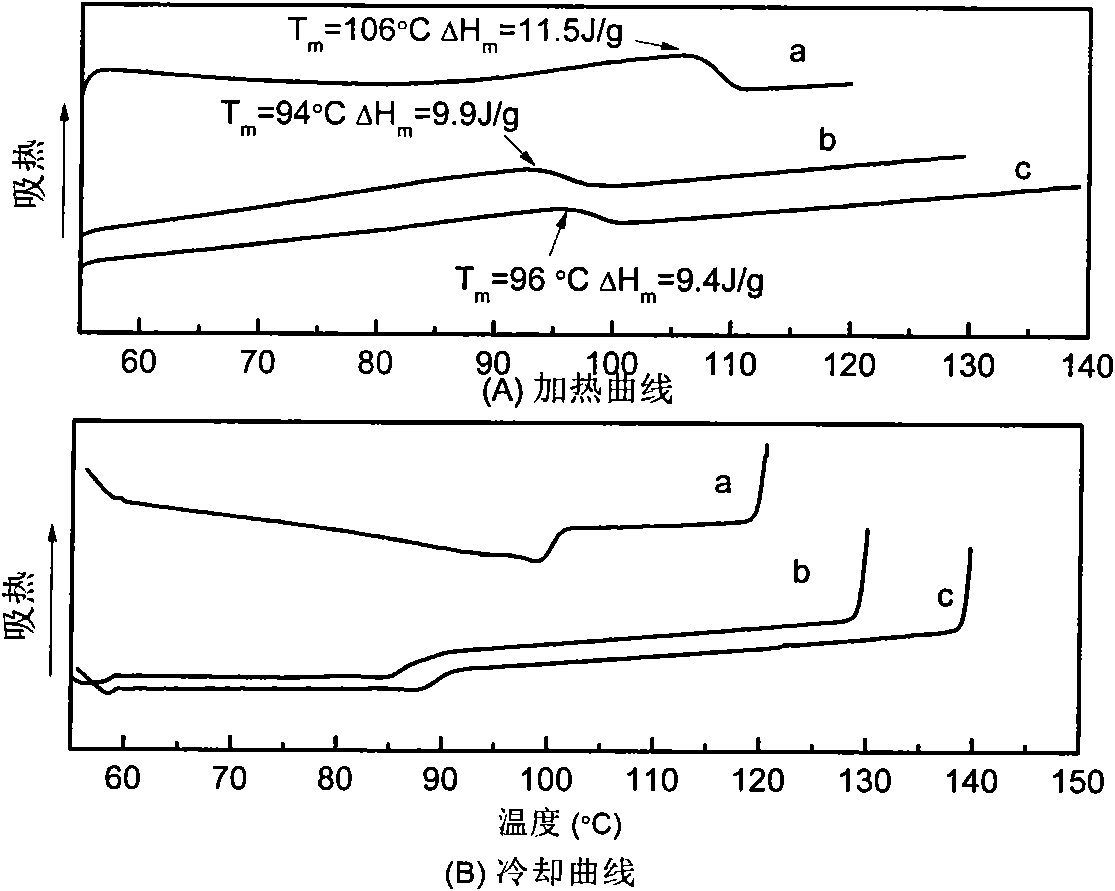
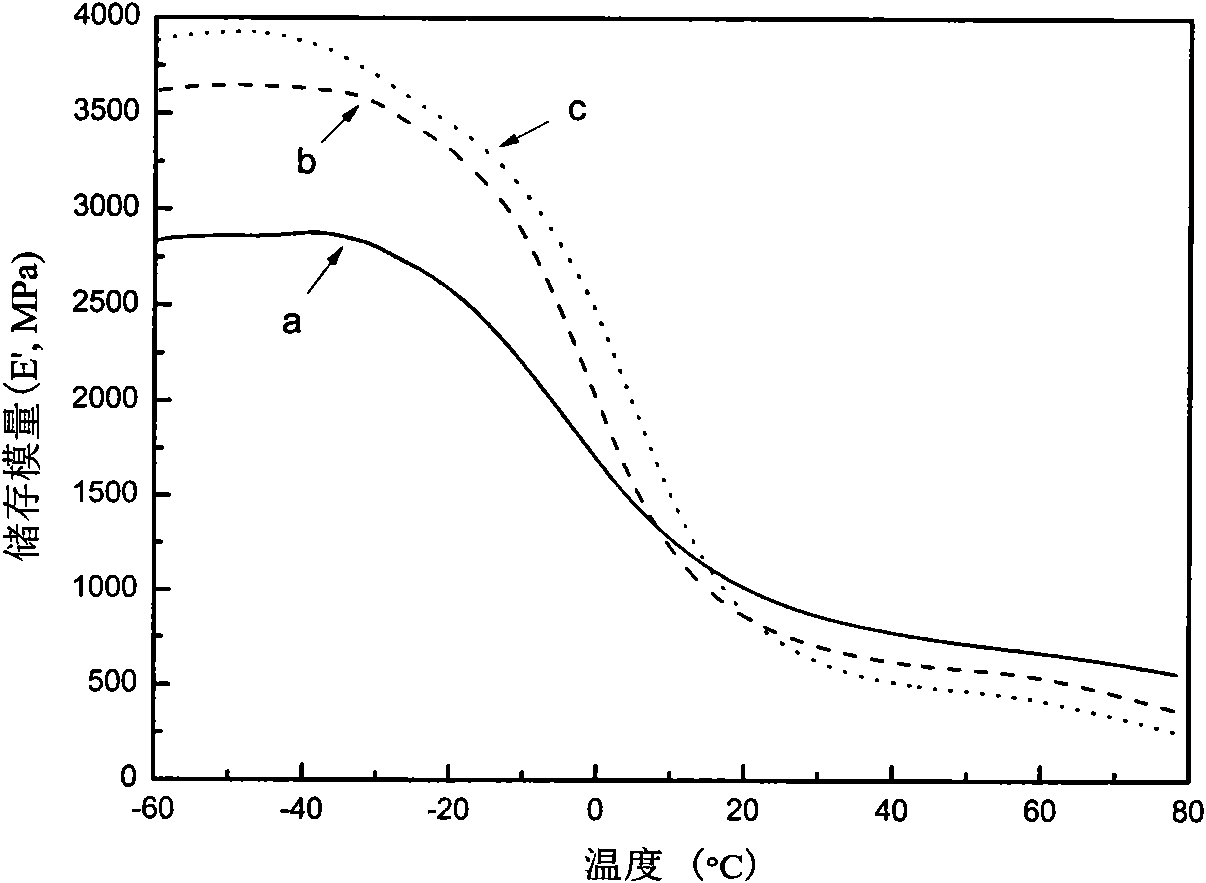
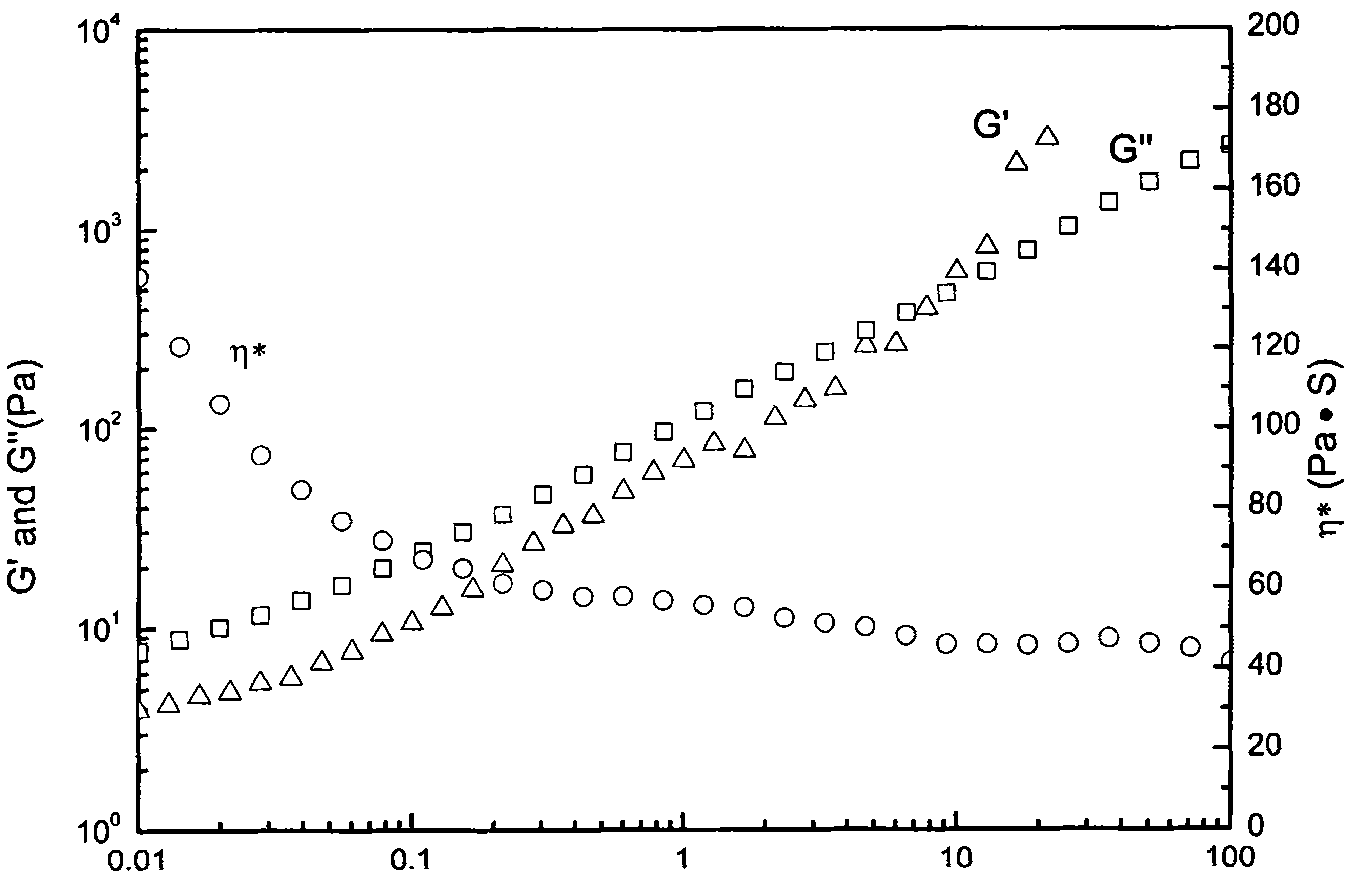
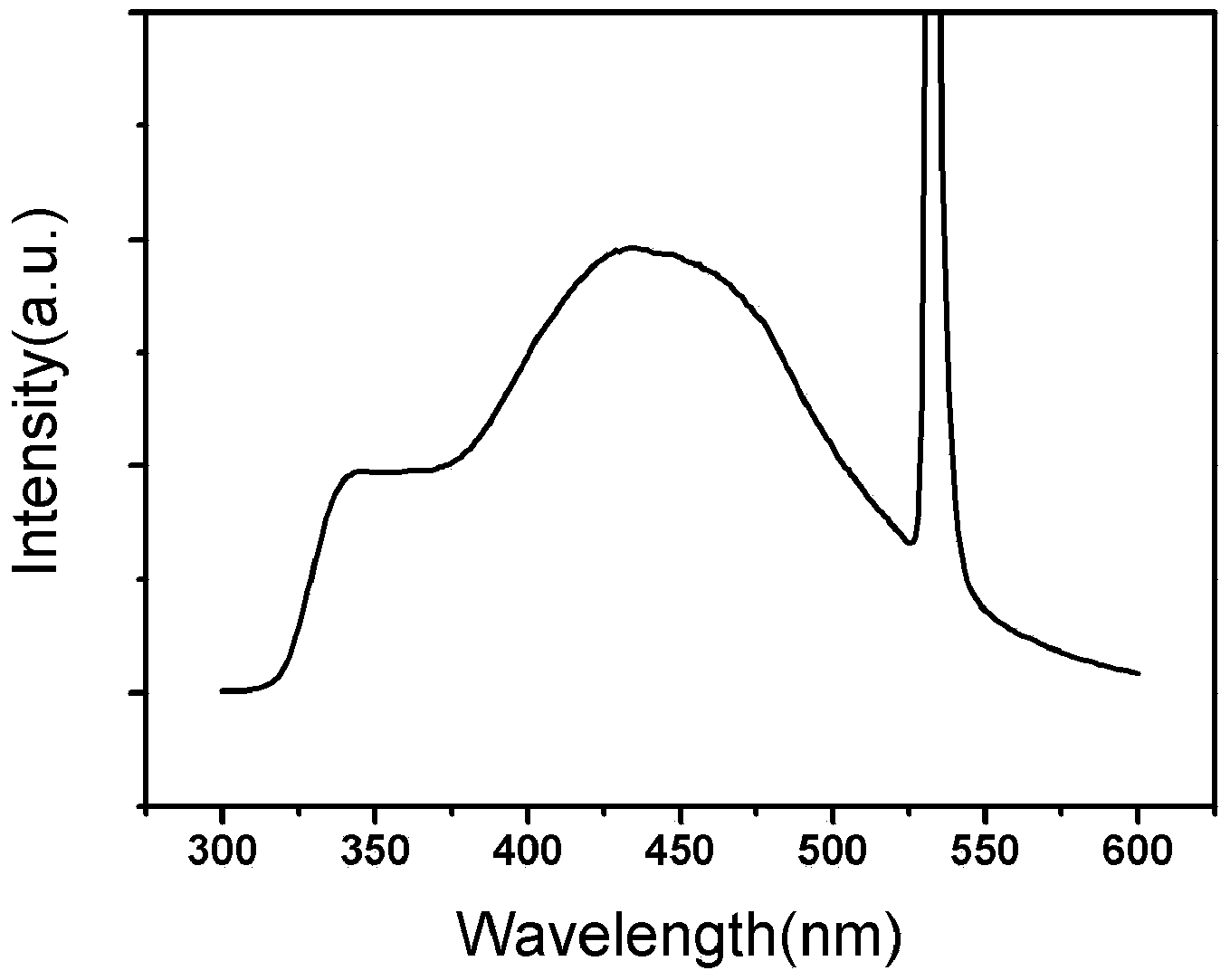
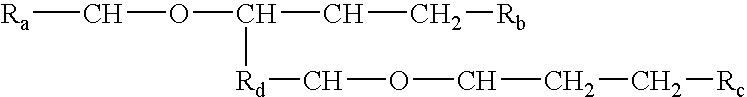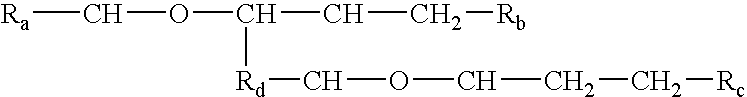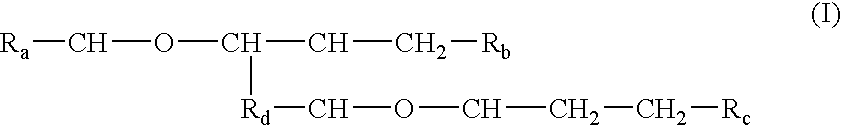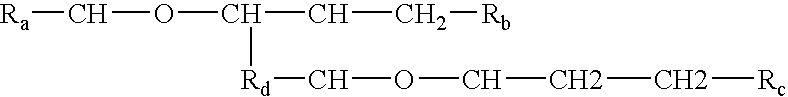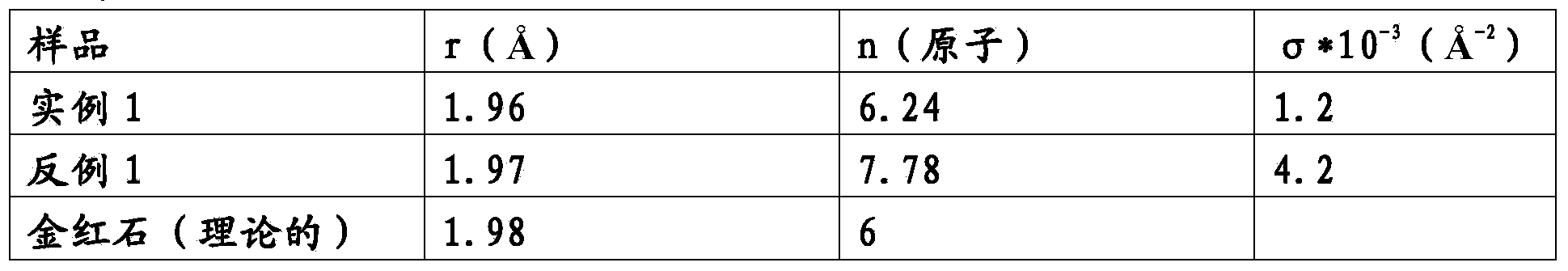Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
84 results about "Bond length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
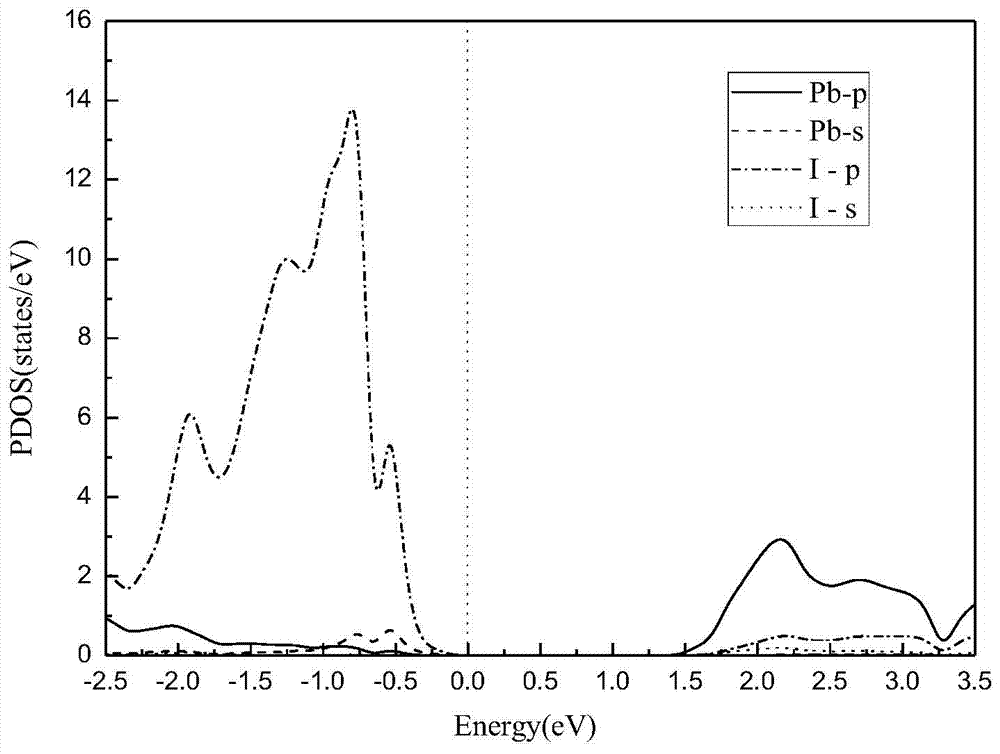
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule.
