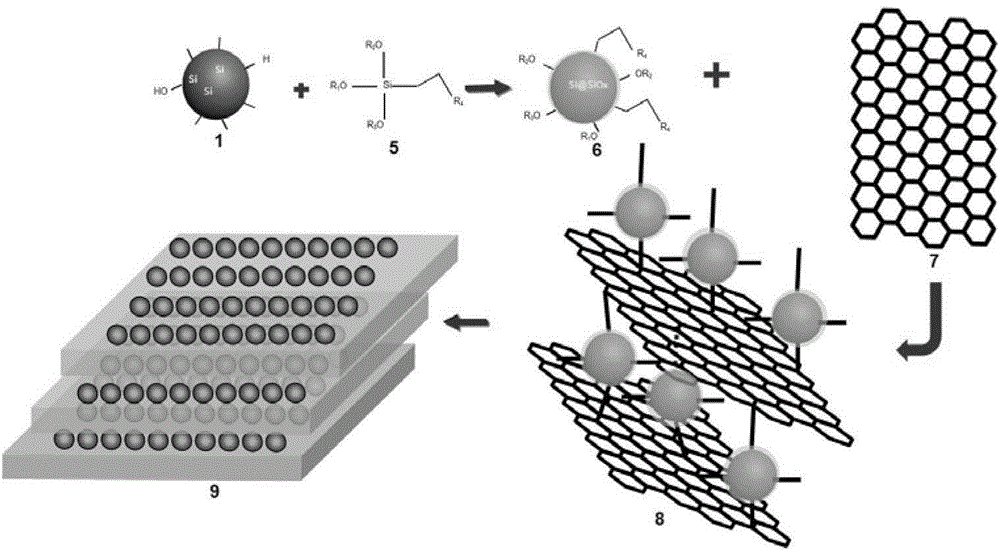
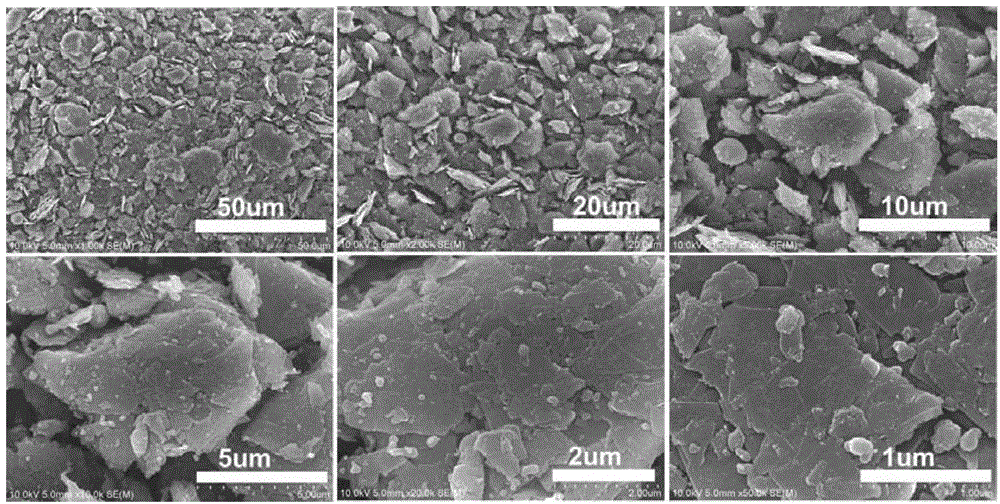
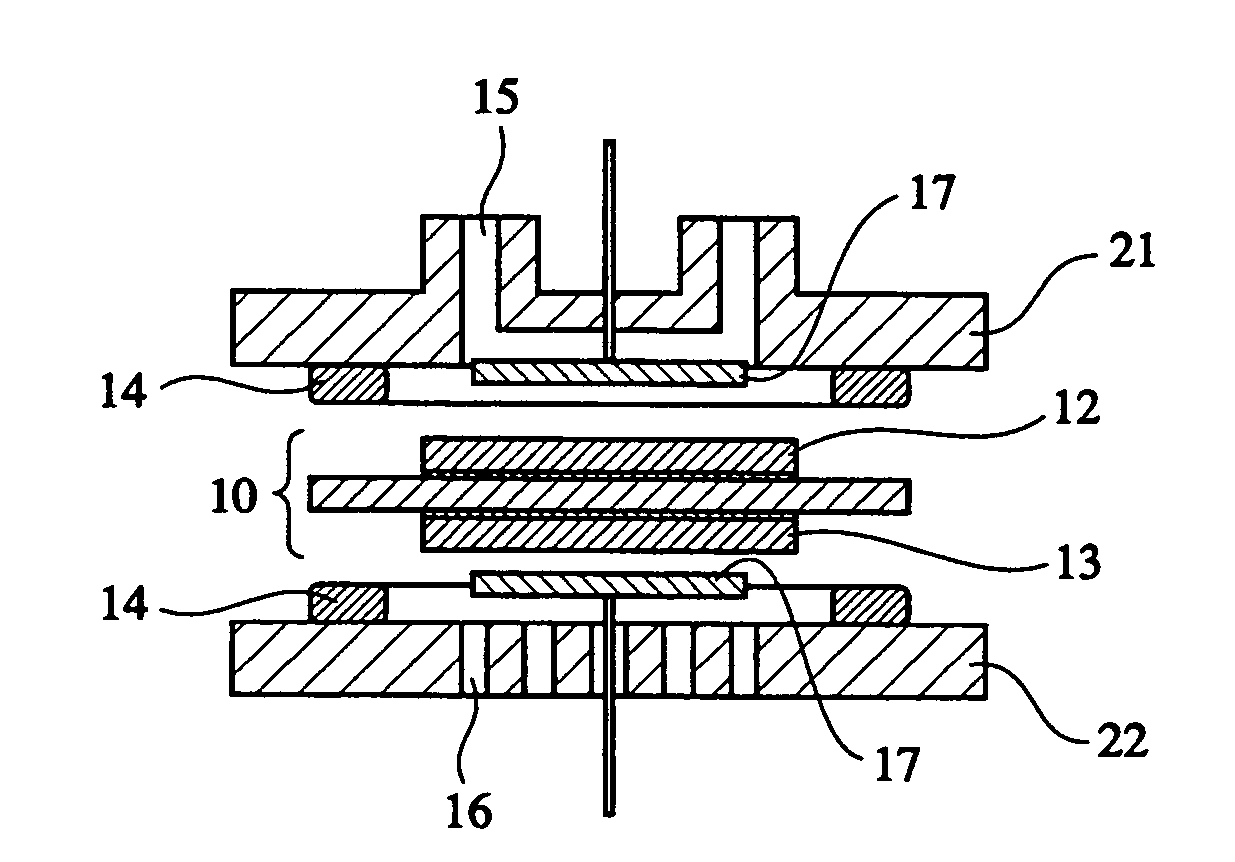
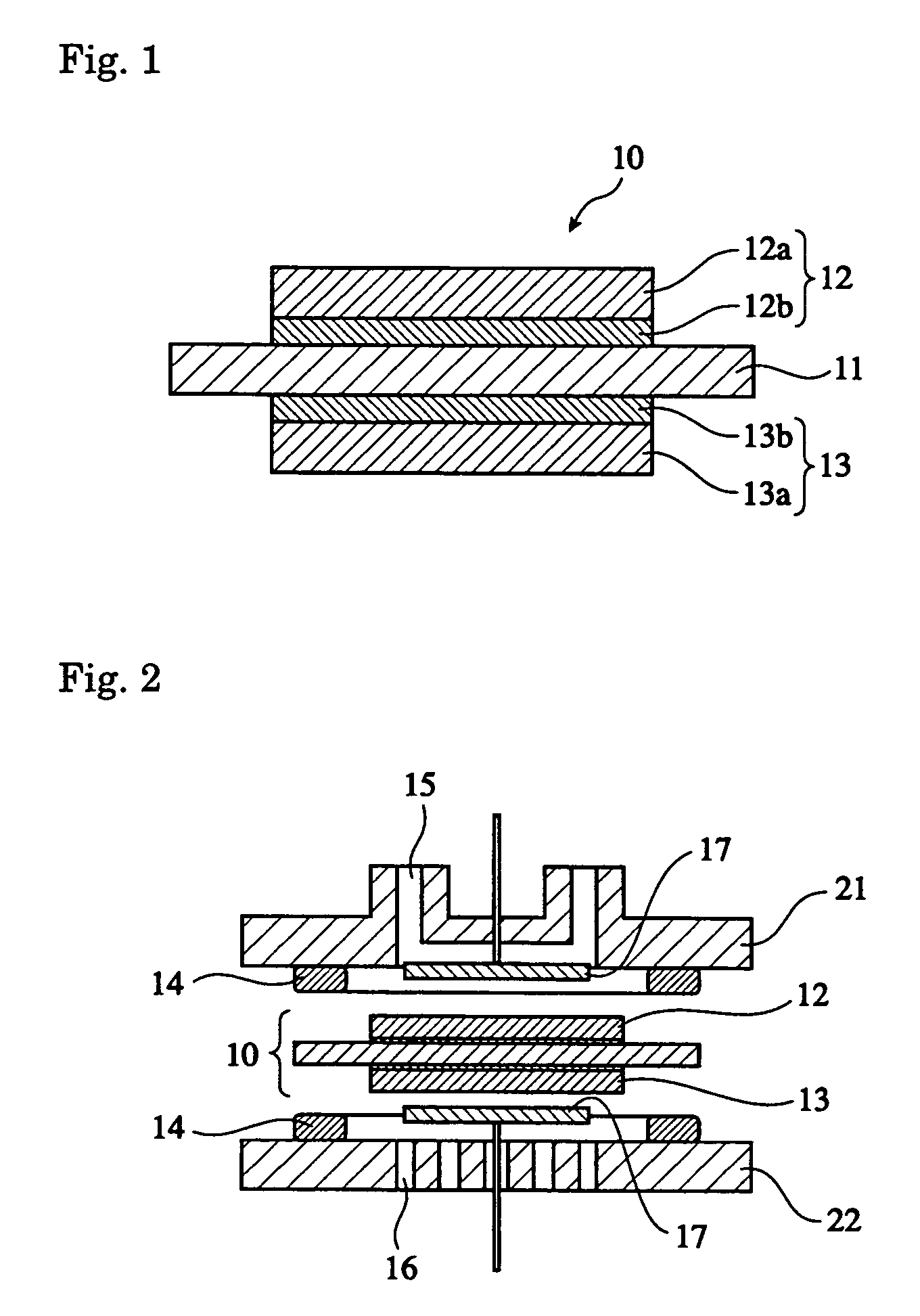
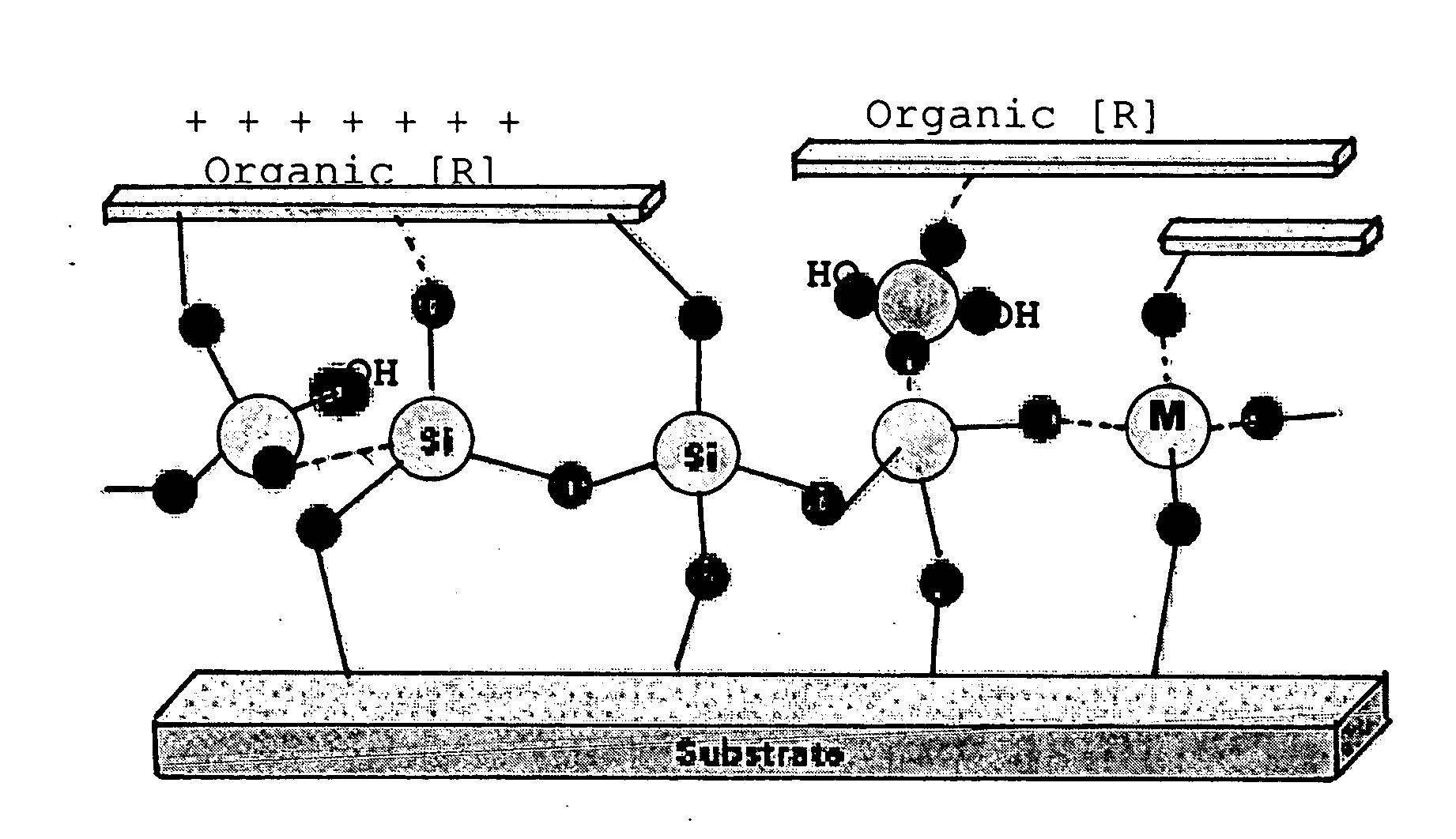
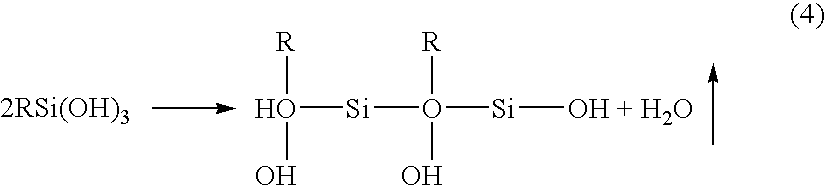
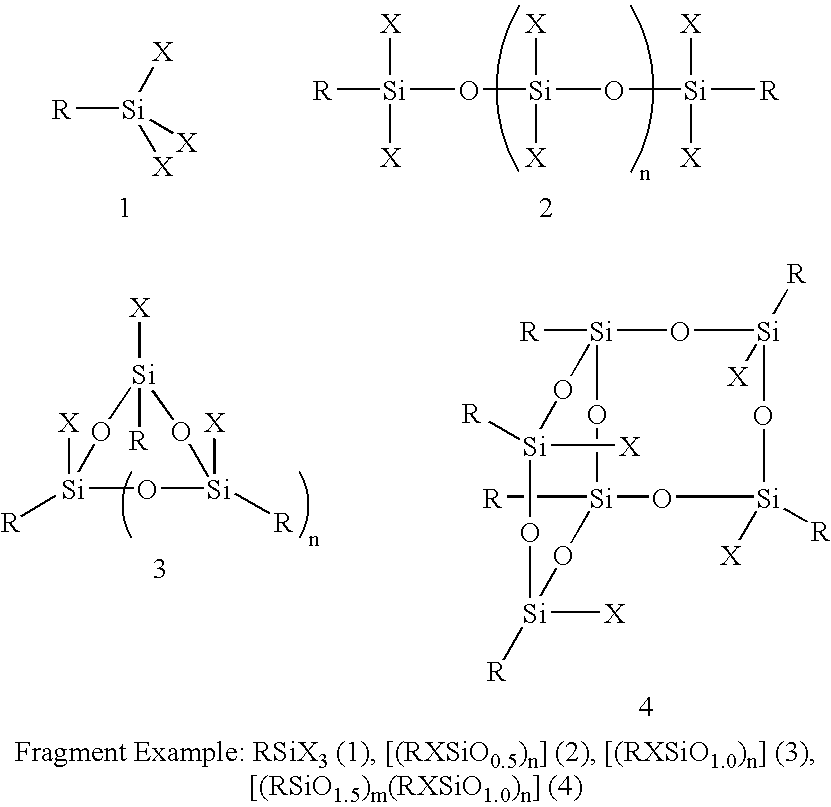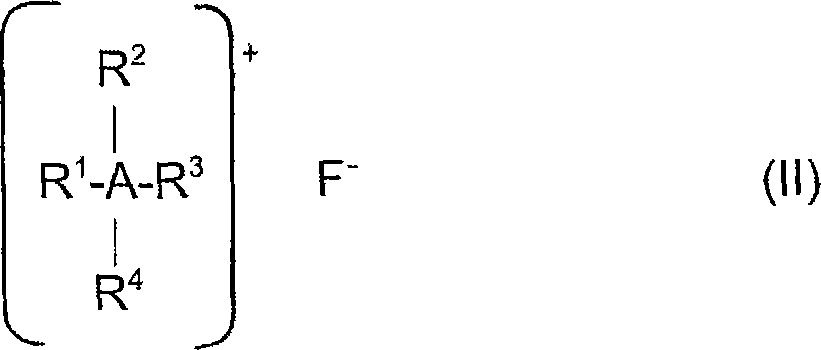Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
792 results about "Silicon oxygen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Silicon therefore can readily form compounds with oxygen where it takes the position of carbon. The electrons in silicon's 3p orbital can combine with the four electrons in oxygen's 2p orbital to complete a molecular orbital with 6 delocalized electrons.
