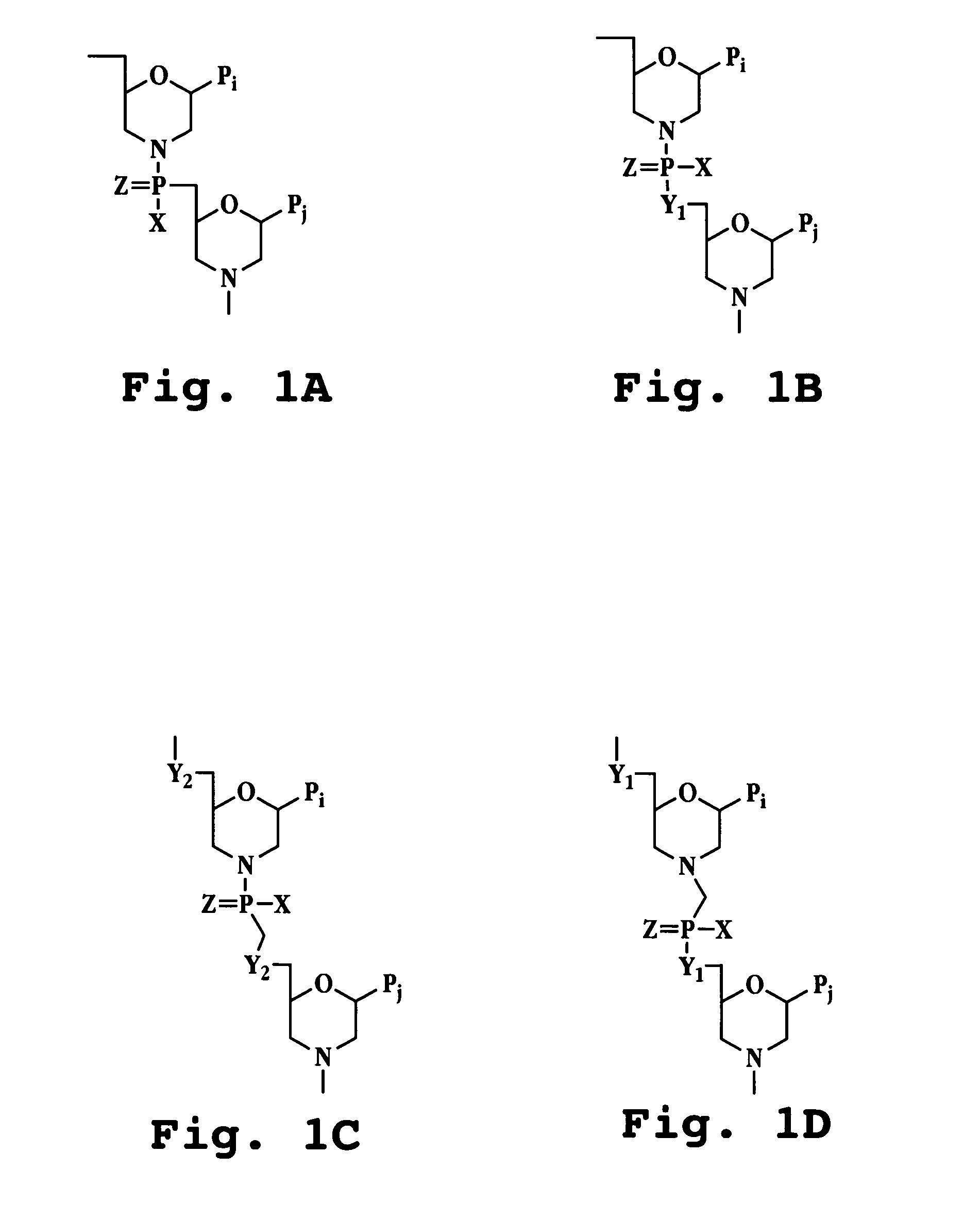
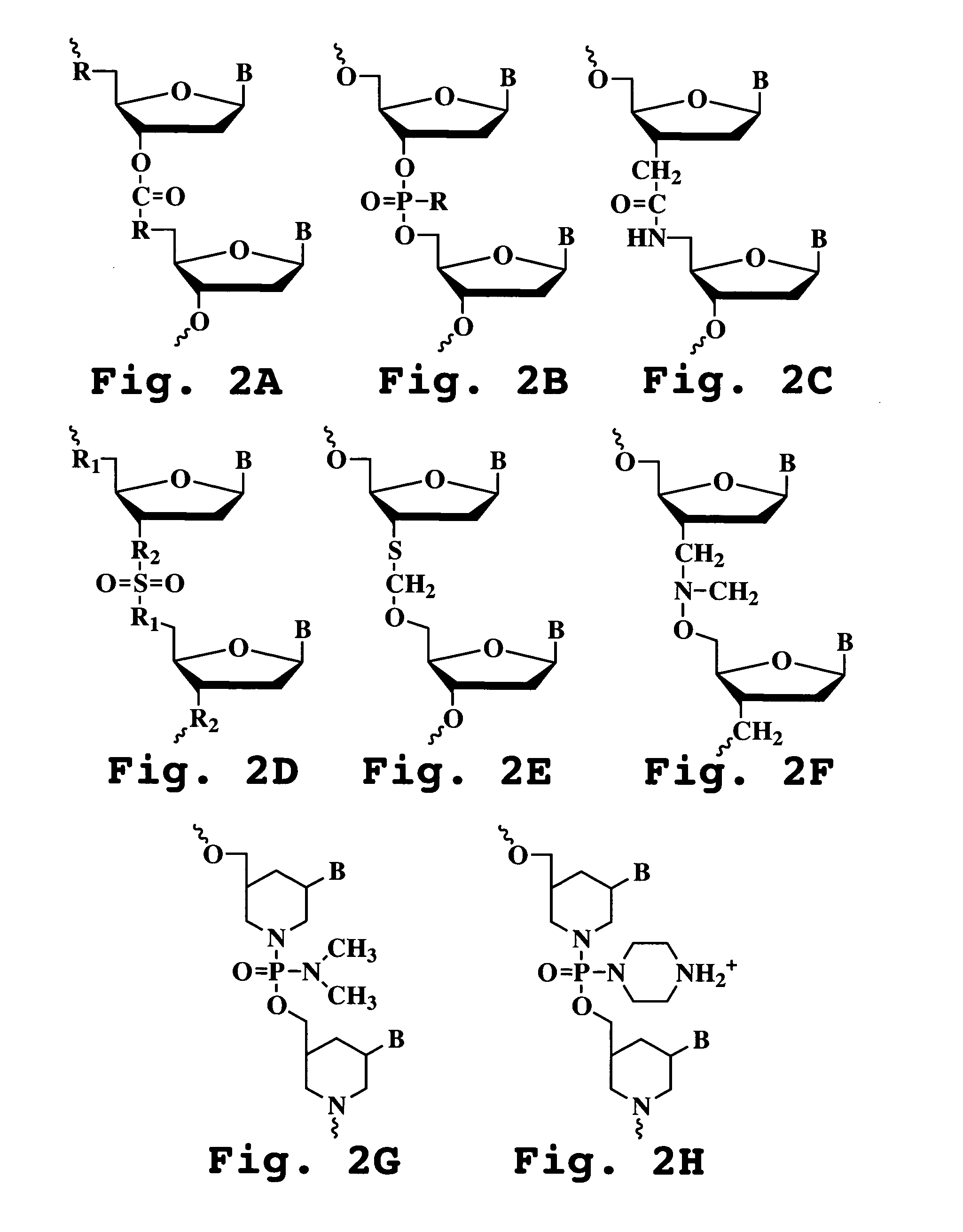
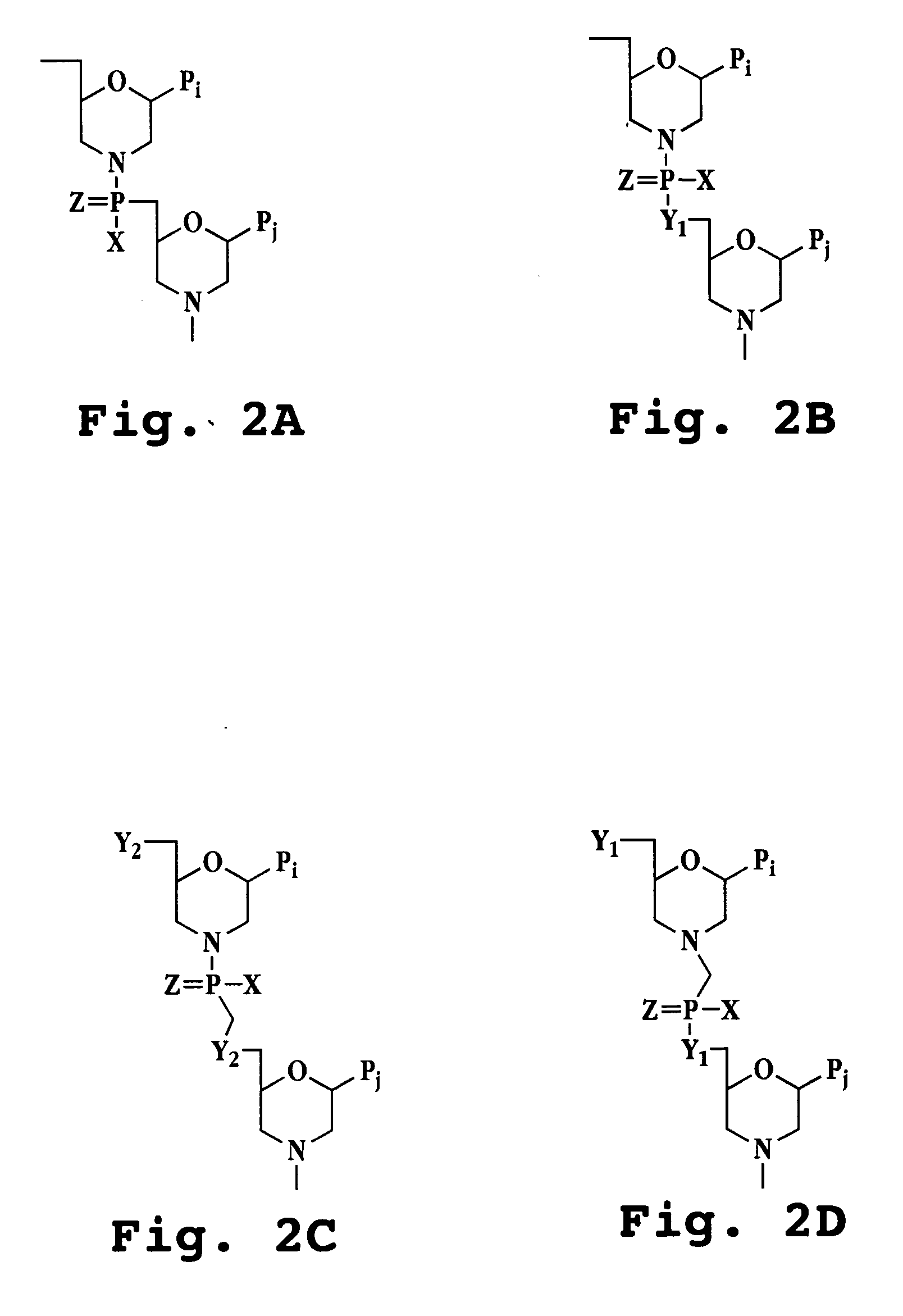
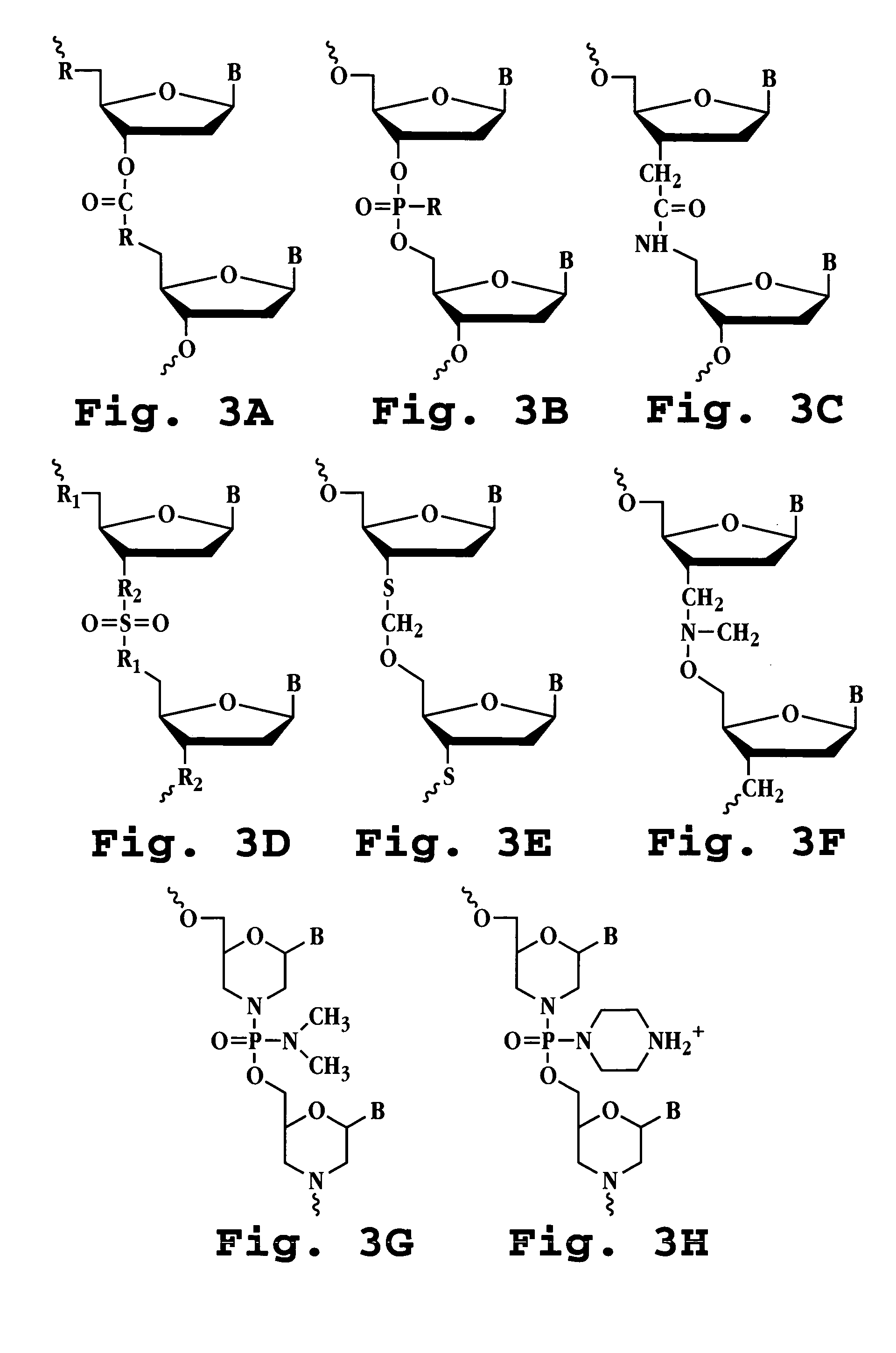
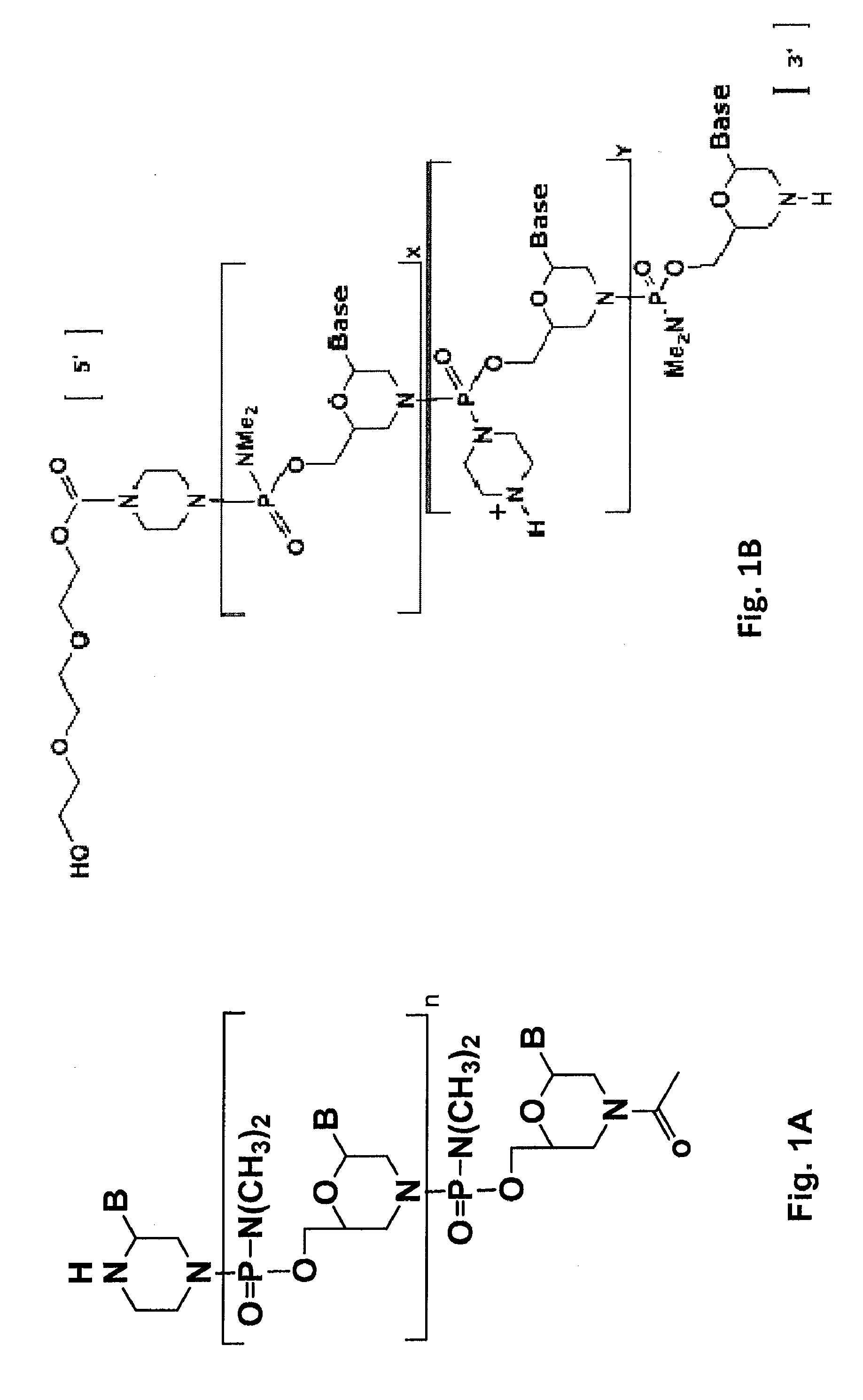
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Target mrna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
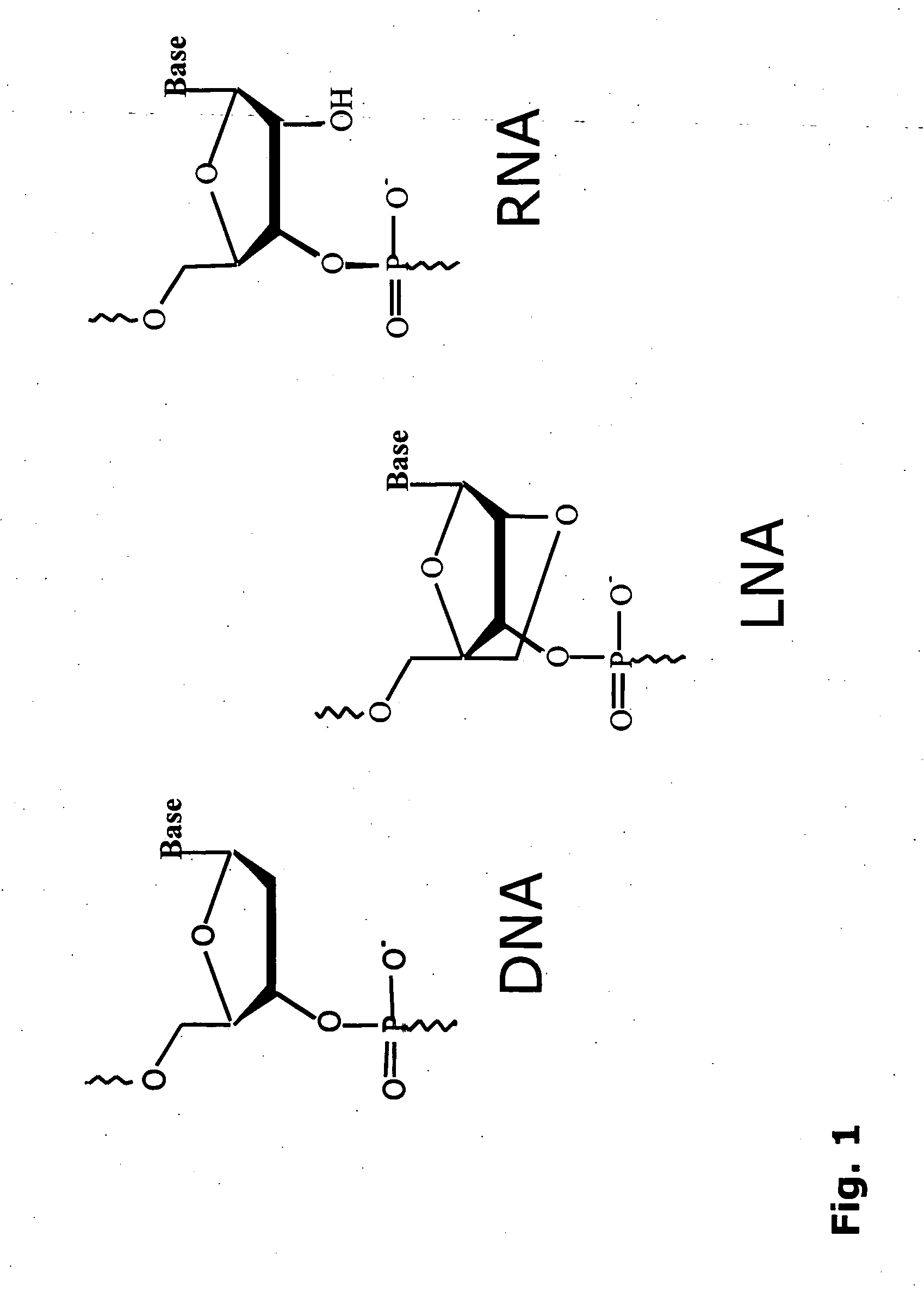
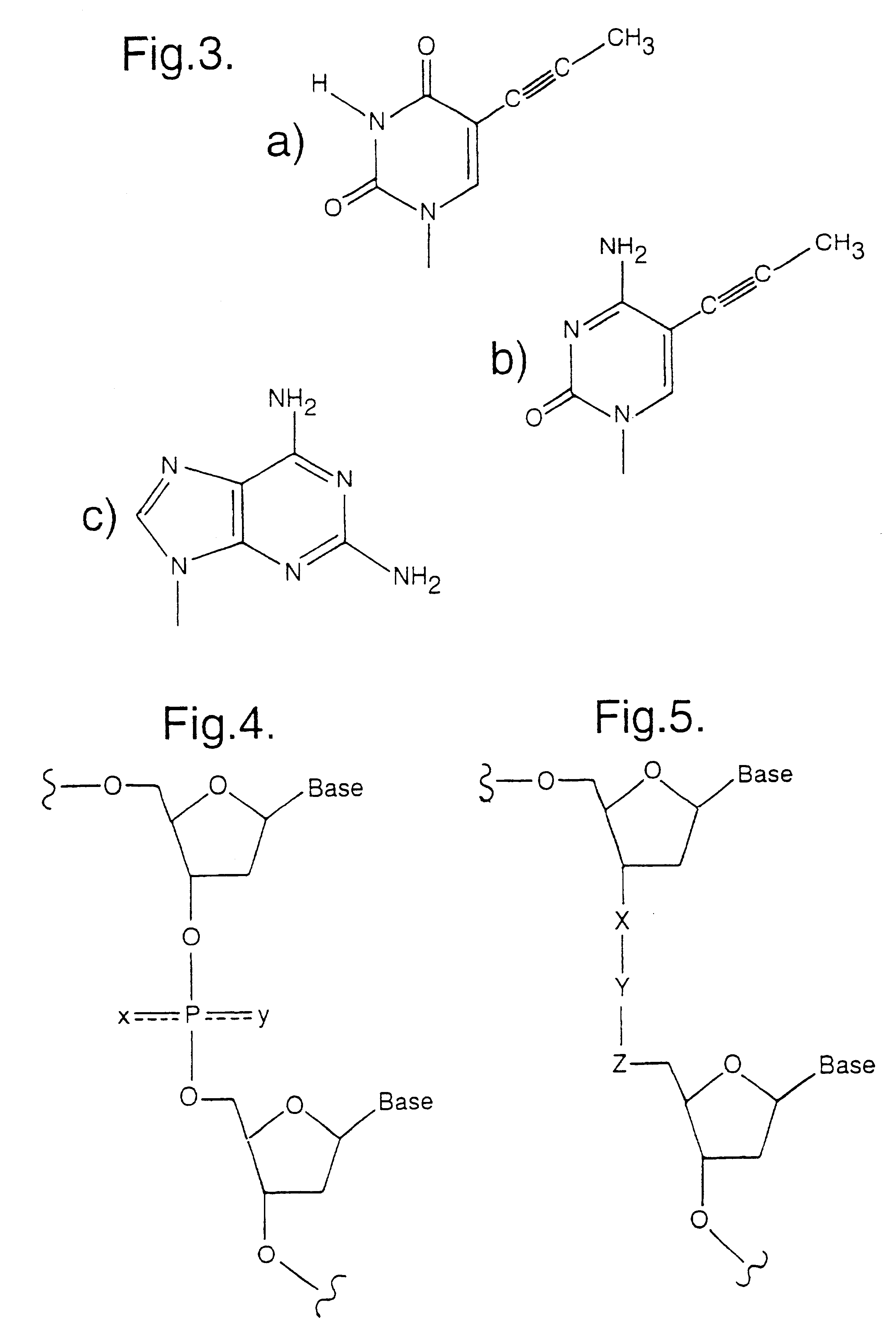
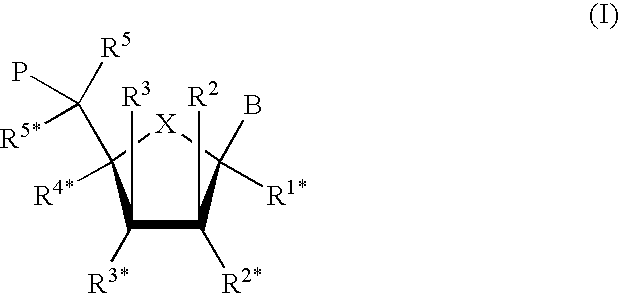
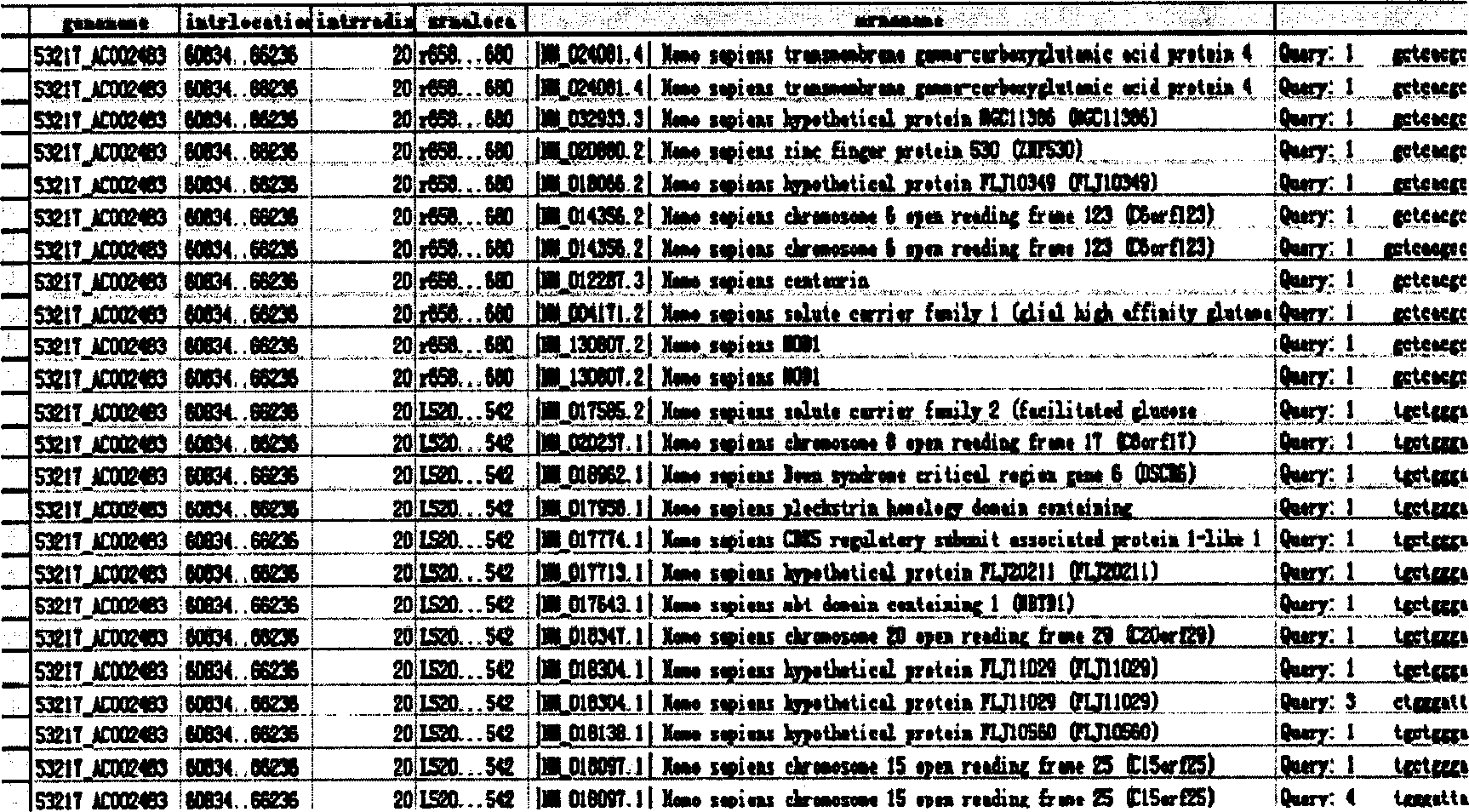
Novel oligonucleotide compositions and probe sequences useful for detection and analysis of micrornas and their target mRNAs
InactiveUS20070099196A1Solve low usageSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsTarget mrna
