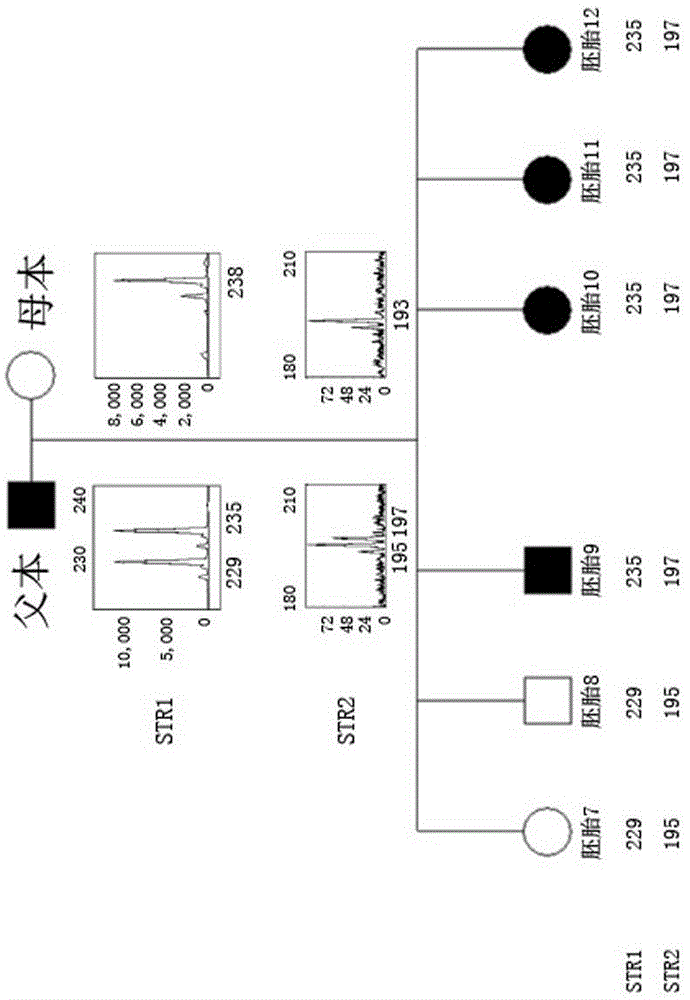
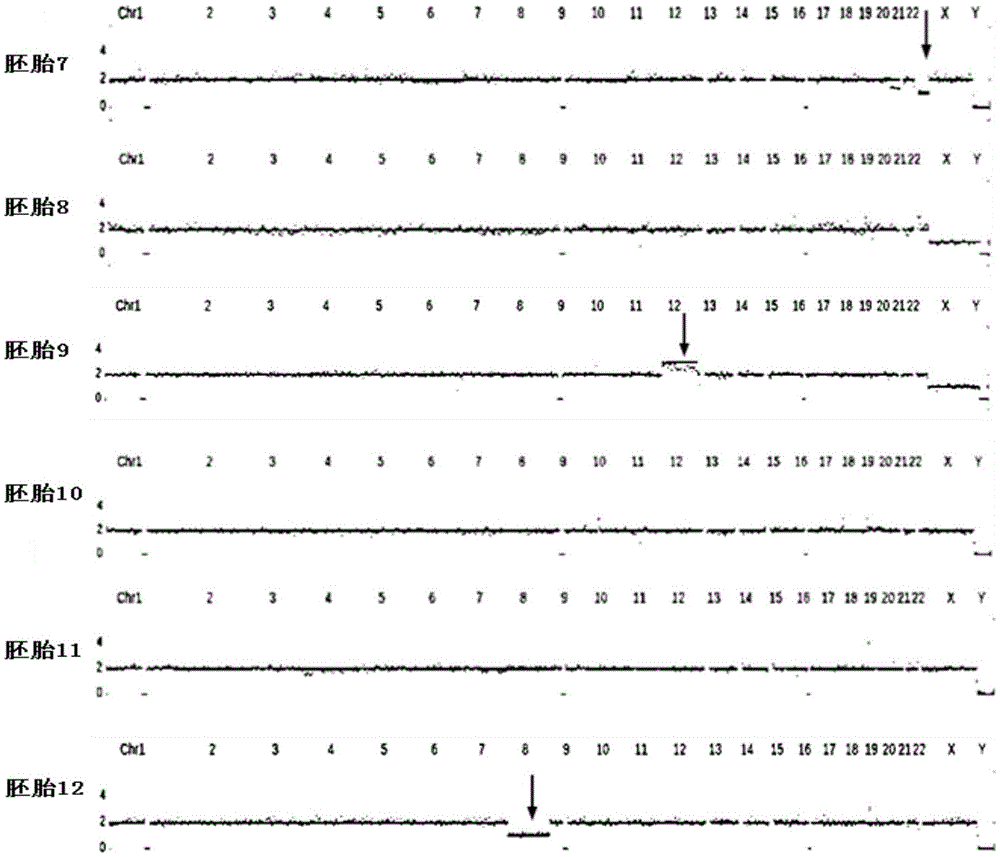
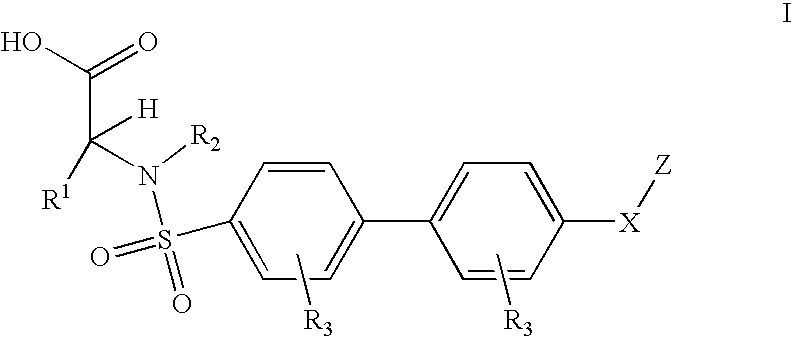
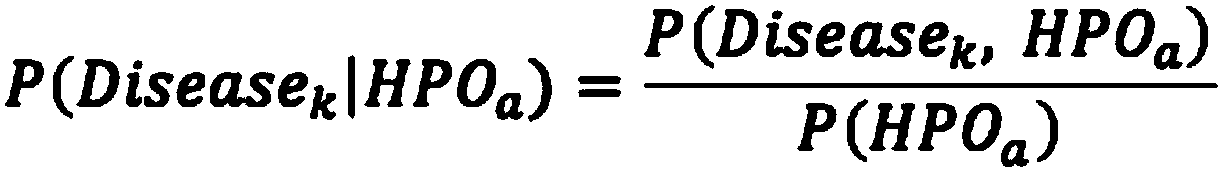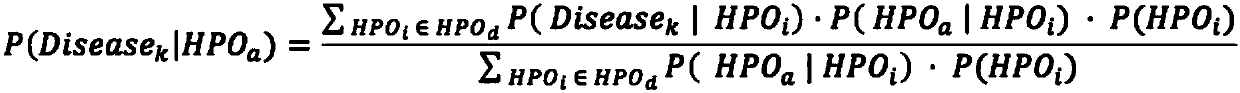Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
365 results about "Single gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single Gene Disorders A gene codes for a protein, which does a job in the body. ... In some cases, single gene disorders are caused by new (also called de novo) mutations. These mutations happen during egg or sperm formation in the parents, or soon after egg and sperm come together to form an embryo.
Herbicide resistance genes
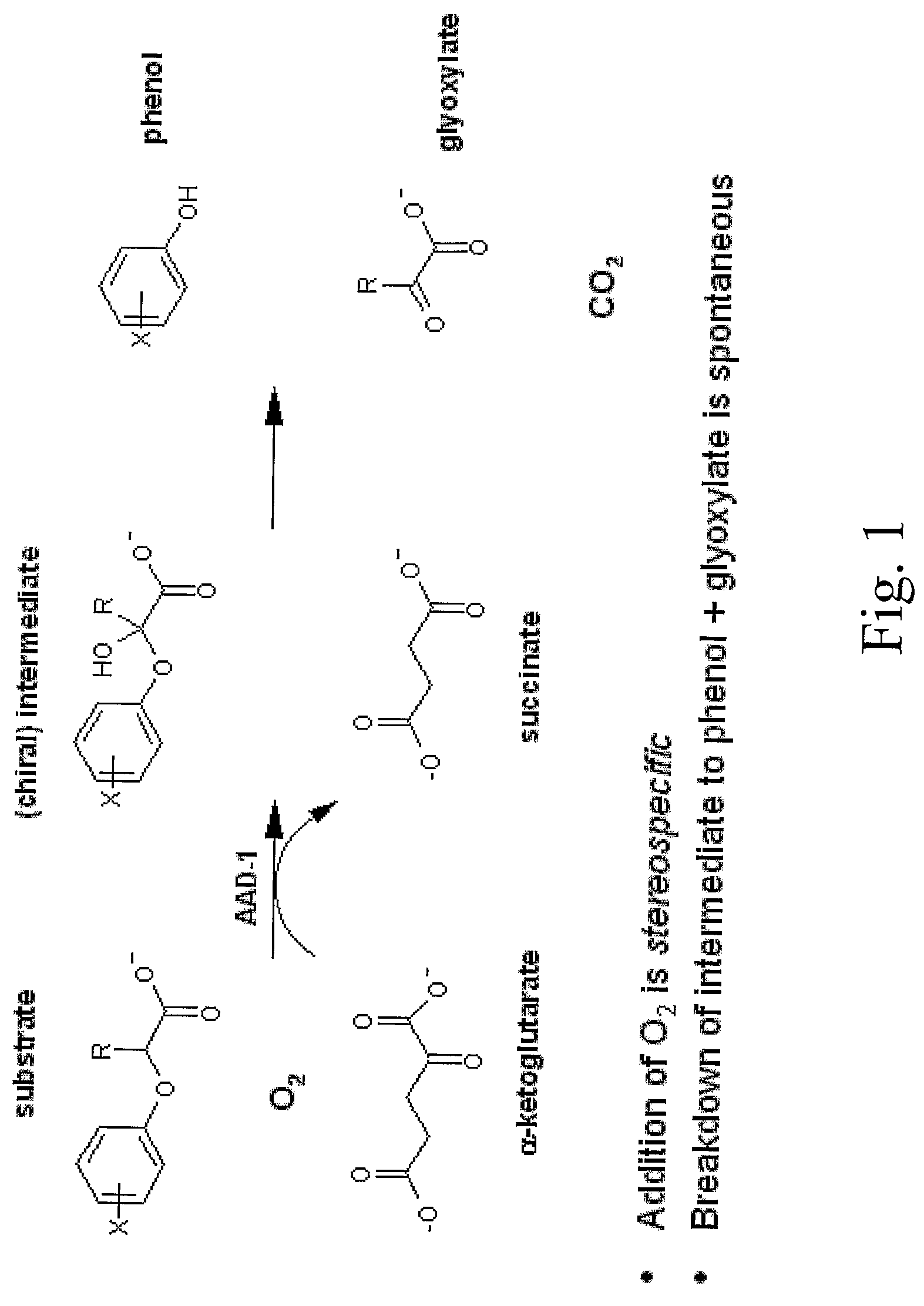
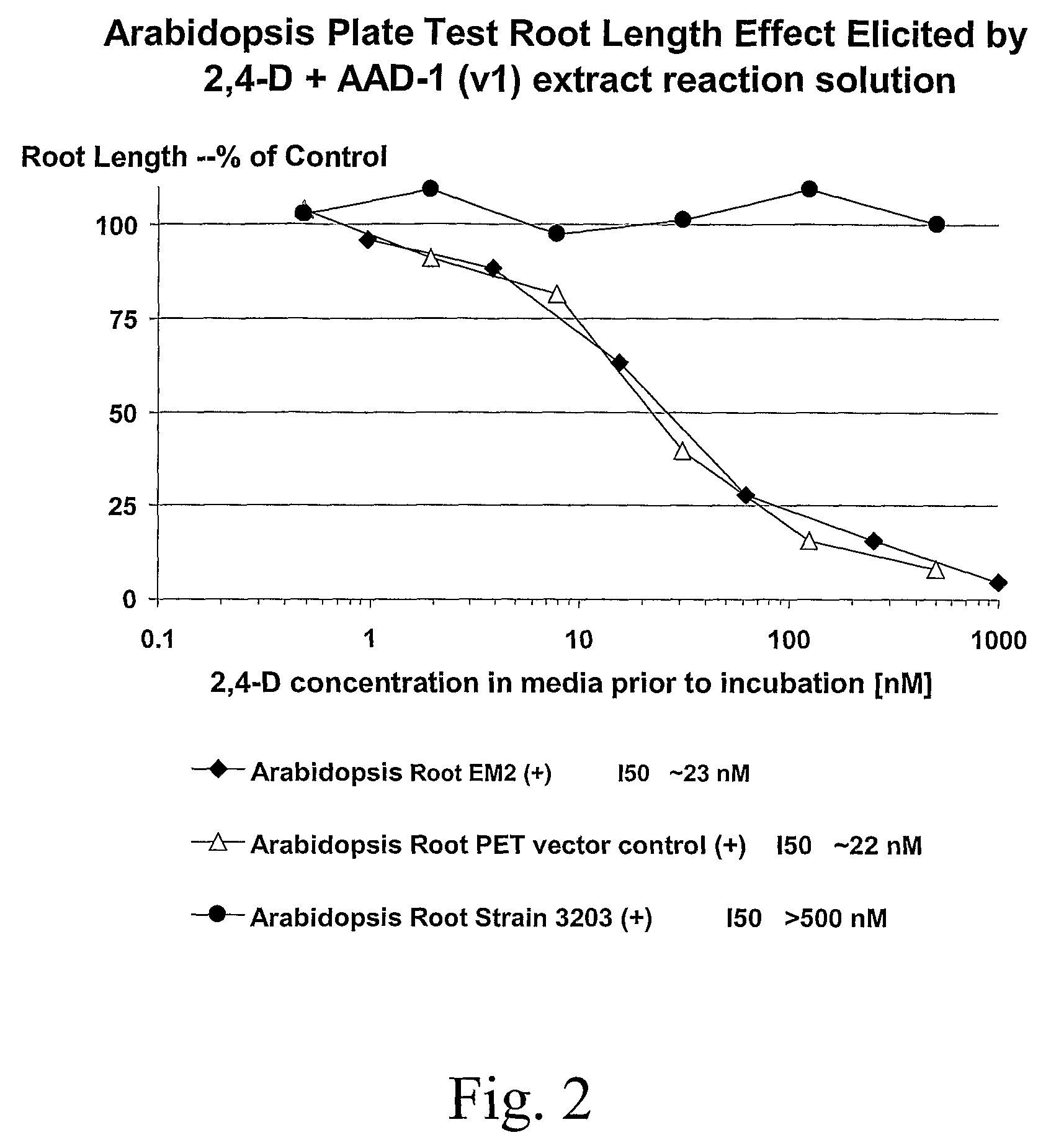
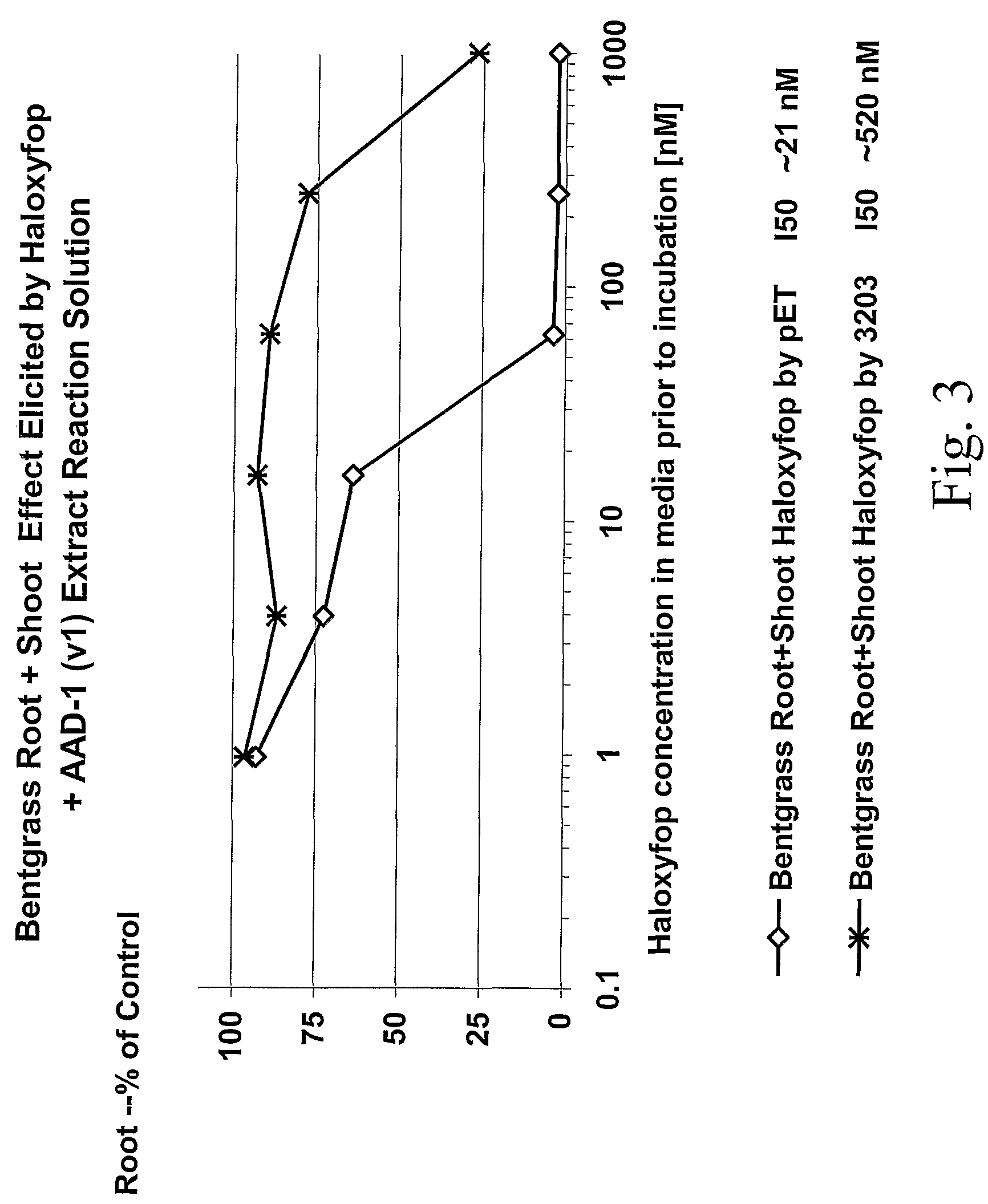
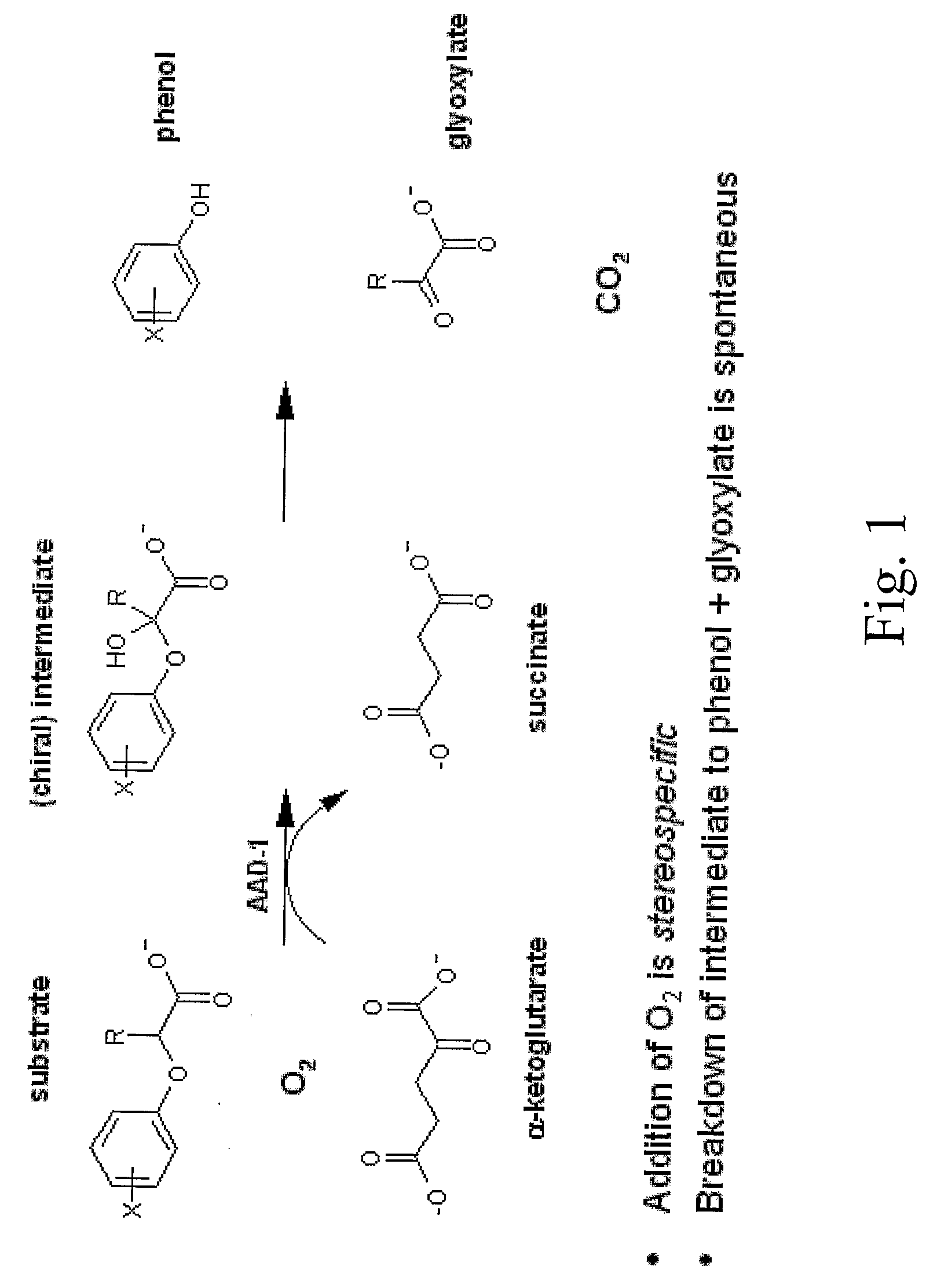
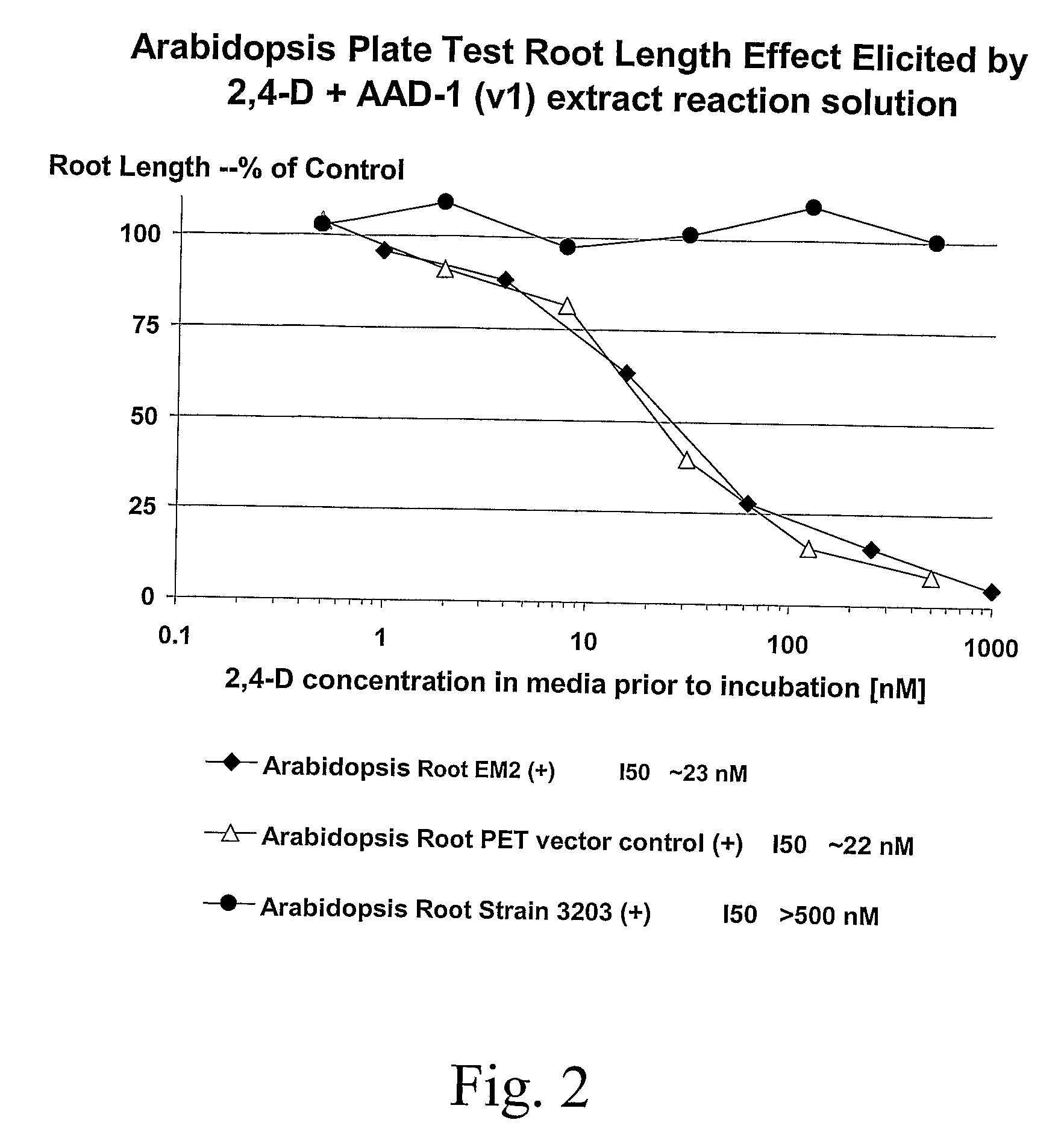
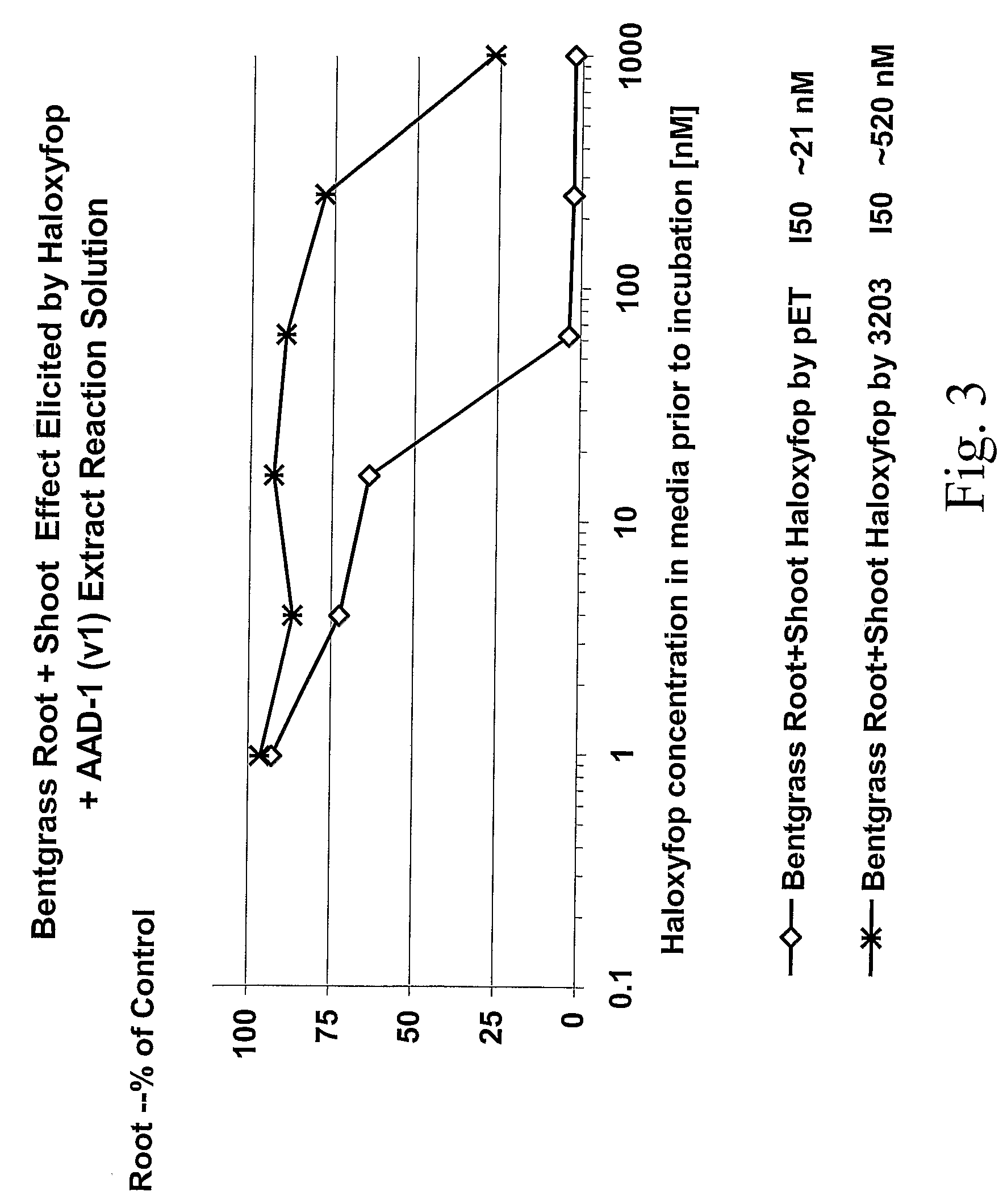
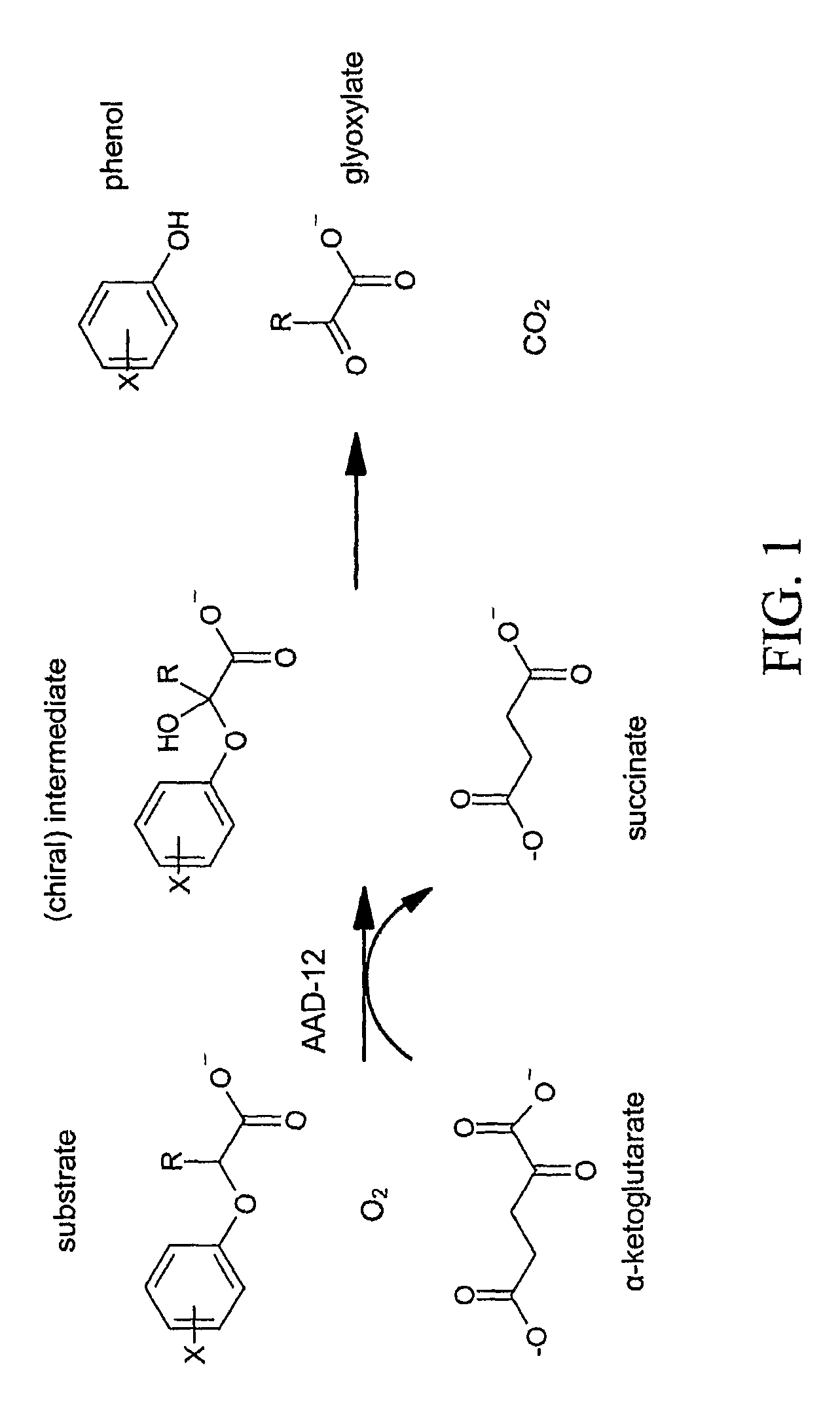
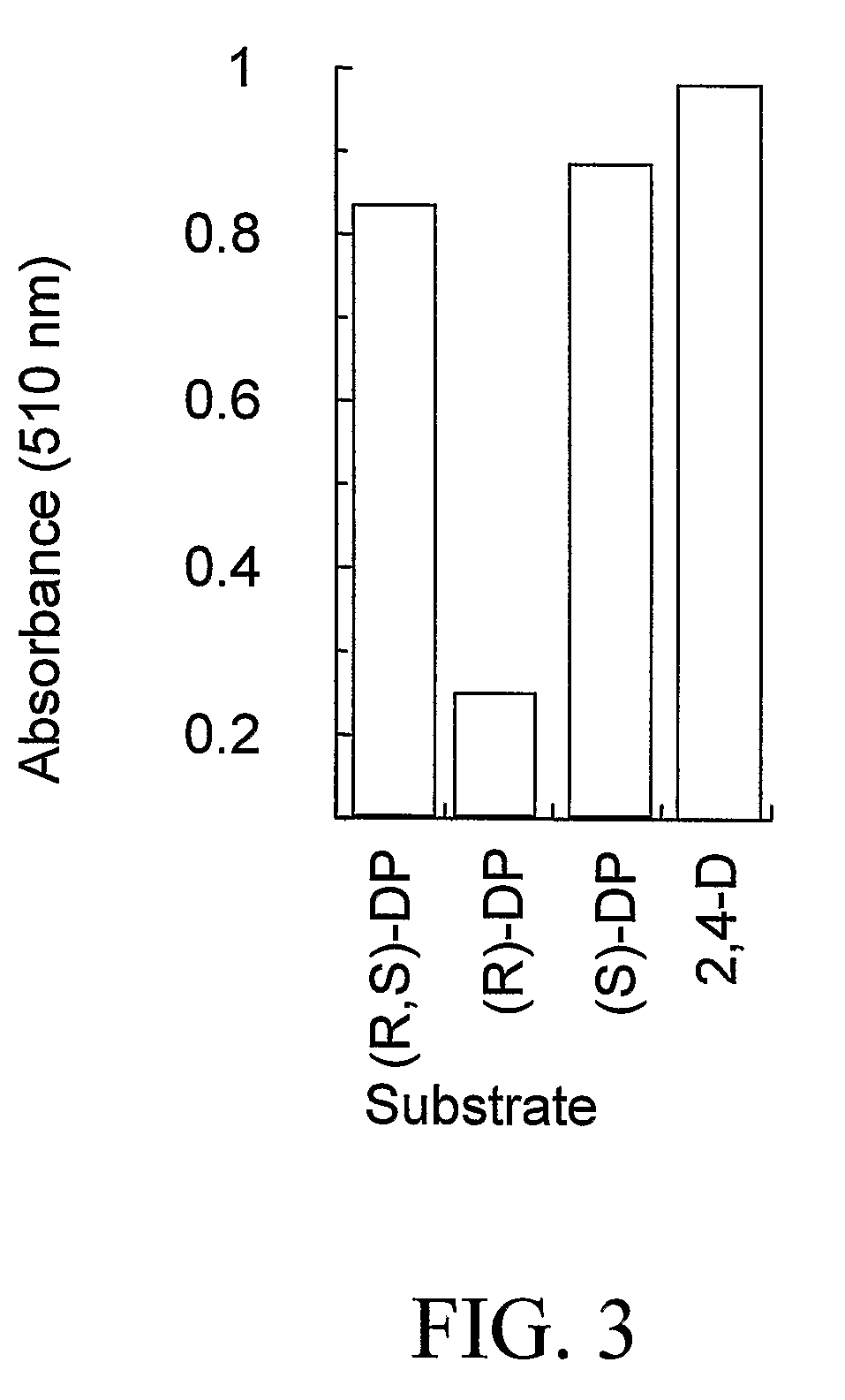
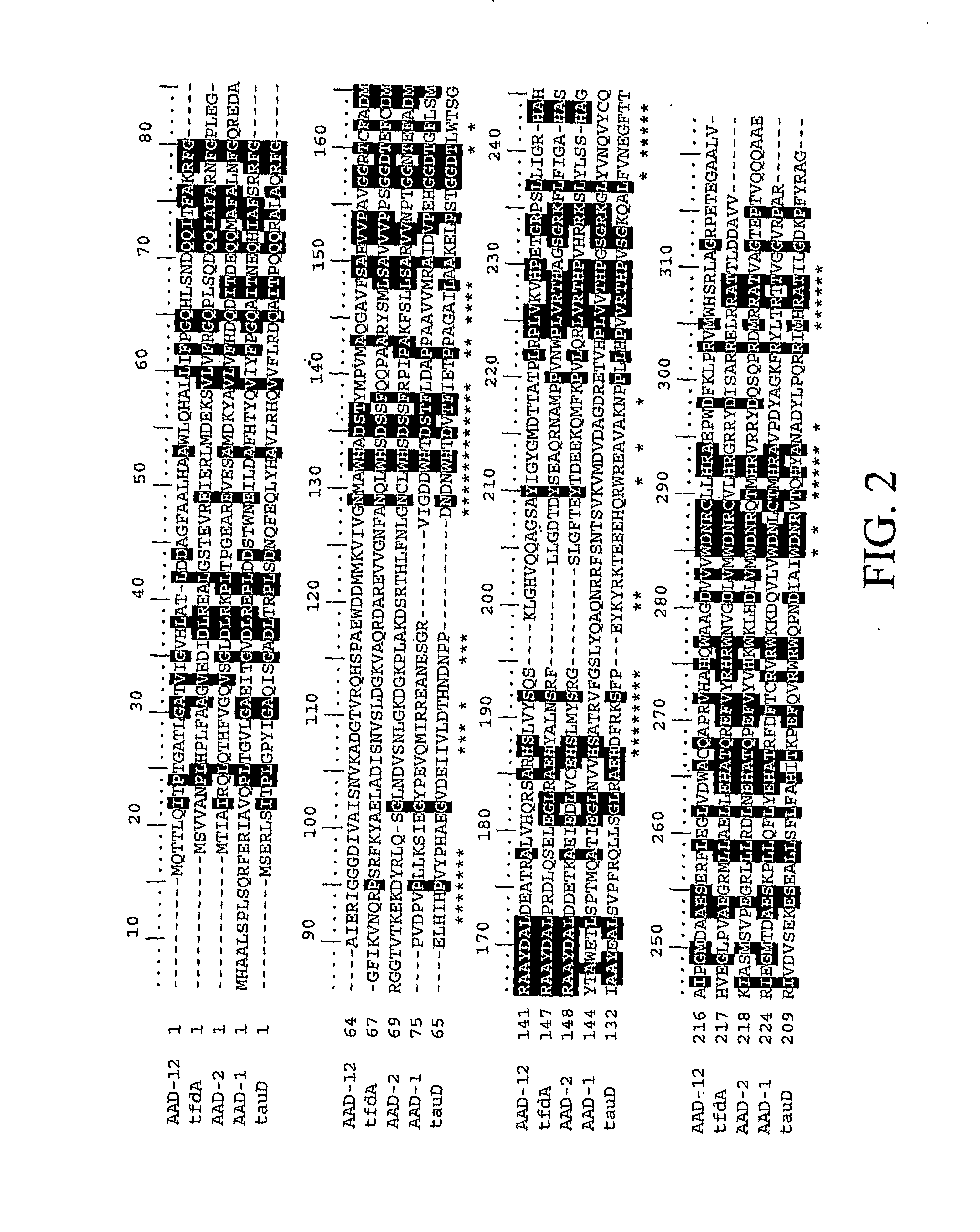
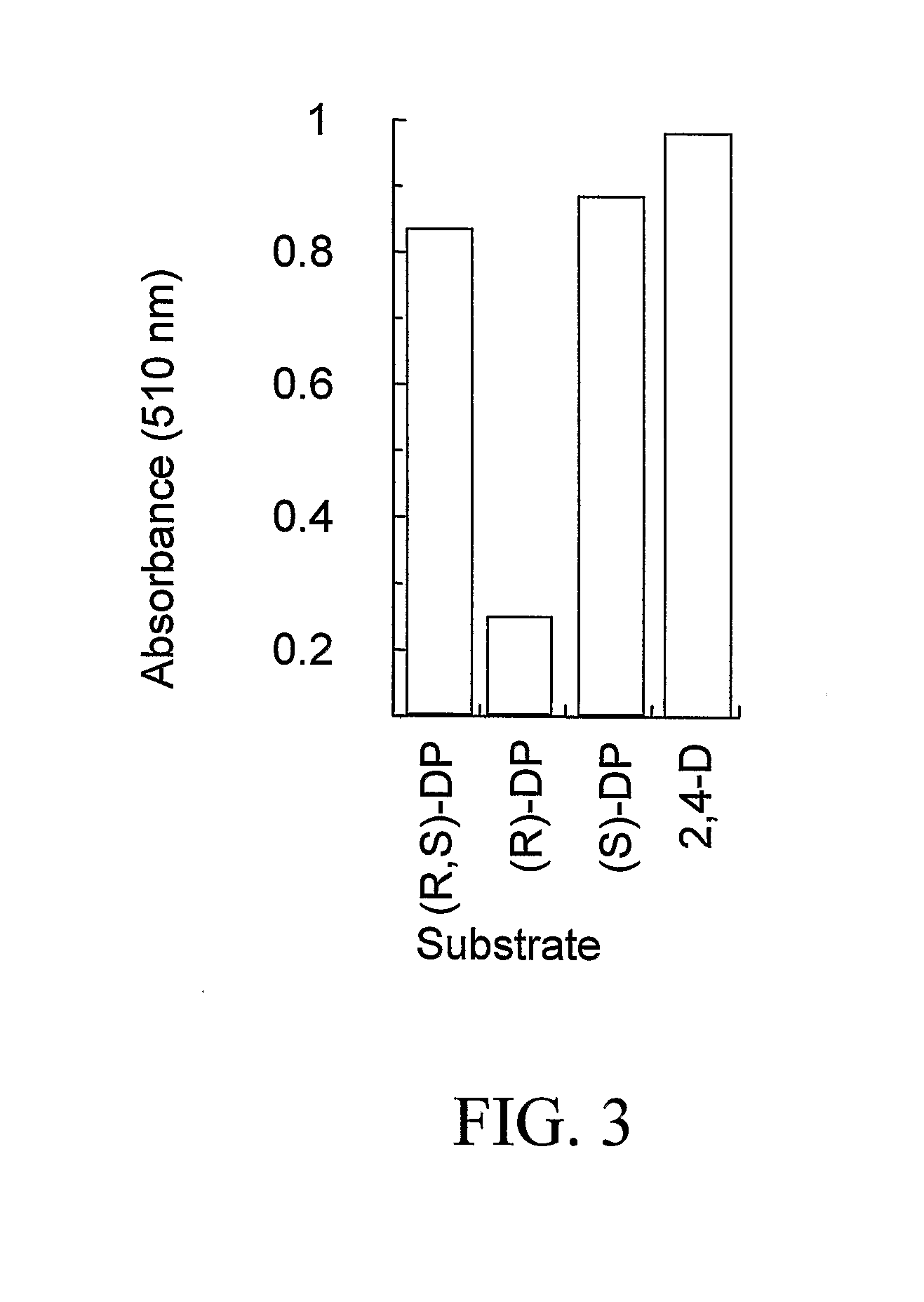
