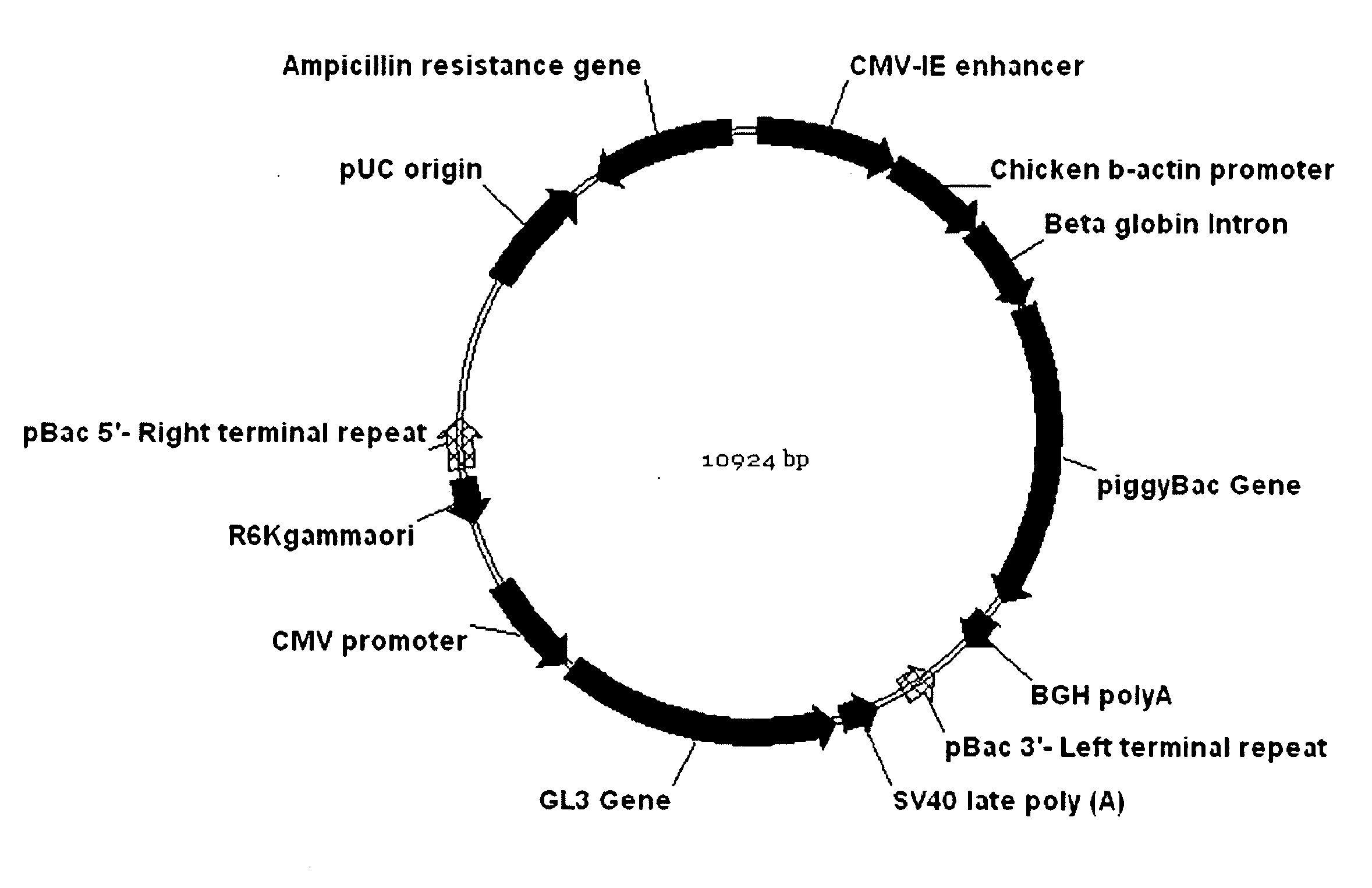
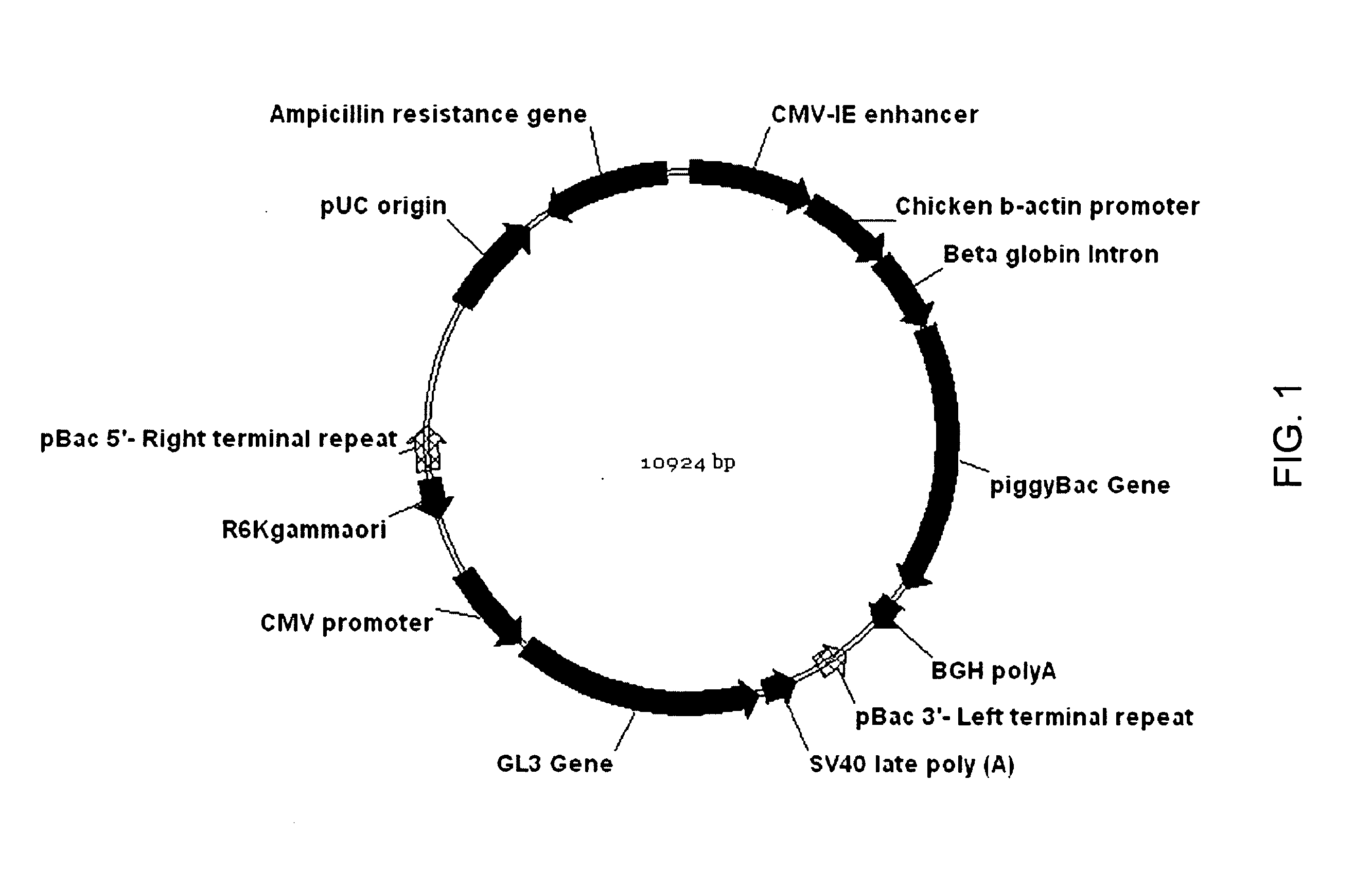
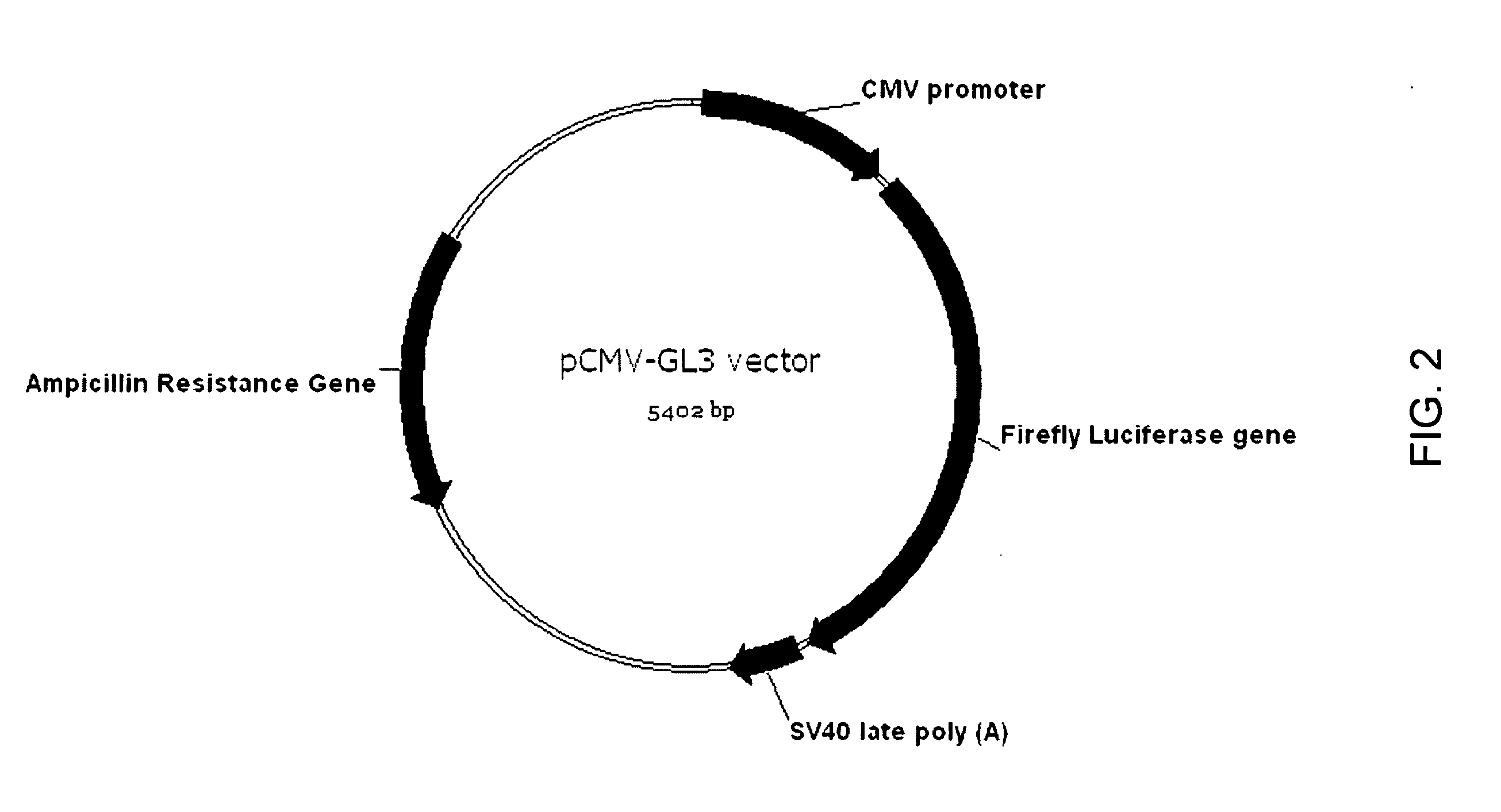
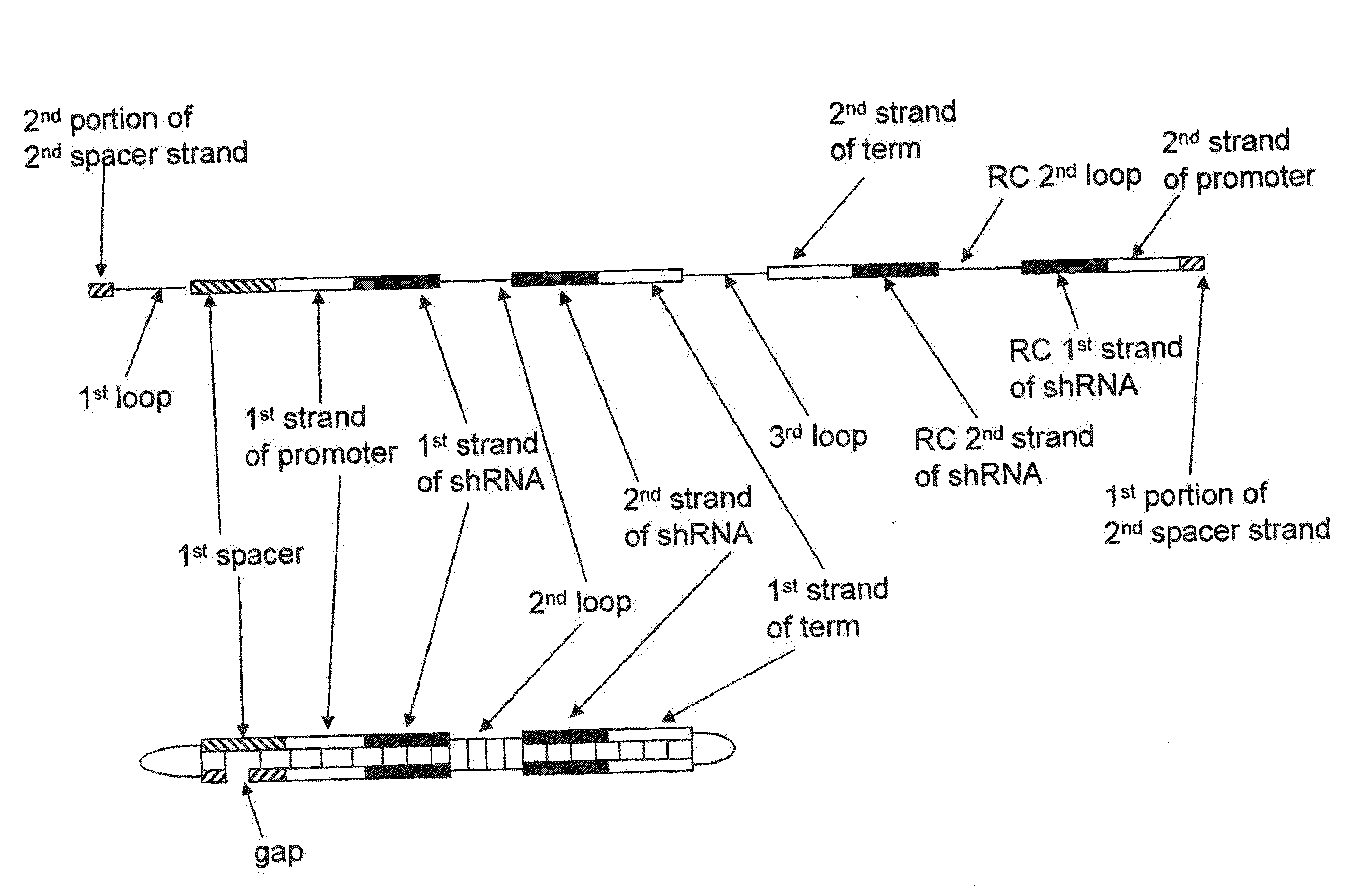
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131 results about "Terminal Repeats" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
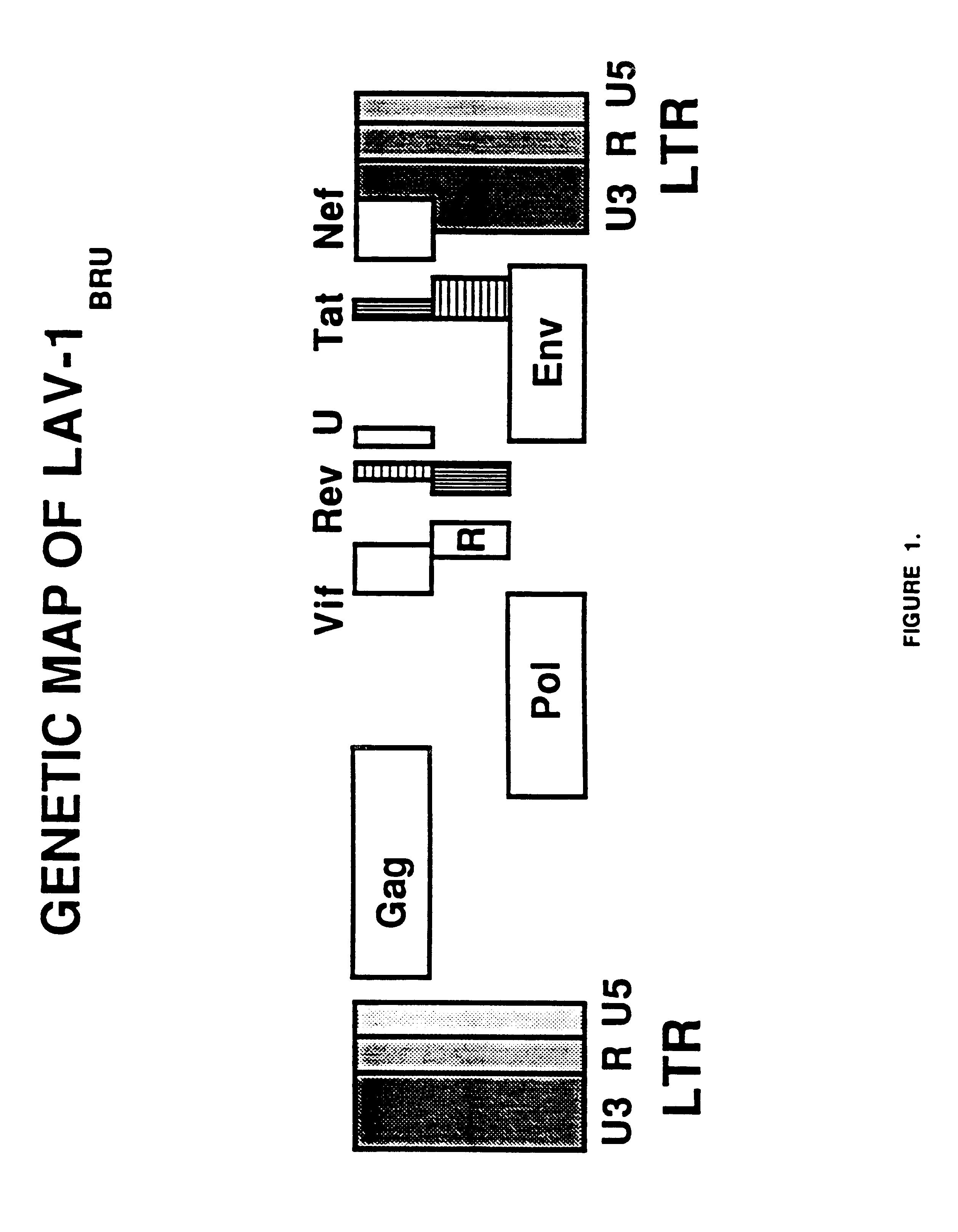
Long terminal repeats (LTRs) are identical sequences of DNA that repeat hundreds or thousands of times found at either end of retrotransposons or proviral DNA formed by reverse transcription of retroviral RNA.
