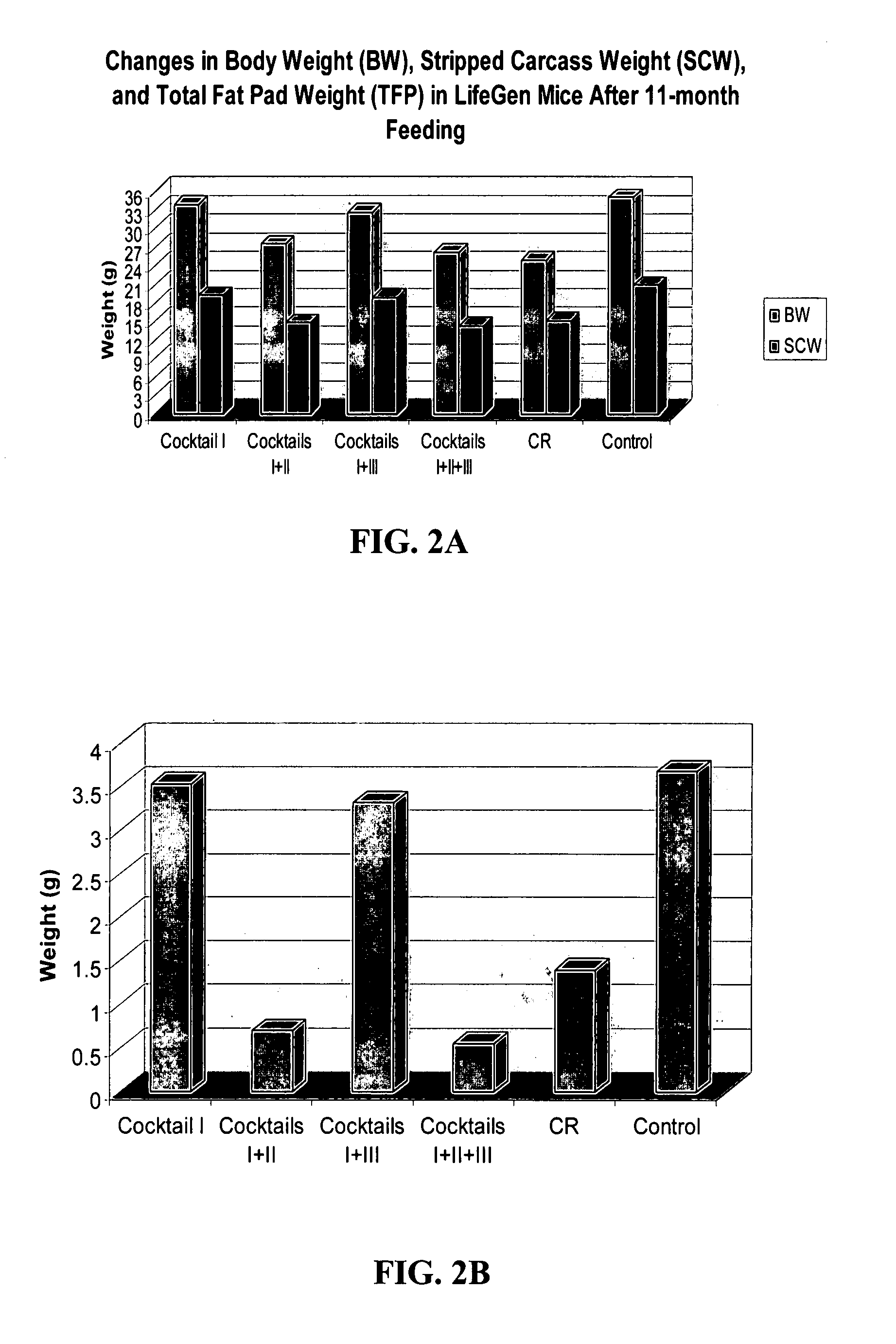
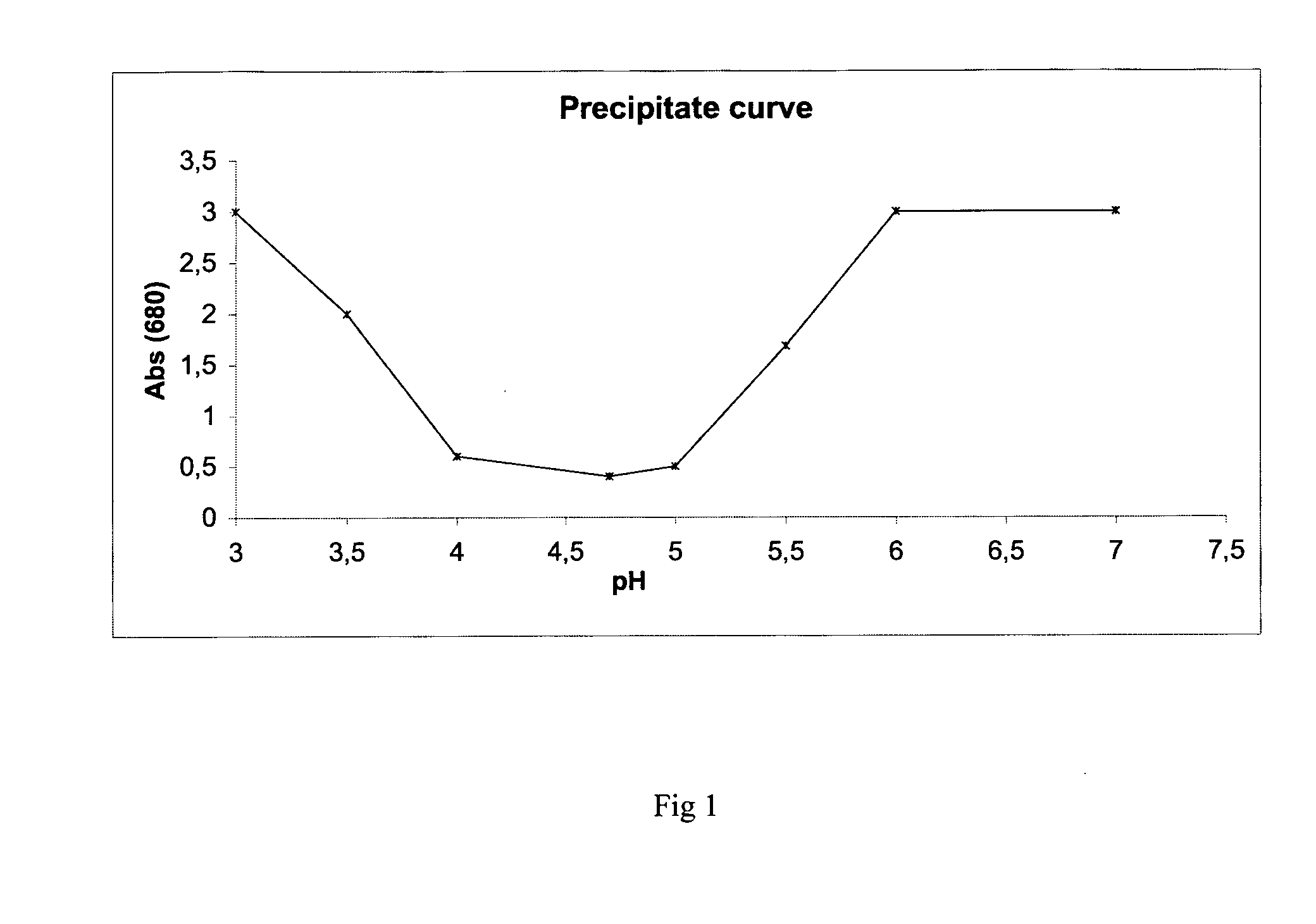
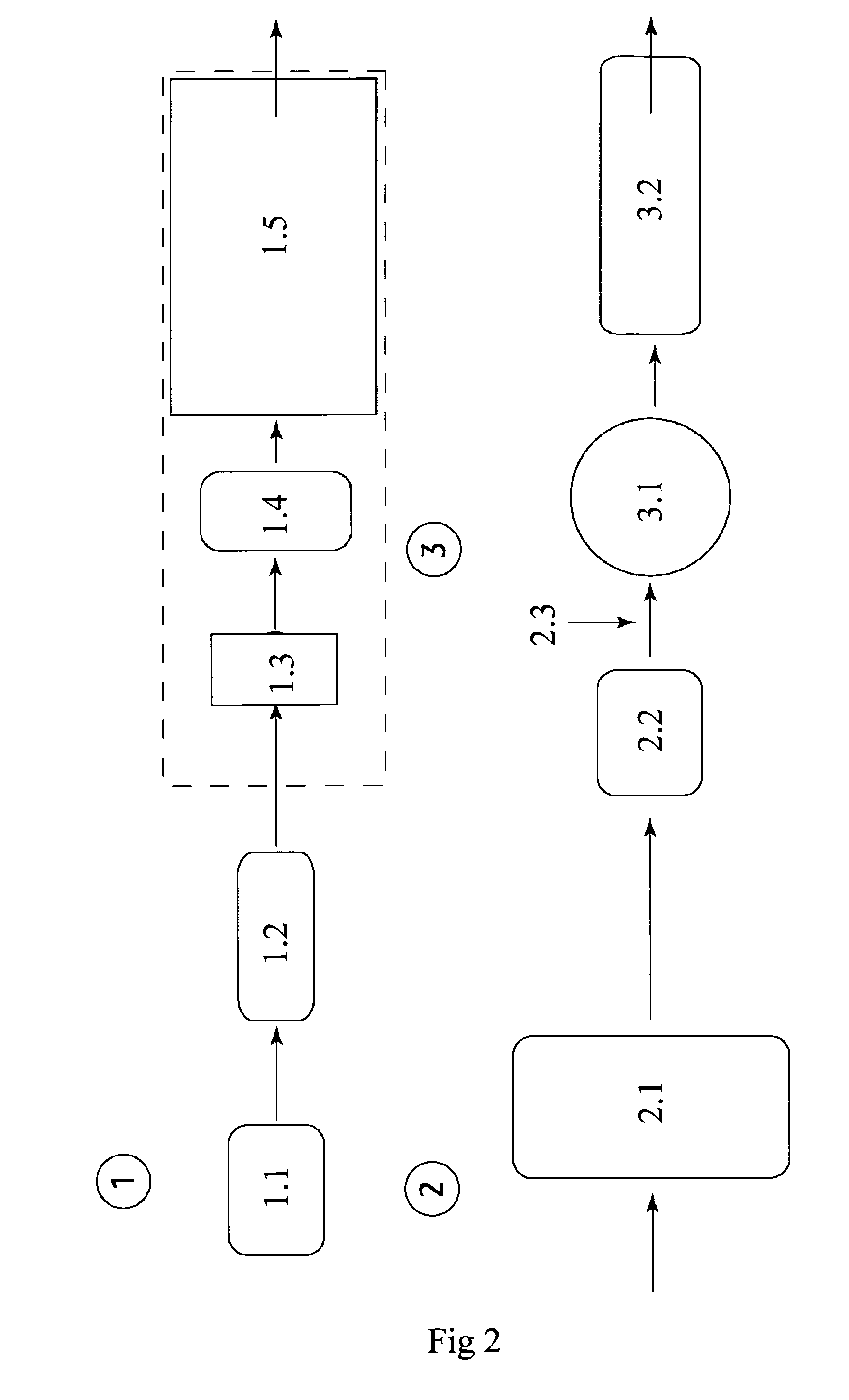
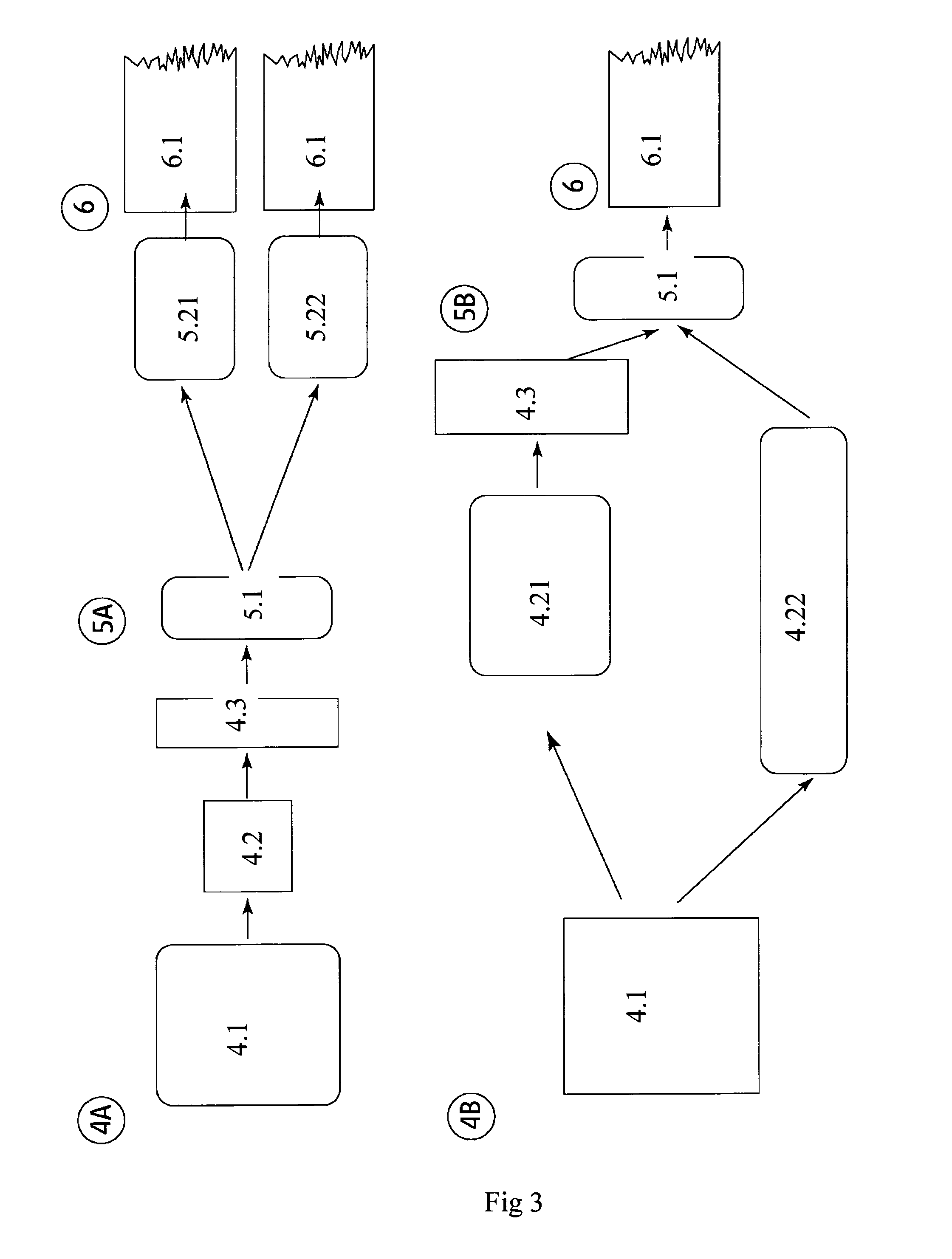
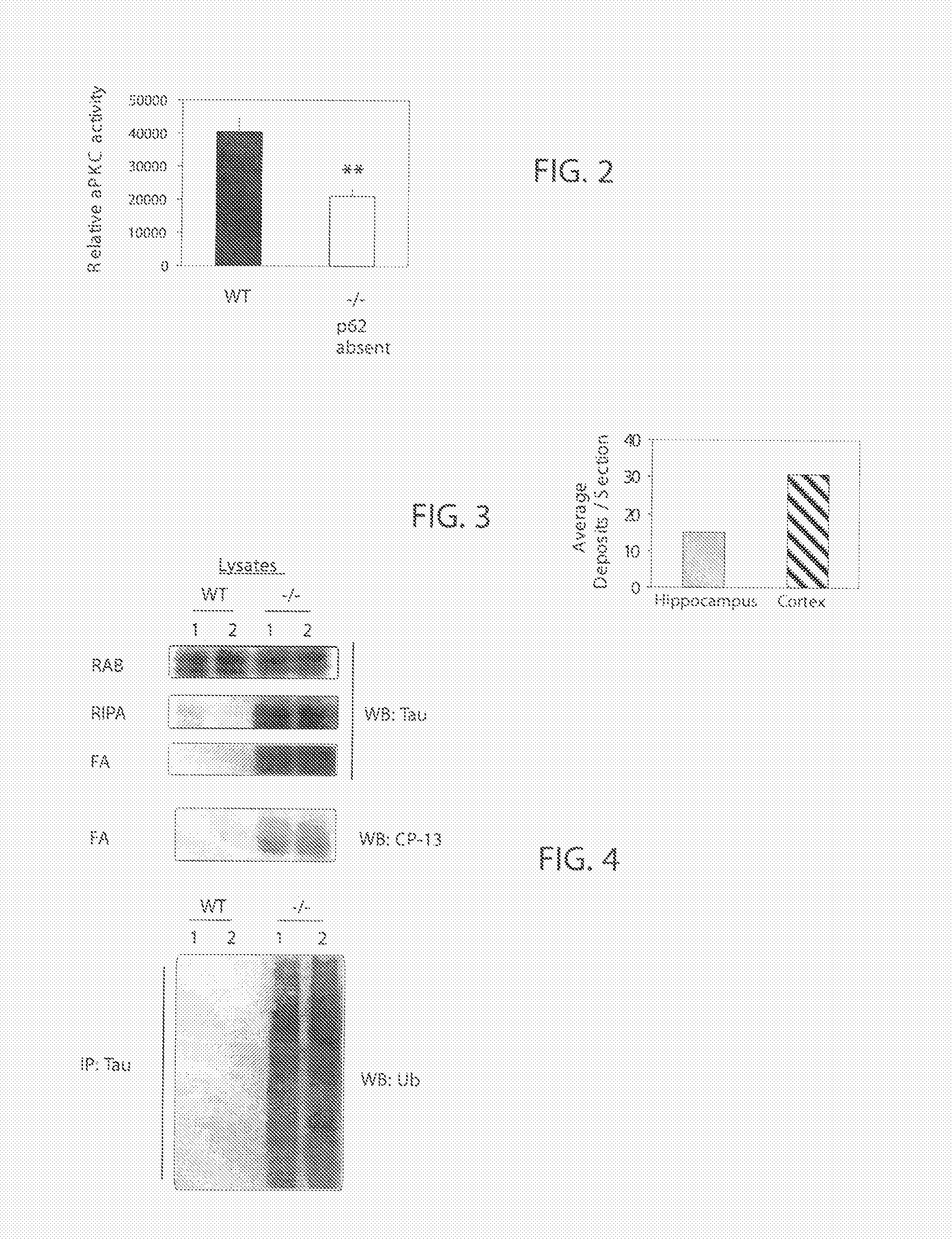Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Blood insulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood glucose level control
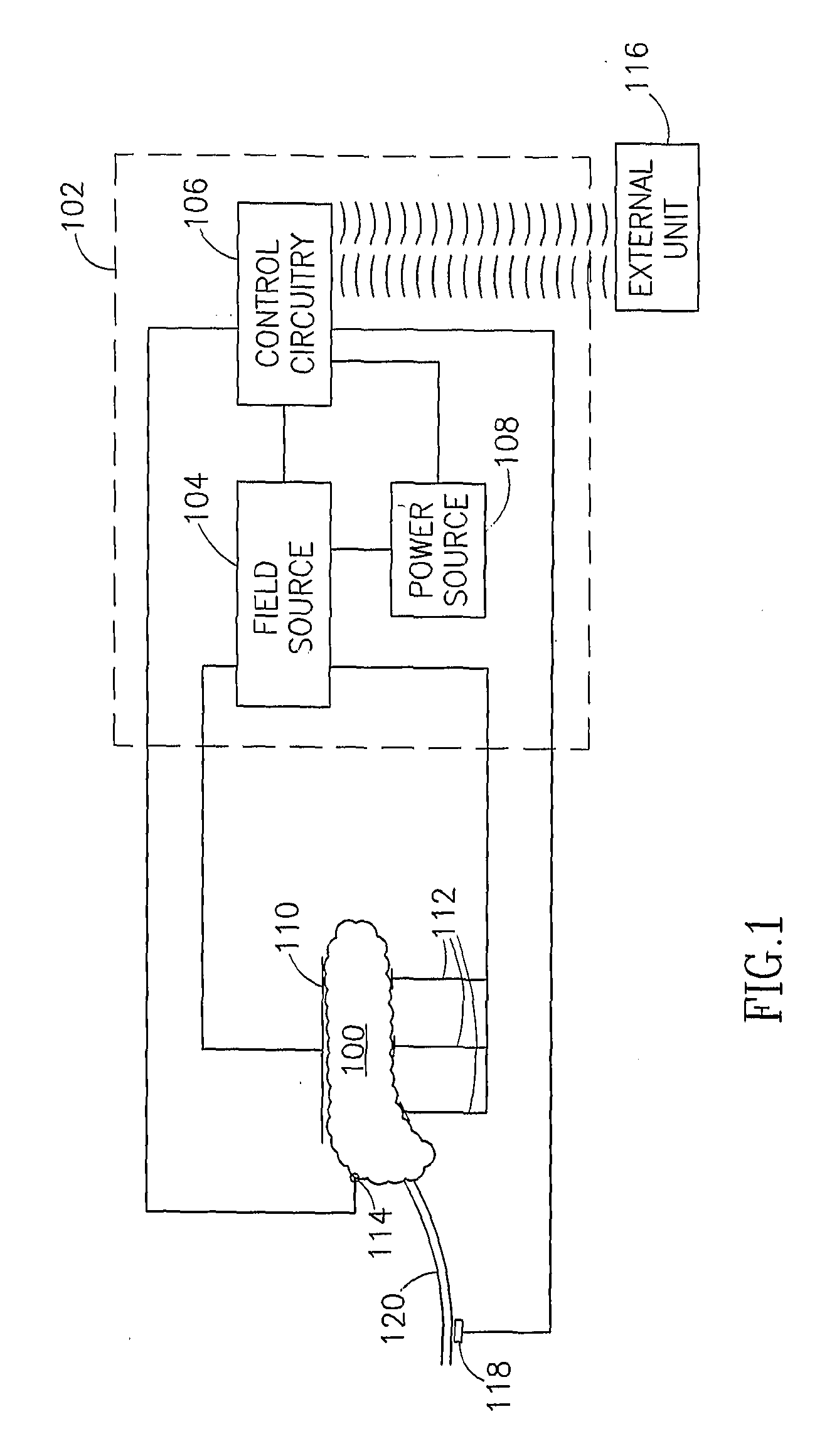
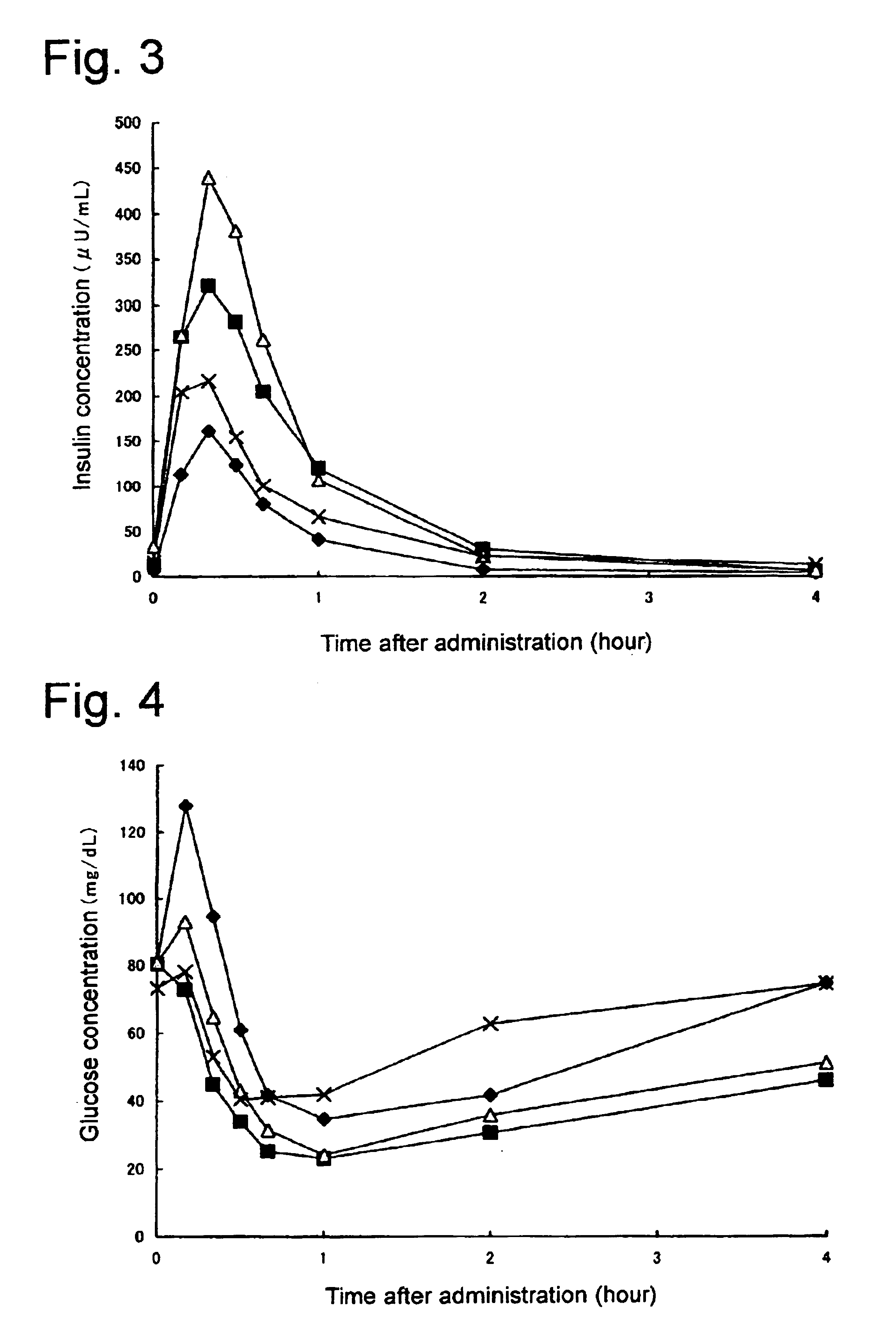
InactiveUS20060085045A1Reduced glucose levelIncrease insulin levelsDigestive electrodesBlood insulinLevel insulin
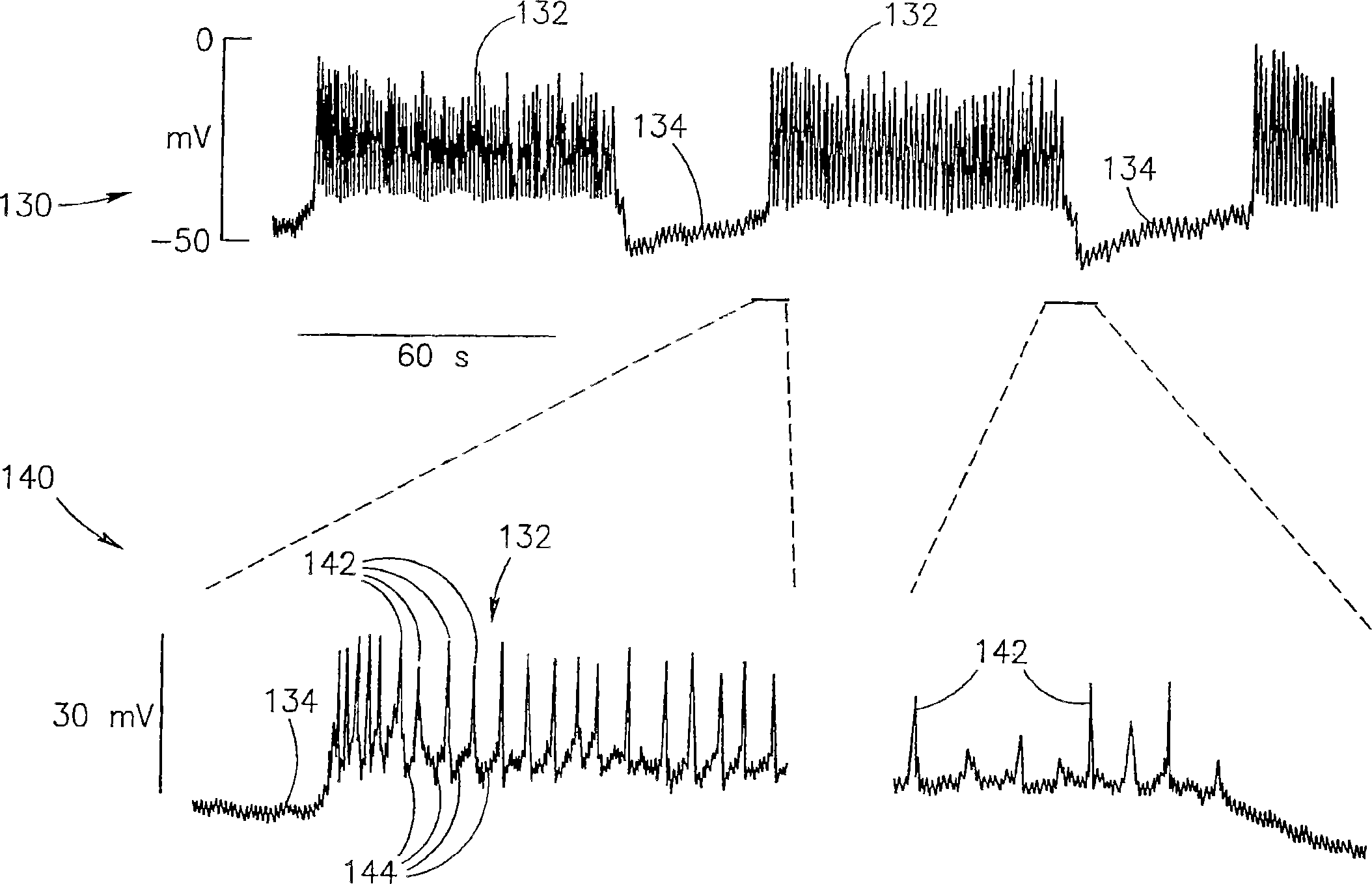
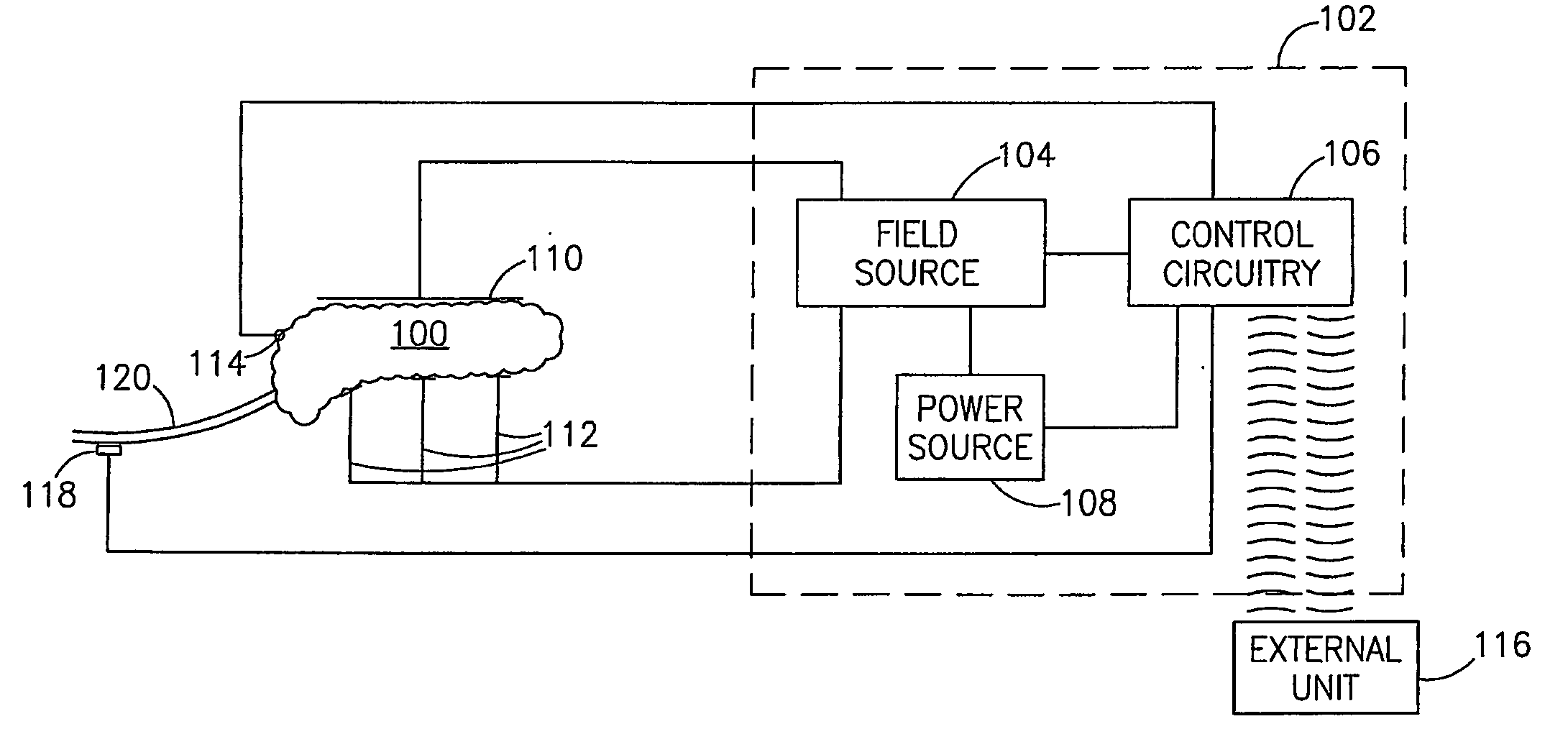
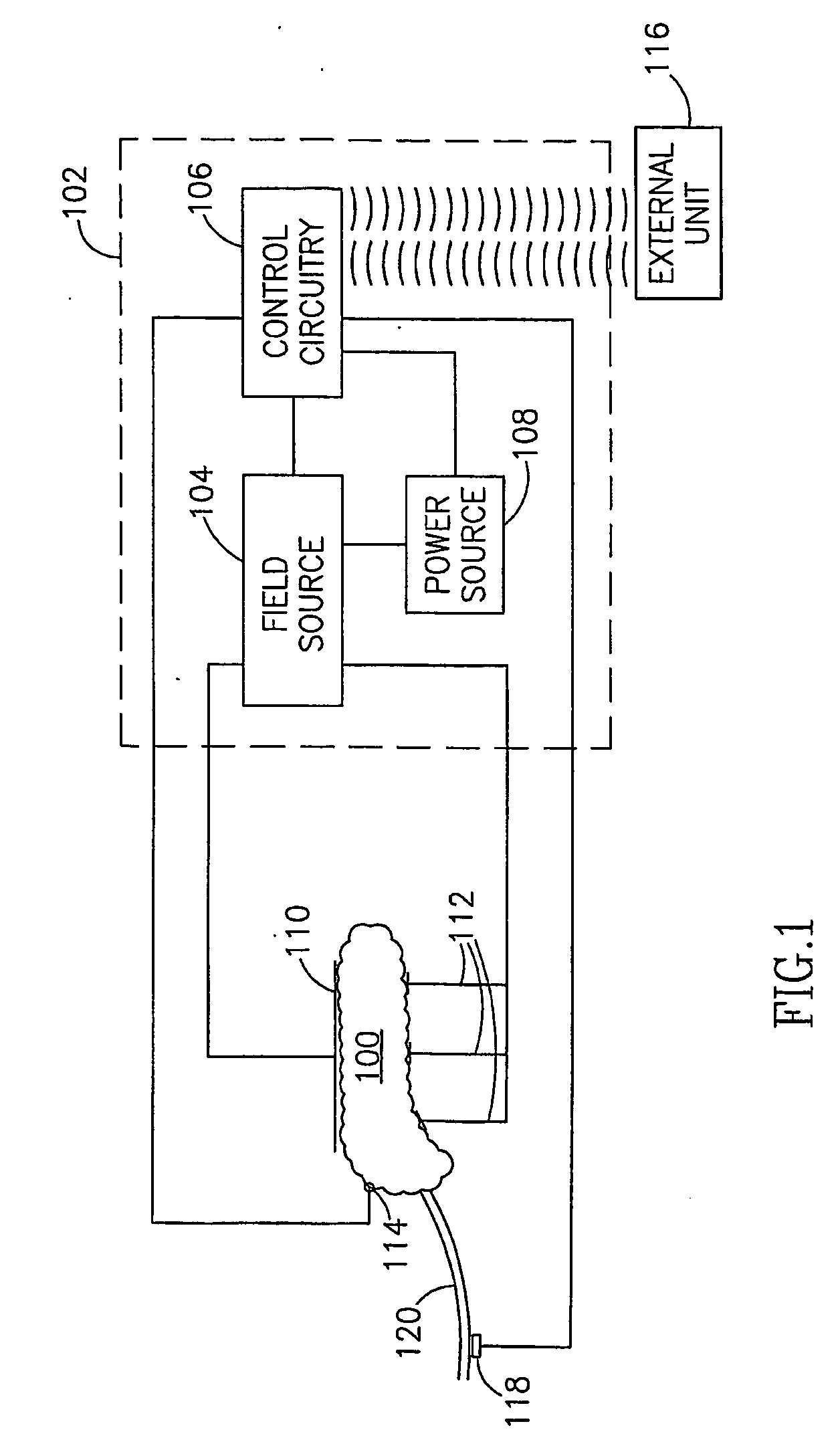
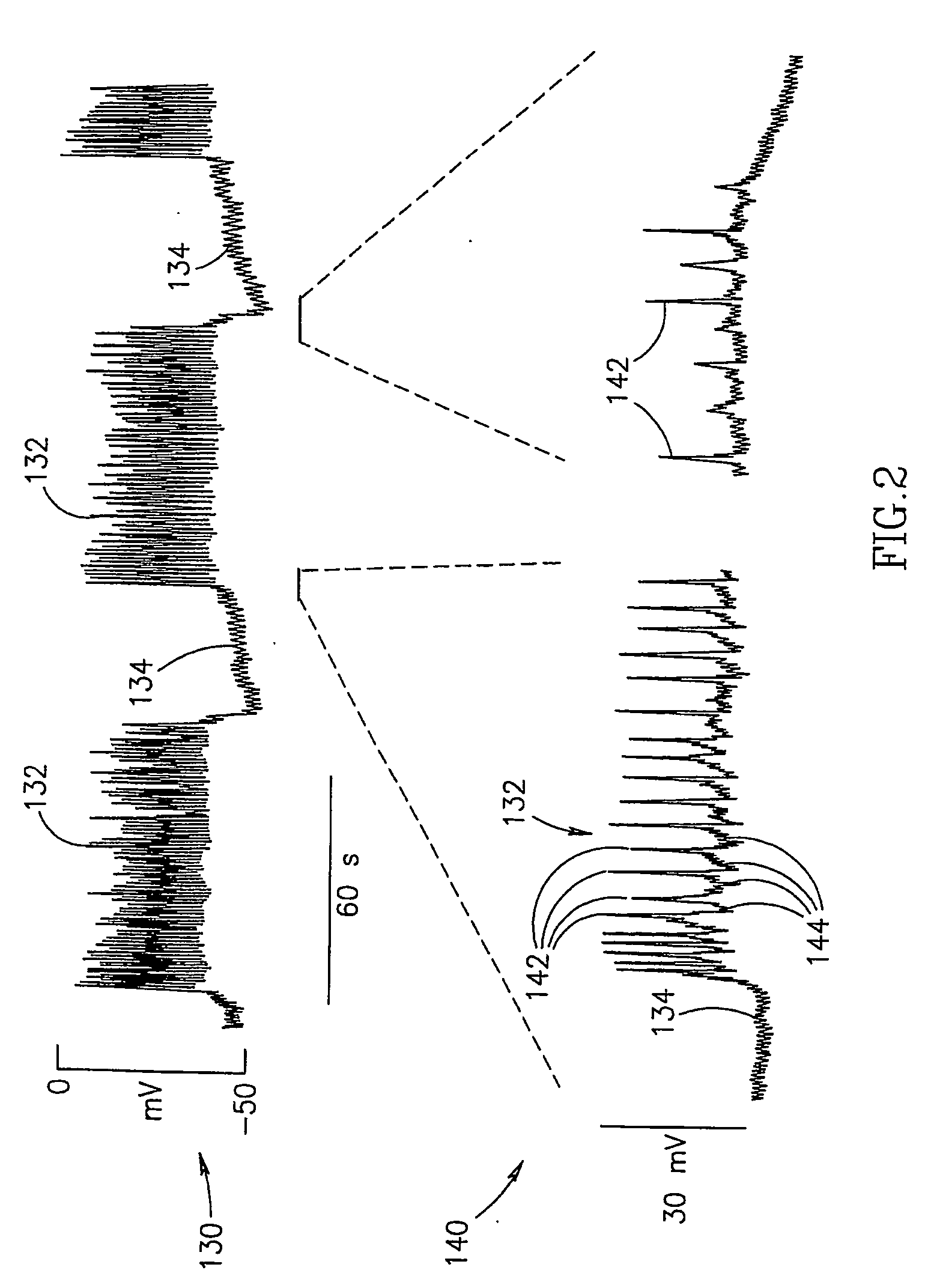
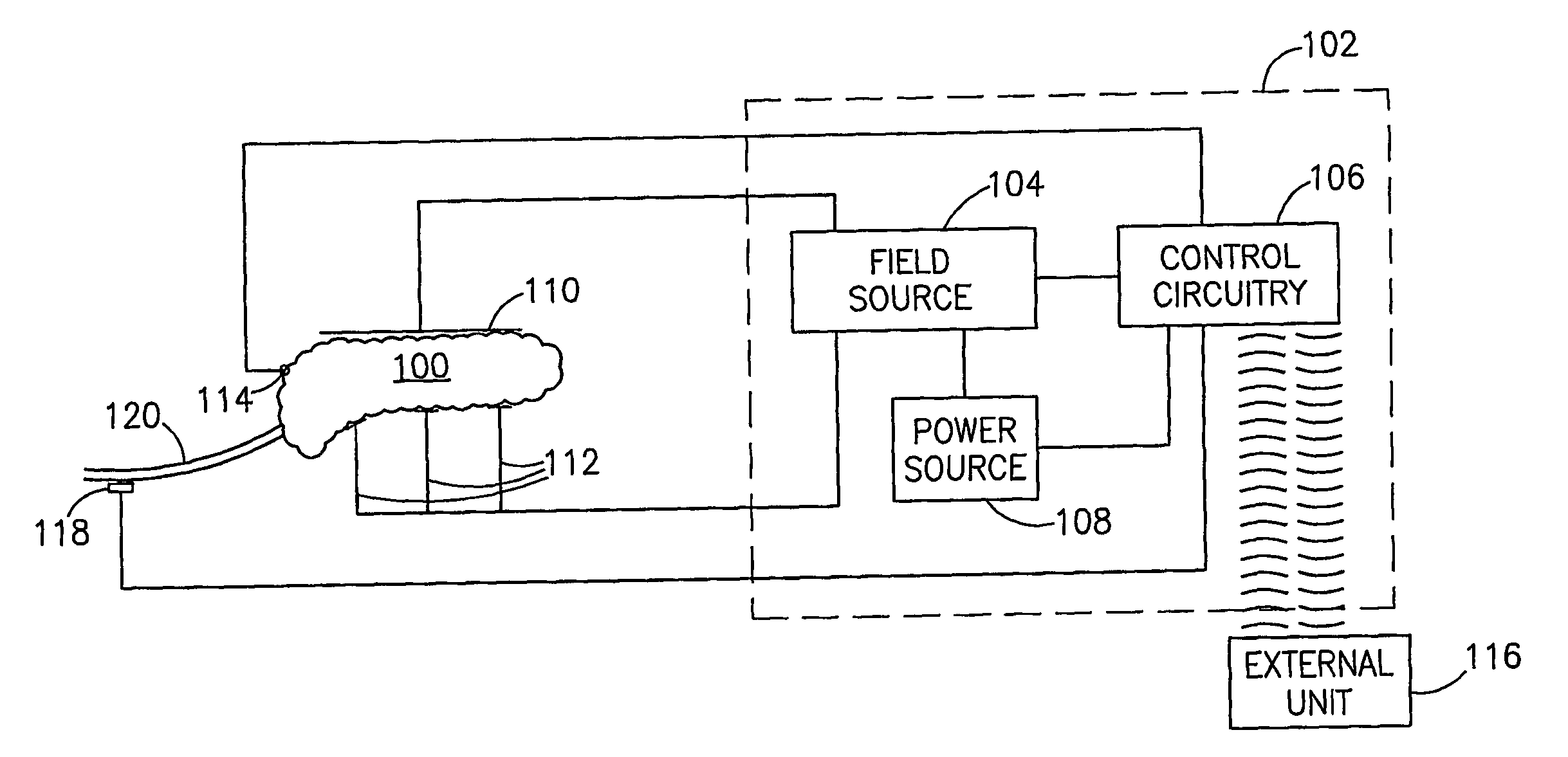
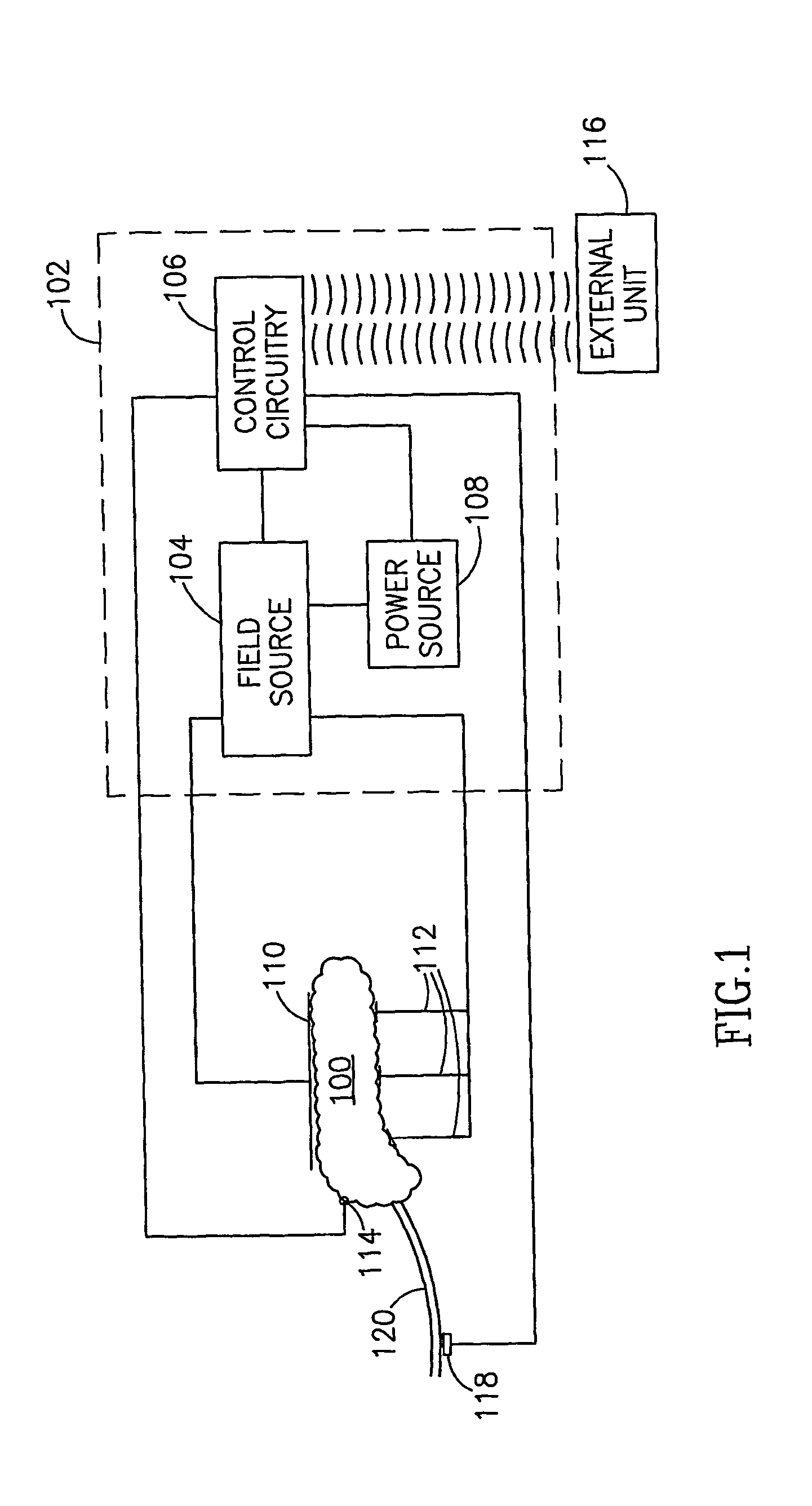
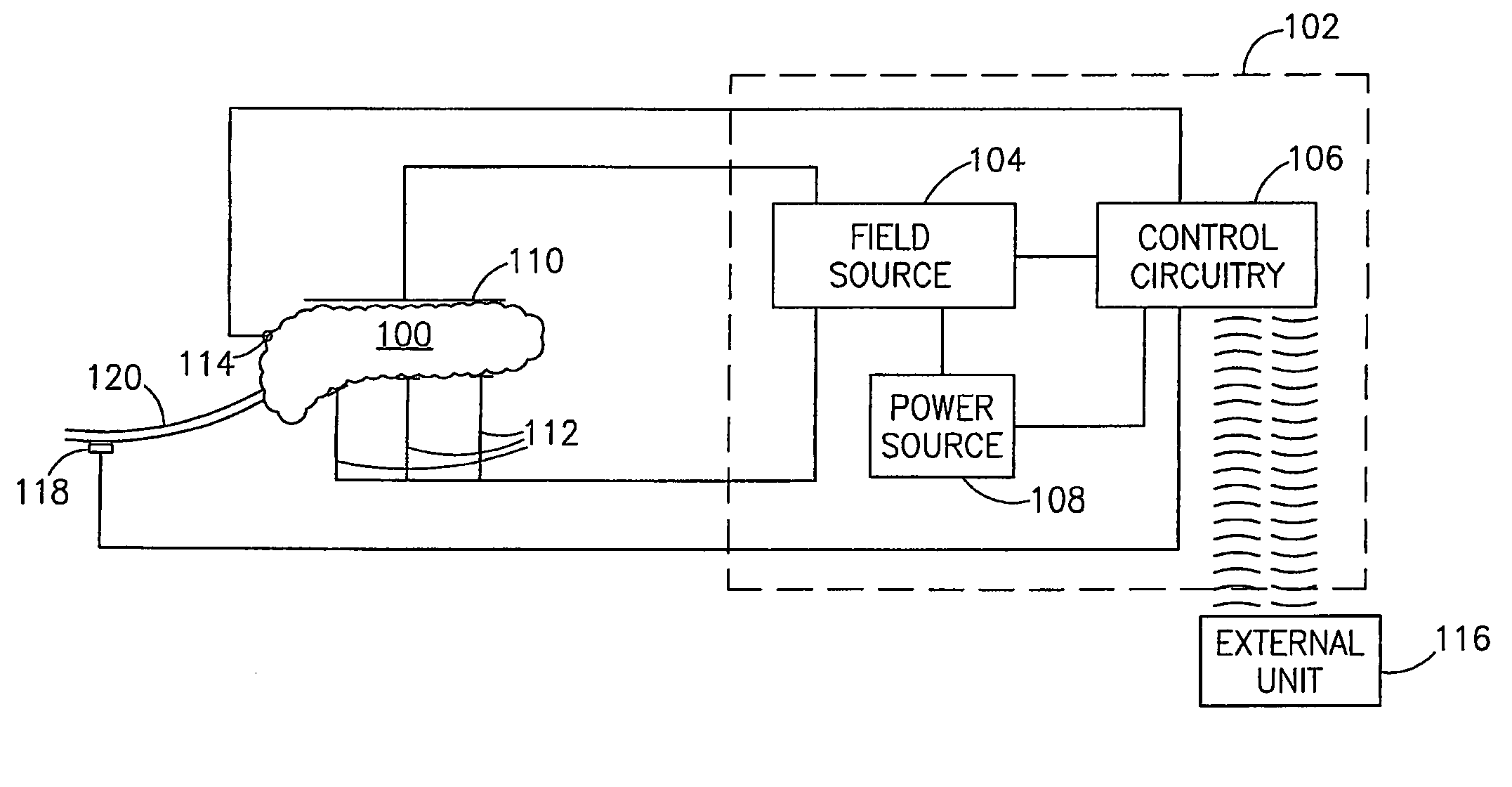
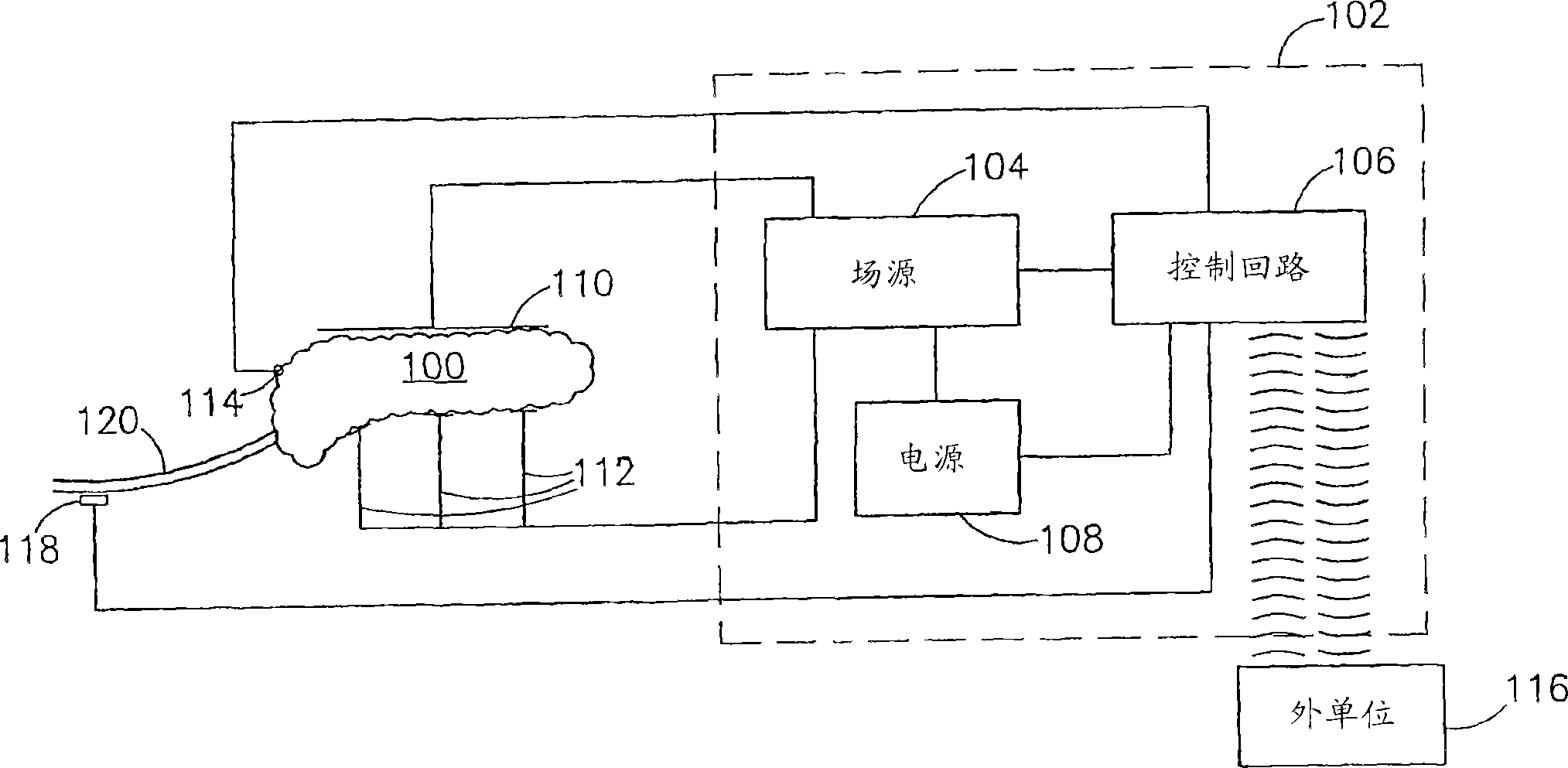
A method of glucose level control, comprising providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using said at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Gastrointestinal Methods And Apparatus For Use In Treating Disorders And Controlling Blood Sugar
InactiveUS20090088816A1Reduced glucose levelAvoid fatigueExternal electrodesDigestive electrodesBlood insulinPhysiology
A method of glucose level control comprising providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using said at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased compared to a regular insulin response in a same person.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Method for delivery of monomeric or dimeric insulin complexed to diketopiperazine microparticles
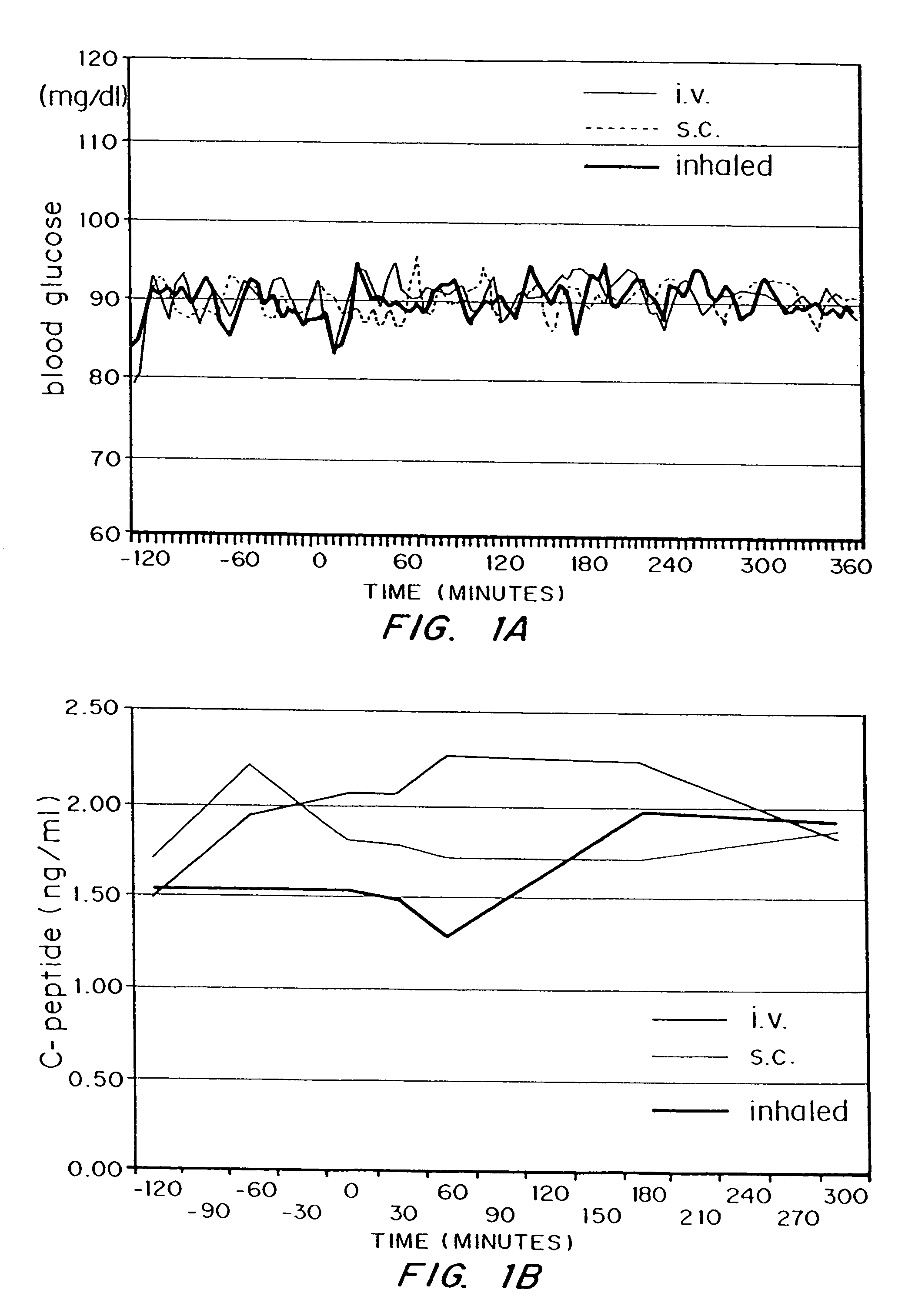
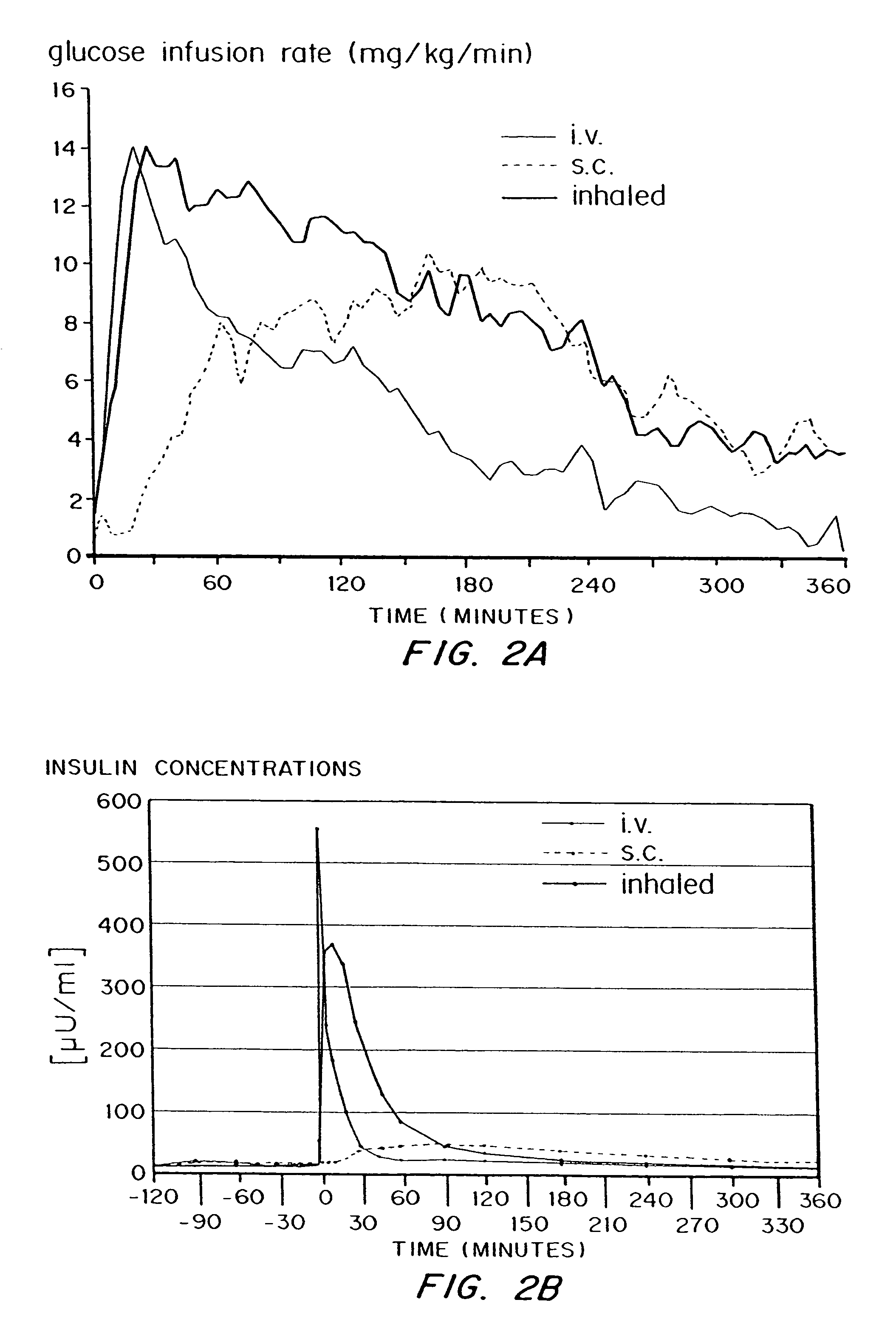
InactiveUS7648960B2Rapid increase in blood agent concentrationEasy to transportPowder deliverySpray deliveryBlood insulinBlood agent
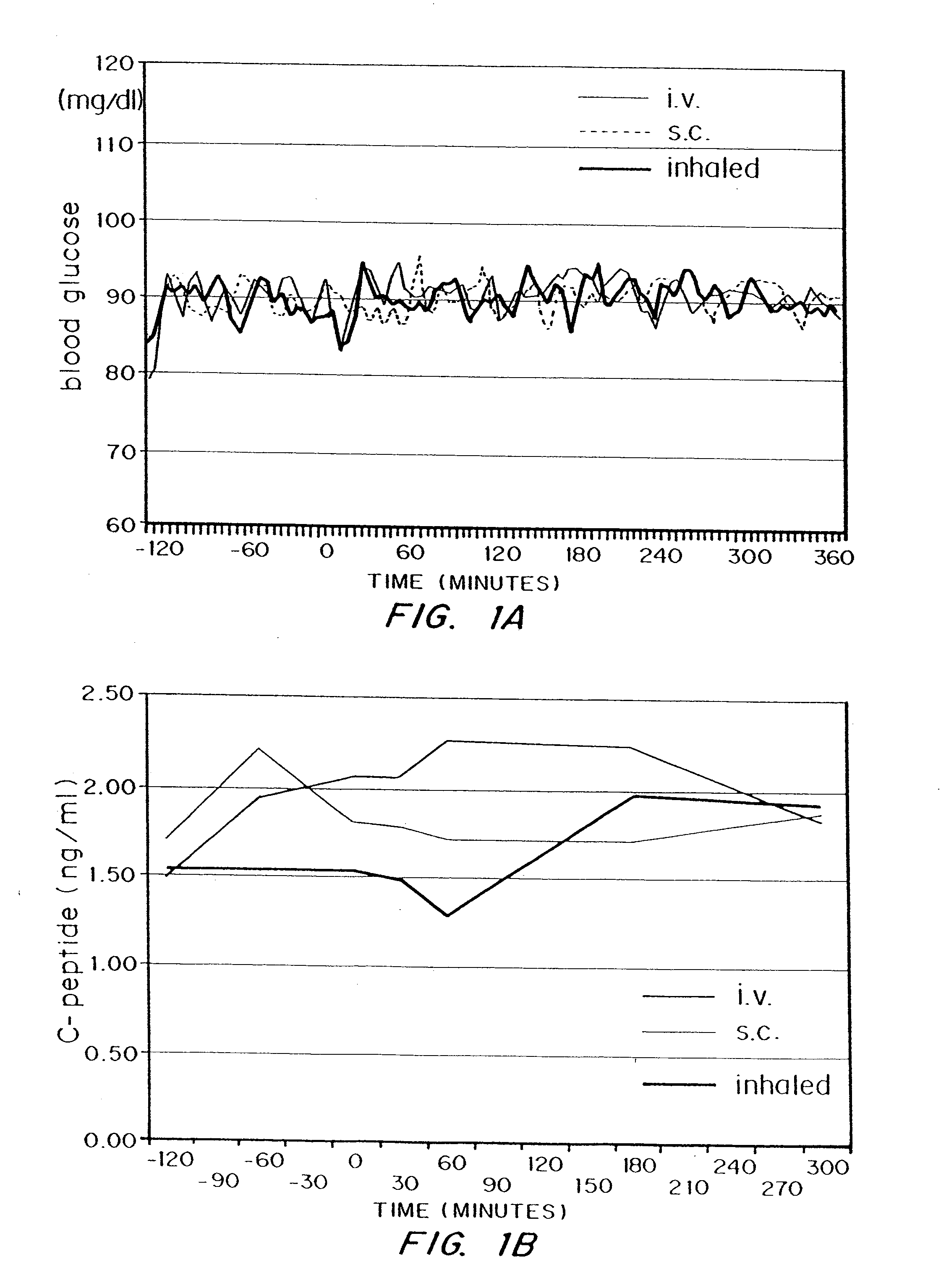
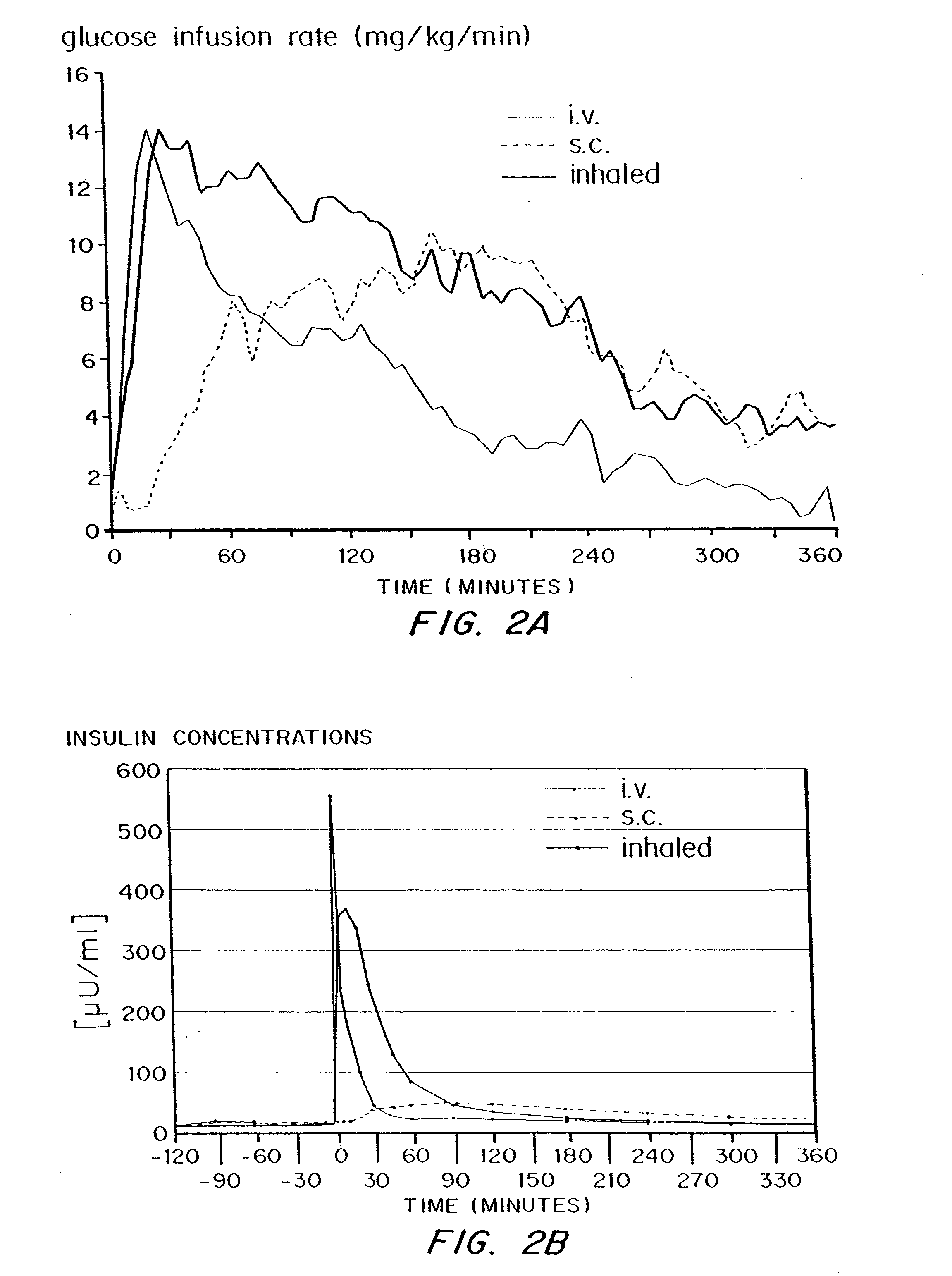
Methods are provided for purifying peptides and proteins by incorporating the peptide or protein into a diketopiperazine or competitive complexing agent to facilitate removal of one or more impurities from the peptide or protein. Formulations and methods also are provided for the improved transport of active agents across biological membranes, resulting for example in a rapid increase in blood agent concentration. The formulations include microparticles formed of (i) the active agent, which may be charged or neutral, and (ii) a transport enhancer that masks the charge of the agent and / or that forms hydrogen bonds with the target biological membrane in order to facilitate transport. In one embodiment insulin is administered via the pulmonary delivery of microparticles comprising fumaryl diketopiperazine and insulin in its biologically active form. This method of delivering insulin results in a rapid increase in blood insulin concentration that is comparable to the increase resulting from intravenous delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS8019421B2Reduced effectivenessOverworking pancreasInternal electrodesSurgical instrument detailsBlood levelBlood insulin
