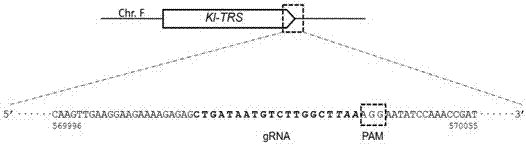
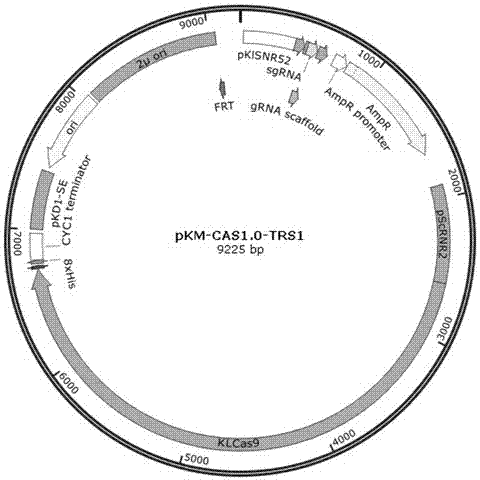
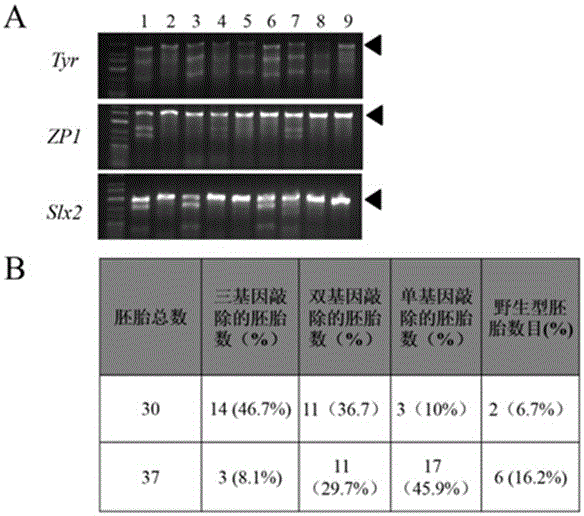
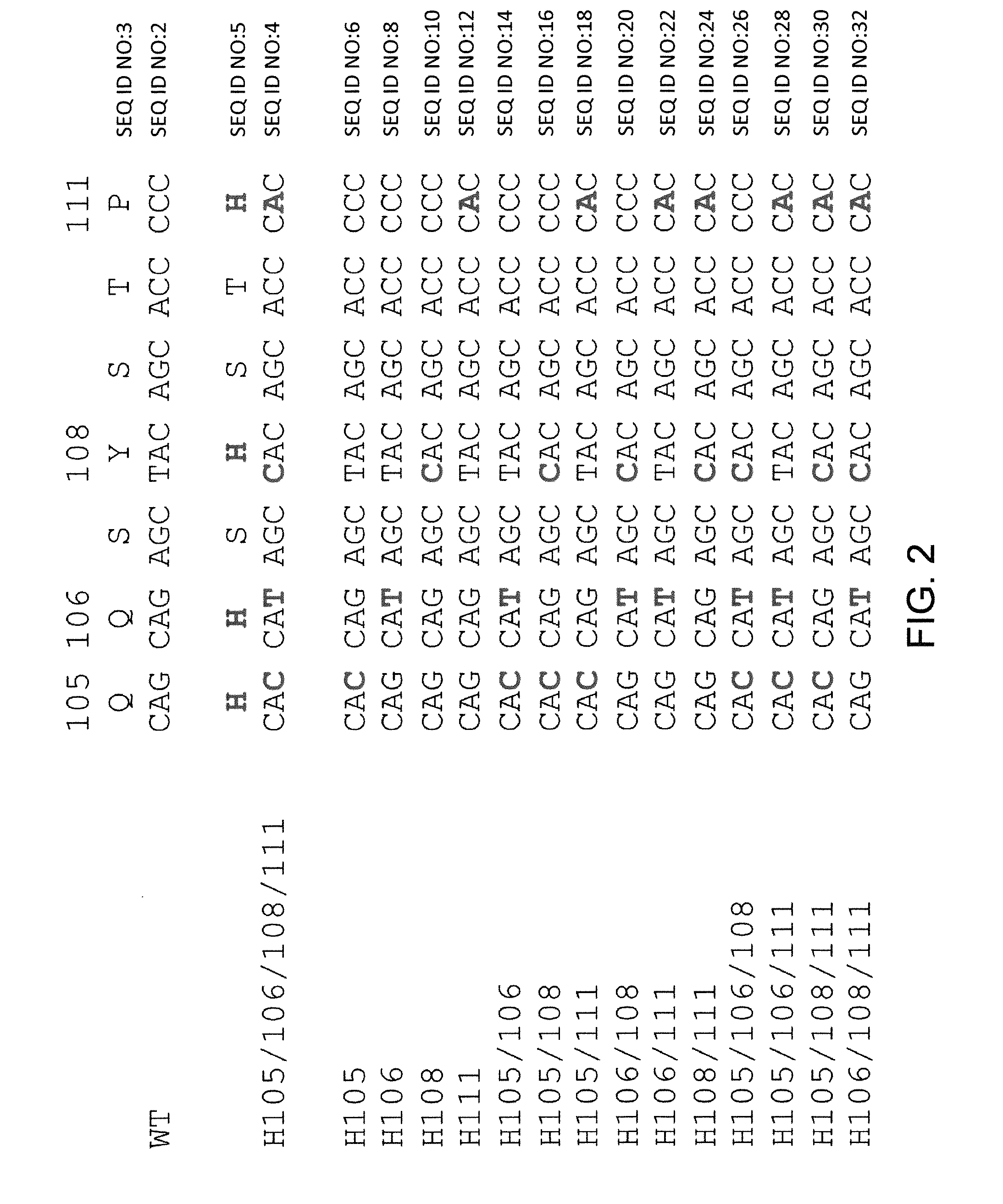
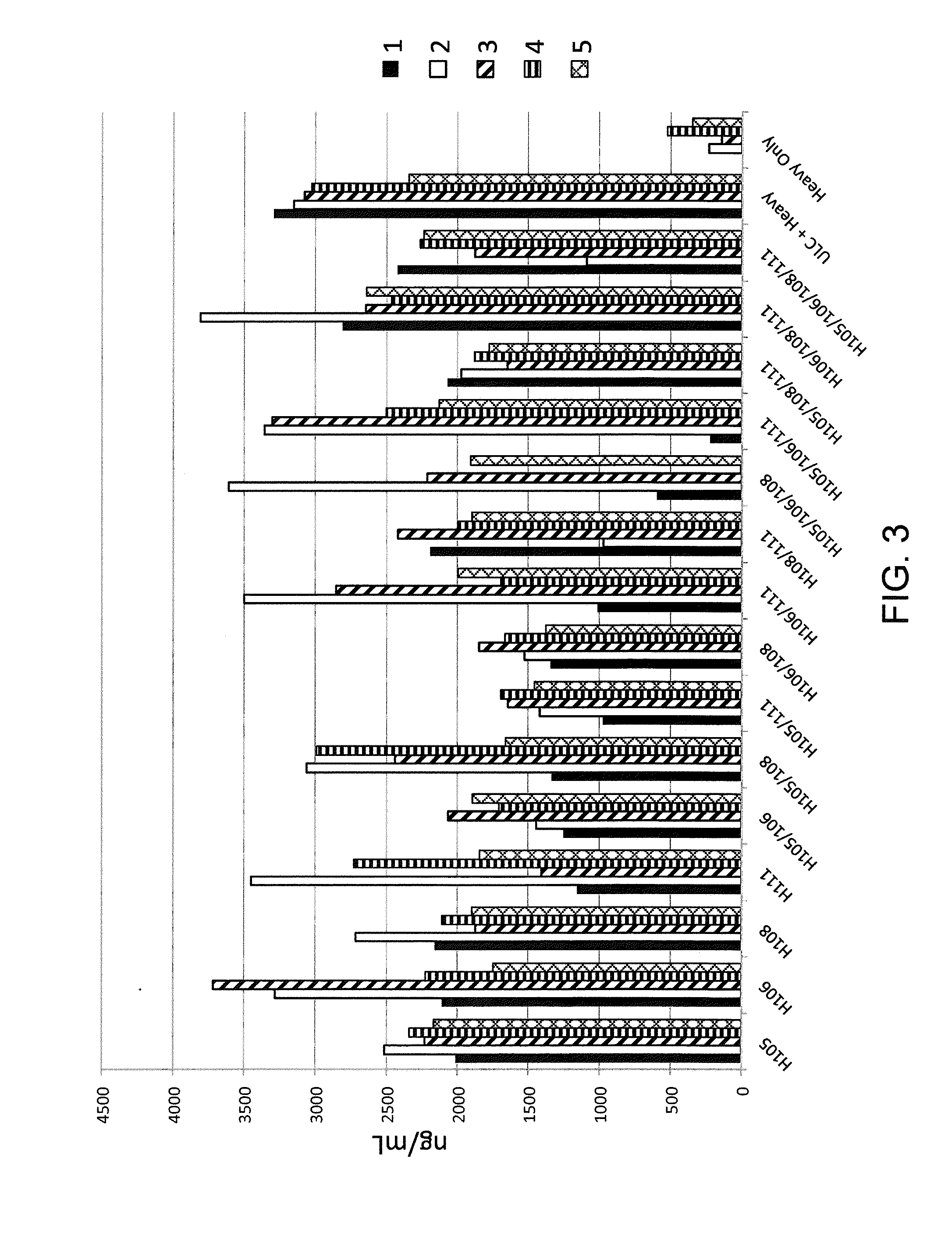
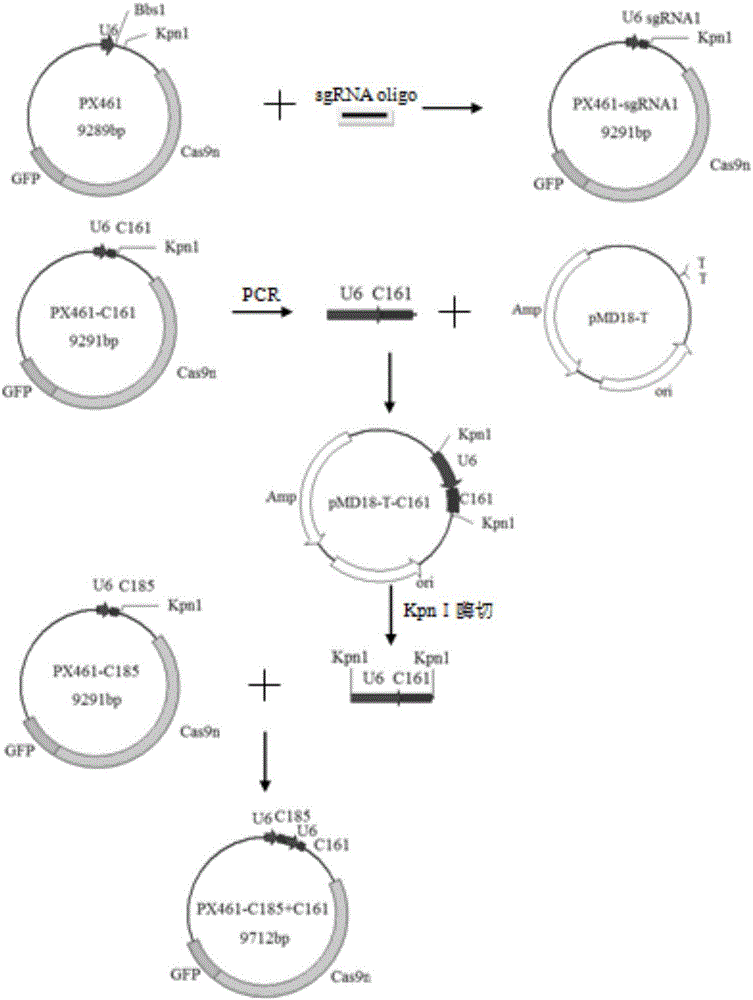
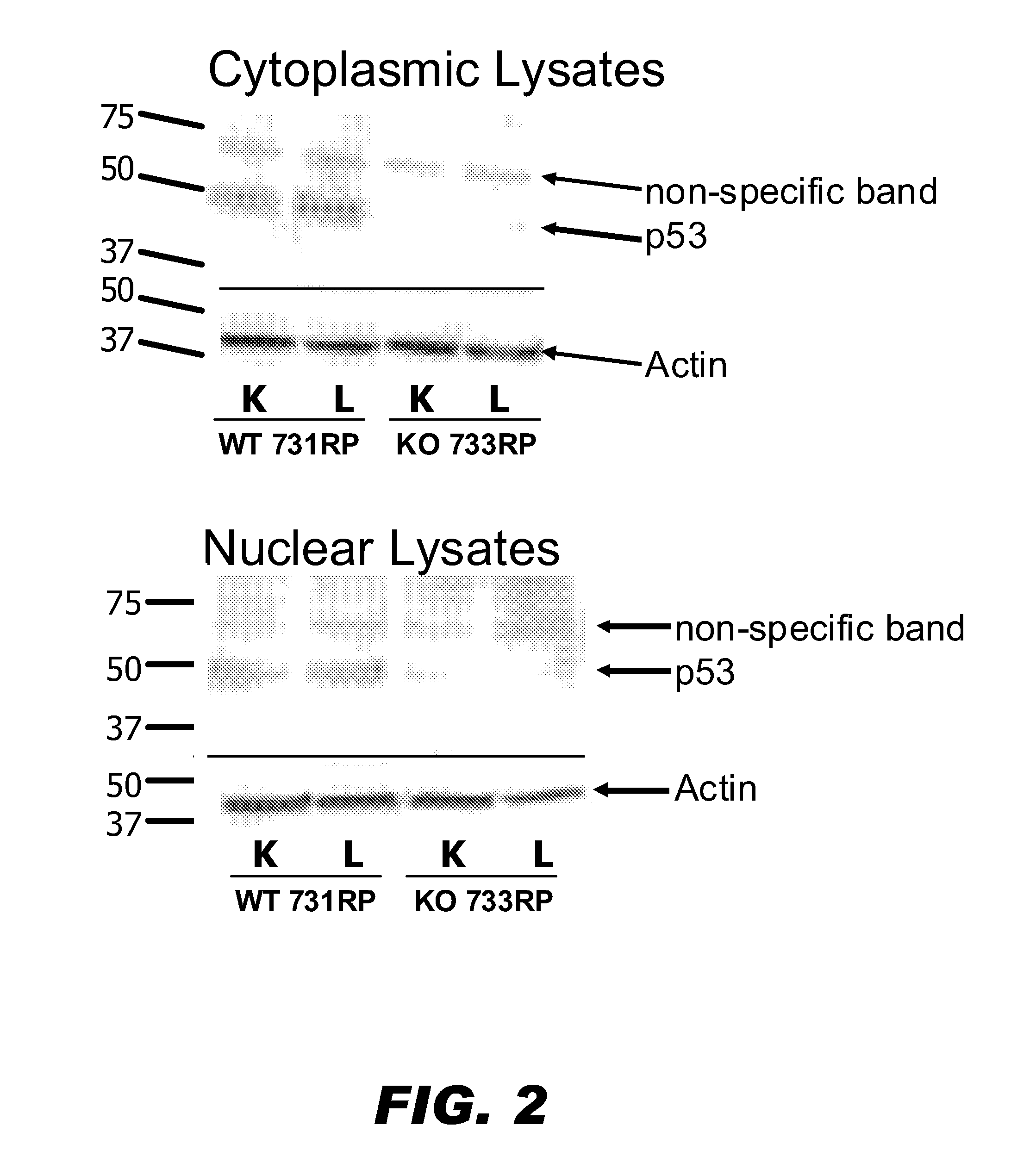
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
724 results about "Gene Modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Germline genetic modification would change the genes in eggs, sperm, or early embryos. Often referred to as “inheritable genetic modification” or “gene editing for reproduction,” these alterations would appear in every cell of the person who developed from that gamete or embryo, and also in all subsequent generations.
