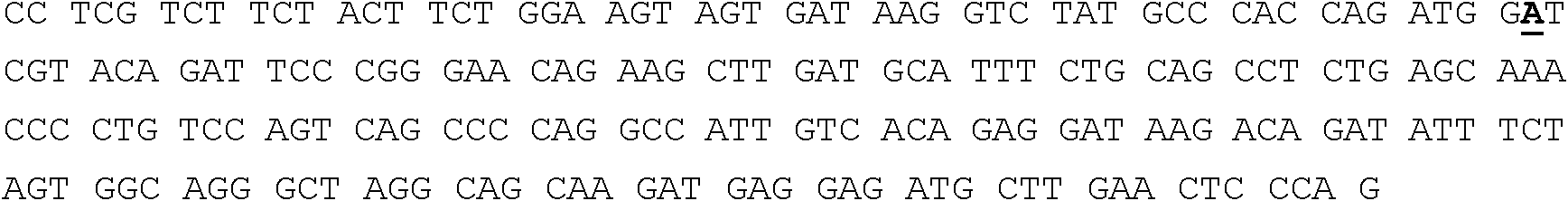Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138results about How to "High mutation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
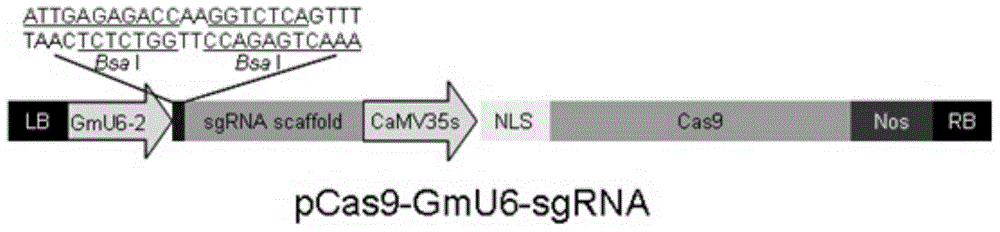
Construction of soybean CRISPR/Cas9 system and application of soybean CRISPR/Cas9 system in soybean gene modification
InactiveCN104450774AFinish quicklyHigh mutation rateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGene ModificationBiology
The invention relates to construction of a soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system. The construction disclosed by the invention is mainly characterized in that a core sequence is designed according to a target gene, and the core sequence is constructed into an expression carrier with cas9. The soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system utilizes the core sequence to identify the target gene, the cas9 shears the target gene, and various mutations can be generated in the process of repairing a broken chain by an organism. The invention also provides application of the soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system in soybean gene modification. With the adoption of the construction and the application provided by the invention, the constructed soybean CRISPR / Cas9 system is simple, the soybean gene can be rapidly and efficiently modified, and the problems of the traditional ZFNs system is too complex, wastes time and is low in efficiency are overcome.