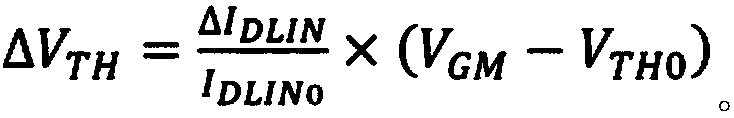Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
180 results about "Negative-bias temperature instability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
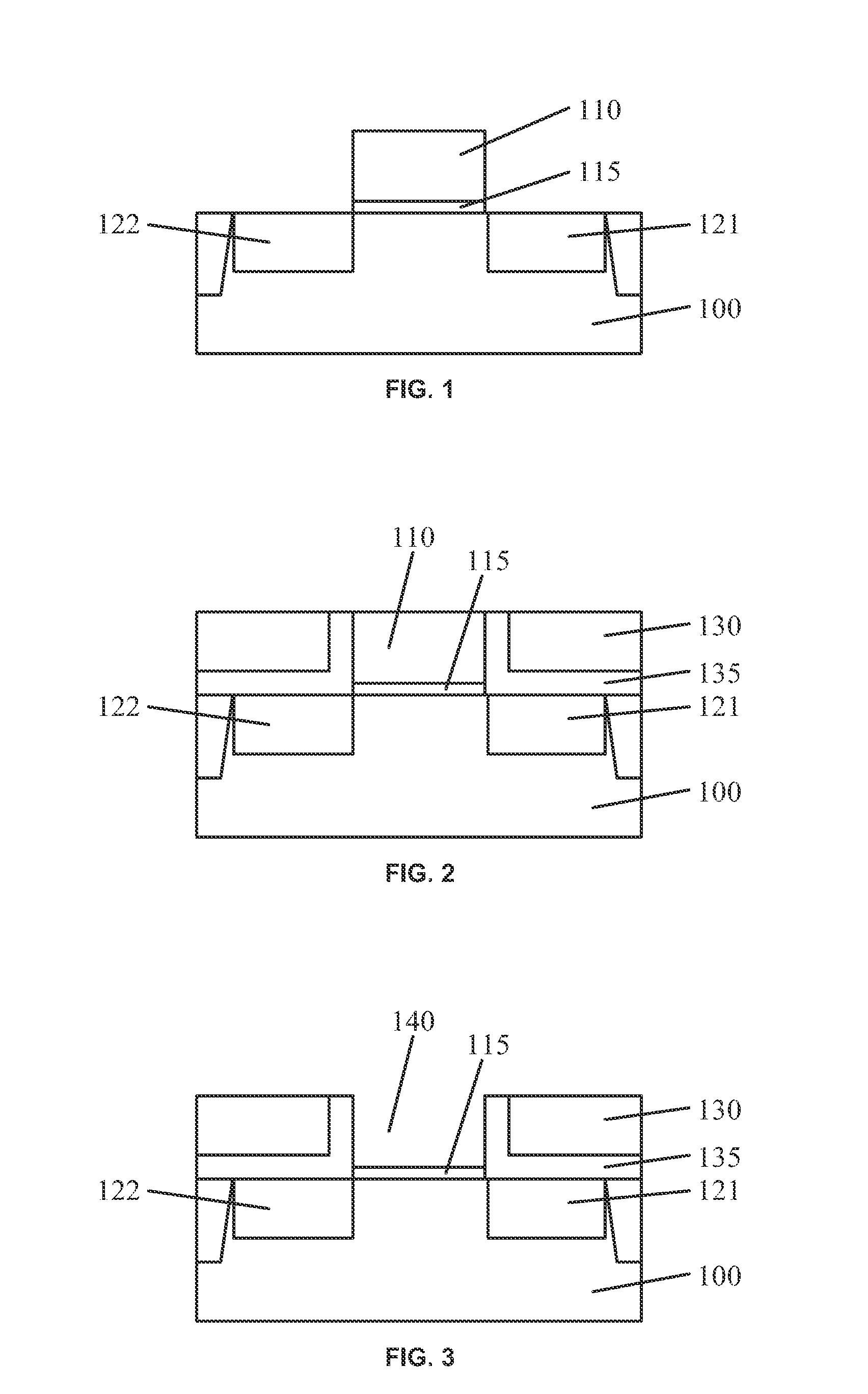
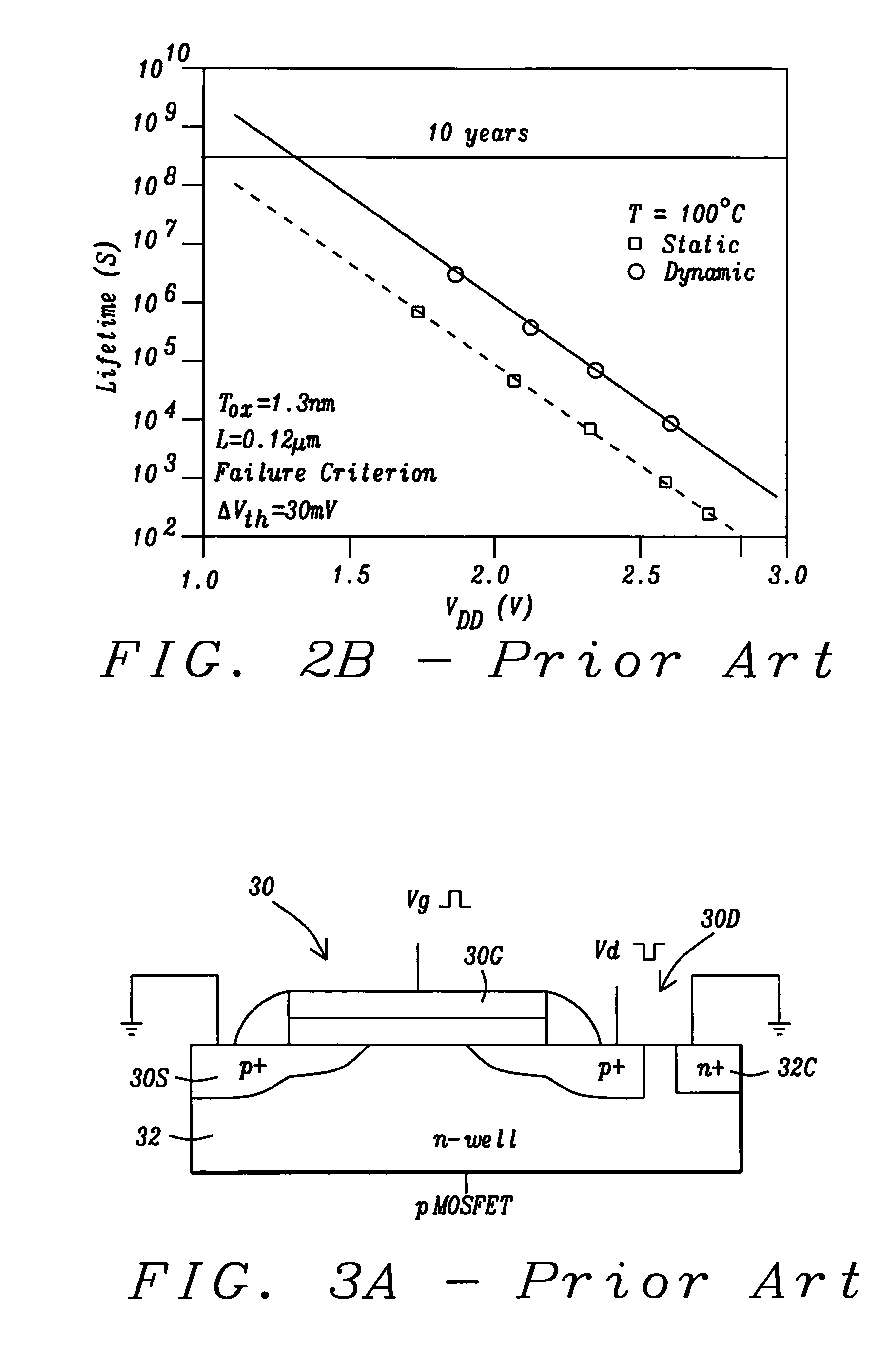
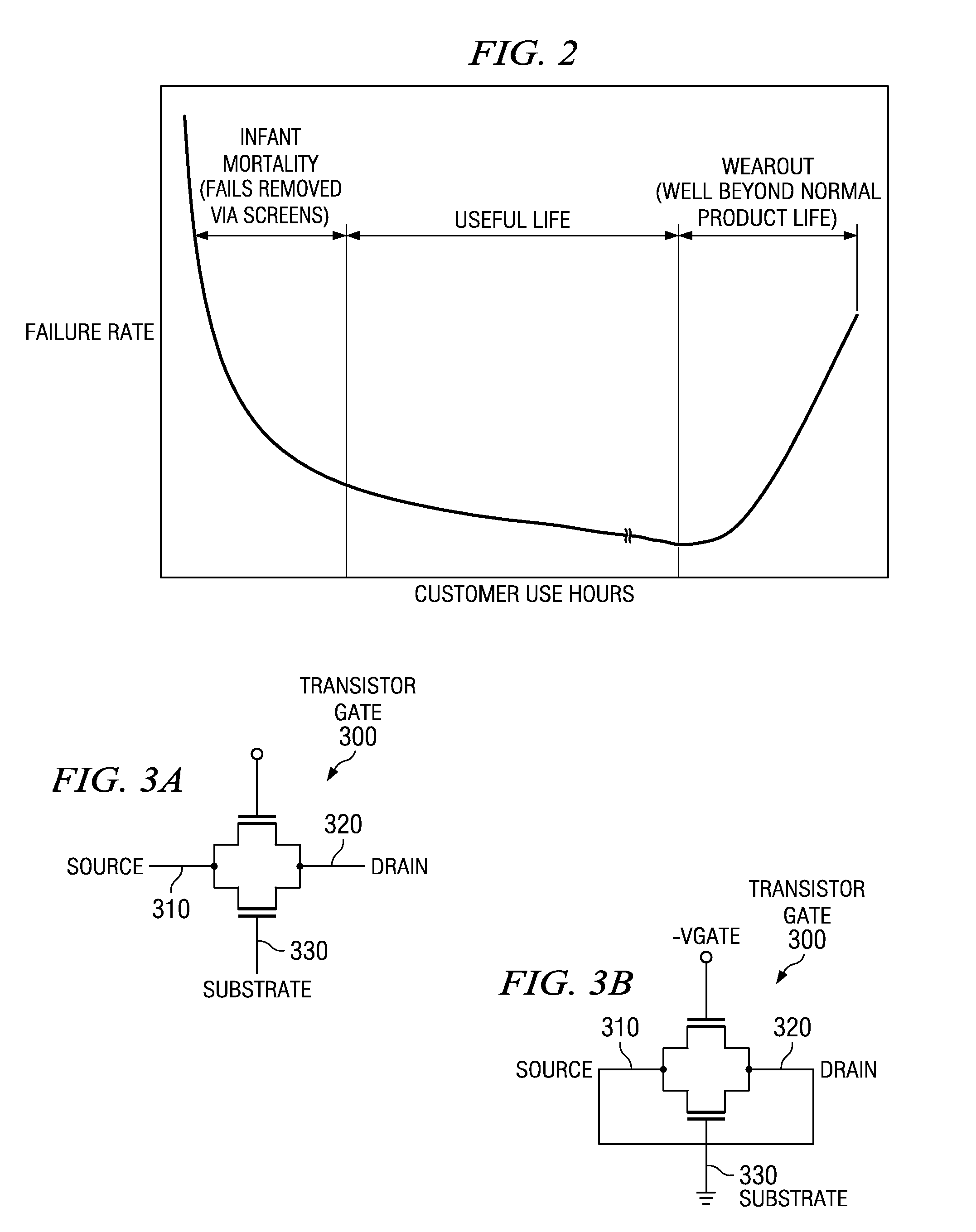
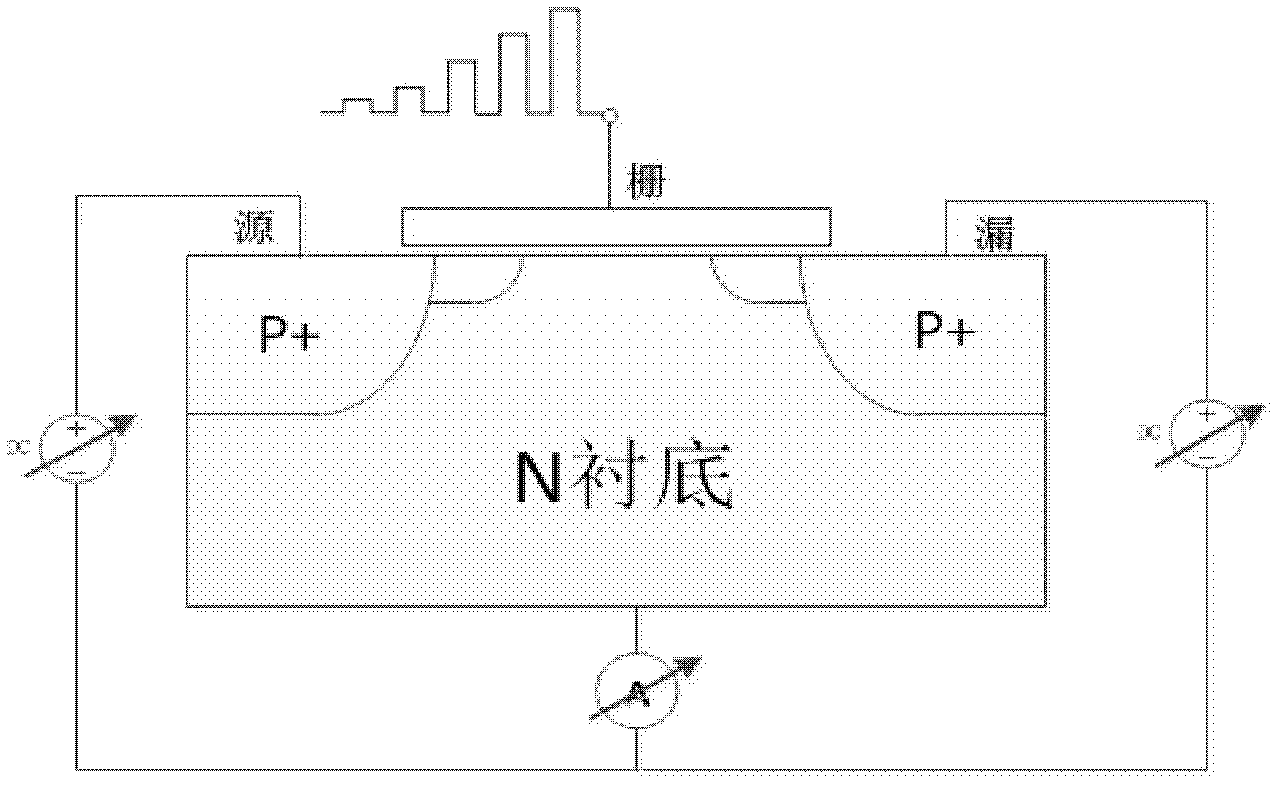
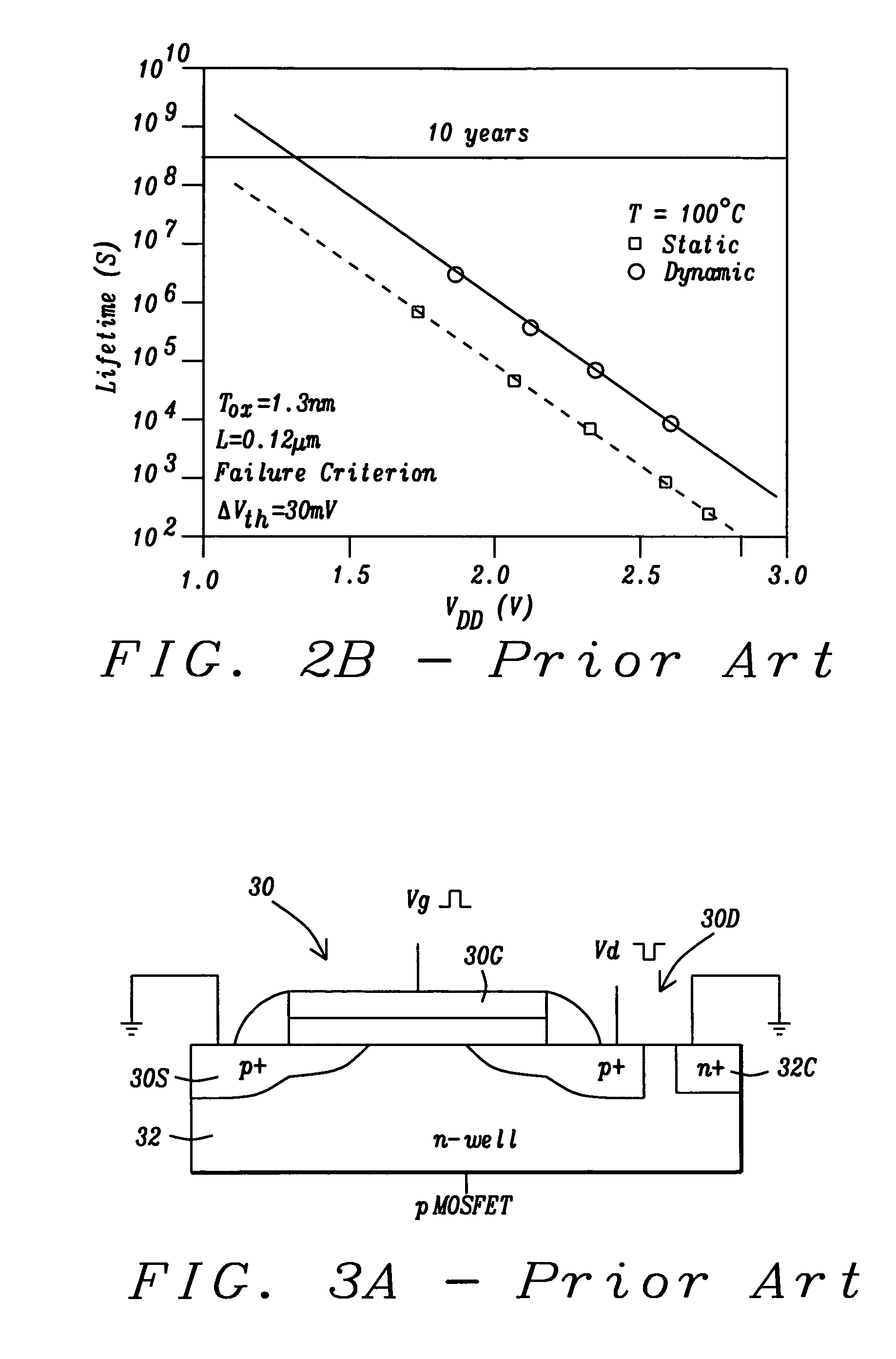
Negative-bias temperature instability (NBTI) is a key reliability issue in MOSFETs. NBTI manifests as an increase in the threshold voltage and consequent decrease in drain current and transconductance of a MOSFET. The degradation is often approximated by a power-law dependence on time. It is of immediate concern in p-channel MOS devices (pMOS), since they almost always operate with negative gate-to-source voltage; however, the very same mechanism also affects nMOS transistors when biased in the accumulation regime, i.e. with a negative bias applied to the gate.
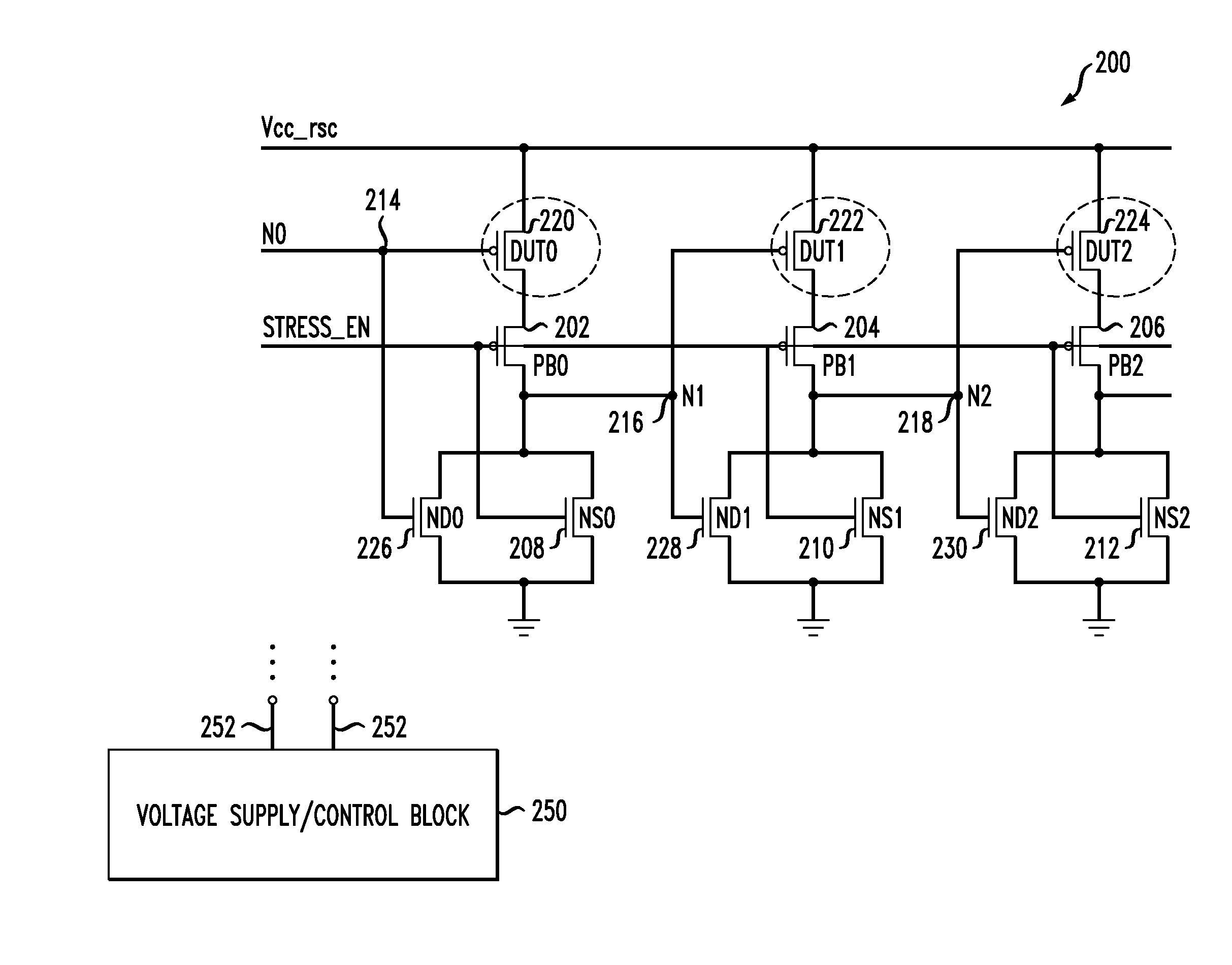
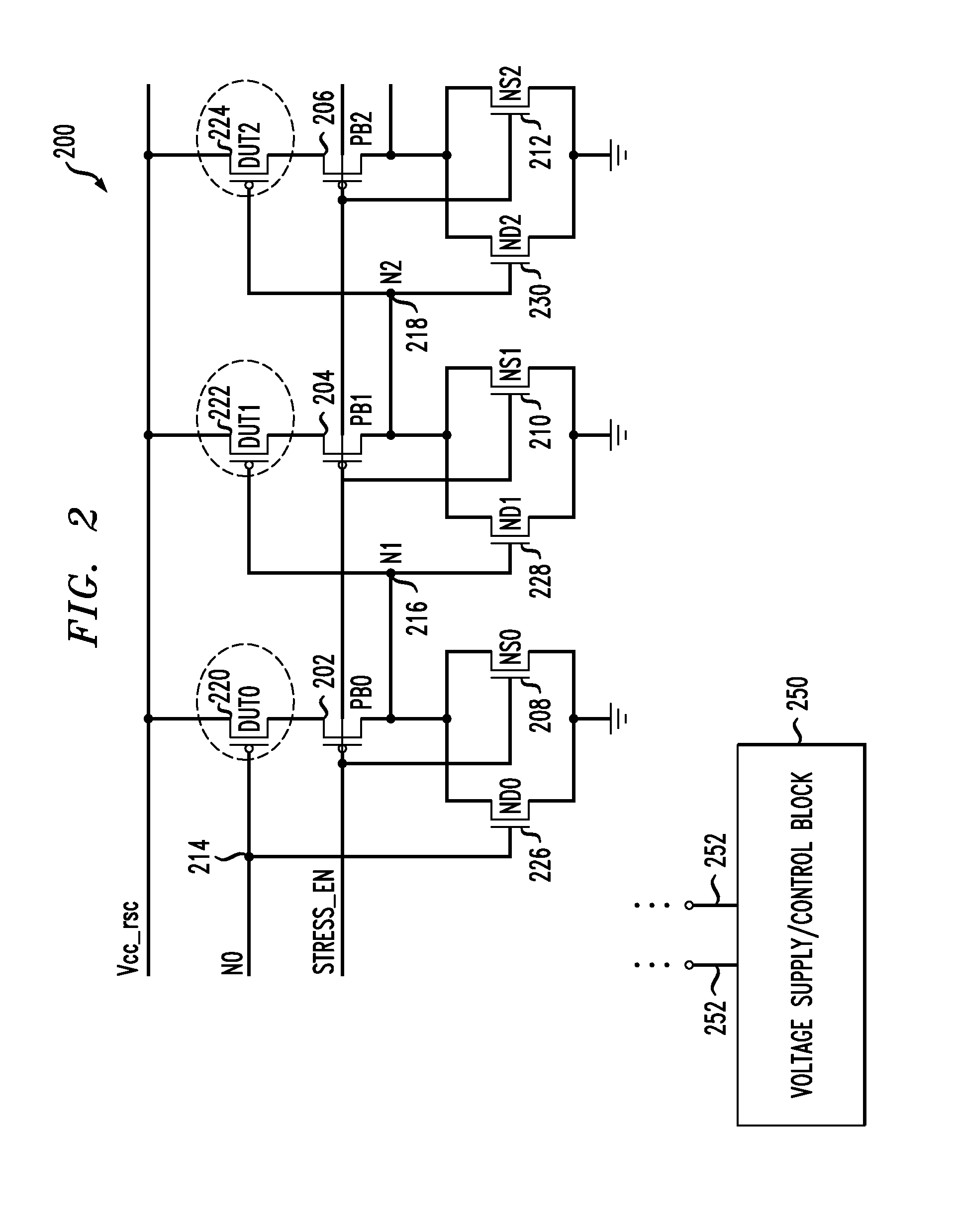
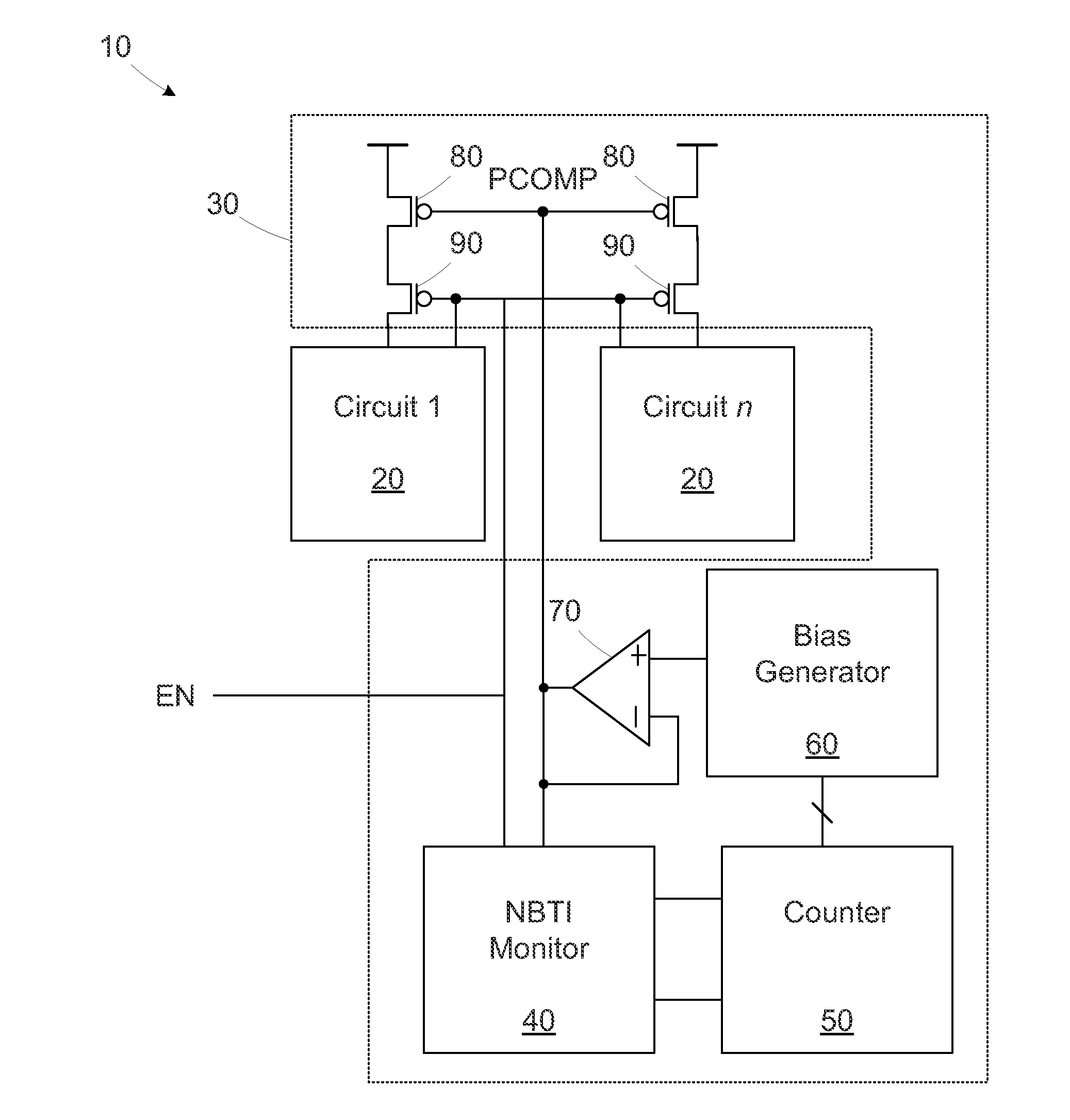
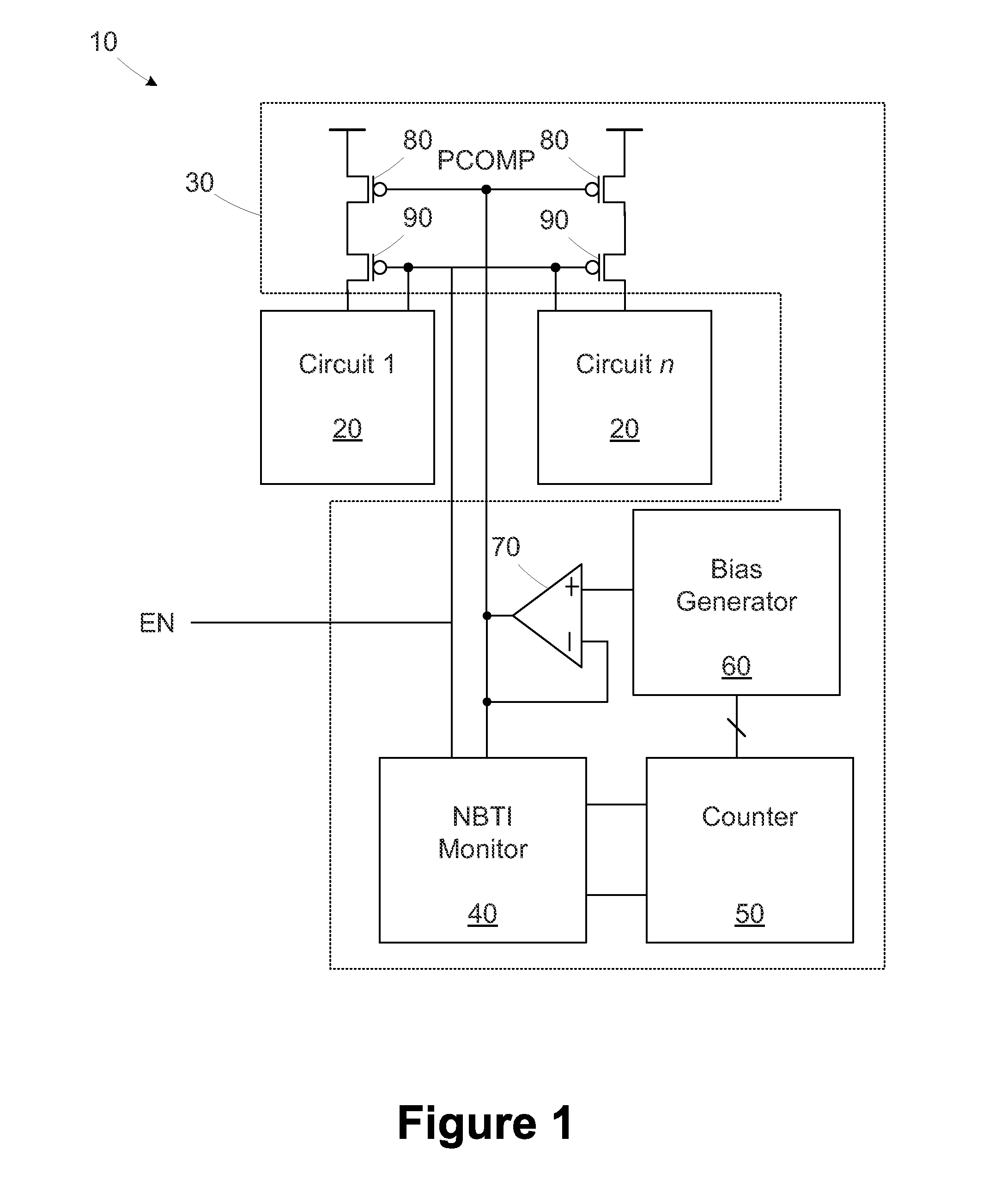
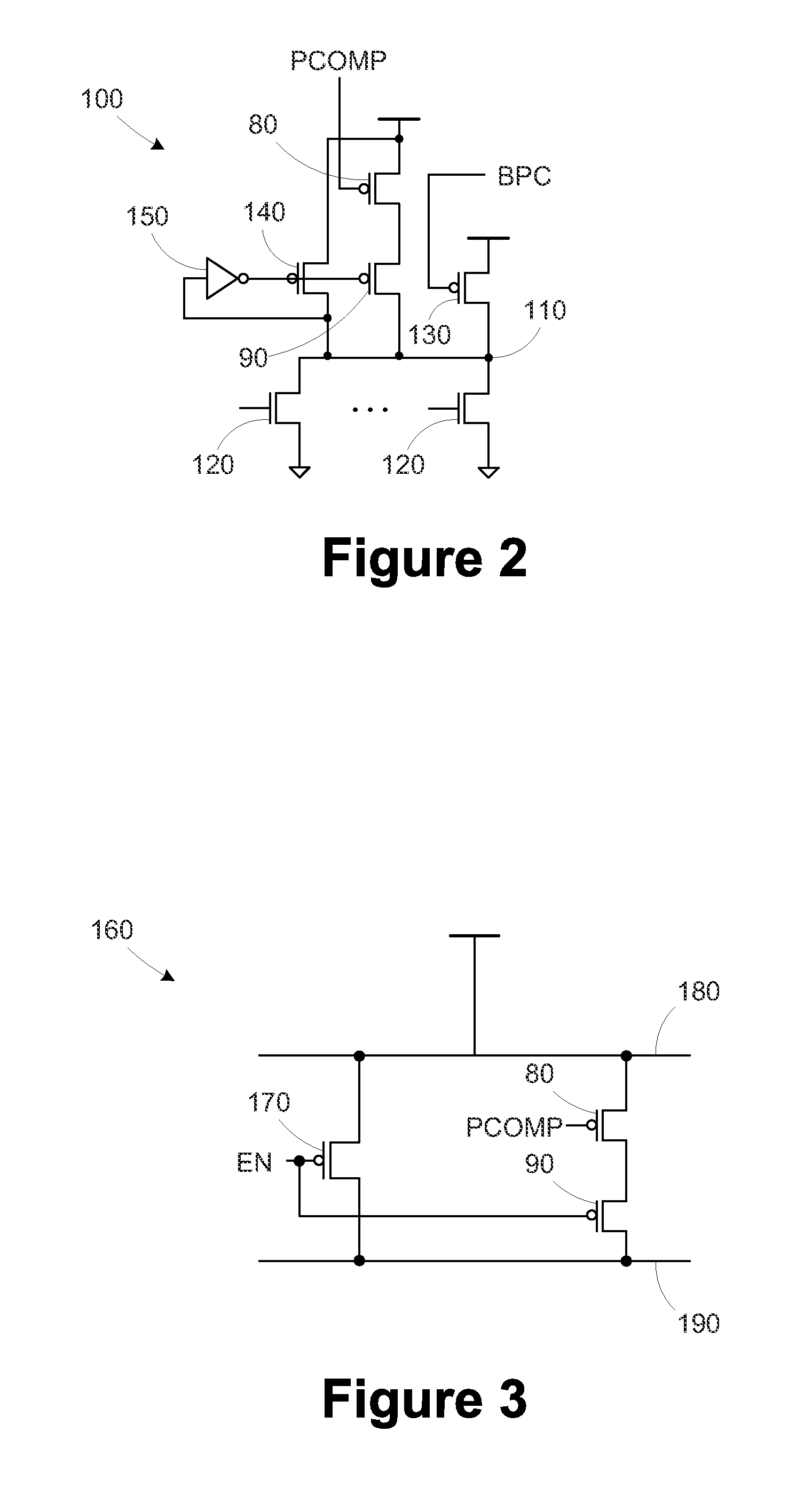
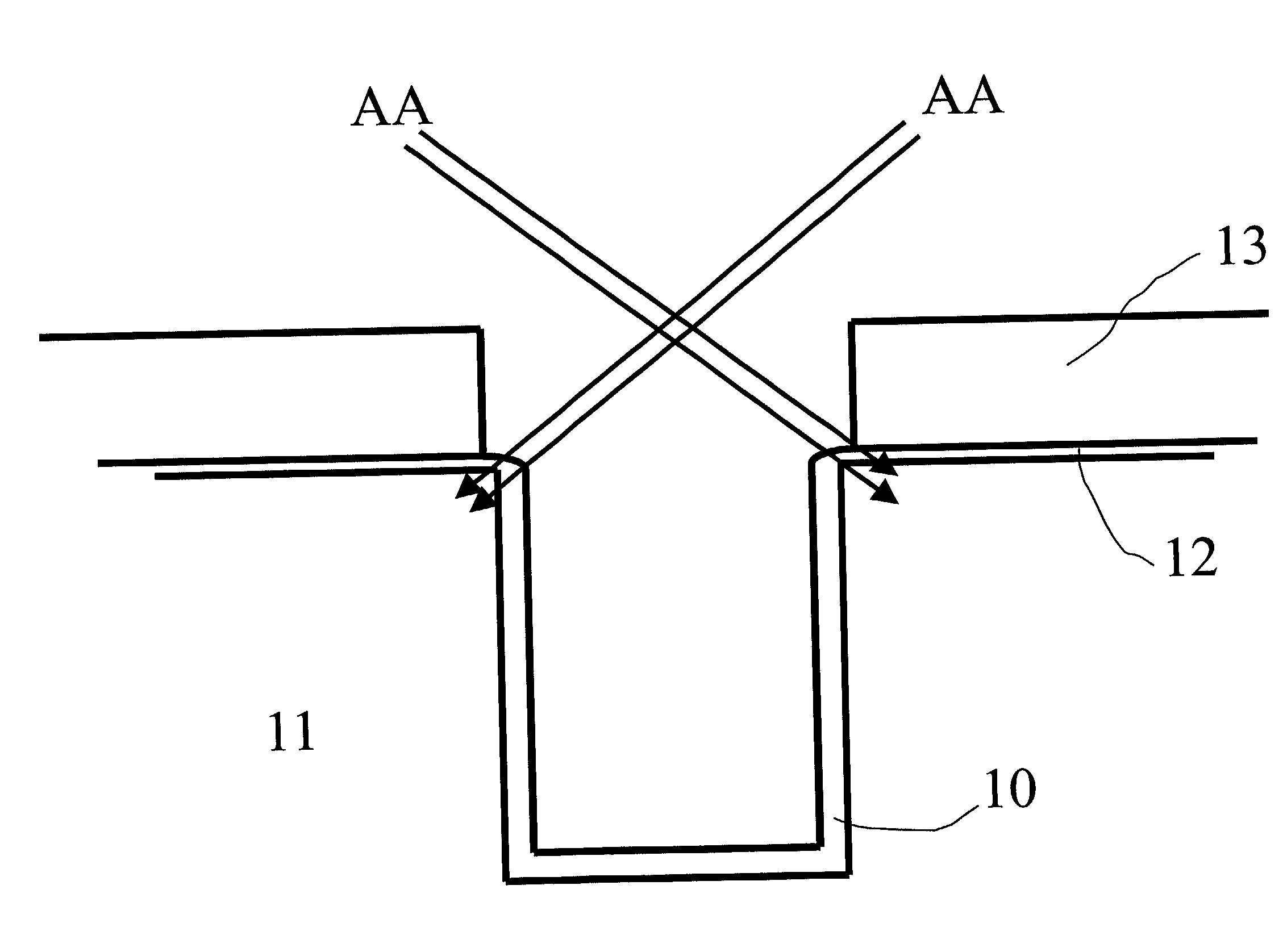
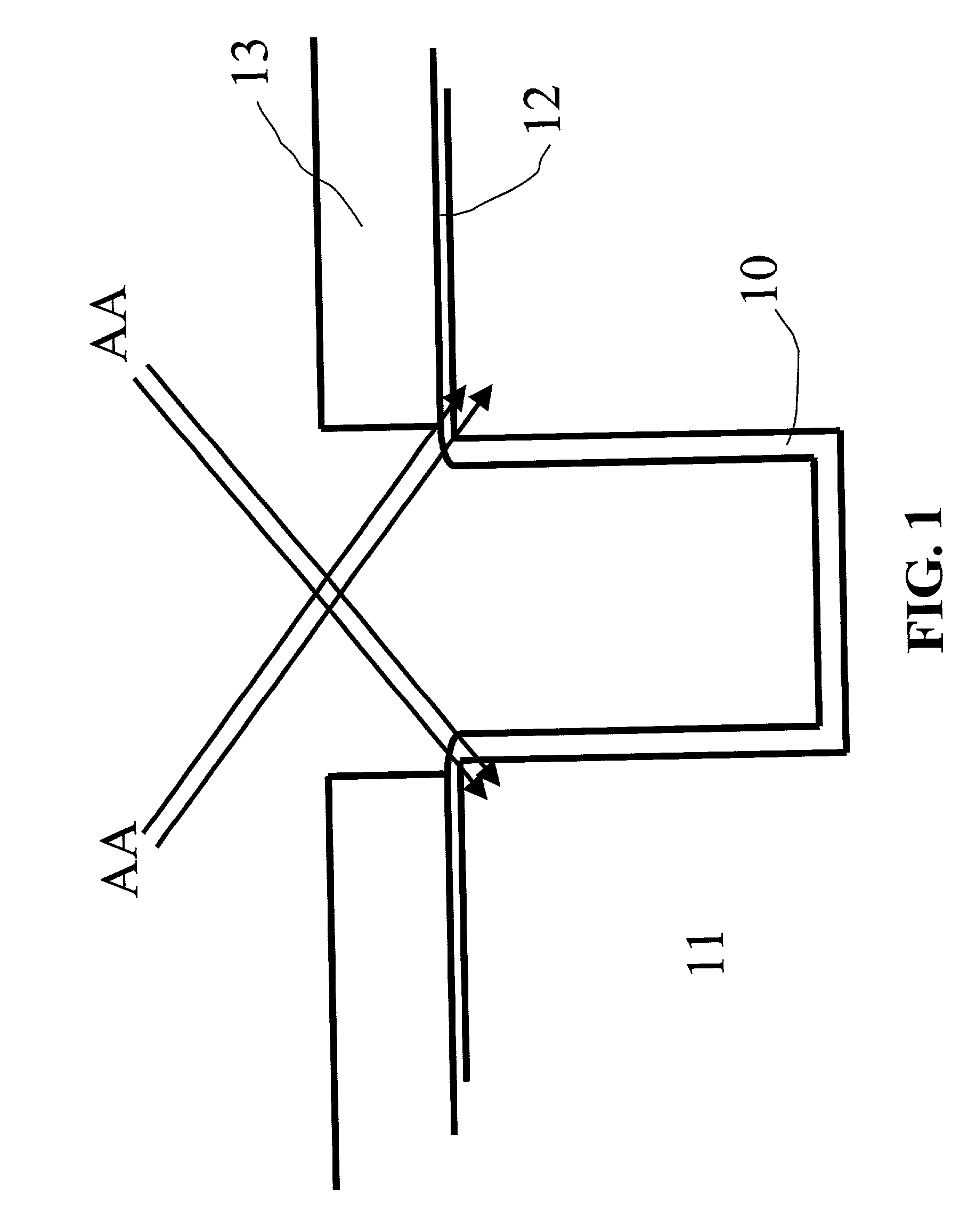
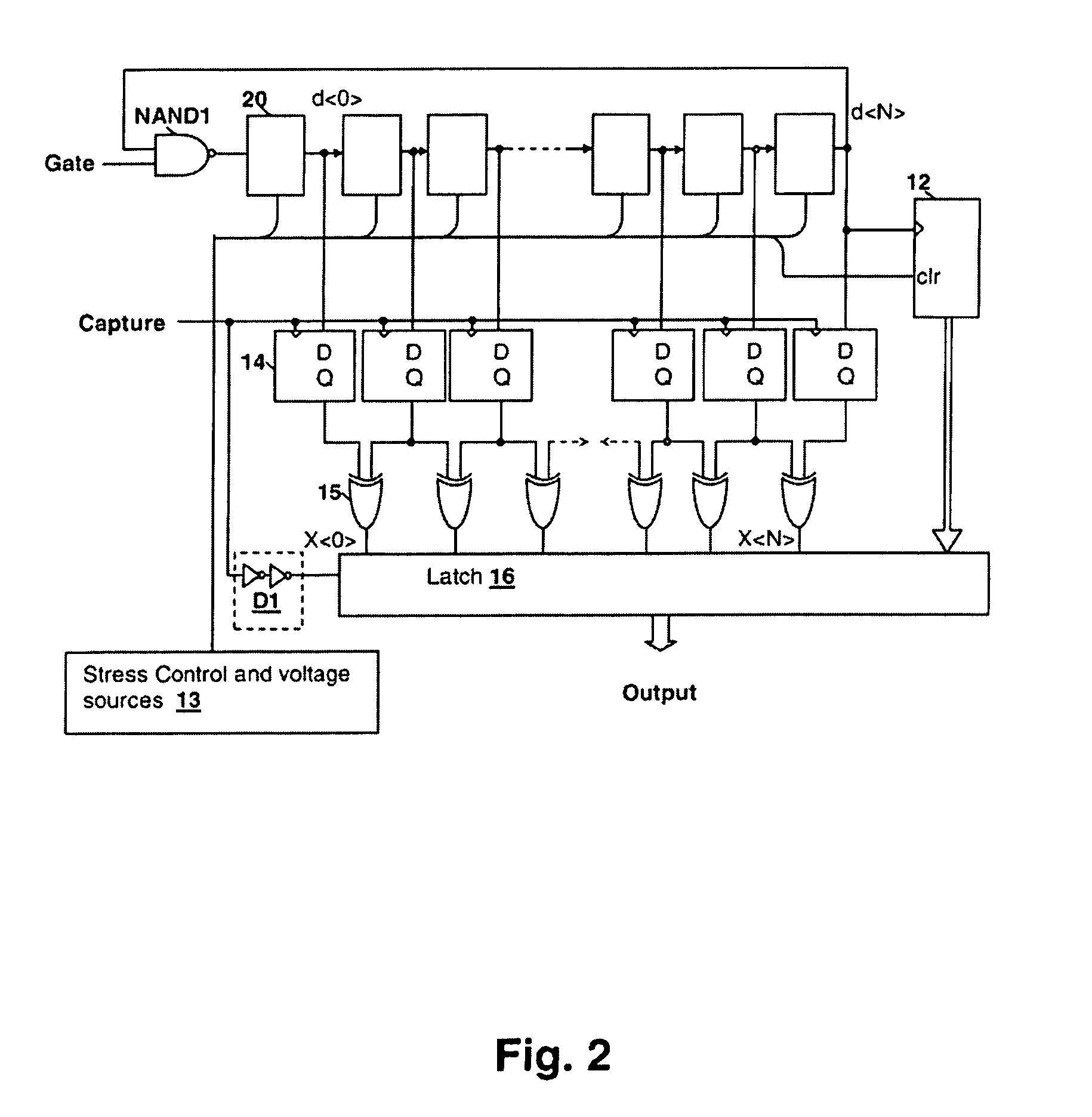
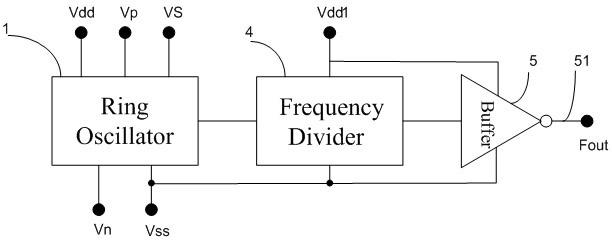
Circuits and design structures for monitoring nbti (negative bias temperature instability) effect and/or pbti (positive bias temperature instability) effect
ActiveUS20090189703A1High power supply voltageResistance/reactance/impedencePulse generation by logic circuitsNOR gateNAND gate
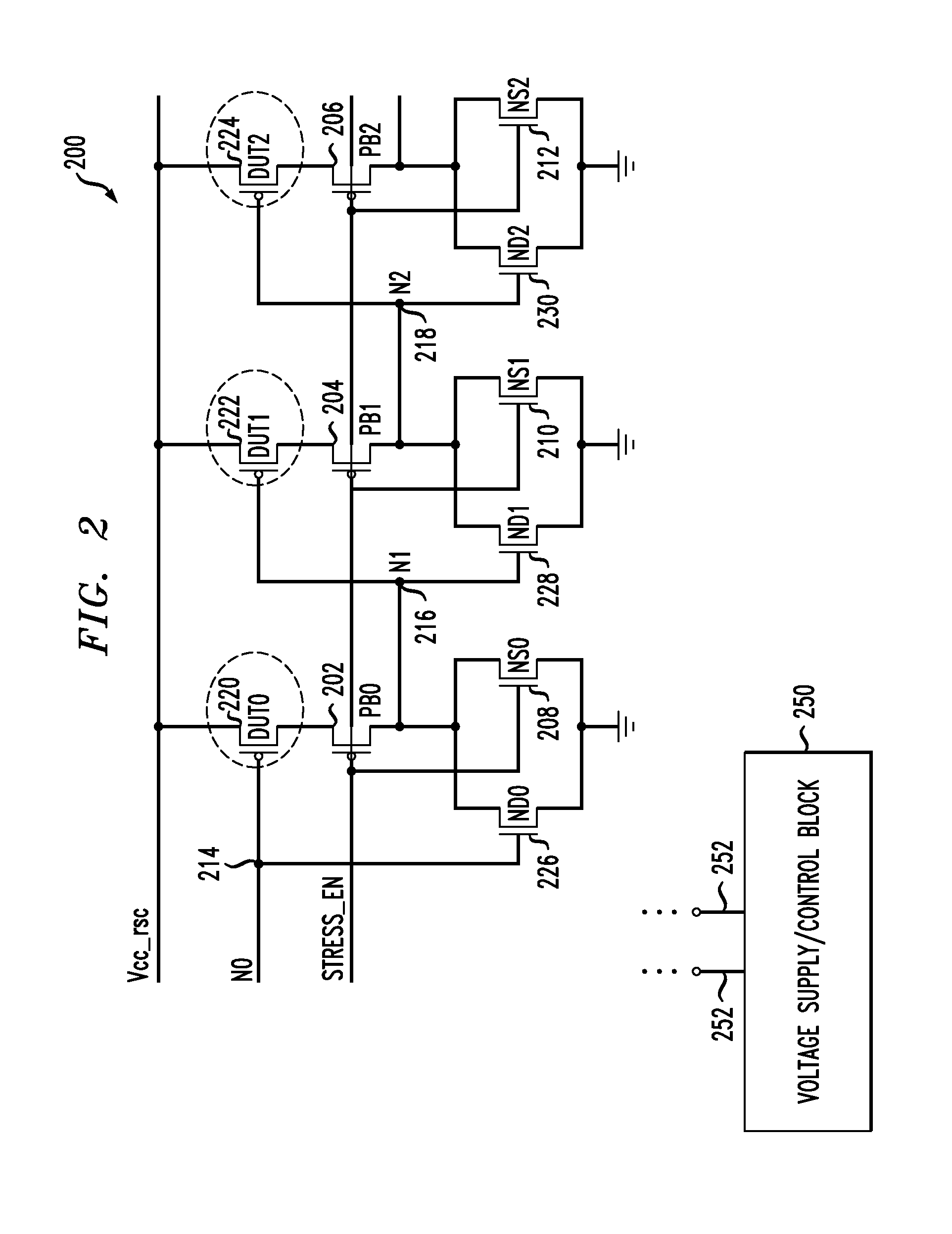
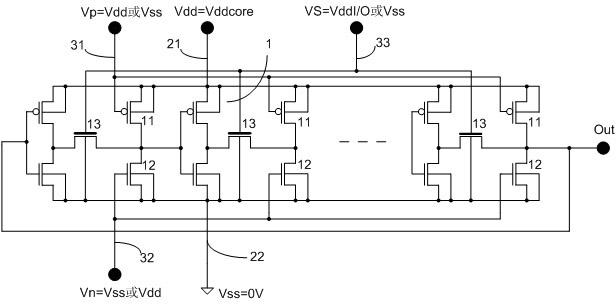
A ring oscillator has an odd number of NOR-gates greater than or equal to three, each with first and second input terminals, a voltage supply terminal, and an output terminal. The first input terminals of all the NOR-gates are interconnected, and each of the NOR-gates has its output terminal connected to the second input terminal of an immediately adjacent one of the NOR-gates. During a stress mode, a voltage supply and control block applies a stress enable signal to the interconnected first input terminals, and an increased supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. During a measurement mode, this block grounds the interconnected first input terminals, and applies a normal supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. Also included are an analogous NAND-gate based circuit, a circuit combining the NAND- and NOR-aspects, a circuit with a ring oscillator where the inverters may be coupled directly or through inverting paths, and circuits for measuring the bias temperature instability effect in pass gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Transistor device and fabrication method