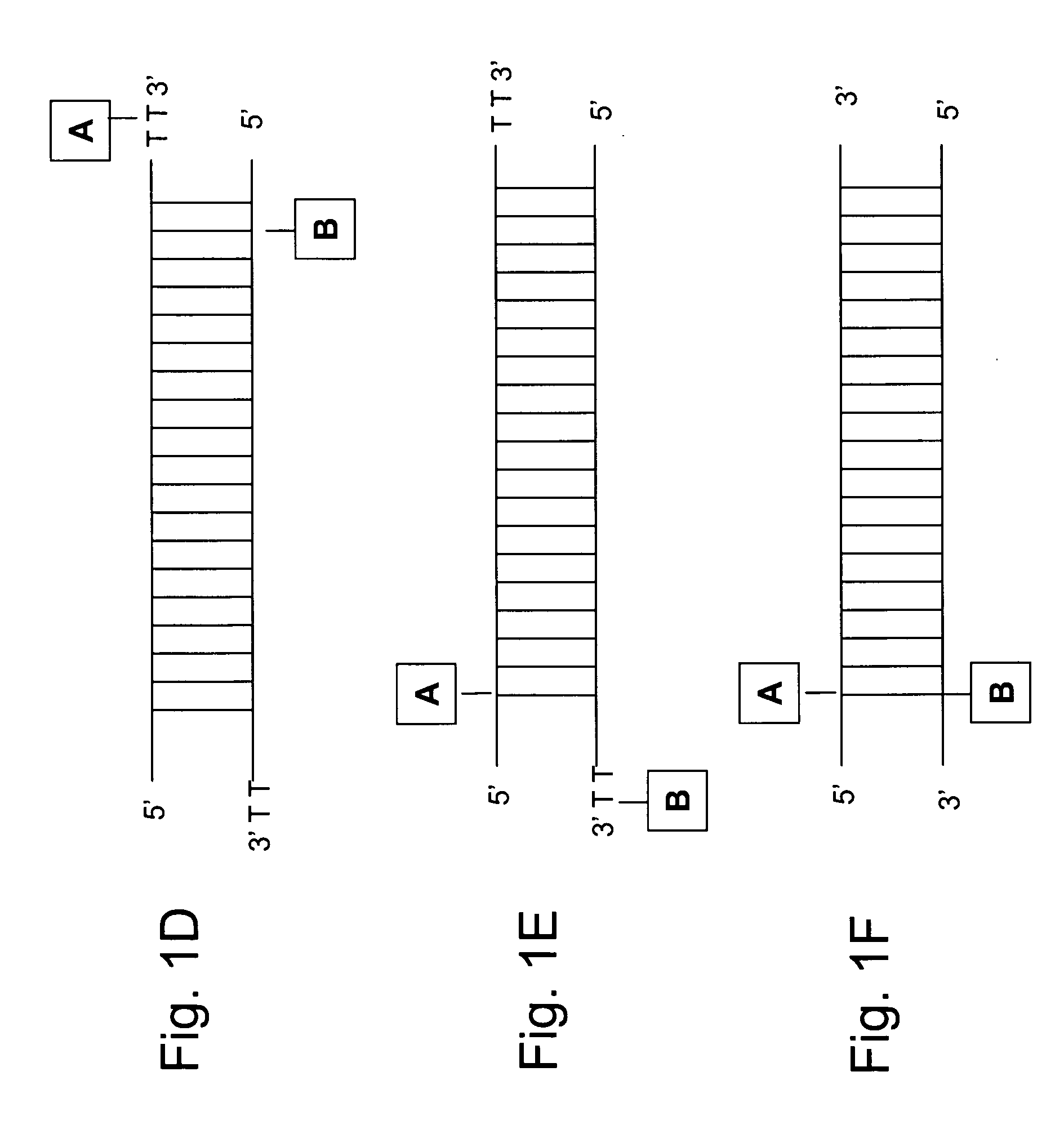
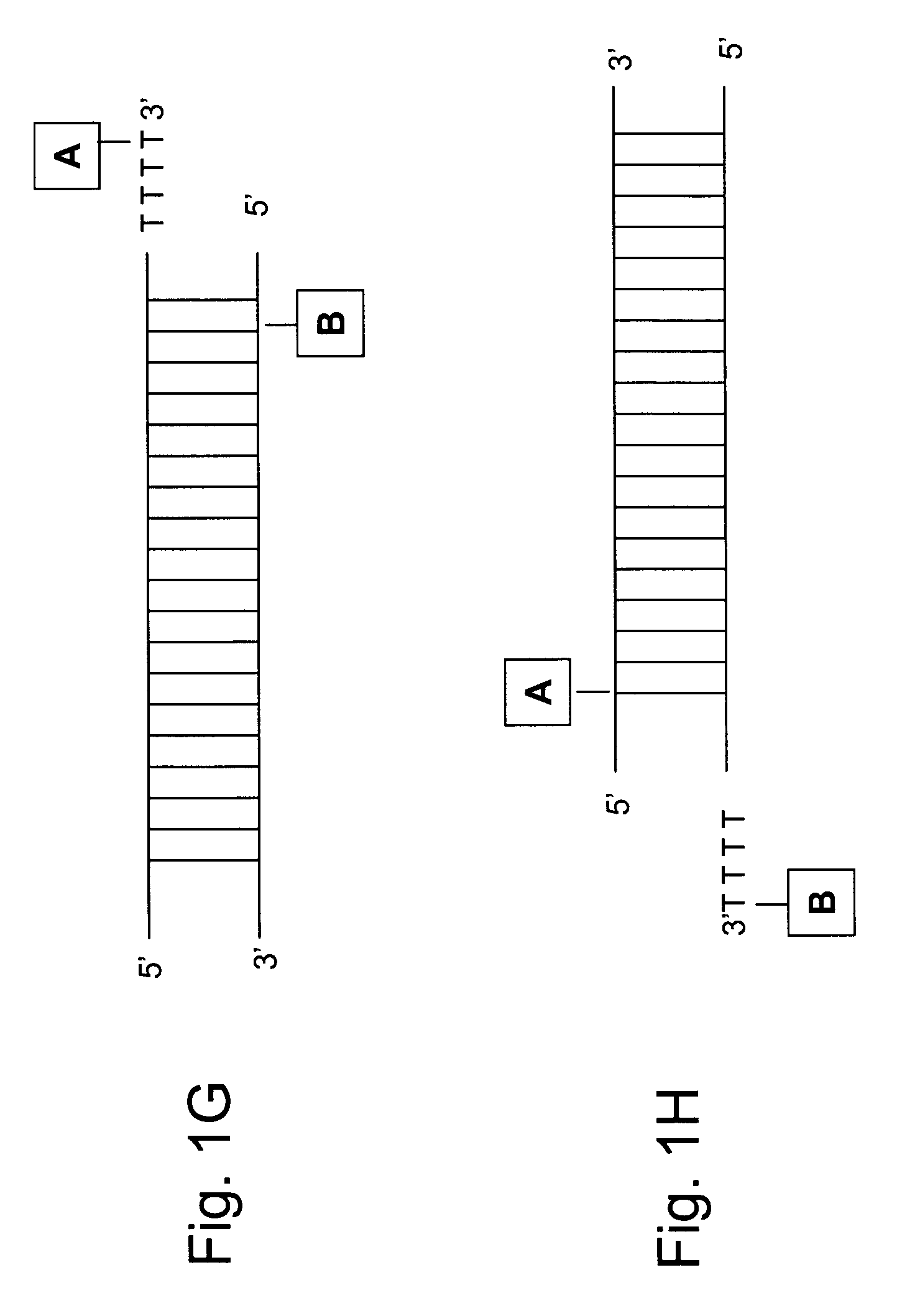
The invention relates relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
Owner:EXIQON AS
Novel oligonucleotide compositions and probe sequences useful for detection and analysis of microRNAS and their target mRNAS
InactiveUS20070065840A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget mrnaAllele
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to oligonucleotide probes for detection and analysis of other non-coding RNAs, mRNAs, mRNA splice variants, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g. alterations associated with human disease, such as cancer.
