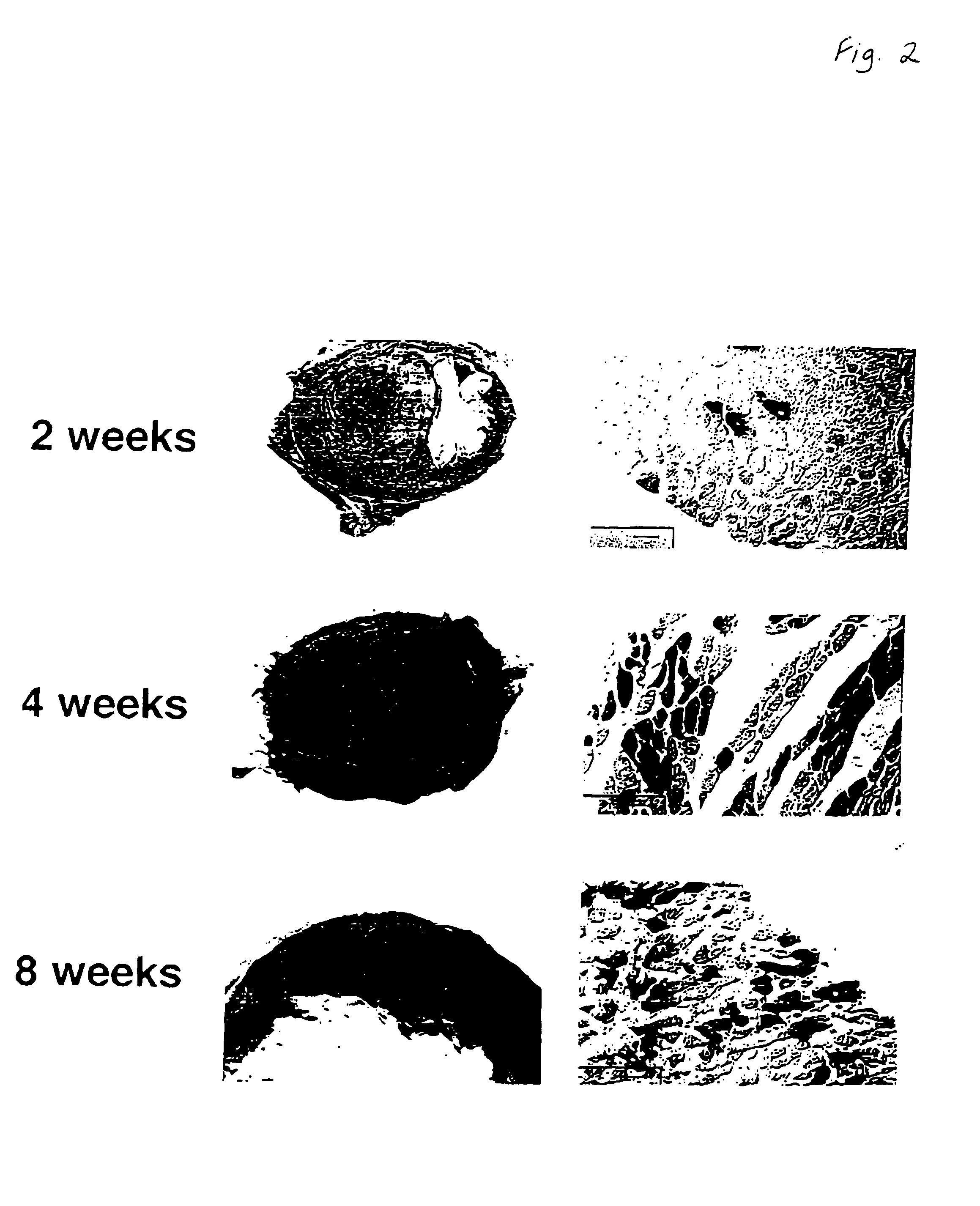
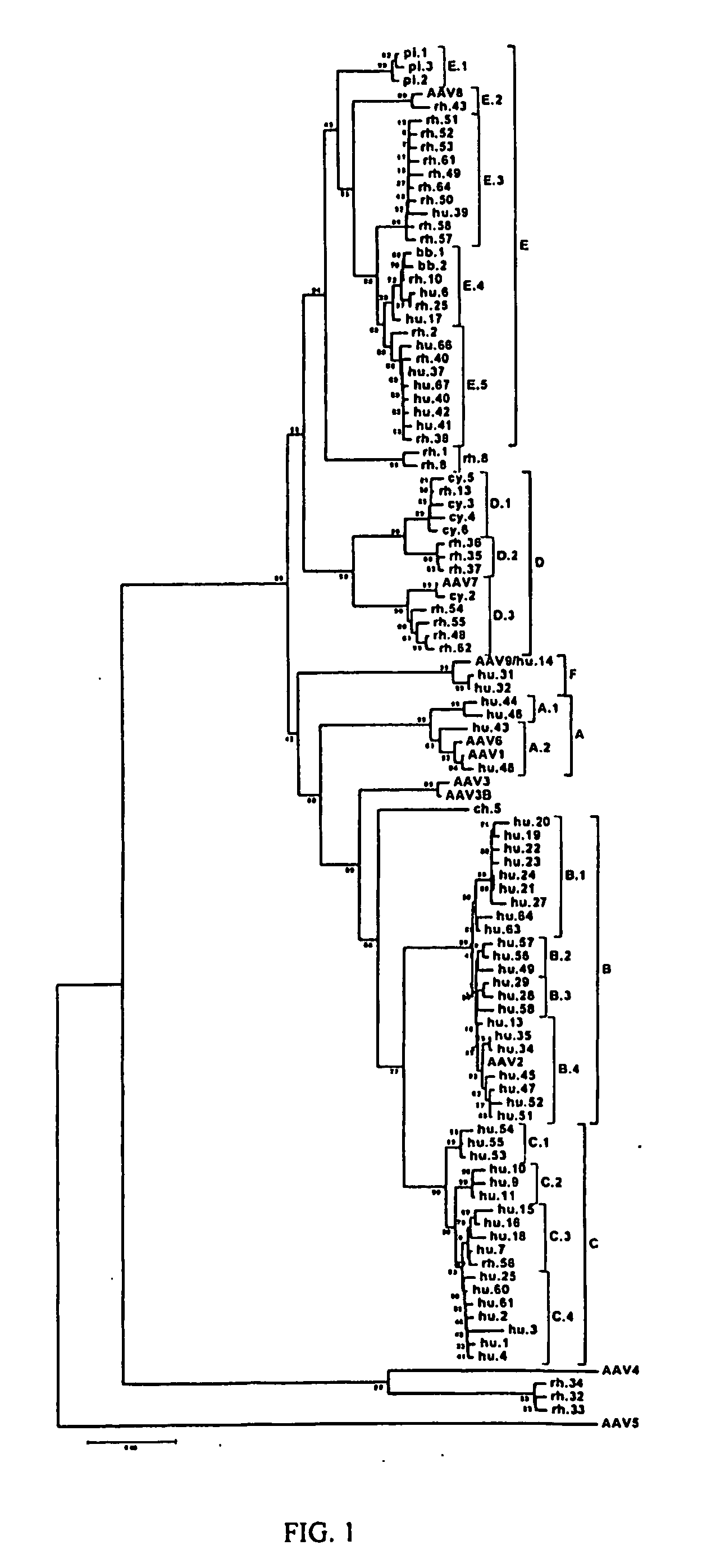
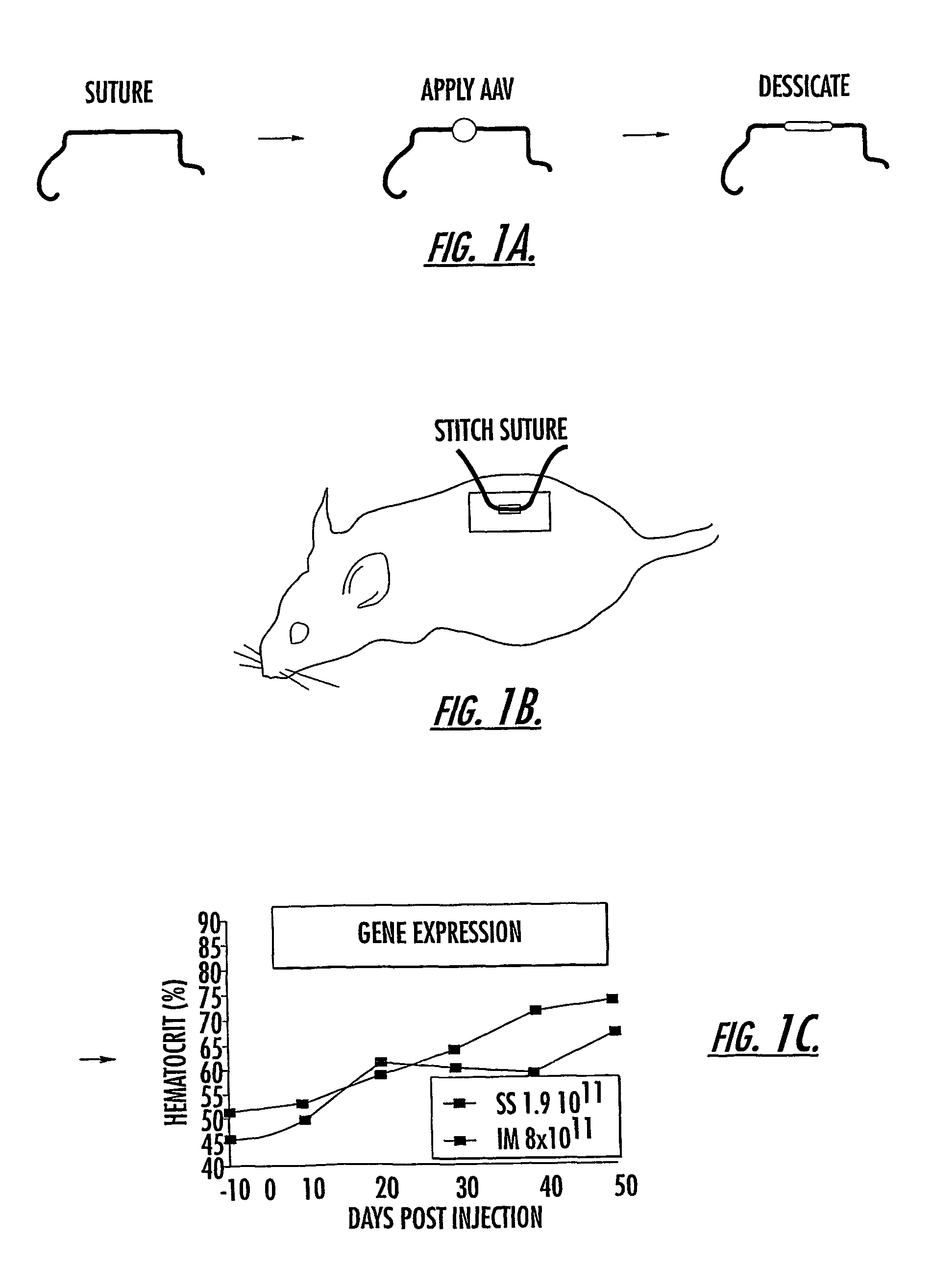
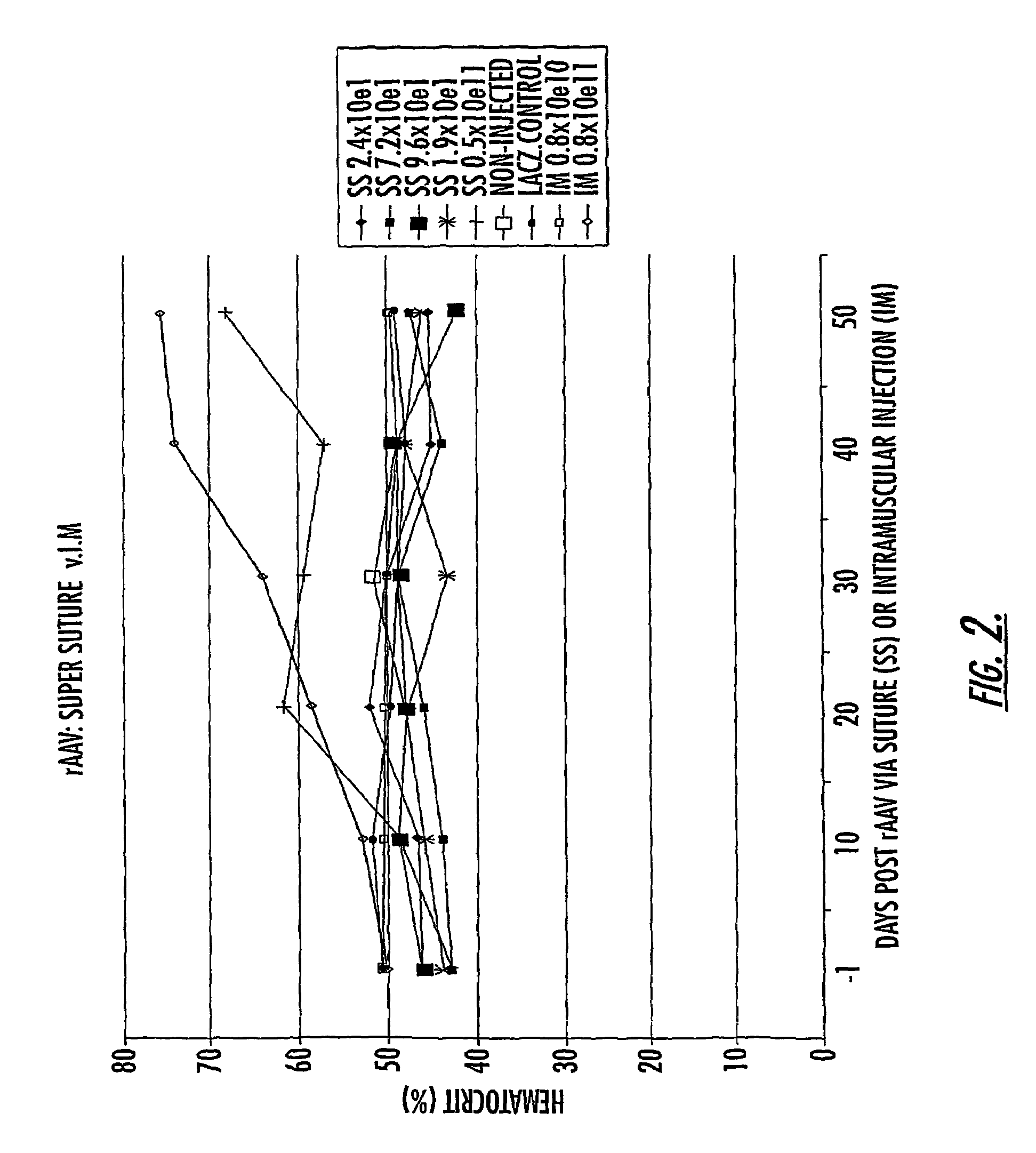
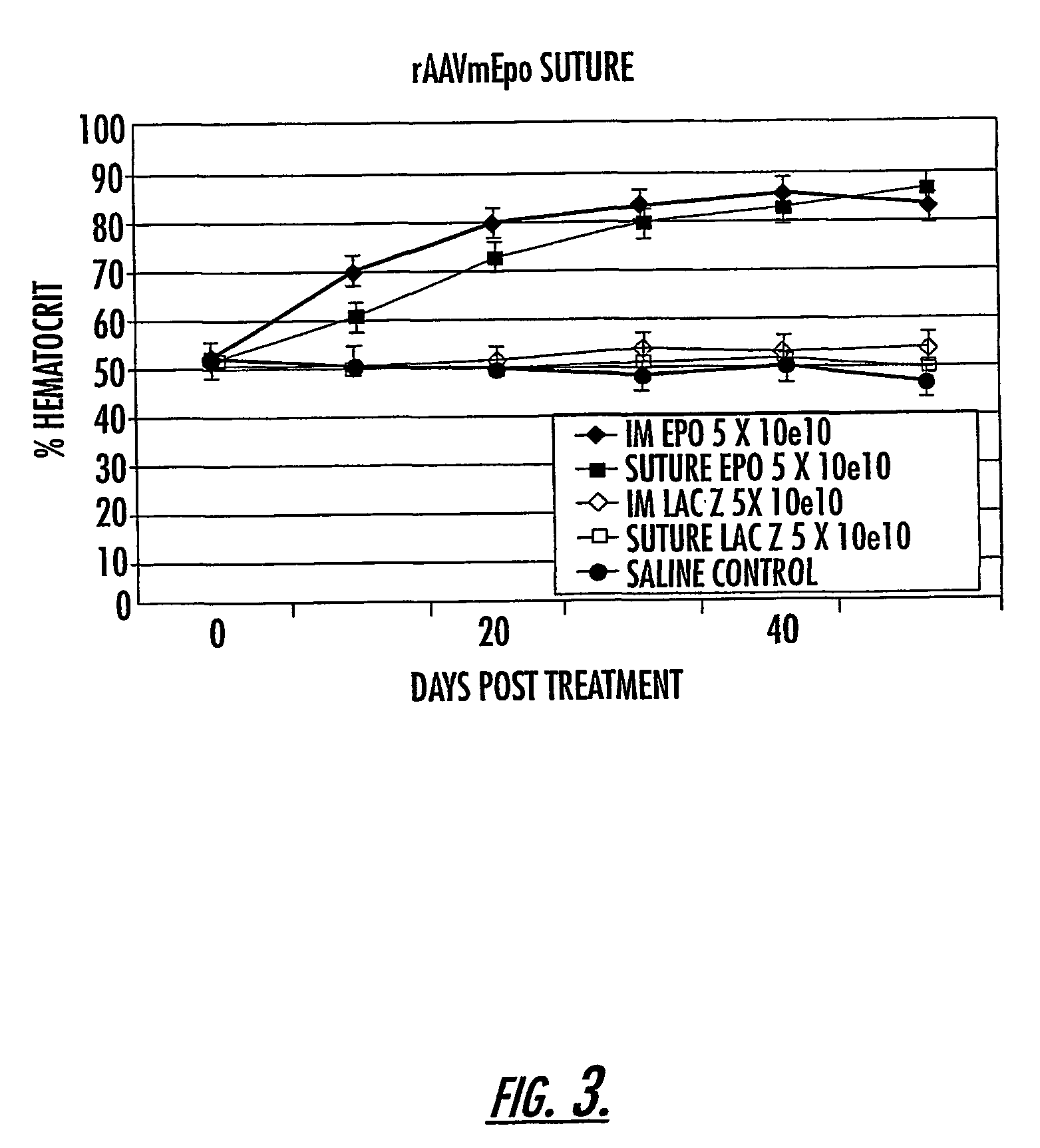
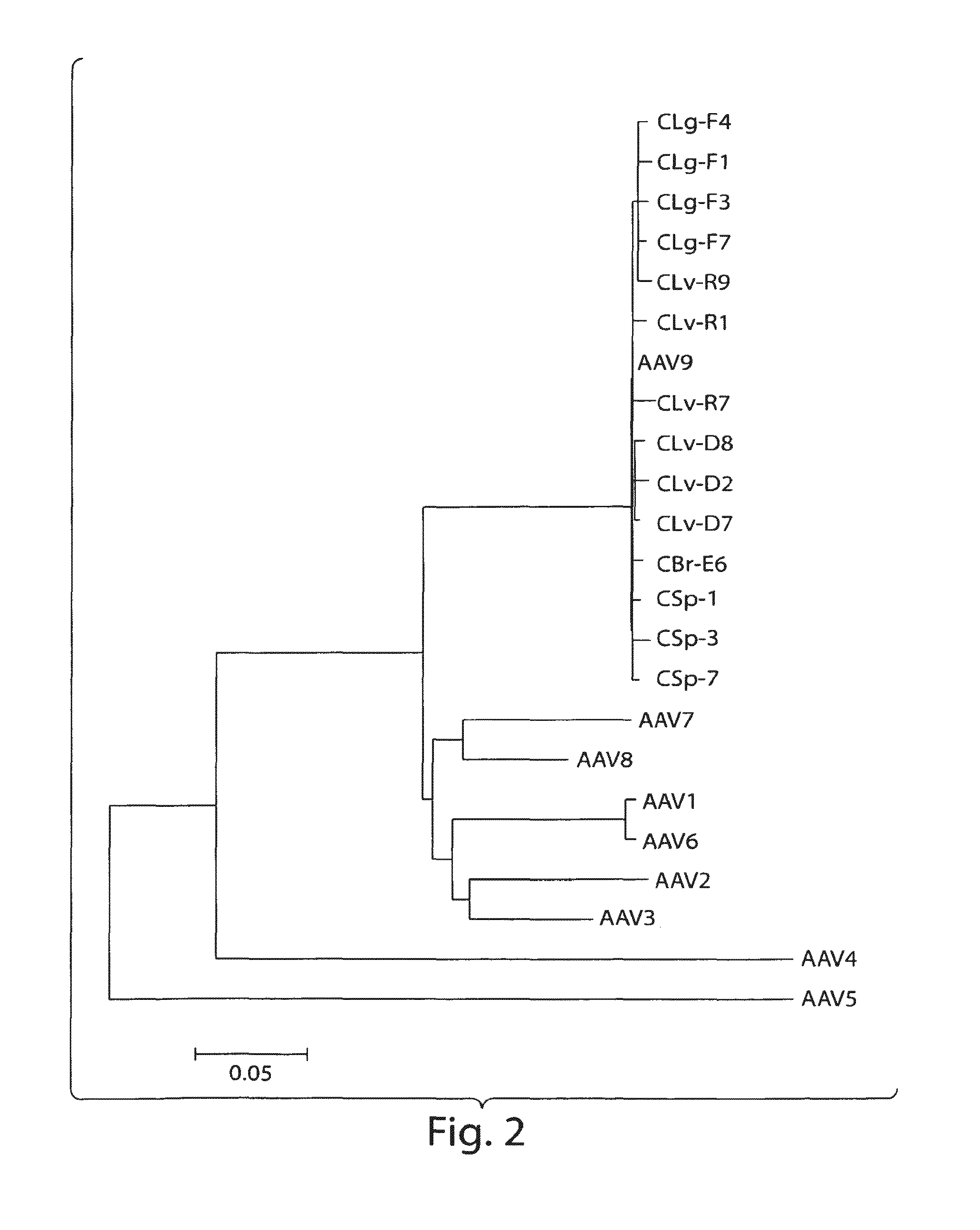
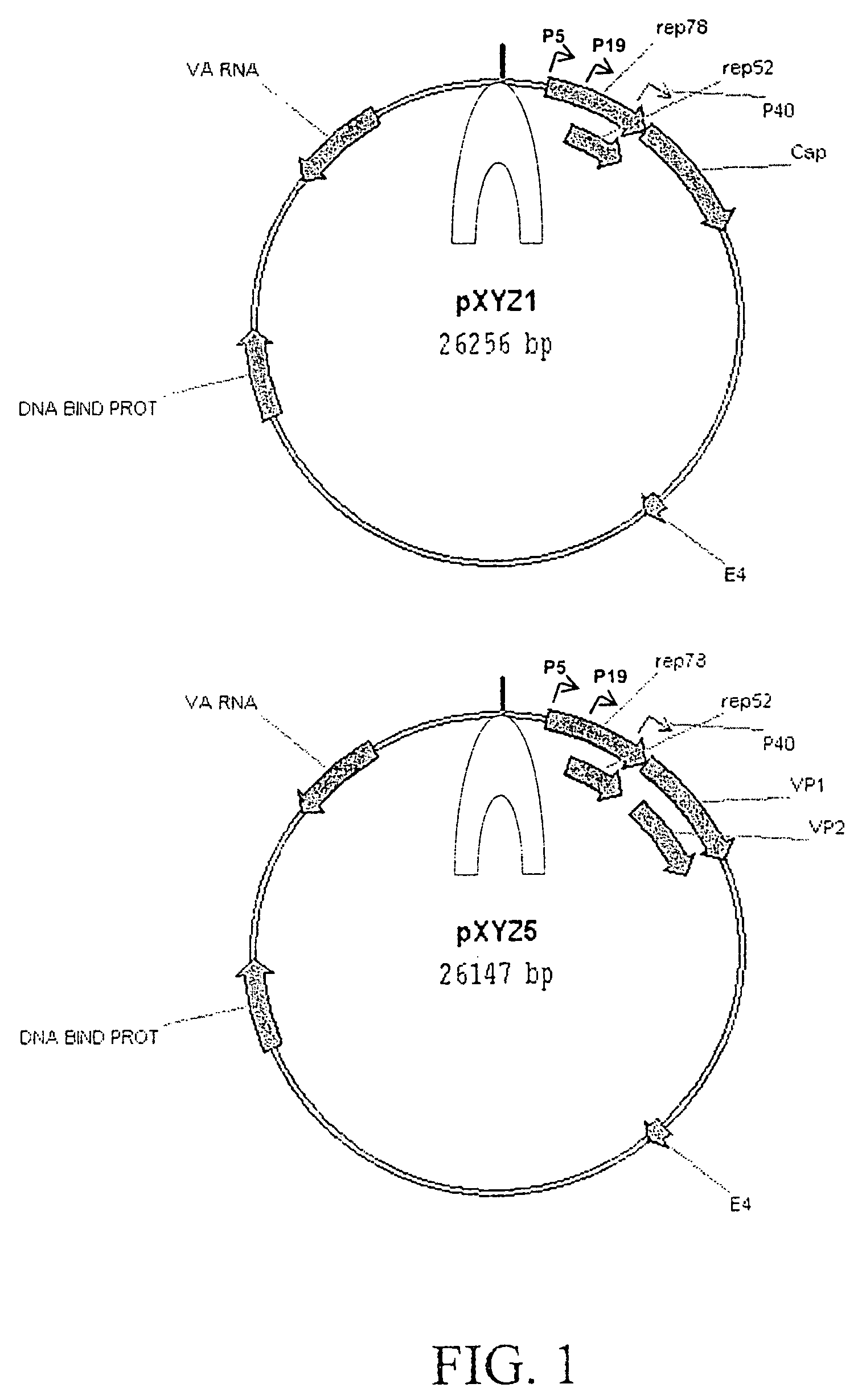
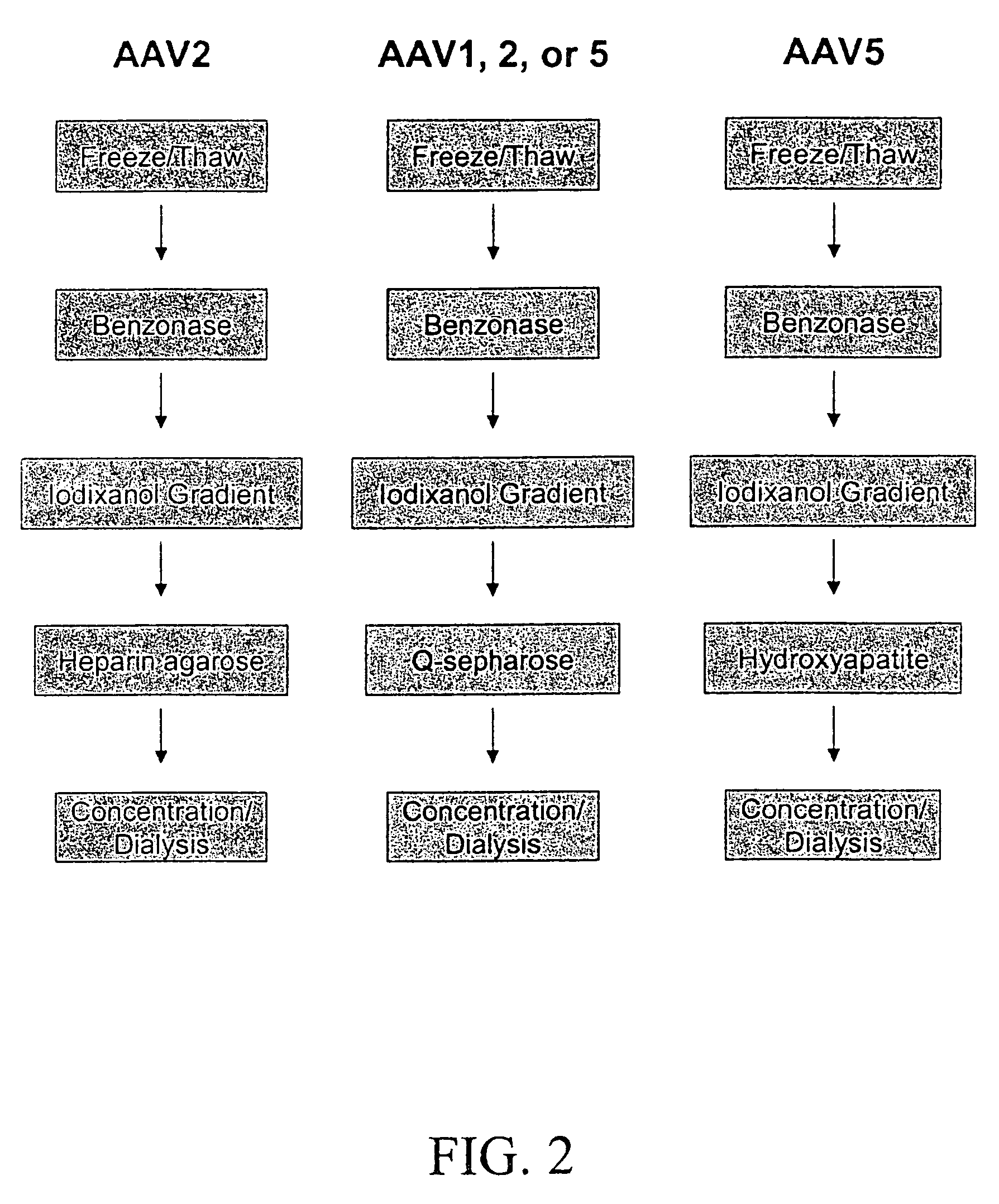
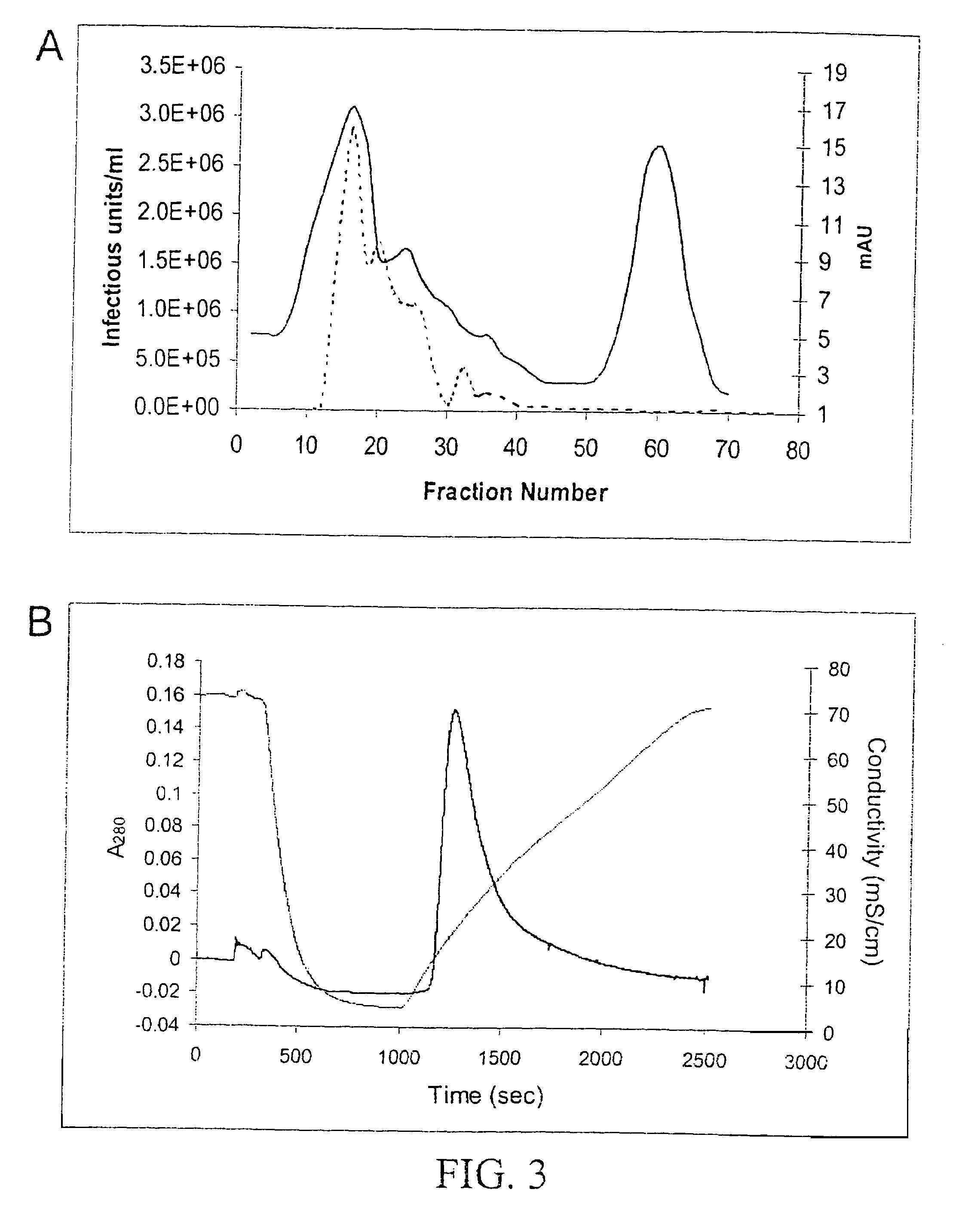
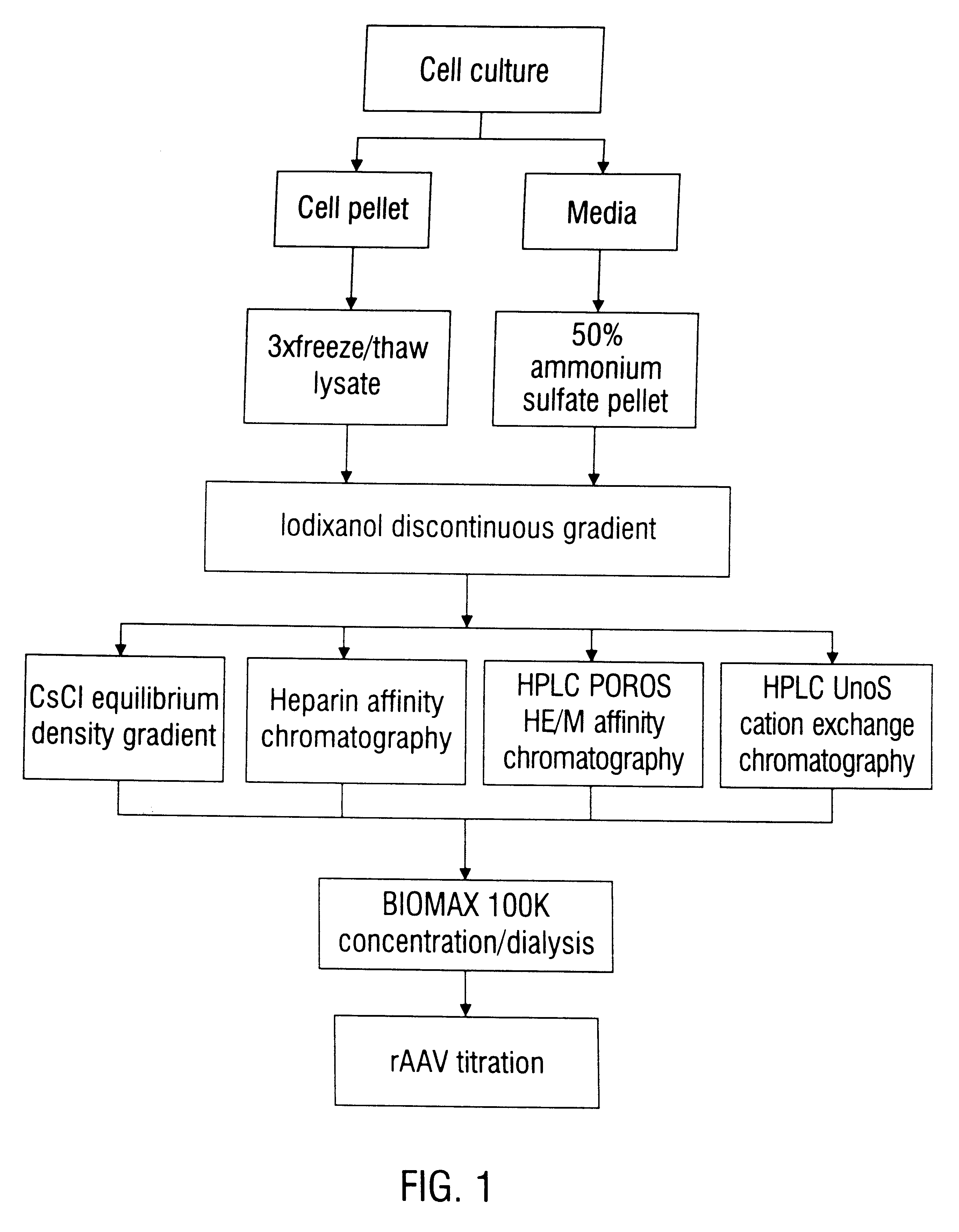
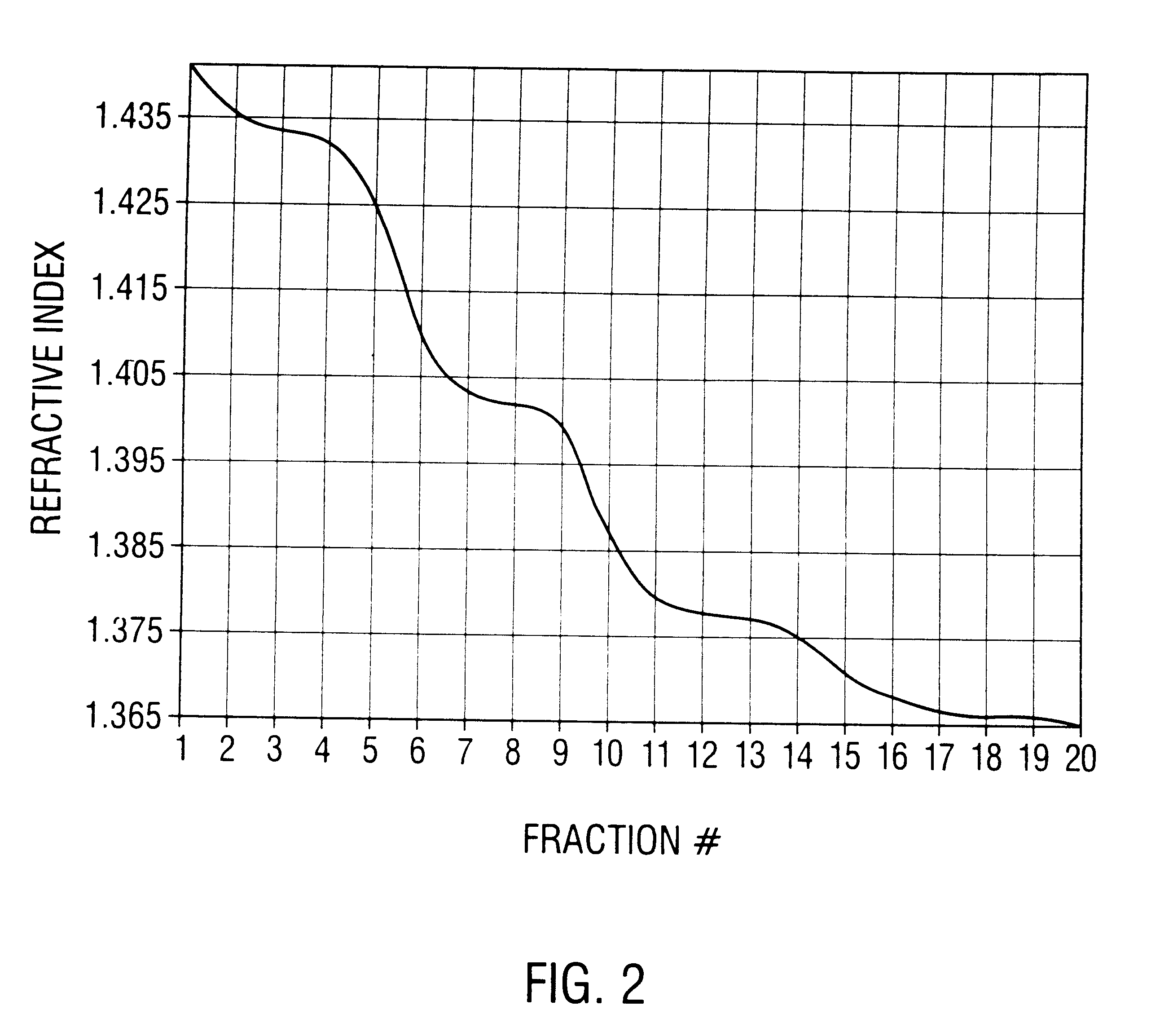
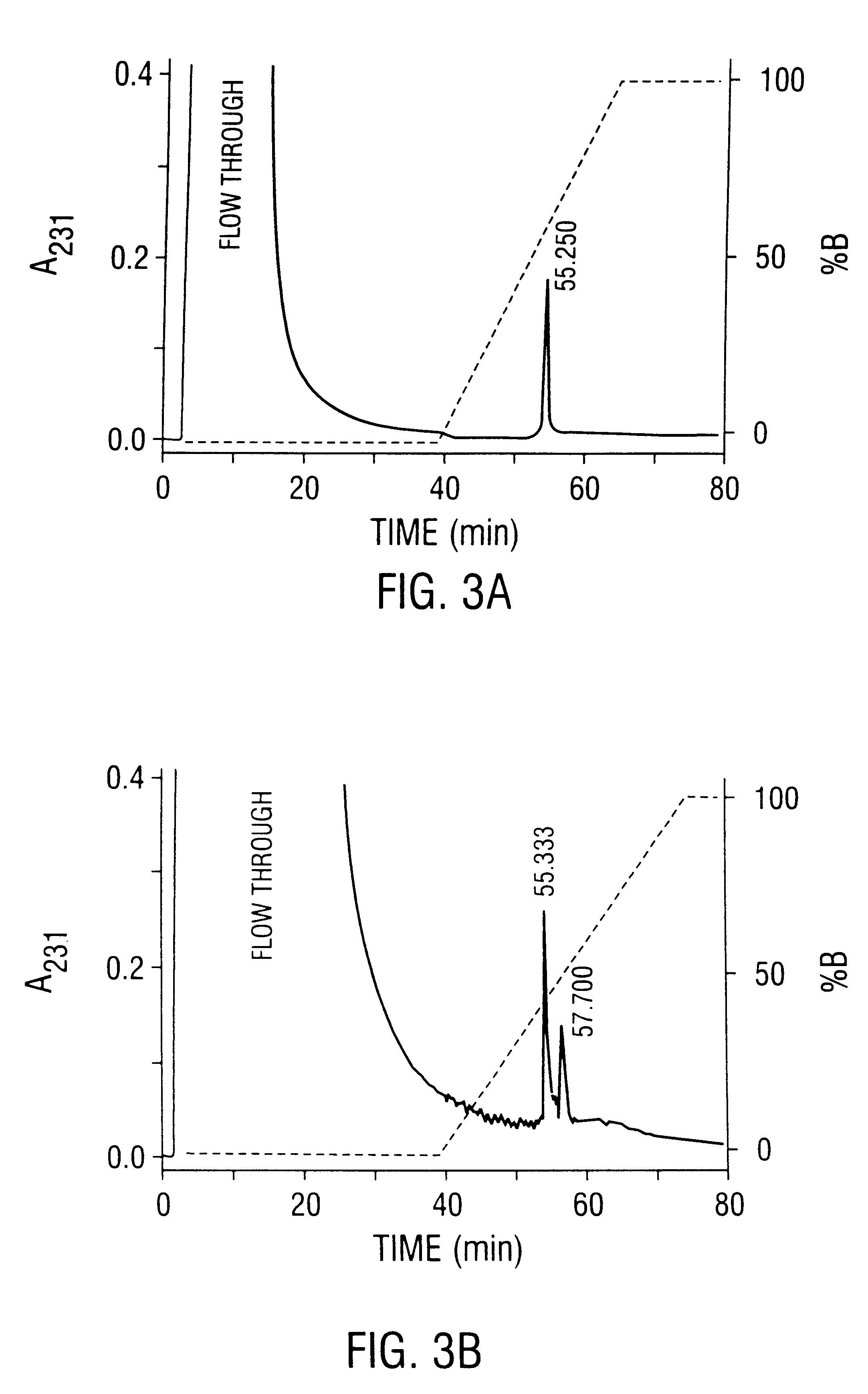
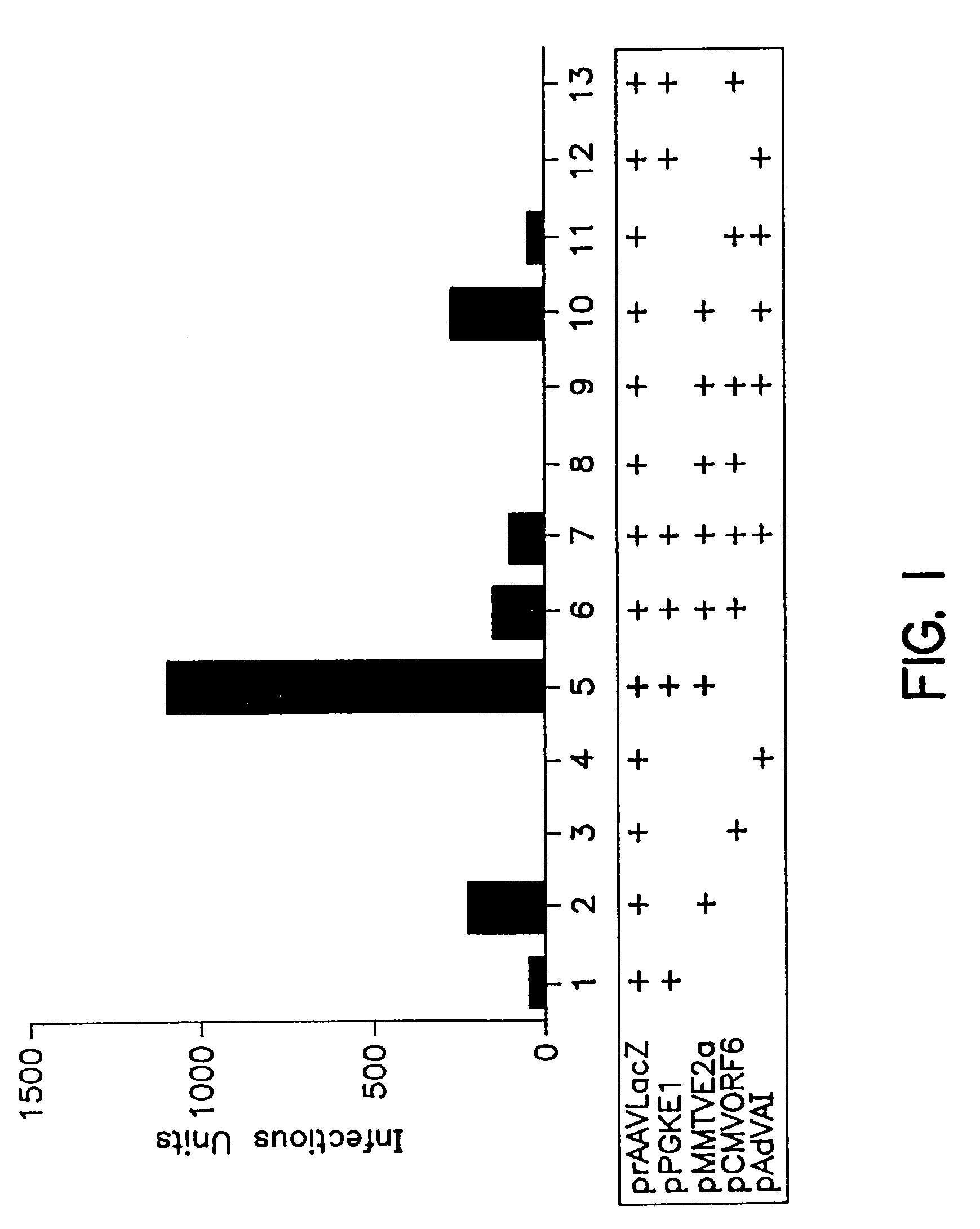
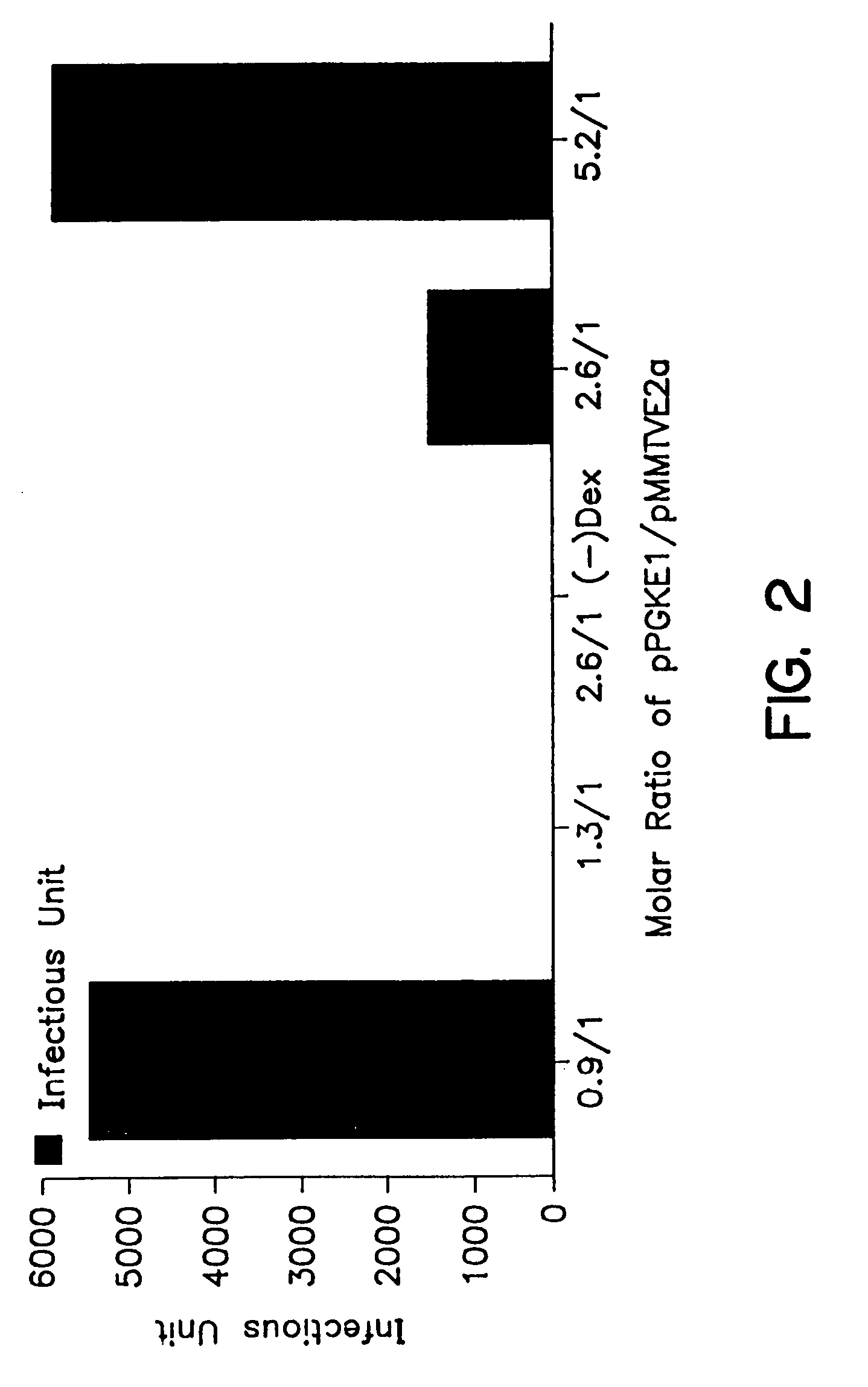
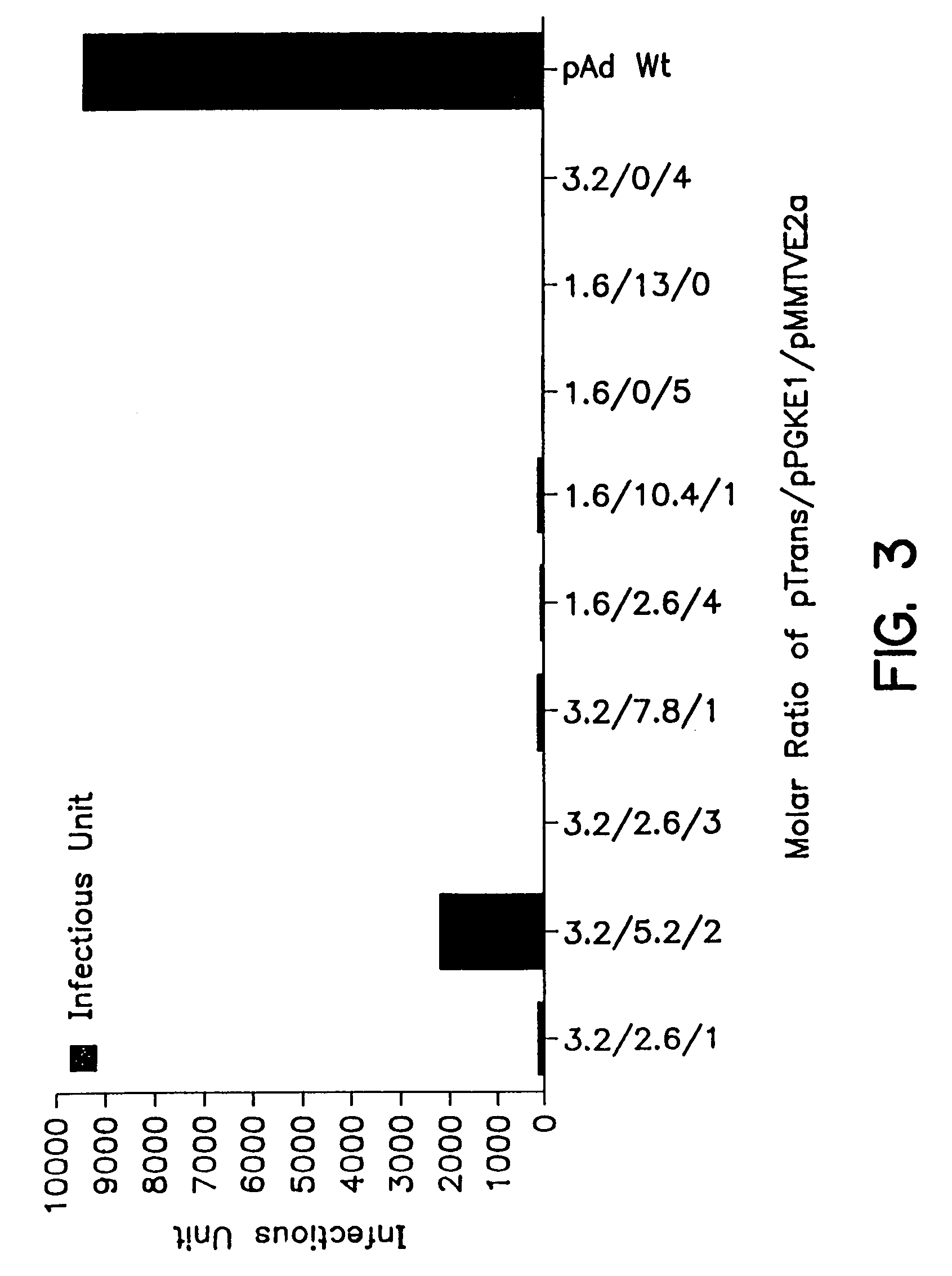