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Induction of viral mutation by incorporation of miscoding ribonucleoside analogs into viral RNA
InactiveUS20050187180A1High mutation rateReduced viabilityOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseRibonucleosideViral replication
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
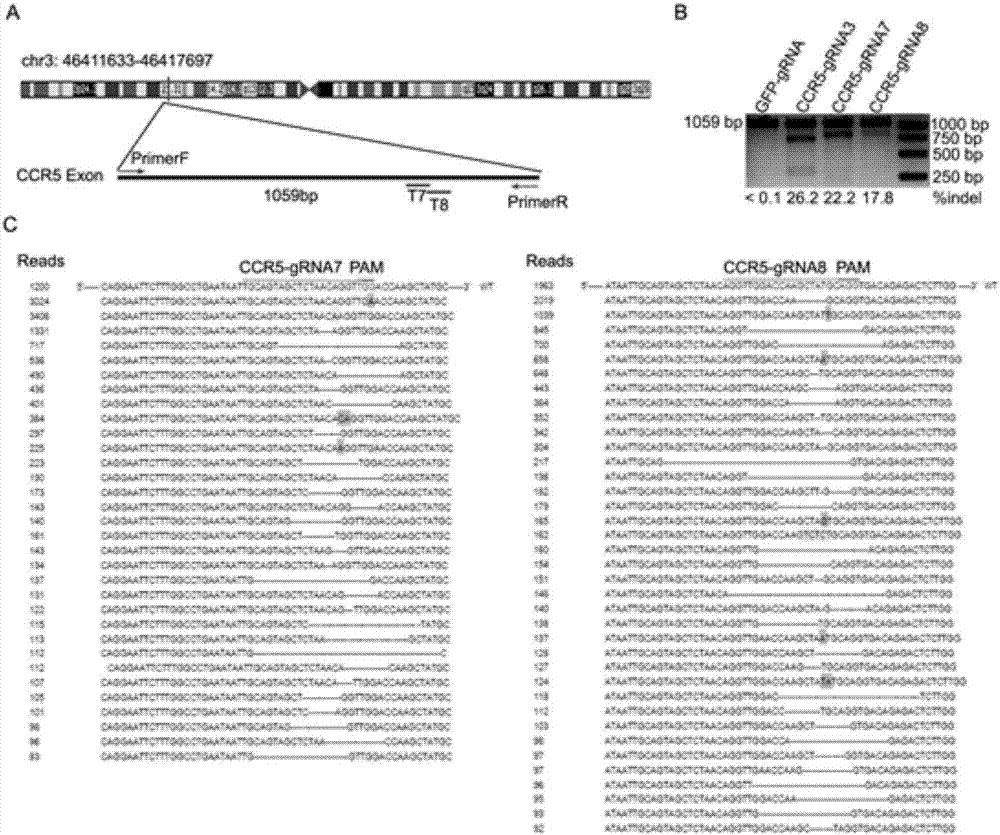
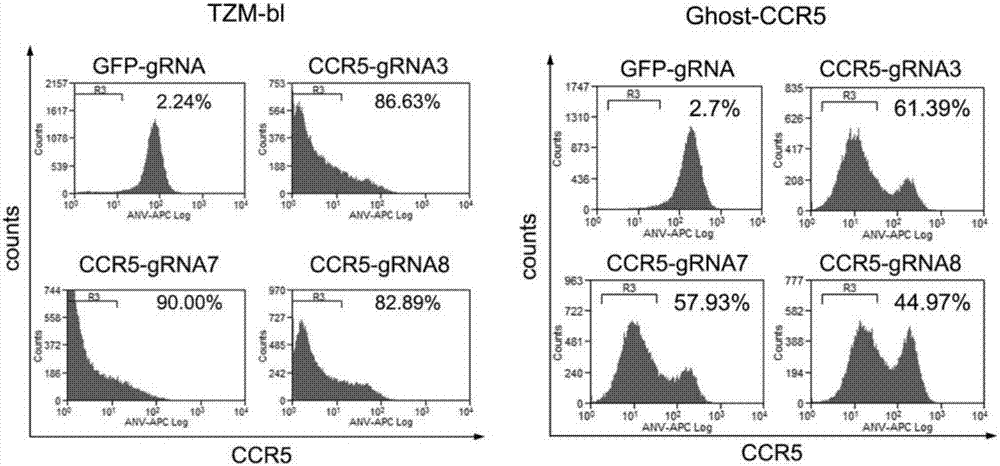
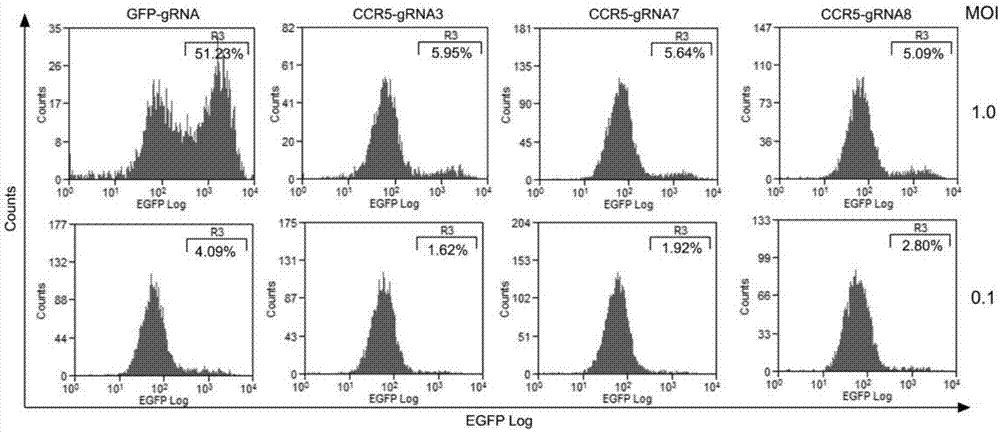
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)/Cas9 Recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 and application thereof
ActiveCN107312798AAvoid infectionInfection efficiency dropsOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRandom mutationLentivirus
The invention discloses a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 and application thereof. A lentivirus of the CRISPR / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 gene Delta 32 region is constructed that the lentivirus can introduce cells into a CRISPR / Cas9 system specific to CCR5, double-chain breakage occurs to a specific site of CCR5 gene, a random mutation is introduced to a breakage site after repairing by means of nonhomogeneous recombinant terminal binding, and the mutation rate reaches 90% and above. As gRNA