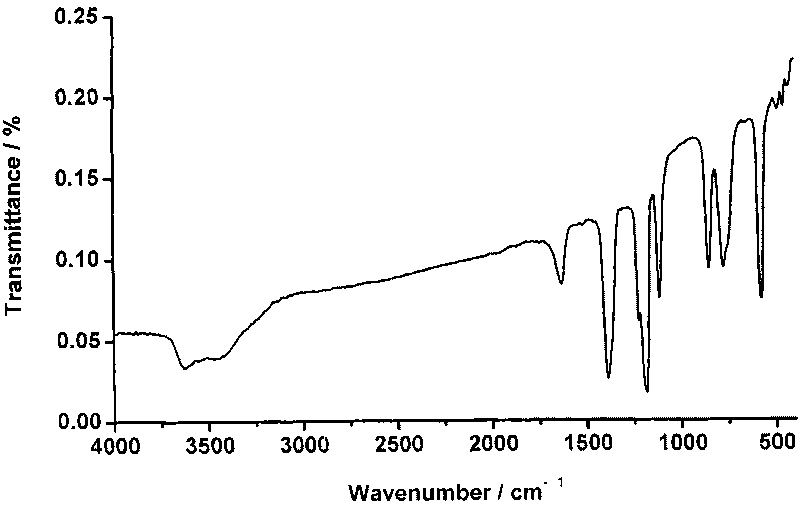
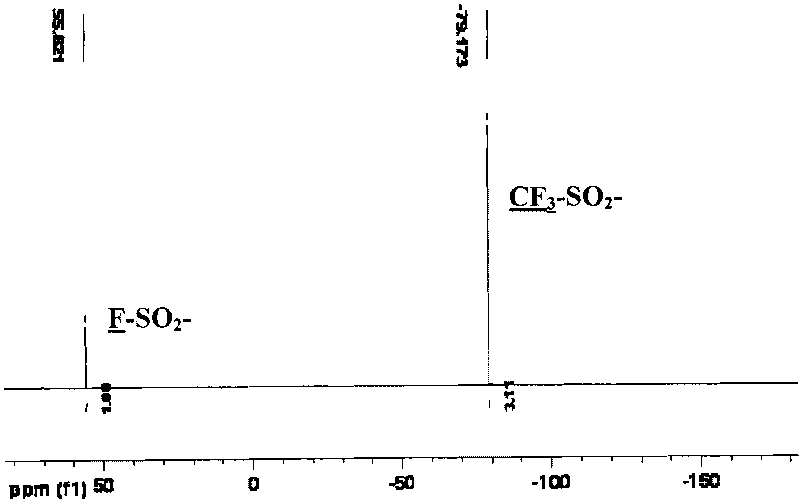
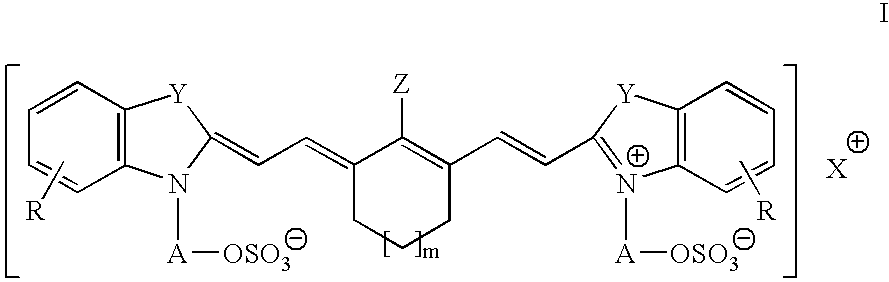
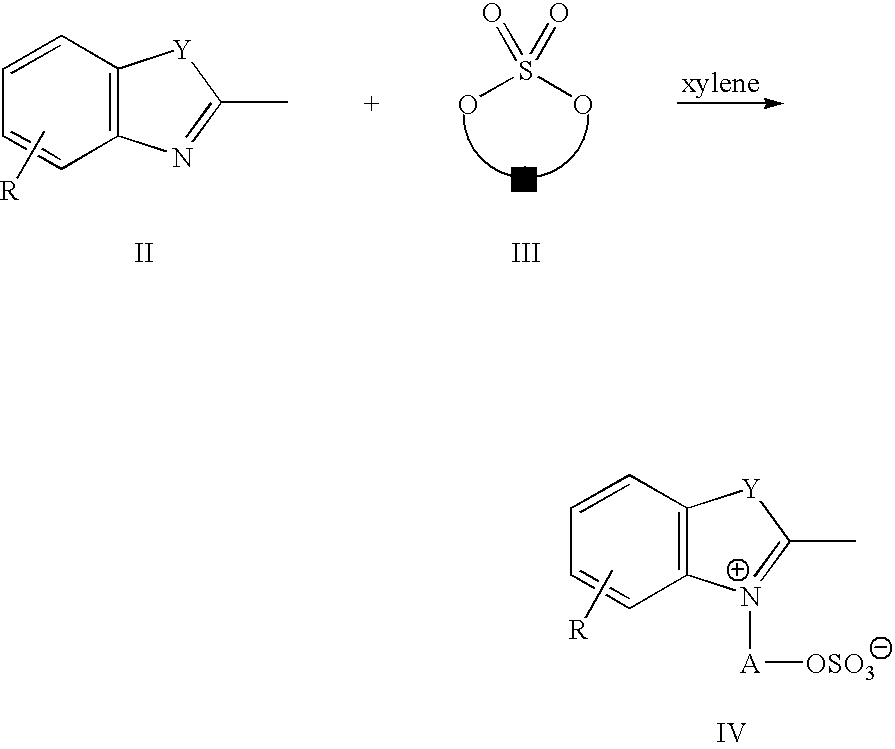
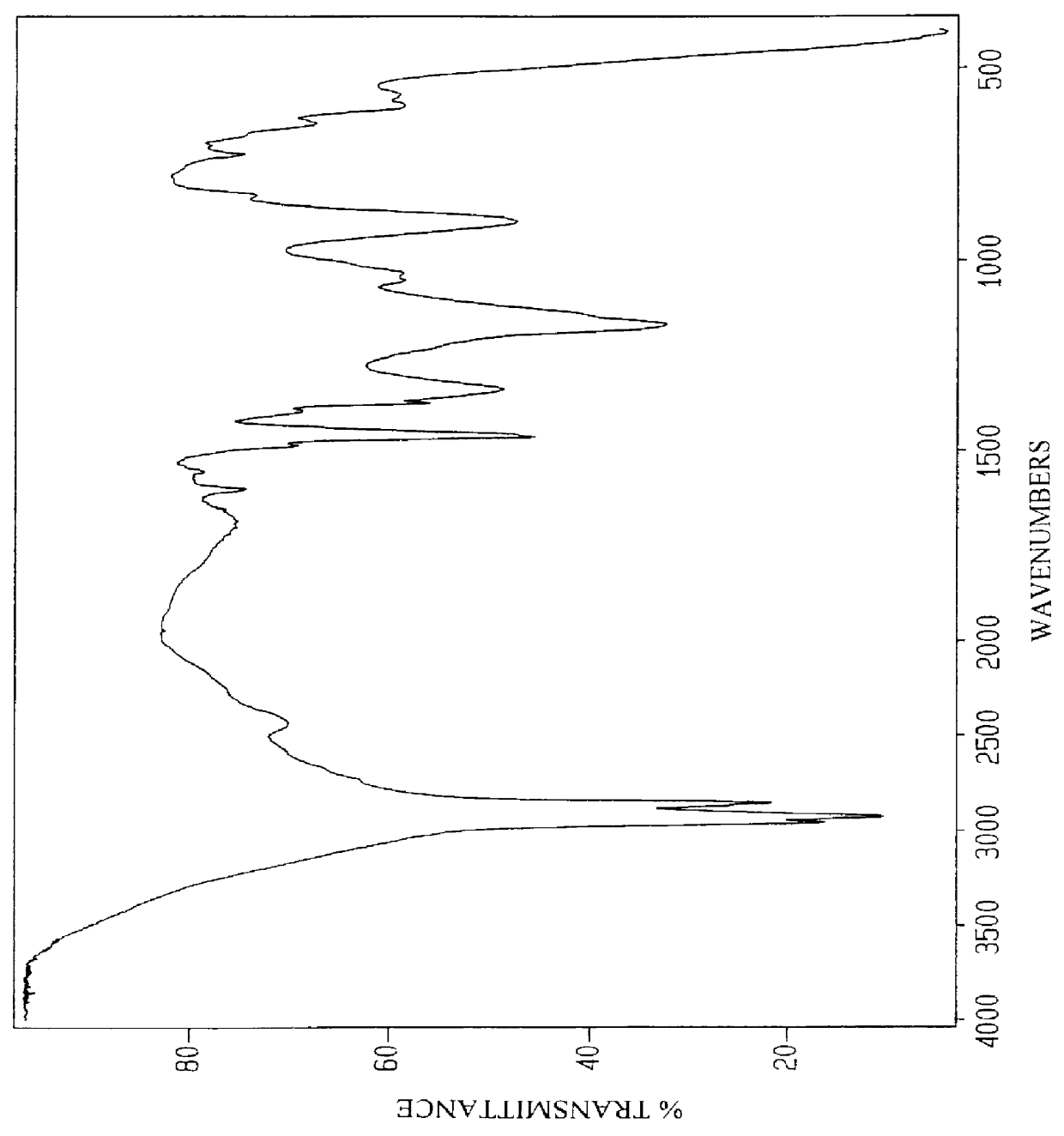
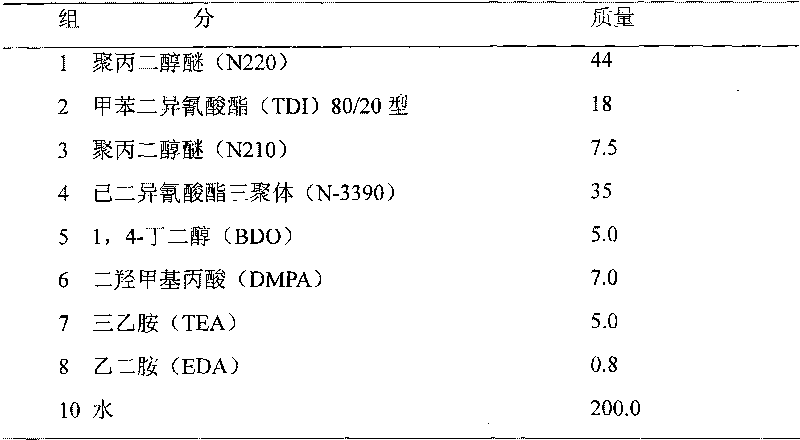
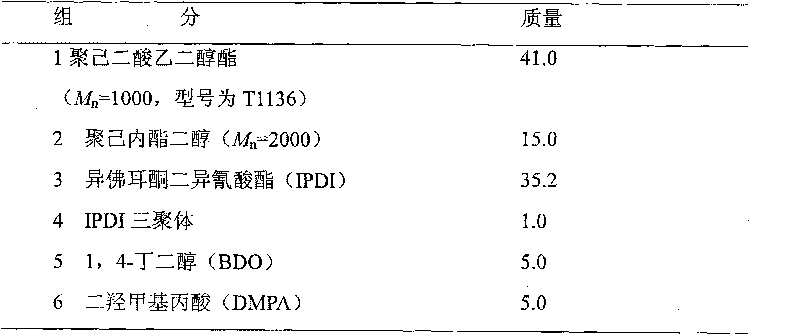
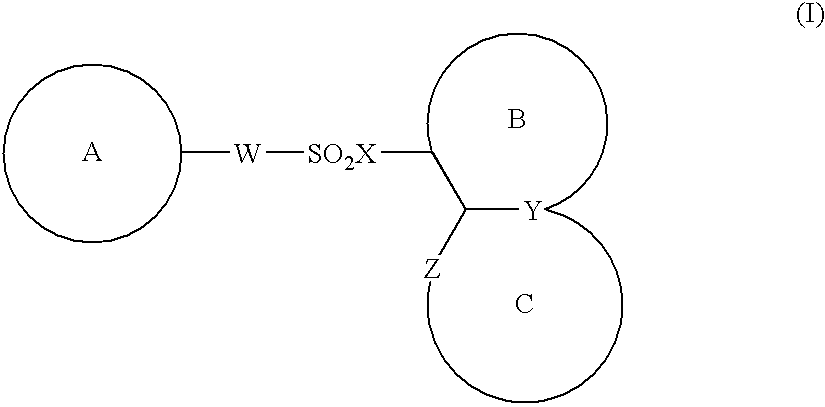
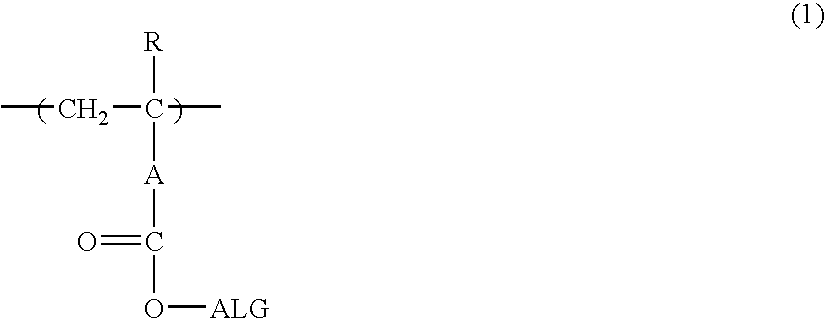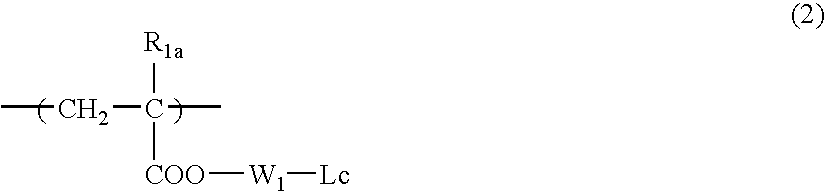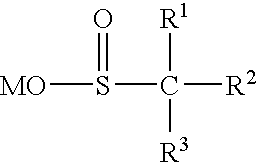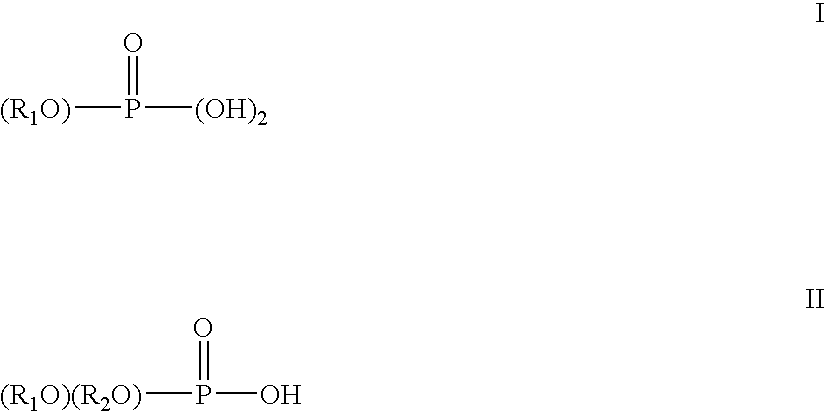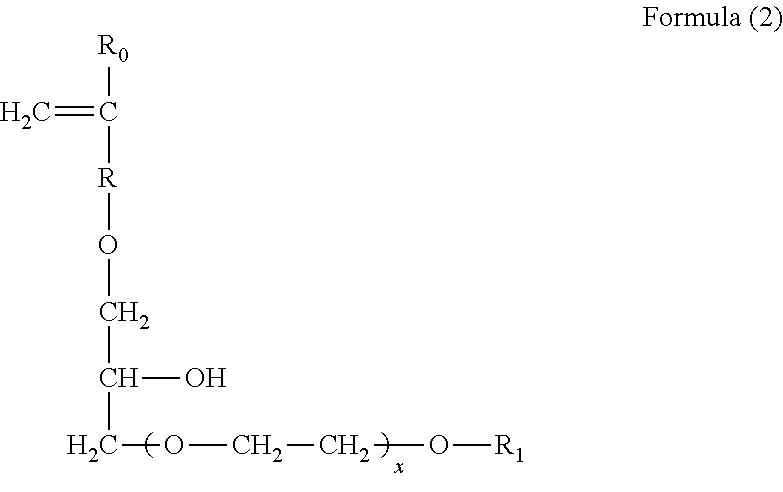Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8968 results about "Sulfonic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sulfonic acid (or sulphonic acid) refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)₂−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)₂(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound (with the organic substituent replaced by hydrogen) is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)₂(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)₂. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
Water-soluble copolymer film packet
Owner:MONOSOL LLC +1
Fluorinated surfactants for use in making a fluoropolymer
InactiveUS20070117914A1Convenient and easy preparationPrepared cost-effectivelyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationEmulsion polymerizationCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a fluorinated surfactant having the general formula:[Rf—(O)t—CQH—CF2—O]n—R-G (I)wherein Rf represents a partially or fully fluorinated aliphatic group optionally interrupted with one or more oxygen atoms, Q is CF3 or F, R is an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon group, G represents a carboxylic or sulphonic acid or salt thereof, t is 0 or 1 and n is 1, 2 or 3. The surfactant is particularly useful in polymerizing fluorinated monomers in an aqueous emulsion polymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
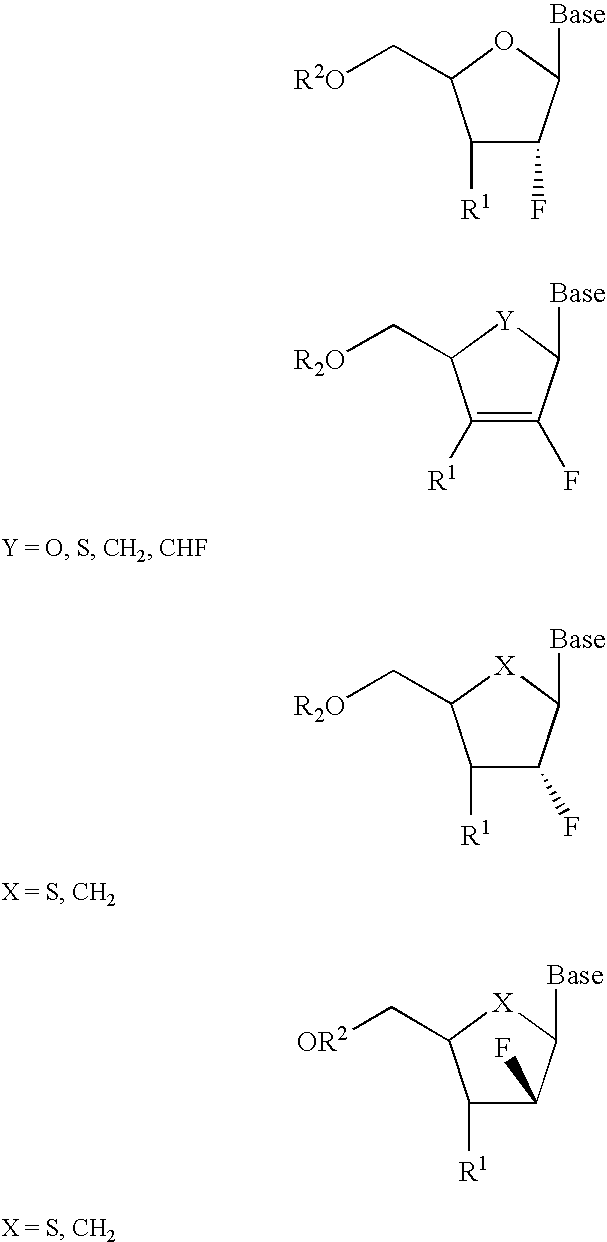
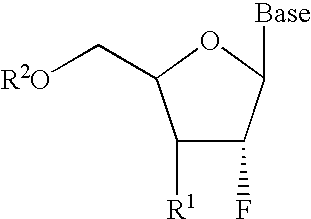
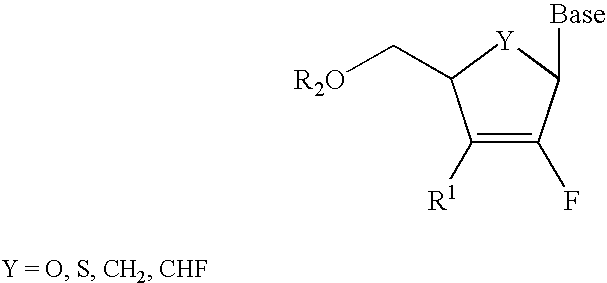
2′-fluoronucleosides
InactiveUS6911424B2Sure easyUseful in treatmentBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersPurine
A class of 2′-fluoro-nucleoside compounds are disclosed which are useful in the treatment of hepatitis B infection, hepatitis C infection, HIV and abnormal cellular proliferation, including tumors and cancer. The compounds have the general formulae: wherein[0001]Base is a purine or pyrimidine base;[0002]R1 is OH, H, OR3, N3, CN, halogen, including F, or CF3, lower alkyl, amino, loweralkylamino, di(lower)alkylamino, or alkoxy, and base refers to a purine or pyrimidine base;[0003]R2 is H, phosphate, including monophosphate, diphosphate, triphosphate, or a stabilized phosphate prodrug; acyl, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of providing a compound wherein R2 is H or phosphate; sulfonate ester including alkyl or arylalkyl sulfonyl including methanesulfonyl, benzyl, wherein the phenyl group is optionally substituted with one or more substituents as described in the definition of aryl given above, a lipid, an amino acid, peptide, or cholesterol; and[0004]R3 is acyl, alkyl, phosphate, or other pharmaceutically acceptable leaving group which when administered in vivo, is capable of being cleaved to the parent compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Hydrogen peroxide disinfectant with increased activity
InactiveUS6346279B1High activityReduced activityBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsDisinfectantPhosphoric acid
An acidic aqueous hydrogen peroxid solution is provided, with improved disinfectant activity. Concentrated solutions preferably contain up to about 8% and as-used concentrations contain about 0.5% peroxide. The solution also contains from 0.1 to 5.0% of at least one acid compound, e.g. phosphoric and / or a phosphonate with from 1 to 5 phosphonic acid groups, and from 0.02 to 5% of at least one anionic surfactant. The surfactant is selected from C8 to C16-alkyl aryl sulphonic acids, sulphonated C12 to C22 carboxylic acids, C8 to C22-alkyl diphenyl oxide sulphonic acids, naphthalene sulphonic acids, C8 to C22 alkyl sulphonic acids, and alkali metal and ammonium salts thereof, and alkali metal C8 to C18 alkyl sulphates, and mixtures thereof. Most preferably the solution has an emulsifier, e.g. a salt of an alkylated diphenyl oxide. The solution may also contain corrosion inhibitors and / or lower alcohols.
Owner:VIROX TECH
Nonaqueous electrolyte and lithium secondary battery employing the same
