Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Positive bias temperature instability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
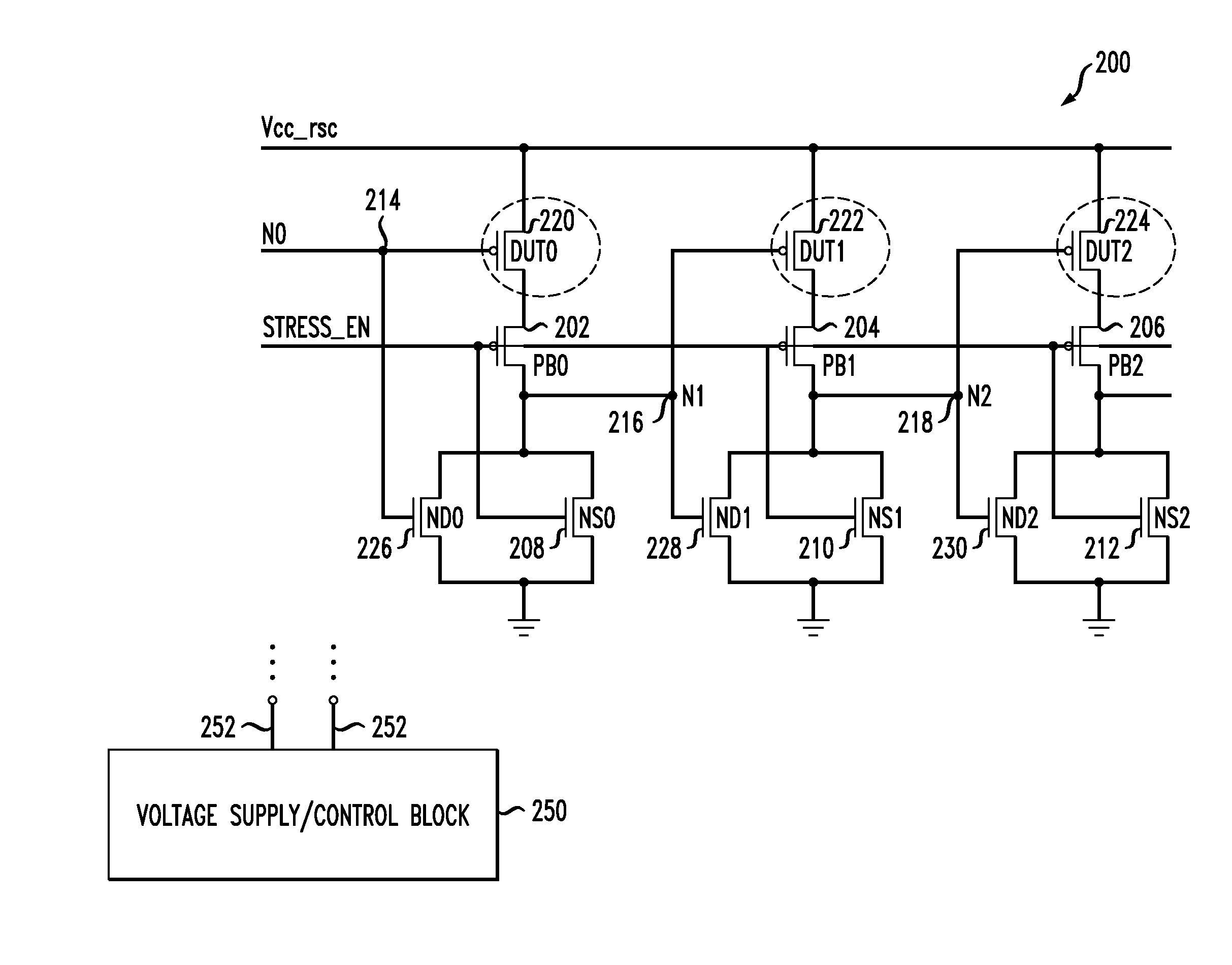
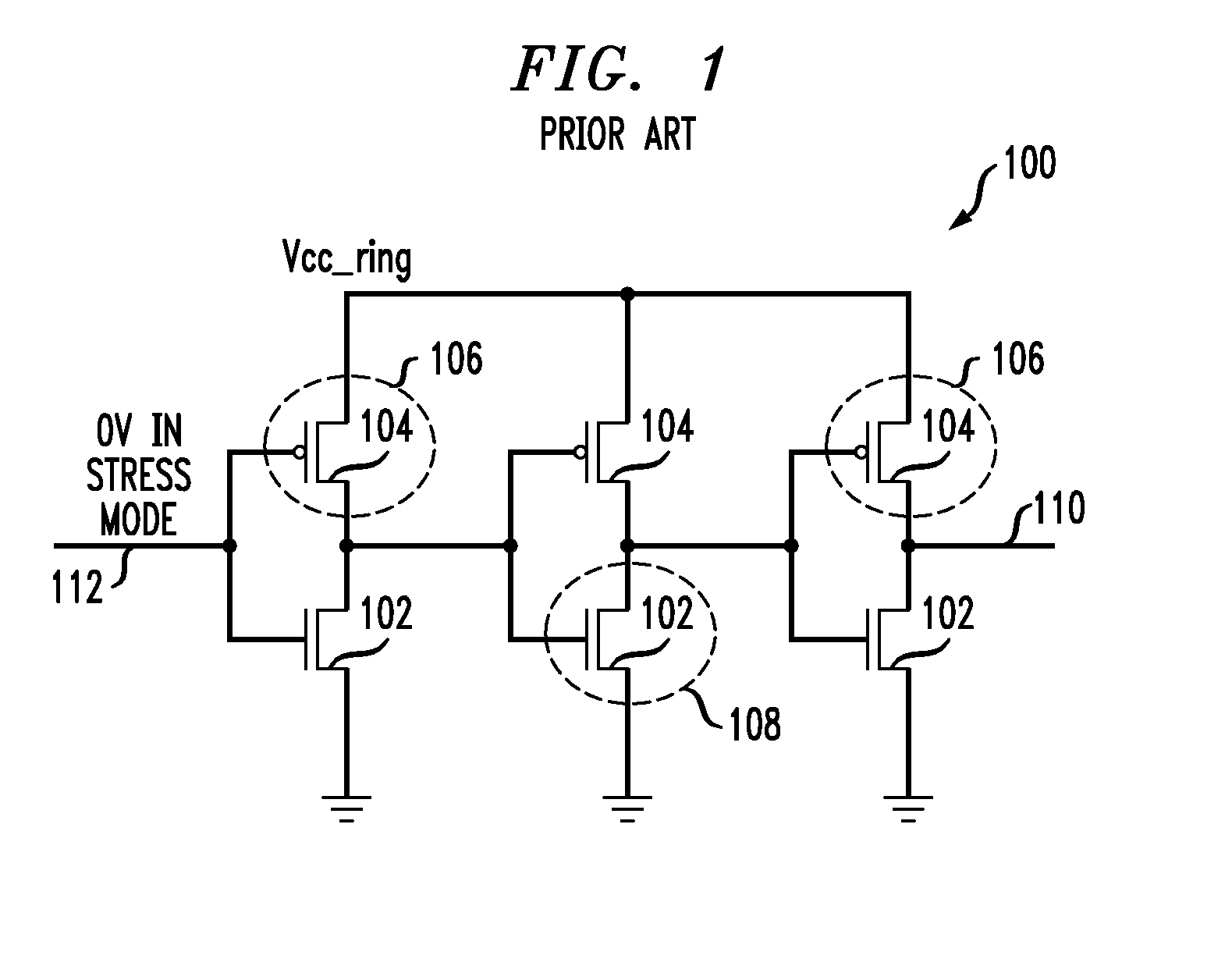
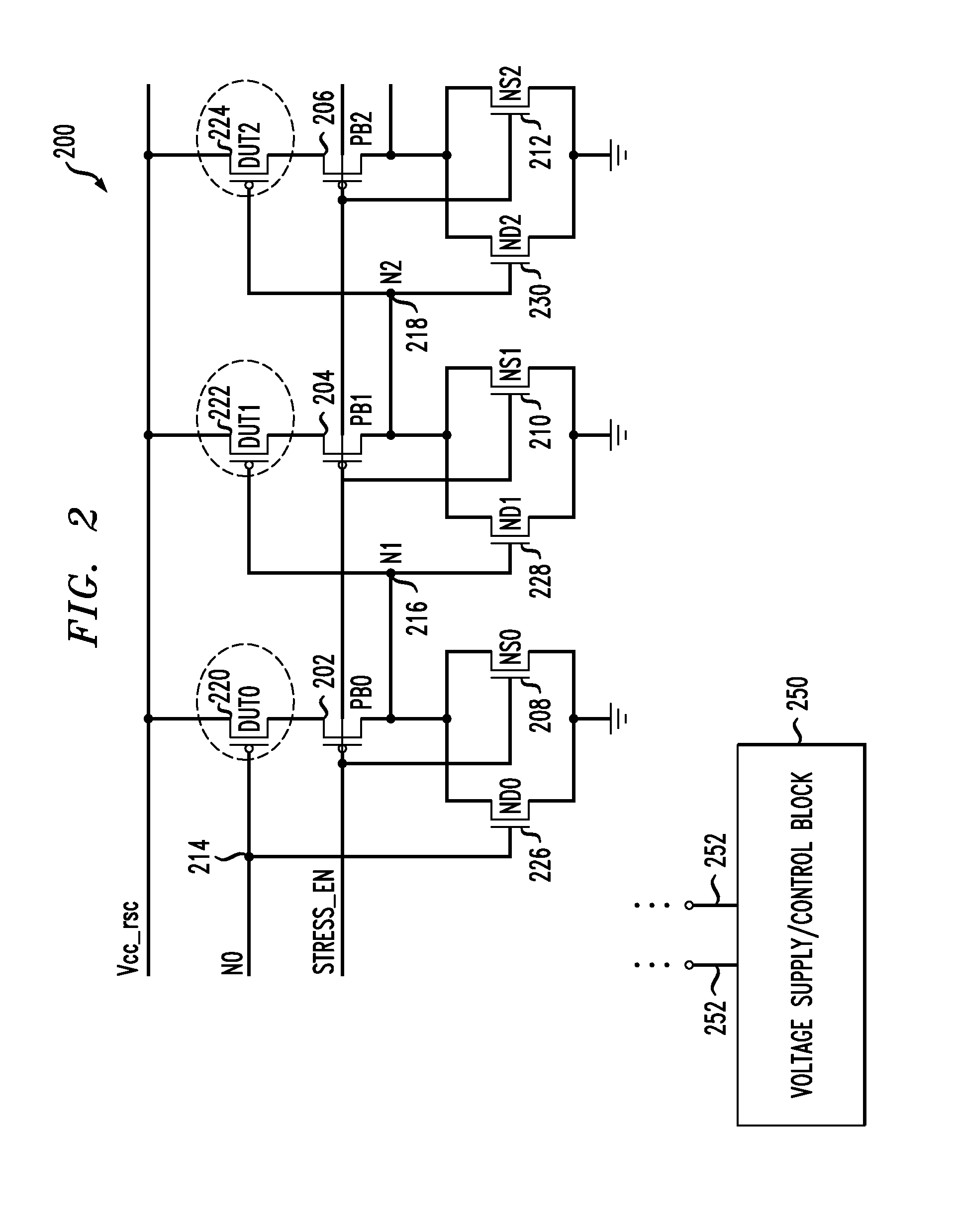
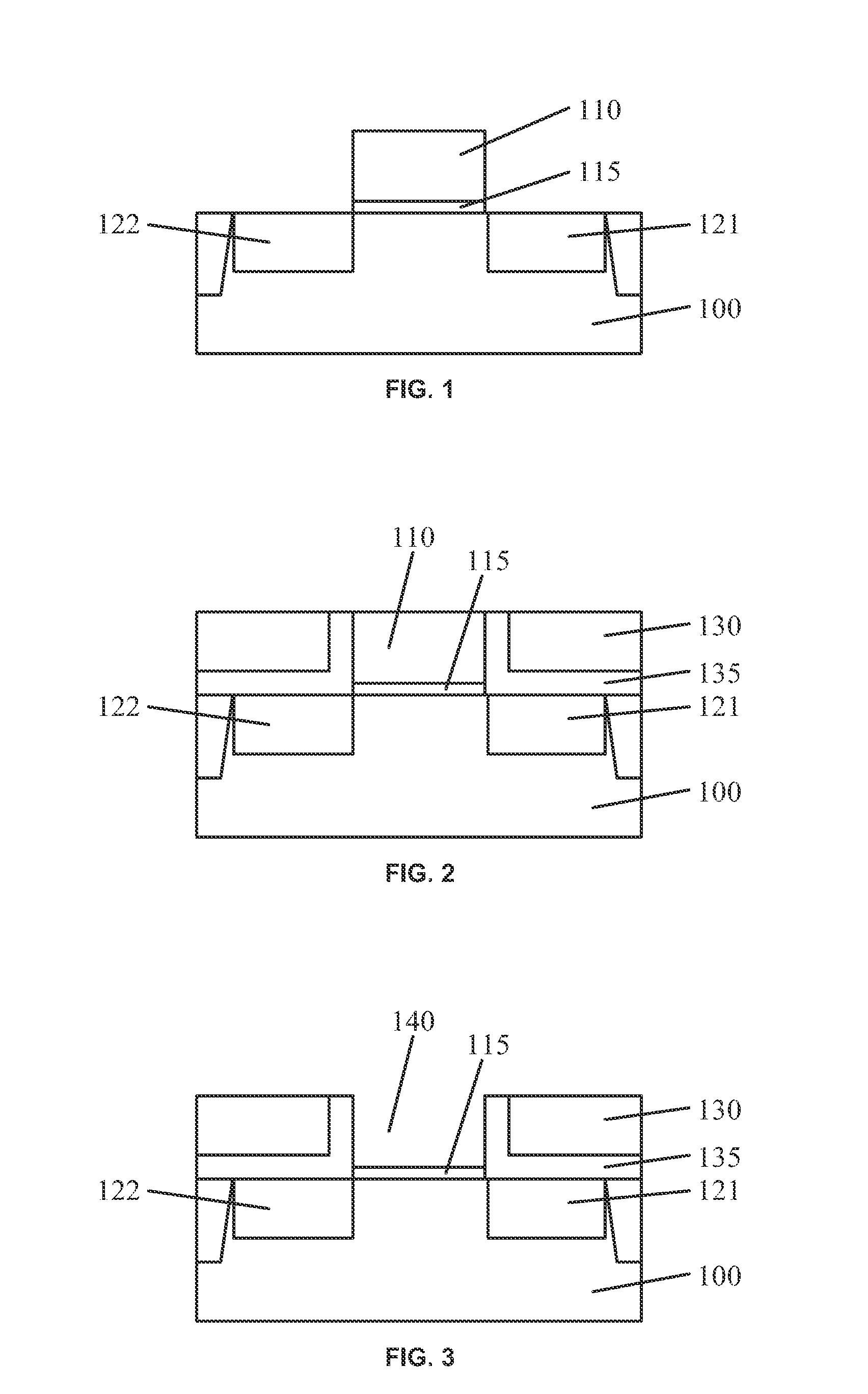
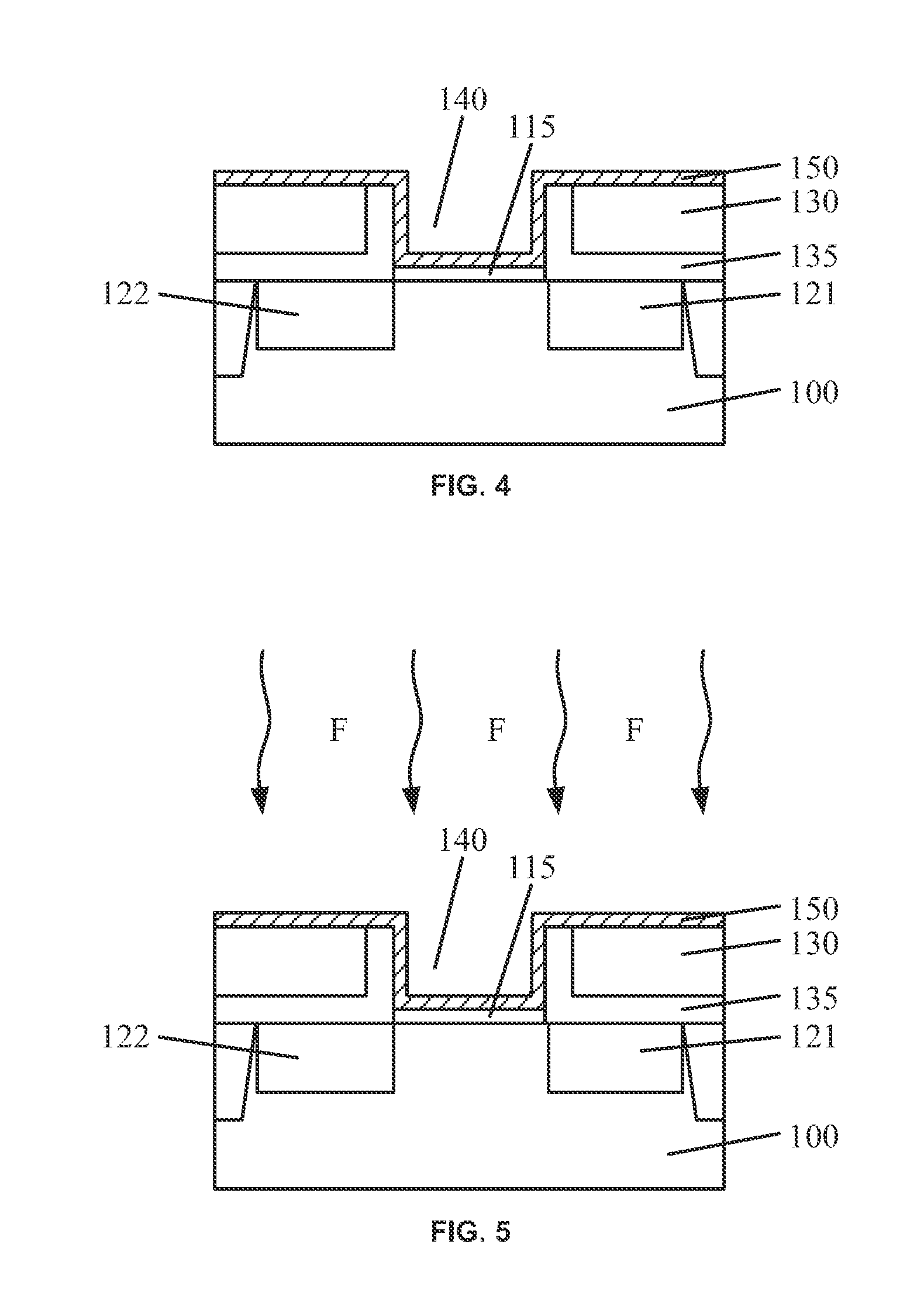
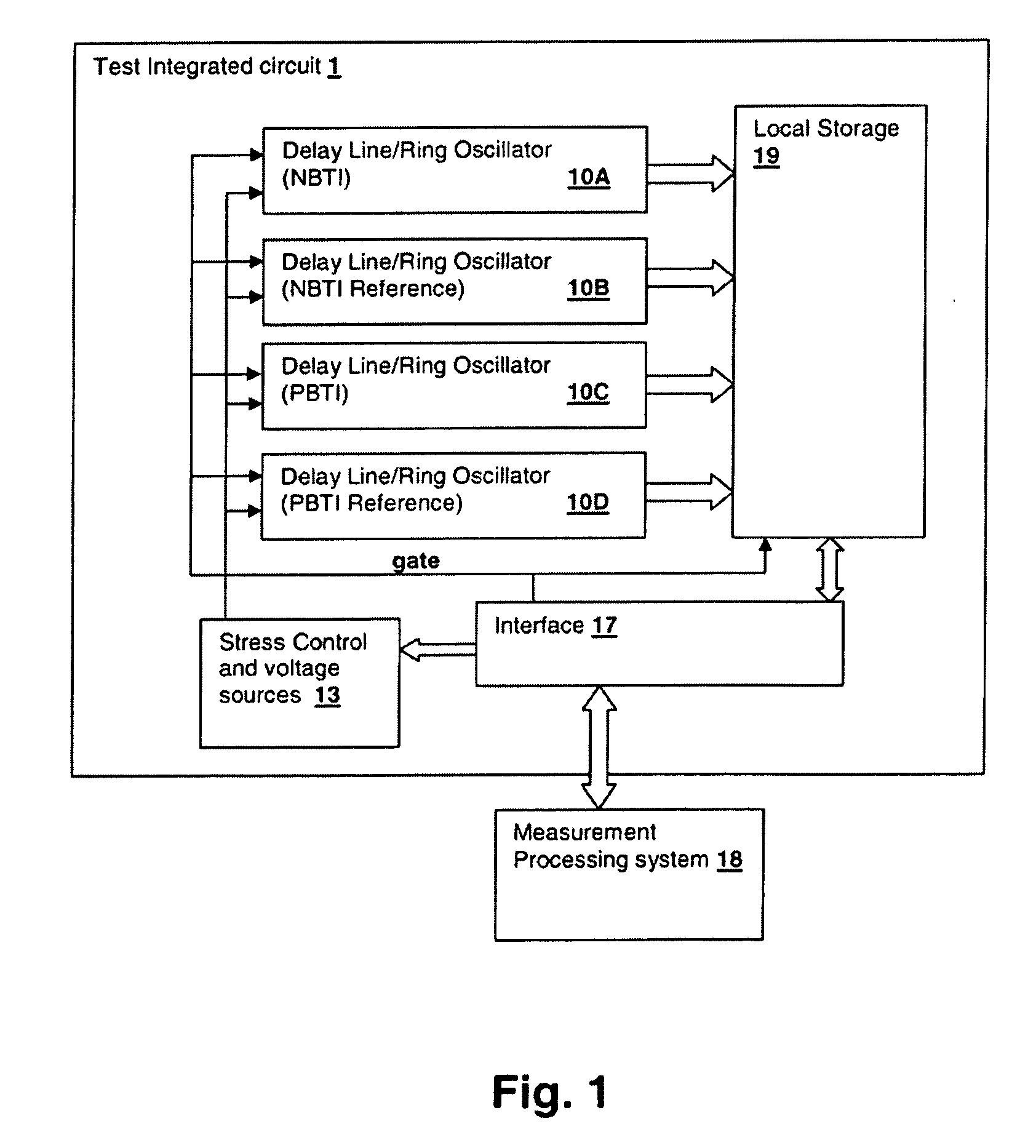
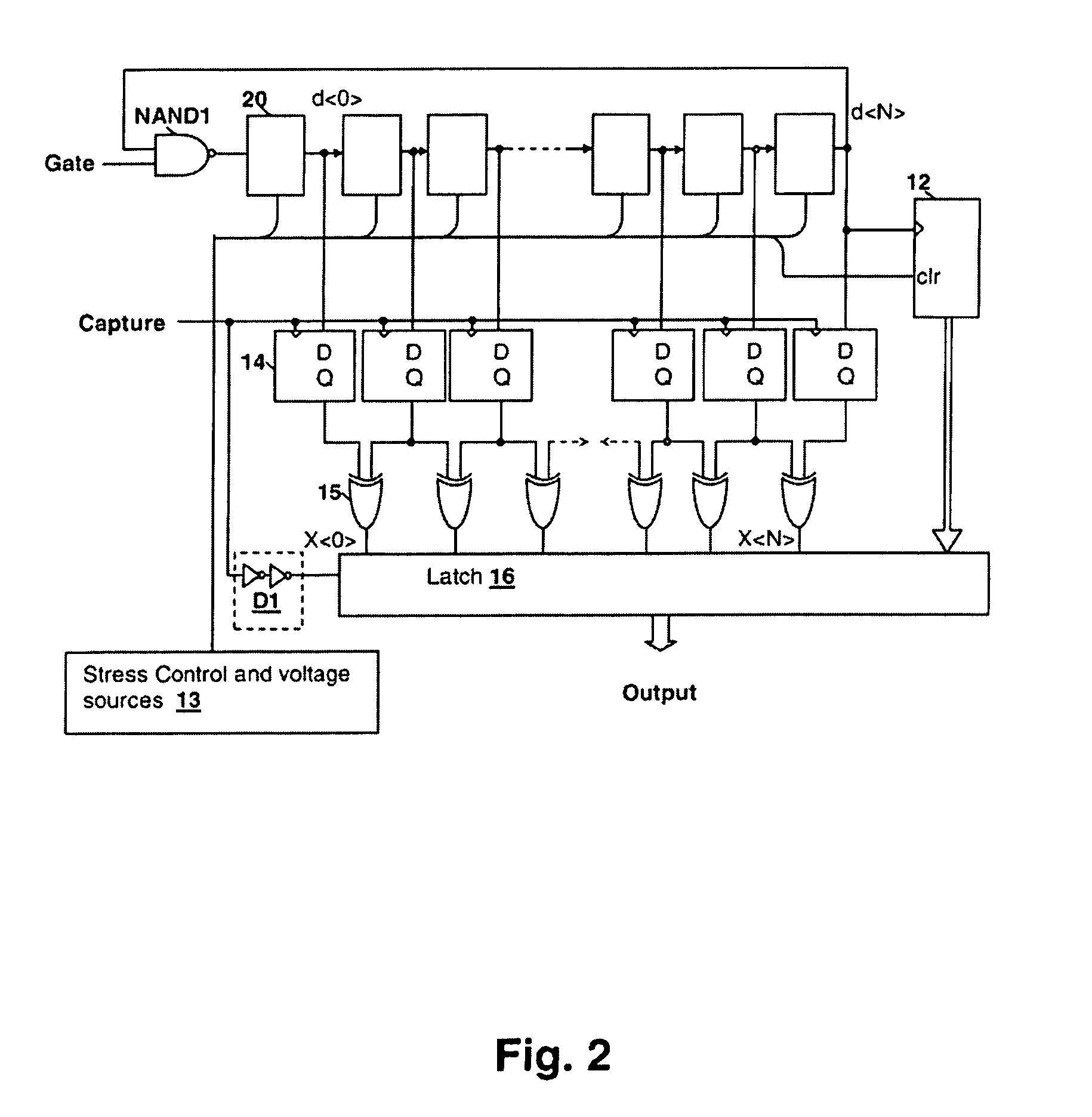
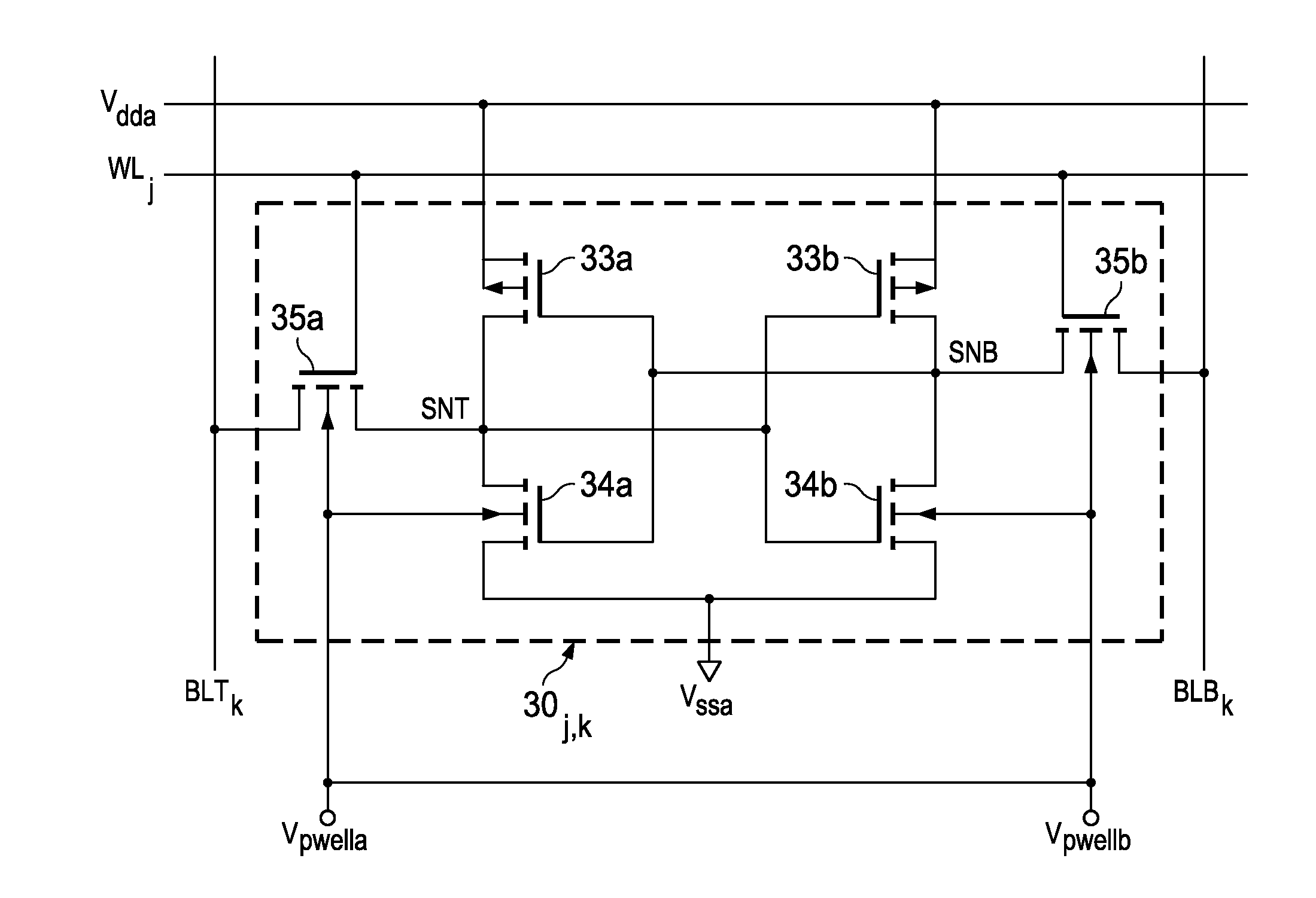
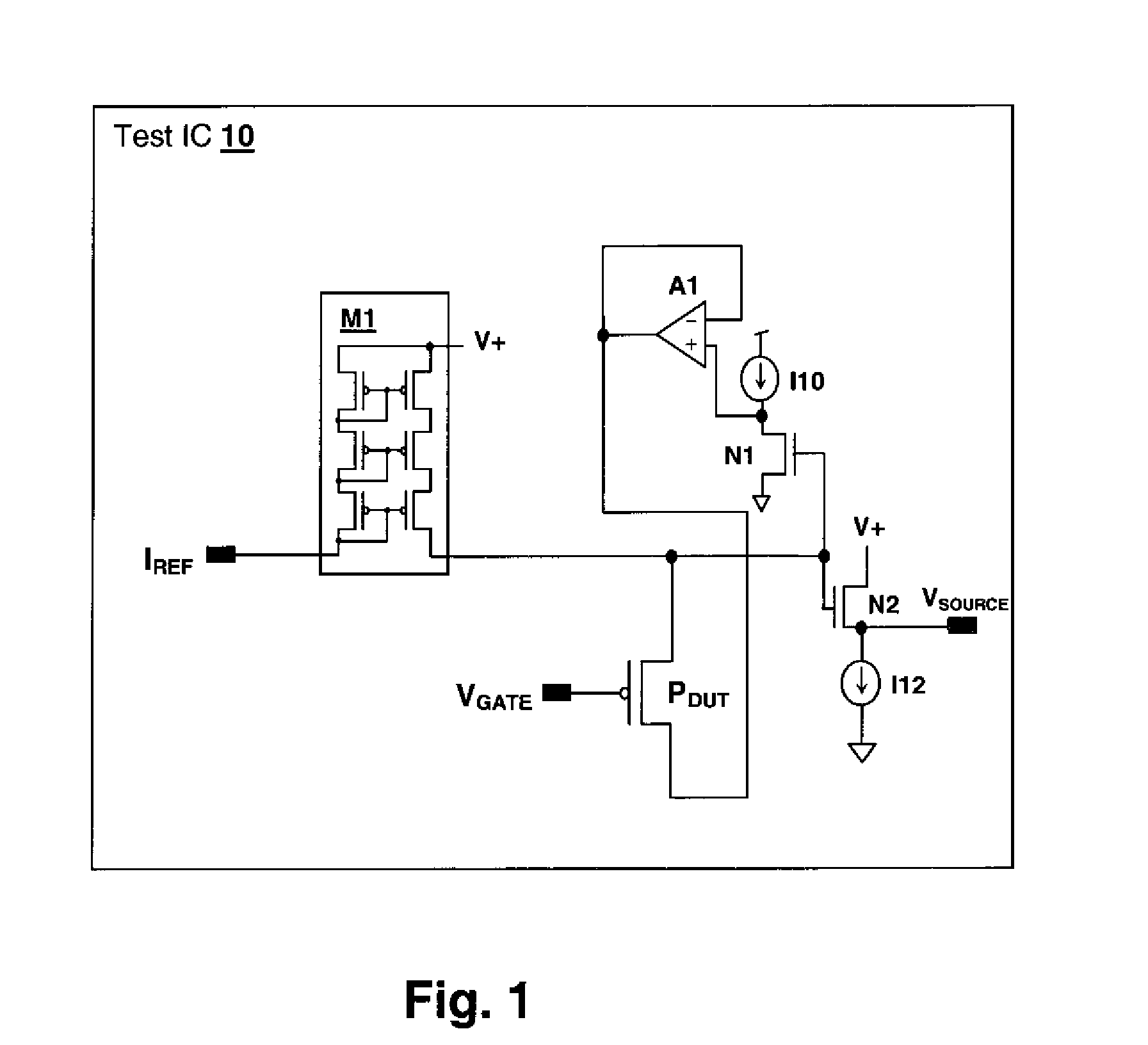
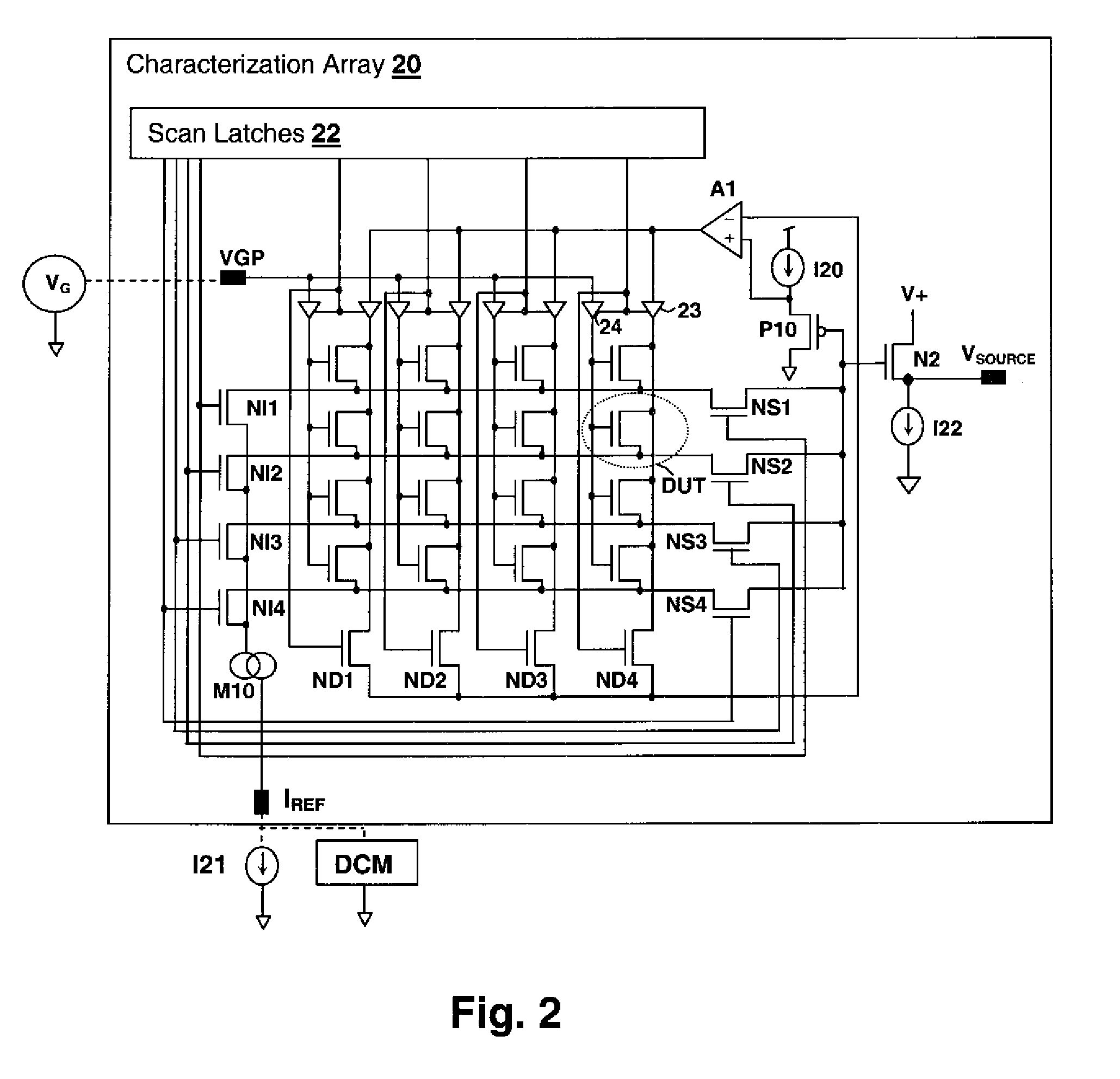
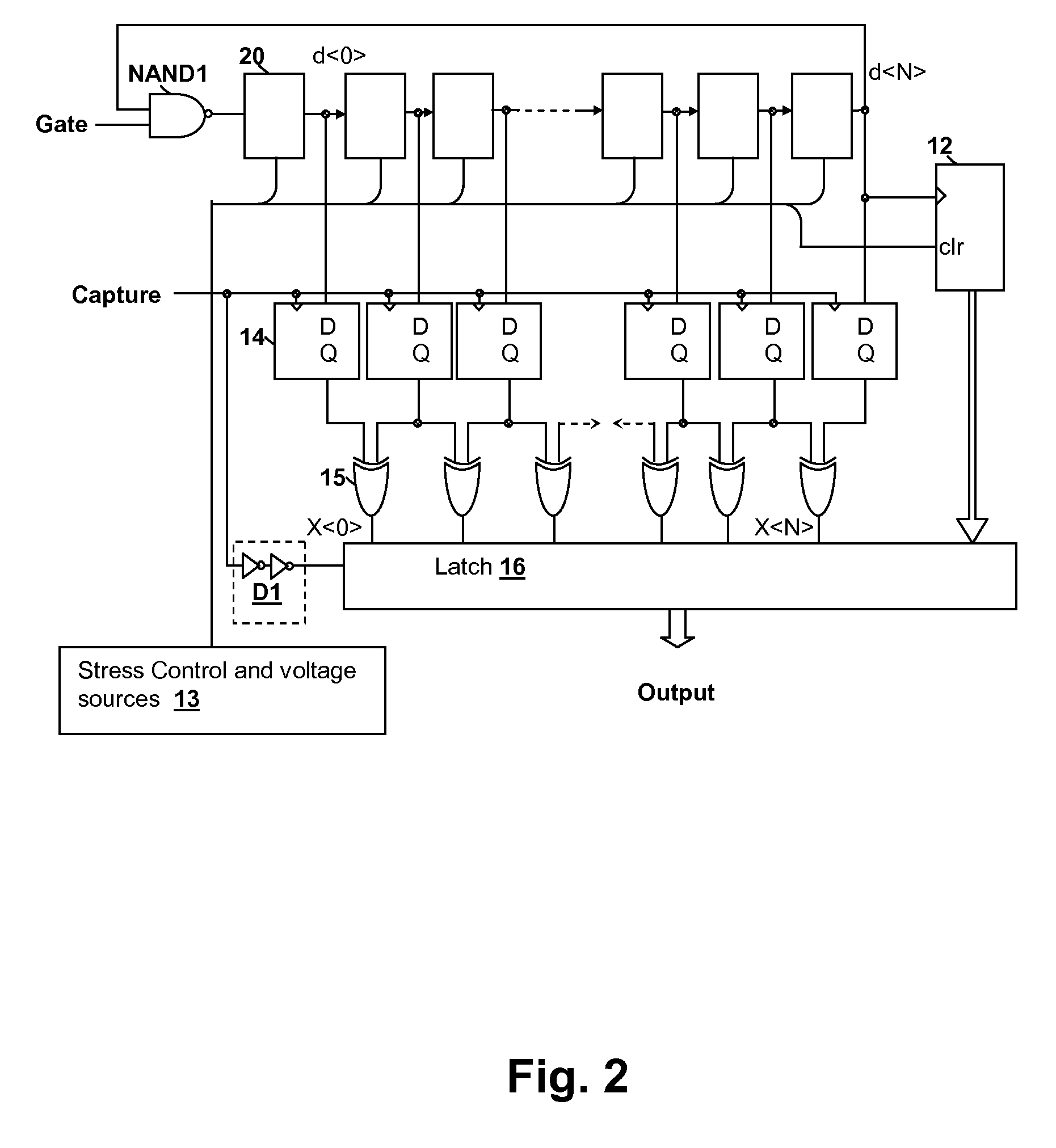
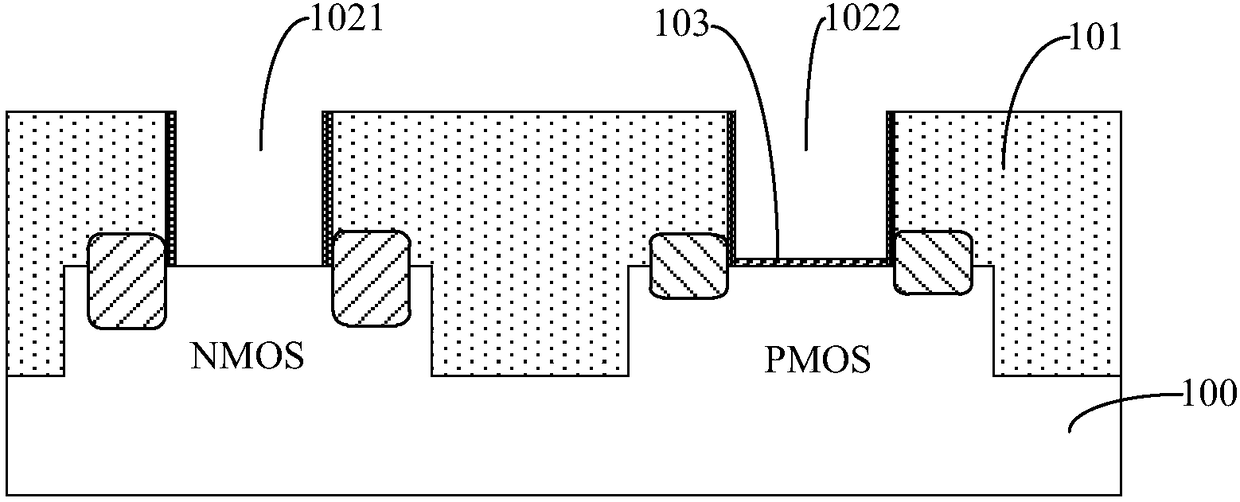
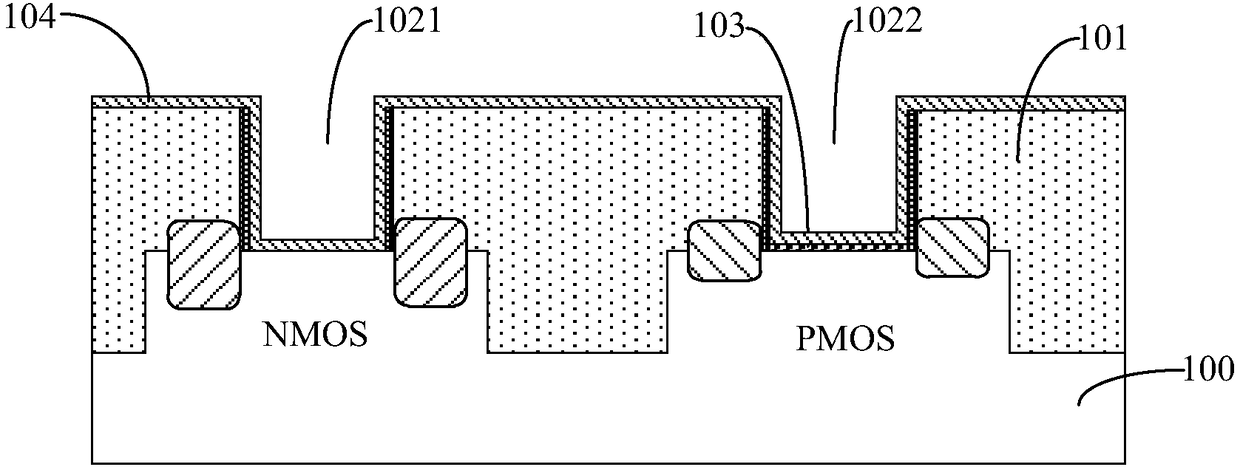
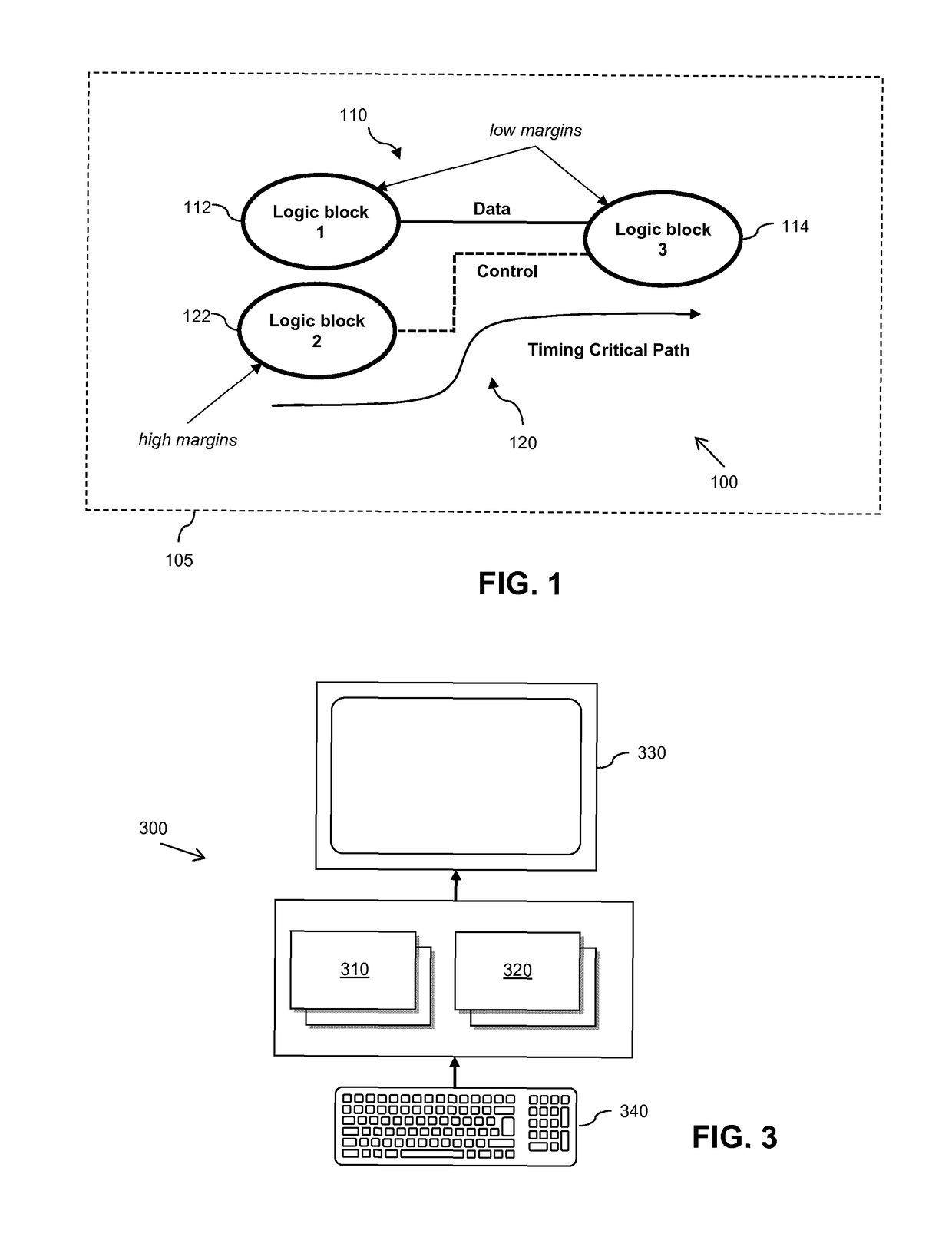
Circuits and design structures for monitoring nbti (negative bias temperature instability) effect and/or pbti (positive bias temperature instability) effect
ActiveUS20090189703A1High power supply voltageResistance/reactance/impedencePulse generation by logic circuitsNOR gateNAND gate
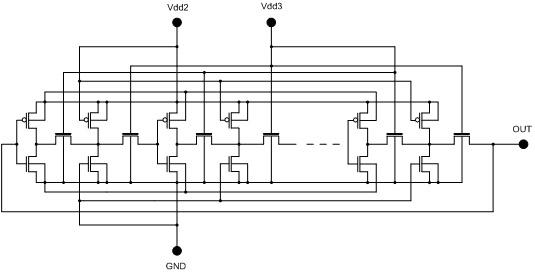
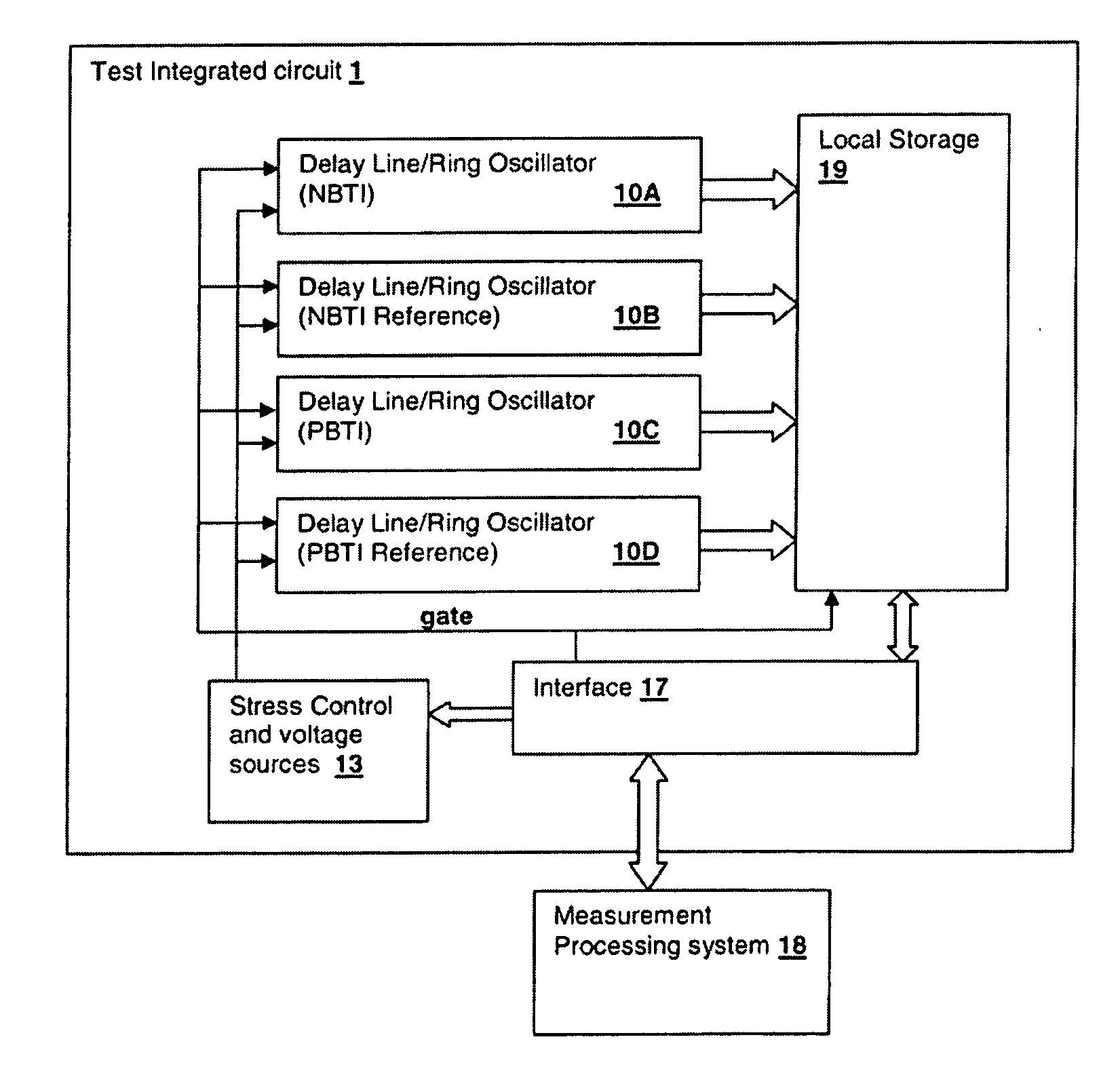
A ring oscillator has an odd number of NOR-gates greater than or equal to three, each with first and second input terminals, a voltage supply terminal, and an output terminal. The first input terminals of all the NOR-gates are interconnected, and each of the NOR-gates has its output terminal connected to the second input terminal of an immediately adjacent one of the NOR-gates. During a stress mode, a voltage supply and control block applies a stress enable signal to the interconnected first input terminals, and an increased supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. During a measurement mode, this block grounds the interconnected first input terminals, and applies a normal supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. Also included are an analogous NAND-gate based circuit, a circuit combining the NAND- and NOR-aspects, a circuit with a ring oscillator where the inverters may be coupled directly or through inverting paths, and circuits for measuring the bias temperature instability effect in pass gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
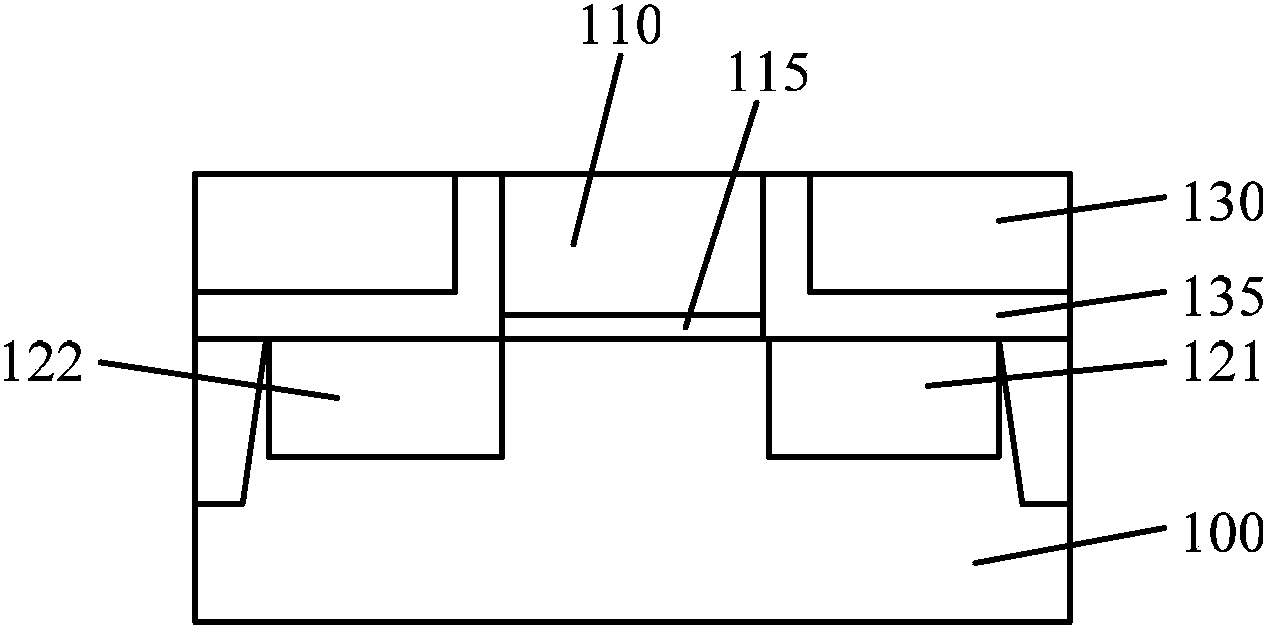
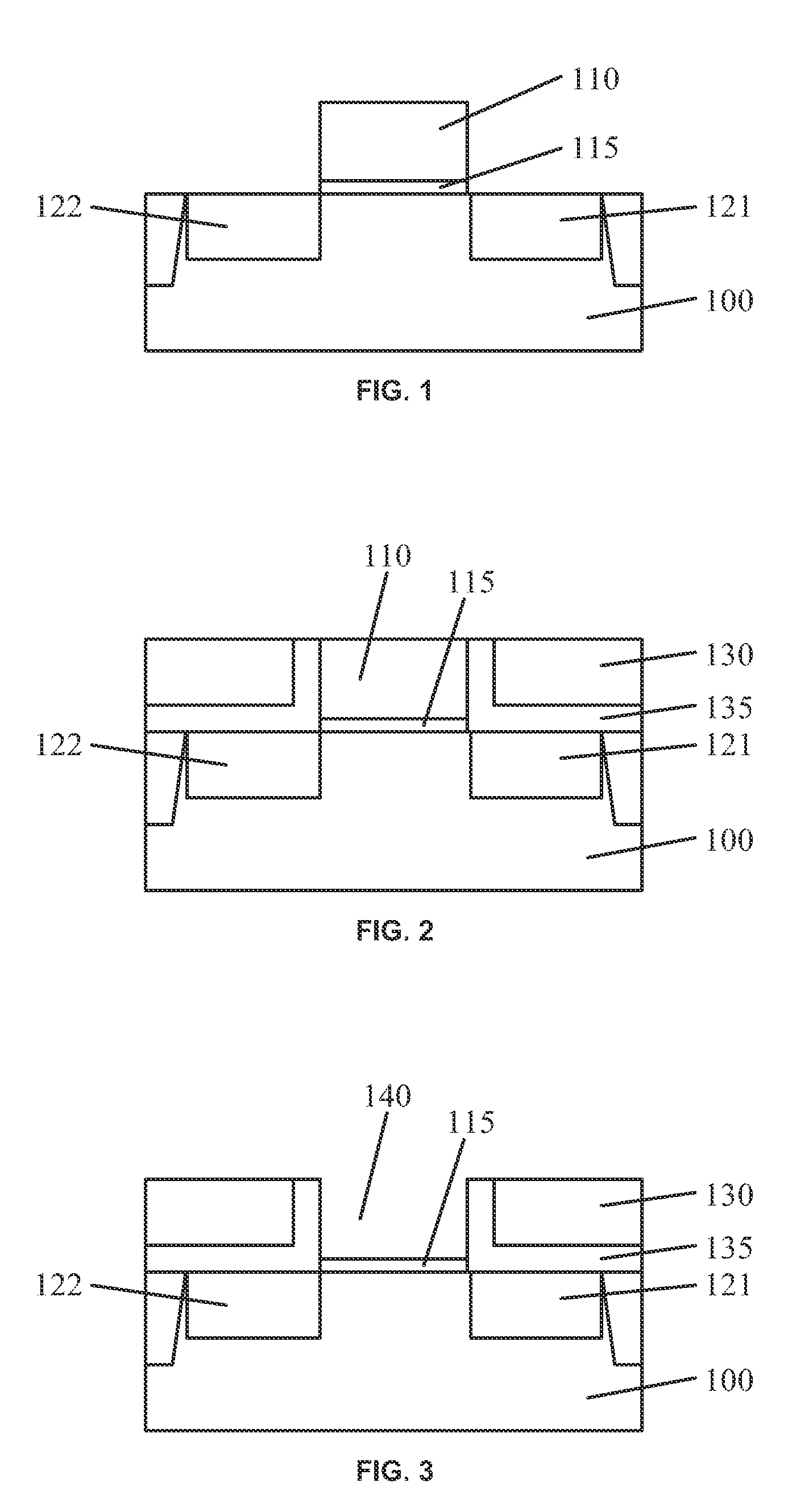
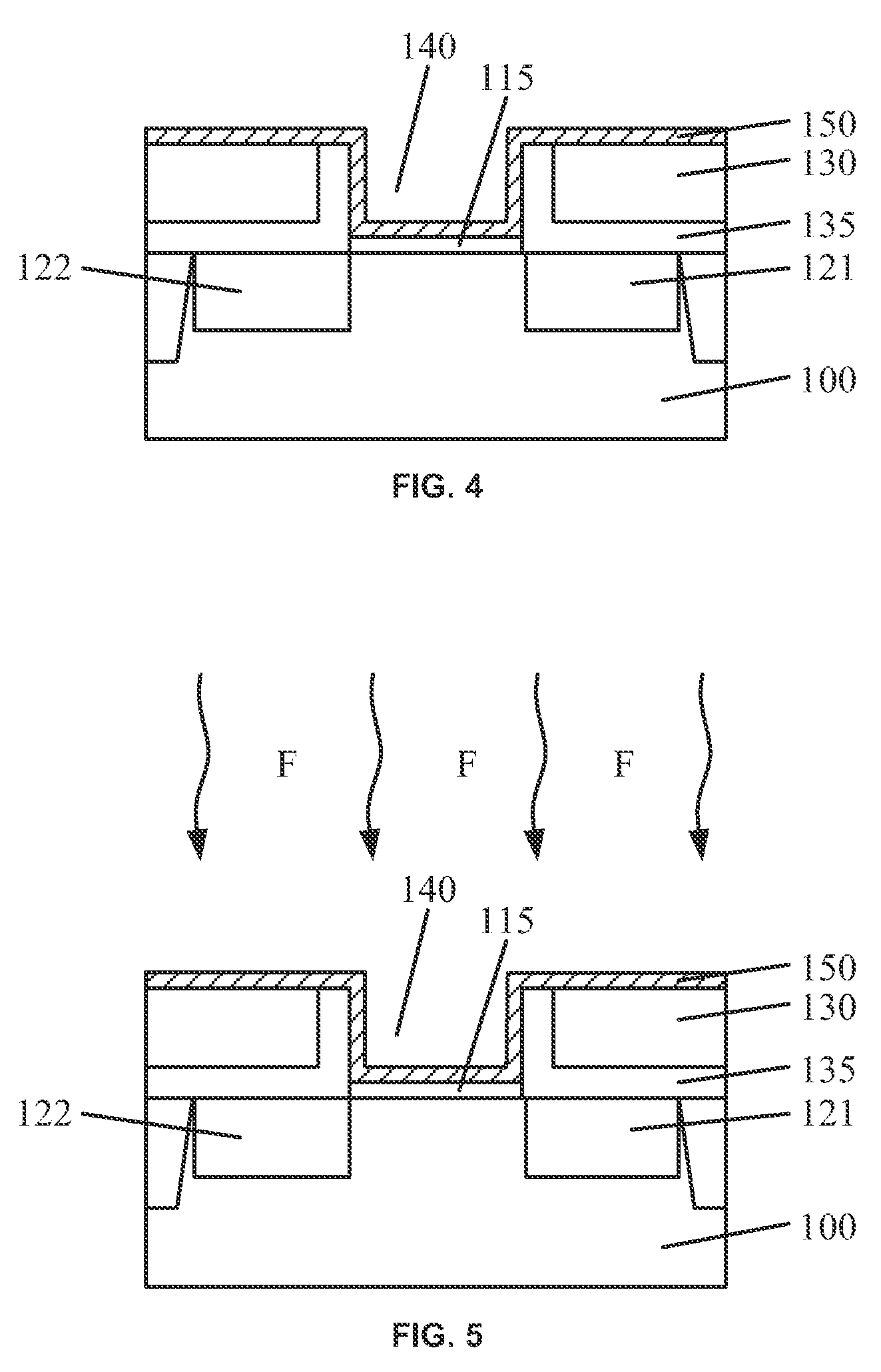
Transistor device and fabrication method
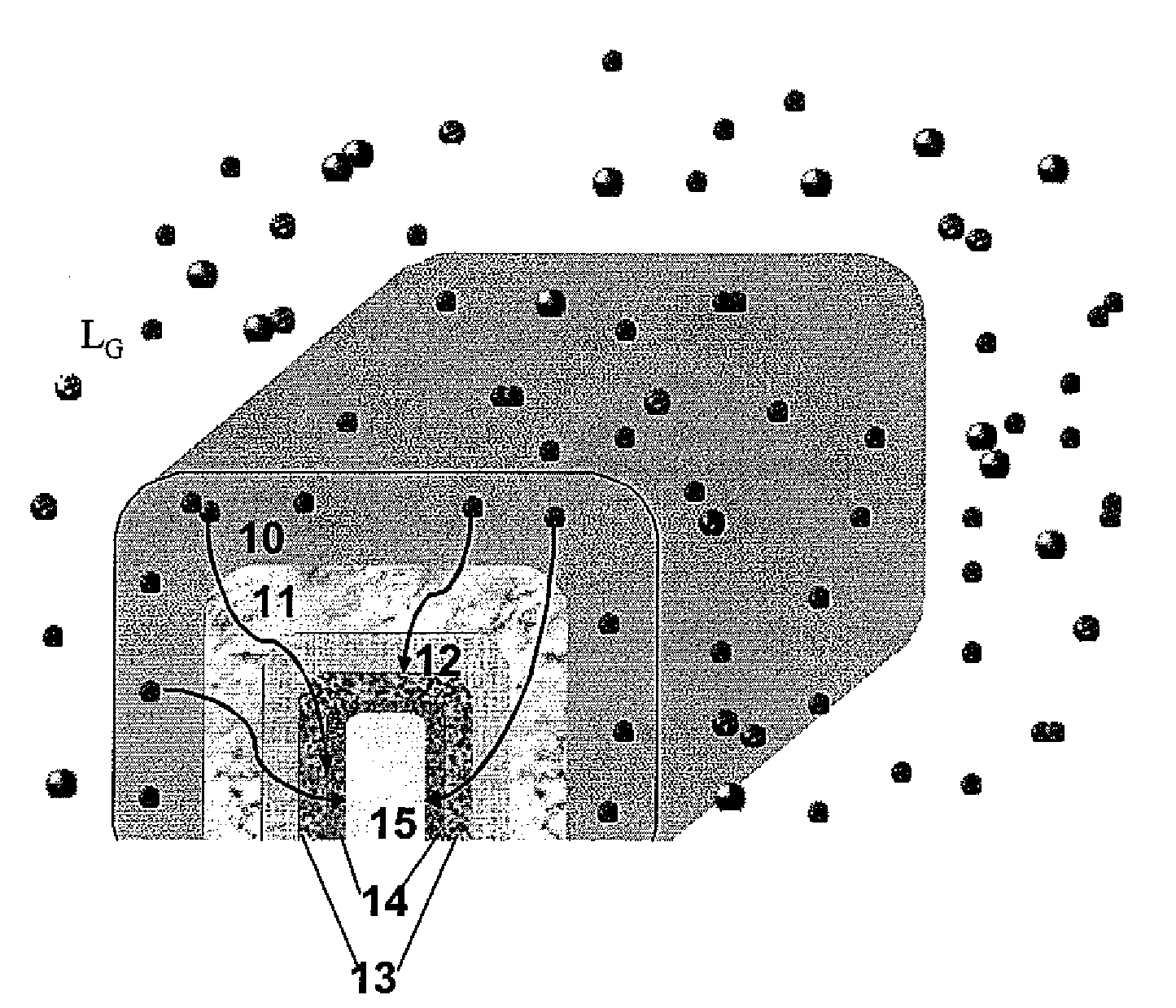
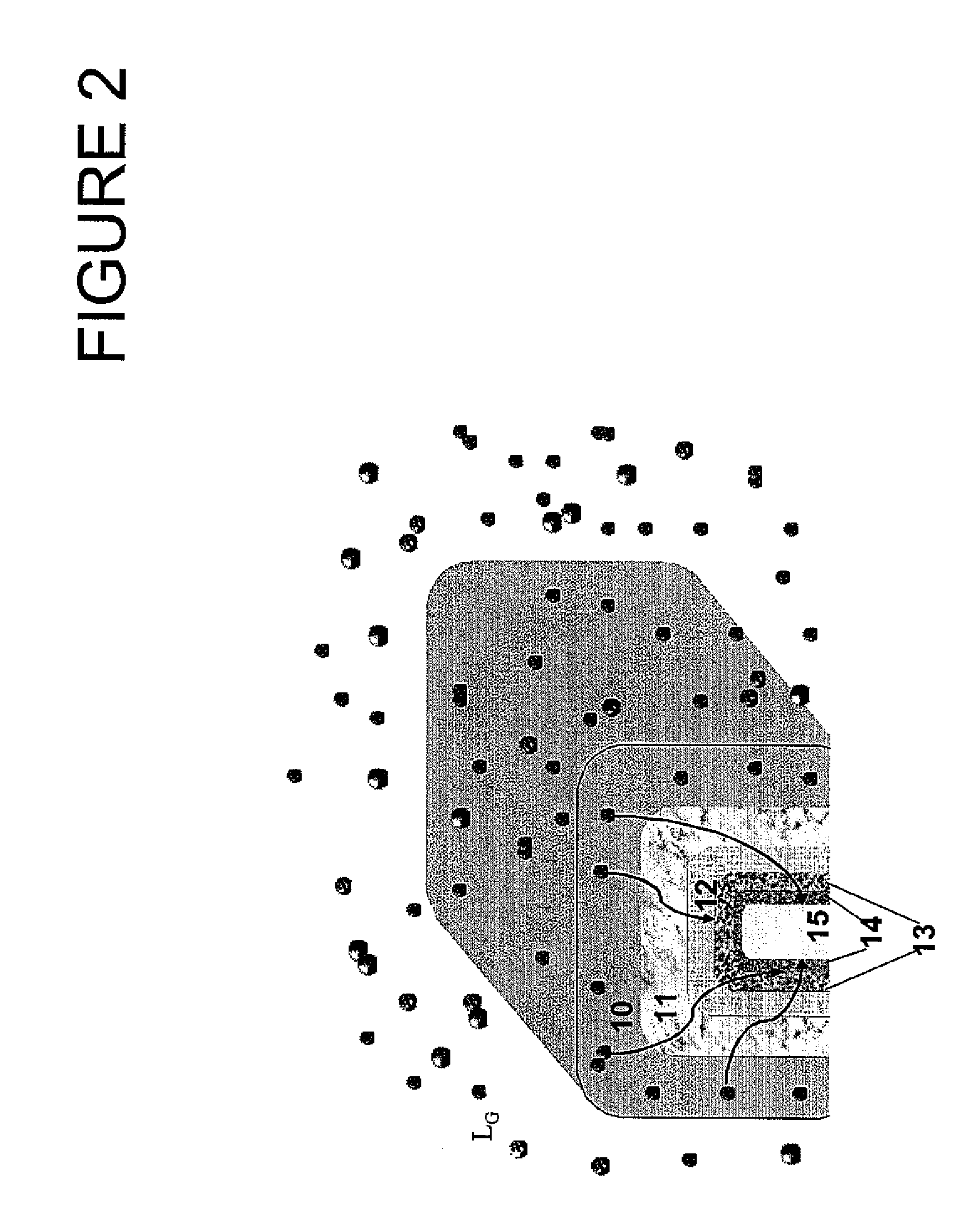
ActiveUS20140077313A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectric layerNegative-bias temperature instability
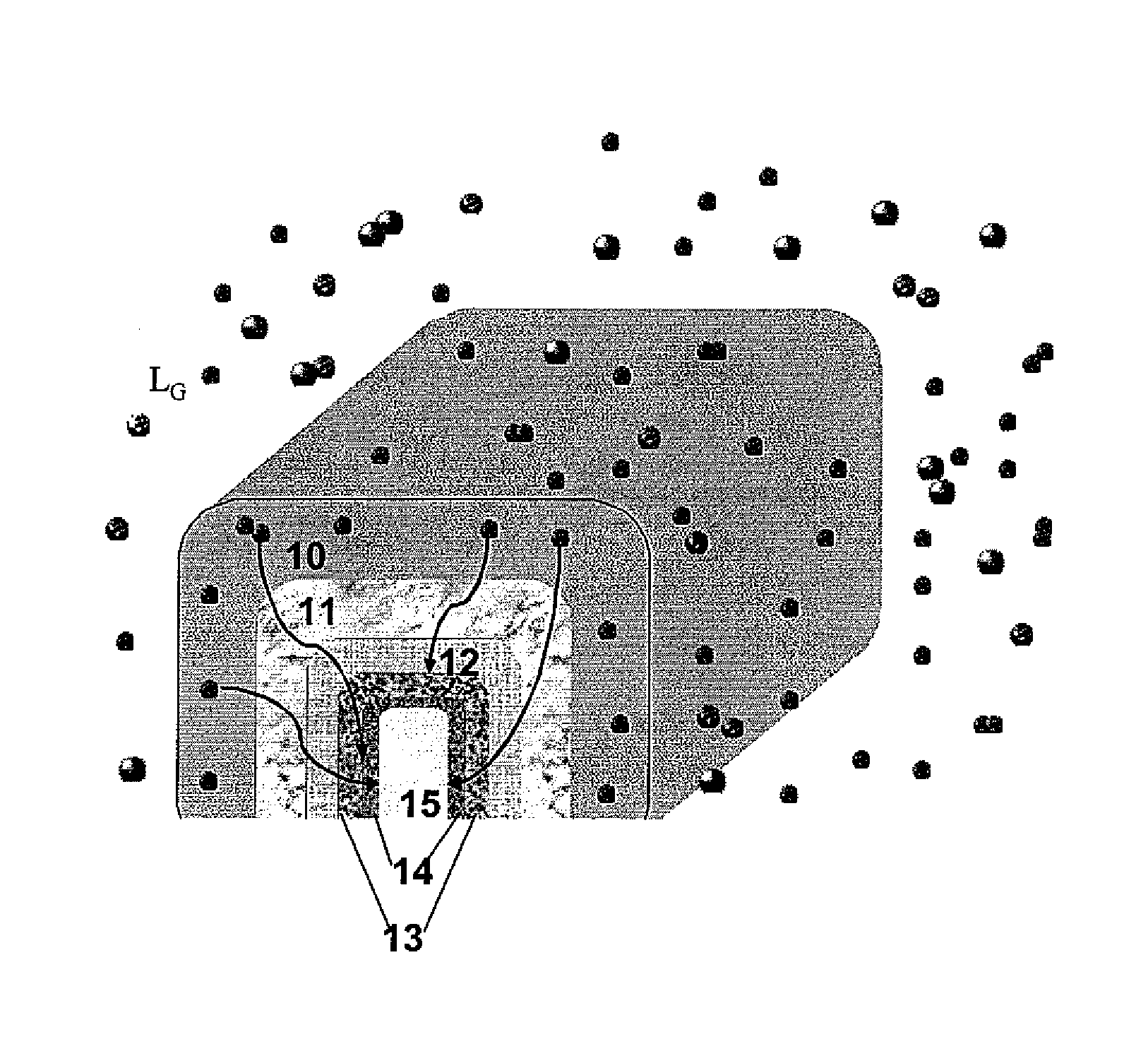
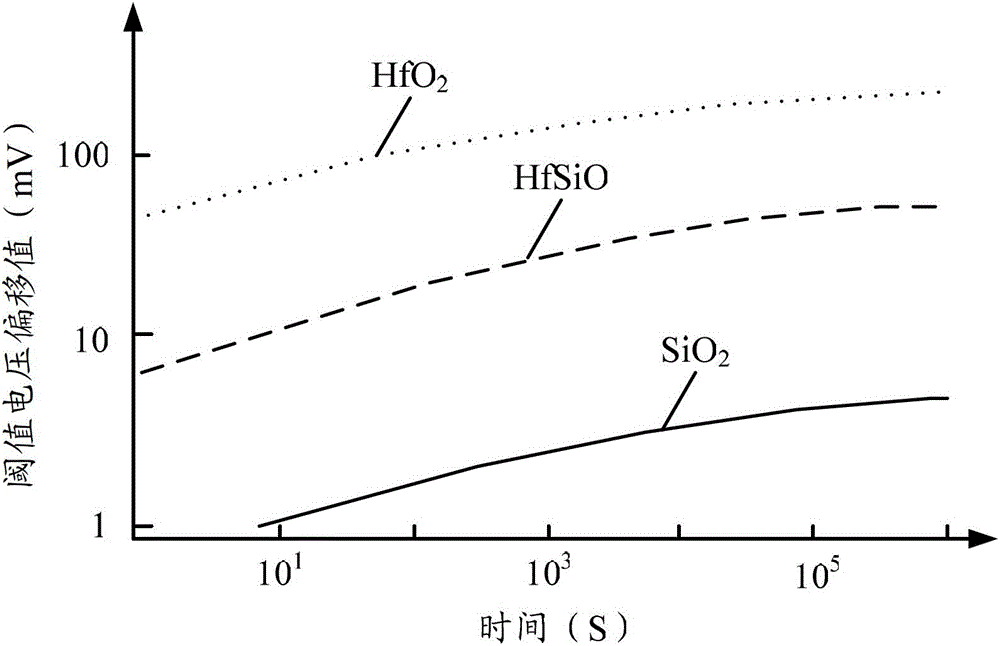
Various embodiments provide transistors and their fabrication methods. An exemplary method for forming a transistor includes removing a dummy gate to form a trench over a semiconductor substrate. A high-k dielectric layer can be conformally formed on surface of the trench and then be fluorinated to form a fluorinated high-k dielectric layer. A functional layer can be formed on the fluorinated high-k dielectric layer and a metal layer can be formed on the functional layer to fill the trench with the metal layer. Due to fluorination of the high-k dielectric layer, negative bias temperature instability of the formed transistor can be reduced and oxygen vacancies can be passivated to reduce positive bias temperature instability of the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Circuits and design structures for monitoring NBTI (negative bias temperature instability) effect and/or PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) effect
A ring oscillator has an odd number of NOR-gates greater than or equal to three, each with first and second input terminals, a voltage supply terminal, and an output terminal. The first input terminals of all the NOR-gates are interconnected, and each of the NOR-gates has its output terminal connected to the second input terminal of an immediately adjacent one of the NOR-gates. During a stress mode, a voltage supply and control block applies a stress enable signal to the interconnected first input terminals, and an increased supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. During a measurement mode, this block grounds the interconnected first input terminals, and applies a normal supply voltage to the voltage supply terminals. Also included are an analogous NAND-gate based circuit, a circuit combining the NAND- and NOR-aspects, a circuit with a ring oscillator where the inverters may be coupled directly or through inverting paths, and circuits for measuring the bias temperature instability effect in pass gates.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
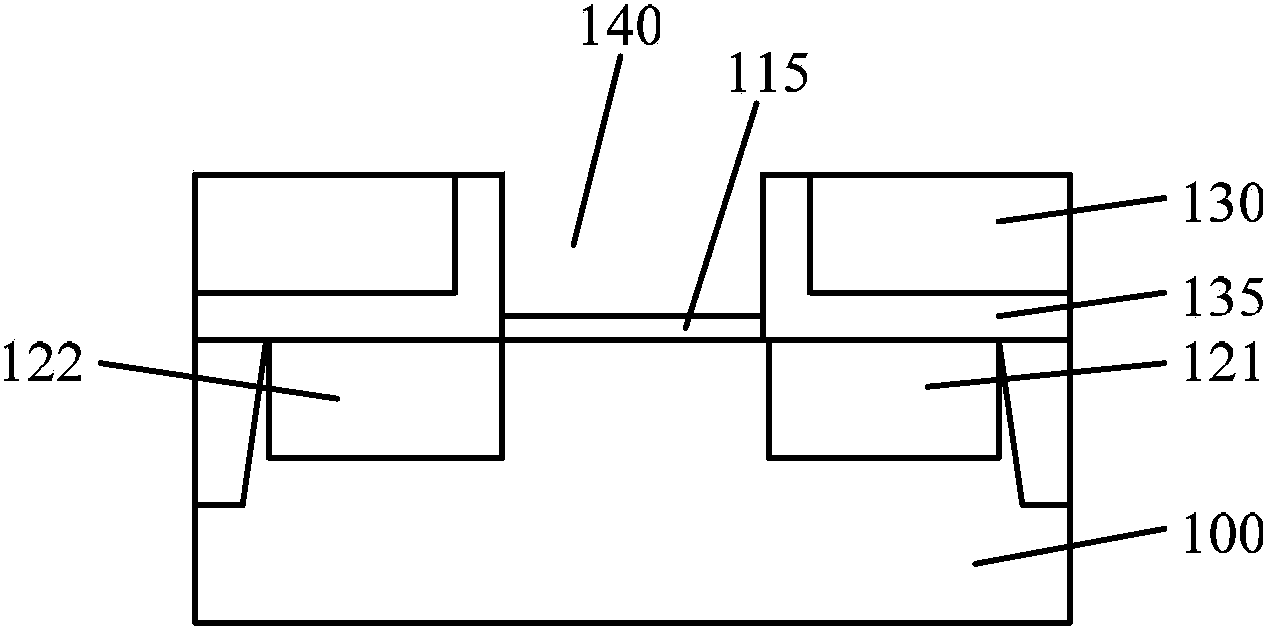
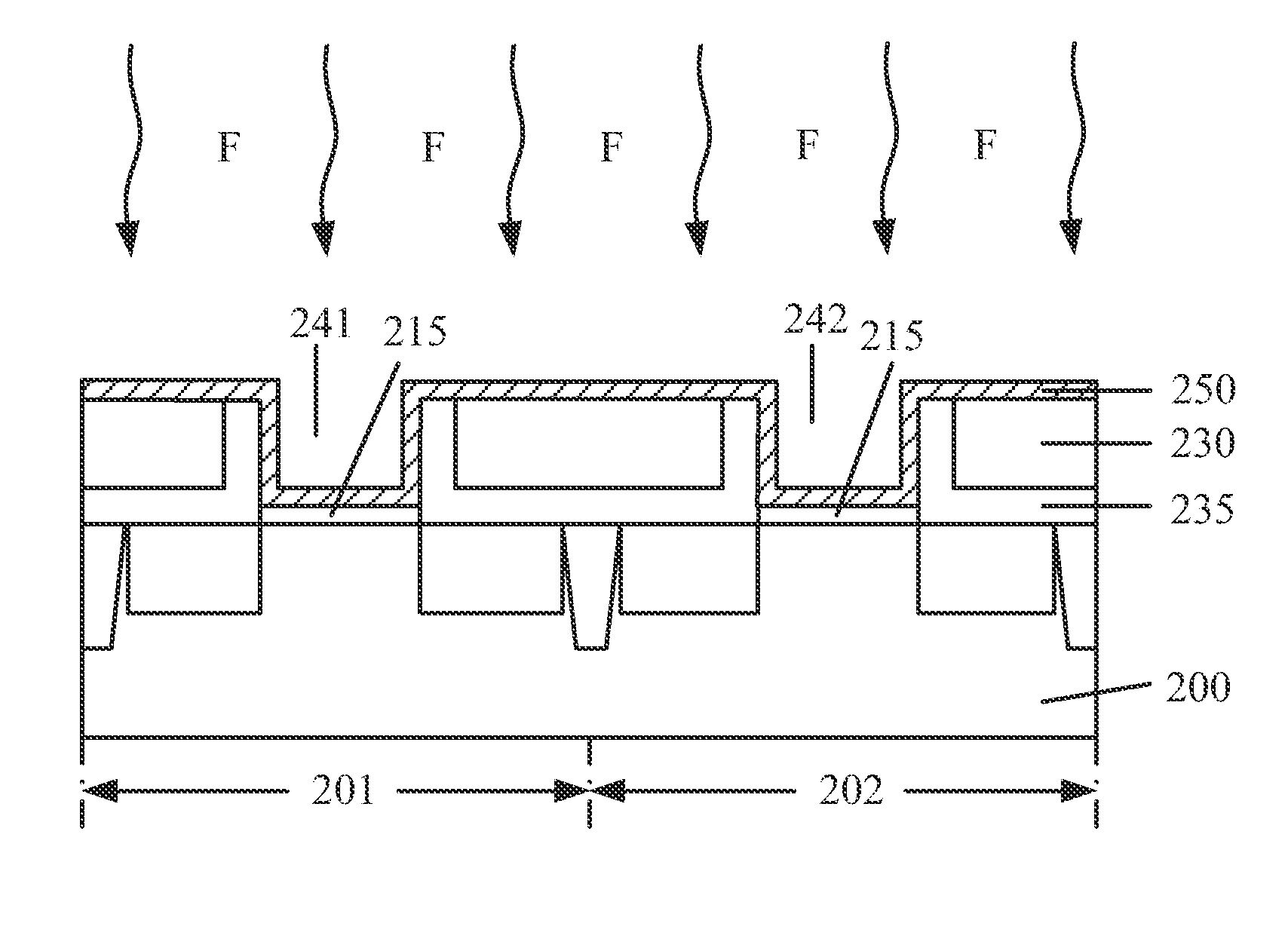
Forming method of metal gate, forming method of MOS transistor and forming method of CMOS structure