A pancreatic controller, comprising:at least one electrode adapted for electrifying at least a portion of a pancreas; anda controller programmed to electrify said electrode so as to positively control at least the effect of at least two members of a group consisting of blood glucose level, blood insulin level and blood level of another pancreatic hormone. In one example, the controller controls insulin, glucagon and / or glucose blood levels.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS20070156177A1Lower Level RequirementsIncrease insulin levelsHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesBlood insulinLevel insulin
A method of glucose level control comprising, providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using said at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased compared to a regular insulin response in a same person.
Owner:METACURE
Blood glucose level control
InactiveUS8700161B2Increase insulin levelsLower Level RequirementsImplantable neurostimulatorsDigestive electrodesBlood insulinPancreas
A method of glucose level control, comprising providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using the above-mentioned at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased.
Owner:TYLERTON INT INC
Nutritional system and methods for increasing longevity
Disclosed herein are dietary formulations and methods to mimic the physiological, biochemical and gene expression effects of calorie restriction without altering dietary intake. The formulations include combinations of nutrients that have various intended functions in the body, falling into three or more of the following activities; (1) antioxidant activity; (2) inhibition of glycation damage; (3) reduction of body weight and fat; and (4) promotion of high insulin sensitivity and low blood insulin / glucose; and (5) anti-inflammatory activity.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Large-scale process for the preparation of thylakoids
InactiveUS20110182930A1Increase satietyLose weightBiocideMetabolism disorderBlood insulinDietary supplement
The present invention relates to a process on a large industrial scale for the production of thylakoids, from photosynthetic organisms, such as from green plant leaf material, to be used as ingredients in food, or additions to food, or dietary supplements, or pharmaceuticals for the purpose of preventing overweight, promoting satiety, reducing food intake, reducing bodyweight, reducing blood insulin concentration and reducing blood fats and percentage body fat in humans and animals.