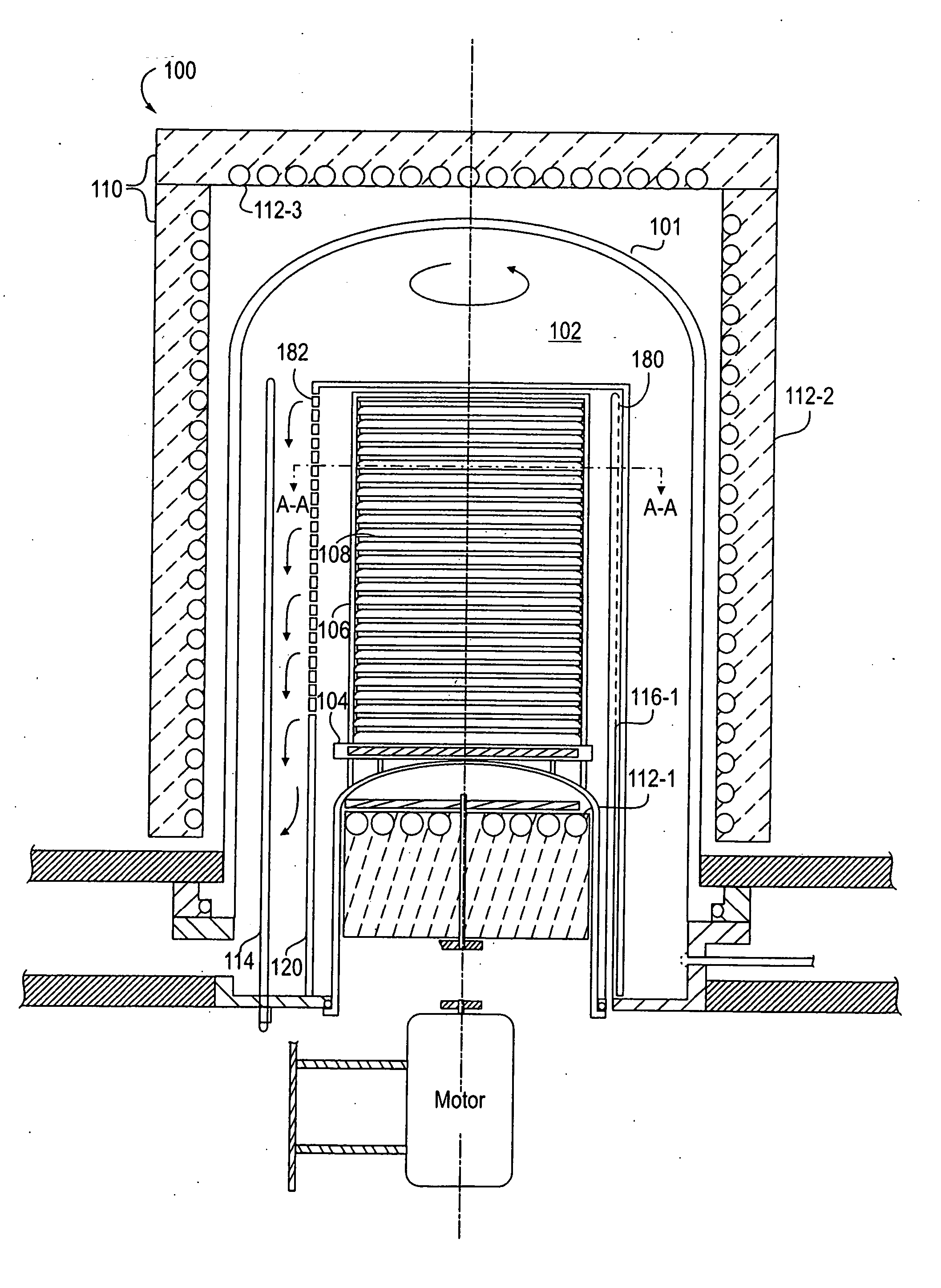
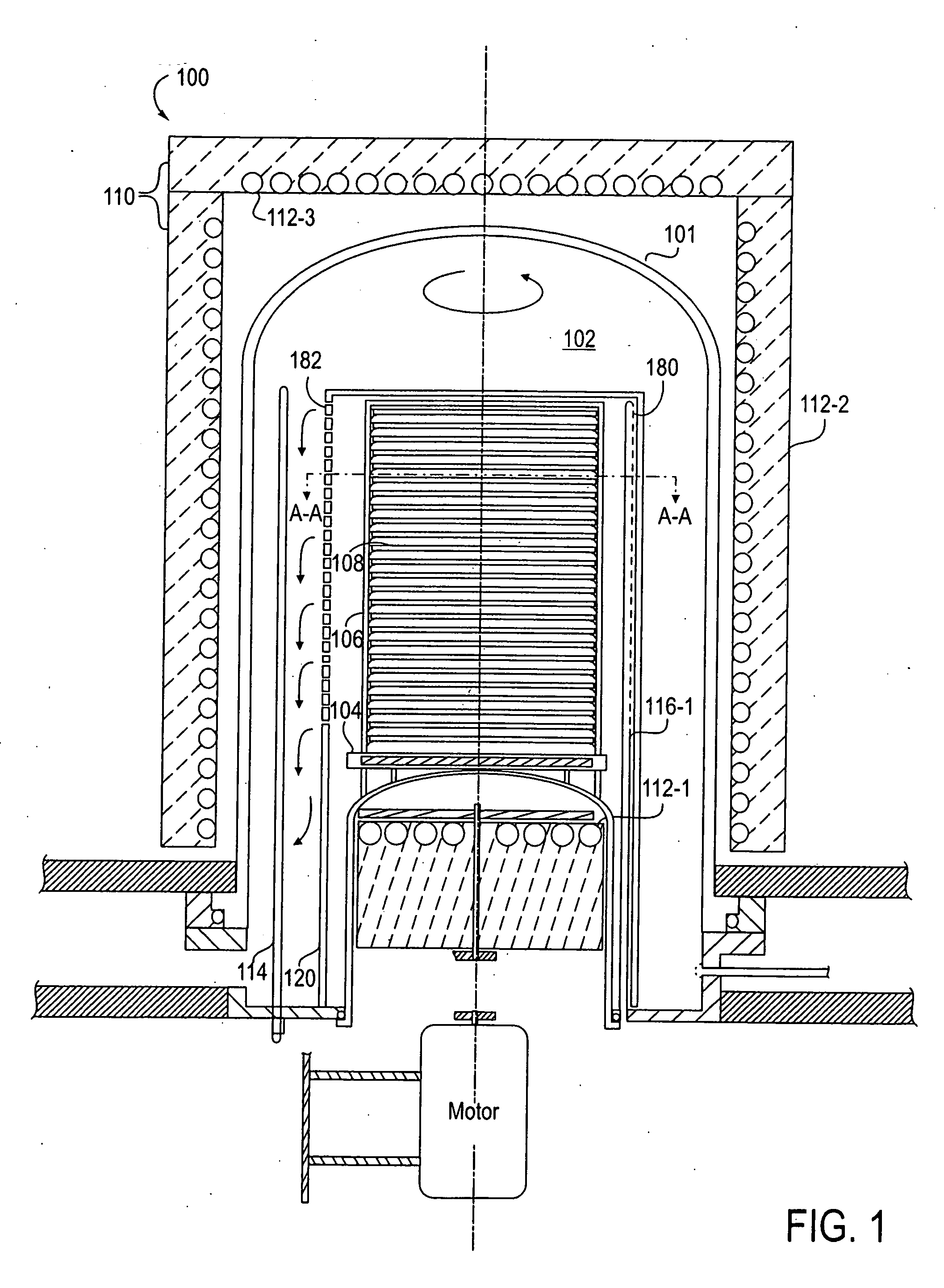
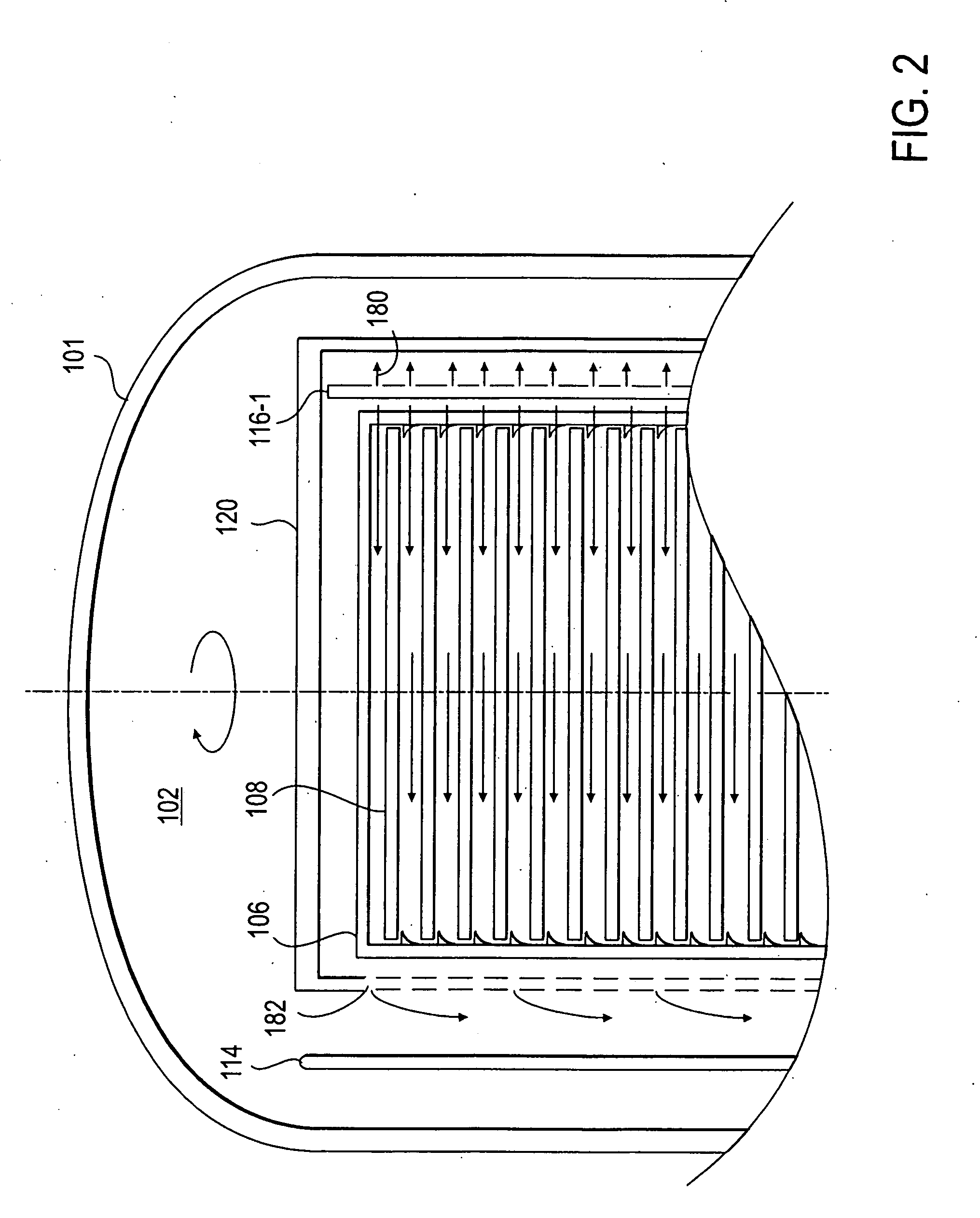
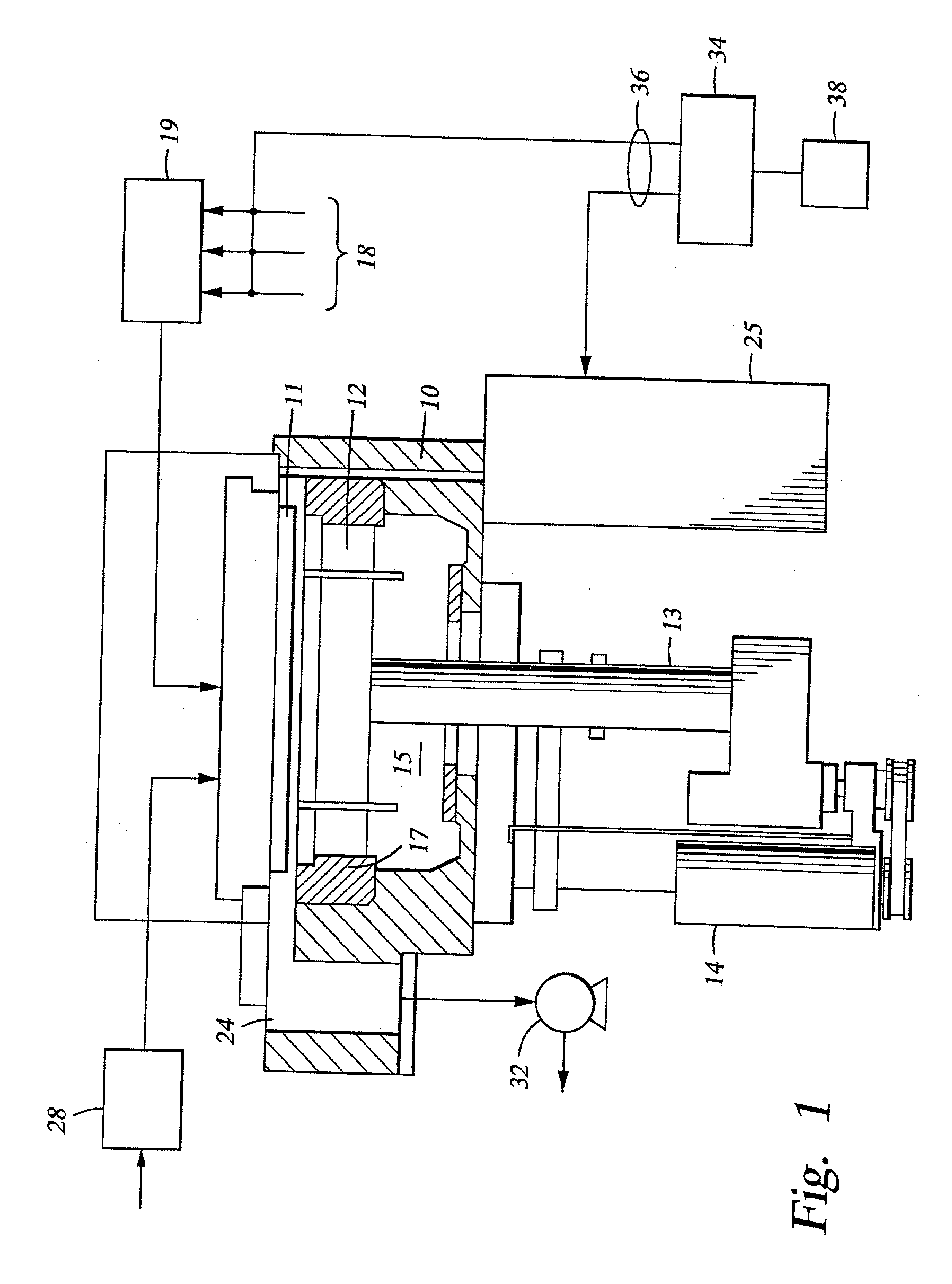
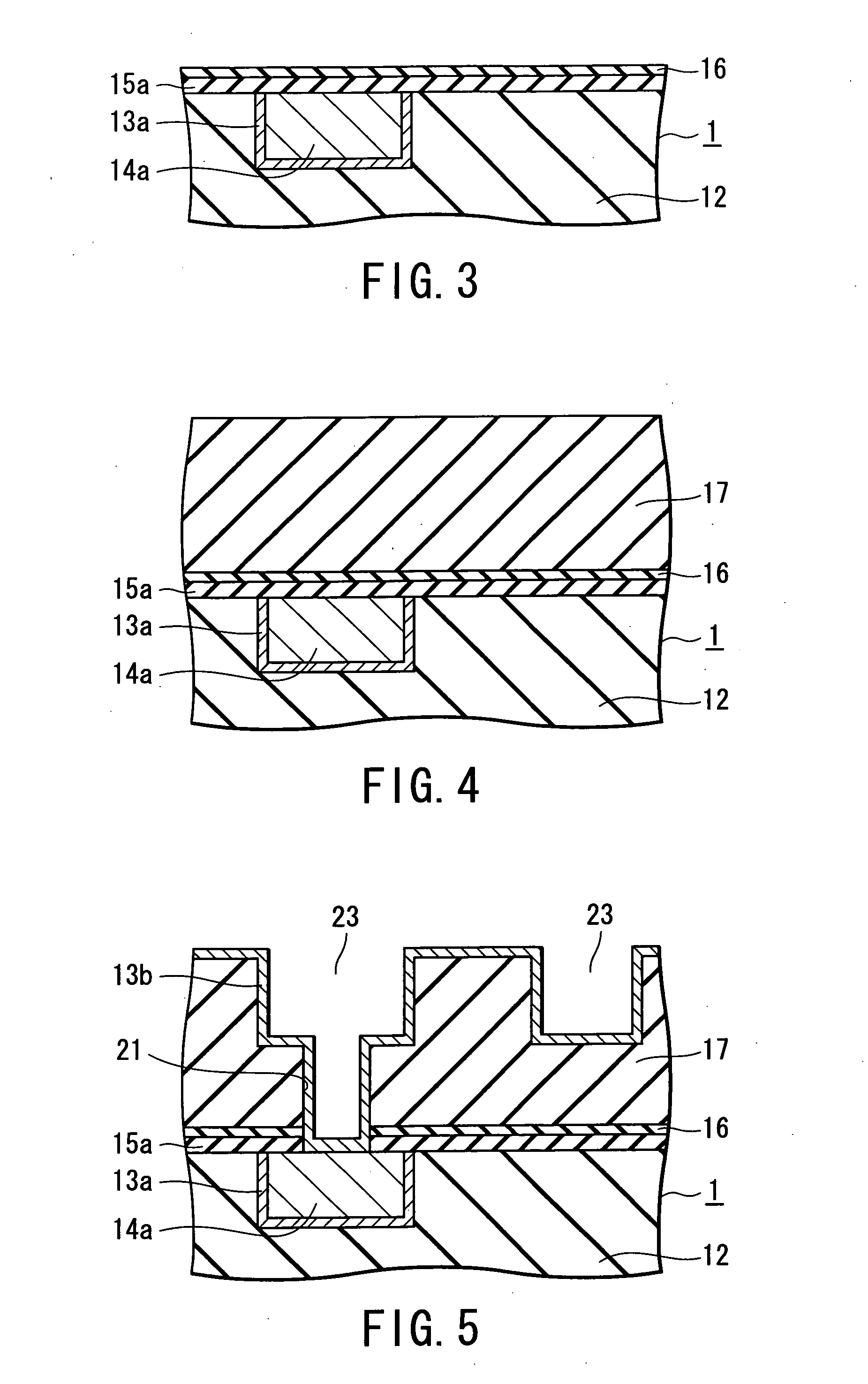
Method for depositing silicon-containing films
InactiveUS20070031598A1Reduce the temperatureChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxygenNitrogen
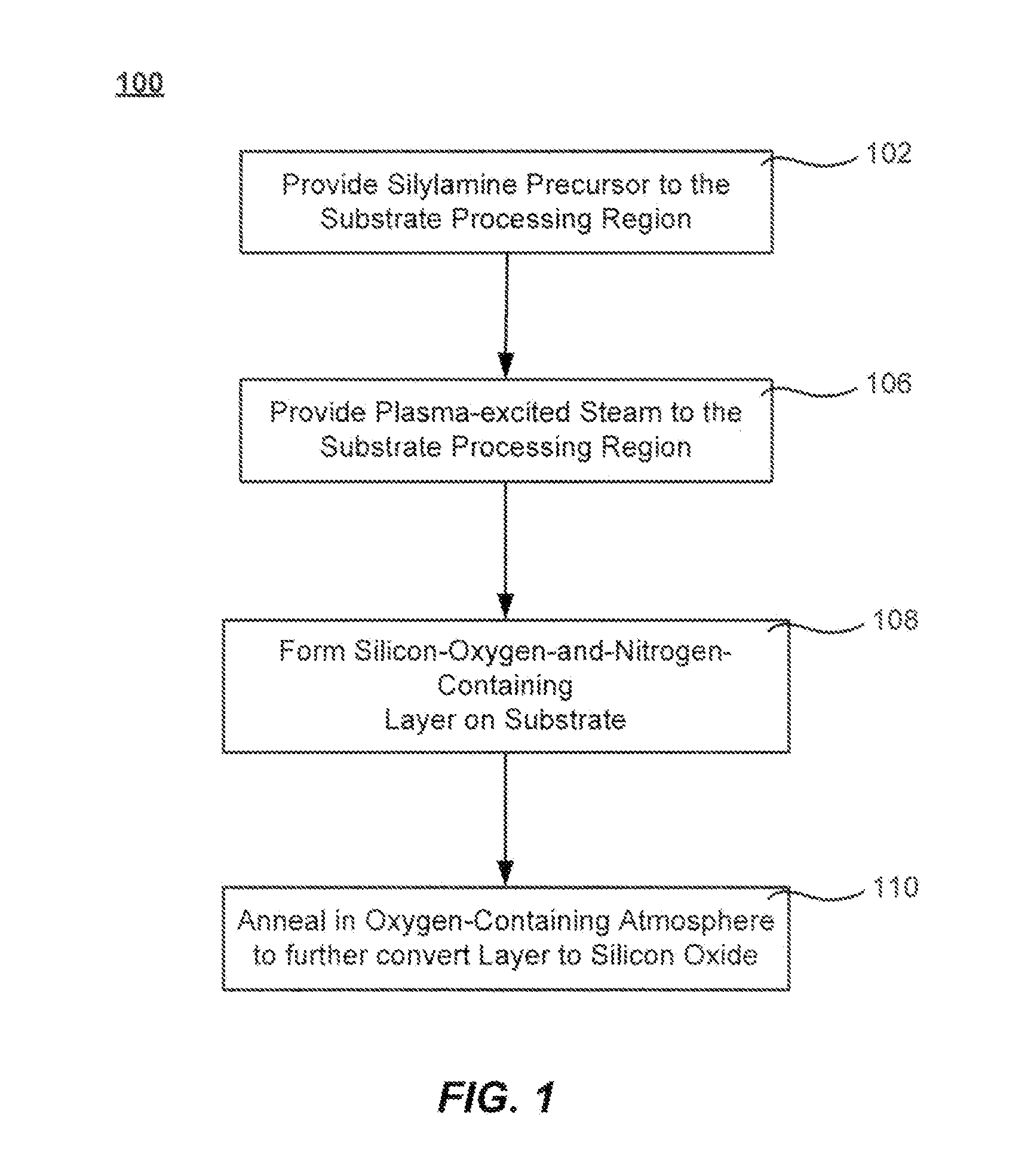
Methods for forming silicon containing films using silylamine moieties are disclosed. In some embodiments, silylamine moieties are employed to deposit silicon-nitrogen, silicon-oxygen, or silicon-nitrogen-oxygen materials at temperatures of less than 550° C. In some embodiments methods are practiced within process chambers adapted to contain a single substrate as well as within process chambers adapted to contain a plurality of substrates, where the silylamine moieties are conveyed to the chambers in across flow type manner.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC
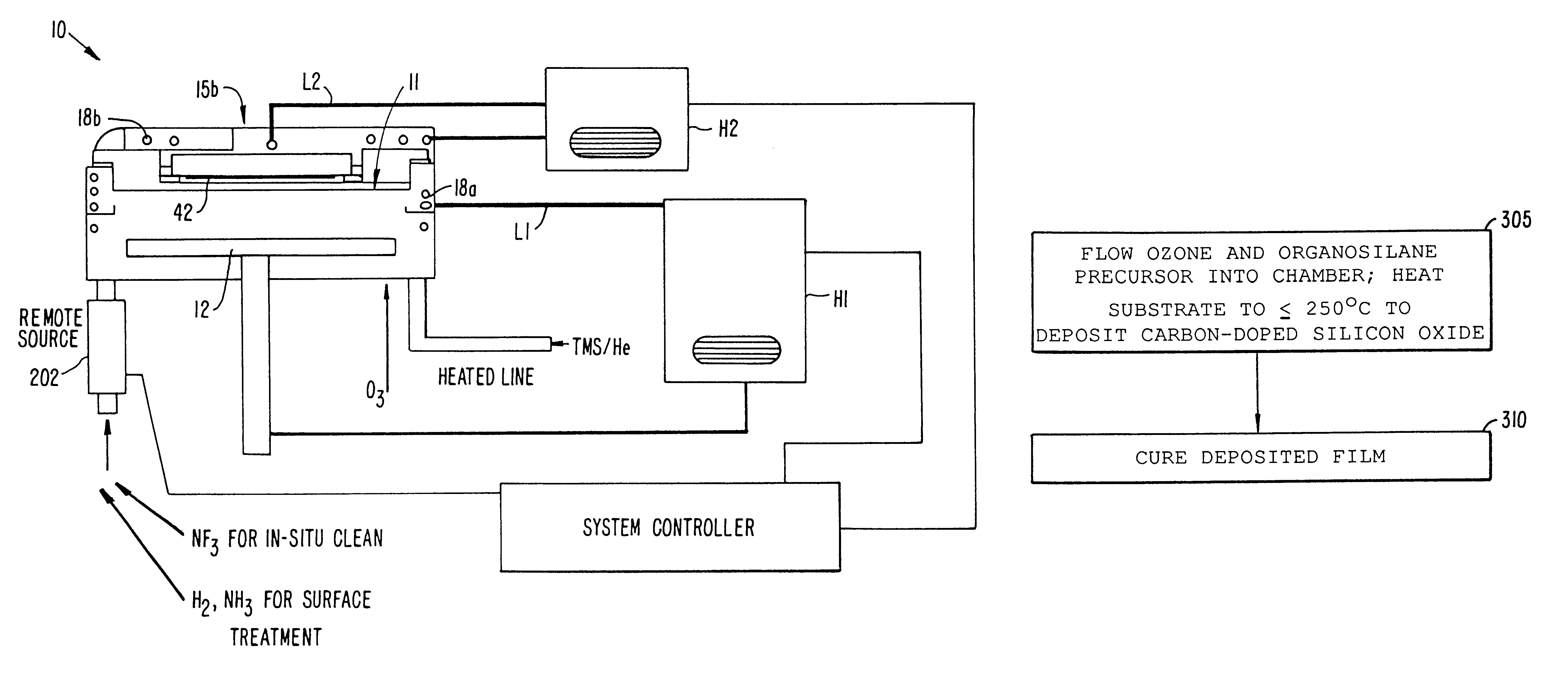
Post-deposition treatment to enhance properties of Si-O-C low K films
InactiveUS6486061B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxygenReducing atmosphere
A method for providing a dielectric film having enhanced adhesion and stability. The method includes a post deposition treatment that densifies the film in a reducing atmosphere to enhance stability if the film is to be cured ex-situ. The densification generally takes place in a reducing environment while heating the substrate. The densification treatment is particularly suitable for silicon-oxygen-carbon low dielectric constant films that have been deposited at low temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
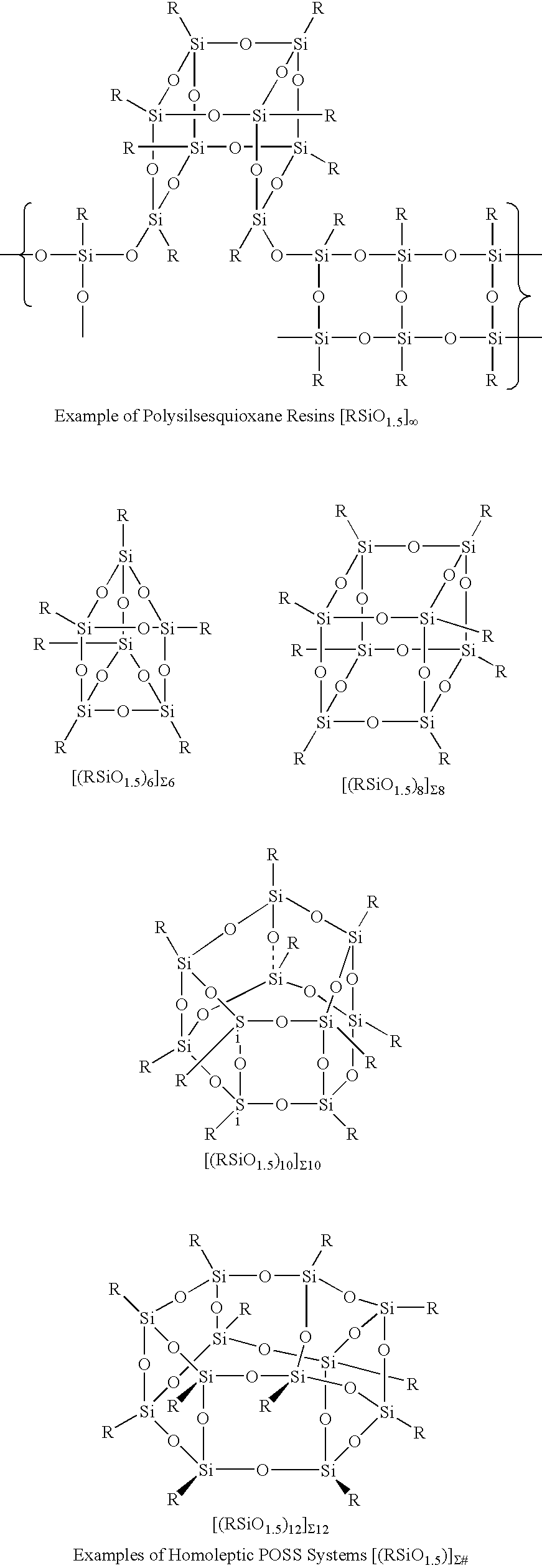
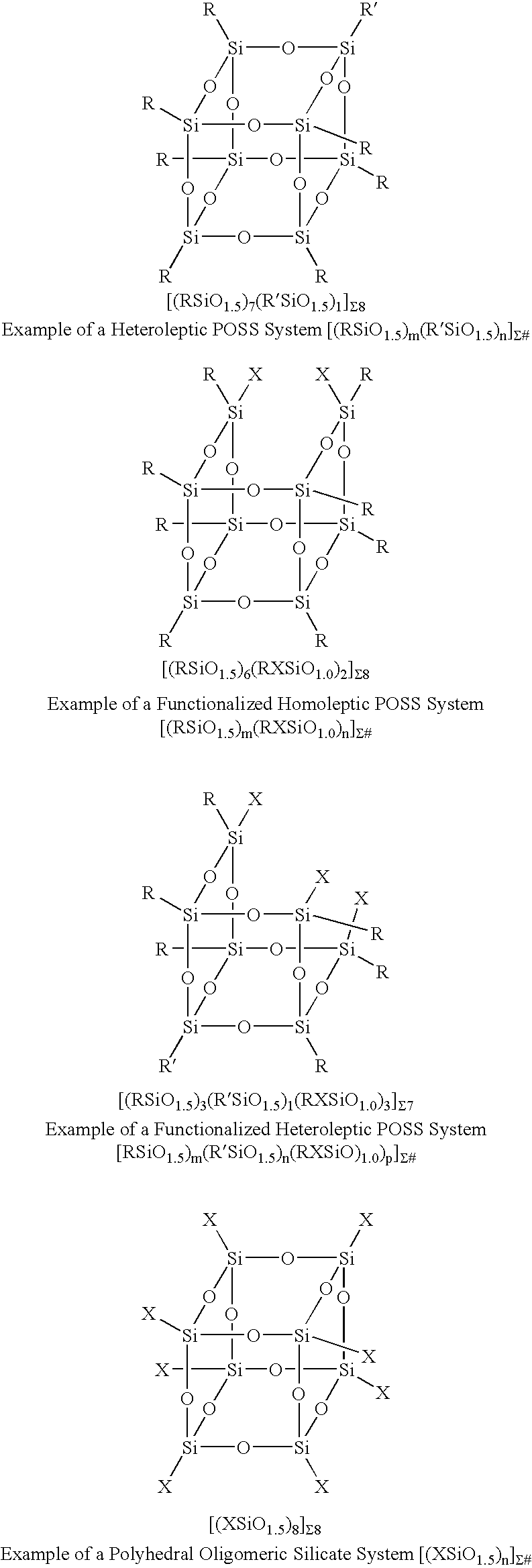
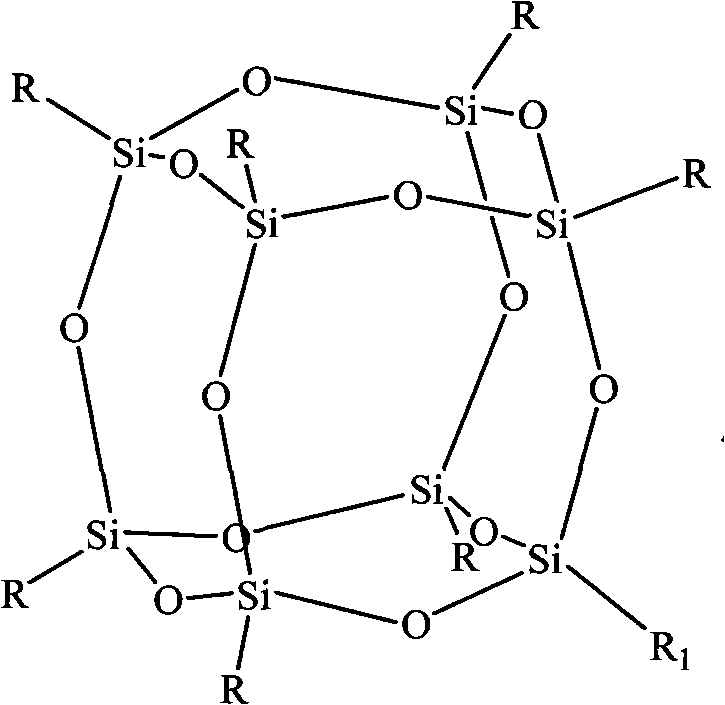
Process for the formation of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes
Three processes for the manufacture of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (POSS) which utilize the action of bases that are capable of either attacking silicon or any compound that can react with a protic solvent (e.g. ROH, H2O etc.) and generate hydroxide [OH]−, alkoxide [RO]−′, etc. The first process utilizes such bases to effectively redistribute the silicon-oxygen frameworks in polymeric silsesquioxanes [RSiO1.5]28 where ∞=1-1,000,000 or higher into POSS nanostructures of formulas [(RSiO1.5)nΣ#, homoleptic, [(RXSiO1.5)n]Σ#, functionalized homoleptic, [(RSiO1.5)m(R′SiO1.5)n]Σ#, heteroleptic, and {(RSiO1.5)m(RXSiO1.0)n}Σ#, functionalized heteroleptic nanostructures. The second process utilizes base to aid in the formation of POSS nanostructures of formulas [(RSiO1.5)n]Σ# homoleptic and [(RSiO1.5)m(R′SiO1.5)n]Σ# heteroleptic and [(RSiO1.5)m(RXSiO1.0)n]Σ# functionalized heteroleptic nanostructures from silanes RSiX3 and linear or cyclic silsesquioxanes of the formula RX2Si—(OSiRX)m—OSiRX2 where m=0-10, X=OH, Cl, Br, I, alkoxide OR, acetate OOCR, peroxide OOR, amine NR2, isocyanate NCO, and R. The third process utilizes base to selectively ring-open the silicon-oxygen-silicon (Si—O—Si) bonds in POSS structures to form POSS species with incompletely condensed nanostructures. These processes also afford stereochemical control over X. The three processes result in new POSS species that can undergo additional chemical manipulations to ultimately be converted into POSS-species suitable for polymerization, grafting, or other desirable chemical reactions.