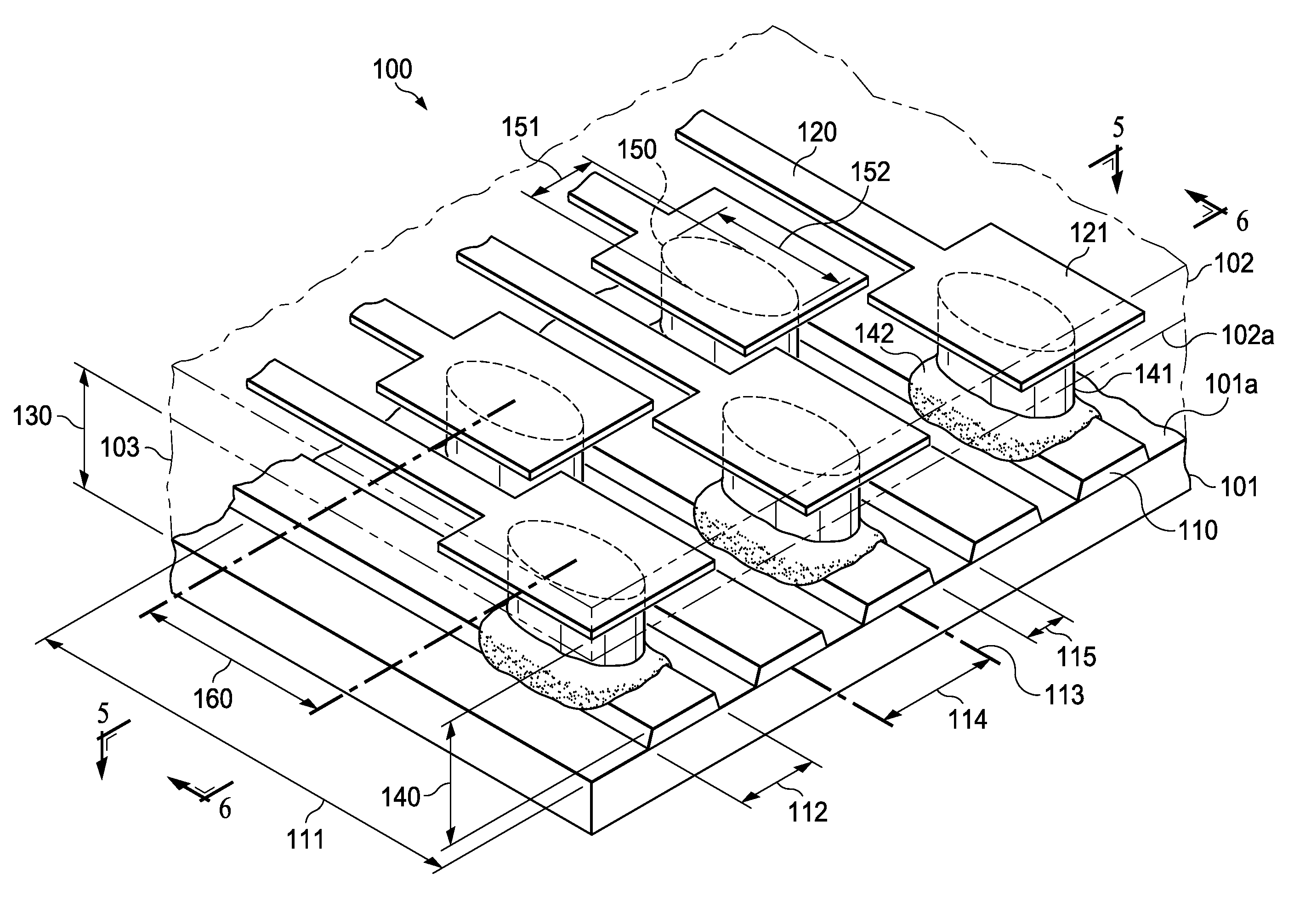
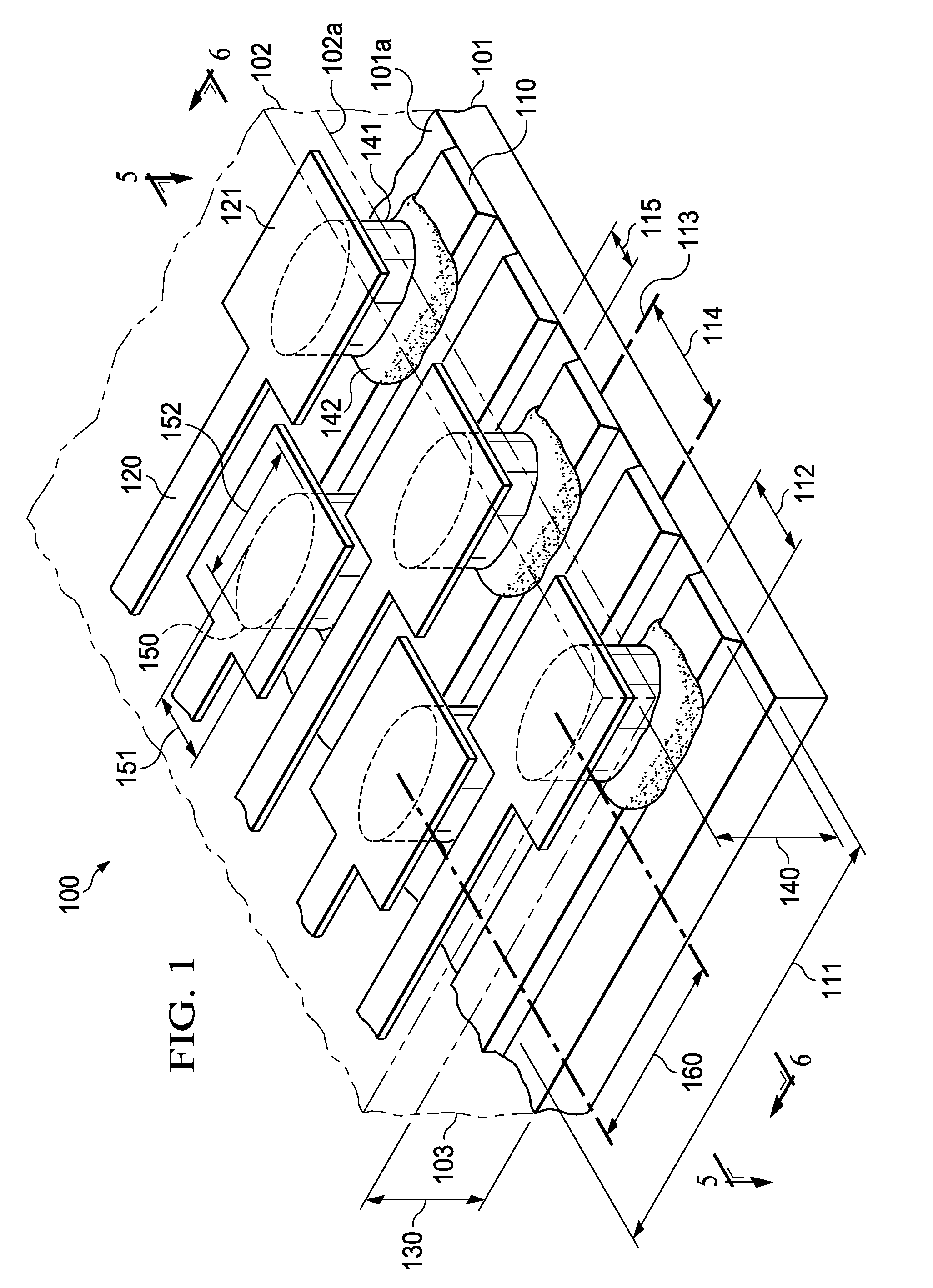
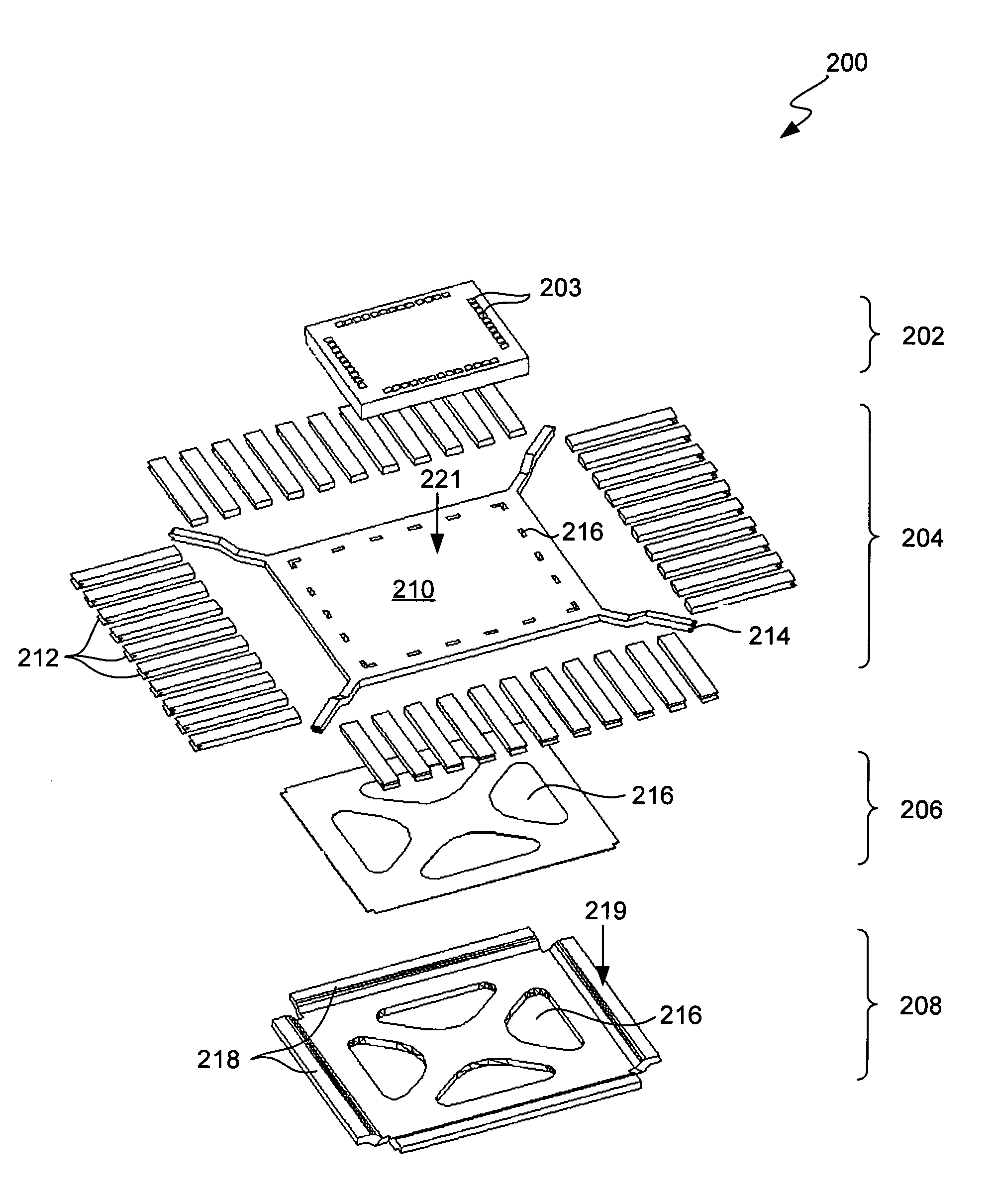
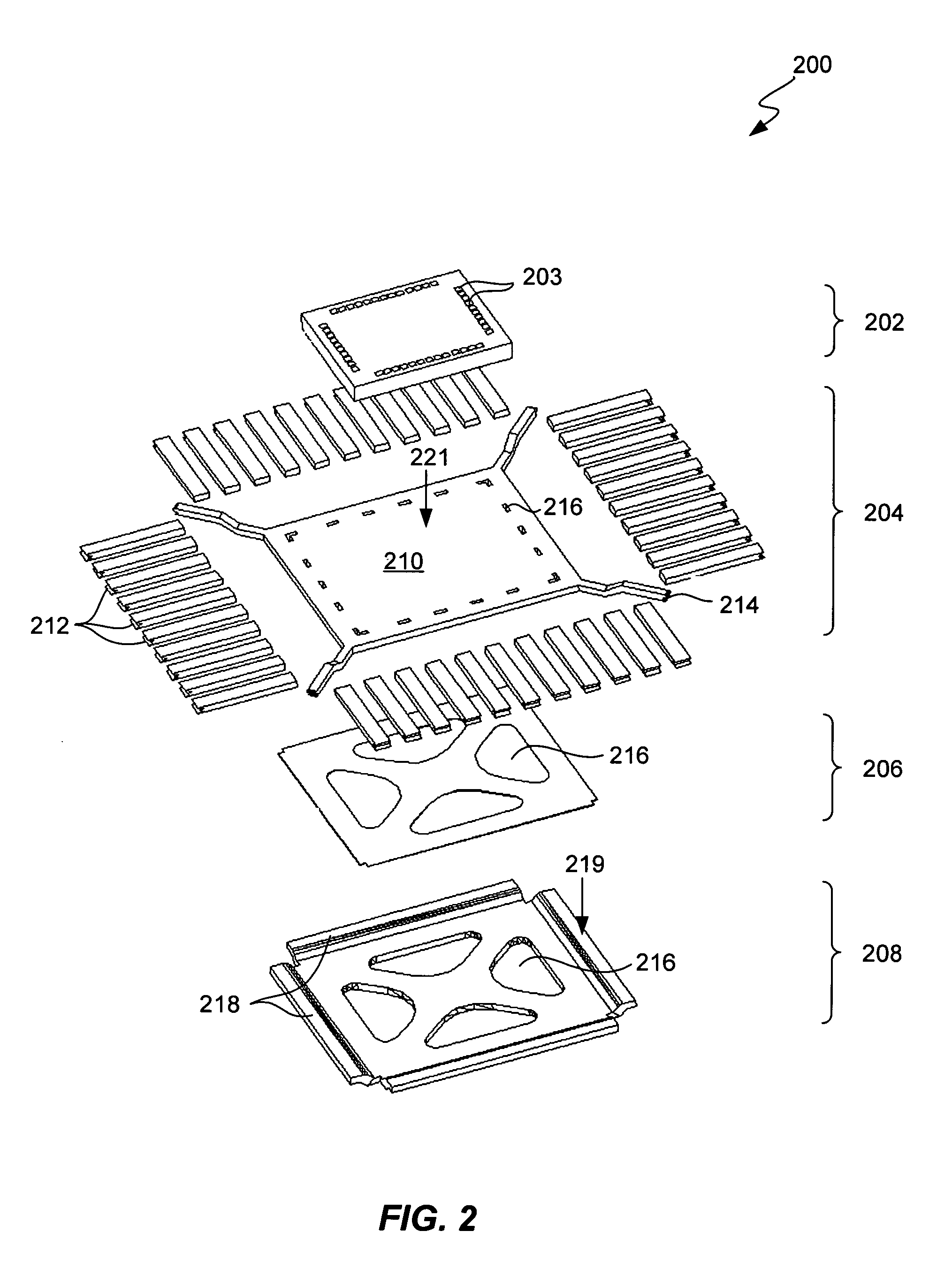
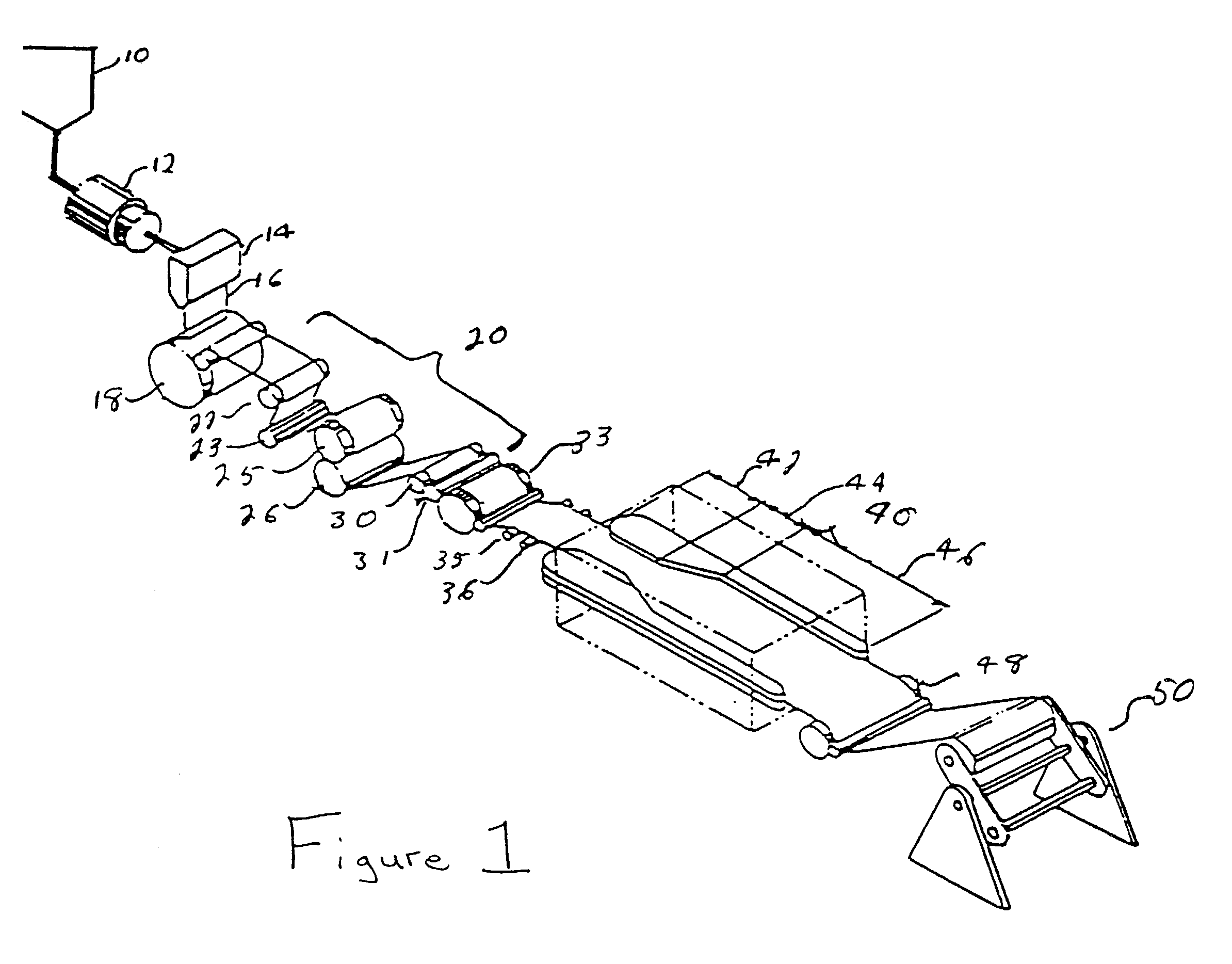
Semiconductor Flip-Chip System Having Oblong Connectors and Reduced Trace Pitches
ActiveUS20100193944A1Increase the number ofSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor chip (102) assembled on a substrate (101). The substrate has a first surface (101a) including conductive traces (110), which have a first length (111) and a first width (112), the first width being uniform along the first length, and further a pitch (114) to respective adjacent traces. The semiconductor chip has a second surface (102a) including contact pads (121); the second surface faces the first surface spaced apart by a gap (130). A conductive pillar (140) contacts each contact pad; the pillar includes a metal core (141) and a solder body (142), which connects the core to the respective trace across the gap. The pillar core (141) has an oblong cross section of a second width (151) and a second length (152) greater than the second width. Trace pitch (141) is equal to or smaller than twice the second width (151). The trace pitch is equal to or smaller than the second length (152).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Photonic polymer-blend structures and method for making
InactiveUS6756117B1Tunable optical and mechanical propertyHighly robustLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringMicroparticle
The present invention comprises the formation of photonic polymer-blend structures having tunable optical and mechanical properties. The photonic polymer-blend structures comprise monomer units of spherical microparticles of a polymer-blend material wherein the spherical microparticles have surfaces partially merged with one another in a robust inter-particle bond having a tunable inter-particle separation or bond length sequentially attached in a desired and programmable architecture. The photonic polymer-blend structures of the present invention can be linked by several hundred individual particles sequentially linked to form complex three-dimensional structures or highly ordered two-dimensional arrays of 3D columns with 2D spacing.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Theoretical method for screening high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer
InactiveCN104778330AImprove efficiencyQuick calculationSpecial data processing applicationsStructure chartFirst principle
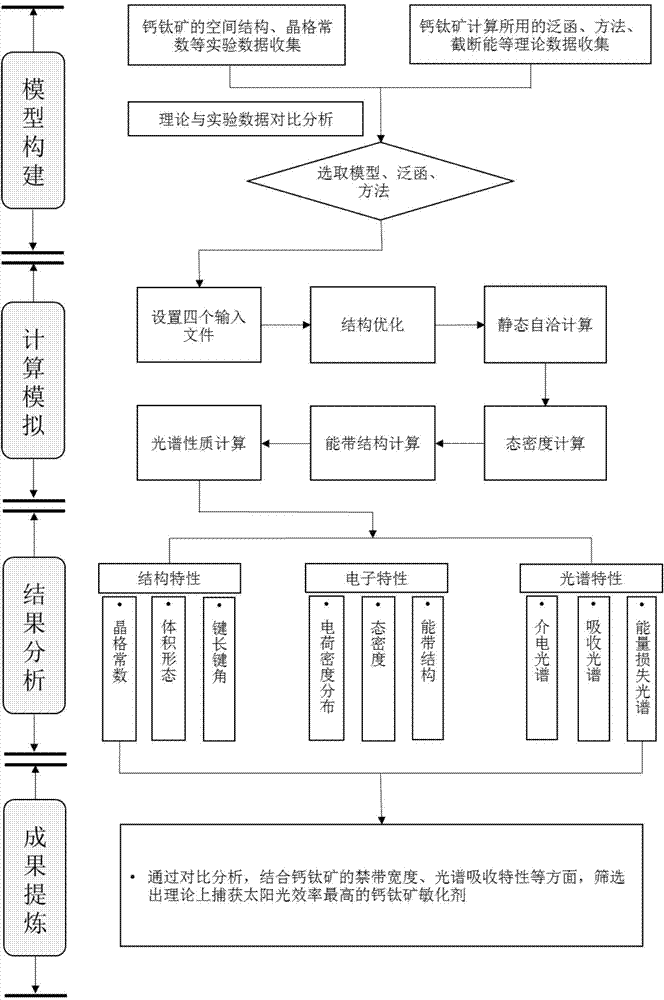
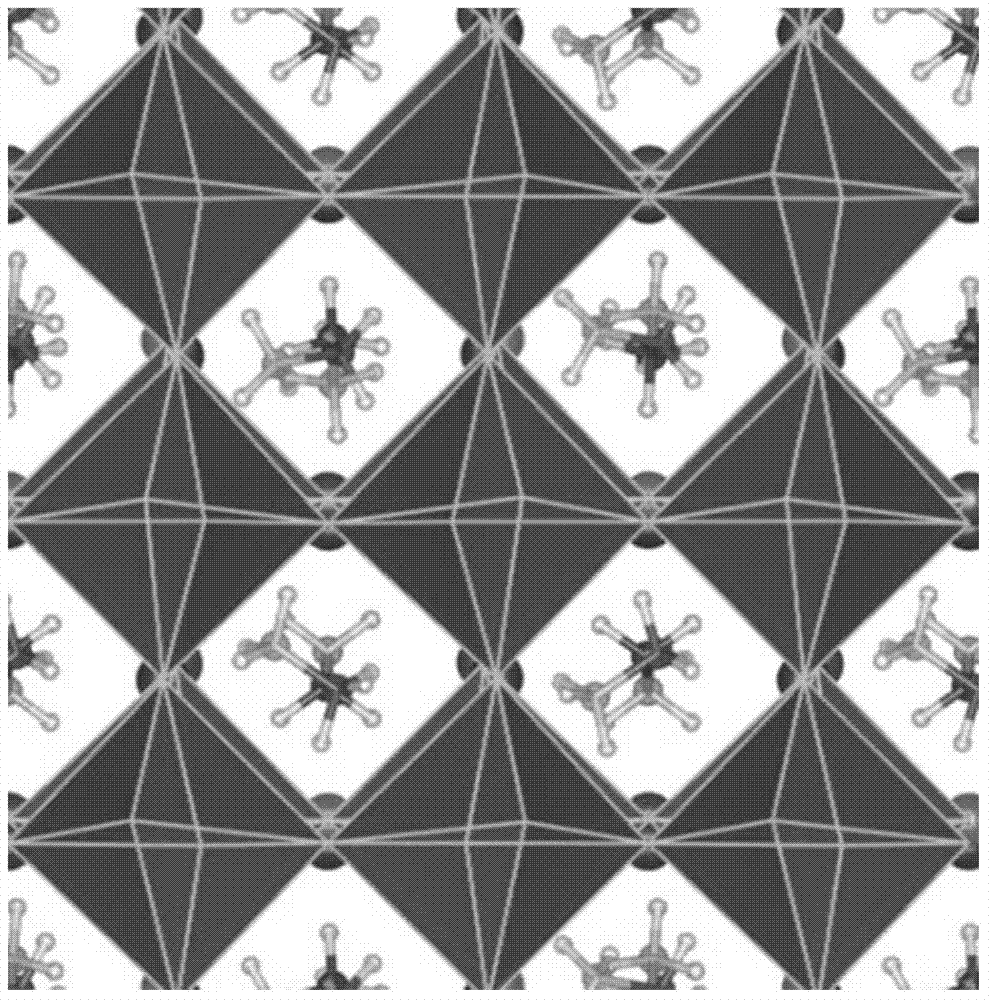
The invention discloses a theoretical method for screening a high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer. The method comprises the following steps: structurally optimizing a perovskite model on the basis of a first principle, and performing electronic and spectral characteristic calculation; analyzing a stable structure to obtain a lattice constant and bond length and bond angle characteristics; performing electronic and spectral characteristic calculation on perovskite by virtue of VASP (Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package) software, drawing a charge density map, a state density map, an energy band structure chart and a spectrum chart by virtue of software such as VESTA and Origin, and analyzing the forbidden bandwidth of perovskite, an electron orbit transition rule, a crystal binding type, frontier orbit compositions and light absorption characteristics by virtue of a valence bond theory and an energy band theory; screening the high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer by comparing spectral absorption characteristics. According to the theoretical method for researching an internal mechanism of perovskite and screening the high-efficiency perovskite sensitizer, a direct theoretical guide is provided for the design of a perovskite solar cell, the research and development cycle of the cell is shortened, and research and development cost is lowered.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Expansion plane for PQFP/TQFP IR-package design
