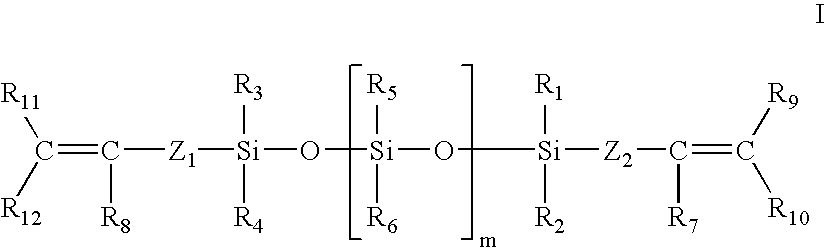Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2682results about How to "Inhibit transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of producing sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6267981B1Maintain good propertiesEnhancement of entrapmentPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEntrapmentBiodegradable polymer
This invention provides a sustained-release preparation comprising a biodegradable polymer metal salt and broactive polypeptide, with enhanced entrapment of the bioactive polypeptides, a suppression of initial burst, and a constant long-term release of the bioactive polypeptides.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Water-soluble fluorescent nanocrystals
InactiveUS6444143B2High quantum yieldHigh spectral purityMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsQuantum yieldOrganic layer
A water soluble semiconductor nanocrystal capable of light emission is provided, including a quantum dot having a selected band gap energy, a layer overcoating the quantum dot, the overcoating layer comprised of a material having a band gap energy greater than that of the quantum dot, and an organic outer layer, the organic layer comprising a compound having a least one linking group for attachment of the compound to the overcoating layer and at least one hydrophilic group space apart from the linking group by a hydrophobic region sufficient to prevent electron charge transfer across the hydrophobic region. The particle size of the nanocrystal core is in the range of about 12.ANG. to about 150.ANG., with a deviation of less than 10% in the core. The coated nanocrystal exhibits photoluminescende having quantum yield of greater than 10% in water.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
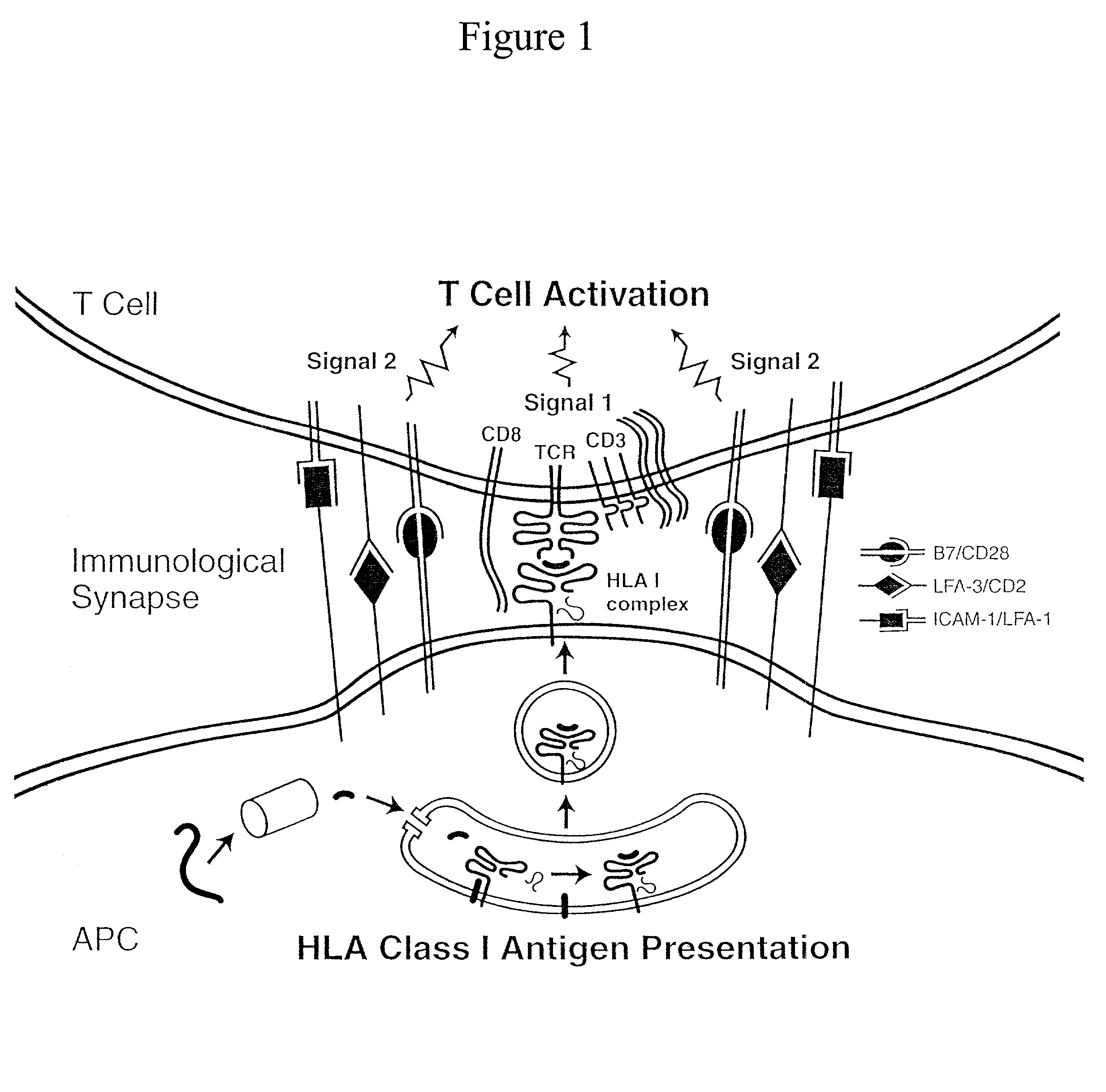
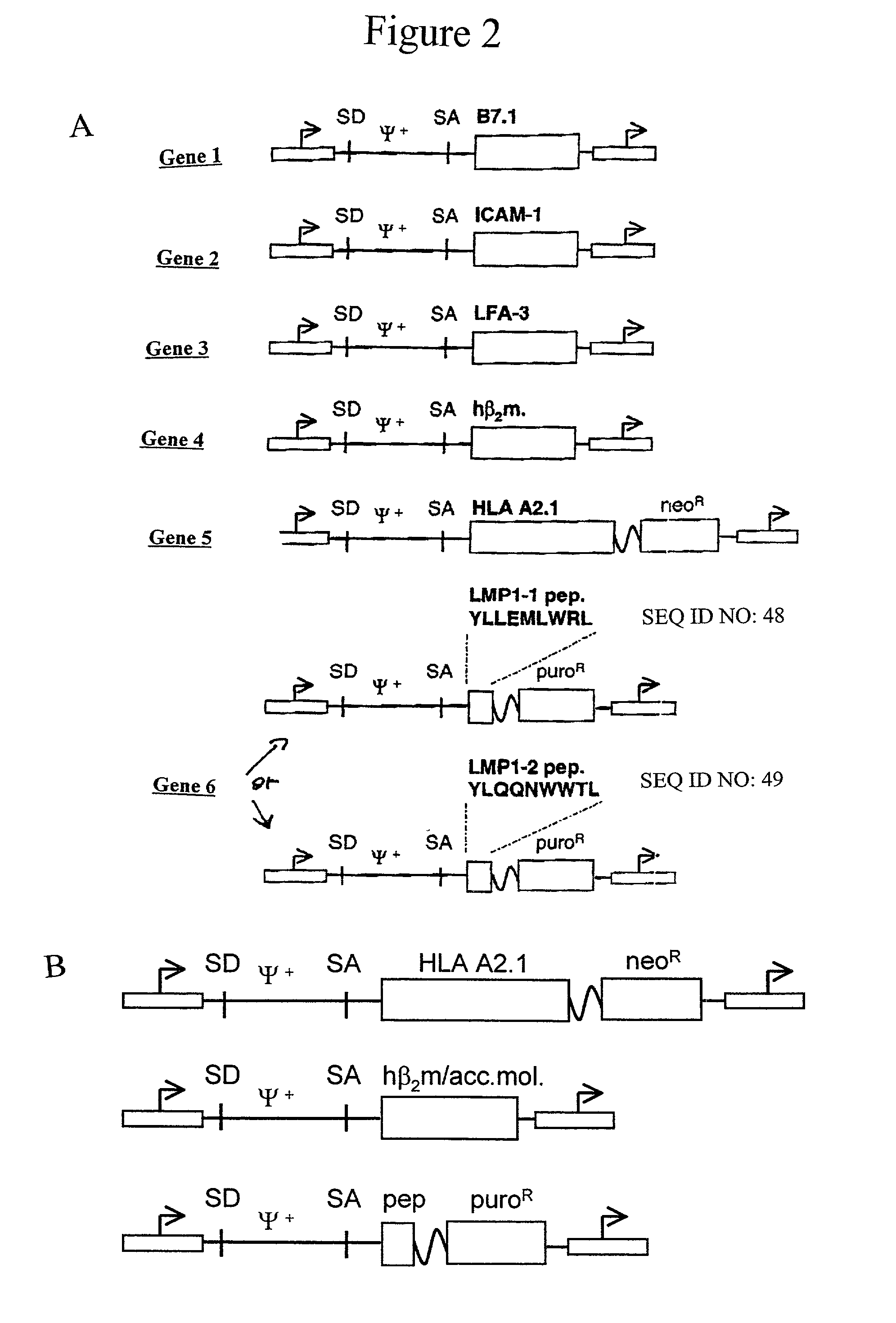
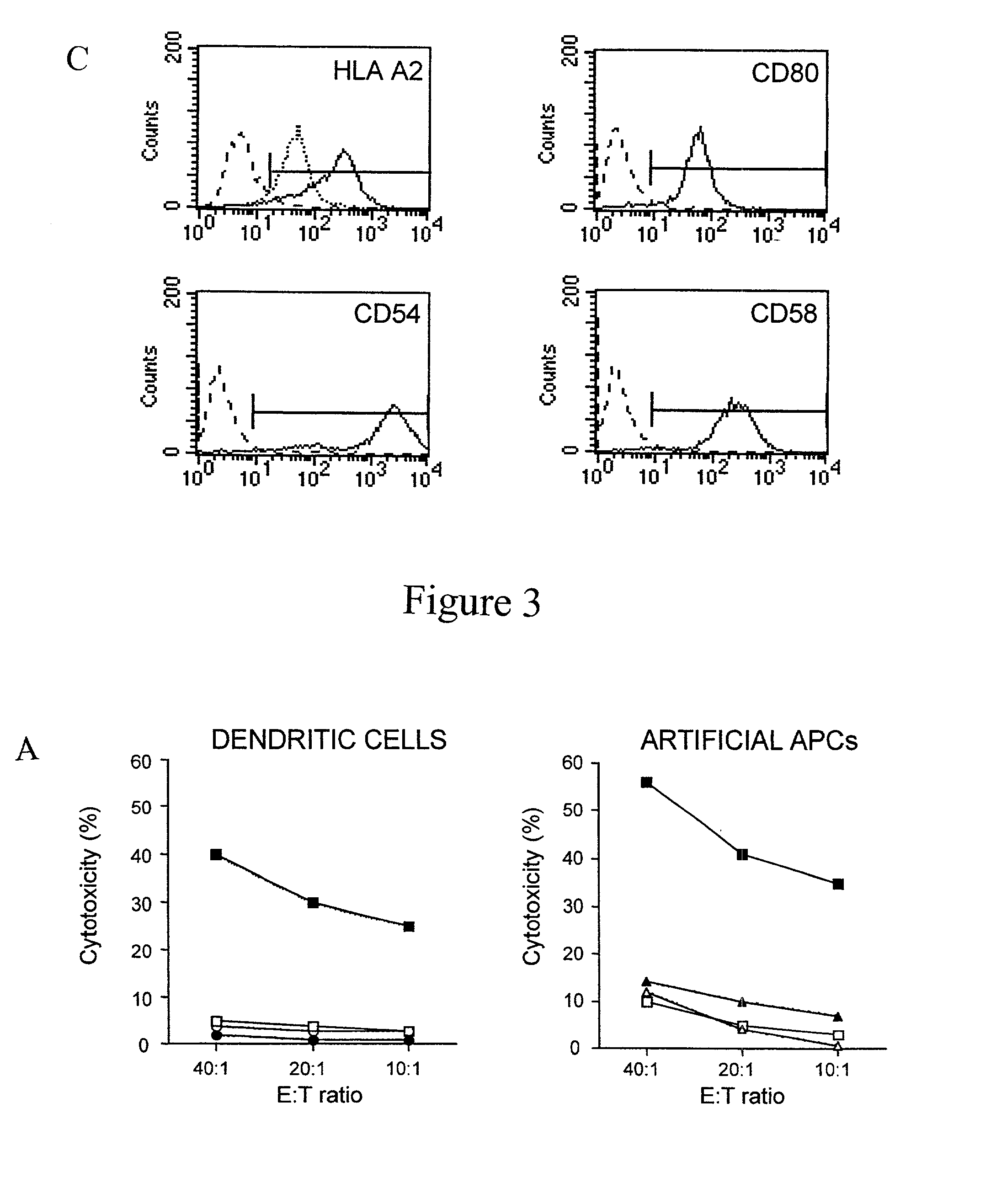
Artificial antigen presenting cells and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20020131960A1Palliating their conditionReduce riskBiocideCompound screeningEpitopeAccessory molecule
The invention provides an artificial antigen presenting cell (AAPC) comprising a eukaryotic cell expressing an antigen presenting complex comprising a human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecule of a single type, at least one exogenous accessory molecule and at least one exogenous T cell-specific epitope. Methods of use for activation of T lymphocytes are also provided.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
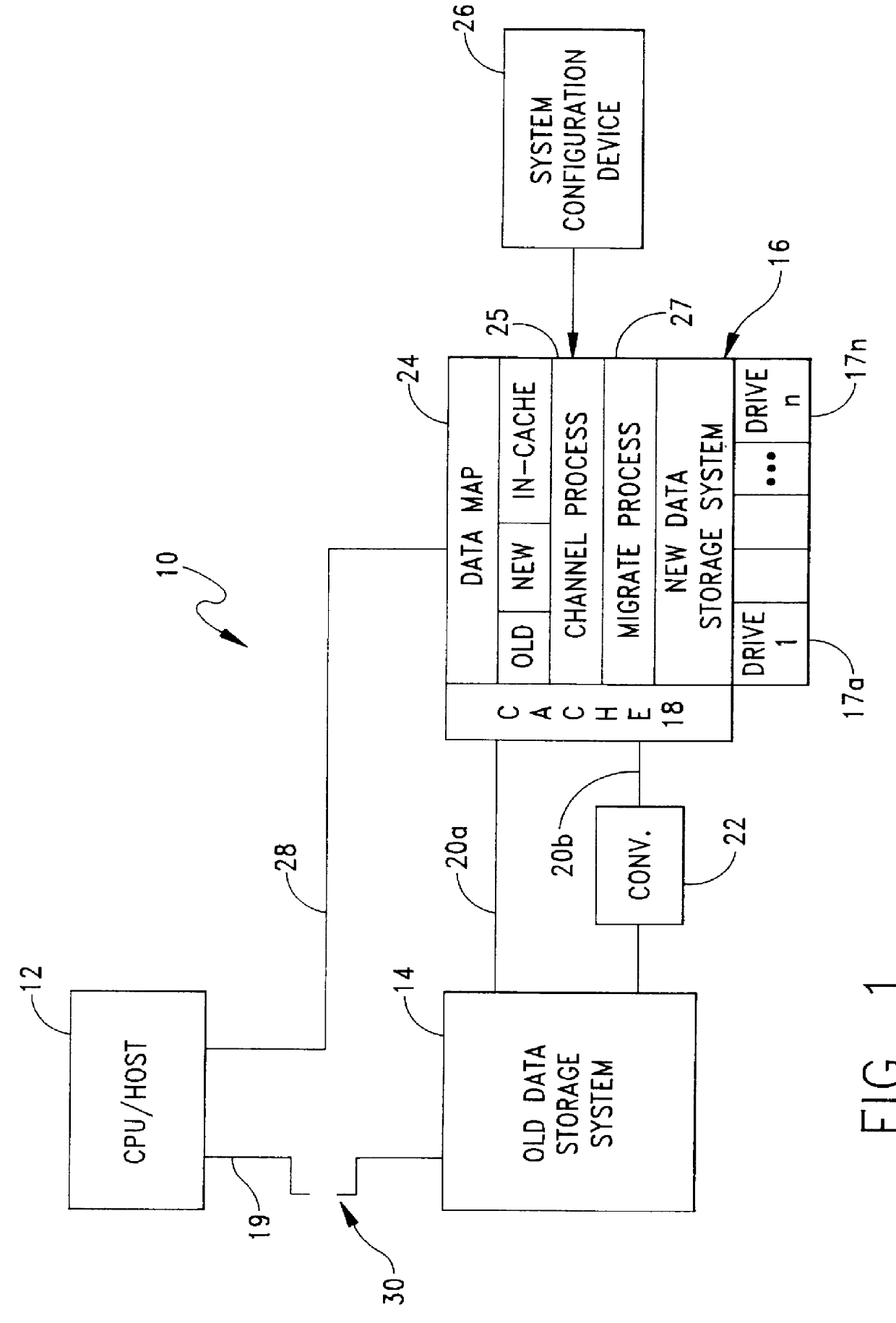
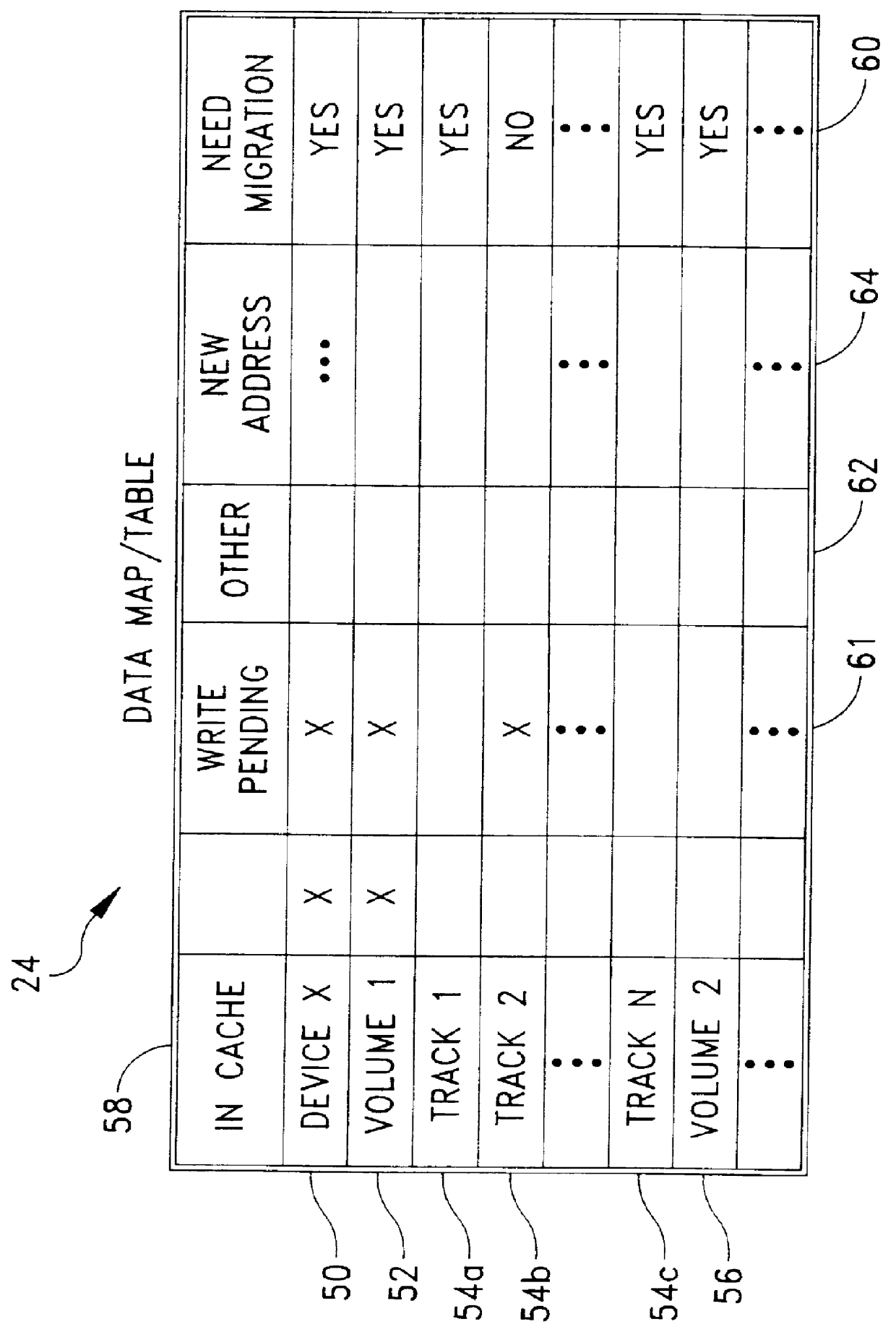
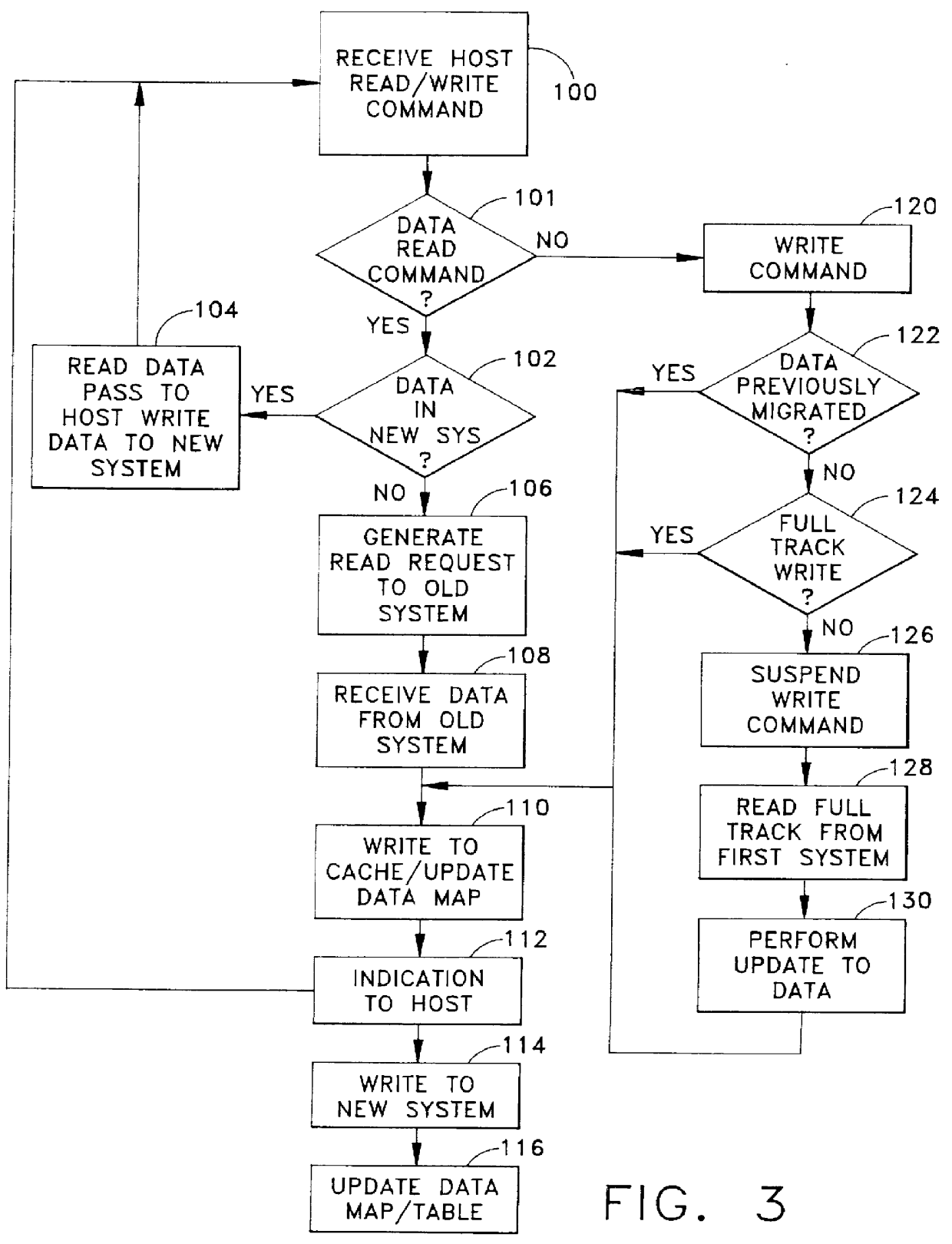
System and method for on-line, real time, data migration
InactiveUS6108748AInhibit transferInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData migrationData transmission
A system and method for providing on-line, real-time, transparent data migration from an existing storage device to a replacement storage device. The existing and replacement storage devices are connected as a composite storage device that is coupled to a host, network or other data processing system. The replacement storage device includes a table which identifies data elements that have migrated to the replacement storage device. When a host system makes a data transfer request for one or more data elements, the replacement storage device determines whether the data elements have been migrated. If the data elements have migrated, the replacement storage device responds to the data transfer request independently of any interaction with the existing storage device. If the data elements have not migrated, the replacement storage device migrates the requested data elements and then responds to the data request and updates the data element map or table. When not busy servicing other requests, the replacement storage device operates in a background mode to migrate data elements so the data migration can occur concurrently with and transparently to system operations.