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D and other phenoxy auxin herbicides, but also to aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention alone or “stacked” together with another herbicide resistance gene, preferably a glyphosate resistance gene, so as to provide broader and more robust weed control, increased treatment flexibility, and improved herbicide resistance management options. More specifically, preferred enzymes and genes for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD (aryloxyalkanoate dioxygenase) genes and proteins. No α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzyme has previously been reported to have the ability to degrade herbicides of different chemical classes and modes of action. This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait opportunities as well as development of selectable marker technology. The subject invention also includes related methods of controlling weeds. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the formation of, and controlling, weeds that are resistant (or naturally more tolerant) to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Herbicide resistance genes
ActiveUS8283522B2Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosateDioxygenase
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to pyridyloxyacetate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-12 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
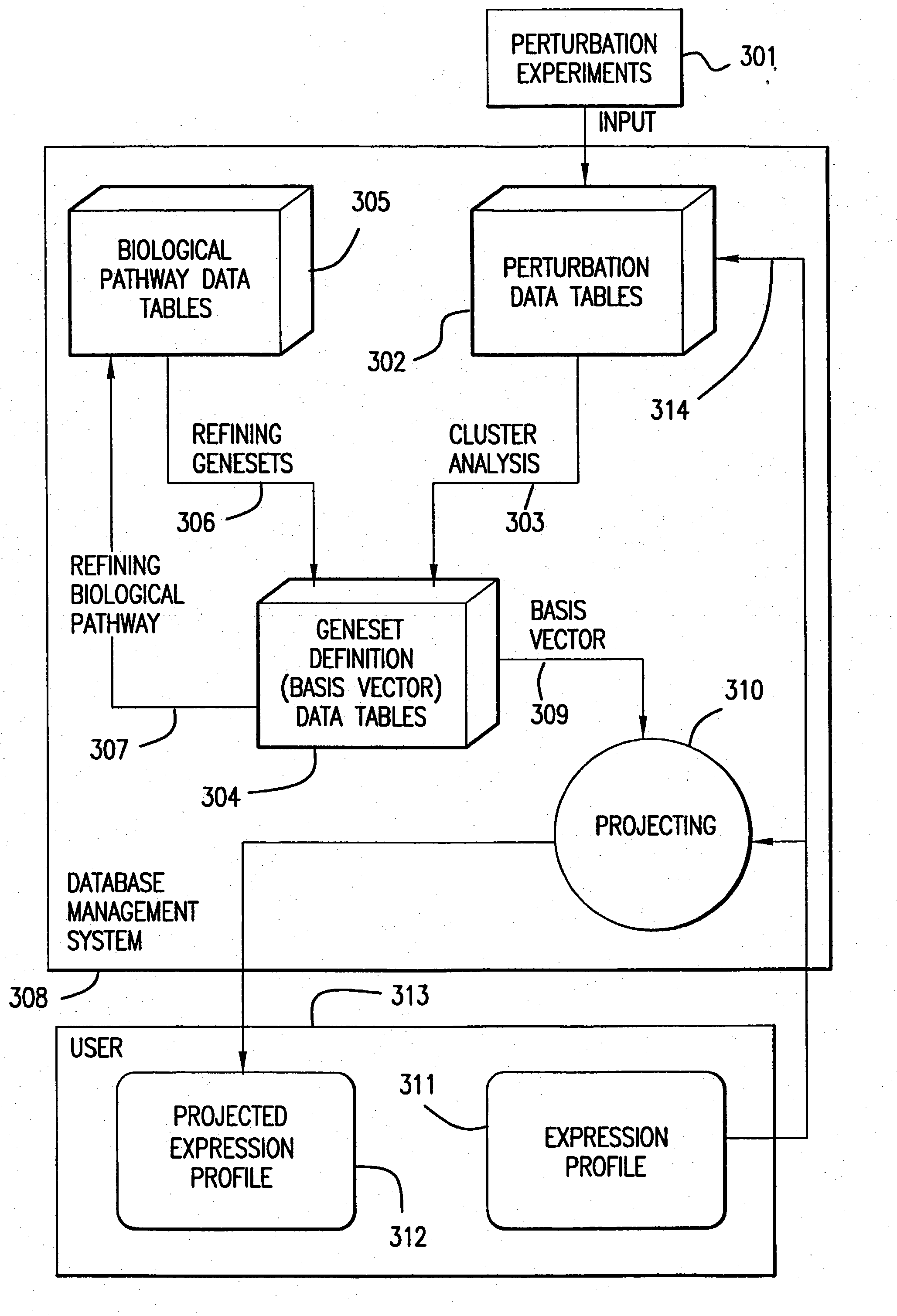
Methods for using co-regulated genesets to enhance detection and classification of gene expression patterns
InactiveUS6203987B1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCo-regulationIndividual gene
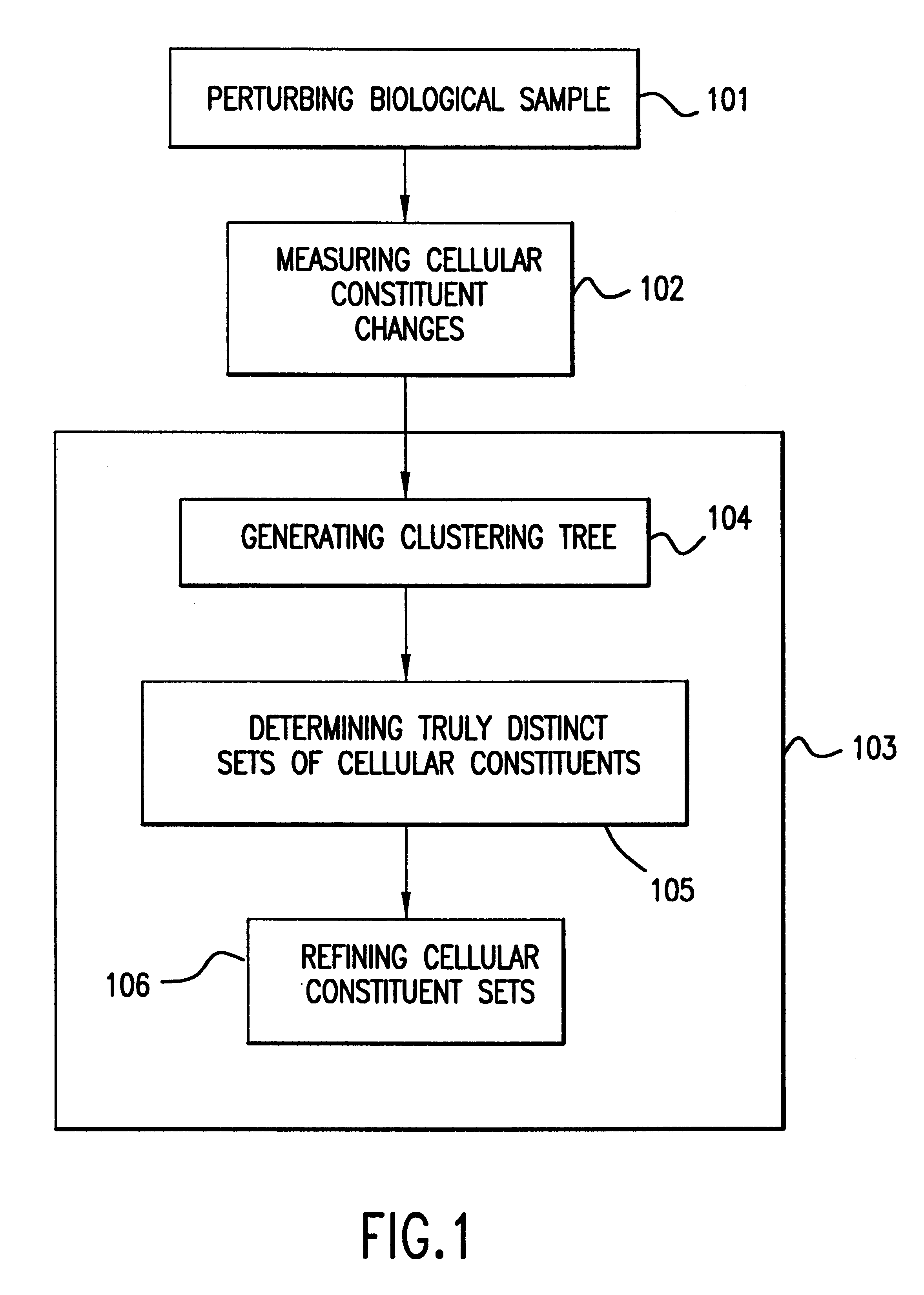
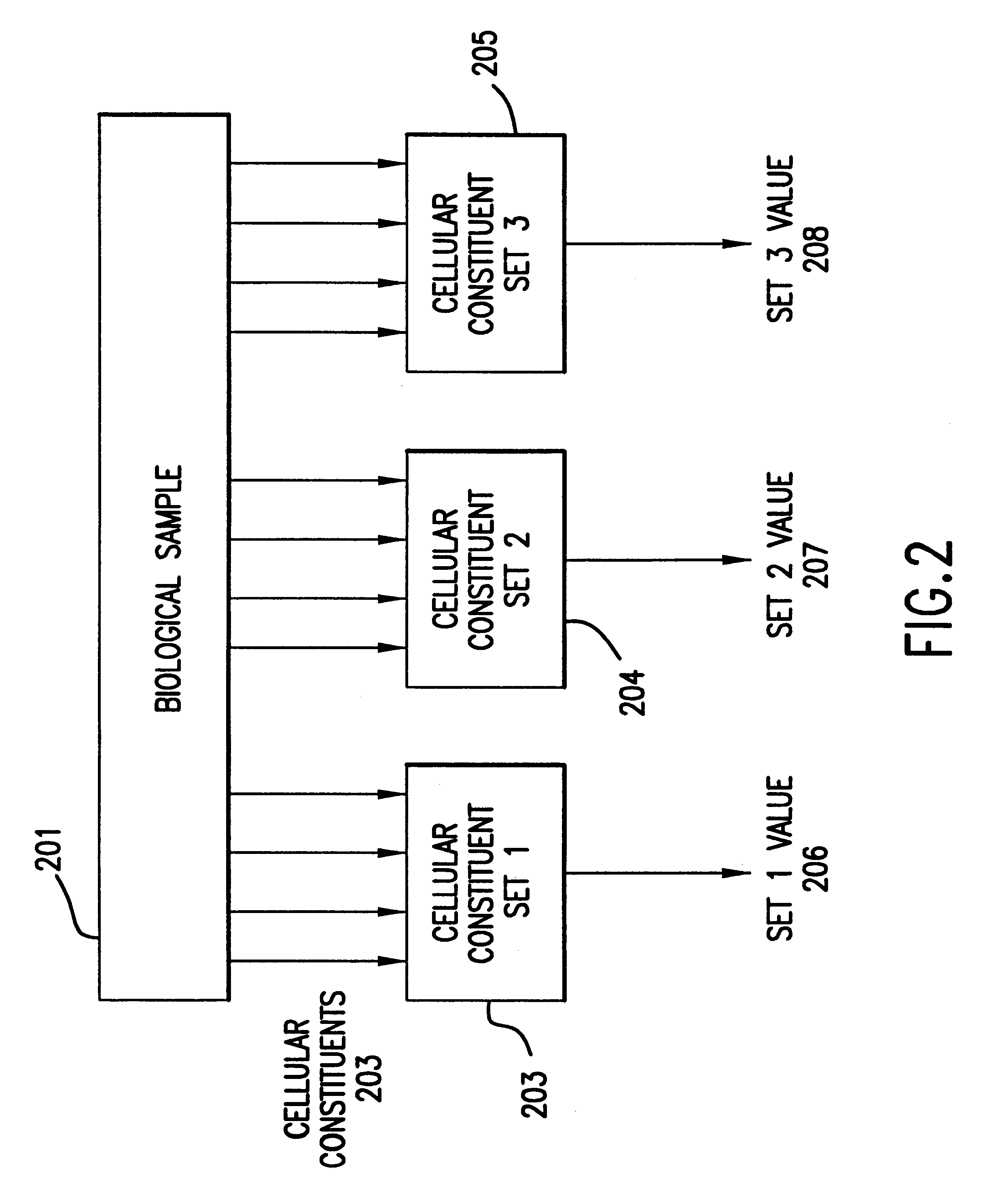
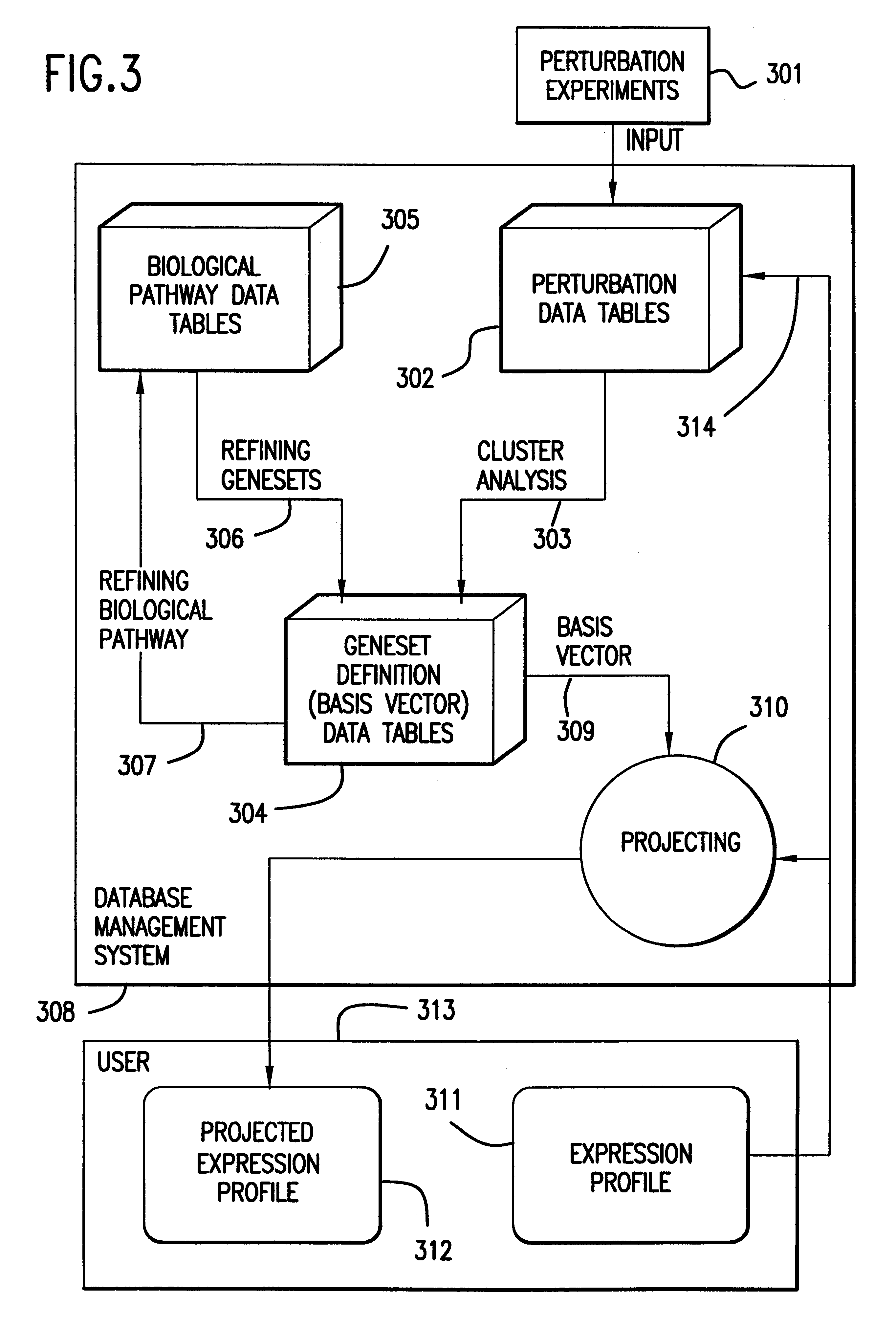
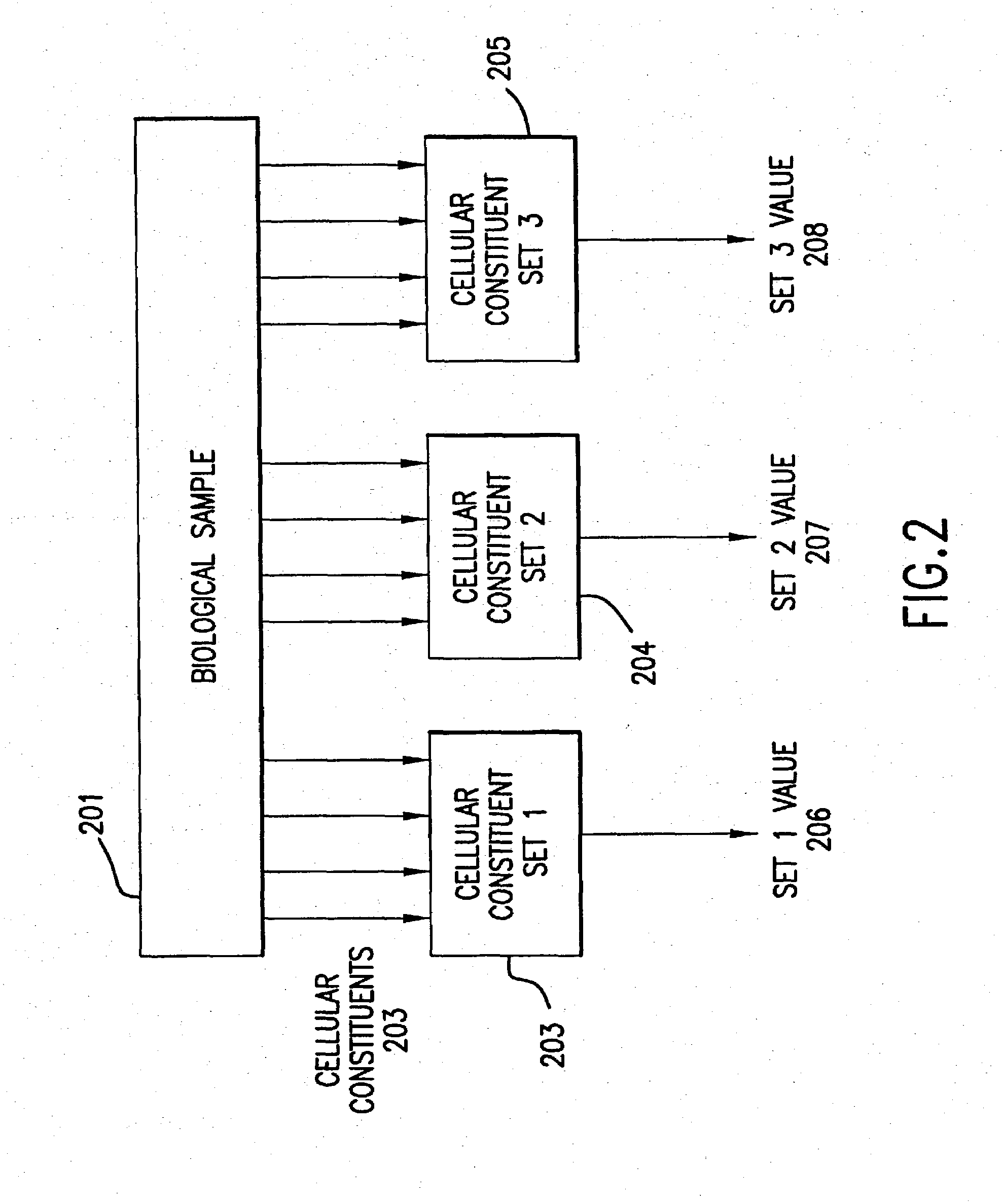
The present invention provides methods for enhanced detection of biological response patterns. In one embodiment of the invention, genes are grouped into basis genesets according to the co-regulation of their expression. Expression of individual genes within a geneset is indicated with a single gene expression value for the geneset by a projection process. The expression values of genesets, rather than the expression of individual genes are then used as the basis for comparison and detection of biological responses with greatly enhanced sensitivity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
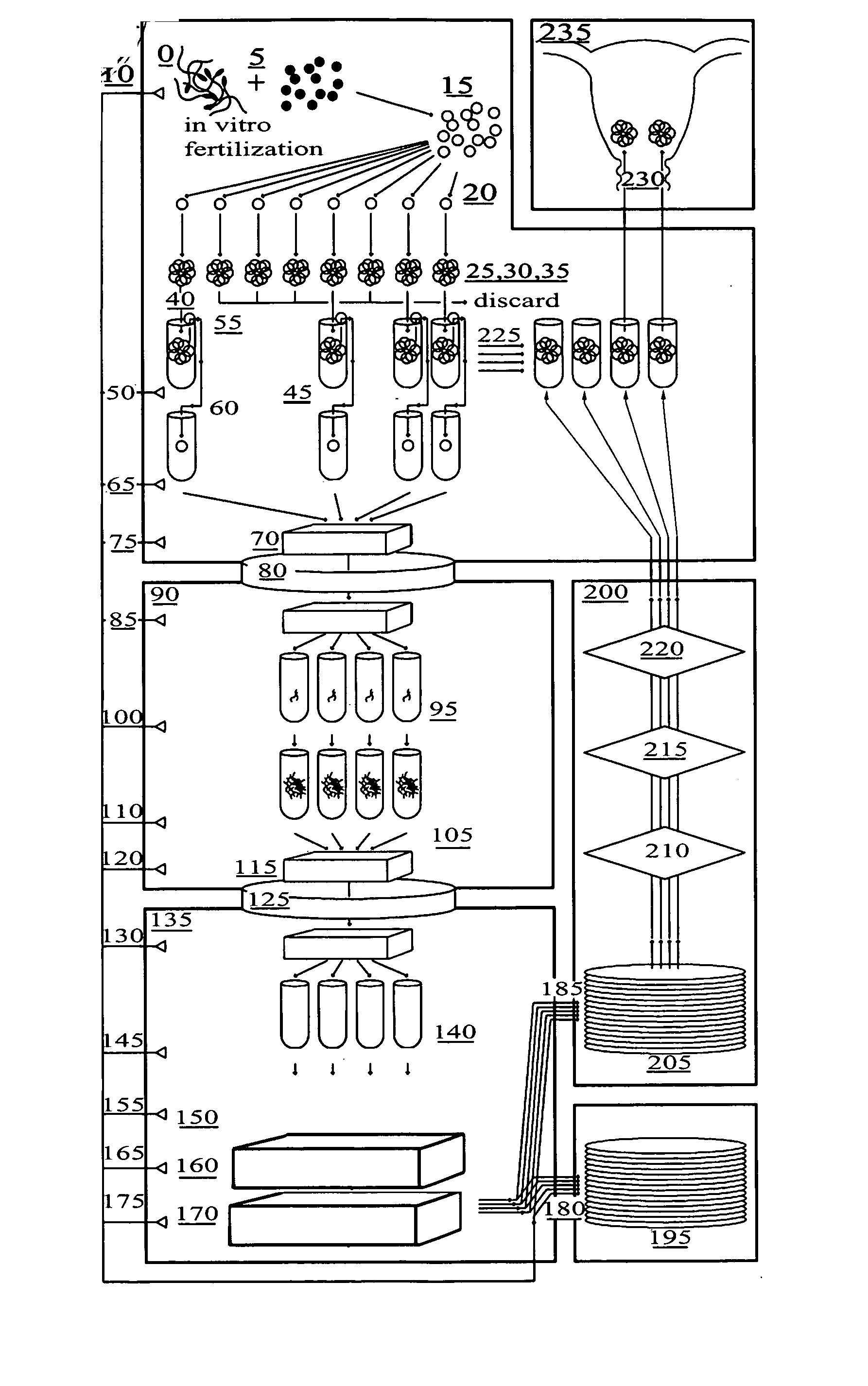
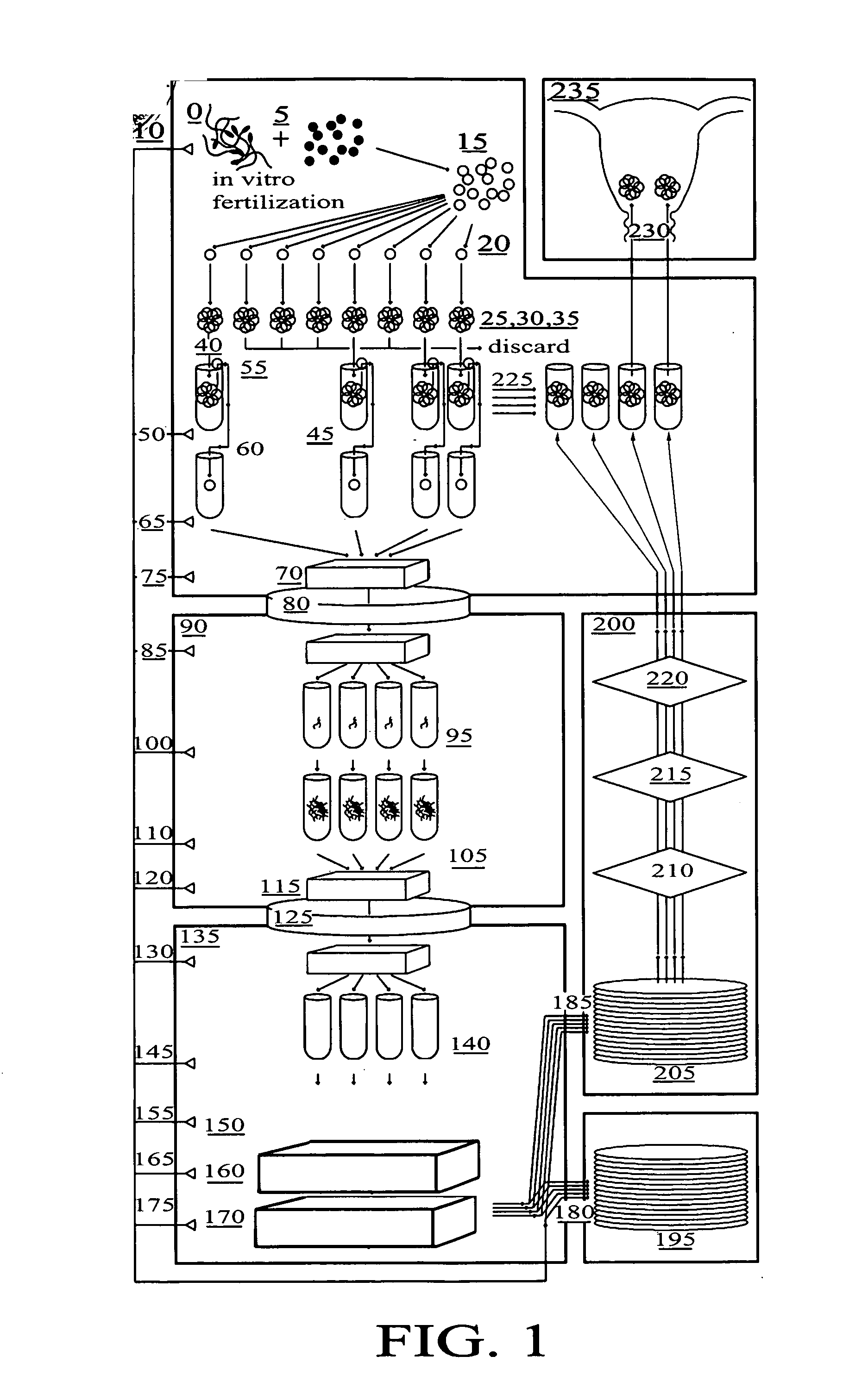