InactiveUS20050118512A1Improve featuresLarge capacityElectrolytic capacitorsCell electrodesOrganic solventPhysical chemistry
An object of the present invention is to provide a battery of high capacity that is excellent in storage, load, cycle, and continuous charge characteristics and that reduces gas generation; and a nonaqueous electrolyte for use in the battery. The invention relates to a nonaqueous electrolyte which comprises a nonaqueous organic solvent and a lithium salt dissolved therein, wherein the nonaqueous organic solvent contains at least one compound selected from the group consisting of acid anhydrides and carbonic esters having an unsaturated bond, and at least one compound selected from the group consisting of sulfonic compounds and fluorine-containing aromatic compounds having 9 carbon atoms or less; and a lithium secondary battery employing the same.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
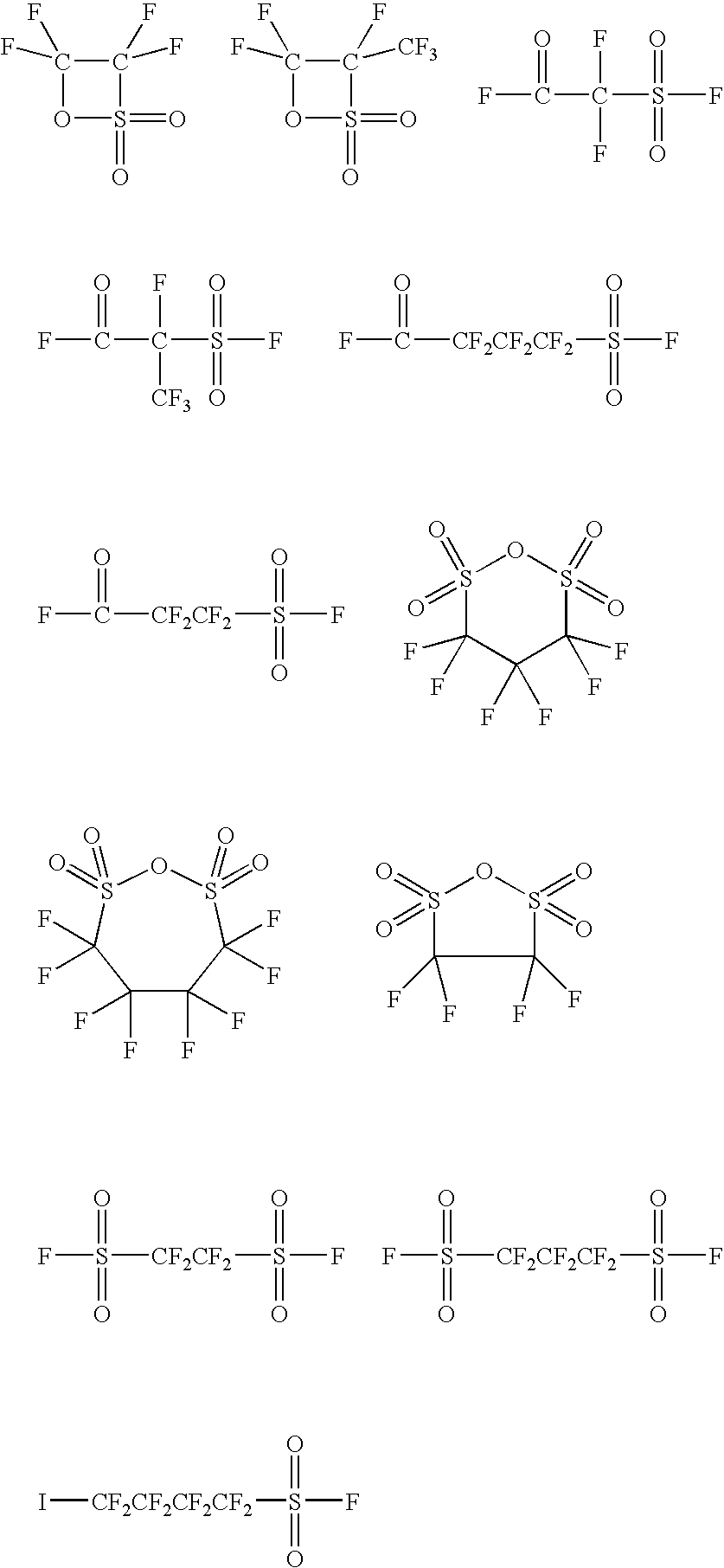
Method for preparing bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine alkali metal salt
ActiveCN101747242AAvoid product agglomerationSimple and efficient operationSulfonic acid amide preparationSolventDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine alkali metal salt. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting sulfamide and thionyl chloride and chlorosulfonic acid to prepare bi-(sulfonyl chlorine) imine and (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl chlorine sulfonyl) imine, reacting with antimony trifluoride and potassium carbonate (rubidium or caesium) to obtain corresponding high-purity bi-(sulfonyl fluoride) imine potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt or (fluorinated alkyl sulfonyl fluorine sulfonyl) imine potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt, performing double decomposition exchange reaction using the potassium (rubidium or caesium) salt with the lithium perchlorate (or sodium) or lithium tetrafluoroborate (or sodium) in the aprotic polar solvent to obtain corresponding lithium (or sodium) salt with high purity. The method in the invention has the characteristics of simple operating steps, easy separation and extraction of output, high purity and yield, no environmental pollution, and the like, and is suitable for mass industrial production.
