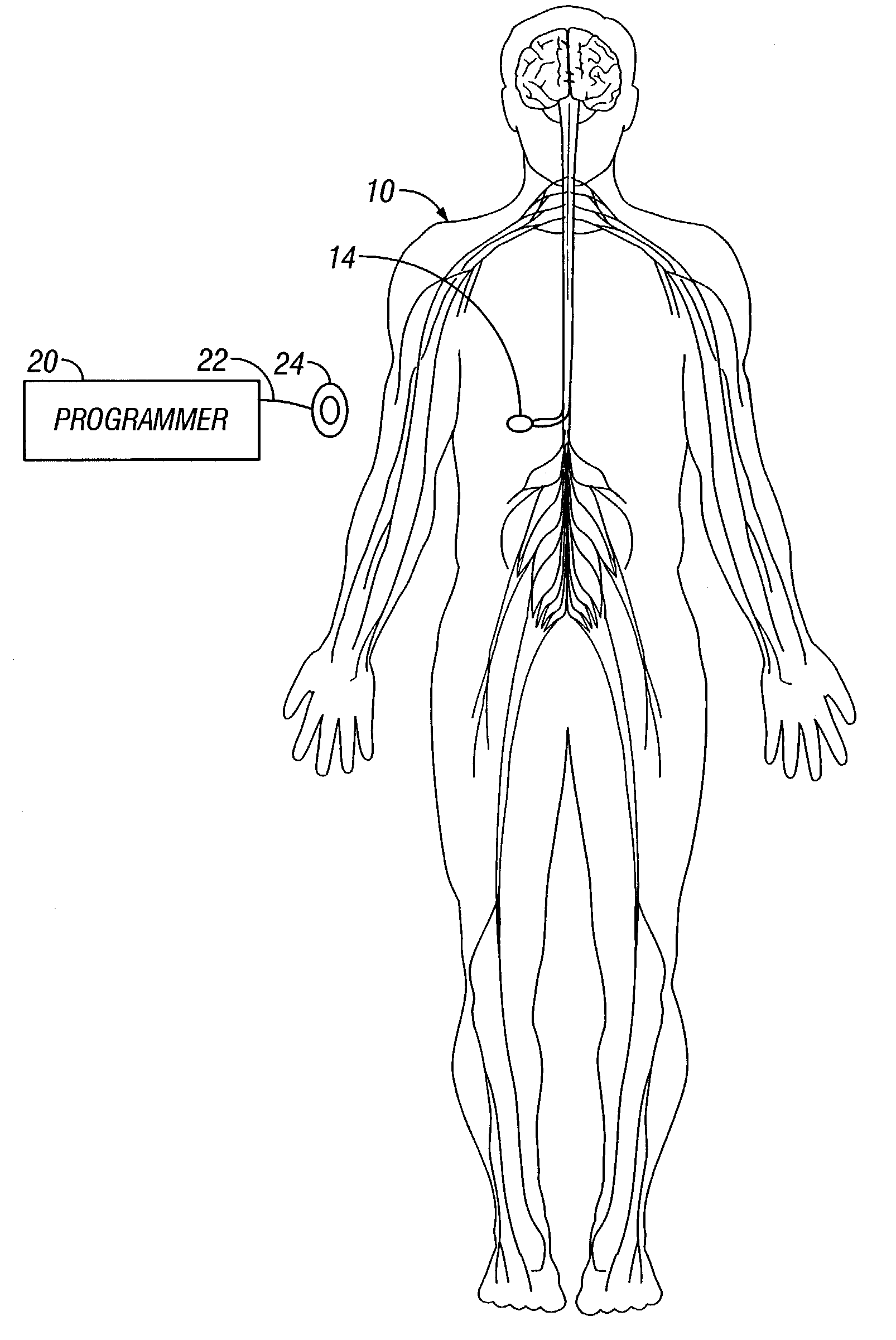
A generic treatment protocol is disclosed for therapeutically treating a patient via an implantable treatment device. Treatment steps can be defined to start and end at absolute times, or can be programmed via telemetry to start a certain amount of time after termination of a previously executed treatment step. Treatment steps have a treatment rate or dose attribute and a duration attribute. Treatment steps may optionally enable patient-activated bolus overlays. Patient-activated rate or dosage adjustments can also optionally be enabled. Repeated-execution treatment-step groups are also provided. Such treatment-step groups can have start and end times, a group duration, and a group total dose, each defined in a manner similar to that for a treatment step. Treatment-step groups include a repetition count, which could be set to a value that causes the group to repeat forever. Single execution treatment steps can, accordingly, be programmed to execute before and / or after a repeated-execution treatment-step group.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of treating stroke with thrombolytic agent
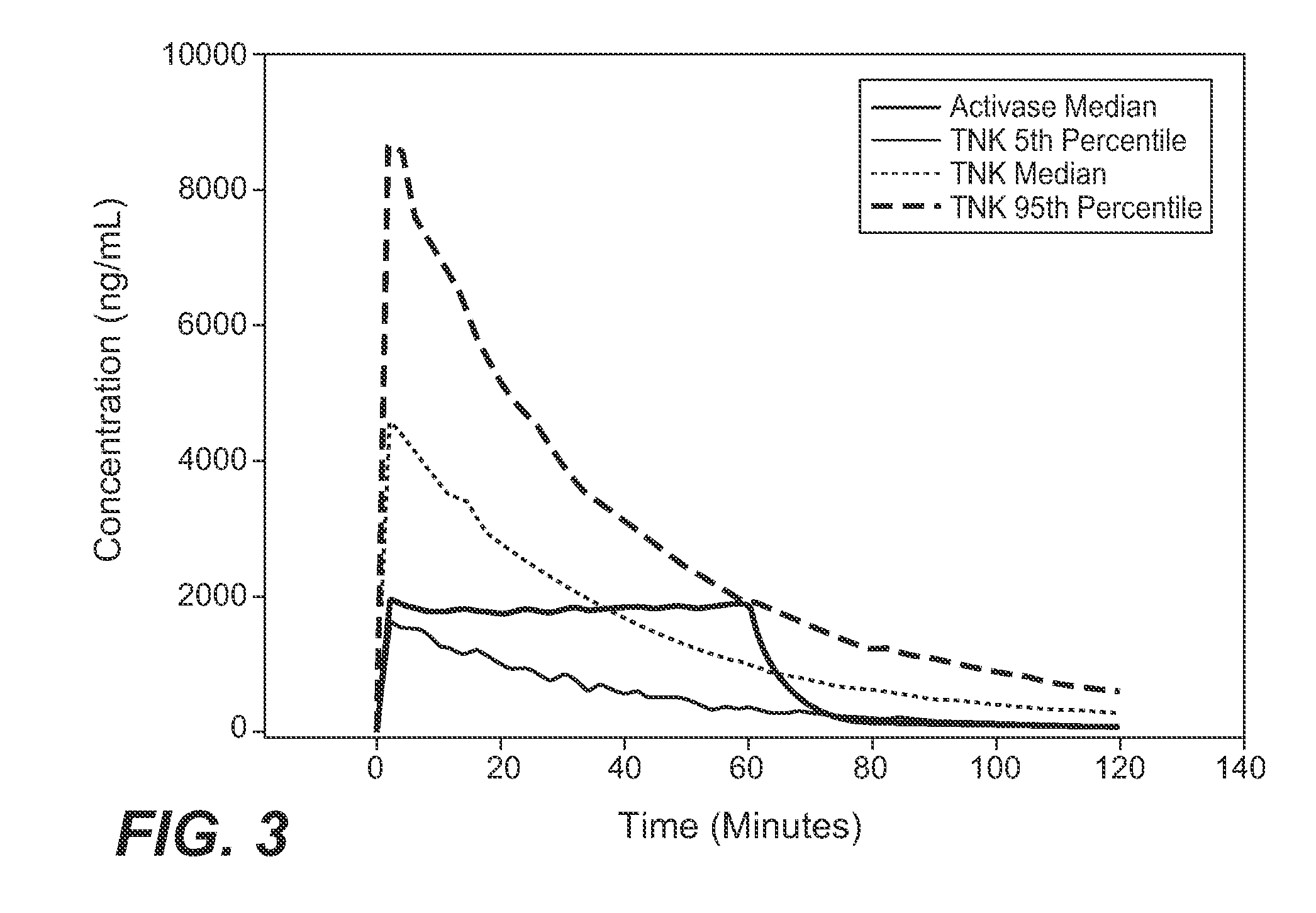
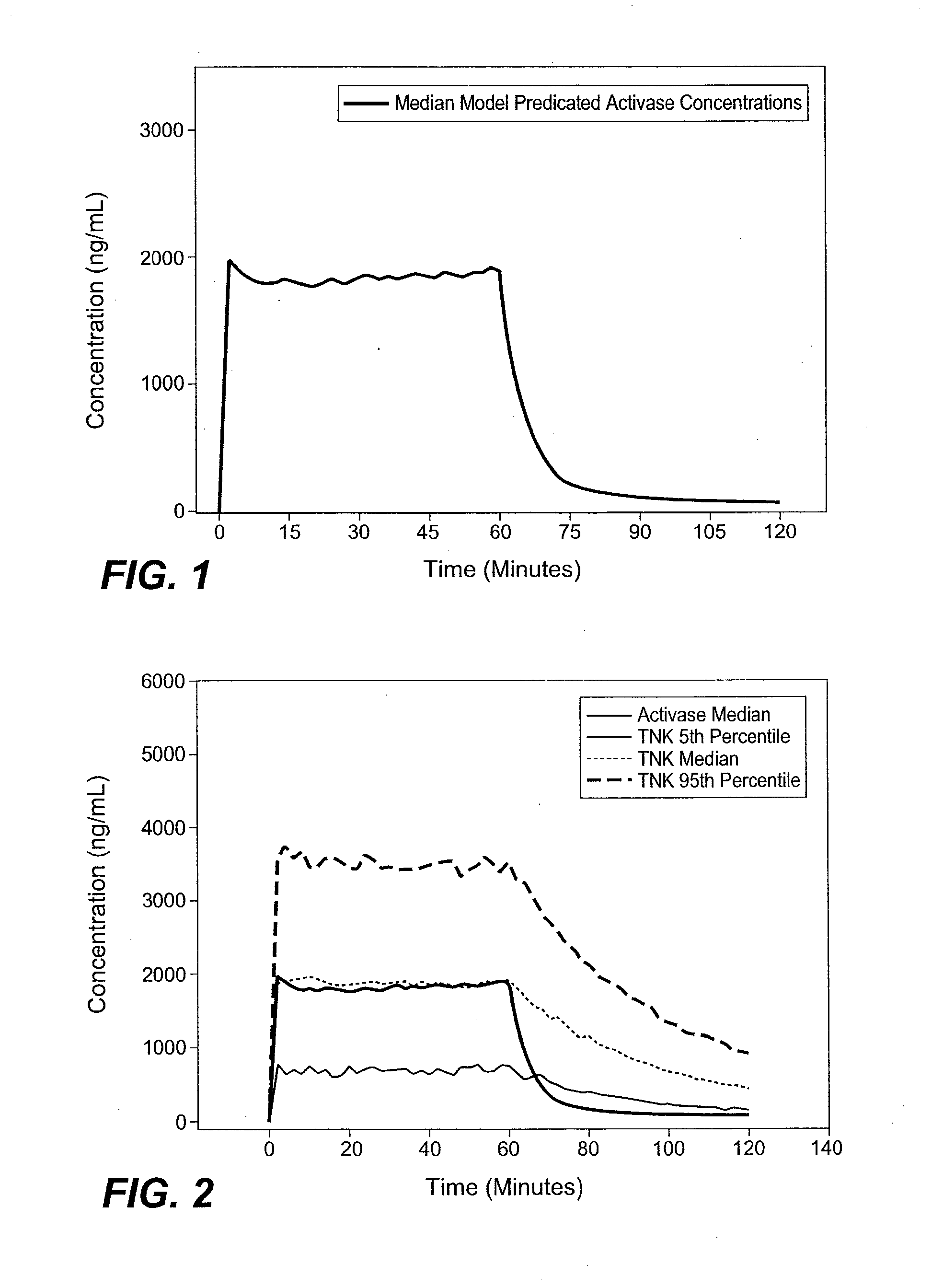
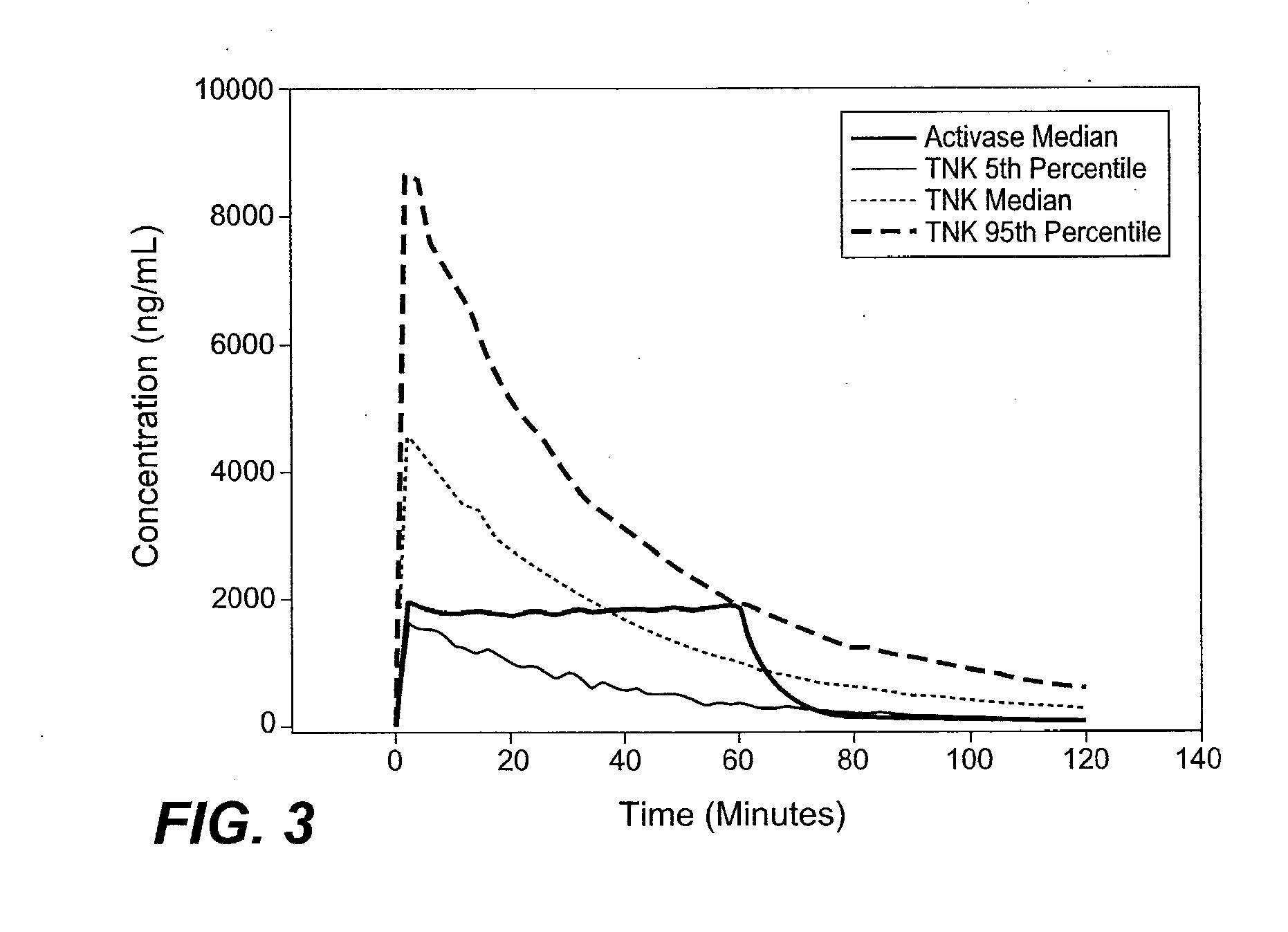
A method for treating acute ischemic stroke in a human comprises administering tenecteplase to the human in a total dose of about 0.05 to 0.5 mg / kg, given as (a) an initial bolus dose of about 0.015 to 0.15 mg / kg, followed by infusion of an amount equaling the total dose minus the initial dose over a period of about 50-90 minutes, or (b) a bolus. Also described are kits for carrying out this method.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Gel composition and methods
InactiveUS20060013879A9Effective distributionLow loading ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineWhole body
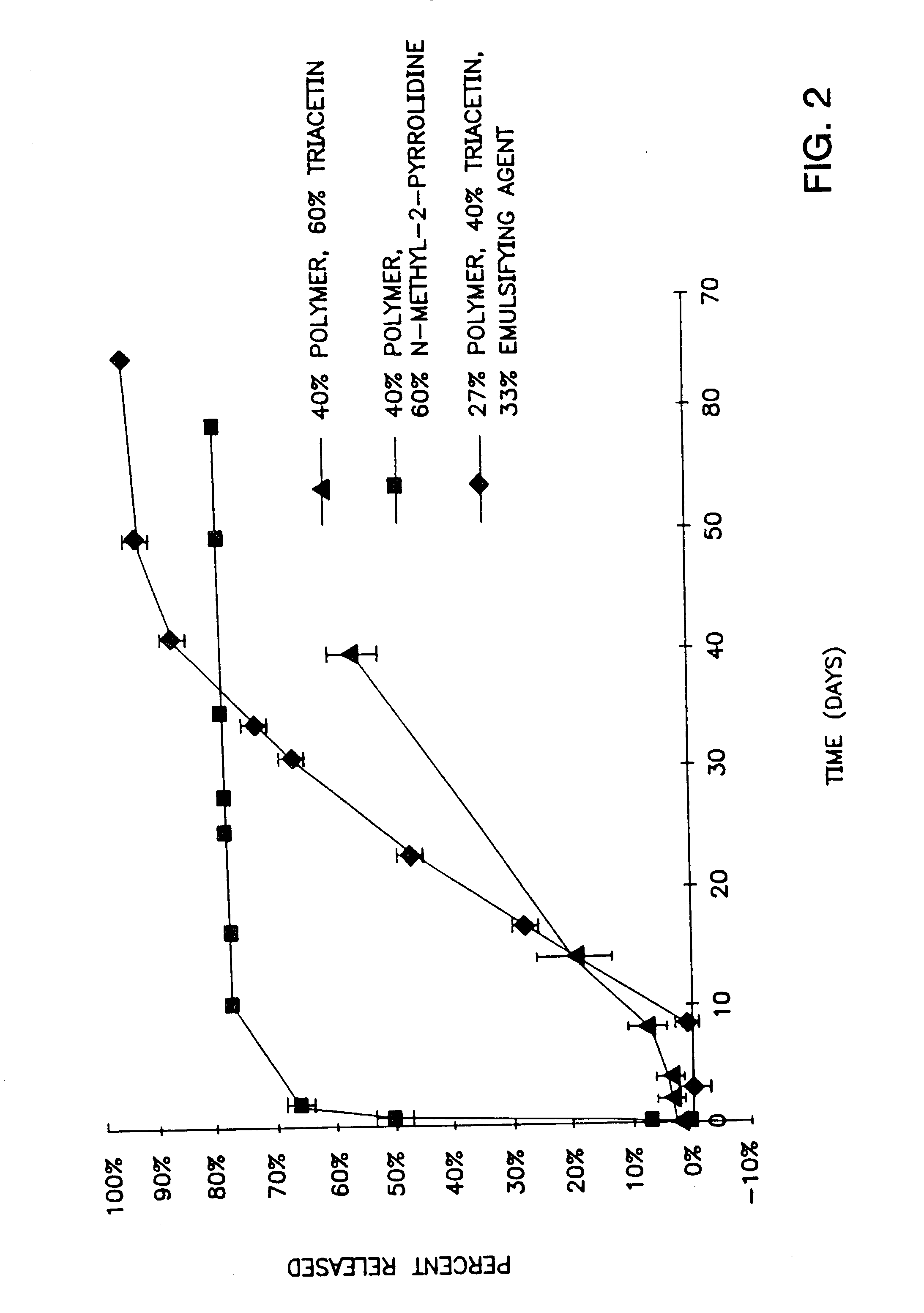
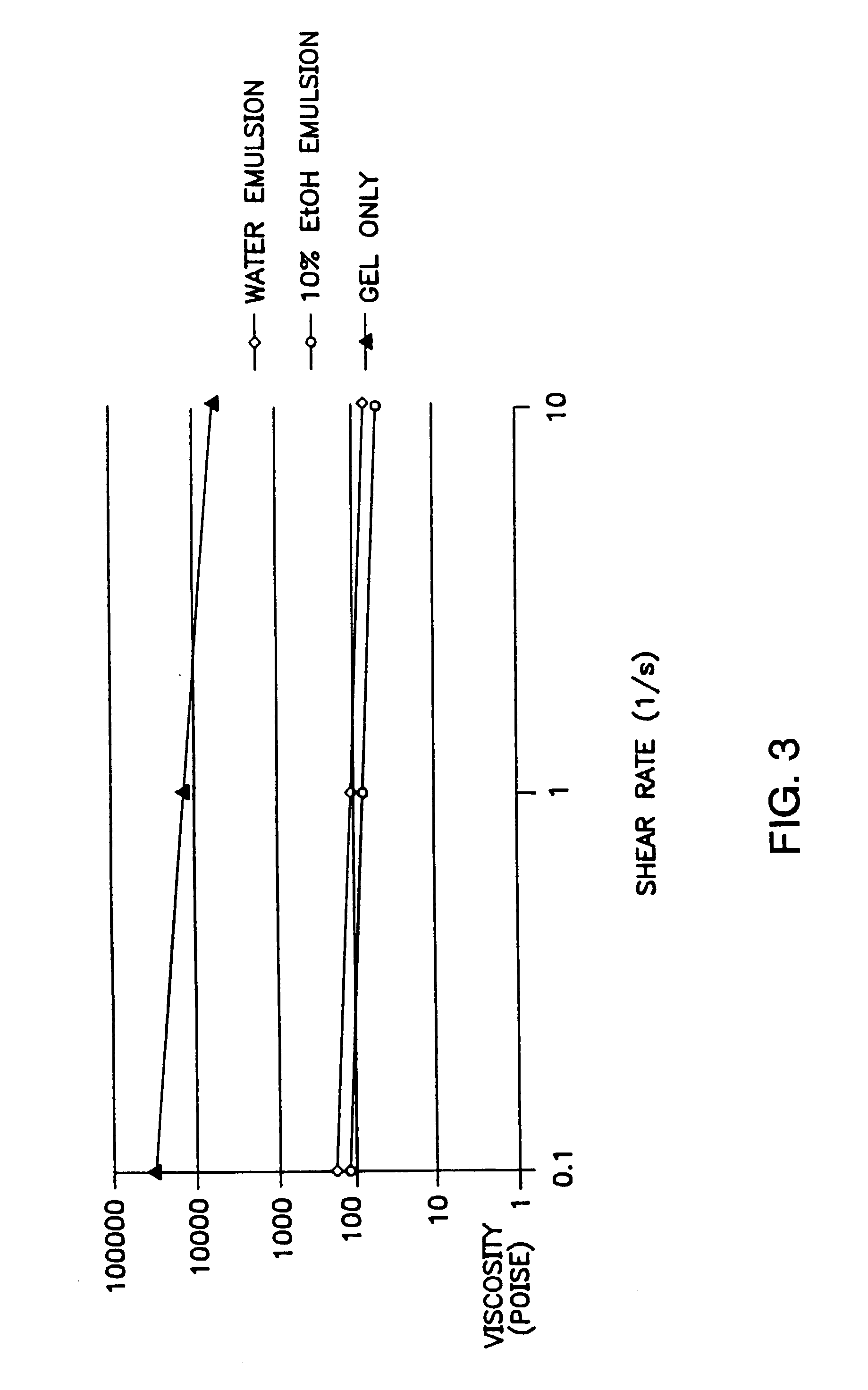
Methods and compositions for systemically or locally administering by implantation a beneficial agent to a subject are described, and include, for example, compositions having burst indices of 8 or less for systemic applications and systems releasing 10% or less of the total dose of beneficial agent in the first 24 hours after implantation for local applications. The compositions include a biocompatible polymer, a biocompatible solvent having low water miscibility that forms a viscous gel with the polymer and limits water uptake by the implant, and a beneficial agent.