Owner:HYBRID PLASTICS INC
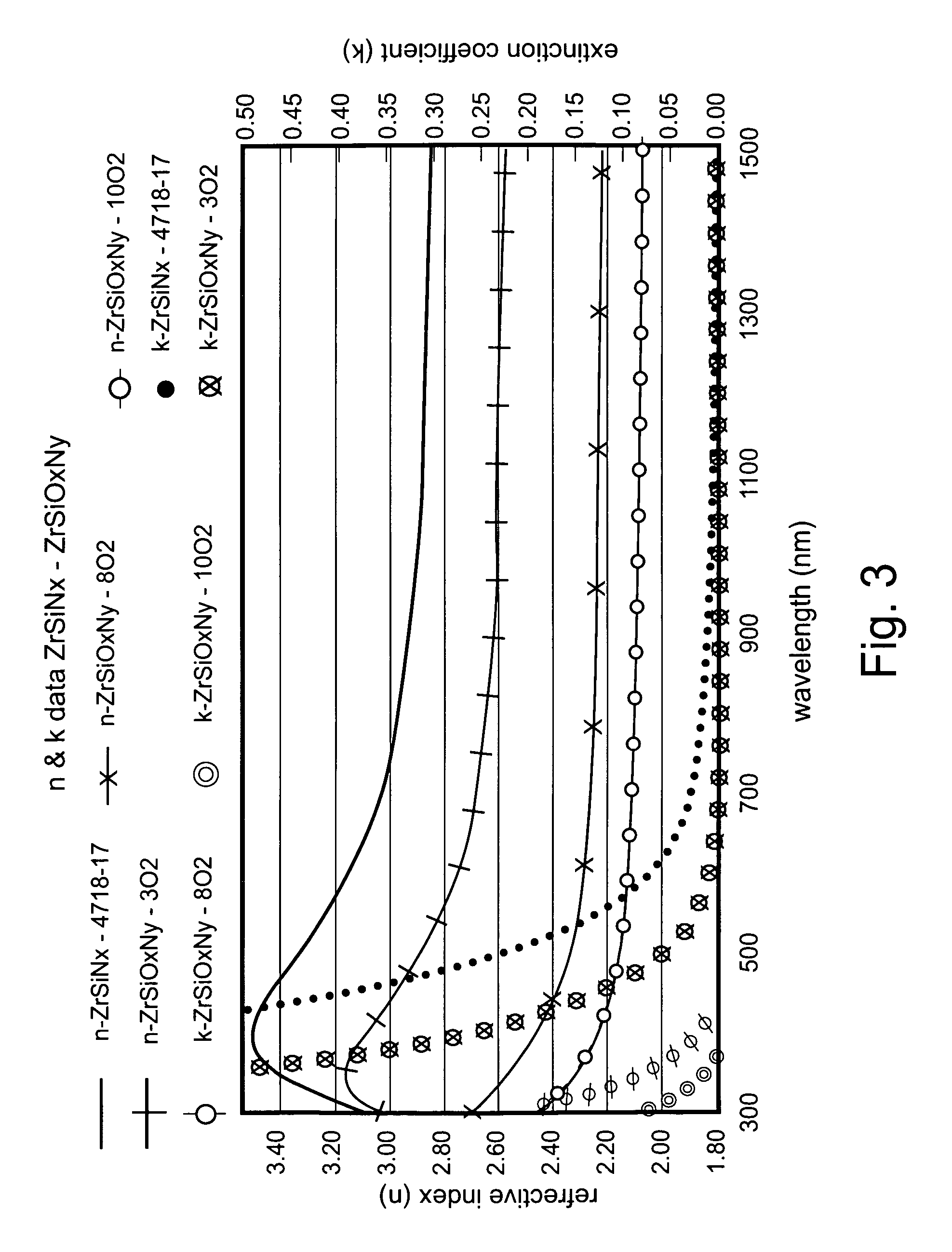
Heat treatable coated article with zirconium silicon oxynitride layer(s) and methods of making same
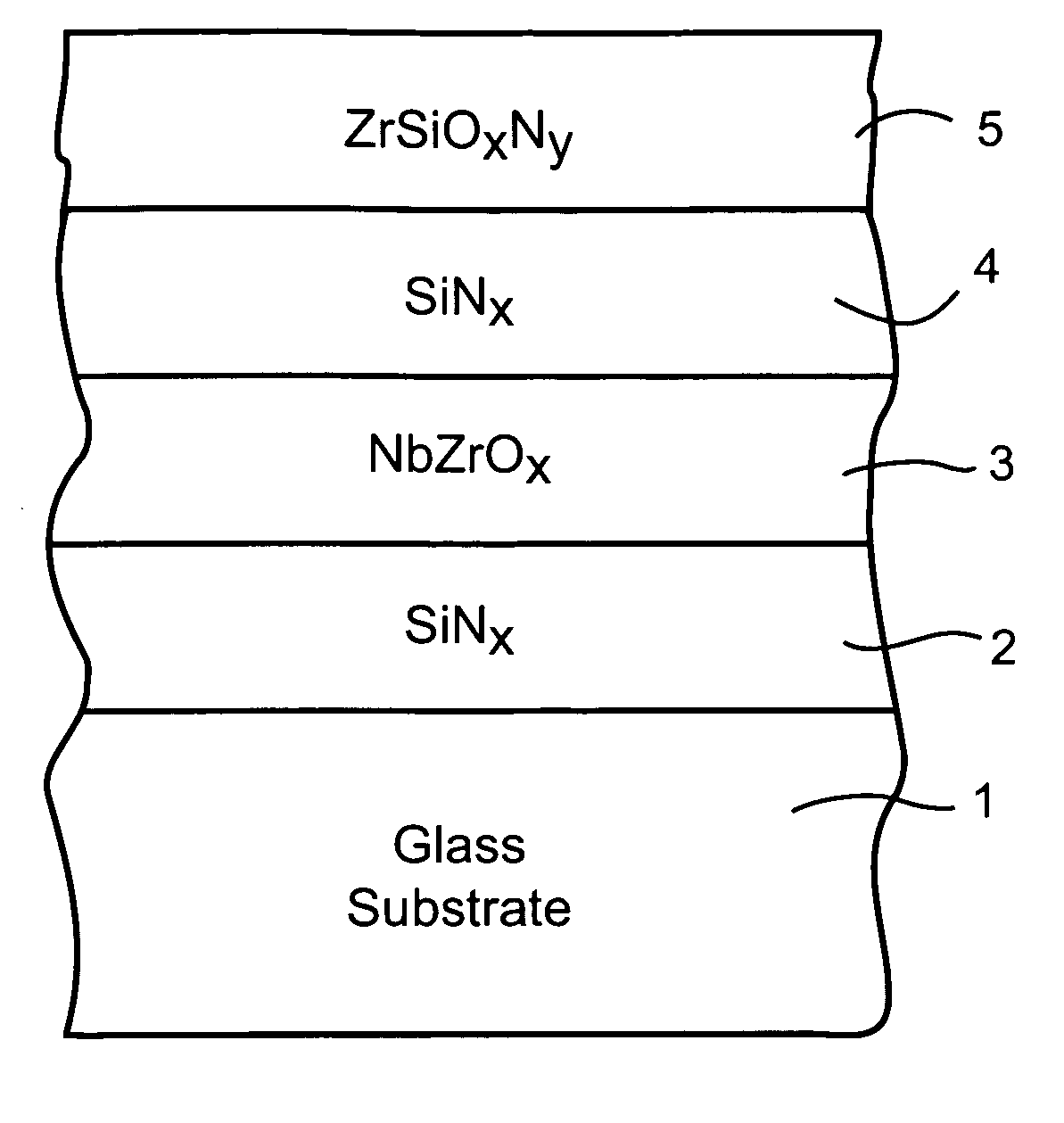
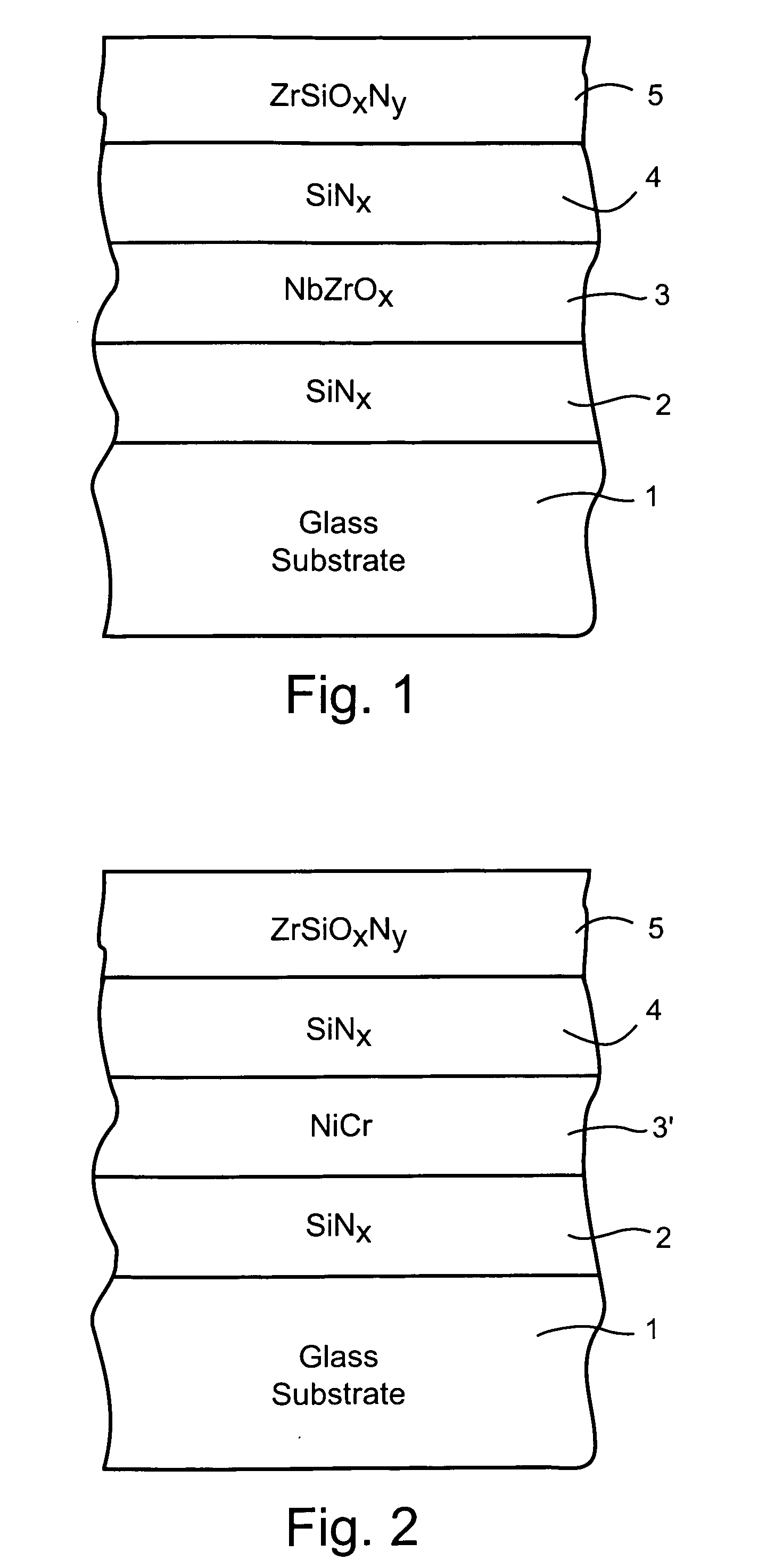
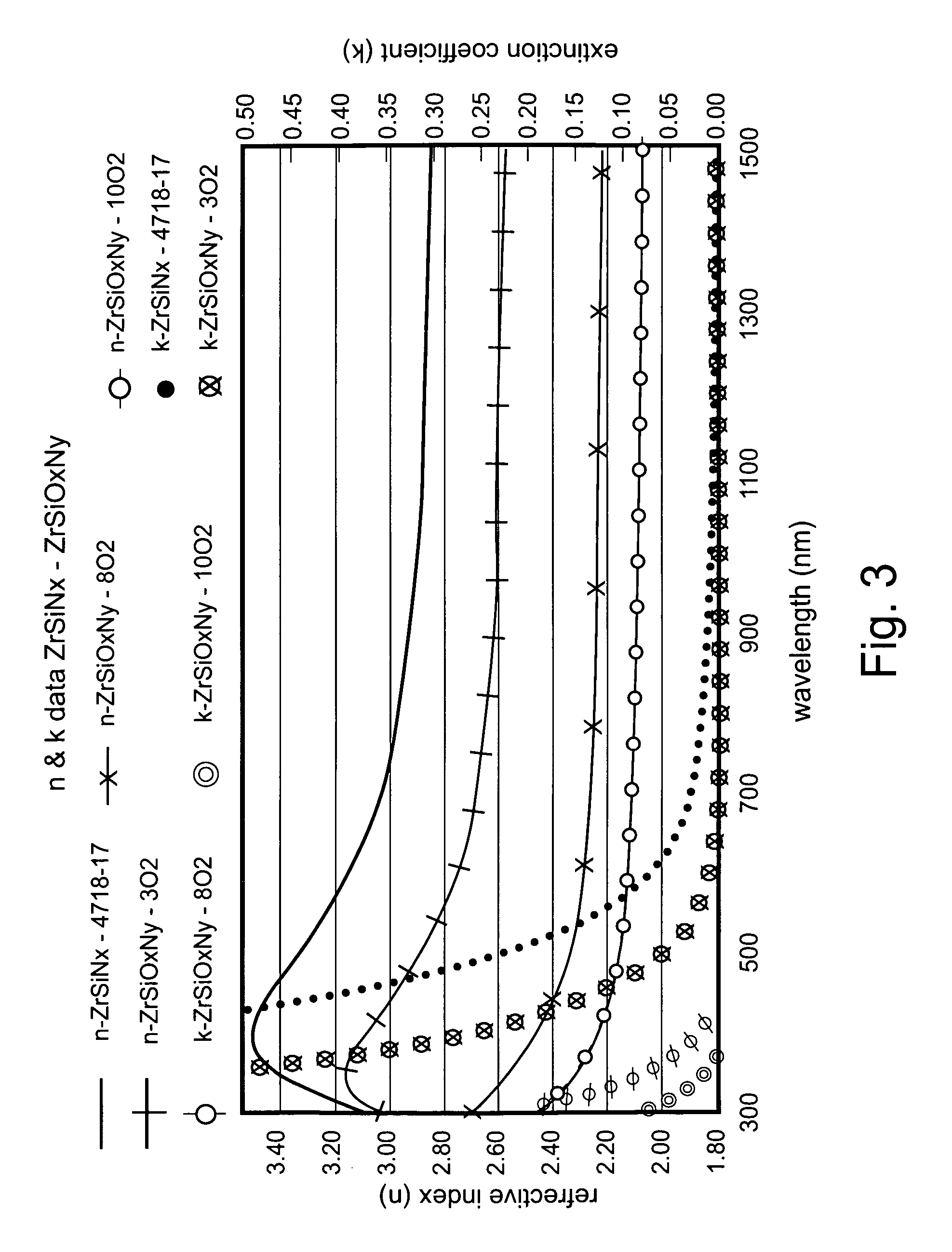
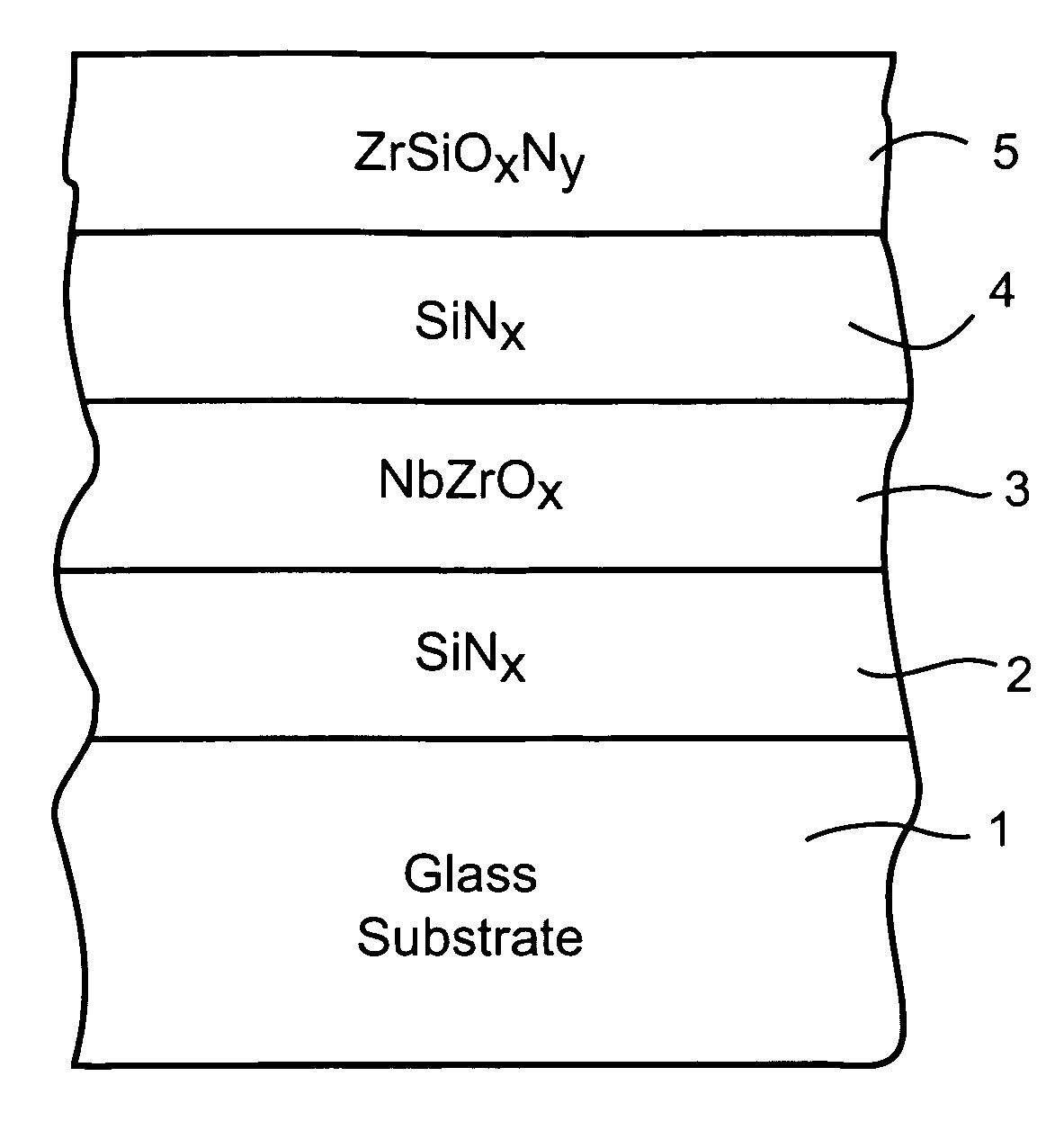
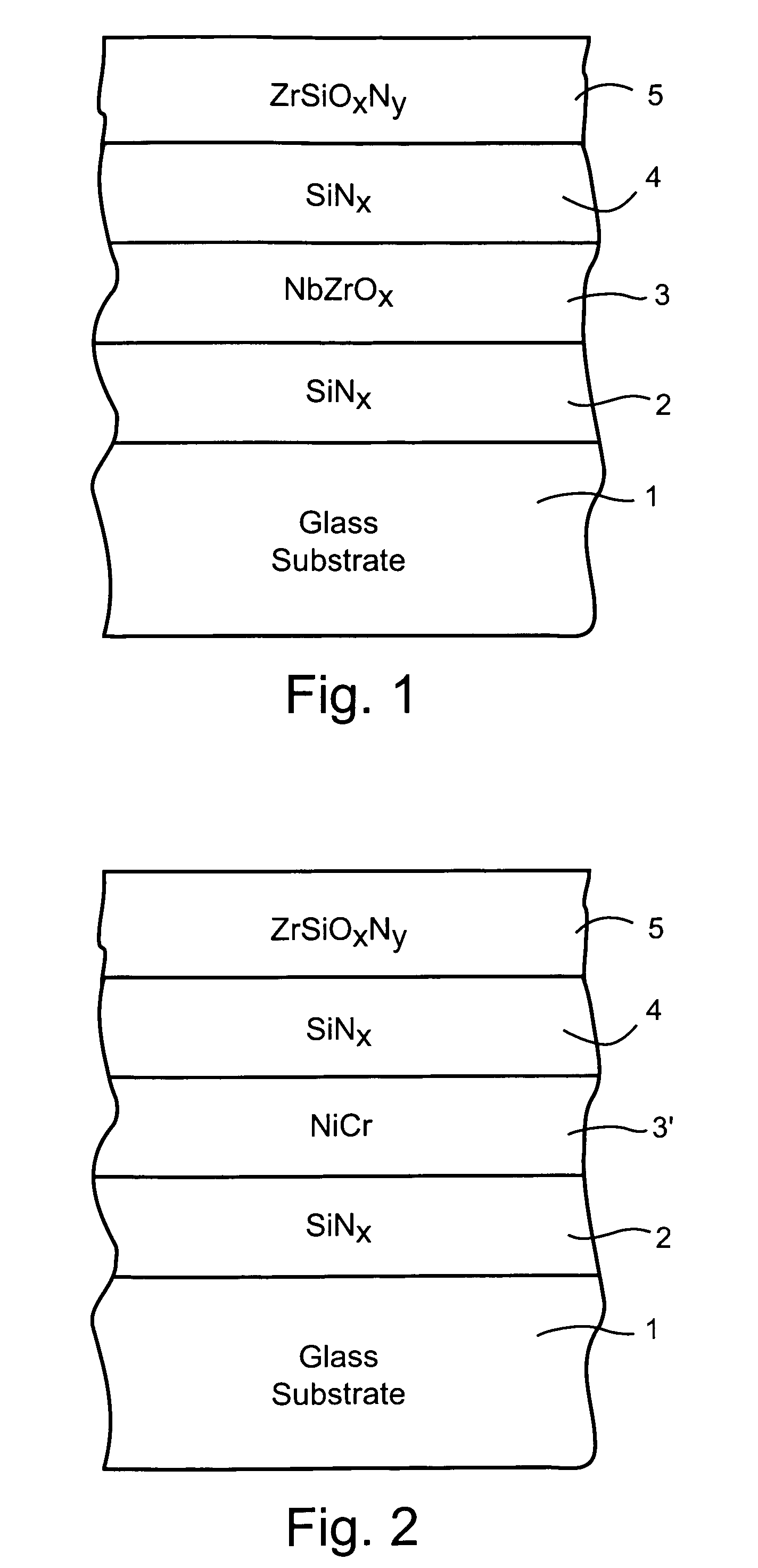
A coated article is provided so as to include a solar control coating having an infrared (IR) reflecting layer sandwiched between at least a pair of dielectric layers. The IR reflecting layer may be of or include NbZrOx, NbZr, NiCr, NiCrNx, or the like in certain embodiments of this invention. In particular, a zirconium silicon oxynitride (e.g., ZrSiOxNy) inclusive layer is provided which unexpectedly improves blocking (reflecting and / or absorption) of UV radiation in a manner which does not significantly degrade other optical properties of a coated article. Moreover, the ZrSiOxNy also has been found to improve (lower) the DeltaE* value upon heat treatment, thereby permitting a coated article when heat treated (HT) to more closely match its non-HT counterpart with respect to glass side reflective color after such HT.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC +1
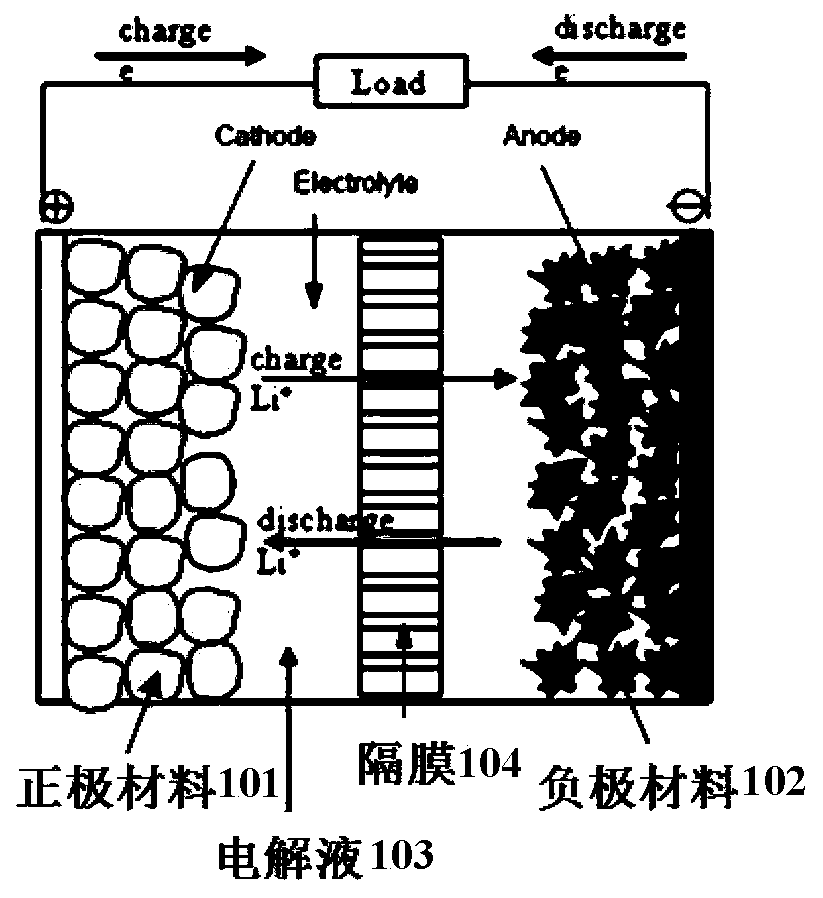
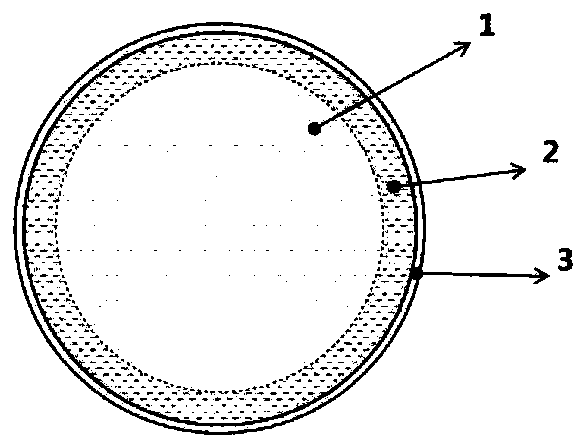
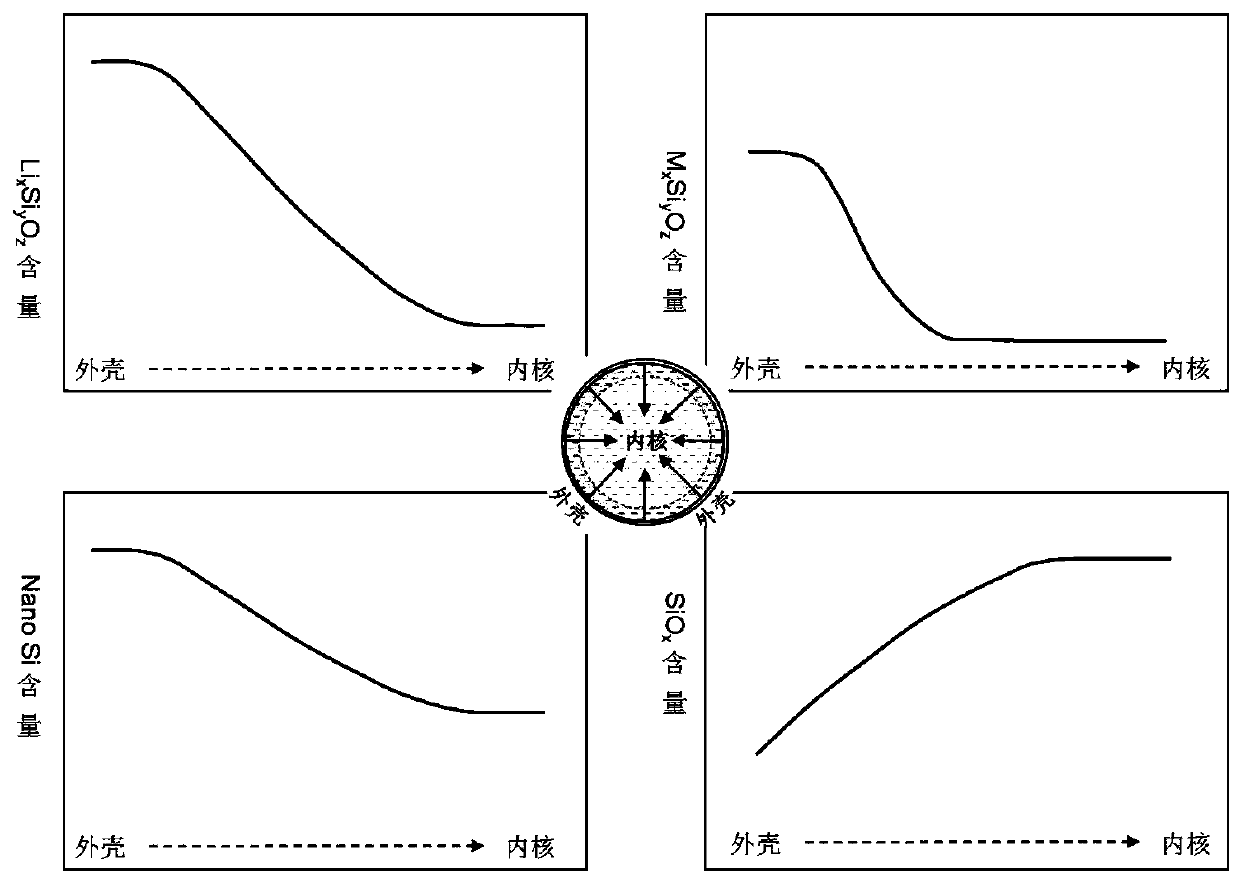
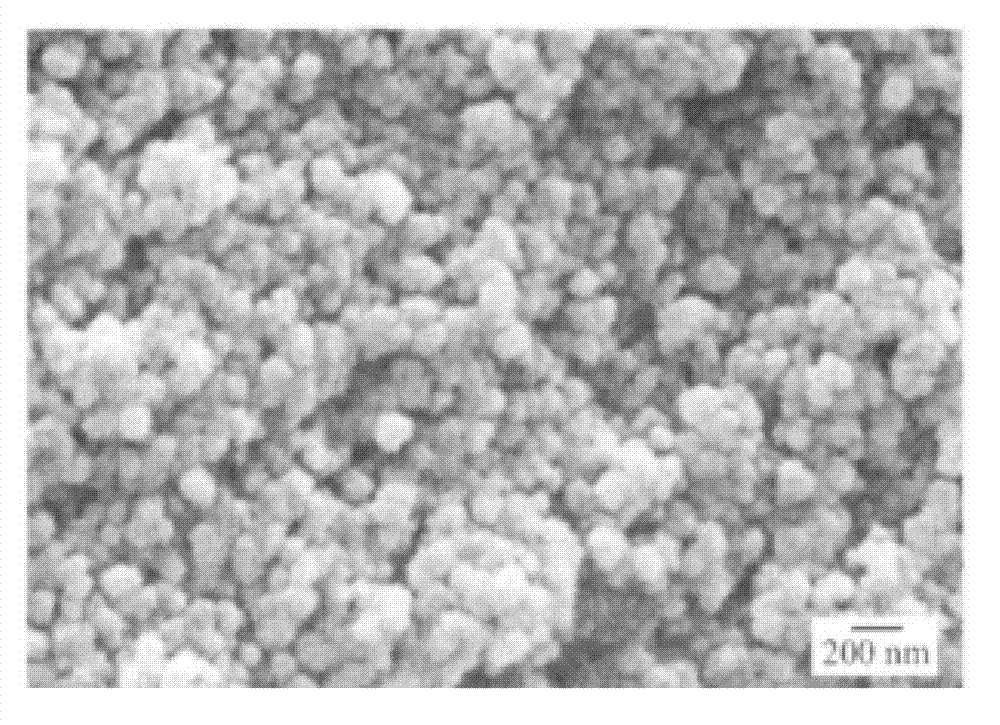
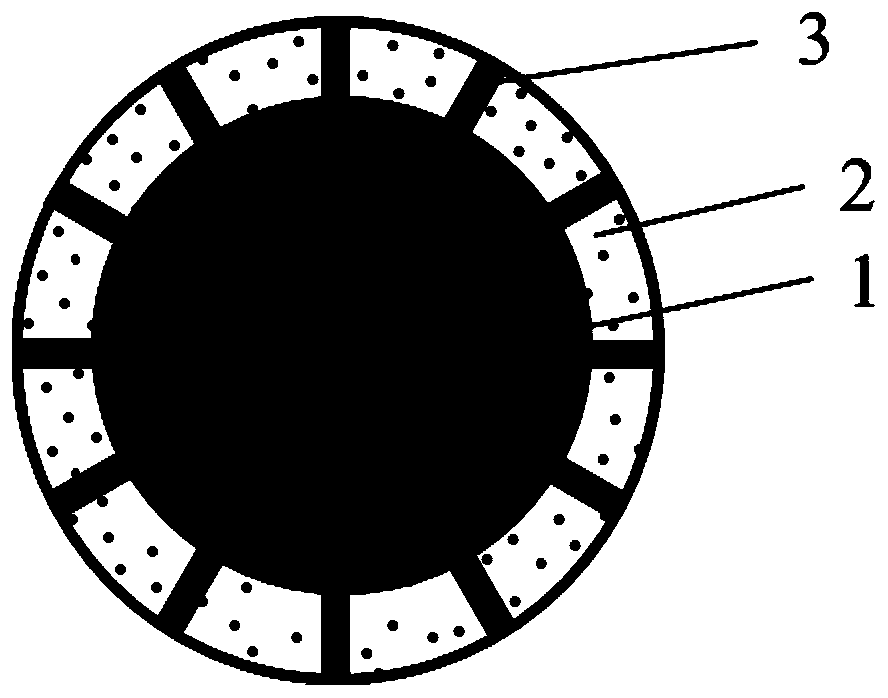
Silicon-oxygen composite negative electrode material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109755500AImprove electronic conductanceReduce lossCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsSilicon oxygenMetallurgy
The invention discloses a silicon-oxygen composite negative electrode material which is used for manufacturing a negative electrode of a lithium battery; the negative electrode material comprises an inner core, a coating layer and a middle layer, wherein the coating layer wraps the inner core, and the middle layer is positioned between the inner core and the coating layer, wherein the middle layercomprises non-lithium silicate, and the non-lithium silicate refers to non-lithium silicate, wherein the mass content of the non-lithium silicate in the middle layer is gradually decreased from the middle layer to the inner core. The decrementing comprises a gradient reduction from the middle layer to the inner core, and the gradient reduction refers to the fact that the mass-duty ratios on the circumference parts which have the same central distance from the inner core are the same, and when the distance from the center of the inner core is reduced, the mass-duty ratio is reduced step by step. The non-lithium silicate is generated in situ on the outer layer of the inner core, and has a non-water-soluble or non-alkaline or weakly alkaline compact structure, so that the dissolution of theinternal water-soluble lithium silicate can be effectively relieved; and the pH value of the ghost-eye composite negative electrode material can be lowered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Crosslink cyclo-siloxane compound with linear bridging group to form ultra low k dielectric
