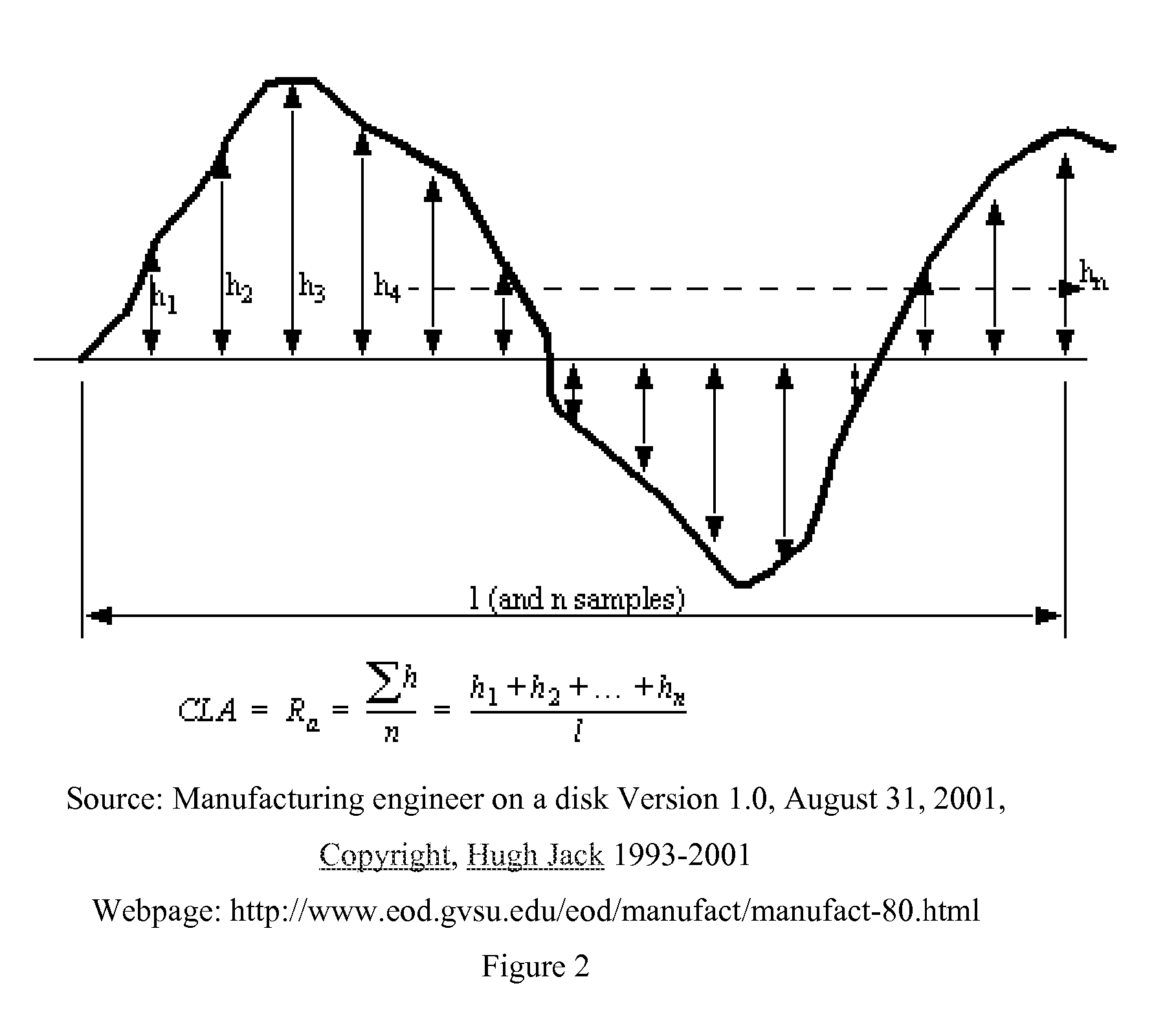
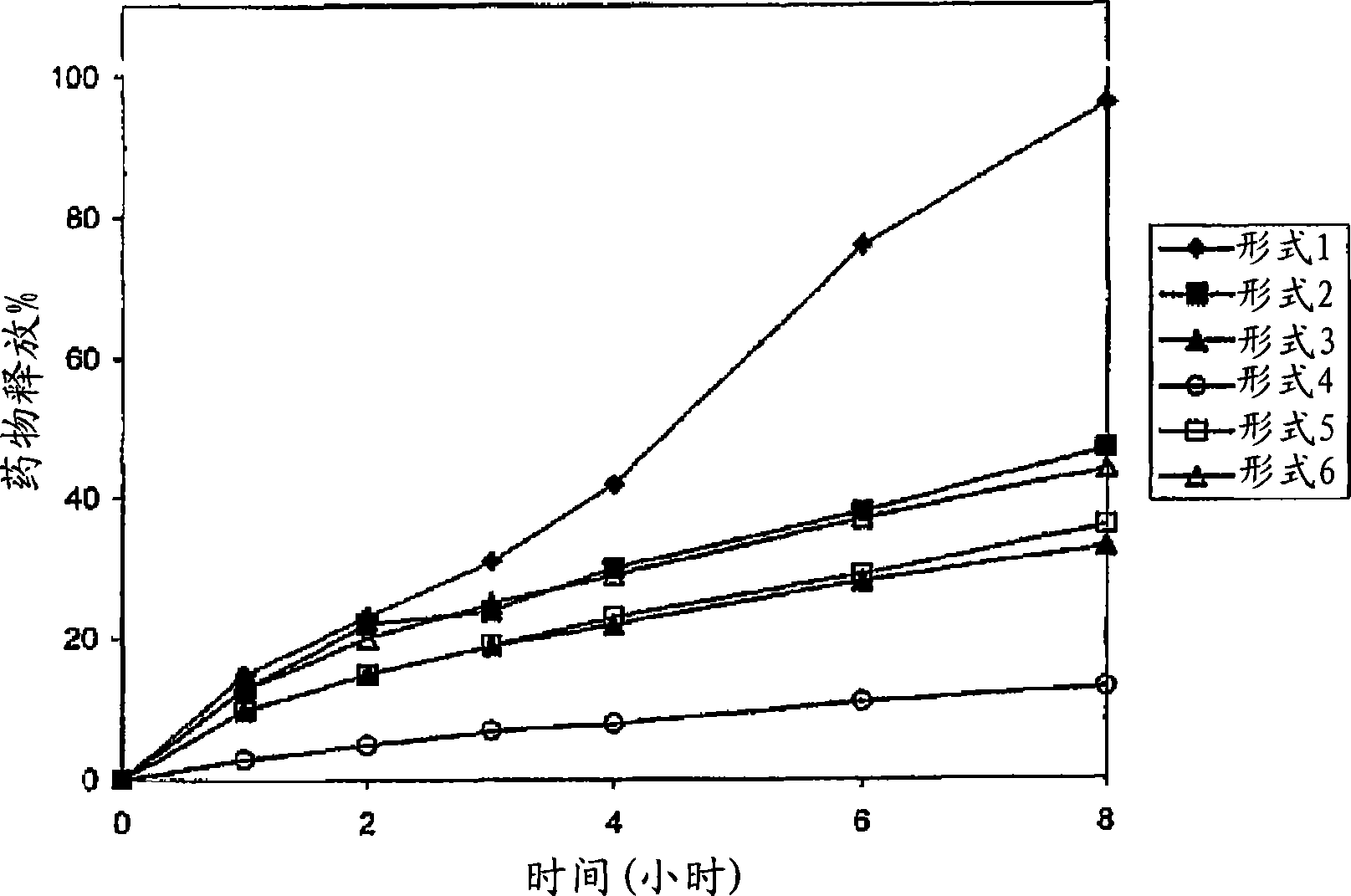
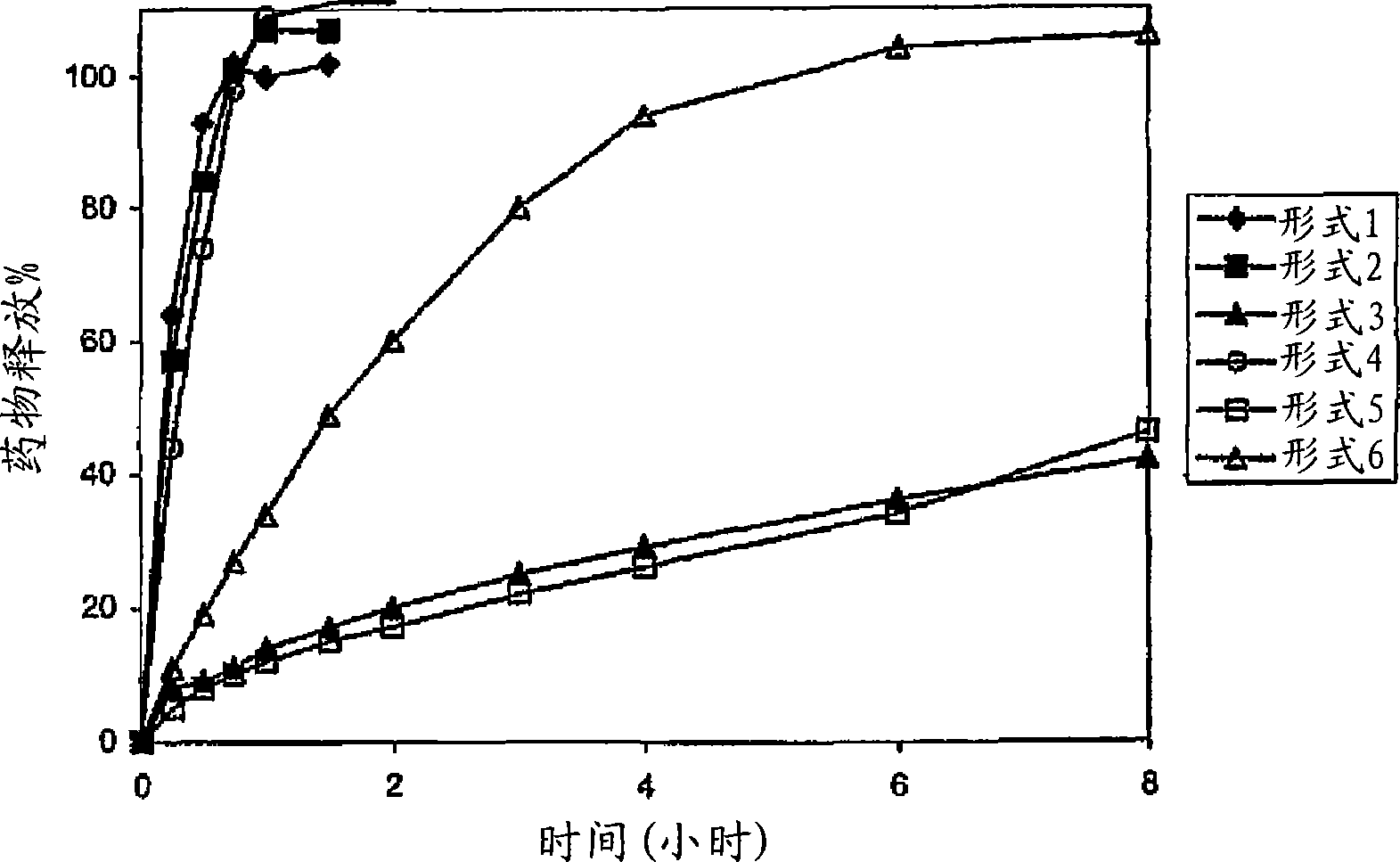
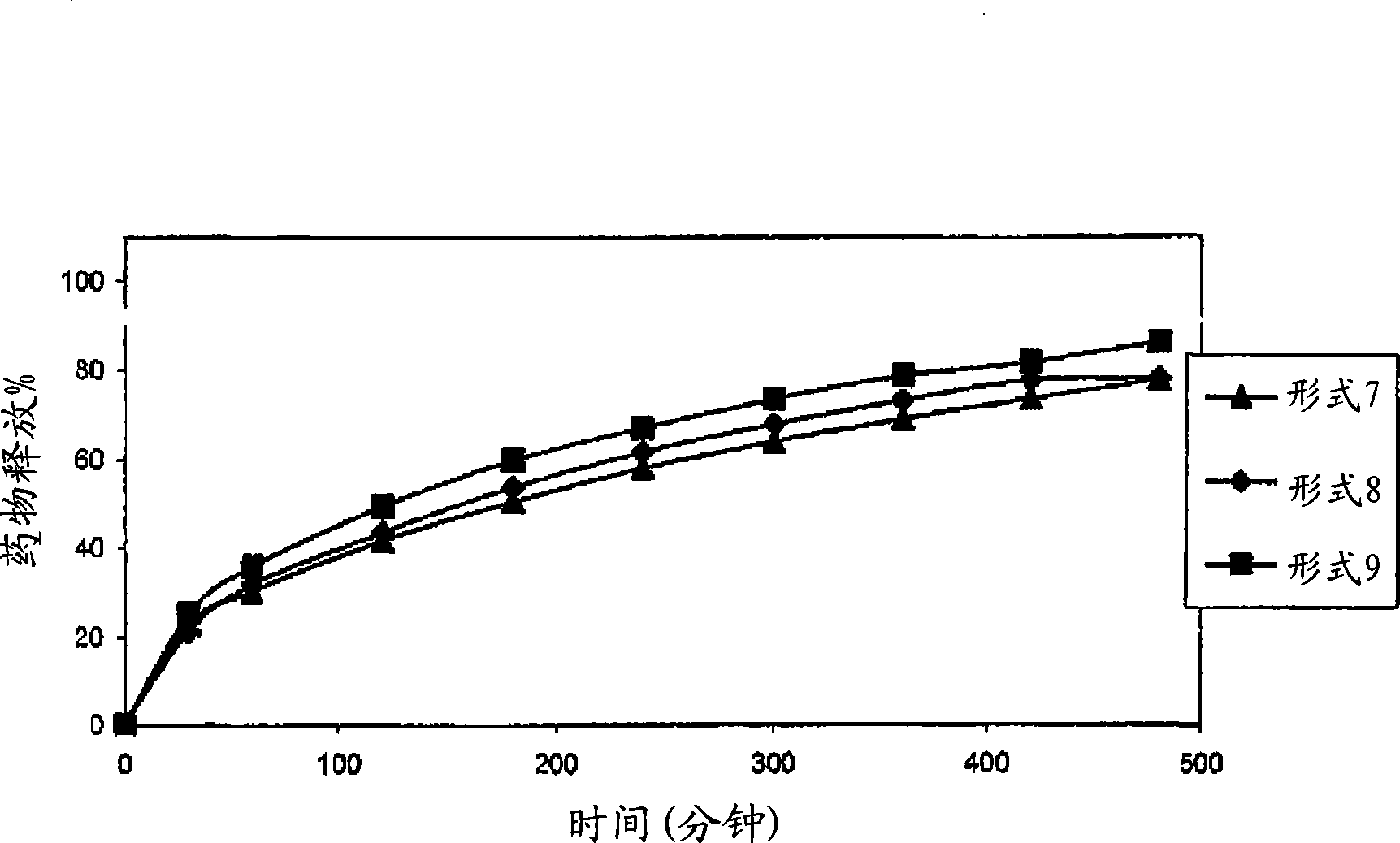
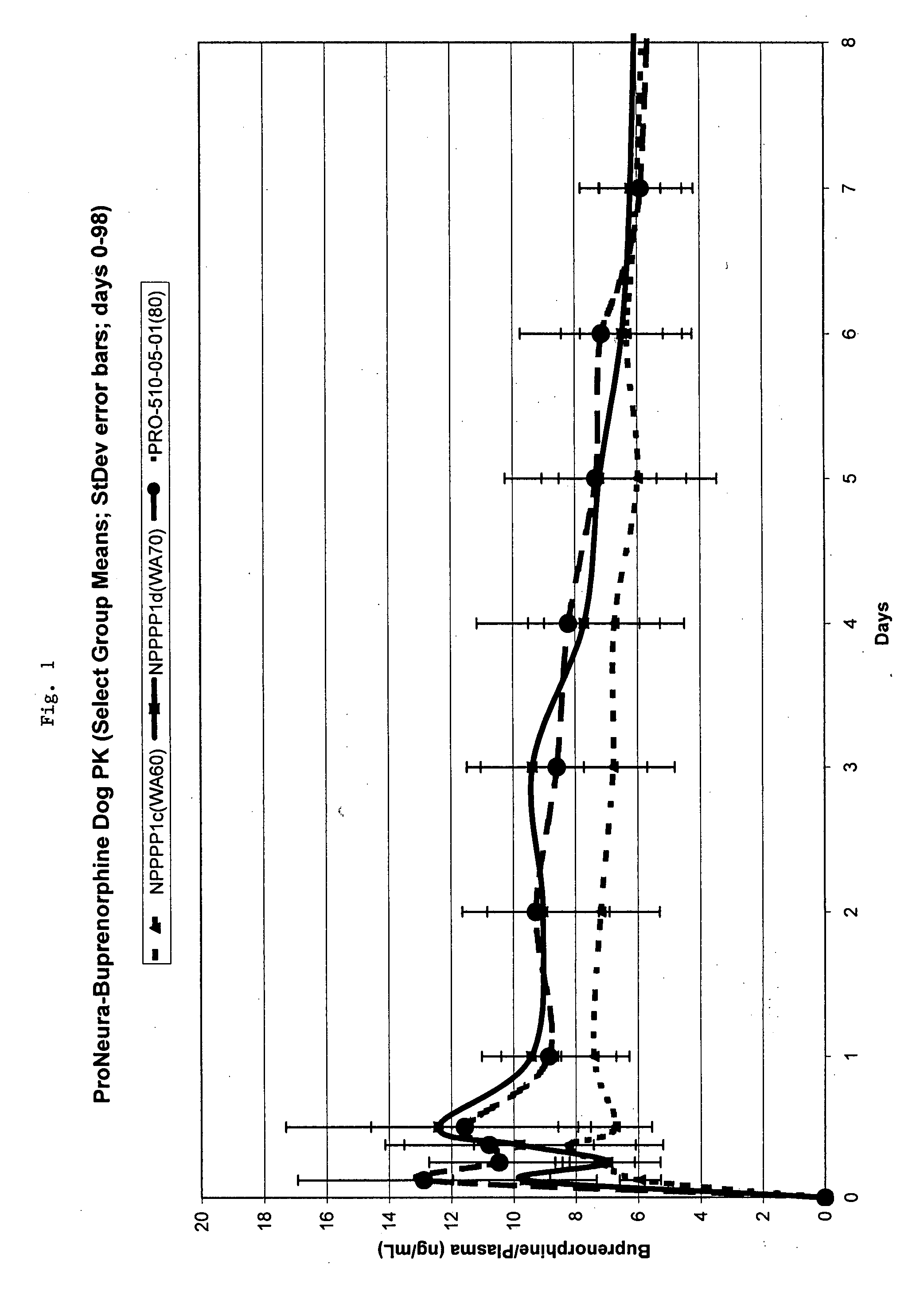
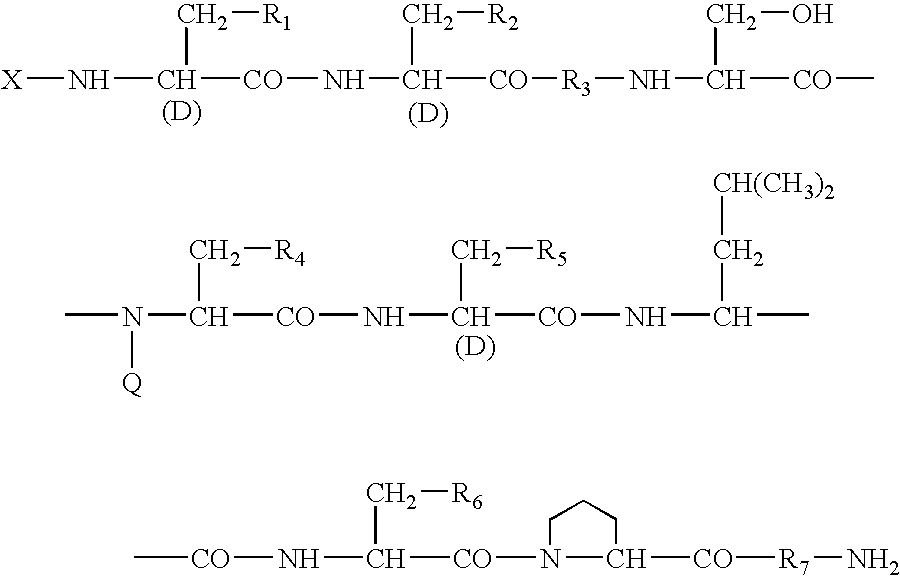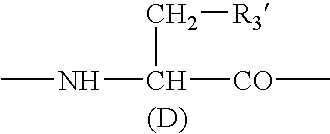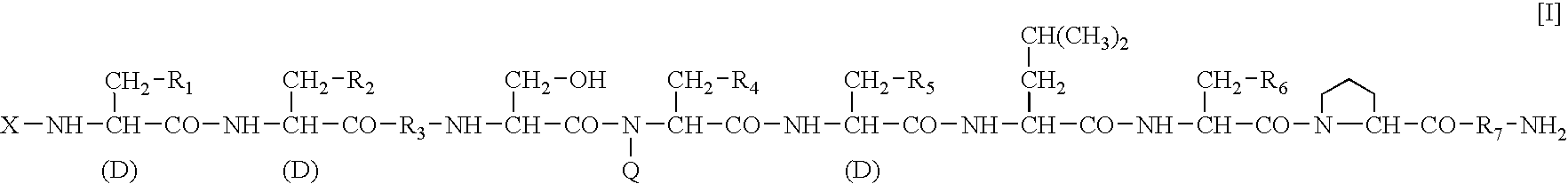Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Initial burst" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of producing sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6267981B1Maintain good propertiesEnhancement of entrapmentPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEntrapmentBiodegradable polymer
This invention provides a sustained-release preparation comprising a biodegradable polymer metal salt and broactive polypeptide, with enhanced entrapment of the bioactive polypeptides, a suppression of initial burst, and a constant long-term release of the bioactive polypeptides.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Formulations of nonopioid and confined opioid analgesics
The preferred exemplary embodiments in the present application provide formulations and methods for the delivery of drugs, particularly drugs of abuse, having an abuse-relevant drug substantially confined in the core and a non-abuse relevant drug in a non-core region. These formulations have reduced potential for abuse. In the formulation, preferably the abuse relevant drug is an opioid and the non-abuse relevant drug is acetaminophen or ibuprofen. More preferably, the opioid is hydrocodone, and the non-abuse relevant analgesic is acetaminophen. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosage forms are characterized by resistance to solvent extraction; tampering, crushing or grinding. Certain embodiments of the inventions provide dosage forms that provide an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Abuse resistant melt extruded formulation having reduced alcohol interaction
InactiveUS20090317355A1Reduced and limited dose-dumping effectReduce interactionBiocideNervous disorderVerapamilOral medication
The present invention relates to compositions for oral administration. The invention preferably comprises at least one abuse-resistant drug delivery composition for delivering a drug having potential for dose dumping in alcohol, related methods of preparing these dosage forms, and methods of treating a patient in need thereof comprising administering the inventive compositions to the patient. Most preferably, the dosage form includes verapamil. These formulations have reduced potential for abuse. In another formulation, preferably the abuse relevant drug is an opioid and the non-abuse relevant drug is acetaminophen or ibuprofen. More preferably, the opioid is hydrocodone, and the non-abuse relevant analgesic is acetaminophen. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosage forms are characterized by resistance to solvent extraction; tampering, crushing or grinding. Certain embodiments of the inventions provide dosage forms that provide an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
Fast wake-up in a gaze tracking system
ActiveUS20140043227A1Lower latencyReduced dynamicsInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPower modeControl signal
A gaze tracking system, leaving a low power mode in response to an activation signal, captures an initial burst of eye pictures in short time by restricting the image area of a sensor, with the purpose of enabling an increased frame rate. Subsequent eye pictures are captured at normal frame rate. The first gaze point value is computed memorylessly based on the initial burst of eye pictures and no additional imagery, while subsequent values may be computed recursively by taking into account previous gaze point values or information from previous eye pictures. The restriction of the image area may be guided by a preliminary overview picture captured using the same or a different sensor. From the gaze point values, the system may derive a control signal to be supplied to a computer device with a visual display.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
Abuse resistant melt extruded formulation having reduced alcohol interaction
InactiveUS20100172989A1Reduced and limited dose-dumping effectReduce interactionPowder deliveryBiocideVerapamilOral medication
The present invention relates to compositions for oral administration. The invention preferably comprises at least one abuse-resistant drug delivery composition for delivering a drug having potential for dose dumping in alcohol, related methods of preparing these dosage forms, and methods of treating a patient in need thereof comprising administering the inventive compositions to the patient. Most preferably, the dosage form includes verapamil. These formulations have reduced potential for abuse. In another formulation, preferably the abuse relevant drug is an opioid and the non-abuse relevant drug is acetaminophen or ibuprofen. More preferably, the opioid is hydrocodone, and the non-abuse relevant analgesic is acetaminophen. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosage forms are characterized by resistance to solvent extraction; tampering, crushing or grinding. Certain embodiments of the inventions provide dosage forms that provide an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG +1
Deposition of calcium-phosphate (CaP) and calcium-phosphate with bone morphogenic protein (CaP+BMP) coatings on metallic and polymeric surfaces
InactiveUS20080097618A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh densityImpression capsBone implantPolymeric surfaceSolubility