ActiveUS20140077313A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectric layerNegative-bias temperature instability
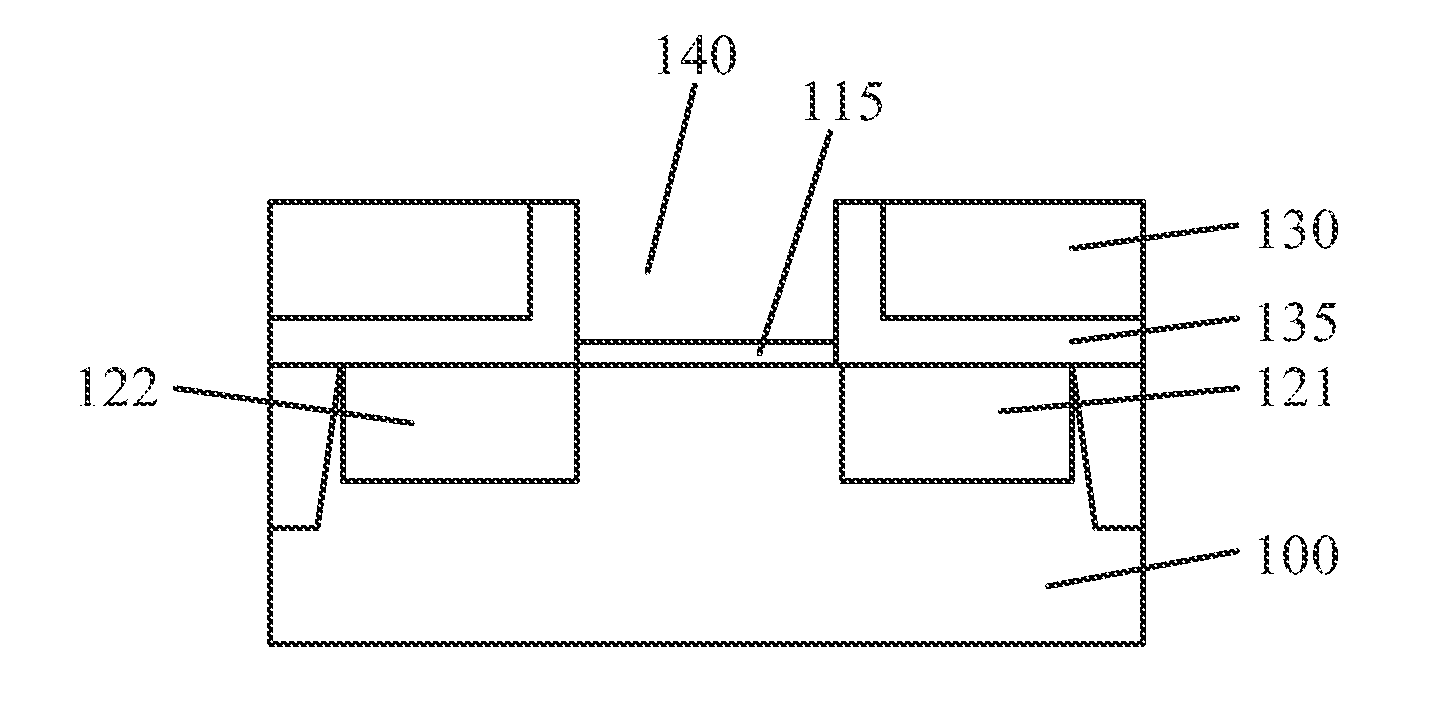
Various embodiments provide transistors and their fabrication methods. An exemplary method for forming a transistor includes removing a dummy gate to form a trench over a semiconductor substrate. A high-k dielectric layer can be conformally formed on surface of the trench and then be fluorinated to form a fluorinated high-k dielectric layer. A functional layer can be formed on the fluorinated high-k dielectric layer and a metal layer can be formed on the functional layer to fill the trench with the metal layer. Due to fluorination of the high-k dielectric layer, negative bias temperature instability of the formed transistor can be reduced and oxygen vacancies can be passivated to reduce positive bias temperature instability of the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
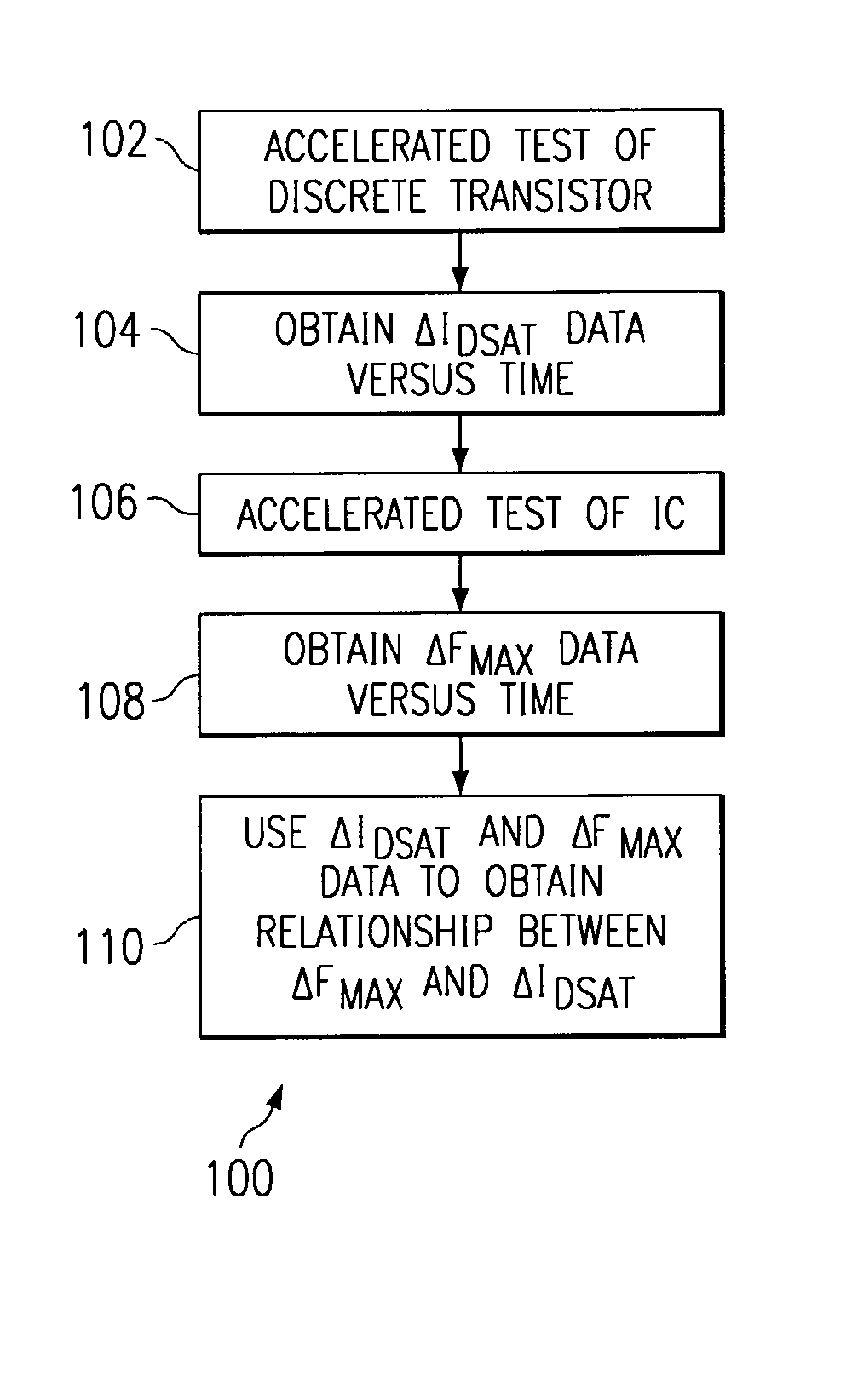
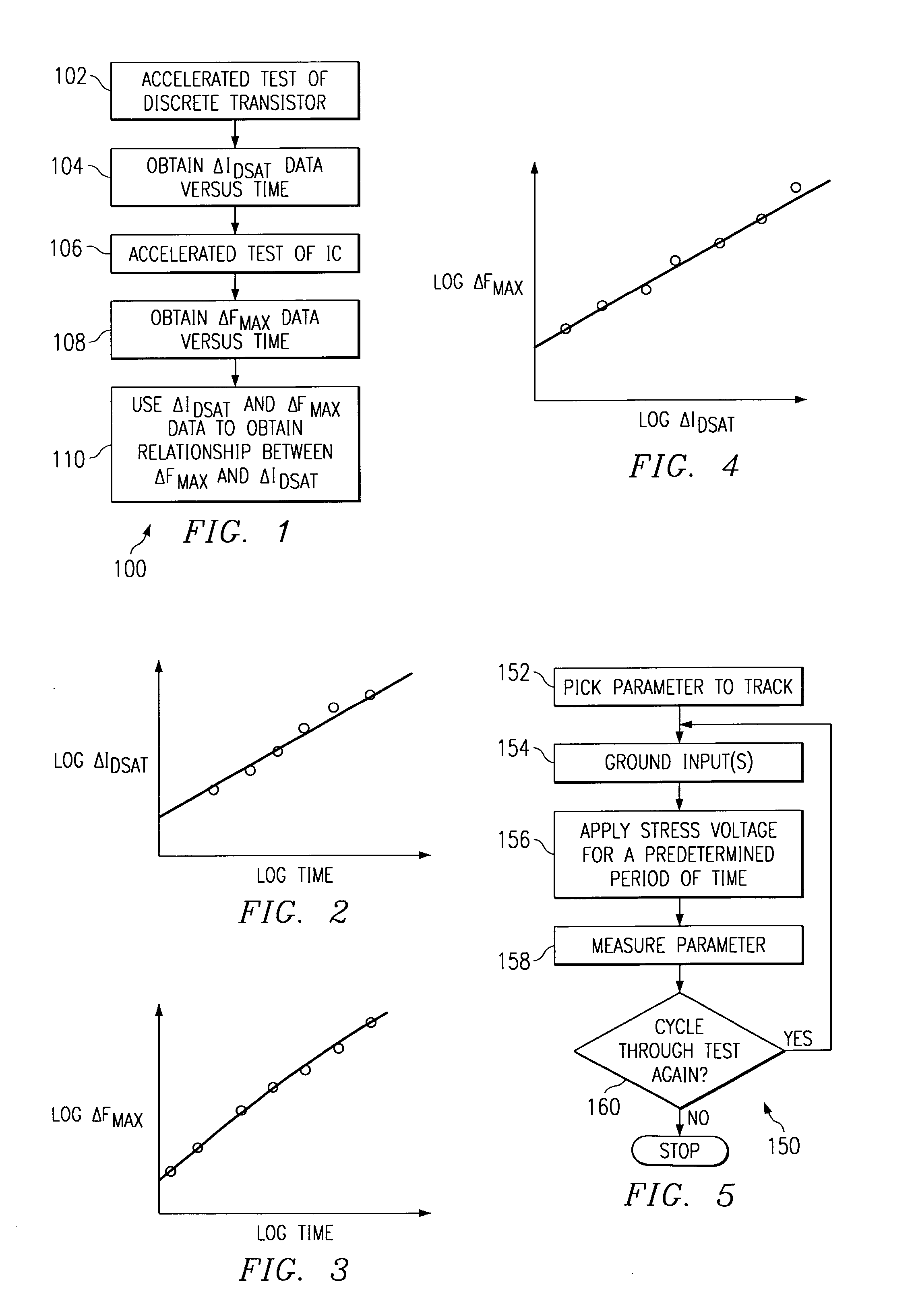
Method for predicting the degradation of an integrated circuit performance due to negative bias temperature instability
InactiveUS20030233624A1Easy and cheap to testEasy and faster and cheap to estimateDigital circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareNegative-bias temperature instabilityIntegrated circuit
A method is provided of correlating integrated circuit NBTI-induced performance degradation to discrete transistor NBTI-induced performance degradation and using that correlation to estimate integrated circuit degradation over time using test results based on a discrete transistor. Because discrete transistors are easier and cheaper to test, the technique described herein makes it easier, faster and cheaper to estimate the degradation of an integrated circuit over time than testing the integrated circuit itself.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of NBTI prediction
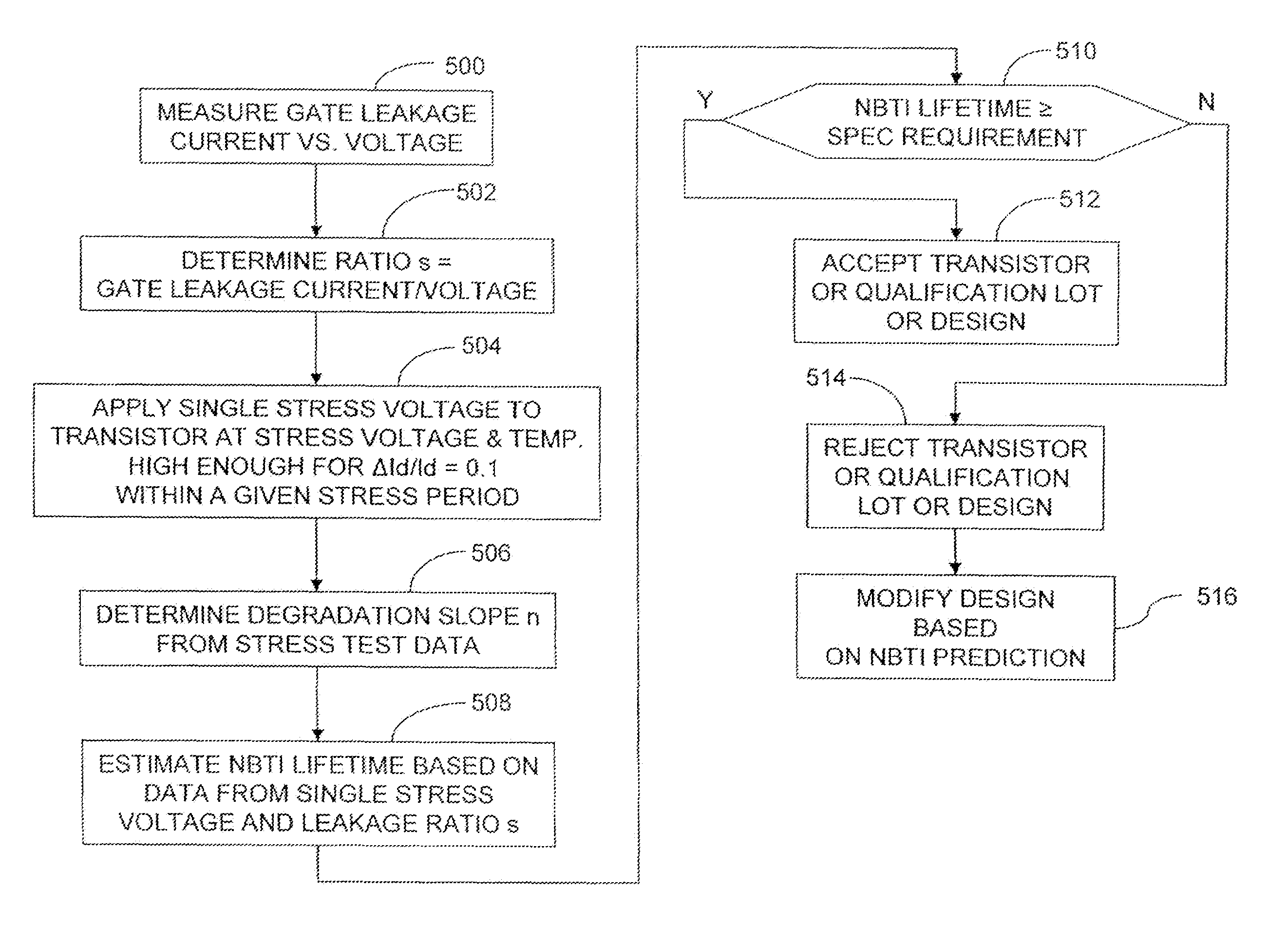
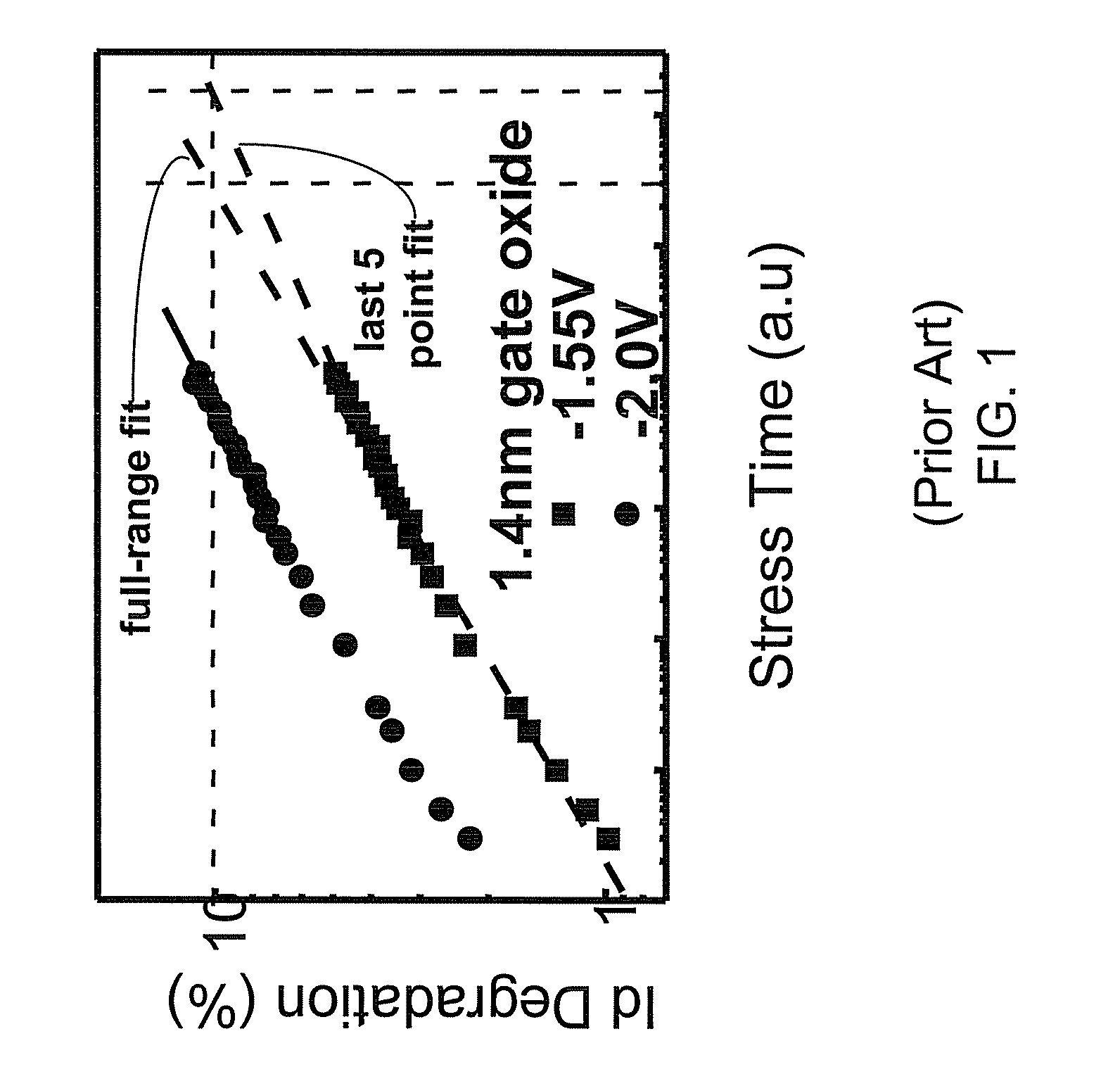
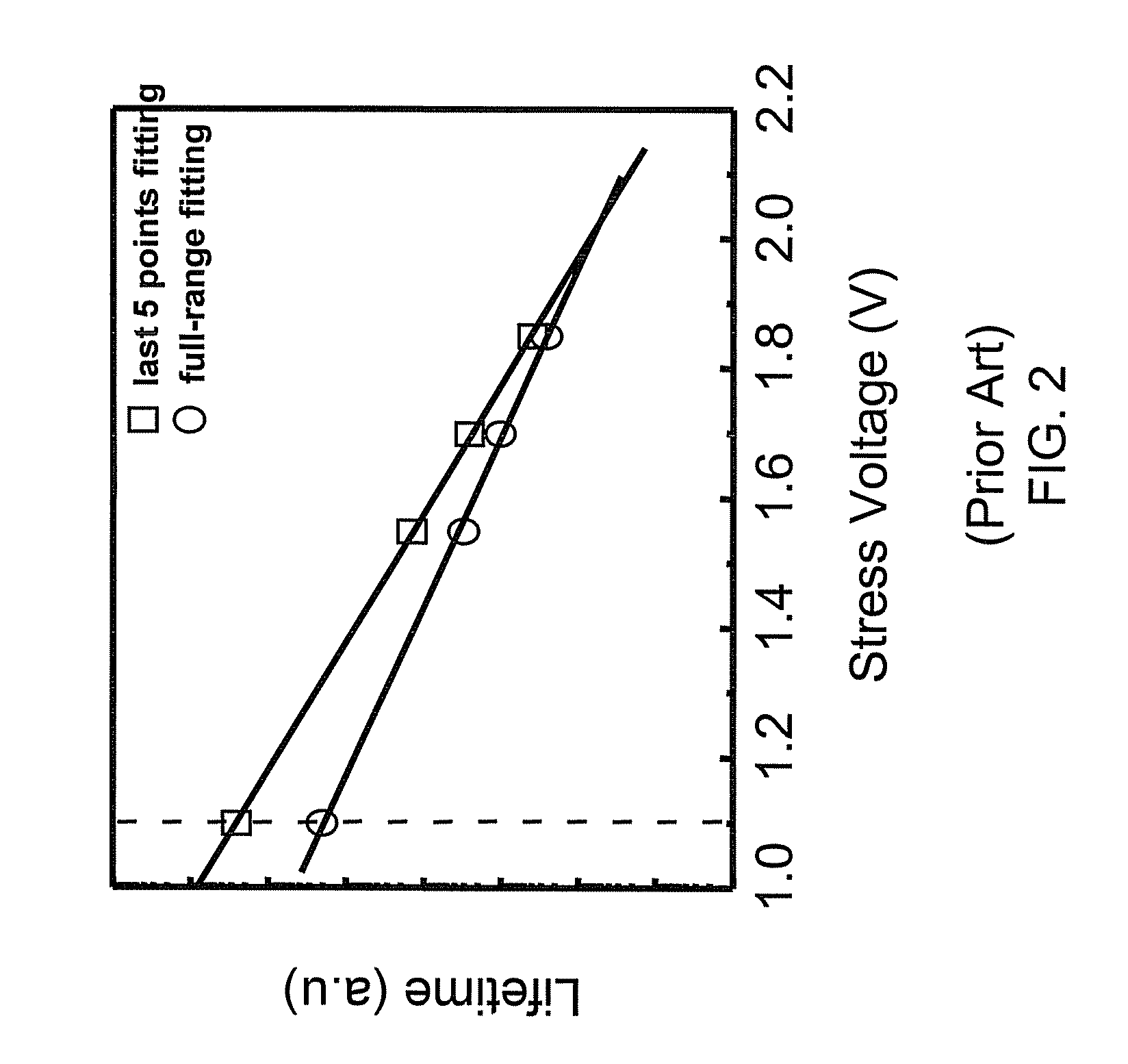
InactiveUS7268575B1Semiconductor operation lifetime testingMarginal circuit testingGate leakage currentDriving current
A method includes measuring a gate leakage current of at least one transistor. A single stress bias voltage is applied to the at least one transistor at a given temperature for a stress period t. The stress bias voltage causes a 10% degradation in a drive current of the transistor at the given temperature within the stress period t. A negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) lifetime τ of the transistor is estimated based on the measured gate leakage current and a relationship between drive current degradation and time observed during the applying step.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