is a nonhomogeneous region of CCR5 and CCR2, detection shows that the missing efficiency of the two gRNAs is lower than 0.2%. Cells modified via the recombinant lentivirus have significantly decreased efficiency of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection. The system is quick to construct, simple and low in price, and is applicable to gene therapy of acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods for determining the presence of sars coronavirus in a sample
InactiveUS20100279276A1High sensitivityHigh mutation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSARS coronavirusTest sample
Methods for determining the presence of SARS-CoV in a test sample that include targeting the SARS-CoV 5′ leader sequence or the SARS-CoV 3′ terminal sequence.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Arthrobacter for fermentative production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and application thereof
ActiveCN102268385AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateBacteriaFermentationArthrobacterAdenosine monophosphate.cyclic
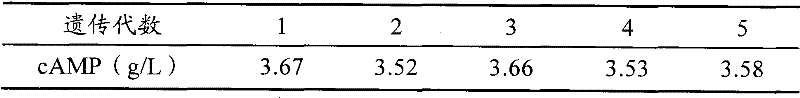
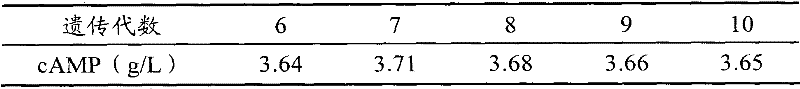
The invention provides arthrobacter for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate through fermentation and application thereof. With a preservation number of CGMCC No.3584, the arthrobacter of the invention