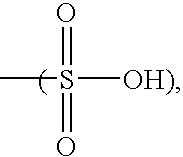
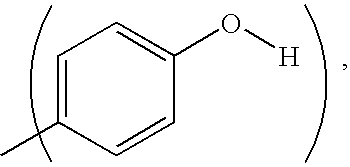
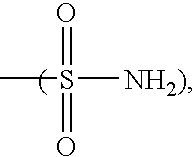Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
281 results about "Bond energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, bond energy (E) or bond enthalpy (H) is the measure of bond strength in a chemical bond. IUPAC defines bond energy as the average value of the gas-phase bond dissociation energies (usually at a temperature of 298 K) for all bonds of the same type within the same chemical species. For example, the carbon–hydrogen bond energy in methane H(C–H) is the enthalpy change involved with breaking up one molecule of methane into a carbon atom and four hydrogen radicals, divided by 4. Tabulated bond energies are generally values of bond energies averaged over a number of selected typical chemical species containing that type of bond. Bond energy (E) or bond enthalpy (H) should not be confused with bond-dissociation energy. Bond energy is the average of all the bond-dissociation energies in a molecule, and will show a different value for a given bond than the bond-dissociation energy would. This is because the energy required to break a single bond in a specific molecule differs for each bond in that molecule. For example, methane has four C–H bonds and the bond-dissociation energies are 435 kJ/mol for D(CH₃–H), 444 kJ/mol for D(CH₂–H), 444 kJ/mol for D(CH–H) and 339 kJ/mol for D(C–H). Their average, and hence the bond energy, is 414 kJ/mol, even though not a single bond required specifically 414 kJ/mol to be broken.
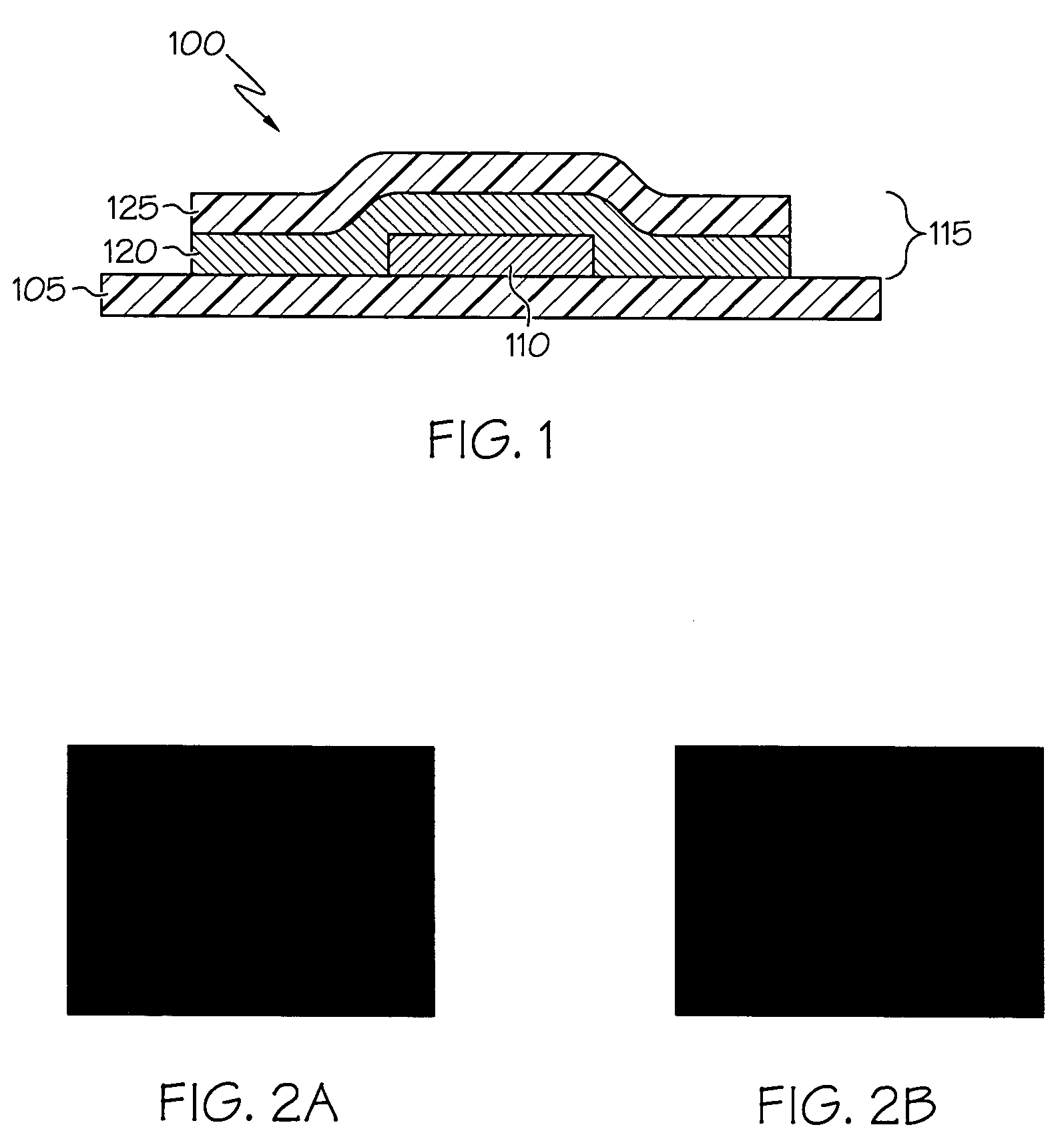
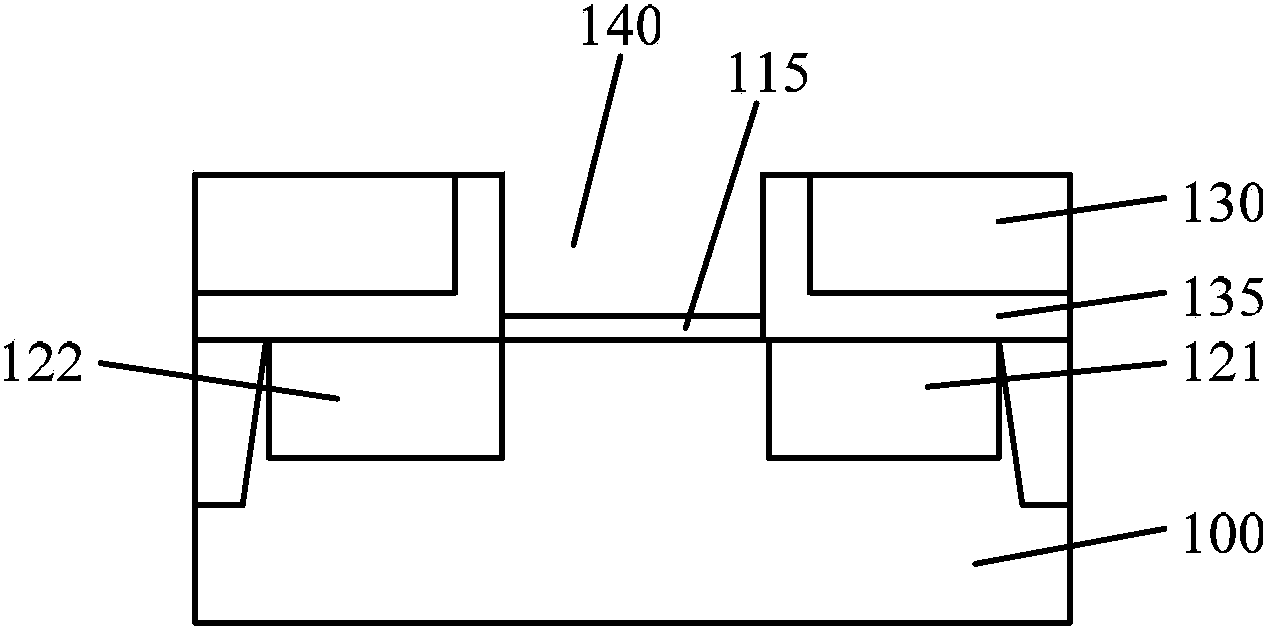
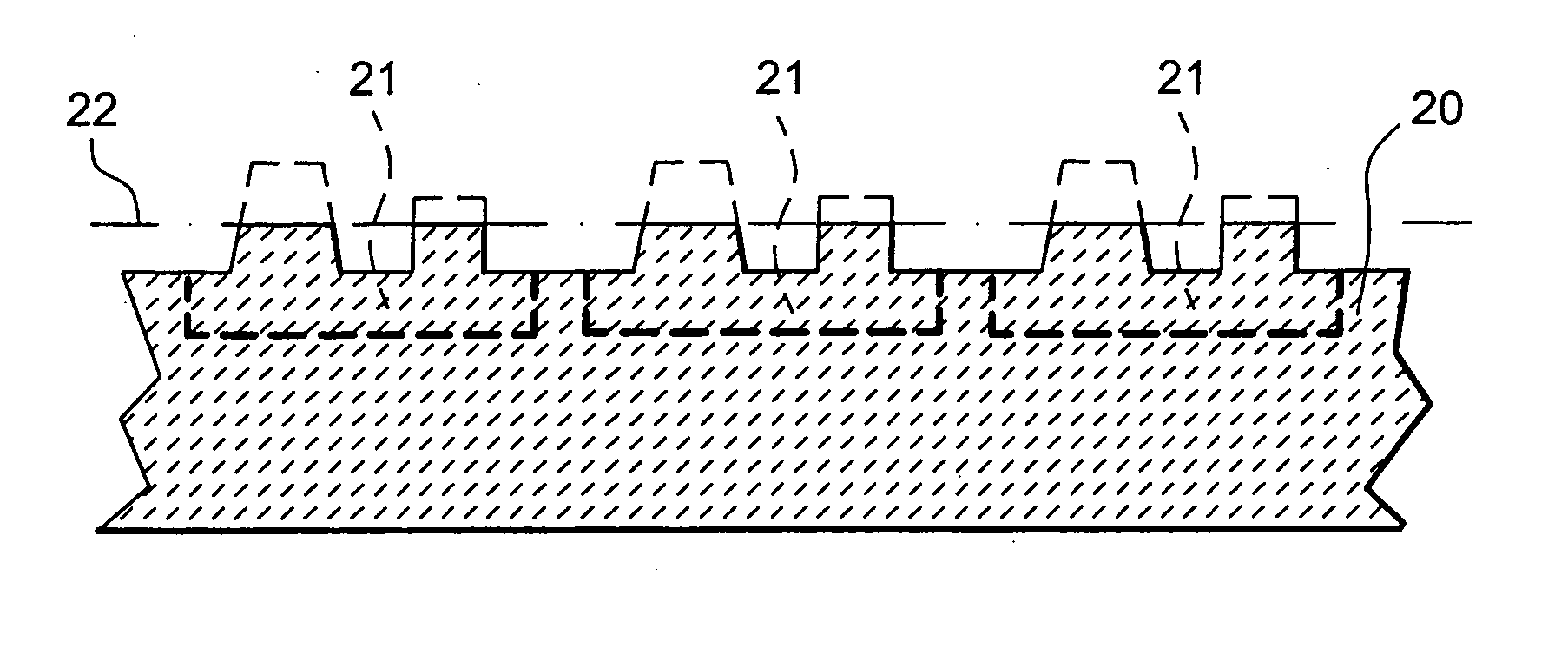
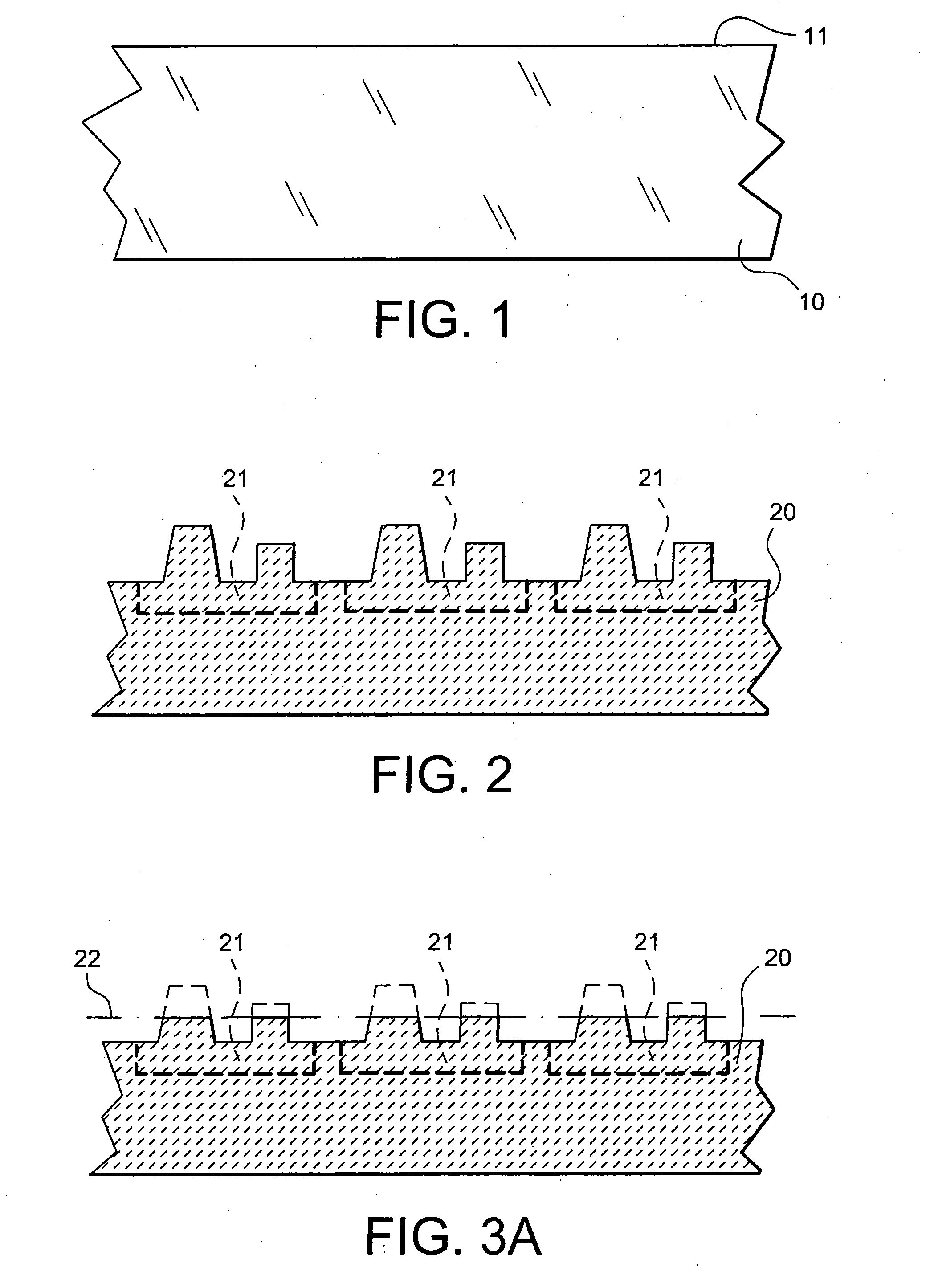
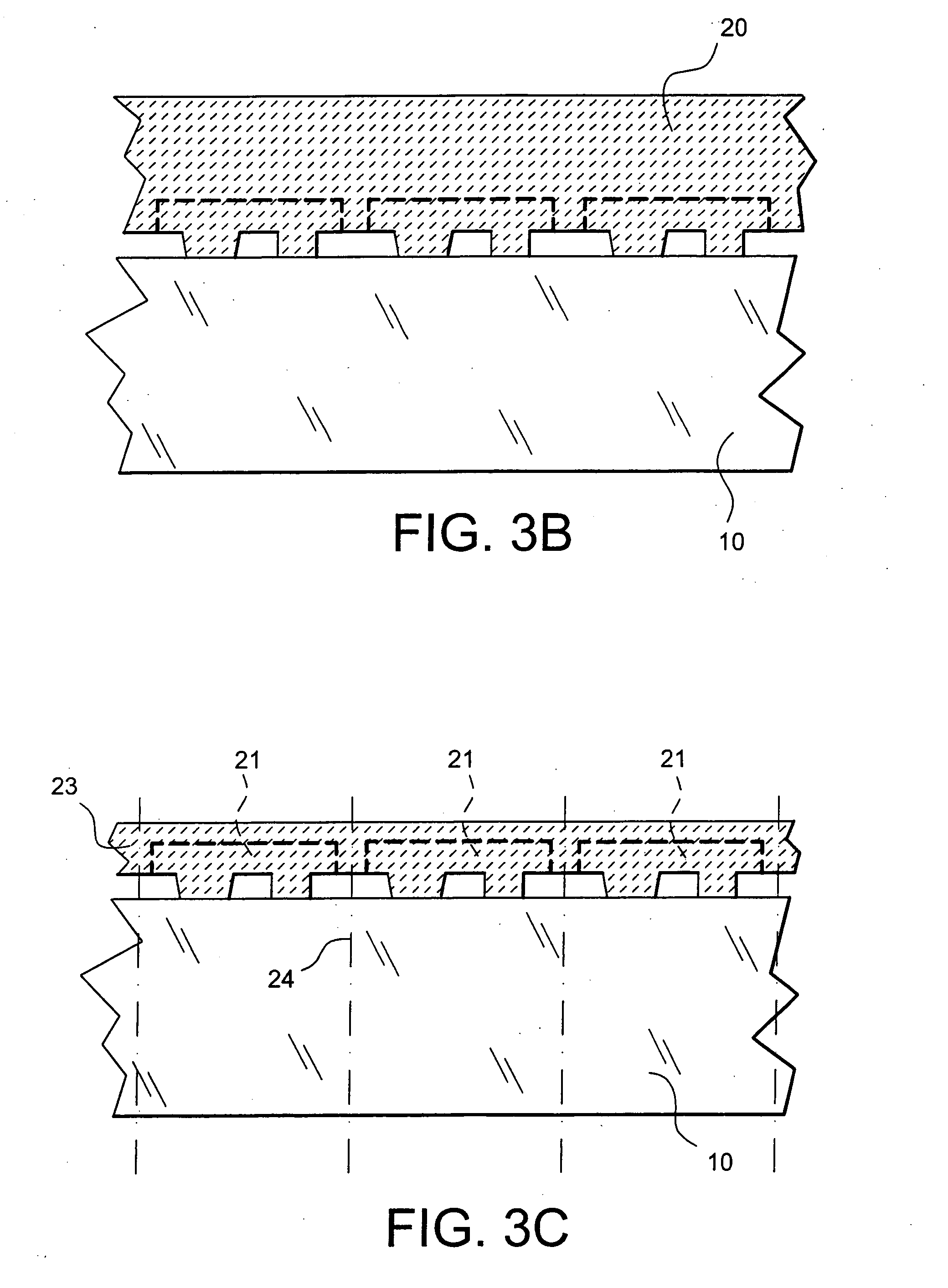
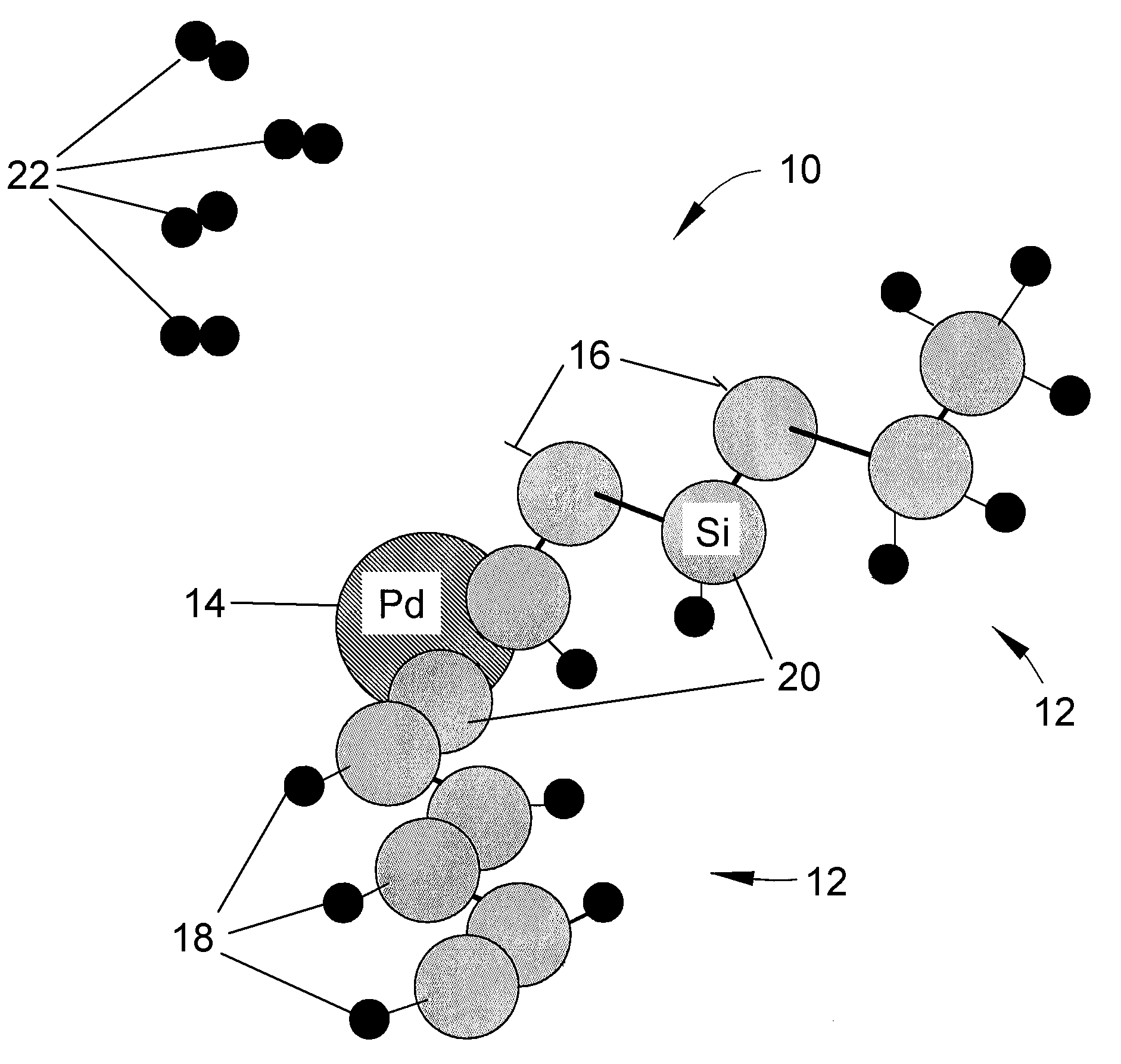
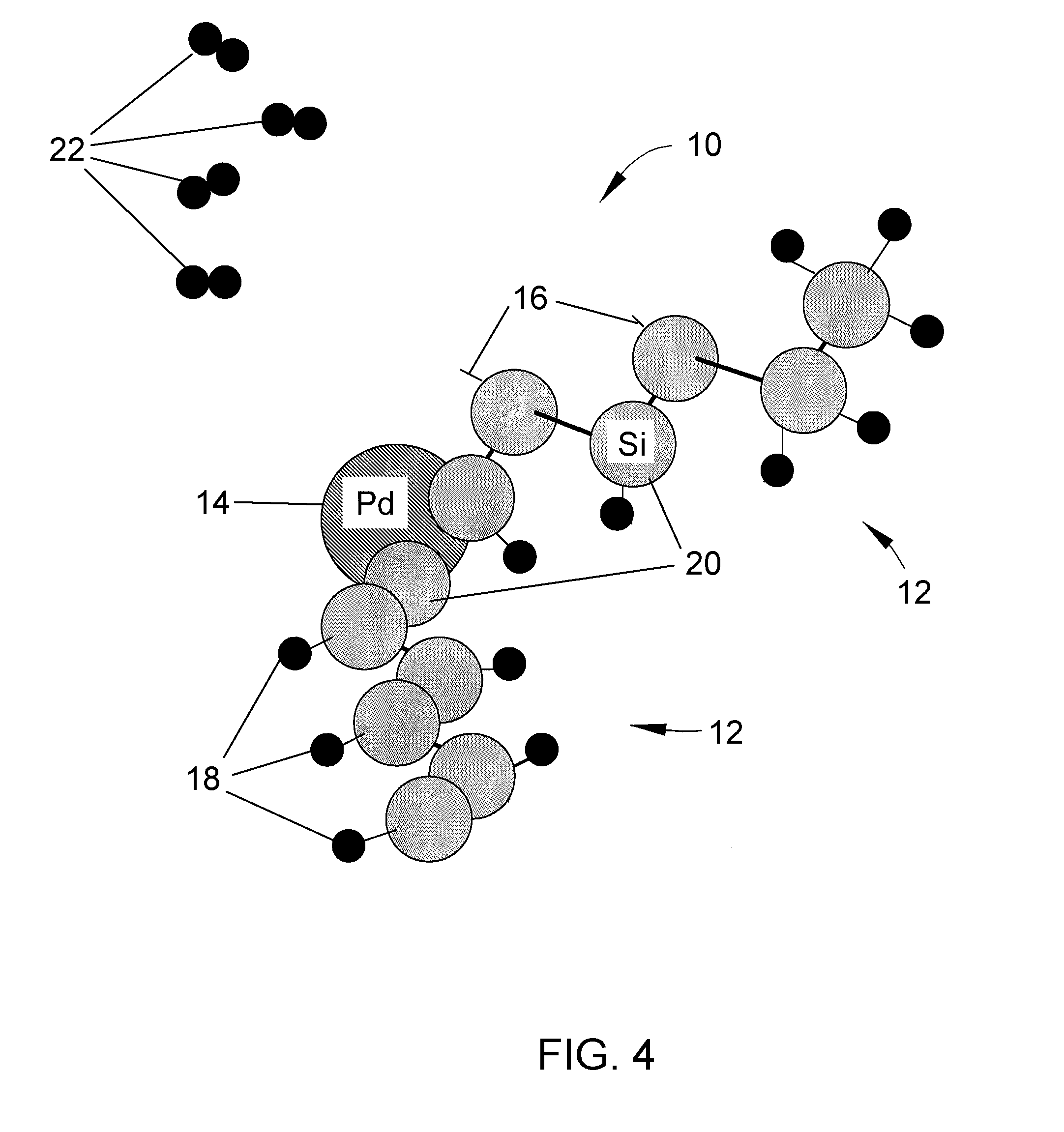
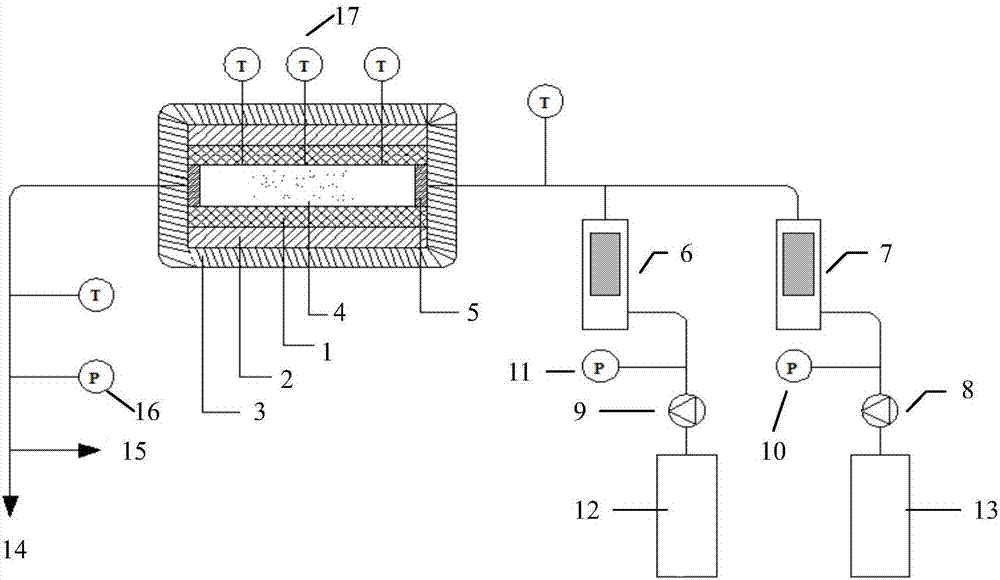
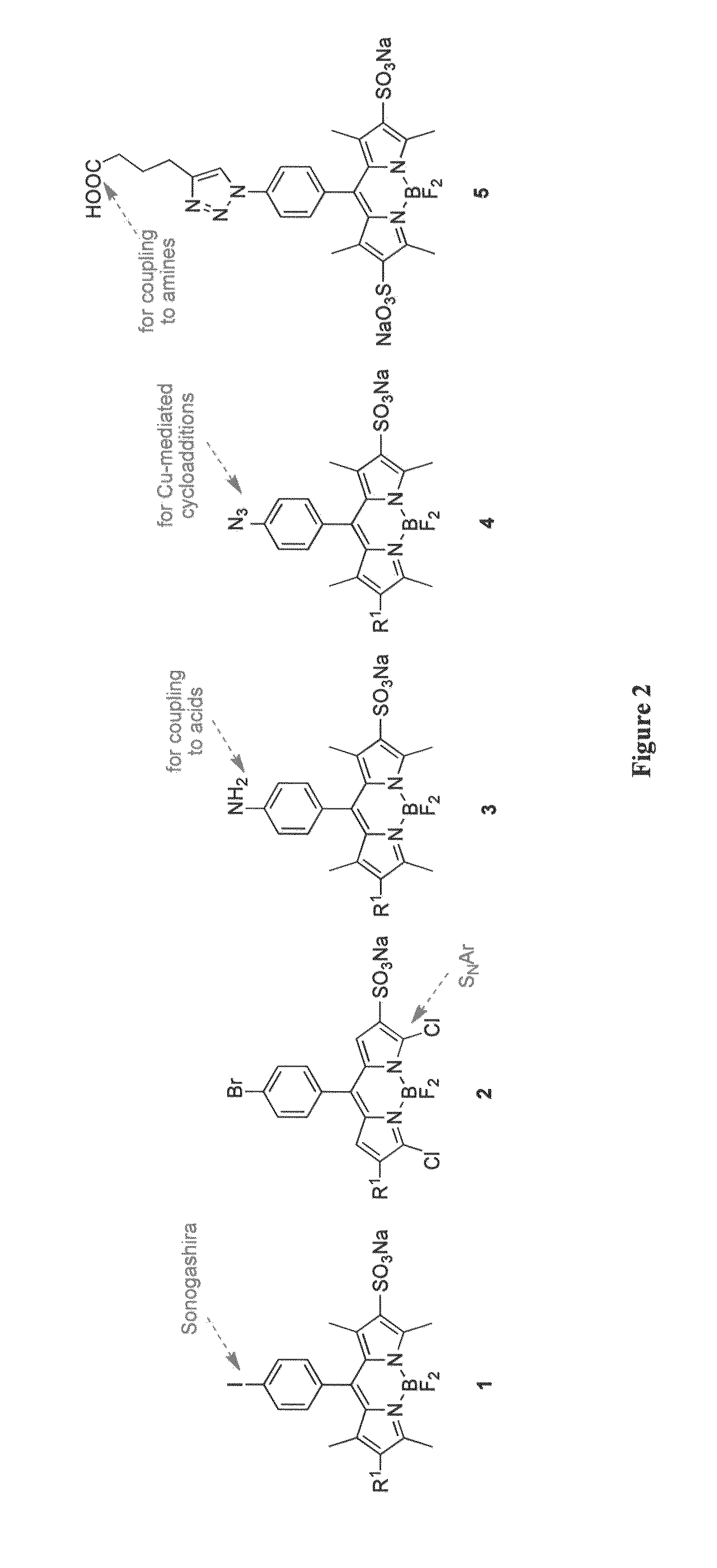
Printed wiring board having highly reliably via hole and process for forming via hole
InactiveUS6280641B1Improve reliabilityImprove productivityLight absorption dielectricsDecorative surface effectsBond energyConductive coating
Disclosed are a printed wiring board having micro-via holes highly reliable for conduction and a method of making the micro-via hole by providing a coating or sheet of an organic substance containing 3 to 97% by volume of at least one selected from a metal compound powder, a carbon powder or a metal powder having a melting point of at least 900° C. and a bond energy of at least 300 kJ / mol on a copper foil as an outermost layer of a copper-clad laminate having at least two copper layers, or providing a coating or sheet of the same after oxidizing a copper foil as an outermost layer, irradiating the coating or sheet with a carbon dioxide gas laser at an output of 20 to 60 mJ / pulse, thereby removing a micro-via-hole-forming portion of at least the copper foil as the outermost layer, then irradiating micro-via-hole-forming portions of the remaining layers with a carbon dioxide gas laser at an output of 5 to 35 mJ / pulse to make a micro-via hole which does not penetrate through the copper foil in a bottom of the micro-via hole, and electrically connecting the copper foil as the outermost layer and the copper foil in the bottom of the micro-via hole with a metal plating or an electrically conductive coating composition.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Dark blue organic light-emitting material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110790782AHigh color purityImprove stabilitySilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesBond energyULTRAMARINE BLUE