The invention is a medical implantable device which is coated by the method according to the invention. The surface of the substrate used for the implantable device, in the raw condition, following a cleaning regime and physiochemical pretreatments, is coated using a biomimetic process in a supersaturated calcium phosphate solution (SCPS) to obtain the desired coating coverage and morphology maintaining a ratio of calcium to phosphorus pH, as well as solution temperature plays a major role in yielding precipitation of the proper phase of CaP so that composition, morphologies, crystal structures, and solubility characteristics are optimal for the deposition process. The biomimetic coating adds the attribute of osteoconductivity to the implant device. To maximize bone growth, the implant must also induce bone growth, or possess the attribute of osteoinductivity. This attribute is acquired by the use of therapeutic agents, i.e. bone morphogenic proteins (BMP), growth factors, stem cells, etc. The preparation of the SCPS solution is slightly altered so that during the immersion of the implant in the SCPS, the therapeutic agents are co-precipitated and bonded with the CaP directly on the underlying surface of the implant device. A final dipping process into a BMP solution provides an initial burst of cellular activity. For delivering stem and / or progenitor cell, after drying the dipped solution of BMP, the cells are cultured on the surface of the implant.
Owner:HERKOWITZ HARRY N
Controlled release formulations using intelligent polymers
InactiveUS6893661B1Promote absorptionMaintenance of therapeutically effective blood levelPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSmart polymerWater contact
An extended release dosage composition of pharmaceutically active substances that have a water contact angle (θ) such that cos θ is between +0.9848 and −0.9848 presented as a matrix tablet containing the said pharmaceutically active substances, with / without suitable pharmaceutical excipients in intimate mixture with two groups of intelligent polymers having opposing wettability characteristics, one demonstrating a stronger tendency towards hydrophobicity and the other a stronger tendency towards hydrophilicity, the polymer combination being between the ratios of 1:50 and 50:1 amounts effective to control the release of said pharmaceutically active substances in a mathematically predictable manner, wherein the polymer demonstrating a stronger tendency towards hydrophobicity is not less than 5% wt / wt and preferably between 5-70% wt / wt of the final formulation composition. The intelligent polymers being ethylcellulose (EC) as a more strongly hydrophobic and hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) and / or hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) as more strongly hydrophilic (the ratio of HEC to HPMC being between 1:100 and 100:1). The matrix tablet is optionally coated with an enteric coat, 0-5%-15% wt / wt to prevent the initial burst effect seen in such systems and to impart gastrointestinal tract (GIT) “stealth” characteristics especially in the presence of food.
Owner:VALEANT INT BERMUDA
Uplink scheduling in wireless networks
InactiveUS20070047553A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationUplink schedulingMedia access control
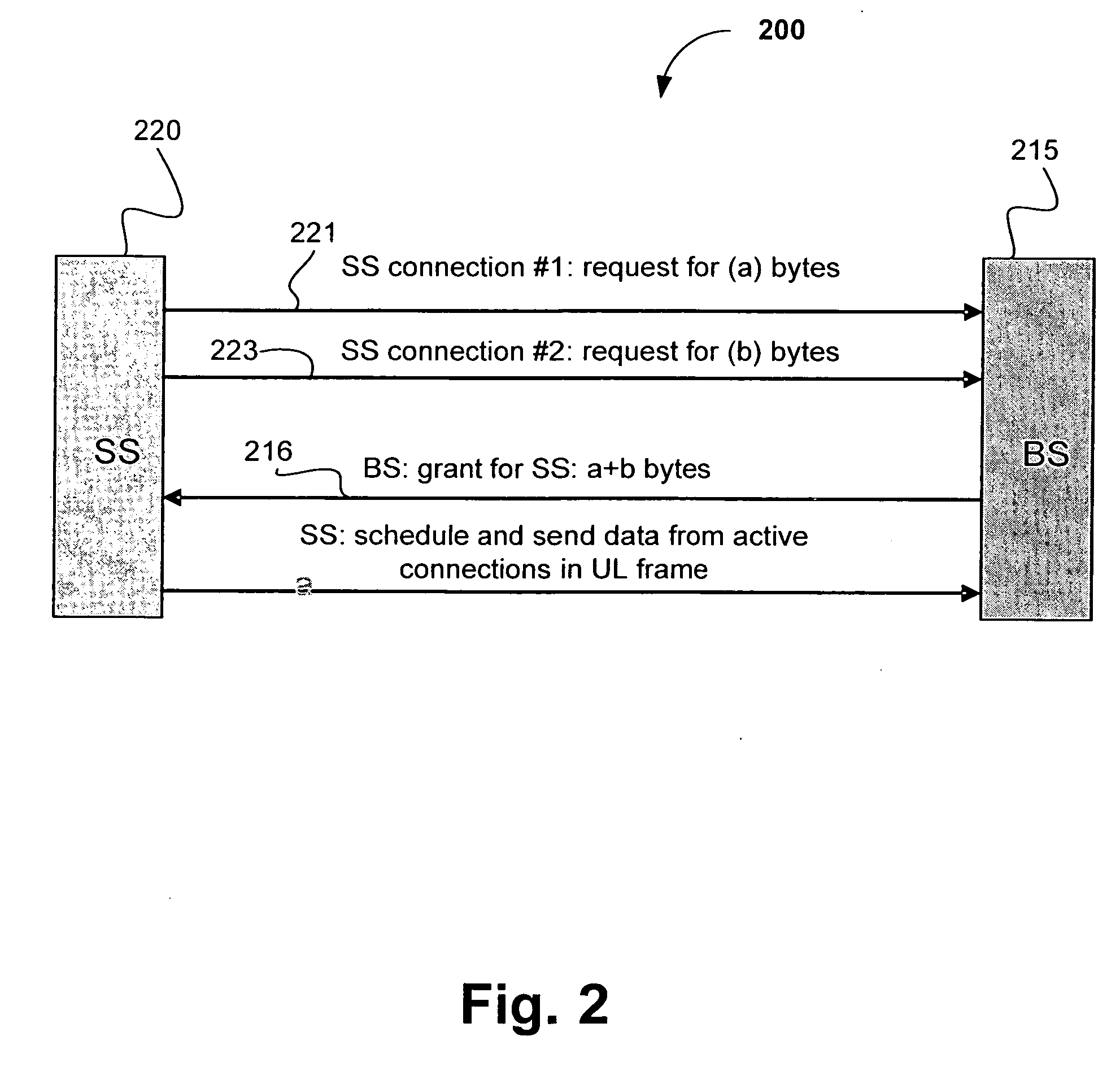
A medium access control (MAC) scheduler is disclosed for scheduling uplink (UL) traffic by a subscriber station having multiple active service connections. The scheduler may include two types of queue sets, a first type of queue for each unsolicited grant service (UGS) connection and a second type of queue for each and all other non-UGS connections. Upon receipt of an overall bandwidth grant from a base station, data in the first type of queues may be sent first and then data in the second type of queues is sent if there is sufficient remaining burst space in the granted UL frame. The second type of queues may be assigned weight value, and thus scheduled, depending on the type of connection. When serving the second type of queues, initial burst space allocation may be reserved for bandwidth requests to the base station. Additional embodiments and variations are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low burst polymers and methods to produce polymer
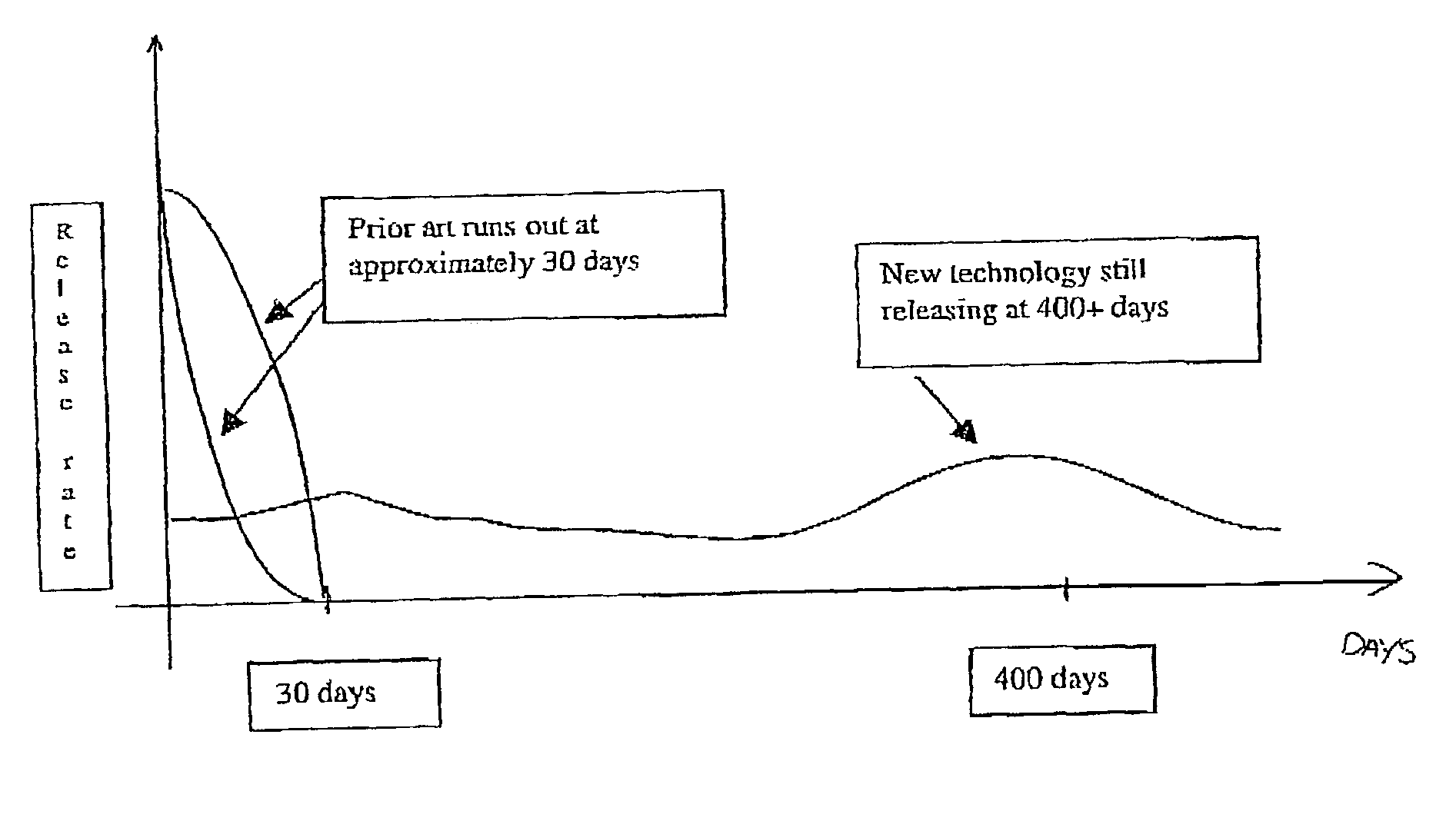
ActiveUS20100292195A1Increase release rateReduced initial burstAntibacterial agentsBiocideDrug biological activityCopolymer
A PLG copolymer material, termed a PLG(p) copolymer material, adapted for use in a controlled release formulation for a bioactive material is provided, wherein the formulation exhibits a reduced “initial burst” effect when introduced into the tissue of a patient in need thereof. A method of preparation of the PLG copolymer material is also provided, as are methods of use.
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Controlled Release Formulation
InactiveUS20080248107A1Reduced initial burst releaseGood physical propertiesPowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityActive agent
The present invention provides a controlled release formulation comprising an therapeutically effective amount of pharmacologically active substance having high water solubility, at least one non-polymeric release retardant, and at least one pH independent non-swelling release retarding polymer. The said dosage form provides controlled release of the active agent with reduced initial burst release.
Owner:RUBICON RES PTY LTD
Touch position coordinate detecting system
InactiveUS7230609B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Surface acoustic wave sensor
A touch position coordinate detecting system is provided that is based on surface acoustic waves and includes arrays of reflective patterns between a touch region of a touch panel. An initial burst that includes two frequency components is sent on the panel. The reflective arrays include two sub-arrays centered respectively at the two frequencies. A touch on the panel involves an absorption of the acoustic waves traveling in the region of the panel, and provides a localized damping in a time output signal. A time localized damping is detected for each reflected frequency components, thereby enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio of the system.
