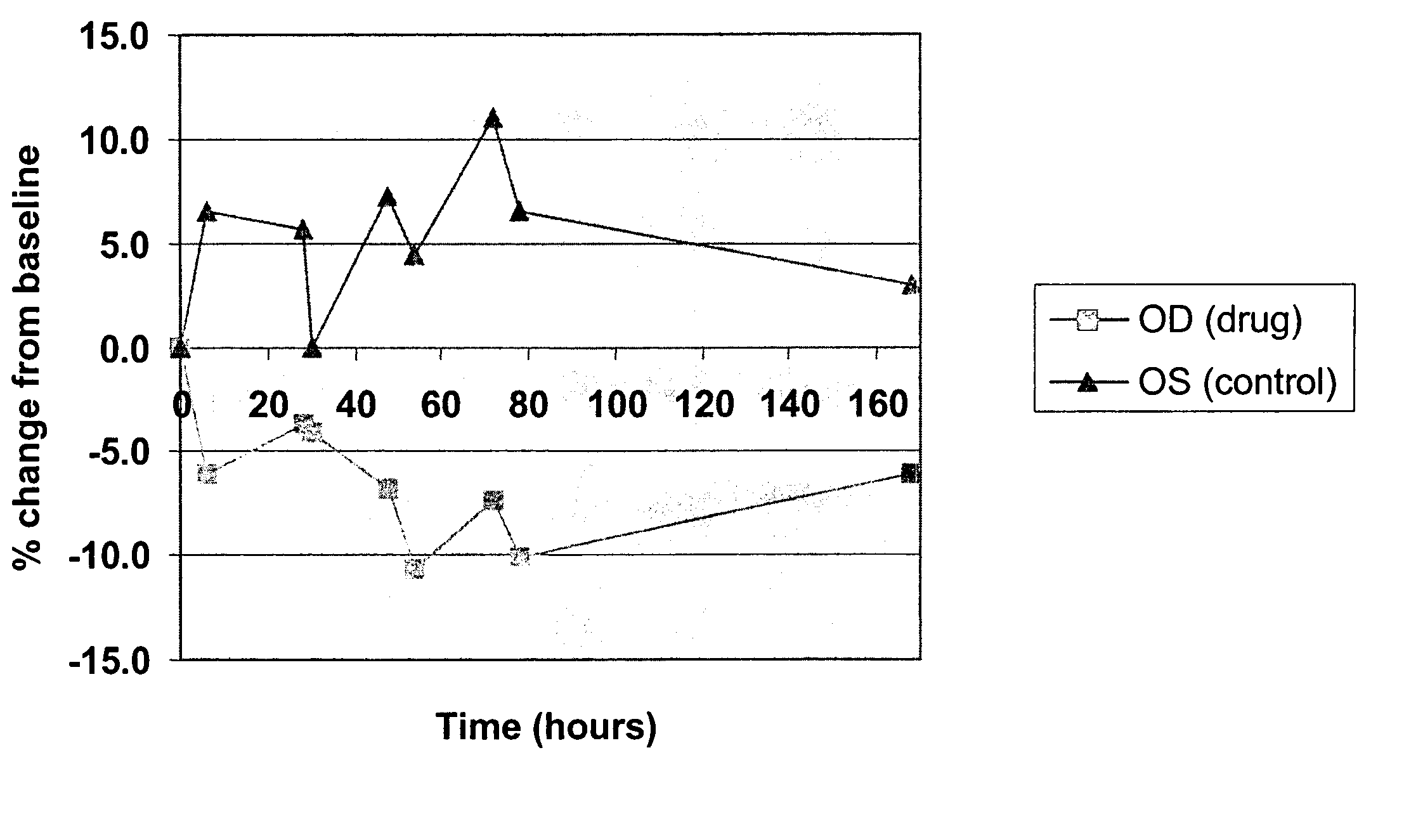
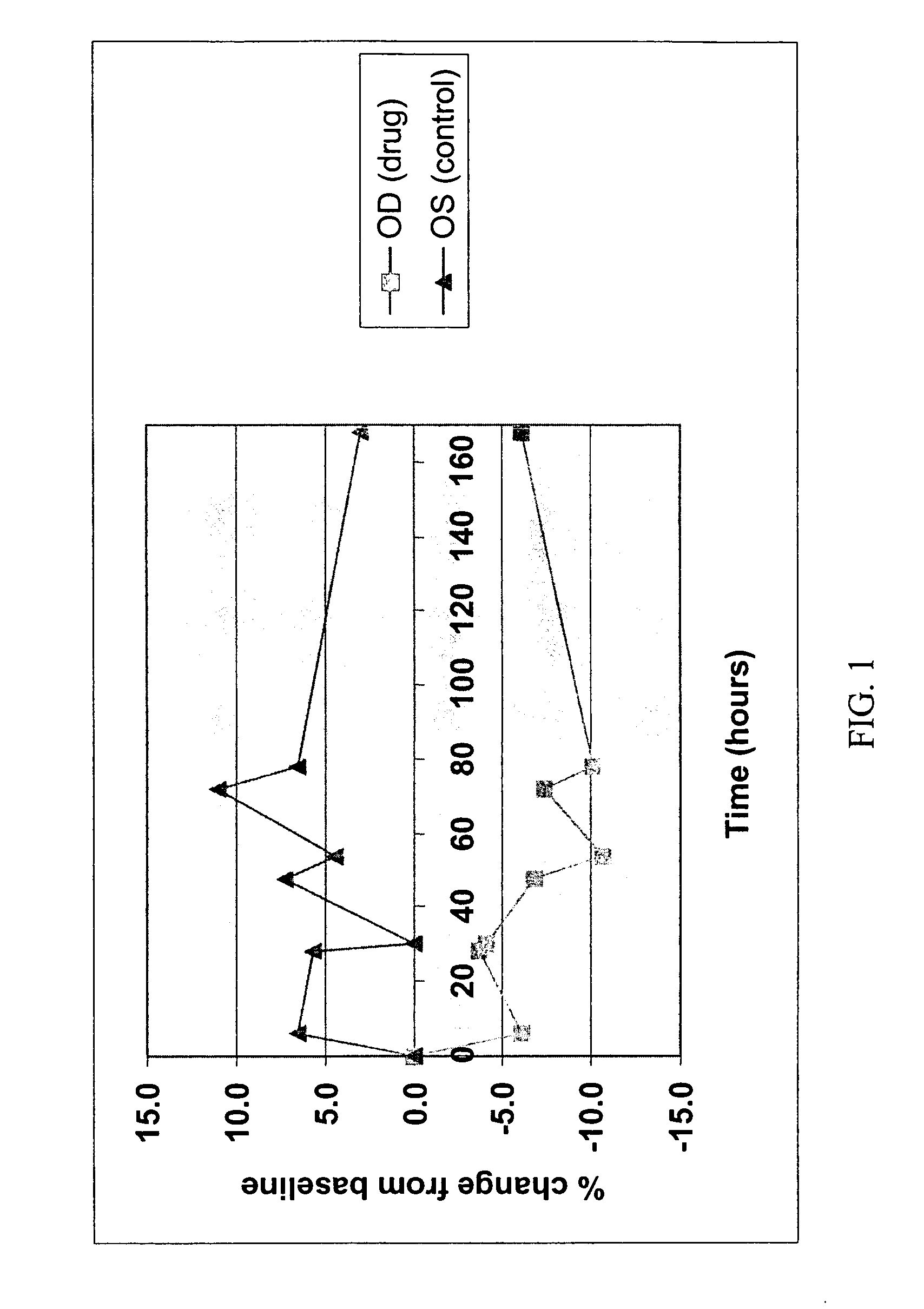
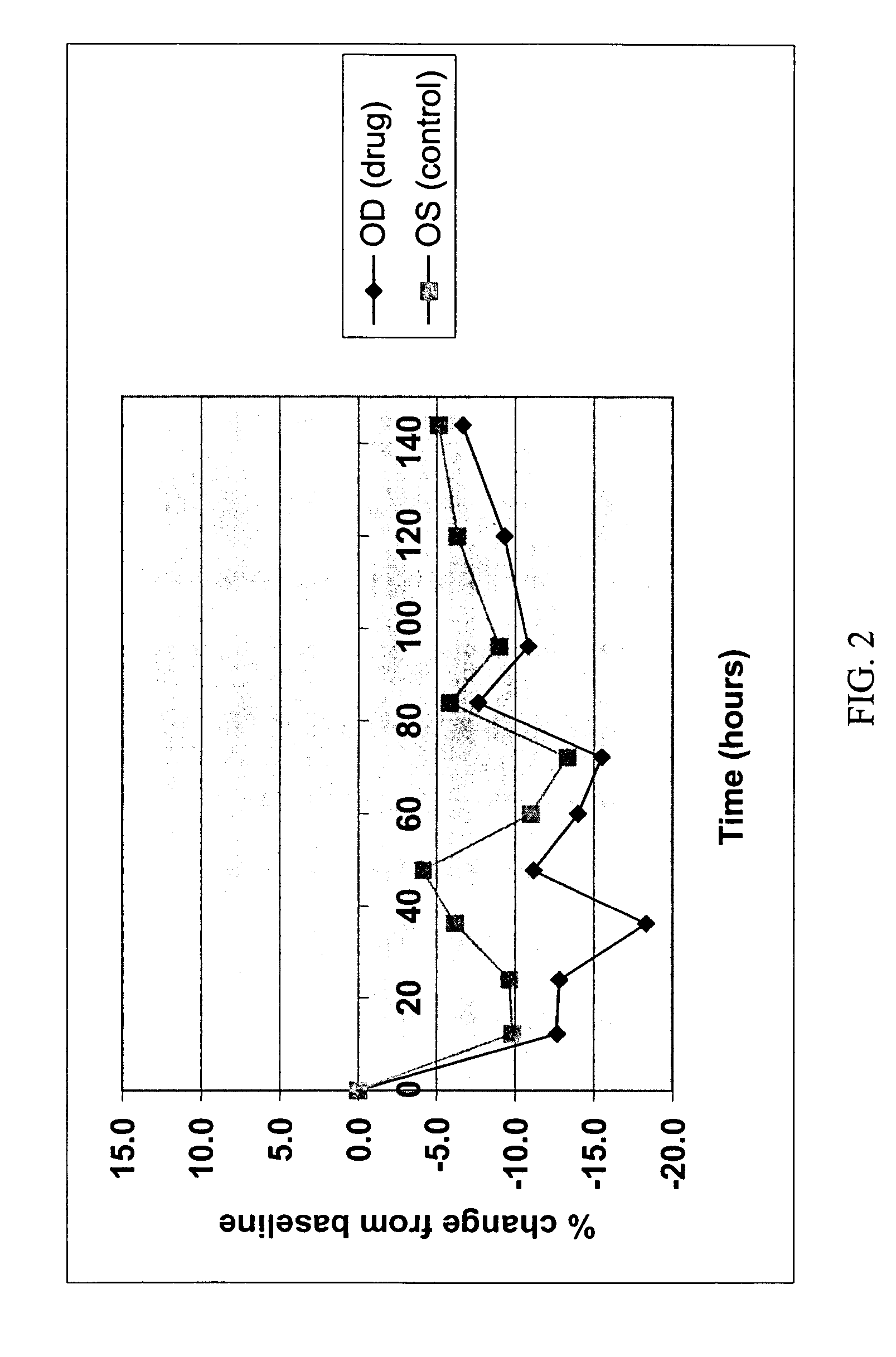
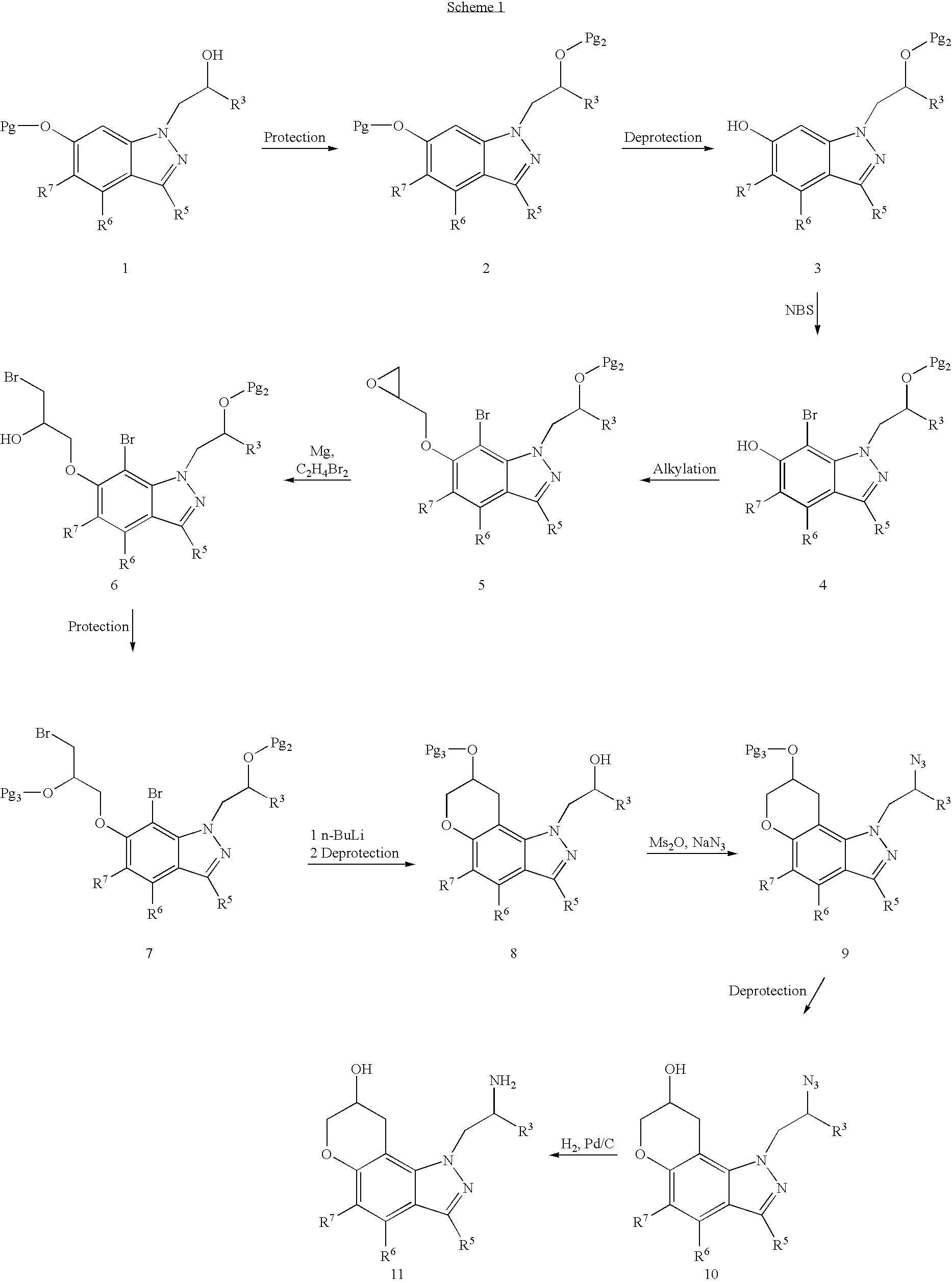
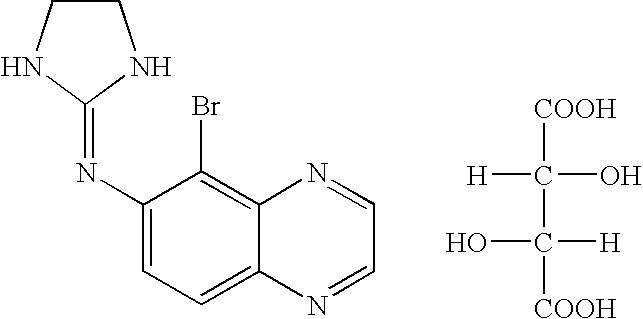
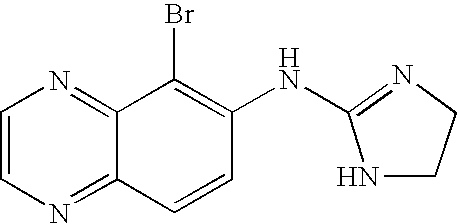
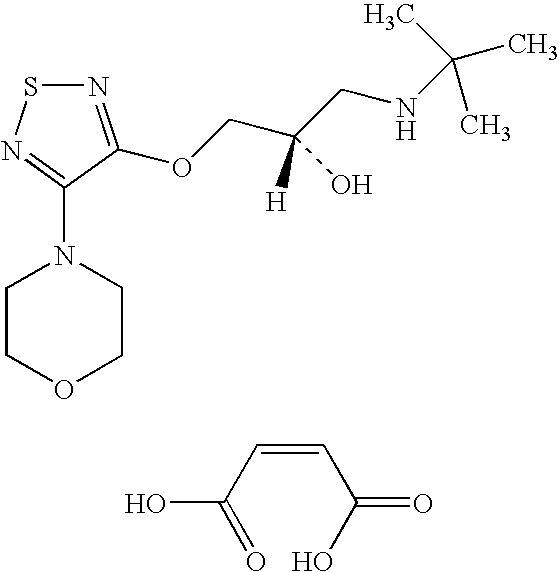
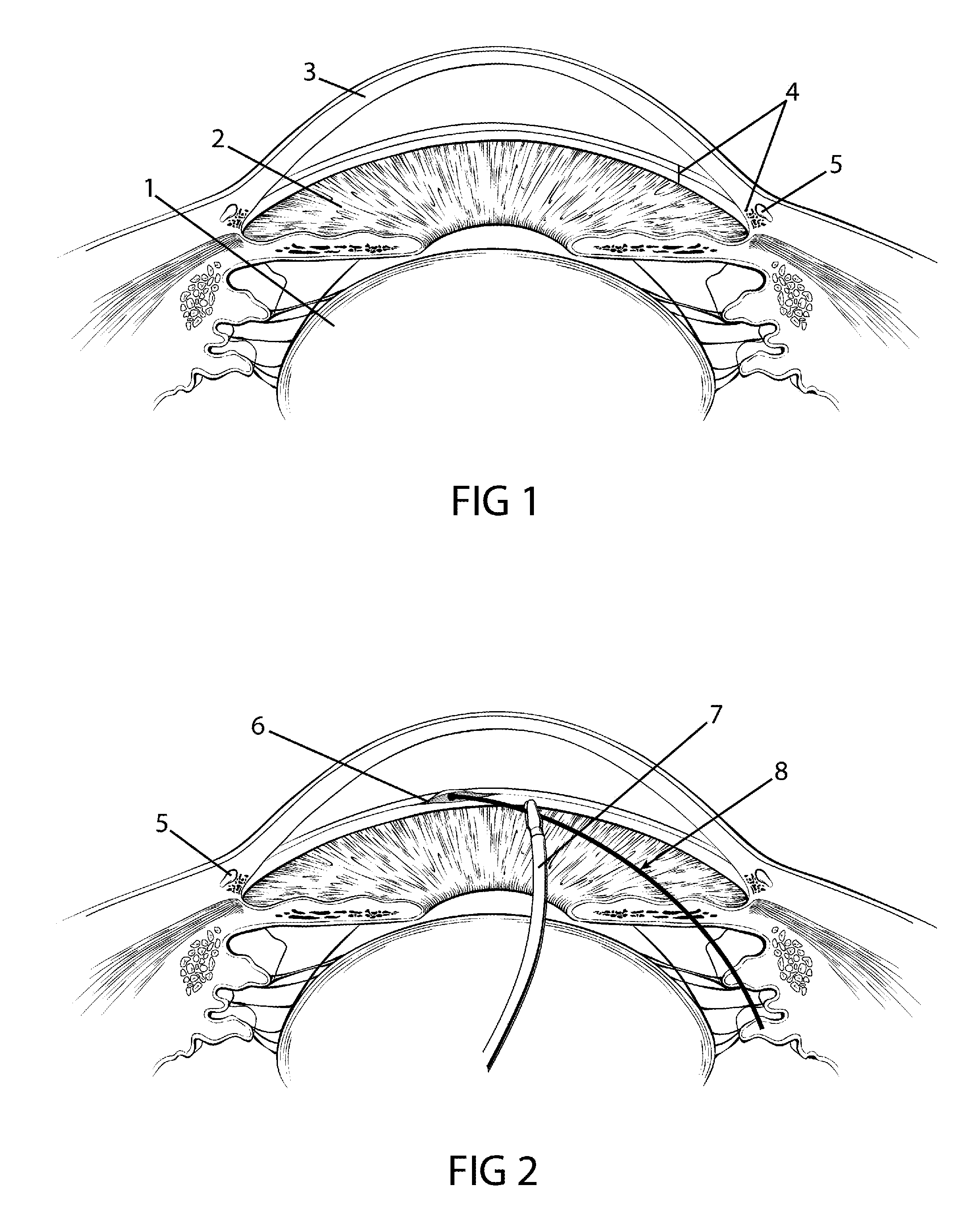
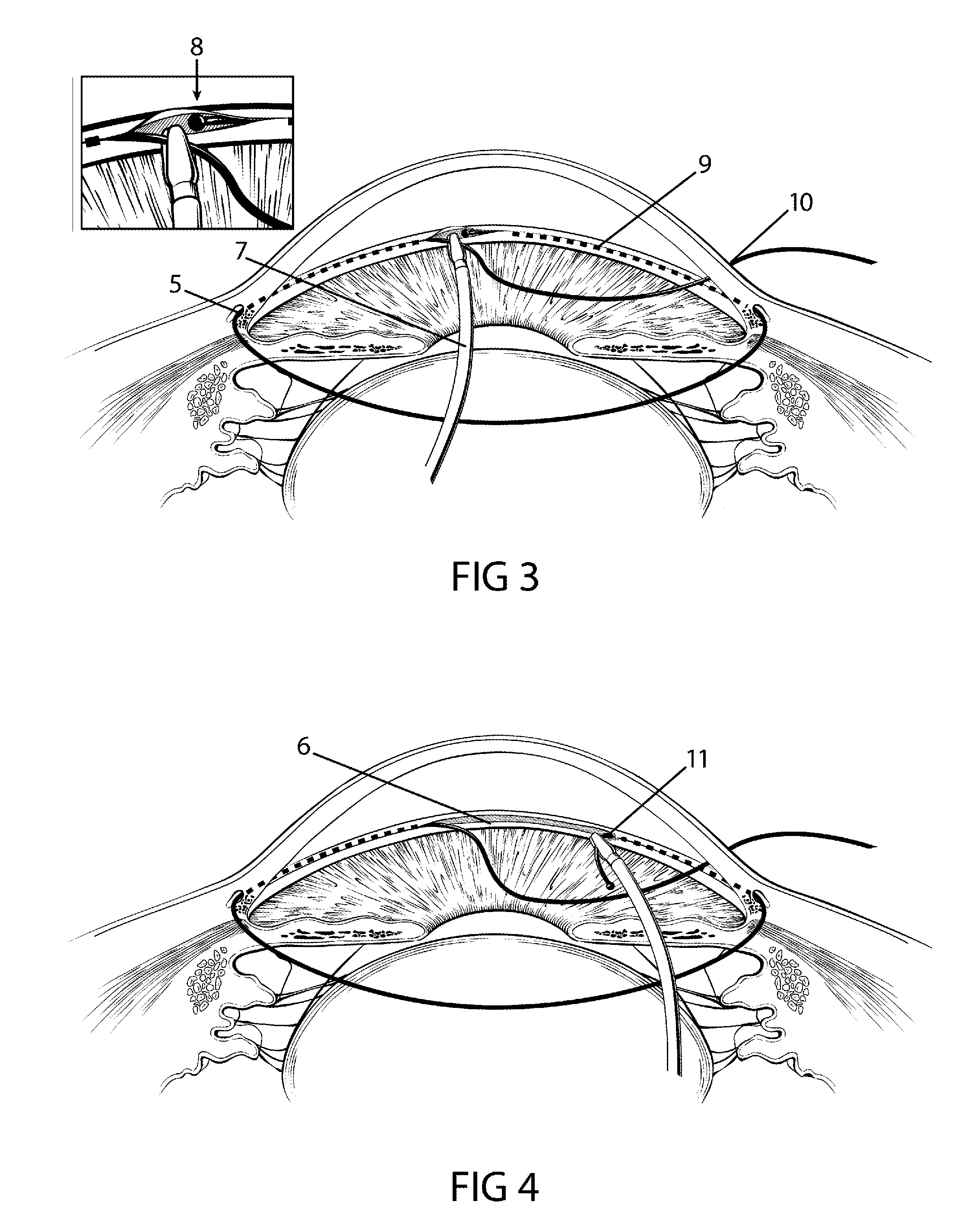
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
155 results about "Elevated intraocular pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
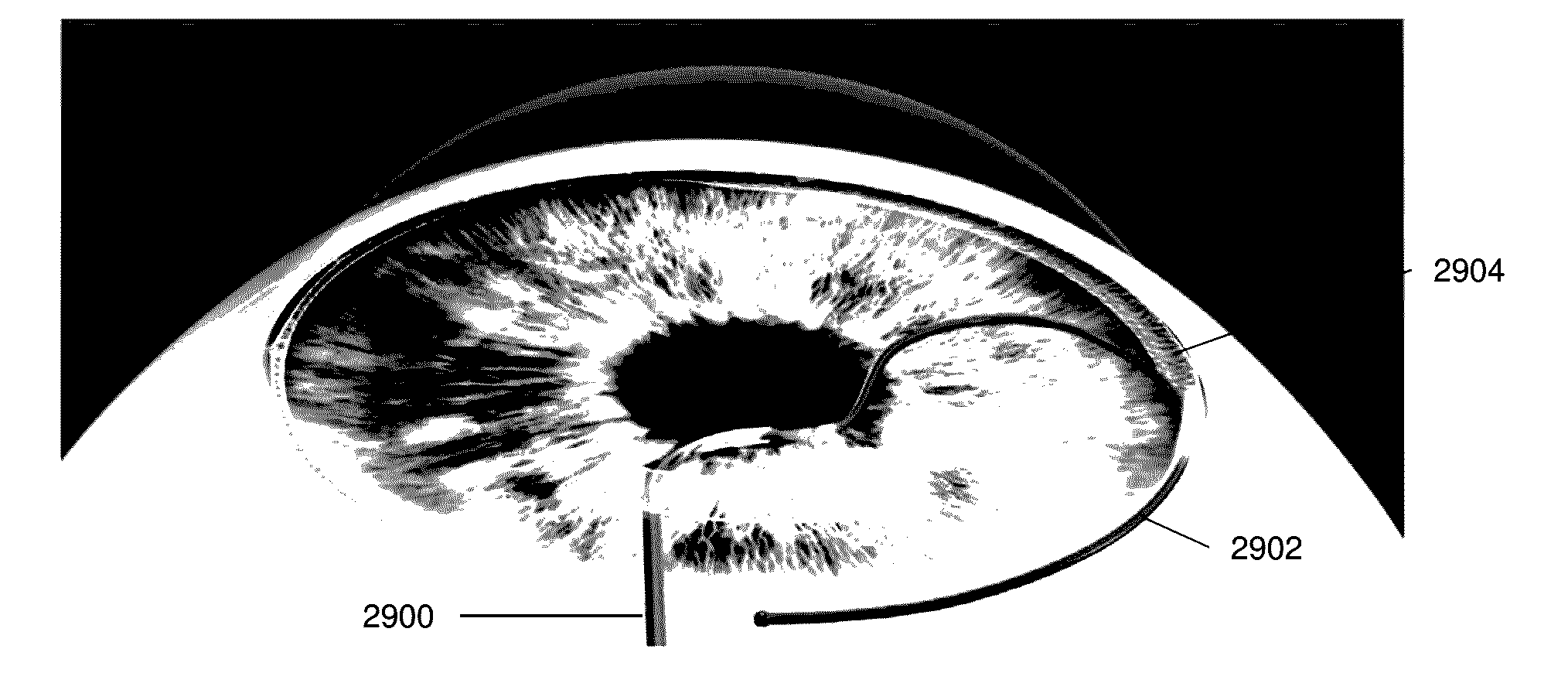
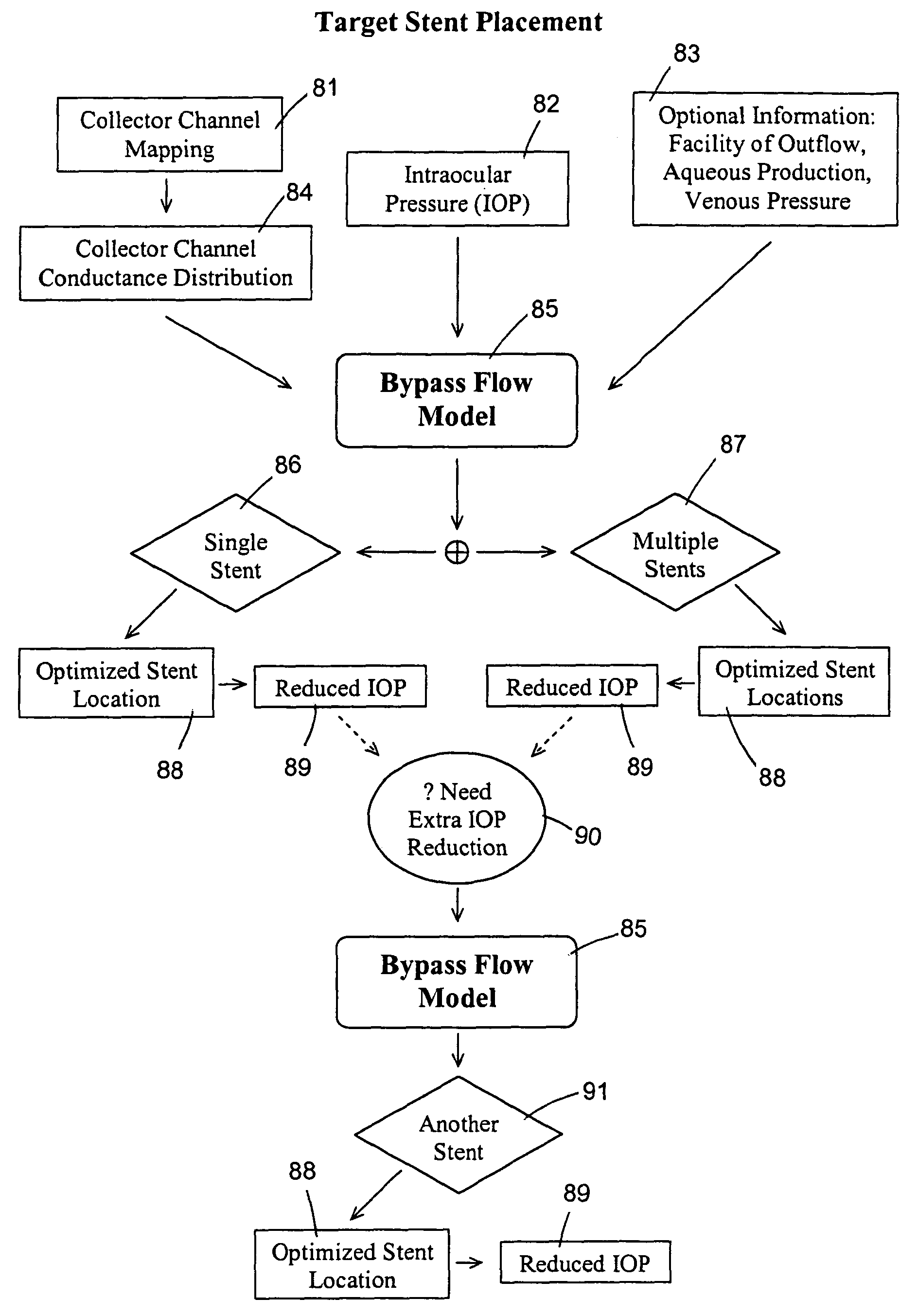
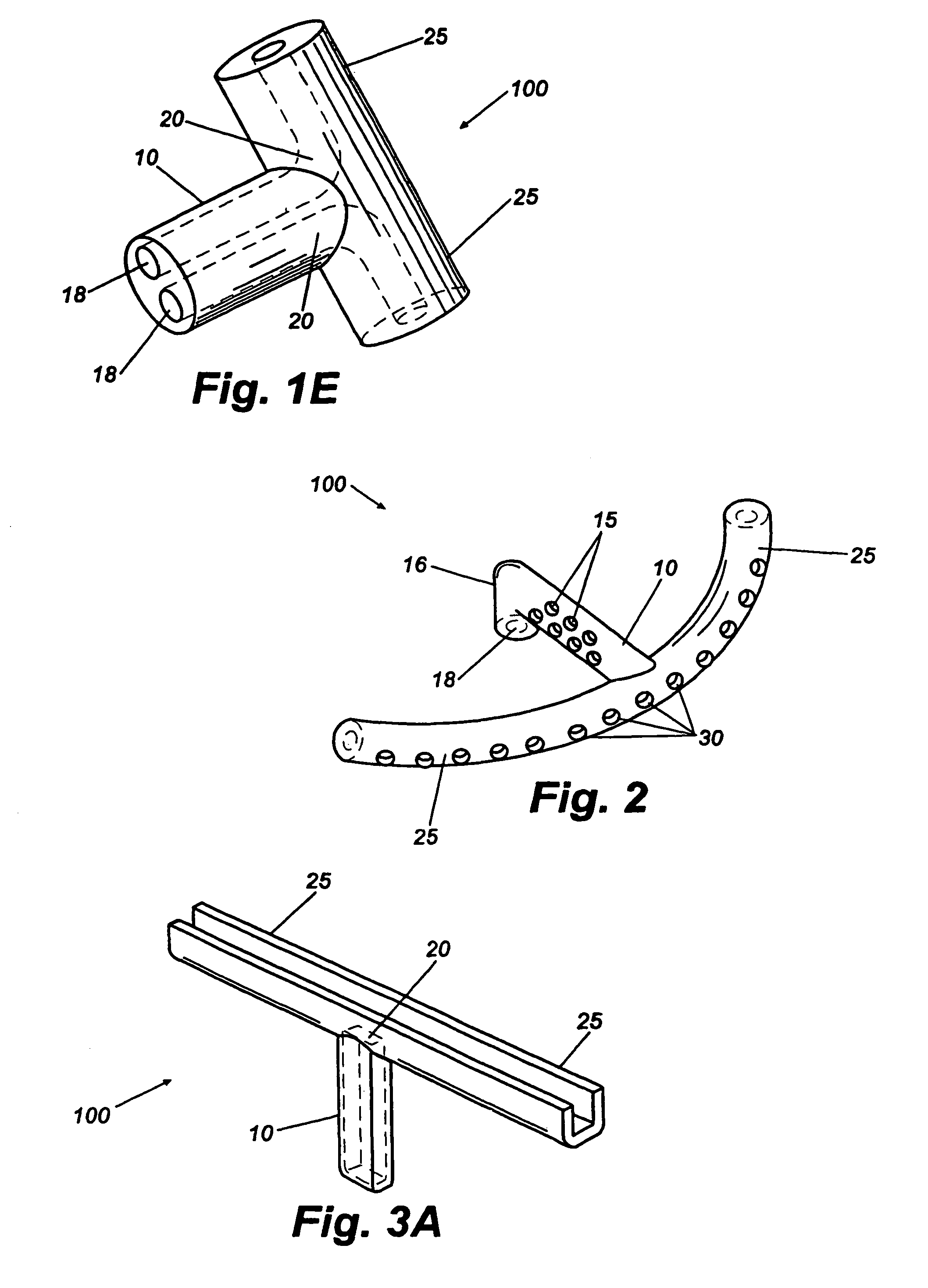
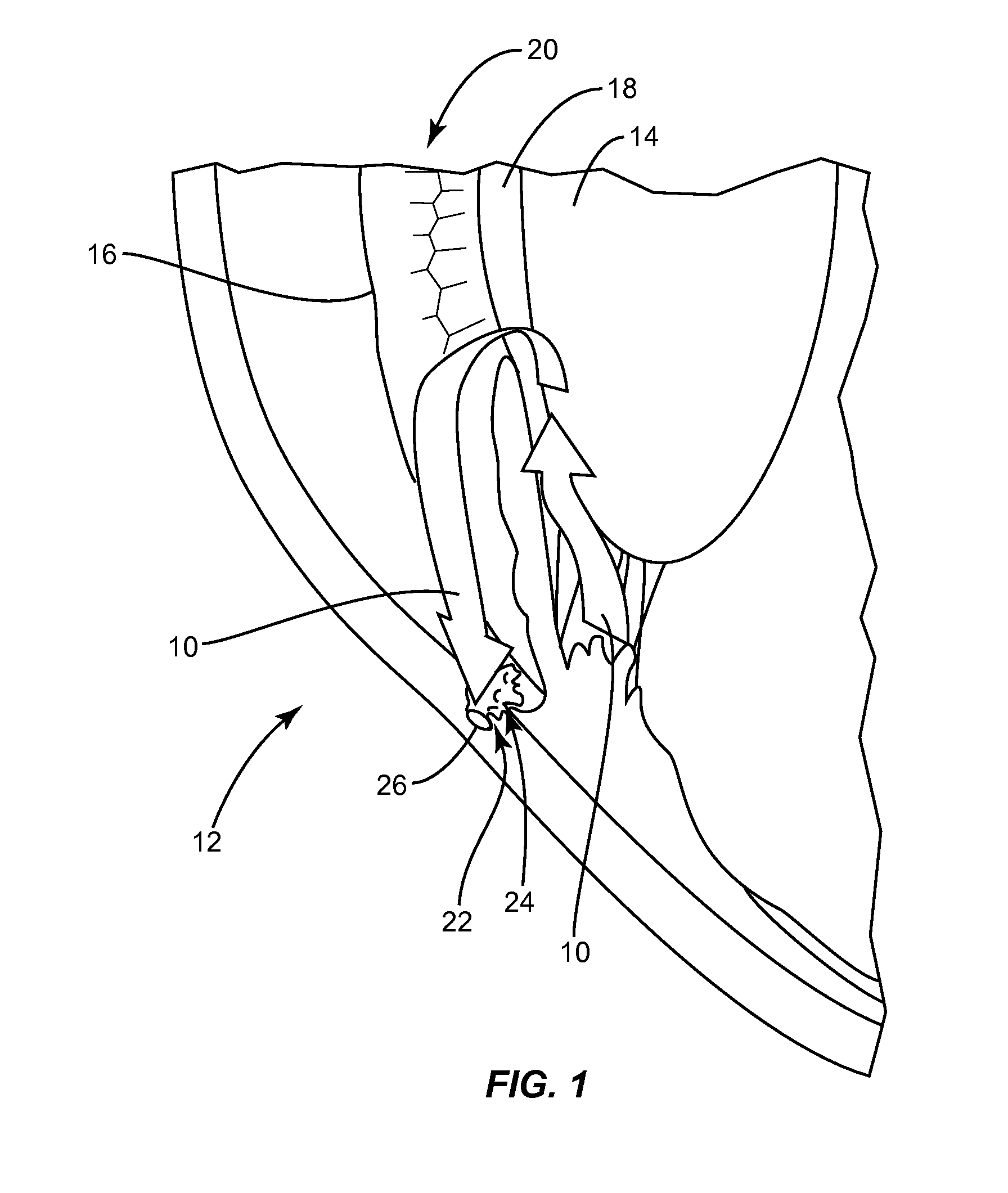
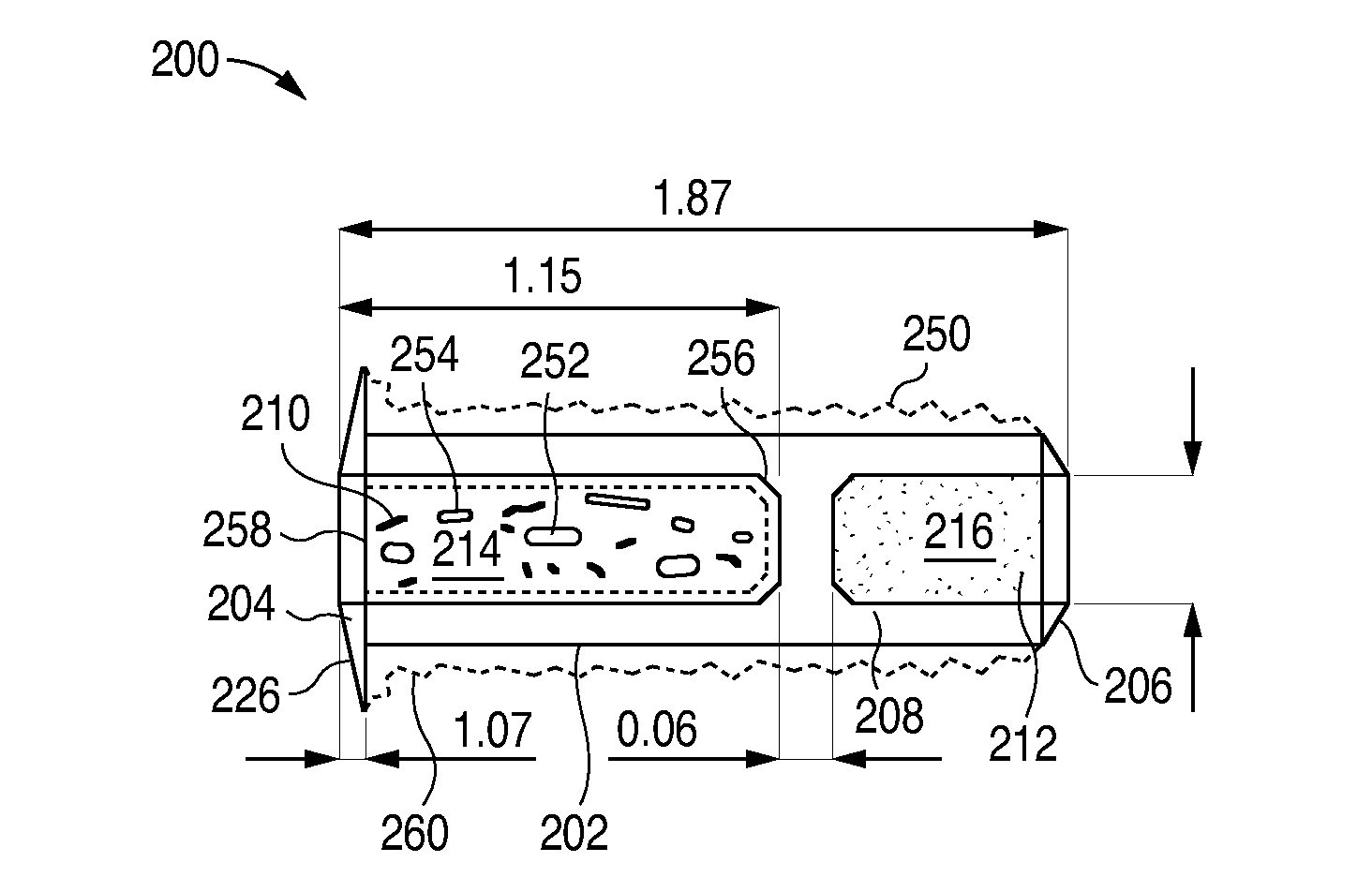