has a A302 strain which is three times higher than an original strain in terms of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate output. Undergoing over 10 generations of passage, the A302 strain of the invention is stable in producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Owner:NANJING BIOTOGETHER
Electrochemical sensor and its prepn process and use
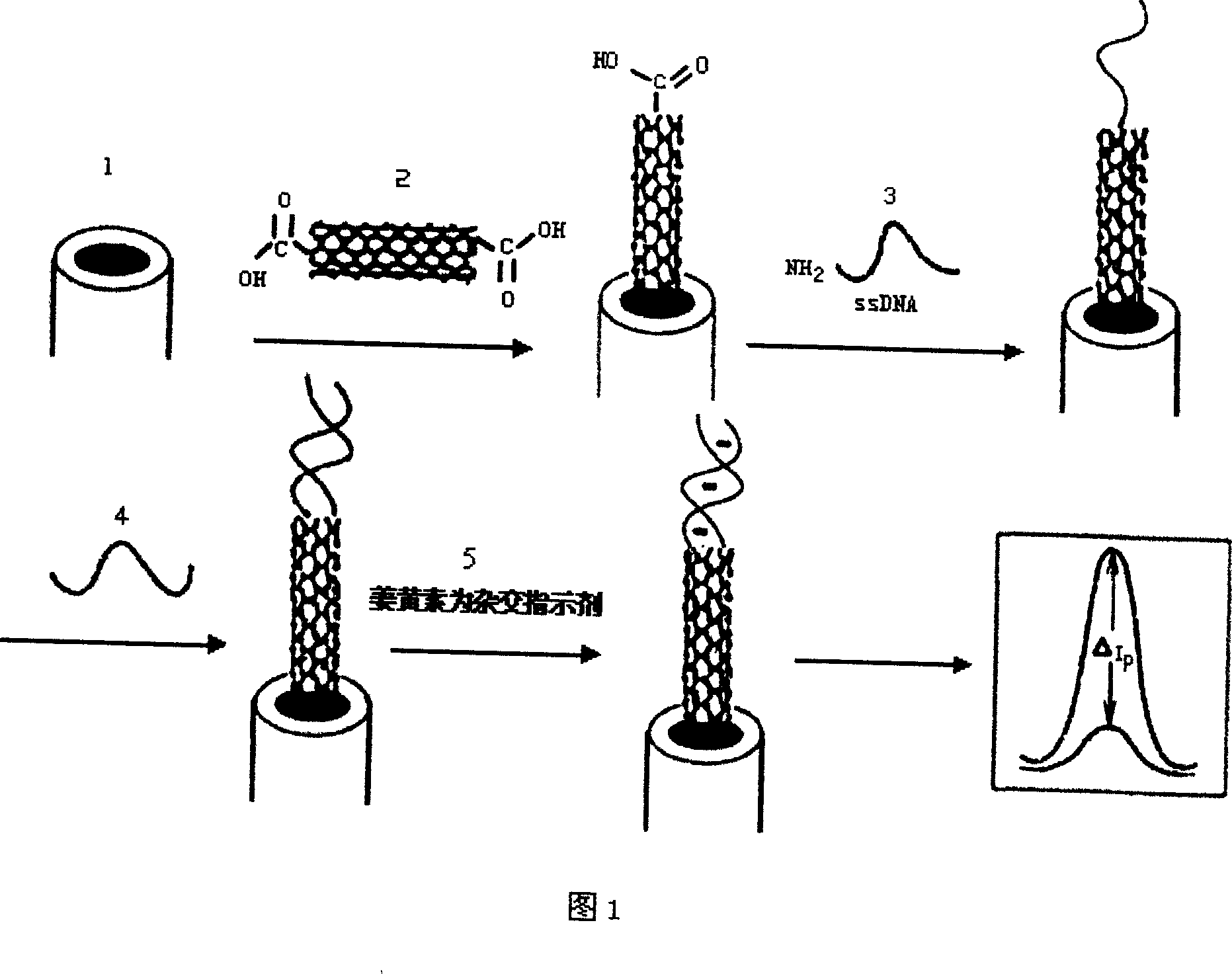
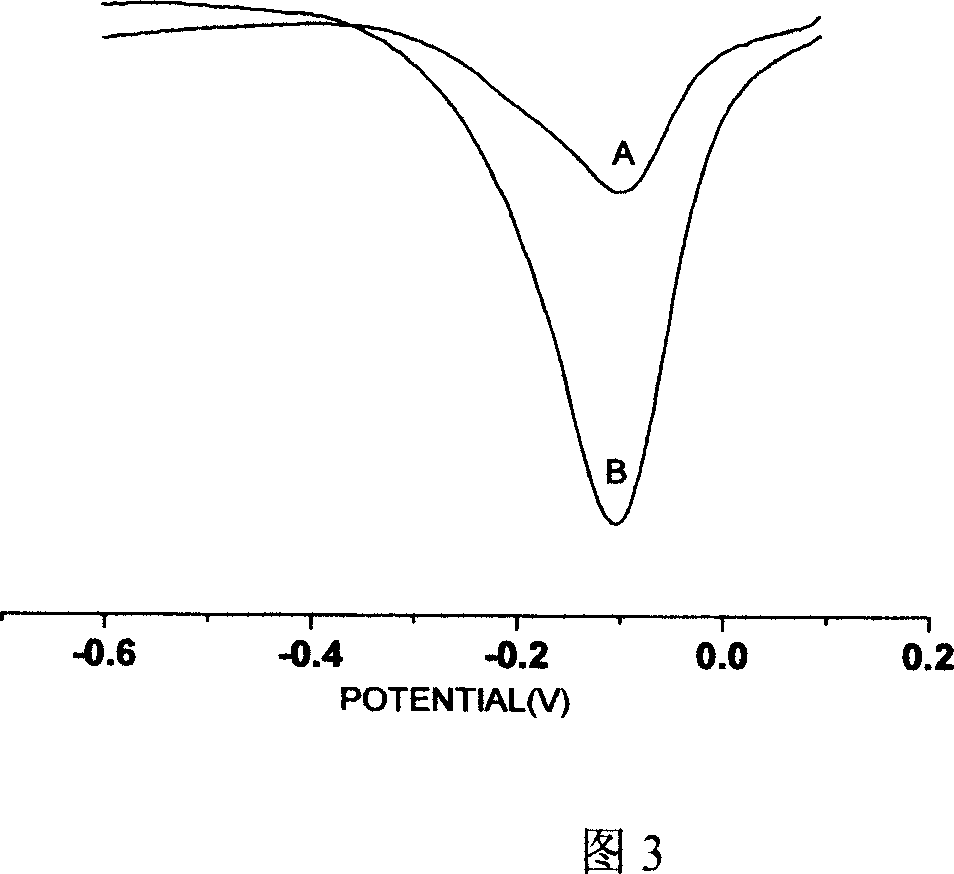
InactiveCN101046461AHigh mutation rateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCarboxyl radicalCarbon nanotube
The present invention discloses one kind of electrochemical sensor and its preparation process and use. The electrochemical sensor is prepared through decorating the surface of glass-carbon electrode with open-mouthed multi-wall carbon nanotube possessing carboxylated end, fixing BCR / ABL b3-a2 type gene probe through covalent decoration onto the end carboxyl radical of carbon nanotube, hybridizing the probe DNA and the target DNA and adopting curcumin as hybridization indicator for researching the recognizing capacity of single strand fixed on the decorated electrode on complementary DNA. The carbon nanotube has great specific surface area favoring the fixing of DNA on the electrode and excellent electron transferring characteristic for high detection sensitivity of sensor. The sensor is used in detecting chronic granulocytic leukemia gene and has high selectivity and high sensitivity.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