Owner:GENERALTOUCH TECH
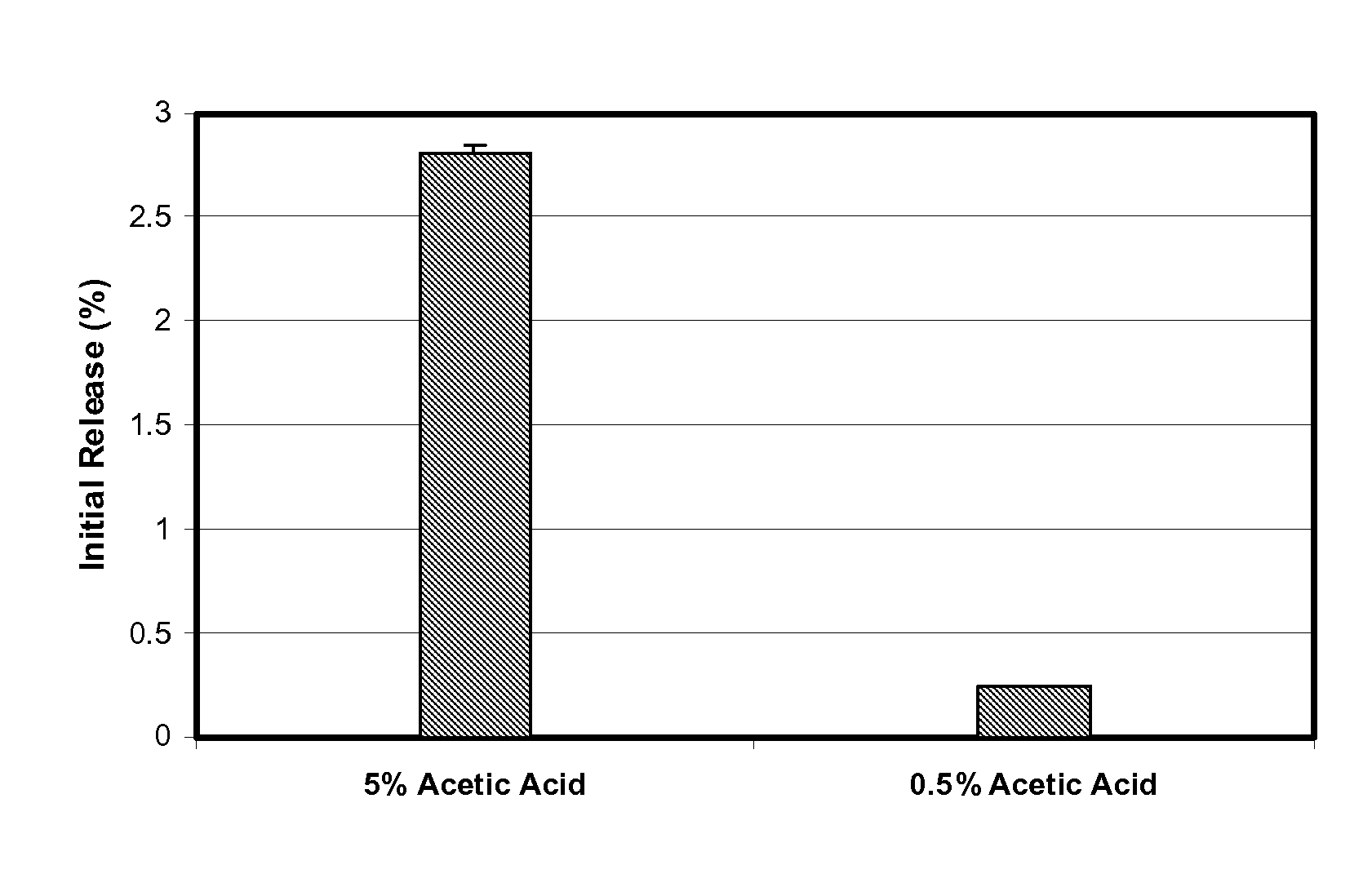
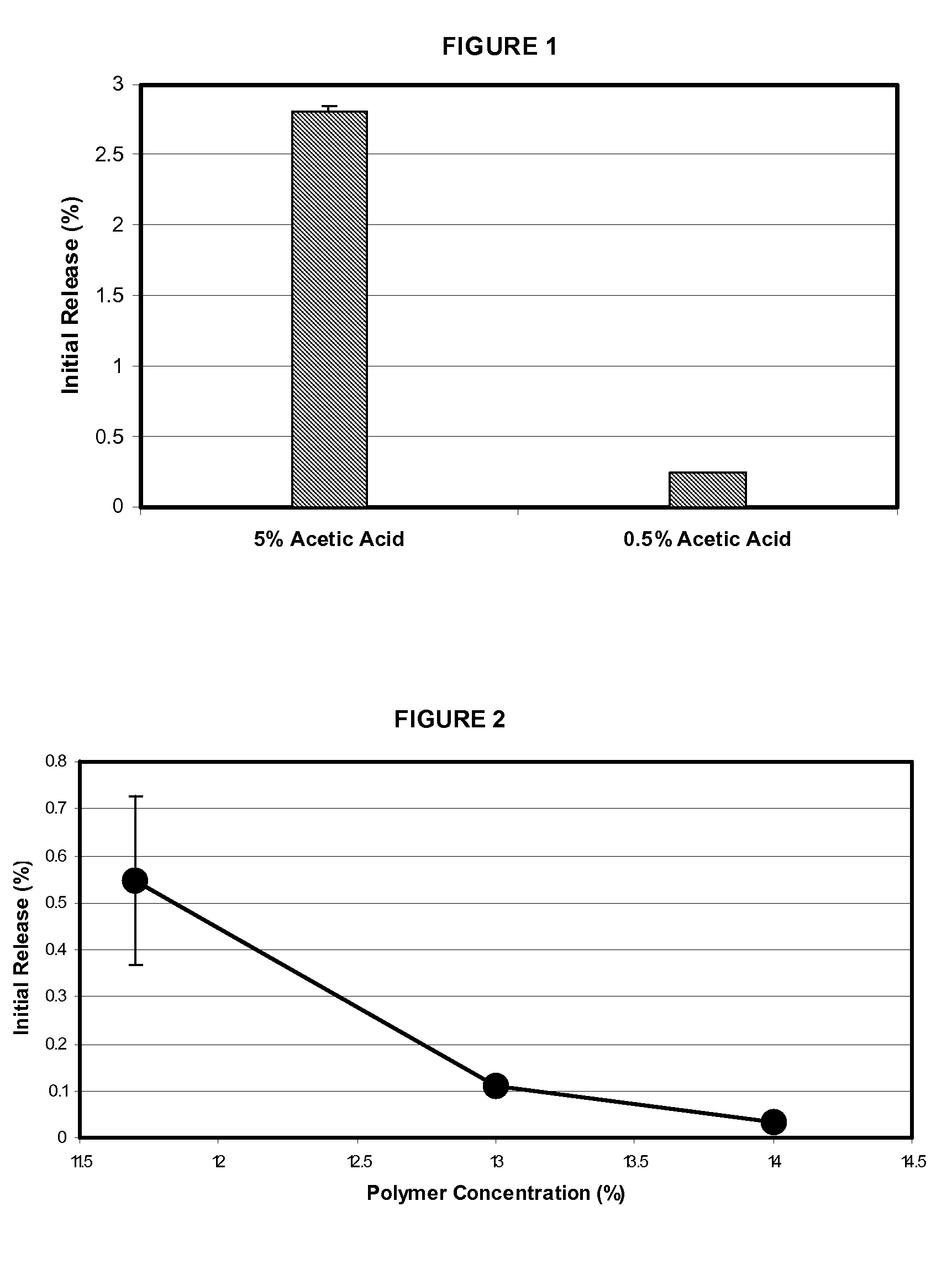
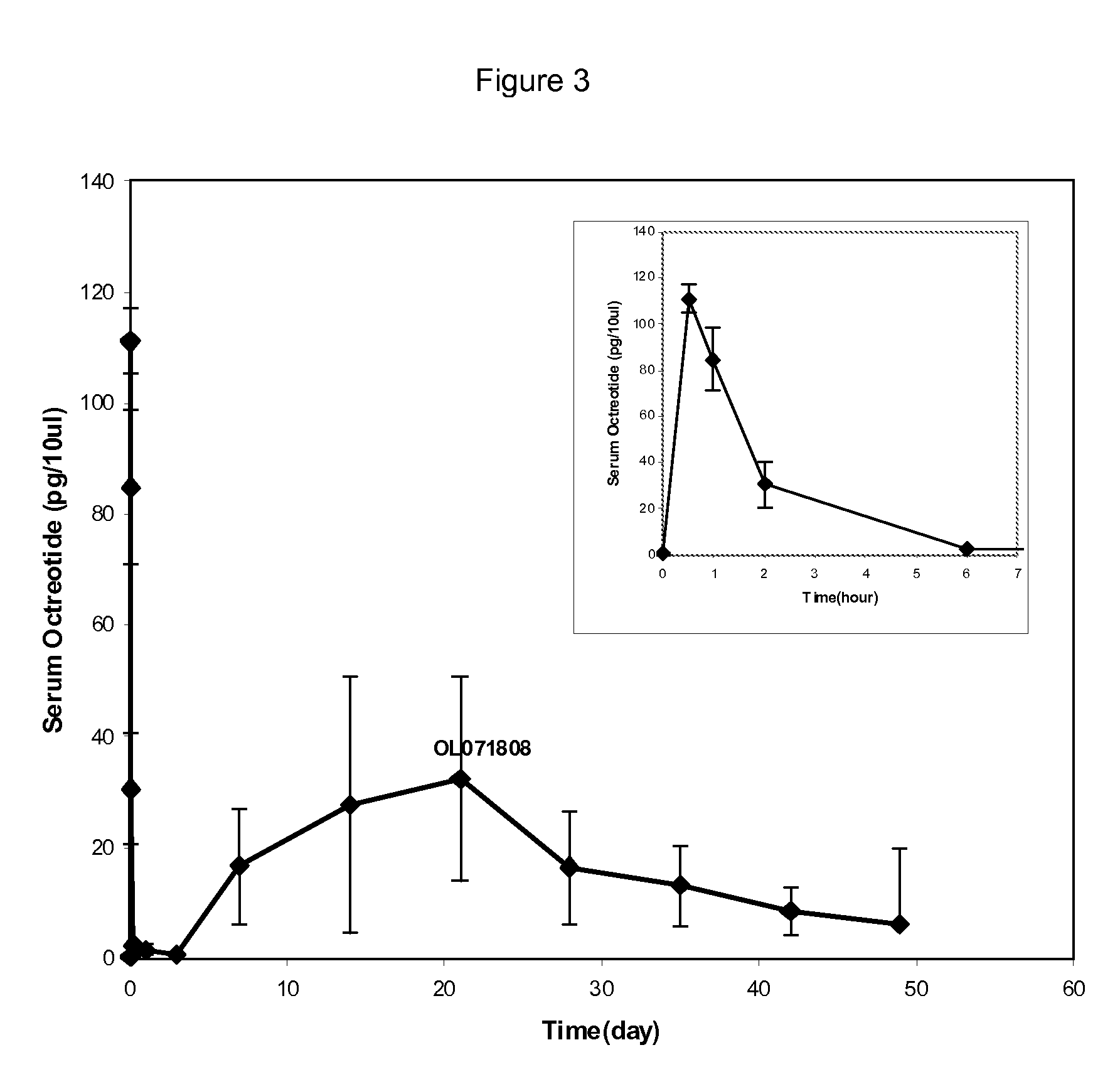
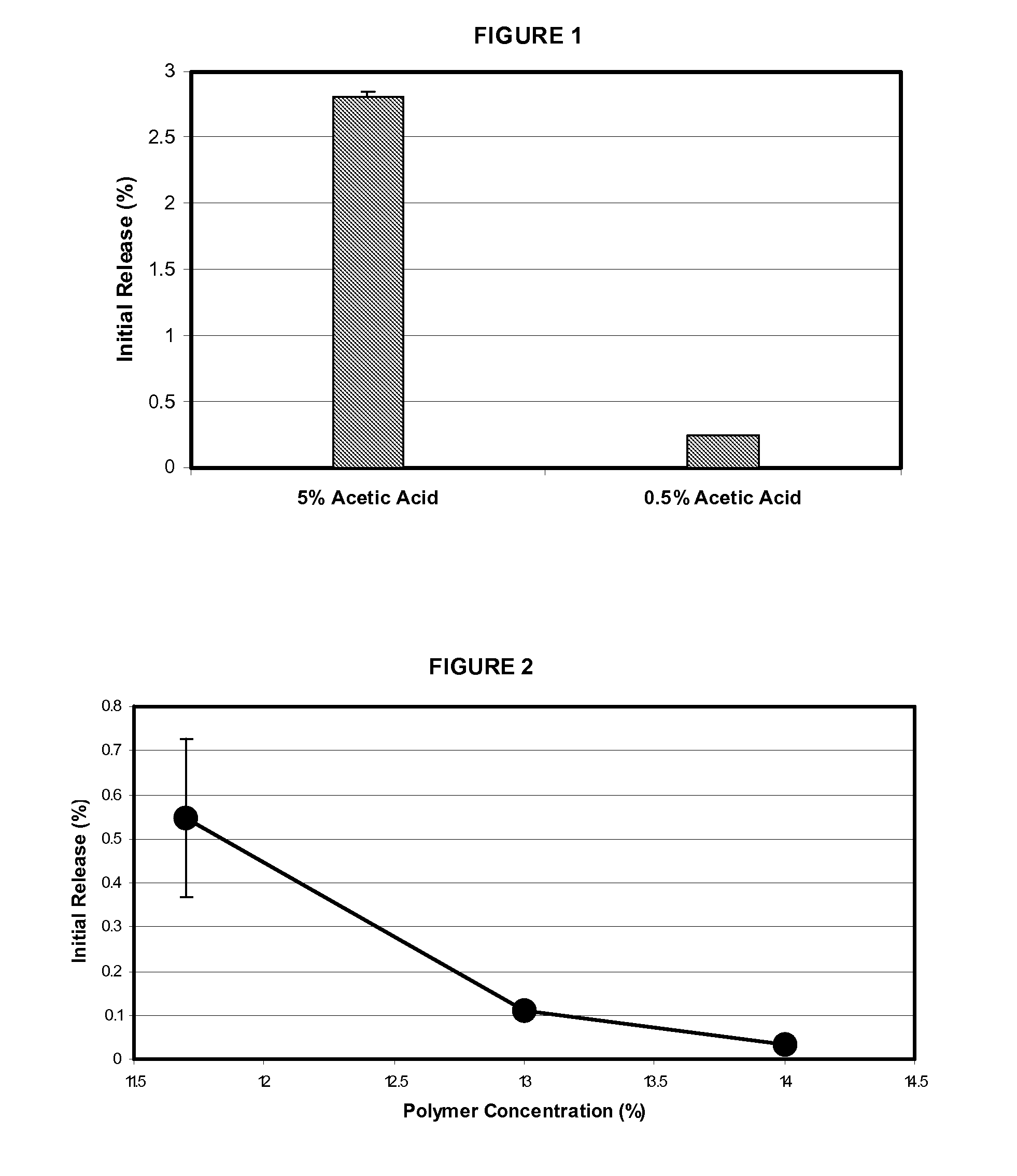
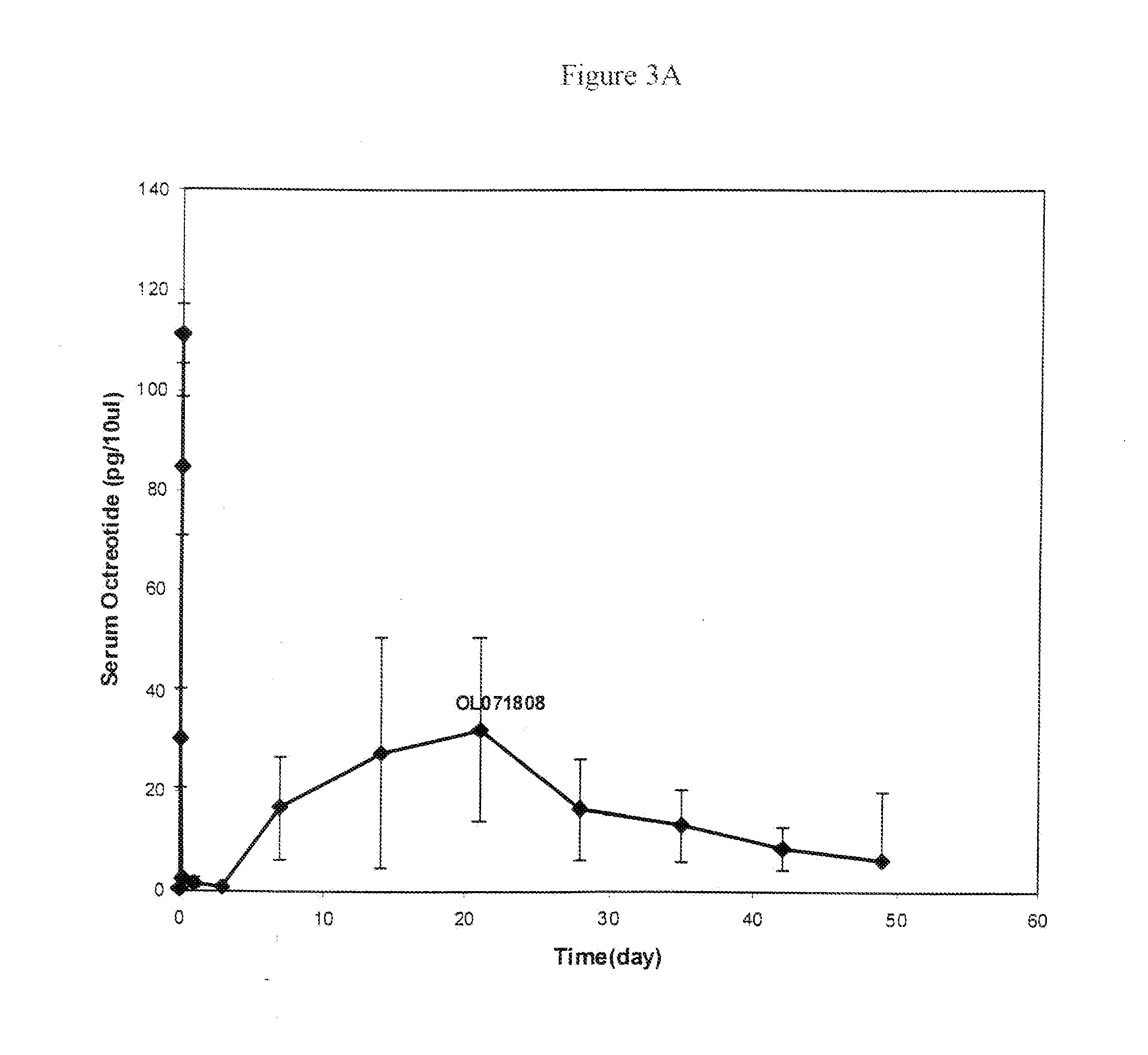
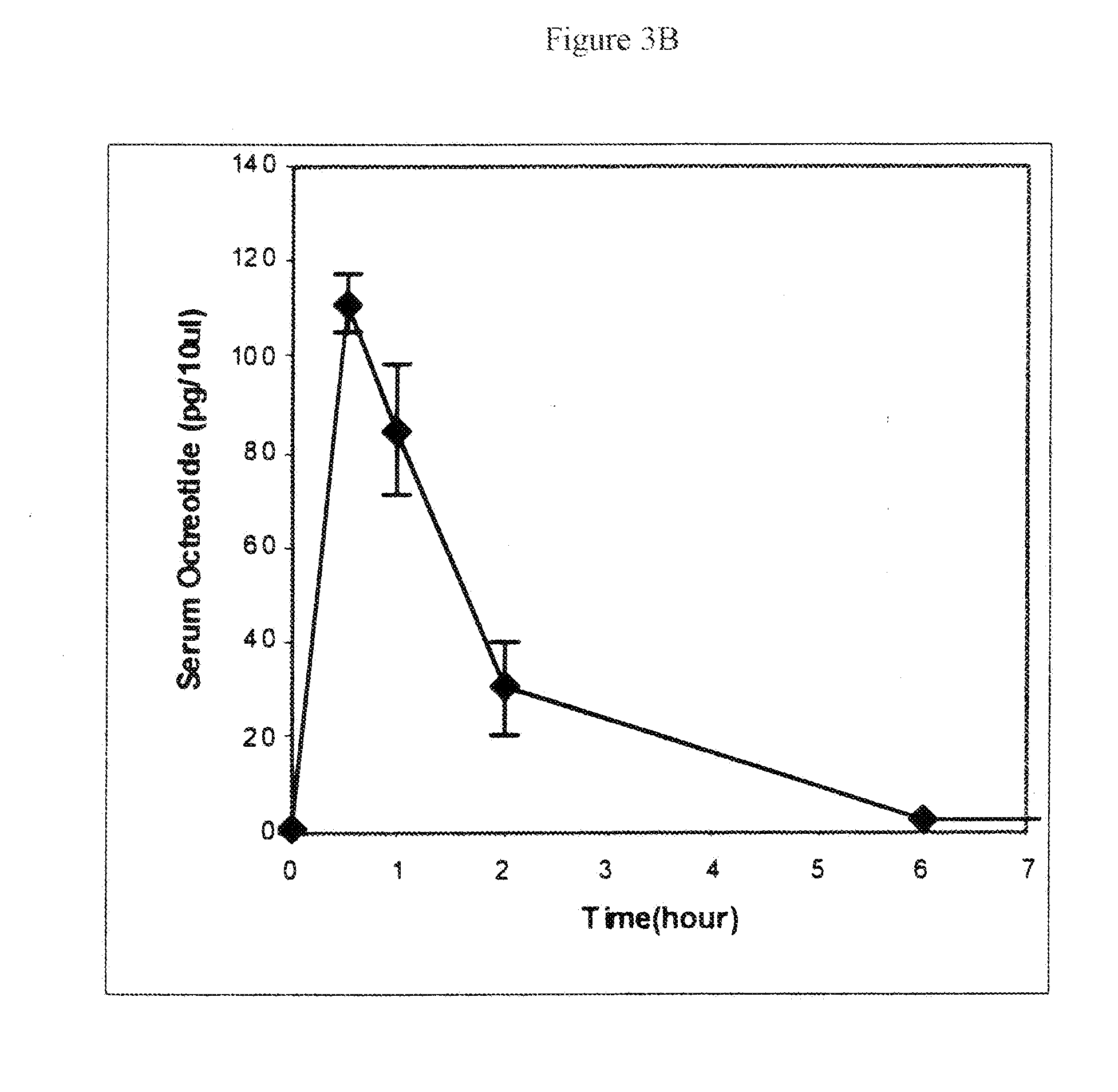
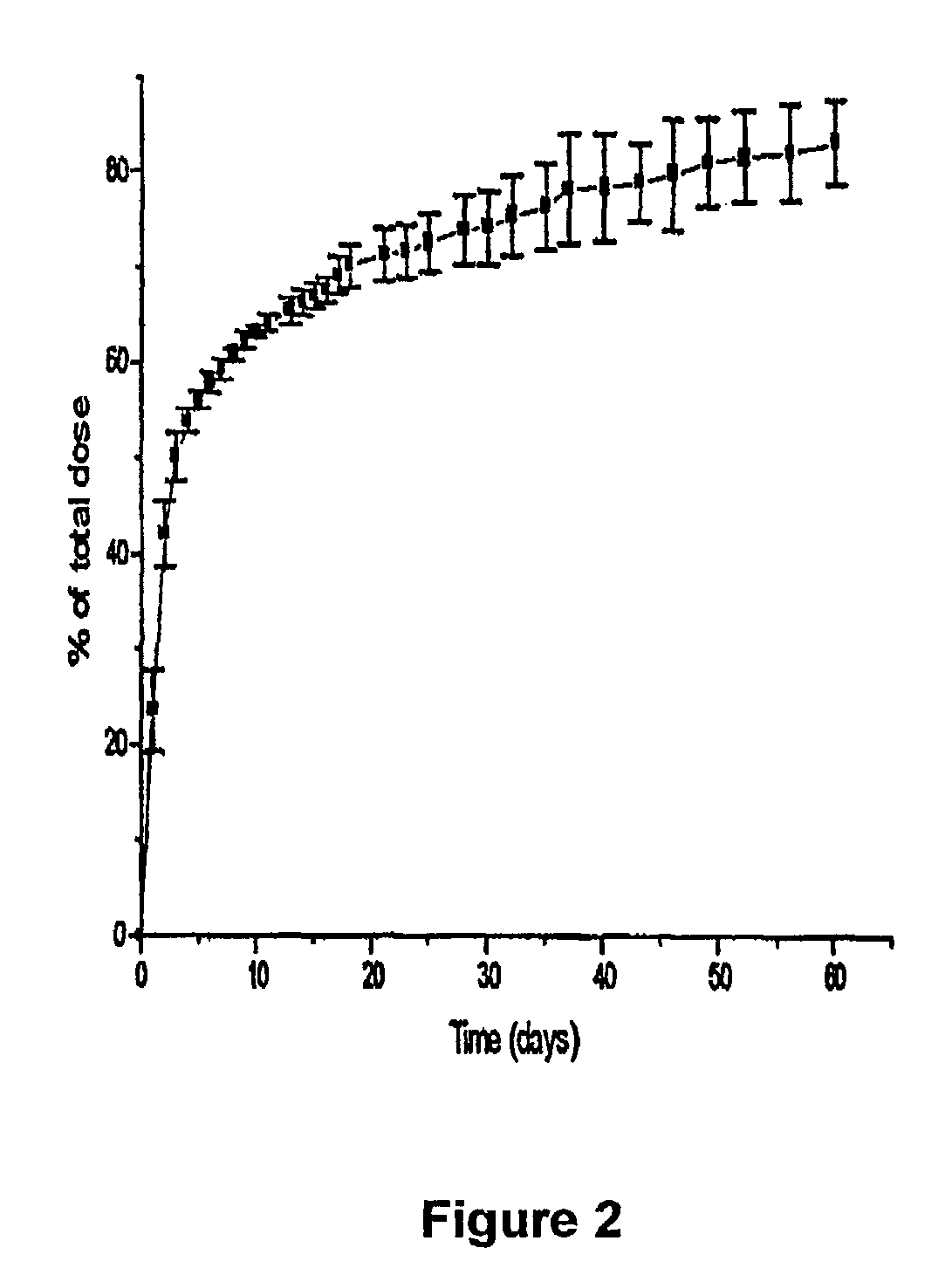
Microspheres for the sustained release of octreotide with a low initial burst
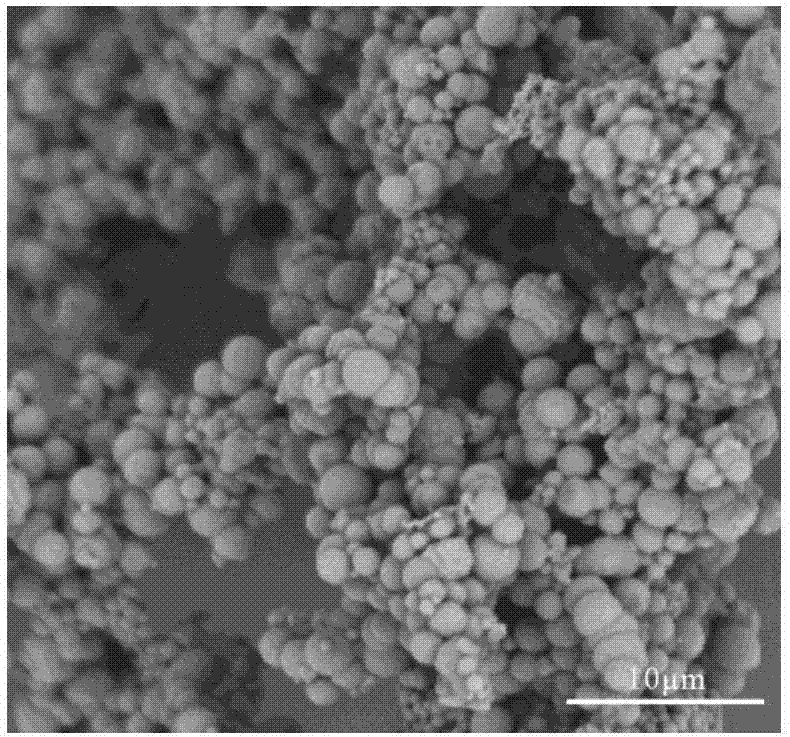
InactiveUS20100086597A1Initial burst can be loweredAvoid painPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrosphereL lactide
This disclosure features microspheres and a method of making them. The microspheres are for sustained release of an octreotide compound with a low initial burst, comprising a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) polymer matrix and an octreotide compound dispersed in the polymer matrix. The microspheres release less than 1% of a total amount of the octreotide compound within 1 hour at 37° C. and pH 7.4.
