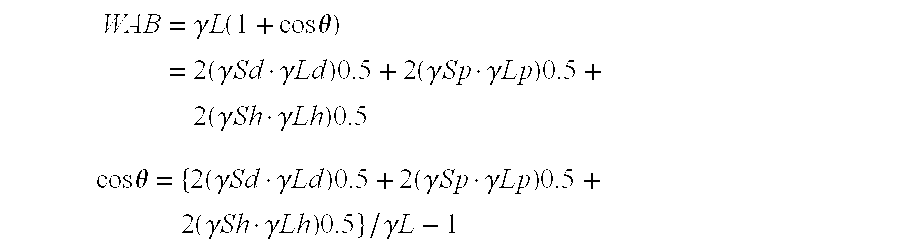Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5525 results about "Hydrogen bond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
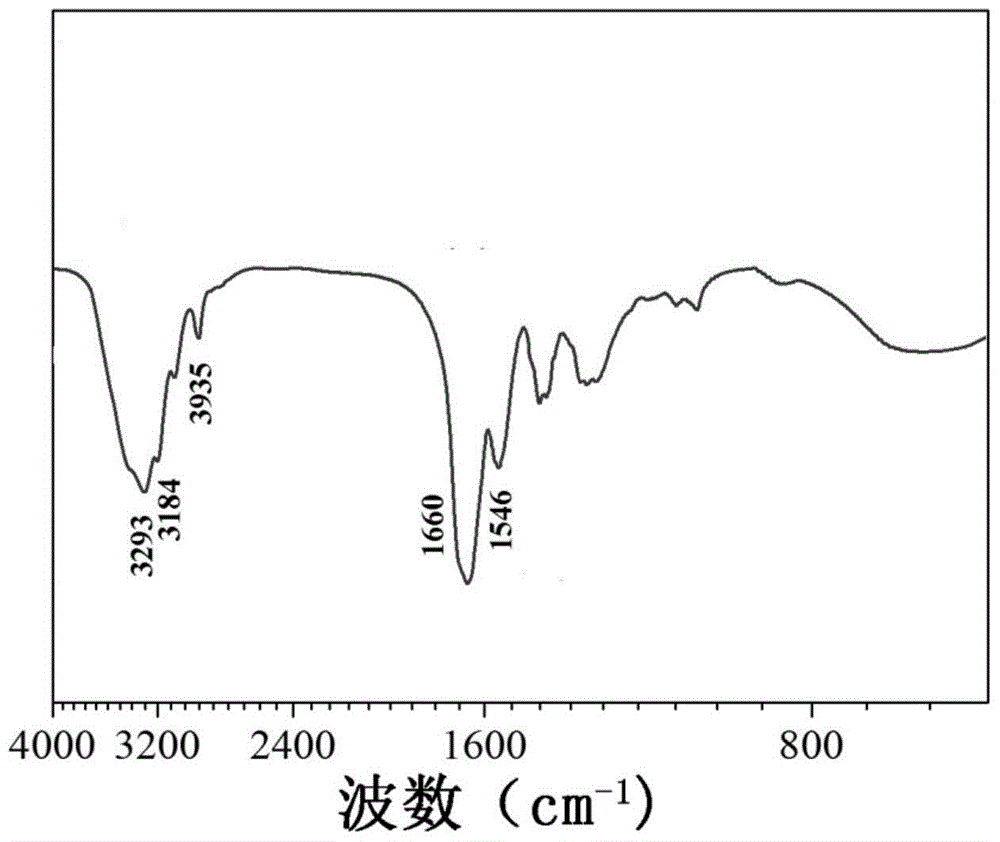
A hydrogen bond (often informally abbreviated H -bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative atom or group, particularly the second-row elements nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F)—the hydrogen bond donor (Dn)—and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Such an interacting system is generally denoted Dn–H···Ac, where the solid line denotes a fully covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The use of three centered dots for the hydrogen bond is specifically recommended by the IUPAC. There is general agreement that there is actually a minor covalent component to hydrogen bonding, especially for moderate to strong hydrogen bonds (> 5 kcal/mol), although the importance of covalency in hydrogen bonding is debated. At the opposite end of the scale, there is no clear boundary between a weak hydrogen bond and a van der Waals (e.g., dipole-dipole) interaction.
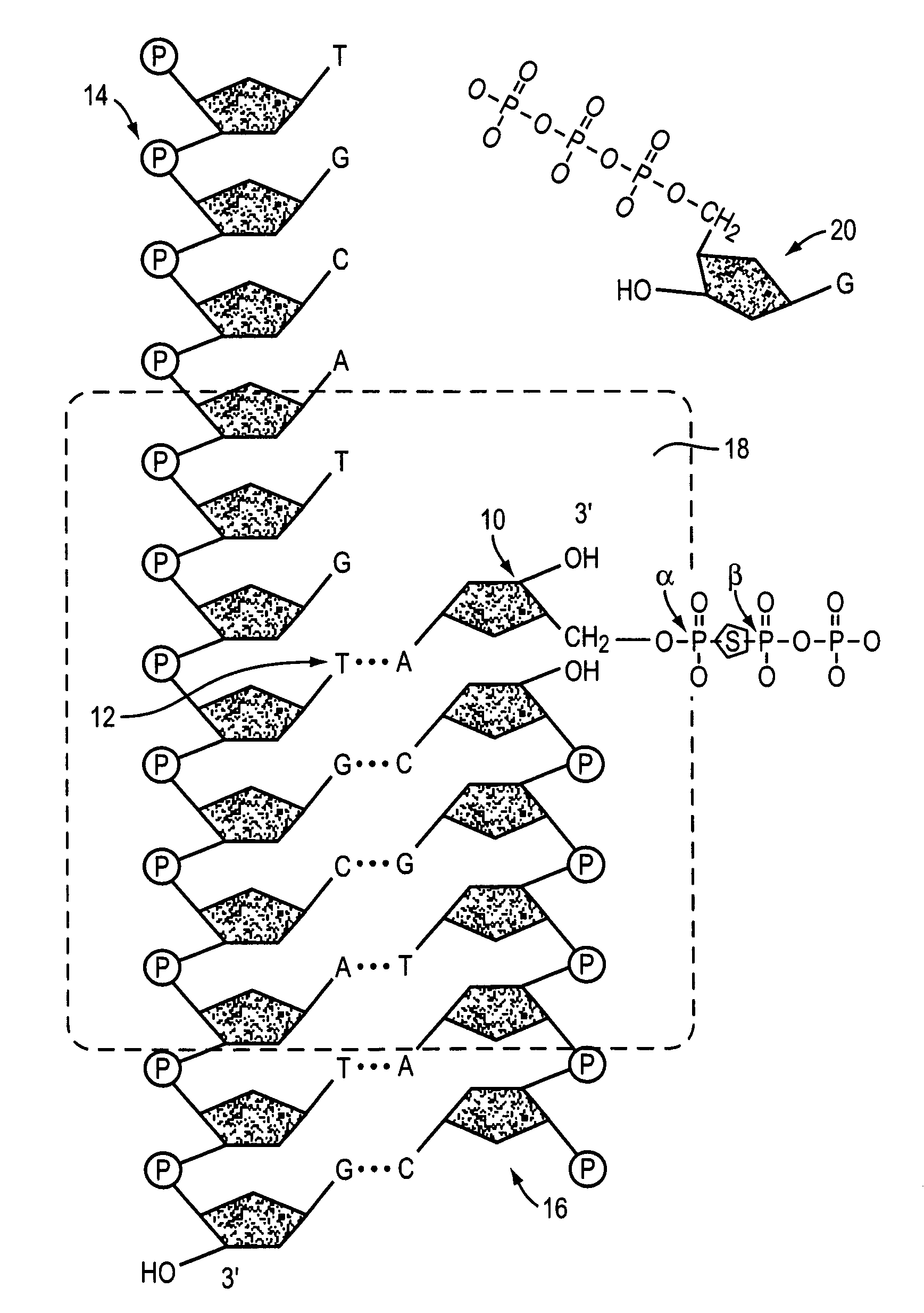
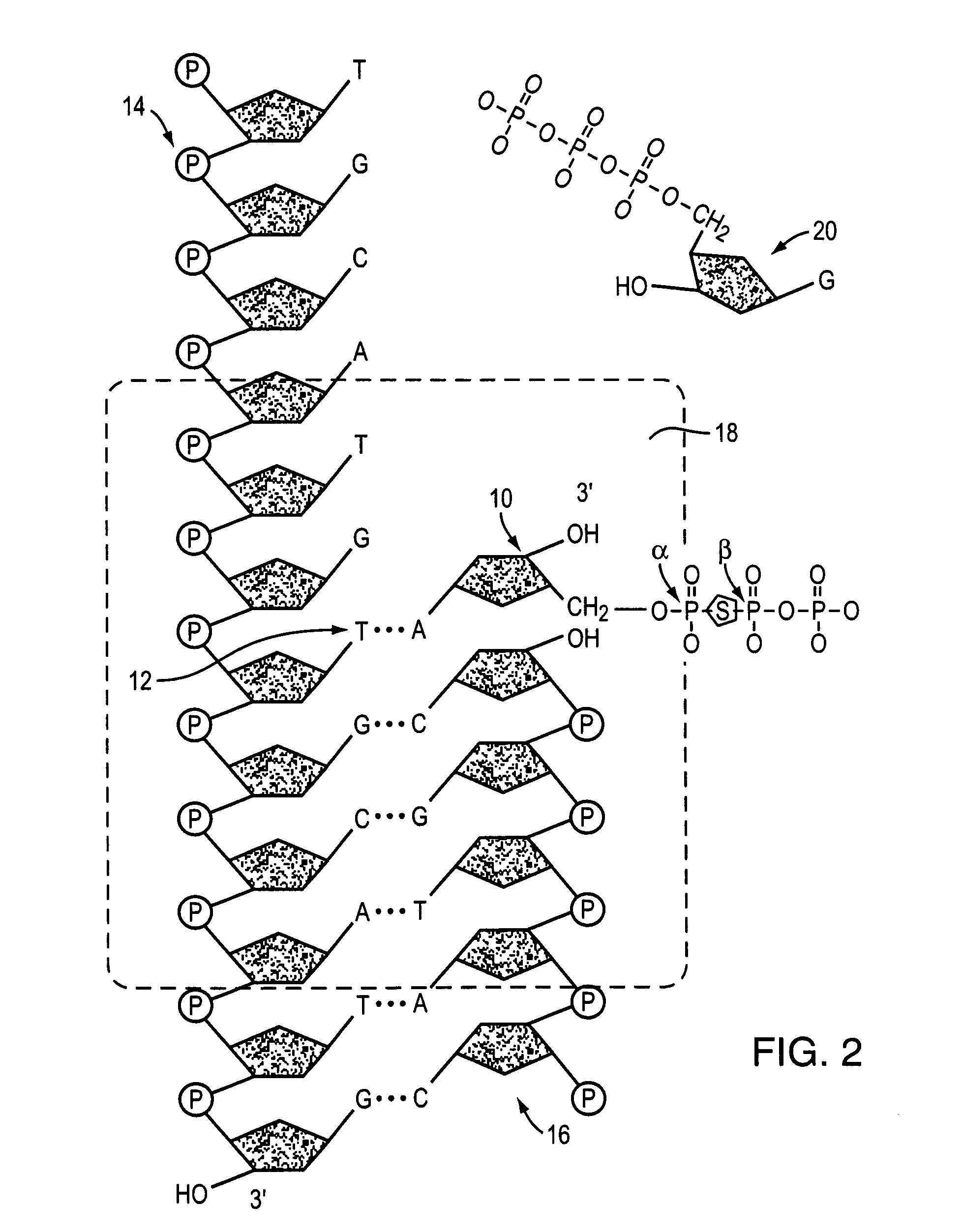
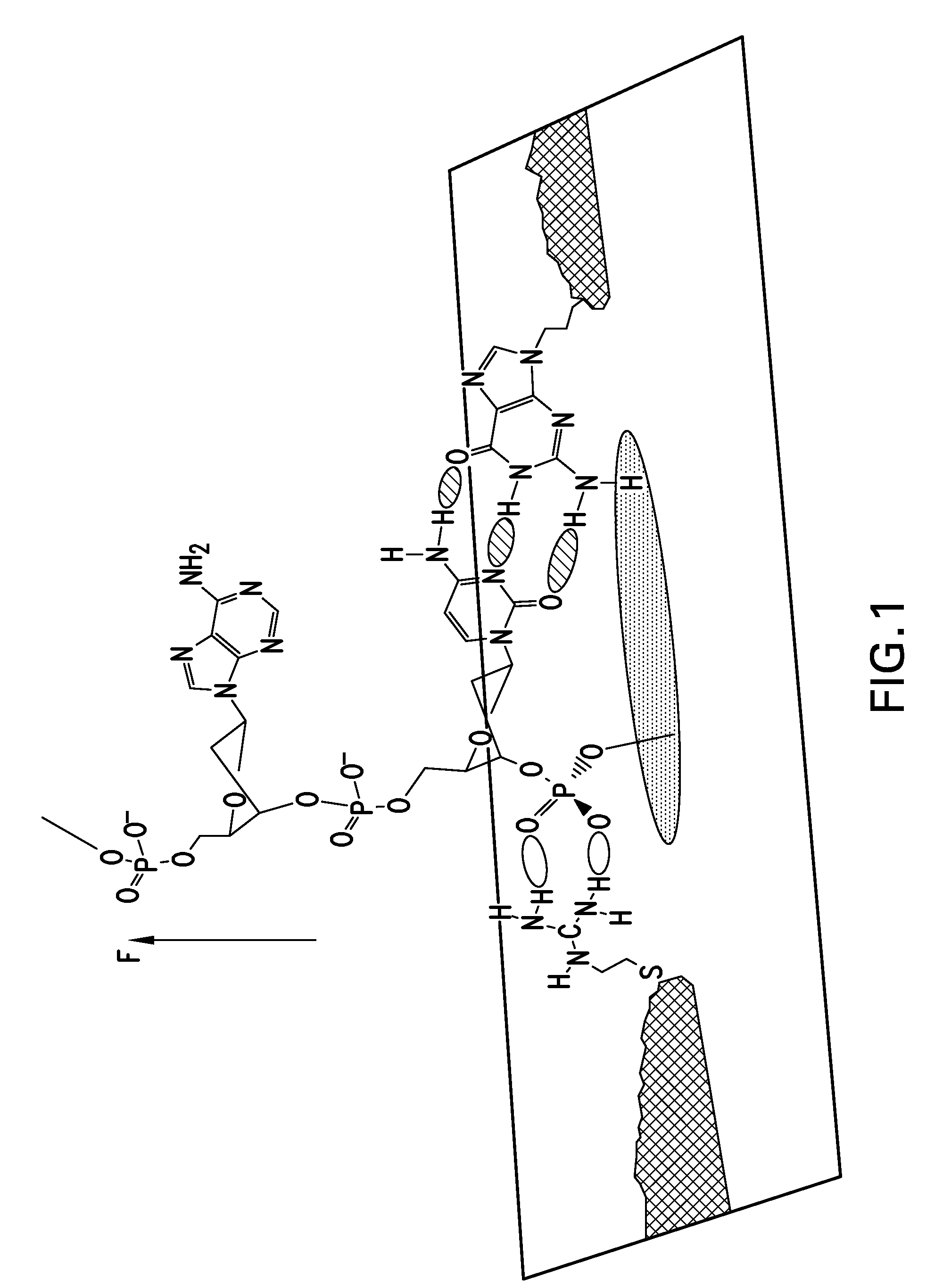
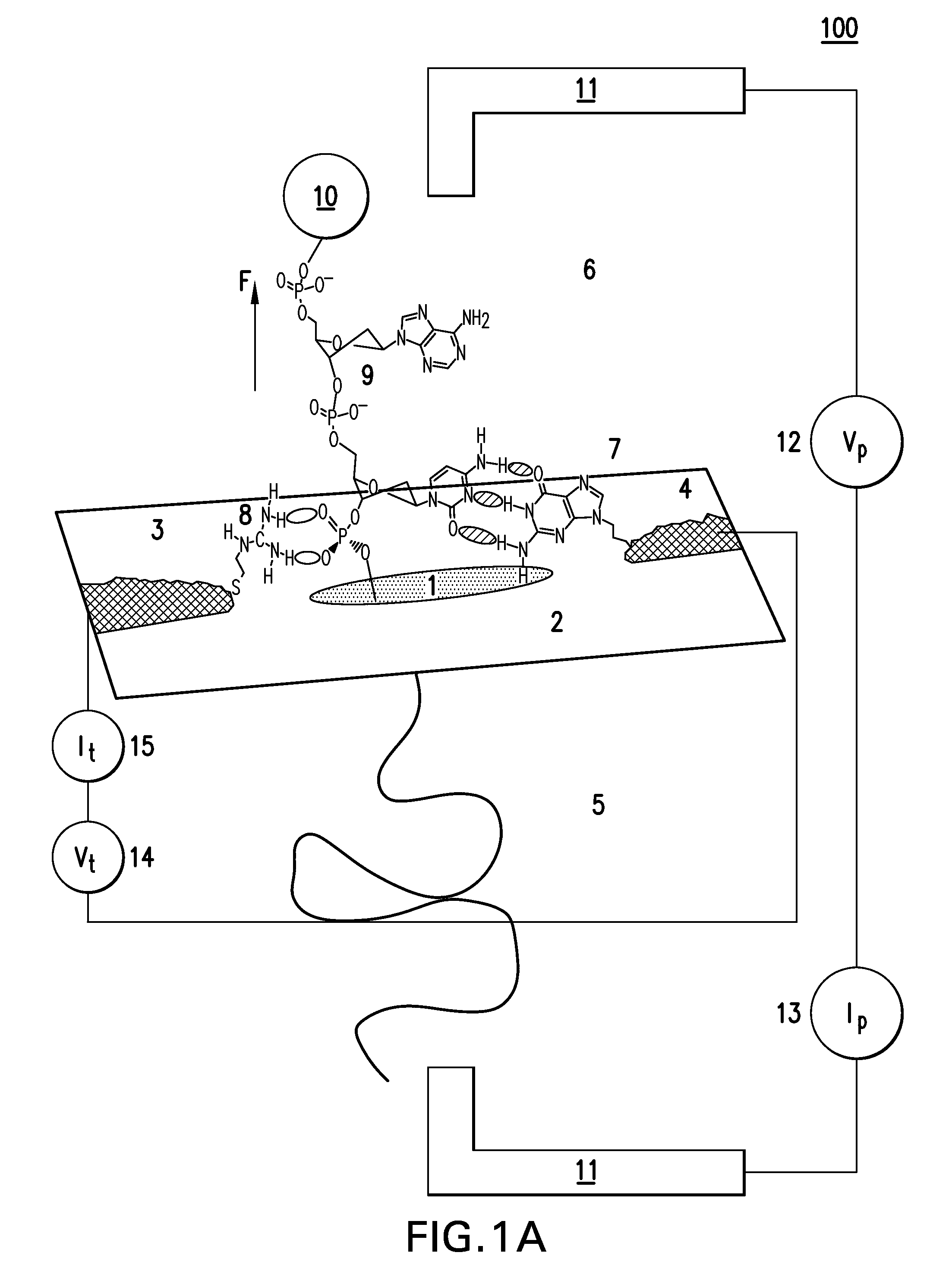
Methods and compositions for improving fidelity in a nucleic acid synthesis reaction
InactiveUS7482120B2Improve fidelityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotidePerylene derivatives
The invention provides methods and compositions for improving the fidelity of a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction by using a nucleotide derivative that forms a hydrogen bond with a complementary nucleotide on a template, but fails to form a phosphodiester bond with the 3′ hydroxyl group of a primer under conditions otherwise suitable for a polymerization reaction; thereby blocking incorporation of a mismatched nucleotide.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Phase change ink compositions
Disclosed is a phase change ink composition comprising a colorant and an ink vehicle, the ink being a solid at temperatures less than about 50° C. and exhibiting a viscosity of no more than about 20 centipoise at a jetting temperature of no more than about 160° C., wherein at a first temperature hydrogen bonds of sufficient strength exist between the ink vehicle molecules so that the ink vehicle forms hydrogen-bonded dimers, oligomers, or polymers, and wherein at a second temperature which is higher than the first temperature the hydrogen bonds between the ink vehicle molecules are sufficiently broken that fewer hydrogen-bonded dimers, oligomers, or polymers are present in the ink at the second temperature than are present in the ink at the first temperature, so that the viscosity of the ink at the second temperature is lower than the viscosity of the ink at the first temperature.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Films and Processes for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20090072194A1Easy to produceEasy to prepareLiquid crystal compositionsDiffusing elementsHydrogenProton
A birefringent film which comprises a compound having a proton-accepting group and a compound having a proton-donating group; and a birefringent film which comprises a compound having a proton-accepting group and a proton-donating group. The proton-accepting group and proton-donating group are combined with each other through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Method for photocatalytically hydrophilifying surface and composite material with photocatalytically hydrophilifiable surface
