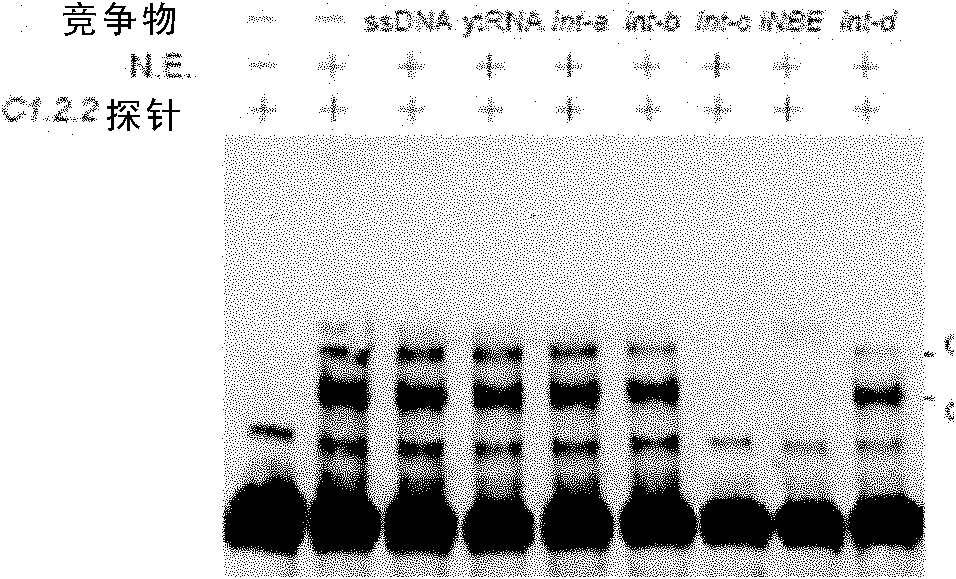Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Eucoenogenes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Eucoenogenes is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Olethreutinae of the family Tortricidae.
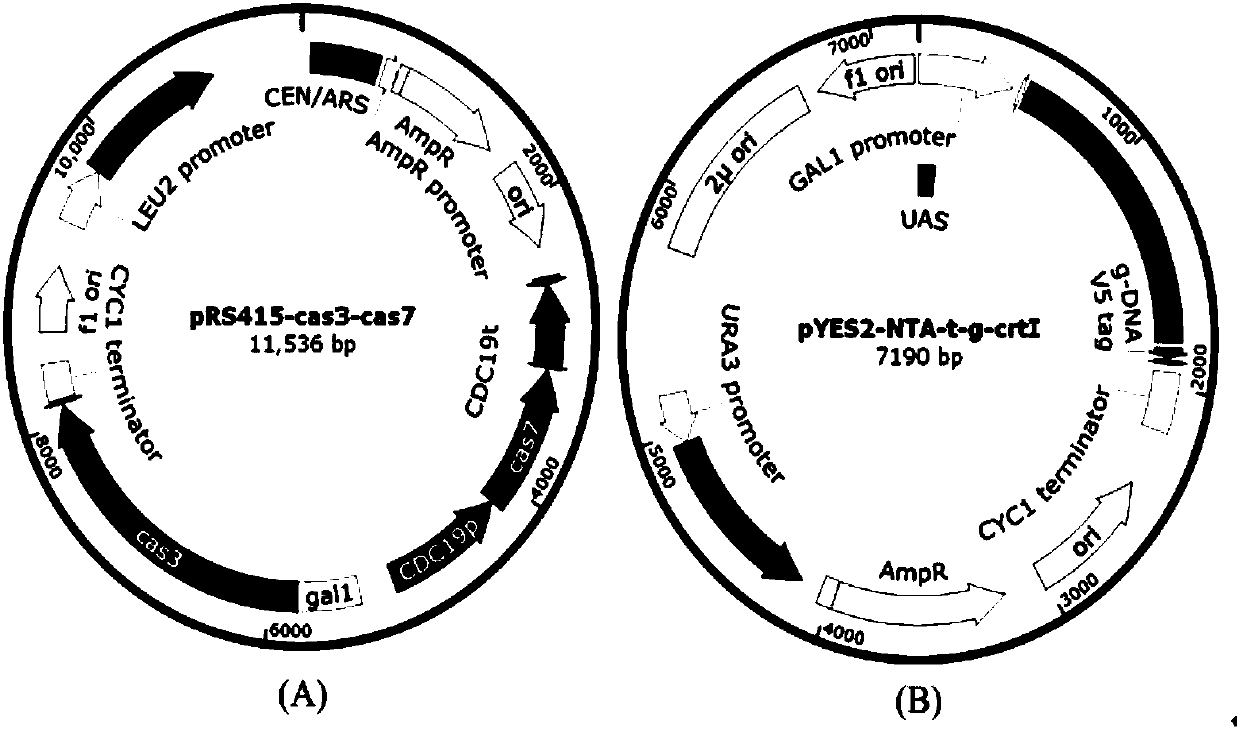
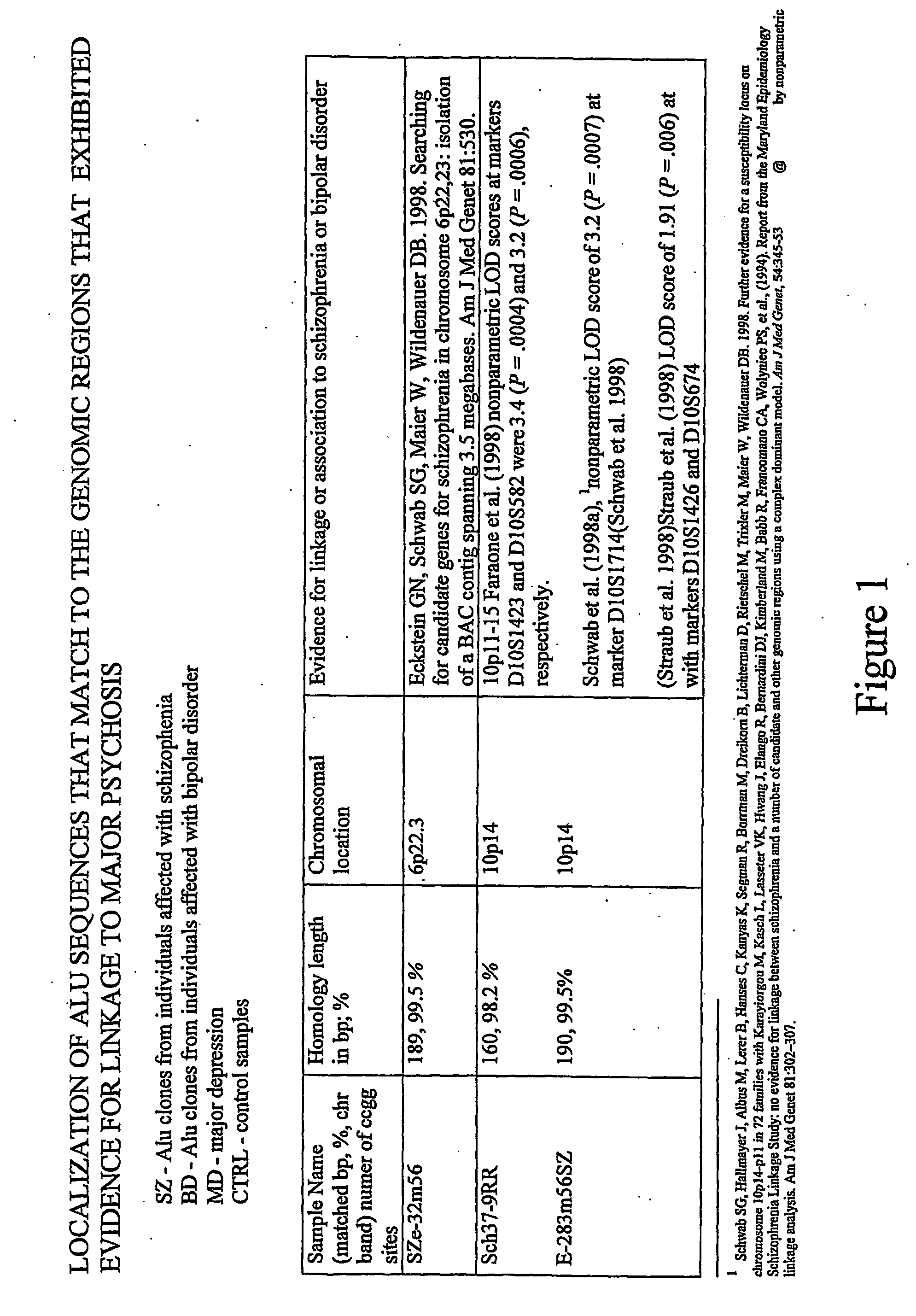
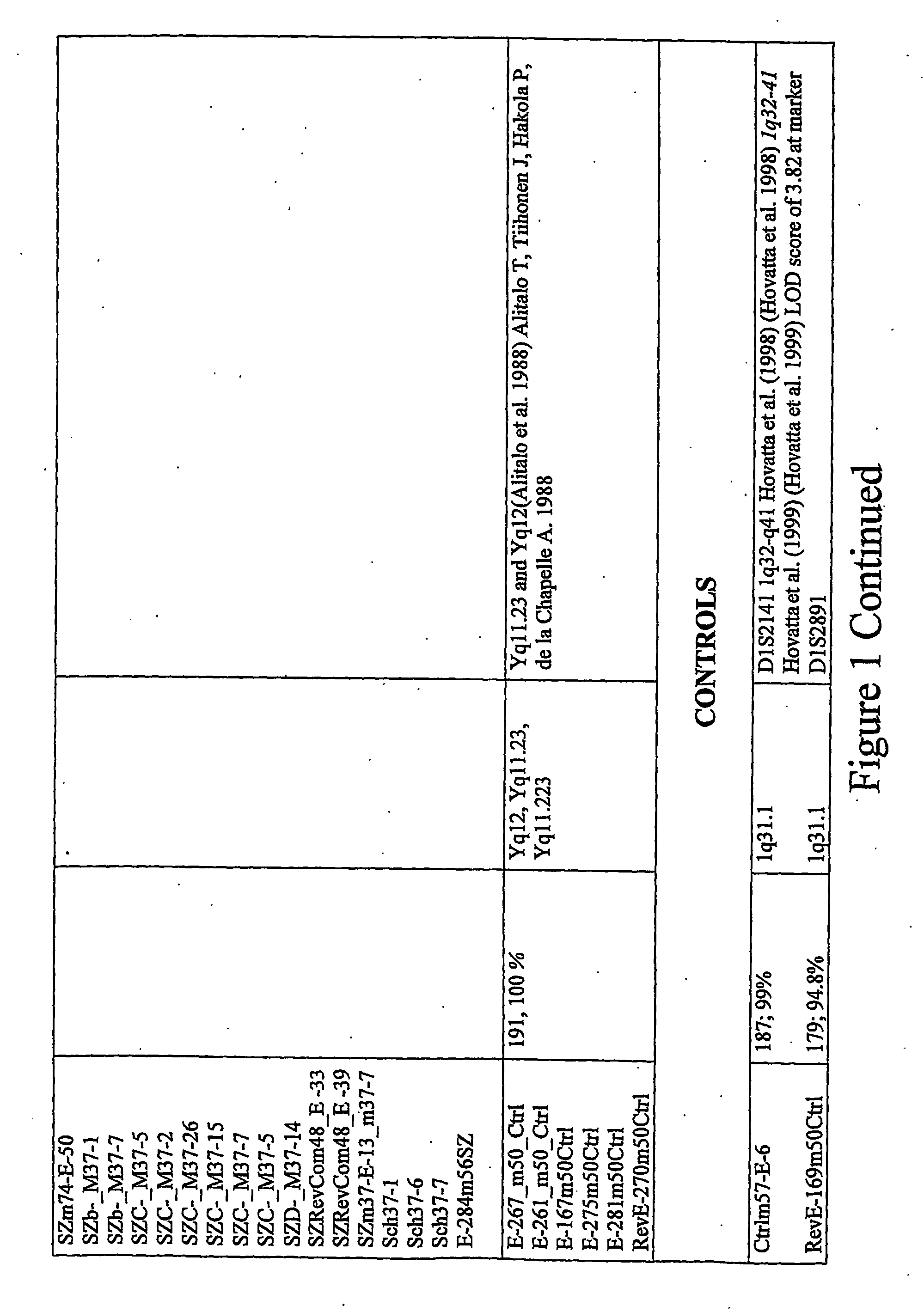
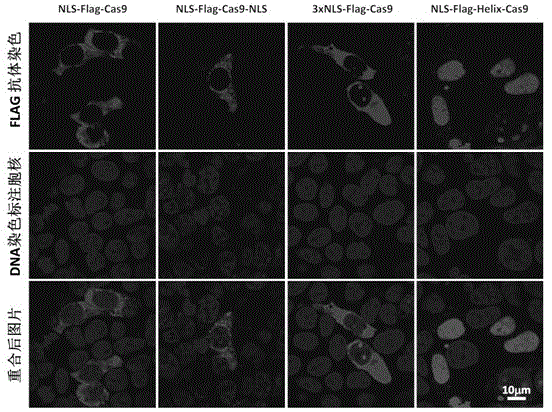
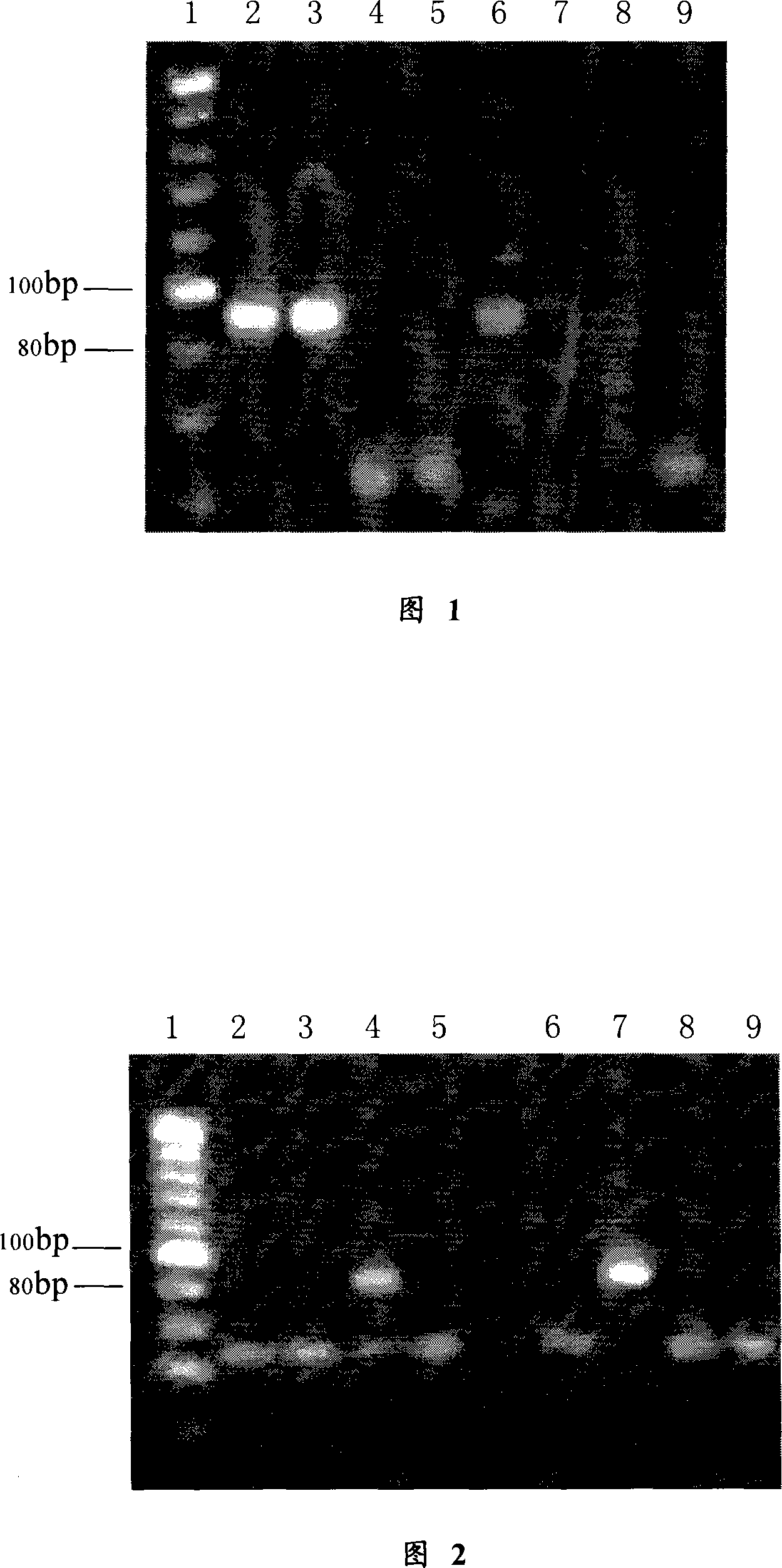
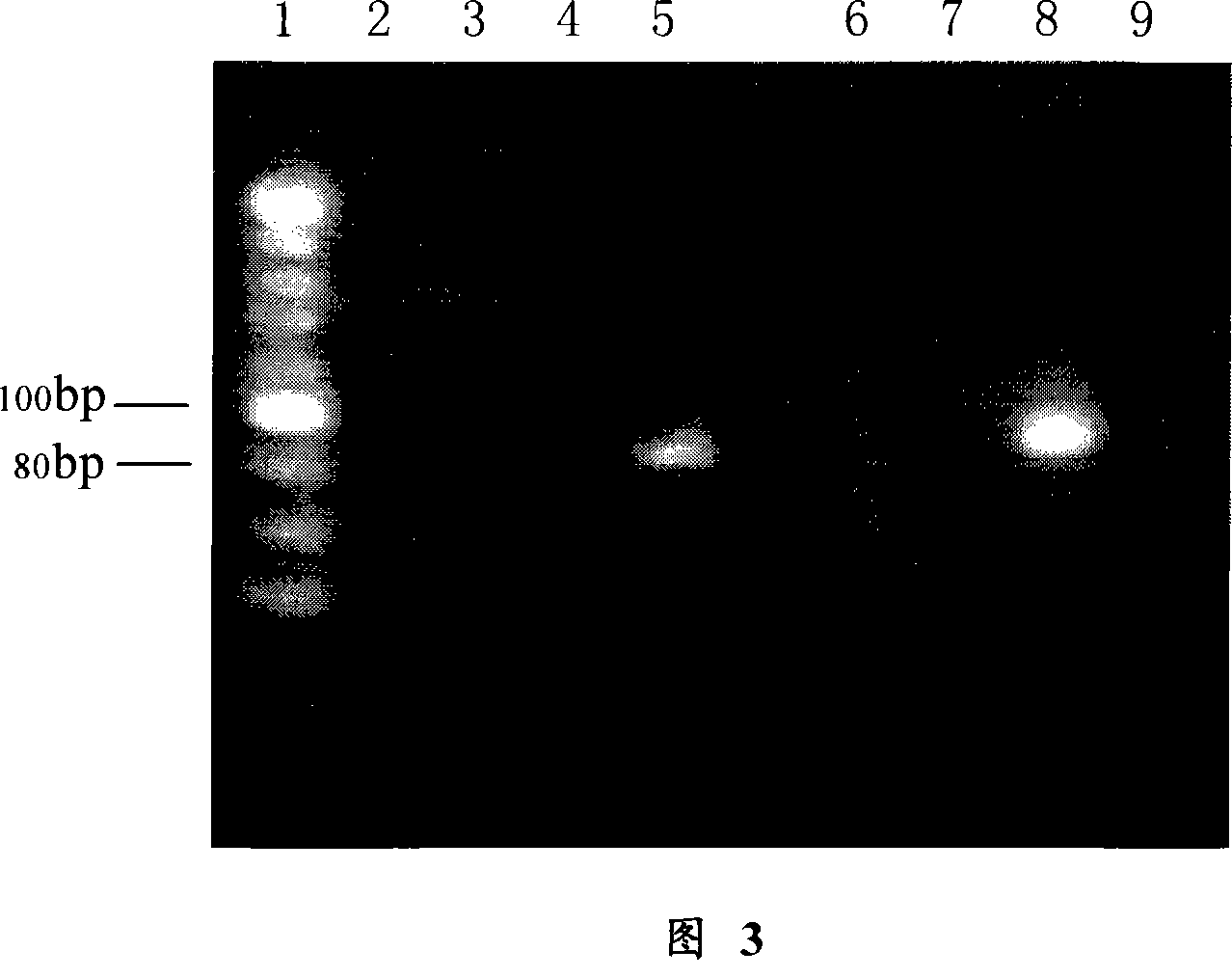
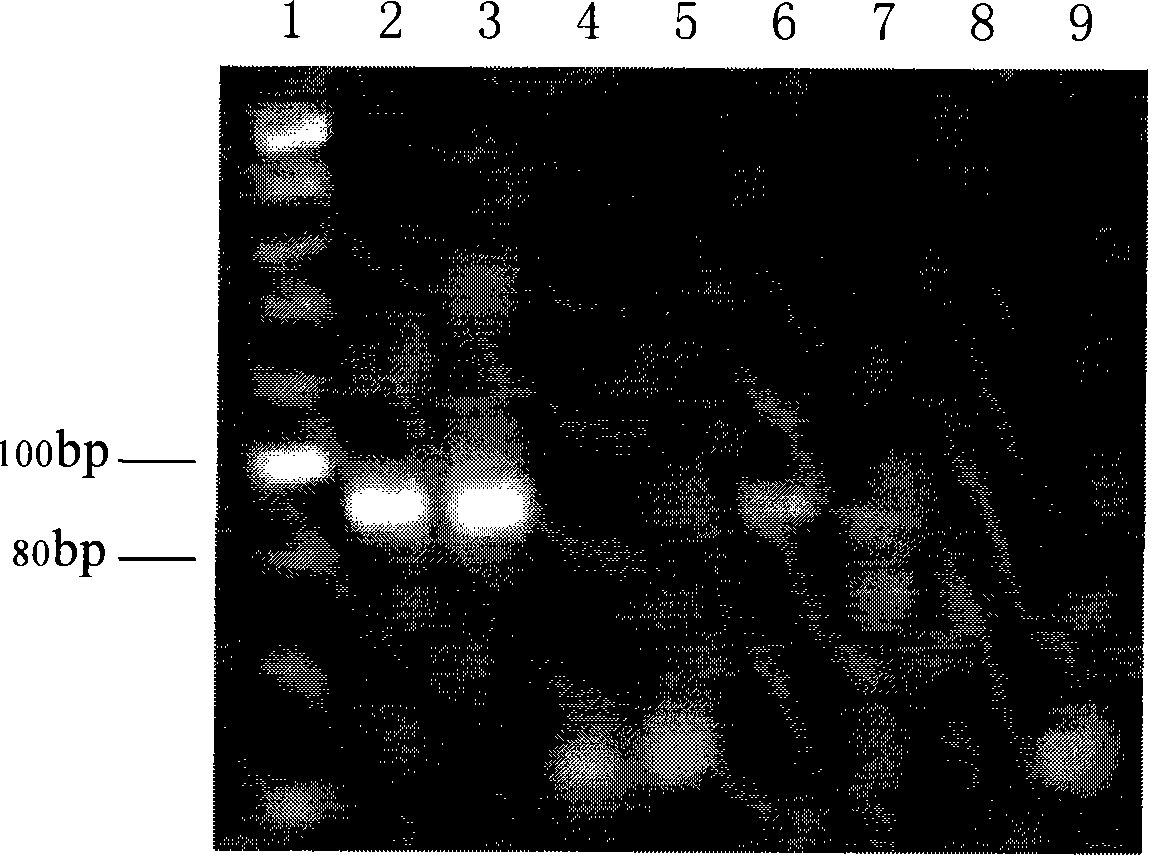
Specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and helical-structure DNA sequence
ActiveCN103233028AUnable to cutImprove accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA repairEucoenogenes
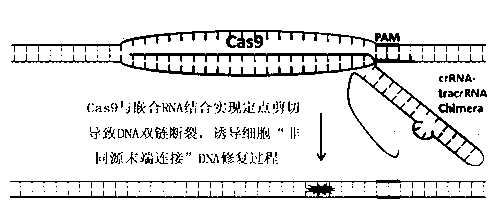
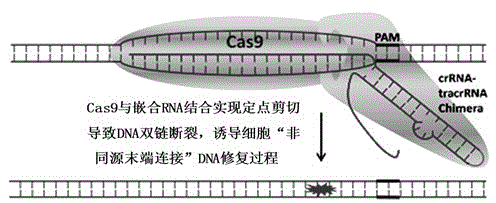
The invention discloses a specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and a helical-structure DNA sequence, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method comprises the following steps of 1, designing and constructing CRISPR / Cas9 and chimeric RNA, and 2, carrying out Cas9mRNA internal translation so that Cas9 nuclease and the chimeric RNA are bonded, carrying out fixed point clipping so that DNA double-chain cleavage is realized after the clipping, and introducing an exogenous DNA by induction of a natural DNA restoration process which is a non-homologous end bonding process of cells so that cell endogenous gene modification is realized. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method has simple processes, realizes flexible site recognition and has low energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING SYNC BIOTECH
Gene editing method based on gene cas3 of I-B type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557373ASmall molecular weightGene editing is correctHydrolasesStable introduction of DNABiological cellEucoenogenes
The invention discloses a novel gene editing system which is established based on gene cas3 of an I-B type CRISPR-Cas system in a chromosome of Virginia streptomycete IBL14, the gene editing of an I type CRISPR-Cas system to a biological cell genome is realized for the first time, and new supplement and choice are provided for the gene editing system which is established by II type commercializedCas9. In the system, a target DNA can be specifically cut by the Cas3 through crRNA guide or t-DNA location. By adopting the system, error-free, simple and rapid gene editing can be performed on prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. The optimized gene editing system is expected to be superior to the commercialized gene editing system which is established based on Cas9 in multiple fields due to low molecular weight and ability to be guided by DNA.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Eukaryotic gene editing method based on gene cas7-3 in I type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557378AEasy gene editingGene editing fastStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionEukaryotic geneEucoenogenes