Owner:THYLABISCO
Methods and Compositions for Delivering Peptides
InactiveUS20100086609A1Improve concentrationEasy to transportPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBlood insulinBlood agent
Methods are provided for purifying peptides and proteins by incorporating the peptide or protein into a diketopiperazine or competitive complexing agent to facilitate removal one or more impurities, from the peptide or protein. Formulations and methods also are provided for the improved transport of active agents across biological membranes, resulting for example in a rapid increase in blood agent concentration. The formulations include microparticles formed of (i) the active agent, which may be charged or neutral, and (ii) a transport enhancer that masks the charge of the agent and / or that forms hydrogen bonds with the target biological membrane in order to facilitate transport. In one embodiment, insulin is administered via the pulmonary delivery of microparticles comprising fumaryl diketopiperazine and insulin in its biologically active form. This method of delivering insulin results in a rapid increase in blood insulin concentration that is comparable to the increase resulting from intravenous delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Uses of NOGO-A inhibitors and related methods
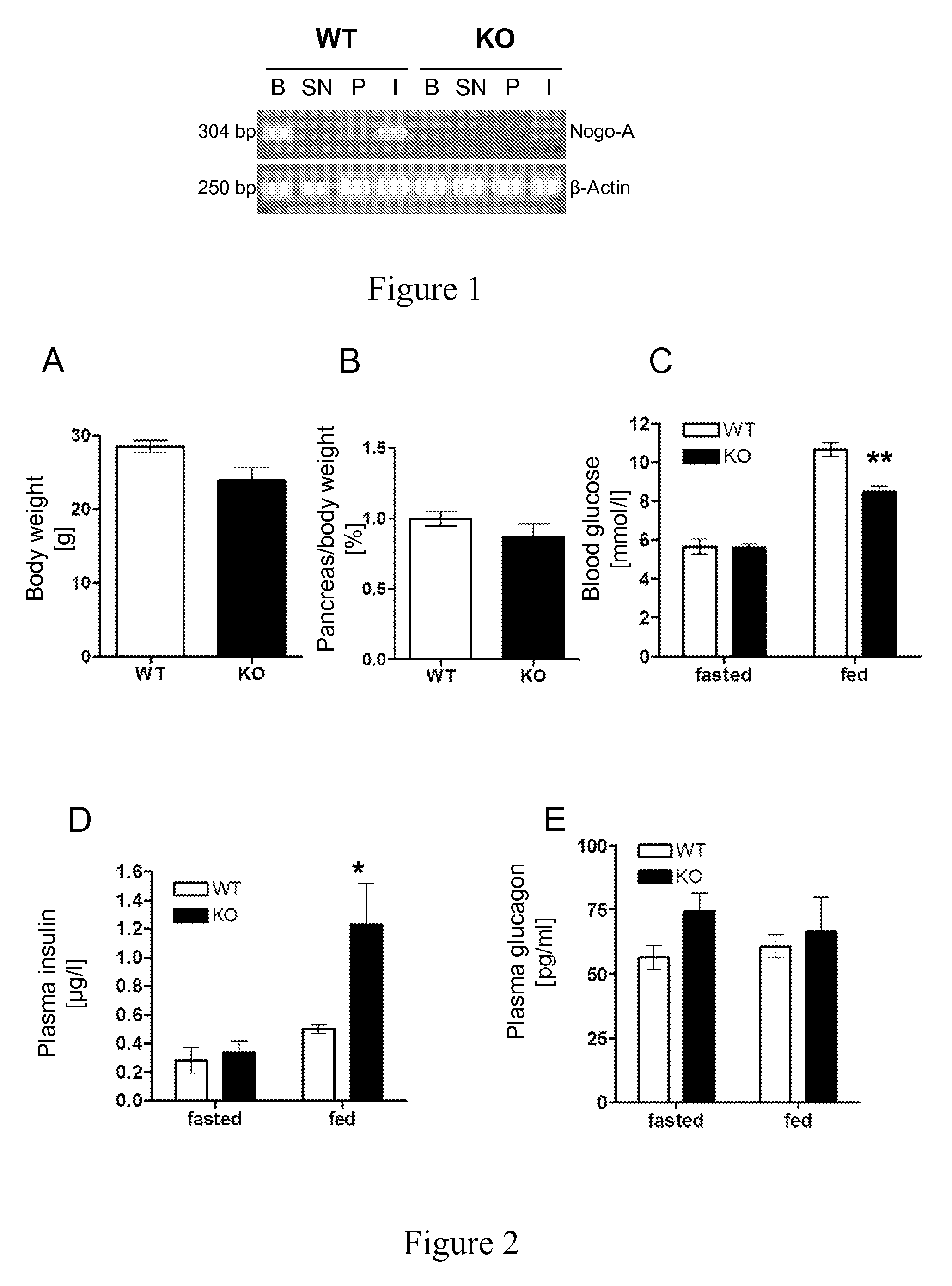
InactiveUS8828390B2High sensitivityIncrease secretionMetabolism disorderSnake antigen ingredientsBlood insulinD-Glucose
The present invention is directed to Nogo-A antagonists useful for the control of blood glucose or blood insulin levels in a subject and related use and formulation thereof. In particular, the invention is directed to Nogo-A antagonists useful for the prevention, repression or treatment insulin secretion deficiency and related methods and pharmaceutical formulations. In particular, the invention relates to Nogo-A antagonists useful in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Method for the treatment of obesity, overweight and fluctuations in blood insuline and/or glucose levels
InactiveUS20030113310A1Low calorific valueLowering indexPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderIntestinal structureBlood insulin