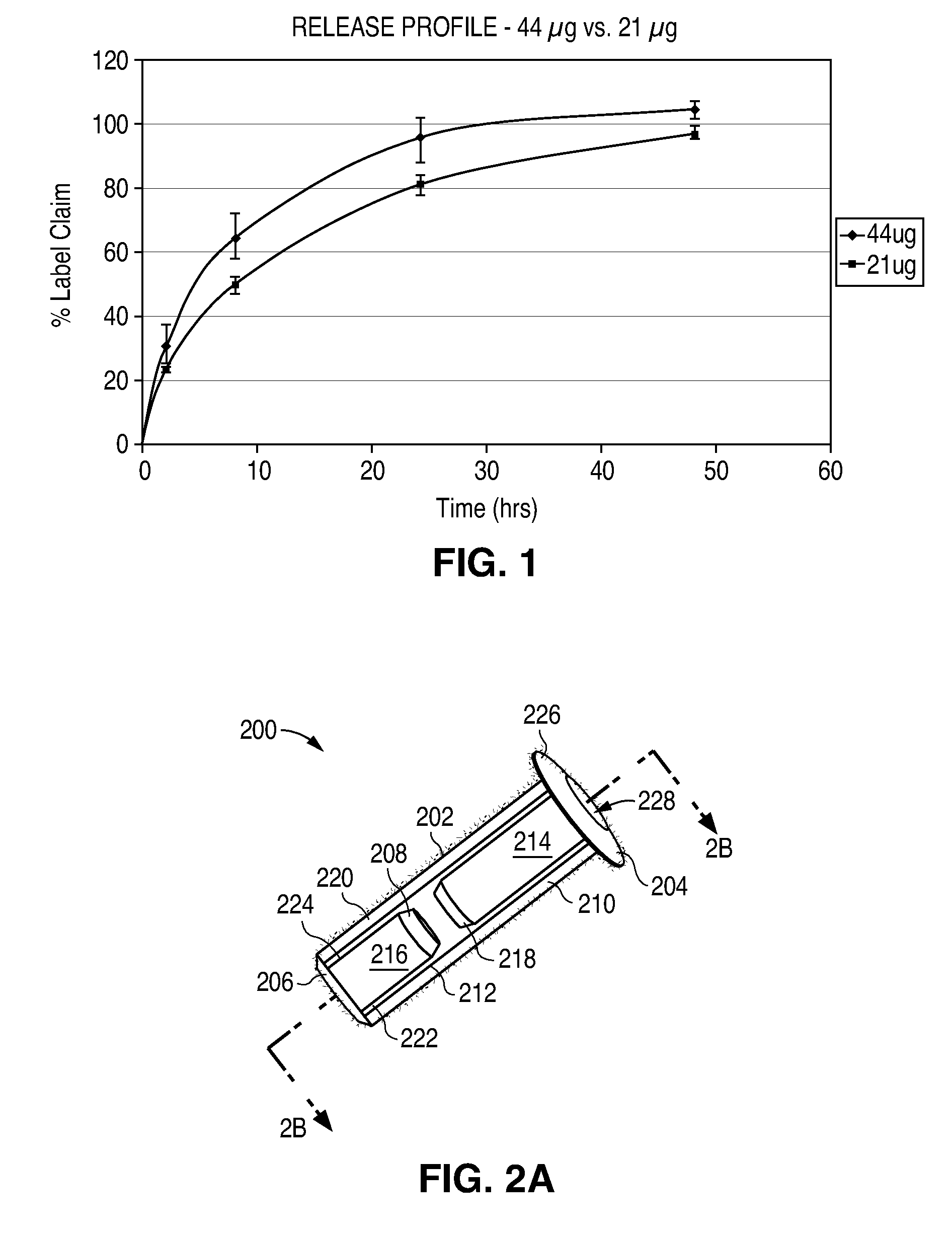
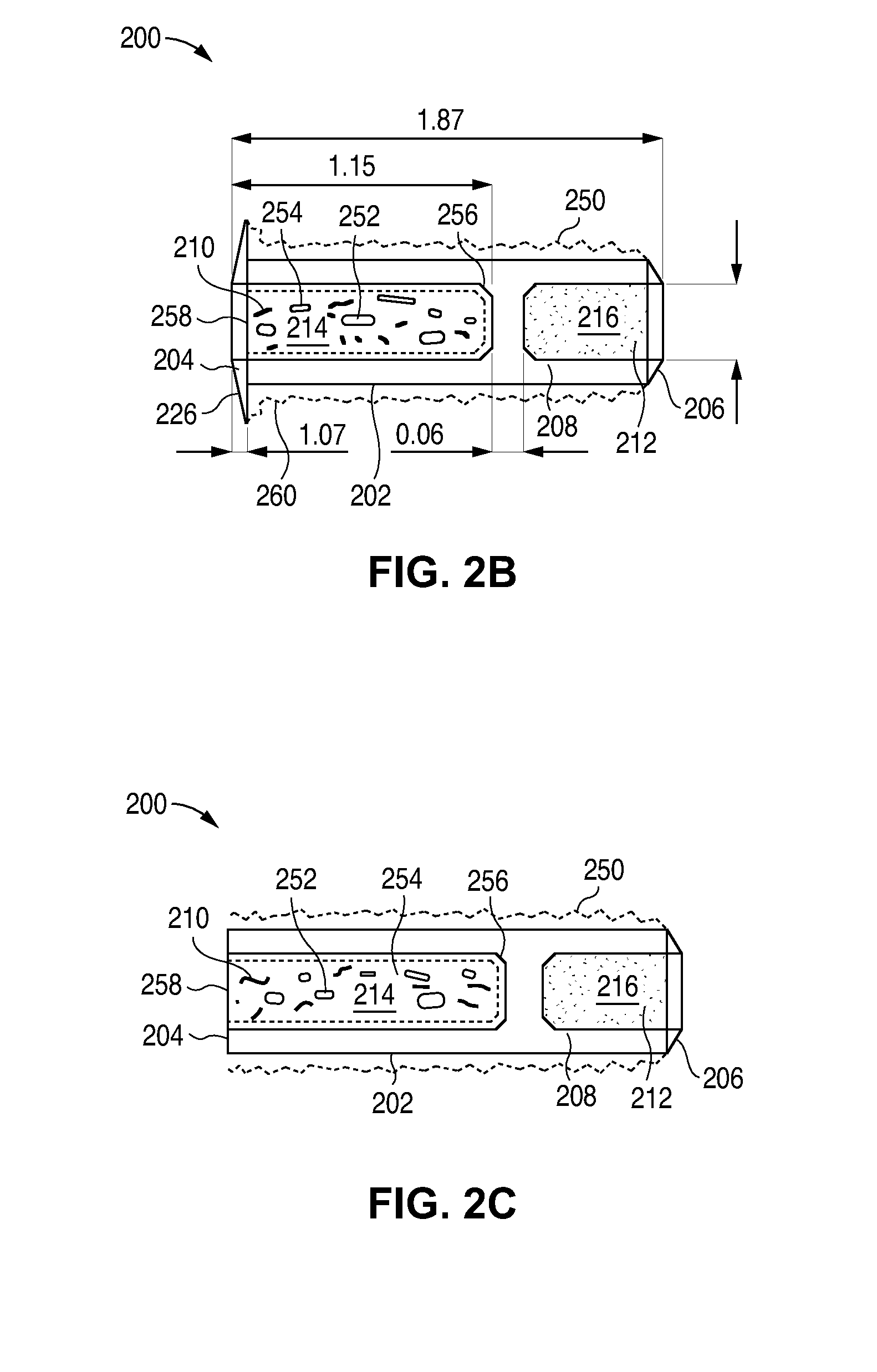
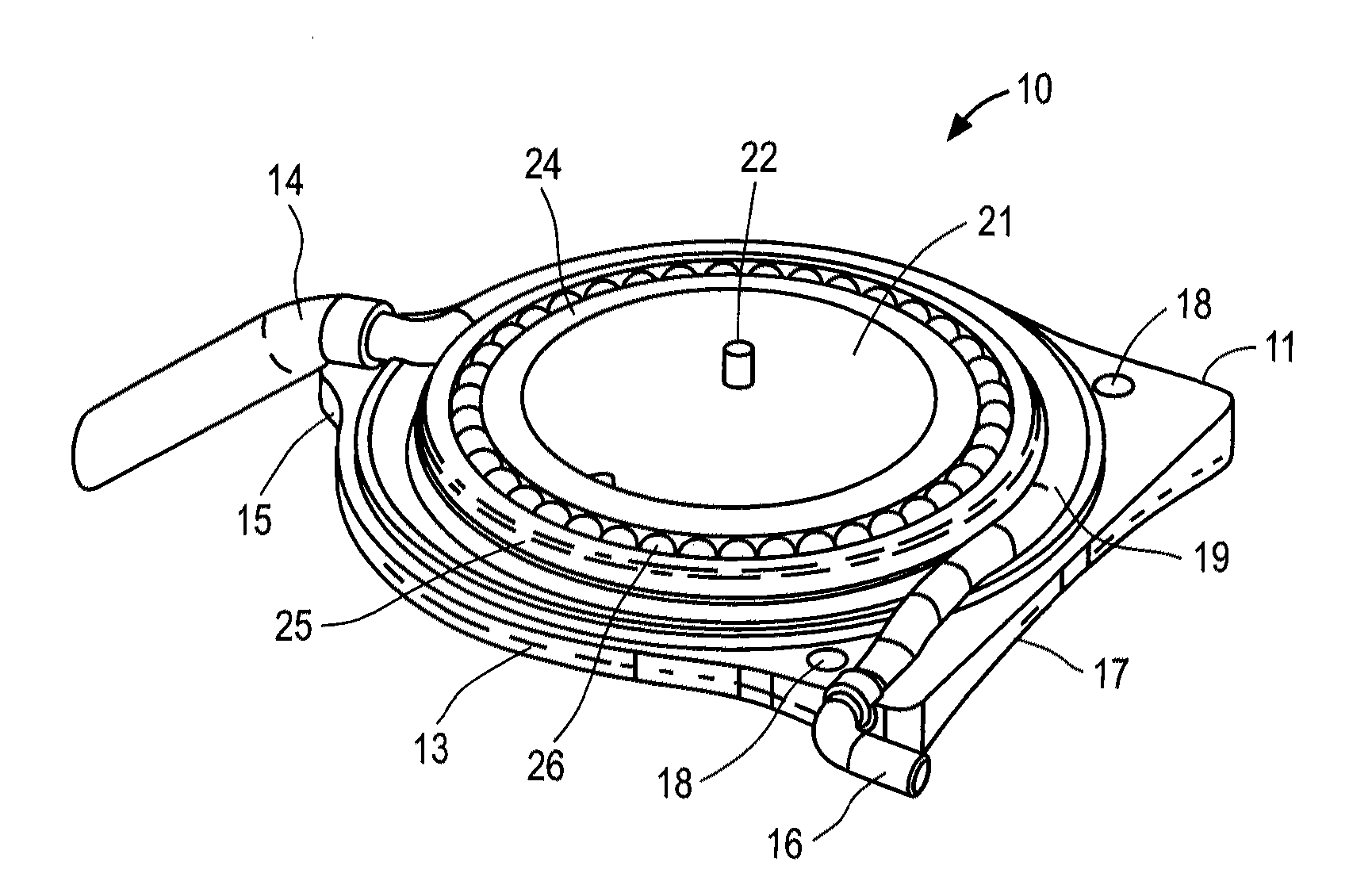
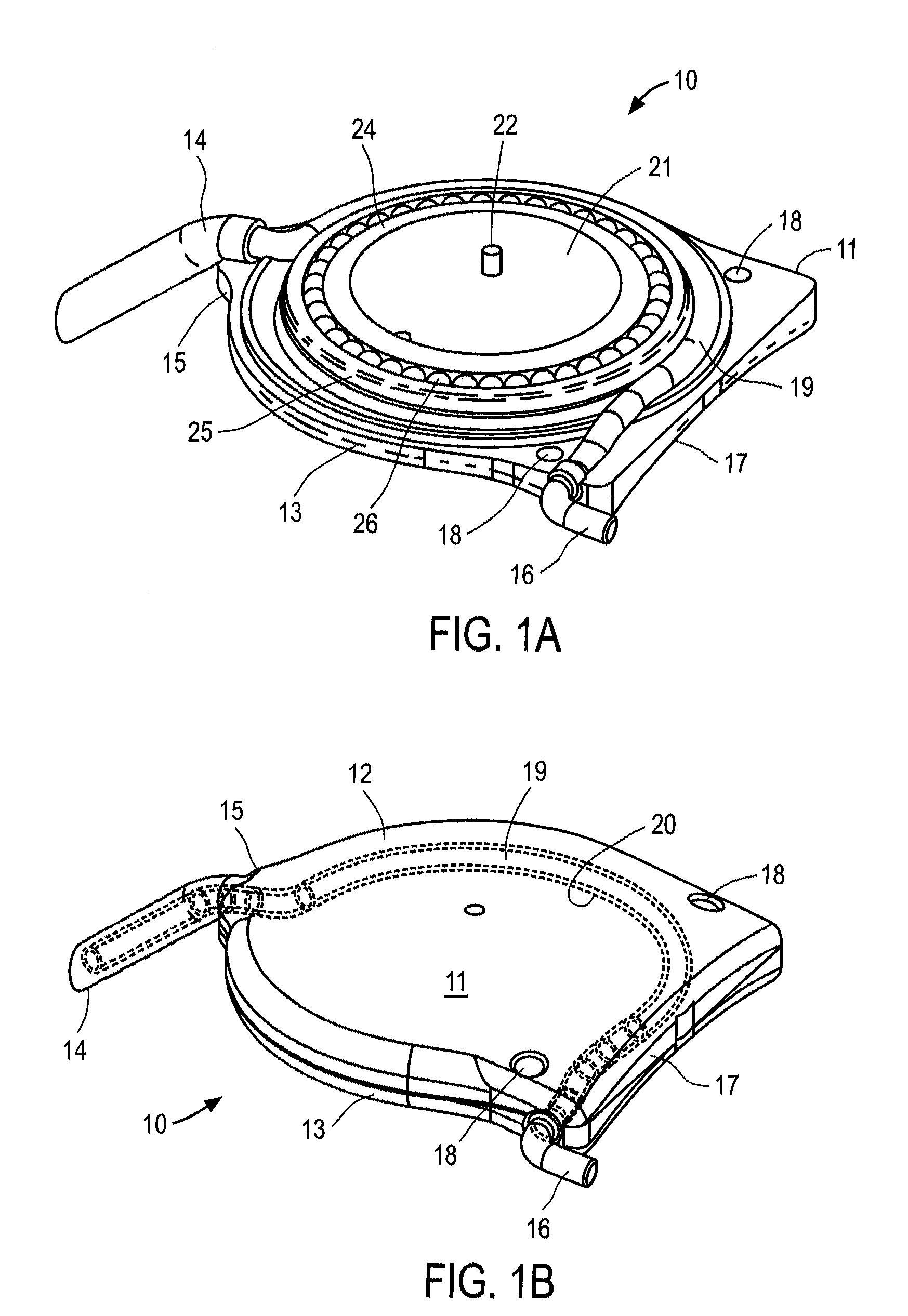
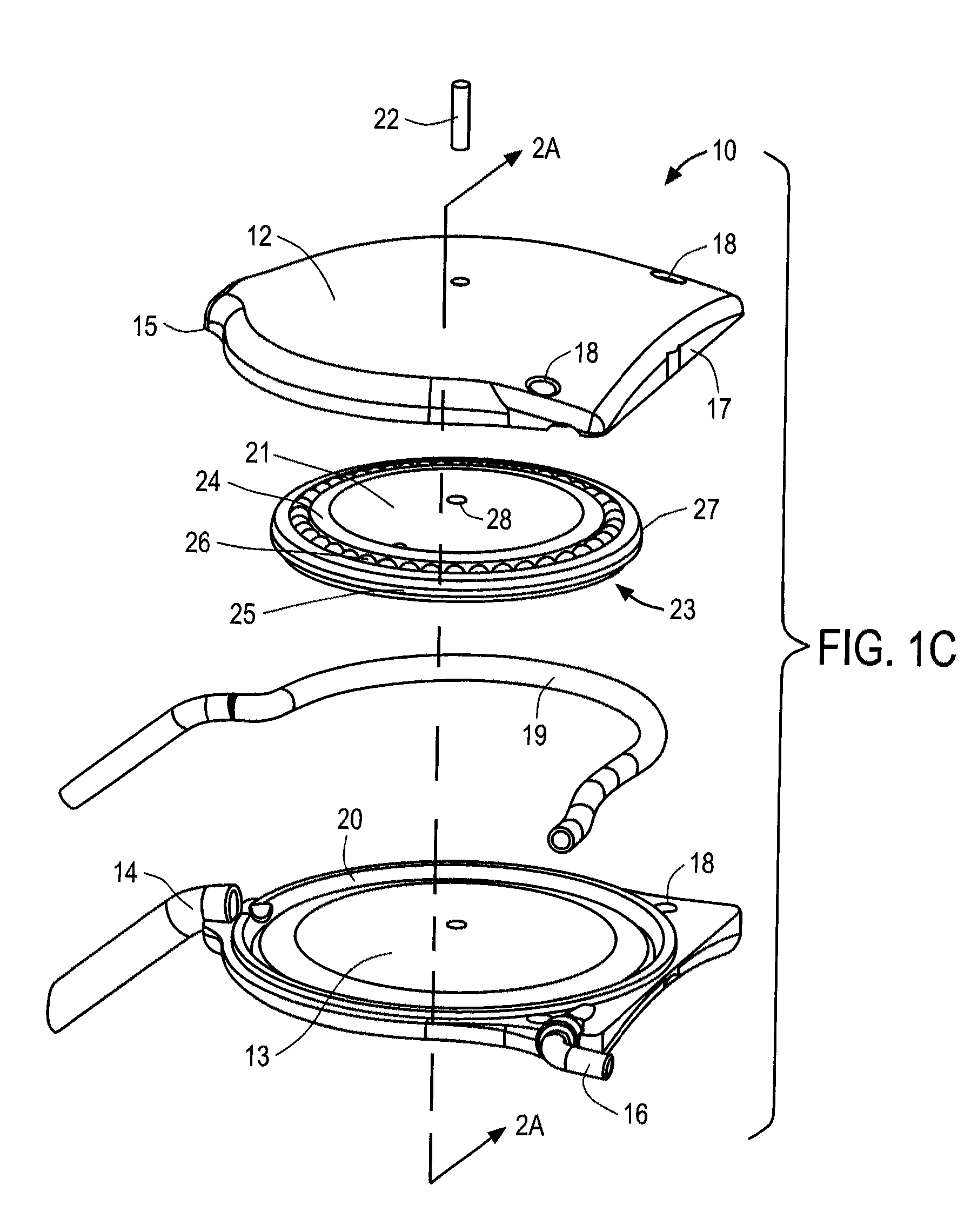
Targeted stent placement and multi-stent therapy
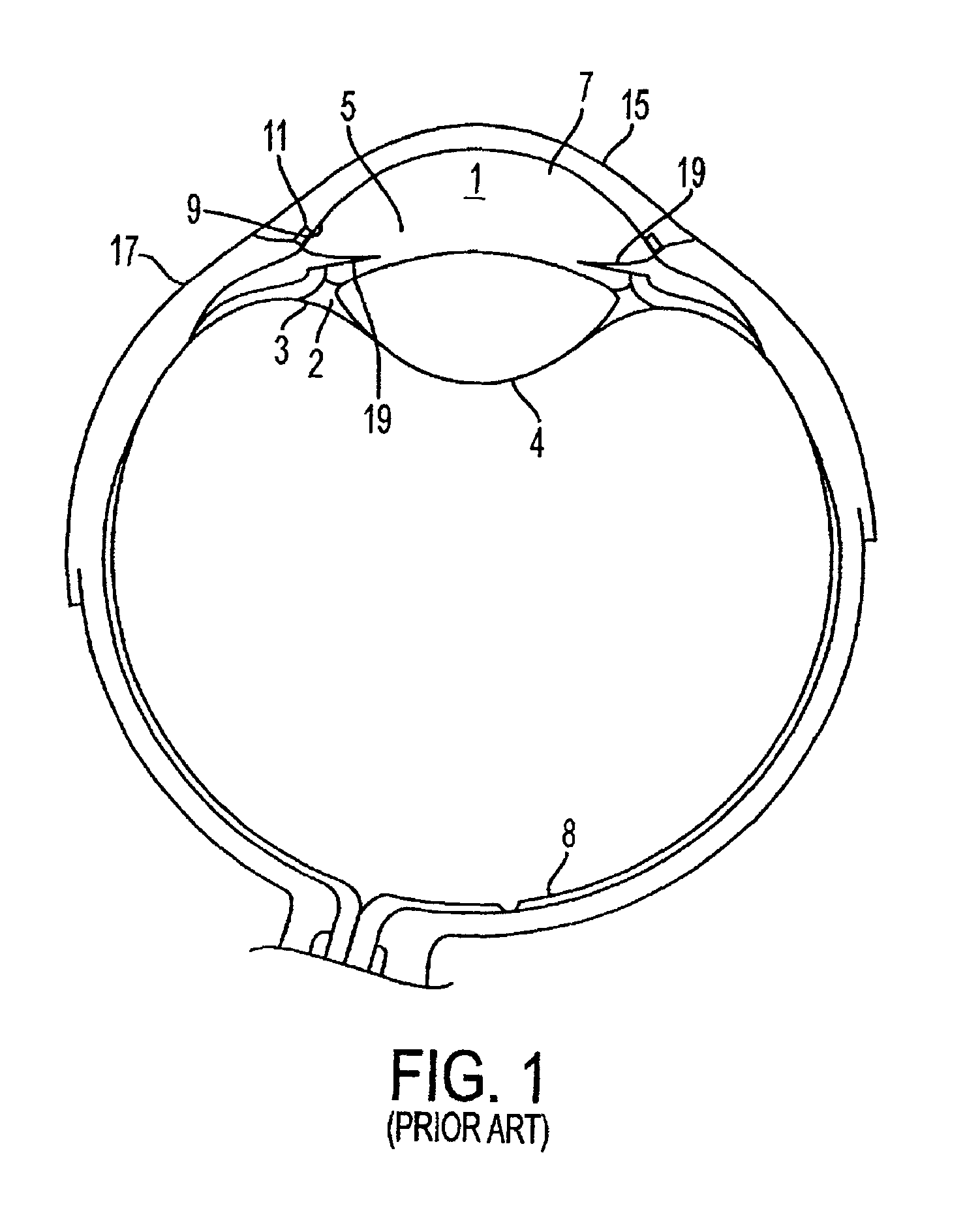
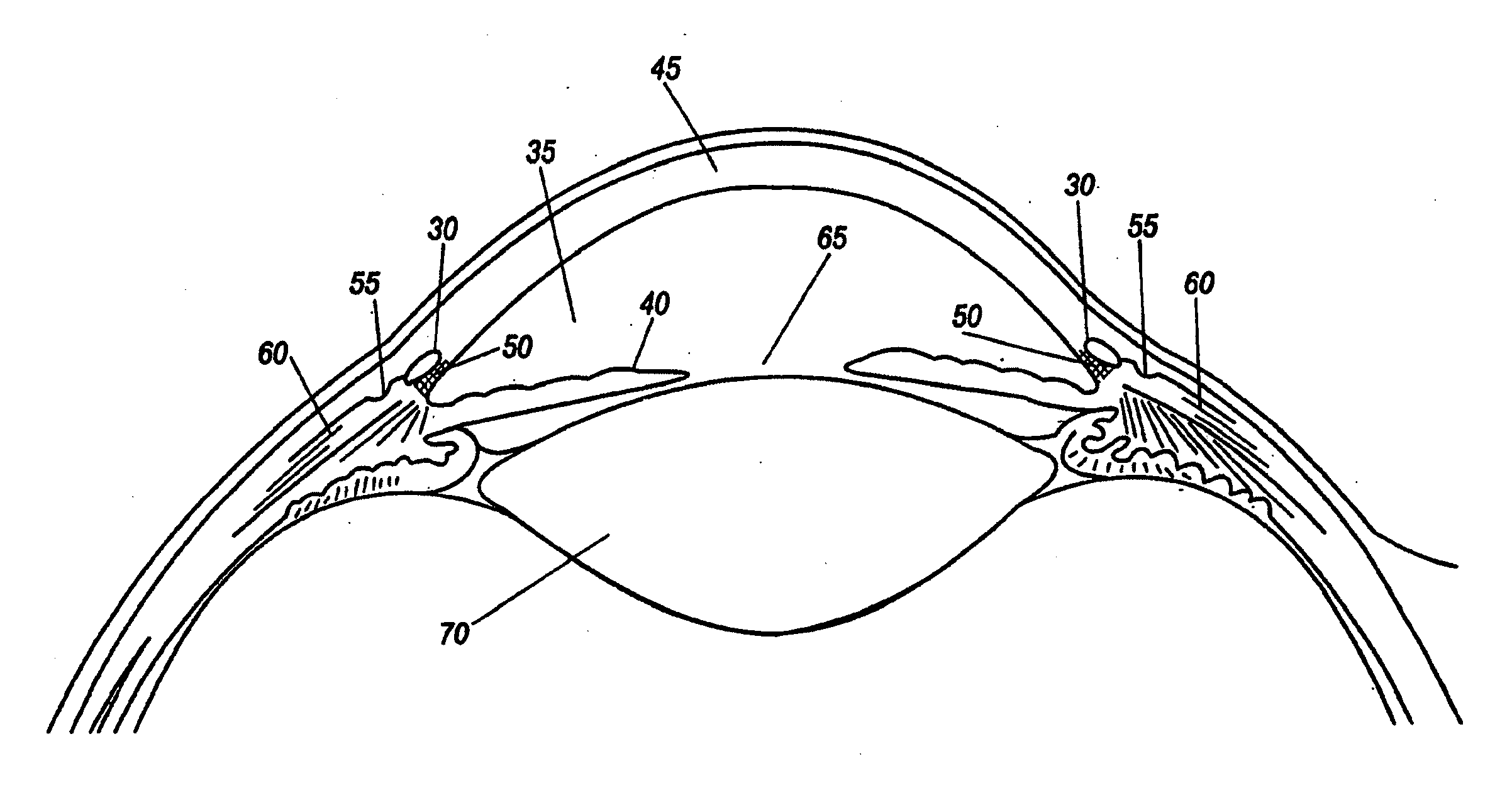
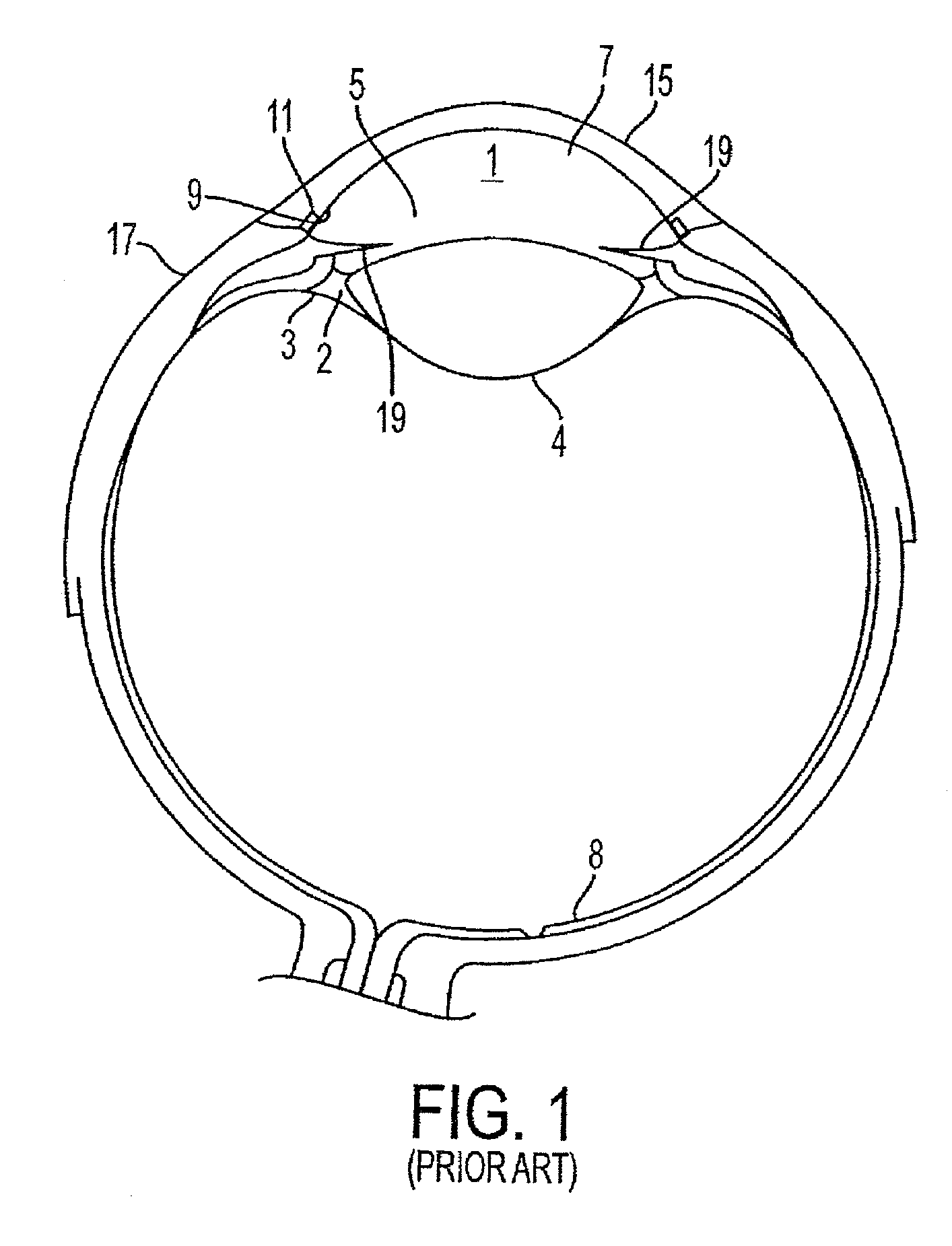
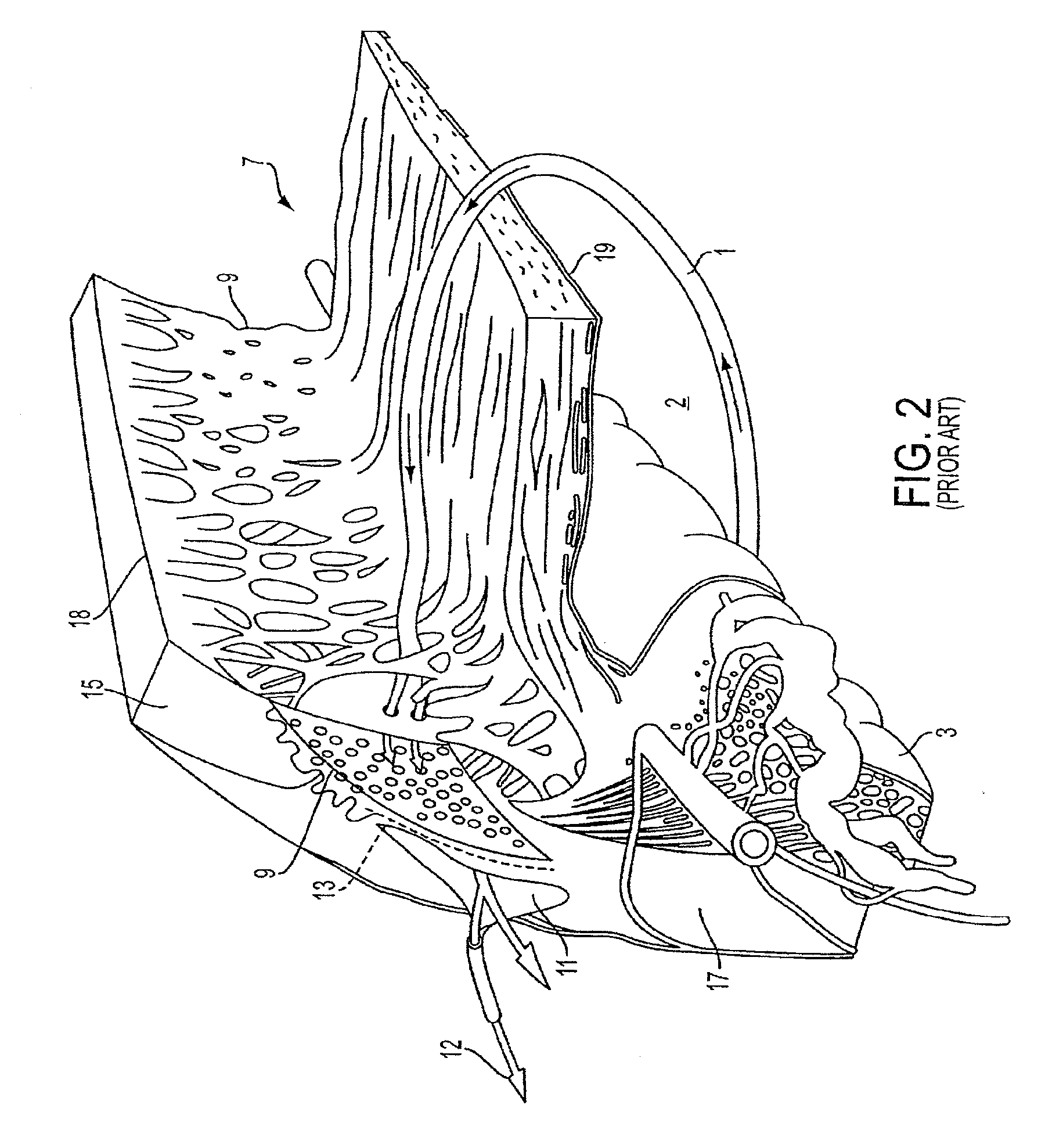
ActiveUS7192412B1Faster and safe and less-expensiveLower eye pressureStentsEye surgerySchlemm's canalElevated intraocular pressure
A trabecular flow model for producing treatment recommendations for patients with elevated intraocular pressure is disclosed. One method includes providing intraocular pressure measurements for a patient; providing