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Method of isolating cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050123914A1Rapid and non-invasive diagnosticHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsTrophoblastNon invasive
The present invention relates to a non-invasive method of retrieving and identifying cells particularly fetal cells and trophoblastic cells. The invention includes methods for use of the cells for identifying chromosomal abnormalities and mutations particularly for prenatal diagnosis by performing genetic diagnosis for chromosomal and single gene disorders. The invention also includes methods of confirming cells of fetal origin.
Owner:MONASH UNIV +1
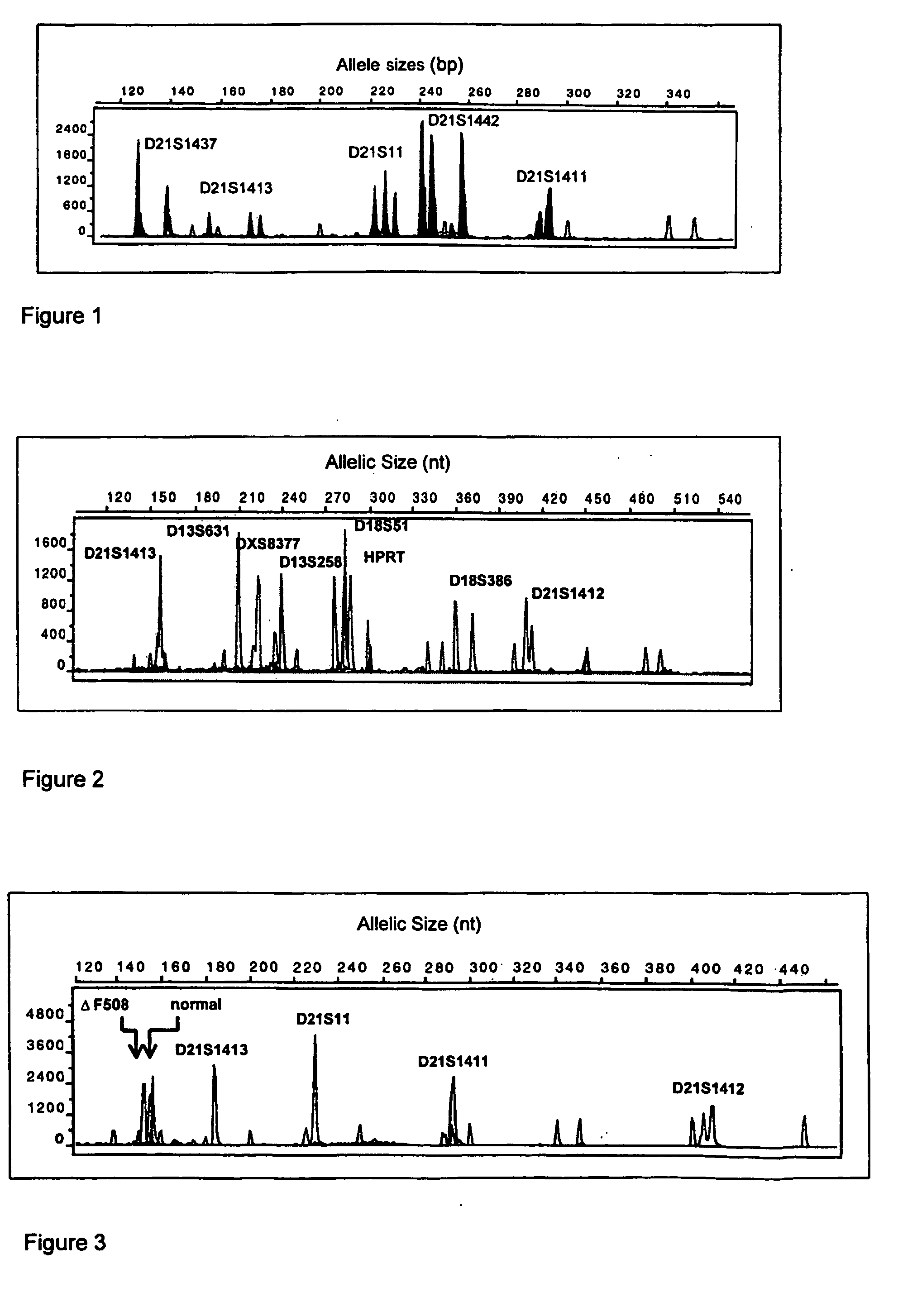
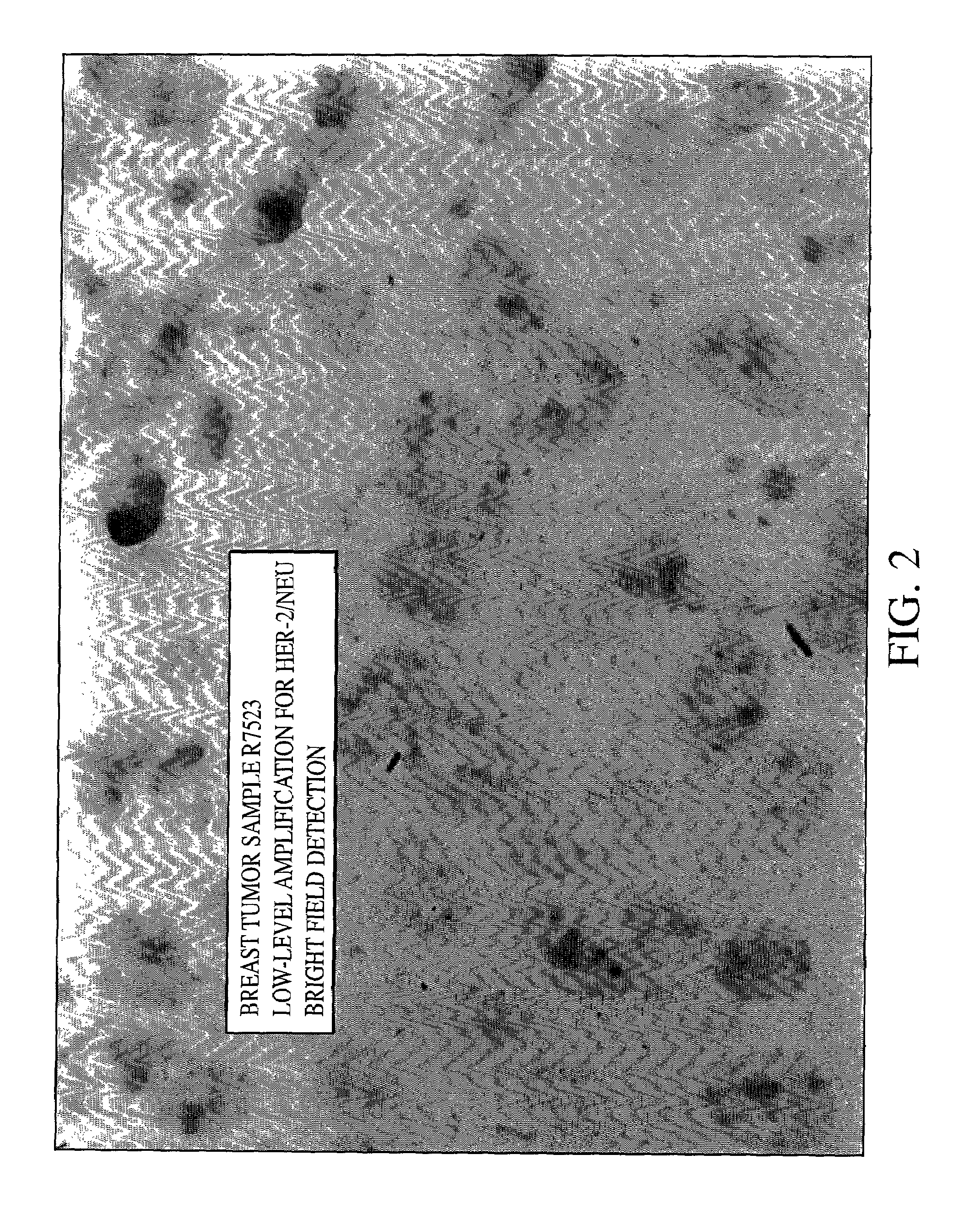
Method of detecting single gene copies in-situ
InactiveUS20020019001A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
A method for detecting single copies of a gene in-situ using brightfield microscopy is used in detection of nucleic acid sequences. Probes are directly or indirectly labeled with alkaline phosphatase with NBT / BCIP used as the chromogen.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Trophic conversion of obligate phototrophic algae through metabolic engineering
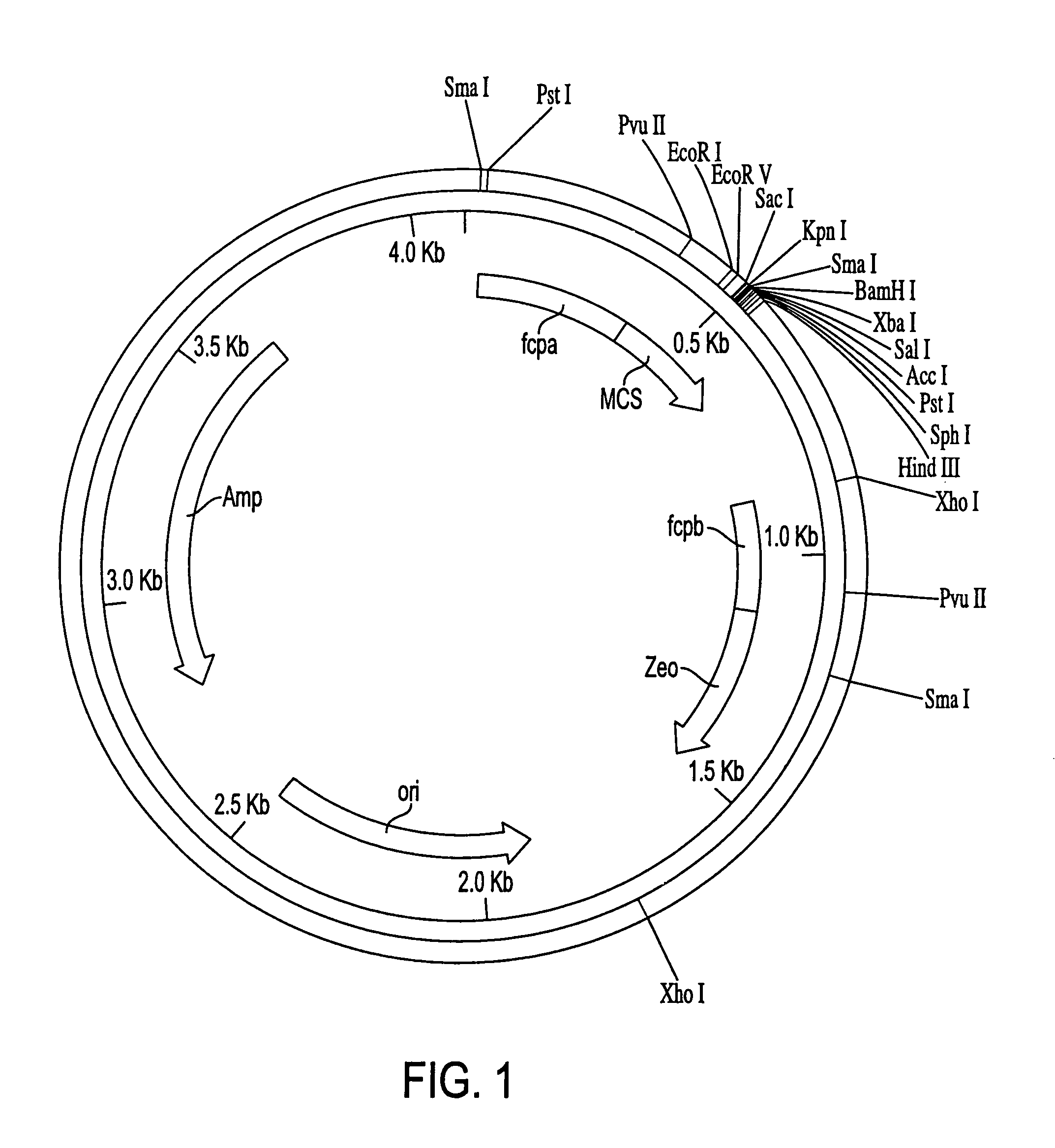
Most microalgae are obligate photoautotrophs and their growth is strictly dependent on the generation of photosynthetically-derived energy. In this study it is shown that the microalga Phaeodaclylurn tricornutum can be engineered to import glucose and grow in the dark through the introduction of genes encoding glucose transporters. Both the human and Chlorella kessleri glucose transporters facilitated the uptake of glucose by P. tricornutum, allowing the cells to metabolize exogenous organic carbon and thrive, independent of light. This is the first successful trophic conversion of an obligate photoautotroph through metabolic engineering, and it demonstrates that methods of cell nourishment can be fundamentally altered with the introduction of a single gene. Since strains transformed with the glucose transport genes are able to grow non-photosynthetically, they can be exploited for the analysis of photosynthetic processes through mutant generation and characterization. Finally, this work also represents critical progress toward large-scale commercial exploitation of obligate phototrophic algae through the use of microbial fermentation technology, eliminating significant limitations resulting from light-dependent growth.