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
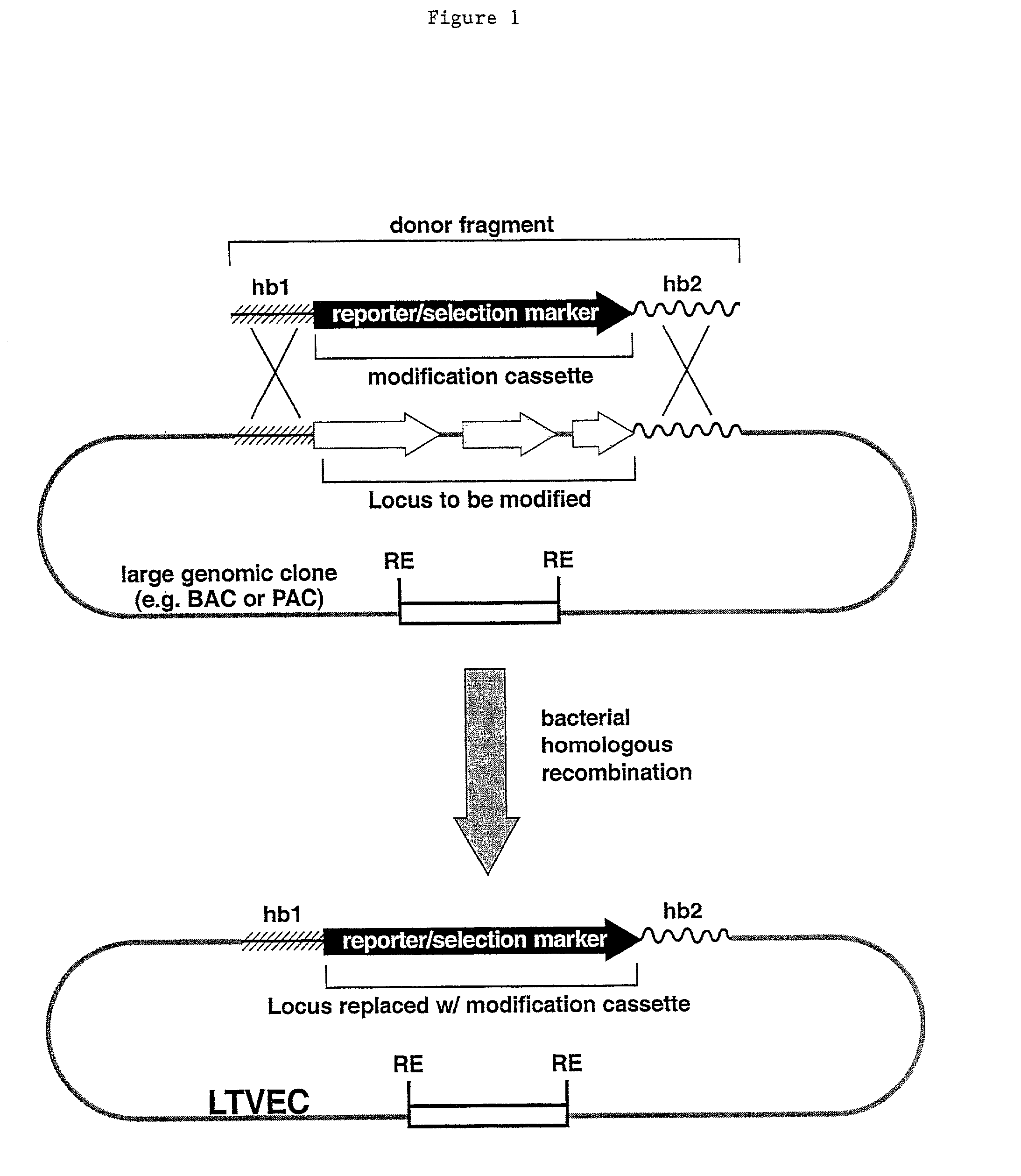
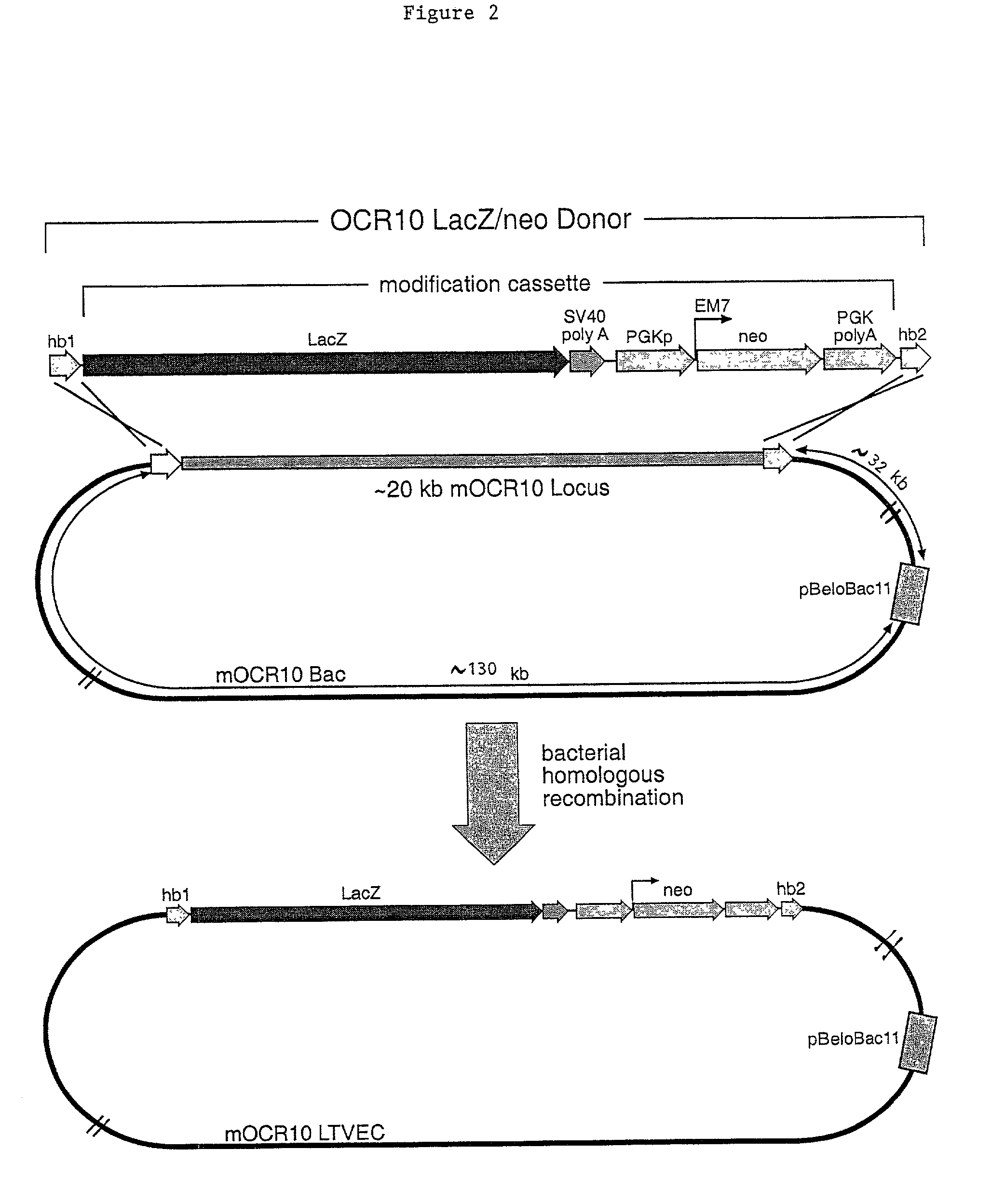
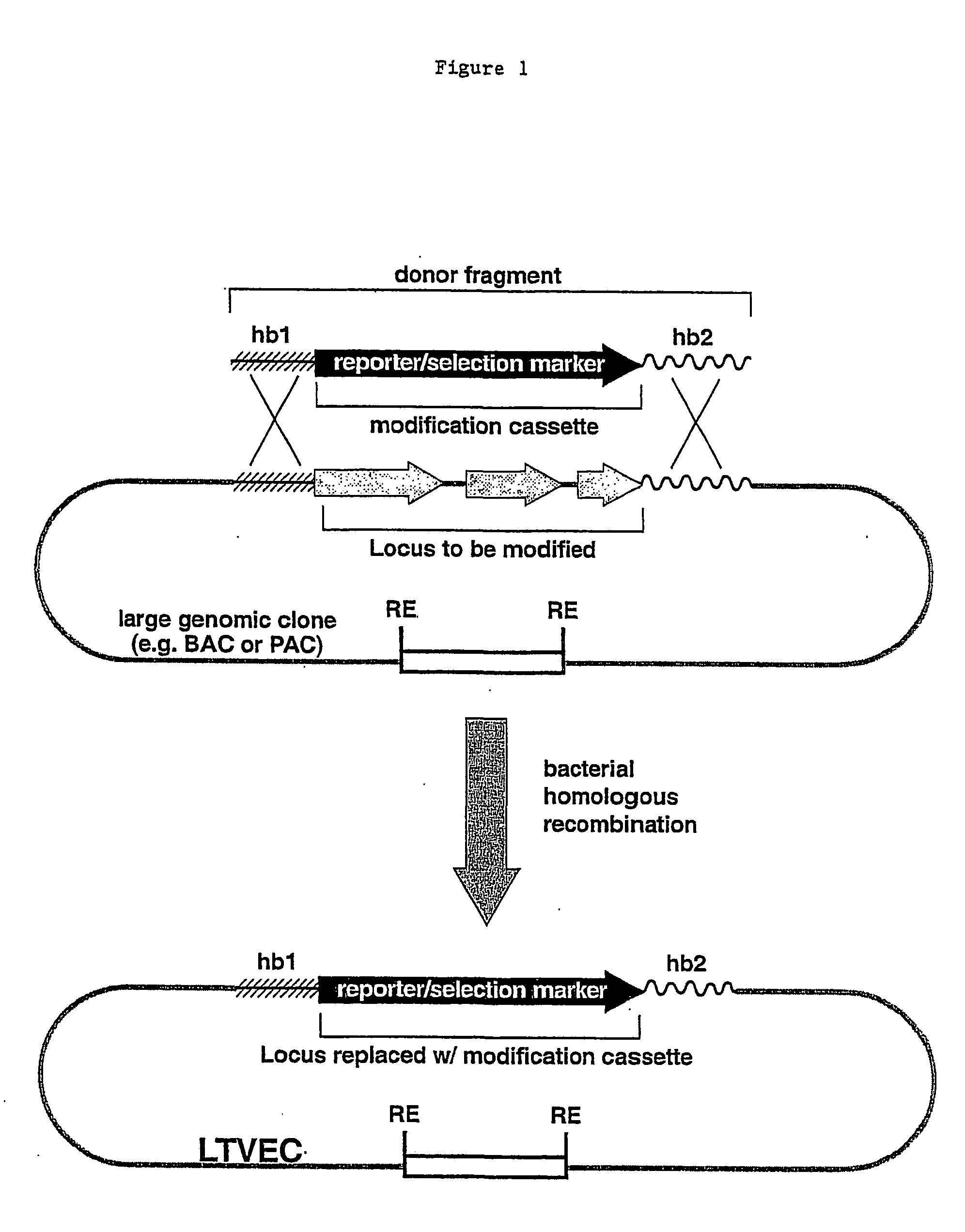
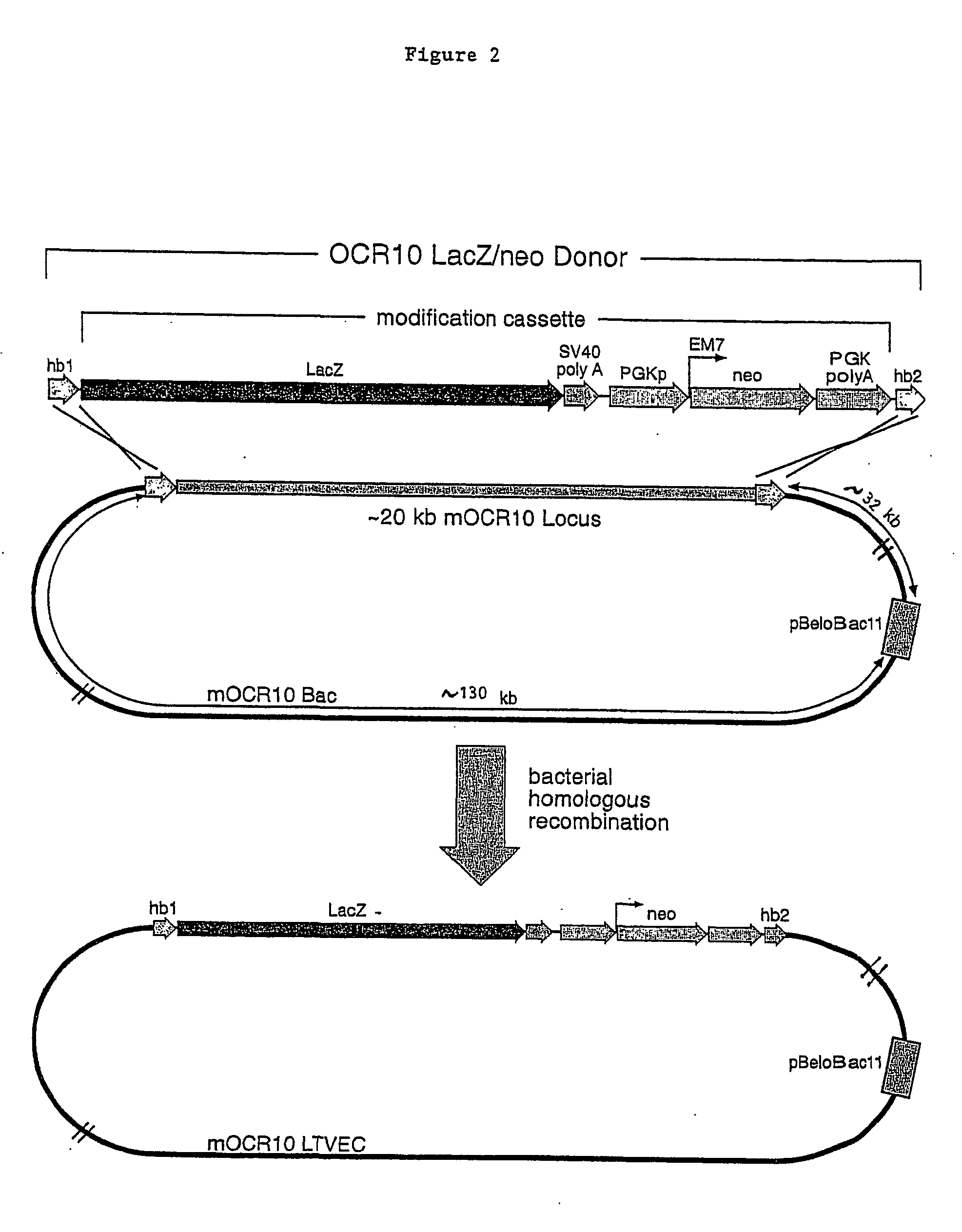
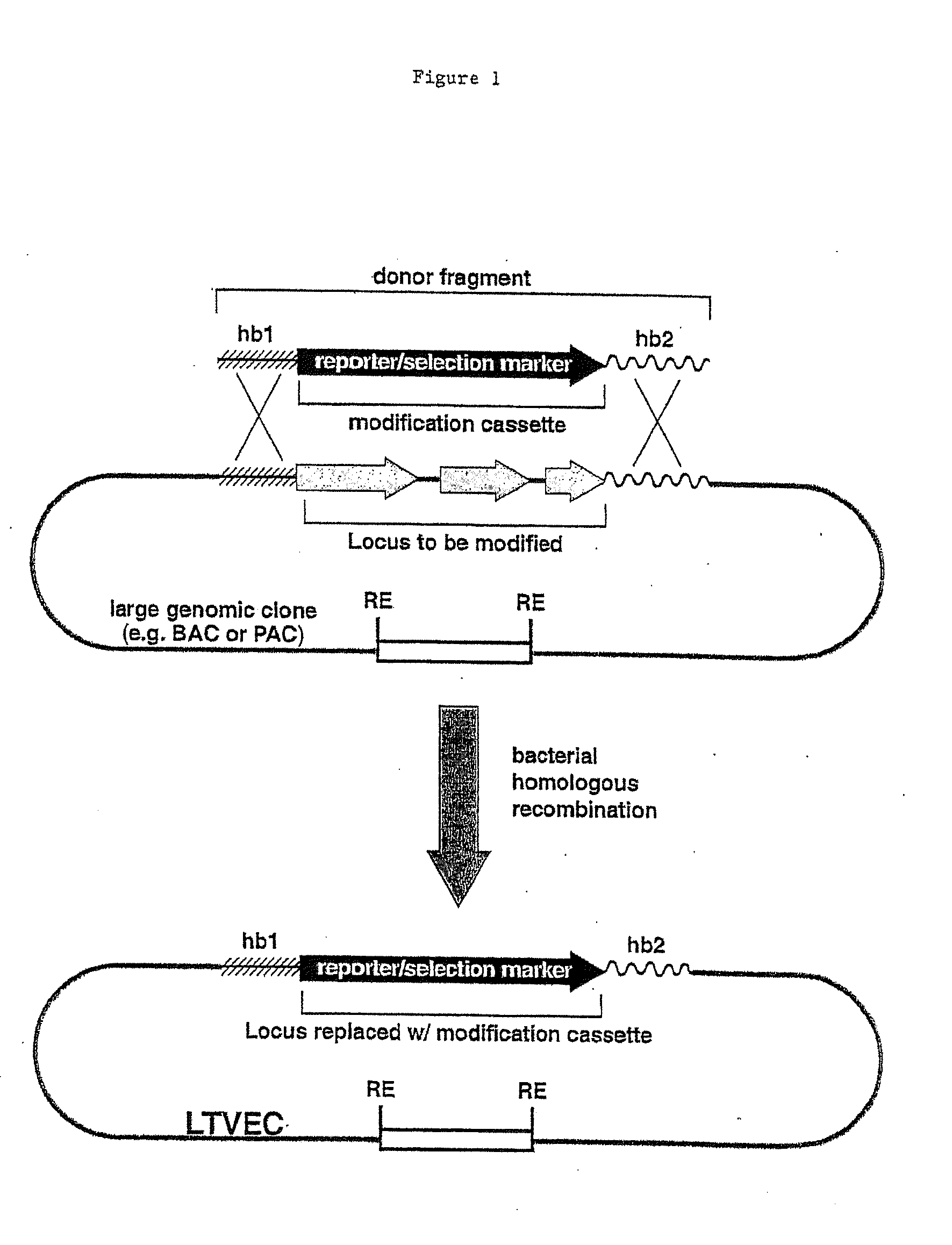
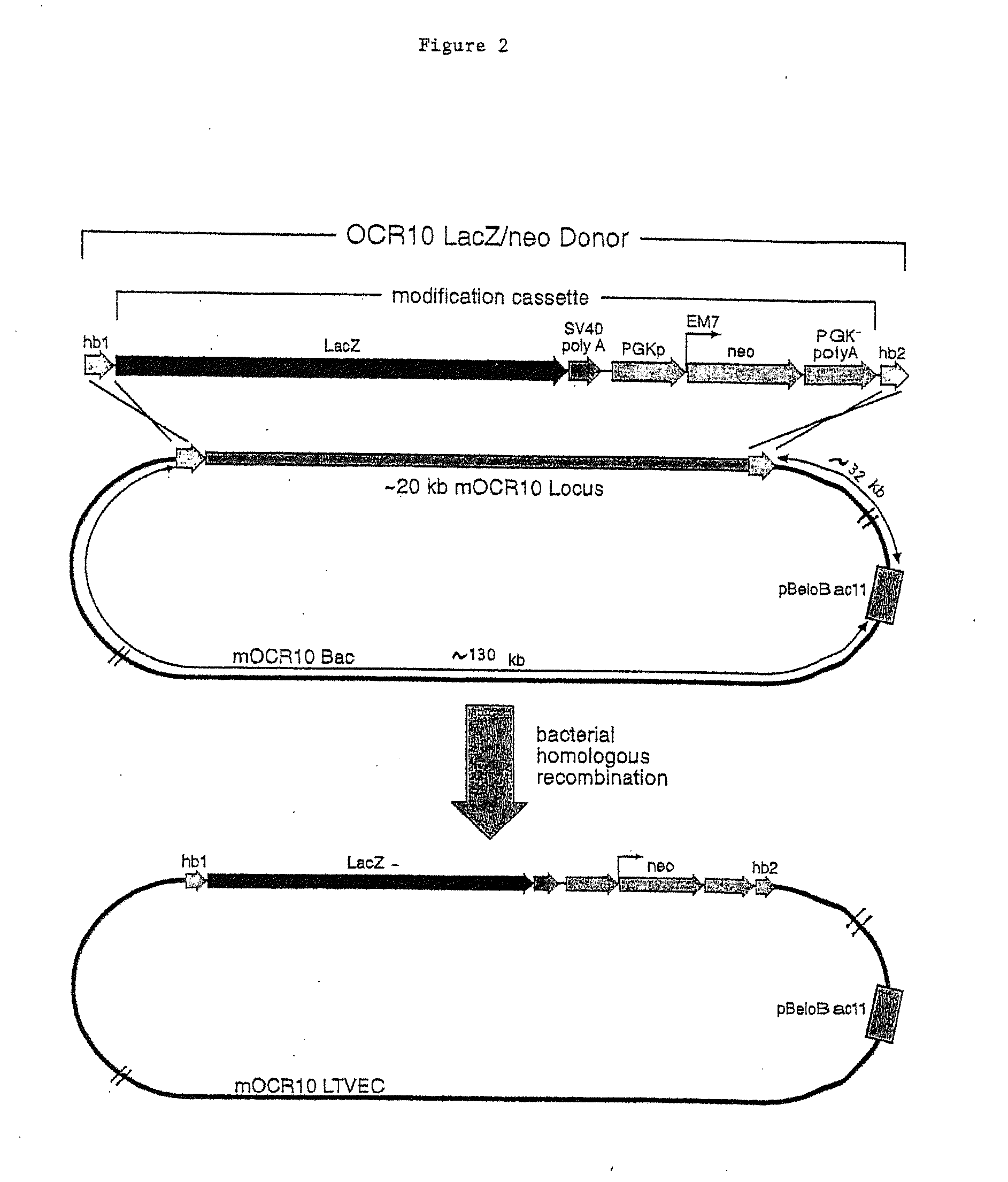
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and helical-structure DNA sequence
ActiveCN103233028AUnable to cutImprove accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA repairEucoenogenes
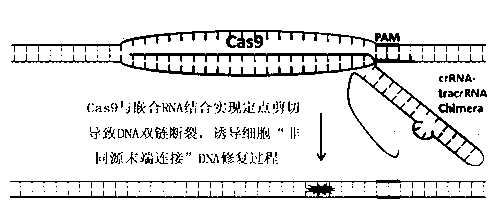
The invention discloses a specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and a helical-structure DNA sequence, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method comprises the following steps of 1, designing and constructing CRISPR / Cas9 and chimeric RNA, and 2, carrying out Cas9mRNA internal translation so that Cas9 nuclease and the chimeric RNA are bonded, carrying out fixed point clipping so that DNA double-chain cleavage is realized after the clipping, and introducing an exogenous DNA by induction of a natural DNA restoration process which is a non-homologous end bonding process of cells so that cell endogenous gene modification is realized. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method has simple processes, realizes flexible site recognition and has low energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING SYNC BIOTECH
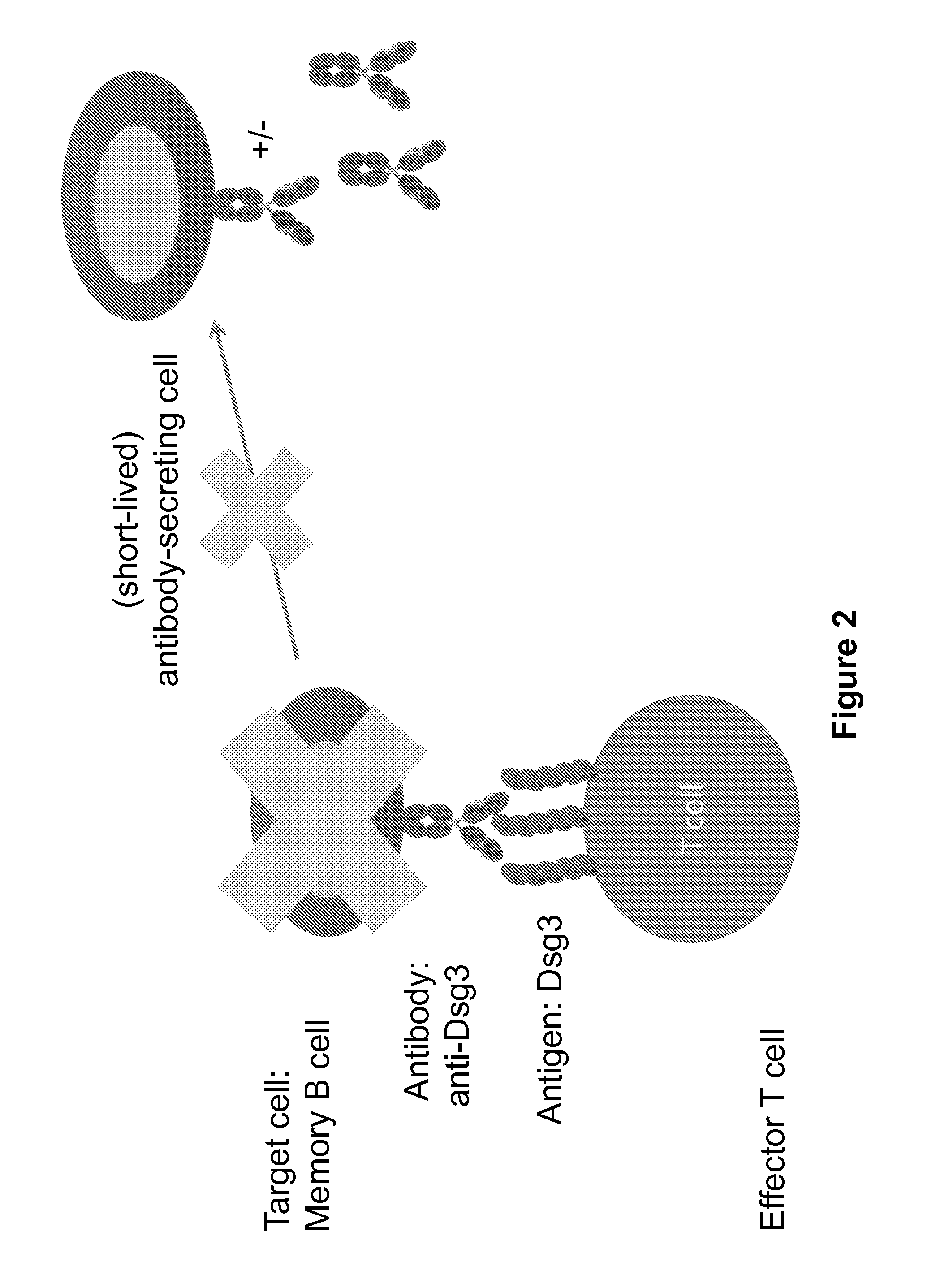
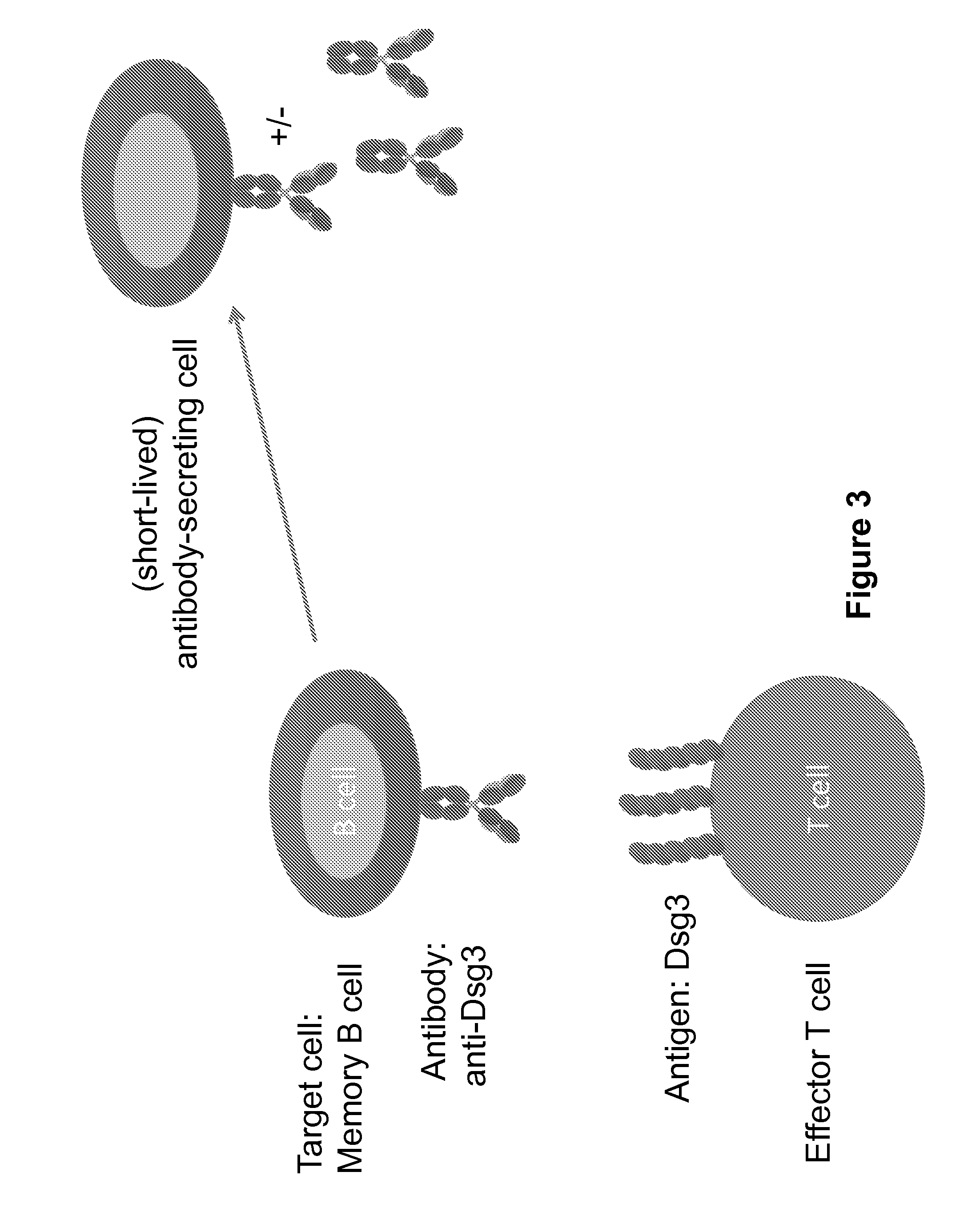
Compositions and methods of chimeric autoantibody receptor t cells
ActiveUS20170051035A1Low toxicityHigh affinityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyDesmoyokinAntibody receptor
The invention includes compositions comprising at least one chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) specific for an autoantibody, vectors comprising the same, compositions comprising CAAR vectors packaged in viral particles, and recombinant T cells comprising the CAAR. The invention also includes methods of making a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAAR (CAART) wherein the expressed CAAR comprises a desmoglein extracellular domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