Owner:OAKWOOD LAB LLC
Formulations of nonopioid and confined opioid analgesics
The preferred exemplary embodiments in the present application provide formulations and methods for the delivery of drugs, particularly drugs of abuse, having an abuse-relevant drug substantially confined in the core and a non-abuse relevant drug in a non-core region. These formulations have reduced potential for abuse. In the formulation, preferably the abuse relevant drug is an opioid and the non-abuse relevant drug is acetaminophen or ibuprofen. More preferably, the opioid is hydrocodone, and the non-abuse relevant analgesic is acetaminophen. In certain preferred embodiments, the dosage forms are characterized by resistance to solvent extraction; tampering, crushing or grinding. Certain embodiments of the inventions provide dosage forms that provide an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBVIE DEUTSHLAND GMBH & CO KG
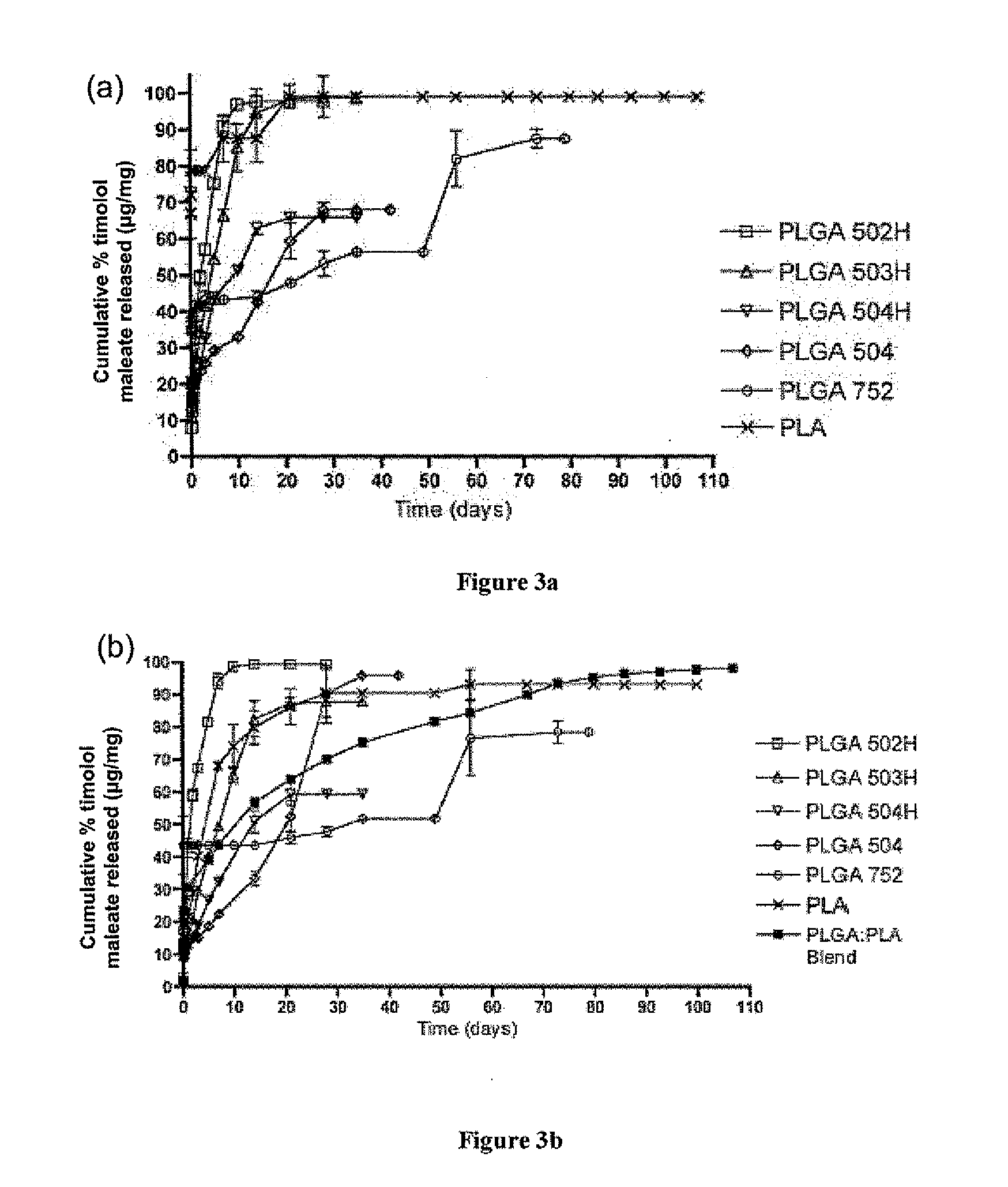
Sustained intraocular delivery of drugs from biodegradable polymeric microparticles
ActiveUS20100261646A1Lower eye pressureSustained releaseHormone peptidesBiocideMicrosphereActive agent
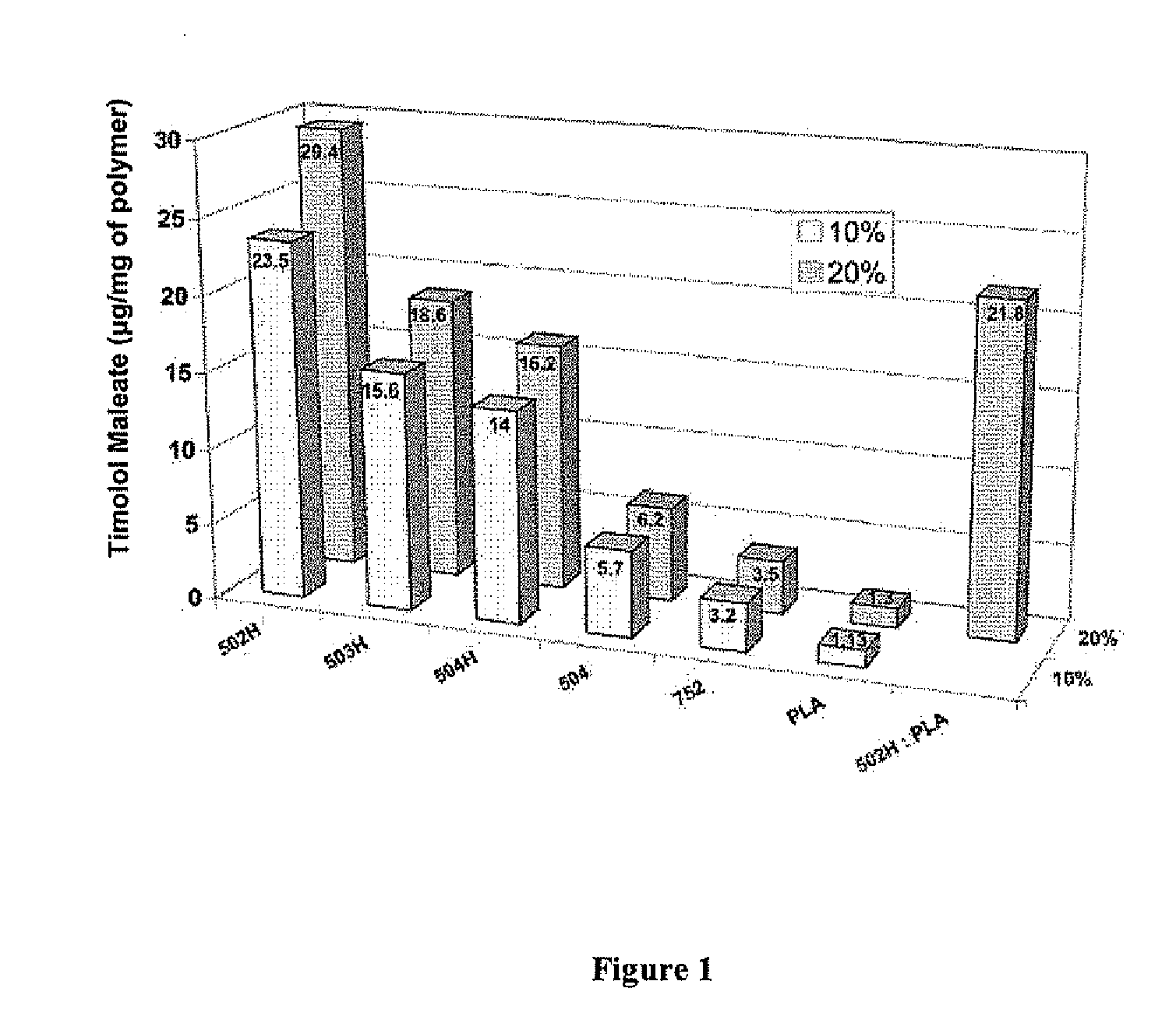
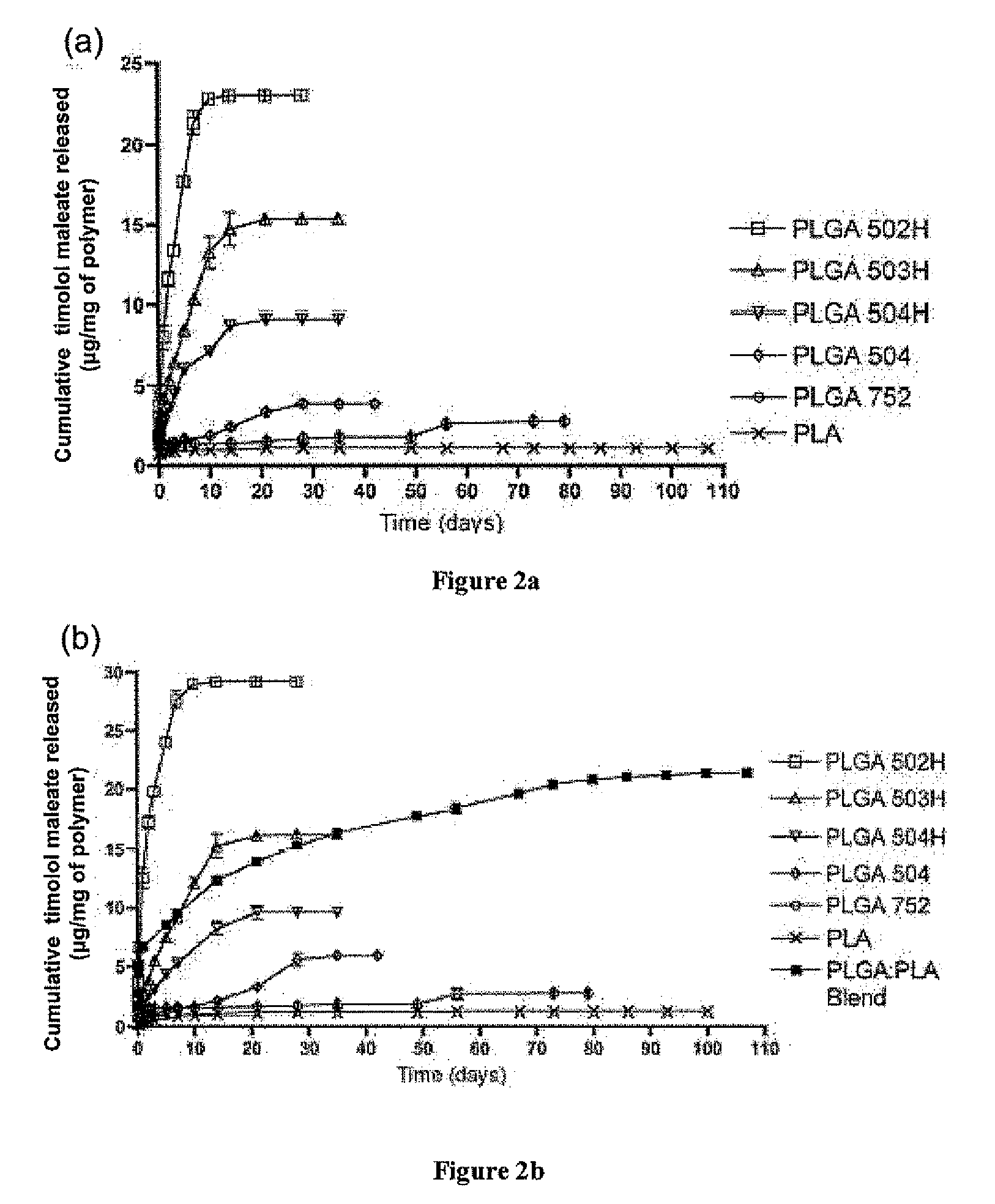
Biodegradable polymeric microparticle compositions containing one or more active agents, especially those useful for treating or preventing or one or more diseases or disorders of the eye, and methods of making and using thereof, are described. The microsphere compositions release an effective amount of the one or more active agents for a period greater than 14 days in vivo, preferably greater than 60 days in vivo, more preferably up to 73 days in vivo, more preferably greater than 90 days in vivo, even more preferably over 100 days in vivo, and most preferably greater than 107 days in vivo. In a preferred embodiment, the microparticle compositions contain one or more active agents useful for managing elevated intraocular pressure (TOP) in the eye. In one embodiment, the microspheres are formed from polylactide-co-glycolide (“PLGA”); in another embodiment, the microspheres are formed from a blend PLGA and poly lactic acid (“PLA”). Relatively hydrophilic, and preferably carboxylated, polymeric materials such as PLGA are used for a drug such as timolol maleate, which is relatively water soluble, to increase drug loading. Higher molecular weight polymers, as well as the ratio of LA (which has a longer degradation time, up to one to two years) to GA (which has a short degradation time, as short as a few days to a week), are used to provide release over a longer period of time. The combination of drug loading and release rate, as well as the minimization of initial burst release, result in prolonged release of a higher amount of drug.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Sustained-release preparation