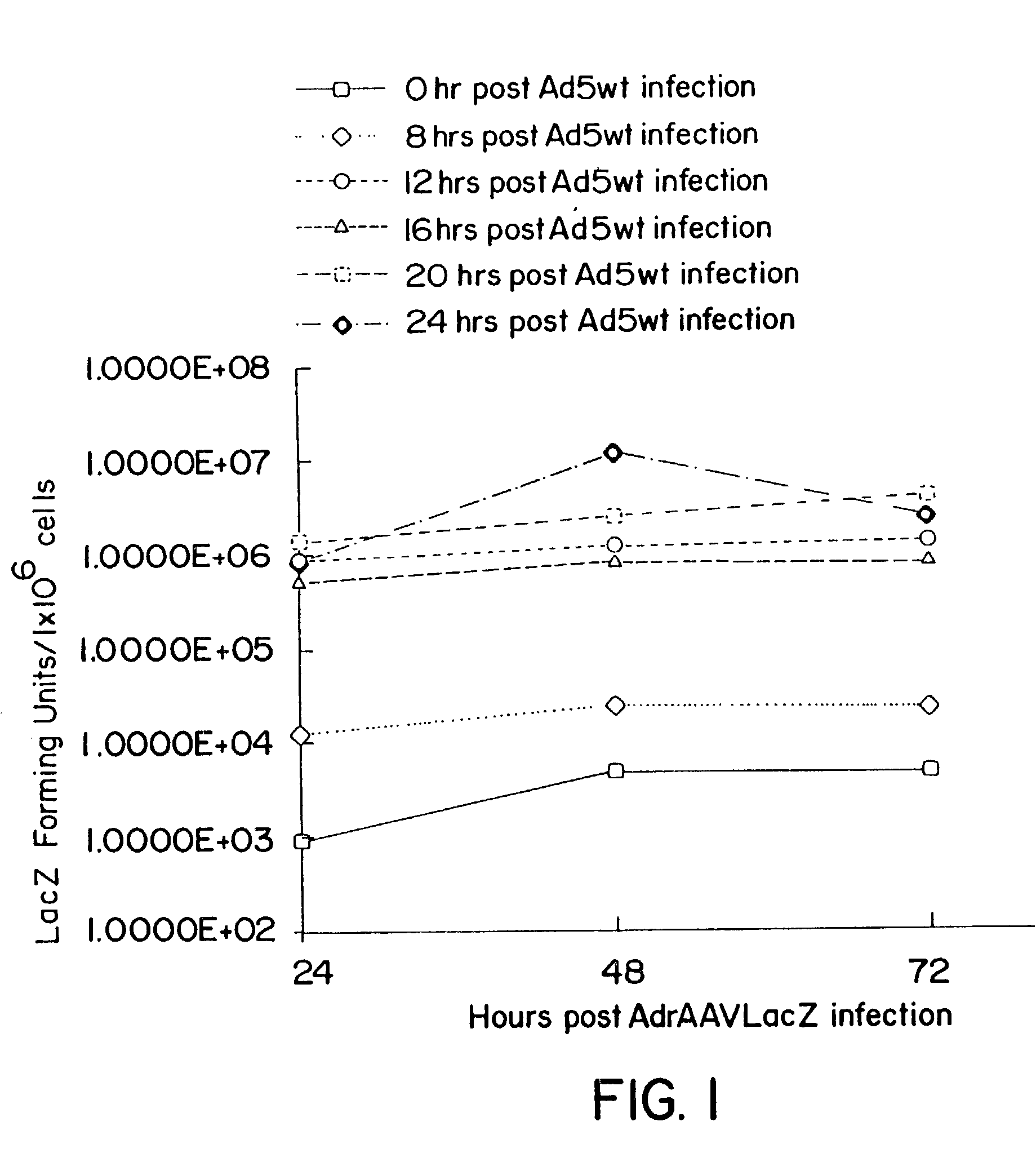
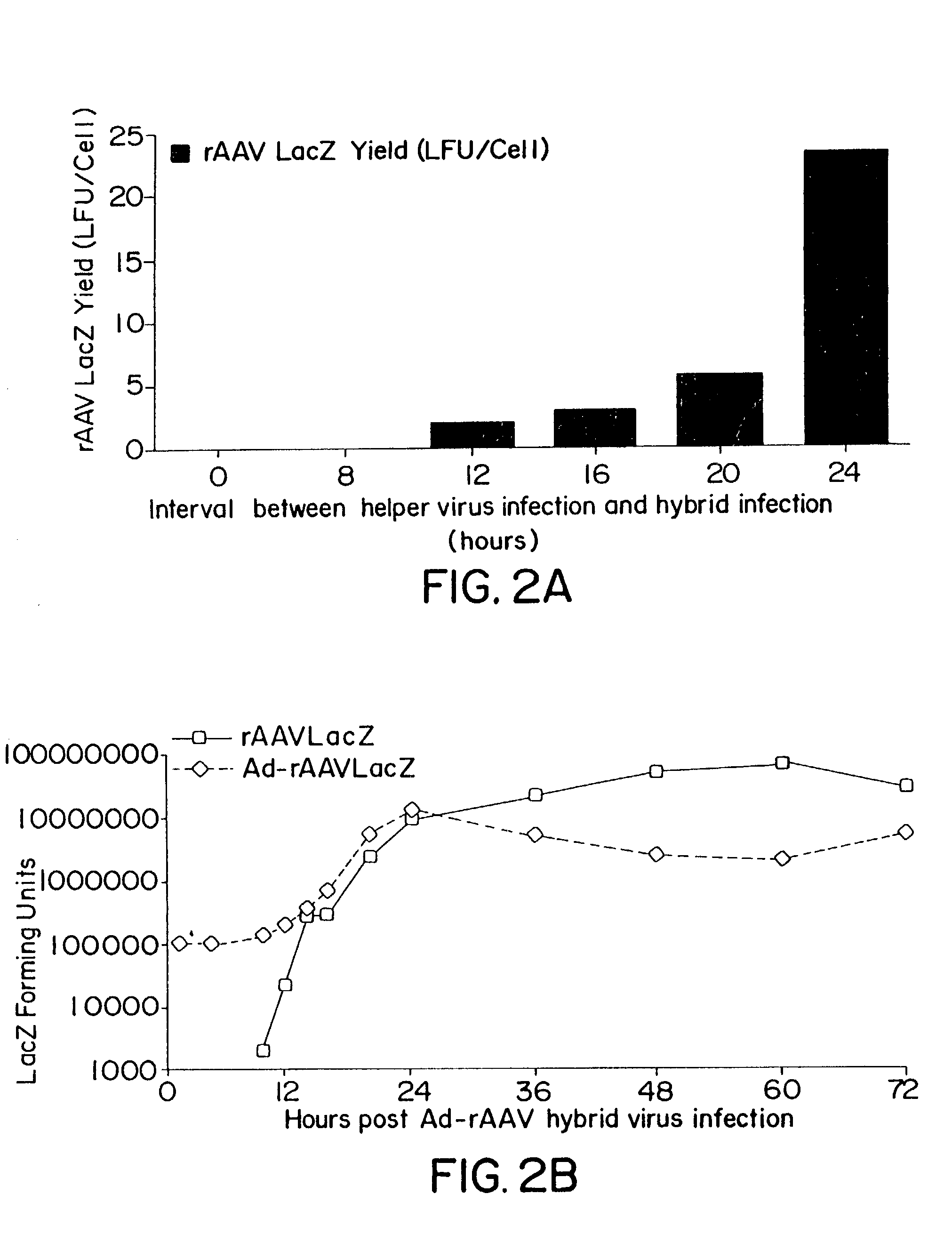
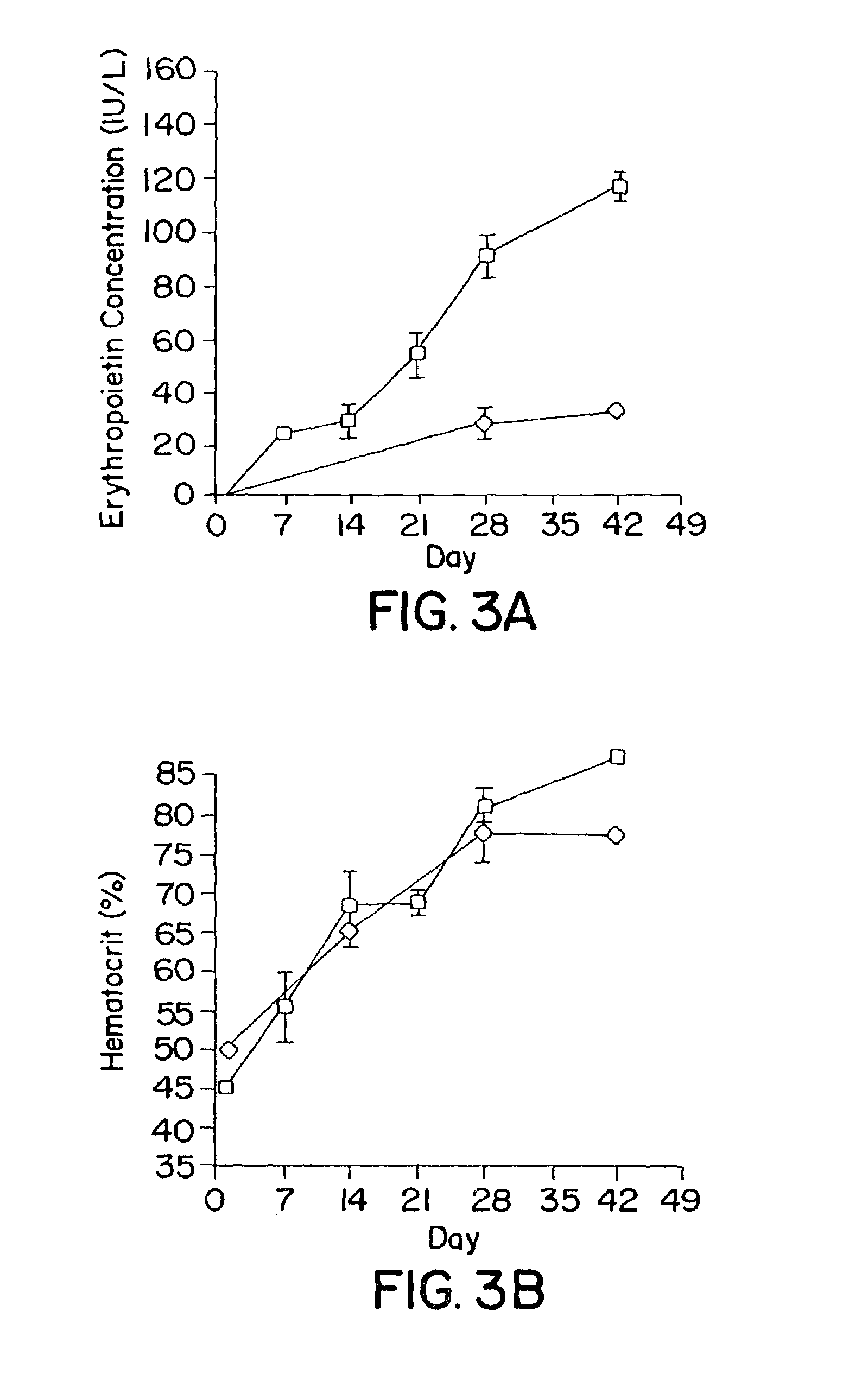
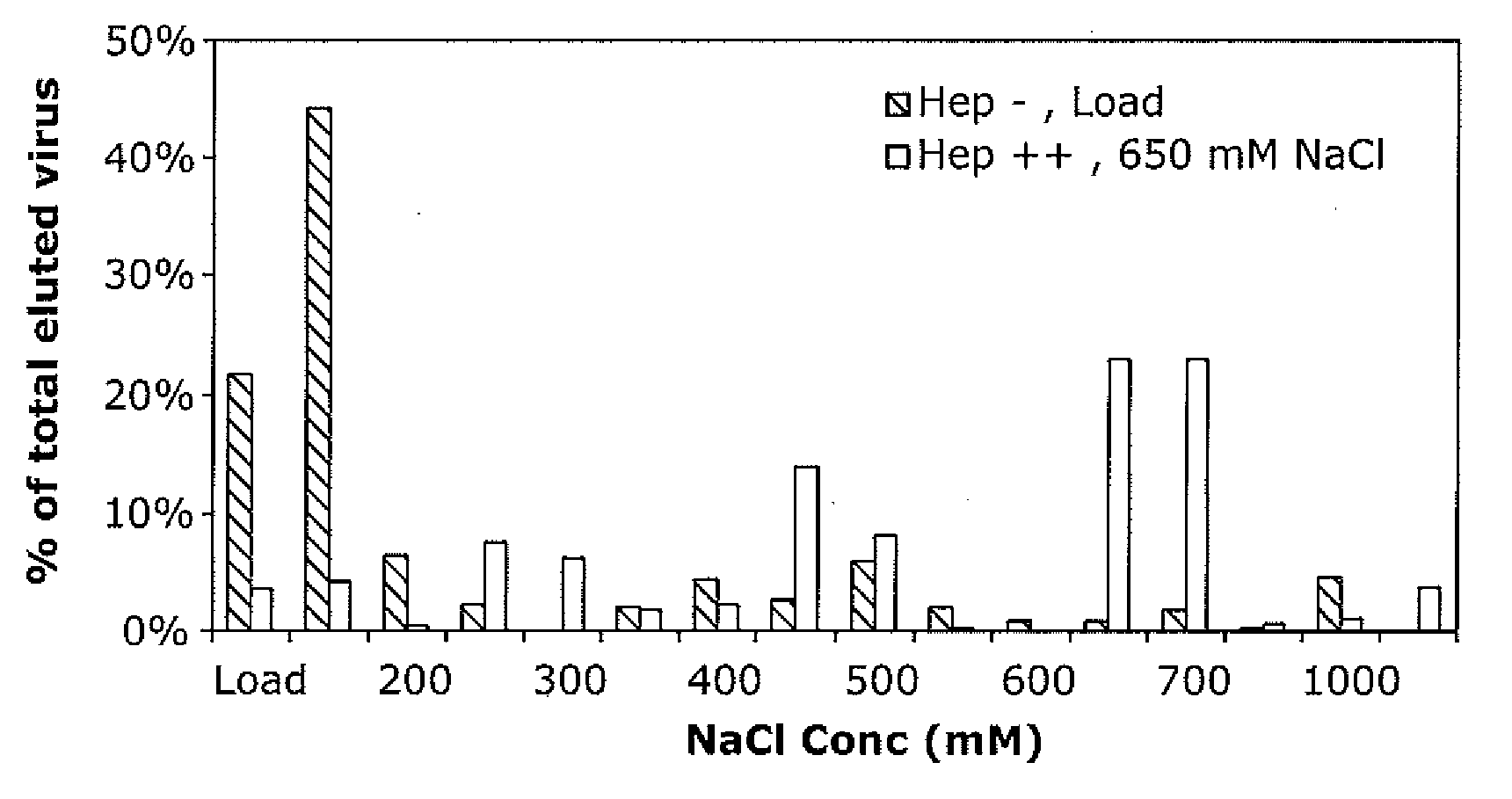
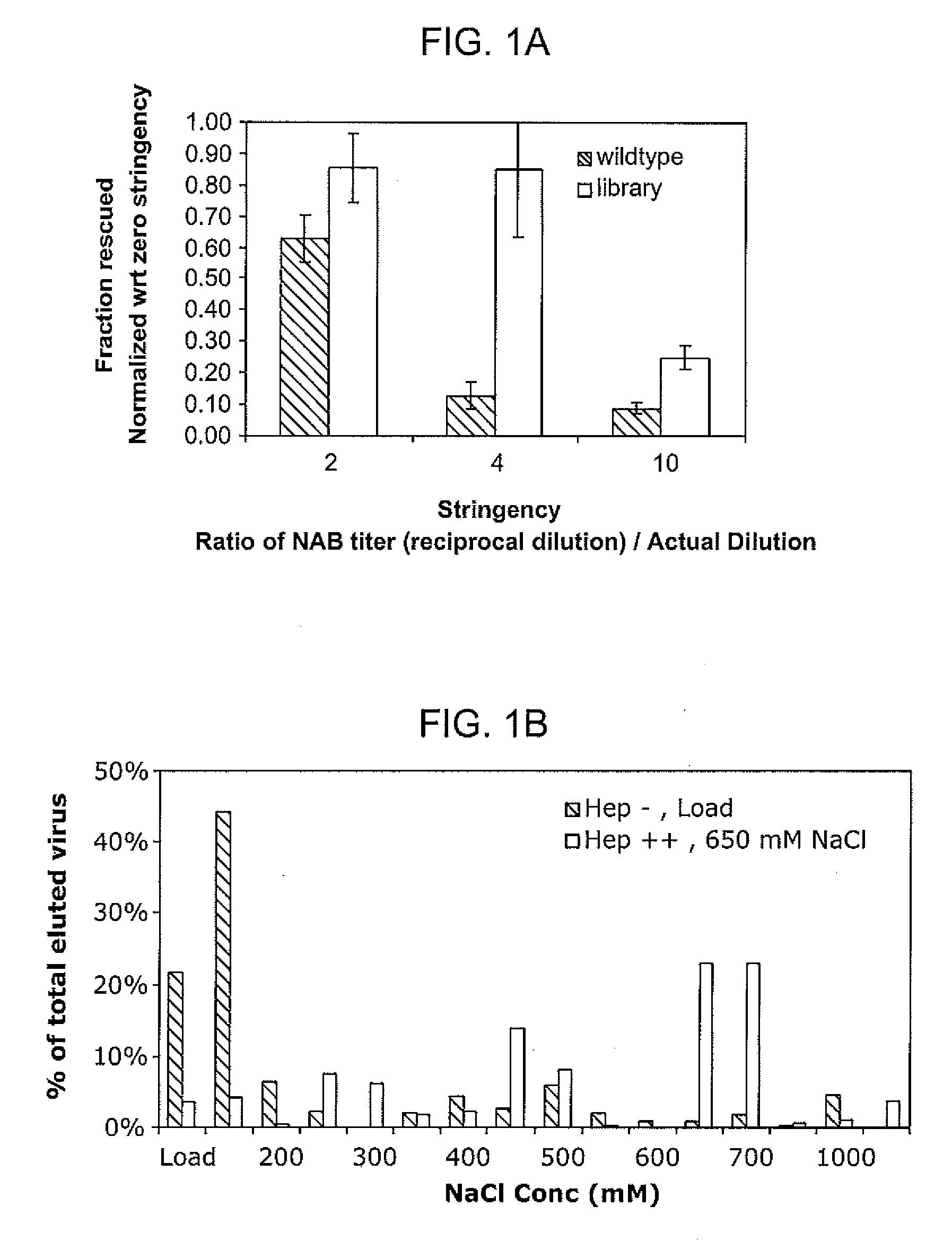
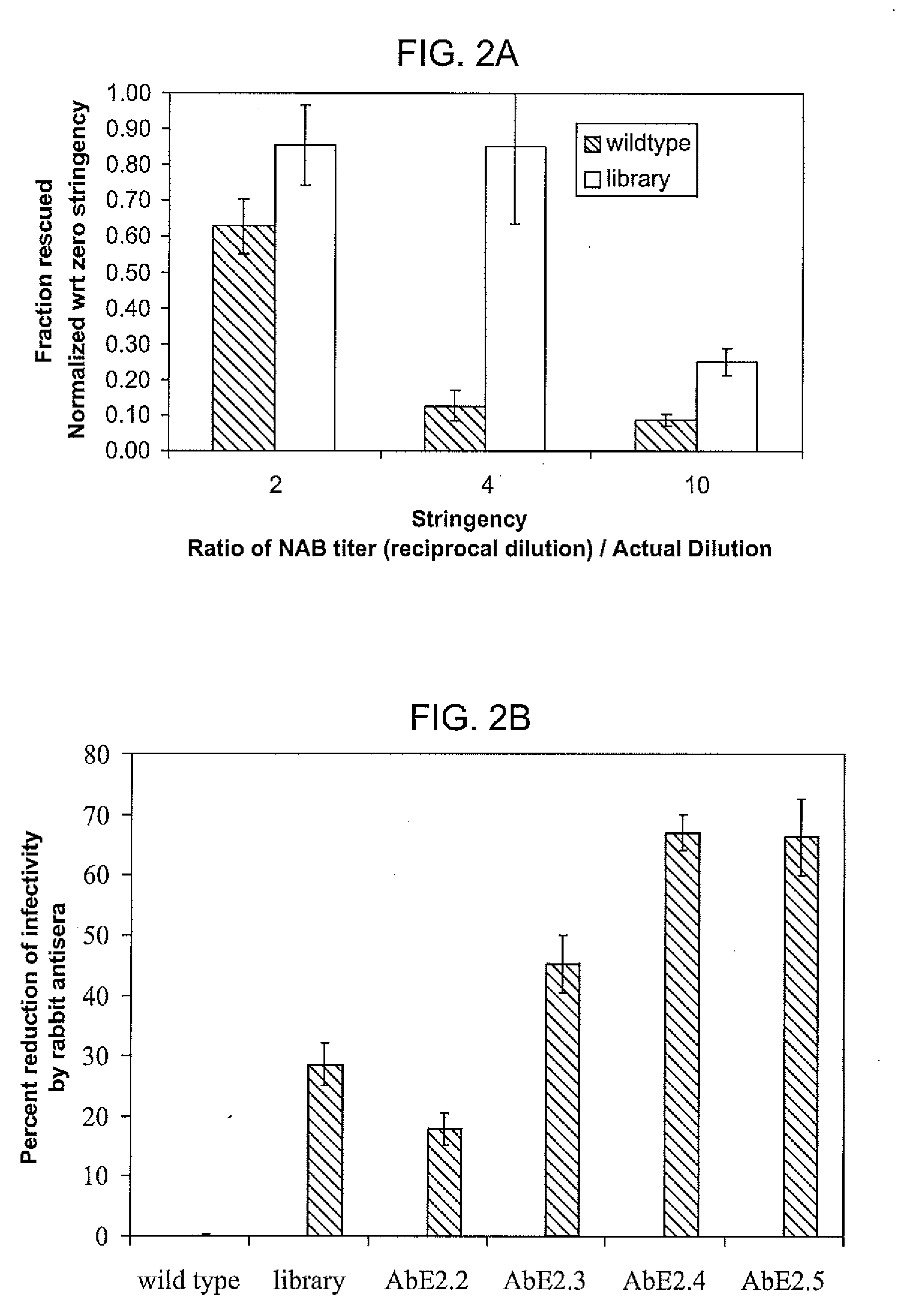
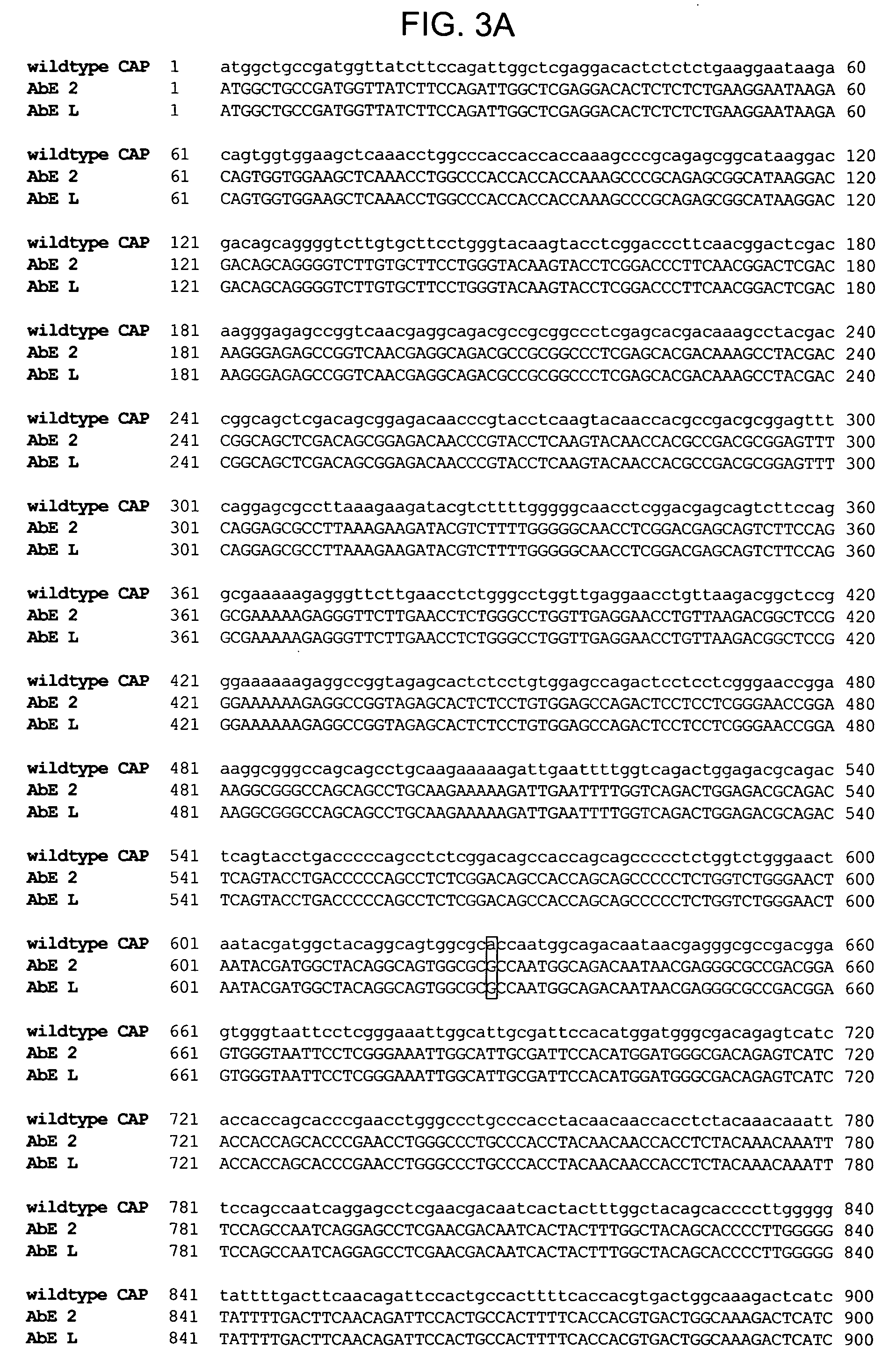
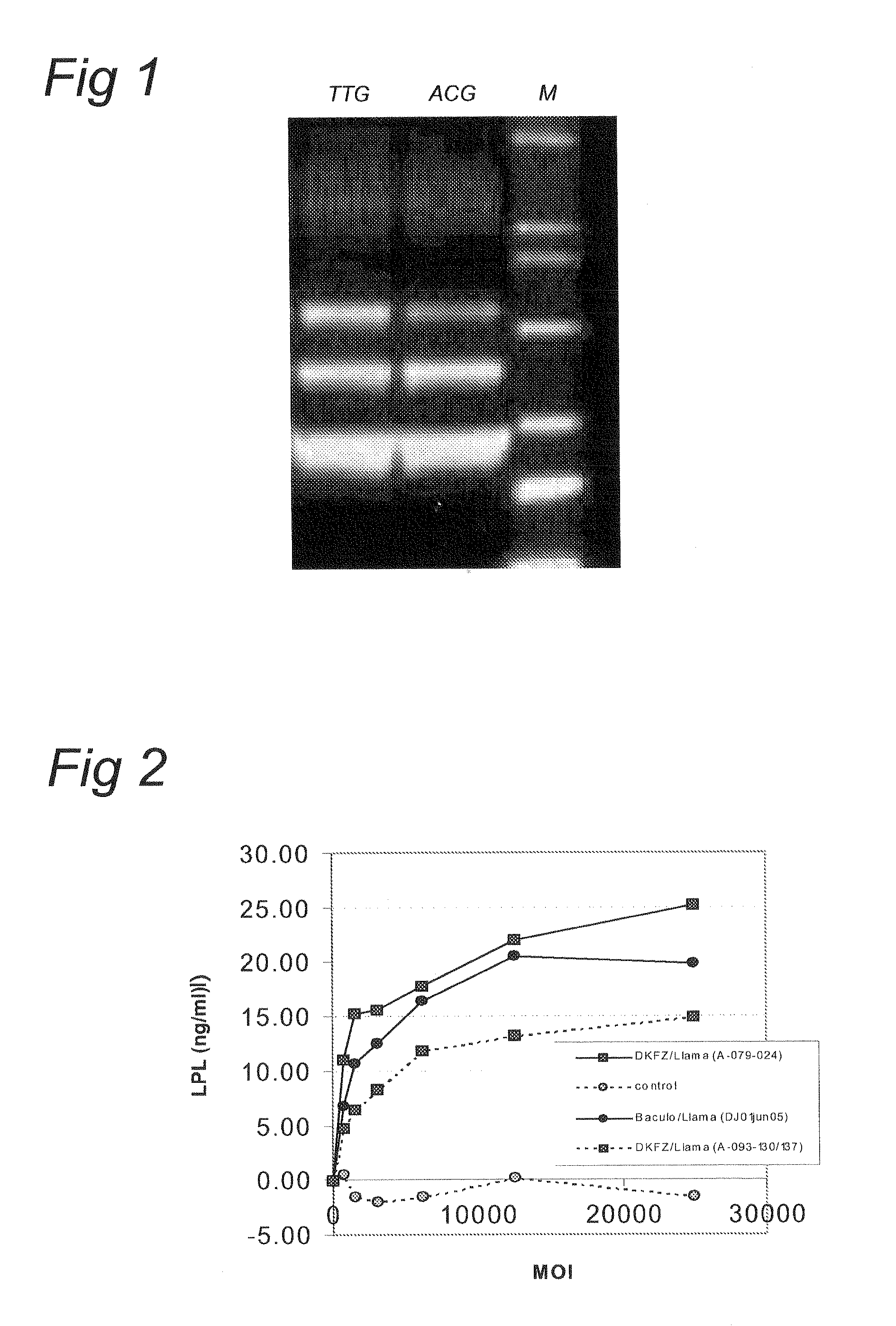
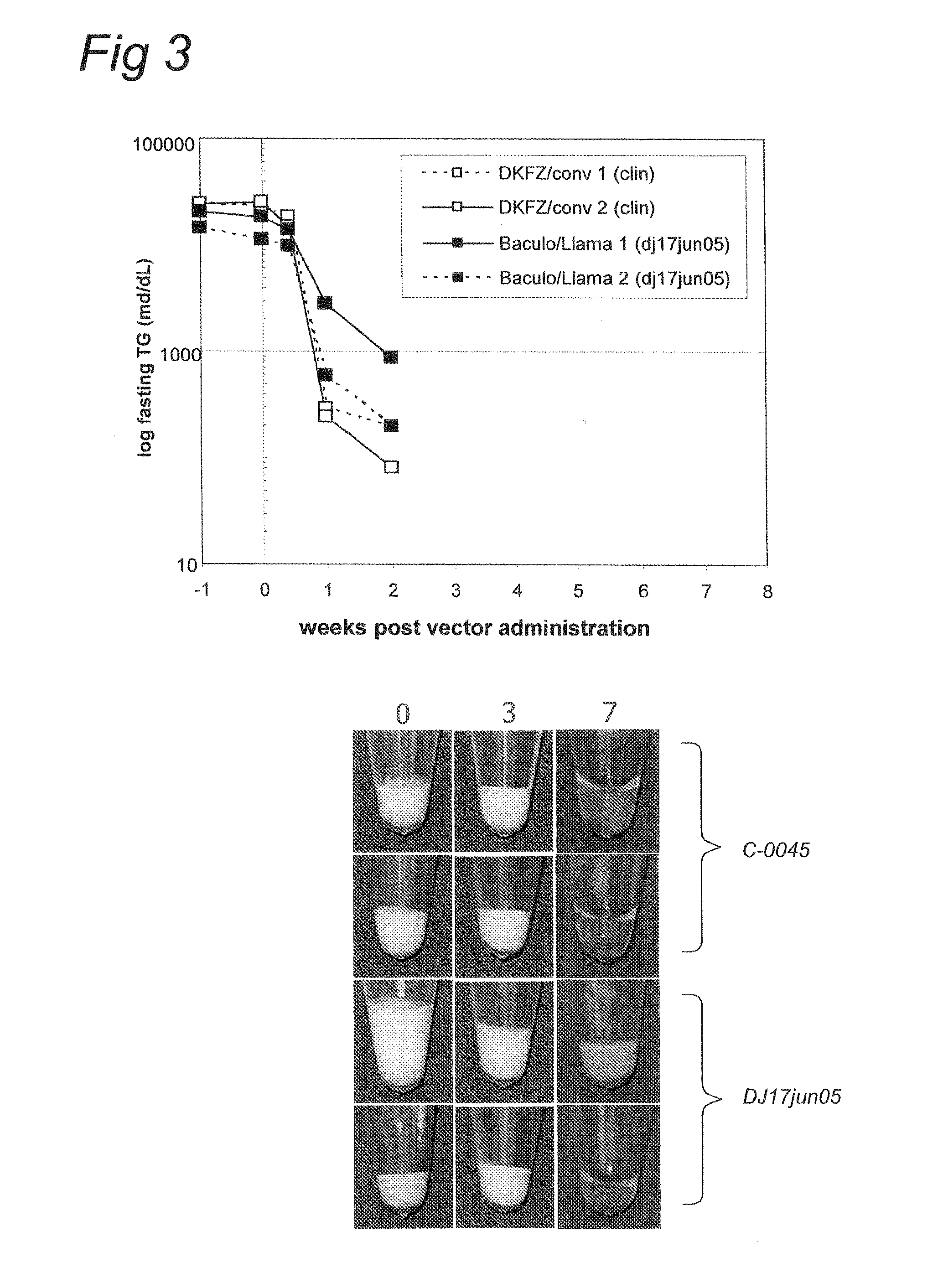
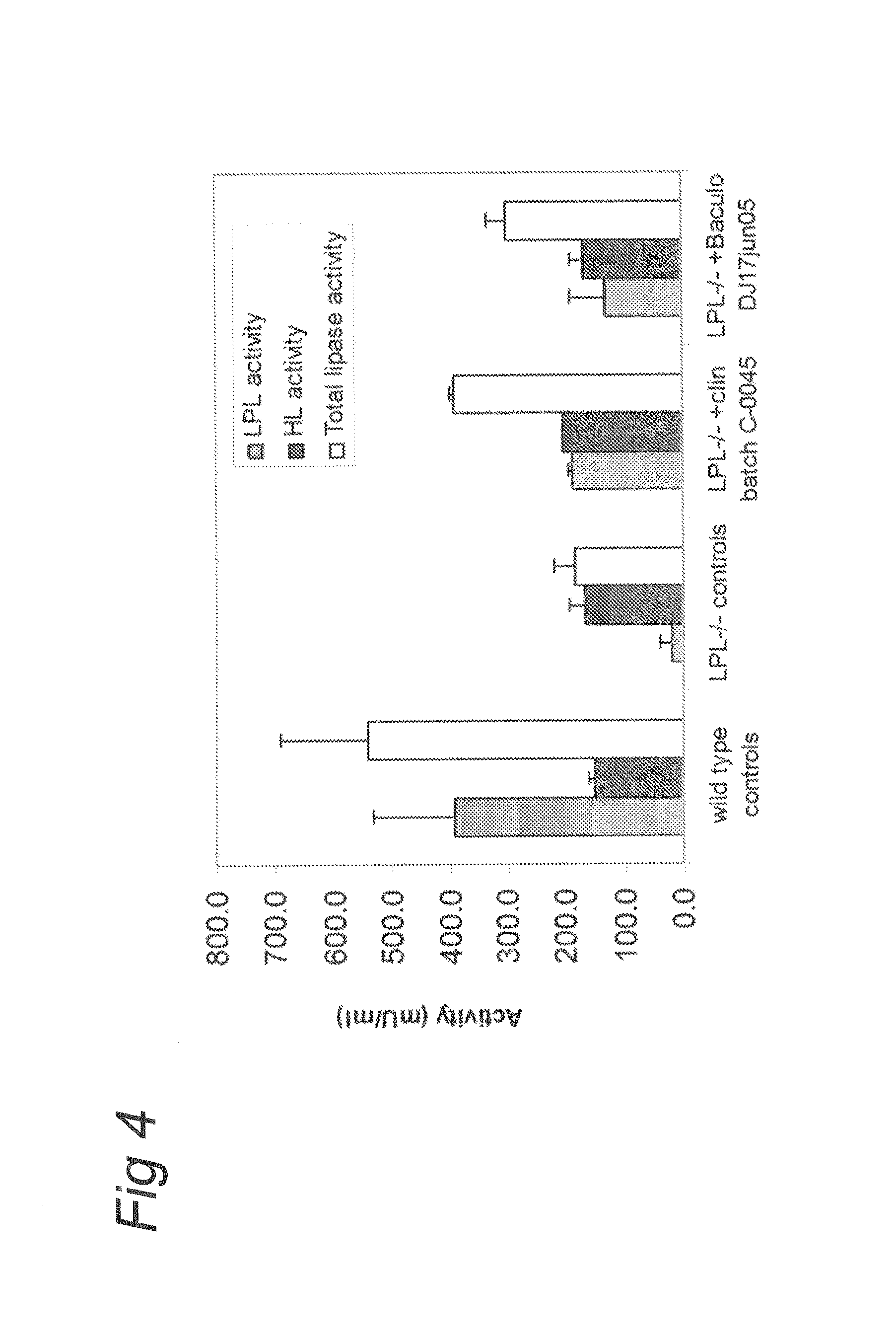
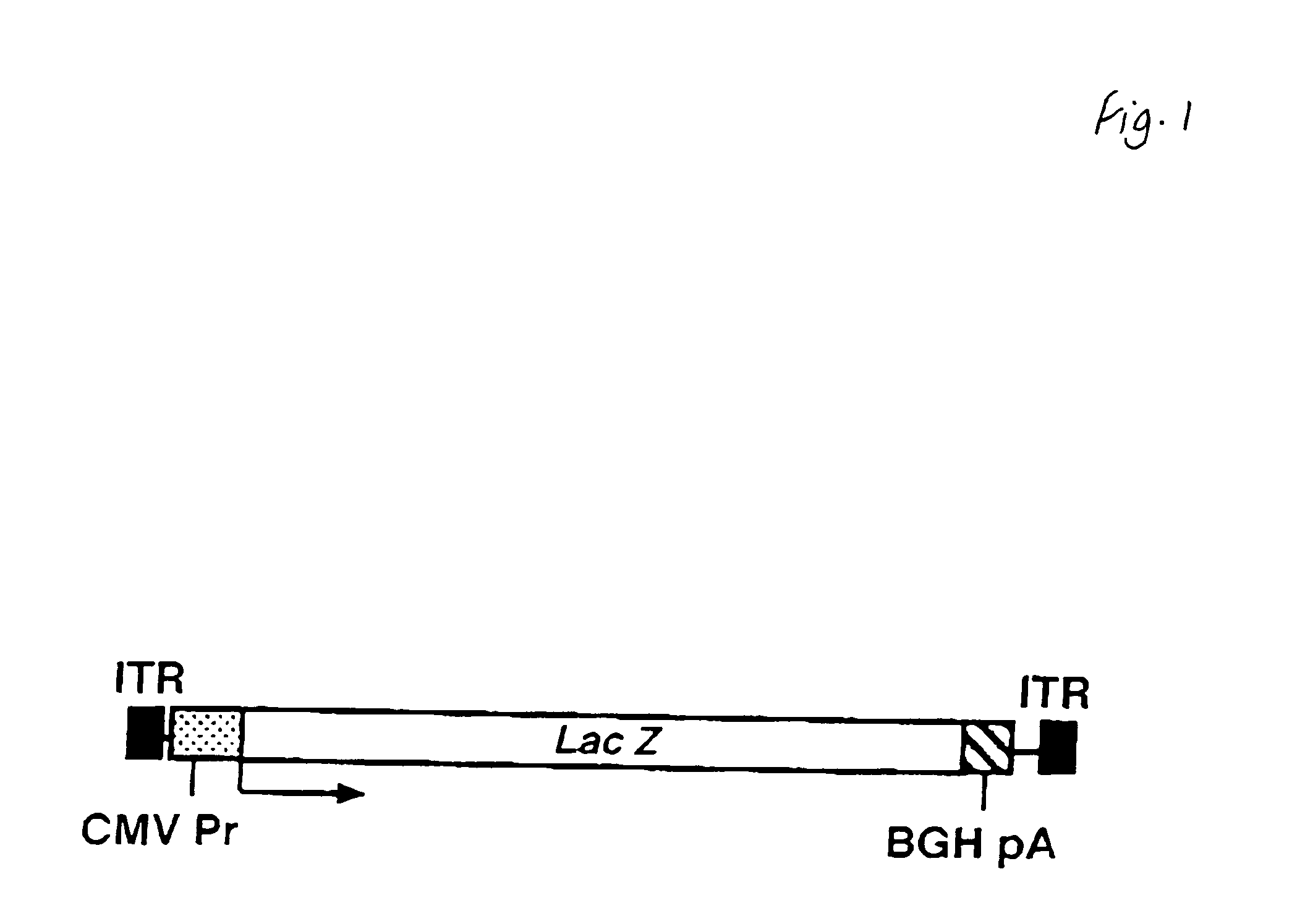
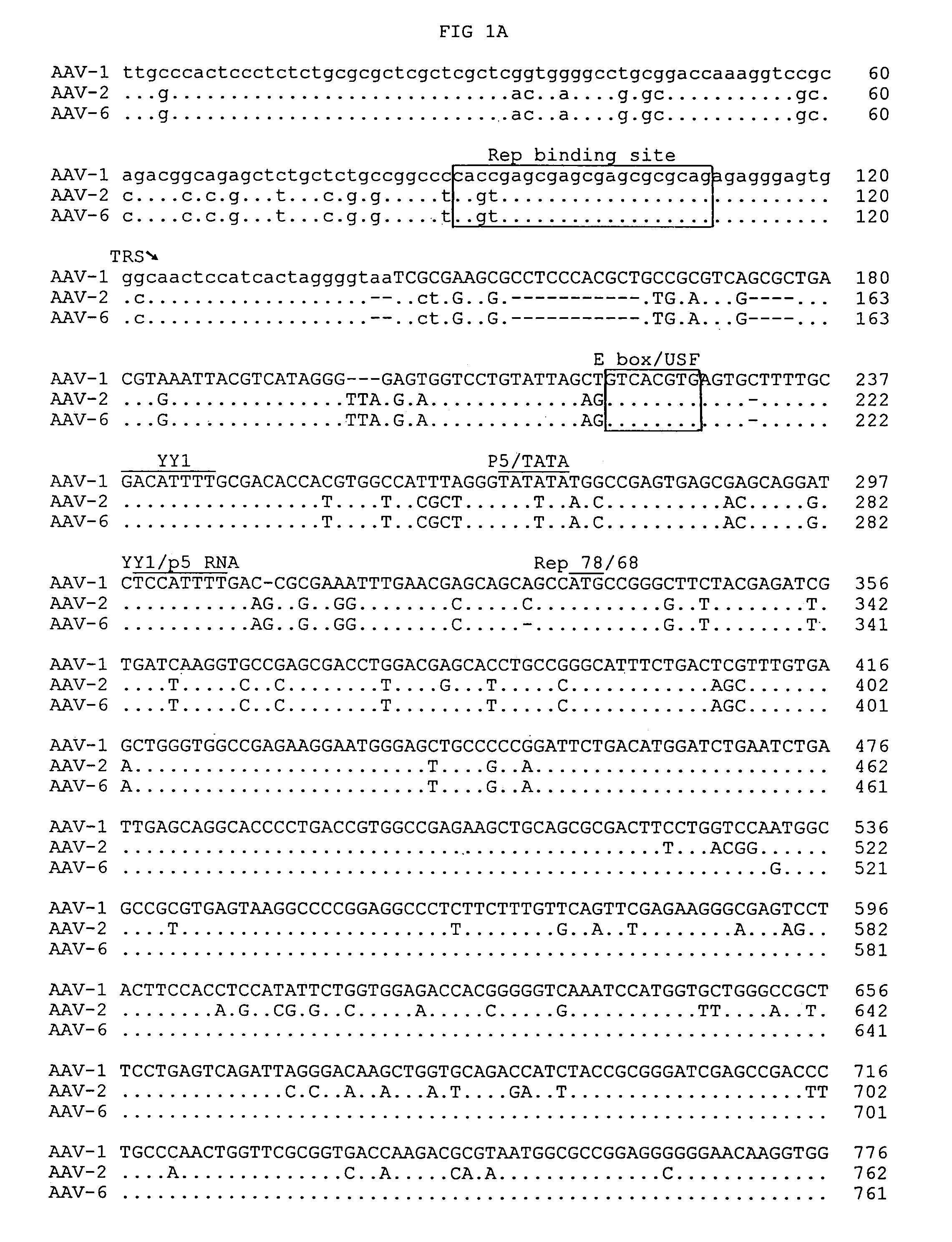
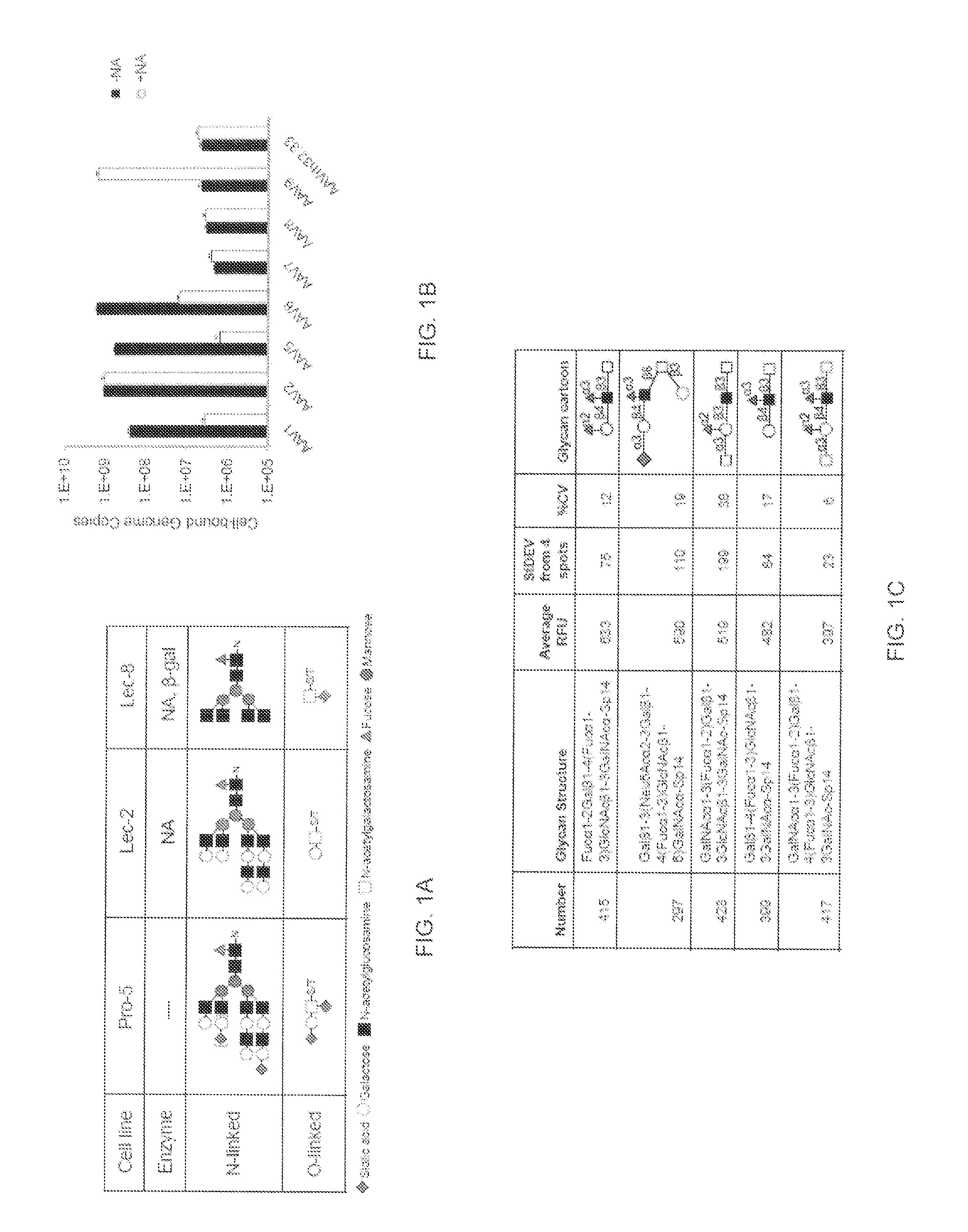
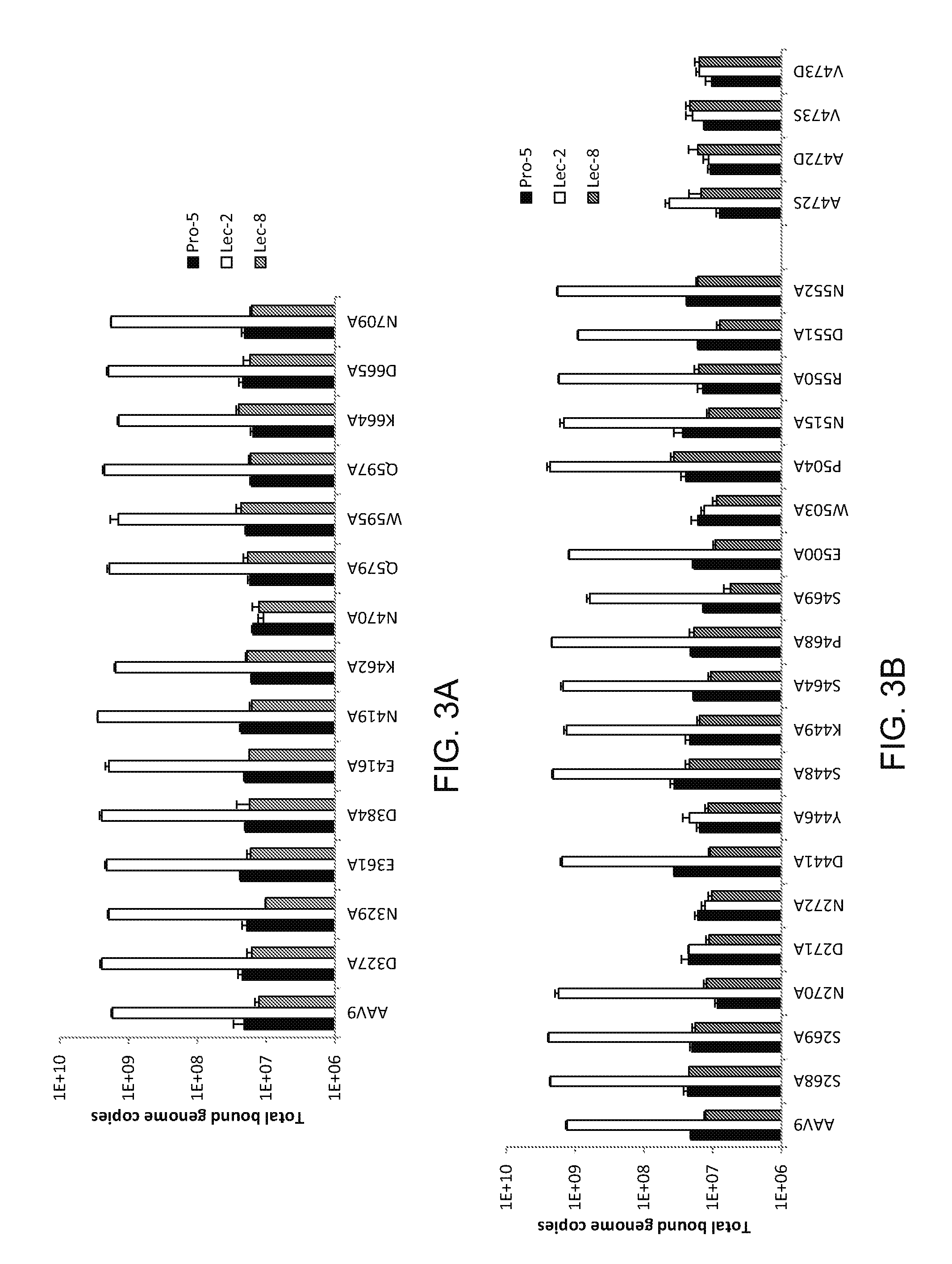