Owner:EMC CORPORATION
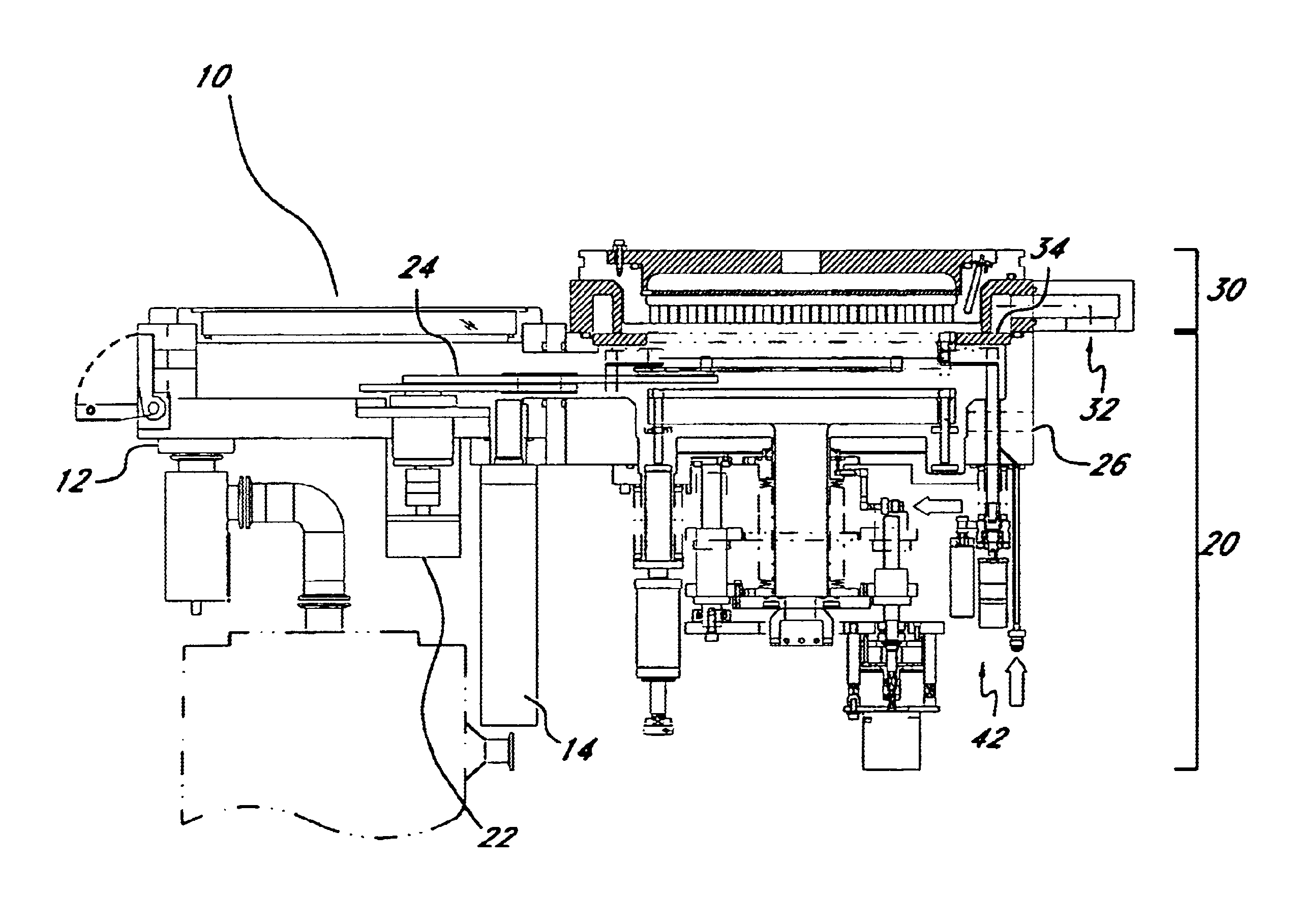
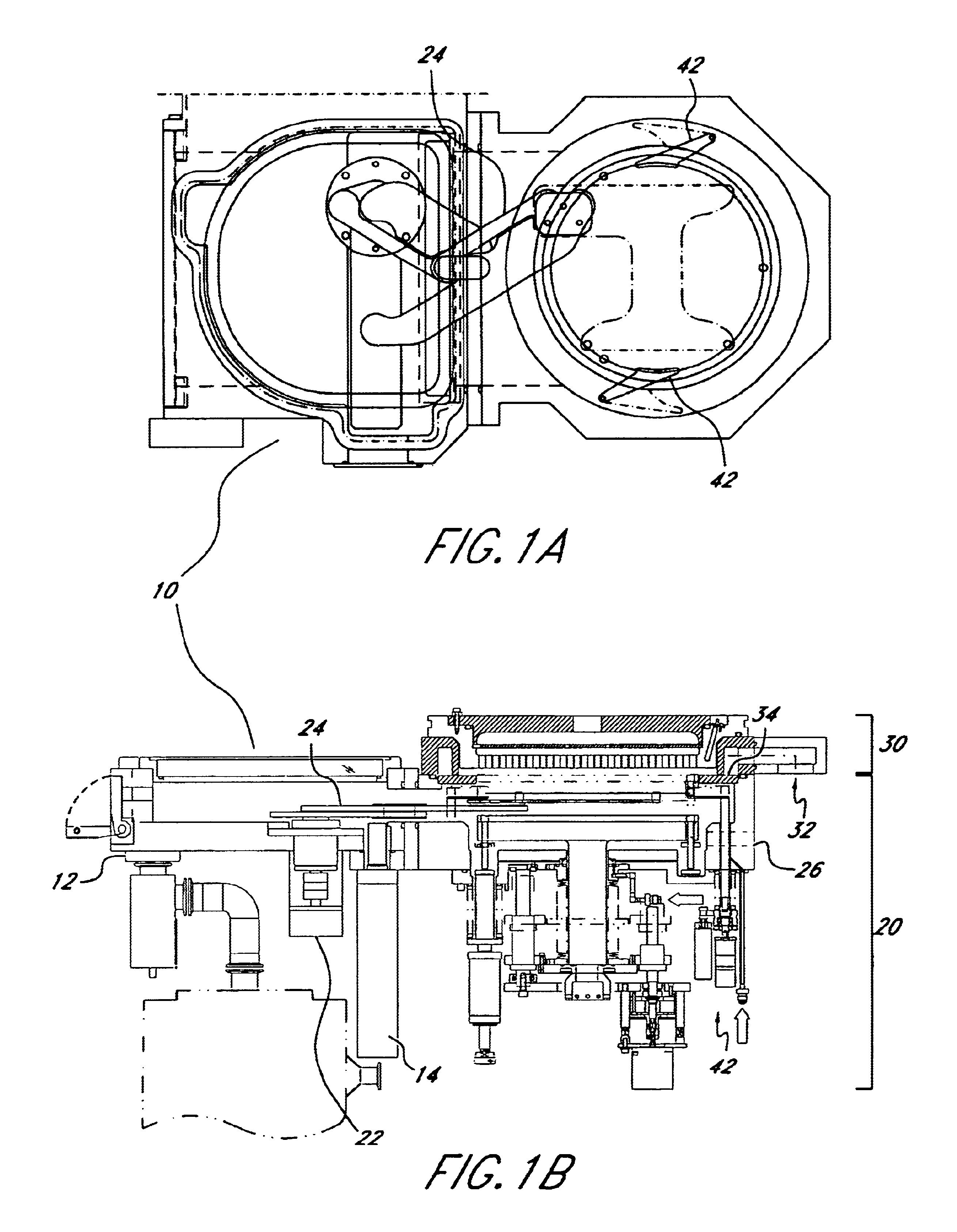
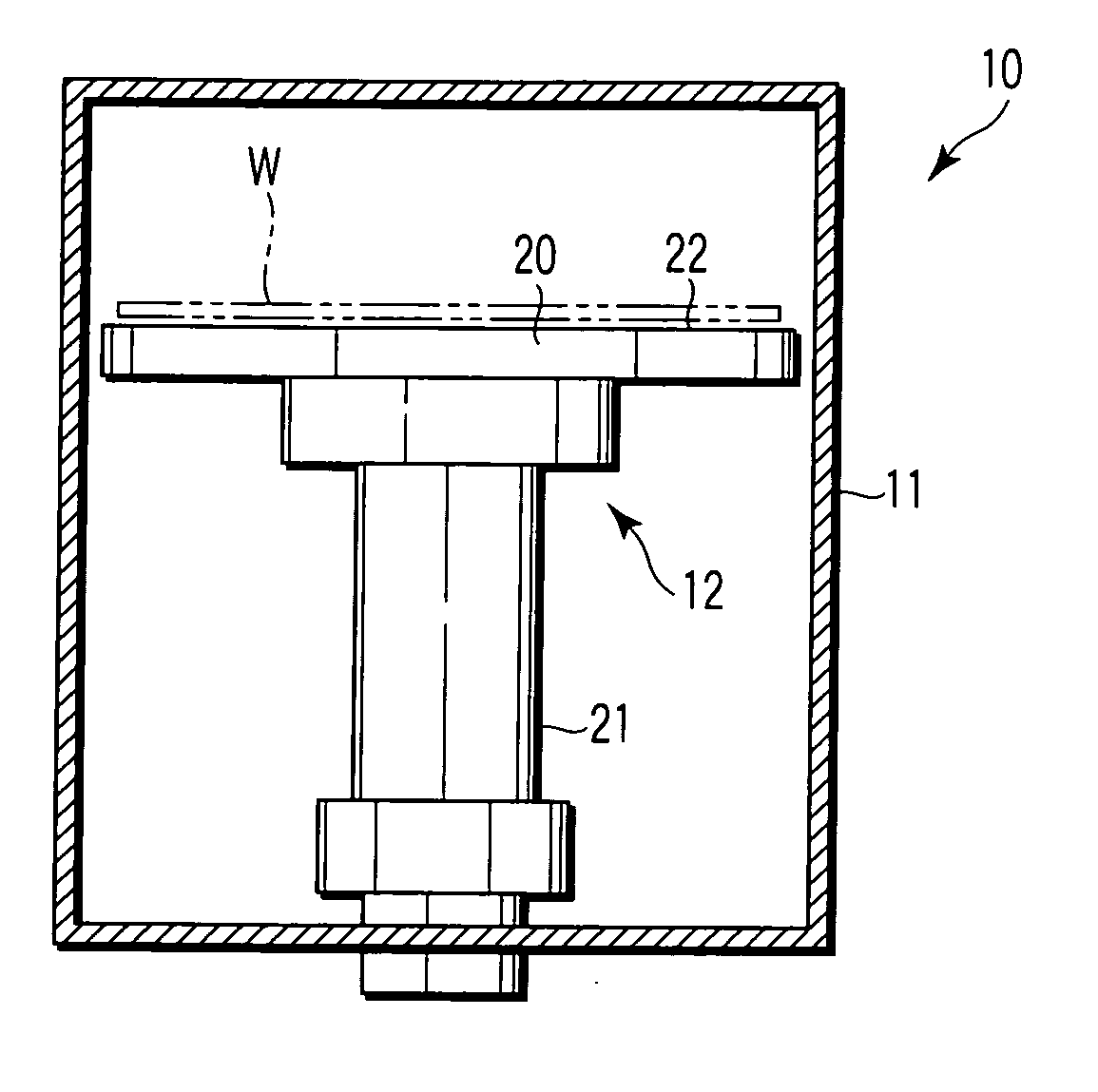
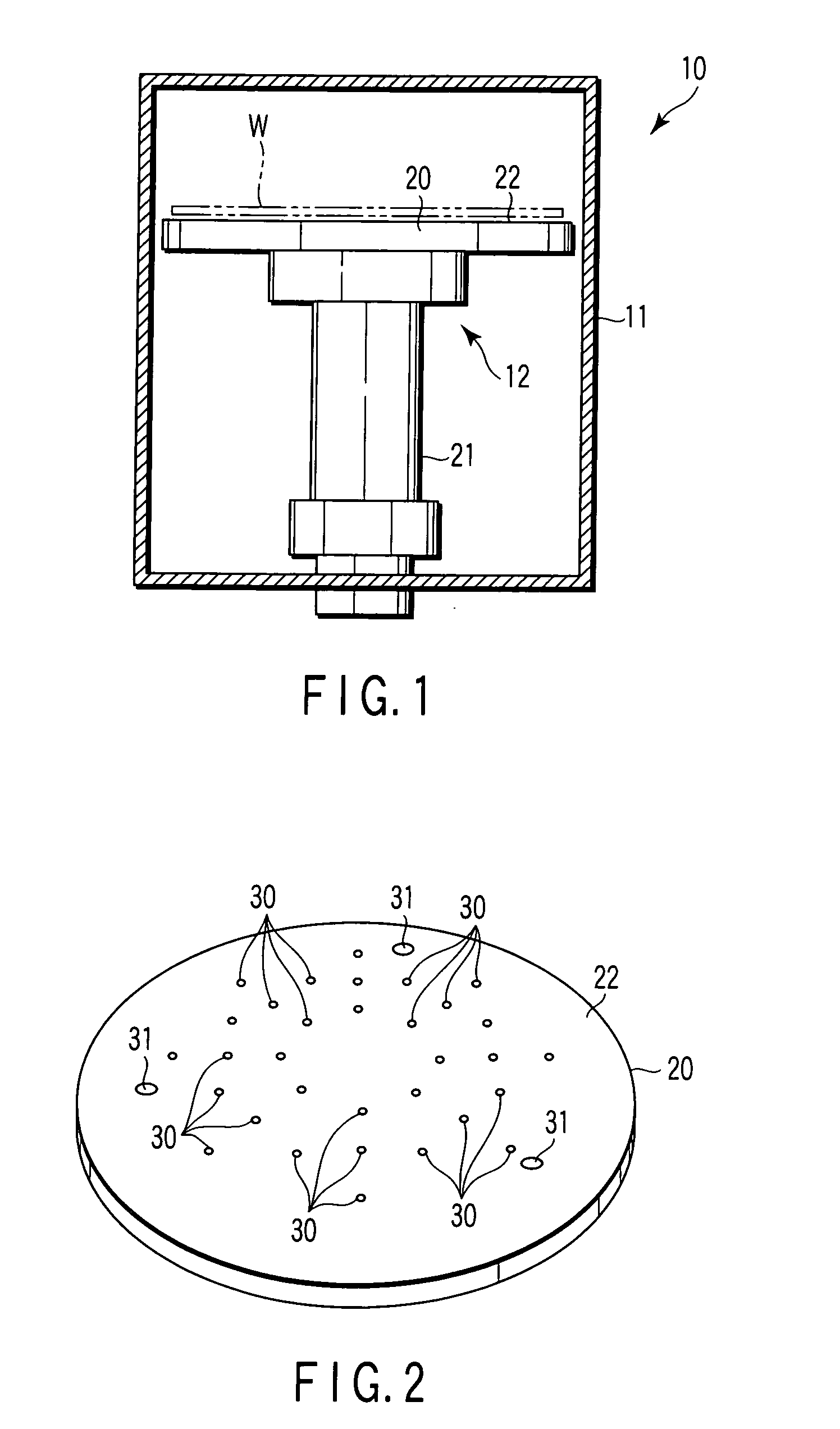
Semiconductor processing apparatus comprising chamber partitioned into reaction and transfer sections
InactiveUS6899507B2Reduce adhesionImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge manipulationEngineeringSemiconductor
Semiconductor processing equipment that has increased efficiency, throughput, and stability, as well as reduced operating cost, footprint, and faceprint is provided. Other than during deposition, the atmosphere of both the reaction chamber and the transfer chamber are evacuated using the transfer chamber exhaust port, which is located below the surface of the semiconductor wafer. This configuration prevents particles generated during wafer transfer or during deposition from adhering to the surface of the semiconductor wafer. Additionally, by introducing a purge gas into the transfer chamber during deposition, and by using an insulation separating plate 34, the atmospheres of the transfer and reaction chambers can be effectively isolated from each other, thereby preventing deposition on the walls and components of the transfer chamber. Finally, the configuration described herein permits a wafer buffer mechanism to be used with the semiconductor processing equipment, thereby further increasing throughput and efficiency.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Substrate supporting apparatus
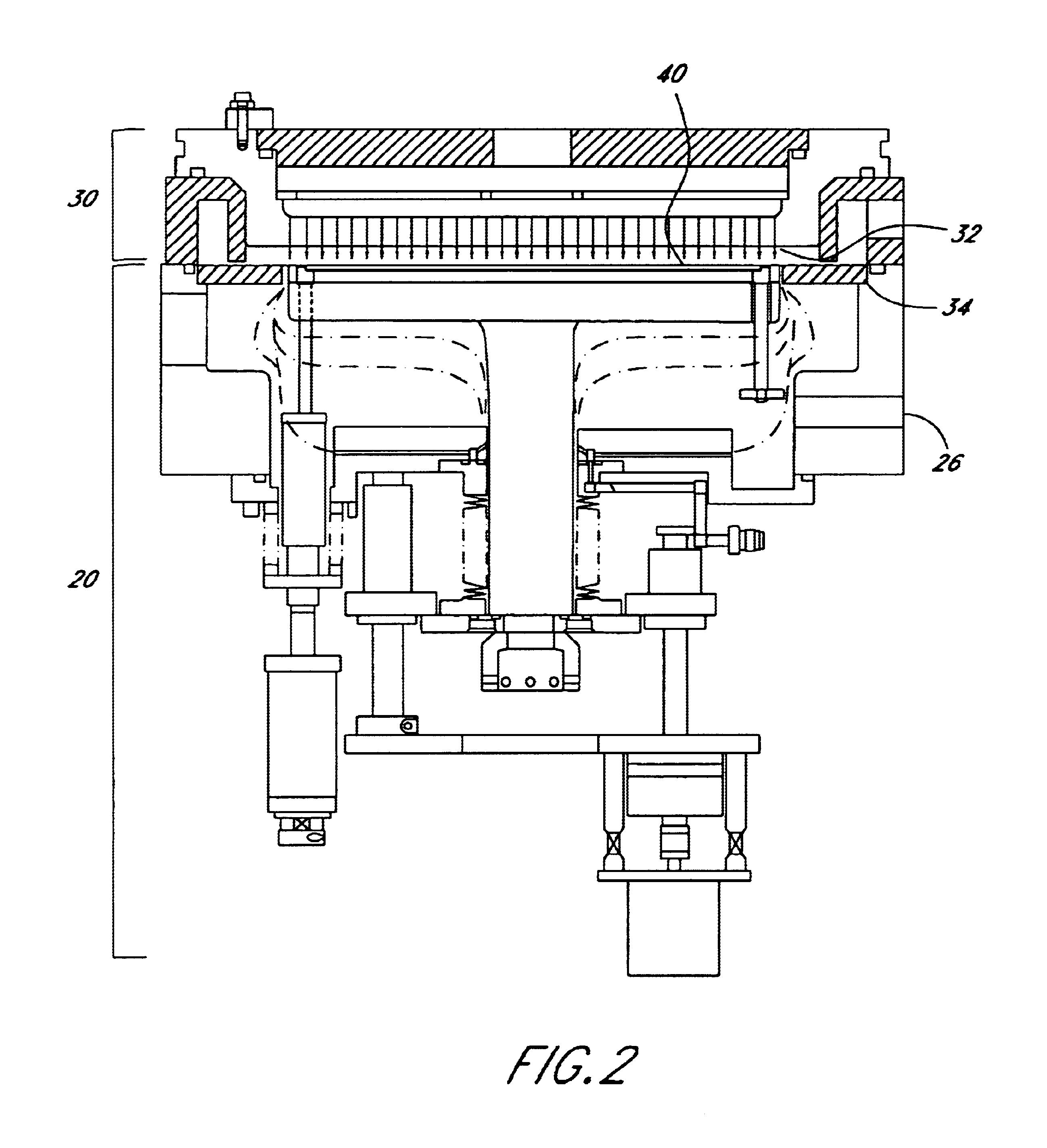
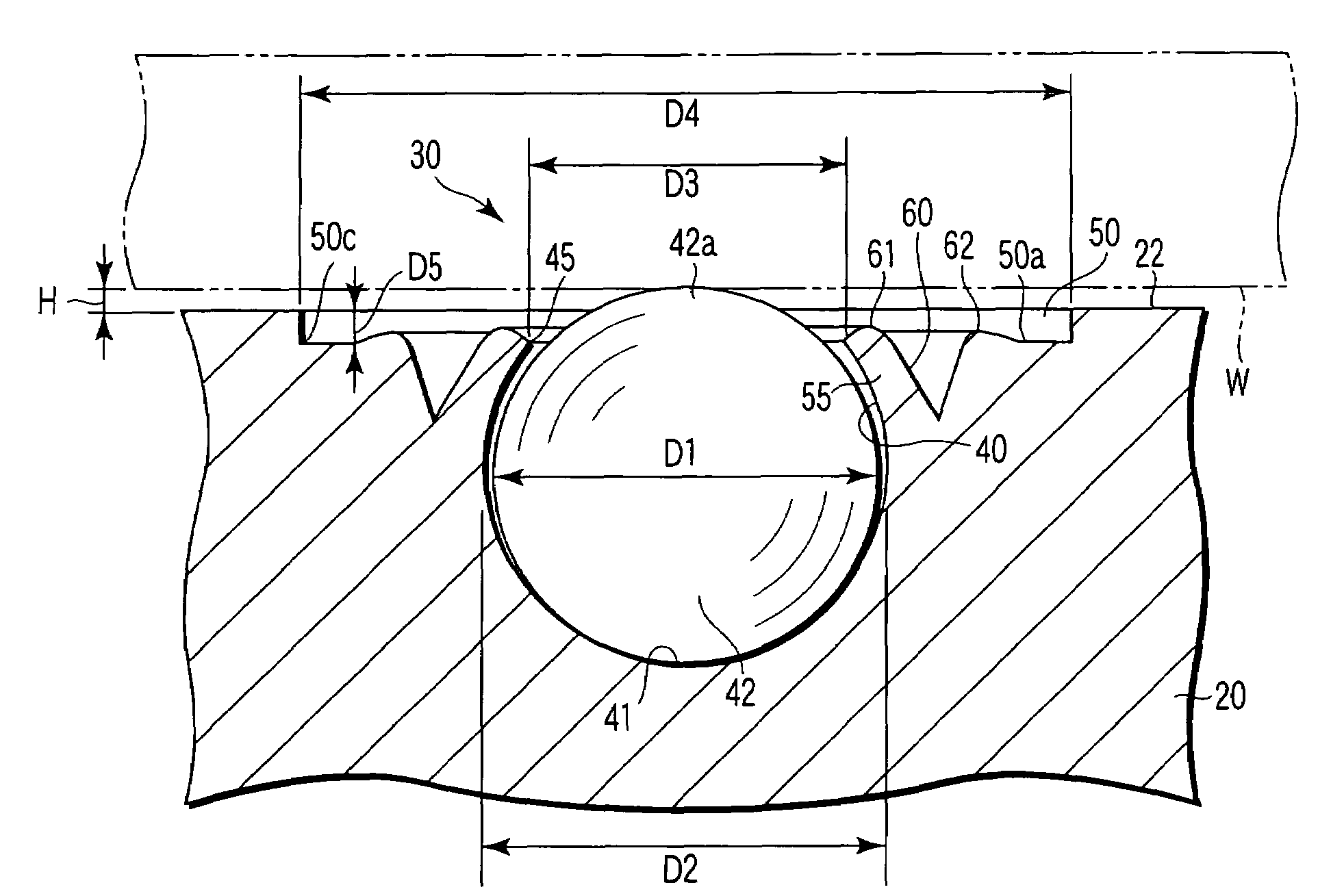
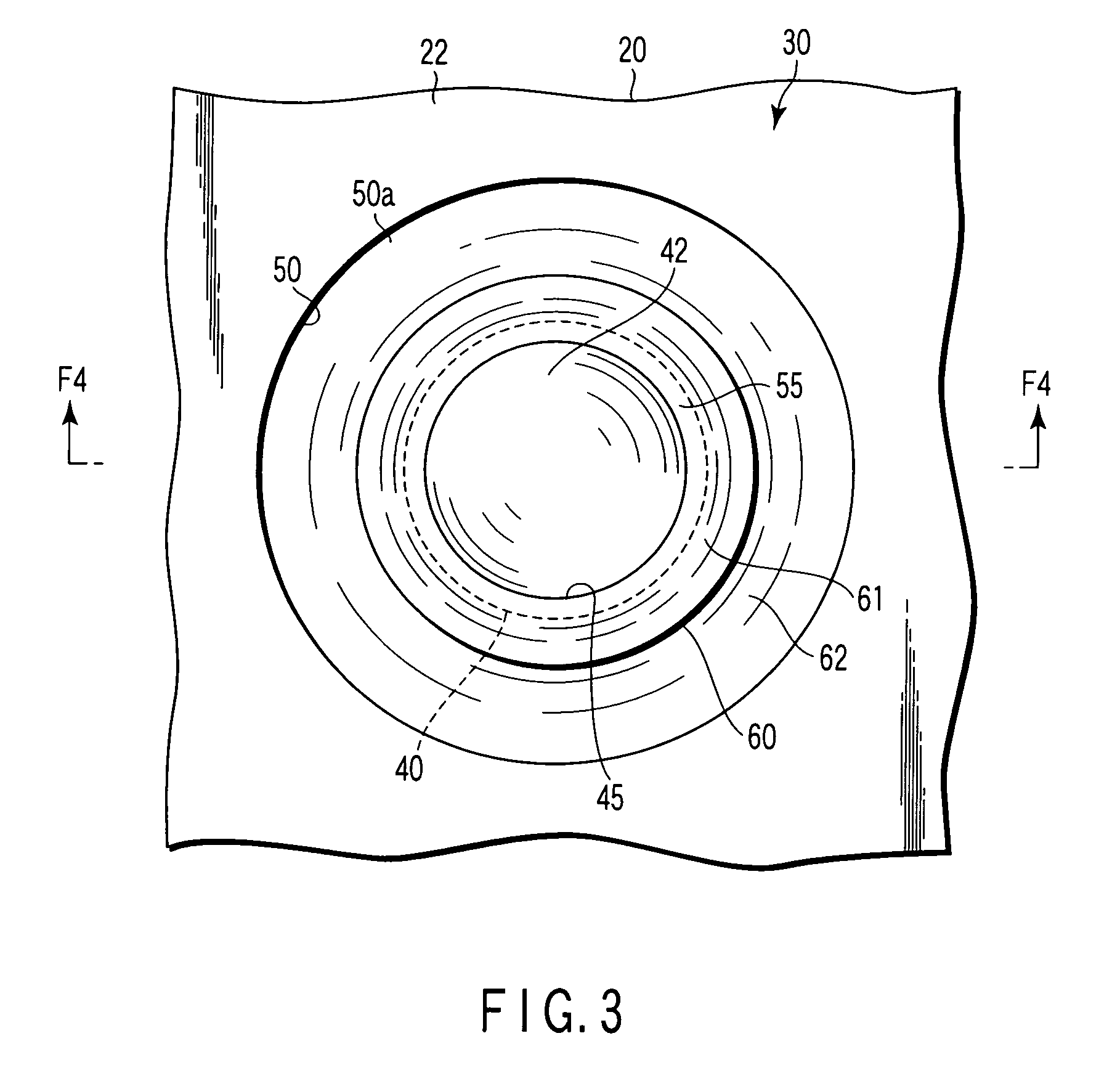
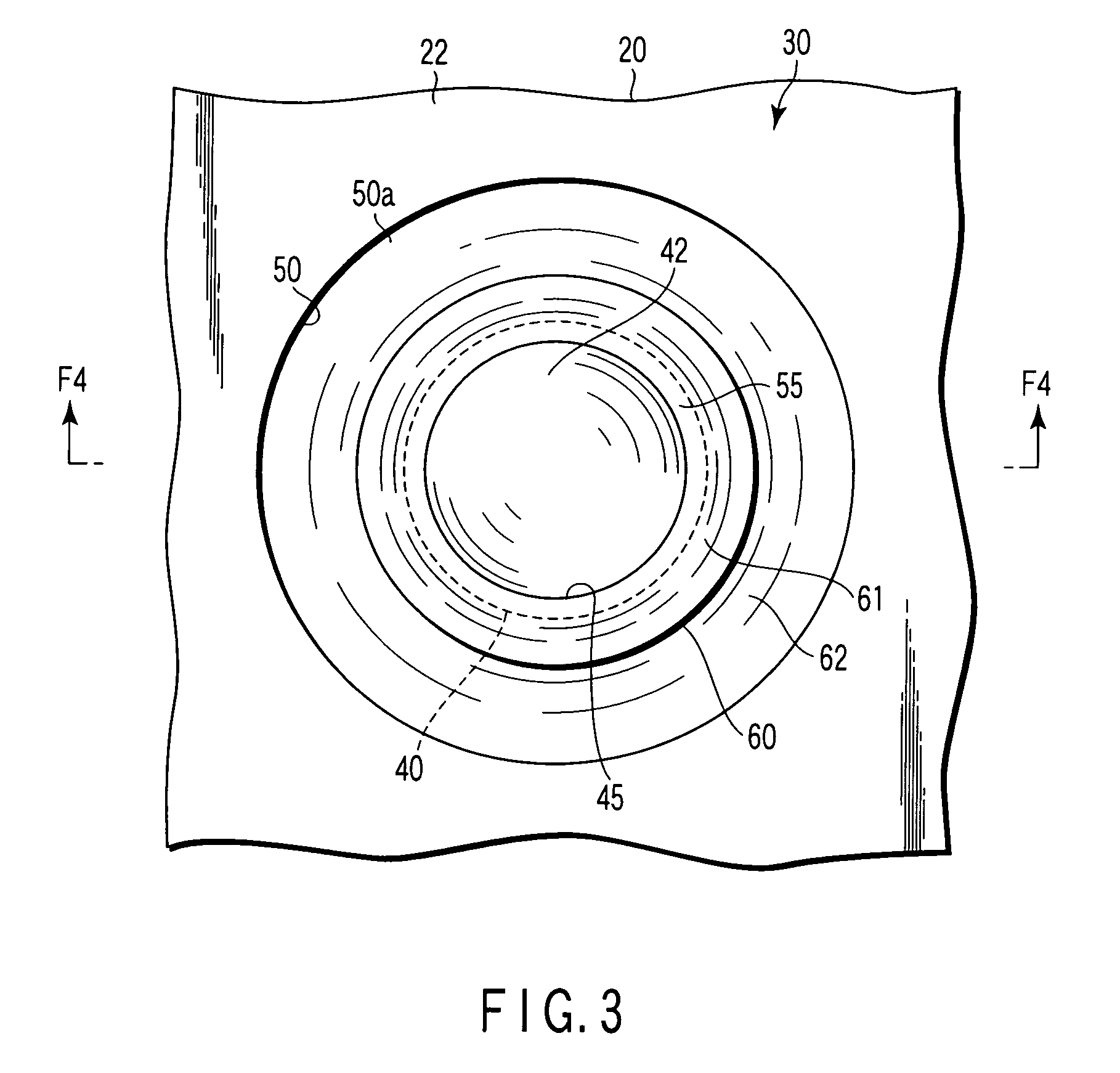
ActiveUS7503980B2Preventing slipping-off and breakageInhibit transferLiquid surface applicatorsLinear bearingsAlloyEngineering
A substrate supporting apparatus includes a plate member of an aluminum alloy having a flat upper surface, bottomed pits formed in the plate member, and spacer members held in the pits, individually. The spacer members are sapphire spheres. The diameter of each spacer member is a little smaller than that of each pit. The upper end of each spacer member projects from the upper surface of the plate member. A spot facing is formed in a region that includes the open edge portion of the pit. A bending portion which is obtained by plastically deforming the open edge portion of the pit toward the spacer member is formed on a bottom surface of the spot facing. A V-shaped groove is formed behind the bending portion.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Substrate supporting apparatus and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20070157466A1Preventing slipping-offAvoid breakingLiquid surface applicatorsLinear bearingsEngineeringAlloy
A substrate supporting apparatus includes a plate member of an aluminum alloy having a flat upper surface, bottomed pits formed in the plate member, and spacer members held in the pits, individually. The spacer members are sapphire spheres. The diameter of each spacer member is a little smaller than that of each pit. The upper end of each spacer member projects from the upper surface of the plate member. A spot facing is formed in a region that includes the open edge portion of the pit. A bending portion which is obtained by plastically deforming the open edge portion of the pit toward the spacer member is formed on a bottom surface of the spot facing. A V-shaped groove is formed behind the bending portion.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
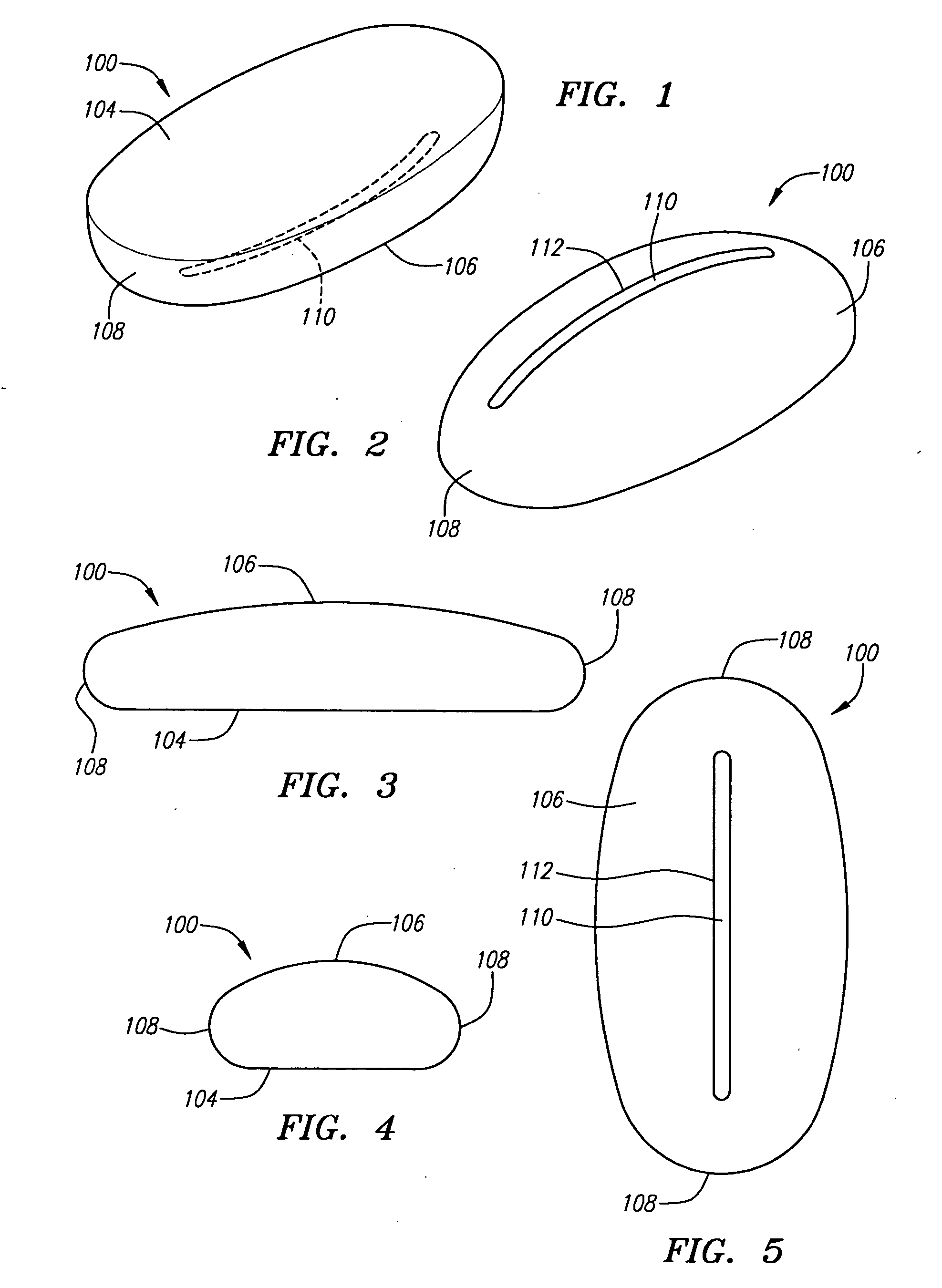
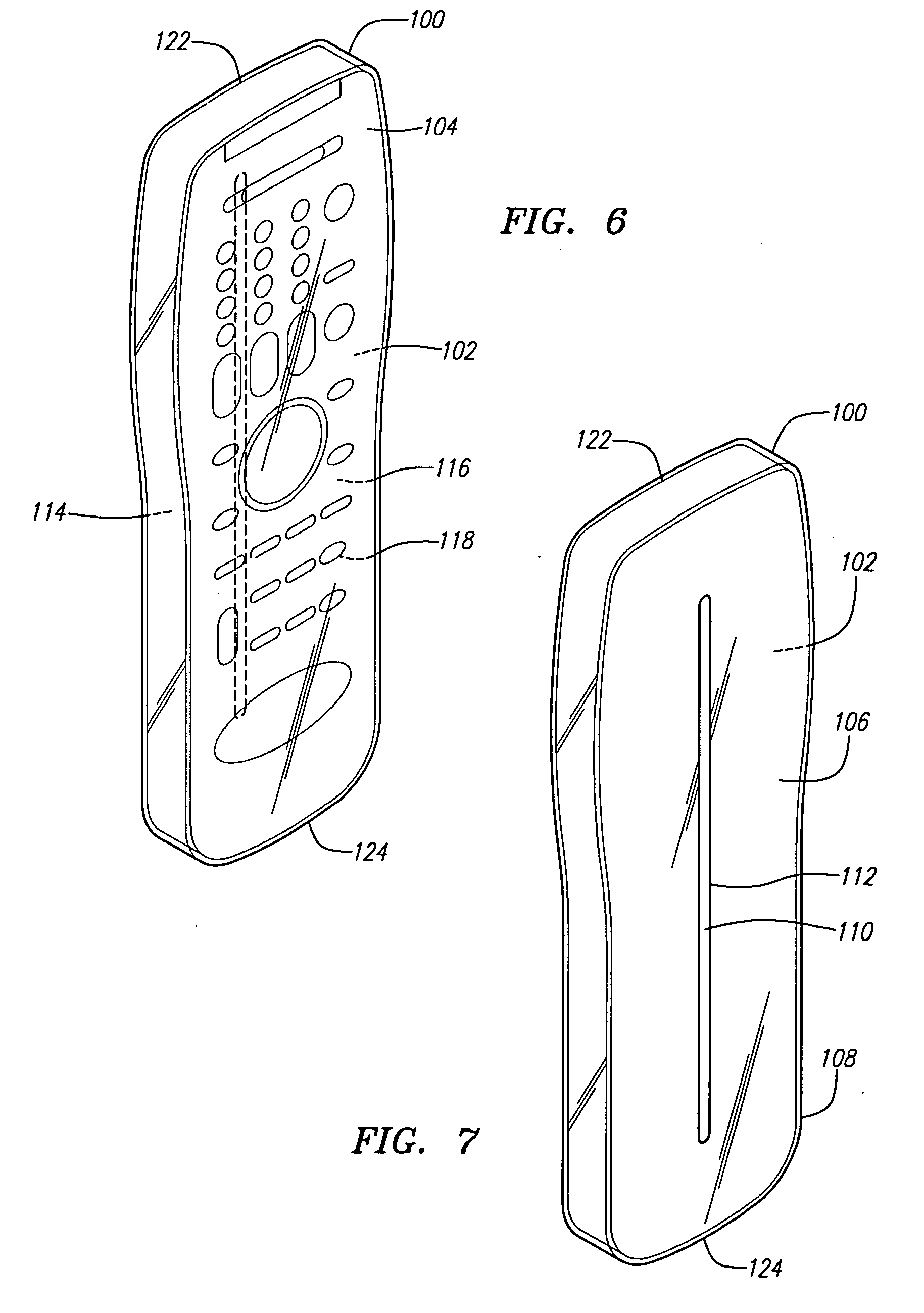
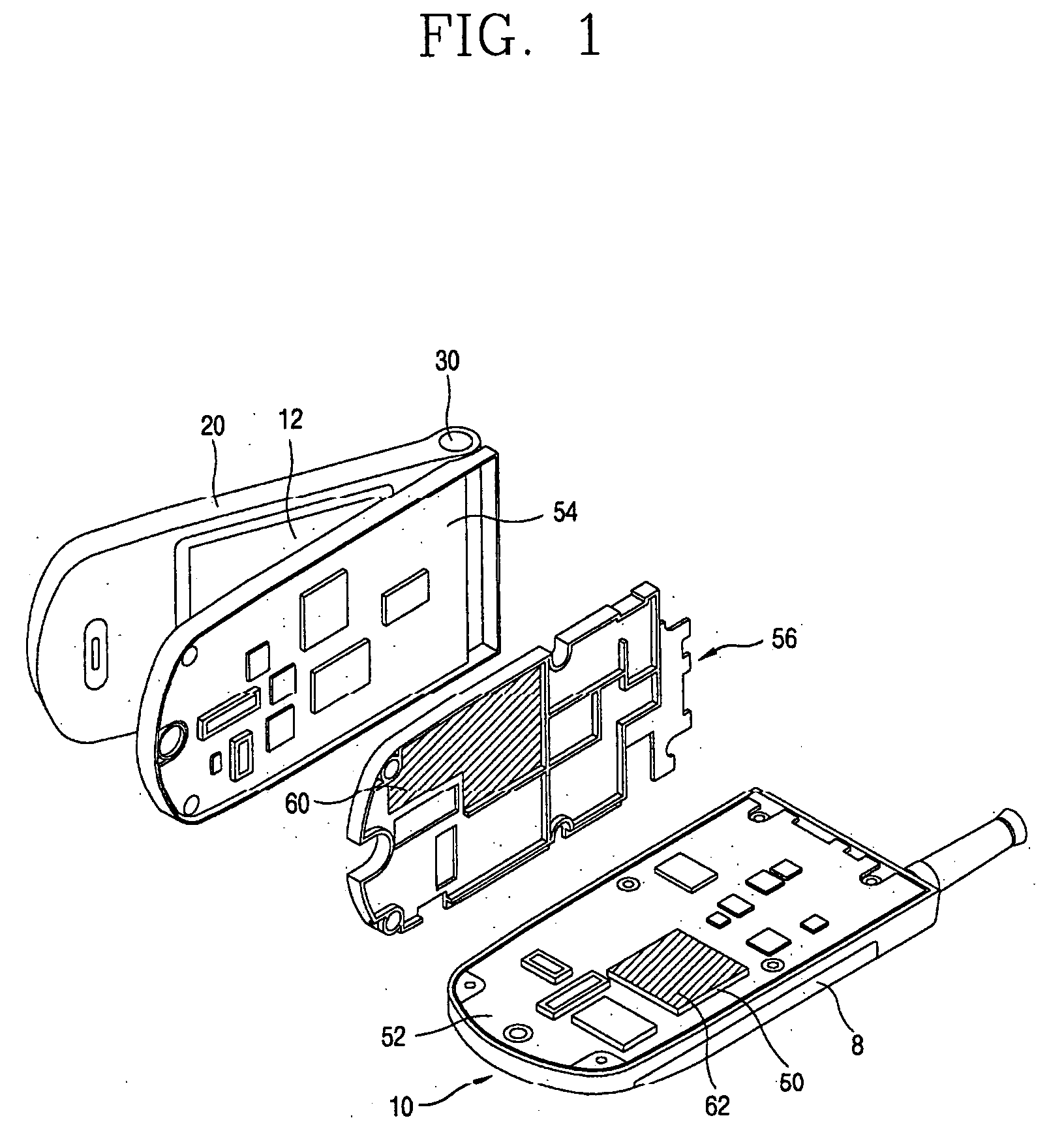
Cover for remote control device