The invention discloses gene knockout and gene insertion on eukaryotic genomes carried out by two Cas proteins (Cas7 and Cas3) in a 1 class I type CRISPR-Cas system for the first time. The developmentof the method breaks the limitation of dependence on single-gene cas9 and cpf1, and provides a new perspective for performing gene editing on the eukaryotes by multi-gene. By applying the system, thegene editing can be conveniently, rapidly and effectively carried out on eukaryote brewer's yeast genomes. The optimized tool is expected to be widely used in the gene editing of other eukaryotes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
PCR determination method for Chinese medicine or Chinese medicinal crops derived from eukaryote
ActiveCN101265500ASensitive and fast identificationValid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementProcessing typeEucoenogenes
The invention provides a PCR identification method derived from eucaryote for Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials. PCR augmentation is processed on DNA samples to obtain augmentation production according to a species-specific primer, wherein, the species-specific primer is designed according to a SINE sequence of eukaryotic genomes. The DNA samples are extracted from the Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials, in particular from the further processing type Chinese traditional medicine. Species categories of eukaryotic species in the further processing type Chinese traditional medicine are estimated by analyzing the augmentation production, and the truth of the identified samples is further estimated. The PCR identification method is suitable for Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials, is particularly suitable for the processing type Chinese traditional medicine, especially for the Chinese traditional medicine which is with extremely little DNA content and extremely short segment due to the further processing. The identification method has the advantages of simple operation, rapidness and sensitivity, low cost and effective truth identification of the Chinese traditional medicine and the traditional Chinese medicinal materials.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for detecting slow virus quality index combination and application of method
ActiveCN108103245AHigh sensitivityEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, particularly relates to a titer detection method for a slow virus carrier, and discloses a quality index detecting method conducting real-time fluorescence quantification nucleic acid amplification detection (qPCR and RT-qPCR) by using a sequence specific primer and a fluorescent dye, a used primer and a standard product. The detecting method isefficient and accurate, the operation is easy, the use amount of a sample is low, the repeatability is good, and the limit problem of inaccurate carrier quantitation in the fields of eucaryon geneticengineering and gene therapy is solved. The method has the advantages of detection time and simple and convenient operation step, the analysis process after the amplification is not needed, comparedwith the Taqman probe method, the SYBR Green I does not need the design of a synthesis fluorescent probe, the design is simplified, the cost is lowered, and a dissolution curve is combined in the analysis to judge the specificity of the reaction.