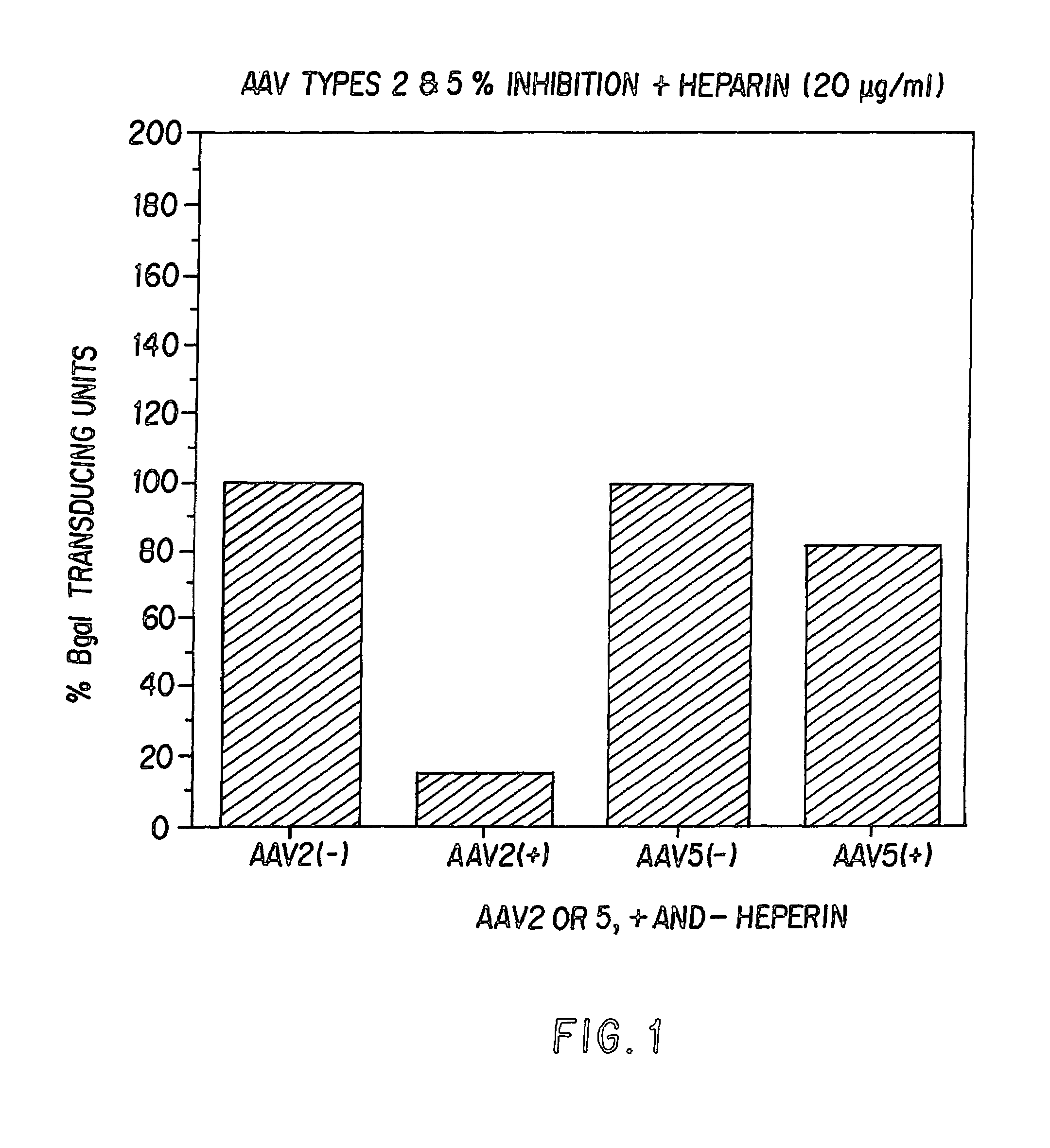
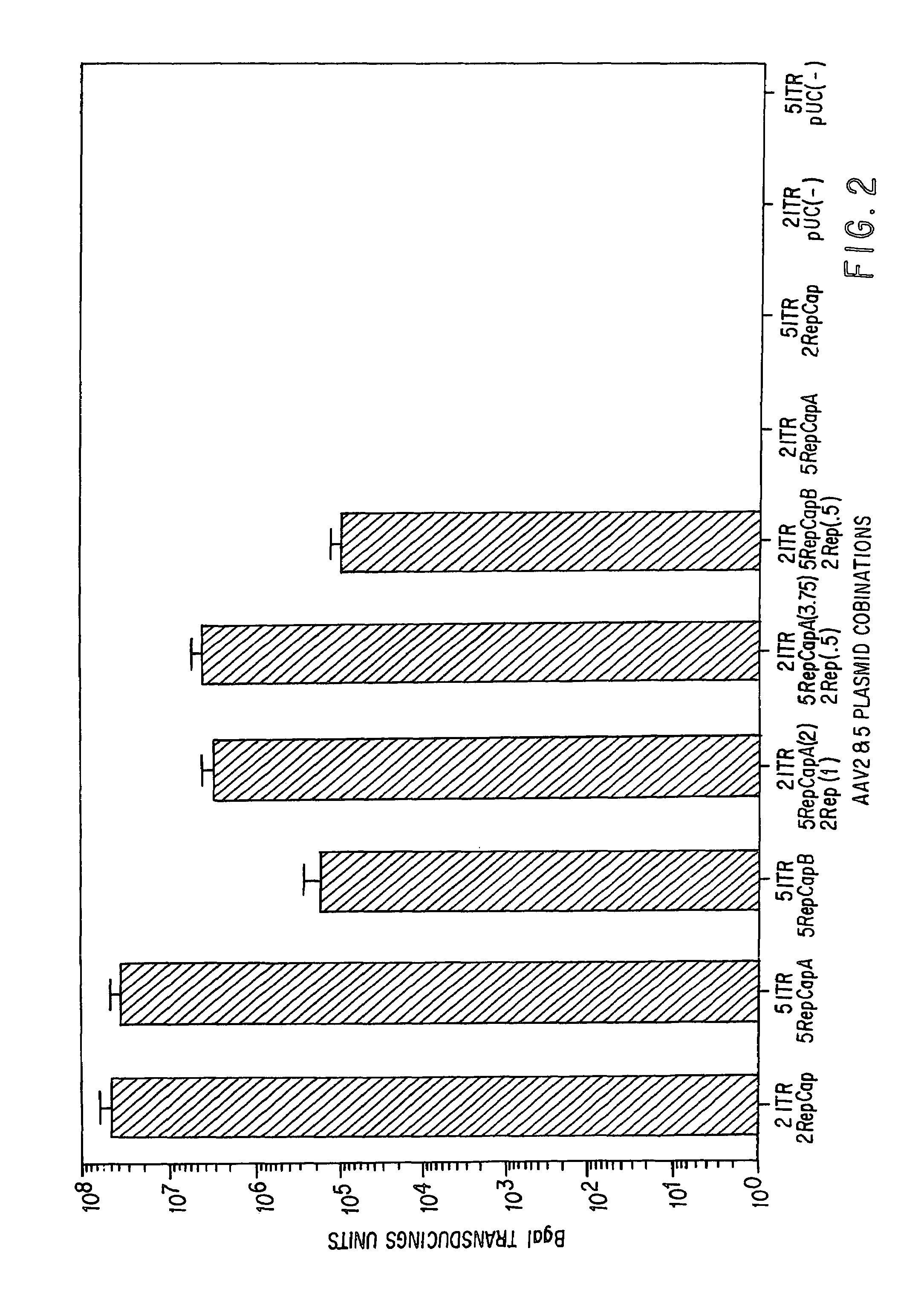
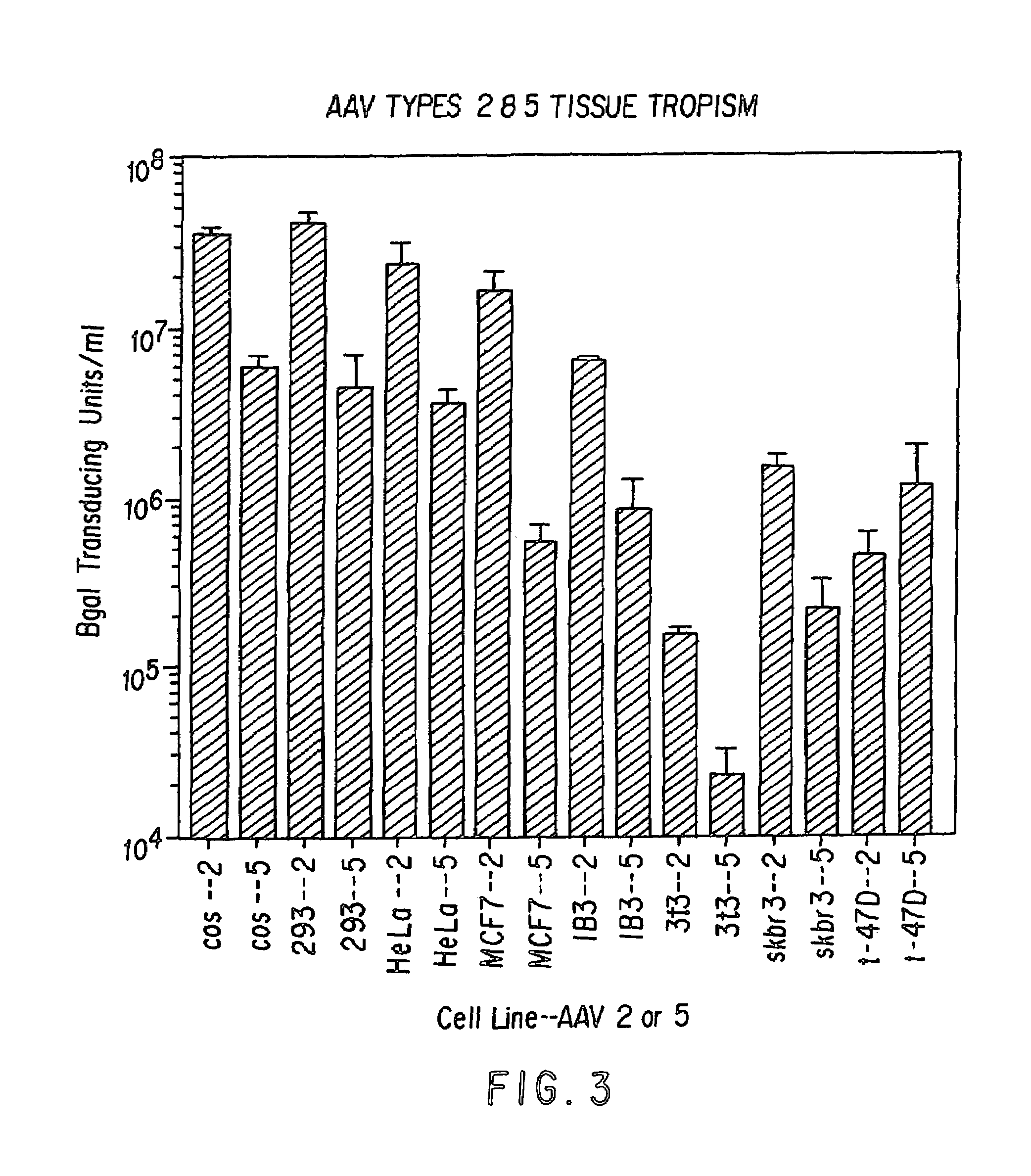
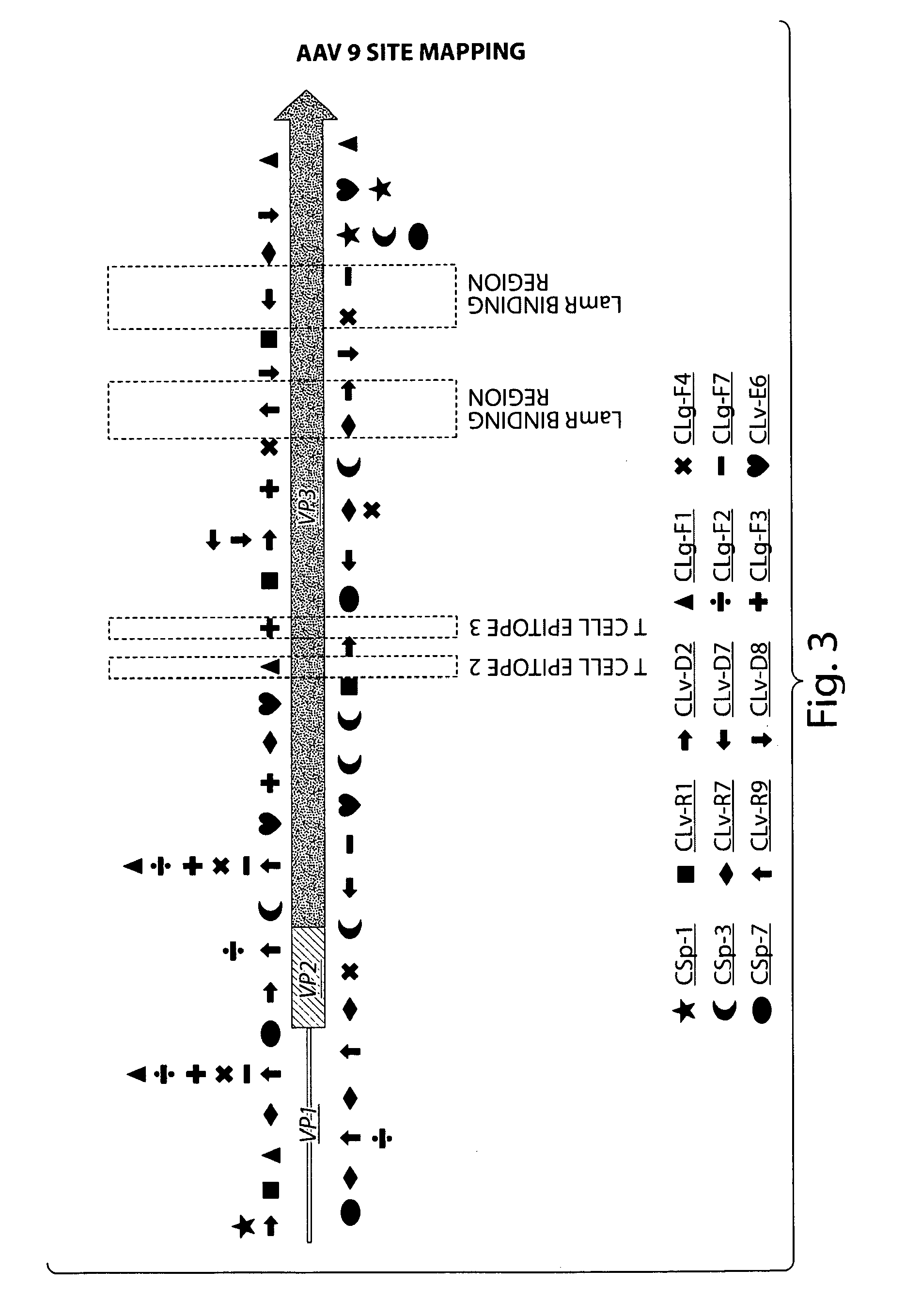
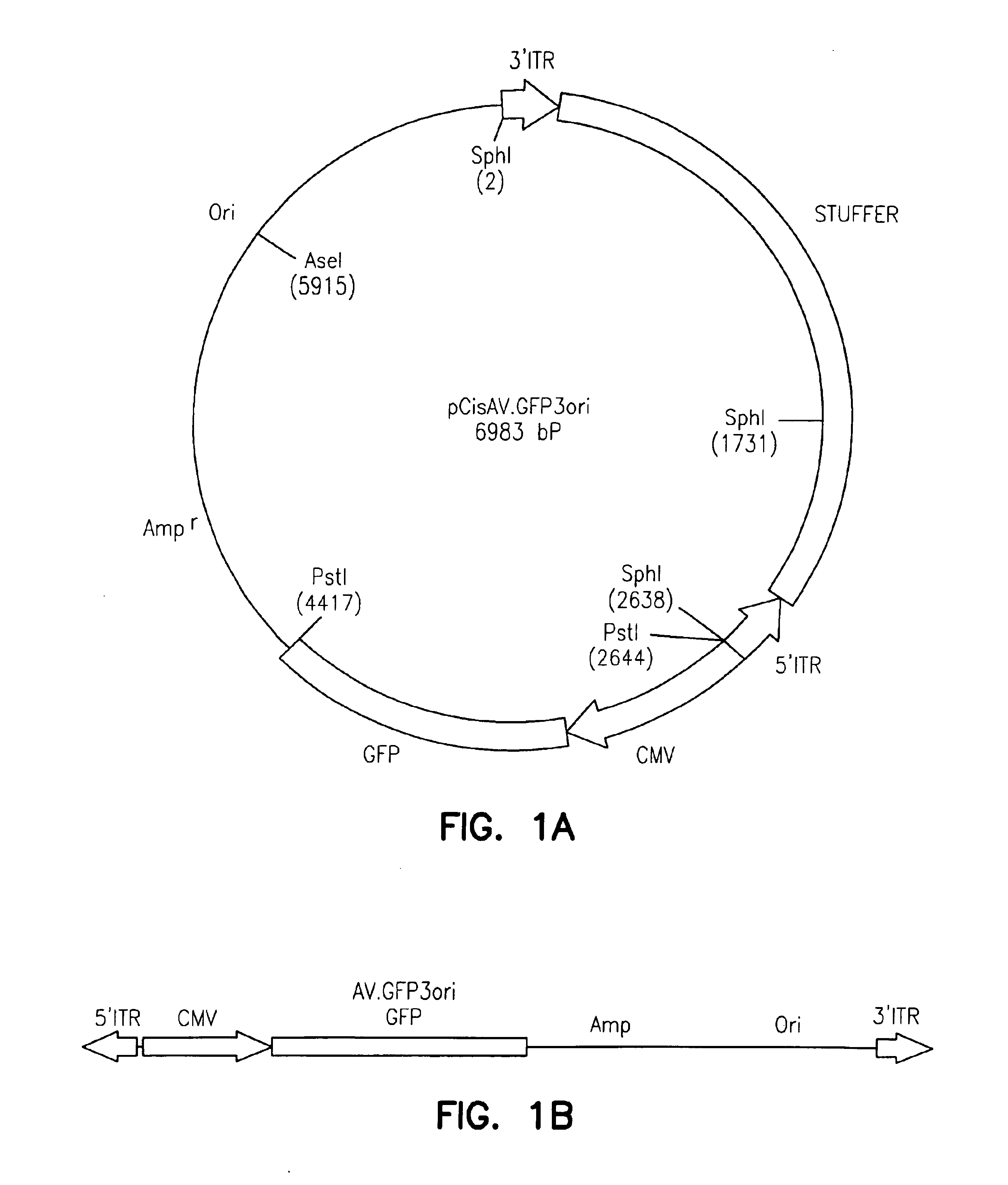
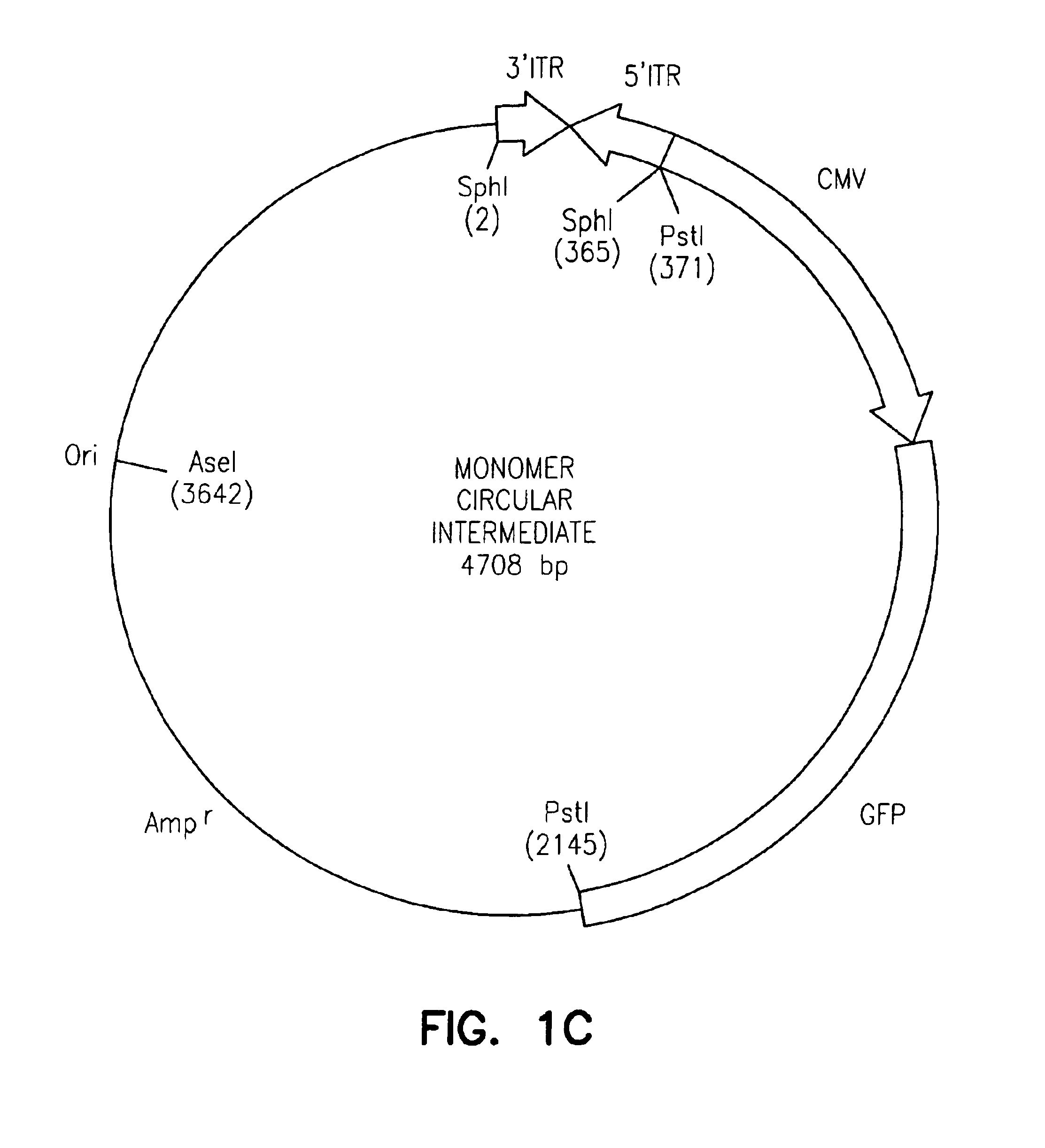
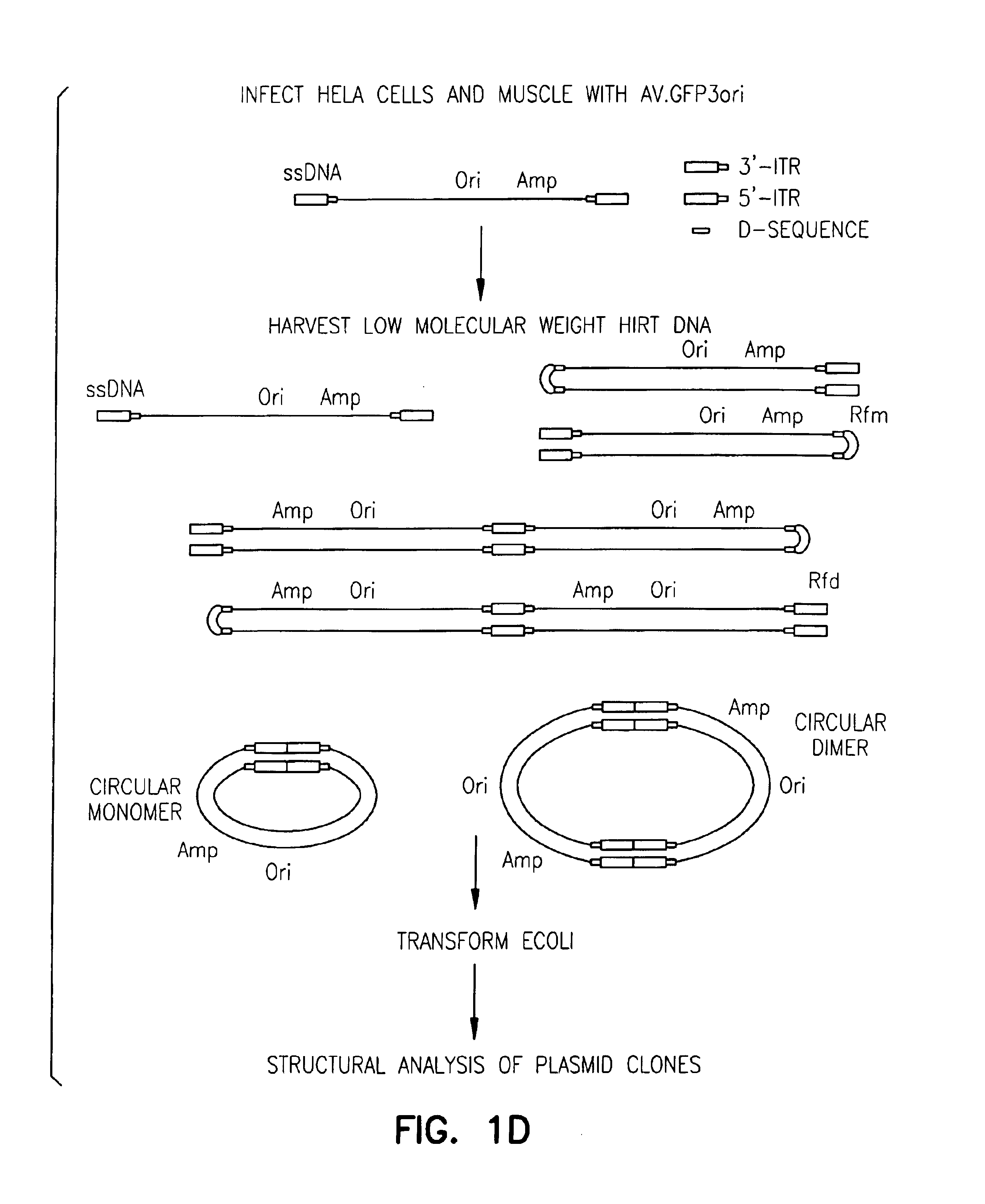
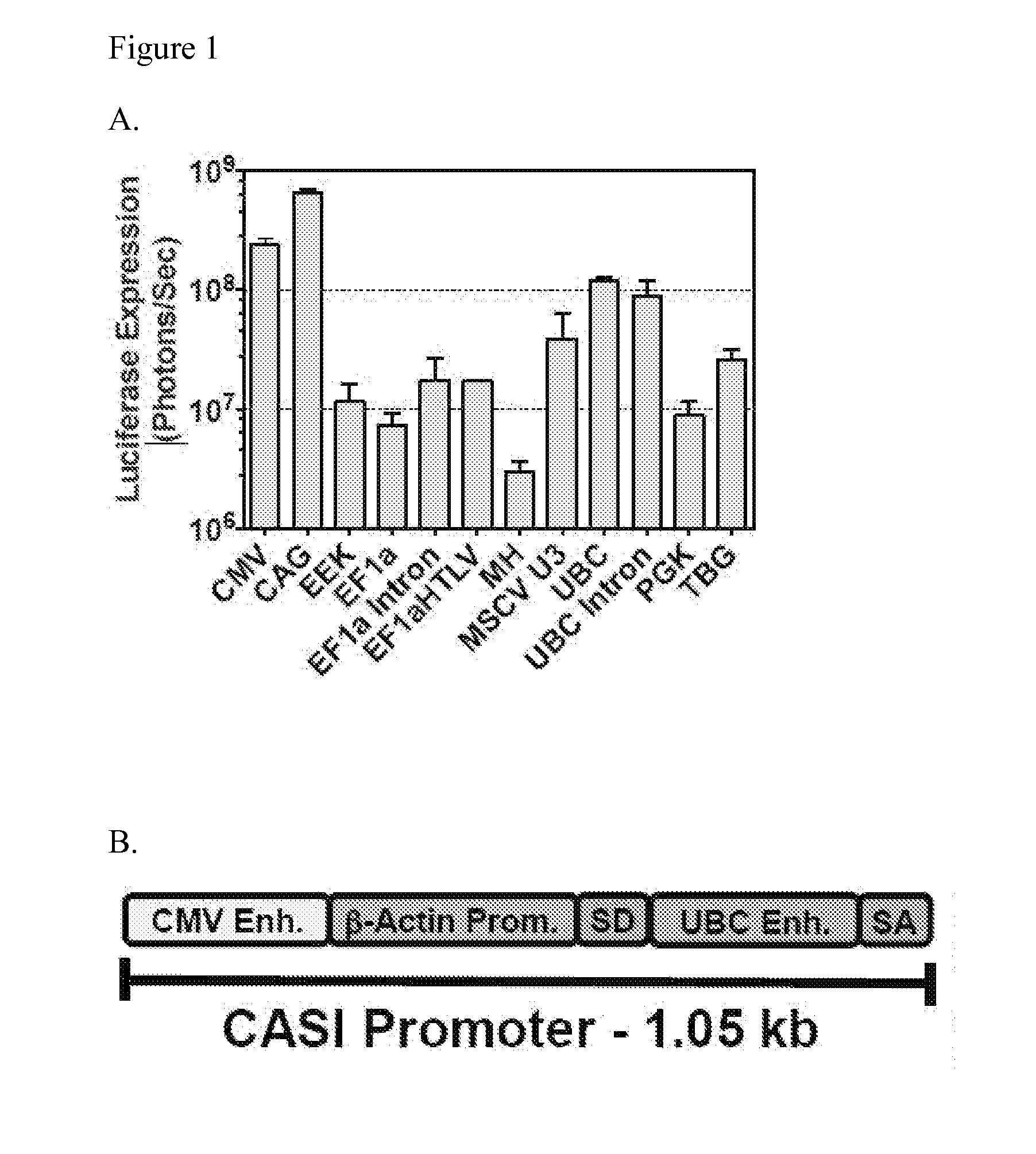
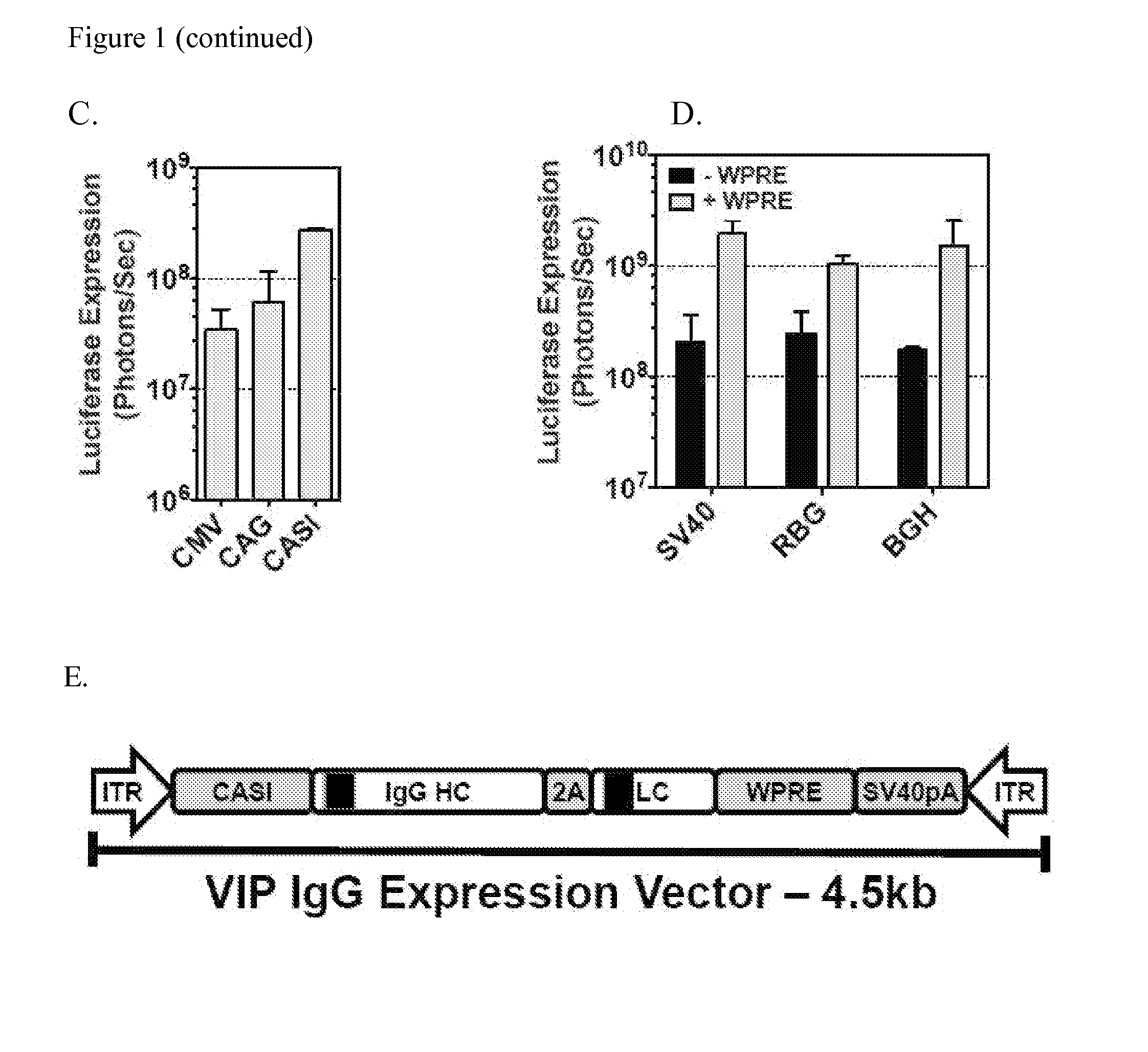
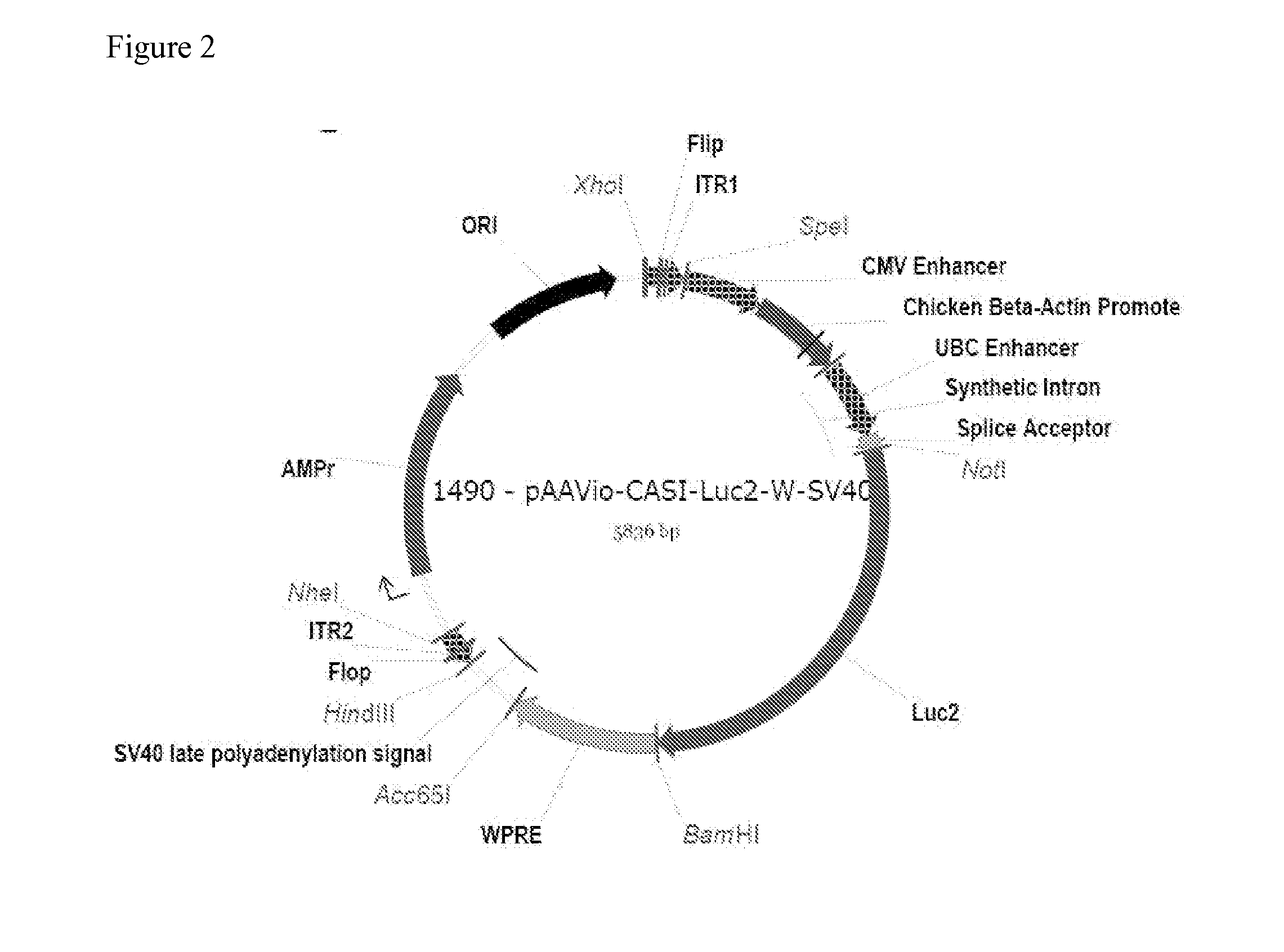
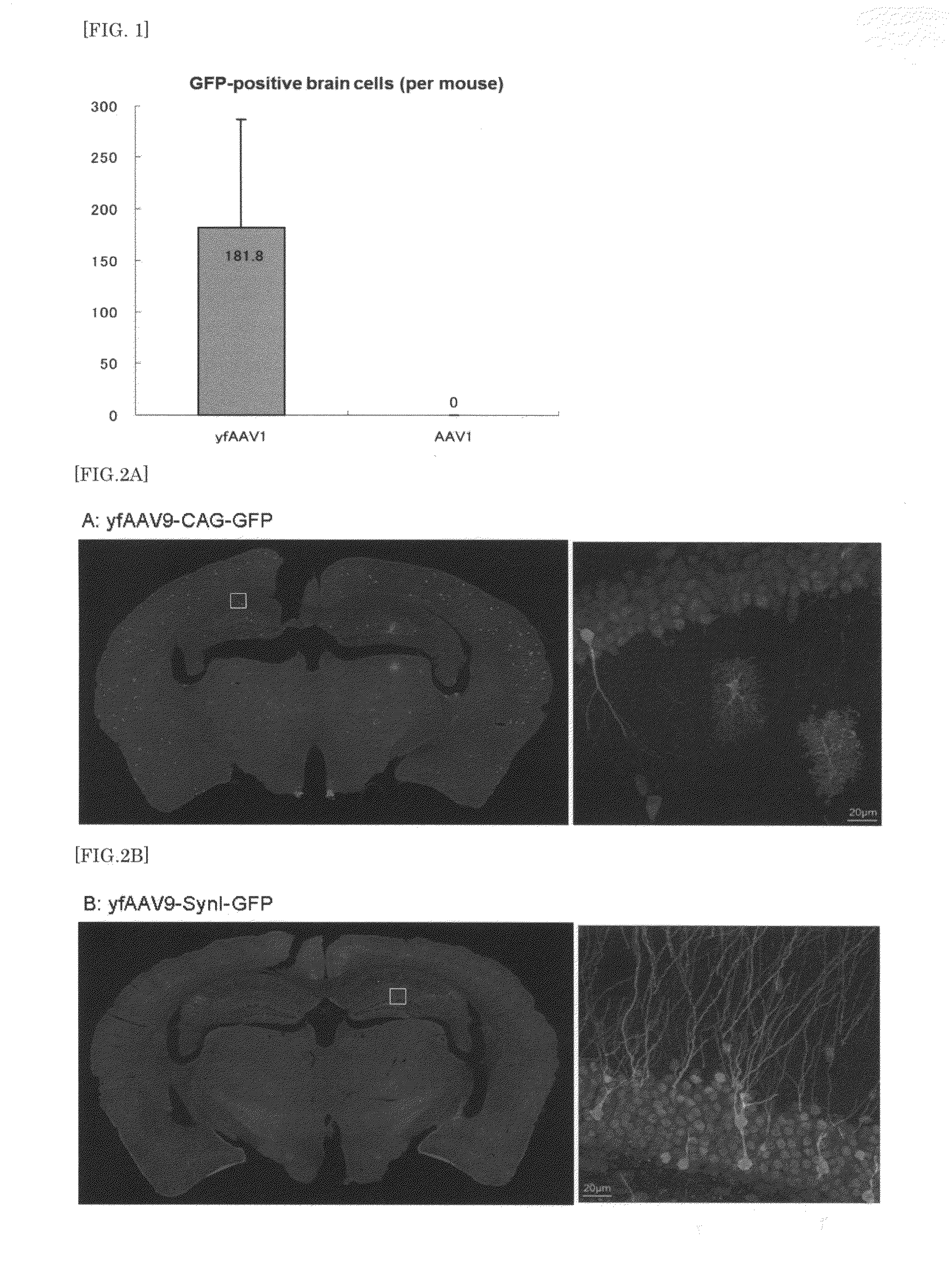
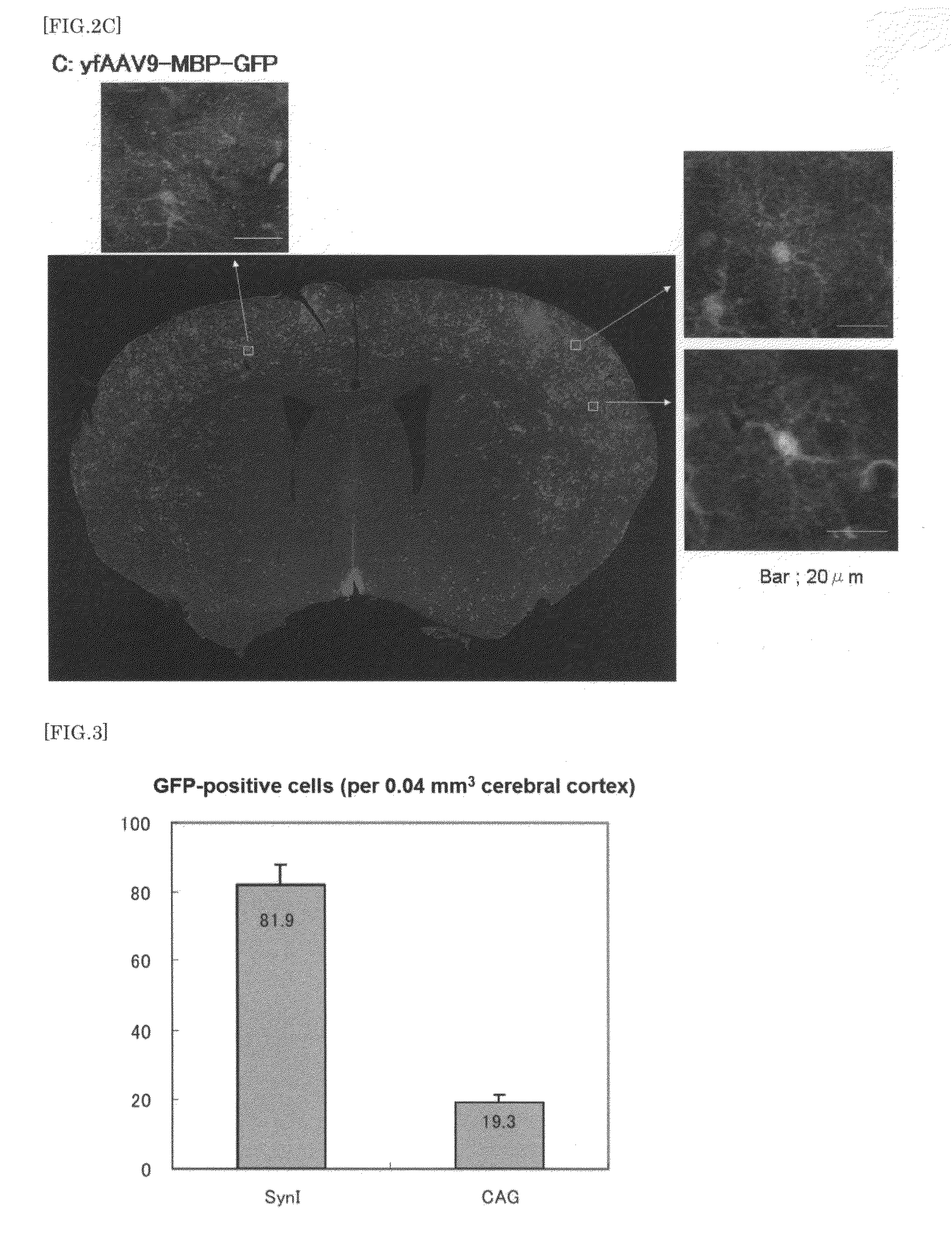
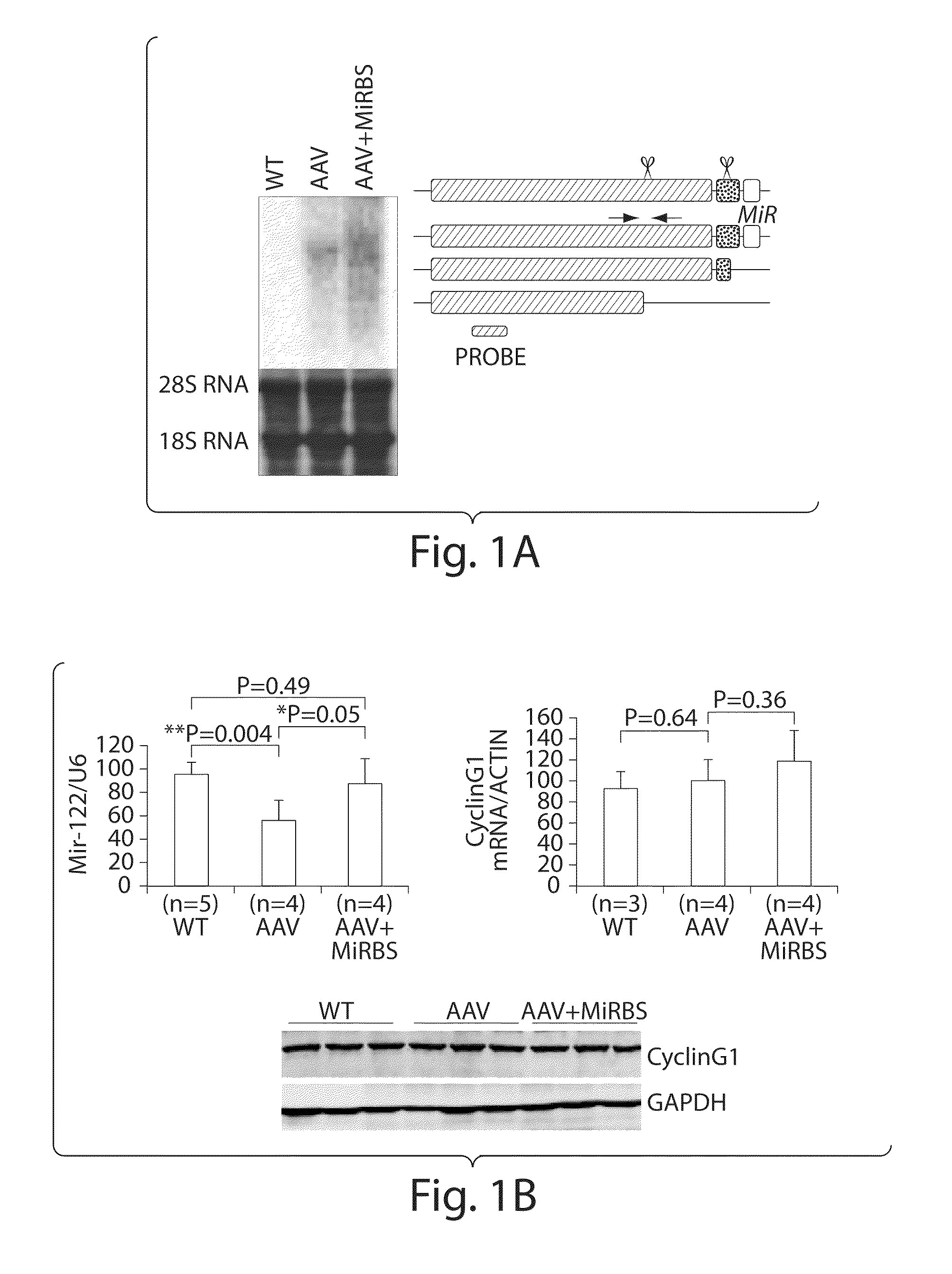
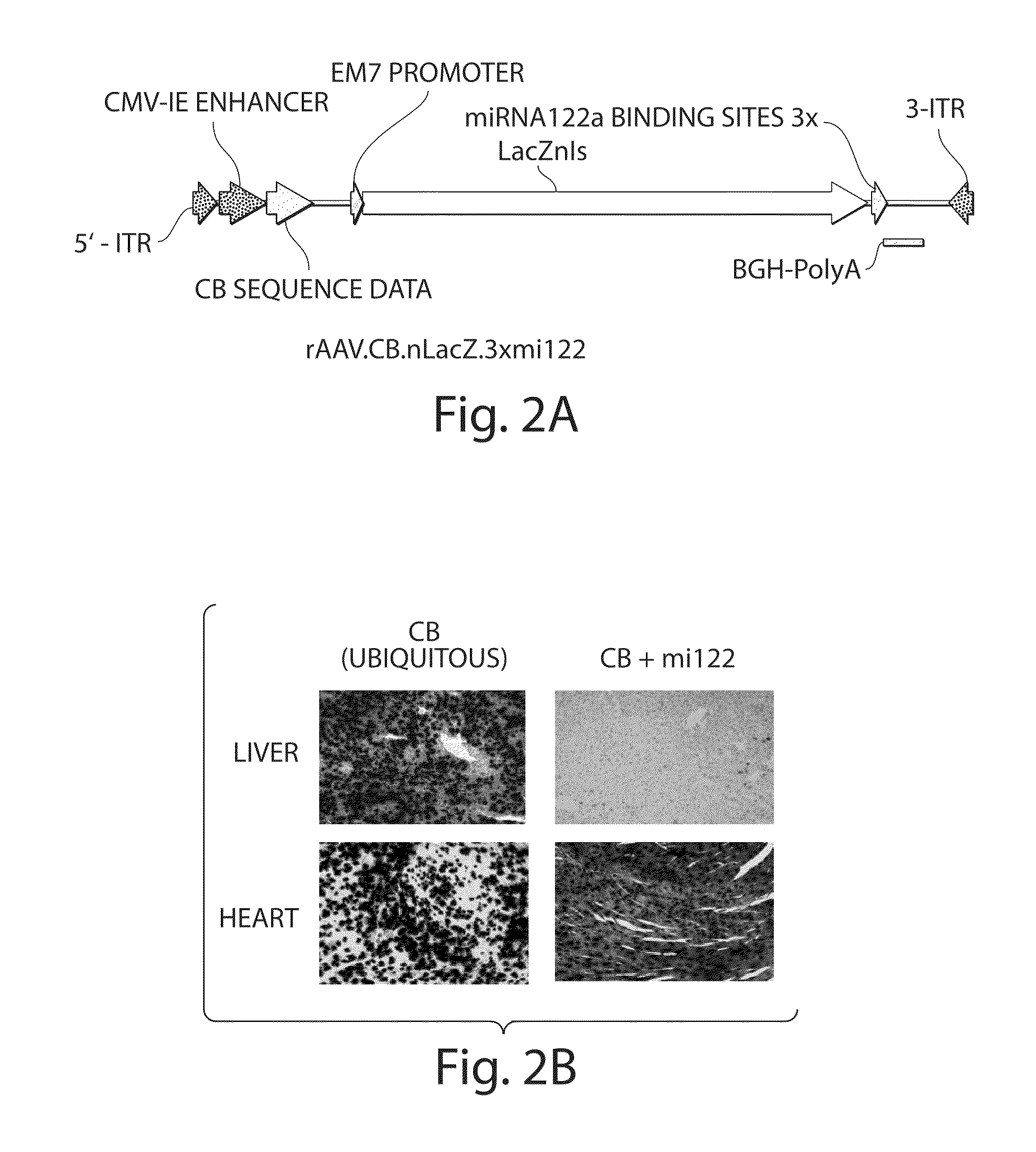
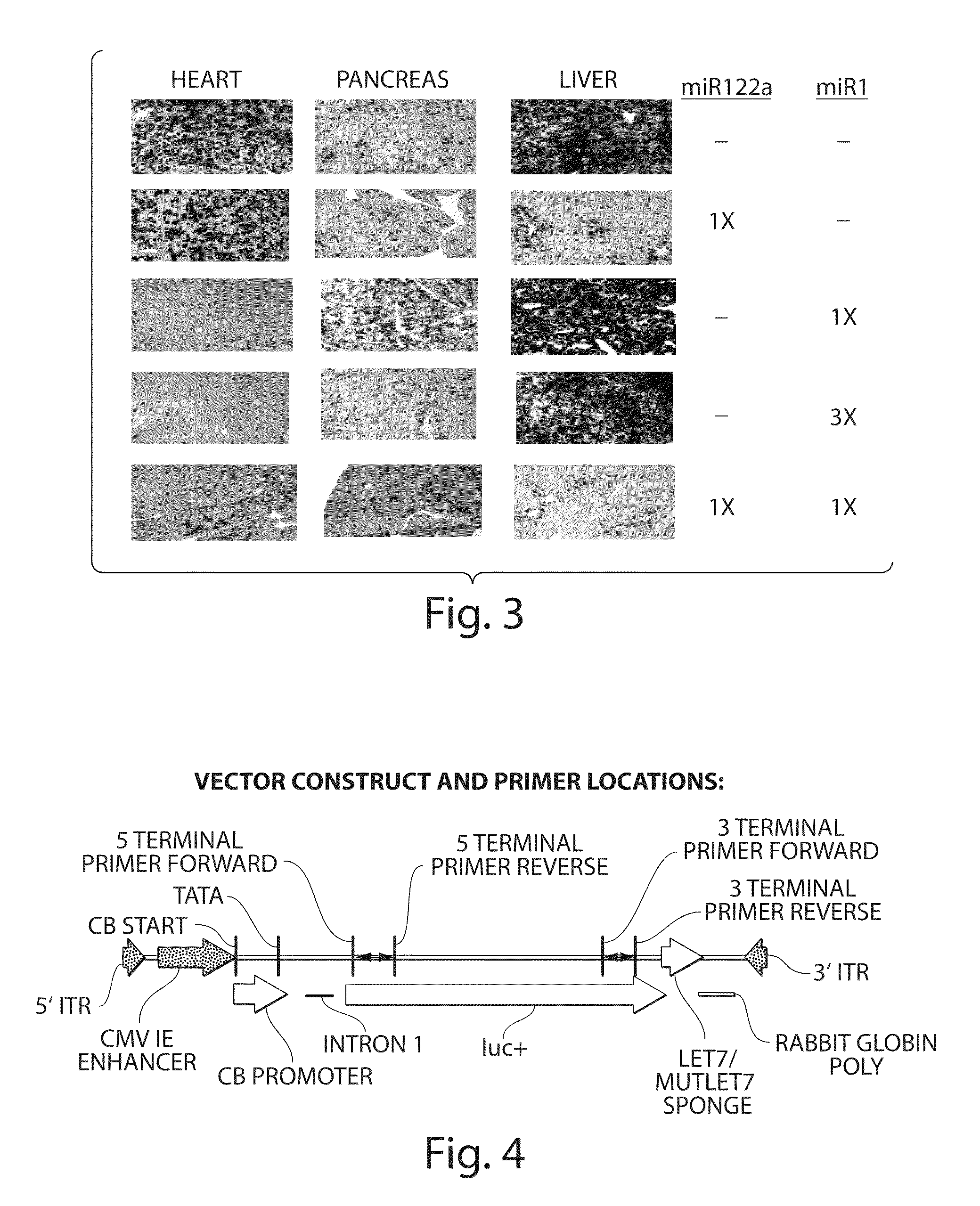
