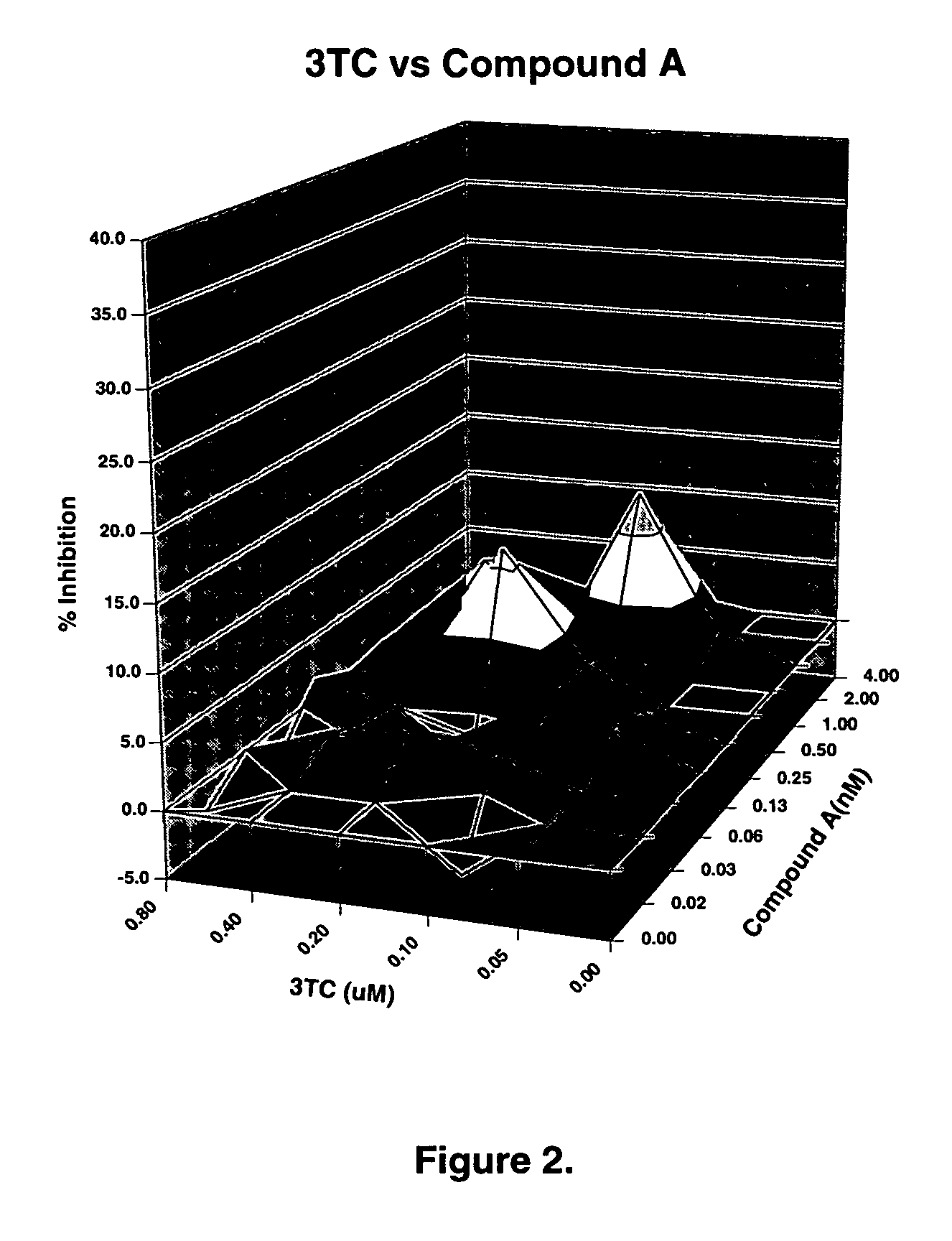
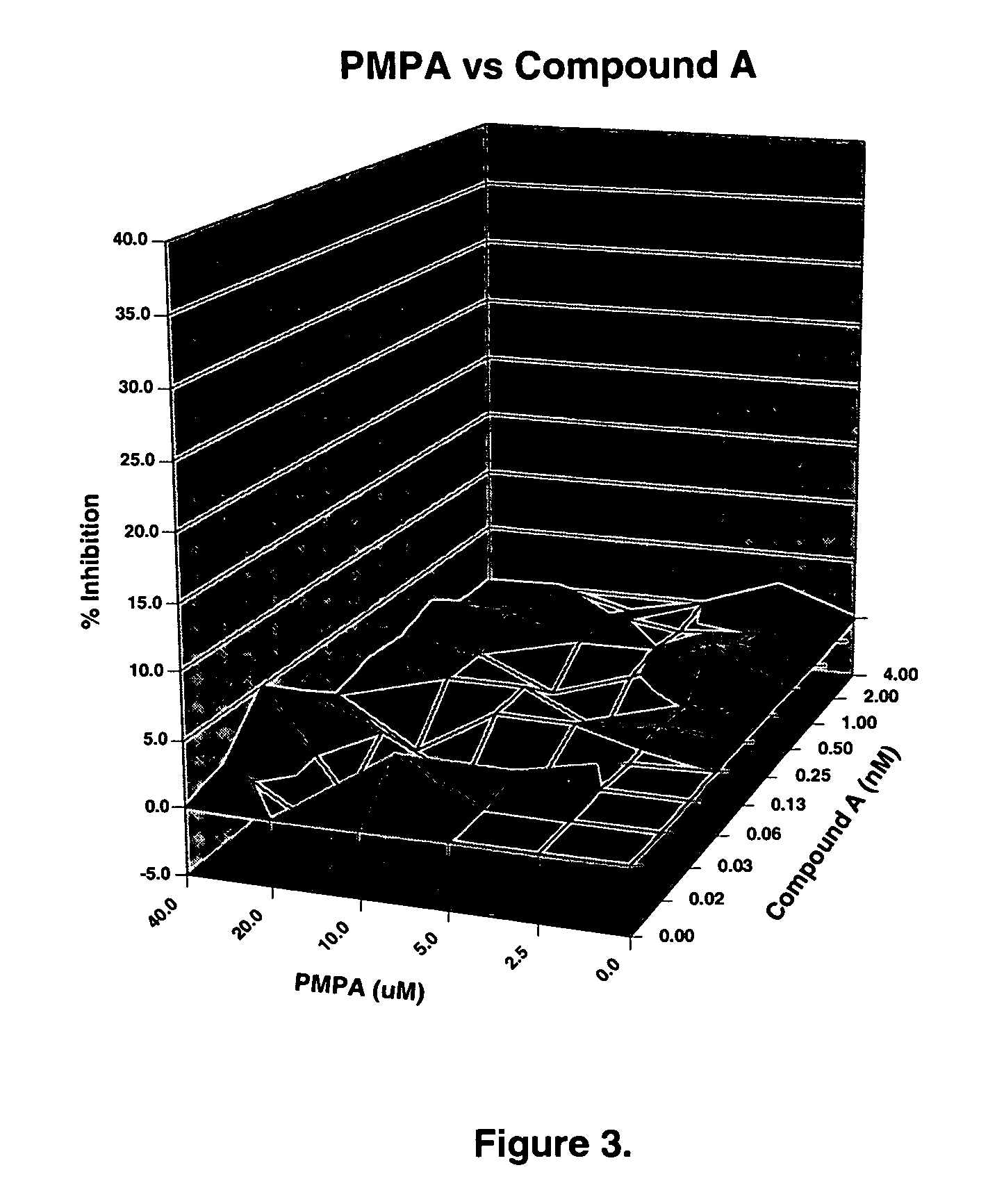
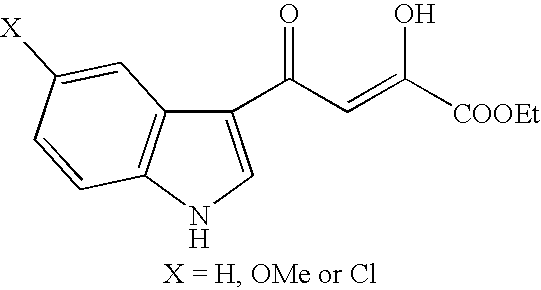
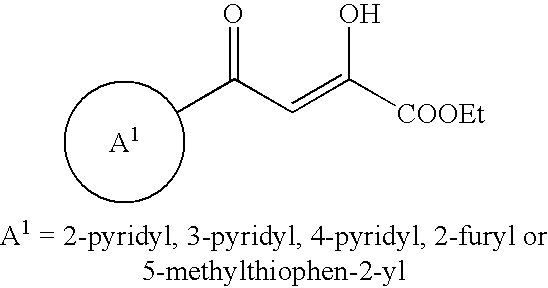
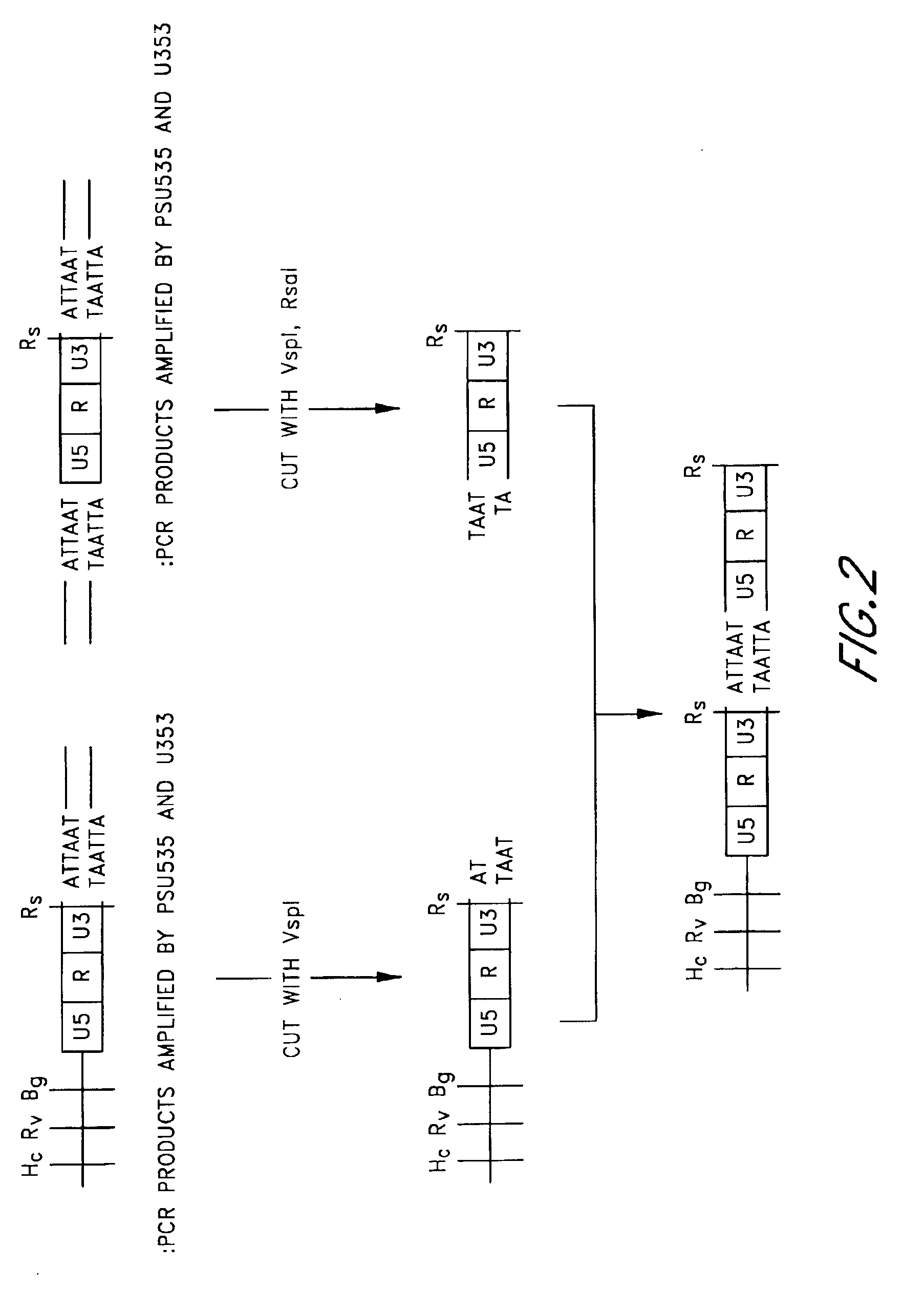
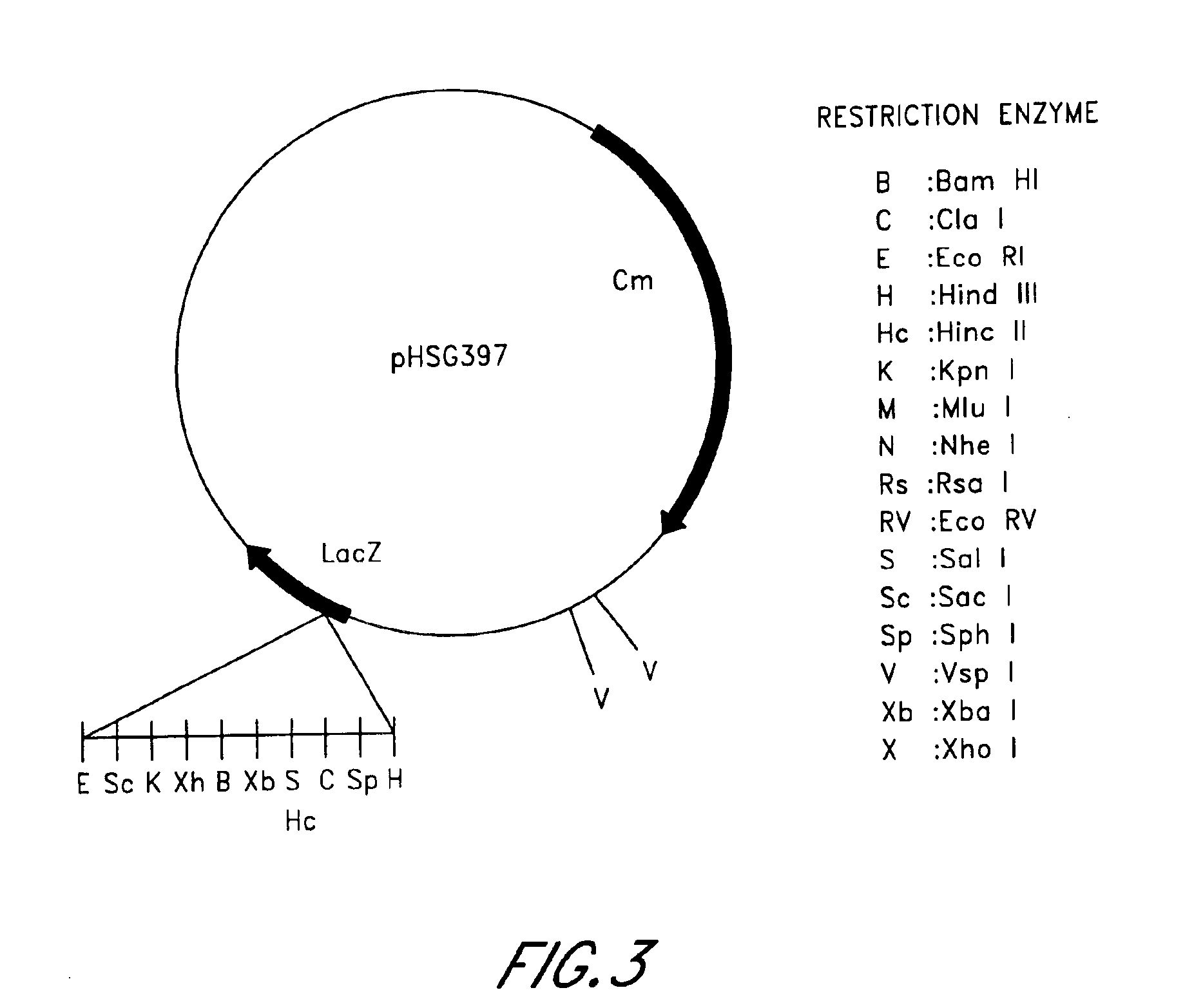
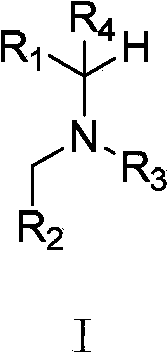
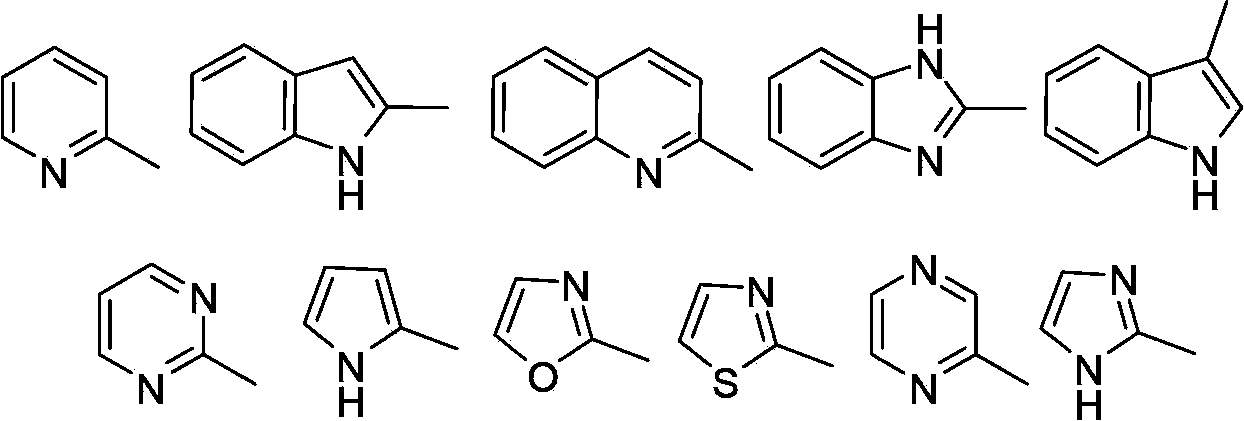
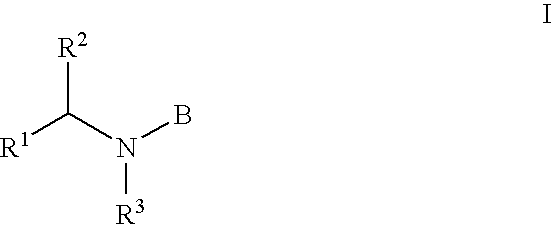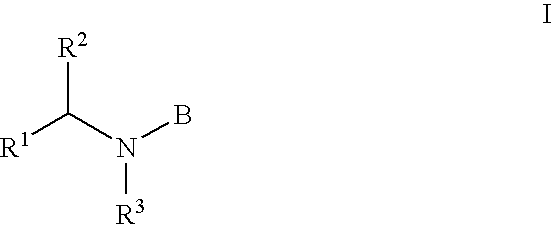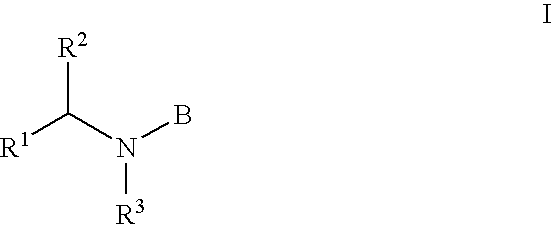Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106 results about "Integrase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
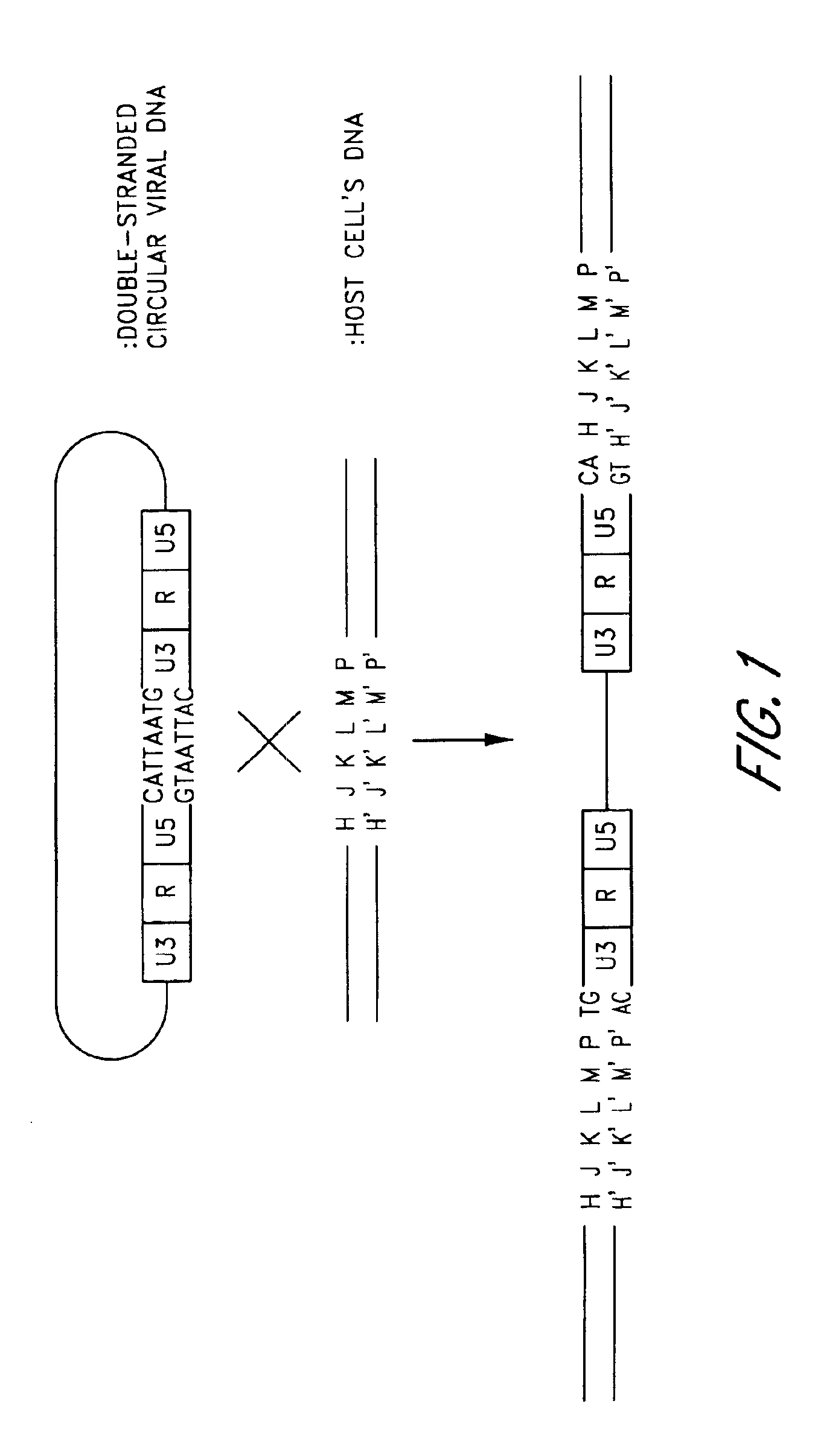
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its DNA (genetic information) into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are distinct from phage integrases, such as λ phage integrase, as discussed in site-specific recombination.