InactiveUS7215009B1Minimize electrical parasiticsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingPackage design
Provided is a lead frame package with an expansion plane to minimize electrical parasitics introduced into the semiconductor chip's electrical system (e.g., power delivery system, signal loops, etc.). Also provided are methods for assembling such lead frame packages into various semiconductor packages. Generally, a lead frame package includes a down set die attach pad over an underlying bottom plate. Both the die attach pad and the bottom plate may be used as intermediary connections for either power or ground connections. As compared to conventional lead frame package having an intermediary connection, the lead frame packages of the present invention can provide for any combination of shorter wire bond lengths, more wire bond connections, improved power delivery system, or reduced amounts of electrical parasitics.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
System for anchoring a load
ActiveUS20130152496A1Increase loadAvoidingBuilding reinforcementsBuilding material handlingEngineeringTendon
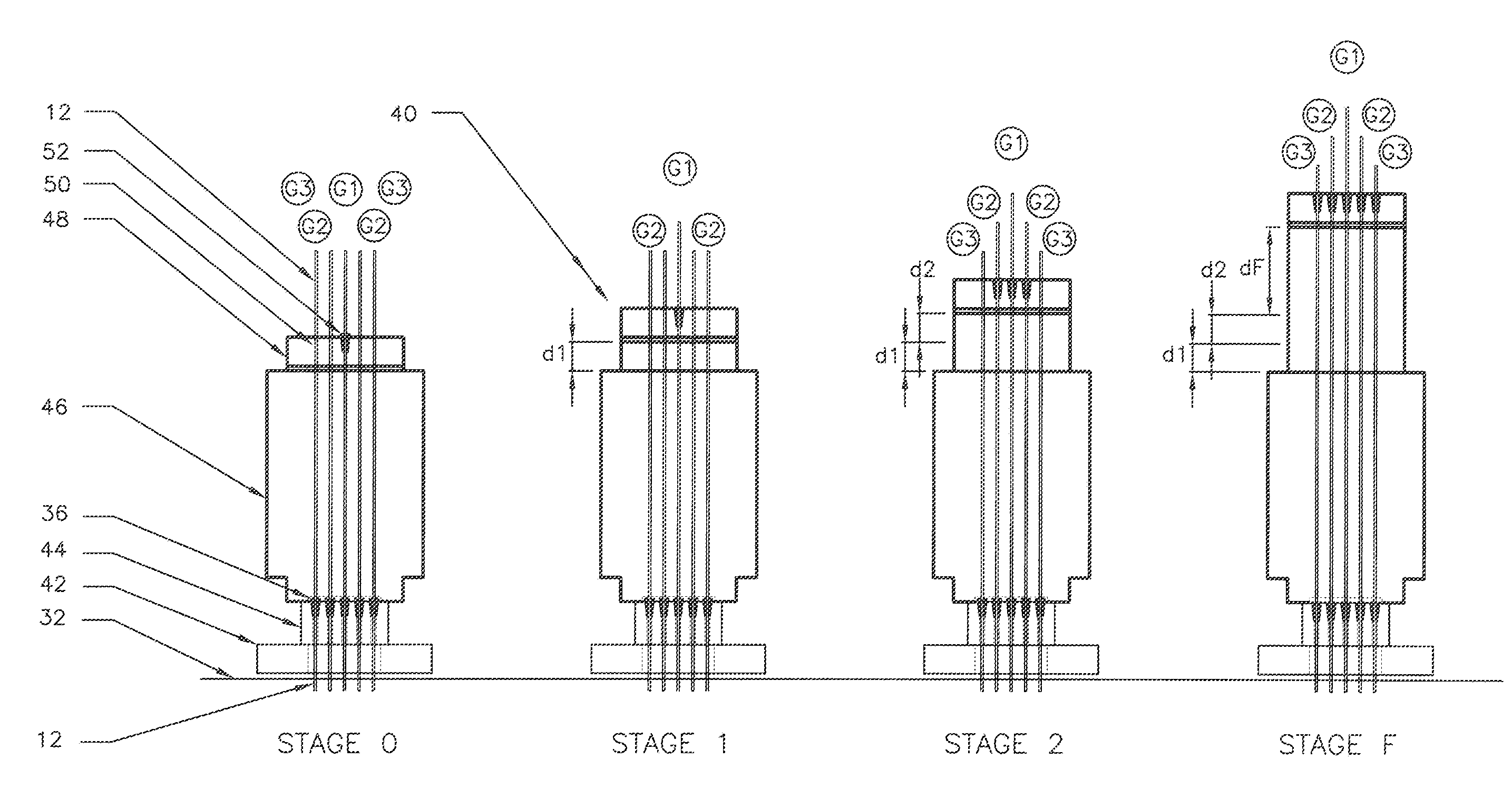
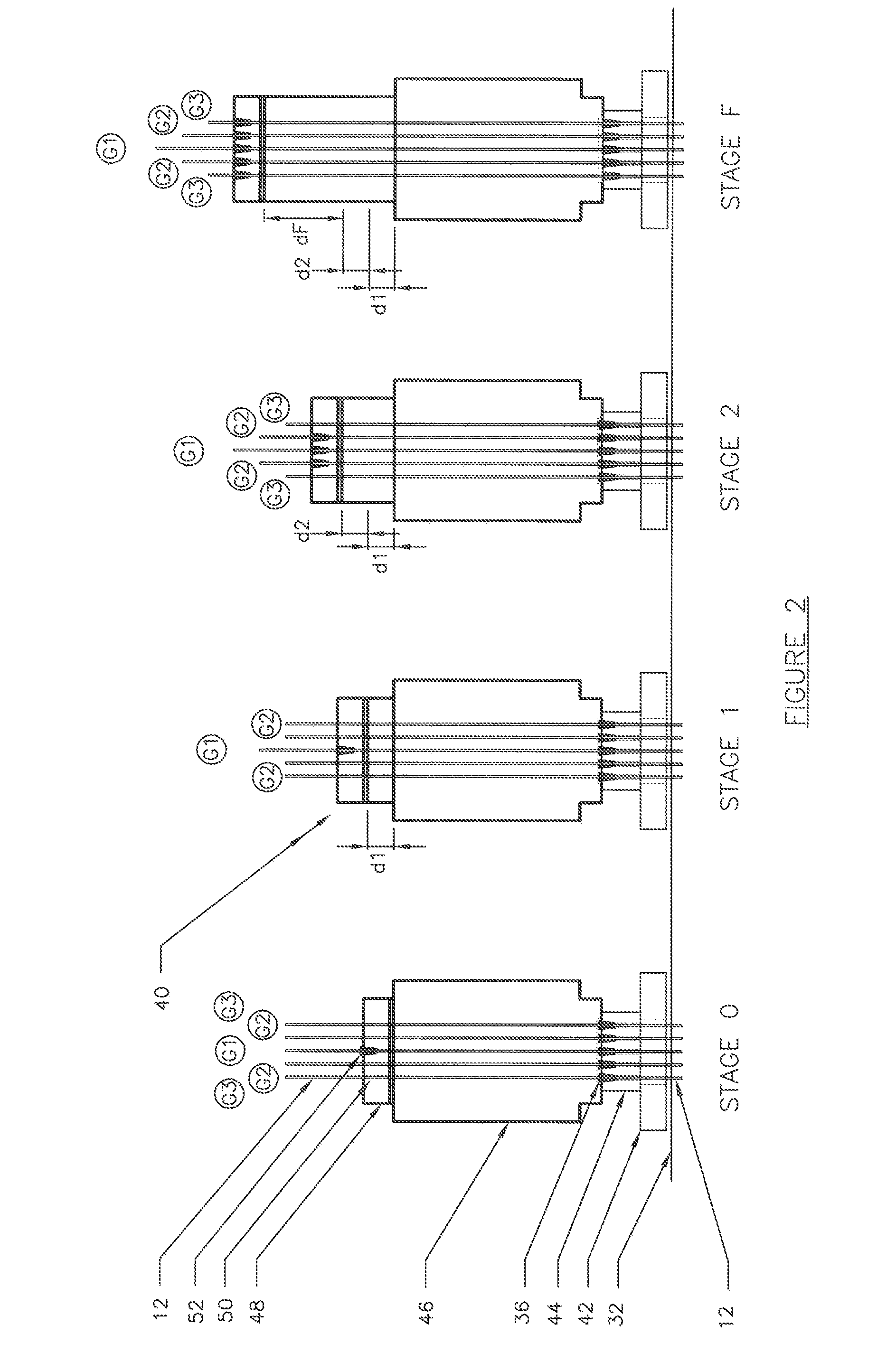
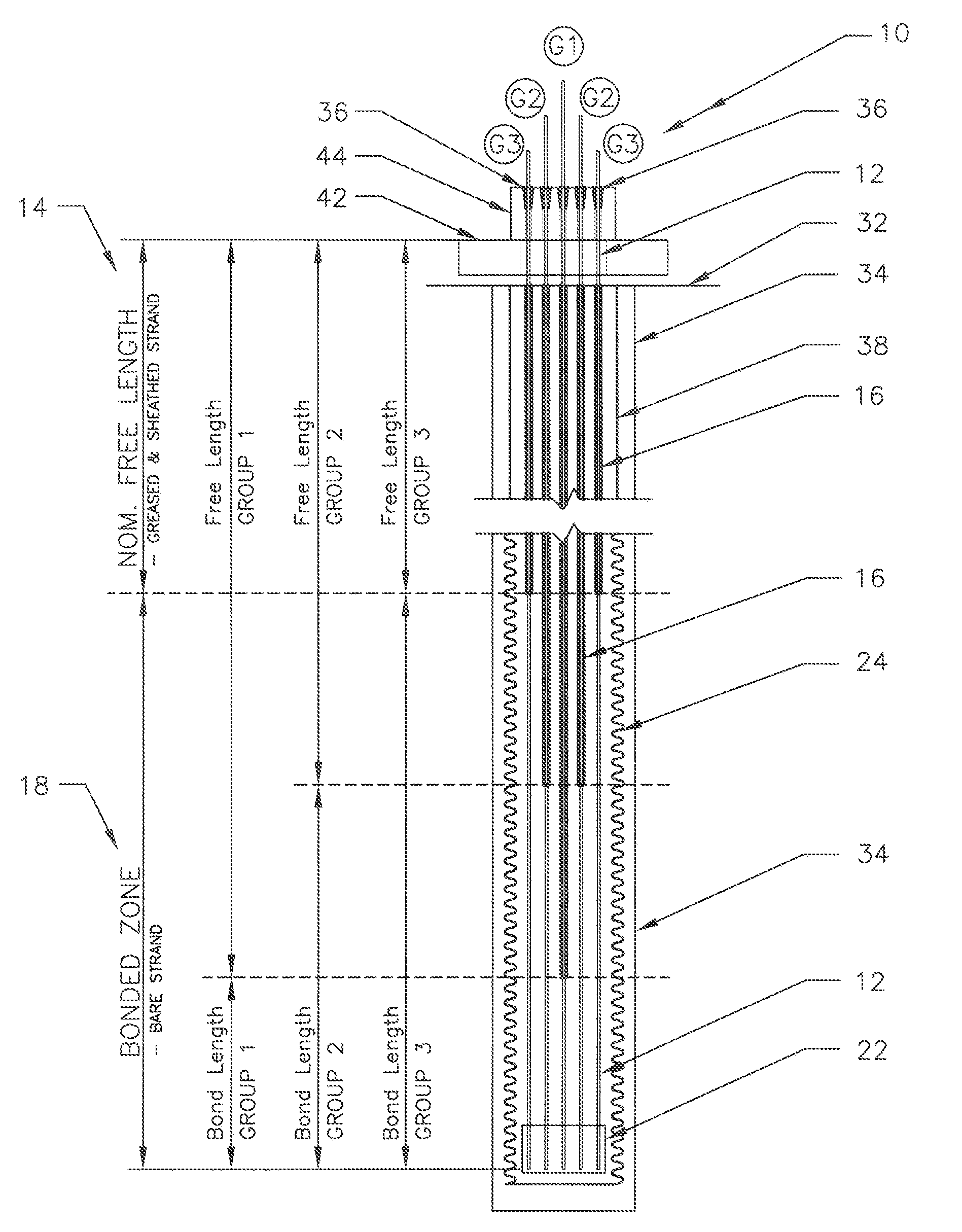
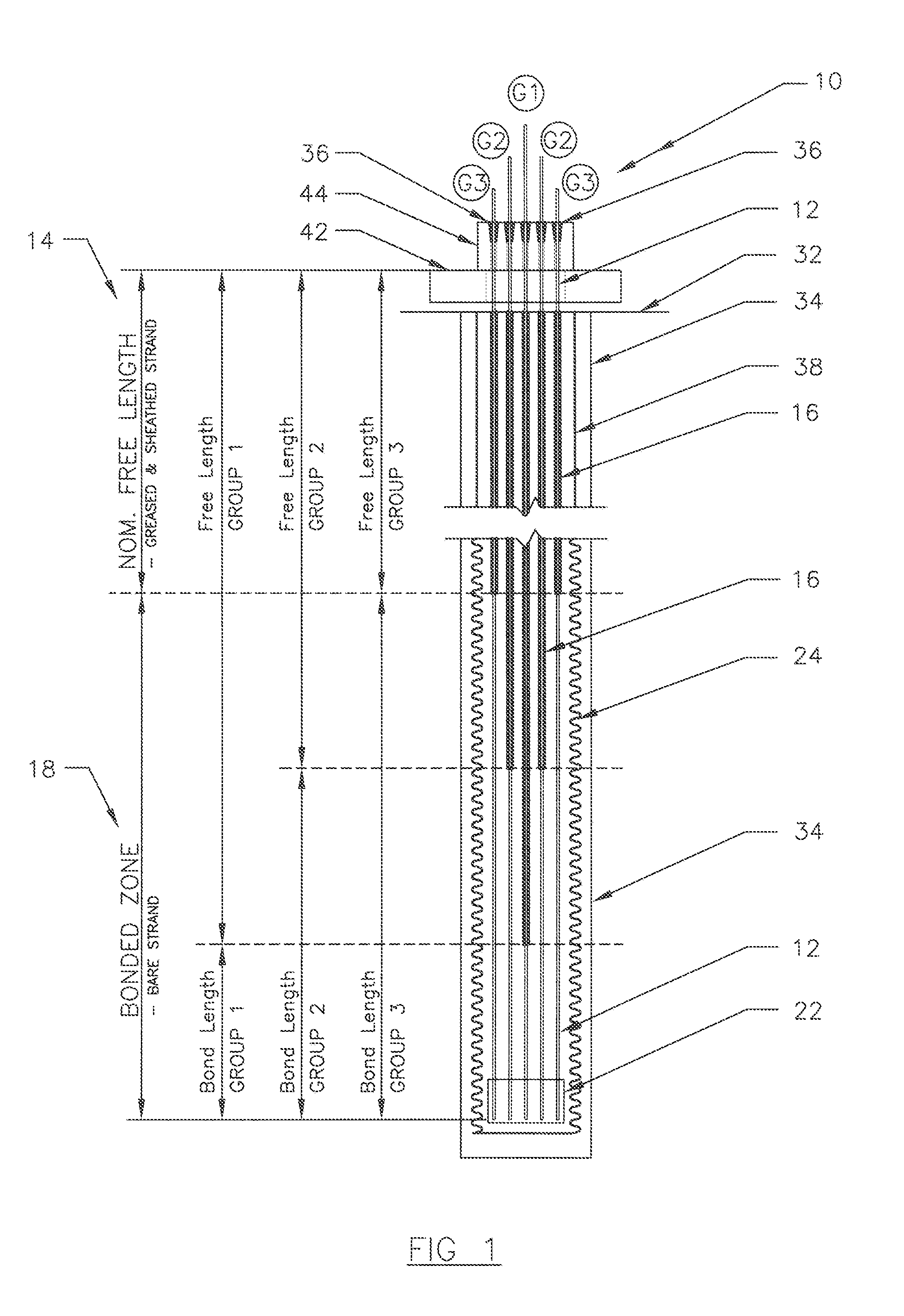
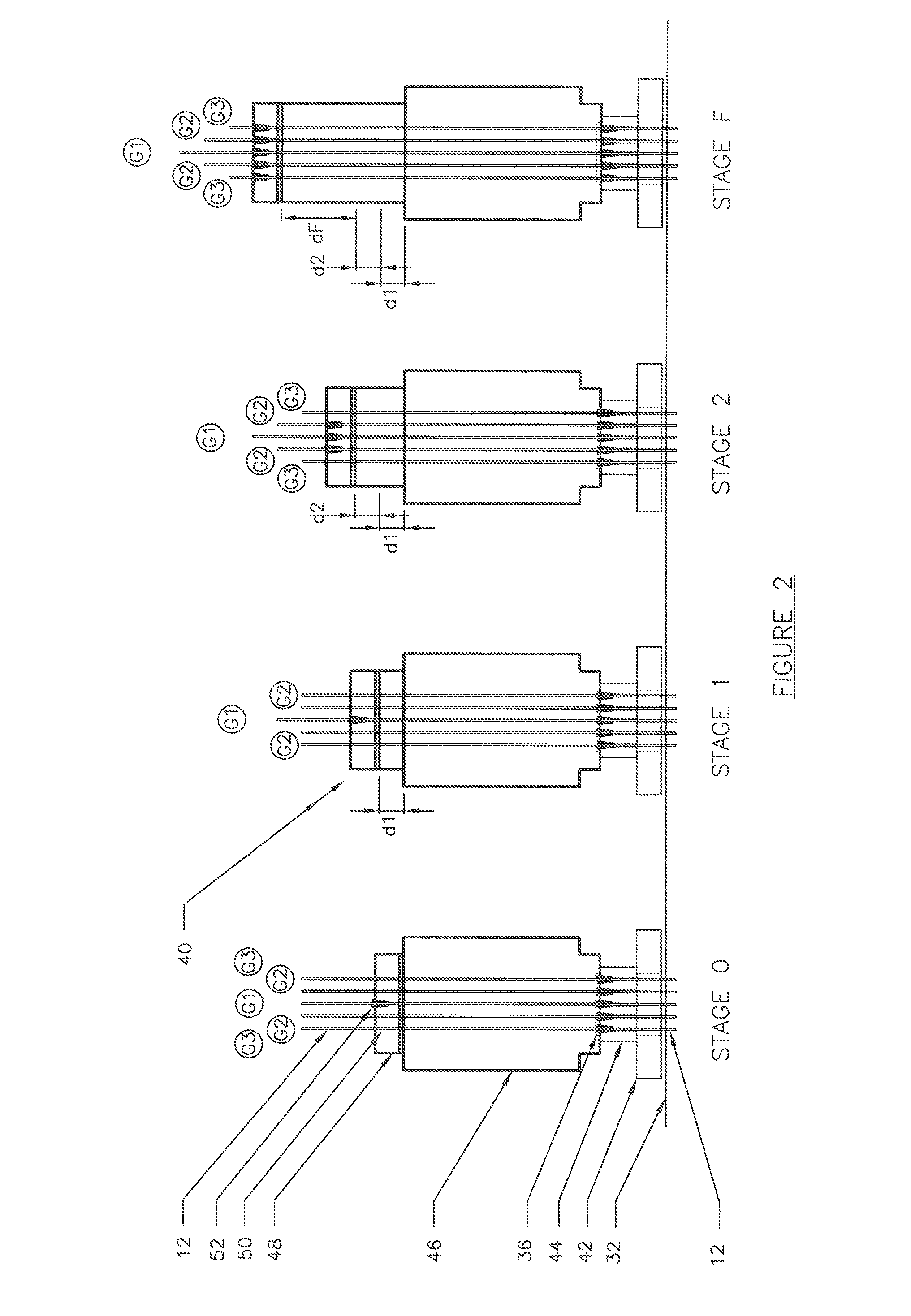
The invention relates to a method for anchoring a load (26) to an anchorage (30) utilising at least one unitary anchoring tendon (10) including a plurality of tensile elements (12) each having a free length (14) and a bond length (18). The tendon is located lengthwise in a bore (34) formed through the load into the anchorage, and different groups (G1, G2, G3) of the strands of the tendon are tensioned in a predetermined sequence to a respective initial displacement length prior to the different groups being collectively tensioned to a respective final displacement length to anchor the load.
Owner:SINCLAIR
Insect characteristic parameter inversion method based on characteristic values of polarization power matrix
ActiveCN107589412AImprove the measurement effectImprove species recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarInsect pest
The invention discloses an insect characteristic parameter inversion method based on the characteristic values of a polarization power matrix. The research on the polarization invariants of a polarization scattering matrix shows that the two characteristic values lambda 1 and lambda 2 (lambda 1 >= lambda 2) of a Graves power matrix have a strong correlation with the body length and body weight oflarge insects and small insects. On the basis, a method for inverting the body length and body weight of insects using lambda 1 of large insects and lambda 2 of small insects is presented, and a method for distinguishing between large insects and small insects is given. The measurement of body length parameters of insects is realized for the first time. The error of body weight inverted using themethod of the invention is lower than the error of body weight inverted using the traditional method. The ability of VLR (Vertical Looking Radar) to measure the biological parameters of insects is significantly enhanced. The ability to identify the species of migratory insects will be greatly improved. The method is of great significance to the research on the air ecological system and the management of insect pests.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Host-guest processes and formulations for delivering bio-affecting compounds