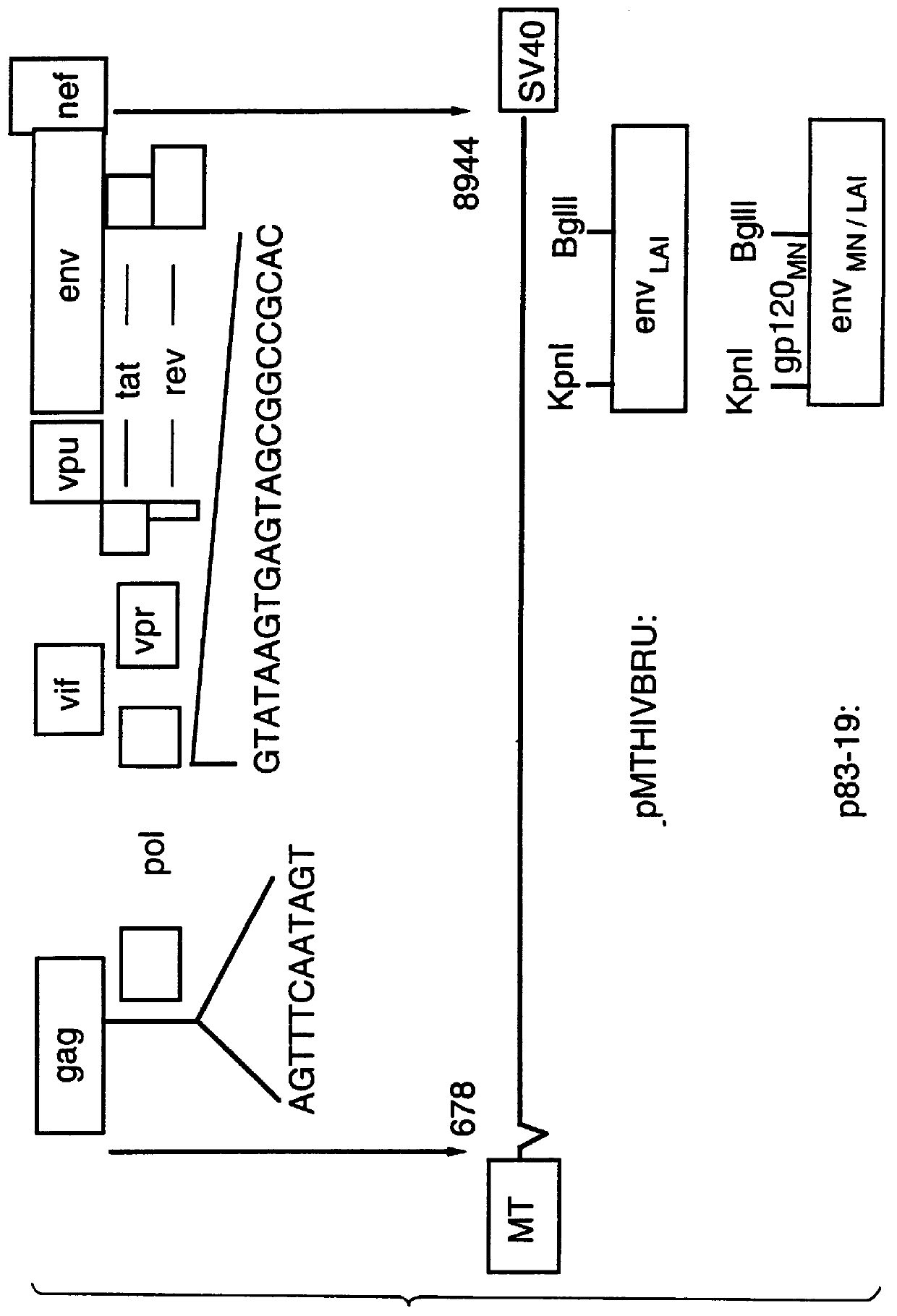
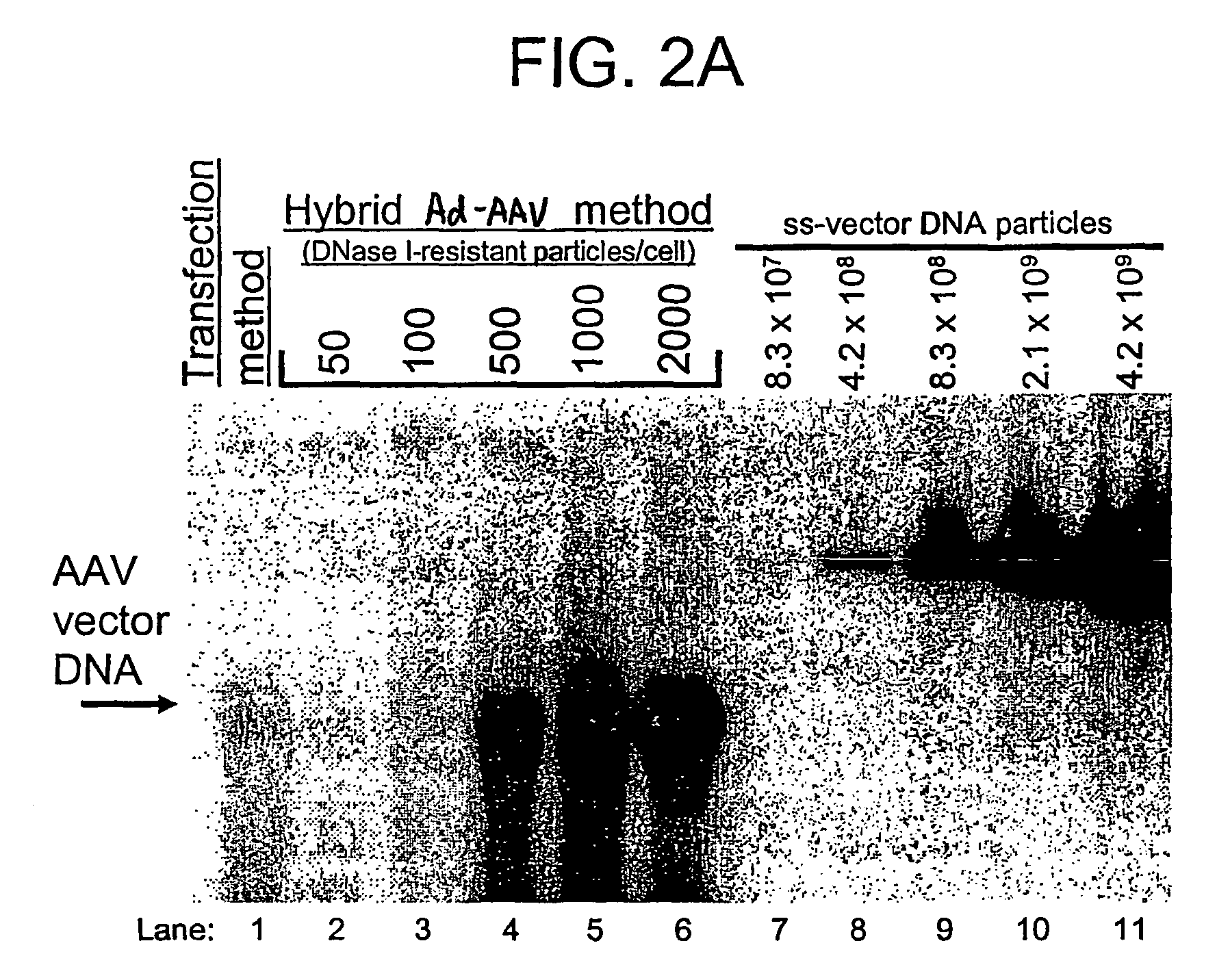
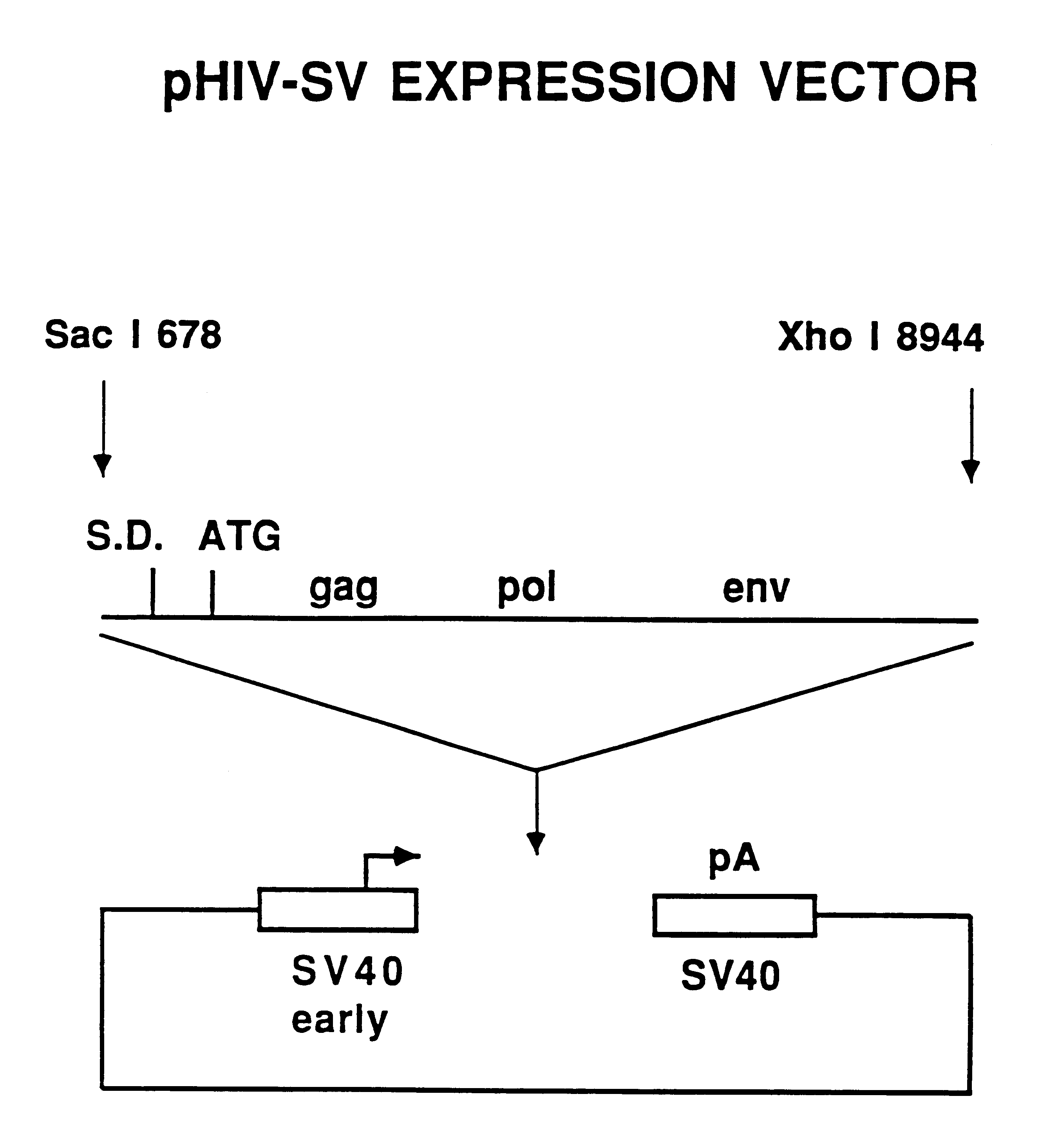
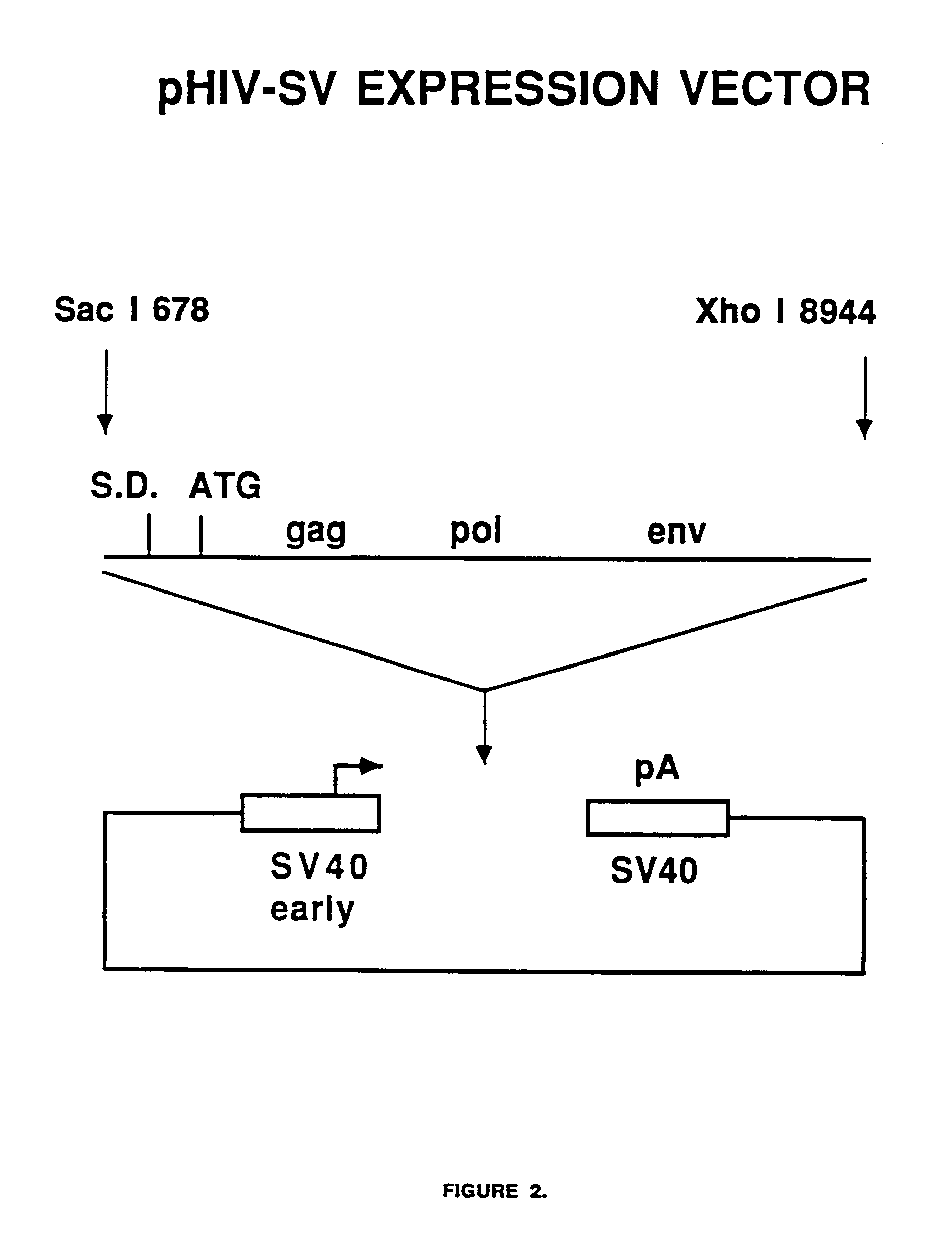
Compositions and methods for helper-free production of recombinant adeno-associated viruses
InactiveUS6953690B1Efficient productionIncrease the number ofBiocideGenetic therapy composition manufactureMammalWild type
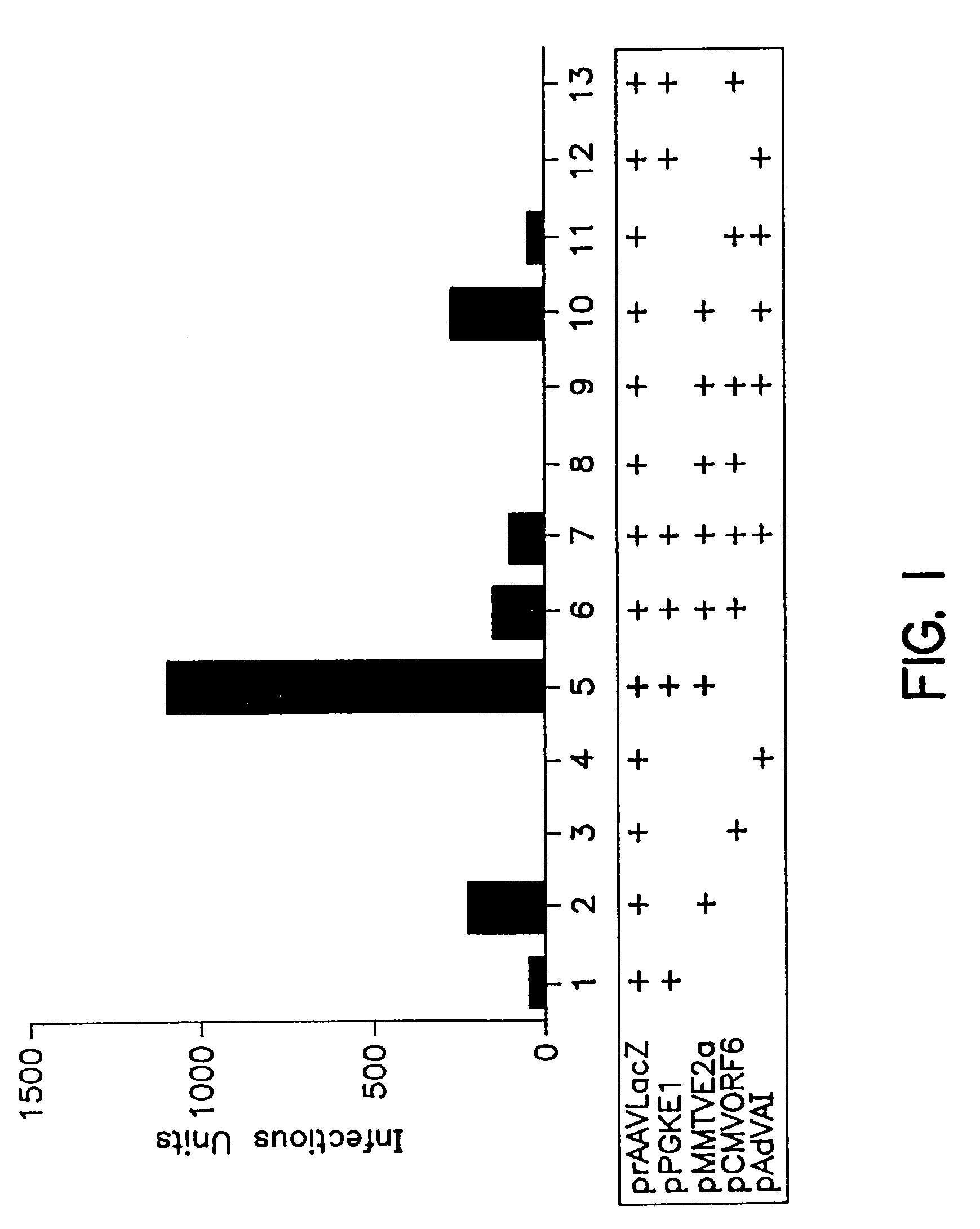
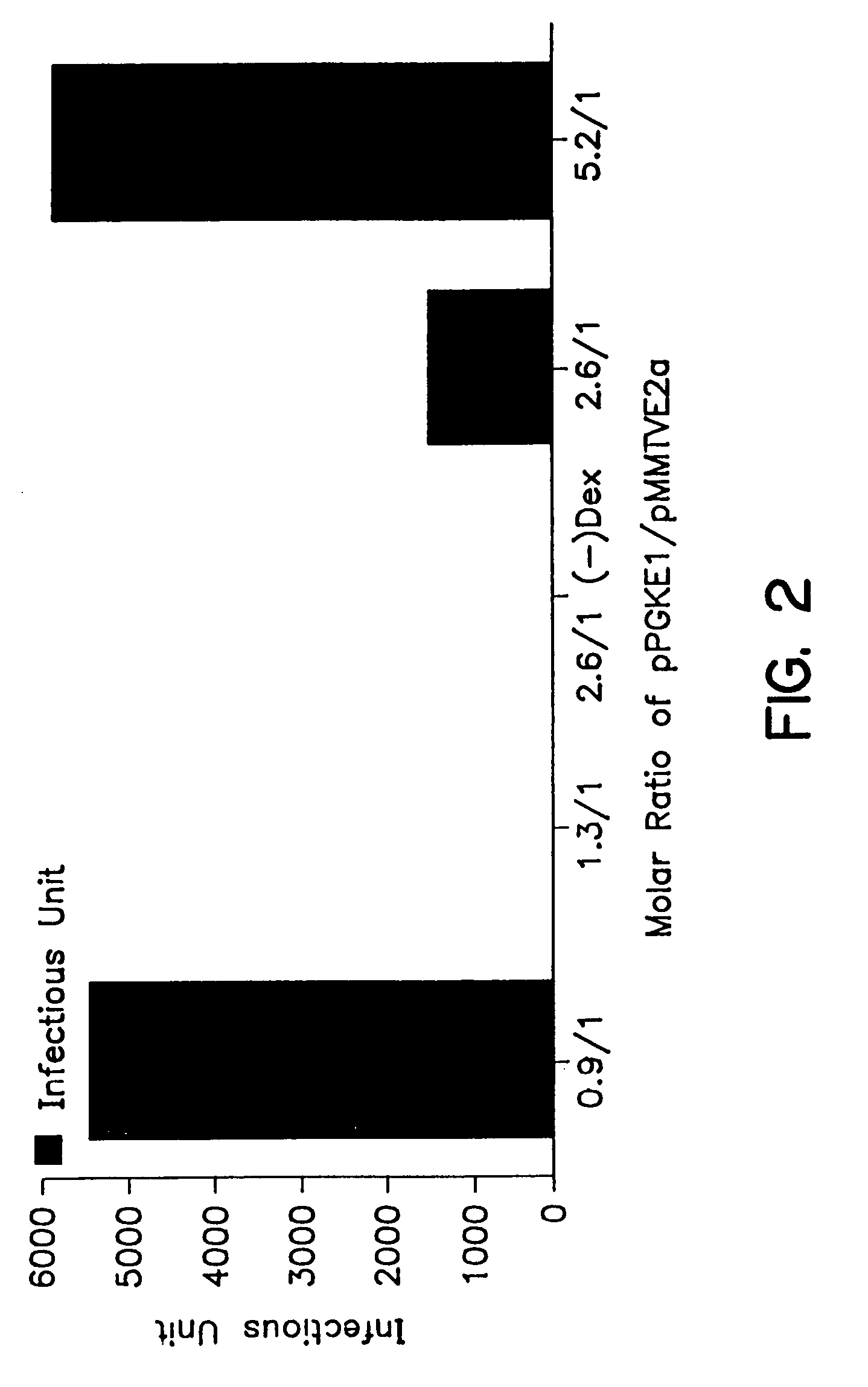
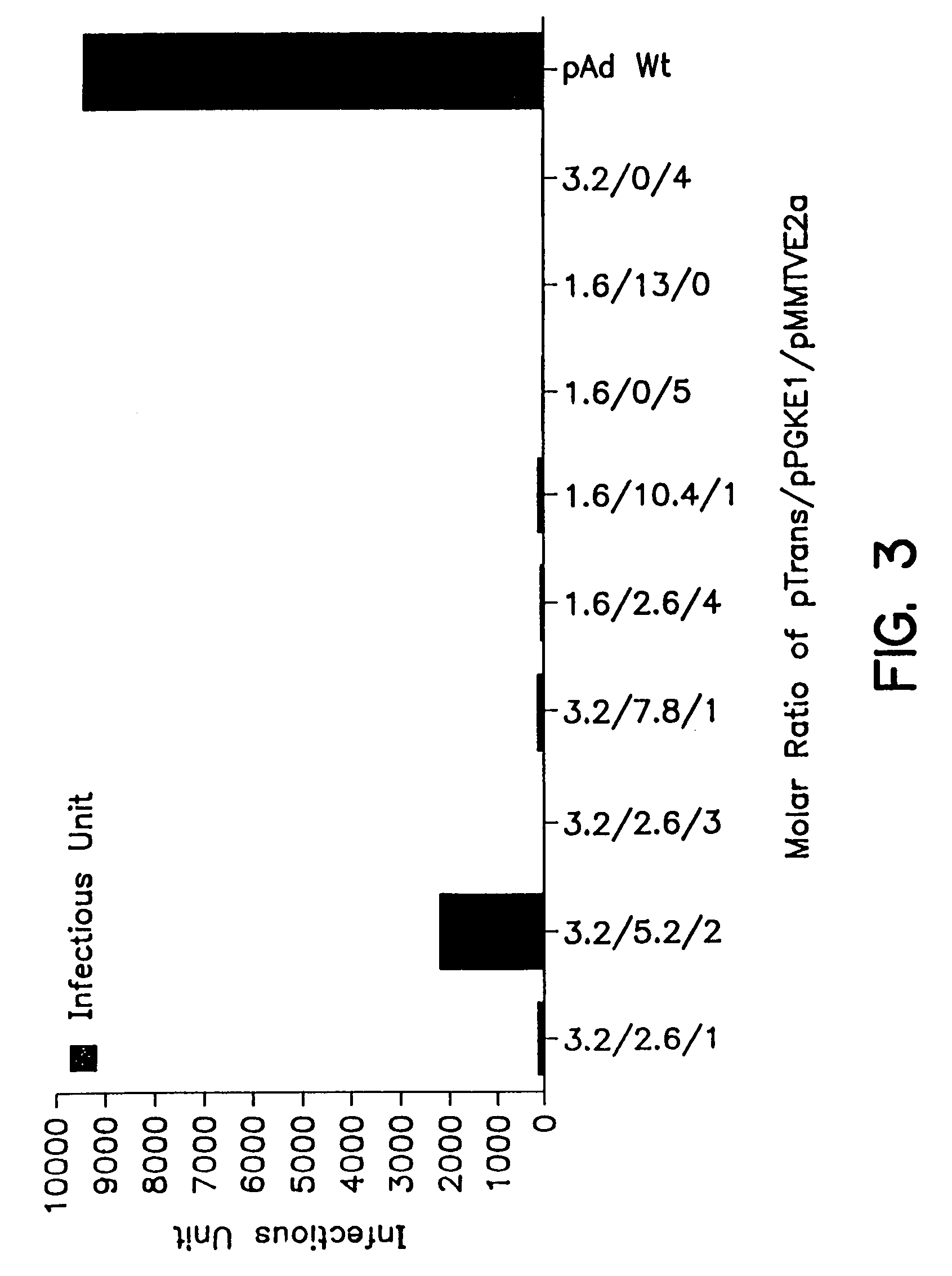
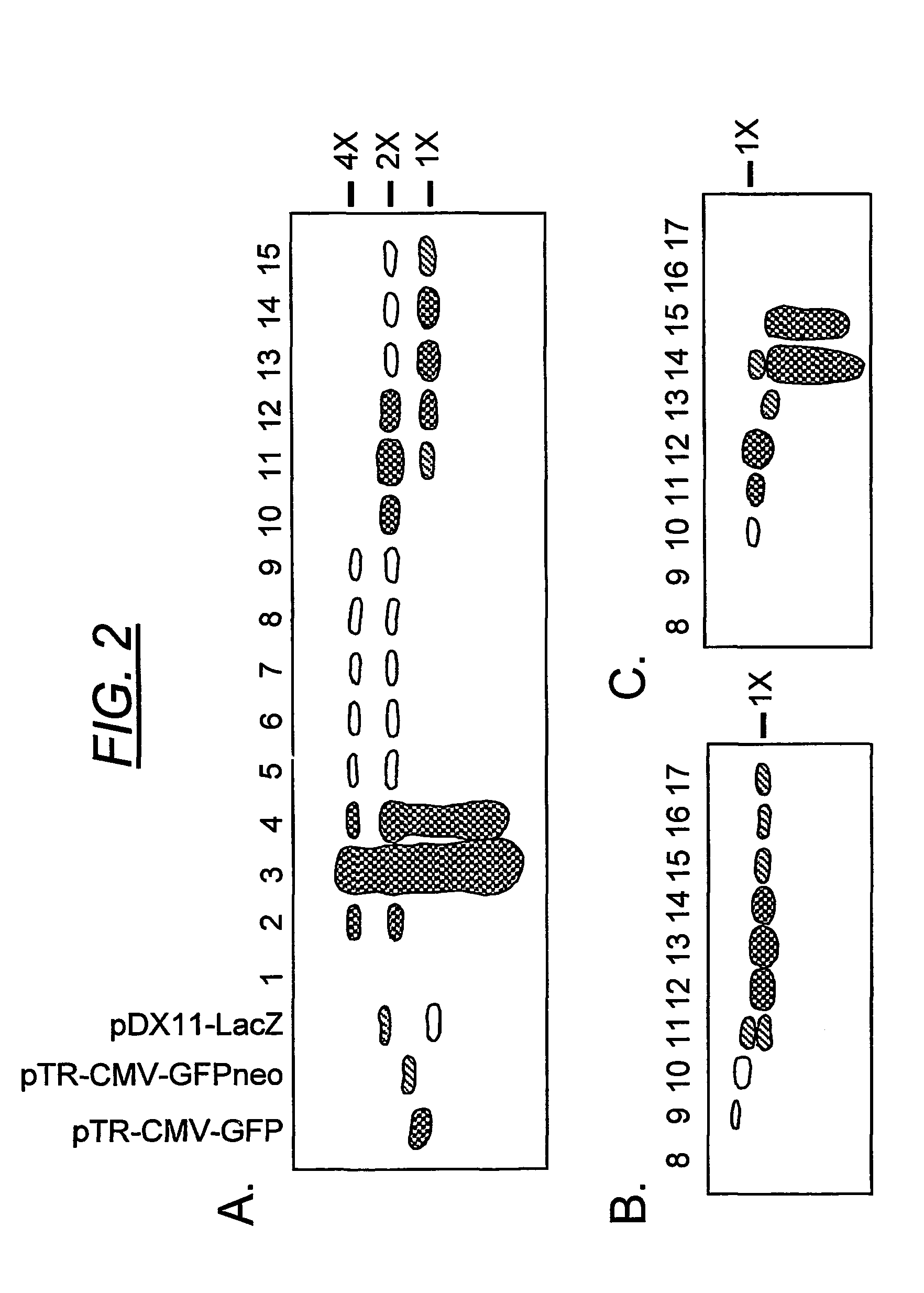
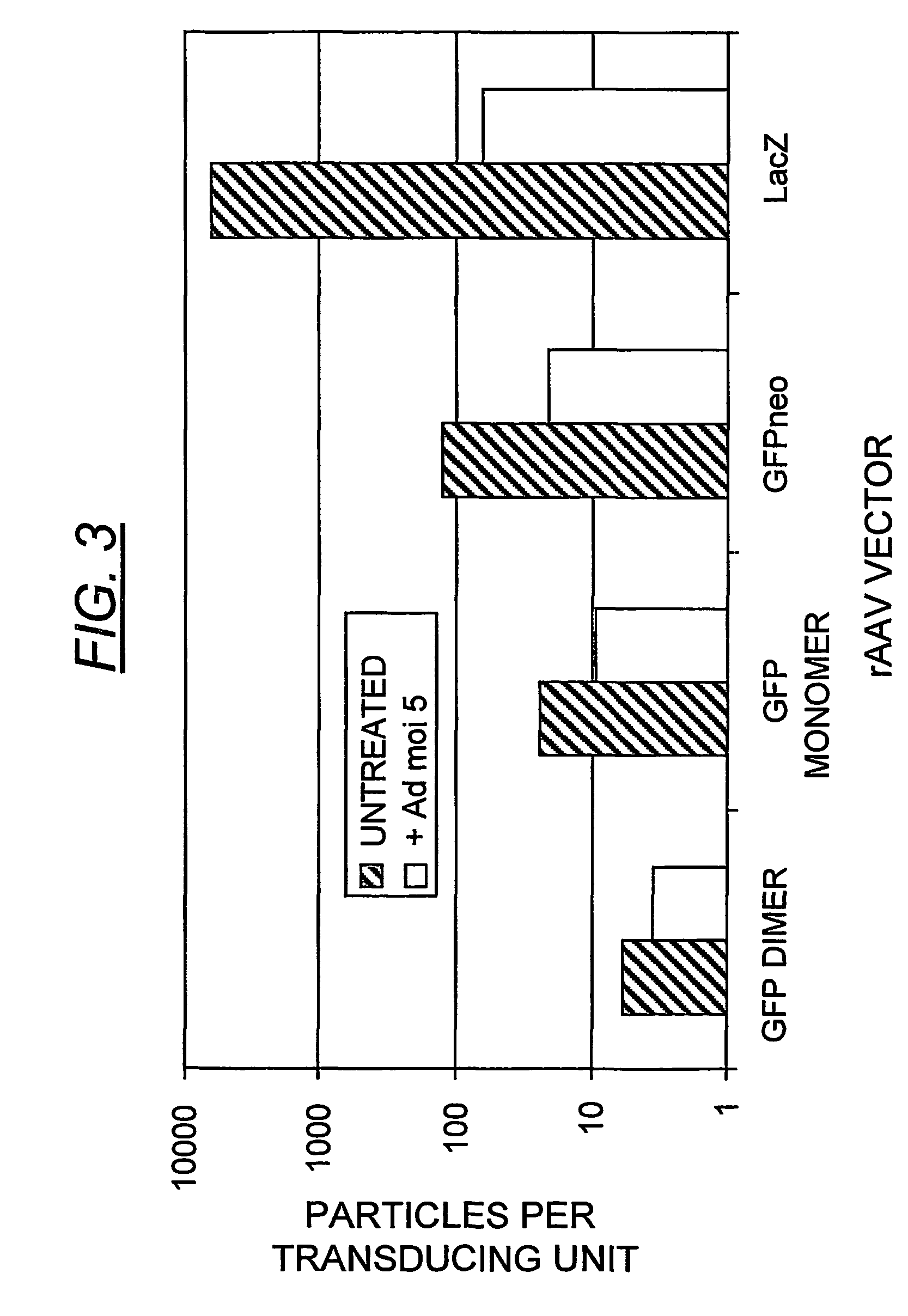
A method for producing recombinant adeno-associated virus in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wild-type virus involves culturing a mammalian host cell containing a transgene flanked by adeno-associated virus (AAV) inverse terminal repeats and under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, an AAV rep sequence and an AAV cap sequence under the control of regulatory sequences directing expression thereof, and the minimum adenovirus DNA required to express an E1a gene product, an E1b gene product and an E2a gene product, and isolating therefrom a recombinant AAV which expresses the transgene in the absence of contaminating helper virus or wildtype AAV. This method obviates a subsequent purification step to purify rAAV from contaminating virus. Also provided are various embodiments of the host cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Duplexed parvovirus vectors
InactiveUS7465583B2High transduction efficiencyRapid onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral vector
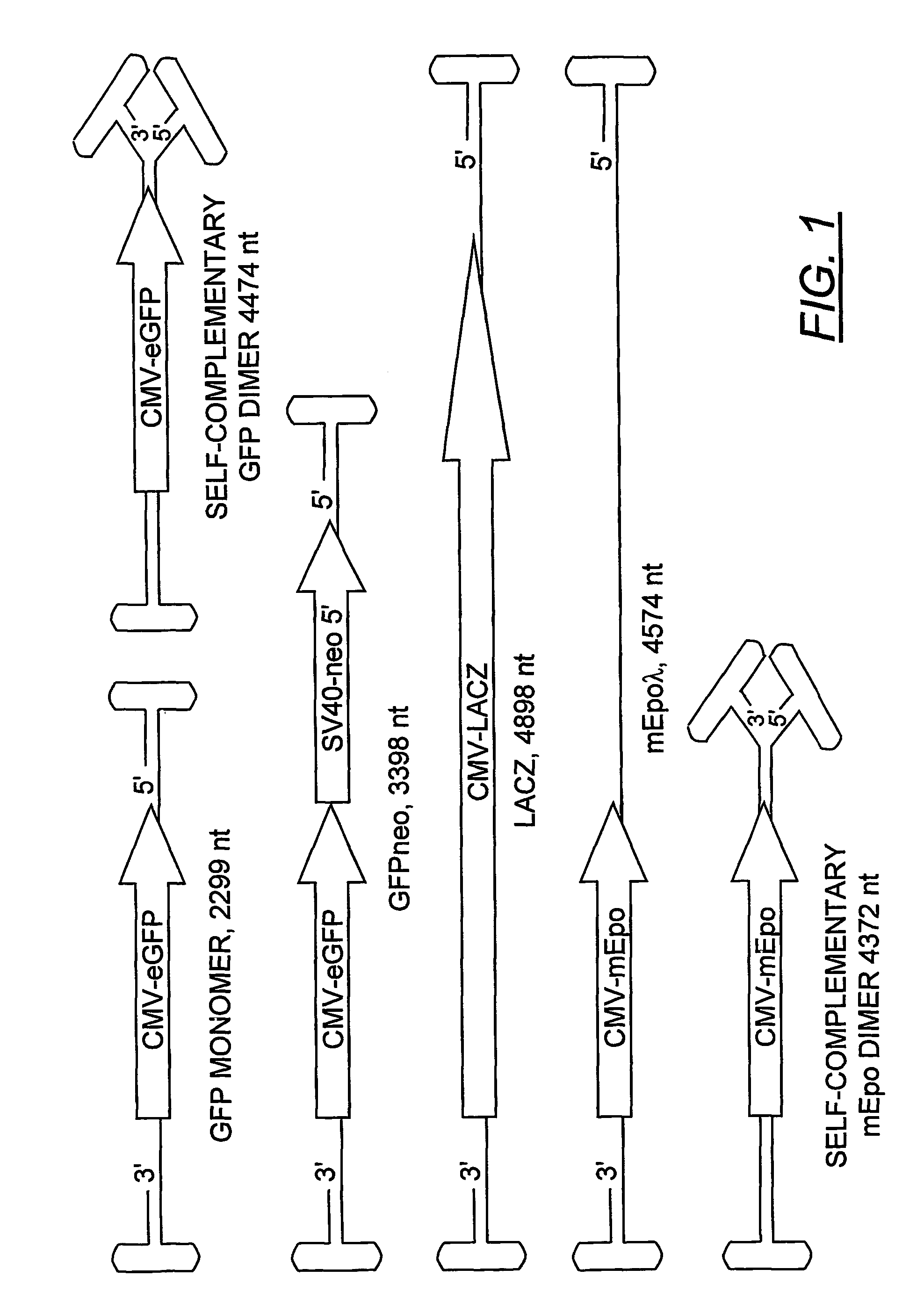
The present invention provides duplexed parvovirus vector genomes that are capable under appropriate conditions of forming a double-stranded molecule by intrastrand base-pairing. Also provided are duplexed parvovirus particles comprising the vector genome. Further disclosed are templates and methods for producing the duplexed vector genomes and duplexed parvovirus particles of the invention. Methods of administering these reagents to a cell or subject are also described. Preferably, the parvovirus capsid is an AAV capsid. It is further preferred that the vector genome comprises AAV terminal repeat sequences.