Owner:NANJING IASO BIOTHERAPEUTICS CO LTD +1
Avena nuda farnesyl diphosphate synthase gene YFPS and detection method for separation and clone, site-specific mutagenesis and enzyme functions
ActiveCN102994527AImprove enzyme catalytic activityIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a detection technology for separation and clone, site-specific mutagenesis, zymoprotein prokaryotic expression, zymoprotein separation and purification and enzyme functions of a branch-point key enzyme gene participating in synthesis of an isoprenoid matter in a wheat mevalonic acid metabolic pathway. The method can provide important technical storage for further performing the gene improvement and modification, constructing an eucaryon gene expression carrier of a farnesyl diphosphate synthase gene, and converting corresponding crops; secondly can be used for obtaining plants with important commercial values in virtue of secondary metabolism, and discussing a relationship of the overexpression of the farnesyl diphosphate synthase gene in a receiver plant and important agronomic traits such as secondary metabolites, crop grain sizes and crop grain weights; and improving the yield of the crops, analyzing structures of introns, exons and promoters, studying functions of the promoters, developing related molecular markers.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Triticum aestivum farnesyl phosphate synthase (TaFPS) gene as well as isolation colonizing and enzyme activity measuring method thereof
InactiveCN102433349AIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzyme GenePhosphate
The invention belongs to molecular biology and relates to a technology for isolation colonizing of a triticum aestivum farnesyl phosphate synthase (TaFPS) gene as a key enzyme gene participating in isoprene-like substances such as wheat chlorophyll, carotenoid and the like as well as prokaryotic expression of enzyme protein, separated purification of the enzyme protein and detection in vitro of the enzyme activity. The invention provides important technical storage for further constructing a eukaryotic gene expression vector of the TaFPS gene and converting the eukaryotic gene expression vector into a corresponding crop, particularly obtaining plants with important commercial value by means of secondary metabolism, discussing the relationships between the overexpression of the TaFPS gene in a receptor plant and important economical characters such as a secondary metabolite, the seed size of crops, the grain weight and the like, further improving the yield of the crops, analyzing the structures of an introne, an exon and a promoter of the TaFPS gene, researching the functions of the promoter and developing a relevant molecular marker.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Detection of epigenetic abnormalities and diagnostic method based thereon
The present invention provides a method of detecting an epigenetic abnormality associated with a disease. The method comprises identifying, within a eukaryotic genome, a locus having a hypomethylated sequence specific for the disease and an endogenous multi-copy DNA element. The method can also comprise separate steps of identifying a disease-specific hypomethylated sequence and identifying an endogenous multi-copy DNA element, where the steps may be performed in any order, so long as a locus is identified that has both a disease-specific hypomethylated sequence and an endogenous multi-copy DNA element. The disease-specific hypomethylated sequences detected in accordance with the present invention indicate putative regions of epigenetic dys-regulation and indicate aberrantly regulated nucleic acid sequences that may cause or predispose a patient to disease, such as, but not limited to, Huntingdon s disease, cancers, diabetes, schizophrenia, or bipolar disorder.
Owner:CENT FOR ADDICTION & MENTAL HEALTH
Identification and assignment of functionally corresponding regulatory sequences for orthologous loci in eukaryotic genomes
The present invention relates to a method and computer program product for identifying a regulatory sequence of a coding sequence within the genome of a eukaroytc organism.
Owner:GENOMATIX SOFTWARE
Accurate and efficient eukaryotic biological gene identification method based on transcriptome
InactiveCN108753994AComplete and compact designMeeting Research NeedsMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsRNA extractionData retrieval
The invention discloses an accurate and efficient eukaryotic biological gene identification method based on a transcriptome. The method comprises 1, quasi-identification gene expression prediction, 2,acquisition of a quasi-identification gene high expressed sample, RNA extraction and reverse transcription, 3, transcriptome sequencing, 4, transcriptome data analysis and storage, 5, transcriptome data retrieval and 6, gene identification primer design and gene identification. Through the close specie research report analysis, the transcriptome of the high expressed sample of the gene to be identified is determined, the target sequence of the gene to be identified is screened in the transcriptome, and the gene is identified and cloned based on the target sequence so that an accurate gene sequence is obtained. The method is suitable for identification of functional genes of most eukaryotes, is very accurate, satisfies the research demands of the functional gene identification in the research process, has a reasonable design, is easy to use, realizes a low cost and is suitable for promotion and use.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Construction method of recombinant plasmid vector p18-kan+/- containing loxP-kanr-loxP segments
InactiveCN102250937AFirmly connectedVector-based foreign material introductionCompetent cellPlasmid Vector
The invention provides a construction method of a recombinant plasmid vector p18-kan+ / - containing loxP-kanr-loxP segments, which relates to a construction method of a recombinant plasmid vector. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring loxP-kanr-loxP segments from a pUG6 plasmid; 2, acquiring a connection product through T-A terminal connection by using a pMD18-T vector as the framework; and 3, converting the connection product into competent cells, picking positive ones for cloning, and extracting the recombinant plasmid. By using the pMD18-T vector as the template, loxP-kanr-loxP gene segments are introduced onto multiple cloning sites of the template, and a pair of recombinant plasmids having opposite connection directions is simultaneously constructed. Thus, both ends of the loxP-kanr-loxP site of each plasmid are provided with multiple common enzyme cutting sites, so that an exogenous gene can be conveniently connected with the loxP-kanr-loxP segments, thereby providing a new operating way for the gene knockout and replacement of eucaryotes.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Autologous upregulation mechanism allowing optimized cell type-specific and regulated gene expression cells