InactiveUS20040228887A1Increase concentrationCosmetic preparationsBiocideSolubilityChemical structure
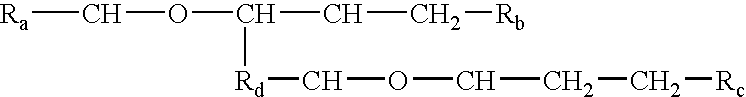
Processes and formulations are provided that are capable of protecting, stabilizing, and / or topically delivering one or more bio-affecting compounds. More particularly, the invention relates to processes of making a composition having a host compound capable of accepting one or more bio-affecting guest compounds, and new compositions formed by the processes. The processes and formulations can be used to protect and stabilize bio-affecting compounds of widely-different solubility characteristics. The processes include formulating a host composition having a host capable of accepting a guest, the processes comprising mixing, in any order: (i) a non-ionic surfactant s elected from the group consisting of compounds having a chemical structure: where "-CH-O-CH-" represents an epoxide group, where Ra and Rb are hydrocarbons that can be the same or different, where at least one of the Ra and Rb hydrocarbons includes an epoxide group within 3 carbons of the hydrocarbon attachment to contribute to the desired hydrolypid balance of 7-9, where Rc is hydrogen or a methyl group, and where Rd is a methylene group (-CH2-), an ethyl group (-CH2-CH2-), or a structurally equivalent link with a bond length range about the same as or shorter than that provided by an ethyl group, and having a hydro-lipid balance in the range of 7-9; (ii) an amphoteric surfactant selected from the group consisting of organic compounds having the chemical formula NH3-R-COOH, where R is a straight, branched, or aromatic hydrocarbon structure having 6-24 carbons; (iii) a solvent for the amphoteric surfactant; (iv) an aromatic selected from the group consisting of compounds having at least one aromatic five or six-member ring; (v) an aluminum cation; (vi) a Lewis acid that is not a Bronsted-Lowry acid; and (vii) a Bronsted-Lowry acid. According to a further aspect of the invention, one or more compounds are selected to be sequentially mixed with the host composition to form a stable molecular environment, which is sometimes referred to herein as a process of molecular stacking.
Owner:CHAMP CHARLES W +1
Host-guest processes and formulations for delivering bio-affecting compounds
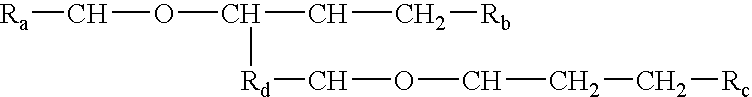
InactiveUS6676951B1Increase concentrationCosmetic preparationsBiocideChemical structureAluminum Cation
The invention relates to processes of making a composition having a host compound capable of accepting one or more bio-affecting guest compounds, and compositions formed by the processes. The processes comprise mixing, in any order: (i) a non-ionic surfactant selected from the group consisting of compounds having chemical structure (I) where "-CH-O-CH-" represents an epoxide group, where Ra and Rb are hydrocarbons that can be the same or different, where at least one of the Ra and Rb hydrocarbons includes an epoxide group within 3 carbons of the hydrocarbon attachment to contribute to the desired hydrolipid balance of 7-9, where Rc is hydrogen or a methyl group, and where Rd is a methylene group, and ethyl group, or a structurally equivalent link with a bond length range about the same as or shorter than that provided by an ethyl group, and having a hydro-lipid balance in the range 7-9; (ii) an amphoteric surfactant selected from the group consisting of organic compounds having the chemical formula NH3-R-COOH, where R is a straight, branched, or aromatic hydrocarbon structure having 6-24 carbons; (iii) a solvent for the amphoteric surfactant; (iv) an aromatic selected from the group consisting of compounds having at (I) least one aromatic five or six-member ring; (v) an aluminum cation; (vi) a Lewis acid that is not a Bronsted-Lowry acid; and (vii) a Bronsted-Lowry acid.