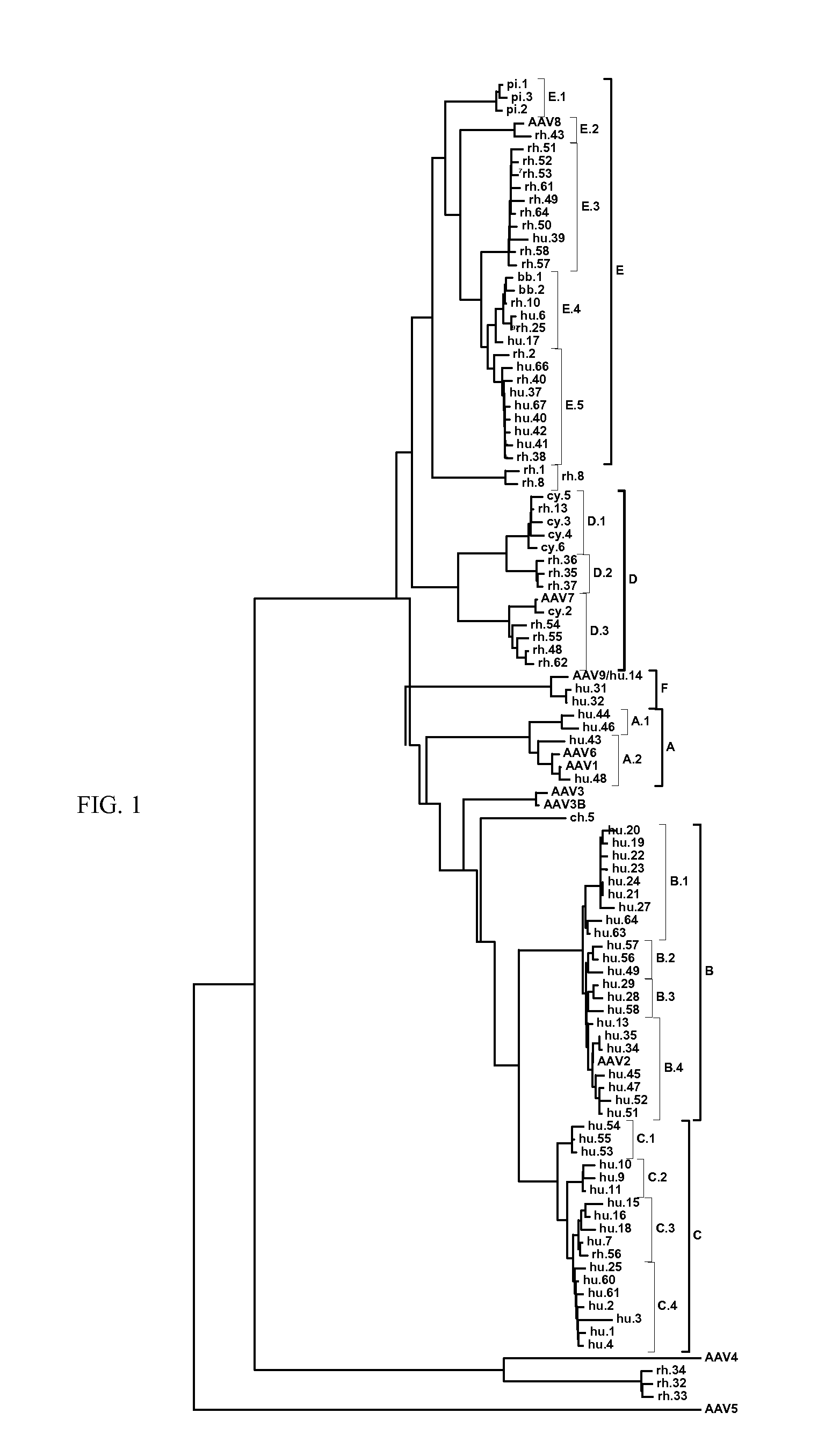
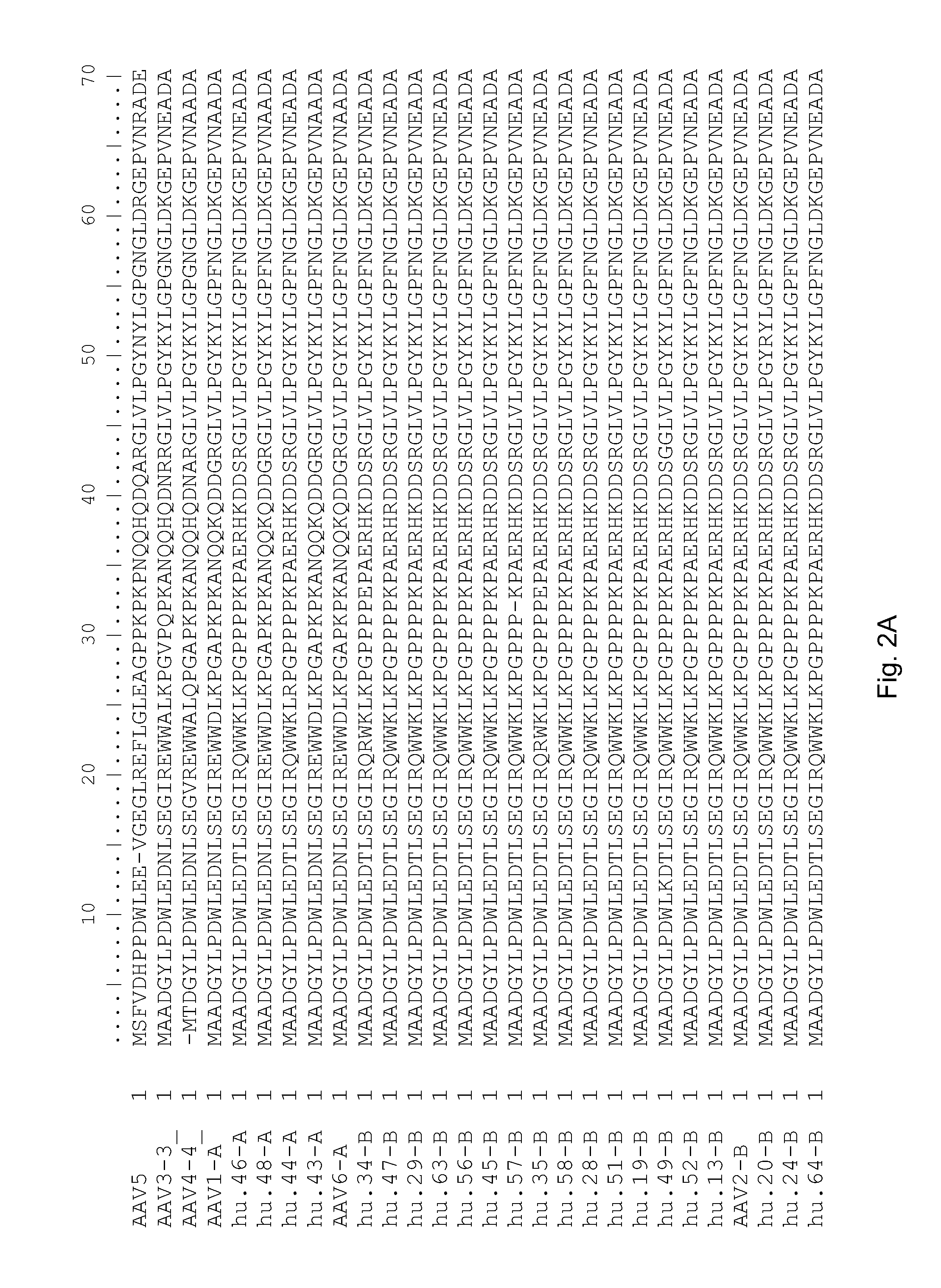
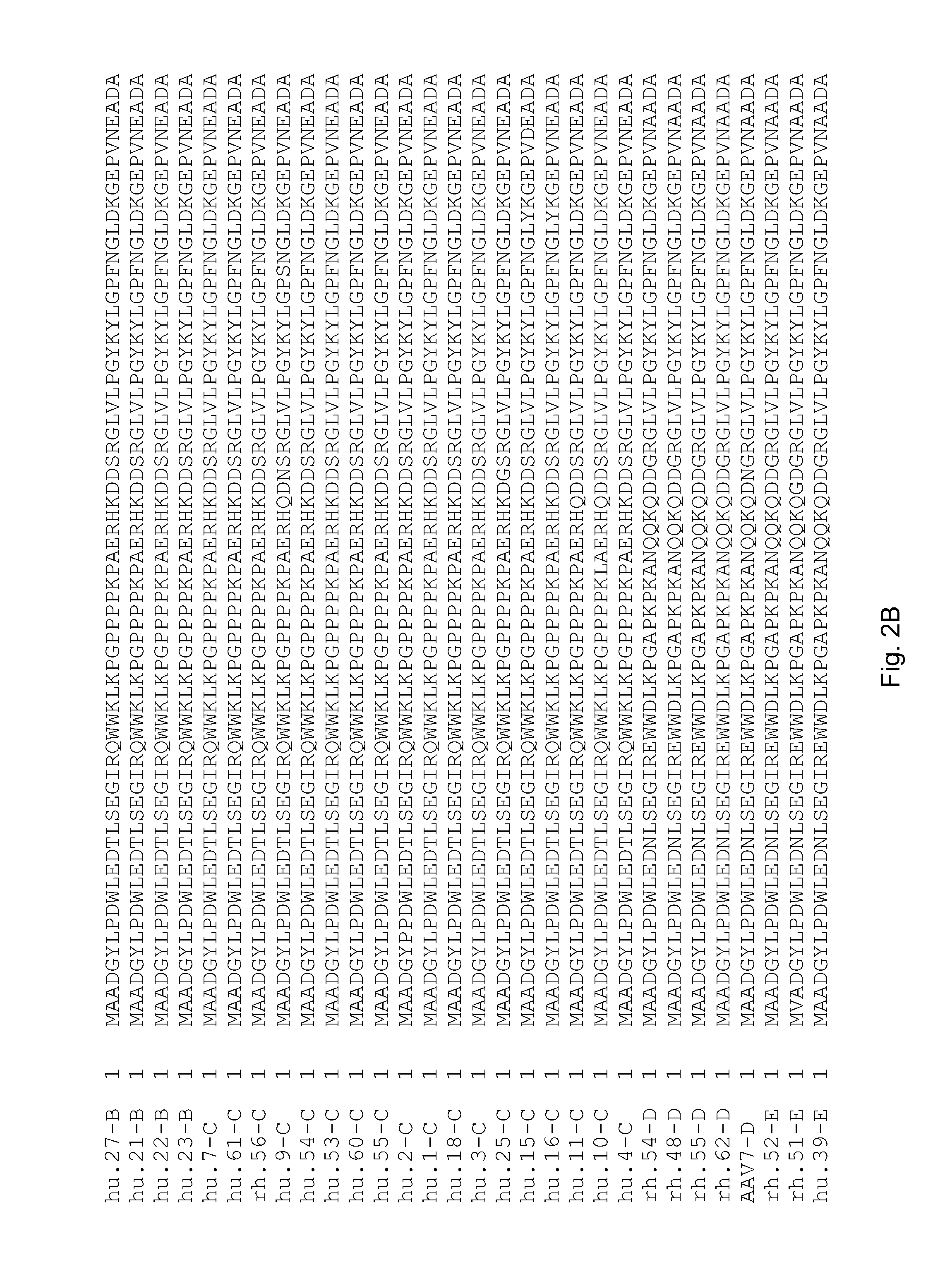
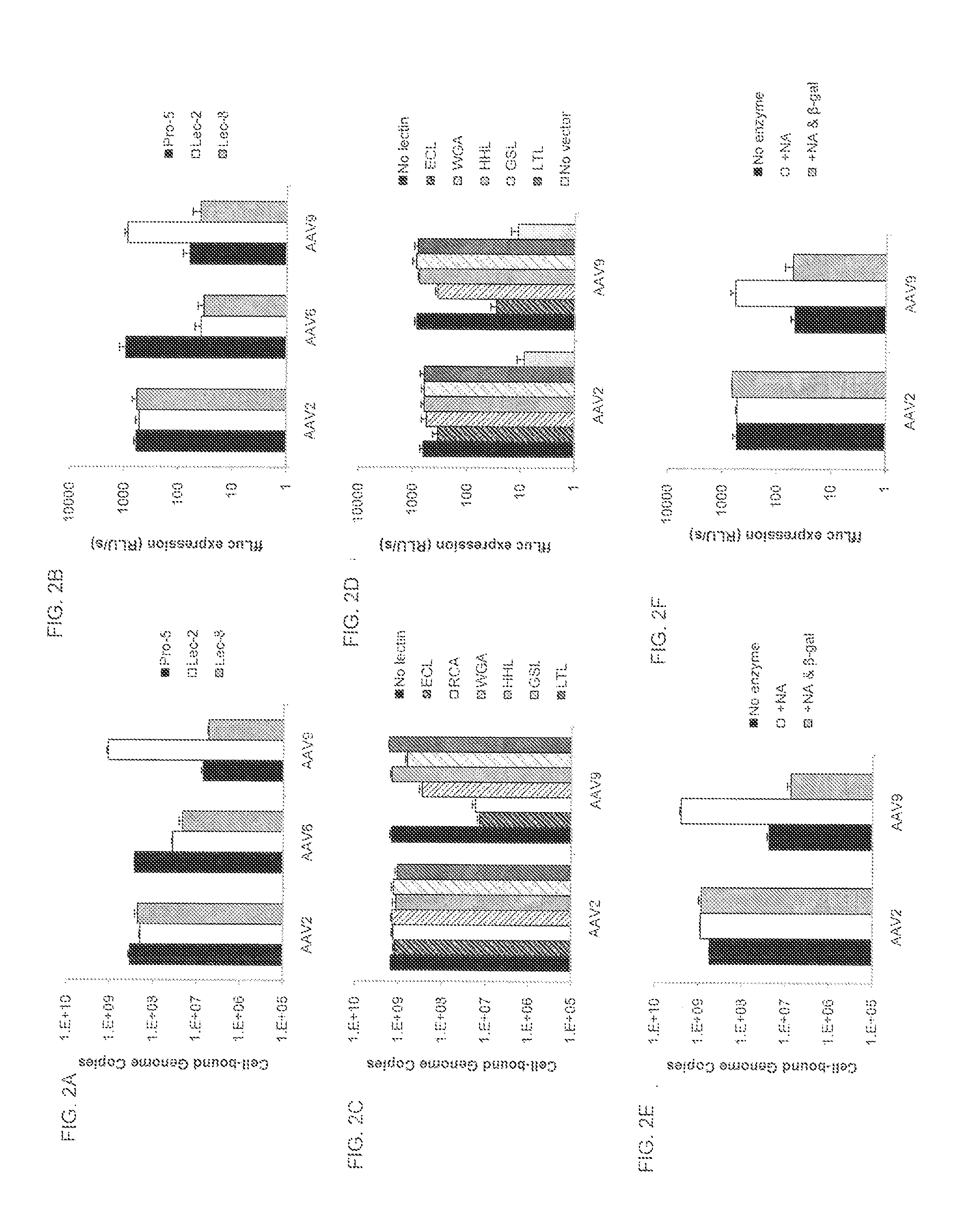Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
964 results about "Adeno-associated virus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a small virus that infects humans and some other primate species. AAV is not currently known to cause disease. The virus causes a very mild immune response, lending further support to its apparent lack of pathogenicity. In many cases, AAV vectors integrate into the host cell genome, which can be important for certain applications, but can also have unwanted consequences. Gene therapy vectors using AAV can infect both dividing and quiescent cells and persist in an extrachromosomal state without integrating into the genome of the host cell, although in the native virus some integration of virally carried genes into the host genome does occur. These features make AAV a very attractive candidate for creating viral vectors for gene therapy, and for the creation of isogenic human disease models. Recent human clinical trials using AAV for gene therapy in the retina have shown promise.