InactiveUS20030194495A1Pretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxygenAliphatic hydrocarbon
A method for depositing a low dielectric constant film having a dielectric constant of about 3.0 or less, preferably about 2.5 or less, is provided by using one or more cyclic organic precursors and one or more aliphatic precursors. In one aspect, a cyclic organosilicon compound, an aliphatic organosilicon, and an aliphatic hydrocarbon compound are reacted with an oxidizing gas at conditions sufficient to deposit a low dielectric constant film on the semiconductor substrate. The cyclic organosilicon compound includes at least one silicon-carbon bond. The aliphatic organosilicon compound includes a silicon-hydrogen bond or a silicon-oxygen bond.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Compound and preparation method thereof as well as negative electrode prepared by adopting compound and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN106356508AImprove consistencyImprove dispersion uniformityCell electrodesSecondary cellsElectrical batterySilicon oxygen
The invention relates to a compound and a preparation method thereof as well as a negative electrode prepared by adopting the compound and a lithium ion battery. The compound comprises silicon, silicon oxide SiOx (x is greater than 0 and is less than or equal to 2) and silicate, wherein positive ion elements of the silicate are reductant elements, and Si, O and the reductant elements in the compound are uniformly distributed. Reductants used in the compound are heated and insulated in the environment of negative pressure, so that SiO steam reacts with reductant steam in the form of a gas phase so as to condense to obtain the compound, and then the compound is further used as a raw material so as to prepare a modified silica negative electrode material. The negative electrode material is suitable for the lithium ion battery, the prepared lithium ion battery has high charge and discharge specific capacity and excellent first coulombic efficiency, the charge capacity is 1447 mAh / g or above, the discharge capacity is 1213 mAh / g or above, and the first coulombic efficiency is 83.8% or above.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
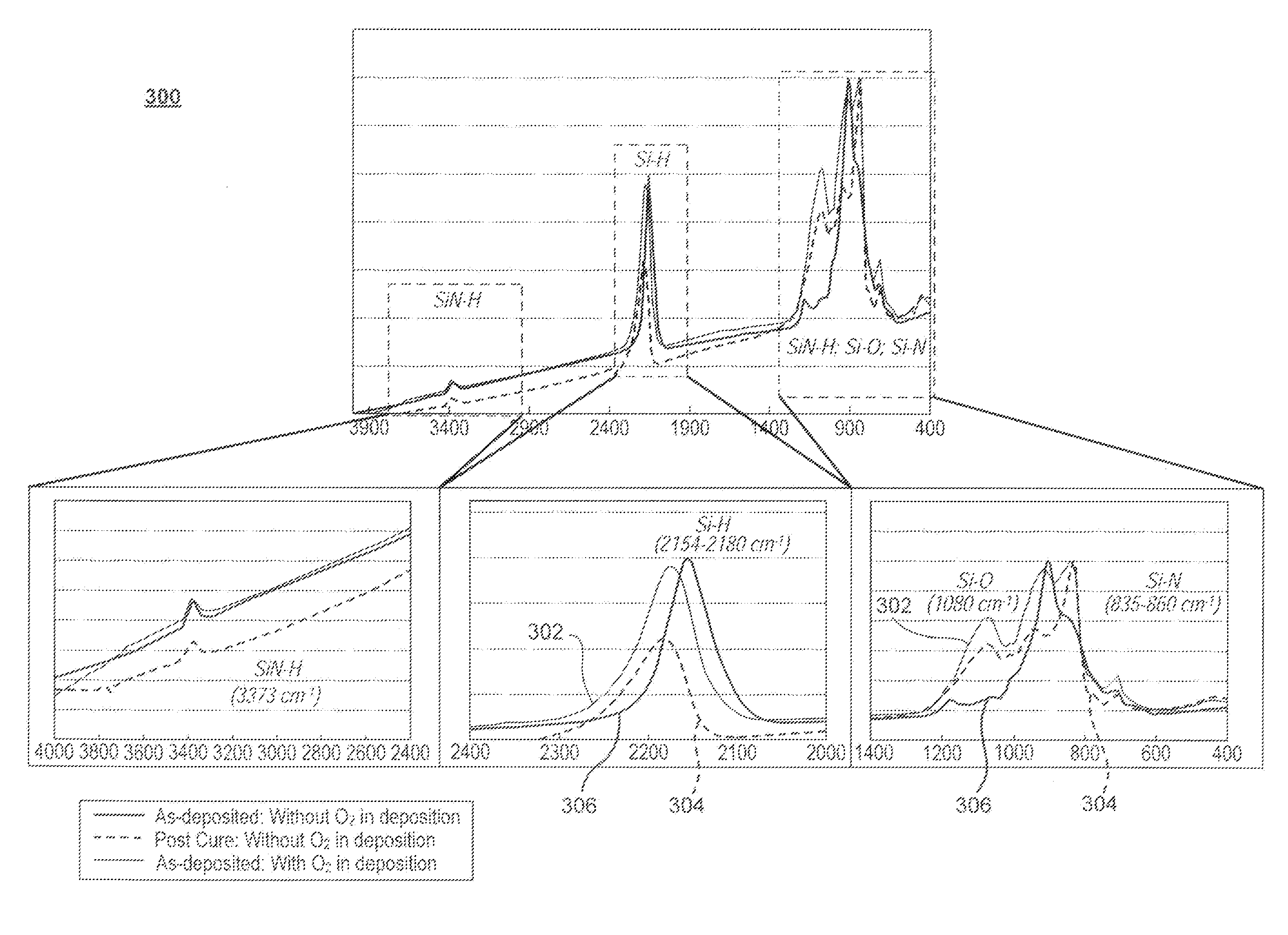
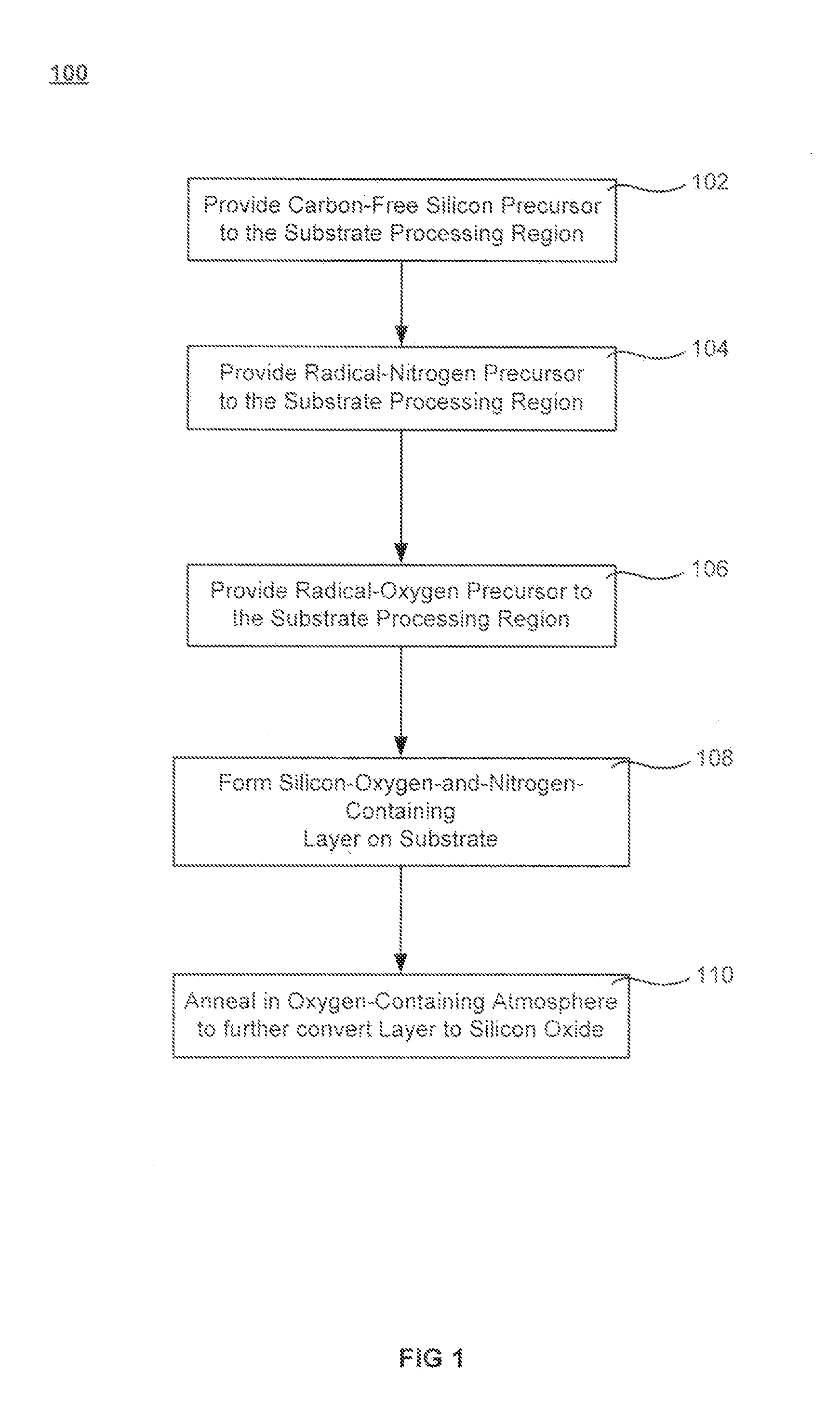
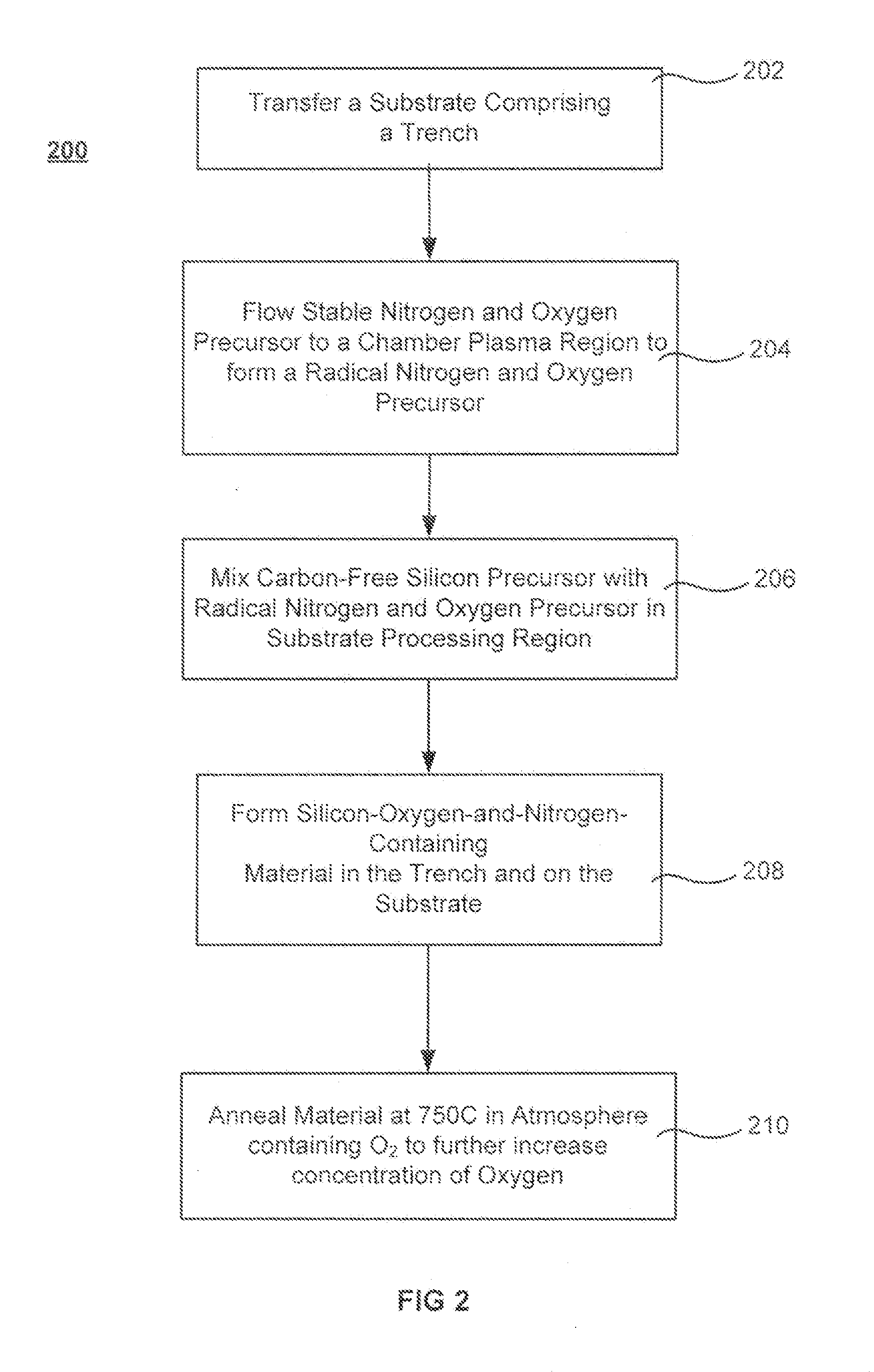
Oxygen-doping for non-carbon radical-component CVD films
Methods of forming silicon oxide layers are described. The methods include the steps of concurrently combining both a radical precursor and a radical-oxygen precursor with a carbon-free silicon-containing precursor. One of the radical precursor and the silicon-containing precursor contain nitrogen. The methods result in depositing a silicon-oxygen-and-nitrogen-containing layer on a substrate. The oxygen content of the silicon-oxygen-and-nitrogen-containing layer is then increased to form a silicon oxide layer which may contain very little nitrogen. The radical-oxygen precursor and the radical precursor may be produced in separate plasmas or the same plasma. The increase in oxygen content may be brought about by annealing the layer in the presence of an oxygen-containing atmosphere and the density of the film may be increased further by raising the temperature even higher in an inert environment.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Preparation method capable of realizing chemical blending of modified nano silicon dioxide particles in acrylate monomer