ActiveCN103681276AStrong oxidation abilityReduced negative bias temperature instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBond energyOxygen vacancy
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
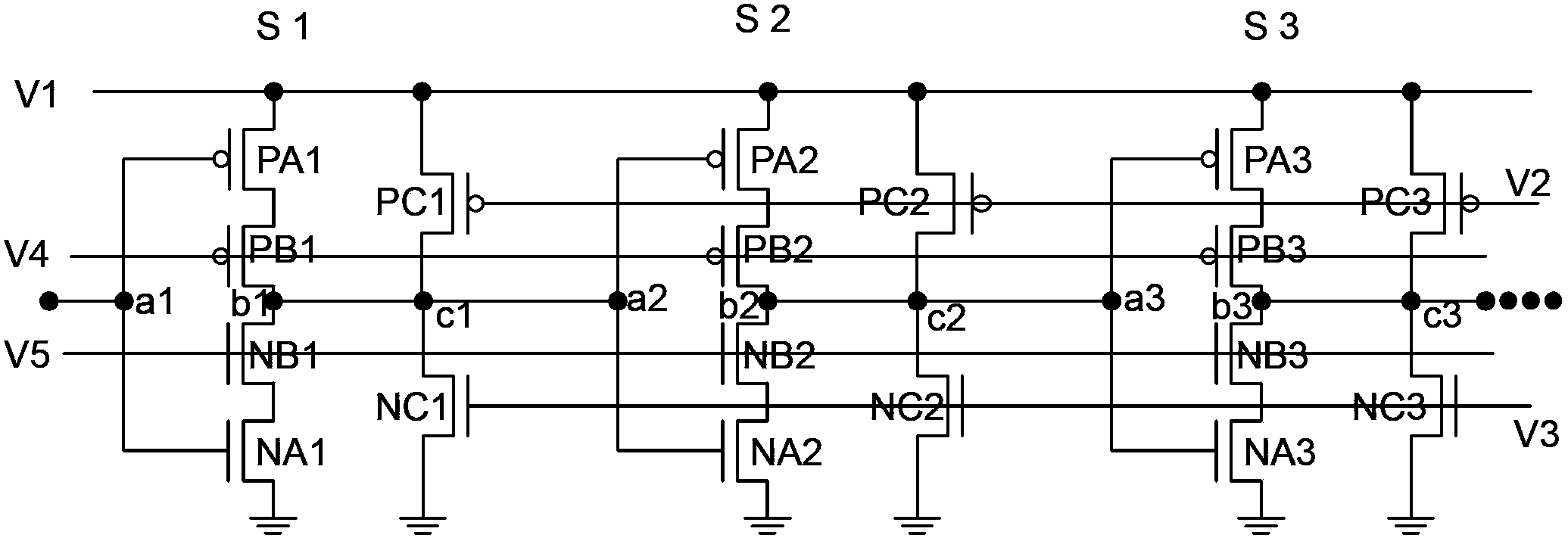
Multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and test method thereof
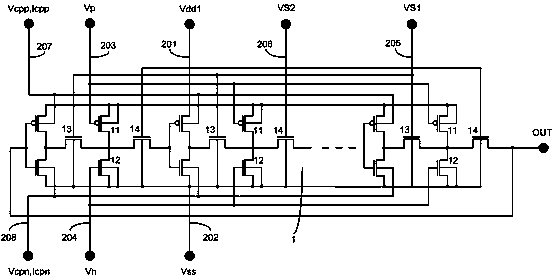
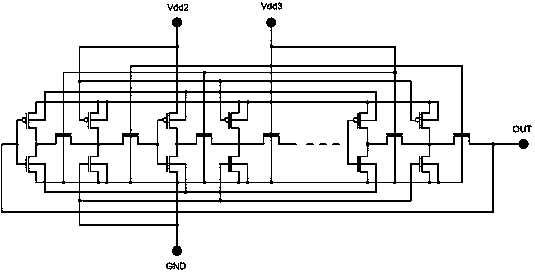
The invention belongs to a integrated circuit reliability test technology field and especially relates to a multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and a test method thereof. A core part of the test circuit takes an annular oscillator as a basis. Several auxiliary transistors, switch transistors and control terminals are added. By using the circuit and the method of the invention, a negative bias temperature instability, a positive bias temperature instability, hot hole injection or hot electron injection stress can be applied to pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in a ring vibration inverter respectively; a ring oscillator is in a normal oscillation and stress oscillation state; the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs of the inverter in the ring oscillator is in a measuring state of a charge pump. The degradation of the MOSFETs in the ring vibration inverter can be shown through changes of a ring oscillator oscillation frequency after the stress and can be shown through the changes of a CP current (Icpp or Icpn) of the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in the ring oscillator.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
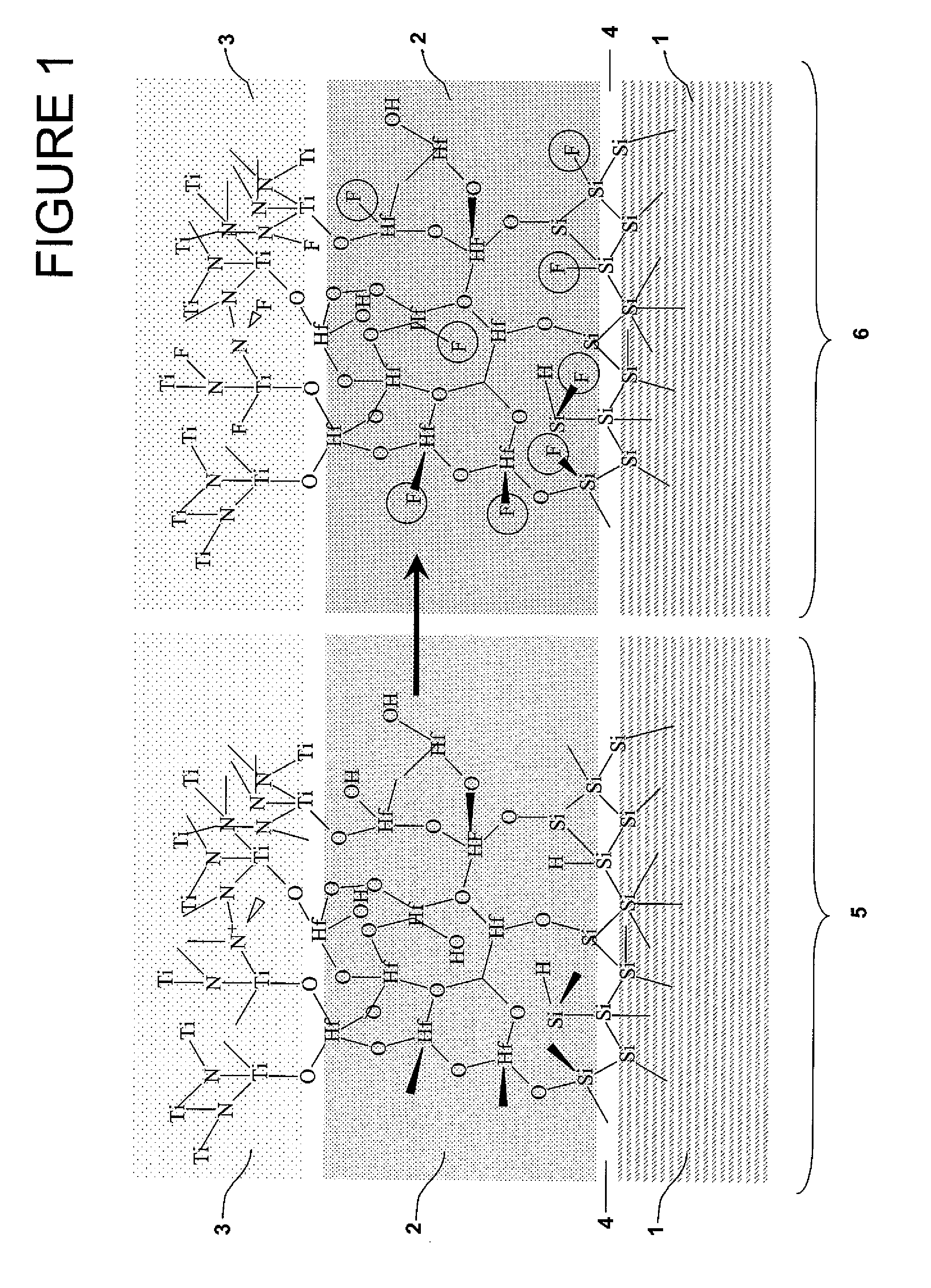
Use of f-based gate etch to passivate the high-k/metal gate stack for deep submicron transistor technologies
ActiveUS20080164539A1Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricDriving current
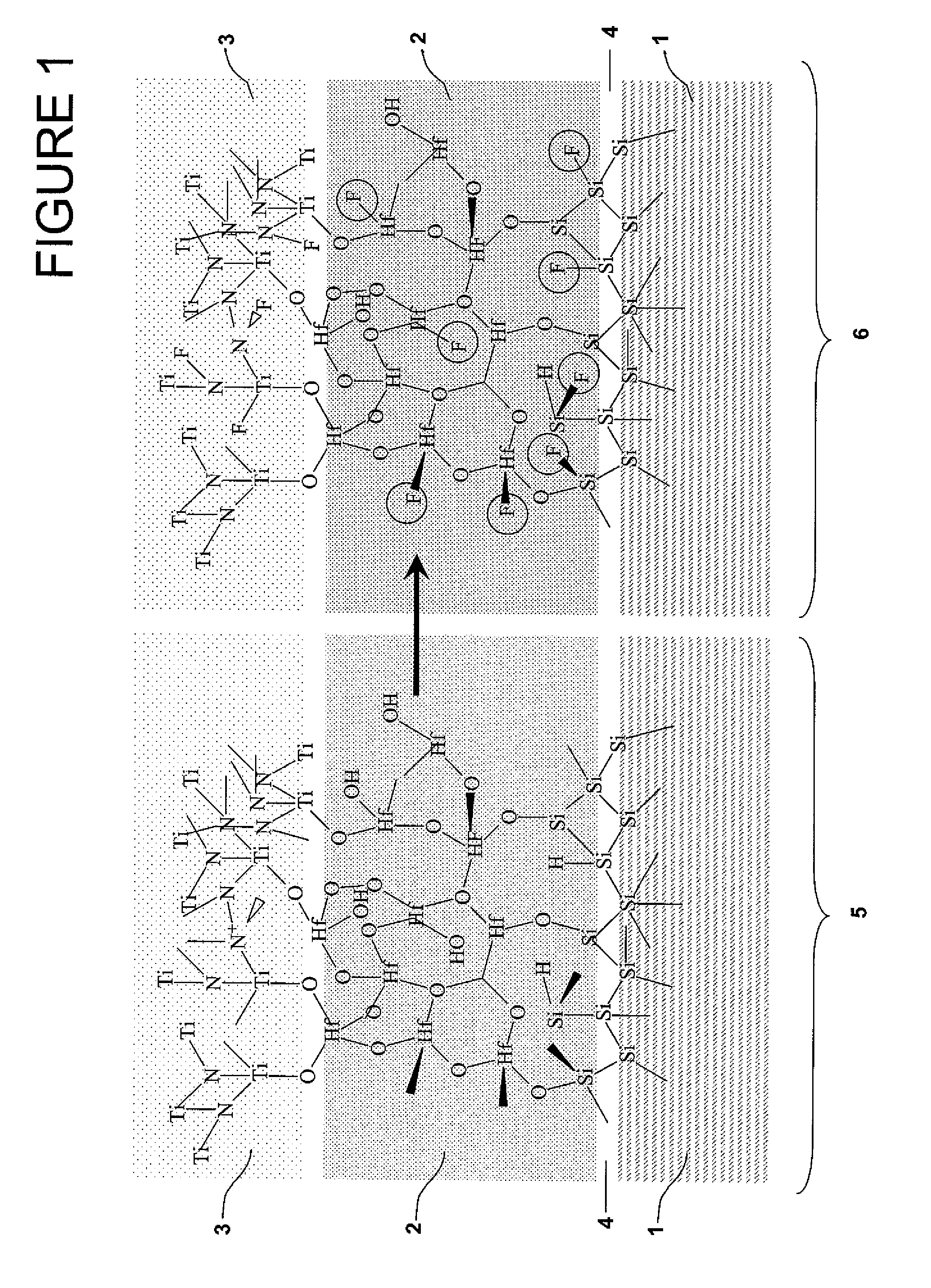
A new, effective and cost-efficient method of introducing Fluorine into Hf-based dielectric gate stacks of planar or multi-gate devices (MuGFET), resulting in a significant improvement in both Negative and Positive Bias Temperature Instabilities (NBTI and PBTI) is provided. The new method uses an SF6 based metal gate etch chemistry for the introduction of Fluorine, which after a thermal budget within the standard process flow, results in excellent F passivation of the interfaces. A key advantage of the method is that it uses the metal gate etch for F introduction, requiring no extra implantations or treatments. In addition to the significant BTI improvement with the novel method, a better Vth control and increased drive current on MuGFET devices is achieved.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Use of F-based gate etch to passivate the high-k/metal gate stack for deep submicron transistor technologies
ActiveUS8319295B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricDriving current
A new, effective and cost-efficient method of introducing Fluorine into Hf-based dielectric gate stacks of planar or multi-gate devices (MuGFET), resulting in a significant improvement in both Negative and Positive Bias Temperature Instabilities (NBTI and PBTI) is provided. The new method uses an SF6 based metal gate etch chemistry for the introduction of Fluorine, which after a thermal budget within the standard process flow, results in excellent F passivation of the interfaces. A key advantage of the method is that it uses the metal gate etch for F introduction, requiring no extra implantations or treatments. In addition to the significant BTI improvement with the novel method, a better Vth control and increased drive current on MuGFET devices is achieved.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
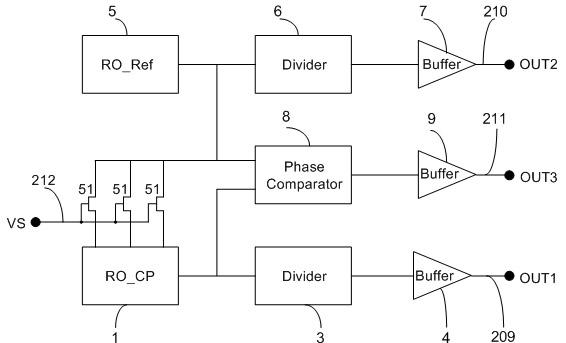
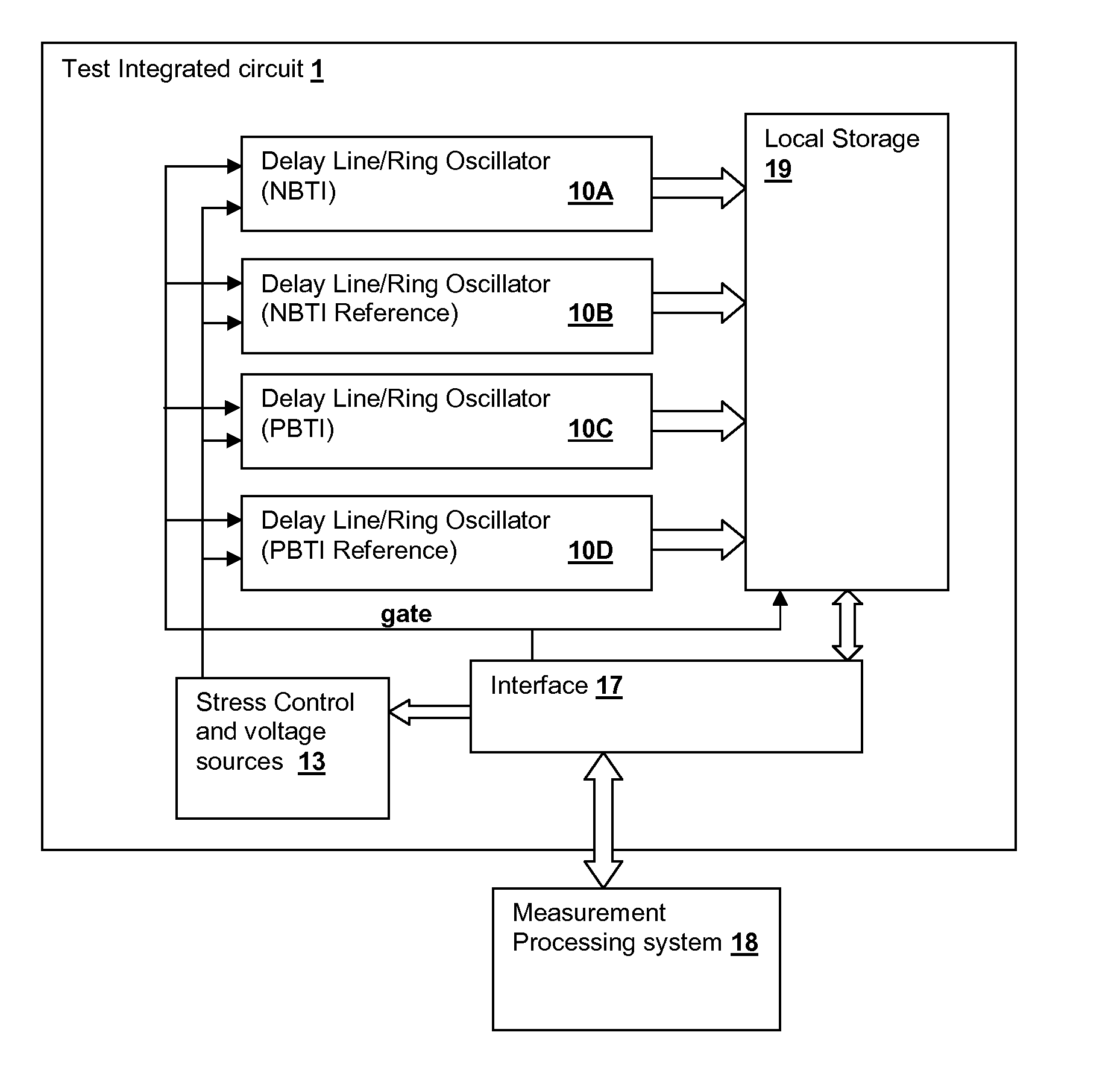
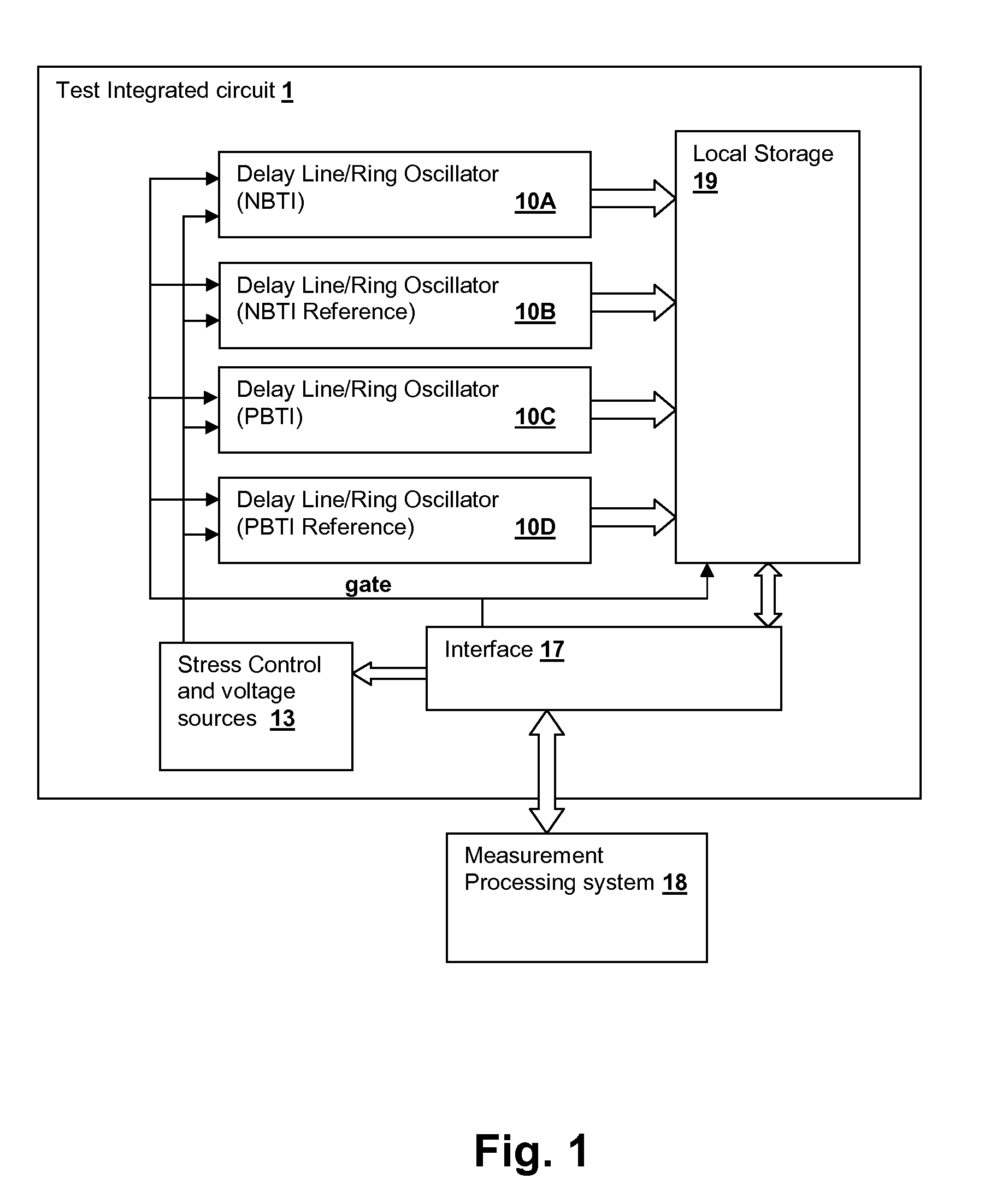
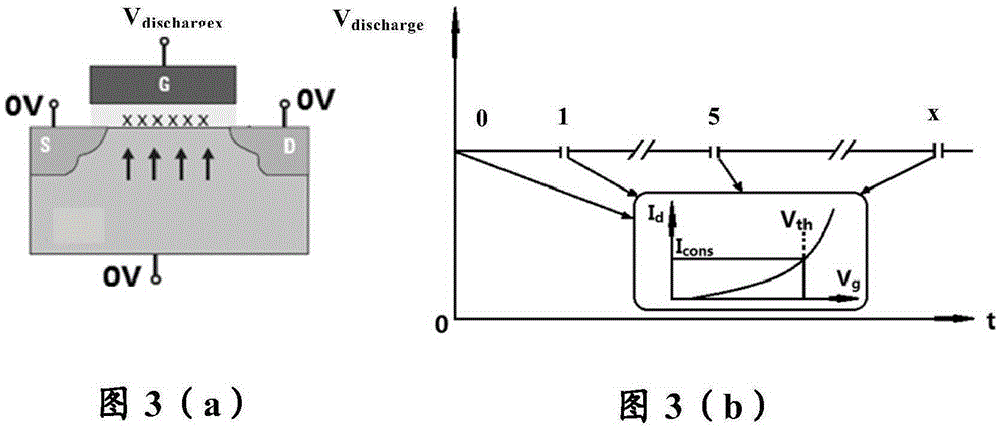
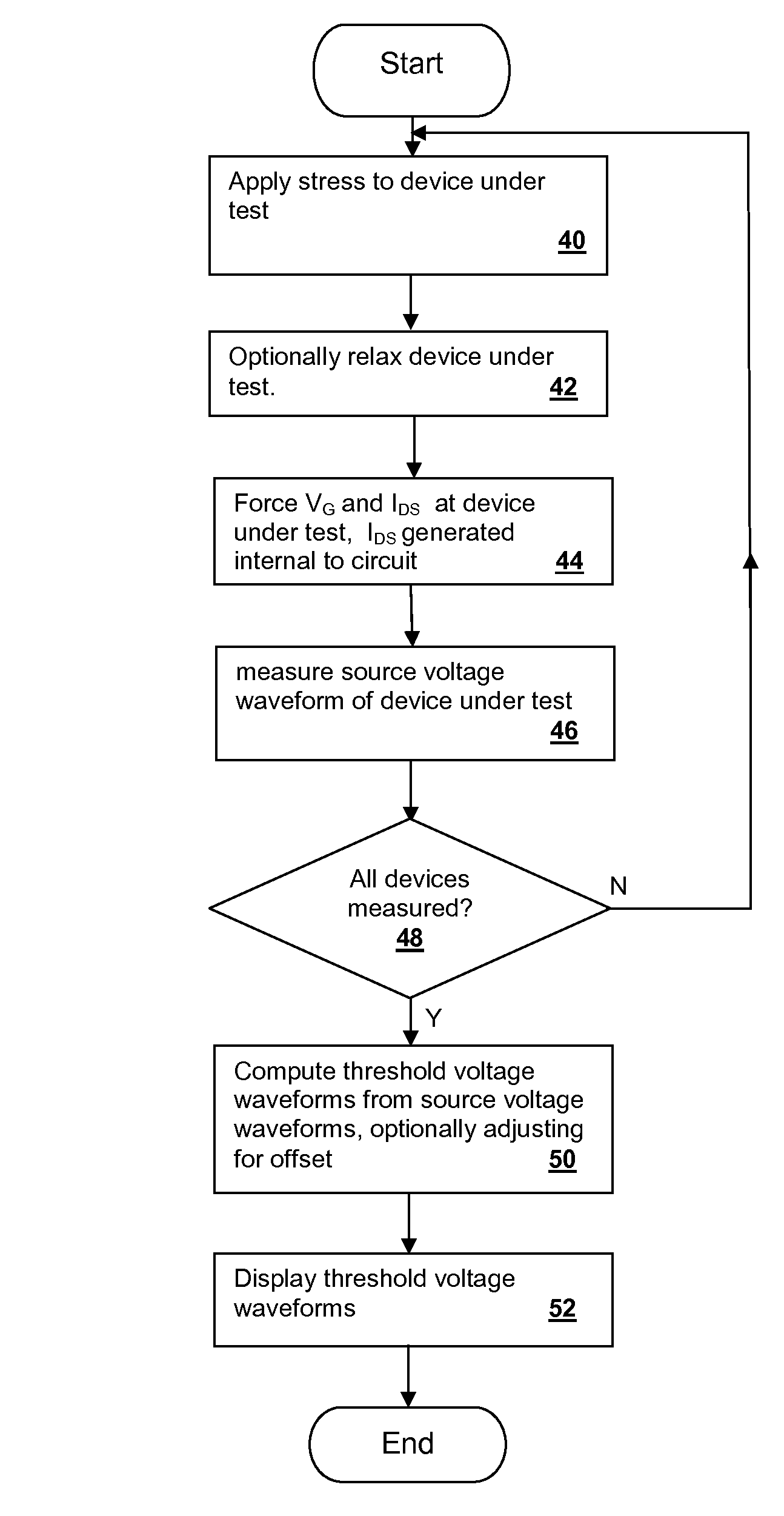
Delay-Based Bias Temperature Instability Recovery Measurements for Characterizing Stress Degradation and Recovery
InactiveUS20090319202A1Improve dynamic rangeHigh resolutionForce measurementWork measurementNanosecondFrequency measurements
A method, test circuit and test system provide measurements to accurately characterize threshold voltage changes due to negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and positive bias temperature instability (PBTI). Both the bias temperature instability recovery profile and / or the bias temperature shifts due to rapid repetitions of stress application can be studied. In order to provide accurate measurements when stresses are applied at intervals on the order of tens of nanoseconds while avoiding unwanted recovery, and / or to achieve recovery profile sampling resolutions in the nanosecond range, multiple delay or ring oscillator frequency measurements are made using a delay line that is formed from delay elements that have delay variation substantially caused only by NBTI or PBTI effects. Devices in the delay elements are stressed, and then the delay line / ring oscillator is operated to measure a threshold voltage change for one or more measurement periods on the order of nanoseconds.