InactiveUS20070166366A1Microencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsEucoenogenesBiological activation
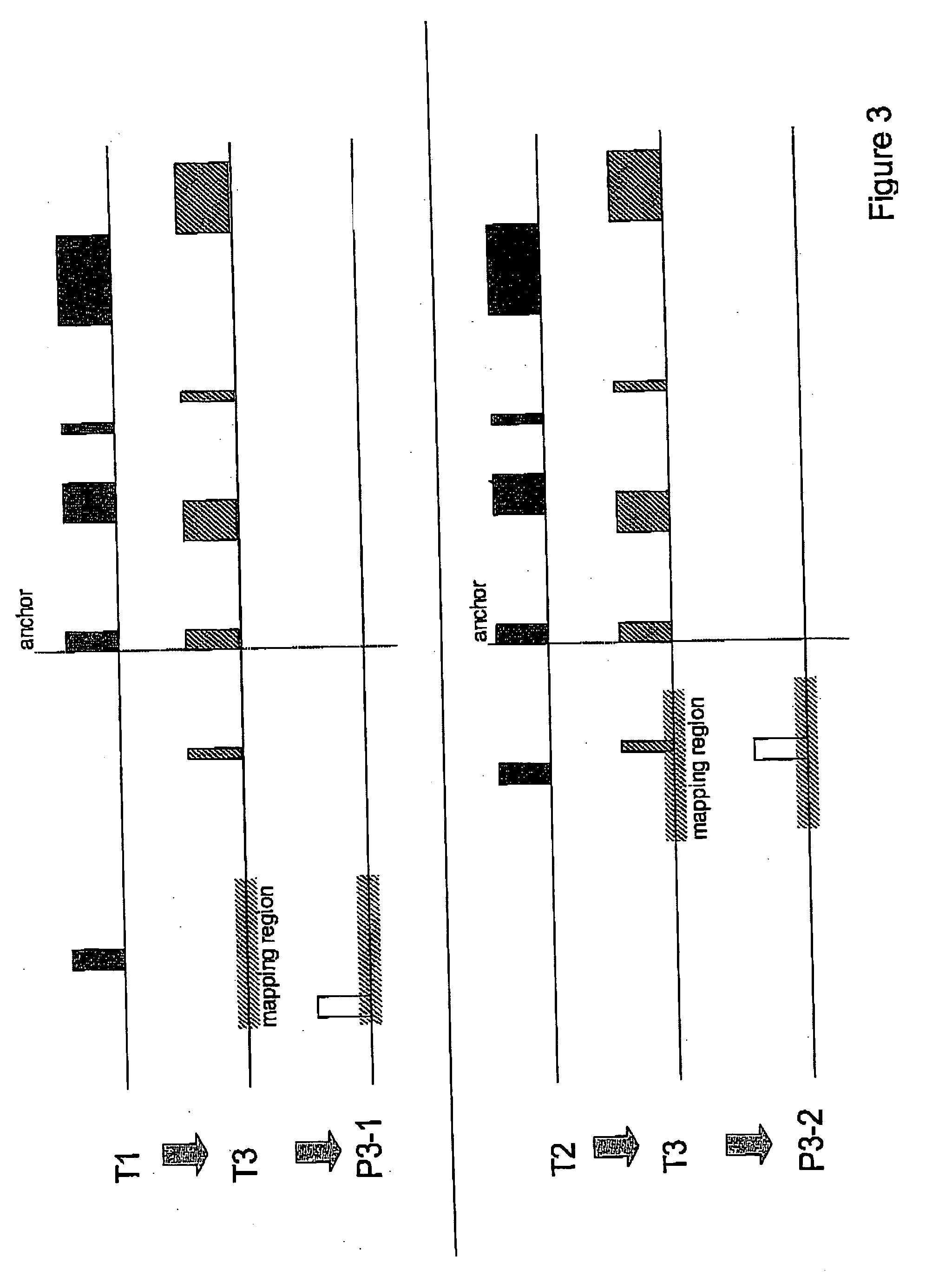
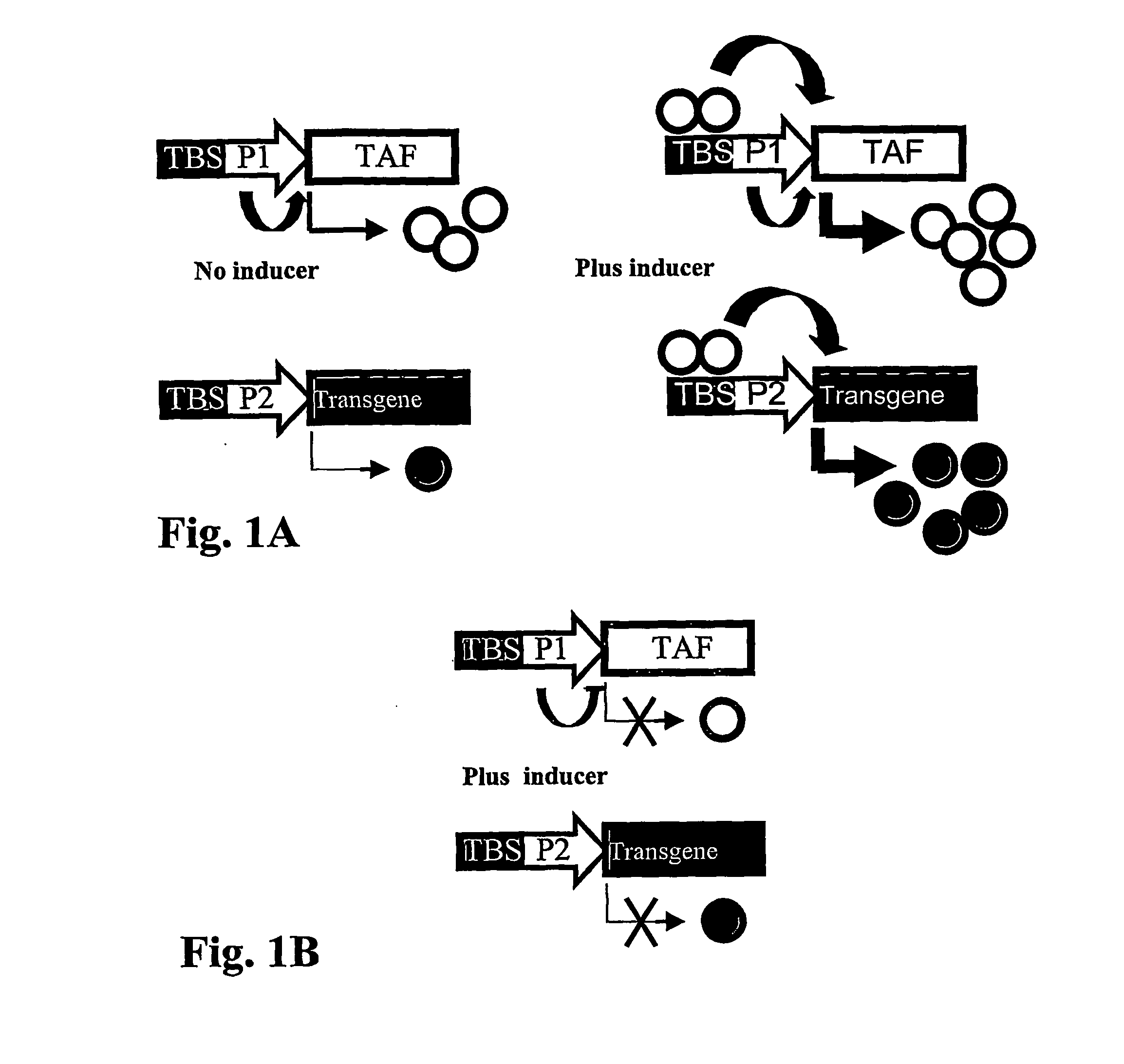
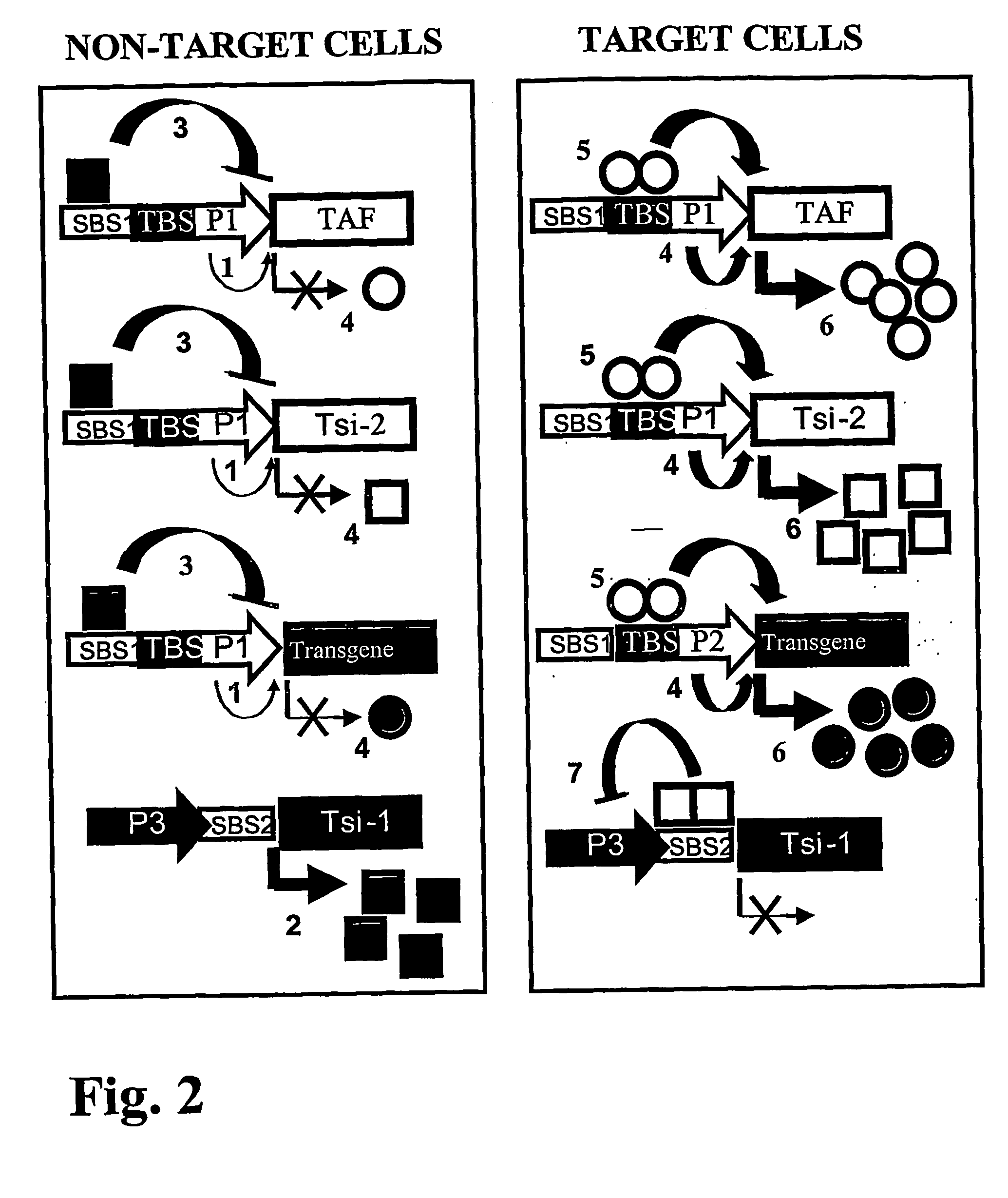
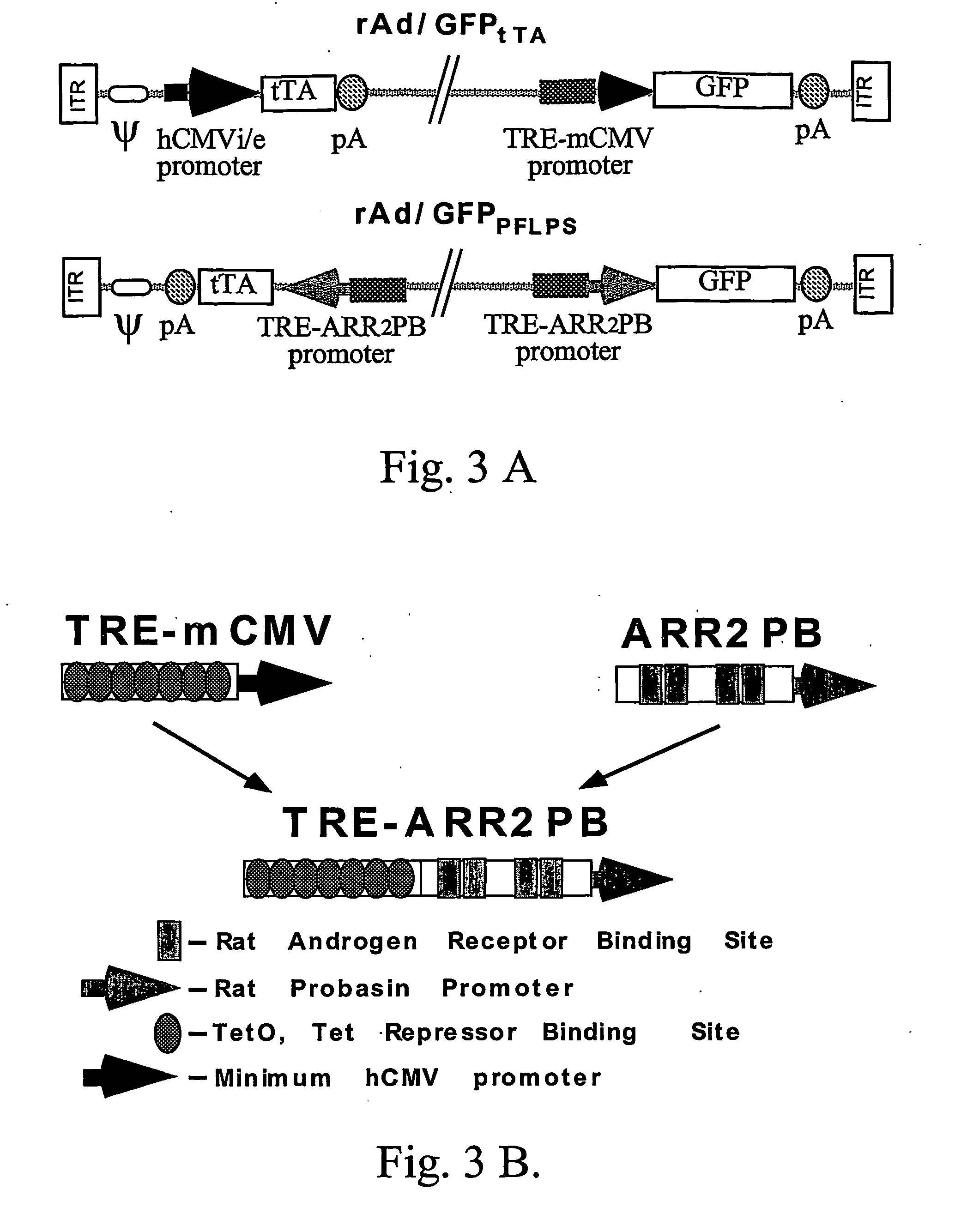
The present invention provides methods for high level, regulated transgene transcription that is restricted to cell populations of specific types. The process is designed to work with any inducible expression regulation systems, adapting them to a tissue-specific expression pattern while simultaneously delivering maximal achievable expression levels. In particular, the invention utilizes hybrid promoters that contain the DNA elements for both cell type-specific and regulated transcription. By placing the gene of the transcriptional activation factor (TAF) under the control of this tissue-specific / drug-regulated (TSDR) promoter, this invention achieves high expression levels of TAF in specific target cells by first initiating TAF expression using cell-type specific transcription elements, and subsequently amplifying transcriptional activity by establishing an autoregulatory positive feedback loop. In non-target cells, cell type-specific elements of the TSDR promoter will be inactive, the TAF expression will not be initiated, and auto-upregulation will not occur. For cell type-specific promoters with leaky low-level activity in non-target cells, a variation of this system has been developed which combines autologous upregulation of TAF with the expression of cross-competing transcriptional silencers (TSi) to achieve a type of eukaryotic “genetic switch”—either shutting off transgene and TAF expression completely or promoting maximal expression levels, depending on the original activity level of the specific promoter in that particular cell.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Tea tree CsANS promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN105543226AWith structureFunctionalOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic sequencingHeterologous
The invention provides a tea tree CsANS promoter and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tea tree CsANS promoter is shown in the SEQ ID No.1. The tea tree CsANS promoter is provided with a basic transcription component of a common promoter and conforms to the characteristics of a eucaryon gene promoter. The promoter can be expressed in a heterogenetic source system (tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana) after driving a reporter gene, and the activity of the promoter is controlled by a plant anthocyanin synthetic route key transcription factor AtPAP. Due to the fact that difficulty exists in tea tree whole genome sequencing and transgenosis, development of tea tree gene promoter cloning and analysis of a gene control mode in a tea tree is quite slow. The promoter of a catechinic acid synthetic route related gene is separated out and identified from a tea tree for the first time, and the tea tree CsANS promoter has the advantages that the promoter can be used for intensively studying CsANS gene transcriptional control and catechinic acid biosynthetic pathways in which the CsANS gene participates and applied to plant genetic engineering and tea tree transgenosis studying.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for excavating difference protein of eucaryotic gene transcriptional regulation group
The invention provides a method for excavating difference protein of a eucaryotic gene transcriptional regulation group. The method comprises the steps of: combining 5' or 3'-end promoter sequence with biotin with a magnetic bead of which the surface absorbs streptavidin to form magnetic bead-promoter binary complex, then extracting nucleoprotein at a specific period from a tissue or a cell, combining with the magnetic bead-promoter binary complex to form a magnetic bead-promoter-nucleoprotein ternary compound; carrying out SDS-PAGE analysis on the ternary compound; finding out a difference band to determine fragment length of target protein to be selected, then carrying out two-dimensional electrophoresis separation to purify the target protein, and carrying out mass spectrometry on the purified target protein so as to determine the contained protein. A new thought is provided for researching adjustment of gene expression from the transcriptional level, searching new protein and understanding the action on transcription regulation, and the foundation is established for further clarifying pathogenesis of certain diseases and gene treatment.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Wheat 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (TaHMGR) gene, isolation and cloning method thereof, site-specific mutagenesis method thereof and enzyme function detection method thereof
ActiveCN105112430AHigh catalytic activityIncrease or decrease catalytic activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and relates to an isolation and cloning, gene site-specific mutagenesis, zymoprotein prokaryotic expression, zymoprotein separation and purification, and enzymatic activity detection technology for a first key enzyme gene participating in isoprenoid substance synthesis in wheat mevalonic acid metabolic pathways. Important technical reserves are provided for further carrying out gene modification and augmentation, constructing eukaryotic genetic expression vectors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) genes and converting corresponding products, and are particularly provided for obtaining plants with the high commercial value through secondary metabolism, discussing the relationship between overexpression of the HMGR genes in the receiver plants and important economical characters such as secondary metabolism products, the crop grain size and the grain weight, then increasing the crop yield, analyzing the structures of introns, exons and promoters of the HMGR genes, researching the functions of the promoters and developing related molecular markers.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Triticum aestivum Mevalonate kinase gene TaMVK, and separation cloning and enzymatic activity determination method thereof
