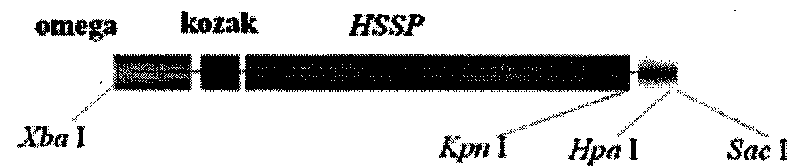Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
334 results about "Enhancer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins (activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers are cis-acting. They can be located up to 1 Mbp (1,000,000 bp) away from the gene, upstream or downstream from the start site. There are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
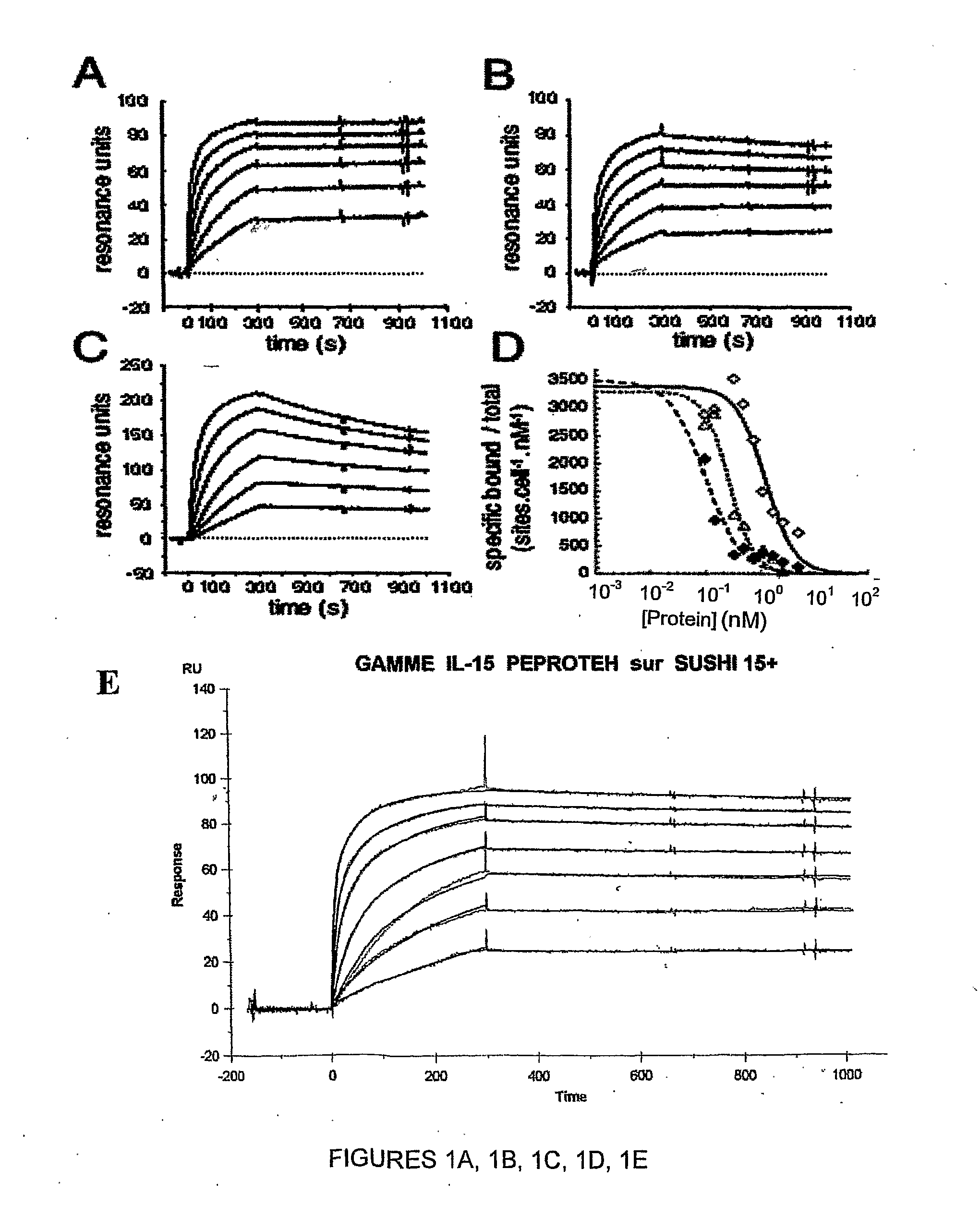
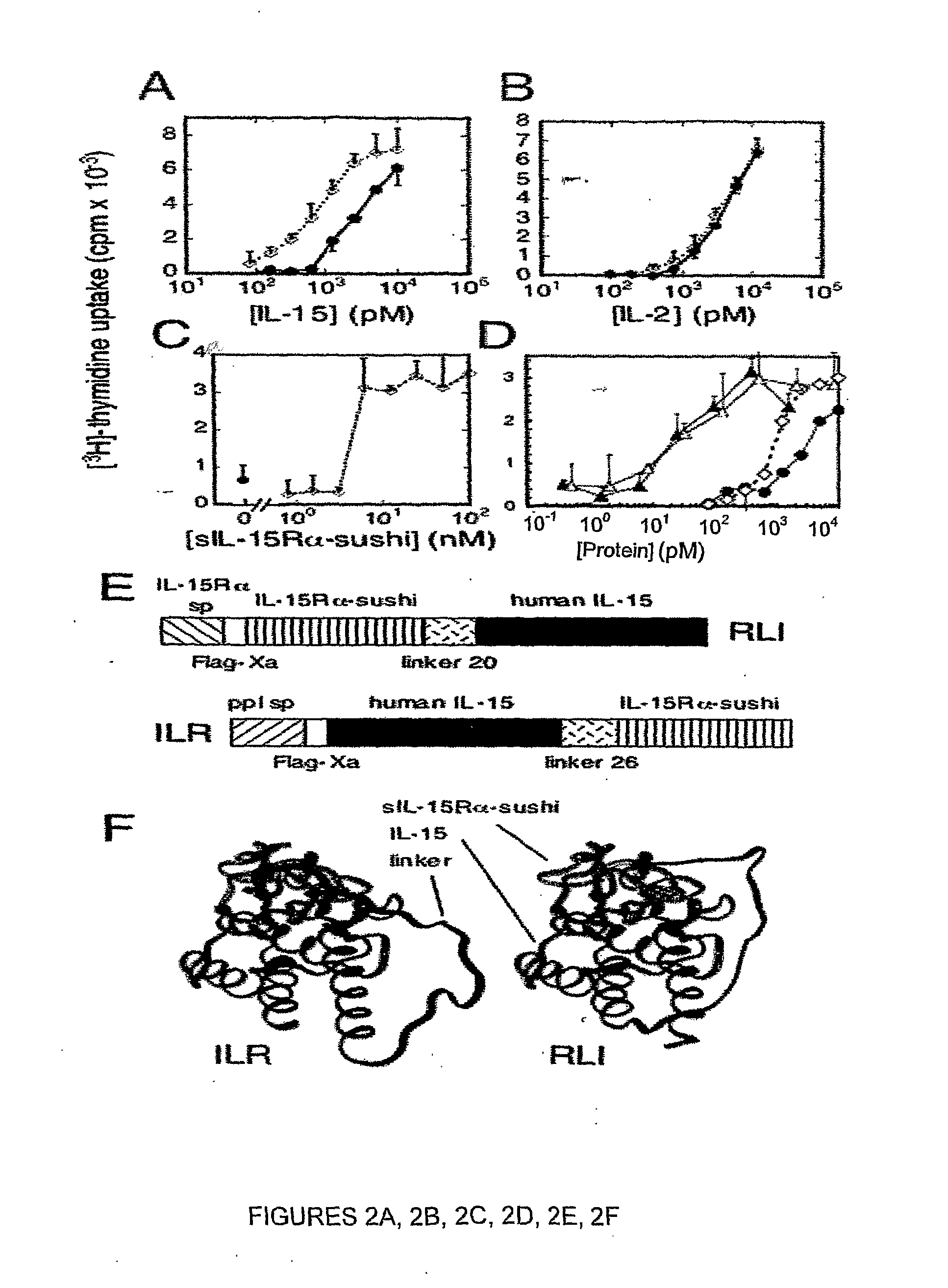
Il-15ralpha sushi domain as a selective and potent enhancer of il-15 action through il-15beta/gamma, and hyperagonist (il-15ralpha sushi - il-15) fusion proteins
ActiveUS20090238791A1Improve efficiencyAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSushi domainBiological activation
The present invention relates to the stimulation of the IL-15R beta / gamma signalling pathway, to thereby induce and / or stimulate the activation and / or proliferation of IL-15Rbeta / gamma-positive cells, such as NK and / or T cells. Appropriate compounds include compounds comprising at least one IL-15Rbeta / gamma binding entity, directly or indirectly linked by covalence to at least one polypeptide which contains the sushi domain of the extracellular region of an IL-15Ralpha.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Human tumor necrosis factor-immunoglobulin(TNFR1-IgG1) chimera composition
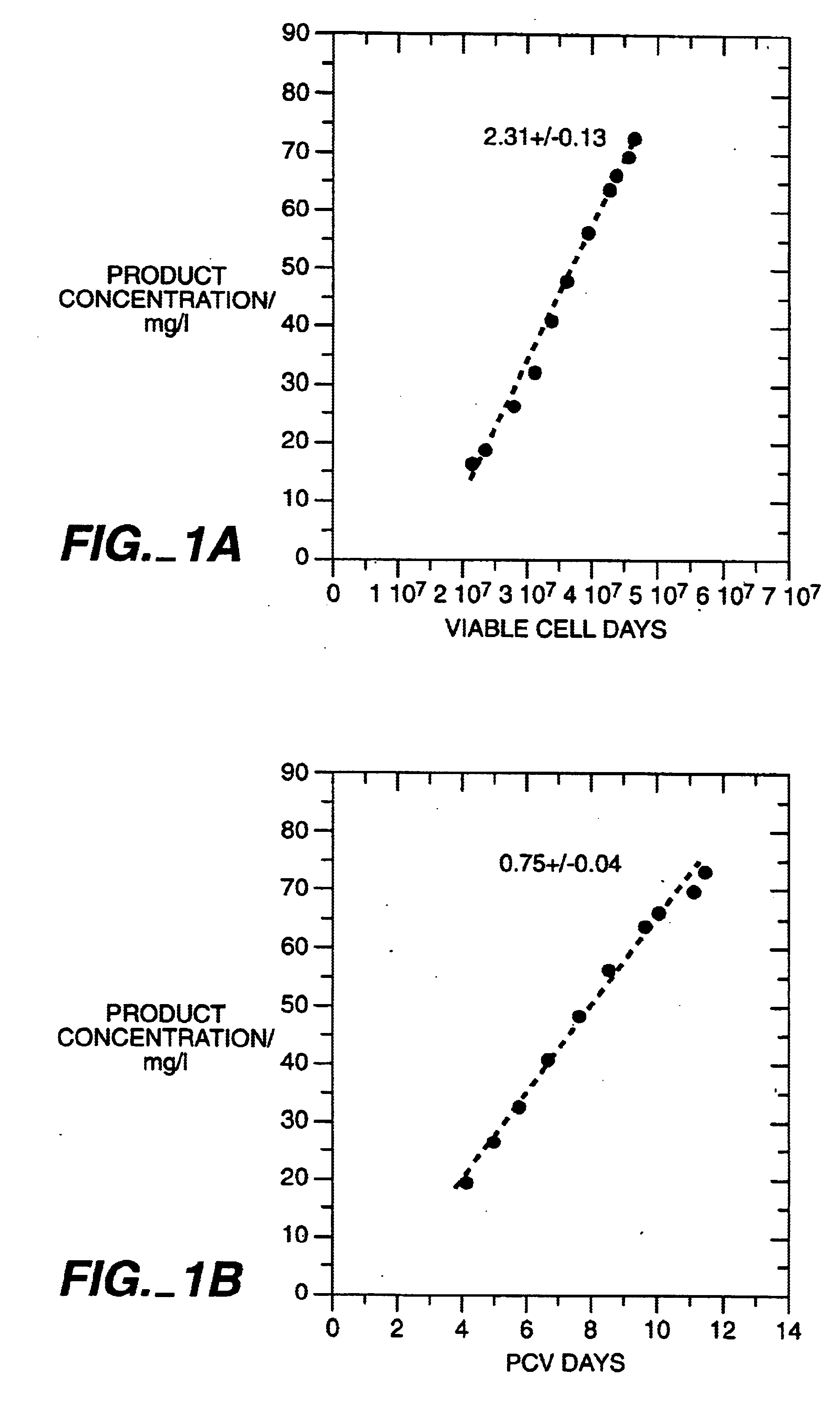
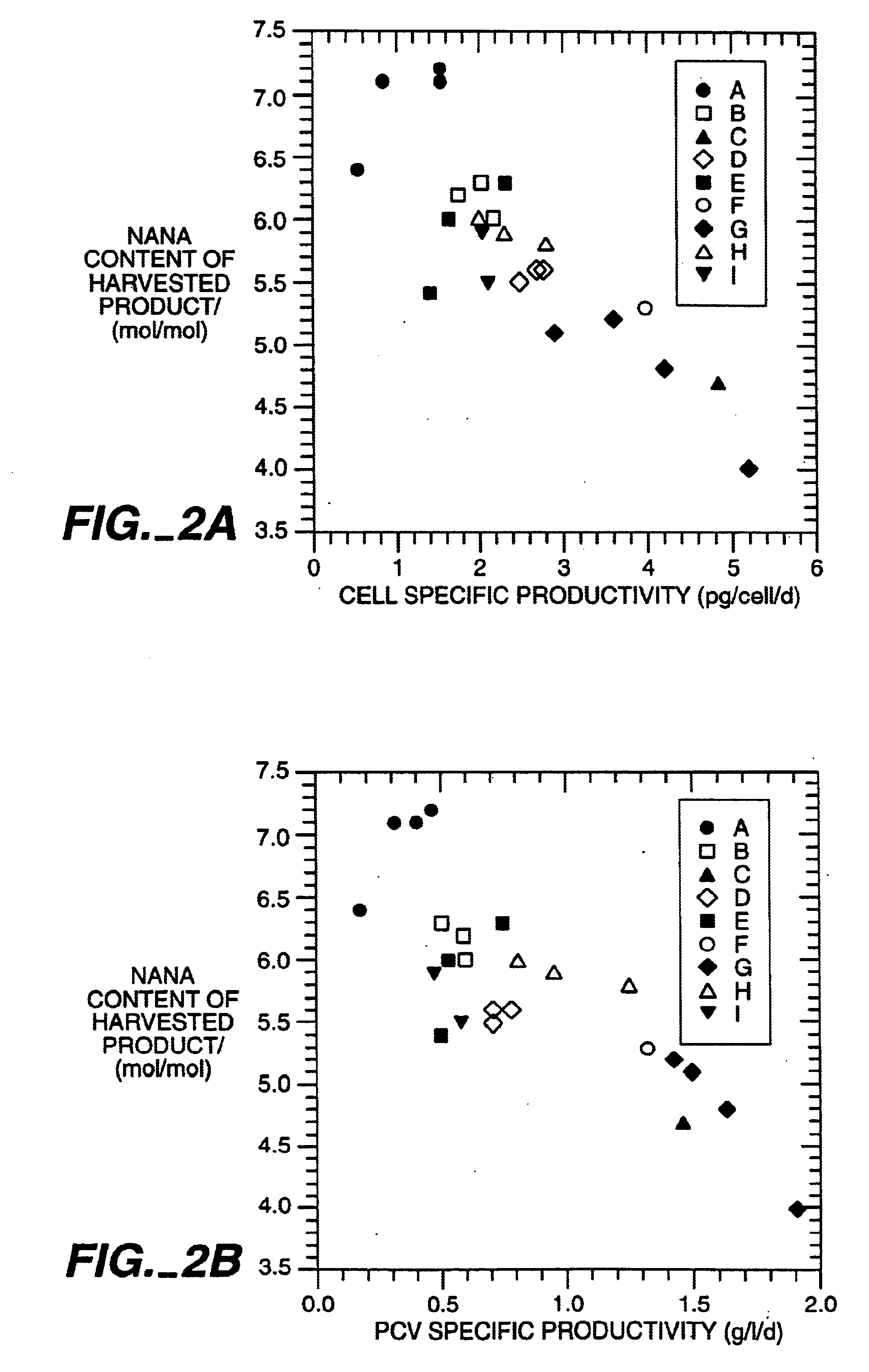
The present invention relates to novel process for the preparation of glycoproteins by mammalian cell culture wherein the sialic acid content of the glycoprotein produced is controlled over a broad range of values by manipulating the cell culture environment. The invention provides for processes in which the sialic acid content of the glycoprotein is modified by changes in cell culture parameters which affect cell specific productivity. Preferred embodiments of the invention include cell culture processes in the osmolality of the cell culture is controlled as well as the concentration of a transcription enhancer during the production phase of the cell culture. The invention further provides for novel preparations of soluble type 1 tumor necrosis factor immunoglobulin G1 and their uses in the treatment of inflammatory or immune related disorders.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
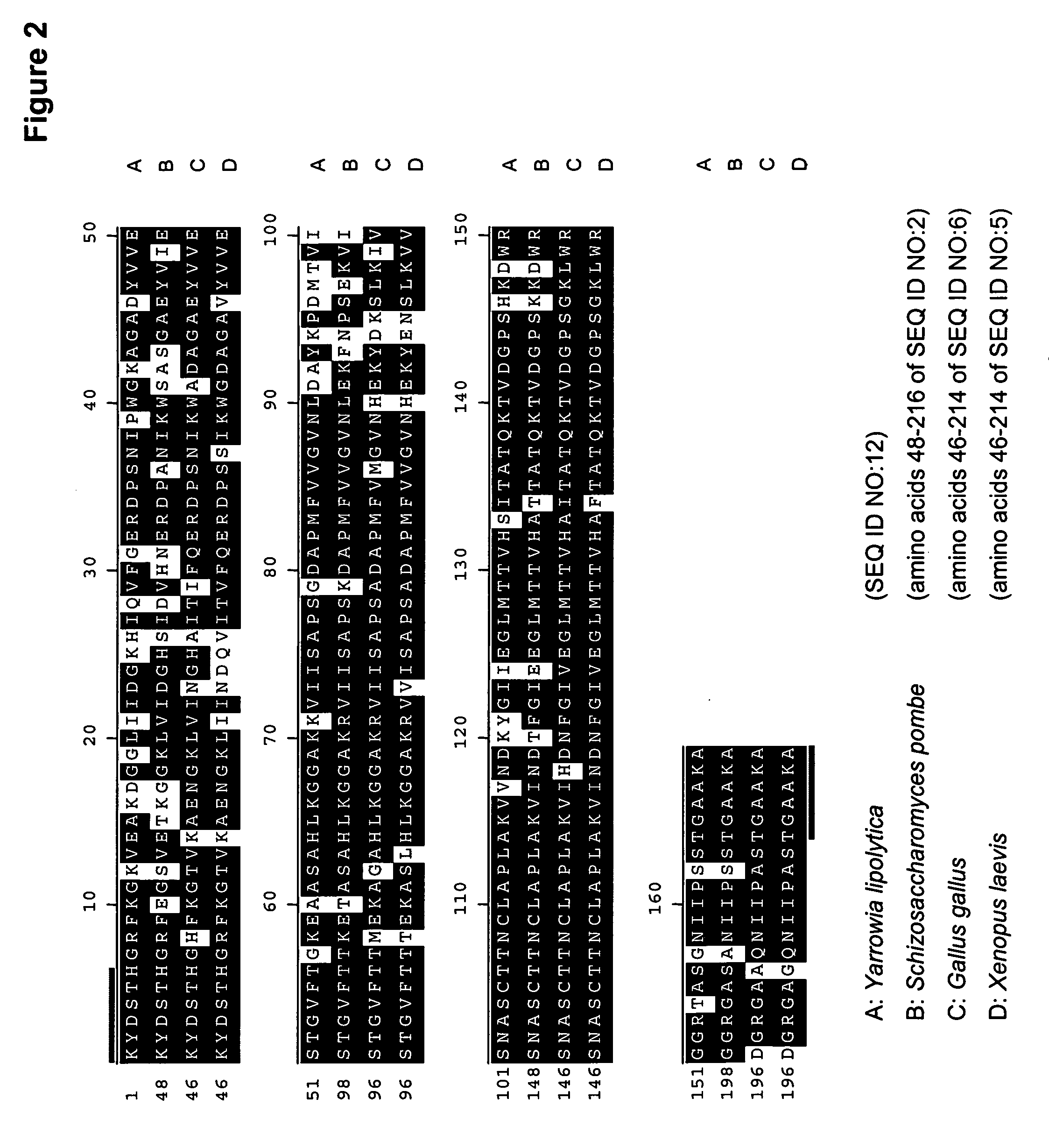
The regulatory sequences associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention, intron and enhancer have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
High-activity T-cell promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN104745581AEfficient expressionSequence stabilityGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAdoptive cellular immunotherapyT cell
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a high-activity T-cell promoter and an application thereof. Particularly, the high-activity T-cell promoter comprises an element 1 and an element 2, wherein the element 1 is an EF1 alpha promoter and / or an EF1 alpha promoter containing an intron; and the element 2 is any one or more of an mCMV promoter, an hCMV promoter and a CD3e promoter. The high-activity T-cell promoter provided by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing a foreign gene in a T cell, has a stable sequence and is free from sequence loss during the transfer process of a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. The high-activity T-cell promoter is applicable to driving the high-efficiency expression of the foreign gene, especially a full-length antibody gene, in the T cell during the process of adoptive cellular immunotherapy.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +2
Protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element
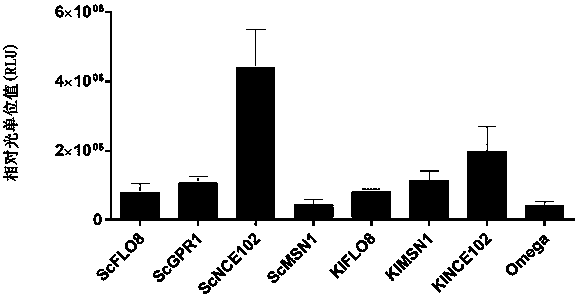
The invention provides a protein synthesis efficiency enhancing RNA element and particularly discloses a nucleic acid structure formed by coding sequences of optional promoters, yeast-derived IRES enhancers (such as ScGPR1, ScFLO8, ScNCE102, ScMSN1, KlFLO8, KlNCE102 and KlMSN1) and heterologous proteins. By application of the nucleic acid structure to a yeast in-vitro protein synthesis system, thesynthesized luciferase activity RLU (relative light unit) is extremely high.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
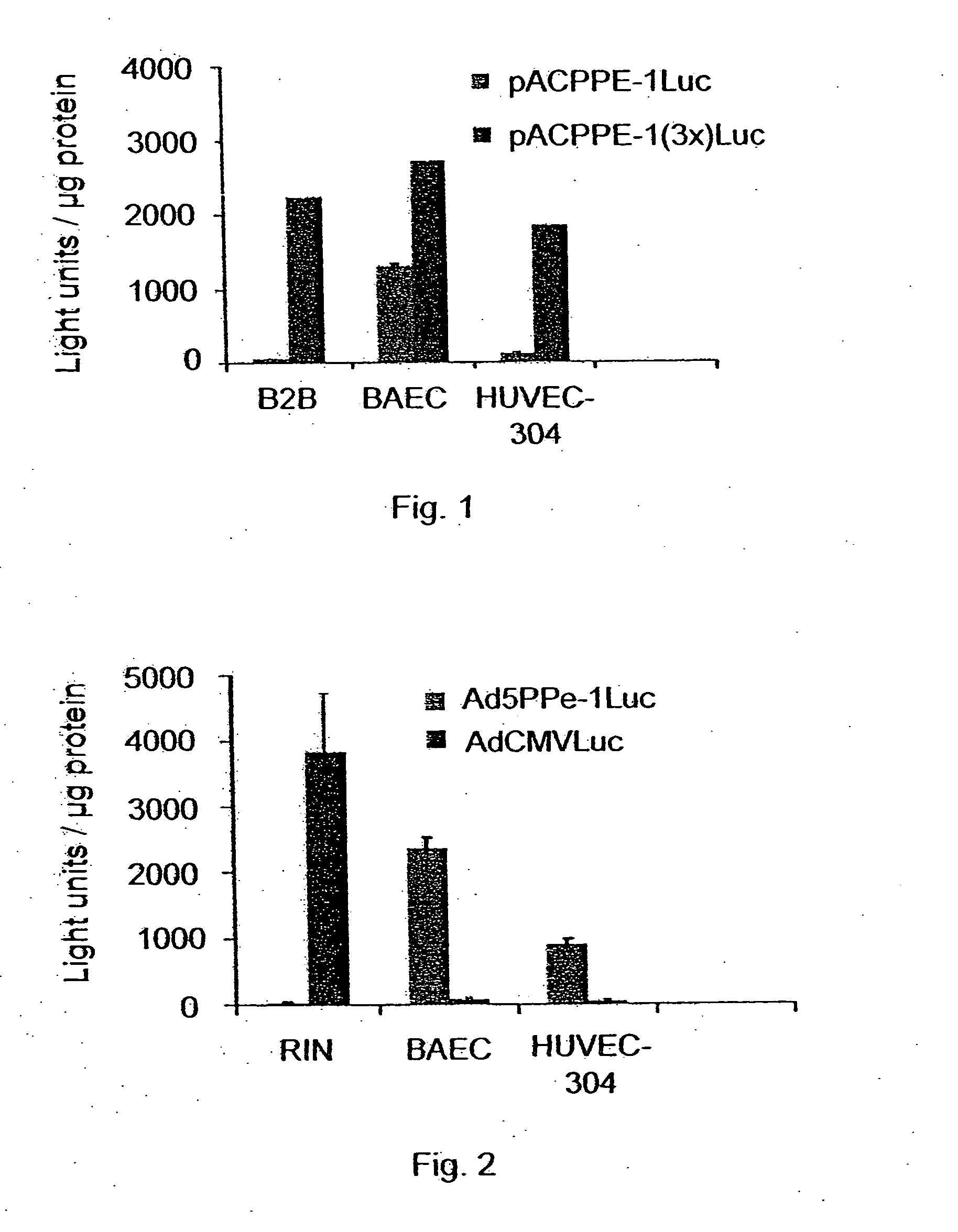
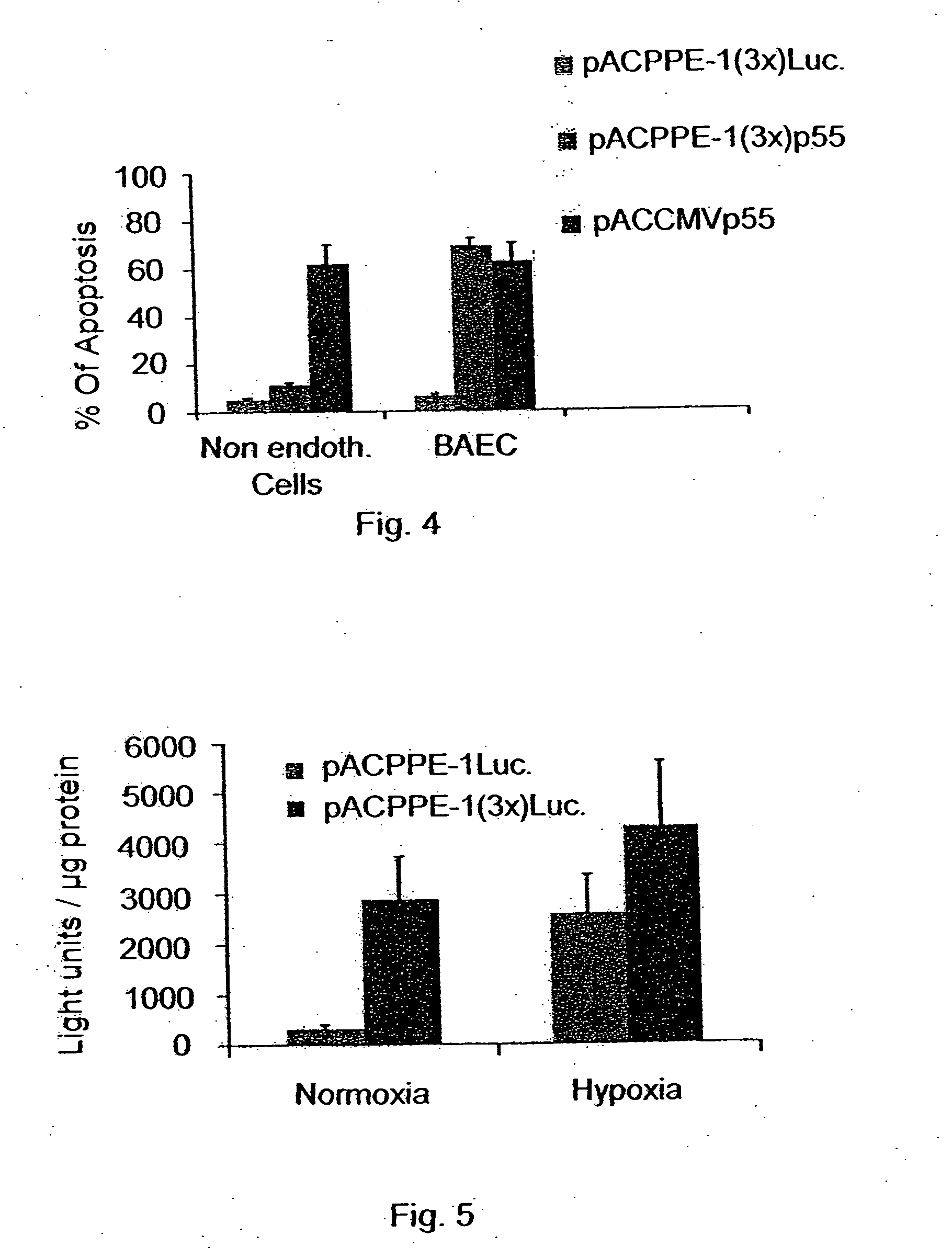
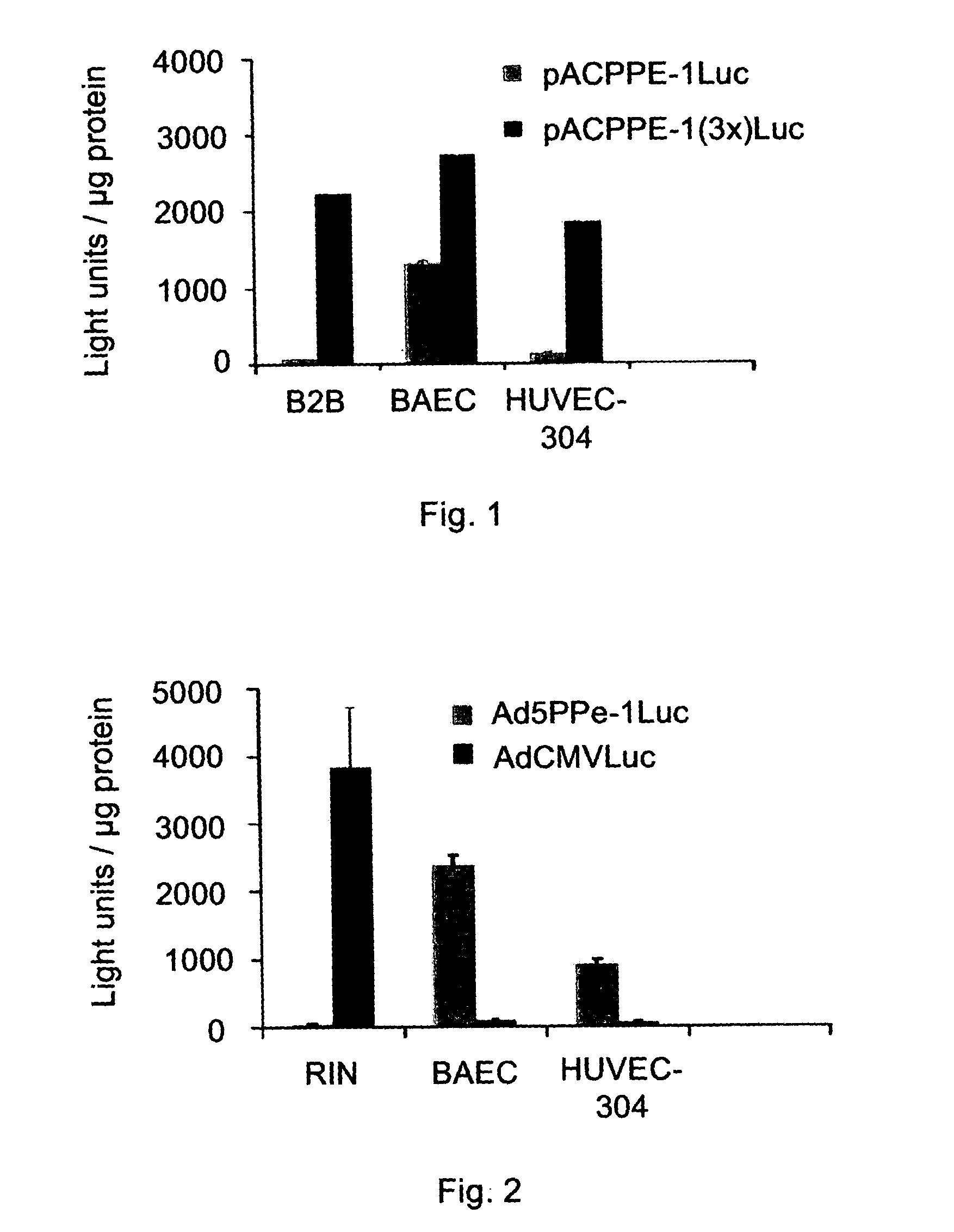
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same
InactiveUS20050112110A1Strong specificityPromotes an increase in inductionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
An isolated polynucleotide functional as a promoter in eukaryotic cells is disclosed. The isolated polynucleotide includes an endothelial specific enhancer element as detailed herein. Further disclosed is a method of expressing a nucleic acid sequence of interest in endothelial cells.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same
InactiveUS20040048280A1Improve responseHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
An isolated polynucleotide functional as a promoter in eukaryotic cells is disclosed. The isolated polynucleotide includes an endothelial specific enhancer element as detailed herein. Further disclosed is a method of expressing a nucleic acid sequence of interest in endothelial cells.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
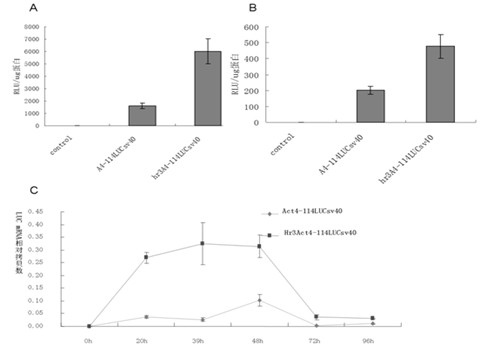
Enhancer Hr3
ActiveCN102492692AIncrease transcriptional activityImprove expression levelVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationRestriction sitePromoter
The invention relates to enhancer Hr3 adopting the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQIDNO: 1. The enhancer Hr3 can be used for preparing and recombining heterologous protein by bombyx mori. The invention further relates to a recombination carrier containing the enhancer Hr3, and the recombination carrier is prepared in such a manner that the enhancer Hr3 is connected with a Nco1 restriction site at the upstream of a promoter of a carrier containing no enhancer through the Nco1 restriction site of the enhancer Hr3. In the invention, functional elements such as the first grade enhancer, activating transcription factor IE1, untranslated region sequences (5' UTR and 3' UTR) and the like which are expressed by intensifier are identified in the cellular level, and an efficient and stable sericin I expression system is built by integrating optimum elements on the basis, so that efficient expression recombination heterologous protein can be made of middle silk gland of transgenic bombyx mori.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Process for protein extraction
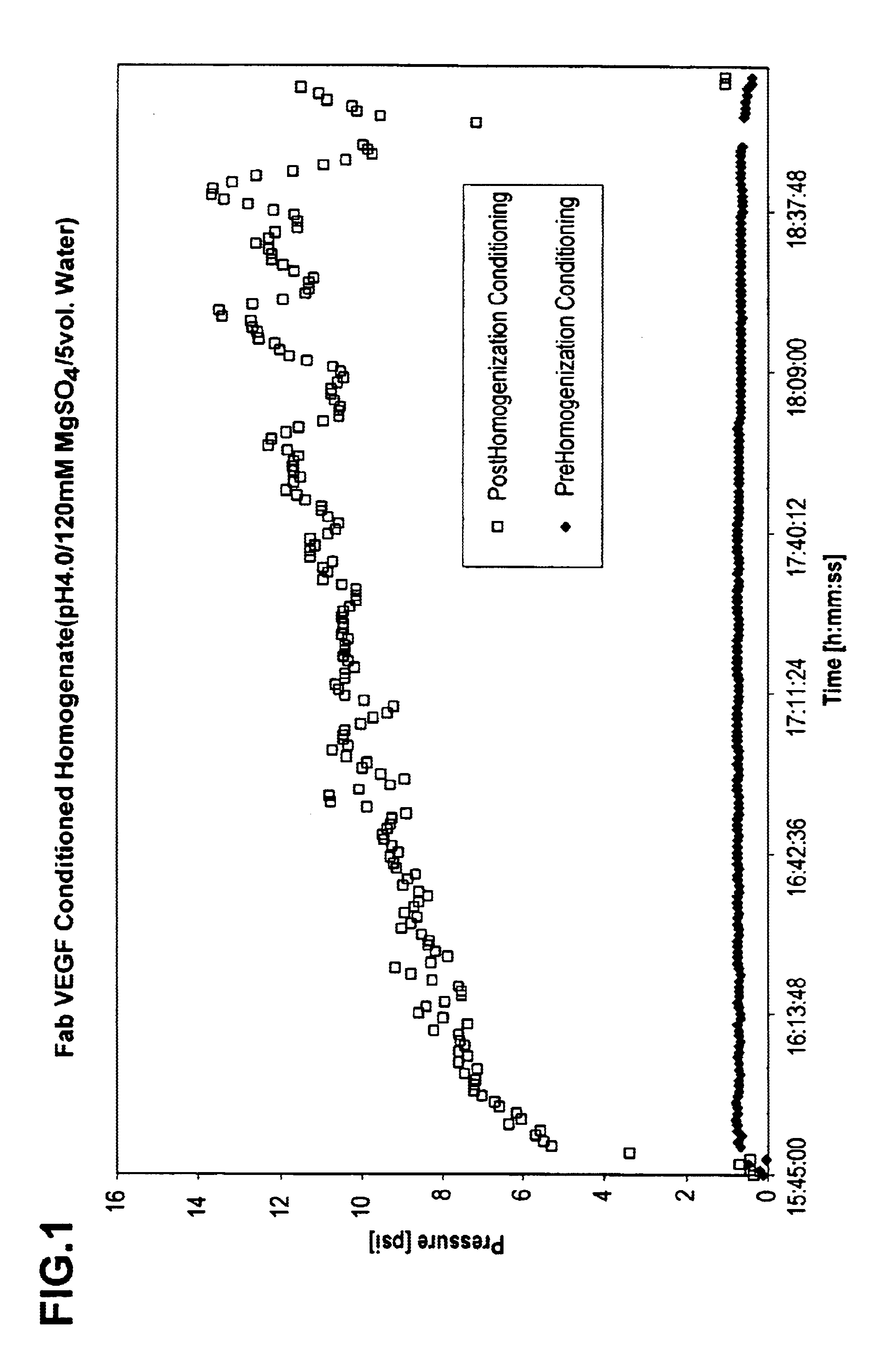
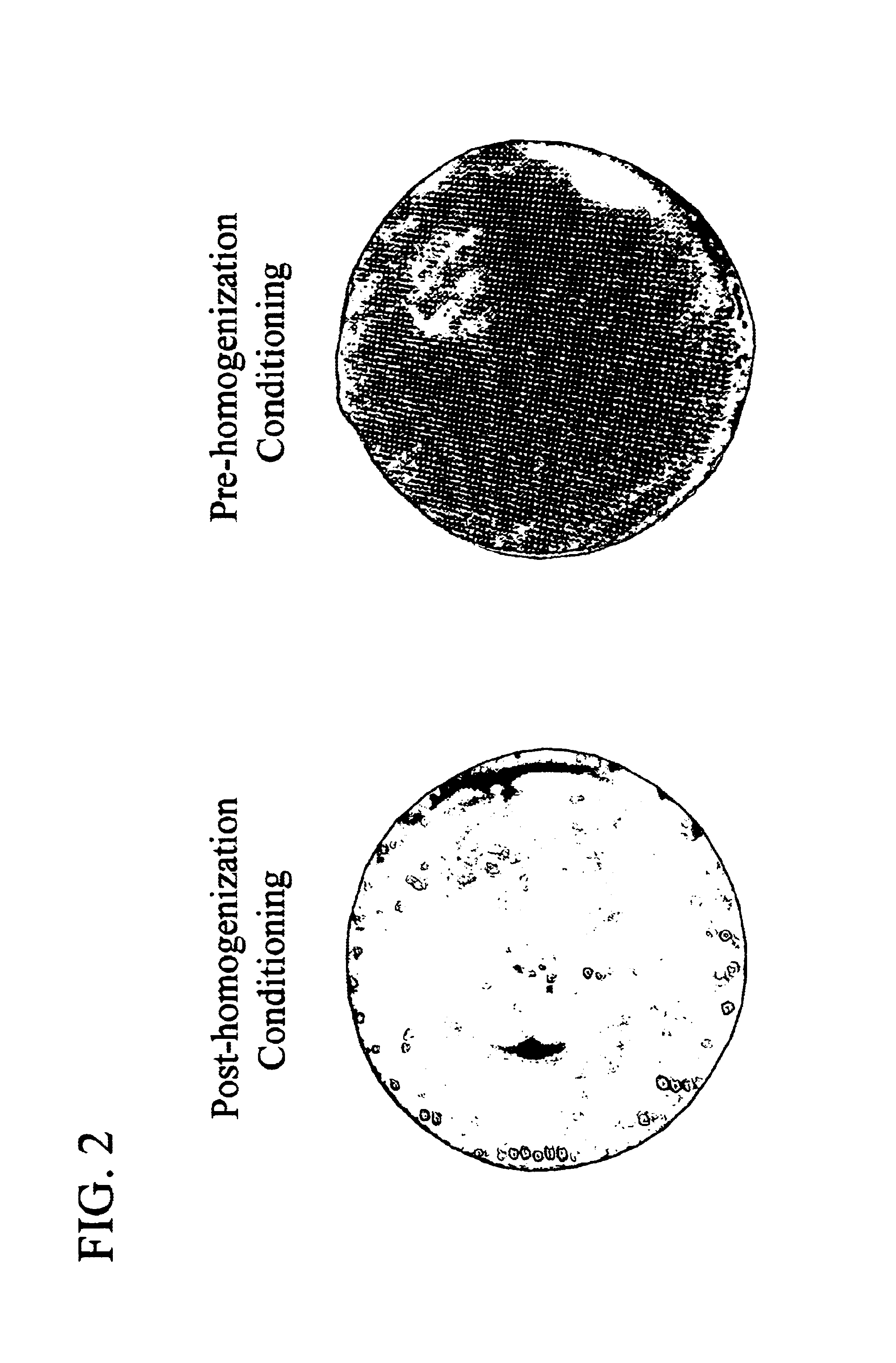
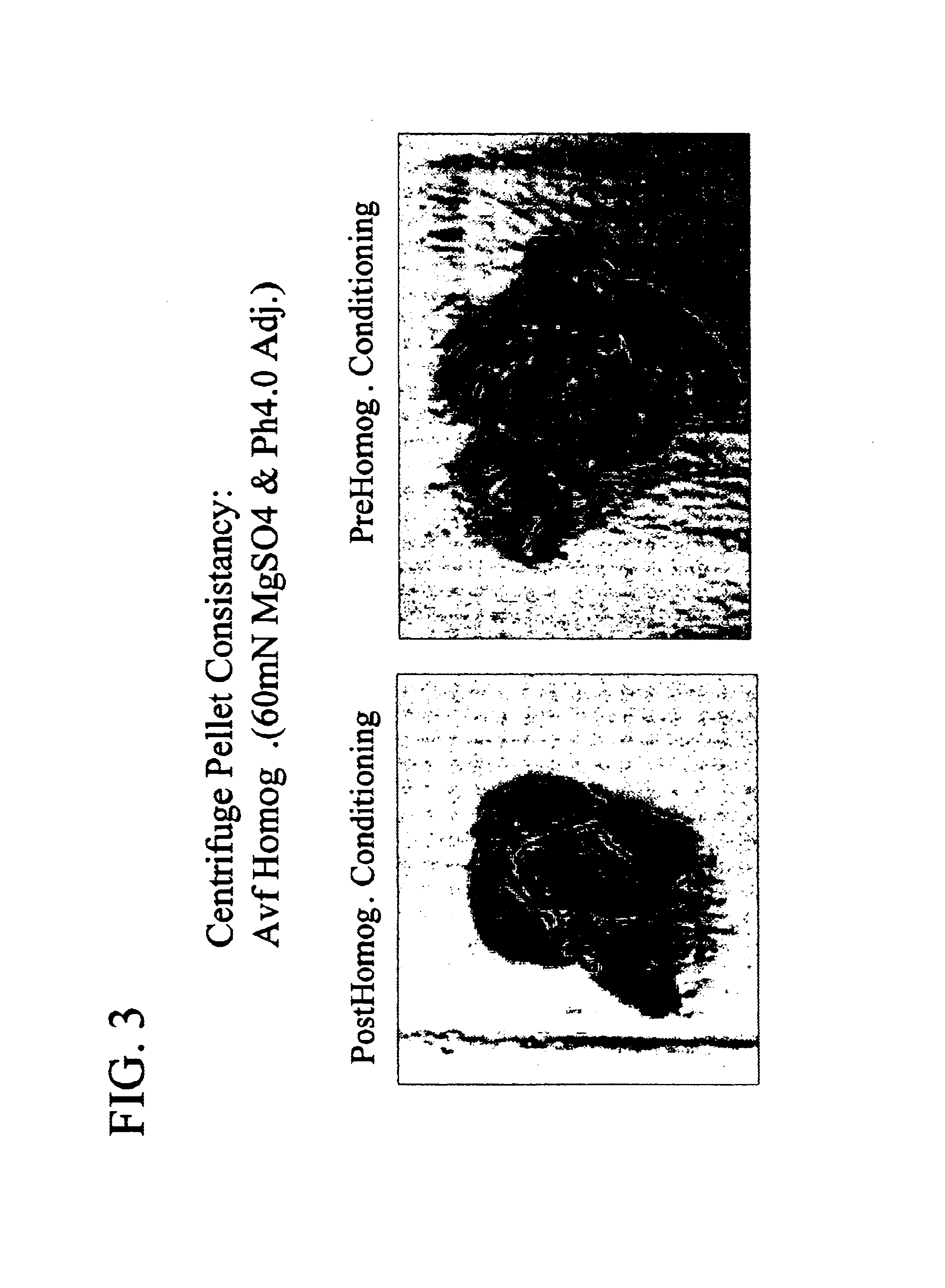
ActiveUS20060106205A1High viscosityReduced pHImmunoglobulins against growth factorsDepsipeptidesSolubilityEscherichia coli