Owner:IBM CORP
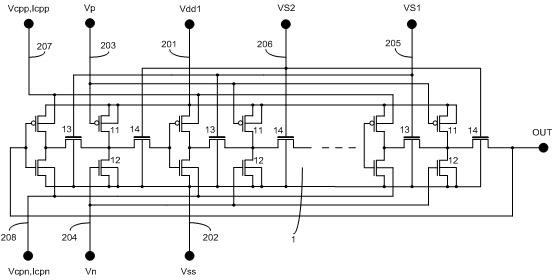
Circuit and method for testing reliability of integrated circuit
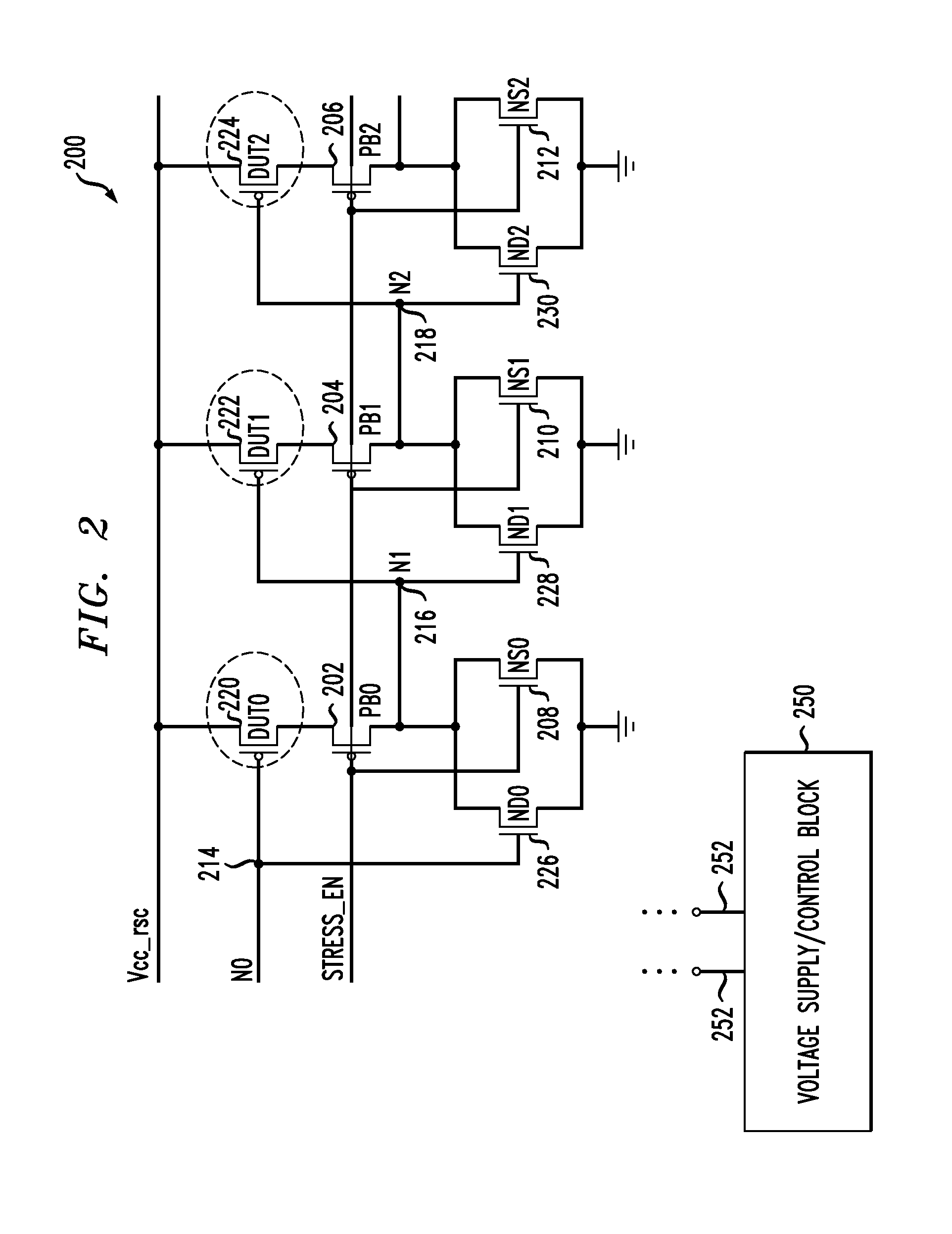
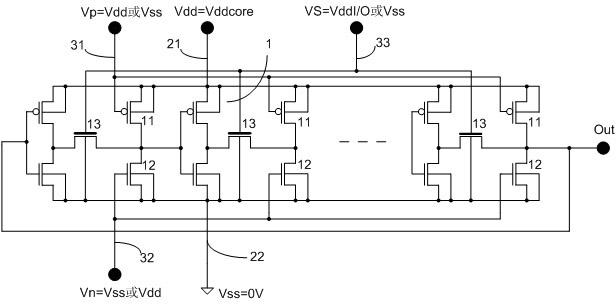
ActiveCN102590735AMeasuring and differentiating degradationElectrical testingCircuit reliabilityHemt circuits
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit test, and in particular relates to a circuit and a method for testing reliability of an integrated circuit. According to the core circuit of the testing circuit, auxiliary p-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (pMOSFETs) and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (nMOSFETs) are connected between every two stages of inverters of a ring oscillator (RO) and between a high level Vdd and low potential Vss, and a switch transistor is plugged in an input and output connecting line. By controlling the grid voltages of the auxiliary transistors and the switch transistor, normal oscillation of the RO can be realized in the core circuit, dynamic stress is applied to complementary metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (CMOSFETs) of the RO, and negative bias temperature instability (NBTI), positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) and hot carrier injection (HCI) stresses are respectively applied to the pMOSFETs or the nMOSFETs of the RO. The testing circuit has the functions of: degradation measurement of the pMOSFETs in the RO under the NBTI stress, degradation measurement of the nMOSFETs under the PBTI stress, degradation measurement of the pMOSFETs under the HCI stress, degradation measurement of the nMOSFETs under the HCI stress, and comparison with degradation measurement of the CMOSFETs under the dynamic stress.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
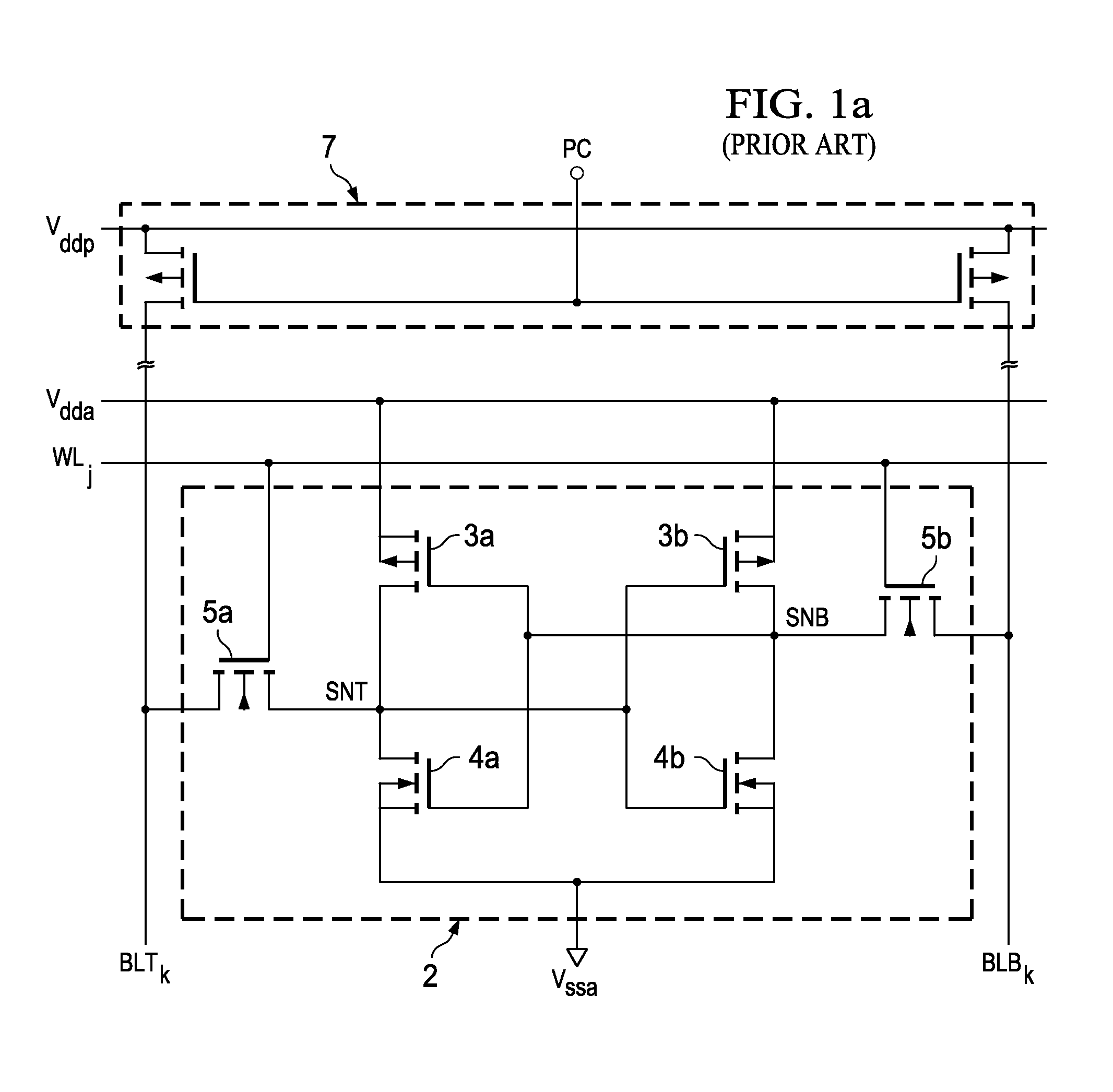
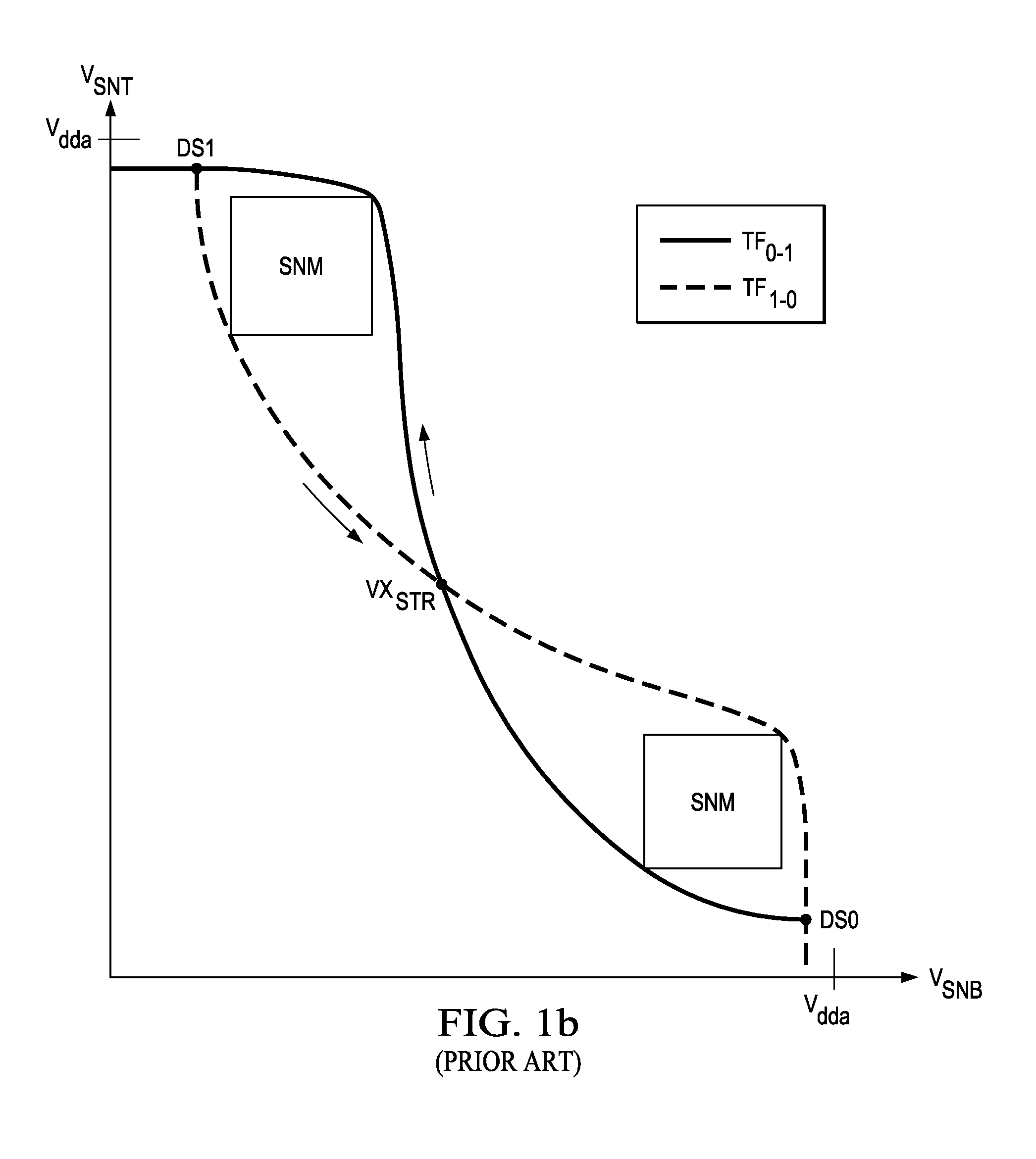
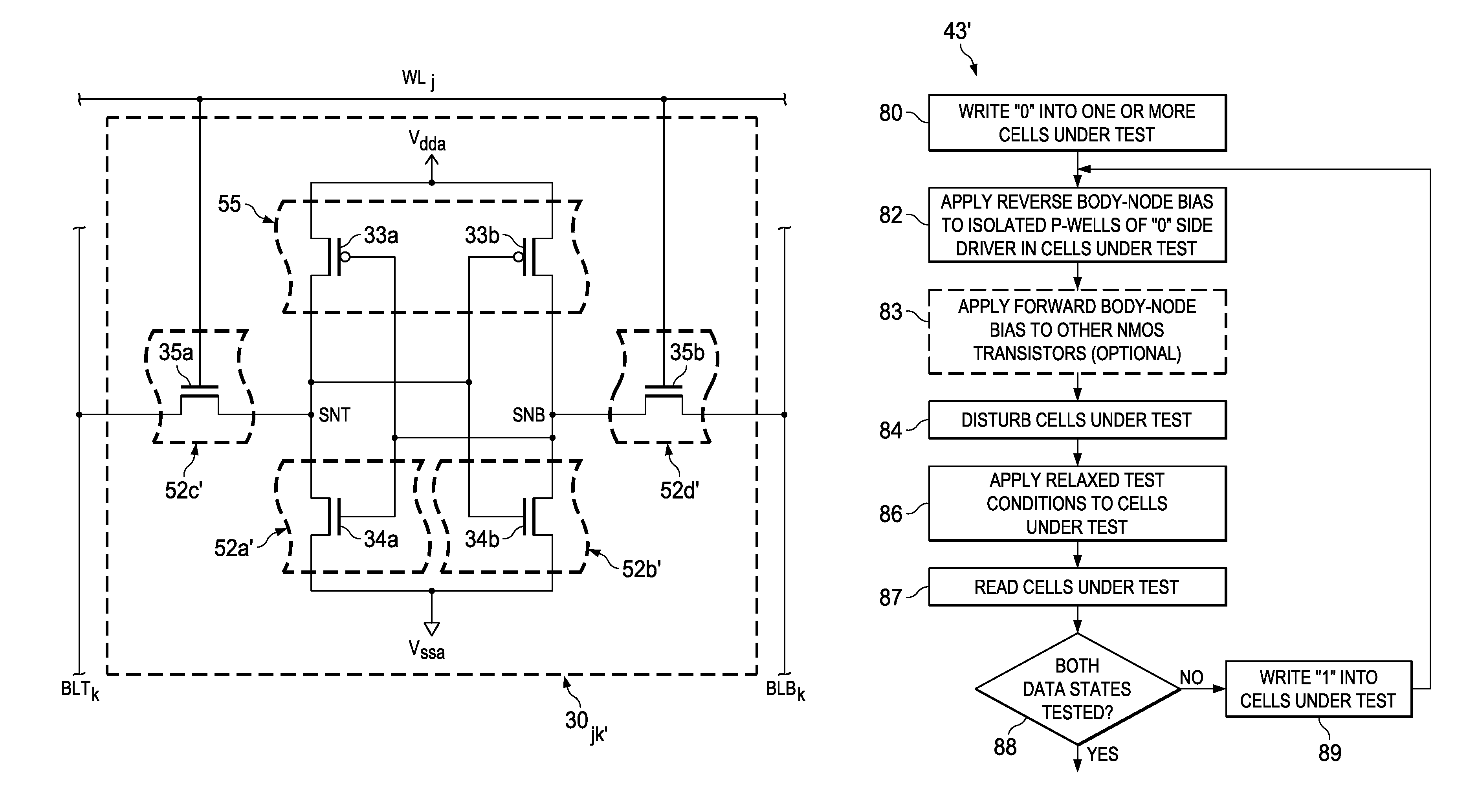
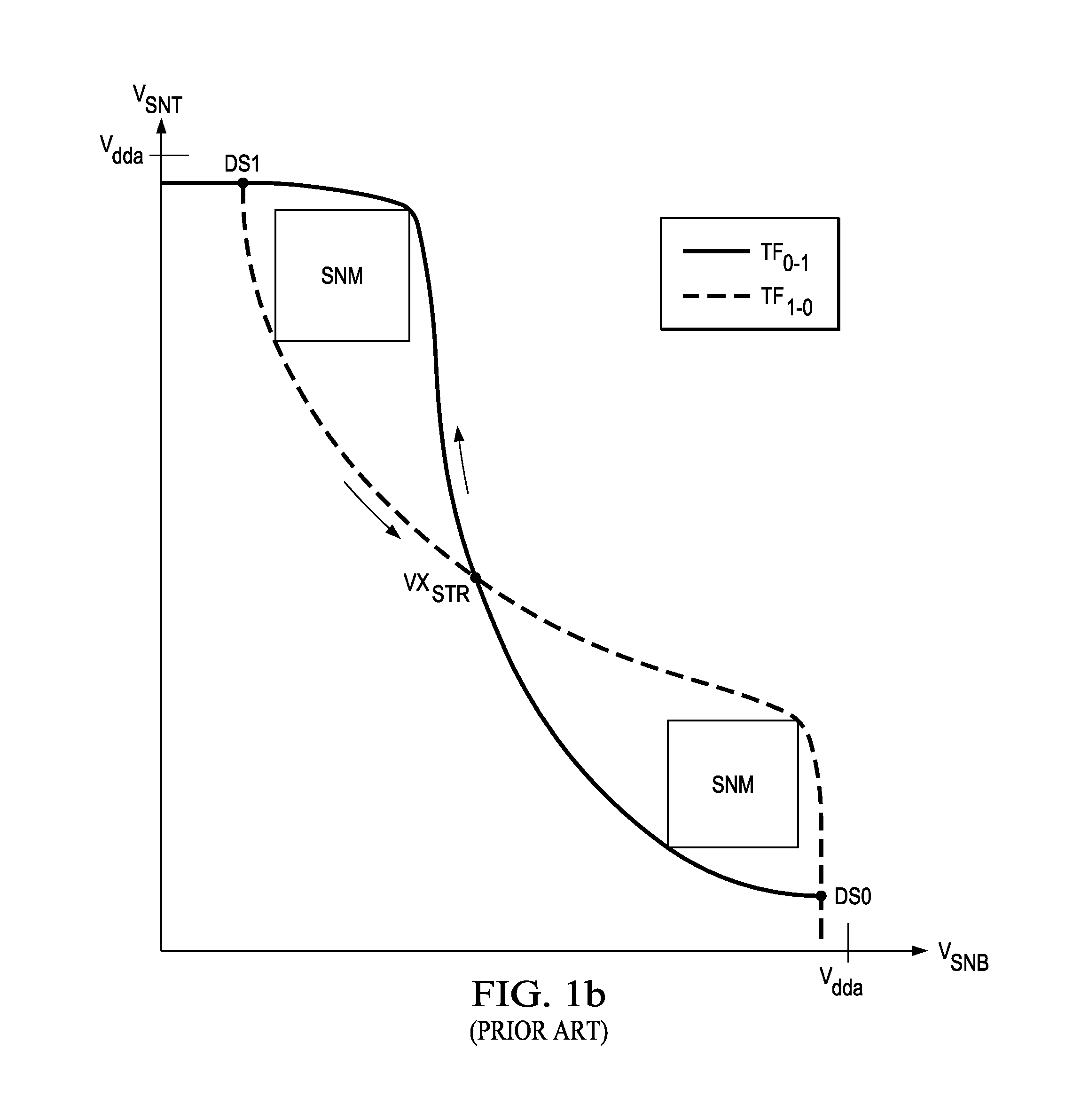
Method of Screening Static Random Access Memory Cells for Positive Bias Temperature Instability
ActiveUS20130058177A1Efficient and accurate identificationYield minimizationDigital storageStatic random-access memorySemiconductor materials
A method of screening complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor CMOS integrated circuits, such as integrated circuits including CMOS static random access memory (SRAM) cells, for n-channel transistors susceptible to transistor characteristic shifts over operating time. For the example of SRAM cells formed of cross-coupled CMOS inverters, static noise margin and writeability (Vtrip) screens are provided. Each of the n-channel transistors in the CMOS SRAM cells are formed within p-wells that are isolated from p-type semiconductor material in peripheral circuitry of the memory and other functions in the integrated circuit. Forward and reverse body node bias voltages are applied to the isolated p-wells of the SRAM cells under test to determine whether such operations as read disturb, or write cycles, disrupt the cells under such bias. Cells that are vulnerable to threshold voltage shift over time can thus be identified.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Device and method thereof for testing bias temperature instability degrading of MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device
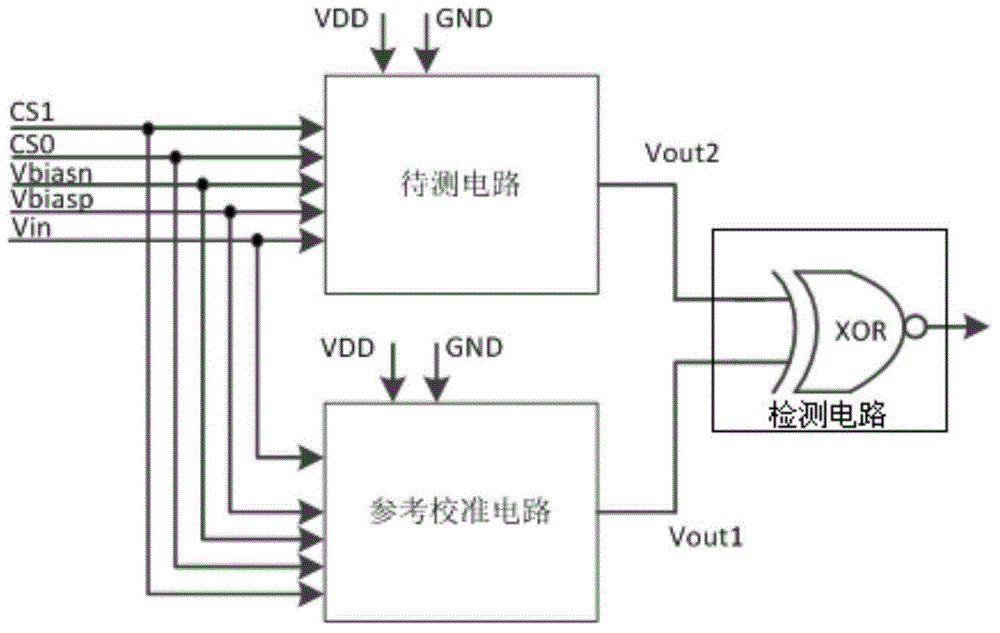
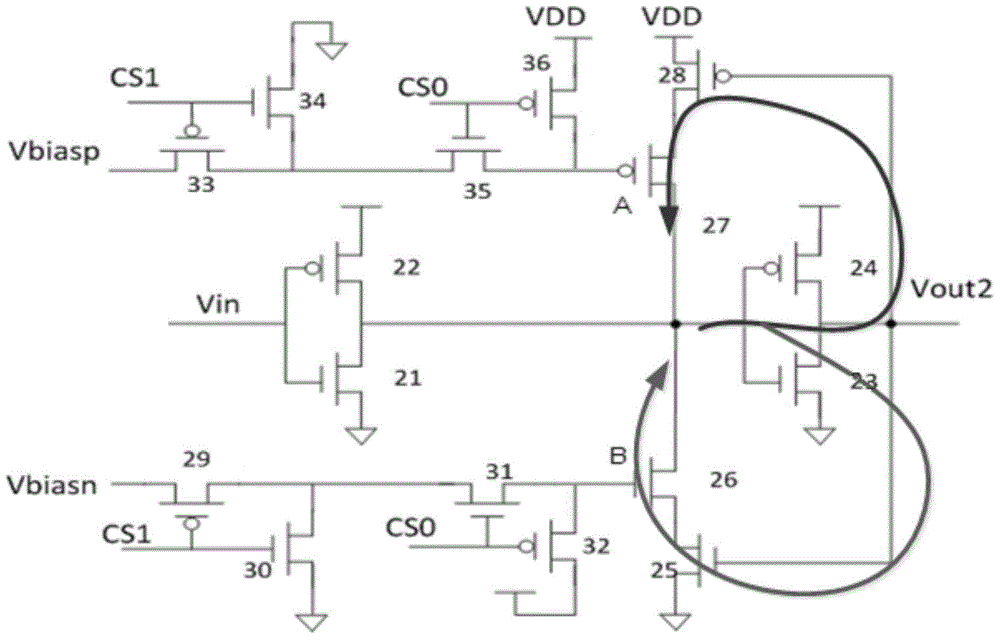
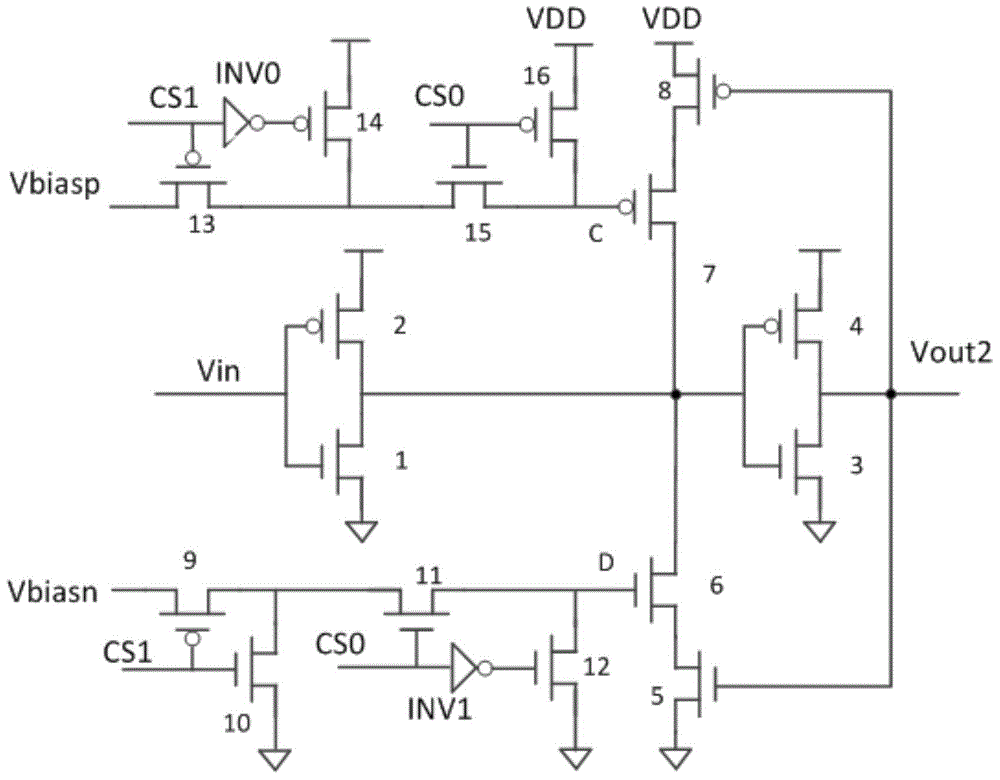
ActiveCN104483611ASimple structureImprove test accuracyIndividual semiconductor device testingHysteresisSchmitt trigger
The invention discloses a device for testing bias temperature instability degrading of a MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) device. The device comprises a to-be-tested circuit, a reference calibration circuit and a detection circuit, wherein the output ends of the to-be-tested circuit and the reference calibration circuit are simultaneously connected with the detection circuit, a first feedback control assembly and a first Schmitt trigger are arranged in the to-be-tested circuit, the first feedback control assembly is used for applying stress on to-be-tested feedback loop components in the first Schmitt trigger so as to generate degrading, the to-be-tested circuit is used for outputting degraded actual hysteresis voltage signals, the reference calibration circuit is used for outputting standard hysteresis voltage signals, and the detection circuit is used for comparing and measuring the difference between the actual hysteresis voltage signals and the reference standard hysteresis voltage signals, so as to test the degrading degree of the feedback loop components. The device has the characteristics that the NBTI (negative bias temperature instability) and PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) properties can be tested, the circuit structure is simple, and the testing accuracy is high. The invention discloses a method for testing the bias temperature instability degrading of the MOS device.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