The invention which belongs to the molecular biological field relates to a technology of key enzymatic gene Triticum aestivum Mevalonate kinase gene TaMVK separation cloning, enzymatic protein prokaryotic expression, enzymatic protein separation purifying, and in vitro detection of the enzymatic activity, wherein the TaMVK is obtained from a Triticum aestivum species Zea mays, and can be synthesized with isoprenoid substances of Triticum aestivum chlorophyll, carotenoid, cytokinin, abscisic acid, gibberellin, dolichol, terpenoids, coenzyme Q, sterol, phytotoxin and the like. An important technological reserve is provided for further constructing an eukaryotic gene expression vector of the Mevalonate kinase gene, converting corresponding crops, especially plants which depend on secondary metabolism to obtain important business values, and discussing relationships of the overexpression of the Mevalonate kinase gene in acceptor plants with important agronomic properties of secondary metabolic products, the grain size, the grain weight, and the like, thereby improving the crop output, dissecting structures of the intron, the exon and the promoter of the Mevalonate kinase gene, researching functions of the promoter, and developing a relevant molecular mark.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Triticum aestivum mevalonate kinase (TaMVK) gene as well as isolation colonizing and enzyme activity measuring method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to technologies for isolation colonizing of a triticum aestivum mevalonate kinase (TaMVK) gene as a key enzyme gene which is obtained from Jinan 13 as a wheat variety and participates in isoprene-like substances such as wheat chlorophyll, carotenoid, cytokinin, abscisic acid, gibberellin, dolichol, terpenoid, coenzyme Q, sterol, phytotoxin and the like as well as prokaryotic expression of enzyme protein, separated purification of the enzyme protein and detection in vitro on the enzyme activity of the TaMVK gene. The invention provides important technical storage for further constructing a eukaryotic gene expression vector of the TaMVK gene and converting the eukaryotic gene expression vector into a corresponding crop, particularly obtaining plants with important commercial value by means of secondary metabolism, discussing the relationships between the overexpression of the TaMVK gene in a receptor plant and important economical characters such as a secondary metabolite, the seed size, the grain weight and the like, further improving the yield of the crops, analyzing the structures of an introne, an exon and a promoter of the TaMVK gene, researching the functions of the promoter and developing a relevant molecular marker.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA sequence regulating eukaryotic gene transcription, and its binding proteins
InactiveCN102618538AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionVirulent characteristicsEucoenogenes
The invention relates to a DNA sequence regulating eukaryotic gene transcription, and its binding proteins. The inventor firstly identifies and separates the non-coding DNA sequence for transcription silencing of a mediated var gene family from Plasmodium falciparum, and its binding proteins actins. The interaction between the DNA sequence and the actins makes the var gene be anchored in a perinuclear heterochromatin zone to lead to gene silencing; and substances adjusting the var gene transcription and then adjusting the virulence of Plasmodium falciparum can be screened based on the new discovery of the invention.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
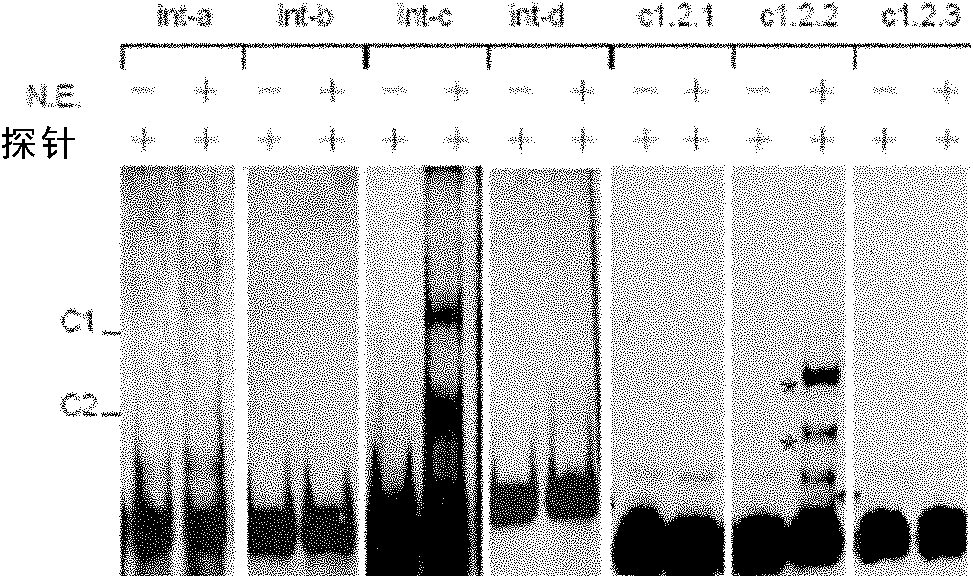
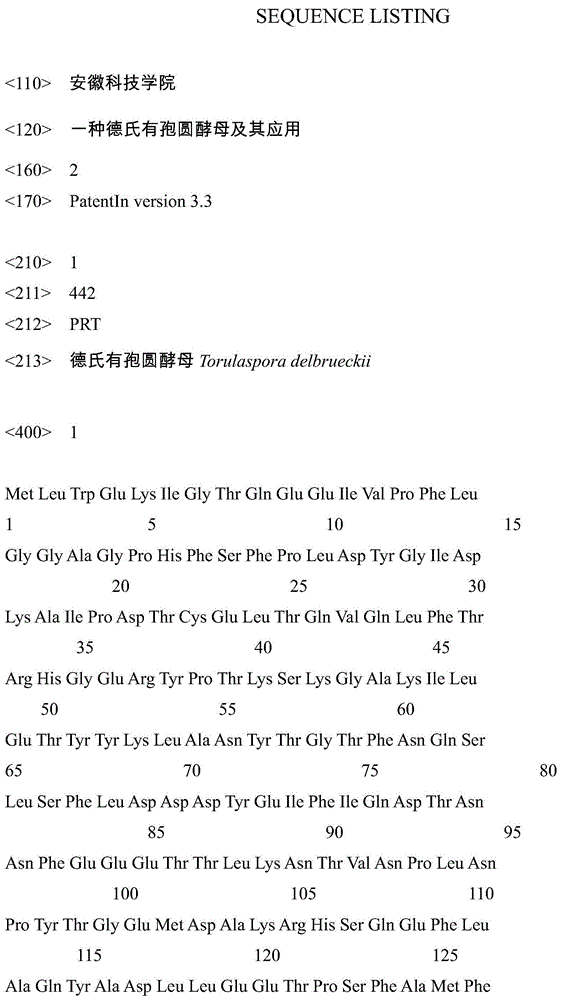
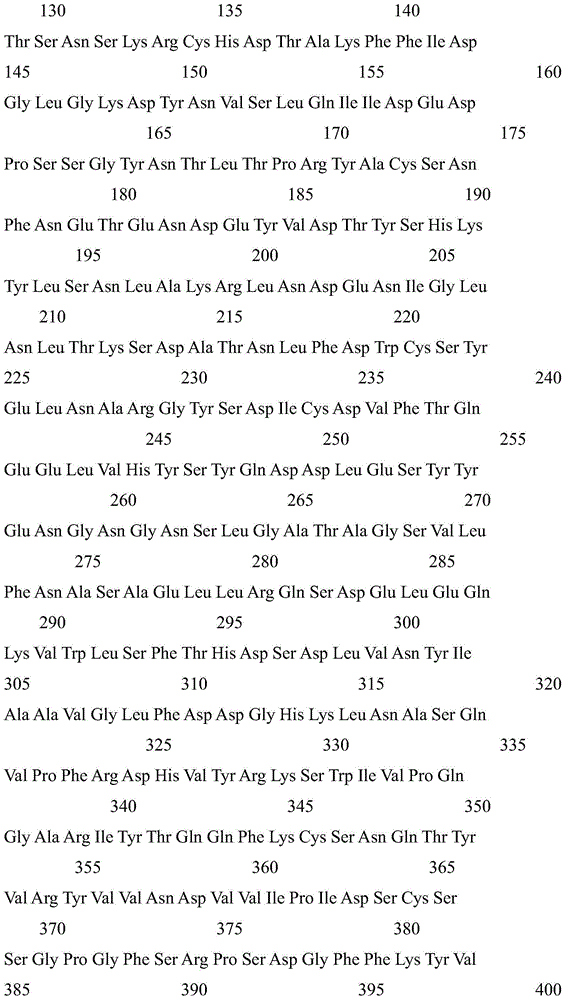
Multi-site mutant strain of phytase gene of Torula delbrueckii and its application
The invention discloses a phytase gene multisite mutant strain of Deshi spore torula yeast and application of the phytase gene multisite mutant strain and relates to the technical field of biology. According to the phytase gene multisite mutant strain disclosed by the invention, the yeast is subjected to ultraviolet mutation to mutate a phytase gene to obtain a high-activity phytase gene mutant strain of which three amino acid sites are mutated; the high-activity phytase gene mutant strain has quite high phytic acid hydrolysis activity in an overall acidic environment and satisfies the requirement of well hydrolyzing phytic acid at a pH condition of a stomach environment. The strain can be used for producing phytase which is used as a feed or a food and can also be used for producing a microbial phosphatic fertilizer and (or) a biological organic phosphatic fertilizer; the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.8738. The mutated phytase gene sequence can be cloned on a pronucleus and (or) eukaryon biological gene expression vector, and a genetic engineering strain and (or) transgenic plants can be built by a genetic engineering technology, so that the phytase gene can be efficiently expressed to produce phytase.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
A kind of Torula delbrueckii and application thereof
The invention discloses Torula delbrueckii and application thereof, and its preservation numbers are CGMCC No.8740 and CGMCC No.8742. The present invention adopts ultraviolet mutagenesis method to carry out mutagenesis to saccharomycete, then screens the mutant strain with high activity phytase under acidic condition, makes the mutant phytase that mutant strain produces can be better under the pH condition of gastric environment. Hydrolyzed phytic acid. The mutant strain can be used to produce feed or edible phytase, and can also be used to produce microbial phosphate fertilizer or biological organic phosphate fertilizer. In addition, the mutated phytase gene sequence can be cloned into prokaryotic or eukaryotic gene expression vectors, and genetically engineered strains or transgenic plants can be constructed by genetic engineering techniques to efficiently express the mutated phytase gene to produce mutated phytase .