InactiveUS6090489AImproved oil repellencyEasy to disassembleOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesAtmospheric airSolid acid
A method for hydrophilifying the surface of a substrate by taking advantage of photocatalytic action. The substrate has a photocatalytic titania coating (10). The surface of the photocatalytic coating (10) bears the solid acid that increases a hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy in the solid / gas interface of the coating. Photoexcitation of the photocatalyst enhances the hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy of the photocatalytic coating (10), accelerating the physical adsorption of molecules of water in the atmosphere through a hydrogen bond (16) onto hydrogen atoms in a terminal OH group (12), bonded to a titanium atom, and a bridge OH group (14) on the surface of the coating. This results in the formation of a high density, physically adsorbed water layer (18) on the surface of the photocatalytic coating (10), thus permitting the surface of the substrate to be easily hydrophilified. The method is applicable to antifogging, antifouling, selfcleaning and cleaning of articles.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Substituted melanocortin receptor-specific piperazine compounds
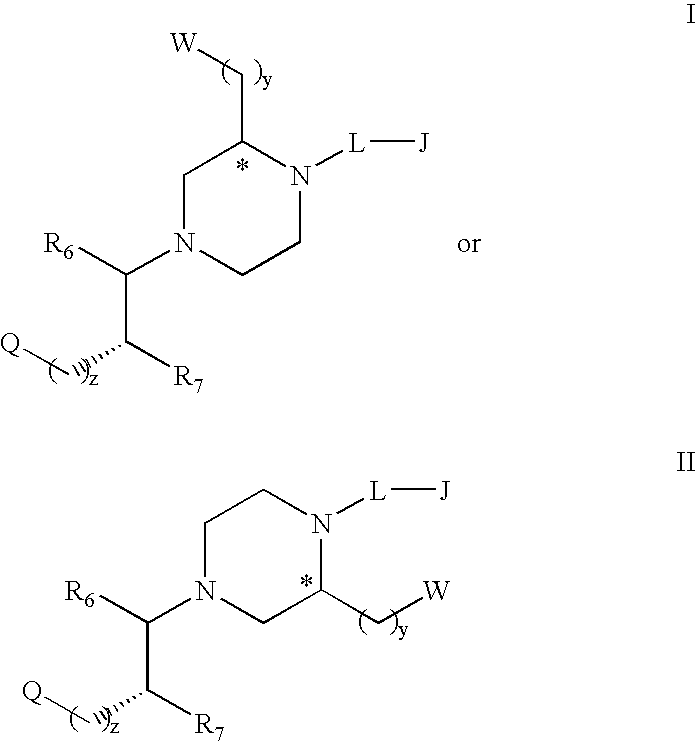
Melanocortin receptor-specific compounds of the general formulas and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, where J is a substituted or unsubstituted monocyclic or bicyclic ring structure, L is a linker, W is a heteroatom unit with at least one cationic center, hydrogen bond donor or hydrogen bond acceptor, Q includes a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic carbocyclic ring, R6, R7, y and z are as defined in the specification, and the carbon atom marked with an asterisk can have any stereochemical configuration, and optionally with one or two additional ring substituents as defined, which compounds bind to one or more melanocortin receptors and are optionally an agonist, a partial agonist, an antagonist, an inverse agonist or an antagonist of an inverse agonist, and may be employed for treatment of one or more melanocortin receptor-associated conditions or disorders, and methods for the use of the compounds of the invention.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Medical devices having a temporary radiopaque coating
A medical device comprising radiopaque water-dispersible metallic nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles are released from the medical device upon implantation of the device. The medical device of the present invention is sufficiently radiopaque for x-ray visualization during implantation, but loses its radiopacity after implantation to allow for subsequent visualization using more sensitive imaging modalities such as CT or MRI.The nanoparticles are formed of a metallic material and have surface modifications that impart water-dispersibility to the nanoparticles. The nanoparticles may be any of the various types of radiopaque water-dispersible metallic nanoparticles that are known in the art. The nanoparticles may be adapted to facilitate clearance through renal