Owner:武汉市瑞华新能源科技有限公司
Method for treating wood with a metal-containing treating agent and wood treated thereby
InactiveUS6541038B1Reduce leachingEasy to fixBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsLignosulfonatesMetal
A method for treating wood, characterized by impregnating wood with a metal-containing treating agent containing lignin and / or lignin derivatives and a metal, a metal compound, and / or a metal ion and oxidizing and / or macromolecularizing of the lignin and / or lignin derivatives in the wood to fix the metal component in the wood, and wood and woody materials obtained by the treating method. According to the method of the present invention, while effectively utilizing lignins, lignosulfonic acids, or lignosulfonic acid salts, leaching of the metal component can be suppressed to a low level to thereby retain the effects due to the incorporation of the metal components for a prolonged period.
Owner:SDS BIOTECH CO LTD
Photosensitive composition and pattern forming method using the same
ActiveUS20050095532A1Increase photosensitivityWide exposure marginRadiation applicationsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentActinic RaysMaterials science
A photosensitive composition containing a compound capable of generating a specific acid having the plural number of sulfonic groups by irradiation with an actinic ray or a radiation and a pattern forming method using the same.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
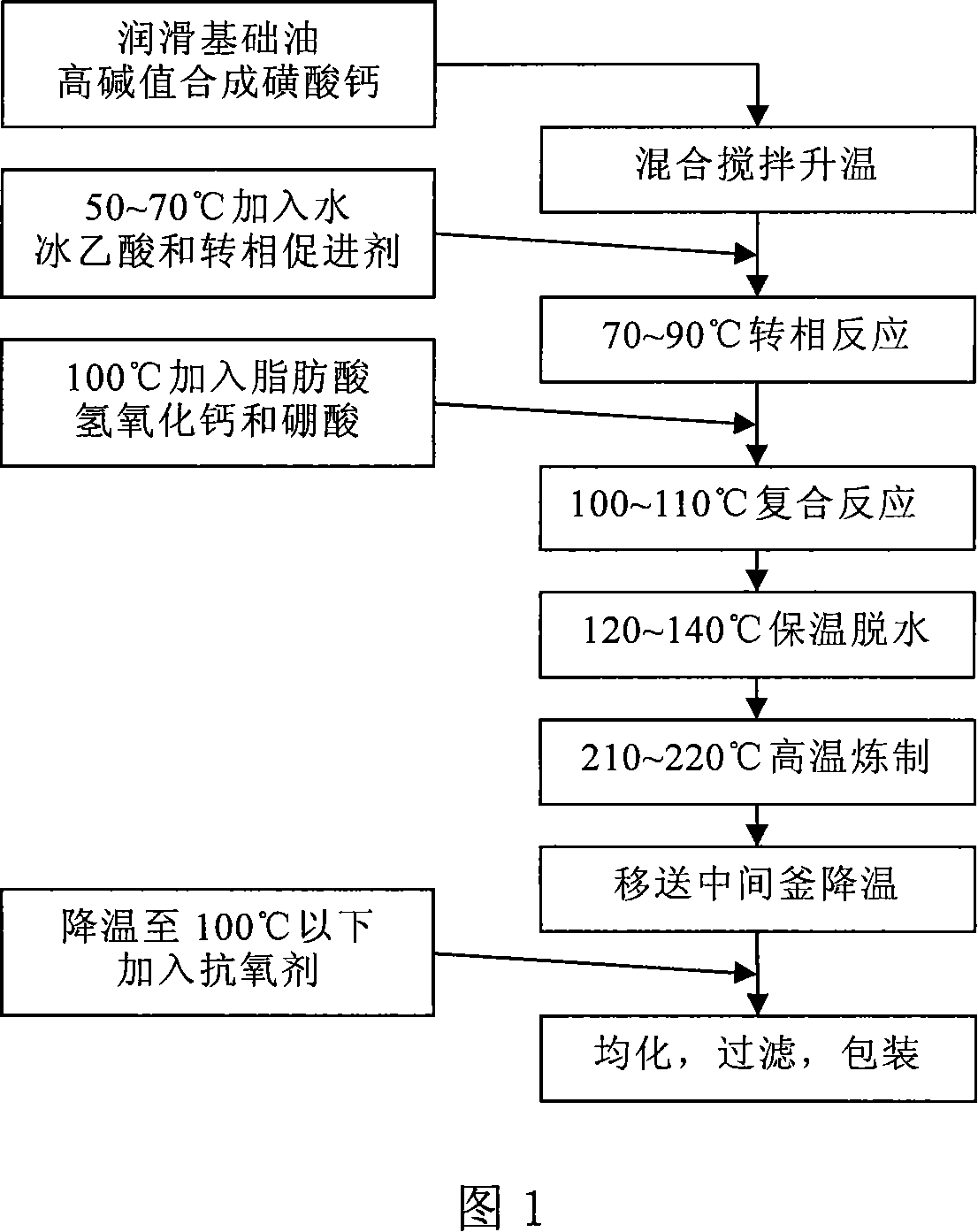
Compound sulphonic acid albany grease and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101153239AImprove performanceImprove water resistanceLubricant compositionAntioxidantManufacturing enterprises
The invention relates to calcium sulfonate complex grease and a manufacture method thereof, in particular to grease producing the thickening agent by synthetic reaction with super-high base value. At first, the lubricating base oil and the calcium sulfonate are added into an opening reaction kettle to be stirred, the phase inversion promoter, the glacial acetic acid and the water are added into the kettle to boost the temperature to make the insulating reaction until the materials are thickened, then the calcium hydroxide, the aliphatic acid and the boric acid are added into make an insulating reaction, a temperature rise, an insulating dehydration and a refining in turn, then the materials are moved into an intermediate kettle, the antioxidant is added to disperse and homogenize, and the finished product is produced after the filtering. The invention has excellent anti-spray performance, excellent high temperature performance, good extreme pressure anti-abrasion performance, prominent anti-shear performance, good pumping performance, anti-rust performance and water adding shear stability; has apparent phase inversion effect and good product performance, decreases the grease exchange times under the same working condition and increases the service life of the equipment, which is proved by the trial applications of a plurality of appliance manufacture enterprises, steel works, paper mills and so on.
Owner:无锡中石油润滑脂有限责任公司
Novel sulfonate salts and derivatives, photoacid generators, resist compositions, and patterning process
ActiveUS20060228648A1Wide spectrum of molecular designReduce molecular weightOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsResistSulfonate
Sulfonate salts have the formula: CF3—CH(OCOR)—CF2SO3−M+ wherein R is C1-C20 alkyl or C6-C14 aryl, and M+ is a lithium, sodium, potassium, ammonium or tetramethylammonium ion. Onium salts, oximesulfonates and sulfonyloxyimides and other compounds derived from these sulfonate salts are effective photoacid generators in chemically amplified resist compositions.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Color-stable superabsorbent polymer composition
ActiveUS20060089611A1Duplicating/marking methodsSynthetic resin layered productsAcetic acidPolymer science
A color-stable superabsorbent polymer having long-term color stability, and methods of manufacturing the polymer, are disclosed. The superabsorbent polymer is prepared using a sulfinic acid derivative, like 2-hydroxy-2-sulfinatoacetic acid, a salt thereof, or a mixture thereof, as the reducing agent in a polymerization initiator system for the preparation of a superabsorbent polymer from monomers. The resulting superabsorbent polymer resists color degradation during periods of extended storage, even at an elevated temperature and humidity.