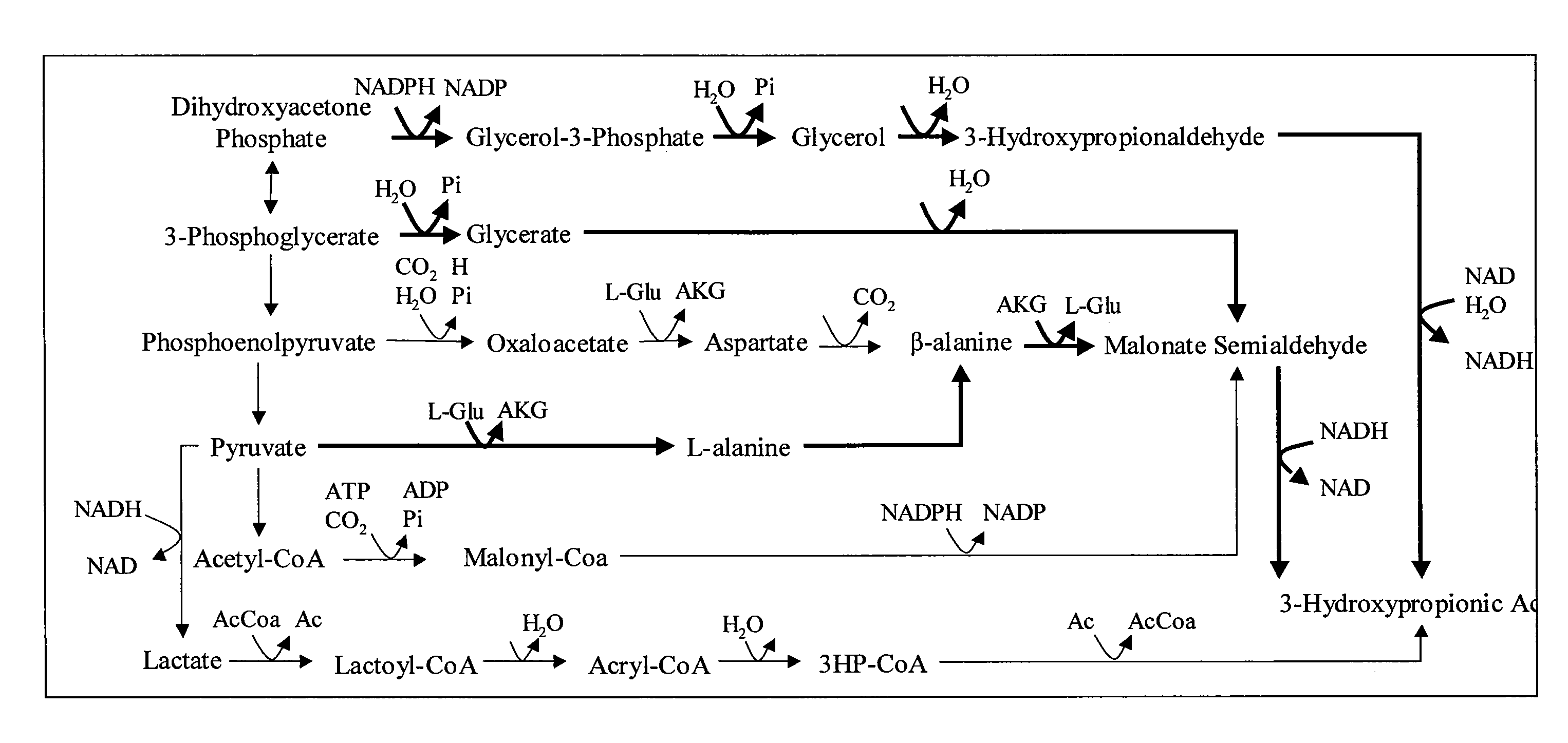
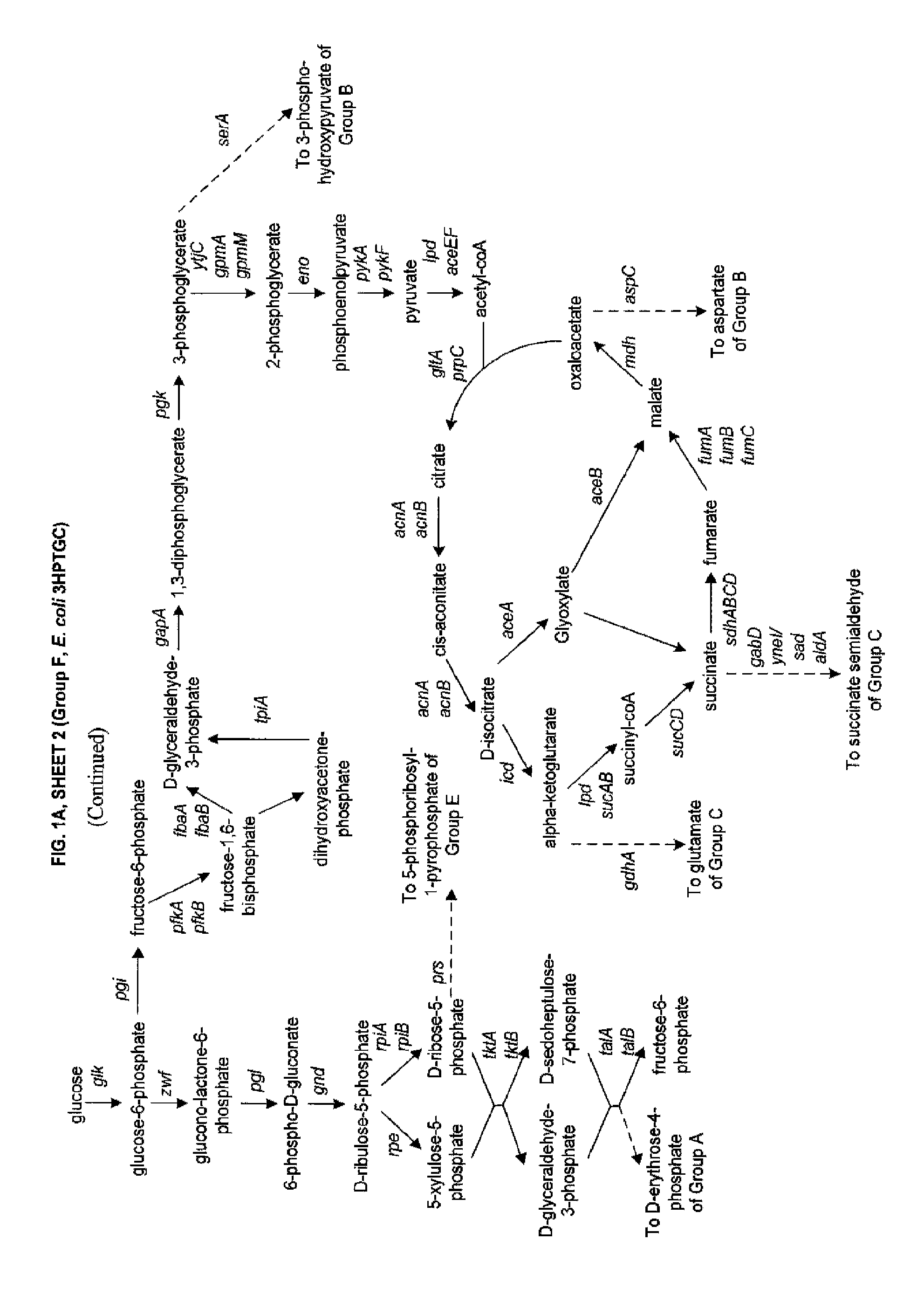
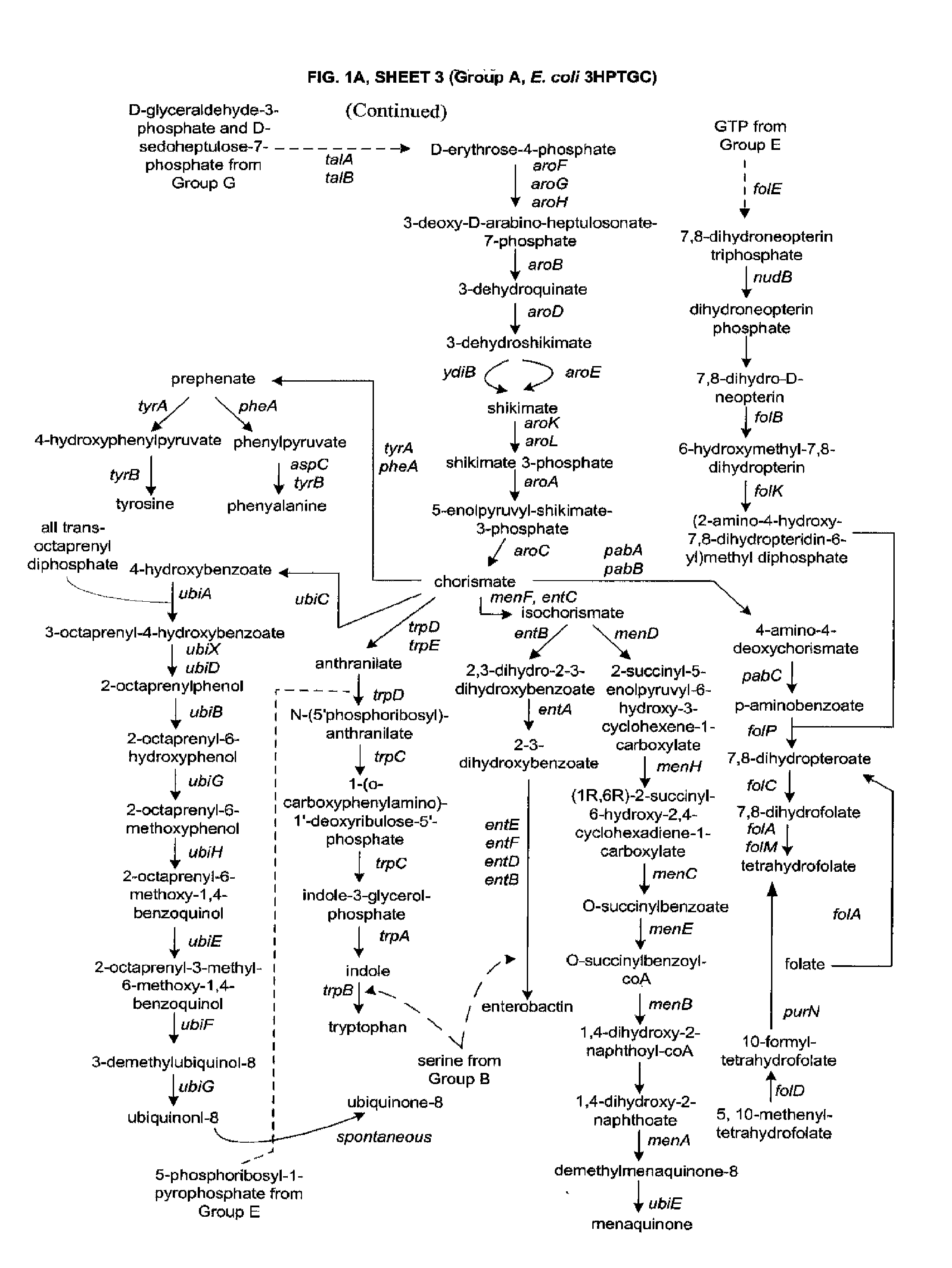
Methods and Organisms for Growth-Coupled Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism having one or more gene disruptions, the one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding an enzyme obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid onto the non-naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications having disruption of one or more genes including: (a) the set of genes selected from: (1) adhE, ldhA, pta-ackA; (2) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD; (3) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, ptsG; (4) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, pntAB; (5) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC; (6) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC, pntAB; (7) pflAB, ldhA, or (8) adhE, ldhA, pgi in a microorganism utilizing an anaerobic β-alanine 3-HP precursor pathway; (b) the set of genes selected from: (1) tpi, zwf; (2) tpi, ybhE; (3) tpi, gnd; (4) fpb, gapA; (5) pgi, edd, or (6) pgi, eda in a microorganism utilizing an aerobic glycerol 3-HP precursor pathway; (c) the set of genes selected from: (1) eno; (2) yibO; (3) eno, atpH, or other atp subunit, or (4) yibO, atpH, or other atp subunit, in a microorganism utilizing a glycerate 3-HP precursor pathway, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid is further provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
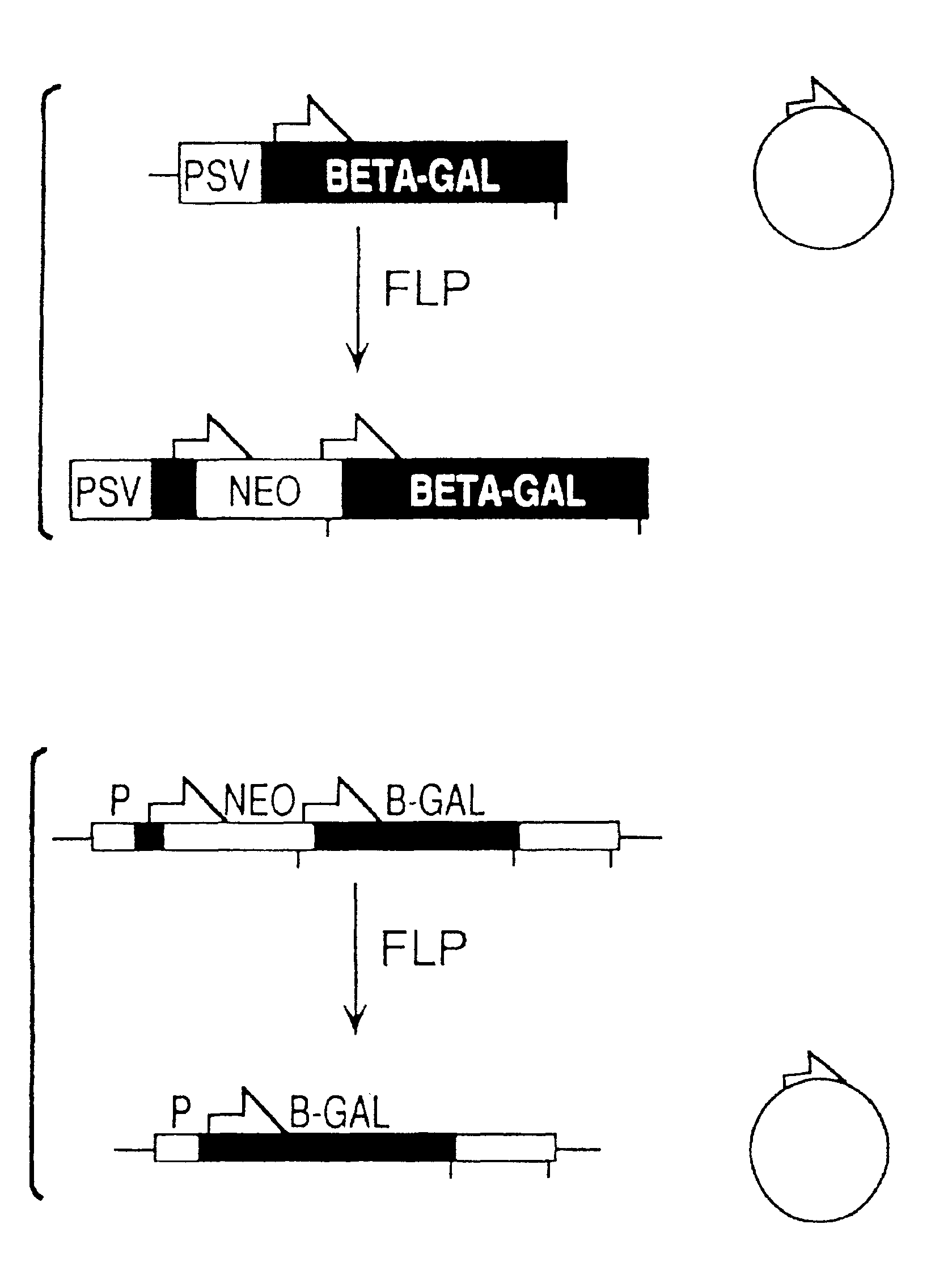
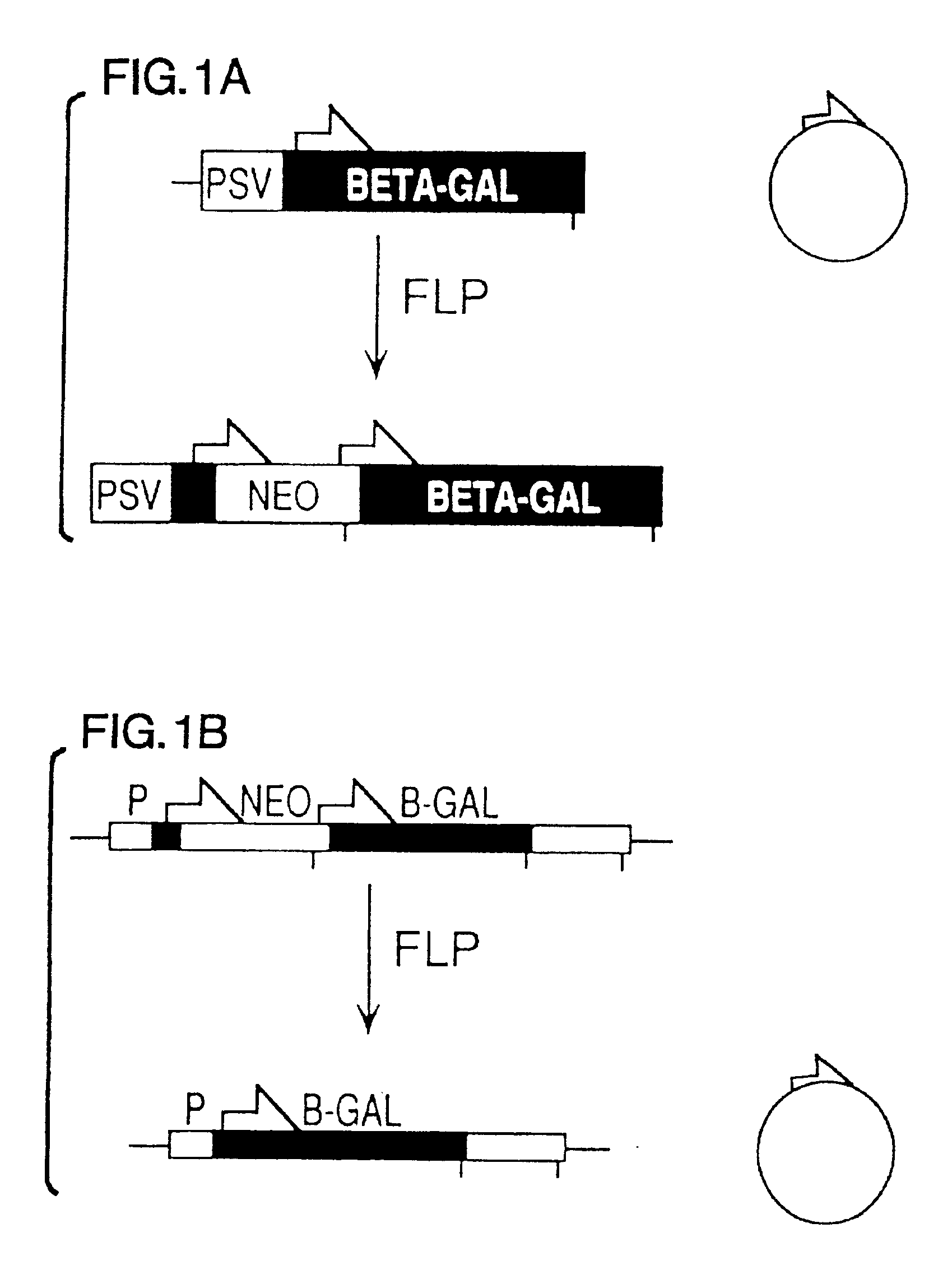
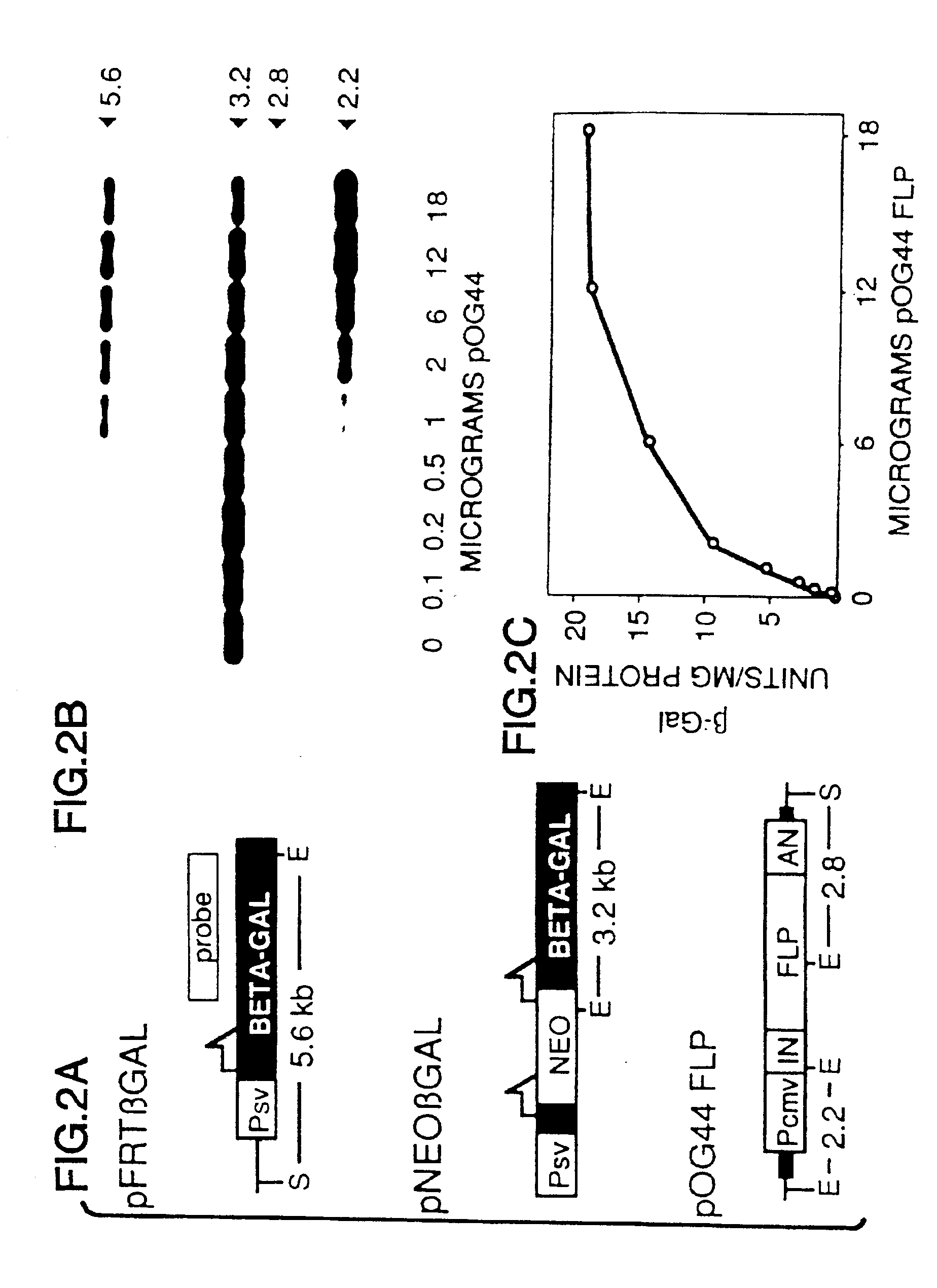
FLP-mediated gene modification in mammalian cells, and compositions and cells useful therefor