filtration or biliary excretion. The nanoparticles may be adapted to reduce tissue accumulation and have reduced toxicity in the human body. The nanoparticles may be applied directly onto the medical device, e.g., as a coating, or be carried on the surface of or within a carrier coating on the medical device, or be dispersed within the pores of a porous layer or porous surface on the medical device. The medical device itself may be biodegradable and may have the nanoparticles embedded within the medical device itself or applied as or within a coating on the biodegradable medical device. The nanoparticles may be released by diffusion through the carrier coating, disruption of hydrogen bonds between the nanoparticles and the carrier coating, degradation of the nanoparticle coating, degradation of the carrier coating, diffusion of the nanoparticles from the medical device, or degradation of the medical device carrying the nanoparticles.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of Drug Formulation Based on Increasing the affinity of Crystalline Microparticle Surfaces for Active Agents
Methods are provided for coating crystalline microparticles with an active agent by altering the surface properties of the microparticles in order to facilitate favorable association on the microparticle by the active agent. Type of surface properties that are altered by the disclosed methods include by electrostatic properties, hydrophobic properties and hydrogen bonding properties.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Devices and Methods for Target Molecule Characterization
The present invention provides a device having at least one constriction that is sized to permit translocation of only a single copy of the molecule. The device has a pair of spaced apart sensing electrodes that border the constriction, which may be a nanopore. The first electrode is connected to a first affinity element and the second electrode is connected to a second affinity element. The first and second affinity elements are configured to temporarily form hydrogen bonds with first and second portions of the target molecule as the latter passes through the constriction.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
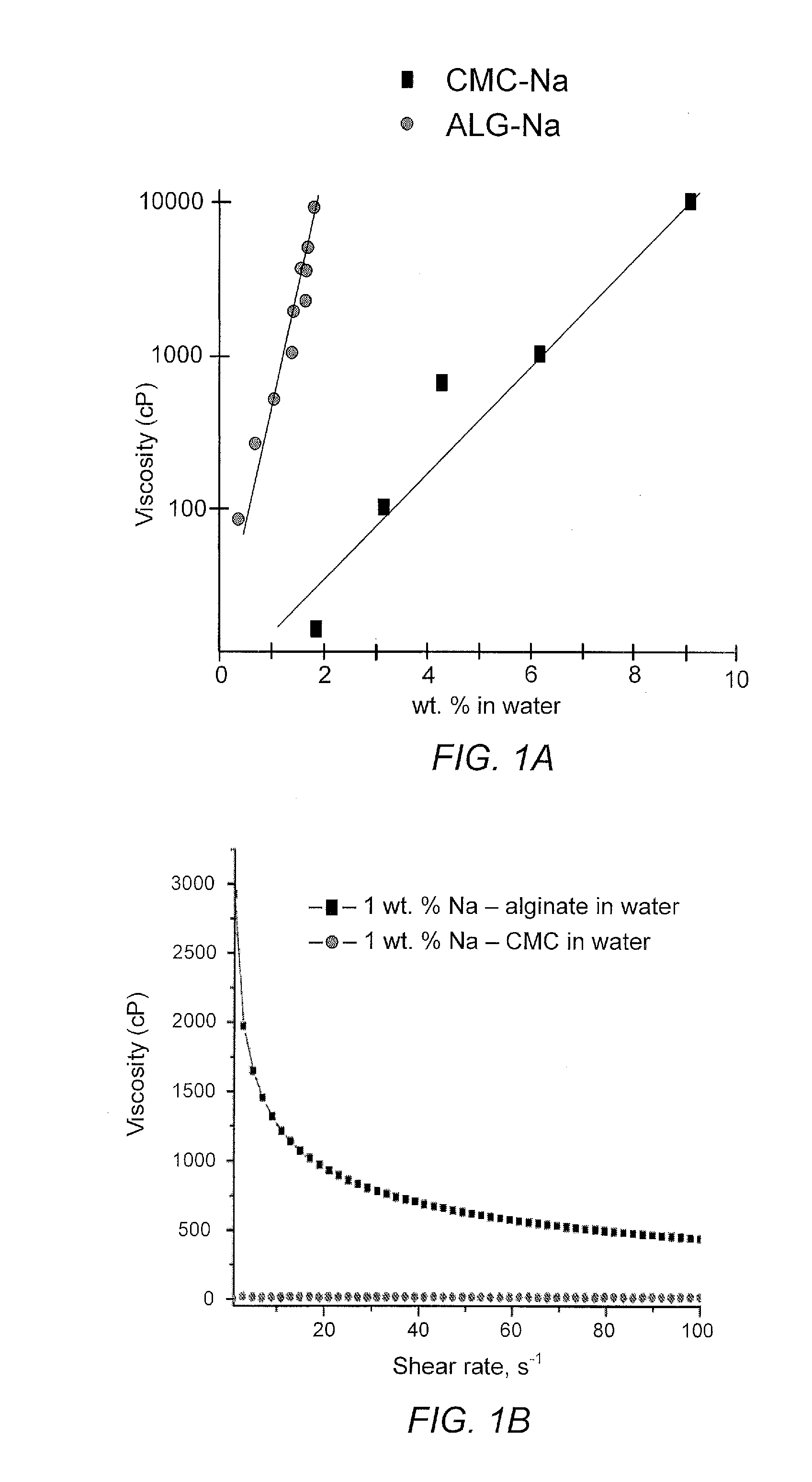
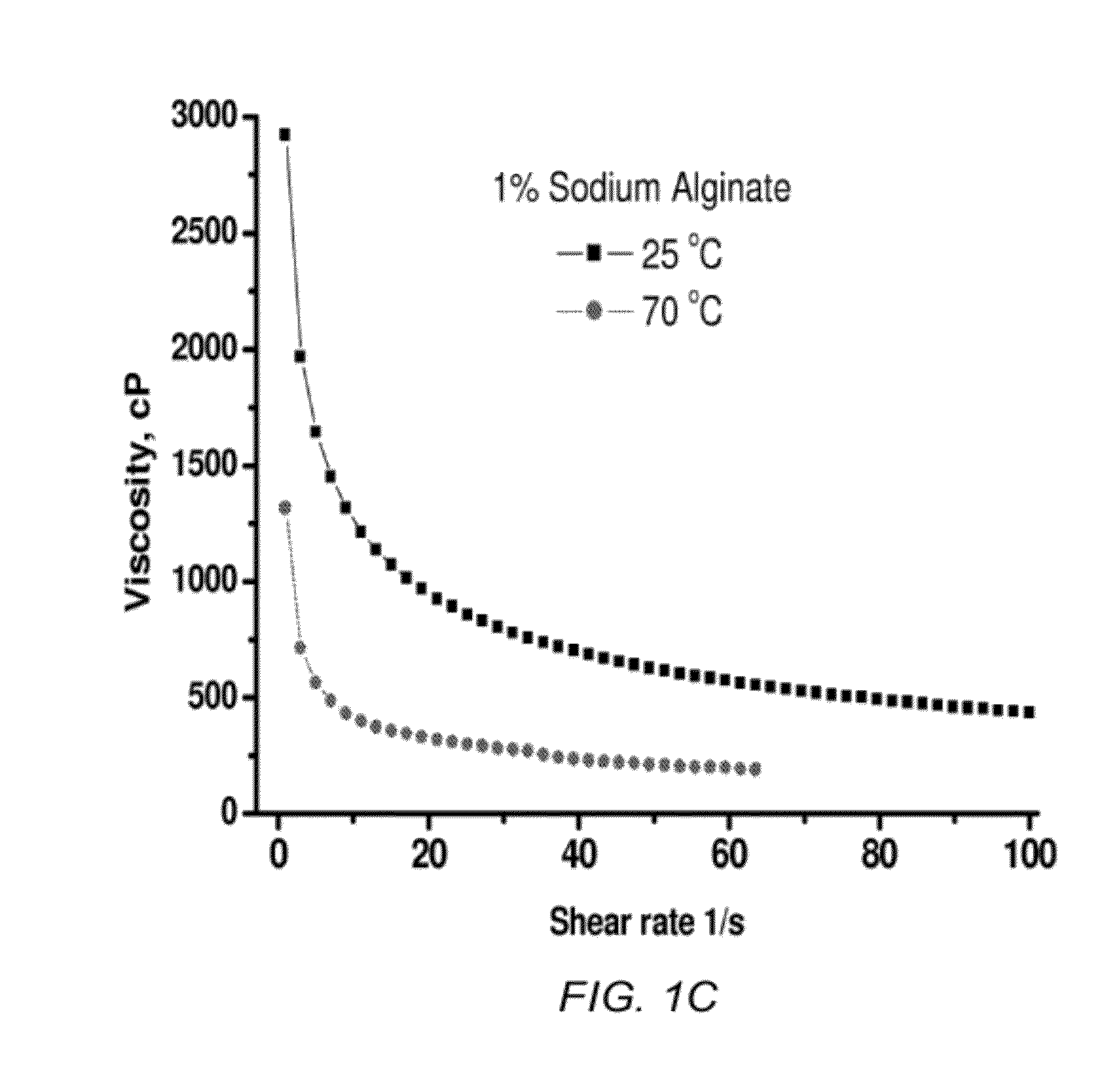
Alginate-containing compositions for use in battery applications
ActiveUS20120088155A1Material nanotechnologyCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersHydrogenMaterials science
A silicon-based anode comprises an alginate-containing binder. The many carboxy groups of alginate bind to a surface of silicon, creating strong, rigid hydrogen bonds that withstand battery cycling. The alginate-containing binder provides good performance to the anode by (1) improving the capacity of the anode in comparison to other commercially-available binders, (2) improving Columbonic efficiency during charging and discharging cycles, and (3) improving stability during charging and discharging cycles.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND +1
Grapheme-organic material layered assembling film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101474897ALow priceLight in massLayered productsPretreated surfacesChemical industryElectromagnetic shielding