Owner:MARTEK BIOSCIENCES CORP
Assay systems for genetic analysis
ActiveUS20120040859A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolygenic traitChromosomal Abnormality
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Novel Herbicide Resistance Genes
ActiveUS20110203017A1Prevent shifting or shiftingAvoid developmentBiocideSugar derivativesGlyphosatePyridine
The subject invention provides novel plants that are not only resistant to 2,4-D, but also to pyridyloxyacetate herbicides. Heretofore, there was no expectation or suggestion that a plant with both of these advantageous properties could be produced by the introduction of a single gene. The subject invention also includes plants that produce one or more enzymes of the subject invention “stacked” together with one or more other herbicide resistance genes. The subject invention enables novel combinations of herbicides to be used in new ways. Furthermore, the subject invention provides novel methods of preventing the development of, and controlling, strains of weeds that are resistant to one or more herbicides such as glyphosate. The preferred enzyme and gene for use according to the subject invention are referred to herein as AAD-12 (AryloxyAlkanoate Dioxygenase). This highly novel discovery is the basis of significant herbicide tolerant crop trait and selectable marker opportunities.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Preparation method of staphylococcus aureus CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of system in constructing mouse model
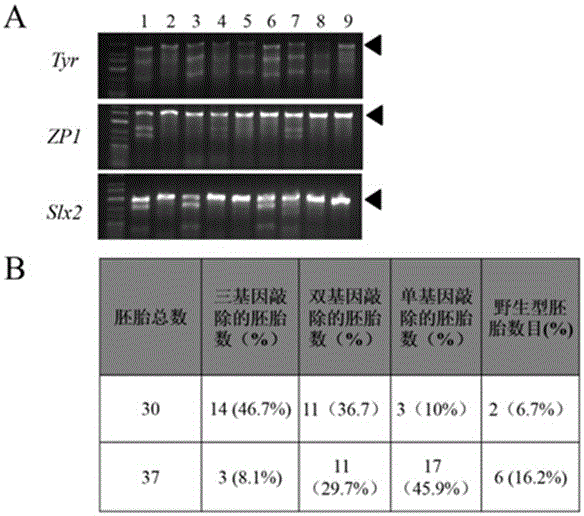
The invention discloses a preparation method of a staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system and an application of the system in constructing a genetically modified mouse model. The staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system is composed of two components, namely Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, wherein a preparation method of the Cas9 mRNA is achieved by adding a T7 promoter to the upstream region of original Cas9 coding DNA, and a preparation method of the gRNA is achieved by adding the T7 promoter to the upstream region of an original gRNA coding sequence. The staphylococcus aureus Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, which are injected to mouse fertilized embryos through micro-injection, can achieve gene editing and modification of various types, such as single-gene knockout, multi-gene knockout and / or gene knock-in and the like, on the mouse fertilized embryos; therefore, the CRISPR / Cas9 system has a good application prospect in the aspects of fertilized embryo gene editing and modification of such animals as mouse and the like as well as construction of animal models.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MAGIGEN BIOTECH
Cloning method for series parallel expression of a plurality of sgRNA based on grading assembling and application
InactiveCN106868031AAvoid lossNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGolden gateLiving cell
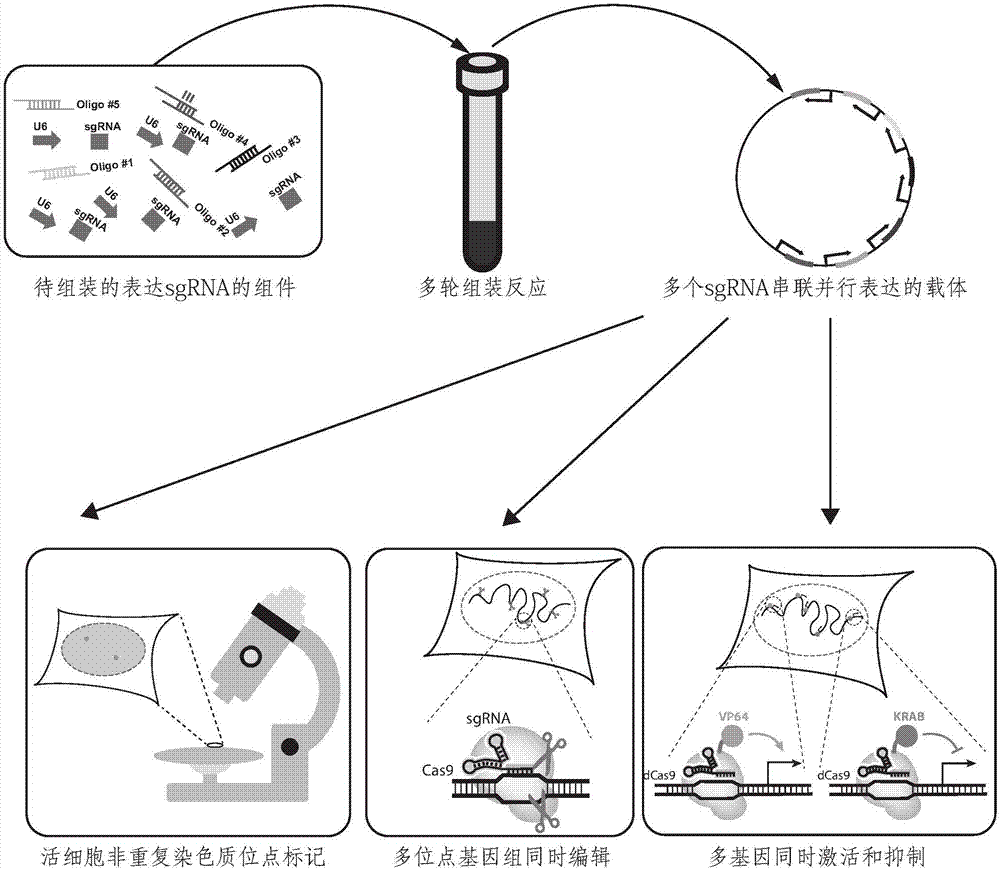
A CRISPR / Cas9 system has an ultrahigh parallel capacity. In order to meet the requirement for expressing a plurality of sgRNA in some cases, the invention provides a quick assembling method for a plurality of parallel expressed sgRNA. The invention utilizes grading Golden Gate reaction to develop a multi-turn amplifying method based on polymerase chain reaction and independent of a carrier, so as to realize the quick connecting assembling for 20 sgRNA within one week. The method for serially assembling a plurality of sgRNA developed by the invention has the advantages of time-saving and labor-saving effect, flexibility, high efficiency and multifunction. The method can be used for quickly assembling 2-20 sgRNA in different quantity onto one carrier. A plurality of parallel expressed sgRNA are utilized to target to a section of DNA, so that the functions of marking and tracking unrepeated sequence chromatin locus in living cells, cooperatively activating or restraining a single gene, simultaneously editing a plurality of genes and simultaneously up-regulating and down-regulating the genes can be achieved. The method can be widely used for editing the gene and understanding the organization structure and dynamic change of chromatin.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and preparation method of liver microsome of the rats
ActiveCN106148416ADiverse in vitro modelsImprove transfer abilityMicroinjection basedFermentationHepaticaMicro injection
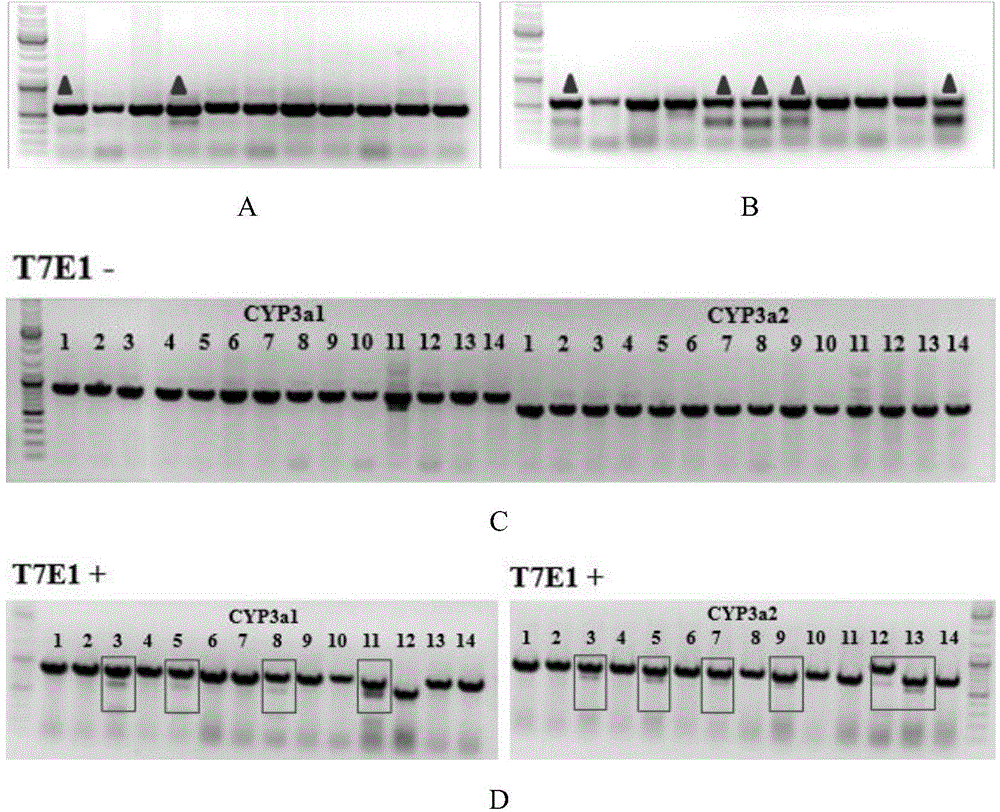
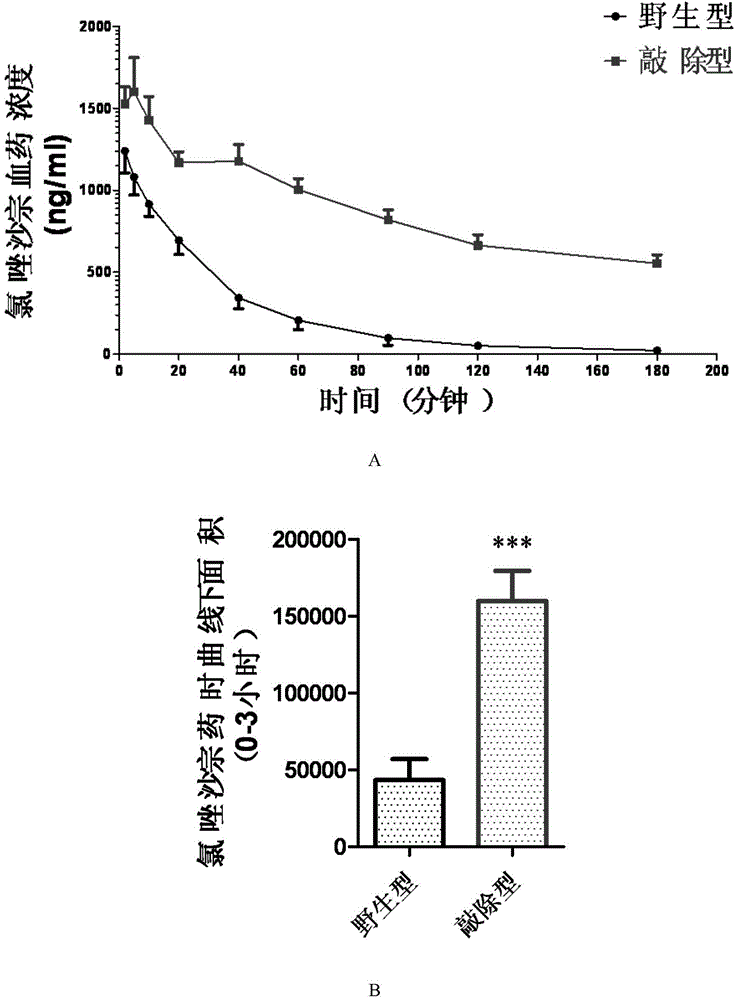
The invention provides a cultivation method of Cyp gene knocked-out rats, and a preparation method of liver microsome of the rats. The Cyp gene knock-out herein includes Cyp single gene knock-out and Cyp multiple gene knock-out. In the method, firstly a Cyp gene knocked-out rat is constructed by means of a CRISPR / Cas system, which includes selection of a knocked-out target site, in-vitro synthesis and transcription of sg RNA and Cas9m RNA, preparation of a pseudopregnant female rat, in-vitro micro-injection and transplanting of a single-cell embryo, and cultivation of the rat, and finally, a homozygote Cyp gene knocked-out rat can be cultured. Furthermore, the liver of the Cyp gene knocked-out rat is extracted and is subjected to homogenization and differential centrifugation to prepare the liver microsome of the rat in Cyp gene deletion. The invention also provides an application of the Cyp gene knocked-out rats and the liver microsome thereof in study on drug metabolism.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Process of knocking out Wnt3a gene and verification method thereof
InactiveCN106434752AHigh targeting accuracyShort experiment cycleFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionValidation methodsWNT3A gene
The invention discloses a process of knocking out Wnt3a gene and a verification method thereof. The knockout and verification of Wnt3a gene are finished through the following steps: establishment of a Cas9 lentiviral vector for Wnt3a gene, culture and passage of HepG2 cell, lentivirus infection and screening of target cell, verification of gene knockout efficiency through a mispairing enzyme method, cell protein analysis and cell proliferation detection by a CCK-8 method. The invention has the following advantages: the Wnt3a gene is knocked out by establishing a Cas9 double-vector lentivirus system for the first time; Crispr / Cas9 is a technology for accurately editing specific site of the genome of any species, and the cell-level single gene or multiple genes can be knocked out by the technology; compared with other gene editing technologies, the method has the advantages that the targeting accuracy is higher; only if the RNA target sequence is completely matched with the genome sequence, can the Cas9 cut the DNA and realize simultaneous knockout of multiple sites of the target gene; and moreover, the experimental period of vector establishment is short, the time and the cost are remarkably saved, and species limit is avoided.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
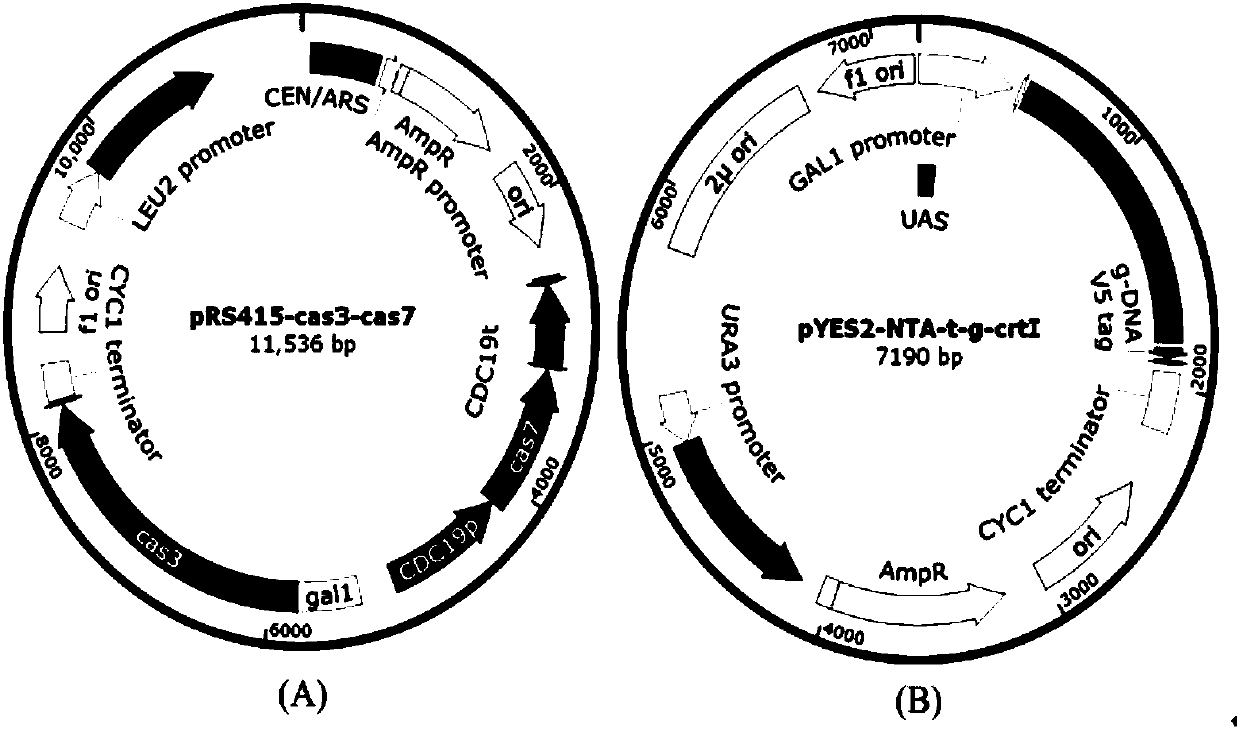
Eukaryotic gene editing method based on gene cas7-3 in I type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557378AEasy gene editingGene editing fastStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionEukaryotic geneEucoenogenes
The invention discloses gene knockout and gene insertion on eukaryotic genomes carried out by two Cas proteins (Cas7 and Cas3) in a 1 class I type CRISPR-Cas system for the first time. The developmentof the method breaks the limitation of dependence on single-gene cas9 and cpf1, and provides a new perspective for performing gene editing on the eukaryotes by multi-gene. By applying the system, thegene editing can be conveniently, rapidly and effectively carried out on eukaryote brewer's yeast genomes. The optimized tool is expected to be widely used in the gene editing of other eukaryotes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Methods for using co-regulated genesets to enhance detection and classification of gene expression patterns