Owner:DURECT CORP
Method of treating stroke with thrombolytic agent
A method for treating acute ischemic stroke in a human comprises administering tenecteplase to the human in a total dose of about 0.05 to 0.5 mg / kg, given as (a) an initial bolus dose of about 0.015 to 0.15 mg / kg, followed by infusion of an amount equaling the total dose minus the initial dose over a period of about 50-90 minutes, or (b) a bolus. Also described are kits for carrying out this method.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Sequentially cross-linked polyethylene
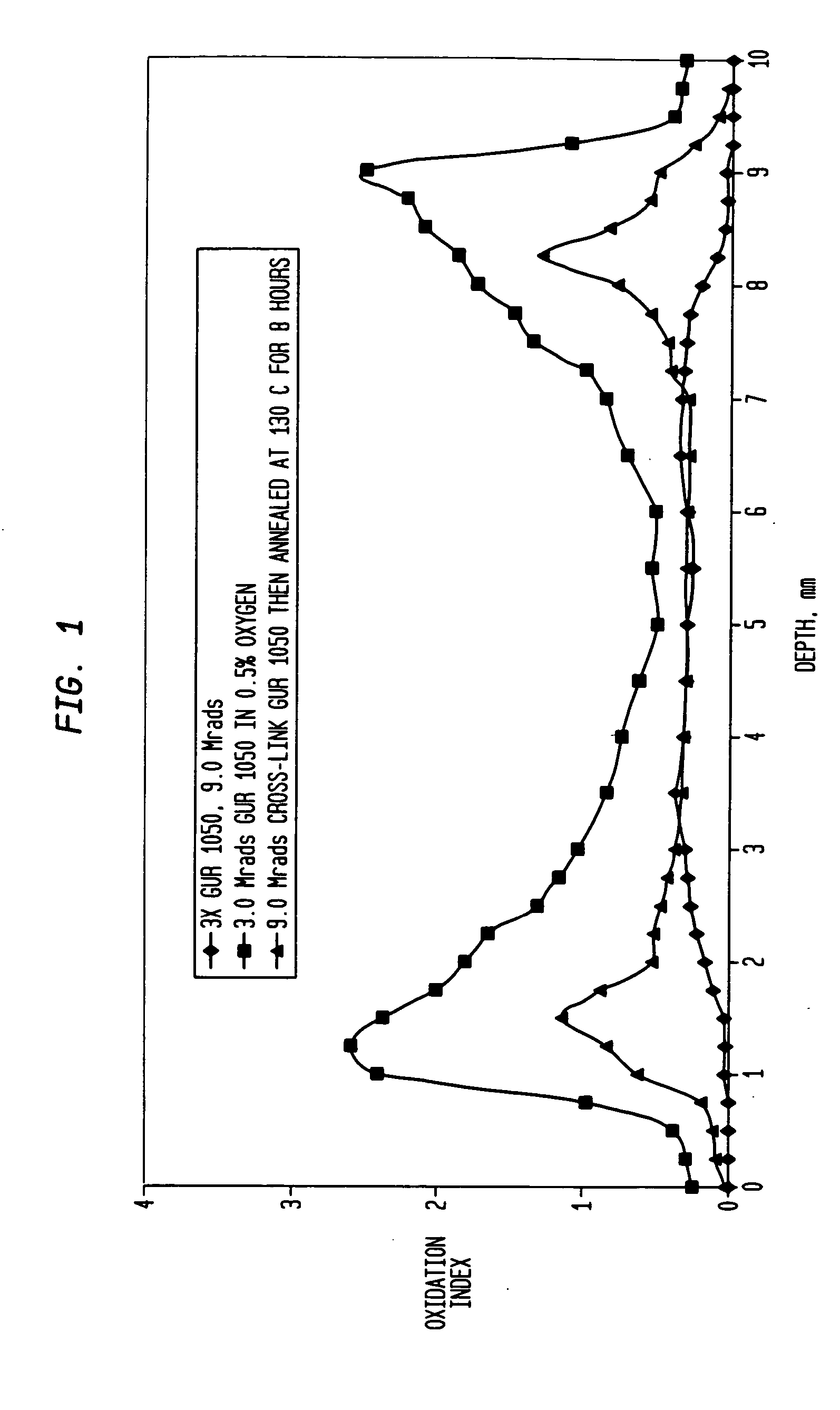
A method of producing an improved polyethylene, especially an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene utilizes a sequential irradiation and annealing process to form a highly cross-linked polyethylene material. The use of sequential irradiation followed by sequential annealing after each irradiation allows each dose of irradiation in the series of doses to be relatively low while achieving a total dose which is sufficiently high to cross-link the material. The process may either be applied to a preformed material such as a rod or bar or sheet made from polyethylene resin or may be applied to a finished polyethylene part. If applied to a finished polyethylene part, the irradiation and annealing must be accomplished with the polyethylene material not in contact with oxygen at a concentration greater than 1% oxygen volume by volume. When applied to a preform, such as a rod, the annealing of the bulk polymer part of the rod from which the finished part is made must take place on the rod before the implant is machined therefrom and exposed to oxygen.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for delivery of pulsed laser radiation
InactiveUS20070224768A1Improve throughputSpeed up the processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning processes and apparatusSurface reactionTotal dose
A method and apparatus delivers pulsed laser energy to a damage-sensitive surface. The pulse scanning method and apparatus allow for the deposition of a total dose of laser radiation that could not be attained by any conventional means without damaging the substrate being exposed. Using a solid-state diode pumped YAG laser and an enclosure with a gas ambient, laser pulses are scanned across a substrate according to one of several programmed approaches. Pulses are deposited that are non-adjacent in time, or non-adjacent in space, or both; conventional methods have the pulses adjacent in both time and space. Using the various approaches of the invention, the degree of spatial and temporal adjacency can be precisely controlled to permit significant laser radiation doses without causing any substrate damage. The present invention novel method and apparatus can be carried out by integrating a computer, laser and scan head with a small chamber into which gas can flow to permit a variety of surface reactions on damage-sensitive substrates that could otherwise not be conducted with conventional methods and systems.
Owner:UVTECH SYST
Pharmaceutical delivery system
InactiveUS20050095245A1Reduce adverse effectsEffectively impact the life cycleAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseGynecology
A pharmaceutical formulation to treat vaginal conditions in a human patient comprises: at least one active agent; a modified release dosage form which provides extended release of the anti-infective agent upon vaginal administration to the patient; and wherein the formulation, when containing a total dose of the anti-infective agent of about 25 μg to about 500 mg based on the active agent will produce a plasma concentration versus time curve (ng / mL versus hours) having an area under the curve (AUC) of less than about 600 ng / mL.hr.
Owner:DRAGTEK CORP
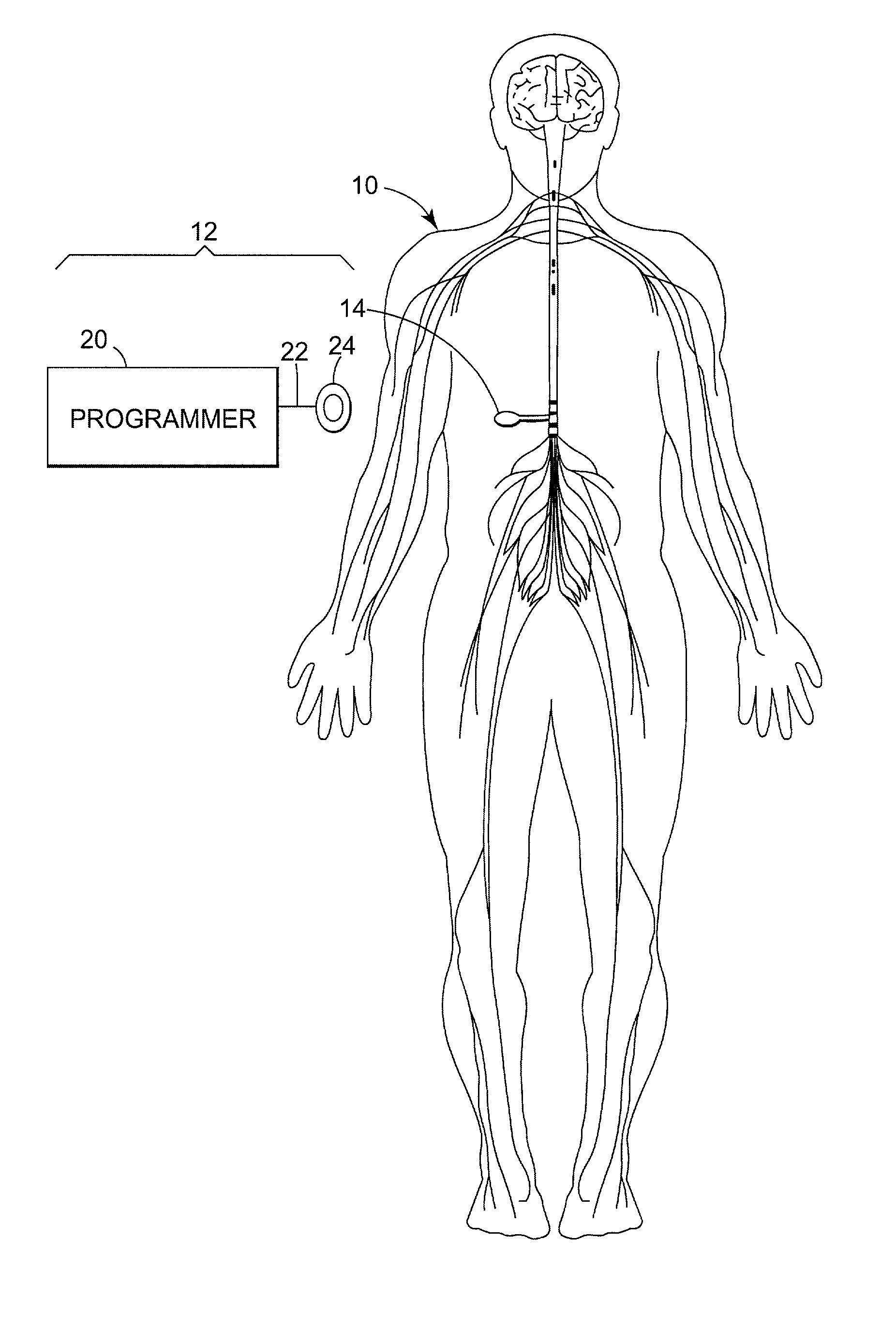
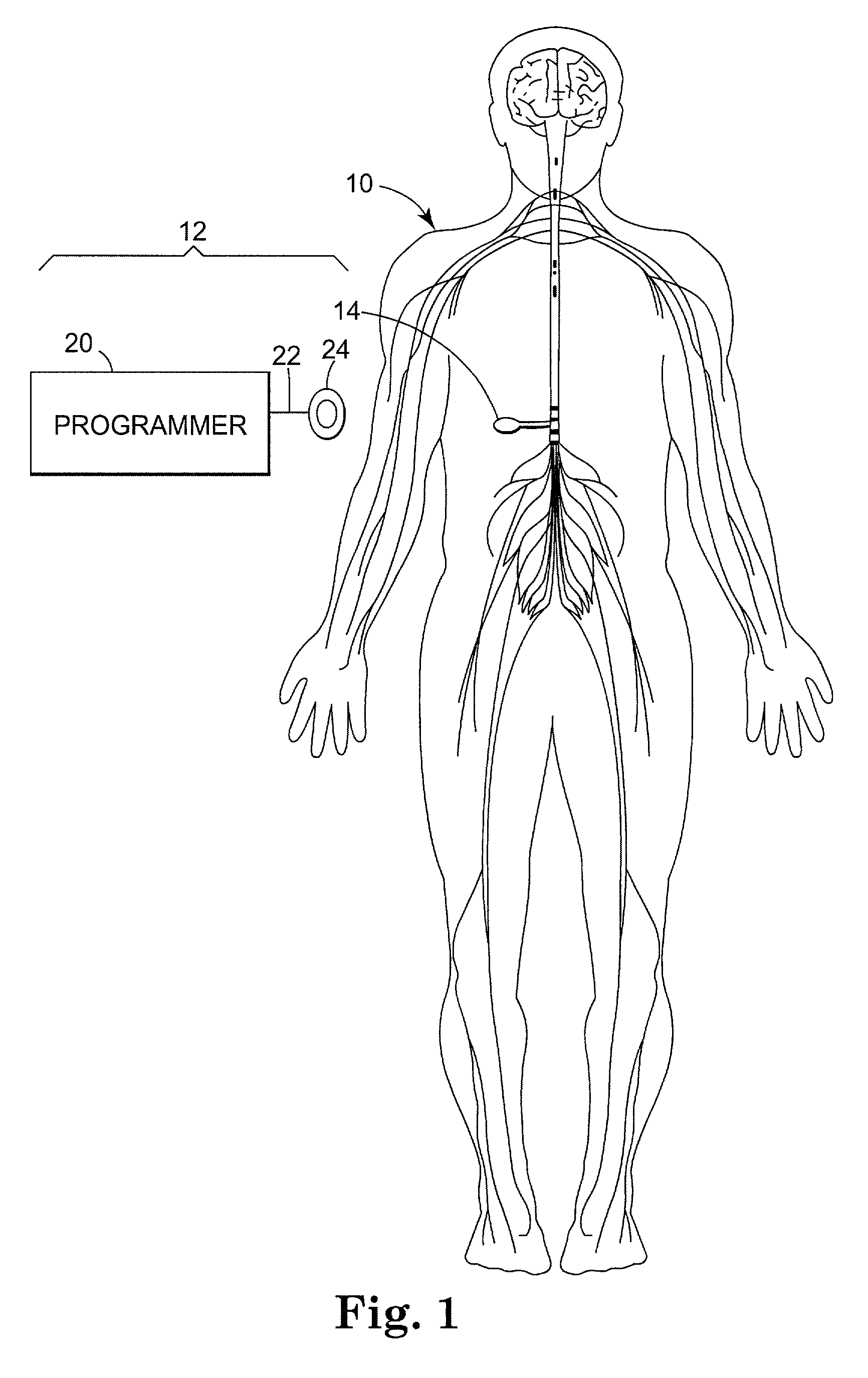
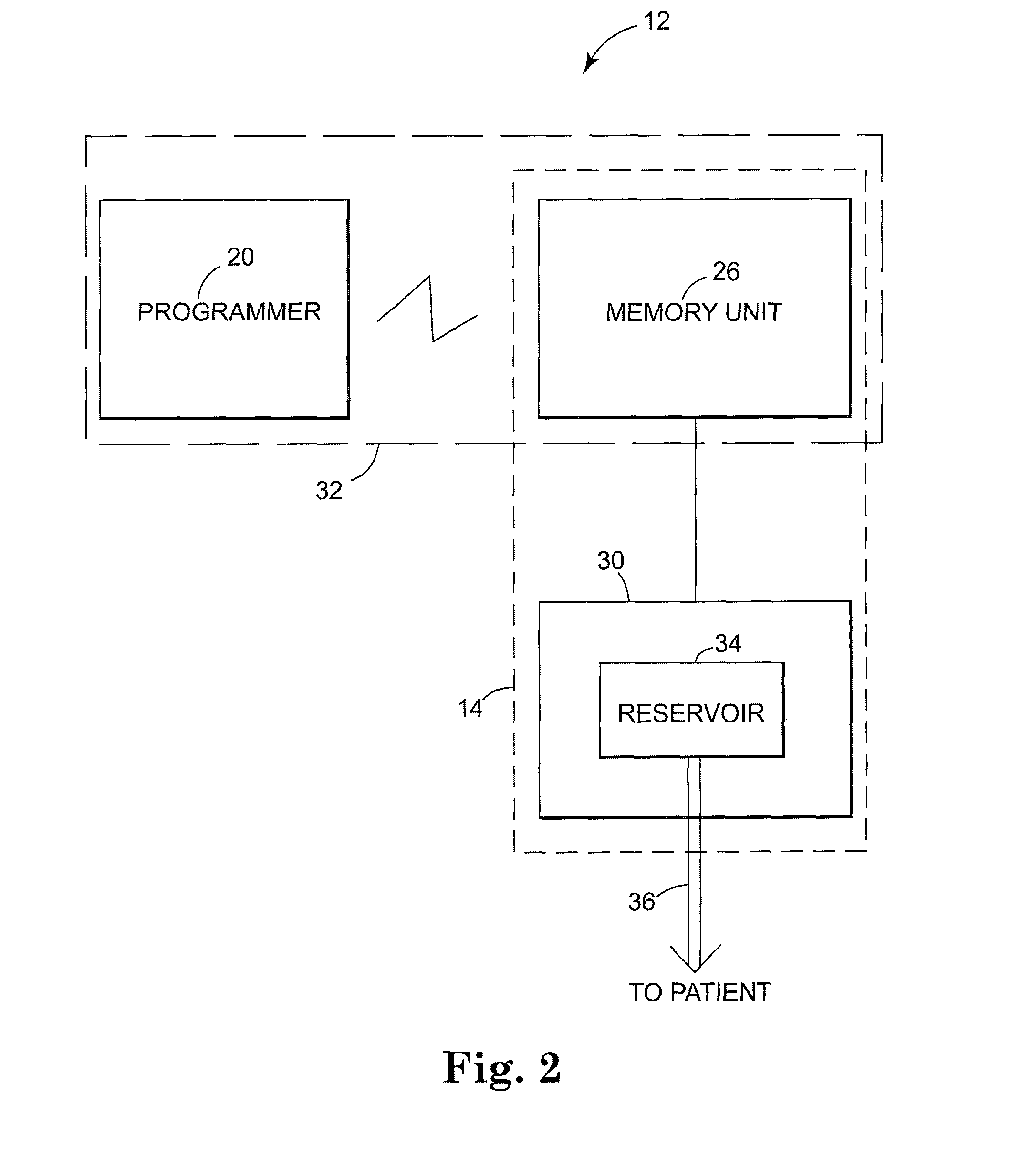
Drug infusion system programmable in flex mode