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nucleic acids devoid of long terminal repeats capable of encoding for non-infectious, immunogenic, retrovirus-like particles
InactiveUS6080408AImprove efficiencyLow backgroundSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsPol genesReverse transcriptase activity
Non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles contain mutations to reduce gag-dependent RNA-packaging of the gag gene product, eliminate reverse transcriptase activity of the pol gene product, eliminate integrase activity of the pol gene product and eliminate RNase H activity of the pol gene product through genetic manipulation of the gag and pol genes. The corresponding nucleic acid molecules are described. The non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles have utility in diagnosis.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
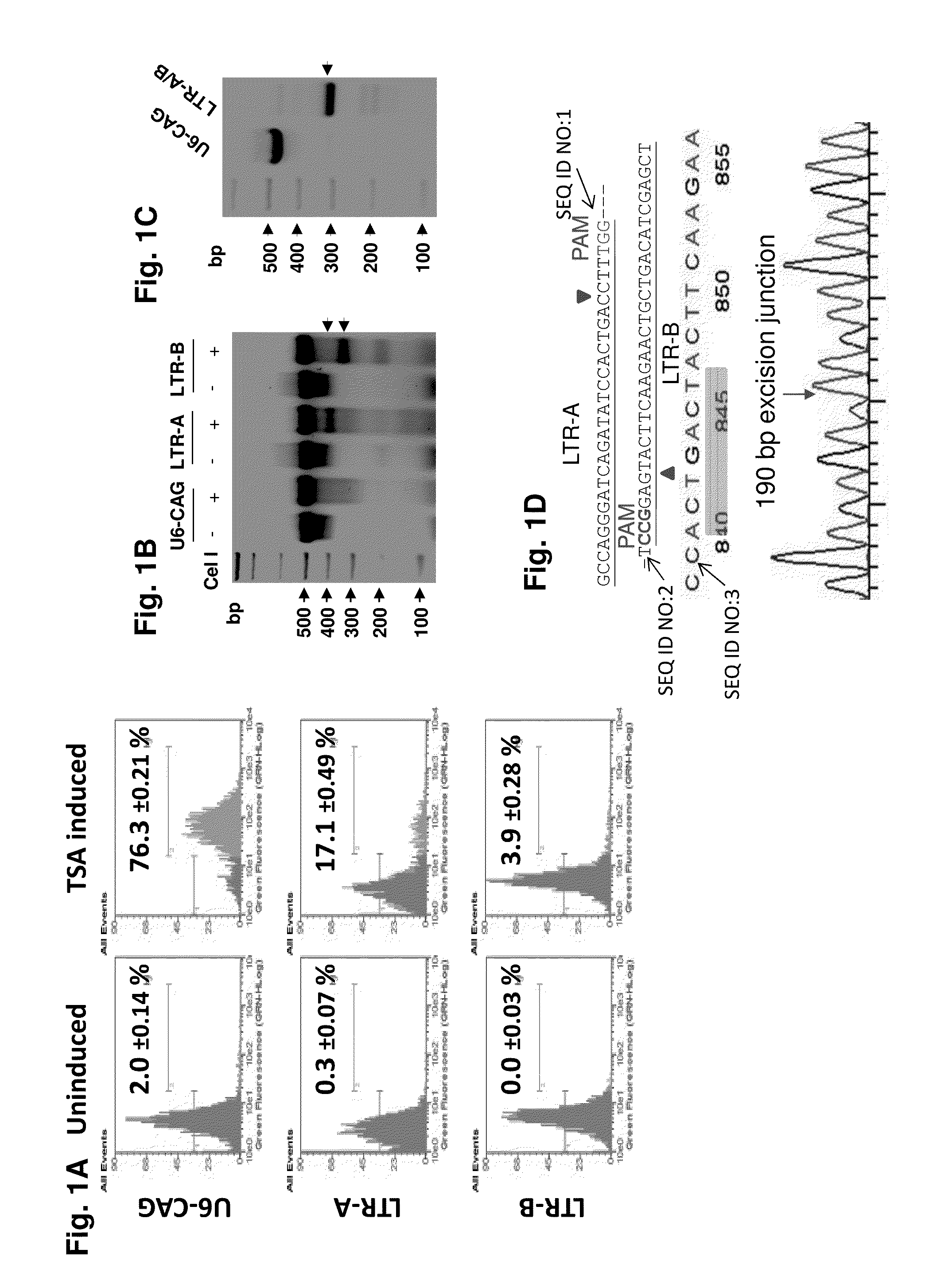
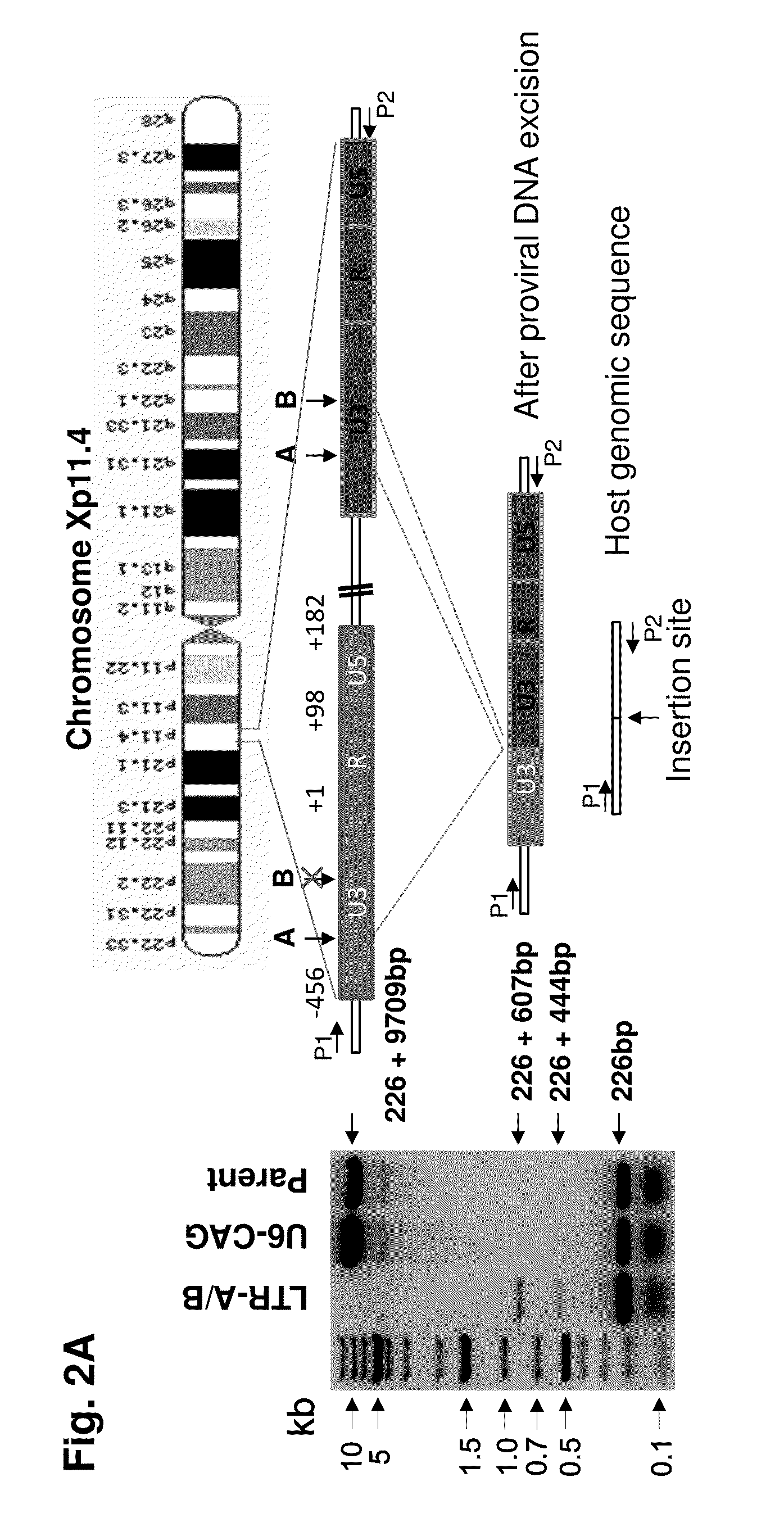
Methods and compositions for rna-guided treatment of HIV infection
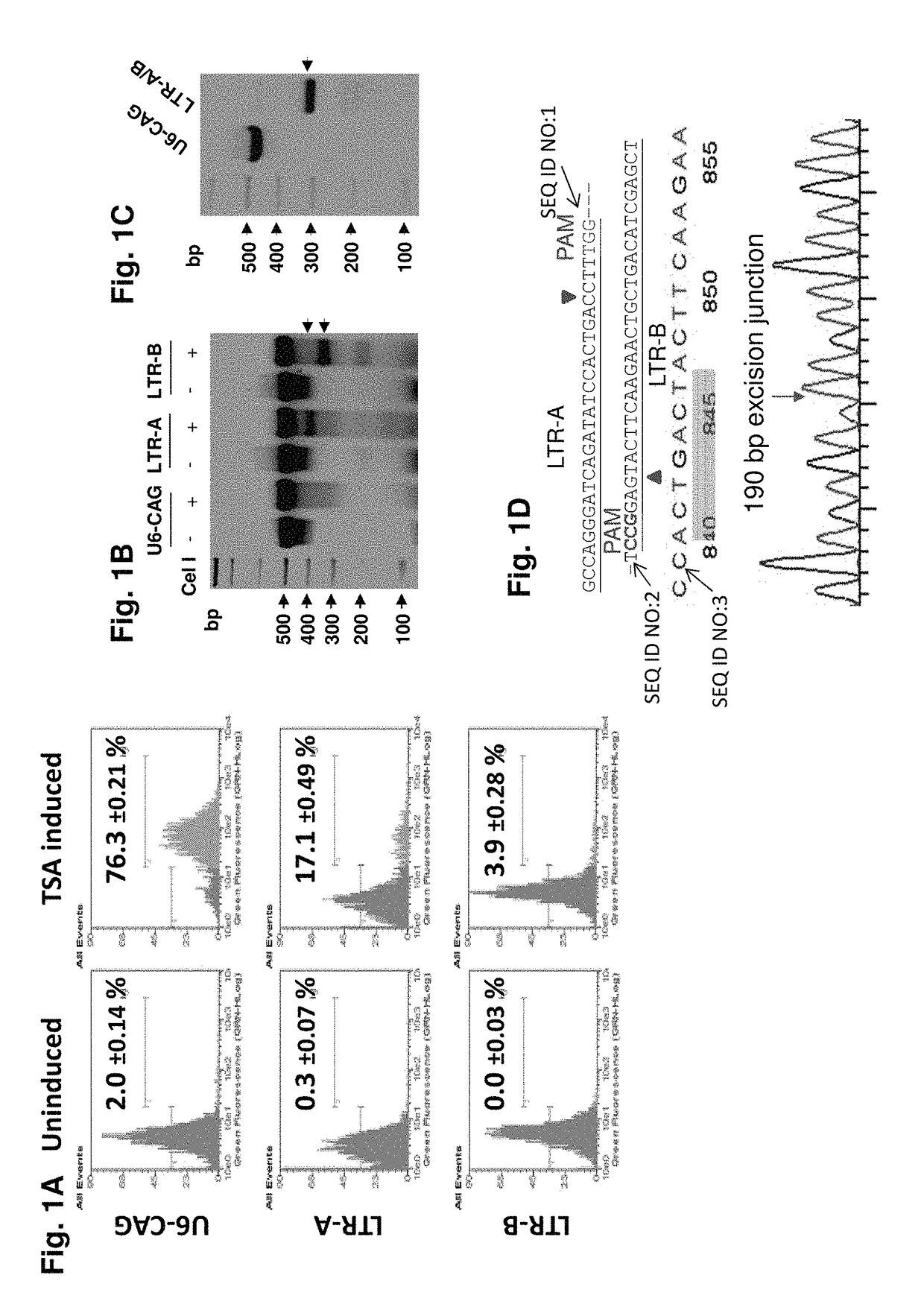
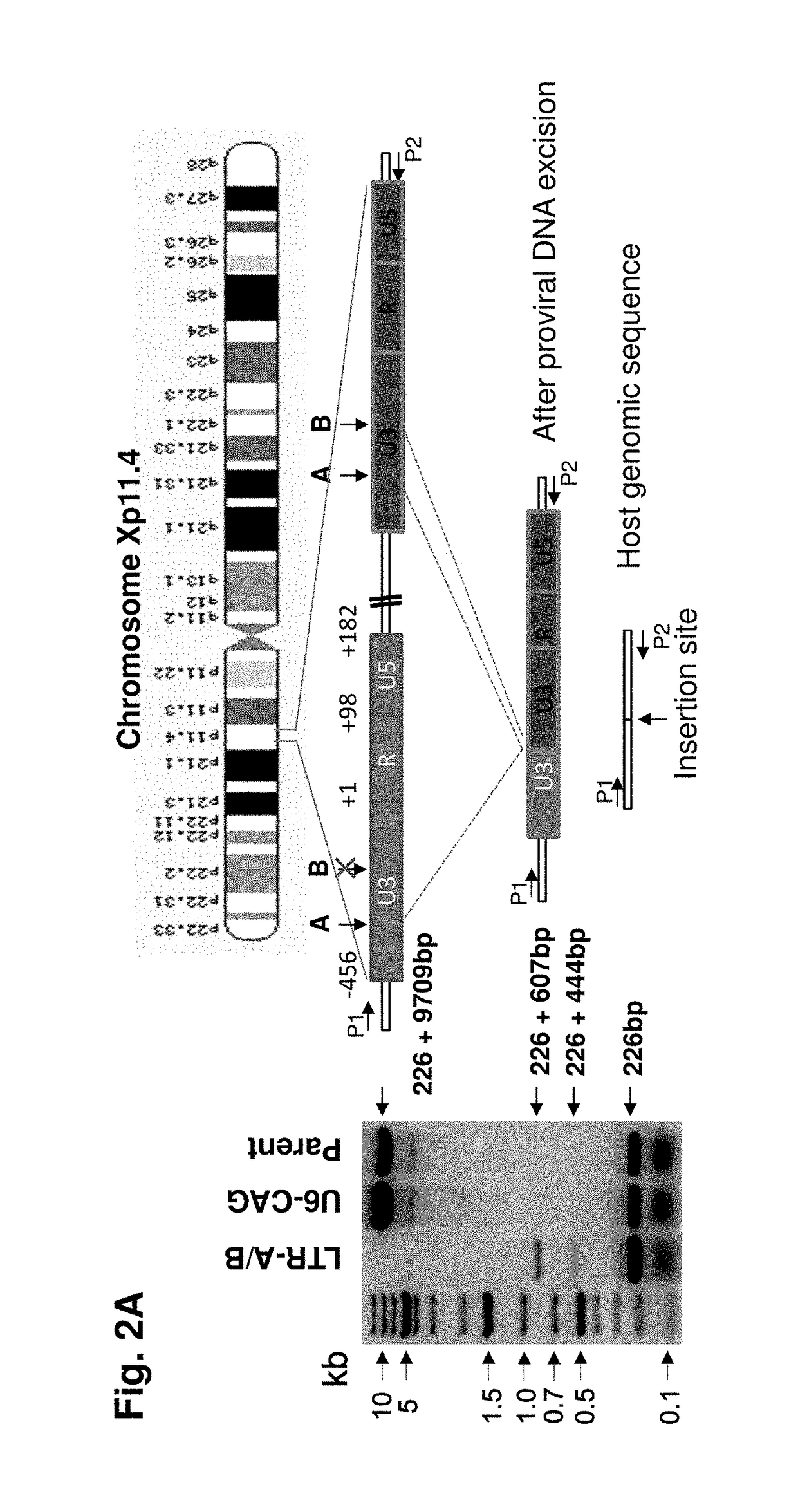
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
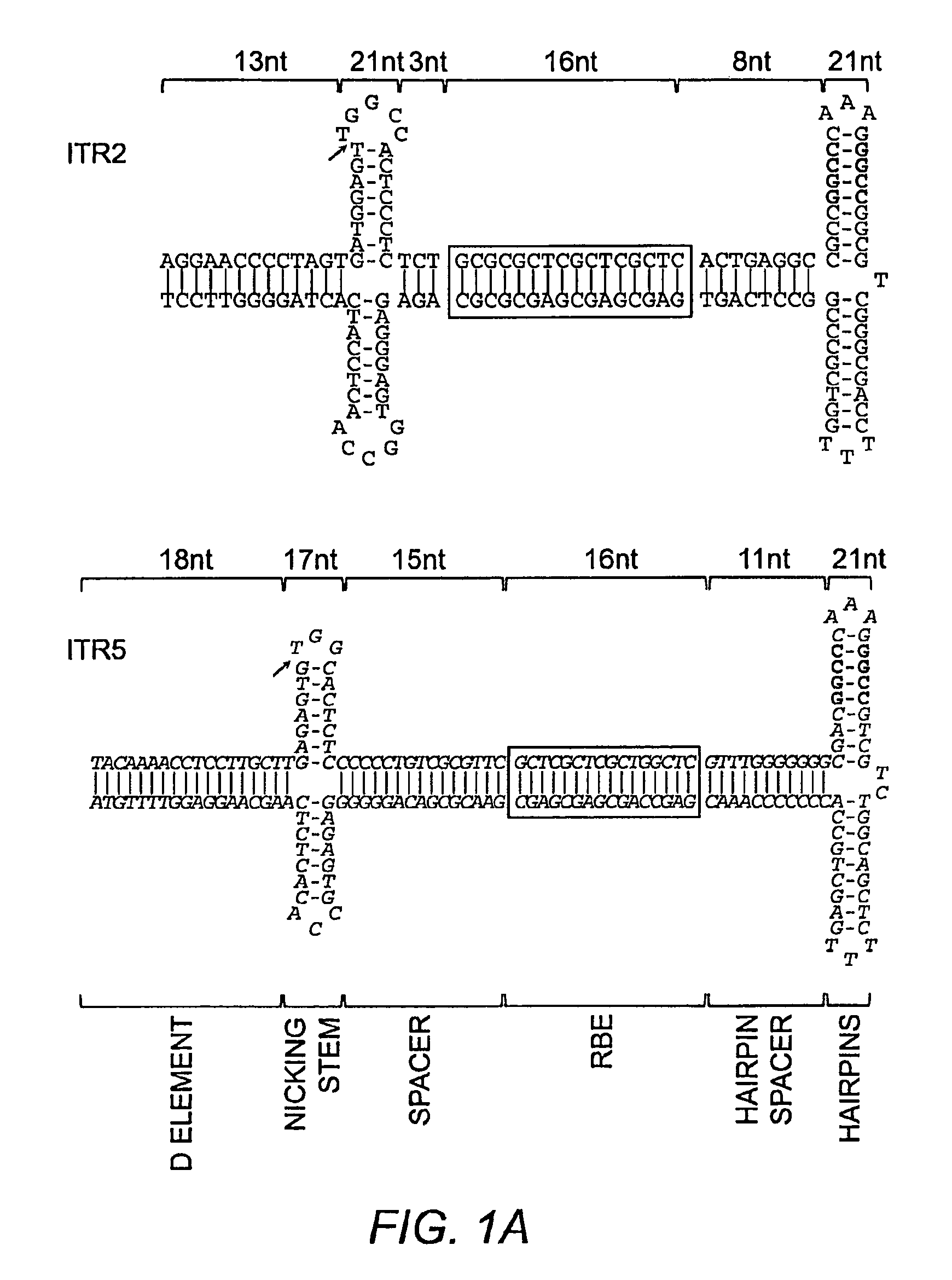
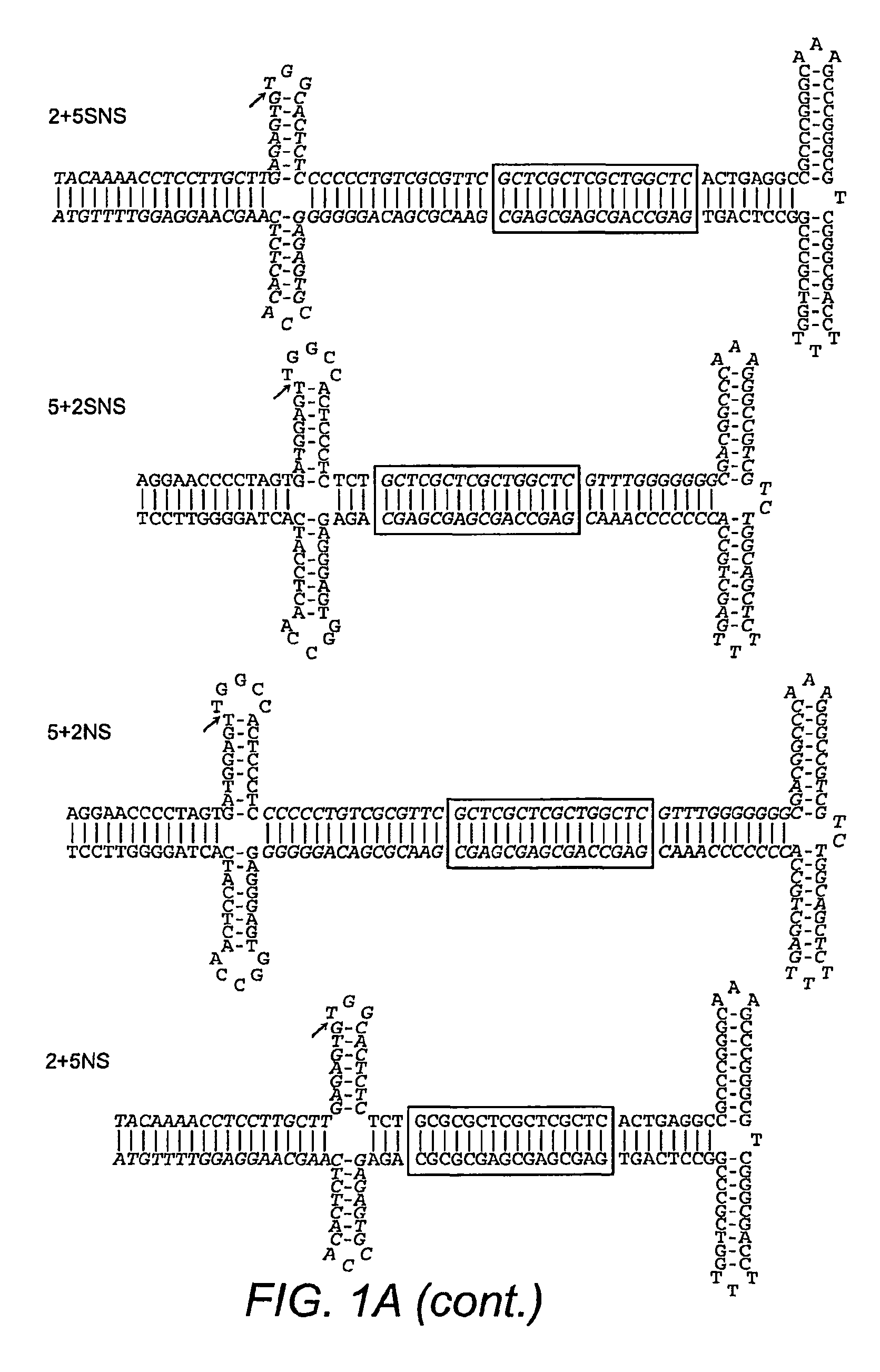
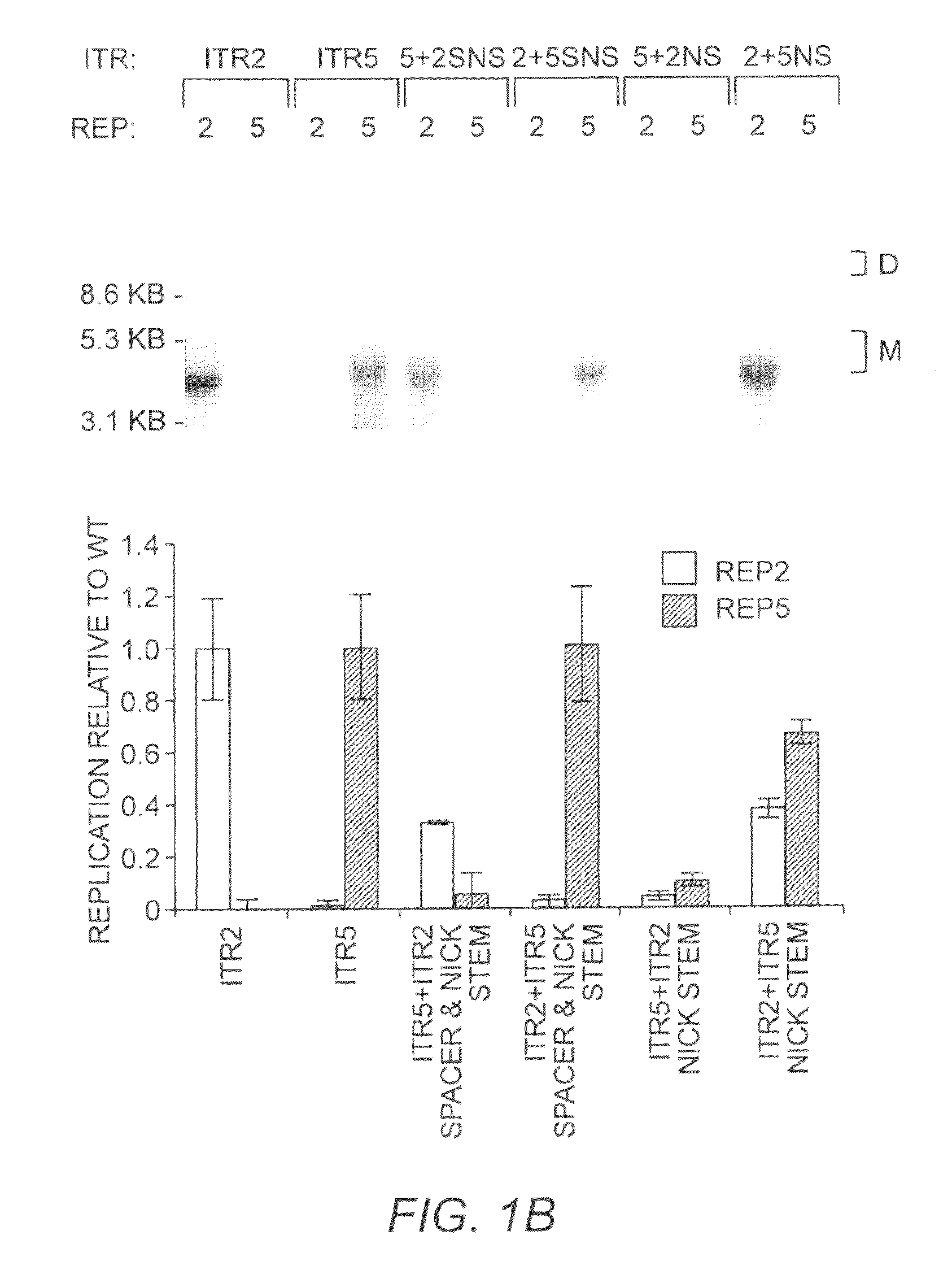
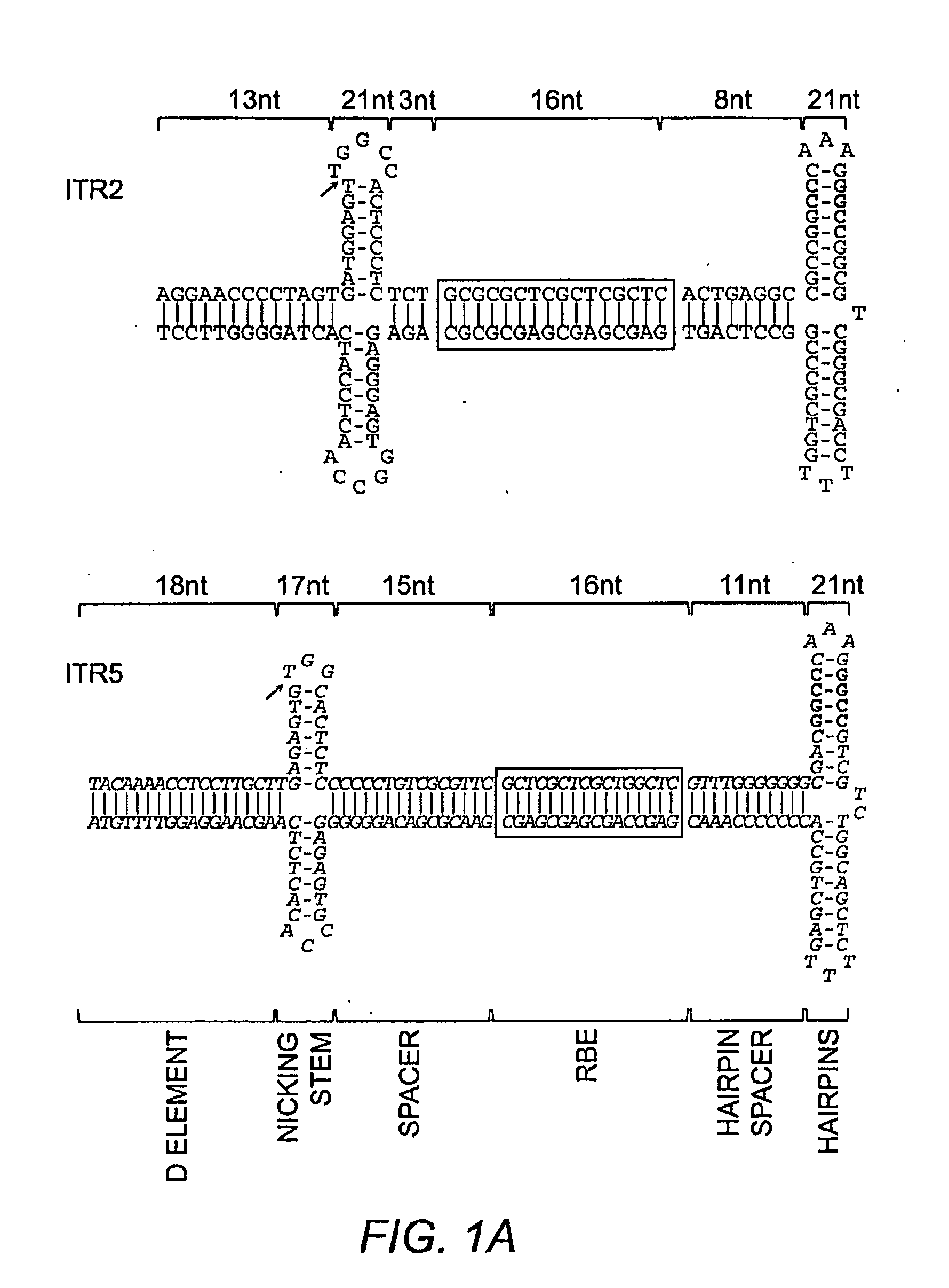
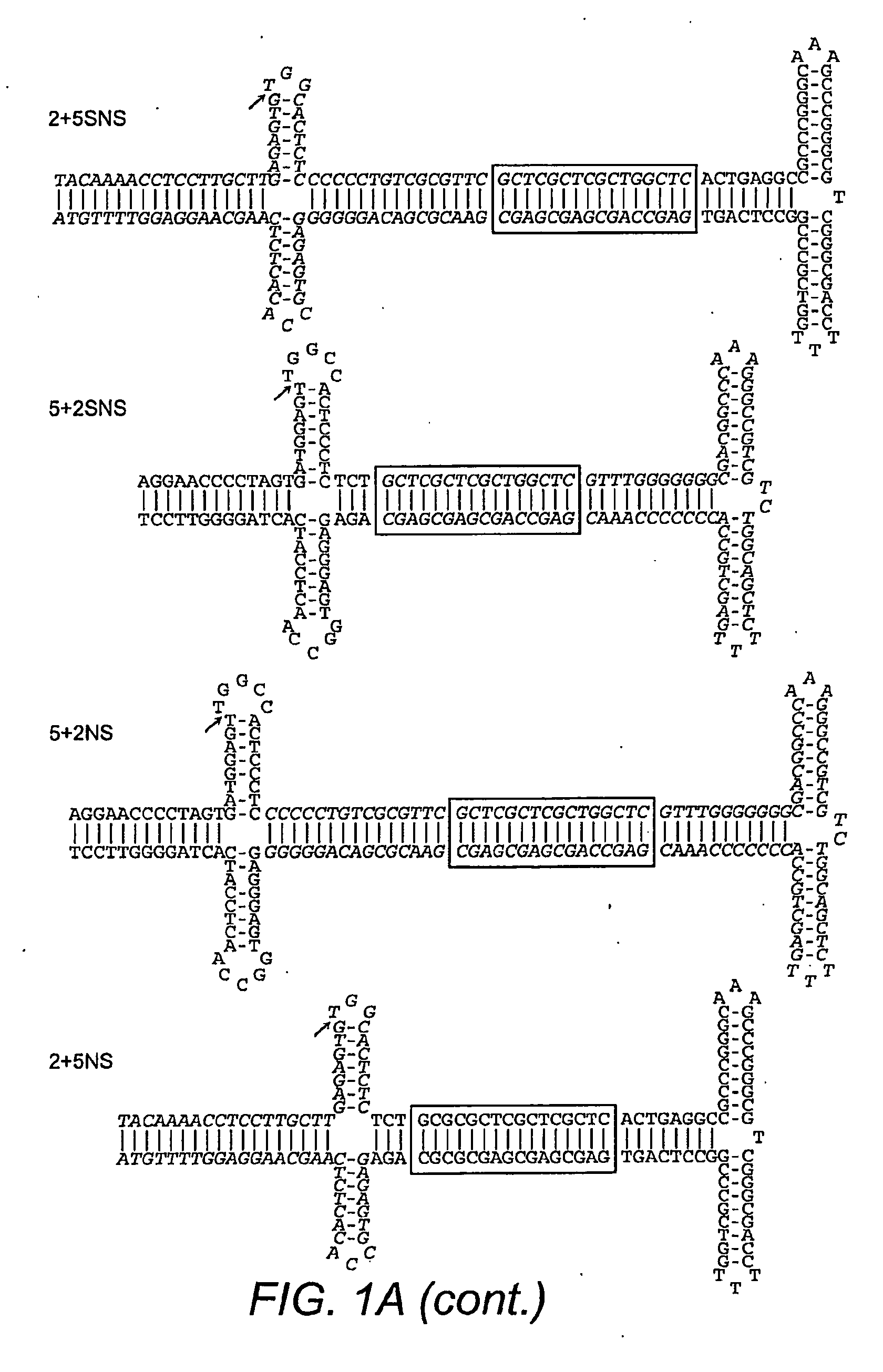
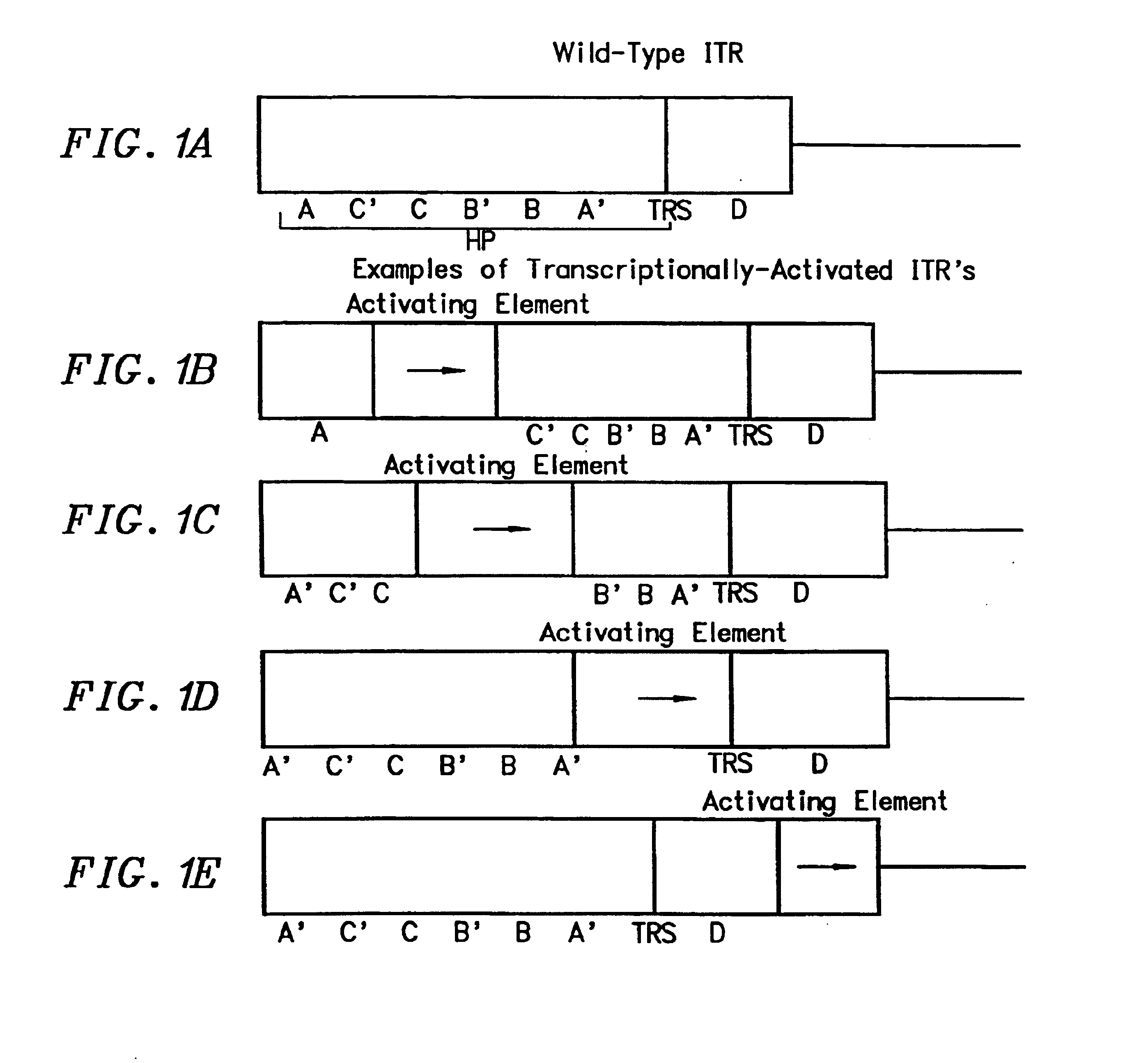
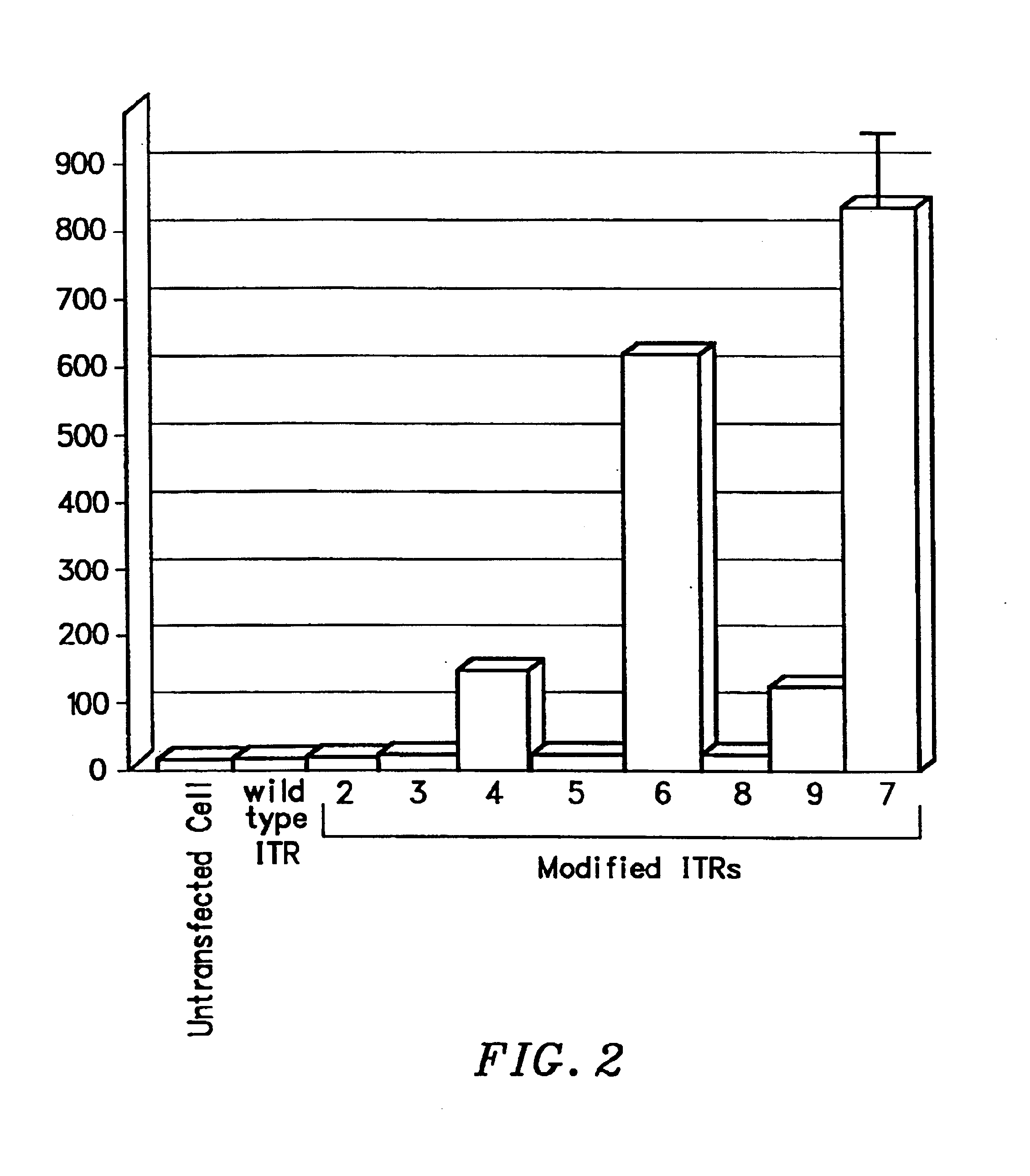
Restrictive inverted terminal repeats for viral vectors
This invention relates to modified parvovirus inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) that do not functionally interact with wild-type large Rep proteins, synthetic Rep proteins that functionally interact with the modified ITRs, and methods of using the same for delivery of nucleic acids to a cell or a subject. The modifications provide a novel Rep-ITR interaction that limits vector mobilization, increasing the safety of viral vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