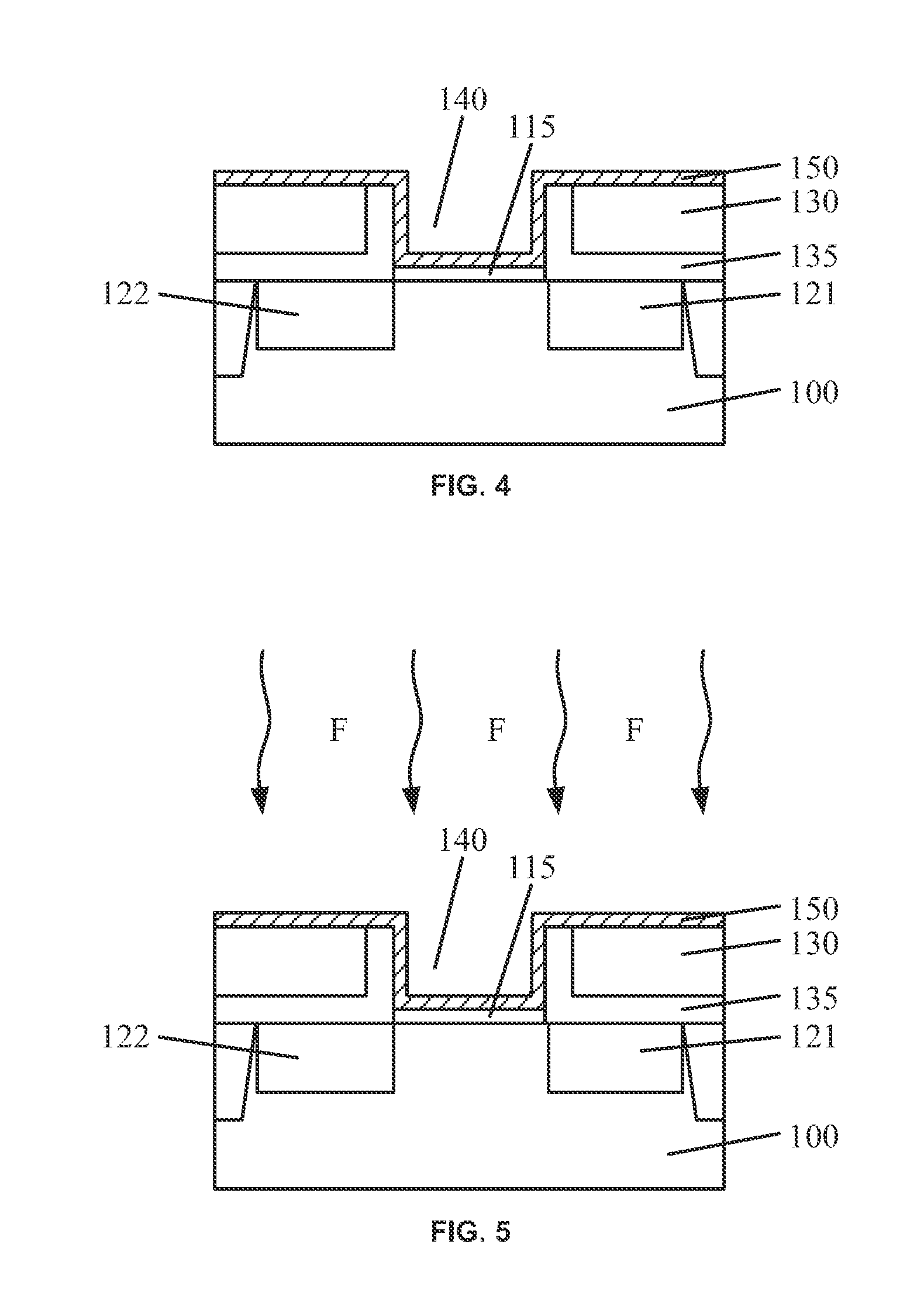
Circuits and design structures for monitoring NBTI (negative bias temperature instability) effect and/or PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) effect
A ring oscillator has an odd number of NOR-gates greater than or equal to three, each with first and second input terminals, a voltage supply terminal, and an output terminal. The first input terminals of all the NOR-gates are interconnected, and each of the NOR-gates has its output terminal connected to the second input terminal of an immediately adjacent one of the NOR-gates. During a stress mode, a voltage supply and control block applies a stress enable signal to the interconnected first input terminals, and an increased supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. During a measurement mode, this block grounds the interconnected first input terminals, and applies a normal supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. Also included are an analogous NAND-gate based circuit, a circuit combining the NAND- and NOR-aspects, a circuit with a ring oscillator where the inverters may be coupled directly or through inverting paths, and circuits for measuring the bias temperature instability effect in pass gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
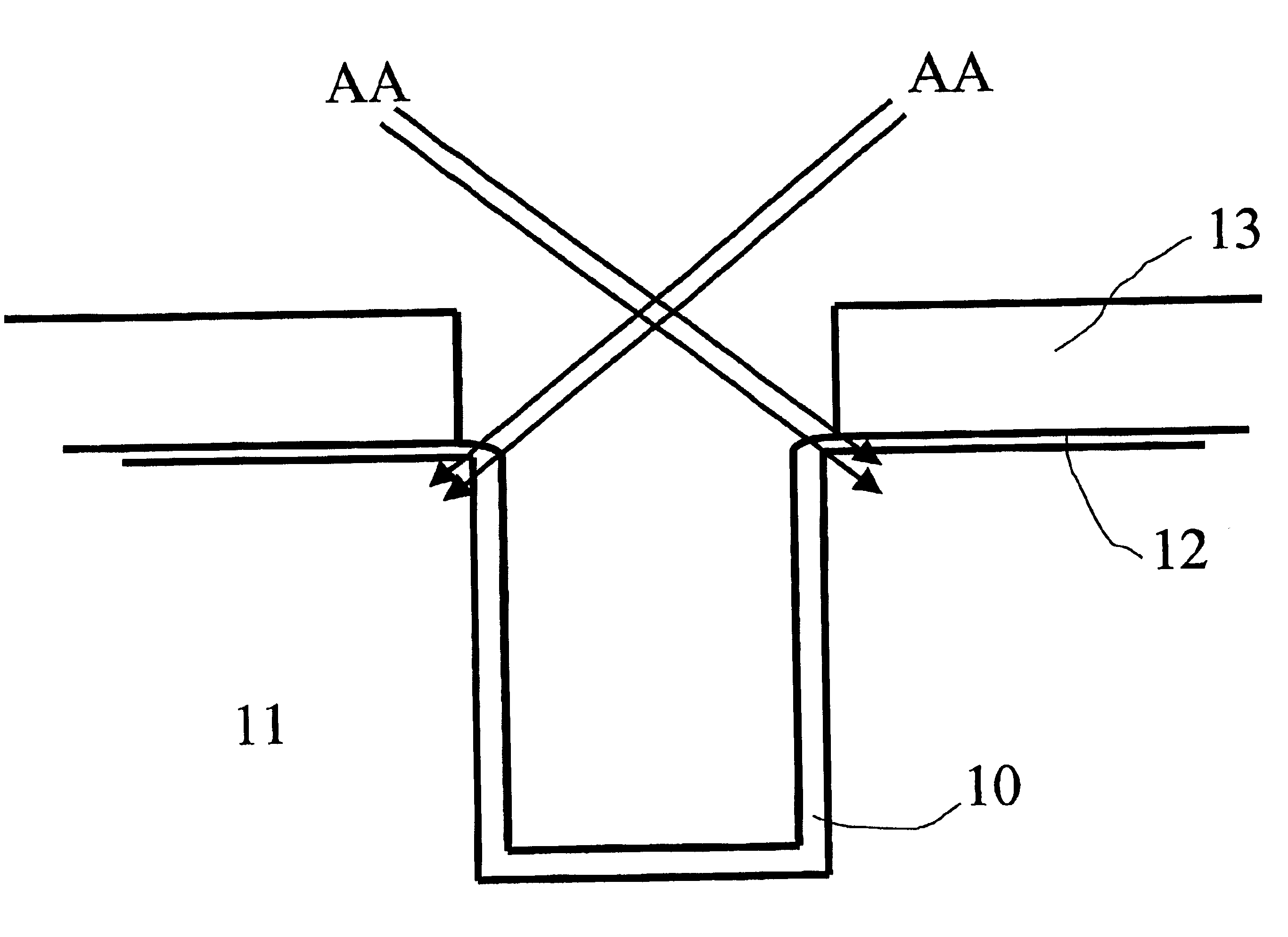
Novel test structure for automatic dynamic negative-bias temperature instability testing
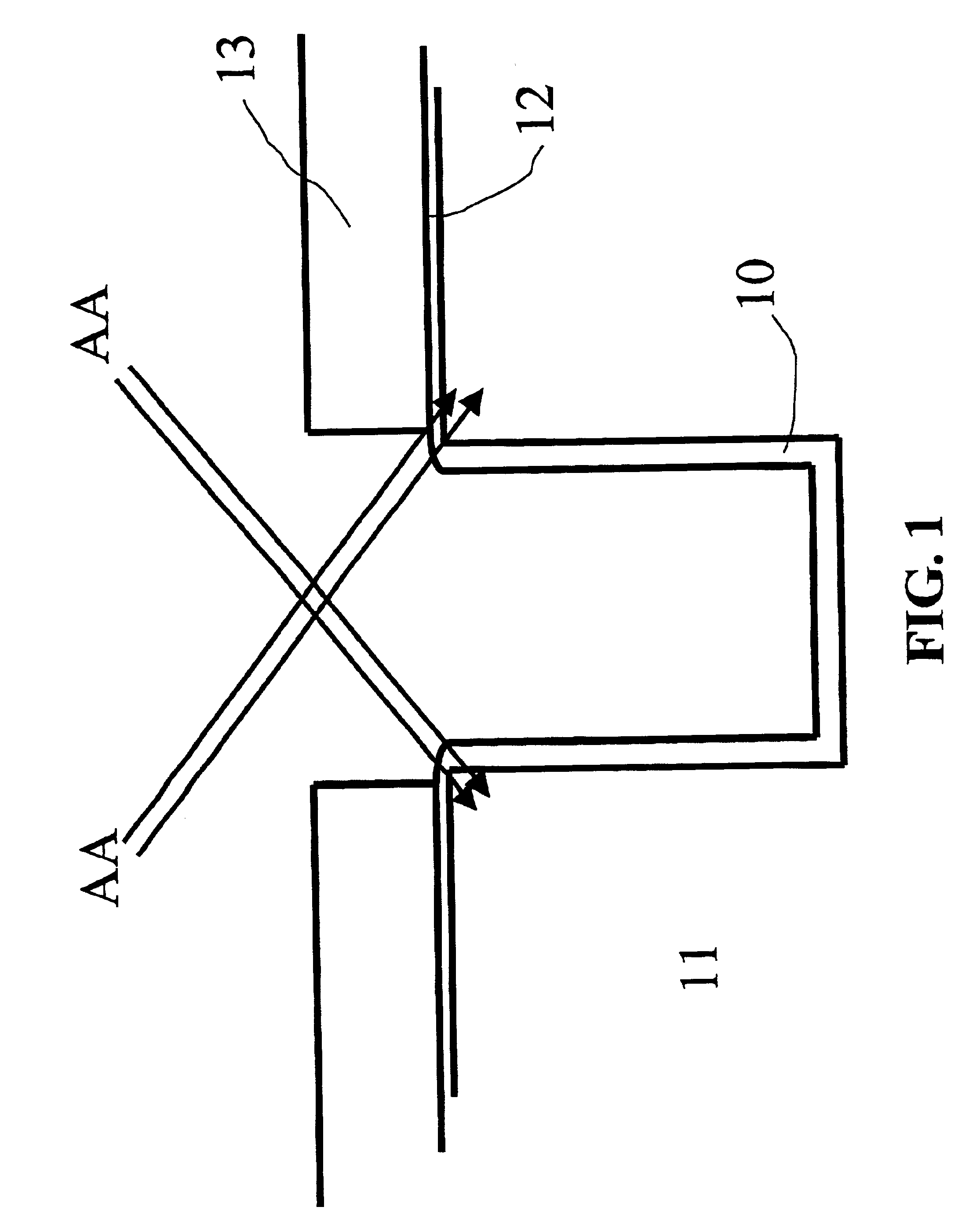
InactiveUS20050278677A1Minimize parasitic capacitanceMinimizes parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronic switchEngineering
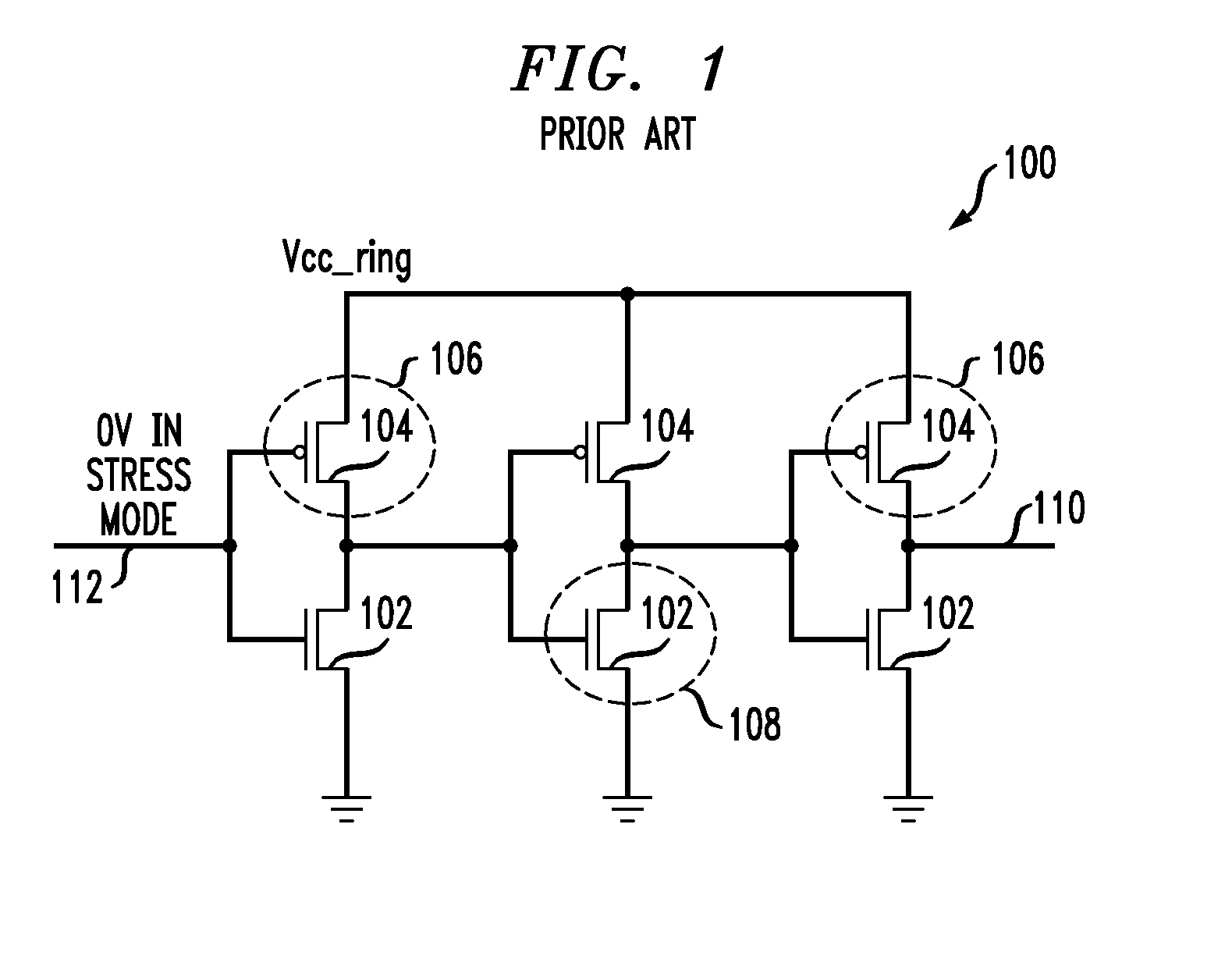
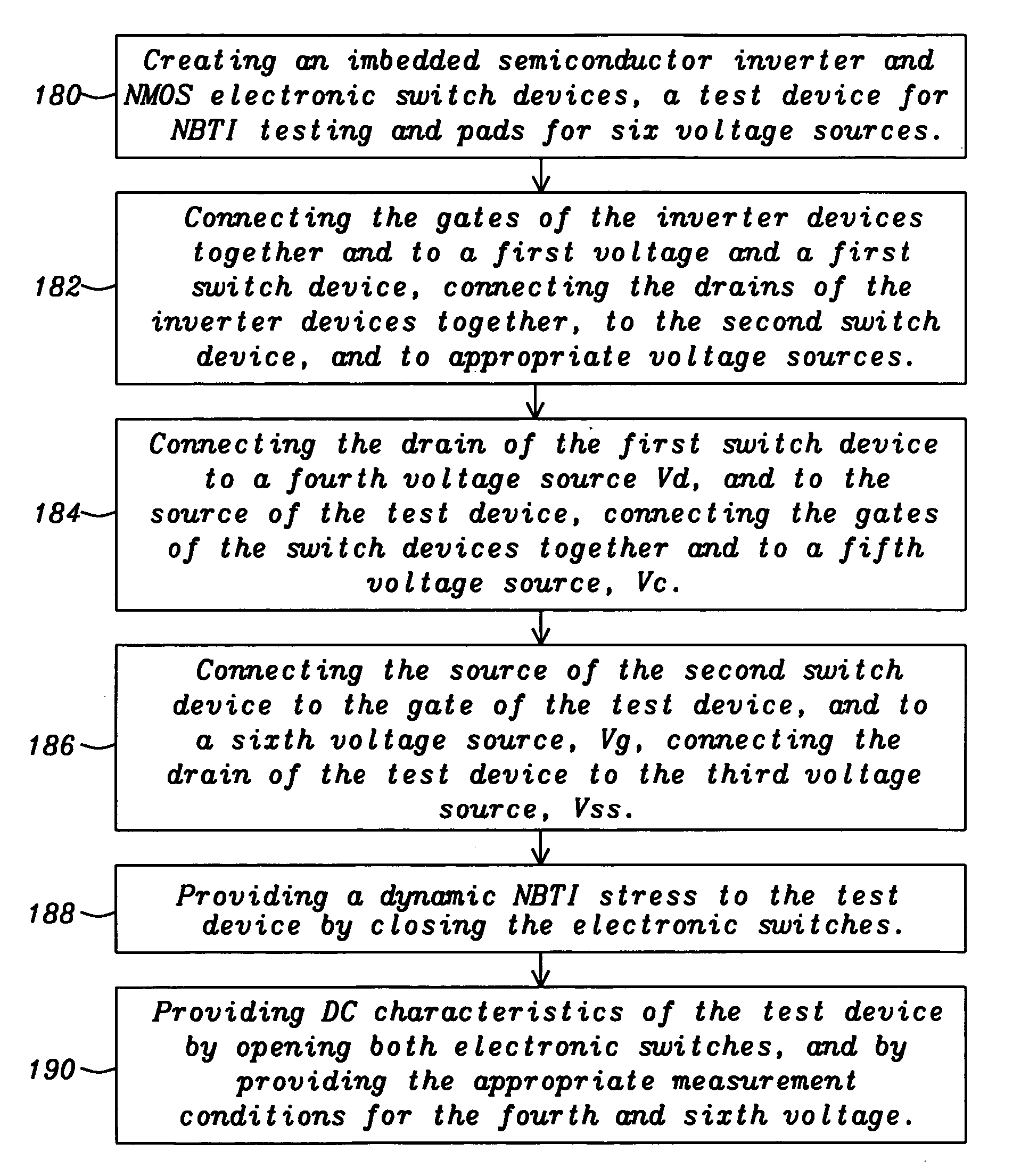
The invention describes a novel test structure and process to create the structure for performing automatic dynamic stress testing of PMOS devices for Negative Bias Temperature Instability (NBTI). The invention consists of an integrated inverter, two integrated electronic switches for switching from stress mode to device DC characterization measurement mode, and a PMOS FET device under test (DUT). The inverter assures the proper 180 degree phase relationship between the test device source and gate voltage while the imbedded electronic switches provide isolation of the test device during DC characterization testing. Another embodiment of the invention enables the testing of multiple devices under test (DUT's).