The present invention relates to a method of treating or preventing obesity, overweight, fluctuations in blood insulin levels and / or fluctuations in blood glucose levels in mammals. The method acording to the invention comprises the enteral administration to a mammal of an effective amount of a preparation containing an enzyme capable of converting an ingested carbohydrate or digestion product thereof into one or more absorbable components, wherein the total metabolic caloric value of the absorbable component(s) is less than the metabolic caloric value of the ingested carbohydrate or digestion product thereof. Thus the present invention effectively provides a method that allows complete digestion of ingested digestible carbohydrates whilst at the same time reducing the actual metabolic caloric value of said ingested carbohydrates. Another aspect of the invention relates to a pill for oral administration provided with an enteric coating and containing 25 to 10.000 IU glucose isomerase per gram.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Composition comprising carbohydrate and peptide material and its use as an energy supplement after or during physical exercise or as a metabolic nutrient for oral consumption
InactiveUS20010031729A1Great tasteImprove responseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBlood insulinDietary supplement
The invention relates to a composition comprising carbohydrate and peptide material as well as an amount of at least one additional free amino acid selected from the group consisting of leucine and phenylalanine. This composition will enhance the blood insulin response after oral intake by humans and is intended for an enhanced recovery air physical exercise or to delay exhaustion during physical exercise.
Owner:QUEST INTERNATIONAL
Composition for nasal administration of insulin
InactiveUS6906027B2Good curative effectPromote absorptionPowder deliveryBiocideCelluloseNasal cavity
Provided is an insulin-containing granulated composition for nasal administration comprising a crystalline cellulose aggregate having a specific particle diameter distribution as a carrier. Such granulated composition for nasal administration can efficiently increase a blood insulin concentration.
Owner:SHIN NIPPON BIOMEDICAL LAB
Composition comprising carbohydrate and peptide material and its use as an energy supplement after or during physical exercise or as a metabolic nutrient for oral consumption
InactiveUS6713082B2Great tasteImprove responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBlood insulinDietary supplement
The invention relates to a composition comprising carbohydrate and peptide material as well as an amount of at least one additional free amino acid selected from the group consisting of leucine and phenylalanine. This composition will enhance the blood insulin response after oral intake by humans and is intended for an enhanced recovery after physical exercise or to delay exhaustion during physical exercise.