A drug infusion system capable of delivering a fluid medication to a patient under direction of a medical professional continually at a basal rate and at an interval rate in each of a plurality of time slots over a specified period of time. The total dose of the fluid medication to be delivered to the patient over the period of time based on the basal rate and the interval rate for each of the plurality of time slots is determined, compared the total dose against a maximum dose. The basal rate is adjusted, if necessary, so that the total dose does not exceed the maximum dose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
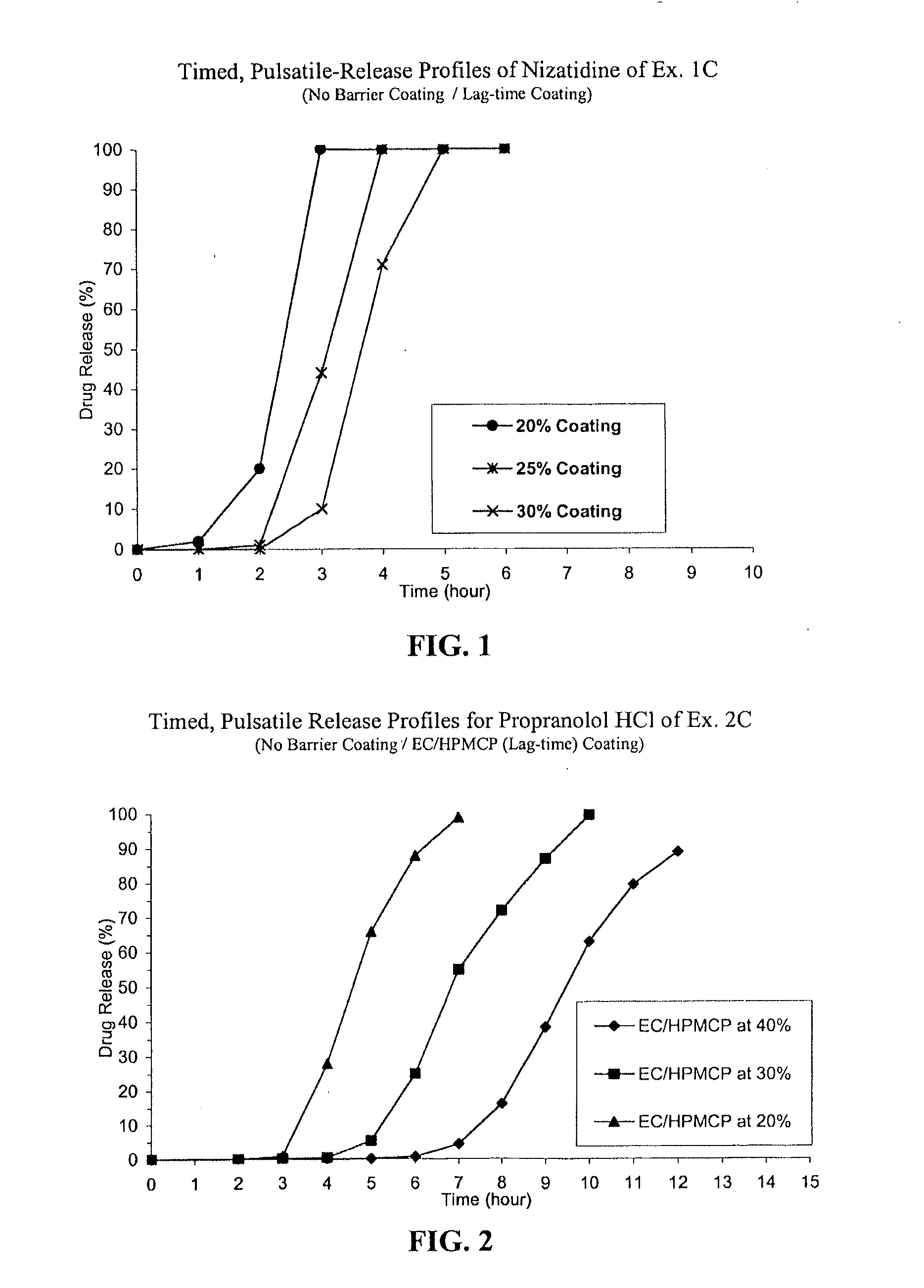
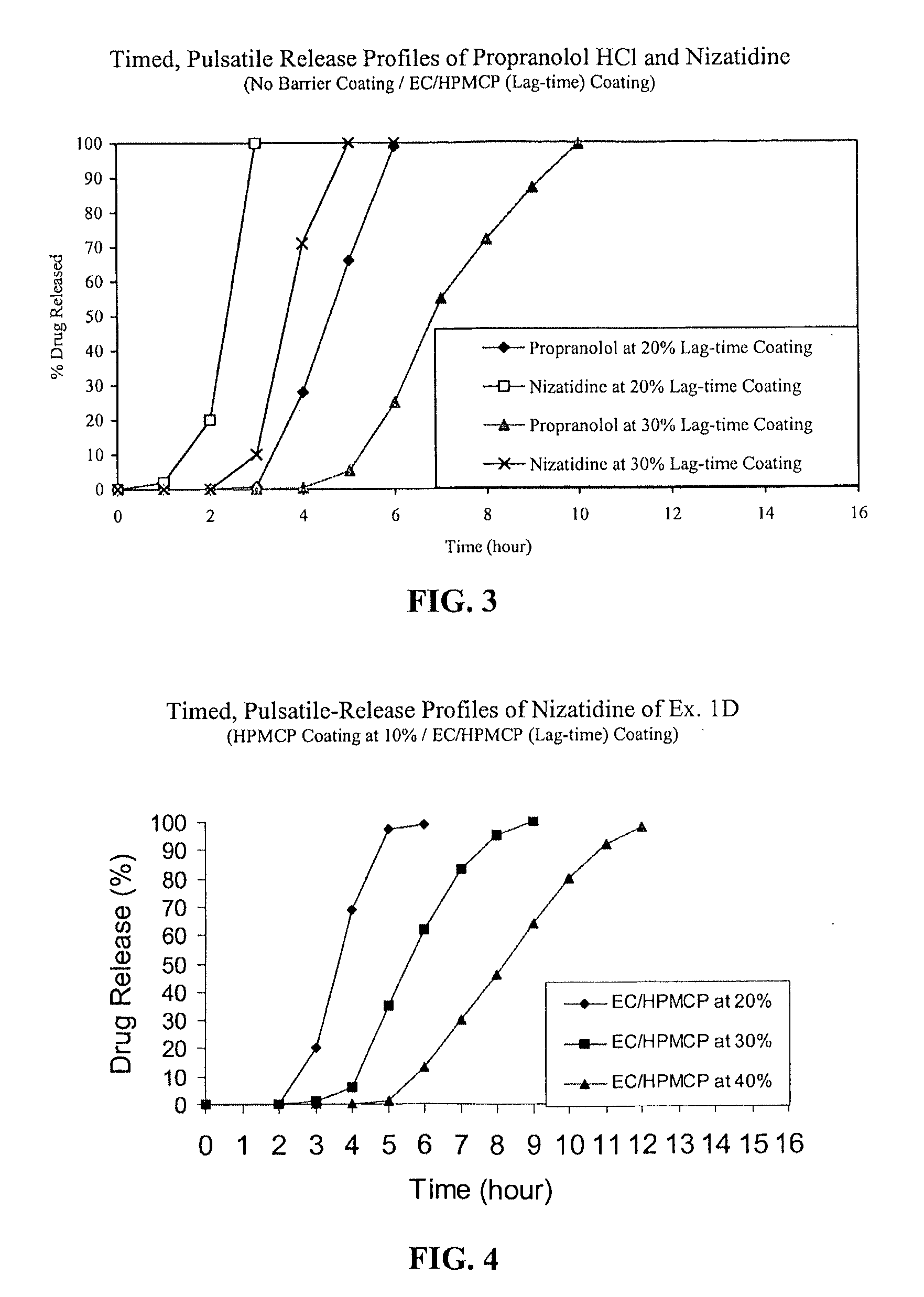
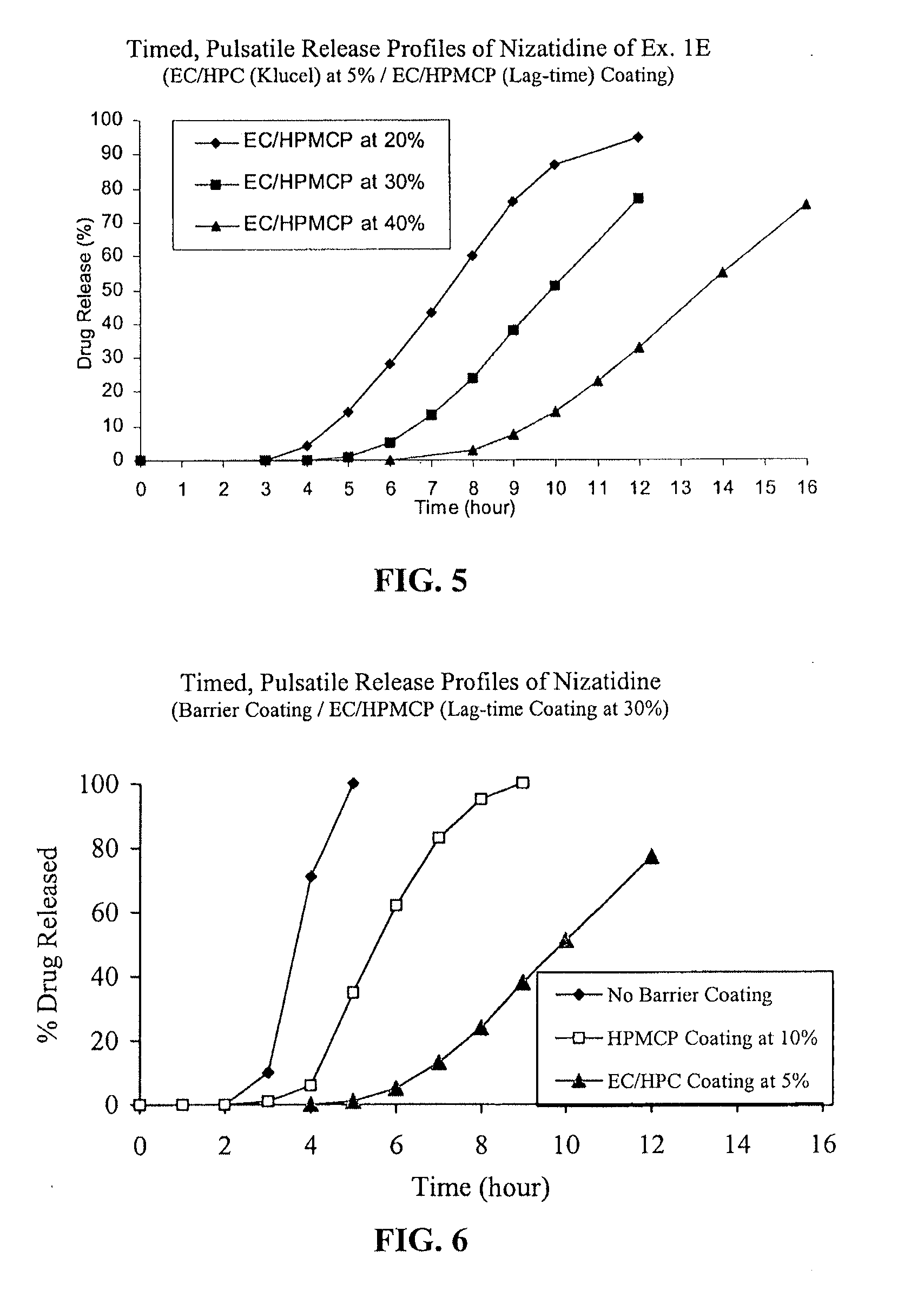
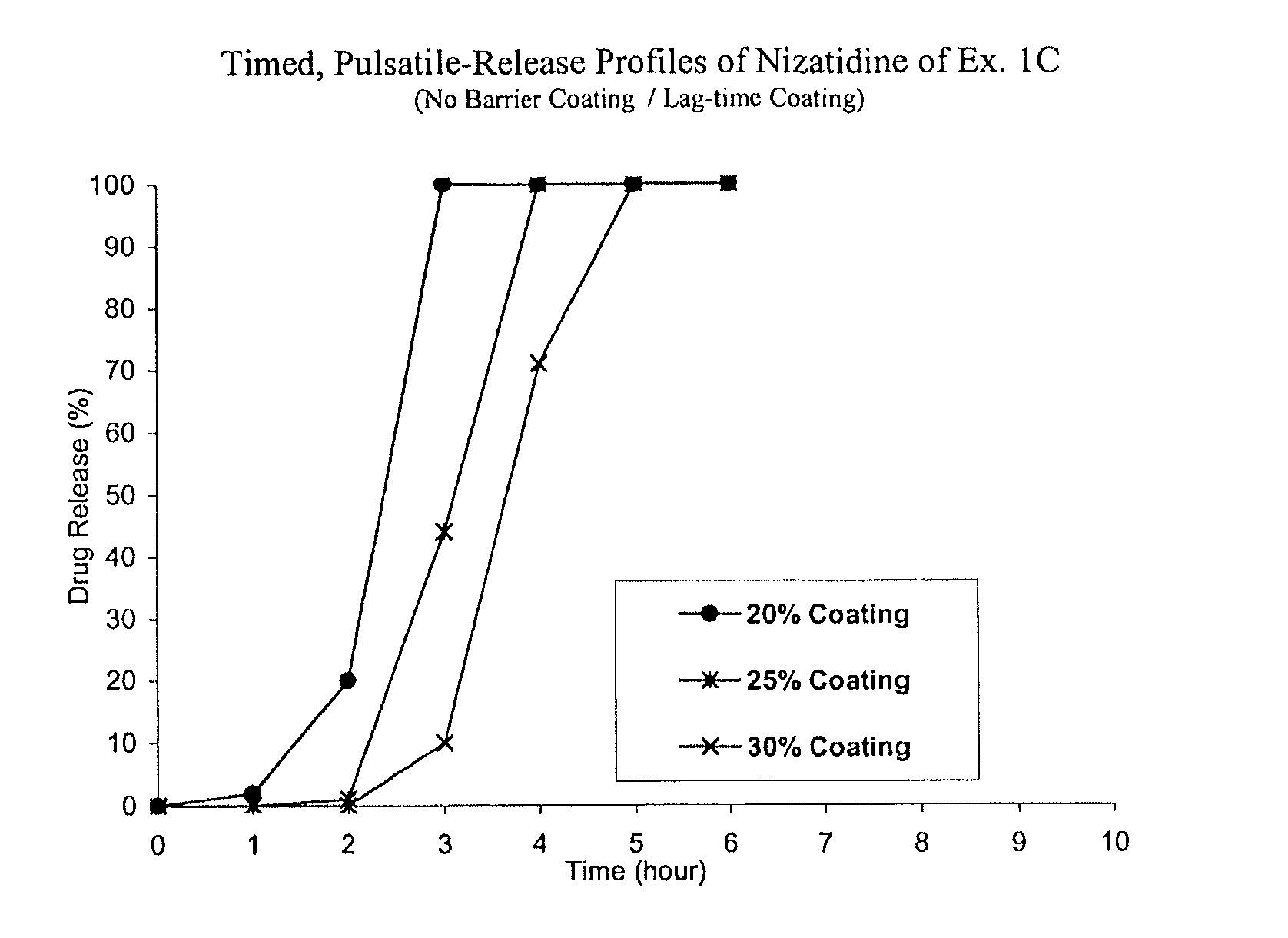
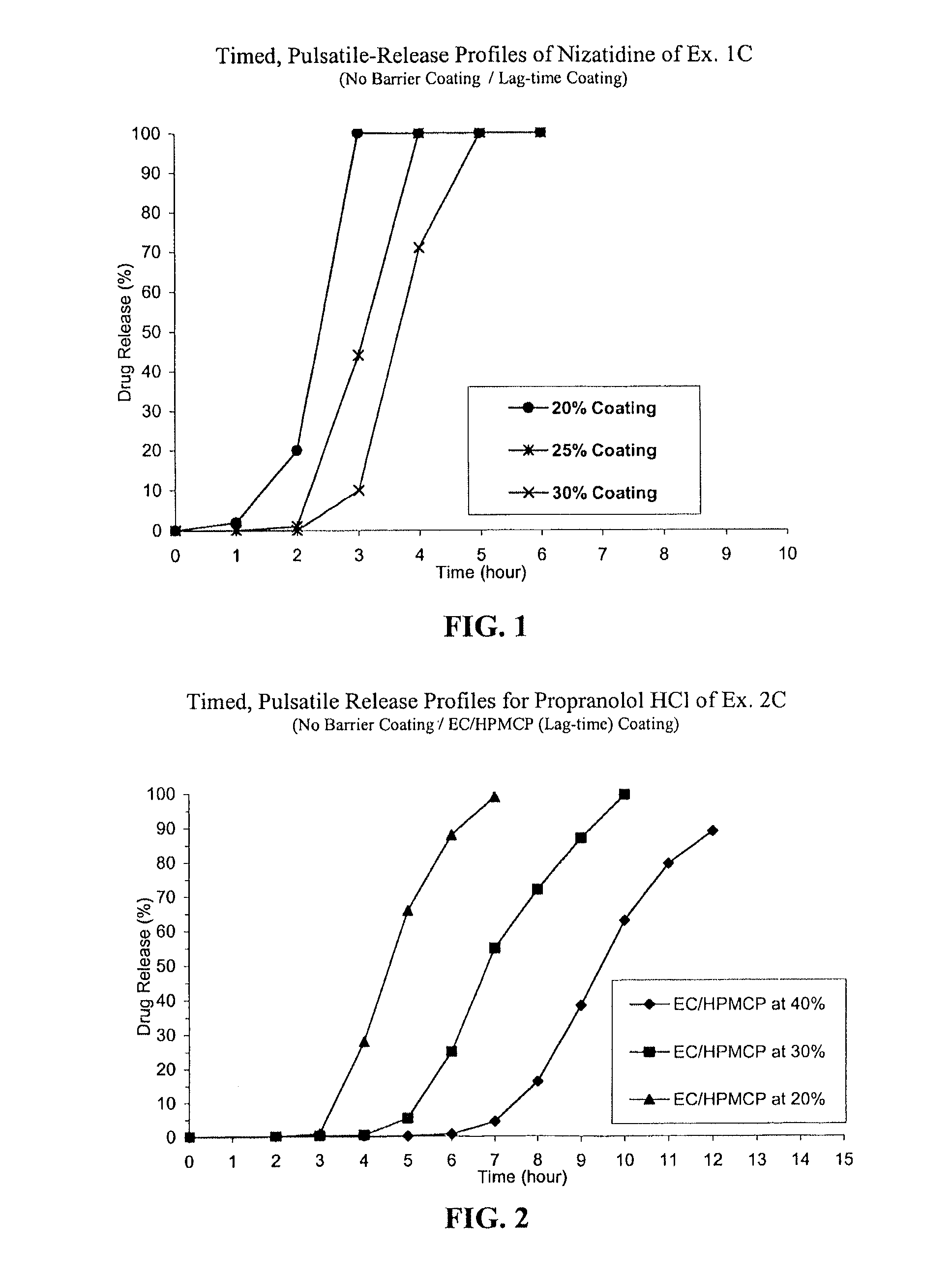
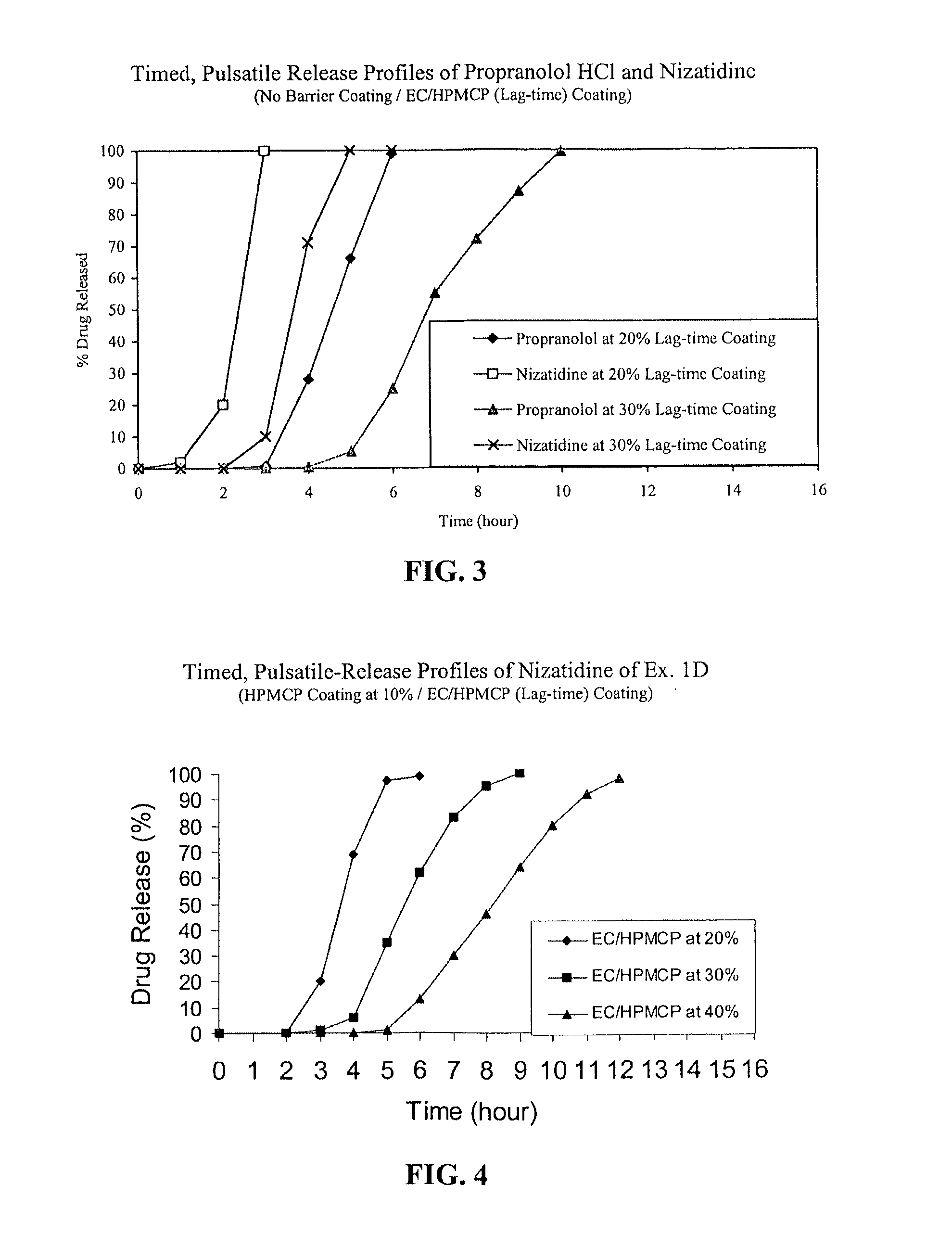
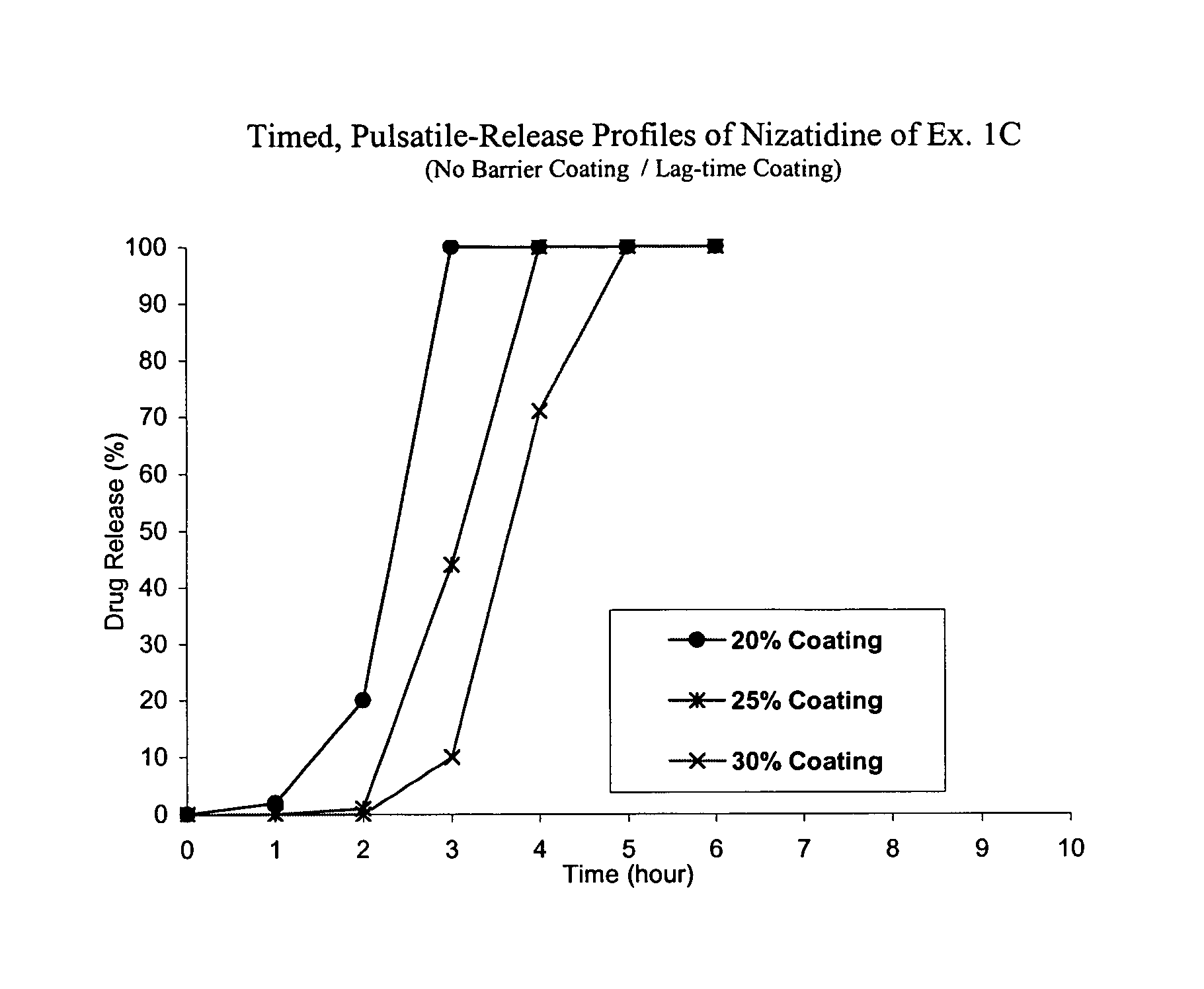
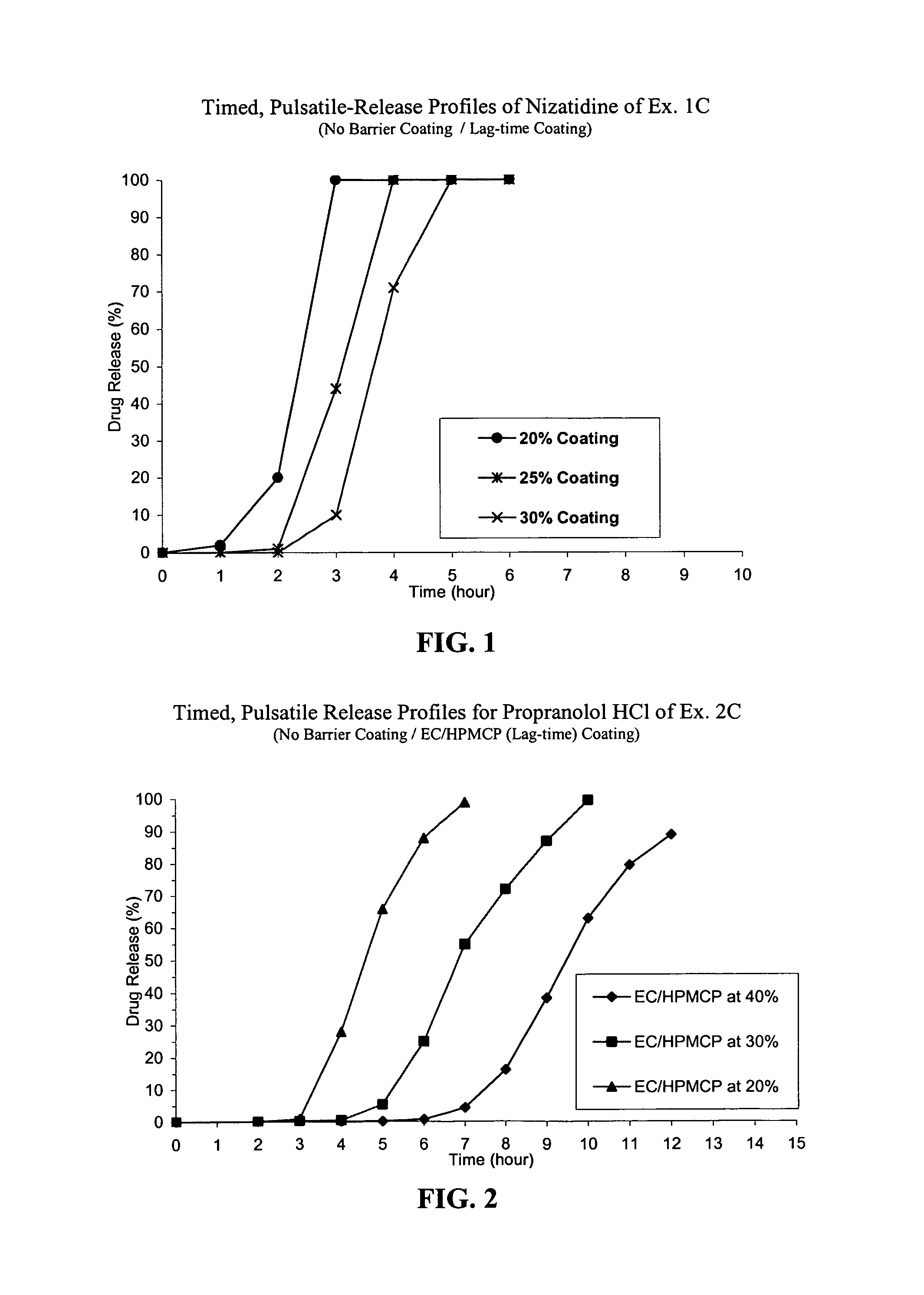
Timed, pulsatile release systems
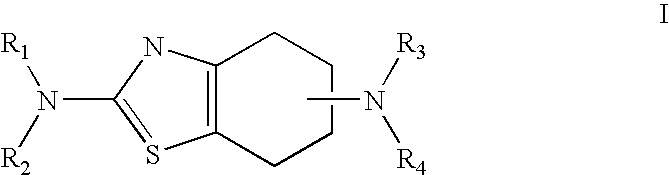
A unit multiparticulate dosage form for delivering one or more basic, active pharmaceutical ingredients into the body in need of such medications to achieve target PK (pharmacokinetics) profiles is described. The dosage form comprises one or more multicoated drug particles (beads, pellets, mini- / micro-tablets) having a barrier coating and a lag-time coating. Each Timed Pulsatile Release (TPR) bead population exhibits pre-determined lag-time followed by differing release characteristics. The composition and thickness of the barrier coating, composition and thickness of the lag-time coating, ratio of IR beads to one or more TPR bead populations and total dose may be varied depending on the alkalinity, pH-dependent solubility and elimination half-life of the active ingredients to achieve target PK profiles (suitable for a once or twice daily dosing regimen) in patients in need of such medications.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
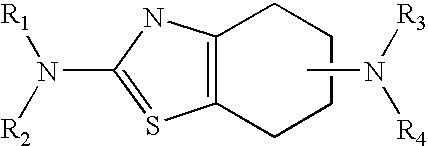
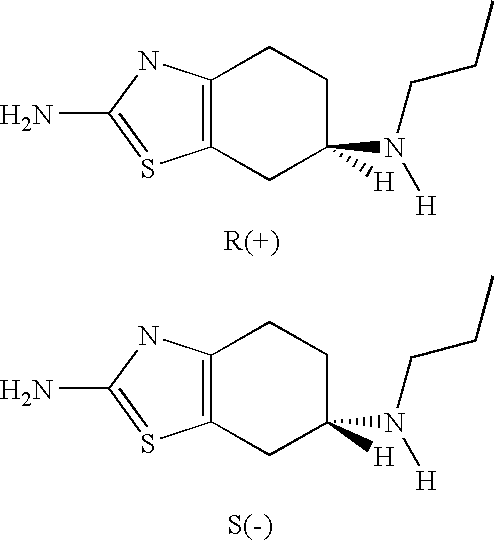
Neurorestoration with R(+) Pramipexole
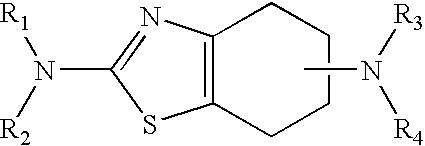
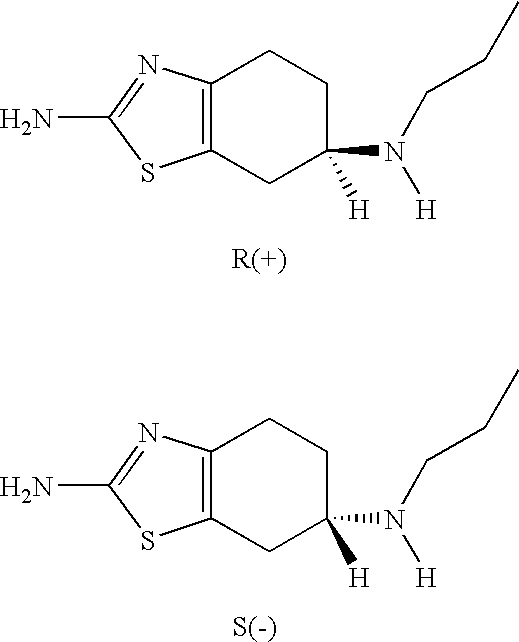
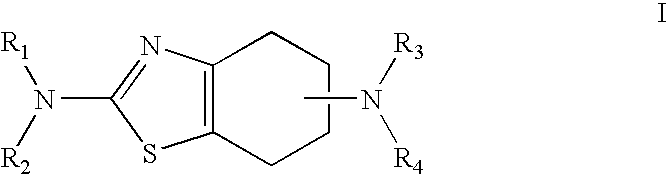
Formulations and methods of use thereof for restoring neuronal, muscular (cardiac and striated) and / or retinal tissue function in children and adults afflicted with chronic neurodegenerative diseases, such as neurodegenerative movement disorders and ataxias, seizure disorders, motor neuron diseases, and inflammatory demyelinating disorders, are described herein. Examples of disorders include Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The method involves administering a pharmaceutical composition containing an effective amount of a tetrahydrobenzathiazole, preferably a formulation consisting substantially of the R(+) enantiomer of pramipexole. R(+) pramipexole is generally administered in doses ranging from 0.1-300 mg / kg / daily, preferably 0.5-50 mg / kg / daily, and most preferably 1-10 mg / kg / daily for oral administration. Daily total doses administered orally are typically between 10 mg and 500 mg. Alternatively, R(+) pramipexole can be administered parenterally to humans with acute brain injury in single doses between 10 mg and 100 mg and / or by continuous intravenous infusions between 10 mg / day and 500 mg / day.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
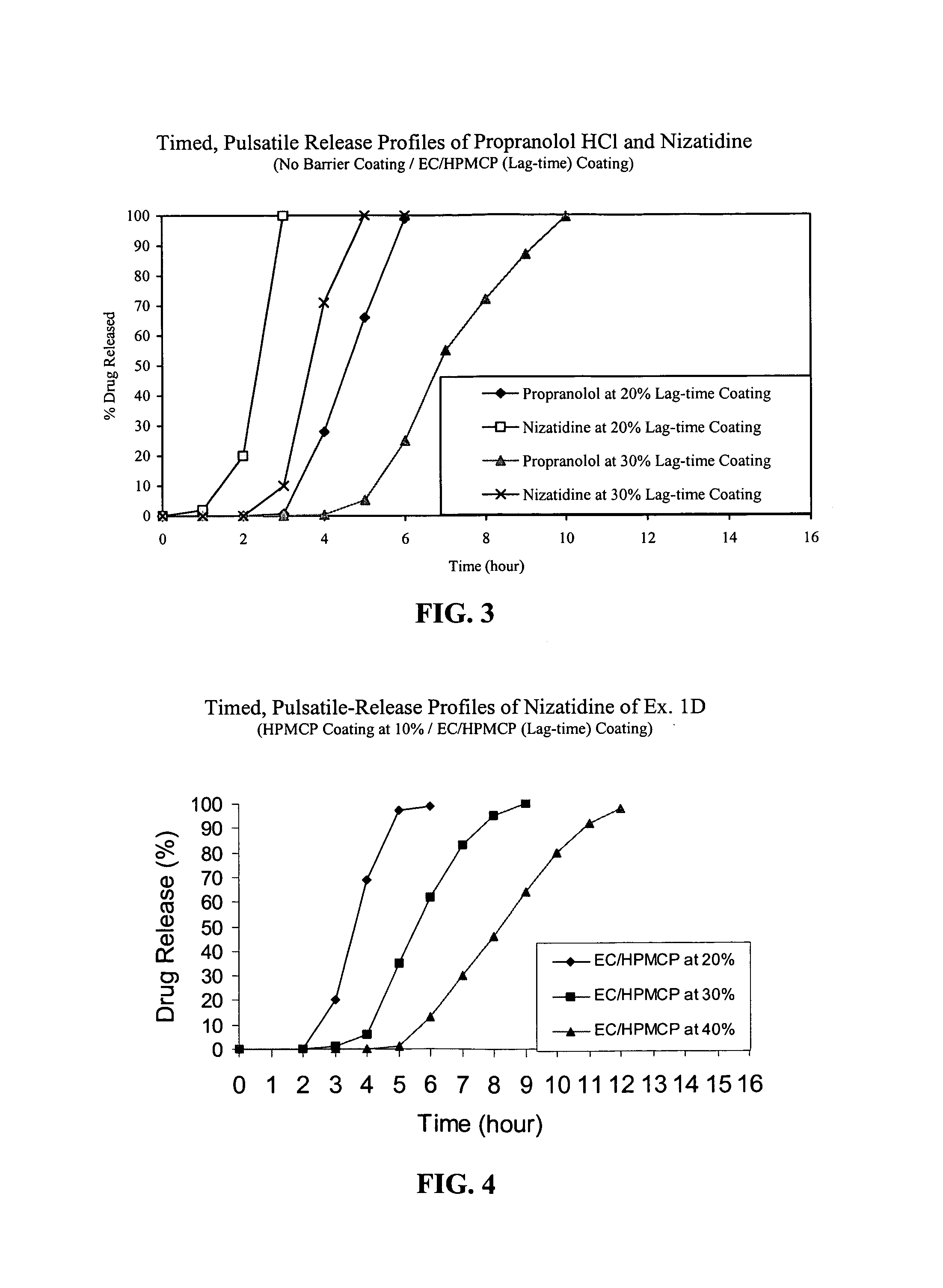
Timed, pulsatile release systems
A unit multiparticulate dosage form for delivering one or more basic, active pharmaceutical ingredients into the body in need of such medications to achieve target PK (pharmacokinetics) profiles is described. The dosage form comprises one or more multicoated drug particles (beads, pellets, mini- / micro-tablets) having a barrier coating and a lag-time coating. Each Timed Pulsatile Release (TPR) bead population exhibits pre-determined lag-time followed by differing release characteristics. The composition and thickness of the barrier coating, composition and thickness of the lag-time coating, ratio of IR beads to one or more TPR bead populations and total dose may be varied depending on the alkalinity, pH-dependent solubility and elimination half-life of the active ingredients to achieve target PK profiles (suitable for a once or twice daily dosing regimen) in patients in need of such medications.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