Owner:博豪(山东)生物科技开发有限公司
Method for constructing eukaryotic expression vector by virtue of designing multiple cloning sites (MCS)
InactiveCN103060365ASpeed up the processRaise the level of developmentVector-based foreign material introductionEucoenogenesA-DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a method for constructing a eukaryotic expression vector by virtue of designing multiple cloning sites (MCS). The eukaryotic expression vector is obtained by connecting restriction enzyme cutting sites without eukaryotic gene promoters, tanscription termination regulatory sequences, selection marker genes, exogenous target genes and primary skeleton vector sequences together, and then cloning the restriction enzyme cutting sites to an MSC-free primary skeleton vector, and finally using a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) recombinant technology to insert the eukaryotic gene promoters, the tanscription termination regulatory sequences, the selection marker genes and the exogenous target genes into the skeleton vector containing a target restriction enzyme cutting site sequence. The method is flexible and practical, is suitable for the construction of all simple and complete eukaryotic expression vectors, and can be used for overcoming the defect that the inherent restriction enzyme cutting sites on the primary skeleton vector cannot meet requirements; and after the proper restriction enzyme cutting sites are determined, and the subsequent vector construction work is fast and efficient, so that the process of the research on a laboratorial eukaryotic gene function is accelerated.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
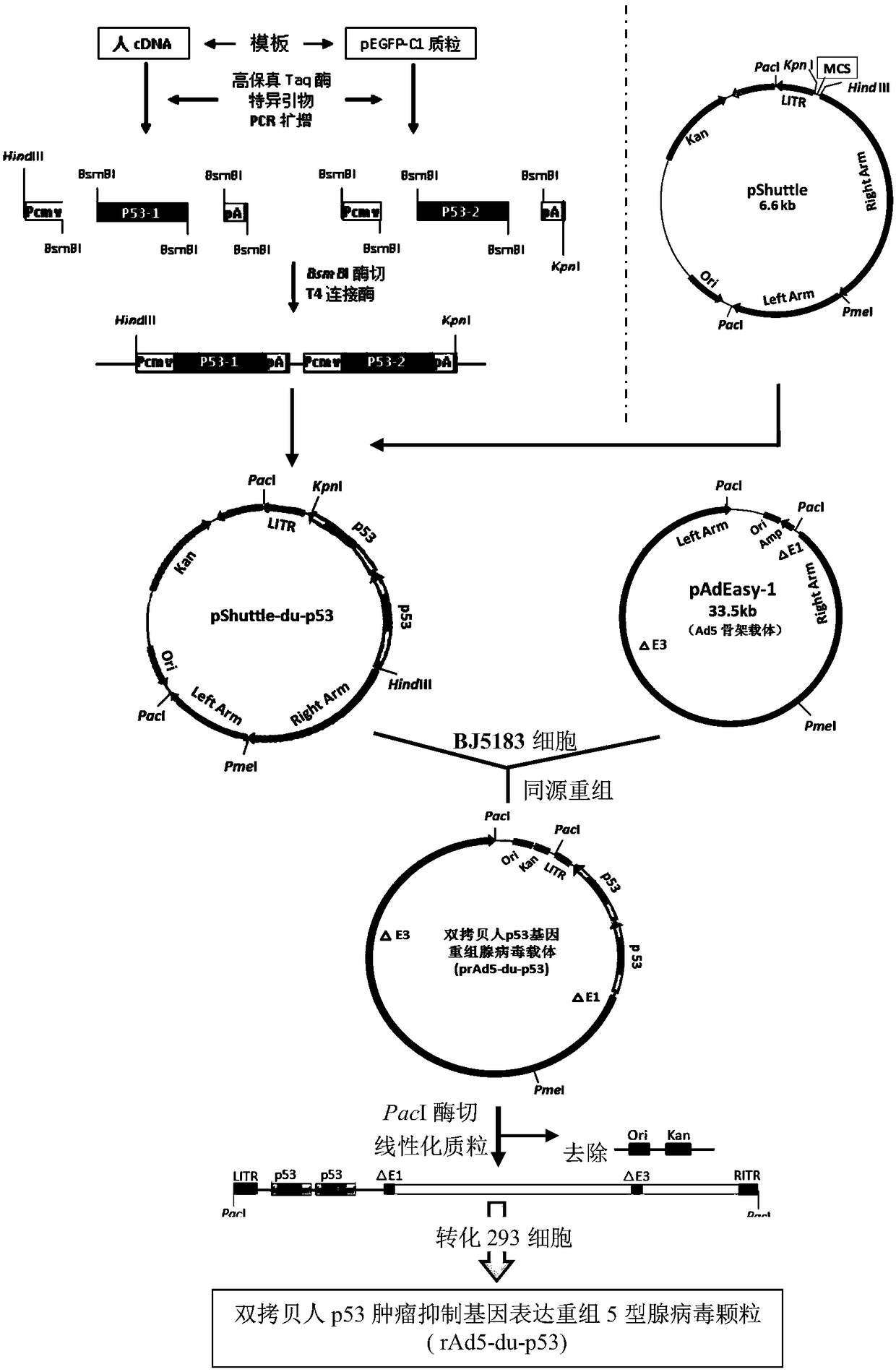
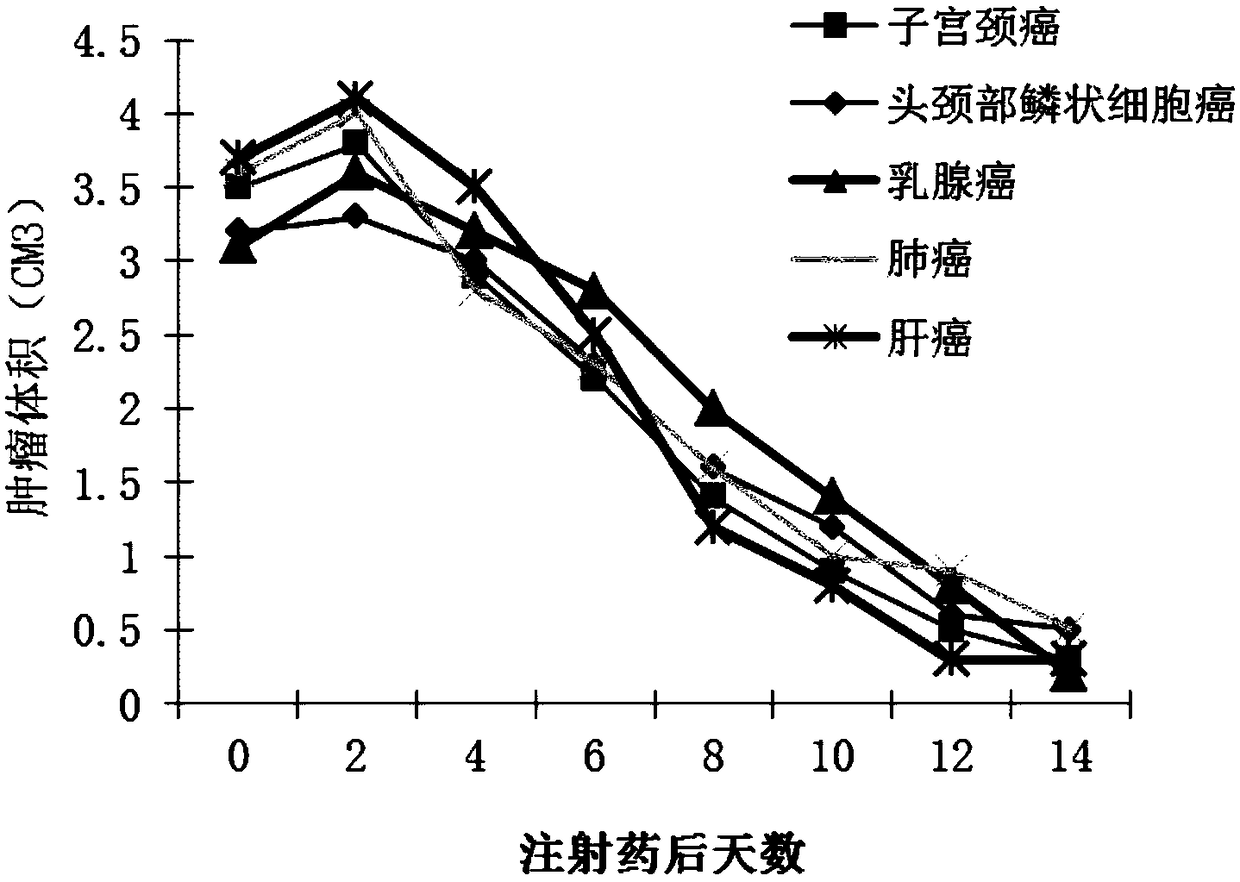
A double-copy human p53 gene recombinant adenovirus and its preparation method
ActiveCN105755043BIncreased expression of functional p53 proteinIncreased and accelerated expression of functional p53 proteinPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationEucoenogenesTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses double-copy human p53 gene recombinant adenovirus and a preparation method thereof. A commercialized 5-type recombinant replication-deficient adenovirus construction system (AdEasy) is inserted into a double-copy human p53 tumor inhibition gene eukaryotic expression box as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to construct a p53 tumor inhibition gene recombinant adenovirus expression carrier system, and recombinant replication-deficient adenovirus granules for expressing double-copy human p53 tumor inhibition gene are further obtained. Experiment shows that after being injected by tumor cells, the double-copy human p53 gene recombinant adenovirus can efficiently express p53 tumor inhibition genes carried by the virus. As the double-copy human p53 tumor inhibition gene eukaryotic expression box is integrated, the p53 tumor inhibition gene expression amount can be greatly increased, meanwhile the virus amount can be reduced, and a relatively good gene treatment effect can be achieved. The double-copy human p53 gene recombinant adenovirus is good in specificity and wide in spectrum, directly aims at gene mutation of tumor cells, and can be applied to malignant tumor of various tissue types at the early stage, the middle stage and the late stage.