InactiveUS20050279661A1Minimizing transferEasy to captureFlexible coversWrappersRemote controlEngineering
A disposable cover for use with a remote control device for providing a protective barrier to human infection comprising a front member having a continuously flat surface and a rear member integrally molded in a seamless unitary, one-piece construction with the front member at a plurality of rounded surfaces for forming a single-use, disposable protective enclosure. An orifice is formed in and parallel to an oblong dimension of the rear member for enabling most any size remote control device to be inserted into and removed from the enclosure. The rounded surfaces designed into the disposable cover facilitate the closing of the orifice for enclosing the remote control device. The front member, rear member and rounded surfaces are each comprised of a flexible, stretchable and transparent material for conforming to the shape of the remote control device and for providing a disposable, protective sanitation barrier to human infection.
Owner:HODGES RICHARD P
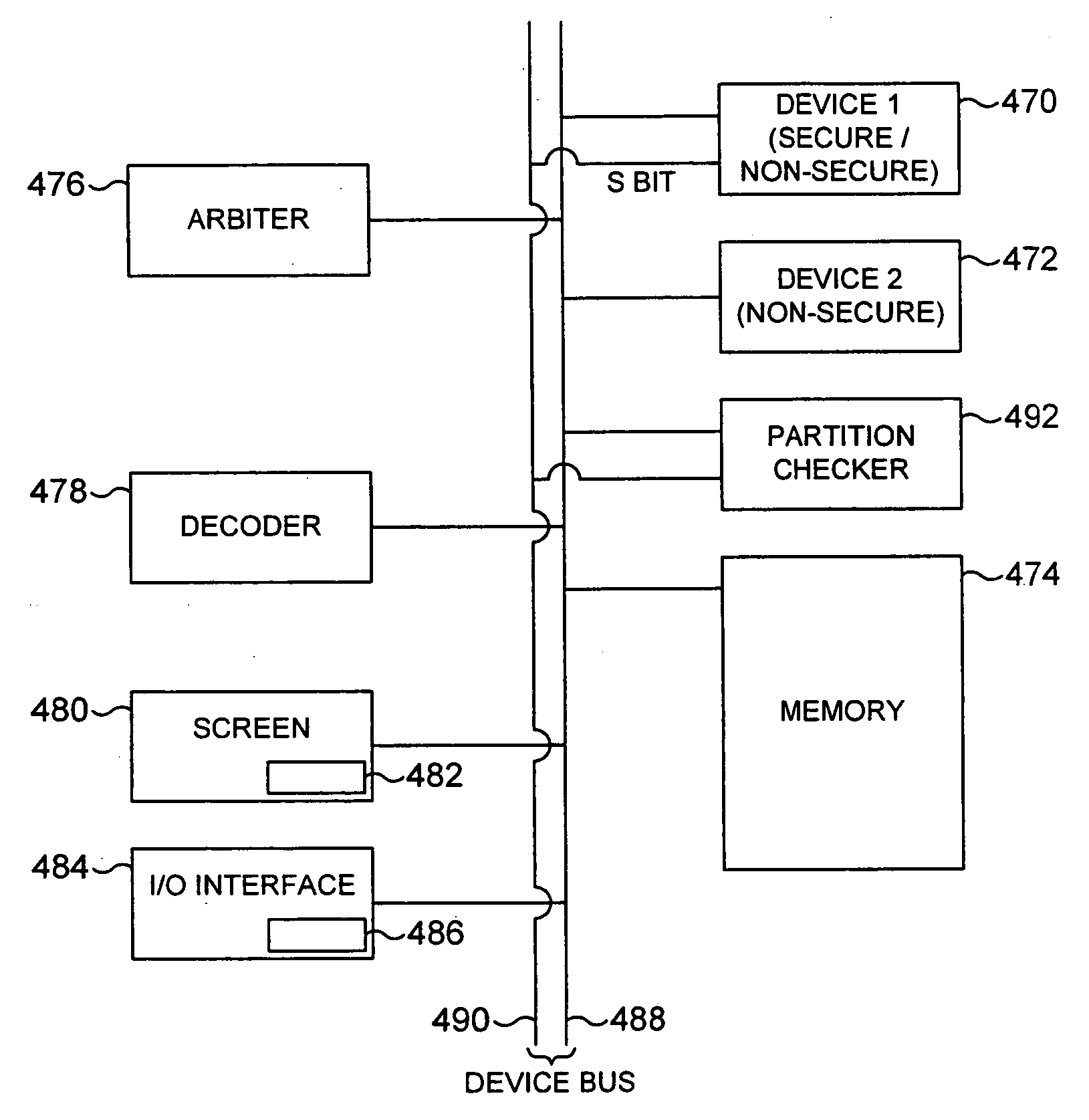
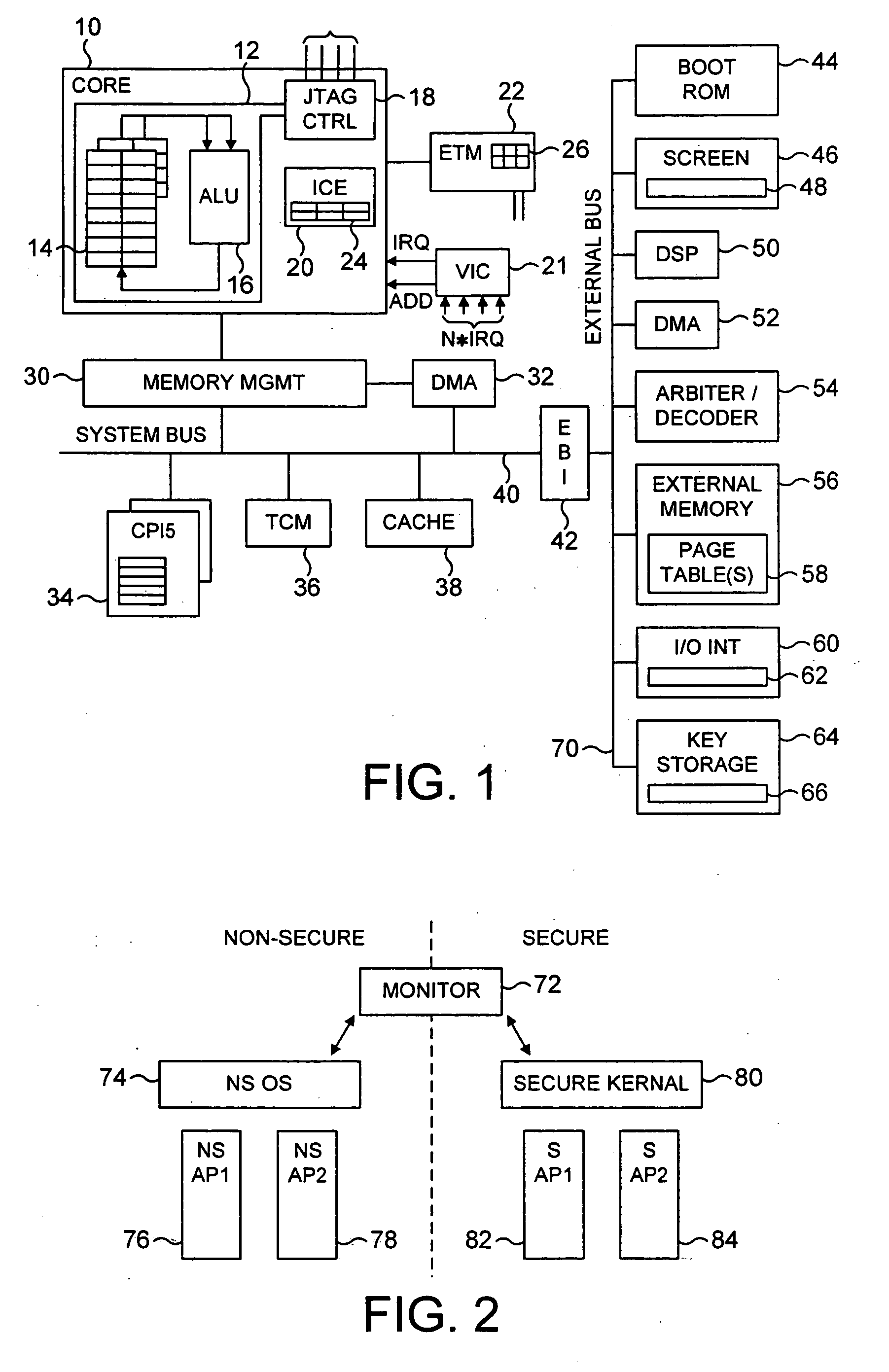
Control of access to a memory by a device
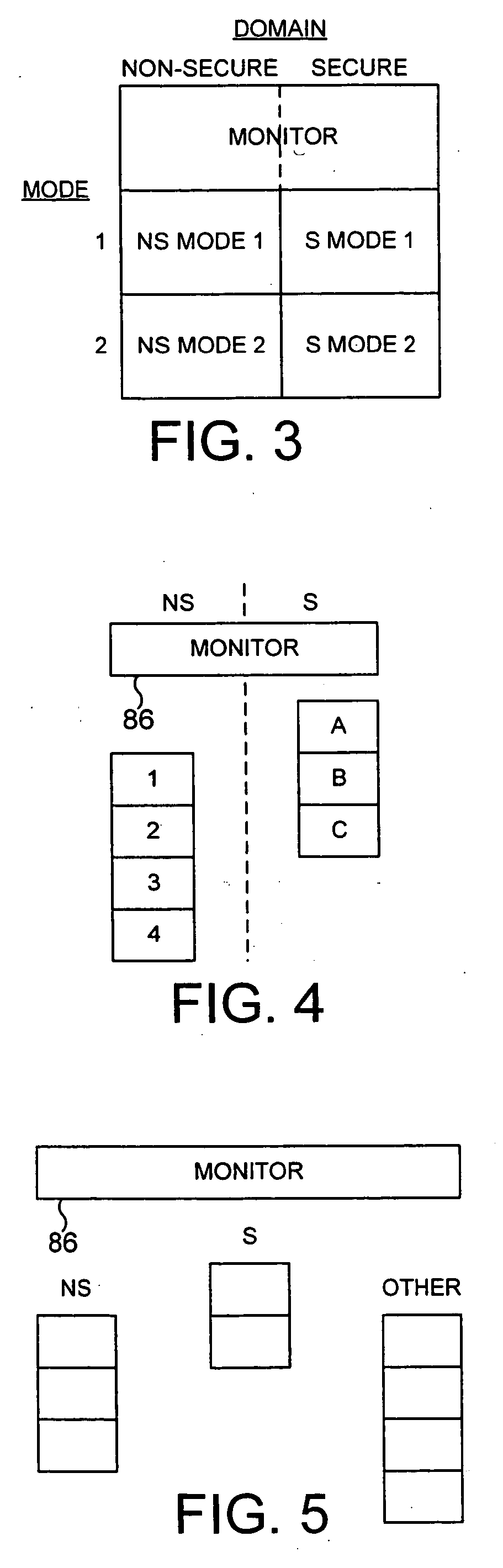
ActiveUS20040177261A1Prevent unauthorized accessAvoid it happening againMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareSecurity domain
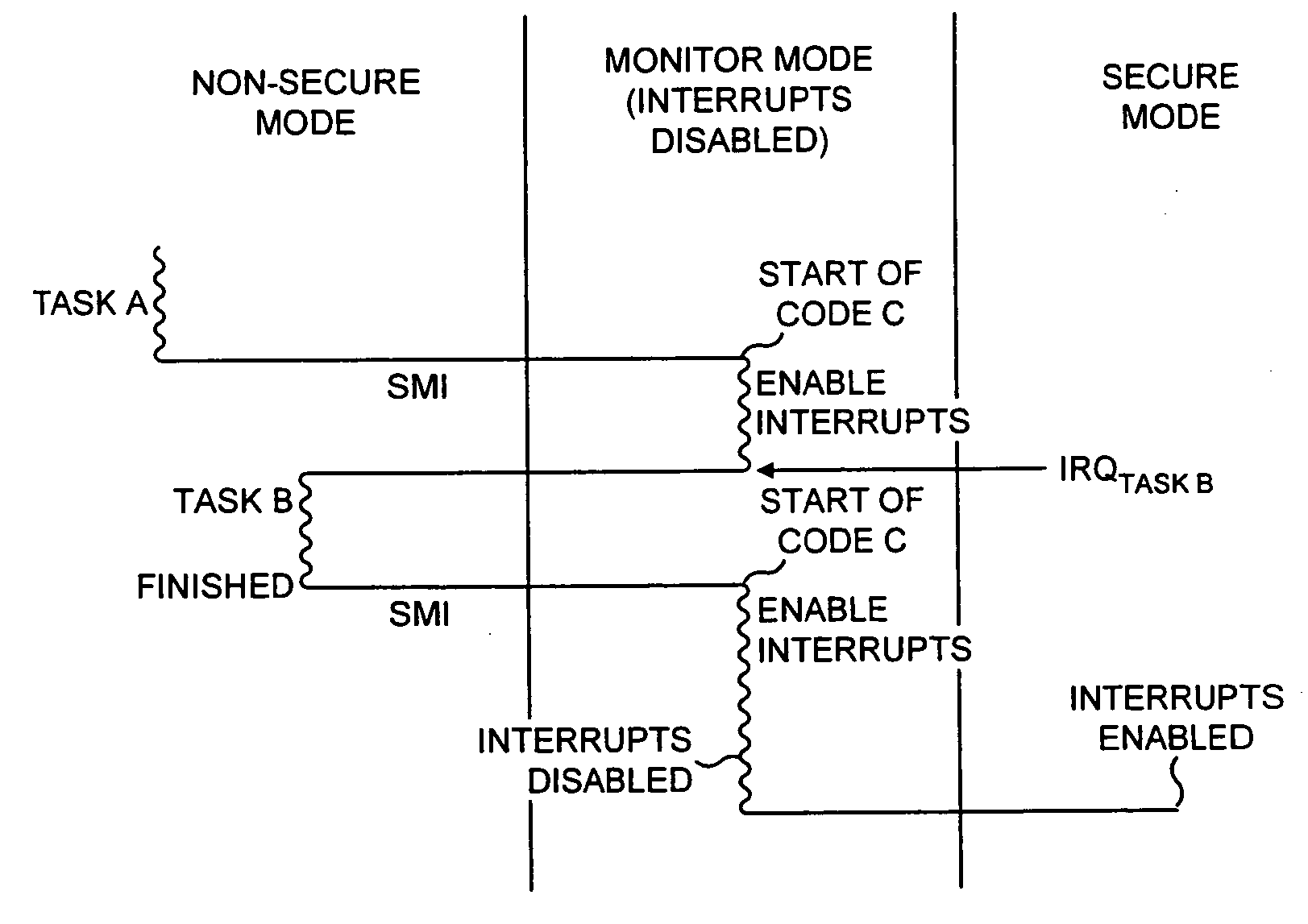
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for controlling access to a memory. The data processing apparatus has a secure domain and a non-secure domain, in the secure domain the data processing apparatus having access to secure data which is not accessible in the non-secure domain. The data processing apparatus comprises a device coupled to a memory via a device bus, and operable, when an item of data in the memory is required by the device, to issue onto the device bus a memory access request pertaining to either the secure domain or the non-secure domain. The memory is operable to store data required by the device, and contains secure memory for storing secure data and non-secure memory for storing non-secure data. In accordance with the present invention, the data processing apparatus further comprises partition checking logic coupled to the device bus and operable whenever the memory access request as issued by the device pertains to the non-secure domain, to detect if the memory access request is seeking to access the secure memory and upon such detection to prevent the access specified by that memory request. This approach significantly improves the security of data contained within a secure portion of memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
Vagus nerve stimulation electrodes and methods of use
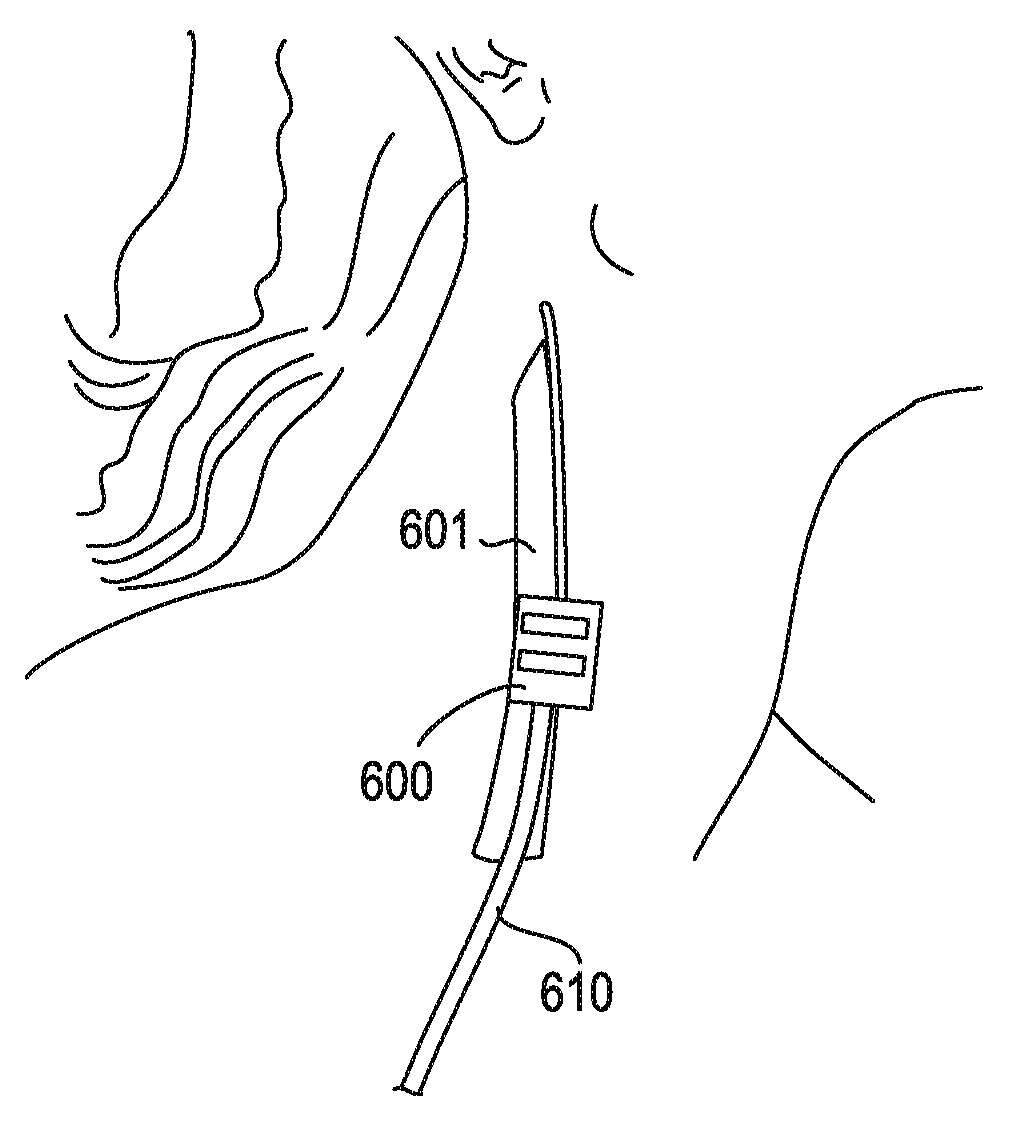
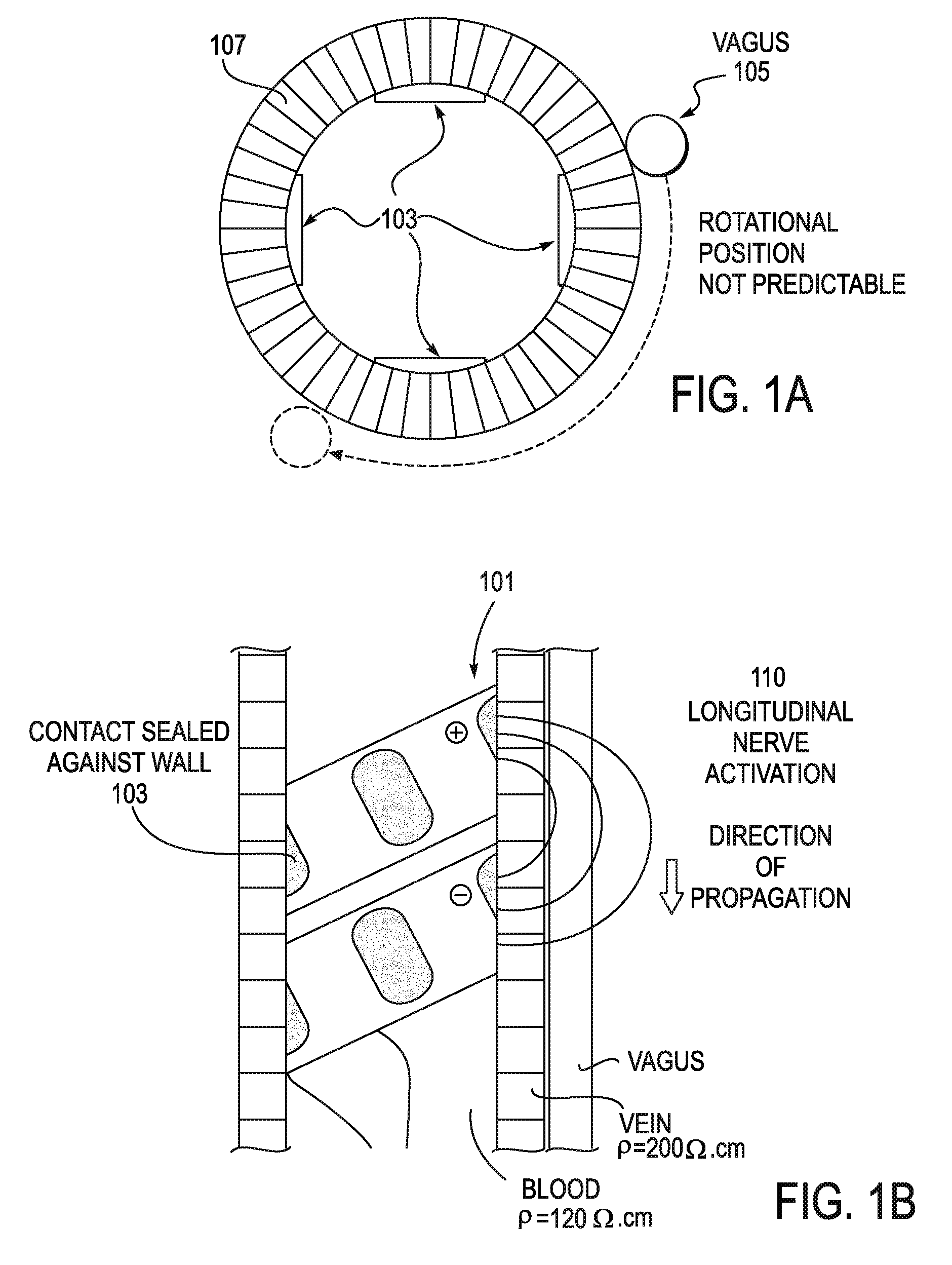
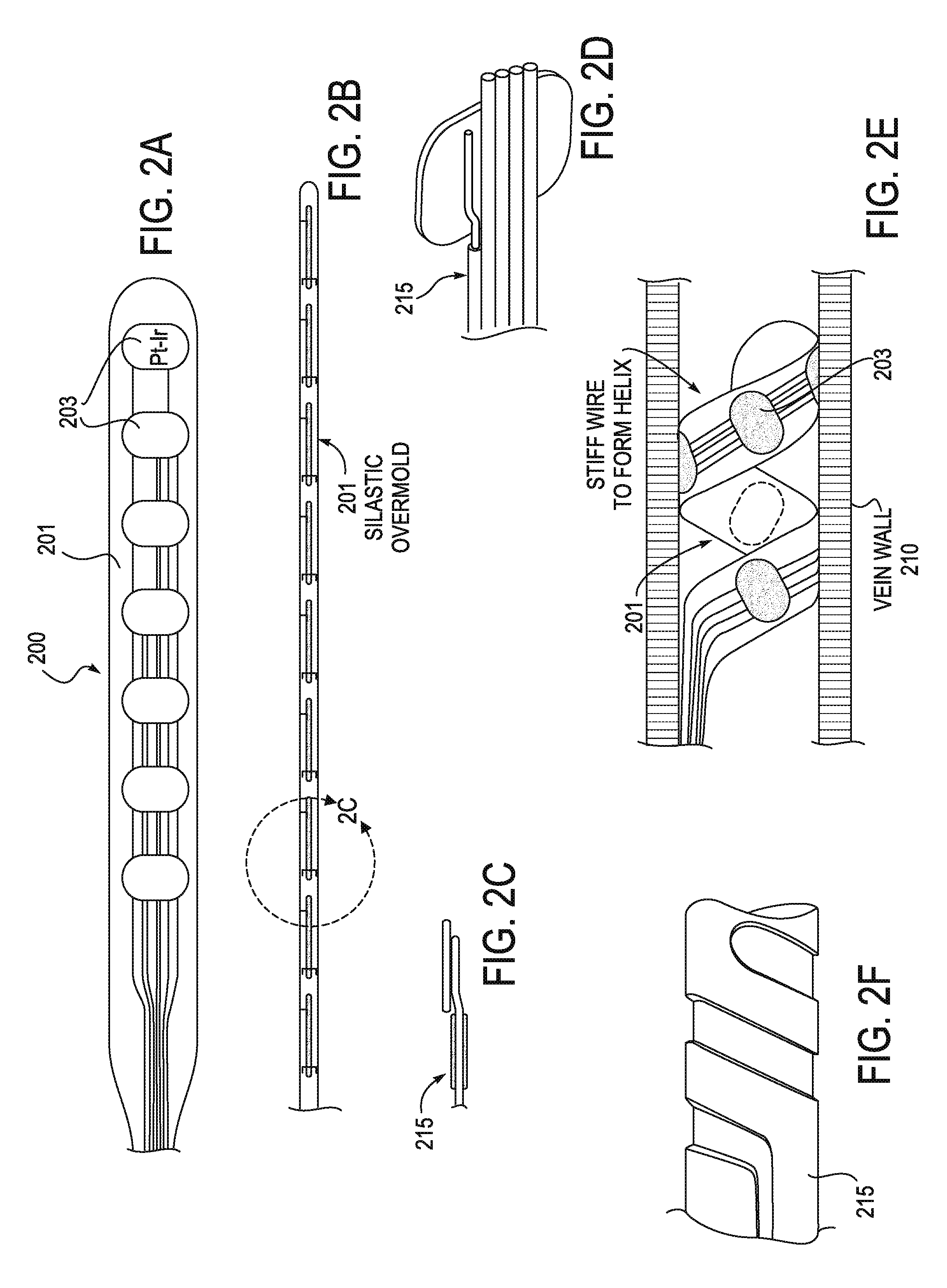
InactiveUS20090275997A1Lower Level RequirementsPrevent adverse side effectsSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesInflammatory reflexVein
Described herein are systems, method and devices for modulating the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The systems described herein may include one or more implantable leads configured to be used to stimulate the inflammatory reflex. These leads typically include a flexible body region, a plurality of electrodes (or contacts) and may be used with a stylet or other inserter. The leads may also include one or more anchors. Exemplary leads may be intra-carotid sheath field-effect leads (“sheath FE” leads), carotid sheath cuff leads (“sheath cuff” leads), intracardiac leads, vagus nerve cuff leads (“vagus cuff” leads), and intravenous leads (“intravascular” leads). Leads (e.g., intravascular leads) may be chronic or acute.