Timed, pulsatile release systems
A unit multiparticulate dosage form for delivering one or more basic, active pharmaceutical ingredients into the body in need of such medications to achieve target PK (pharmacokinetics) profiles is described. The dosage form comprises one or more multicoated drug particles (beads, pellets, mini- / micro-tablets) having a barrier coating and a lag-time coating. Each Timed Pulsatile Release (TPR) bead population exhibits pre-determined lag-time followed by differing release characteristics. The composition and thickness of the barrier coating, composition and thickness of the lag-time coating, ratio of IR beads to one or more TPR bead populations and total dose may be varied depending on the alkalinity, pH-dependent solubility and elimination half-life of the active ingredients to achieve target PK profiles (suitable for a once or twice daily dosing regimen) in patients in need of such medications.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
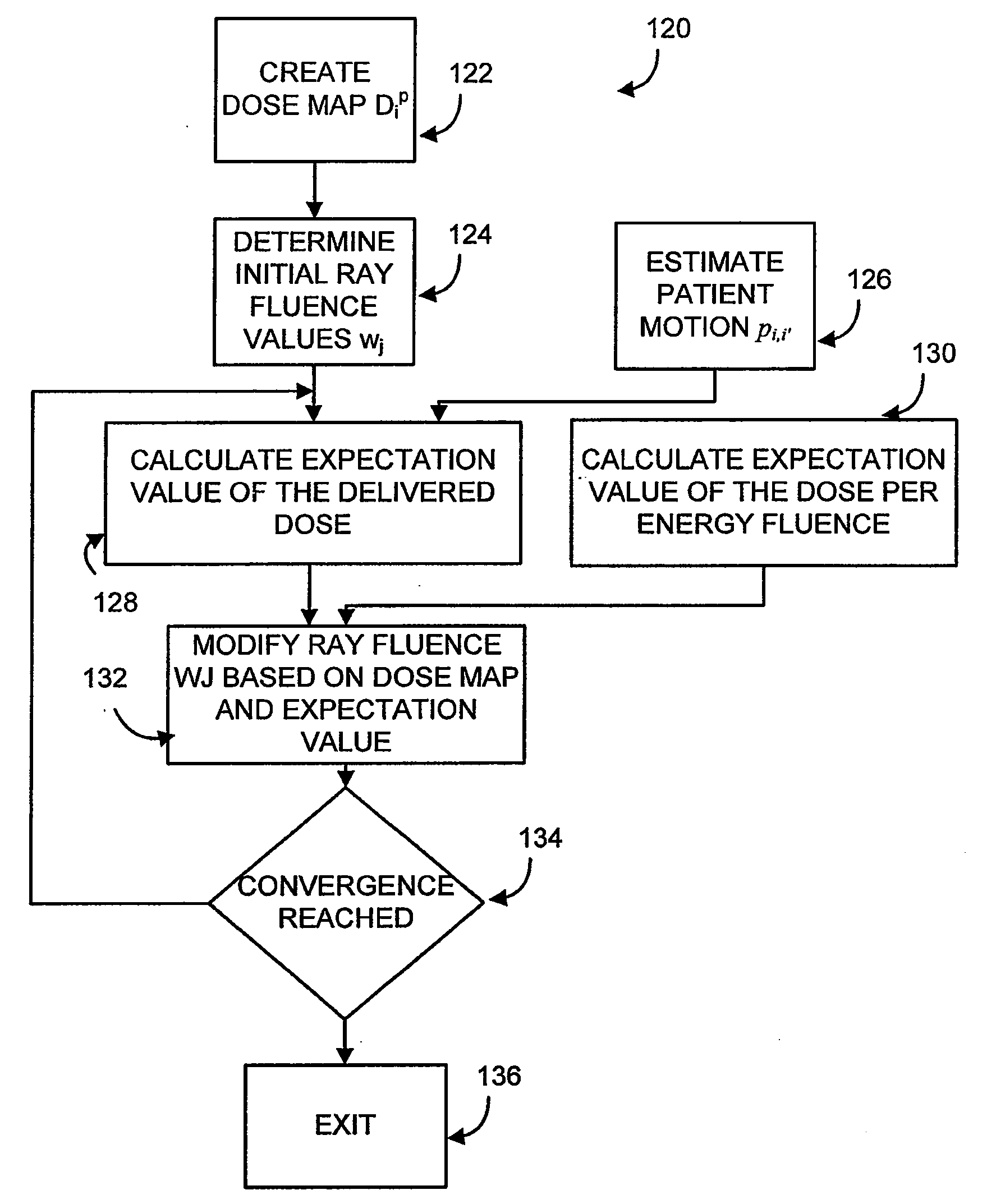
System and method for optimization of a radiation therapy plan in the presence of motion
A computer-implemented method for optimizing a radiation treatment plan for a radiotherapy machine providing independently controlled radiation along a plurality of rays j directed toward a patient and configured to account for the effects of patient motion. The method includes generating a probability distribution function quantitatively expressing patient motion, identifying a prescribed total dose Dip at the voxels i in a treatment area, assigning a fluence value wj for each ray j based on an iterative function, calculating an actual total dose Did produced each voxel i within the assigned fluence values and calculating an expectation value of the dose per energy fluence, dij based on the actual total dose Did and the probability distribution function.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
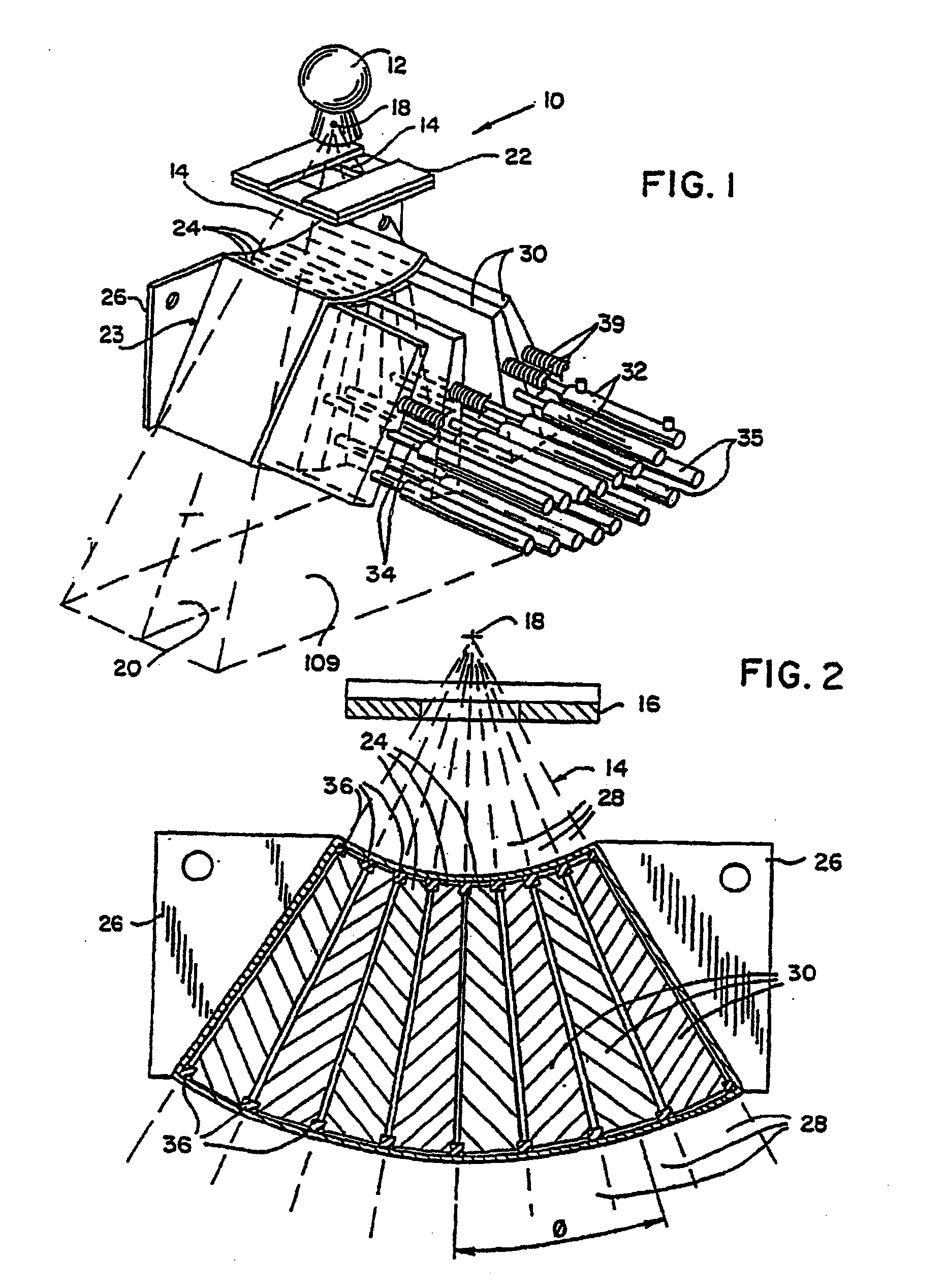
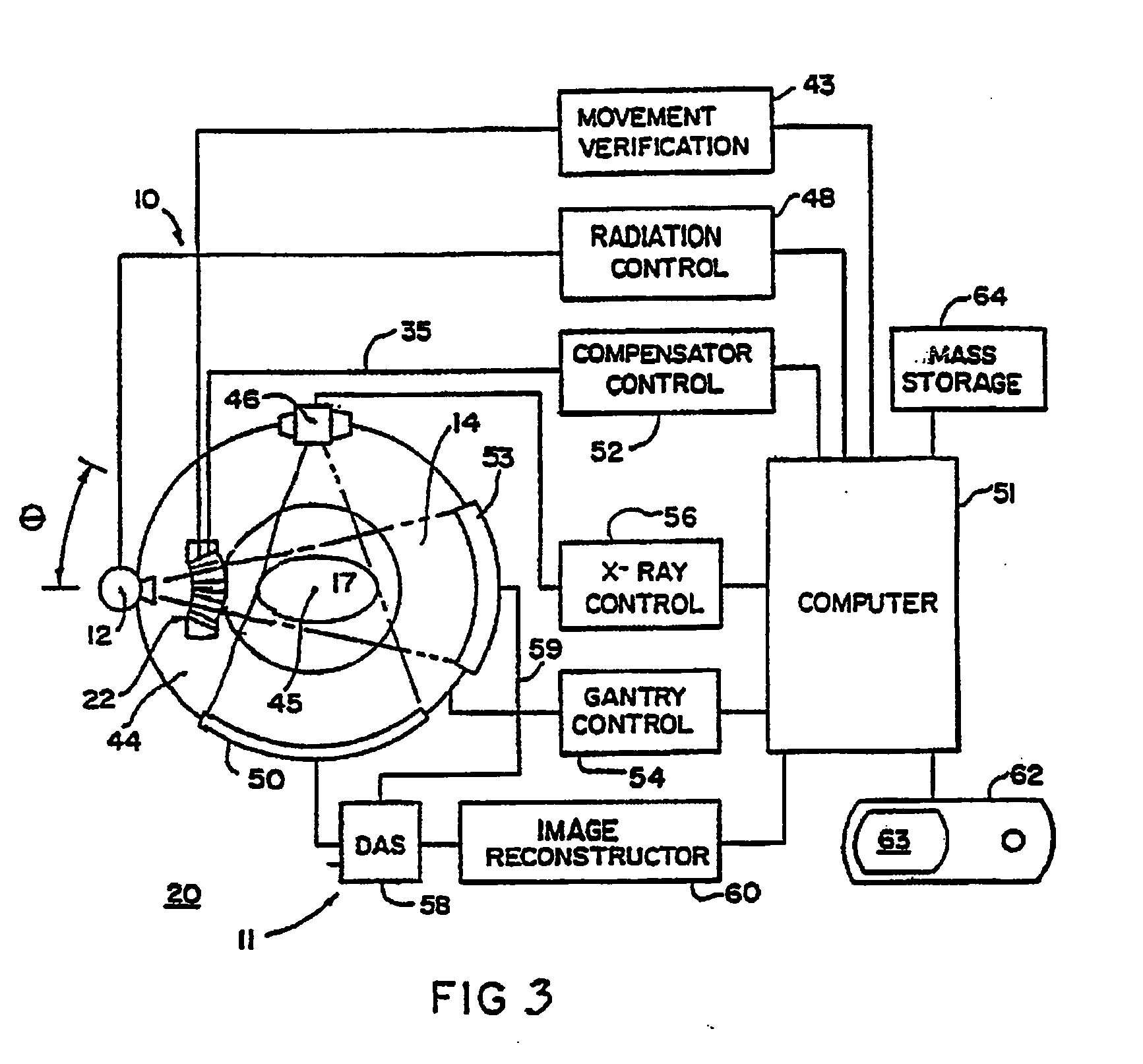
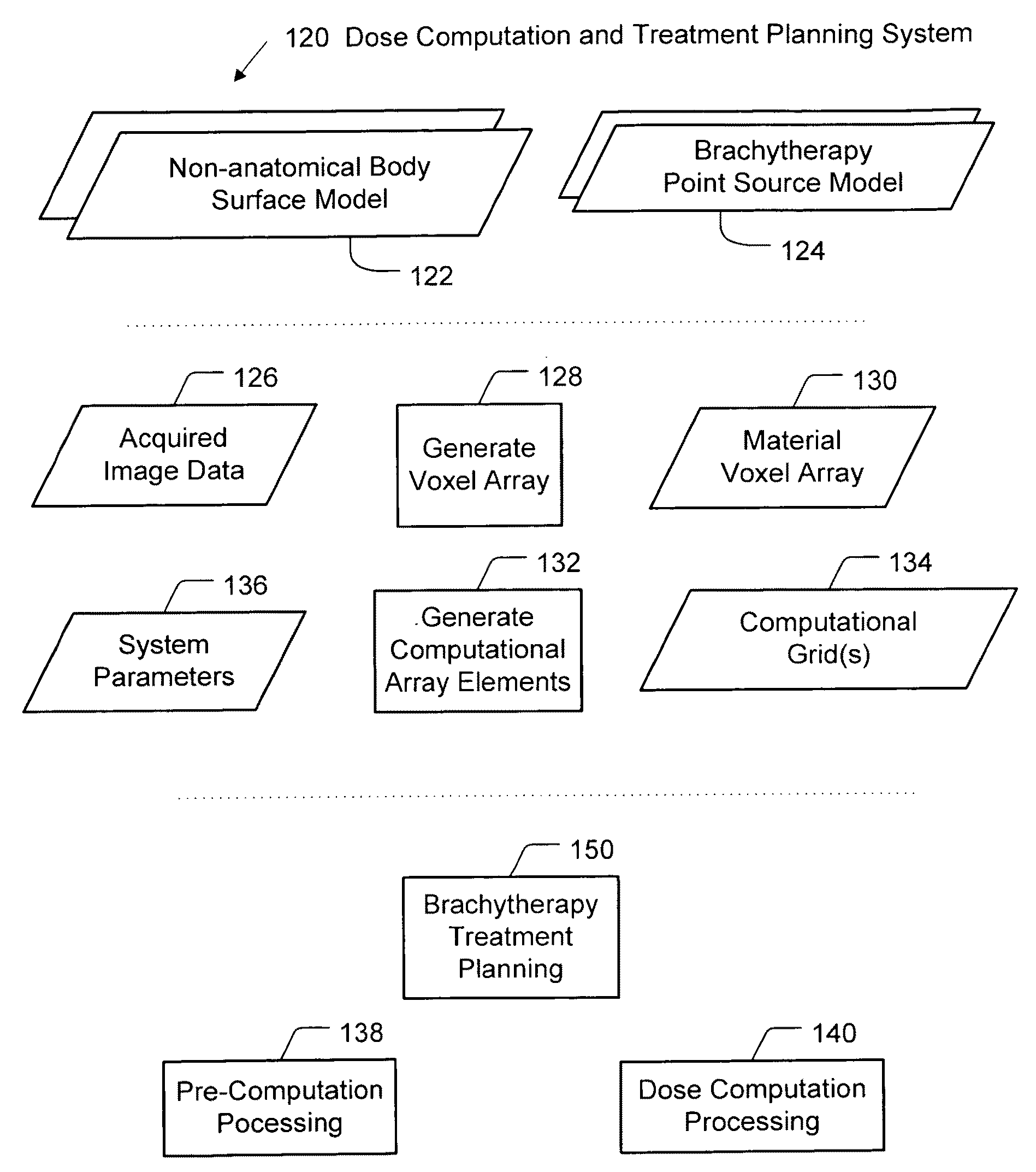
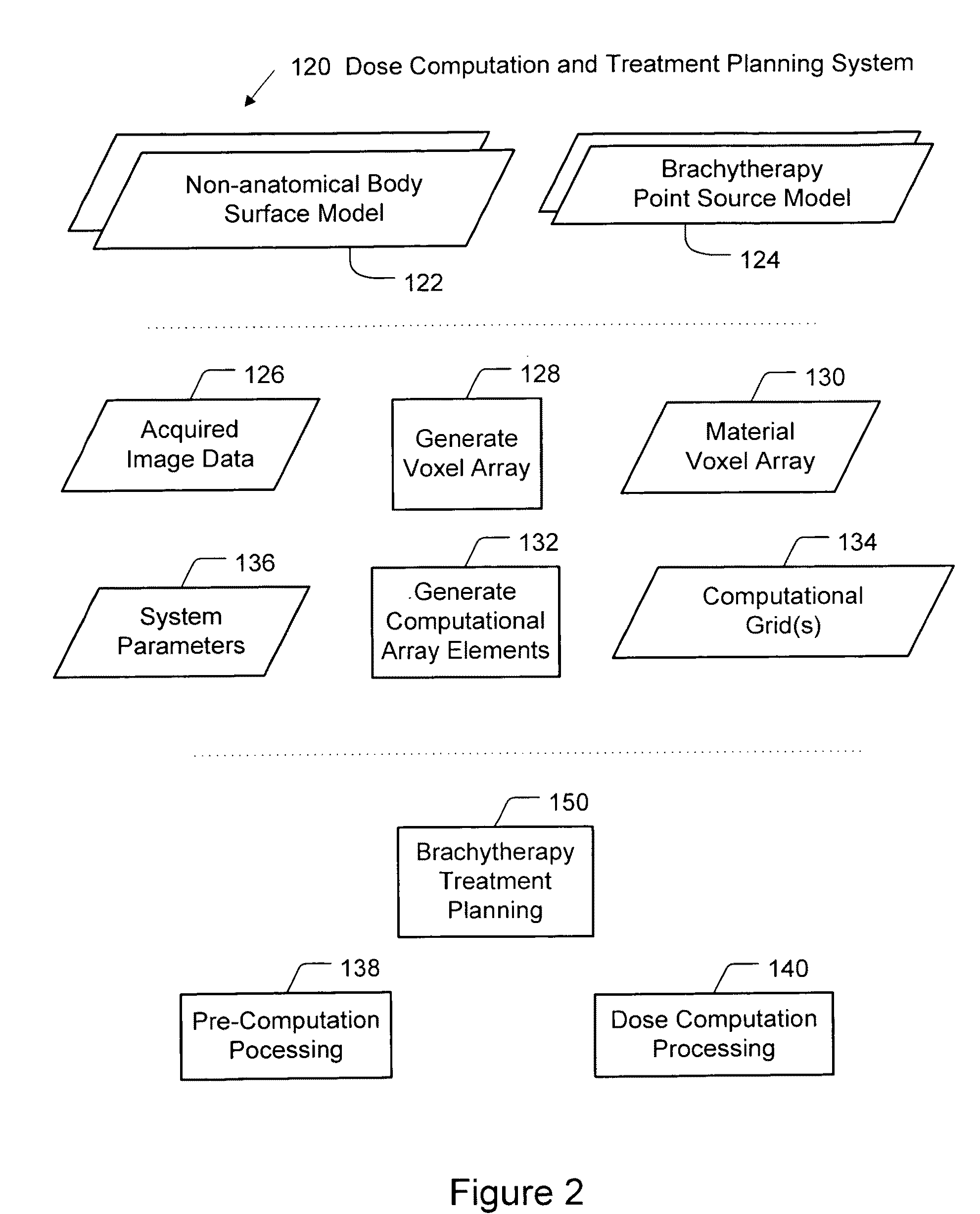
Brachytherapy dose computation system and method
InactiveUS20090063110A1Medical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVoxelCritical structure
Brachytherapy dose attributable to a brachytherapy source is computed for portions of a patient treatment volume corresponding to a pathological target volume and critical structures. Patient image data is accessed to derive a material voxel array. Multiple computation grids are derived. Primary particle fluence is computed for each first grid element using a ray tracing process from which a primary dose and a first scattered particle source are derived. Scattered particle fluence of the first scattered particle source is derived for each second grid element from which a secondary dose is derived. Each first grid element corresponds to a plurality of second grid elements. Primary dose and scattered dose combine to provide total dose at specific volumes. Brachytherapy source models and non-anatomical body surface models may be applied as applicable.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
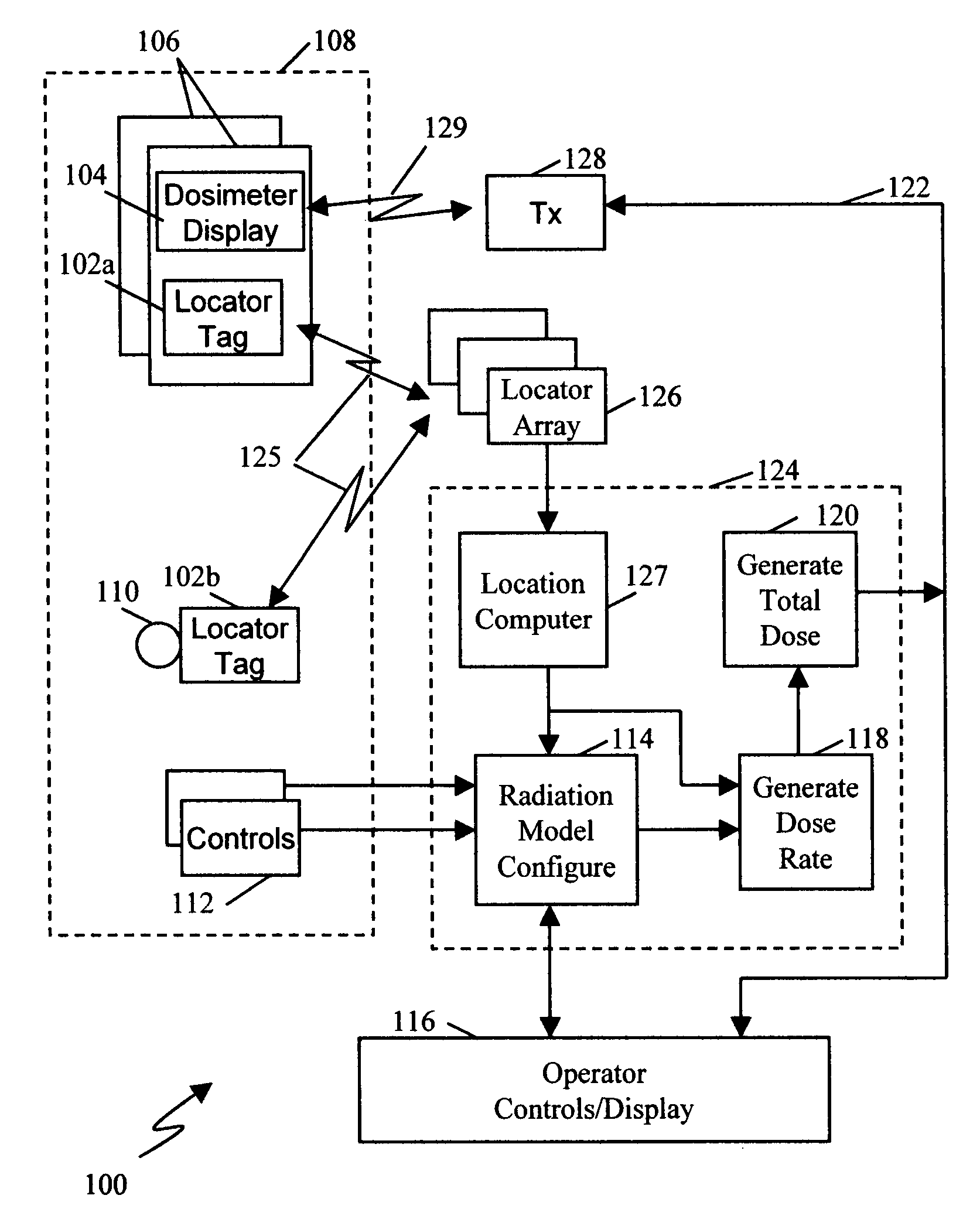
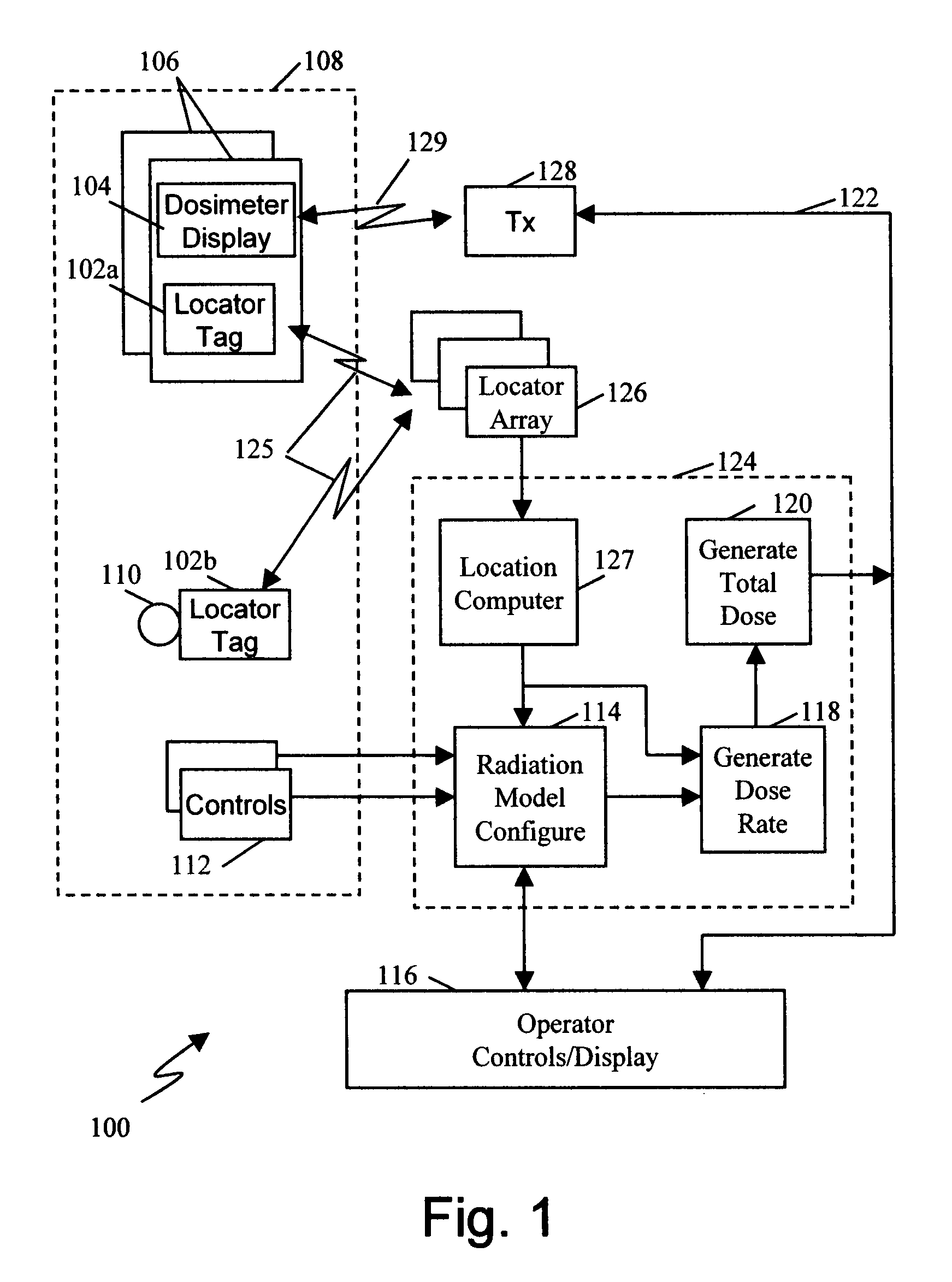
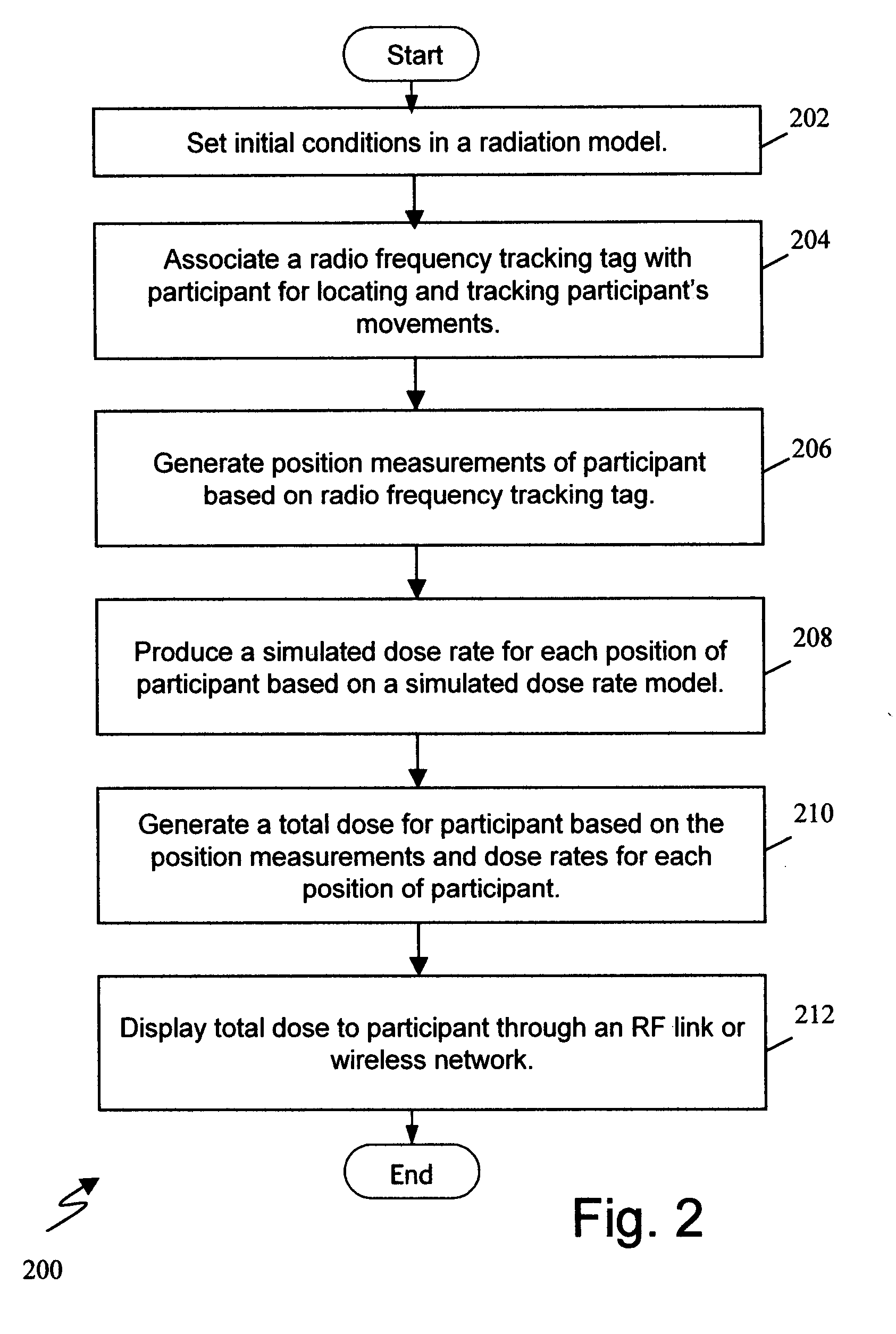
System and method for simulated dosimetry using a real time locating system
InactiveUS20080241805A1Automatic collectionCosmonautic condition simulationsVacuum evaporation coatingDosimetry radiationTotal dose