aqueous cavity information, such as collector channel resistance and Schlemm's canal resistance, and determining a treatment recommendation for the patient based on the aforementioned parameters.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
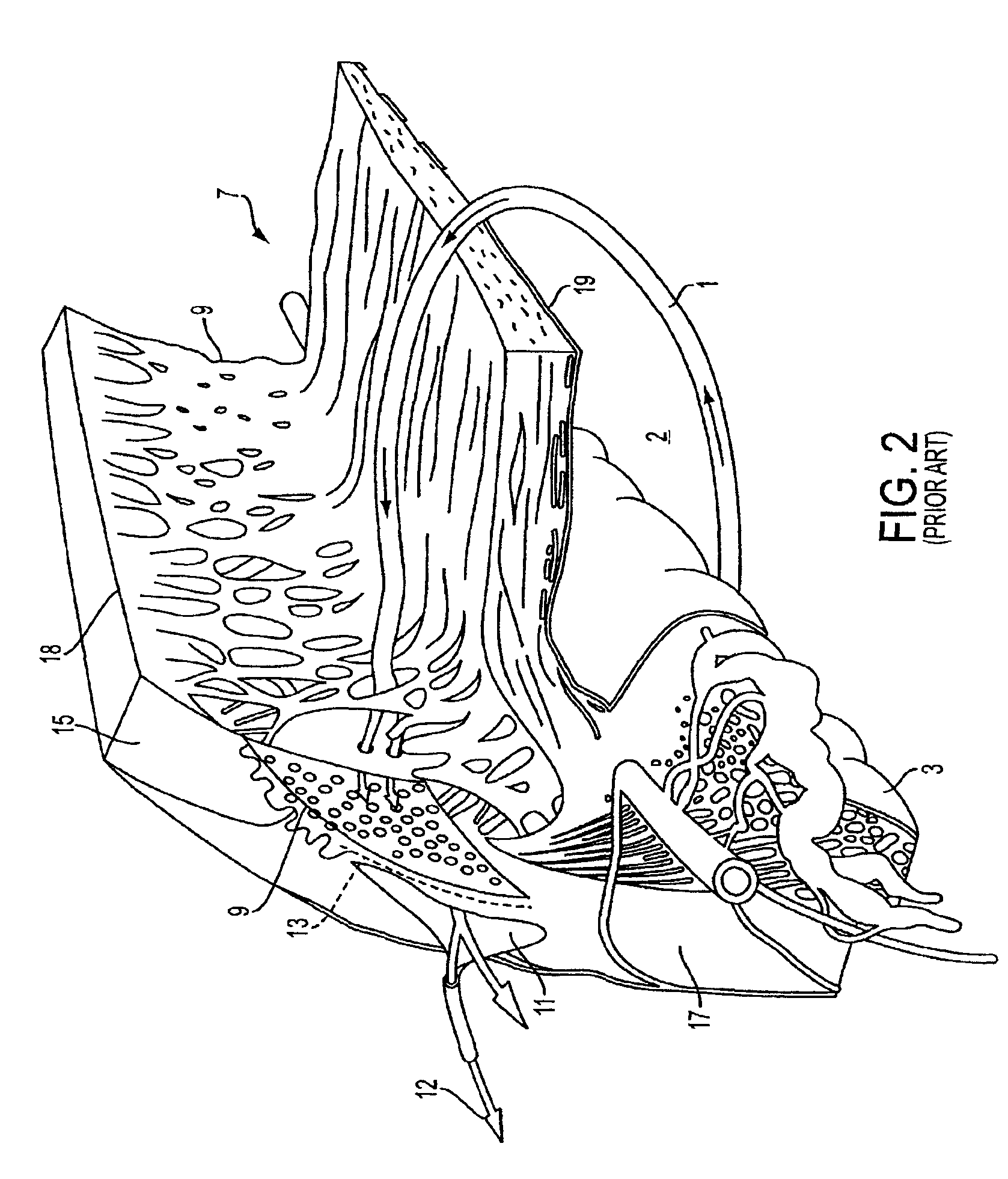
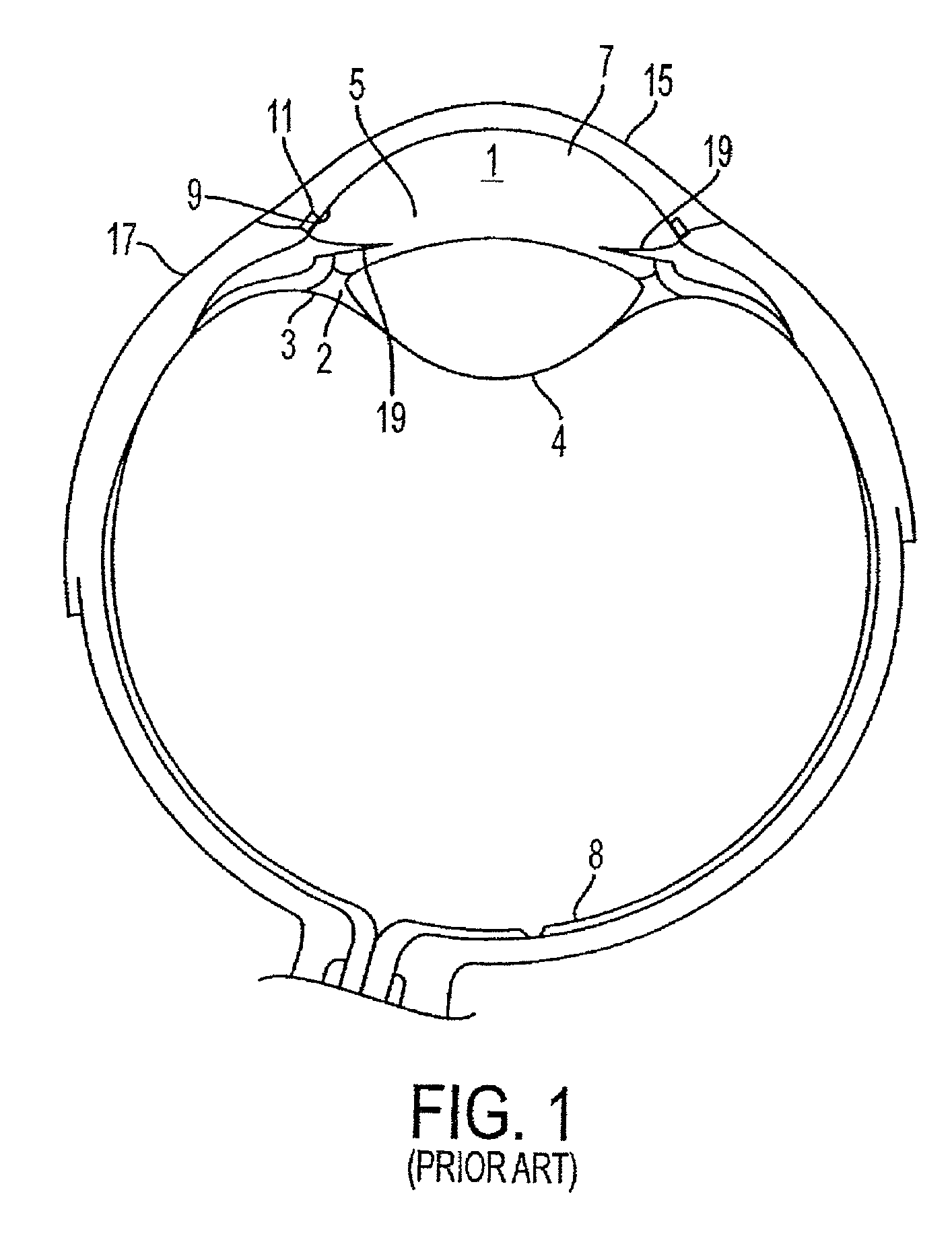
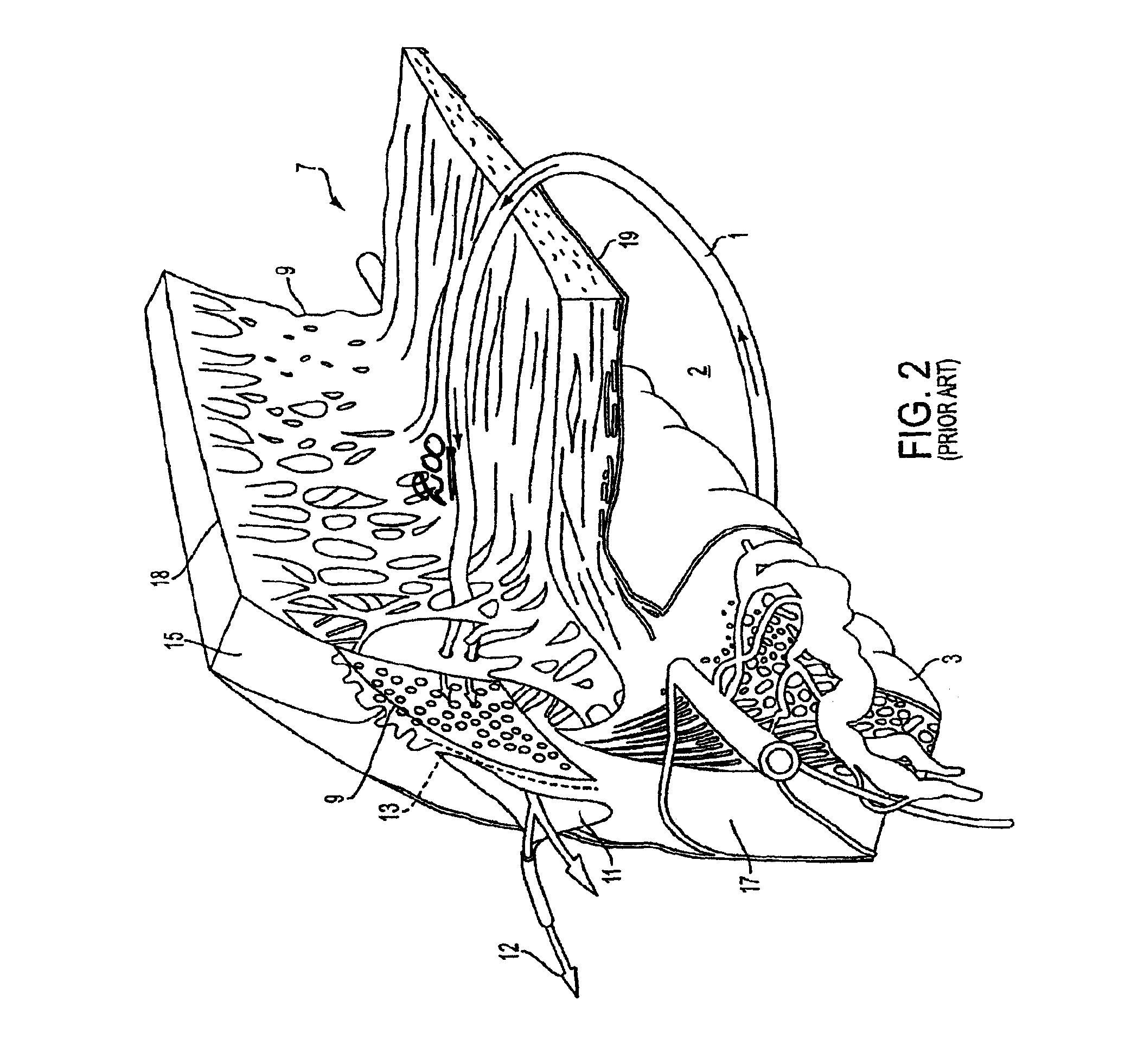
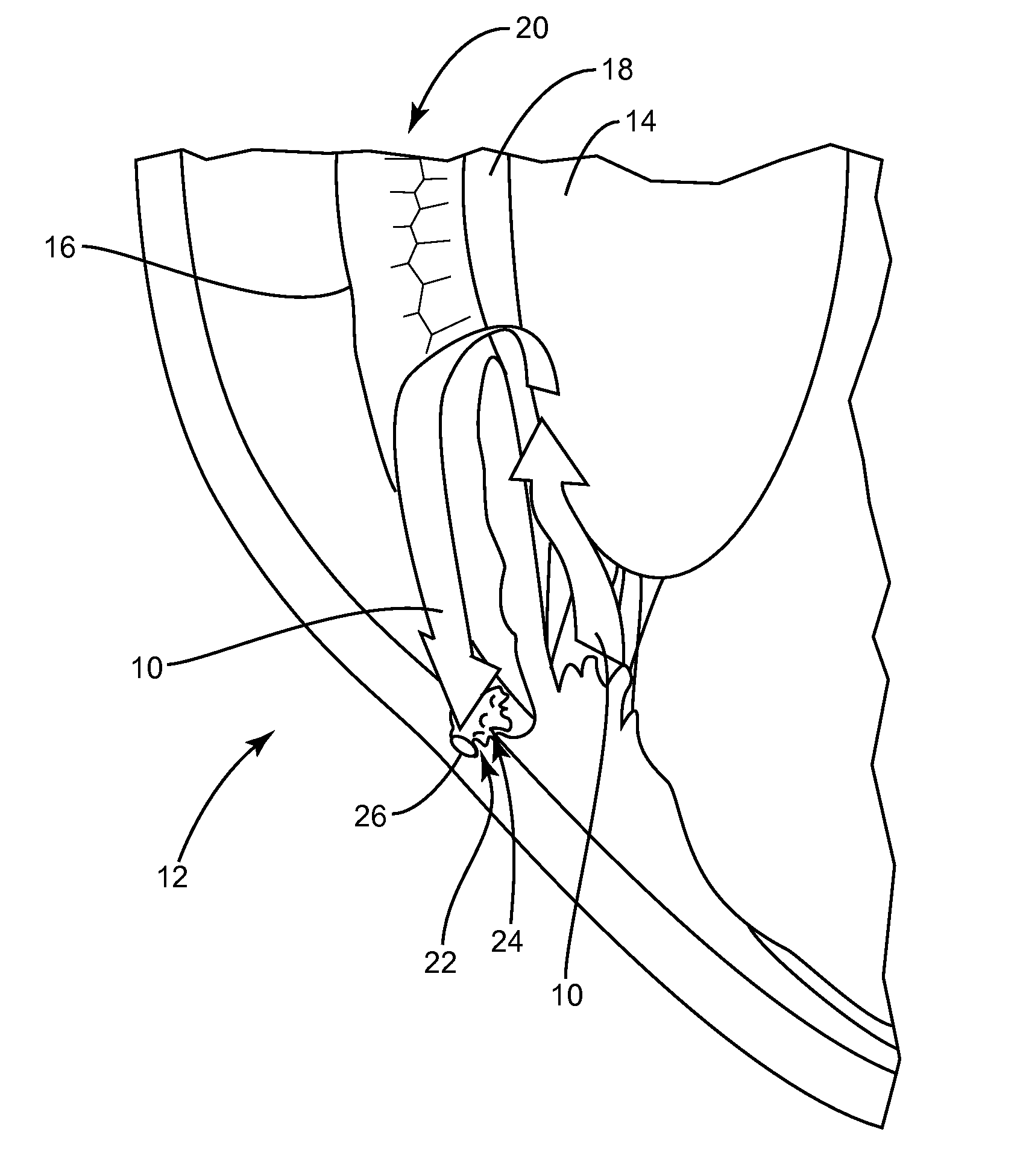
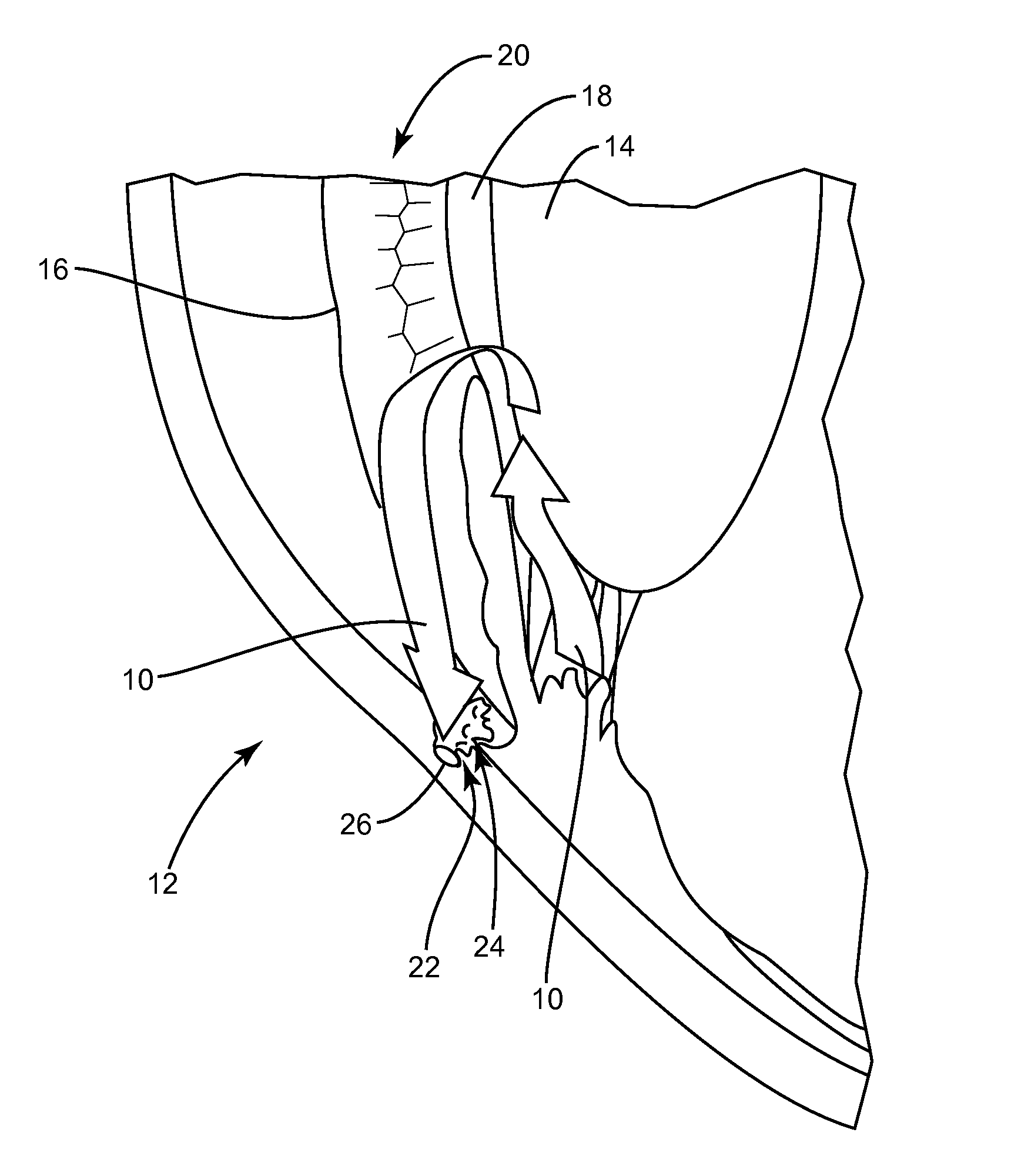
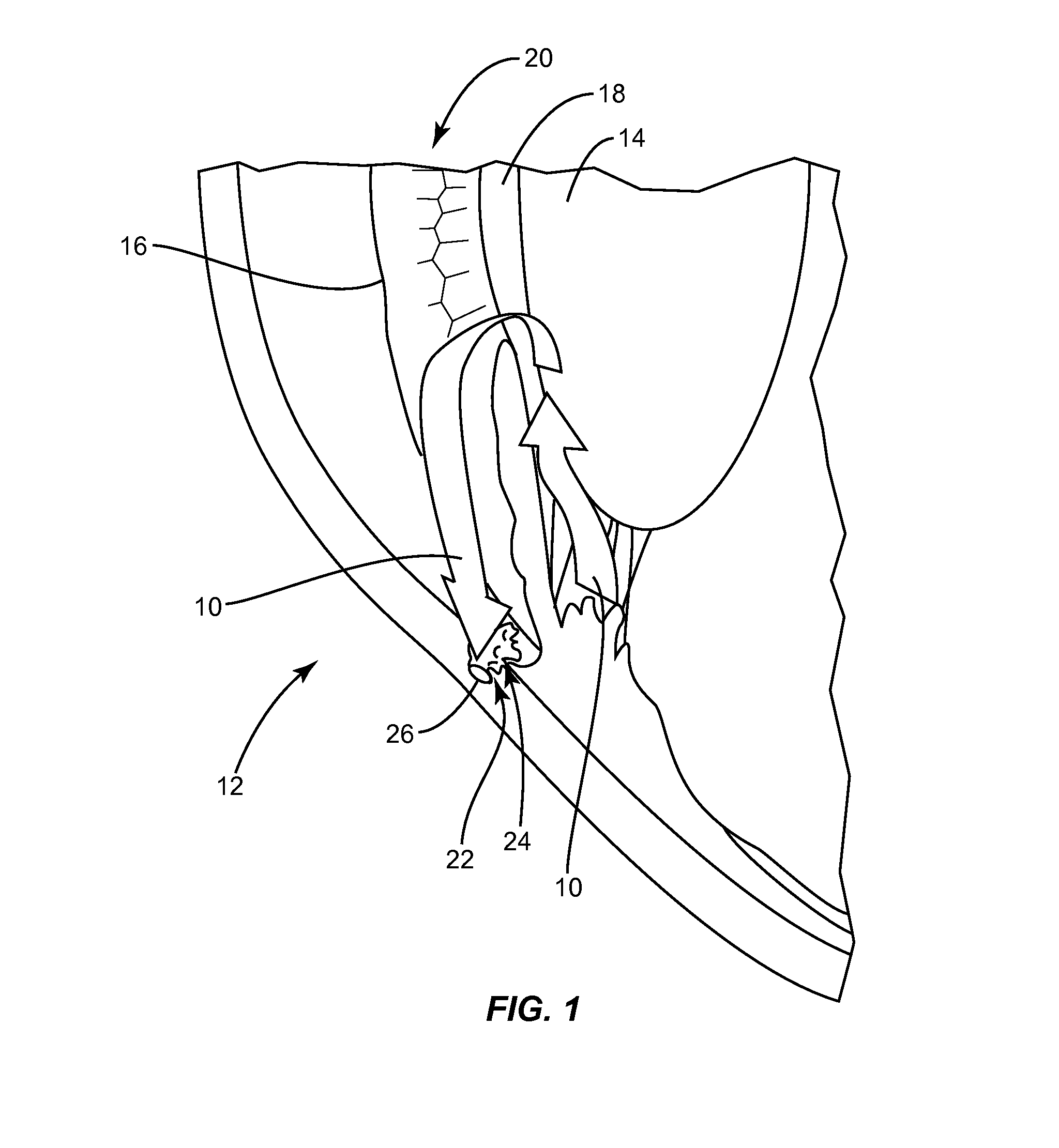
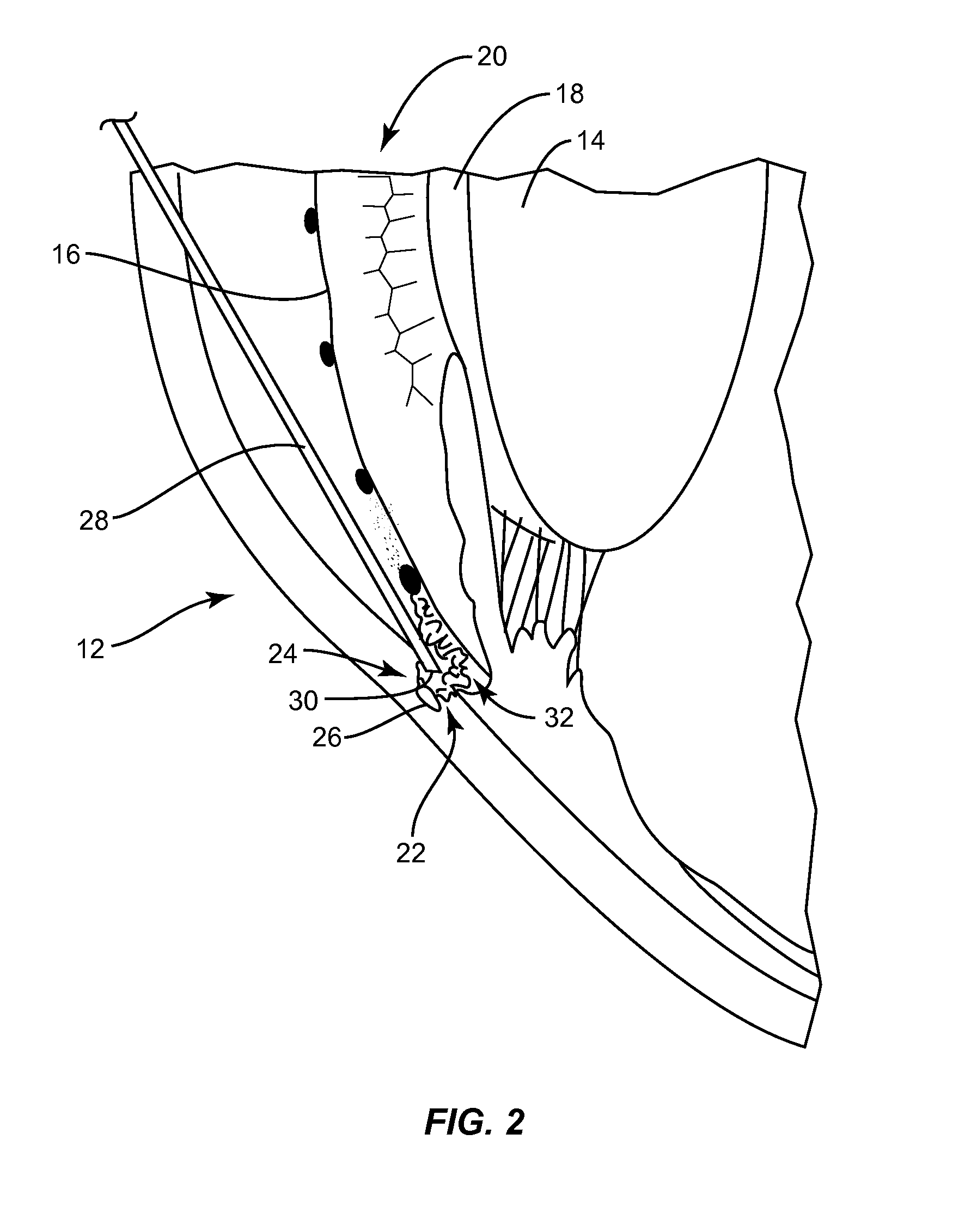
Glaucoma surgery methods and systems
InactiveUS20080082078A1Reducing collateral tissue damageObviating benefitLaser surgeryElectrotherapyAqueous flowSchlemm's canal
Methods and systems are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Some embodiments described apparatus and methods useful in photoablation of tissues. In some embodiments, a photoablation apparatus is used to perforate a tissue, forming an aperture into a space behind the tissue. Gases formed during a photoablation process can be used to pressurize the space behind the tissue to enhance patency of the space. In some embodiments the tissue is the trabecular meshwork of the eye and a wall of Schlemm's canal, and the space behind the tissue is a portion of the lumen of Schlemm's canal. In some embodiments, the method is useful in the treatment of glaucoma by improving outflow from the anterior chamber of the eye into Schlemm's canal, reducing intraocular pressure.