Owner:BASF AG
Liquid detergent composition for improved grease cleaning
InactiveUS20070275868A1Organic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsSulphate IonSURFACTANT BLEND
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
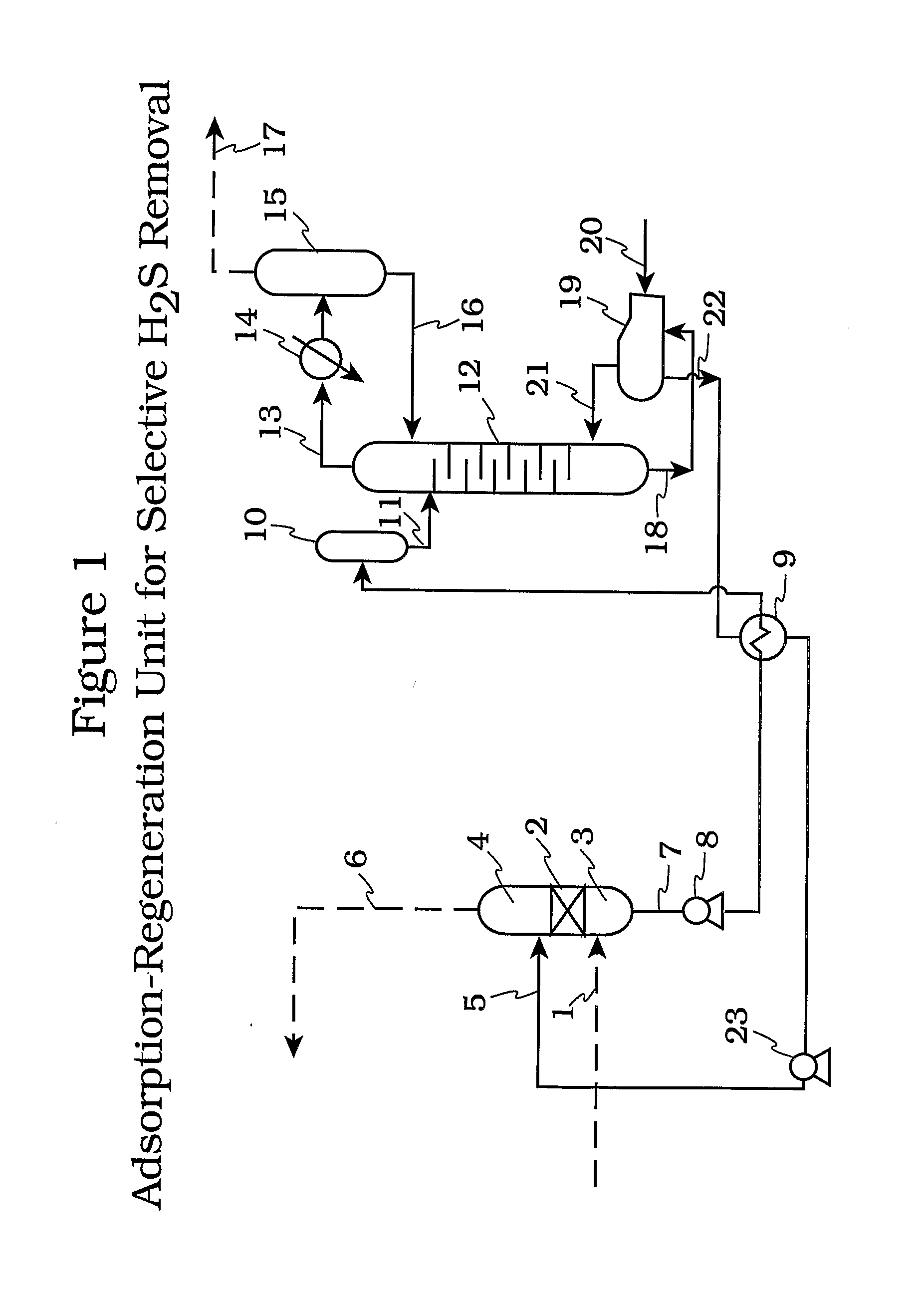
Absorbent composition containing molecules with a hindered amine and a metal sulfonate, phosphonate or carboxylate structure for acid gas scrubbing process
An acid gas absorbent comprising a metal sulfonate, phosphonate or carboxylate of a hindered amine and a process for the selective removal Of H2S as well as other acidic components such as carbon disulfide, carbonyl sulfide and oxygen and sulfur derivatives of C1 to C4 hydrocarbons from mixtures containing such acidic components and CO2 using said absorbent.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Infrared absorbing compounds and their use in imageable elements
Infrared absorbing compounds are disclosed. The compounds are co-polymers that comprise covalently attached ammonium, sulfonium, phosphonium, and / or iodonium cations, and infrared absorbing cyanine anions that have two to four sulfonate groups and / or sulfate groups, and / or infrared absorbing oxonol anions. The infrared absorbing compounds can be used in aqueous developable lithographic printing plate precursors.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
Anionic surfactants based on alkene sulfonic acid
InactiveUS6043391AIncrease productionImprove yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFlushingAlkylphenolAlpha-olefin
New anionic surfactants and methods of preparation which are derived from aromatic or substituted aromatic molecules and alkenesulfonic acid. Wherein the aryl compound is alkylated and sulfonated in one-step with an alkene sulfonic acid prior to sulfonic acid neutralization. The methods allow the functional sulfonate group to be attached to the end of the alkyl chain rather than to the aromatic ring thus allowing for selective substituted groups, either branched, linear or alkoxylated or combinations thereof to be placed on the aryl compound prior to sulfonation and alkylation. The invention uses the alkene sulfonic acid produced from thin-film sulfonation of an alpha-olefin to alkylate benzene, mono-substituted aromatic, poly-substituted aromatic, alkylbenzene, alkoxylated benzene, polycyclic aromatic, mono-substituted polycyclic aromatic, poly-substituted polycyclic aromatic, naphthalene, alkylnaphthalene, phenol, alkylphenol, alkoxylated phenol, and alkoxylated alkylphenolalkyl substituted or polysubstituted cyclic or polycyclic compounds to produce the corresponding sulfonic acid having an additional alkyl group derived from the alpha-olefin used during the thin-film sulfonation which is either linear or branched.
Owner:OIL CHEM TECH
Preparation method and application of modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of polyisocyanate curing agents
InactiveCN101696262ASimple processEasy to operatePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsLeather surface finishingPolyesterSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of polyisocyanate curing agents. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out prepolymerization reaction by using polyester polyol, vulcabond monomer and a polyisocyanate curing agent; reacting with a hydrophilic chain-extending agent and a micro-molecule chain-extending agent to obtain polyurethane prepolymer containing hydrophilic groups (carboxyl or sulfonic groups) and isocyanate(NCO)-terminated groups; neutralizing the polymer into salt, and then dispersing the salt into water; and preparing the modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of the polyisocyanate curing agents by the chain extending of a polyamine chain-extending agent. The modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions of the polyisocyanate curing agents have self-crosslinking function at room temperature, and the self-crosslinking density is over 85%. Compared with non-modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions prepared under the same condition, the modified polyurethane aqueous dispersions have superior film forming property, water resistance, alcohol resistance, pollution resistance, cold resistance, dry / wet rubbing resistance and chemical solvent resistance; and coating films have especially high drying speed, high hardness increment speed and high final hardness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Medicinal compositions for concomitant use as anticancer agent
InactiveUS20030215523A1Good synergyEliminate side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCarboplatinAnticarcinogen
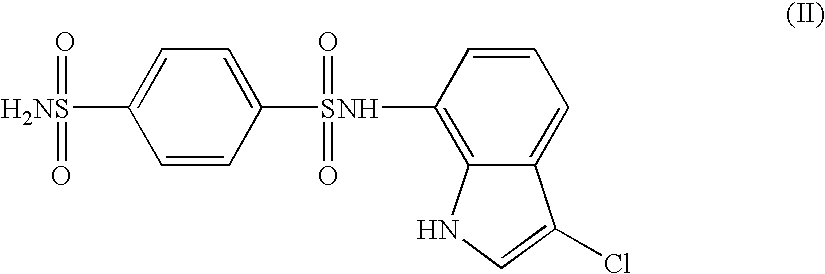
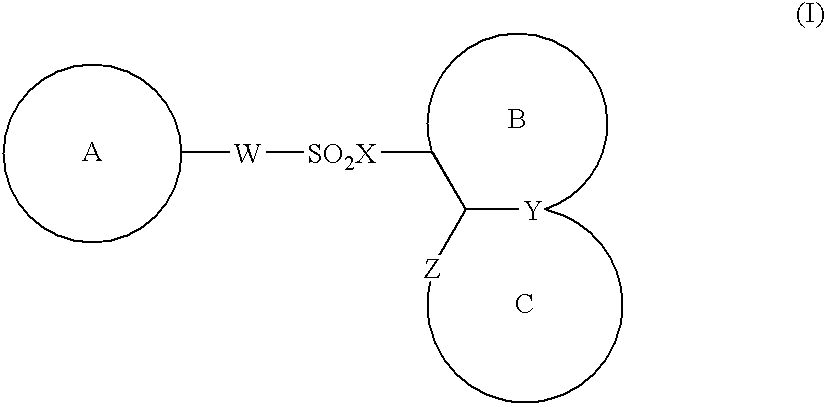
The present invention provides a medicinal composition having an excellent antitumor activity. That is, it provides a medicinal composition comprising a sulfonamide compound, a sulfonate compound or a salt of them, which is represented by the following formula: (wherein ring A represents an aromatic ring which may have a substituent group; ring B represents a 6-membered unsaturated hydrocarbon ring which may have a substituent group etc.; ring C represents a 5-membered hetero-ring containing one or two nitrogen atoms, and the ring C may have a substituent group; W represents a single bond or -CH=CH-; X represents -NH- etc.; and Y represents a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom; and Z represents -NH- etc.), particularly N-(3-chloro-1H-indol-7-yl)-4-sulfamoylbenzenesulfonamide or a salt thereof, combined with at least one substance selected from (1) irinotecan hydrochloride trihydrate; (2) mitomycin C; (3) 5-fluorouracil; (4) cisplatin; (5) gemcitabine hydrochloride; (6) doxorubicin; (7) taxol; (8) carboplatin; (9) oxaliplatin; (10) capecitabine; and (11) a salt of the above-mentioned (1) to (10).