A system for providing a simulated total dose exposure measurement during a nuclear facility training exercise by locating participants using a real time location system, modeling incremental exposure as a function of location and summing incremental exposure to produce a total dose for each of the participants. Total dose may be displayed via a wireless link to a simulated dosimiter worn by each participant. Radiation sources may also have location tags and the exposure model may be modified in real time according to the tracked location of the radiation source. In one embodiment, the locating technology comprises near field locating technology based on comparing near field signal characteristics. Alternative locating technologies may be used.
Owner:Q TRACK CORP
Neurorestoration With R(+) Pramipexole
Formulations and methods of use thereof for restoring neuronal tissue function in children and adults afflicted with chronic neurodegenerative diseases, such as neurodegenerative movement disorders and ataxias, seizure disorders, motor neuron diseases, and inflammatory demyelinating disorders. Examples of disorders include Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The method involves administering a pharmaceutical composition containing an effective amount of a tetrahydrobenzathiazole, preferably a formulation consisting substantially of the R(+) enantiomer of pramipexole. R(+) pramipexole is generally administered in doses ranging from 0.1-300 mg / kg / daily, preferably 0.5-50 mg / kg / daily, and most preferably 1-10 mg / kg / daily for oral administration. Daily total doses administered orally are typically between 10 mg and 500 mg. Alternatively, R(+) pramipexole can be administered parenterally to humans with acute brain injury in single doses between 10 mg and 100 mg, and / or by continuous intravenous infusions between 10 mg / day and 500 mg / day.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
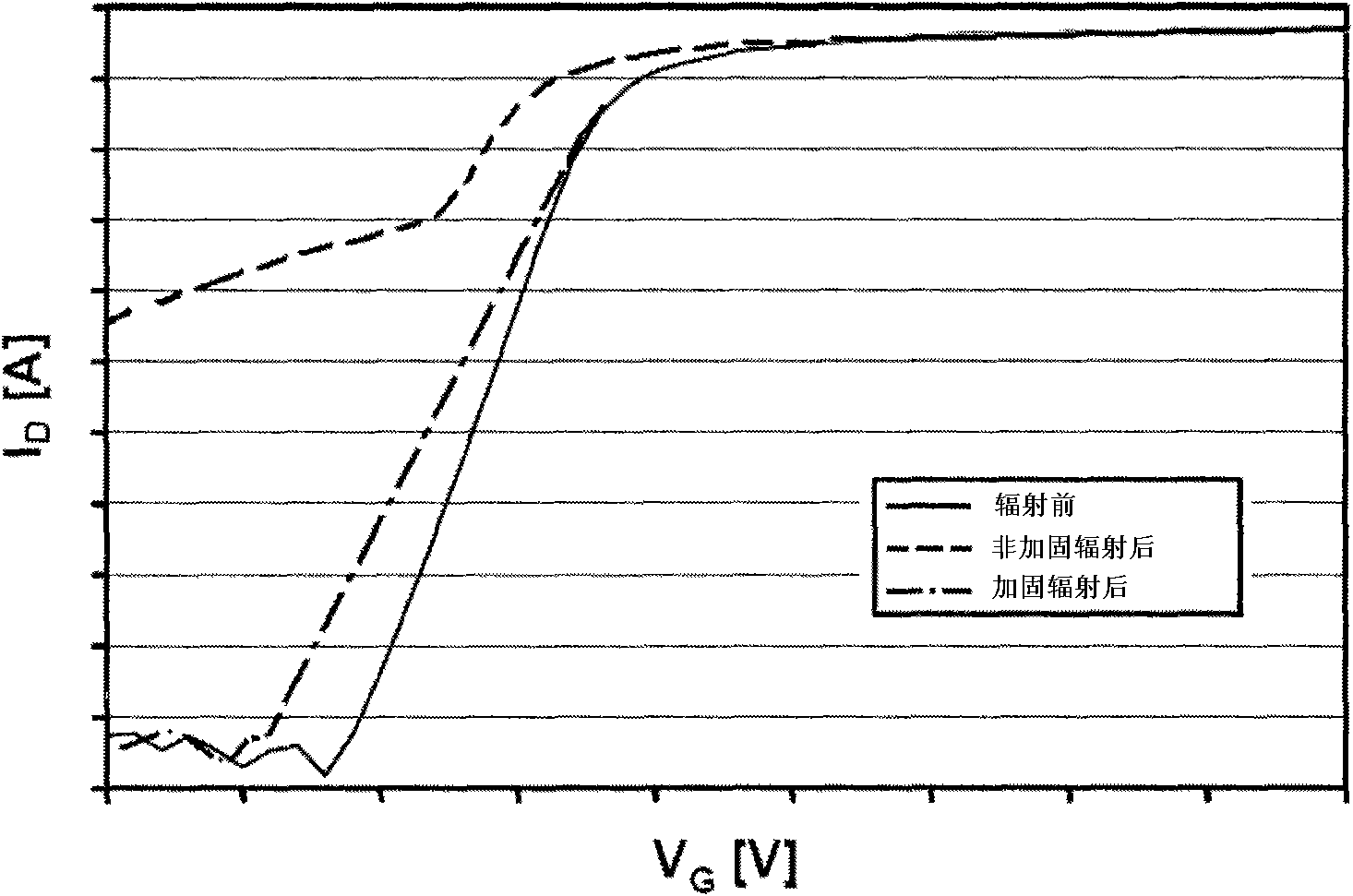
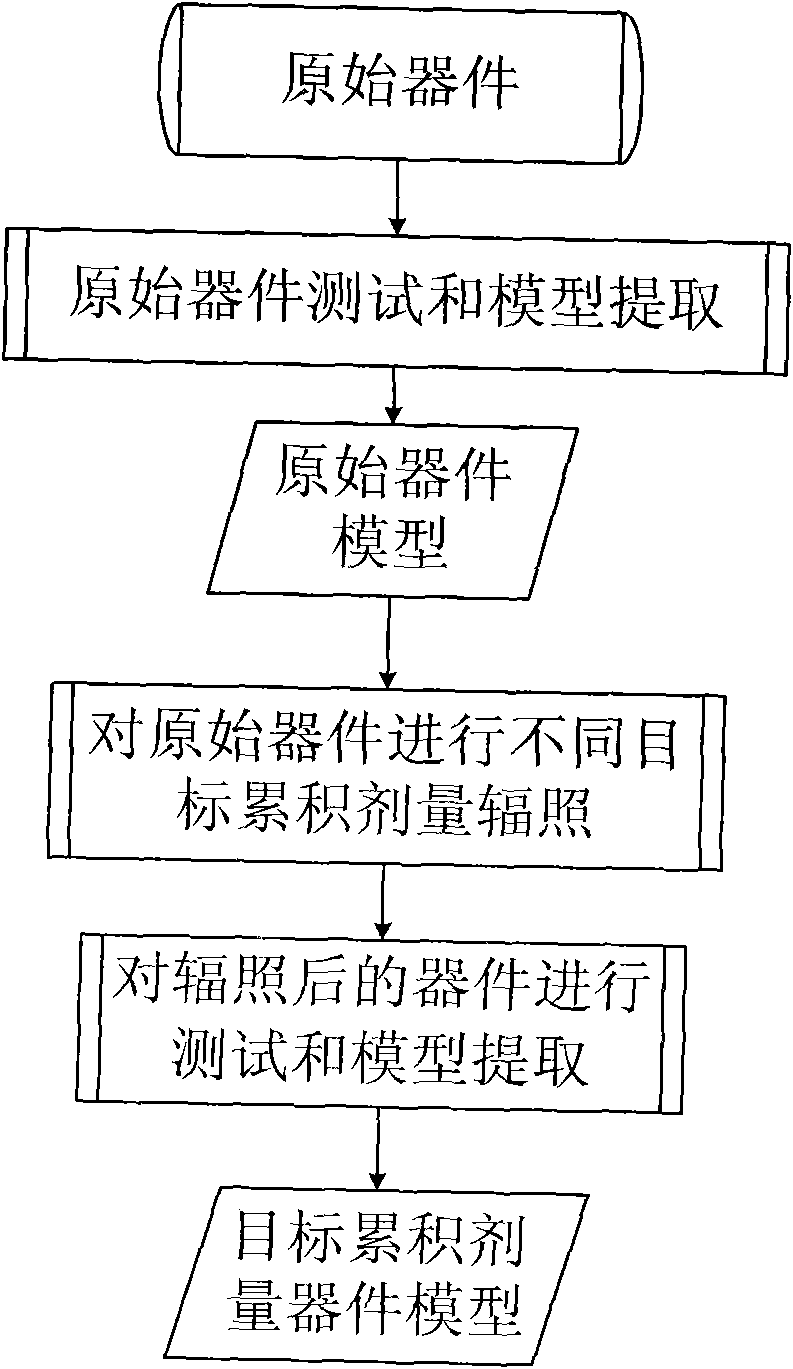
A device modeling method in relation to total dose radiation
InactiveCN101551831ASolve modeling problemsHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsModel extractionComputational physics
A device modeling method in relation to total dose radiation, wherein firstly, an original electronic device is designed and undergoes testing and model extraction to obtain the model of the original device, secondly, the obtained original device undergoes radiation at different target cumulative doses and model extraction to obtain the device model after radiation at all target cumulative doses, and lastly, the obtained original device model and the device model that has received radiation at all target cumulative doses jointly constitute the device model in relation to total dose radiation. Through testing and parameter extraction of the original device and the device that has received radiation at all target cumulative doses, the present invention provides a method for accurate modeling of hardened devices and unhardened devices. Meanwhile it adds radiation dose as a variable into the realization method of device model so that the performance of the circuit that has received radiation at different doses can be accurately predicted through simulation, thus raising the design efficiency and success rate of the circuits.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Programmable segmented volumetric modulated arc therapy for respiratory coordination
ActiveUS20130193351A1Radiation therapyChemical conversion by chemical reactionMedicineVolumetric modulated arc therapy
The invention designs the segmented short-arc VMAT plan, modified from the original long-arc VMAT, to fit the breath-hold interval. The modified VMAT of the invention has the advantages of its applicability to different planning systems for variously long arcs and its preprogrammed arc segmentation for summated dose consistency. Using segmented short-arc modification from the original long-arc VMAT plan is accurate for dose planning and delivery, as well as tolerable for breath-hold VMAT.