Owner:EXIQON AS
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular targets
InactiveUS20060172965A1Lower eye pressureOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderATPaseOpen angle glaucoma
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
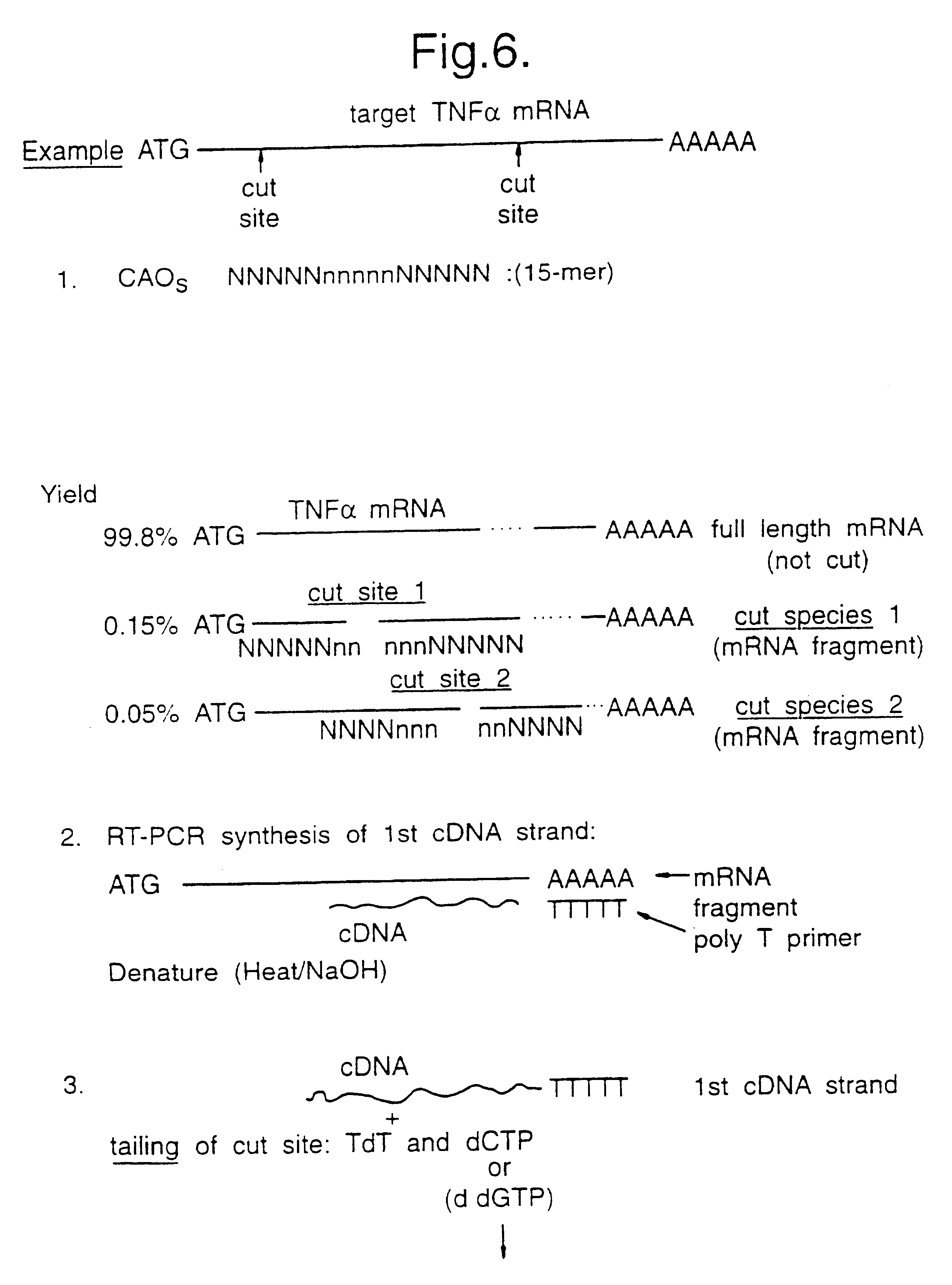
Methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20050266417A1Rapid and accurate hybridizationReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesSplice Site SNPTarget mrna
The present invention relates to methods for identifying target nucleic acid molecules differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, deletions, or translocations; and identifying one or more target mRNA molecules differing by one or more splice site variations in a plurality of mRNA molecules. Also disclosed is a method of generating a linearly amplified representation of a whole genome. Other aspects of the present invention relate to labeled detection oligonucleotide probes and translational oligonucleotide probes as well as to methods of designing such probes.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and compositions for delivering siRNA into mammalian cells
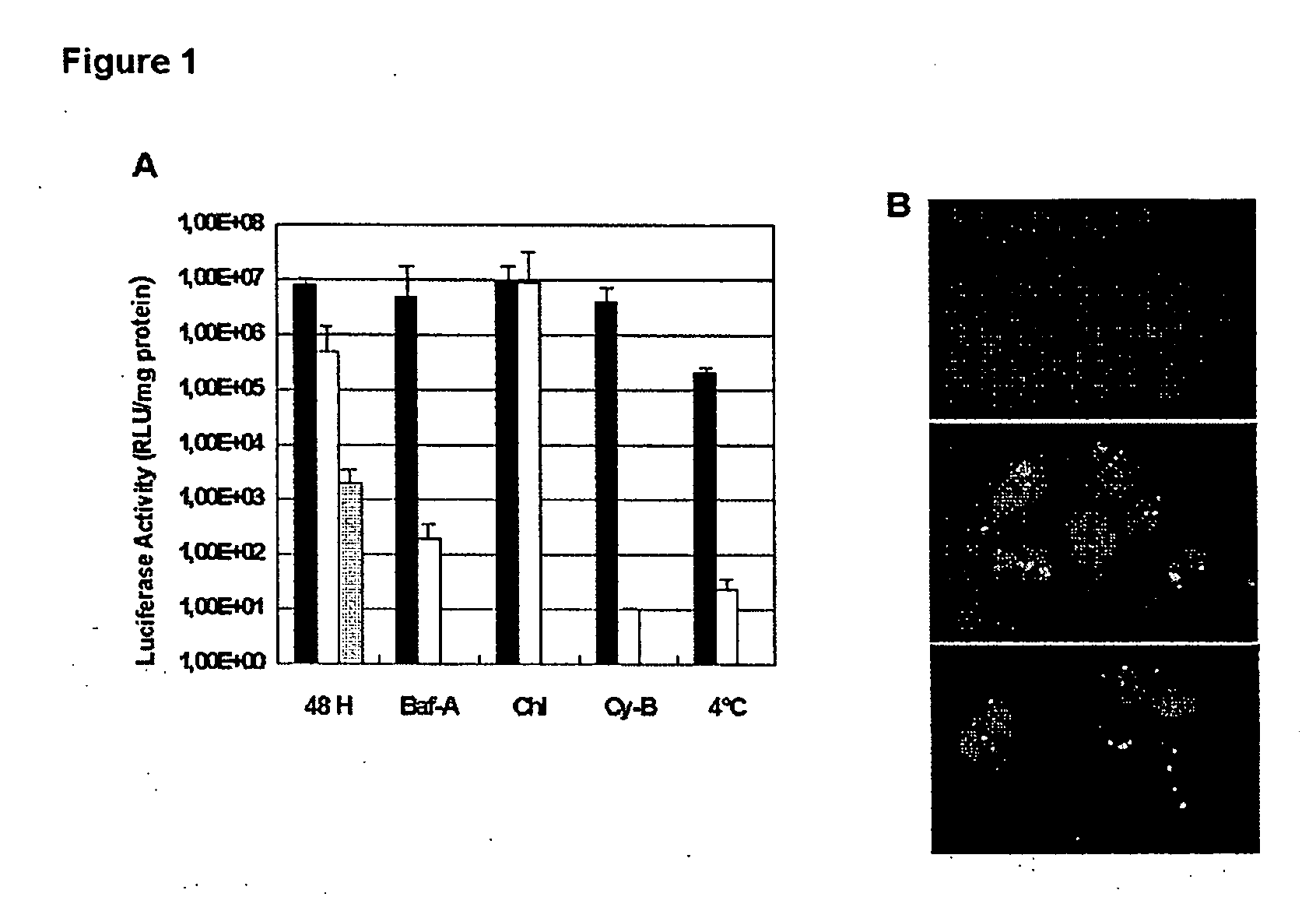
ActiveUS20050239687A1Quick releaseRobust downregulation of target mRNABiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationCysteine thiolate
Complex comprising a peptide carrier of SEQ ID NO:1 GALFLGFLGAAGSTMGAWSQPKR1KRKVR2 and an appropriate siRNA, wherein R1 represents any amino acid residue and more preferably K or S, R2 is null or represents one of the following groups: cysteamide, cysteine, thiol, amide, linear or ramified C1-C6 alkyl optionally substituted, primary or secondary amine, osidic derivative, lipid, phospholipid or cholesterol and said siRNA is selected to silence a target mRNA.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Identifying antisense oligonucleotide binding
A method for identifying an antisense oligonucleotide capable of binding to a target mRNA, which comprises contacting the target mRNA with each member of an oligonucleotide library separately under hybridization conditions, removing unhybridized material and determining which member or members hybridize; wherein the oligonucleotide library comprises a plurality of distinct nucleotide sequences of a predetermined common length, and wherein each nucleotide sequence comprises a known sequence of 4 to 8 bases and all possible combinations of the known sequence are present in the library.