Owner:CHAMP CHARLES WALTON +1
Preparation method of high-performance supported metal silicide catalyst and application thereof
ActiveCN101658804AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMetal silicideAlkyne
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-performance supported metal silicide catalyst and application thereof, and belongs to the field of catalytic science and technology. In the catalyst, silicon atoms enter metal lattices, and cause the metal lattices to be expanded and metallic bond length to be increased, and structural changes, physical property changes and the like provide metal silicides with special catalytic properties. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a carbonyl compound and an organic silicon compound are used as raw materials, and a metal organic silicide precursor is obtained after low temperature reaction and purification by sublimation; and the metal organic silicide precursor is sublimated to a carrier in a fluidized bed reactor for metal organic chemical vapor deposition, thus obtaining the high-performance supported metal silicide catalyst. The catalyst can be applied to multi-phase hydrogen-related catalytic reactions such as naphthalene hydrogenation, selective hydrogenation of alkyne or diene, hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrogenation reactions. The preparation method solves the problem of low surface area of metal silicides prepared by traditional methods, and has advantages of simple operation and easy control.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Quantum limit catalysts and hydrogen storage materials
InactiveUS20050014640A1Promote formationMaintain good propertiesHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationChemical elementElectron density
A quantum limit catalyst. The quantum limit corresponds to a size domain in which material properties are no longer constrained by the structure and bonding requirements imposed by the macroscopic length scale. The instant quantum limit catalyst is comprised of atomic aggregations whose dimensions correspond to the quantum limit. In the quantum limit, the atomic aggregations acquire structural configurations and electronic interactions not attainable in the macroscopic limit. The structural configurations possible in the quantum limit correspond to atomic aggregations having bond lengths, bond angles, topologies and coordination environments that differ from those found in the macroscopic limit. The electronic interactions possible in the quantum limit originate from wavefunction overlap and tunneling between atoms and lead to modifications in the magnitude and / or spatial distribution of electron density at catalytic sites to provide improved catalytic properties. The modifications in electron density and wavefunction characteristics (overlap and directionality) achieved in the quantum limit provide, in effect, “new” or “virtual” chemical elements whose structure and bonding deviate from those associated with the “standard” chemical elements of conventional materials. Combinations of virtual elements provide virtual alloys having structures and properties not available in conventional alloys. Representative quantum limit catalysts include materials comprised of quantum scale atomic aggregations of metal atoms. The aggregations include one or more metals and have sizes in the angstrom scale range. Examples including catalysts derived from Fe, Mg, V and Co are disclosed. Catalytic properties are exemplified in the context of hydrogen storage. Methods that may be used to prepare quantum limit catalysts include sonochemical synthesis, thermal decomposition, and reduction.
Owner:HARNYSS IP LLC +1
Acrylic urn vault
The sealing acrylic urn vault of the invention includes a generally square sheet of ⅝″ cast acrylic serving as the base and a generally square top portion which will have four adjacent side walls bonded to its edges and protruding downward. Each opposing side wall will be bonded length-wise to each adjoining side, creating a seamless cast acrylic box, open at the bottom, that lowers onto the acrylic base. Attached to the base are four 0.625″ tall ⅝″ thick acrylic guide rails, bonded equidistant from the outside base edge on all four sides of the base. This “railing system” is the fastening guide for the acrylic top portion which lowers onto the base with the inside of the four side walls bonded with the outside edges of the four guide rails.
Owner:WILBERT FUNERAL SERVICES
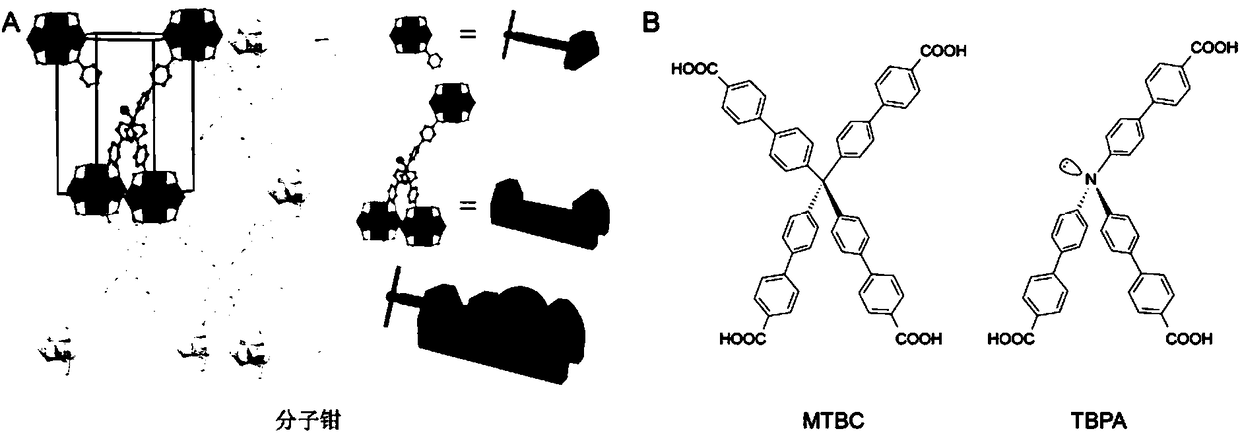
Preparation method of molecular forcipiform metal organic frame material having fixed coordination configuration and accurate regulation and control of coordination bond length
ActiveCN108285538APrecise continuous regulationImprove performanceGas treatmentDispersed particle separationFluorescenceMetal
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molecular forcipiform metal organic frame material having fixed coordination configuration and accurate regulation and control of a coordination bondlength. The material is prepared by three ligands of a fluorescence ligand TBPA, a material building ligand MTBC and an ion coordination environment regulation and control ligand. Through limitation of a metal organic frame structure, the 3 coordinated TBPA ligand and a series of a 1 coordinated ligand combinations partially replace the 4 coordinated organic ligand in a frame, the coordination configuration can be fixed, and the 1 coordinated ligand is changed to change the coordination bond length. The method has the advantages that based on unchanged metal coordination configuration, the coordination bond length is changed, the method can accurately and continuously regulate and control the metal coordination environment, and performance optimization can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Borosilicate rare earth luminescent microcrystalline glass, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110467351AHigh luminous intensityControl colorSemiconductor devicesChemical compositionLuminous intensity
The invention belongs to the technical field of luminescent materials, and particularly relates to borosilicate rare earth luminescent microcrystalline glass, and a preparation method and applicationthereof. The chemical composition of the borosilicate rare earth luminescent microcrystalline glass is aMO.bLn<2>O<3>.cB<2>O<3>.dSiO<2>.eAl<2>O<3>: xBi, yGe, zRE. According to the invention, rare earth ions including RE, Bi, Ge, Al and the like are doped into the microcrystalline glass, and a crystal field around the rare earth ions is further adjusted by utilizing different ion radiuses, coordination potentials, bond types, bond lengths, coordination numbers and the like of the rare earth ions, so the control of color and luminous intensity is facilitated; and through sensitization of Bi ionsto other rare earth ions (such as Tb<3+>, Eu<3+>, Tm<3+>, Dy<3+> and the like), the microcrystalline glass has higher luminous intensity and can be applied to LED luminescent devices.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
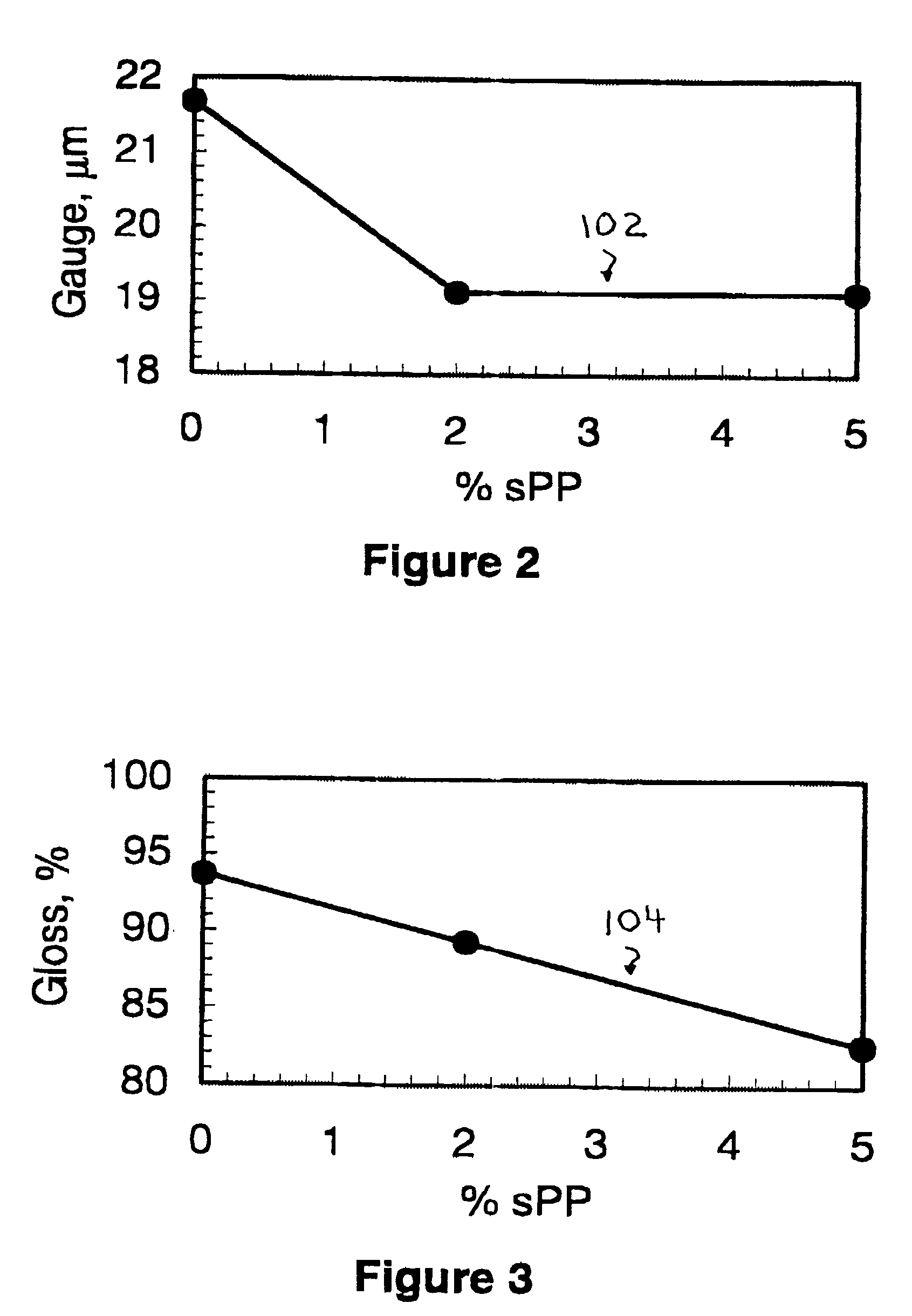
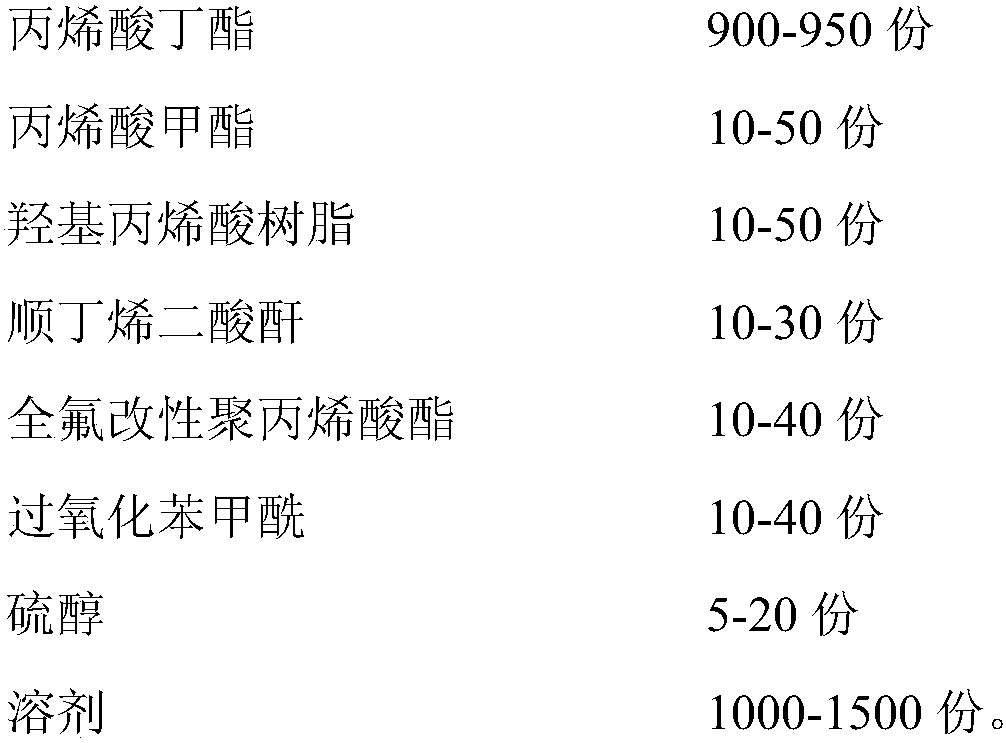
Metal bond strength in polypropylene films
InactiveUS7026055B2Synthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingOptical propertyEthylene Homopolymers
The present invention relates to the improvement of metal bond strength in polypropylene films surface treated at higher levels through the addition to the basic isotactic polypropylene (iPP) polymer of an amount of syndiotactic polypropylene (sPP) in an amount no more than about 10 percent by weight and preferably in an amount between about 0.5 percent and about 8 percent by weight. The invention encompasses both the resulting metallized polypropylene films with enhanced bond strength and the process for producing such films. The prescribed use provides improved bonding properties over a simple non-blended isotactic polypropylene homopolymer, while maintaining at acceptable levels the optical and physical characteristics of a film made from non-blended iPP homopolymer. At increasing percentages of sPP above the preferred levels, bond strength continues to increase, but a deterioration in other properties may be noted, particularly in the optical property haze.
Owner:FINA TECH
Construction method for food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model
ActiveCN103714266AGood correlationSpecial data processing applicationsEntity–relationship modelHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention relates to a construction method and application for a food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model. The method comprises the steps of using a food-borne polypeptide with known activity as a research object, utilizing the three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship technology for establishing the food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model, and adopting the MM+ method the semi-empirical quantum chemistry method AM1, the DFT method and other quantum chemistry technologies to obtain quantum chemistry parameters. According to the construction method, analysis and statistics are carried out on the food-borne polypeptide quantum chemistry parameters, the antioxidant activity sites of the food-borne polypeptide are determined, and quantitative structure-activity model is constructed by utilizing the bond length, charge distribution, frontier molecular orbit energy parameters of the activity sites and food-borne polypeptide antioxidant activity values. The constructed model can rapidly and accurately predict the activity value of the food-borne polypeptide with the unknown activity, and the relationship between the antioxidant activity and structural features can be reasonably explained; compared with a traditional high throughput screening technology, the screening efficiency is greatly improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
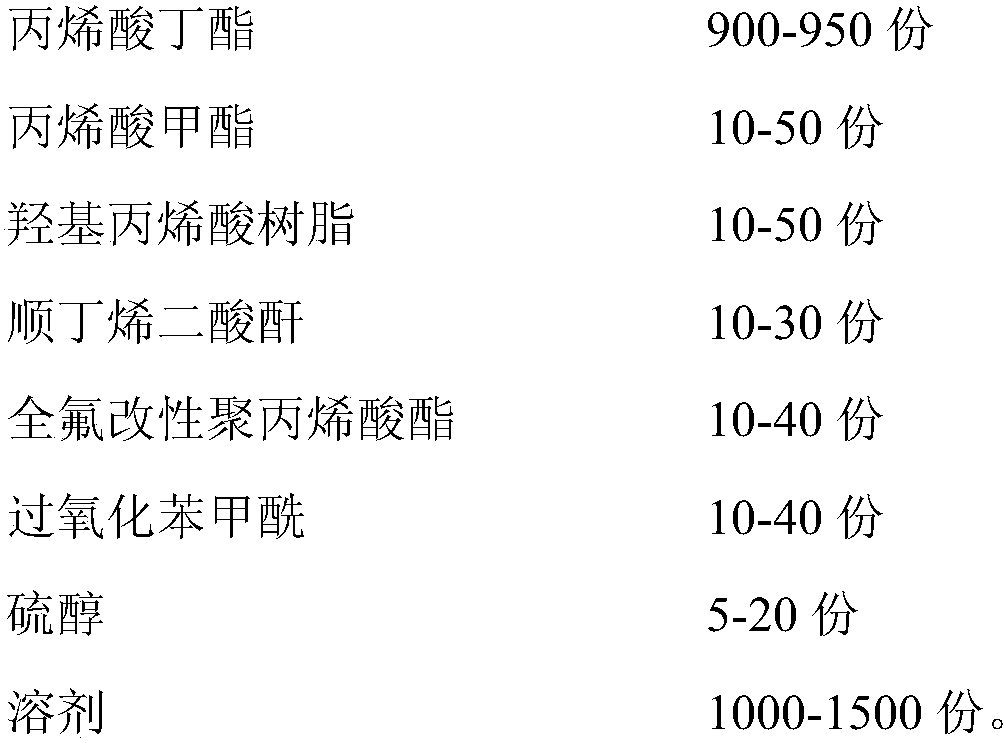
Leveling agent for powdered coating and preparation method of leveling agent
InactiveCN107793822AImprove thermal stabilityGood chemical stabilityAnti-corrosive paintsPowdery paintsChemical synthesisBond energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis, and particularly relates to a leveling agent for powdered coating and a preparation method of the leveling agent. The leveling agentfor powdered coating is prepared from the following raw materials: butyl acrylate, methyl acrylate, hydroxy acrylic resin, maleic anhydride, perfluoro modified polyacrylate, benzoyl peroxide, mercaptan and a solvent. By the adding of the perfluoro modified polyacrylate into the acrylates leveling agent, as a fluorine carbon bond is small in bond length, high in bond energy and low in fluorine atom polarizability, introduction of a fluorine-containing polymer improves the heat stability, the chemical stability, the glossiness, the low surface energy, the chemical corrosion resistance and the like of the leveling agent, which are higher than the properties of the same type of acrylate products.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFENG CHEM
System for anchoring a load
ActiveUS8931236B2Increase loadLevel loadingBuilding repairsBridge erection/assemblyEngineeringBond length
The invention relates to a method for anchoring a load (26) to an anchorage (30) utilizing at least one unitary anchoring tendon (10) including a plurality of tensile elements (12) each having a free length (14) and a bond length (18). The tendon is located lengthwise in a bore (34) formed through the load into the anchorage, and different groups (G1, G2, G3) of the strands of the tendon are tensioned in a predetermined sequence to a respective initial displacement length prior to the different groups being collectively tensioned to a respective final displacement length to anchor the load.