Piggybac transposon-based vectors and methods of nucleic acid integration
InactiveUS20090042297A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPiggybac transposonInfection disease
Disclosed herein are compositions comprising integrating enzymes that can deliver nucleic acids to a target DNA. Additionally, the methods of using the compositions disclosed herein relate to treatments for a variety of infections, conditions, and genetic disorders.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Aromatic heterocycle compounds having HIV integrase inhibiting activities
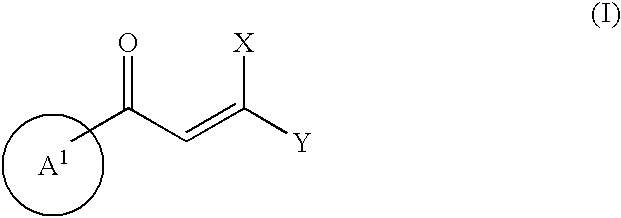
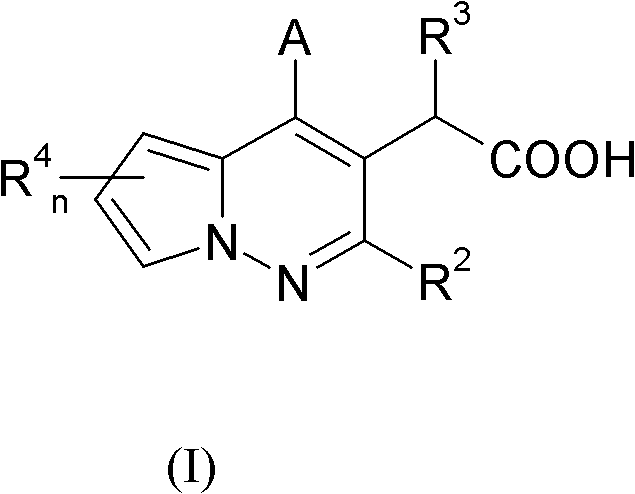
A compound of the formula (I):wherein X is hydroxy, protected hydroxy or optionally substituted amino; Y is -COORA wherein RA is hydrogen or ester residue, -CONRBRC wherein RB and RC each is independently hydrogen or amide residue, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl; and A1 is optionally substituted heteroaryl; provided that a compound wherein Y and / or A1 is optionally substituted indol-3-yl is excluded, a tautomer, a prodrug, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a hydrate thereof has an inhibitory activity against an integrase.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
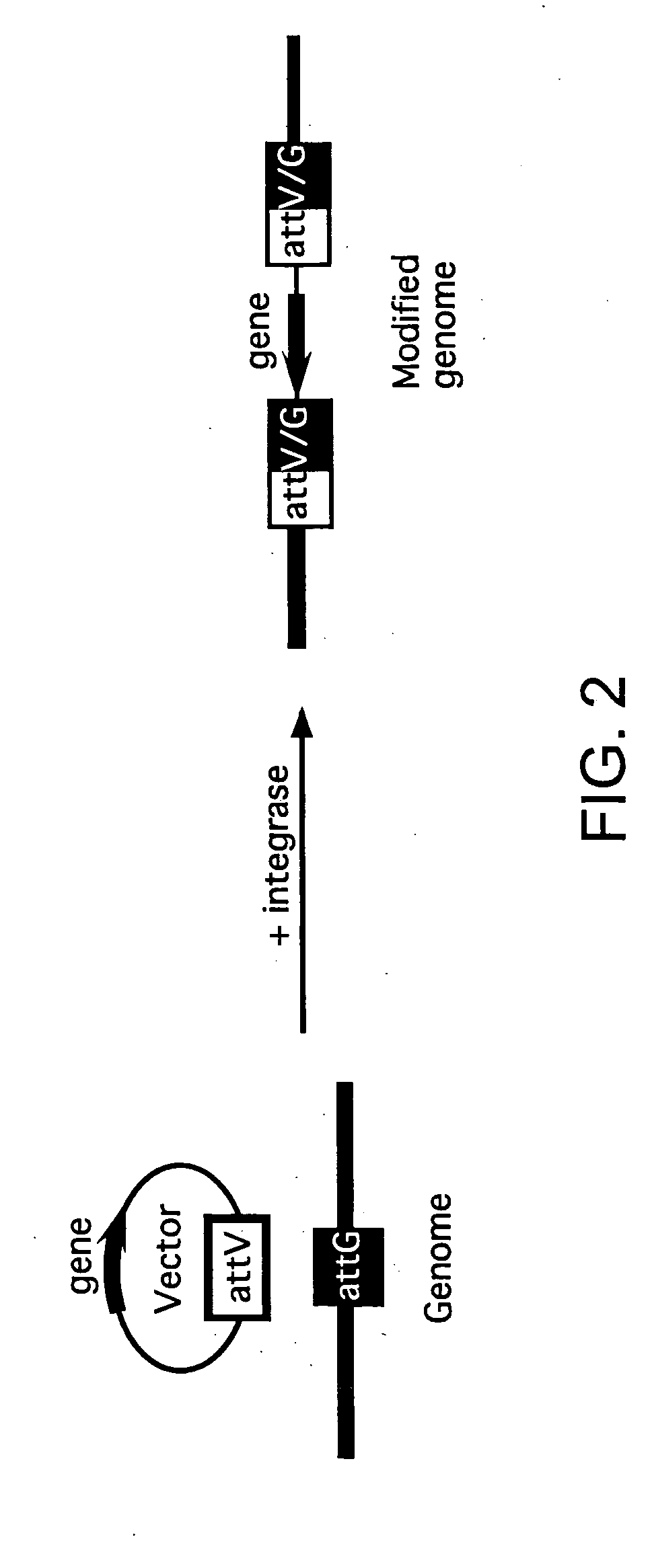
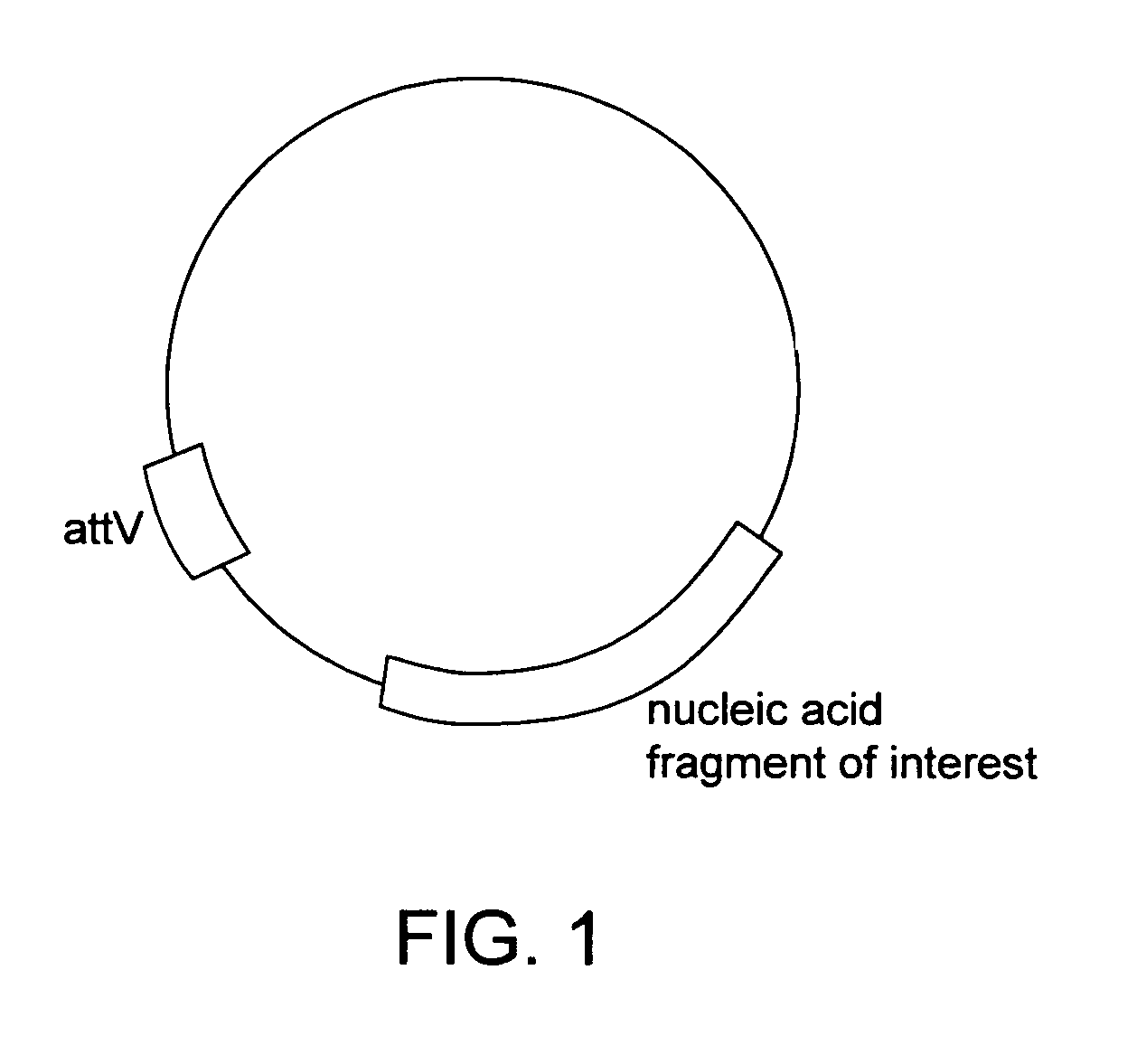
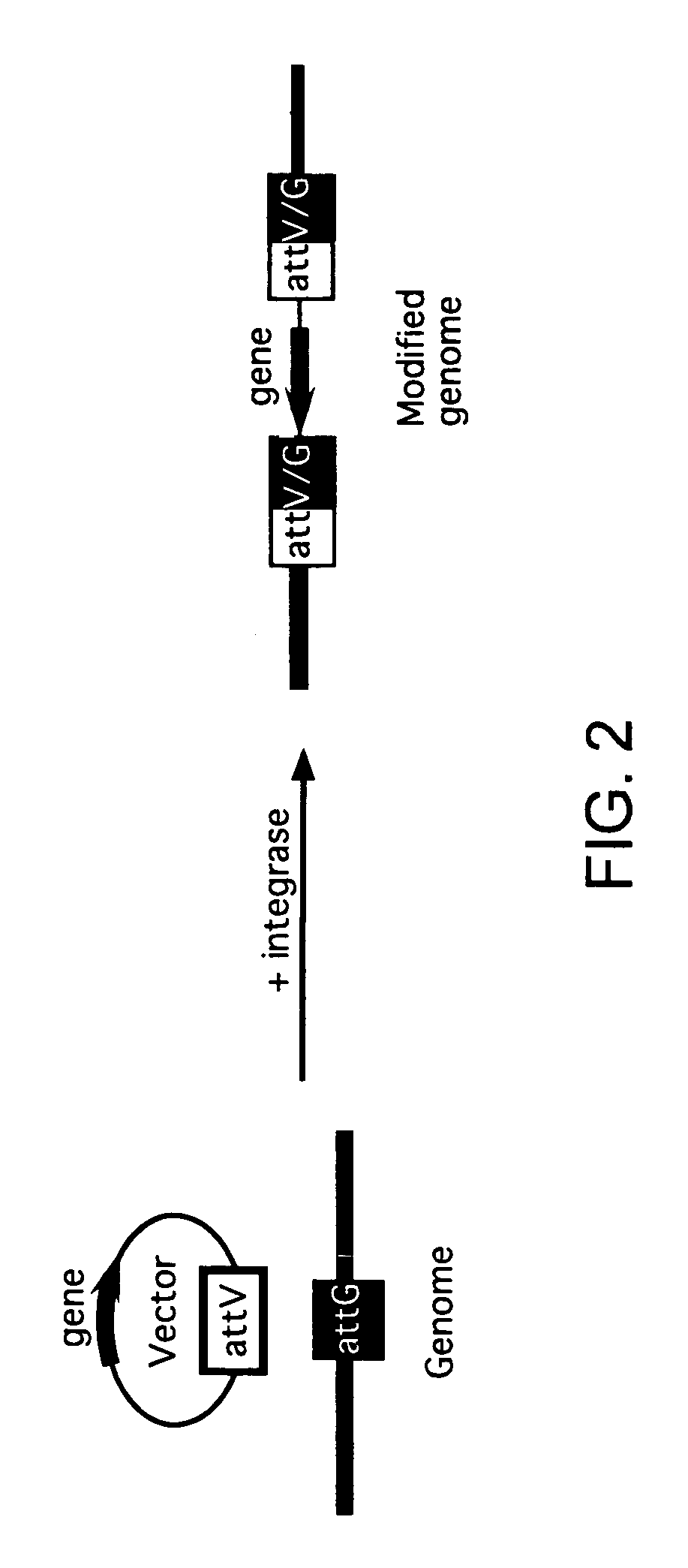
Methods of unidirectional, site-specific integration into a genome, compositions and kits for practicing the same
InactiveUS20060128020A1Facilitate site-specific recombinationReducing and avoiding secondary recombination eventSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNAIntegrasesSite-specific recombination
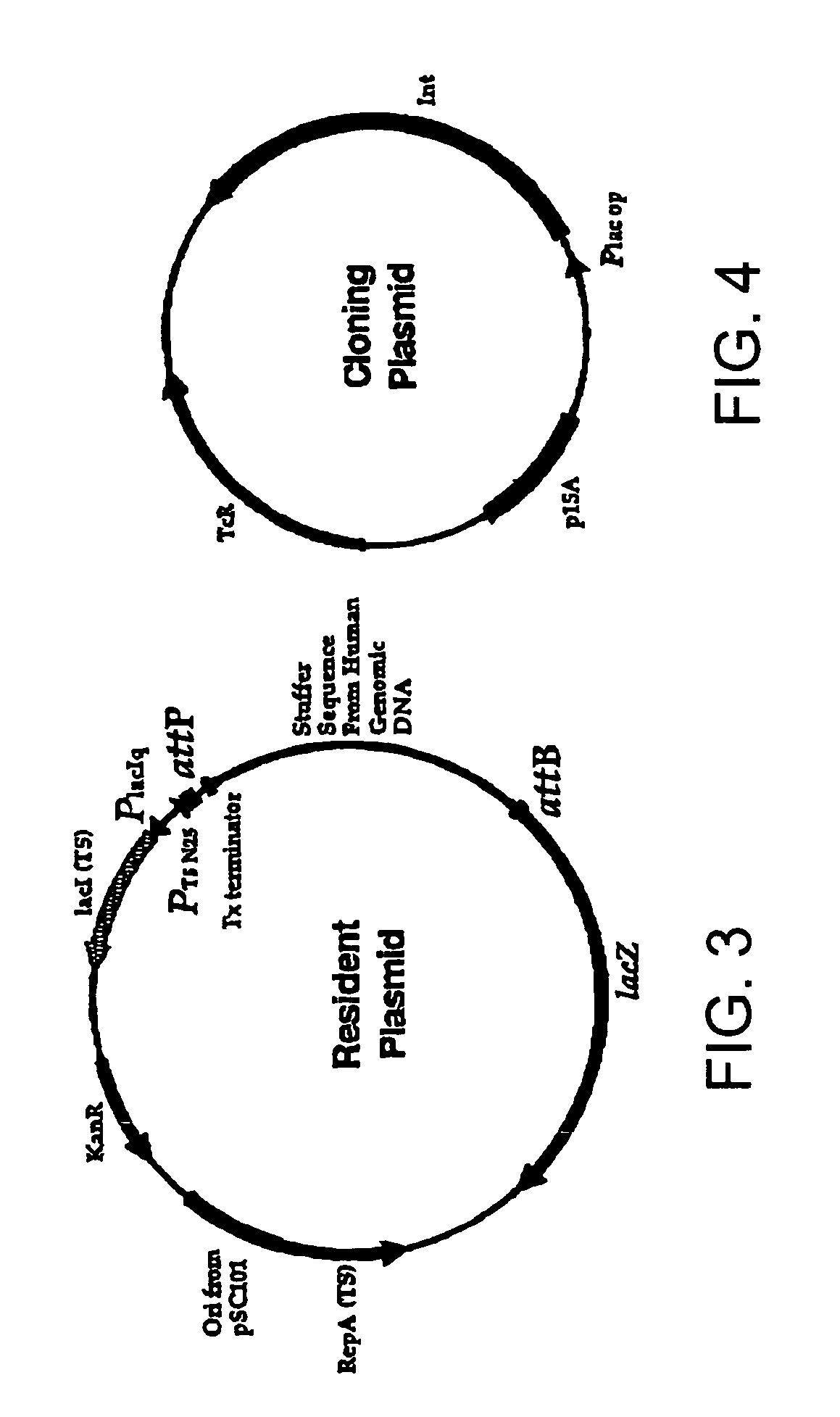
The subject invention provides a unidirectional site-specific integration system for integrating a nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell. The provided system includes a site-specific integrating expression cassette (INTEC) vector, consisting of (a) a polynucleotide of interest operably linked to a promoter, (b) a single recombination site, and (c) a hybrid recombination site. In using the subject systems for site-specific integration, the INTEC vector and integrase are introduced into the target cell and the cell is maintained under conditions sufficient to provide for site-specific integration of the nucleic acid into the target cell genome via a recombination event mediated by the site-specific recombinase. Also provided are kits that include the subject systems. The subjects systems, methods and kits find use in a variety of different applications, several representative ones of which are described in detail as well.
Owner:POETIC GENETICS +1
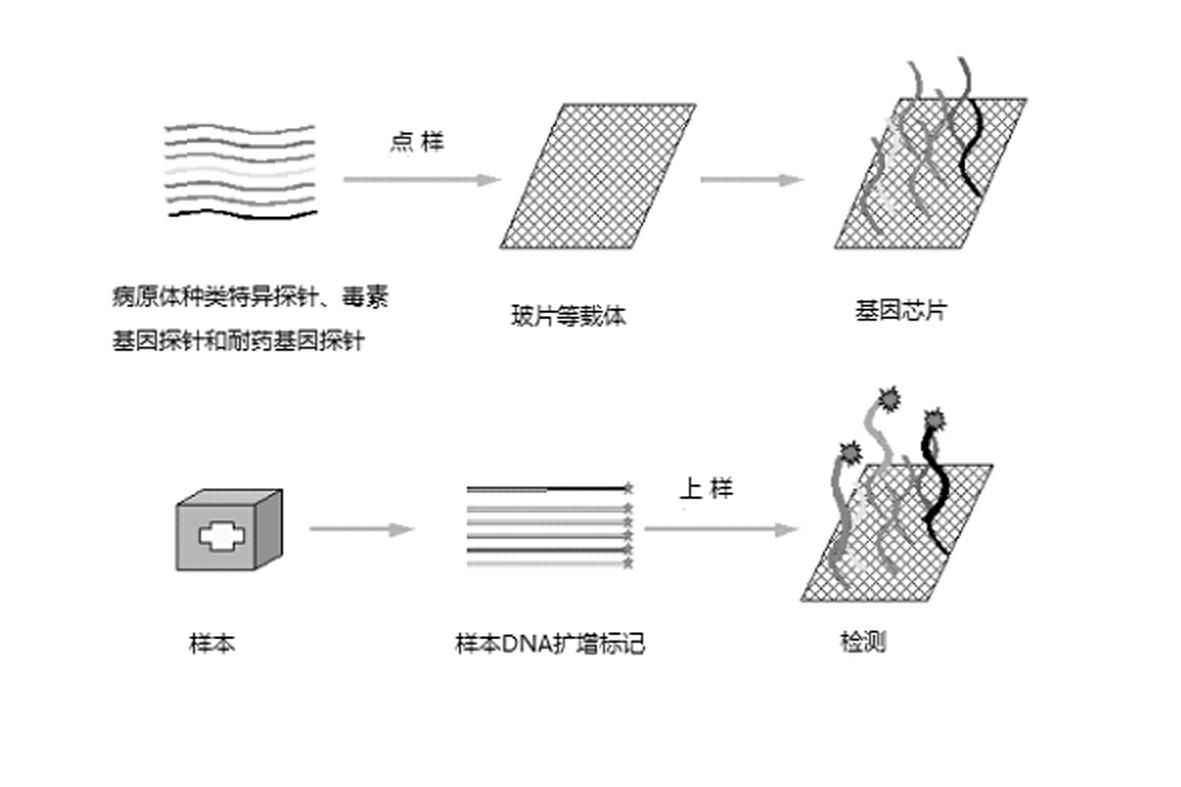
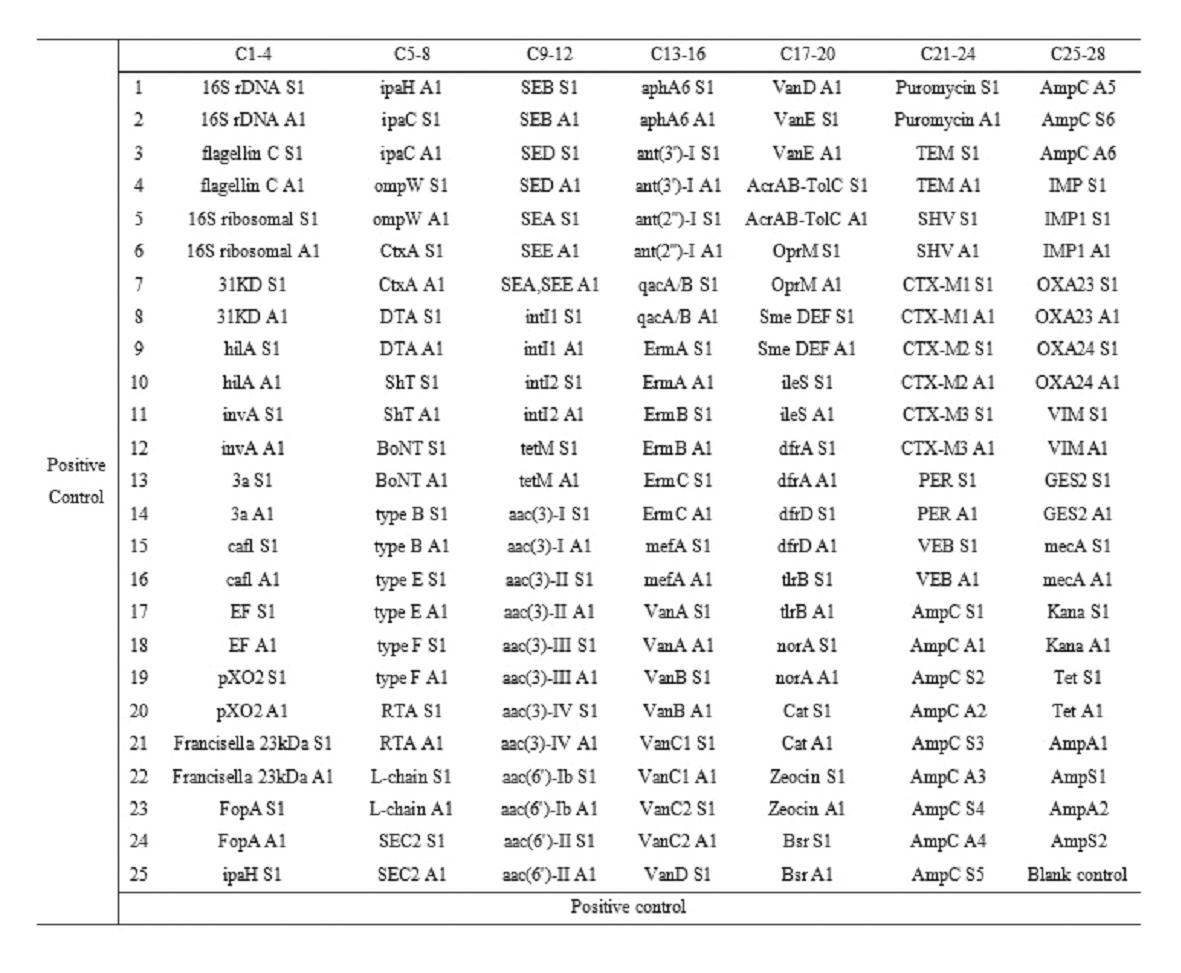
Gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof
InactiveCN102534013AStrong specificityDetermine the typeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesYersinia pestisBrucella
The invention relates to a gene chip for high-flux detection of pathogens and application thereof. The gene comprises (1) a combination of 174 oligonucleotide probes of pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes; and (2) a probe array, which is formed by curing the oligonucleotide probes on a carrier material by arm molecules. The gene chip comprises 174 gene probes, namely 32 pathogen variety specific gene probes of the following 8 pathogens of Burkholderia mallei, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Brucella, salmonella, Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, comma bacillus and the like, 25 toxin gene probe of the following 7 toxins of diphtheria toxin, Shiga toxin, staphylococcus enterotoxin, choleratoxin and the like, and 117 drug-resistant gene probes of 17 drug-resistant genes of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, cephalosporinase, carbapenemase, integrase gene, common gene engineering carrier drug-resistant gene and the like. The gene chip can be used to detect multiple pathogen variety specific genes, toxin genes and drug-resistant genes.