Owner:XZILLION
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular hypertension targets
InactiveUS20060172963A1Lower eye pressureOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderIntra ocular pressureATPase
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:ARROWHEAD RES CORP +1
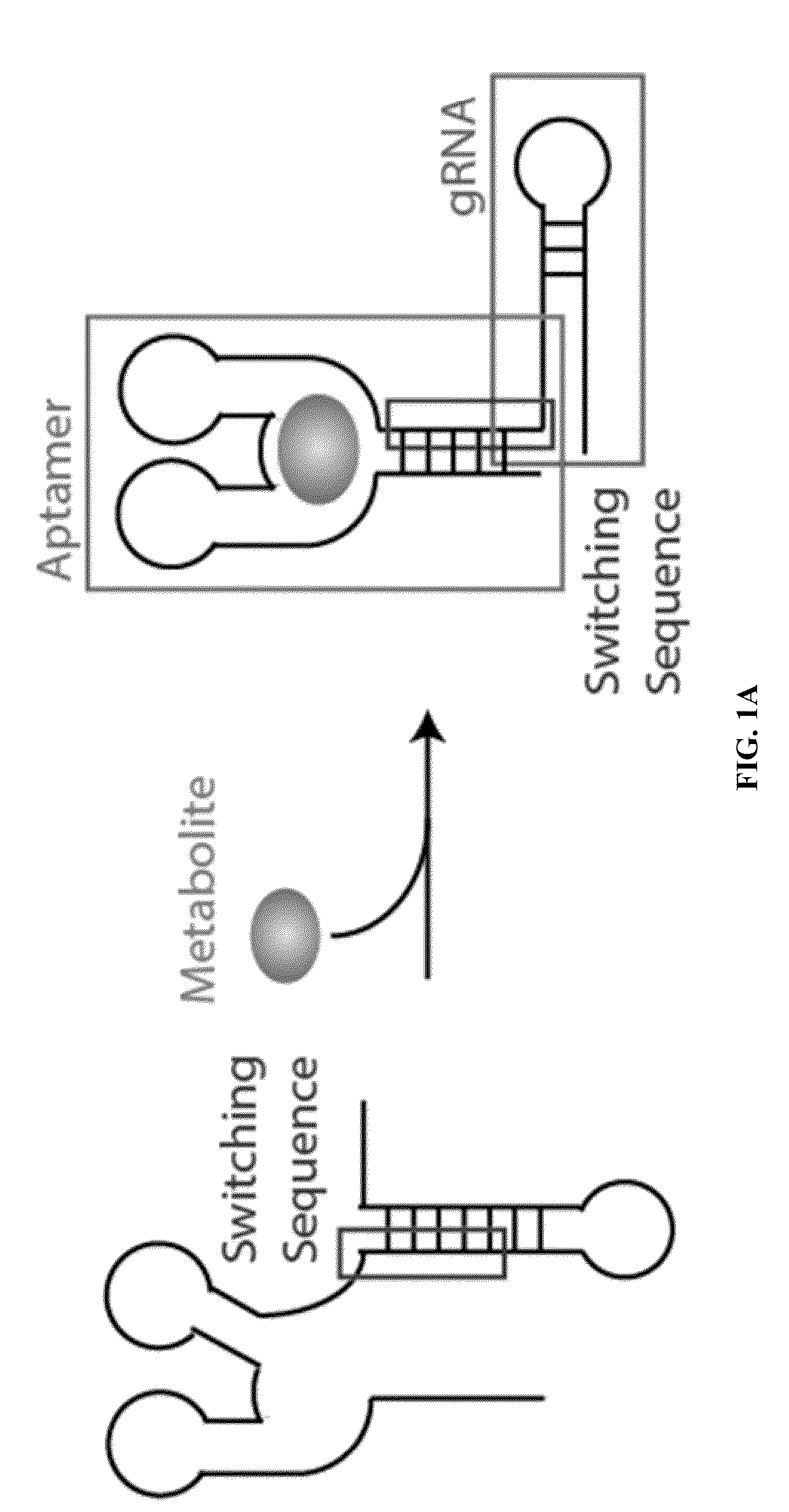
mRNA-Sensing Switchable gRNAs
ActiveUS20150071901A1Reduce the possibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsActivity regulationTarget mrnaBiology
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, systems, and kits for controlling the activity and / or improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. For example, provided are guide RNAs (gRNAs) that are engineered to exist in an “on” or “off” state, which control the binding and hence cleavage activity of RNA-programmable endonucleases. Some aspects of this disclosure provide mRNA-sensing gRNAs that modulate the activity of RNA-programmable endonucleases based on the presence or absence of a target mRNA.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
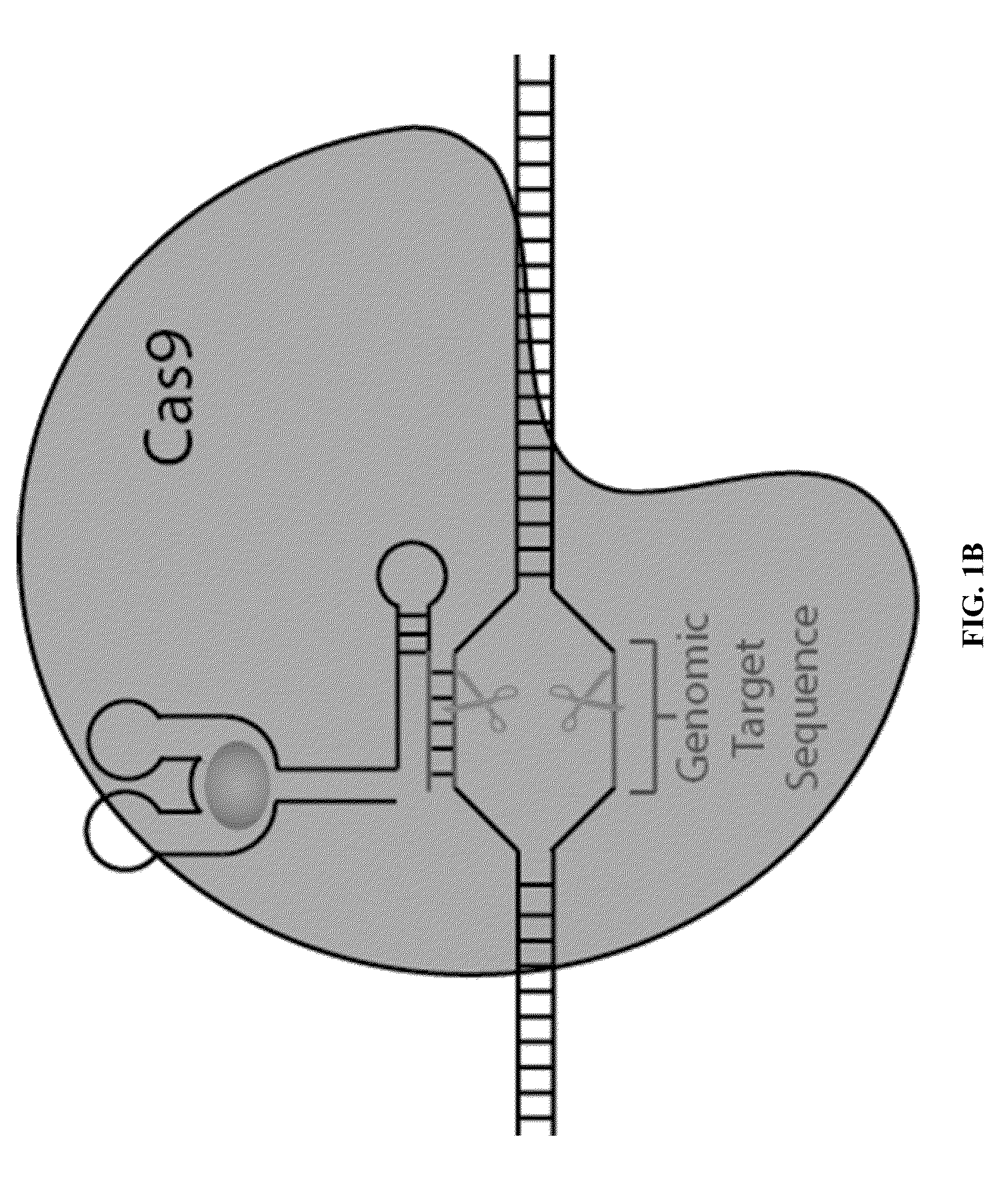
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
ActiveUS20070135333A1Inhibition of replicationSimple designAntibacterial agentsBiocideArginineNucleotide
An antibacterial antisense conjugate and method of using the same for treating a bacterial infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The conjugate includes an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotide contains 10-20 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 12 amino acids.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Peptide carrier for delivering siRNA into mammalian cells
ActiveUS7514530B2Quick releaseRobust downregulation of target mRNABiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationThiol
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
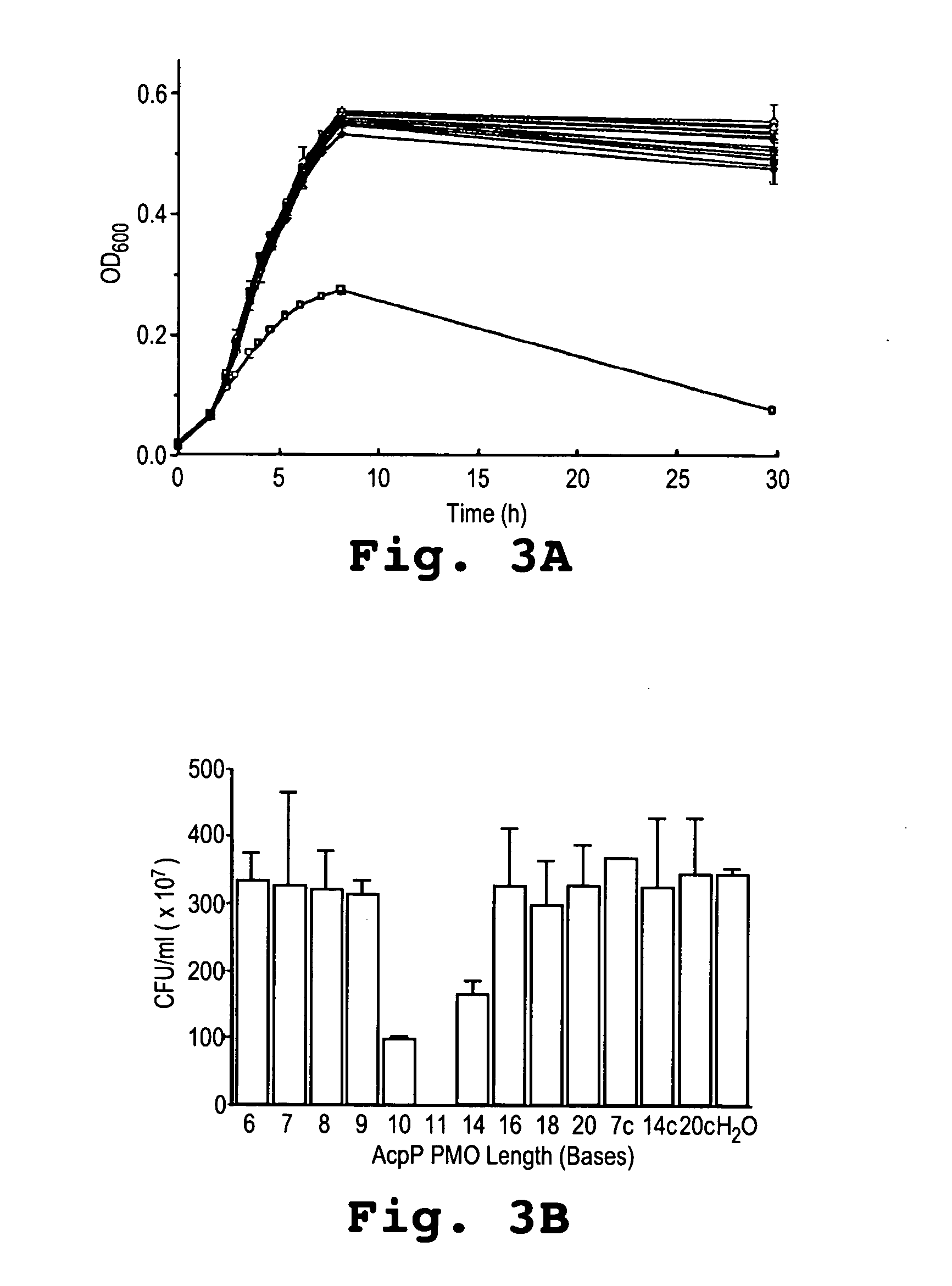
ActiveUS20070021362A1Growth inhibitionSimple designAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound aStart codon
A method and antisense compound for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells are disclosed. The compound contains no more than 12 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence of no fewer than 10 bases in length that is complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication. The compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The relatively short antisense compounds are substantially more active than conventional antisense compounds having a targeting base sequence of 15 or more bases.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
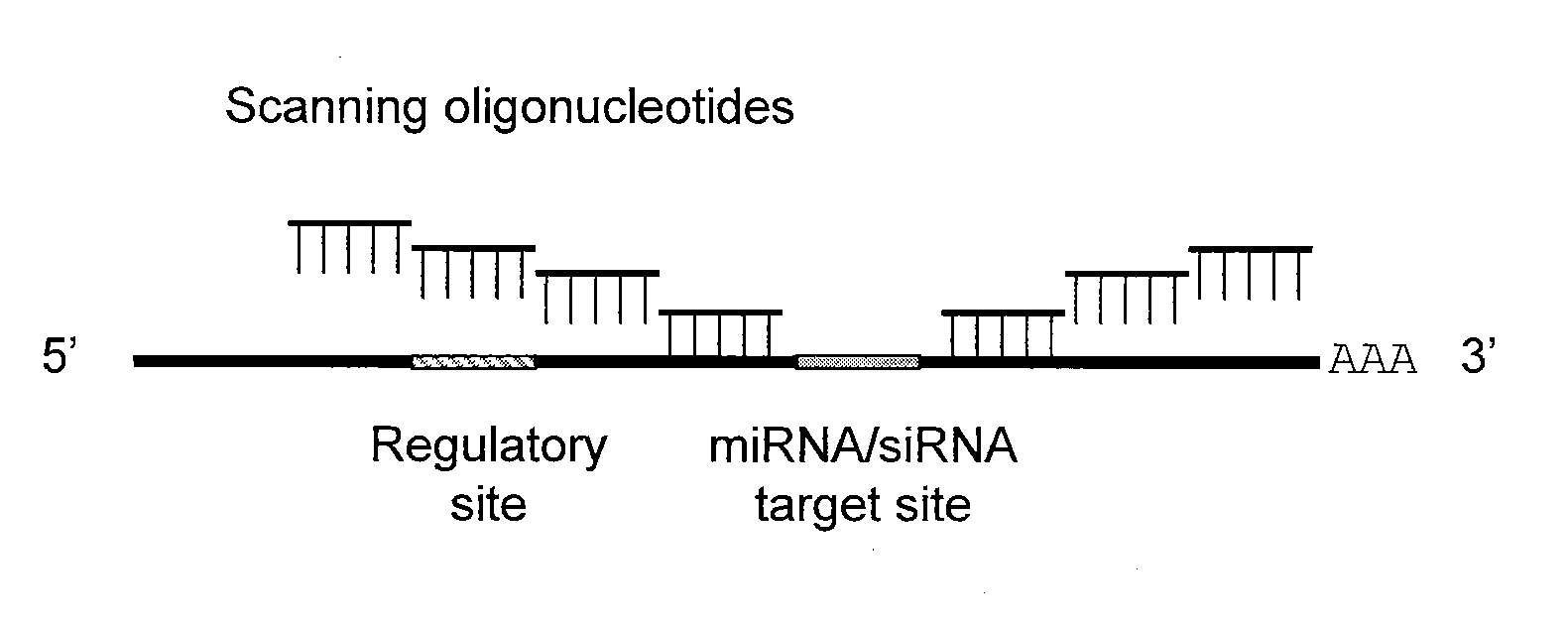
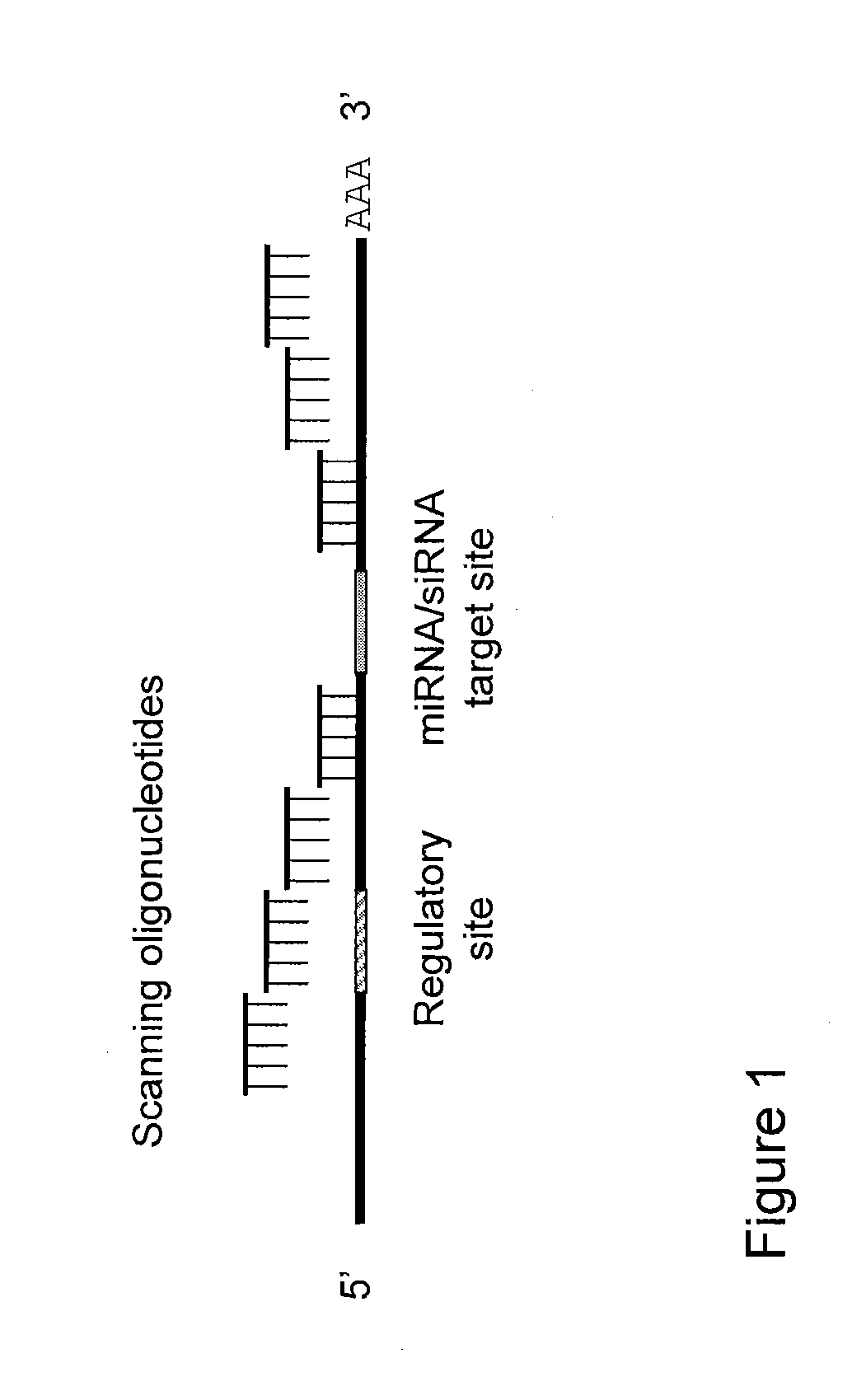
Blocking oligos for inhibition of microrna and sirna activity and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090326049A1High sensitivityHigh sequence specificityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesTarget mrnaMiRNA binding
The present invention relates to methods of identifying sites in the 3′- and / or 5′-UTR of mRNA involved in the binding of miRNA and / or siRNA to their target sites and nucleic acids designed to prevent the binding of endogenous or exogenous miRNA and / or siRNA to their target mRNA and uses thereof.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Antisense antibacterial method and compound
A method and antisense compound for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacterial cells are disclosed. The compound contains no more than 12 nucleotide bases and has a targeting nucleic acid sequence of no fewer than 10 bases in length that is complementary to a target sequence containing or within 10 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication. The compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 50° to 60° C. The relatively short antisense compounds are substantially more active than conventional antisense compounds having a targeting base sequence of 15 or more bases.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
NOVEL OLIGONUCLEOTIDE COMPOSITIONS AND PROBE SEQUENCES USEFUL FOR DETECTION AND ANALYSIS OF microRNAs AND THEIR TARGET mRNAs
InactiveUS20090053718A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processTarget mrnaAllele
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The invention furthermore relates to oligonucleotide probes for detection and analysis of other non-coding RNAs, mRNAs, mRNA splice variants, allelic variants of single transcripts, mutations, deletions, or duplications of particular exons in transcripts, e.g. alterations associated with human disease, such as cancer.