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Method and device for analyzing reliability of integrated circuit
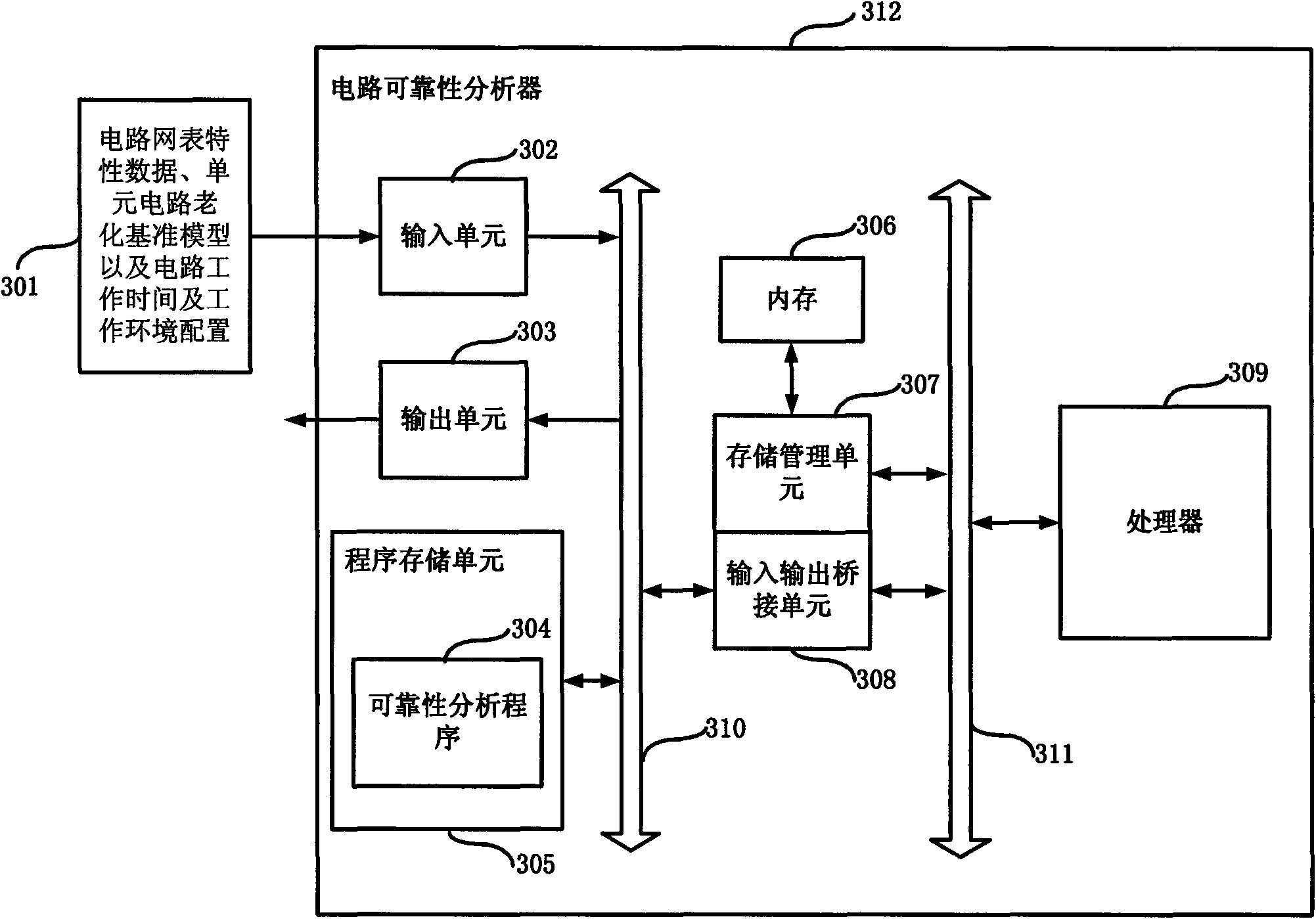
ActiveCN101964003AMeet analysis needsExtension of timeSpecial data processing applicationsProcess deviationsCircuit delay
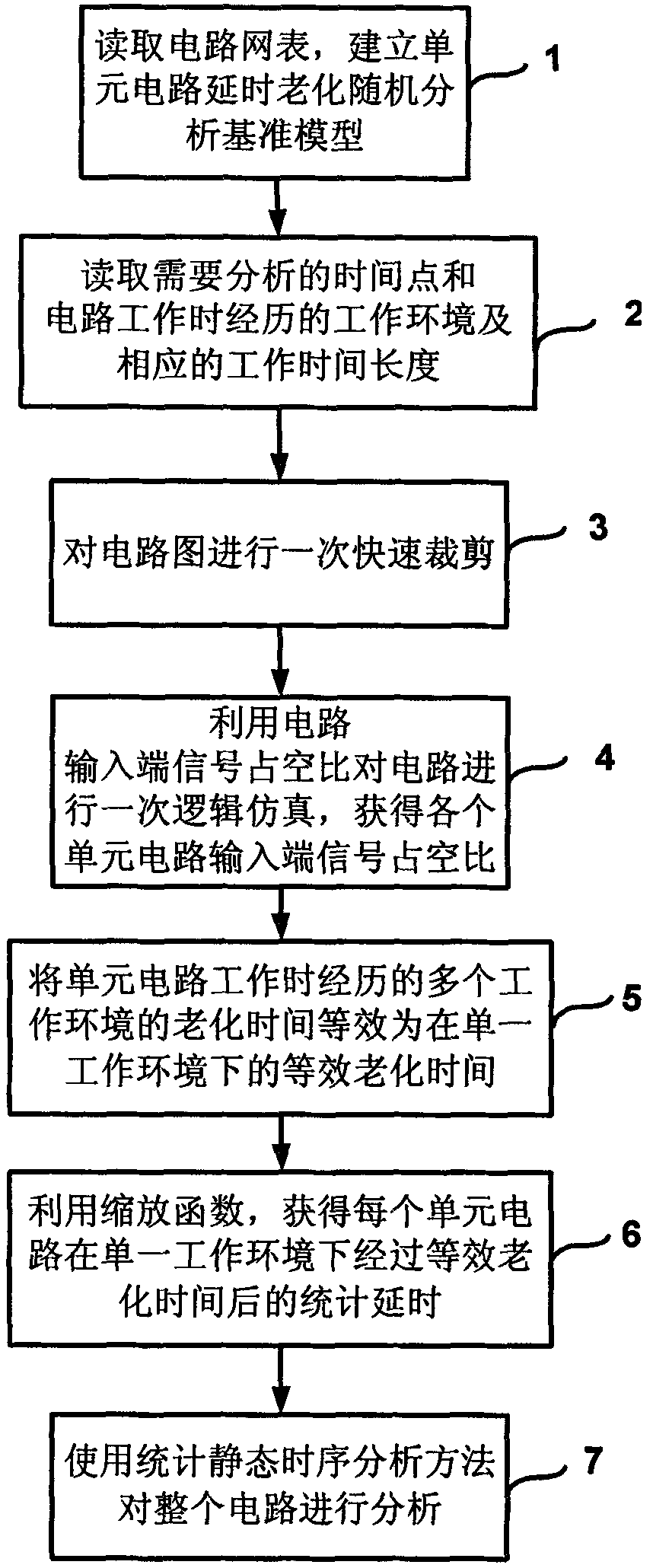
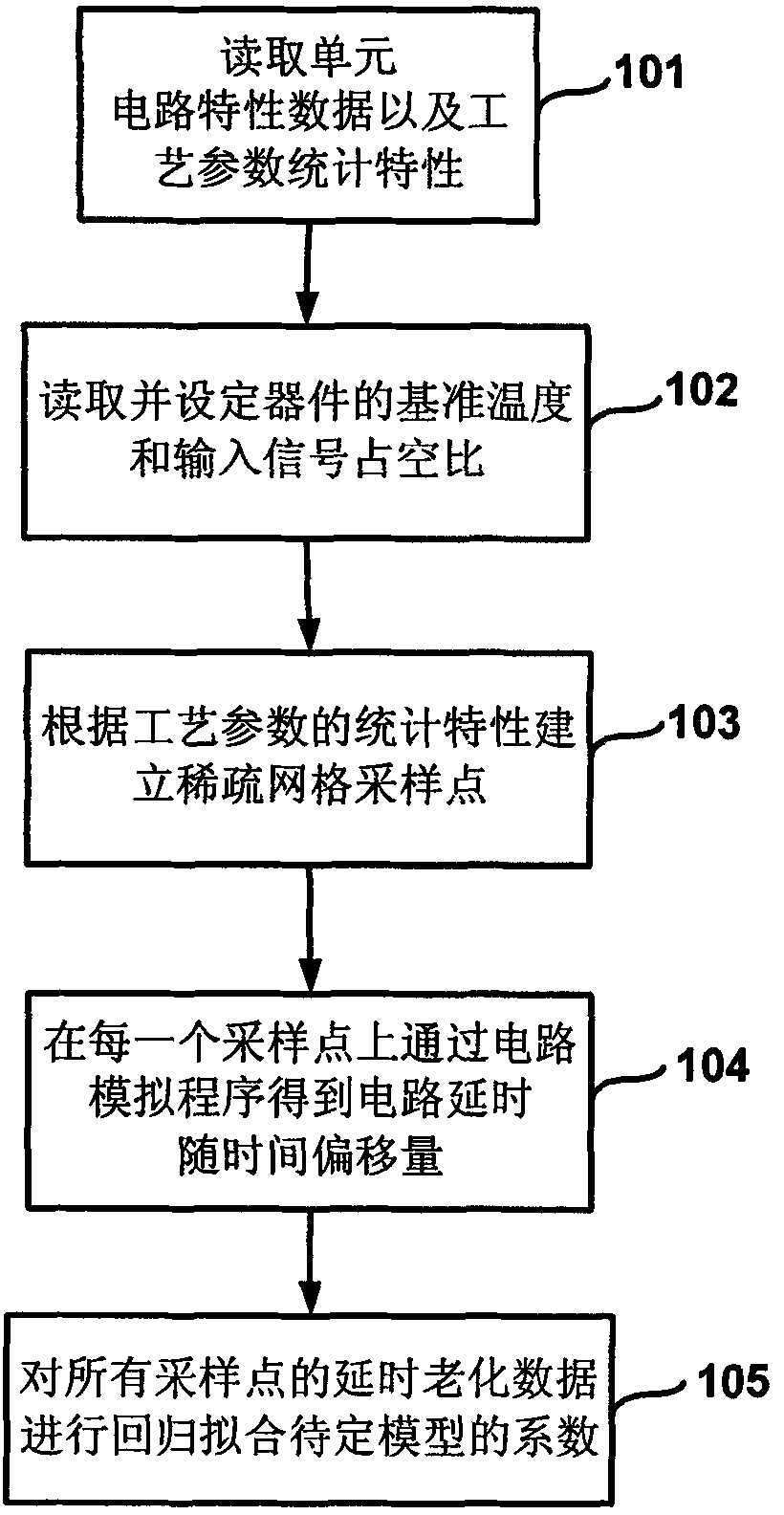
The invention relates to a method and a device for analyzing the reliability of an integrated circuit. In the analytical method, a unit circuit delayed aging stochastic analysis reference model in consideration with both negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) effect and process parameter perturbation is established, a scaling function and an equivalent aging time concept are provided to solve the delayed statistical distribution of a unit circuit under the actual work environment quickly from the reference model, and the pre-clipping process of the circuit is provided to reduce the complexity of reliable analysis. The device of the invention comprises an input unit, an output unit, a program storage unit, an external bus, a memory, a storage administration unit, an input / output bridging unit, a system bus and a processor. In the method and the device, the effect of the process parameter perturbation, the NBTI effect and the work environment of the circuit on reliability are considered simultaneously, and the complexity of the reliable analysis can be reduced effectively by utilizing the scaling function, equivalent aging time and the pre-clipping technology so as to realize the quick analysis on the reliability of super-large-scale integrated circuits in consideration with process deviation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and test method thereof
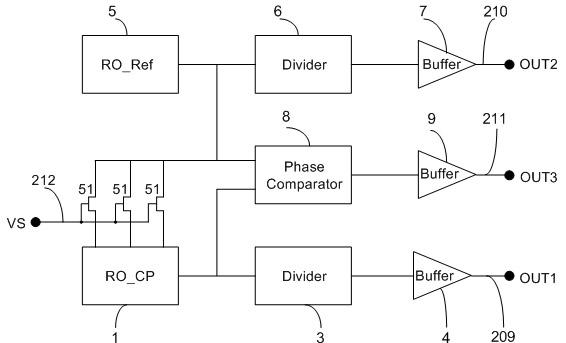
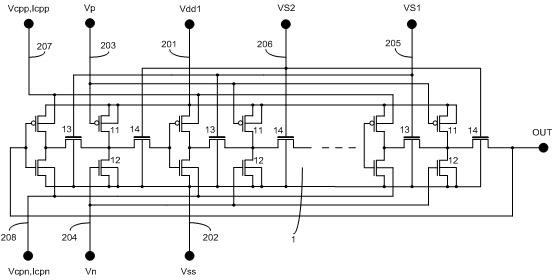
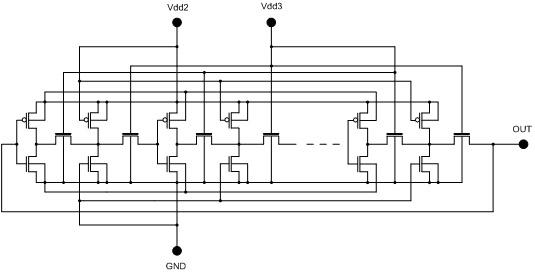
The invention belongs to a integrated circuit reliability test technology field and especially relates to a multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and a test method thereof. A core part of the test circuit takes an annular oscillator as a basis. Several auxiliary transistors, switch transistors and control terminals are added. By using the circuit and the method of the invention, a negative bias temperature instability, a positive bias temperature instability, hot hole injection or hot electron injection stress can be applied to pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in a ring vibration inverter respectively; a ring oscillator is in a normal oscillation and stress oscillation state; the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs of the inverter in the ring oscillator is in a measuring state of a charge pump. The degradation of the MOSFETs in the ring vibration inverter can be shown through changes of a ring oscillator oscillation frequency after the stress and can be shown through the changes of a CP current (Icpp or Icpn) of the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in the ring oscillator.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
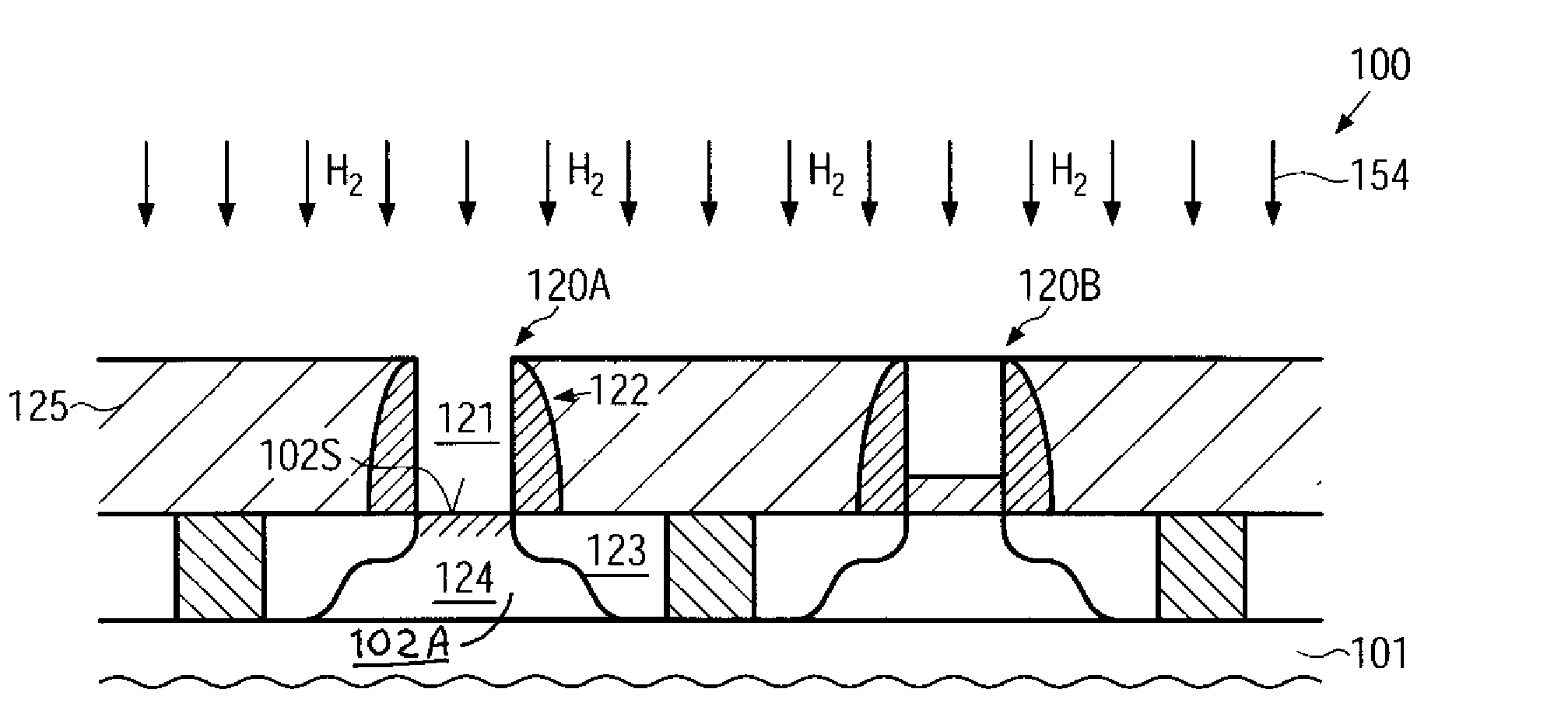
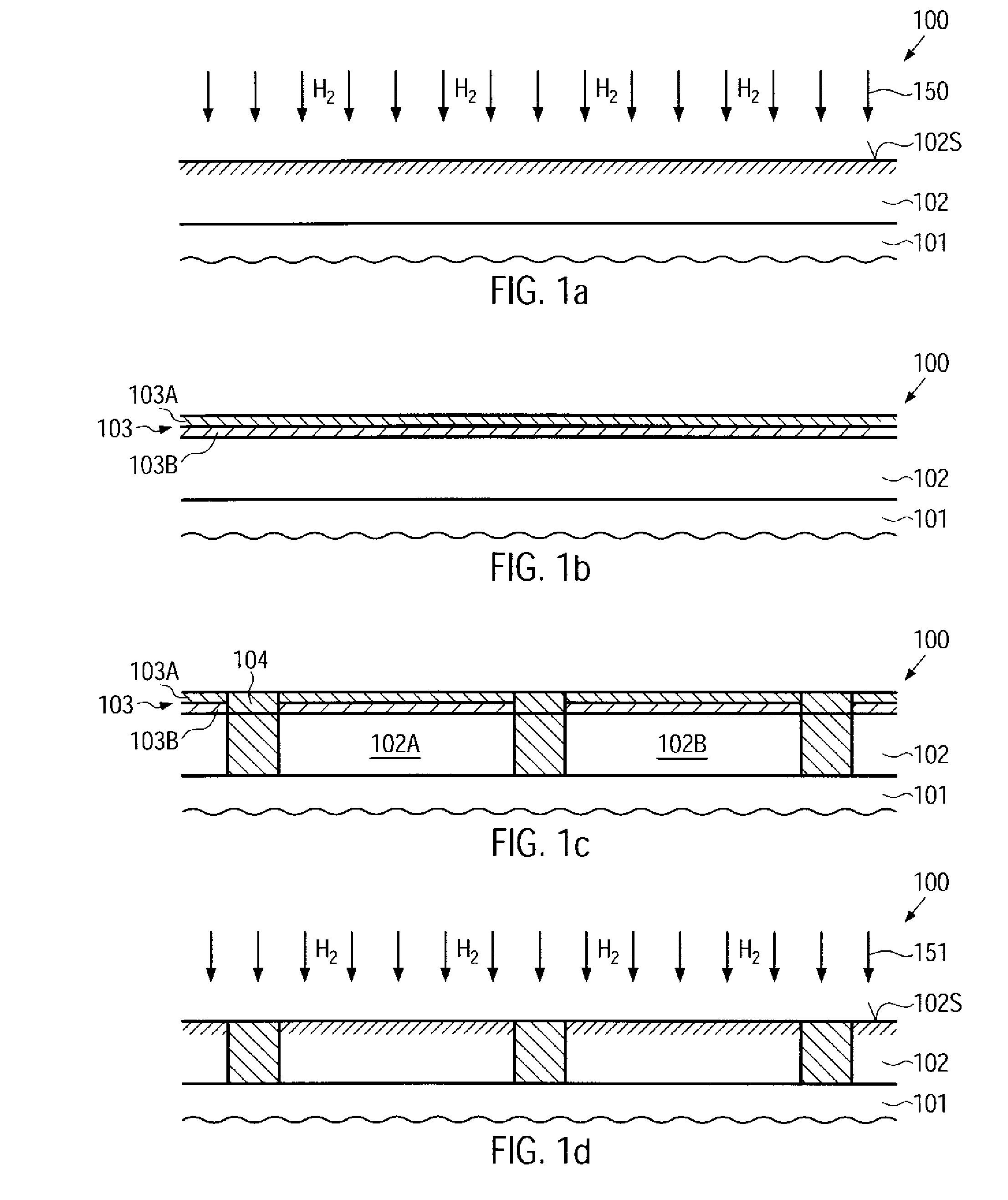
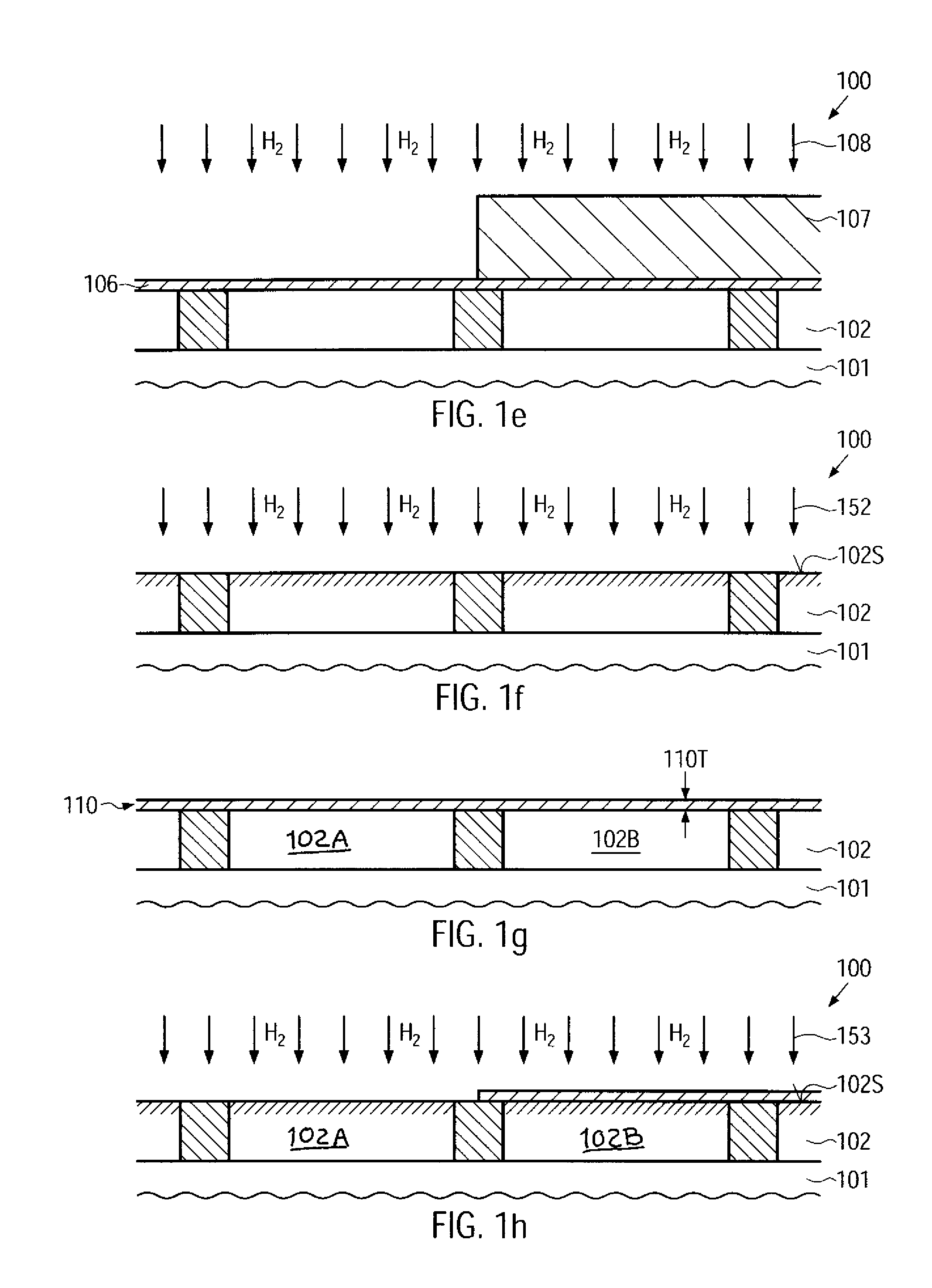
Reducing the creation of charge traps at gate dielectrics in mos transistors by performing a hydrogen treatment
InactiveUS20090170339A1Improve featuresHigh crystallinityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
By performing a heat treatment on the basis of a hydrogen ambient, exposed silicon-containing surface portions may be reorganized prior to the formation of gate dielectric materials. Hence, the interface quality and the material characteristics of the gate dielectrics may be improved, thereby reducing negative bias temperature instability effects in highly scaled P-channel transistors.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
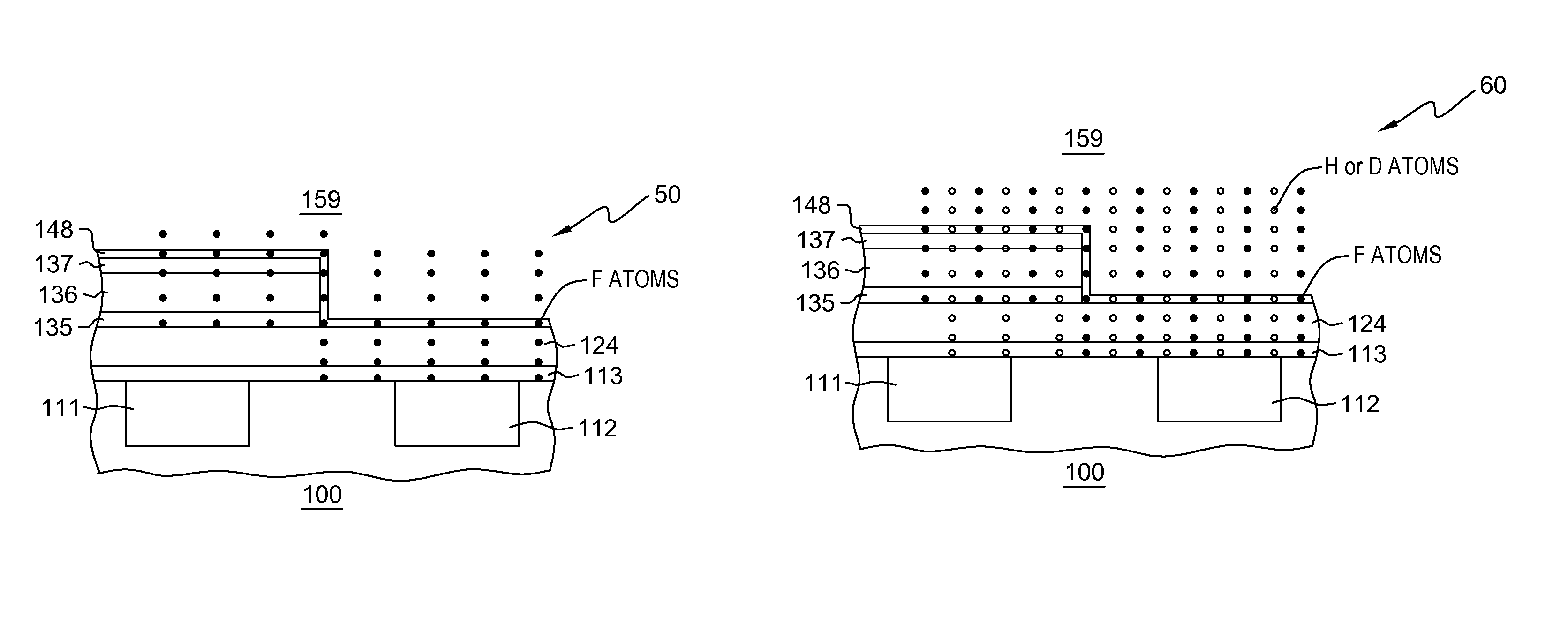
Reduction of negative bias temperature instability in narrow width PMOS using F2 implantation
InactiveUS6780730B2Suppress instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh densityEngineering
In a process of fabricating a narrow channel width PMOSFET device, the improvement of affecting reduction of negative bias temperature instability by use of F2 side wall implantation, comprising:a) forming a shallow trench isolation (STI) region in a substrate;b) forming a gate on a gate oxide in the substrate;c) forming a liner layer in said shallow trench isolation region and subjecting the liner layer to oxidation to form a STI liner oxidation layer;d) implanting F2 into side walls of the STI liner oxidation layer at a large tilted angle in sufficient amounts to affect reduction of negative bias temperature instability after a high density plasma fill of the STI F2 implanted liner oxidation layer; ande) filling the STI F2 implanted structure from step d) with a high density plasma (HDP) fill to affect reduction of negative bias temperature instability.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Method for testing reliability of semiconductor devices
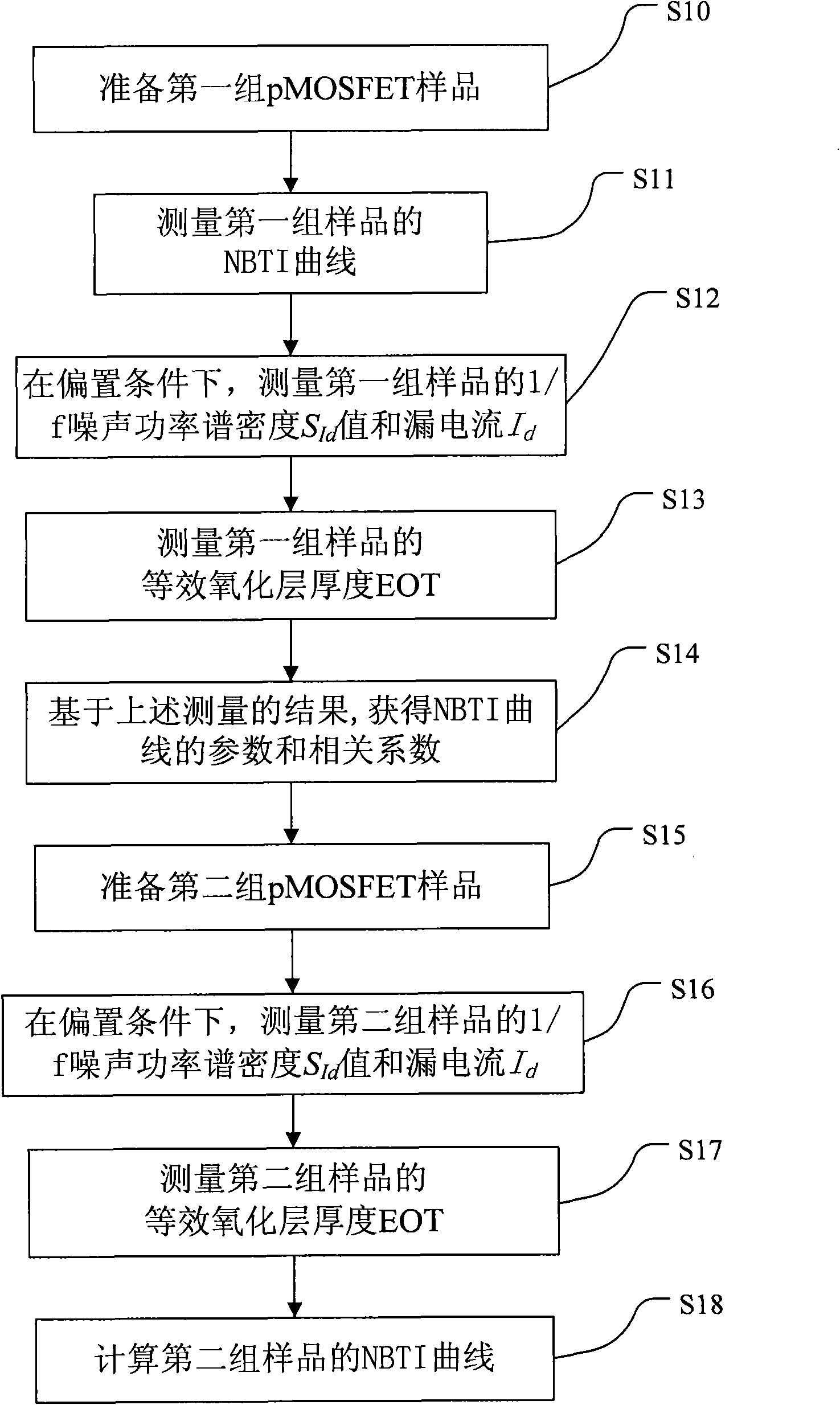
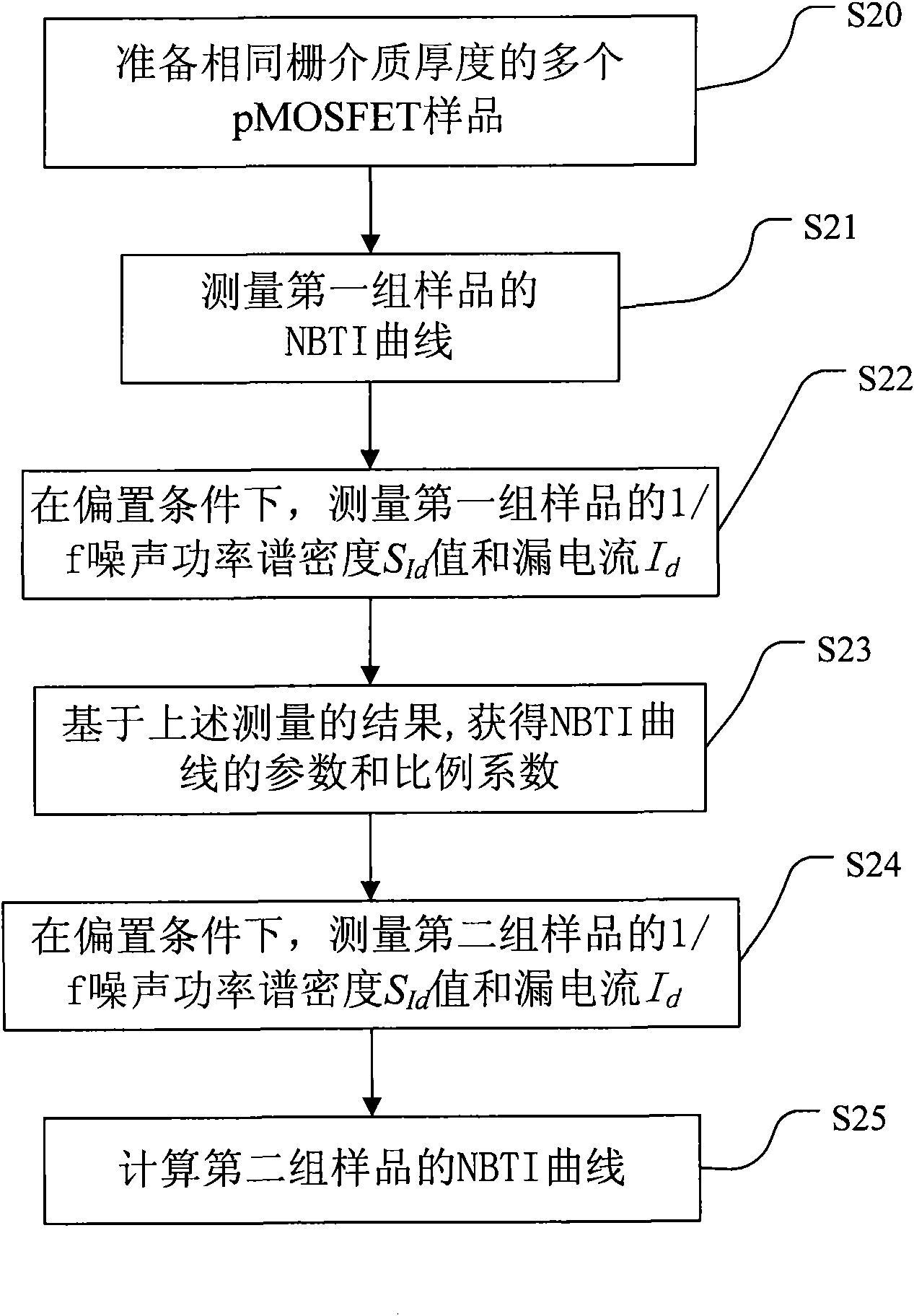
InactiveCN102073004AIncrease usageDegradation of electrical characteristicsIndividual semiconductor device testingGate dielectricLayer thickness
The invention discloses a method for testing reliability of semiconductor devices which have negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The method comprises the following steps: measuring the NBTI curve of a first set of semiconductor devices; measuring the 1 / f noise power spectral density and drain current of the first set of semiconductor devices at a predetermined frequency under the condition that the first set of semiconductor devices is biased in a gate electric field; measuring the equivalent oxide layer thickness of the gate dielectric of the first set of semiconductor devices; measuring the 1 / f noise power spectral density and drain current of a second set of semiconductor devices at the predetermined frequency under the condition that the second set of semiconductor devices is biased in the gate electric field; measuring the equivalent oxide layer thickness of the gate dielectric of the second set of semiconductor devices; and evaluating the deterioration characteristic of the second set of semiconductor devices by using the NBTI curve of the first set of semiconductor devices. The method disclosed by the invention saves the time required for testing the reliability of a large number of semiconductor devices, and can not damage the second set of semiconductor devices.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
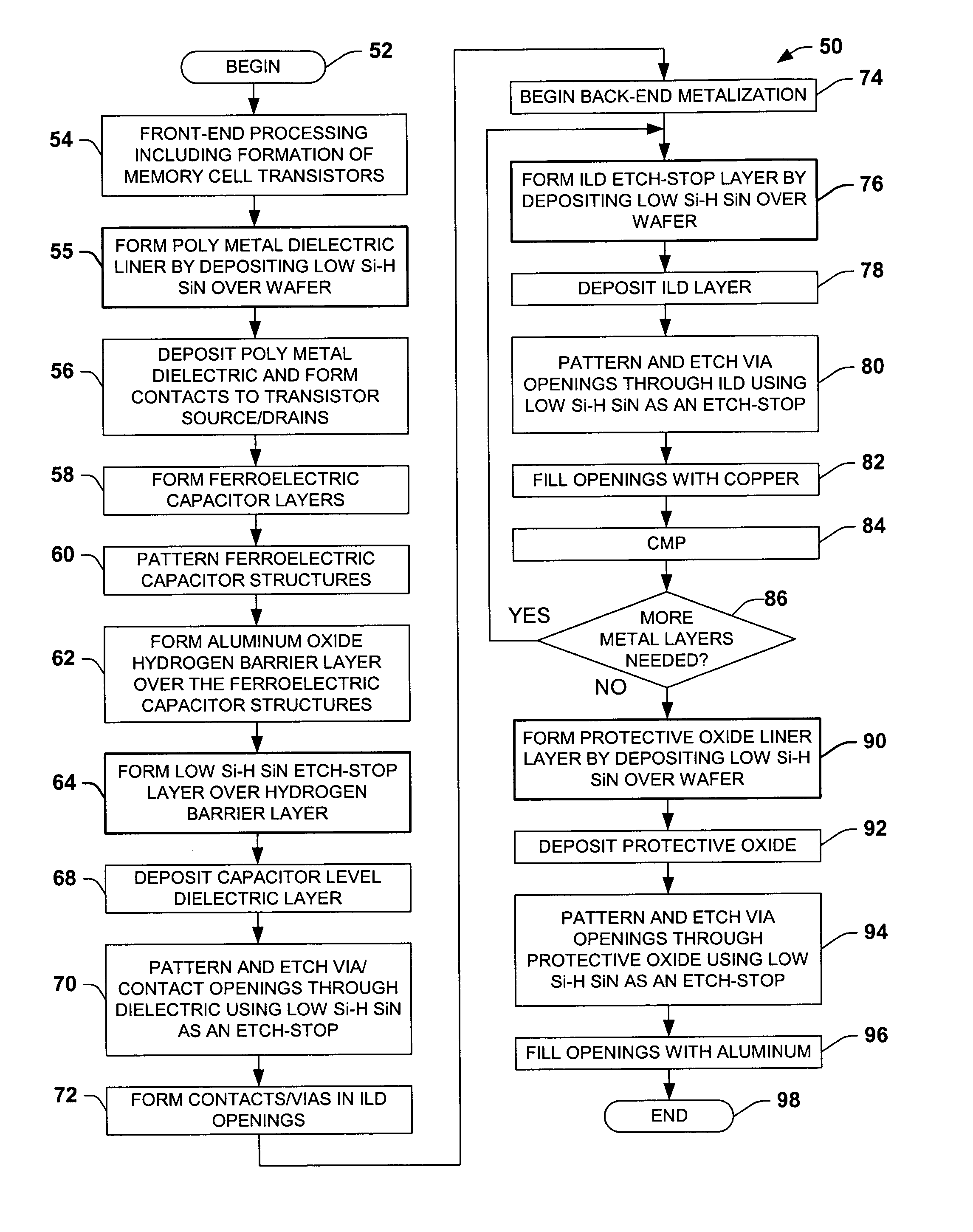
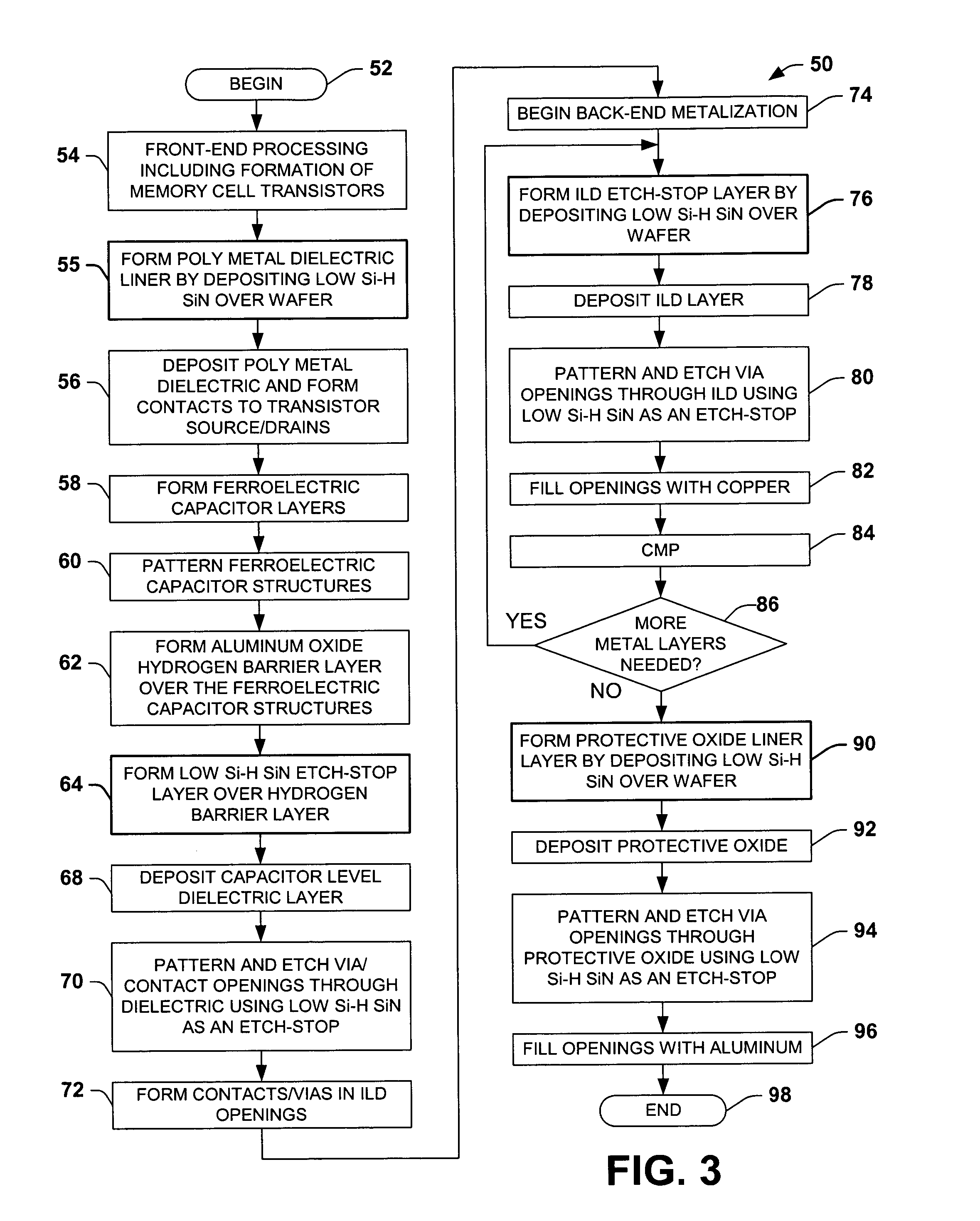
Low silicon-hydrogen sin layer to inhibit hydrogen related degradation in semiconductor devices having ferroelectric components