A preparation method capable of realizing chemical blending of modified nano silicon dioxide particles in an acrylate monomer relates to the field of the application of uniform dispersity of acryloyl oxygen radical contained silane couplint agent modified nano silicon dioxide particles in the acrylate monomer and the application of photocuring products in coating material. According to the method, the modified silicon dioxide is formed in a way that alkoxy on silane couplint agent and hydroxy on the surfaces of the nano silicon dioxide particles are reacted to form firm silicon-oxygen-silicon bonds; the double-bond silane couplint agent modified nano silicon dioxide is mixed in the monomer; during the photopolymerization process of the product, the acryloyl oxygen radical contained silane couplint agent modified nano silicon dioxide and the monomer are polymerized through the chemical bonds, so as to allow the nano silicon dioxide to be more uniformly distributed in the polymer; and the acryloyl oxygen radical contained silane couplint agent modified nano silicon dioxide particles are subjected to laser size analysis and transmission electron microscopy. The purpose of improving the application of the nano silicon dioxide composite acrylate monomer in the coating material field is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for treatment of sea red tides and fresh water bloom
InactiveCN1417136AReduce concentrationImprove flocculation efficiencySedimentation separationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processOctahedronSilicon oxygen
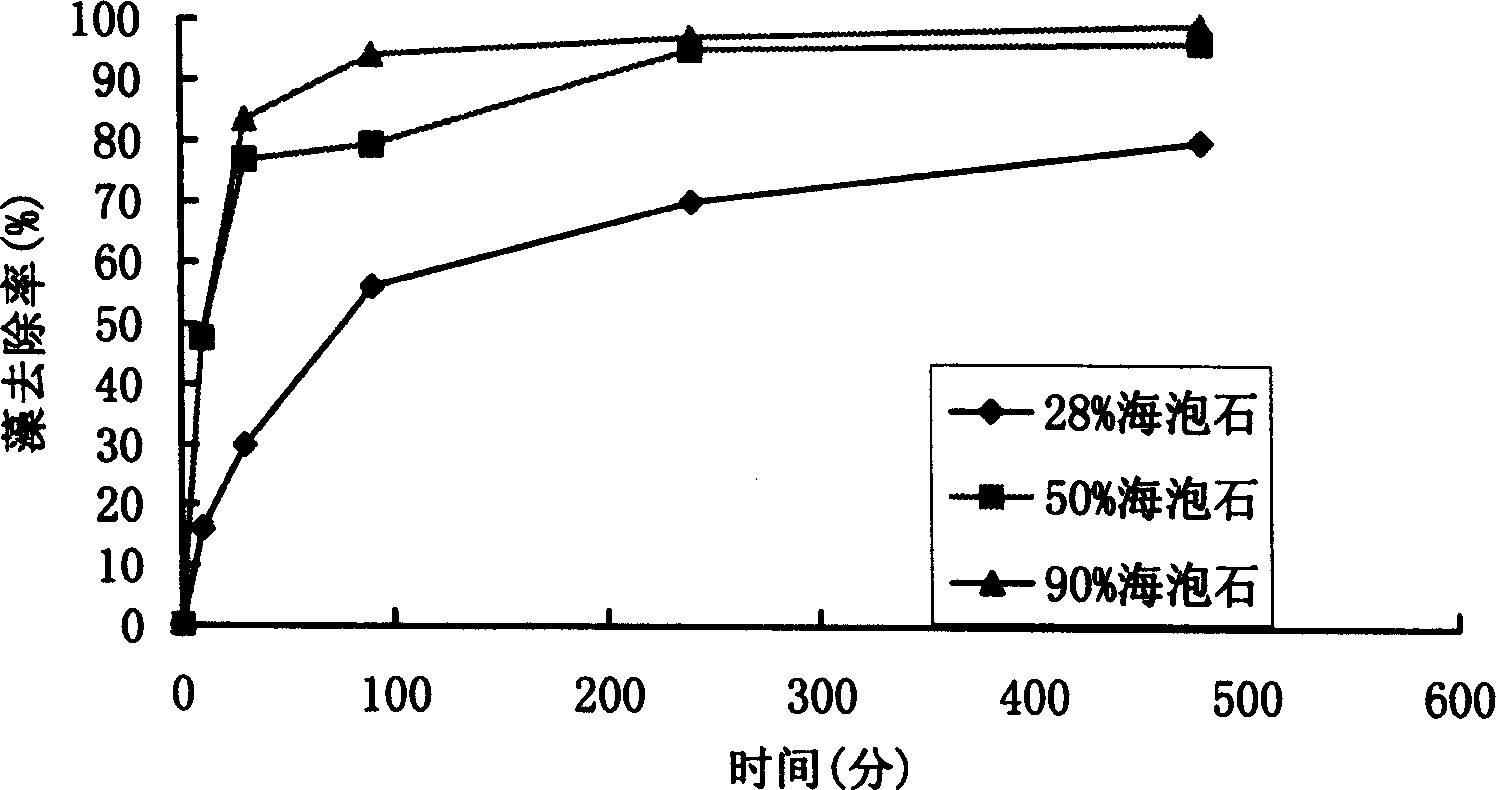
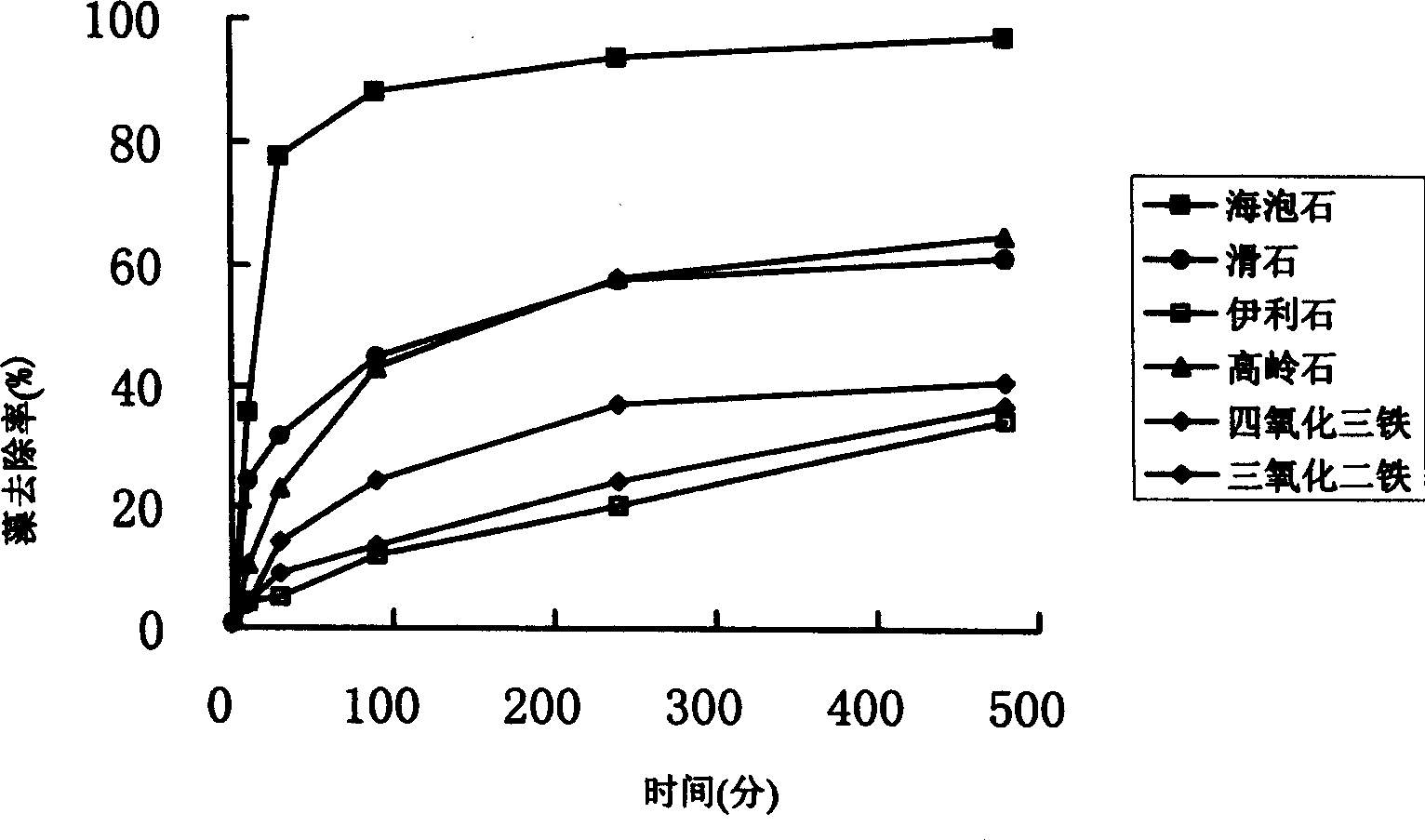
The present invention relates to a method of tackling sea red tides and fresh water bloom using clay as algae flocculant. The effective component of the flocculant is hydrated magnesio-silicate salt in the laminated structure including upper and lower silicon-oxygen tetrahedron layers and sandwiched magnesium-oxygen octahedron layer. The hydrated magnesio-silicate salt is easy to prepare, low in cost and high in algae flocculating elimination effect.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radiation-curable composition and method for manufacturing cured-product patterns therefrom
InactiveUS6096483AHighly radiation curabilityHigh sensitivityImpression capsOrganic chemistrySilicon oxygenUltraviolet lights
The present invention provides a curable composition which comprises (A) a base-generating substance which generates a base when exposed to the action of ultraviolet light, (B) a siloxane polymer which has silicon-hydrogen bonds (Si-H) capable of reacting with hydroxy groups under the effect of the base to form silicon-oxygen bonds (Si-O) and hydrogen molecules (H2), and (C) an acid substance. This composition is cured by irradiation with ultraviolet light. During this ultraviolet irradiation, a mask is placed between a coating film of the composition and the radiation source, and the uncured portions of the composition are dissolved and removed so that a pattern is formed. The residual portions are then heated to produce a pattern-cured product.