A gene activation / inactivation and site-specific integration system has been developed for mammalian cells. The invention system is based on the recombination of transfected sequences by FLP, a recombinase derived from Saccharomyces. In several cell lines, FLP has been shown to rapidly and precisely recombine copies of its specific target sequence. For example, a chromosomally integrated, silent β-galactosidase reporter gene was activated for expression by FLP-mediated removal of intervening sequences to generate clones of marked cells. Alternatively, the reverse reaction can be used to target transfected DNA to specific chromosomal sites. These results demonstrate that FLP can be used, for example, to mosaically activate or inactivate transgenes for a variety of therapeutic purposes, as well as for analysis of vertebrate development. The FLP recombination system of the present invention can be incorporated in transgenic, non-human mammals to achieve site-specific integration of transgenes, to construct functional genes or to disrupt existing genes.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Treatment of cancer using humanized anti-EGFRvIII chimeric antigen receptor
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating diseases associated with expression of EGFRvIII. The invention also relates to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) specific to EGFRvIII, vectors encoding the same, and recombinant T cells comprising the anti-EGFRvIII CAR. The invention also includes methods of administering a genetically modified T cell expressing a CAR that comprises an anti-EGFRvIII binding domain.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +2
Targeted chromosomal mutagenasis using zinc finger nucleases
The present invention provides for a method or methods of targeted genetic recombination or mutagenesis in a host cell or organism, and compositions useful for carrying out the method. The targeting method of the present invention exploits endogenous cellular mechanisms for homologous recombination and repair of double stranded breaks in genetic material. The present invention provides numerous improvements over previous mutagenesis methods, such advantages include that the method is generally applicable to a wide variety of organisms, the