The invention discloses a dark blue organic light-emitting material and a preparation method and application thereof. The dark blue organic light-emitting material contains a structural unit disclosedin the invention, wherein, M is B or Bi; X is O, S or NR4; R1-R4 are independently selected from connecting bonds or groups obtained from H-H, H-F, H-O-H, H-S-H, H-CN, saturated hydrocarbons, unsaturated hydrocarbons, fluorinated hydrocarbons, heterocyclic compounds, organoboron, organosilicone, alcohols, mercaptans, ethers, thioethers, phenols, thiophenol, aldehydes, ketones, amines, amides, nitriles or sulfones losing one or more H; R1-R3 are located at any substitution position on rings of the structural unit where R1-R3 are located, and the bond energy between the ring where R3 is locatedand M is greater than or equal to the bond energy between the ring where R2 is located and M. The dark blue organic light-emitting material containing the B / Bi-N main body structure has very narrow light-emitting spectrum and TADF properties; the color purity is high, and the stability is good.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
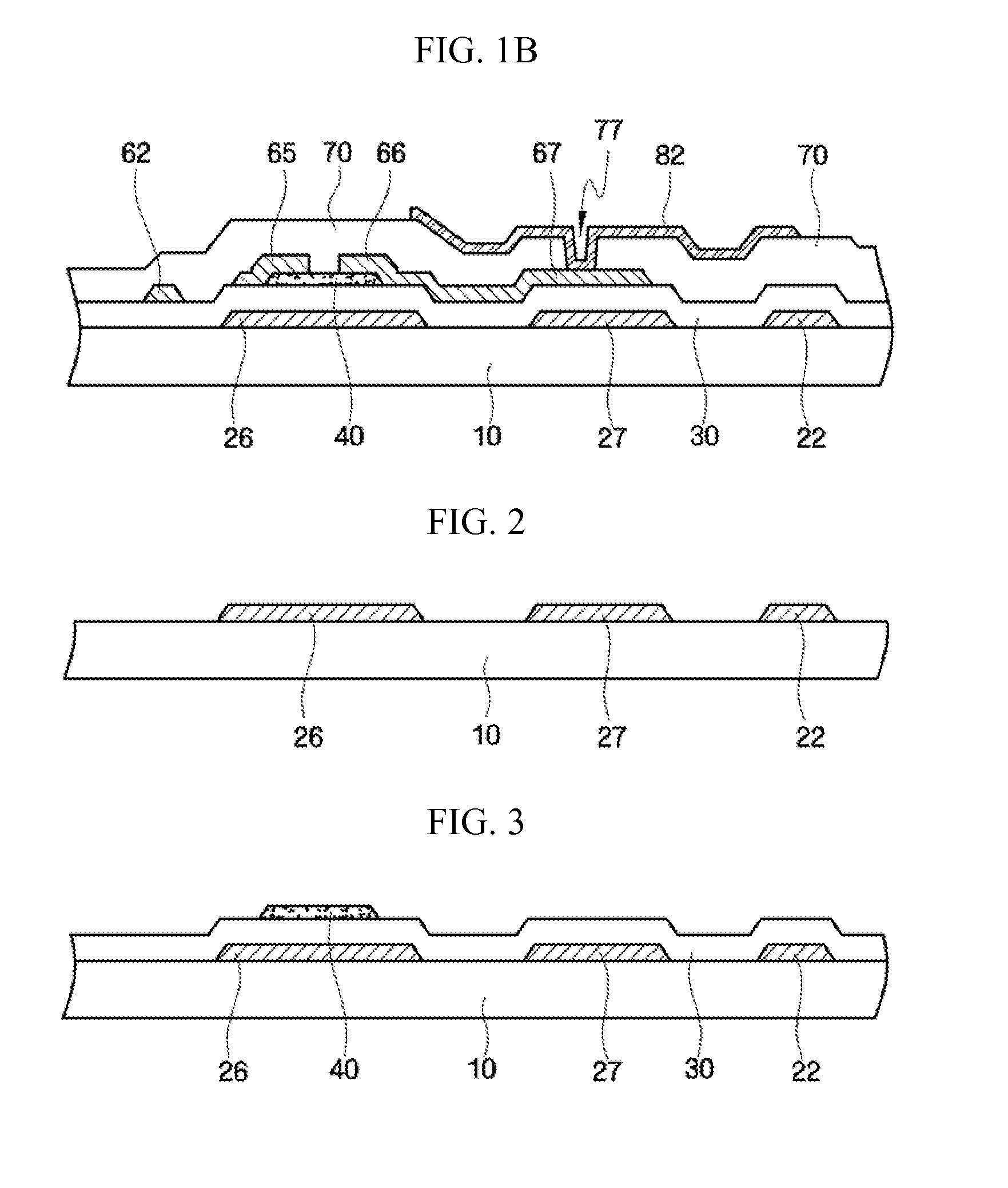
Thin film transistor array substrate and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100155721A1Improve propertiesImprove stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesBond energyOxygen
A thin film transistor (TFT) array substrate is provided. The thin film transistor (TFT) array substrate includes an insulating substrate, an oxide semiconductor layer formed on the insulating substrate and including an additive element, a gate electrode overlapping the oxide semiconductor layer, and a gate insulating layer interposed between the oxide semiconductor layer and the gate electrode, wherein the oxygen bond energy of the additive element is greater than that of a base element of the oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Prefabricated and attached interconnect structure
InactiveUS6965245B2Eliminate momentumSimple structureElectrical apparatusElectrical measurement instrument detailsBond energyManufacturing technology
A interconnect assembly features a prefabricated interconnect structure metallurgically bonded to a terminal of a larger structure. Fabrication of the interconnect structure's independently and seperate from the larger structure enables the use of economic mass fabrication techniques that are well-known for miniature scale sheet metal parts. During fabrication, positioning and attachment, each interconnect structure is combined with and / or held in a carrier structure from which it is separated after attachment to the terminal. The interconnect structure is configured such that an attachment tool may be brought into close proximity to the attachment interface between the interconnect structure and the terminal for a short and direct transmission of bonding energy onto the attachment interface. The attachment interface provides for an electrically conductive and a bending stress opposing mechanical connection between the interconnect structure and the terminal. The interconnect assembly is preferably part of a probe apparatus.