Owner:李越希
Combination therapy
ActiveUS8633219B2Low effective doseEffective treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistrySide effectCombined Modality Therapy
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Heteroaromatic derivatives having an inhibitory activity against HIV integrase
A compound of the formula (I): 1 wherein X is hydroxy, protected hydroxy or optionally substituted amino; Y is --COOR.sup.A wherein R.sup.A is hydrogen or ester residue, --CONR.sup.BR.sup.C wherein R.sup.B and R.sup.C each is independently hydrogen or amide residue, optionally substituted aryl or optionally substituted heteroaryl; and A.sup.1 is optionally substituted heteroaryl; provided that a compound wherein Y and / or A.sup.1 is optionally substituted indol-3-yl is excluded, a tautomer, a prodrug, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a hydrate thereof has an inhibitory activity against an integrase.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
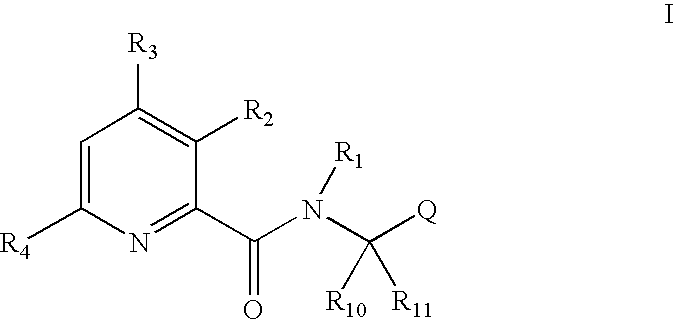
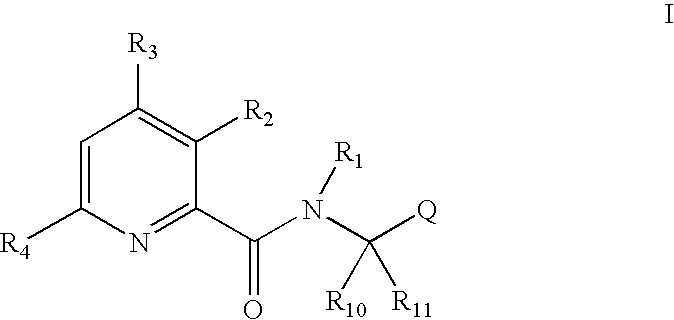
Pyridine carboxamide and methods for inhibiting HIV integrase
InactiveUS20050176767A1Prevent integrationInhibit transferBiocideOrganic chemistryIntegrasesMedicine
Owner:VIROCHEM PHARMA INC (CA)
Methods of unidirectional, site-specific integration into a genome, compositions and kits for practicing the same
InactiveUS20050208021A1Facilitate site-specific recombinationReducing and avoiding secondary recombination eventBiocideHydrolasesIntegrasesAttachment site
The subject invention provides a unidirectional site-specific integration system for integrating a nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell. The provided systems include a (1) a mutant, unidirectional site specific integrase, which can be provided by an integrase vector encoding the mutant integrase and (2) a targeting vector that includes: (a) a nucleic acid to be integrated; and (b) a vector attachment site, where the targeting vector attachment site serves as a substrate for the mutant, unidirectional site-specific integrase. In using the subject systems for site-specific integration, the targeting vector and integrase are introduced into the target cell and the cell is maintained under conditions sufficient to provide for site-specific integration of the nucleic acid into the target cell genome via a recombination event mediated by the site-specific integrase. Also provided are kits that include the subject systems. The subjects systems, methods and kits find use in a variety of different applications, several representative ones of which are described in detail as well.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Pharmaceutical formulation containing a release rate controlling composition
ActiveUS20070292504A1Treatment or prophylaxis of HIV infectionDelay in the onset, or prophylaxis of AIDSOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOral medicationCompound (substance)