Owner:QUEST INTERNATIONAL
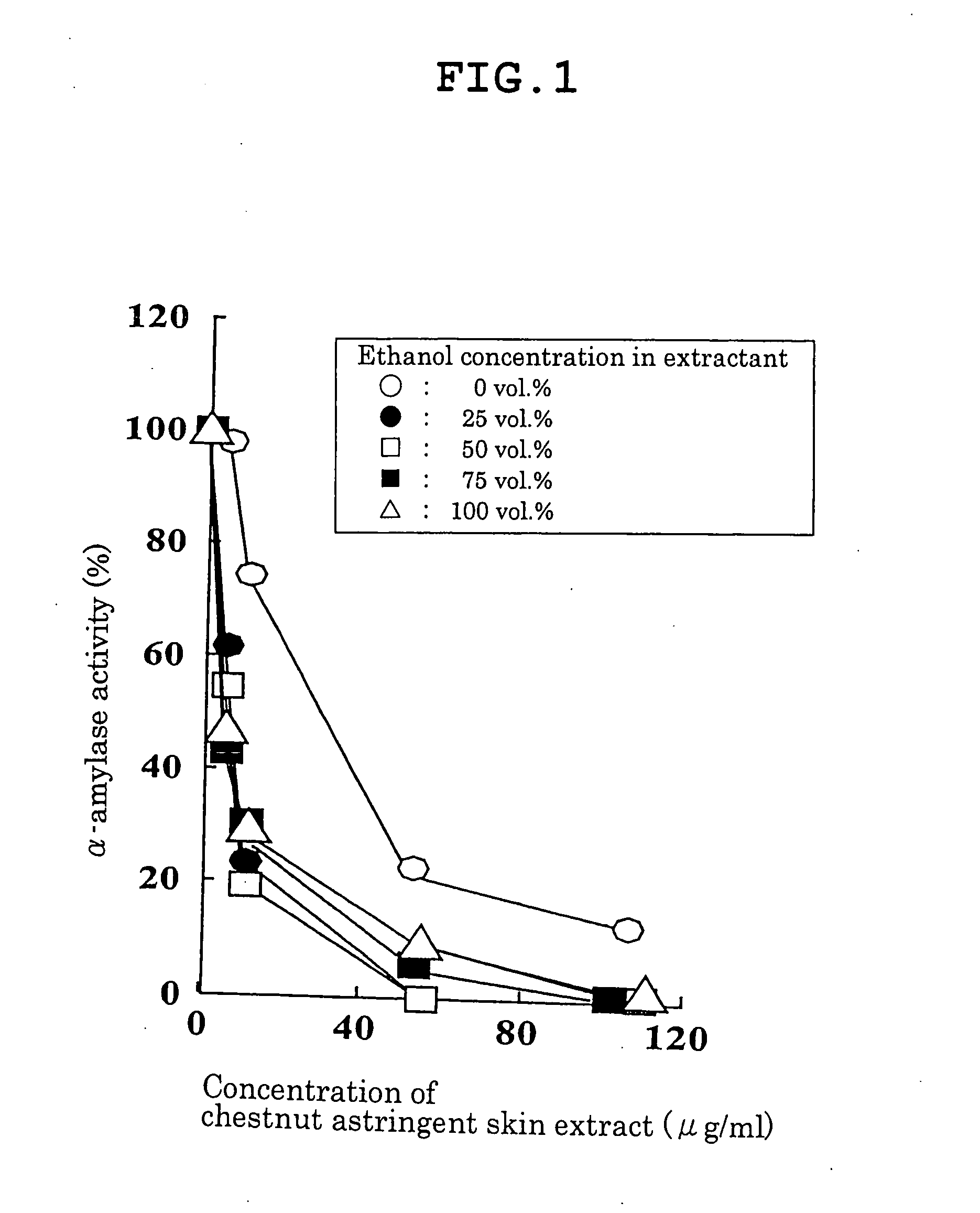
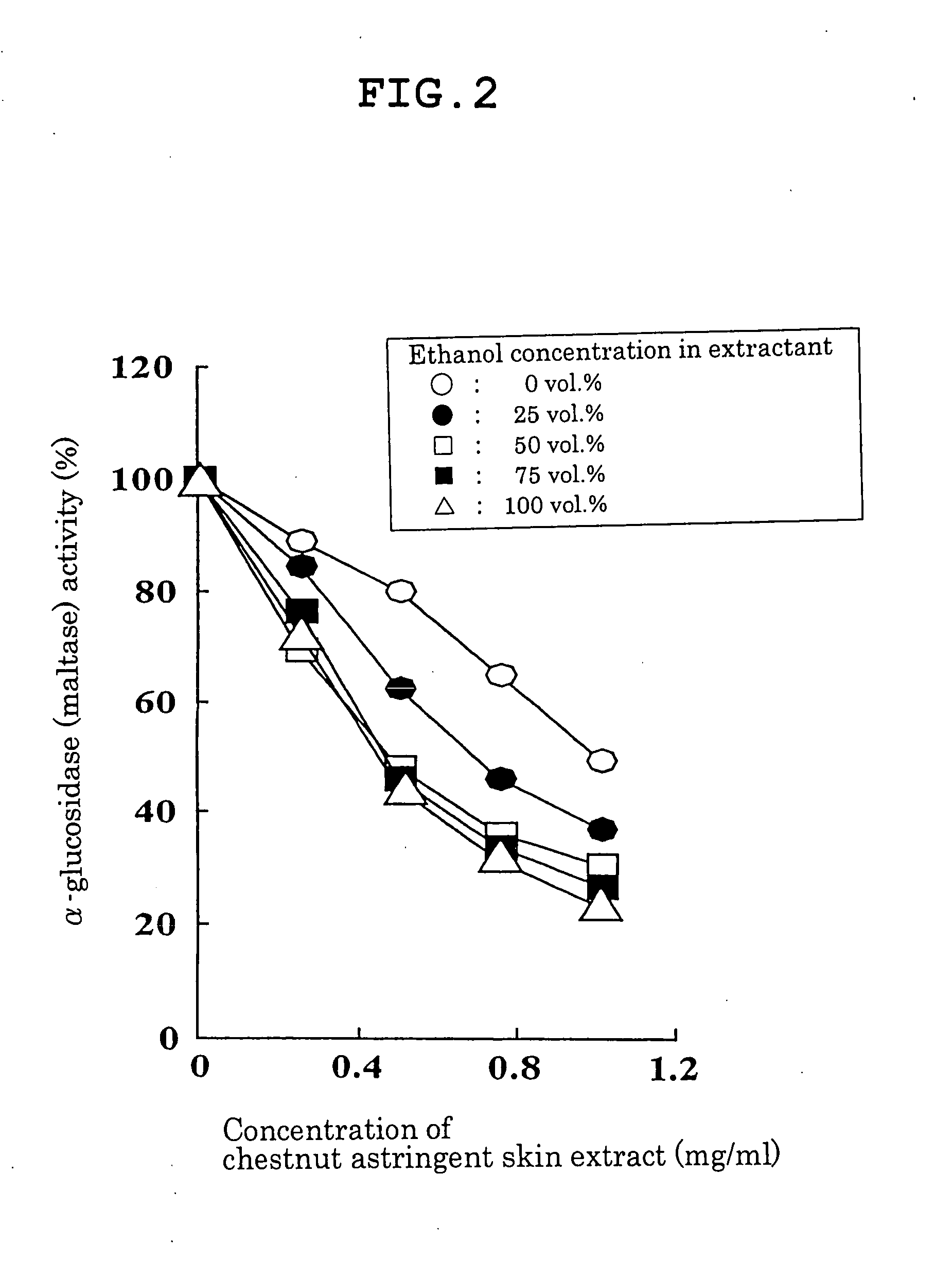
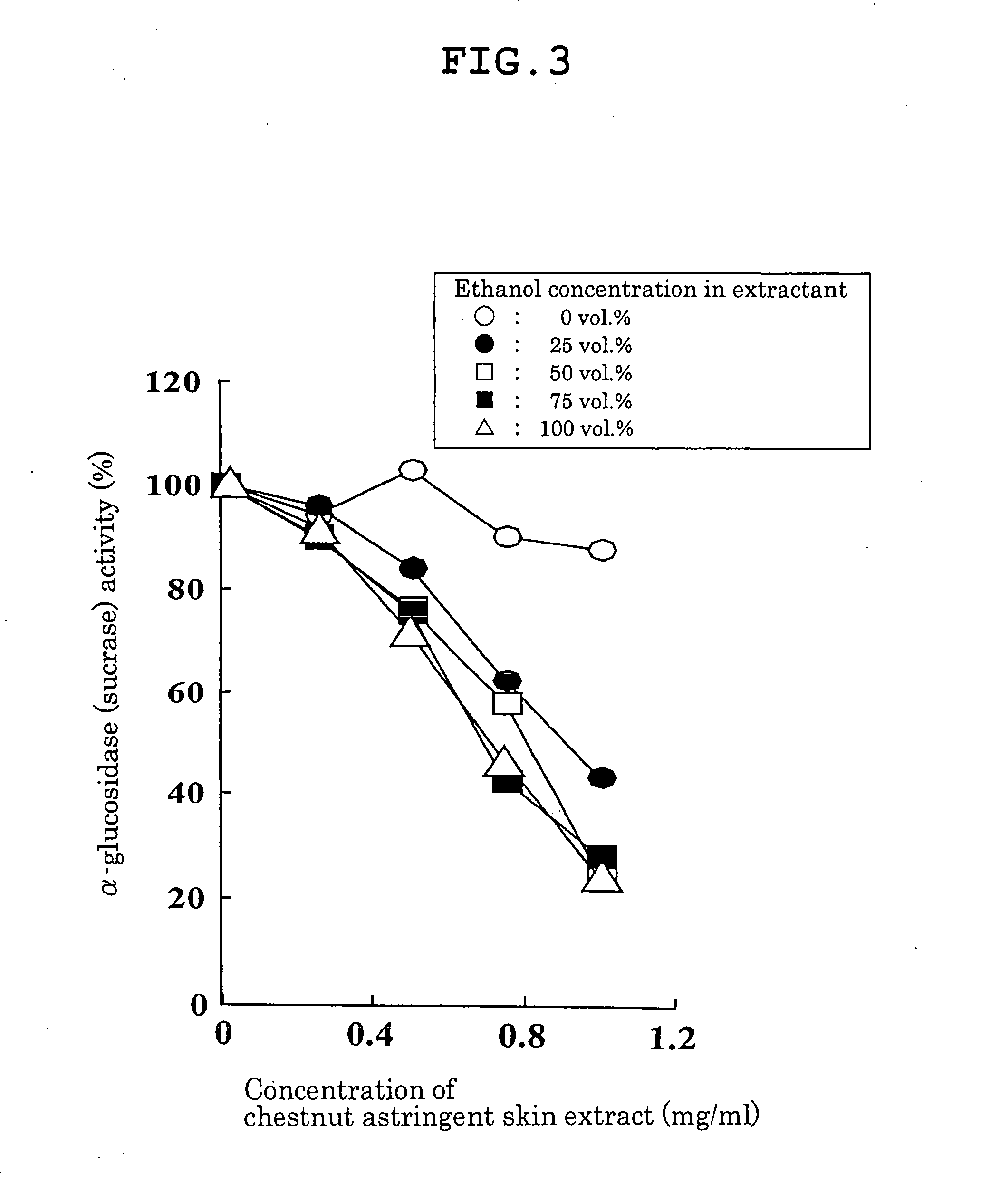
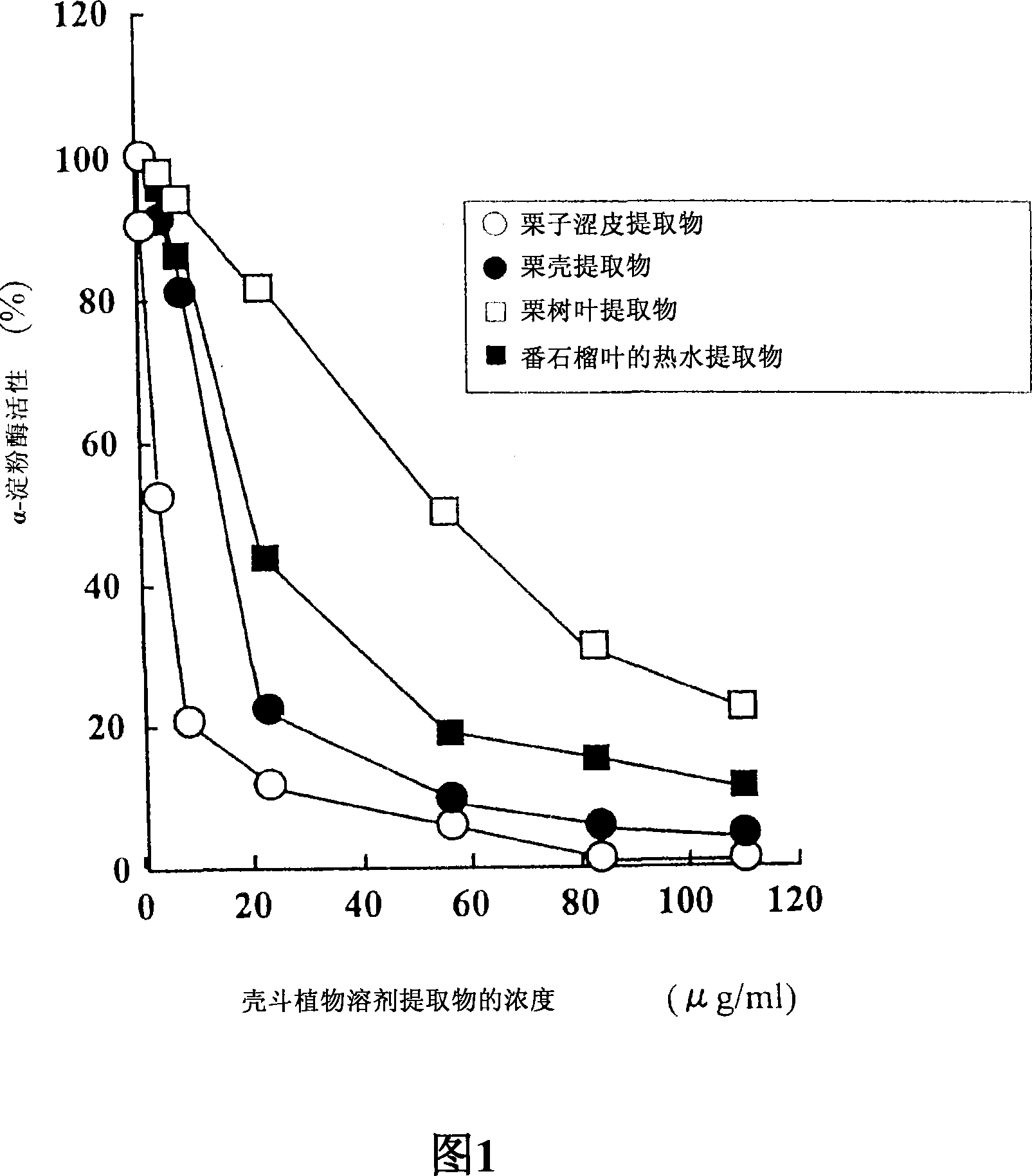
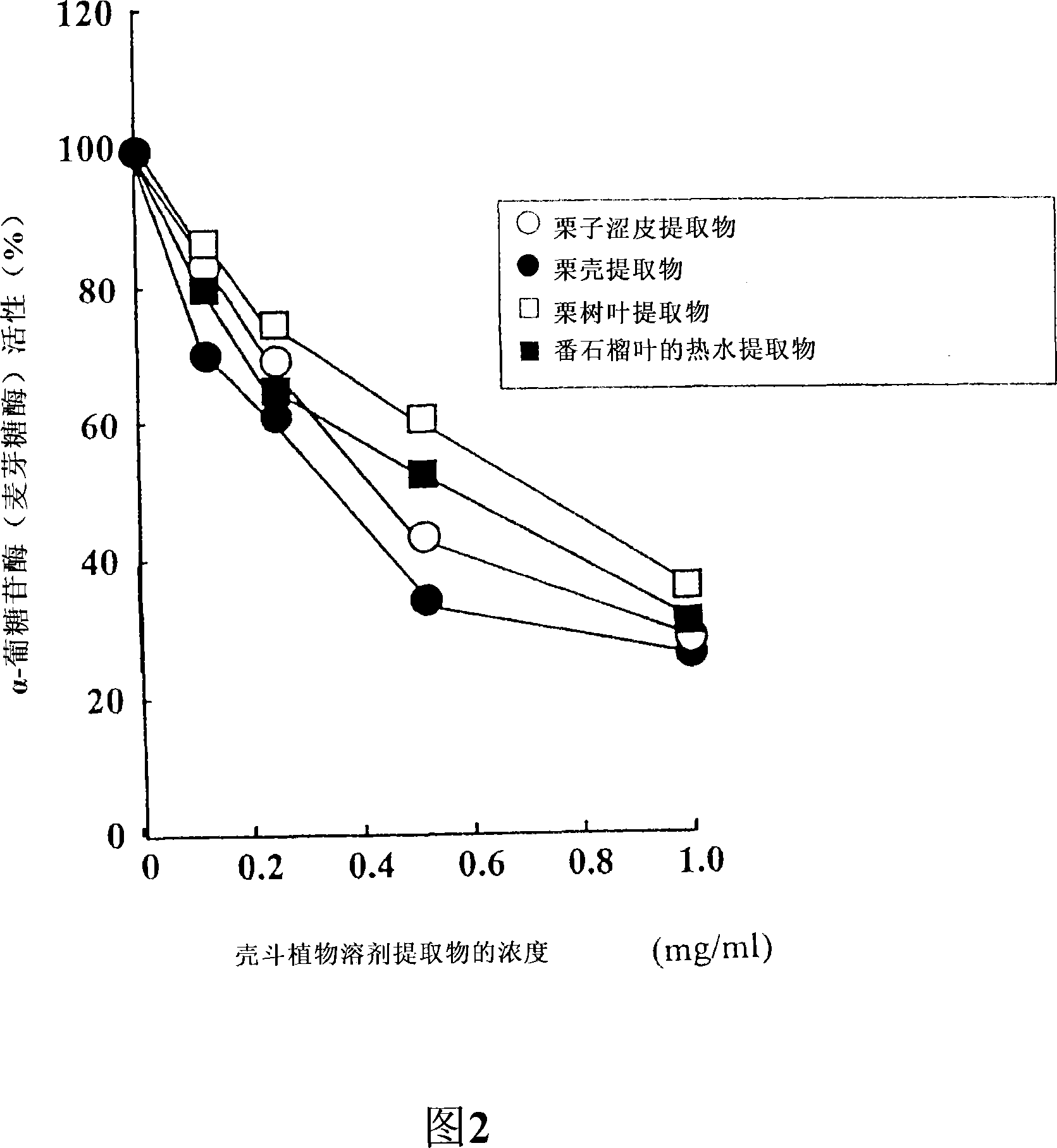
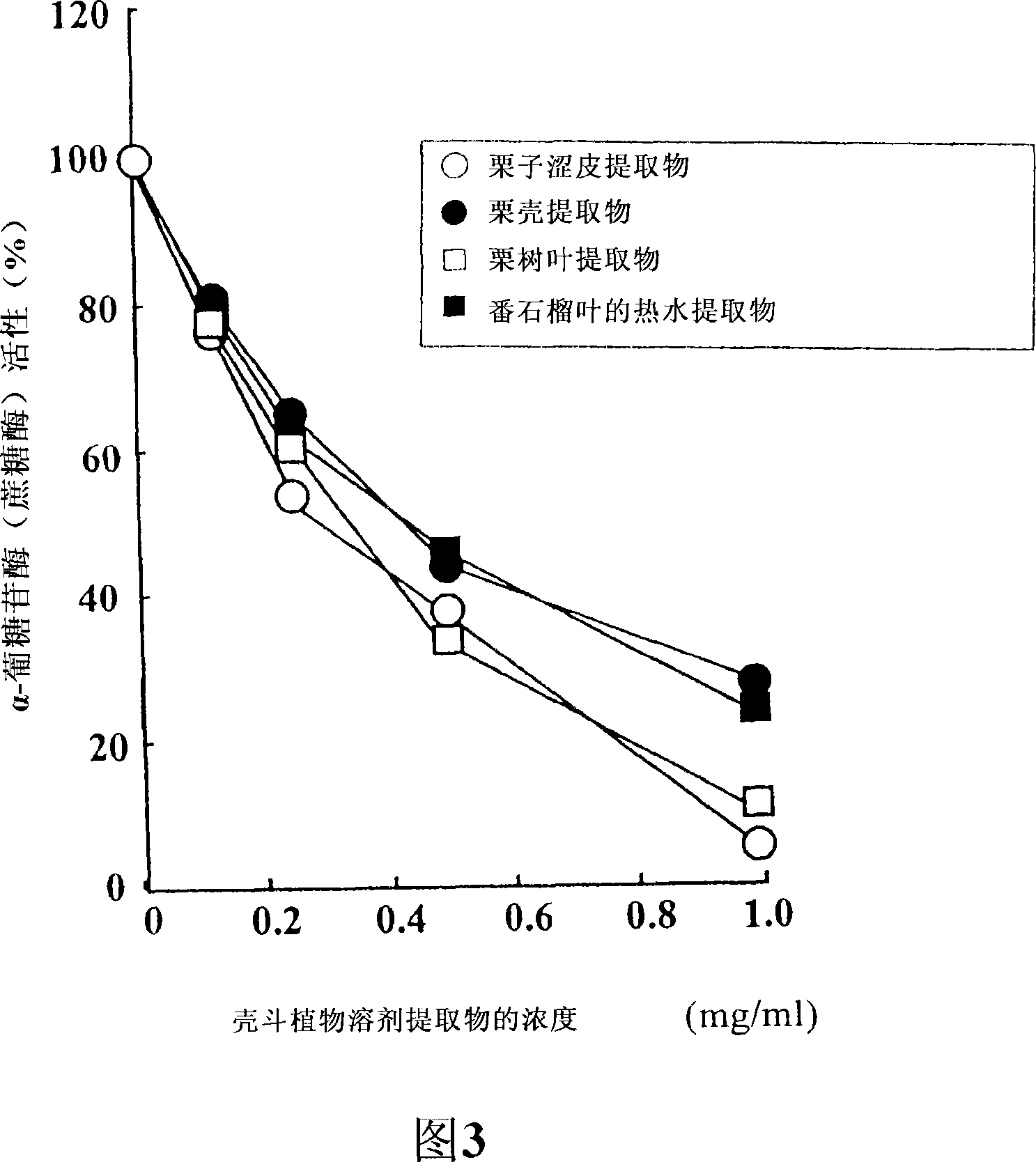
Carbohydrase Inhibitors Derived From Chestnut And Use Thereof
InactiveUS20070202205A1Stable supplyReduce digestion and absorptionBiocideSenses disorderAmylase inhibitorsBlood insulin
The present invention provides a plant-derived carbohydrase inhibitor, wherein the inhibitor is effective for preventing or alleviating diabetes, or preventing obesity, and foods, drinks, and medicines containing the same. The present invention is accomplished by use of an α-amylase inhibitor or an α-glucosidase inhibitor as a carbohydrase inhibitor that is extracted from astringent skins of a chestnut using ethanol or aqueous ethanol solution. The present invention can also be accomplished by adding the carbohydrase inhibitor to a food or medical composition as an active ingredient for delaying saccharide digestion or absorption, suppressing a rise in postprandial blood glucose levels or blood insulin levels, or preventing obesity.