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Biocidal applications of concentrated aqueous bromine chloride solutions
Methods for disinfecting surfaces and for sanitizing bodies of water using a single-feed, bromine-based biocide are described. These methods use concentrated liquid biocide compositions comprising biocidally active bromine as the biocide. Also described is a process of producing the concentrated liquid biocide composition: mixed together are (a) bromine chloride and (b) an aqueous solution of alkali metal salt of sulfamic acid having a pH of at least about 7, in amounts such that (i) the active bromine content of the composition is at least about 100,000 ppm (wt / wt), and (ii) the atom ratio of nitrogen to active bromine in the composition is greater than 0.93. Use of bromine chloride as the source of the active bromine in the process is advantageous because in the resulting aqueous compositions, all of the bromine of the bromine chloride is made available as active bromine in solution. In other words, the chlorine of the bromine chloride is converted in the process to dissolved alkali metal chloride salt, thereby liberating all of the bromine as the active bromine content of the biocidal composition.
Owner:ALBEMARLE CORP
Additives for enhancing corrosion protection of metals
InactiveUS6054514AImprove corrosion inhibitionProvide protectionSynthetic resin layered productsAnti-corrosive paintsOrganic filmOrganic sulfonic acid
A corrosion inhibiting paint composition comprises from about 1 to 20 parts by weight of a corrosion inhibiting additive mixture comprising 1 to 25 parts by weight of an organic sulfonic acid in a mixture of 75 to 99 parts by weight of butyrolactone; from about 10 to 99 parts by weight of film forming polymer; and from about 0 to 89 parts by weight of a liquid medium selected from the group consisting of water, organic solvents for the film forming polymer and mixtures thereof. Another corrosion inhibiting paint composition comprises from about 1 to 20 parts by weight of a corrosion inhibiting additive mixture comprising 1 to 25 parts by weight of an organic sulfonic acid in a mixture of 75 to 99 parts by weight of butyrolactone; from about 10 to 98.5 parts by weight of film forming polymer; from about 0.5 to 20 parts of an intrinsically conductive polymer; and from about 0 to 89 parts of liquid medium selected from the group consisting of water and organic solvents for the film forming polymer and mixtures thereof. Metal substrates containing a coating composition comprise an organic film forming matrix and an additive mixture comprising organic sulfonic acid and butyrolactone. A method for imparting corrosion resistance to metal substrates comprises providing a layer of a coating composition on at least one surface of the substrate, formed from an organic film forming matrix and an additive mixture comprising an organic sulfonic acid and butyrolactone.
Owner:AMERICHEM INC
Modification of lubricant properties in an operating all loss lubricating system
ActiveUS20040144355A1Lubrication of auxillariesLubricant conduit arrangementsSulfonateAlkylphosphate
A marine diesel engine system includes a diesel engine having a plurality of cylinders. The system also includes, proximate the engine, a primary engine lubricant and an additive selected from certain alkylamine-alkylphosphates, 500 TBN calcium sulfonate and mixtures thereof. A means for blending the lubricant and additives into a mixture for introduction into a cylinder is provided. Thus lubricant properties may be modified depending upon engine conditions.
Owner:EXXOMOBIL RES & EINGIEERING
High solid content latent curing polyurethane acroleic acid hybrid emulsion
InactiveCN101481451AHigh solid contentHigh glossPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterPolymer science
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high solid content latent cured polyurethane acrylic acid heterozygous latex and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pre-polymerizing polyester polyalcohol, hydrophilic chain extender and diisocyanate monomer to obtain the polyurethane prepolymer containing a hydrophilic group (carboxyl or sulfo group) and a terminal NCO group; then, neutralizing the polymer into salt and dispersing the salt in water to prepare the polyurethane water dispersoid; finally, using the dispersoid as macro molecular emulsifying agent and reactant to emulsify and disperse the acrylic ester monomer, initiating the polymerization by heating, dropping initiator to perform the latex polymerization, and regulating the pH of the latex by adding a latent curing agent to obtain the high solid content latent cured polyurethane acrylic acid heterozygous latex. The high solid content latent cured polyurethane acrylic acid heterozygous latex has a solid content of above 45%; the storage of the high solid content latent cured polyurethane acrylic acid heterozygous latex is stable; and high hardness film coating can be formed at the room temperature. Compared with acrylic acid latex and polyurethane latex, the high solid content latent cured polyurethane acrylic acid heterozygous latex has better film forming performance, water resistance, alcohol resistance, pollution resistance, dry / wet cleaning resistance and chemical solvent resistance, as well as high hardness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
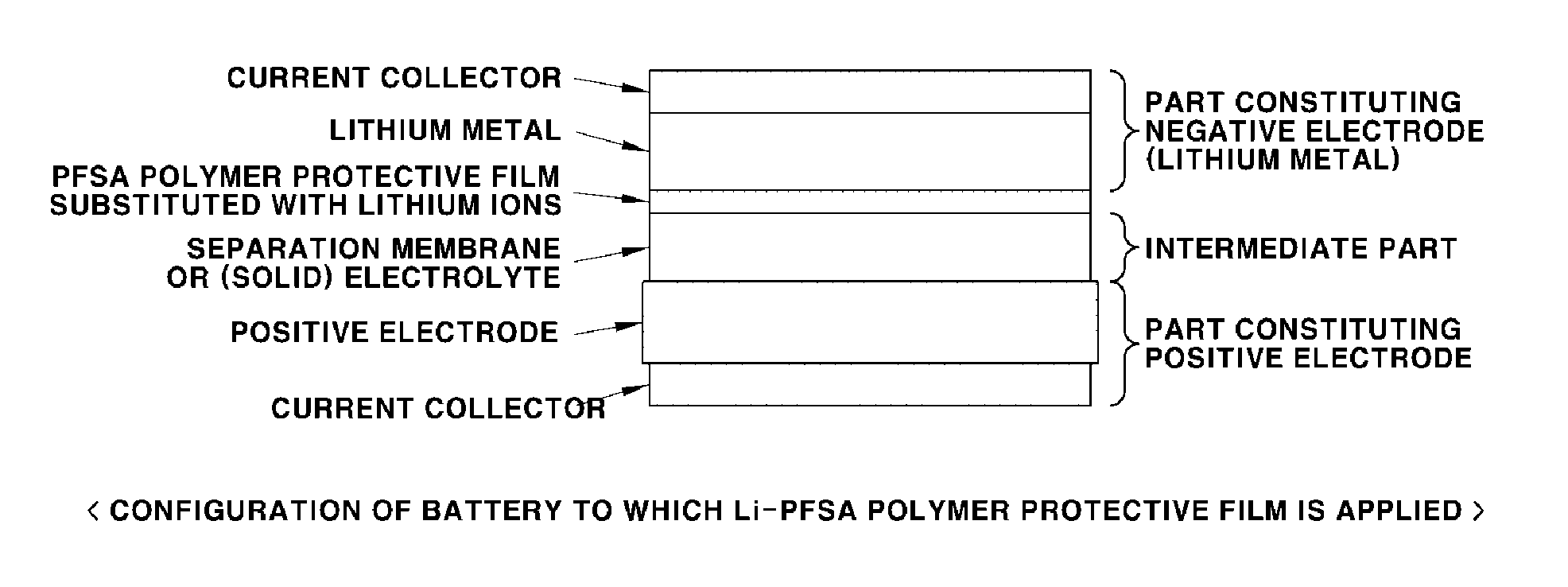
Separation membrane for lithium sulfur batteries
InactiveUS20150255782A1Improve lithium ion conductivityImprove stabilityFuel and secondary cellsElectrode thermal treatmentLithium–sulfur batteryLithium metal
Disclosed is a material which enhances stability for lithium in all the batteries, which use the lithium metal as an electrode material, by using and applying a lithium-substituted perfluoro sulfonic acid (PFSA) material in the form of a membrane or a powder to a lithium anode. Methods of manufacturing the material are also enclosed.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
High base number composite calcium sulfonate lubricating grease and its preparation method
A composite lubricating grease contains high-basicity petroleum calcium sulfonate or synthetic calcium sulfonate, acetic acid, C12-C22 hydroxy fatty acid, boric acid, arylamine-type antioxidizing agent and basic lubricating oil. Its advantages are excellent extreme-pressure resistance to friction, water, salt fog and corrosion, high drop point and thermal stability, good viscosity and long service life.