Owner:SV PROBE PTE LTD
Method of epitaxial-like wafer bonding at low temperature and bonded structure
InactiveUS20030141502A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond energyHydrogen
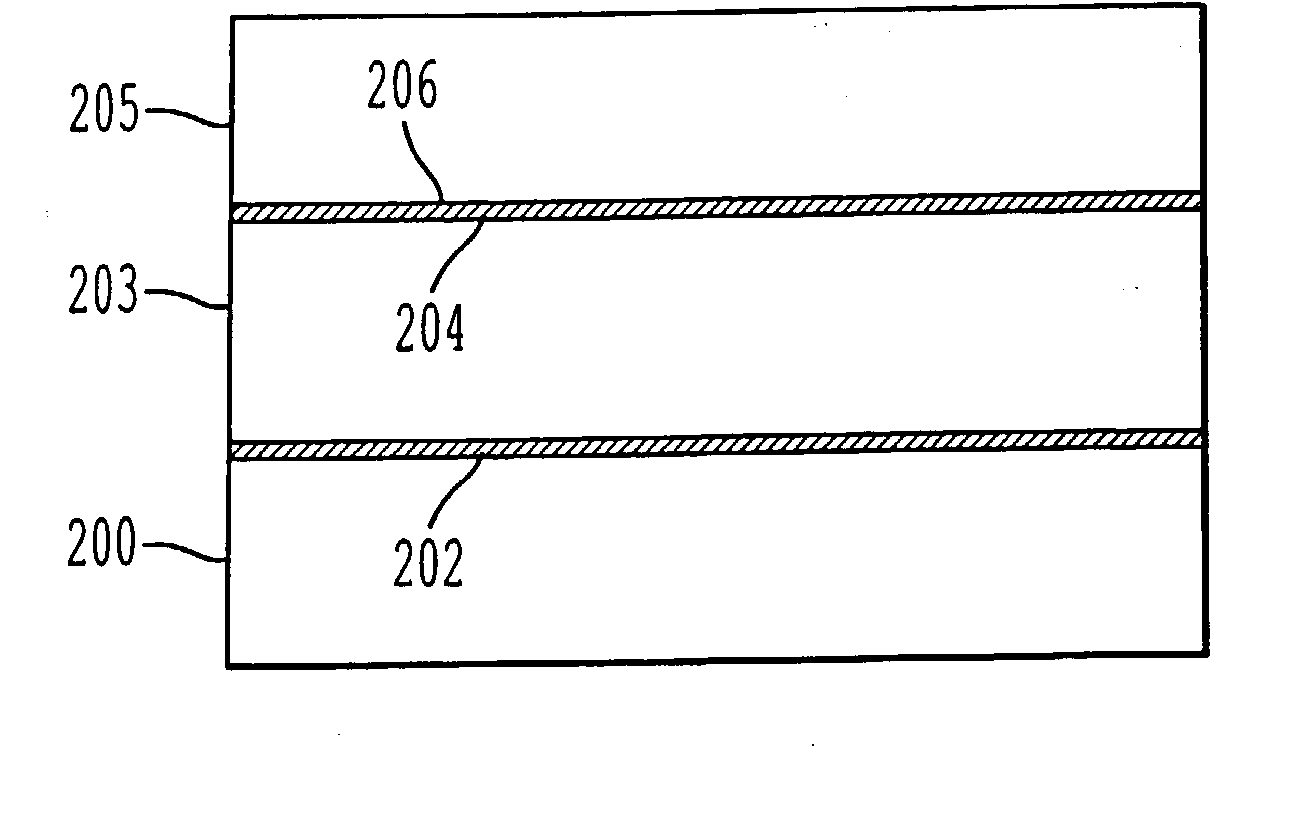
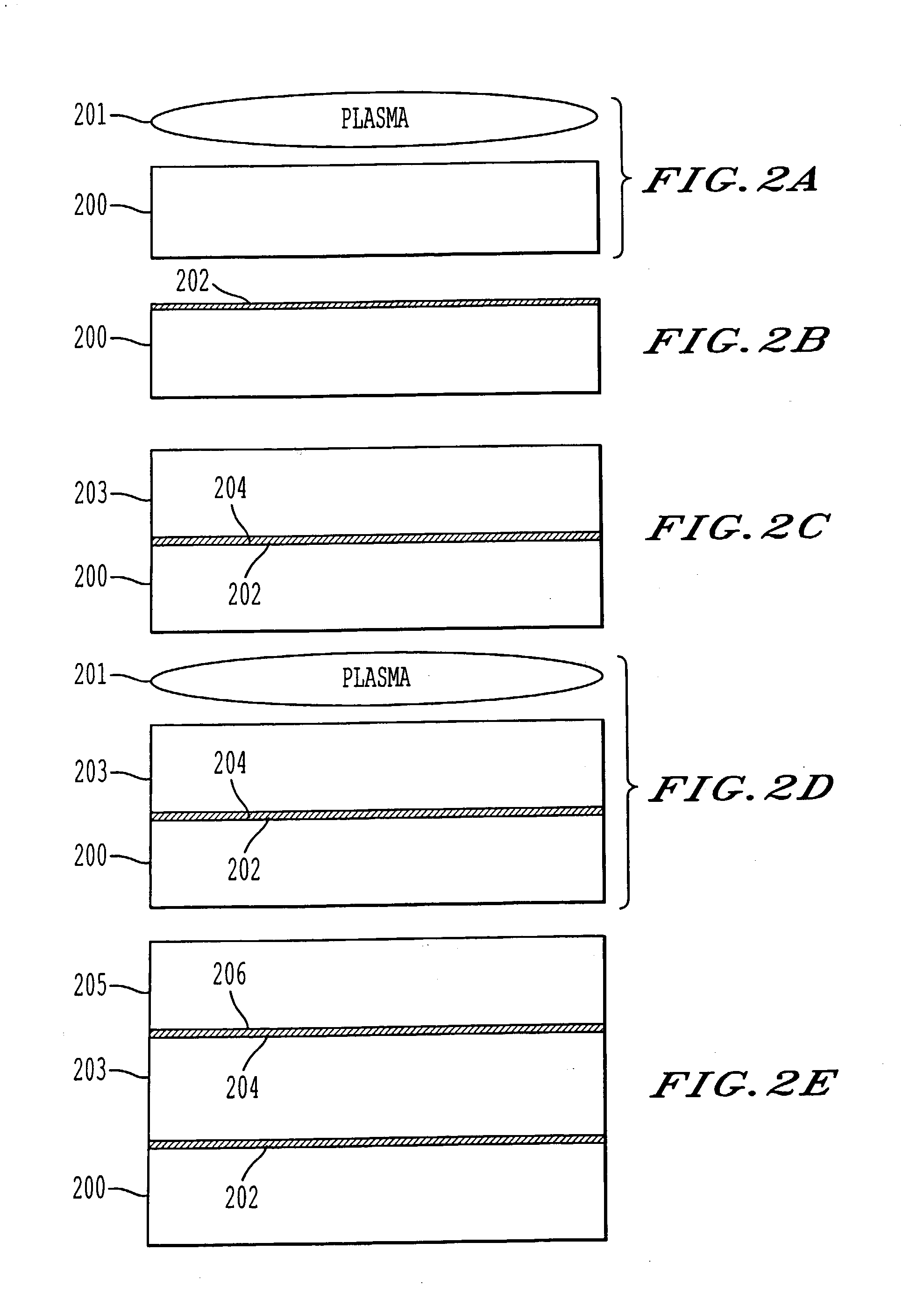
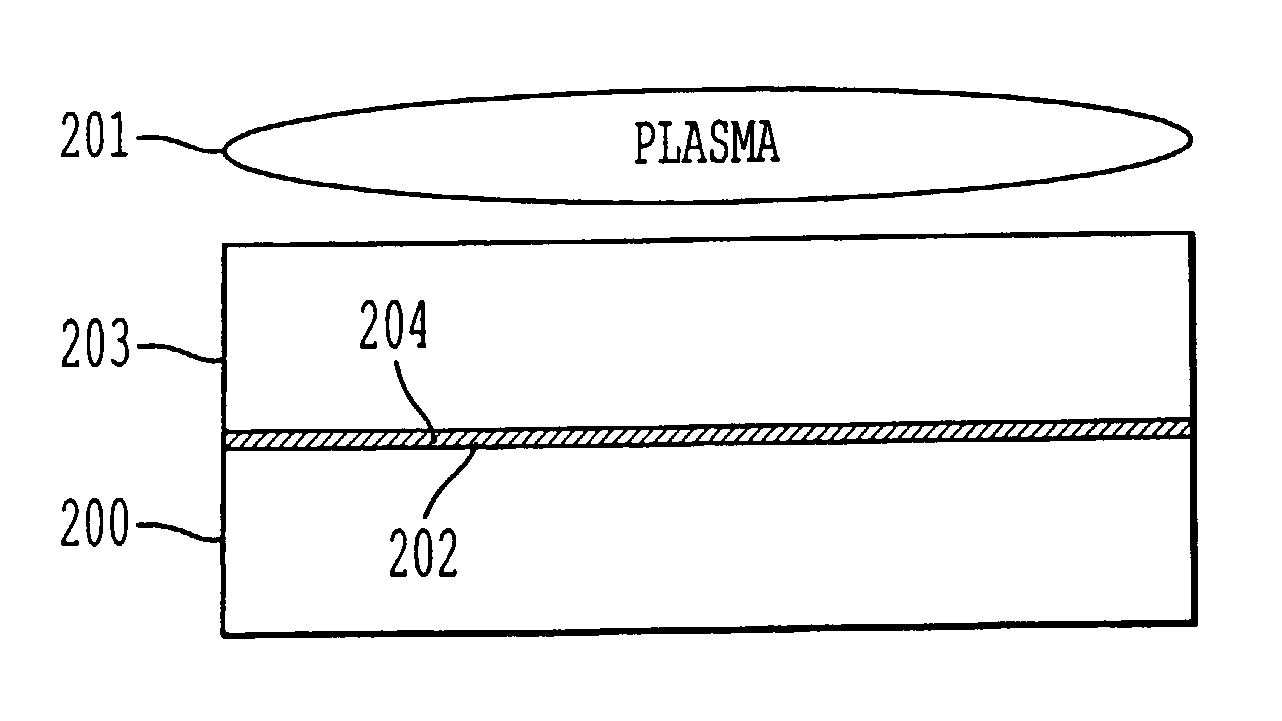
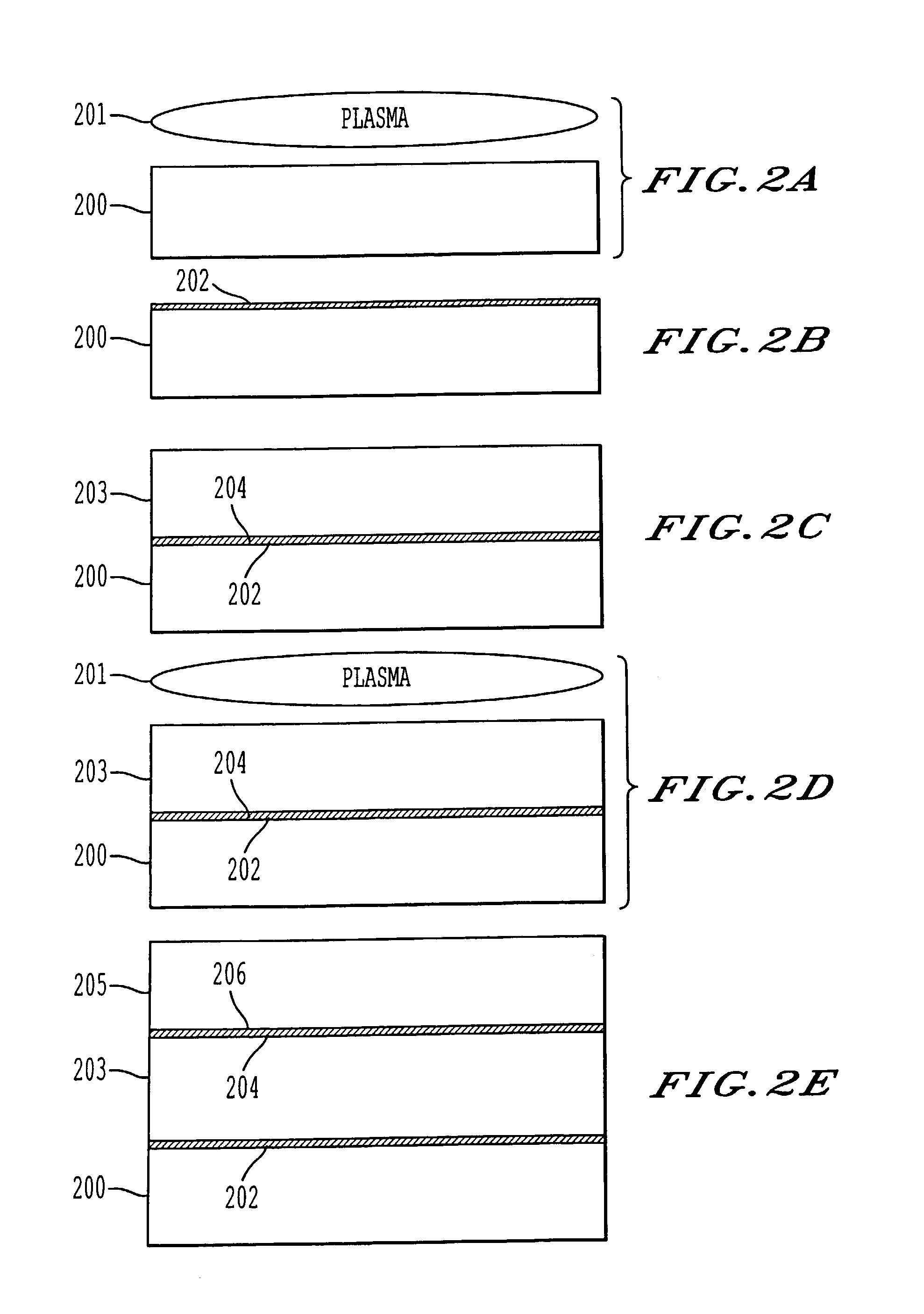
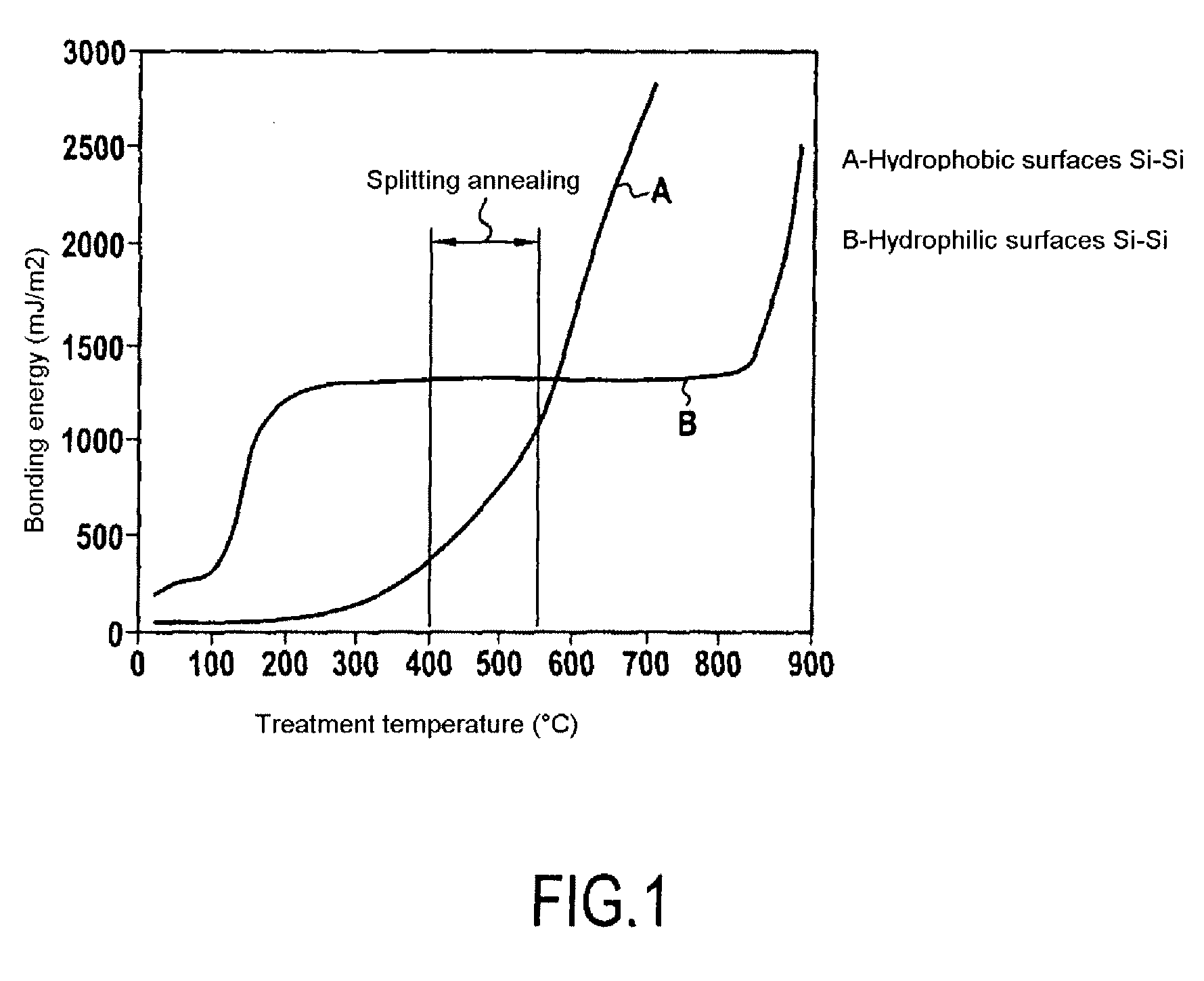
A process for bonding oxide-free silicon substrate pairs and other substrates at low temperature. This process involves modifying the surface of the silicon wafers to create defect regions, for example by plasma-treating the surface to be bonded with a or boron-containing plasmas such as a B2H6 plasma. The surface defect regions may also be created by ion implantation, preferably using boron. The surfaces may also be amorphized. The treated surfaces are placed together, thus forming an attached pair at room temperature in ambient air. The bonding energy reaches approximately 400 mJ / m2 at room temperature, 900 mJ / m2 at 150° C., and 1800 mJ / m2 at 250° C. The bulk silicon fracture energy of 2500 mJ / m2 was achieved after annealing at 350-400° C. The release of hydrogen from B-H complexes and the subsequent absorption of the hydrogen by the plasma induced modified layers on the bonding surfaces at low temperature is most likely responsible for the enhanced bonding energy.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Encapsulated devices and method of making
ActiveUS7767498B2High bulk densityReduce in quantitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond energyPolymer science
A method of encapsulating an environmentally sensitive device. The method includes providing a substrate; placing at least one environmentally sensitive device adjacent to the substrate; and depositing at least one barrier stack adjacent to the environmentally sensitive device, the at least one barrier stack comprising at least one barrier layer and at least one polymeric decoupling layer, wherein the at least one polymeric decoupling layer is made from at least one polymer precursor, and wherein the polymeric decoupling layer has at least one of: a reduced number of polar regions; a high packing density; a reduced number of regions that have bond energies weaker than a C—C covalent bond; a reduced number of ester moieties; increased Mw of the at least one polymer precursor; increased chain length of the at least one polymer precursor; or reduced conversion of C═C bonds. An encapsulated environmentally sensitive device is also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
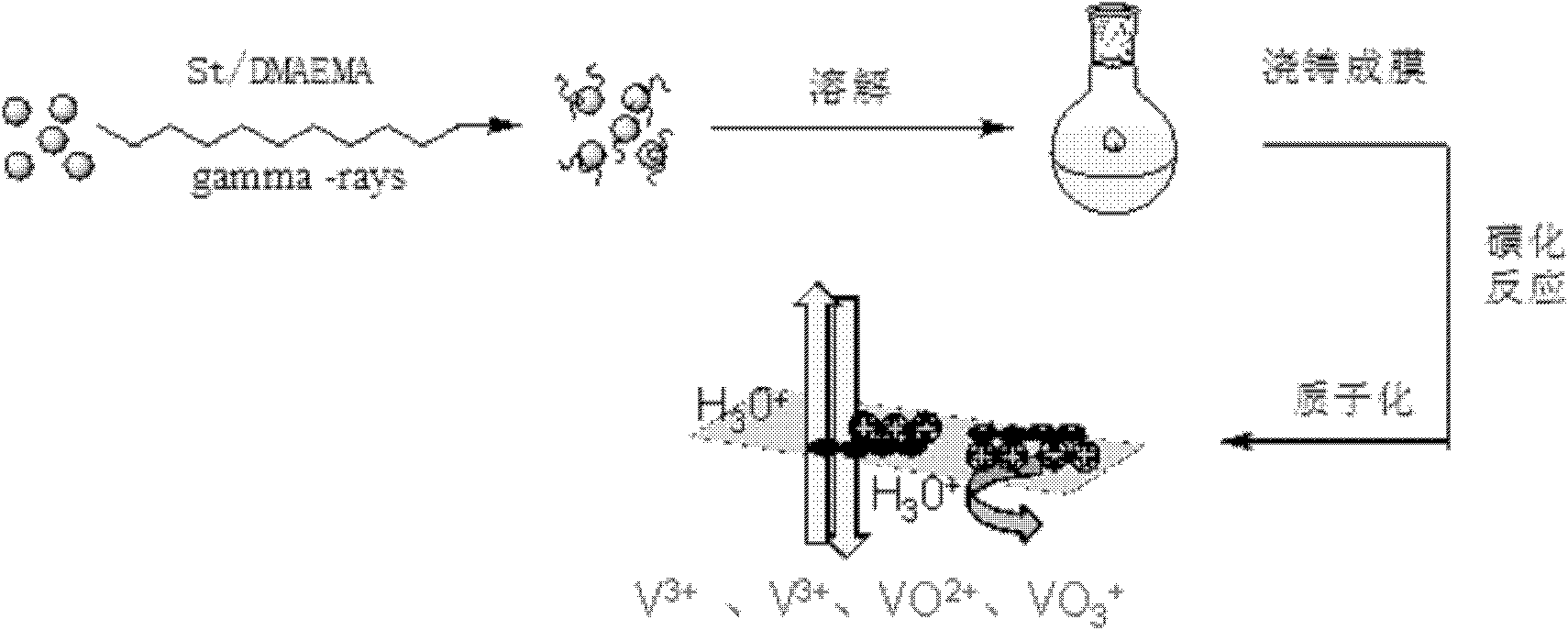
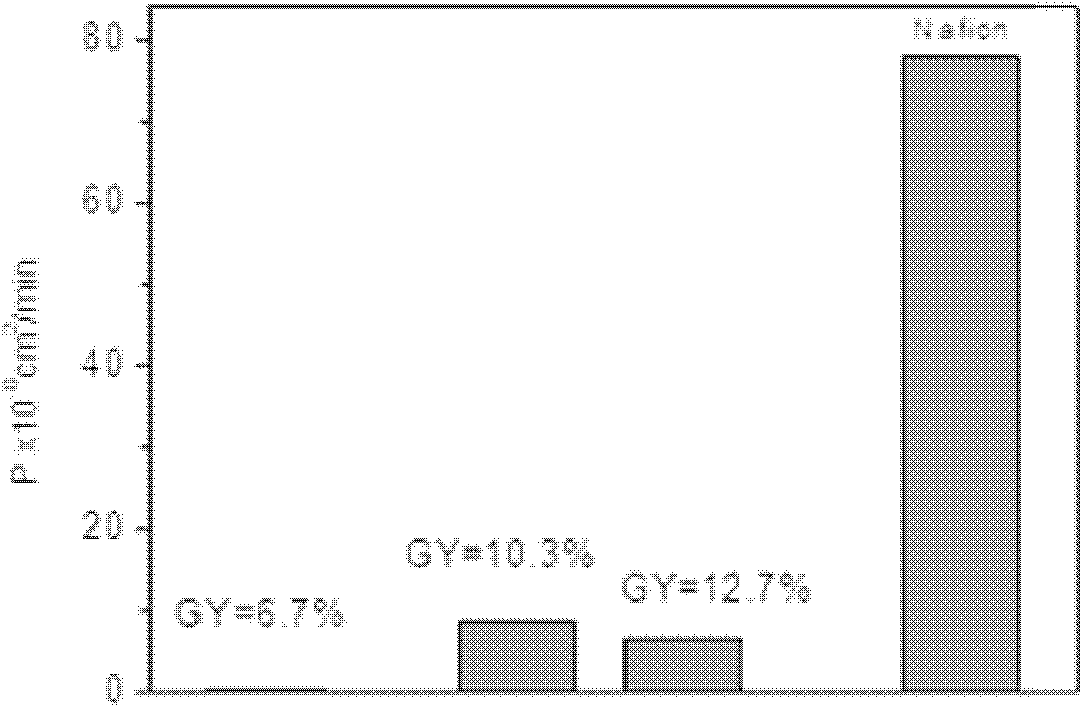
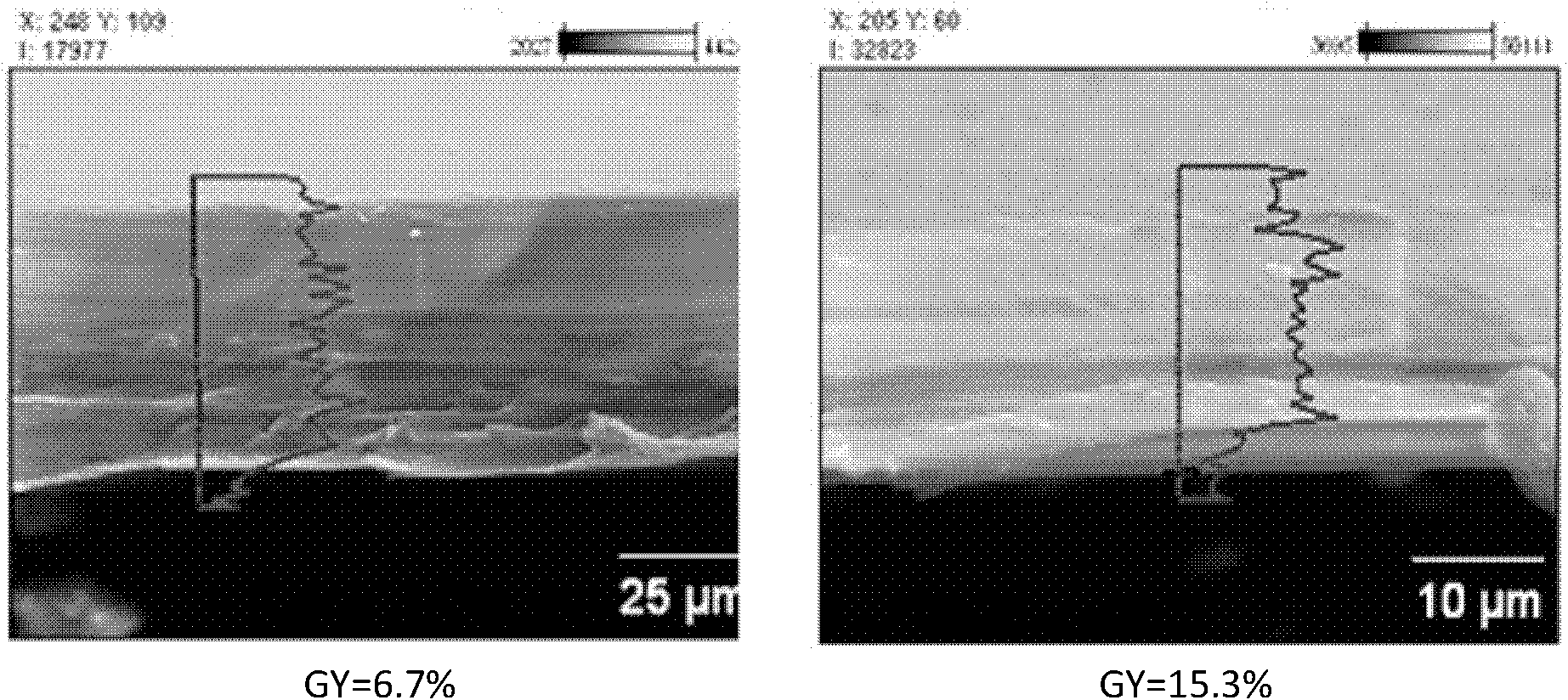
Preparation method of amphoteric ion exchange membrane
ActiveCN102181069AKeep hydrophilicEnsure normal conductionAmphoteric ion-exchangersCell component detailsProtonationBond energy
The invention discloses a preparation method of an amphoteric ion exchange membrane and relates to a preparation method of an amphoteric ion exchange membrane for an all-vanadium redox flow battery. According to the scheme, the preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing irradiation grafting on polymer powder poly(vinylidene fluoride); transforming the irradiation-grafted polymer powder into a membrane material; and sulfonating the membrane material, hydrolyzing, introducing a sulfonate radical group with a cationic exchange function, putting the membrane material into a hydrochloric acid aqueous solution for undergoing a protonation reaction and introducing basic nitril with an anion exchange function to obtain the amphoteric ion exchange membrane. In the method, commercial poly(vinylidene fluoride) resin with low price is taken as a raw material, so that the membrane making cost can be lowered; a C-F bond has large bond energy, so that the membrane can keep high chemical stability in a strong acid and high oxidizing electrochemical environment; and meanwhile, the problem of non-uniform distribution of grafted chains of the conventional heterogeneous irradiation-grafted membrane in the vertical direction of the membrane is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Hair treatment compositions incorporating hair substantive polymers