The invention relates to a graphene-organic material layered assembly film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: using a graphene material and an organic material as raw materials, utilizing interaction of static electricity, hydrogen bonds, coordinate bonds or charge transfer and the like between the graphene and the organic material, and superposing films layer by layer through the film preparation methods such as spin coating, spraying, dipping, lifting and pulling and the like to prepare the film, wherein the thickness of each layer of the film can be controlled between 10 nanometers and 2 millimeters according to requirement. The layered assembly film and the preparation method have the characteristics that multilayer film materials with different functions are prepared by utilizing unique electric, magnetic, mechanical and chemical properties of the grapheme, and can be used as biomaterials, conductive materials, electromagnetic shielding and wave absorbing materials, photovoltaic materials, electrode materials, film filtering and separating materials, and the like to be applied to chemistry and chemical industry, biology and precision instruments, and manufacture of micro electrons, machinery and aviation and aerospace devices according to the selected different organic materials.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Fiberglass nonwoven binder
A fiberglass non-woven binder composition containing a carboxy-functional copolymer binder crosslinker and a compound capable of forming a hydrogen-bonding complex with the carboxy-functional copolymer binder. The binder composition provides a strong, yet flexible bond that allows a compressed fiberglass mat to easily expand once the compression is released. The binder composition is capable of being cured at lower cure temperatures than those binders prepared using conventional crosslinkers.
Owner:NAT STARCH & CHEM INVESTMENT HLDG CORP
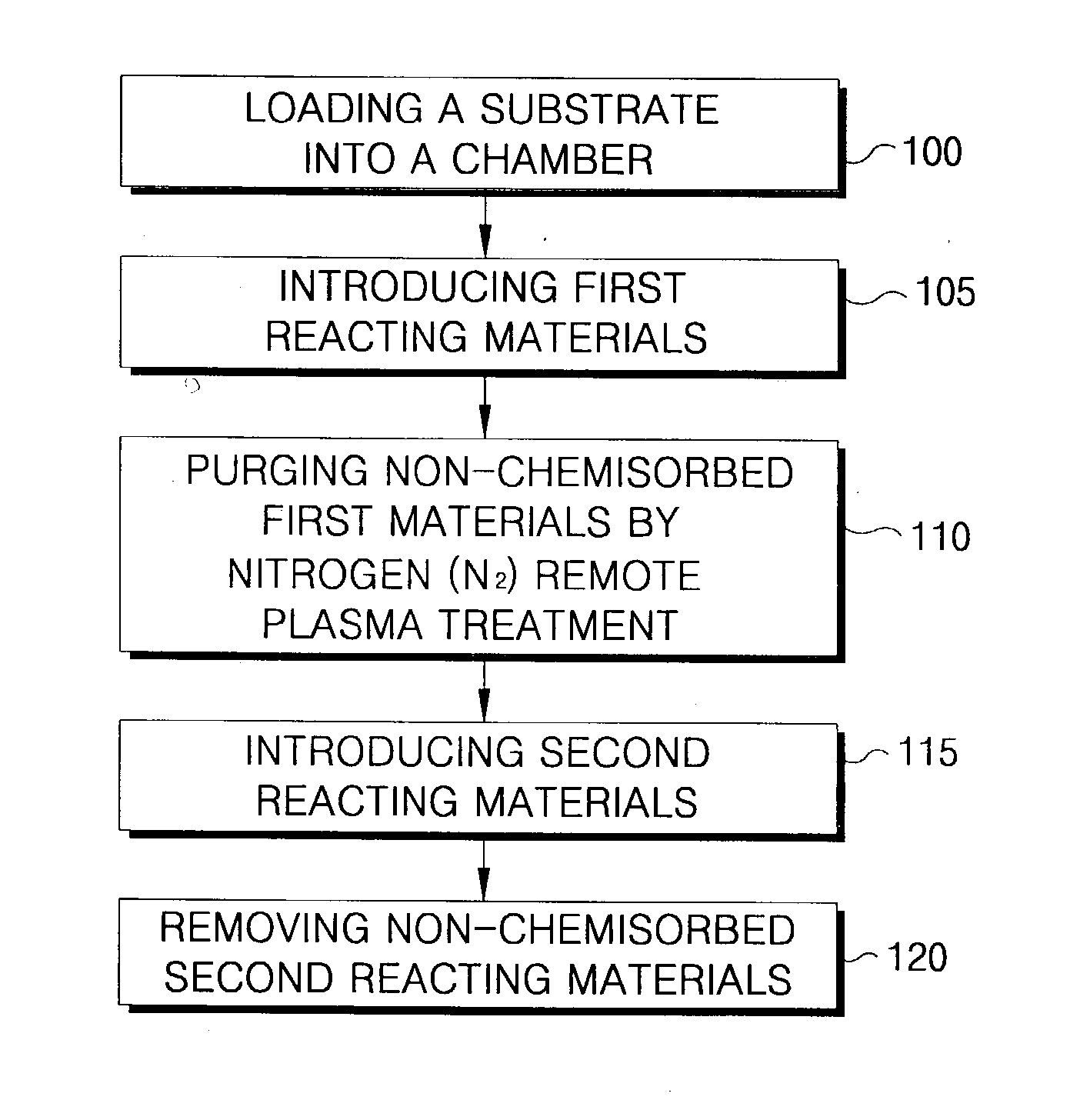
Method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen content on a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20030228770A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaDevice material
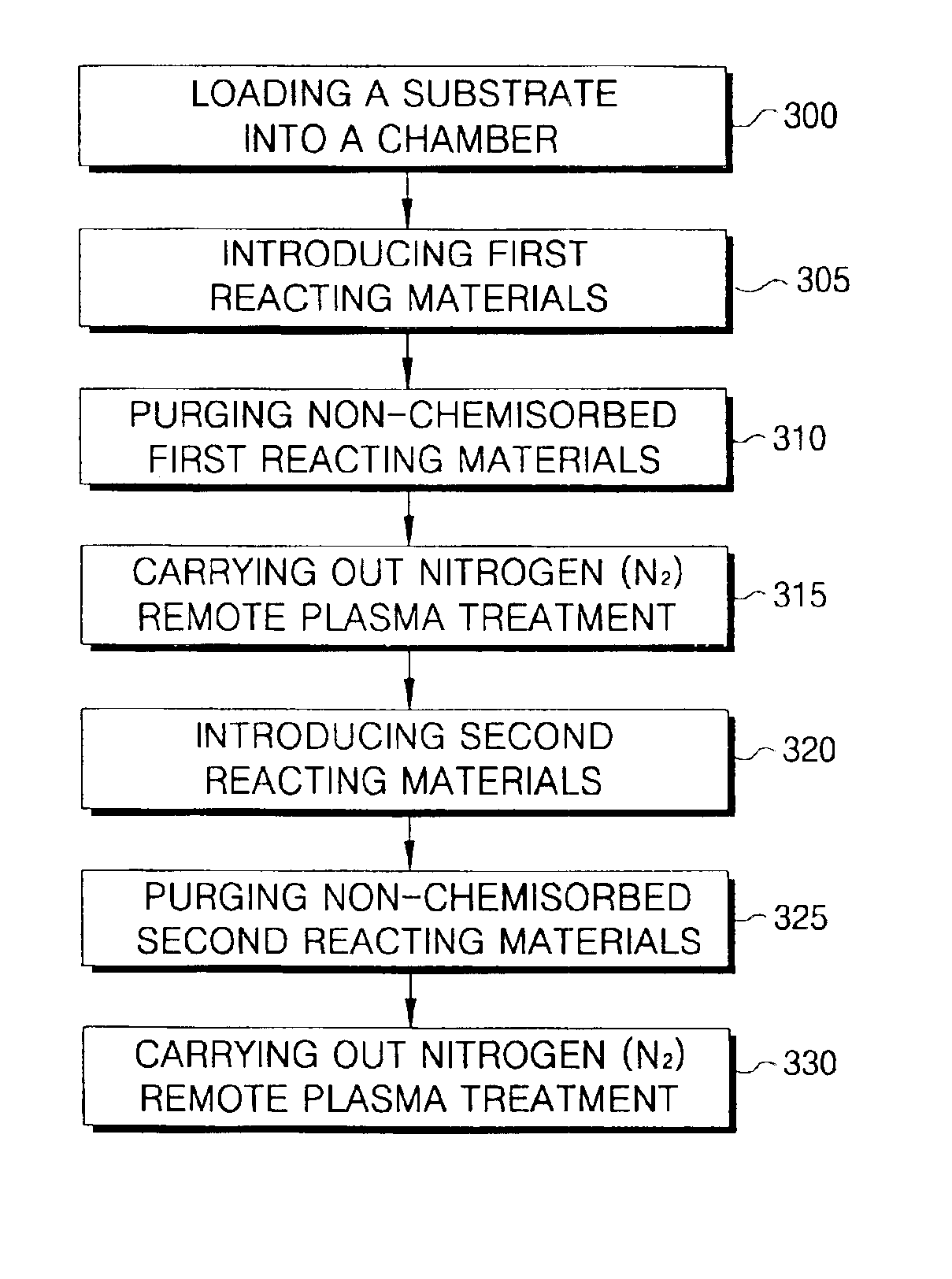
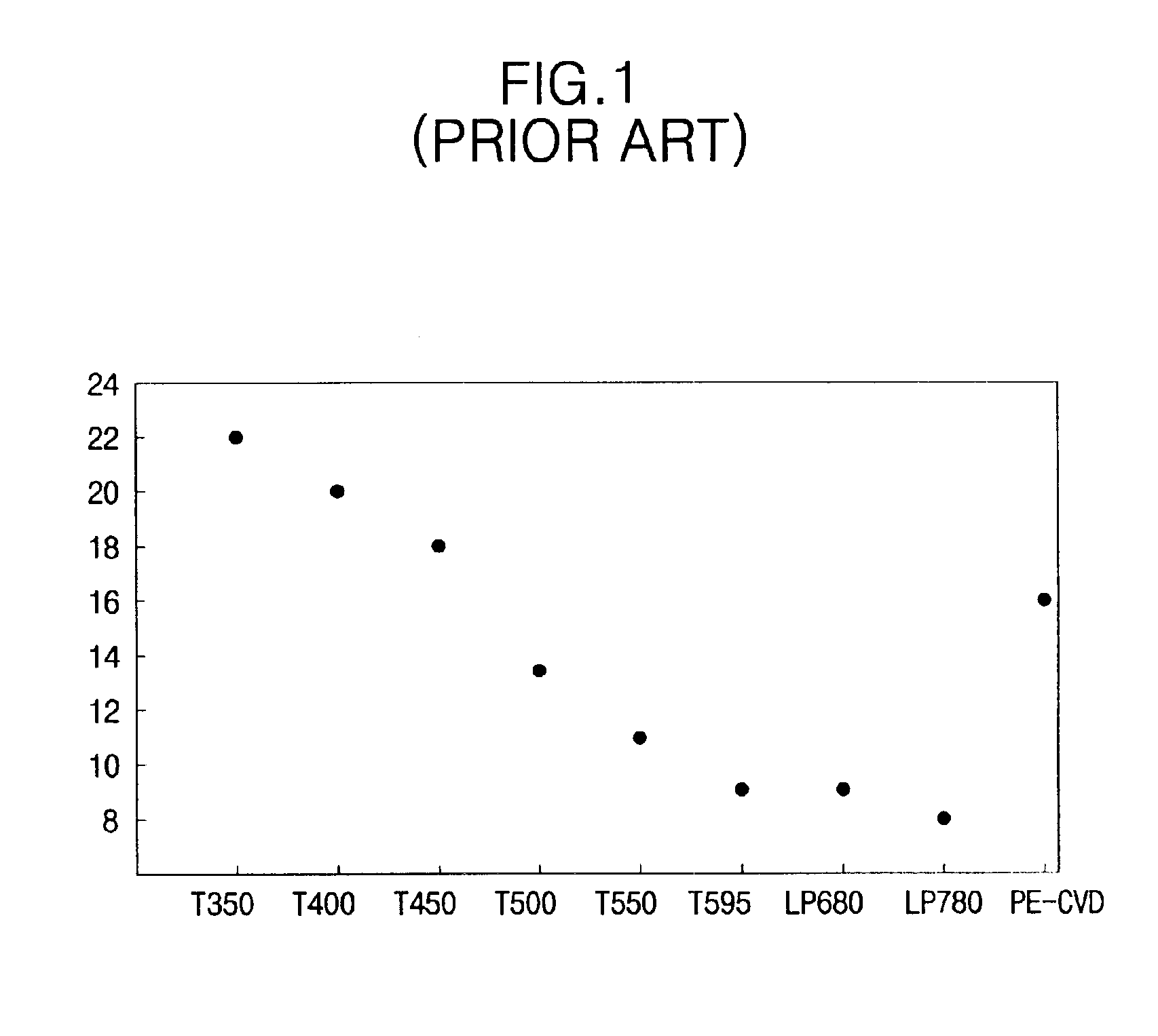
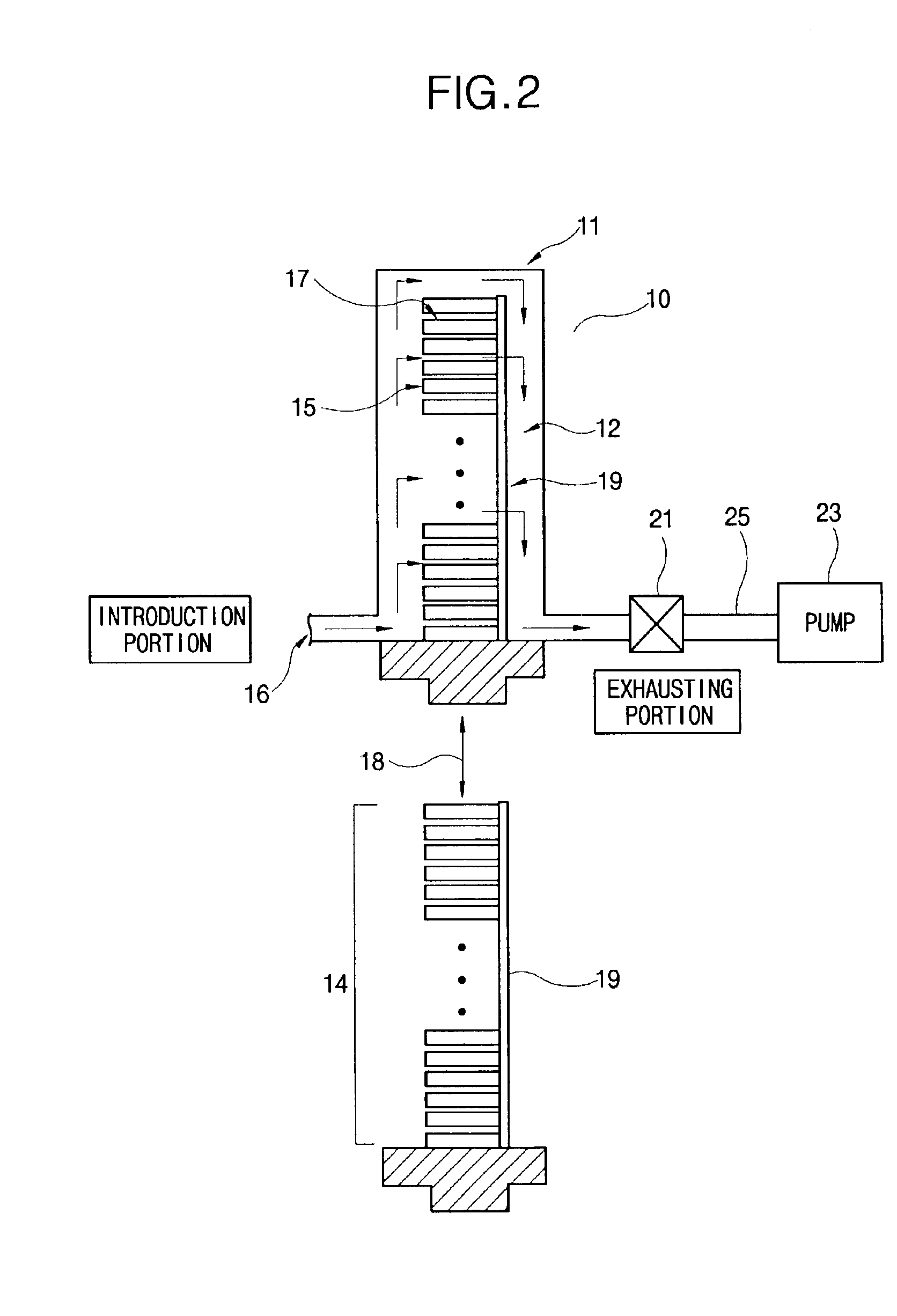
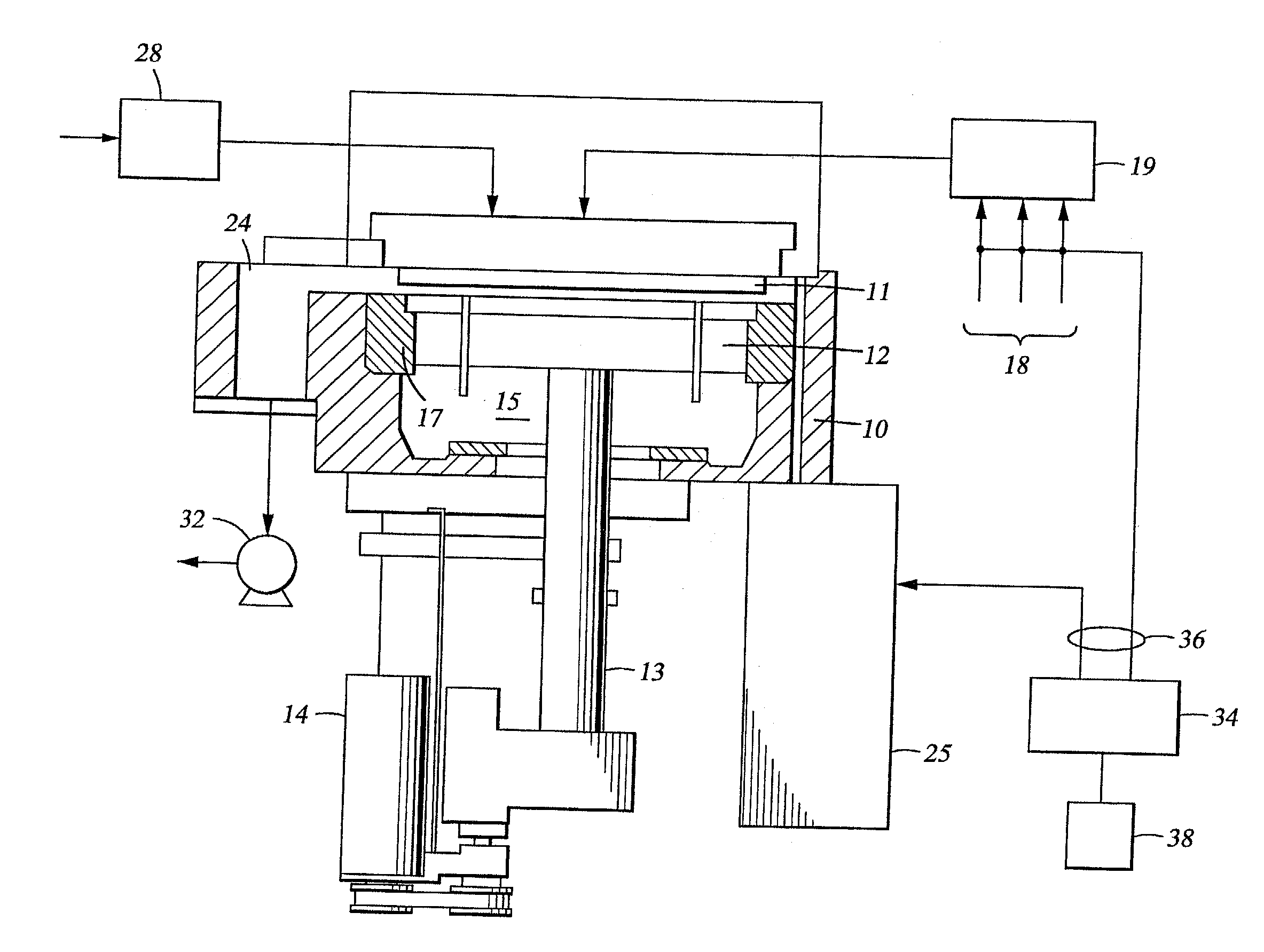
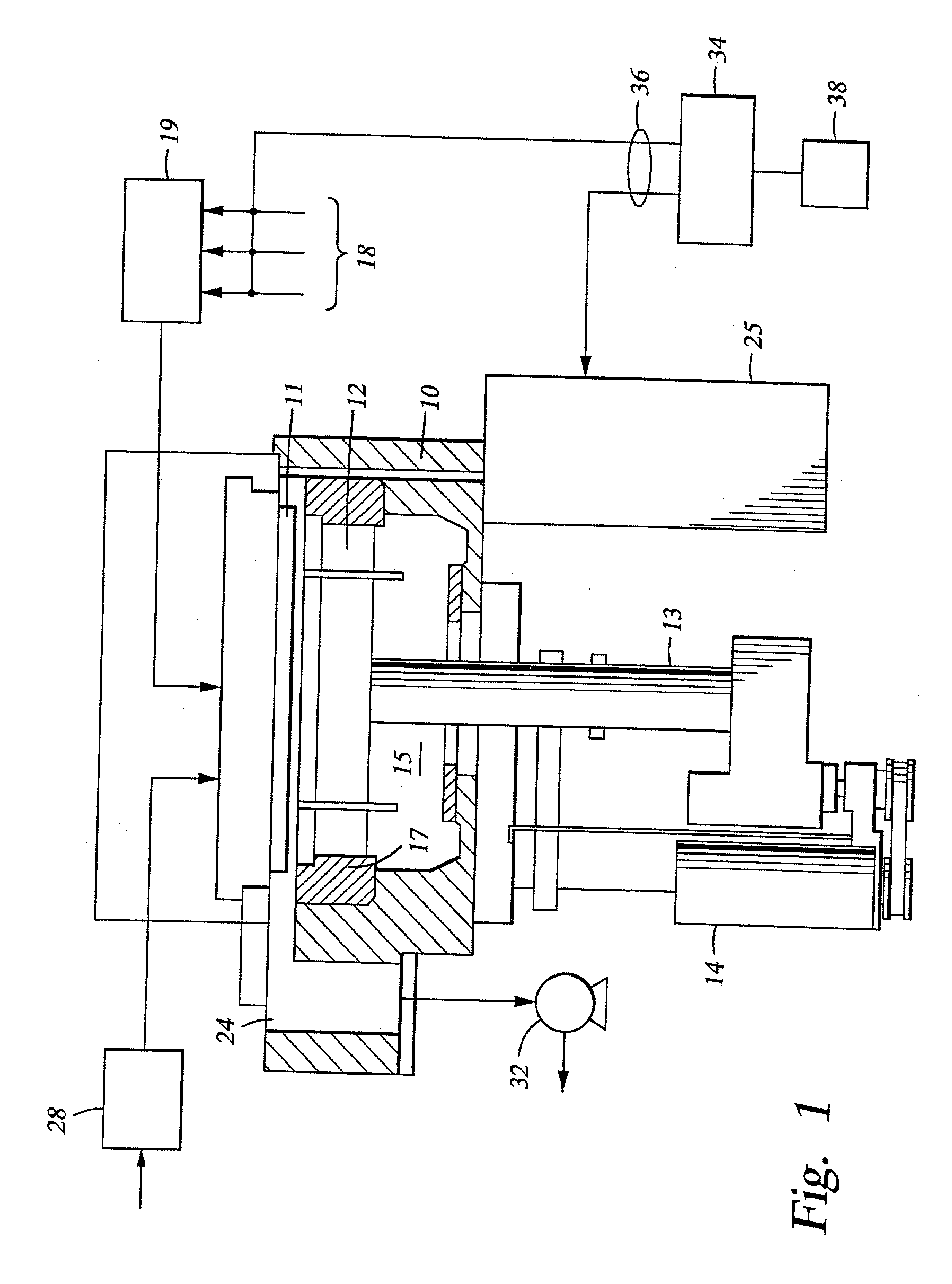
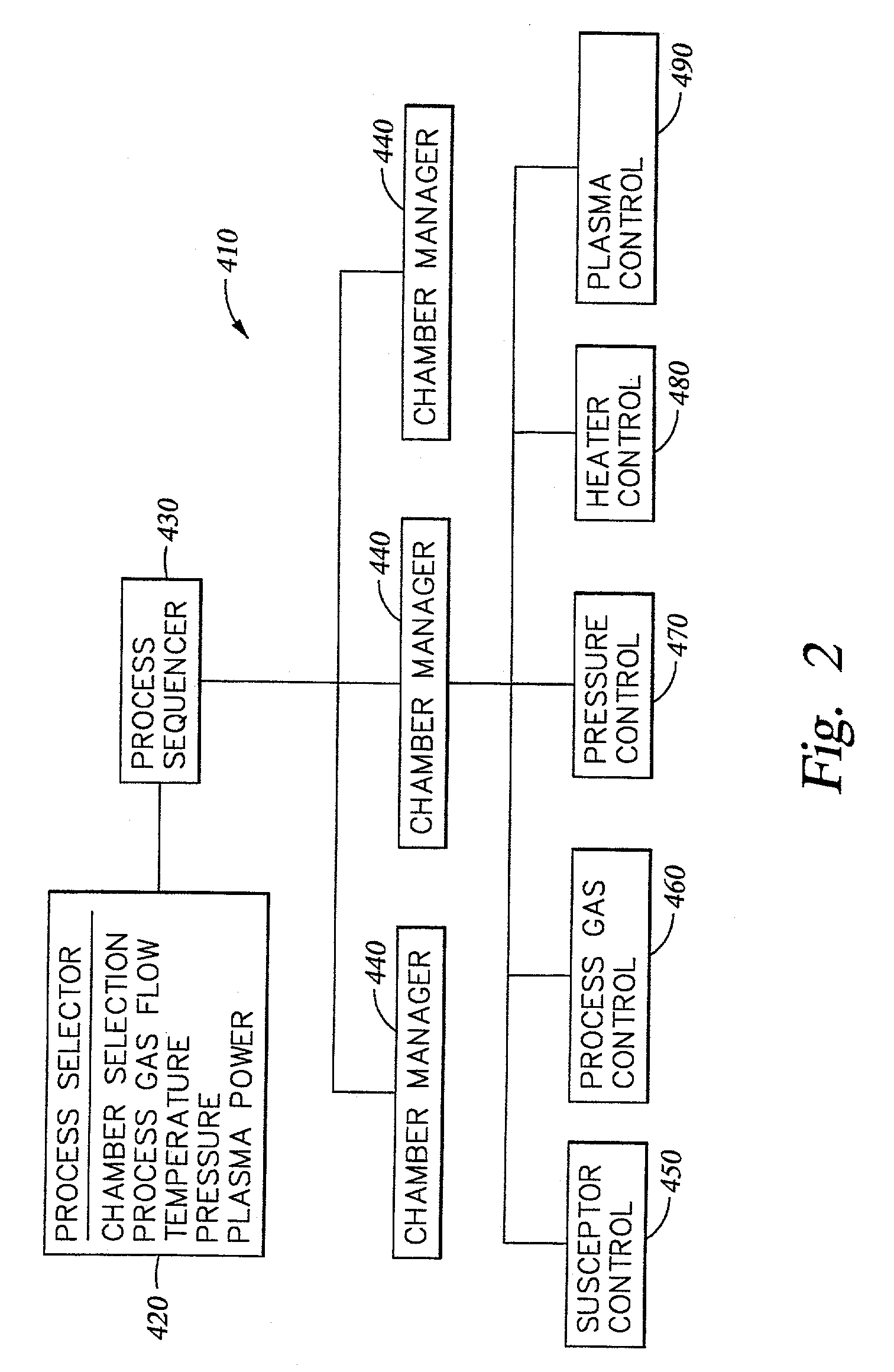
A method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen contents is provided by positioning a substrate inside a processing chamber, and supplying reacting materials into the chamber, chemisorbing a portion of the reacting materials onto the substrate. Then, a nitrogen (N2) remote plasma treatment is performed to reduce the hydrogen content of thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials on the substrate. Accordingly, a thin film is formed having a low hydrogen content, since the hydrogen bonds in the thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials are removed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of drug formulation based on increasing the affinity of crystalline microparticle surfaces for active agents
Methods are provided for coating crystalline microparticles with an active agent by altering the surface properties of the microparticles in order to facilitate favorable association on the microparticle by the active agent. Type of surface properties that are altered by the disclosed methods include by electrostatic properties, hydrophobic properties and hydrogen bonding properties.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Beneficial Effects of Increasing Local Blood Flow