Owner:FALTYS MICHAEL ALLEN +2
Apparatus and method for managing access to a memory
ActiveUS20040177269A1Performance is not affectedEasy to operateMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsManagement unitMultiple modes
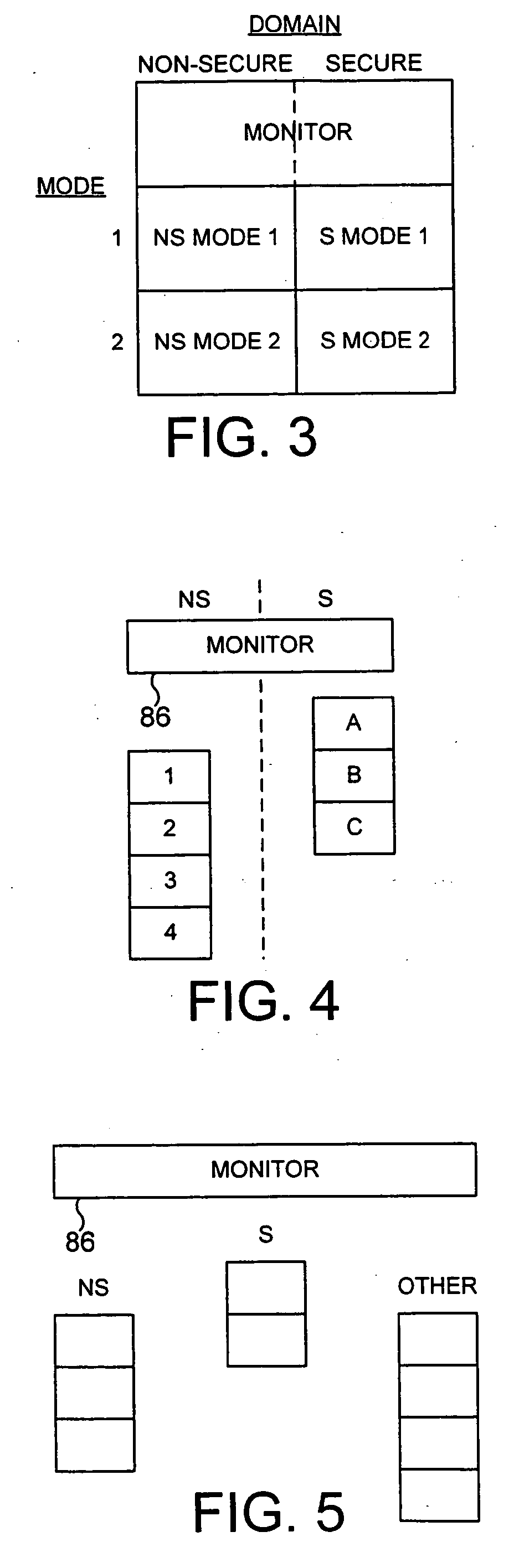
The present invention provides a data processing apparatus and method for managing access to a memory within the data processing apparatus. The data processing apparatus comprises a processor operable in a plurality of modes and a plurality of domains, said plurality of domains comprising a secure domain and a non-secure domain, said plurality of modes including at least one non-secure mode being a mode in the non-secure domain and at least one secure mode being a mode in the secure domain, said processor being operable such that when executing a program in a secure mode said program has access to secure data which is not accessible when said processor is operating in a non-secure mode. Further, a memory is provided for storing data required by the processor, and consists of secure memory for storing secure data and non-secure memory for storing non-secure data. The memory further contains a non-secure table and a secure table, the non-secure table being within the non-secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of first memory regions an associated descriptor, and the secure table being within the secure memory and arranged to contain for each of a number of second memory regions an associated descriptor. When access to an item of data in the memory is required by the processor, the processor issues a memory access request, and a memory management unit is provided to perform one or more predetermined access control functions to control issuance of the memory access request to the memory. The memory management unit comprises an internal storage unit operable to store descriptors retrieved by the memory management unit from either the non-secure table or the secure table, and in accordance with the present invention the internal storage unit comprises a flag associated with each descriptor stored within the internal storage unit to identify whether that descriptor is from the non-secure table or the secure table. By this approach, when the processor is operating in a non-secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the non-secure table. In contrast, when the processor is operating in a secure mode, the memory management unit is operable to perform the predetermined access control functions for the memory access request with reference to access control information derived from the descriptors in the internal storage unit retrieved from the secure table. This approach enables different descriptors to be used for the control of accesses to memory in either the secure domain or the non-secure domain, whilst enabling such different descriptors to co-exist within the memory management unit's internal storage unit, thereby avoiding the requirement to flush the contents of such an internal storage unit when the operation of the processor changes from the secure domain to the non-secure domain, or vice versa.
Owner:ARM LTD
Aromatic amine compound, and light-emitting element, light-emitting device, and electronic appliance using the aromatic amine compound
InactiveUS20070215889A1High luminous efficiencyInhibit transferOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceElectron
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel aromatic amine compound, and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, and an electronic appliance with high luminous efficiency. An aromatic amine compound expressed by General Formula (1) and a light-emitting element, a light-emitting device, and an electronic appliance formed using the aromatic amine compound expressed by General Formula (1) are provided. By the use of the aromatic amine compound expressed by General Formula (1), the light-emitting element, the light-emitting device, and the electronic appliance can have high luminous efficiency.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Wet/dry automatic injector assembly
InactiveUS6953445B2Extended shelf lifeObstruct passageAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesBiological activationBiomedical engineering
Owner:MERIDIAN MEDICAL TECH
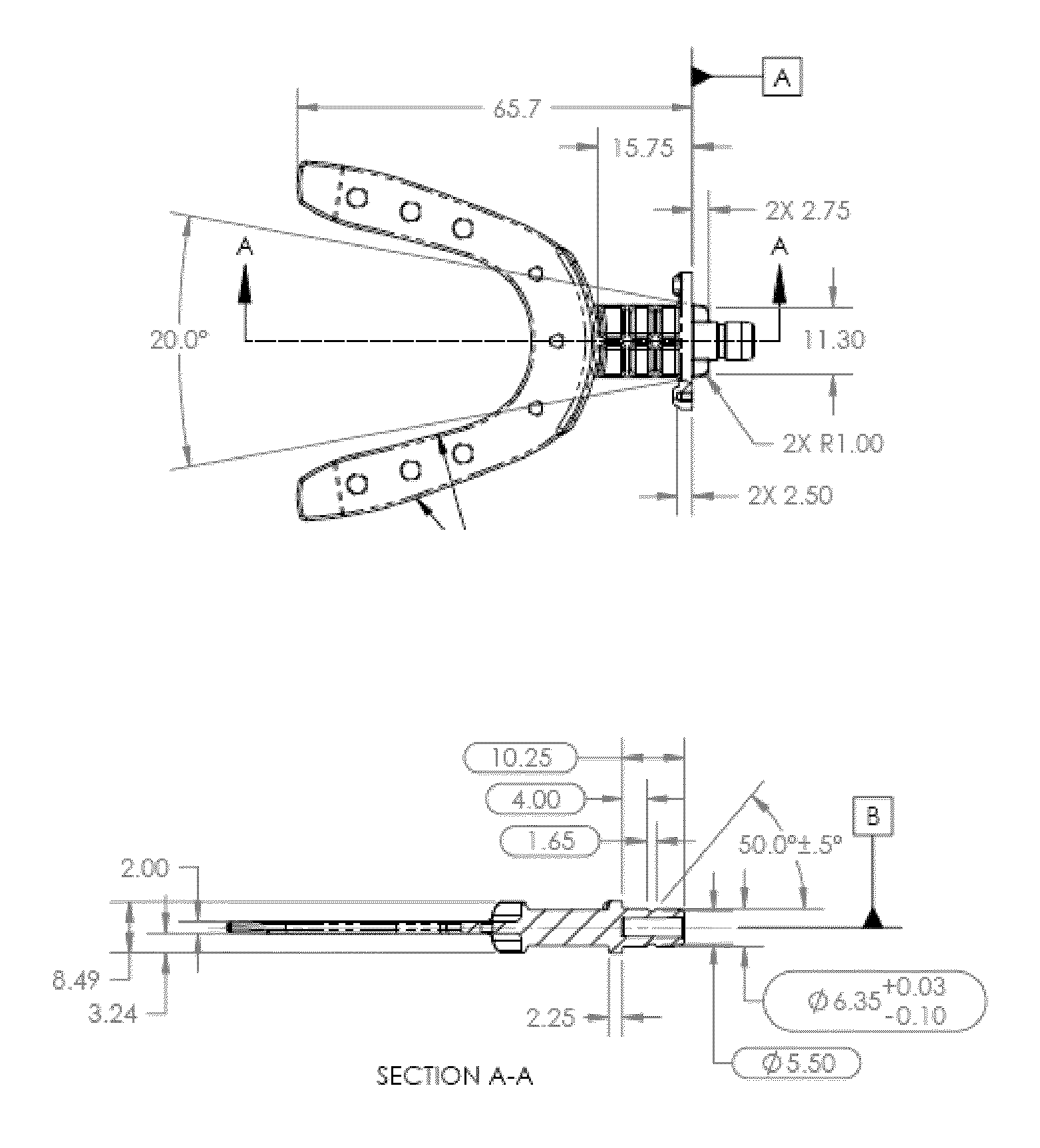
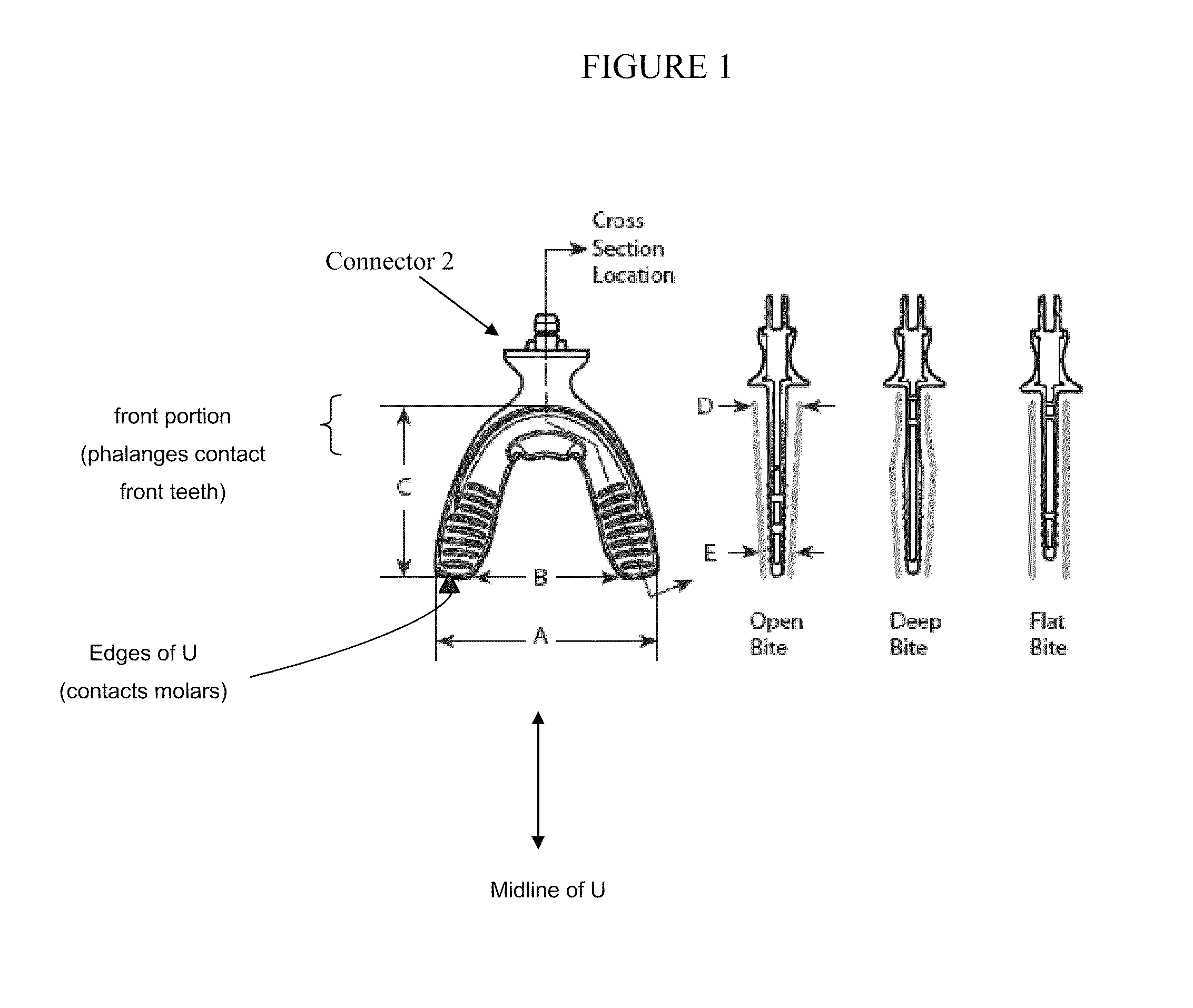
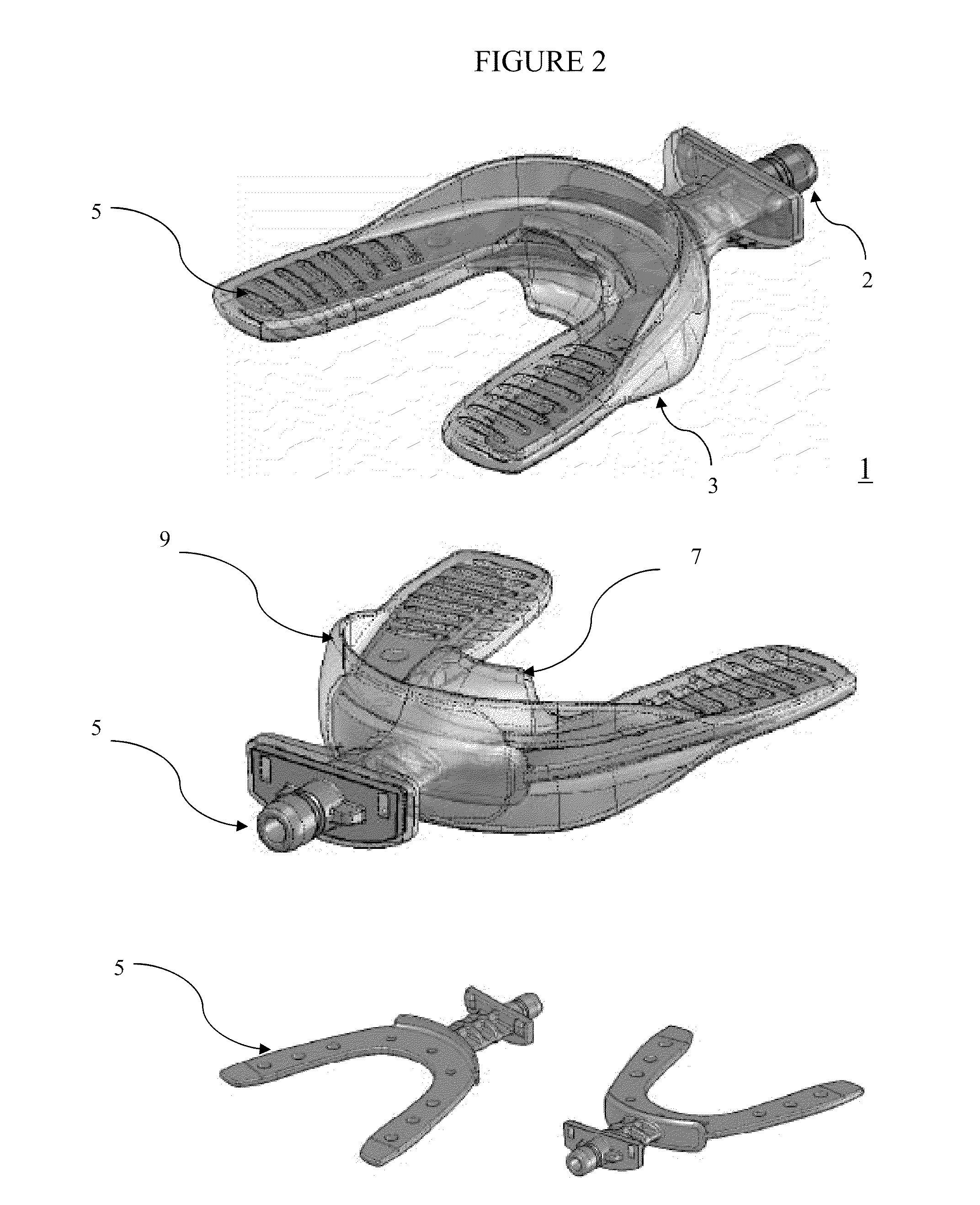
Vibrating dental devices
InactiveUS20100055634A1Speed boney remodelingEnhance boney remodelingBracketsDental toolsDental EquipmentBite plates
A variety of improvements to the vibrating devices for dental remodeling are provided, including improved bite plate designs that accommodate common patient bite structure, a connector for a bite plate, a sizing tray for same, as well as better motors providing improved performance characteristics for an extraoral vibrator, and a completely intraoral vibrating dental plate with very thin cross section.