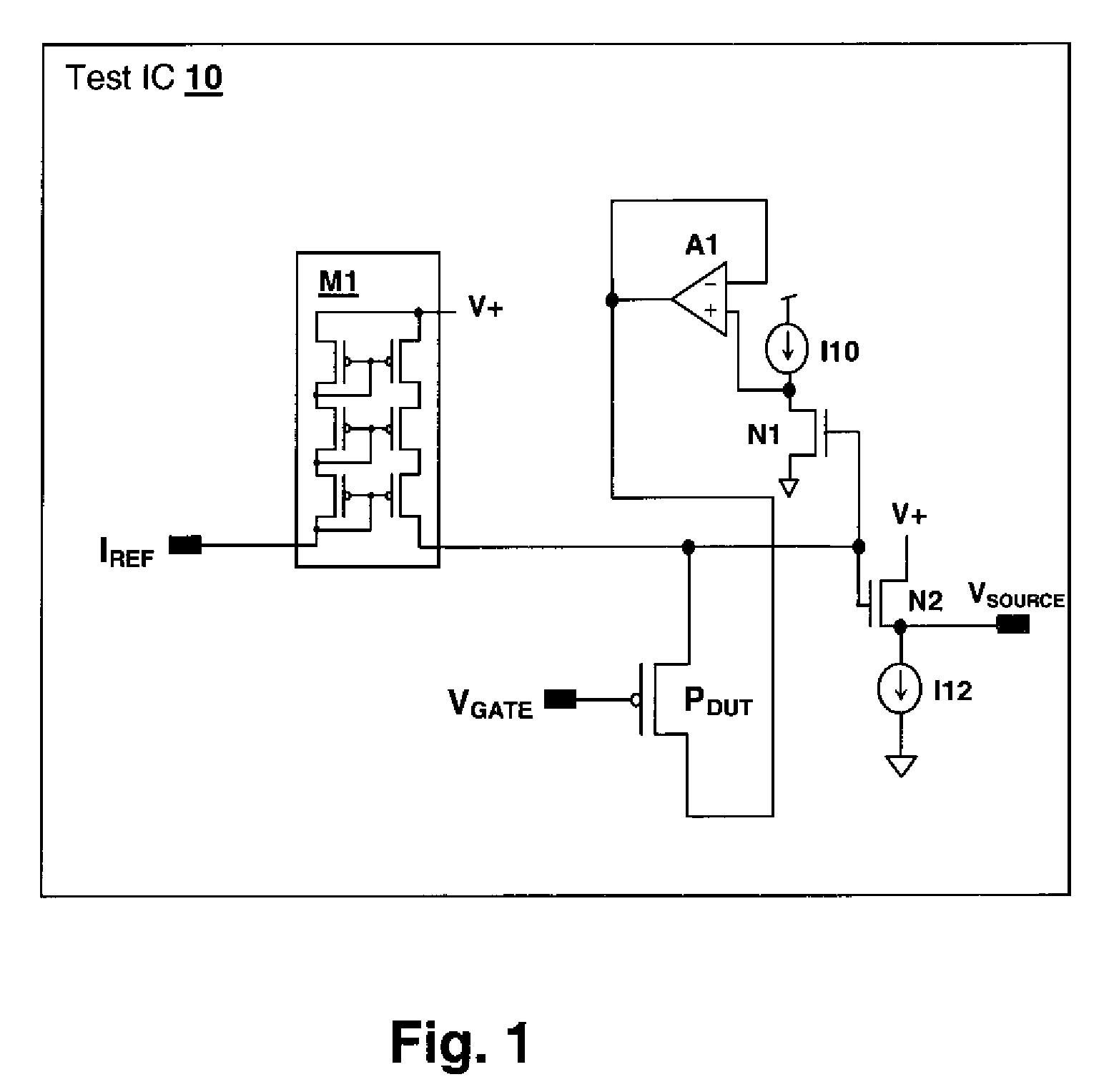
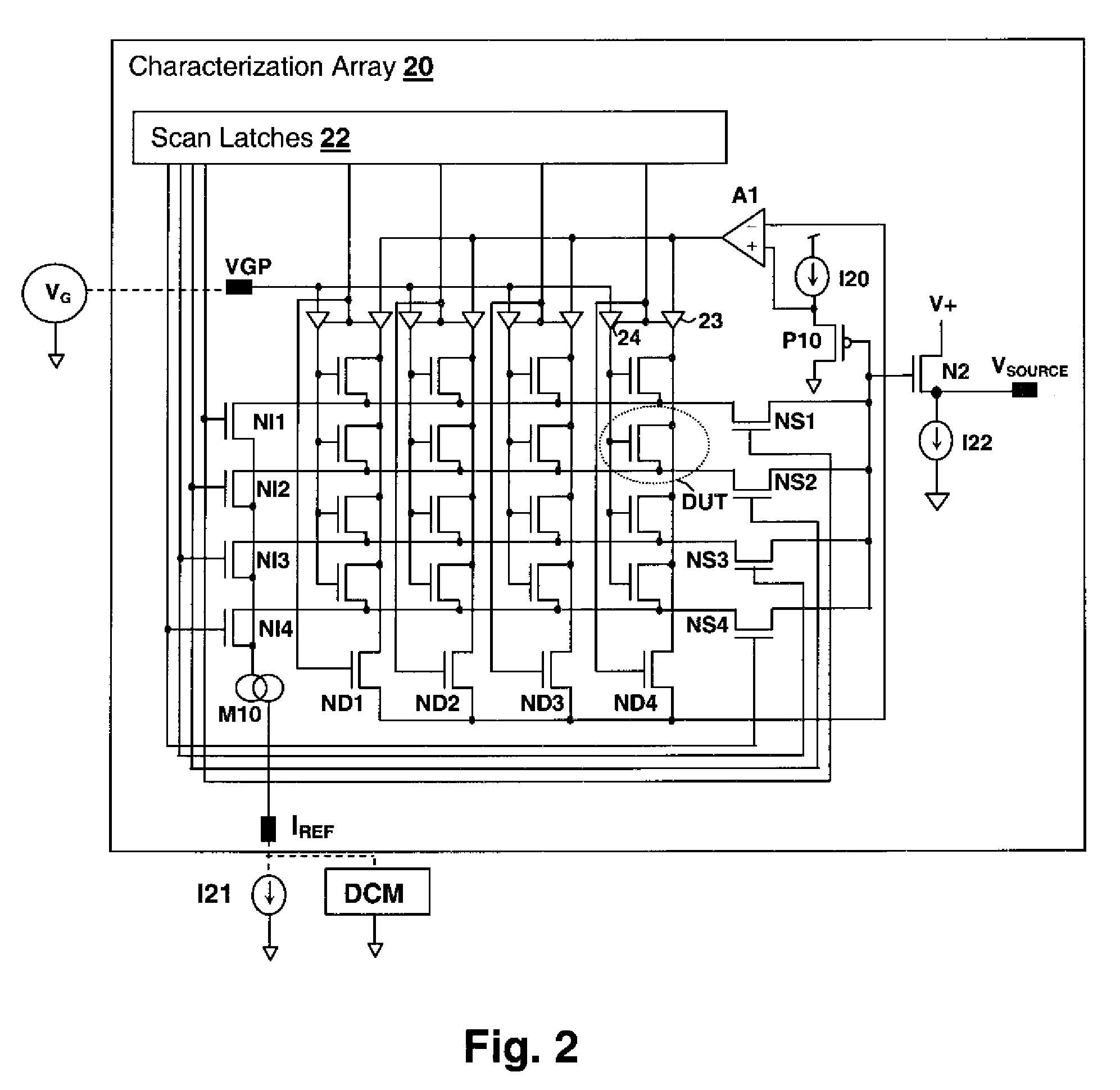
Array-Based Early Threshold Voltage Recovery Characterization Measurement
InactiveUS20090251167A1Marginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringVoltage source
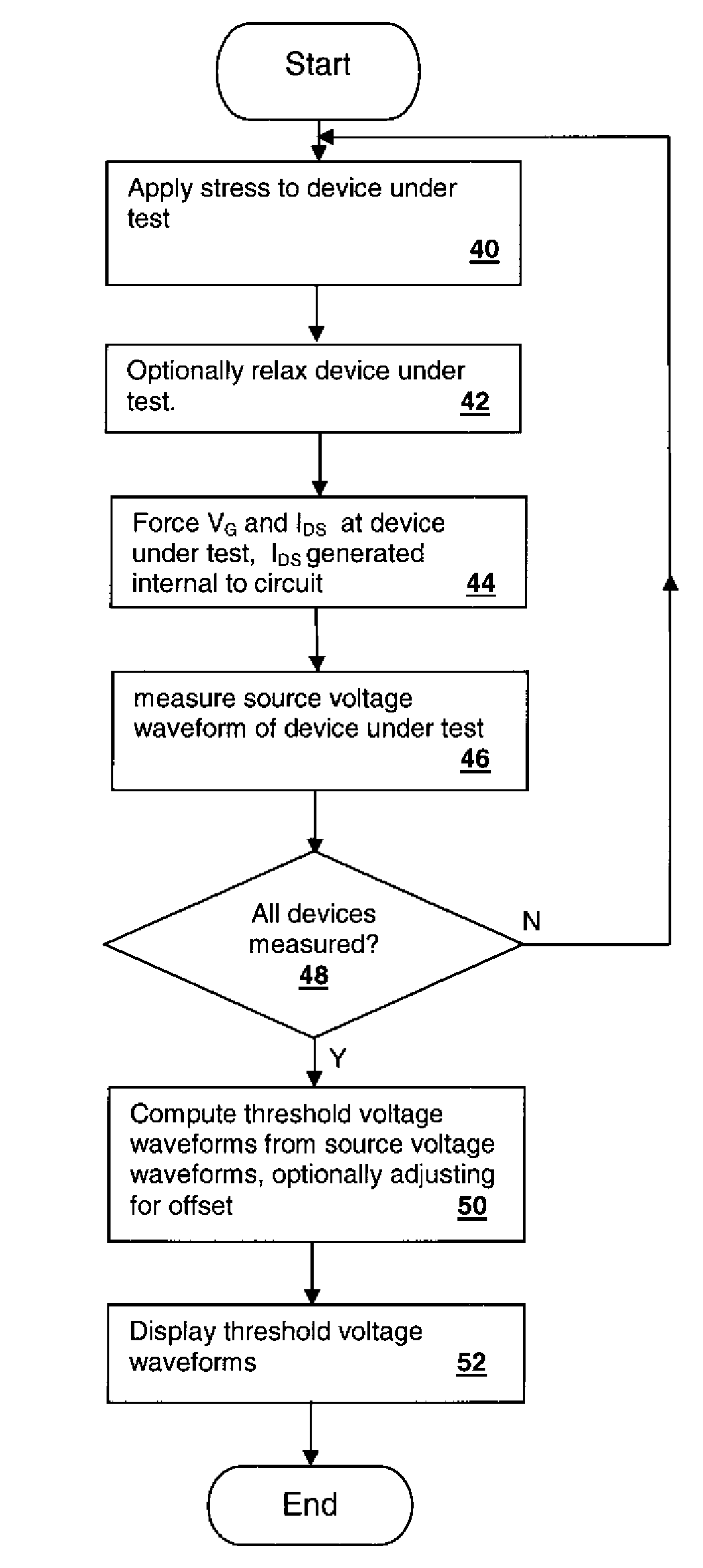
A method and test circuit provide measurements to aid in the understanding of time-varying threshold voltage changes such as negative bias temperature instability and positive bias temperature instability. In order to provide accurate measurements during an early stage in the threshold variation, a current generating circuit is integrated on a substrate with the device under test, which may be a device selected from among an array of devices. The current generating circuit may be a current mirror that responds to an externally-supplied current provided by a test system. A voltage source circuit may be included to hold the drain-source voltage of the transistor constant, although not required. A stress is applied prior to the measurement phase, which may include a controllable relaxation period after the stress is removed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Test circuit for bias temperature instability recovery measurements
InactiveUS20110074394A1Improve dynamic rangeHigh resolutionCurrent/voltage measurementSpecial tariff metersNanosecondImage resolution
A method, test circuit and test system provide measurements to accurately characterize threshold voltage changes due to negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and positive bias temperature instability (PBTI). Both the bias temperature instability recovery profile and / or the bias temperature shifts due to rapid repetitions of stress application can be studied. In order to provide accurate measurements when stresses are applied at intervals on the order of tens of nanoseconds while avoiding unwanted recovery, and / or to achieve recovery profile sampling resolutions in the nanosecond range, multiple delay or ring oscillator frequency measurements are made using a delay line that is formed from delay elements that have delay variation substantially caused only by NBTI or PBTI effects. Devices in the delay elements are stressed, and then the delay line / ring oscillator is operated to measure a threshold voltage change for one or more measurement periods on the order of nanoseconds.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
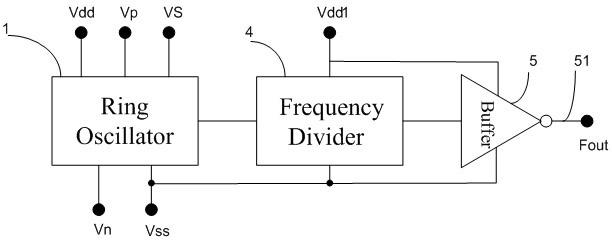
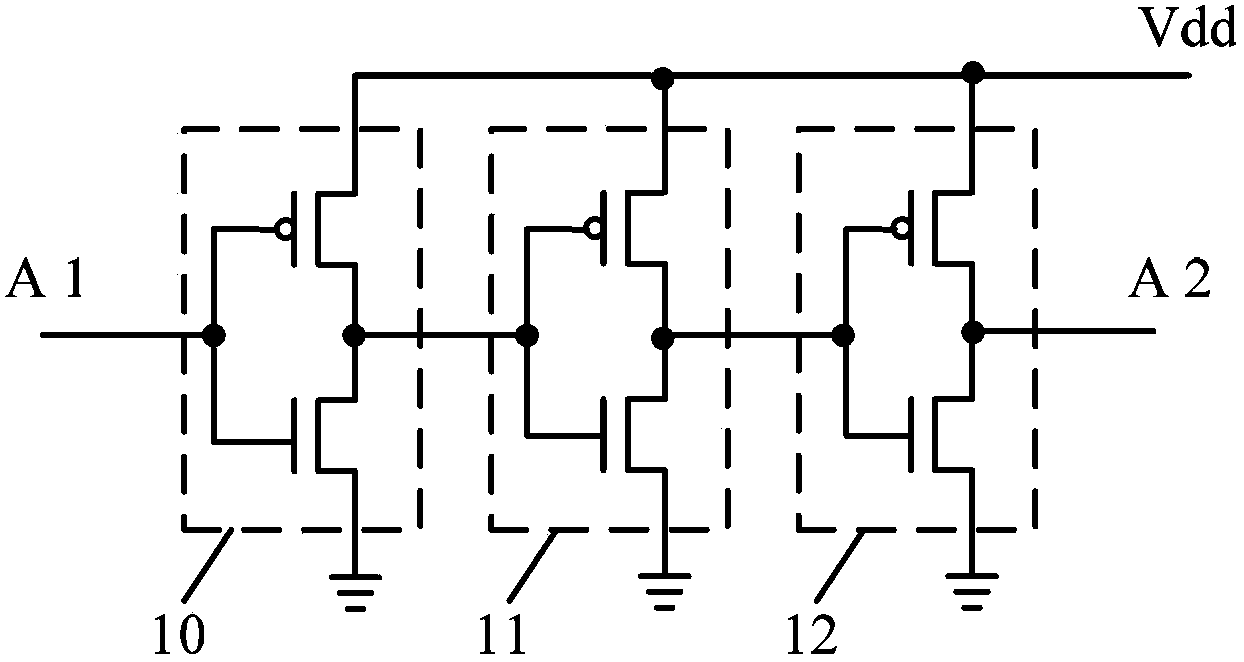
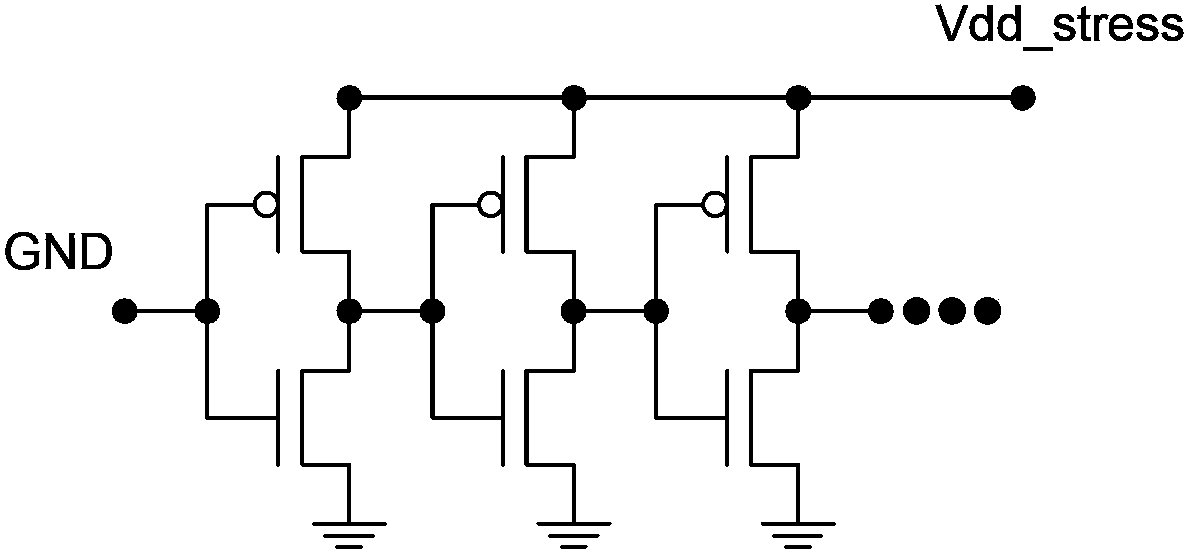
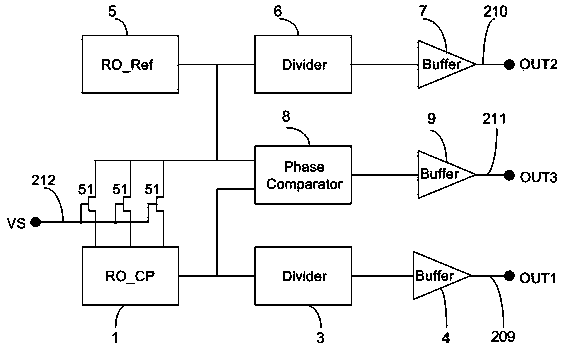
Bias voltage temperature instability detection circuit and detection method
ActiveCN103424684AZoom in on test resultsHigh precisionElectronic circuit testingEngineeringNegative bias
The invention provides bias voltage temperature instability detection circuit and detection method. The bias voltage temperature instability detection circuit comprises an odd number of fundamental oscillation units. Each fundamental oscillation unit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor, a first control transistor, a second control transistor, an input end and an output end. The detection circuit further comprises third transistors which are located between adjacent fundamental oscillation units. The fundamental oscillation units and the third transistors are connected in series to form an annular oscillator. According to the embodiment of the invention, the bias voltage temperature instability detection circuit can respectively detect the degree of threshold voltage degradation, which is caused by negative bias voltage temperature instability, of a PMOS transistor and the degree of threshold voltage degradation, which is caused by positive bias voltage temperature instability, of an NMOS transistor; by using the third transistors, the degree of threshold voltage degradation, which is caused by bias voltage temperature instability, of an MOS transistor can be amplified; and the final detection result is sensitive and the detection precision is high.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
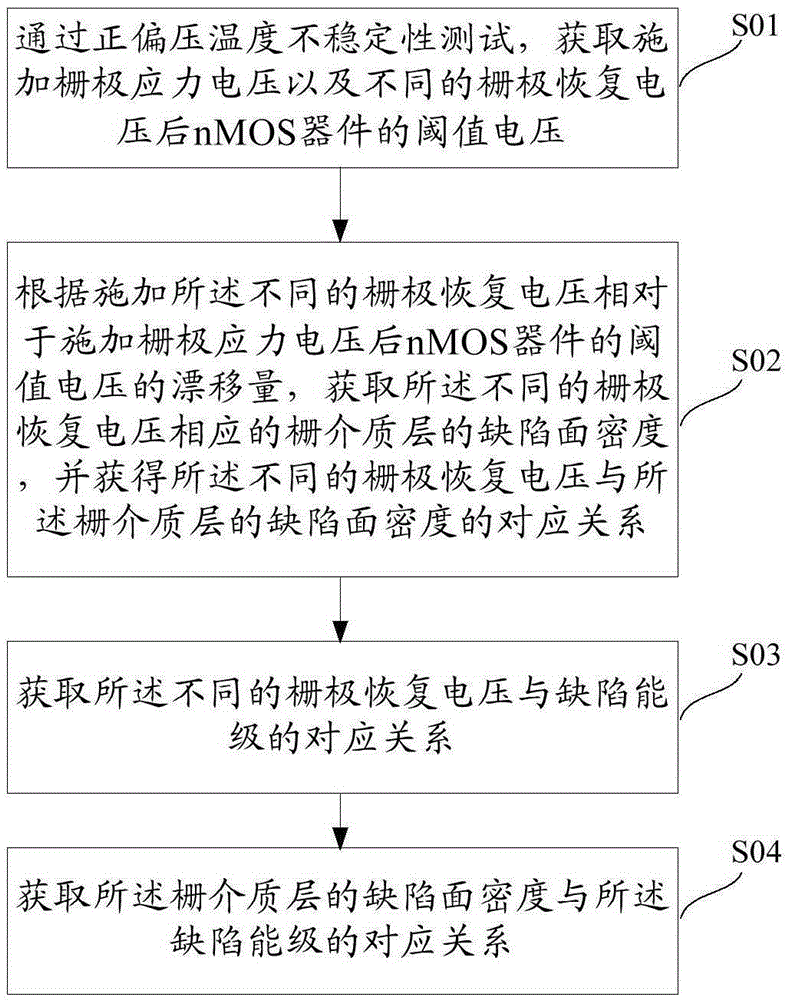
Method and system for extracting semiconductor defect level
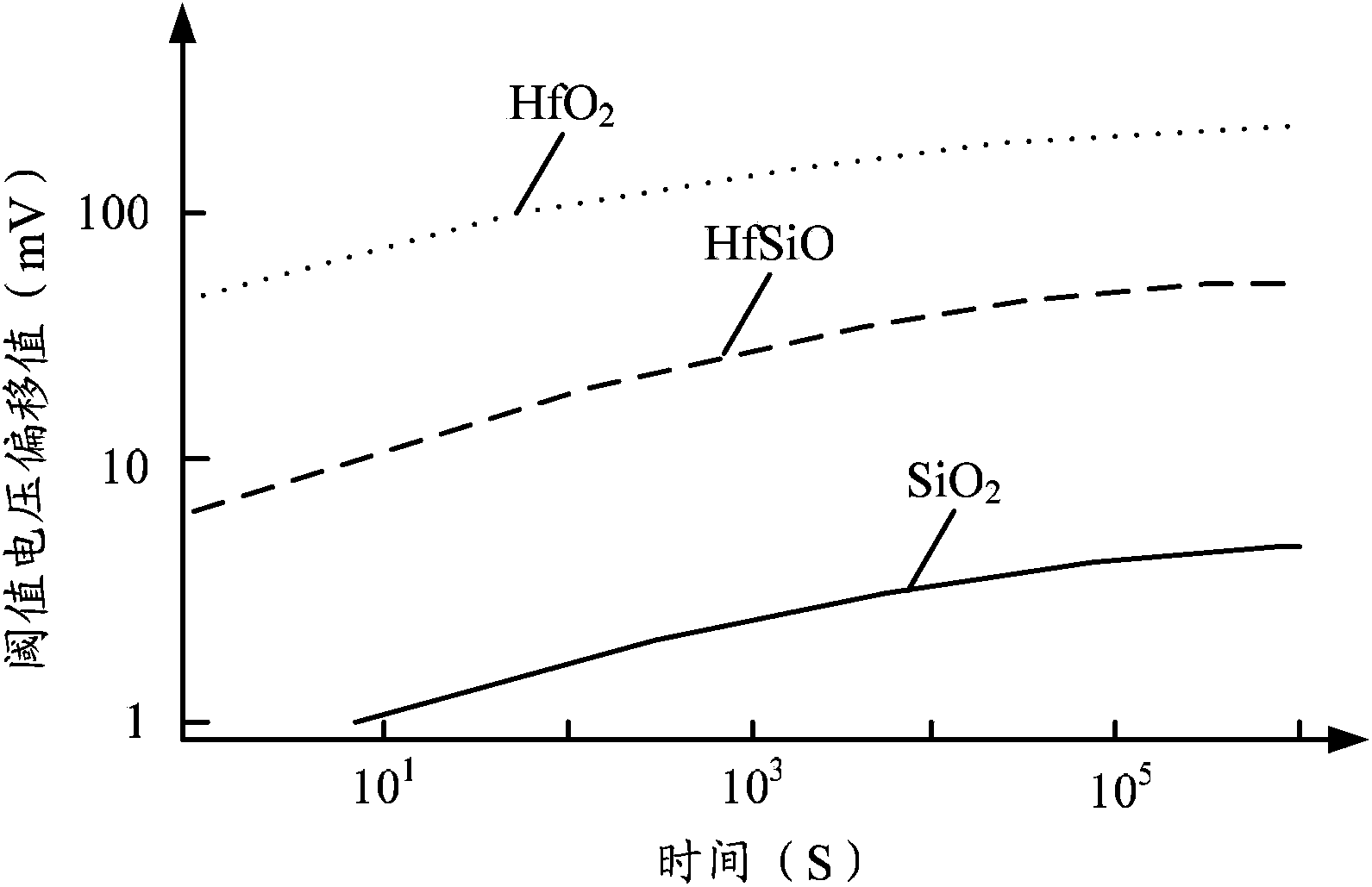
InactiveCN106556789AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityIndividual semiconductor device testingGate dielectricSemiconductor