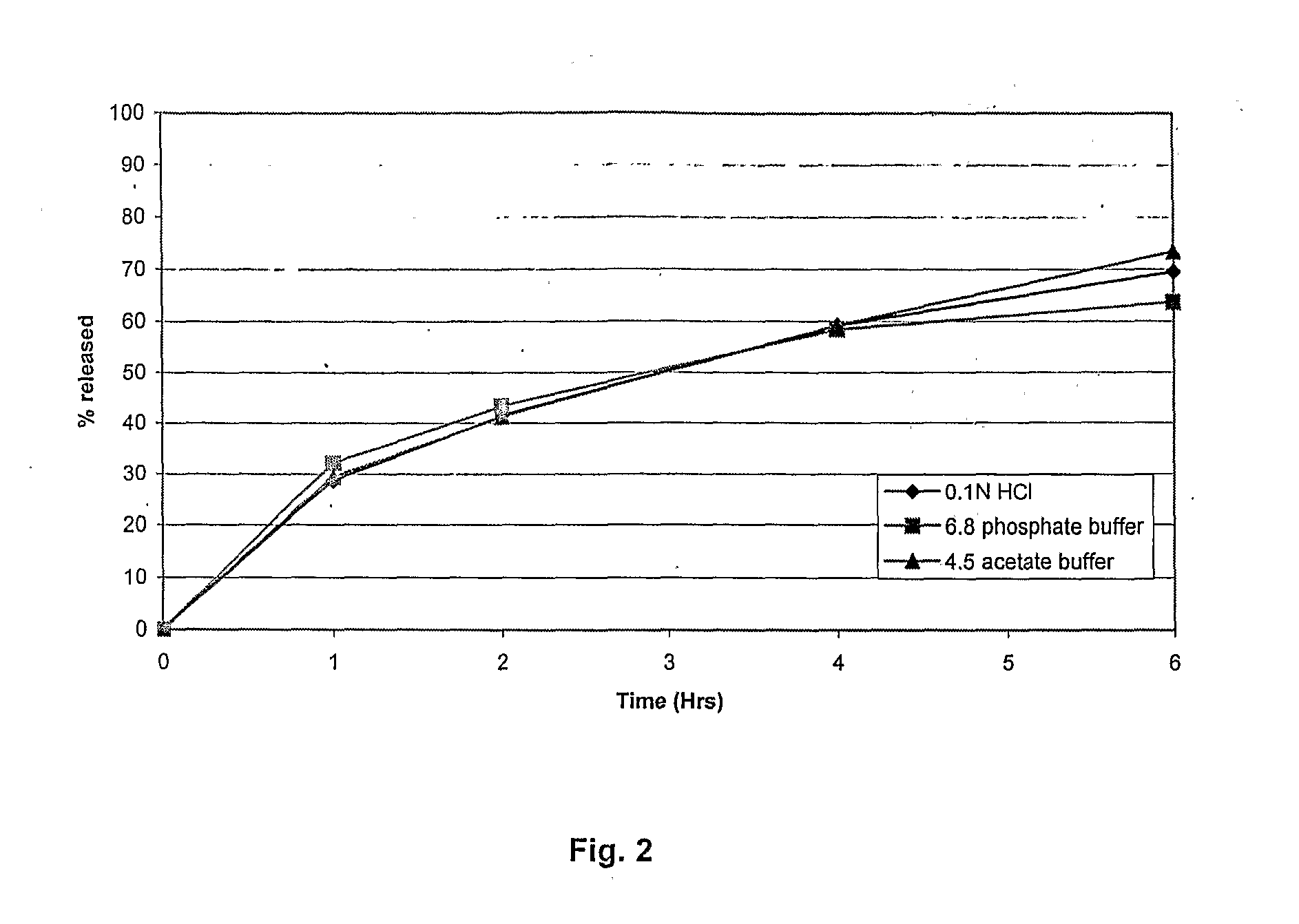
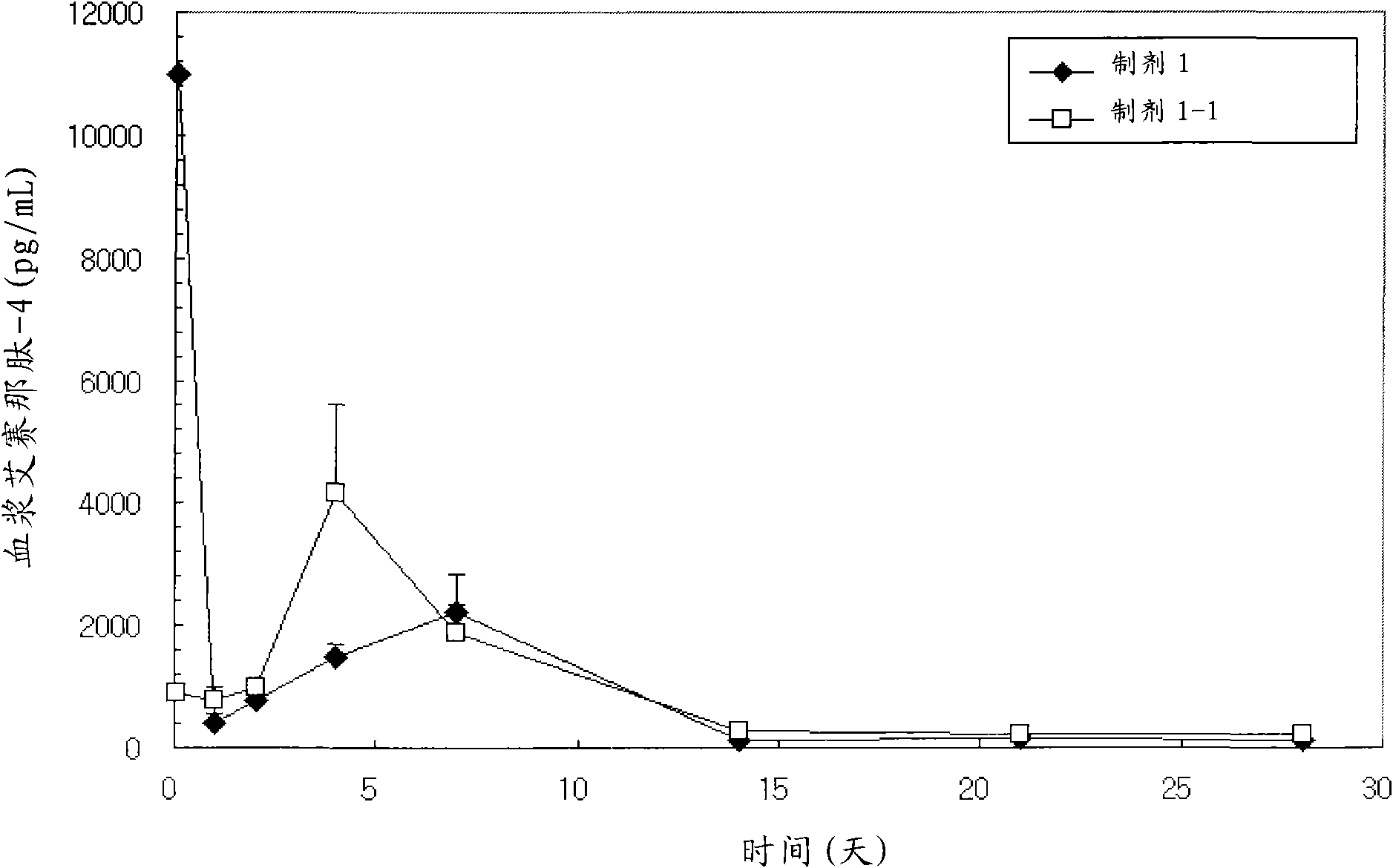
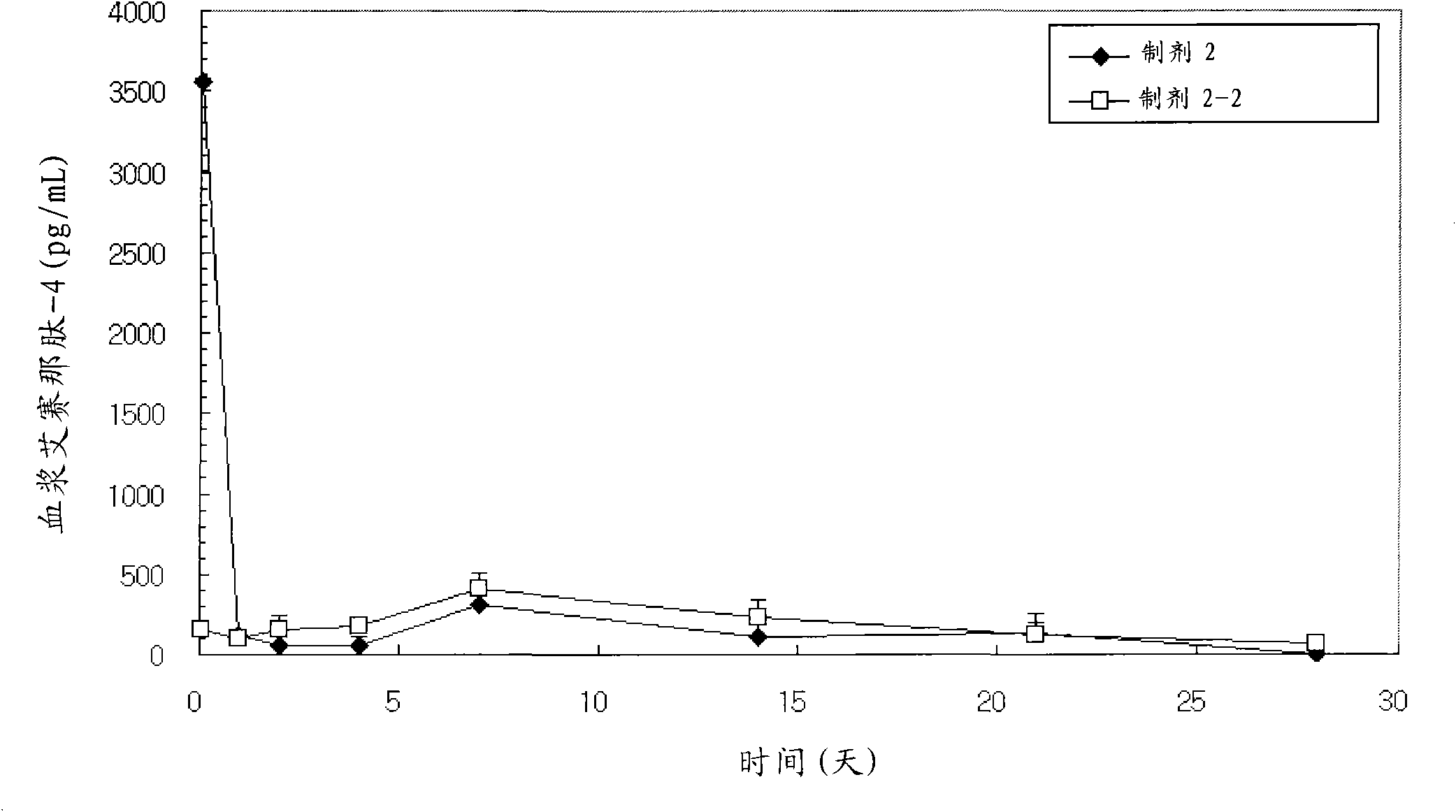
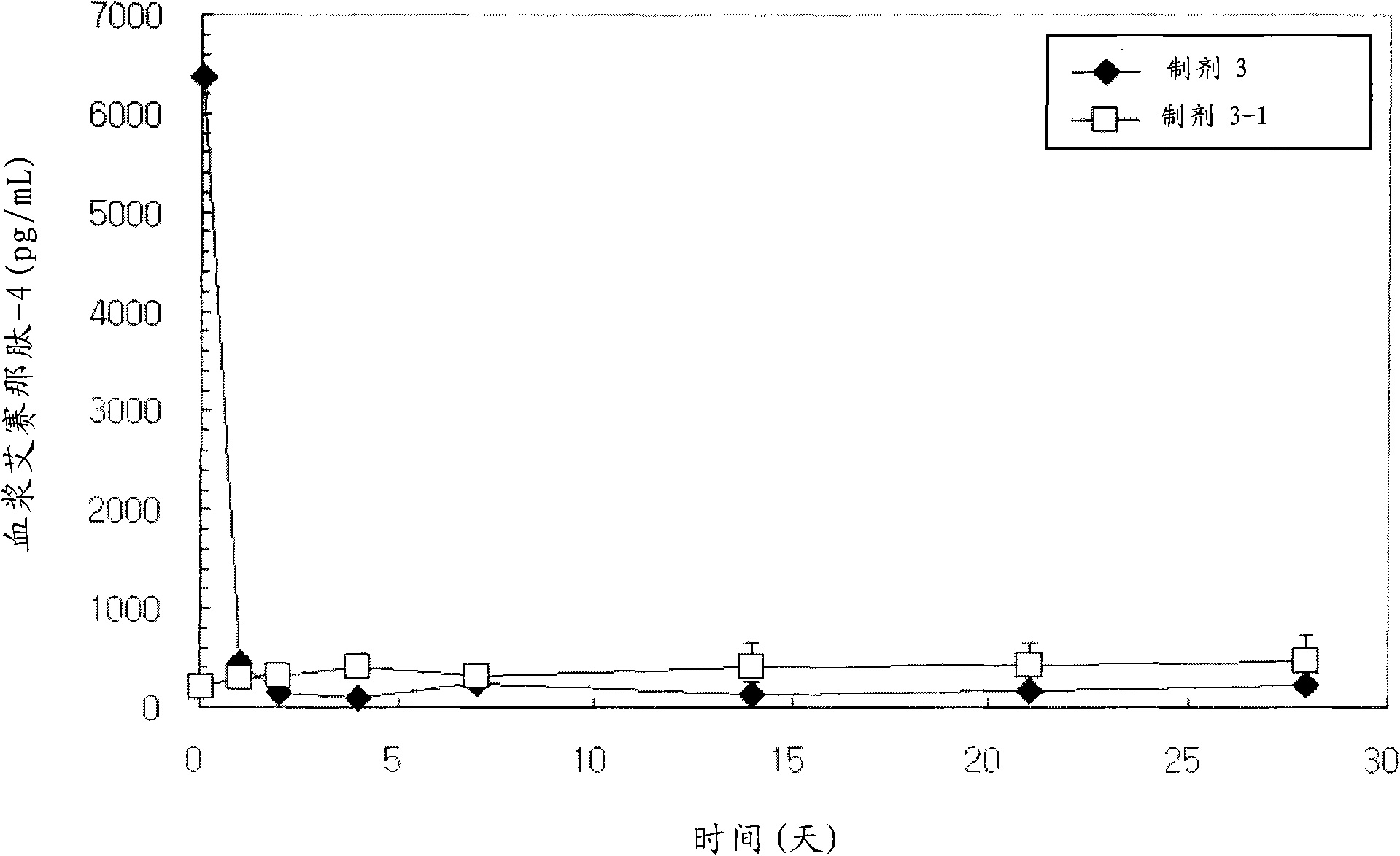
A sustained-release preparation which comprises a physiologically active peptide of general formulawherein X represents an acyl group;R1, R2 and R4 each represents an aromatic cyclic group;R3 represents a D-amino acid residue or a group of the formulawherein R3′ is a heterocyclic group;R5 represents a group of the formula —(CH2)n—R5′ wherein n is 2 or 3, and R5′ is an amino group which may optionally be substituted, an aromatic cyclic group or an O-glycosyl group;R6 represents a group of the formula —(CH2)n—R6′ wherein n is 2 or 3, and R6′ is an amino group which may optionally be substituted;R7 represents a D-amino acid residue or an azaglycyl residue; andQ represents hydrogen or a lower alkyl group, or a salt thereof and a biodegradable polymer having a terminal carboxyl group.The sustained-release preparation shows a constant release of the peptide over a long time and is substantially free from an initial burst.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Dosage form and method for the delivery of drugs of abuse
A dosage form and method for the delivery of drugs, particularly drugs of abuse, characterized by resistance to solvent extraction, tampering, crushing, or grinding, and providing an initial burst of release of drug followed by a prolonged period of controllable drug release.
Owner:ABBOTTGMBH & CO
Implantable polymeric device for sustained release of buprenorphine with minimal initial burst
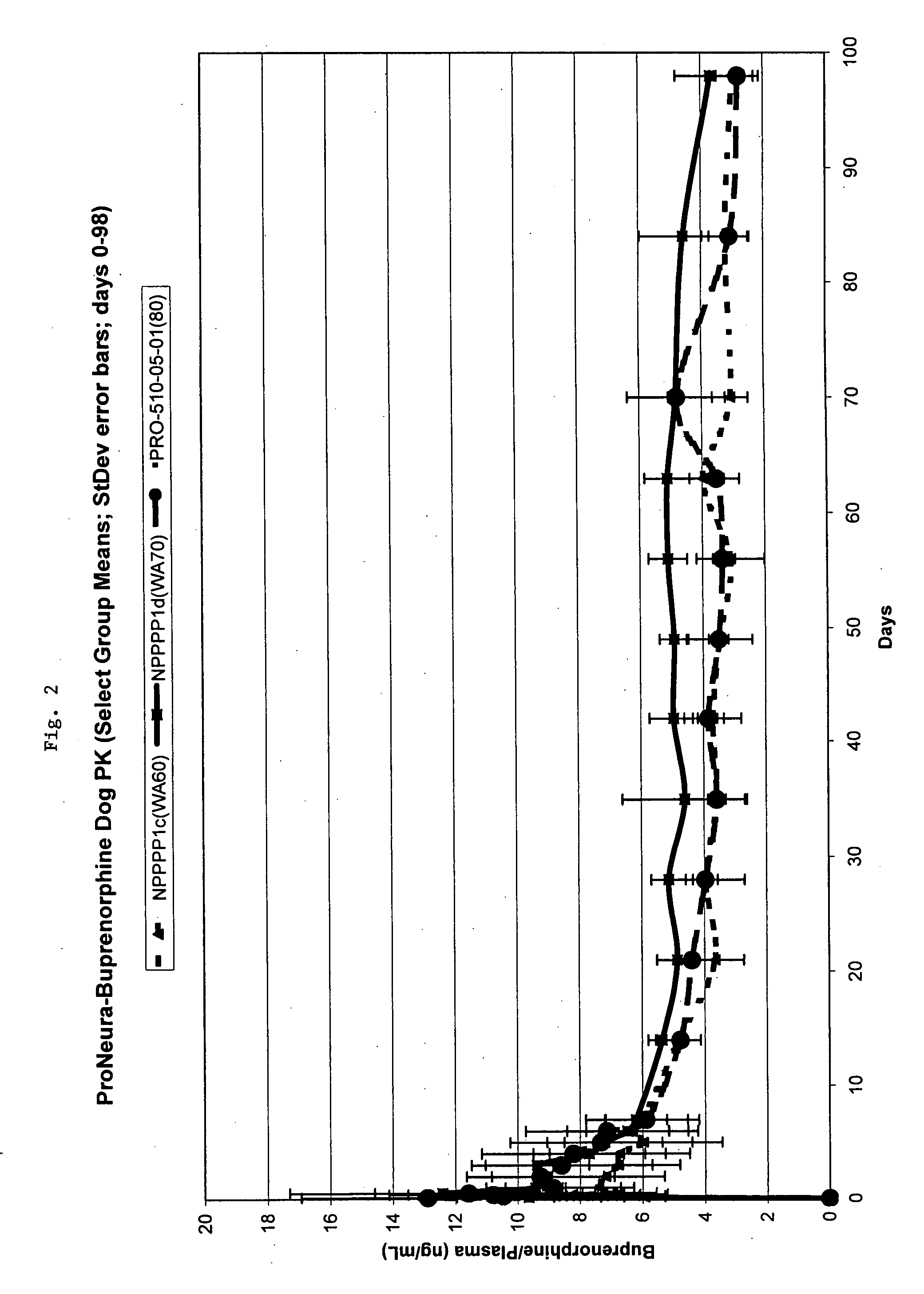
InactiveUS20070275031A1Low in steady stateLow initial burstBiocideGranular deliverySubcutaneous implantationBlood plasma
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for treatment of pain. The invention provides a biocompatible nonerodible polymeric device which releases buprenorphine continuously with generally linear release kinetics for extended periods of time, and exhibits minimal initial burst upon subcutaneous implantation. Buprenorphine is released through pores that open to the surface of the polymeric matrix in which it is encapsulated. The device may be administered subcutaneously to an individual in need of continuous treatment with buprenorphine. Devices of the invention are washed with ethanol for greater than 30 minutes prior to subcutaneous implantation or have release characteristics of a device that has been washed with ethanol for greater than 30 minutes, such as a low peak to steady state plasma level ratio.