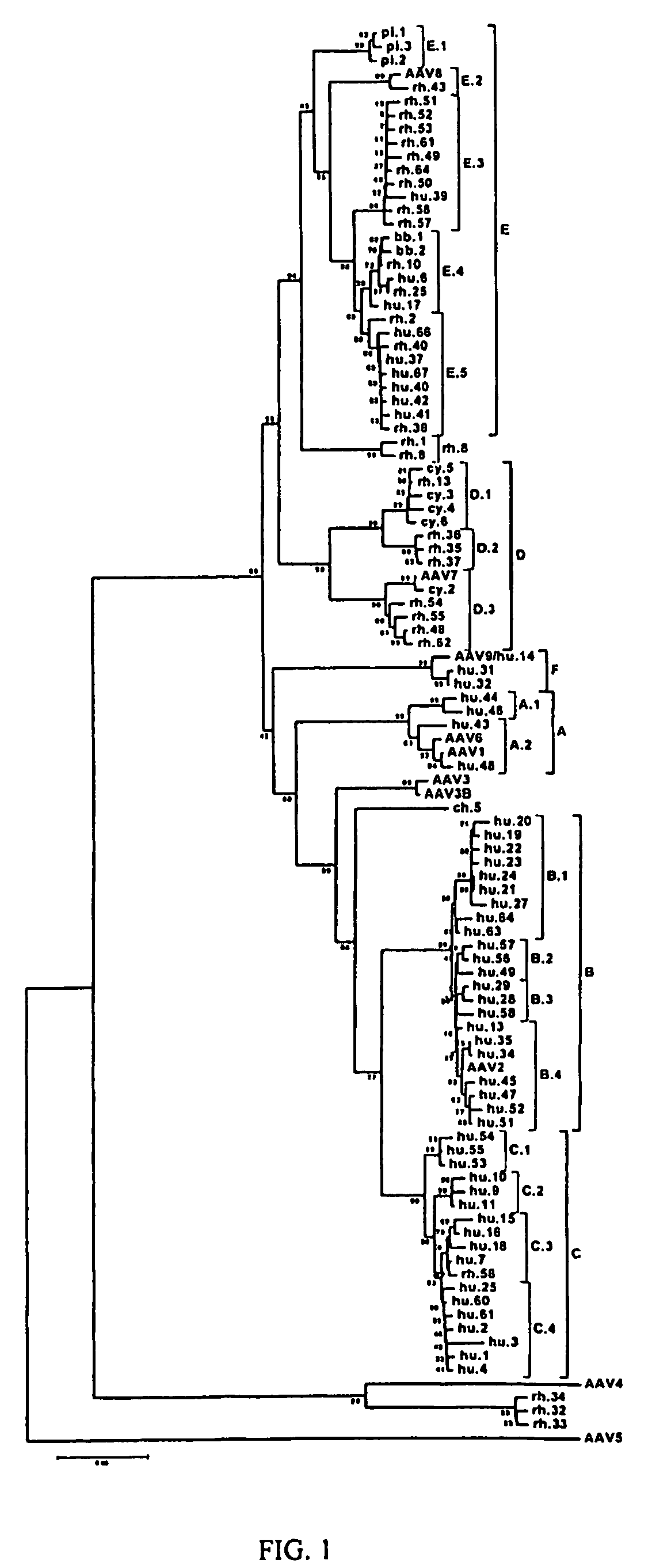
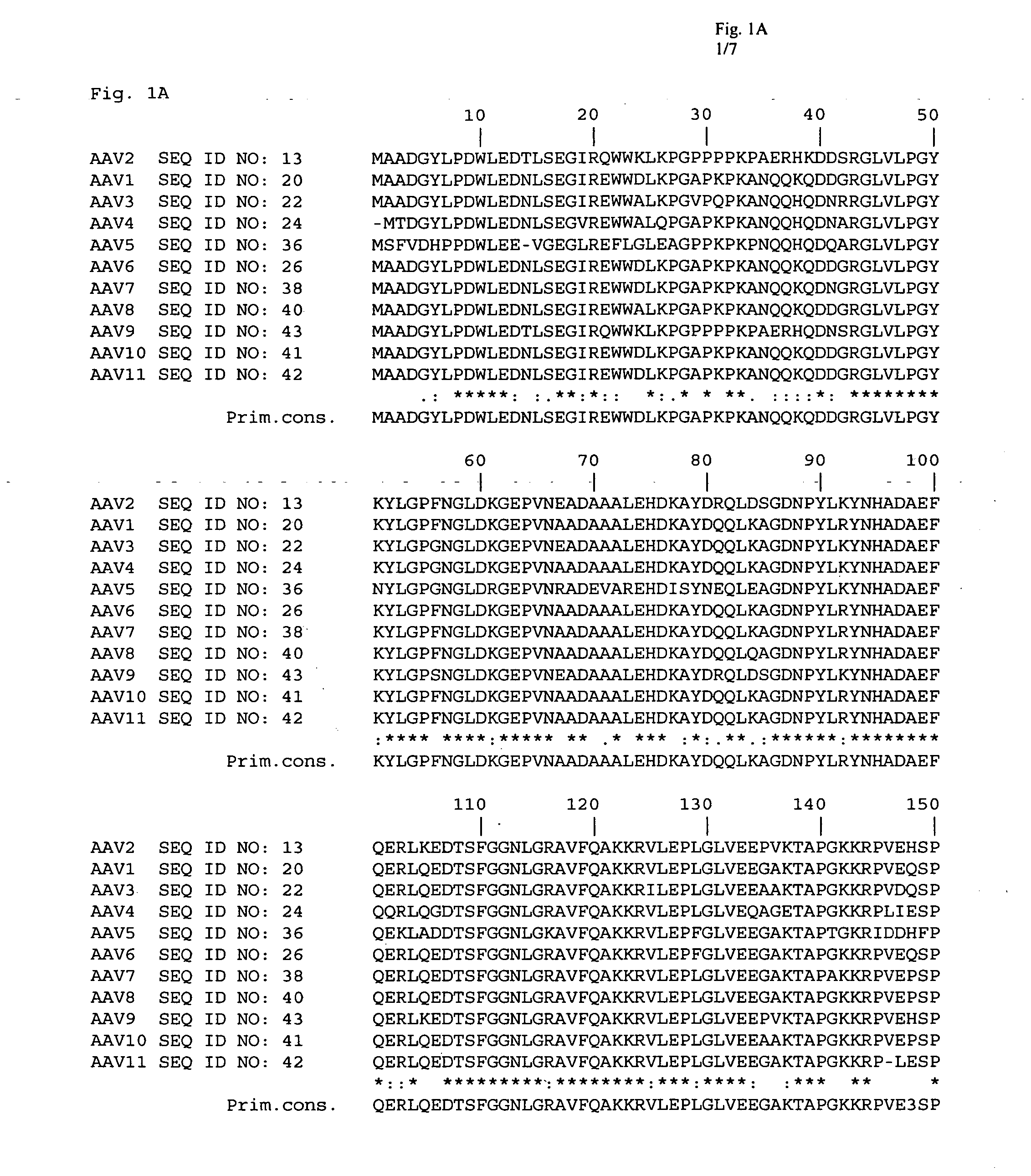
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
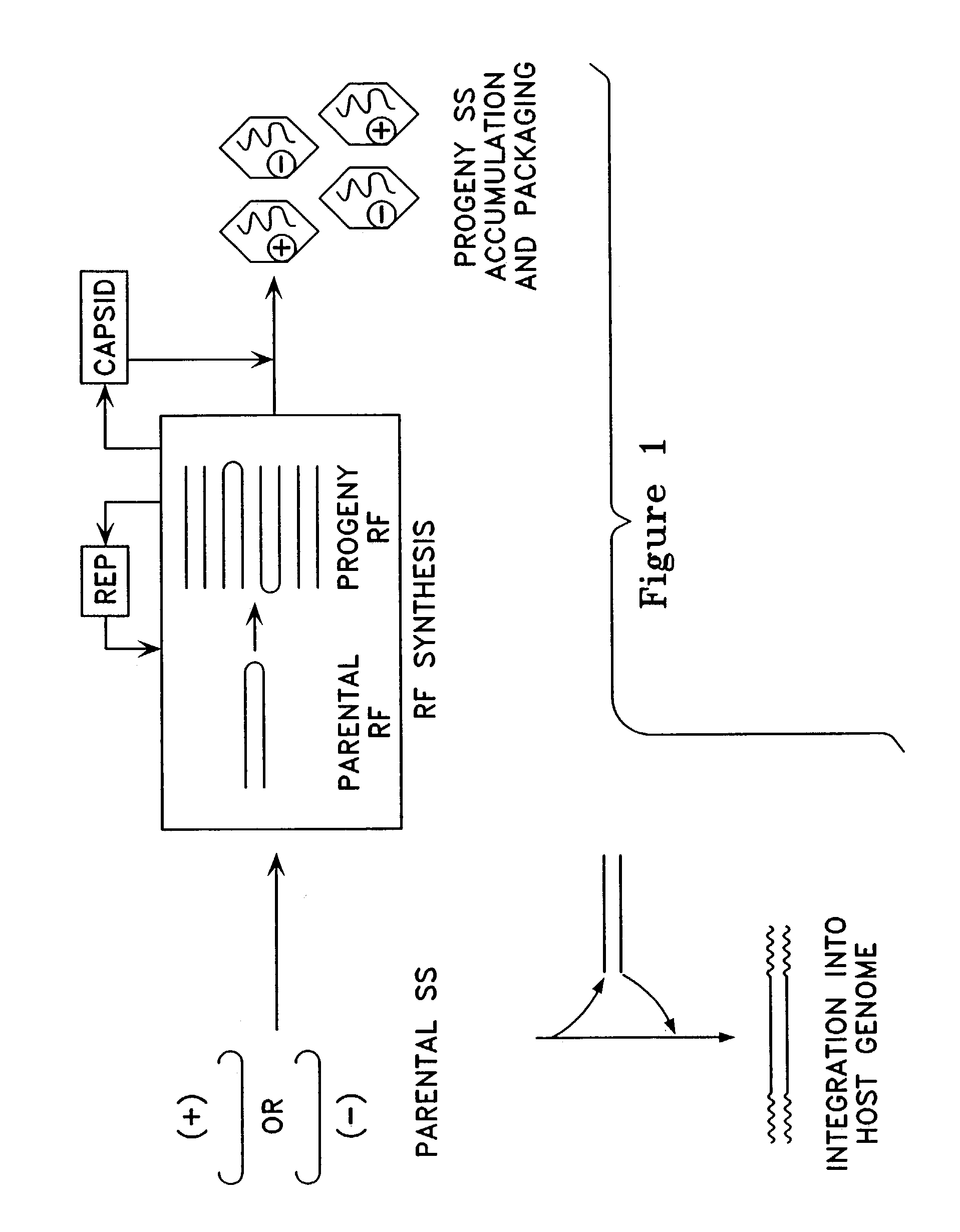
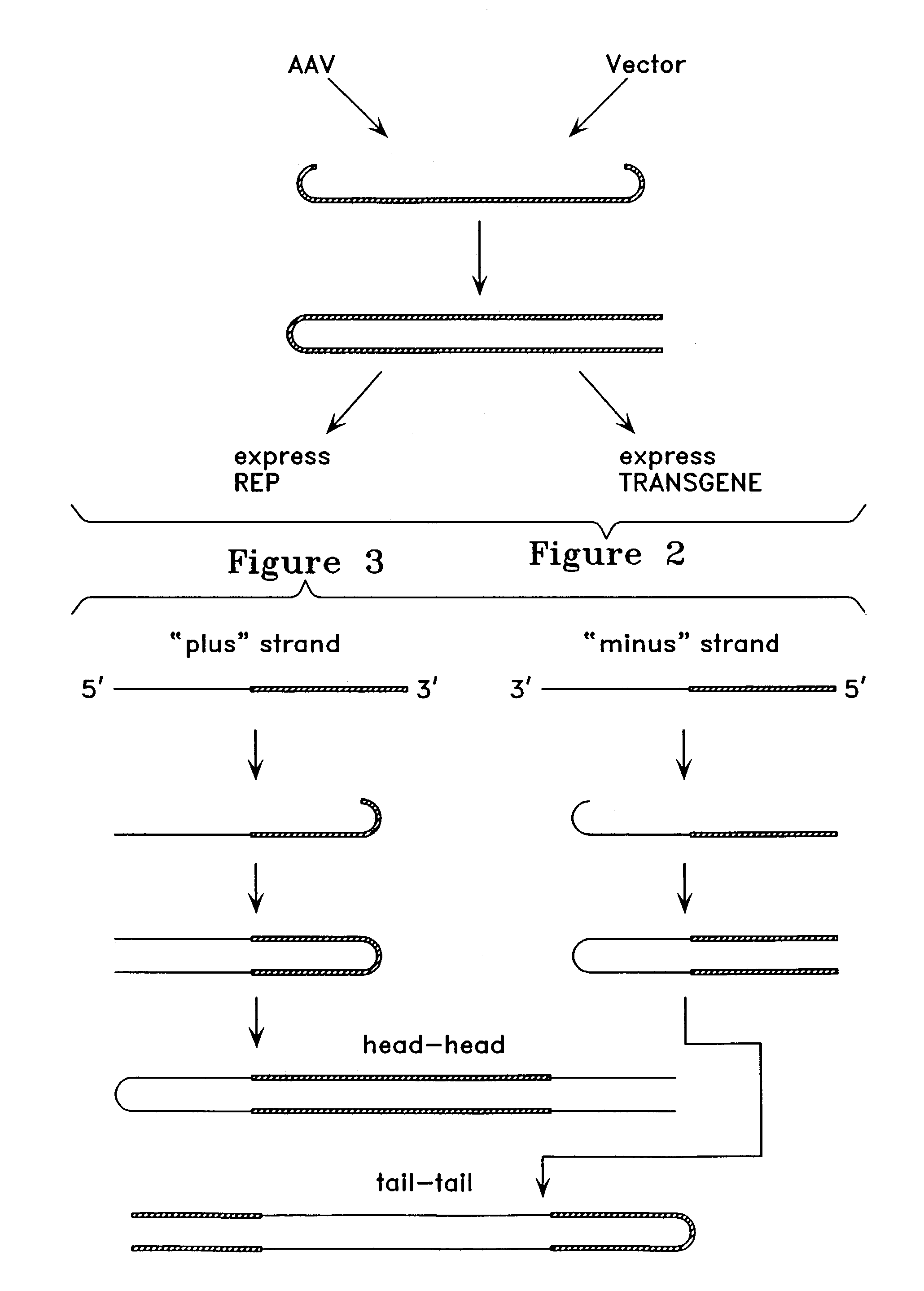
Metabolically activated recombinant viral vectors and methods for their preparation and use
Recombinant viral vectors, especially parvovirus vectors such as adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, capable of enhanced expression of heterologous sequences, and methods for their construction and use, are provided. The vectors have a structure, or are capable of rapidly adopting a structure, which involves intrastrand base pairing of at least one region in a heterologous sequence.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Adeno-associated virus (aav) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods and compounds for controlled release of recombinant parvovirus vectors
InactiveUS7201898B2Prevent relapseImproved pulmonary mechanicsSuture equipmentsAntibacterial agentsControlled releaseSupport matrix
The invention uses recombinant parvoviruses, and particularly recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) to deliver genes and DNA sequences for gene therapy following manipulation of the therapeutic virus for packaging and transport. The invention delivers therapeutic viral vectors via rAAV affixed to support matrixes (i.e., sutures, surgically implantable materials, grafts, and the like).
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL THE UNIV OF
RNA interference for the treatment of heart failure
InactiveUS8404658B2Reduce expressionDecreasing ventricular arrhythmiasOrganic active ingredientsTissue culturePhospholambanTransfection
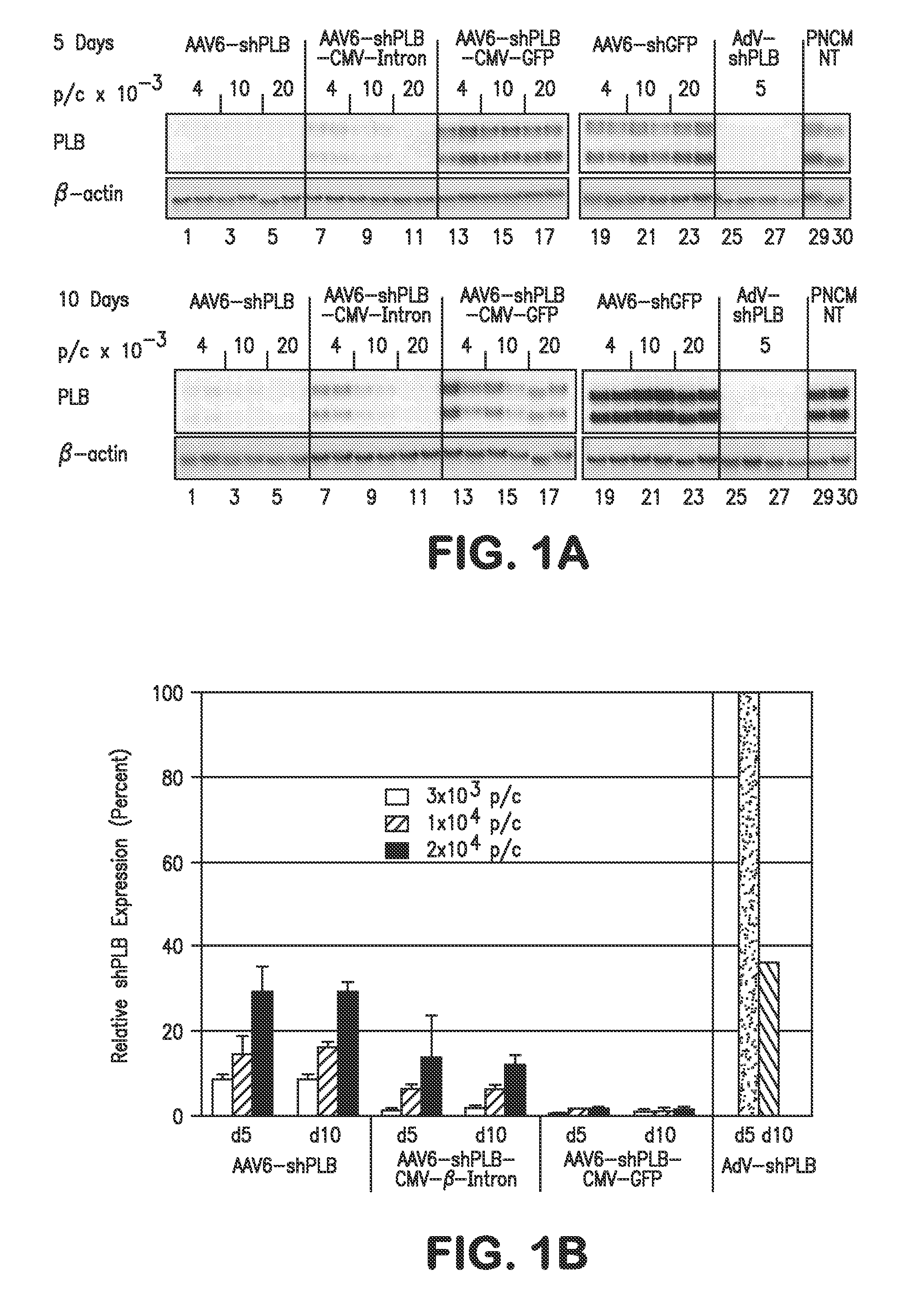
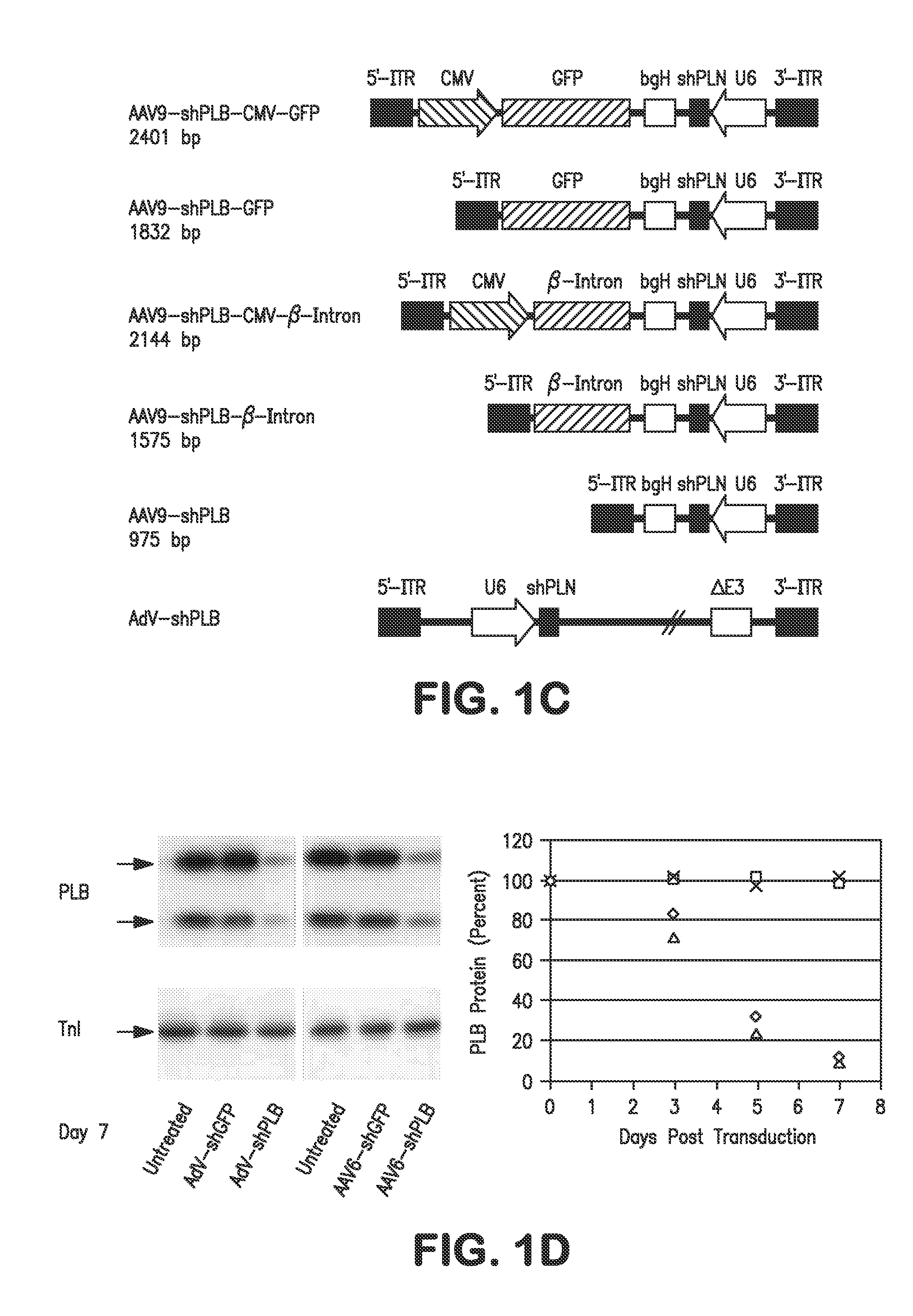
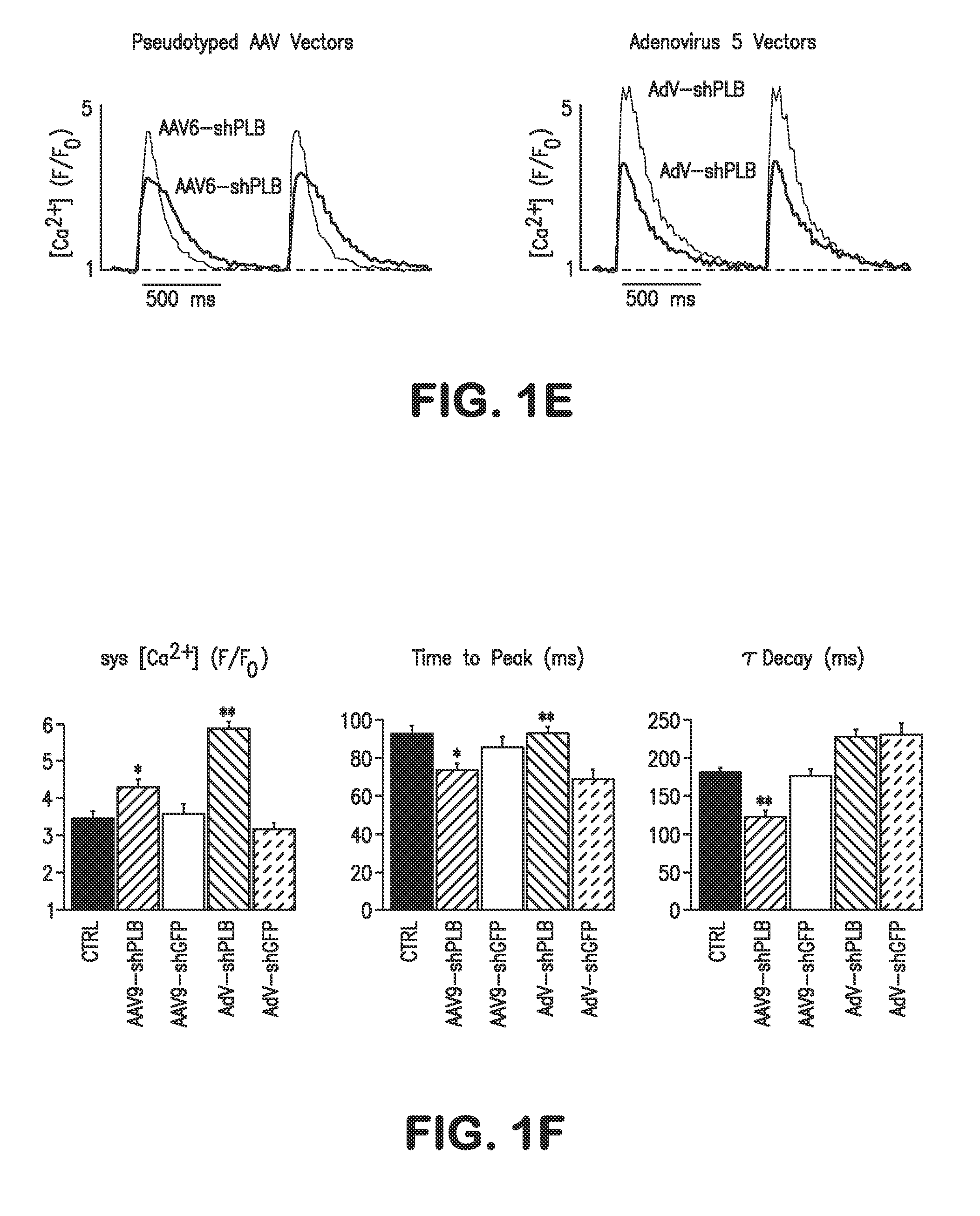
The present invention relates to targeted RNAi for the treatment of heart failure by modulating defective cardiac Ca2+ homeostasis via decreasing expression or activity of phospholamban (PLB) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) transfection of cardiomyocytes. Methods for decreasing ventricular arrhythmias, as well as methods for overall improvement of survival from heart failure in subjects are also disclosed. Further, the present invention provides methods which can be used to diagnose susceptibility to treatment by RNAi, and includes pharmaceutical compositions, kits and vectors including an RNAi sequence.
Owner:NANOCOR THERAPEUTICS +1
Adeno-associated virus vectors for expression of factor VIII by target cells
InactiveUS6200560B1Easily transfectedConvenient platformBiocideFactor VIIHigh level expressionHuman cell
The present invention provides improved viral vectors useful for the expression of genes at high levels in human cells. In particular, the present invention provides recombinant adeno-associated vectors (AAV) suitable for gene therapy. These vectors are capable of delivering nucleic acid containing constructs which result in the production of full-length therapeutic levels of biologically active Factor VIII in the recipient individual in vivo. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such AAV vectors, as well as methods for making and using these constructs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
AAV's and uses thereof
The invention in some aspects relates to recombinant adeno-associated viruses having distinct tissue targeting capabilities. In some aspects, the invention relates to gene transfer methods using the recombinant adeno-associate viruses. In some aspects, the invention relates to isolated AAV capsid proteins and isolated nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Production of pseudotyped recombinant AAV virions
InactiveUS7094604B2Highly purified and concentratedEfficient and large-scale productionVectorsSugar derivativesPurification methodsSerotype
Vectors that encode Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Rep and Cap proteins of different serotypes and Adenovirus transcription products that provide helper functions were used to produce pseudotyped recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions. Purification methods generated pseudotyped rAAV virion stocks that were 99% pure with titers of 1×1012–1×1013 vector genomes / ml.