InactiveUS20090204333A1Less vulnerableReduced dimensionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologic responseMethod comparison
The present invention provides methods for enhanced detection of biological response patterns. In one embodiment of the invention, genes are grouped into basis genesets according to the co-regulation of their expression. Expression of individual genes within a geneset is indicated with a single gene expression value for the geneset by a projection process. The expression values of genesets, rather than the expression of individual genes, are then used as the basis for comparison and detection of biological response with greatly enhanced sensitivity. In another embodiment of the invention, biological responses are grouped according to the similarity of their biological profile.The methods of the invention have many useful applications, particularly in the fields of drug development and discovery. For example, the methods of the invention may be used to compare biological responses with greatly enhanced sensitivity. The biological responses that may be compared according to these methods include responses to single perturbations, such as a biological response to a mutation or temperature change, as well as graded perturbations such as titration with a particular drug. The methods are also useful to identify cellular constituents, particularly genes, associated with a particular type of biological response. Further, the methods may also be used to identify perturbations, such as novel drugs or mutations, which effect one or more particular genesets. The methods may still further be used to remove experimental artifacts in biological response data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
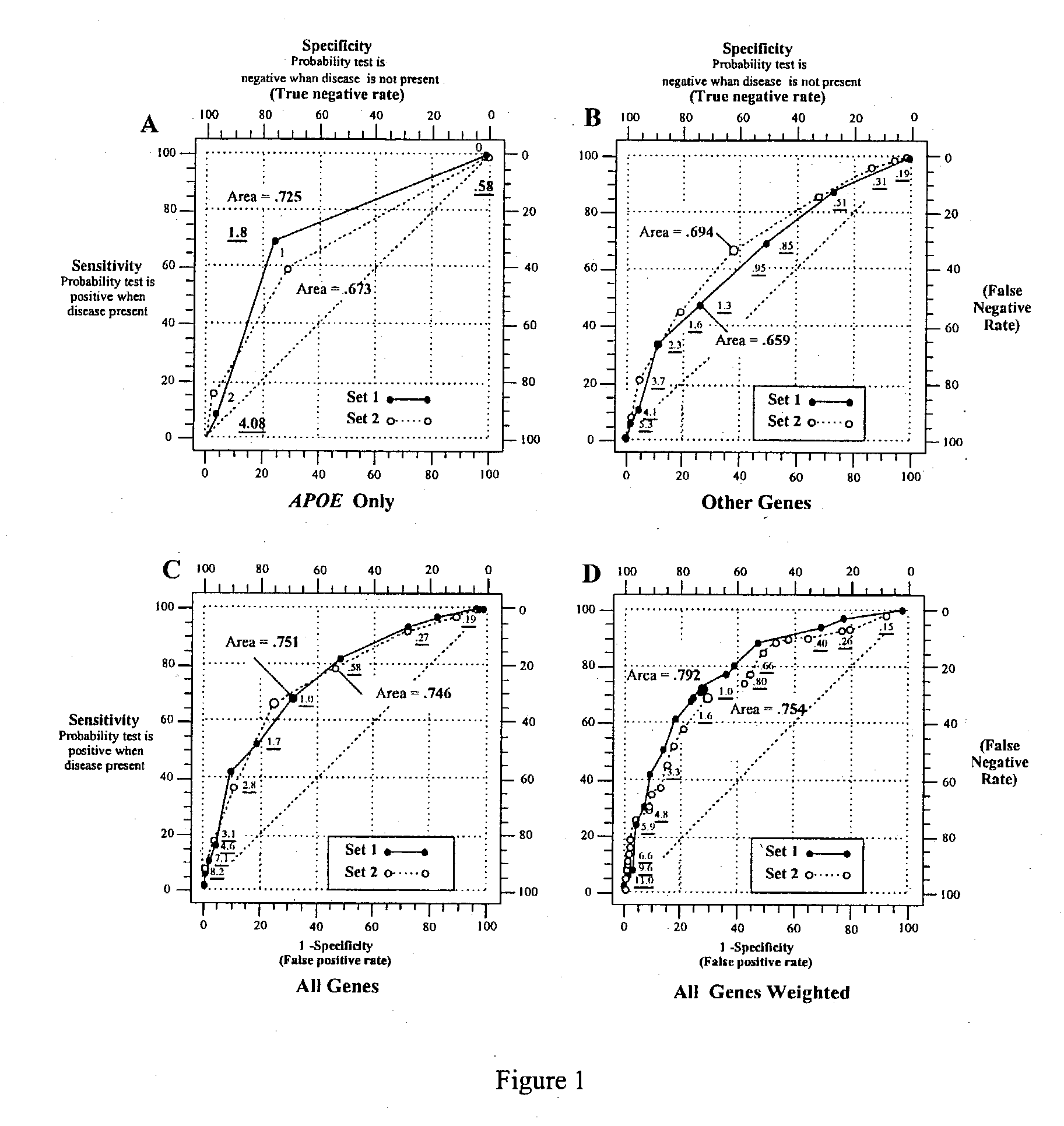
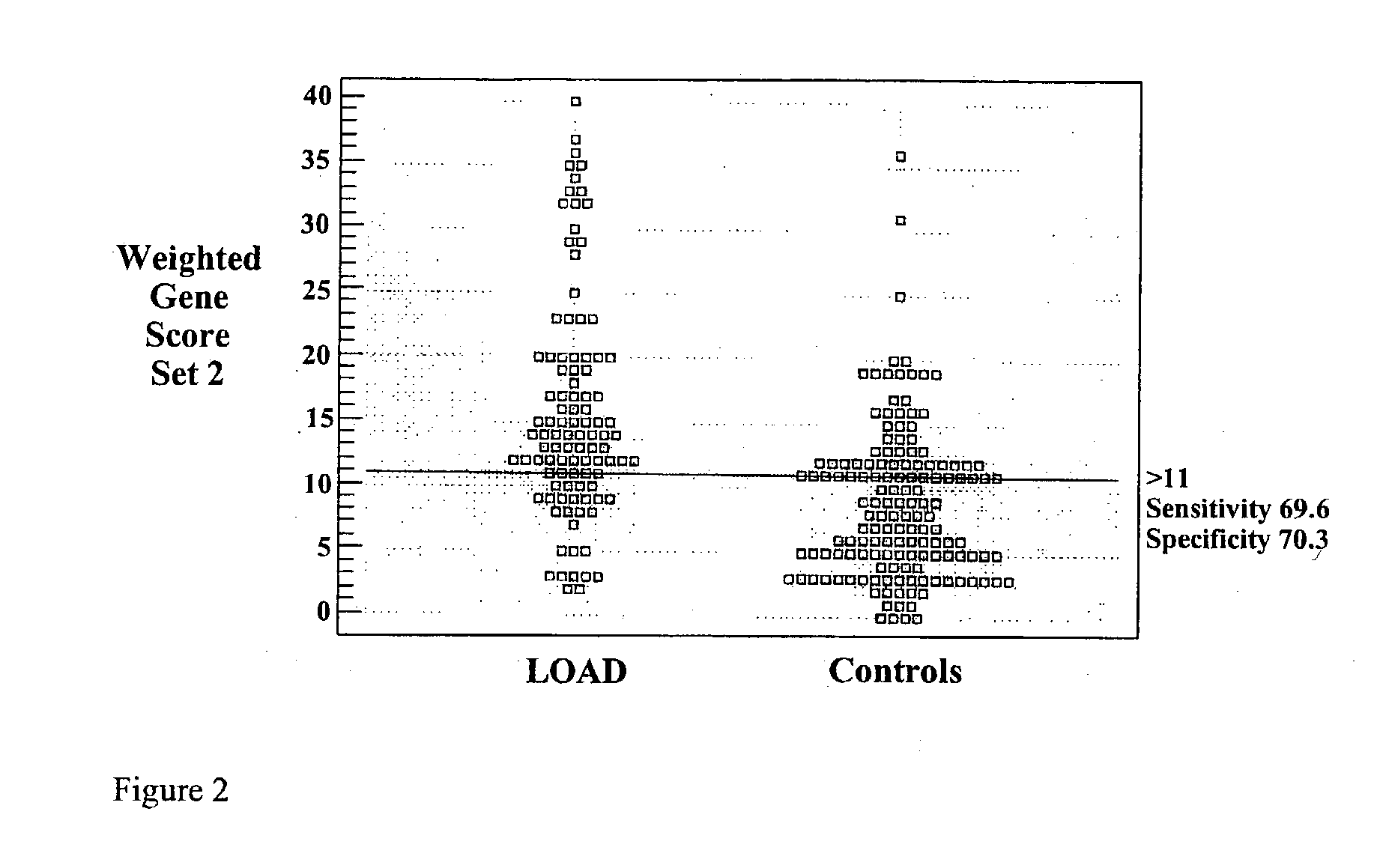
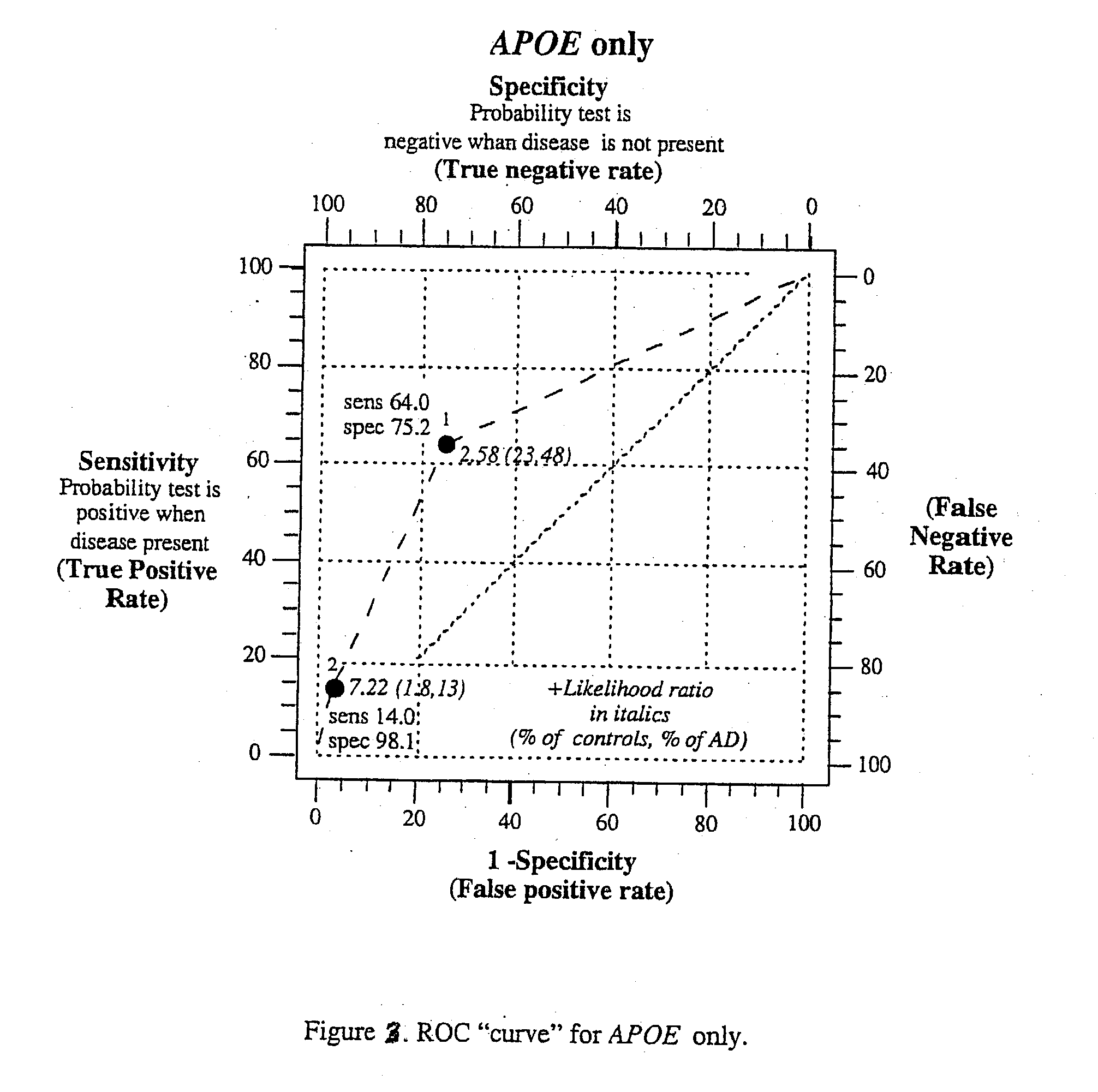
Multi-gene tests with ROC plots for the assessment of risk for polygenic disorders
InactiveUS20030162207A1Microbiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnostic testPolygenic disease
Polygenic disorders are due to the additive effect of multiple genes interacting with the environment. Because of the small effect size of each gene and considerable genetic heterogeneity, when single genes are examined, the outcome of association and linkage analyses are variable from study to study. Techniques are needed that take these unique characteristics of polygenic disorders into consideration. The present invention discloses that the formation of a polygenic score, consisting of the additive effect of multiple candidate genes, and its assessment using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) plots, provides such a technique. Six genes previously shown to be associated with Alzheimer's disease were examined, APOE, ACE, ACP1, ESR1, PNMT and SLC6A4. The total fraction of the variance, the area under the ROC plots, and the range of risks were similar for both groups indicating that despite genetic heterogeneity and the small effect size of most genes, consistent risk analyses could be obtained by examining the additive effect of these multiple genes. The present invention also discloses diagnostic tests for determining a subject's risk of developing Alzheimer's Disease or specifically Late Onset Alzheimer's Disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Method of detecting single gene copies in-situ
InactiveUS7087379B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingBioinformatics
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Inbred maize line NP2460
An inbred maize line, designated NP2460, seeds of inbred maize line NP2460, to plants of inbred maize line NP2460, to inbred maize line NP2460 into which one or more specific, single gene traits, for example, transgenes, have been transformed and / or introgressed.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
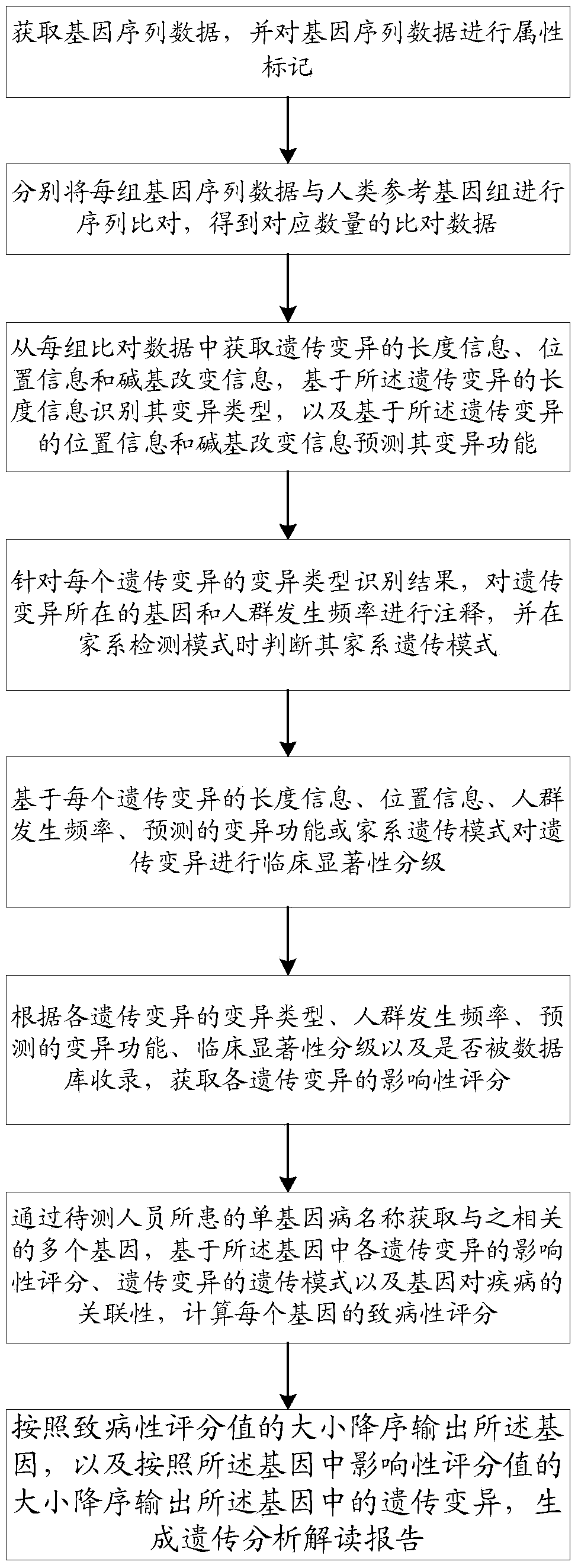
A method and system for intelligently interpreting and reporting genetic variation of monogenic diseases
ActiveCN109086571ARealize full automationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsSequence alignment
The invention discloses a method and a system for intelligently interpreting and reporting the genetic variation of a single gene disease, which can automatically analyze the genetic variation resultbased on the original sequence data of a gene of a patient, and provide a professional genetic variation analysis report, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment efficiency of the genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps of: gene sequence data is acquired and attribute marking is performed on the gene sequence data; sequence alignment of each set of gene sequence data withhuman reference genome is performed to obtain corresponding amount of alignment data; based on the length information of genetic variation, the variation type is identified, and the variation function is predicted based on the position information and base change information of genetic variation. According to the identification results of each genetic variation type, the gene and population frequencies of genetic variation were annotated, and the family genetic pattern was judged when the family detection mode was used. The system comprises the method proposed in the technical proposal.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
Assay systems for genetic analysis
ActiveUS20130004950A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayPolygenic trait
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for simultaneously completing gene locus, chromosome and linkage analysis
ActiveCN105543339AEasy to operateStrong practical feasibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEmbryoRecurrent abortion
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously completing gene locus, chromosome and linkage analysis. The method concretely and mainly comprises the following steps: collecting an embryo cell sample, amplifying a whole genome, amplifying a target gene mutation locus, establishing a whole genome and target gene mutation locus library, carrying out high flux sequencing, and carrying out data analysis. Multiple-item comprehensive detection is completed through one step by combining a whole genome amplification technology with the high flux sequencing, so respective detection of single-gene genetic disease mutation site, chromosome diseases and linkage analysis through using multiple methods and multiple steps is avoided. The method provided by the invention provides favorable conditions for a tiny amount of a sample, can be used for PGD detection to determine whether an embryo carries a pathogenic gene and chromosome copy number abnormity or not, is also suitable for genetic screening of embryos of recurrent abortion older women, and realizes multi-item detection of a plurality of single samples through one step. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short period and strong feasibility, so promotion and application of the method are facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Soybean cultivar BA922834
ActiveUS7304217B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSoybean cyst nematodeHeterodera
A soybean cultivar designated BA922834 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, MG VI maturity, resistance to race 3 of soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines), and resistance to frogeye leaf spot, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar BA922834, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar BA922834 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar BA922834 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar BA922834 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Method for treating ADAMTS-5-associated disease
