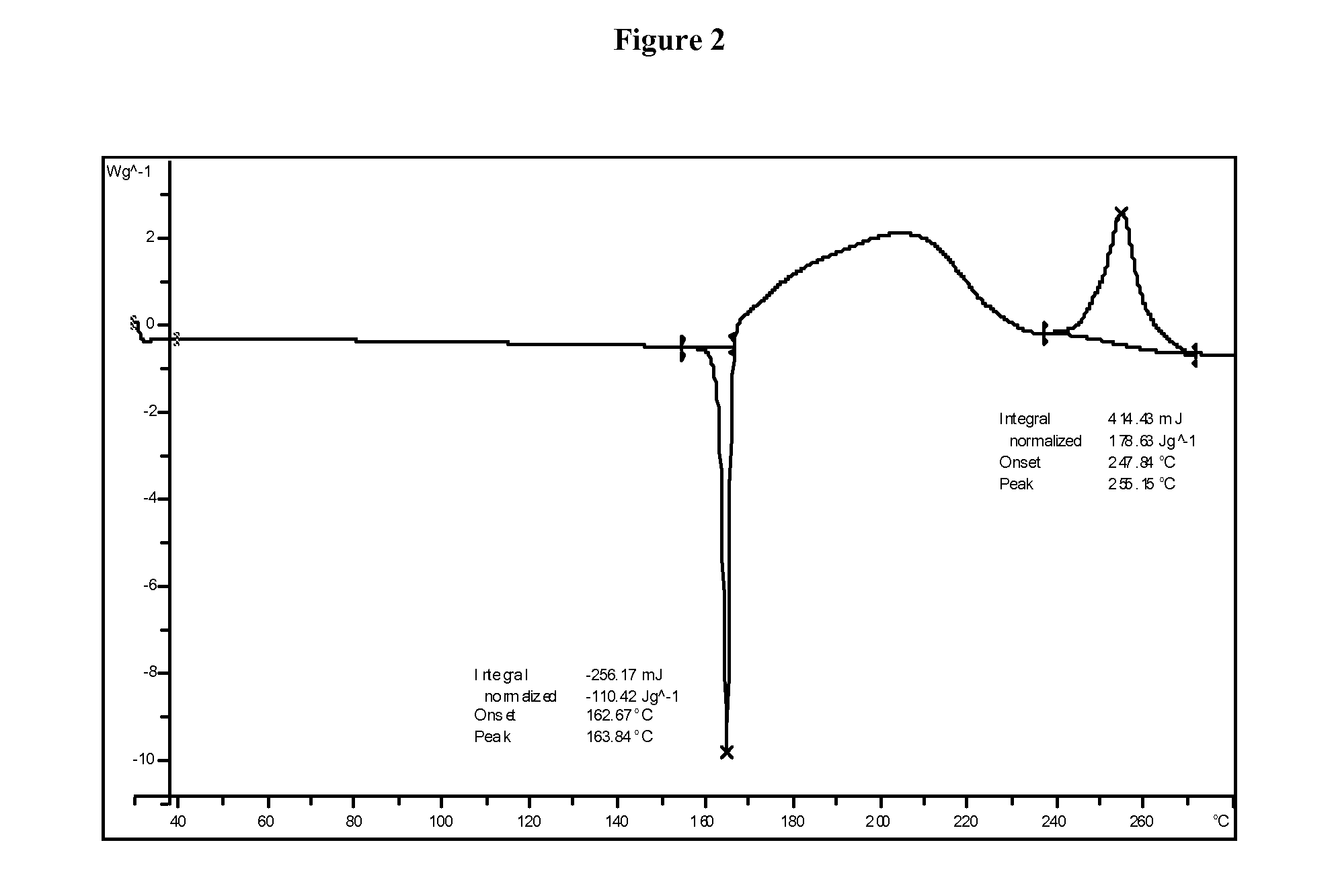
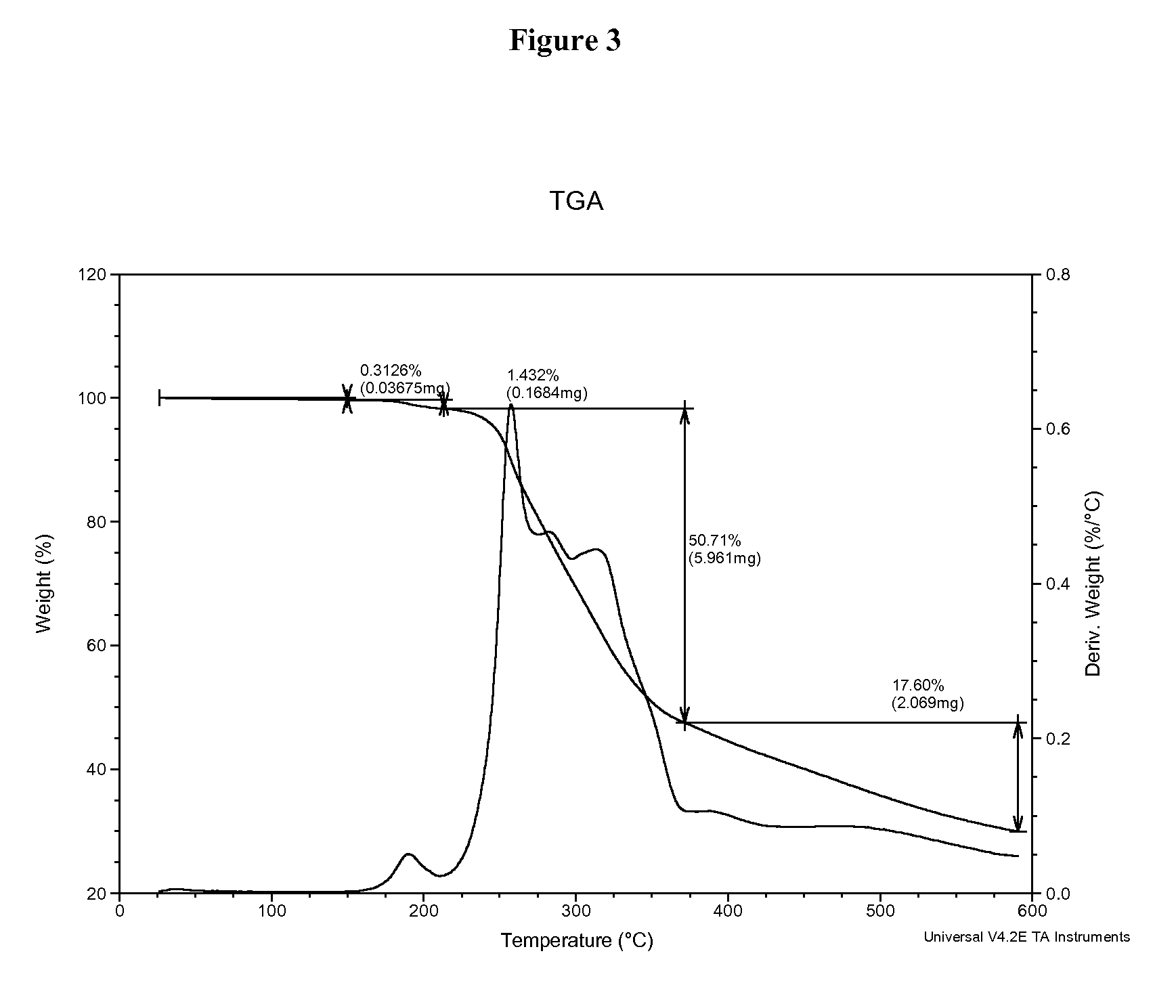
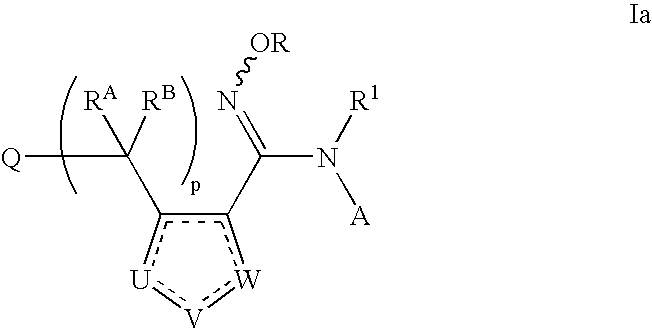
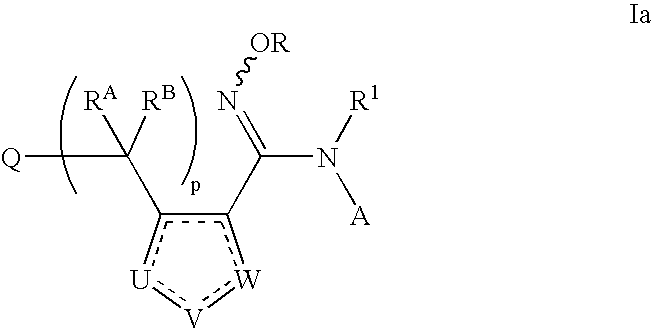
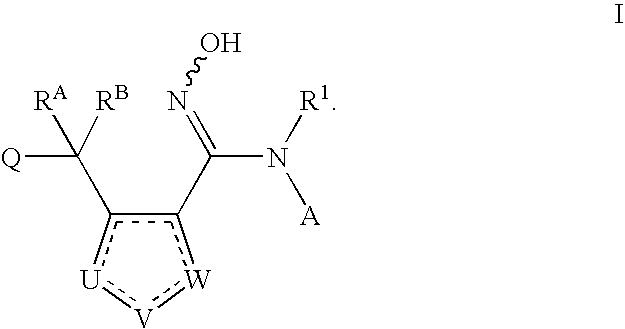
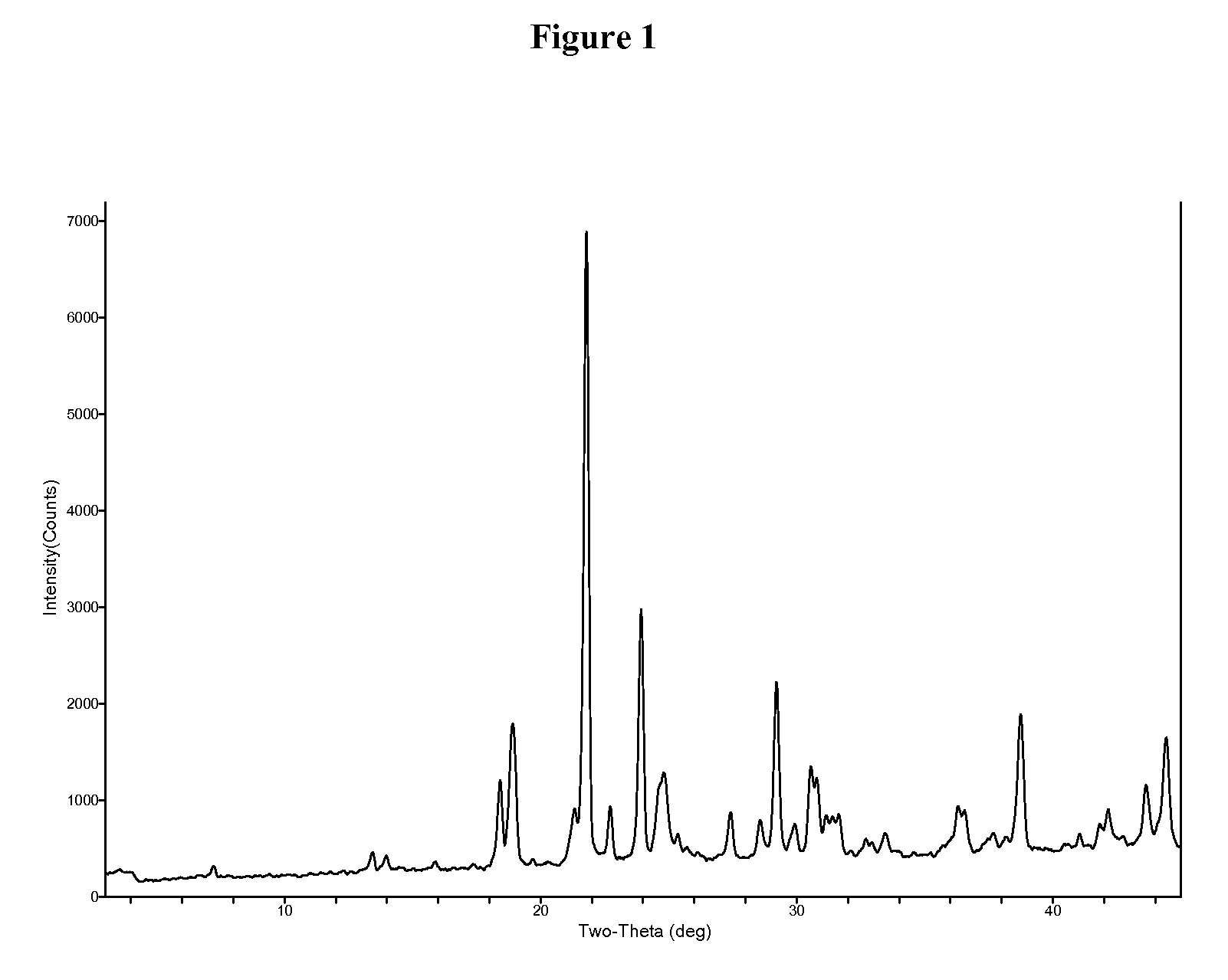
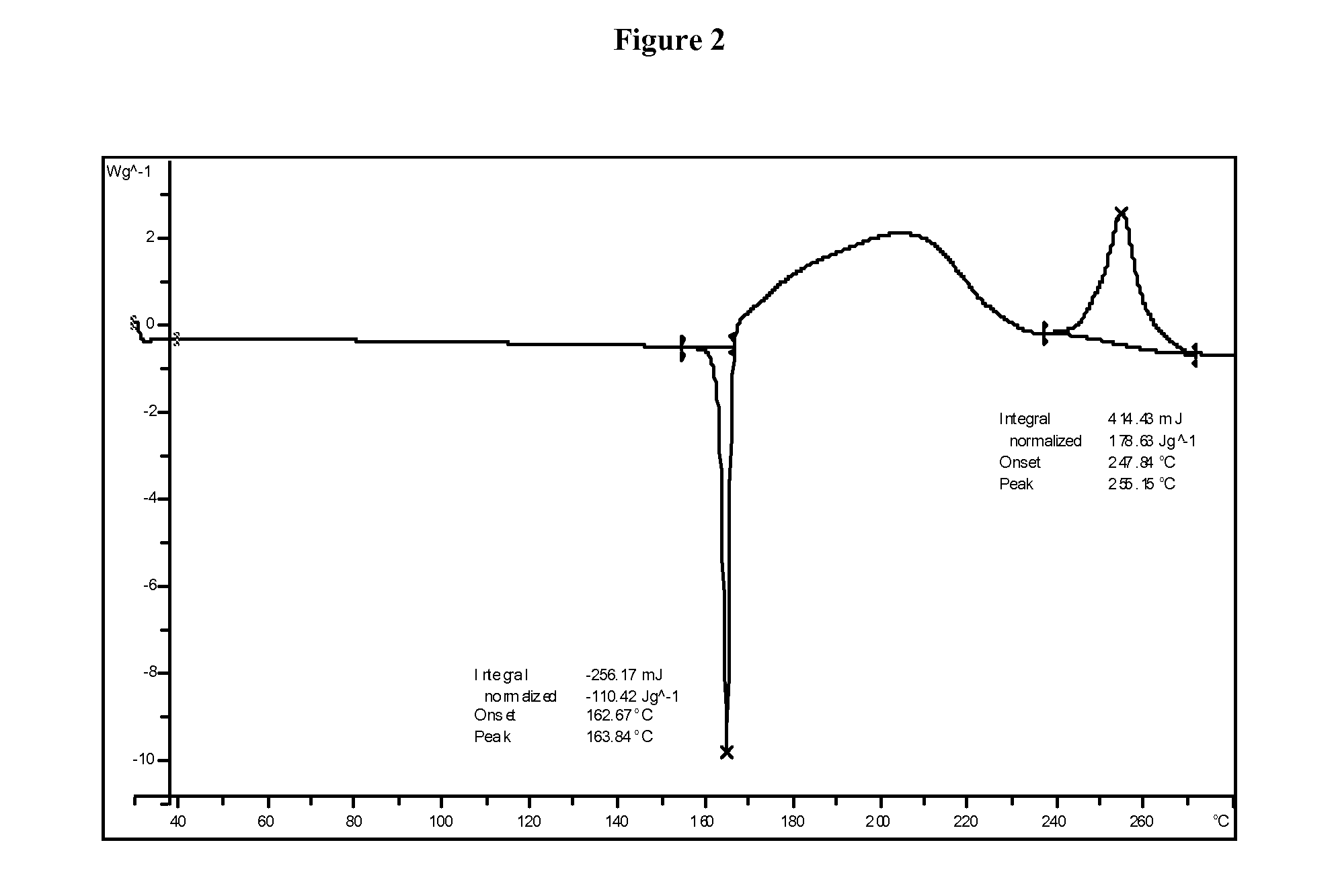
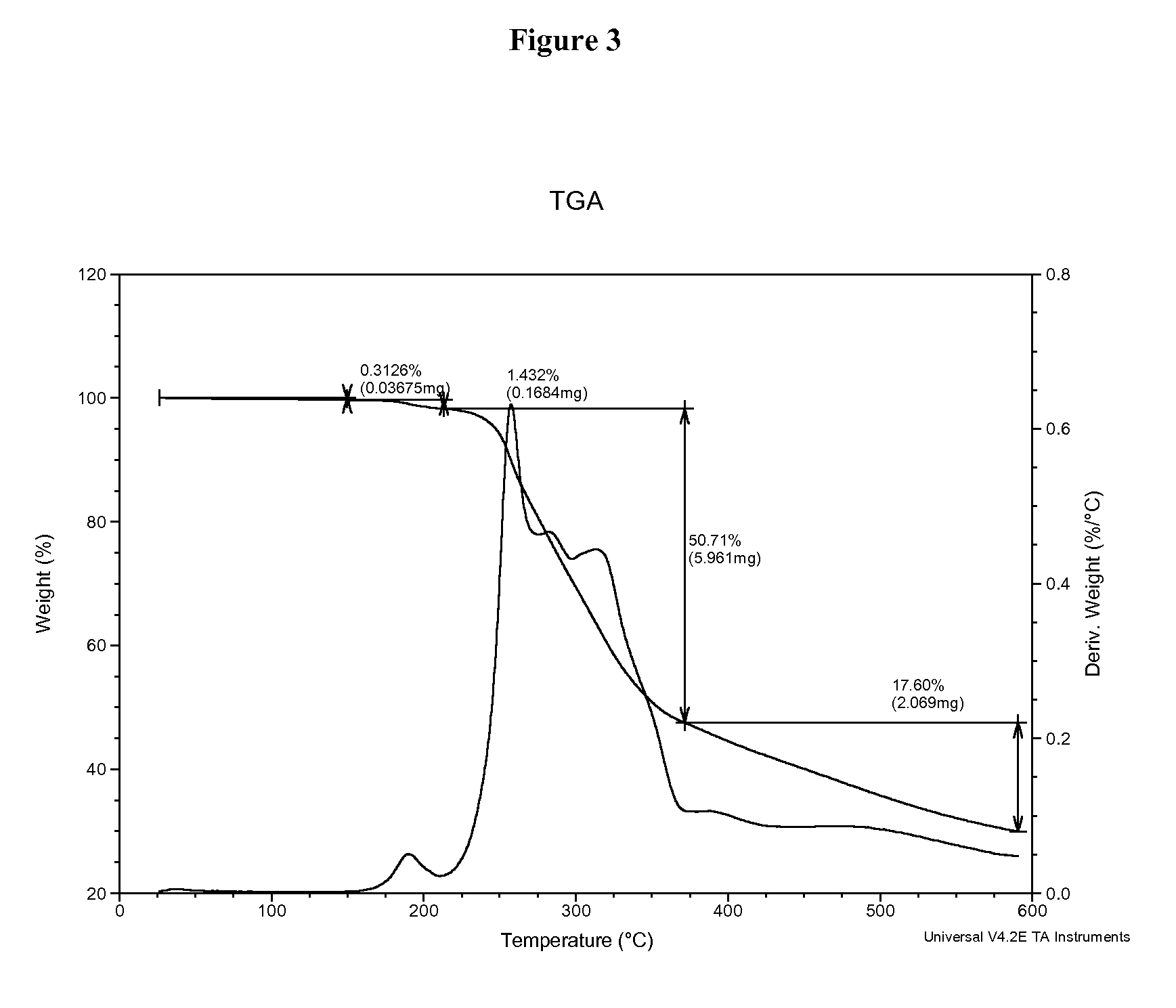
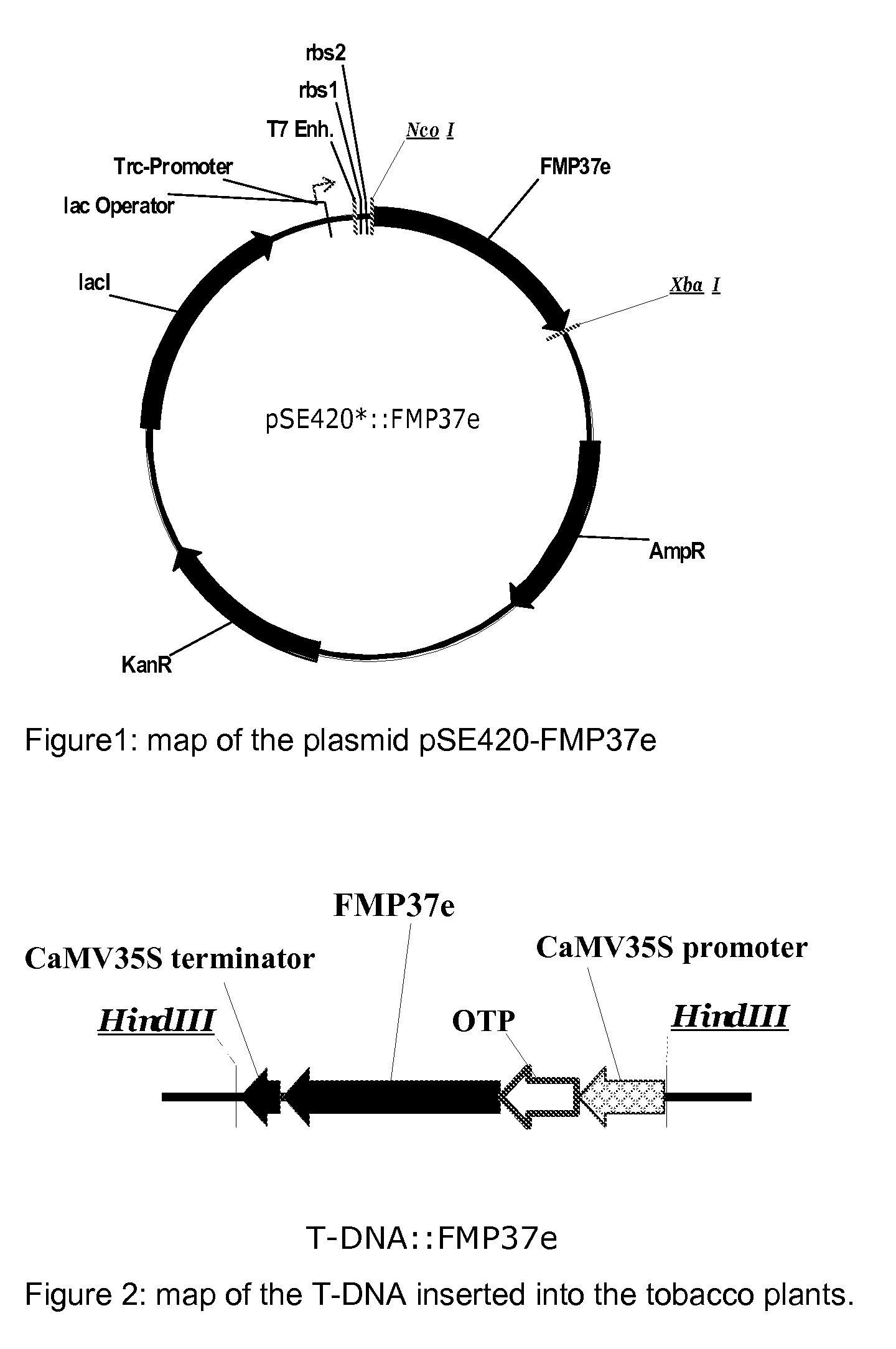
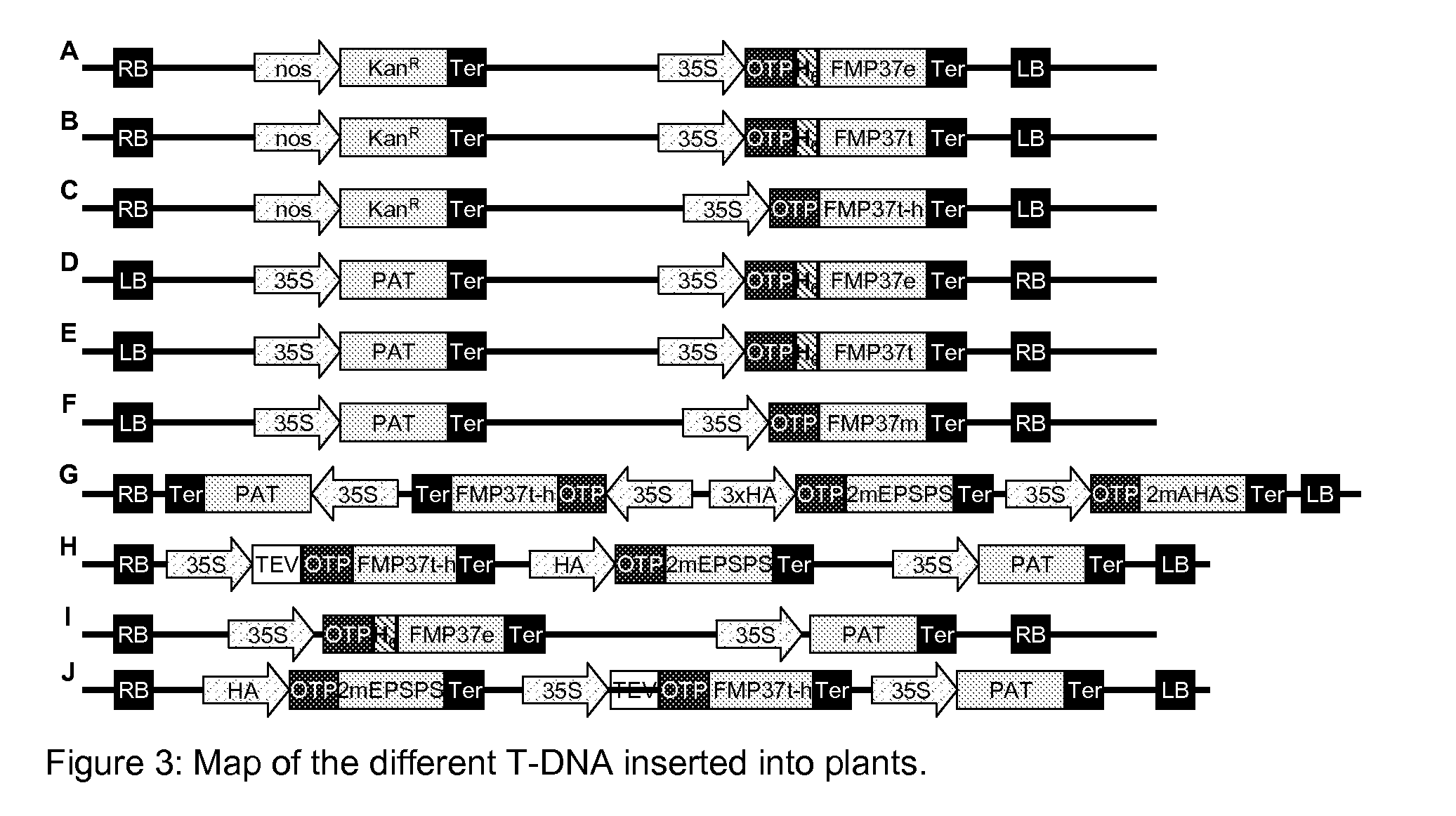
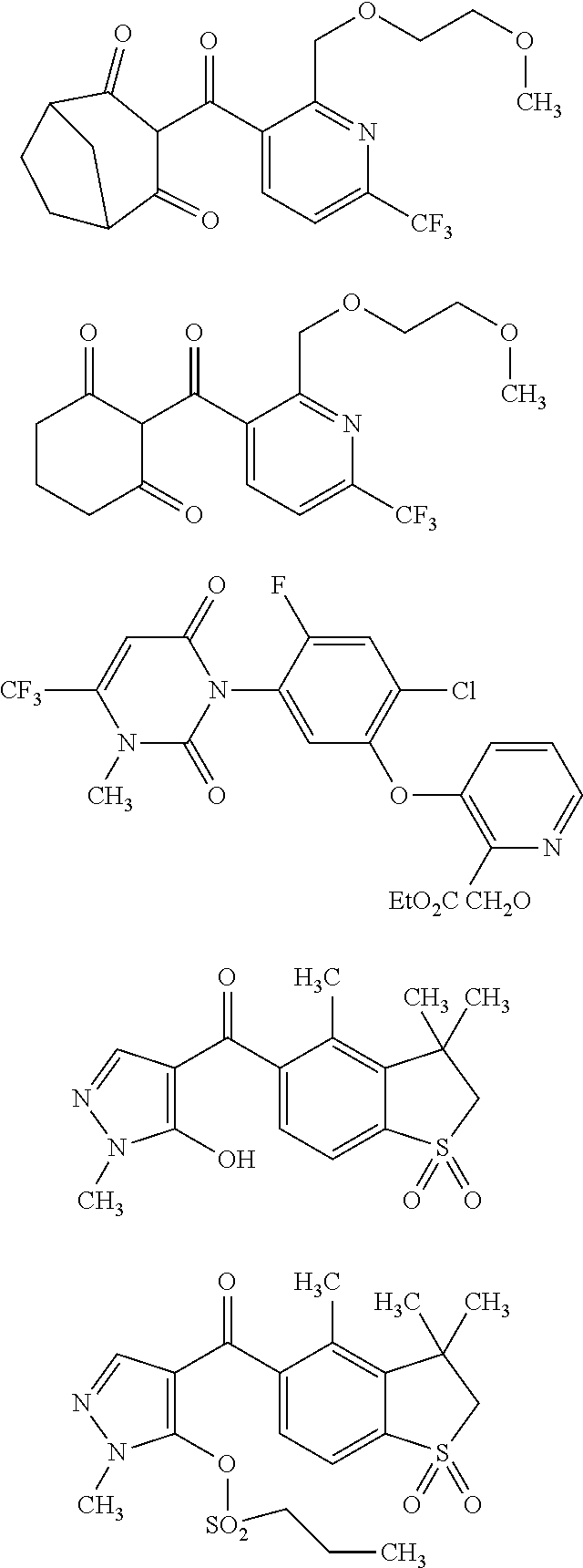
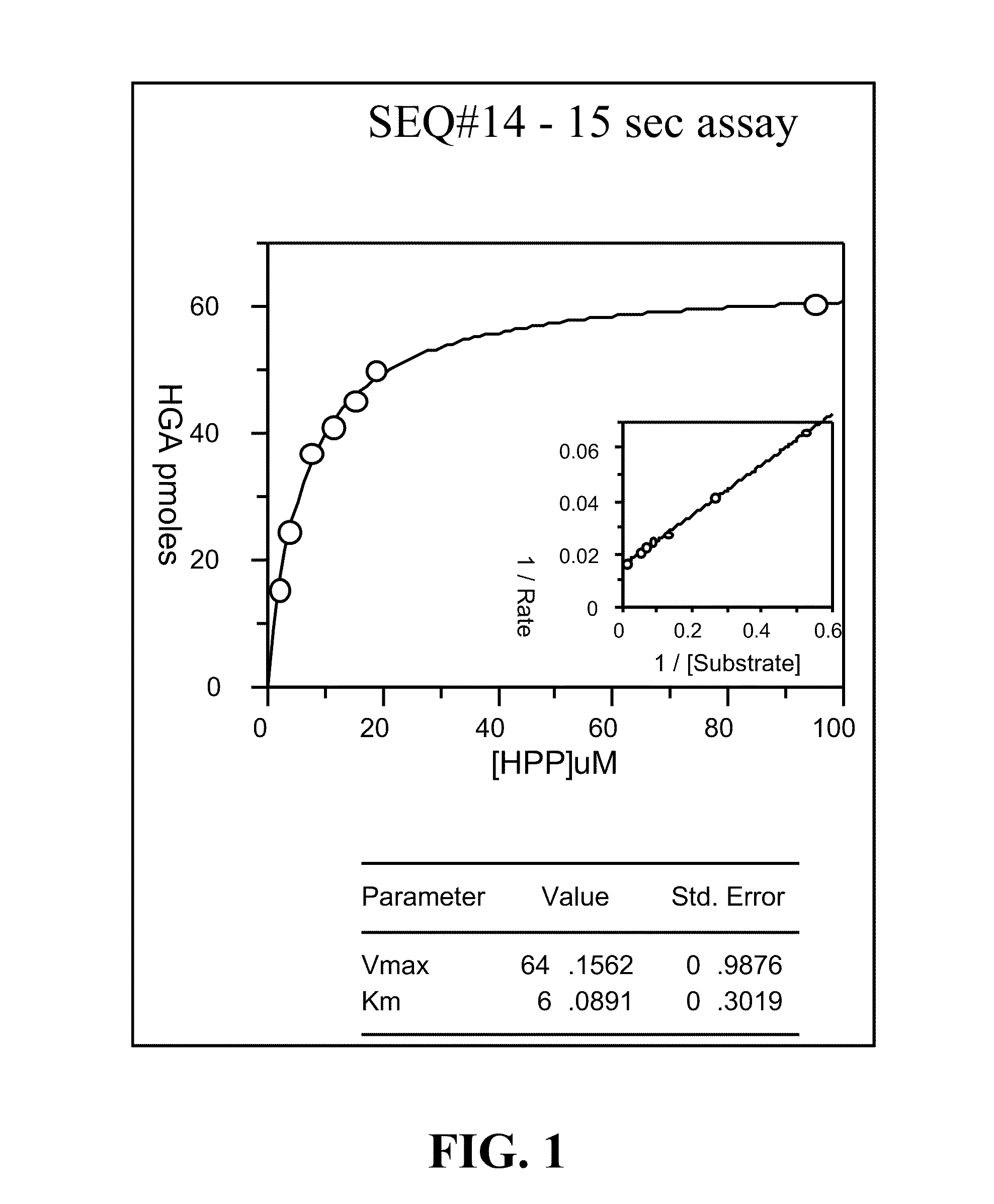