Owner:TSUJITA TAKAHIRO +2
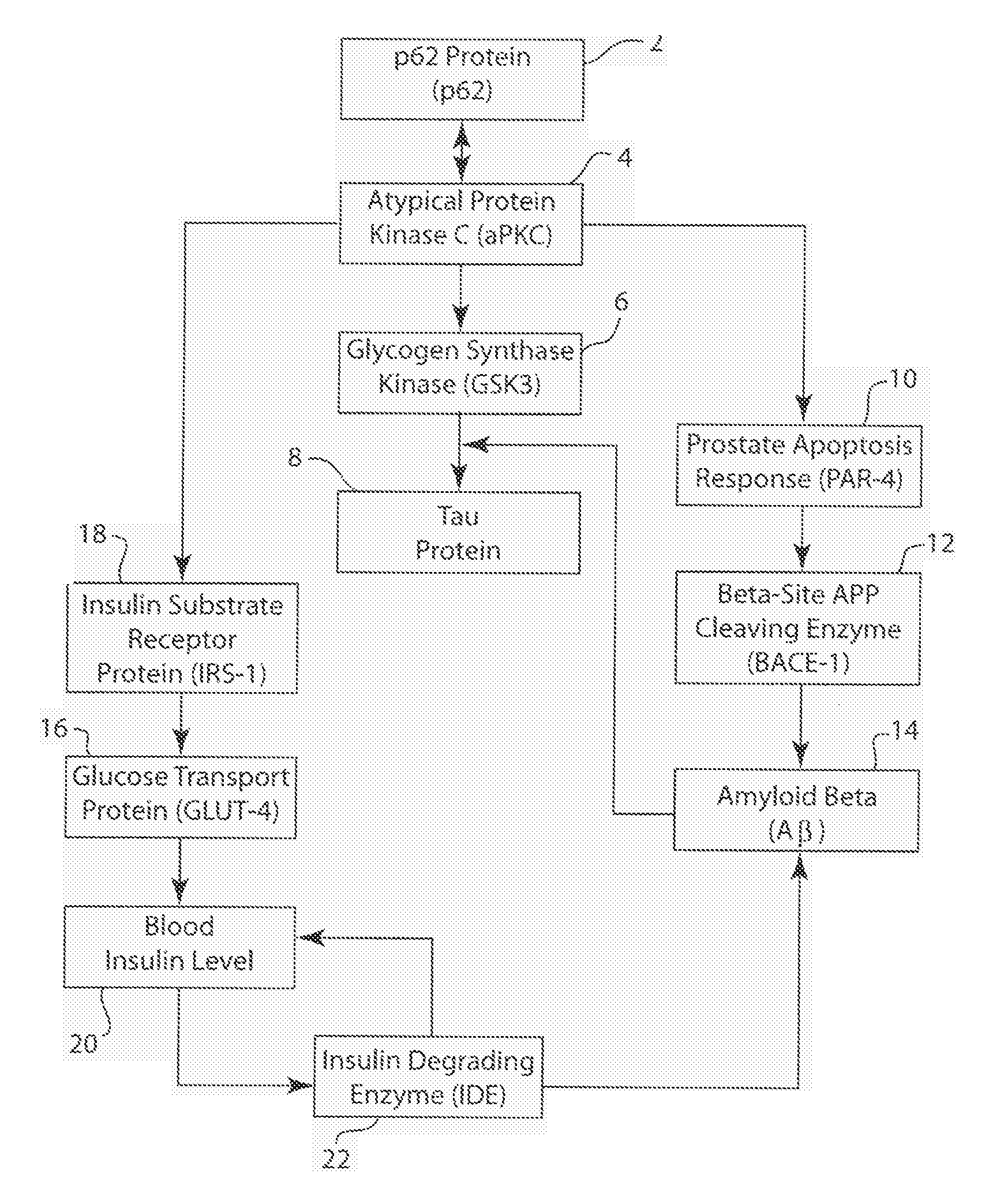
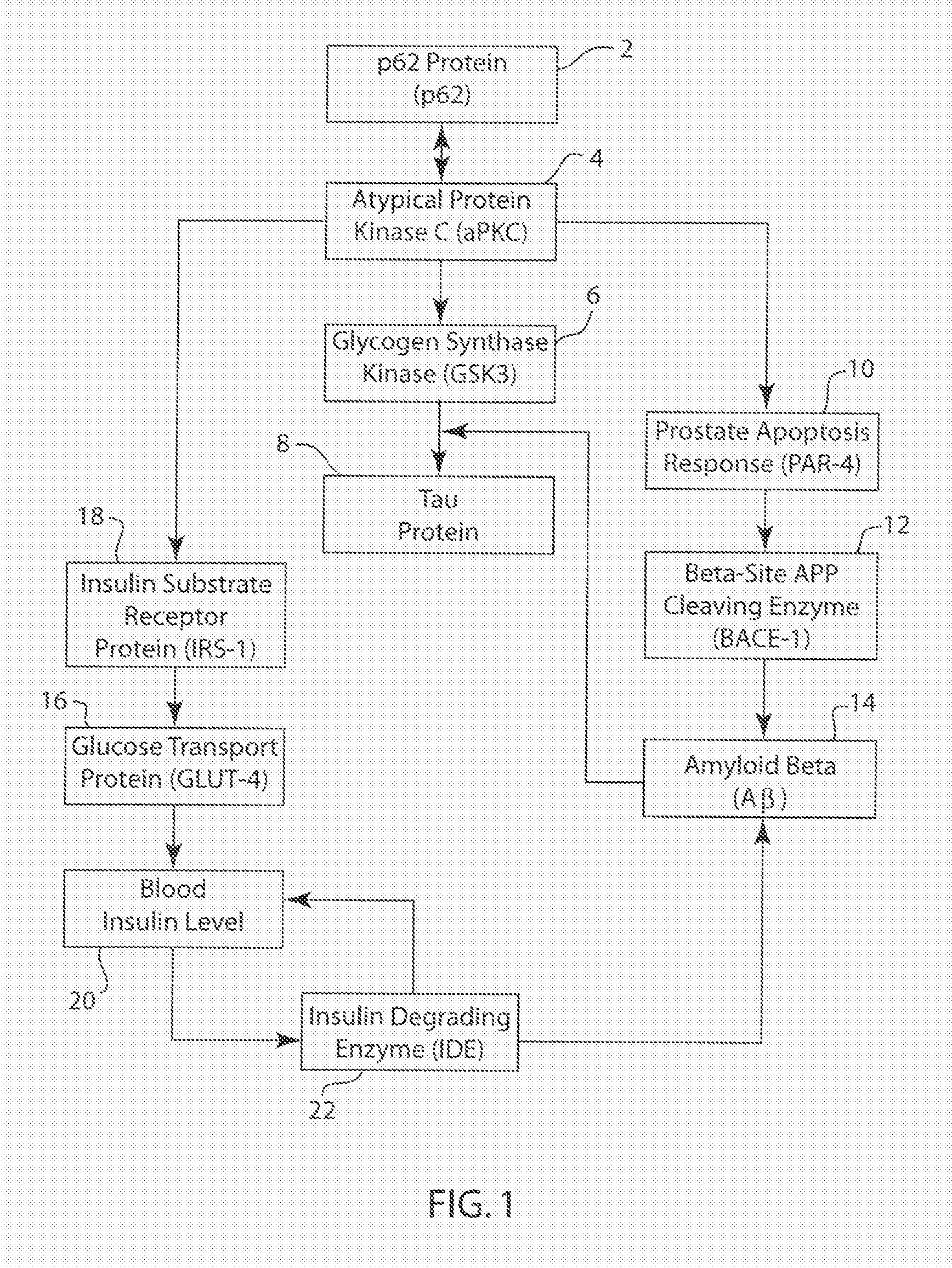
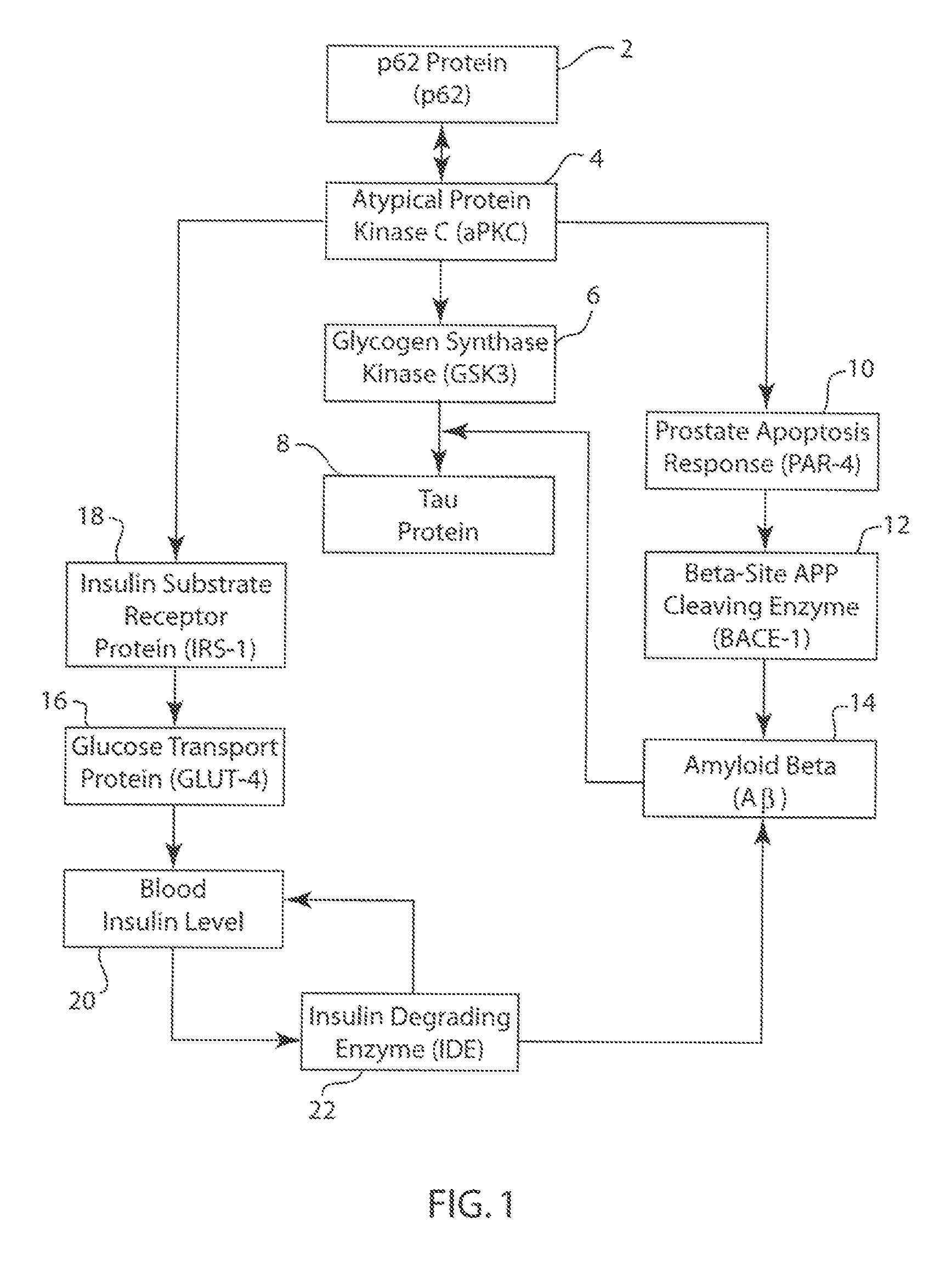
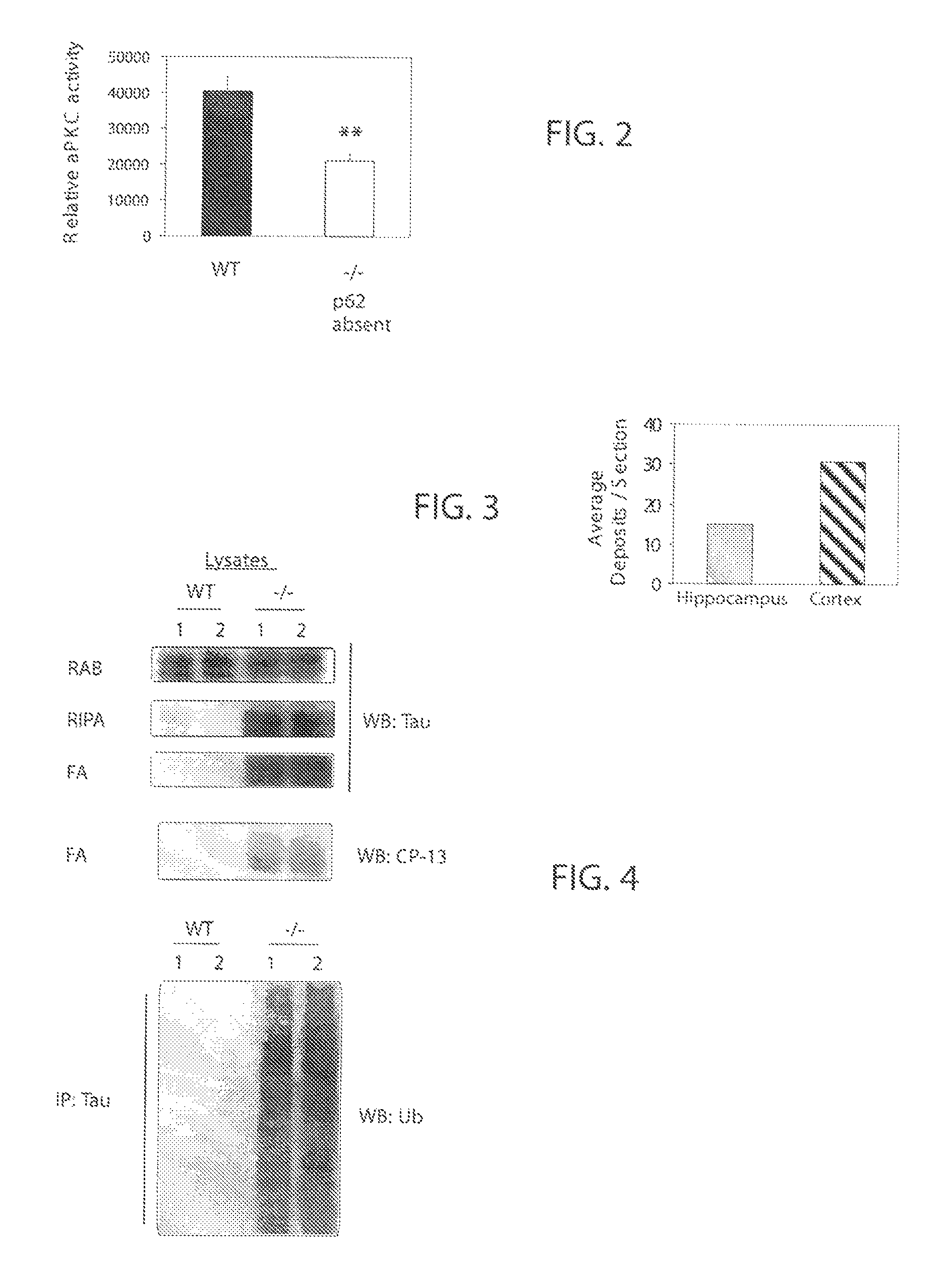
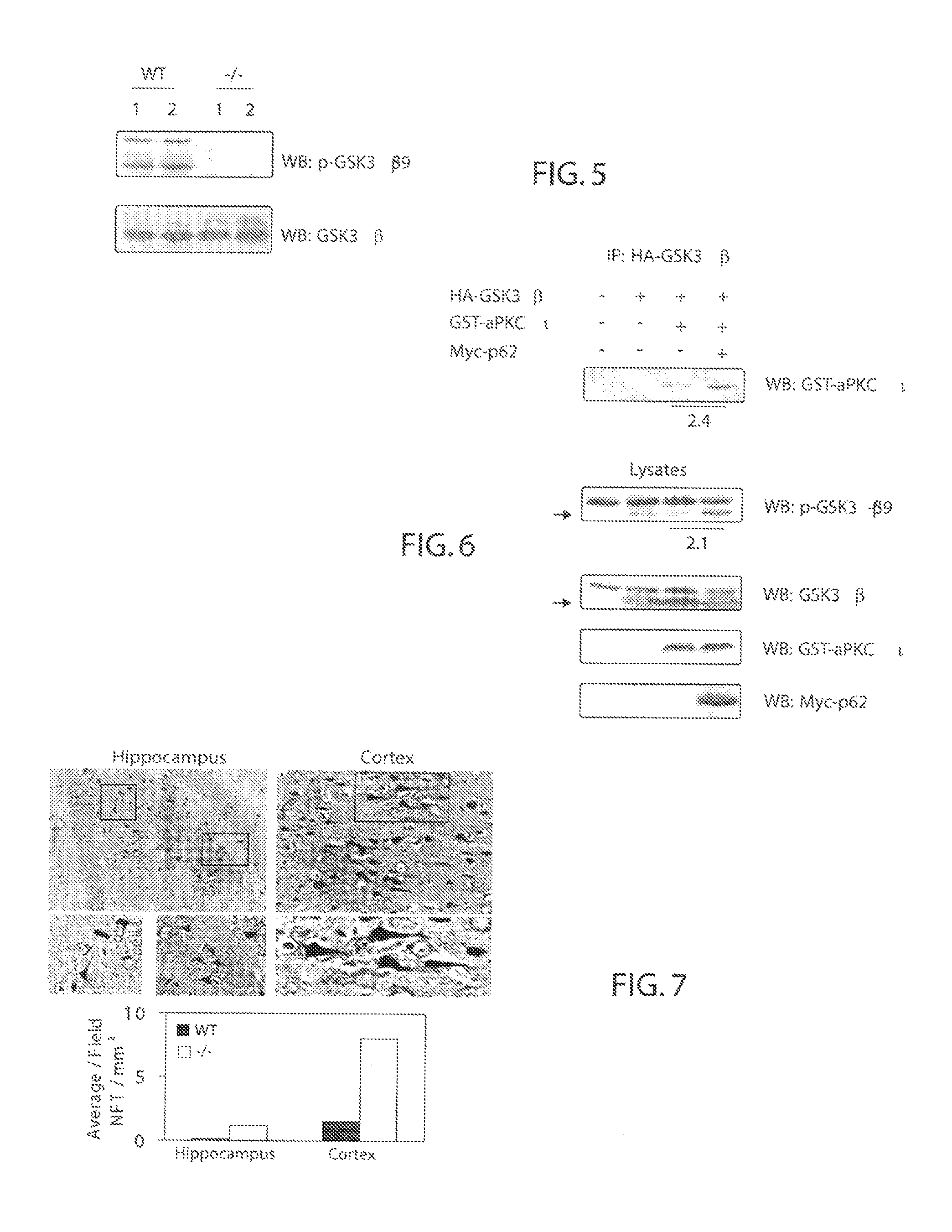
P62 as a risk determinant for metabolic syndrome
The p62 protein has been analyzed and identified as the significant contributor to several metabolic pathways that lead to metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer's Disease, and other related diseases. The absence of the p62 protein has a profound effect on the accumulation of tau protein, amyloid beta protein and an increase in blood insulin levels. The accumulation of tau protein and amyloid beta protein in neurological tissues is a hallmark of neurological metabolic diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease and related dementias. Moreover, increase blood insulin levels is an indicator of insulin resistance in mammals. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for screening a mammal for metabolic disease comprising the step of detecting the absence of the p62 protein. The present invention also contemplates a method of screening a mammal for a metabolic syndrome comprising the steps of detecting the level of p62 protein in a metabolic pathway and determining whether the level of p62 protein falls below a threshold level. A pharmaceutical composition is also contemplated for therapeutic supplementation of a metabolic pathway, the pharmaceutical composition comprising a p62 protein or an amide, ester or salt thereof and a pharmaceutically effective carrier. Such pharmaceutical composition will have an inhibitory action on the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, accumulation of tau protein, an inhibitory effect on the accumulation of APP / amyloid beta and may operate to lower blood insulin levels.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Uses of sesquiterpene derivatives
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, diabetes and obesity comprising a sesquiterpene derivative as an active ingredient. The sesquiterpene derivatives of the present invention leads to decrease in body fat weight, visceral fat weight and total cholesterol levels, triglyceride of plasma and liver tissue, blood glucose and blood insulin levels in a fast state, finally exhibiting efficacies on prevention or treatment of hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, diabetes and obesity.
Owner:KWANG DONG PHARMA CO LTD
P62 as a diagnostic tool for alzheimer's disease
The p62 protein has been analyzed and identified as the significant contributor to several metabolic pathways that lead to metabolic syndrome, Alzheimer's Disease, and other related diseases. The absence of the p62 protein has a profound effect on the accumulation of tau protein, amyloid beta protein and an increase in blood insulin levels. The accumulation of tau protein and amyloid beta protein in neurological tissues is a hallmark of neurological metabolic diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease and related dementias. Moreover, increase blood insulin levels is an indicator of insulin resistance in mammals. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for screening a mammal for metabolic disease comprising the step of detecting the absence of the p62 protein. The present invention also contemplates a method of screening a mammal for a metabolic syndrome comprising the steps of detecting the level of p62 protein in a metabolic pathway and determining whether the level of p62 protein falls below a threshold level. A pharmaceutical composition is also contemplated for therapeutic supplementation of a metabolic pathway, the pharmaceutical composition comprising a p62 protein or an amide, ester or salt thereof and a pharmaceutically effective carrier. Such pharmaceutical composition will have an inhibitory action on the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, accumulation of tau protein, an inhibitory effect on the accumulation of APP / amyloid beta and may operate to lower blood insulin levels.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Carbohydrase inhibitors derived from chestnut and use thereof
The present invention provides a plant-derived carbohydrase inhibitor, wherein the inhibitor is effective for preventing or alleviating diabetes, or preventing obesity, and foods, drinks, and medicines containing the same. The present invention is accomplished by use of an alpha-amylase inhibitor or an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor as a carbohydrase inhibitor that is extracted from astringent skins of a chestnut using ethanol or aqueous ethanol solution. The present invention can also be accomplished by adding the carbohydrase inhibitor to a food or medical composition as an active ingredient for delaying saccharide digestion or absorption, suppressing a rise in postprandial blood glucose levels or blood insulin levels, or preventing obesity.