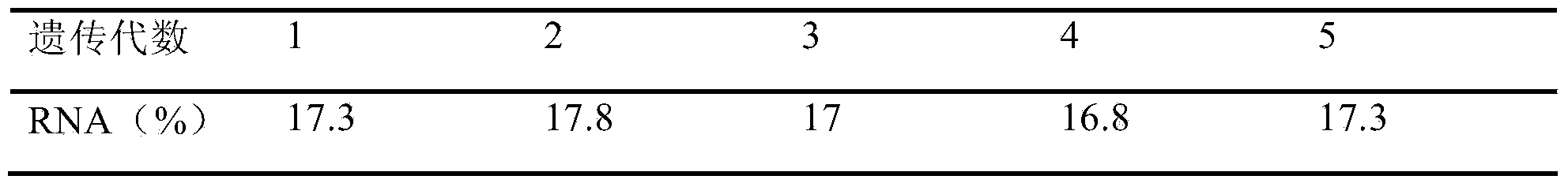
Saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ribonucleic acid by fermentation, and application thereof
ActiveCN103820337AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismDry weight
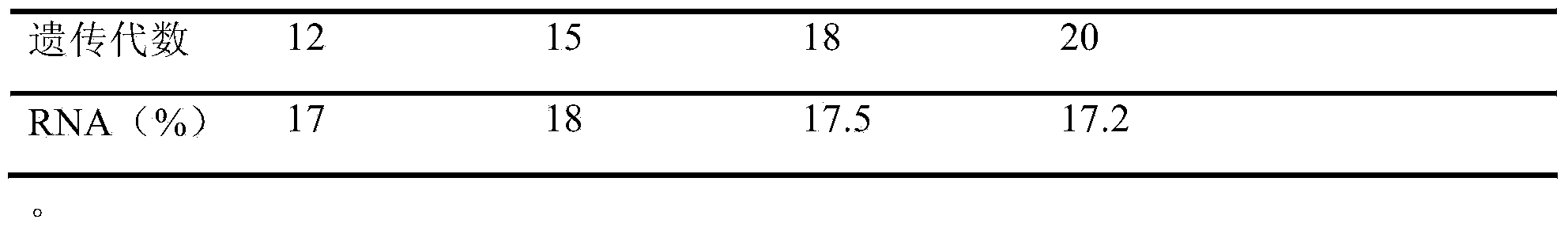
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ribonucleic acid by fermentation. The saccharomyces cerevisiae has a strain number of TKZZY-06 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, on April 26th, 2013, with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 7522. The invention also discloses an application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA content of the TKZY-06 strain thallus can reach 17.5% that of dry weight of the thallus and is increased by 9.5% than RNA yield of an original strain. The strain is subcultured by over 10 generations; and the performance for producing the ribonucleic acid can be kept stable.
Owner:NANJING BIOTOGETHER
Activation induced deaminase (AID)
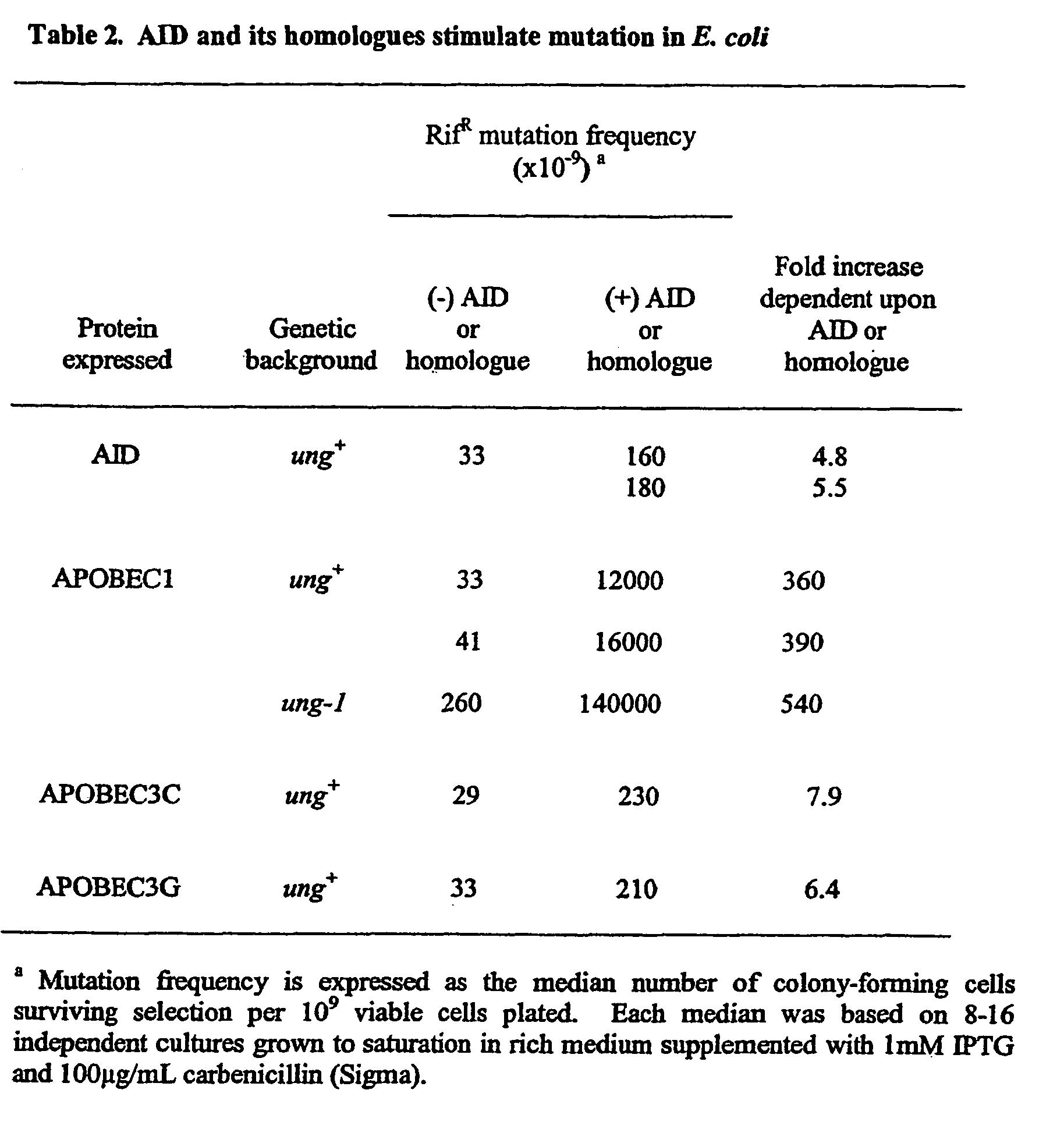
InactiveUS20060019262A1Increase mutation frequencyGood effectBacteriaHydrolasesGene productBiological activation
The present invention identifies that the expression of Activation Induced Deaminase (AID) or its homologues in cells confers a mutator phenotype and thus provides a method for generating diversity in a gene or gene product as well as cell lines capable of generating diversity in defined gene products. The invention also provides methods of modulating a mutator phenotype by modulating AID expression or activity.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Targeting opposite strand replication intermediates of single-stranded viruses by rnai
ActiveUS20100267805A1High activityReduce eliminateOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsSingle-Stranded RNASingle strand
The invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating viral replication through double-stranded RNA-mediated gene silencing (RNAi), wherein the antiviral methods and compositions preferentially target opposite strand replication intermediates of single-stranded RNA viruses.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Methods for generating hypermutable yeast
Yeast cells are mutagenized to obtain desirable mutants. Mutagenesis is mediated by a defective mismatch repair system which can be enhanced using conventional exogenously applied mutagens. Yeast cells with the defective mismatch repair system are hypermutable, but after selection of desired mutant yeast strains, they can be rendered genetically stable by restoring the mismatch repair system to proper functionality.