The invention provides a hair treatment composition comprising a hair substantive polymer, the hair substantive polymer comprising a polymeric backbone bearing: (a) at least one side chain which is formed from a hair fiber targeting group which is covalently linked to the polymeric backbone, the hair fiber targeting group being a non-cationic species which is capable of specifically interacting with the protein surface of the hair fiber in a non-covalent interaction having a bond energy ranging from 0.5 to 3 Kcal / mol, when the composition is applied to hair; (b) preferably, at least one side chain which is different to side chain (a) and which comprises a hair benefit agent. Compositions of the invention provide for deposition and delivery of benefit agents to hair in a more efficient and targeted manner.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Molecular complexes and release agents
A molecular complex for application to fuser members in toner fusing systems. The complex is formed from molecules with complementary acid and base functional groups. These groups interact to provide a noncovalent bond having a bond energy of about 20 kJ / mol or more.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO +1
Positive electrode material of multi-element layered lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a positive electrode material of a multi-element layered lithium ion battery. The chemical general formula of the positive electrode material is LiNiaMbNcO2, and the Li-Ni mixed ranging degree is less than 2%; in the chemical general formula, M is a transition-metal element, N is one or more of Al, Mg, Ti and Zr, and the values of a, or b, or c meet conditions that a+b+c=1, a>0.3, and c<0.03. The preparation method is as follows: preparing a multi-element precursor by virtue of utilizing a coprecipitation method, and then performing lithiation and sintering, thereby obtaining the positive electrode material of a multi-element layered solid solution. Compared with the prior art, the positive electrode material of the multi-element layered lithium ion battery has the advantages that the Li-Ni mixed ranging degree is reduced to less than 2%, so that the positive electrode material has higher coulomb efficiency, better layer structure and stronger bond energy and shorter bond length of metal-oxygen bond and also has better cycle performance and obviously improved thermal stability at a high temperature and a high pressure.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH
Synthesis of high mechanical stability non-metal element doped ordered mosopore carbon material
InactiveCN100999316ALarge specific surface areaUniform pore size distributionBond energyMolecular adsorption
This invention discloses a preparation method of functional order mesoporous carbon without metal. Make water-soluble phenol formaldehyde and response type of acid for polymerization, utilize predecessor and nonionic wetting agent to carry out organism-organism self assembly, get resin-nonionic wetting agent composite containing boron and phosphonium, remove surface acting agent by calcinating in inert atmosphere, carbonize with high temperature, get non-metal element functional ordered mesoporous polymer, and make order mesoporous carbon with boron or phosphonium. Its ordered meso-scale structure is divided into two kinds. It has characteristics of uniform large specific surface, pore diameter, bore, and path. Because boron oxygen bond of high bond energy is leaded in molecular constitution, it makes order mesoporous carbon with boron have strong mechanical stability. It can be used as wear-resisting stuff. It has lubricating, abrasion improving, service life of friction materials extending effects. It has extensive application prospect in catalytic action, heavy metal ion, and colorant molecular adsorption and electrode materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Forming method of metal gate, forming method of MOS transistor and forming method of CMOS structure
ActiveCN103681276AStrong oxidation abilityReduced negative bias temperature instabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBond energyOxygen vacancy
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Foam drainage agent for gas well drainage gas recovery
ActiveCN104140802AImprove stabilityGood water carrying effectDrilling compositionBond energyChemical agent