AAV vectors
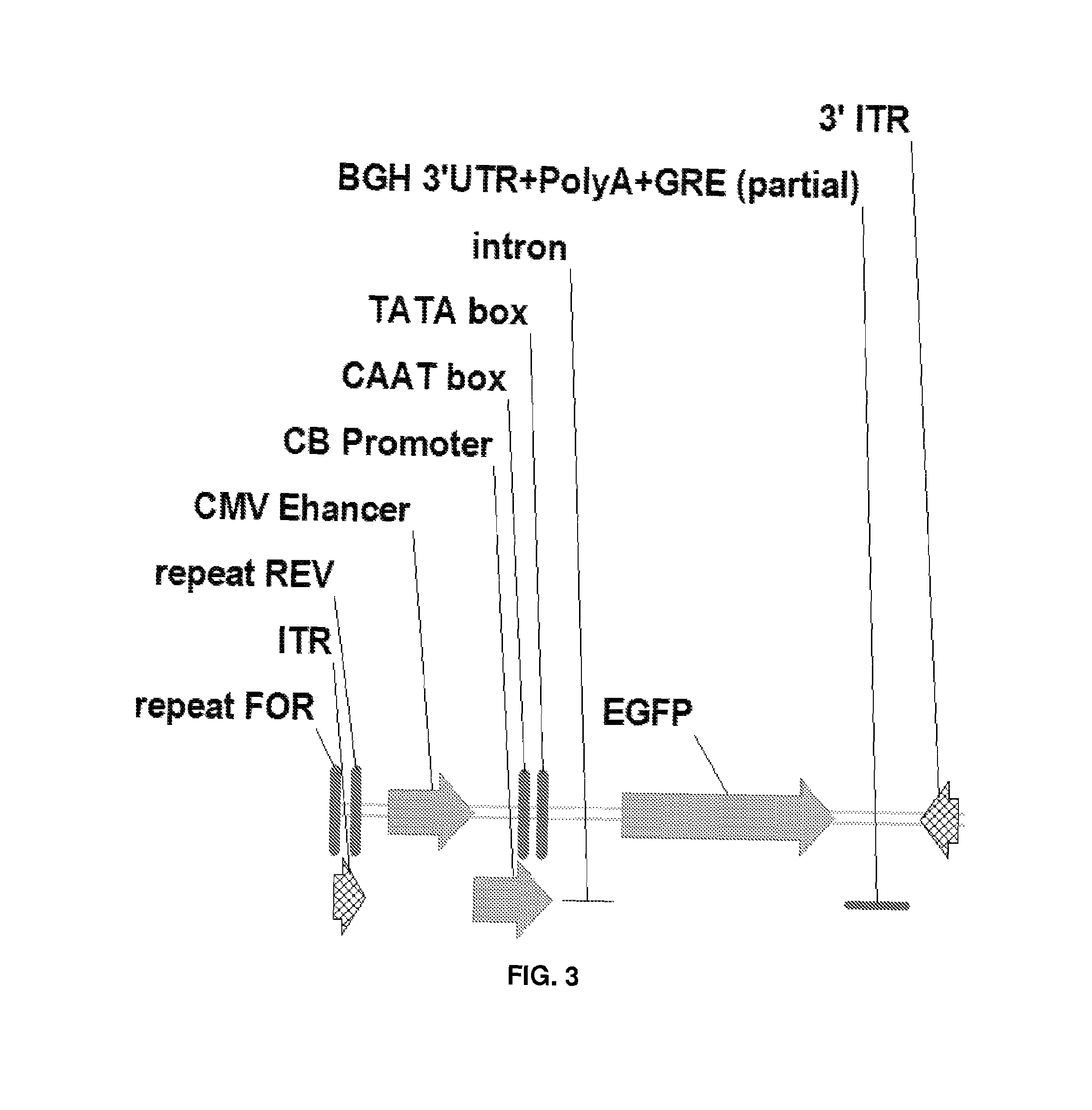
InactiveUS6521225B1Prevent and limit expressionPrevents terminal glycosylation and translationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLong terminal repeatNucleotide
The present invention is directed to a recombinant adenovirus vector comprising two inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) each of which comprises a D-sequence having (i) from 5 to 15 native nucleotides and (ii) one or more deletions or substitutions therein.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST +1
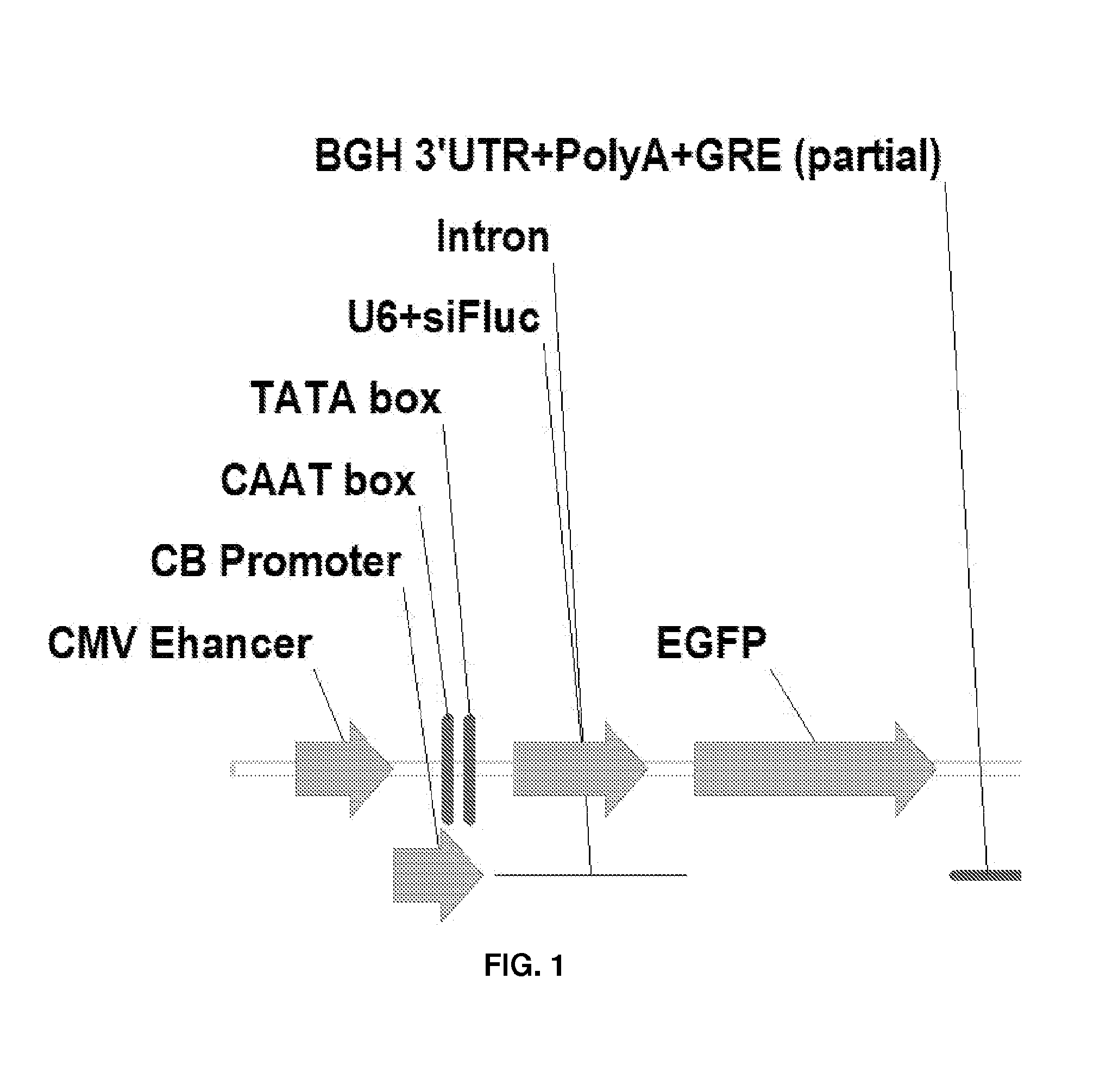
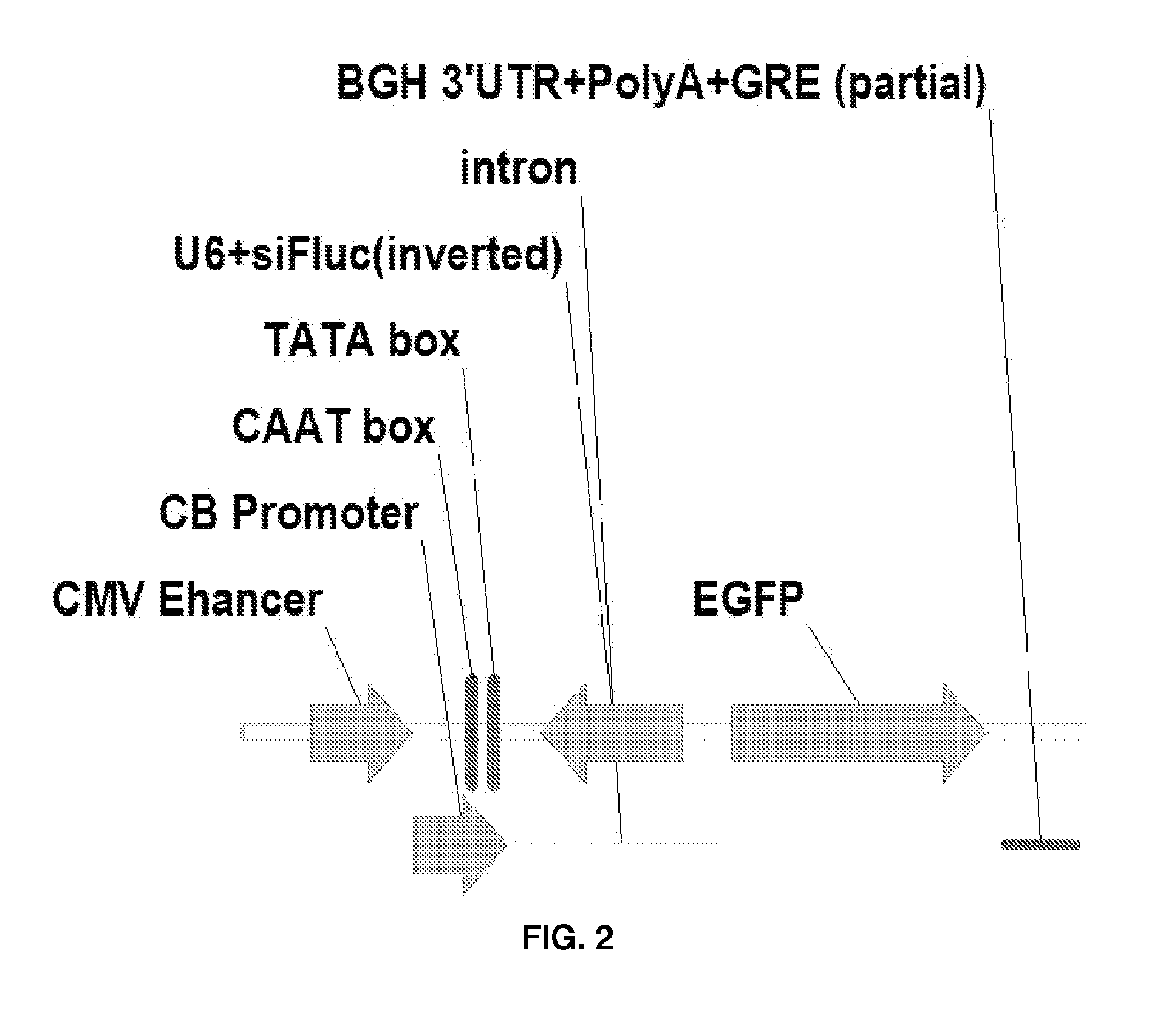
Multicistronic expression constructs
ActiveUS20130281516A1Efficient expressionVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
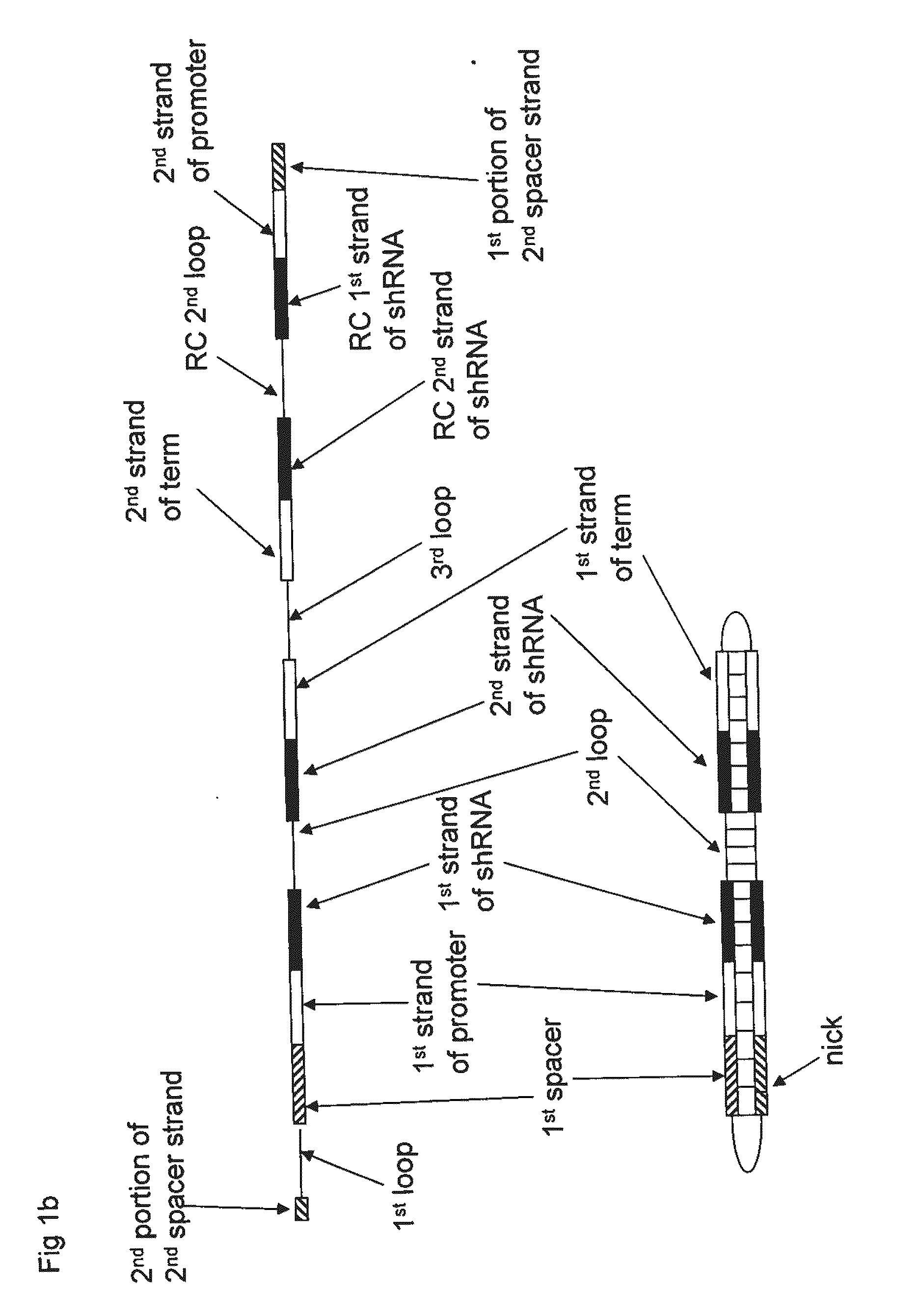
Some aspect of this invention provide nucleic acid constructs for transgene expression. Some aspects of this invention provide multicistronic nucleic acid constructs, for example, comprising an expression cassette encoding a hairpin RNA and a reporter expression cassette. Some aspects of this invention provide nucleic acid constructs comprising two or more self-complementary nucleic acid sequences, for example, hairpin RNA encoding nucleic acid sequences and AAV inverse terminal repeats. Methods for the use of the constructs in therapy and research are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Restrictive Inverted Terminal Repeats for Viral Vectors
This invention relates to modified parvovirus inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) that do not functionally interact with wild-type large Rep proteins, synthetic Rep proteins that functionally interact with the modified ITRs, and methods of using the same for delivery of nucleic acids to a cell or a subject. The modifications provide a novel Rep-ITR interaction that limits vector mobilization, increasing the safety of viral vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS20050220766A1Improve AAV production titerReduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPolymerase LNucleic acid sequencing