The invention provides a method and a system for extracting a semiconductor defect level. The method comprises steps: through a positive bias temperature instability test, the threshold voltage of an nMOS device after applying gate stress voltage and different gate recovery voltage is acquired; according to the shift of the threshold voltage of the nMOS device after applying the different gate recovery voltage relative to applying the gate stress voltage, the defect surface density of a gate dielectric layer corresponding to the different gate recovery voltage is acquired, and the corresponding relationship between the different gate recovery voltage and the defect surface density of the gate dielectric layer is acquired; the corresponding relationship between the different gate recovery voltage and a defect level is acquired; and the corresponding relationship between the defect surface density of the gate dielectric layer and the defect level is acquired. According to the method provided by the invention, the relationship between the defect level and the defect surface density of the gate dielectric layer can be extracted, and the device performance and the reliability can be improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Array-based early threshold voltage recovery characterization measurement
InactiveUS7868640B2Marginal circuit testingIndividual semiconductor device testingInstabilityEngineering
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
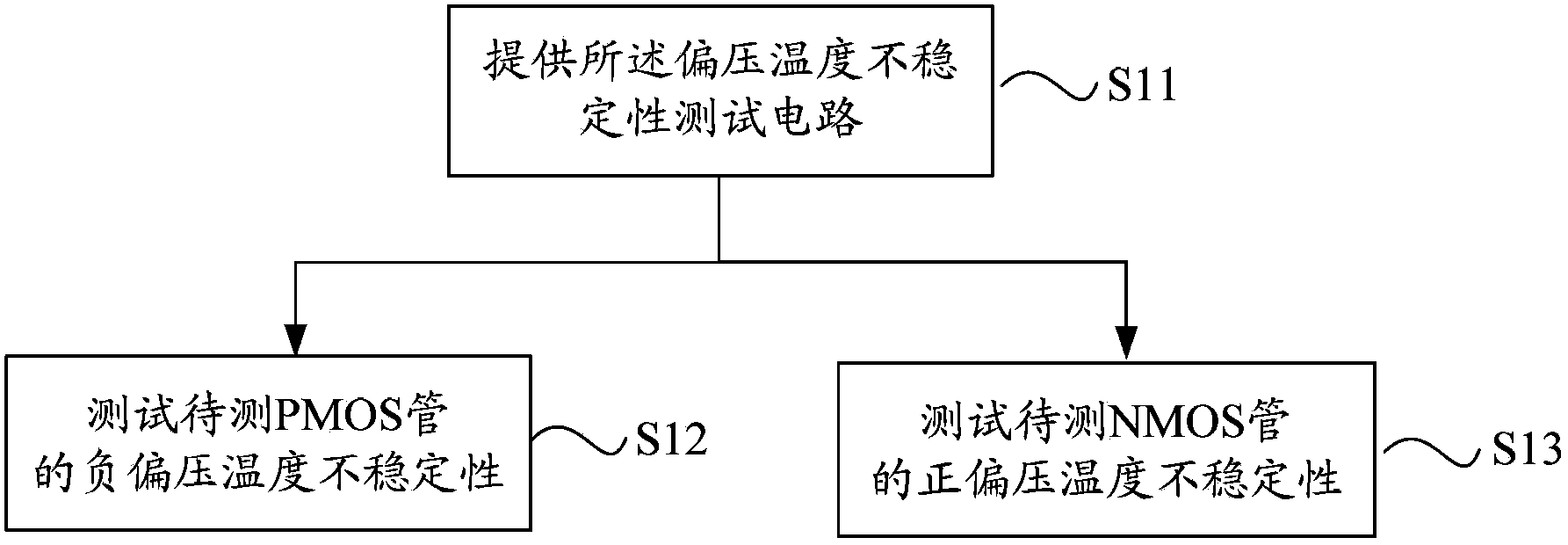
Bias voltage temperature instability testing circuit and testing method thereof
InactiveCN103576067AMeasurement stabilityMeasuring Forward Bias Temperature InstabilityIndividual semiconductor device testingInstabilityNegative bias
The invention discloses a bias voltage temperature instability testing circuit which comprises a circular vibrator circuit. The vibrator circuit comprises n grades of testing circuits which are the same in structure. Each testing circuit comprises a first node, a second node and a third node. The third node of each testing circuit is connected with the first node of a former testing circuit. Each testing circuit comprises a PMOS tube to be tested, an NMOS tube to be tested, a switch PMOS tube, a switch NMOS tube and at least one pair of partial pressure PMOS tube and partial pressure NMOS tube, wherein the PMOS tube to be tested and the NMOS tube to be tested are complementary, the switch PMOS tube and the switch NMOS tube are complementary, and the partial pressure PMOS tube and the partial pressure NMOS tube are complementary. The invention further discloses a testing method for the bias voltage temperature instability testing circuit. The method comprises the steps of providing the bias voltage temperature instability testing circuit, testing the negative bias pressure temperature instability of the PMOS tube to be tested and testing the positive bias pressure temperature instability of the NMOS tube to be tested. The bias voltage temperature instability testing circuit can test the negative bias pressure temperature instability of the PMOS tube to be tested and the positive bias pressure temperature instability of the NMOS tube to be tested.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
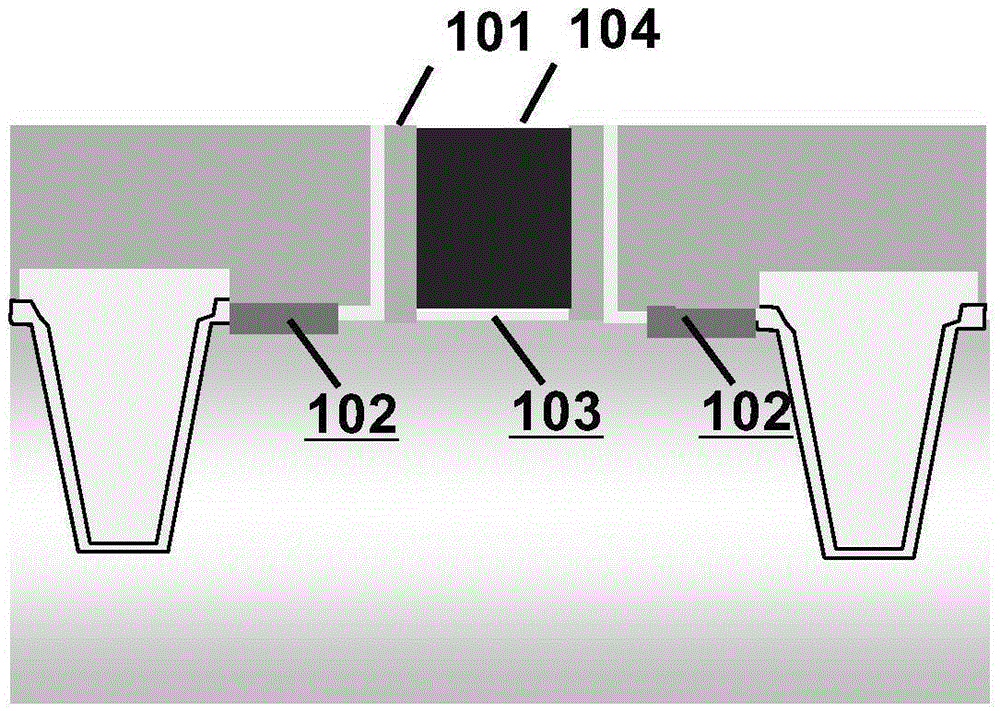
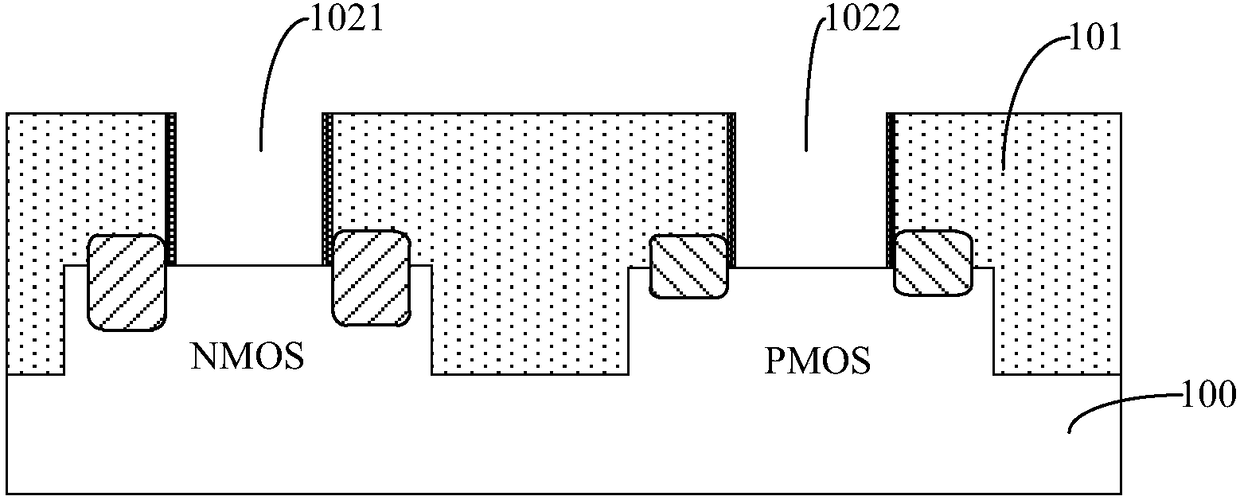
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof and electronic device
InactiveCN108400115AImprove performanceImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceHydrogen
The invention provides a semiconductor device, a manufacturing method thereof and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate, wherein a gate groove isformed on the semiconductor substrate; and forming a high-k dielectric layer at the bottom of the gate groove and also comprises the following steps of performing first annealing under an atmosphere containing a hydrogen element before the high-k dielectric layer is formed so that a suspension bond exposed out of the gate groove and in the semiconductor substrate is passivated, and / or performing second annealing after the high-k dielectric layer is formed so that oxygen vacancy in the high-k dielectric layer is passivated. According to the manufacturing method, first annealing is performed under the atmosphere containing the hydrogen element before the high-k dielectric layer is formed so that the exposed suspension bond in the semiconductor substrate is passivated, hot carrier injection (HCI) and negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) of the device are improved, second annealing is performed after the high-k dielectric layer is formed so that the oxygen vacancy in the high-k dielectric layer is passivated, positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) is further improved, and the performance and the reliability of the device are improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