Belonging to the technical field of oil-gas field chemical agents, the invention relates to a foaming drainage agent for gas well drainage gas recovery. The foaming drainage agent for gas well drainage gas recovery is formed by mixing of a gemini surfactant, a zwitterionic surfactant, a high-bond energy surfactant and a macromolecular polymer. The foaming drainage agent provided by the invention has high temperature environment resistance (up to 180DEG C), suitability to environment with wide pH value (of 1-10), high mineralization degree resistance (greater than or equal to 320000mg / L), and resistance to hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide atmosphere (with the hydrogen sulfide partial pressure being greater than or equal to 25% and the carbon dioxide partial pressure being greater than or equal to 20%). And the foaming drainage agent also has the advantages of excellent foaming performance, good foam stability, good water-carrying effect, low surface tension, and foam volume mostly higher than 8 times.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of epitaxial-like wafer bonding at low temperature and bonded structure
A process for bonding oxide-free silicon substrate pairs and other substrates at low temperature. This process involves modifying the surface of the silicon wafers to create defect regions, for example by plasma-treating the surface to be bonded with a or boron-containing plasmas such as a B2H6 plasma. The surface defect regions may also be created by ion implantation, preferably using boron. The surfaces may also be amorphized. The treated surfaces are placed together, thus forming an attached pair at room temperature in ambient air. The bonding energy reaches approximately 400 mJ / m2 at room temperature, 900 mJ / m2 at 150° C., and 1800 mJ / m2 at 250° C. The bulk silicon fracture energy of 2500 mJ / m2 was achieved after annealing at 350-400° C. The release of hydrogen from B—H complexes and the subsequent absorption of the hydrogen by the plasma induced modified layers on the bonding surfaces at low temperature is most likely responsible for the enhanced bonding energy.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Forming method of grid oxidation layer
InactiveCN102486999AAvoid breakingReduce interface defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBond energyReactive gas
The invention provides a forming method of a grid oxidation layer. The forming method comprises the following steps of: providing a substrate, and forming a grid oxide layer on the substrate by a thermal oxidation process, wherein reactive gas in the thermal oxidation process is mixed gas at least containing deuterium. According to the forming method, a deuterium element is introduced into the thermal-oxidation growth process of the grid oxidation layer, silicon dangling bonds in a saturated interface state form silicon-deuterium bonds with stronger combination so as to reduce the silicon dangling bonds positioned in the interface state or replace hydrogen of silicon-hydrogen bonds to further form the silicon-deuterium bonds with stronger combination. Simultaneously, the silicon-deuterium bond energy is more than the silicon-hydrogen bond energy; and under the semiconductor process environment, the silicon-deuterium bonds are not easily broken due to external stress, so that the silicon dangling bonds positioned in the interface state are further reduced, the interface defects are reduced, and further the hot-electron effect is restrained.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
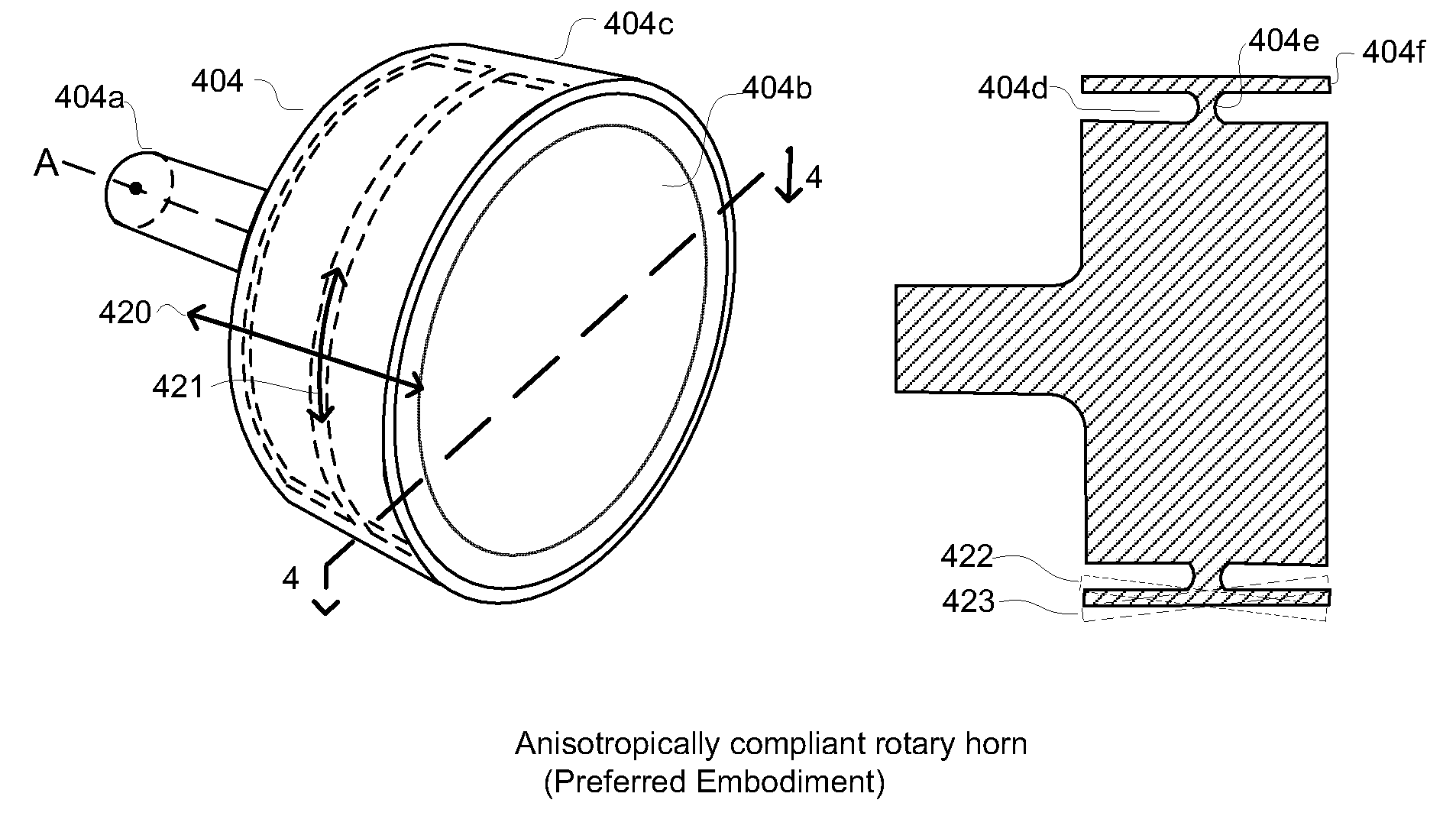
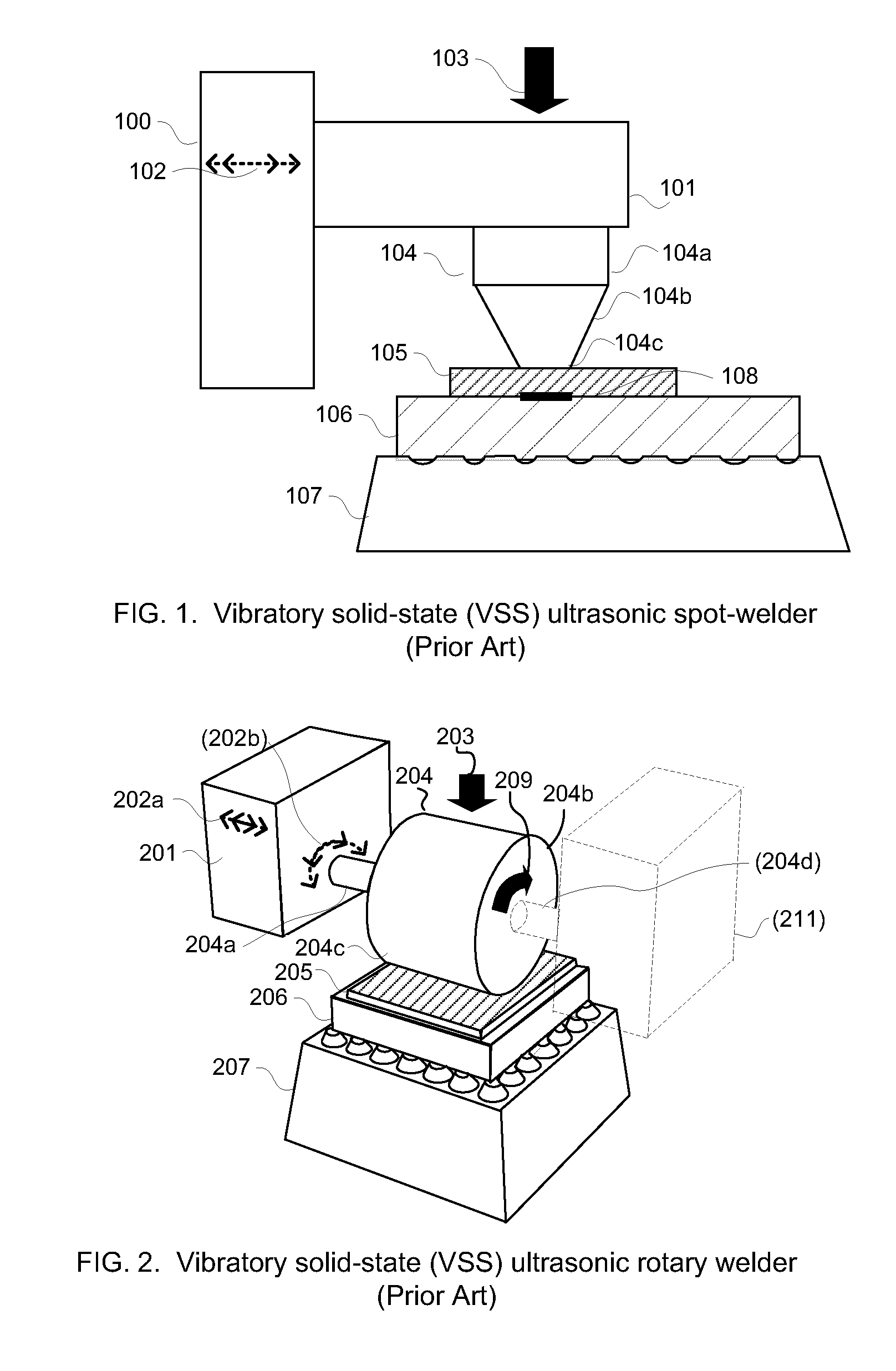
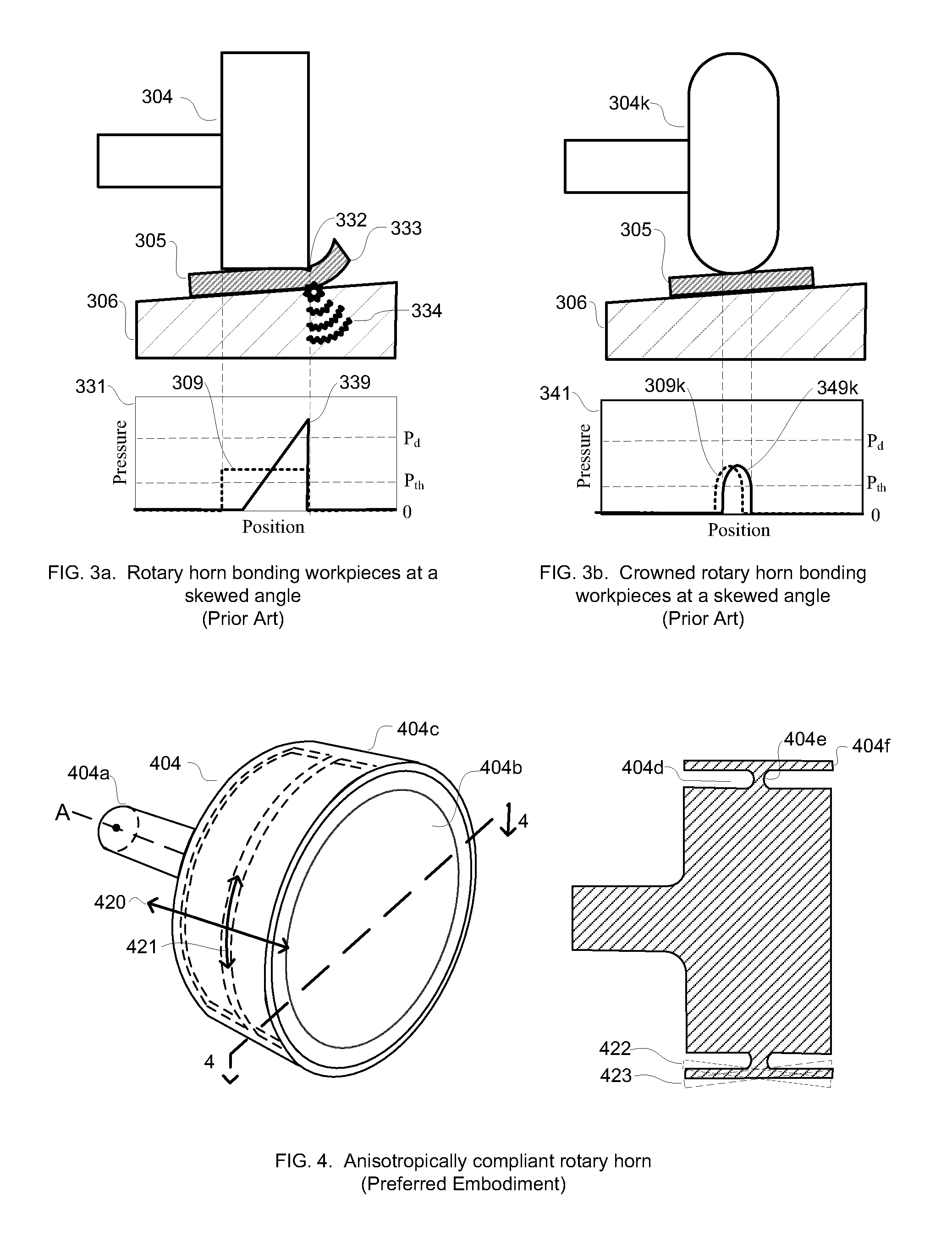
Anisotropically compliant horns for ultrasonic vibratory solid-state bonding
InactiveUS20100040903A1Minimize complianceReduce areaWelding/cutting auxillary devicesSolid-state devicesBond energySonification
A horn for vibratory solid-state ultrasonic welding of metals and similarly-behaved materials “self-levels” to produce wide continuous seams or large-area spot-welds between delicate workpieces without damage, even if the workpieces are not perfectly flat and parallel to the nominal toolface angle. The horn toolface flexes under pressure to conform to skew-angled workpieces because it is disposed on a tool head supported by a tool neck cut from the tool body. The tool head, the tool neck, or both are anisotropically compliant. When resonances are properly optimized for typical VSS modes of vibration, atypical but useful localized modes are excited at the compliant toolface edges, actually intensifying the bond energy where one might normally expect unwanted damping. Various design approaches optimize the characteristics of the tool head and tool neck to various materials and bonding configurations. The horns can be configured for use with existing ultrasonic welders.