The invention includes a process for extracting a target protein from E. coli cells that includes lowering the pH of a whole E. coli cell solution to form an acidic solution, disrupting the cells to release the protein into the acidic solution, and separating the cellular debris from the released protein to obtain a protein product enriched in the heterologous target protein. The invention also includes addition of a solubility enhancer.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Superior hybridization probes and methods for their use in detection of polynucleotide targets
InactiveUS20090170719A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Hybridization probe
We describe new hybridization probes and methods for their use in detection, identification, and quantitation of polynucleotides such as RNA and DNA. Ordinary short oligonucleotide probes usually provide higher sequence-specificity but lower efficacy of hybridization than longer ordinary polynucleotide probes where both are fully complementary to the target polynucleotide. Our new polynucleotide probes combine the hybridization efficacy of long probes with the sequence-specificity of short probes. The polynucleotide probes contain a target binding domain and a binding enhancer domain, where the binding enhancer domain does not for stable structures under hybridizing conditions with the target binding domain or its corresponding target. These binding enhancer domains are able to improve the hybridization features of the target binding domain as well as the signal-to-noise ratio for target detection. Detection methods based on these probes allow fast, accurate, and sensitive detection of target polynucleotides (either qualitatively or quantitatively) and can be easily multiplexed.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
Eukaryotic expression vector for expressing shRNA (short hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) in manner of targeting in cancer cells
InactiveCN101993892ASolve the problem of non-specific interferenceGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesCancer cellReverse transcriptase
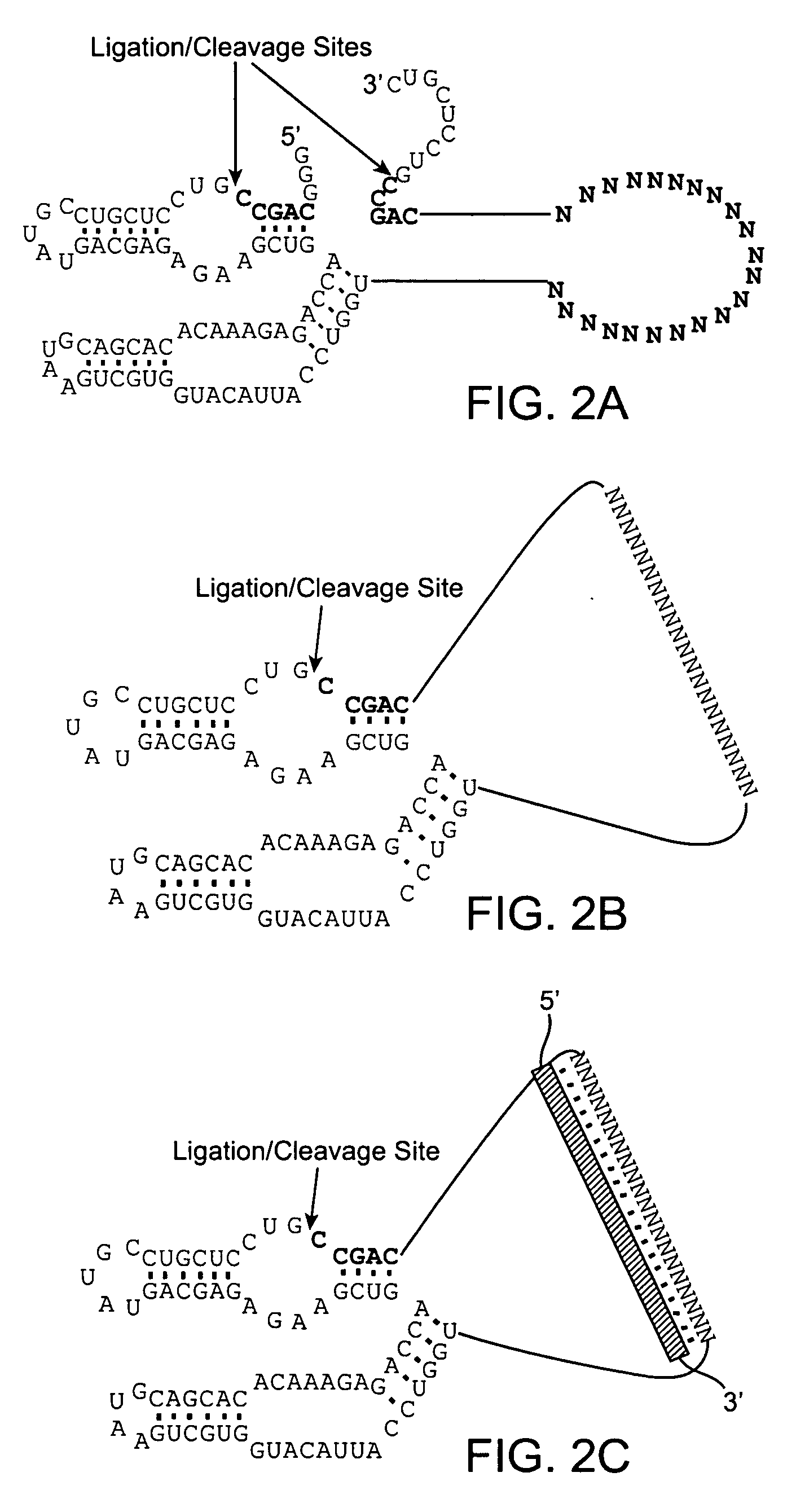
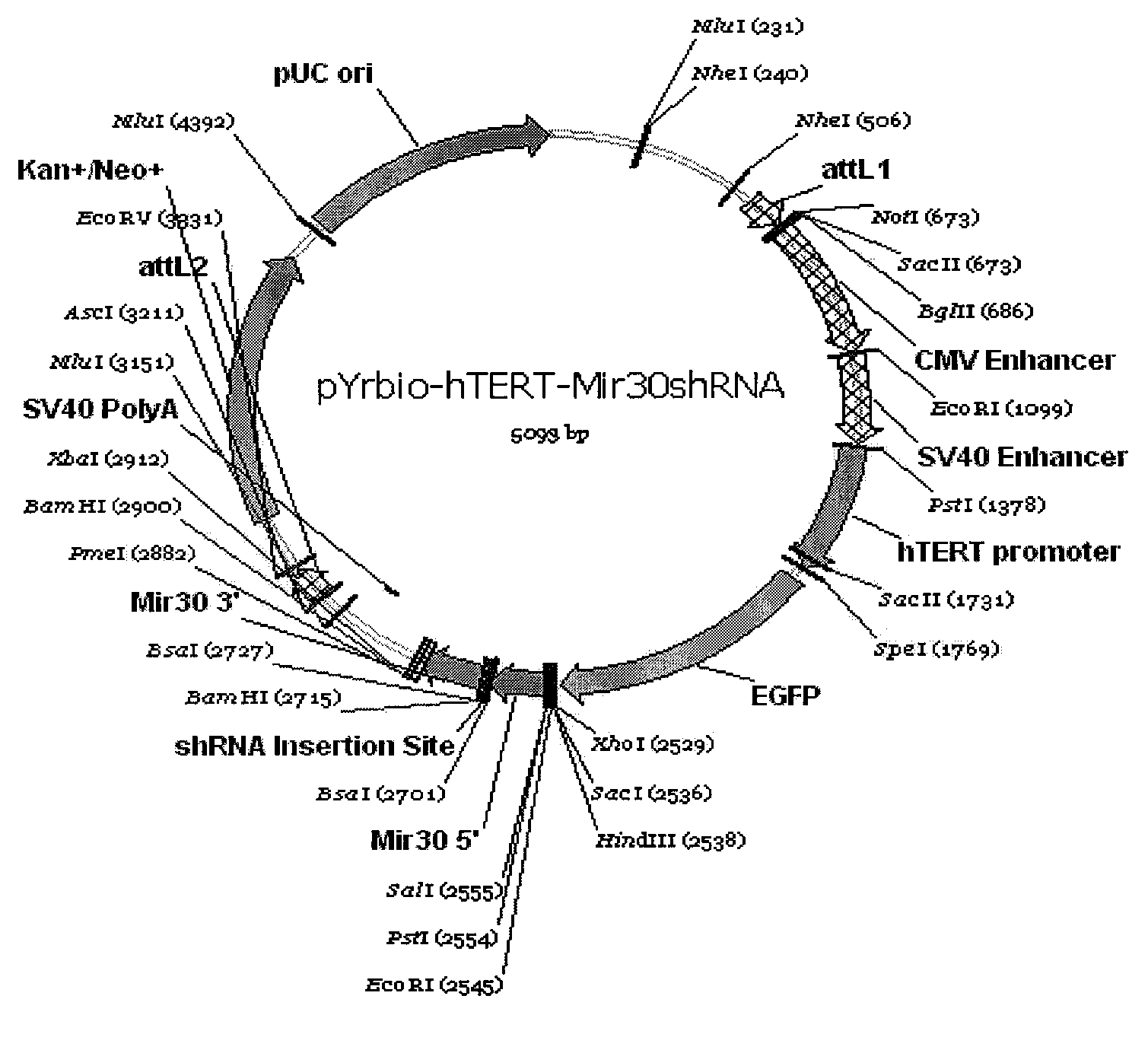
The invention provides a eukaryotic expression vector for expressing shRNA (short hairpin Ribonucleic Acid) in manner of targeting in cancer cells, comprising the structure as follows: (1) an expression cassette structure which is driven by a polII-type promoter and connects a fluorescent protein gene and a mirshRNA structure in series together; (2) a hTERT (human telomerase reverse transcriptase) promoter enhanced by a CMV (cytomegalovirus) enhancer and a SV40 (simian virus 40) enhancer; (3) mirshRNA structures based on mir30: mir30 left arm-shRNA-mir30 right arm, and multiple mirshRNA structures can be connected in series; (4) a Kan or Amp resistance selection marker; and (5) LR homologous recombination arms. By utilizing the method to construct the shRNA eukaryotic expression vector, one or more than one shRNA can be specifically expressed in the cancer cells in manner of targeting; normal cells are not influenced while the RNA interference and the gene therapy are carried out on the cancer cells, thereby solving the problem of non-specific interference during carrying out the gene therapy by utilizing the RNA interference and being beneficial to the research and the application of the RNA interference in the cancer gene therapy aspect.
Owner:HUNAN NENGRUN MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS TECH
Cell-specific molecule and method for importing DNA into osteoblast nuclei
ActiveUS20060242725A1Easy to transportOvercome obstaclesPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesCore binding factorPromoter
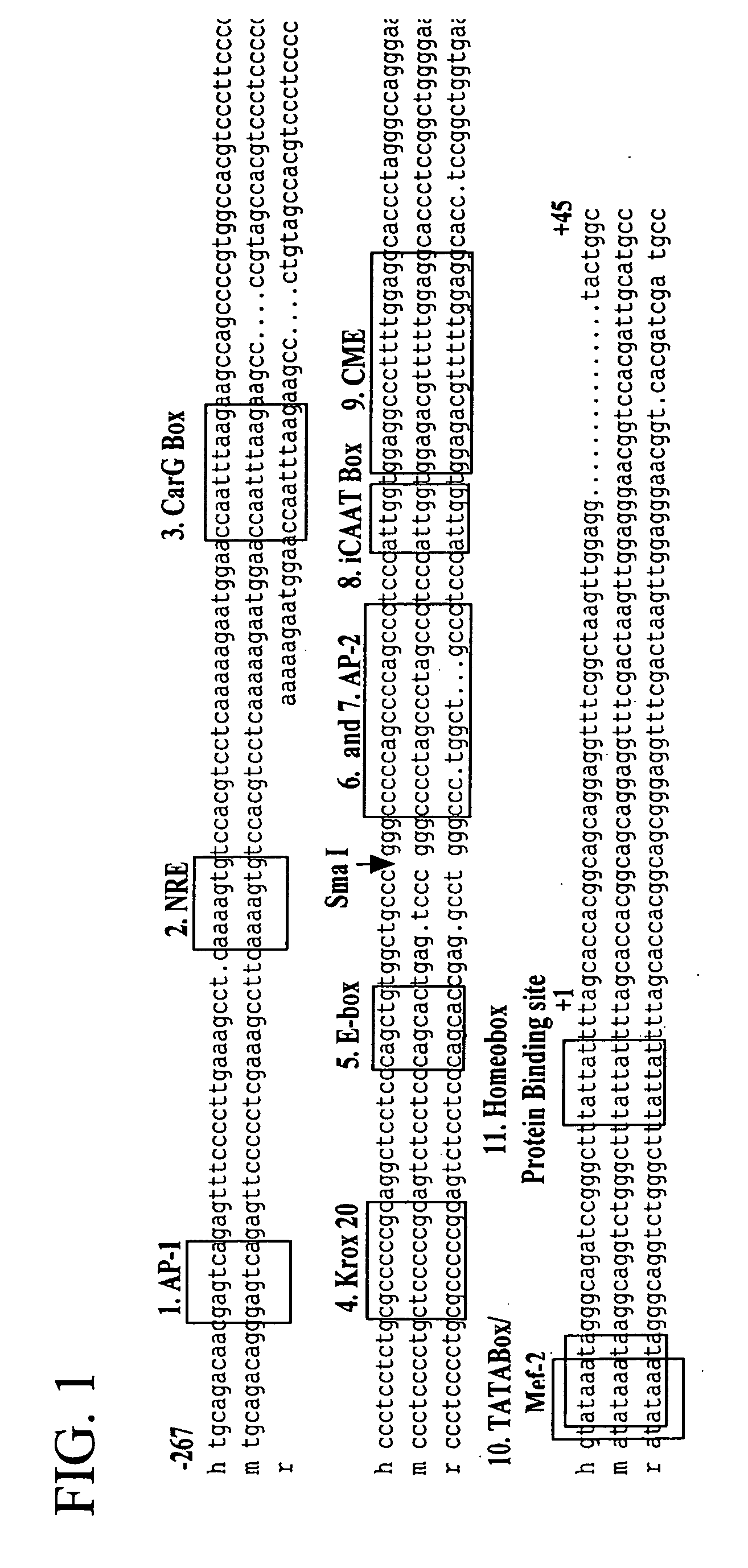
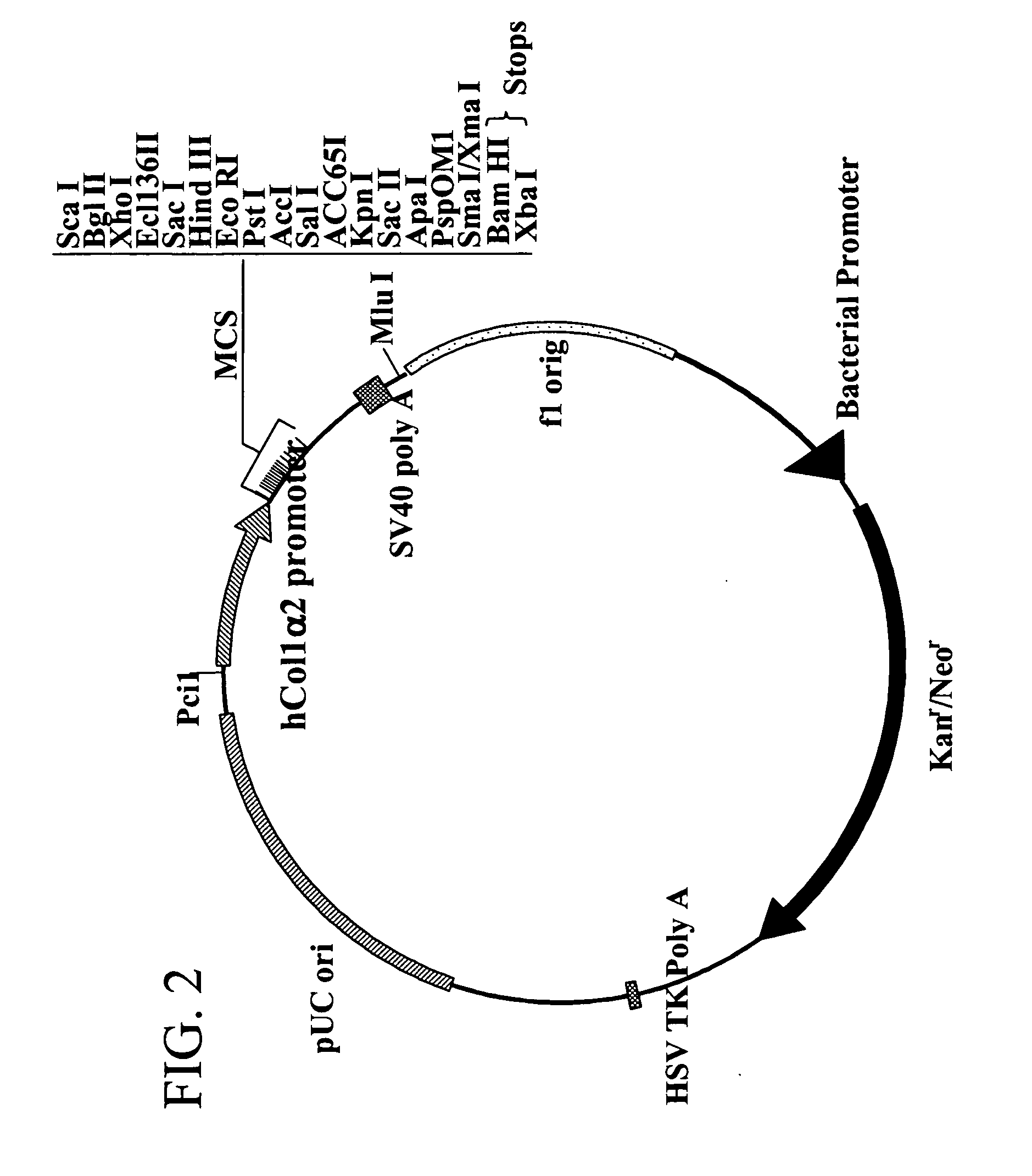