InactiveUS20090105336A1Increase oxygenationImprove tissue nutritionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTopical creamArginine
The present invention provides a treatment for enhancing the ability of the body to heal wounds. A topical cream is described which improves blood flow by the transdermal delivery of the nitric oxide precursor L-Arginine either alone or with an adjunct, theophylline. The delivery of the active agents is accomplished by use of a vehicle which contains a hostile biophysical environment which is also hostile to hydrogen bond formation.
Owner:STRATEGIC SCI & TECH
Member for semiconductor light emitting device and method for manufacturing such member, and semiconductor light emitting device using such member
InactiveUS20090045422A1Improve heat resistanceImprove light resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeat resistancePhosphor
To provide novel semiconductor light-emitting device member superior in transparency, light resistance, and heat resistance and capable of sealing semiconductor light-emitting device and holding phosphor without generating cracks or peelings even after use for a long time, the member meets the following requirements: (1) comprising functional group forming hydrogen bond with hydroxyl group or oxygen in a metalloxane bond, on the surface of ceramic or metal, (2) maintenance rate of transmittance at 400 nm wavelength before and after left at 200° C. for 500 hours is between 80% to 110%, (3) no change is observed by visual inspection after irradiated with light having 380 nm to 500 nm wavelength, whose center wavelength is between 400 nm and 450 nm both inclusive, for 24 hours with 4500 W / m2 illumination intensity at 436 nm wavelength, and (4) refractive index at 550 nm wavelength is 1.45 or larger.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Absorbent, nonwoven material exhibiting z-direction density gradient
InactiveUS20100318047A1Inhibition releaseMaintain integrityPersonal careCellulosic plastic layered productsAbsorbent materialVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an absorbent material that can be used as an absorbent core in absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, pantiliners, incontinence products, disposable diapers, etc. The material of the present invention is a nonwoven sheet, consisting of cellulosic fibers, optionally superabsorbent polymeric material, containing no binders, latexes, etc, relying on hydrogen bonding to produce the necessary structure. The material contains density gradients which direct fluid into the material and distribute it providing more effective fluid transport and efficient utilization of storage capacity. The material consists of two regions. In the first region, the material has a low-density stratum adjacent to one surface, overlaying at least one higher density stratum adjacent to the opposite surface of the sheet. These strata create a density gradient in the thickness direction (Z-direction) of the sheet. The second region consists of a fluid distribution structure that has a higher density than at least the lower density of the strata comprising the first region. The fluid distribution structure is in direct fluid communication with the adjacent strata in the first region, along their boundaries.