Owner:FOREFRONT INNOVATIVE TECH
Process for high temperature layer transfer
InactiveUS20080064182A1Inhibition defectImproved bonding energySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond energyThin layer
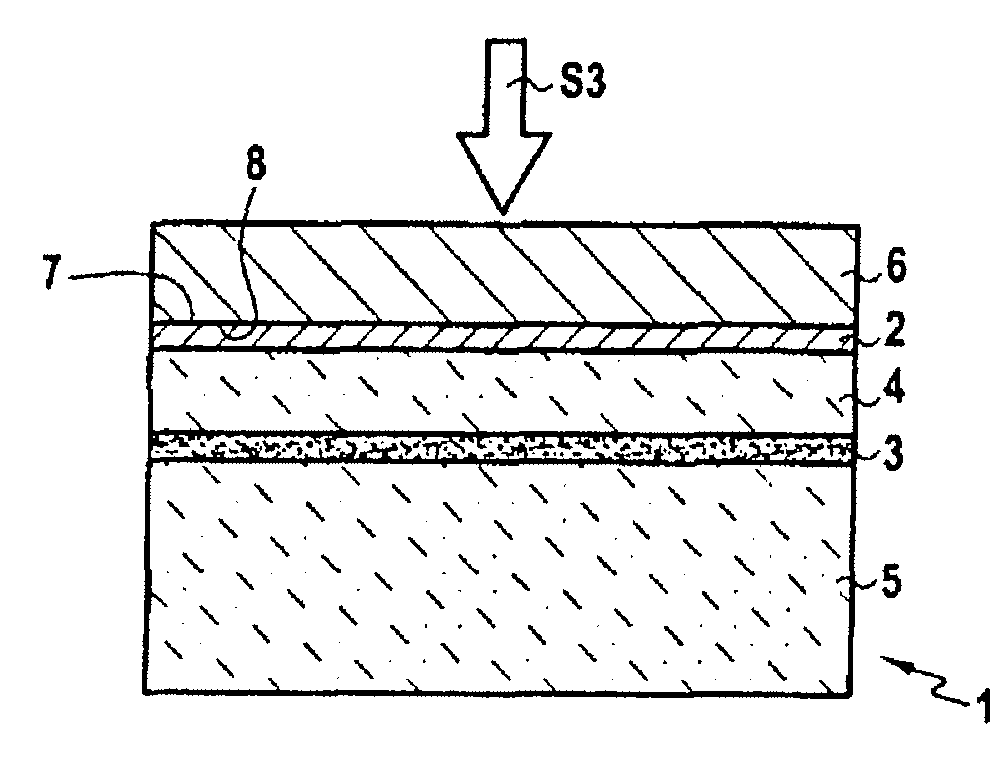
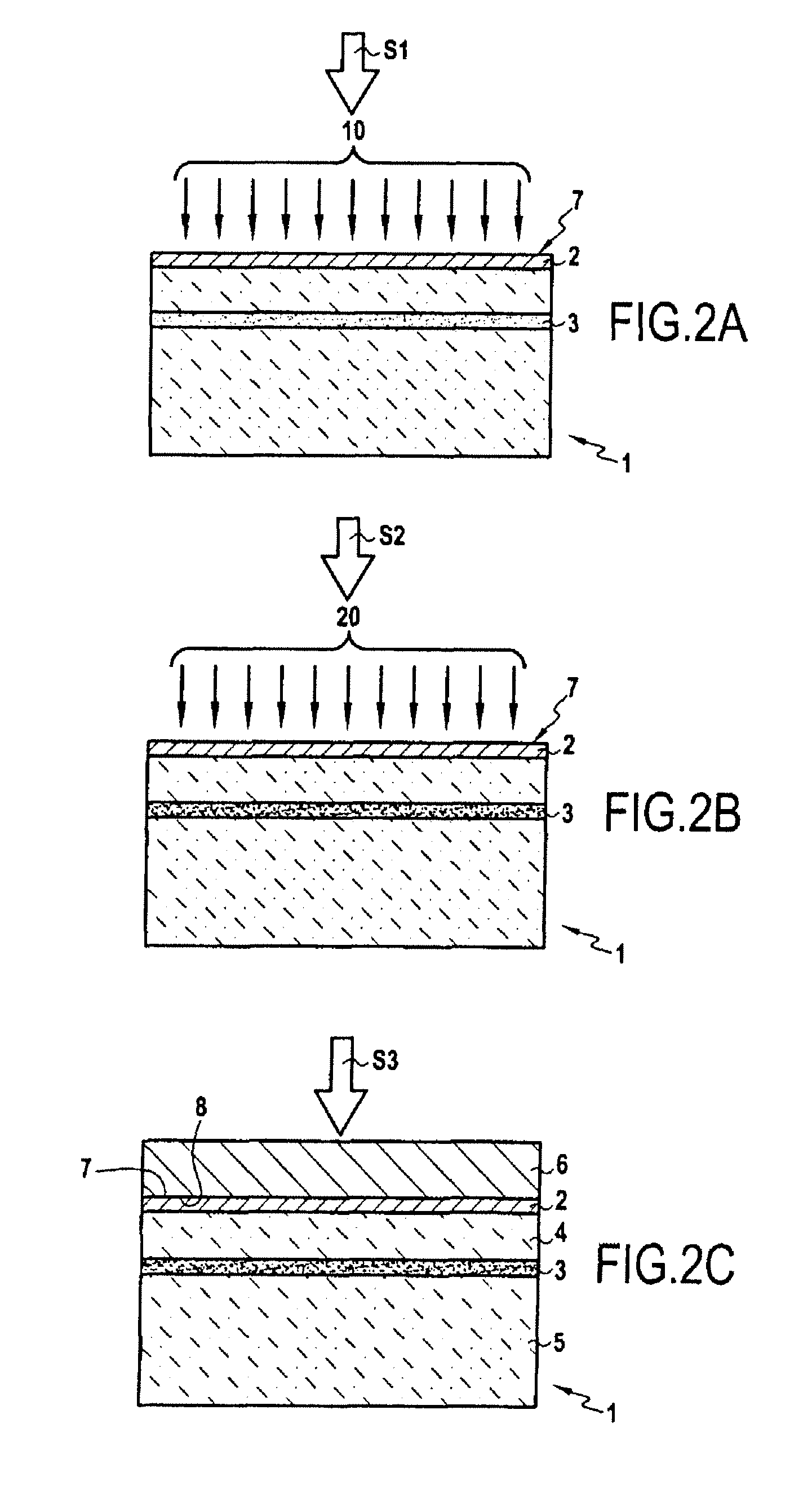
The invention concerns a method for transferring a thin layer from a donor wafer onto a receiving wafer by implanting at least one atomic species into the donor wafer to form a weakened zone therein, with the weakened zone being including microcavities or platelets therein, and the thin layer being defined between the weakened zone and a surface of the donor wafer; molecular bonding of the surface of the donor wafer onto a surface of the receiving wafer; splitting the thin layer at the zone of weakness by heating to a high temperature to transfer the thin layer to the receiving substrate; and treating the donor wafer to block or limit the formation of microcavities or platelets by trapping the atoms of at least one of the implanted atomic species at least until a certain release temperature is reached during the splitting. This method enables bonding energy to be reinforced adjacent the layer to be transferred and hence limits defects in the resulting heterostructure.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Method for handling semiconductor layers in such a way as to thin same
InactiveUS7205211B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond energyThin layer
This invention relates to a method for making a thin layer starting from a wafer comprising a front face with a given relief, and a back face, comprising steps consisting of:a) obtaining a support handle with a face acting as a bonding face;b) preparing the front face of the wafer, this preparation including incomplete planarisation of the front face of the wafer, to obtain a bonding energy E0 between a first value corresponding to the minimum bonding energy compatible with the later thinning step, and a second value corresponding to the maximum bonding energy compatible with the subsequent desolidarisation operation, the bonding energy E0 being such that E0=α.E, where E is the bonding energy that would be obtained if the front face of the wafer was completely planarised, α is the ratio between the incompletely planarised area of the front face of the wafer and the area of the front face of the wafer if it were completely planarised;c) solidarising the front face of the wafer on the bonding face of the support handle, by direct bonding;d) thinning the wafer starting from its back face until the thin layer is obtained;e) transferring the thin layer onto a usage support, involving separation from the support handle.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Anode material of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an anode material of a lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The anode material which is granular comprises: an internal nucleus which is a substance having a molecular formula of LixMn2-yMyNzO4; and an external surface crystal shell which is nitrogen-containing nanometer oxide particles. According to the anode material of the lithium ion batter disclosed in the invention, M is doped to replace partial Mn, and the crystal lattice volume is reduced because the bond energy of M-O is greater than the bond energy of Mn-O, so the spinel structure of lithium manganate is stabilized, the manganese solution in the cycle process is reduced, and the product cycle performance is improved. The preparation method of the anode material of the lithium ion battery disclosed in the invention, which allows the lithium manganese oxide to be doped and coated through a two-step reaction, has the advantages of simple production technology, no pollution, no waste discharge, simple equipment, low cost of raw materials and the production cost, and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO HUAGUAN HENGYUAN LI TECH
Method for handling semiconductor layers in such a way as to thin same
InactiveUS20050124138A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond energyThin layer
This invention relates to a method for making a thin layer starting from a wafer comprising a front face with a given relief, and a back face, comprising steps consisting of: a) obtaining a support handle with a face acting as a bonding face; [0001]b) preparing the front face of the wafer, this preparation including incomplete planarisation of the front face of the wafer, to obtain a bonding energy E0 between a first value corresponding to the minimum bonding energy compatible with the later thinning step, and a second value corresponding to the maximum bonding energy compatible with the subsequent desolidarisation operation, the bonding energy E0 being such that E0=α.E, where E is the bonding energy that would be obtained if the front face of the wafer was completely planarised, α is the ratio between the incompletely planarised area of the front face of the wafer and the area of the front face of the wafer if it were completely planarised; c) solidarising the front face of the wafer on the bonding face of the support handle, by direct bonding; d) thinning the wafer starting from its back face until the thin layer is obtained; e) transferring the thin layer onto a usage support, involving separation from the support handle.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Production method of superhydrophobic antifog glass
The invention relates to a production method of a superhydrophobic antifog glass and belongs to the technical field of materials. The superhydrophobic antifog glass is produced with hydrophobic nano silica particles; the surface of a glass material is coated with a layer of hydrophobic nano silica particles, so that surface wet state of the glass material is improved, small waterdrops formed of condensed vapor slip off under their gravity action, the surface pollutants are easily brought away by the waterdrops, and good self-cleaning effect is achieved. Trimethoxy(1H,1H,2H,2H-heptadecafluorodecyl)silane and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane are added herein to produce superhydrophobic antifog glass; since a superhydrophobic coating on the antifog glass contains F and Si atoms; F is an element of greatest electronegativity in the periodic table of elements, has very small atom radius and forms a very short F-Si bond having great bond energy; the surrounding of carbon chains of a fluorine atom polymer is in tight arrangement, so that the fluorine-bearing polymer has excellent weatherability, surface self-cleaning property, high temperature resistance, chemicals resistance and the like.
Owner:邹玉
Solid-state hydrogen storage media and catalytic hydrogen recharging thereof
ActiveUS20080274873A1Low costIncrease activation energyMolecular sieve catalystsReversible hydrogen uptakeBond energyHydrogen atom
A solid-state hydrogen storage material and process for making the material more thoroughly rechargeable. The process entails forming a porous matrix material to contain atoms of a first element and hydrogen atoms, in which the atoms of the first element are capable of bonding with more than one hydrogen atom per atom of the first element, and the atoms of the first element are molecularly arranged within the porous matrix material so that different atoms of the first element are bonded to different numbers of hydrogen atoms at correspondingly different levels of bonding energy. At least some of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the atoms of the first element at the lowest bond energies are then removed without removing hydrogen atoms bonded at higher bond energies, after which atoms of a second element are bonded to those atoms of the first element from which hydrogen atoms were removed.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
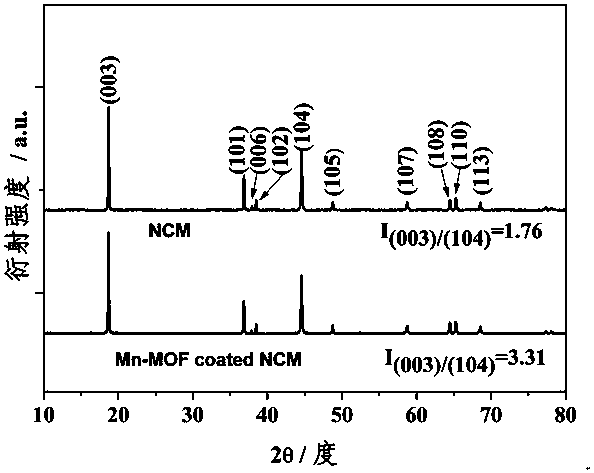
Manganese-based metal organic framework compound-coated lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107910529AImprove electrochemical performanceLarge specific surface areaCell electrodesSecondary cellsBond energyHigh rate
The invention discloses a manganese-based metal organic framework compound-coated lithium ion battery ternary positive electrode material. Based on the self-assembling performance of an MOFs material,coating of a spherical ternary positive electrode material is realized through a simple one-step method; the positive electrode material has a layered structure, is free of impurity phase, and structural changing of the material is not caused by coating; and the positive electrode material has a two-stage spherical-like structure formed by sheet-rod-like small particles in an clustering manner. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1) preparation of a precursor; 2) preparation of a spherical ternary positive electrode material; and 3) preparation of the manganese-based metal organic framework compound-coated ternary positive electrode material. According to the application as the battery positive electrode material, the discharge specific capacity is 160-180mAh g<-1> after 50 cycles of constant current charging and discharging at 0.5C; and the discharge specific capacity is 140-160mAh g<-1> at high rate of 10C. The positive electrode material has the advantages of providing porous channels, improving wetting degree, improving cycling stability and high-rate cycle performance, reinforcing stability of M-O bond energy, low cost, simple operation and suitability of large-scale production.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
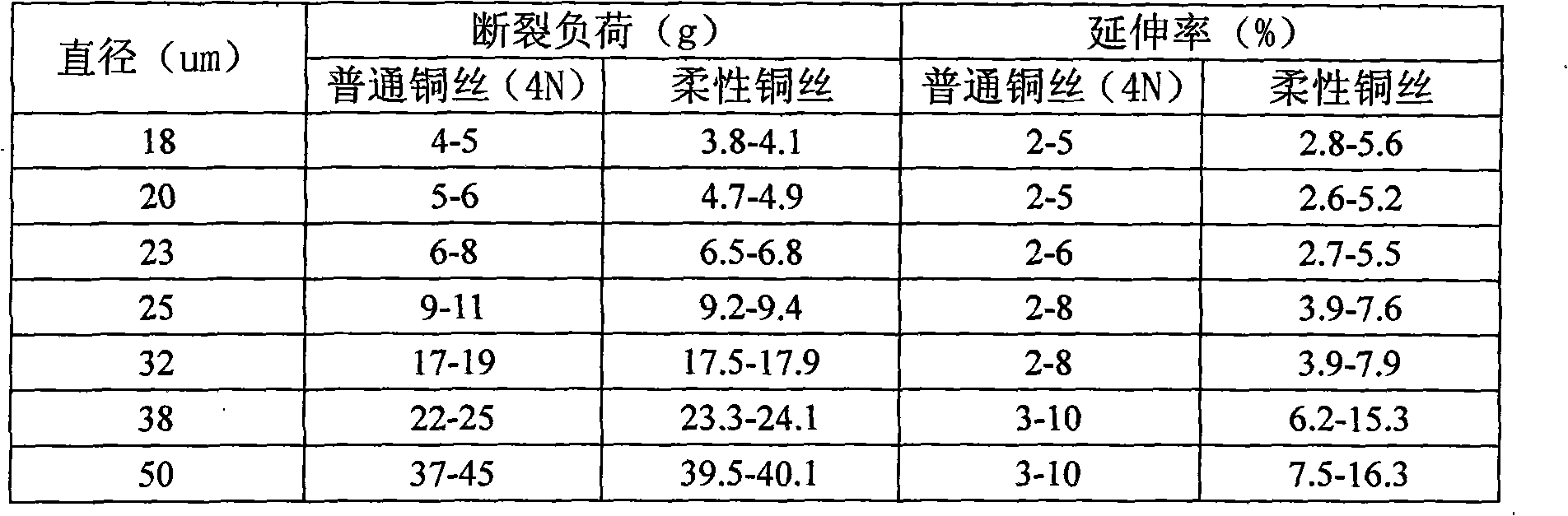
Flexible bonding copper wire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101626006AReduce hardnessReduce impactSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond energyInterfacial oxide
The invention relates to a flexible bonding copper wire and a preparation method thereof. The flexible bonding copper wire comprises the components: 0.001-0.005% of Ce, 0.003-0.005% of Pd, 0.005-0.009% of Pt and the rest of Cu. The invention adopts multielement doped alloy which is added with other components, so as to reduce the rigidity of copper, especially the balling rigidity, reduce the impact force and the damage for a chip, lower the bonding energy, prevent the generation of interfacial oxide and the crack, and ensure the combination performance to be stable, thus improving the combination performance, the electrical conductivity and the inoxidizability; by controlling the conditions of fusion casting, processing and hot treatment, the invention further optimizes the structure and guarantees the proper mechanical capacity, so as to meet different needs.