Owner:EXIQON AS
RNAi-mediated inhibition of ocular targets
RNA interference is provided for inhibition of ocular hypertension target mRNA expression for lowering elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Ocular hypertension targets include carbonic anhydrase II, IV, and XII; β1- and β2 adrenergic receptors; acetylcholinesterase; Na+ / K+-ATPase; and Na—K-2Cl cotransporter. Ocular hypertension is treated by administering interfering RNAs of the present invention.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Compositions and methods for treating inflammatory disorders
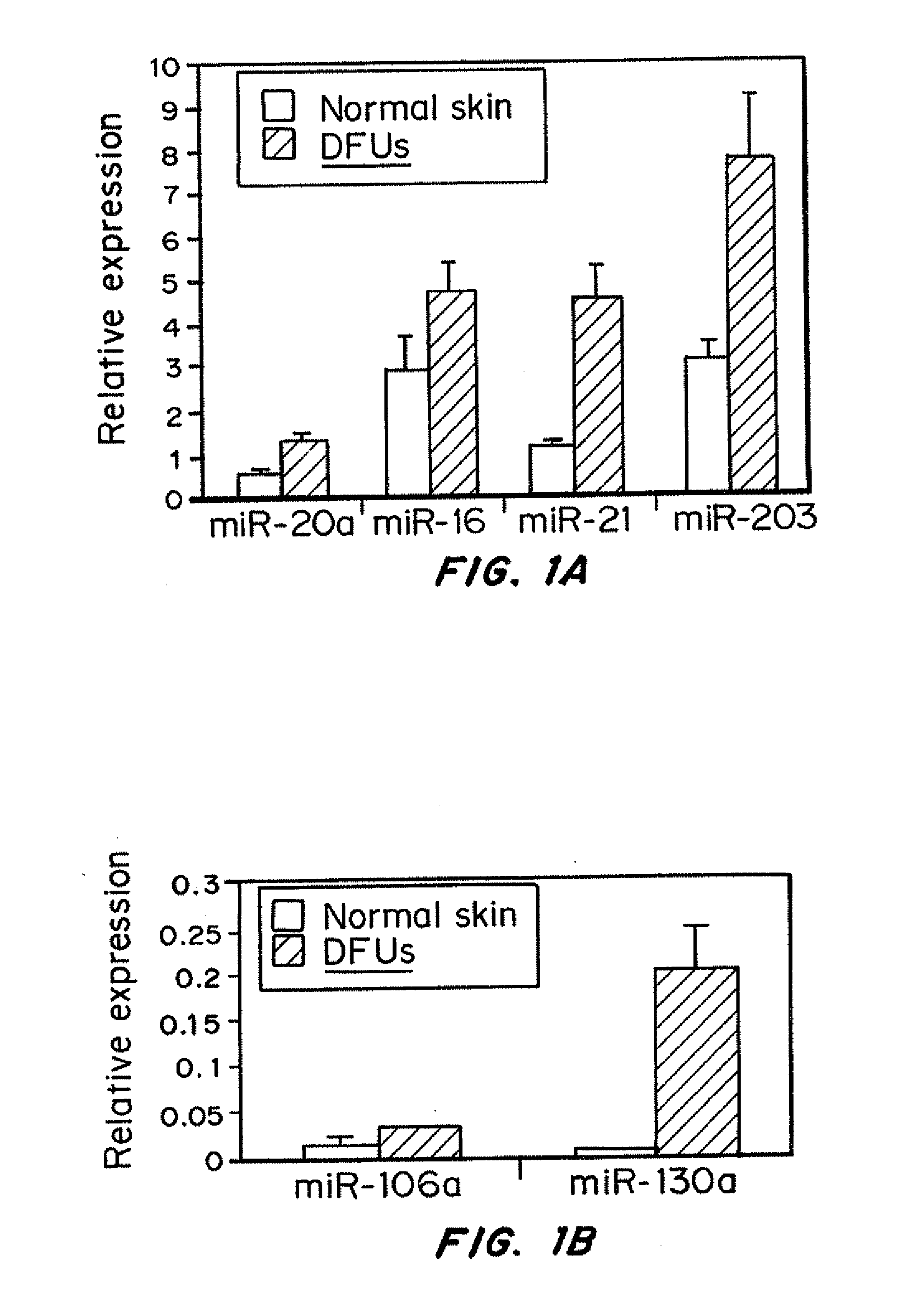
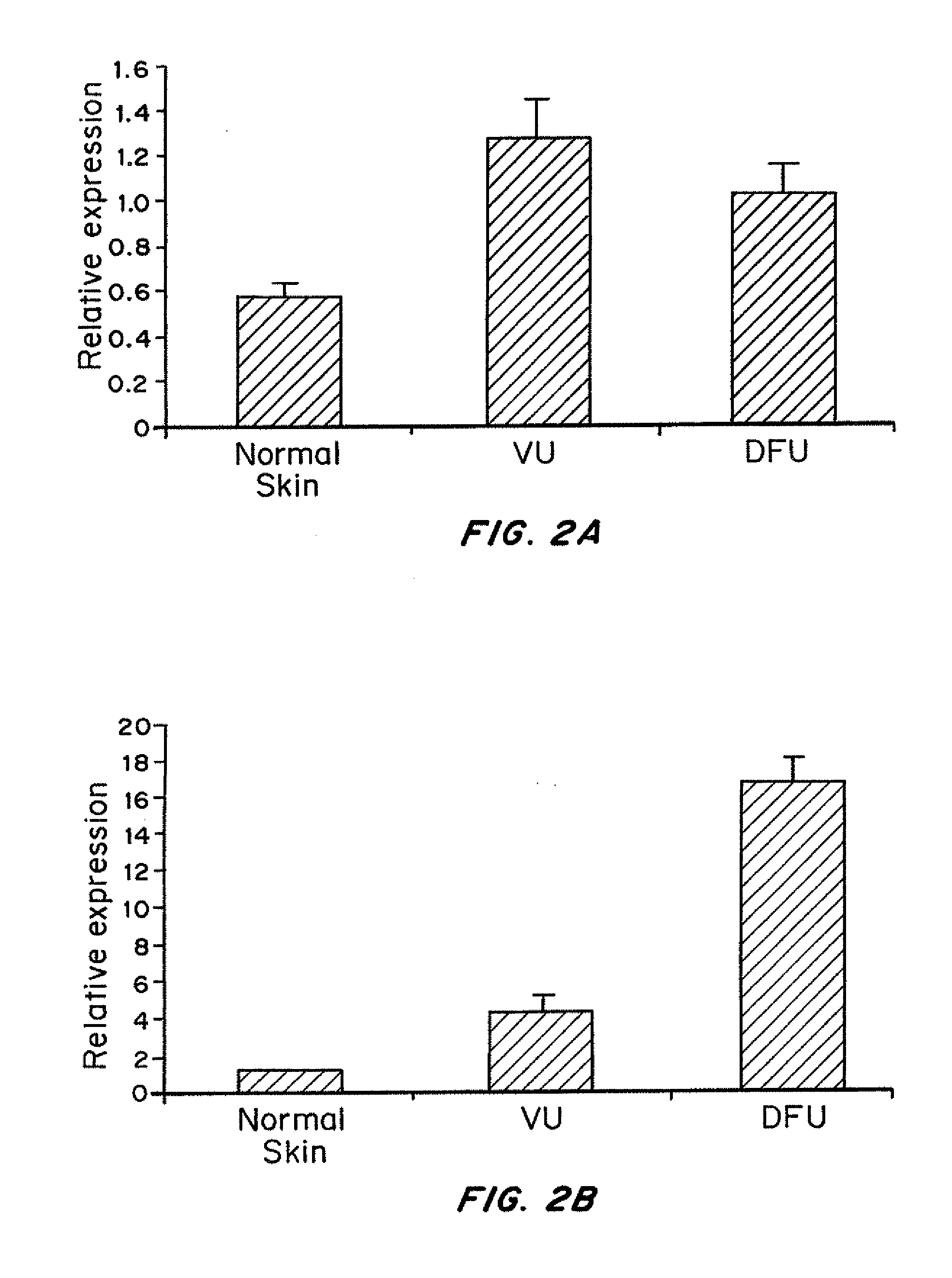
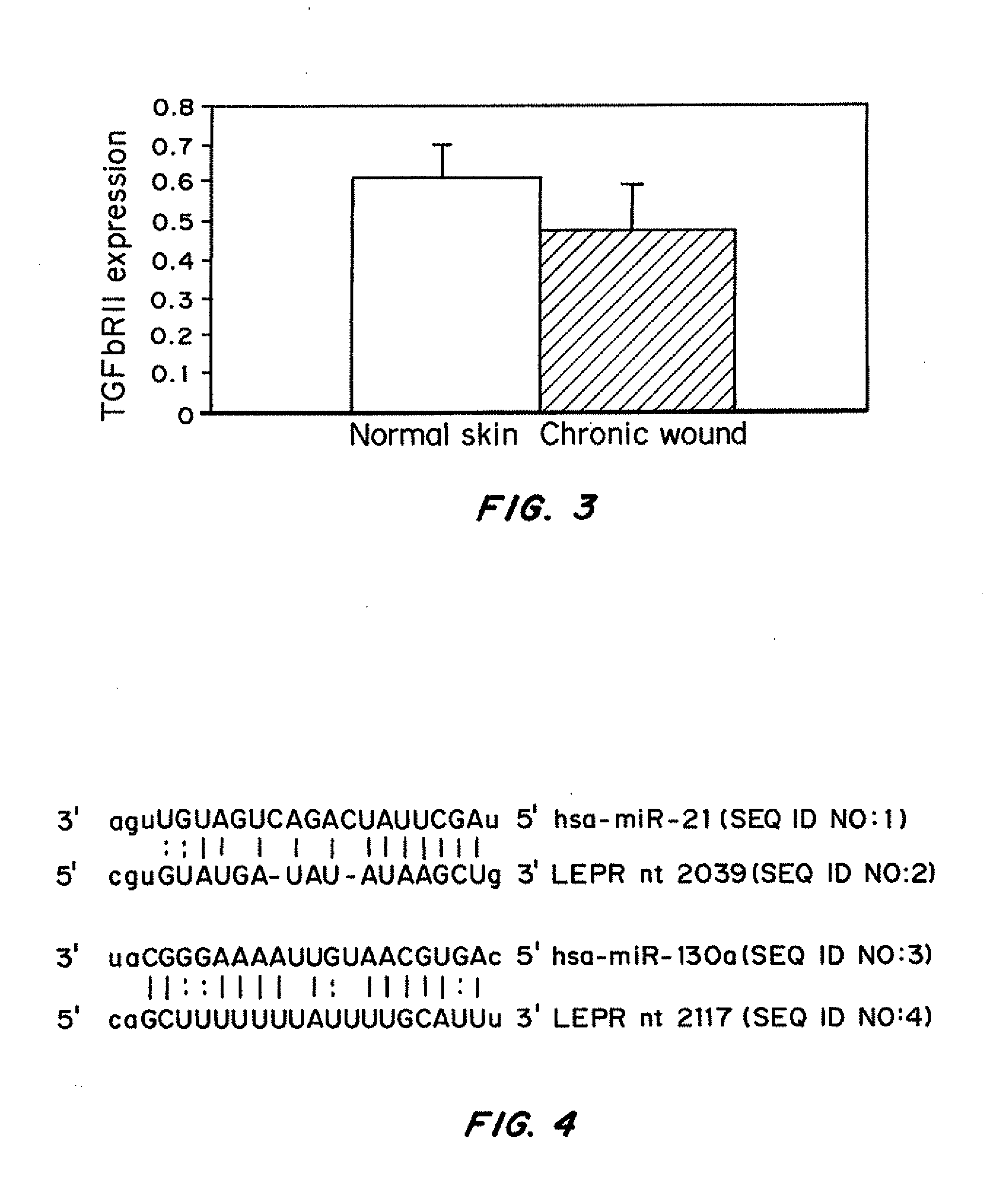
Compositions and methods for antagonizing miRNAs that are overexpressed in chronic, non-healing wounds, as compared to healthy tissue, are disclosed. The miRNA antagonists are oligonucleotides that hybridize to selected pre-miRNA or mature miRNAs and prevent the miRNAs from binding to and downregulating their target mRNAs. Methods of using the miRNA antagonists to treat inflammatory disorders, including to promote healing of chronic, non-healing wounds and acute wounds are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Human autogenous siRNA sequence, its application and screening method
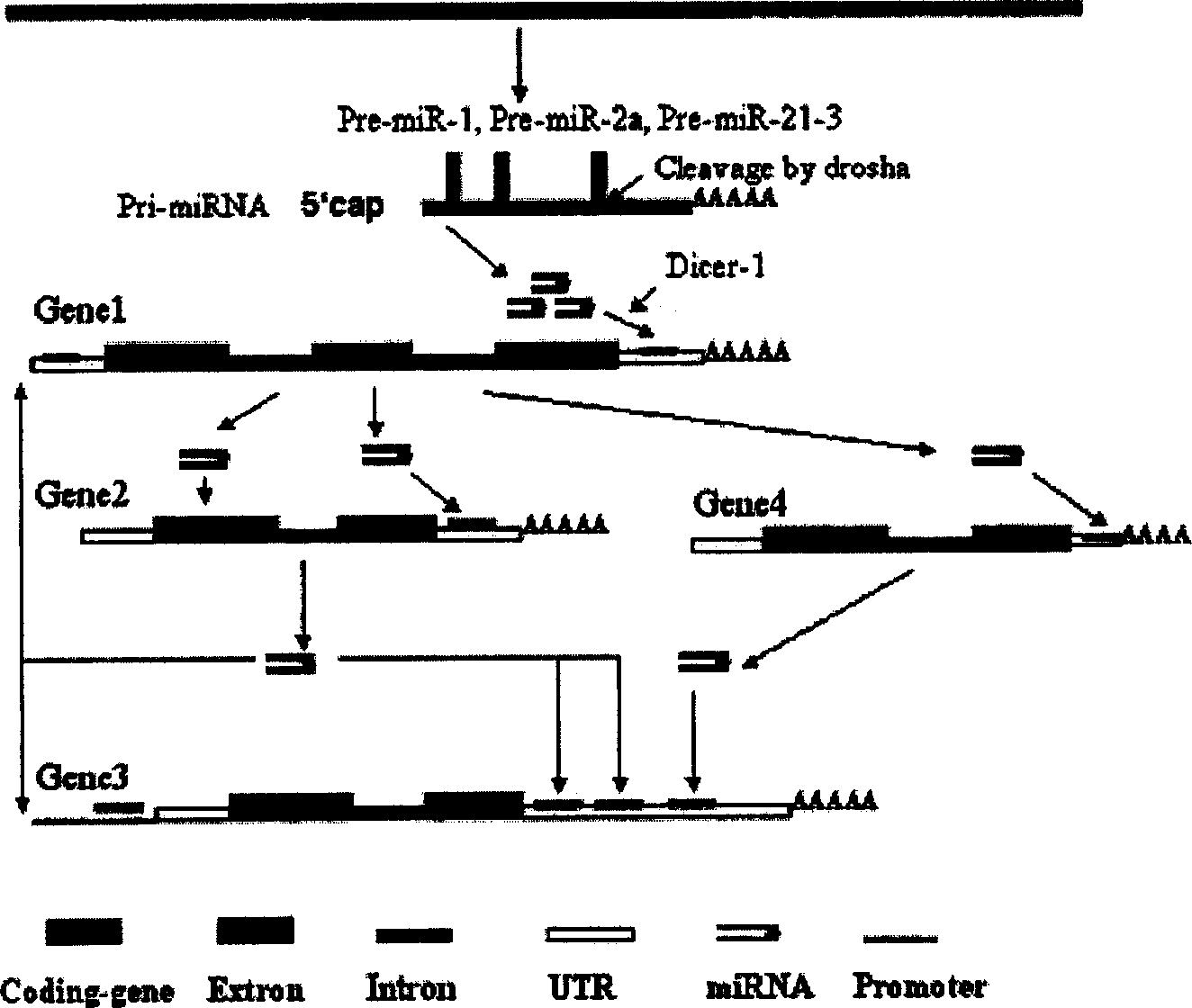
The invention relates to a computer algorithmic language and relative application software. It could rapidly select and predict internal source siRNA gene and siRNA molecule. Especially, it relates to an entire finding method for internal source siRNA gene and internal source siRNA molecule, and gaining 255 new siRNAs and target mRNAs from coding gene intron. The siRNA molecules could be used to research develop, differentiation and growth of cell, organization and organic, discuss the function and express adjusting network and discuss function of genes. It also could be used to develop medicines to prevent and cure kinds of disease.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Dual functional oligonucleotides for use as anti-viral agents
InactiveUS20060293267A1Improve in vivo stabilitySugar derivativesActivity regulationTarget mrnaViral infection
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that endogenous mRNAs, such as viral miRNAs, can be recruited for translational repression of target mRNAs, such as viral target mRNAs. The RNA-silencing agents and the methods described herein, thereby provide a means of treating viral infections, of treating diseases or disorders caused by viral infections, or for preventing viral propagation. The RNA-silencing agents of the present invention have an mRNA targeting moiety, a linking moiety, and a viral miRNA recruiting moiety.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
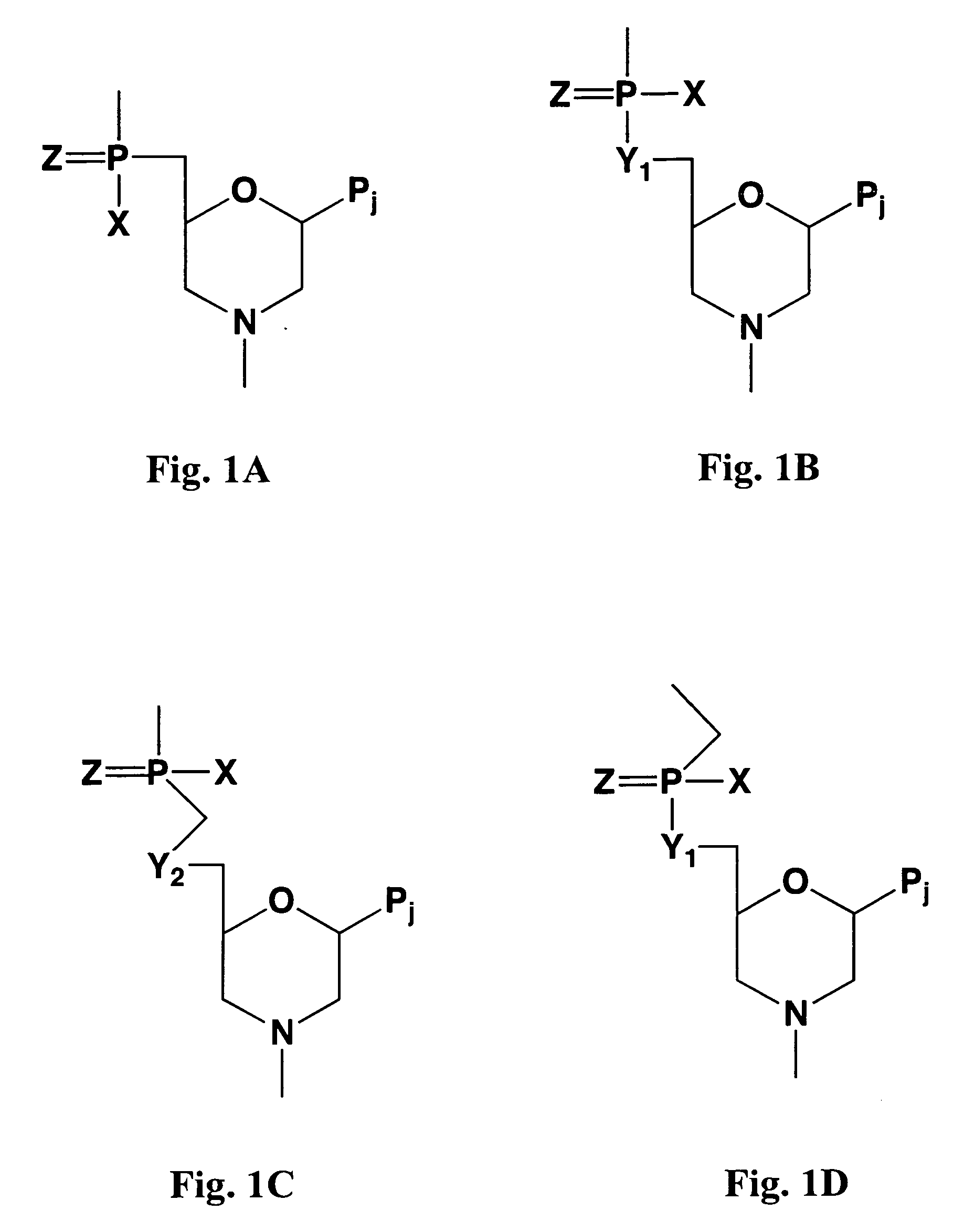
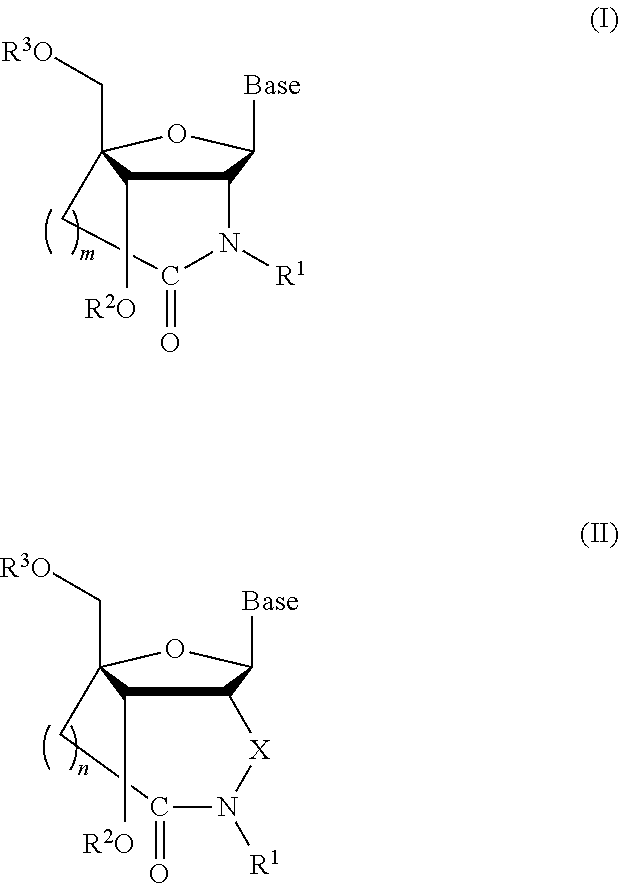
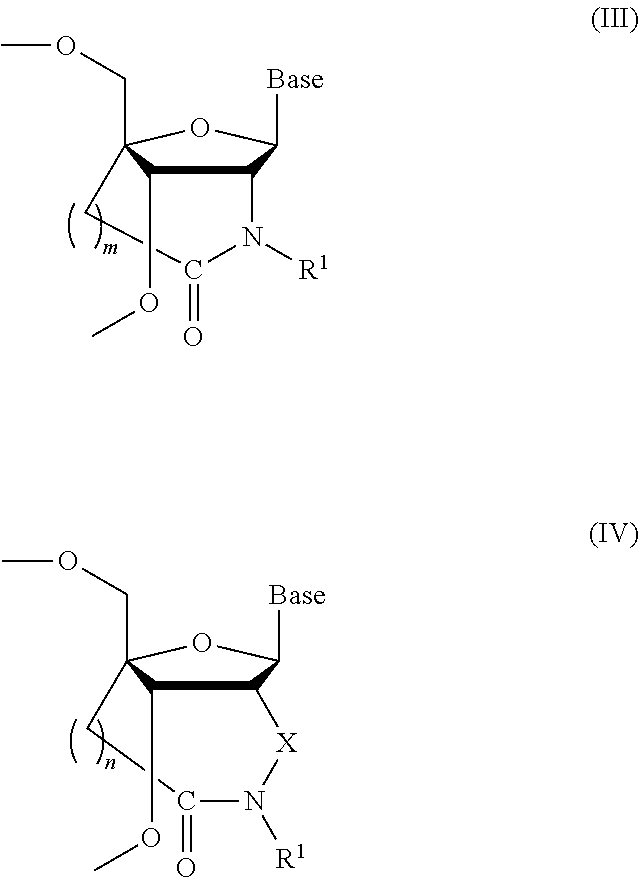
Bridged artificial nucleoside and nucleotide
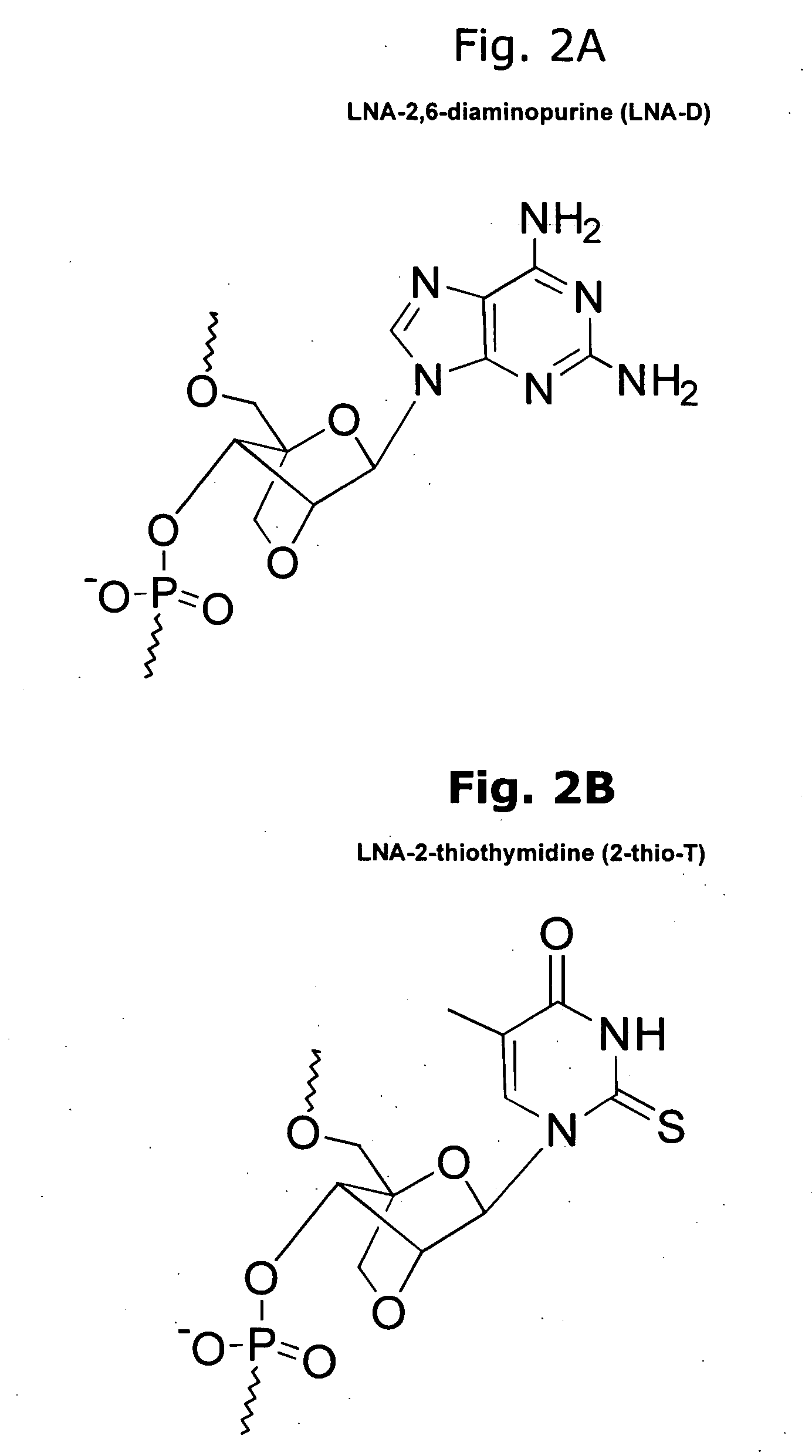
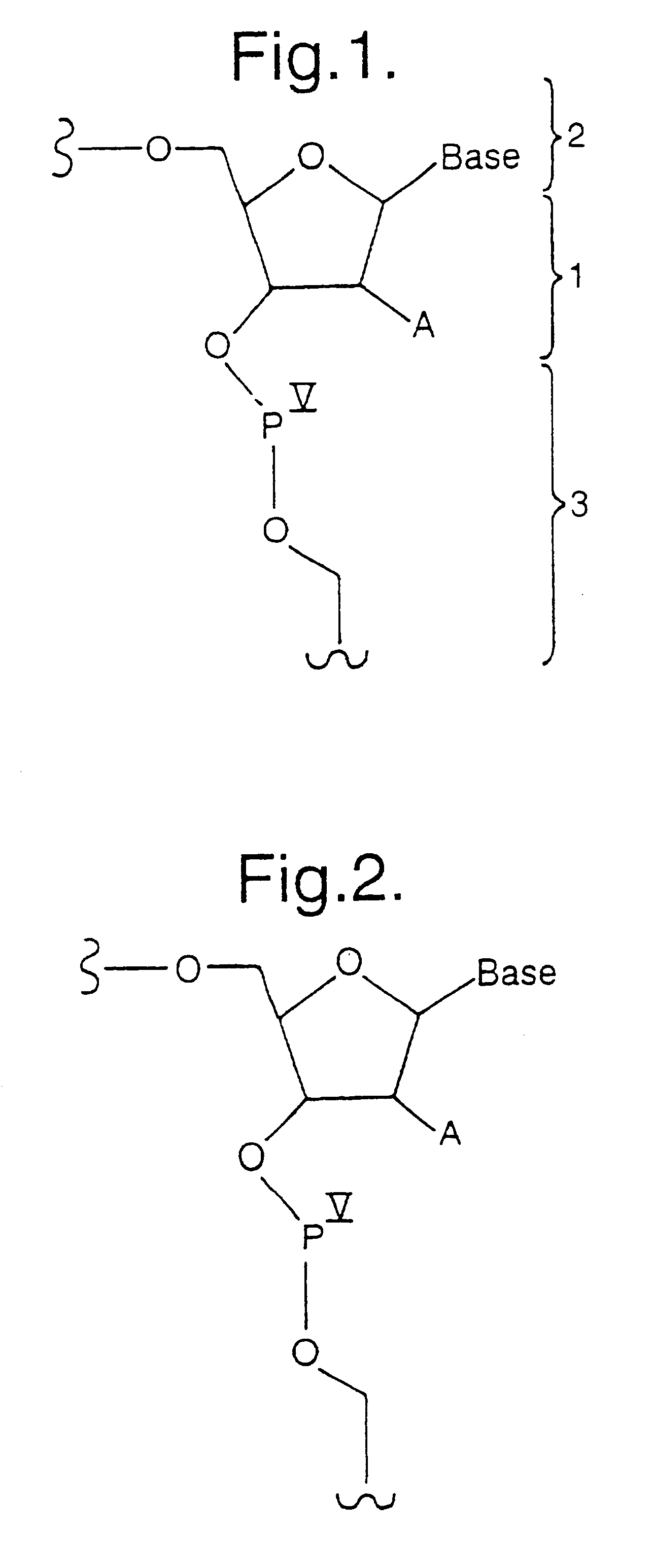