Owner:SINCLAIR
Heteropolycopper niobate, preparation method thereof and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater
InactiveCN106563460AEasy to synthesizeLow costWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsHeteroatomOxygen
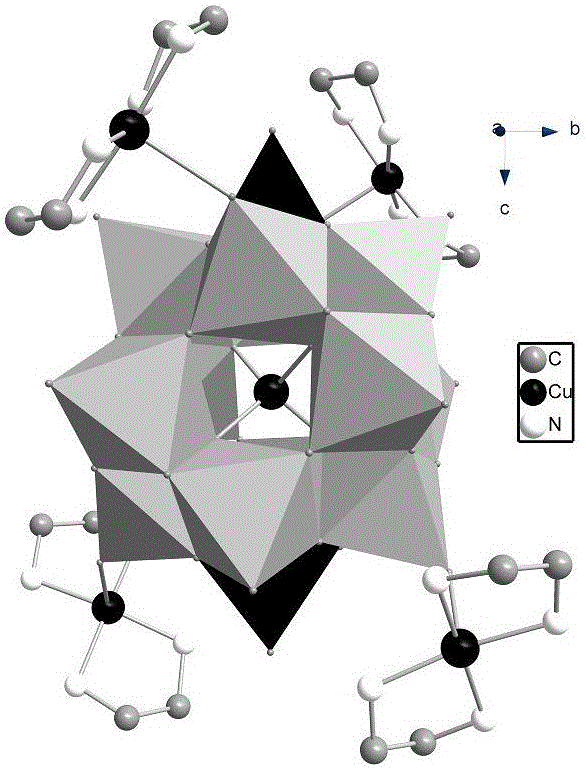
The invention discloses heteropolycopper niobate, a preparation method thereof and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of synthesis and photocatalysis of polyniobate. The key points of the technical scheme are as follows: the molecular formula of the heteropolycopper niobate is H6[Cu(en)2]4[CuNb12O40(VO)2].7H2O; in a polyanion [CuNb12O40(VO)2]14, the bond length of the Cu-O bonds of central heteroatomic copper and surrounding oxygen atoms are 1.728A'; two V4+ cover caps are located at the two poles of the polyanion; in a cationic complex [Cu(en)2]2+, the bond length of the Cu-N bond is 2.022 A'; and each polyanion is respectively connected with four cationic complex through Cu-O(t) bonds. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the heteropolycopper niobate and application of the heteropolycopper niobate in the photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater. The heteropolycopper niobate prepared in the invention is the first heteropoly niobate which regards late transition metal as a heteroatom, is simple in synthesis process and low in cost, is absorbed in a UV region and a visible light region, and has relatively good application prospect in the field of photocatalysis.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
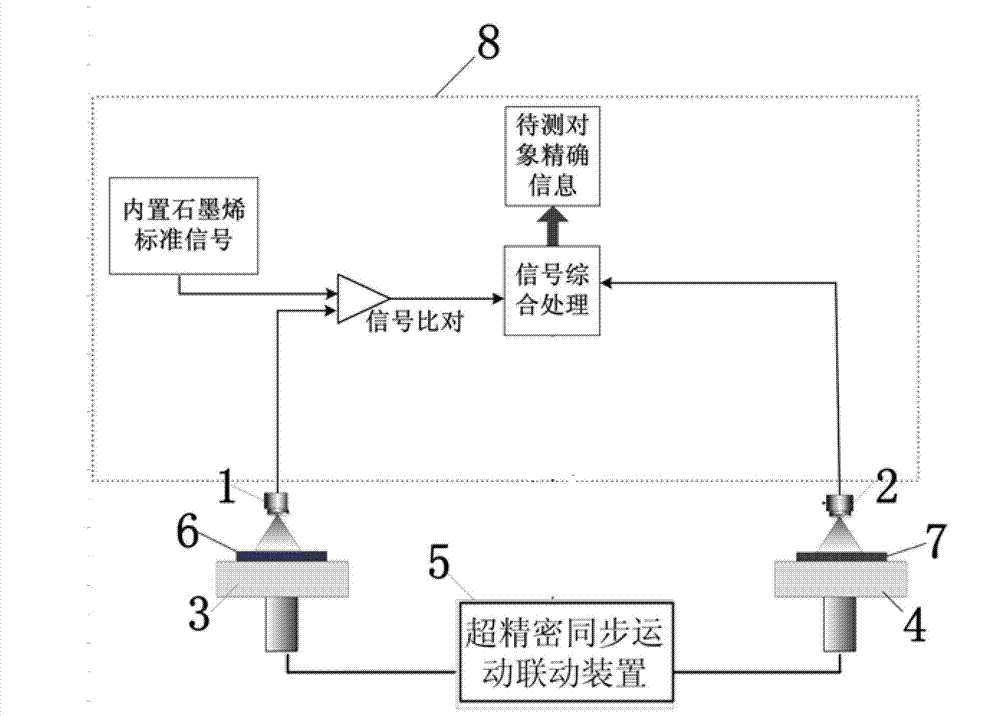
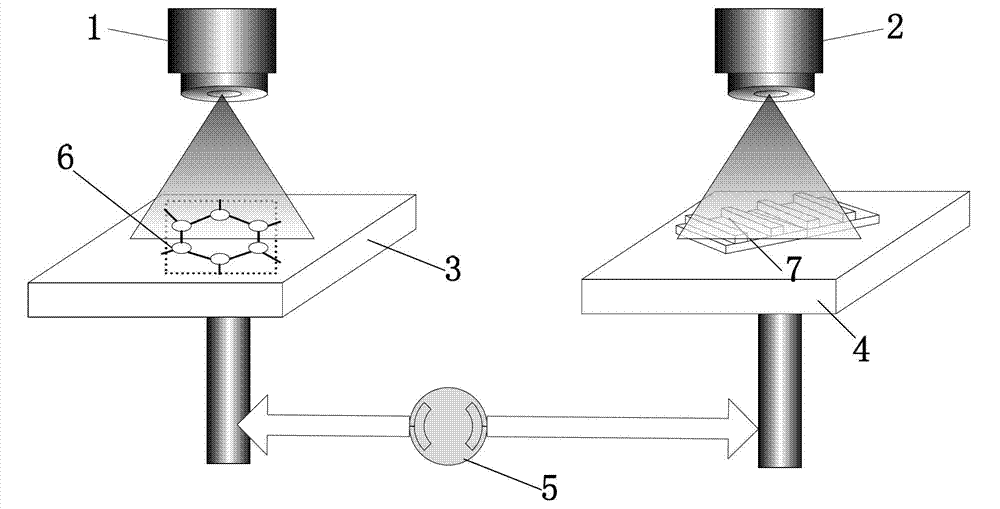
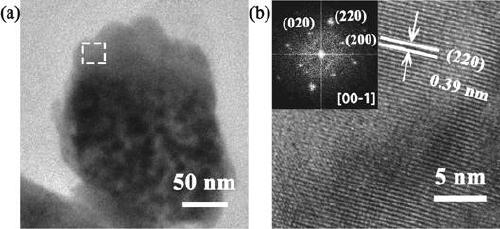
Length measuring and tracing method using graphene bond length as measuring reference
InactiveCN102889866ALong-term stabilityGuaranteed long-term stabilityUsing wave/particle radiation meansReference sampleGraphene
The invention discloses a length measuring and tracing method using a graphene bond length as a measuring reference. The graphene bond length is used as a length measuring and tracing reference, length measuring and tracing are carried out on an object to be detected by the number of detected graphene bond lengths, and sub-nanometer grade precision length measuring and tracing are realized. Ultra-precision synchronous motion control connection is carried out on the object to be detected and a graphene reference sample bearing table, the number of the graphene bond lengths is scanned to represent the motion length of the graphene reference sample bearing table, and the motion of the graphene reference sample bearing table is detected in real time, so that the sub-nanometer grade precision length measuring is carried out on the object to be detected, and sub-nanometer grade precision length measuring and tracing are realized. As graphene lattices are used as the length measuring and tracing reference, the length measuring and tracing method has the characteristics of high stability, high measuring precision capable of reaching a sub-nanometer grade, simpleness, reliability and the like and has wide application prospects in the field of ultra-precision measuring and tracing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Lead-MOF complex with fluorescent performance
InactiveCN108912163ASimple reaction conditionsRapid responseGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic chemistry methodsFluorescenceCoordination geometry
The invention discloses preparation for a lead-MOF complex with fluorescent performance. The lead-MOF complex has a molecular formula of [Pb(L)0.5(DMA)(H2O)].DMA.2H2O, a structure of the complex belongs to a monoclinic crystal system C2 / c space group, a basic structural unit of the crystal is obtained by symmetric operation of asymmetric units, a symmetric operation code is <1>-1 / 2+X, -1 / 2+Y, +Z;<2>1 / 2+X, 1 / 2+Y, +Z; <3>1-X, 1-Y, 1-Z, the asymmetric units have a 1 / 2 coordination ligand, a Pb<2+>, a coordinated DMA molecule, the Pb<2+> adopts a five-coordination mode, wherein four oxygen atomsare respectively from two different perylene derivative ligands, and another oxygen atom is from the coordinated DMA molecule DMA molecule, and an average bond length of Pb-O is shown in the description. The lead-MOF complex disclosed by the invention has the advantages of controllable preparation of the fluorescent complex
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Evaluation method for simulating oil-water interface characteristics of alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant based on molecular dynamics
PendingCN111028891AThe evaluation result is accurateEvaluation time period is shortChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationActive agentOil phase