A recombinant hybrid virus, including: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome comprising the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation, and further comprising a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the group consisting of: (i) the polymerase region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase protein from said deleted region and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein, (ii) the preterminal protein region, wherein said deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional preterminal protein from said deleted region, and said hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional preterminal protein, and (iii) both the regions of (i) and (ii); and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), said recombinant AAV vector genome comprising (i) AAV 5′ and 3′ inverted terminal repeats, (ii) an AAV packaging sequence, and (iii) a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein said heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by the 5′ and the 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats of (i). Methods of making and using the recombinant hybrid virus are also disclosed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Tetracycline-regulated adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors for gene delivery to the nervous system
Owner:CHILDRENS MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
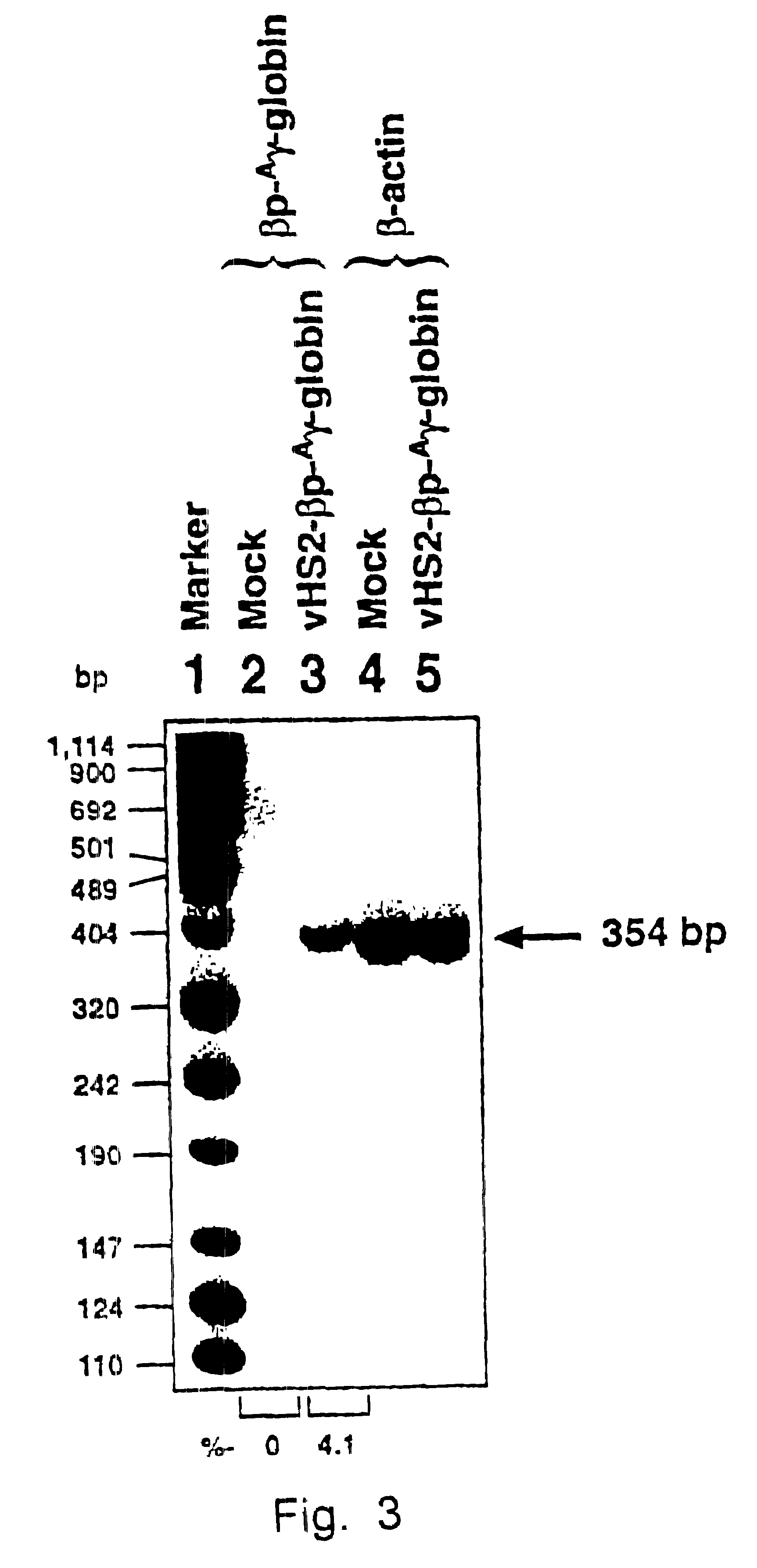
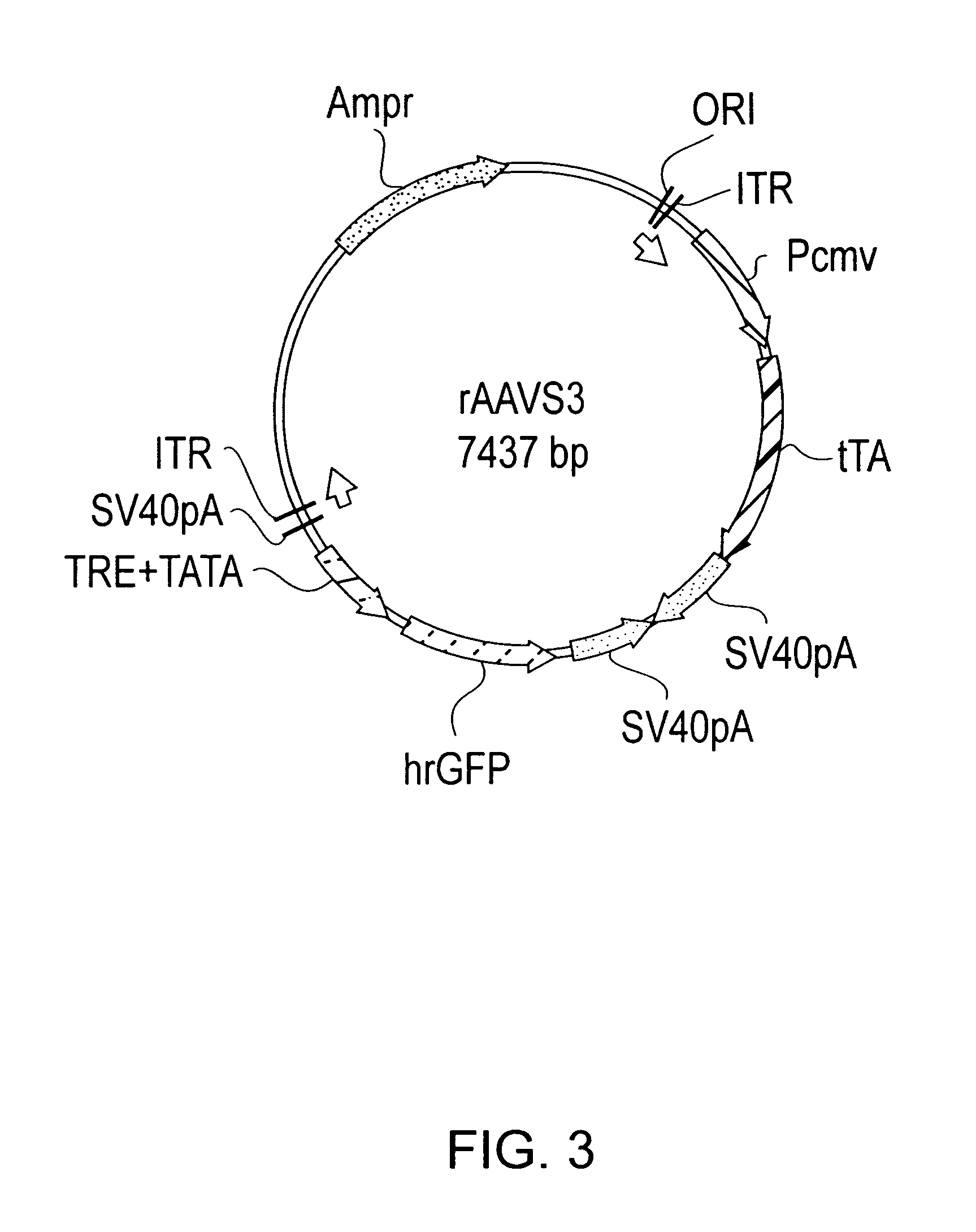
Transcriptionally-activated AAV inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) for use with recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS6936466B2Increase transcriptional activityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationLong terminal repeatGenetics
This invention provides transcriptionally-activated AAV ITRs (inverted terminal repeats) which are small and transcriptionally active and uses thereof to optimize the expression of relatively large transgenes packaged in recombinant AAV vectors.