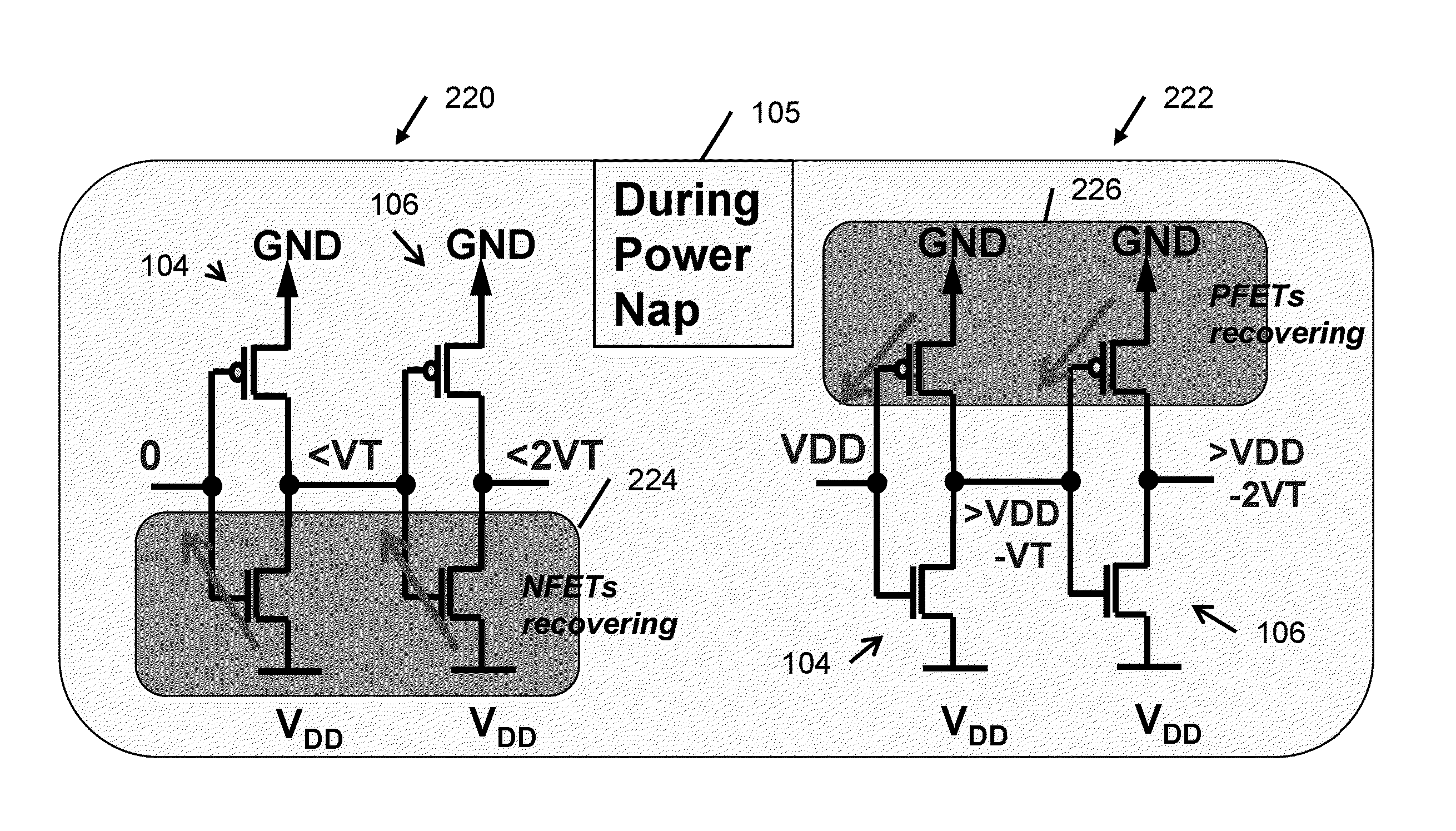
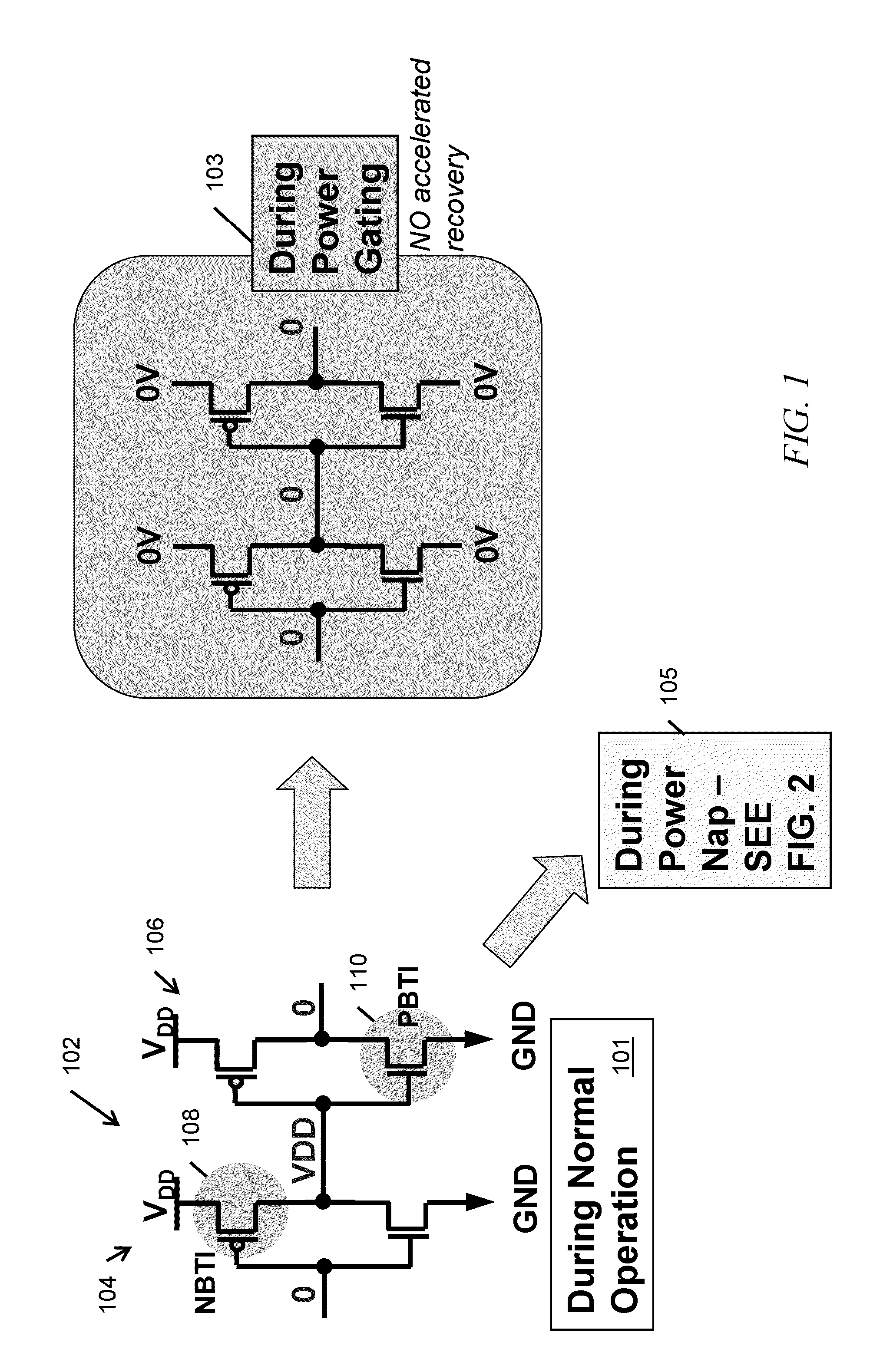
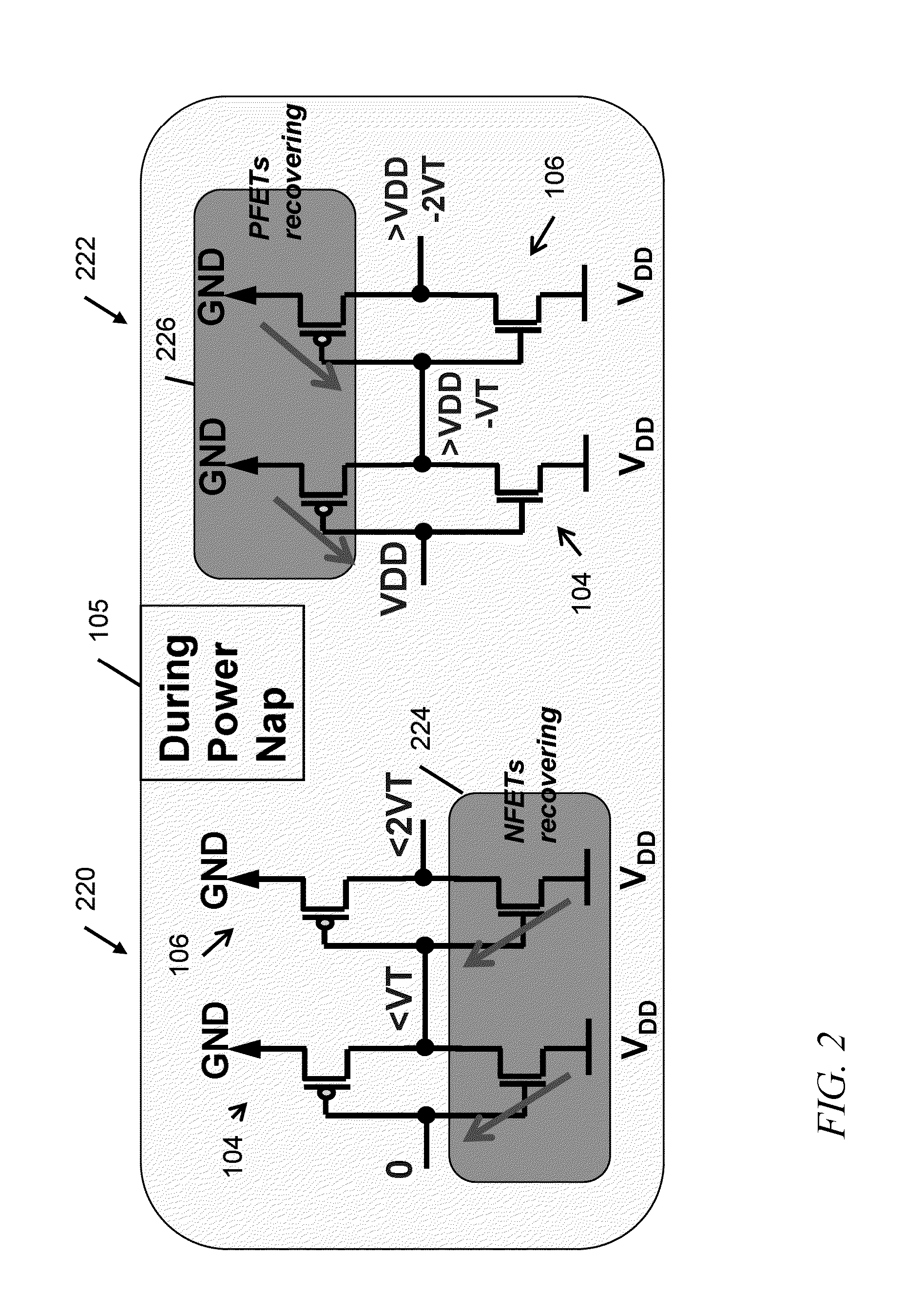
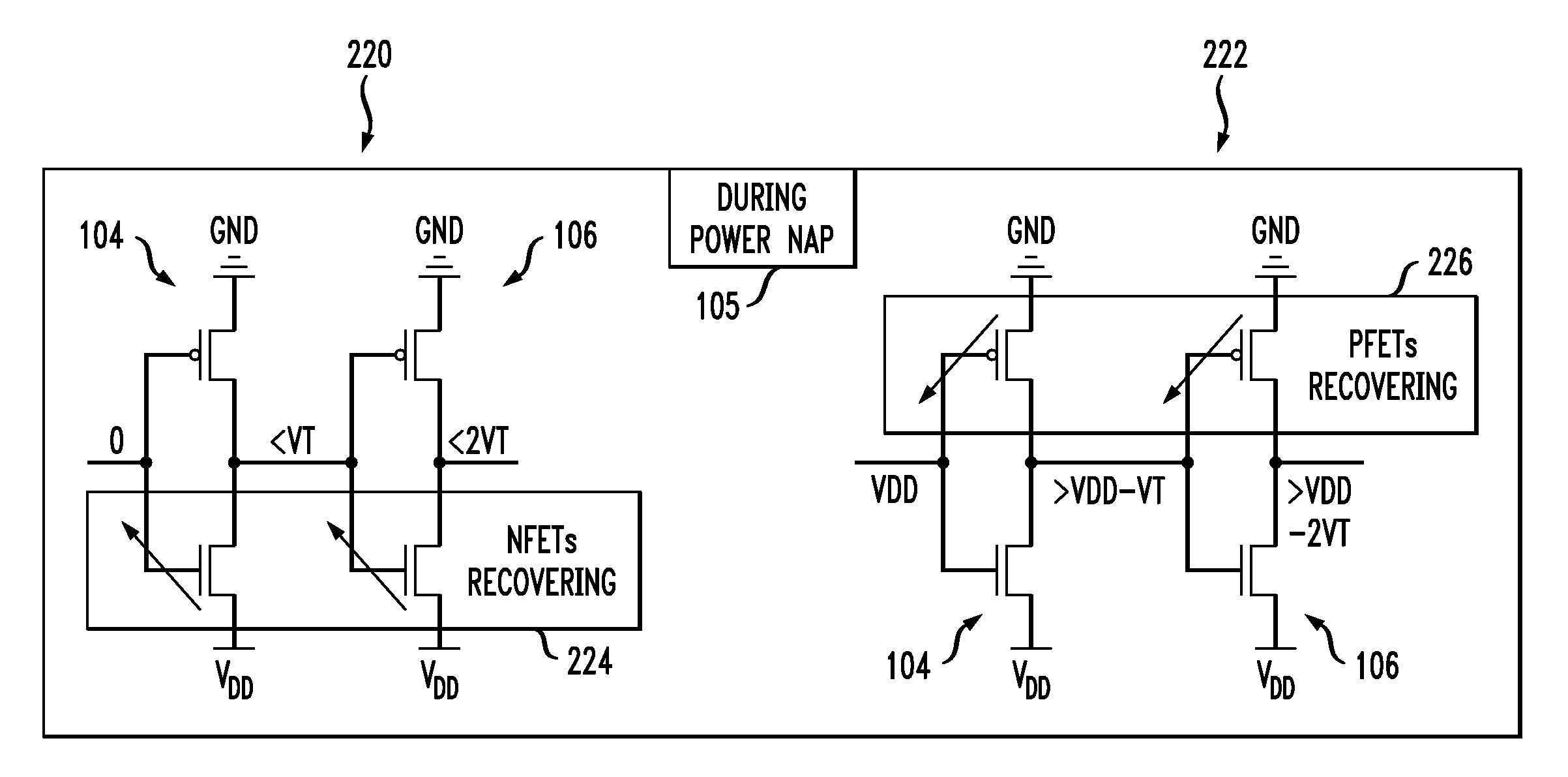
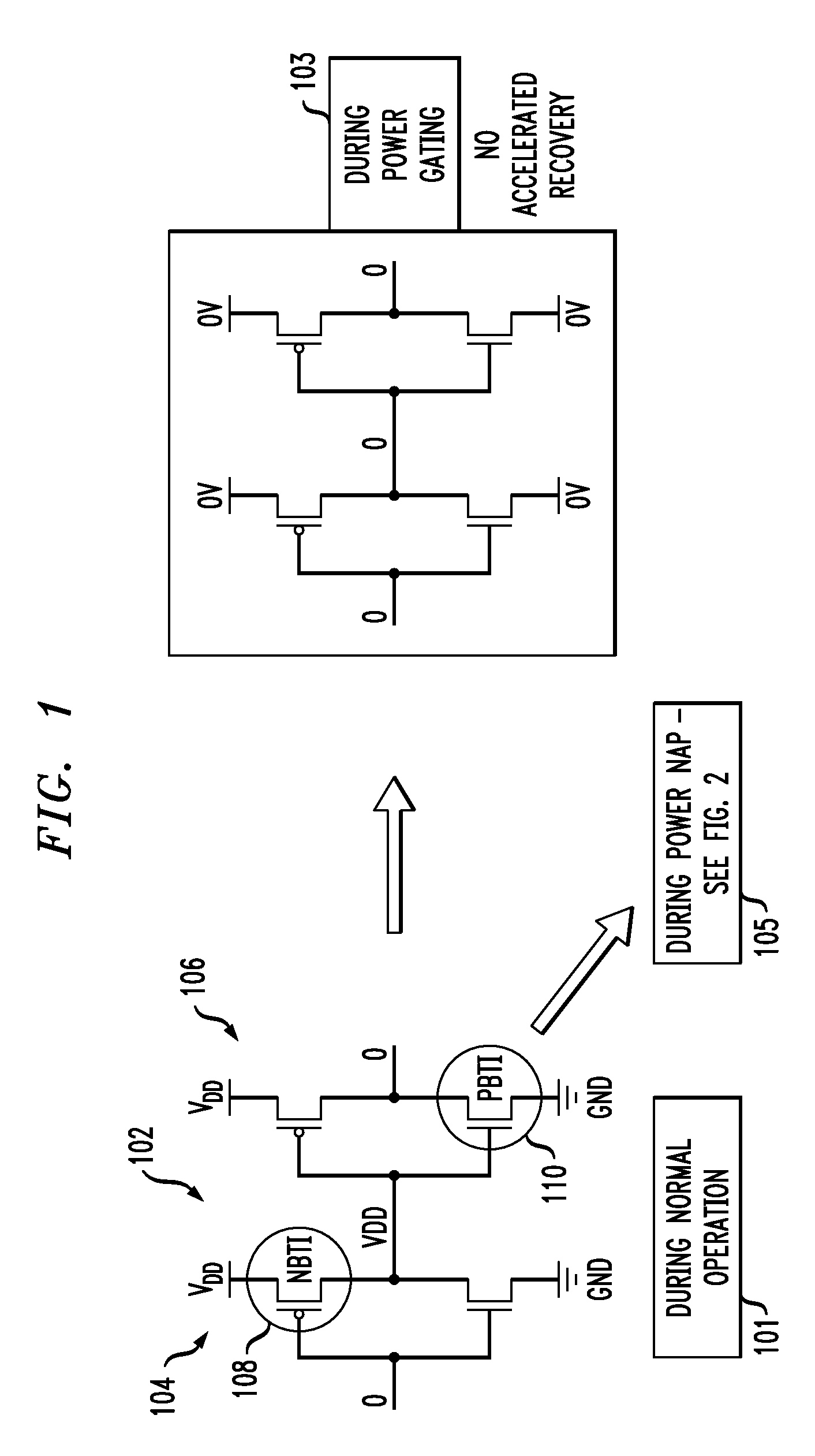
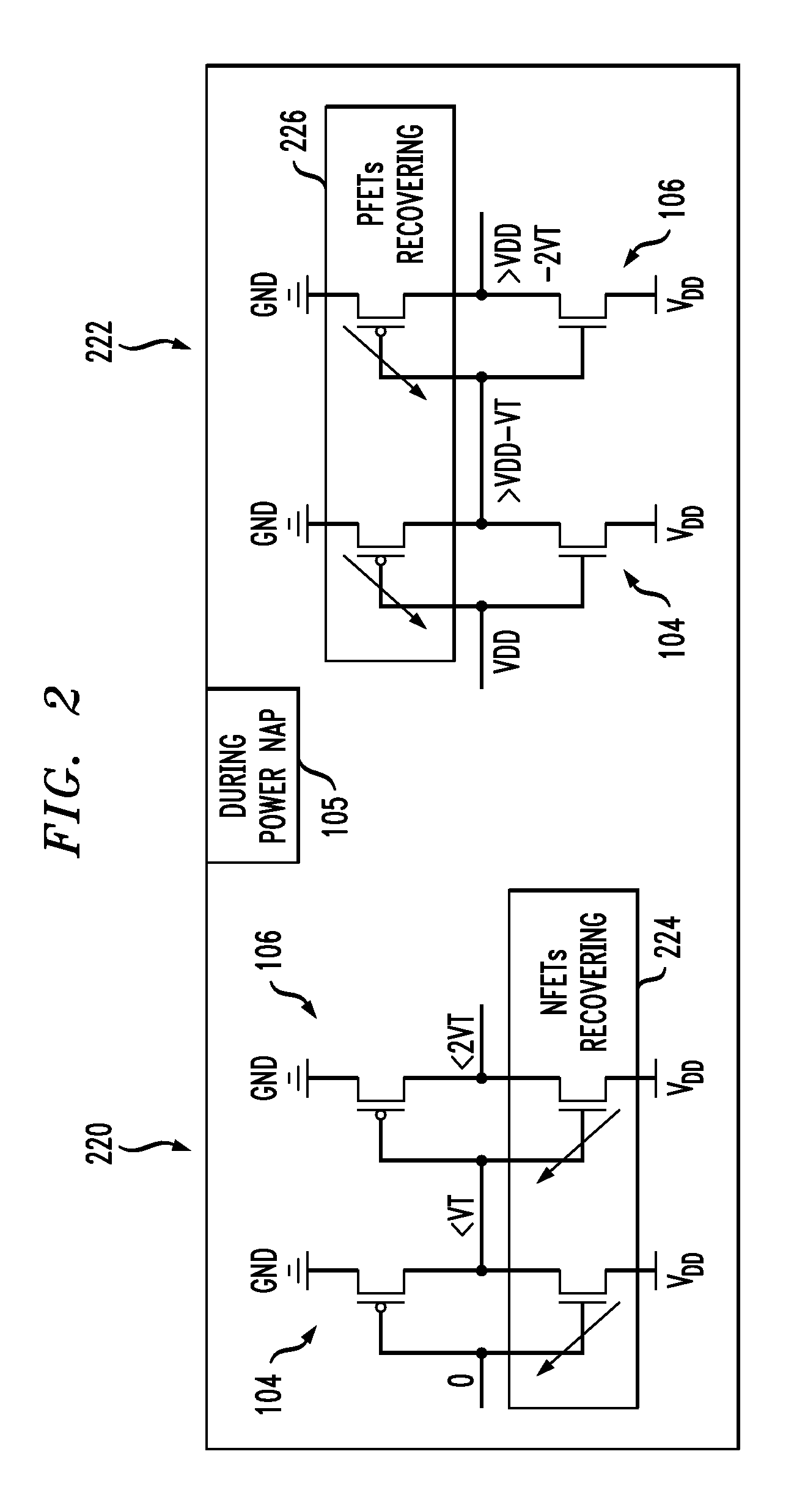
Power napping technique for accelerated negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and/or positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) recovery
InactiveUS20140013131A1Improve negative bias temperature instabilityVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingInstabilityNormal mode
A logic circuit is operated in a normal mode, with a supply voltage coupled to a supply rail of the logic circuit, and with a ground rail of the logic circuit grounded; It is determined that at least a portion of the logic circuit has experienced degradation due to bias temperature instability. Responsive to the determining, the logic circuit is operated in a power napping mode, with the supply voltage coupled to the ground rail of the circuit, with the supply rail of the circuit grounded, and with primary inputs of the circuit toggled between logical zero and logical one at low frequency. A logic circuit and corresponding design structures are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
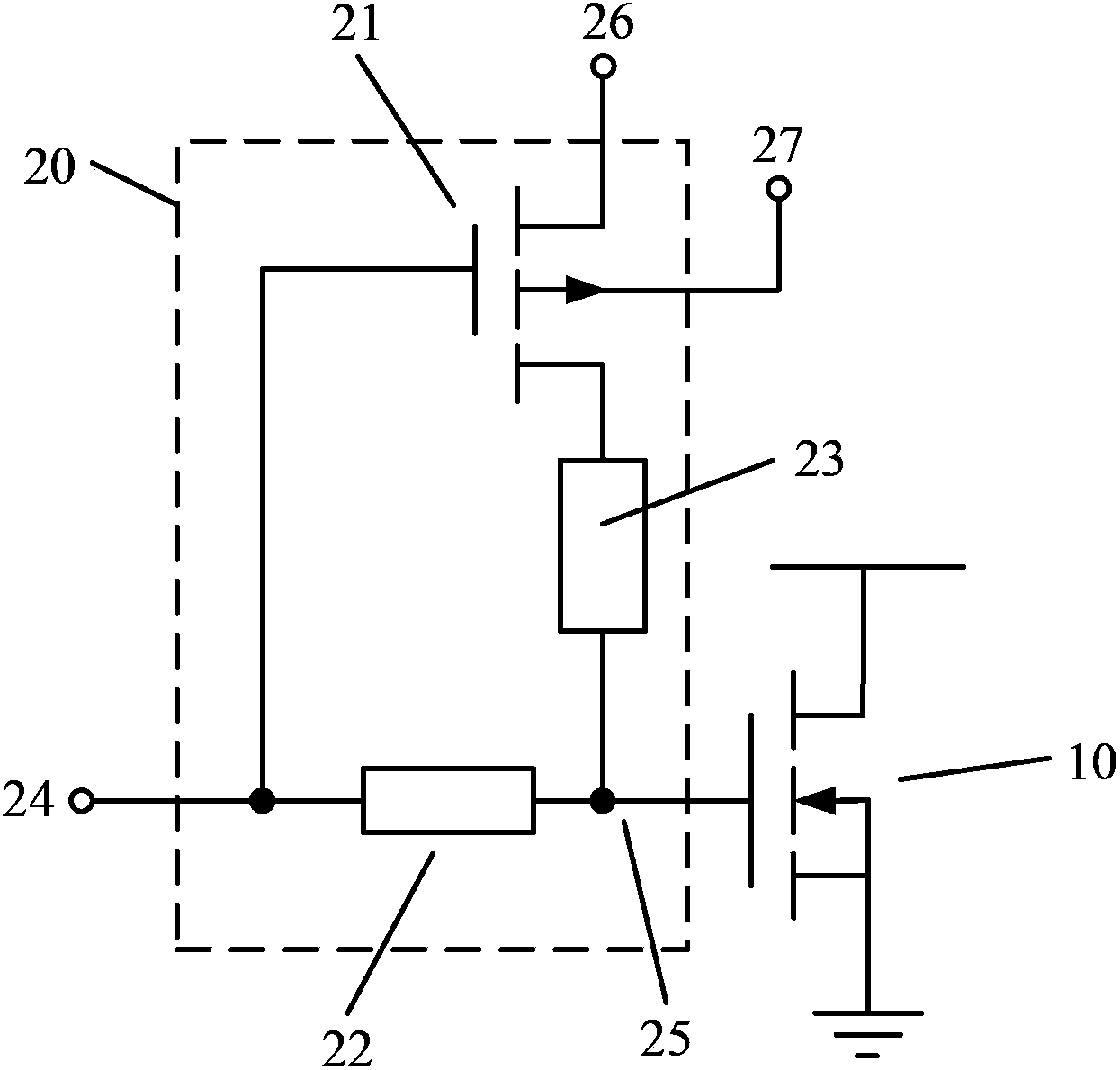
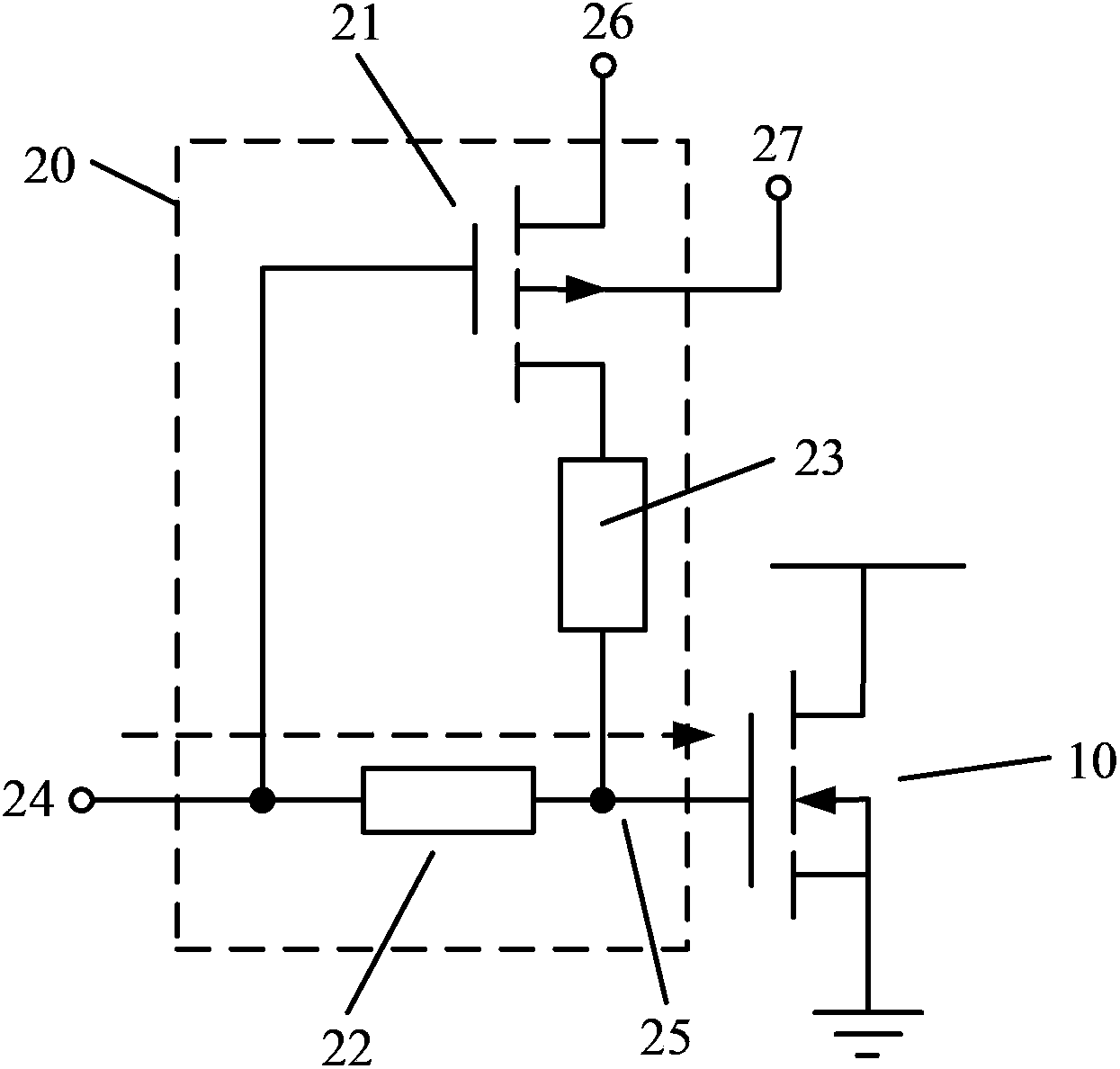
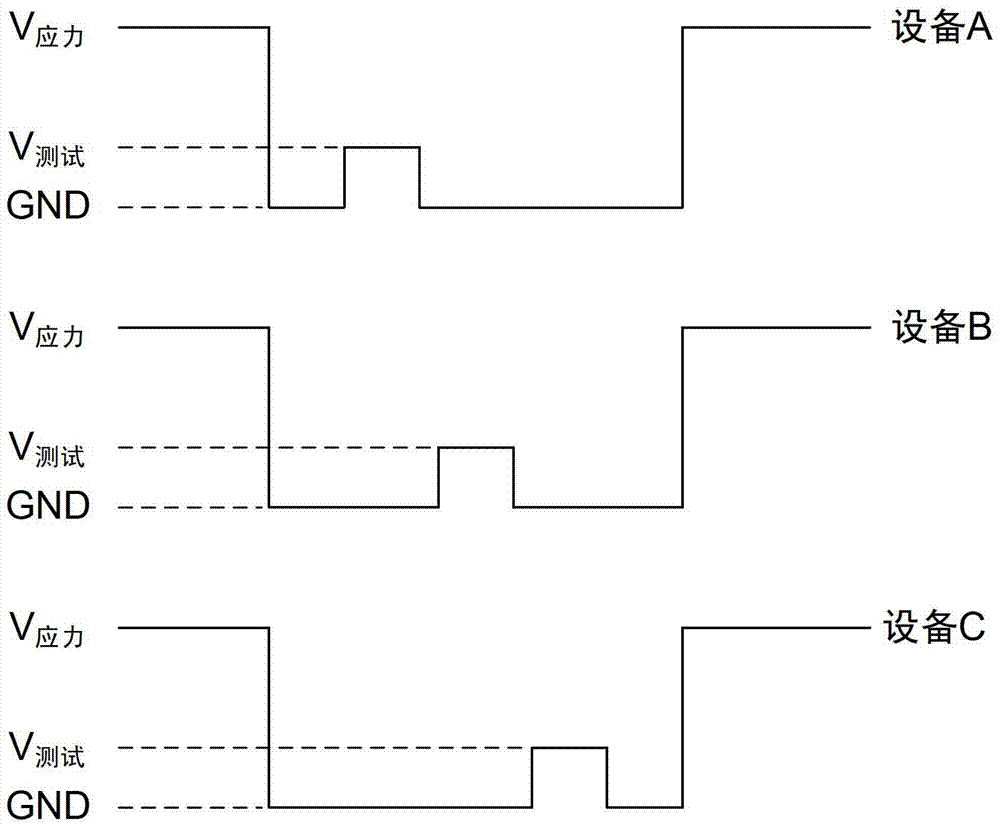
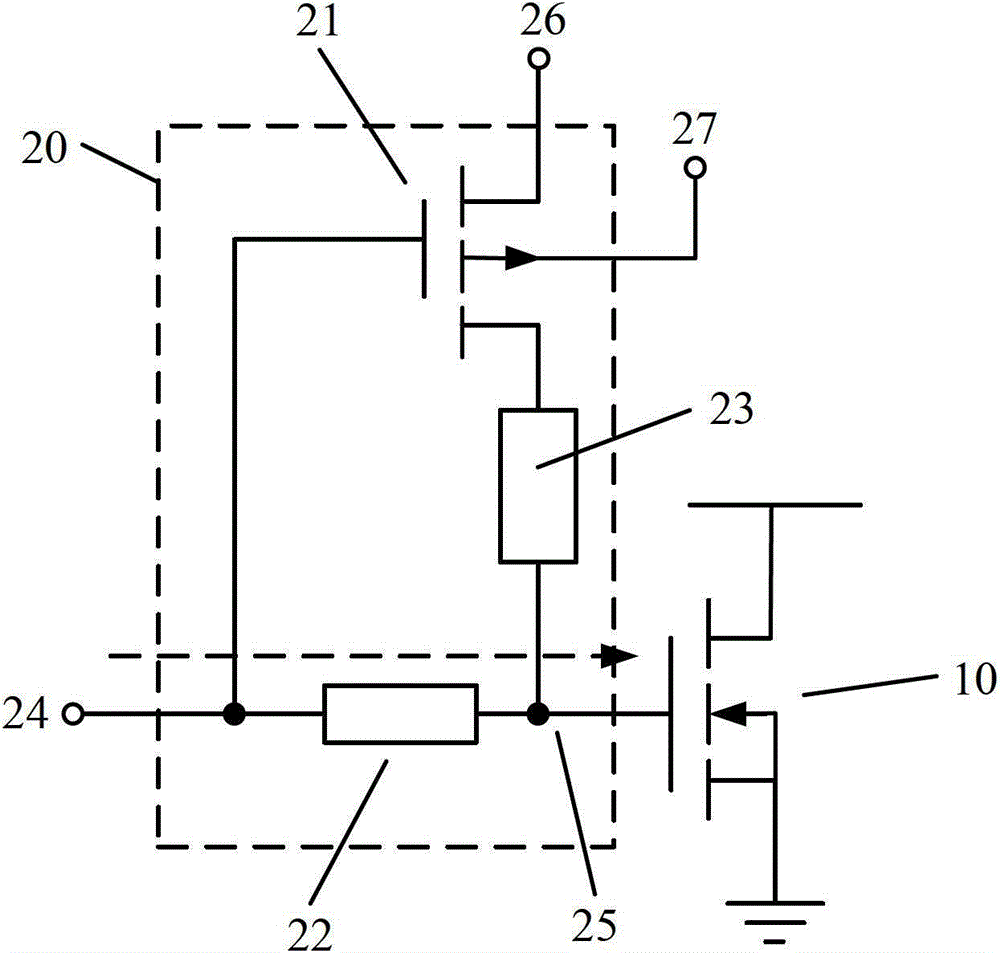
Restoring circuit and restoring method against positive bias temperature instability
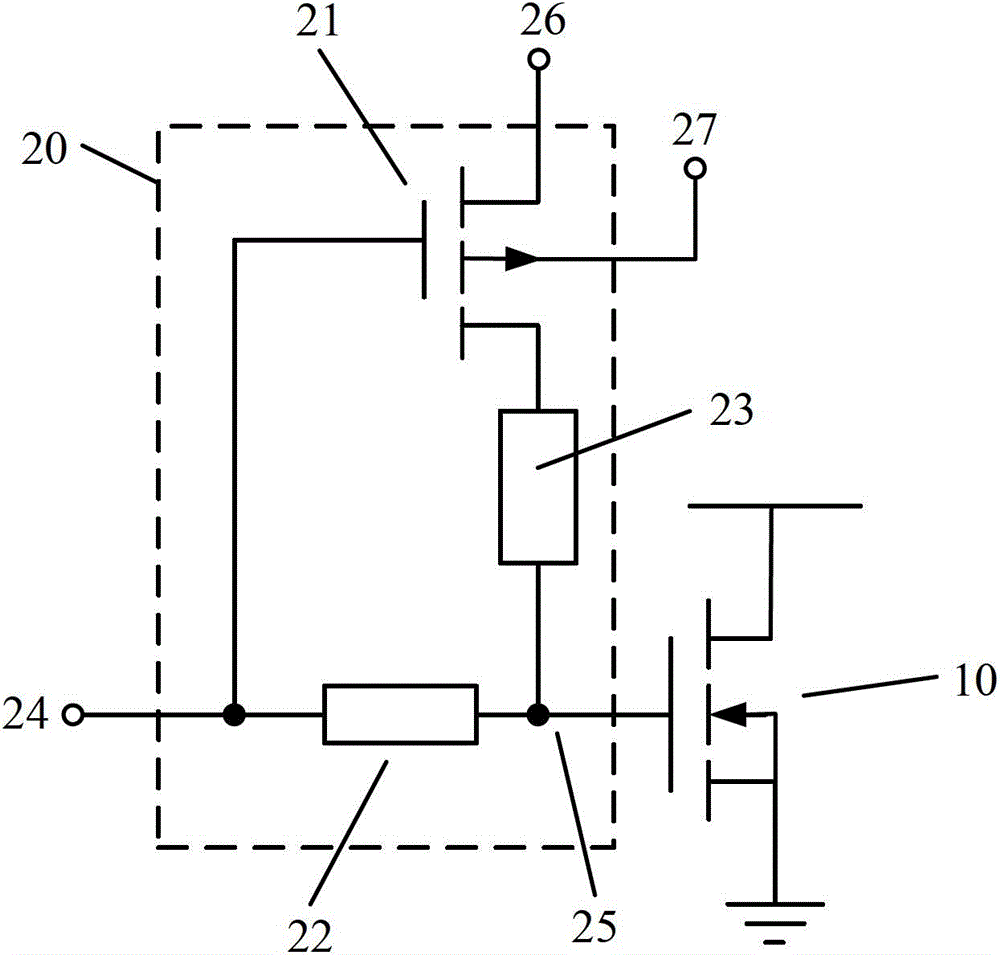
ActiveCN103427827AGood recovery effect of PBTI characteristicsLogic circuitsPositive bias temperature instabilityResistor
Provided are a restoring circuit and restoring method against positive bias temperature instability. The restoring circuit comprises a to-be-restored N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistor and a restoring unit. A grid electrode of the to-be-restored NMOS transistor is connected with the restoring unit. According to the restoring unit, a grid electrode of a switch transistor is connected with a signal input end, a drain electrode of the switch transistor is connected with a first voltage end, the first voltage end provides a negative first working voltage, a substrate of the switch transistor is connected with a second voltage end, a source electrode of the switch transistor is connected with one end of a second resistor, the other end of the second resistor is connected with a signal output end, one end of a first resistor is connected with a signal input end, and the other end of the first resistor is connected with the signal output end. Due to the fact that the voltage of the first voltage end is negative, by adjusting resistance values of the first resistor and the second resistor, grid electrode voltage applied to the to-be-restored NMOS transistor can be negative pressure, and good positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) characteristic restoration effect can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
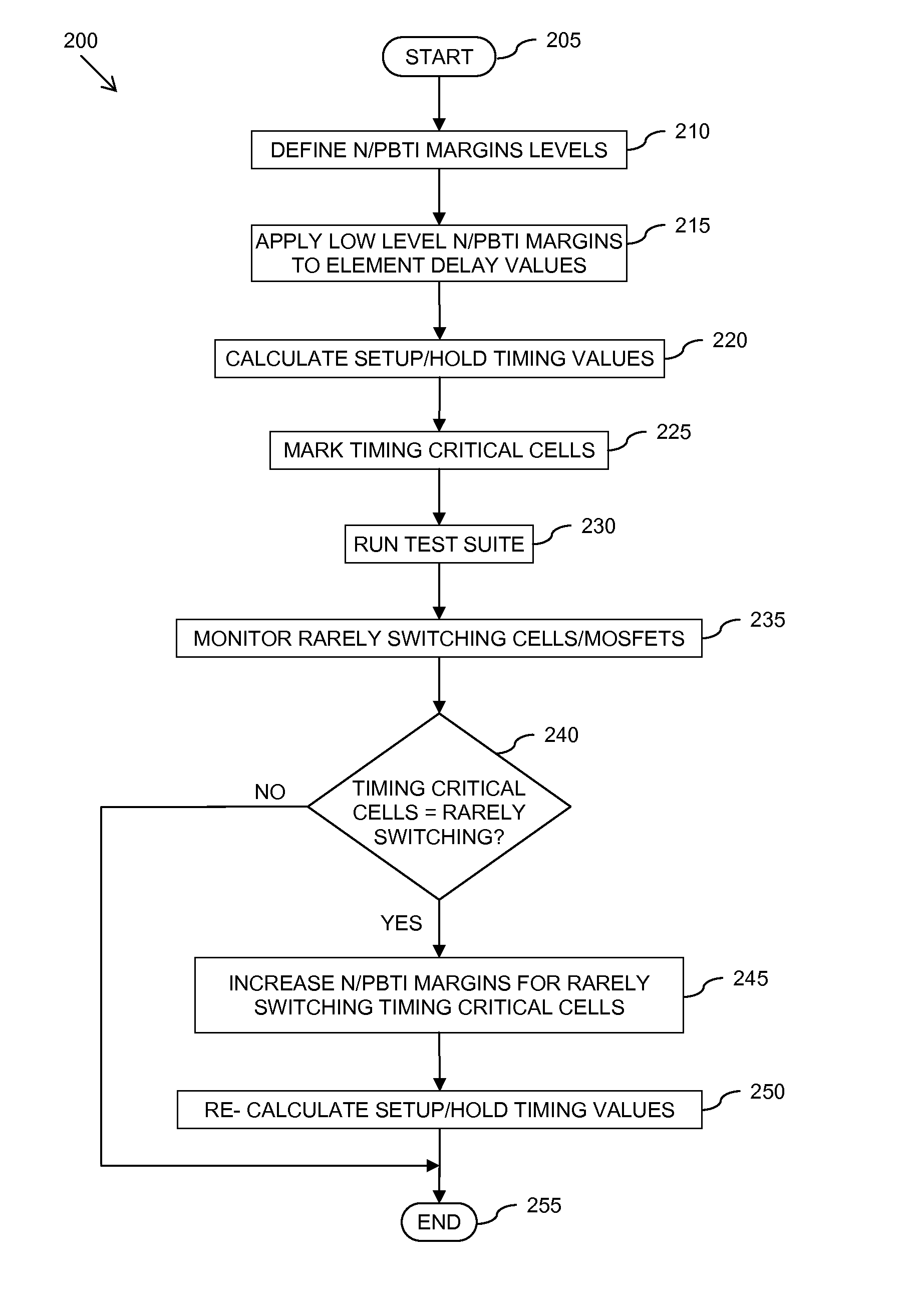
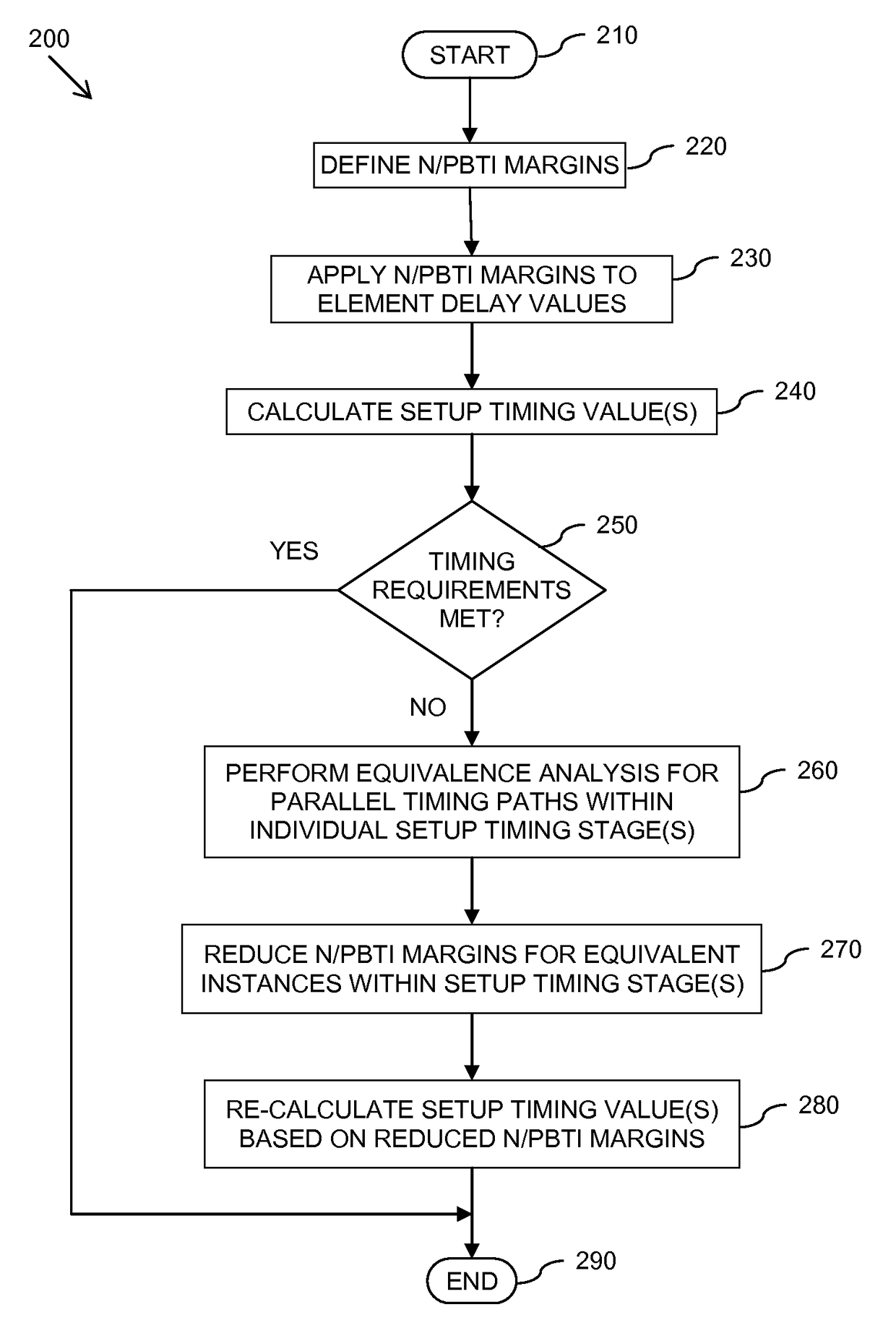
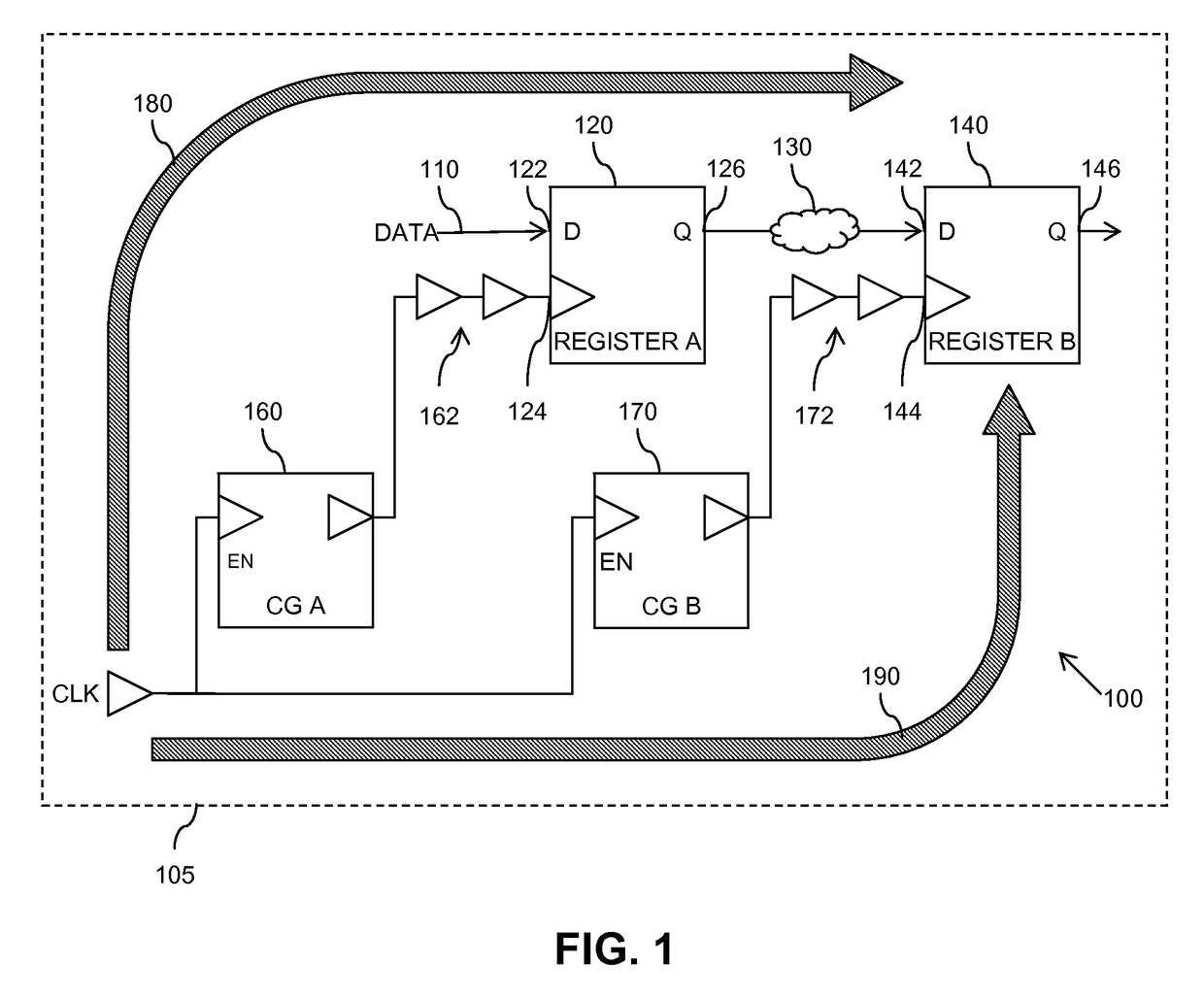
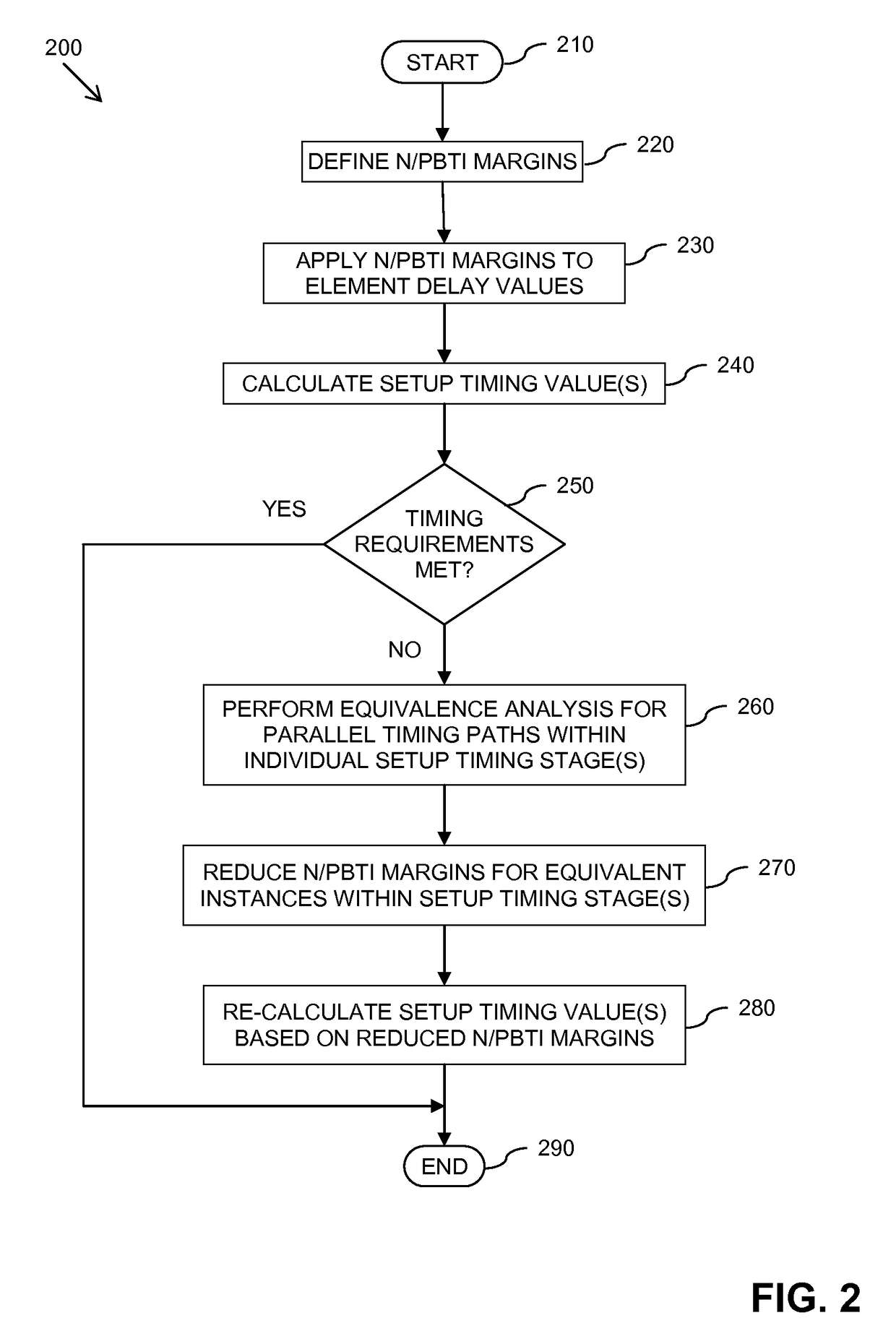
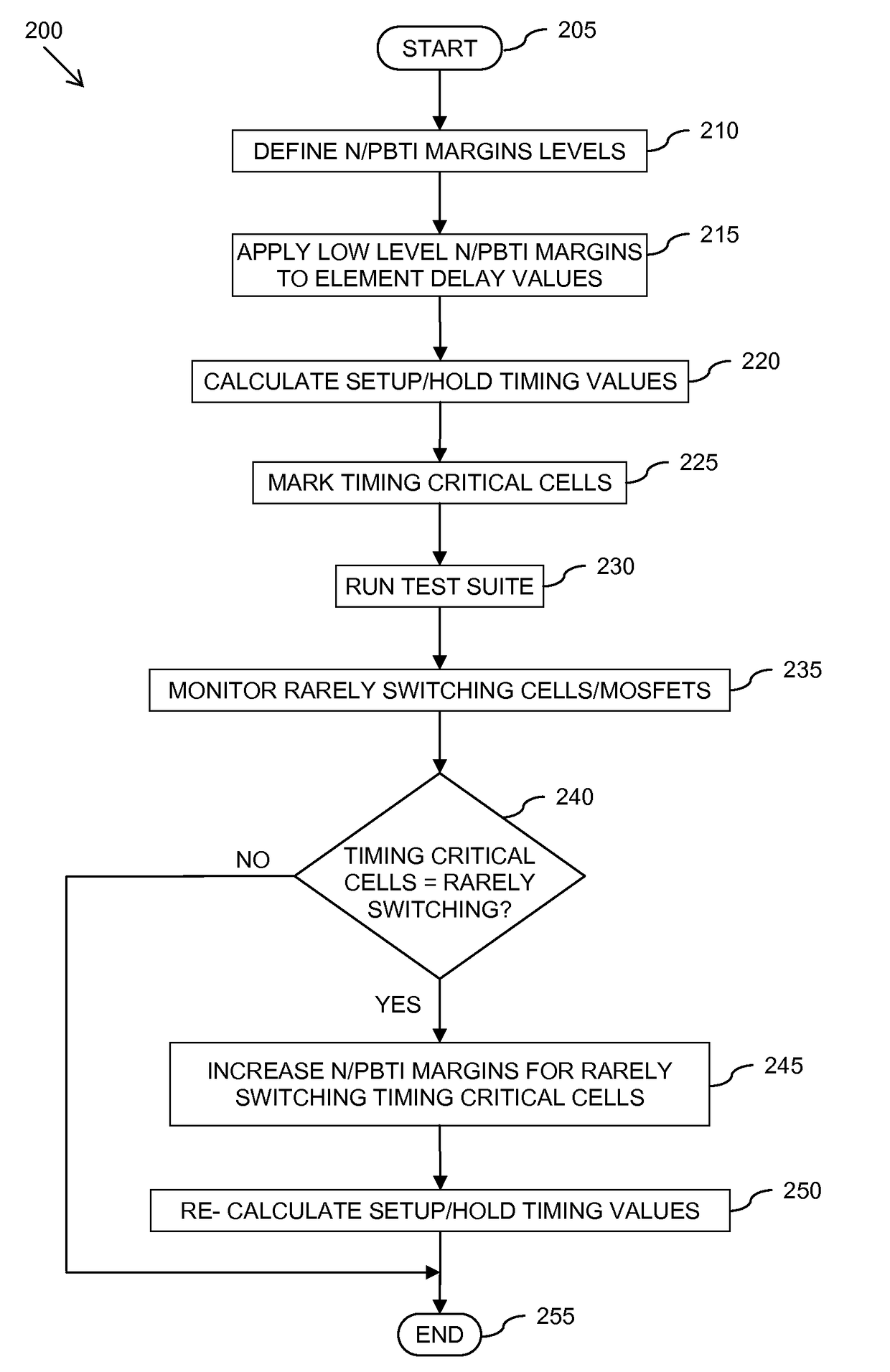
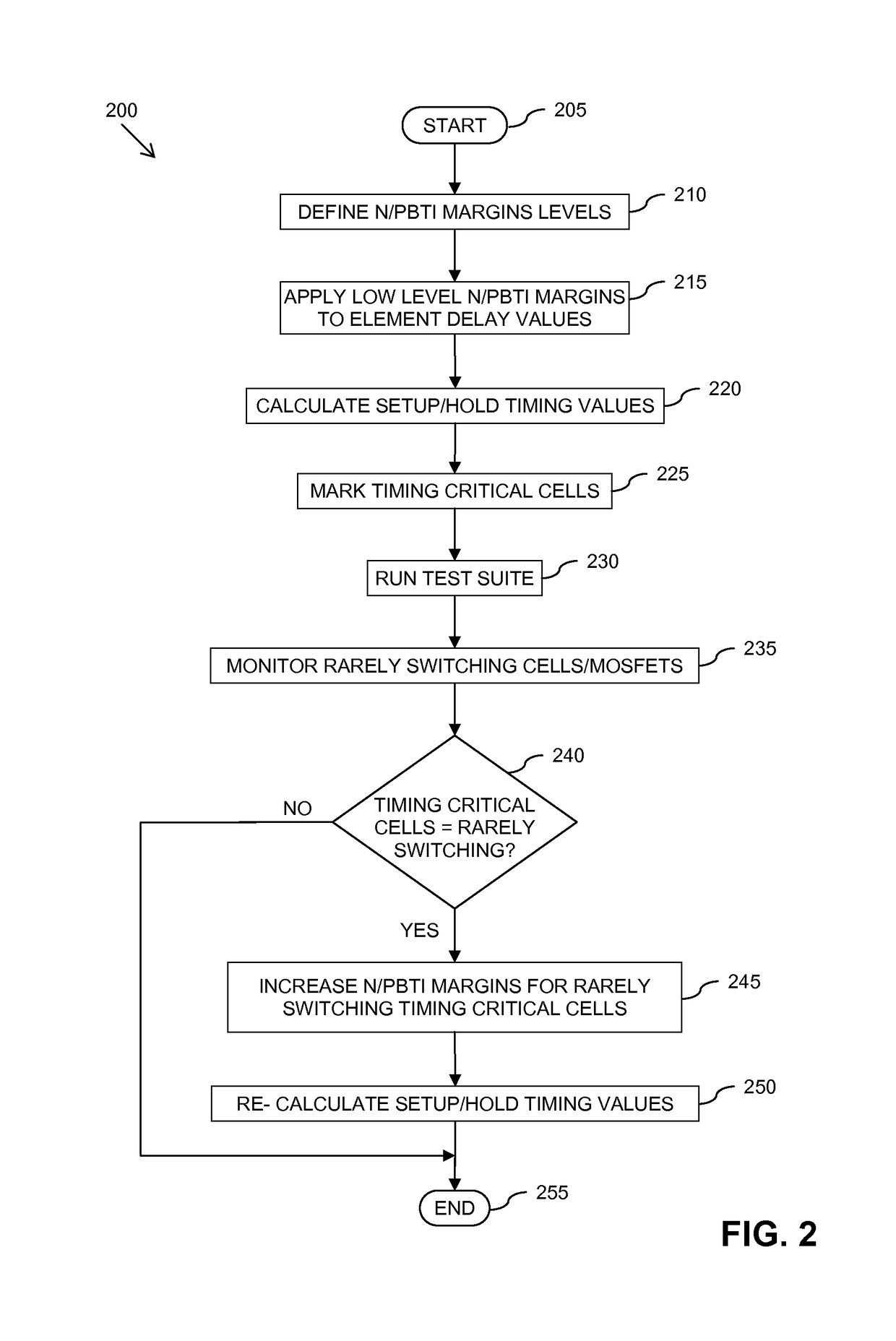
Method and apparatus for calculating delay timing values for an integrated circuit design
InactiveUS20150347653A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInstabilityPositive bias temperature instability
A method and apparatus for calculating delay timing values for at least a part of an integrated circuit design. The method comprises applying a first Negative / Positive Bias Temperature Instability compensation margin to delay values for elements within the at least part of the IC design, identifying at least one lower-rate switching element within the at least part of the IC design, and applying at least one further, increased N / PBTI compensation margin to the delay value(s) for the at least one identified lower-rate switching element.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Power napping technique for accelerated negative bias temperature instability (NBTI) and/or positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) recovery
InactiveUS9086865B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingInstabilityNormal mode
A logic circuit is operated in a normal mode, with a supply voltage coupled to a supply rail of the logic circuit, and with a ground rail of the logic circuit grounded; It is determined that at least a portion of the logic circuit has experienced degradation due to bias temperature instability. Responsive to the determining, the logic circuit is operated in a power napping mode, with the supply voltage coupled to the ground rail of the circuit, with the supply rail of the circuit grounded, and with primary inputs of the circuit toggled between logical zero and logical one at low frequency. A logic circuit and corresponding design structures are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of screening static random access memory cells for positive bias temperature instability