Owner:SINOSHENG SHENZHEN GENE IND DEV CO LTD
Single primer capable of multi-species molecular marking and marking method thereof
ActiveCN106906289AHigh amplification efficiencyPolymorphism richMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEucoenogenesEukaryotic genome
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院经济作物研究所
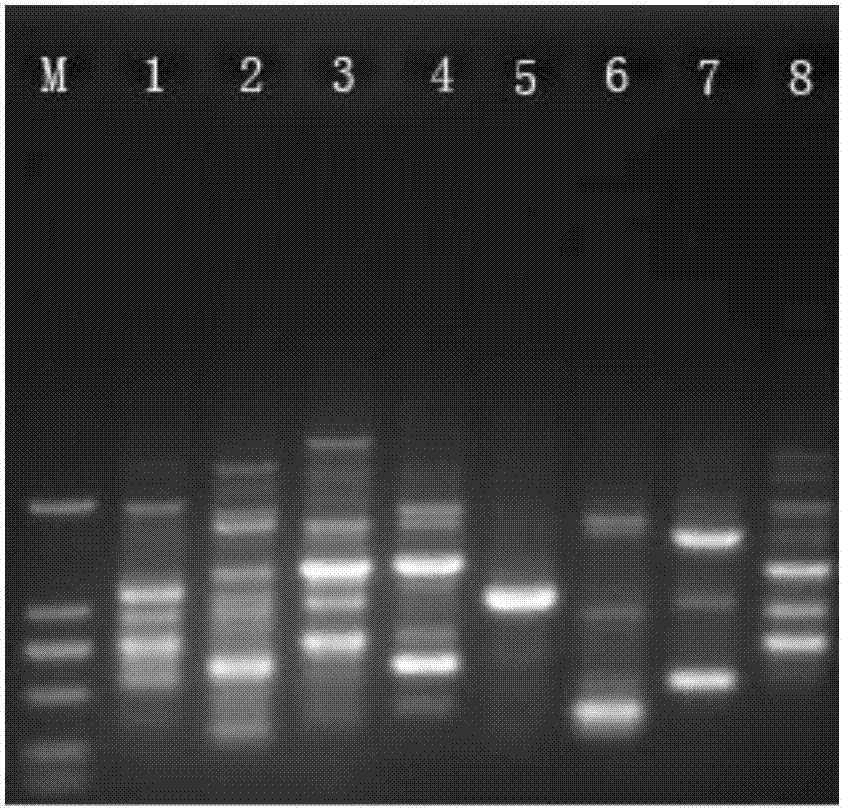
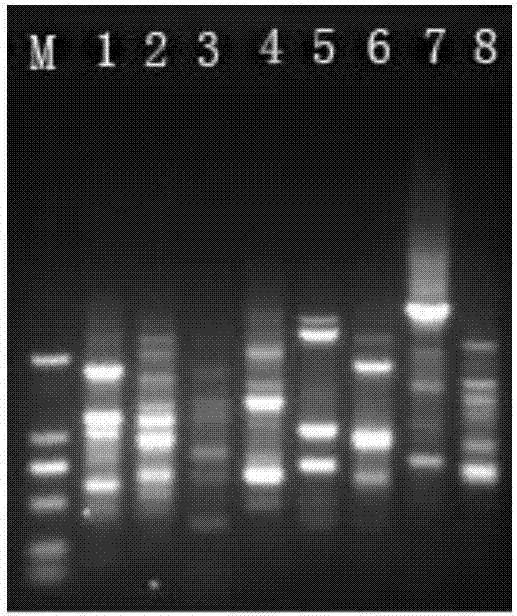
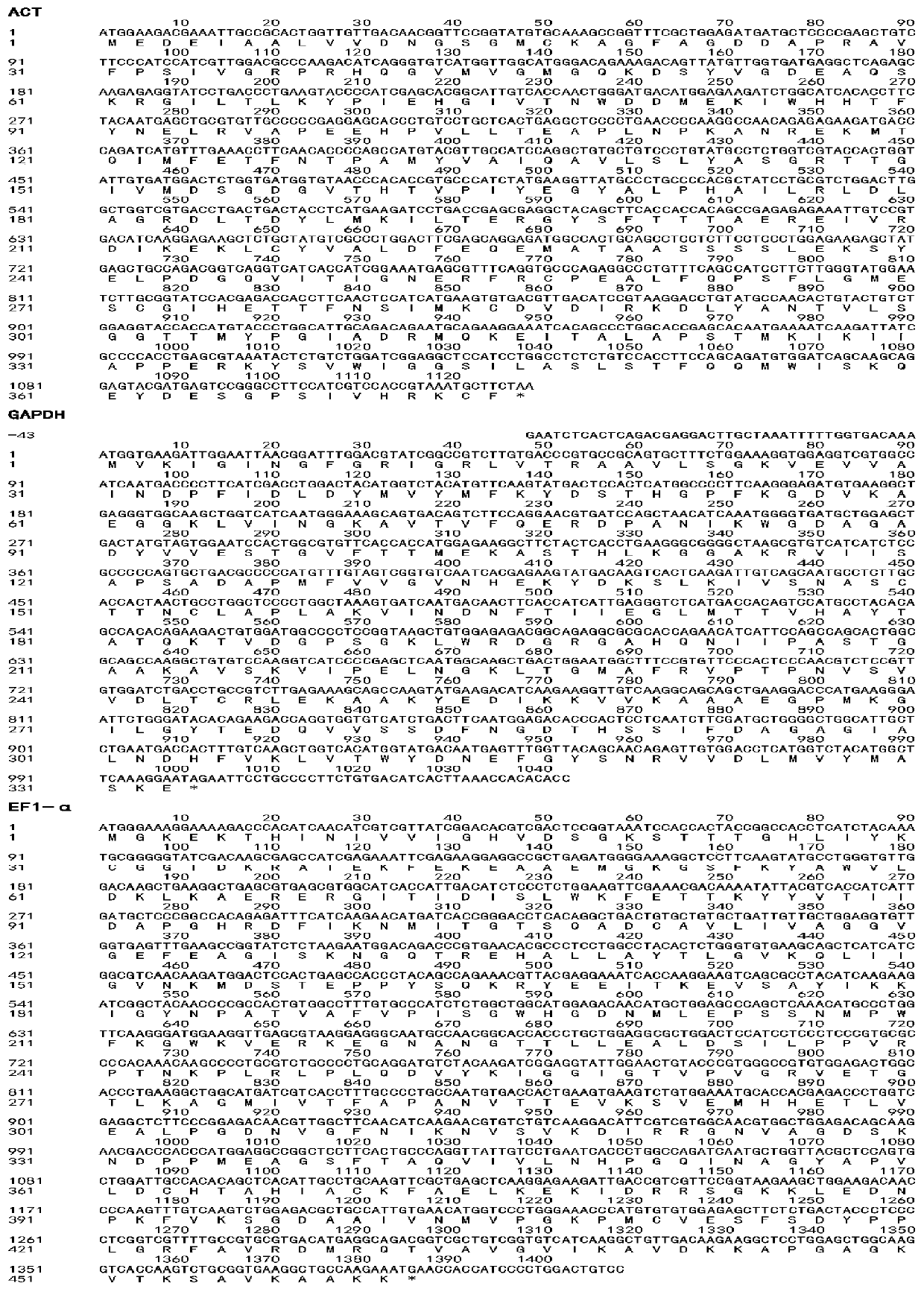
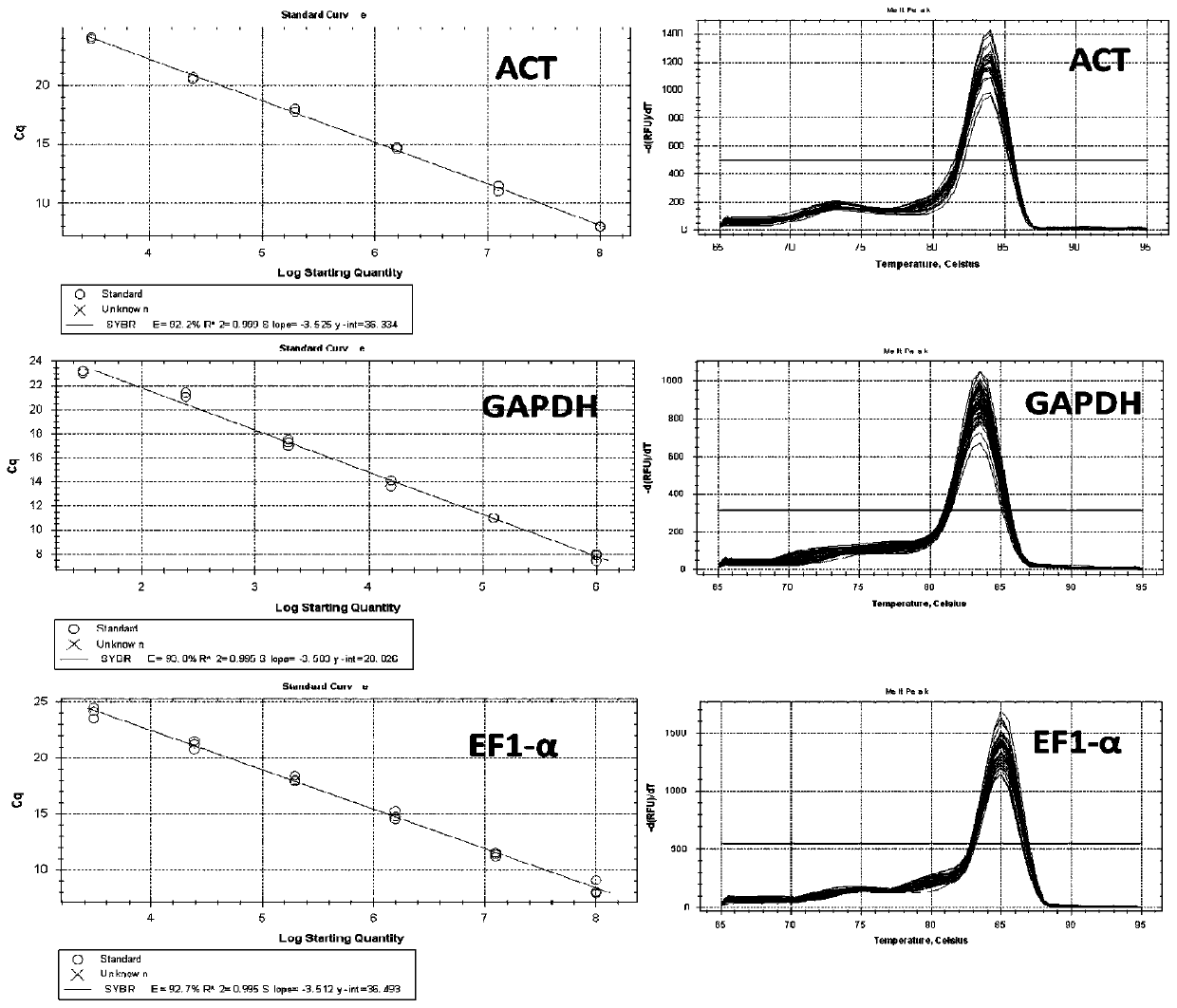
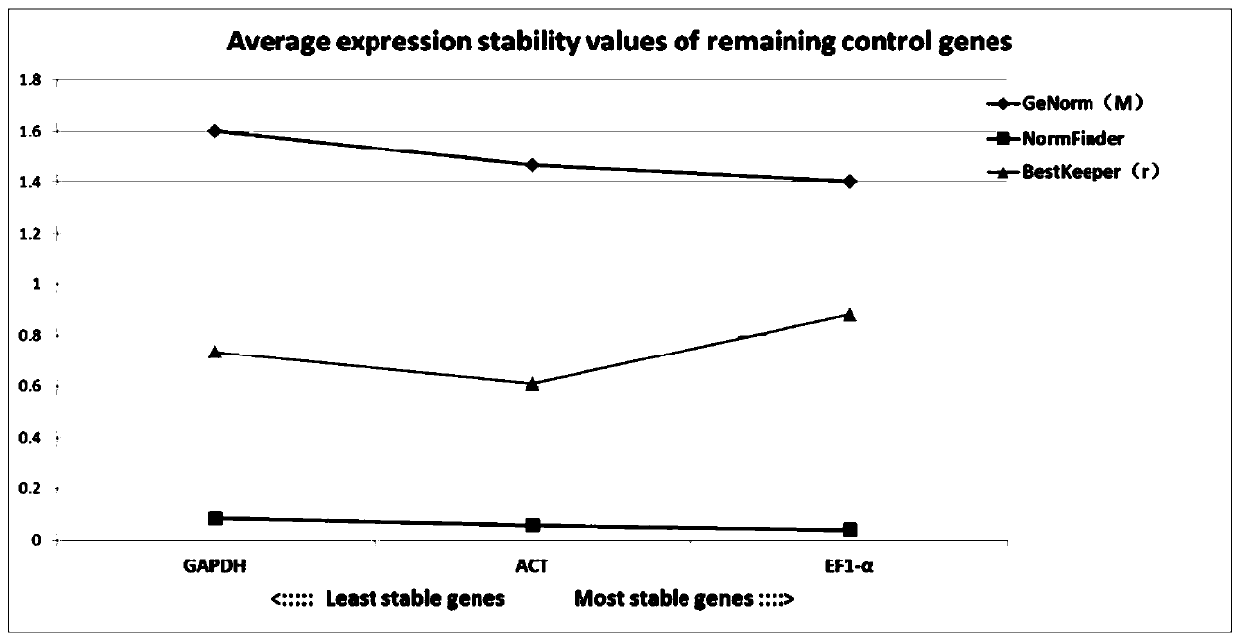
Three internal reference genes of acipenser dabryanus, primer development and stability evaluation technique
InactiveCN110295239AOvercome the defect that only Actin can be usedImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesFluorescence
The invention discloses an accurate and highly efficient transcriptome-based eukaryotic gene identification method. The method includes the following steps that three internal reference genes of acipenser dabryanus are obtained through PCR amplification reaction of a high-fidelity enzyme, real-time fluorescence quantitative primers of the three internal reference genes of the acipenser dabryanus are developed, the quality of the primers of the three internal reference genes of the acipenser dabryanus are evaluated based on a standard curve and a melting curve, and the stability of the three internal reference genes of the acipenser dabryanus in tissue expression is evaluated. According to the accurate and highly efficient transcriptome-based eukaryotic gene identification method, by providing full-length coding regions of the three internal reference genes (ACT, GAPDH and EF1-alpha genes), more internal reference gene choices are provided for fluorescence quantitative research of the acipenser dabryanus; by developing the fluorescence quantitative primers based on nucleotide sequences of ACT, GAPDH and EF1-alpha, the reliability and reproducibility of fluorescence quantitative research are greatly improved; the stability of ACT, GAPDH and EF1-alpha in tissue expression is evaluated, and stable and suitable internal reference genes are provided for the fluorescence quantitativeresearch of the acipenser dabryanus.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A kind of tea tree csans promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN105543226BFunctionalMeet the characteristicsOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousGenomic sequencing
The invention provides a tea tree CsANS promoter and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tea tree CsANS promoter is shown in SEQ ID No.1, which has the basic transcription elements of a general promoter and conforms to the characteristics of eukaryotic gene promoters. The promoter can be expressed in heterologous systems (tobacco and Arabidopsis) after driving the reporter gene, and its activity is regulated by AtPAP, a key transcription factor in the plant anthocyanin synthesis pathway. Due to the great difficulties in tea tree whole genome sequencing and transgenic, the progress of tea tree gene promoter cloning and gene regulation mode analysis in tea tree is very slow. This is the first time that the promoters of genes related to catechin synthesis pathways have been isolated and identified from tea trees. The results of this invention can be used for in-depth research on the transcriptional regulation of CsANS genes and the catechin biosynthesis pathways involved in them, and can be applied to plant genetic engineering and Tea tree transgenic research.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Wheat 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene tahmgr and its isolation and clone, site-directed mutagenesis and detection method of enzyme function
ActiveCN105112430BHigh catalytic activityIncrease or decrease catalytic activityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and relates to an isolation and cloning, gene site-specific mutagenesis, zymoprotein prokaryotic expression, zymoprotein separation and purification, and enzymatic activity detection technology for a first key enzyme gene participating in isoprenoid substance synthesis in wheat mevalonic acid metabolic pathways. Important technical reserves are provided for further carrying out gene modification and augmentation, constructing eukaryotic genetic expression vectors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) genes and converting corresponding products, and are particularly provided for obtaining plants with the high commercial value through secondary metabolism, discussing the relationship between overexpression of the HMGR genes in the receiver plants and important economical characters such as secondary metabolism products, the crop grain size and the grain weight, then increasing the crop yield, analyzing the structures of introns, exons and promoters of the HMGR genes, researching the functions of the promoters and developing related molecular markers.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and helical-structure DNA sequence