method is targeted so that the disadvantages associated with random insertion of DNA in-to host genetic material are eliminated, and certain embodiments require relatively little manipulation of the host genetic material for success. Additionally, it provides a method that produces organisms with specific gene modifications in a short period of time.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
CAS9-carrying recombinant adenovirus and application thereof
ActiveCN104178461ARapid knockoutImprove efficiencyViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationNucleotideGene Modification
The invention discloses a CAS9-carrying recombinant adenovirus and application thereof. The invention protects a recombinant adenovirus carrying coding gene of CAS9 protein; and the CAS9 protein is disclosed as Sequence 7 in the sequence table. The coding gene of the CAS9 protein is disclosed as 789th-5045th nucleotides from the 5' terminal of Sequence 6 in the sequence table. The invention also protects application of the recombinant adenovirus in preparing a kit for knocking out target gene. The CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) method has the characteristics of high efficiency, high speed and low cost. The CAS9 recombinant adenovirus disclosed by the invention can be used in a protein function cell platform (1) for quick gene modification and high flux screening, a liver protein function platform (2) for implementing quick and specific gene knock-out at the liver, and a mouse gene modification platform (3) for preparing a gene knock-out / knock-in mouse.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT
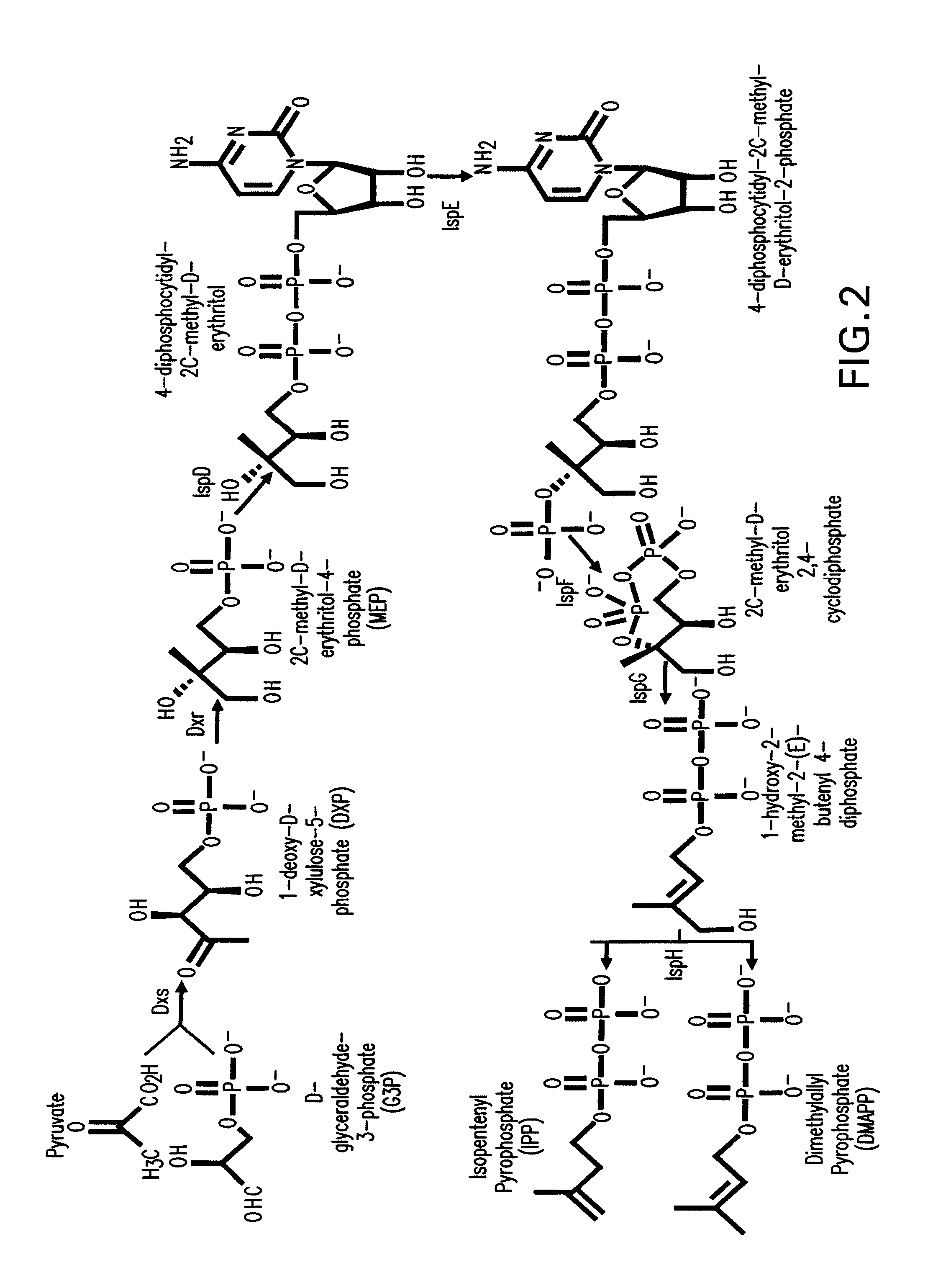
Production of isoprenoids
Provided herein are methods for a robust production of isoprenoids via one or more biosynthetic pathways. Also provided herein are nucleic acids, enzymes, expression vectors, and genetically modified host cells for carrying out the subject methods. Also provided herein are fermentation methods for high productivity of isoprenoids from genetically modified host cells.