Owner:TITAN PHARMA
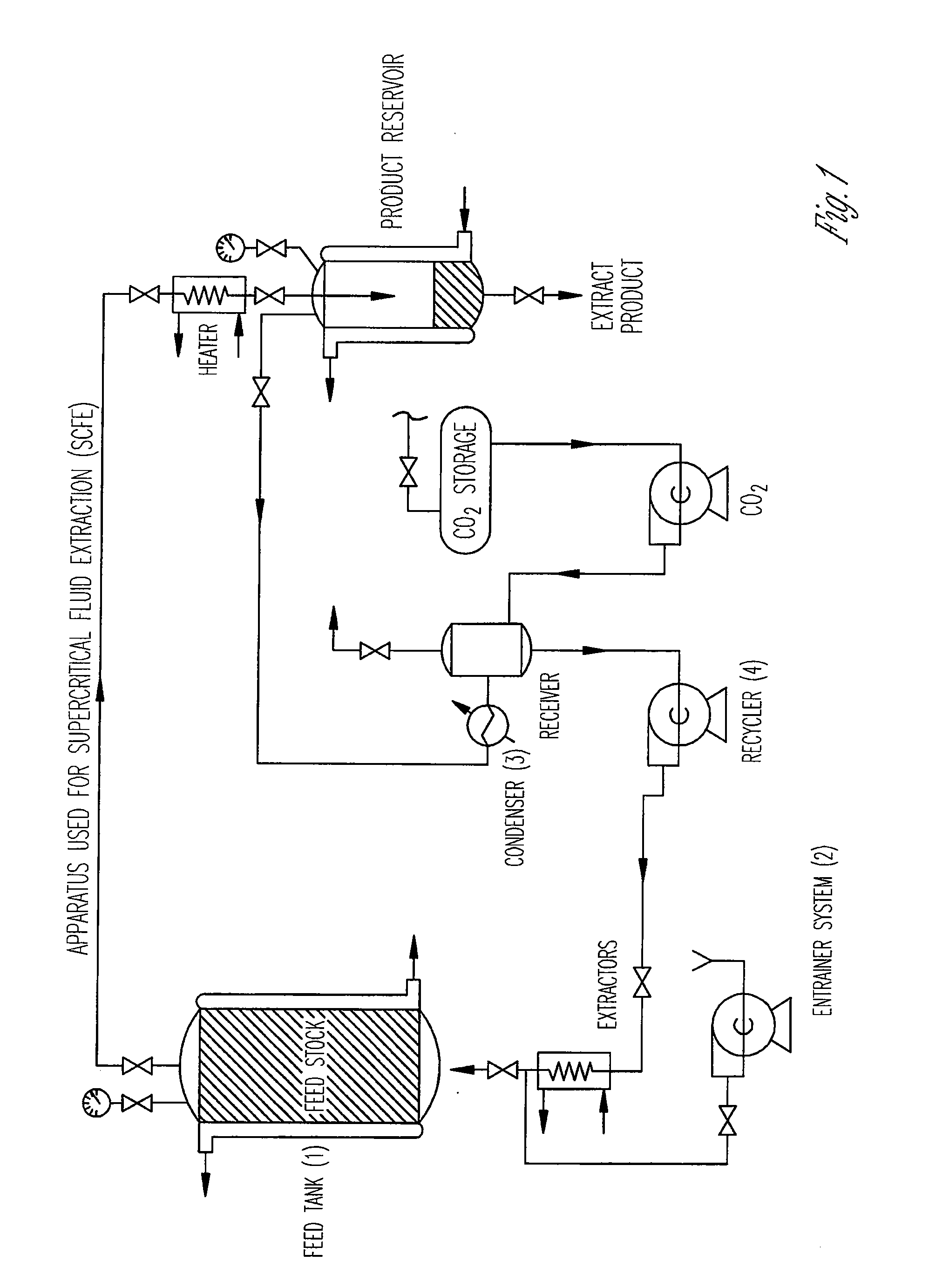
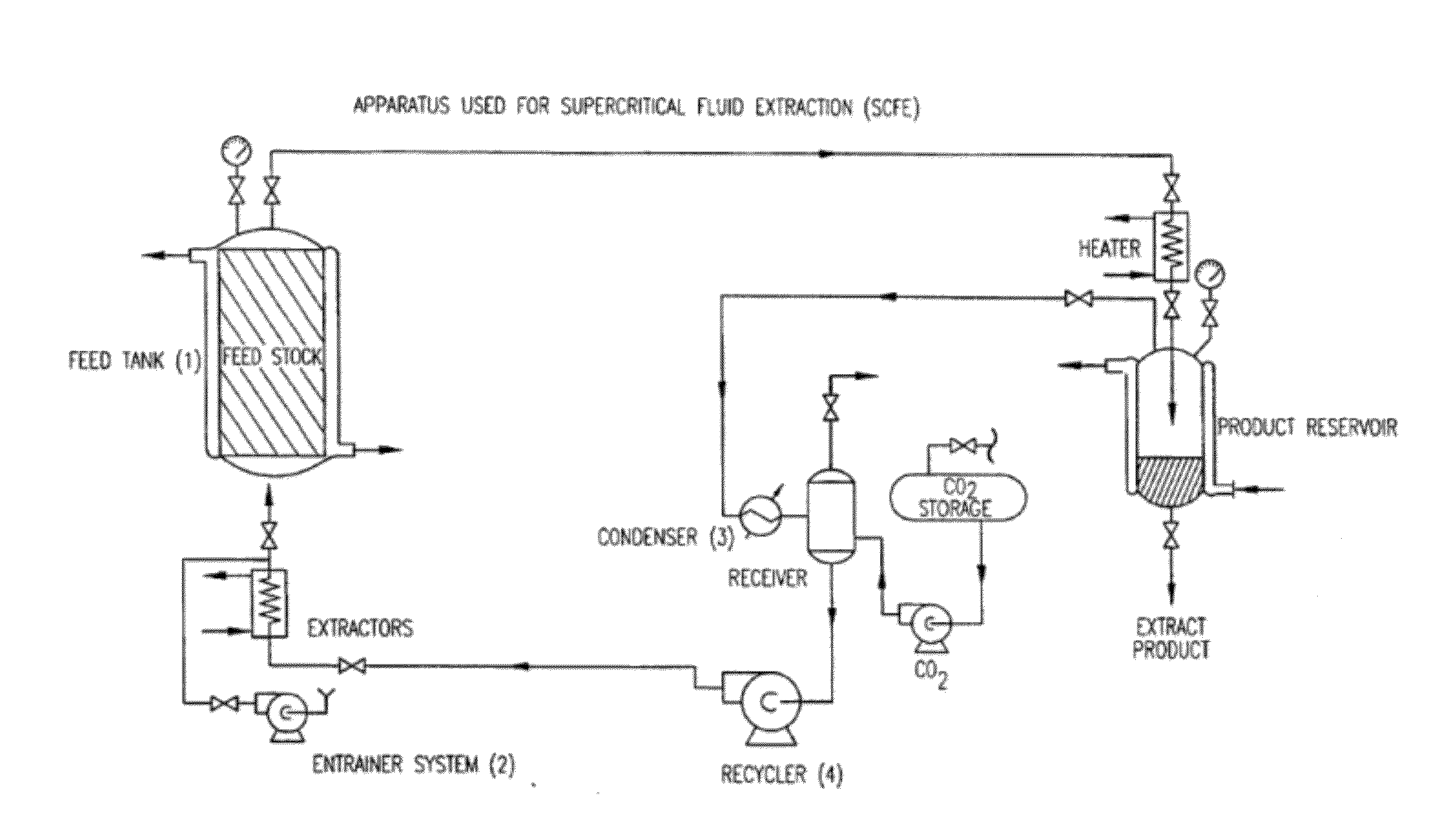
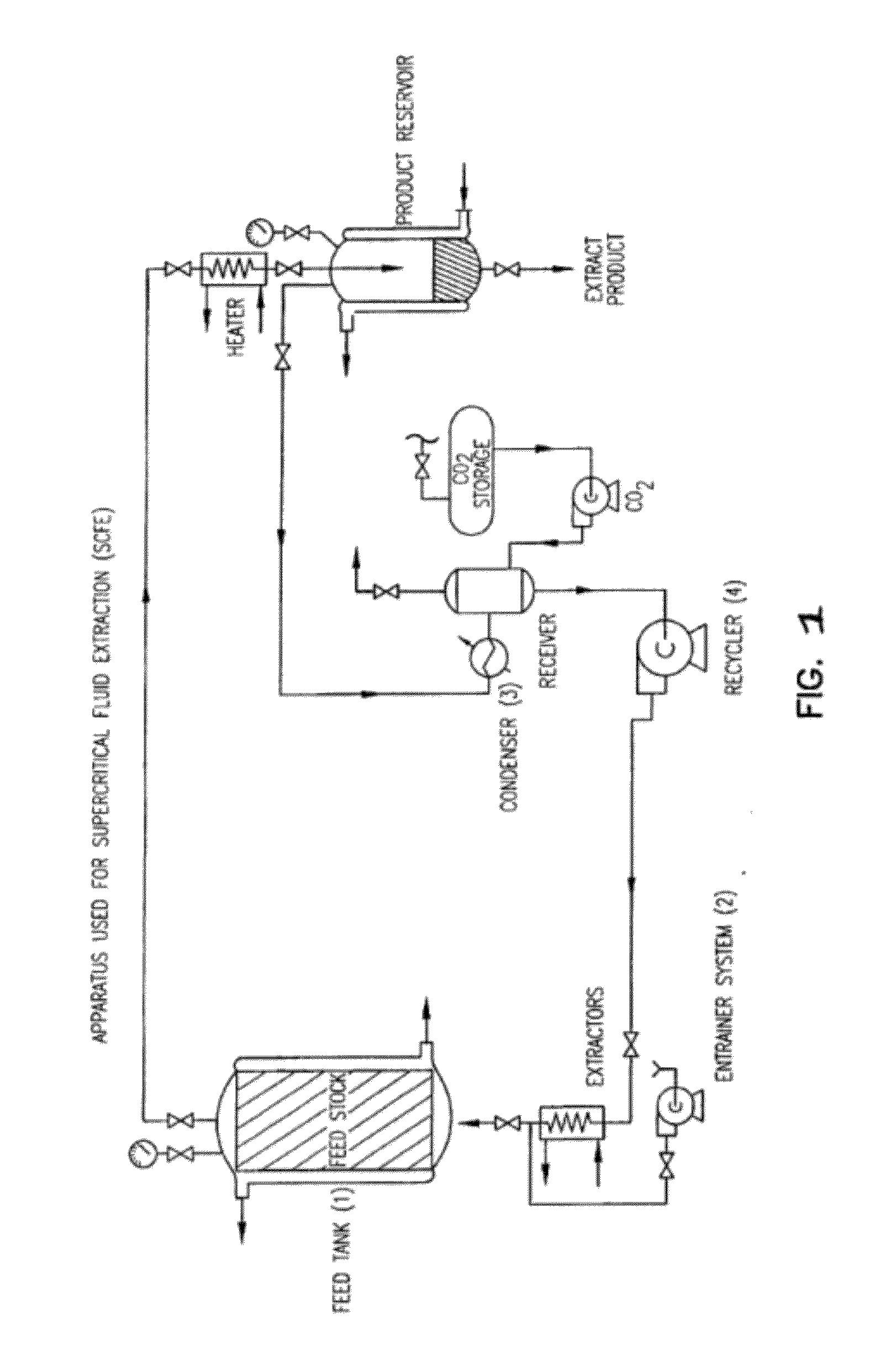
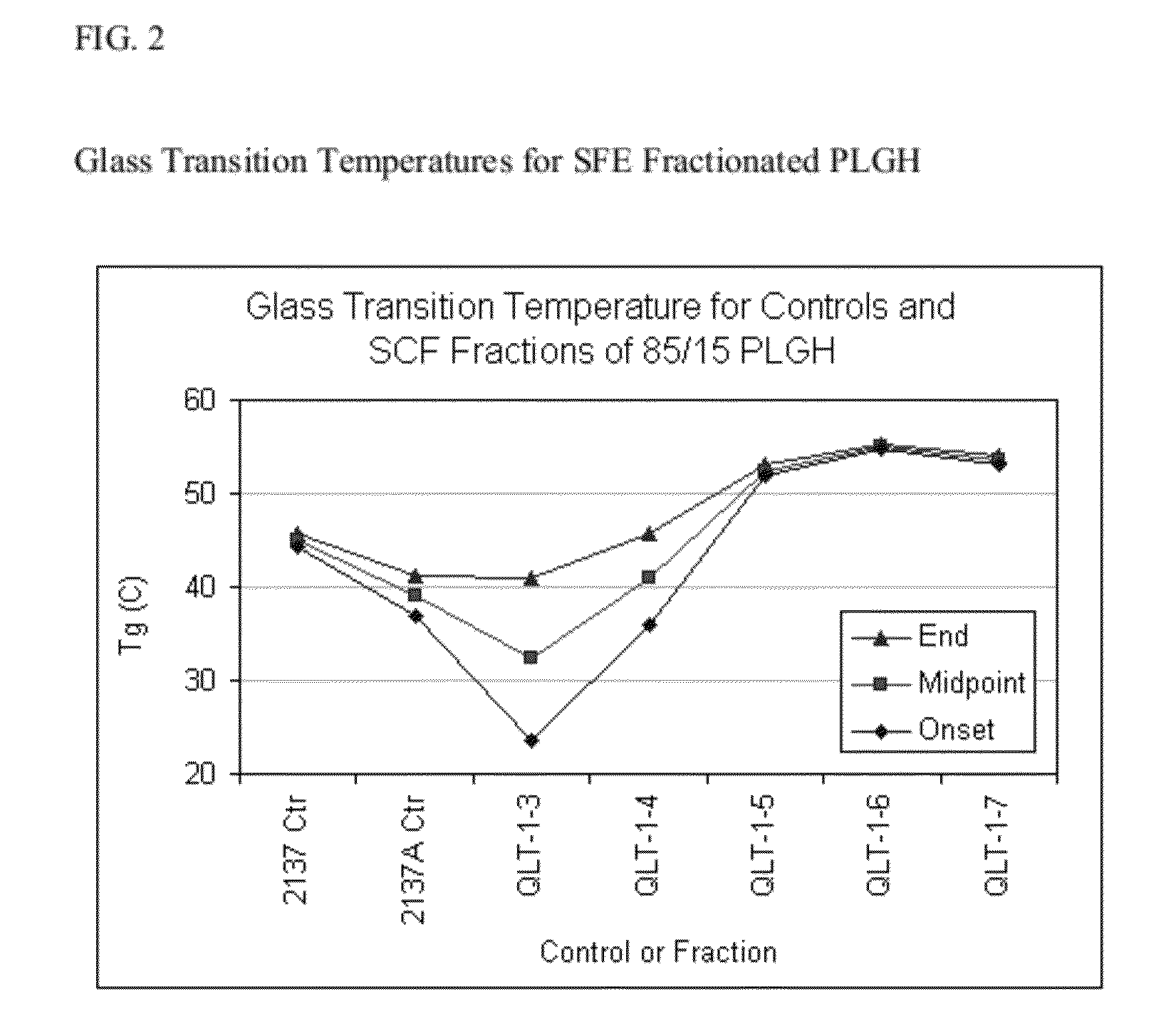
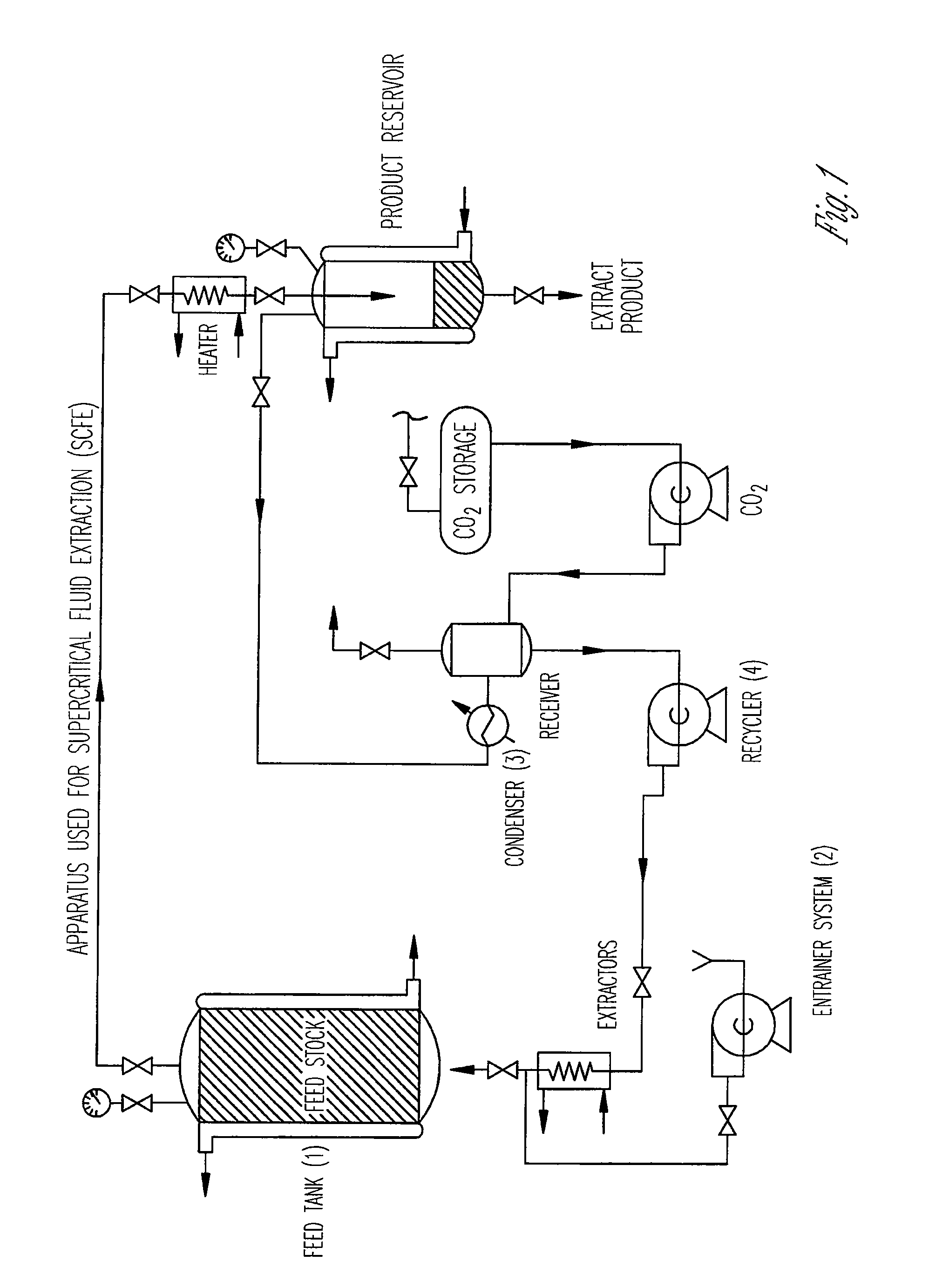
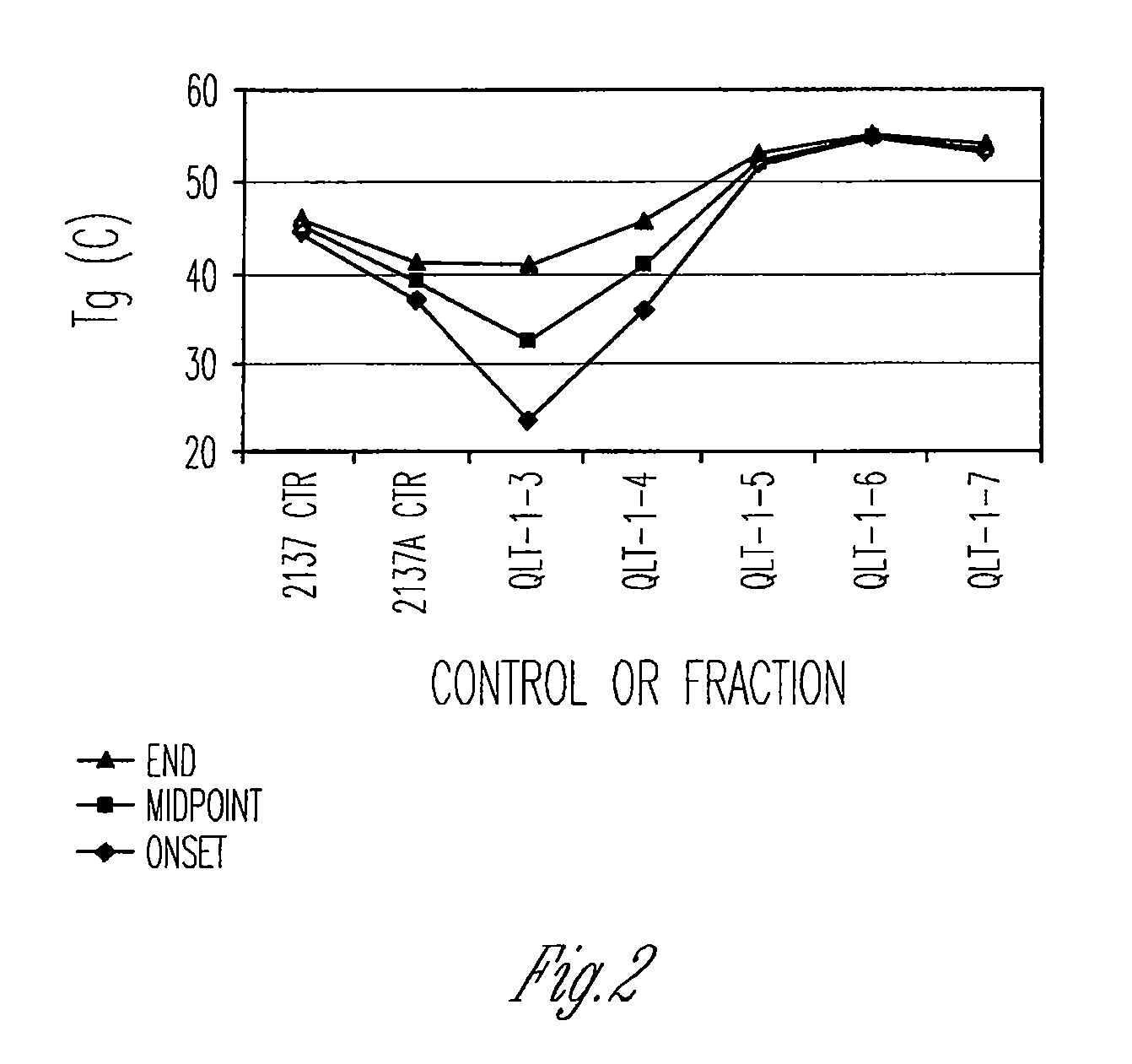
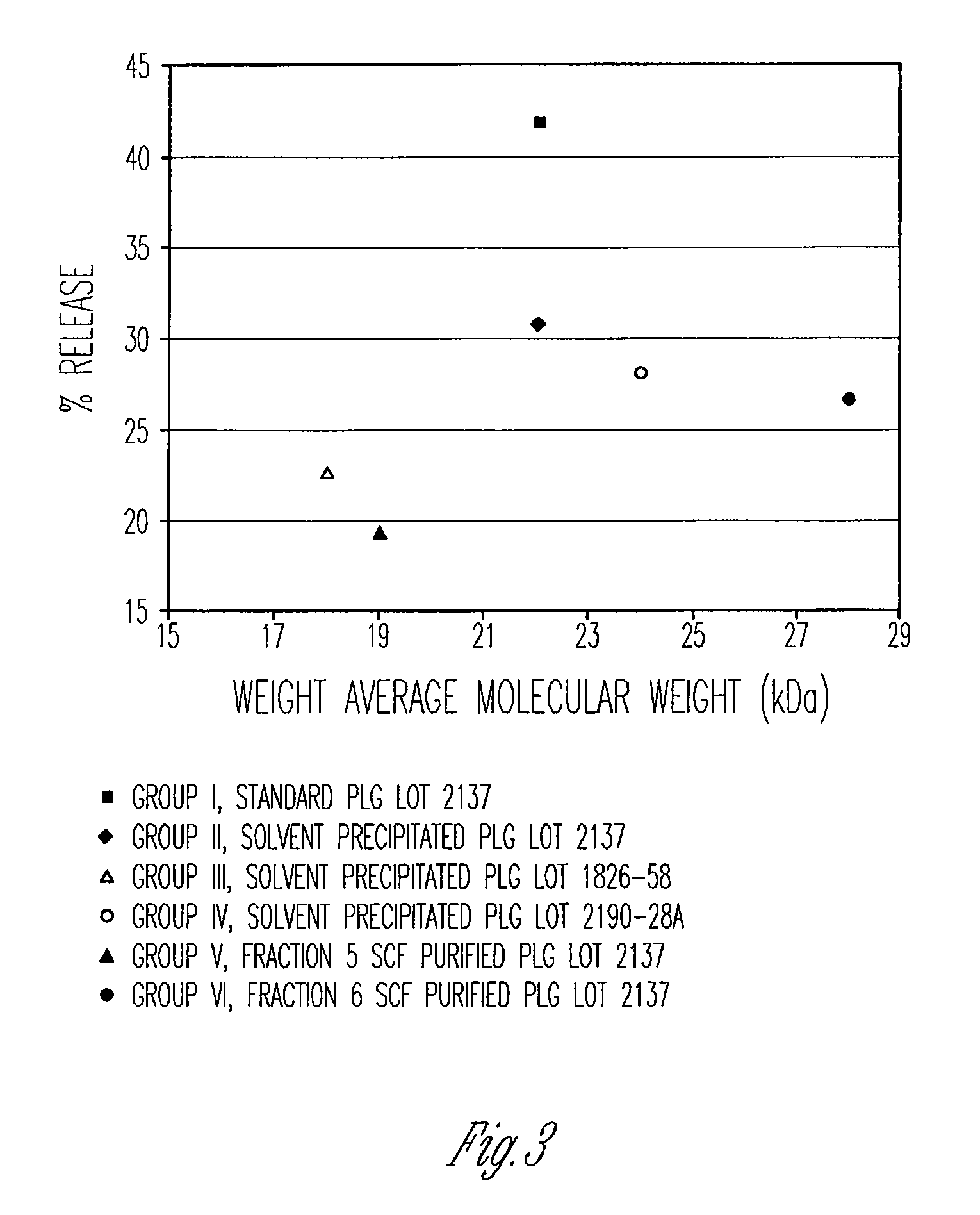
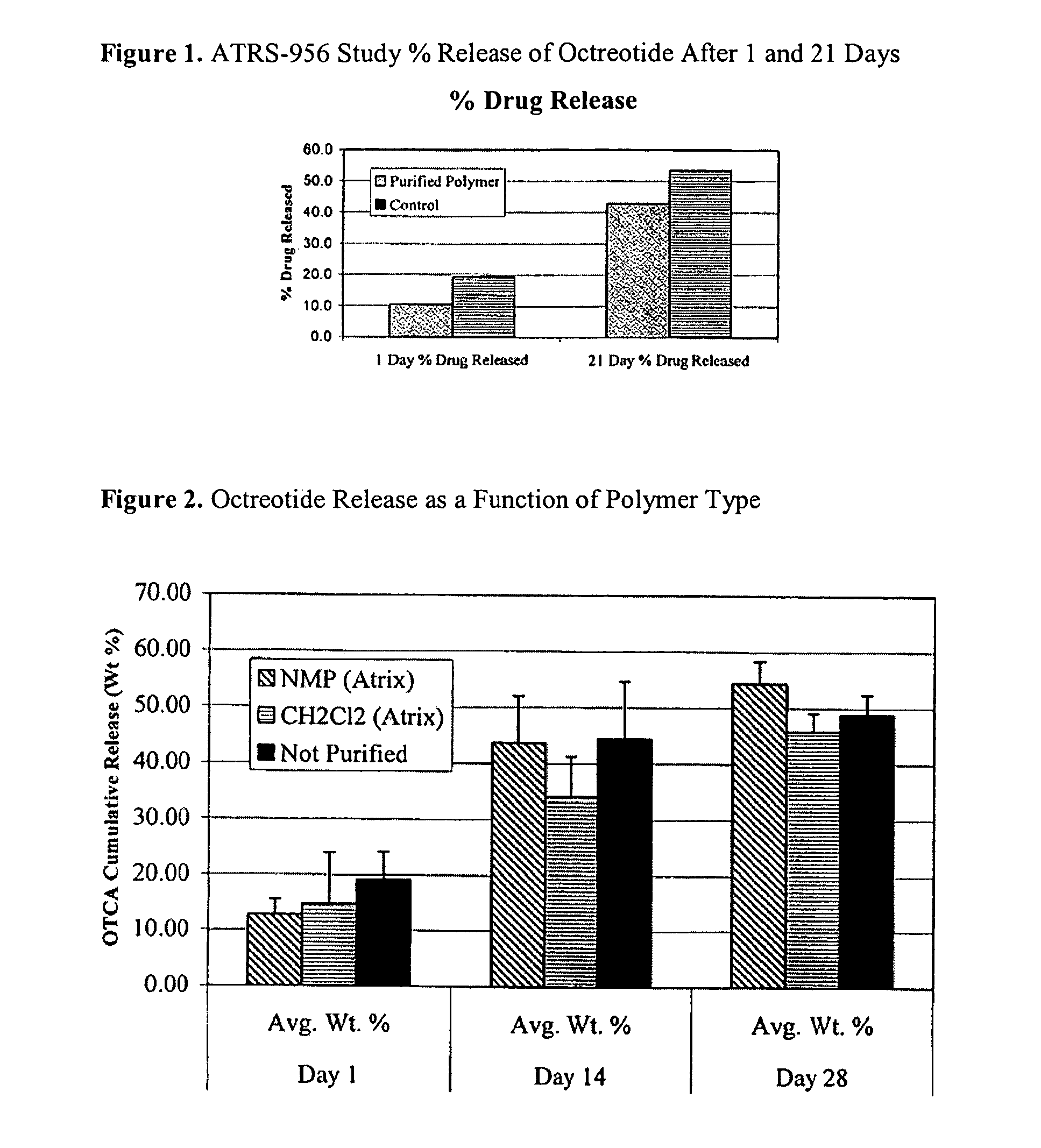
Preparation of biodegradable polyesters with low-burst properties by supercritical fluid extraction
ActiveUS20090305957A1Reduced initial burst effectNarrow molecular weight distributionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLactideSolvent
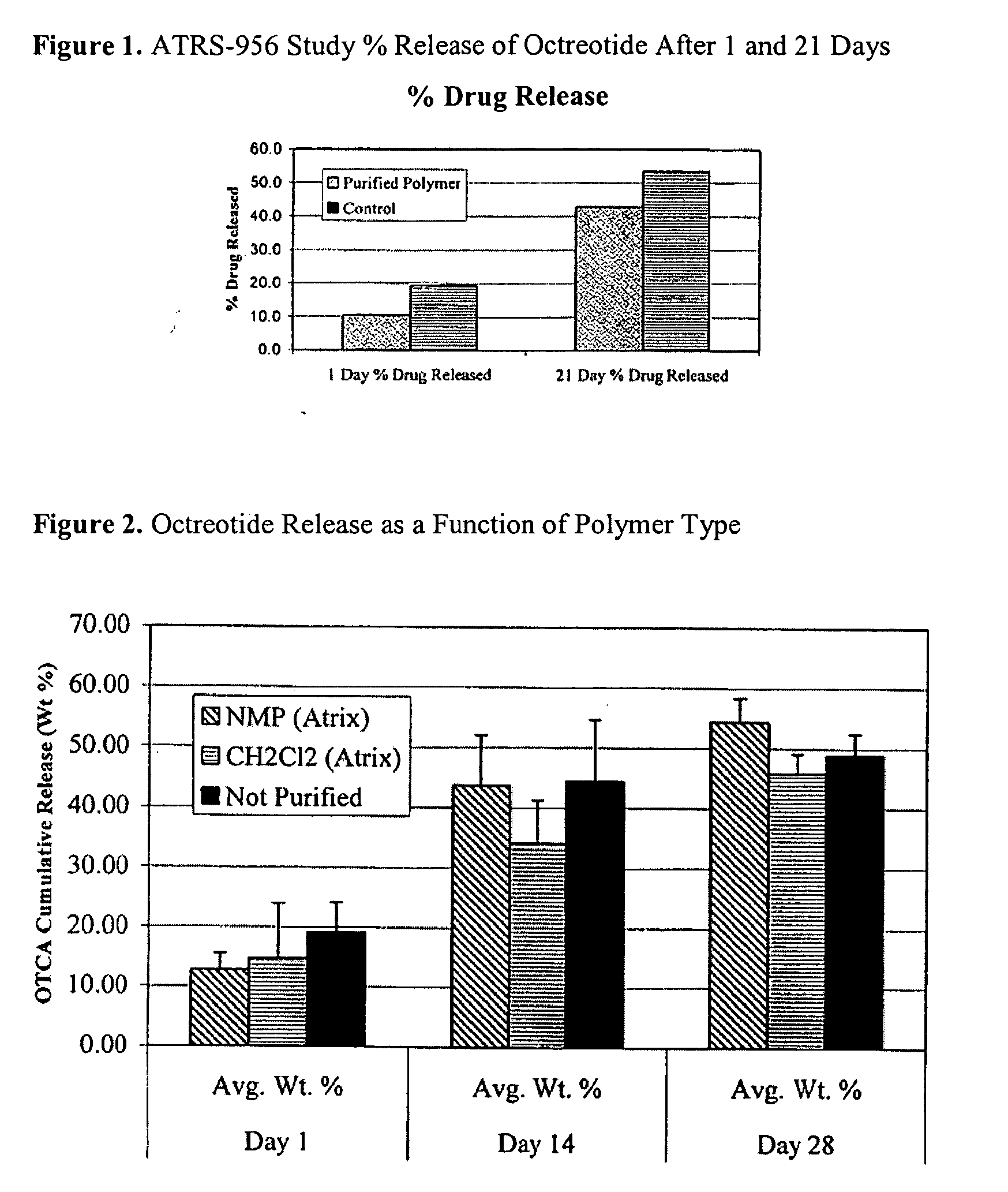
The invention provides methods of extracting a biodegradable polyester with a supercritical fluid effective to obtain a purified biodegradable polyester, such as a purified biodegradable poly(lactide-glycolide) (PLG). The supercritical fluid can be carbon dioxide at an elevated pressure, or can be carbon dioxide with one or more cosolvents. Methods for carrying out stepwise purification of the biodegradable polyester at multiple pressures or multiple temperatures, or both, are also provided. When the polyester is PLG, a purified PLG copolymer is obtained having a narrowed molecular weight distribution with respect to the unpurified polyester. The purified PLG copolymer can have a polydispersity index of less than about 1.7, less than about 2% monomers, and less than about 10% oligomers. The purified PLG copolymer can exhibit a reduced initial burst effect when incorporated into a controlled release formulation such as a flowable implant adapted to be injected into body tissues.
Owner:TOLMAR THERAPEUTICS
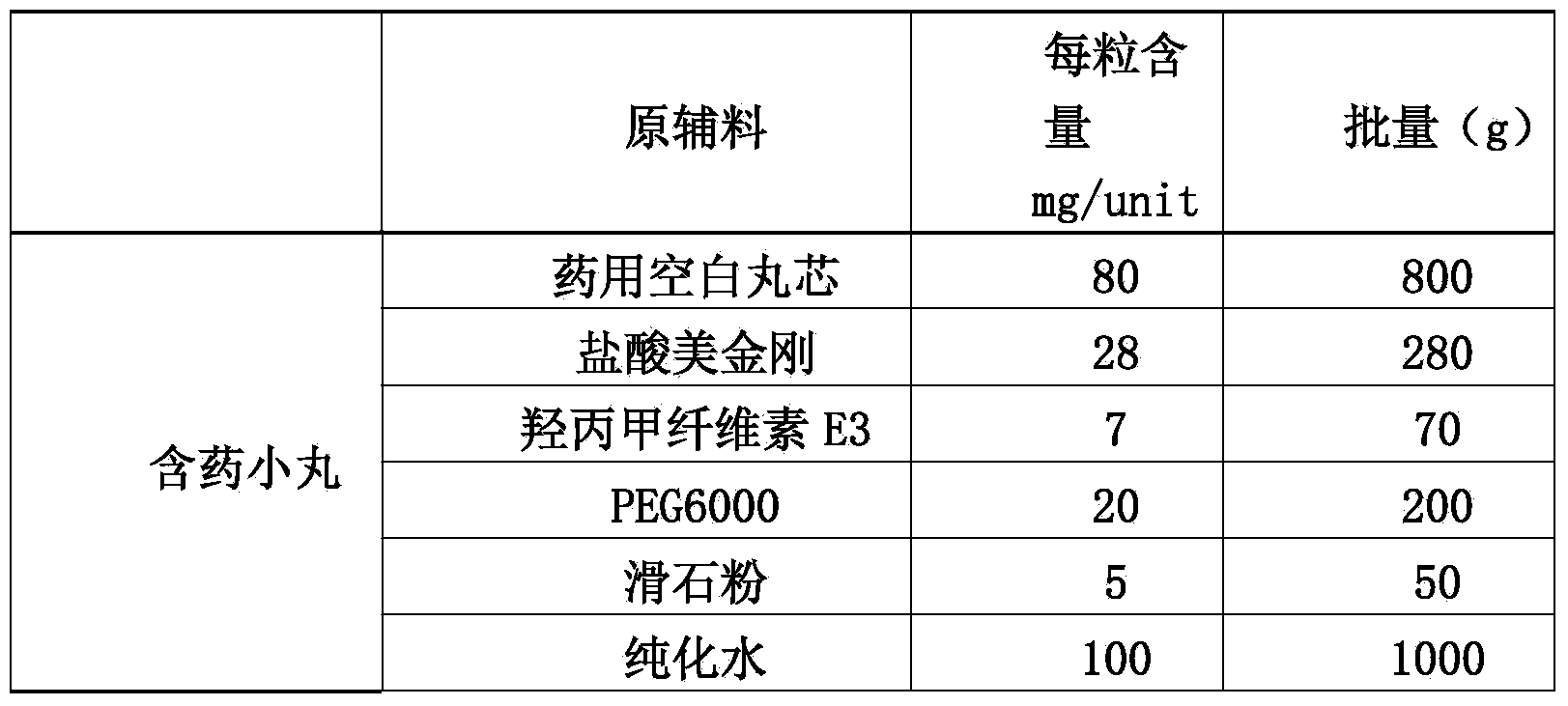
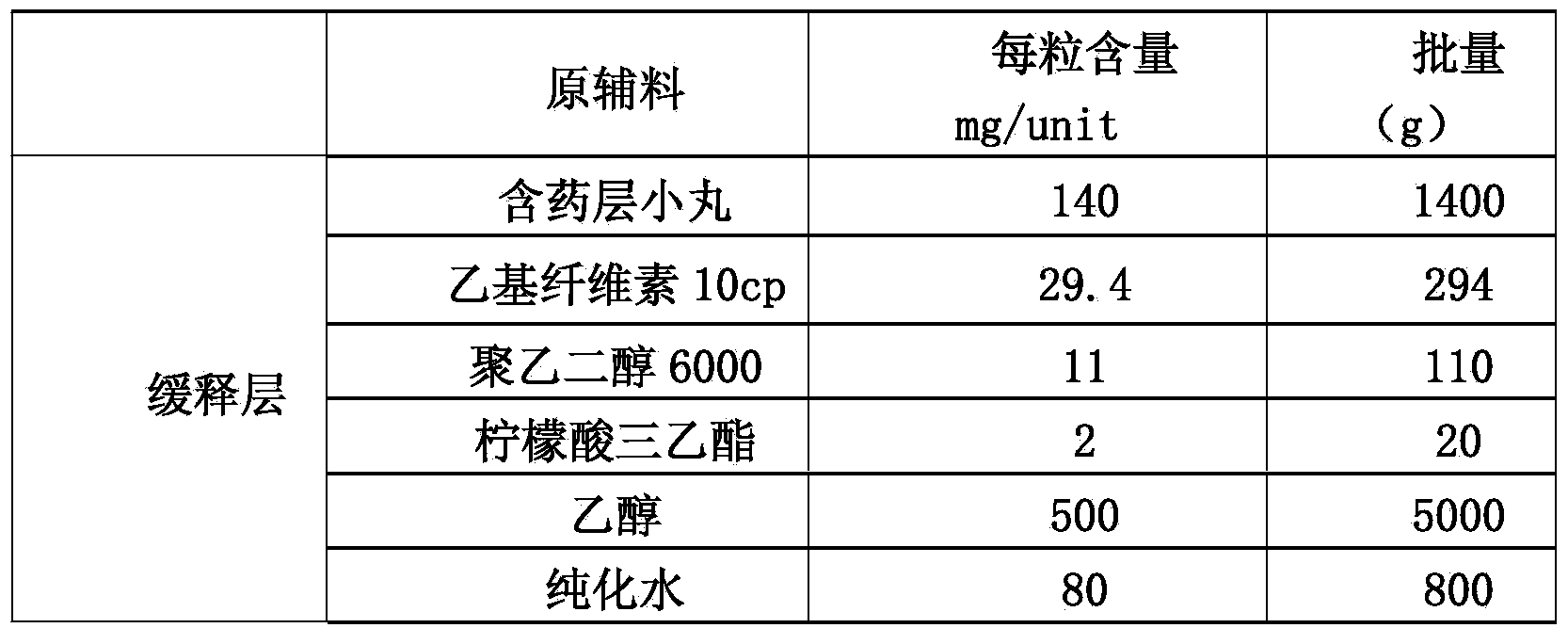
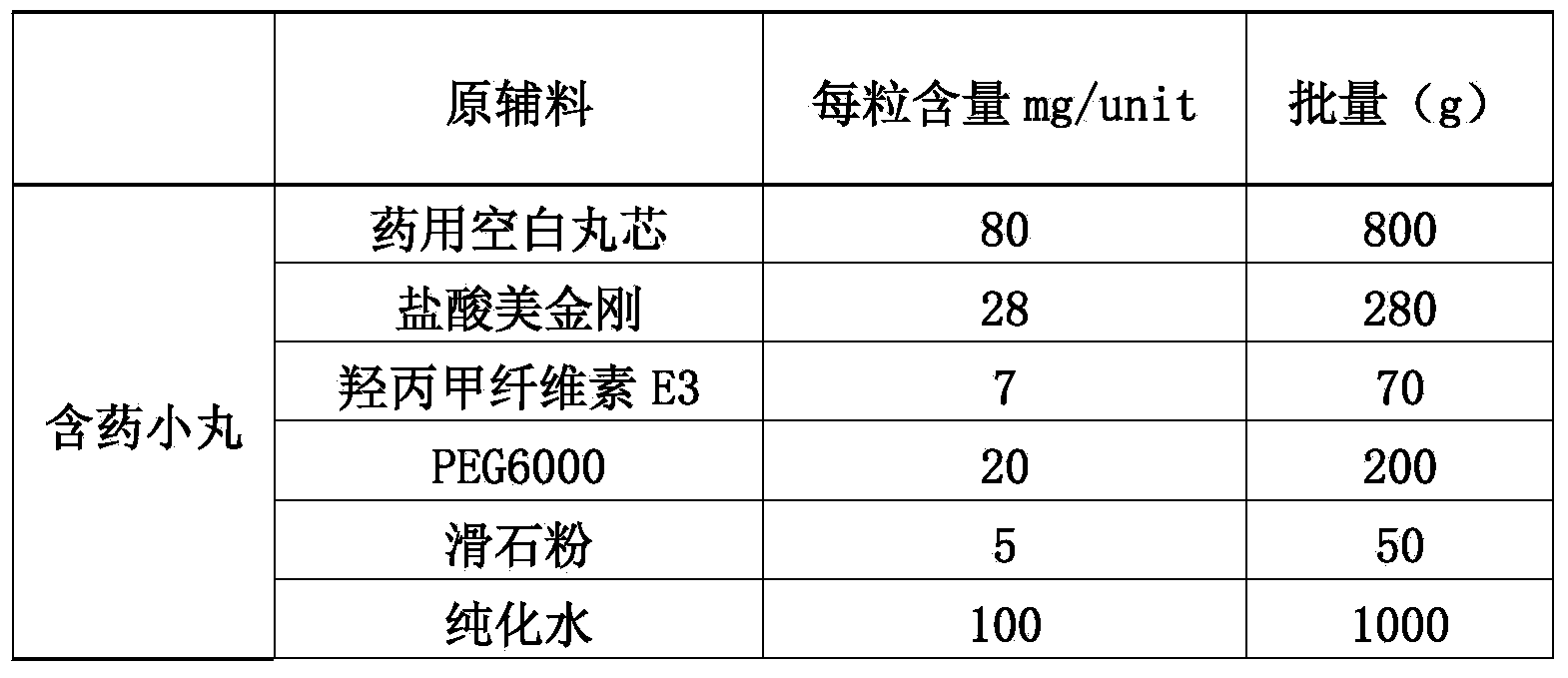
Memantine hydrochloride slow-release pill and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104013592ASolve the problem of easy releaseReduce the risk of sudden releaseNervous disorderPharmaceutical product form changeMemantine HydrochlorideCurative effect