Owner:TARGETED GENETICS CORPORTION
Multicistronic expression constructs
ActiveUS9546369B2VectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
Some aspects of this invention provide nucleic acid constructs for transgene expression. Some aspects of this invention provide multicistronic nucleic acid constructs, for example, comprising an expression cassette encoding a hairpin RNA and a reporter expression cassette. Some aspects of this invention provide nucleic acid constructs comprising two or more self-complementary nucleic acid sequences, for example, hairpin RNA encoding nucleic acid sequences and AAV inverse terminal repeats. Methods for the use of the constructs in therapy and research are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Viral vectors and methods for producing and using the same
InactiveUS7858367B2Reduce and even essentially eliminate contaminationReduce dependenceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousPolymerase L
A recombinant hybrid virus which includes: (a) a deleted adenovirus vector genome having the adenovirus 5′ and 3′ cis-elements for viral replication and encapsidation and a deletion in an adenovirus genomic region selected from the polymerase region and / or the preterminal protein region, wherein the deletion essentially prevents the expression of a functional polymerase and / or preterminal protein from the deleted region and the hybrid virus does not otherwise express a functional polymerase protein; and (b) a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector genome flanked by the adenovirus vector genome sequences of (a), wherein the recombinant AAV vector genome includes an AAV packaging sequence and a heterologous nucleic acid sequence, wherein the heterologous nucleic acid sequence is flanked by 5′ and 3′ AAV inverted terminal repeats.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
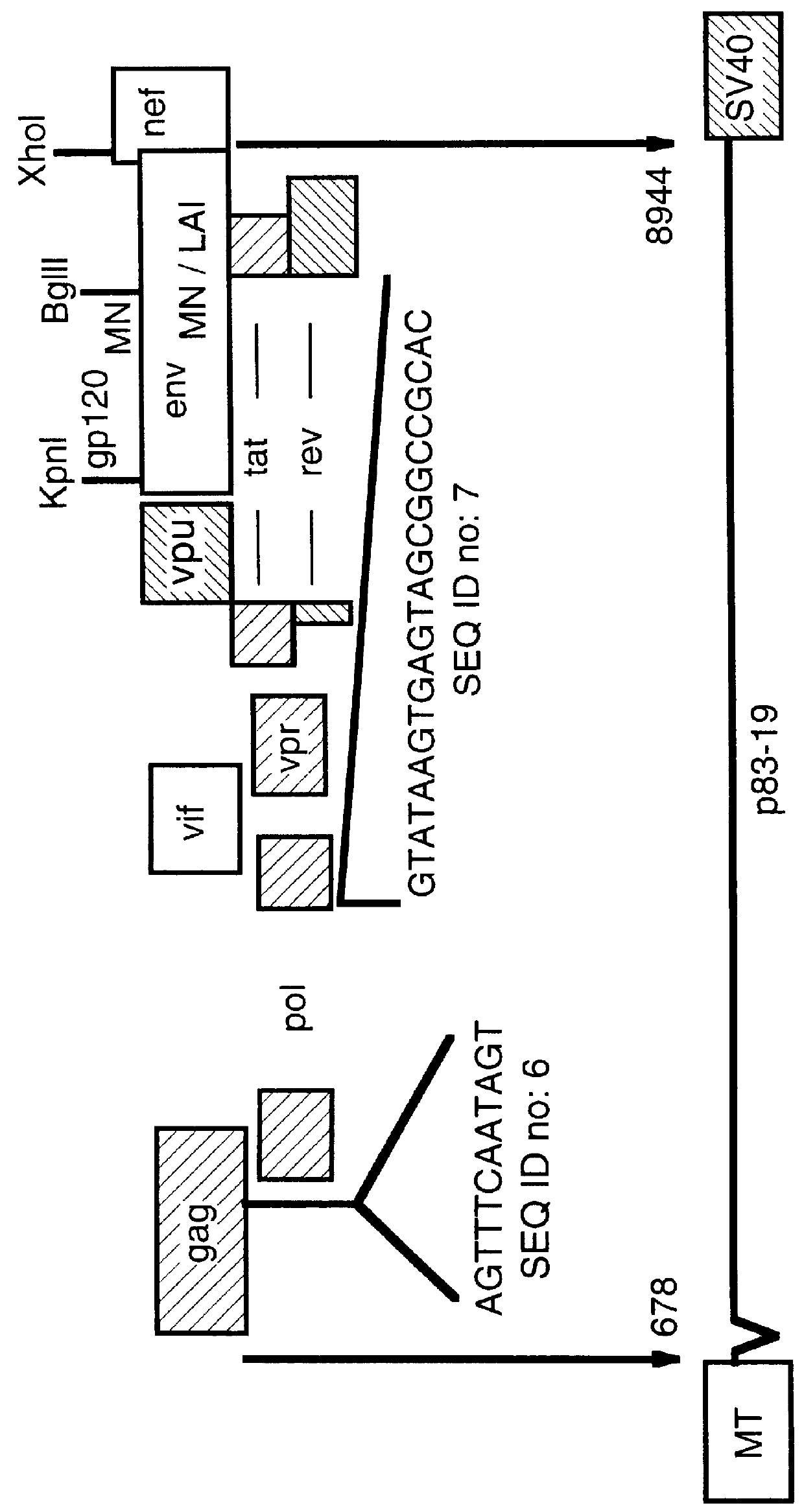
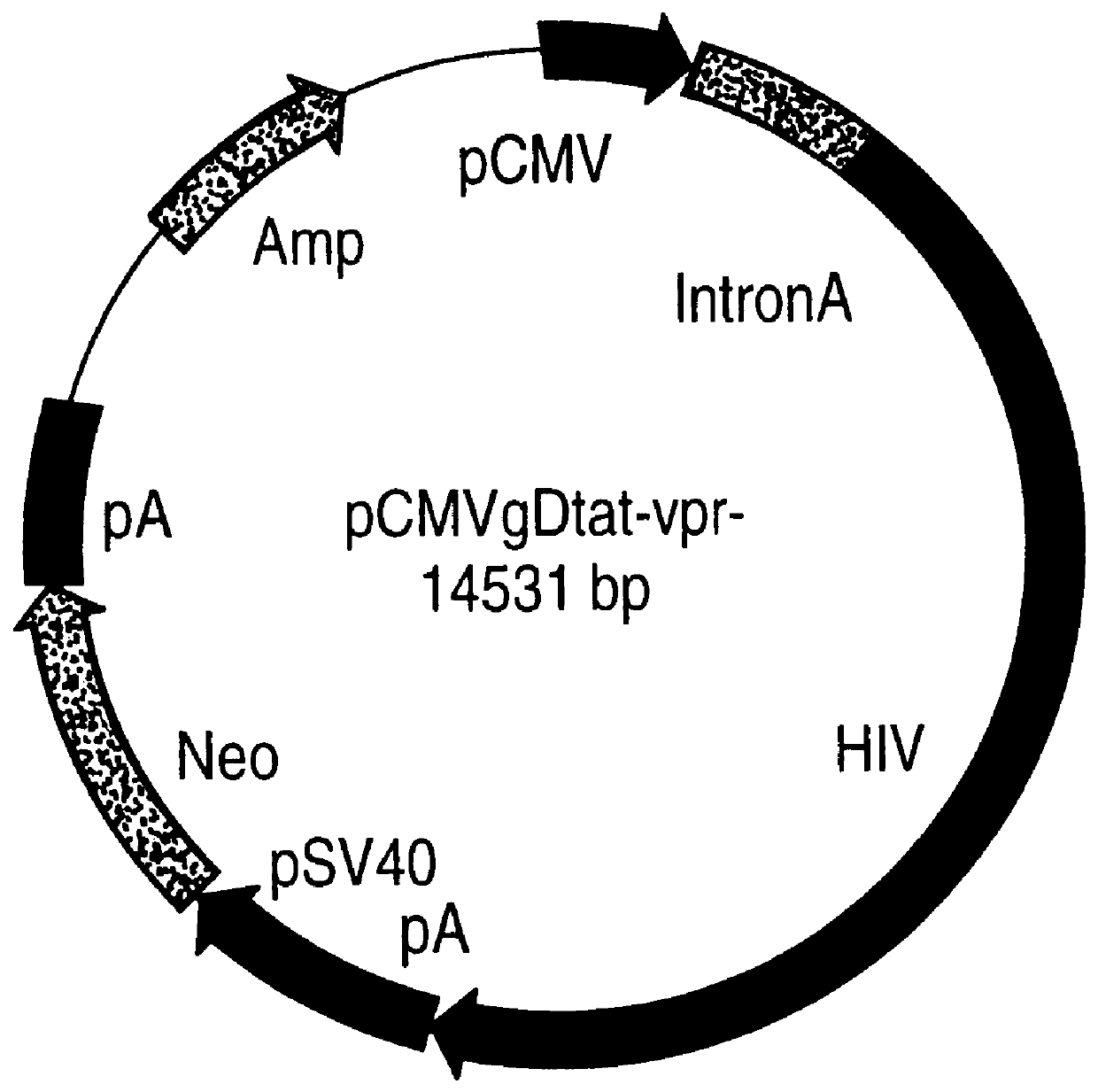
Constitutive expression of non-infectious HIV-like particles
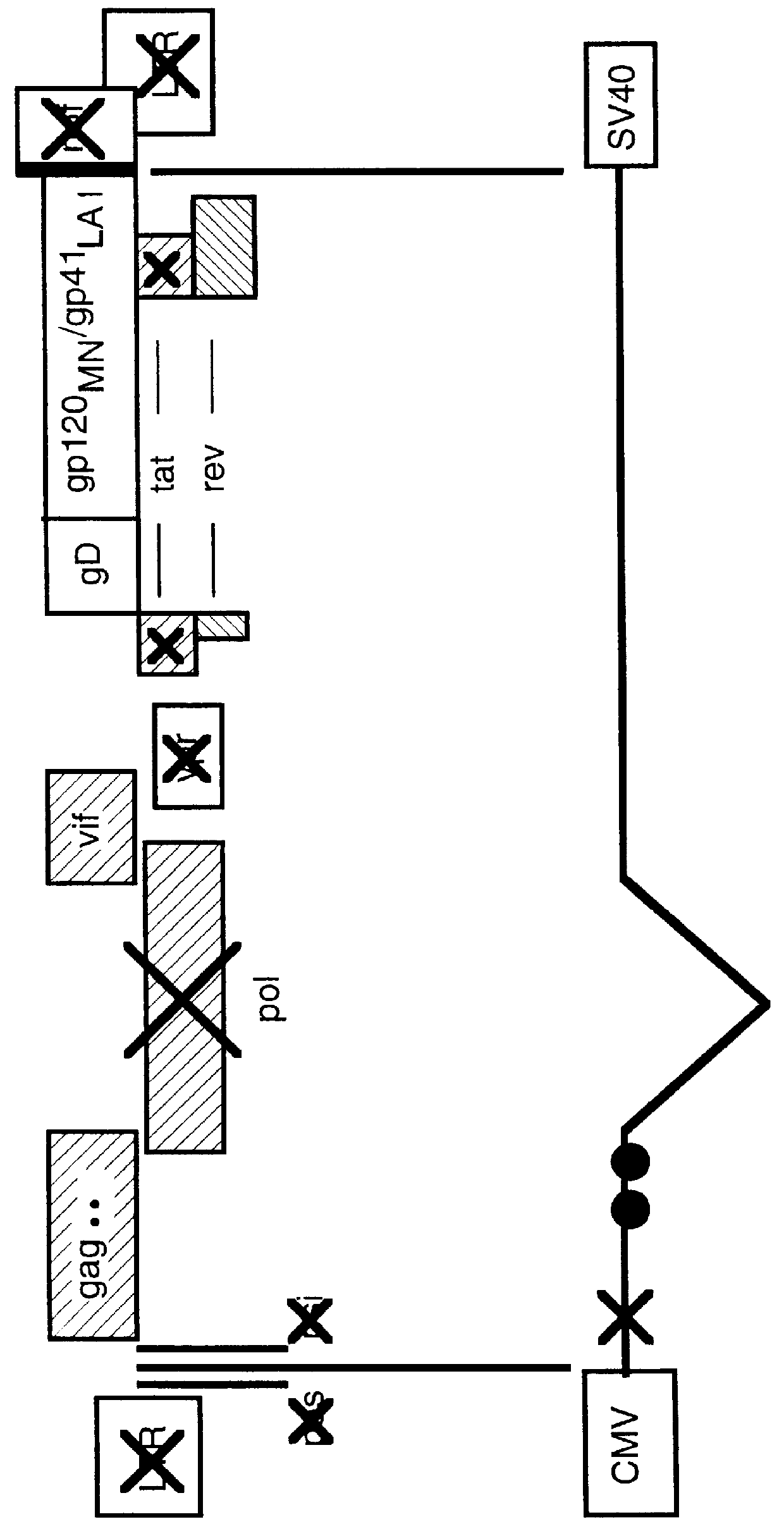
Non-infectious, non-replicating immunogenic HIV-like particles are produced by stable longn-term constitutive expression in mammalian cells by eliminating elements toxic to the mammalian cells. An expression vector contains a nucleic acid molecule comprising a modified HIV genome devoid of long terminal repeats and wherein Tat and vpr sequences are functionally disabled and a constitutive promoter operatively connected to the modified HIV genome for constitutive expression of the modified genome to produce the HIV-like particles.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Wireless Device
ActiveUS20070243892A1Easy to addReduce processing burdenError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless lanWireless network
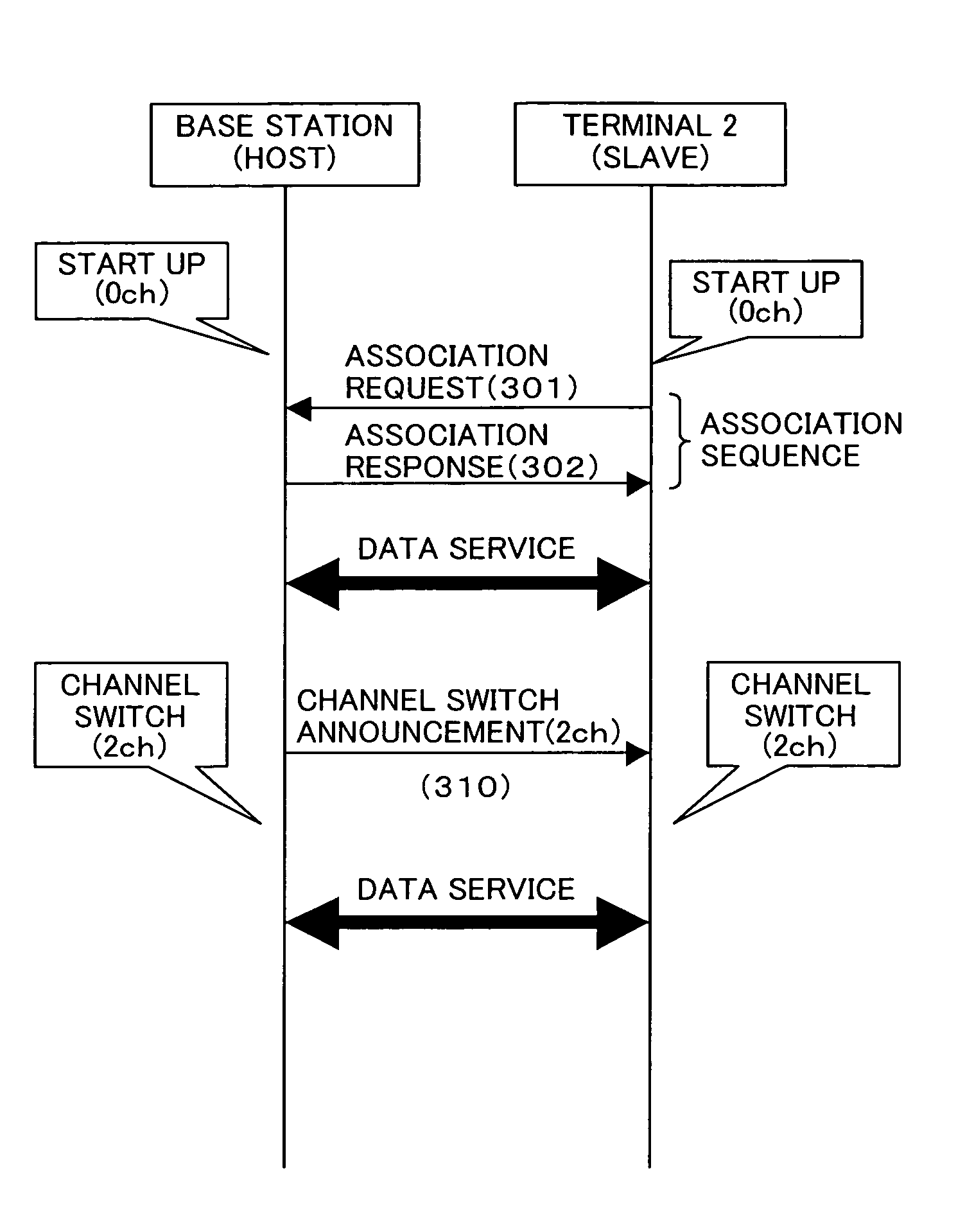
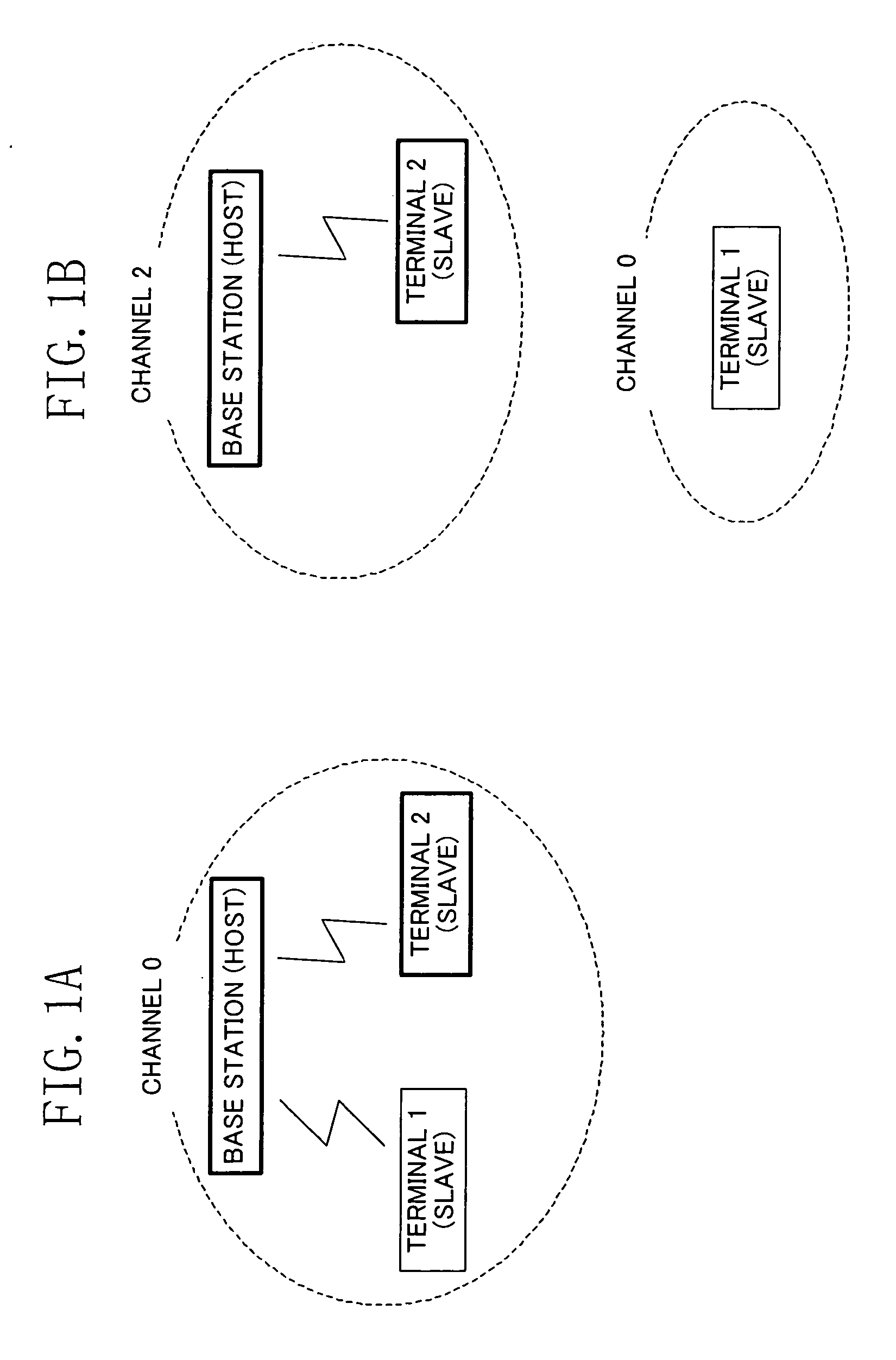
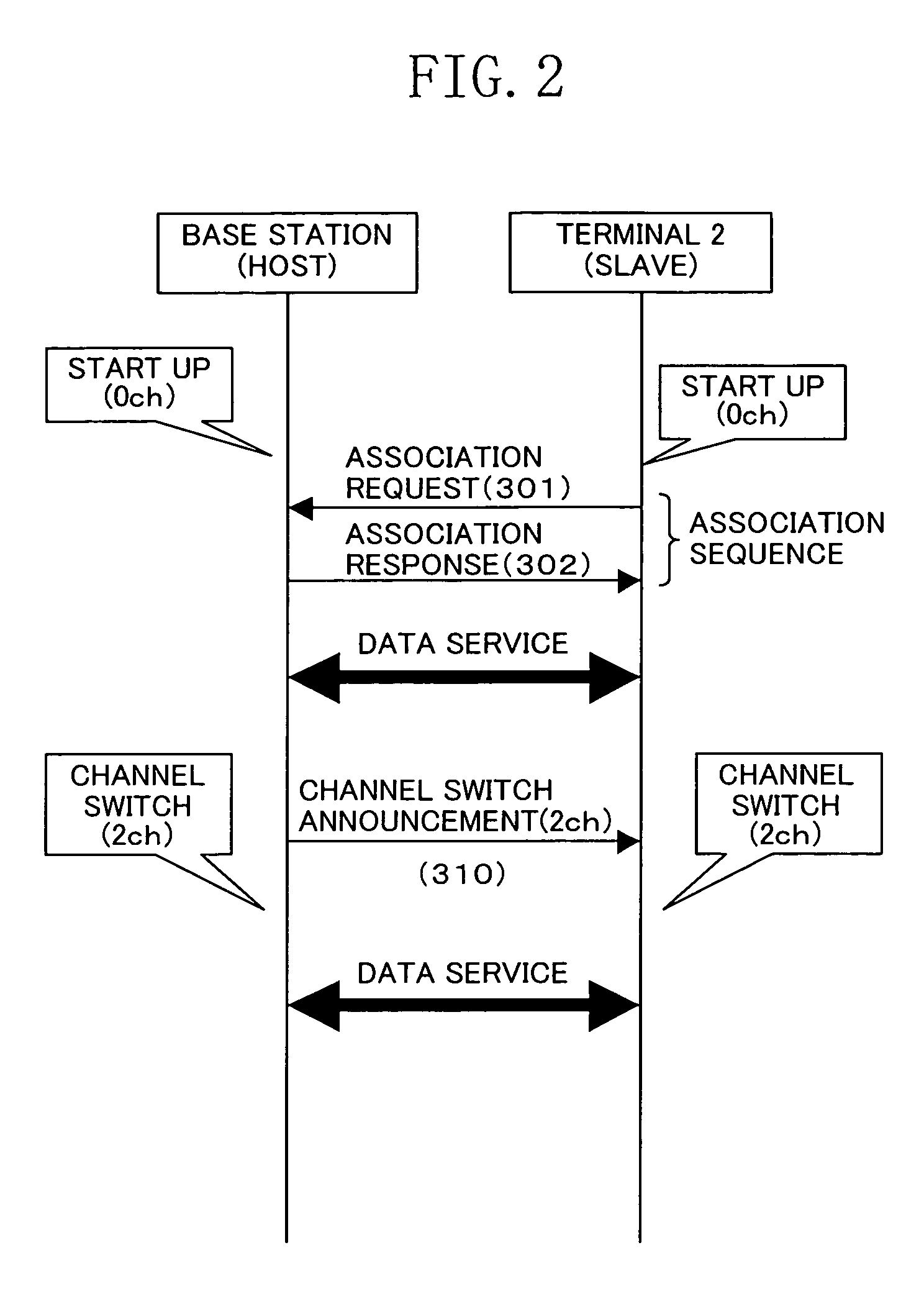
In a wireless network structure which includes a wireless LAN device having a base station function (host device) which is compliant with IEEE802.11h and at least one wireless LAN device having a terminal function (slave device) which is not compliant with IEEE802.11h, the incompliant terminal transmits a probe request to the base station for confirming the presence of the base station. When the base station has dynamically switched its channel (frequency), a probe response is not returned from the base station to the terminal. Thus, the incompliant terminal transmits a probe request through a different channel in order to confirm the presence of the base station. The incompliant terminal repeats the above channel search process till the base station is found.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
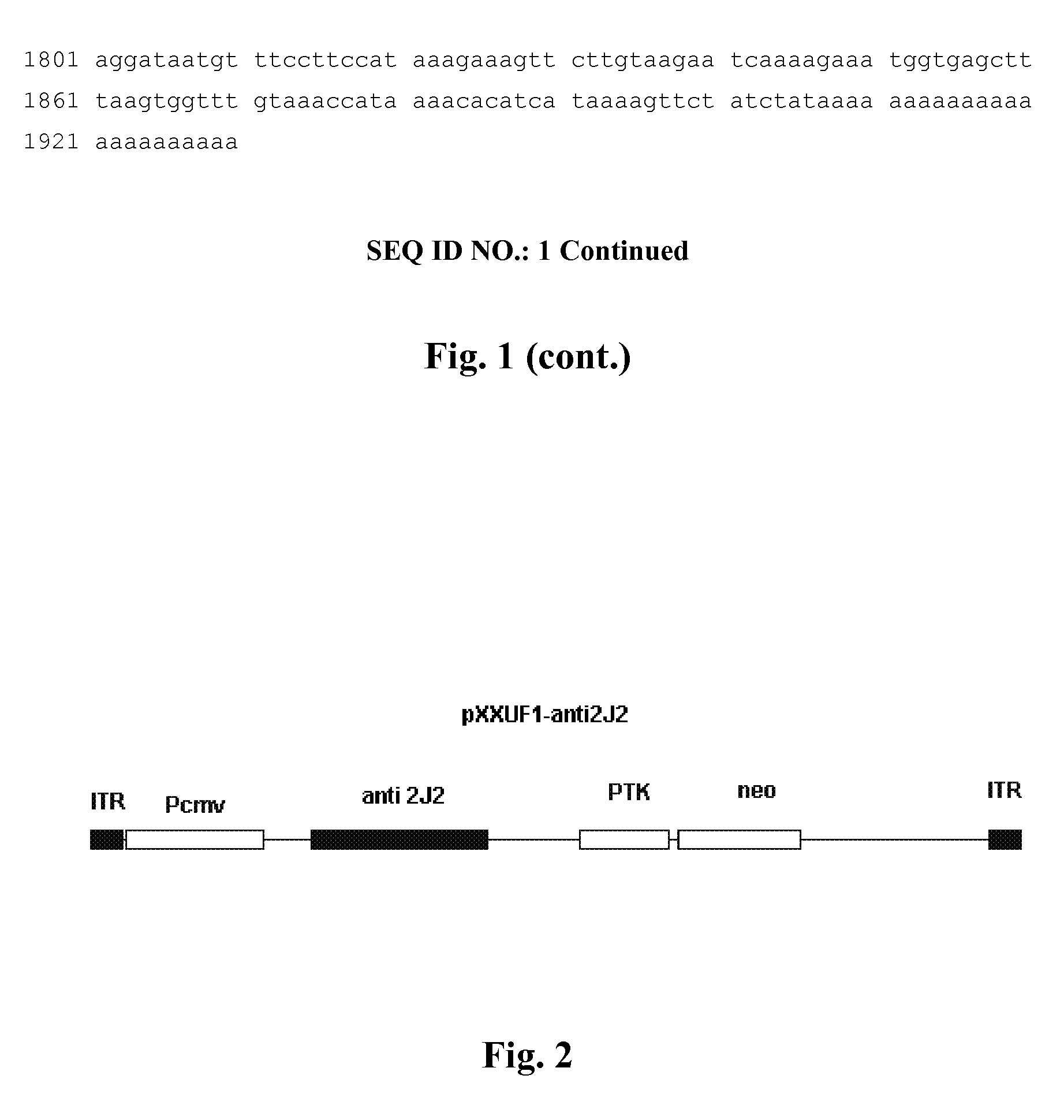
Recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing human antisense gene CyP2J2 and its preparation methods
ActiveUS8273344B2Inhibit proliferation and migrationPromote apoptosisBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Method for quantifying adeno-associated virus
ActiveUS20160273058A1Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAdeno associate virusNucleotide sequencing
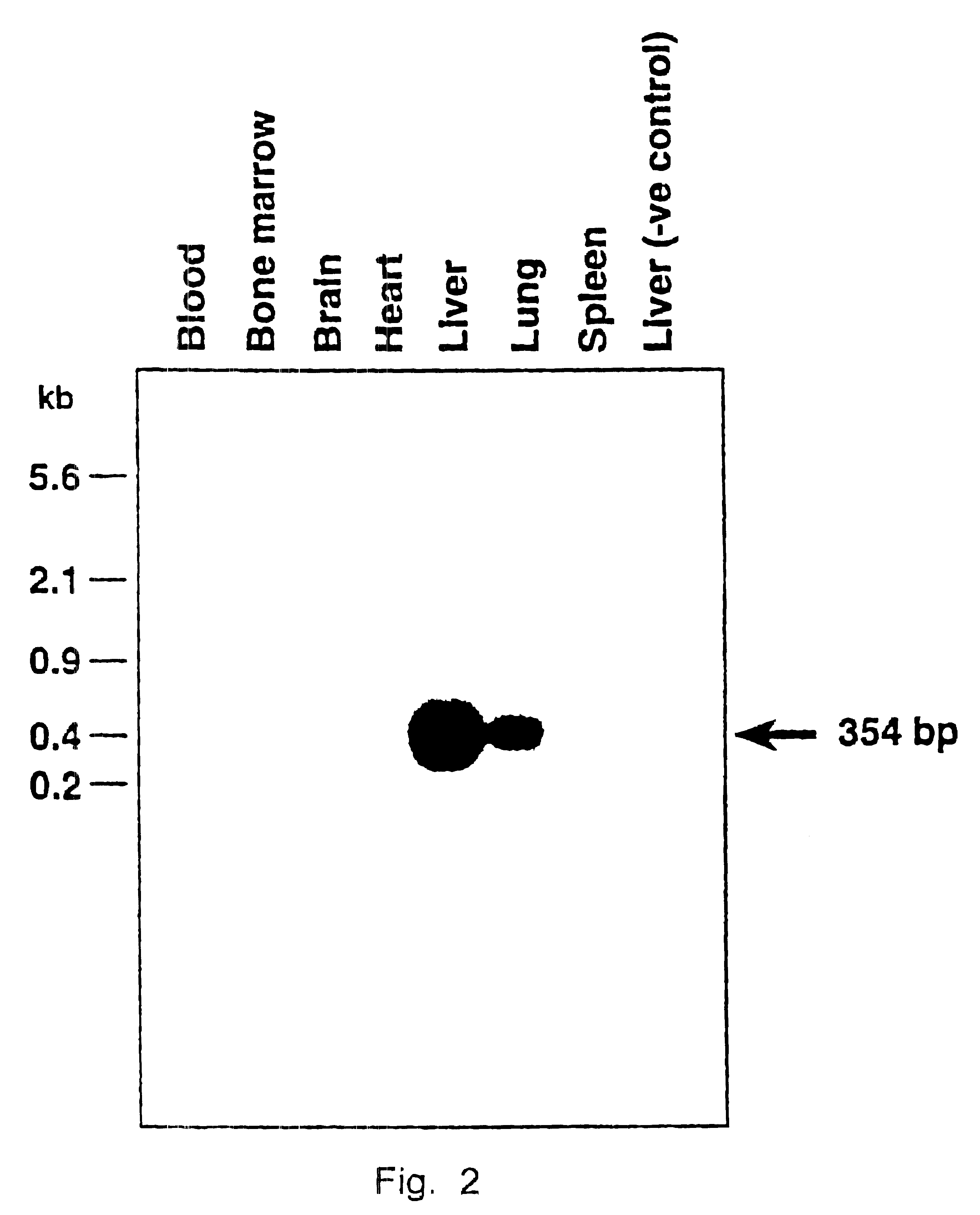
A method for quantification of an adeno-associated virus genome, including the steps of (a) preparing a composition containing a sample, at least one primer pair for use in amplification of only a nucleotide sequence contained in inverted terminal repeats of an adeno-associated virus, and an intercalating dye; (b) performing nucleic acid amplification reaction using the composition prepared in the step (a); and (c) detecting an amplified product obtained in the step (b). The present invention is especially useful in the fields of medicine, gene engineering, and biology.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Schistosome infectious oncomelania detection kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101457258ASuitable for useSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceOncomelaniaBiology
A blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection kit and a detection method thereof belongs to the verminosis transmission medium detecting field. The invention provides a kit and a detection method for detecting blood fluke infectious oncomelania based on a loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification technology (LAMP). According to the LAMP technology principle, six pairs of specific primers for amplifying a DNA fragment between the 20bp and 231bp of the schistosoma japonicum non-long terminal repeated inverse transcription transposon gene (AF412214) are designed. The LAMP method is constructed for detecting blood fluke gene in the body of the infectious oncomelania and the objective for distinguishing the blood fluke infectious oncomelania from the non-infectious oncomelania is reached. Comparing to the conventional blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection method the method of the invention has advantages of easy and fast operation, sensitive and specific without especial equipment and is suitable for bilharziasis controlling personnel use on site.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
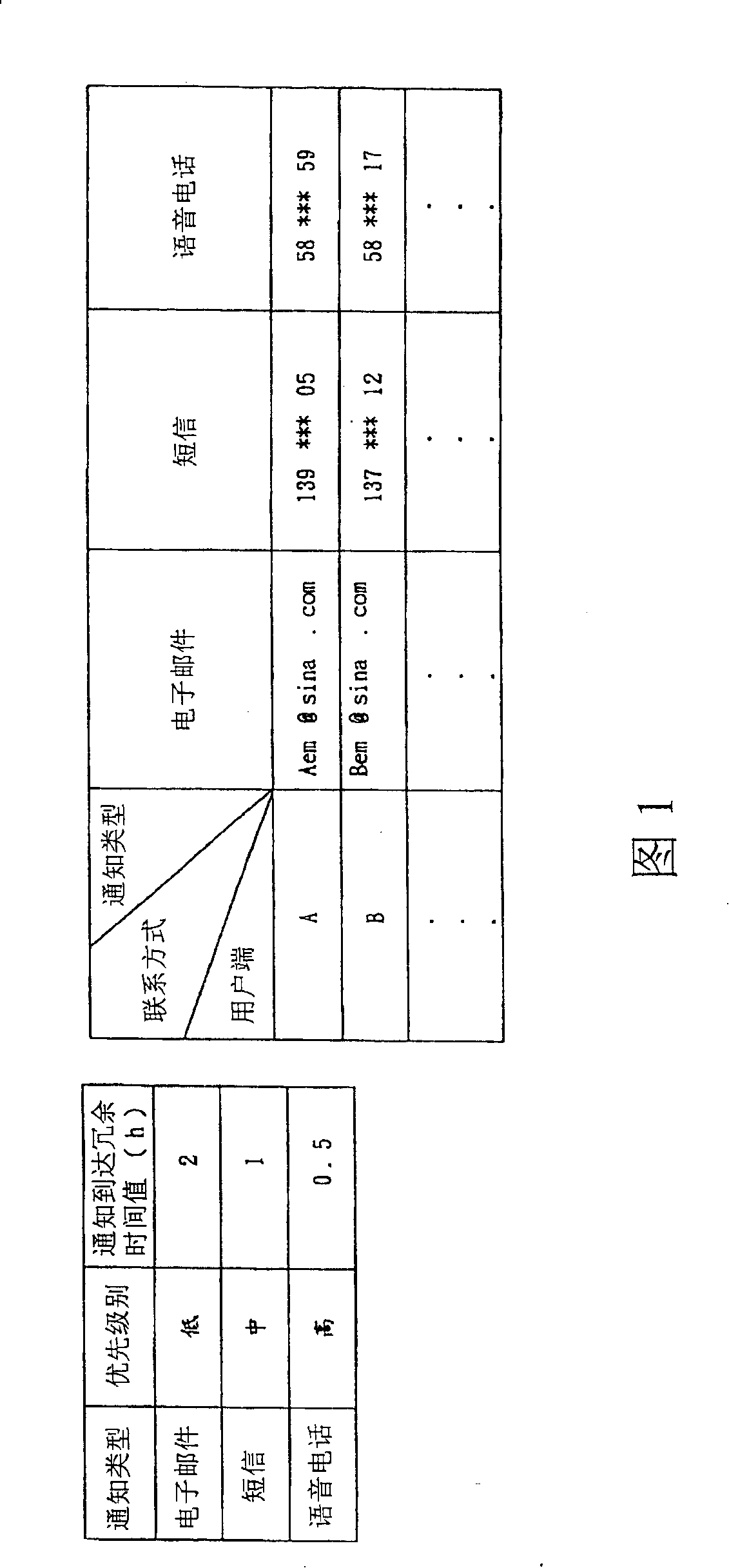
Method for conveying information
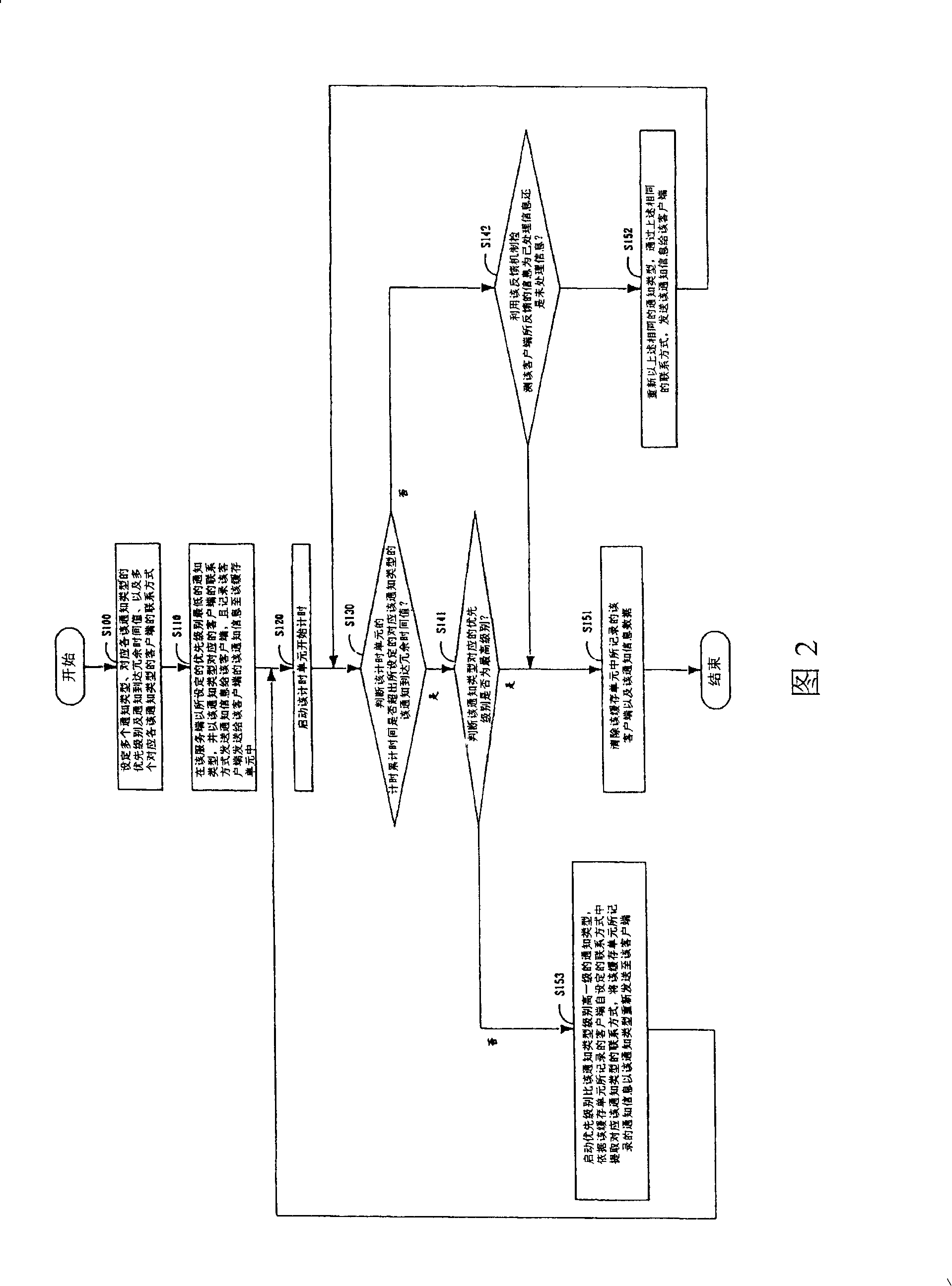
ActiveCN101202712ASave human effortSave energySpecial service for subscribersData switching networksClient-sideProcess information
An information communicating method provides a feedback mechanism, which transmits notice information to a client through a classified control server terminal. The notice information is transmitted to the client by the notice type of a preset lowest PRI and a client contact way corresponding to the notice type; simultaneously, a treatment state report of the notice information from a user is informed to a server terminal in real time by the feedback mechanism; if the client feeds back the treated information to the server terminal, the server terminal stops the information transmitting process; if not, the server terminal retransmits the notice information to the client by the notice type; if the client has no response in the preset time, the server terminal repeats the steps and informs the information report to the client by the notice type, the preset PRI of which is one grade higher than the notice type and repeats the steps until the server terminal receives the treated information fed back by the client or the PRI of the notice type reaches the highest preset level, thus improving the notice standard-reaching rate of the server terminal.
Owner:ZHIGU HLDG
Method of communication and base station
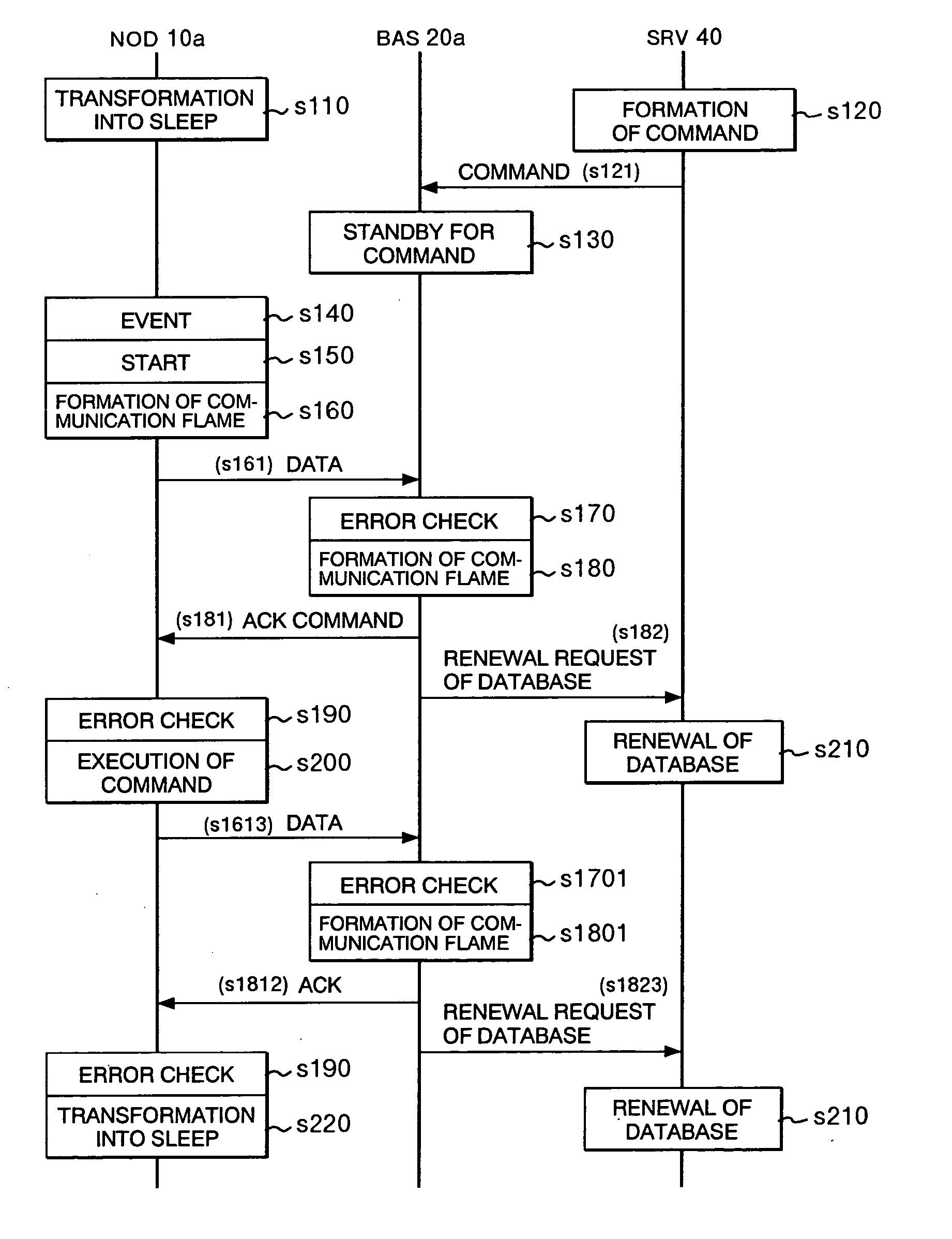
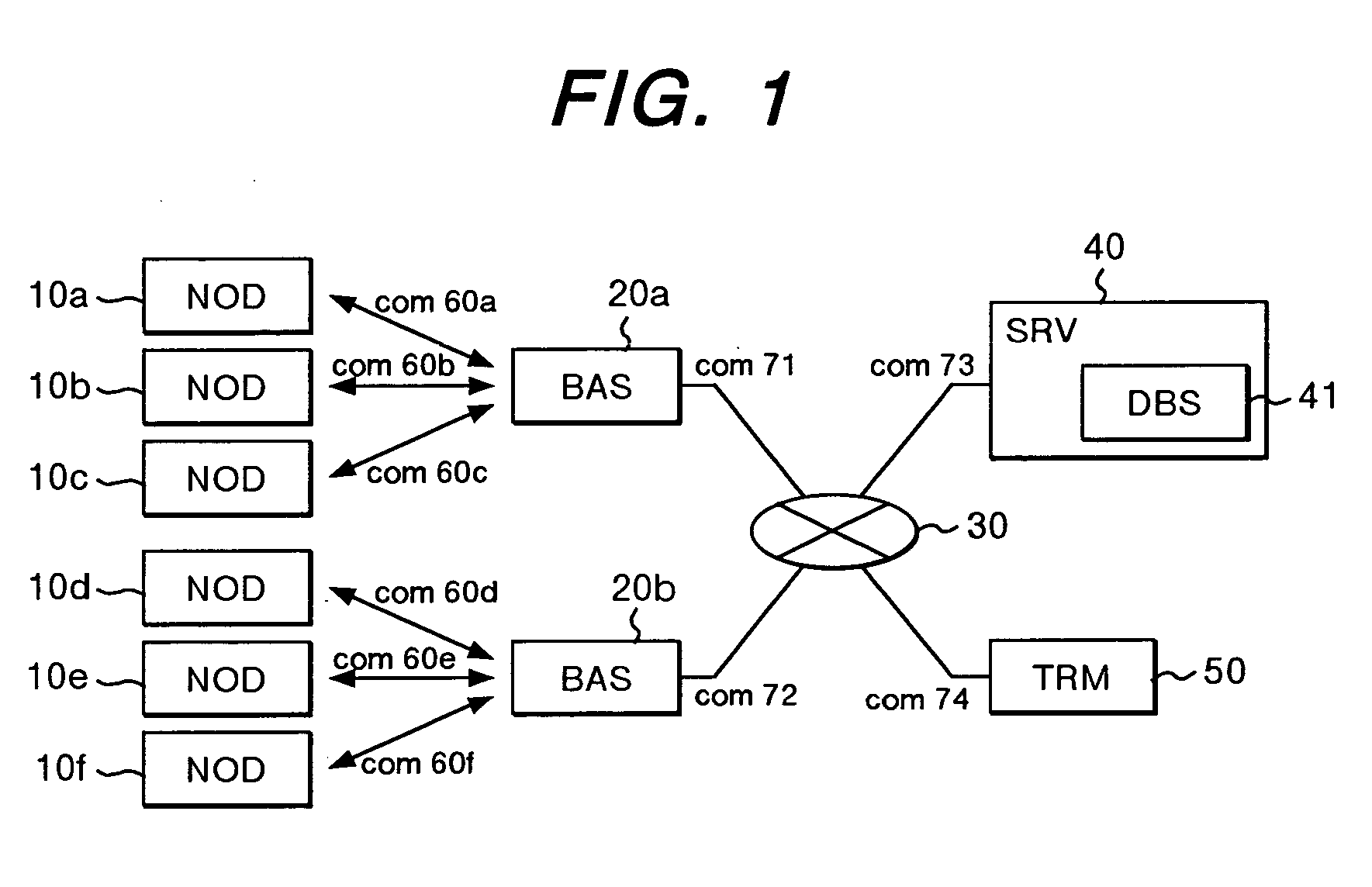
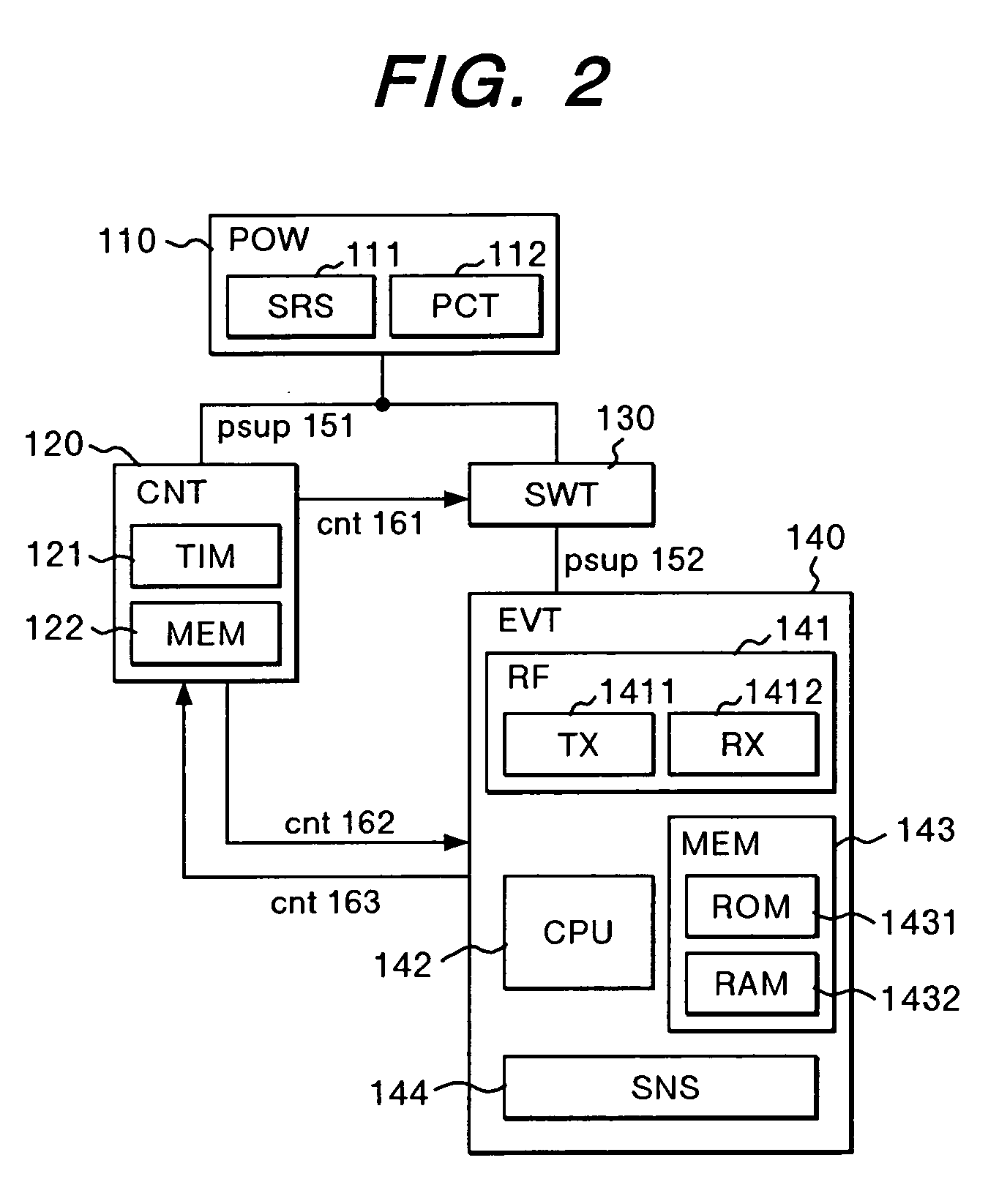
InactiveUS20060019695A1Reduce power consumptionReduce consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsEnergy efficient ICTPower consumptionTerminal Repeats
There are provided a method of communication which can reliably transmit information from a base station to a wireless terminal in a system which can reduce power consumption by intermittent operation in which the wireless terminal repeats operating state and suspended state by power on and off and the base station used for the method. The method includes the steps of storing base station information such as a command or data supplied to the wireless terminal in the base station, transferring the wireless terminal from the suspended state to the operating state to transmit information from the sensor to the base station, coupling the base station information stored in the base station to a response signal to transmit it to the wireless terminal in the operating state for transmitting the sensor information, and returning the wireless terminal to the suspended state after completing the transmission of the base station information and sensor information.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
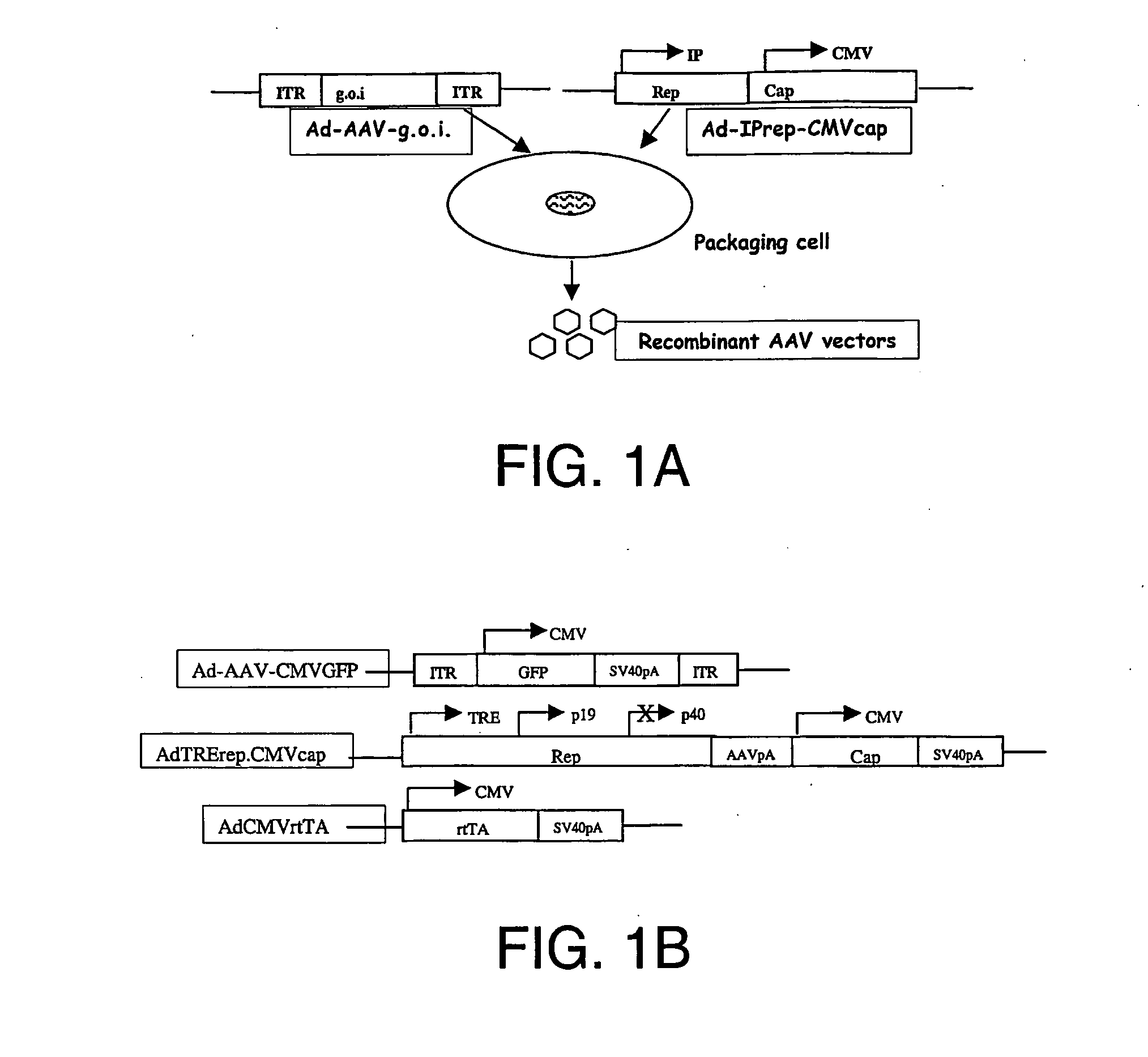
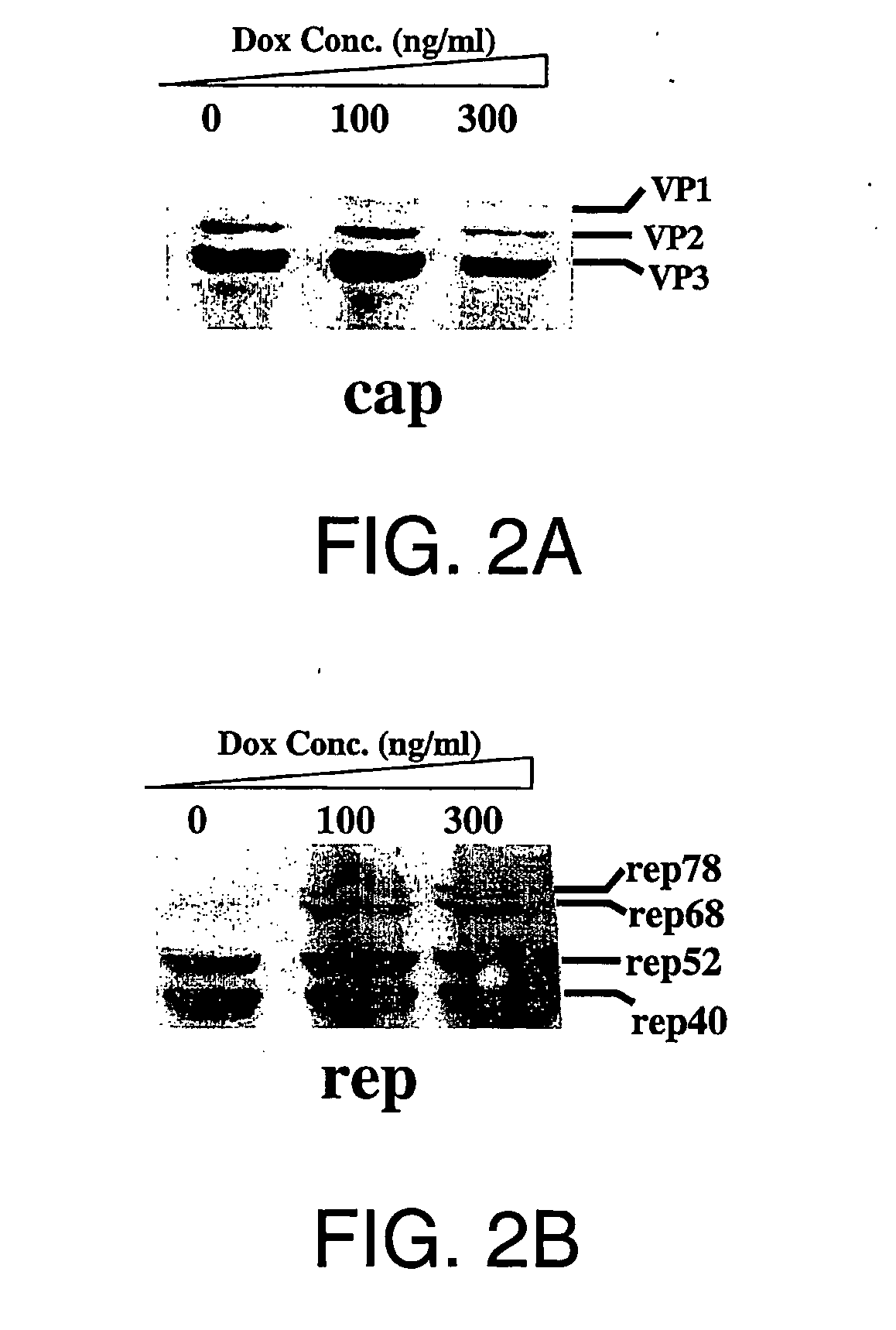
Generation of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors by a complete adenovirus-mediated approach
A complete virus-mediated system for recombinant AAV production including: (a) a first recombinant adenovirus encoding one or more AAV REP78 / 68 polypeptides and one or more viral capsid polypeptides; (b) a second recombinant adenovirus encoding a gene of interest and including AAV inverted terminal repeats, wherein the AAV inverted terminal repeats flank the gene of interest; (c) viral helper functions; and (d) a host cell transduced with the first recombinant adenovirus, the second recombinant adenovirus, and the viral helper functions.