Owner:辻田隆广 +2
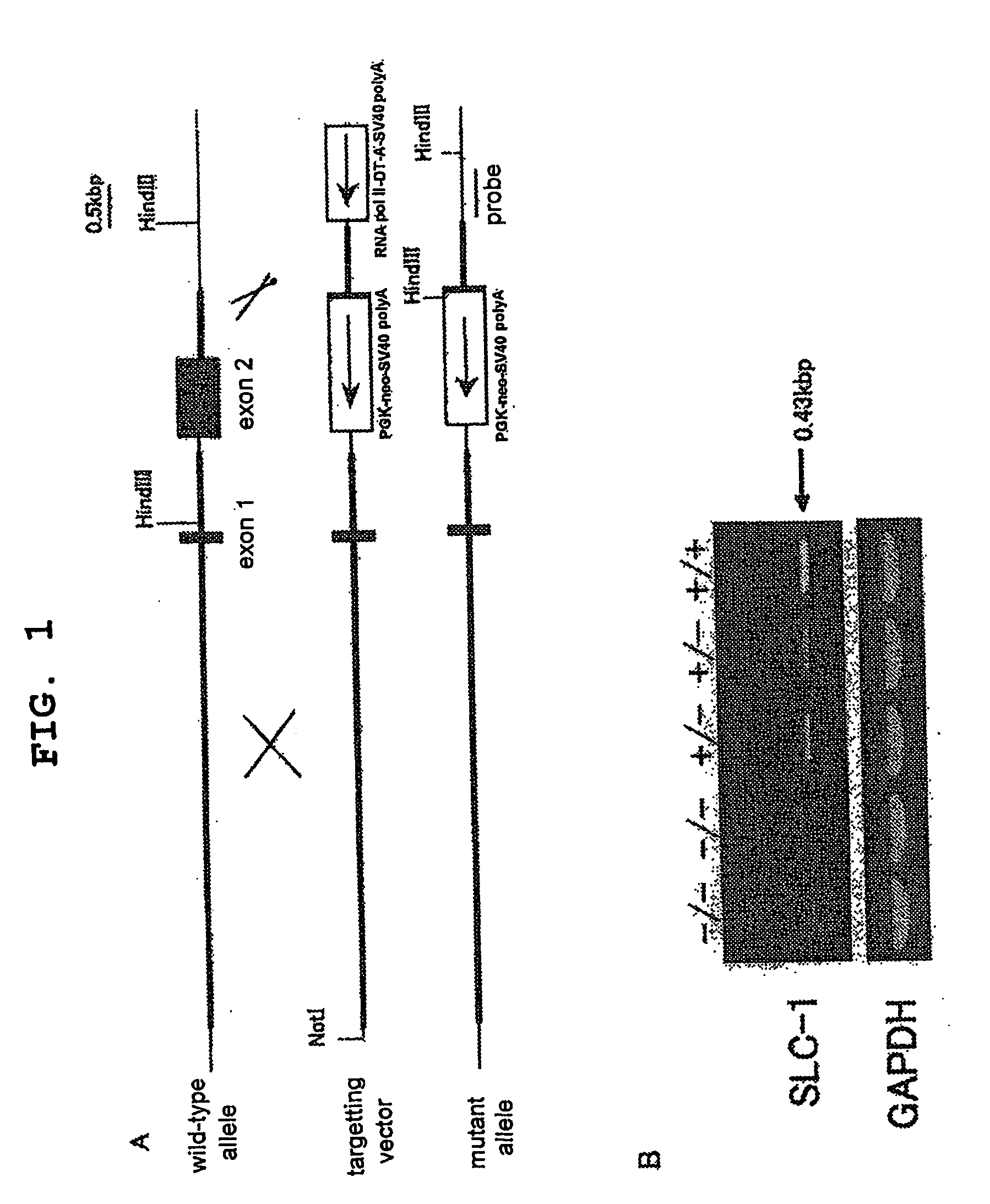
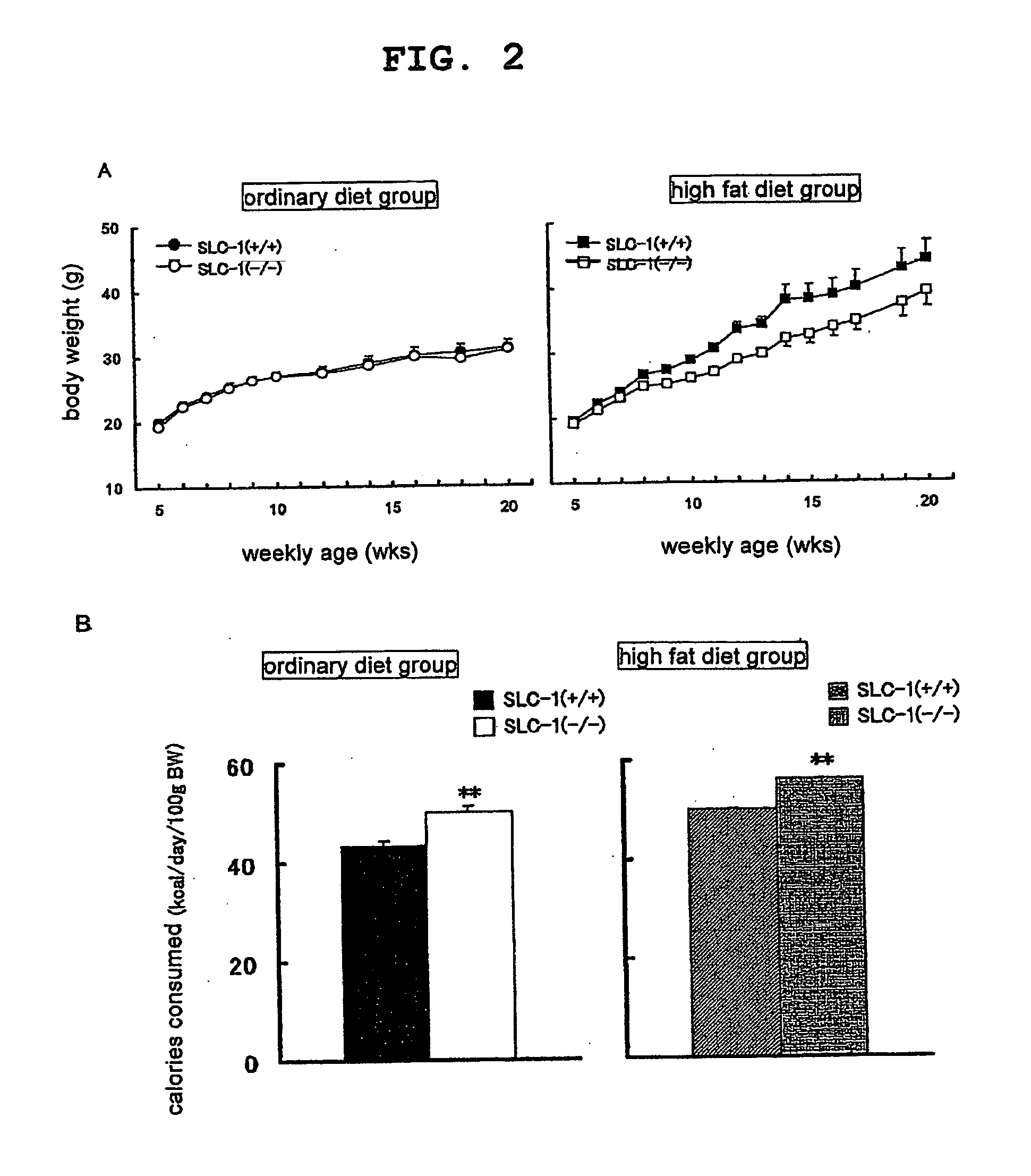
Genetically Modified Animal and Use Thereof
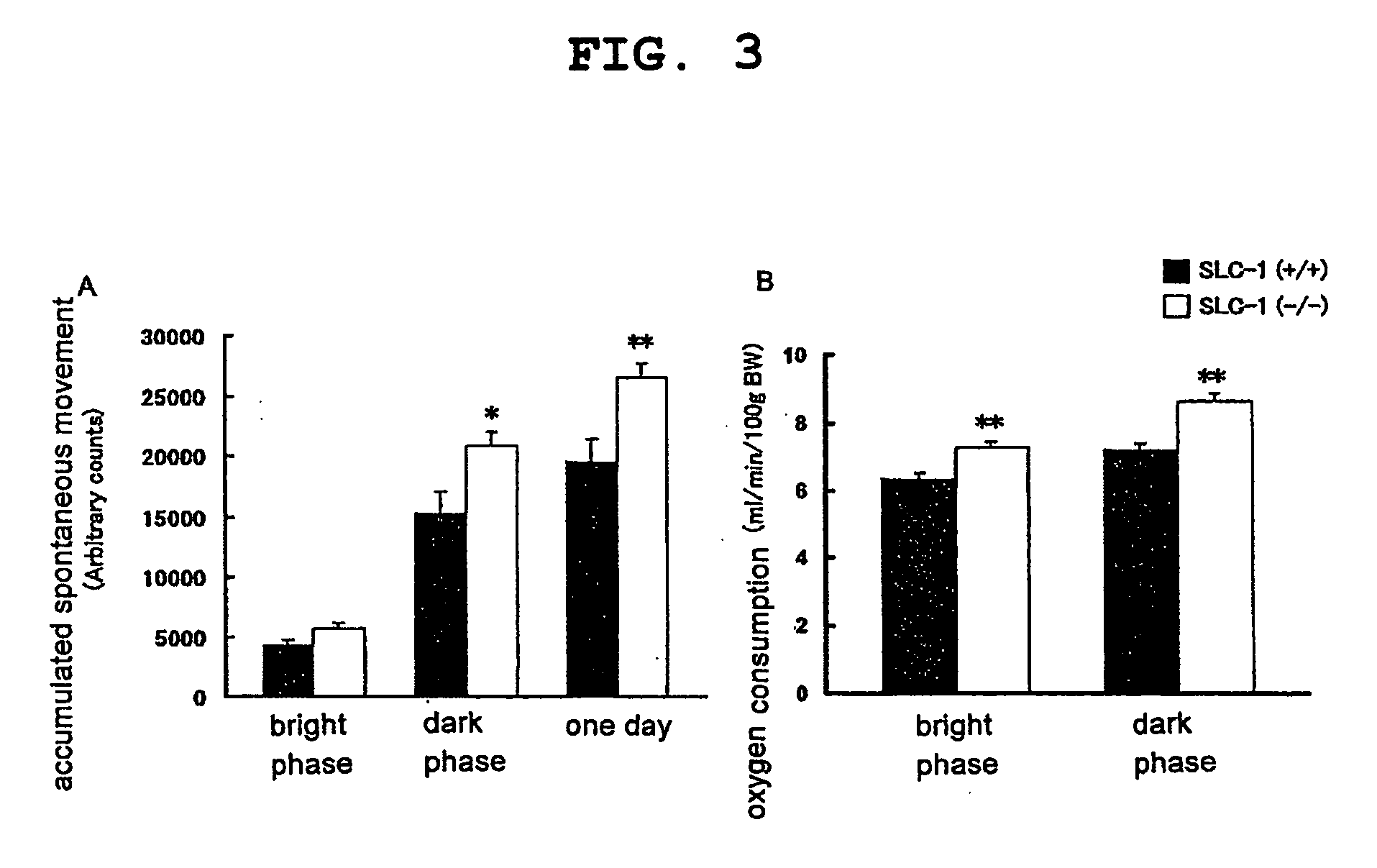
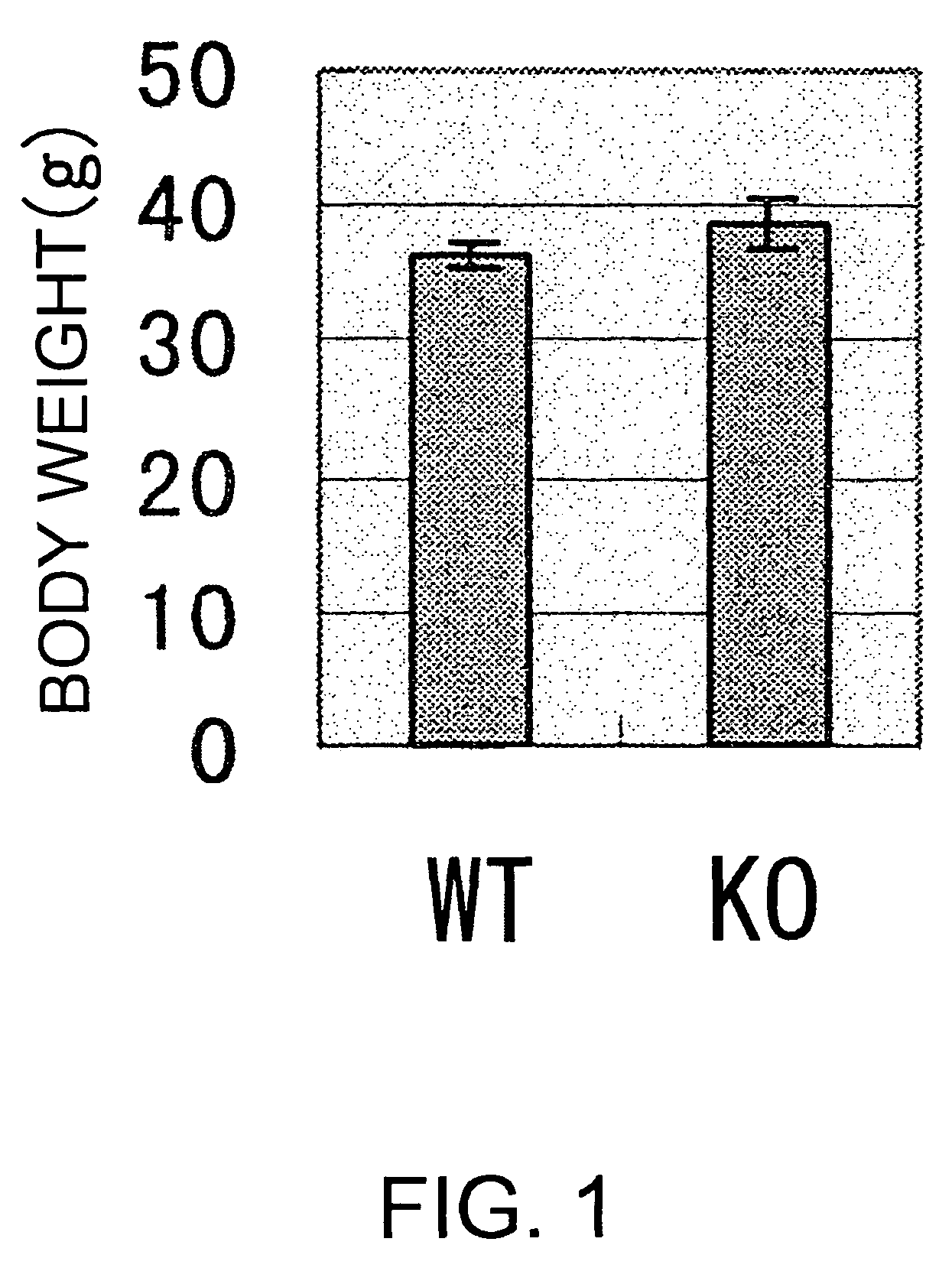
InactiveUS20090186946A1Small fat cell sizeIncrease insulin sensitivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHigh resistanceAcute hyperglycaemia
The present invention provides a non-human mammal deficient in the expression of the SLC-1 gene, having the characteristics of (1) a lower blood insulin level in glucose tolerance test, (2) increased insulin sensitivity, (3) higher resistance to obesity even on high fat diet, (4) a smaller white fat cell size, and (5) accentuated lipolysis, compared with the corresponding wild-type animal, or a portion of the body thereof. Also provided is an obesity and / or type II diabetes model non-human mammal that is deficient in the expression of the SLC-1 gene, having the characteristics of (1) elevated expression of adiponectin, (2) delayed onset of hyperglycemia, (3) a lower blood glycohemoglobin level, and (4) accentuated energy consumption, compared with the corresponding obesity and / or type II diabetes model non-human mammal wherein the expression of the gene is normal, or a portion of the body thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Composition of insulin for nasal administration
InactiveUS20050158250A1Good curative effectPromote absorptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsCelluloseNasal cavity
Provided is an insulin-containing granulated composition for nasal administration comprising a crystalline cellulose aggregate having a specific particle diameter distribution as a carrier. Such granulated composition for nasal administration can efficiently increase a blood insulin concentration.
Owner:OKI TOSHIKAZU +2
Blood glucose level control
A method of glucose level control comprising, providing at least one electrode adapted to apply an electric field to a pancreas; and applying an electric field to the pancreas using said at least one electrode such that blood glucose levels are significantly reduced and blood insulin levels are not significantly increased compared to a regular insulin response in a same person.
Owner:梅塔库尔公司
Large-scale process for the preparation of thylakoids
InactiveCN102088986AReduce intakeReduce blood fatty acidAntipyreticMetabolism disorderBiotechnologyBlood insulin
The present invention relates to a process on a large industrial scale for the production of thylakoids, from photosynthetic organisms, such as from green plant leaf material, to be used as ingredients in food, or additions to food, or dietary supplements, or pharmaceuticals for the purpose of preventing overweight, promoting satiety, reducing food intake, reducing bodyweight, reducing blood insulin concentration and reducing blood fats and percentage body fat in humans and animals.
Owner:THYLABISCO
Insulin sustained-release oral preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101167699AStable physical and chemical propertiesGood repeatabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBlood insulinFiltration
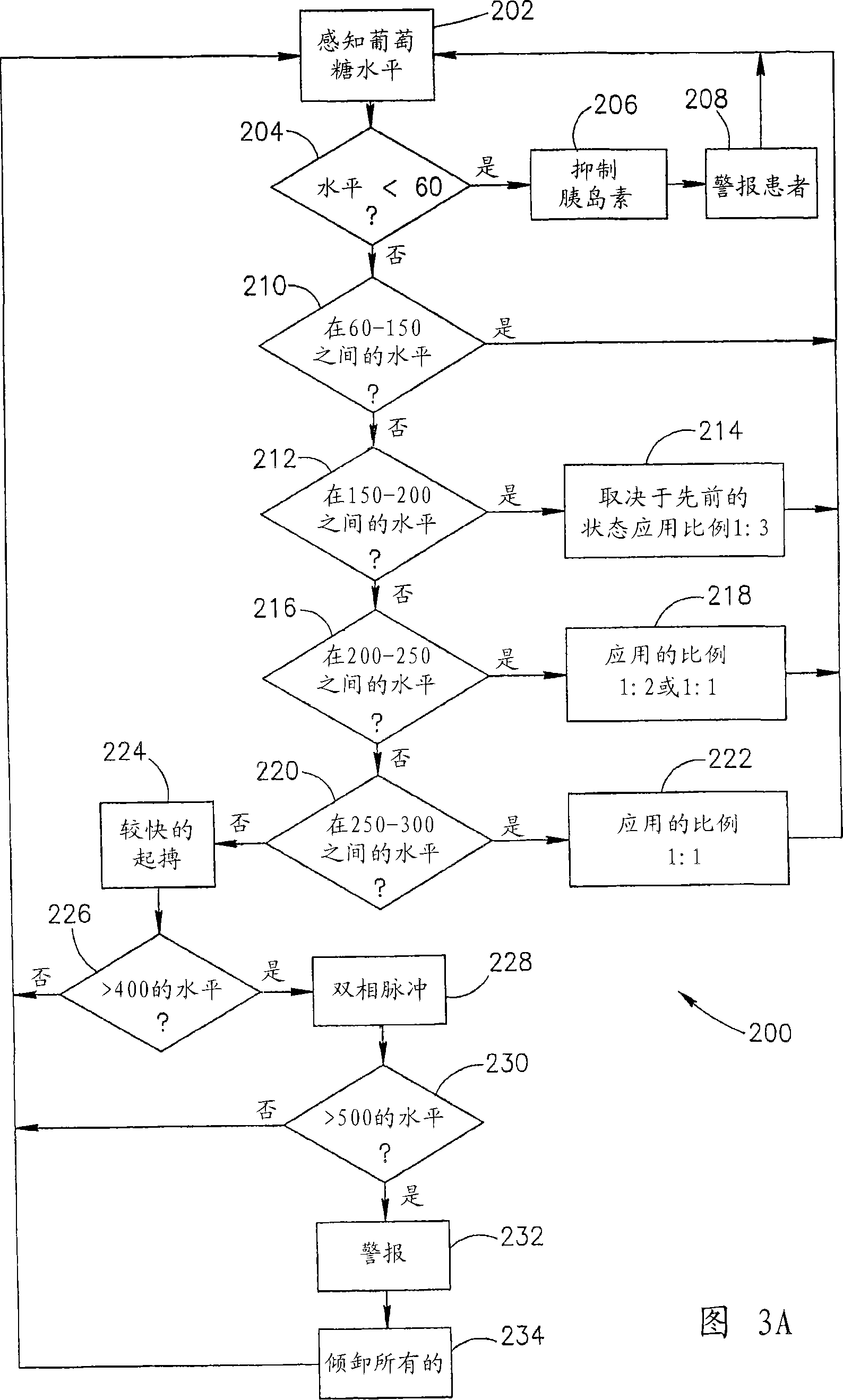
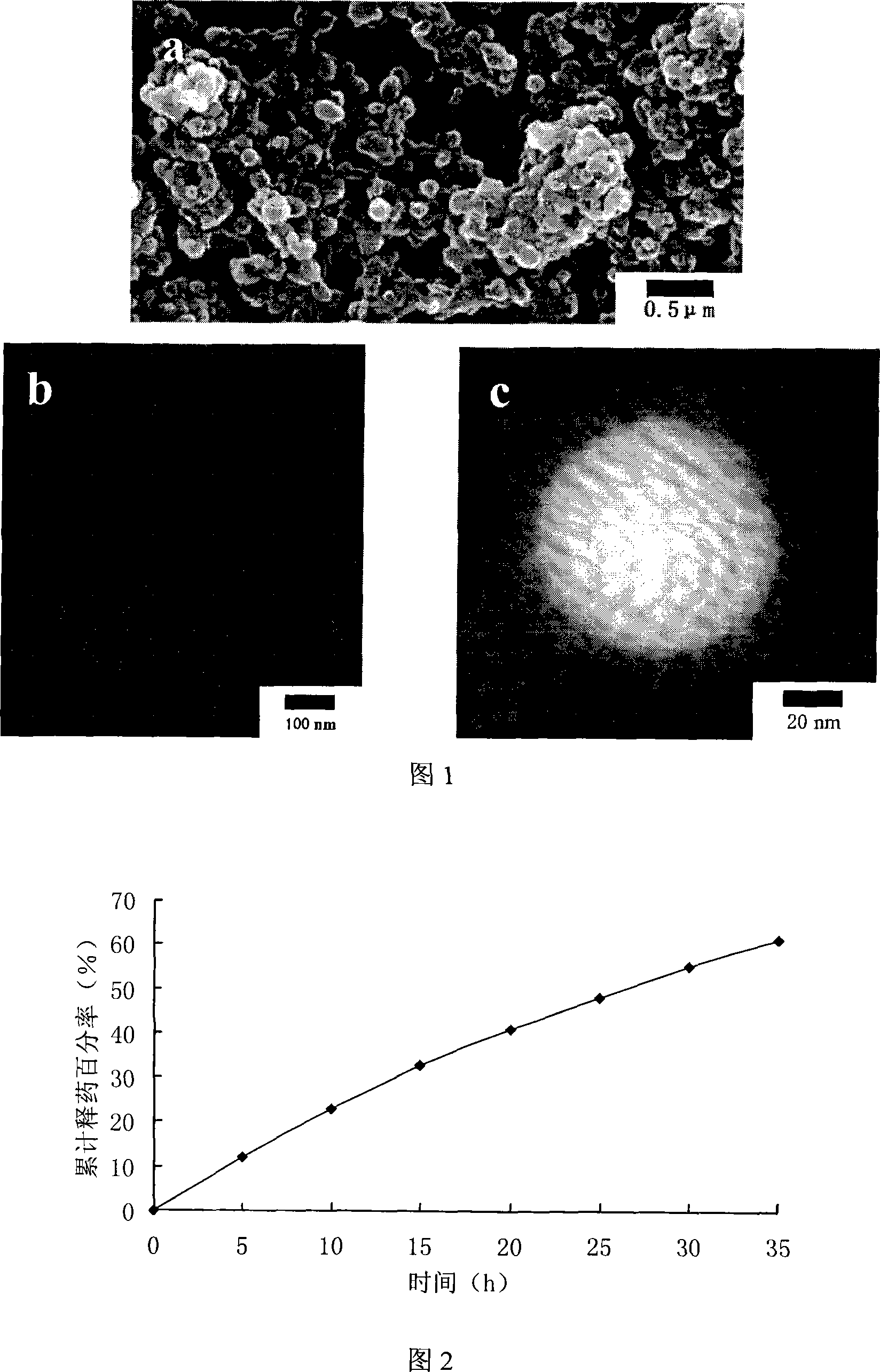
A sustained releasing medicament of insulin for oral administration and a process for preparation relates to insulin for oral administration. The invention provides insulin sustained releasing medicament for oral administration and a process for preparation for the diabetic to reduce blood sugars. The invention is made of nanometer grains of dragon's blood insulin, which contains dragon's blood and insulin. The nanometer grain of dragon's blood insulin takes the insulin as the core, and the dragon's blood as the coating layer. The process comprises getting miscible liquids by confecting the dragon's blood alcohol solution with the concentration of 1-5%, and filtering, charging 1-3g of insulin with the activity unit of 26.7 IU / mg to 100ml dextran-70, and charging tween 20 or tween 80, regulating the pH level of the miscible liquids by NaOH solution until the solution become lacte, charging the dragon's blood alcohol solution after filtration to the lacte solution, getting the lateritious colloidal solution of nanometer grain of dragon's blood insulin by churning up, getting the deposition by centrifugation, washing the deposition with acid solution. The insulin sustained releasing medicament for oral administration is made by freezing and drying the deposition.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Utilization of histamine receptor h3 gene participating in body weight or food intake control
InactiveUS7767881B2Decrease in hybridization efficiencyHybridization efficiency can be reducedBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseBlood insulin
To clarify histamine receptor H3 protein function in vivo, the present inventors constructed a nonhuman higher animal in which the expression of a histamine receptor H3 gene was artificially inhibited. As a result, the present inventors found that this nonhuman higher animal showed increased body weight, food intake, blood insulin level, or blood leptin level compared with a control. Thus, the present inventors found that abnormalities in the histamine receptor H3 protein relate to diseases characterized by changes in body weight or food intake, and this has made it possible to screen drugs for treatment or prevention of these diseases, and to examine these diseases.