Owner:AMYRIS INC
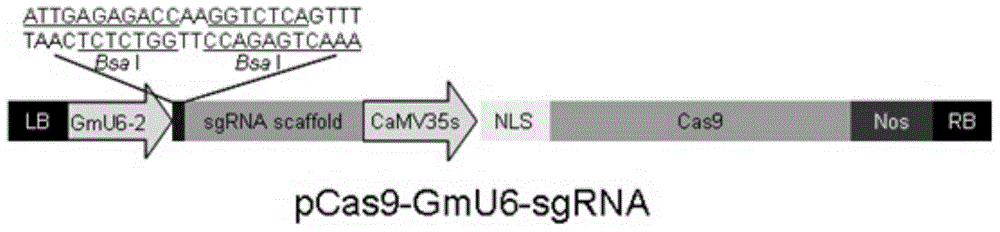
Construction of soybean CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of soybean CRISPR/Cas9 system in soybean gene modification
InactiveCN104450774AFinish quicklyHigh mutation rateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGene ModificationBiology
The invention relates to construction of a soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system. The construction disclosed by the invention is mainly characterized in that a core sequence is designed according to a target gene, and the core sequence is constructed into an expression carrier with cas9. The soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system utilizes the core sequence to identify the target gene, the cas9 shears the target gene, and various mutations can be generated in the process of repairing a broken chain by an organism. The invention also provides application of the soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system in soybean gene modification. With the adoption of the construction and the application provided by the invention, the constructed soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system is simple, the soybean gene can be rapidly and efficiently modified, and the problems of the traditional ZFNs system is too complex, wastes time and is low in efficiency are overcome.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
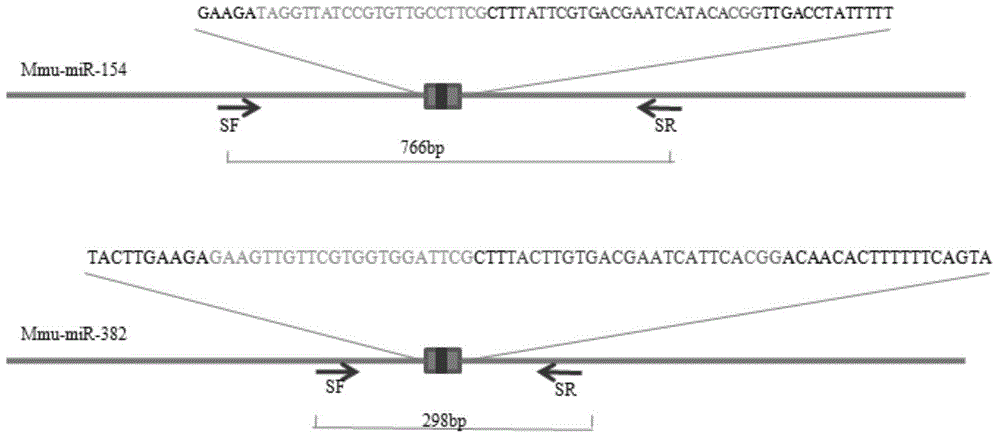
Method for knocking out microRNA gene family by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 specificity
InactiveCN104651398AShort cycleReduce investmentVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryF1 generationMicroRNA Gene
The invention discloses a method for knocking out a microRNA gene family by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 specificity, wherein a target gene is knocked out by mainly adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The microRNA family is knocked out by utilizing the specificity of the CRISPR / Cas9 system for the first time; the disadvantage that only one gene can be knocked out for one time in traditional transgenosis can be overcome by utilizing the novel method; the time for establishing a model organism is reduced to three weeks; furthermore, the construction step is simple; an expensive molecular reagent is also reduced; the period for constructing a genetically modified mouse is greatly shortened to four months; multiple genes constructed for one time can be knocked out simultaneously; the fund investment is obviously reduced; F1 generations of mice can be obtained only in need of 50000 Yuan; the gene modification efficiency can be above 90%; the unreliability of the traditional technology is reduced; the operation technology is simple; and a series of complex steps including constructing a targeting vector, screening ES (Embryonic Stem) cells, selectively breeding chimeric mice and the like are unnecessary.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Genome editing of sensory-related genes in animals
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences encoding proteins that are associated with nociception or taste disorders. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. Also provided are methods of using the genetically modified animals or cells disclosed herein to screen agents for toxicity and other effects.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Genetically-modified cells comprising a modified human T cell receptor alpha constant region gene
ActiveUS9889160B2Efficient insertionConvenient treatmentAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseGene Modification
Disclosed herein is a genetically-modified cell comprising in its genome a modified human T cell receptor alpha constant region gene, wherein the cell has reduced cell-surface expression of the endogenous T cell receptor. The present disclosure further relates to methods for producing such a genetically-modified cell, and to methods of using such a cell for treating a disease in a subject.
Owner:PRECISION BIOSCI
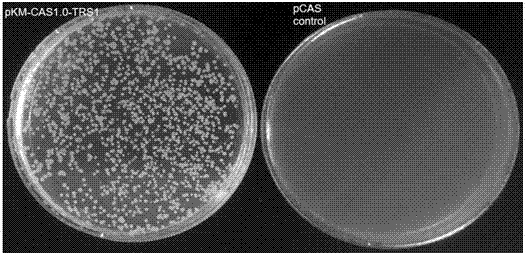
Efficient CRISPR/Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization
ActiveCN107574179AStable gene editingEfficient gene editingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTime transformation
The invention relates to a special safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas (Clustered Regulatory Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated) 9 gene editing system for Kluyveromyces optimization, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. In the prior art, pCAS plasmids used in saccharomyces cerevisiae have Cas9 gene sequences and gRNA (guide RNA) elements at the same time, and efficient genomemodification in the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be realized through one-time transformation, but stable copying and expression cannot be realized in Kluyveromyces. According to the system, Cas9 / gRNAfusion plasmids are transformed in Kluyveromyces cells, the plasmids are targetedly delivered to endogenous DNA sequences of the Kluyveromyces cells, and double strand breaks are generated; and donorDNA sequences are transformed in the Kluyveromyces cells, the sequences generate homologous recombination at the double strand breaks and target sites, and Tag sequences are inserted in the target sites. Through the modification, the new safe and efficient CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system which is specially used for the Kluyveromyces and can perform stable copying and expression in the Kluyveromyces and perform gene modification is established.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
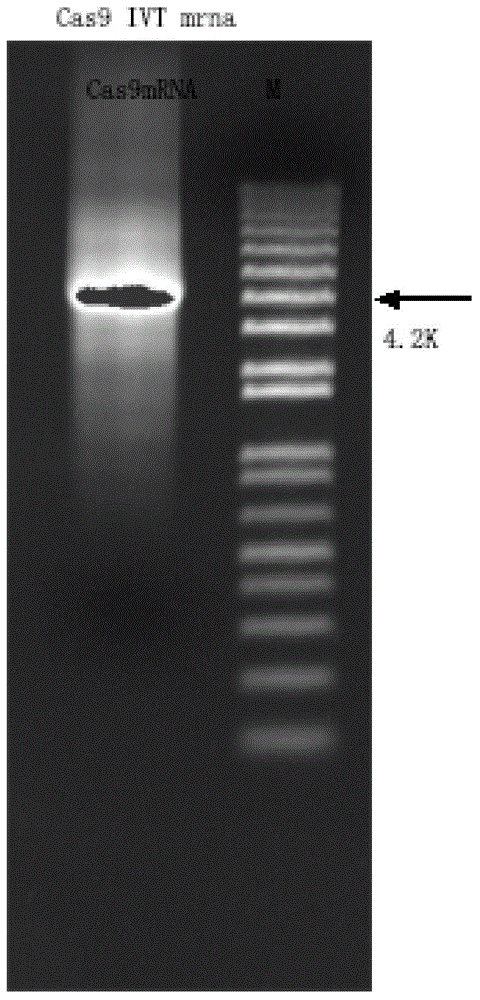
Preparation method of staphylococcus aureus CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of system in constructing mouse model
The invention discloses a preparation method of a staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system and an application of the system in constructing a genetically modified mouse model. The staphylococcus aureus CRISPR / Cas9 system is composed of two components, namely Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, wherein a preparation method of the Cas9 mRNA is achieved by adding a T7 promoter to the upstream region of original Cas9 coding DNA, and a preparation method of the gRNA is achieved by adding the T7 promoter to the upstream region of an original gRNA coding sequence. The staphylococcus aureus Cas9 mRNA and gRNA, which are injected to mouse fertilized embryos through micro-injection, can achieve gene editing and modification of various types, such as single-gene knockout, multi-gene knockout and / or gene knock-in and the like, on the mouse fertilized embryos; therefore, the CRISPR / Cas9 system has a good application prospect in the aspects of fertilized embryo gene editing and modification of such animals as mouse and the like as well as construction of animal models.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MAGIGEN BIOTECH
Methods of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
ActiveUS20130247234A1Reduce the binding forceImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHuman animalVariable domain
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses a single light chain variable domain derived from a single rearranged light chain variable region gene in the germline of the non-human animal, wherein the single rearranged light chain variable region gene comprises a substitution of at least one non-histidine encoding codon with a histidine encoding codon. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising a histidine-containing universal light chain are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Targeting sgRNA for pig CD163 gene editing, modification vector, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107177595AReduce economic lossStrong specificityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNADiseaseGene Modification
The invention provides a targeting sgRNA for pig CD163 gene editing, a modification vector, and a preparation method and application thereof, which relate to the technical field of gene engineering. The sgRNA and the gene modification vector provided by the invention have high specificity, and can be used for efficiently editing a pig CD163 gene on a cell level through a CRISPR / Cas9n system. According to the preparation method of a blue-eared disease resistant pig provided by the invention, a blue-eared disease virus receptor is damaged, the target gene CD163 is edited, no other exogenous gene is intruded, no non-specific editing is carried out on a non-CD163 gene area on a genome, a genetic background is clean and clear, and the work of later transgene safety evaluation is greatly reduced. The blue-eared disease resistant pig obtained by utilizing the invention can be ensured to survive normally, and resists the infection of a blue-eared disease virus, so that the economic loss caused by the blue-eared disease in pig husbandry is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for improving gene targeting efficiency and method for carrying out in-situ repair on base on beta-globulin gene locus
InactiveCN106244555AShorten the construction experiment cycleHigh miss rateNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsGene Modification
The invention provides a method for improving the gene targeting efficiency and a method for carrying out in-situ repair on the base on a beta-globulin gene locus. The method for improving the gene targeting efficiency comprises the following steps of: S10, determining a gene locus to undergo in-situ repair; and S20, introducing a CRISPR / Ca system to cleave editing lotus DNA to cause DNA damage and simultaneously providing a repair template segment. Based on the deficiency of existing gene modification, the gene modification efficiency, the timeliness and the modification quality are improved after single-stranded oligonucleotides (ss ODNs) and a small molecule compound participate in a CRISPR / Cas9 gene modification system.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Fixed-point gene editing method based on intratestis injection
InactiveCN105296537AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryMatingGene Modification
The invention discloses a simple, convenient and efficient fixed-point gene editing method relating to the fields of transgenic animal preparation, gene functional study and biomedicines. A testis injection method is a sperm-mediated gene transferring method developed by utilizing the sperm capacity of actively combining, transferring and integrating an exogenous DNA. By using the method disclosed by the invention, an animal testis injection method is optimized, a carrier constructed by utilizing a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat system (CRISPR / Cas9) is integrated with a sperm chromosome through multi-point testis injection or seminiferous tubule microinjection, so that the aims of deleting, replacing and inserting genes are achieved. Then, a transgenic animal descendant is obtained through various approaches such as natural mating and artificial insemination. According to the method, the advantages of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system are sufficiently utilized, and the existing transgenic animal system is combined, so that the complexity of in-vitro cell operation and requirement on expensive precise instruments / equipment are avoided while the gene modification animal obtaining efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
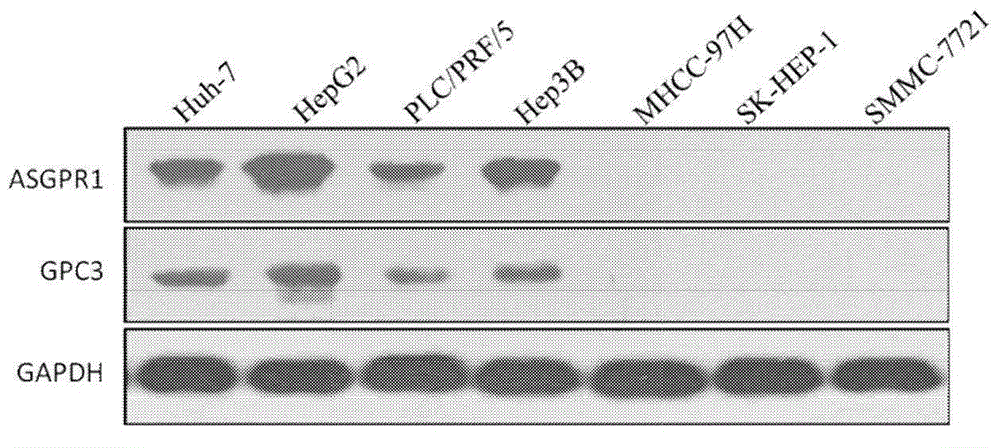
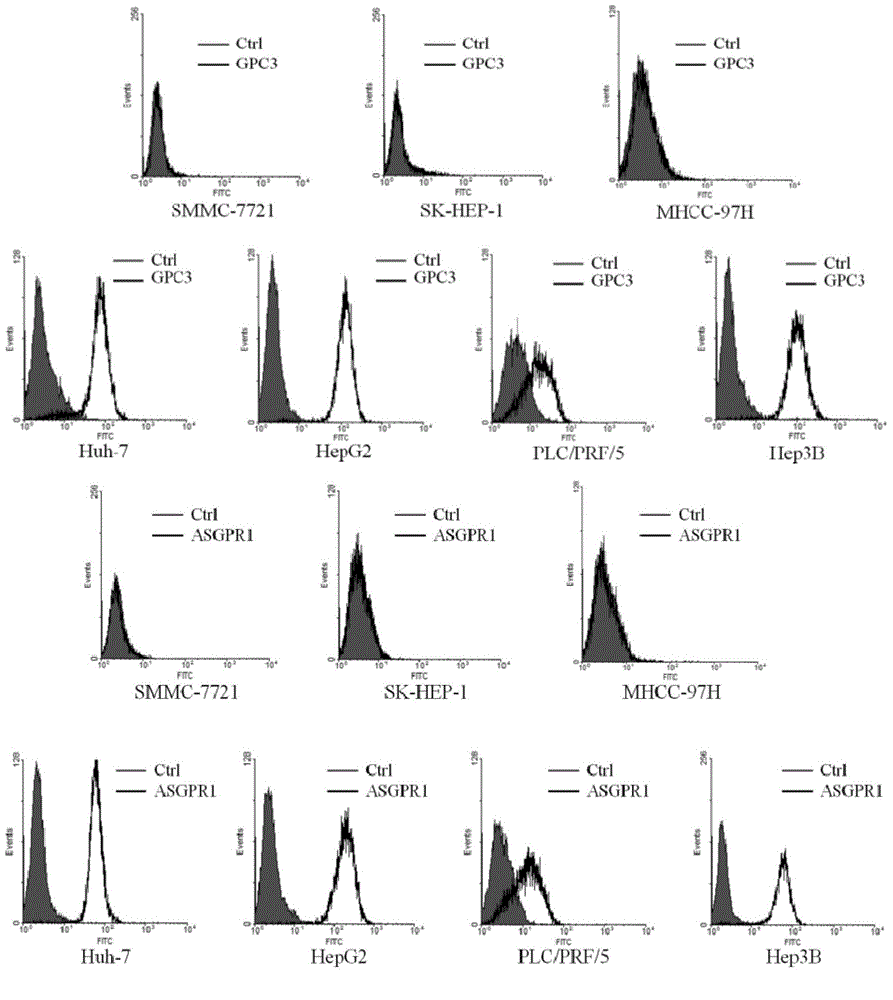
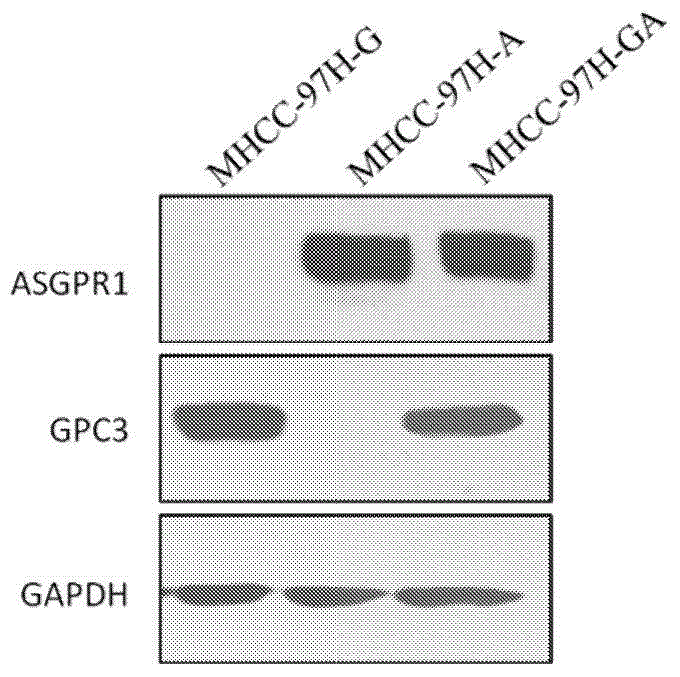
Dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (Glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell
ActiveCN105713881APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmune effector cellEffector cell
The invention relates to a dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of the dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell. The invention discloses the gene-modified immunologic effector cell capable of simultaneously identifying GPC3 and ASGPR1 for the first time, and the gene-modified immunologic effector cell can be used for the treatment of the GPC3 and ASGPR1 double-positive tumor, such as liver cancer.