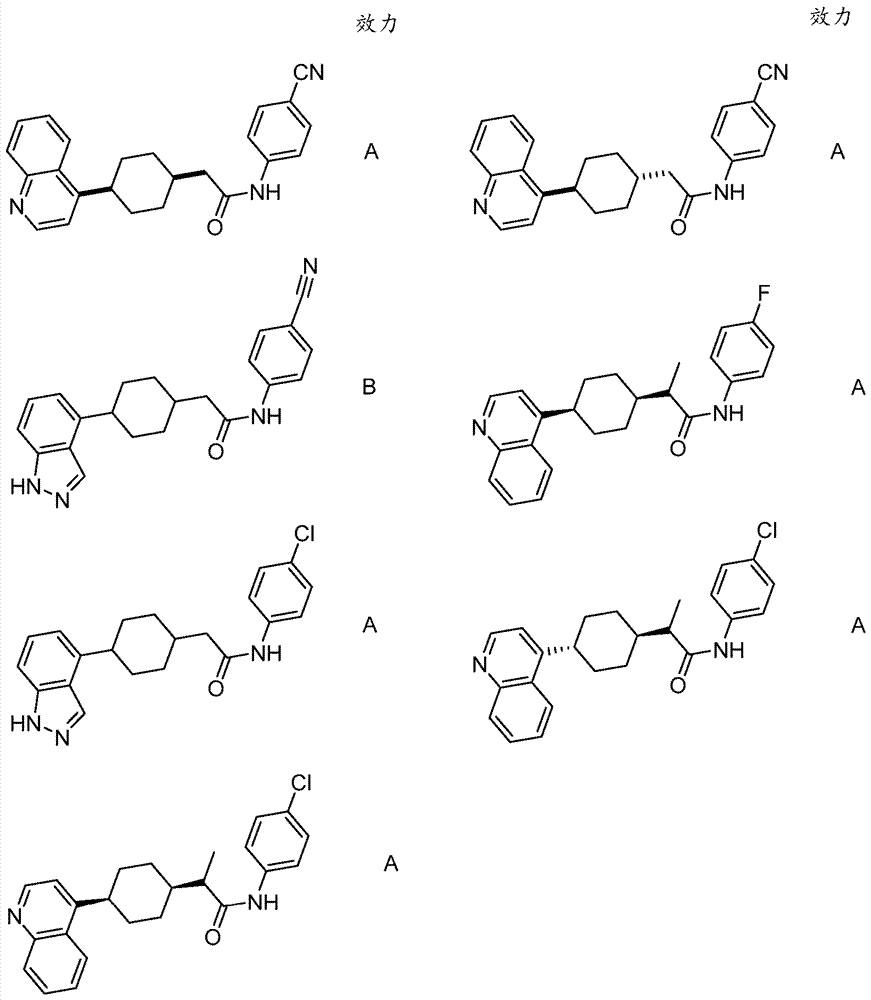
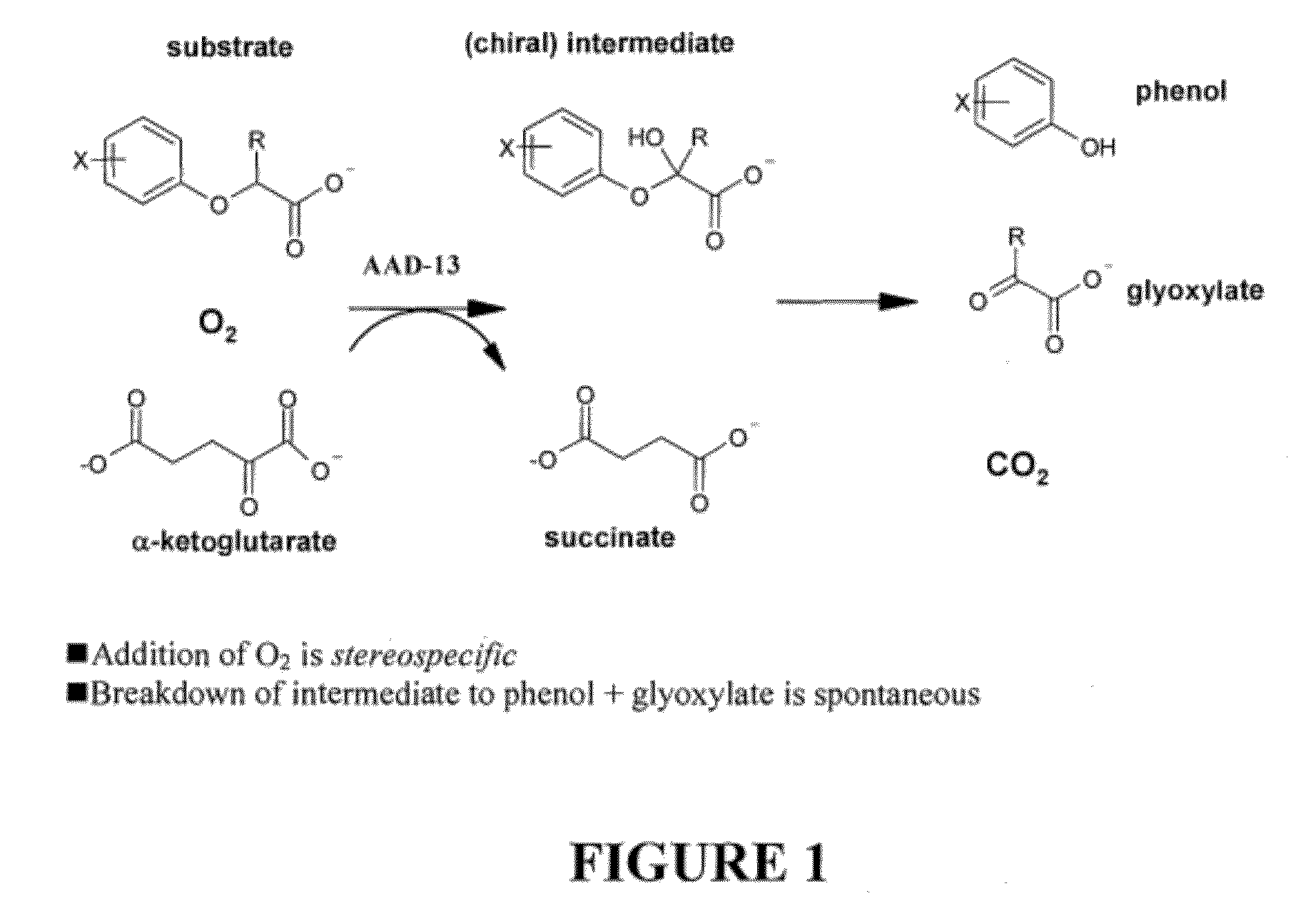
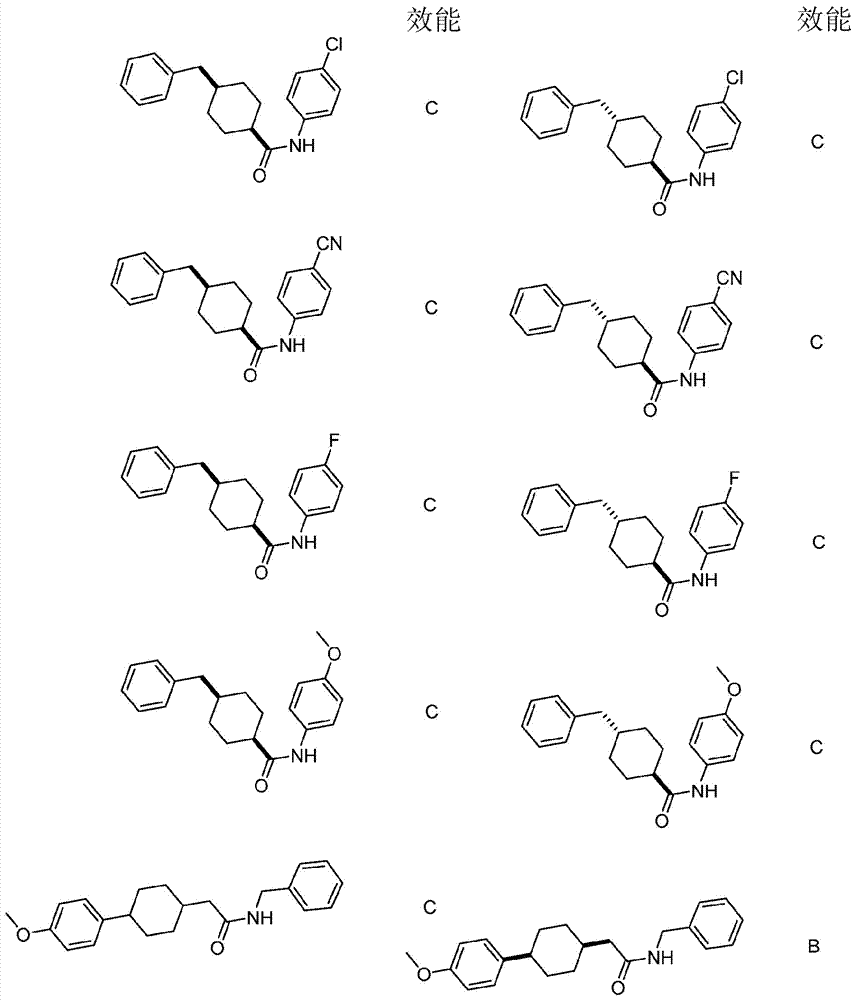
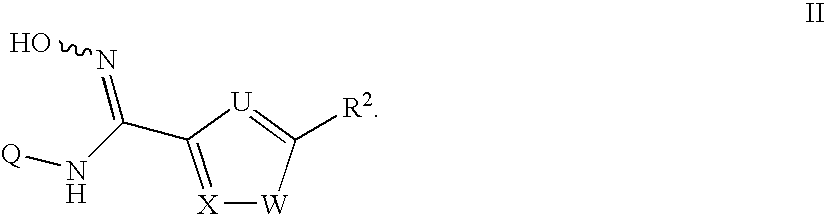Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
612 results about "Dioxygenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
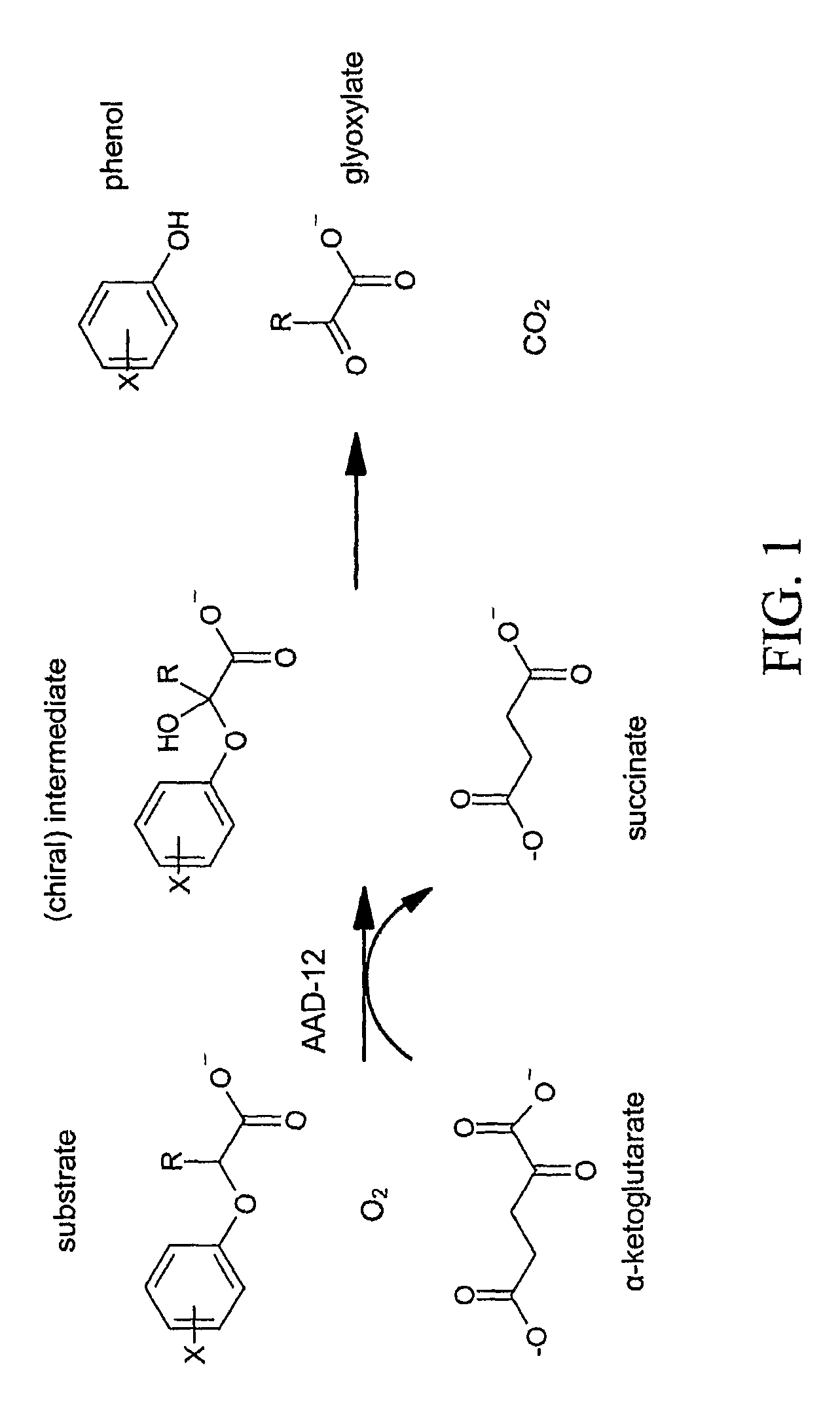
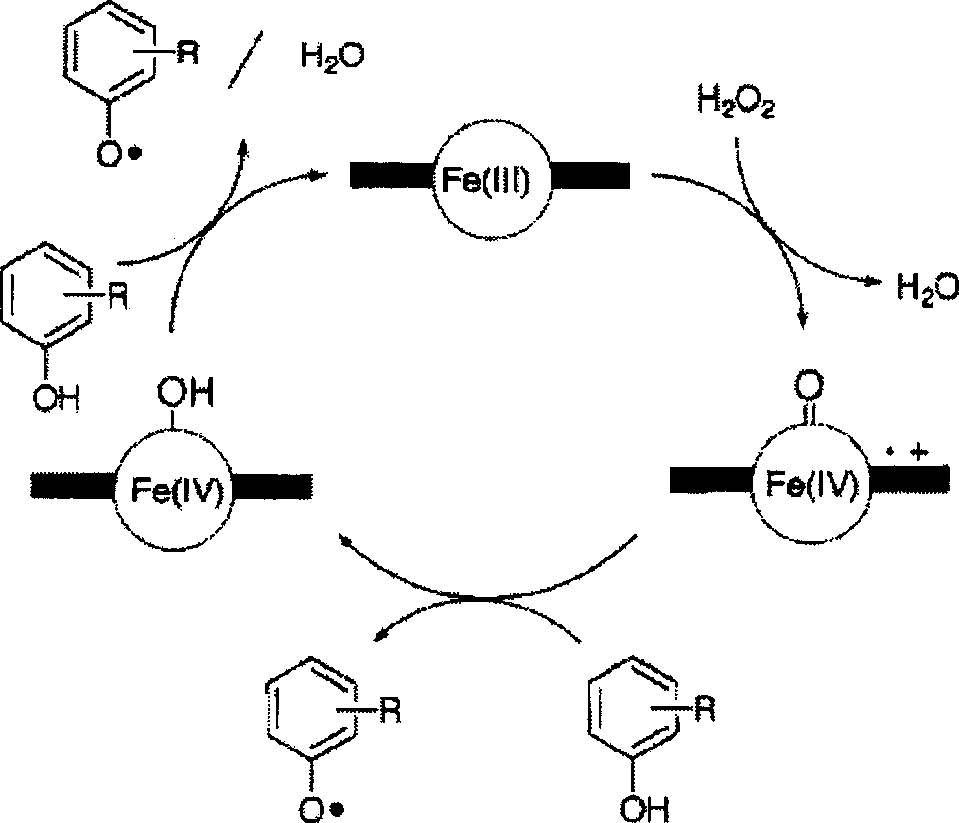
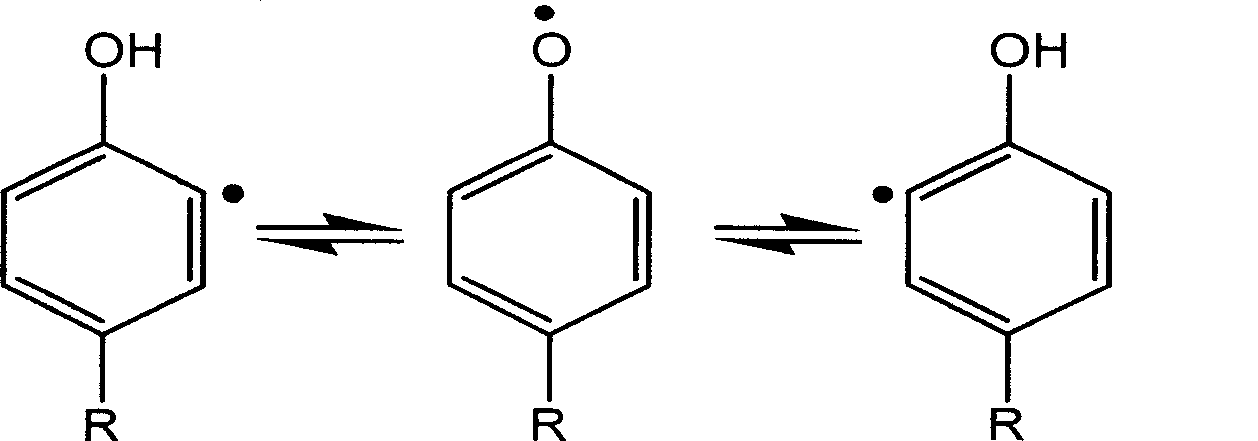
Dioxygenases are oxidoreductase enzymes. Aerobic life, from simple single-celled bacteria species to complex eukaryotic organisms, has evolved to depend on the oxidizing power of dioxygen in various metabolic pathways. From energetic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation to xenobiotic degradation, the use of dioxygen as a biological oxidant is widespread and varied in the exact mechanism of its use. Enzymes employ many different schemes to use dioxygen, and this largely depends on the substrate and reaction at hand.