The invention discloses an evaluation method for simulating oil-water interface characteristics of an alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant based on molecular dynamics. The method comprises establishing amolecular structure model of alkylbenzene sulfonate by adopting software; then, performing quantum chemistry calculation by utilizing software to obtain optimized molecular conformation and all-atomic structure charge parameters of alkylbenzene sulfonate; optimizing the molecular structure of alkylbenzene sulfonate to obtain optimized molecular topological structure parameters of the bond length,the bond angle and the dihedral angle; establishing a system model of oil-phase molecules, water molecules and alkylbenzene sulfonate by utilizing molecular accumulation software; and finally carrying out molecular dynamics calculation on a simulation system by utilizing molecular dynamics calculation software to evaluate the oil-water interface characteristics of alkylbenzene sulfonate. According to the method, the oil-water interface microcosmic action mechanism of the alkylbenzene sulfonate surfactant for chemical flooding can be clarified from molecular and atomic scales, and certain theoretical guidance is provided for application of alkylbenzene sulfonate in the field of oilfield chemical flooding.
Owner:NANJING POLYTECHNIC INSITUTE
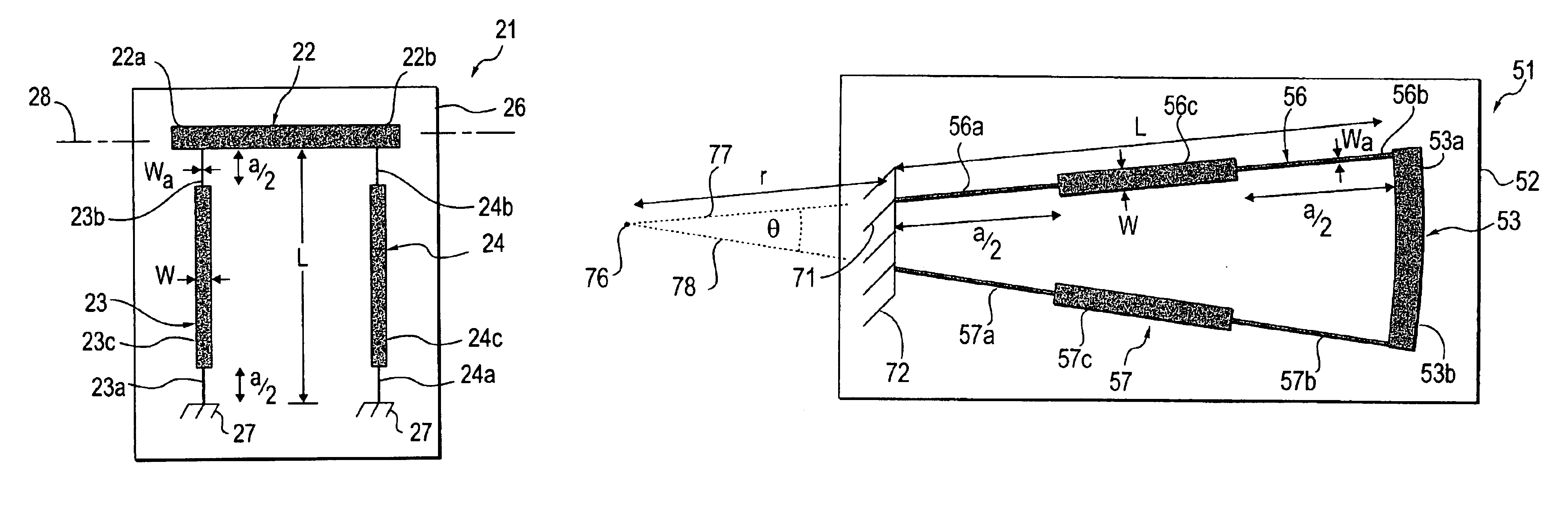
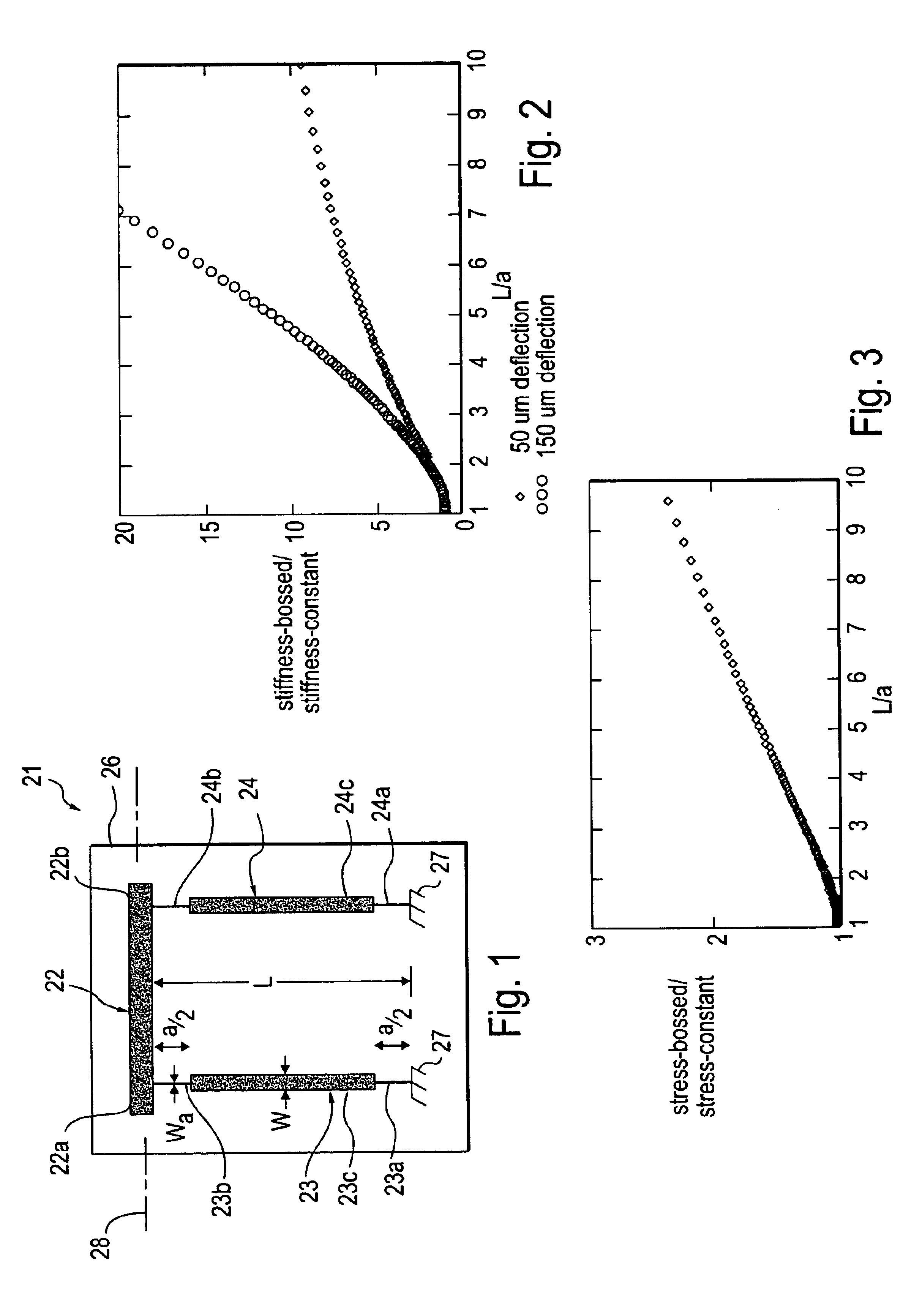
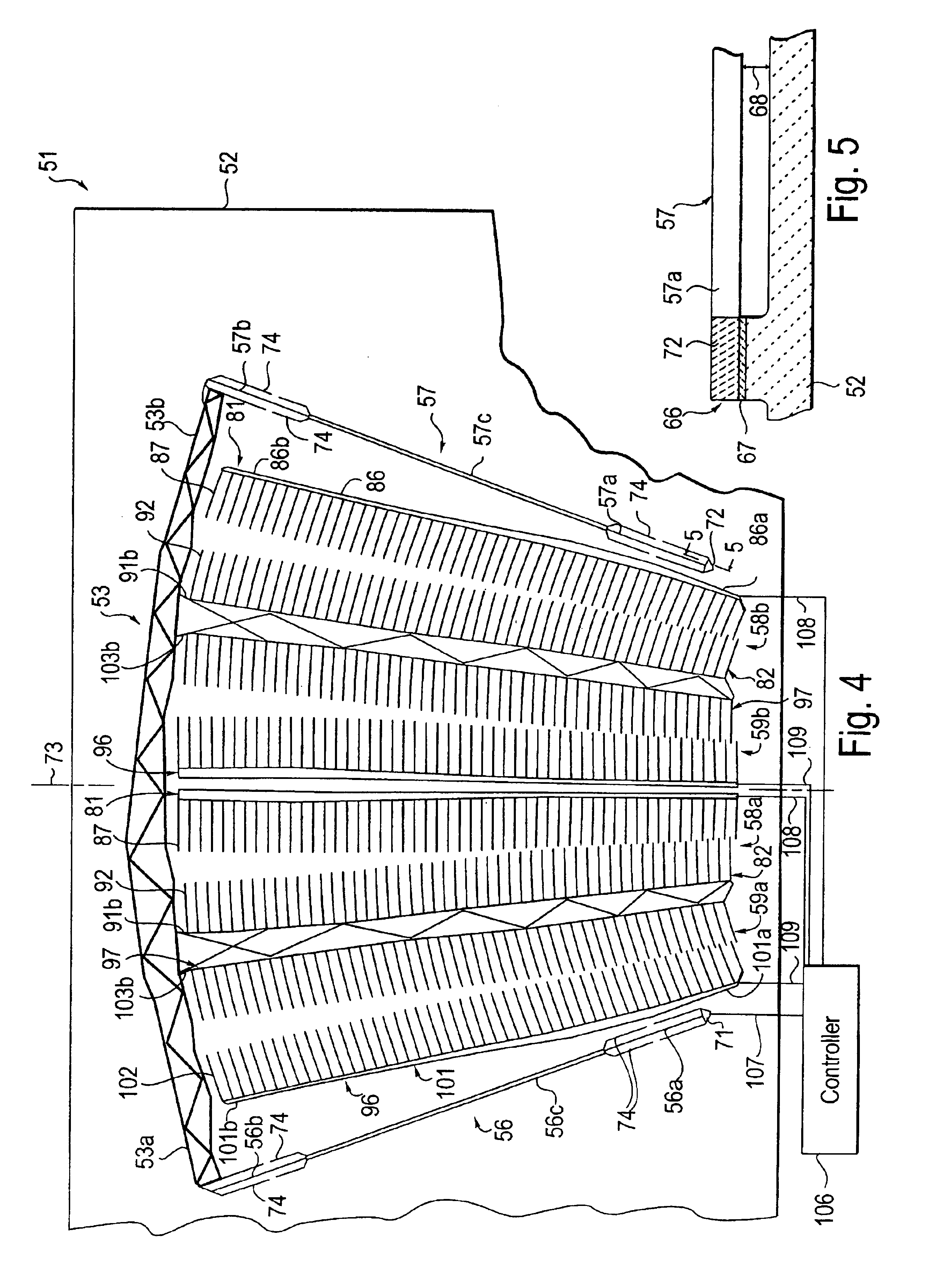
Miniature device with bossed suspension member
InactiveUS6882083B2Constant widthAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsBiomedical engineeringBond length
Owner:COHERENT INC
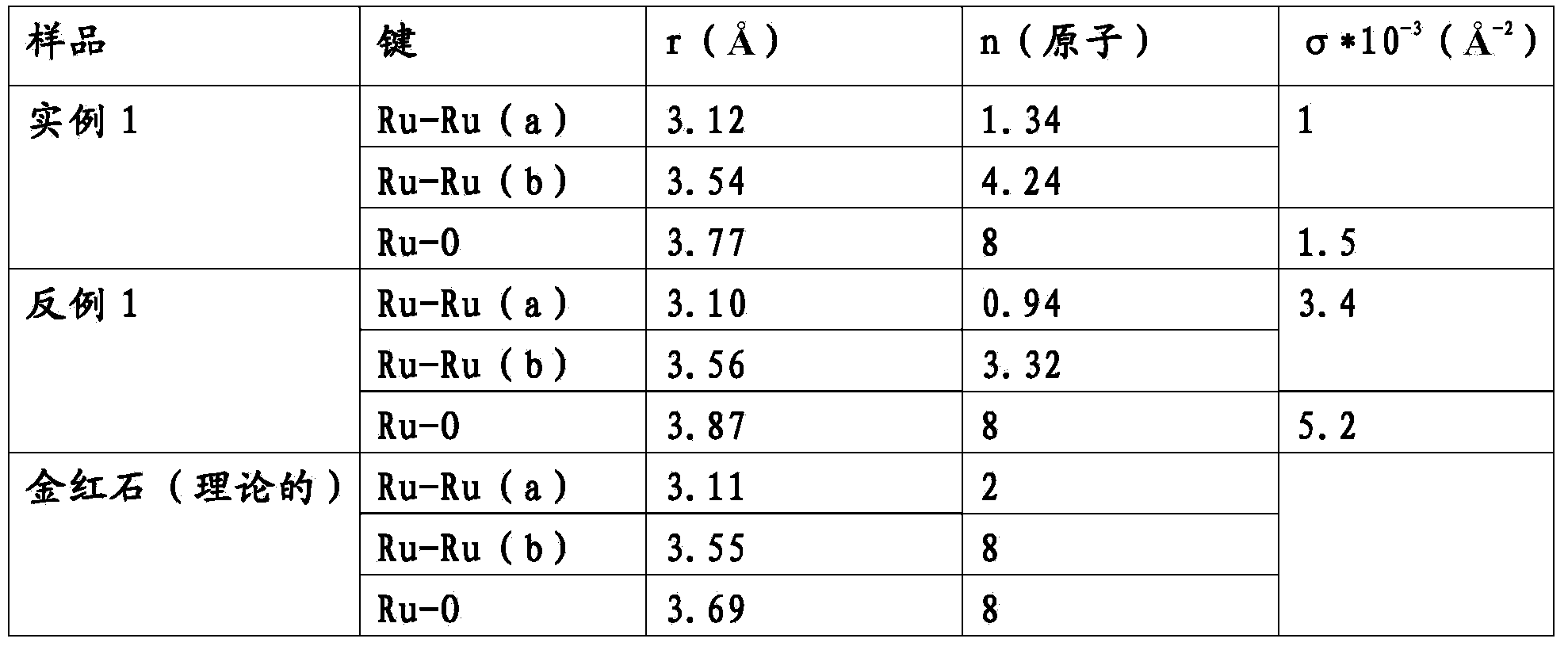
Electrode for electrolytic processes and method of manufacturing thereof
The invention relates to an electrode for electrolytic processes, particularly to a cathode suitable for hydrogen evolution in an industrial electrolysis process comprising a metal substrate coated with an external catalytic layer containing crystalline ruthenium oxide having a highly ordered rutile-type structure with Ru Ru and Ru O bond length characterised by a Debye-Waller factor lower than a critical value. The catalytic outer layer may contain rare earth oxides, such as praseodymium. The electrode may also comprise an internal catalytic thin layer platinum-based, which gives an enhanced protection against accidental current reversal events.
Owner:IND DE NORA SPA
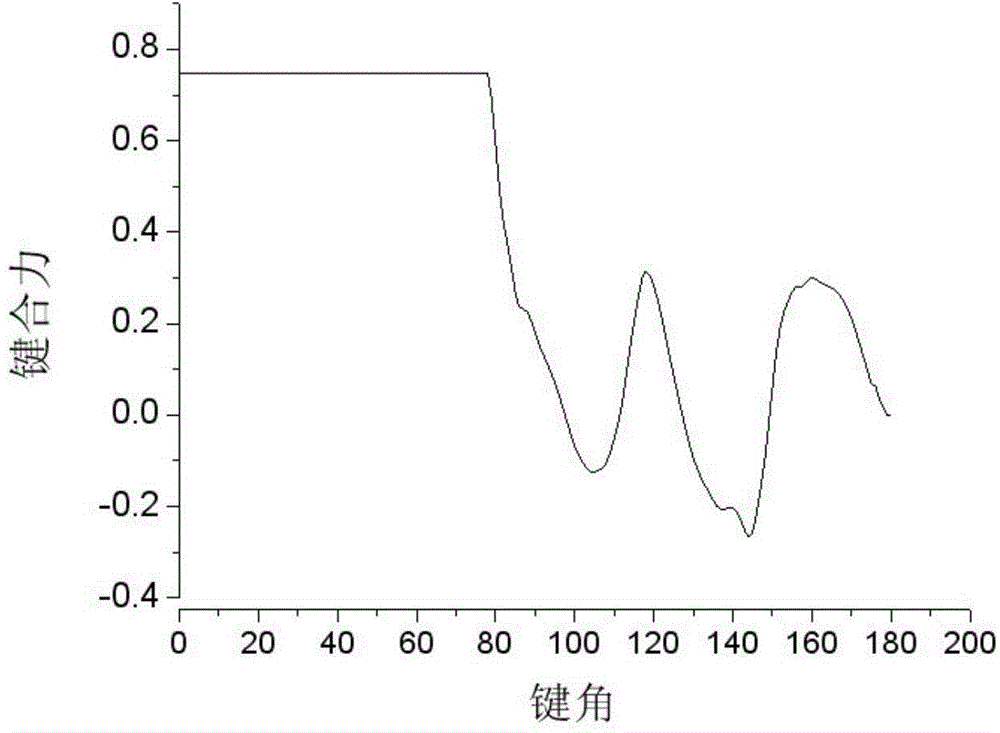
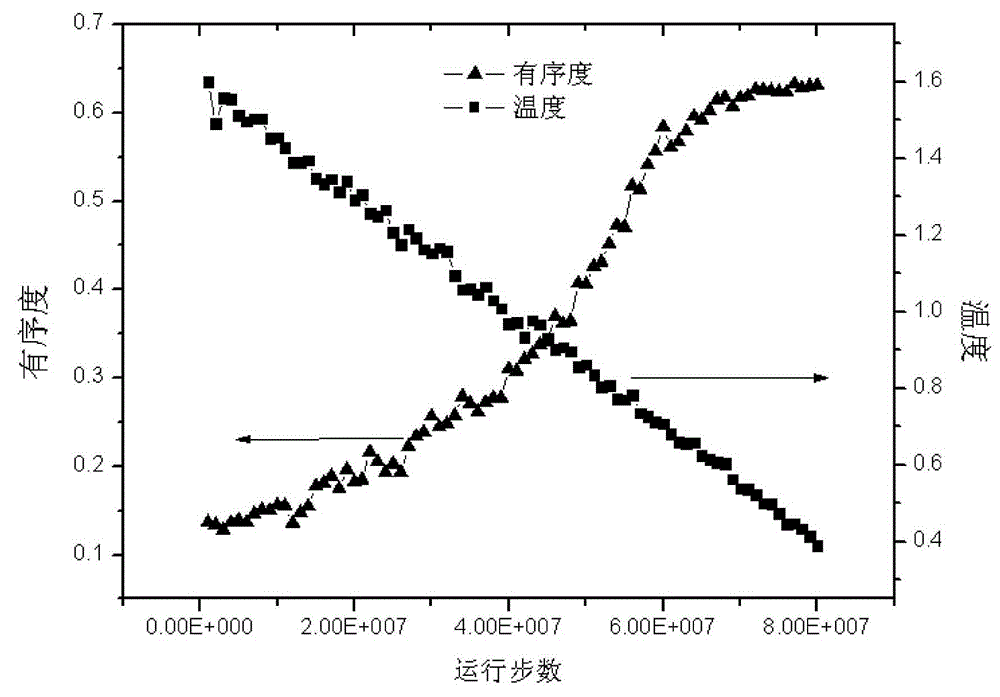
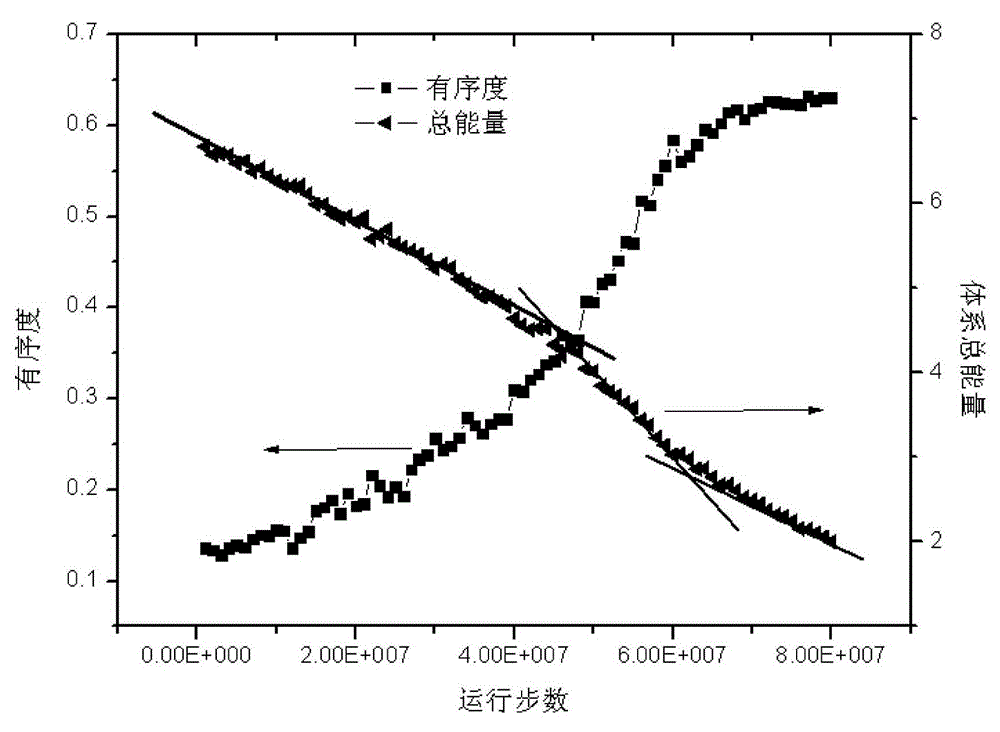
Method for simulating linear polymer crystallization
The invention discloses a method for simulating linear polymer crystallization. The method comprises the following steps of building a polymer model, simulating crystallization, building a polymer coarse-grained model, and setting particle position, particle initial velocity, bond length and bond angle; setting a corresponding force field for the polymer model, i.e. adopting LJ-96 potential for intermolecular forces, and adopting corresponding energy potential for bond length and bond angle; initially setting corresponding periodic boundary conditions for the model; sequentially performing down balance when T* is equal to 0.1, temperature raising NPT movement from T* which is equal to 0.1 to T* which is equal to 1.6, NPT balance movement when T* is equal to 1.6, temperature reducing NPT movement from T* which is equal to 1.6 to T* which is equal to 0.4 under the experiment temperature, and NPT balance movement when T* is equal to 0.4 on the model. According to the computer simulation method provided by the invention, the defect of the traditional observation experiment method is overcome; integral and real-time observation can be performed, and the result shows that computer simulated data can be well identical to the traditional experiment data.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
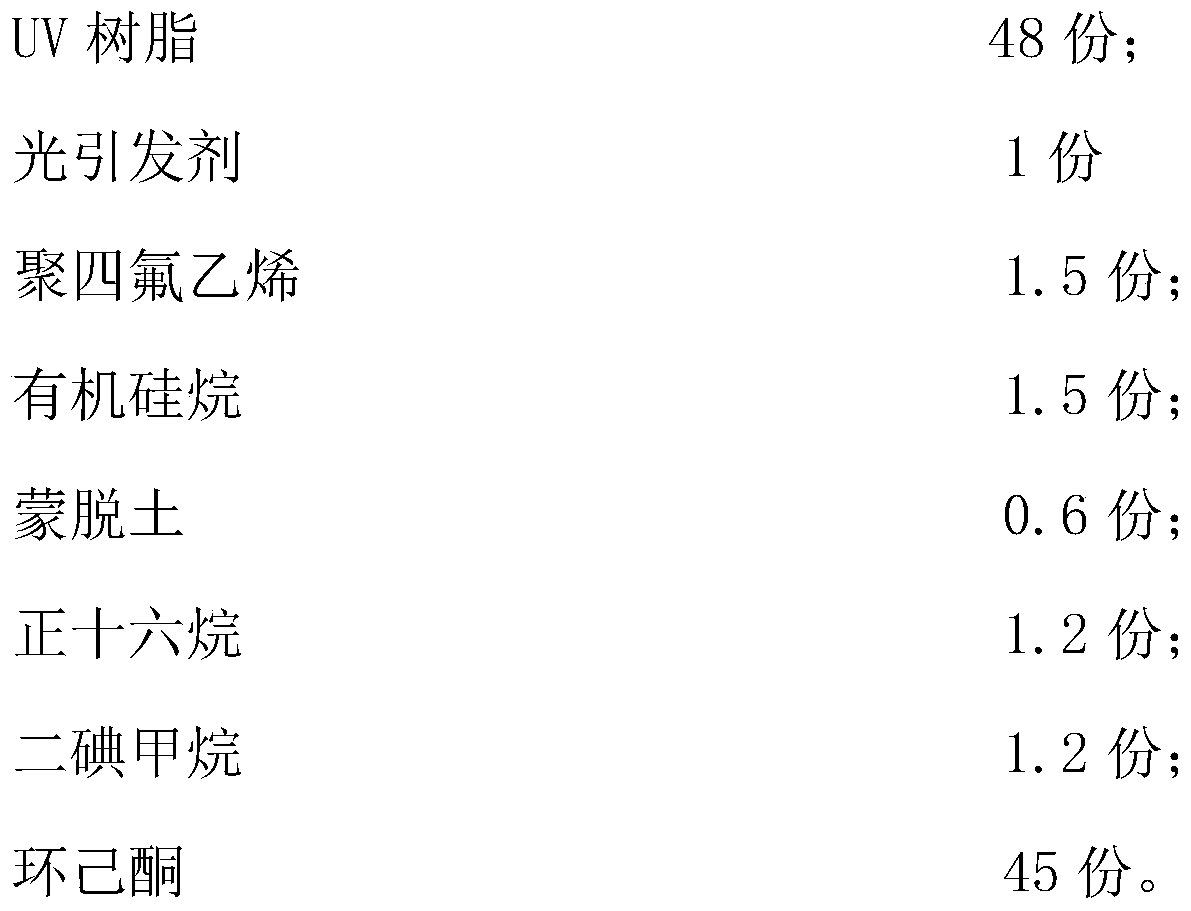
Light weather resistant optical grade PET rigid film
InactiveCN110437730AReduce thicknessHigh hardness on the basis of small thicknessPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsCyclohexanonePolyester
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical grade polyester films, and particularly relates to a light weather resistant optical grade PET rigid film. The hardening film is prepared from the raw materials of UV curing resin, a photoinitiator, polytetrafluoroethylene, organosilane, montmorillonoid, n-hexadecane, diiodomethane and cyclohexanone, the hardening film adopts UV curing hardening liquid, thus the hardness of the hardening film is large on the basis of the small thickness, the screen protection ability is high, the polytetrafluoroethylene, the organosilane and the montmorillonoid make surface energy of the hardening film low, thus the hardening film is prevented from being deformed by influence of the low temperature, a silicon oxygen bond in the organosilane has long bond length, large bond angle and easy internal rotation, molecules are helical, methyl groups are arranged outwardly and rotated around the silicon oxygen bond, the surface energy is very low, the good hydrophobic and oleophobic properties are achieved, the surface of the hardening film is not prone to being dirty, and the visual effect of a screen is affected to the low extent while the screen isprotected.