The invention discloses a memantine hydrochloride slow-release pill and a preparation method thereof. Packing inside a capsule is a memantine hydrochloride slow-release pill; the memantine hydrochloride slow-release pill sequentially comprises a hollow pill core, a main medicine layer containing memantine hydrochloride, an isolated coating layer and a slow-release coating layer from inside to outside. The memantine hydrochloride slow-release pill is good in stability and free of an initial burst release phenomenon, the condition that the medicine is lastingly, evenly and slowly released is ensured, and the curative effect of the product is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINGXIN PHARMA
Preparation of biodegradable polyesters with low-burst properties by supercritical fluid extraction
InactiveUS20120108511A1Reduced initial burst effectNarrow molecular weight distributionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLactideHigh pressure
The invention provides methods of extracting a biodegradable polyester with a supercritical fluid effective to obtain a purified biodegradable polyester, such as a purified biodegradable poly(lactide-glycolide) (PLG). The supercritical fluid can be carbon dioxide at an elevated pressure, or can be carbon dioxide with one or more cosolvents. Methods for carrying out stepwise purification of the biodegradable polyester at multiple pressures or multiple temperatures, or both, are also provided. When the polyester is PLG, a purified PLG copolymer is obtained having a narrowed molecular weight distribution with respect to the unpurified polyester. The purified PLG copolymer can have a polydispersity index of less than about 1.7, less than about 2% monomers, and less than about 10% oligomers. The purified PLG copolymer can exhibit a reduced initial burst effect when incorporated into a controlled release formulation such as a flowable implant adapted to be injected into body tissues.