Owner:CARSGEN THERAPEUTICS
Transgenic bovine comprising human immunoglobulin loci and producing human immunoglobulin
Owner:SAB LLC
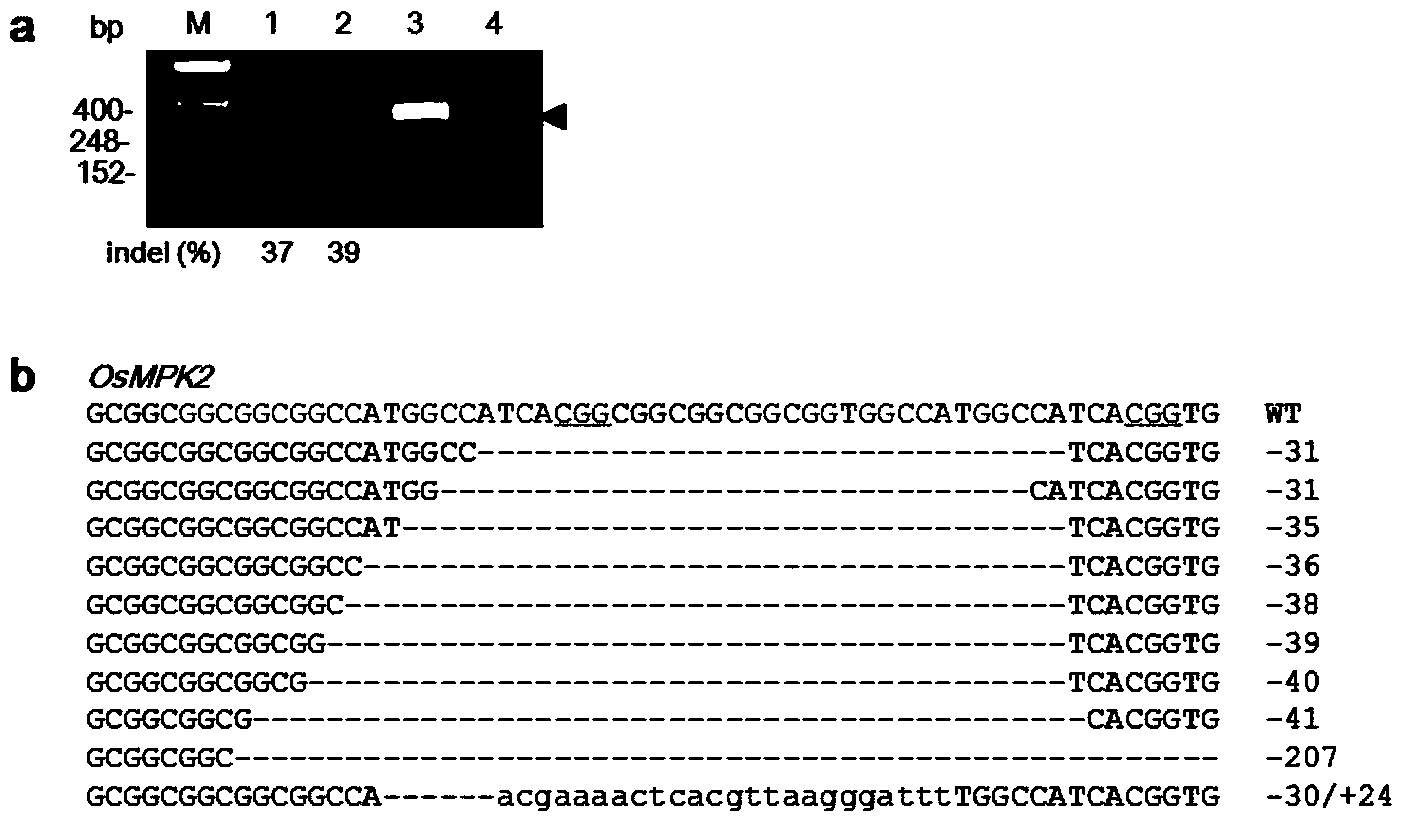
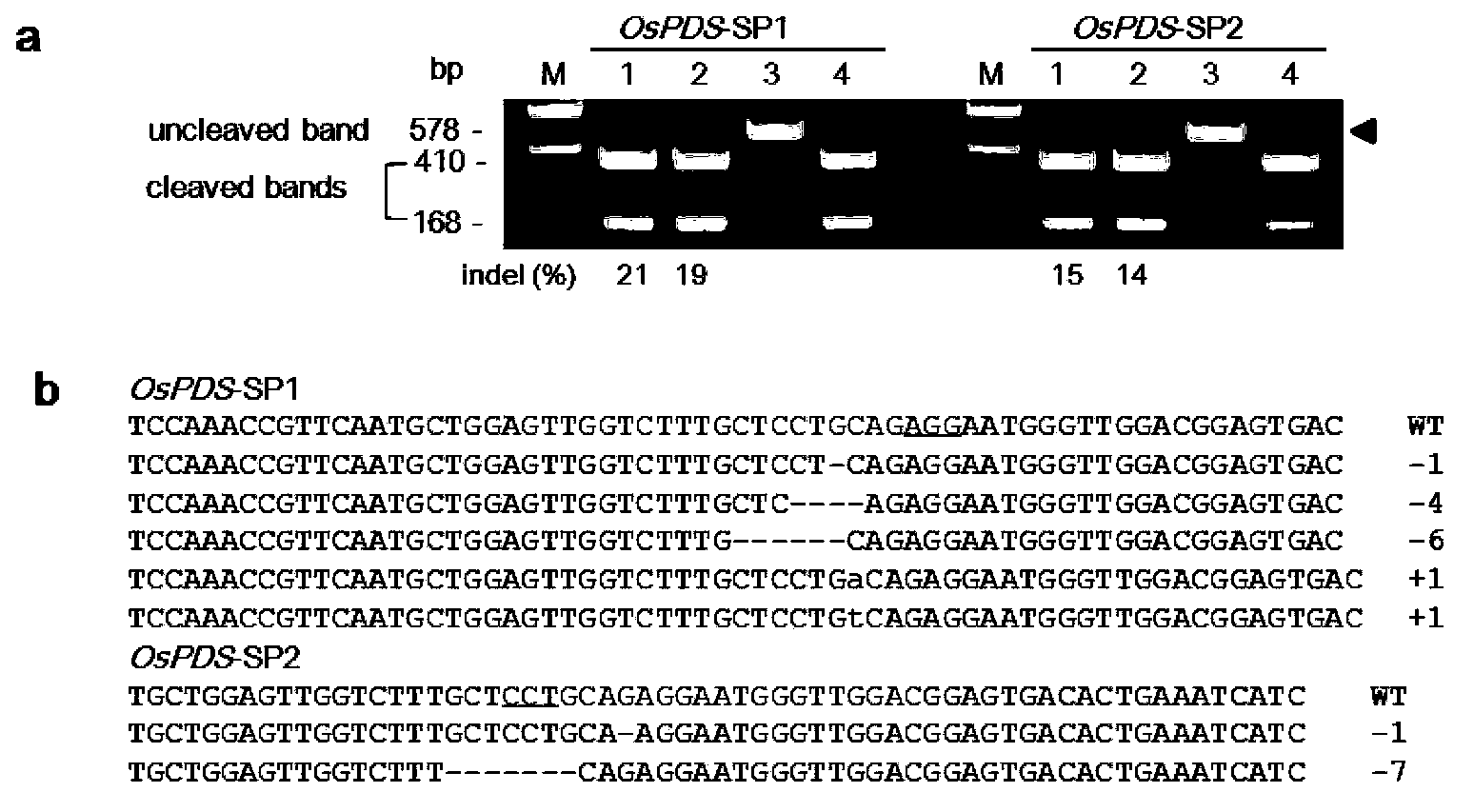
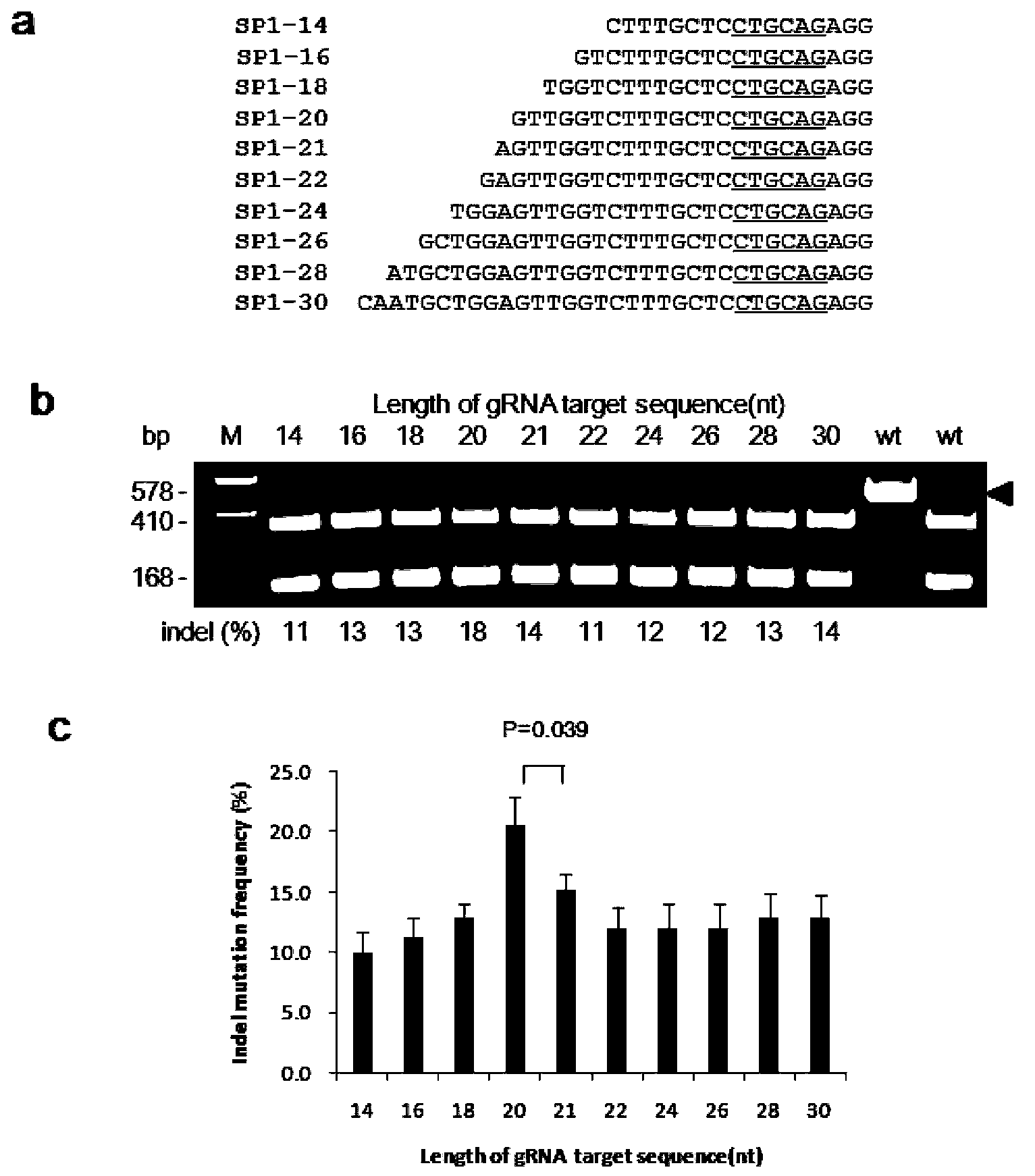
Site-directed modification method of rice genome
The invention discloses a gene modification method which is capable of realizing random insertion and / or random deletion on a target segment of a rice target gene. The gene modification method comprises following steps: a guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease are induced in rice tissues; the double-chain target segment of the target gene is sliced because of the combined effect of the guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease; and then the random insertion and / or random deletion on the target segment of the rice target gene are / is realized because of DNA self-repairing function of rice cells. The gene modification method is capable of inducing gene mutation of rice.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetically modified major histocompatibility complex mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express a humanized MHC II protein (humanized MHC II α and β polypeptides), as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the humanized MHC II protein. Also provided are constructs for and methods of making the genetically modified non-human animals. Methods of using the genetically modified non-human animals to study various aspects of the human immune system are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
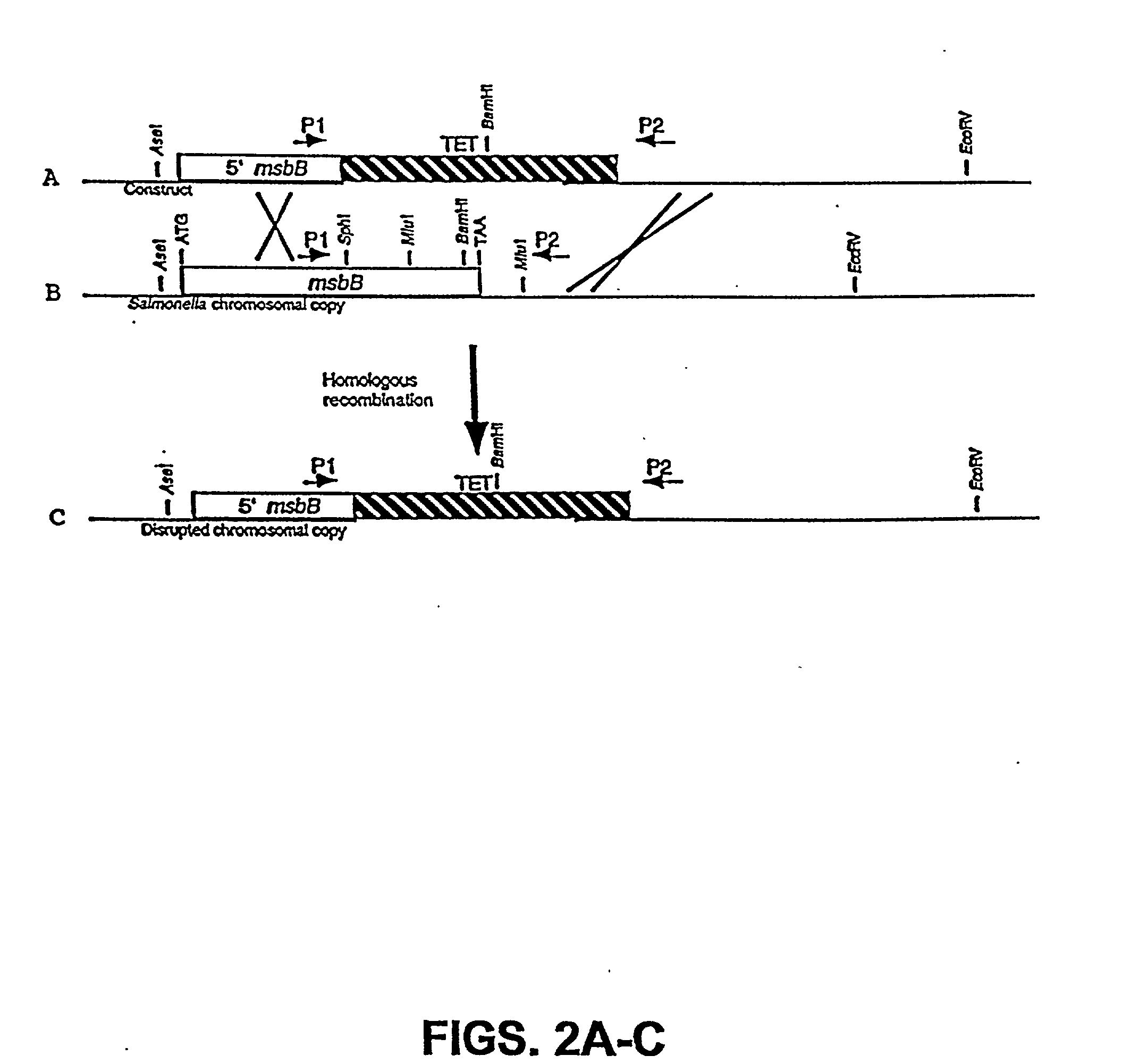
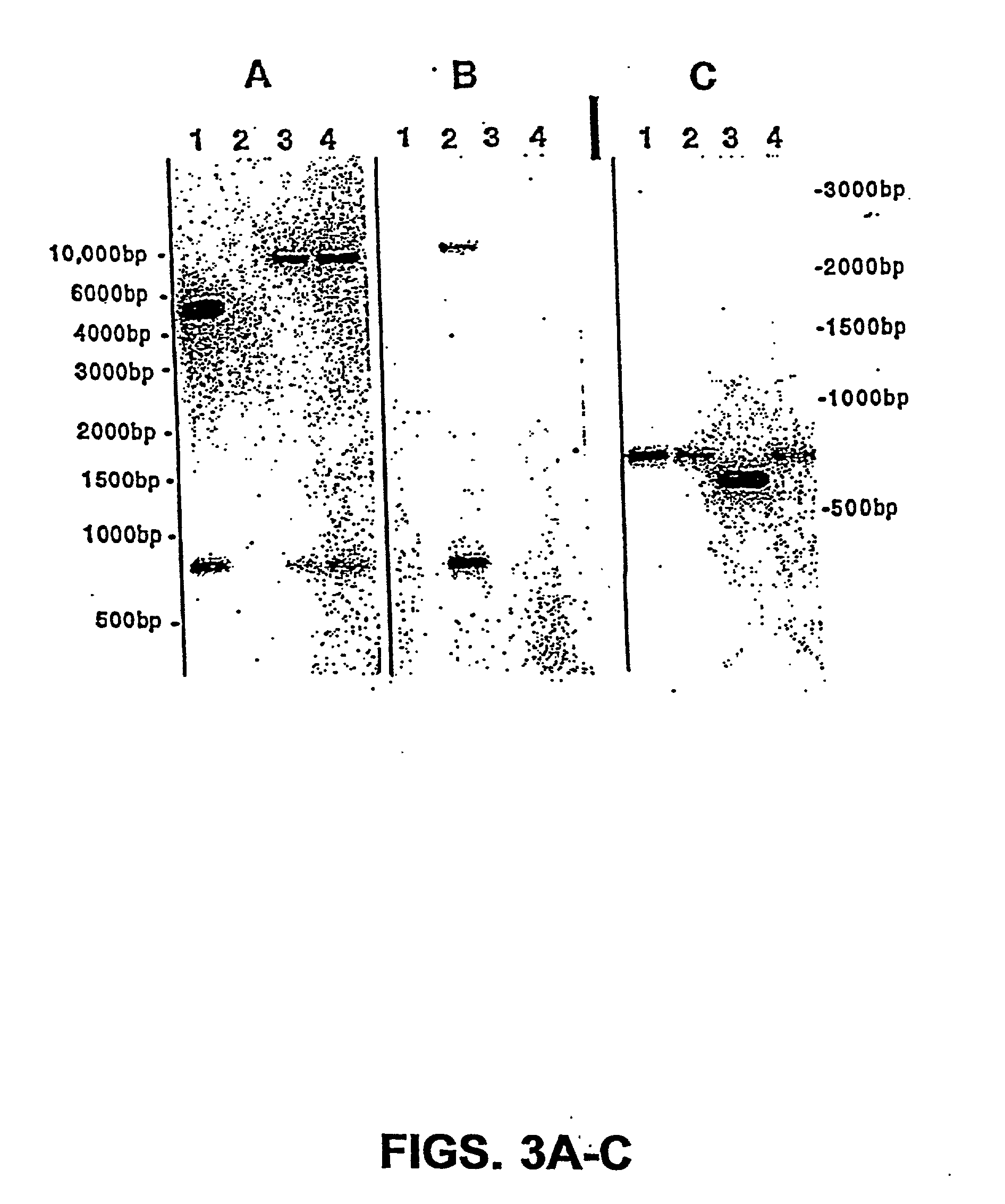
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20020026655A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purl gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Methods, Systems and Compositions for Increased Microorganism Tolerance to and Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid (3-HP)
InactiveUS20120264902A1Increase productionImprove the level ofOrganic chemistryFermentationMicroorganism3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The present invention relates to methods, systems and compositions, including genetically modified microorganisms, adapted to exhibit increased tolerance to 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP), particularly through alterations to interrelated metabolic pathways identified herein as the 3-HP toleragenic pathway complex (“3HPTGC”). In various embodiments these organisms are genetically modified so that an increased 3-HP tolerance is achieved. Also, genetic modifications may be made to provide at least one genetic modification to any of one or more 3-HP biosynthesis pathways in microorganisms comprising one or more genetic modifications of the 3HPTGC.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Genomic editing of genes involved in tumor suppression in animals