A plasmid, viral or linear DNA molecule containing a nucleic acid sequence derived from the promoter region of the hCol1α2 gene, which is selectively transported into the nuclei of cells in the osteoblast lineage. The sequence can be used independently as a nuclear entry sequence only, and / or as a nuclear entry sequence without regard to position, in a vector or linear DNA that directs gene expression and nuclear entry. The disclosure further includes a chimeric DNA sequence derived by the addition of osteoblast-specific enhancer sequences to the nuclear entry sequence / promoter sequence, to increase osteoblast-specific expression while retaining osteoblast-specific nuclear import. An enhancer sequence is derived from the promoter region of the human Core Binding Factor alpha 1 (Cbfa1 / Runx2) gene. The Cbfa1 / Runx2 promoter can be added to the sequence derived from, or alternatively, comprising the promoter region of the hCol1α2 gene. Also provided are methods of use of the novel sequences.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +3
Human beta-globin gene and recombinant adeno related viral vector thereof
ActiveCN101348786AImprove expression efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAdeno associate virusAdeno-associated virus
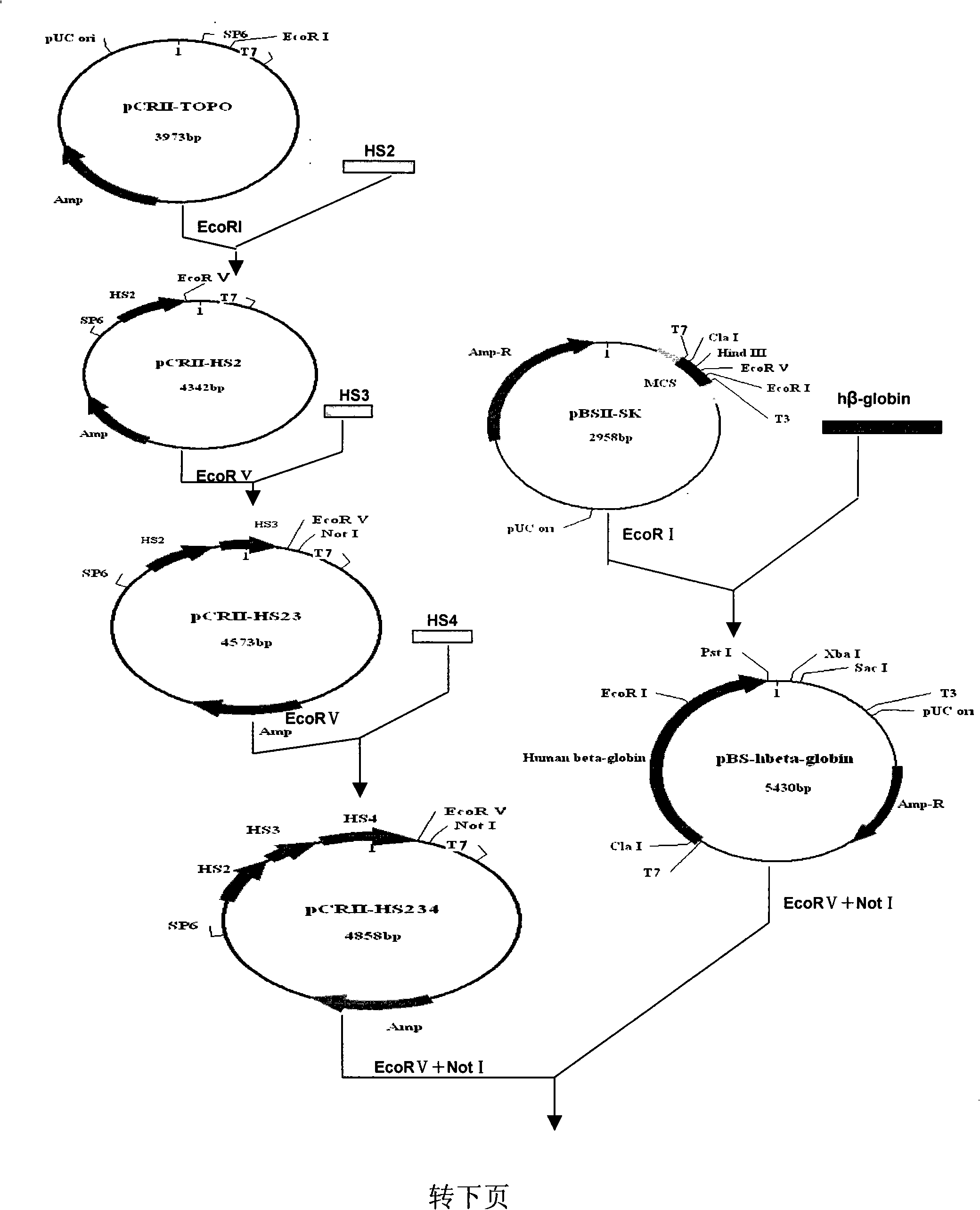
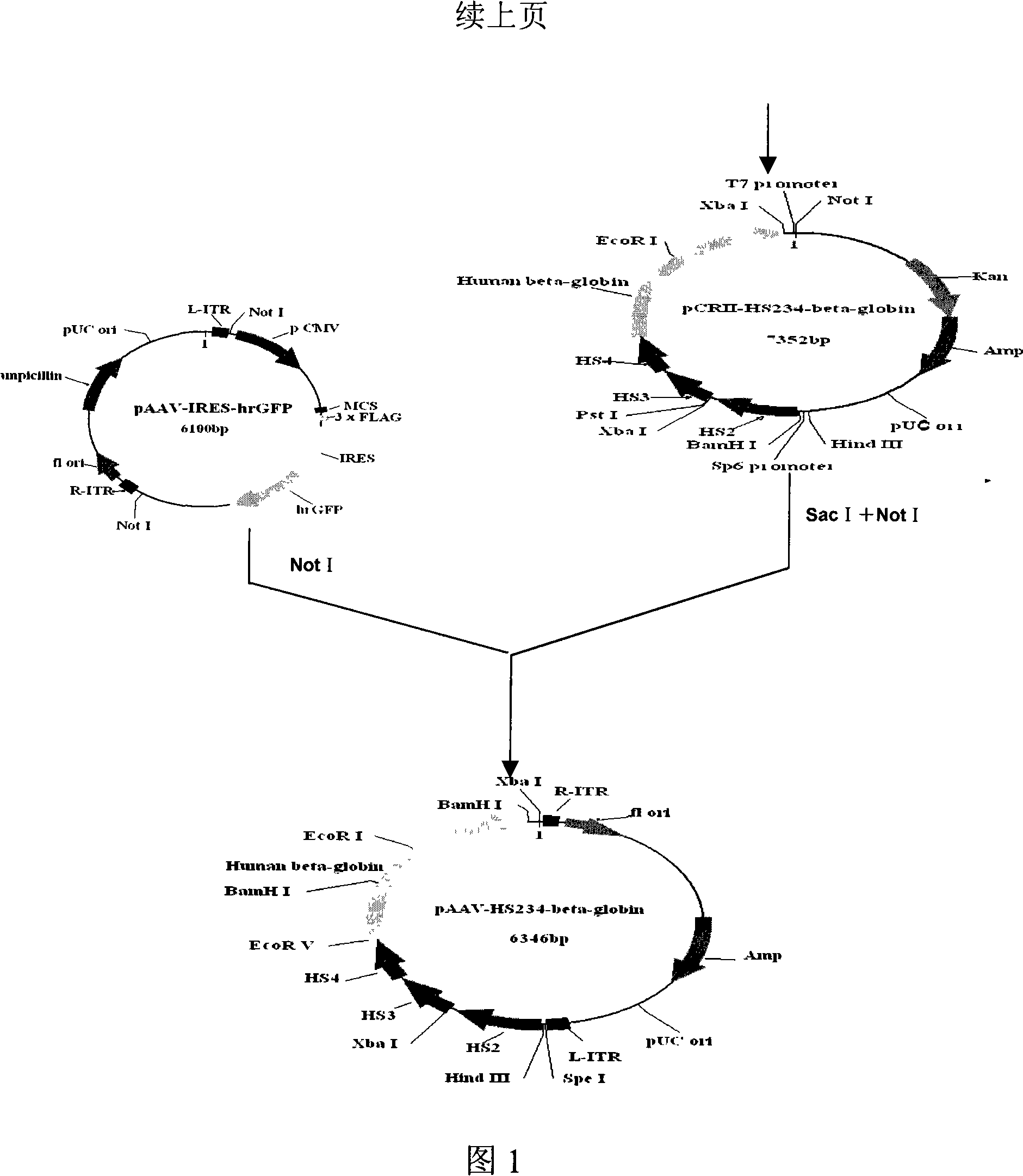
The invention discloses a human beta globin gene containing a human beta globin gene promoter, a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing the human beta globin gene, and a method for preparing the recombinant vector. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector inserts an HS2 segment, an HS3 segment and an HS4 segment of a human beta globin gene cluster enhancer core sequence and a human beta globin gene sequence containing the human beta globin gene promoter into repeated sequence ITRs on the reverse terminal of an adeno-associated virus. The recombinant vector has high transfection efficiency; and mediated exogenous genes can be expressed in vivo for a long time, have good safety and can be used for gene therapy of beta Mediterranean anemia.
Owner:DONGGUAN ZHENGXING BEITE MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
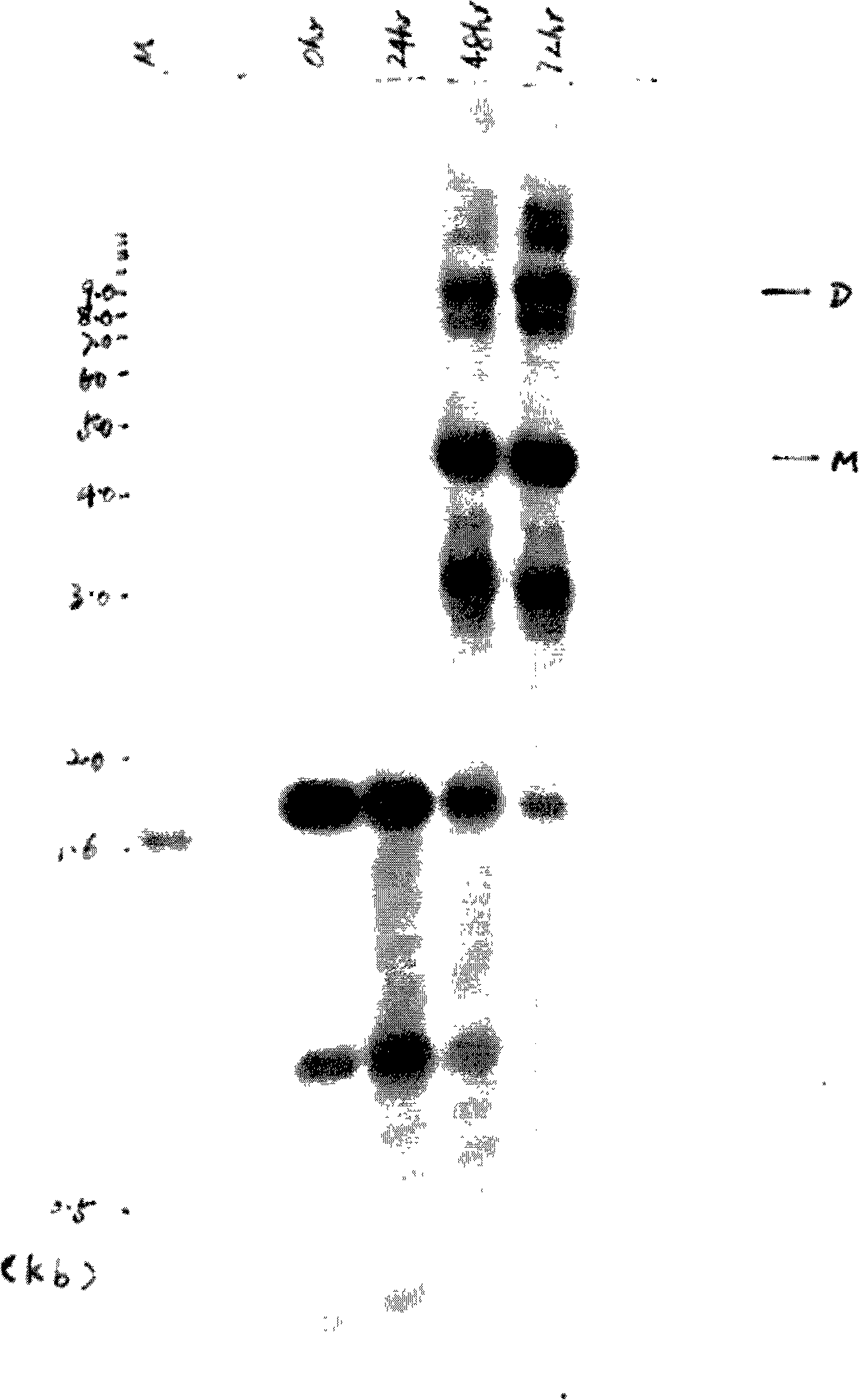
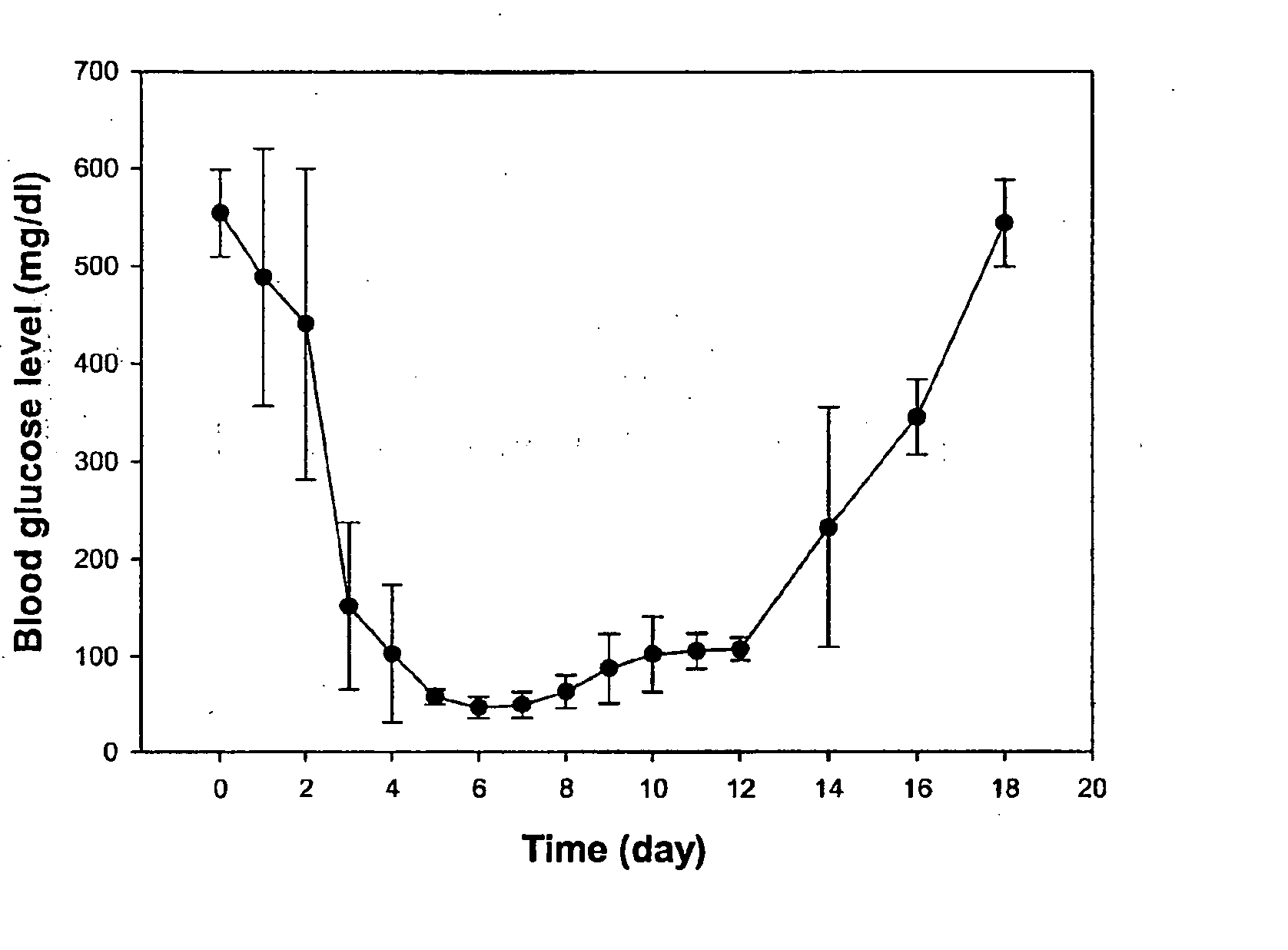
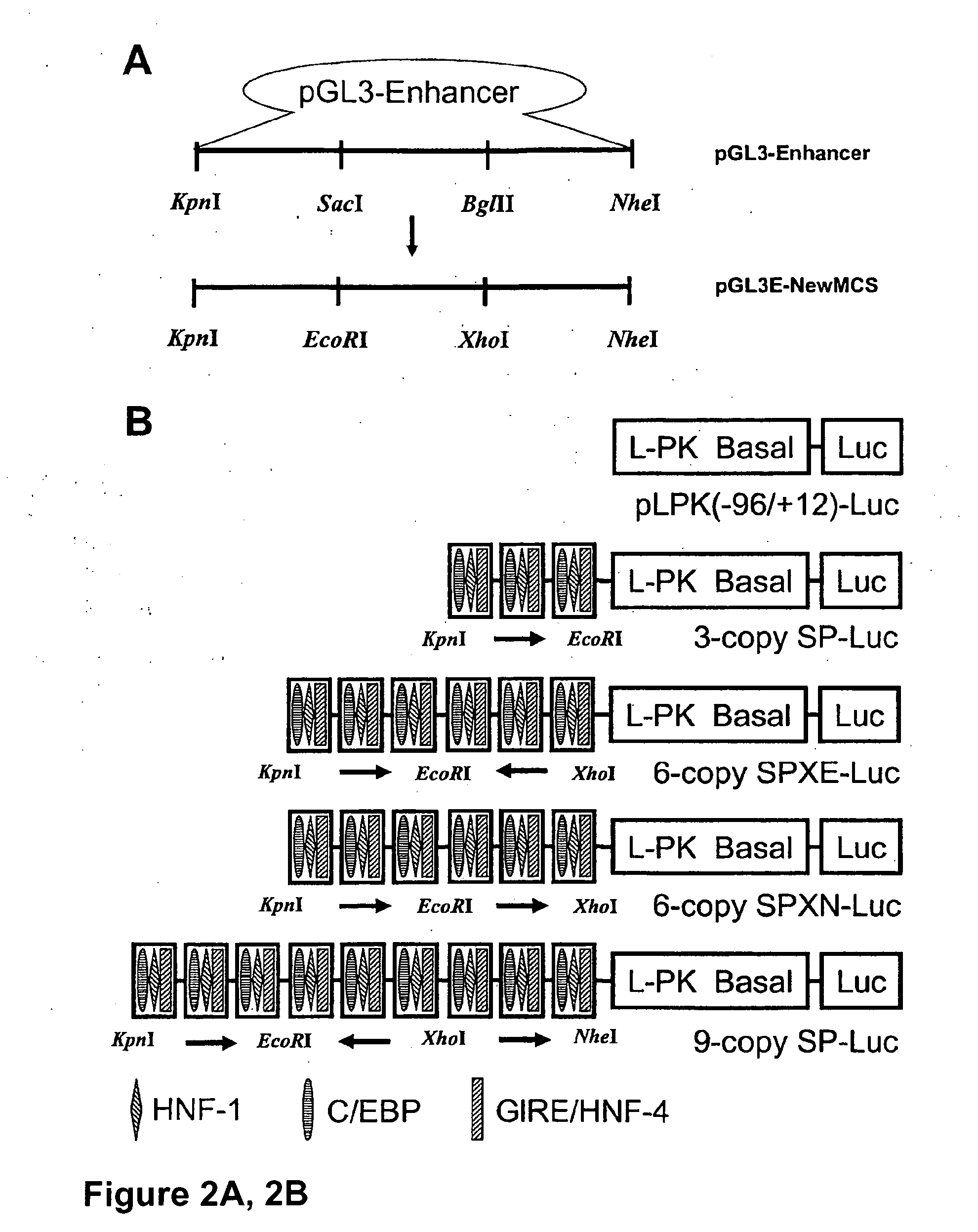
Glucose inducible insulin expression and methods of treating diabetes
The invention provides an isolated tissue specific glucose responsive promoter having a polymerase binding domain 3′ to at least one tripartite transcription factor binding cis element having a hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 (HNF-1) element, a CAAT / enhancer binding protein (C / EBP) response element and a glucose-response element (GRE). The promoter can include a second or third tripartite transcription factor binding cis element. A host cell including the tissue specific glucose responsive promoter of the invention also are provided. Further provided is a method of treating or preventing diabetes. The method includes administering to an individual an effective amount of a viral particle having a vector comprising a tissue specific glucose responsive promoter comprising a polymerase binding domain 3′ to at least one tripartite transcription factor binding cis element having a hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 (HNF-1) element, a CAAT / enhancer binding protein (C / EBP) response element and a glucose-response element (GRE) operationally linked to an insulin encoding nucleic acid, wherein expression of the insulin encoding nucleic acid is tissue specific and glucose responsive.