Pharmaceutical formulations suitable for oral administration in solid dosage forms are described. The compositions comprise an effective amount of a base salt of a compound of Formula (I) and a release rate controlling composition comprising a solubilizing agent, a gelling agent, and a water soluble filler; wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are defined herein. The formulations are suitable for use in the inhibition of HIV integrase, the treatment and prophylaxis of HIV infection, and the treatment, prophylaxis and delay in the onset of AIDS.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
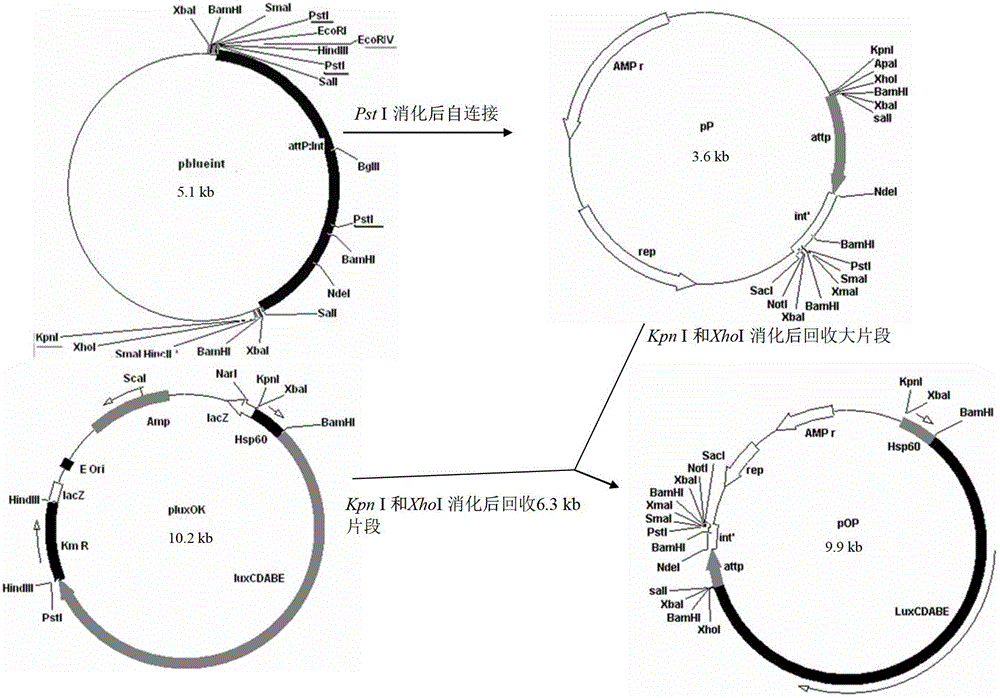
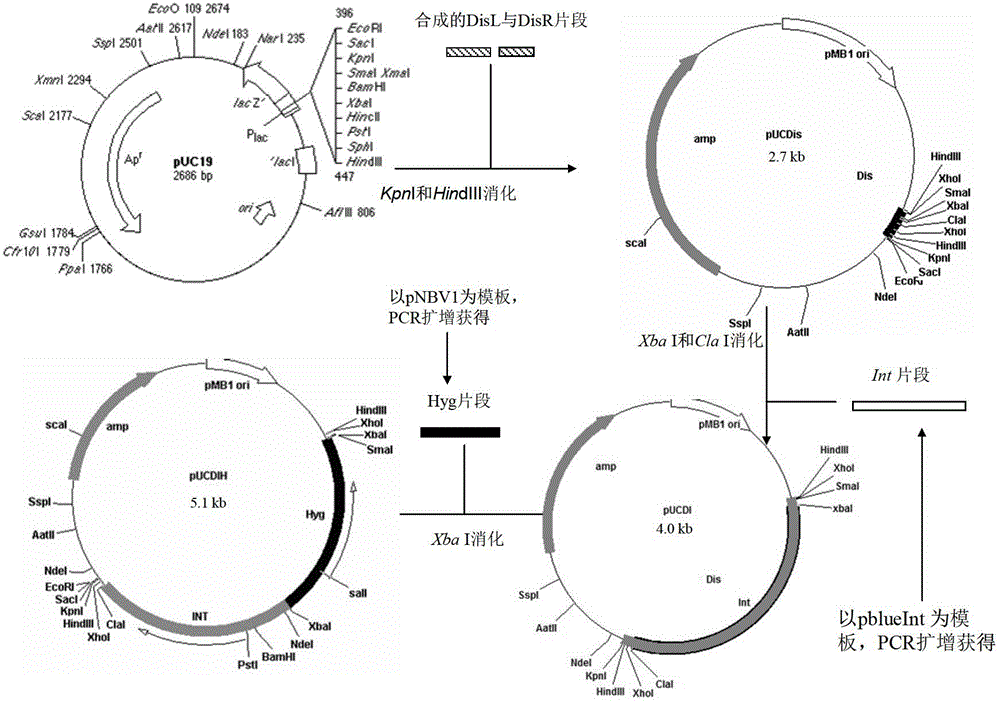
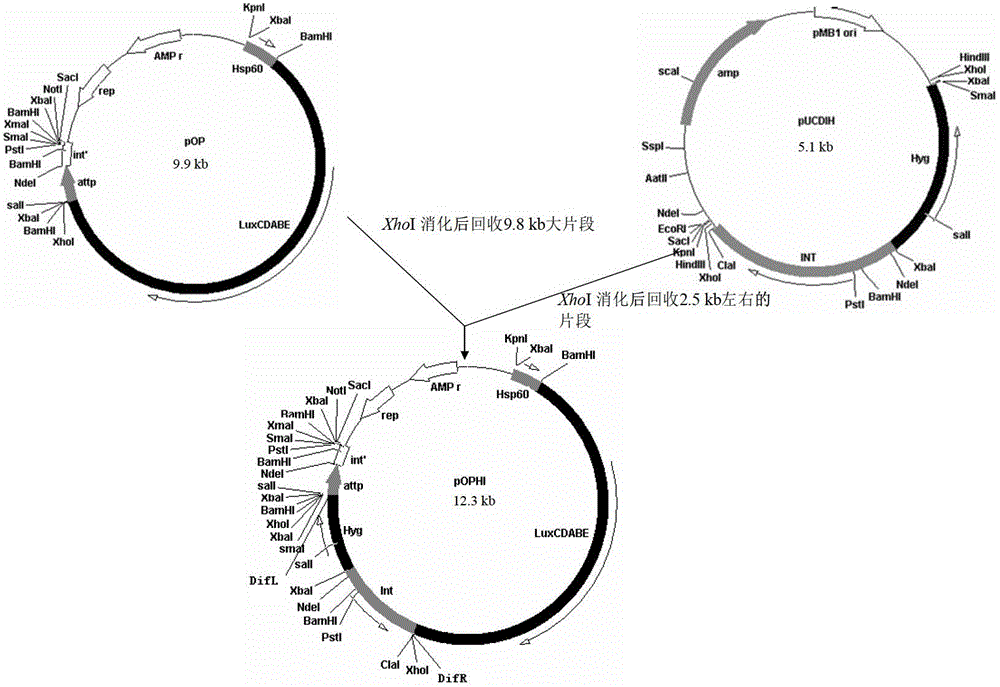
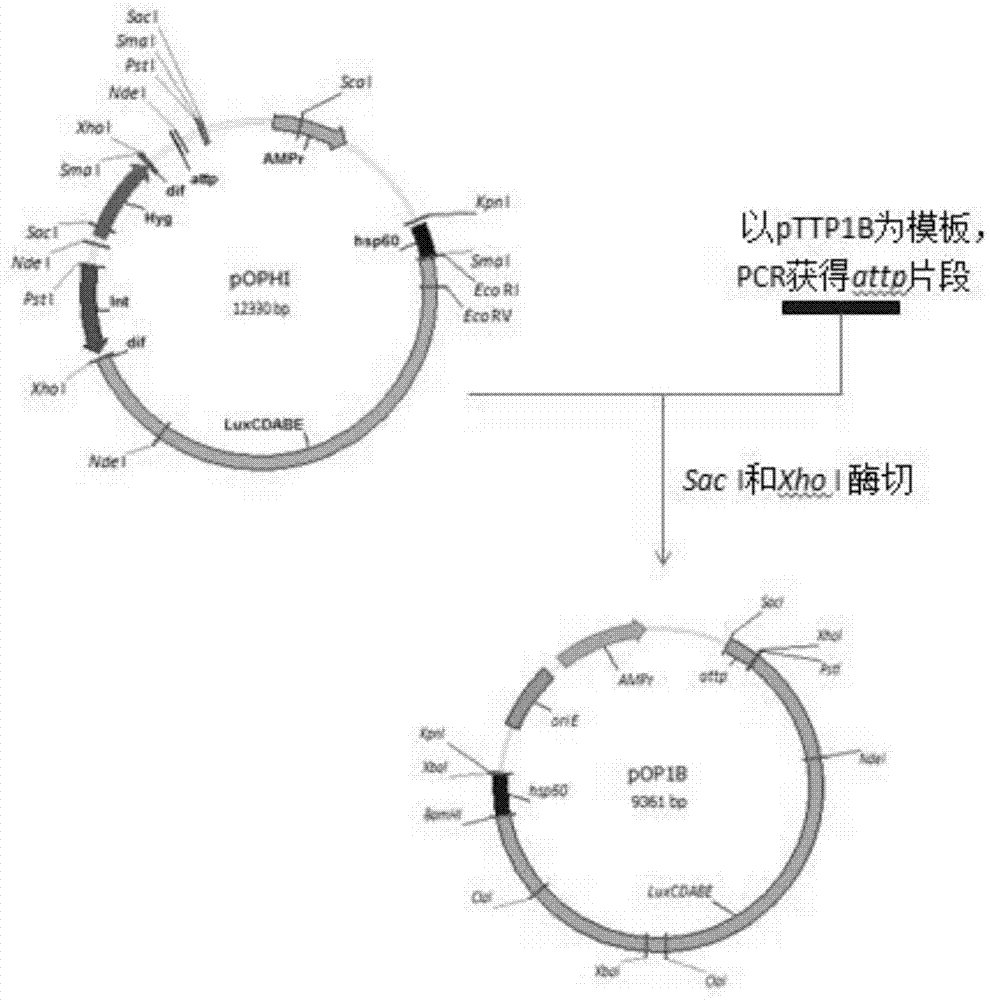
Integrative plasmid pOPHI and resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium
ActiveCN102719471AExperimental data is credibleHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses an integrative plasmid pOPHI and a resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. The integrative plasmid pOPHI comprises a promoter, an enzyme gene (LuxCDABE) needed for luminescence, a fusion gene of an integrase gene (Int) and a resistance screening gene, direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL positioned on two ends of the fusion gene, a phage integration site (attP) and a replicon. After the integrative plasmid pOPHI is transferred into the mycobacteria, a photobacterium of which the resistance gene and the integrase gene are lost is screened out by subculturing, and the photobacterium is the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. Whether the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium obtained by construction is dead or not is judged according to whether the bacterium is luminescent or not, the mycobacterium can be used for a plurality of detections of experiments, and credible experimental data can be quickly obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
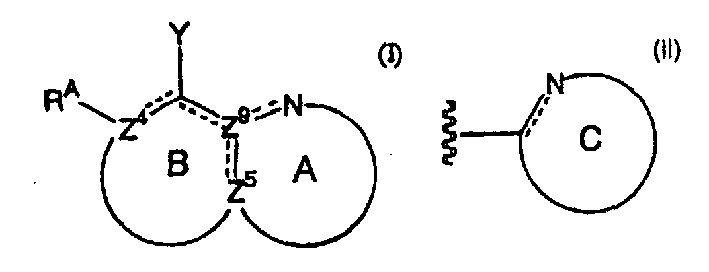
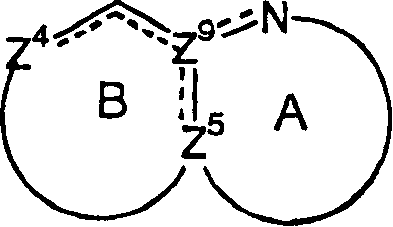
Nitrogen-containing heteroaryl compounds having HIV integrase inhibitory activity
A compound of the formula (I) wherein Z<4>, Z<5> and Z<9> each is independently carbon atom or nitrogen atom; Y is hydroxy, mercapto or amino; R is a group of the formula (II) (wherein C ring is nitrogen-containing heteroaryl) has an inhibitory activity against integrase.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
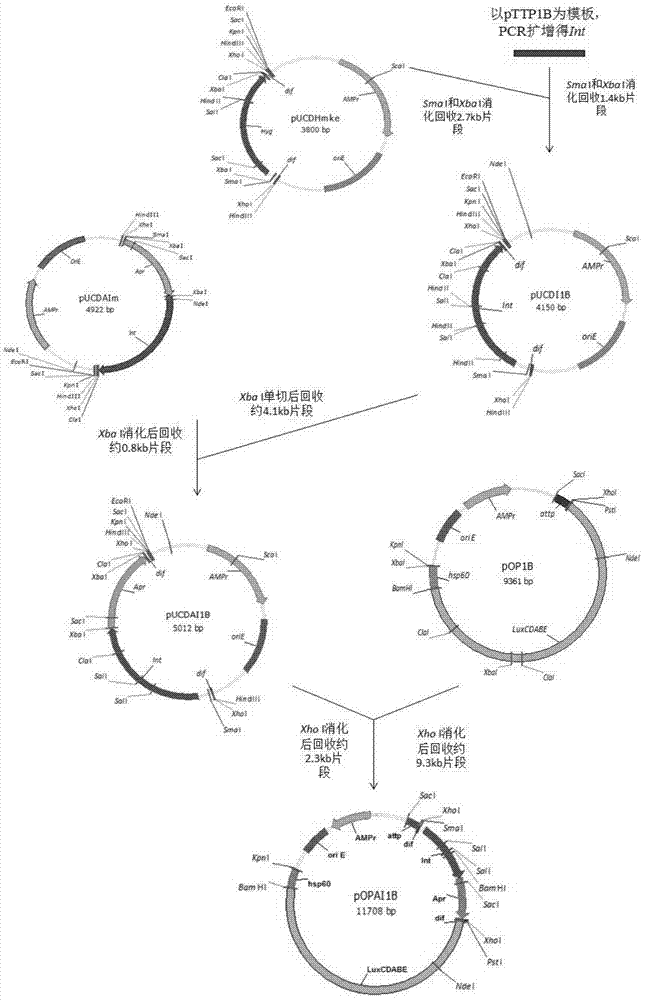
Method of constructing selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus and establishment of corresponding in-vitro high-flux medicine-screening model
InactiveCN104762312ANo effect on growthNo effect on drug sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses a method of constructing selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus and establishment of a corresponding in-vitro high-flux medicine-screening model. During the construction process, a key factor is the construction of a recombinant plasmid pOPAI1B, which contains a fused gene including a luminescent required enzyme gene LuxCDABE, a resistance screening gene Apr and an integrase gene Int; direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL at the two ends of the fused gene respectively; and a phage integration site attP and a replicon. The recombinant plasmid pOPAI1B is transformed into the mycobacterium abscessus and then is screened to obtain the selection-marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus of which a resistance gene and the integrase gene are both lost. The self-luminescent mycobacterium abscessus can screen drugs in a high flux, can determine sterilizing or bacteria-resistant effects of the drug by means of detection of luminescent situation of bacteria, can be used for in-vitro drug activity detection, is free of any substrates, can continuously detect the same sample, is high in sensitivity and is strong in repeatability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