Herbicide resistance genes
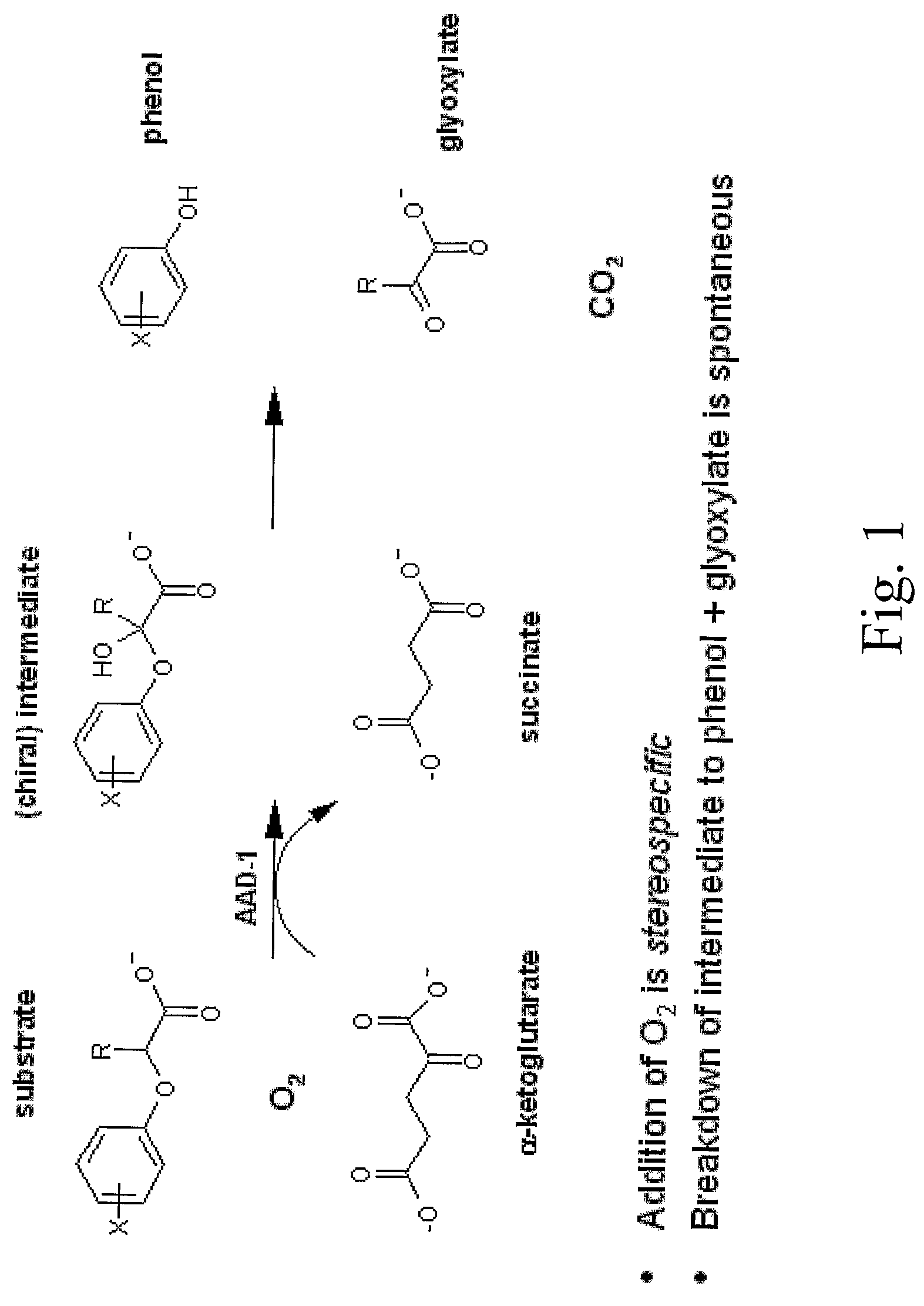
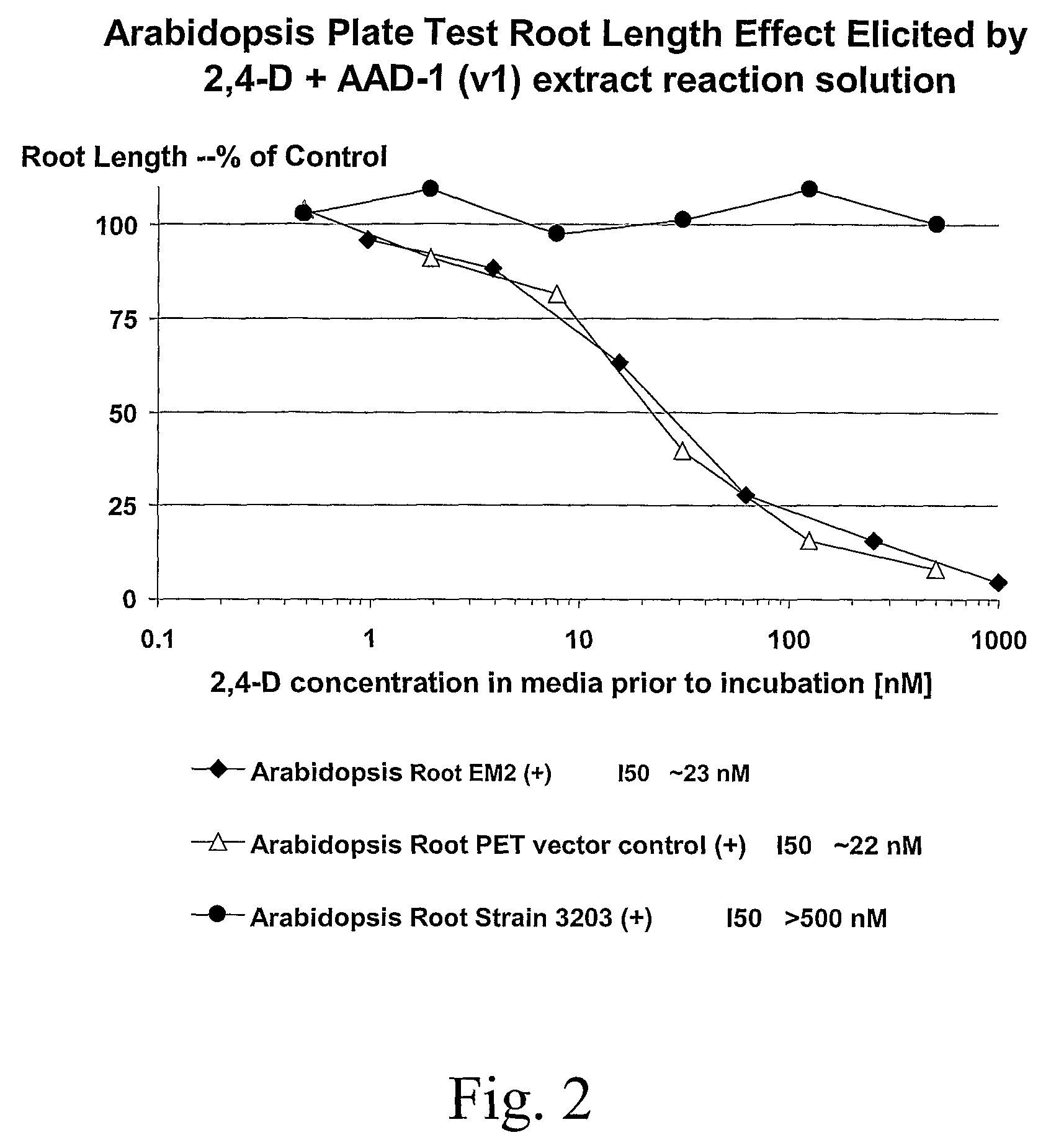
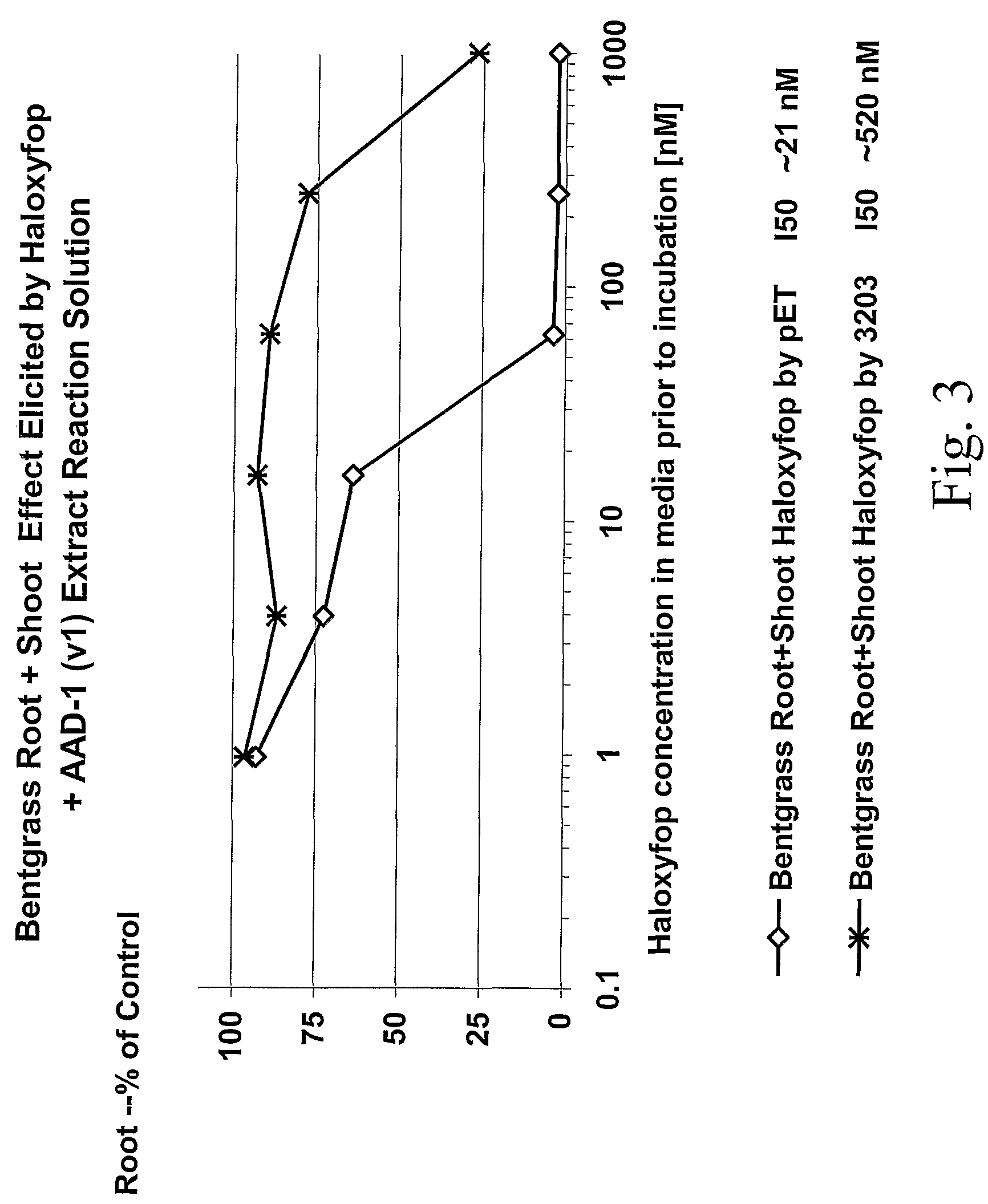
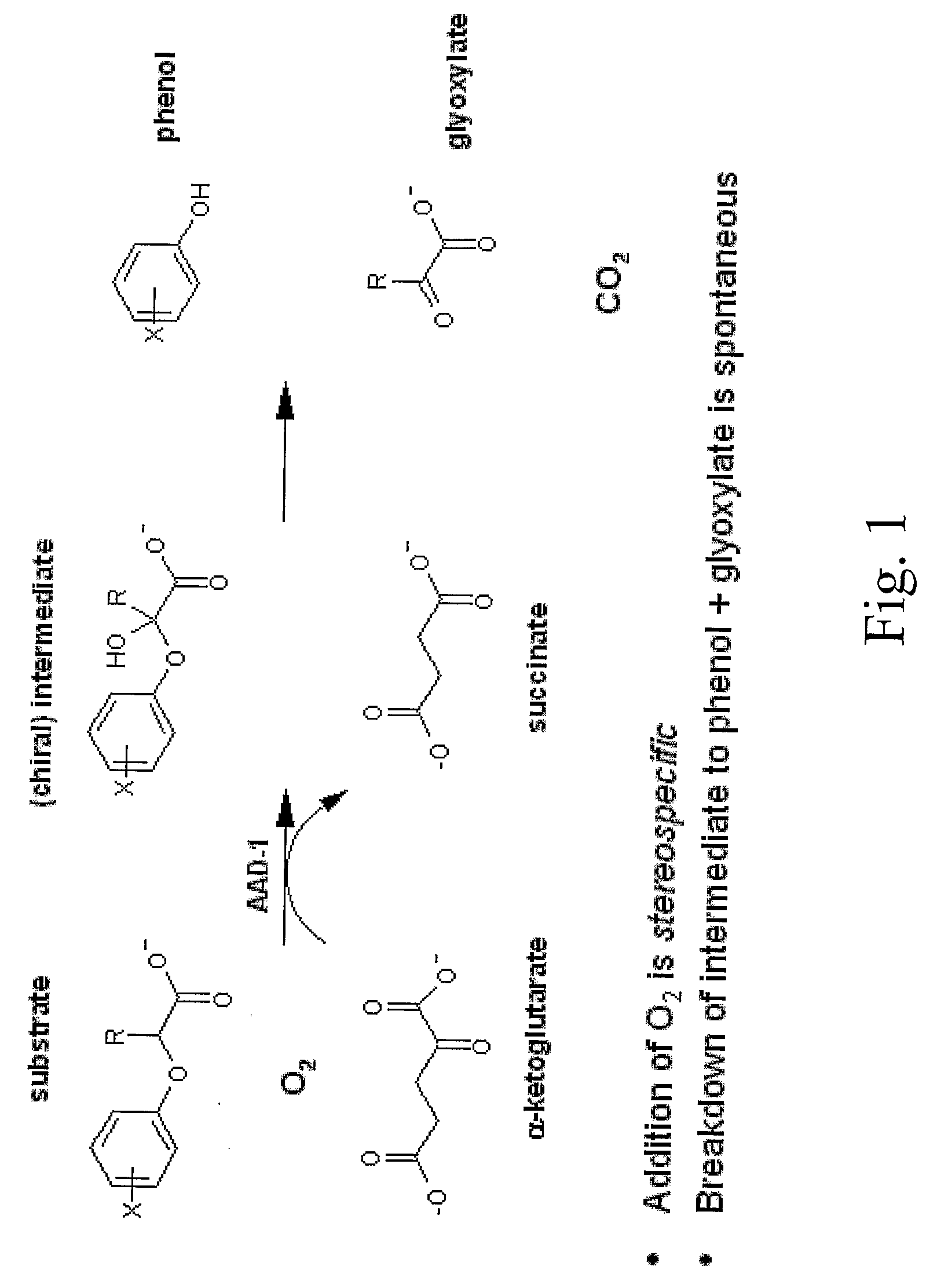
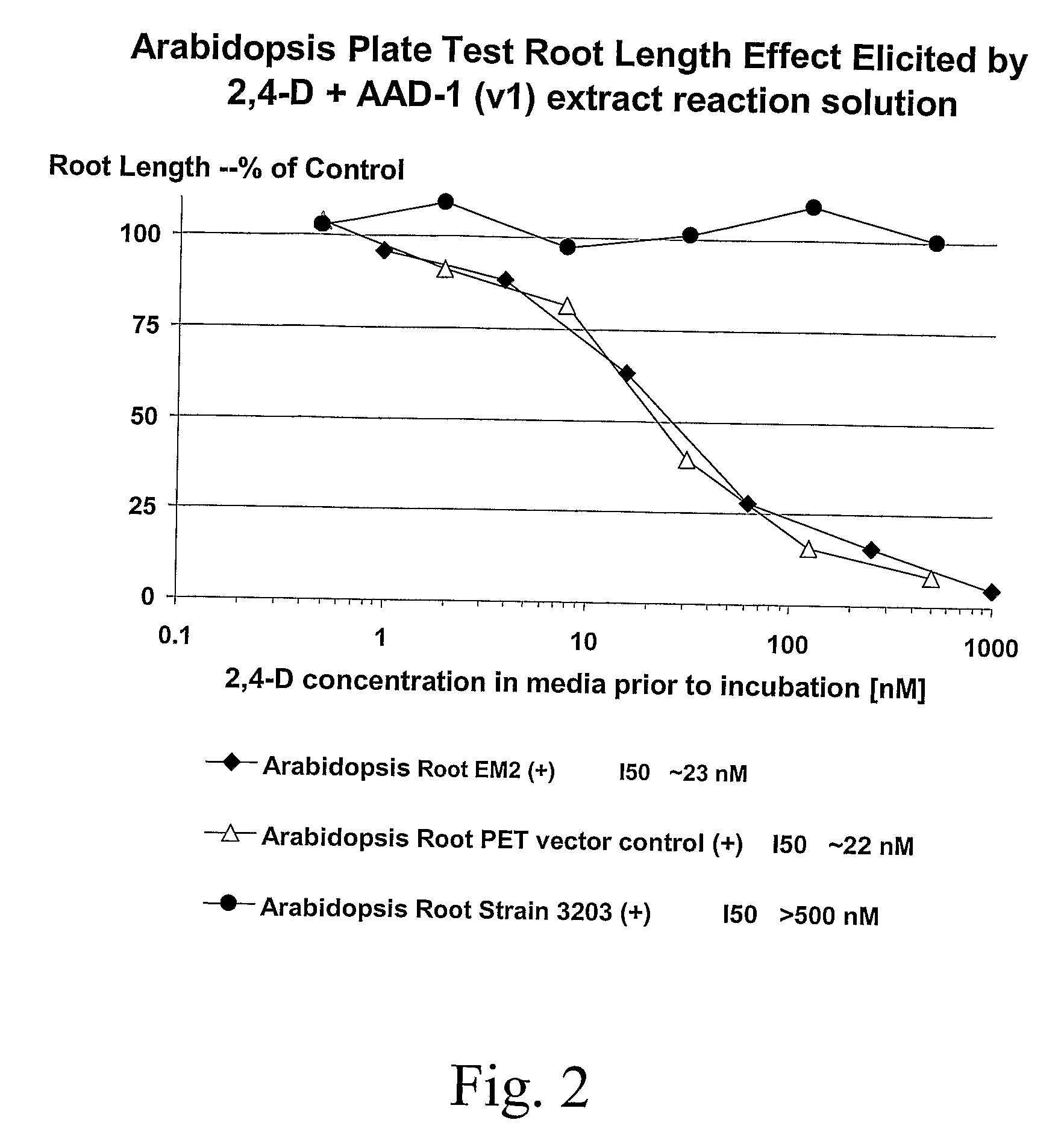
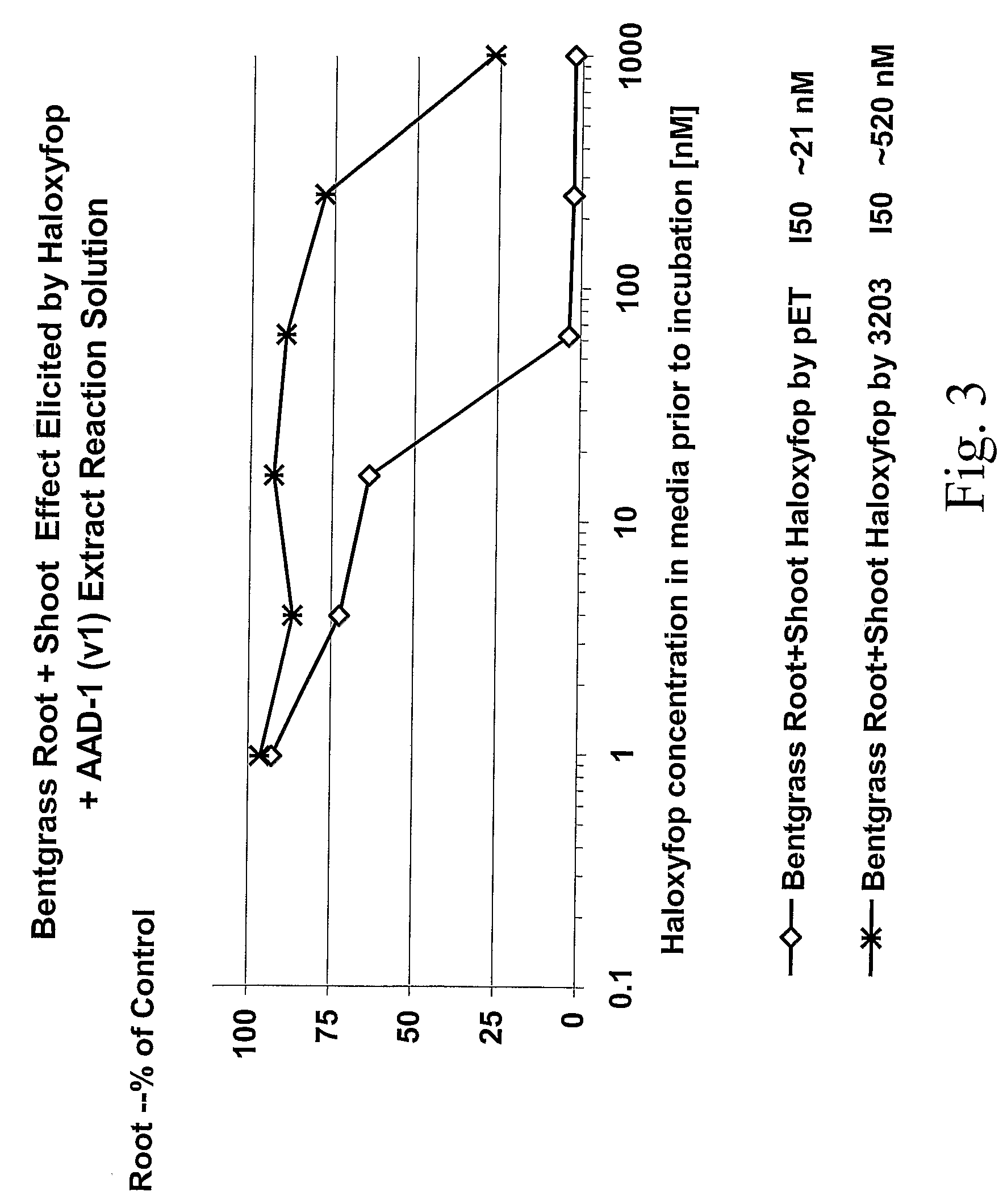
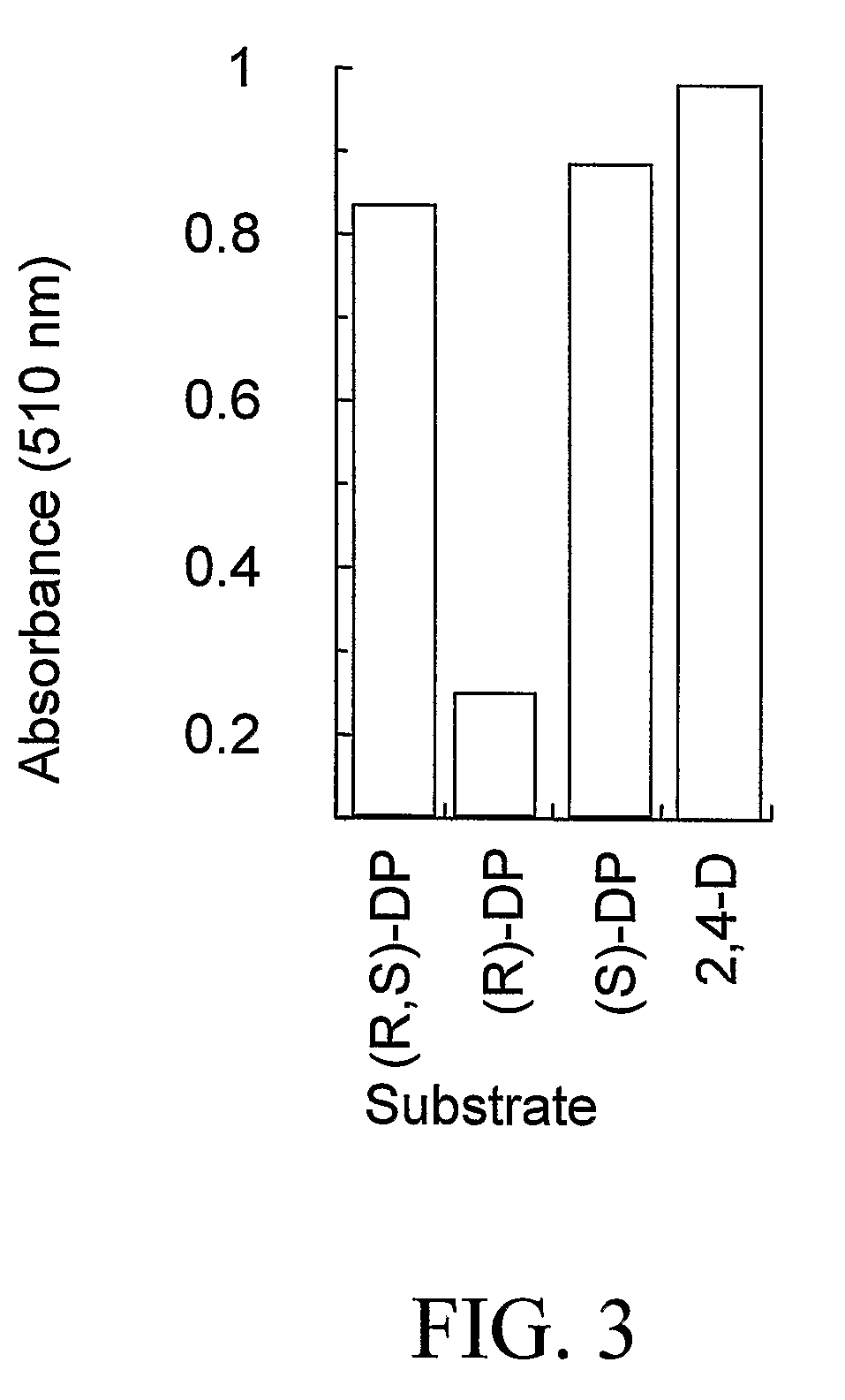
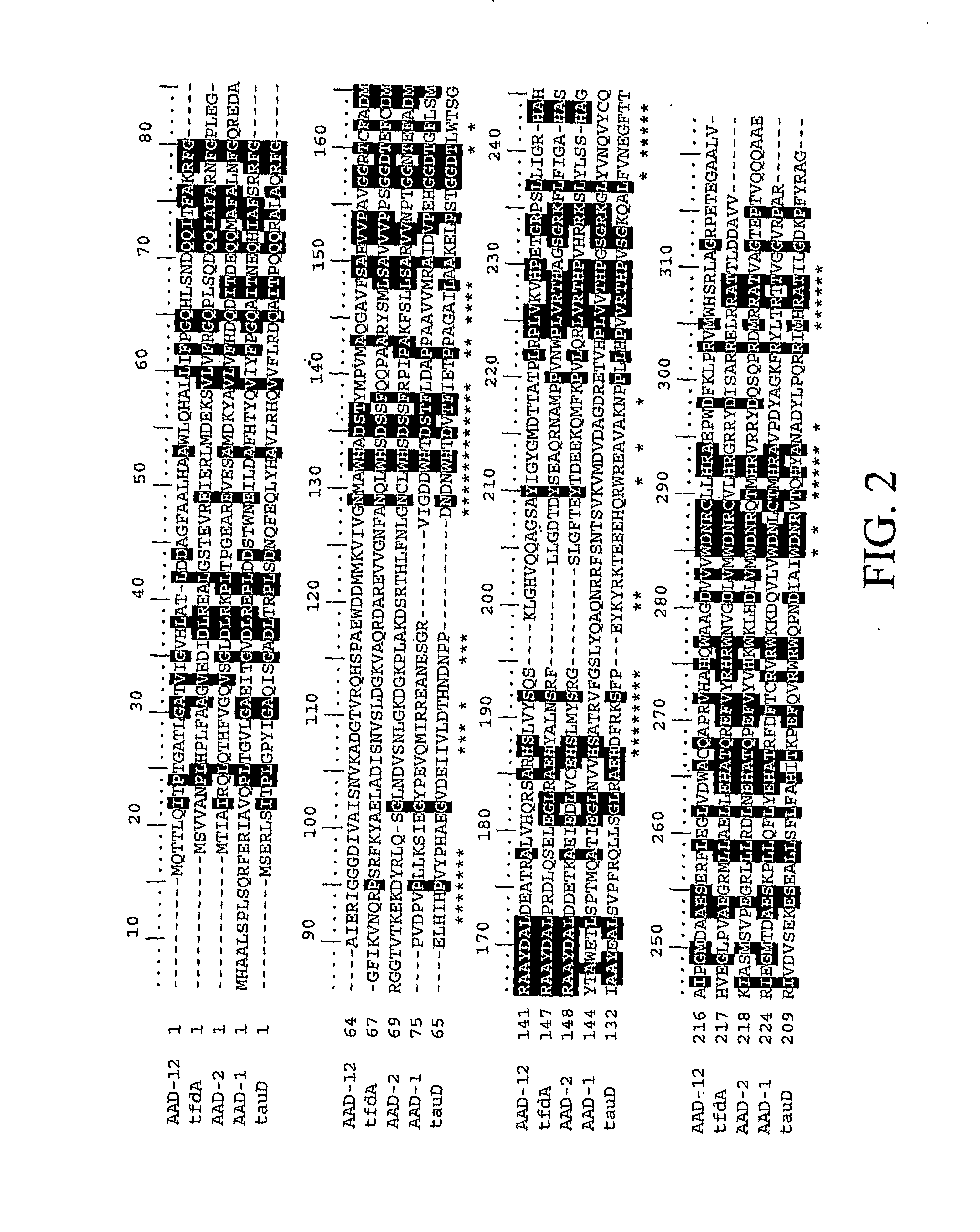
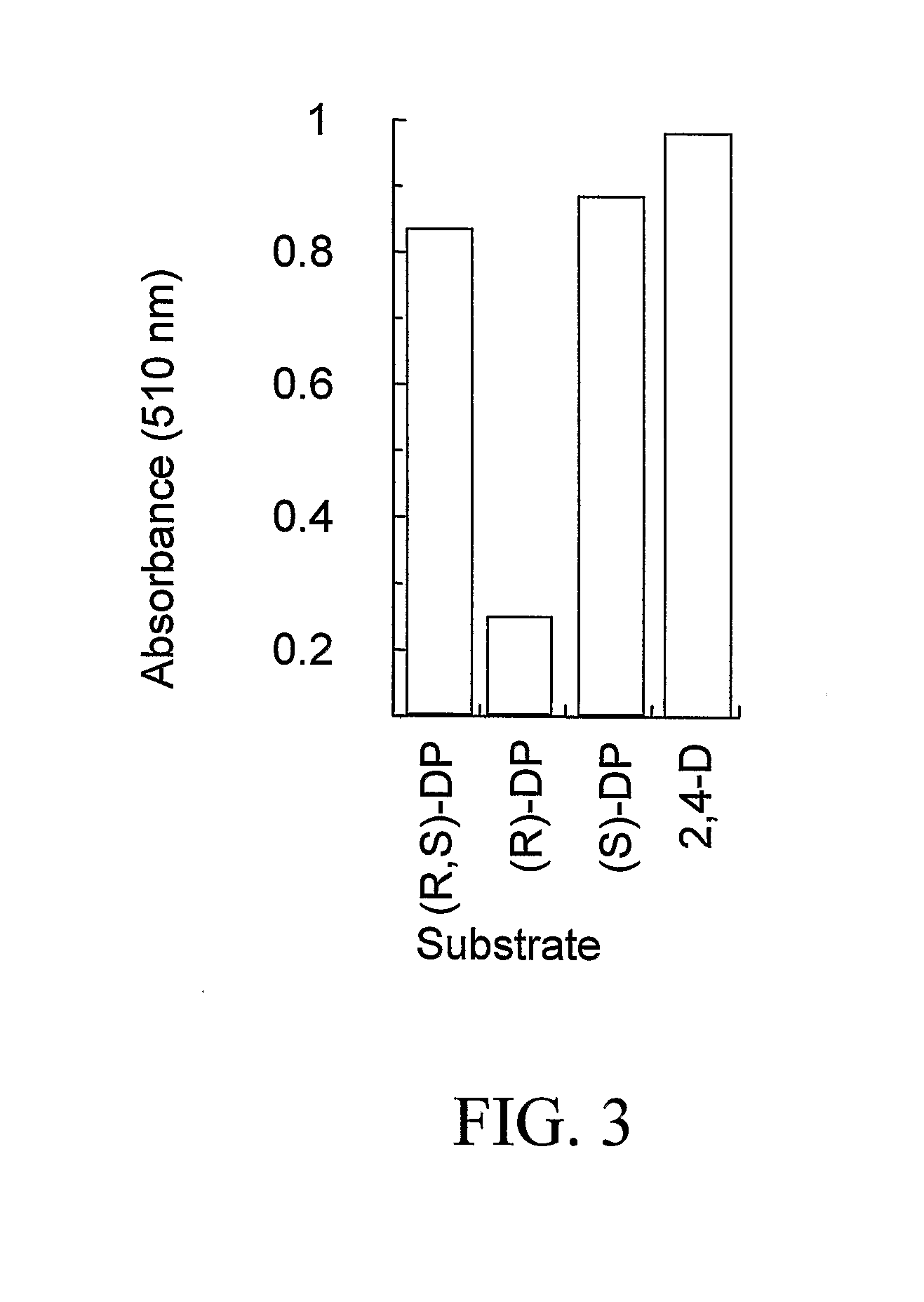
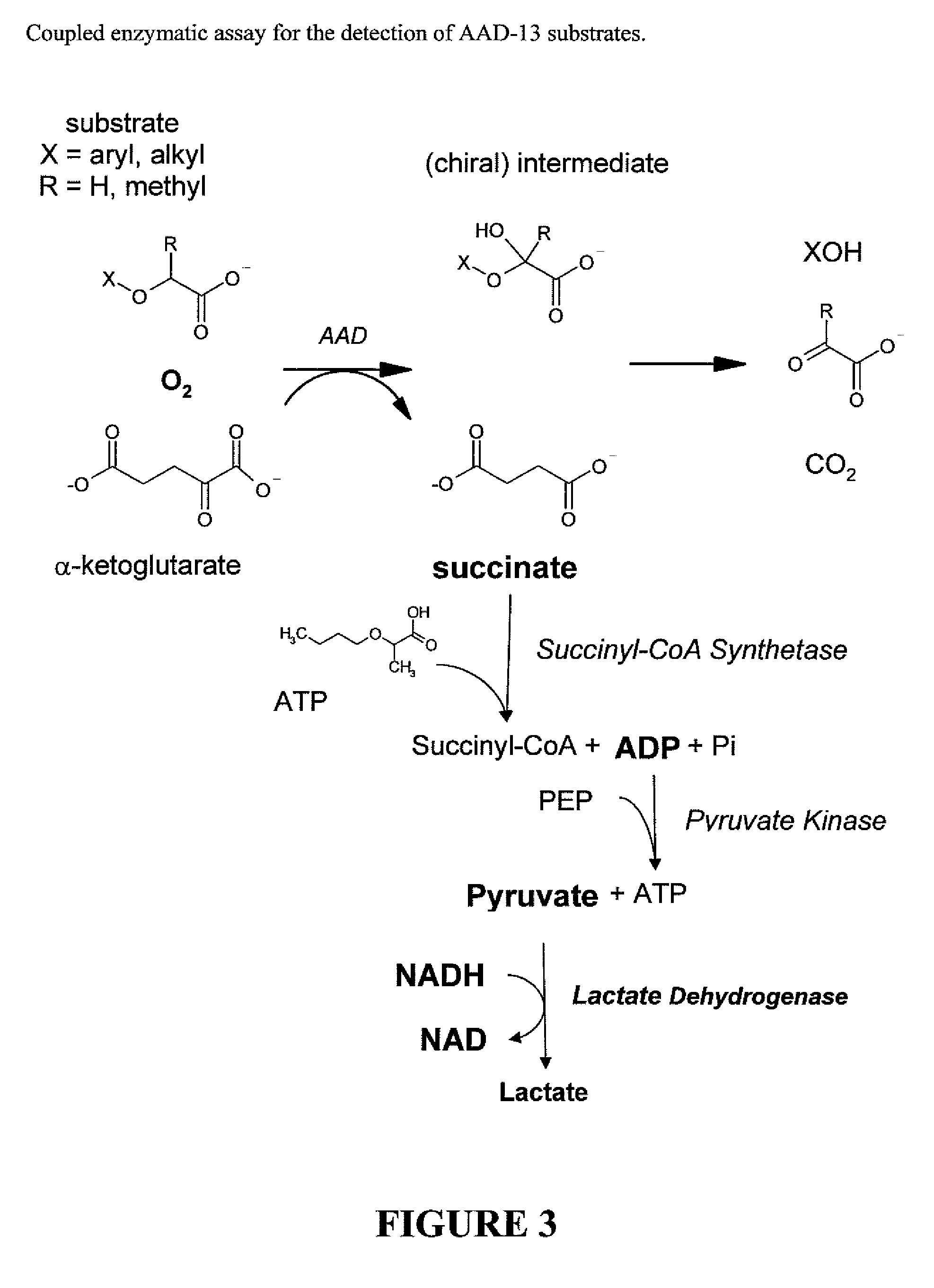
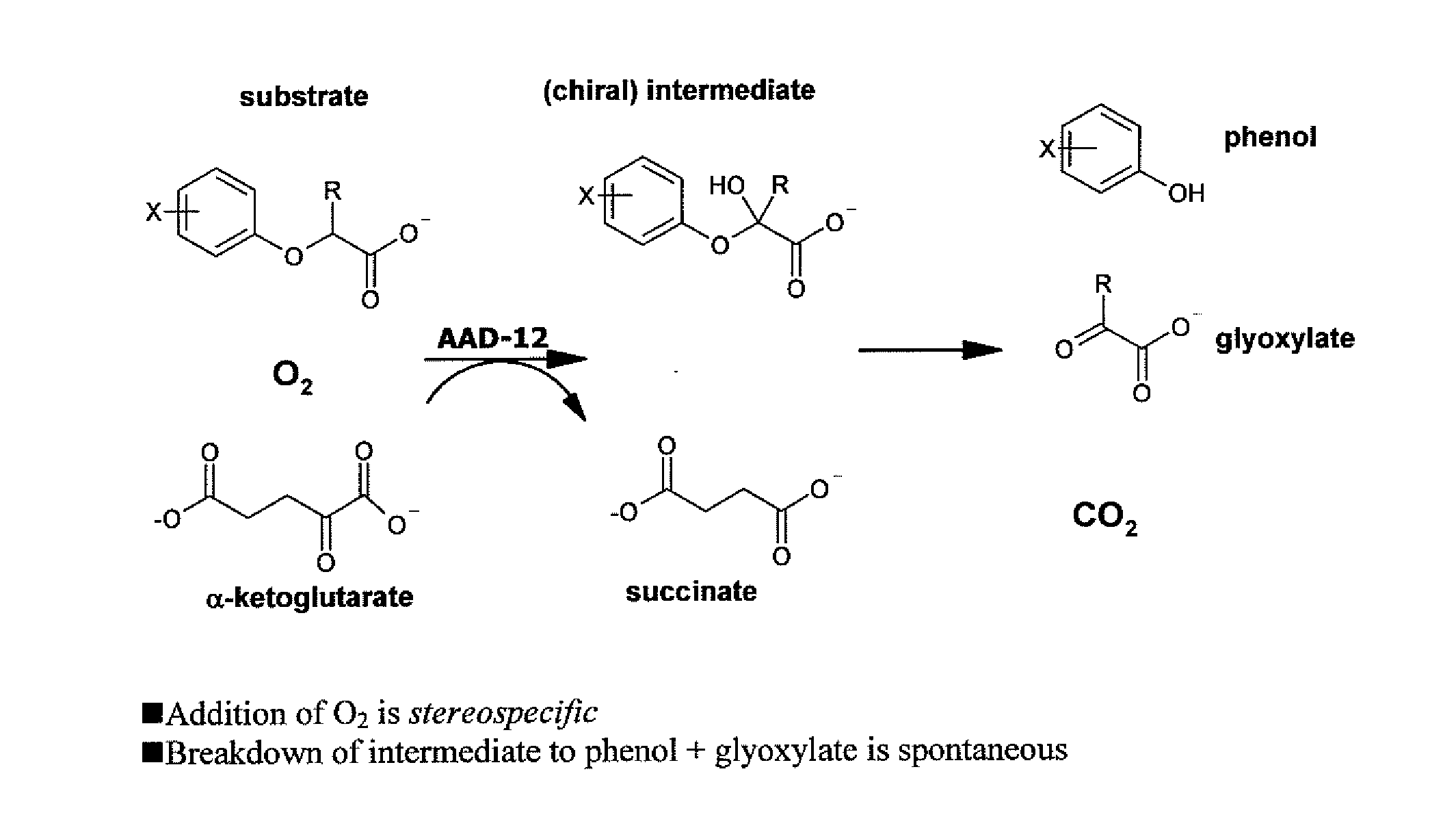
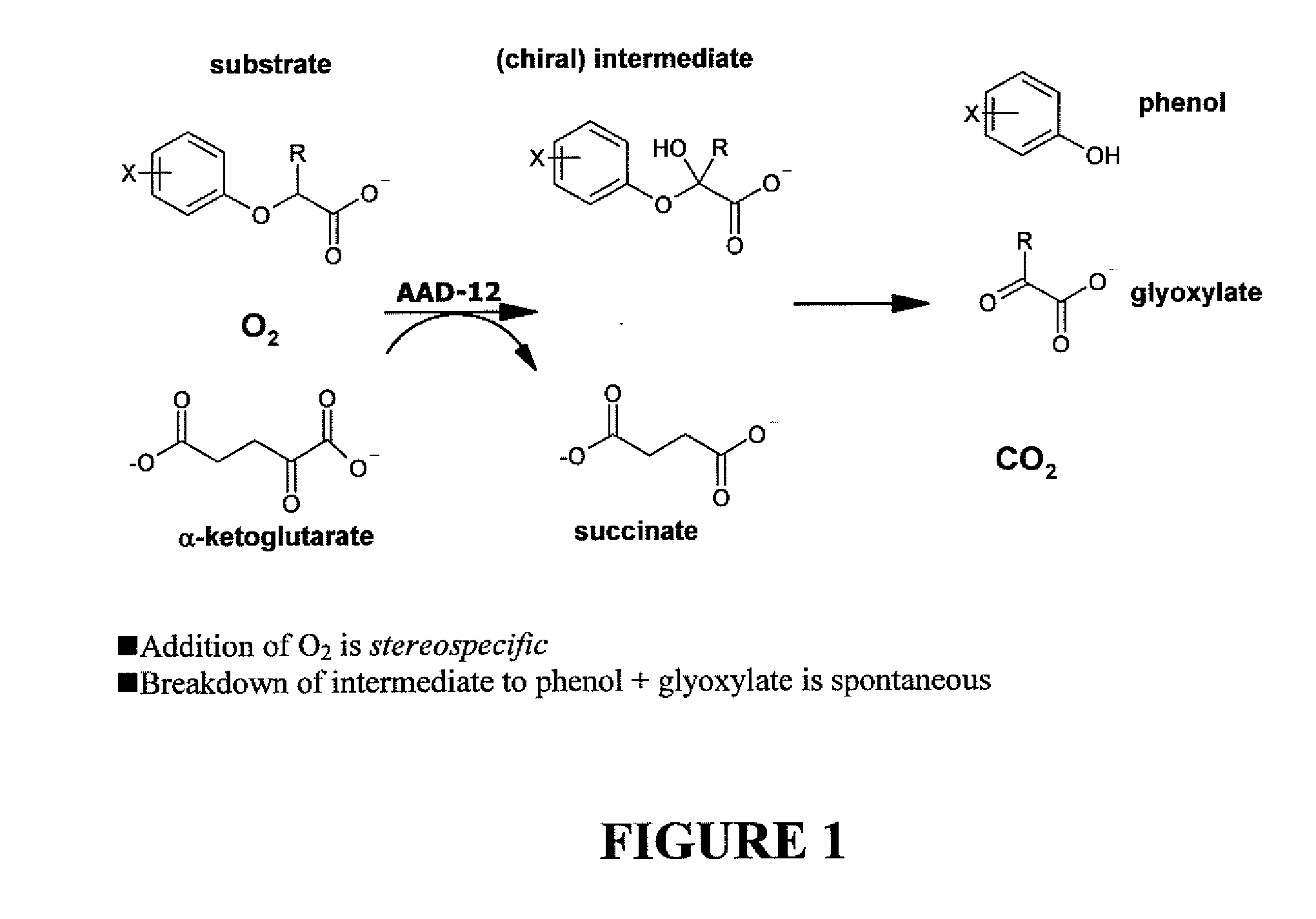
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Herbicide resistance genes
ActiveUS8283522B2Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosateDioxygenase
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to pyridyloxyacetate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-12 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Monoclonal antibodies detection methods for enzymes that confer resistance to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in plants
ActiveUS8460891B2Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsMonoclonal antibodyDioxygenase
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and methods of using the same
The present invention is directed to modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as compositions and pharmaceutical methods thereof.
Owner:INCYTE
1,2,5-oxadiazoles as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