ActiveUS8971138B2Efficient and accurate identificationYield minimizationDigital storageStatic random-access memorySemiconductor materials
A method of screening complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor CMOS integrated circuits, such as integrated circuits including CMOS static random access memory (SRAM) cells, for n-channel transistors susceptible to transistor characteristic shifts over operating time. For the example of SRAM cells formed of cross-coupled CMOS inverters, static noise margin and writeability (Vtrip) screens are provided. Each of the n-channel transistors in the CMOS SRAM cells are formed within p-wells that are isolated from p-type semiconductor material in peripheral circuitry of the memory and other functions in the integrated circuit. Forward and reverse body node bias voltages are applied to the isolated p-wells of the SRAM cells under test to determine whether such operations as read disturb, or write cycles, disrupt the cells under such bias. Cells that are vulnerable to threshold voltage shift over time can thus be identified.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for calculating delay timing values for an integrated circuit design
A method of calculating at least one delay timing value for at least one setup timing stage within an integrated circuit design includes applying Negative / Positive Bias Temperature Instability (N / PBTI) compensation margins to delay values for elements within the at least one setup timing stage, and calculating the at least one delay timing value for the at least one setup timing stage based at least partly on the N / PBTI compensation margins applied to the delay values. The method further includes identifying at least partially equivalent elements within the parallel timing paths of the at least one setup timing stage, and applying reduced N / PBTI compensation margins to delay values for the identified at least partially equivalent elements within parallel timing paths of the at least one setup timing stage.
Owner:NXP USA INC
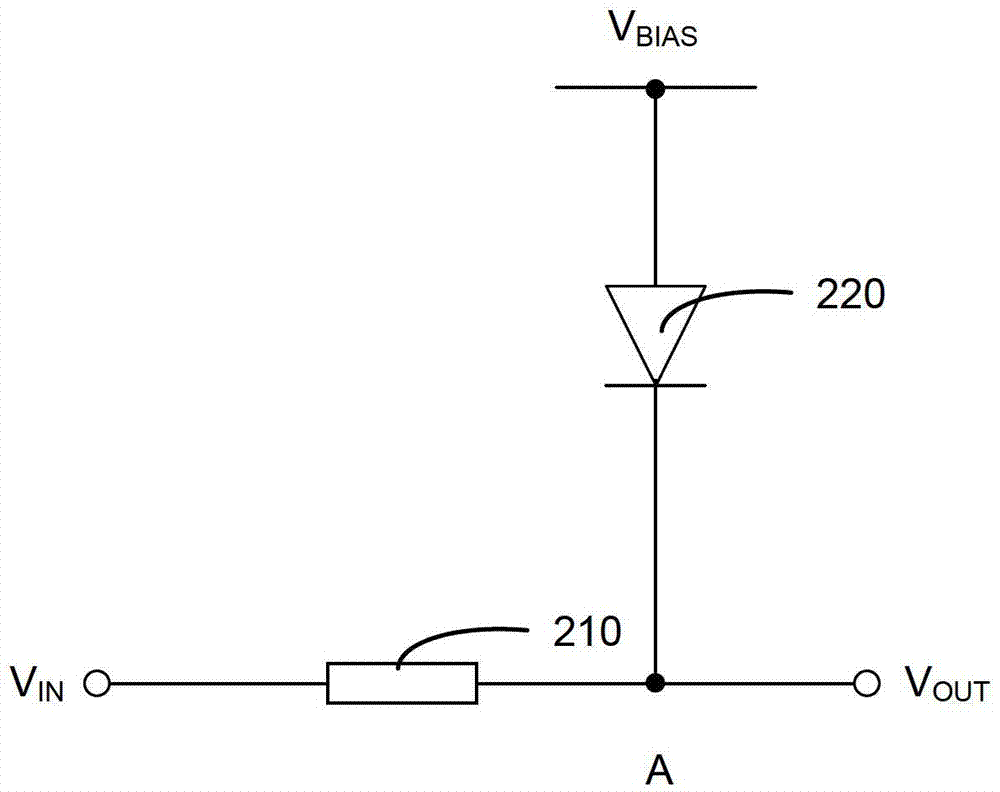
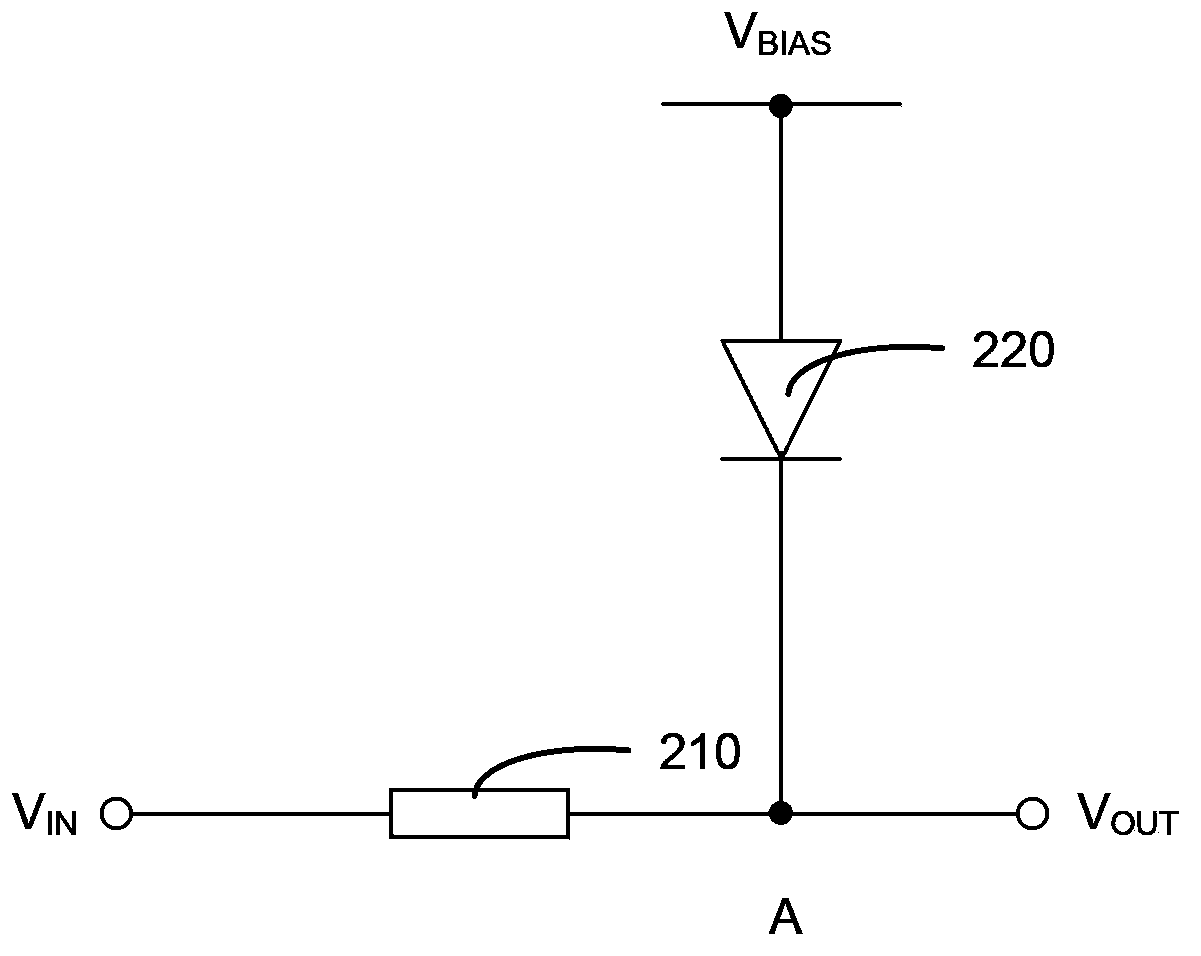
A test device and test method for high-k metal gate nmos transistors
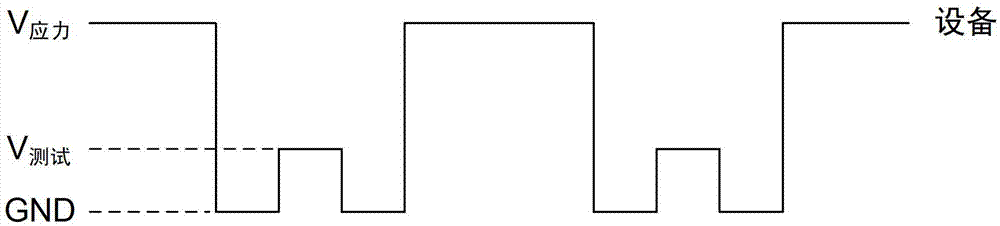
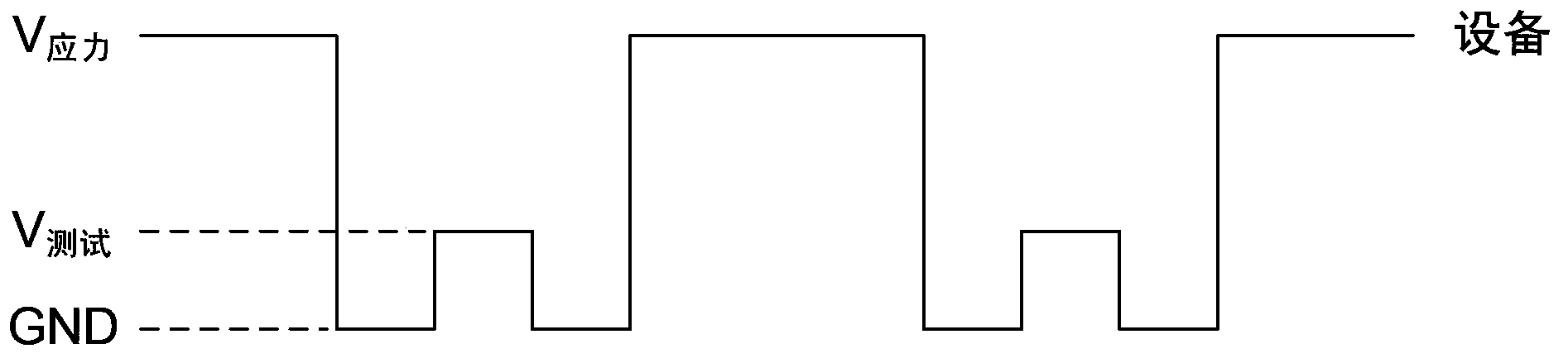
ActiveCN103543396BAvoid recovery effectsTroubleshooting Restoration EffectsIndividual semiconductor device testingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The invention discloses a testing device and a testing method used for an NMOS (n-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor in a high-k metal gate. The testing device comprises a resistor and a diode. The resistor is connected between an input end and an output end of the testing device, a positive pole of the diode is used for being connected with a bias voltage source, a negative pole of the diode is connected to the output end of the testing device, the input end of the testing device is used for receiving testing signals, and the output end of the testing device is used for connecting the gate of a to-be-tested NMOS transistor. The testing device is capable of exerting stress upon the to-be-tested NMOS transistor continuously and automatically during the PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) testing process, so that the problem of restoration effect during the PBTI testing process can be effectively solved; besides, the testing device is easy to operate and basically free of additional hardware, thereby being low in cost.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and test method thereof
The invention belongs to a integrated circuit reliability test technology field and especially relates to a multifunctional test circuit of integrated circuit stress degradation and a test method thereof. A core part of the test circuit takes an annular oscillator as a basis. Several auxiliary transistors, switch transistors and control terminals are added. By using the circuit and the method of the invention, a negative bias temperature instability, a positive bias temperature instability, hot hole injection or hot electron injection stress can be applied to pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in a ring vibration inverter respectively; a ring oscillator is in a normal oscillation and stress oscillation state; the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs of the inverter in the ring oscillator is in a measuring state of a charge pump. The degradation of the MOSFETs in the ring vibration inverter can be shown through changes of a ring oscillator oscillation frequency after the stress and can be shown through the changes of a CP current (Icpp or Icpn) of the pMOSFETs or nMOSFETs in the ring oscillator.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Recovery circuit and recovery method for positive bias temperature instability