Owner:LI CHUAN YAN +1
Method for producing heart-specific fluorescence of non-human eukaryotic animals
A method of expressing in vivo heart-specific fluorescence in transgenic line of zebrafish is developed, which provides a research model for studying heart-related gene functions and performing gene therapies in the future. The method comprises the following steps. Firstly, a plasmid is constructed. This plasmid construct includes the upstream regulatory region, the exon 1, the intron 1, and the exon 2 of cmlc2 gene, cDNA of GFP, wherein the cmlc2 gene and GFP cDNA form a cassette, and inverted terminal repeats from adeno-associated virus are flanked at both sides of this cassette. The plasmid construct is linearized and microinjected into one-celled zebrafish fertilized eggs. Lastly, the heart-specific fluorescent expressed zebrafish are selected and the germline-transmitting transgenic strain is generated.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Methods and compositions for treating brain diseases
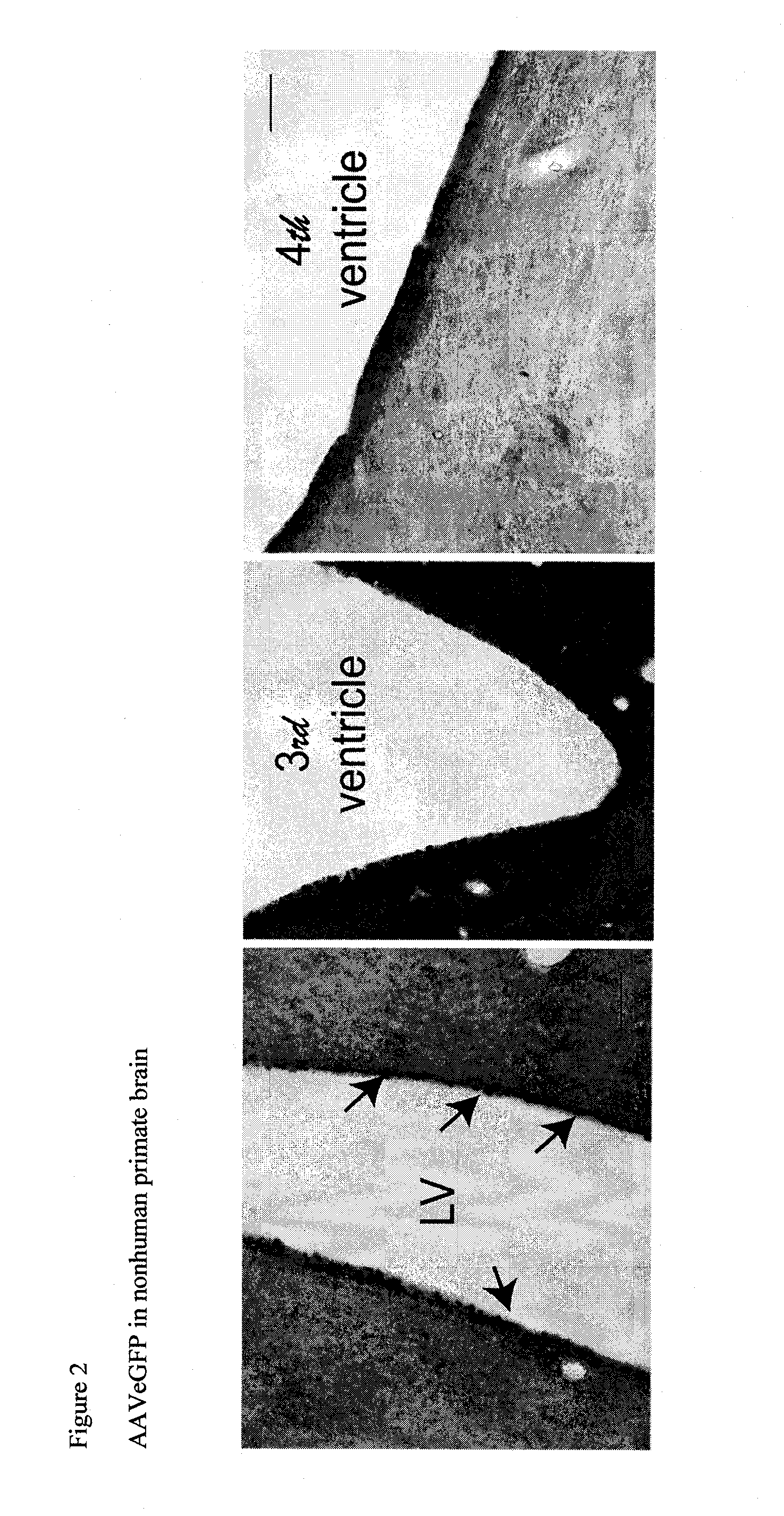
The present disclosure provides methods of treating a disease in a non-rodent mammal comprising administering to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the non-rodent mammal an rAAV2 particle containing a vector comprising a nucleic acid encoding a therapeutic protein inserted between a pair of AAV inverted terminal repeats in a manner effective to infect an ependymal cell in the non-rodent mammal, wherein the ependymal cell secretes the therapeutic protein so as to treat the disease.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Non-infectious, non-replicating, immunogenic human immunodeficiency virus-like particles
InactiveUS7008784B1Improving immunogenicitySafe preparationNanotechVirus peptidesHeterologousPol genes
The present invention is directed toward methods for the production of non-infectious, replication-deficient, immunogenic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-like particles. These particles are prepared from a recombinant expression vector comprising a heterologous promoter operatively connected to a DNA molecule comprising a modified HIV genome devoid of the long terminal repeat (LTR) regulatory regions but containing at least the gag and pol genes in their natural genomic arrangement. This vector is introduced into mammalian cells to produce the particles of interest. These particles should prove useful in a number of diagnostic, virologic, and immunologic applications.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Methods and compositions for targeted delivery of gene therapeutic vectors
InactiveUS20110130444A1Organic active ingredientsFusion with DNA-binding domainFocus ultrasoundMicrobubbles
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods and compositions for tissue- specific delivery of a gene therapeutic, transgenic nucleic acid in mammals. Methods and compositions of the invention include the steps of providing a nucleic acid comprising a transgene flanked by two terminal repeats and, within the same or on a separate nucleic acid, a nucleotide sequence encoding a transposase, wherein the transgene comprises a biotherapeutic gene, contacting the nucleic acid with perfluorocarbon gas-filled microbubbles to form a mixture, introducing the mixture into the bloodstream of a mammal, and focusing ultrasound pulses on a specific tissue of said mammal, wherein said pulses disrupt said microbubbles of said mixture and release said nucleic acid into the bloodstream within the target tissue, thereby enabling uptake of the transgenic nucleic acid into the cells of said target tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Compositions, Methods, and Systems for SIRNA Delivery
InactiveUS20110052666A1Reduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPyrimidine NucleotidesBiology
The instant invention provides silencer expression cassettes for delivery of RNAi therapy. The silencer cassettes of the instant invention encode an RNAi agent and lack means for replication within a host cell, inverted terminal repeats and further lacking one or more selectable markers. Optionally, the silencer cassettes lack CpG dinucleotides and / or the RNAi agent is within a scaffold of a naturally occurring miRNA. The composition comprising the silencer cassettes of the instant invention, as well as methods of use and suitable systems are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and compositions for RNA-guided treatment of HIV infection
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Method for producing heart-specific fluorescence of non-human eukaryotic animals
A method of expressing in vivo heart-specific fluorescence in transgenic line of zebrafish is developed, which provides a research model for studying heart-related gene functions and performing gene therapies in the future. The method comprises the following steps. Firstly, a plasmid is constructed. This plasmid construct includes the upstream regulatory region, the exon 1, the intron 1, and the exon 2 of cmlc2 gene, cDNA of GFP, wherein the cmlc2 gene and GFP cDNA form a cassette, and inverted terminal repeats from adeno-associated virus are flanked at both sides of this cassette. The plasmid construct is linearized and microinjected into one-celled zebrafish fertilized eggs. Lastly, the heart-specific fluorescent expressed zebrafish are selected and the germline-transmitting transgenic strain is generated.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
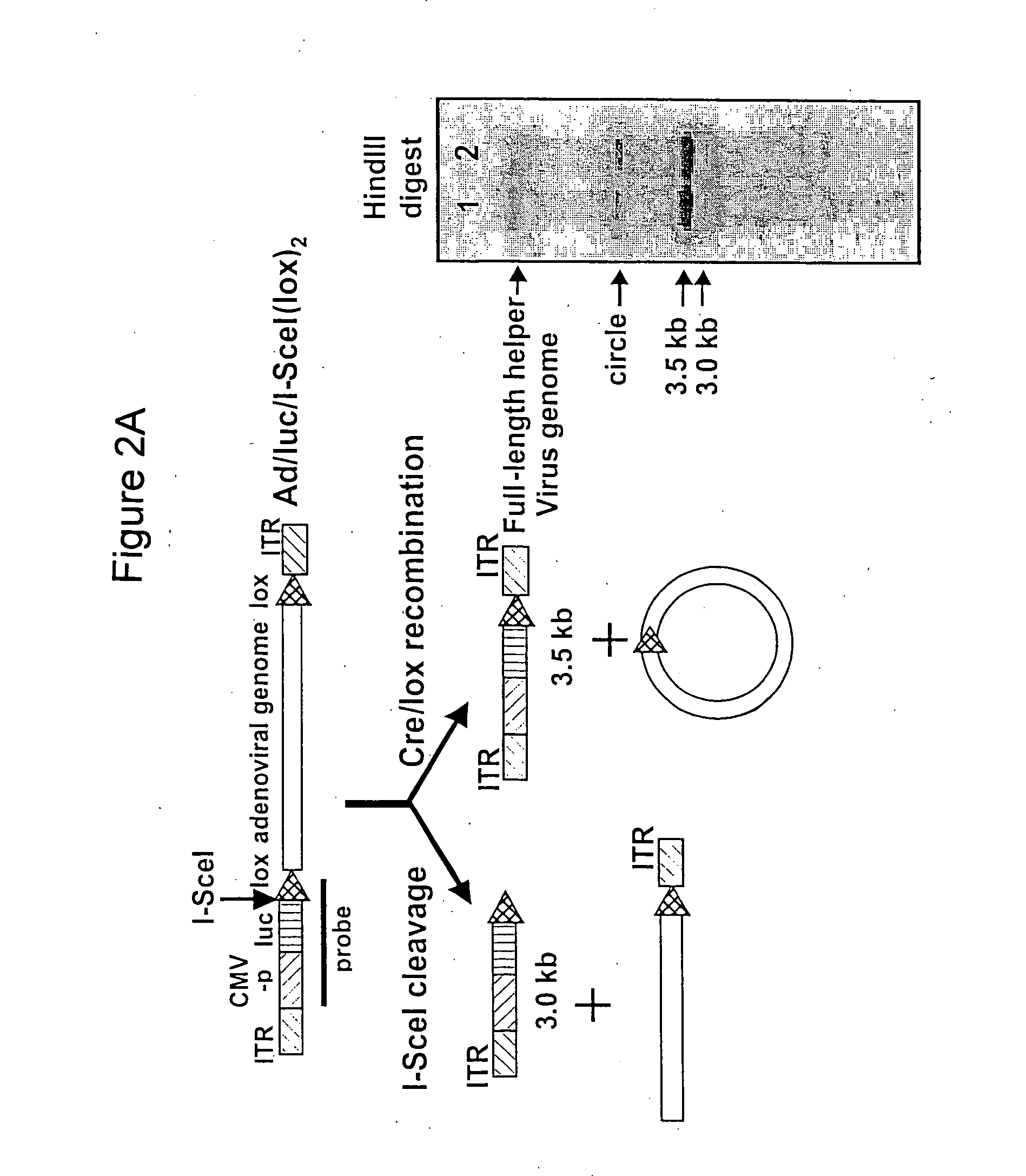
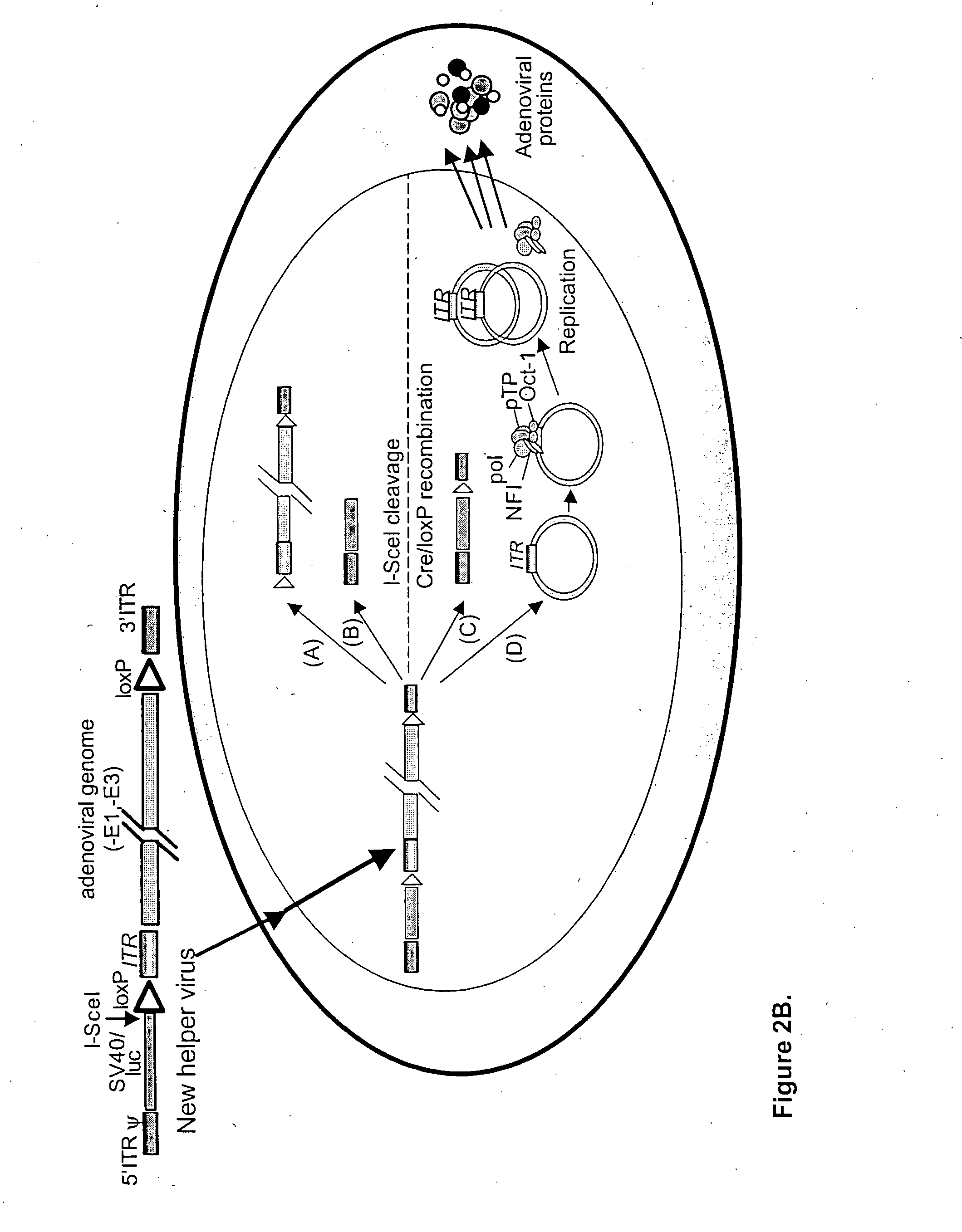
Helper dependent adenoviral vector system and methods for using the same
A helper dependent adenoviral vector system is provided. The subject helper dependent adenoviral vector system is made up of: (1) a "gutless" adenoviral vector, which in certain embodiments includes cis-acting human stuffer DNA that provides for in vivo long term, high level expression of a coding sequence present on the vector, where in certain embodiments the vector includes an integrating domain; (2) an adenoviral helper vector that is characterized by having an adenoviral genome region flanked by recombinase recognition sites, where the helper vectors further include a non-mammalian endonuclease recognition site positioned outside of the adenoviral genome region and in certain embodiments a third adenoviral inverted terminal repeat (ITR) sequence positioned between first and second terminal ITRs; and (3) a mammalian cell that expresses the corresponding recombinase and endonuclease, as well as the adenoviral preterminal and polymerase proteins. Also provided are methods of using the subject systems to produce virions having the subject helper dependent adenoviral vectors encapsulated in an adenoviral capsid. In addition, kits for use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
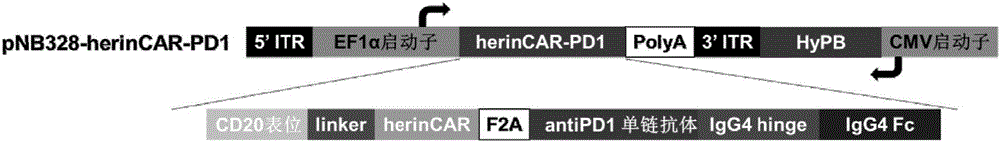
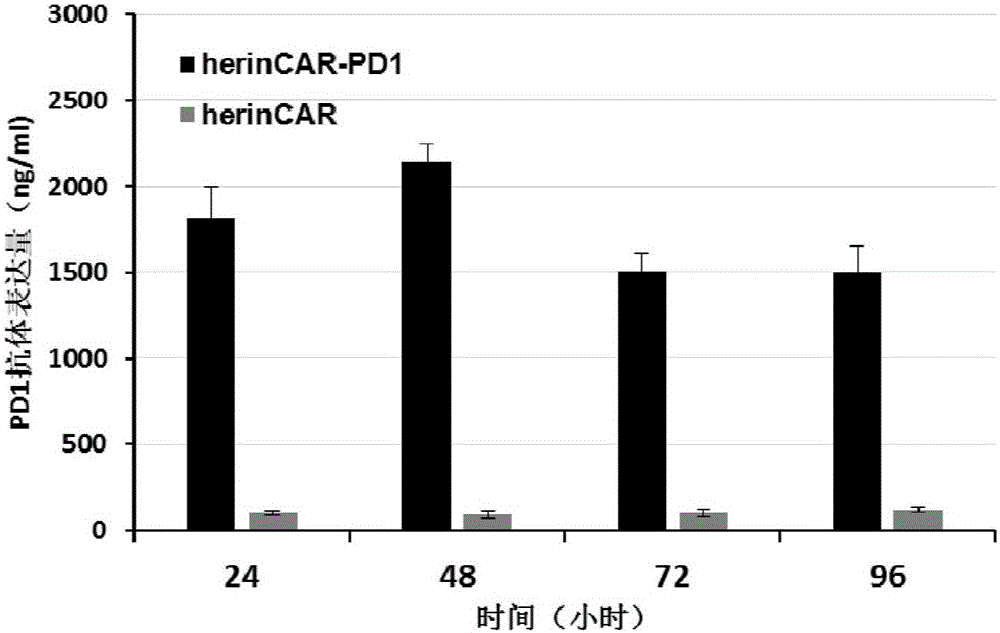
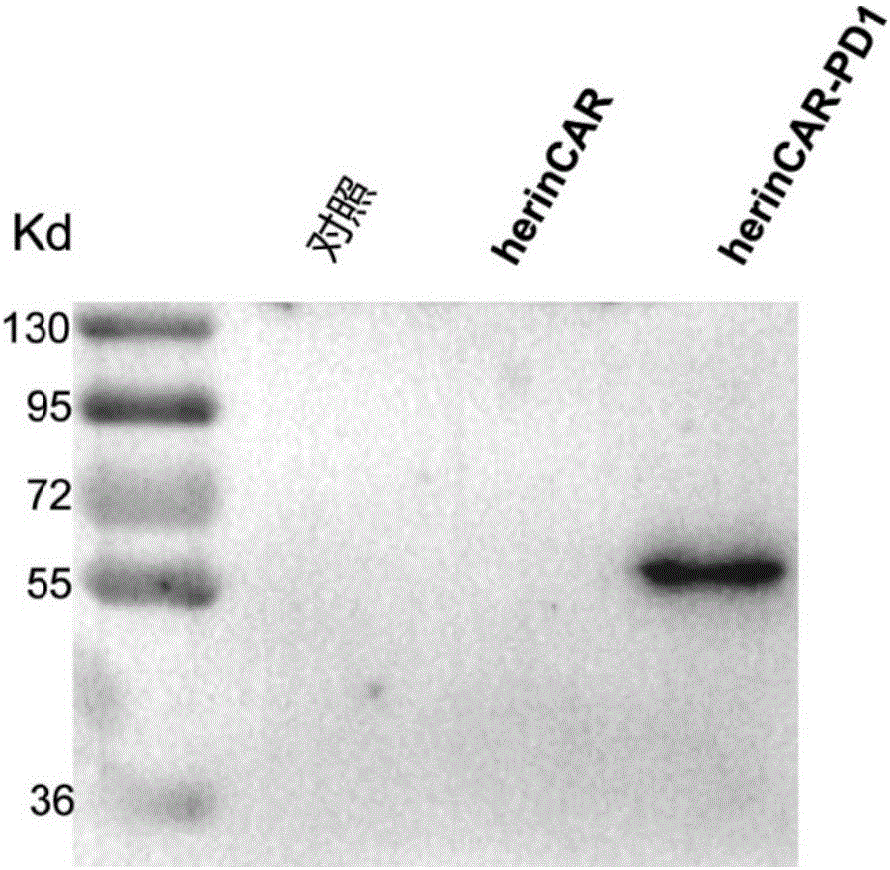
CAR-T cell capable of efficiently and stably expressing inhibiting antibody and application thereof
PendingCN107523547AAntibacterial agentsGenetically modified cellsCAR T-cell therapyAntigen receptors
The invention provides a CAR-T cell capable of efficiently and stably expressing an inhibiting antibody and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a transgenic T cell, and the genome of the transgenic T cell is stably integrated with expression cassettes containing nucleic acid sequences coding chimeric antigen receptors and immune checkpoint inhibiting antibodies, wherein two ends of the expression cassettes contain inverted terminal repeats of transposons. In the genome of the pluripotent CAR-T cell, the expression cassettes of the inhibiting antibodies are stably integrated via a transposon system, so the CAR-T cell has the activity of stably and efficiently expressing the inhibiting antibodies on the premise that original killing activity of the T cell is maintained, transfer-back CAR-T cells are prevented from inhibition by a tumor microenvironment, and residual tumor-specific T cells can be activated in situ. Meanwhile, a molecular brake system is introduced to ensure the security of CAR-T cell therapy, and transfer-back pluripotent CAR-T cells can be timely removed if necessary.
Owner:SHANGHAI CELL THERAPY RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com