ActiveUS20050032301A1Reduce and prevent diffusion of hydrogenMitigate negative bias temperature instabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricHydrogen
Semiconductor devices and fabrication methods are disclosed, in which one or more low silicon-hydrogen SiN barriers are provided to inhibit hydrogen diffusion into ferroelectric capacitors and into transistor gate dielectric interface areas. The barriers may be used as etch stop layers in various levels of the semiconductor device structure above and / or below the level at which the ferroelectric capacitors are formed so as to reduce the hydrogen related degradation of the switched polarization properties of the ferroelectric capacitors and to reduce negative bias temperature instability in the device transistors.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Life Prediction Method of Pmosfet Device Negative Bias Temperature Instability
ActiveCN102262206AShort failure timeLow costIndividual semiconductor device testingField-effect transistorGate voltage
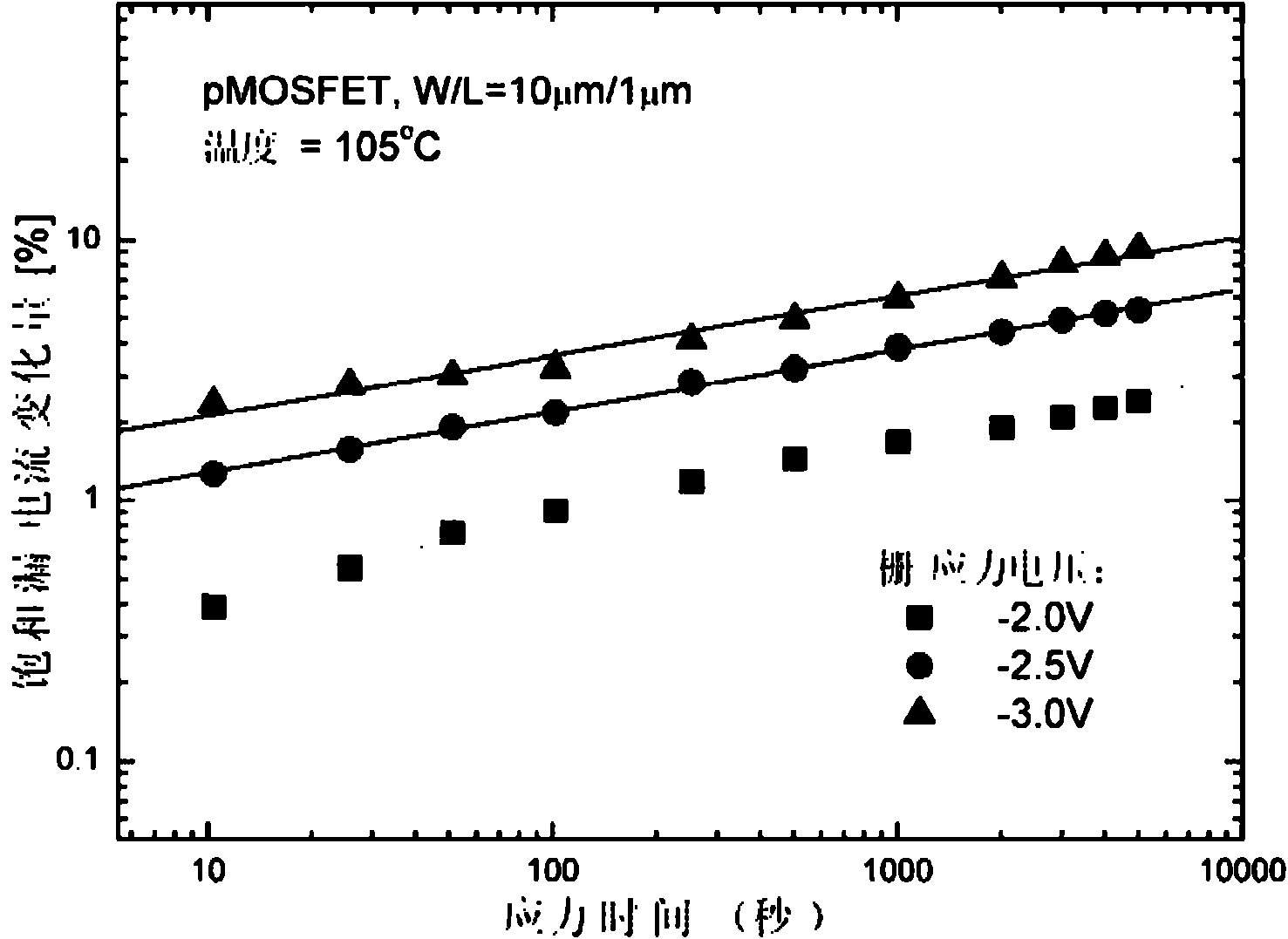
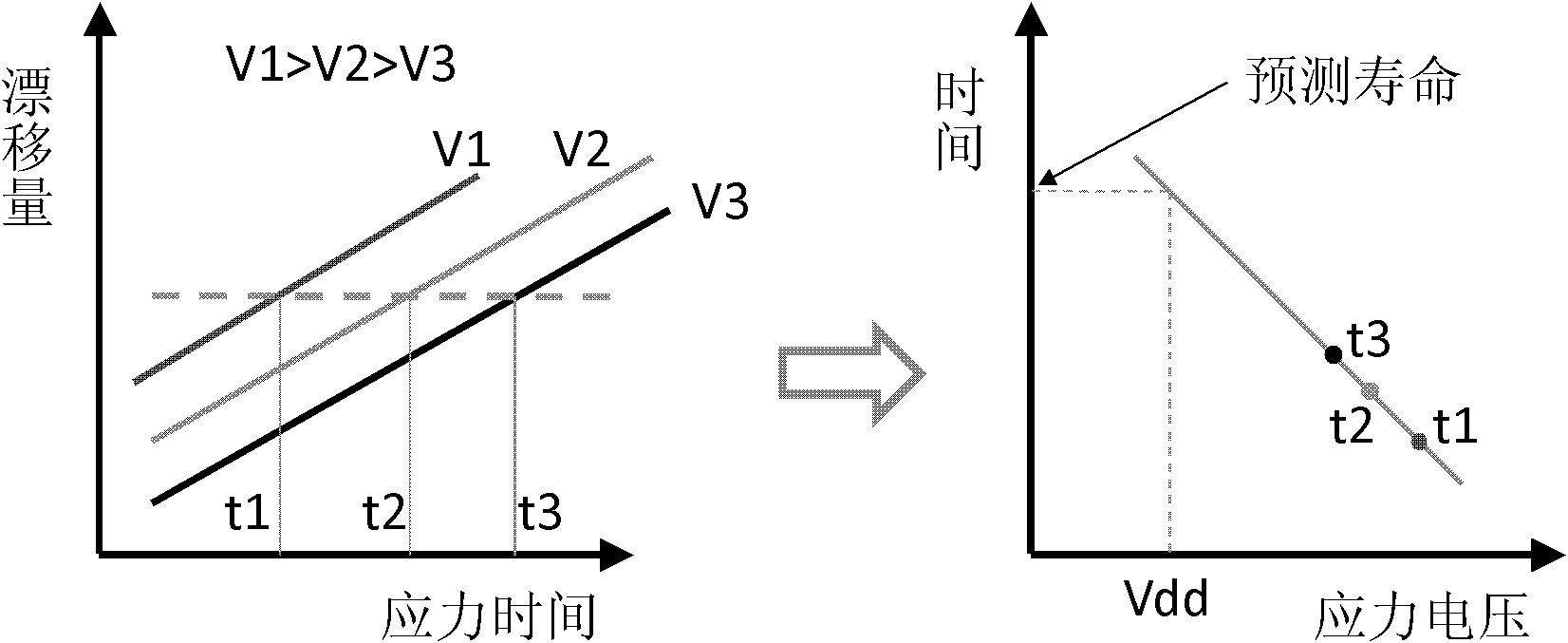
The invention discloses a method for predicting a negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) service life of a pMOSFET (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) device. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, before applying negative bias stress, measuring initial characteristics of the pMOSFET device to obtain initial parameters of the device; S2, applying a stress condition to a grid of the device, wherein drain voltage is normal working voltage; performing stress aging test to the device within a pre-set time interval; S3, testing the parameters of the device to obtain device parameters related to the aging time until the total stress time is ended; S4, when the drain voltage is the normal working voltage, repeating the steps S2 and S3; testing different stress conditions; referencing to the device parameters retrograded to a critical point; obtaining failure times of the pMOSFET device under the relative stress conditions; and S5, using the failure times of the pMOSFET device under the different stress conditions, predicting the reliability service life of the device when the gate voltage is the normal working voltage. Because the failure time of the device obtained by the method in the invention is shorter than that obtained by the conventional method, the NBTI service life of the pMOSFET device can be well reflected.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Circuit for negative bias temperature instability compensation
ActiveUS20120119825A1Well formedDigital storageElectric variable regulationEngineeringNegative-bias temperature instability
An integrated circuit device includes a first circuit for providing current to a first node, and a degradation compensator including a first compensation circuit coupled to the first node to provide compensation current to the first node. The degradation compensator is operable to estimate a degree of degradation in the first circuit and provide a compensation signal to the first compensation circuit to control the amount of compensation current based on the estimated degree of degradation.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
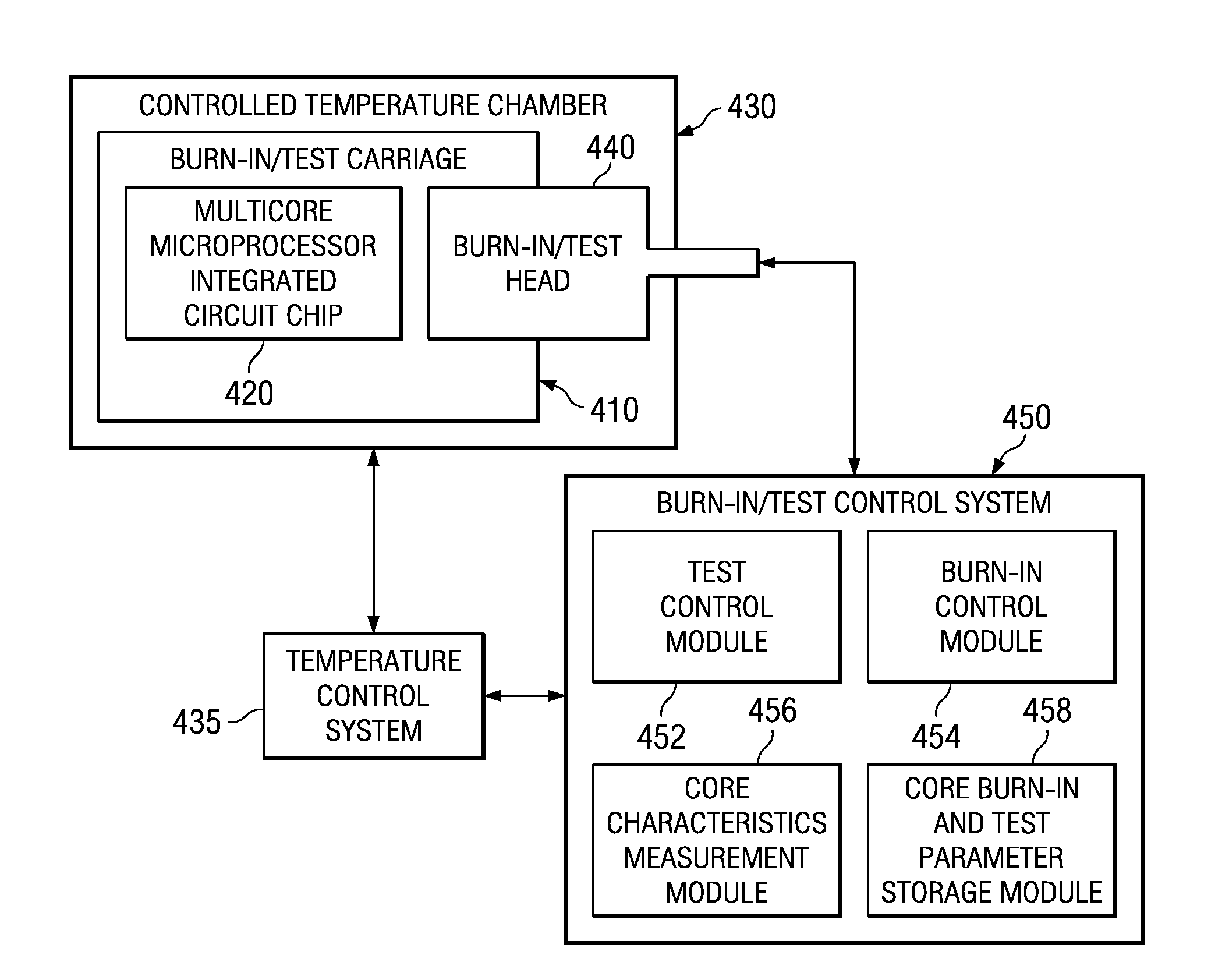
Apparatus and method for customized burn-in of cores on a multicore microprocessor integrated circuit chip
InactiveUS7268570B1Reduce chip costUniform powerFault location by increasing destruction at faultPeak valueEngineering
An apparatus and method for providing a multi-core integrated circuit chip that reduces the cost of the package and board while optimizing performance of the cores for use with a single voltage plane. The apparatus and method of the illustrative embodiments make use of a dynamic burn-in technique that optimizes all of the cores on the chip to run at peak performance at a single voltage. Each core is burned-in with a customized burn-in voltage that provides uniform power and performance across the whole chip. This results in a higher burn-in yield and lower overall power in the integrated circuit chip. The optimization of the cores to run at peak performance at a single voltage is achieved through use of the negative bias temperature instability affects on the cores imparted by the burn-in voltages applied.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Reduction of negative bias temperature instability in narrow width PMOS using F2 implanation
InactiveUS20030143812A1Suppress instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh densityEngineering
In a process of fabricating a narrow channel width PMOSFET device, the improvement of affecting reduction of negative bias temperature instability by use of F2 side wall implantation, comprising: a) forming a shallow trench isolation (STI) region in a substrate; b) forming a gate on a gate oxide in the substrate; c) forming a liner layer in said shallow trench isolation region and subjecting the liner layer to oxidation to form a STI liner oxidation layer; d) implanting F2 into side walls of said STI liner oxidation layer at a large tilted angle in sufficient amounts to affect reduction of negative bias temperature instability after a high density plasma fill of the STI F2 implanted liner oxidation layer; and e) filling the STI F2 implanted structure from step c) with a high density plasma (HDP) fill to affect reduction of negative bias temperature instability.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
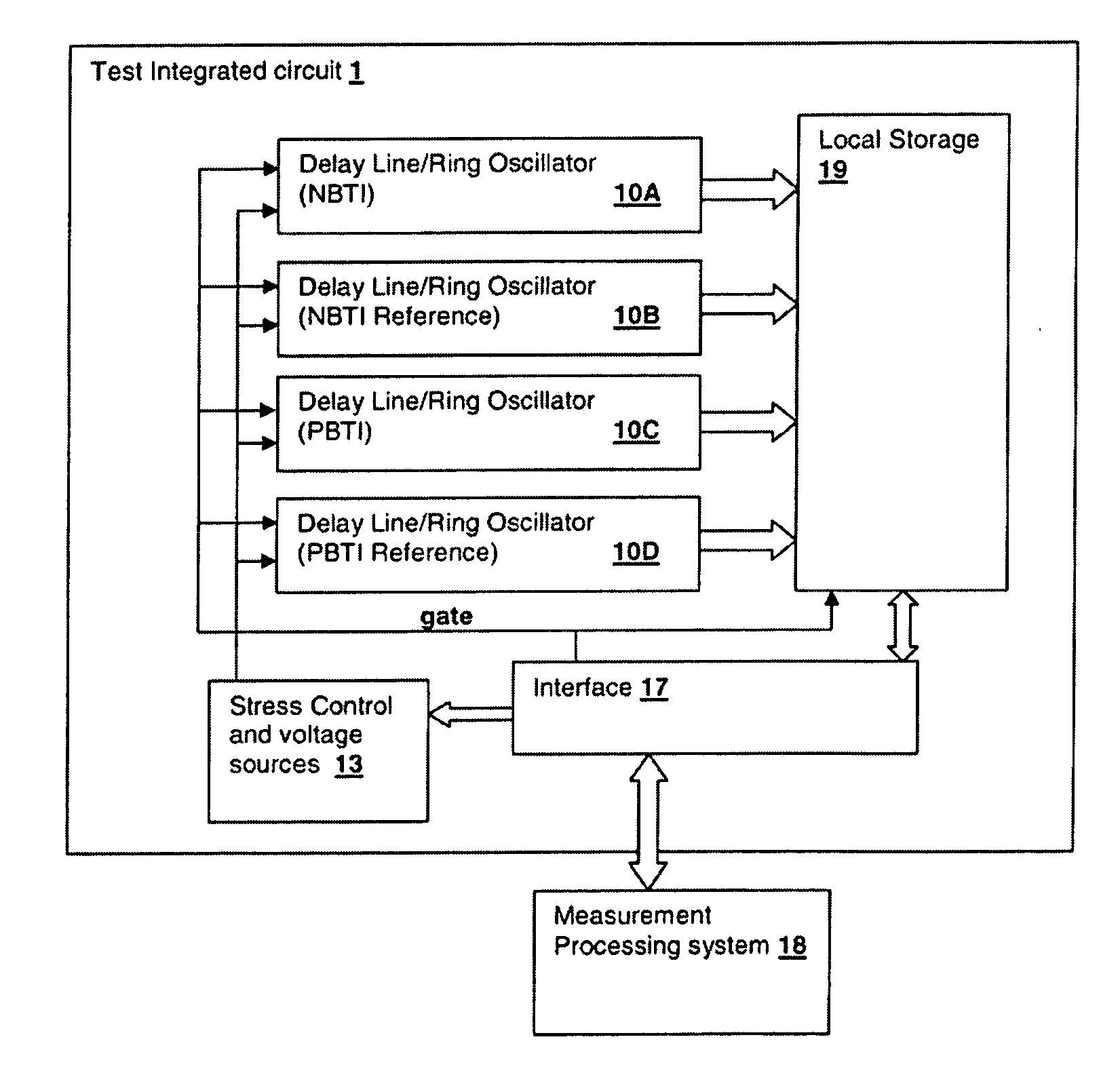
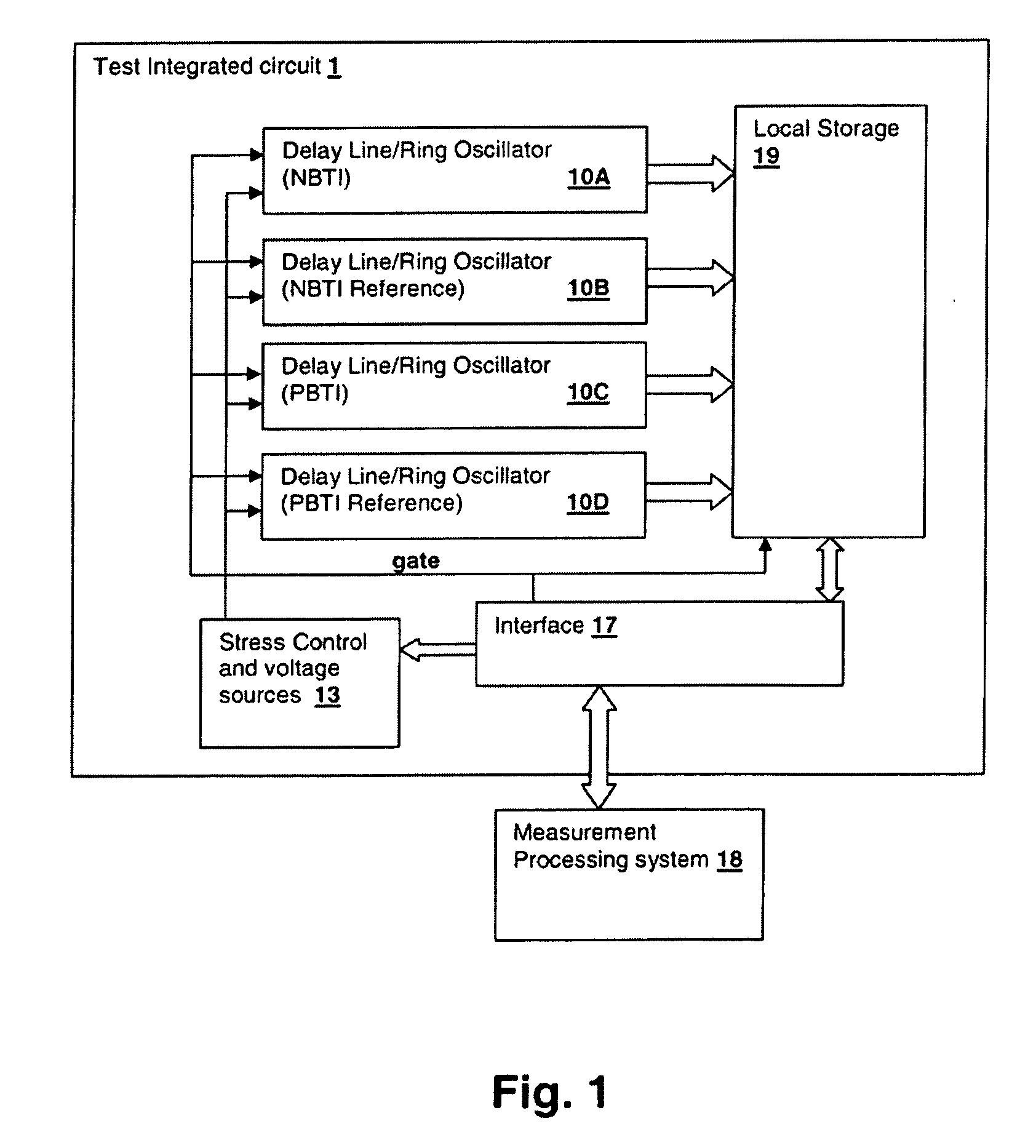
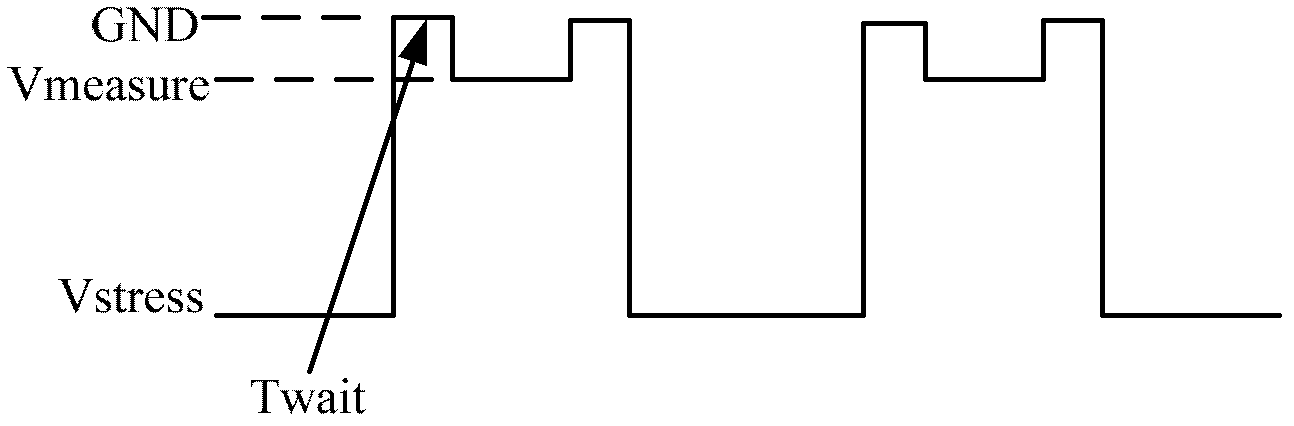
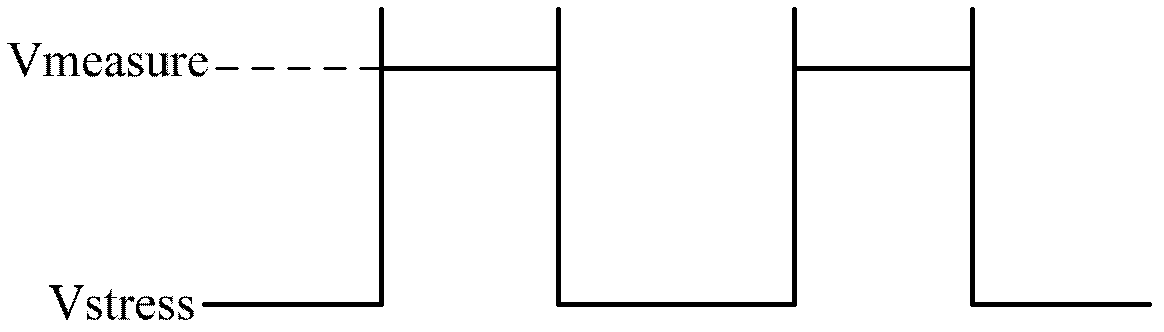
Delay-Based Bias Temperature Instability Recovery Measurements for Characterizing Stress Degradation and Recovery
InactiveUS20090319202A1Improve dynamic rangeHigh resolutionForce measurementWork measurementNanosecondFrequency measurements
A method, test circuit and test system provide measurements to accurately characterize threshold voltage changes due to negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and positive bias temperature instability (PBTI). Both the bias temperature instability recovery profile and / or the bias temperature shifts due to rapid repetitions of stress application can be studied. In order to provide accurate measurements when stresses are applied at intervals on the order of tens of nanoseconds while avoiding unwanted recovery, and / or to achieve recovery profile sampling resolutions in the nanosecond range, multiple delay or ring oscillator frequency measurements are made using a delay line that is formed from delay elements that have delay variation substantially caused only by NBTI or PBTI effects. Devices in the delay elements are stressed, and then the delay line / ring oscillator is operated to measure a threshold voltage change for one or more measurement periods on the order of nanoseconds.
Owner:IBM CORP