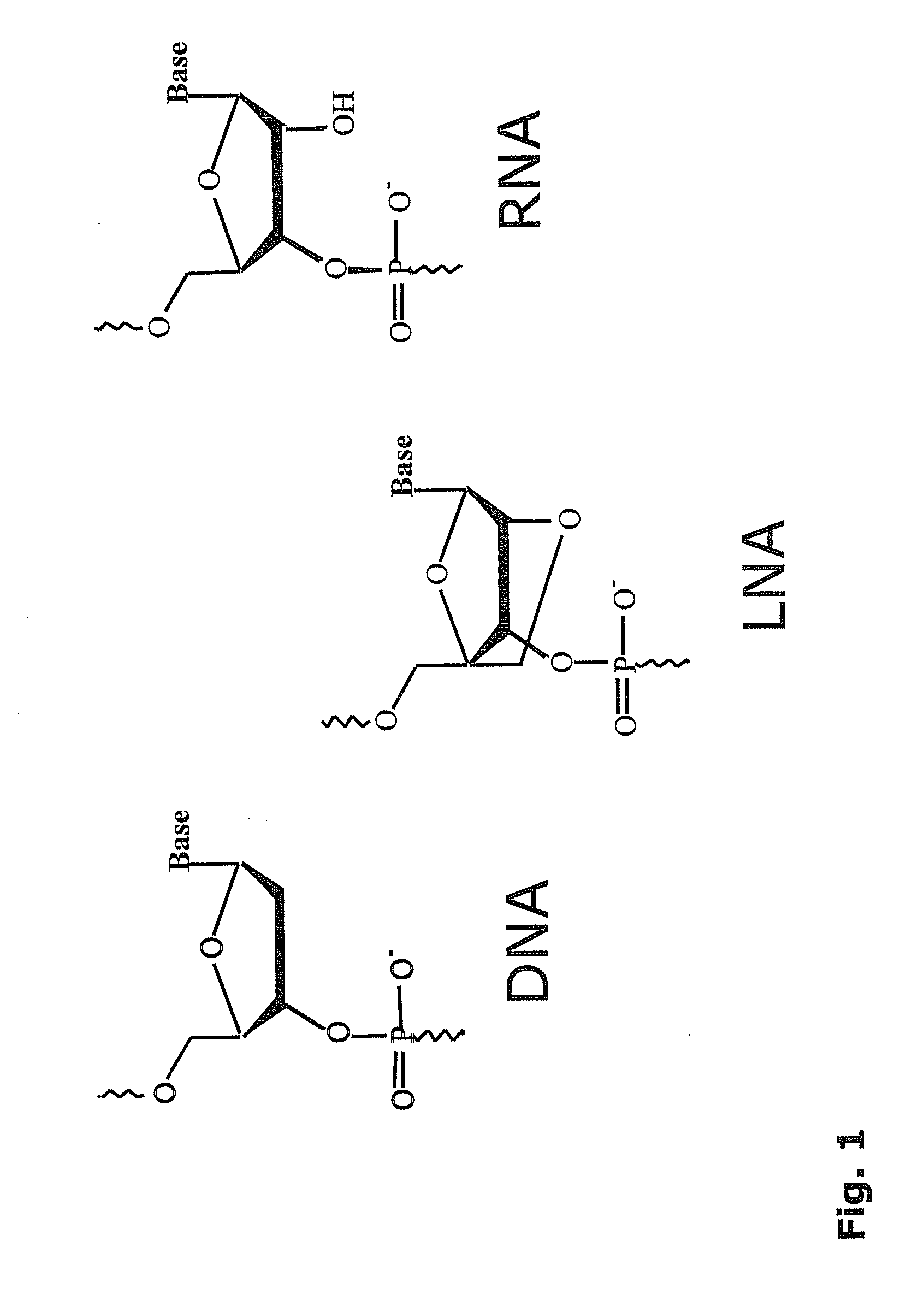
ActiveUS8541562B2Increase resistanceSugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle-Stranded RNANucleotide
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Antisense antibacterial compounds and methods
Antibacterial antisense compounds and methods of their use in treating a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a mammalian host are disclosed. The compounds include an antisense oligonucleotide conjugated to a carrier peptide that significantly enhances the antibacterial activity of the oligonucleotide. The antisense oligonucleotides contain 10-20 nucleotide bases and have a targeting nucleic acid sequence complementary to a target sequence containing or within 20 bases, in a downstream direction, of the translational start codon of a bacterial mRNA that encodes a bacterial protein essential for bacterial replication, where the compound binds to a target mRNA with a Tm of between 45° to 60° C. The carrier peptide is an arginine-rich peptide containing between 6 and 14 amino acids. Antisense compounds that target host factor genes that facilitate Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are also provided, as are methods of using these compounds to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections, alone or in combination with other therapies.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Delivery Of Double-Stranded RNA Into The Central Nervous System
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for in vivo delivery of a cell-permeable complex to cells of the central nervous system, wherein the cell-permeable complex decreases the level of a functional target protein encoded by a target mRNA molecule. In preferred embodiments of the invention, the cell-permeable complex comprises an siRNA nucleic acid molecule operably linked to a cell-penetrating peptide, wherein the cell-penetrating peptide facilitates transport of the cell-permeable complex across both the blood brain barrier and cell membrane of a target cell. The methods of the invention further encompass the utilization of convection-enhanced delivery methods such as intracerebral clysis (ICC) to deliver the cell-permeable complex to the target cells of the central nervous system.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Bridged artificial nucleoside and nucleotide
ActiveUS20120208991A1Increased nuclease resistanceIncrease resistanceSugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle-Stranded RNANucleotide
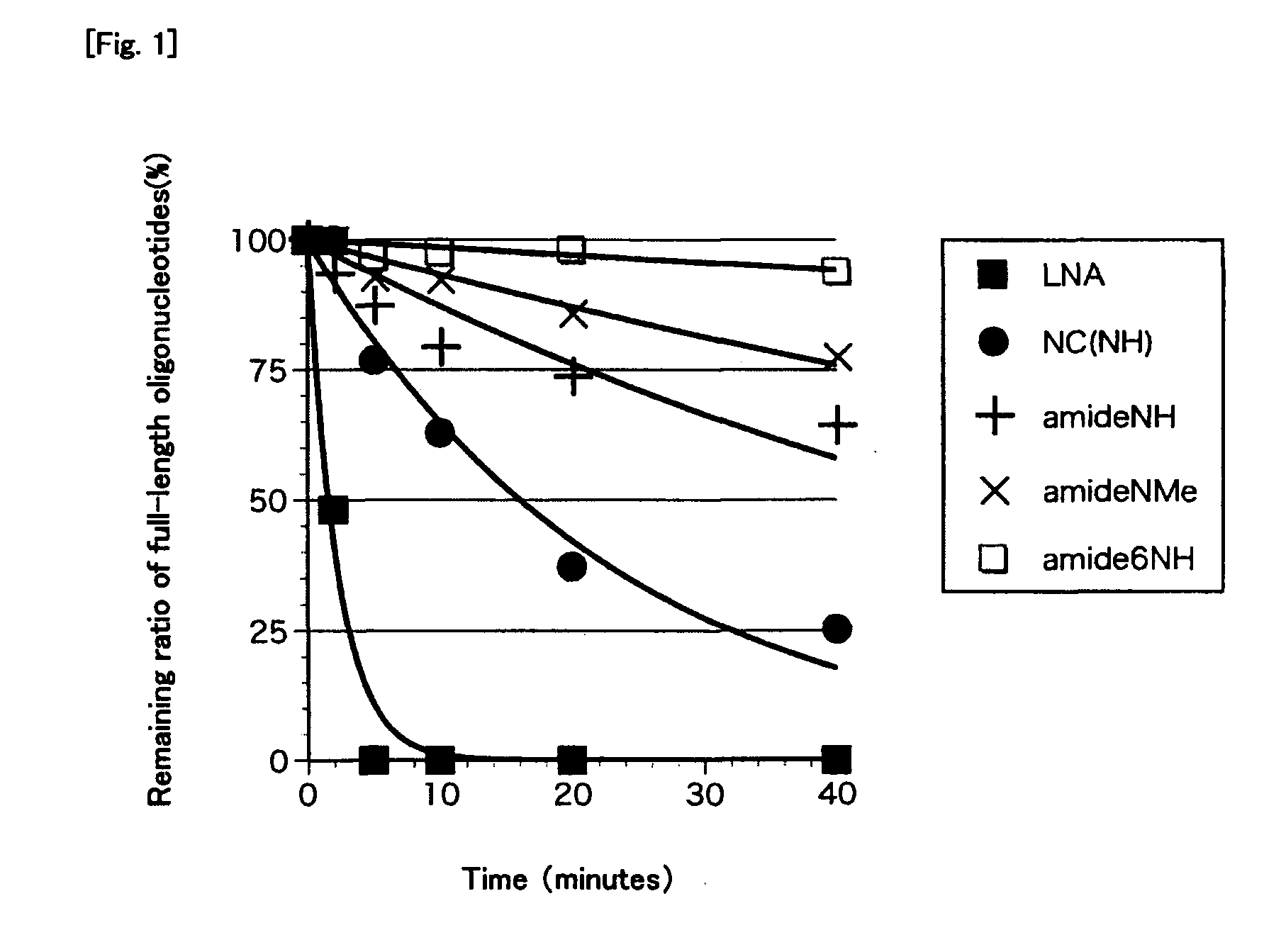
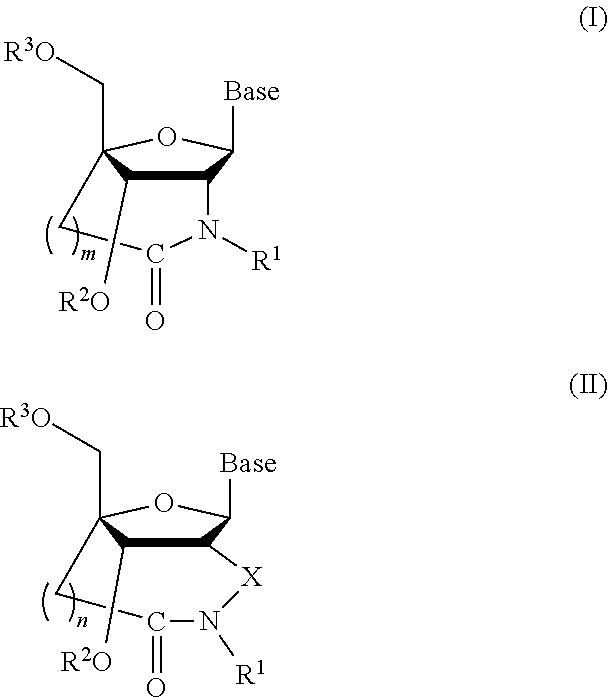
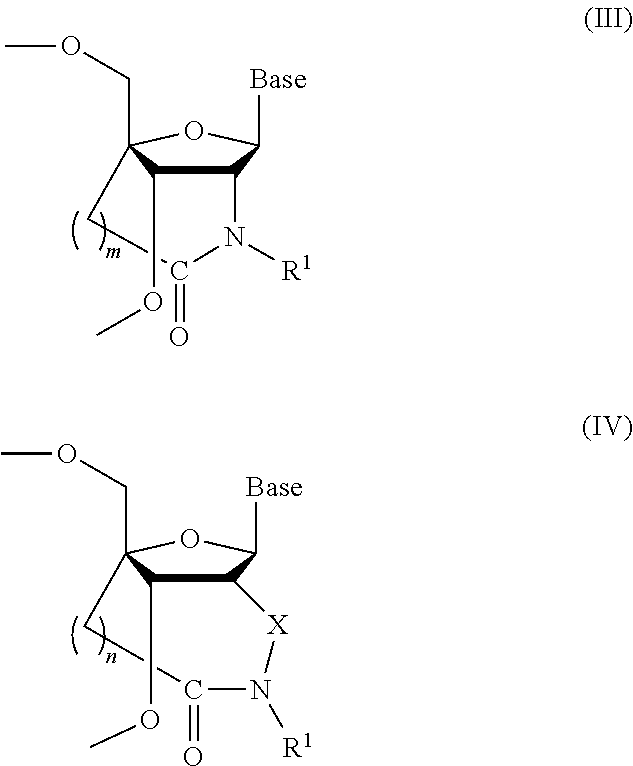
It is an object of the present invention to provide a novel molecule for antisense therapies which is not susceptible to nuclease degradation in vivo and has a high binding affinity and specificity for the target mRNAs and which can efficiently regulate expression of specific genes. The novel artificial nucleoside of the present invention has an amide bond introduced into a bridge structure of 2′,4′-BNA / LNA. The oligonucleotide containing the 2′,4′-bridged artificial nucleotide has a binding affinity for a single-stranded RNA comparable to known 2′,4′-BNA / LNA and has an increased nuclease resistance over LNA. Particularly, it is expected to be applied to nucleic acid drugs because of its much stronger binding affinity for single-stranded RNAs than S-oligo's affinity