Owner:BERLIN MICHAEL S
Shunt device and method for treating glaucoma
InactiveUS7850637B2Expand exportsFacilitates the normal physiologic pathwayEye implantsEar treatmentShunt DeviceAqueous humor
Shunt devices and a method for continuously decompressing elevated intraocular pressure in eyes affected by glaucoma by diverting excess aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye into Schlemm's canal where post-operative patency can be maintained with an indwelling shunt device which surgically connects the canal with the anterior chamber. The shunt devices provide uni- or bi-directional flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS8540659B2Minimal thermal effectLower eye pressureLaser surgeryEye implantsFiberPhotoablation
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for reducing intraocular pressure as a means of preventing or treating open-angle glaucoma
InactiveUS20090043365A1Lower Level RequirementsSustainably reduce IOPUltrasound therapyEye surgeryAqueous humorOpen angle glaucoma
Embodiments include methods, apparatuses, and systems for reducing elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in a patient to either prevent or treat open-angle glaucoma. Heat is applied to the trabecular meshwork in the patient's eye without damaging proteins in the trabecular meshwork. The application of heat to the trabecular meshwork has the effect of relaxing or loosening protein clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork, which are either reducing or obstructing of the outflow of aqueous humor, thereby increasing the patient's IOP and causing ocular hypertension (OHT). By loosening or relaxing clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork, the outflow path for aqueous humor is increased or restored, which can lower IOP and either prevent or treat glaucoma. Force may also be applied to the patient's eye to apply pressure to the trabecular meshwork to further assist in the loosening or relaxing of clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork.
Owner:TEARSCIENCE INC
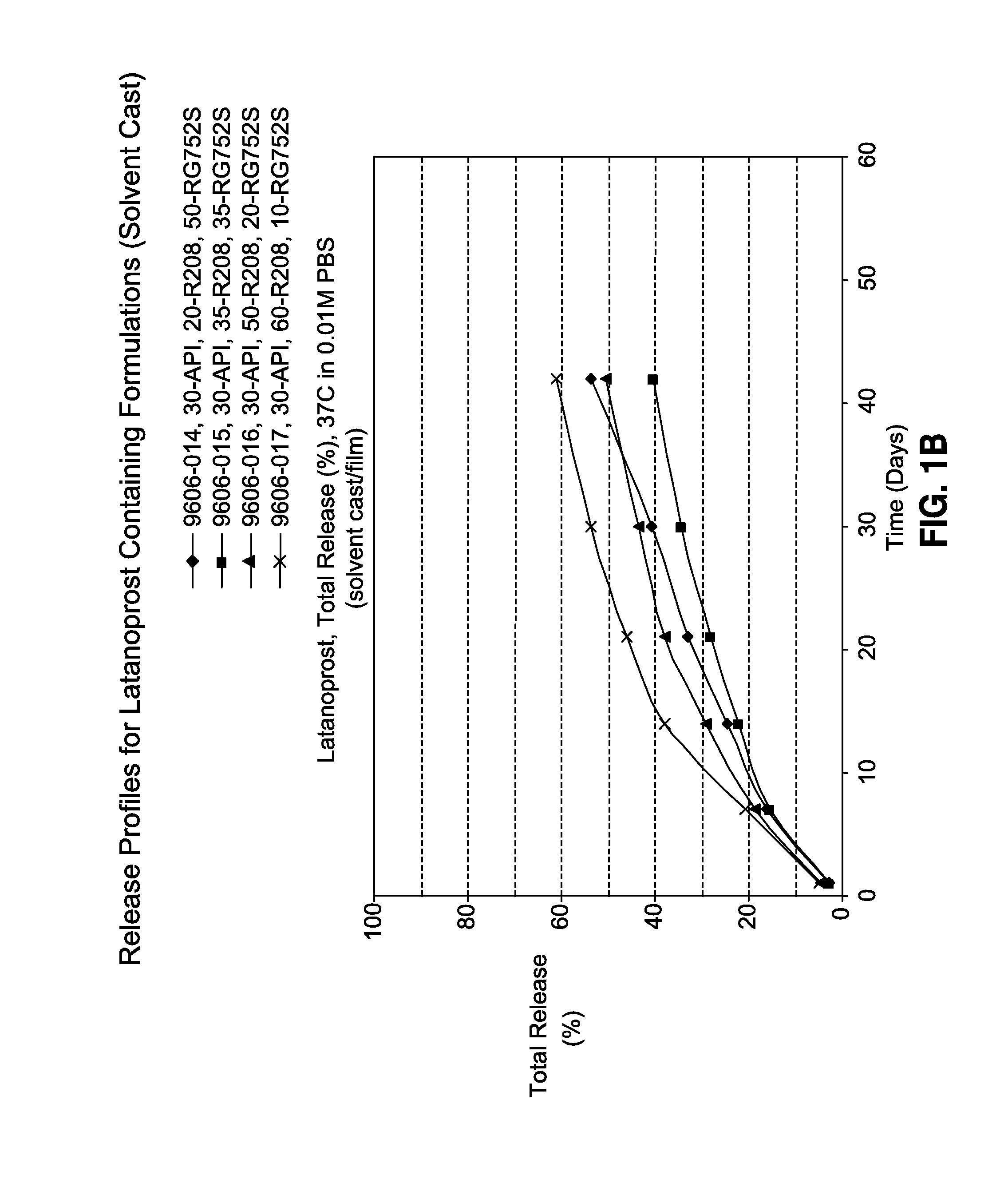
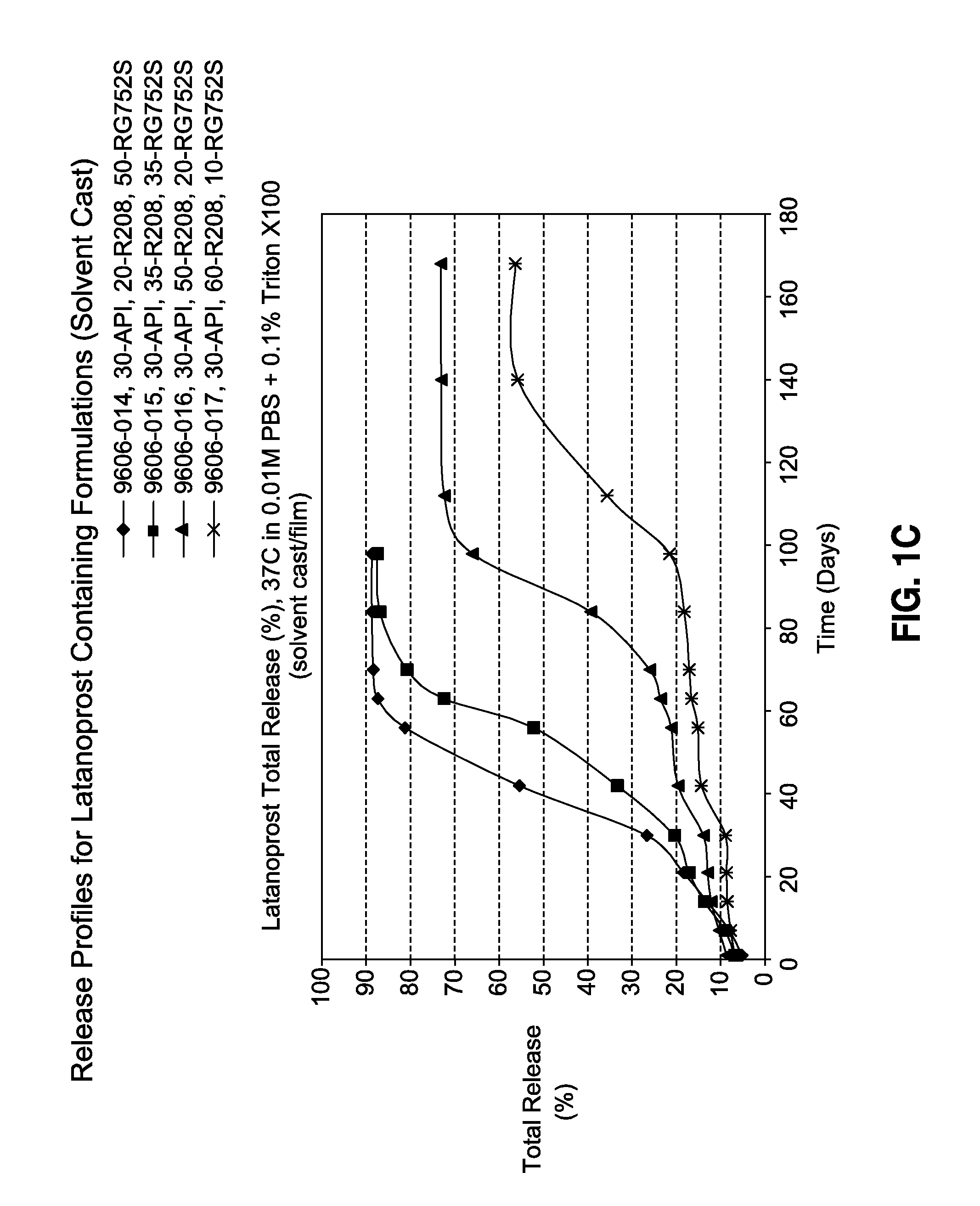
Sustained release delivery of active agents to treat glaucoma and ocular hypertension
ActiveUS20090280158A1Lower eye pressureReduction in patient noncomplianceBiocideSenses disorderLatanoprostActive agent
The methods described herein provide treatment of glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and elevated intraocular pressure with latanoprost or other therapeutic agent(s). Implant devices for insertion into a punctum of a patient provide sustained release of latanoprost or other therapeutic agent(s) that is maintained for 7, 14, 21, 30, 45, 60, or 90 days or more, thus avoiding patient noncompliance and reducing or lowering adverse events associated with eye drop administration of latanoprost or other therapeutic agent(s) and other therapeutic agent(s).
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
Sustained release delivery of one or more agents
InactiveUS20100209477A1Improve permeabilityReduce the amount requiredBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkExcipient
The lacrimal implant delivery systems and methods described herein provide for controlled release of a therapeutic agent for the treatment of disease, including the treatment of glaucoma, ocular hypertension, or elevated intraocular pressure with latanoprost or other anti-glaucoma agents. Treatment of disease, including glaucoma, ocular hypertension, or elevated intraocular pressure with latanoprost or other anti-glaucoma agent in conjunction with penetration enhancer, such as benzalkonium chloride, and / or artificial tears is also provided. Also provided are implants containing a drug core emplacable in a punctum adjacent to an eye of a patient for controlled release of a therapeutic agent such as latanoprost for the treatment of glaucoma, the drug core containing a polymer such as cross-linked silicone, a therapeutic agent, and an excipient, wherein the excipient can increase the rate of release of the agent from the drug core, or can increase the drug loading in the core without loss of desirable homogeneity of the agent within the core, or can improve retention of the agent in the eye or in tear fluid, or can increase corneal penetration of the agent into the eye.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
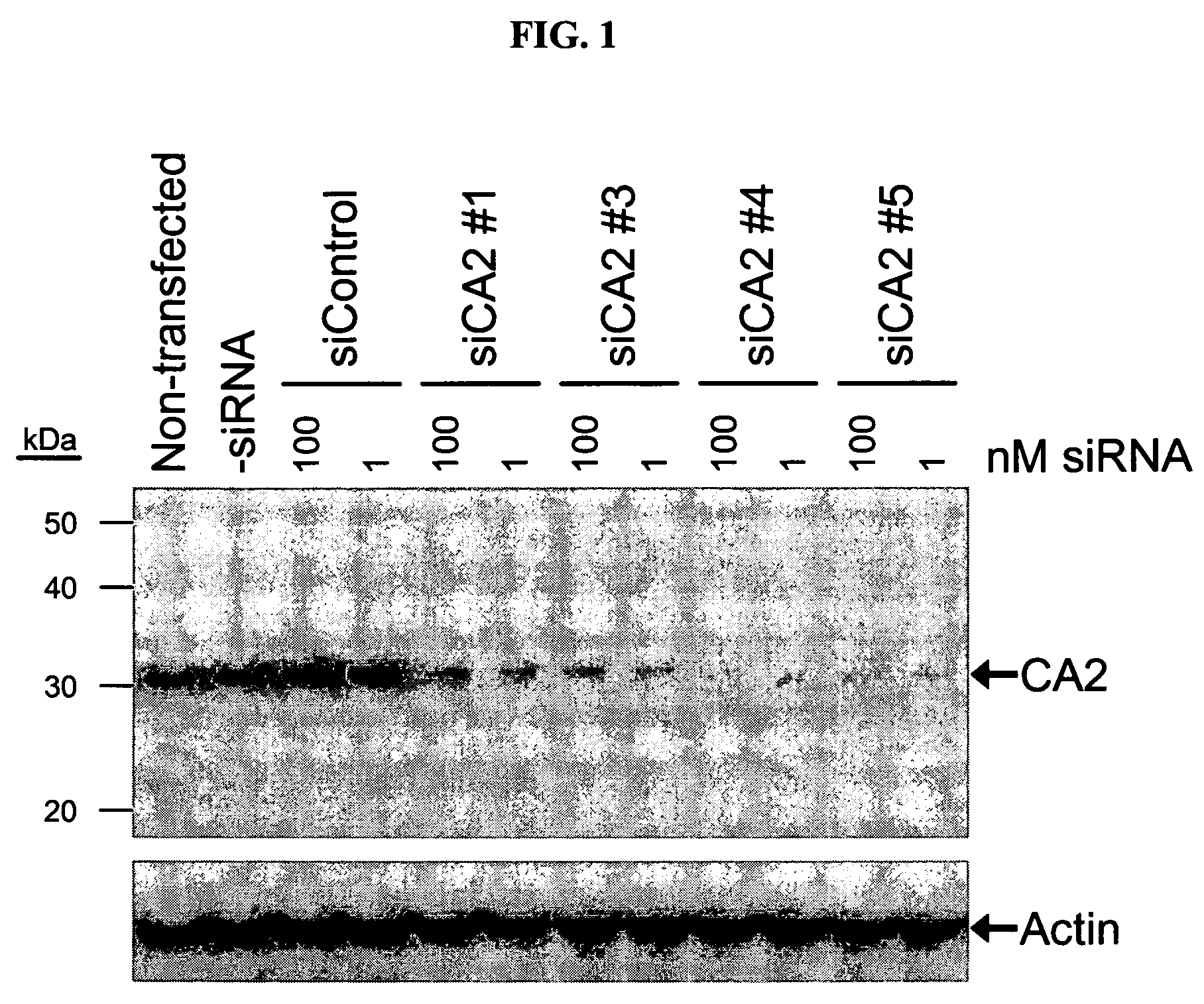
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular targets
InactiveUS20060172965A1Lower eye pressureOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderATPaseOpen angle glaucoma
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Glaucoma surgery methods and systems
InactiveUS8679089B2Minimal thermal effectLower eye pressureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLaser surgeryAqueous flowSchlemm's canal
Methods and systems are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Some embodiments described apparatus and methods useful in photoablation of tissues. In some embodiments, a photoablation apparatus is used to perforate a tissue, forming an aperture into a space behind the tissue. Gases formed during a photoablation process can be used to pressurize the space behind the tissue to enhance patency of the space. In some embodiments the tissue is the trabecular meshwork of the eye and a wall of Schlemm's canal, and the space behind the tissue is a portion of the lumen of Schlemm's canal. In some embodiments, the method is useful in the treatment of glaucoma by improving outflow from the anterior chamber of the eye into Schlemm's canal, reducing intraocular pressure.