Owner:QLT USA INC
Preparation of biodegradable polyesters with low-burst properties by supercritical fluid extraction
ActiveUS8076448B2Reduced initial burst effectNarrow molecular weight distributionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOligomerLactide
Owner:TOLMAR THERAPEUTICS
Microspheres for the sustained release of octreotide with a low initial burst
InactiveUS20120021018A1Initial burst can be loweredAvoid painPowder deliveryCyclic peptide ingredientsMicrosphereL lactide
This disclosure features microspheres and a method of making them. The microspheres are for sustained release of an octreotide compound with a low initial burst, comprising a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) polymer matrix and an octreotide compound dispersed in the polymer matrix. The microspheres release less than 1% of a total amount of the octreotide compound within 1 hour at 37° C. and pH 7.4.
Owner:OAKWOOD LAB LLC
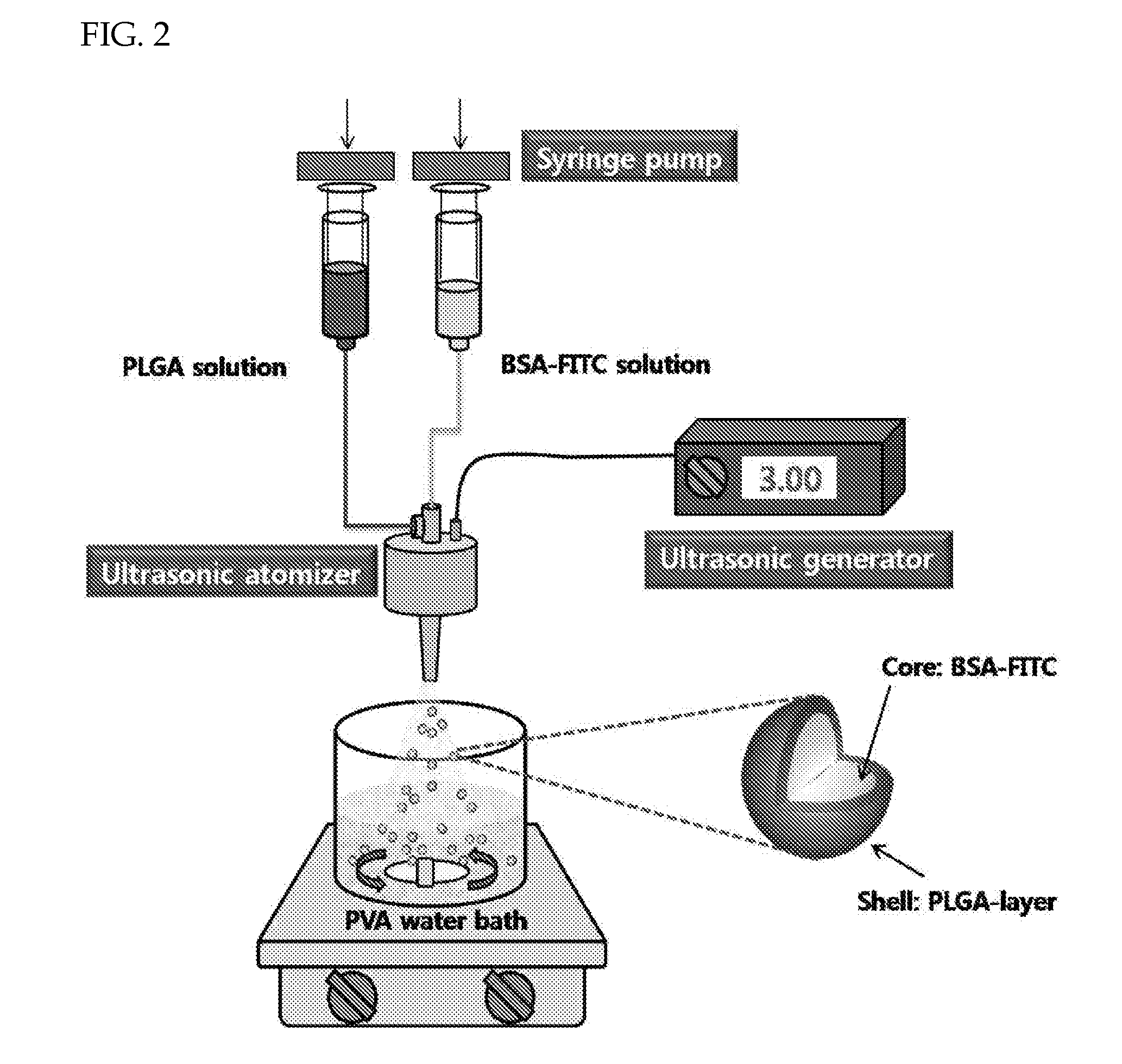
Method for manufacturing sustained release microsphere by solvent flow evaporation method
InactiveUS20110200679A1Eliminate the effects ofSuppresses burst releasePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrospherePharmaceutical Substances
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a sustained-release microsphere which can control the long-term release of a drug. More particularly, as the preparation of a microsphere in which a drug is loaded in a carrier comprising a biodegradable polymer, the present invention relates to a method for preparing a sustained-release microsphere wherein a solvent intra-exchange evaporation method by means of co-solvent is used for suppressing the initial burst release of physiologically active substance, to release the physiologically active substance in the body continuously and uniformly.
Owner:DONG KOOK PHARMA CO LTD
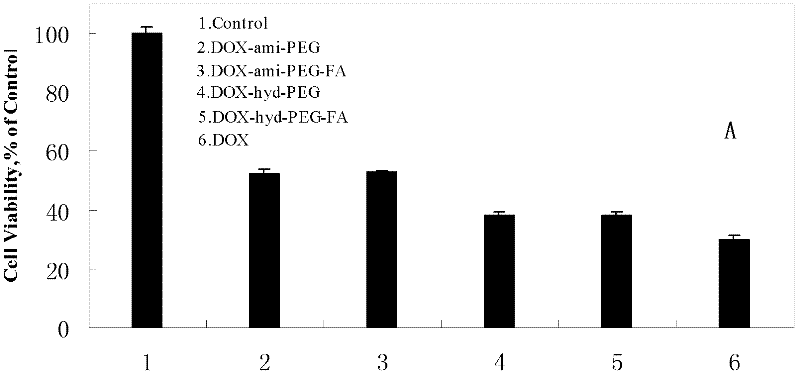
Preparation method and application of folacin mediated tumor targeting adriamycin prodrugs
InactiveCN102343099AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetSide effect
The invention provides a preparation method and application of two types of adriamycin prodrugs. The two types of prodrugs with tumor active targeting and acid-sensitive initial burst release properties can be prepared by virtue of connection of hydrazone bonds and introduction of folacin. By utilizing the two types of prodrugs, the tumor resistance of adriamycin can be reinforced, the toxic and side effects of the medicament can be reduced, and the targeting property can be improved. Therefore, the preparation method provides a novel idea for the development of anti-tumor medicaments.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
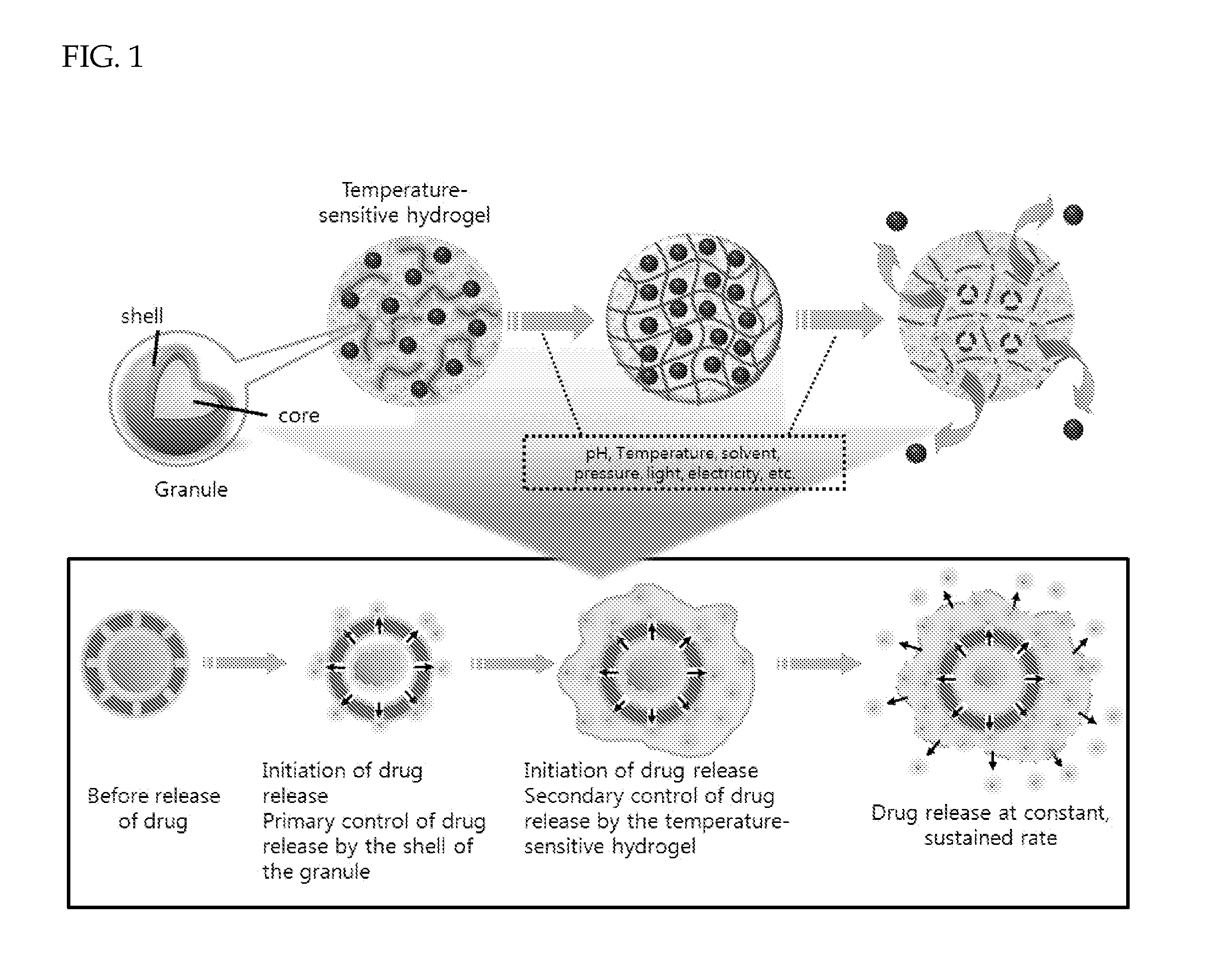
Drug delivery formulation for controlling of initial burst and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120177740A1Maintain blood levelsMaximizing its therapeutic effectPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood levelBiodegradable polymer
Provided is a drug delivery system for control of initial burst of a drug. More particularly, there are provided a drug delivery formulation including: a granule containing a biodegradable polymer and a drug; and a temperature-sensitive hydrogel, and a method for preparing the same. The presently disclosed drug delivery formulation can be prepared via a relatively simple process and allows a drug to be released slowly at a constant rate without initial burst and thus maintains a constant blood level of the drug for a long period of time. Consequently, it is capable of preventing the initial burst of the existing injection-type drug delivery formulations and slow-release granules and providing a desired release profile, including sustained release with time.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Composition and microsphere for controlled-release of exendin, and method of preparing the same
A controlled-release composition and controlled-release microspheres containing an exendin as an active ingredient, and a method of preparing the same are provided. More specifically, a controlled-release composition containing an exendin as an active ingredient, a biodegradable polymer with a specific viscosity, and coating materials, having high bioavailability and showing sustained release of the active ingredient in an effective concentration for a certain period without an excessive initial burst of the active ingredient; controlled-release microspheres containing a core including an exendin as an active ingredient and a biodegradable polymer, and a coating layer coating the core; and a method of preparing controlled-release microspheres including the steps of mixing an exendin, a biodegradable polymer, and a solvent, removing the solvent from the mixture to prepare hardened microspheres, and coating the hardened microspheres to form a coating layer on the surface of each microsphere, are provided.
Owner:FITLEN CO LTD
CaCO3-(PLO/Fucoidan)<4> self-assembly carriers and preparation method
InactiveCN107375217AGood biocompatibilityUniform particle size distributionOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsSide effectMicrosphere
The invention discloses CaCO3-(PLO / Fucoidan)<4> self-assembly carriers and a preparation method. CaCO3 microspheres with good biocompatibility are prepared through a coprecipitation method firstly, and growth of the CaCO3 microspheres is controlled by utilizing carboxymethyl chitosan; and polyelectrolytes of PLO and Fucoidan are assembled on the surfaces of the CaCO3 microspheres layer by layer, wherein the polyelectrolytes have nutrient and pharmacological efficacies and are degradable, and thus LbL microspheres, namely the CaCO3-(PLO / Fucoidan)<4> self-assembly carriers, are prepared. According to the preparation method, the coprecipitation method and an LbL technique are combined, the technology is simple, operation is convenient, a complex instrument and equipment are not needed, and the problems of poor biocompatibility of carriers, initial burst release in drug release and the like are solved. The LbL microspheres are of core-shell type structures, can enhance the adsorbing capacity of a drug, reduces the toxic and side effects caused by pure use of the drug and can obviously slow down the release rate of the drug.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Slow release pharmaceutical preparation and method of administering same
InactiveUS7914804B2High strengthIncrease pressureOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryActive agentDilator
A pharmaceutical preparation adopted for sustained release of an active agent(s) over an extended period of time at a therapeutic rate without an initial burst release of the agent(s) upon administration, wherein the preparation comprises: (i) an outer portion prepared from one or more layers of a biodegradable polymer, which is selected to release an active agent over an extended period of time when positioned in situ in a patient, and (ii) an inner portion comprising a plurality of micro-capsules formed from at least a biodegradable polymer, said micro capsules containing at least an active agent, wherein the micro-capsules are compressed into the form of a tablet under suitable pressure to suppress the rate of release of the active agent from the micro-capsules. The present specification also relates to a method for inserting one or more implants(s) into a tissue of a mammal comprising the following steps: a) making a small incision into the tissue with a needle and a first sheath; b) withdrawing the needle from the first sheath but leaving the first sheath in the tissue; c) dilating the opening of the incision by inserting a dilator and second sheath of larger diameter through the body of the first sheath; d) withdrawing the dilator from the second sheath, but leaving the second sheath in the tissue; e) disturbing the implant(s) from a sheath filled with implant(s) by inserting said sheath into the final sheath inserted into the tissue and pushing a dilator into the sheath thereby releasing said implant(s) into the tissue.
Owner:PALMAYA
Low burst polymers and methods to produce polymer
ActiveUS9187593B2Increase release rateReduced initial burstAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPolymer chemistryControlled-Release Formulations
Owner:TOLMAR INC
Biodegradable Drug Delivery Composition
InactiveUS20120225033A1Low viscosityGood injectabilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEmulsionViscosity
The present disclosure provides a biodegradable drug delivery composition including a vehicle and an insoluble component comprising beneficial agent dispersed in the vehicle. Typically, the composition is not an emulsion, but has a low viscosity and further provides for minimized initial burst and sustained release of the beneficial agent over time. Also provided, are kits including the biodegradable drug delivery composition or components thereof, as well as methods of making and using the biodegradable drug delivery composition.
Owner:DURECT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com