ActiveUS20100015178A1Prevent immunosuppressionUseful in preparationBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseDioxygenase
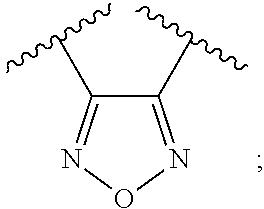
The present invention is directed to 1,2,5-oxadiazole derivatives, and compositions of the same, which are inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and are useful in the treatment of cancer and other disorders, and to the processes and intermediates for making such 1,2,5-oxadiazole derivatives.
Owner:INCYTE
N-hydroxyamidinoheterocycles as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
The present invention is directed to N-hydroxyamidino compounds which are modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of use thereof relating to the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:INCYTE
1,2,5-oxadiazoles as inhibitors of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
Plants Tolerant to HPPD Inhibitor Herbicides
ActiveUS20110191897A1Effectively actEliminate side effectsBiocideAnimal repellantsNucleic acid sequencingDioxygenase
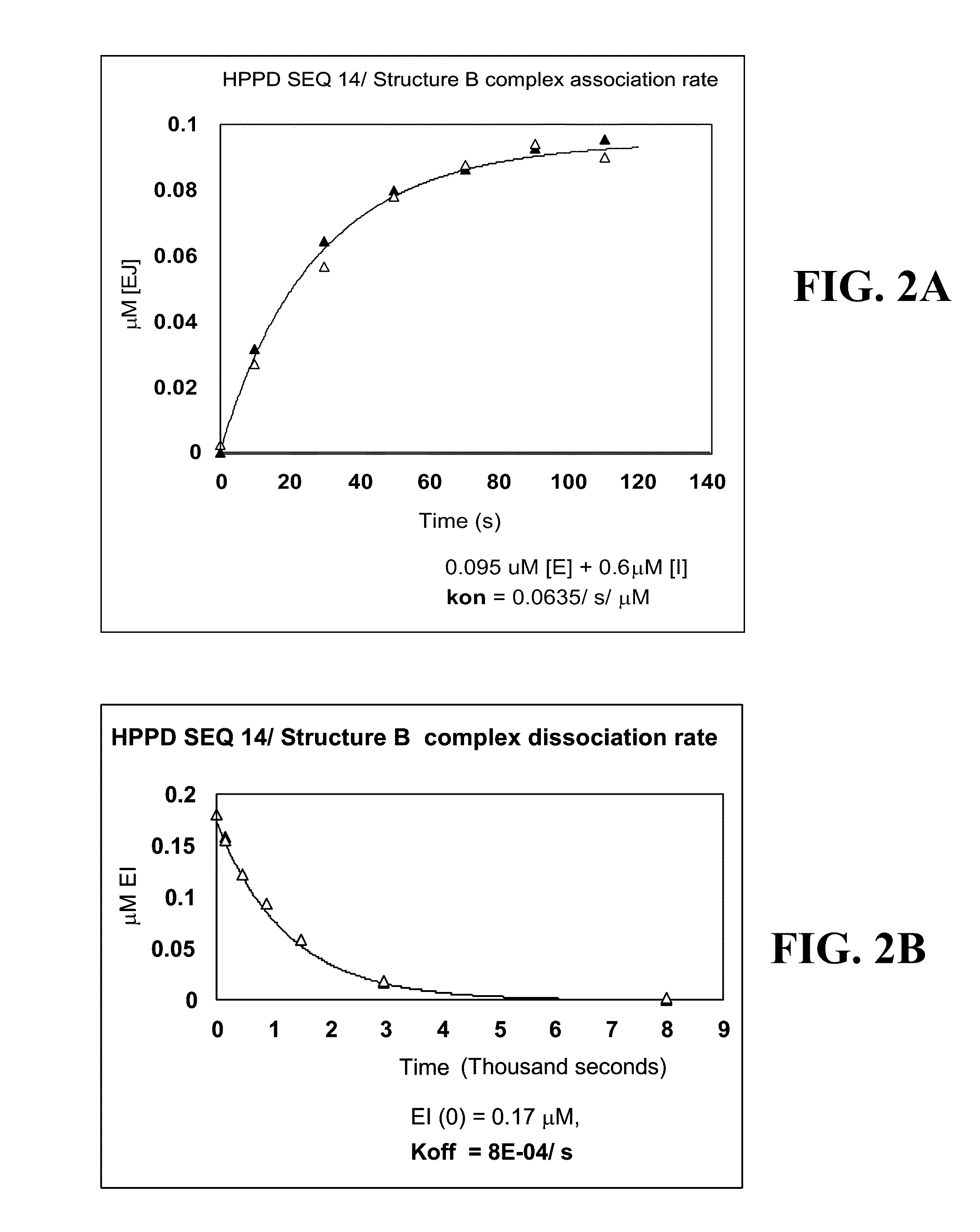
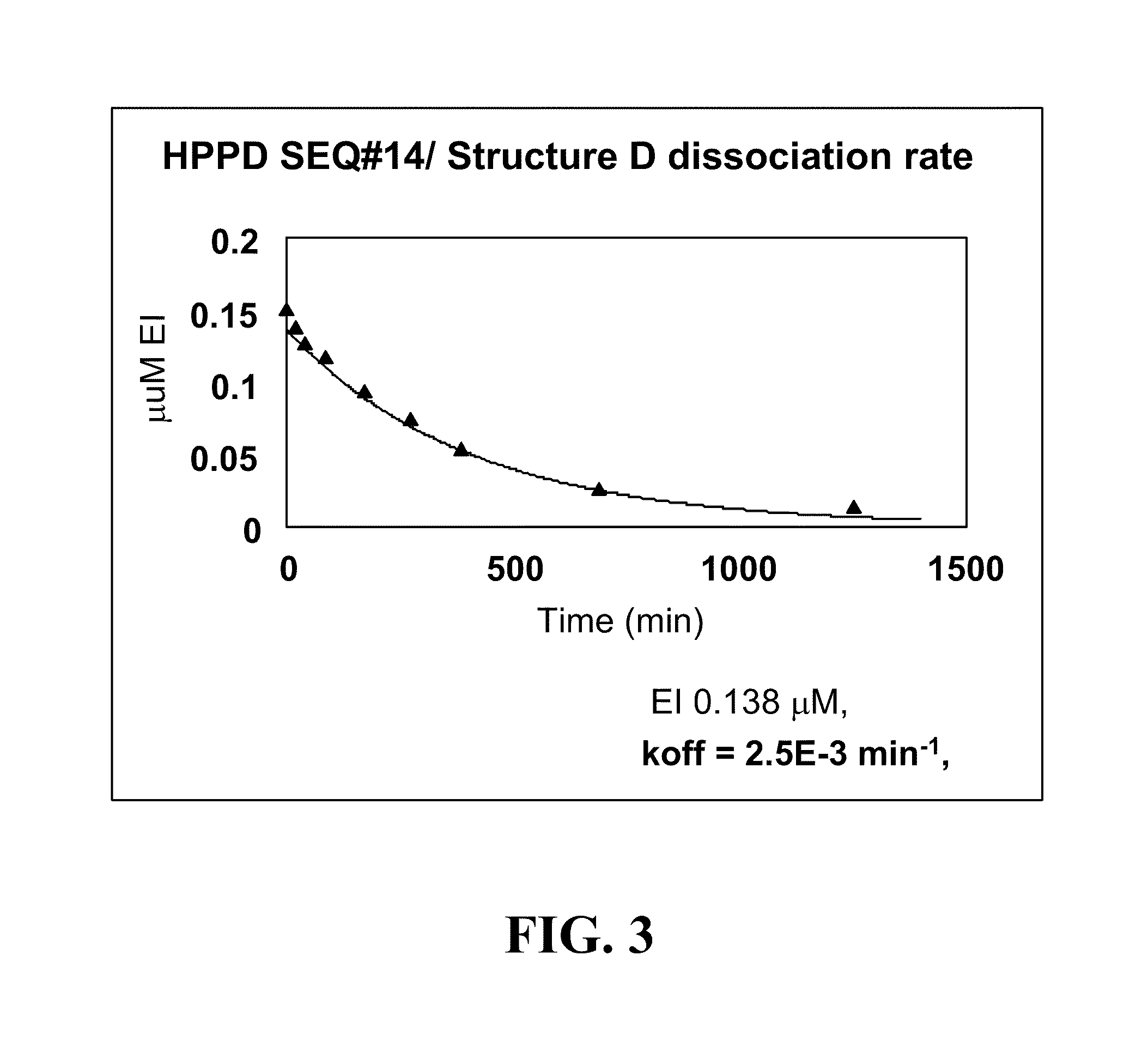
The present invention relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding a hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.27, abbreviated herein as HPPD) obtained from protists belonging to the family Blepharismidae, as well as the proteins encoded thereby, and to a chimeric gene which comprises such nucleic acid sequence, and to the use of such nucleic acid sequences, proteins or chimeric genes for obtaining plants which are tolerant to HPPD inhibitor herbicides.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Mutant Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Polypeptides and Methods of Use
Compositions and methods for conferring hydroxyphenyl pyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) herbicide resistance or tolerance to plants are provided. Compositions include amino acid sequences, and variants and fragments thereof, for mutant HPPD polypeptides. Nucleic acids that encode the mutant HPPD polypeptides are also provided. Methods for conferring herbicide resistance or tolerance, particularly resistance or tolerance to certain classes of herbicides that inhibit HPPD, in plants are further provided. Methods are also provided for selectively controlling weeds in a field at a crop locus and for the assay, characterization, identification and selection of the mutant HPPDs of the current invention that provide herbicide tolerance.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and methods of using the same
The present invention is directed to modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as compositions and pharmaceutical methods thereof.