Owner:MSD KK
Application of hexadienoic acid in preparation of pig feed additive and pig feed
ActiveCN102008024AFacilitated releaseImprove qualityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAnimal scienceBlood insulin
The invention provides application of hexadienoic acid in preparation of pig feed additive and pig feed, which is novel important application of the hexadienoic acid, and can be applied to preparation of the pig feed additive or the pig feed. The pig feed added with the hexadienoic acid is a safe feed, and does not contain substances which are toxic or harmful to growth and health of pigs. Compared with conventional feed additives, the pig feed additive can effectively improve the pork quality while improving the secretion level of blood insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) by the specificityof the pig feed additive and improving the growing performance of the pigs, so that the slaughtering speed can be increased, the grade of meat products can be improved, and the pork products have higher market values. In the application, additive amount of the hexadienoic acid is small, and can be directly added into premix, the adding process is convenient and rapid, and the preparation method is simple without special requirement for equipment, so the hexadienoic acid has quite wide popularization and application prospect.
Owner:沃曼(广东)生物科技有限公司
Gi and pancreatic device for treating obesity and diabetes
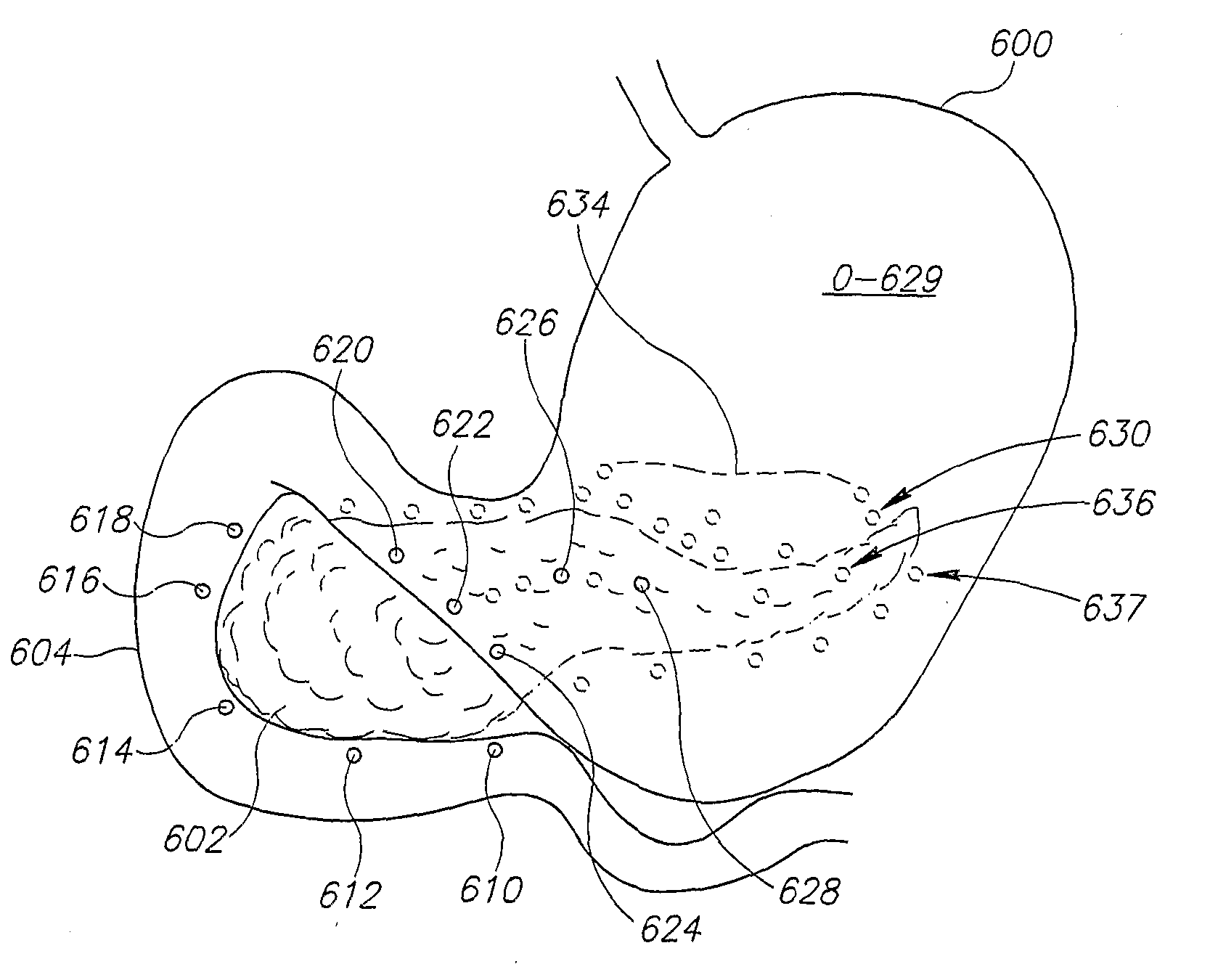
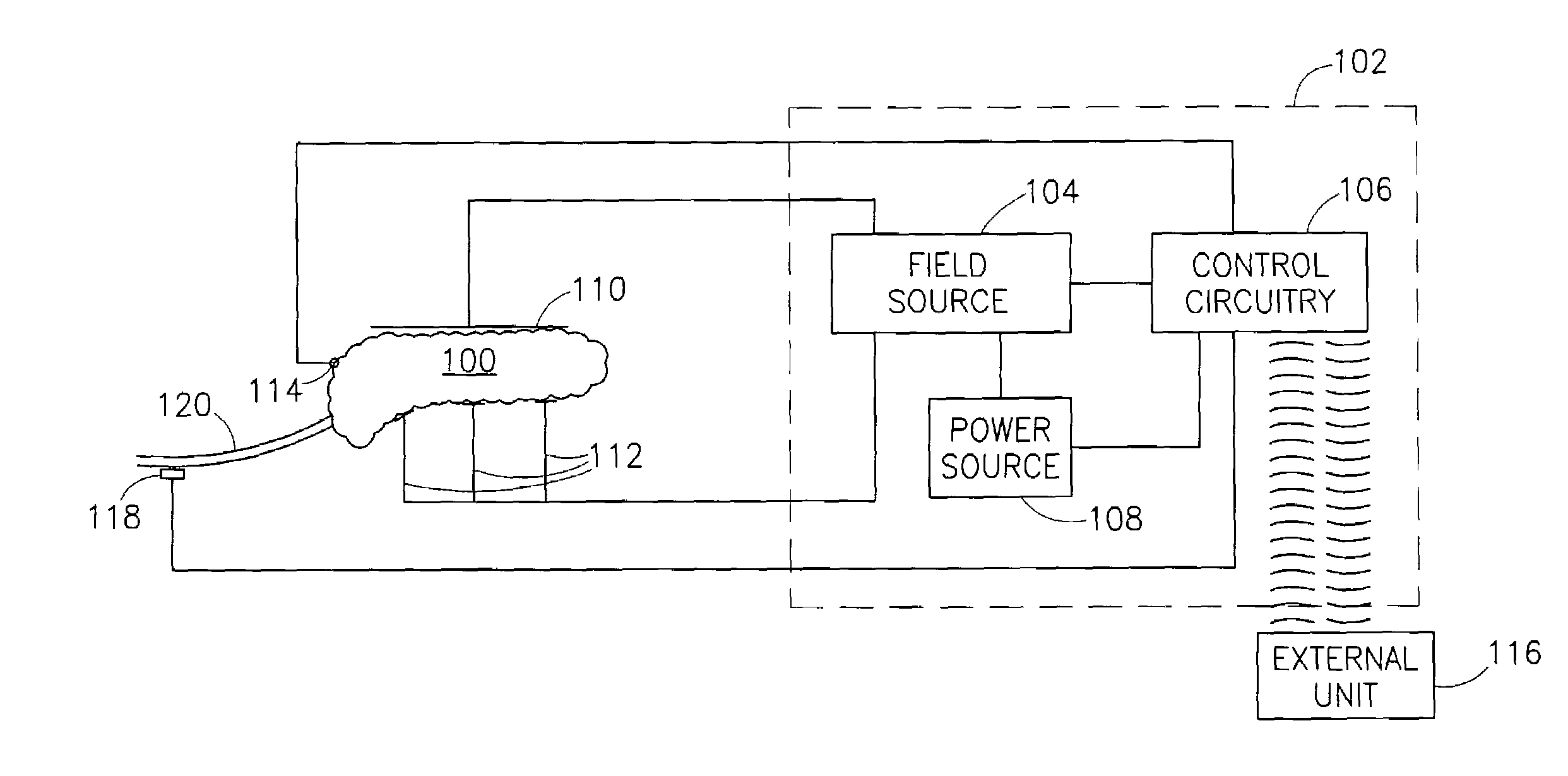
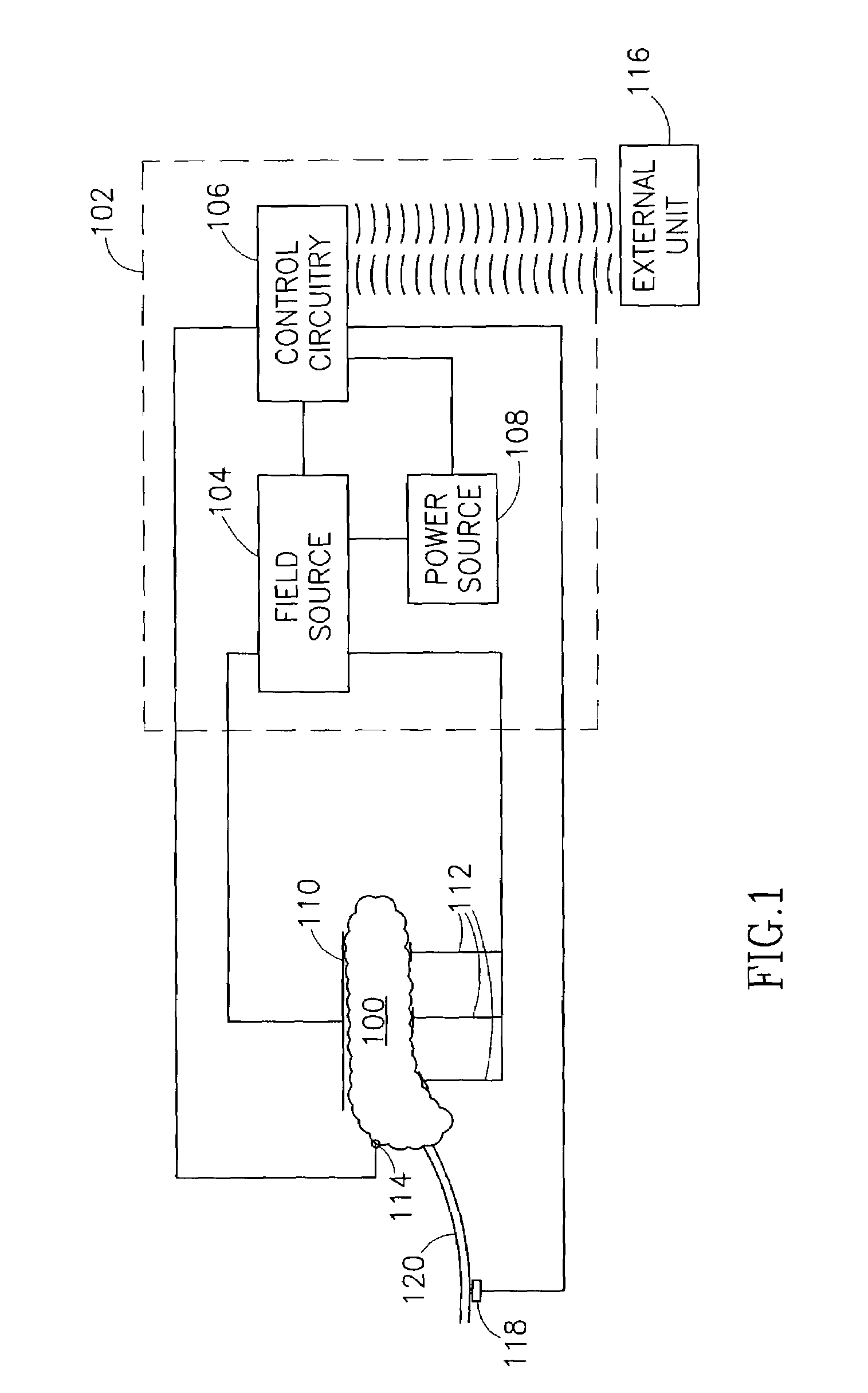
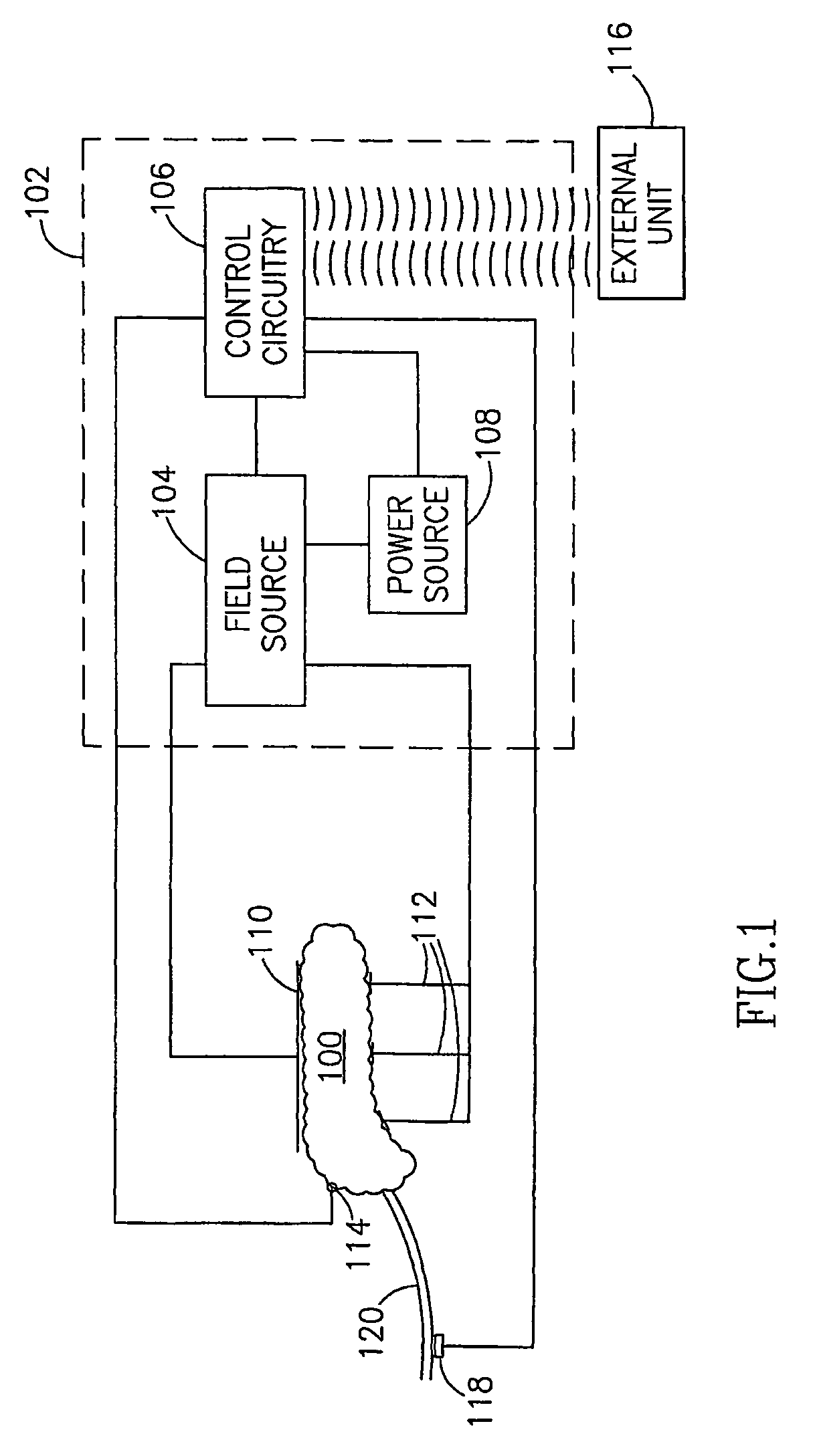
The invention provides a method, including placing first and second electrodes (90) at respective first and second sites of a duodenum (40) of a subject, and activating the electrodes (90) to increase a blood insulin level of the subject. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:BETASTIM LTD
Inhibitor of increase in postprandial blood insulin level
InactiveUS20090124691A1Preventing and ameliorating obesityBiocideMetabolism disorderBlood insulinLevel insulin
The present invention provides an agent for inhibiting a postprandial increase in blood insulin level, wherein the agent containing a monoacylglycerol as an active ingredient. An agent of the invention for inhibiting a postprandial increase in blood insulin level contains a monoacylglycerol as an active ingredient.
Owner:KAO CORP
Preventive/Remedy for Obesity
InactiveUS20080096842A1Inhibit fat accumulationImprove lipid metabolismBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWide areaElevated insulin
Owner:KAO CORP
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating diabetes or fatty liver containing a cyp4a inhibitor as an active ingredient
ActiveUS20140275198A1Reduce ER stressReduce stressBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiabetes mellitusFatty liver
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating diabetes or fatty liver, and more specifically relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating diabetes or fatty liver containing a CYP4A (cytochrome P450A) inhibitor as an active ingredient. According to the present invention, the CYP4A inhibitor suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress, reduces the blood insulin concentration and suppresses apoptosis of liver cells, and hence exhibits effects in preventing or treating diabetes or fatty liver.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com