The present invention relates to methods of treating ADAMTS-5-associated diseases and particularly osteoarthritis comprising administering an agent capable of modulating ADMATS-5 activity to a subject afflicted with the disease. The agent is preferably a biaryl sulfonamide compound. The invention is based, in part, on the discovery that transgenic animals that do not express functional ADAMTS-5 show a reduction in the degree of osteoarthritis after the induction of osteoarthritis as compared to WT animals. Furthermore, the ADAMTS-5 transgenic animals have reduced aggrecanase activity in articular tissue as compared to WT animals. These animals are good models for ADAMTS-5-associated diseases, and for screening of drugs useful in the treatment and / or prevention of these diseases. There are no other animal models in which the deletion of the activity of a single gene is capable of abrogating the course of osteoarthritis. Accordingly, these animals also show that osteoarthritis can be prevented and / or treated by administering to a subject an ADAMTS-5 inhibitory agent and particularly an agent capable of inhibiting the aggrecanase activity of ADAMTS-5.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Zoonosis tuberculosis fluorescence PCR rapid diagnosis kit
InactiveCN101168780AQuick monitoringQuick solveMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMycobacterium
The invention discloses a fluorescence PCR quick diagnosis reagent box of the zoonosis tuberculosis, which belongs to the biological technology field. A group of nucleotide sequence for detecting the zoonosis tuberculosis is the nucleotide sequence shown from the sequence table SEQ ID No.1 to the sequence table SEQ ID No.12. The content disclosed by the invention comprises a fluorescence PCR primer and a probe sequence for a mycobacterium tuberculosis composite group, mycobacterium tuberculosis, cow mycobacterium and fowl mycobacterium, a fluorescence PCR reaction system, a detection program, a reaction parameter and a judging method of various reagent boxes, and the preliminary treatment and the nucleic acid extraction method of various clinic samples of bacteria fluid, milk sample, blood sample, sputum, fecal sample and lymph nodes. The invention provides diagnosis reagent for the zoonosis tuberculosis diagnosis of which the technology method is special, sensitive and quick and the quality is reliable. The adoption of the reagent box provided by the invention can accomplish the whole process from the sample treatment to the fluorescence PCR detection within a day, and the detection sensitivity can reach the single gene copy or the signal bacterial cell.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish
InactiveCN106191110AShorten the growth cycleGood medical researchNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionLiving bodyGenome
The invention discloses a wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish. Compared with the prior art, specific genes in the genome of a living body can be muted more efficiently and precisely; moreover, the manufacturing is simple, the cost is lower, multiple sites on target genes can be sheared at the same time, and any number of single gene can be muted. The wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish can be applied to research related with gene and skeleton growth and other research for finding whether deletion of wnt16 gene is related with growth of other organs such as heart or not, and thus the wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish has a good medical research value. At the same time, the growth period of zebra fishes without wnt16 gene is obviously shortened, and the wnt16 gene deletion type zebra fish also has a good commercial value therefore.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
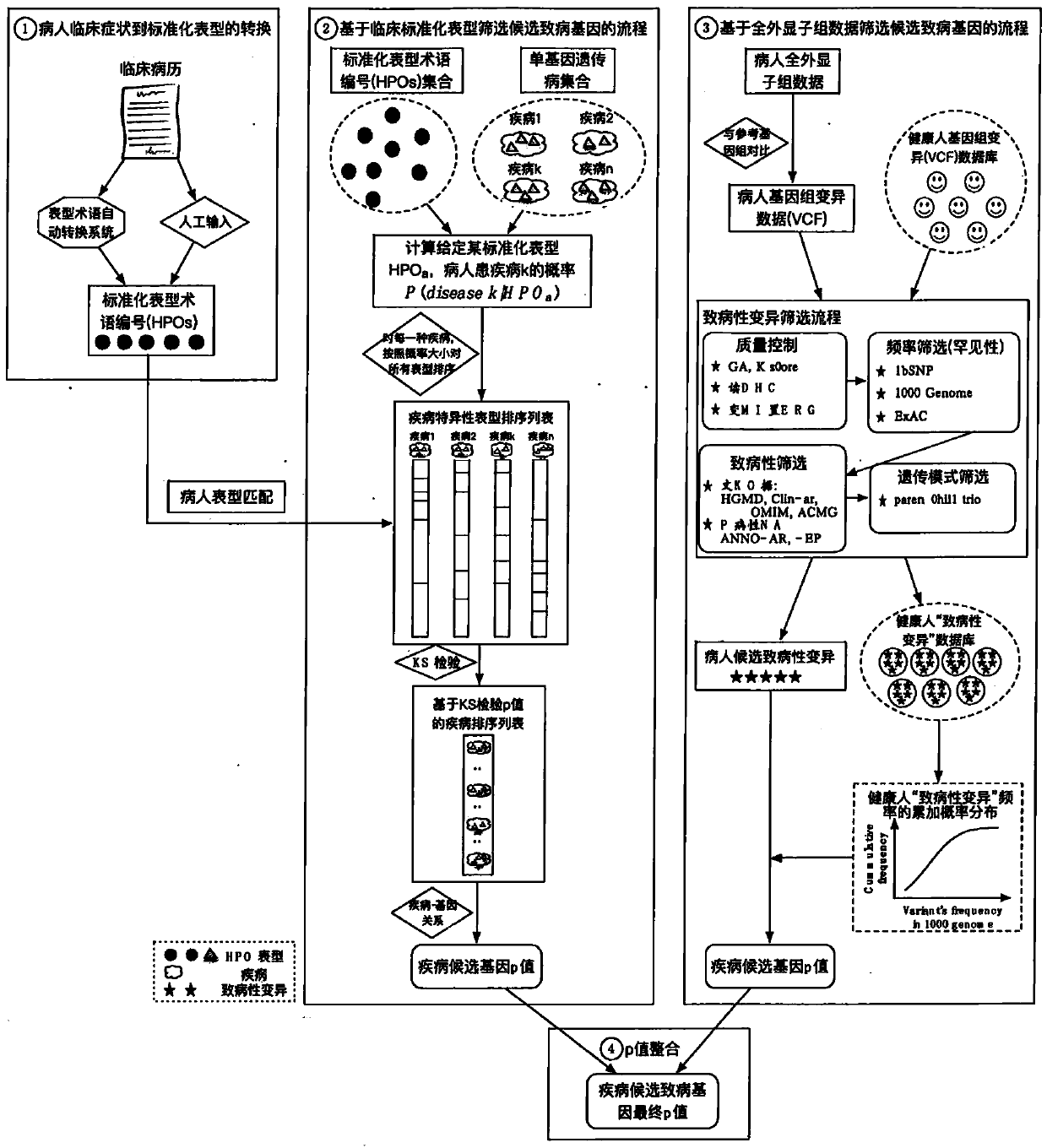
Analysis detection system for screening single gene hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical symptom data and whole exome sequencing data
The invention relates to an automated analysis system for automatically screening the single gene disease and hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical phenotype information and whole exome sequencing data. The system comprises four automatic analysis modules: (1) an automatic transferring subsystem for automatic transferring from patient clinical report to standardized phenotype term (HPO, human phenotype ontology); (2) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient standardized phenotype; (3) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient whole exome sequencing data; and (4) a p value integration system. The system adopts a possibility model to calculate the possibility of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease under the situation that a certain standard phenotype of the patient is provided, and utilizes a computer statistic check method to systematically evaluate the significance level of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease after all standard phenotype of the patient are provided, so as to accordingly achieve the purpose of screening candidate disease pathogenic gene based on clinical standard phenotype.
Owner:上海睿视健康科技有限公司
Methods of identifying spike morphology and fusarium head blight resistance, and the use of these methods for improving barley and related triticeae plants
InactiveUS7518040B2Efficient identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyTriticeaeHordeum vulgare
Using crossbred segregating populations of two-rowed and six-rowed barley cultivars, the row type of individual plants was precisely determined. The results indicate that row type is controlled by a single gene. In addition, it was discovered that molecular markers linked with this gene could be used to identify whether a test barley or related Triticeae plant is two-rowed or six-rowed. Furthermore, molecular markers can be used to identify Fusarium head blight resistance, which is linked with the two-rowed or six-rowed gene.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Construction method of genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid
InactiveCN102304539AReduce the content of intermediate productsIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneTryptophan
The invention discloses a construction method of a genetic engineering strain for producing shikimic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, constructing an escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out; 2, constructing a recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 containing key enzyme genes aroGFBR, aroE, aroB, aroD, tktA and ppsA in the metabolic pathway of the shikimic acid, so that the genes are subjected to transcriptional control of a tryptophan promoter Ptrp; and 3, transferring the recombinant expression plasmid pAR63 into the escherichia coli strain of which the aroA gene is knocked out to obtain a production strain for expressing the shikimic acid. In the method, the aim of interrupting the metabolism of the shikimic acid is fulfilled by the knock-out of the single gene aroA, a small number of genes are knocked out, the operating difficulty is low, and the expression of the genes is in the state of starting and stopping automatically and is started automatically in the middle and late period without the induction of inducers, so the possibility of adding toxic substances into a culture medium is reduced, and the shikimic acid has high yield.
Owner:河南孟成生物药业股份有限公司
Soybean cultivar M03393
InactiveUS7071391B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationMutagenic ProcessSingle gene
A soybean cultivar designated M03393 with high yield potential and tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar M03393, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar M03393 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar M03393 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar M03393 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com