Owner:CHENG JASON CHIA HSIEN
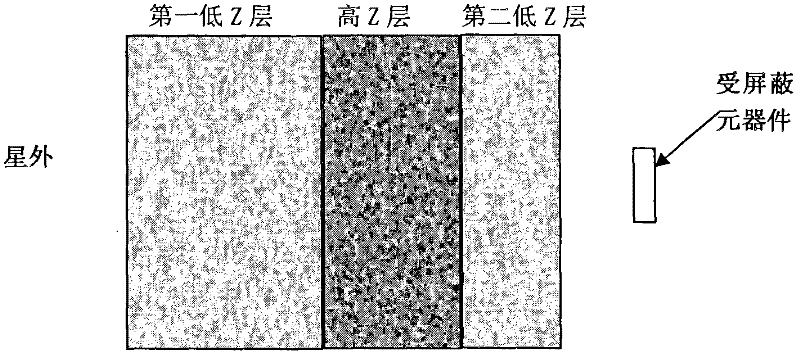
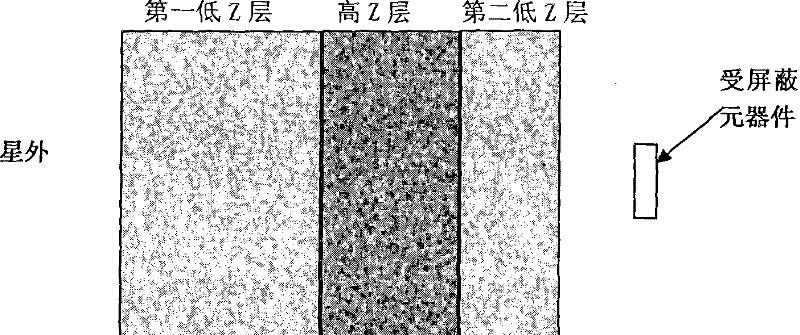
Anti-total-dose shielding device
InactiveCN102490913AImprove total dose resistanceExtend your lifeCosmonautic radiation protectionSoft x rayX-ray
The invention provides an anti-total-dose shielding device, which comprises a first low Z layer, a high Z layer and a second low Z layer, wherein the first low Z layer is used for moderating and shielding primary electrons, the high Z layer is used for scattering electrons and absorbing secondary bremsstrahlung photons, and the second low Z layer is used for absorbing photoelectrons and back scattered electrons generated in high Z materials and restraining secondary photoelectron emission and electron back scattering generated by action of X-rays and materials. The first low Z layer is the outmost layer and close to the space outside a satellite, and the second low Z layer is the innermost layer and close to a component to be shielded. The first low Z layer and the second low Z layer are made of materials formed by elements of atomic numbers smaller than or equal to 30. The thickness of the first low Z layer ranges from 1 to 3mm, and the thickness of the second low Z layer ranges from 0.2 to 0.4mm. The high Z layer is made of materials formed by elements of atomic numbers larger than or equal to 50, and the thickness of the high Z layer ranges from 0.1 to 0.3mm.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
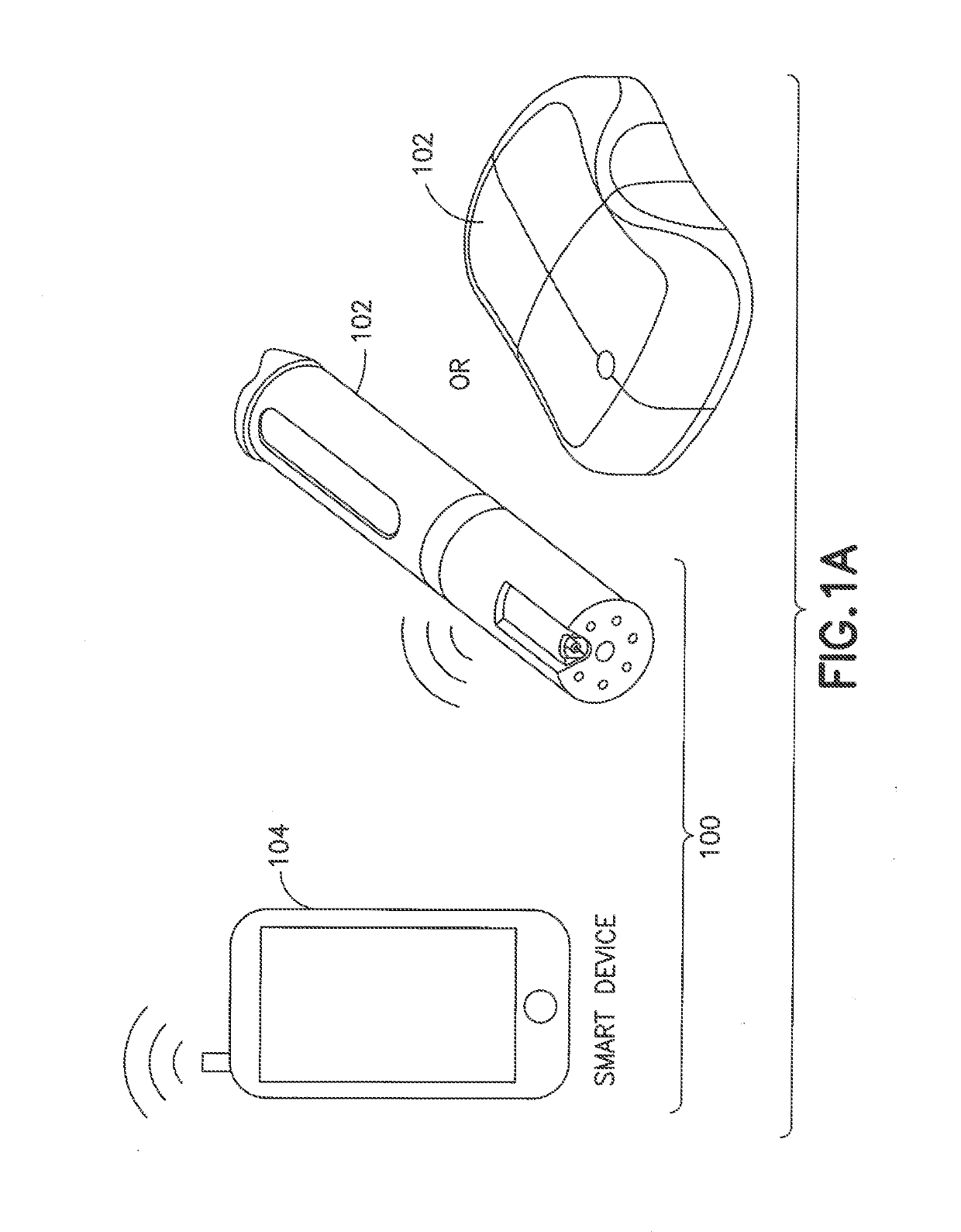
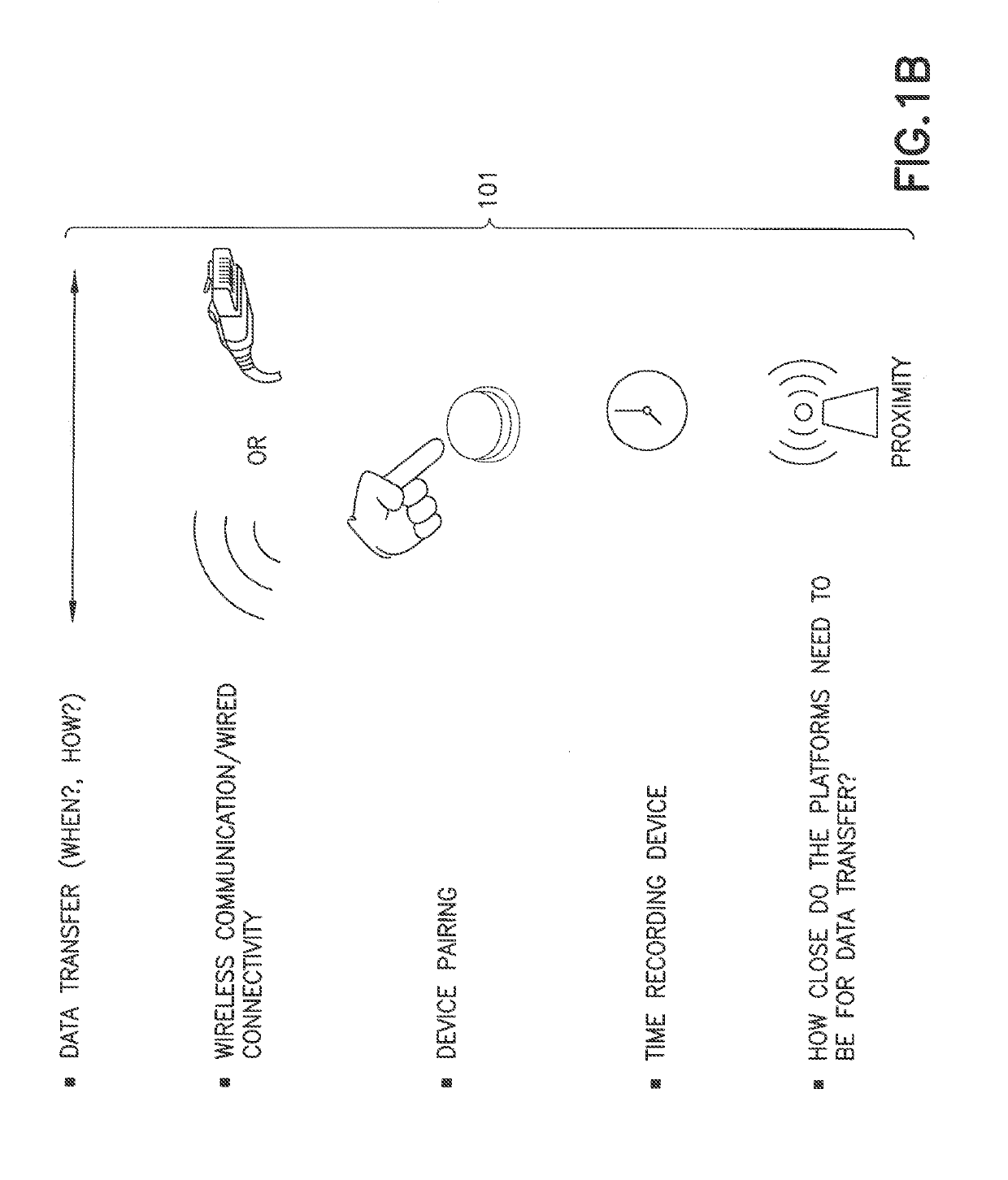
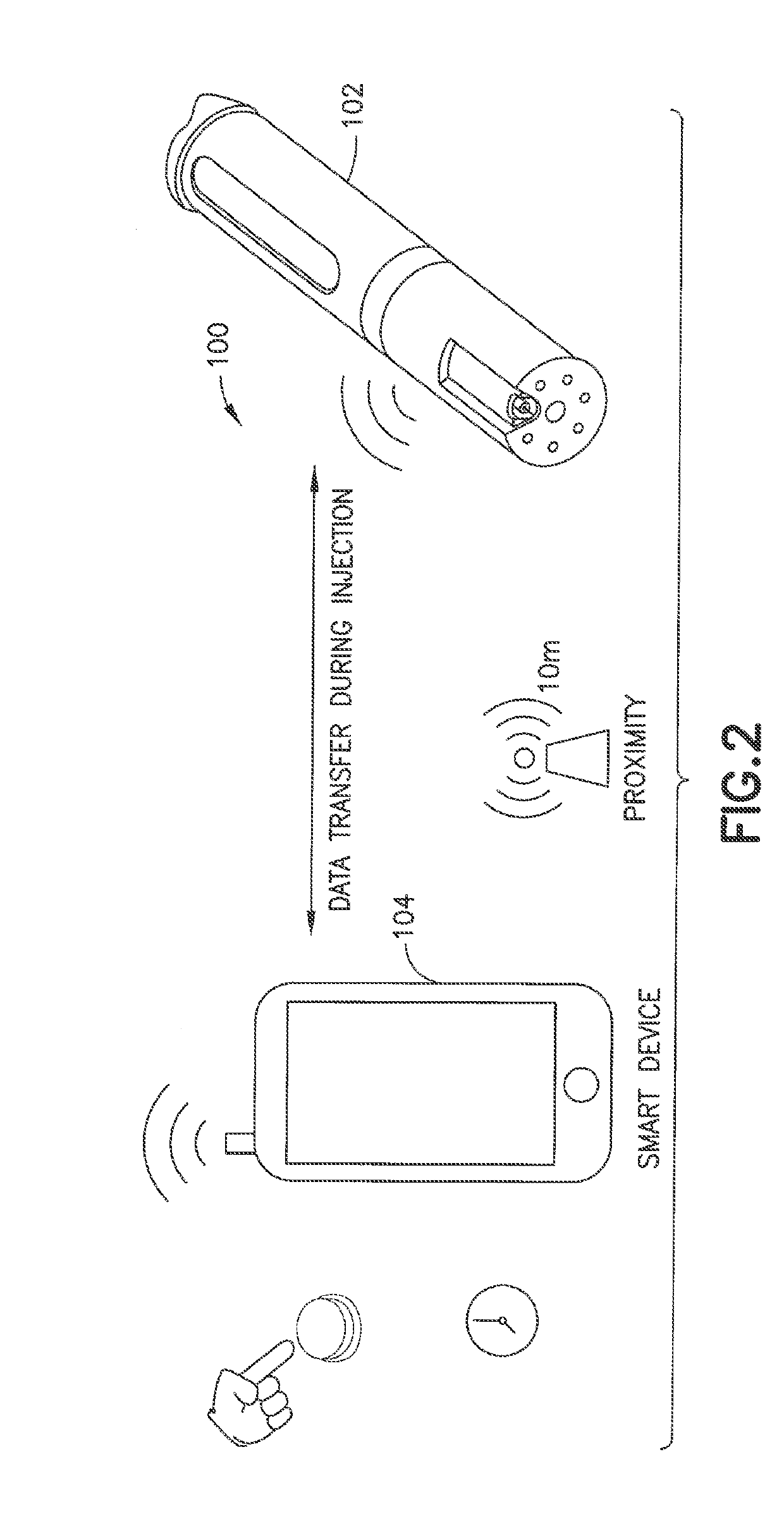
Smart medication delivery devices for providing users with delivery infomatics and methods of using same
ActiveUS20190134305A1Optimization rangeNear-field transmissionAutomatic syringesCompletion StatusFlow transducer
A medication delivery device (MDD) (e.g., injection pen, wearable pump) is paired with an external device (e.g., smart phone, iPad, computer) via wireless link or wireline connection. The MDD provides to the external device captured data from the flow sensor relating to medicine delivery to a patient to ensure complete delivery and minimize MDD misuse or malfunction or inaccuracies in dosing. The MDD can have Bluetooth™ and / or near field communication (NFC) communication circuits for proximity-based pairing and connectivity with the external device for real-time or deferred transfer of captured data to the external device, depending on memory and power availability at the MDD. The MDD or external device can use captured data and corresponding time stamps to determine flow infomatics such as flow rate, total dose delivered, and dose completion status. An LED on the MDD indicates states such as powered on, paired, delivery in progress and delivery completion.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
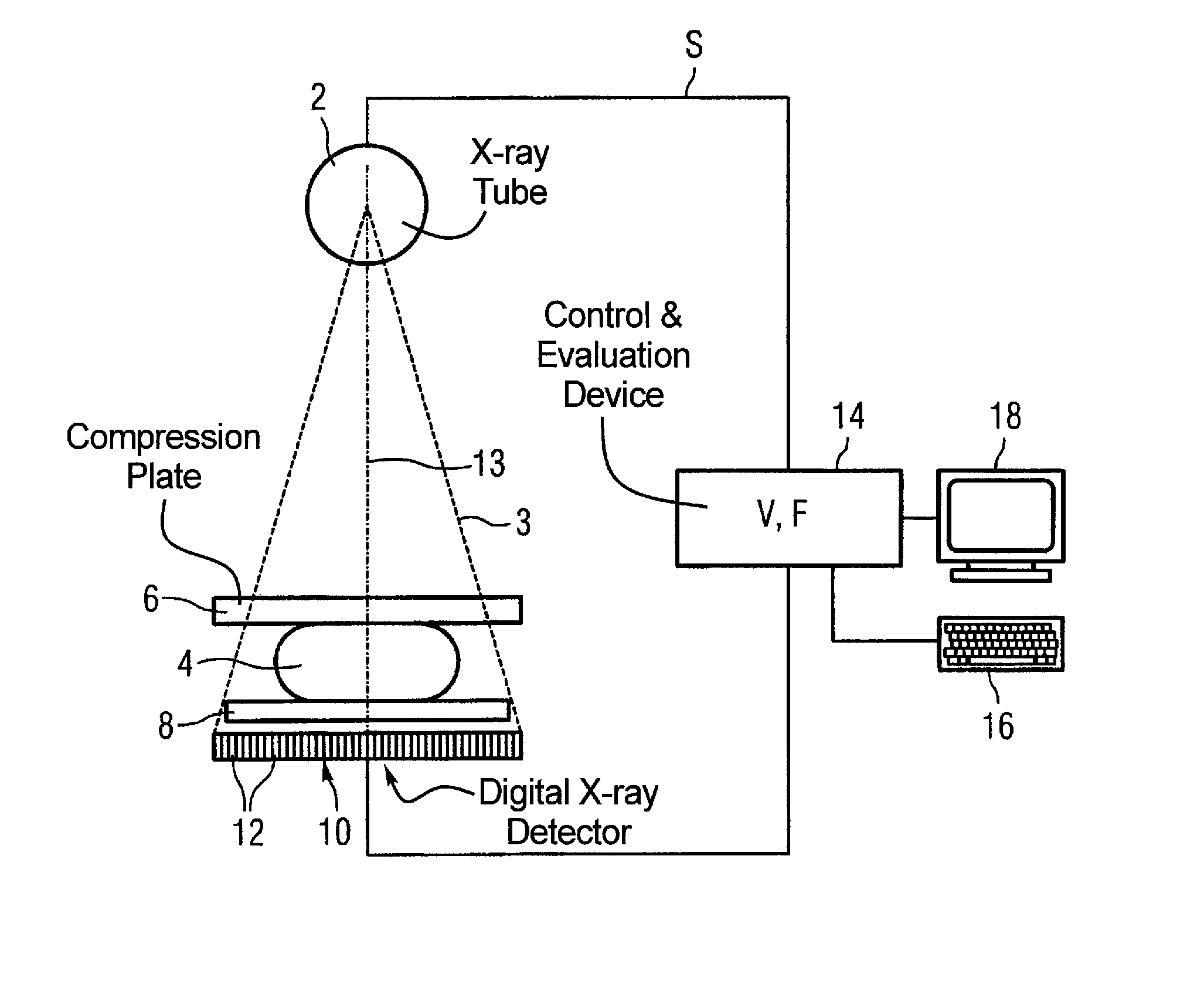
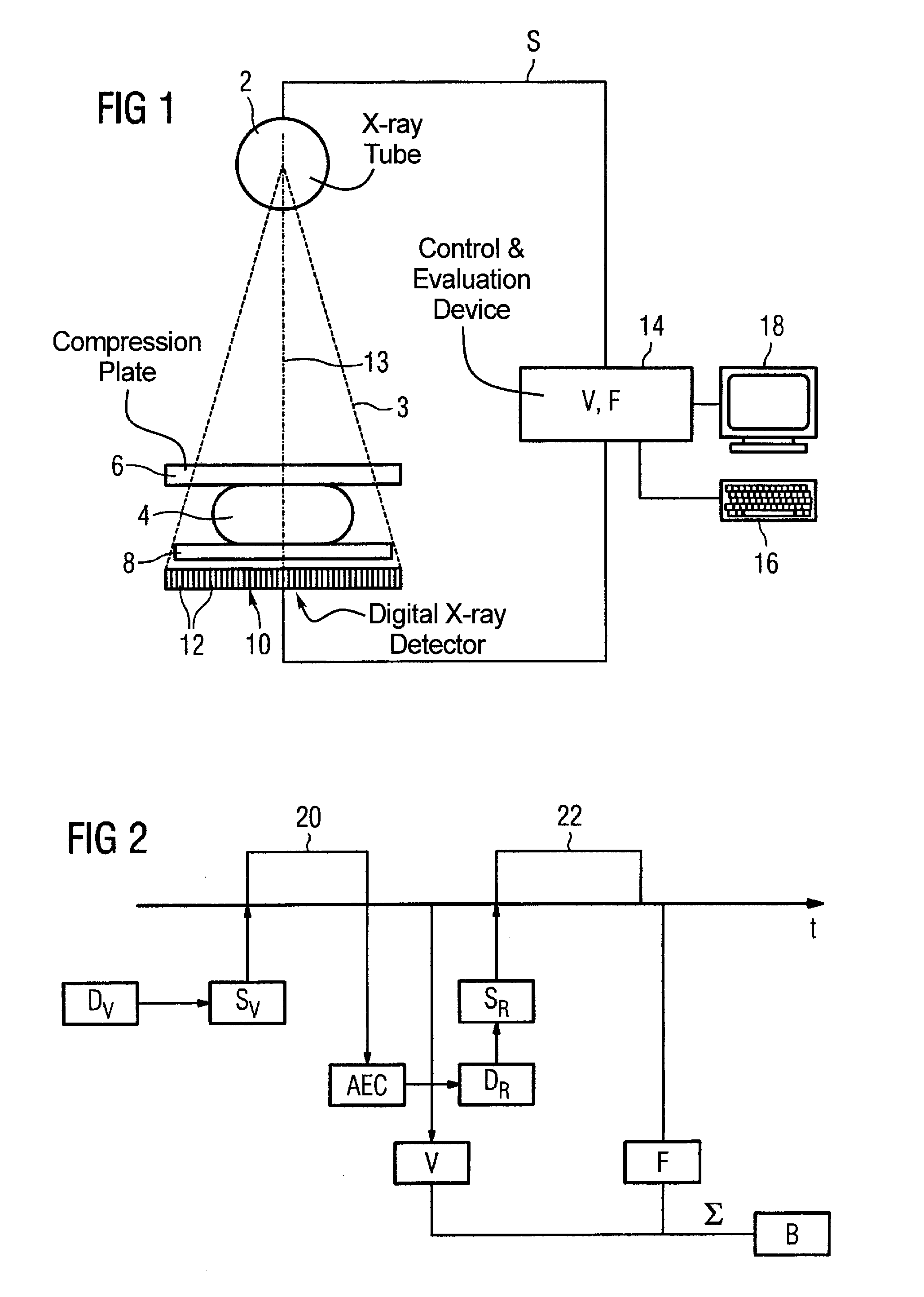
Method and apparatus for generation of a digital x-ray image of an examination subject
ActiveUS7342999B2Avoid disadvantagesNoise minimizationPatient positioning for diagnosticsMammographySoft x rayImage evaluation
In a method and apparatus for generation of a digital x-ray image of an examination subject with an x-ray tube and a digital x-ray detector, a preliminary total dose required for correct exposure is determined using prior knowledge and a complete pre-image of the examination subject is acquired with a partial dose that is smaller than the preliminary total dose. A remaining dose is determined from the pre-image by image evaluation. A complete following image is acquired with this remaining dose, and the final x-ray image is assembled from the pre-image and the following image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
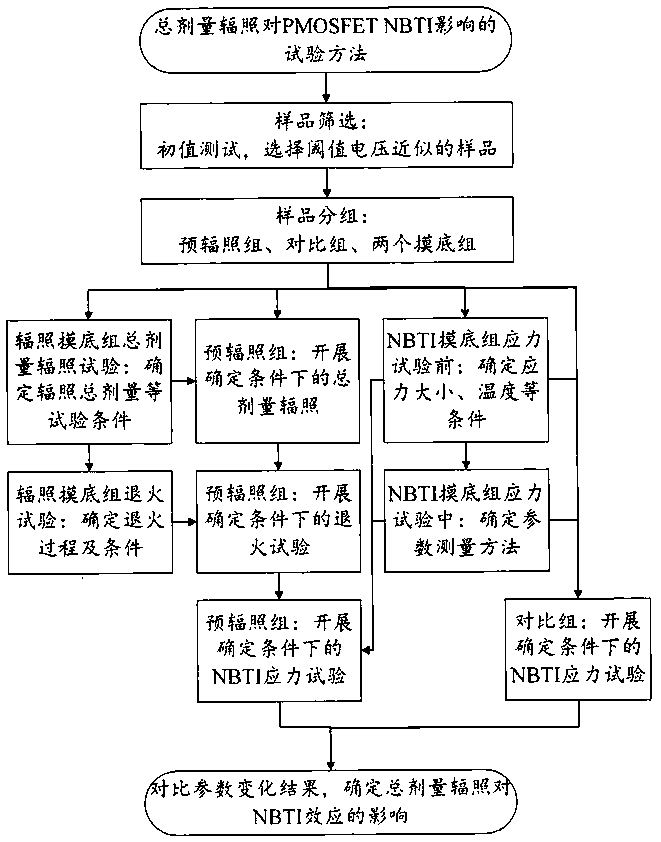
Test method for influence of total dose irradiation on PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability
ActiveCN108037438AEnsure consistencySemiconductor operation lifetime testingPre irradiationTest sample
The invention relates to a method for testing the influence of total dose irradiation on the PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability. The method includes test sample grouping and test parameterselection; the total dose irradiation and annealing tests of the test sample; and the negative bias temperature instability measurement of the test sample. In order to ensure the consistency and accuracy of the test result, the sample is divided into a pre-irradiation group, a comparison group and two pre-test groups, and on the basis of the pre-test, the total dose irradiation and annealing testsare carried out on the pre-irradiation group under the determination condition, the comparison group and the pre-irradiation group are subjected to a negative bias temperature instability test underthe same condition, and the test result is compared, the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of the sample is obtained. The method provided by the invention can represent the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