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
ActiveUS20110203017A1Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosatePyridine
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to pyridyloxyacetate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-12 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor, as well as preparation method and application thereof
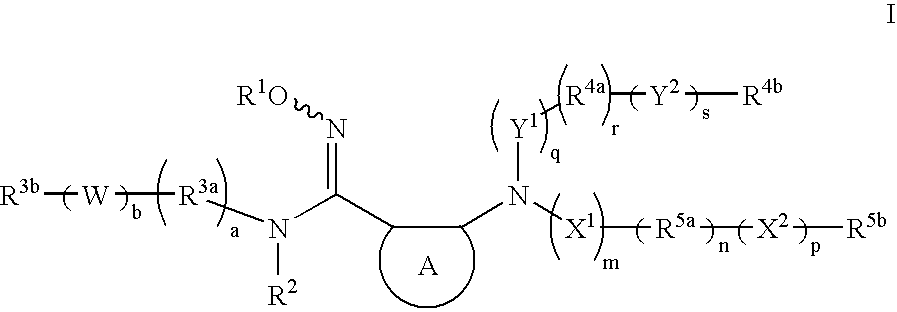
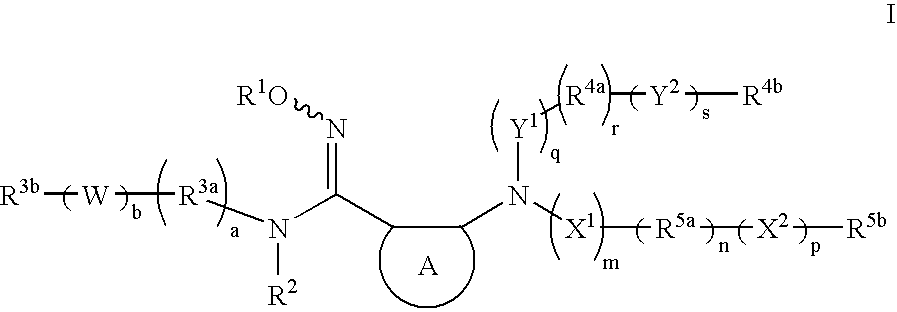
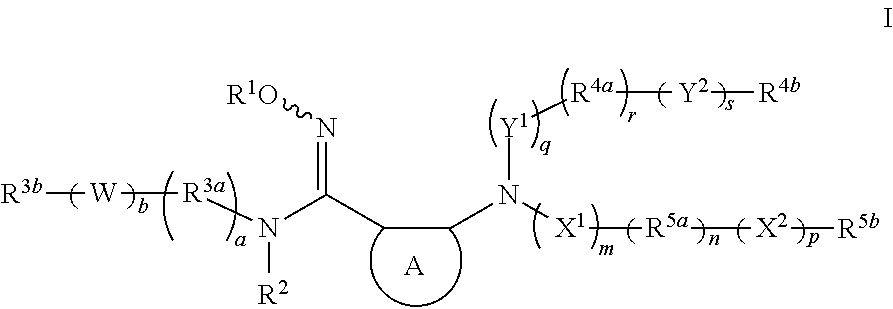
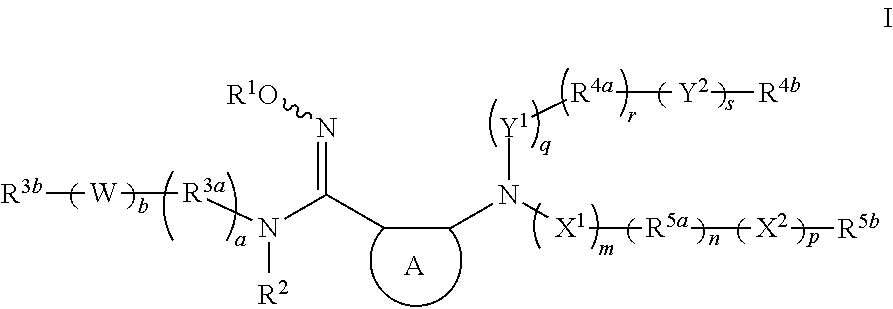
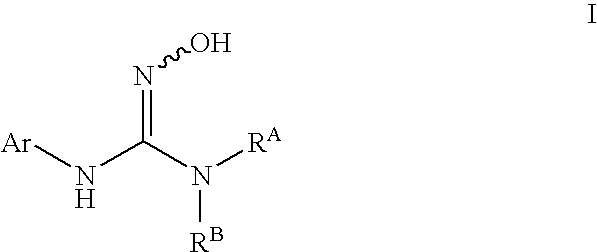
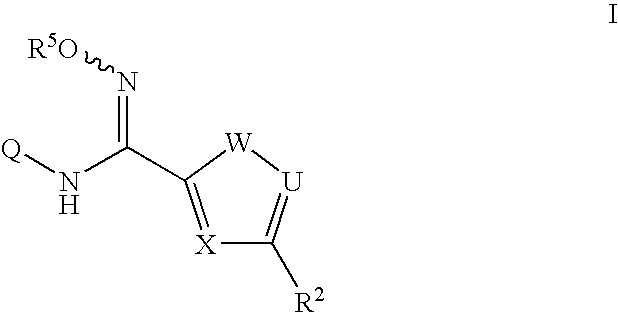
The invention relates to an indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor having a structure as shown in a formula (I), as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The IDO inhibitor is (Z)-N'-hydroxyl-N-benzoate derivative, has high inhibiting activity for IDO, can be used for effectively inhibiting the IDO activity and inhibiting immunosuppression of patients, can be widely applied to treatment or prevention of cancer or tumors, virus infection, depression, neural degeneration disease, trauma, age related cataract, organ transplant rejection or autoimmune disease, and is expected to be developed into a new generation of immunosuppressors.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANSOH BIOMEDICAL +1
Immunoregulatory agents
ActiveCN107427499ARaise countIncrease in opportunistic infectionsOrganic chemistryAntibody medical ingredientsDiseaseOxygenase
Compounds that modulate the oxidoreductase enzyme indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase, and compositions containing the compounds, are described herein. The use of such compounds and compositions for the treatment and / or prevention of a diverse array of diseases, disorders and conditions, including cancer- and immune-related disorders, that are mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is also provided.
Owner:FLEXUS BIOSCI
N-hydroxyguanidines as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
The present invention is directed to modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as pharmaceutical compositions containing the same and methods for the treatment of IDO-associated diseases.
Owner:INCYTE
Ido inhibitors
Presently provided are methods for (a) modulating an activity of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase comprising contacting an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase with a modulation effective amount of a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein; (b) treating indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) mediated immunosuppression in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering an effective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibiting amount of a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein; (c) treating a medical conditions that benefit from the inhibition of enzymatic activity of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase comprising administering an effective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibiting amount of a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein; (d) enhancing the effectiveness of an anti-cancer treatment comprising administering an anti-cancer agent and a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein; (e) treating tumor-specific immunosuppression associated with cancer comprising administering an effective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibiting amount of a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein; and (f) treating immunosuppression associated with an infectious disease, e.g., HIV-I infection, comprising administering an effective indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibiting amount a compound as described in one of the aspects described herein.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS
Herbicide resistance genes for resistance to aryloxyalkanoate herbicides
ActiveUS8278505B2Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosatePyridine
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to a pyridyloxyacetate herbicide. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-13 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
N-hydroxyamidinoheterocycles as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
The present invention is directed to N-hydroxyamidino compounds which are modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as compositions and pharmaceutical methods thereof.
Owner:INCYTE
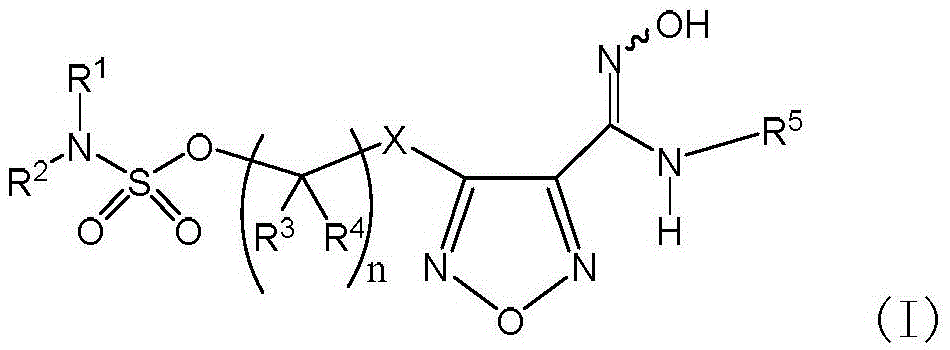
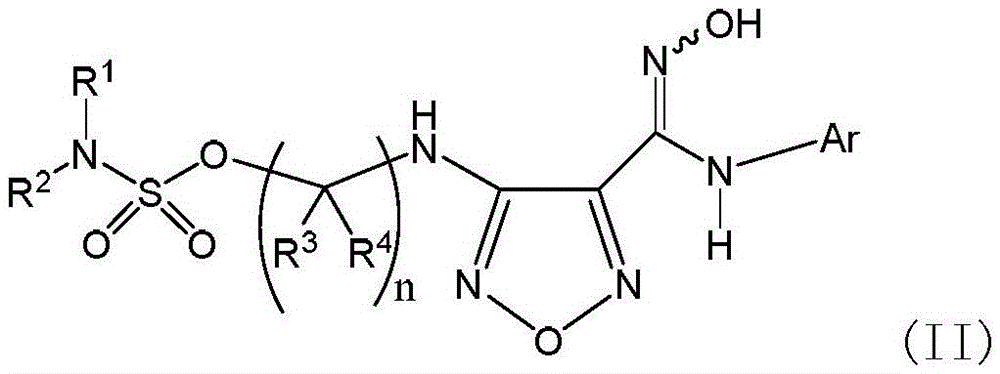
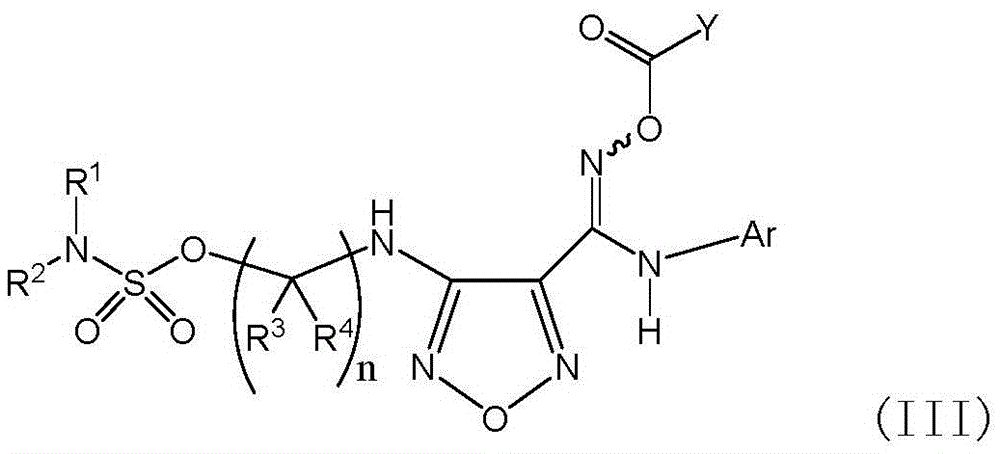
Sulfamate serving as indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105646389ANovel structureGentle synthesis methodOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseDioxygenase
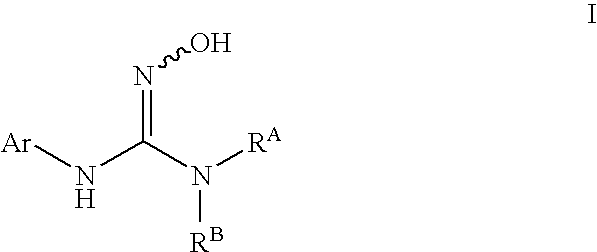
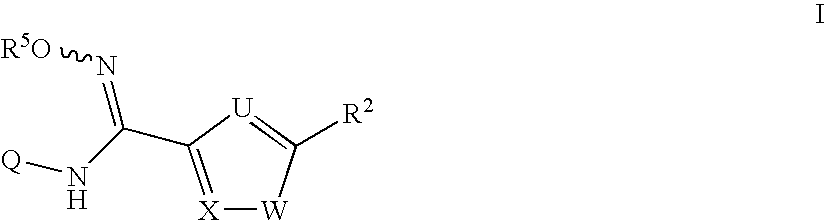
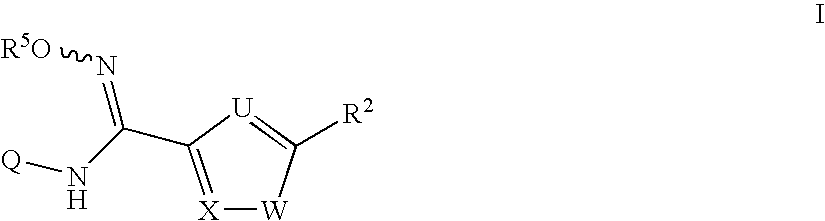
The invention provides sulfamate serving as an indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the inhibitor is shown in the general formula I, wherein definitions of X, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and n are shown in the description and the claim. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the inhibitor. The compound shown in the general formula I can serve as the indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor and is used for preparing medicine for preventing and / or treating indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase mediated diseases. The general formula I is shown in the description.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
N-hydroxyamidinoheterocycles as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
The present invention is directed to N-hydroxyamidino compounds which are modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as compositions and pharmaceutical methods thereof.
Owner:INCYTE
Immunoregulatory agents
ActiveCN106999450AReduce loadRaise countImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmide active ingredientsOxygenaseBiochemistry
Compounds that modulate the oxidoreductase enzyme indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase, and compositions containing the compounds, are described herein. The use of such compounds and compositions for the treatment and / or prevention of a diverse array of diseases, disorders and conditions, including cancer- and immune-related disorders, that are mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is also provided.
Owner:FLEXUS BIOSCI
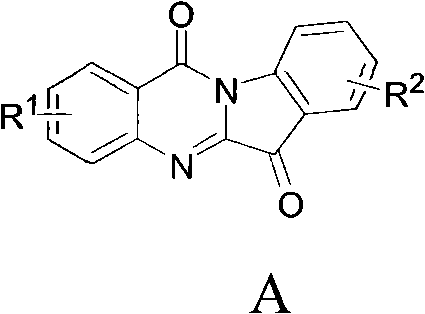
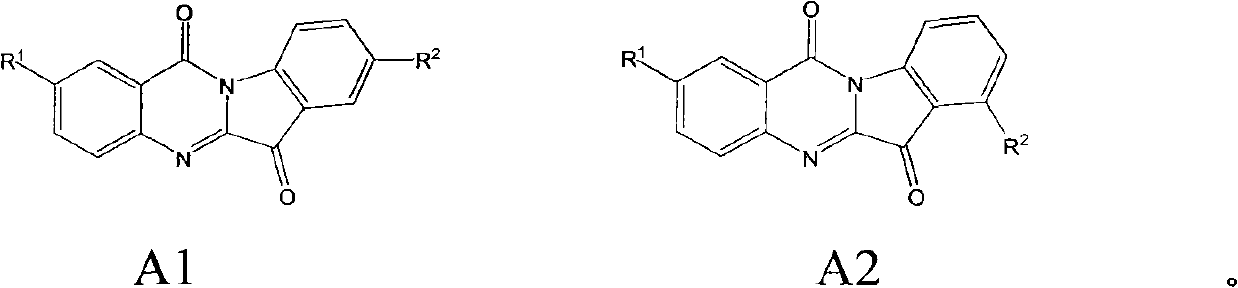
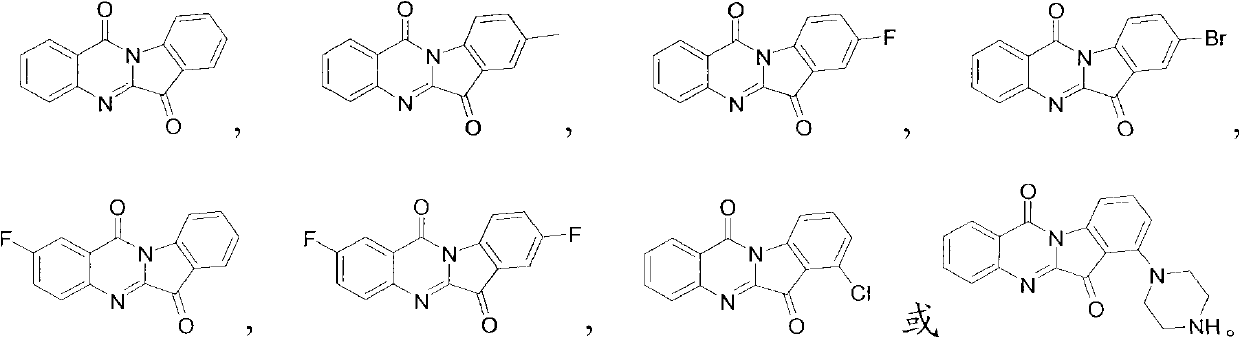
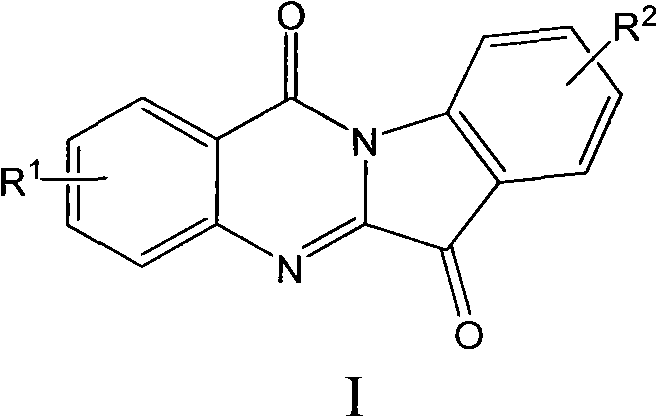
Preparation method of tryptanthrin compound and new application of tryptanthrin compound in preparing indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor
The invention relates to a preparation method of tryptanthrin compound and a new application of tryptanthrin compound in preparing indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor, in particular to an application of tryptanthrin compound in preparing IDO inhibitor and in preparing medicine for preventing and / or treating diseases having pathological characteristics of tryptophan metabolic disturbance mediated by IDO. The structure of the tryptanthrin compound is shown in formula A in the description, wherein R1 and R2 are respectively and independently selected from hydrogen, nitryl, C1 to C5 alkyl, halogen or piperazinyl. The tryptanthrin compound can be used as an IDO inhibitor with high activity and is used for treating diseases having pathological characteristics of tryptophan metabolic disturbance mediated by IDO such as tumor, cancer, Alzheimer disease, autoimmune disease, cataract, mental block, tristimania, anxiety neurosis, acquired immure deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and other serious diseases, and as a medicinal resource which is very difficult to get, the tryptanthrin compound has good potential on researching and developing new medicine.