System and method for detection of HIV integrase variants
InactiveUS20100136516A1Reduce frequencyMicrobiological testing/measurementIntegrasesNucleic acid sequencing
An embodiment of a method for detecting low frequency occurrence of one or more HIV sequence variants associated with integrase is described that comprises the steps of: (a) generating a cDNA species from a plurality of RNA molecules in an HIV sample population; (b) amplifying a plurality of first amplicons from the cDNA species, wherein each first amplicon is amplified with a pair of nucleic acid primers; (c) clonally amplifying the amplified copies of the first amplicons to produce a plurality of second amplicons; (d) determining a nucleic acid sequence composition of the second amplicons; (e) detecting one or more sequence variants that occur at a frequency of 5% or less in the nucleic acid sequence composition of the second amplicons; and (f) correlating the detected sequence variants with variation associated with HIV integrase.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Nitrogen-containing polyhydroxy fragrant compounds, preparation and uses thereof
InactiveCN101429142AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsHydrogenIntegrases
The invention relates to a nitrogen-containing polyhydroxy arometic compound having a structure as shown in a general formula 1, wherein R1 is hydrogen, methyl or fluorine; R2 is hydrogen, methyl, acetyl, fluorine, chlorine or bromine; R3 is hydrogen, methyl, butyl, methoxyl, ethoxyl, fluorine, chlorine, bromine or nitro; R4 is hydrogen, methyl, acetyl, fluorine, chlorine or bromine; and n is 0 or 1. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the nitrogen-containing polyhydroxy arometic compound in the general formula 1. The compound has obvious inhibitory activity to HIV integrase, and is used for preparing anti-AIDS medicine. The n is equal to 0 or 1.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation method of pseudotype virus for nucleic acid detection of 2019-nCoV
ActiveCN111471717AEasy loadingSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesViral nucleic acidViral vector
The invention discloses a preparation method of a pseudotype virus for nucleic acid detection of 2019-nCoV, and relates to the technical field of biology. The preparation method comprises a method forpreparing standard quality control products which contain but are not limited to a 2019-nCoV nucleotide sequence and are used for nucleic acid detection through a non-integrated slow virus vector system, a method which is used for preparing the standard quality control products for nucleic acid detection, and a method for constructing a non-integrated slow virus through mutating 64-locus amino acid Asp of integrase of slow virus auxiliary plasmid into Asn, and amino acids Arg, Arg and Lys at 262-264 loci into Ala, Ala and His. In the manner of removing elements of promoters and the like of slow viruses, the load quantity of virus vectors can be promoted, a pseudotype virus which can be used for nucleic acid detection and complete flow quality control is constructed, and the preparation method can be used for constructing a pseudotype virus for corona viruses and can also be used for constructing a pseudotype virus for SARS-COV, MERS-COV, influenza viruses and the like.