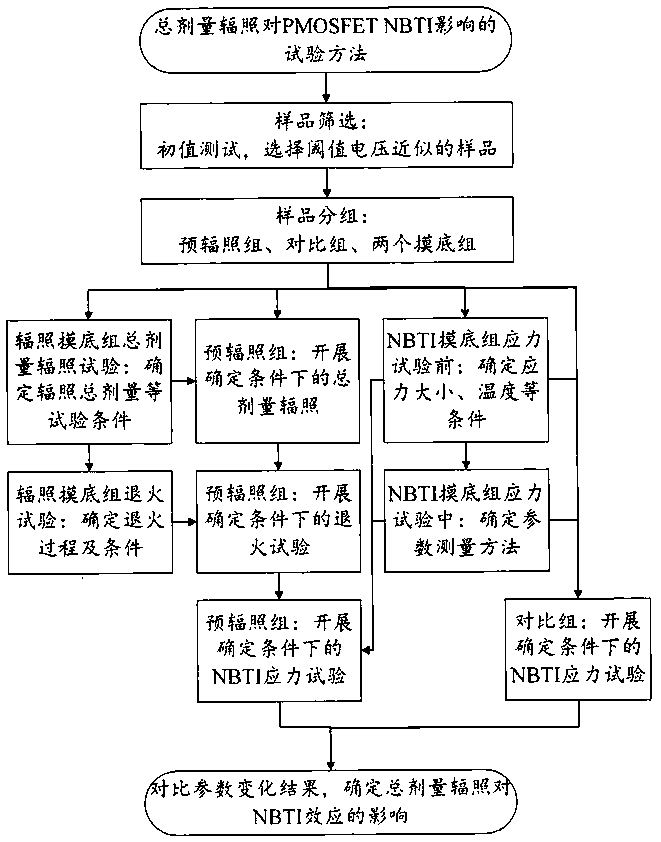
Test method for influence of total dose irradiation on PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability
ActiveCN108037438AEnsure consistencySemiconductor operation lifetime testingPre irradiationTest sample
The invention relates to a method for testing the influence of total dose irradiation on the PMOSFET negative bias temperature instability. The method includes test sample grouping and test parameterselection; the total dose irradiation and annealing tests of the test sample; and the negative bias temperature instability measurement of the test sample. In order to ensure the consistency and accuracy of the test result, the sample is divided into a pre-irradiation group, a comparison group and two pre-test groups, and on the basis of the pre-test, the total dose irradiation and annealing testsare carried out on the pre-irradiation group under the determination condition, the comparison group and the pre-irradiation group are subjected to a negative bias temperature instability test underthe same condition, and the test result is compared, the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of the sample is obtained. The method provided by the invention can represent the influence of the total dose irradiation on the negative bias temperature instability of a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Circuit and method for testing reliability of integrated circuit
ActiveCN102590735AMeasuring and differentiating degradationElectrical testingCircuit reliabilityHemt circuits
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit test, and in particular relates to a circuit and a method for testing reliability of an integrated circuit. According to the core circuit of the testing circuit, auxiliary p-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (pMOSFETs) and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (nMOSFETs) are connected between every two stages of inverters of a ring oscillator (RO) and between a high level Vdd and low potential Vss, and a switch transistor is plugged in an input and output connecting line. By controlling the grid voltages of the auxiliary transistors and the switch transistor, normal oscillation of the RO can be realized in the core circuit, dynamic stress is applied to complementary metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (CMOSFETs) of the RO, and negative bias temperature instability (NBTI), positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) and hot carrier injection (HCI) stresses are respectively applied to the pMOSFETs or the nMOSFETs of the RO. The testing circuit has the functions of: degradation measurement of the pMOSFETs in the RO under the NBTI stress, degradation measurement of the nMOSFETs under the PBTI stress, degradation measurement of the pMOSFETs under the HCI stress, degradation measurement of the nMOSFETs under the HCI stress, and comparison with degradation measurement of the CMOSFETs under the dynamic stress.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Building-out circuit and testing method for testing negative bias temperature instability
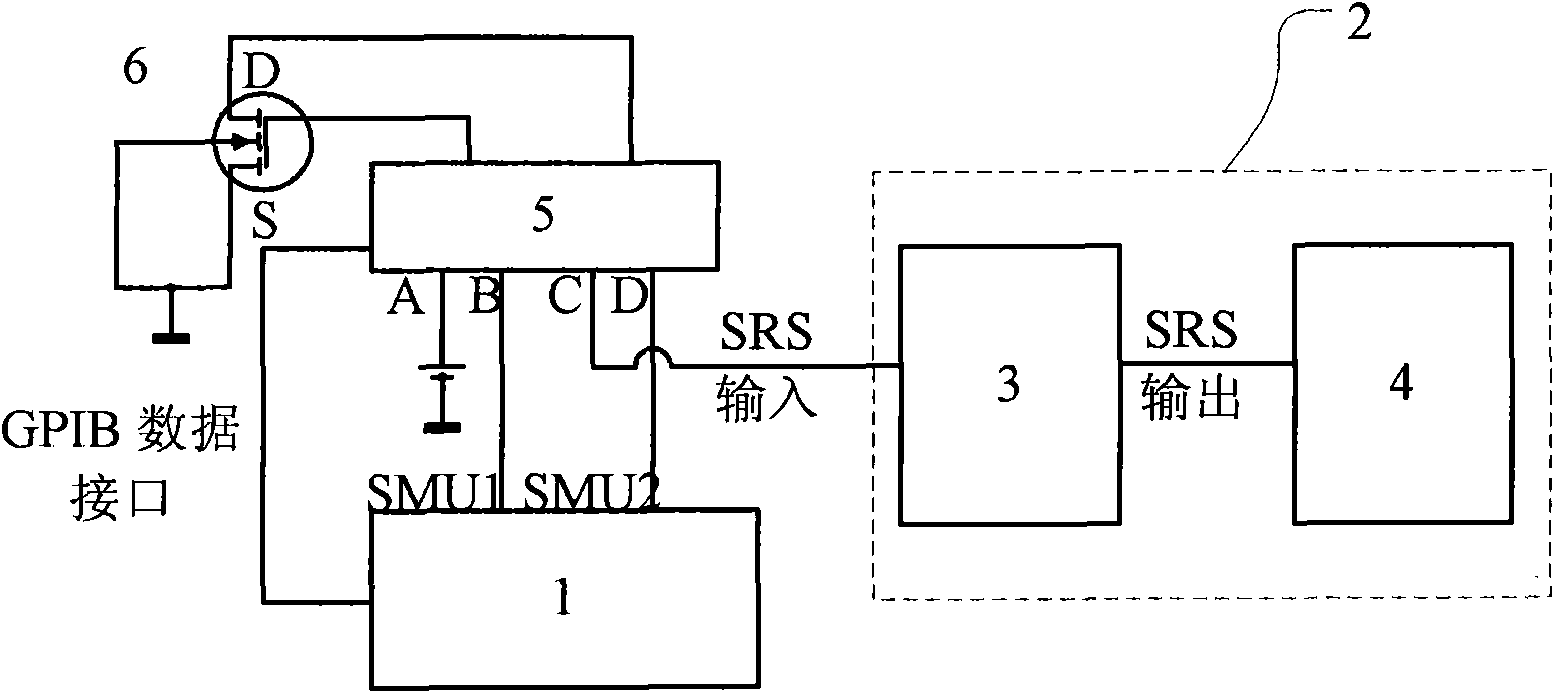
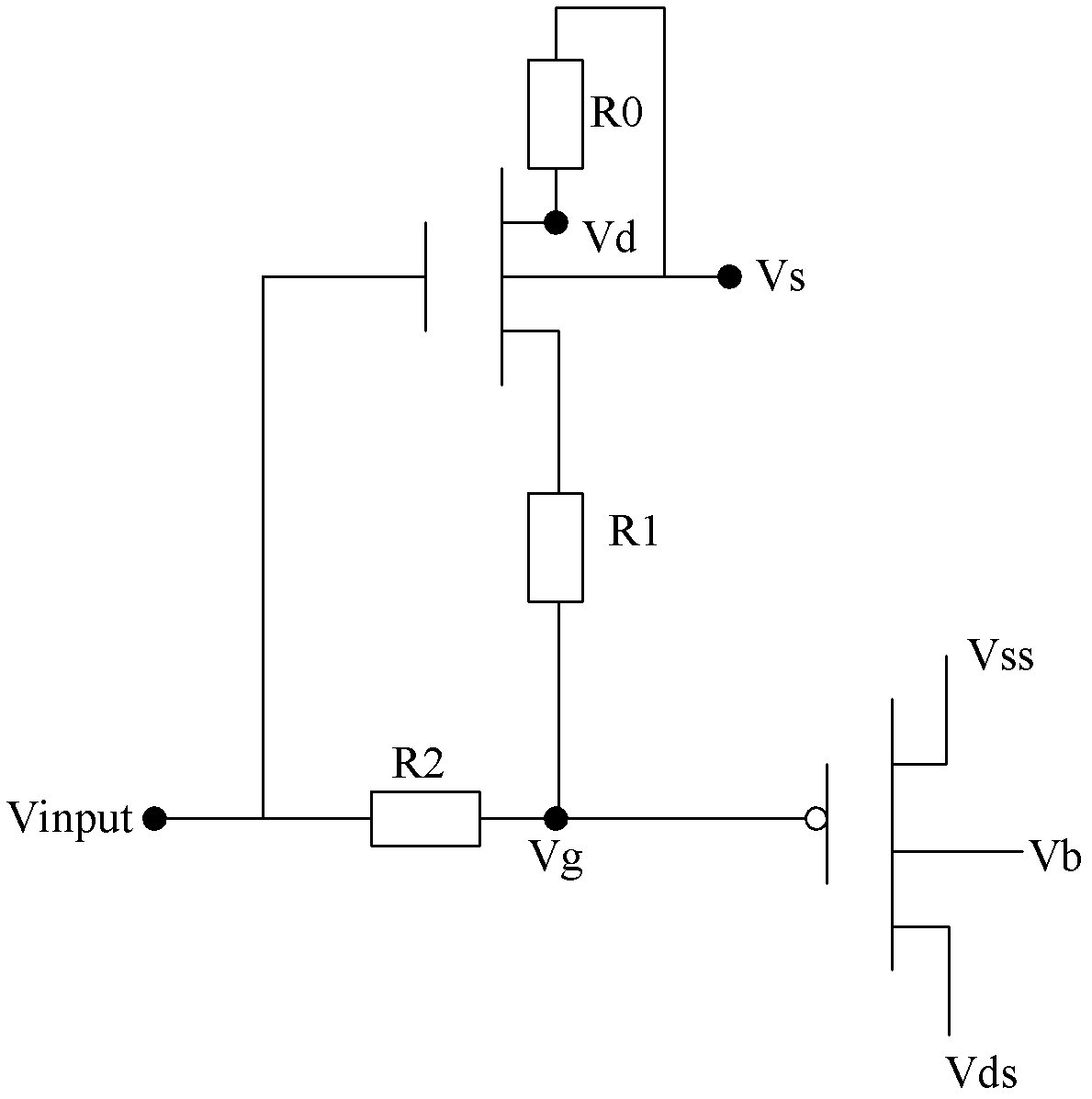
ActiveCN102866340ARestoration Effect InhibitionAccurate measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringP channel
The invention provides a building-out circuit and a testing method for testing the negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The building-out circuit is respectively connected with a source-measurement unit and a PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) to be measured; the building-out circuit comprises an NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor); a base electrode of the NMOS is electrically connected with a source electrode of the NMOS by a resistor R0; a drain electrode fo the NMOS is electrically connected with a grid electrode of the PMOS to be measured by a resistor R1; a grid electrode fo the NMOS is electrically connected with the grid electrode of the PMOS to be measured by a resistor R2; the potential of the base electrode of the NMOS is set into a value of less than 0V; and the voltage input end of the source-measurement unit is connected with the grid electrode of the NMOS. When an input voltage of the source-measurement unit is changed into 0V, due to the voltage division of the resistor R2, the voltage of the grid electrode of the PMOS to be measured is less than 0V, i.e. when the NBTI recovery effect occurs after the stress voltage is switched off, a partial pressure of the R2 is still applied to the grid electrode of the PMOS to be measured to inhibit the NBTI recovery effect in the PMOS, so that the measurement result is more accurate.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Microprocessor performance improvement by dynamic nbti compensation through transistor forward biasing
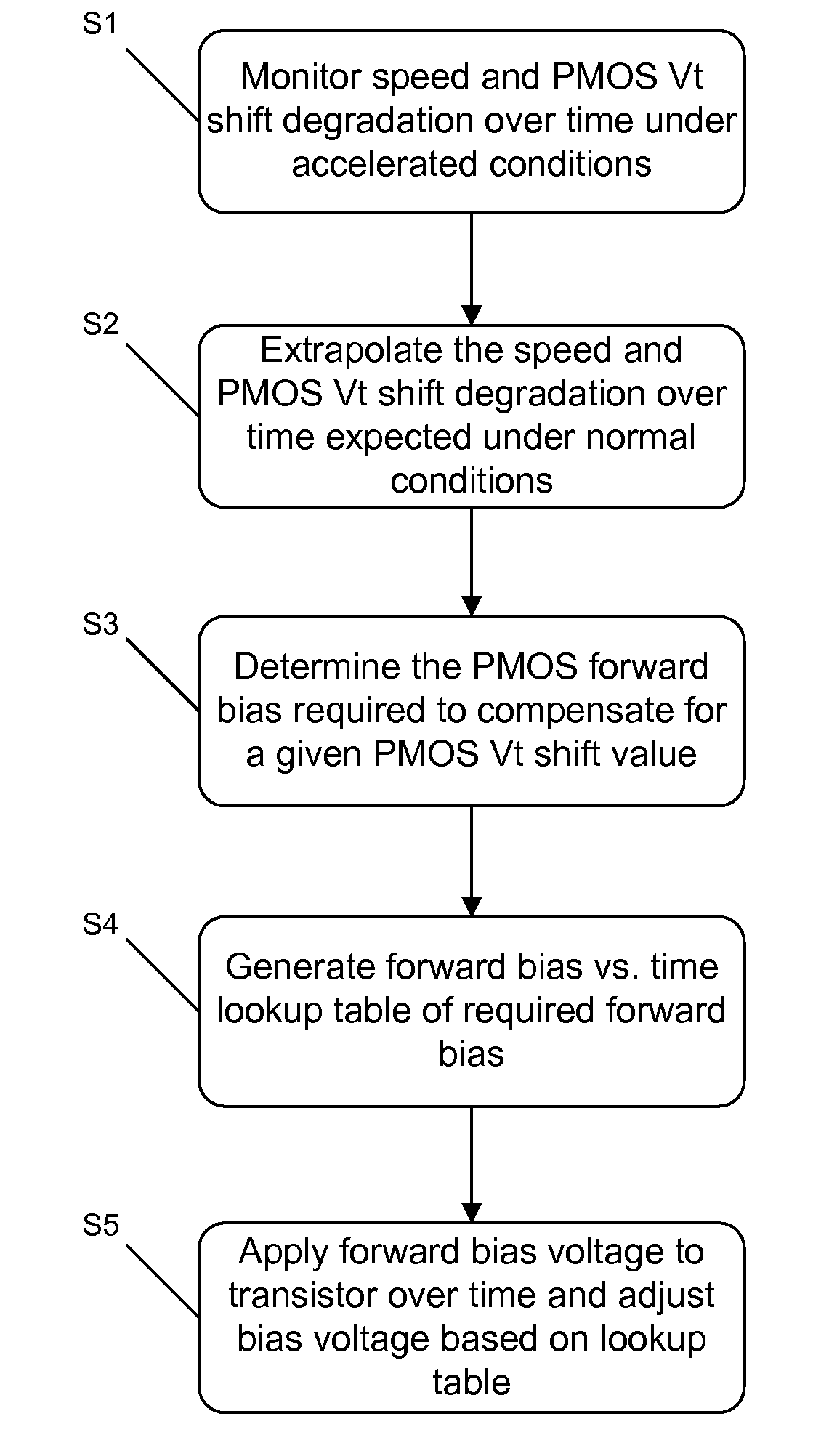
ActiveUS20100214007A1Electrical testingElectronic switchingLookup tableNegative-bias temperature instability
A method for compensating negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) effects on a given model of transistors includes monitoring the NBTI effects on the transistors over time, determining a change in a threshold voltage of the transistors over time based on the monitoring, determining a forward bias voltage based on the change in threshold voltage, and applying the forward bias voltage to the transistors over time. The method may further include storing the monitoring results in a lookup table, and adjusting the forward bias voltage based on the lookup table. The monitoring may include emulating the NBTI effects on a system comprising a plurality of semiconductor devices in which the transistors are used.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Forming a semiconductor structure for reduced negative bias temperature instability
InactiveUS9502307B1Improve negative bias temperature instabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricSemiconductor structure
An approach to forming a semiconductor structure with improved negative bias temperature instability includes forming an interfacial layer on a semiconductor substrate with an nFET and a pFET. The approach includes depositing a gate dielectric layer on the interfacial layer. Additionally, the approach includes an nFET work function metal layer deposited on the interfacial layer. Additionally, the approach includes removing the nFET work function metal from an area above the pFET and depositing a pFET work function metal layer on a portion of the exposed gate dielectric layer where the portion of the exposed gate dielectric layer is over the pFET. Furthermore, the approach includes depositing a gate metal on the pFET work function metal layer where the gate metal is deposited in an environment with a fluorine containing gas followed by an anneal in a reducing environment.