Owner:SHENYANG XINMA PHARMA
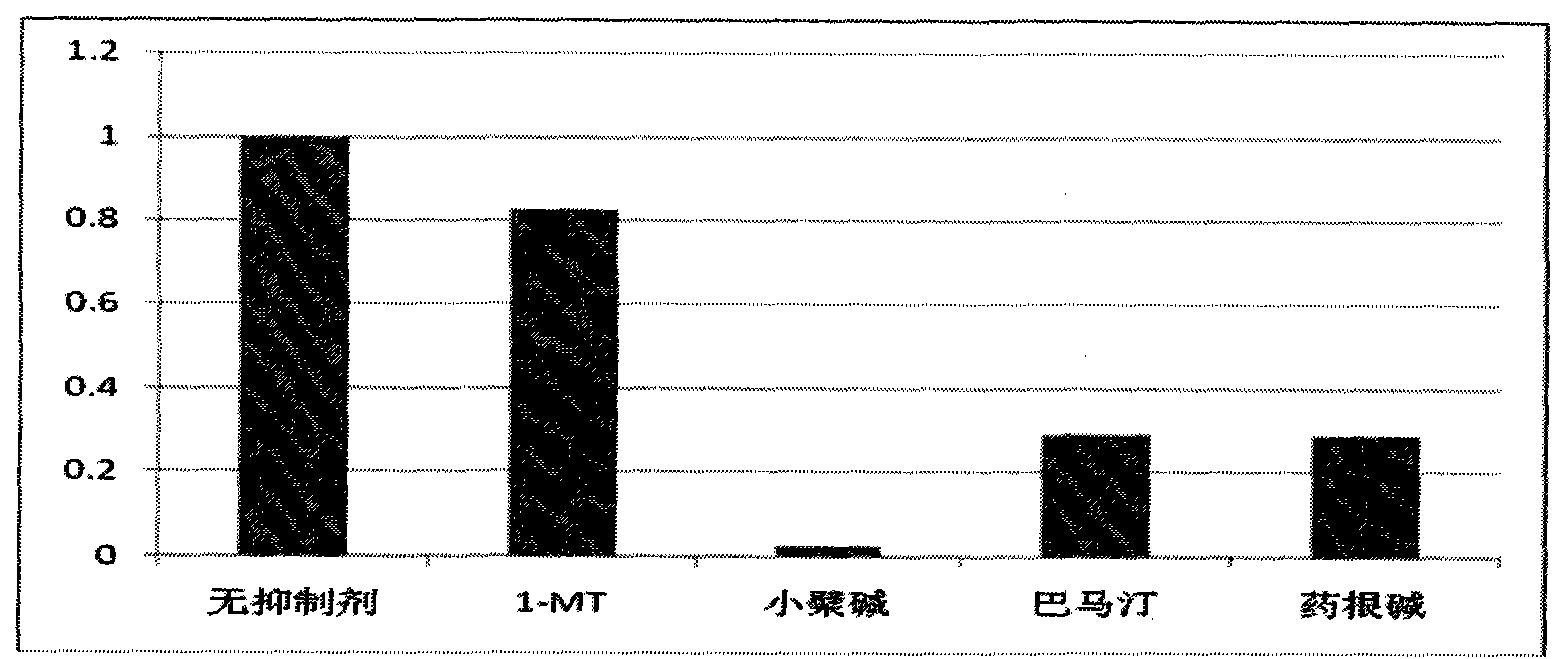
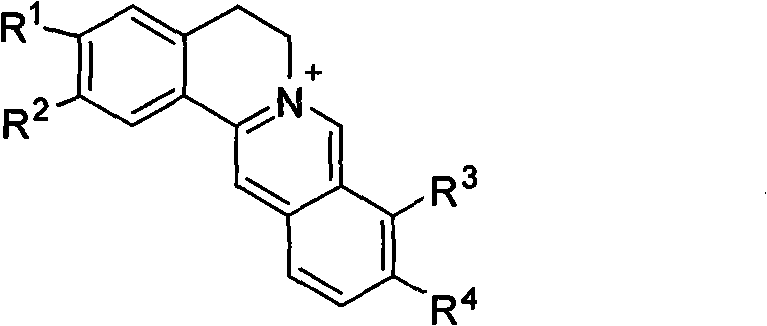
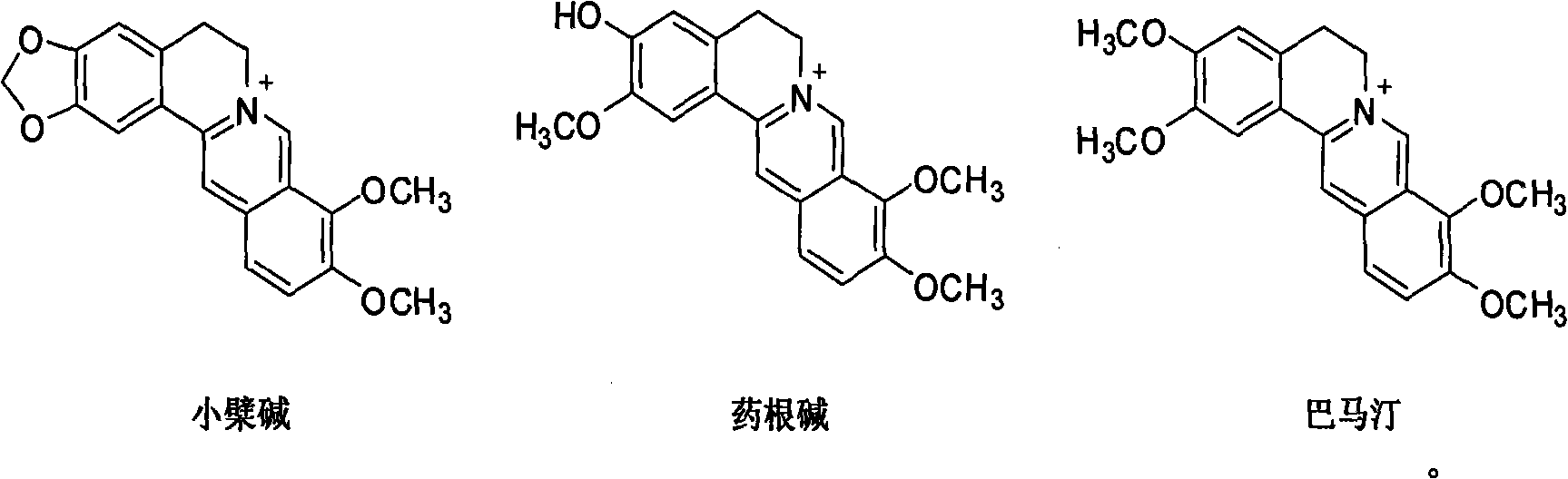
Application of berberine and derivatives thereof in preparation of indole amine 2, 3-dioxygenase inhibitor
The invention relates to novel application of berberine and derivatives thereof in preparation of medicines, in particular to application of berberine and derivatives thereof in preparation of indole amine 2, 3-dioxygenase IDO inhibitor, belonging to the medicine field. According to IDO inhibition activity detection, reversible inhibition judgment, inhibitor type judgment, Ki value determination and median effective inhibition concentration IC50 determination, the results show that berberine is reversible inhibitor and inhibition constant Ki is 8muM; and jatrorrhizine hydrochloride and palmatine hydrochloride are irreversible inhibitors, and the median effective inhibition concentrations IC50 thereof are respectively 123muM and 126muM. When the berberine and the derivatives thereof disclosed in the invention are used as IDO inhibitors, the application prospect is wide and the IDO inhibitors can be used for treating serious diseases such as cancers, AIDS, Alzheimer diseases, tristimania, cataract and the like with pathological feature of IDO-mediated tryptophan metabolism.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
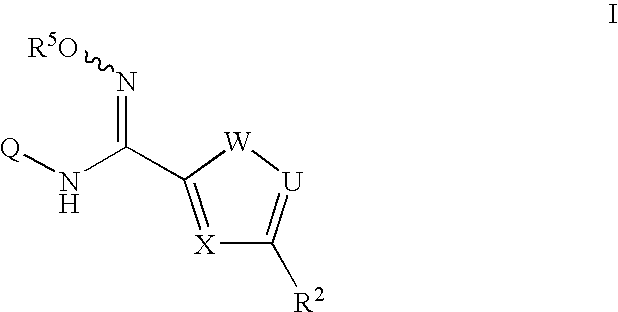
Novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102532144AImprove solubilityImprove pharmacological activityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention relates to a novel indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The inhibitor is compounds of a formula I or pharmaceutically-acceptable salt, solvate, polymorph, enantiomer or racemic mixture thereof, wherein R1 or R2 is independently selected from H, C1-C5 alkyl, halogen and a substituent of a formula II and either of R1 and R2 is the substituent of the formula II; R3 is an aryl group; and n is equal to 0, 1, 2 or 3. Compared with the know IDO inhibitors, the novel IDO inhibitor has significant inhibitory effect on IDO and can be used for treatment of diseases having IDO-mediated tryptophan metabolic pathway pathological features, such as tumors, cancers, Alzheimer's disease, autoimmune diseases, cataract, psychological disorders, depression and / or anxiety. The preparation method of the novel IDO inhibitor has the advantages of being convenient in operation, having mild reaction conditions and reducing solvent consumption and pollution, thereby facilitating industrial production.
Owner:SHENYANG XINMA PHARMA
Production of omega-amino fatty acids
The invention provides a whole cell catalyst which expresses a recombinant α-dioxygenase or the combination of a recombinant fatty acid reductase and a phosphopantetheinyl transferase phosphopantetheinylating the fatty acid reductase, and which in addition to the α-dioxygenase and / or the combination of fatty acid reductase and phosphopantetheinyl transferase expresses a transaminase, characterized in that the phosphopantetheinyl transferase and / or transaminase is preferably recombinant; and a method for the conversion of a fatty acid, ω-hydroxy fatty acid, ω-oxo fatty acid or a monoester thereof to an amine, comprising oxidation of the fatty acid, ω-hydroxy fatty acid, ω-oxo fatty acid or the monoester thereof to an oxidation product by contacting with an alkane hydroxylase and / or alcohol dehydrogenase, contacting the oxidation product with a phosphopantetheinylated fatty acid reductase or a α-dioxygenase to give an aldehyde, and contacting the aldehyde with a transaminase.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
IDO inhibitors and methods of use thereof
Novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitors, compositions comprising the same, and methods of use thereof are disclosed.
Owner:LANKENAU INST FOR MEDICAL RES
N-hydroxyamidinoheterocycles as modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
The present invention is directed to N-hydroxyamidino compounds which are modulators of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), as well as pharmaceutical compositions thereof and methods of use thereof relating to the treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
ActiveUS20100251432A1Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosateDioxygenase
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to a pyridyloxyacetate herbicide. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-13 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Regulation of T cell-mediated immunity by D isomers of inhibitors of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
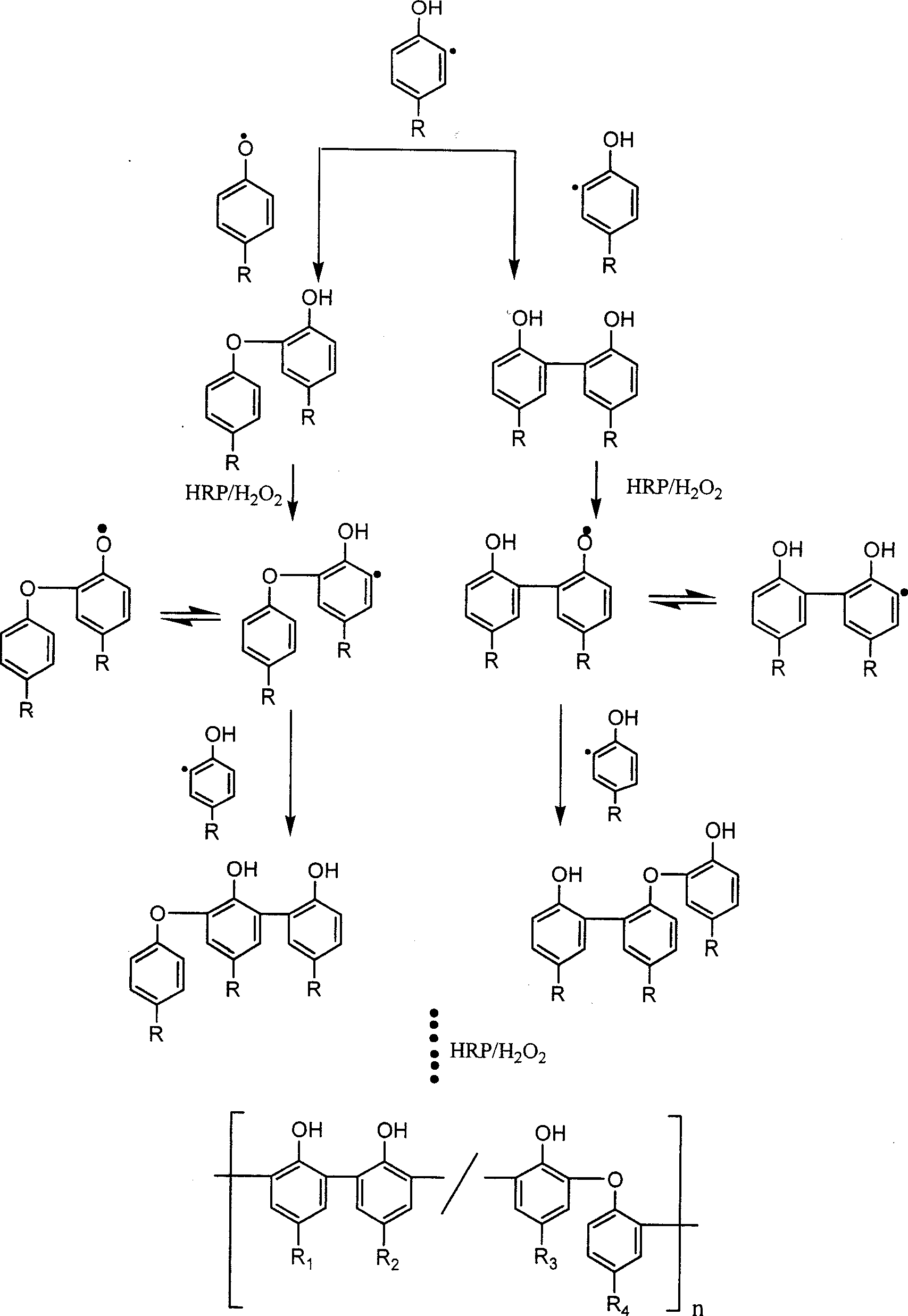
Preparation of enzyme-catalyzed rapid-solidified hydrogel and use thereof
InactiveCN101439206AGood biocompatibilityEasy to transportSurgical drugsSurgeryCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hydrogel rapidly crosslinked by enzyme catalysis, and application thereof. A precursor of the hydrogel consists of a mixture (hereinafter referred to as No. 1 solution) of good-biocompatibility macromonomer aqueous solution with an active phenolic hydroxyl unit and dioxygenase aqueous solution which is taken as a catalyst, and the aqueous solution of the precursor can rapidly react to form a 3D polymer cross-linked network after an oxidant (usually low-concentration oxydol, hereinafter referred to as No. 2 solution) is injected. As the No. 1 solution and the No. 2 solution have low-viscosity characteristic, are suitable for being transported and injected, and can rapidly crosslink to form a gel network, the hydrogel can be used for vascular embolization treatment, cancer treatment, family planning operation blocking agents, injectable tissue engineering scaffold materials, soft tissue fillers of human body, controlled release drug carriers, anti-adhesive membranes used in operations and the like after adding one or a plurality of components with specific properties to the No. 1 solution or the No. 2 solution or the gel network.
Owner:郭倩 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com