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Novel oligonucleotide compositions and probe sequences useful for detection and analysis of micrornas and their target mrnas
InactiveUS20090286753A1Solve low usageSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsTarget mrna
The invention relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of microRNAs and their target mRNAs, as well as small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).
Owner:EXIQON AS
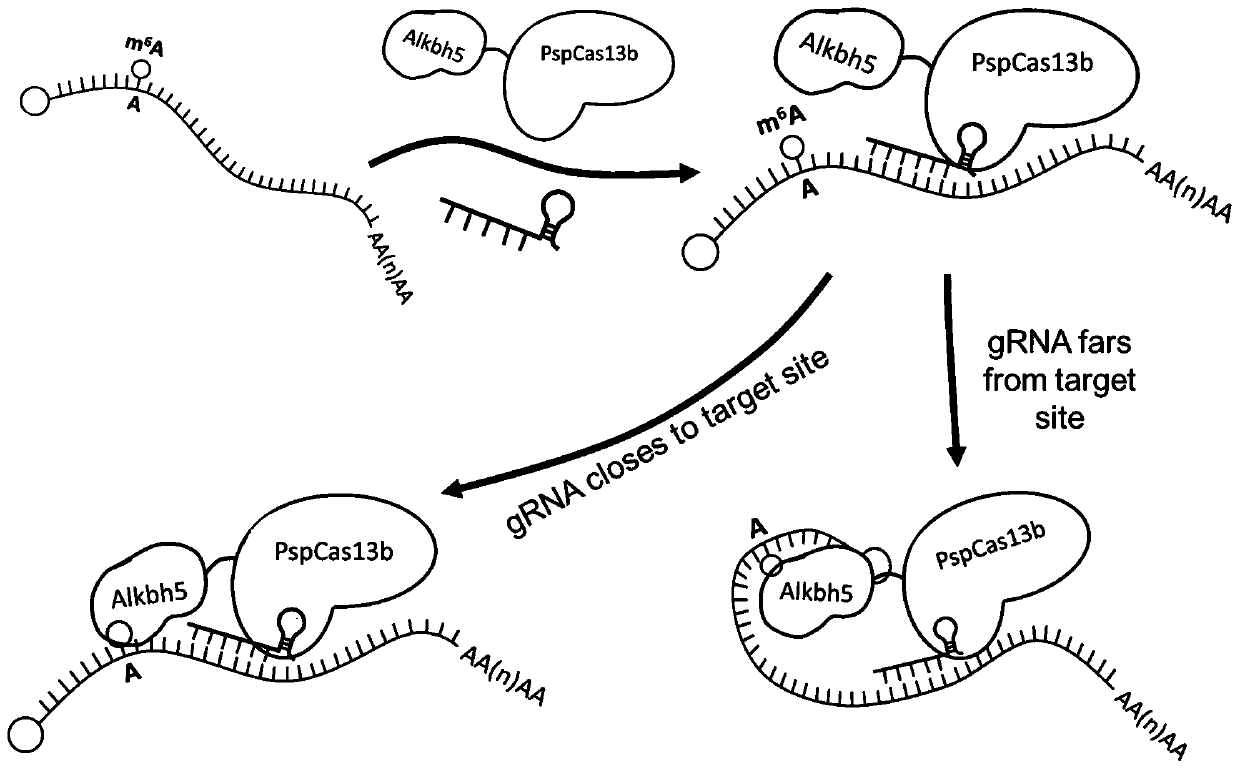
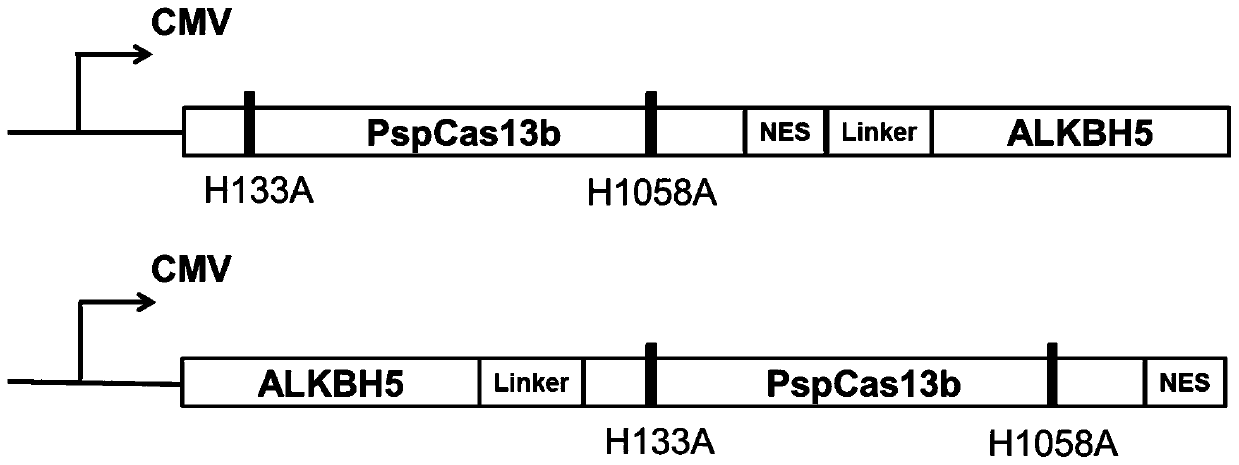
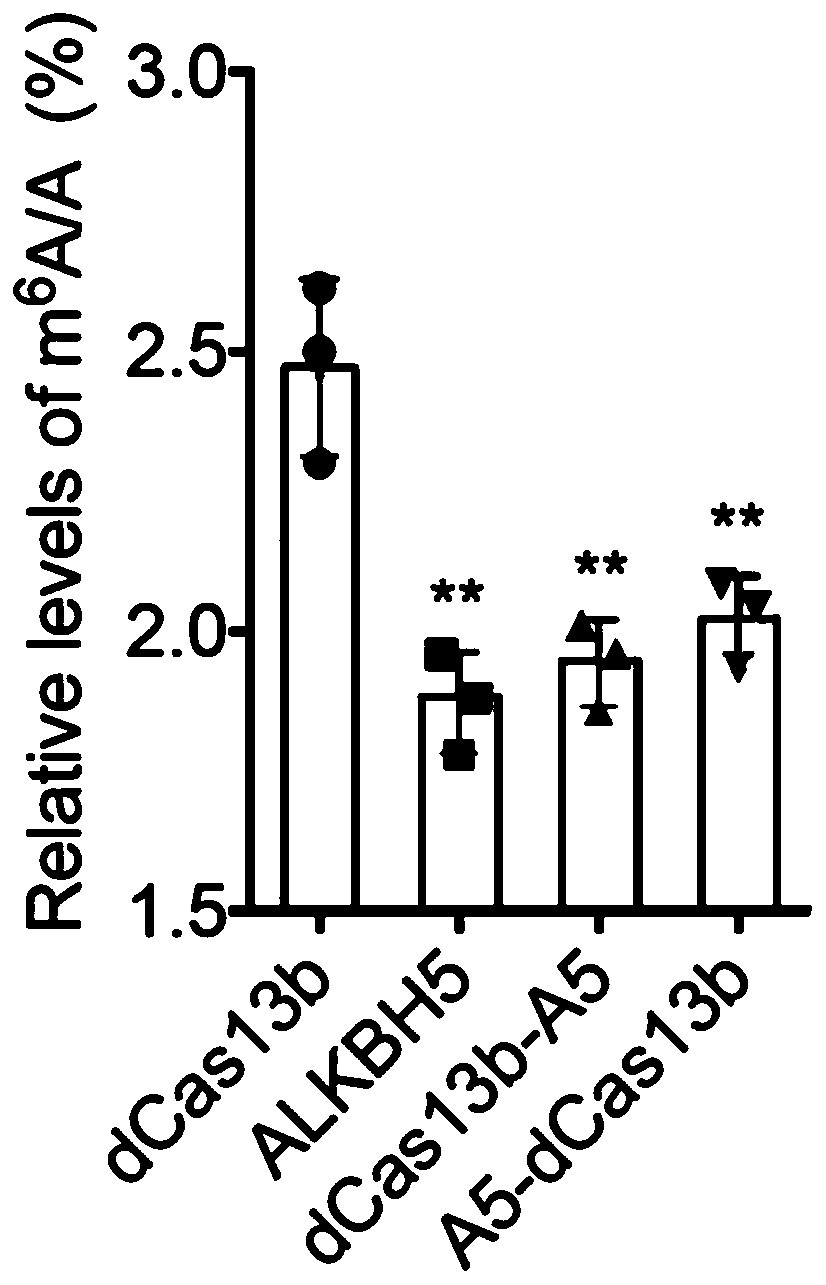
PspCas13b-Alkbh5 single gene specific m6A modification editing method
The invention discloses application of demethylation modification of targeted mRNA by using PspCas13b in combination with m6A demethylase Alkbh5. A study shows that a PspCas13b-Alkbh5 fusion protein can perform demethylation modification by targeting target gene (such as CYB5A and CTNNB1) mRNA through the specific gRNA to further regulate the target gene expression. m6A RNA immunoprecipitation assays and m6A site quantitative PCR results show that the PspCas13b-Alkbh5 fusion protein can effectively reduce the m6A methylation level of the target gene mRNA in the cell, and no off-target phenomenon is found. The PspCas13b is used as a means and combined with the m6A demethylase Alkbh5 to achieve the demethylation modification of the targeted mRNA for the first time and regulate the expressionof the specific purpose and application accordingly. The method breaks through the previous specific protein expression regulation based on previous change of DNA genetic information, provides a newpotential treatment mode and strategy for treatment of various diseases in the future, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods for Disease Therapy
InactiveUS20100130526A1Improve isolationHigh throughput analysisBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDisease phenotypeCoronary artery disease
The present invention discloses disease-linked SNPs, microRNAs, and microRNA-targeted mRNAs relevant to the pathogenesis of several major human disorders including, but not limited to, multiple types of cancers, type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes, Crohn's disease, coronary artery disease, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, bipolar disorder. Also provided are methods for the identification of disease phenotype-defining sets of SNPs, microRNAs, and mRNAs that are defined here as a “consensus disease phenocode” as well as methods of using the information provided by these consensus disease phenocodes for various diagnostic, prognostic, and / or therapeutic applications.