Owner:复百澳(苏州)生物医药科技有限公司
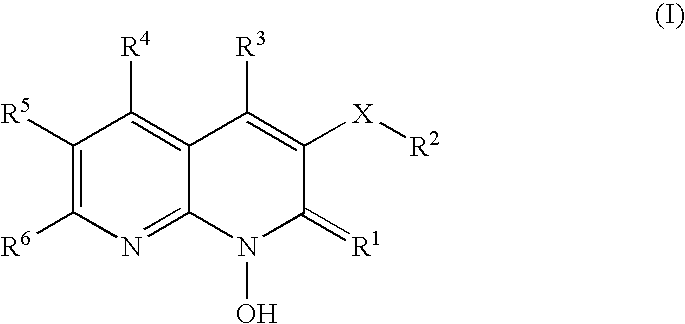
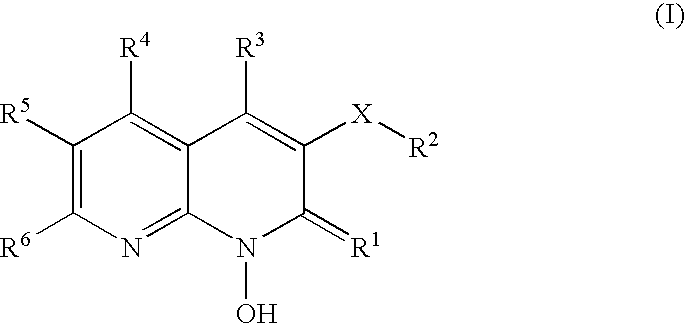
1-hydroxy naphthyridine compounds as Anti-hiv agents
1-Hydroxy naphthyridine compounds (e.g., 1-hydroxy naphthyridin-2(1H)-one compounds of Formula I are inhibitors of HIV integrase and / or HIV RNase H and inhibitors of HIV replication: (I) wherein X and R1-R6 are as defined herein. The compounds are useful in the prophylaxis and treatment of infection by HIV and in the prophylaxis, delay in the onset, and treatment of AIDS. The compounds are employed against HIV infection and AIDS as compounds per se or in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable salts. The compounds and their salts can be employed as ingredients in pharmaceutical compositions, optionally in combination with other anti-HIV agents such as HIV antivirals, immunomodulators, antibiotics and vaccines.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
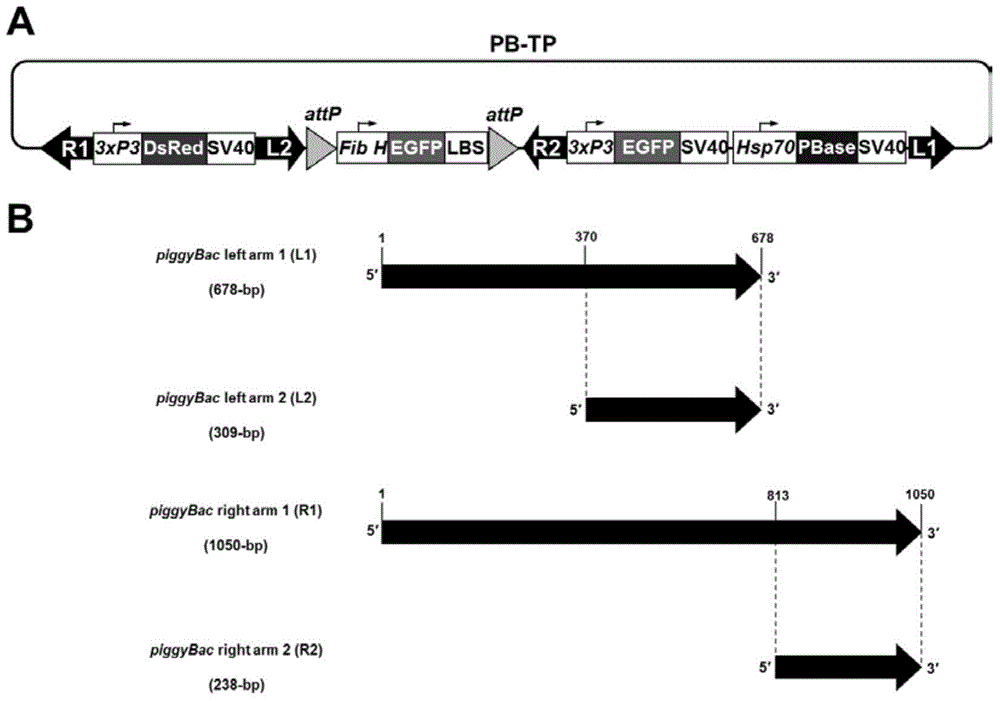
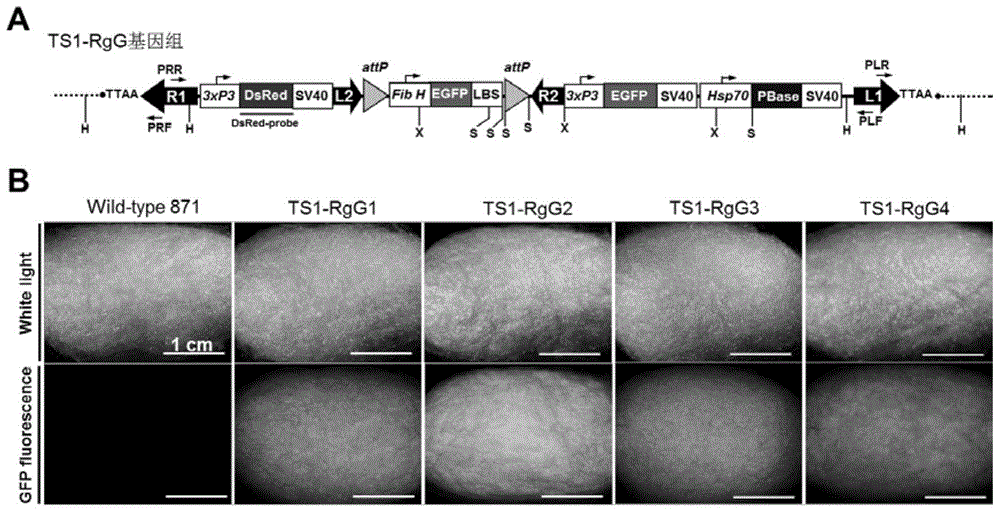
Compound type piggyBac recombinant vector as well as preparation method and application of compound type piggyBac recombinant vector
InactiveCN104673815AIntegration and stabilityNo retranspositionVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryHeat shockFrame sequence
The invention discloses a compound type piggyBac recombinant vector as well as a preparation method and an application of the compound type piggyBac recombinant vector. According to the recombinant vector, a target gene expression frame, selection marker gene expression frames I and II, piggyBac transposase expression frame regulated by a heat shock promoter and truncated type piggyBac transposon arms L2 and R2 are inserted between wild type piggyBac transposon arms R1 and L1, integration of target gene, selection marker gene, piggyBac transposase expression frame sequence in silkworm genome can be conveniently mediated, complete deletion of all of transposon sequences and selection marker gene sequences in progeny transgenosis silkworm genome can be realized through establishing and screening a transgenosis silkworm line with high target gene expression and then inducing piggyBac to express in the transgenosis silkworm by heat shock treatment, replacement of other exogenous gene and the target gene can be conveniently realized through box type exchange reaction mediated by phiC31 integrase by surplus target gene expression frame anchored by attP locus, and then fixed point integration of other exogenous genes in the genome locus is further realized.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Acyl sulfonamides as inhibitors of HIV integrase
The present invention relates a series of compounds of Formula I wherein R1, R2, R3, and B are as defined in the specification. The compounds are useful for the inhibition of HIV integrase and for the treatment of AIDS or ARC by administering compounds of the formula.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
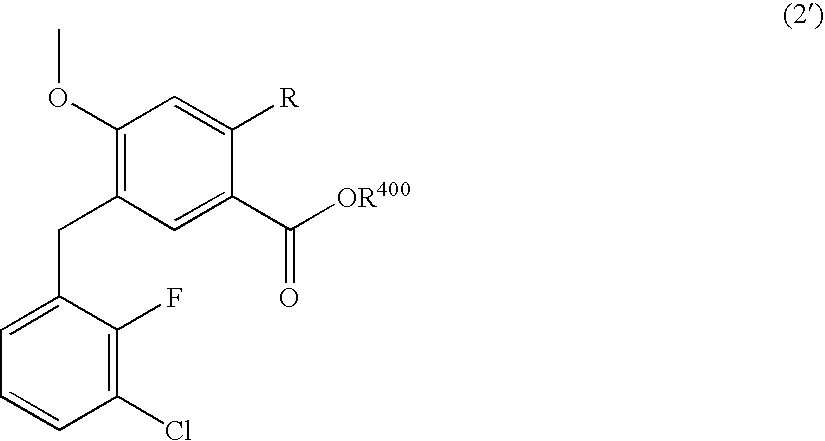
Method for producing 4-oxoquinoline compound
ActiveUS8383819B2Reduce yieldAvoid it happening againOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAnti-HIV AgentHydrogen atom
The present invention provides a compound useful as a synthetic intermediate for an anti-HIV agent having an integrase inhibitory activity, and a production method thereof, and a production method of an anti-HIV agent using the synthetic intermediate. Specifically, for example, a compound represented by the formula (2′):wherein R is a fluorine atom or a methoxy group, and R400 is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C4 alkyl group, or a salt thereof, and a production method thereof, and a production method of an anti-HIV agent using the synthetic intermediate.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
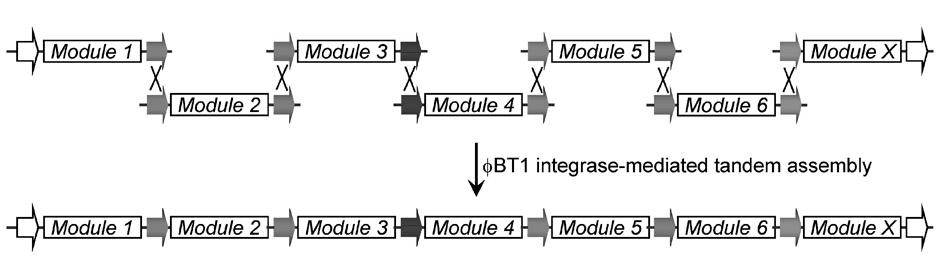
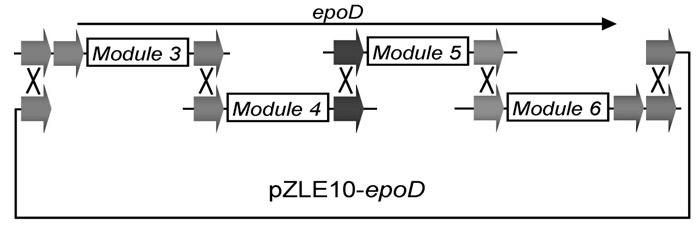
Multi-fragment deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) series connection recombination assembly method based on site-specific recombination
InactiveCN102286512AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationEscherichia coliSite-specific recombination
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering and synthetic biology, and particularly relates to a multi-fragment deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) series connection recombination assembly method based on BT1 integrase and mutation recognition sites thereof. In the method, sixteen pairs of mutational integrase recognition sequences are provided through mutation screening and verification, on the basis, a complete set of related carriers is constructed and comprises a framework carrier and seven TA cloning vectors, the framework carrier can realize escherichia coli-streptomyces coelicolor shuttle, the seven TA cloning vectors comprise mutation substrates and are used for DNA element construction and screening, and a concrete method for multi-fragment external series connection recombination reaction is provided. The method of the invention is simple, fast and efficient and can be used for the multi-fragment fast series connection recombination assembly, and the amplification of series connection products is realized through escherichia coli transformation. The method can be widely used for combination and assembly of standard modules and elements in the synthetic biology.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods of unidirectional, site-specific integration into a genome, compositions and kits for practicing the same
InactiveUS8304233B2Promote recombinationSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNASite-specific recombinationPolynucleotide
Owner:POETIC GENETICS +1
Bovine genome pseudo-attP site and its use
ActiveCN1982452ADoes not affect expressionWill not disrupt normal functionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionIntegrasesBio engineering
Method for separating and determining bovine genome pseudo attp site and its usage are disclosed. The process is carried out by separating out tow pseudo attp sites from bovine gene, having 38% and 41% homology with attp site of streptomycete phagicin phiC31 genome, discriminating by streptomycete phagicin phiC31 integrase and integrating foreign gene containing attB site with the site of bovine geneome under mediation of integrase. It has higher integration efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV AFFILIATED CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
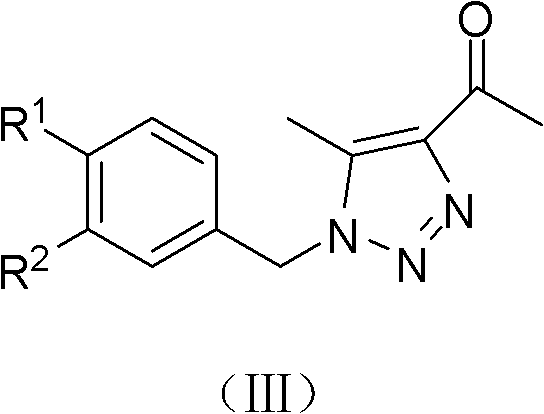
(Z)-1-(1-substituted benzyl-5-methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-yl)-3-substituted benzyl-3-hydroxy-2-propylene-1-ketone compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102503900AMild reaction conditionsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBenzoyl bromideCarboxylic acid
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Plasmid vector comprising a retroviral integrase gene and an integrase recognition region