Owner:DOW CORNING ASIA
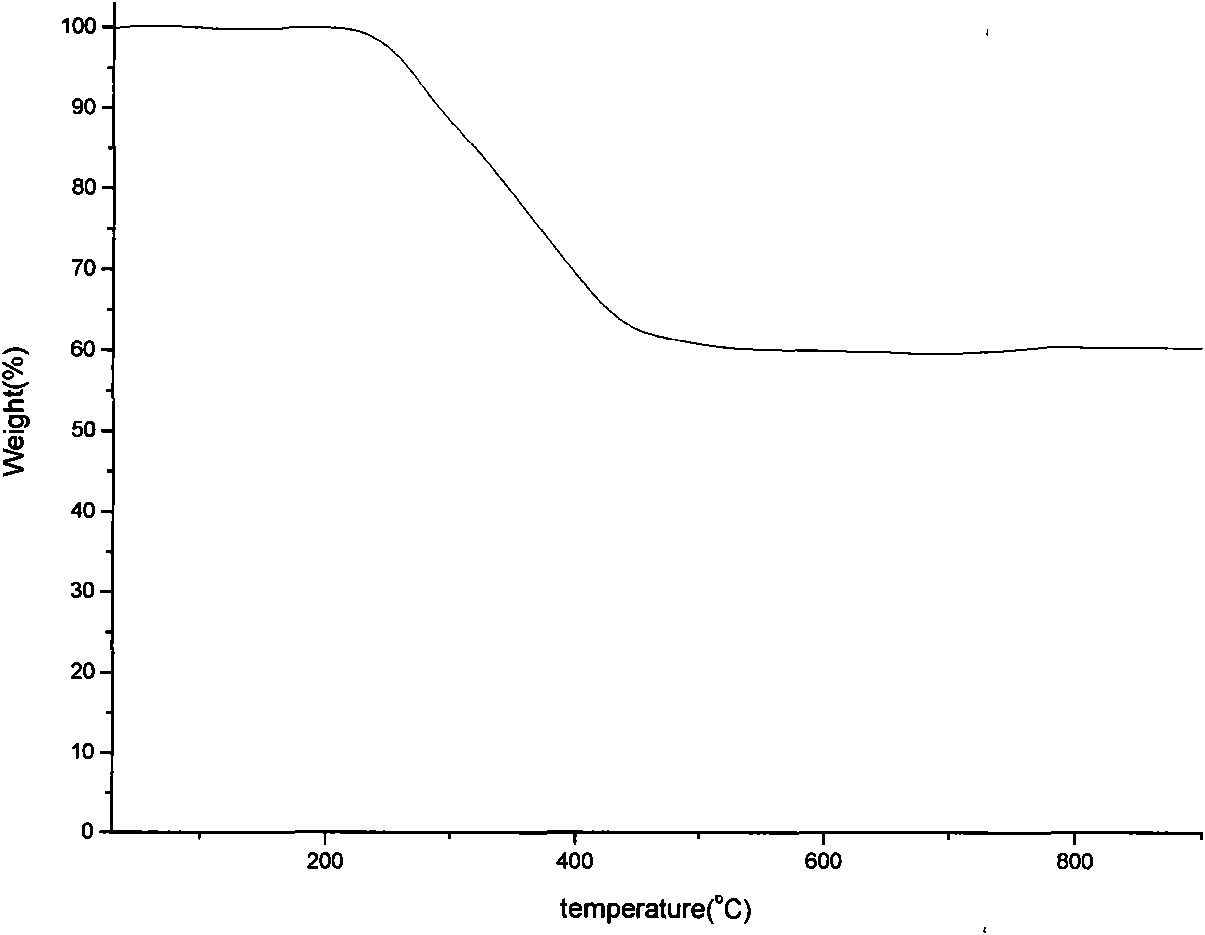
Preparation method of silicon dioxide aerogel
The invention provides a preparation method of a silicon dioxide aerogel, which comprises the following steps: regulating the pH value of a silicasol to 4-10 with reducing acid, adding ethanol, heating, and keeping the temperature to obtain a wet gel; mixing the wet gel with ethyl orthosilicate and ethanol to carry out aging; and finally, mixing with a drying-control chemical additive, and drying to obtain the silicon dioxide aerogel. In the aging process, the active hydroxy groups and ethyl orthosilicate on the wet gel surface and the region with weak network skeleton structure react to reinforce the silicon-oxygen bridge bond and enhance the networking degree and strength of the gel skeleton, thereby reducing the shrinkage and cracking phenomena in the drying process. Atoms with large electronegativity and small radius in the drying-control chemical additive and SiOH on the colloidal particle surface form a hydrogen bond, thereby generating a wide shielding network on the periphery; polycondensation is also generated in the system under the action of the hydrogen bond, thereby reducing the polycondensation speed; and many branched chains are increased in the skeleton network structure formation process, thereby promoting the formation of large and uniform nanopores.
Owner:BEIJING BOTIANZIRUI TECH CO LTD
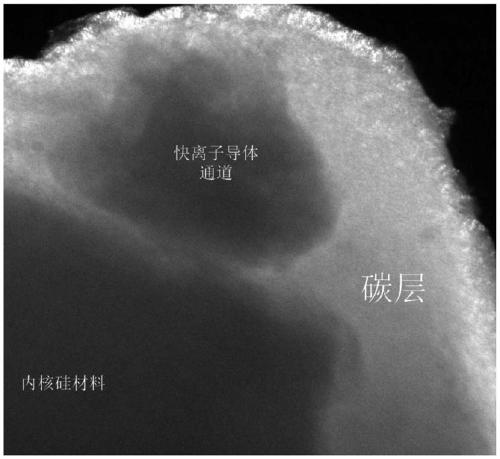
High-conductivity silicon-oxygen negative electrode material and application thereof
PendingCN111048756AEasy transferIncrease capacityCell electrodesSecondary cellsSilicon oxygenHigh conductivity
The invention provides a high-conductivity silicon-oxygen negative electrode material which comprises a silicon-based inner core and a coating layer formed on a surface of the silicon-based inner core. The coating layer comprises carbon and a fast ion conductor, and the fast ion conductor forms a complete ion transmission channel on the coating layer, is directly connected with the silicon-based inner core and extends to the surface of the coating layer. The fast ion conductor forms the complete ion channel in the coating layer so that the silicon-oxygen negative electrode material can give consideration to both electron conductivity and ion conductivity, meanwhile, an SEI film is stabilized, and a capacity and electrochemical performance of the material are effectively improved.
Owner:LANXI ZHIDE ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Inner surface coating technique of medicinal glass bottle
The invention relates to an inner surface coating technique of medicinal glass bottle, comprising the following steps: taking organosiloxane to prepare 2 to 10 wt% of dispersion solution by adding water; coating the solution to the inner surface of the medicinal glass bottle; then obtaining the finished product by heating and curing. The invention can connect a polymer film with a silicon-oxytetrahedron in the glass by dint of a common silicon-oxygen bond when the polymer film material is coated to the inner surface of the glass bottle; since the hydroxyl has certain orienting effect, a layer of compact polyorganosiloxane hydrophobic film in the inner surface of the glass bottle.
Owner:肖特药品包装(浙江)有限公司
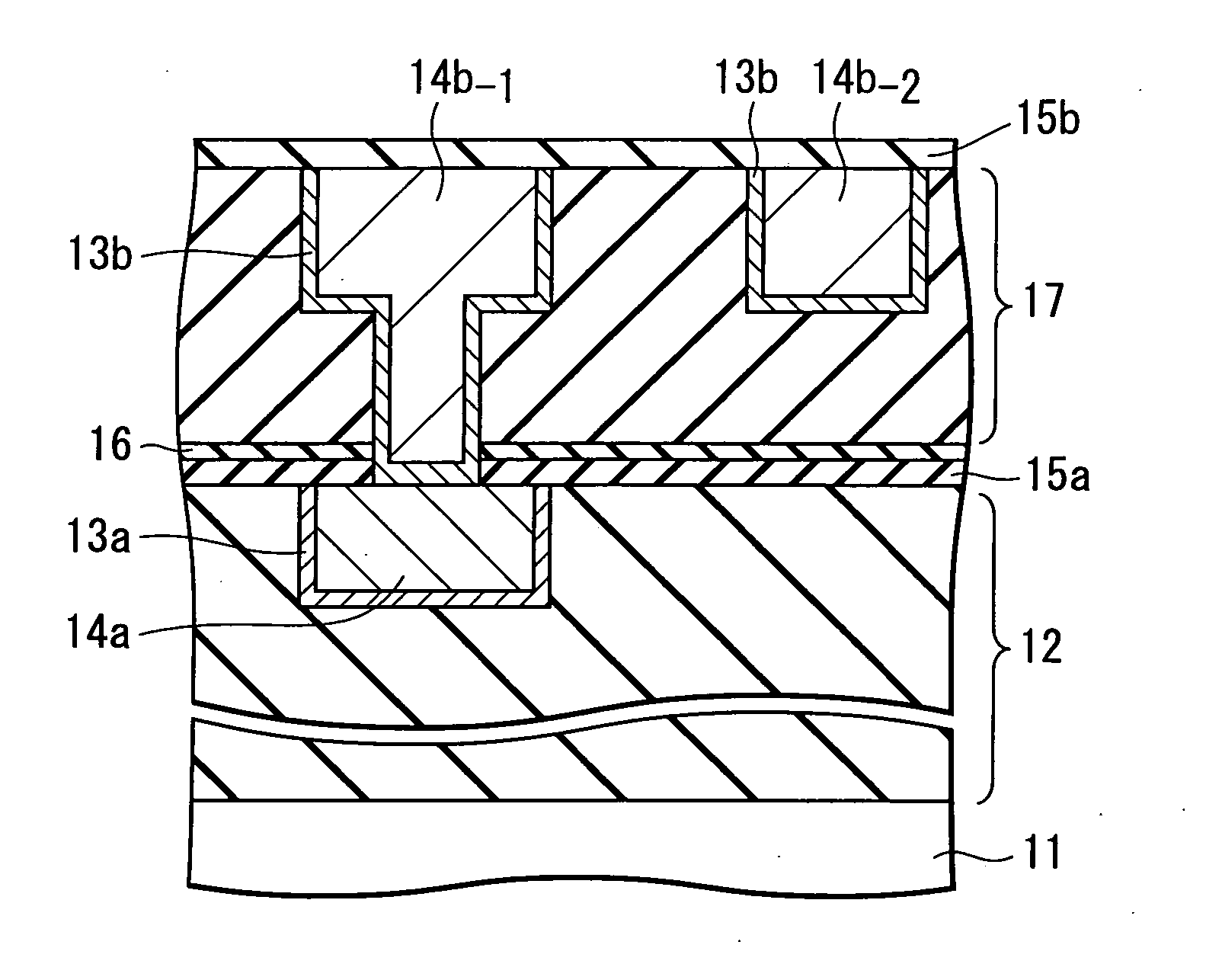
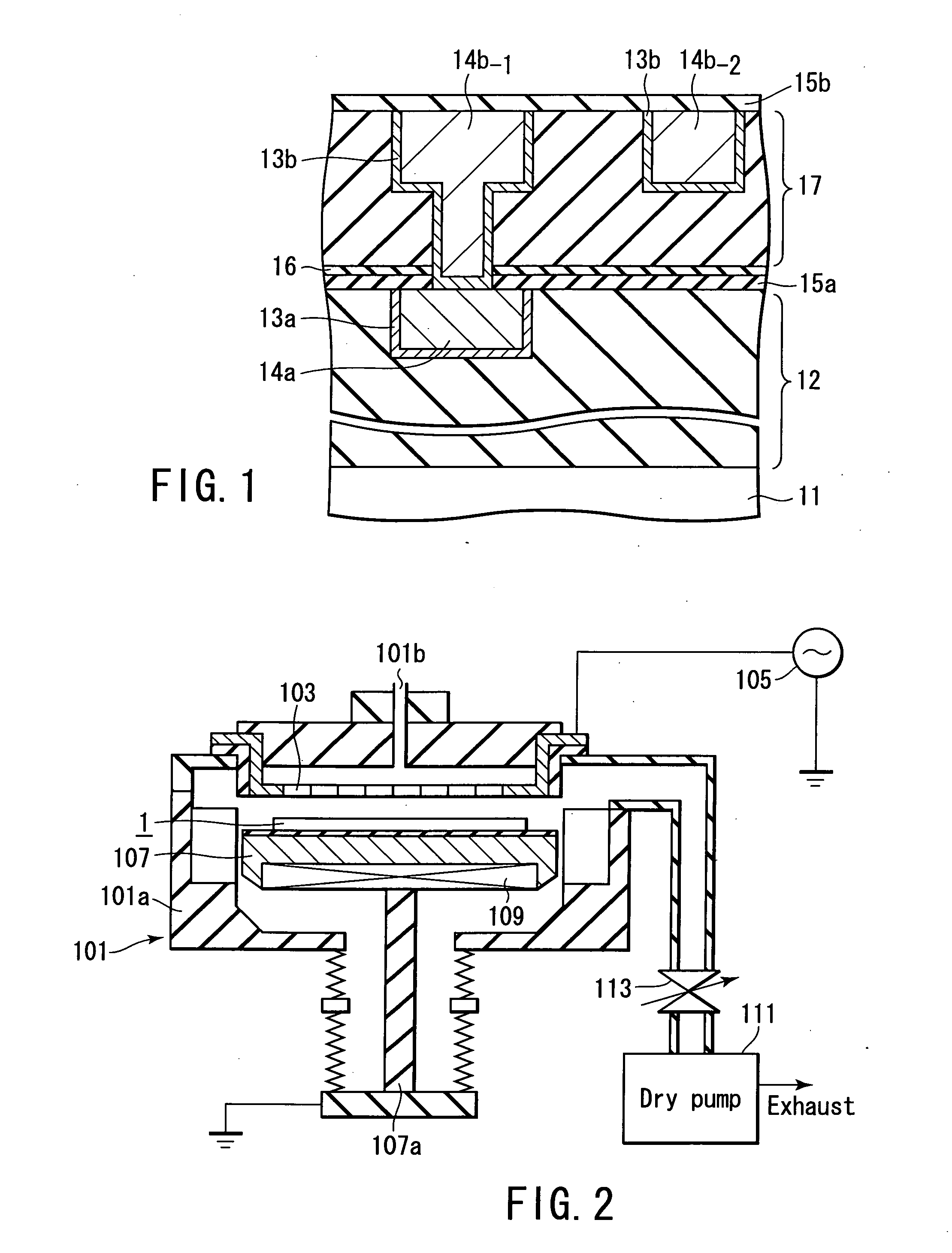
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050023691A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSilicon oxygen
A semiconductor device includes a metal wiring provided on a semiconductor substrate. The device further includes an anti-metal diffusion film formed on the metal wiring, a buffer layer which is formed on the anti-metal diffusion film and includes at least a silicon-methyl radical bond and a silicon-oxygen bond, and a low-dielectric constant film layer which is formed on the buffer layer and includes at least the silicon-methyl radical bond and the silicon-oxygen bond, wherein the silicon-methyl radical bonding density of the buffer layer is less than the silicon-methyl radical bonding density of the low-dielectric constant film layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
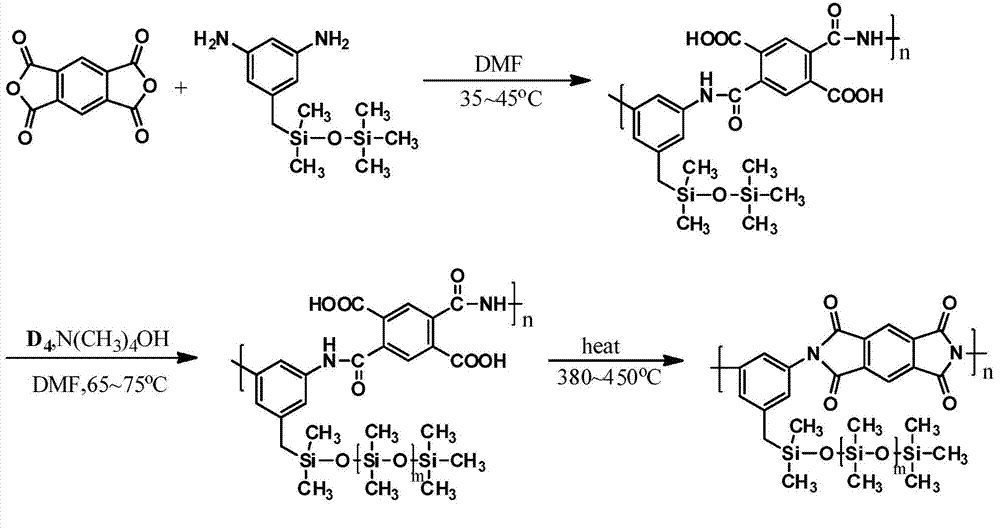
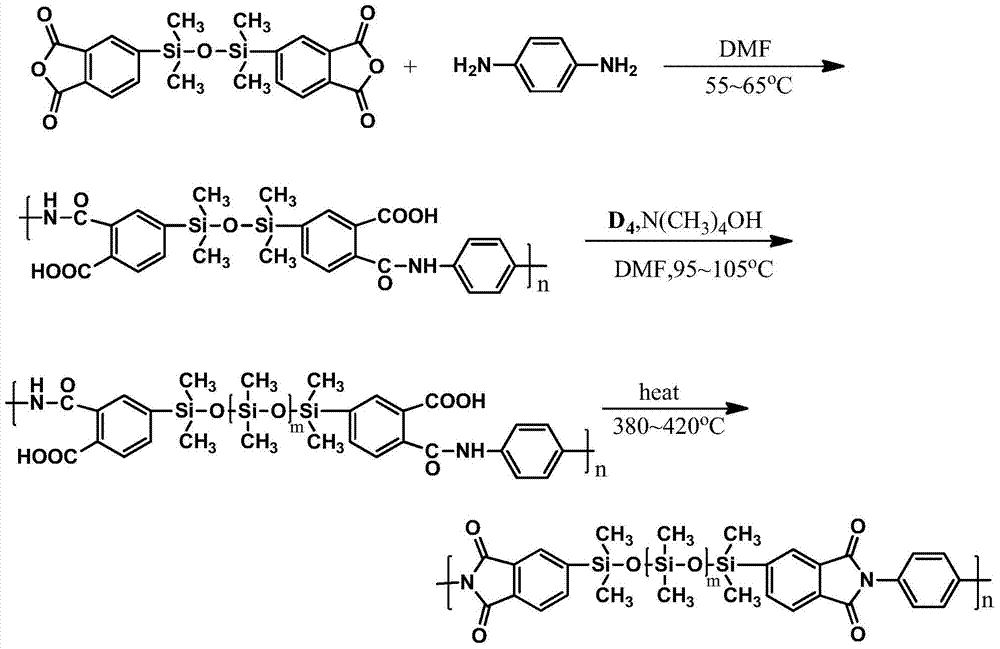
Novel electronic-grade polyimide film with low linear expansion coefficient and production method thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electronic-grade polyimide film with low linear expansion coefficient. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the step-by-step condensation polymerization technology is used for obtaining polybasic block copolymerization polyamide acid glue solutions comprising one or more bar-shaped rigid chain sections containing para-benzene or biphenyl and one or more soft chain sections containing ether bonds or silicon-oxygen bonds and the like; (2) polyamide acid comprising one or more bar-shaped rigid chain structures containing para-benzene or biphenyl and polyamide acid comprising one or more soft chain structures containing ether bonds or silicon-oxygen bonds are independently compounded, and the two or more polyamide acid glue solutions different in rigidity and softness are mixed and compounded; (3) the compounded glue solutions are subjected to filtration, vacuum defoamation, casting filming, bidirectional stretching, chemical amidization or thermal amidization, infrared complete amidization, high-temperature thermal forming processing, corona processing and a reeling process, and therefore the electronic-grade polyimide film with the thickness being 7.5-125 micrometers, the linear expansion coefficient being 5-18ppm / DEG C, and good physical mechanical performance is obtained.