Owner:EISAI INC
Bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin
InactiveCN101974444AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateBacteriaMutant preparationBacterial strainButanediol
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin, which is preserved in a China general microbiological culture collection center with CGMCC No.3720 and the preservation data of April eighth, 2010. The invention also discloses a method for producing the D-ribose and co-producing the acetoin by fermenting the bacillus subtilis. The selected bacterial strains can produce produce the D-ribose and co-produce the acetoin by using the fermentation of a plurality of types of carbon and nitrogen sources, the operation is convenient and simple, the conditions of culture are extensive, and the industrialization is easy. In the invention, an organic acid is added to a fermentation medium, therefore, the yield of the D-ribose is improved by 64.5g / L compared with the original strains, and the acetoin is improved by 17.3g / L. The bacillus subtilis has higher capability for synthetizing the D-ribose and the acetoin, and the yield of reduced by-products of 2,3-butanediol of the acetoin is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
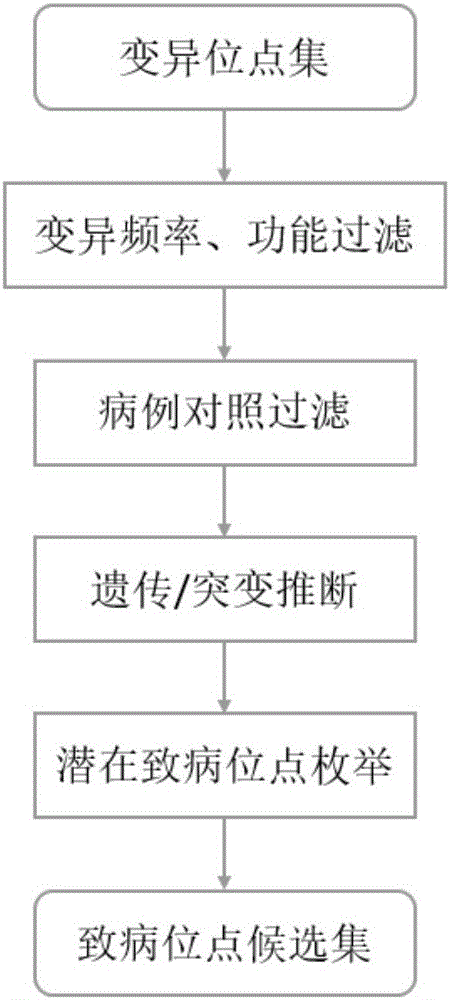
Exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on family line
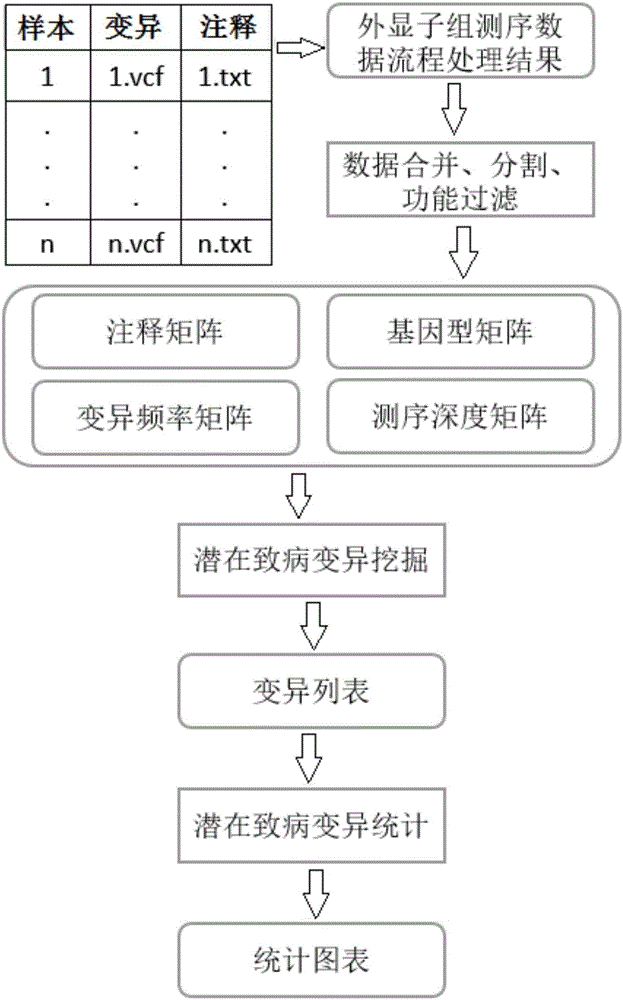
InactiveCN105925685ASolve the problem of mining potential pathogenic variantsImprove heterogeneityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsFiltrationSingle mutation