Owner:UNIVIRSITY OF FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method of preparing recombinant adeno-associated virus compositions
InactiveUS6660514B1Reduce concentrationImprove yield and recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyBiochemistryAdeno-associated virus
Disclosed are methods for the isolation and purification of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) compositions. Also disclosed are methods for reducing or eliminating the concentration of helper adenovirus in rAAV samples. Methods are disclosed that provide highly-purified rAAV stocks having titers up to about 10<13 >particles / ml at particle-to-infectivity ratios of less than 100 in processes that are accomplished about 24 hours or less.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS6953690B1Efficient productionIncrease the number ofBiocideGenetic therapy composition manufactureMammalWild type
A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wild-type virus involves culturing a mammalian host cell containing a transgene flanked by adeno-associated virus (AAV) inverse terminal repeats and under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, an AAV rep sequence and an AAV cap sequence under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, and the minimum adenovirus DNA required to express an E1a gene product, an E1b gene product and an E2a gene product, and isolating therefrom a recombinant AAV which expresses the transgene in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wildtype AAV. This method obviates a subsequent purification step to purify rAAV from contaminating virus. Also provided are various embodiments of the host cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods and cell line useful for production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS7238526B2High yieldInduce expressionGenetically modified cellsGenetic material ingredientsPlasmid VectorAdeno associate virus
Methods for efficient production of recombinant AAV employ a host cell which comprising AAV rep and cap genes stably integrated within the cell's chromosomes, wherein the AAV rep and cap genes are each operatively linked to regulatory sequences capable of directing the expression of the rep and cap gene products upon infection of the cell with a helper virus, a helper gene, and a helper gene product. A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) involves infecting such a host cell with a helper virus, gene or gene product and infecting the infected host cell with a recombinant hybrid virus or plasmid vector containing adenovirus cis-elements necessary for replication and virion encapsidation, AAV sequences comprising the 5′ and 3′ ITRs of an AAV, and a selected gene operatively linked to regulatory sequences directing its expression, which is flanked by the above-mentioned AAV sequences.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
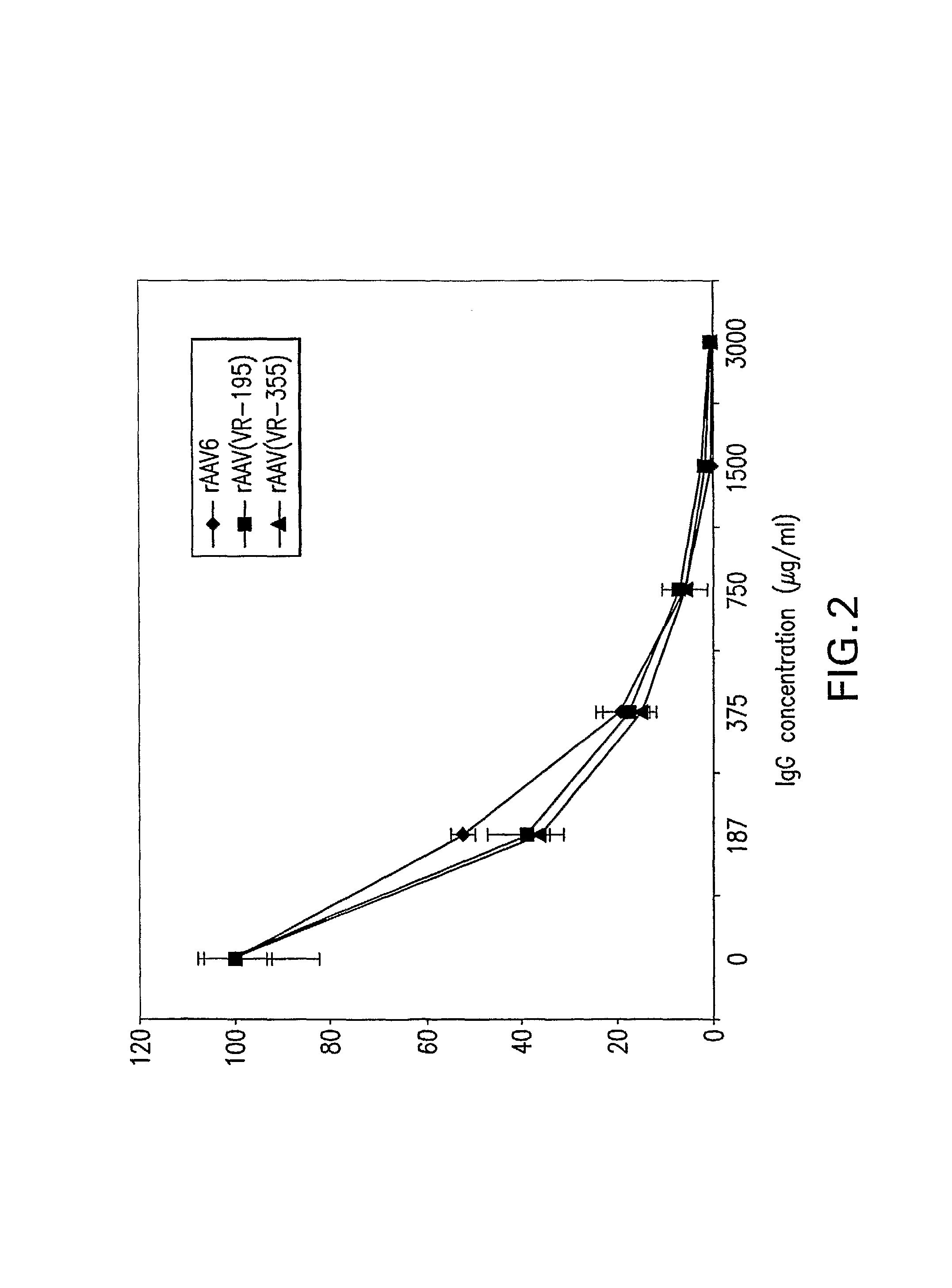
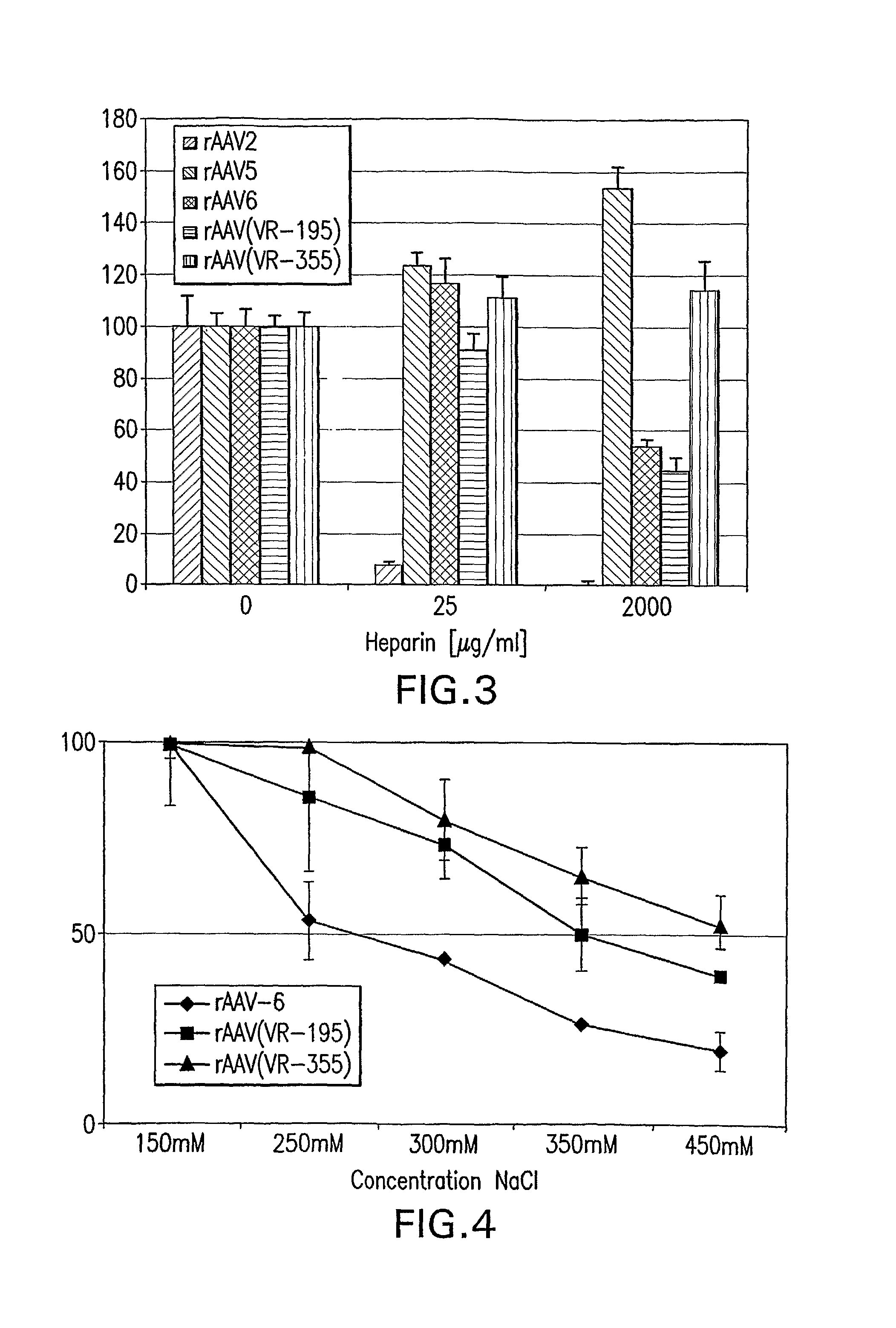
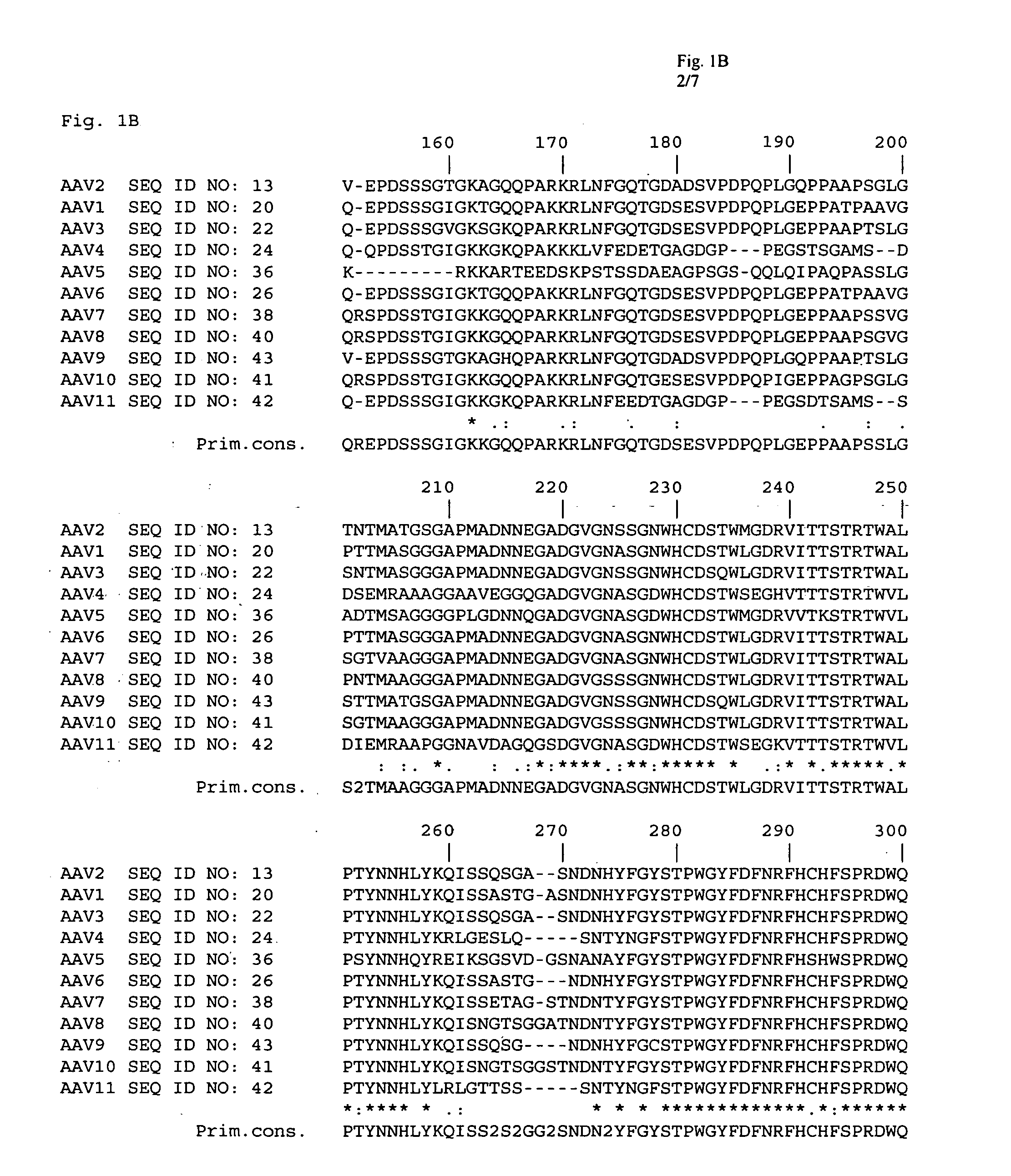
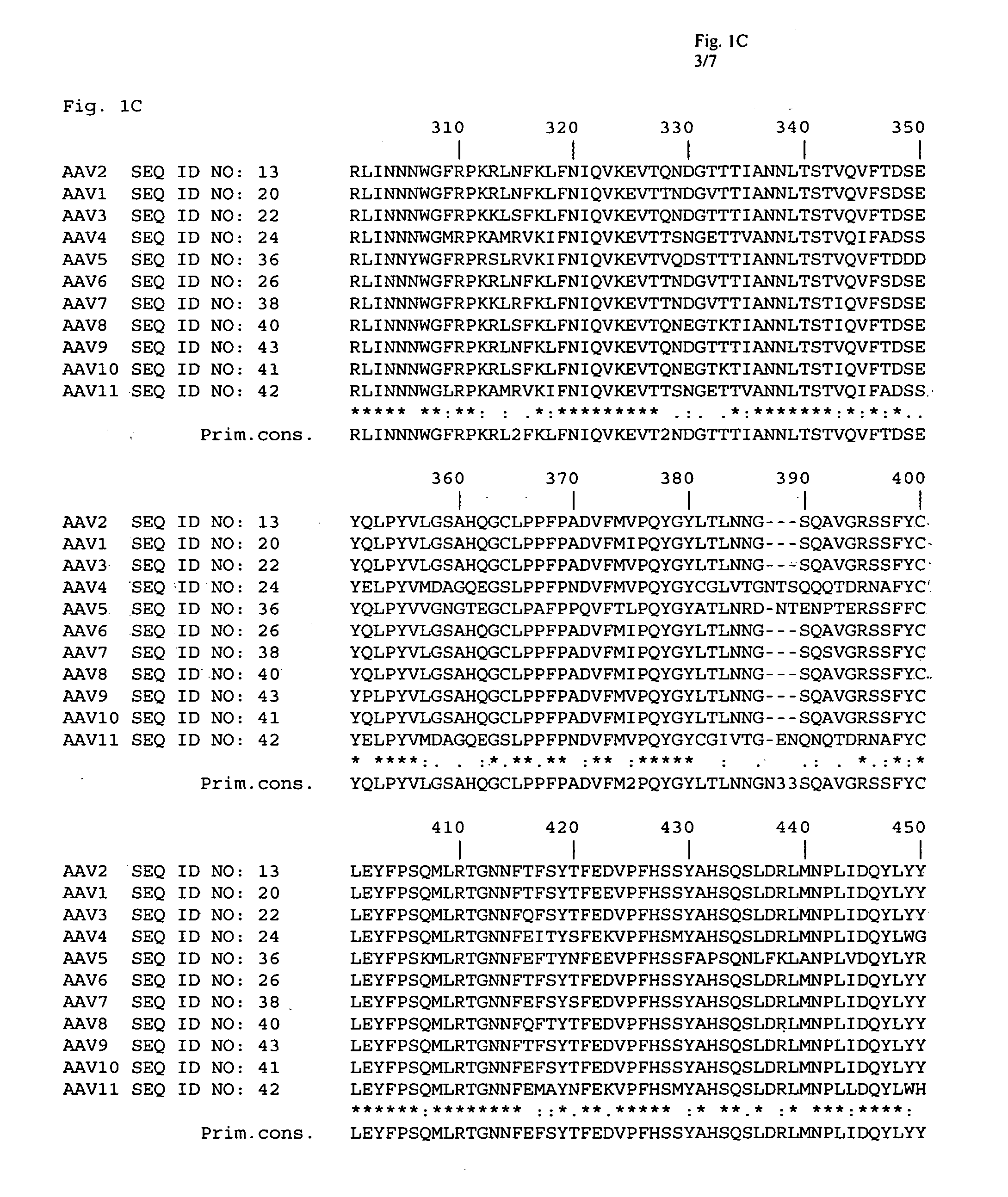
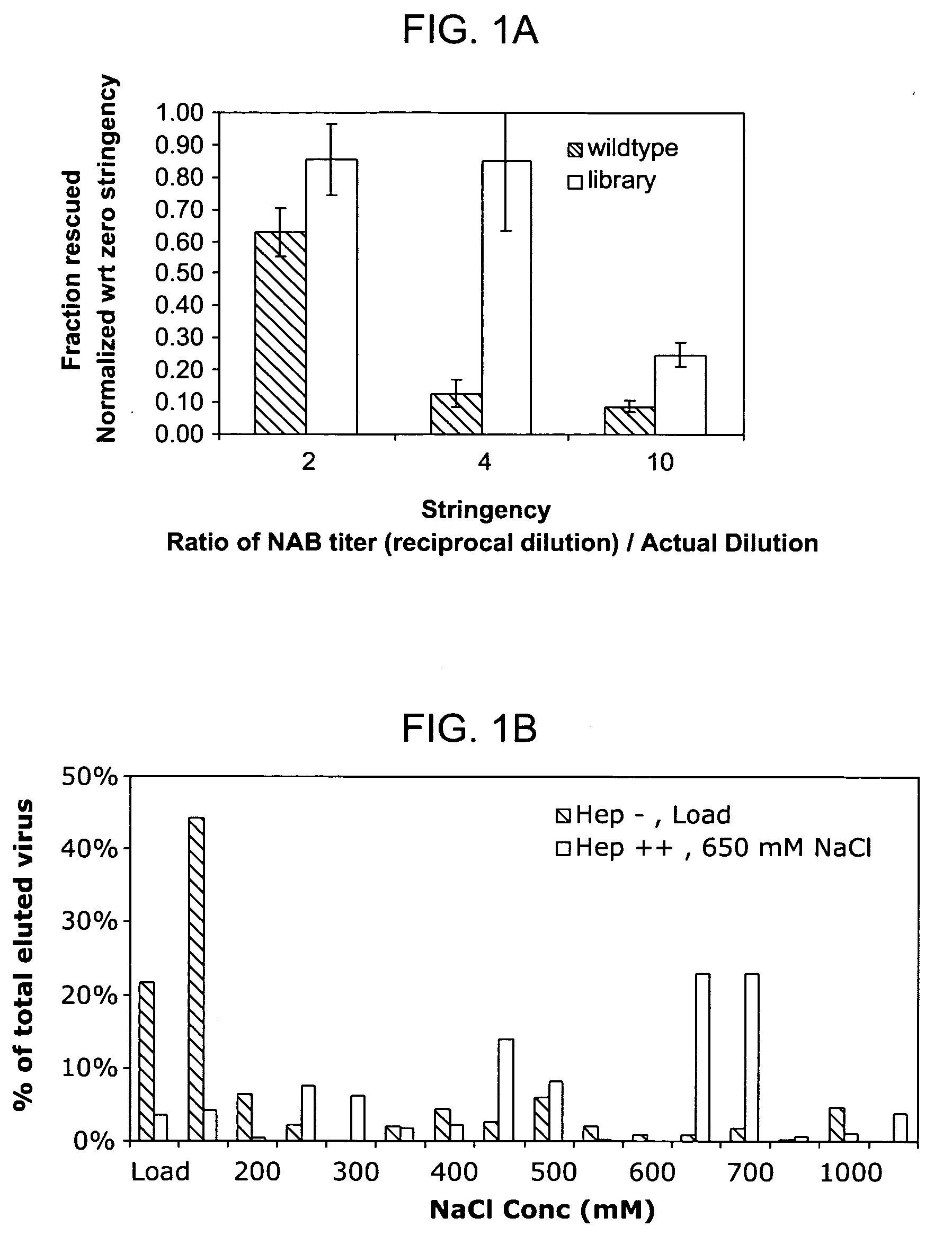
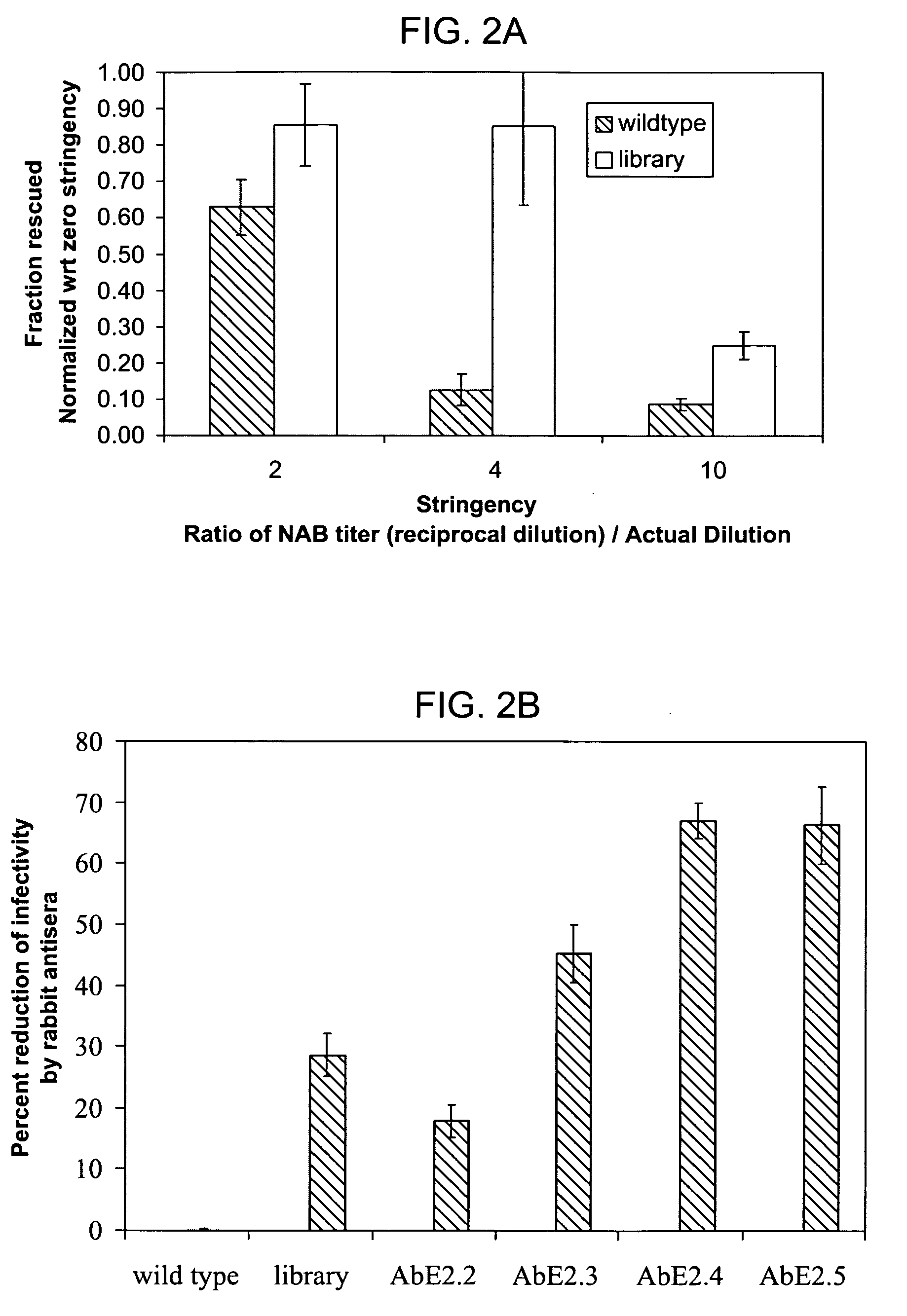
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20090202490A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCell type specificNeutralizing antibody
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
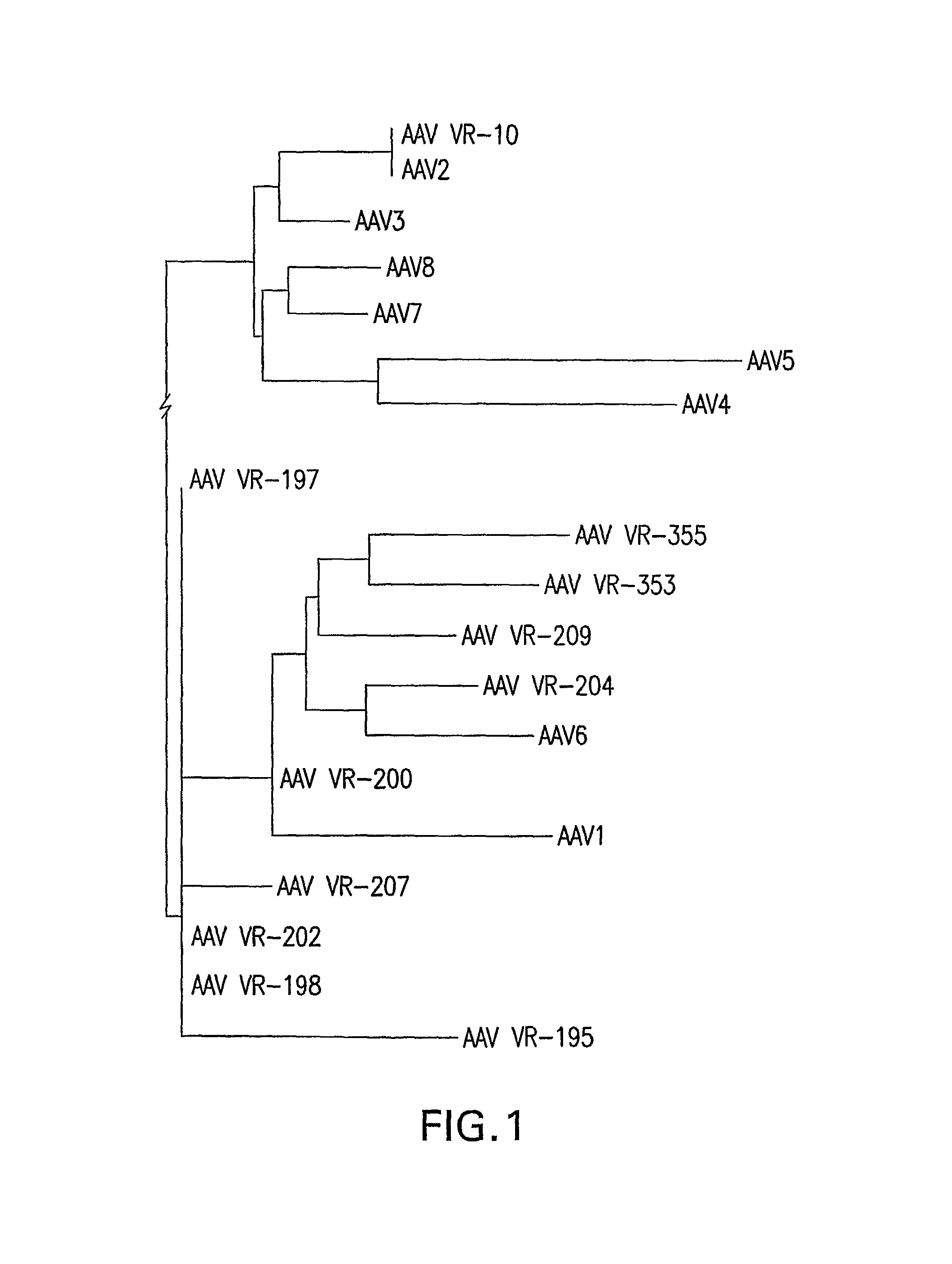
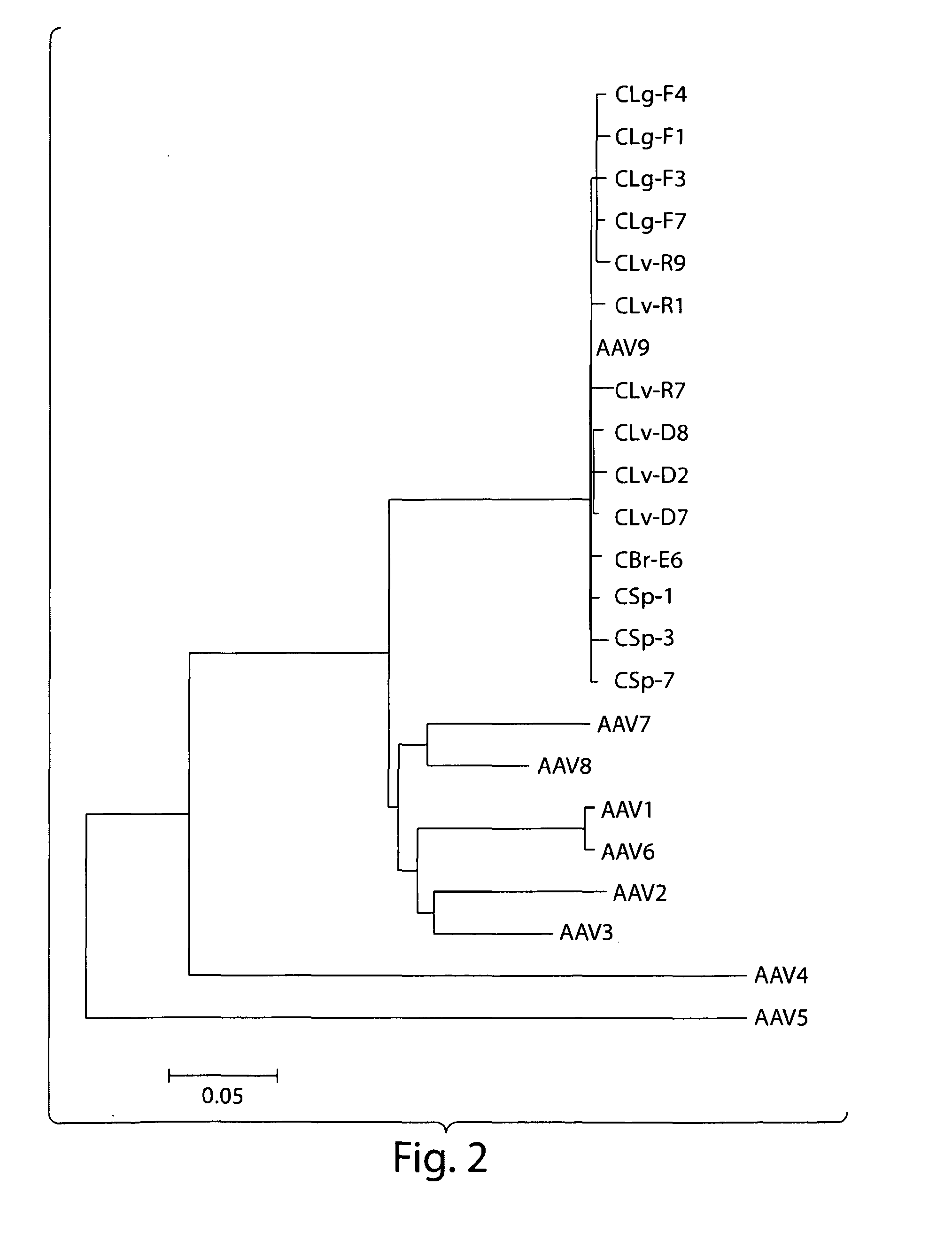
Isolation, cloning and characterization of new adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotypes
The present invention provides new adeno-associated virus (AAV) viruses and vectors, and particles derived therefrom. In addition, the present invention provides methods of delivering a nucleic acid to a cell using the AAV vectors and particles.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
AAV vectors and methods
InactiveUS20050287122A1Easy to adaptSuitable for mass productionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCapsidAdeno-associated virus
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL +1
Mutant adeno-associated virus virions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20050053922A1Reduce the binding forceAltered infectivityAntibacterial agentsVirusesReassortant VirusesNeutralizing antibody
The present invention provides mutant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that exhibit altered capsid properties, e.g., reduced binding to neutralizing antibodies in serum and / or altered heparin binding and / or altered infectivity of particular cell types. The present invention further provides libraries of mutant AAV comprising one or more mutations in a capsid gene. The present invention further provides methods of generating the mutant AAV and mutant AAV libraries, and compositions comprising the mutant AAV. The present invention further provides recombinant AAV (rAAV) virions that comprise a mutant capsid protein. The present invention further provides nucleic acids comprising nucleotide sequences that encode mutant capsid proteins, and host cells comprising the nucleic acids. The present invention further provides methods of delivering a gene product to an individual, the methods generally involving administering an effective amount of a subject rAAV virion to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE GENE THERAPEUTICS +1
AAV2 vectors and methods
InactiveUS6962815B2Easy to adaptSuitable for mass productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsViral vectorCapsid
Owner:NATIONWIDE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
AAV vectors produced in insect cells
ActiveUS8163543B2Improve stabilityReduced expression levelAnimal cellsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideViral vector
The present invention relates to the production of adeno-associated viral vectors in insect cells. The insect cells therefore comprise a first nucleotide sequence encoding the adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsid proteins, whereby the initiation codon for translation of the AAV VP1 capsid protein is a non-ATG, suboptimal initiation codon. The insect cell further comprises a second nucleotide sequence comprising at least one AAV inverted terminal repeat (ITR) nucleotide sequence; a third nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep52 or a Rep40 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell; and, a fourth nucleotide sequence comprising a Rep78 or a Rep68 coding sequence operably linked to expression control sequences for expression in an insect cell. The invention further relates to adeno-associated viral vectors with an altered ratio of the viral capsid proteins that provides improved infectivity of the viral particles.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Efficient and stable in vivo gene transfer to cardiomyocytes using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS7078387B1The process is stable and efficientBiocideSugar derivativesCoronary sinusAdeno associate virus
This invention relates to the use of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors to transduce cardiomyocytes in vivo by infusing the rAAV into a coronary artery or coronary sinus. rAAV infection is not associated with detectable myocardial inflammation or myocyte necrosis. Thus, rAAV is a useful vector for the stable expression of therapeutic genes in the myocardium and can be used to deliver genes for inducing angiogenesis, inhibiting angiogenesis, stimulating cell proliferation, inhibiting cell proliferation and / or treating or ameliorating other cardiovascular conditions.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
Adeno-associated virus serotype 1 nucleic acid sequences, vectors and host cells containing same
The nucleic acid sequences of adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 1 are provided, as are vectors and host cells containing these sequences and functional fragments thereof. Also provided are methods of delivering genes via AAV-1 derived vectors.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
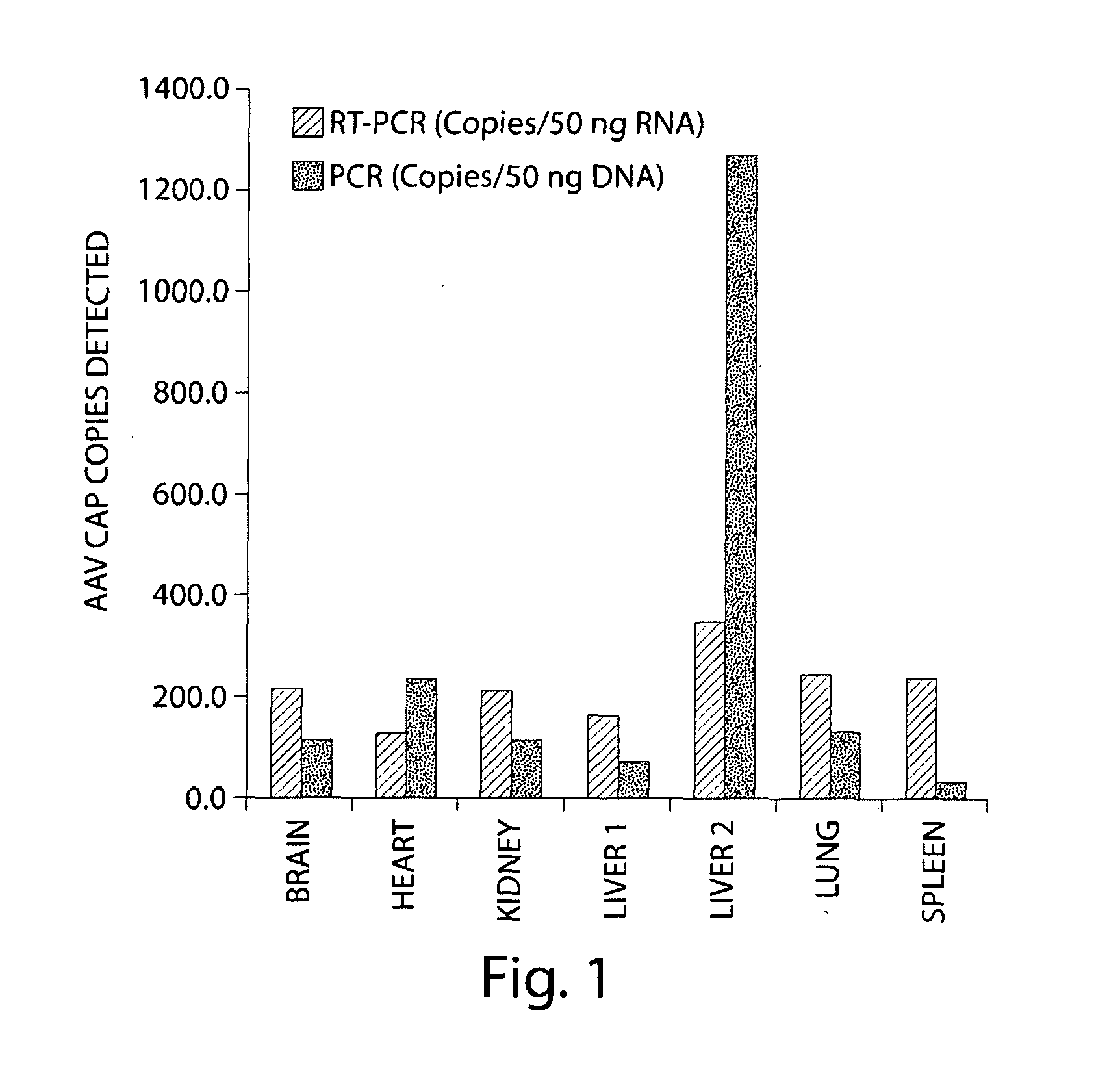
Compositions and Methods for Altering Tissue Specificity and Improving AAV9-Mediated Gene Transfer
ActiveUS20130323226A1Improve efficiencyImprove usabilityOrganic active ingredientsVectorsViral vectorFhit gene