A plasmid vector having components (D1), (D2), and (D3) enables the efficient integration of foreign DNA into host cells. The components are (D1) an integrase gene, (D2) a segment of DNA forming a region for controlling the expression of the integrase gene, and (D3) a segment of DNA serving as an integrase recognition region when integrase catalyzes the integration reaction.
Owner:NIHON SEIBUTSU KAGAKU KENKYUSHO
Multi-substituted amine compound, as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN103570683AAvoid interactionInhibition of dimerizationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTherapy HIVIntegrase
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and specifically provides a multi-substituted amine compound as shown in a general formula I or an isomer thereof or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester, pro-medicament or hydrate thereof or a pharmaceutical composition, as well as a preparation method and use thereof in preparation of medicaments for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome. The compound or the pharmaceutical composition containing the compound can be used as an inhibitor for inhibiting the protein-protein interaction between HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) integrase and LEDGF / p75 and the dimerization of the HIV integrase, and further can be used for treating the acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel integrase and application thereof to efficiently modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa
The invention provides a novel integrase and application thereof to genetically modifying saccharopolyspora spinosa. The integrase particularly comes from saccharopolyspora endophytica CCTCC AA208003, and exogenous DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be specifically locally integrated on saccharopolyspora endophytica chromosome by the integrase via specific cis-form components. In addition, independent free replication regions of different strain sources are discovered in the saccharopolyspora spinosa by an inventor via research on genetic factors of different strains of the saccharopolyspora spinosa. The novel integrase and the application have the advantages that vectors constructed on the basis of the integrase and sequences of the replication regions can be used for genetically modifying the saccharopolyspora spinosa, accordingly, novel spinosad analogues can be possibly discovered, and the spinosad fermentation yields can be possibly increased; different resistance molecular markers can be carried by plasmids, accordingly, the novel integrase can be used for inter-species or intergenetic genome shuffling operation on the saccharopolyspora spinosa, and efficient genome shuffling can be implemented.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for detecting the presence of bacterial strains resistant to antibiotics in a biological sample
InactiveUS20130183679A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic YBacterial strain
The invention relates to the field of molecular diagnostic, in particular for the detection of the presence of gram-negative bacterial strains resistant to antibiotic in a biological sample. The invention more specifically relates to an in vitro method for detecting the presence of gram-negative bacterial strains resistant to antibiotics in a biological sample, said method comprising the steps of: a) providing a biological sample; b) preparing said biological sample for nucleic acid amplification; c) performing nucleic acid amplification using (i) nucleic acid from said biological sample as a template, (ii) at least one or more set of primers specific of bacterial genes encoding integrase of integrons of class 1, 2 and 3, and, (iii) at least one or more set of primers specific of bacterial genes encoding CTX-M type β-lactamases; and, d) determining the presence or absence of amplicons; wherein the presence of at least one amplicon is indicative of a high likelihood that said biological sample contains bacterial strains resistant to antibiotics. The method may be carried out directly on clinical samples, e.g. from septic patients.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
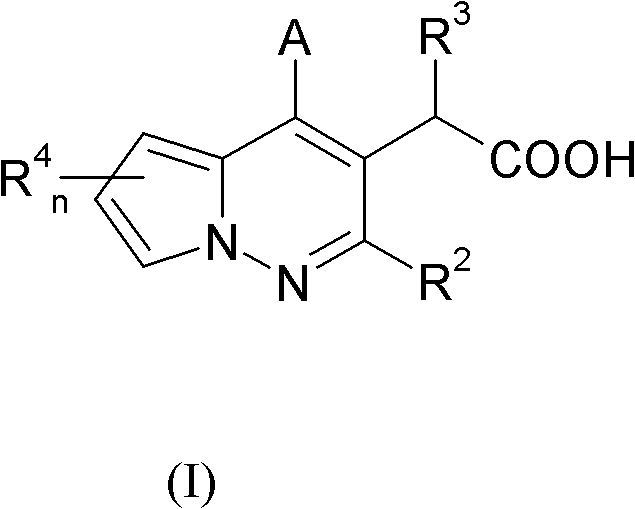
Pyrrolopyridazine compounds with antiviral properties
The invention discloses pyrrolopyridazine compounds used for treating or preventing HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection or other virus infections. The compounds can be used for as inhibitors for inhibiting HIV replication and can be used with other treatment drugs (particularly other antiviral drugs). Specifically, the invention discloses compounds for inhibiting HIV replication, a drug containing the compounds and a method for treating retrovirus infection through the compounds, for example, HIV infection. More specifically, the invention discloses an integrase allosteric inhibitor.
Owner:世方科技(杭州)有限公司
Hiv-1 integrase derived stimulatory peptides interfering with integrase -- rev protein binding
ActiveUS20110257082A1Useful in treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiocideInfected cellHiv 1 integrase
Isolated peptides comprising sequences derived from the protein integrase of HIV-1, as well as their analogs, mixtures, conjugates with permeability enhancing moieties, and pharmaceutical compositions are disclosed. The peptides and compositions are capable of selectively killing HIV-1 infected cells and are used in treatment of HIV infection and AIDS.
Owner:CODE PHARMA BV
Method for quickly constructing gene targeting vector based on site specificity recombination
InactiveCN101967475AEasy to buildBuild methods are fast and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliSite-specific recombination
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biotechnology and gene engineering, and in particular relates to a method for quickly constructing a gene targeting vector based on phi BT1 integrase and a mutation recognition site thereof. The invention provides three pairs of mutative intergrase recognition sequences by strict mutation screening and verification, and the mutative substrate pair has equal reaction efficiency to that of a wild type, and appears as incompatible in the same system. On the basis, the method constructs a set of related vectors comprising a backbone vector capable of realizing Escherichia coli-streptomyces coelicolor shuttle, and three TA clone vectors containing mutative substrate pairs for constructing and screening homology arms, and provides a concrete method of series recombination and reaction of four DNA fragments in vitro. The method of the invention is simple, quick and high-efficiency, can be used for constructing the gene targeting vector of streptomyces, and can be widely used for quickly constructing gene targeting vectors of different species by corresponding original substitution.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com