Owner:IBM CORP
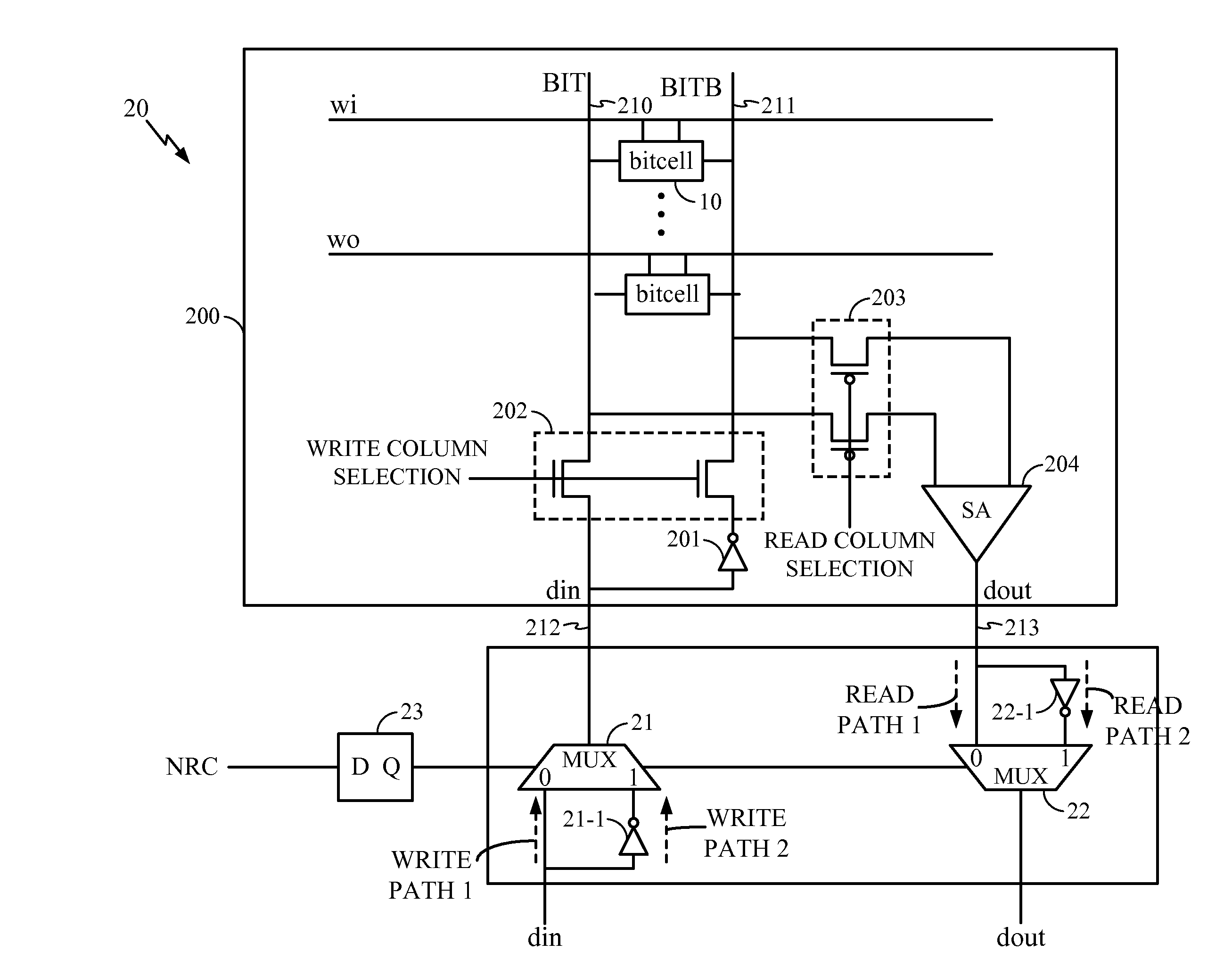
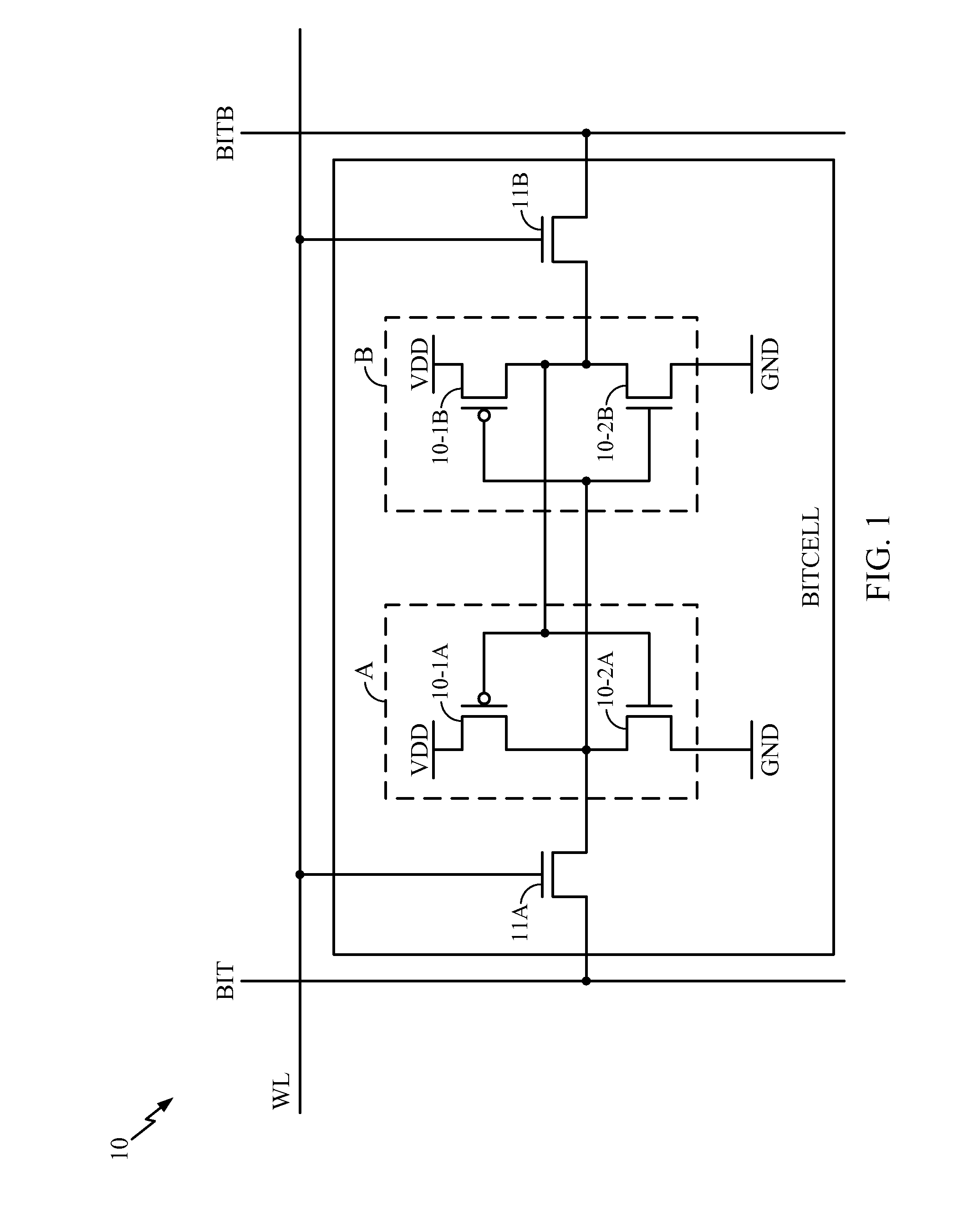
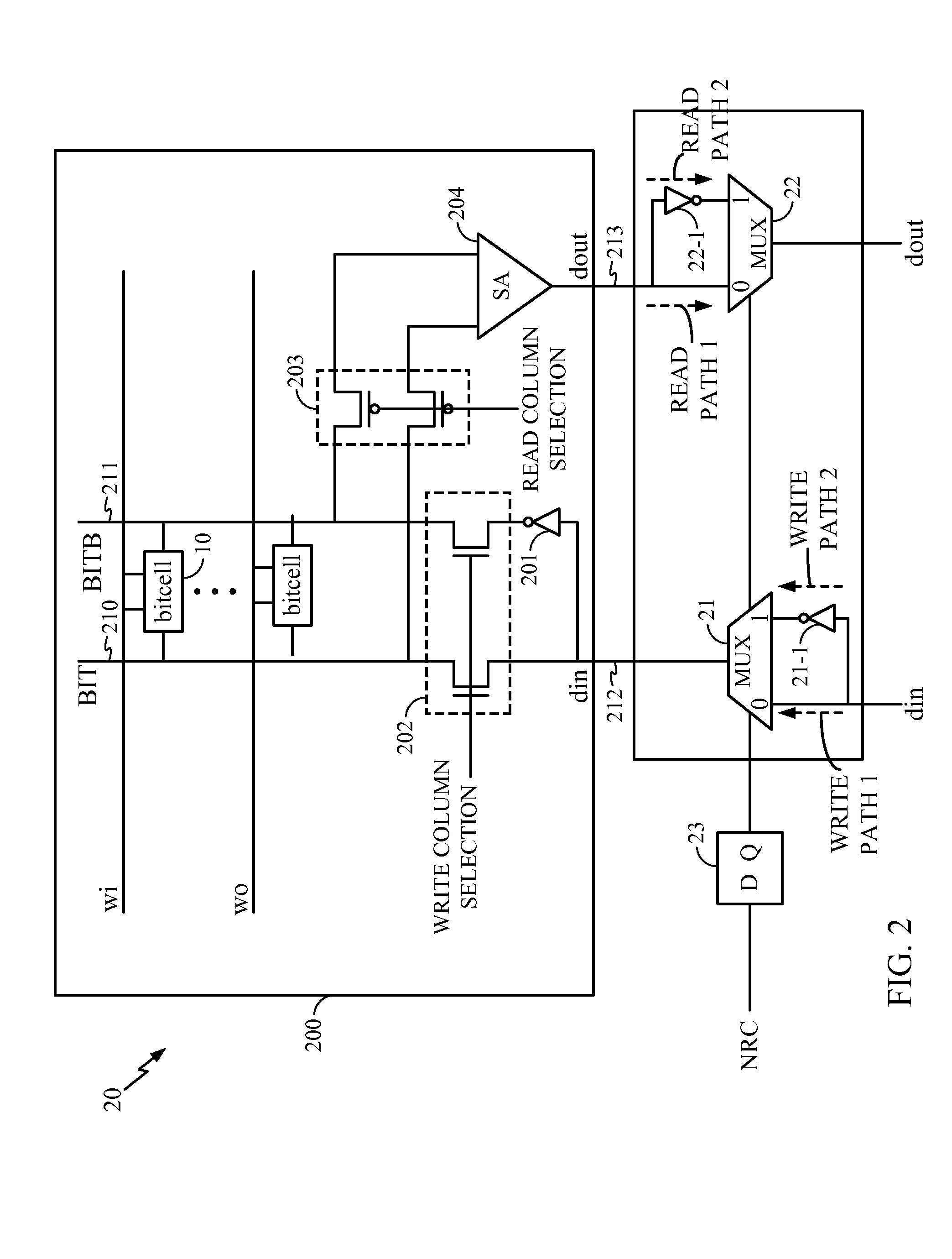
Systems and Methods for Handling Negative Bias Temperature Instability Stress in Memory Bitcells
A system and method reduce stress caused by NBTI effects by determining if a trigger event has occurred and if so inverting all input data values to the memory and all output data values from the memory during a period of time defined by the determined trigger event. In one embodiment, the trigger event is an alternate memory power-up.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
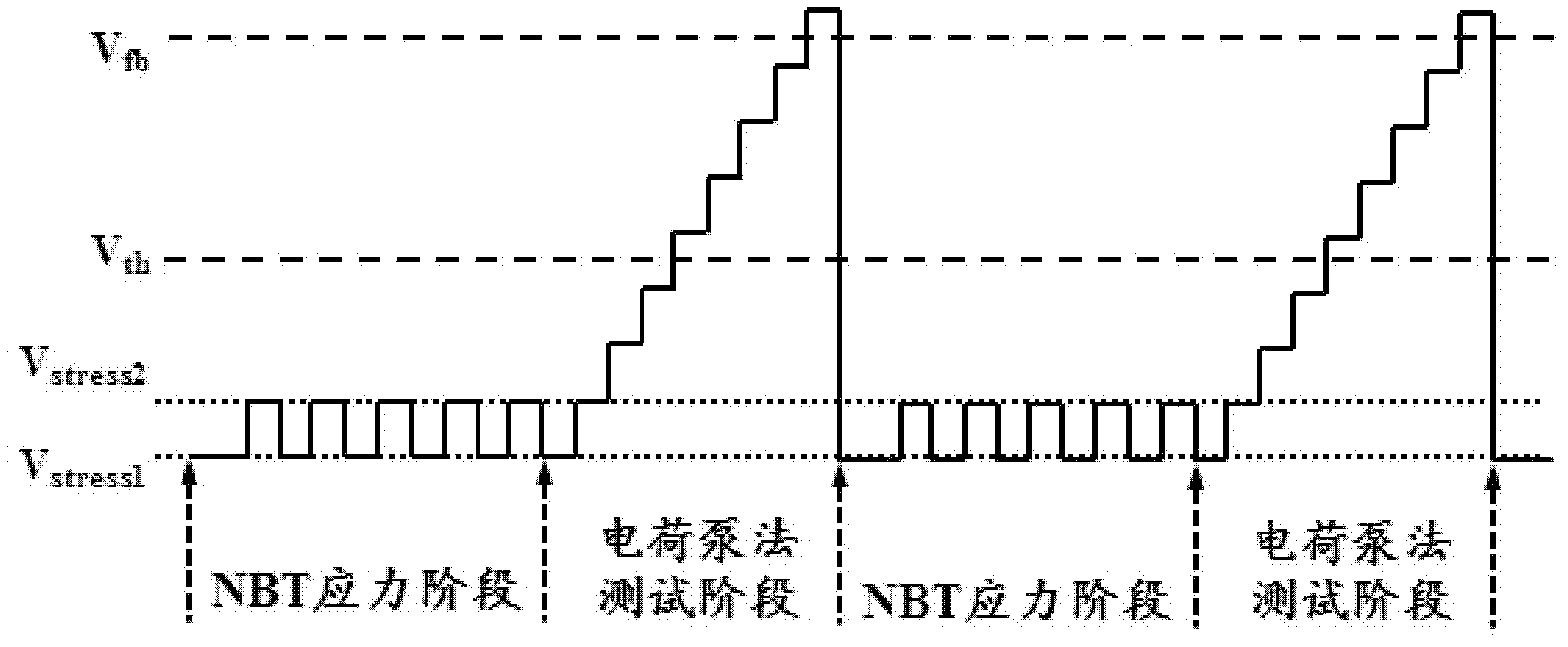
Test method generated by monitoring negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) effect interface states in real time
ActiveCN102621473AEffective assessmentReal-timeIndividual semiconductor device testingDependabilityNegative bias
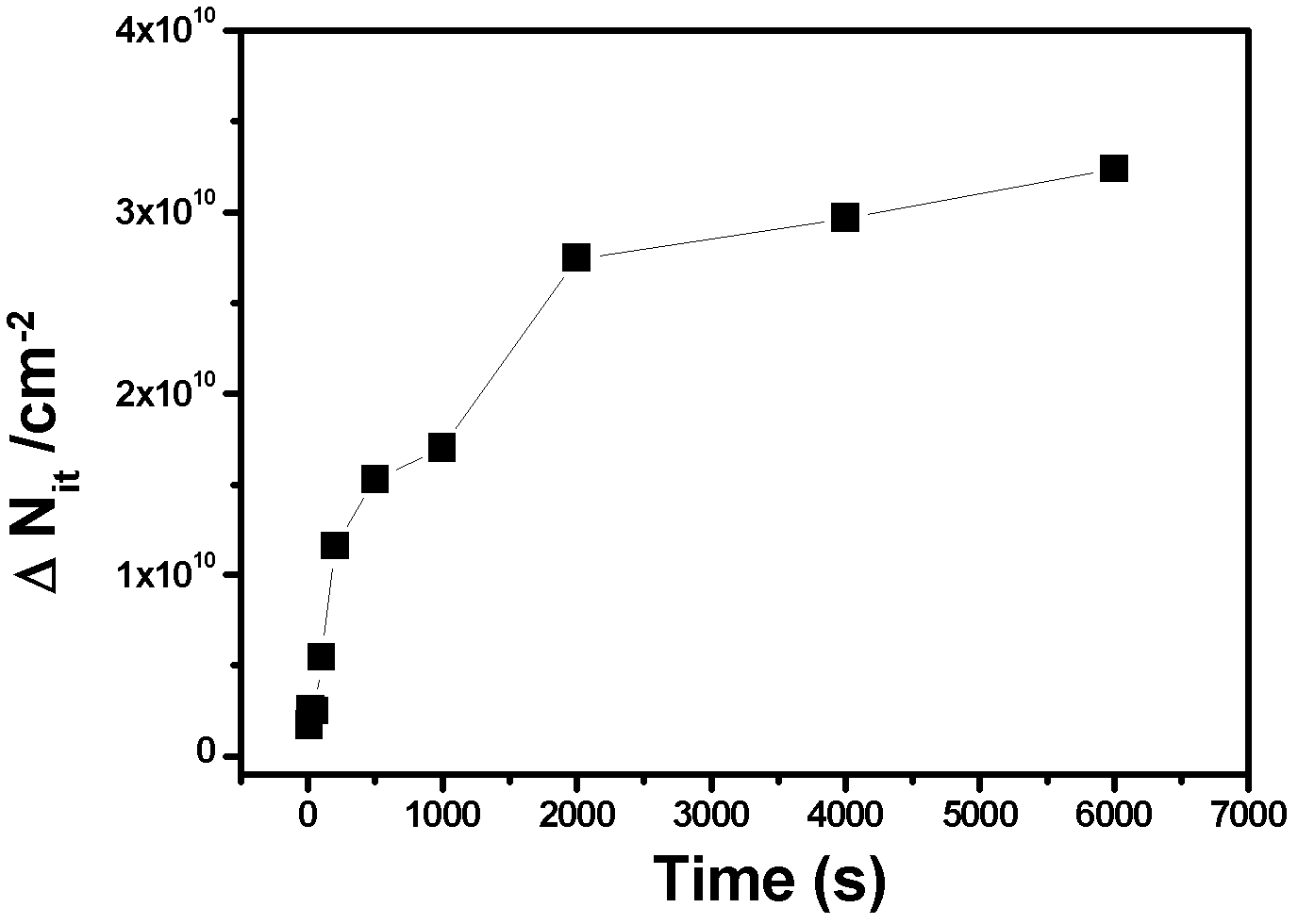
The invention discloses a test method generated by monitoring a negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) effect interface states in real time, which belongs to the field of reliable testing of semiconductor devices. The method enables a direct voltage signal source at negative bias temperature (NBT) stress polarization middle gate end to be changed into a pulse signal source, adopts a charge pump method to measure current on a substrate after NBT stress with different time, and immediately monitors increase of interface state charge caused by the NBTI effect. Compared with commonly-used test method of monitoring interface state charge changes, the test method has instantaneity, reduces recovery amount of NBTI degeneration, and can effectively assess influences of the NBTI effect on characteristics of devices.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Device and method thereof for testing bias temperature instability degrading of MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device
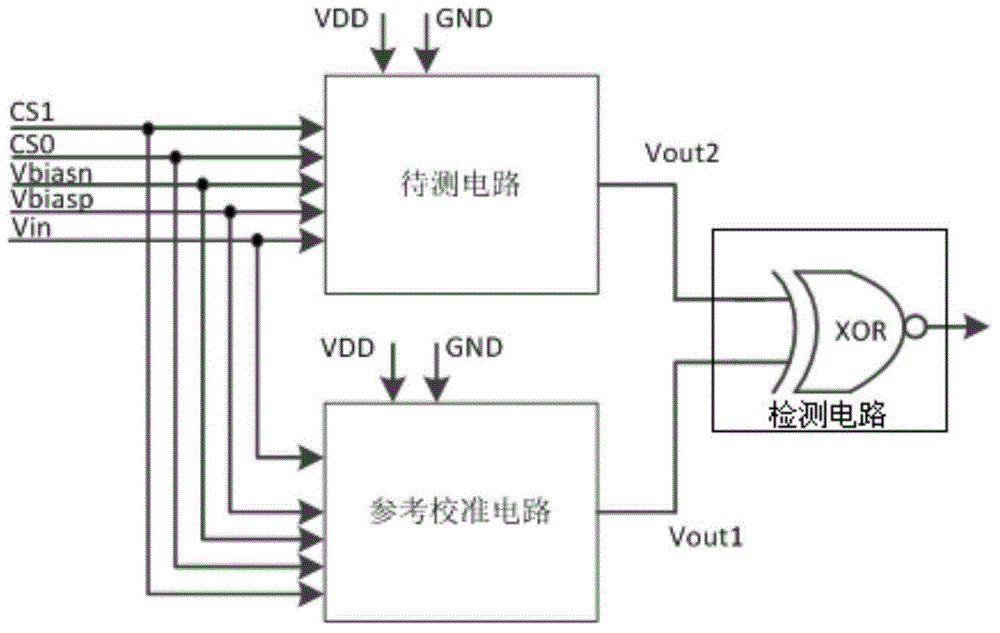
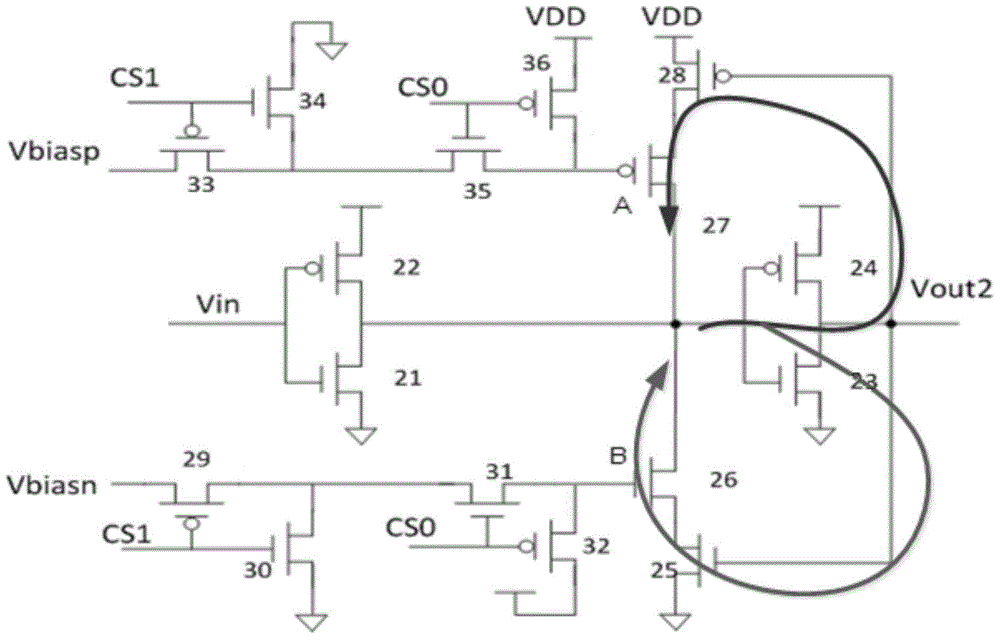
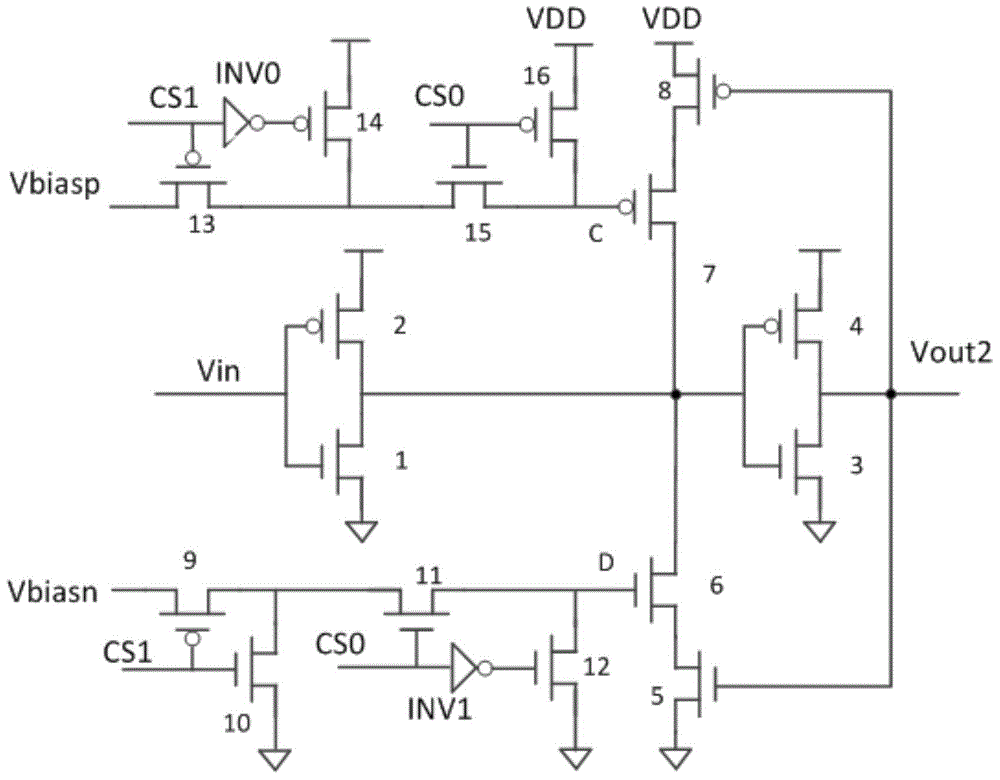
ActiveCN104483611ASimple structureImprove test accuracyIndividual semiconductor device testingHysteresisSchmitt trigger
The invention discloses a device for testing bias temperature instability degrading of a MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device. The device comprises a to-be-tested circuit, a reference calibration circuit and a detection circuit, wherein the output ends of the to-be-tested circuit and the reference calibration circuit are simultaneously connected with the detection circuit, a first feedback control assembly and a first Schmitt trigger are arranged in the to-be-tested circuit, the first feedback control assembly is used for applying stress on to-be-tested feedback loop components in the first Schmitt trigger so as to generate degrading, the to-be-tested circuit is used for outputting degraded actual hysteresis voltage signals, the reference calibration circuit is used for outputting standard hysteresis voltage signals, and the detection circuit is used for comparing and measuring the difference between the actual hysteresis voltage signals and the reference standard hysteresis voltage signals, so as to test the degrading degree of the feedback loop components. The device has the characteristics that the NBTI (negative bias temperature instability) and PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) properties can be tested, the circuit structure is simple, and the testing accuracy is high. The invention discloses a method for testing the bias temperature instability degrading of the MOS device.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Threshold voltage measuring method and system
InactiveCN101825680AImprove accuracyShorten the timeIndividual semiconductor device testingDrain currentNegative-bias temperature instability
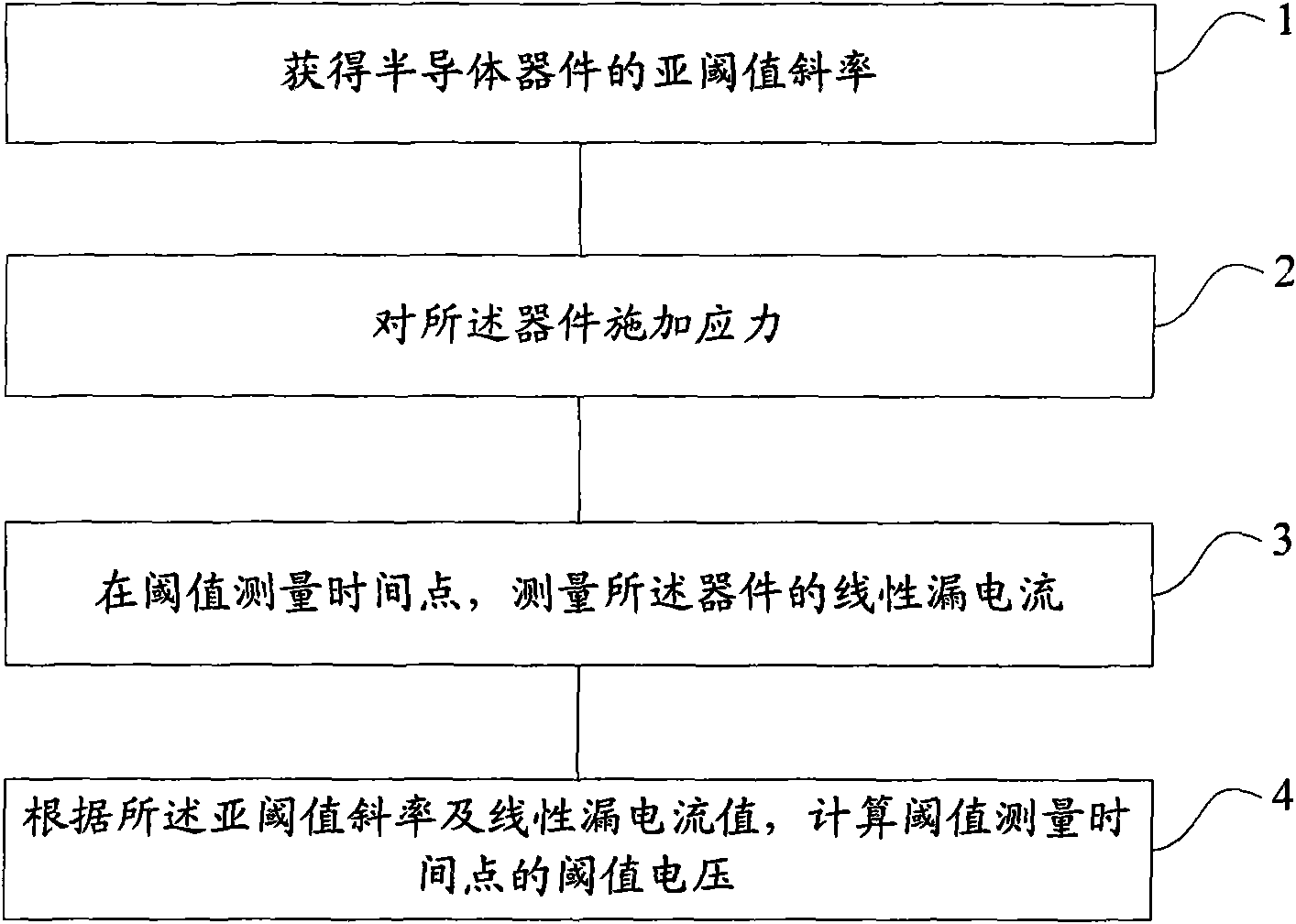
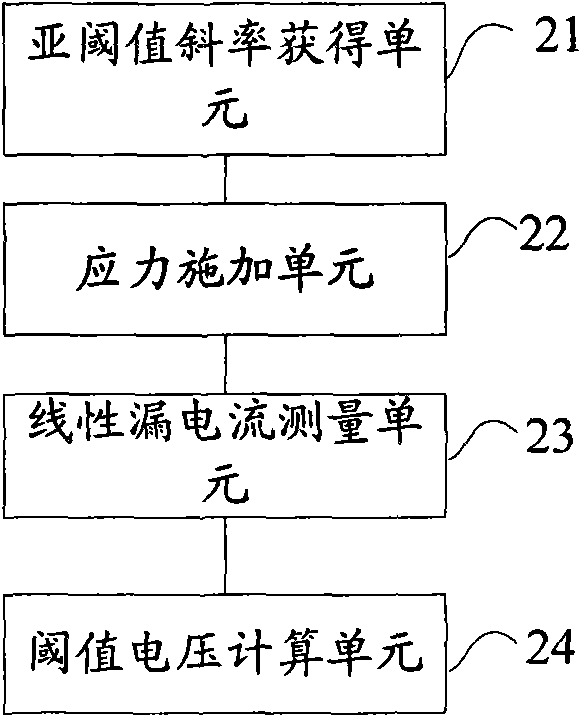
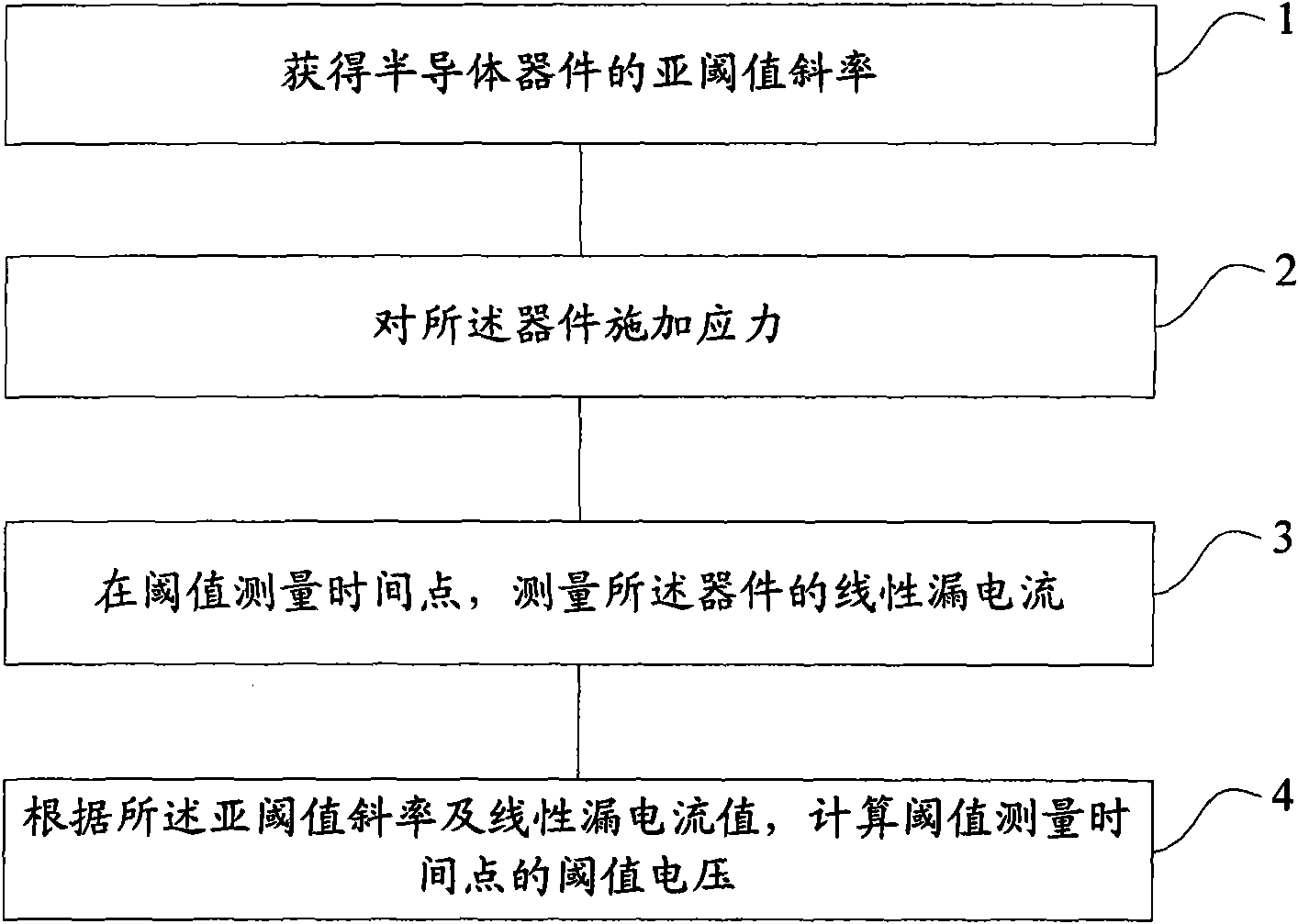
The invention provides a threshold voltage measuring method and a system, which are used for improving the accuracy of the measured threshold voltage and further improving the accuracy of a NBTI (Negative Bias Temperature Instability) test. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the subthreshold slope of a semiconductor device; applying the stress on the device; measuring the linear leakage current of the device at the threshold measuring time point; calculating the threshold voltage of the threshold measuring time point according to the subthreshold slope and the linear leakage current value, wherein the process of measuring the linear leakage current comprises the steps of removing the stress; connecting the test voltage to the device; and measuring the linear leakage current of the device under the test voltage.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