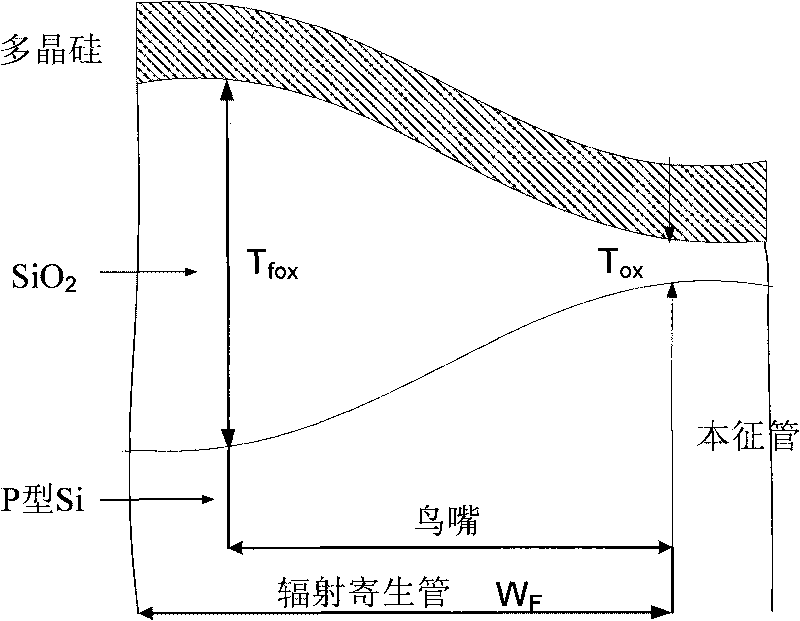
Total dose radiation hardening I-shaped gate layout structure
The invention relates to a total dose radiation hardening I-shaped gate layout structure, which comprises an active region, a field oxidation region outside the active region, and an I-shaped gate overlapped with the active region. The part on the active region, which is not overlapped with the I-shaped gate, is divided into a rectangle source region and a rectangle drain region. The total dose radiation hardening I-shaped gate layout structure arranges a gate oxidation layer below the I-shaped gate layer of the whole region where the I-shaped gate and the active region are overlapped, not only comprises an a region between the source region and the drain region, but also comprises b regions on the upper and lower parts of the source region and the drain region. The formation of the b regions pushes off the distances among the source region, the drain region and the field oxidation region, thus, the total dose radiation hardening I-shaped gate layout structure avoids a field region, cuts off the accesses between an edge radiation parasitic channel of the field oxidation region and the source region and the drain region, better solves the parasitic leakage problem caused by the ionizing radiation total-dose effect, improves the ionizing radiation resistance of the circuit, reduces the chip layout area, and can be applied into the large scale integrated circuit system.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Dosage form comprising means for changing drug delivery shape
InactiveUS20020006439A1Keeps its physical integrityAvoidance and reduction of riskPill deliveryOsmotic deliveryTotal doseDosage form
Owner:ALZA CORP
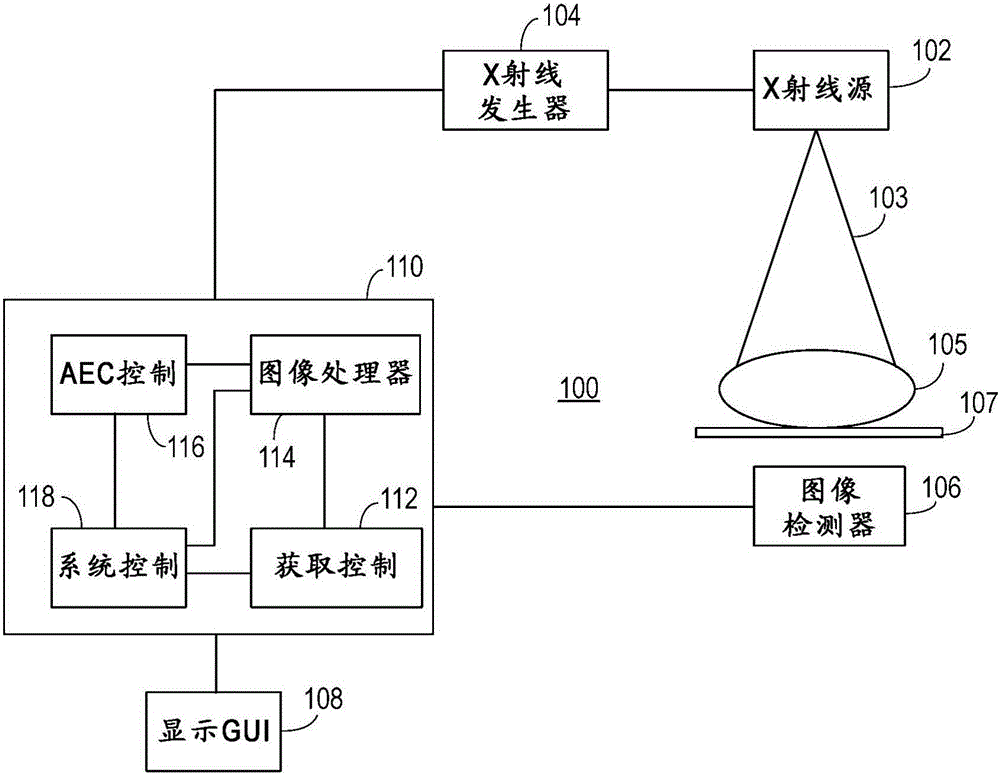
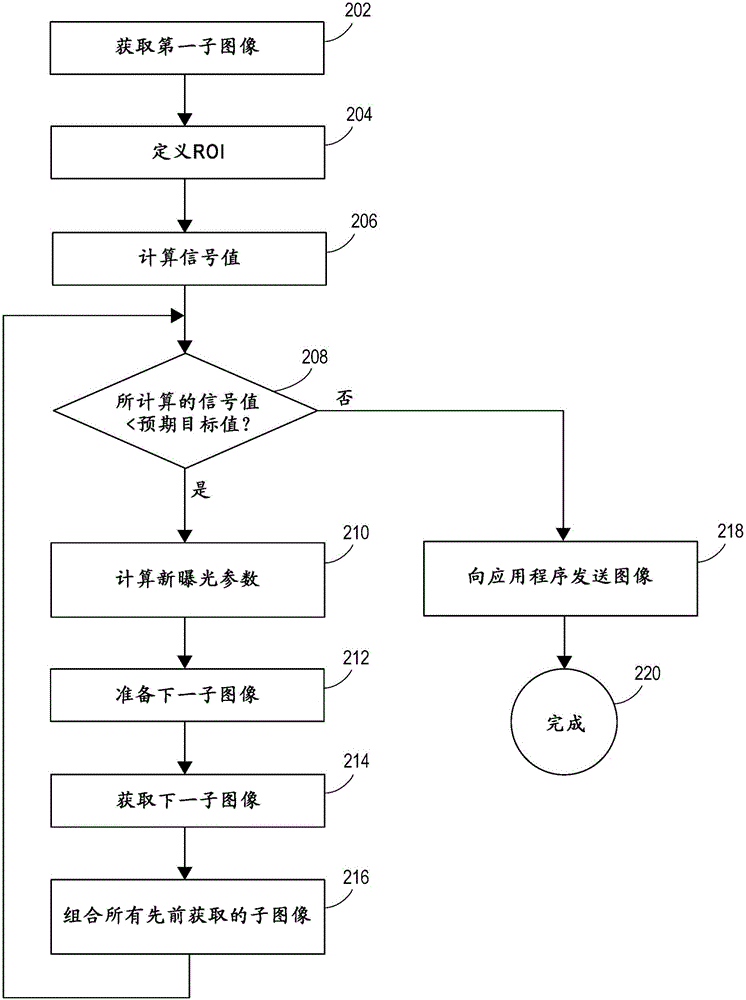
Automatice exposure control for x-ray imaging
In an x-ray imaging method, the acquisition of a signal image is split off into acquisition of two or more subimages or frames. The first subimage may be acquired with an exposure of a low dose followed by a readout cycle. The dose of the exposure for acquiring the first subimage can be chosen such that it is below the default dose for a particular anatomy. The first subimage may be used to calculate or estimate the parameters of exposure for acquiring a second or subsequent images subimage. The estimation may be such that the total dose received by the imager, in acquiring the first and second subimages, achieves an expected target value to provide an image of good quality. The first and second subimages can be combined to form the final image. A detector array supporting automatic exposure control (AEC) includes AEC pixels providing AEC signals. The AEC pixels are independently or individually addressable and / or readable.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Automatic quantitative dosing device under oil well
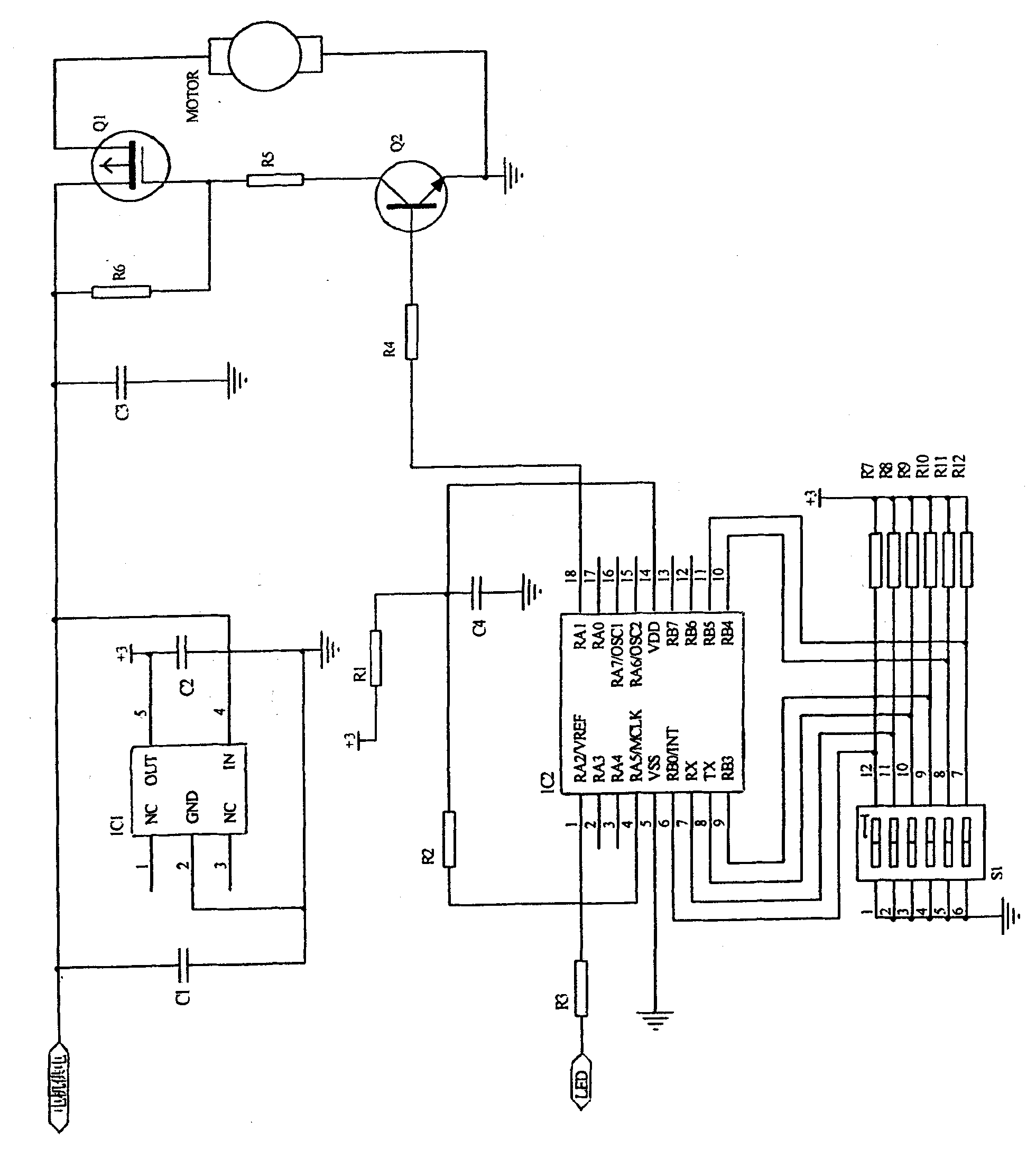
InactiveCN102155205AReduce workloadInjected smoothlyCleaning apparatusFluid removalMicrocontrollerStart time
The invention relates to an automatic quantitative dosing device under an oil well. In the device, the upper part of a charging pipe is connected with a communicating joint, and the lower part of the charging pipe is connected with a pump body joint of a dosing pump; a piston rod of the dosing pump is connected with a cam, a connecting rod and a motor in sequence; the motor is connected with a control circuit and a battery; a singlechip IC2 of the control circuit is connected with a dial switch S1; a triode Q2 is connected with a triode Q1; the Q1 is connected with the motor; and a power supply is connected with the triode Q1 through a voltage regulating chip IC1. The motor starting time interval and every dosing amount can be set according to the total dosing amount of the oil well, the piston rod of the dosing pump reciprocates to spray a liquid medicine into the annular space of an oil sleeve during dosing, and the dosing pump stops working and waits for the next dosing time when a designed medicine amount is reached so that automatic timing and quantitative continuous dosing are realized. The automatic quantitative dosing device has a high automatic degree, a good dosing effect, low construction cost and high long-term working reliability, and is easy to operate; and underground dosing can be realized without detaching an instrument or performing pipe column operation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Infusion system programmable in flex mode