InactiveUS20110023149A1Improve effectivenessUntoward effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesZinc finger nucleaseMedicine
The present invention provides genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences involved in tumor suppression. In particular, the animals or cells are generated using a zinc finger nuclease-mediated editing process. The invention also provides zinc finger nucleases that target chromosomal sequence involved in tumor suppression and the nucleic acids encoding the zinc finger nucleases. Also provided are methods of assessing the effects of agents in genetically modified animals and cells comprising edited chromosomal sequences involved in tumor suppression.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Preparation method and application of tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells
InactiveCN104630146AHigh killing efficiencyApparent tumor cell specificityMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCell specificPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention relates to the technical fields of molecular biology and cellular immunology and in particular relates to a preparation method of tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells. The preparation method of the tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining peripheral blood mononuclear cells; (2) mixing the obtained peripheral blood mononuclear cells with gene modifying tumour cells; and (3) resuspending the obtained mixed cells in a culture medium containing cell factors which can maintain cell growth, proliferation and differentiation. The prepared tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells are mainly applied to medicines which are sued for preventing or treating cancers. The preparation method of the tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells has the advantages that the prepared tumour cell specific polyclonal T cells have the characteristics of large quantity, high specificity and strong killing capability; besides, a technology is simple, and the preparation cost is obviously reduced compared with the prior art.
Owner:马飞
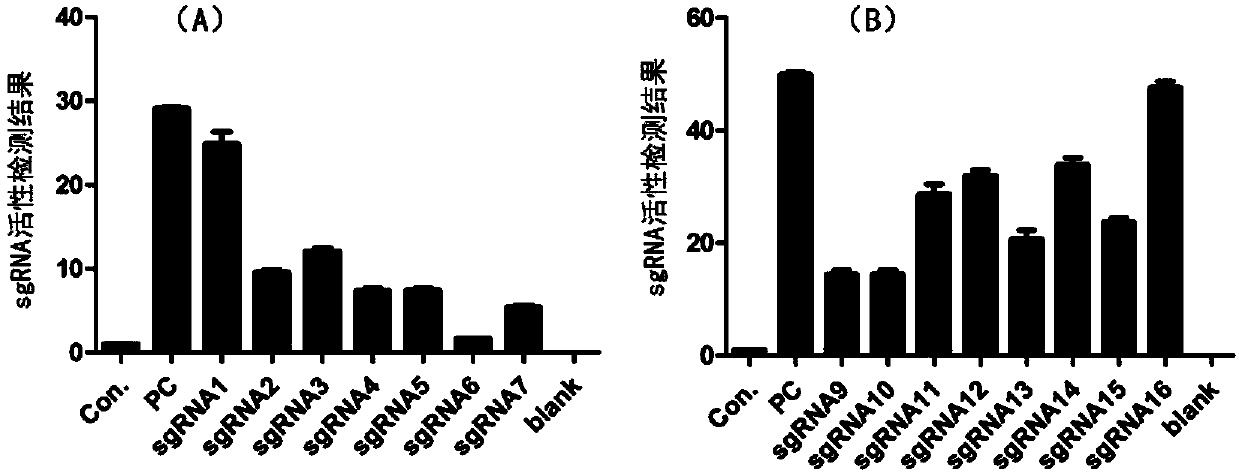
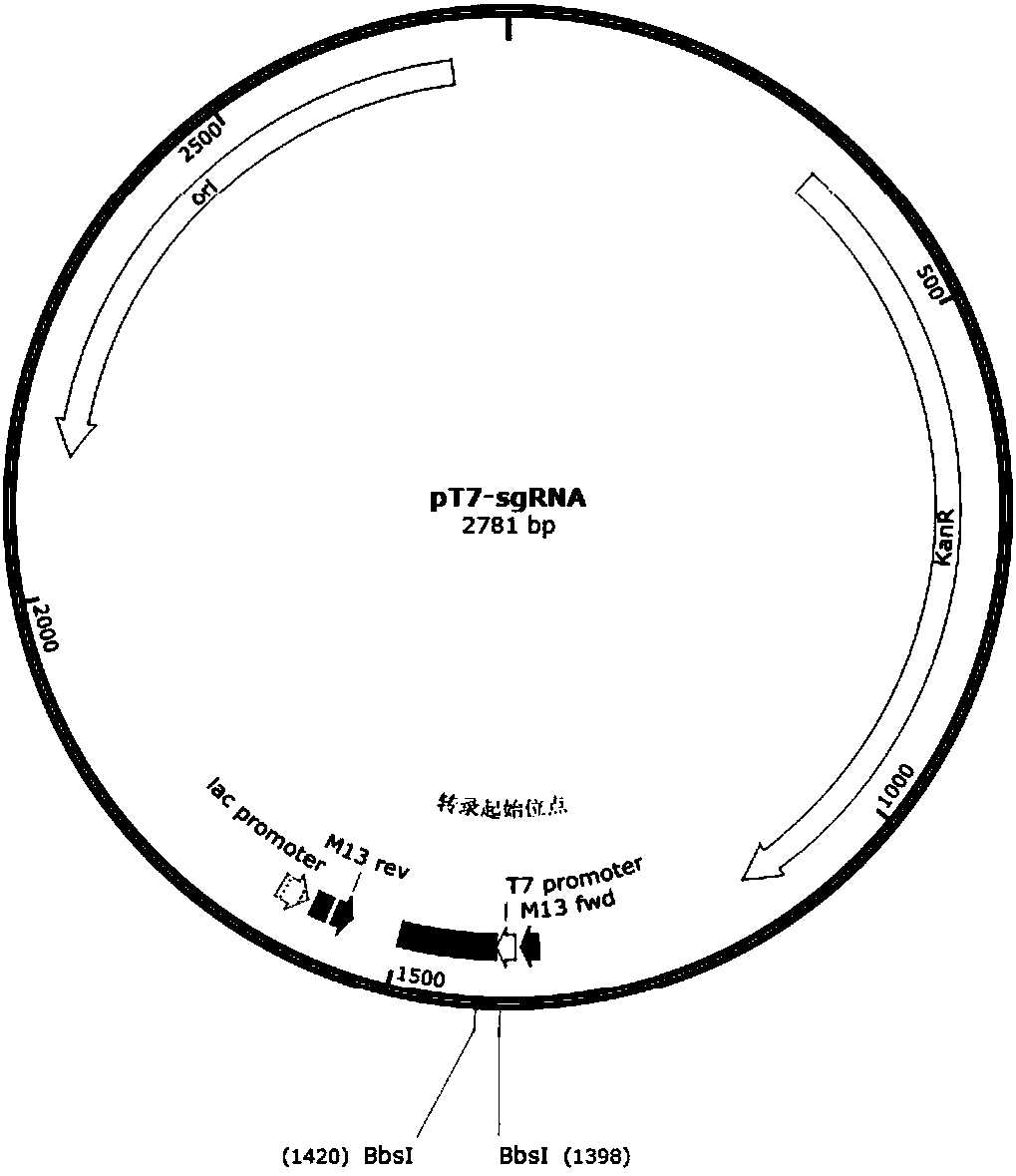
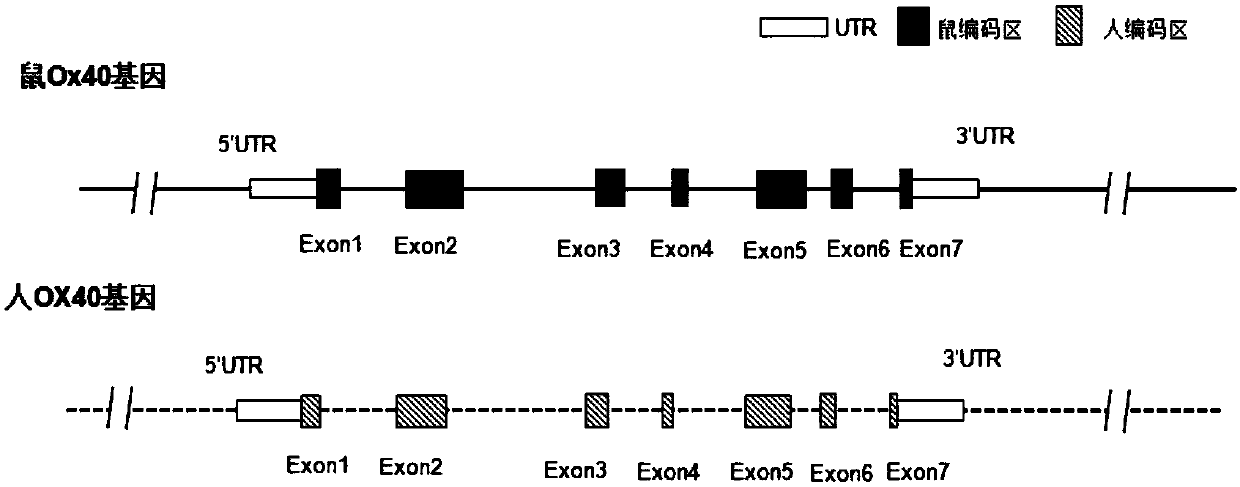
Preparation method and application of humanized gene modification animal model
ActiveCN107815465AReduce development riskSpeed up the R&D processNGF/TNF-superfamilyStable introduction of DNAGene ModificationGenetically modified mouse
The invention relates to a humanized gene genetically modified non-human animal, particularly a genetically modified rodent, especially a genetically modified mouse, and in particular relates to a construction method of a humanized OX-40 gene animal model and application of the model in the biomedicine field.
Owner:BIOCYTOGEN PHARMACEUTICALS (BEIJING) CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com