Owner:ORDWAY RES INST
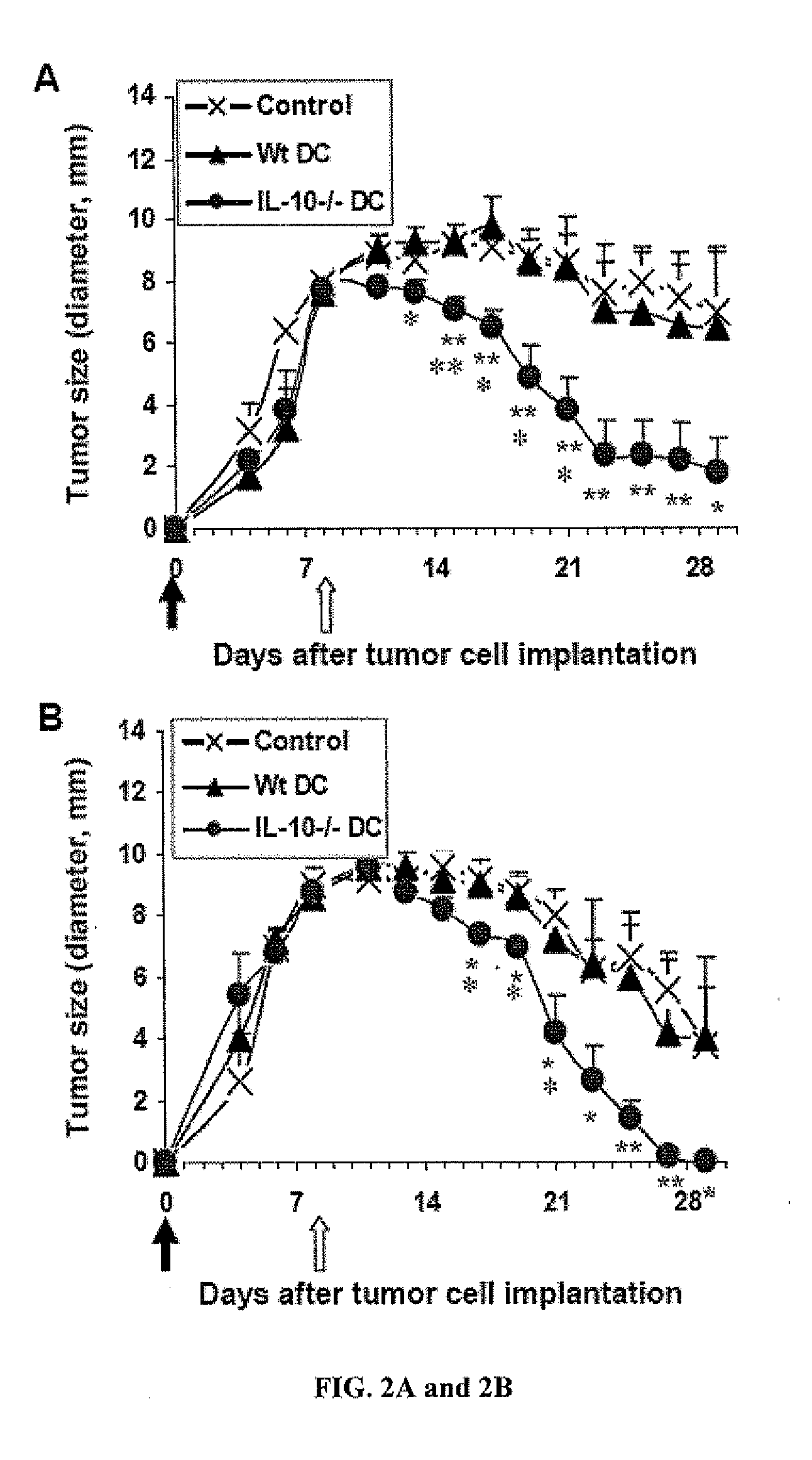
Anti-tumor vaccines delivered by dendritic cells devoid of interleukin-10
InactiveUS20090010948A1Highly effectiveBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDendritic cellInterleukin 10
It has been discovered that reducing, inhibiting or preventing the expression of immunosuppressive cytokines or tolergenic agents in antigen presenting cells improves the ability of the antigen presenting cell to promote an immune response. One embodiment provides a genetically engineered antigen presenting cell that has reduced or no expression of IL-10. Preferred antigen presenting cells are dendritic cells. Expression of IL-10 can be inhibited or blocked by genetically engineering the antigen presenting cell to express inhibitory nucleic acids that inhibit or prevent the expression mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Inhibitory nucleic acids include siRNA, antisense RNA, antisense DNA, microRNA, and enzymatic nucleic acids that target mRNA encoding immunosuppressive cytokines. Immunosuppressive cytokines include, but are not limited to IL-10, TGF-β, IL-27, IL-35, or combinations thereof. Tolerogenic agents include but are not limited to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Caged RNAs and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050282203A1Sugar derivativesSpectrum investigationLipid formationProtein transduction domain
Methods of using labeled interfering RNAs to detect and / or quantitate target mRNAs in cells are provided. Related compositions, systems, and kits are also provided. Caged interfering RNAs (e.g., photoactivatable interfering RNAs), methods of using such caged RNAs, and related systems and kits are also provided. Caged RNAs capable of repressing translation of a target mRNA or silencing transcription of a target gene are also provided, along with related methods, systems, and kits. Methods and compositions for introducing RNAs into cells, using RNAs covalently associated with protein transduction domains and / or lipids, are provided. Also provided are methods and compositions for selectively attenuating expression of a target mRNA by controlling expression of an interfering RNA, an RNA capable of initiating translation repression, or an RNA capable of initiating transcriptional silencing.
Owner:PANOMICS
Methods and compositions relating to gene silencing
InactiveUS7700758B2Reduce expressionImprove featuresSugar derivativesHydrolasesHeterologousNucleotide
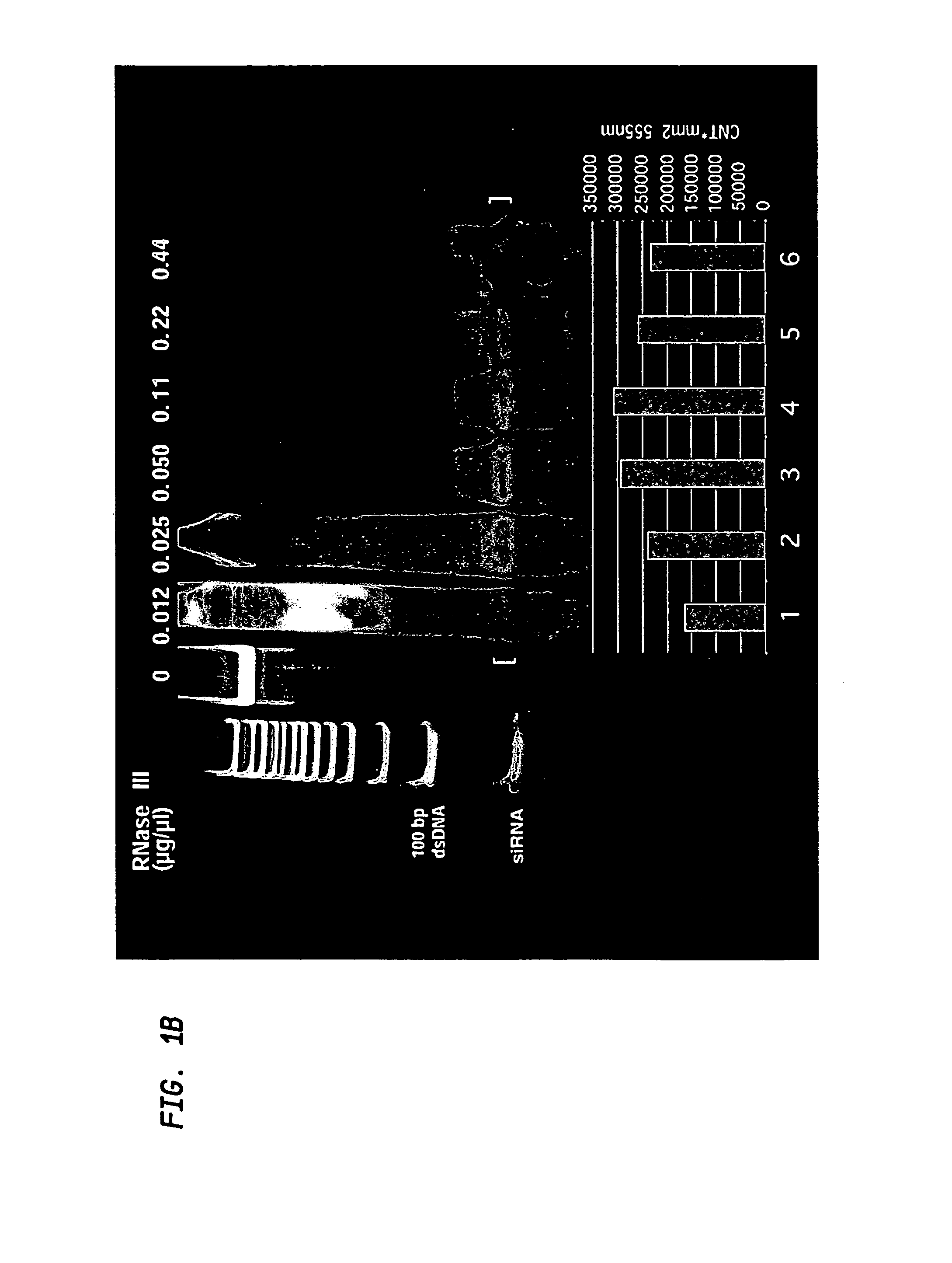
A method for obtaining a mixture of heterogenous short double-stranded RNA molecules suitable for use in gene silencing (hsiRNA) by subjecting large double-stranded RNA to enzymatic cleavage under specified conditions. The resulting mixture consistently includes enhanced representation of fragments having a size of 21-22 nucleotides absent any fractionation step. The fragments contain sequences that collectively span the entire length of the large double-stranded RNA from which they are derived. Double-stranded RNA with sequences that individually represent segments of a target mRNA may be analyzed using the methods described herein to identify the most active subset of hsiRNA fragments or individual siRNA fragments for achieving gene silencing for any gene or transcribed sequences. A method is additionally provided for preparing and cloning DNA encoding selected siRNA, hsiRNA mixtures or hairpin sequences to provide a continuous supply of a gene silencing reagent derived from any long double-stranded RNA.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
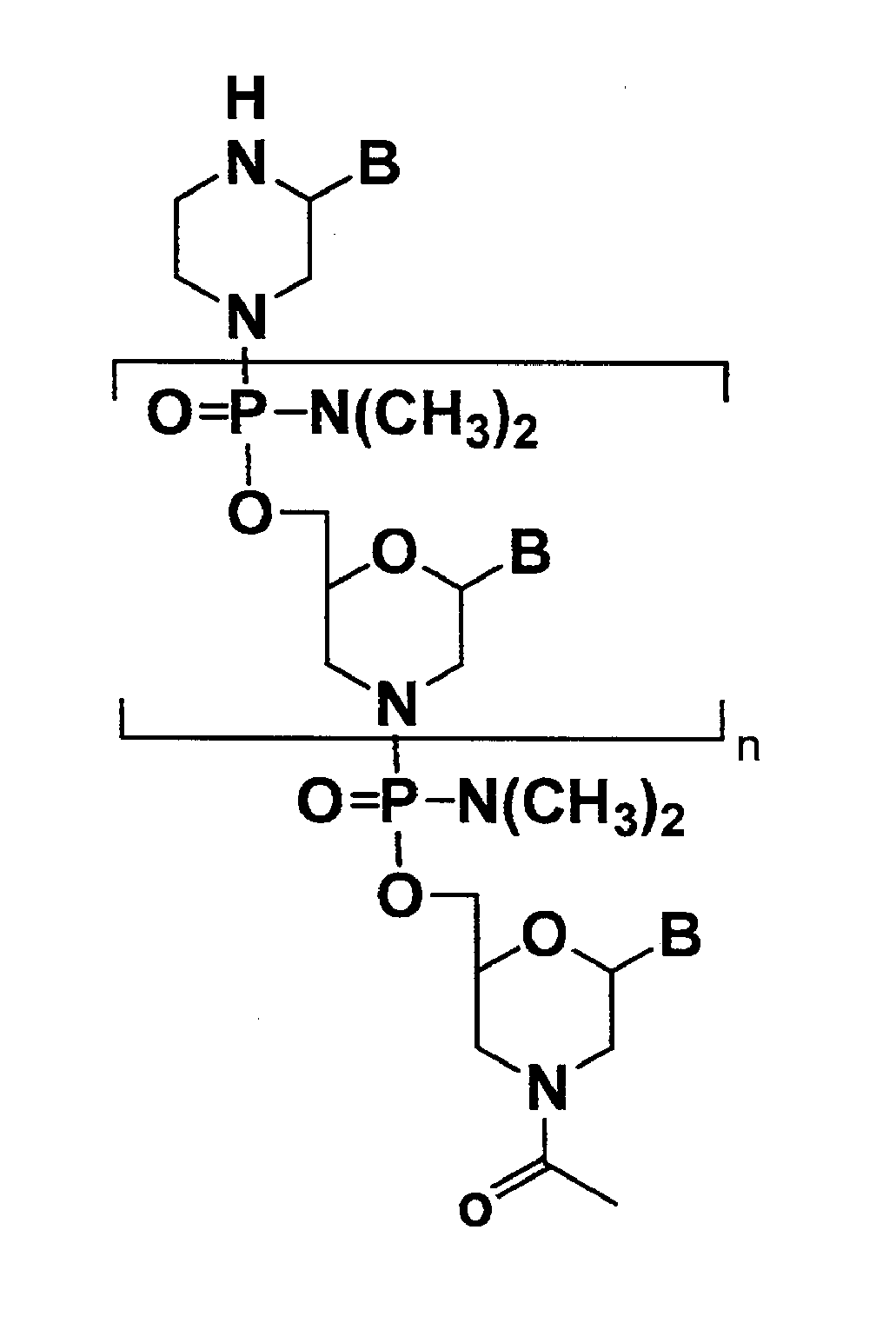
Three component chimeric antisense oligonucleotides
Owner:WOOLF TOD MITCHELL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com