Owner:BERLIN MICHAEL S
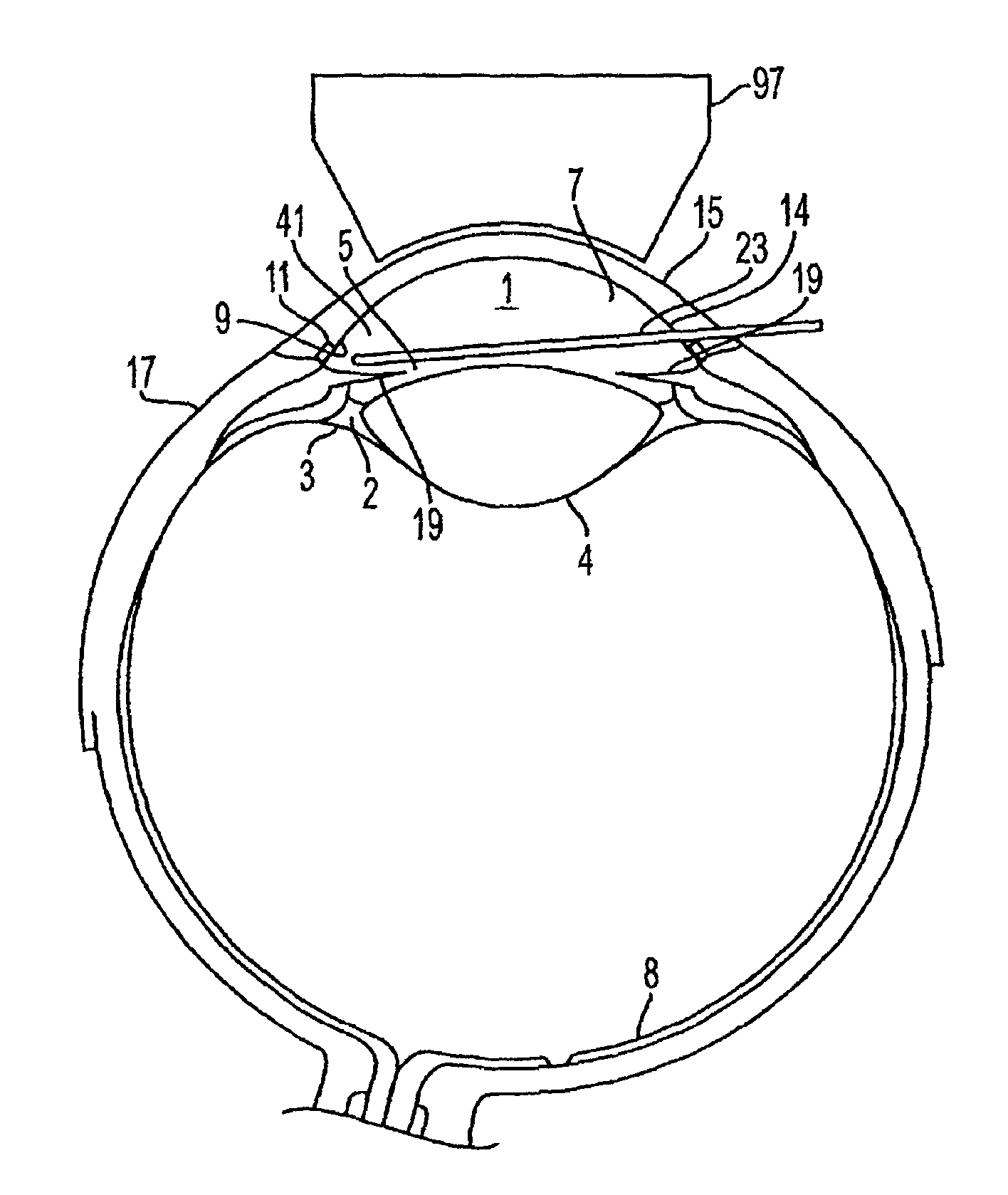
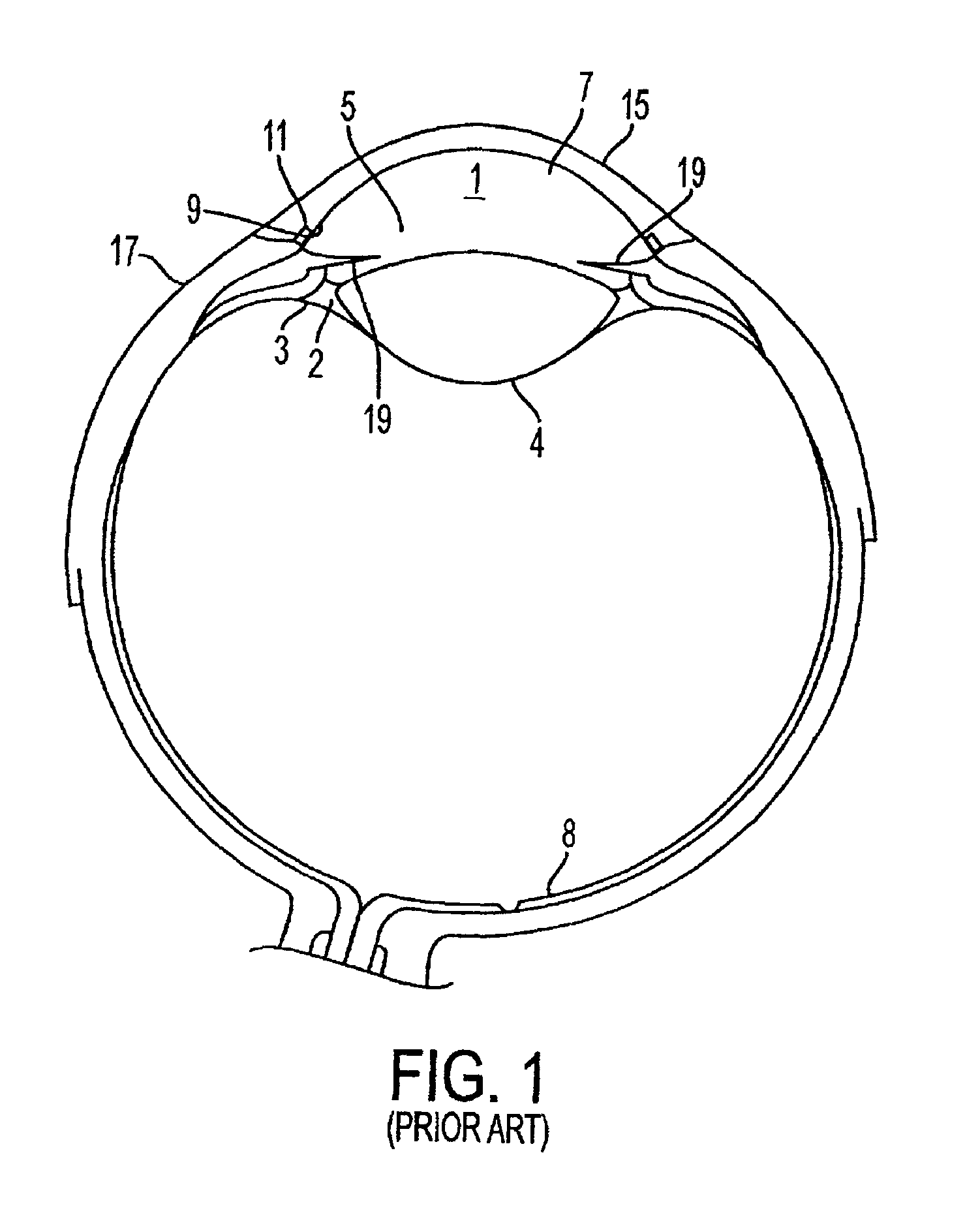
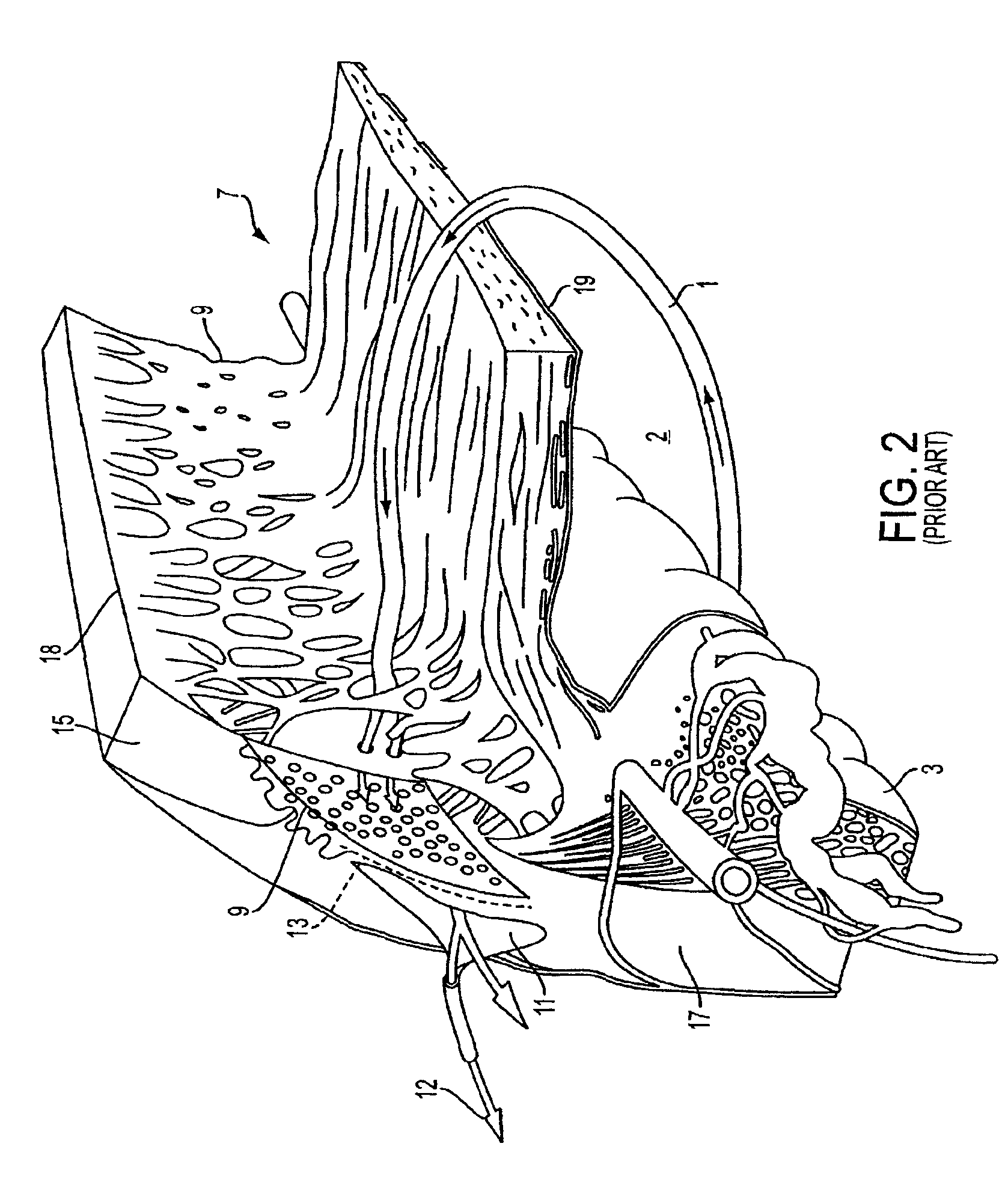
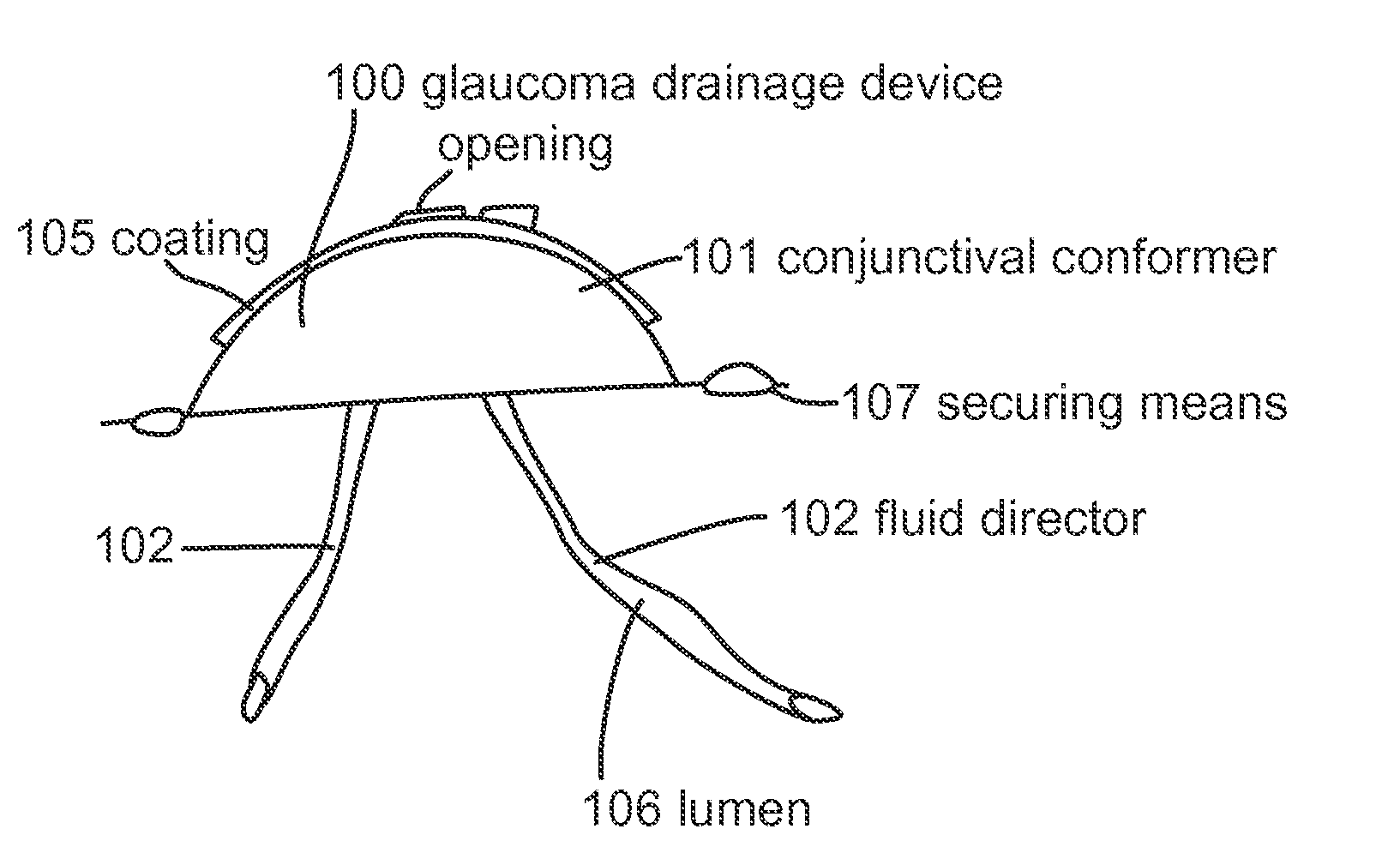
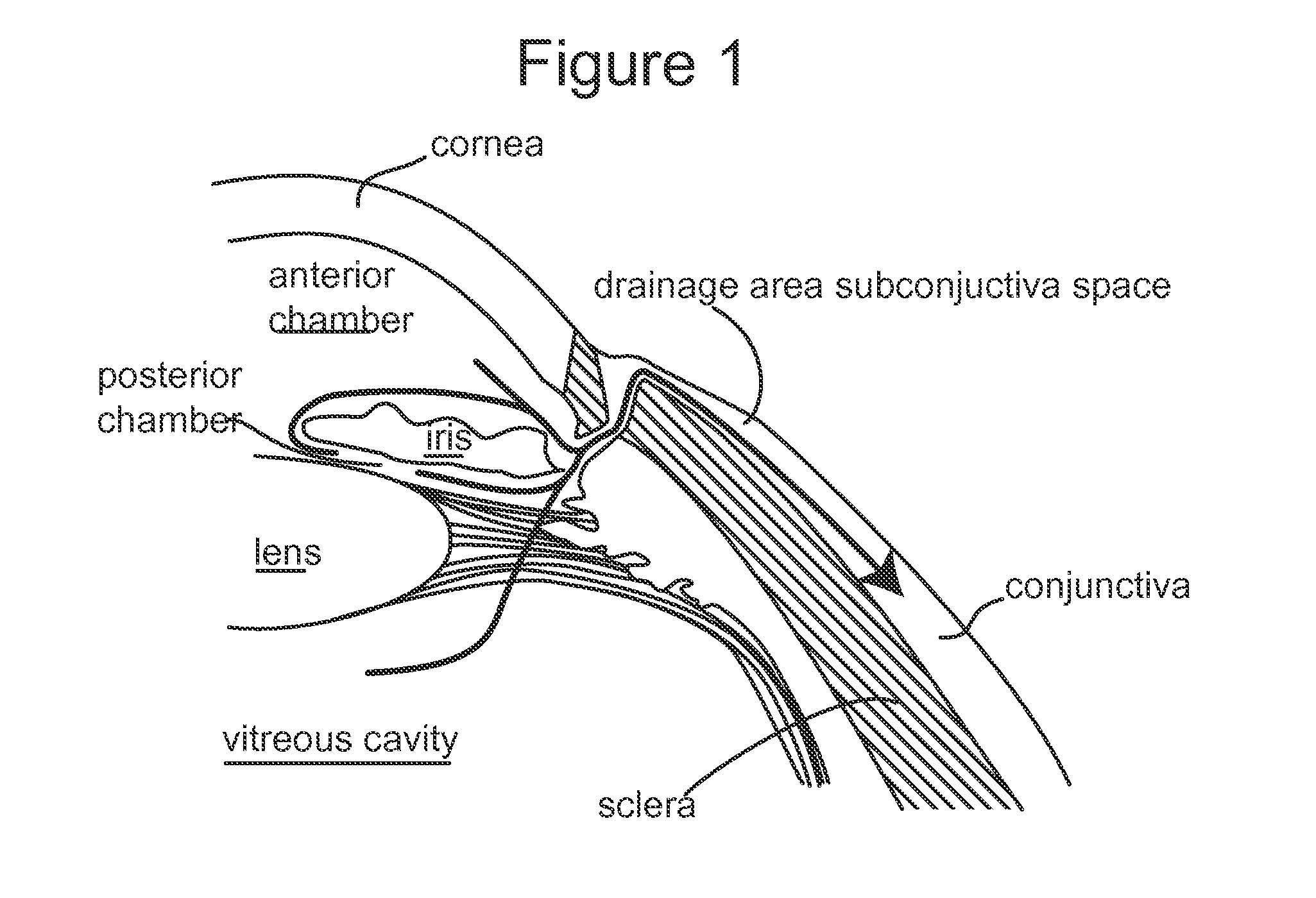
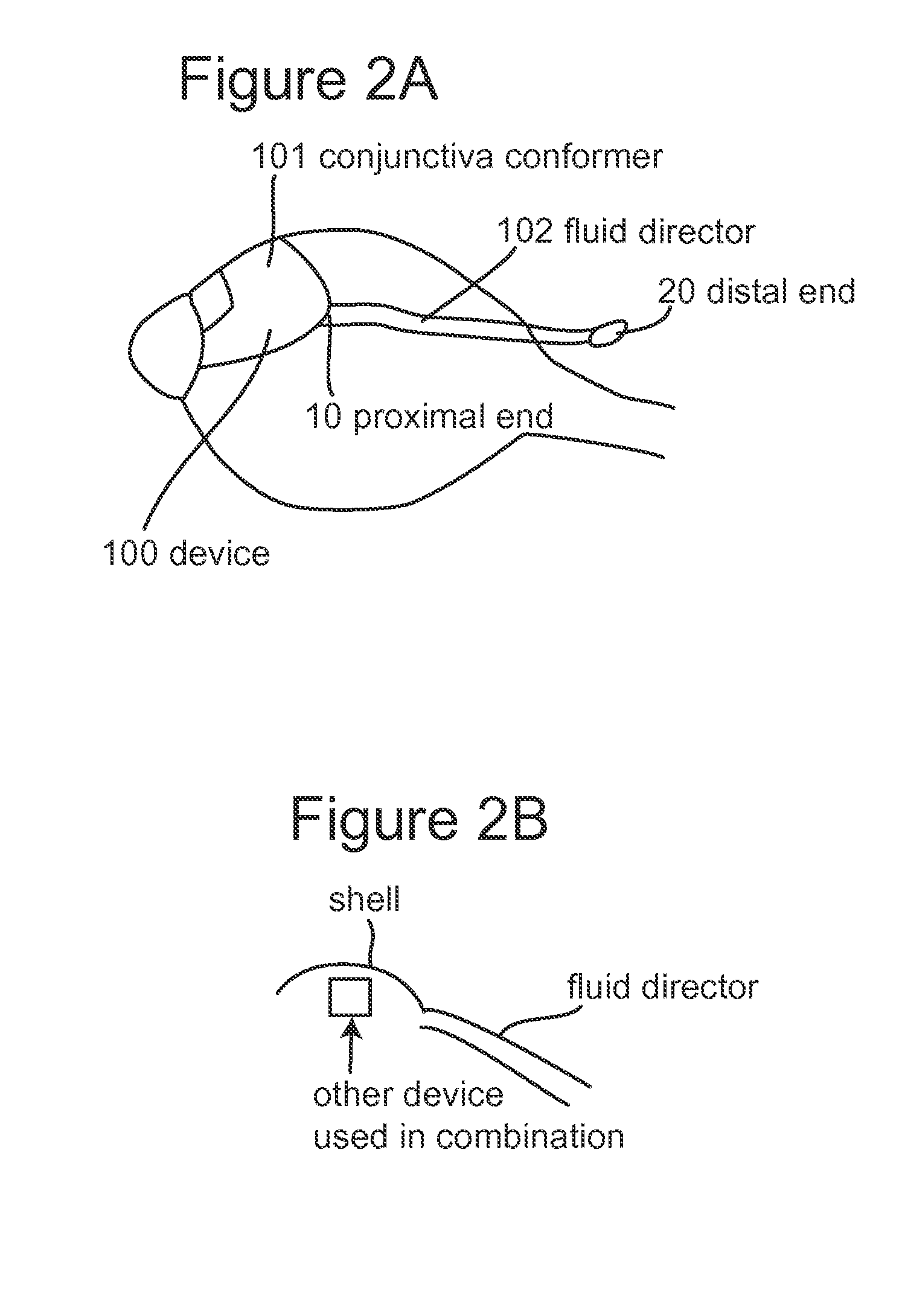
Subconjunctival conformer device and uses thereof
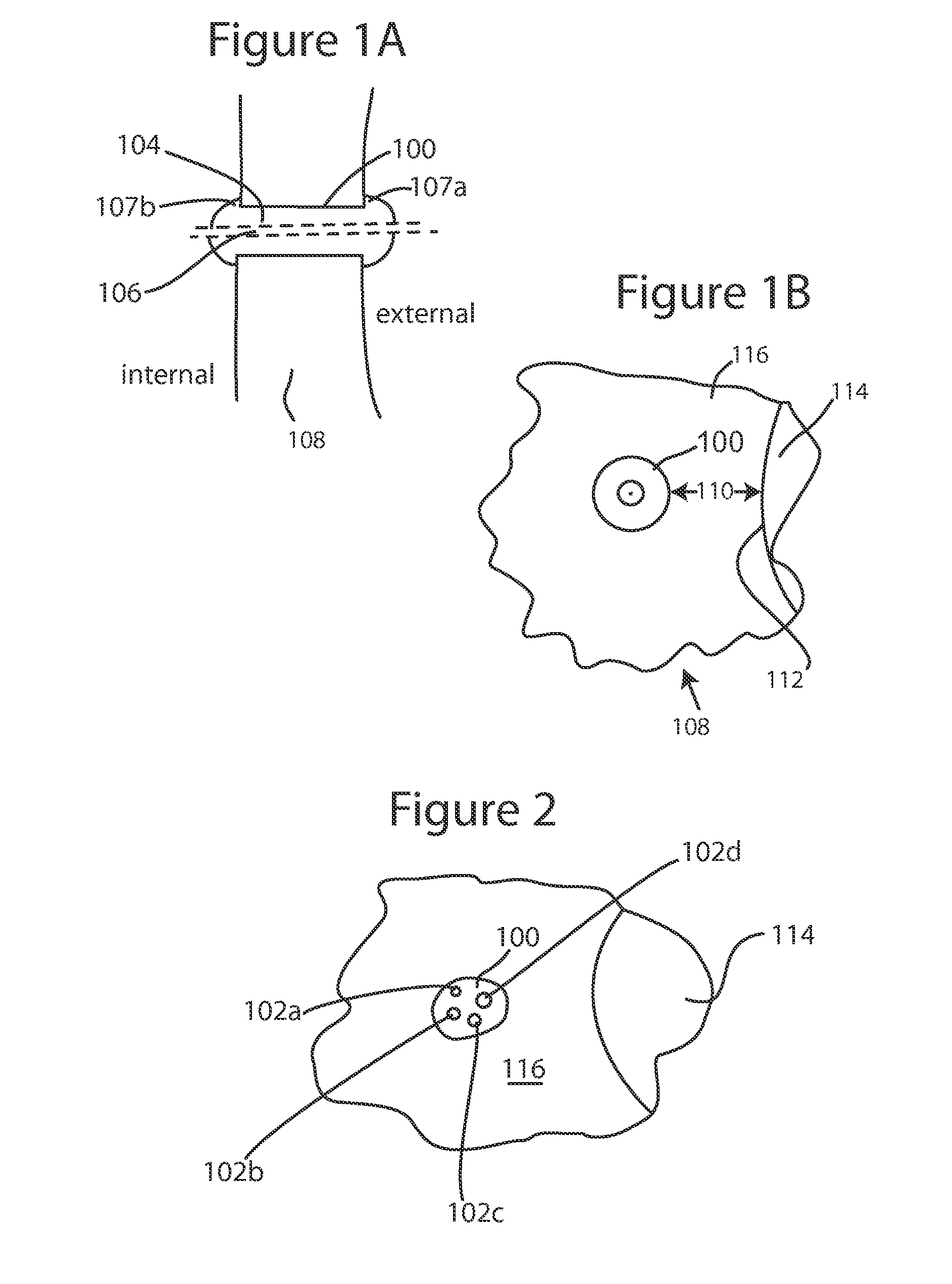
ActiveUS20120089072A1Minimize inflammationMinimize scarringEye surgeryIntravenous devicesConjunctivaElevated intraocular pressure
The present invention provides a device for use in an eye with elevated intraocular pressure or glaucoma, the device comprising a subconjunctival conformer shaped to conform to the eye wall and a fluid director that directs or facilitates the flow of intraocular fluid out of the eye and into the subconjunctival or retrobulbar space. The present invention also provides a method of lowering intraocular pressure using the device of the present invention.