A drug infusion system capable of delivering a fluid medication to a patient under direction of a medical professional continually at a basal rate and at an interval rate in each of a plurality of time slots over a specified period of time. The total dose of the fluid medication to be delivered to the patient over the period of time based on the basal rate and the interval rate for each of the plurality of time slots is determined, compared the total dose against a maximum dose. The basal rate is adjusted, if necessary, so that the total dose does not exceed the maximum dose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
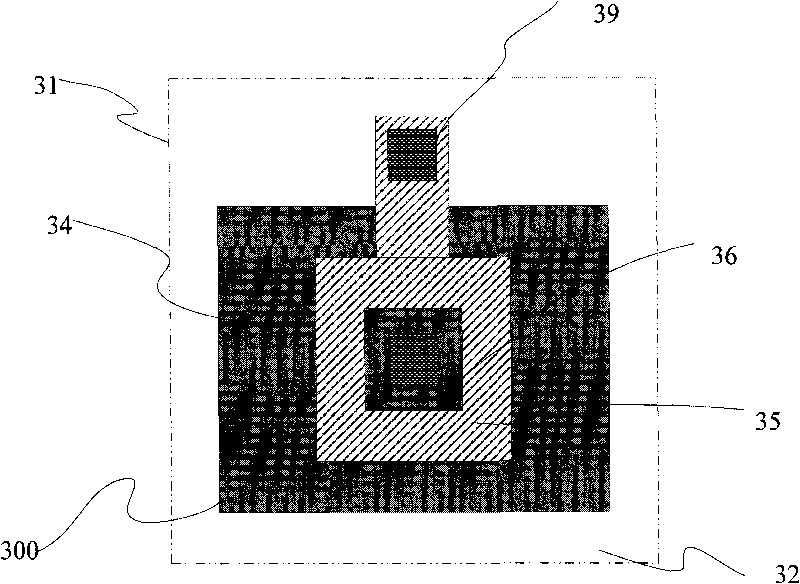
Double edge total dose resistant radiation reinforcement pattern construction preventing edge electricity leakage
The invention discloses an anti-total dose radiation double-edge hardened layout structure which prevents edge electric leakage. The layout structure comprises an active region, an implantation region as well as a field oxide region and a field oxide gate which are outside the active region, overlap section of the active region and the implantation region form a source region and a drain region; the gate is a double-edge structure the two sides of which is beyond the active region, the gate separates the source region from the drain region, the region covered by the gate between the source region and the drain region is a channel region, and a non-implantation active region is arranged between the channel region and the field oxide region which is covered by the gate. The anti-total dose radiation double-edge hardened layout structure can suppress parasitic leakage on device edges caused by the total dose radiation effect with less area cost, and realizes high integration level.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Radiotherapeutic apparatus
ActiveUS20090213991A1Avoid less flexibilityReduce doseX-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose rateClassical mechanics
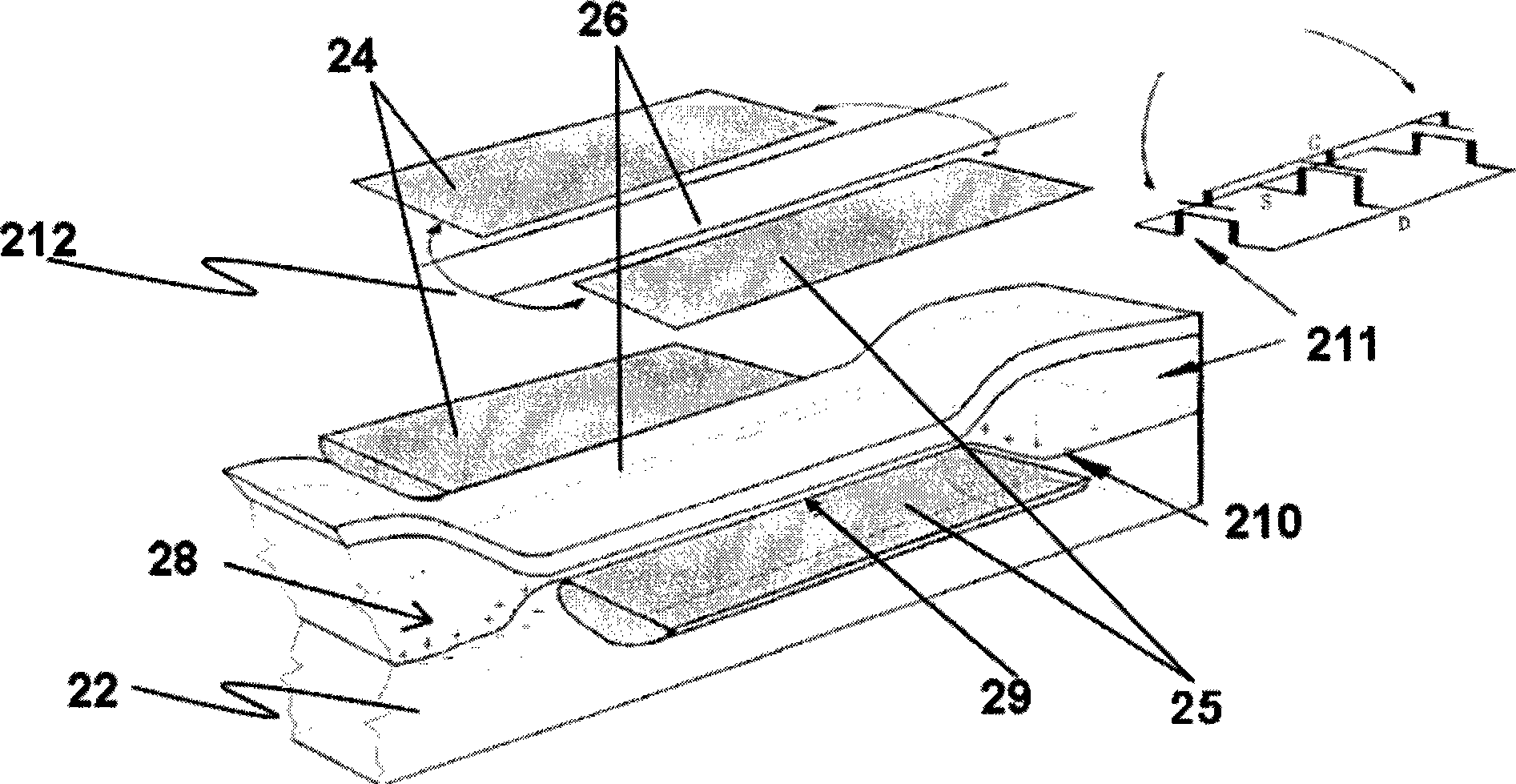
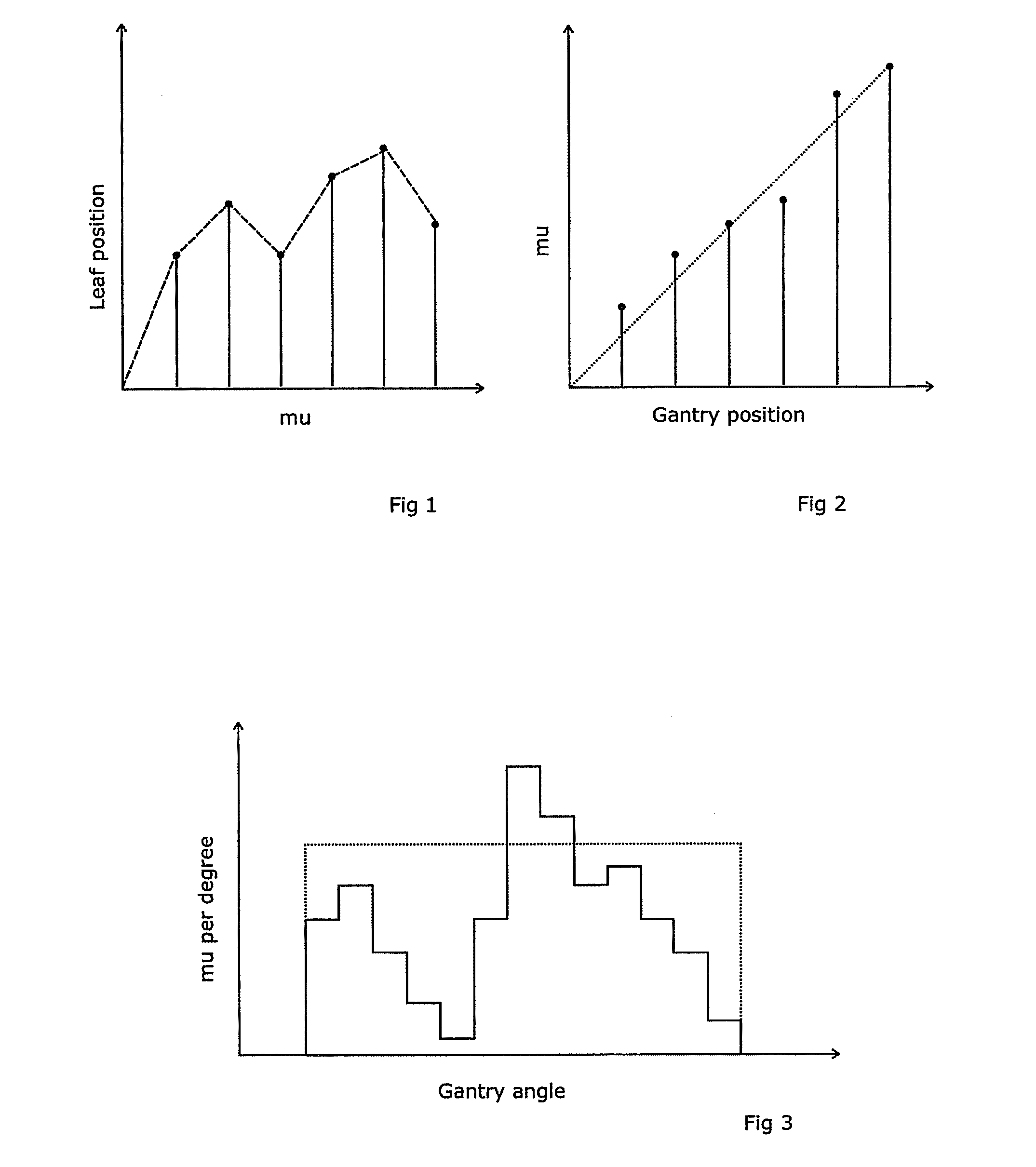
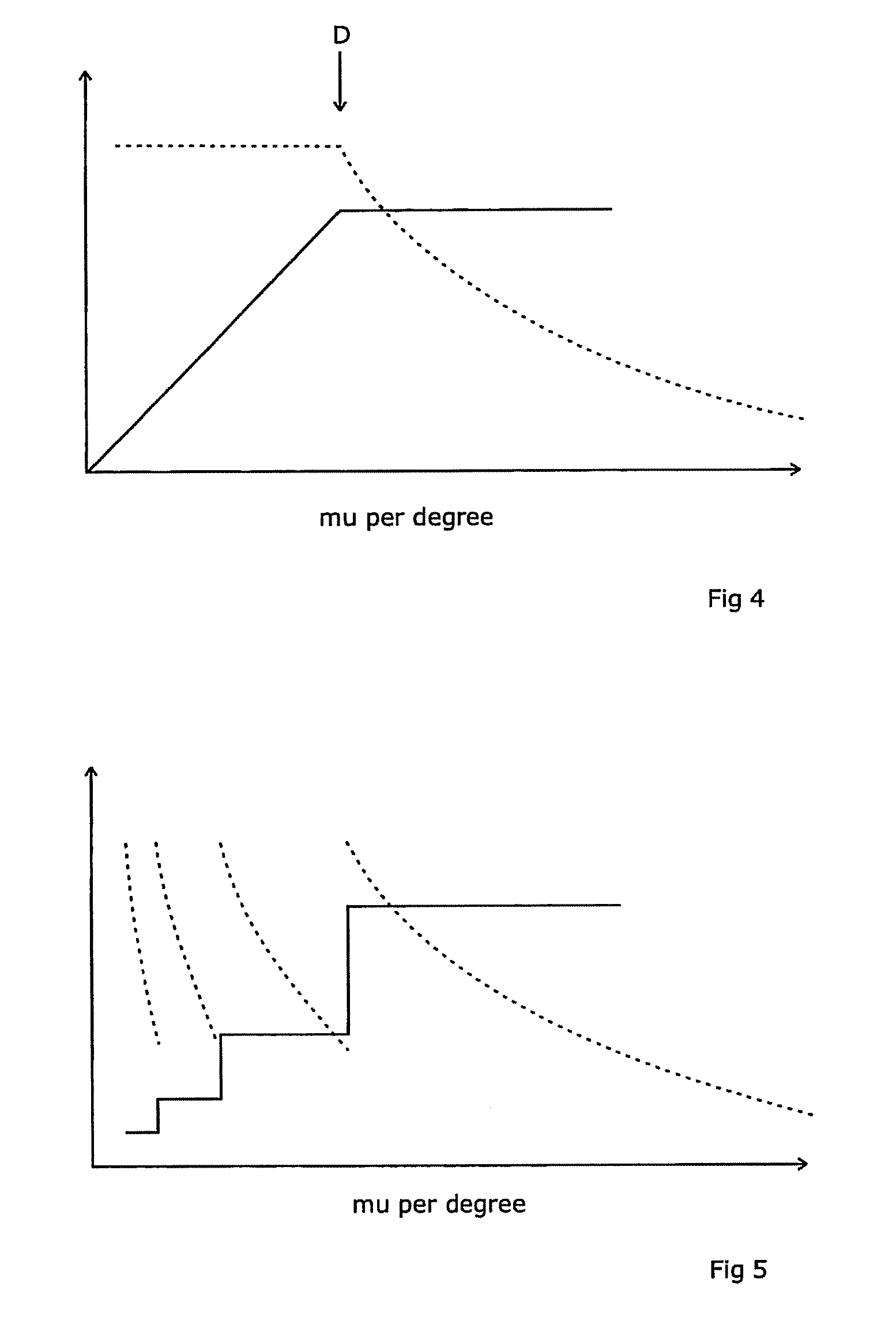
A radiotherapeutic apparatus comprises a source able to emit a beam of therapeutic radiation along a beam axis, a multi-leaf collimator arranged to collimate the beam to a desired shape, wherein the source is rotateable about a rotation axis that is substantially orthogonal and intersects with the beam axis thereby to describe an arc around that axis, and further comprises a control means able to control the dose / time rate of the source, the rotation speed of the source, and the multi-leaf collimator position. The control means is arranged to receive a treatment plan in which the arc is divided into a plurality of notional arc-segments, and specifying the total dose for the arc-segment and a start and end MLC position. It then controls the source in accordance with that plan over an first arc-segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant and the multi-leaf collimator changes shape, and a second arc segment such that at least one of the rotation speed and dose rate are constant at a level different to the constant level adopted during the first arc-segment. It achieves this by calculating the total time required for the arc segment for a plurality of factors including an MLC leaf movement from a prescribed position at the start of the arc-segment to a prescribed position at the end of the arc-segment, at a maximum leaf speed, rotation of the source from the start to the end of the arc-segment at a maximum source rotation speed, delivery of the dose at a maximum dose rate per time, selecting the factor dictating the longest time, and controlling the apparatus so that the selected factor operates at its respective maximum and the remaining factors are operated at a reduced rate selected to match that longest time.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
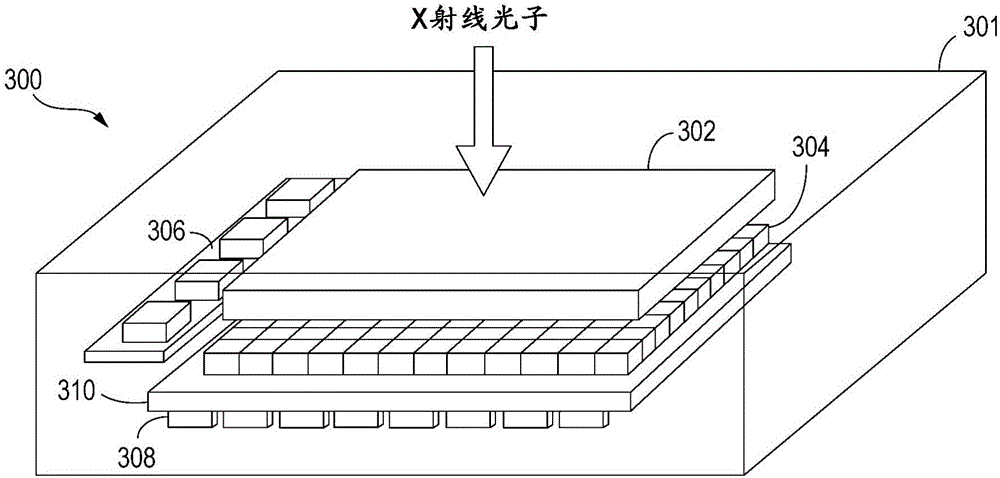
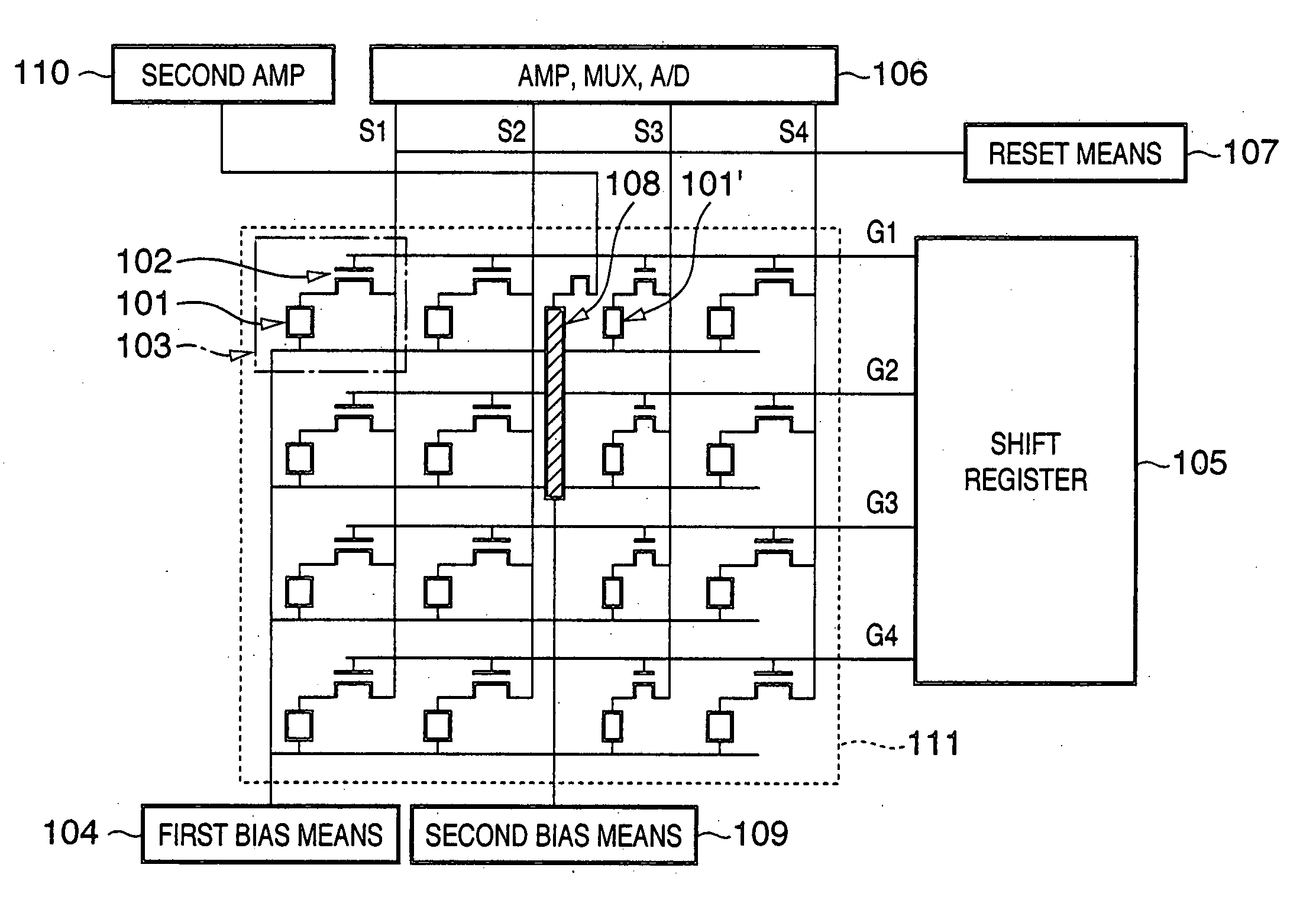
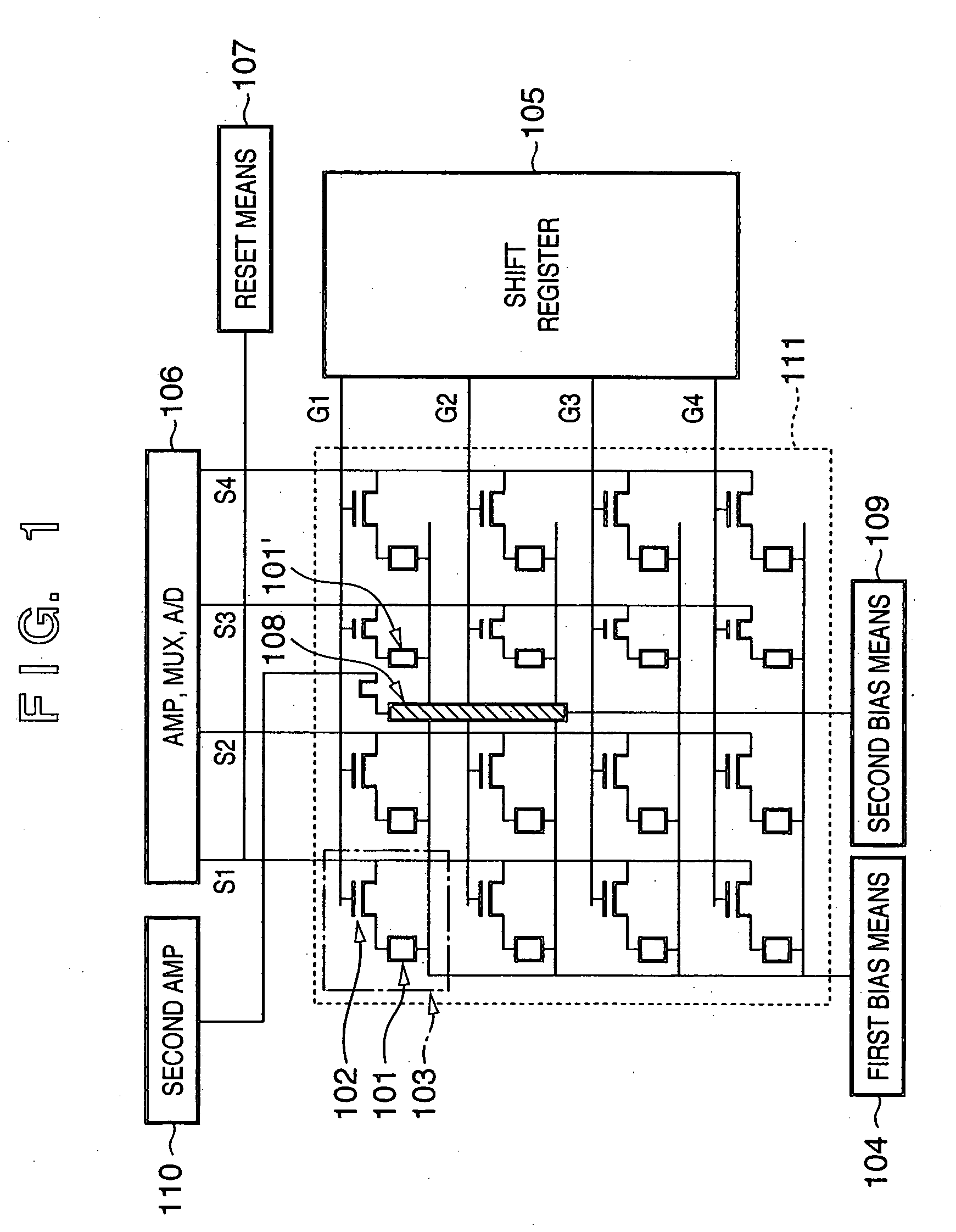
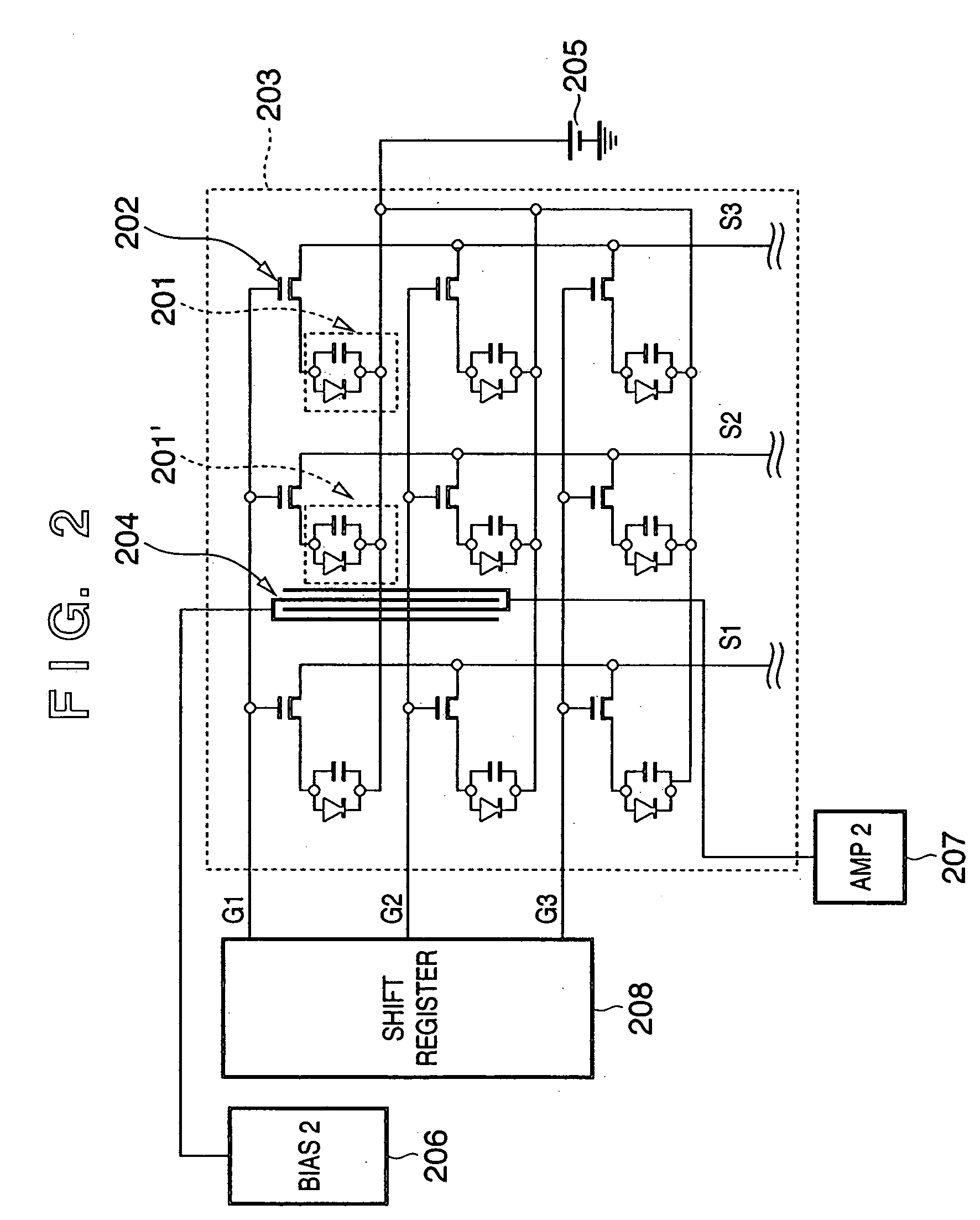
Radiation image sensing apparatus and its driving method
InactiveUS20050279943A1Television system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoelectric conversionIncident radiation dose
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com