Owner:烟台一诺电子材料有限公司
Hard layer-coated tool
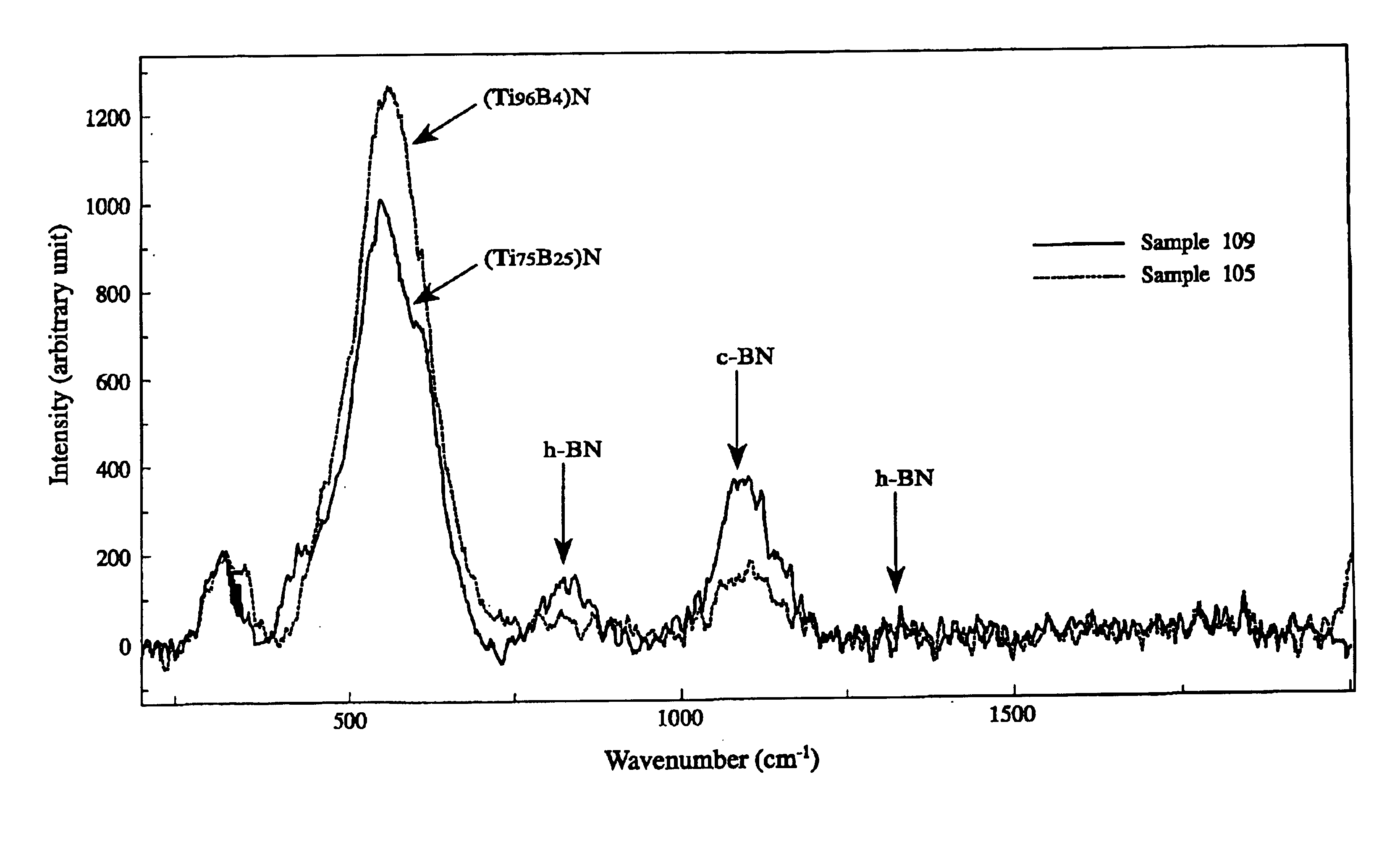
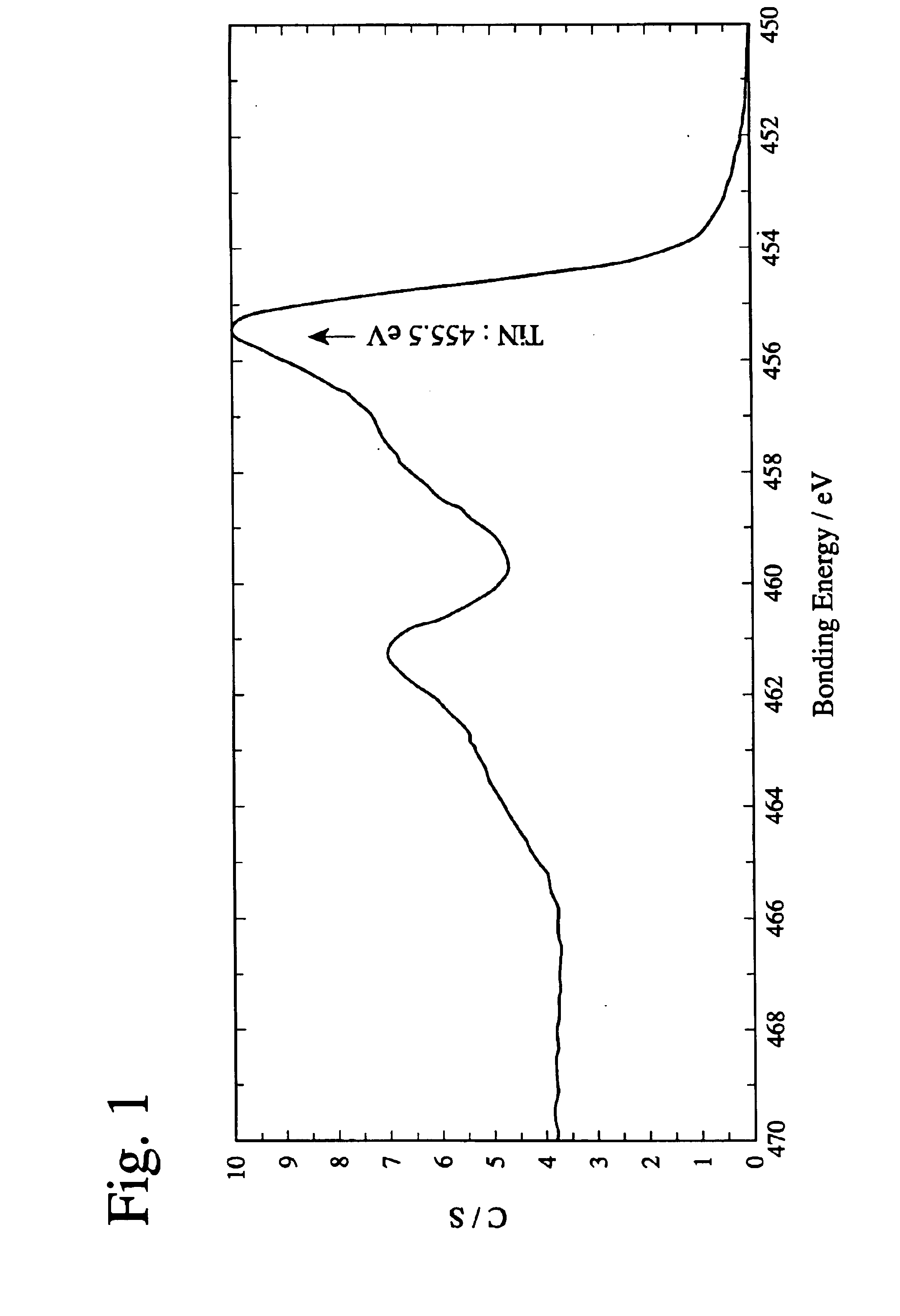
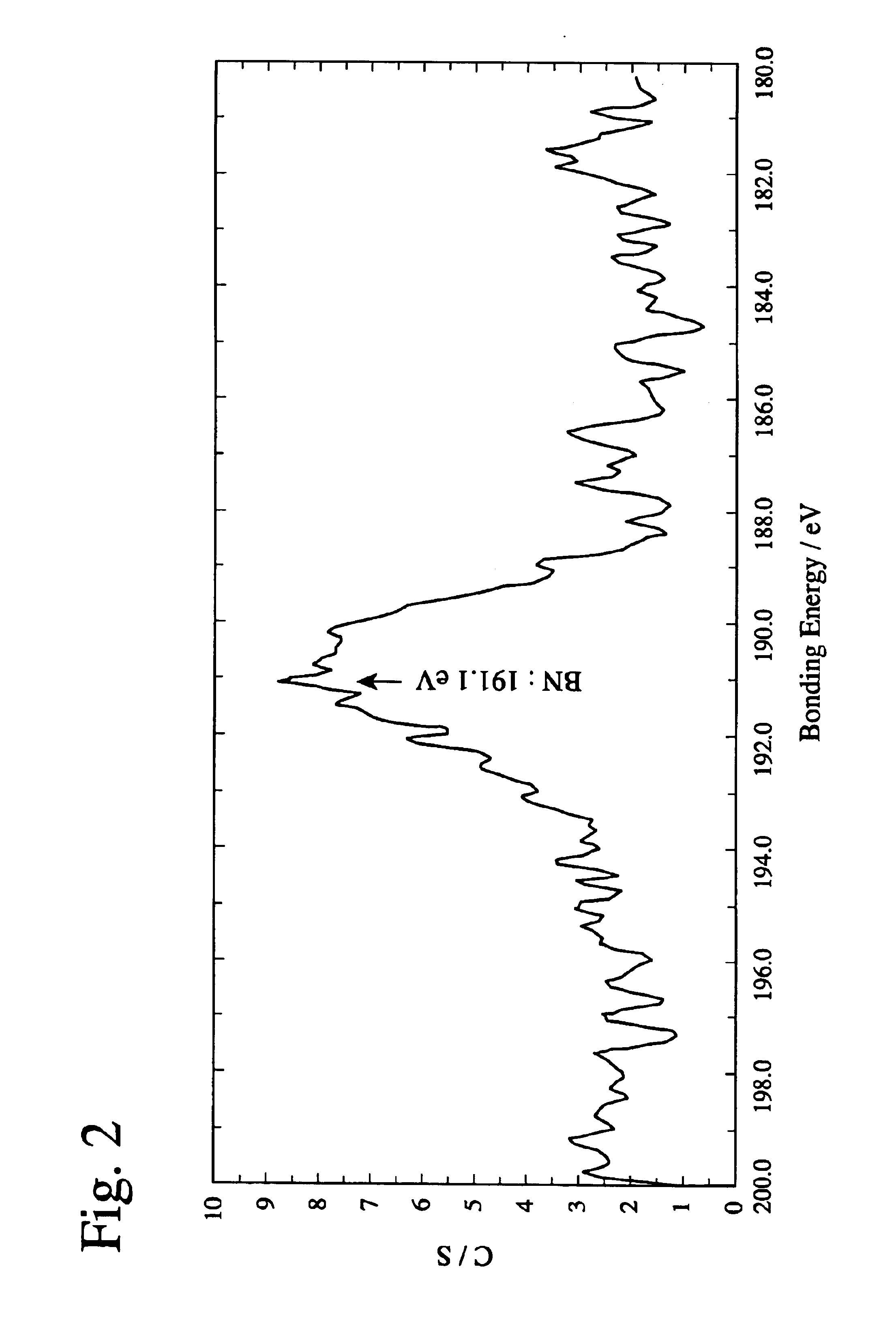
InactiveUS6790543B2Improved seizure resistanceSuppress DiffusePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBond energyChemical reaction
A tool coated with a hard Ti / B layer having fine boron nitride particles dispersed therein, wherein the bonding energy of B and N is observed in an ESCA analysis of the hard coating layer; wherein peaks of c-BN and h-BN is detected in an Raman spectroscopy of the hard coating layer; wherein a ratio Q1 / Q2 of a peak intensity Q1 of c-BN to a peak intensity Q2 of h-BN is 1.0 or more; wherein a half-value width Z of a (200) face in an X-ray diffraction of the hard coating layer is in a range of 0.3° to 0.6°; and wherein a ratio K / L of a face thickness K to a flank thickness L in the tool is 1.0 or more, whereby the hard coating layer has high hardness, high lubricating properties and excellent crater wear resistance, with chemical reactions with a work suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI TOOL ENG LTD
Innocent treatment method for sulfur-bearing VOC
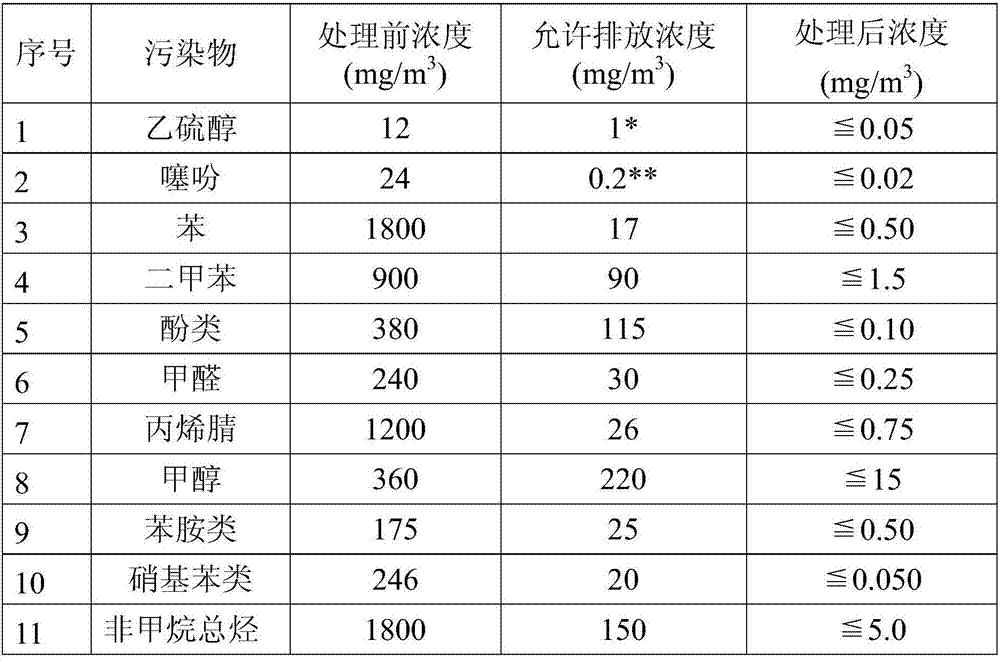
InactiveCN107202333AEasy to handleRealize harmless treatmentIncinerator apparatusChemical LinkageBond energy
The invention belongs to the field of environmental protection and discloses a method for harmless treatment of sulfur-containing VOC. The method is as follows: (1) the catalyst is placed in the combustion furnace of the sulfur-containing VOC combustion treatment device, and the sulfur-containing VOC gas and the combustion-supporting gas are introduced; (2) the mixed sulfur-containing VOC gas and the combustion-supporting gas are placed in the catalytic combustion furnace Carry out catalytic combustion under the effect of the catalyzer, the gas gained after combustion is absorbed by alkaline substance at last; The catalyst described in step (1) is main catalyst, main catalyst and co-catalyst, main catalyst and carrier or main catalyst, co-catalyst and carrier. The method of the present invention is simple and efficient, and the catalyst used can increase the local concentration of sulfur-containing VOC gas and combustion-supporting gas, and can also weaken its chemical bond energy, increase its reactivity, and make the catalytic combustion of sulfur-containing VOC easier to carry out, and the reaction is more efficient. Thoroughly and effectively realize the harmless treatment of sulfur-containing VOC.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
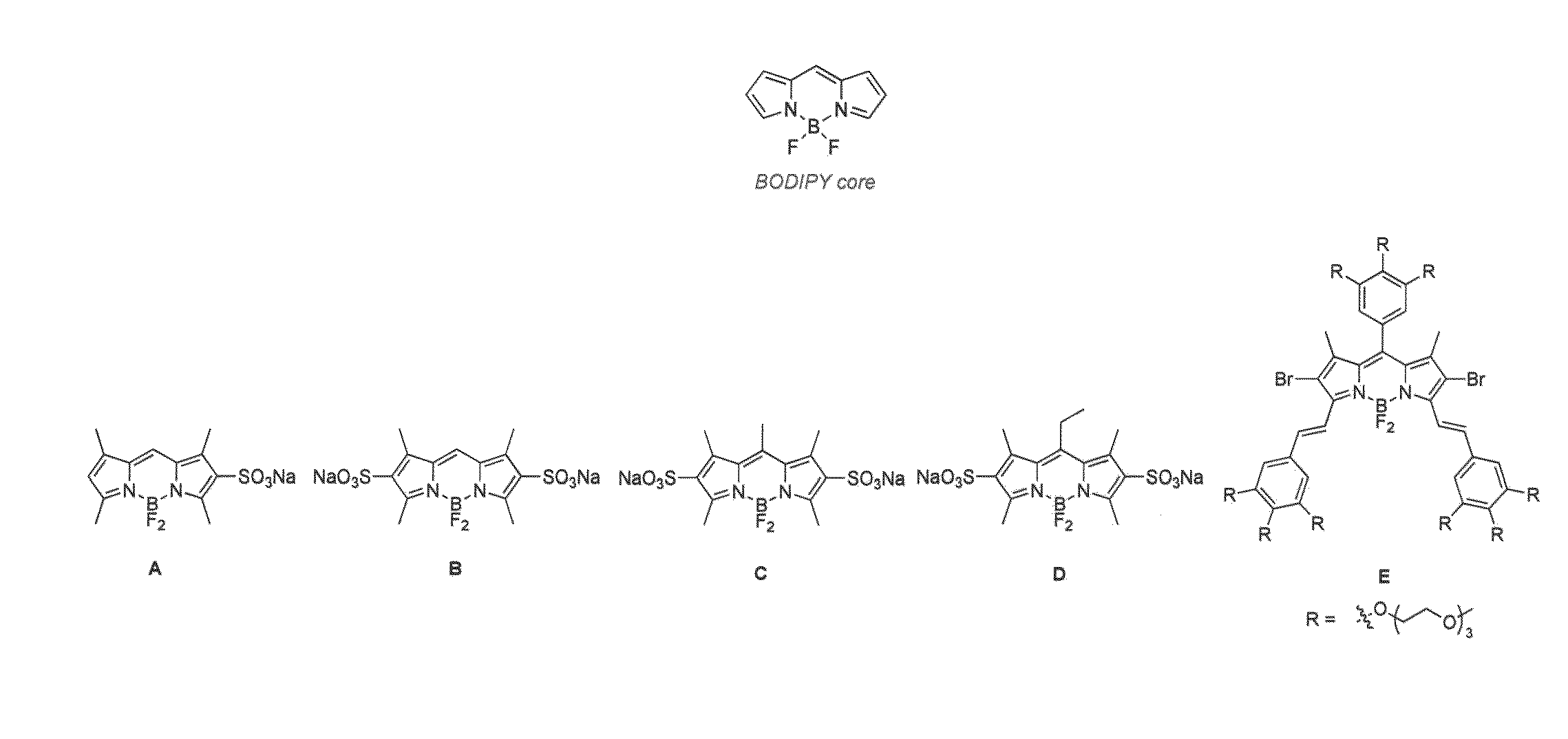
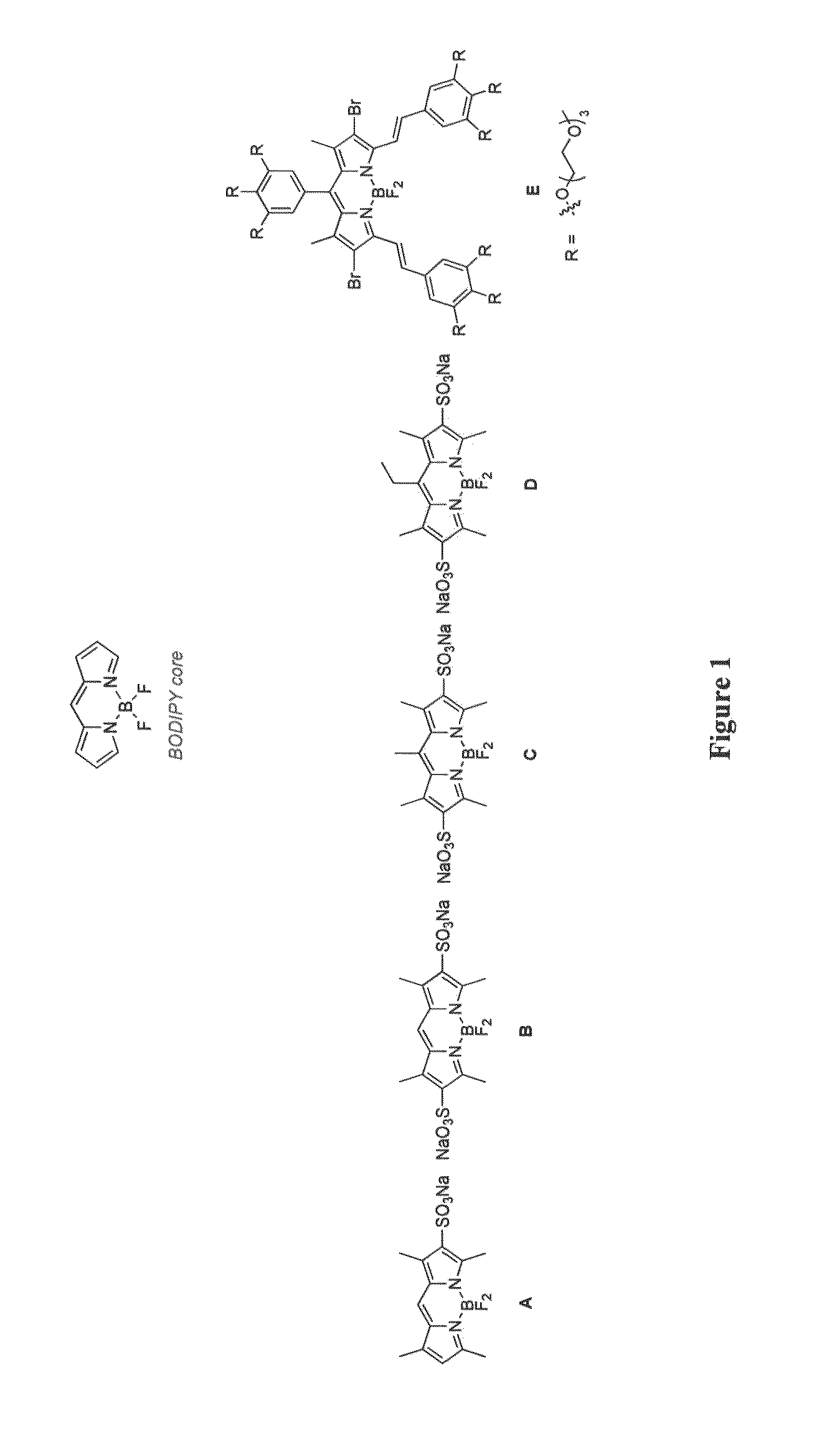
Through-bond energy transfer cassettes, systems and methods
InactiveUS20090192298A1Slow and accelerate warmingSilicon organic compoundsSugar derivativesBond energyFluorescence
The present disclosure relates, according to some embodiments, to compositions, systems, and methods for preparing and using fluorescent through-bond energy transfer cassettes.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
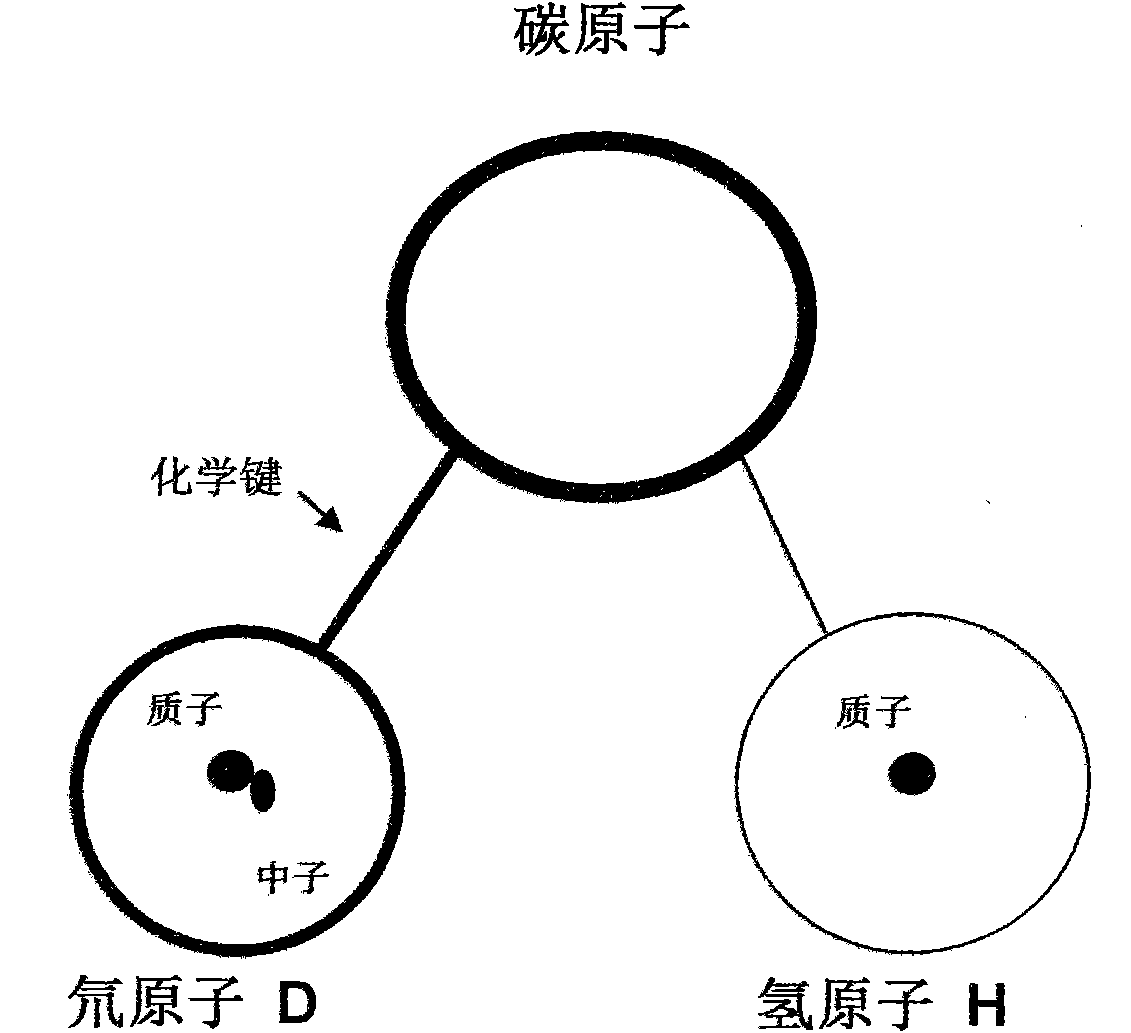