Owner:EAM
Preparation method of three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel material and product thereof
ActiveCN103285789AImprove pore structureWide pore structure adjustable rangeColloidal chemistry detailsSolubilityFiber
The invention relates to a preparation method of a three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel material and a product thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly dispersing fibers in solvents which do not have fiber solubility to form turbid liquid; secondly curing the turbid liquid to form cured pieces; thirdly removing cured solvents in the cured pieces to form non-crosslinked fiber-based aerogel; and finally carrying out crosslinking stabilization treatment on the non-crosslinked fiber-based aerogel to obtain the fiber crossing point bonded and fixed three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel material. The product is a three-dimensional network-shaped material formed through mutual penetration and stagger of fibers. The fiber crossing points are effectively interconnected through non-hydrogen-bond bonding. The three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel material has volume density of 0.1-500mg / cm<3>, average pore size of 0.01-2000mu m and specific surface area of 0.2-2000m<2> / g. The preparation method and the product have the advantages that the preparation process is simple; the raw material limitations are less; and the aerogel product has good flexibility and connectivity and has broad application prospects in numerous fields.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Super-hydrophobic coating material, preparation method thereof and super-hydrophobic coating
InactiveCN102051120AThe preparation method is simple and easy to obtainEasy to realize industrial applicationCoatingsOrganic solventHydrogen
The invention provides a super-hydrophobic coating material, which comprises water or emulsifier or organic solvent, a polysiloxane compound having more than three silicon-hydrogen bonds and solid particles. The invention also provides the preparation method of the super-hydrophobic coating material and the preparation method of a super-hydrophobic coating. The invention provides the super-hydrophobic coating material which is prepared by a simple method, has high mechanical strength, is durable, practical and capable of self-cleaning and the preparation method of the super-hydrophobic coating material. The super-hydrophobic coating material provided by the invention can solidify in a wider temperature range and is applicable to substrates made of various materials such as metal, glass and high polymer materials.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Silicone containing polymers formed from non-reactive silicone containing prepolymers
The present invention relates to polymer compositions formed from a reactive mixture comprising at least one substantially non-reactive prepolymer comprising silicone containing groups and compatibilizing groups and a hydrophilic component comprising at least one monomer capable of hydrogen bonding with said prepolymer.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Magnetic disk and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7722968B2Improve securityEfficient preparationProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageHydrogenFree energies
In a magnetic disk having a magnetic layer, a protection layer, and a lubrication layer formed on a substrate in this order, a surface free energy γS of a surface of the magnetic disk derived by an extended Fowkes equation is greater than 0 and no greater than 24 mN / m. γSd (dispersion force component of surface free energy) forming the surface free energy γS is greater than 0 and no greater than 17 mN / m, γSp (dipole component of surface free energy) forming the surface free energy γS is greater than 0 and no greater than 1 mN / m, and γSh (hydrogen bonding force component of surface free energy) forming the surface free energy γS is greater than 0 and no greater than 6 mN / m.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
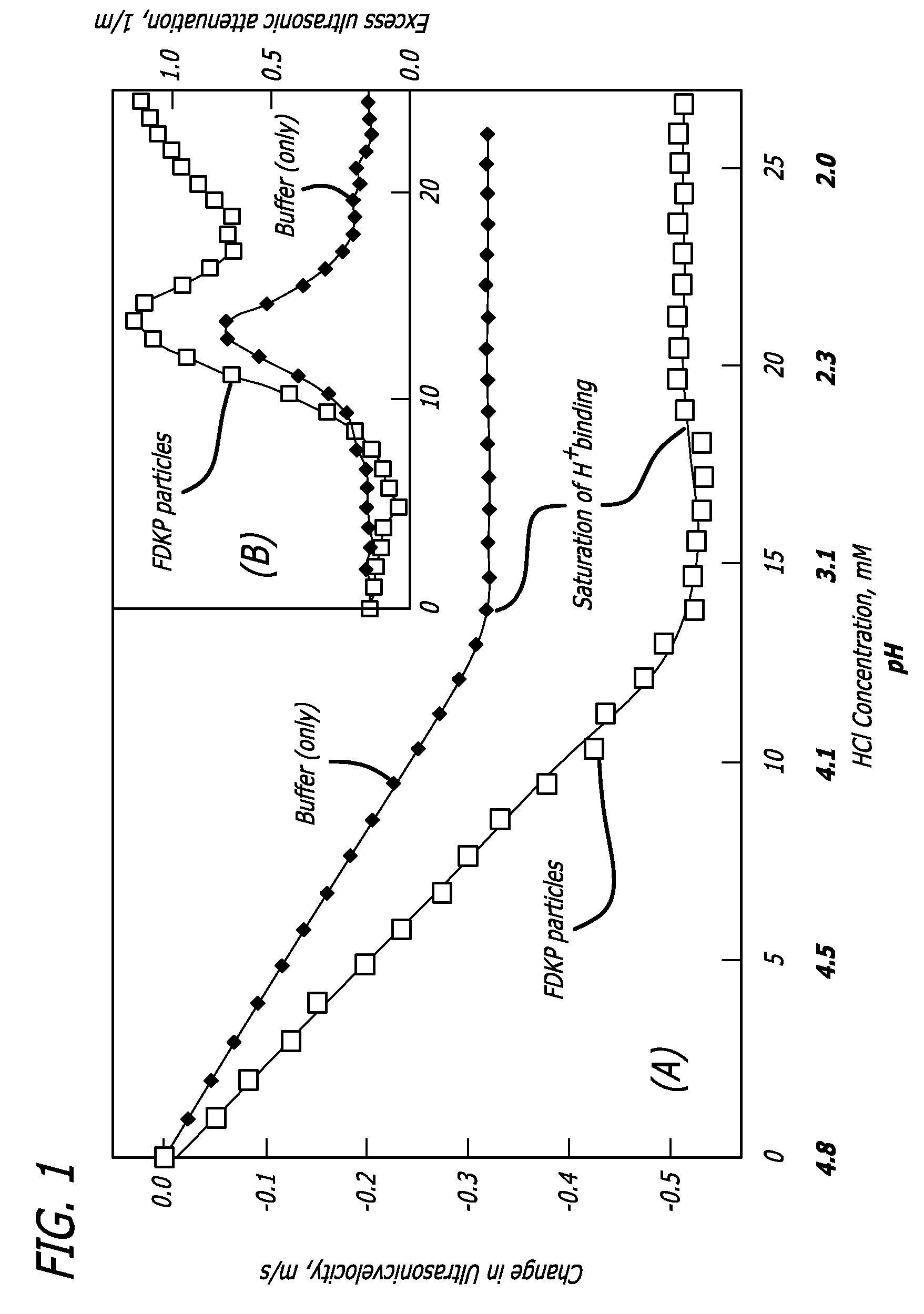
Method for delivery of monomeric or dimeric insulin complexed to diketopiperazine microparticles
InactiveUS7648960B2Rapid increase in blood agent concentrationEasy to transportPowder deliverySpray deliveryBlood insulinBlood agent
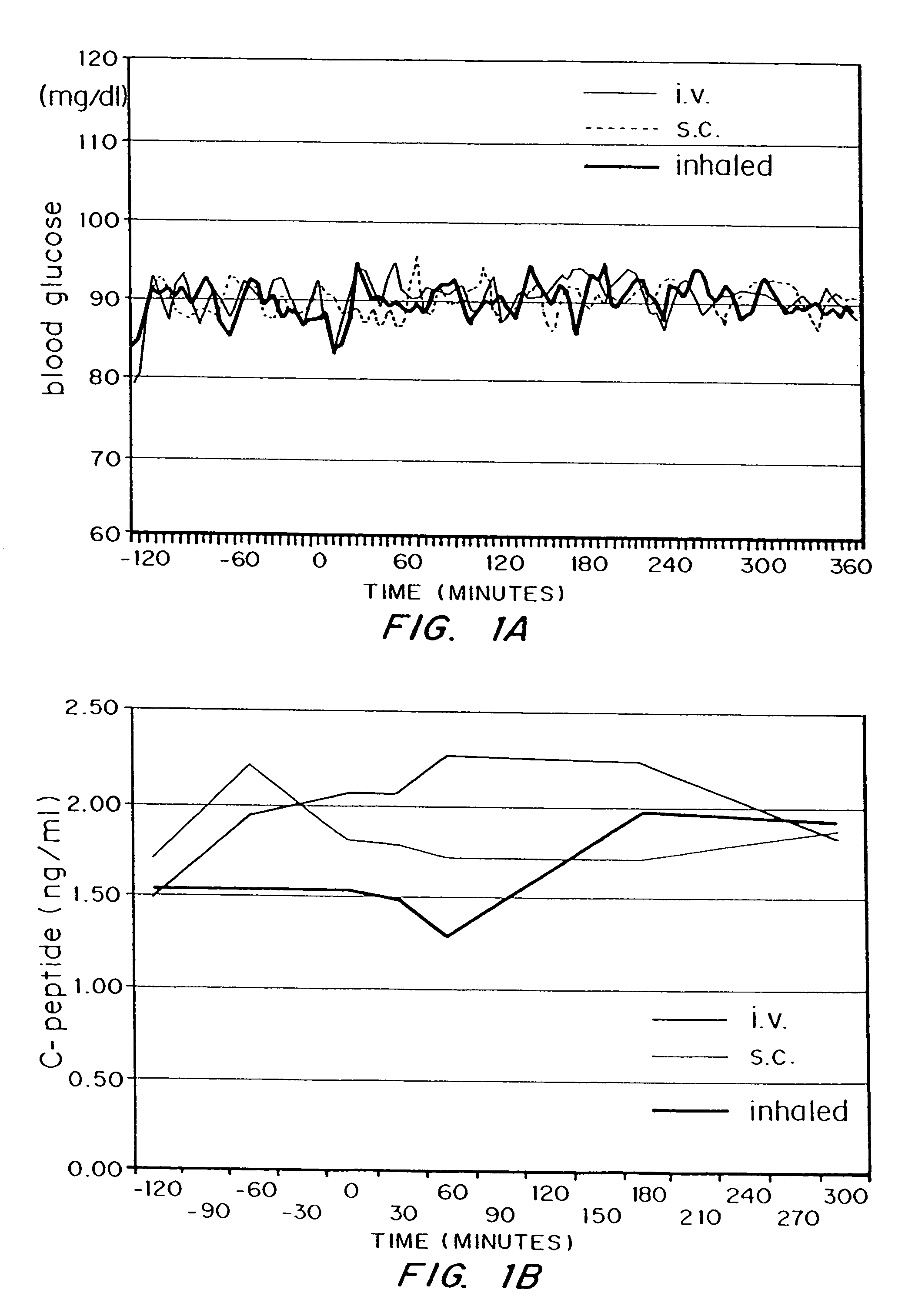
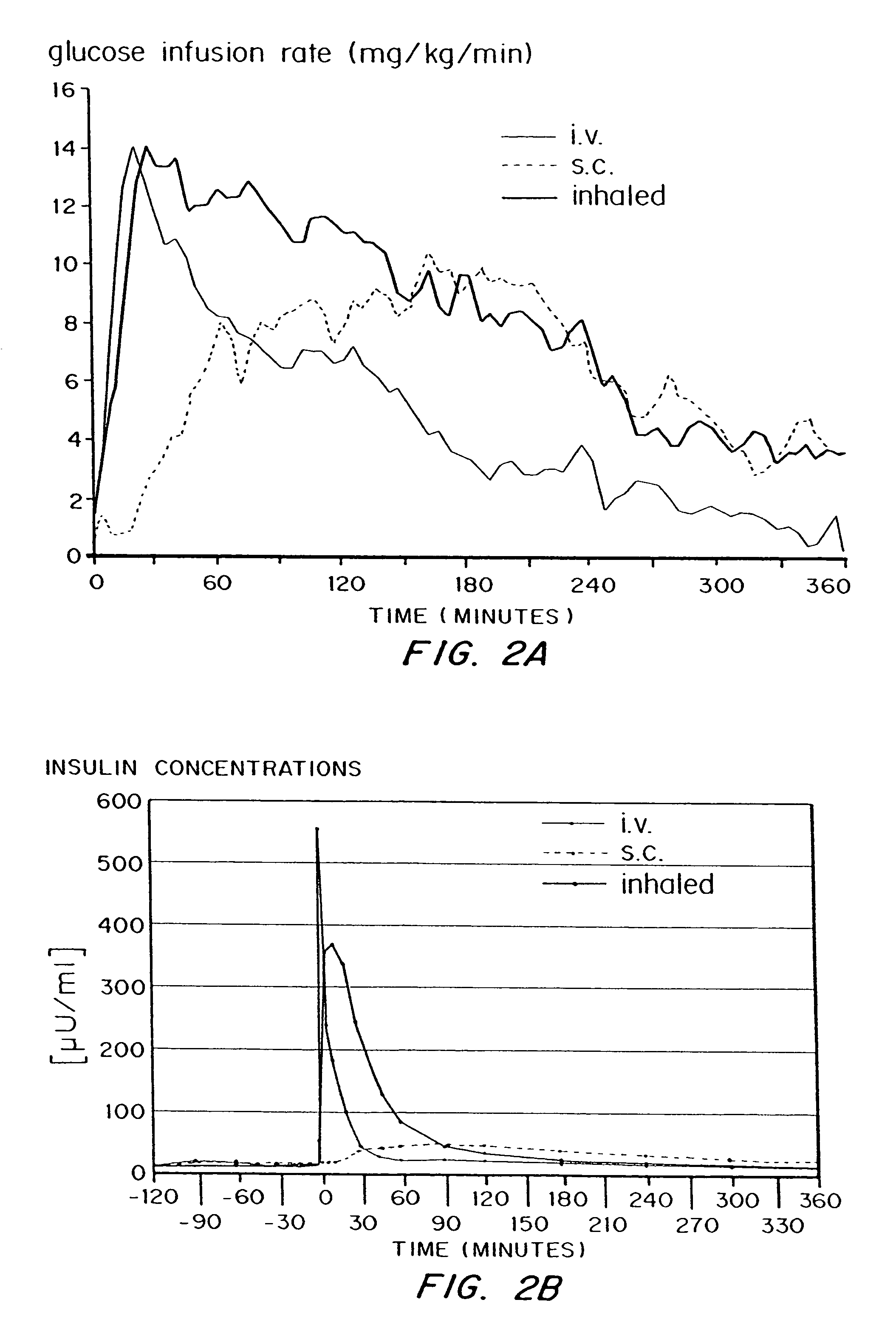
Methods are provided for purifying peptides and proteins by incorporating the peptide or protein into a diketopiperazine or competitive complexing agent to facilitate removal of one or more impurities from the peptide or protein. Formulations and methods also are provided for the improved transport of active agents across biological membranes, resulting for example in a rapid increase in blood agent concentration. The formulations include microparticles formed of (i) the active agent, which may be charged or neutral, and (ii) a transport enhancer that masks the charge of the agent and / or that forms hydrogen bonds with the target biological membrane in order to facilitate transport. In one embodiment insulin is administered via the pulmonary delivery of microparticles comprising fumaryl diketopiperazine and insulin in its biologically active form. This method of delivering insulin results in a rapid increase in blood insulin concentration that is comparable to the increase resulting from intravenous delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Three-dimensional carbon fiber based aerogel material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103265010AImprove conductivityStrong modifiabilityCarbon preparation/purificationFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a