Owner:BIOTECH INST FOR INT INNOVATION
Expression vector
ActiveCN105238816AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGeneticsOrgyia pseudotsugata
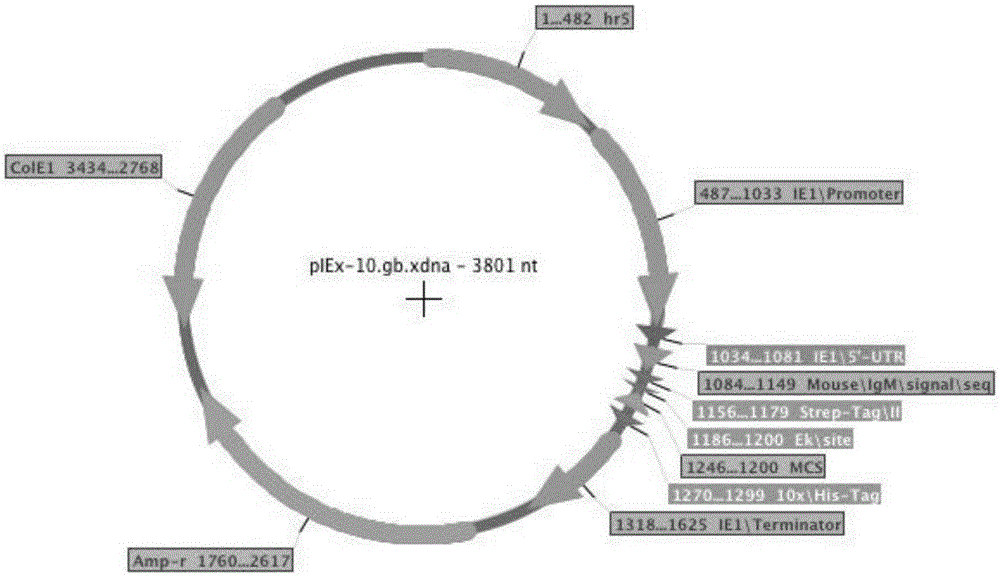
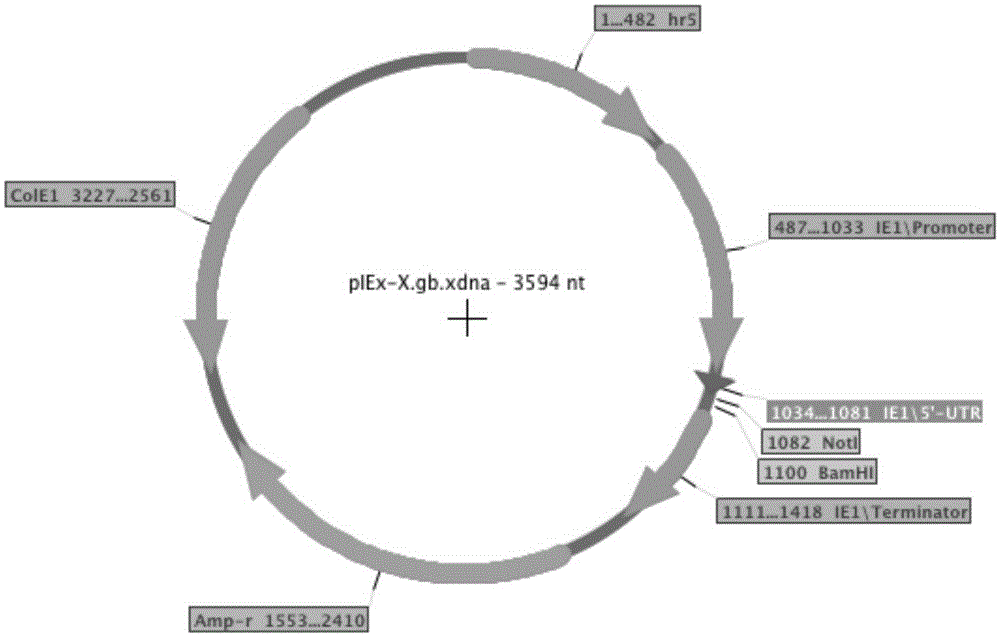
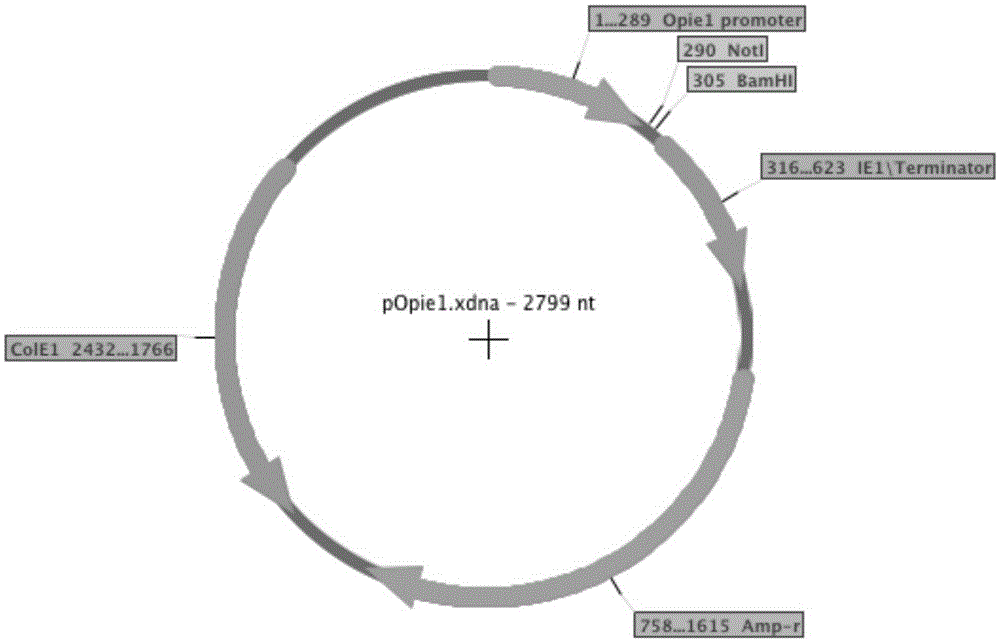
The invention belongs to the field of a biology technology, and relates to an expression vector. The expression vector is an expression vector for insect, and contains an AcIE1 promoter of Autographa californica multicapsid nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) and a hr5 enhancer of a homologous region 5 and an Opie2 promoter of Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus (OpMNPV). An insect host cell containing the expression vector and a method for preparing a recombinant protein by using the expression vector are provided.
Owner:CANTONBIO CO LTD
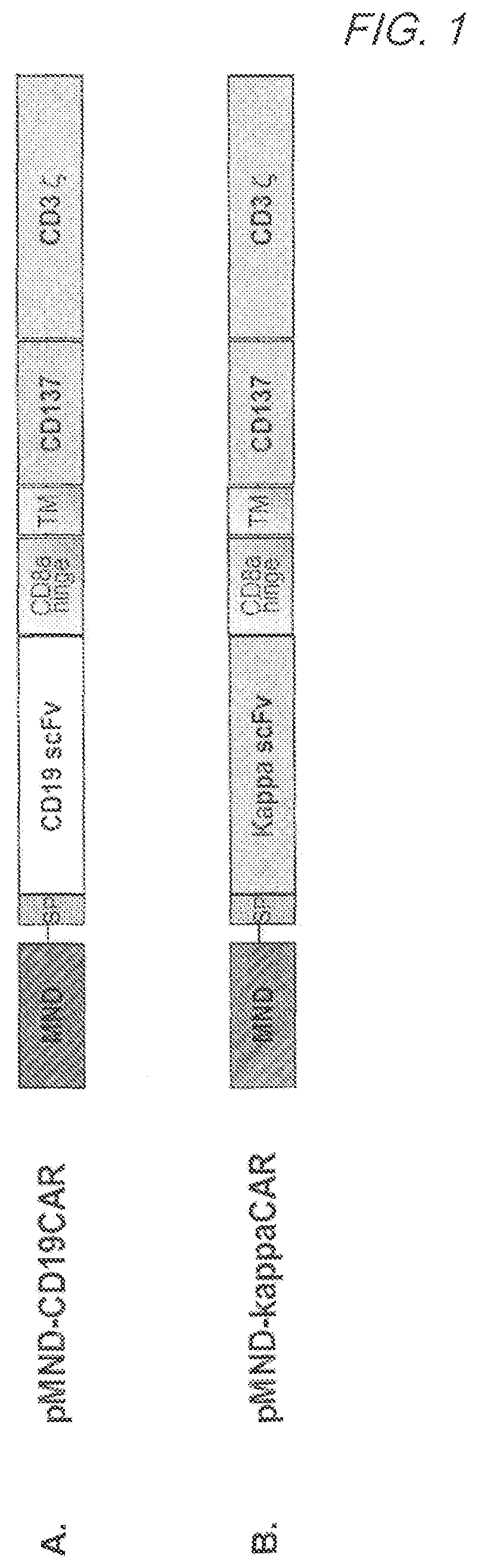
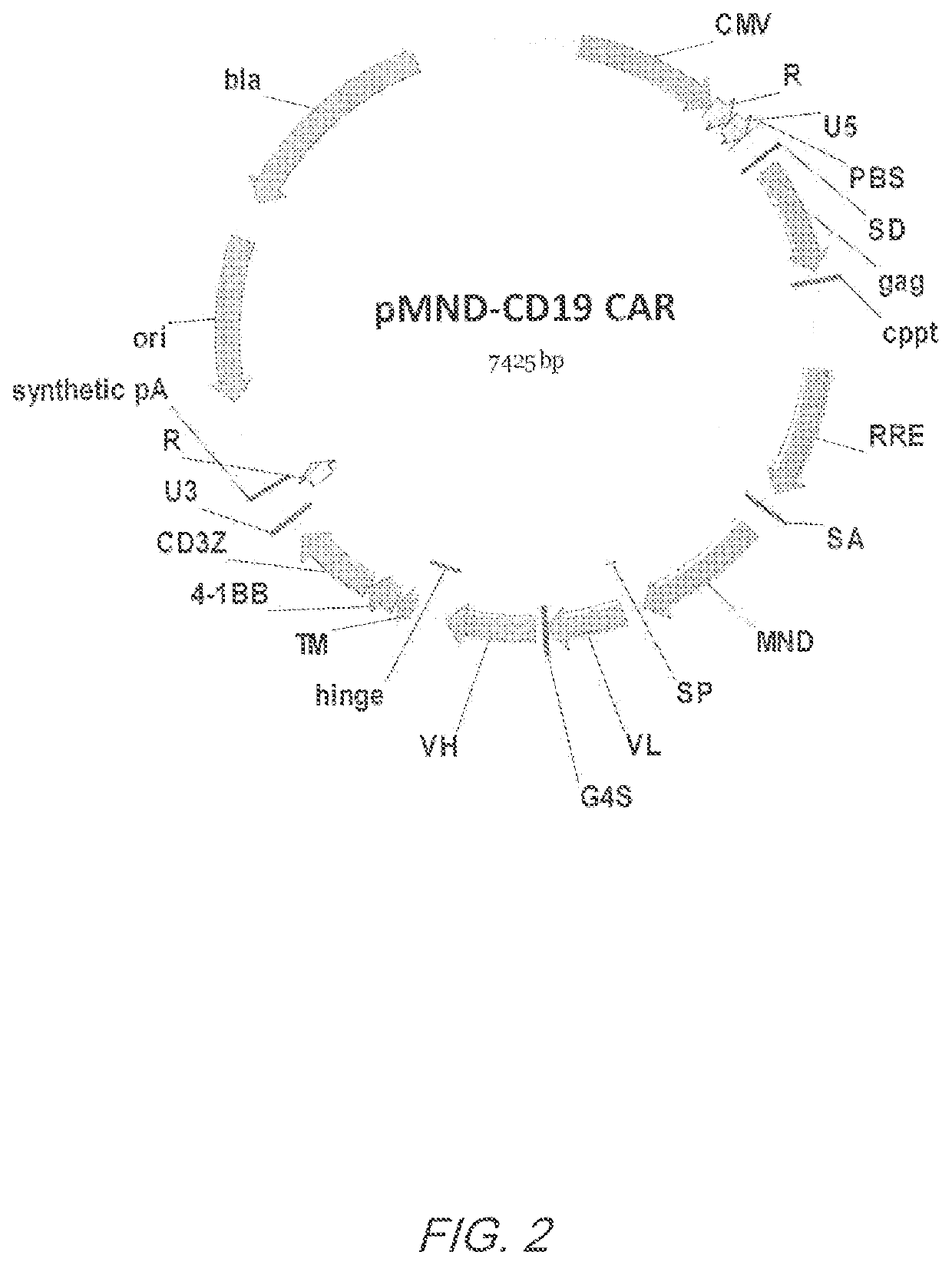
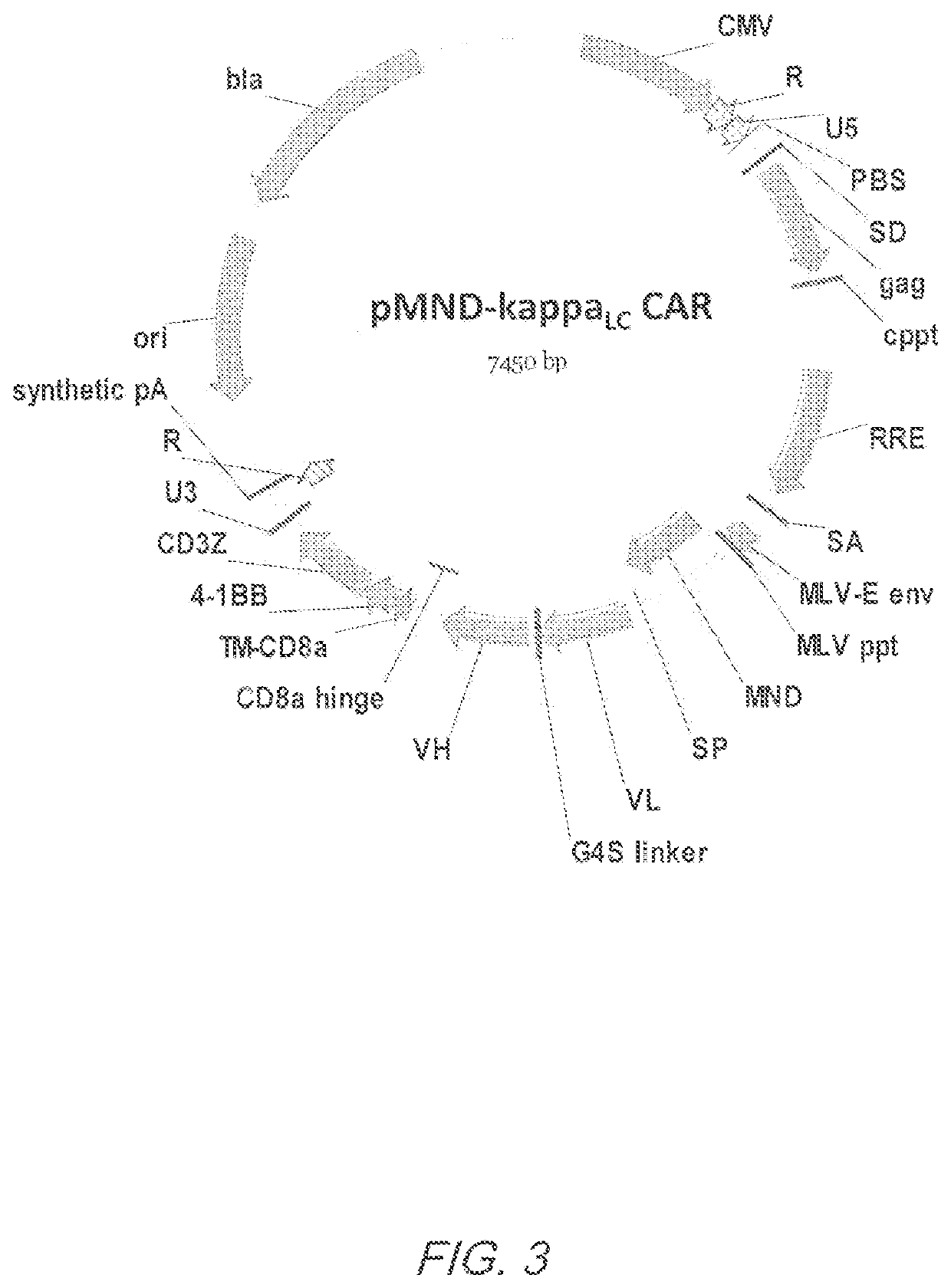
MND promoter chimeric antigen receptors
ActiveUS10774343B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsBinding siteAntigen receptors
Vector compositions comprising a myeloproliferative sarcoma virus enhancer, negative control region deleted, dl587rev primer-binding site substituted (MND) promoter operably linked to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) are provided.
Owner:2SEVENTY BIO INC
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of DNA and pichia pastoris expression vector
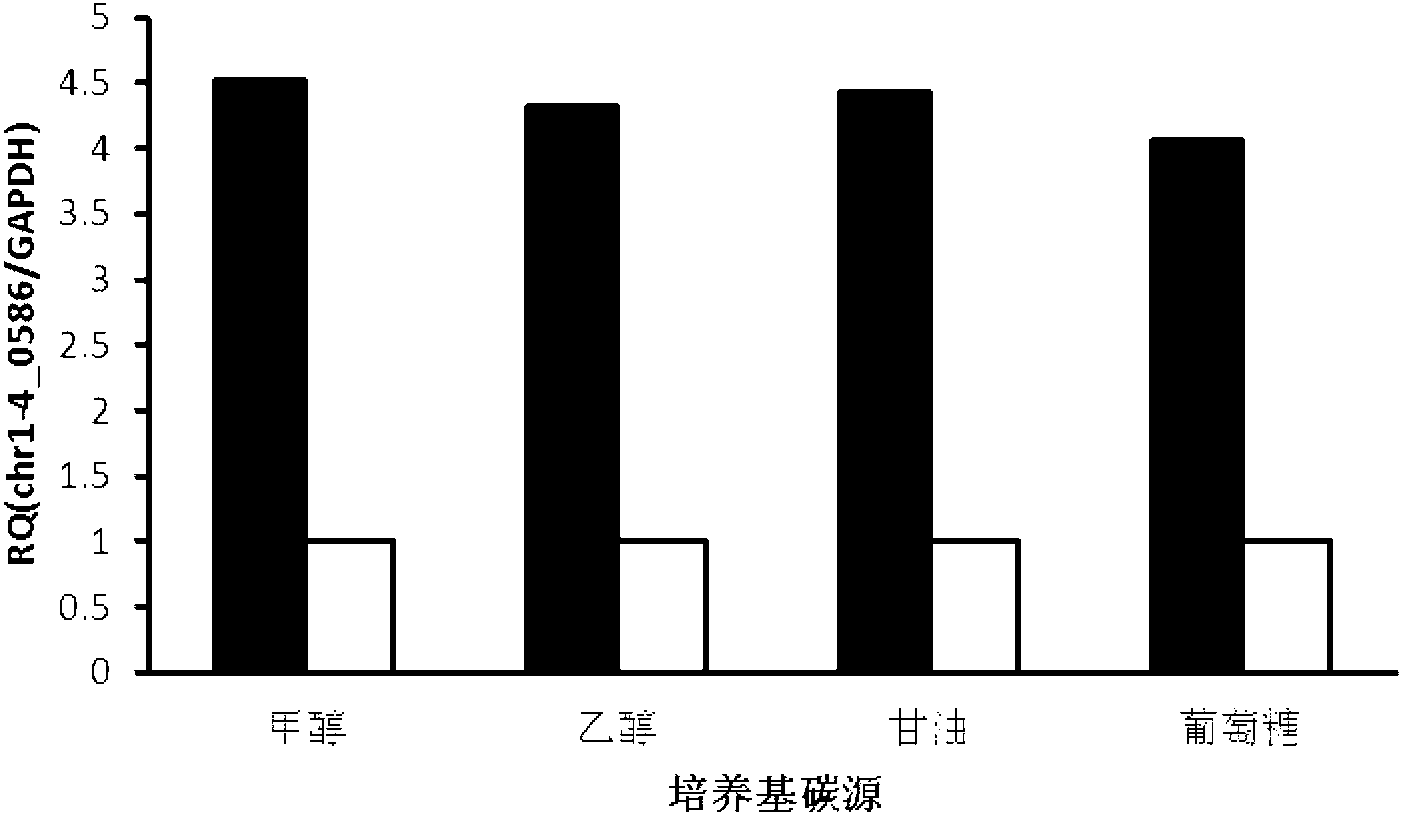
ActiveCN102994501ALittle change in transcriptional activityIncrease transcriptional activityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisBase J
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) with constitutive promoter activity, application of the DNA and a pichia pastoris expression vector. The DNA has a base sequence as shown in SEQ No.1 (Sequence Number); and the application of the DNA relates to the application of the DNA in construction of the pichia pastoris (Pinchia Pastoris) expression vector. The DNA disclosed by the invention has the constitutive promoter activity, and can activate the transcription of a downstream structural gene without an inductor; the transcriptional activity shows little change in four different culture mediums, namely, ethanol, methanol, glucose and glycerol; the promoter activity is efficient, and the efficiency of the initiation transcription is four times more than the pichia pastoris GAPDH (Reduced Glyceraldehyde-phosphate Dehydrogenase) promoter. The pichia pastoris expression vector, constructed by the DNA disclosed by the invention, can efficiently express the extrinsic protein without methanol induction, and the efficiency of expressing the extrinsic protein (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) is about 6 to 8 times that of the expression system of the GAPDH promoter and 1.5 to 2 times that of the expression system of a TEF1 (Transcription Enhancer Factor 1) promoter.