ActiveCN103233028BUnable to cutImprove accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA repairEucoenogenes
The invention discloses a specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and a helical-structure DNA sequence, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method comprises the following steps of 1, designing and constructing CRISPR / Cas9 and chimeric RNA, and 2, carrying out Cas9mRNA internal translation so that Cas9 nuclease and the chimeric RNA are bonded, carrying out fixed point clipping so that DNA double-chain cleavage is realized after the clipping, and introducing an exogenous DNA by induction of a natural DNA restoration process which is a non-homologous end bonding process of cells so that cell endogenous gene modification is realized. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method has simple processes, realizes flexible site recognition and has low energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING SYNC BIOTECH
PCR determination method for Chinese medicine or Chinese medicinal crops derived from eukaryote
ActiveCN101265500BSensitive and fast identificationValid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementProcessing typeEucoenogenes
The invention provides a PCR identification method derived from eucaryote for Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials. PCR augmentation is processed on DNA samples to obtain augmentation production according to a species-specific primer, wherein, the species-specific primer is designed according to a SINE sequence of eukaryotic genomes. The DNA samples are extracted from the Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials, in particular from the further processing type Chinese traditional medicine. Species categories of eukaryotic species in the further processing type Chinese traditional medicine are estimated by analyzing the augmentation production, and the truth of the identified samples is further estimated. The PCR identification method is suitable for Chinese traditional medicine and traditional Chinese medicinal materials, is particularly suitable for the processing type Chinese traditional medicine, especially for the Chinese traditional medicine which is with extremely little DNA content and extremely short segment due to the further processing. The identification method has the advantages of simple operation, rapidness and sensitivity, low cost and effective truth identification of the Chinese traditional medicine and the traditional Chinese medicinal materials.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
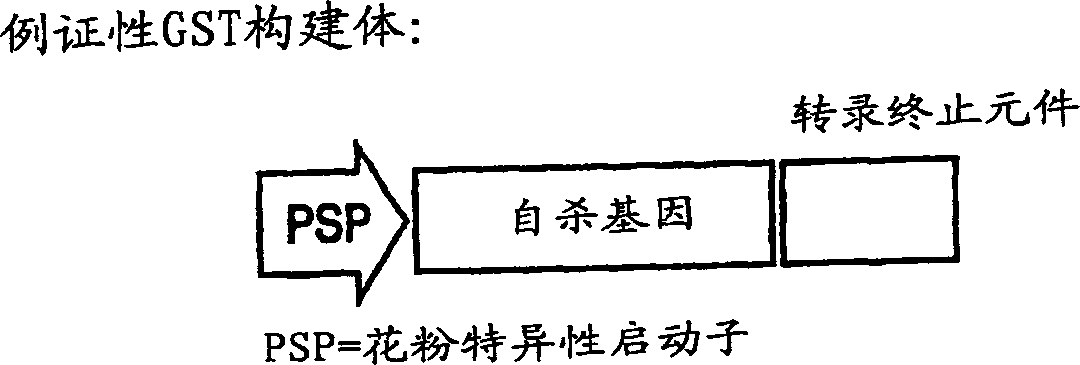
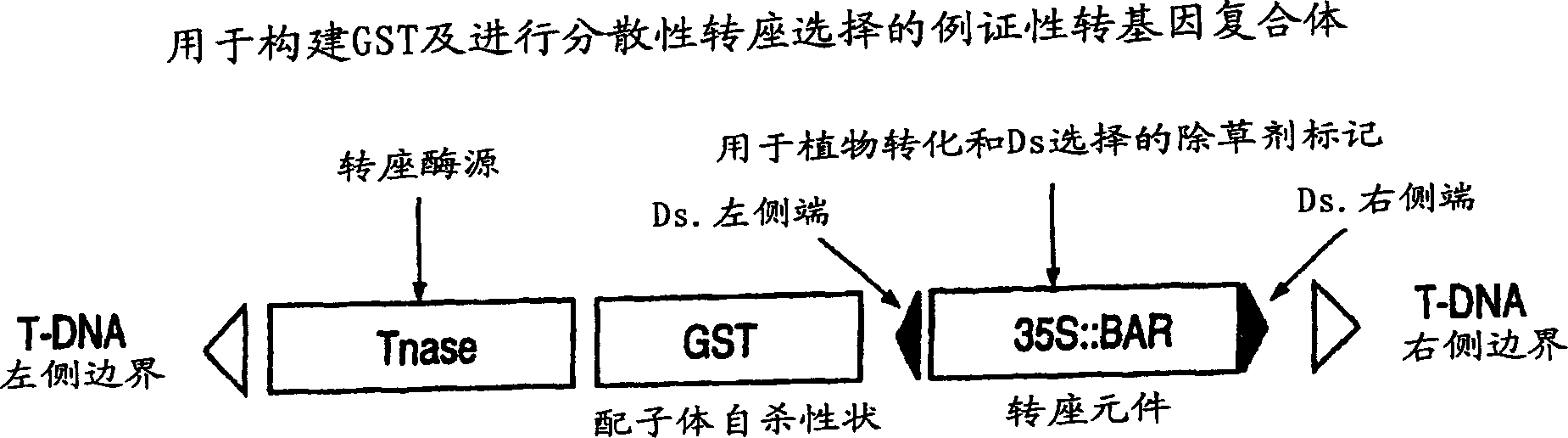
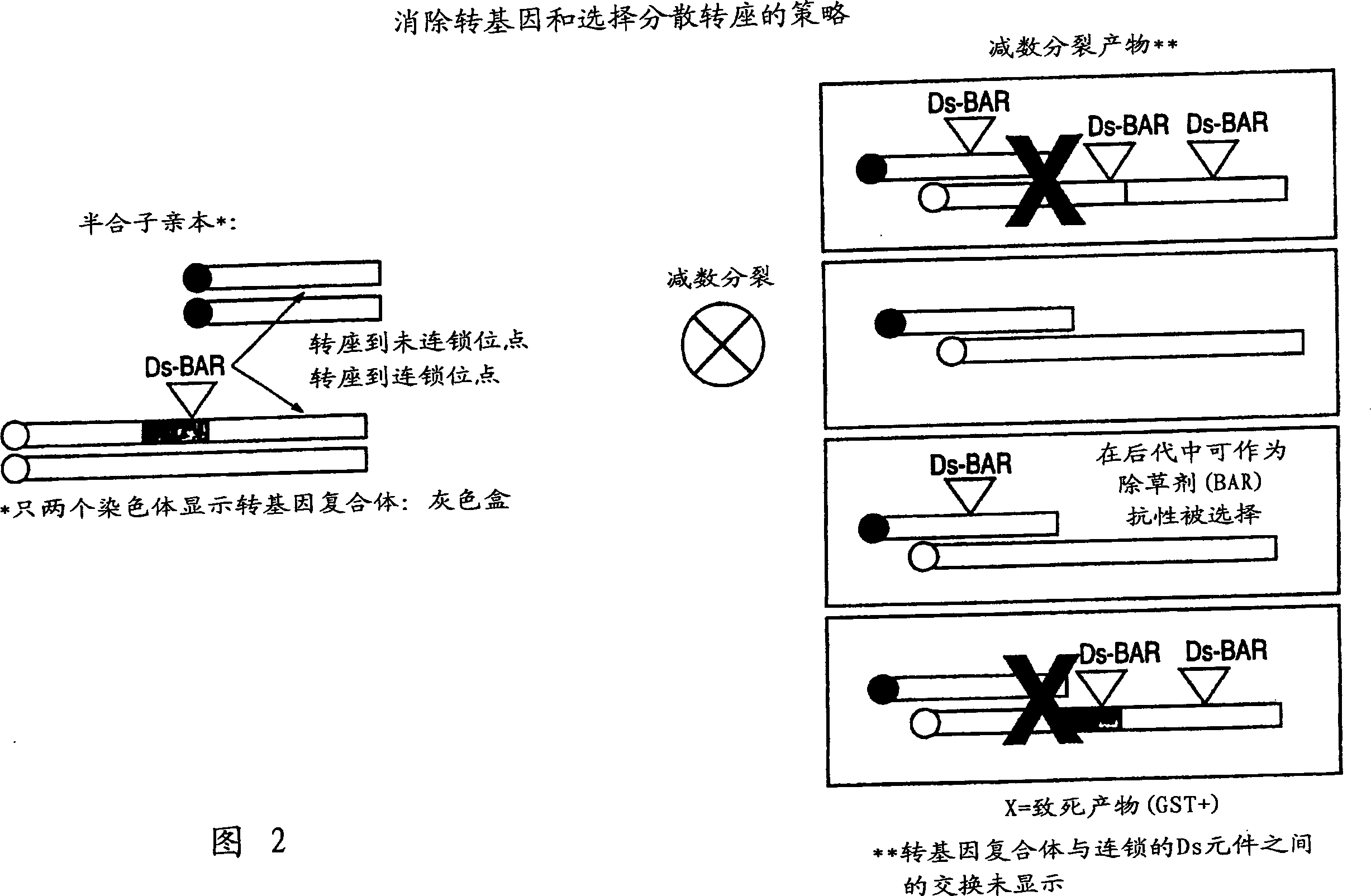
Method and compositions to reduce or eliminate transmission of transgene
Genetic constructs and methods are disclosed for the production, maintenance and control of transgenes in transgenic eukaryotic organisms that undergo meiosis in which pollen or sperm can be outcrossed; this includes: transgenic animals, plant cells, plant tissues and whole plants. More specifically, this invention relates to the control of transgene transmission by male and / or female gametes or gametophytes using a gametophytic sterility trait (GST). The genetic constructs and methodologies of the present invention provide the ability to control the undesired spread of transgenes. In addition, this invention also provides the tools and methodologies to enrich a plant or other eukaryotic genome for dispersed and / or stable transposition events.
Owner:YALE UNIV
A single primer capable of multi-species molecular labeling and its labeling method
ActiveCN106906289BHigh amplification efficiencyPolymorphism richMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyEucoenogenes
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, especially to a single primer capable of multi-species molecular marking and a marking method thereof. The primer is designed according to the AT-rich intron region and regulatory region of a gene in a eukaryotic genome, and primer sequence length is 17 bp. A filling sequence is any sequence rich in GC bases; a core-region sequence is formed by random arrangement of AT bases; a selective base sequence is any base sequence. The primer can be used among eukaryote. Thus, synthesis cost of the primer is reduced, and utilization rate of the primer is greatly raised. Meanwhile, the DNA molecular marking method is based on a PCR reaction, polymorphism begins with intron sequence mutation and insertion / deletion. The method is simple and efficient; polymorphism is high; there are abundant amplified bands; results are reliable; and the bands are easy for separation and sequencing.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院经济作物研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com