three-dimensional carbon fiber based aerogel material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: first, dispersing fiber in a solvent to form a turbid liquid; then, curing the turbid liquid to form a cured block; then, removing the cured solvent in the cured block to form an uncrosslinked fiber based aerogel; and crosslinking and stabilizing the uncrosslinked fiber based aerogel and pre-oxidizing and carbonizing to obtain the three-dimensional carbon fiber based aerogel material. The product is a three-dimensional network-shaped material formed by carbon fibers in a penetrated and staggered mode. The fiber crosslinking points show effective bonding and interconnection of bonding effect of non-hydrogen bond. The volume density is 0.1-500mg / cm<3>, the average aperture is 0.01-200mu m, and the specific surface area is 0.2-2000m<2> / g. The preparation process is simple and the raw material limit is less. The three-dimensional carbon fiber based aerogel product has good flexibility, connectivity and conductivity, and has a wide application prospect in many fields.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of a three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel tissue engineering scaffold and a product thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly dispersing fibers in solvents to form turbid liquid; secondly curing the turbid liquid to form cured pieces; thirdly removing cured solvents to form non-crosslinked fiber-based aerogel; finally carrying out crosslinking stabilization treatment and then carrying out sterilization treatment, thus obtaining the three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel tissue engineering scaffold. The product is a three-dimensional network-shaped material formed through mutual penetration and stagger of fibers. The fiber crossing points are effectively interconnected through non-hydrogen-bond bonding. The three-dimensional fiber-based aerogel tissue engineering scaffold has volume density of 0.1-500mg / cm<3>, average pore size of 0.01-2000mu m and specific surface area of 0.2-2000m<2> / g. The preparation method and the product have the advantages that the preparation process is simple; the raw material limitations are less; the aerogel tissue engineering scaffold product has good flexibility, connectivity and tissue growing environment and has broad application prospects in the tissue engineering field.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen content on a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6933245B2Reduce hydrogen contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaChemisorption
A method of forming a thin film with a low hydrogen contents is provided by positioning a substrate inside a processing chamber, and supplying reacting materials into the chamber, chemisorbing a portion of the reacting materials onto the substrate. Then, a nitrogen (N2) remote plasma treatment is performed to reduce the hydrogen content of thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials on the substrate. Accordingly, a thin film is formed having a low hydrogen content, since the hydrogen bonds in the thin film layer formed by chemisorption of the reacting materials are removed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-strength supramolecular hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104804115AHigh mechanical strengthStrong toughnessProsthesisHydrogenBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a high-strength supramolecular hydrogel and a preparation method and application thereof. The high-strength supramolecular hydrogel is prepared by using acryloyl glycinamide as a monomer and triggering in the presence of an initiator; because of the synergistic effect of hydrogen bonds, the supramolecular hydrogel is high in tensile strength and anti-tear while being compressed, can realize functions of thermoplasticity and self-repair at a high temperature, and is good in biocompatibility.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
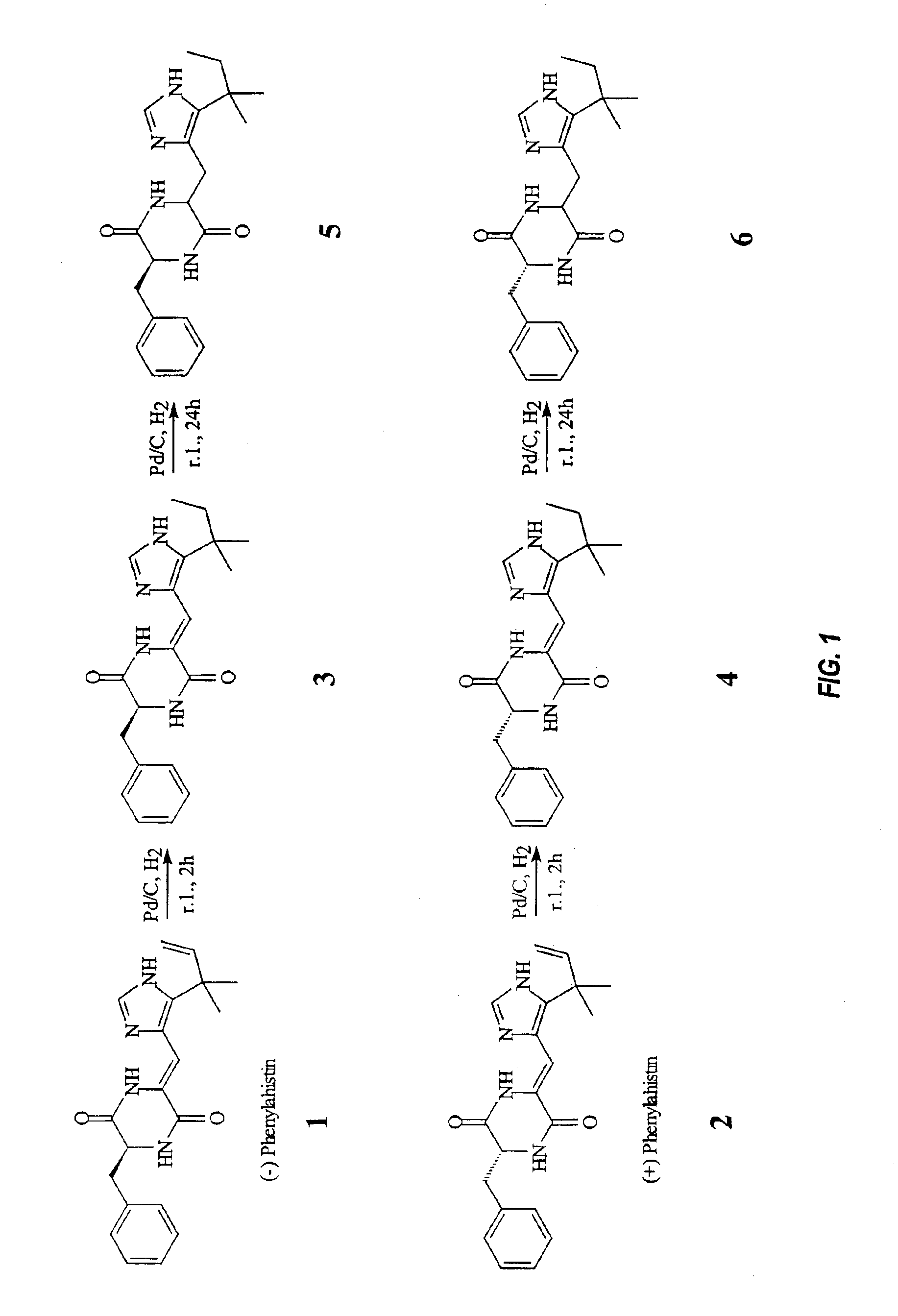
Phenylahistin and the phenylahistin analogs, a new class of anti-tumor compounds
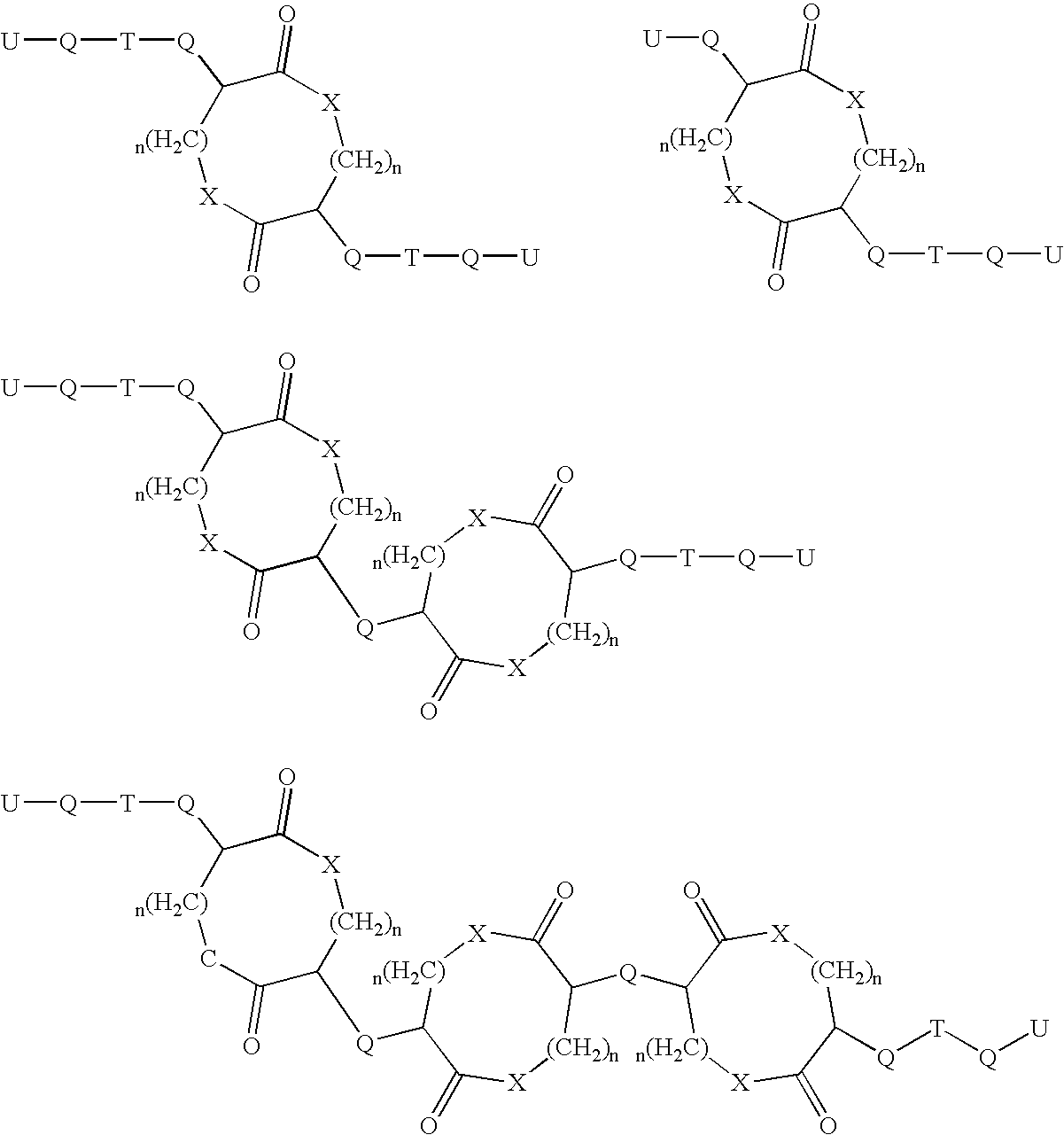
Methods of using a compound, its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, and / or its pro-drug esters, in isolated form, to treat cancer, and methods for isolating, for formulating, and for administering the compound, salt, and / or pro-drug ester as an antitumor agent, wherein the compound, salt, or pro-drug ester has the following structure: wherein:R1, R2, R5, R7, and R8 are each separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, and saturated C1-C24 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C24 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, cycloalkenyl, alkoxy, cycloalkoxy, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, amino, substituted amino, nitro, substituted nitro, phenyl, and substituted phenyl groups,R3, R4, and R6 are each separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, and saturated C1-C12 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C12 alkenyl, cycloalkyl, alkoxy, cycloalkoxy, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, amino, substituted amino, nitro, and substituted nitro groups,X1 and X2 are separately selected from the group consisting of an oxygen atom, and a sulfur atom, andthe dashed bond represents a bond selected from the group consisting of a carbon-carbon single bond and a carbon-carbon double bond. Most preferably, R3 and R4 are hydrogen, and each are involved in hydrogen bonds, and / or the dashed bond is a double bond, such that the chemical backbone of the compound substantially retains a substantially planar conformation.