Owner:SINOPEC LUBRICANTS TIANJIN
Ionic photoacid generators with segmented hydrocarbon-fluorocarbon sulfonate anions
InactiveUS6841333B2Improve solubilitySolubility in organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationPhotosensitive materialsSolubilityAcid catalyzed
Photoacid generator salts comprising photoactive cationic moieties and segmented, highly fluorinated-hydrocarbon anionic moieties are disclosed which provide high photoacid strength and can be tailored for solubility and polarity. The present invention further relates to photoacid generators as they are used in photoinitiated acid-catalyzed processes for uses such as photoresists for microlithography and photopolymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Sulfonate group-containing copolymers and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110245132A1Inhibition is effectiveSuperior deposition-inhibiting abilityNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsSulfonateCarboxyl radical
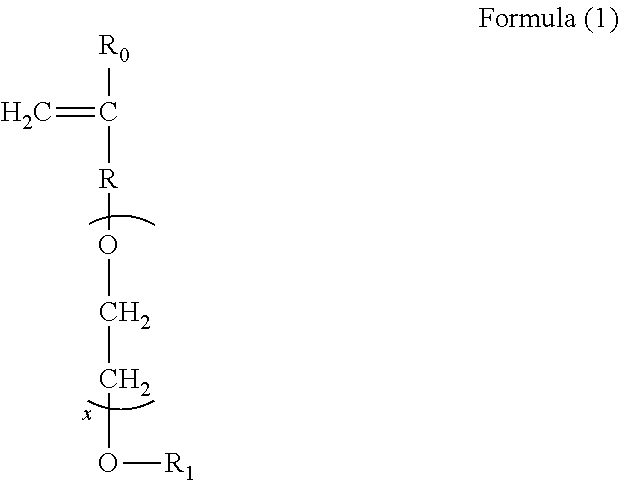
[Problem] To provide detergent compositions with superior surfactant deposition-inhibiting ability and anti-gelling properties that exhibit good cleaning effectiveness even when laundering under harsh conditions such as laundering in residual bath water.[Solution] A laundry detergent or cleaning composition which comprises a copolymer containing sulfonate groups containing from 1 to 50 mass percent of structural units (a) derived from 1 or more kinds of monomers (A) selected from ether bond-containing monomers represented by Formulas (1) and (2), 50 mass % or more and less than 98 mass % of structural units (b) derived from a carboxyl group-containing monomer (B), and 1 mass % or more and less than 50 mass % of structural units (c) de-rived from a sulfonate group-containing monomer (C).
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Microemulsion heavy wax crystal emulsifying dispersant applied to oil well for tertiary oil recovery
InactiveCN103614128AUnique penetrationImprove permeabilityDrilling compositionHigh carbonAromatic solvents
The invention relates to a microemulsion heavy wax crystal emulsifying dispersant applied to an oil well for tertiary oil recovery, and is mainly used for solving the problem that the oil production rate is influenced due to the high return pressure and the short thermal washing period of the oil recovery well caused by that serious wax precipitations are generated by the oil well which contains thickened oil and is high in polymer flooding and viscosity. The emulsifying dispersant is prepared from the following components by weight percent: 1% to 3% of high-molecular polymer wax inhibitor, 13% to 25% of organic aromatic solvent, 1% to 3.5% of emulsifying agent, 8% to 12% of sulfonate, 10% to 12.5% of alcohol, 10% to 20% of demulsifier and 25% to 35% of water. The emulsifying dispersant has the dual effects of eliminating and preventing the waxy bitumen colloid precipitations with long molecular chains or high carbon number in crude oil from being precipitated, so that the wall sticking quantity of condensate oil is greatly decreased; the running load of the oil well is reduced; and the well washing period is prolonged. Thus, the oil production rate is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Detergent mixture
InactiveUS20040048766A1Good cleaning and foaming propertyProcess economyCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsActive agentSugar amine
A process for making a surfactant composition involving: (a) providing a starting mixture containing: (i) an aqueous alkali solution; (ii) at least one amino acid and / or a salt thereof; (iii) a fatty acid chloride; (iv) an acylatable surfactant precursor selected from the group consisting of a protein hydrolyzate, a polyamino acid, an aminosulfonic acid, an amino sugar, a nonionic surfactant, and mixtures thereof; and (v) up to about 15% by weight, based on the weight of the starting mixture, of a polyol component; (b) providing a stirring mechanism; and (c) reacting (ii) and (iii), with stirring, to form the surfactant composition.