Owner:CUNNINGHAM JR EMMETT T
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular hypertension targets
InactiveUS20060172963A1Lower eye pressureOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderIntra ocular pressureATPase
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:ARROWHEAD RES CORP +1
Glaucoma drainage device and uses thereof
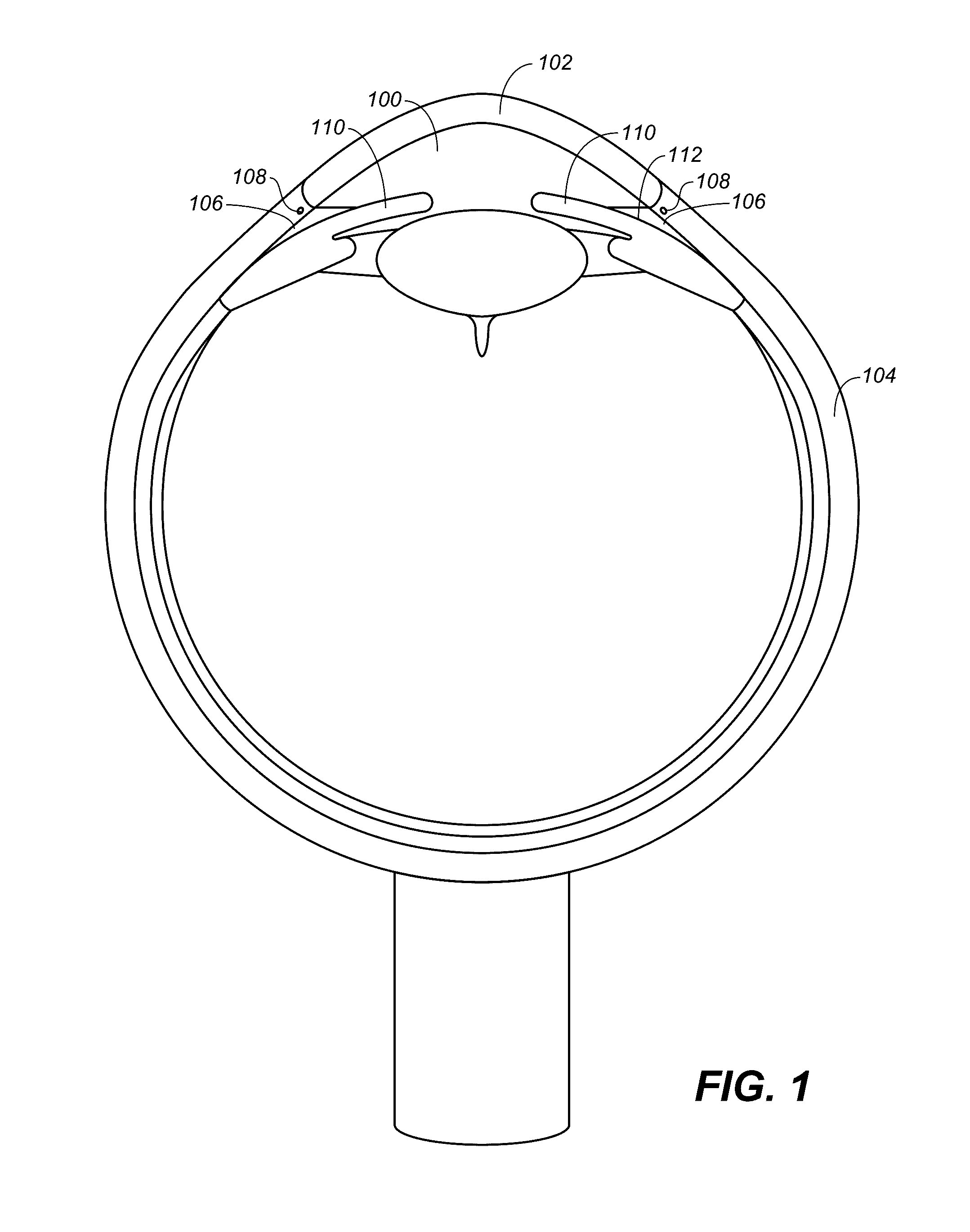
InactiveUS20120089073A1Elevated intraocular pressure or glaucomaPrevent dislocationEye surgeryNanomedicineElevated intraocular pressureImplanted device
In one aspect, the present invention provides an implant device for use in an eye with elevated intraocular pressure or glaucoma. In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for lowering intraocular pressure and / or treating a condition associated with elevated intraocular pressure using the implant device of the present invention.
Owner:CUNNINGHAM JR EMMETT T
Pde1 inhibitors for ophthalmic disorders
ActiveUS20110312978A1Reduce dosageEliminate side effectsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseWhole body
Compounds that inhibit phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1) are useful to treat glaucoma or elevated intraocular pressure. The PDE1 inhibitors may be administered as monotherapy or in combination with additional intraocular-pressure lowering agents. In addition, the invention provides ophthalmic compositions comprising PDE 1 inhibitors and optionally one or more additional intraocular pressure-lowering agents. Topical and systemic therapy may be used.
Owner:INTRA CELLULAR THERAPIES INC
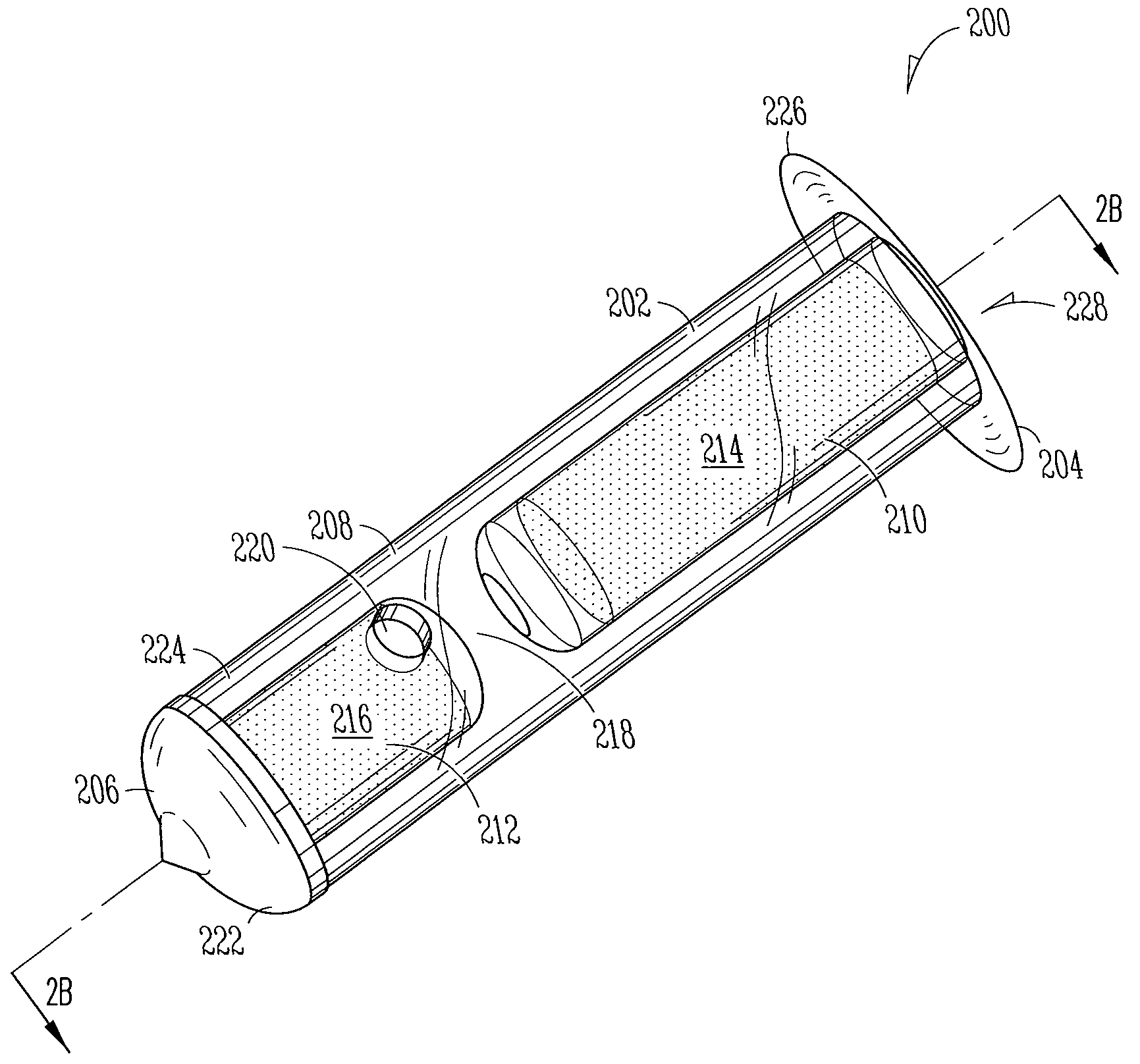
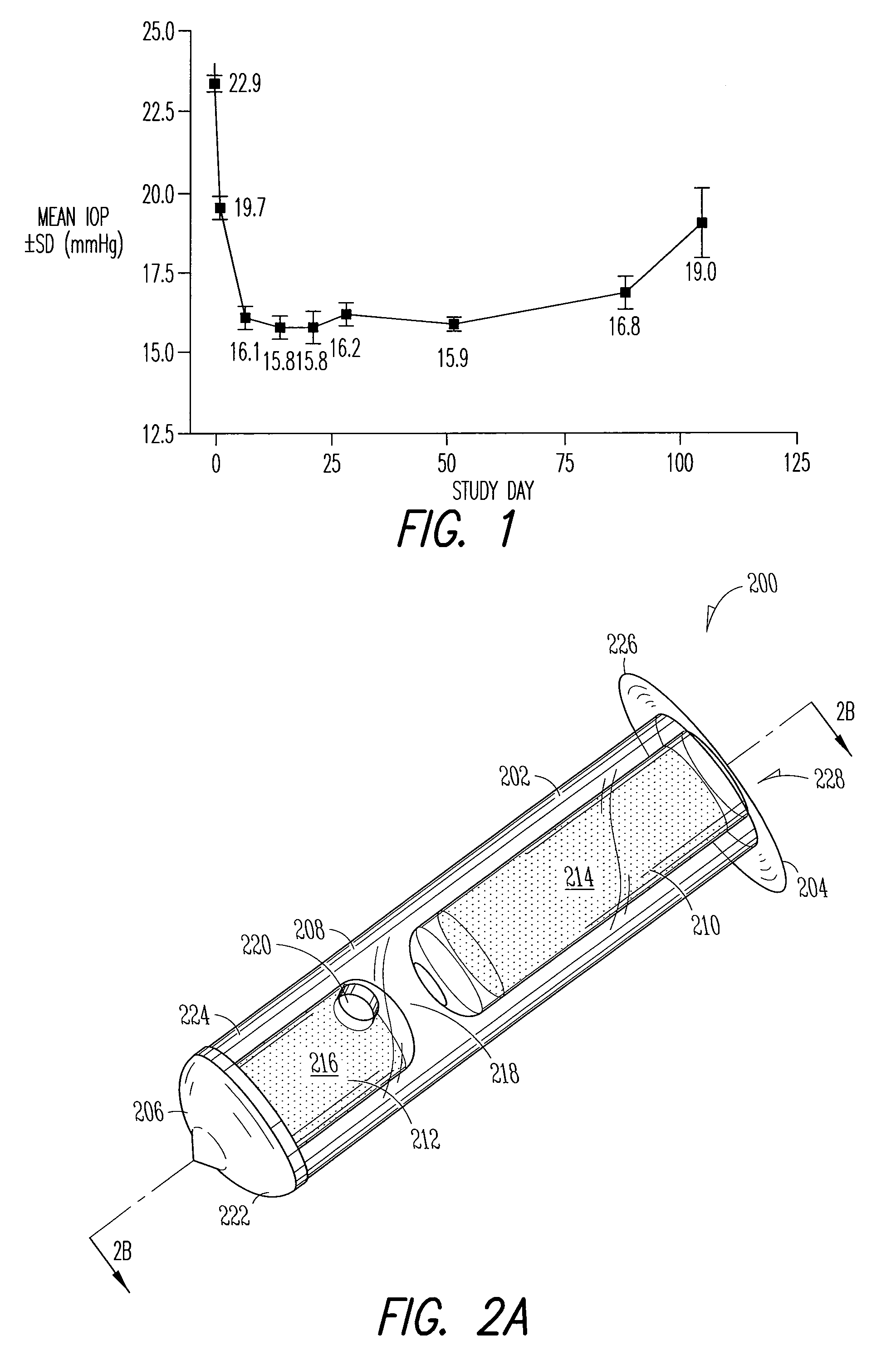
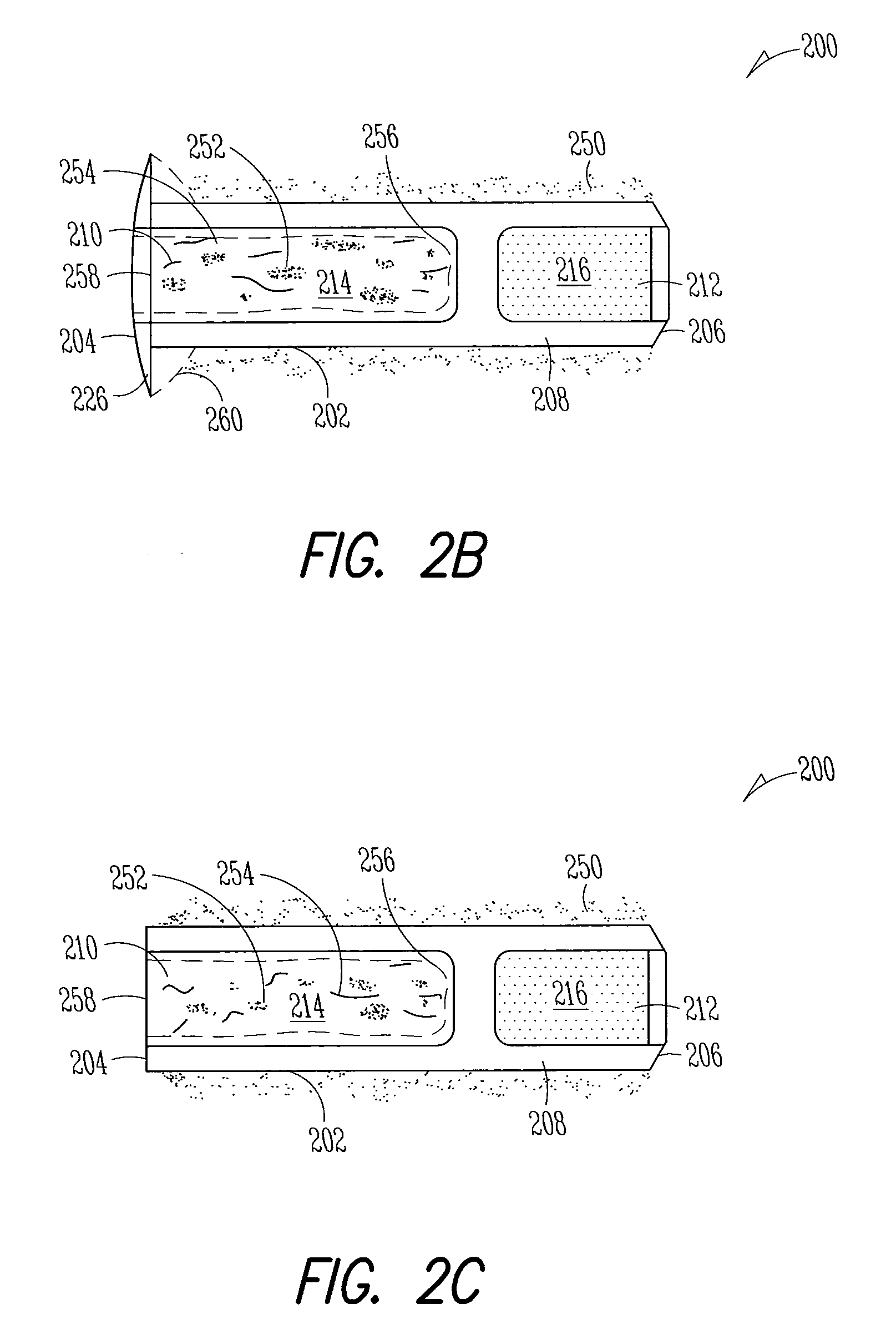
Ocular delivery systems and methods
ActiveUS20160287438A1Easily and reliably accessingMinimal and reduced traumaGuide needlesOrganic active ingredientsAqueous humorSchlemm's canal
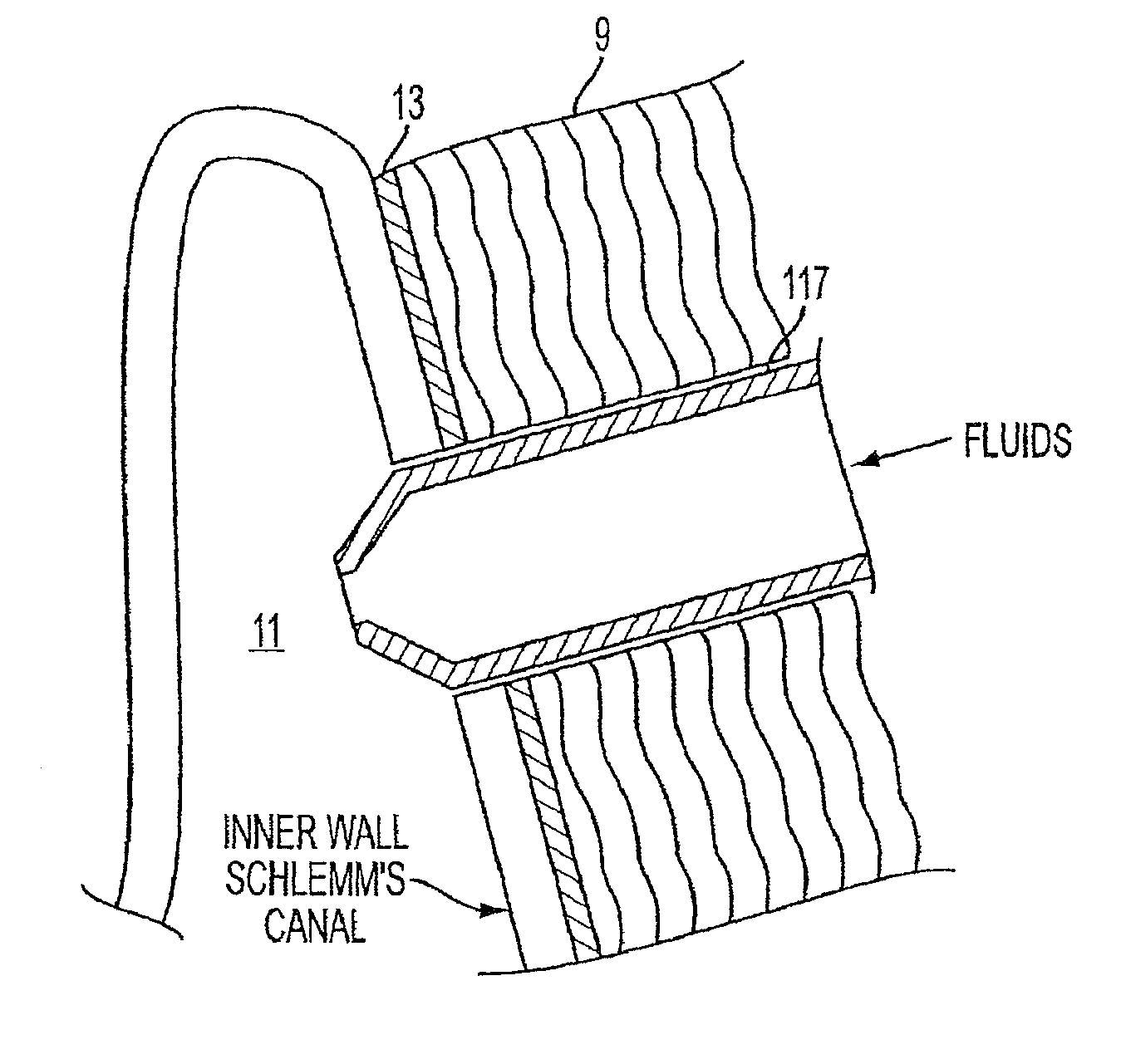
Described here are systems and methods for accessing Schlemm's canal and for delivering an ocular device, tool, or fluid composition therein. The ocular devices may maintain the patency of Schlemm's canal without substantially interfering with transmural fluid flow across the canal. The fluid composition may be a viscoelastic fluid that is delivered into the canal to facilitate drainage of aqueous humor by disrupting the canal and surrounding trabeculocanalicular tissues. Some systems described here may be configured to cut or tear the trabecular meshwork with the body of an elongate member located within Schlemm's canal. Other tools for disrupting these tissues and minimally invasive methods for treating medical conditions associated with elevated intraocular pressure, including glaucoma, are also described.
Owner:SIGHT SCI
Shunt device and method for treating ocular disorders
InactiveUS20100004580A1Expand exportsFacilitates the normal physiologic pathwayEye surgeryWound drainsShunt DeviceAqueous humor
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Delivery system and method of use for the eye
InactiveUS20080108934A1Reduce elevated intraocular pressureMinimal thermal effectLaser surgeryEye implantsPhotoablationFiber
A method and delivery system are disclosed for creating an aqueous flow pathway in the trabecular meshwork, juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal of an eye for reducing elevated intraocular pressure. Pulsed laser radiation is delivered from the distal end of a fiber-optic probe sufficient to cause photoablation of selected portions of the trabecular meshwork, the juxtacanalicular trabecular meshwork and an inner wall of Schlemm's canal in the target site. The fiber-optic probe may be advanced so as to create an aperture in the inner wall of Schlemm's canal in which fluid from the anterior chamber of the eye flows. The method and delivery system may further be used on any tissue types in the body.
Owner:IVANTIS INC
Apparatus and methods for treating excess intraocular fluid
ActiveUS20120184892A1Minimize buildupAvoiding hypotonyEye surgeryFlexible member pumpsDiseaseElevated intraocular pressure
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for reducing intraocular pressure as a means of preventing or treating open-angle glaucoma
ActiveUS20140066821A1Lower Level RequirementsLower eye pressureUltrasound therapyEye surgeryAqueous humorOpen angle glaucoma
Embodiments include methods, apparatuses, and systems for reducing elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in a patient to either prevent or treat open-angle glaucoma. Heat is applied to the trabecular meshwork in the patient's eye without damaging proteins in the trabecular meshwork. The application of heat to the trabecular meshwork has the effect of relaxing or loosening protein clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork, which are either reducing or obstructing of the outflow of aqueous humor, thereby increasing the patient's IOP and causing ocular hypertension (OHT). By loosening or relaxing clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork, the outflow path for aqueous humor is increased or restored, which can lower IOP and either prevent or treat glaucoma. Force may also be applied to the patient's eye to apply pressure to the trabecular meshwork to further assist in the loosening or relaxing of clogs or other inhibitors in the trabecular meshwork.