Owner:BEYONDSPRING PHARMA INC
Medical device rapid drug releasing coatings comprising oils, fatty acids, and/or lipids
ActiveUS8414526B2Improve permeabilityEnhanced rate and extent of absorptionOrganic active ingredientsStentsHydrogenChemical compound
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Crosslink cyclo-siloxane compound with linear bridging group to form ultra low k dielectric
InactiveUS20030194495A1Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxygenAliphatic hydrocarbon
A method for depositing a low dielectric constant film having a dielectric constant of about 3.0 or less, preferably about 2.5 or less, is provided by using one or more cyclic organic precursors and one or more aliphatic precursors. In one aspect, a cyclic organosilicon compound, an aliphatic organosilicon, and an aliphatic hydrocarbon compound are reacted with an oxidizing gas at conditions sufficient to deposit a low dielectric constant film on the semiconductor substrate. The cyclic organosilicon compound includes at least one silicon-carbon bond. The aliphatic organosilicon compound includes a silicon-hydrogen bond or a silicon-oxygen bond.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of binding particles to binder treated fibers
InactiveUS7144474B1Efficiently and economically attachedIncreases absorptive efficiency of productNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberHydrogen
Fiber treated with an organic nonpolymeric binder is combined with superabsorbent particles in order to bind the particles to the fiber. The nonpolymeric organic binder comprises binder molecules that include at least one functional group capable of forming a hydrogen bond or a coordinate covalent bond with the particles and at least one functional group capable of forming a hydrogen bond with the fiber. The superabsorbent particles have a hydrogen or coordinate covalent bonding functional site. The binder serves to bind the particles to the fiber through formation of hydrogen and / or coordinate covalent bonds.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER CO
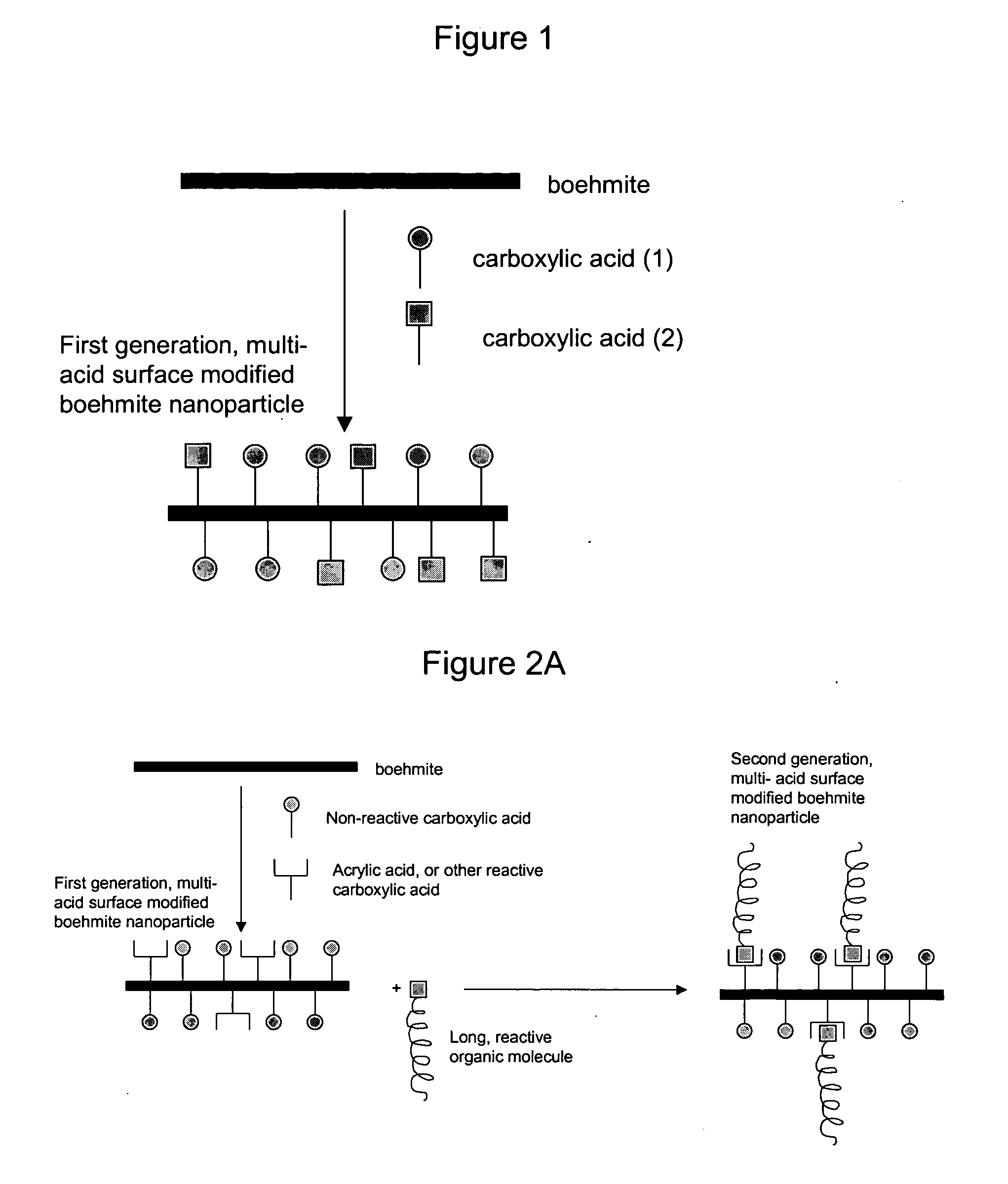
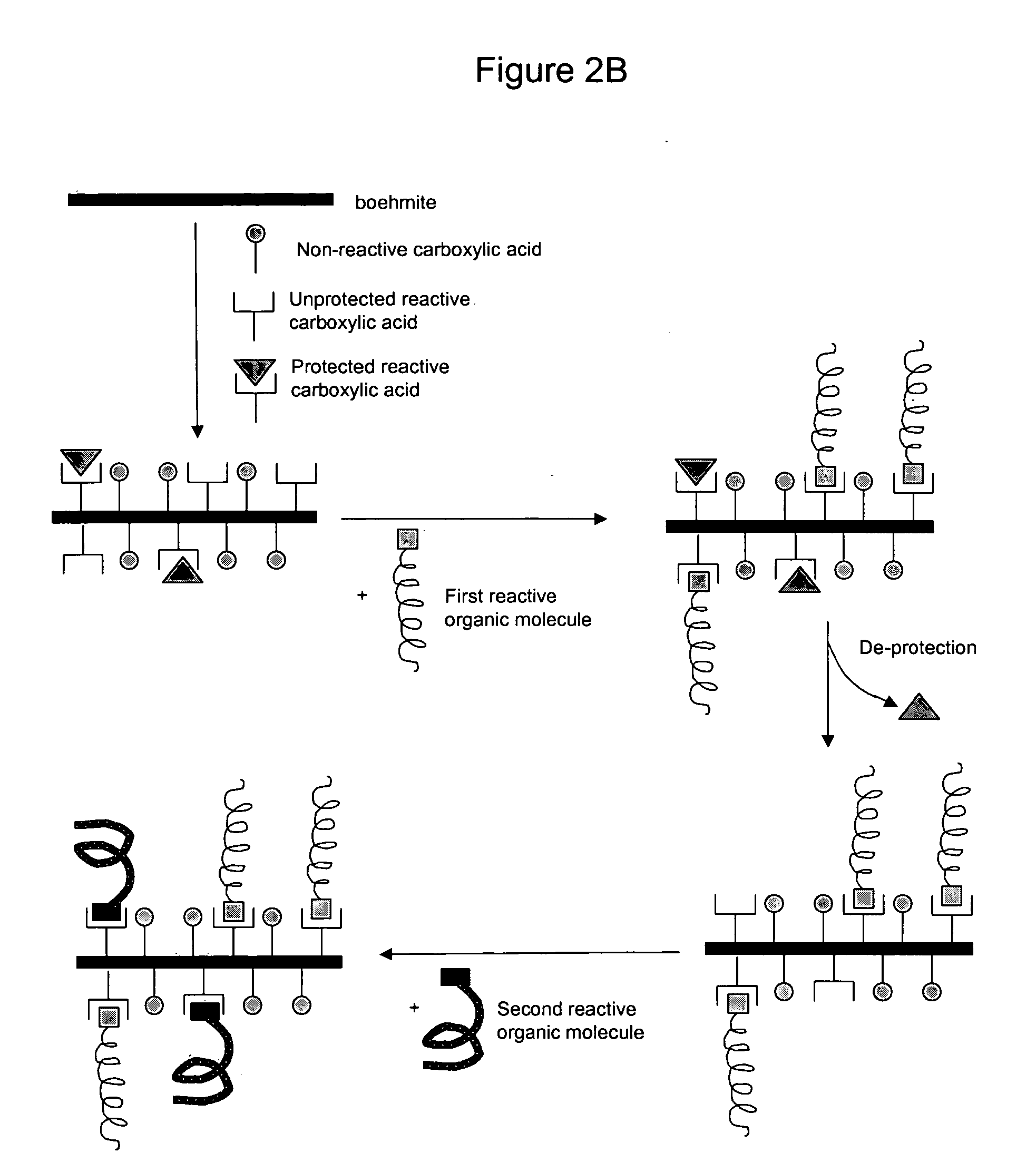
Nanoparticles modified with multiple organic acids
InactiveUS20070098990A1Reduce the amount requiredPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologySolubilityOrganic acid
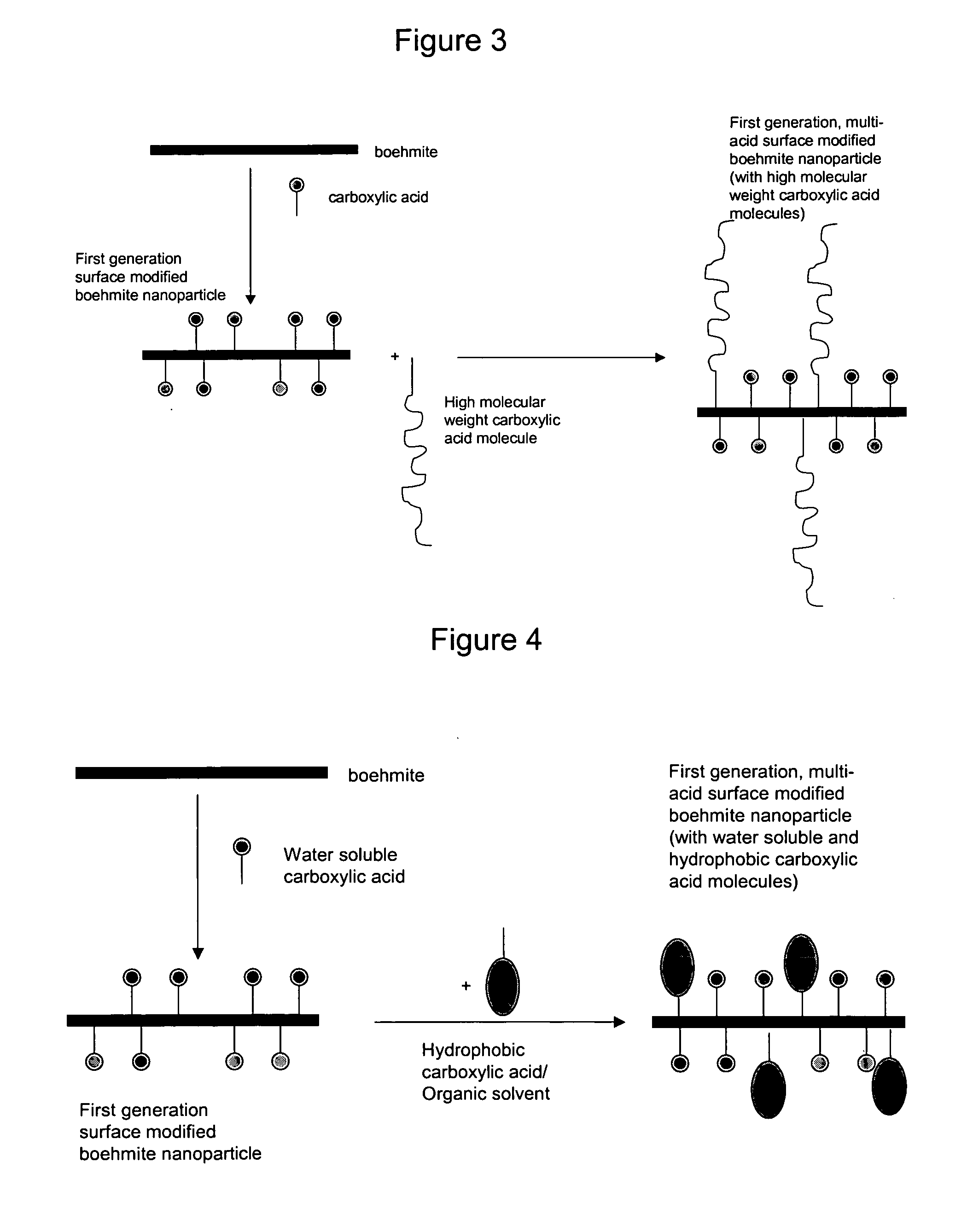
Surface-modified nanoparticles of boehmite, and methods for preparing the same. Aluminum oxyhydroxide nanoparticles are surface modified by reaction with selected amounts of organic acids. In particular, the nanoparticle surface is modified by reactions with two or more different carboxylic acids, at least one of which is an organic carboxylic acid. The product is a surface modified boehmite nanoparticle that has an inorganic aluminum oxyhydroxide core, or part aluminum oxyhydroxide core and a surface-bonded organic shell. Organic carboxylic acids of this invention contain at least one carboxylic acid group and one carbon-hydrogen bond. One embodiment of this invention provides boehmite nanoparticles that have been surface modified with two or more acids one of which additional carries at least one reactive functional group. Another embodiment of this invention provides boehmite nanoparticles that have been surface modified with multiple acids one of which has molecular weight or average molecular weight greater than or equal to 500 Daltons. Yet, another embodiment of this invention provides boehmite nanoparticles that are surface modified with two or more acids one of which is hydrophobic in nature and has solubility in water of less than 15 by weight. The products of the methods of this invention have specific useful properties when used in mixture with liquids, as filler in solids, or as stand-alone entities.
Owner:TDA RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com