A method of altering the targeting and / or cellular uptake efficiency of an adeno-associated virus (AAV) viral vector having a capsid containing an AAV9 cell surface binding domain is described. The method involves modifying a clade F cell surface receptor which comprises a glycan having a terminal sialic acid residue and a penultimate β-galactose residue. The modification may involve retargeting the vector by temporarily functionally ablate AAV9 binding in a subset of cells, thereby redirecting the vector to another subset of cells. Alternatively, the modification may involve increasing cellular update efficiency by treating the cells with a neuraminidase to expose cell surface β-galactose. Also provided are compositions containing the AAV9 vector and a neuraminidase. Also provided is a method for purifying AAV9 using β-galactose linked to solid support. Also provided are mutant vectors which have been modified to alter their targeting specificity, including mutant AAV9 in which the galactose binding domain is mutated and AAV in which an AAV9 galactose binding domain is engineered.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
AAV5 vector and uses thereof
The present invention provides an adeno-associated virus 5 (AAV5) virus and vectors and particles derived therefrom. In addition, the present invention provides methods of delivering a nucleic acid to a cell using the AAV5 vectors and particles.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Methods of treating Parkinson's disease using recombinant adeno-associated virus virions
ActiveUS7588757B2Reduce deliveryIncrease in fine motor taskingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryDisease
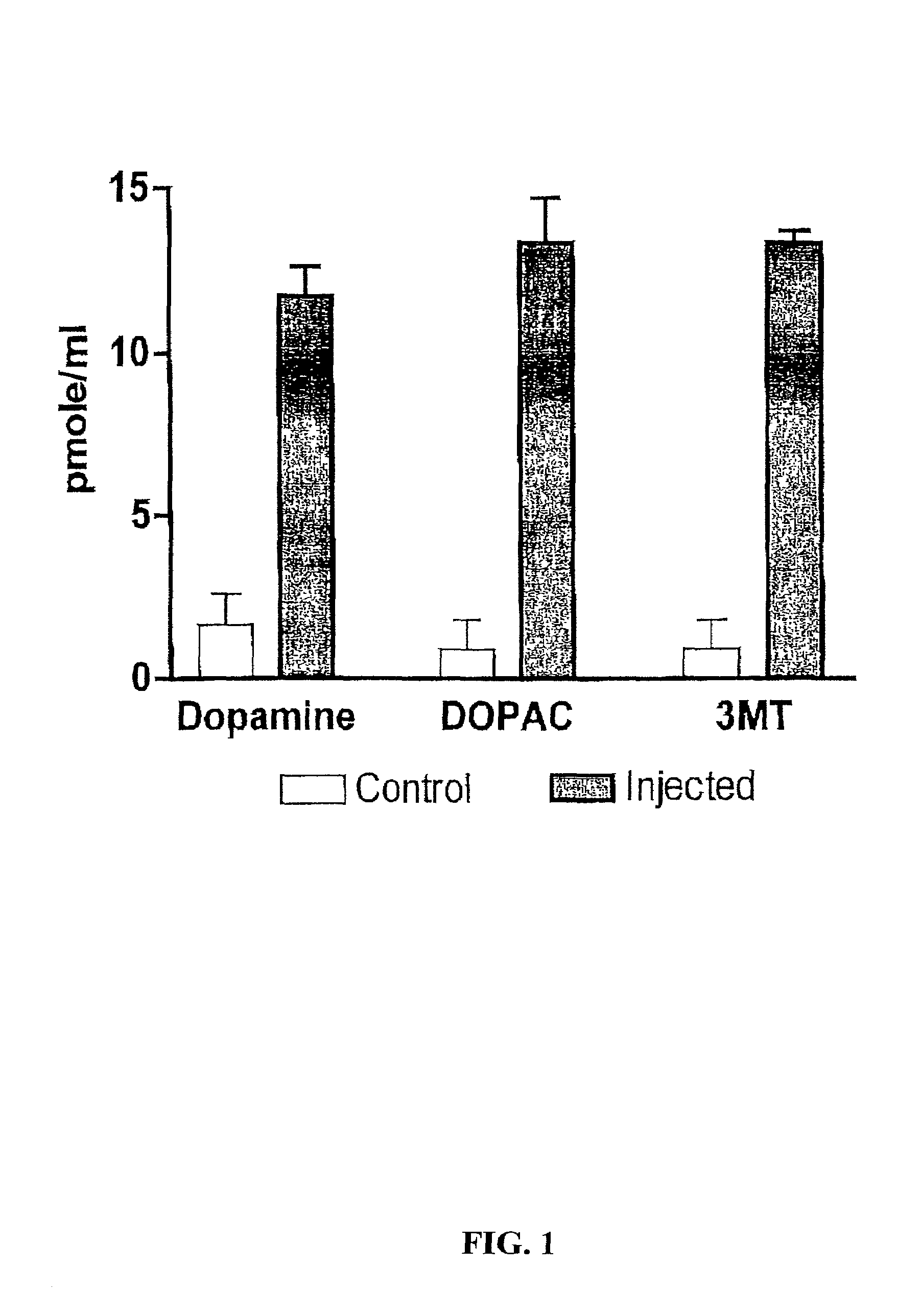
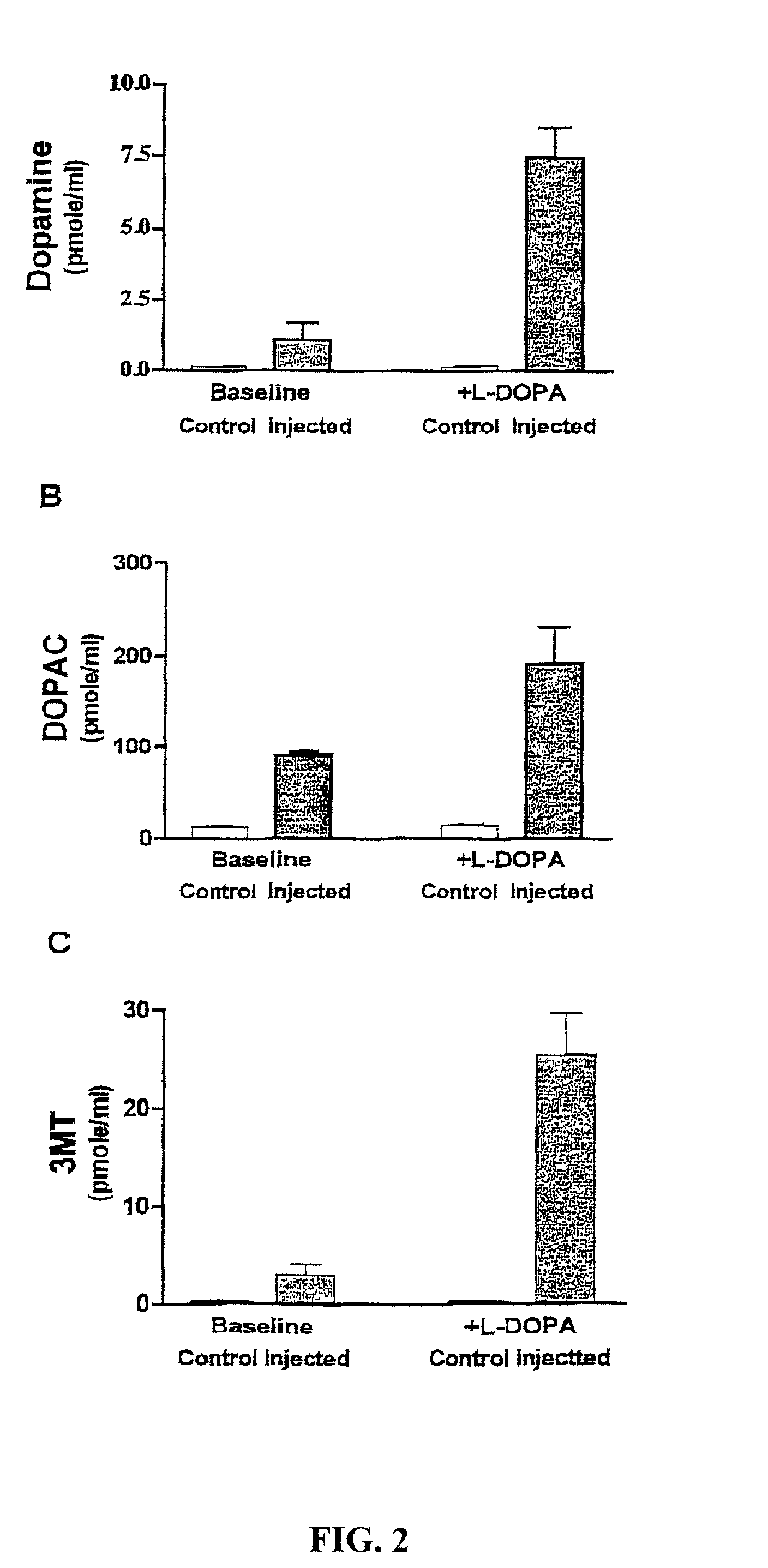
Methods for treating Parkinson's disease (PD) are provided. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virions are used to deliver genes encoding dopamine-synthesizing enzymes to the central nervous system of a primate. Once delivered, the genes are expressed, which then results in dopamine synthesis and amelioration in the clinical signs and symptoms of PD. The methods of the present invention can be used to deliver the three central dopamine synthesizing enzymes: tyrosine hydroxylase, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, and guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I thereby enhancing dopamine biosynthesis and providing for enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Novel aav's and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120137379A1Determining effectOrganic active ingredientsVirusesTissue targetingAdeno associate virus
The invention in some aspects relates to recombinant adeno-associated viruses having distinct tissue targeting capabilities. In some aspects, the invention relates to gene transfer methods using the recombinant adeno-associate viruses. In some aspects, the invention relates to isolated AAV capsid proteins and isolated nucleic acids encoding the same.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
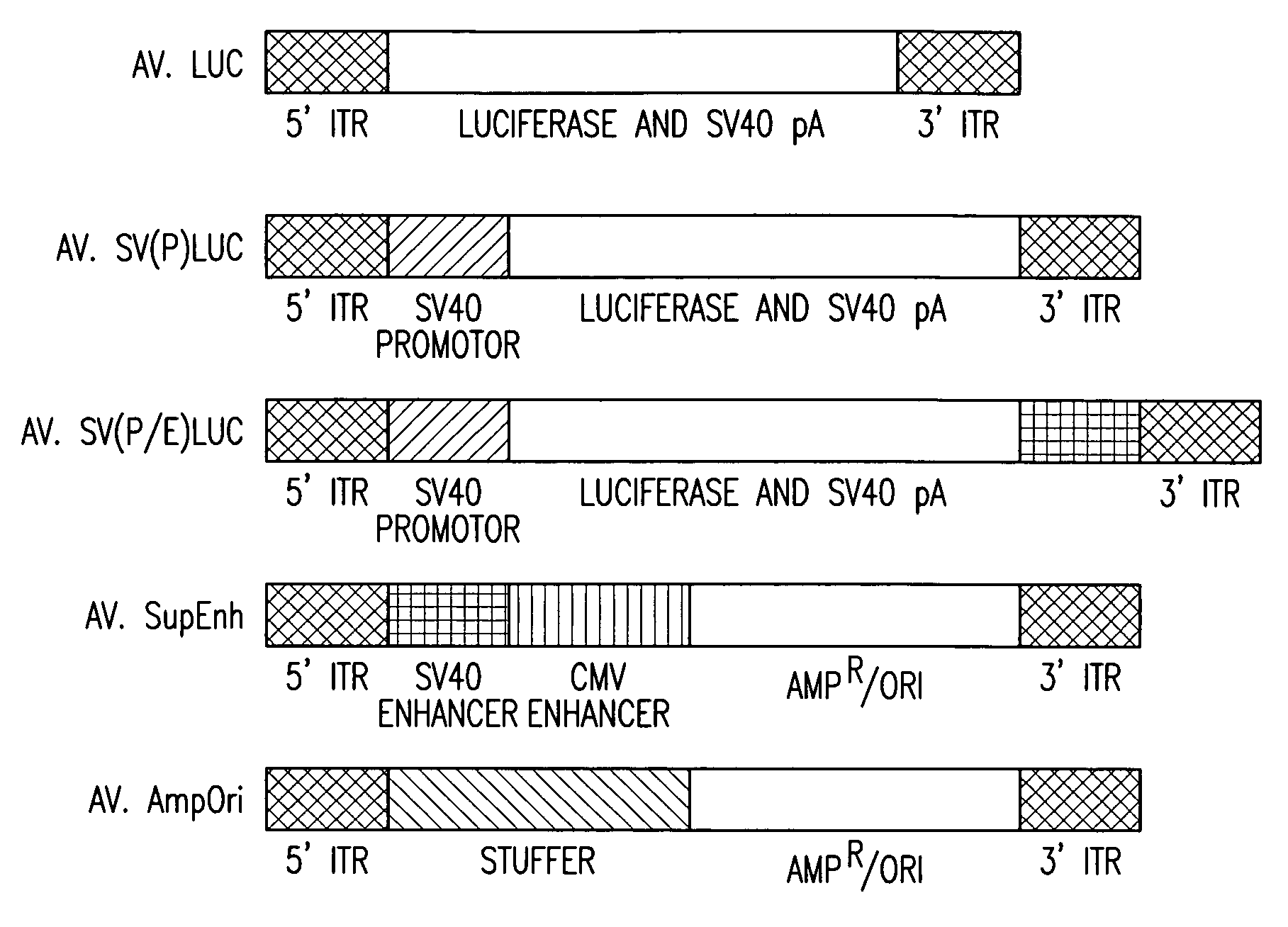
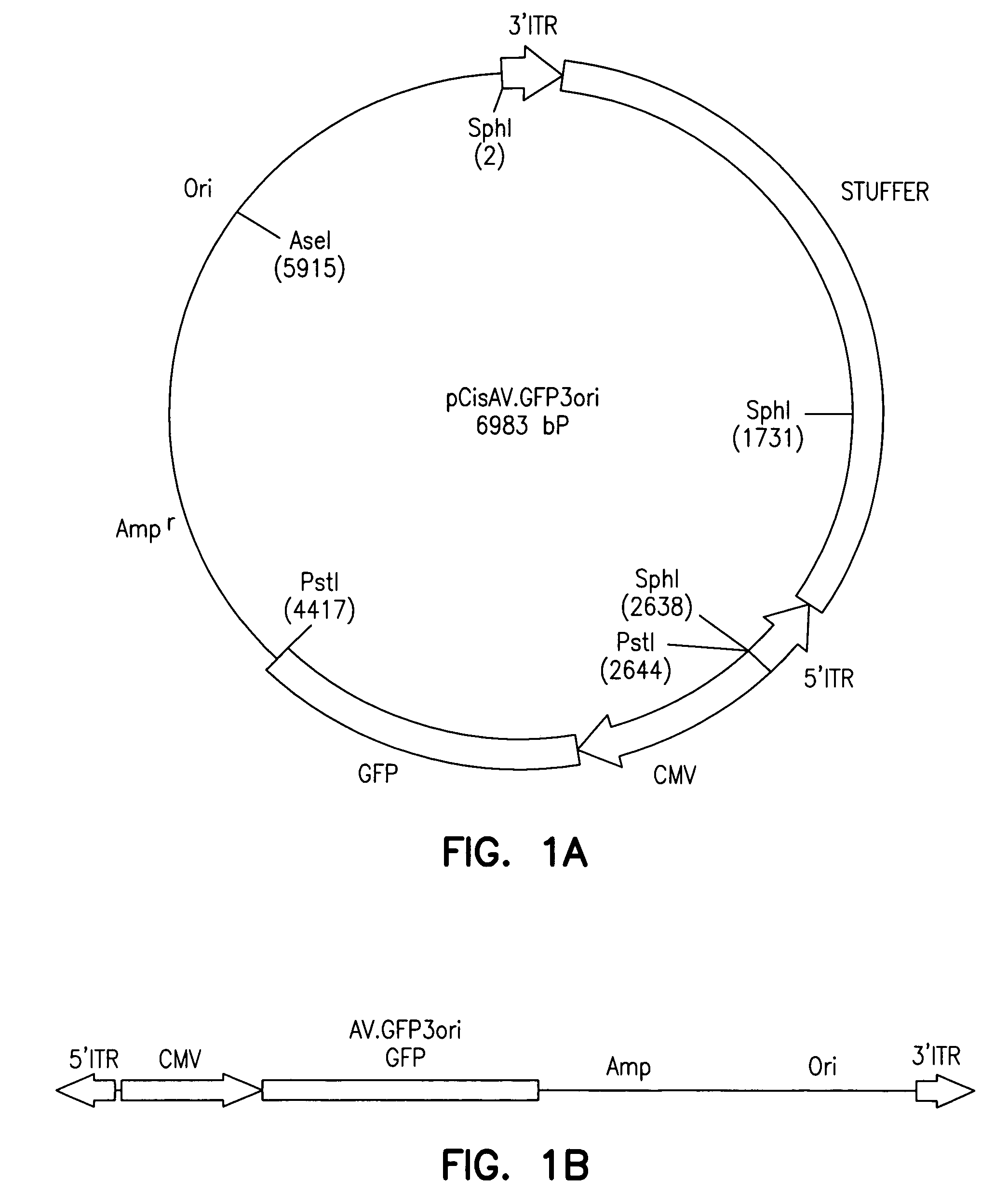
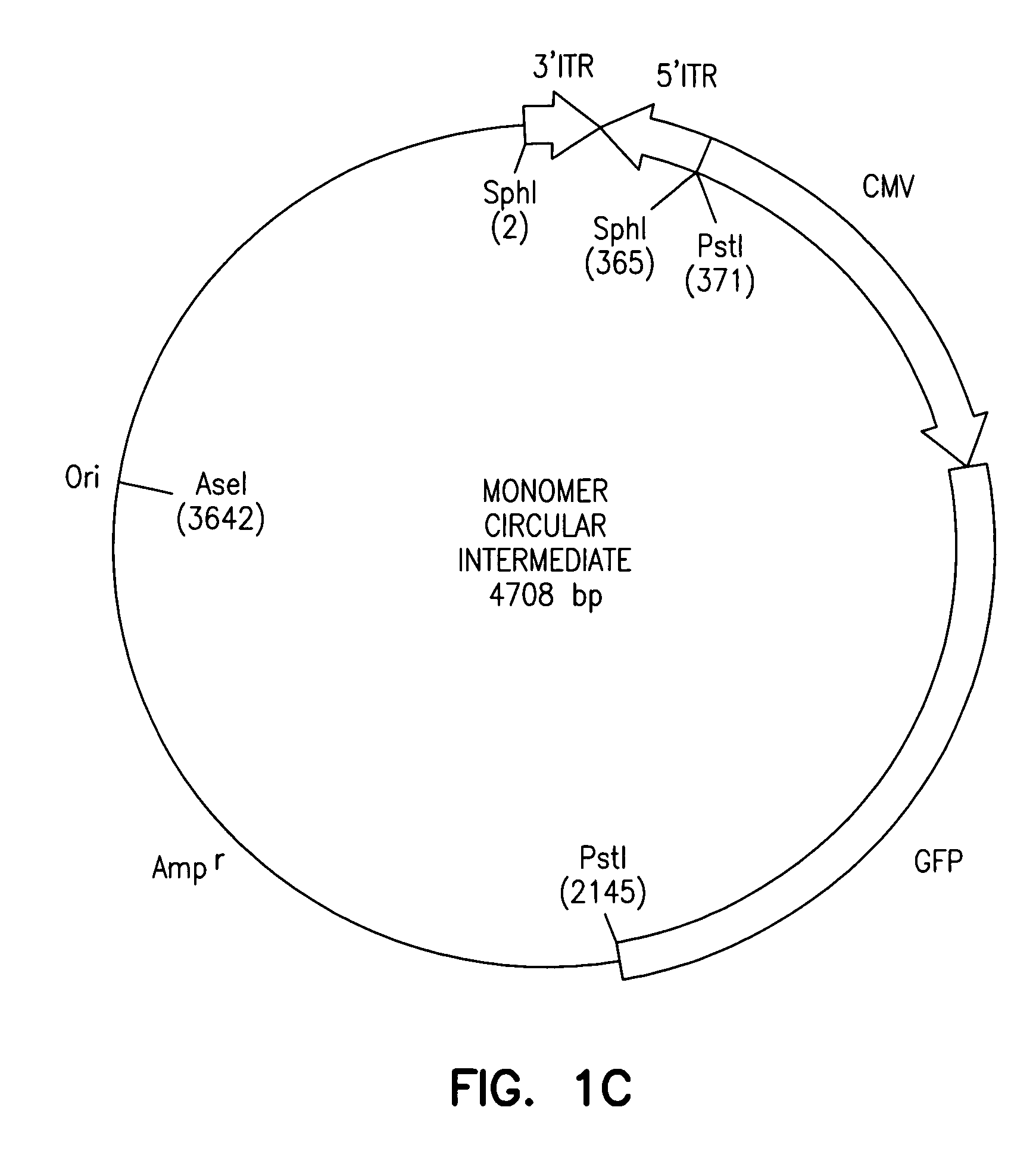
Adeno-associated virus vectors
InactiveUS6897045B2Improve stabilityIncreased episomal stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideVirusAdeno-associated virus
The invention provides an isolated and purified DNA molecule comprising at least one DNA segment, a biologically active subunit or variant thereof, of a circular intermediate of adeno-associated virus, which DNA segment confers increased episomal stability, persistence or abundance of the isolated DNA molecule in a host cell. The invention also provides a composition comprising at least two adeno-associated virus vectors.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Delivery of proteins using adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors
ActiveUS20120232133A1Reduce the risk of infectionAvoid virus infectionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAdeno-associated virusVirology
Disclosed herein are compositions, systems and methods for delivery of proteins of interest using adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Adeno-Associated Virus Virion for Gene Transfer to Nervous System Cells
ActiveUS20130224836A1Improve efficiencyLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderSpecial deliveryNervous systemAdeno associate virus
The present invention provides a means for transferring a therapeutic gene of interest into a nervous system cell by a highly-efficient and simpler means. More specifically, the present invention provides a recombinant vector that uses an adeno-associated virus (AAV), a method for manufacturing the recombinant vector, and a method for using the recombinant vector. More specifically, recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, which are capable of passing through the brain-brain barrier, for transferring a therapeutic genes of interest into a nervous system cell in a highly-efficient manner, a drug composition containing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, a method for manufacturing the recombinant adeno-associated virus virions, and a kit or the like are provided.
Owner:JICHI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Isolation Of Novel AAV'S And Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20100186103A1Determine effectAvoid time-consume and costly processVectorsSpecial deliveryAdeno associate virusBinding site
The invention in some aspects relates to isolated nucleic acids, compositions, and kits useful for identifying adeno-associated viruses in cells. In some aspects, the invention provides kits and methods for producing somatic transgenic animal models using recombinant AAV (rAAV) to an animal having at least one transgene that expresses a small interfering nucleic acid or at least one binding site for a miRNA.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) clades, sequences, vectors containing same, and uses therefor
Sequences of novel adeno-associated virus capsids and vectors and host cells containing these sequences are provided. Also described are methods of using such host cells and vectors in production of rAAV particles. AAV-mediated delivery of therapeutic and immunogenic genes using the vectors of the invention is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Adeno-associated virus vectors and uses thereof
InactiveUS7241447B1Improve stabilityIncreased episomal stabilityBiocideViral antigen ingredientsAdeno associate virusAdeno-associated virus
The invention provides an isolated and purified DNA molecule comprising at least one DNA segment, a biologically active subunit or variant thereof, of a circular intermediate of adeno-associated virus, which DNA segment confers increased episomal stability, persistence or abundance of the isolated DNA molecule in a host cell. The invention also provides a composition comprising at least two adeno-associated virus vectors.
Owner:RES FOUND UNIV OF IOWA
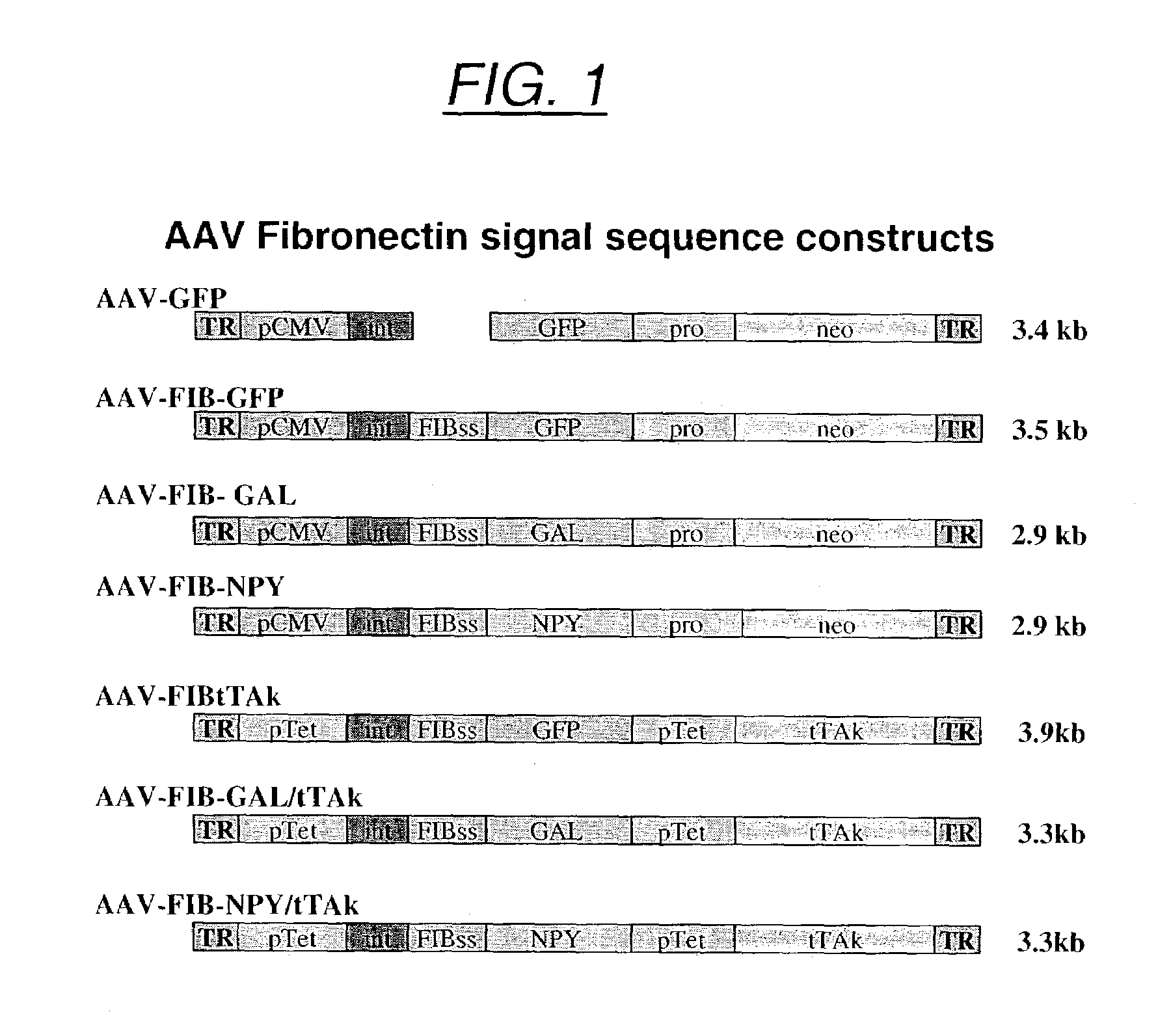
Secretion signal vectors
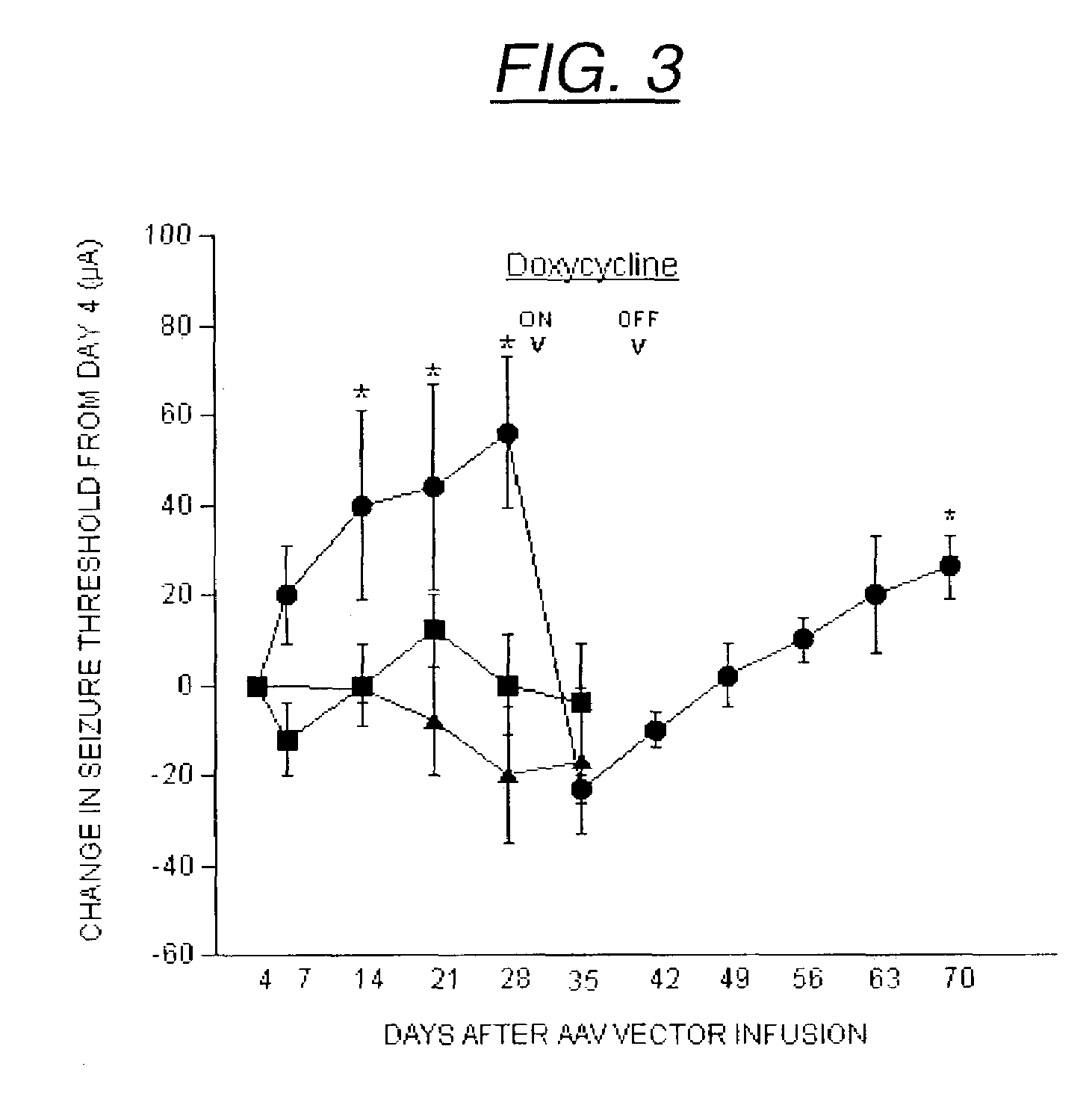
InactiveUS7071172B2Minimize potential deleterious side effectAttenuate seizure activityBiocideAnimal repellantsHeterologousAdeno associate virus
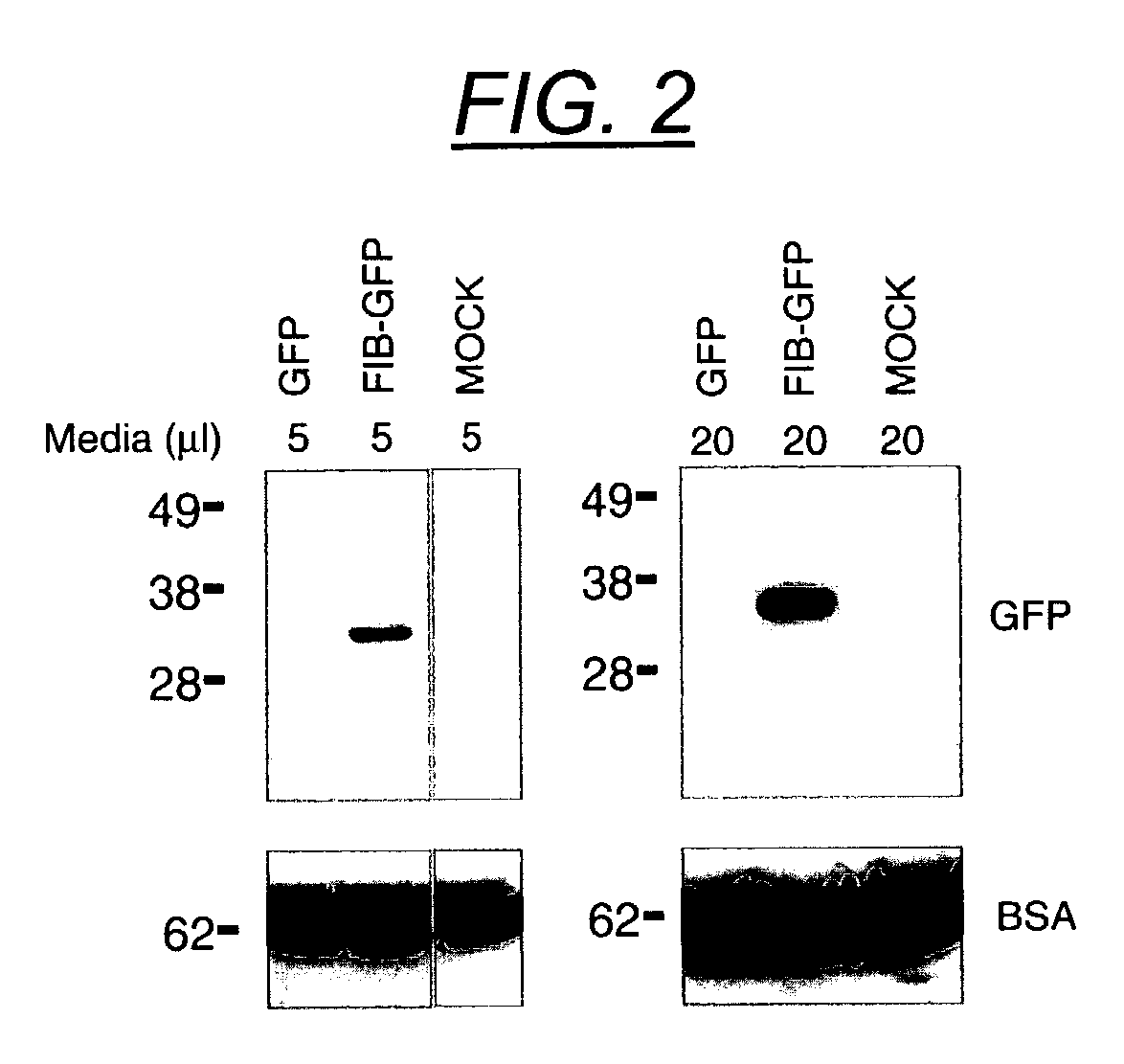
The present invention provides delivery vectors for transferring a nucleic acid sequence to a cell in vitro, ex vivo or in vivo. The delivery vector comprises a segment encoding a secretory signal peptide. In embodiments of the invention, the delivery vector is an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector. In other embodiments, the secretory signal peptide is a fibronectin secretory signal peptide (including variations and modifications, thereof). The delivery vectors of the invention may further comprise a heterologous nucleic acid sequence encoding a polypeptide of interest for transfer to a target cell, where the polypeptide of interest is operably associated with the secretory signal. Also disclosed are methods of transferring a nucleic acid of interest to a cell using the delivery vectors of the invention.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com