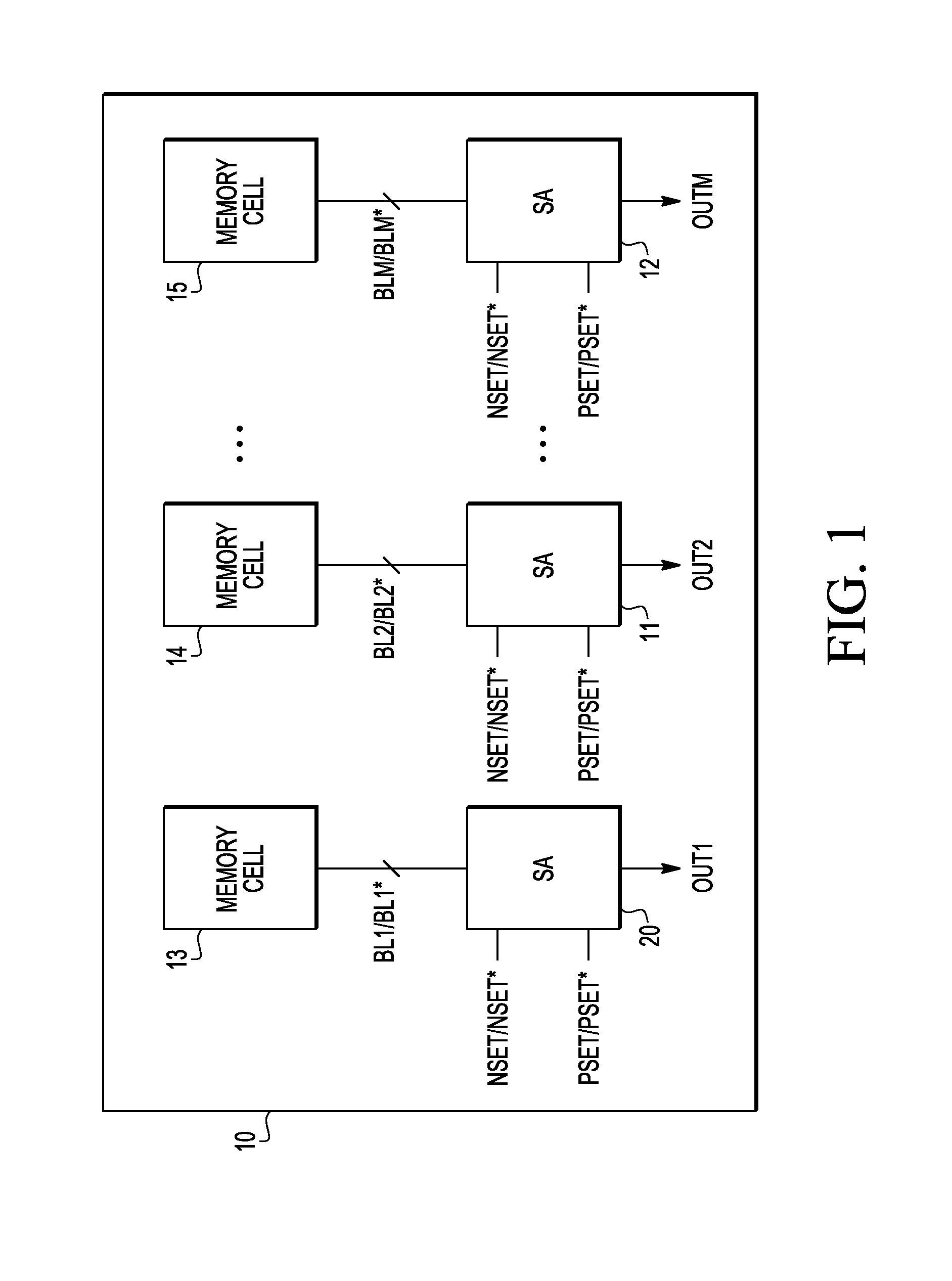
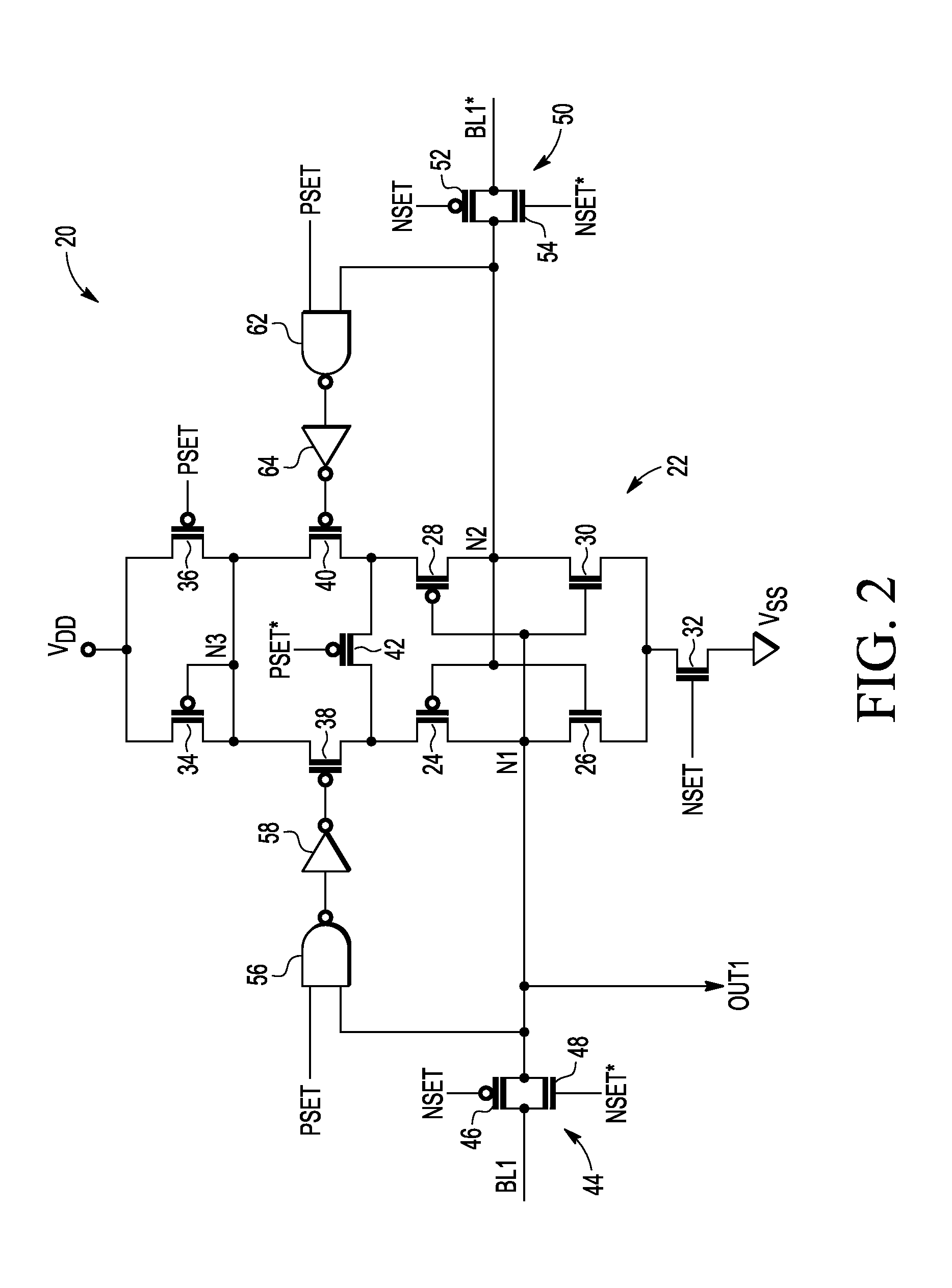
Memory having a latching sense amplifier resistant to negative bias temperature instability and method therefor
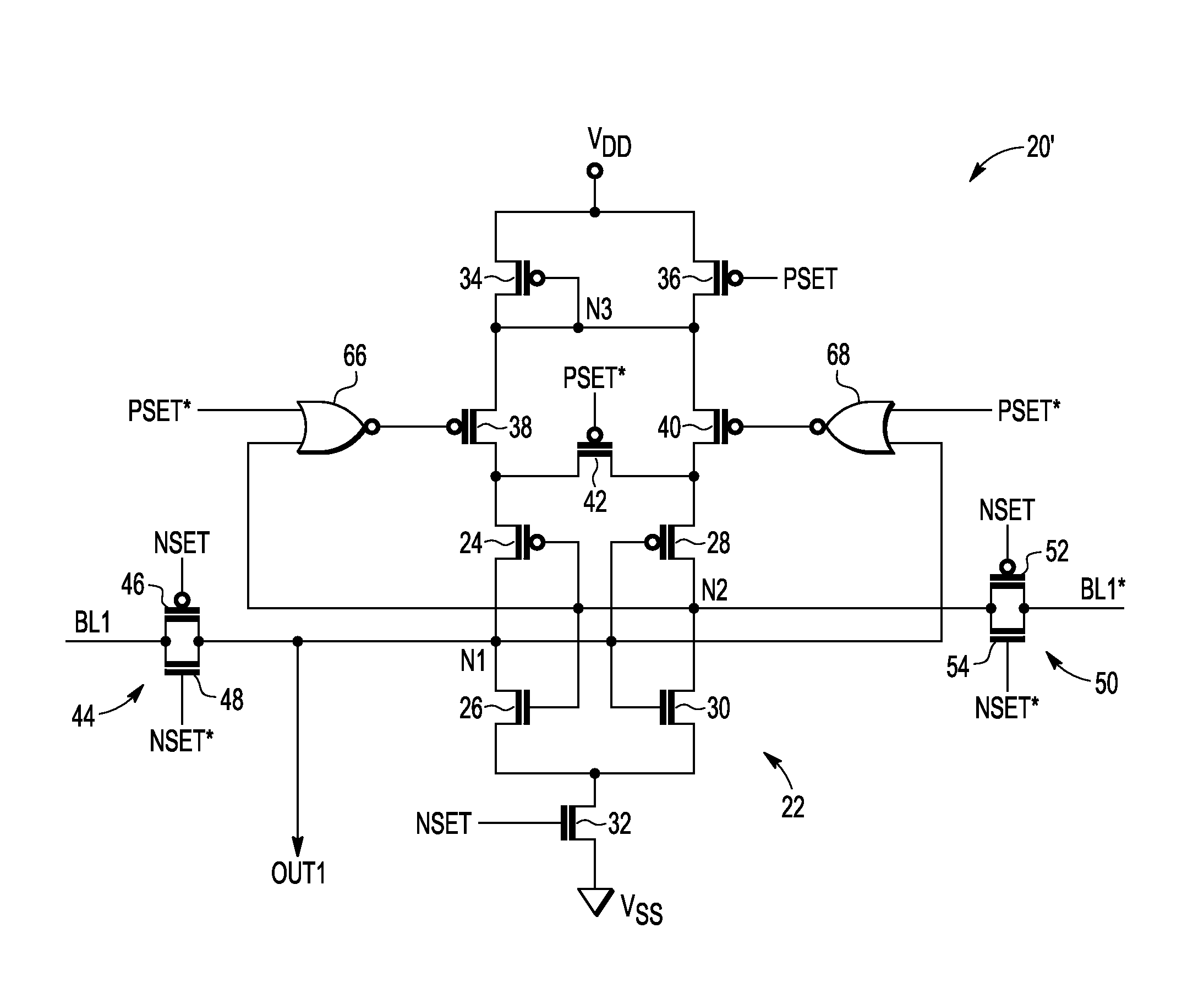
An integrated circuit includes a memory cell and a sense amplifier coupled to the memory cell via a first bit line and a second bit line. The sense amplifier includes first and second inverters cross-coupled to provide a latch. The first inverter is responsive to a first data signal provided by the memory cell over the first bit line. The second inverter is responsive to a second data signal as provided by the memory cell over the second bit line. A first negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) compensation transistor includes a source electrode coupled to receive a reference voltage, a drain electrode coupled to a source electrode of the first inverter, and a gate electrode coupled to first logic responsive to the first data signal. A second NBTI compensation transistor includes a source electrode coupled to receive the reference voltage, a drain electrode coupled to a source electrode of the second inverter, and a gate electrode coupled to second logic responsive to the second data signal, wherein the second data signal is a logical complement of the first data signal.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Test structure for automatic dynamic negative-bias temperature instability testing
InactiveUS7103861B2Minimizes parasitic capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectronic switchElectron
The invention describes a novel test structure and process to create the structure for performing automatic dynamic stress testing of PMOS devices for Negative Bias Temperature Instability (NBTI). The invention consists of an integrated inverter, two integrated electronic switches for switching from stress mode to device DC characterization measurement mode, and a PMOS FET device under test (DUT). The inverter assures the proper 180 degree phase relationship between the test device source and gate voltage while the imbedded electronic switches provide isolation of the test device during DC characterization testing. Another embodiment of the invention enables the testing of multiple devices under test (DUT's).
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Semiconductor On-Chip Repair Scheme for Negative Bias Temperature Instability
InactiveUS20090179689A1Avoid insufficient heatingAvoid insufficient temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor chipTransmission-line pulse
Disclosed are embodiments of a semiconductor chip structure and a method that incorporate a localized, on-chip, repair scheme for devices that exhibit performance degradation as a result of negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The repair scheme utilizes a heating element above each device. The heating element is configured so that it can receive transmission line pulses and, thereby generate enough heat to raise the adjacent device to a temperature sufficient to allow for performance recovery. Specifically, high temperatures (e.g., between approximately 300-400° C. or greater) in the absence of bias can accelerate the recovery process to a matter of seconds as opposed to days or months. The heating element can be activated, for example, on demand, according to a pre-set service schedule, and / or in response to feedback from a device performance monitor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Circuitry and method for measuring negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and hot carrier injection (HCI) aging effects using edge sensitive sampling
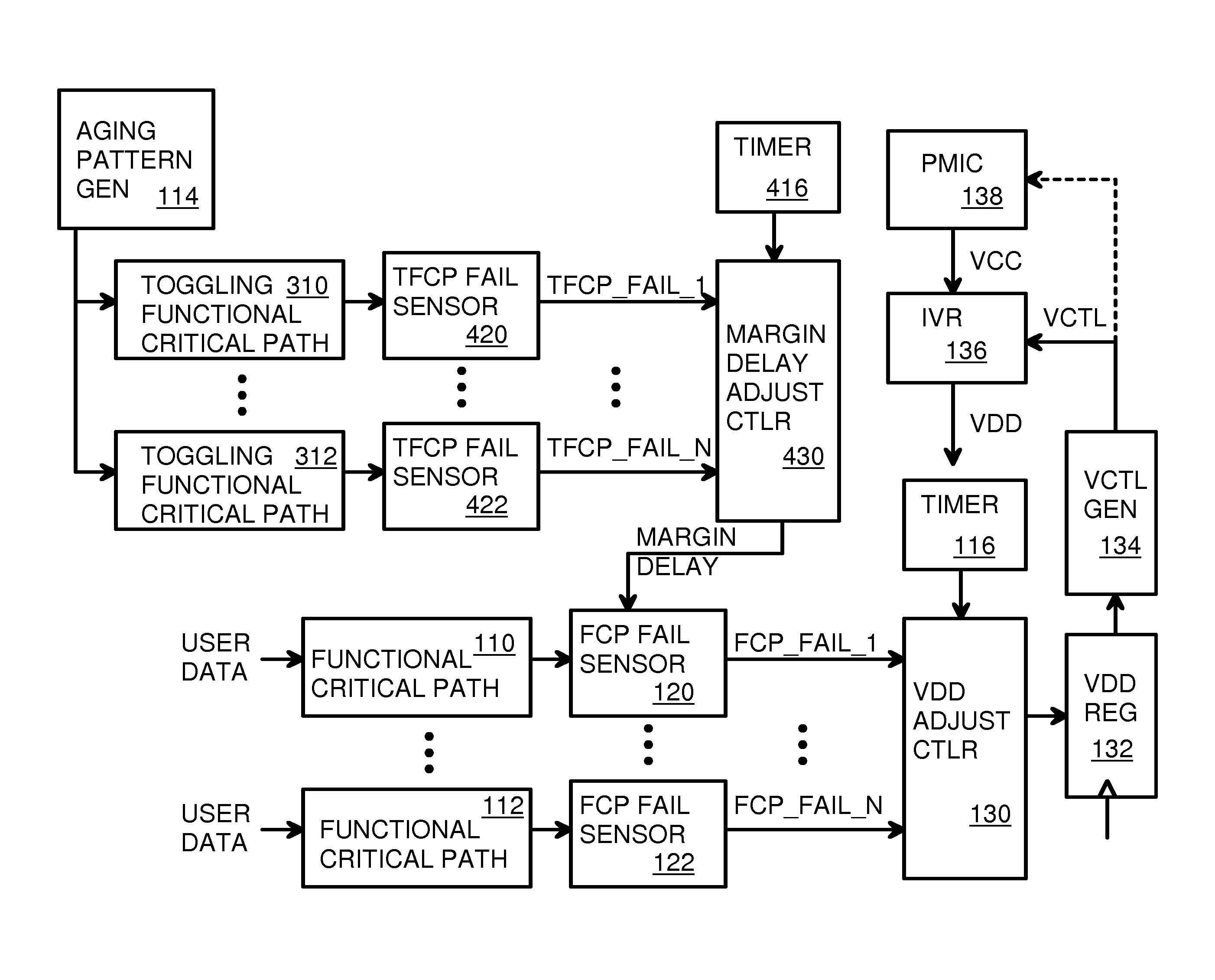
InactiveUS9564884B1Electrical testingSingle output arrangementsTransition densityCritical path method
Toggling functional critical path timing sensors measure delays in toggling functional critical paths that continuously receive patterns from an aging pattern generator. Wear is accelerated. A margin delay adjustment controller sweeps margin delays until failures occur to measure delays. The margin delay is then adjusted in functional critical path timing sensors that add the margin delay to functional critical paths that carry user data or chip controls during normal operation. When the path delays fail to meet requirements, the functional critical path timing sensors signal a controller to increase VDD. When no failures occur over a period of time, the controller decreases VDD. Wear on the toggling functional critical paths is accelerated using both toggle and low-transition-density patterns. Circuit aging is compensated for by increasing margin delays to timing sensors.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com