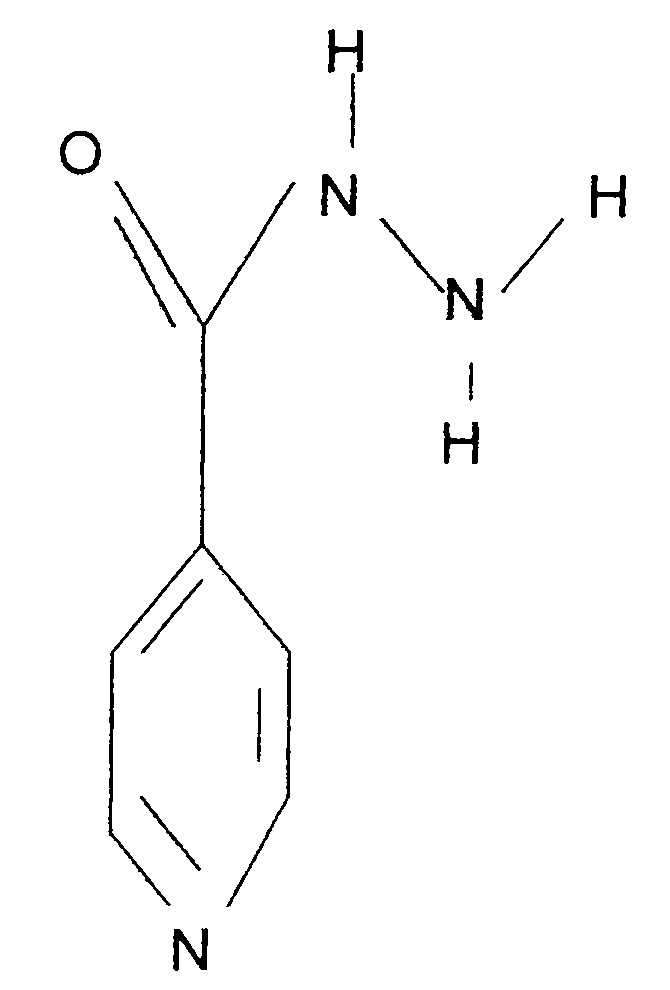
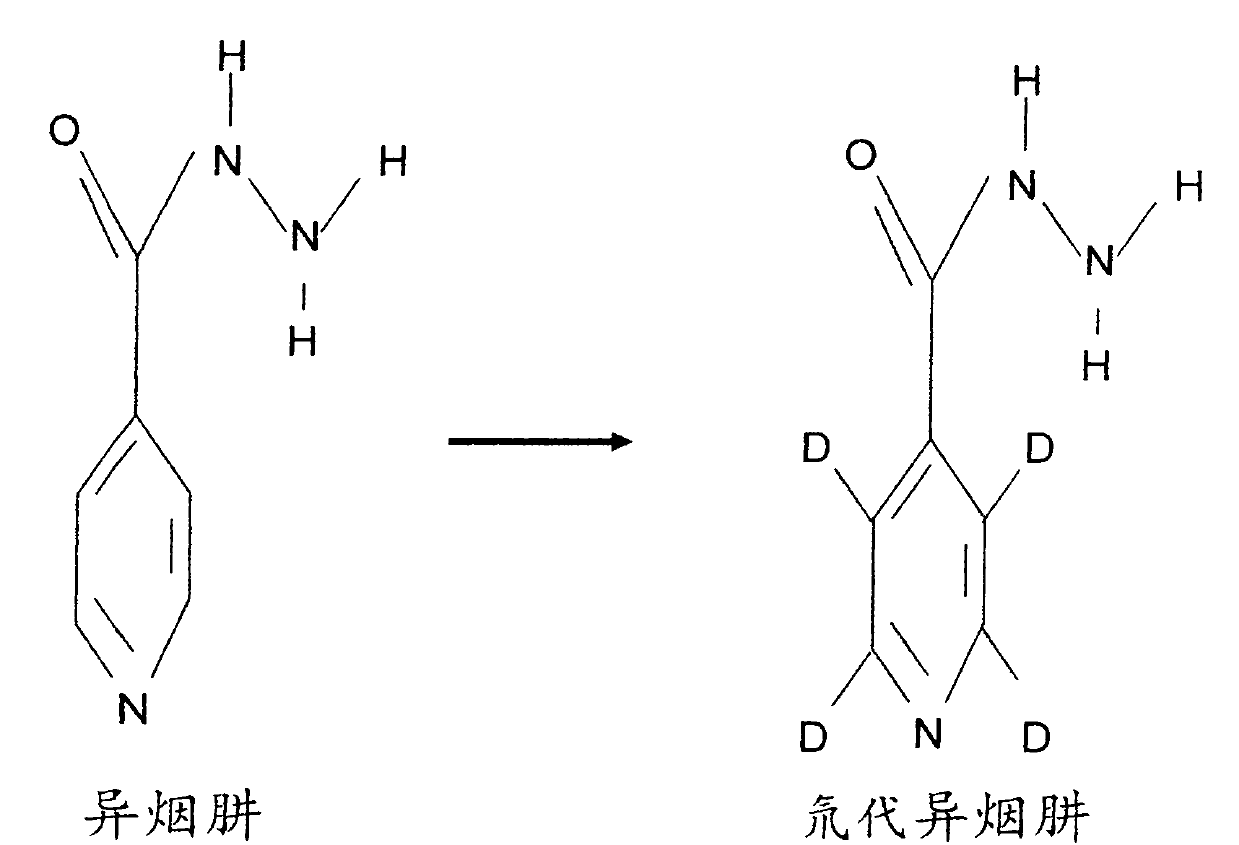
Preparation method and application of deuterated drugs
InactiveCN102020522AReduce toxicity and side effectsAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBond energy
A carbon hydrogen structure (C: H) is one of the basic structures in the pharmaceutical chemistry structure and a formed C-H bond is the basic chemical bond. The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of deuterated drugs which can change the chemical bond energy and the hydrogen bond energy in the structure of pharmaceutical compound. The hydrogen atom (H) in pharmaceutical compound structure is substituted by the A deuterium atom (D) which is the isotope of hydrogen, therefore changing the molecular structure and the bond energy of the substituted pharmaceutical compound so as to form a new deuterated drug. The deuterated drugs can be used for pharmacokinetics research, can obviously enhance the disease-preventing or treating function of the drugs, and can reduce the toxic and side effect of the drugs.
Owner:陈松源
Methods for preparing a bonding surface of a semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS20050218111A1Improved bonding energyFully removedDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesBond energySemiconductor structure
A method for preparing an oxidized surface of a first wafer for bonding with a second wafer. The method includes treating the oxidized surface using a mix of NH4OH / H2O2 to increase the bonding energy between the first and second wafers. The treatment parameters are chosen such that etching occurs that is sufficient to remove isolated particles from the oxidized surface, but that is sufficiently weak to smooth the surface without creating rough patches thereon. Also described is a thin layer removal process, which may advantageously be used to fabricate a semiconductor on insulator structure.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Method of preparing porous carbon and porous carbon
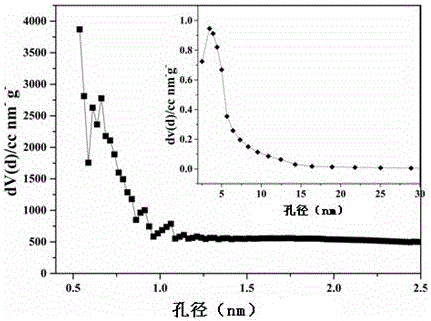
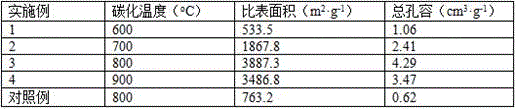
ActiveCN106744803AIncrease the areaHigh porosityCarbon preparation/purificationBond energyPorous carbon
The invention discloses a method of preparing porous carbon and porous carbon. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a carbon source and an activator; drying the mixture; and carbonizing the mixture in an inert atmosphere to obtain porous carbon, wherein the carbon source contains one or more elements of N, P, B and S. By taking some materials containing elements such as N, P, B and C as the carbon source, the carbon source is activated through an activator to obtain porous carbon with a high specific surface area. As a C-N bond, a C-P bond, a C-B bond and a C-S bond are weaker than a C-C bond in bond energy, the activator will preferably etch impure elements such as N, P, B and S and surrounding carbon thereof so as to form uniform holes, so that the etching efficiency is improved and the specific surface area is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com