Owner:宏威高新材料有限公司 +1
Silicon/silicon oxycarbide/graphite composite negative electrode material
ActiveCN104466142AAdjustable capacityStable structureElectrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cellsSilicon oxygenLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a silicon / silicon oxycarbide / graphite composite negative electrode material which is a silicon-containing material which has the size being lower than 3 microns uniformly and is firmly distributed on the surface of a negative electrode of graphite. The invention further provides a preparation method of the composite negative electrode material. The preparation method comprises the steps of dispersing a silicon-containing material in a liquid organo-siloxane monomer, sequentially adding an acid liquid of alcohol and water, a curing agent and a graphite negative electrode material, then carrying out ball milling or mechanical stirring, pinching and mixing to obtain a paste-type mixture; calcining the paste-type mixture at high temperature under a protective atmosphere, crushing and sieving to obtain different-particle-size silicon / silicon oxycarbide / graphite lithium-ion battery negative electrode material. The silicon-containing materials of the silicon / silicon-oxygen carbon / graphite composite negative electrode material are firmly and uniformly distributed on the surface of a graphite material; due to the structure, the silicon-containing materials can be effectively adsorbed on the surface of the graphite, the self agglomeration of the silicon-containing material can be avoided and the silicon-containing material is prevented from peeling off from the graphite; the silicon / silicon oxycarbide / graphite composite negative electrode material has the characteristics that the charge and discharge specific capacities are adjustable, and the electrochemical cycle stability is high.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE BATTERY RES INST CO LTD
Silica sol composition, membrane electrode assembly with proton-exchange membrane, and fuel cell
InactiveUS7371480B2Process stabilityLow methanol permeabilityIon-exchanger regenerationConductive materialSilicon oxygenMethanol crossover
Provided are a proton-exchange membrane of which the ionic conductivity is high and the methanol crossover is low, and a fuel cell of high power that comprises the proton-exchange membrane. The proton-exchange membrane has a structure of mesogen-containing organic molecular chains and a proton-donating group-containing group covalent-bonding to a silicon-oxygen three-dimensional crosslinked matrix, in which at least a part of the organic molecular chains are oriented to form an aggregate thereof; and the fuel cell comprises the membrane.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
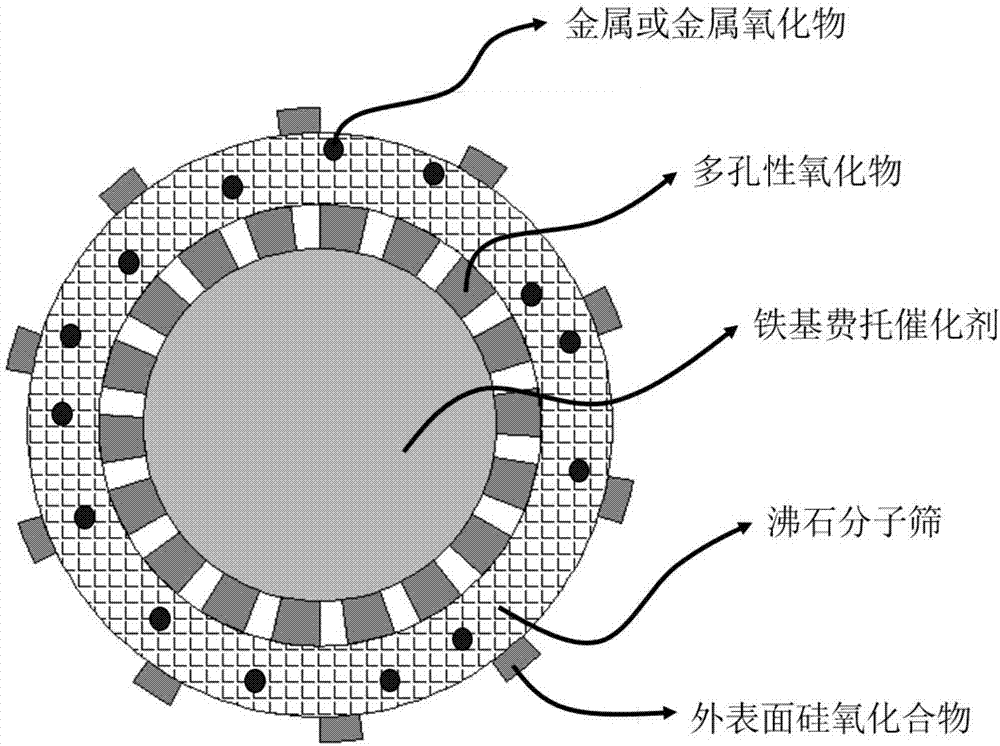
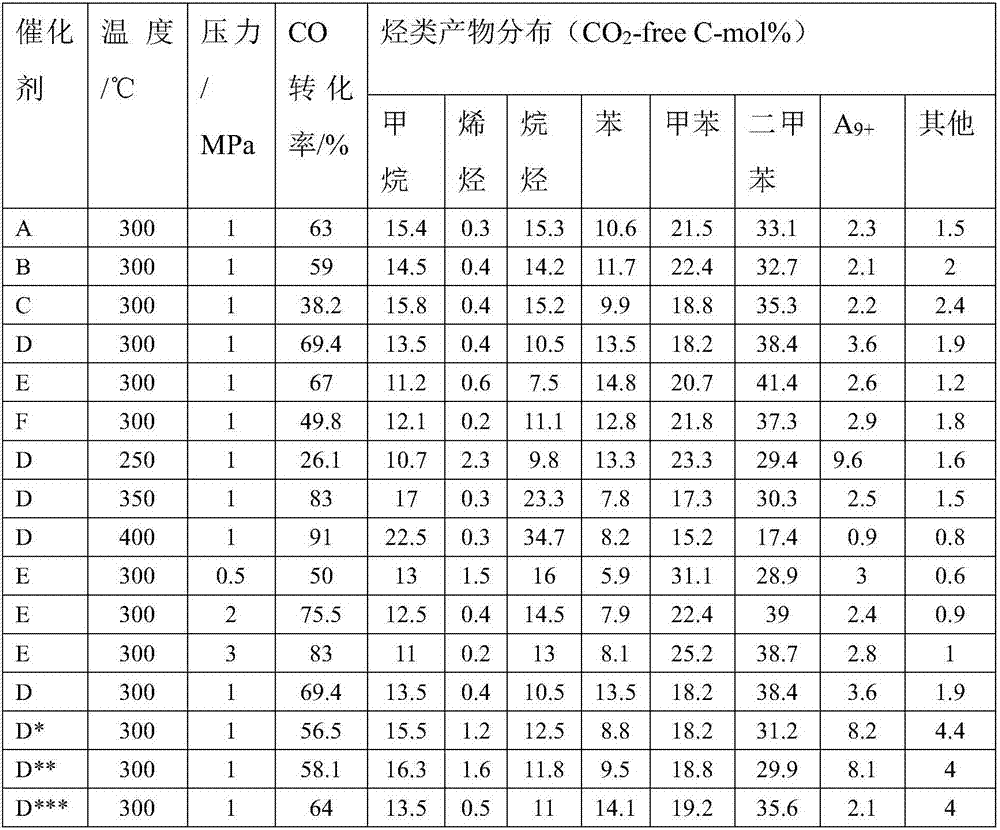
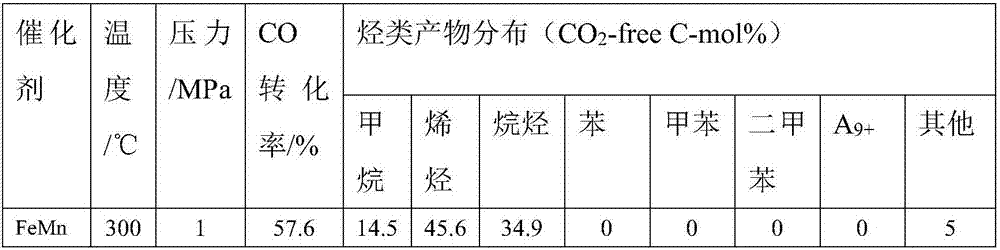
Multistage nano-reactor catalyst for direct preparation of aromatic compounds from synthetic gas, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107349954AAvoid influenceImprove conversion rateHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsNanoreactorPorous carbon
The invention discloses a multistage nano-reactor catalyst for one-step direct preparation of aromatic hydrocarbons from synthetic gas, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst comprises a core layer iron-based Fischer-Tropsch catalyst, a porous oxide or porous carbon material transition layer and a molecular sieve shell layer having an aromatization function, wherein the shell layer molecular sieve can be further modified with a metal element or a nonmetal element, and the external surface of the molecular sieve is further modified with a silicon-oxygen compound to adjust the acidic site of the external surface and the aperture of the molecular sieve in order to inhibit the formation of heavy aromatic hydrocarbons. The preparation method of the multistage nano-reactor catalyst is characterized in that the transition shell layer can be prepared from the Fischer-Tropsch catalyst through multiple steps, the shell layer contains or does not contain an assistant, and the shell layer molecular sieve undergoes or does not undergo surface modification. The catalyst can be used for the direct preparation of the aromatic compounds, especially lightweight aromatic hydrocarbons, from the synthetic gas; the selectivity of the lightweight aromatic hydrocarbons in the hydrocarbons can reach 75% or more, and the content of the aromatic hydrocarbons aromatic hydrocarbons in a liquid phase product is not less than 95%; and the catalyst has a good stability and has a very good industrial application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of resisting contaminant build up and oxidation of vehicle surfaces and other surfaces
Coating compositions and methods for applying reactive silanol coating compositions having electron deficient surfaces when cured wherein organic radical groups from the silanes are forced to the surface of the coating. The interpenetrating silicon-oxygen structure below the surface skews the electron cloud downward creating a net positively charged surface which is hydrophobic and oleophobic to repel contaminants by discouraging light hydrogen bonding. The surface is also extremely tight and thereby absent nutrients for microorganisms, discourages organic growth. These unique qualities provide cleanliness solutions for automotive and marine applications, including substrates subjected to elevated temperatures typically destructive to organic coatings (paints). Substrate examples are: brakes to repel brake dust on wheels; coating of engines and engine accessories, high-temperature exhausts / stacks / eductors, and engine compartments; automotive, architectural, industrial, and marine exterior substrates; and preservation and restoration of vehicles and boat interiors, seats, and instrument panels / dashboards and the like.
Owner:GEDEON ANTHONY
Silicon oxide-based silicon-oxygen-carbon composite material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106025220AImprove conductivityImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesSilicon oxygen
The invention discloses a silicon oxide-based silicon-oxygen-carbon composite material, which is of a three-layer structure comprising an inner layer, an intermediate layer and an outer layer, wherein the inner layer is an SiOx substrate; the intermediate layer is a carbon coating layer; the outer layer is graphite; the SiOx substrate has the characteristics consistent with SiO or a compound of Si and SiOx in the crystal structure characteristic; the value range of x is greater than 0 and smaller than 2; the SiOx substrate is of a powdery structure; the average grain diameter of the SiOx substrate is 2.0-5.0 microns; and the SiOx substrate is prepared through technical details of Si and SiO2 high-temperature reaction, sublimation and condensation. The silicon oxide-based silicon-oxygen-carbon composite material has the most obvious characteristics that added polyethylene powder is decomposed to form small pores in a high-temperature pyrolysis carbon coating process; and meanwhile, the decomposed product and introduced carbon source gas can be cracked to form a carbon coating layer, so that the carbon coating efficiency and thickness are improved. Active material particles obtained by the method are controllable in size, good in conductivity and stable in structure; and the silicon-oxygen-carbon composite material has high reversible capacity and excellent cycling stability when used as a negative electrode of a lithium-ion battery.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN ENERGY STORAGE TECH
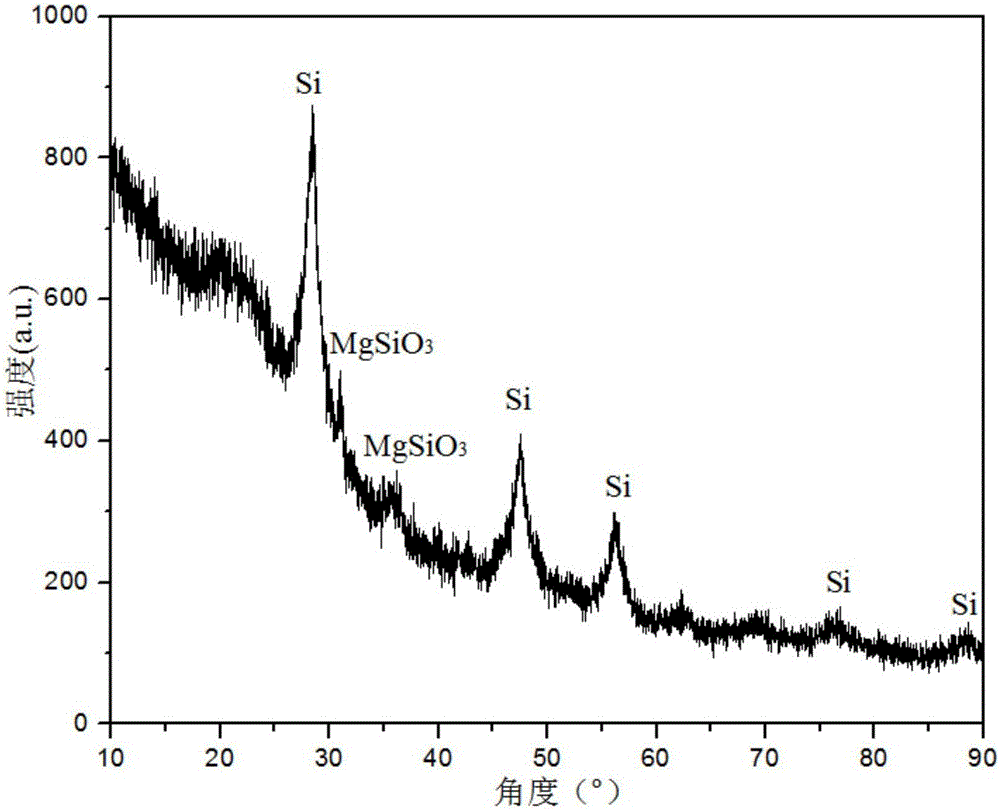
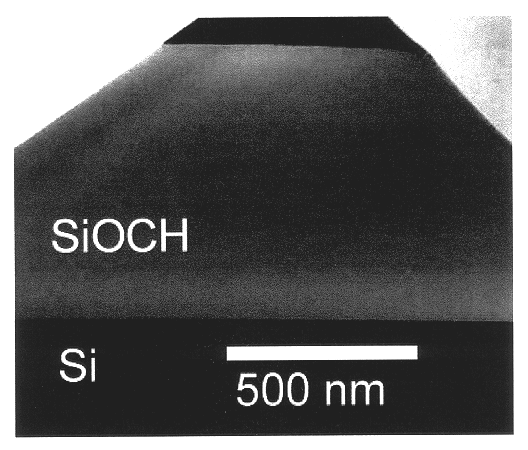
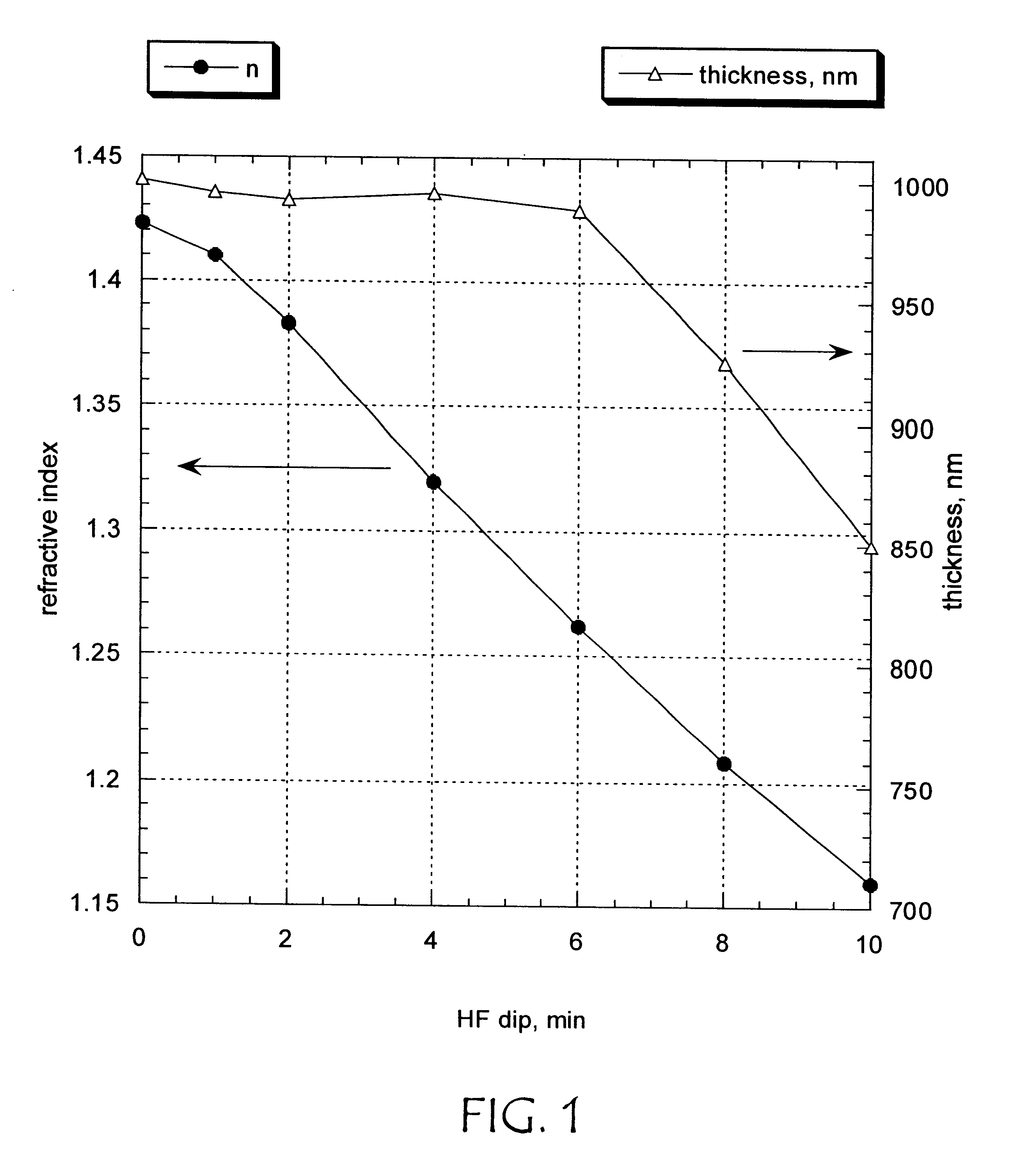
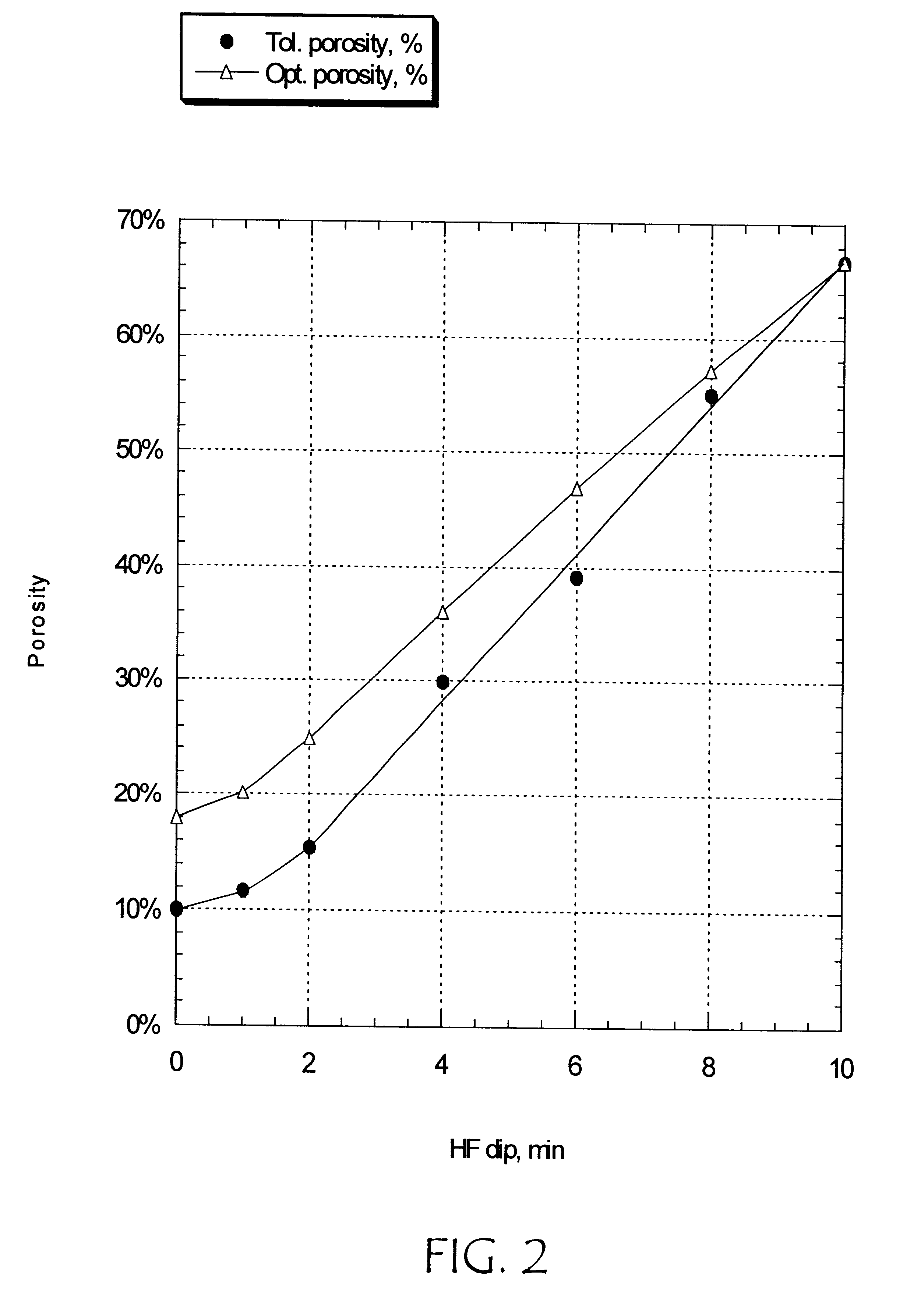
Method to produce a porous oxygen-silicon layer
InactiveUS6593251B2High porosityAvoid changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxygenOxygen
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Selective wet etching of oxides
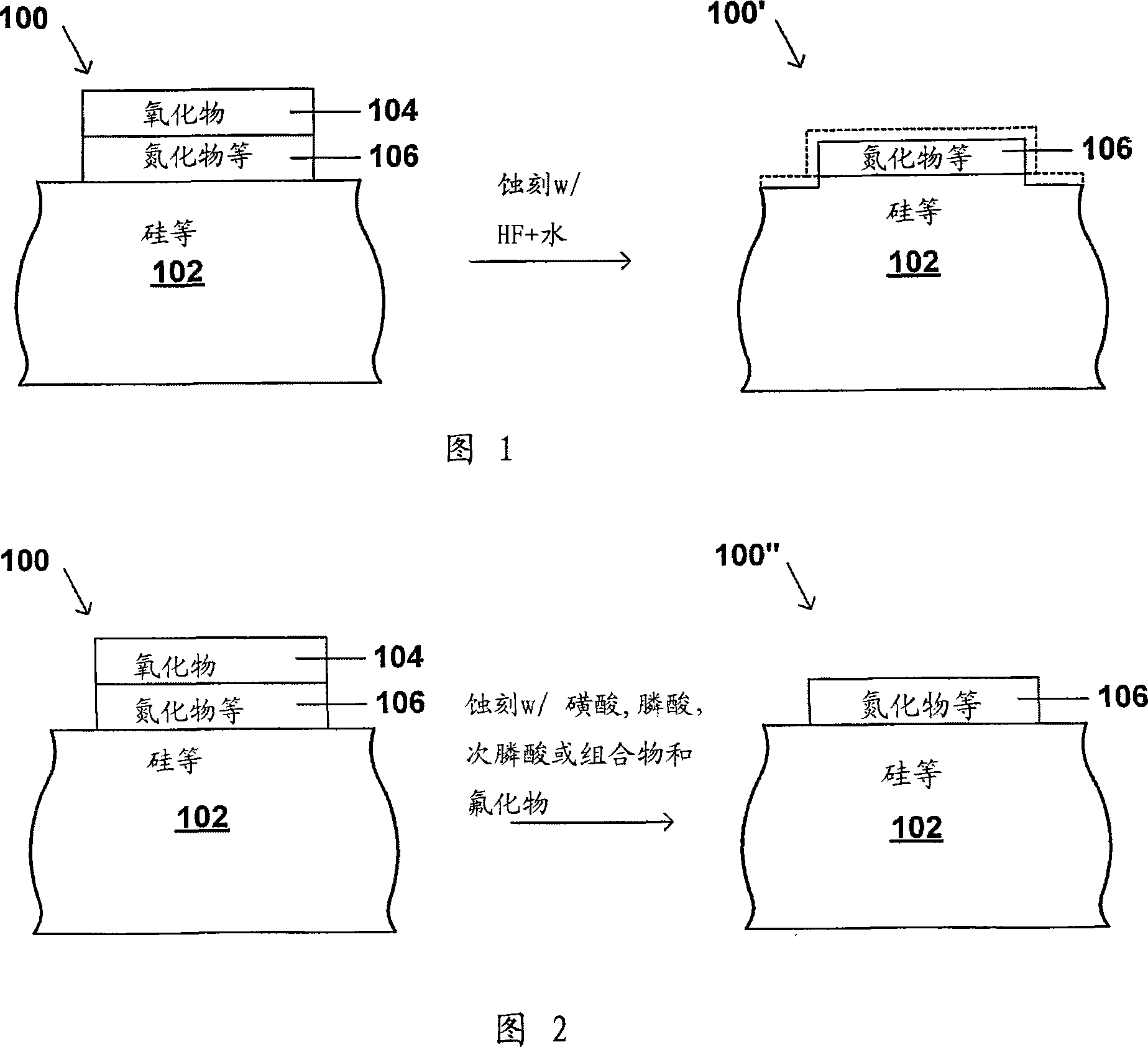
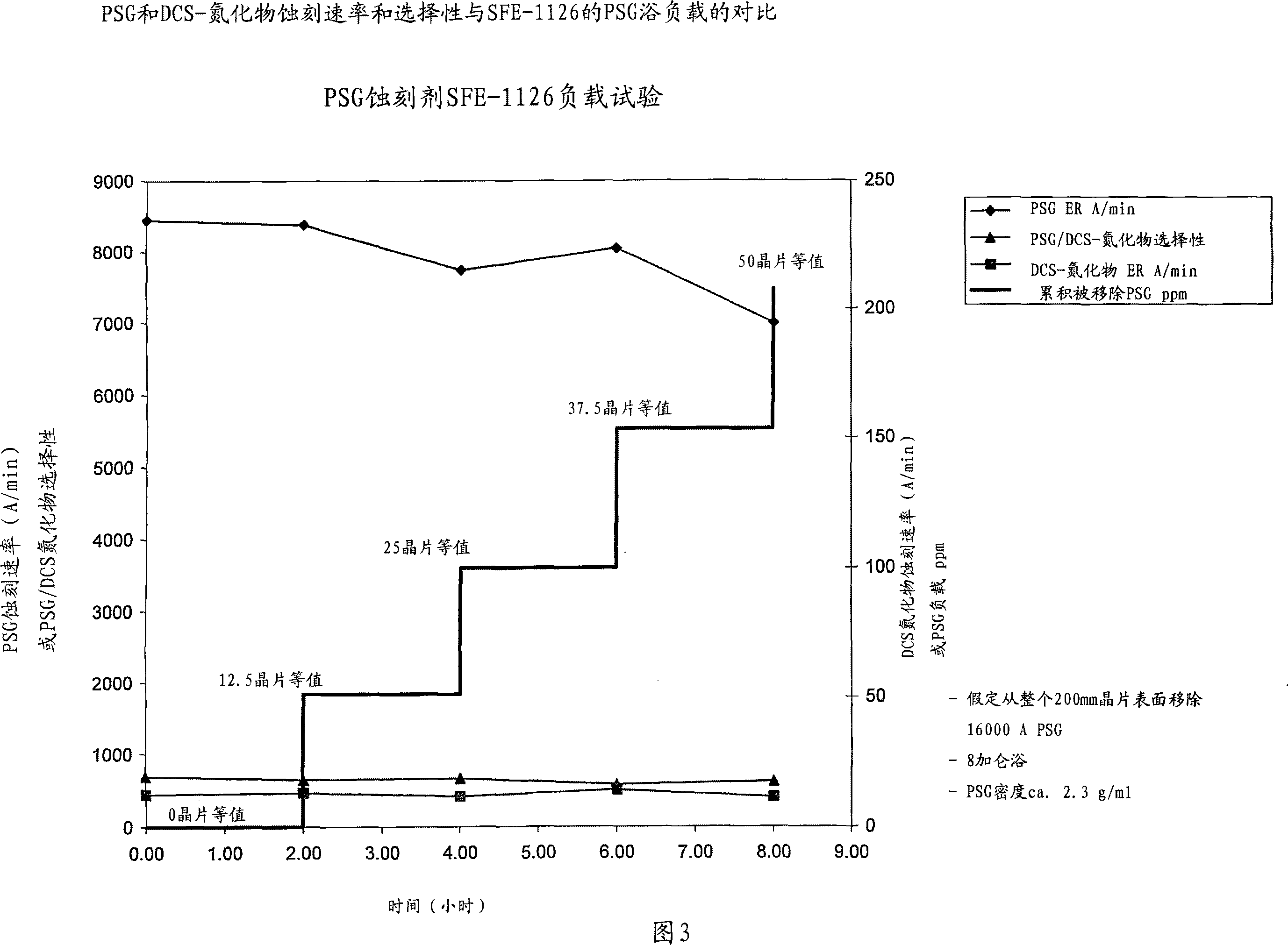