Owner:ADVANCED ORTHODONTICS & EDUCATION ASSOC LLC
Heat radiating system and method for a mobile communication terminal
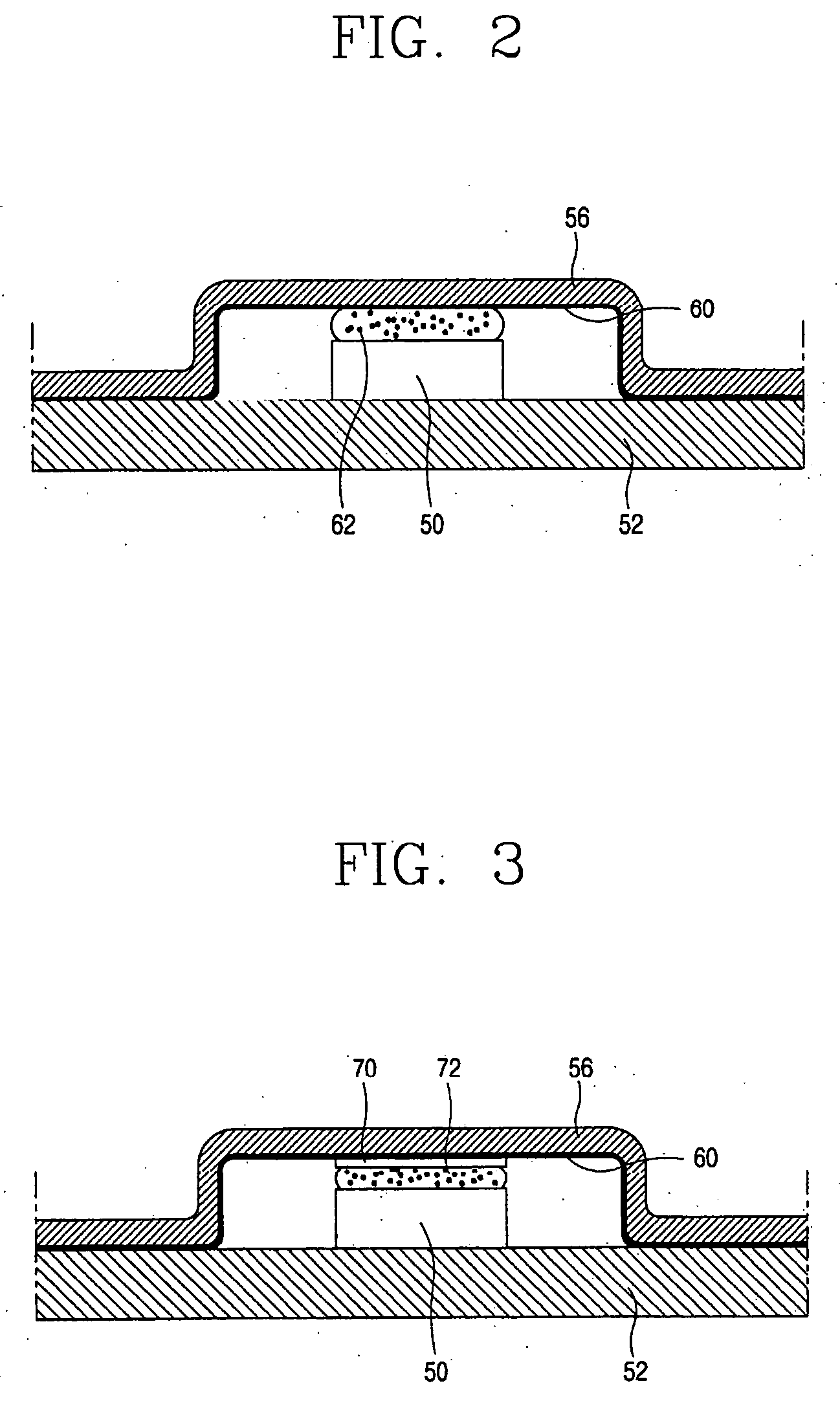
ActiveUS20050111194A1Prevent heat transferLow heat generationMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMobile communication systems
A system and method for transferring heat from a terminal in a mobile communication system. The system comprises a circuit board mounted to a terminal body, in which a heat generating component is mounted, and a shield frame for shielding electromagnetic waves generated from the circuit board and supporting the circuit board. At least one heat radiating apparatus is installed between the heat generating component and the shield frame. The at least one heat radiating apparatus transfers heat generated by the heat generating component away from the circuit board and substantially directly to the shield frame. The heat transfer prevents an impact of the generated heat being transferred to the circuit board from the shield frame.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
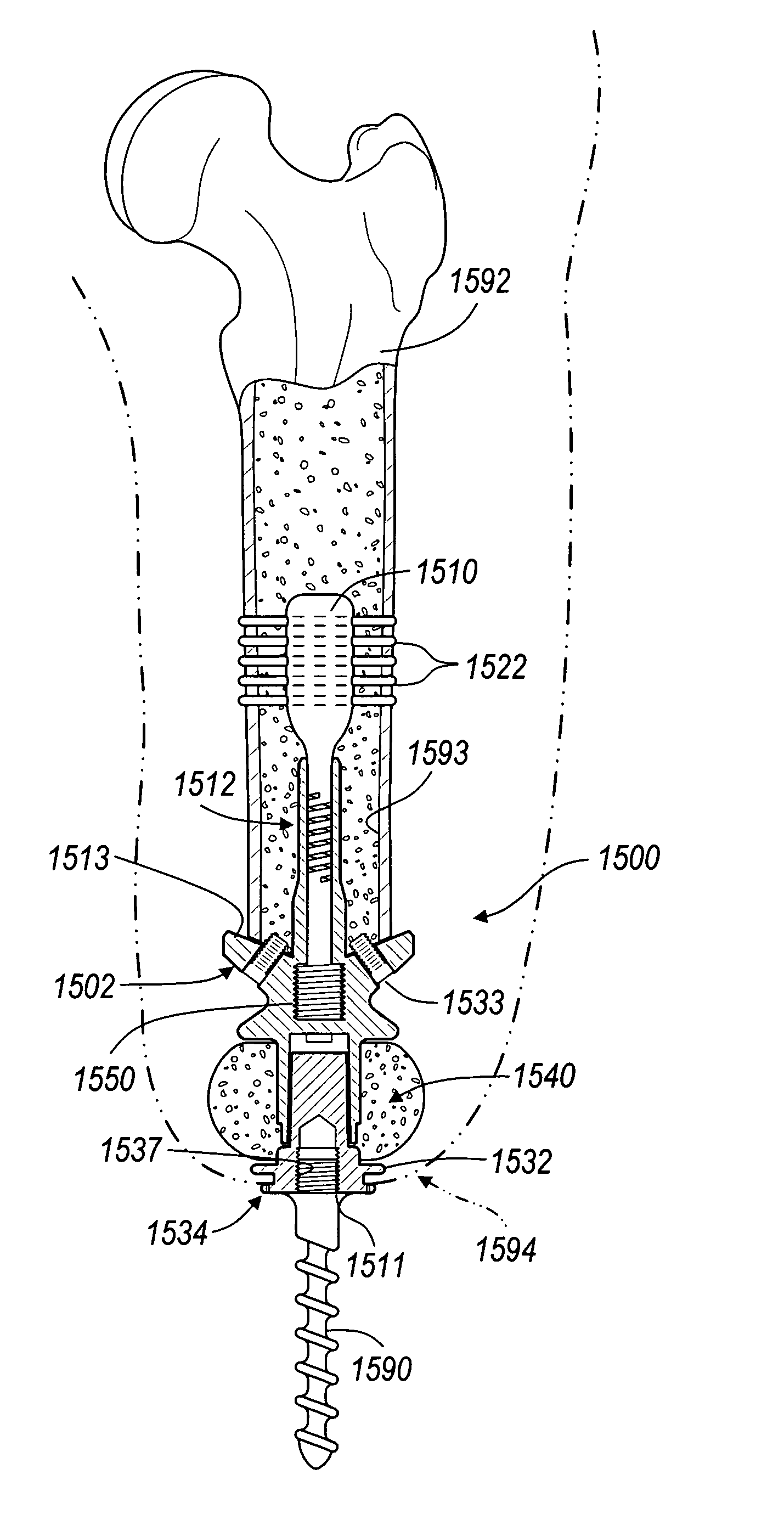
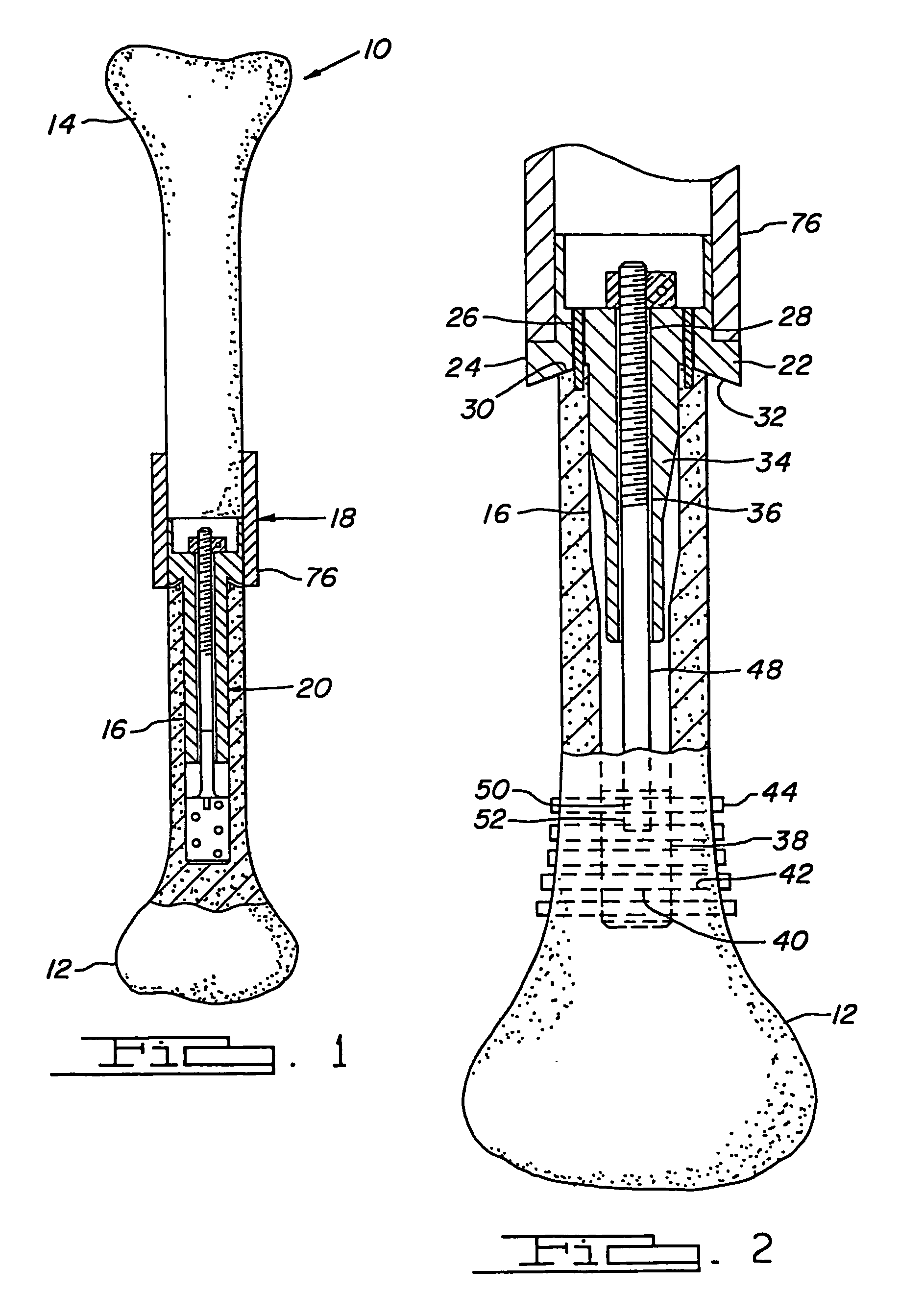
Compliant fixation of external prosthesis
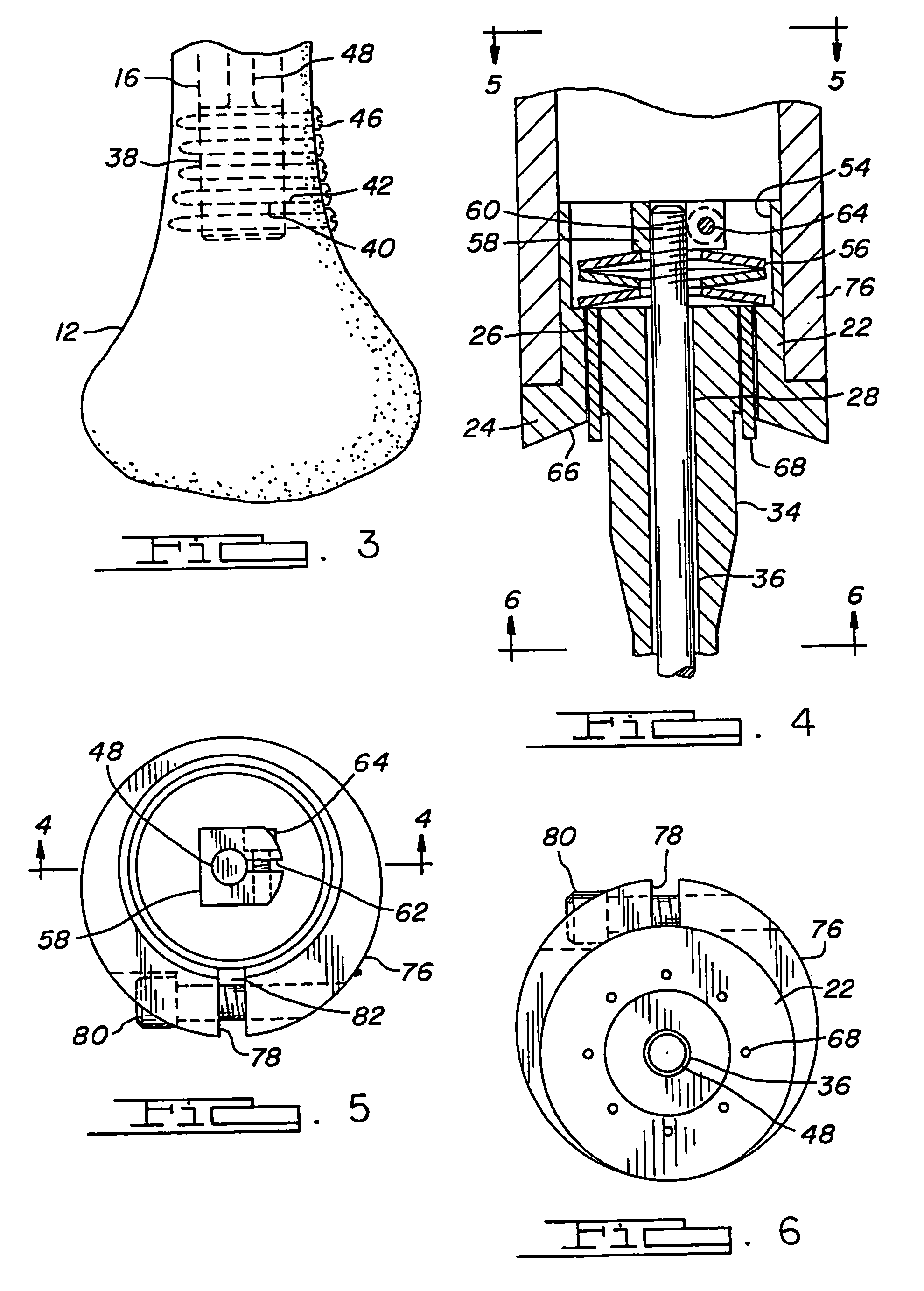
InactiveUS7141073B2Improve securityPreventing secure wedgingInternal osteosythesisBone implantBiomedical engineeringExternal prosthesis
A fixation device and method for attaching an external prosthesis to a bone. The fixation device includes a main body having a compliant portion operable to be expanded and contracted. The main body has a first end fixedly retained in the bone and a second end coupled to an extension for receiving the external prosthesis. The main body and the extension define respectively first and second engagement surfaces for constraining a bone graft therebetween.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Drive unit with coolant flow through a space separating an inverter from a casing housing an electric motor
InactiveUS6201365B1Avoid contactLow thermal conductivityPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingElectric motor speed/torque regulationEngineeringCoolant flow
A drive unit which uses an electric motor as a power source and has an integrated inverter, with a cooling circuit for the electric motor and the inverter. The drive unit includes a drive unit case, the electric motor housed within the case, and the inverter fixed to the case. A coolant flow passage is provided between the drive unit case and the inverter. The inverter is fixed to the drive unit case through a panel wall, and a partition divides the coolant flow passage into chambers which are coextensive in parallel. As a result, the coolant which flows through the coolant flow passage acts as a two-stage heat shield, barring the heat generated by the electric motor from being transmitted to the inverter.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
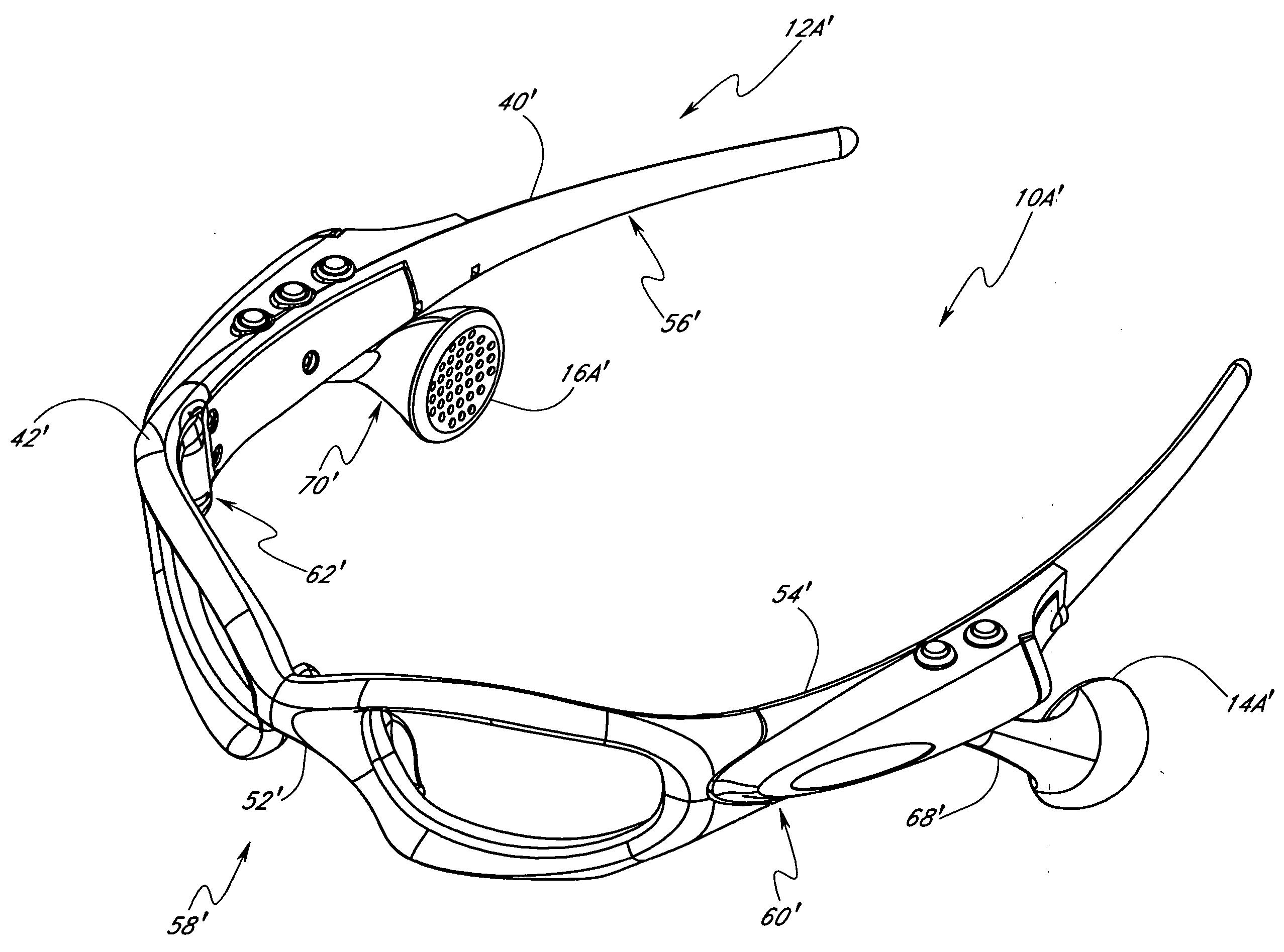
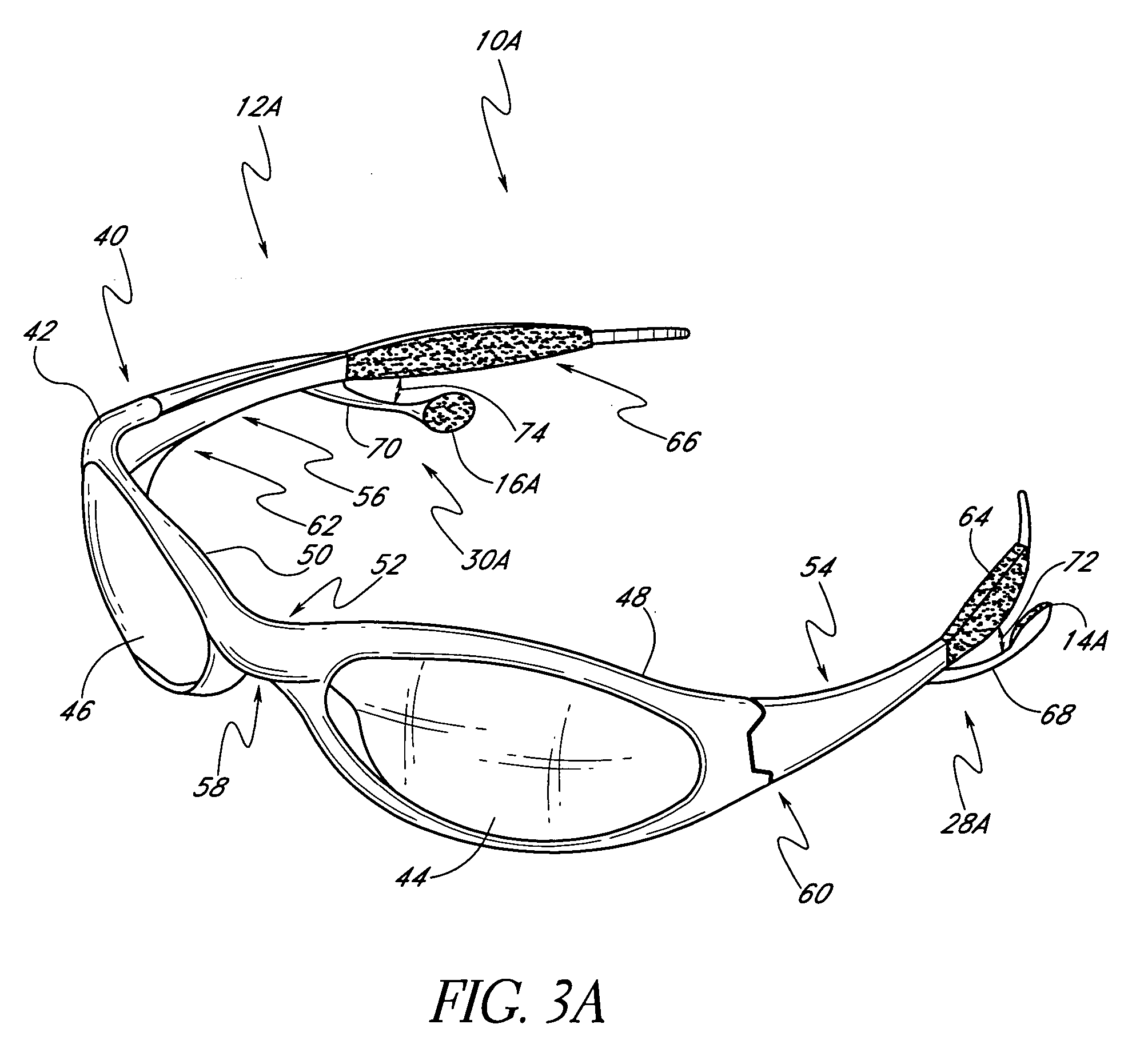
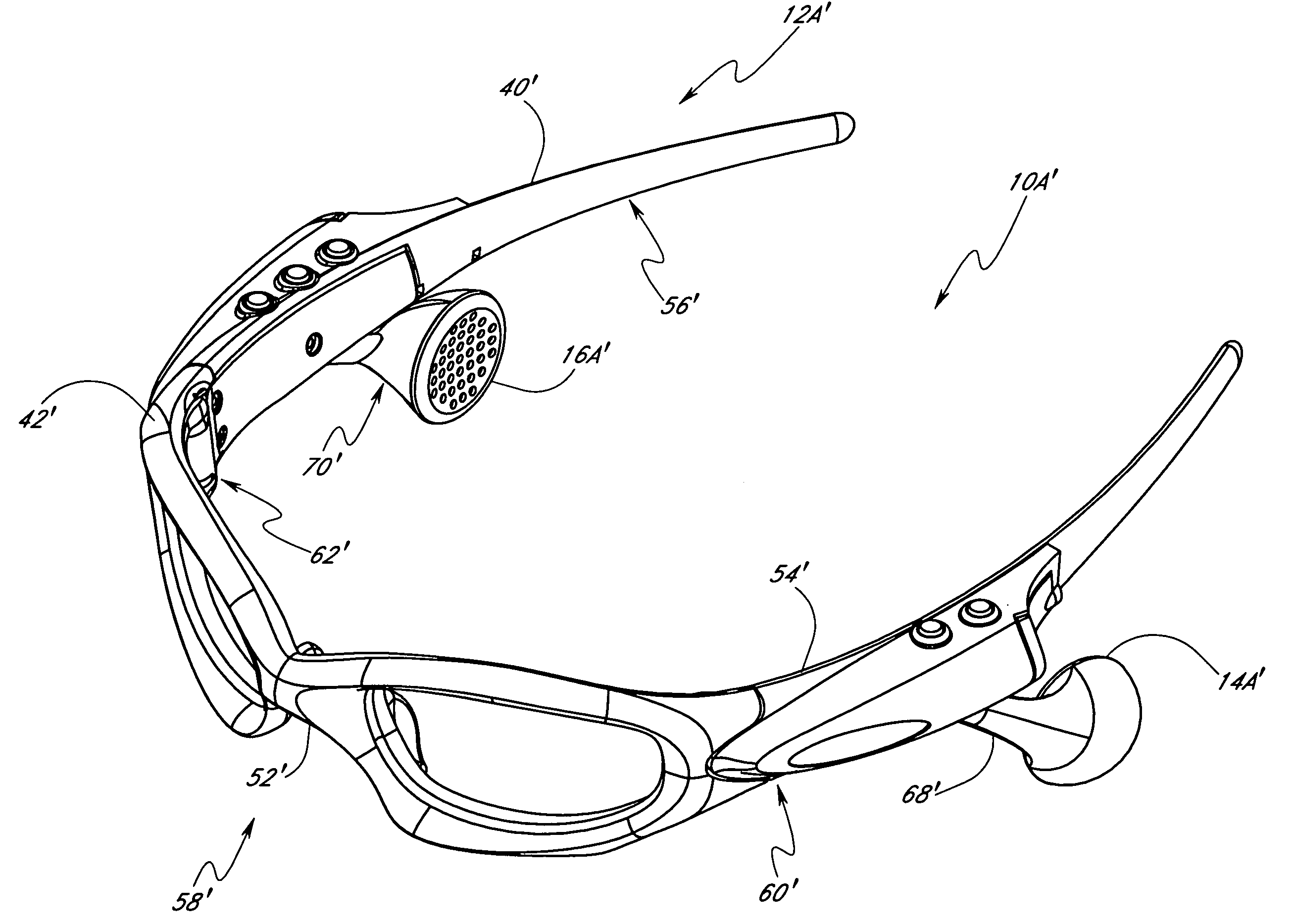
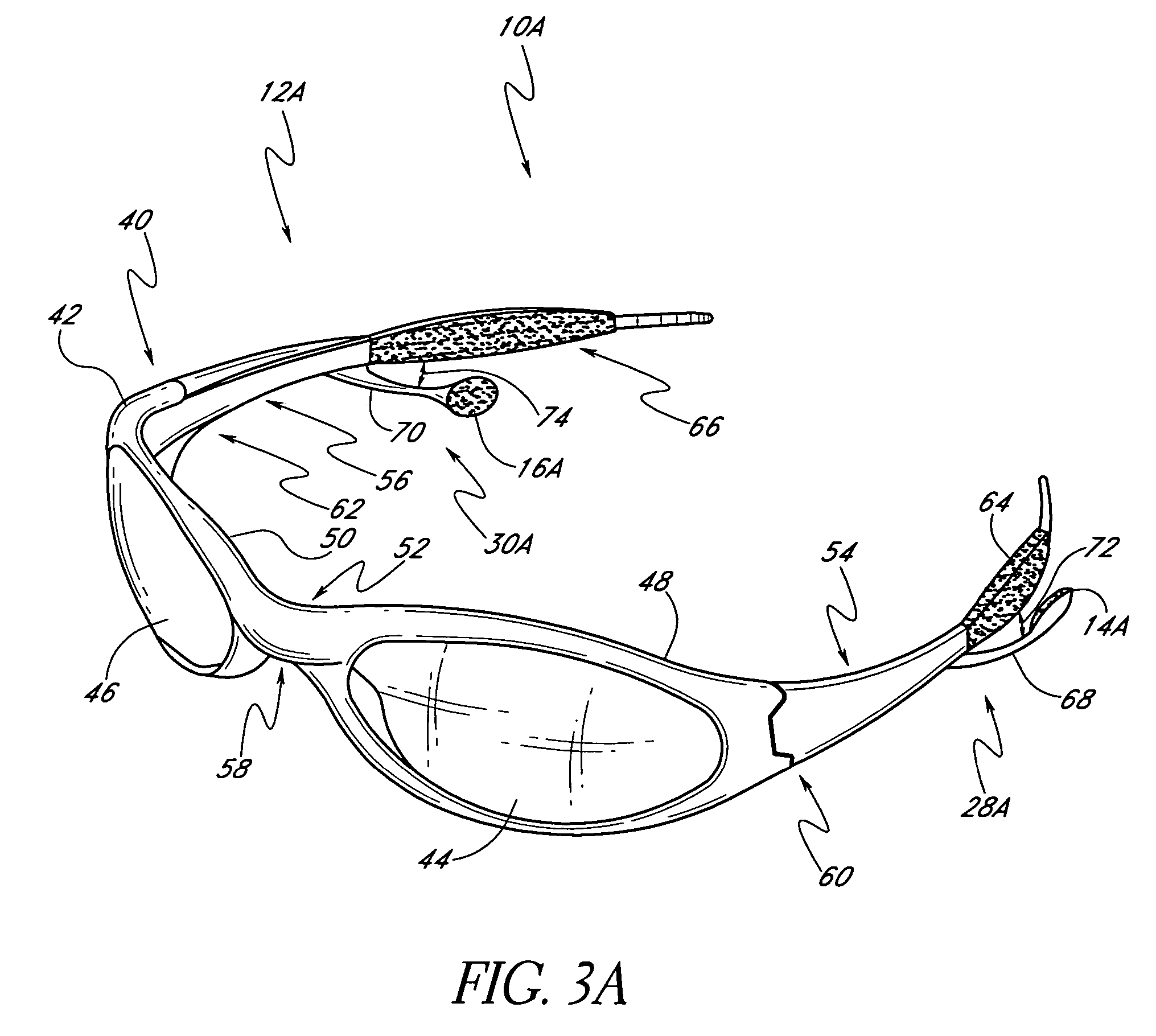
Speaker mounts for eyeglass with MP3 player
InactiveUS20050046790A1Reduce weightInhibit transferSubstation speech amplifiersTelephone set constructionsEyewearEngineering
A wearable audio device in the form of eyeglasses speaker mounts supported by the frames of the eyeglass. The speaker mounts are constructed so as to be translatable along the ear stems of the eyeglass. This allows a wearer to move the speakers without changing the shape of the speaker mount, which can occur where the speaker mounts are made from some flexible materials.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