Owner:林影 +1
Reic-expressing adenovirus vector
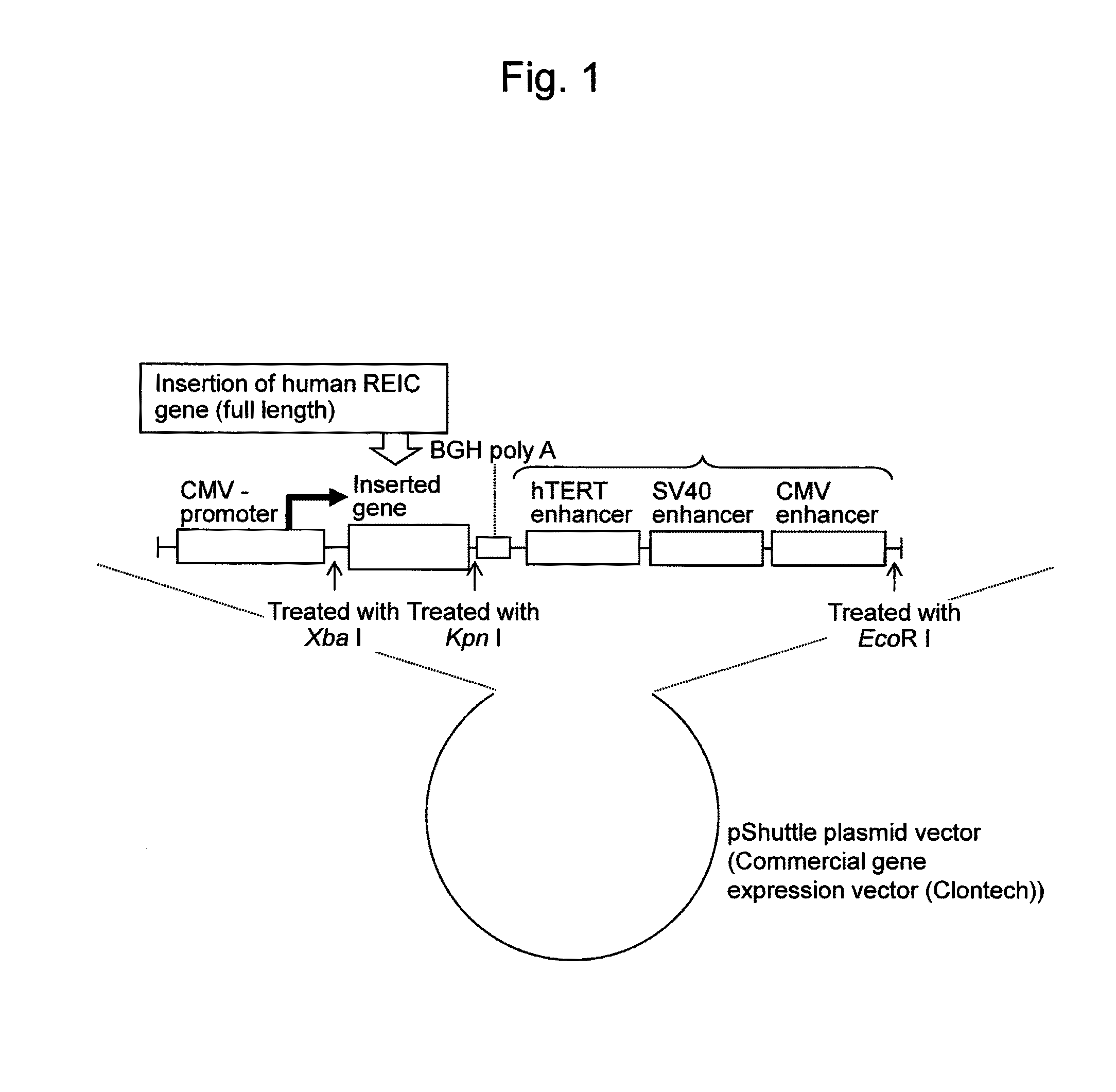
ActiveUS20140147917A1Increased gene expression levelsInhibit tumor growthVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructBiology
An objective of the present invention is to provide an adenovirus vector expressing a REIC / Dkk-3 protein at a high level and containing a DNA construct for expression of REIC / Dkk-3 DNA, wherein the DNA construct is prepared by ligating, from the 5′ terminal side,(i) a CMV promoter,(ii) REIC / Dkk-3 DNA,(iii) a polyA addition sequence, and(iv) enhancers prepared by linking an hTERT (Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase) enhancer, an SV40 enhancer, and a CMV enhancer in this order.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
Protein expression system
ActiveUS8674084B2Improve expression levelBoost protein levelsSugar derivativesVirus peptidesGenomic SegmentCowpea mosaic potyvirus
The inventions is based on an expression enhancer sequence derived from the RNA-2 genome segment of a bipartite RNA virus, in which a target initiation site in the RNA-2 genome segment has been mutated. Deletion of appropriate start codons upstream of the main RNA2 translation initiation can greatly increase in foreign protein accumulation without the need for viral replication. Also provided are methods, vectors and systems, including the ‘hyper-translatable’ Cowpea Mosaic Virus (‘CPMV-HT’) based protein expression system.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
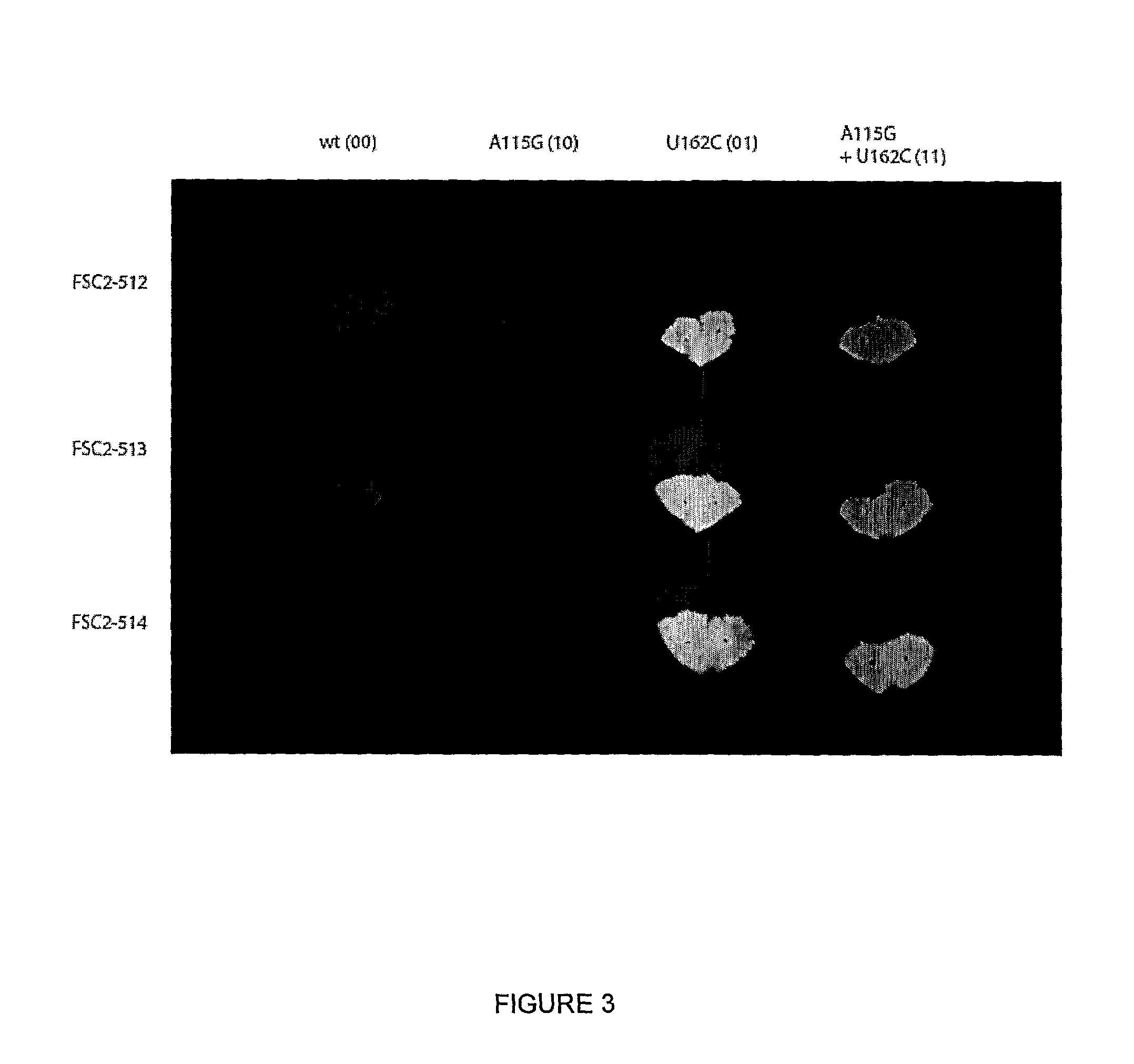
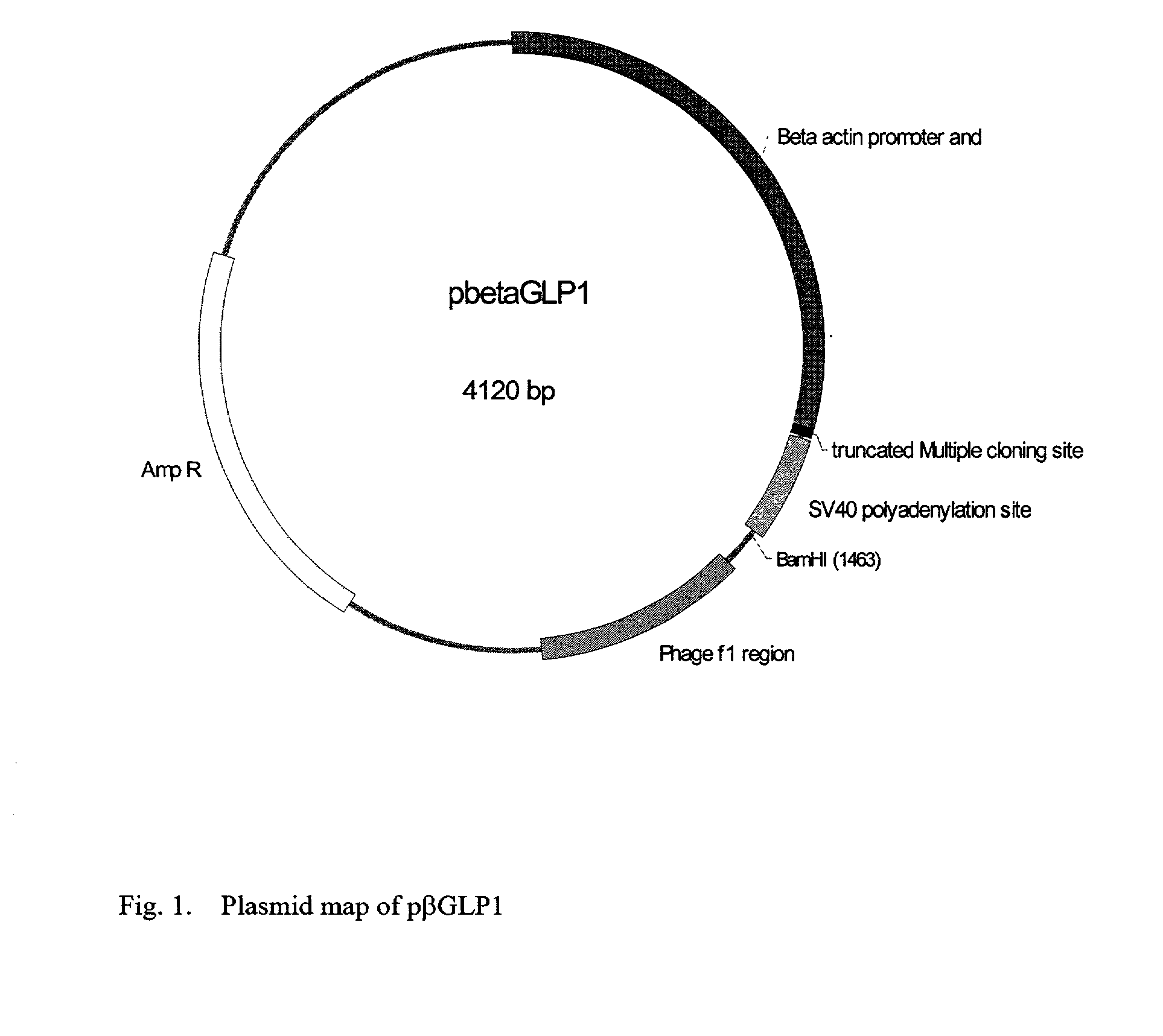
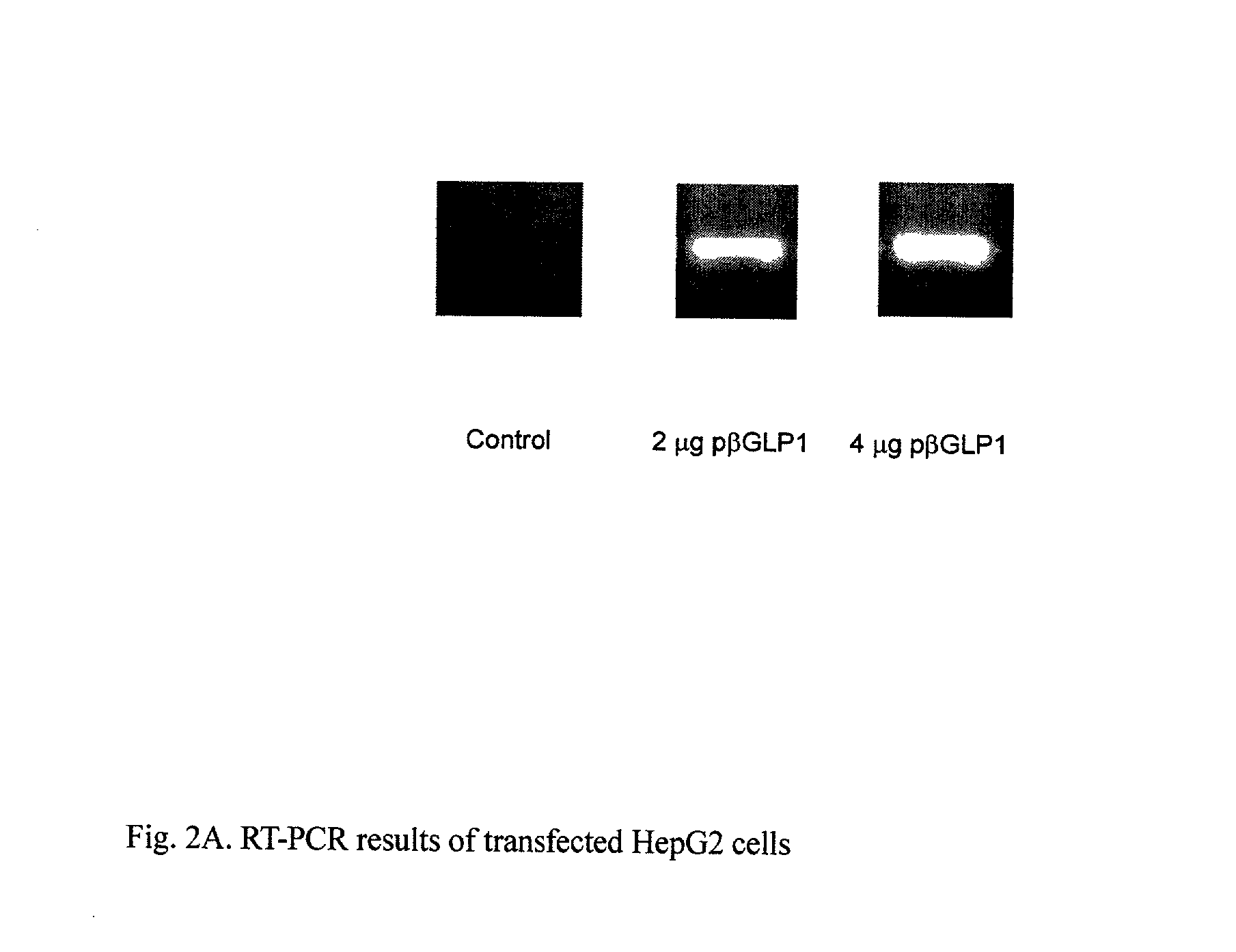
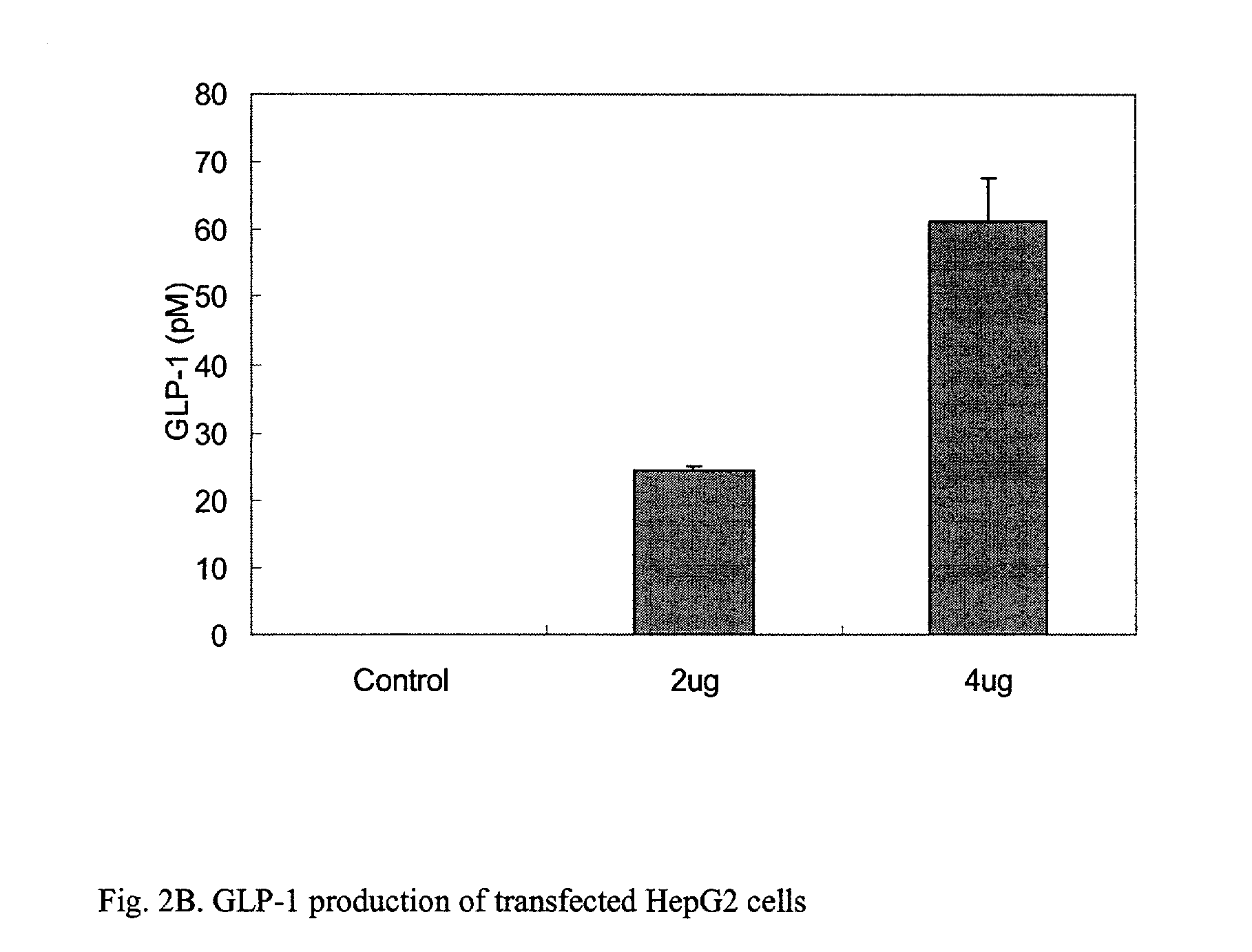
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS20030220274A1Rapid clearanceEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken beta actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pbetaGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Process for protein extraction
ActiveUS6967241B2Reduced pHReduce the amount requiredPowder deliveryBacteriaSolubilityCellular Debris
The invention includes a process for extracting a target protein from E. coli cells that includes lowering the pH of a whole E. coli cell solution to form an acidic solution, disrupting the cells to release the protein into the acidic solution, and separating the cellular debris from the released protein to obtain a protein product enriched in the heterologous target protein. The invention also includes addition of a solubility enhancer.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
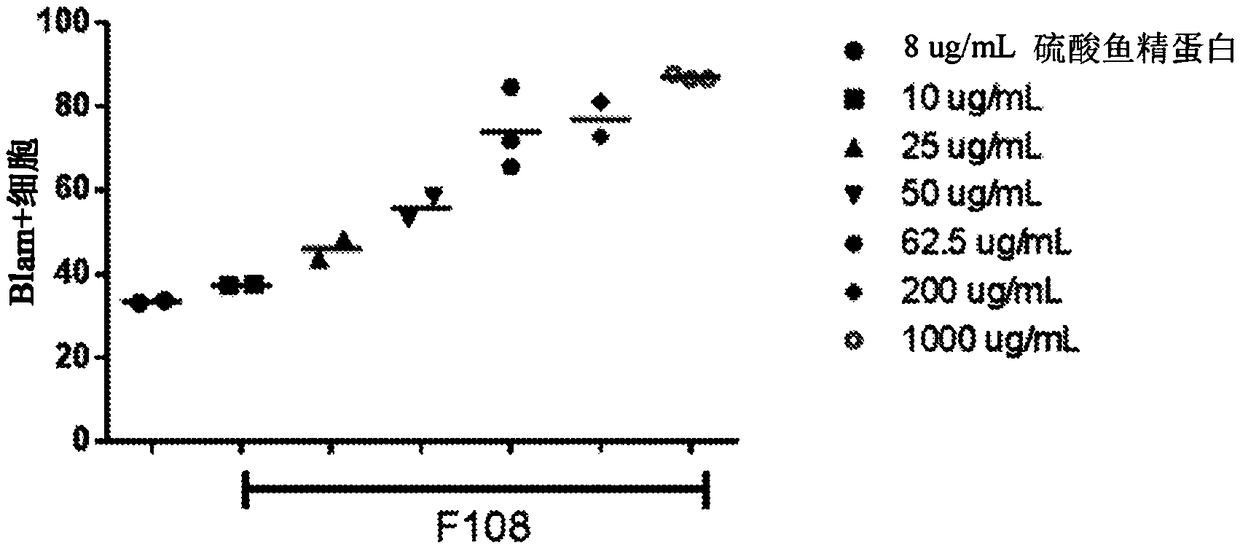
Compositions for improving gene amplification
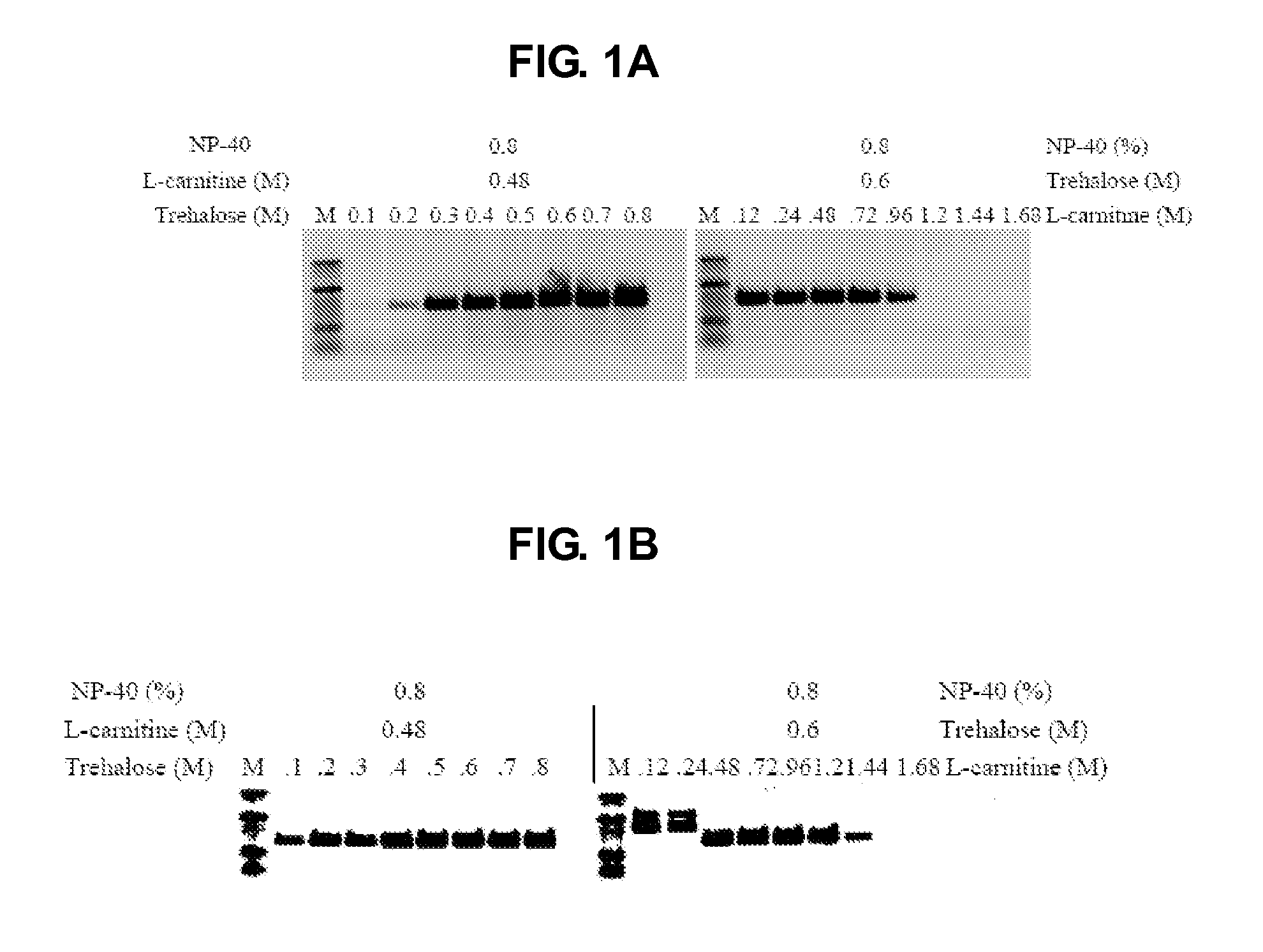
InactiveUS20120028259A1Improve polymerase performanceImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBlood componentGC-content
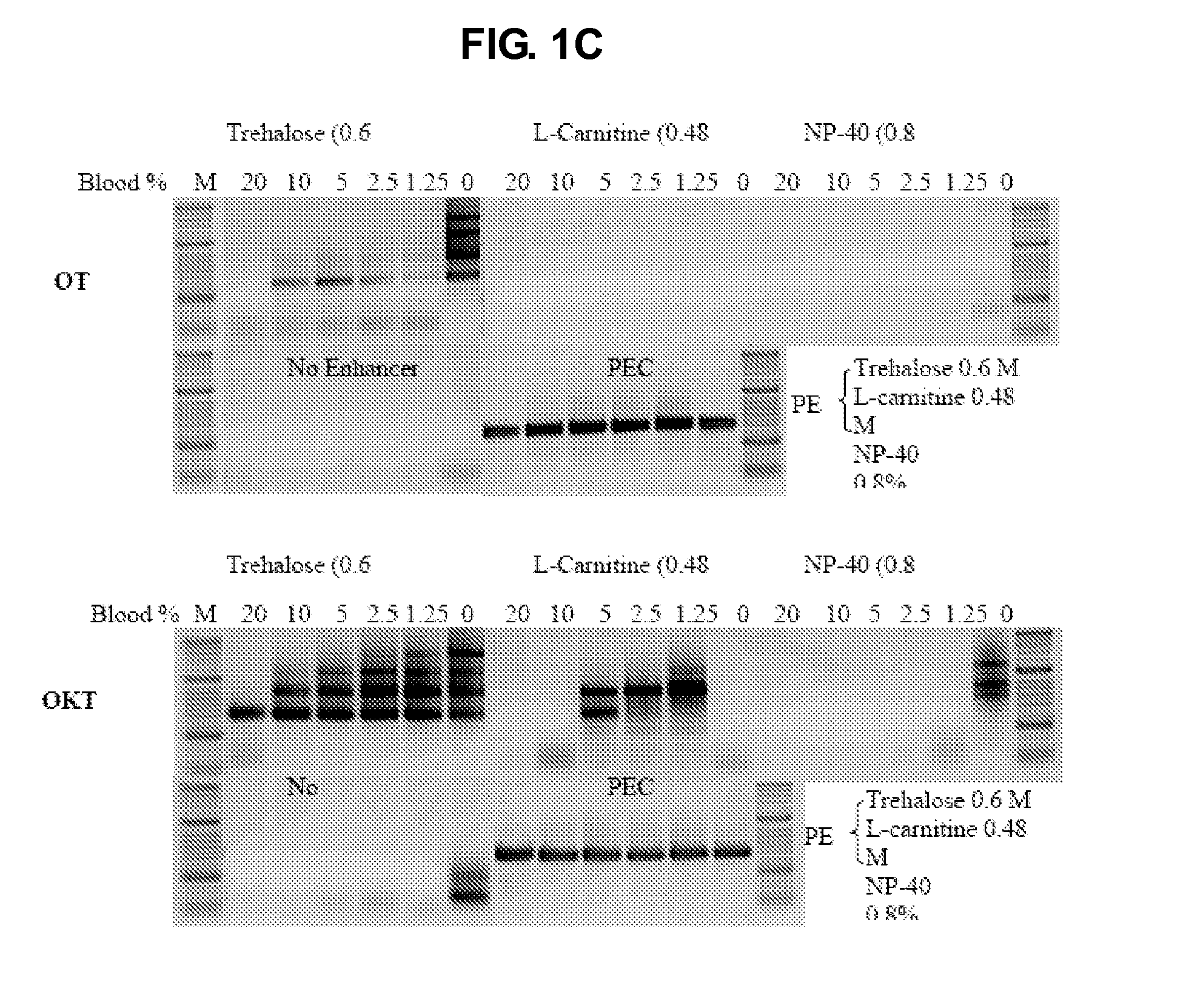
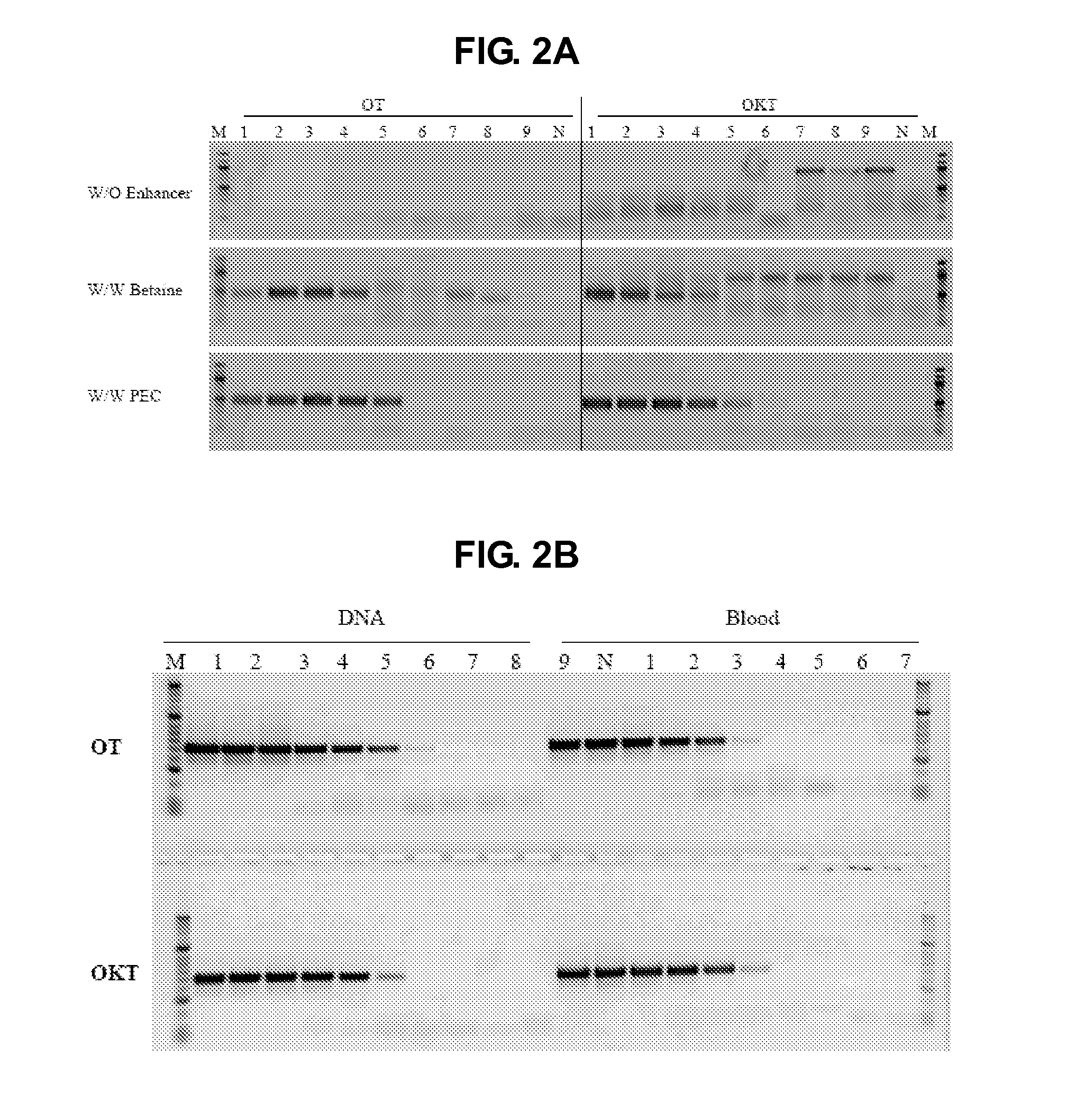
The present invention generally relates to amplfication reactions. One aspect of the invention provides amplification reaction enhancer compositions comprising trehalose, carnitine, and a non-ionic detergent, such as NP40. These enhancer compositions can improve efficiency, specificity, and sensitivity of amplification reactions in conventional and real-time PCR and RT-PCR. In addition, these compositions permit nucleic acid amplification directly in crude samples containing blood, blood components, or soil extract with little or no nucleic acid extraction prior to amplification. Another aspect of the invention provides a method of enhancing an amplification reaction containing a crude blood sample with heparin. Another improvement derived from the invention is improved detection of difficult, high GC content nucleic acid targets.