The present invention relates to a wet etching composition including a sulfonic acid, a phosphonic acid, a phosphinic acid or a mixture of any two or more thereof, and a fluoride, and to a process of selectively etching oxides relative to nitrides, high-nitrogen content silicon oxynitride, metal, silicon or silicide. The process includes providing a substrate comprising oxide and one or more of nitride, high-nitrogen content silicon oxynitride, metal, silicon or silicide in which the oxide is to be etched; applying to the substrate for a time sufficient to remove a desired quantity of oxide from the substrate the etching composition; and removing the etching composition, in which the oxide is removed selectively.
Owner:SACHEM INC
Radical steam CVD
InactiveUS20120177846A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxygenNitrogen
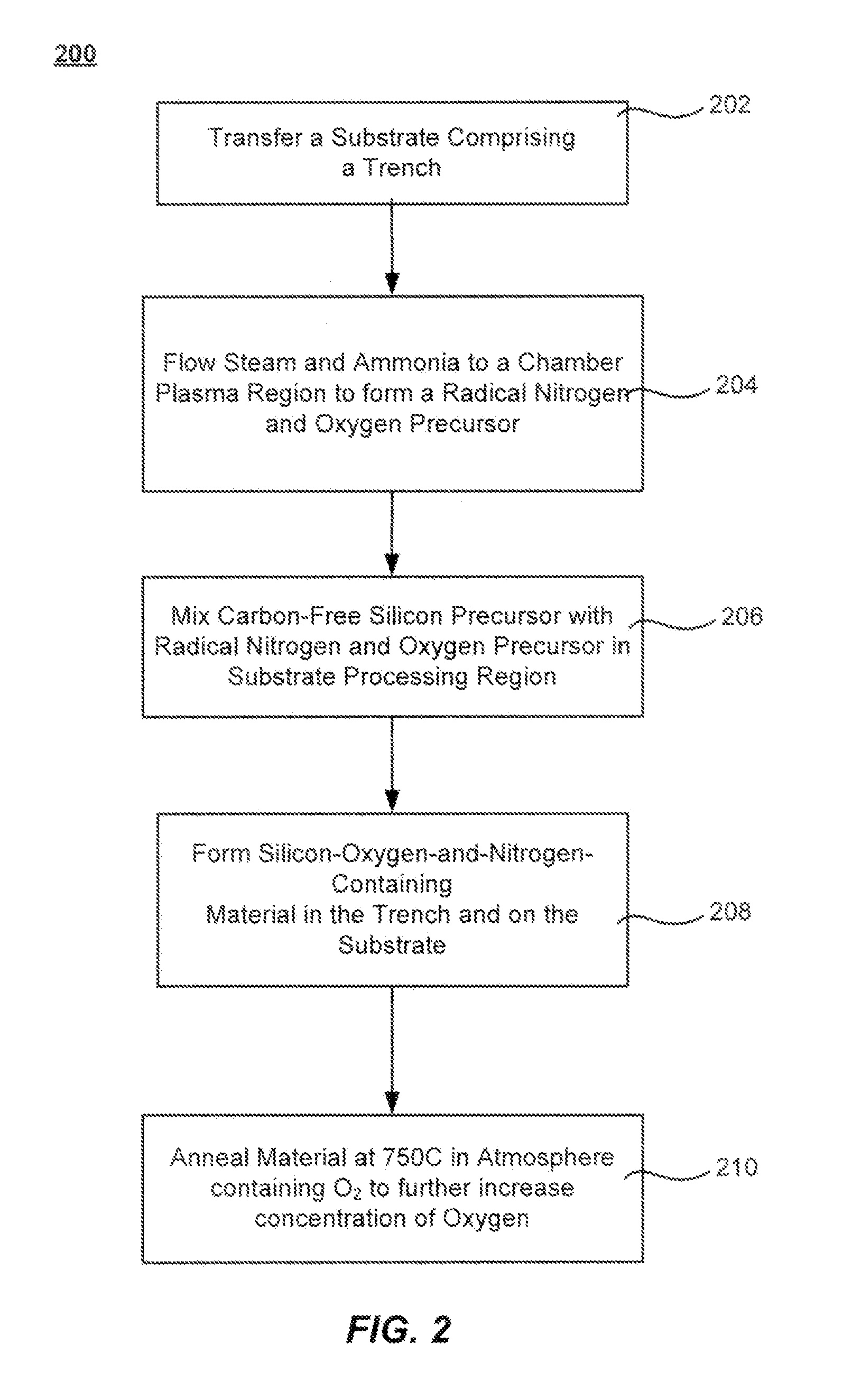
Methods of forming silicon oxide layers are described. The methods include concurrently combining plasma-excited (radical) steam with an unexcited silicon precursor. Nitrogen may be supplied through the plasma-excited route (e.g. by adding ammonia to the steam) and / or by choosing a nitrogen-containing unexcited silicon precursor. The methods result in depositing a silicon-oxygen-and-nitrogen-containing layer on a substrate. The oxygen content of the silicon-oxygen-and-nitrogen-containing layer is then increased to form a silicon oxide layer which may contain little or no nitrogen. The increase in oxygen content may be brought about by annealing the layer in the presence of an oxygen-containing atmosphere and the density of the film may be increased further by raising the temperature even higher in an inert environment.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Heat treatable coated article with zirconium silicon oxynitride layer(s) and methods of making same
A coated article is provided so as to include a solar control coating having an infrared (IR) reflecting layer sandwiched between at least a pair of dielectric layers. The IR reflecting layer may be of or include NbZrOx, NbZr, NiCr, NiCrNx, or the like in certain embodiments of this invention. In particular, a zirconium silicon oxynitride (e.g., ZrSiOxNy) inclusive layer is provided which unexpectedly improves blocking (reflecting and / or absorption) of UV radiation in a manner which does not significantly degrade other optical properties of a coated article. Moreover, the ZrSiOxNy also has been found to improve (lower) the ΔE* value upon heat treatment, thereby permitting a coated article when heat treated (HT) to more closely match its non-HT counterpart with respect to glass side reflective color after such HT.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC +1
Heat radiation material, heat radiation structure, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103205149AGood compatibilityImprove stabilityLayered productsFilm/foil adhesivesDispersion stabilitySilicon oxygen
The invention provides a heat radiation material, a heat radiation structure, and preparation methods thereof. The heat radiation material comprises, by weight, 10-30 parts of inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material aqueous slurry, 40-80 parts of aqueous high-molecular resin, 0.5-5 parts of an auxiliary agent, and 5-20 parts of a diluting agent. The inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material aqueous slurry comprises, by weight, 10-25 parts of an inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material, 0.5-20 parts of a bi-functional large-molecular modifier, and 50-100 parts of a solvent. According to the inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material, the bi-functional large-molecular modifier is used in surface modification. Selective absorption and grafting hybridization reaction are carried out on the surface of the inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material, such that coordination self-assembly behaviors of ester bond, silicon-oxygen bond, hydrogen bond, and the like are formed on the surface of the material. Therefore, inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material interface performance is controlled, compatibility and system dispersion stability of the inorganic heat radiation nano-grade material are improved, and better heat radiation performance can be obtained.
Owner:REGAL PAPER TECH
Proton-conducting membrane, method for producing the same, and fuel cell using the same
InactiveUS6864006B2Improve proton conductivityExcellent characteristicsNon-metal conductorsSemi-permeable membranesFuel cellsHeat resistance
A proton-conducting membrane, excellent in resistance to heat, durability, dimensional stability and fuel barrier characteristics, and showing excellent proton conductivity at high temperature and a method for producing the same. A proton-conducting membrane includes a carbon-containing compound and inorganic acid, characterized by a phase-separated structure containing a carbon-containing phase containing at least 80% by volume of the carbon-containing compound and inorganic phase containing at least 80% by volume of the inorganic acid, the inorganic phase forming the continuous ion-conducting paths. The method for producing the above proton-conducting membrane includes steps of preparing a mixture of a carbon-containing compound (D) having one or more hydrolyzable silyl groups and inorganic acid (C), forming the above mixture into a film, and hydrolyzing / condensing the hydrolyzable silyl group contained in the mixture formed into the film, to form a three-dimensionally crosslinked silicon-oxygen structure (A). The above proton-conducting membrane is incorporated in a fuel cell.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +2
Semiconductor device having improved insulation film and manufacturing method thereof
A semiconductor device which has an interlayer insulating film comprised of molecules with silicon-oxygen bonds and silicon-fluorine bonds and contains a rare gas in concentration higher than 1011 atoms per cm2. The interlayer insulating film is preferably a fluorine-containing silicon oxide film which contains a rare gas. In a manufacturing process, an interlayer insulating is formed by a chemical vapor deposition from a material gas including a silicon-containing gas, a fluorine compound gas, a rare gas, and oxygen. The silicon-containing gas is preferably SiH4 gas, and the fluorine compound gas is preferably SiF4 gas. The flow rate of the rare gas is greater than three times the total flow rate of the SiH4 gas and SiF4 gas. The rare gas is at least one type of gas selected from neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), and xenon (Xe).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Preparation method of modified ultra-thin fire-resistant coating polymer matrix based on silsesquioxane
The invention relates to a method of POSS modified ultra-thin fire-resistant coating polymer matrix, and in the method, non-reactive POSS or reactive POSS is introduced in the polymer matrix by a physical or chemical method to form the real nanometer fire-retardant polymer matrix; the nanometer fire-retardant polymer matrix has good heat resistance in high temperature, and can form silicon oxygen compound which is deposited on the surface of unburned polymer after burning to form a protective layer, thus slowing the heat transfer to a certain extent, inhibiting the combustible gas from releasing, separating the mixture of the combustible gas and oxygen and improving the fire-retardant property.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
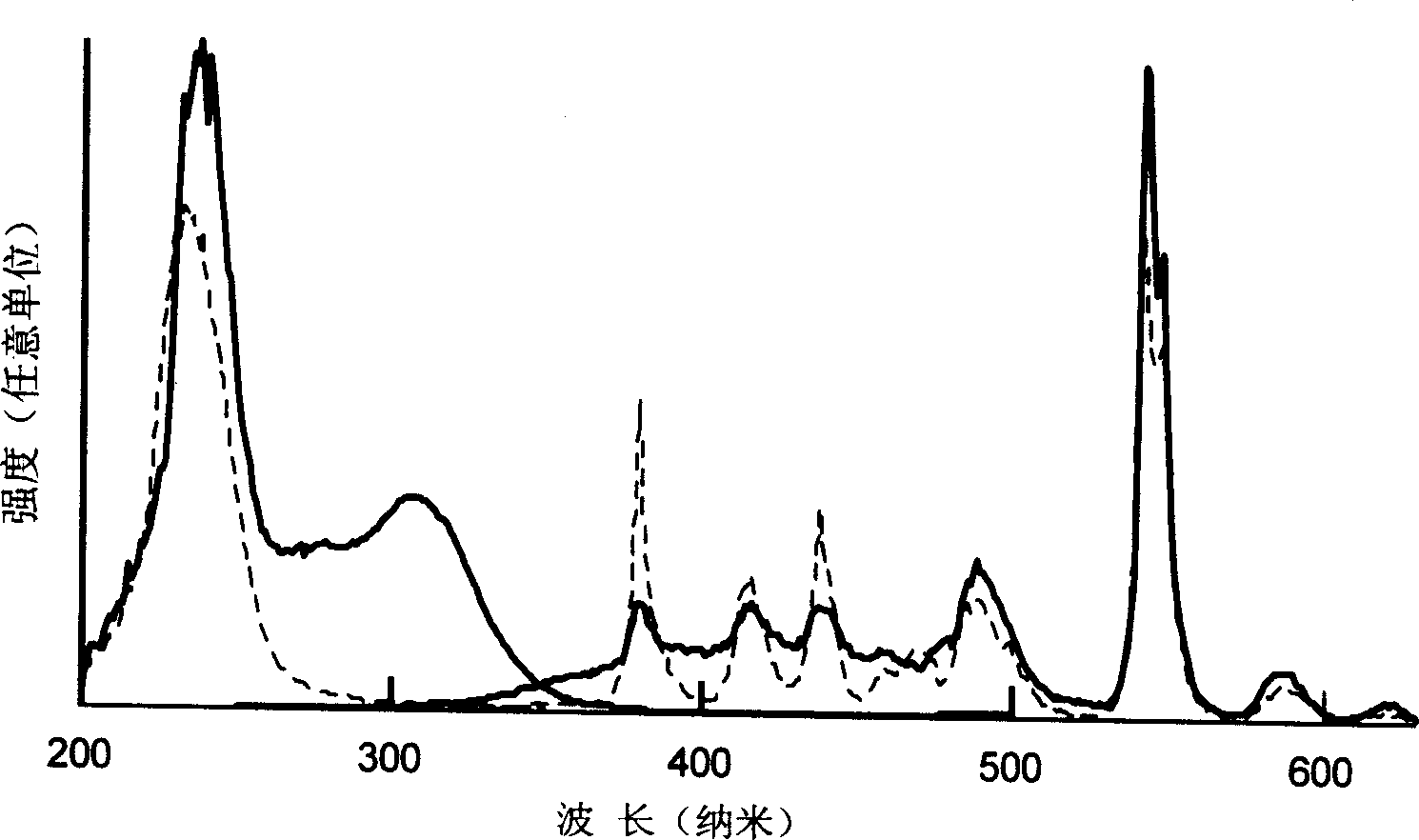
Geen light emitting vycor glass production method
The preparation method for vycor glass that emits green light comprises, using porous glass with SiO2 content over 95wt%, wherein, the aperture is 1.0-10nm and pore takes up volume of 23-28%; dipping the said glass into solution that contains rare-earth ion, such as Tb ion, or Tb ion and Ce ion, or gadolinium ion and Yt ion; sintering at temperature more than 1050Deg. The product has green light of 545nm when activating by ultraviolet light of 254nm.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com