Dry prosthetic heart valve packaging system
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
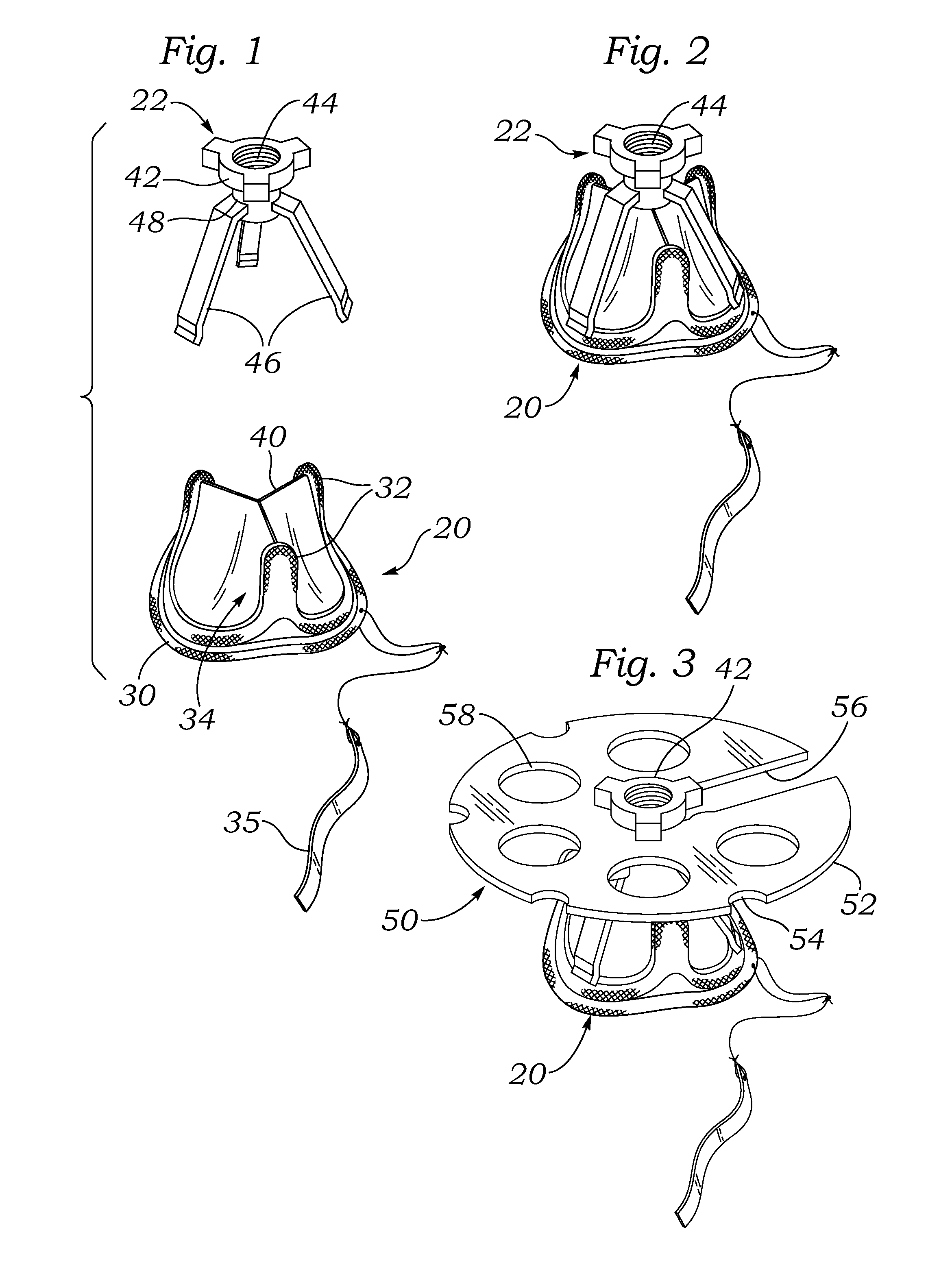
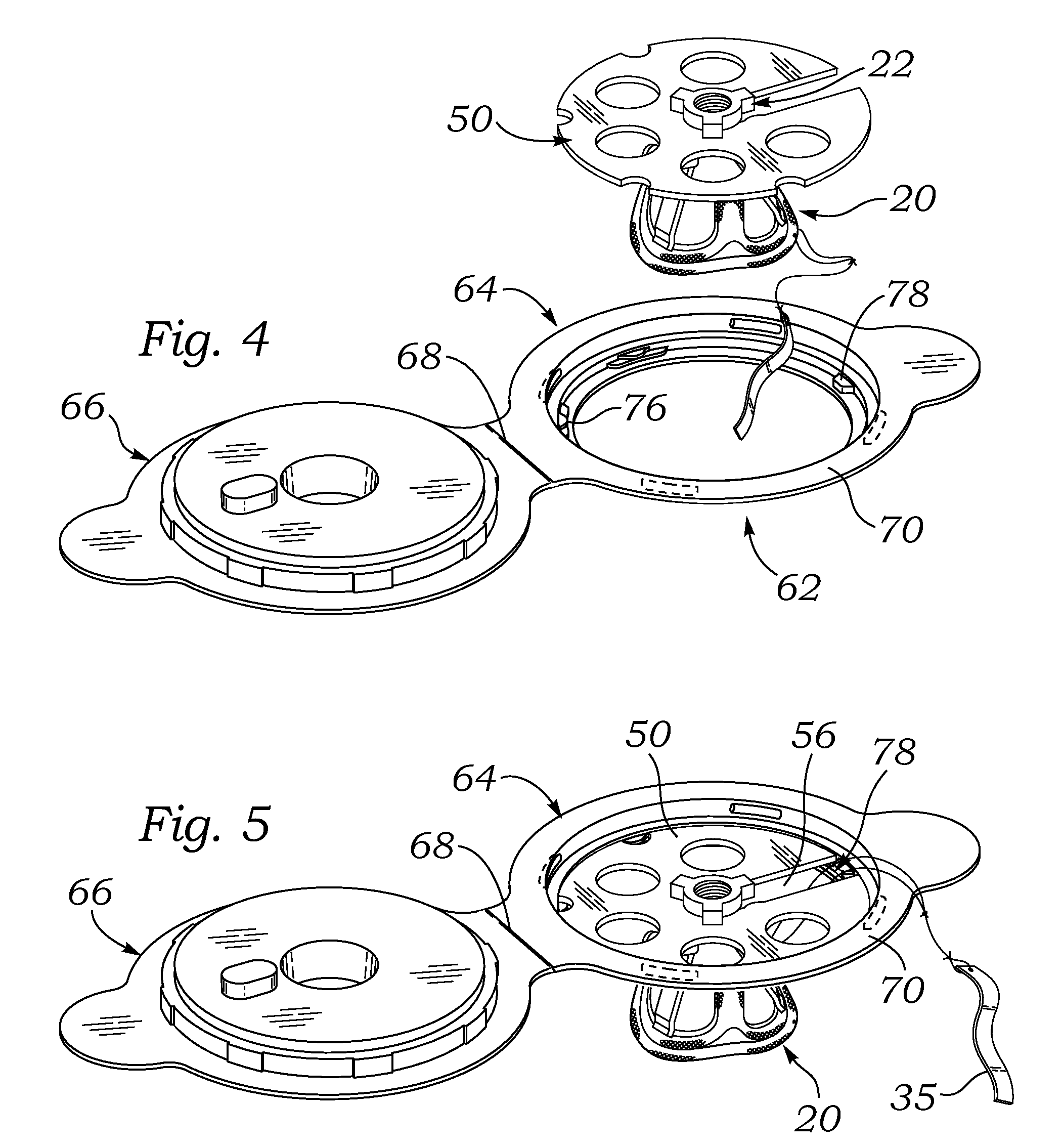
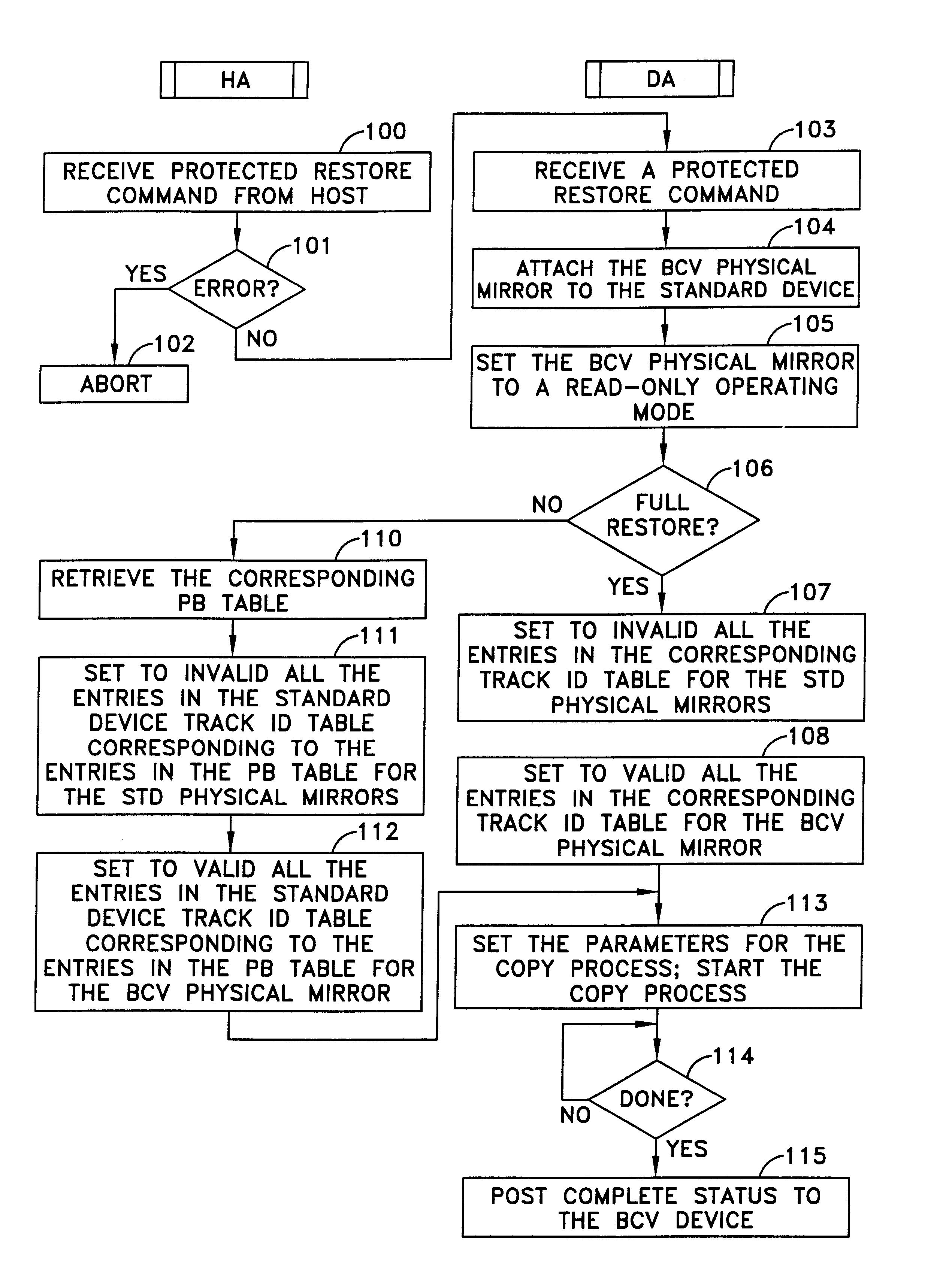
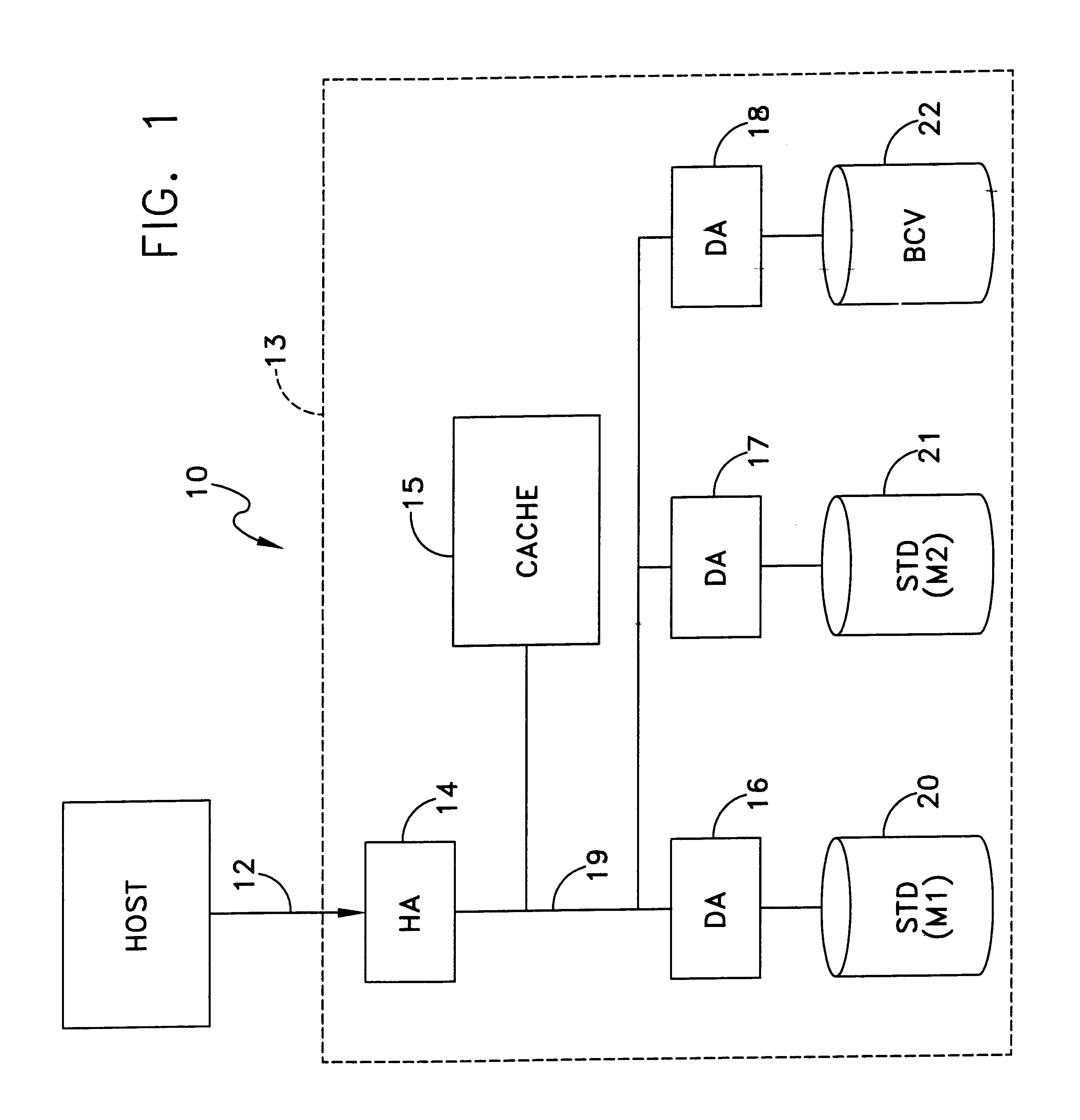
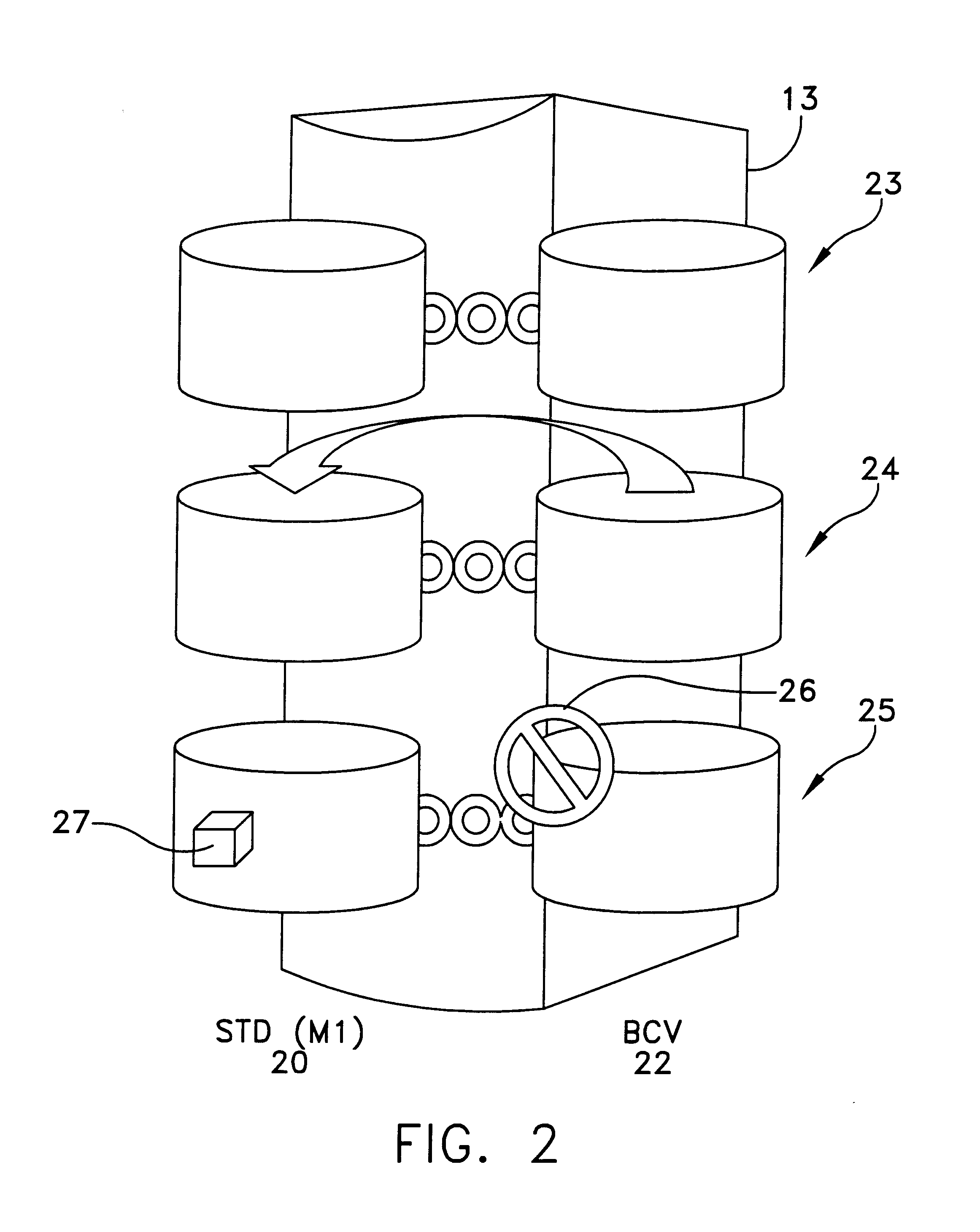
Data recovery method and apparatus
InactiveUS6742138B1Easy Data RecoveryAvoid data transferEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionRedundant operation error correctionRecovery methodData memory
A method and apparatus for data recovery in a system involving a first data store acting as a standard device and a physical moving mirror data store that operates as moving mirror with a first mode to be synchronized and in a second, isolated mode. In response to a command to establish a third or protected restore operating mode, the data to be transferred in response to that command is identified. A restoration procedure copies data from the second data store to the first store to recover any data that may have been corrupted in the second data store. An update procedure acts on the restored data concurrently with the restoration procedure.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
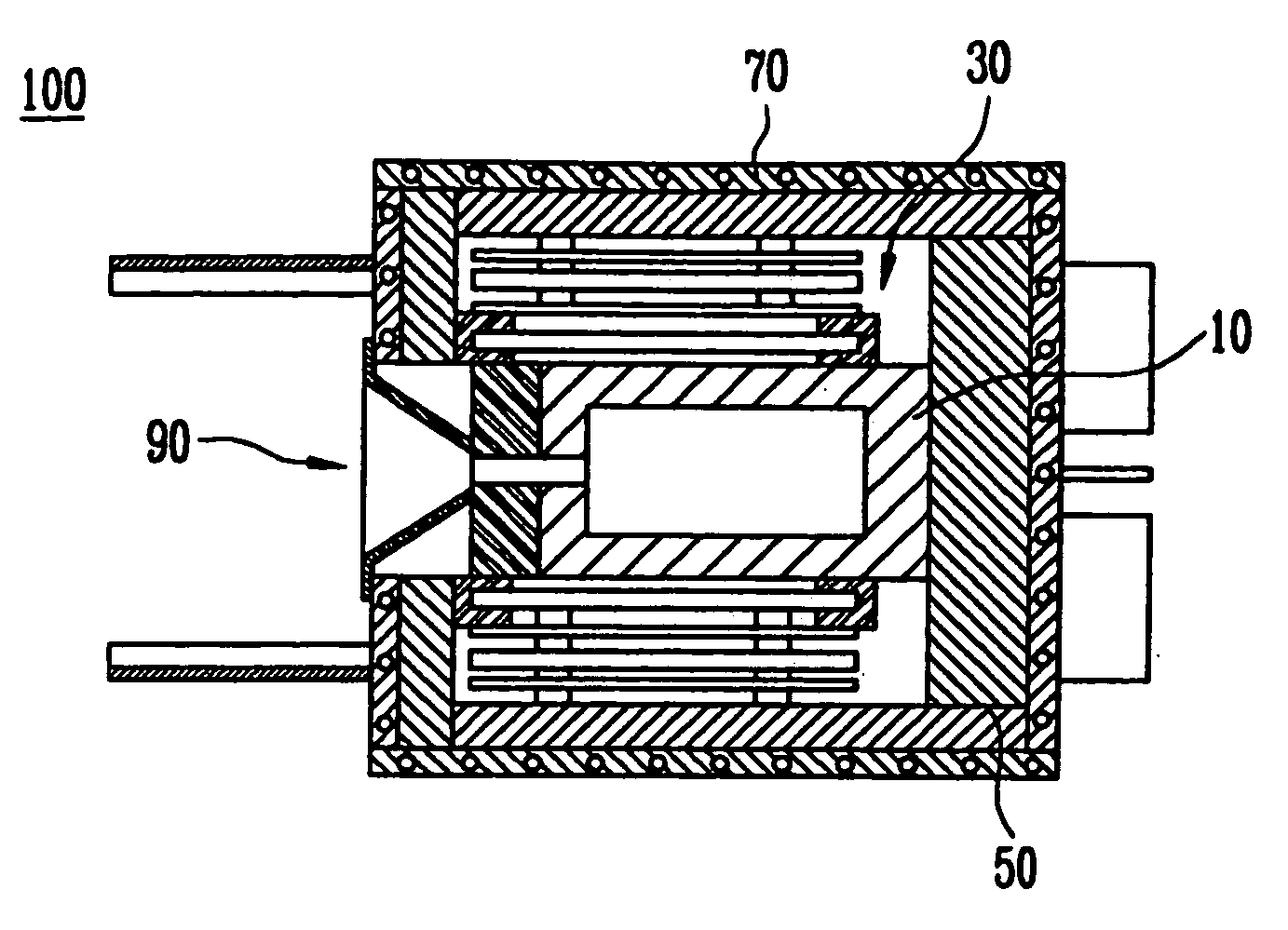
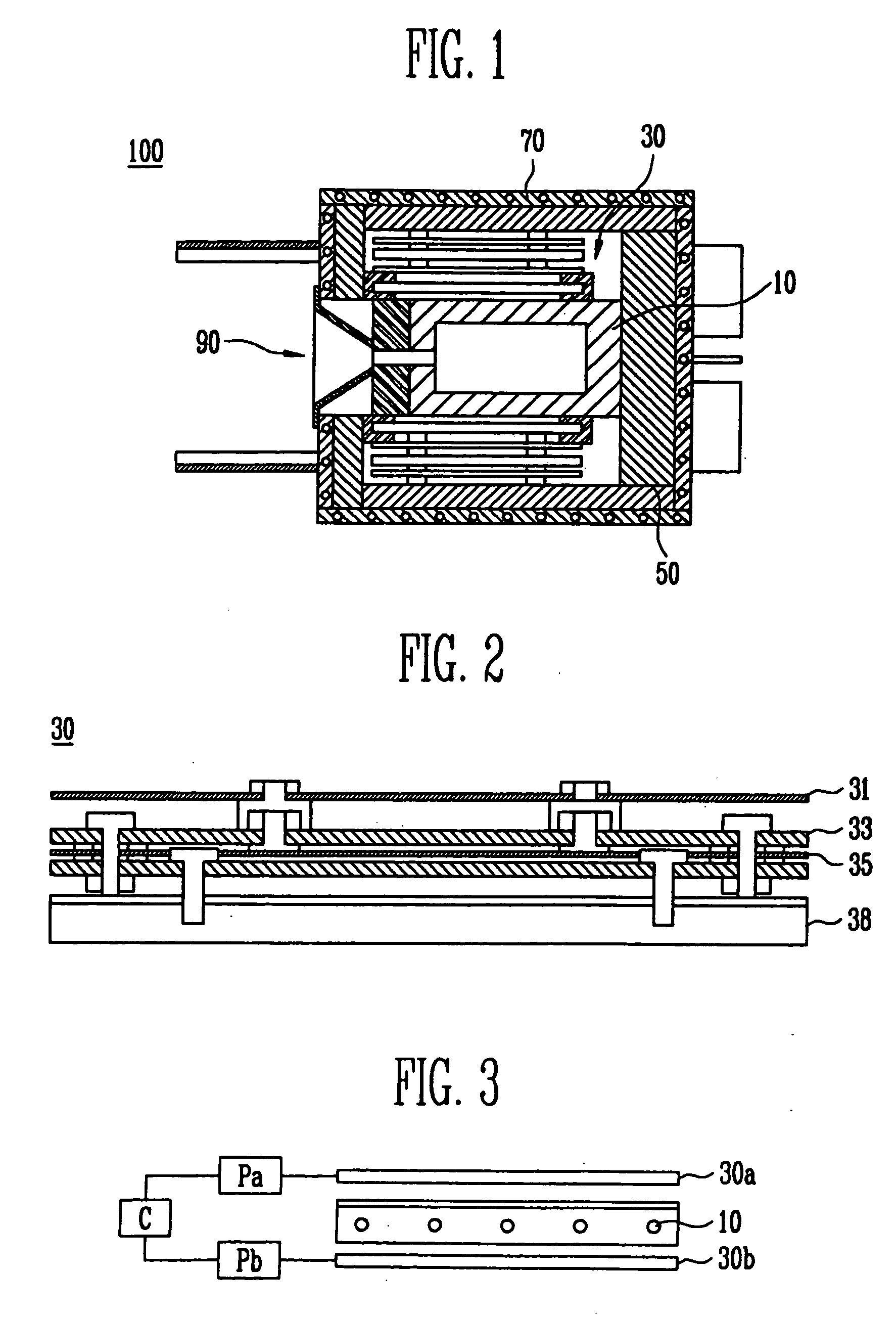
Apparatus for depositing an organic layer and method for controlling a heating unit thereof
InactiveUS20070077358A1Improve heating efficiencyMinimize timeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCrucibleEvaporation
An apparatus for depositing an organic layer and a method for controlling the heating unit thereof are provided. The apparatus includes a crucible positioned in a deposition chamber and containing materials for evaporation. The apparatus also includes a heating unit having first and second heat sources for heating the crucible. A housing isolates the heat emitted from the heating unit and an outer wall anchors the crucible. A nozzle sprays the materials evaporated from the crucible. The first and second heat sources are positioned on first and second sides of the crucible, respectively, and are independently controlled to minimize the time required to stabilize the deposition rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
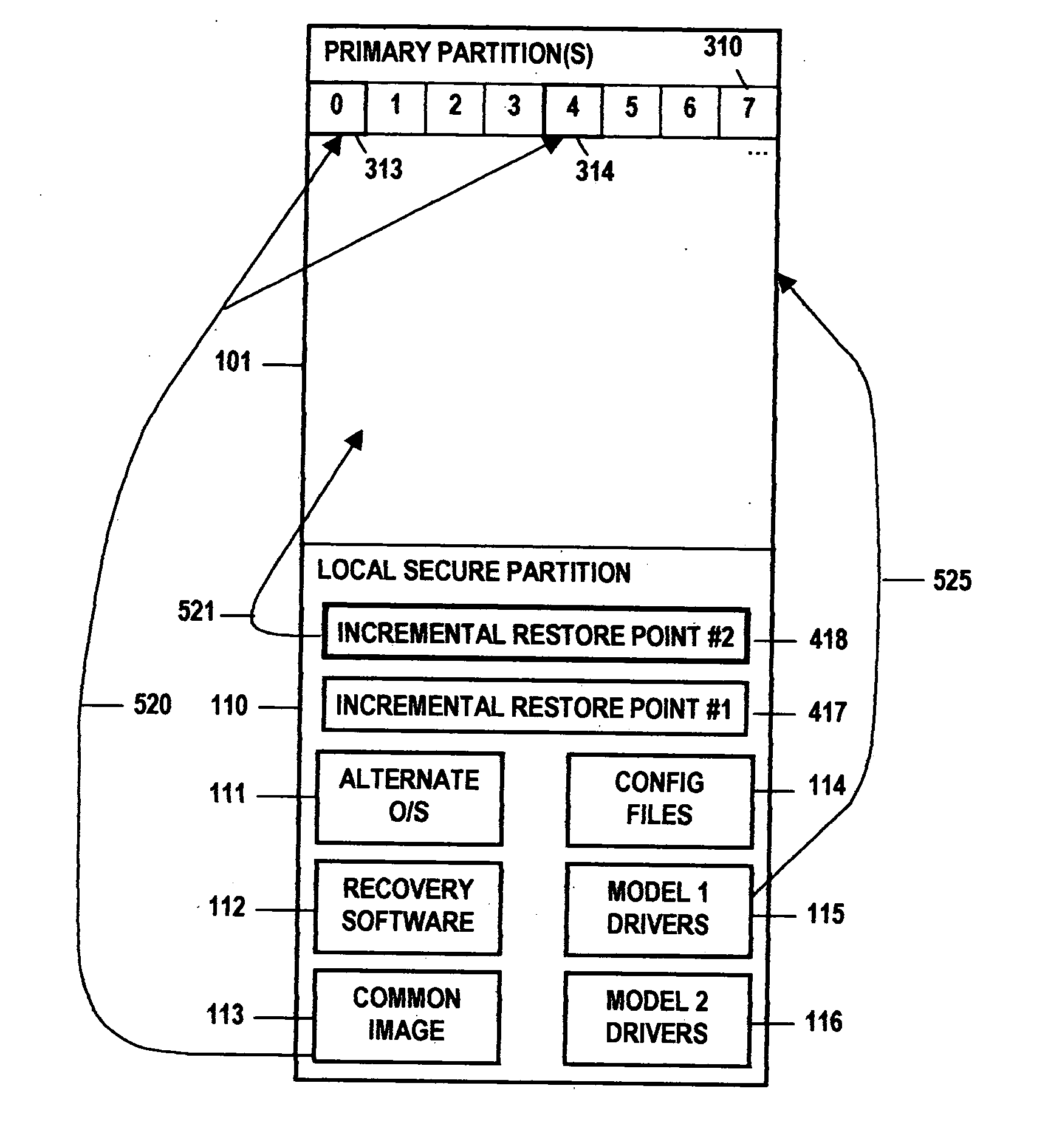
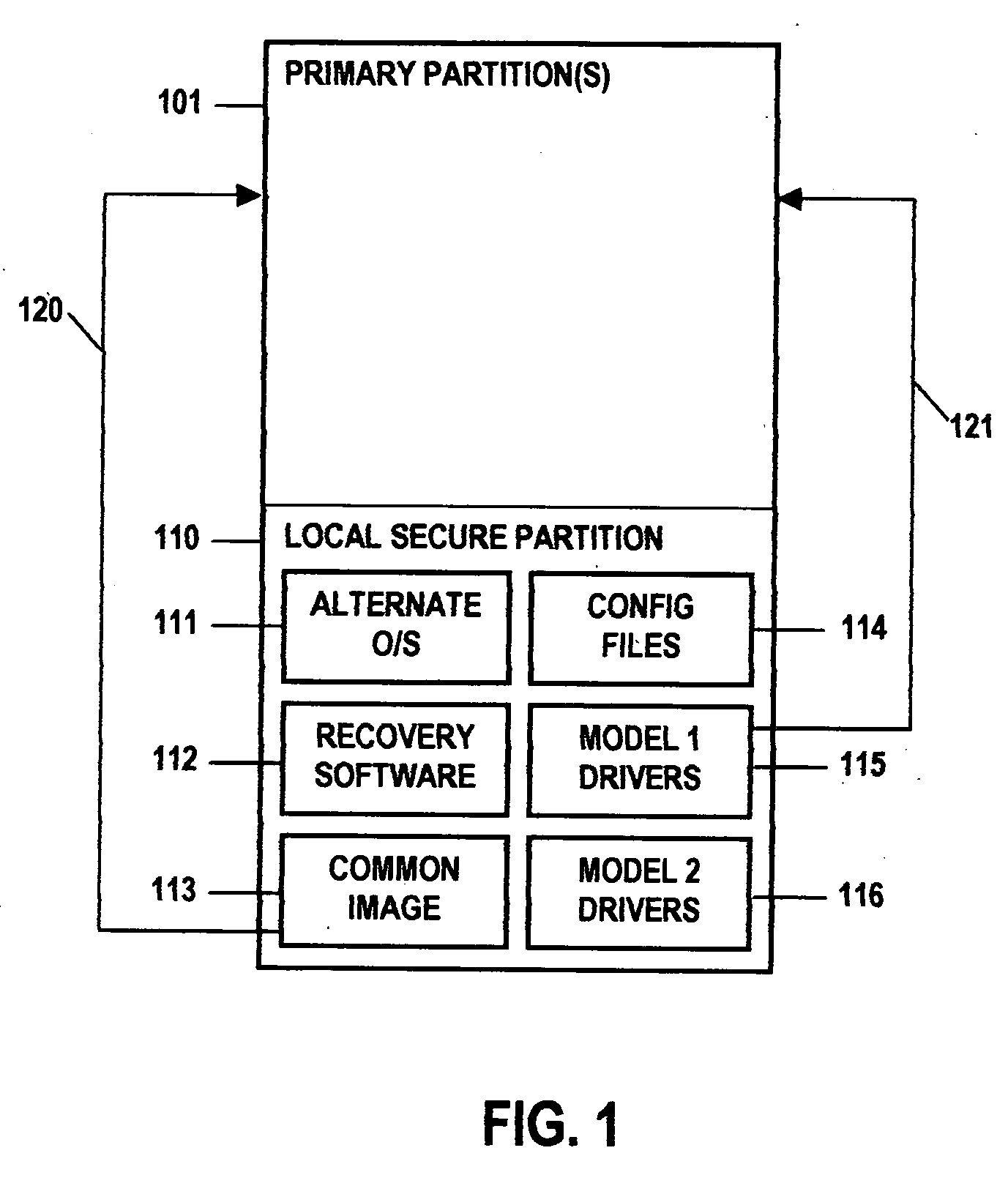
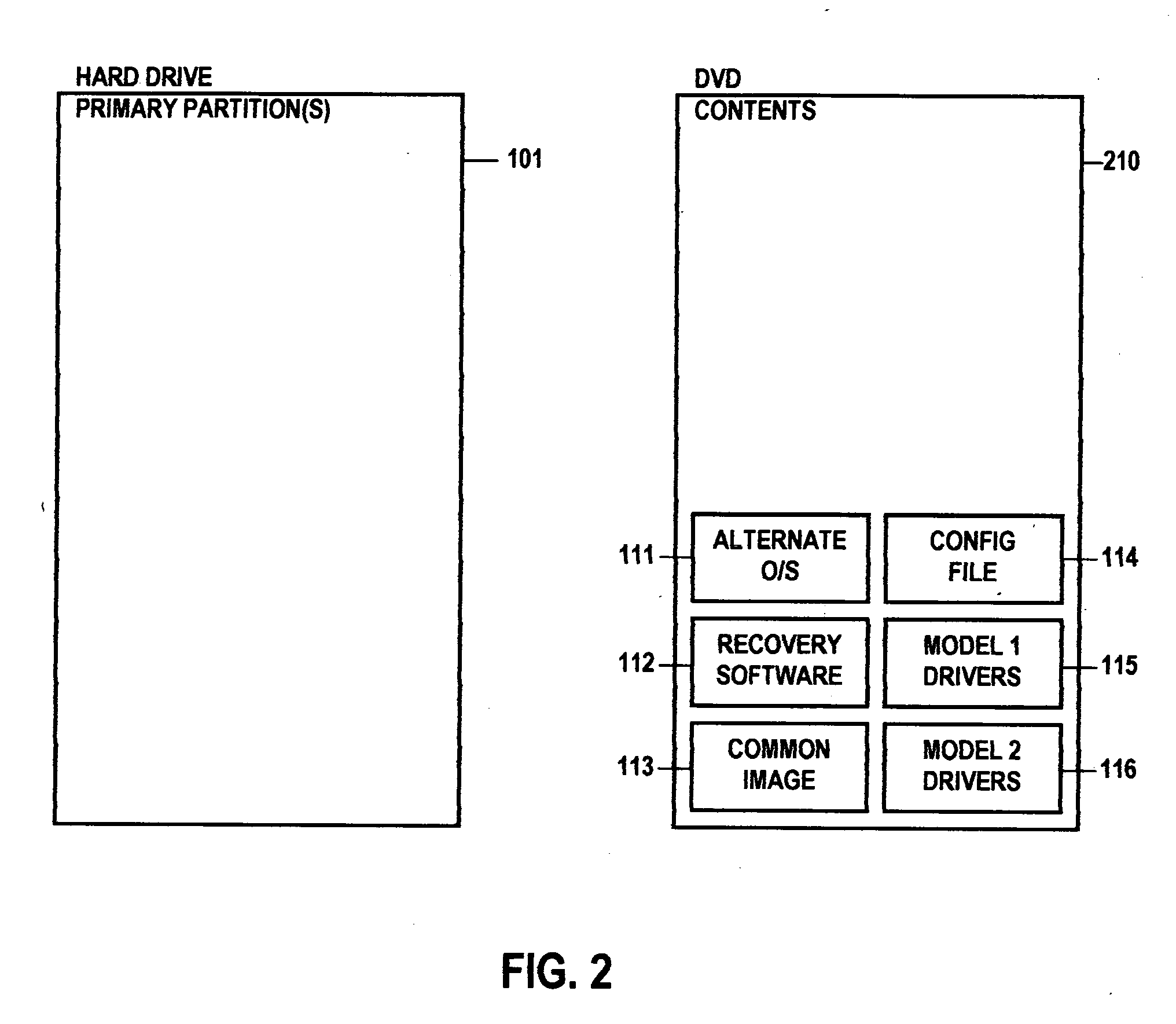
Method and system for updating a software image
ActiveUS20050289533A1Improve performanceShorten the timeError detection/correctionPlatform integrity maintainanceHard disc driveOperational system
A method and system for updating or recovering a computer device's software image using a single portable operating system image stored on a bootable, secure partition on local storage (hard drive); a method and system utilizing delta image patching technology to allow the single image to work on a large number of diverse computer device platforms; and a method for distributing software patches and updates via a, secure local partition to ensure patches and updates are applied to well known software images that have not been modified to include malicious software and do not include any other undesirable changes that have been made to the primary, running operating system image.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
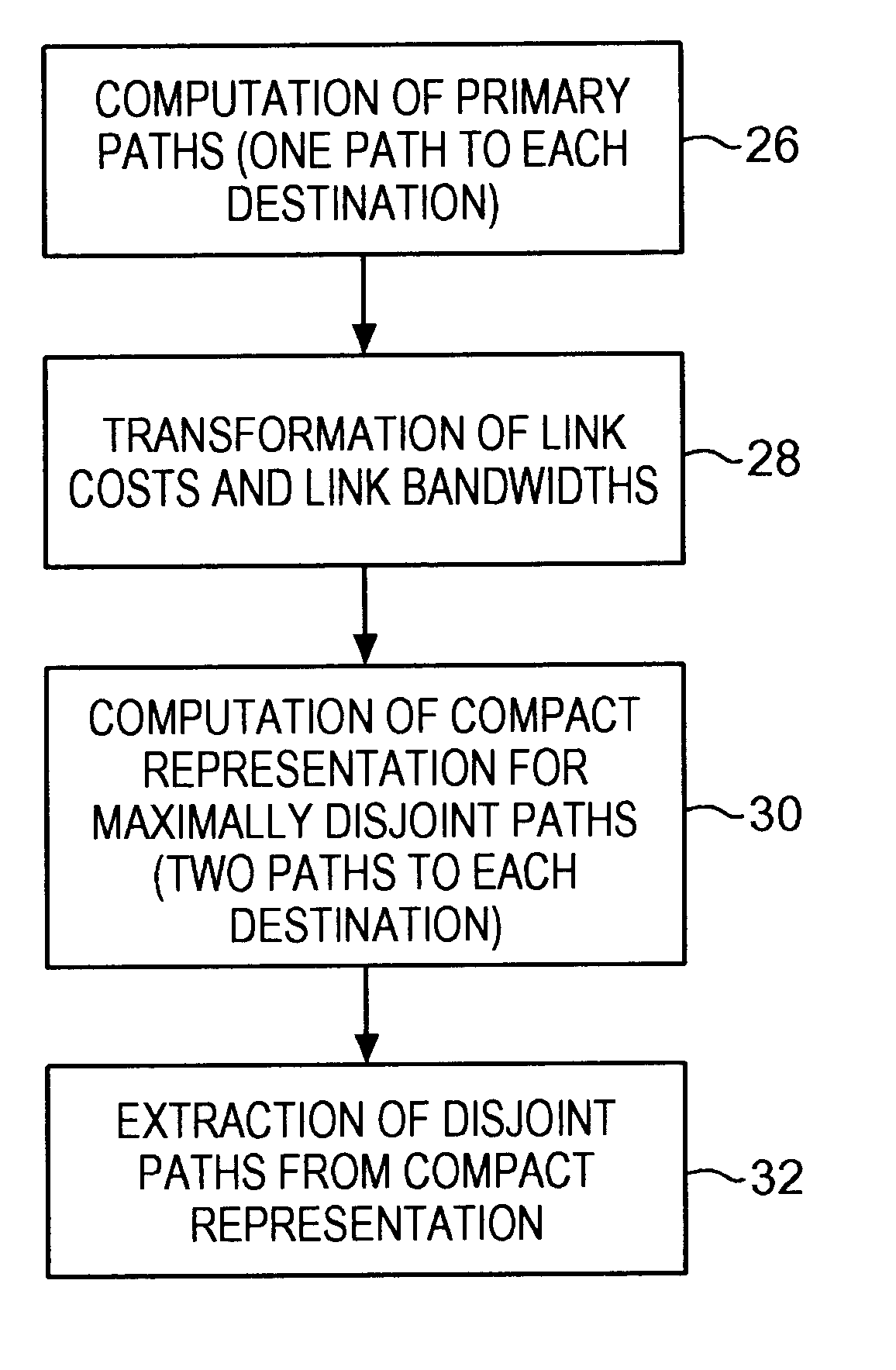
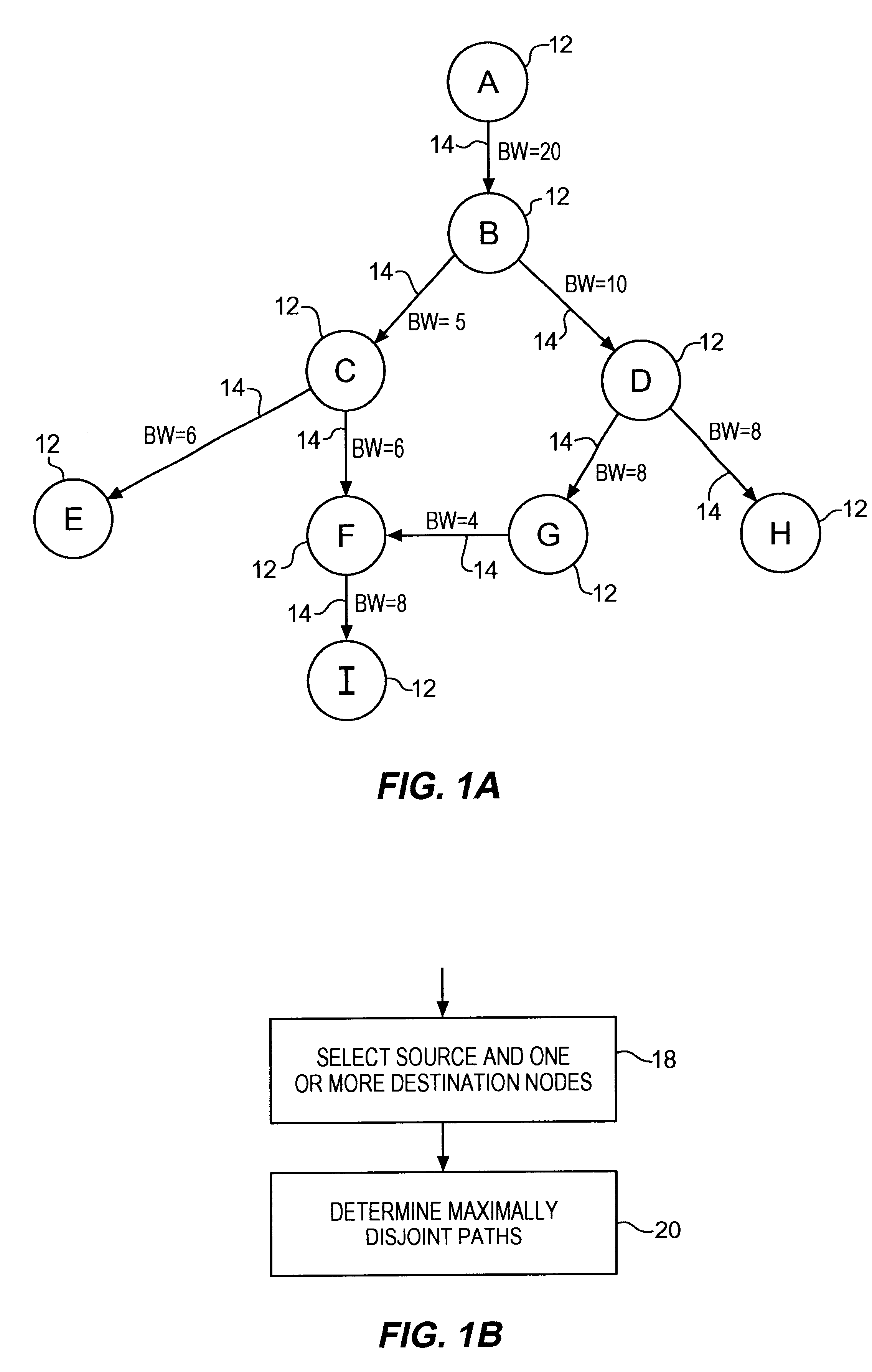
Communications network system and method for routing based on disjoint pairs of path
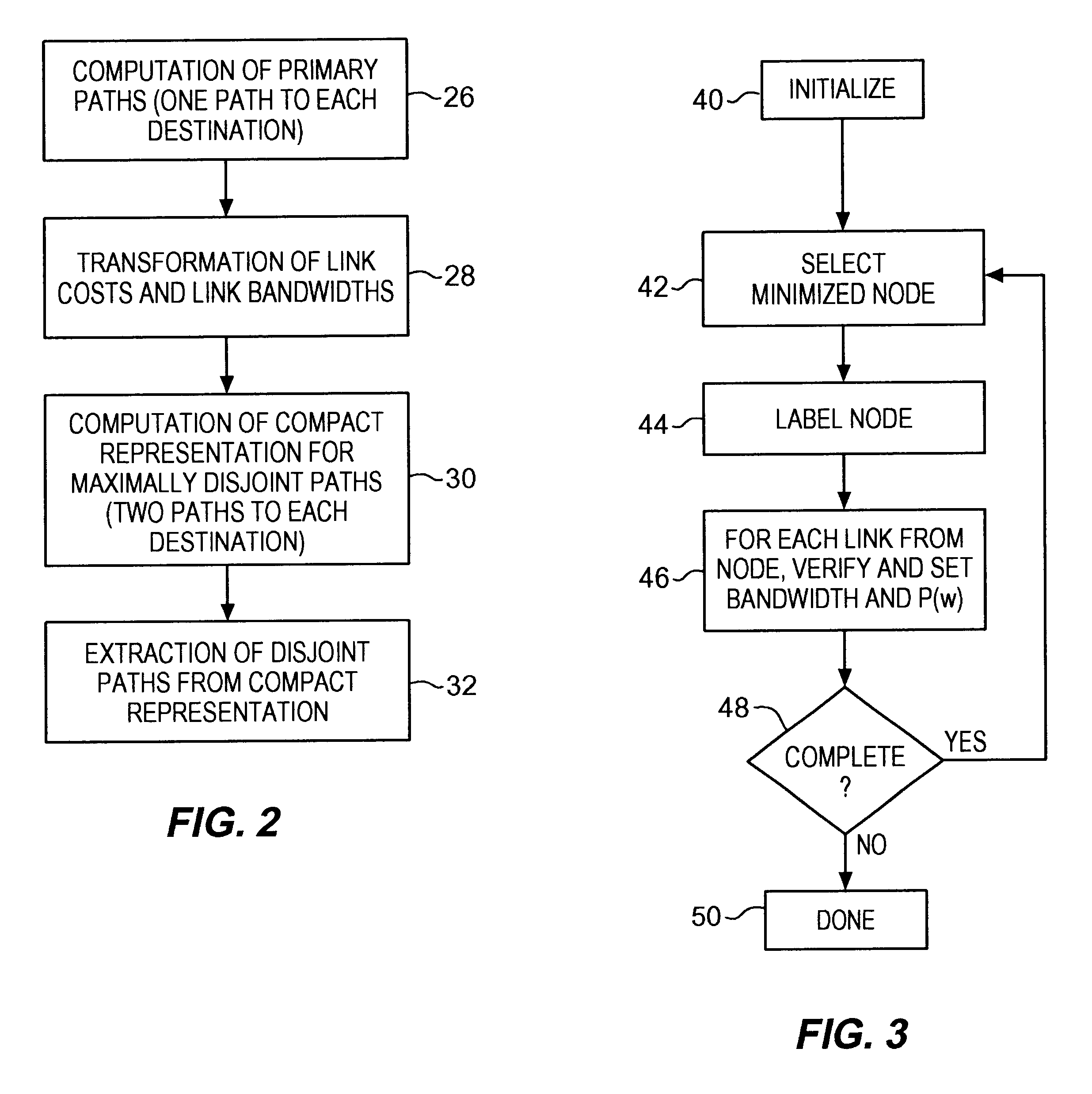
InactiveUS6542469B1Raise the possibilityMinimizes probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingHigh bandwidth