Owner:DNA POLYMERASE TECH
Compositions and method for reducing seizures
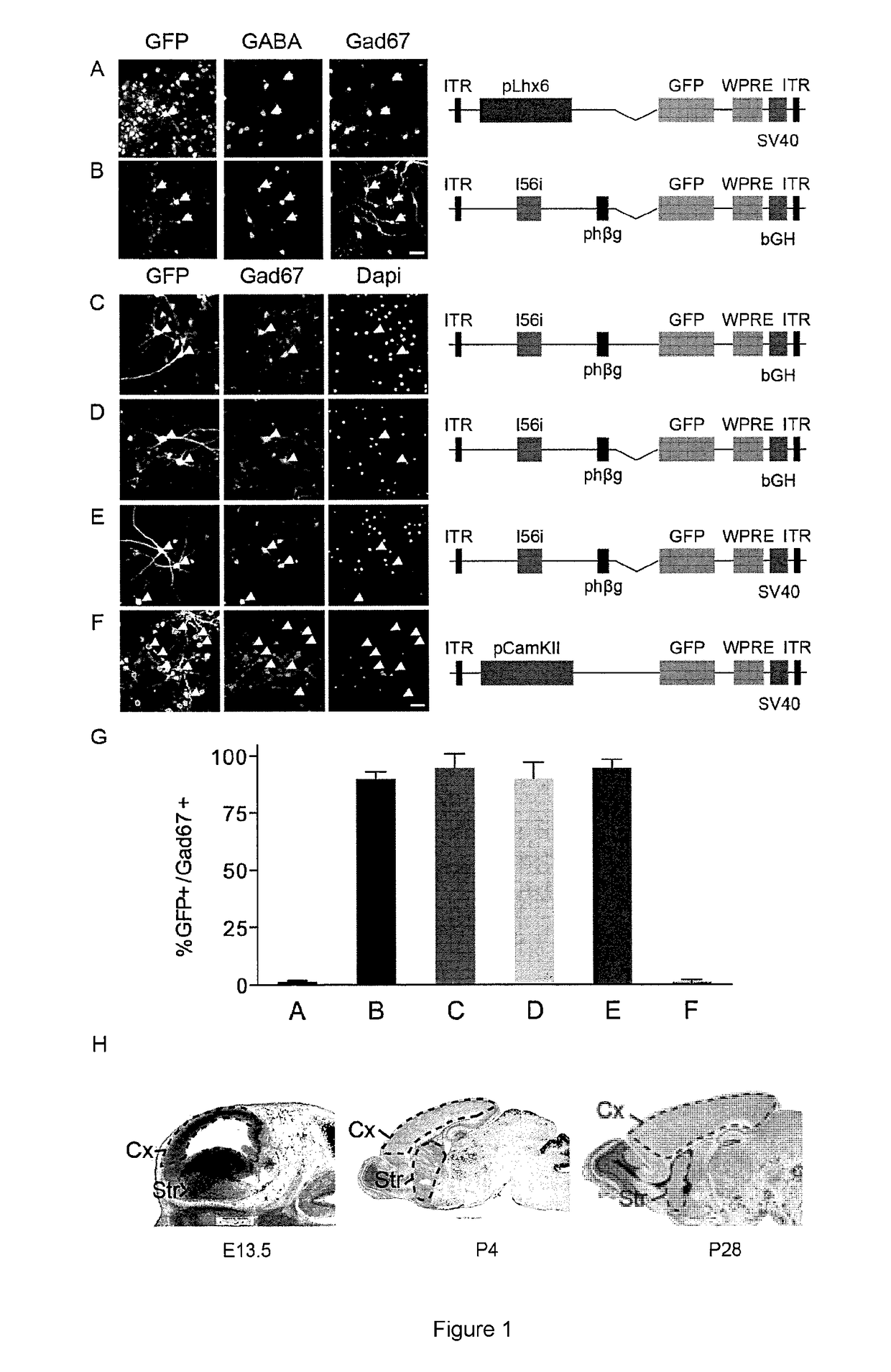
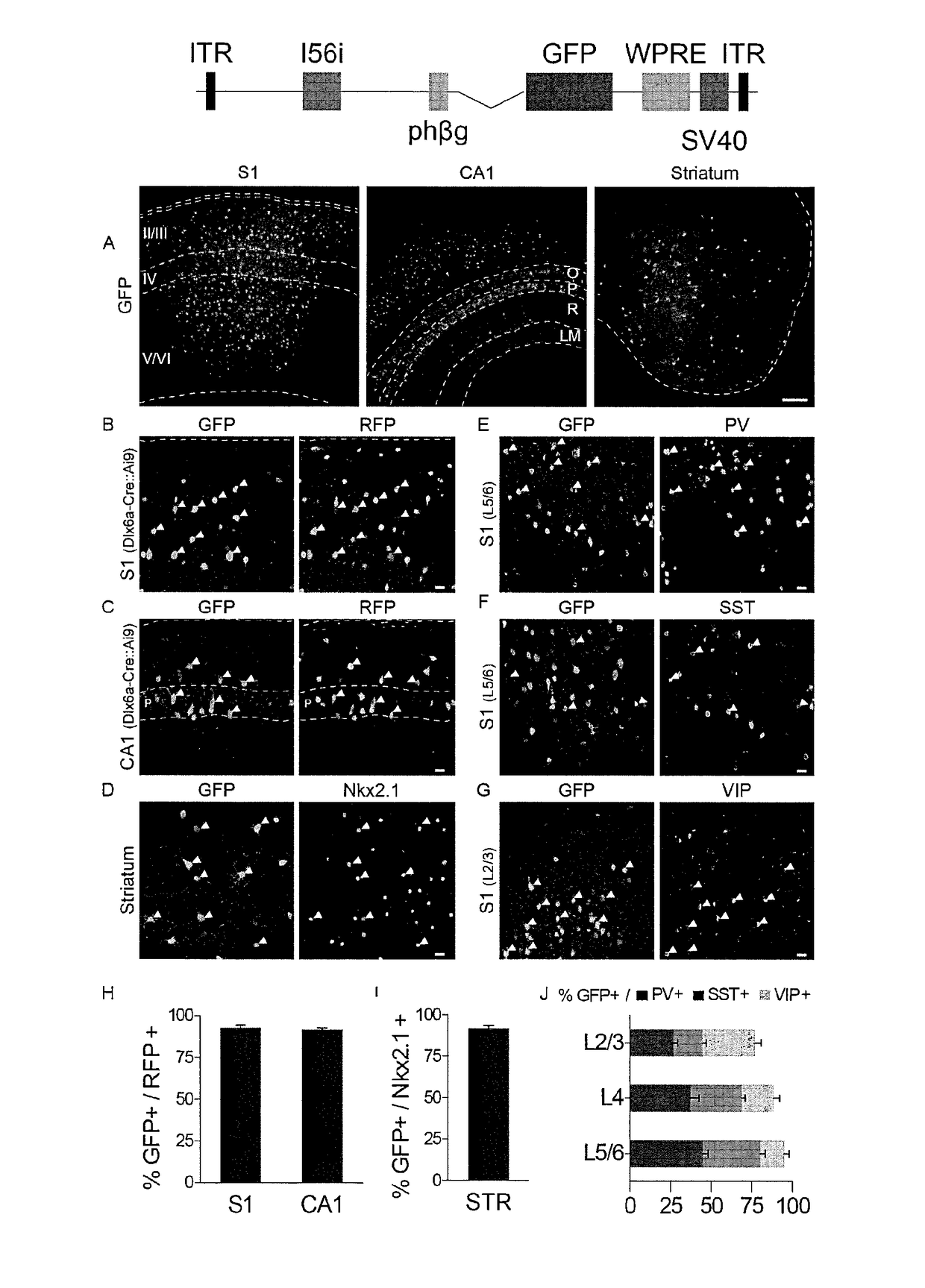
Provided are compositions and methods for prophylaxis and / or therapy of disorders that involve seizures. The compositions and methods relate to a recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) comprising a I56i enhancer sequence, and a sequence encoding hM3Dq modified muscarinic receptor (Gq-DREADD). The method includes introducing the rAAV into interneurons of an individual such that Gq-DREADD is expressed in interneurons of the individual. The method can further comprise administering to the individual an agonist of the Gq-DREADD, such for reducing or preventing seizures.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
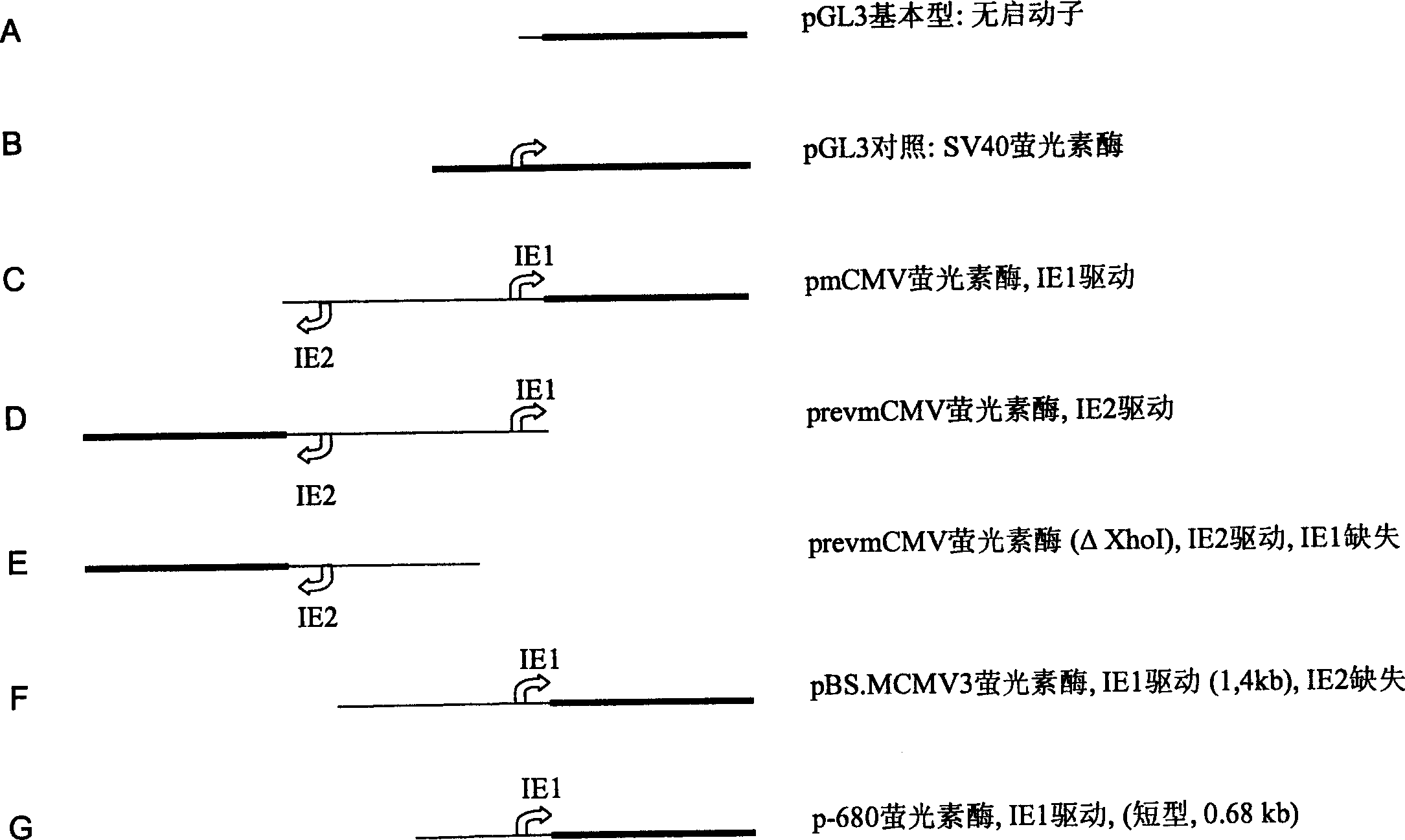
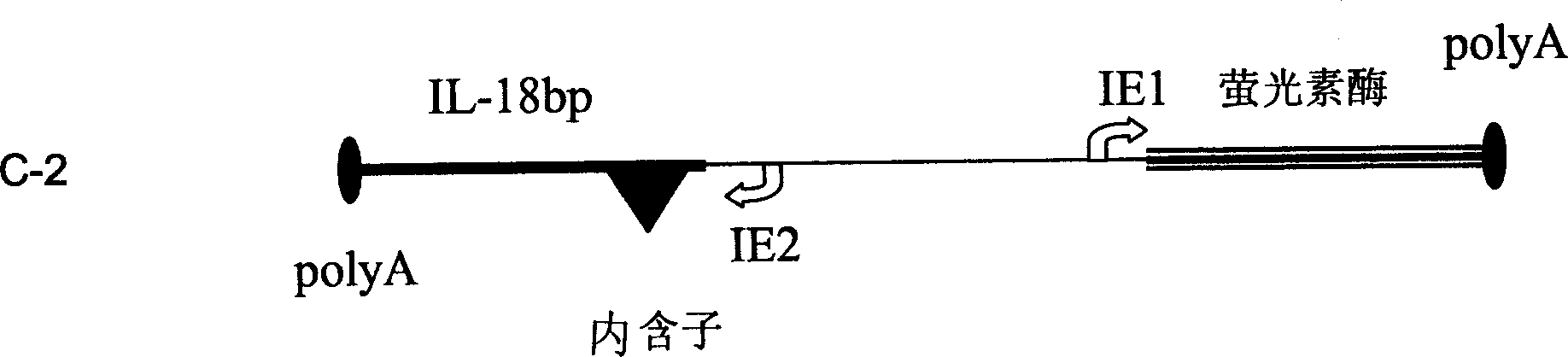
Expression vectors comprising the MCMV IE2 promoter
The invention relates to an expression vector comprising the promoter of the mCMV-IE2 gene, or a functional expression promoting fragment thereof, and / or an enhancer of the mCMV-IE2 gene, or a functional expression enhancing fragment thereof, wherein the expression vector does not contain any complete gene of the mCMV.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
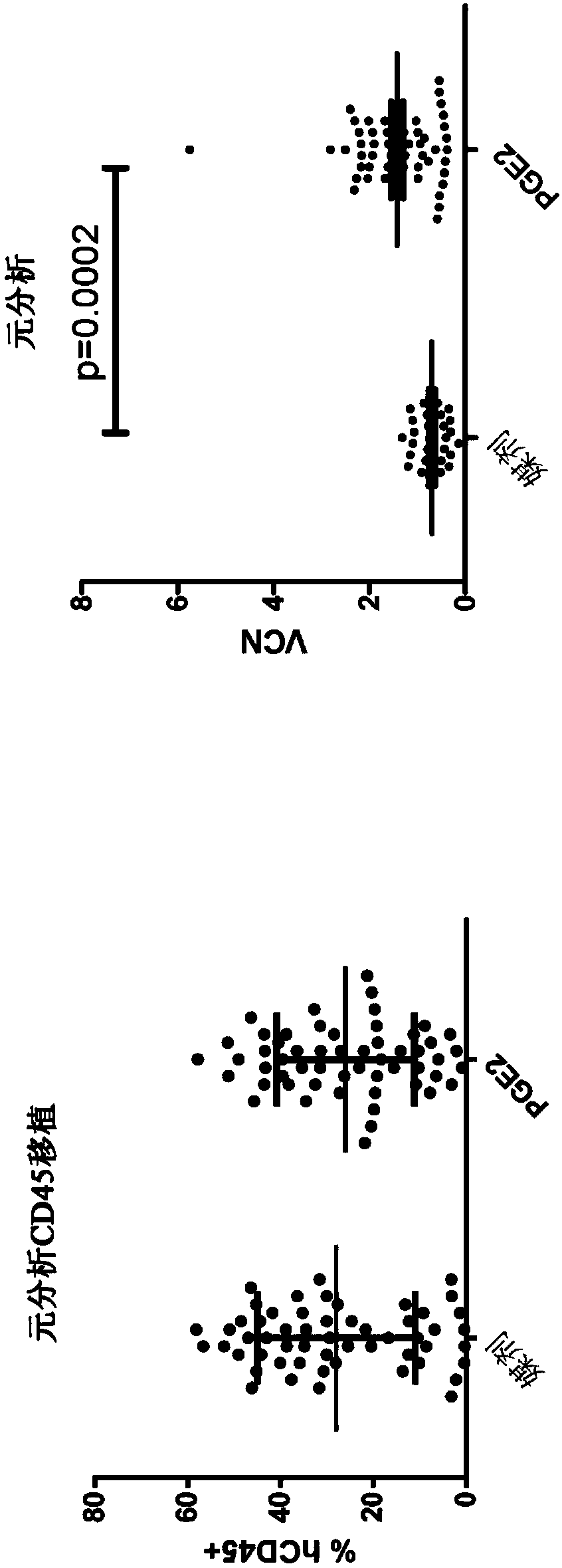
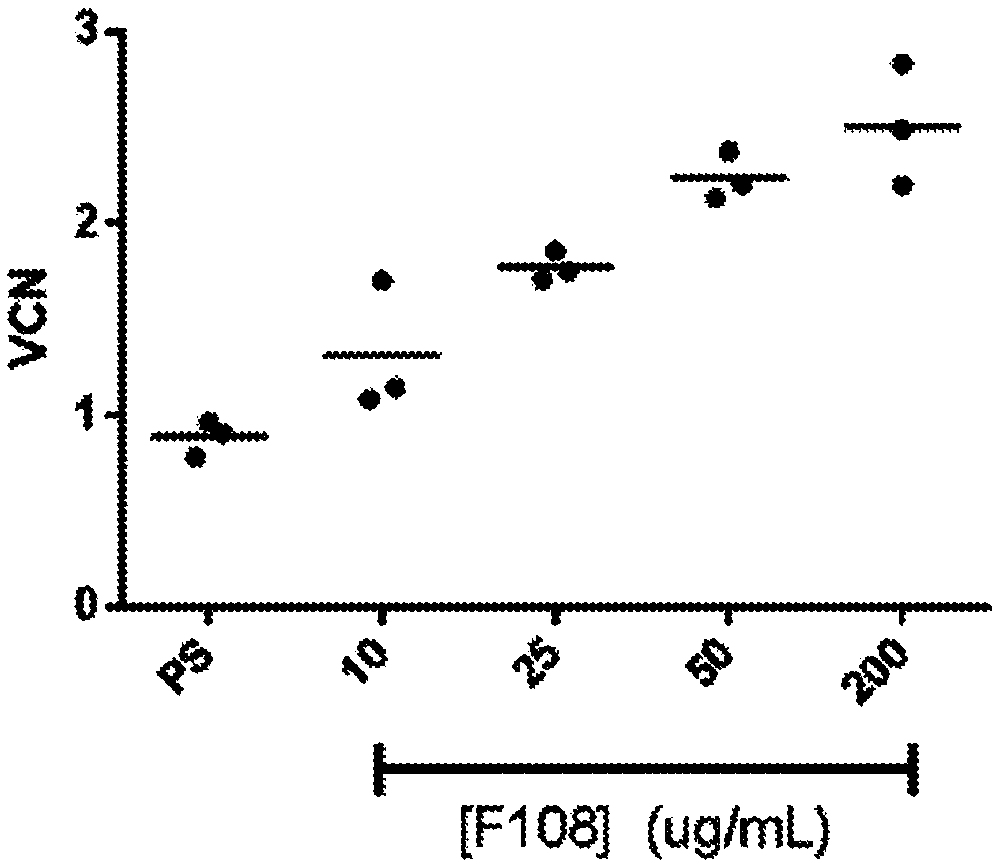
Vcn enhancer compositions and methods of using the same
Owner:BLUEBIRD BIO INC
Enhance-like element gene for enhancing foreign protein expression and application of gene
InactiveCN102965375AIncreased expression level propertiesIncrease resistanceVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBacterial strainCapsid
The invention discloses an enhance-like element gene ER1 for enhancing foreign protein expression in prokaryotic cells. The enhance-like element gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 (Sequence Identity No) or a truncated sequence of the nucleotide sequence, wherein the gene sequence is screened by establishing a fusion expression reporter gene recombinant vector; the fusion reporter gene consists of major capsid protein L1 gene of human papilloma virus and chloramphnicol acetyltransferase (CAT); the gene fragments to be selected are linked with the sieving recombinant vector and is transformed so as to establish a gene library; and the recombinant bacterial strain containing the enhance-like element gene sequence is screened based on the chloramphenicol resistance, so as to obtain the enhance-like element sequence which can improve the activity of chloramphenicol of the fusion reporter gene of the strain and promotes the foreign protein expression.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Parenteral formulations of peptides for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
InactiveUS20050008634A1Relieve symptomsEffective amountPowder deliveryImpression capsComplementarity determining regionPotentiator