Owner:四川羽玺新材料股份有限公司
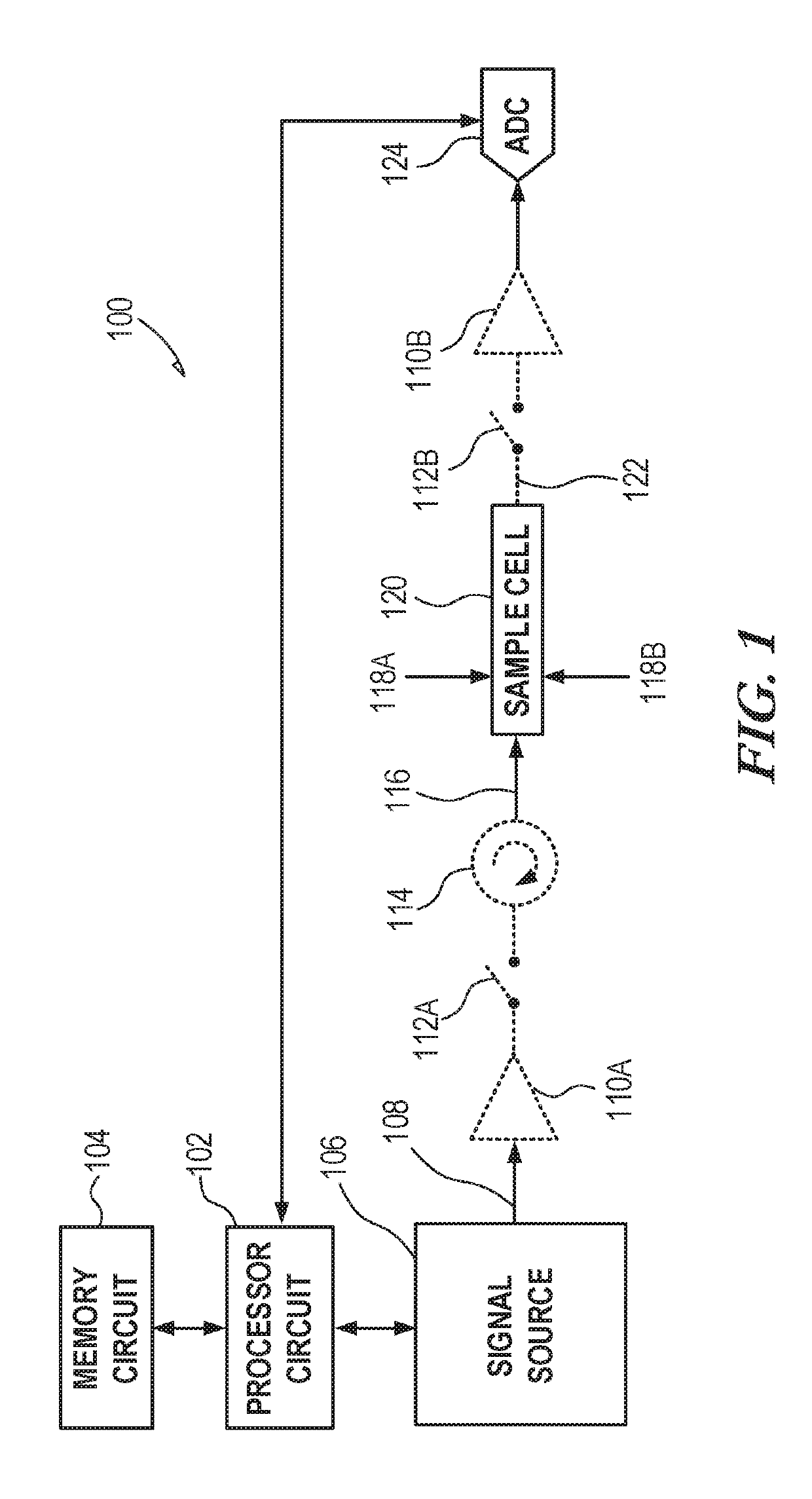
Cavity-enhanced fourier transform spectroscopy for chiral analysis
ActiveUS20190302015A1Photometry using reference valuePolarisation spectroscopyRotational spectroscopyResonant cavity
A chiral molecule can be defined as a molecule that has a non-superimposable mirror image. These mirror images can be referred to as enantiomers. The enantiomers generally have the same set of bond lengths and bond angles in their three-dimensional geometry. Apparatus and techniques described herein can be used to perform analysis of chiral molecules using cavity-enhanced molecular rotational spectroscopy. A sample cell can define a resonant cavity, and a sample introduction port can provide pulse jet injection of an analyte molecule and a chiral tag to allow analysis of a complex comprising the analyte and chiral tag.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method for broadening the light emitting range of lead-free double perovskite
ActiveCN110437831ABroaden the fluorescence spectral rangeReduce manufacturing costLuminescent compositionsOctahedronFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for broadening the light emitting range of lead-free double perovskite. The method comprises: placing submicron-scale Cs2AgBiBr6 as a sample in a pressure chamber, continuously pressurizing the sample by using a diamond anvil cell press as a pressurizing device and using silicone oil as a pressure transmitting medium, and releasing the pressure to achieve a normalpressure so as to obtain the Cs2AgBiBr6 perovskite with a broadened fluorescence range. According to the present invention, by applying external pressure, the pressure can change the atom arrangementmode and the electronic structure so as to affect the interaction between the atoms; and the inorganic octahedrons AgBr6 and BiBr6 in Cs2AgBiBr6 are twisted under the pressure, such that the same length of the Ag-Br bond and the Bi-Br bond is respectively converted into the two bond lengths so as to increase the number of the STEE states between the band gaps and expand the fluorescence emissionrange, wherein the fluorescence range of the Cs2AgBiBr6 material is broadened to 520-1000 nm, and the full width at half maximum is broadened to 230-245 nm.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
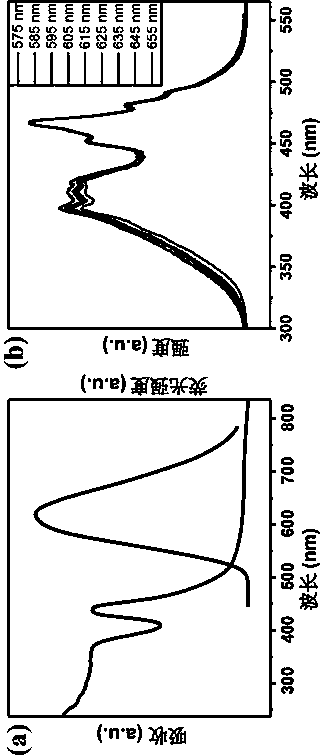
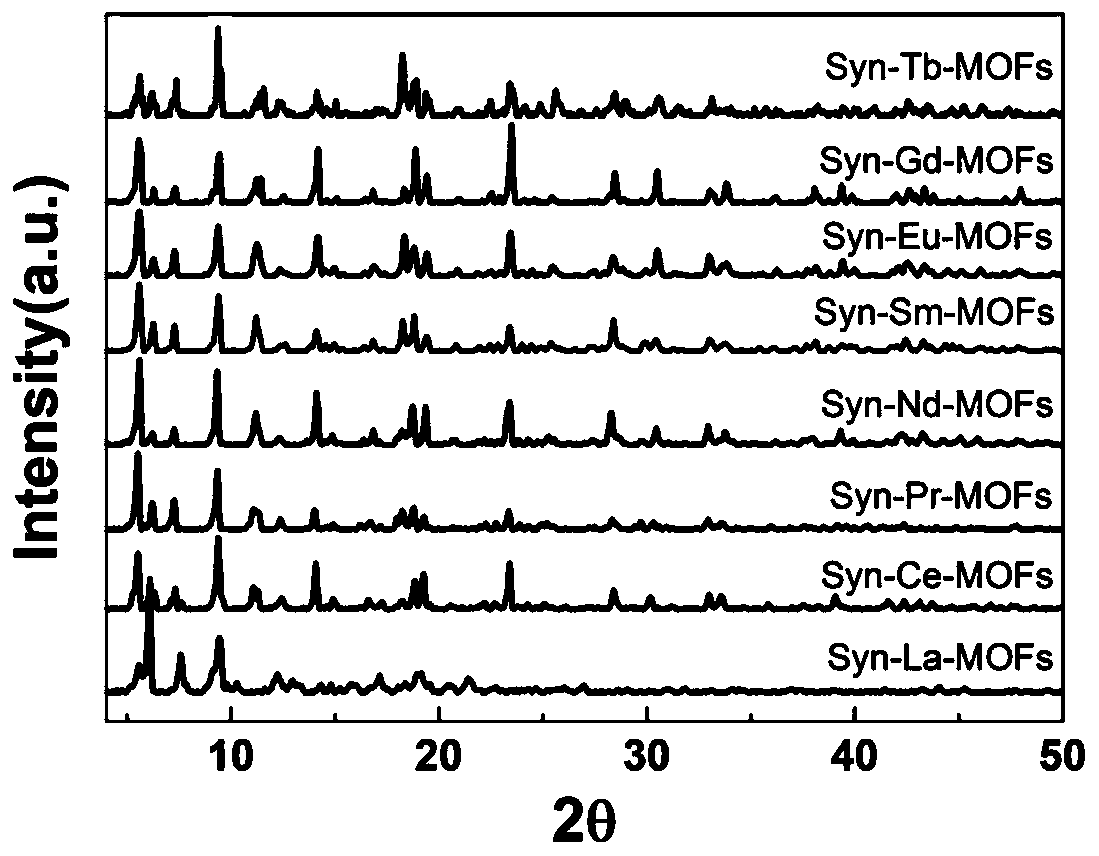
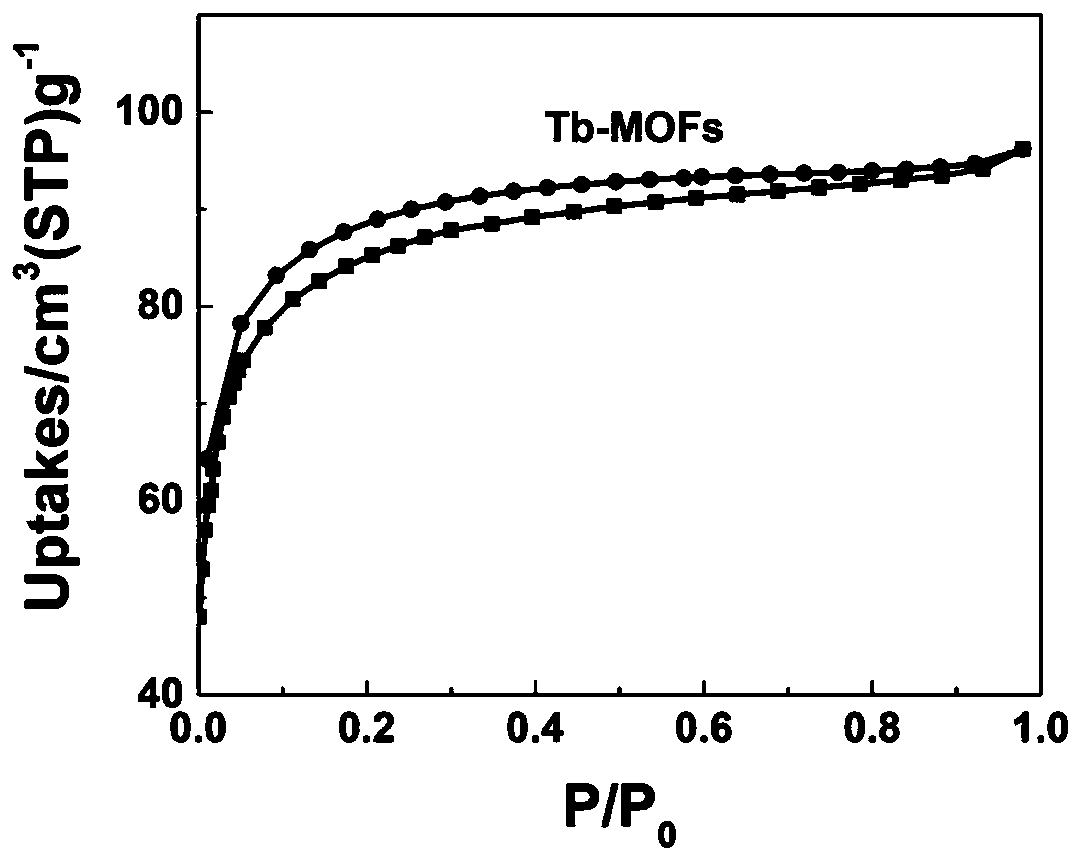
Lanthanide series metal-organic framework material with excellent second harmonic performance and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111187420AExcellent second harmonic performanceVerify microwell featuresLuminescent compositionsSolvent moleculePhosphate crystals
The invention discloses a lanthanide series metal-organic framework material with excellent second harmonic performance and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the material is M(L)<x>(G)<y>, wherein M is a metal atom, L is a flexible organic ligand containing a hexacarboxylic acid group, and G is a solvent molecule. The material is prepared by adopting a solvothermal method. Thelanthanide series metal-organic framework material disclosed by the invention has a non-centrosymmetric C121 space group, so the lanthanide series metal-organic framework material has second harmonicperformance, and the highest second harmonic performance can reach 4 times or more of the second harmonic performance of a potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystal. In general, the strength of SHG of La-Tb-MOFs shows a rising trend along with the increase of a metal atomic number, and experiments find that the SHG of La-Tb-MOFs is inversely related to average coordination bond length; that is, the SHG of La-Tb-MOFs is consistent with the electron push-and-pull capacity of the metal atom; and MOFs with sizes of 170-300 meshes show optimal SHG performance under various pumping wavelengths.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Thermal restoring net-structured hydrogen bond supermolecule elastomeric polymer and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polymer with the following hydrogen bond supermolecule net-structure, which has significant thermal restoring performance and good mechanical strength and elasticity, and facilitates the low temperature shaping process and cyclic utilization of the material. The synthesized oligomer is used as the skeleton of the hydrogen bond net-structured supermolecule polymer, and themain chain of the synthesized oligomer is provided with groups of hydrogen bond-forming factors such as carbonyl group (C=O), amino-group (-NH- or -NH2), sulfonyl group (O=S=O) and the like. Because the acting force of the hydrogen bond is much smaller than the force of the covalent bond, the length of the hydrogen bond is increased and the association speed is accelerated during the process of raising the temperature, so that the hydrogen bond supermolecule polymer has a lower melting point, thereby having better thermal restoring performance. In addition, though the single hydrogen bond force is smaller, the hydrogen bond supermolecule net-structure has good mechanical strength and elasticity due to the stable structure of the hydrogen bond supermolecule net-structure.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Blue light-ultraviolet continuously-adjustable aluminate fluorescent powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103468257AImprove stabilityImprove luminescence stabilityLuminescent compositionsUltraviolet lightsElectronegativity
The invention provides a blue light-ultraviolet continuously-adjustable aluminate fluorescent powder and a preparation method thereof. A Si-N bond is substituted for a Al-O bond; after the substitution, the internal structure of the fluorescent powder is improved; and thus, the luminescent spectrum of the fluorescent powder is continuously adjustable from blue light to ultraviolet light according to different substitution proportions. The fluorescent powder is more stable due to the doping of the Si-N key. The Si-N bond and Al-O bond have similar bond lengths, Si and Al, and O and N have similar bonding characteristics according to the diagonal line principle, so the Al-O bond in the aluminate-base fluorescent powder can be easily partially substituted by the Si-N bond; according to the charge compensation effect, after (SiN)+ is substituted for (AlO)+, the charge balance can be maintained; the bond length of the Si-N bond is slightly smaller than that of the Al-O bond, so that the matrix lattice constant is reduced, the cell volume is correspondingly reduced, and the atomic arrangement in the matrix is closer; and N with relatively smaller electronegativity can stabilize the Ce<2+>, so the material stability and light-emitting stability of the fluorescent powder are enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com