ActiveCN103427827BGood recovery effect of PBTI characteristicsLogic circuitsEngineeringPositive bias temperature instability
Provided are a restoring circuit and restoring method against positive bias temperature instability. The restoring circuit comprises a to-be-restored N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) transistor and a restoring unit. A grid electrode of the to-be-restored NMOS transistor is connected with the restoring unit. According to the restoring unit, a grid electrode of a switch transistor is connected with a signal input end, a drain electrode of the switch transistor is connected with a first voltage end, the first voltage end provides a negative first working voltage, a substrate of the switch transistor is connected with a second voltage end, a source electrode of the switch transistor is connected with one end of a second resistor, the other end of the second resistor is connected with a signal output end, one end of a first resistor is connected with a signal input end, and the other end of the first resistor is connected with the signal output end. Due to the fact that the voltage of the first voltage end is negative, by adjusting resistance values of the first resistor and the second resistor, grid electrode voltage applied to the to-be-restored NMOS transistor can be negative pressure, and good positive bias temperature instability (PBTI) characteristic restoration effect can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Transistor device and fabrication method
ActiveUS9147614B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOxygen vacancyOptoelectronics
Various embodiments provide transistors and their fabrication methods. An exemplary method for forming a transistor includes removing a dummy gate to form a trench over a semiconductor substrate. A high-k dielectric layer can be conformally formed on surface of the trench and then be fluorinated to form a fluorinated high-k dielectric layer. A functional layer can be formed on the fluorinated high-k dielectric layer and a metal layer can be formed on the functional layer to fill the trench with the metal layer. Due to fluorination of the high-k dielectric layer, negative bias temperature instability of the formed transistor can be reduced and oxygen vacancies can be passivated to reduce positive bias temperature instability of the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
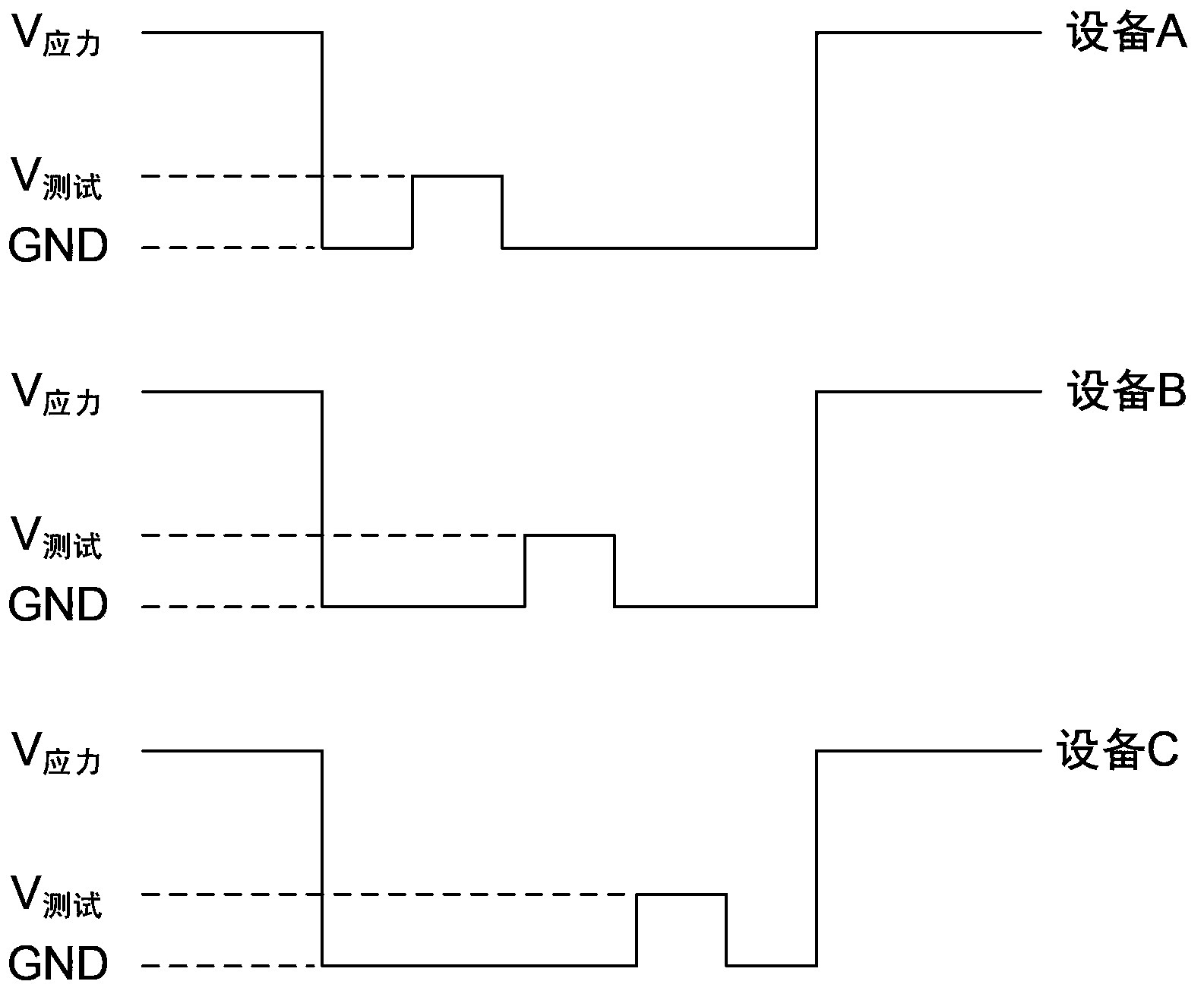
Testing device and testing method used for NMOS (n-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor in high-k metal gate
ActiveCN103543396AAvoid recovery effectsTroubleshooting Restoration EffectsIndividual semiconductor device testingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The invention discloses a testing device and a testing method used for an NMOS (n-channel metal oxide semiconductor) transistor in a high-k metal gate. The testing device comprises a resistor and a diode. The resistor is connected between an input end and an output end of the testing device, a positive pole of the diode is used for being connected with a bias voltage source, a negative pole of the diode is connected to the output end of the testing device, the input end of the testing device is used for receiving testing signals, and the output end of the testing device is used for connecting the gate of a to-be-tested NMOS transistor. The testing device is capable of exerting stress upon the to-be-tested NMOS transistor continuously and automatically during the PBTI (positive bias temperature instability) testing process, so that the problem of restoration effect during the PBTI testing process can be effectively solved; besides, the testing device is easy to operate and basically free of additional hardware, thereby being low in cost.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Method and apparatus for calculating delay timing values for an integrated circuit design
A method and apparatus for calculating delay timing values for at least a part of an integrated circuit design. The method comprises applying a first Negative / Positive Bias Temperature Instability compensation margin to delay values for elements within the at least part of the IC design, identifying at least one lower-rate switching element within the at least part of the IC design, and applying at least one further, increased N / PBTI compensation margin to the delay value(s) for the at least one identified lower-rate switching element.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com