Methods for determining at least two pre-computed paths to a destination in a communications network are provided. The two paths are maximally disjoint. Maximally disjoint paths are paths where the number of links or nodes common to the two paths is minimized. This minimization is given a priority over other path considerations, such as bandwidth or cost metrics. By pre-computing a maximally disjoint pair of paths, the probability that an inoperable link or node is in both paths is minimized. The probability that the inoperable link or node blocks a transfer of data is minimized. Additionally, a pair of maximally disjoint paths is determined even if absolutely disjoint paths are not possible. The communications network may include at least four nodes, and maximally disjoint pairs of paths are pre-computed from each node to each other node. A third path from each node to each other node may also be computed as a function of bandwidth or a cost metric. Therefore, the advantages of the maximally disjoint pair of paths are provided as discussed above and a path associated with a higher bandwidth or lower cost is provided to more likely satisfy the user requirements of a data transfer.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
Soi substrate and method for manufacturing soi substrate
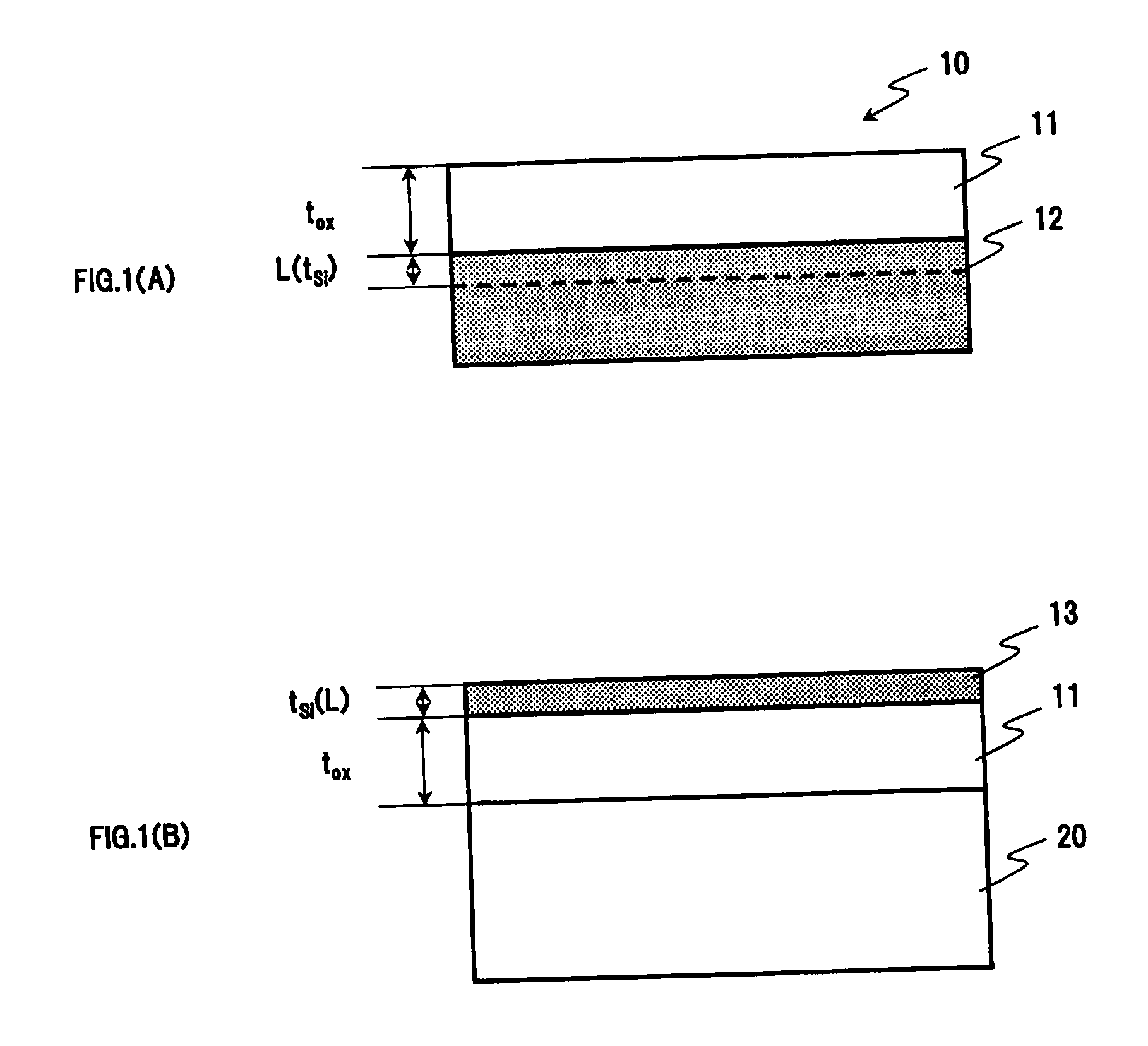
InactiveUS20100289115A1Prevent transfer defectIncrease productionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal expansionSoi substrate
An oxide film having a thickness “tox” of not less than 0.2 μm is provided on the bonding surface of a single-crystal silicon substrate. In a method for manufacturing an SOI substrate according to the present invention, a low-temperature process is employed to suppress the occurrence of thermal strain attributable to a difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the silicon substrate and a quartz substrate. To this end, the thickness “tox” of the oxide film is set to a large value of not less than 0.2 μm to provide sufficient mechanical strength to the thin film to be separated and, at the same time, to allow strain to be absorbed in and relaxed by the relatively thick oxide film to suppress the occurrence of transfer defects during the step of separation.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
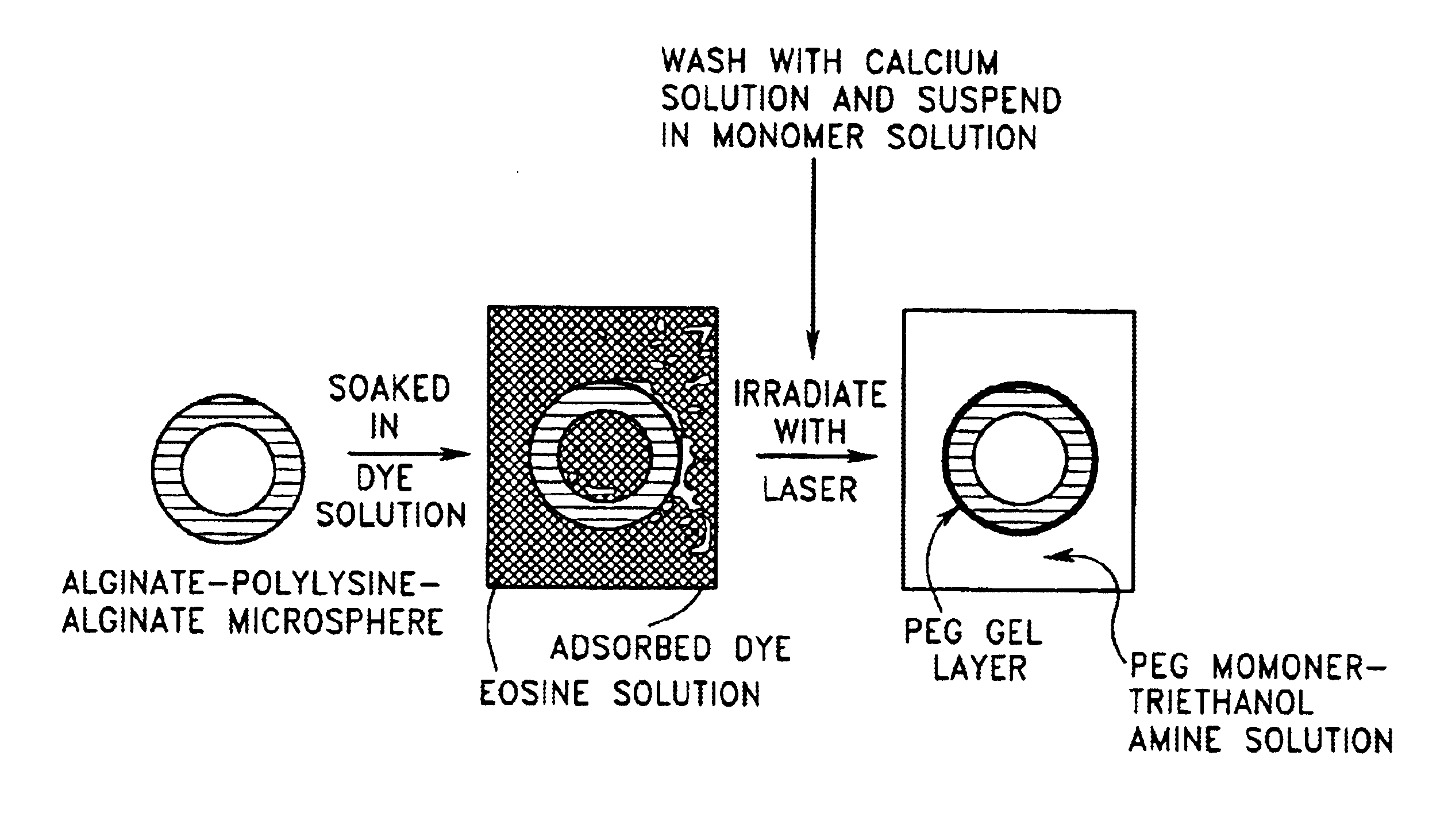
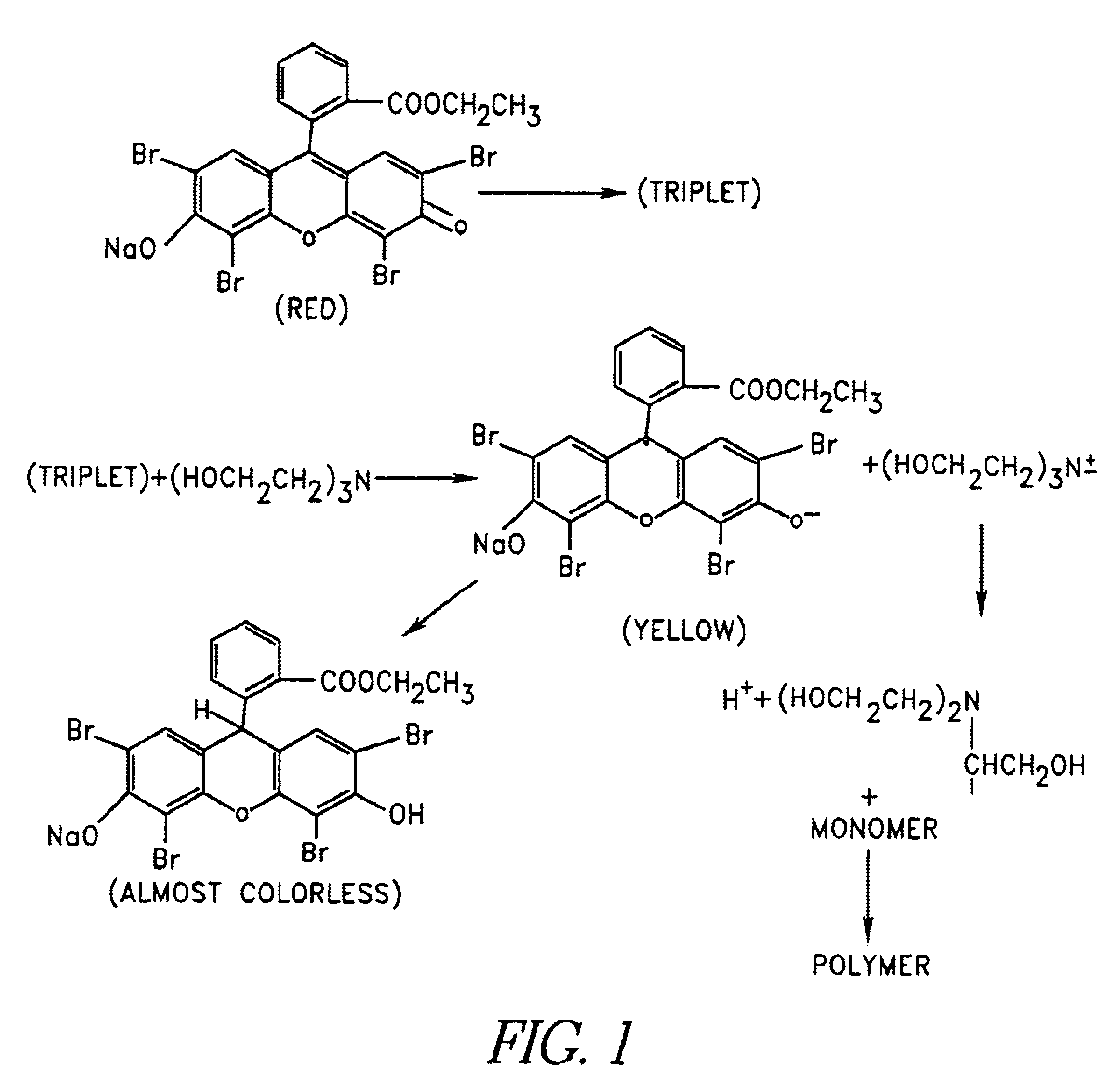
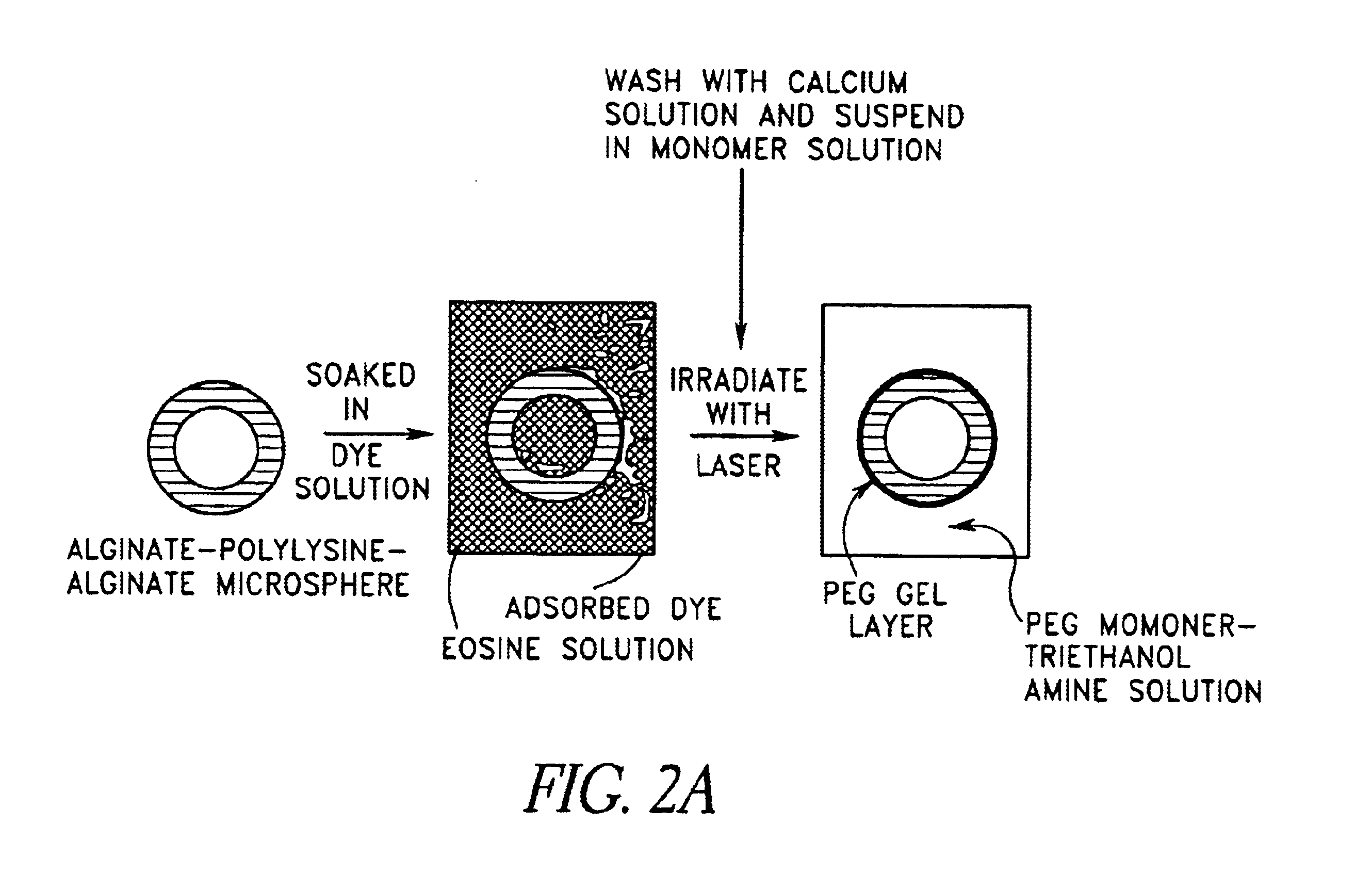
Gels for encapsulation of biological materials
InactiveUS6911227B2Efficient gluingFacilitated DiffusionImmobilised enzymesSurgical adhesivesActive matterWater soluble
This invention provides novel methods for the formation of biocompatible membranes around biological materials using photopolymerization of water soluble molecules. The membranes can be used as a covering to encapsulate biological materials or biomedical devices, as a “glue” to cause more than one biological substance to adhere together, or as carriers for biologically active species. Several methods for forming these membranes are provided. Each of these methods utilizes a polymerization system containing water-soluble macromers, species, which are at once polymers and macromolecules capable of further polymerization. The macromers are polymerized using a photoinitiator (such as a dye), optionally a cocatalyst, optionally an accelerator, and radiation in the form of visible or long wavelength UV light. The reaction occurs either by suspension polymerization or by interfacial polymerization. The polymer membrane can be formed directly on the surface of the biological material, or it can be formed on material, which is already encapsulated.