The subject invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: an aqueous carrier; from 0.1 mg / ml to 20 mg / ml of the composition of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of a) a peptide comprising at least 12 and at most 30 consecutive amino acids having a sequence corresponding to (i) a sequence of amino acids found within a complementarity-determining region (CDR) of a heavy or a light chain of a human monoclonal anti-DNA 16 / 6 Id antibody, or (ii) a sequence of amino acids found within a complementarity-determining region (CDR) of a heavy or a light chain of a pathogenic anti-DNA monoclonal antibody that induces a systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)-like disease response in mice, or b) a peptide comprising consecutive amino acids having the sequence shown by any of SEQ ID NOS. 8-17, or c) a peptide comprising consecutive amino acids having a sequence of any of a) and b), or at least two of the sequences in (a) (i), (a) (ii) and (b)(i) through (b)(x), or d) a peptide comprising consecutive amino acids having a sequence comprising at least two identical sequences included in (a) (i), (a) (ii) and (b) (i) through (b) (x); and a solubility enhancer, wherein both the peptide and the solubility enhancer are dissolved in the aqueous carrier; and wherein the composition has a pH between 4 and 9, and a method of alleviating symptoms of SLE in a human by administering an effective amount of the composition.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD +1
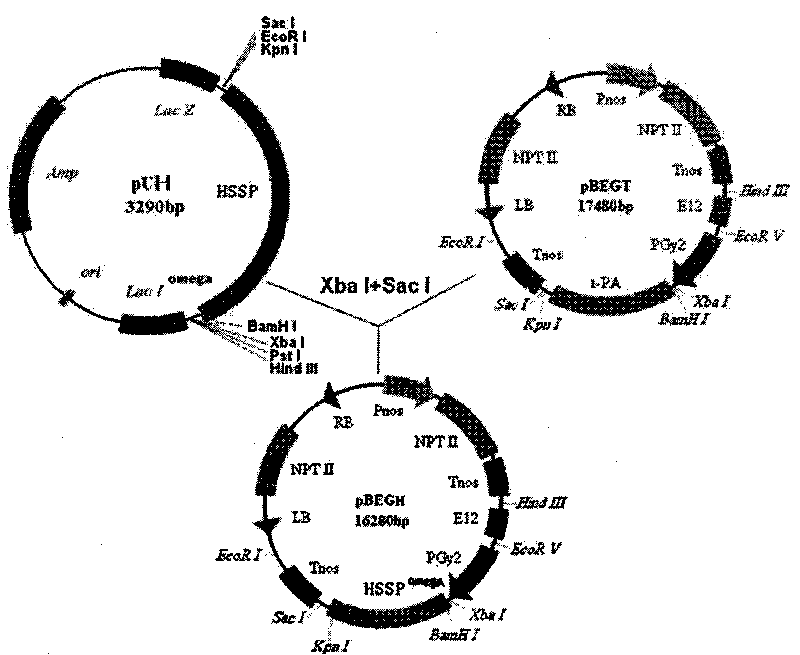
Artificial sequence for increasing methionine content of soy and plant expression vector thereof
ActiveCN101698841AIncrease methionine contentStable expressionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyTransgenic technology
The invention relates to an artificial sequence for increasing the methionine content of soy and a plant expression vector thereof, which solve the problem of the poor stability of the prior methods for increasing the methionine content of the soy in the prior transgenic technology. In the artificial sequence HSSP for increasing the methionine content of the soy of the invention, the sequence of the HSSP is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The plant expression vector of the artificial sequence for increasing the methionine content of the soy comprises the artificial sequence HSSP, wherein the upstream of the artificial sequence HSSP of the plant expression vector comprises an E12 enhancer sequence and a seed specific expression promoter PGY2, while the downstream comprises a Tnos terminator sequence. The technical scheme of the invention can be used for cultivating transgenic soy with high methionine content.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
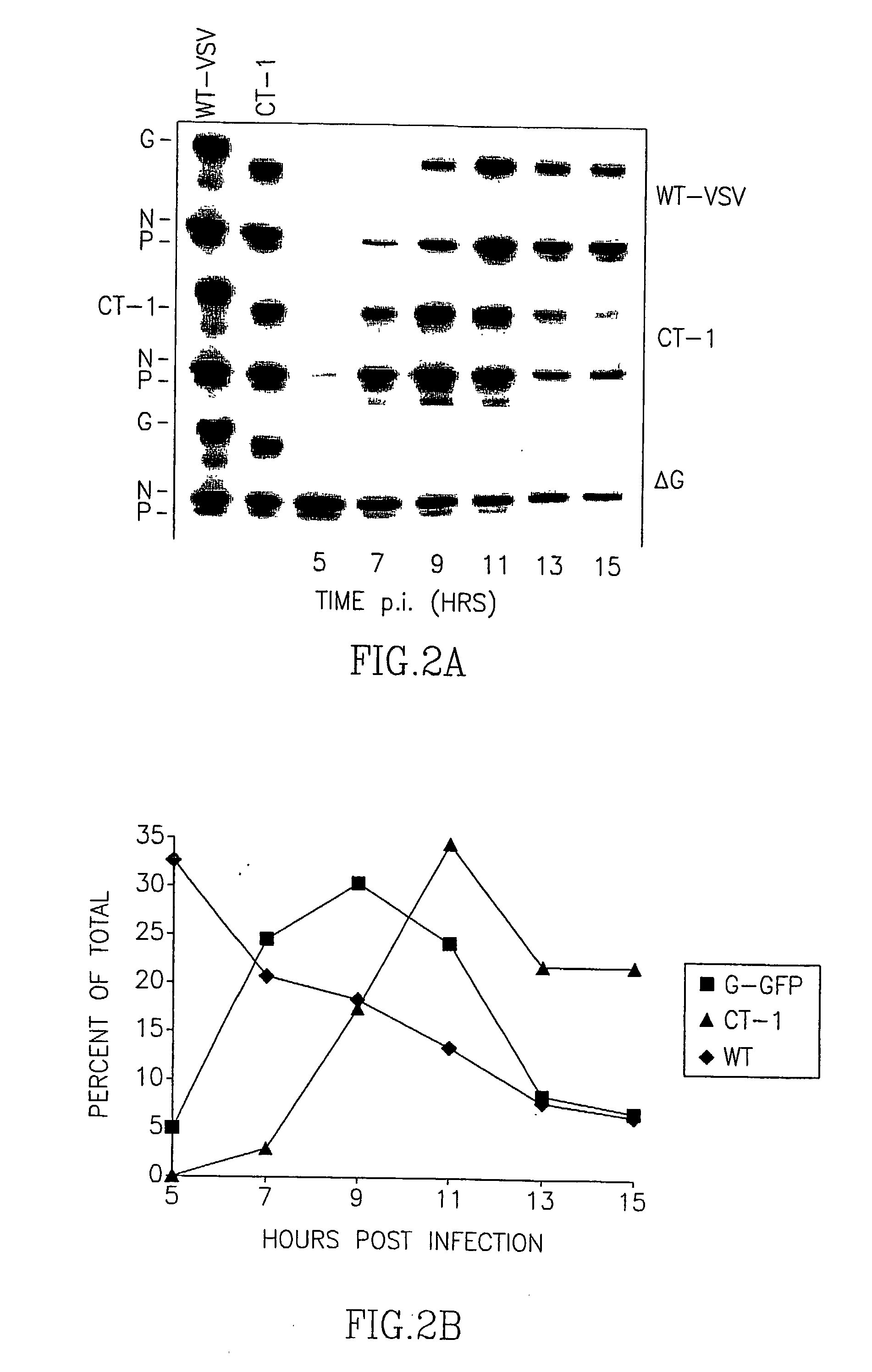
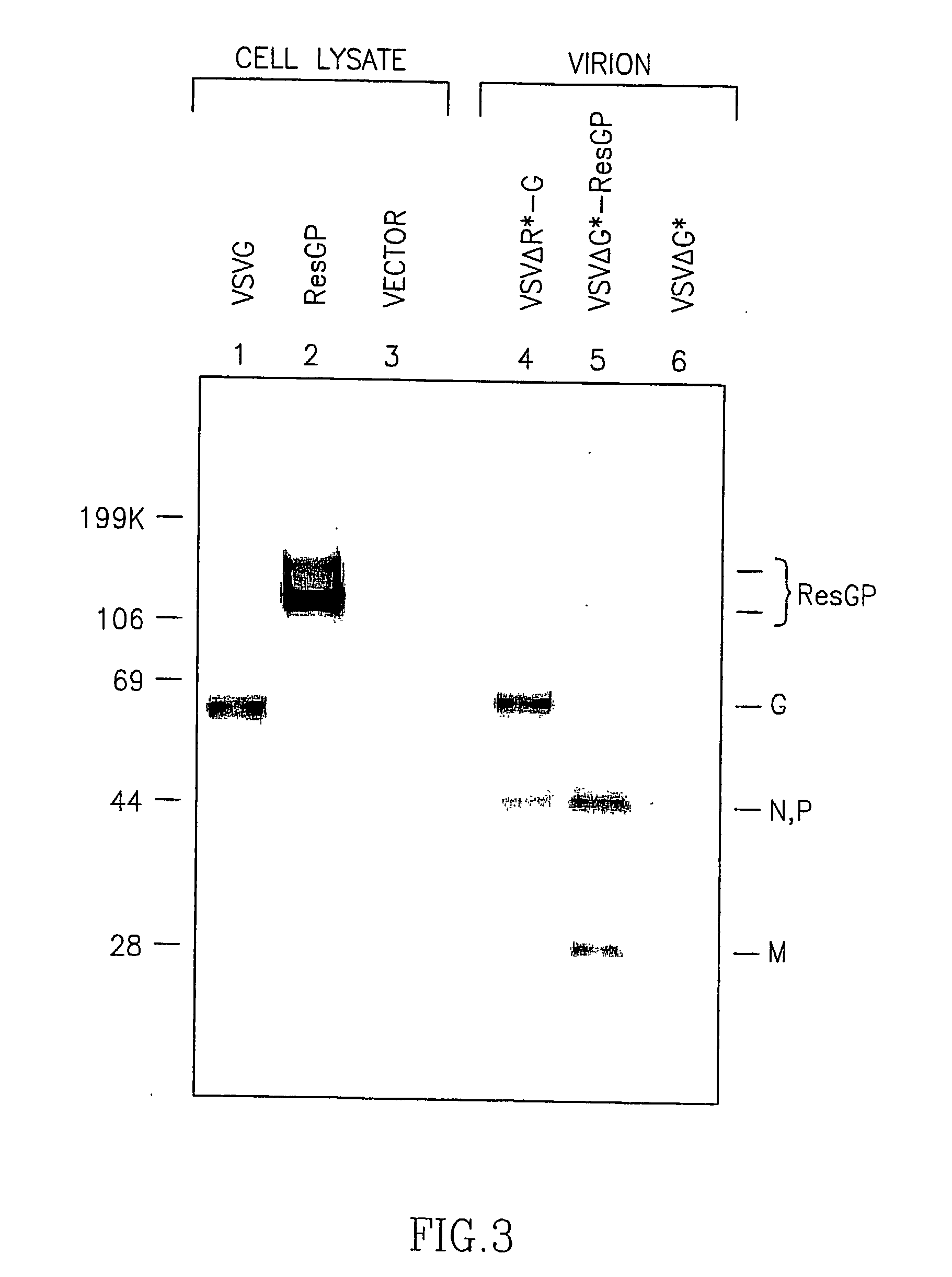
Recombinant Rhabdovirus containing a heterologous fusion protein
InactiveUS20030138457A1Easy to integrateOvercome limitationsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousAttachment protein
This invention relates to a composition comprising a recombinant or genetically engineered Rhabdovirus that expresses a Fusion Protein, such as the F protein of the Paramyxovirus SV5 strain. This recombinant Rhabdovirus may express other non-Rhabdovirus attachment proteins and / or an enhancer protein. The invention also relates to methods of making recombinant Rhabdoviruses which express an F Protein. These recombinant compositions can be used for purposes of research, as well as for diagnostic and therapeutic compositions for treatment of diseases.
Owner:TENNESSEE RESEARCH CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com