Owner:TEARSCIENCE INC
Ophthamological drugs
InactiveUS20060135609A1Improve permeabilityEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideMedicineElevated intraocular pressure
The present invention relates generally to ophthamological drugs. More specifically, the inventon relates to a method of modifying (derivatizing) ophthamological drugs so as to increase their penetration through the cornea. The invention also relates to drugs modified (derivatized) in accordance with the instant method and to the use of same in treating conditions associated with elevated intraocular pressure, particularly, glaucoma.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Pyranoindazoles and their use for the treatment of glaucoma
InactiveUS6696476B2Good chemical stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideElevated intraocular pressureTreatment glaucoma
Pyranoindazoles are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for the lowering and controlling of normal or elevated intraocular pressure as well as a method for the treatment of glaucoma using compositions containing one or more of the compounds of the present invention.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Sustained intraocular delivery of drugs from biodegradable polymeric microparticles
ActiveUS20100261646A1Lower eye pressureSustained releaseHormone peptidesBiocideMicrosphereActive agent
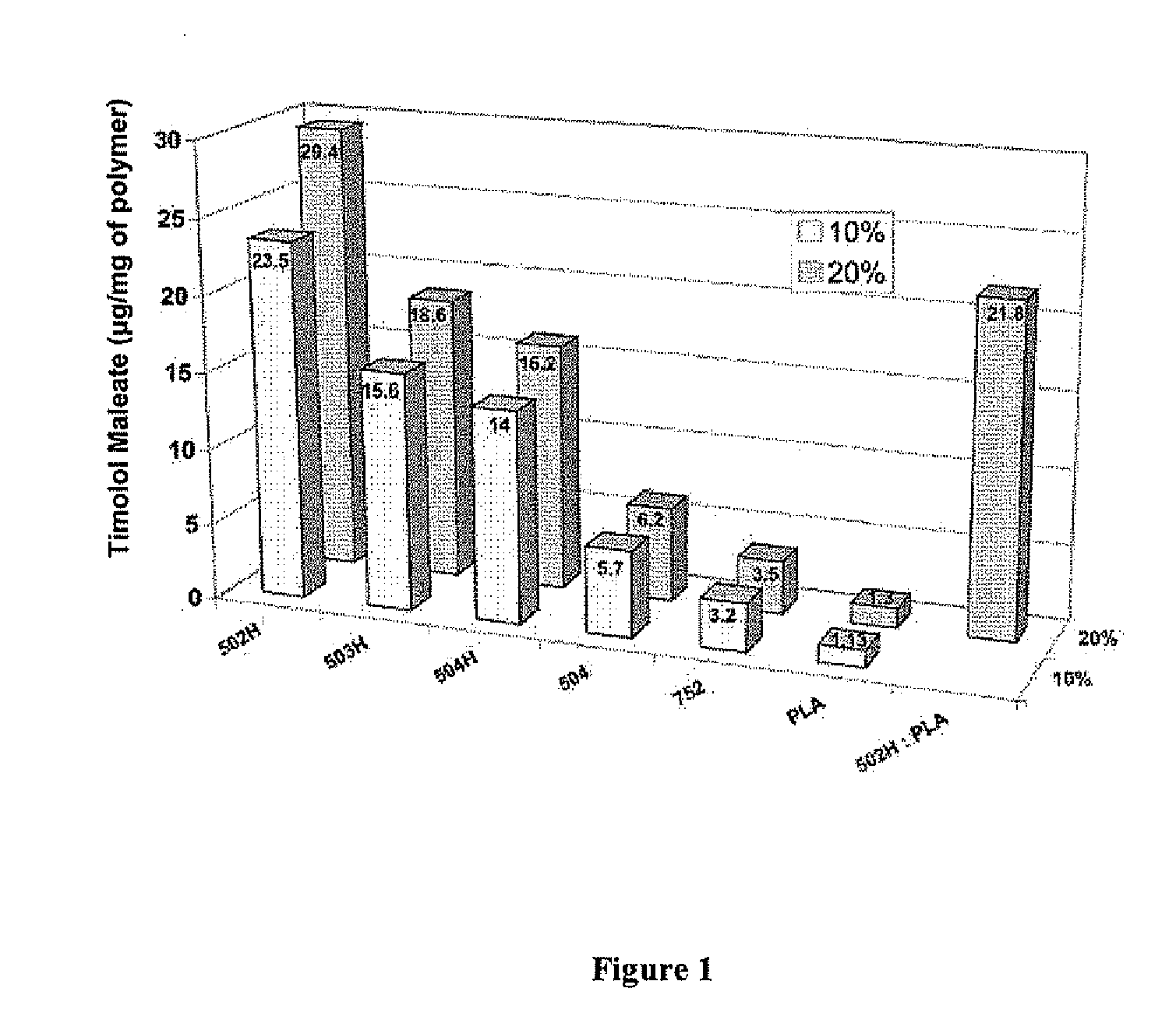
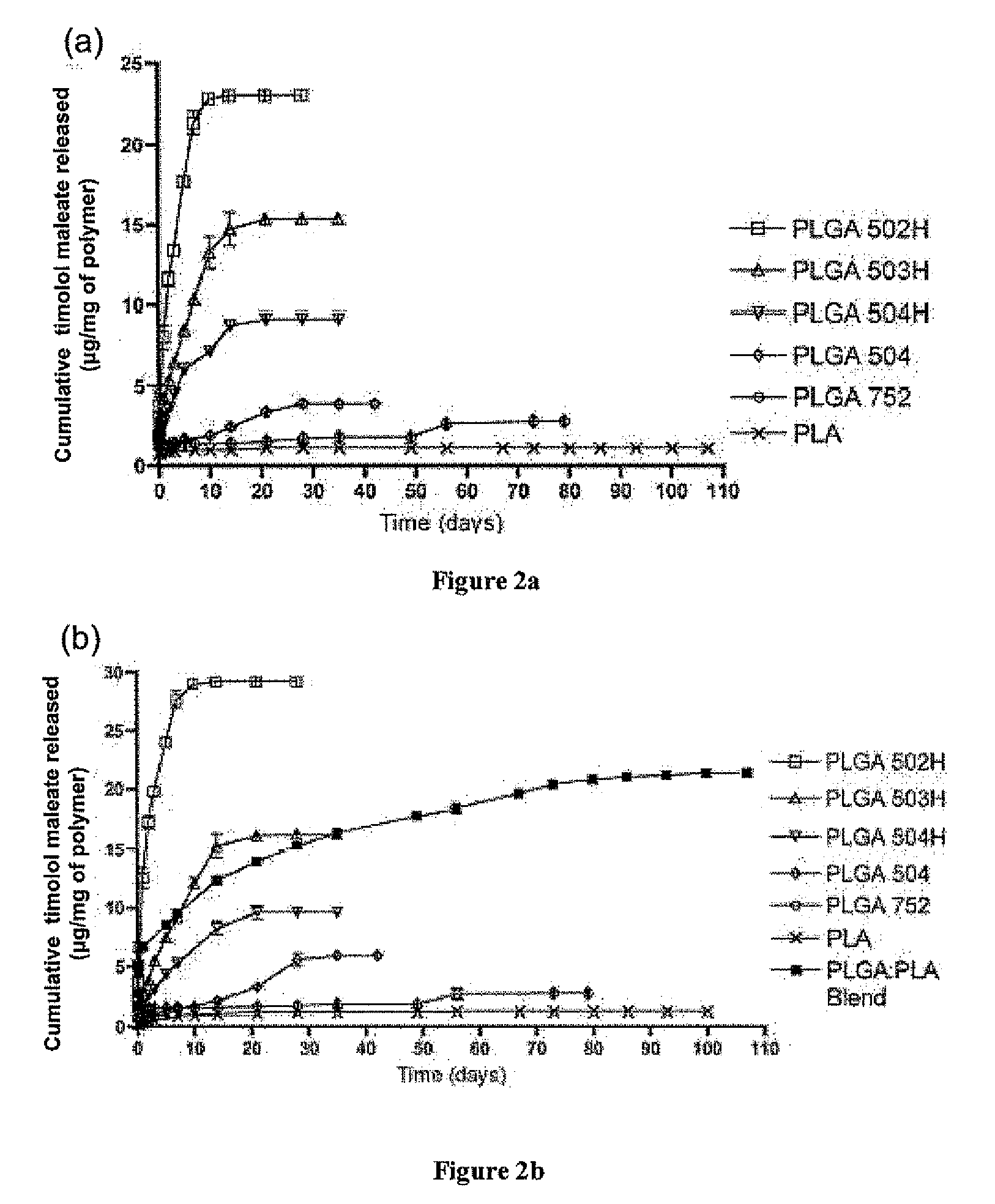
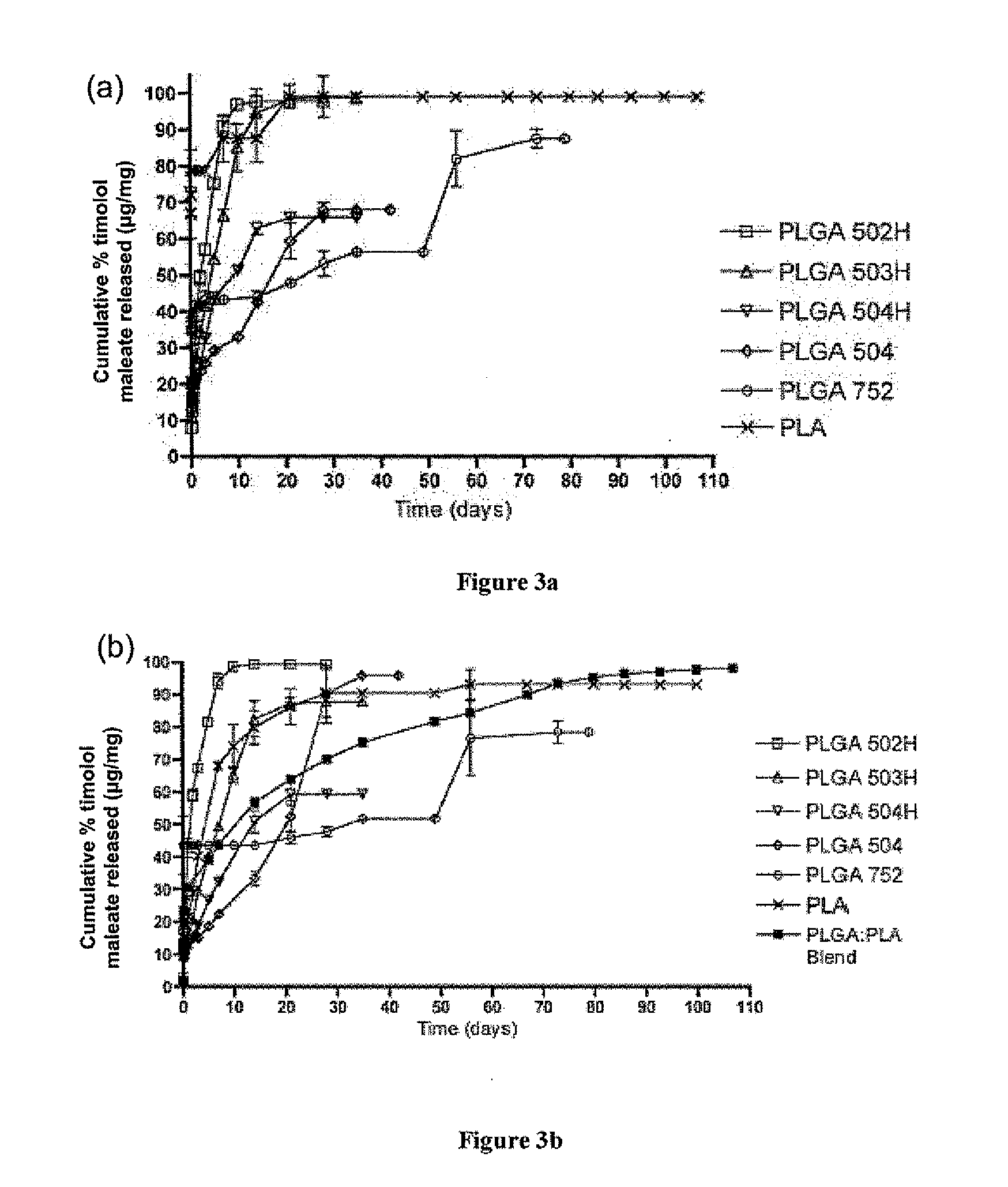
Biodegradable polymeric microparticle compositions containing one or more active agents, especially those useful for treating or preventing or one or more diseases or disorders of the eye, and methods of making and using thereof, are described. The microsphere compositions release an effective amount of the one or more active agents for a period greater than 14 days in vivo, preferably greater than 60 days in vivo, more preferably up to 73 days in vivo, more preferably greater than 90 days in vivo, even more preferably over 100 days in vivo, and most preferably greater than 107 days in vivo. In a preferred embodiment, the microparticle compositions contain one or more active agents useful for managing elevated intraocular pressure (TOP) in the eye. In one embodiment, the microspheres are formed from polylactide-co-glycolide (“PLGA”); in another embodiment, the microspheres are formed from a blend PLGA and poly lactic acid (“PLA”). Relatively hydrophilic, and preferably carboxylated, polymeric materials such as PLGA are used for a drug such as timolol maleate, which is relatively water soluble, to increase drug loading. Higher molecular weight polymers, as well as the ratio of LA (which has a longer degradation time, up to one to two years) to GA (which has a short degradation time, as short as a few days to a week), are used to provide release over a longer period of time. The combination of drug loading and release rate, as well as the minimization of initial burst release, result in prolonged release of a higher amount of drug.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
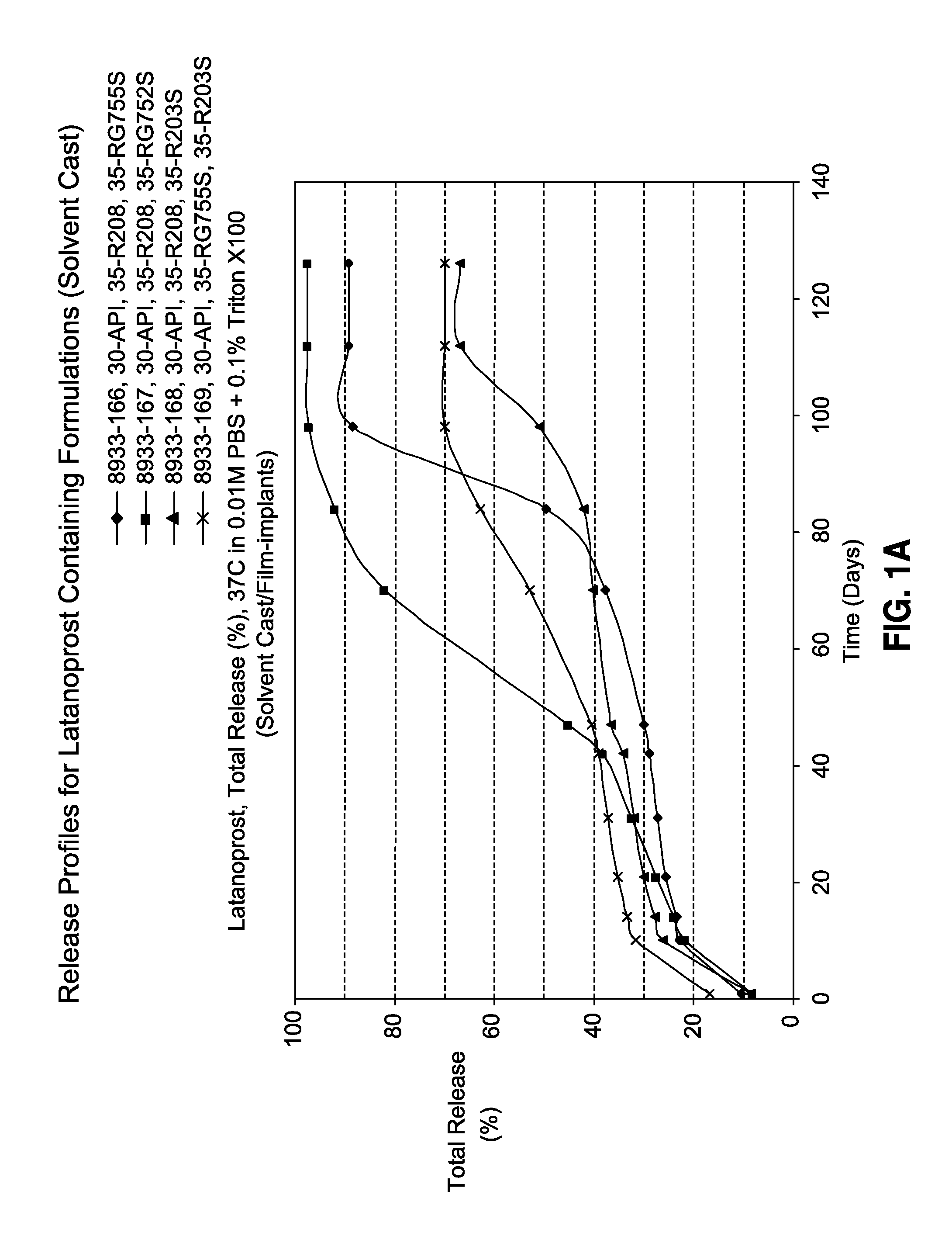
Sustained release latanoprost implant
InactiveUS20120276186A1Preserve latanoprost activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLatanoprostProstate implant
The present invention provides a sustained release, biodegradable intraocular latanoprost implant for reducing elevated intraocular pressure in an individual in need thereof. The implant can be configured as a film (e.g., a rolled film) or extruded filament, either of which can be inserted into the eye of the individual to provide for extended release of latanoprost for several days. Upon insertion into the eye, a rolled film may unroll to provide a film having a high surface area to volume ratio for drug diffusion.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular targets
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Combination of brimonidine and timolol for topical ophthalmic use
Owner:ALLERGAN SALES LLC
Apparatus for treating excess intraocular fluid
ActiveUS20170348149A1Avoiding hypotonyConstant forceEye surgeryWound drainsDiseaseElevated intraocular pressure
Apparatus and methods are provided for treating diseases that produce elevated intraocular pressures, such as glaucoma, wherein the device operates on the principles of a Starling resistor, and includes a housing, a deformable structure and a spring mounted within a housing, such that the spring applies a substantially constant spring force over a predetermined working range on the deformable structure to thereby self-regulate flow of fluid through the deformable structure.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Cyclopentane 1-hydroxy alkyl or alkenyl-2-one or 2-hydroxy derivatives as therapeutic agents
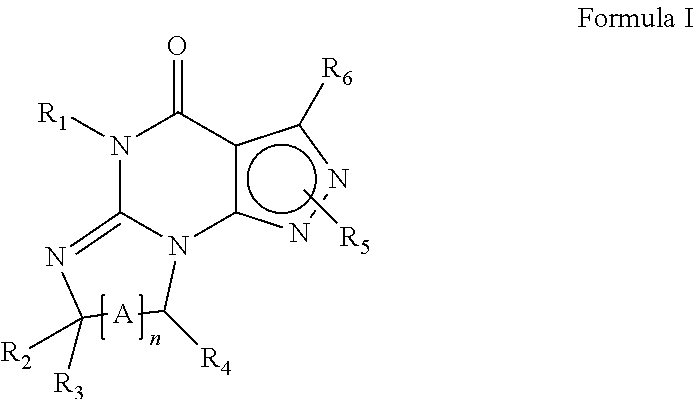
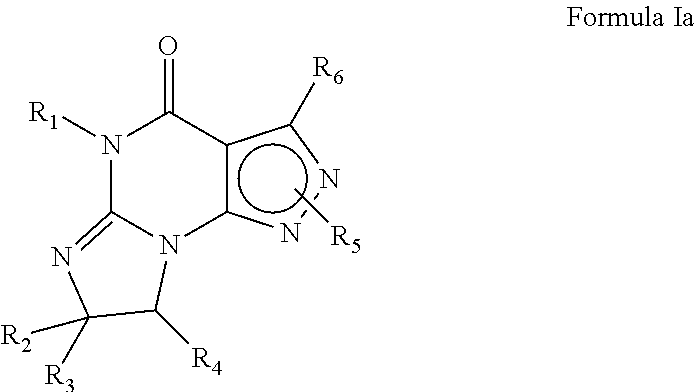
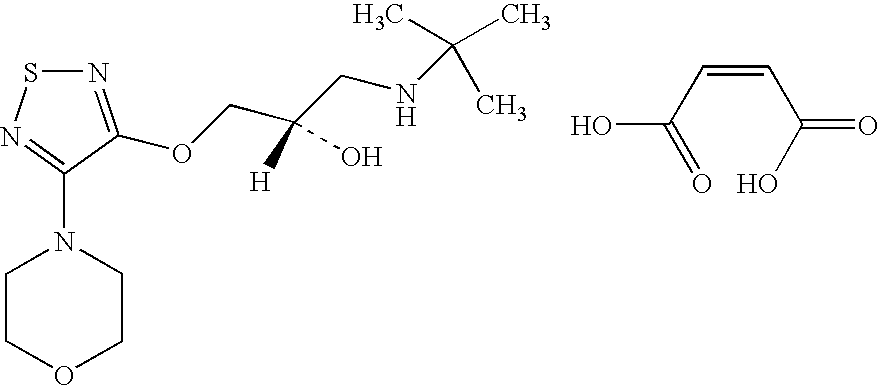
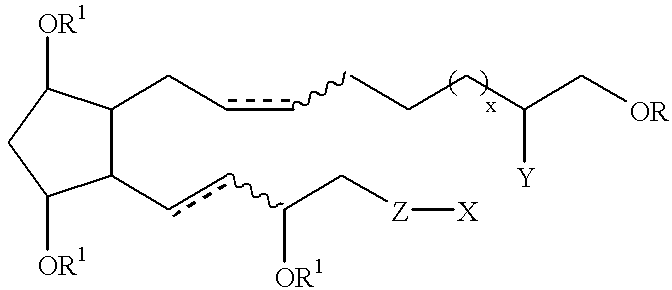
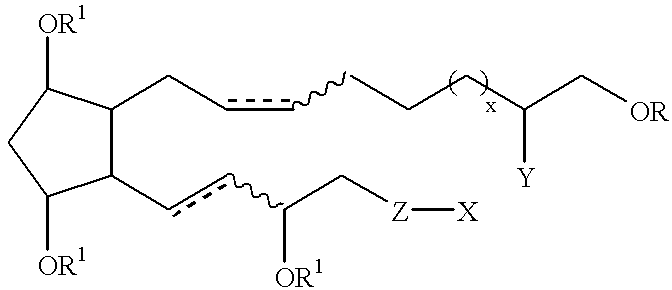
The present invention provides a novel compound represented by the general formula I;wherein R is H or COR3;R1 is H, R2, phenyl, or COR3, wherein R2 is C1-C5 lower alkyl and R3 is R2 or phenyl;Z is CH2 or O;Y is OH or OCOR3;x is 0 or 1; andX is C1-C5 n-alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, phenyl, furanyl, thienyl or substituted derivatives thereof, wherein the substituents maybe selected from the group consisting of C1-C5 alkyl, halogen, CF3, CN, NO2, NR42, CO2R4 and OR4 wherein R4 is hydrogen or C1-C5 alkyl and dotted lines represent the presence or absence of a double bond and wavy lines represent a cis or trans bond. These novel compounds are especially useful for treating elevated intraocular pressure (ocular hypertension) and glaucoma.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Ep4 receptor agonists
InactiveUS20060167081A1Elevated intraocular pressureBiocideSenses disorderOsteoblastElevated intraocular pressure
This invention relates to potent selective agonists of the EP, subtype of prostaglandin E2 receptors, their use or a formulation thereof in the treatment of glaucoma and other conditions which are related to elevated intraocular pressure in the eye of a patient. This invention further relates to the use of the compounds of this invention for mediating the bone modeling and remodeling processes of the osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Owner:MERCK FROSST CANADA INC
Combination of brimonidine and timolol for topical ophthalmic use
Disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising brimondine and timolol for topical ophthalmic delivery and a method of treatment comprising administering said composition when indicated for glaucoma and associated conditions such as elevated intraocular pressure in the eyes of humans.
Owner:ALLERGAN SALES LLC
Ocular devices
Ocular devices are provided for placement in the upper fornix of the eye and having a body that encompasses a low-level light source, an energy source, a microcontroller, and an antenna for delivering a programmable, fade in-out, light therapy regimen to treat neurological and ophthalmic diseases and disorders. In one embodiment the ocular device delivers a programmable green light therapy to reduce elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) and retinal hypoxia during the nocturnal period, that is, when these risk factors are at their highest level especially in glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy patients.
Owner:ALVALUX MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for treating an ocular disorder
Embodiments of the claimed invention are directed to the treatment of glaucoma (or conditions of elevated intraocular pressure) using a novel ab interno trabeculotomy procedure that uses a flexible device. At least one advantage of the present method is that it does not require a conjunctival or scleral incision, which in turn improves patient recovery time and healing.
Owner:NOVA EYE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com