Owner:COGNIS DEUT GMBH & CO KG
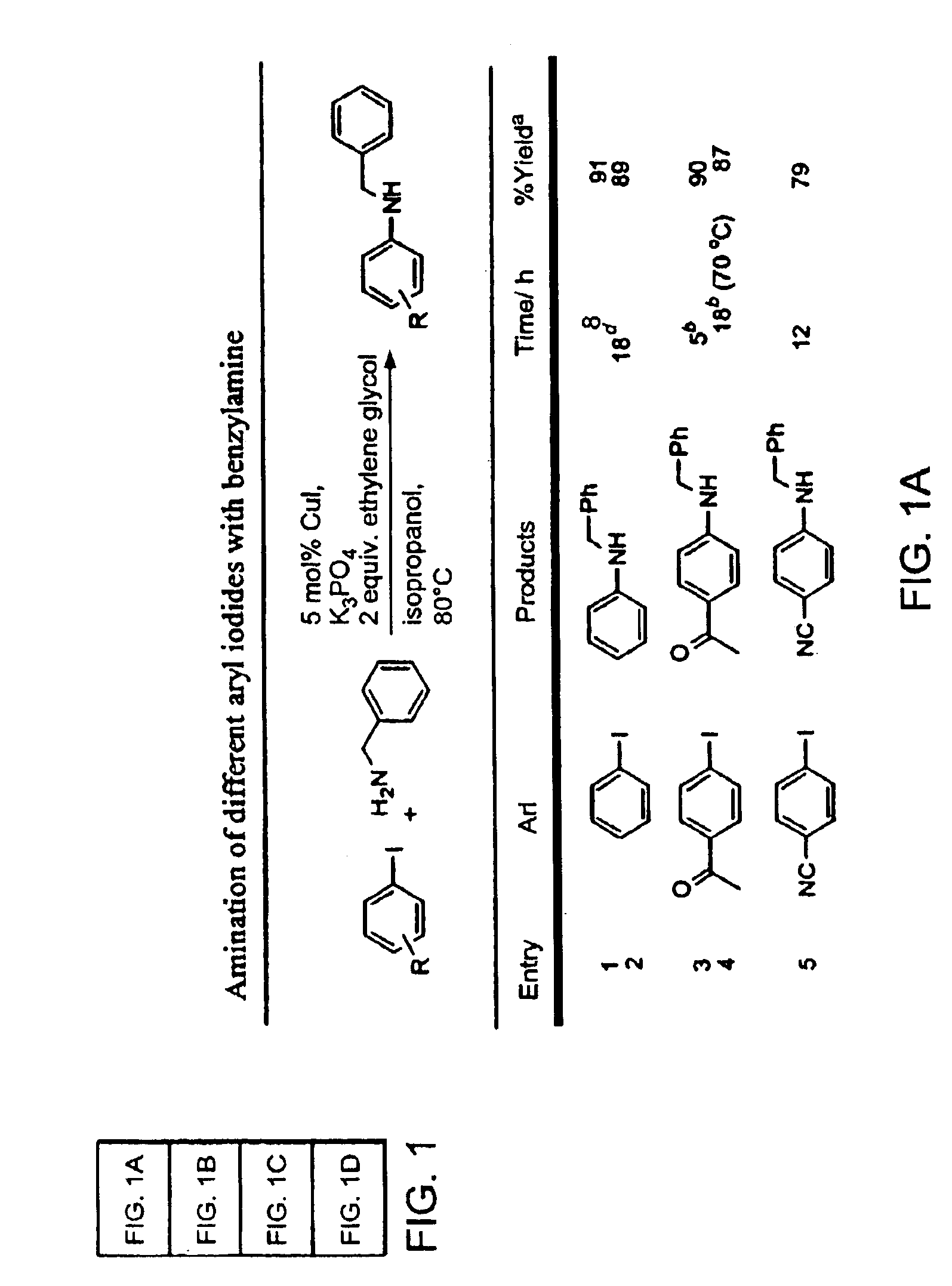
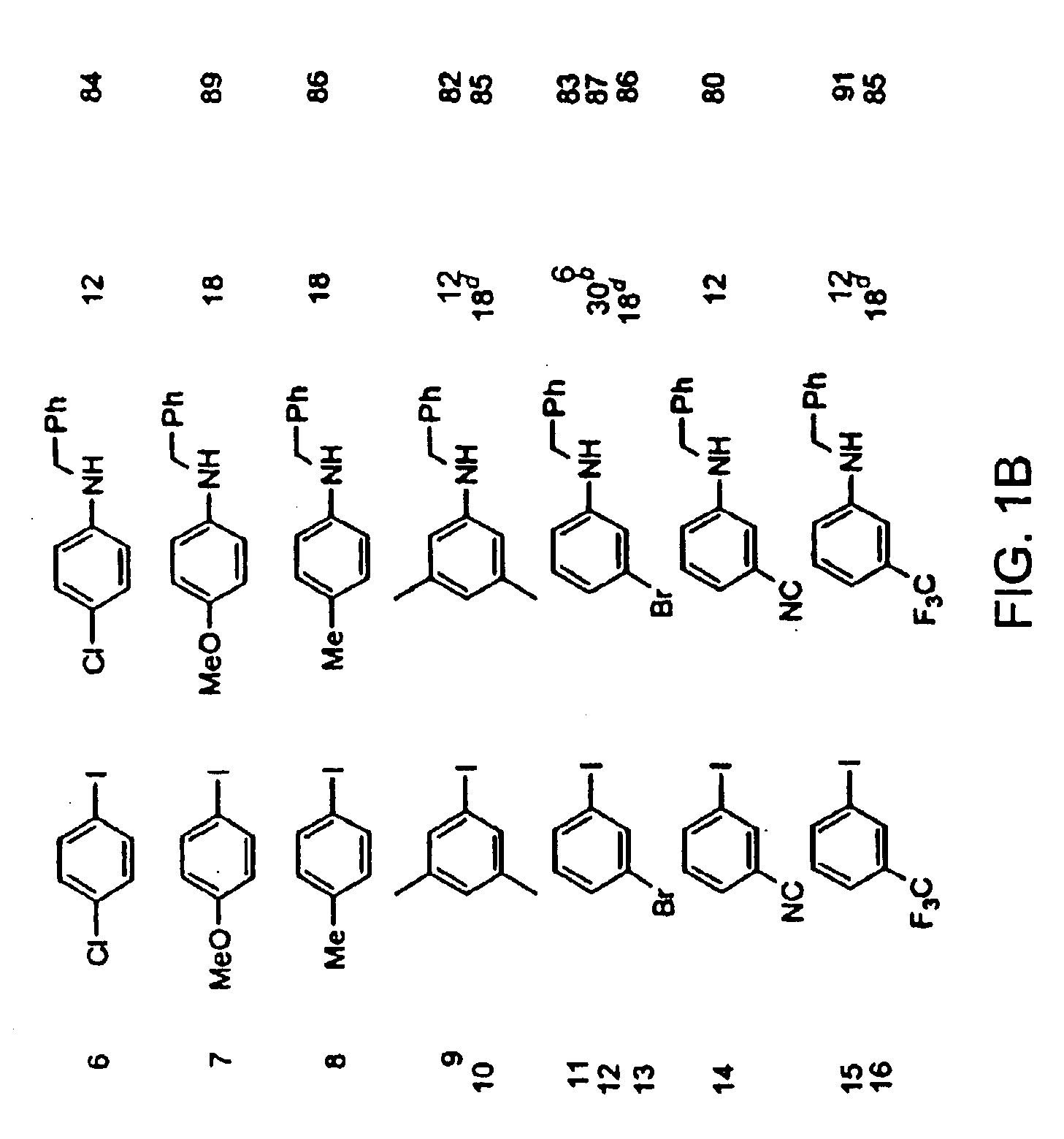
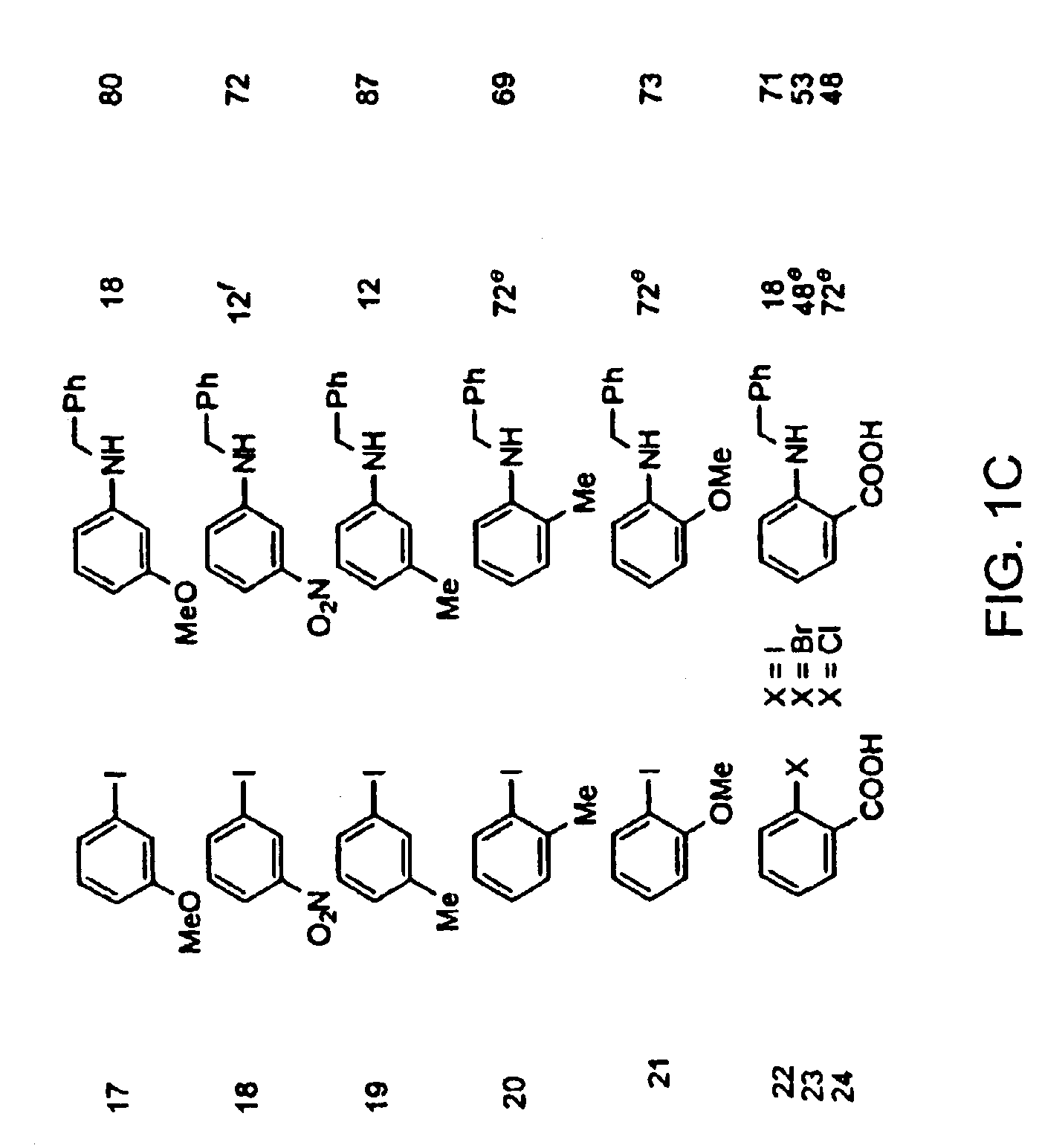
Copper-catalyzed formation of carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bonds
InactiveUS6867298B2Cheap and practicalLow costUrea derivatives preparationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCarbon–oxygen bondHydrazine compound
The present invention relates to copper-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming methods. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of an amide or amine moiety and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In additional embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between a nitrogen atom of an acyl hydrazine and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of a nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic, e.g., indole, pyrazole, and indazole, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-oxygen bond between the oxygen atom of an alcohol and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. The present invention also relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-carbon bond between a reactant comprising a nucleophilic carbon atom, e.g., an enolate or malonate anion, and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. Importantly, all the methods of the present invention are relatively inexpensive to practice due to the low cost of the copper comprised by the catalysts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel sulfonate salts and derivatives, photoacid generators, resist compositions, and patterning process
ActiveUS20080124656A1Increase acidityInhibits the formation of defectsLithium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationResistPhotoacid
Sulfonate salts have the formula: R1COOCH2CH2CF2CF2SO3−M+ wherein R1 is alkyl, aryl or hetero-aryl, M+ is a Li, Na, K, ammonium or tetramethylammonium ion. Onium salts, oxime sulfonates and sulfonyloxyimides derived from these salts are effective photoacid generators in chemically amplified resist compositions.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Nano calcium carbonate-containing calcium sulfonate complex grease and production method thereof
InactiveCN101993767AImprove thermal stabilityImprove extreme pressure and anti-wear performanceLubricant compositionMetallurgyPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to nano calcium carbonate-containing calcium sulfonate complex grease and a production method thereof. The grease comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 10 to 40 percent of high base-value calcium alkylbenzenesulfonate, 50 to 85 percent of base oil, 1 to 10 percent of nano calcium carbonate, 0.5 to 5 percent of boric acid, 0.5 to 5 percent of saturated fatty acid with 12 to 22 carbon atoms, 0.1 to 5 percent of anti-oxidant additive and 1 to 5 percent of composite transformation accelerator HBS. The grease and the production method have the advantages that: a nano calcium carbonate material is added into the formula of the calcium sulfonate complex grease for the first time, so that the thermal stability and extreme pressure wearing resistance of the ordinary calcium sulfonate complex grease are enhanced and a preparation and operation process is simplified. Simultaneously, the composite transformation accelerator is adopted, so that transformation speed and transformation rate are increased and production cost is lowered.
Owner:WUXI HUIYUAN PACKAGING TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com