Owner:NOVOCELL
Multiplayer handheld computer game system having tiled display and method of use
InactiveUS20090280905A1Prevent transferLarge effective screenVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsDisplay deviceComputer game
A multiplayer handheld game employs individual game units having individual displays. Players can prepare their moves in secret on their game unit using controls and the individual displays, but when the game units are joined together, the game plays out on the aggregated screen. The game units employ digital signatures to ensure that all play is fair and that the virtual game pieces and characters in play have not been doctored or are otherwise fraudulent. Game results can be uploaded to a remote, secure server, which also serves as a backup for user data. Customization, improvements, and additions to the virtual game pieces and characters can be performed in conjunction with the secure server.
Owner:WEISMAN JORDAN K +1
Multi-directional adjustment devices for speaker mounts for eyeglass with MP3 player
InactiveUS20050128431A1Reduce weightInhibit transferSubstation speech amplifiersTelephone set constructionsEyewearEngineering
Owner:OAKLEY INC
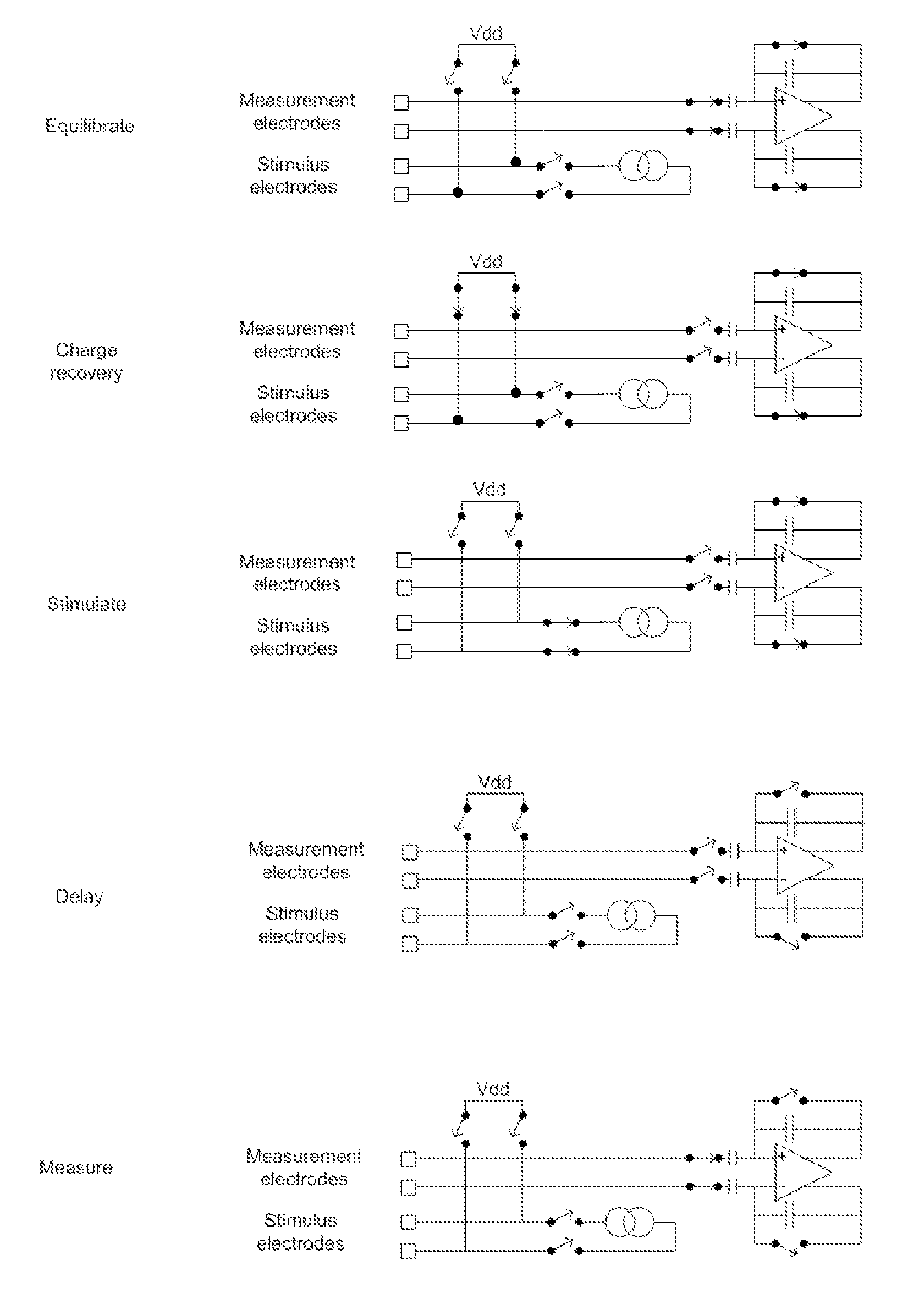
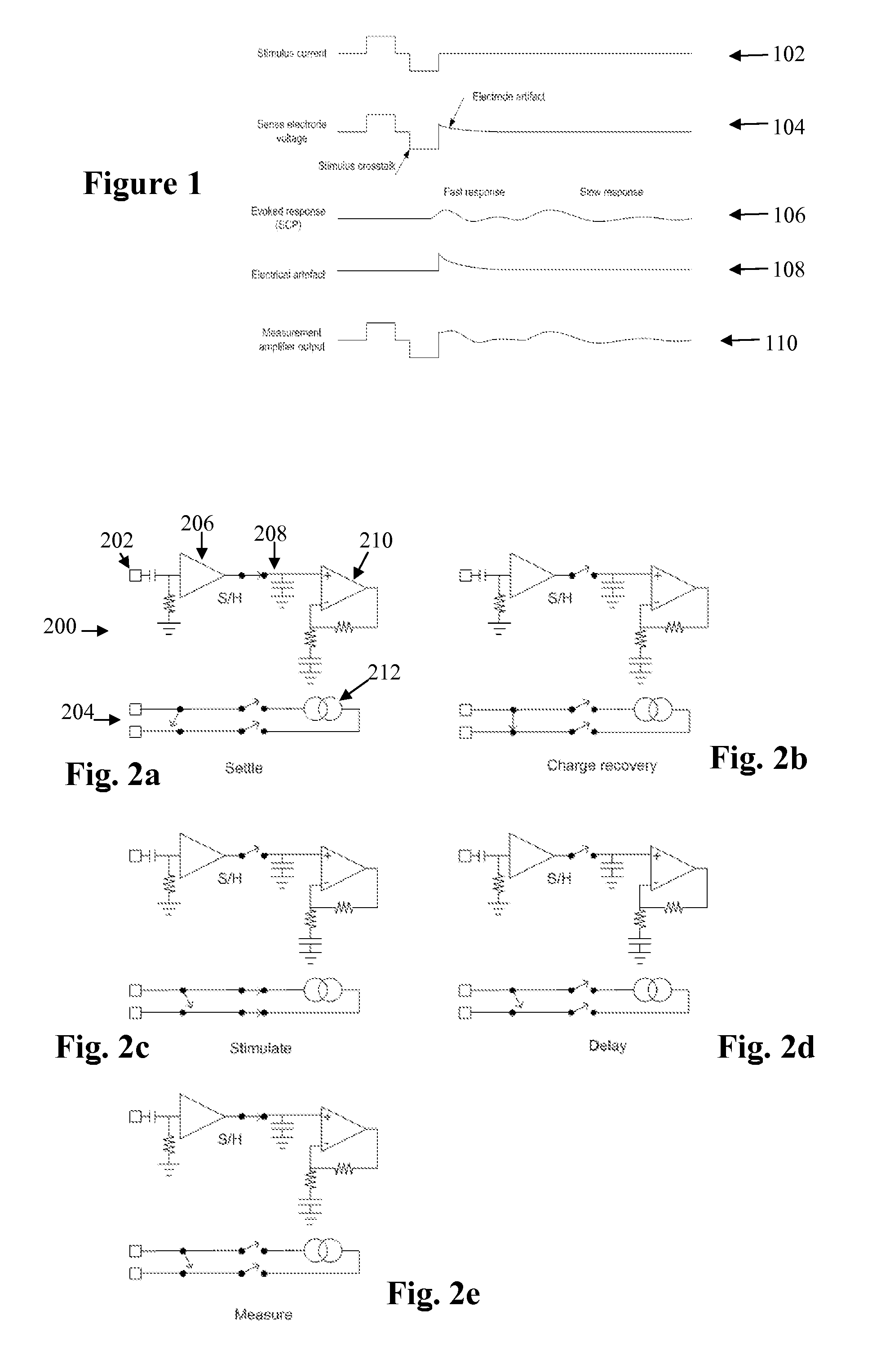
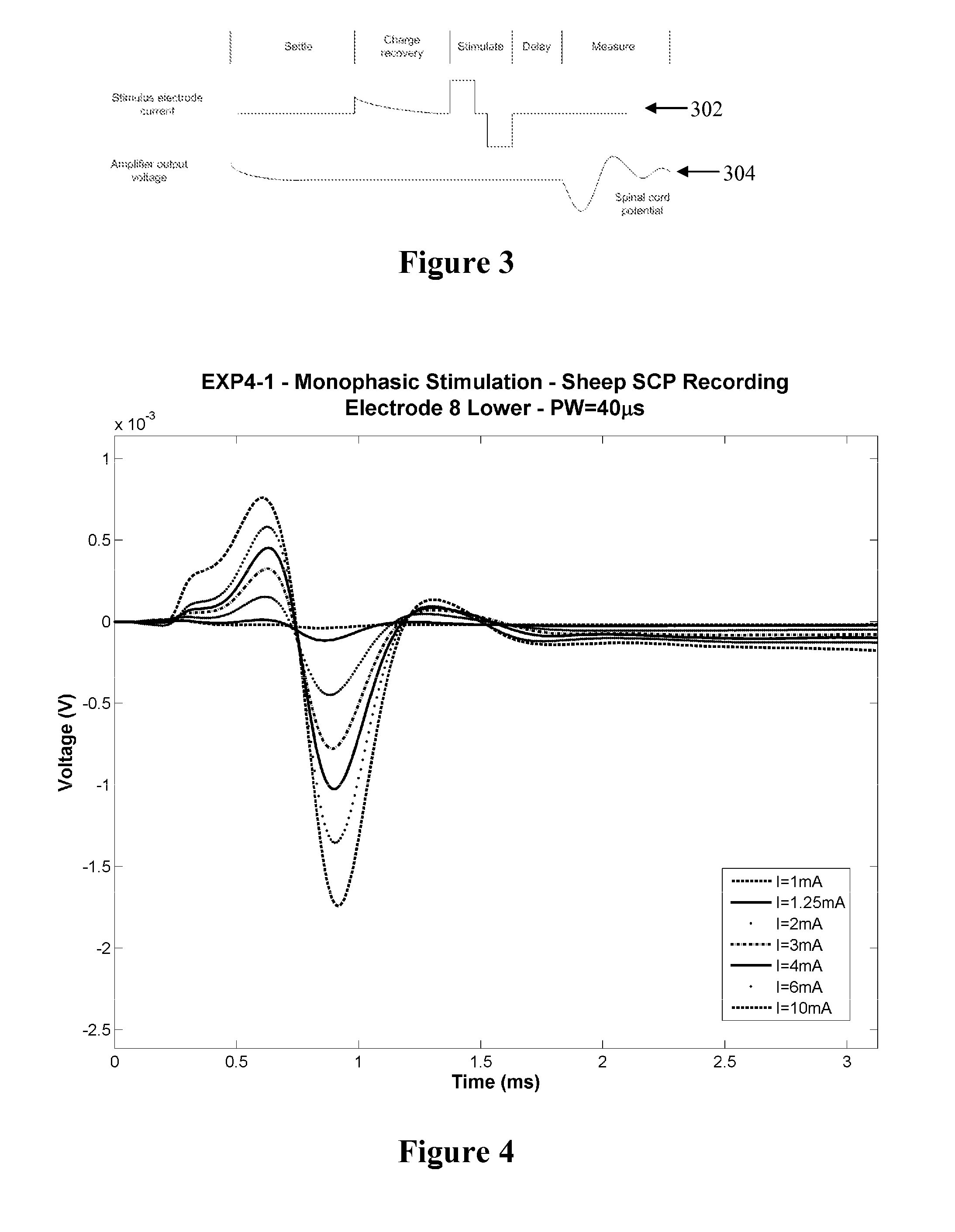
Method and apparatus for measurement of neural response
A method for measuring a neural response to a stimulus. Measurement circuitry is settled prior to a stimulus, by connecting a sense electrode to the measurement circuitry to allow the measurement circuitry to settle towards a bio-electrically defined steady state. Charge is recovered on stimulus electrodes by short circuiting the stimulus electrodes to each other. An electrical stimulus is then applied from the stimulus electrodes to neural tissue, while keeping the sense electrode disconnected from the measurement circuitry. After the stimulus, a delay is imposed during which the stimulus electrodes are open circuited and the sense electrode is disconnected from the measurement circuitry and from the stimulus electrodes. After the delay, a neural response signal present at the sense electrode is measured by connecting the sense electrode to the measurement circuitry.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
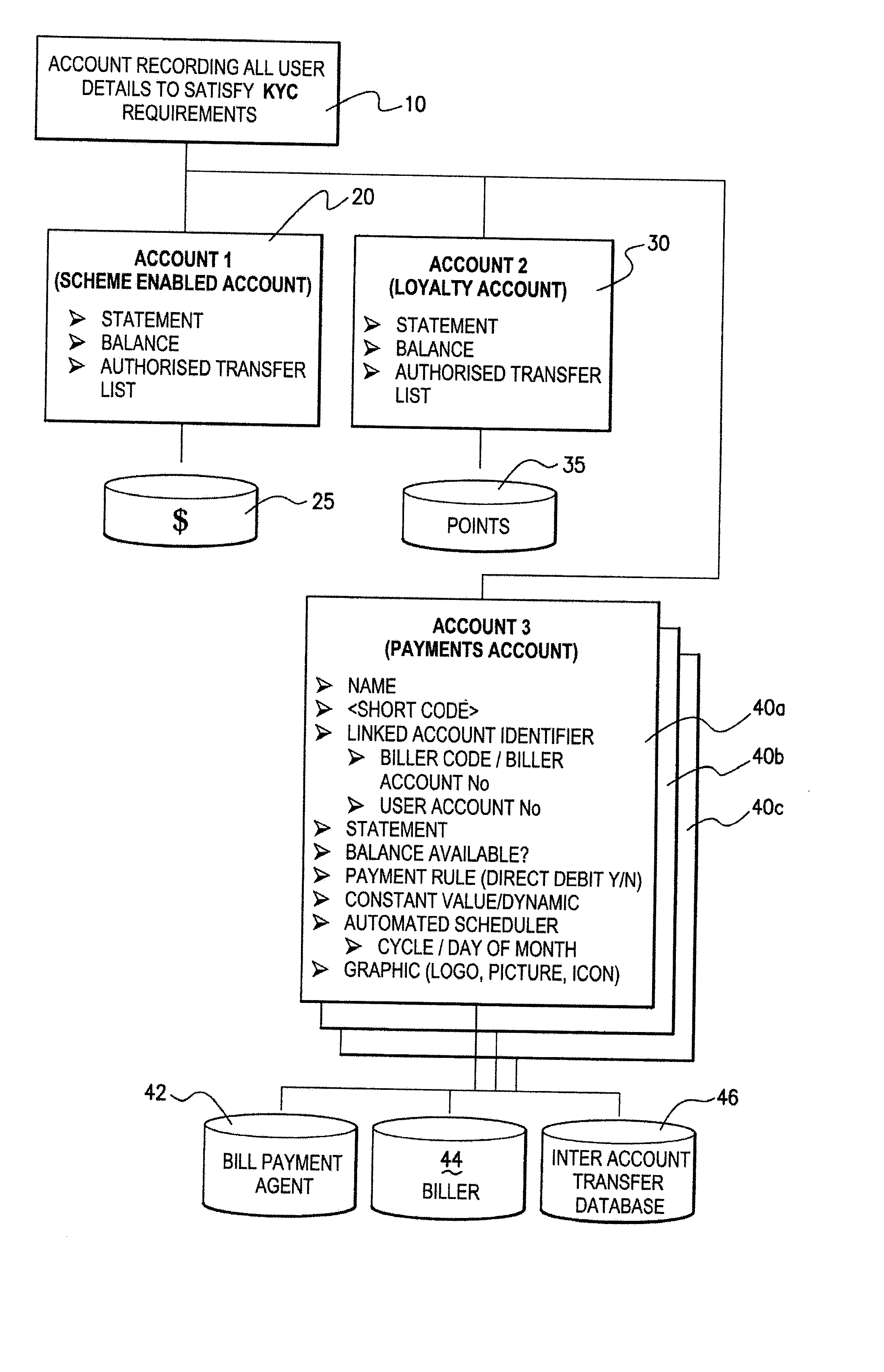
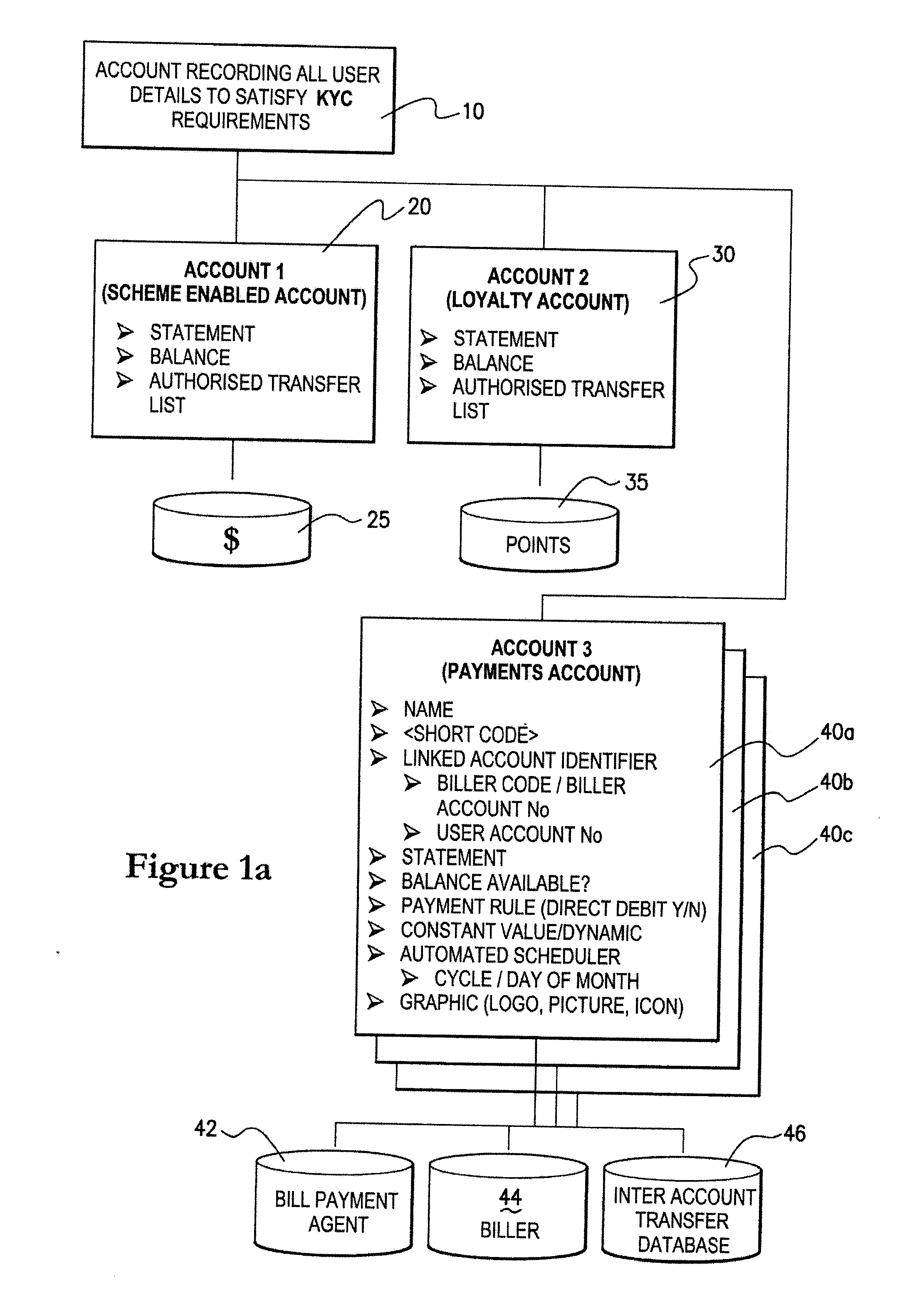
System and Method for Organising and Operating an Electronic Account
A method for a user to operate accounts with a user device when the user device is operably connected to a communications network, the user having at least one transaction account, the method including the steps of: (a) the user establishing any number of linked transaction accounts and associating same with the at least one transaction account; (b) the user establishing account operating rules for the at least one transaction account and any linked transaction accounts; and (c) the user operating a user device to access the at least one transaction account and / or any linked transaction accounts.
Owner:ON Q TECH PTY LTD
Cosmetic compositions having in-situ hydrosilylation cross-linking
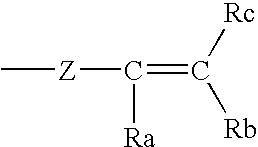
InactiveUS20070142575A1Inhibit migrationInhibit transferCosmetic preparationsMake-upCross-linkHydrosilylation
Compositions and methods for the in situ formation of hydrosilylation (addition) cross-linked organosiloxane films are disclosed. The disclosed films are long-lasting, flexible, transfer-resistant, and water-proof. The film-forming compositions generally comprise alkoxy-terminated organosiloxane polymers and a catalyst and are useful for formulating cosmetics and personal care products.
Owner:AVON PROD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com