The invention provides an exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on a family line. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) reading a result file of an exome sequencing data processing flow, and conducting function filtering; 2) reading the file obtained in the last step, extracting mutations in all samples, calculating a union set, and then combining all samples, so that a matrix is constituted; 3) extracting mutation information in the matrix obtained in the last step, enumerating and assessing pathogenicity of single mutation and pathogenicity of combined dual-site mutation, so that a potential pathogenic mutation list is obtained; and 4) in accordance with the list obtained in the last step, calculating the appearance situations of sites in various samples and target genes. According to the method disclosed by the invention, data integration and basic filtration are completed by taking an output result of the common exome sequencing processing flow as an input condition; by virtue of a special mutation screening algorithm, a candidate set of the potential pathogenic mutations is provided; and the method focuses on solving a problem on potential pathogenic mutation mining of sequencing data with high heterogeneity, high mutation rate and high noise.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for determining the presence of SARS coronavirus in a sample
InactiveUS20060134609A1High sensitivityMinimizes reduction in sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSARS coronavirusTest sample
The present invention relates to oligonucleotides useful for determining the presence of SARS coronavirus in a test sample. The oligonucleotides of the present invention may be incorporated into detection probes, capture probes and amplification oligonucleotides, or used in various combinations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
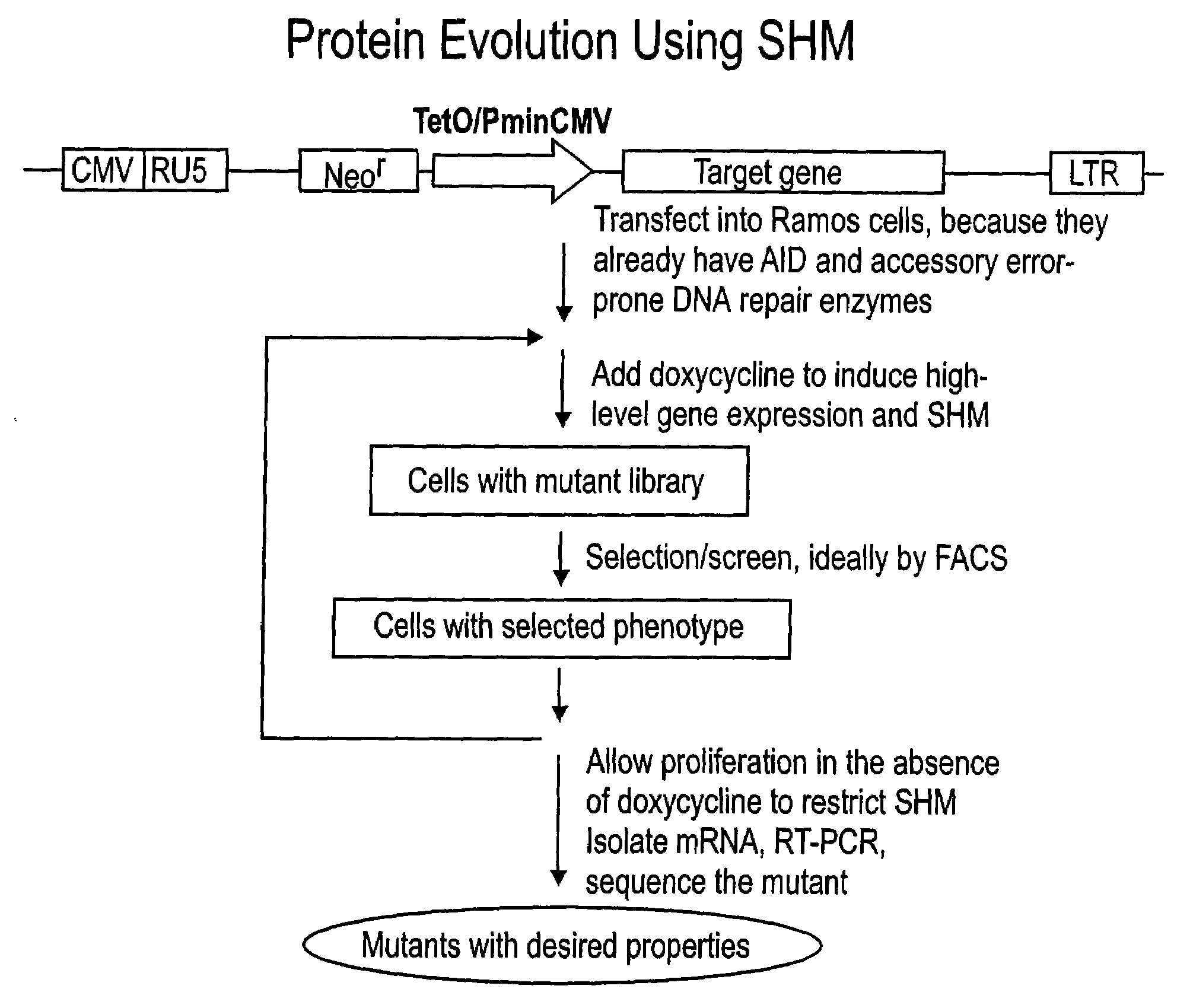
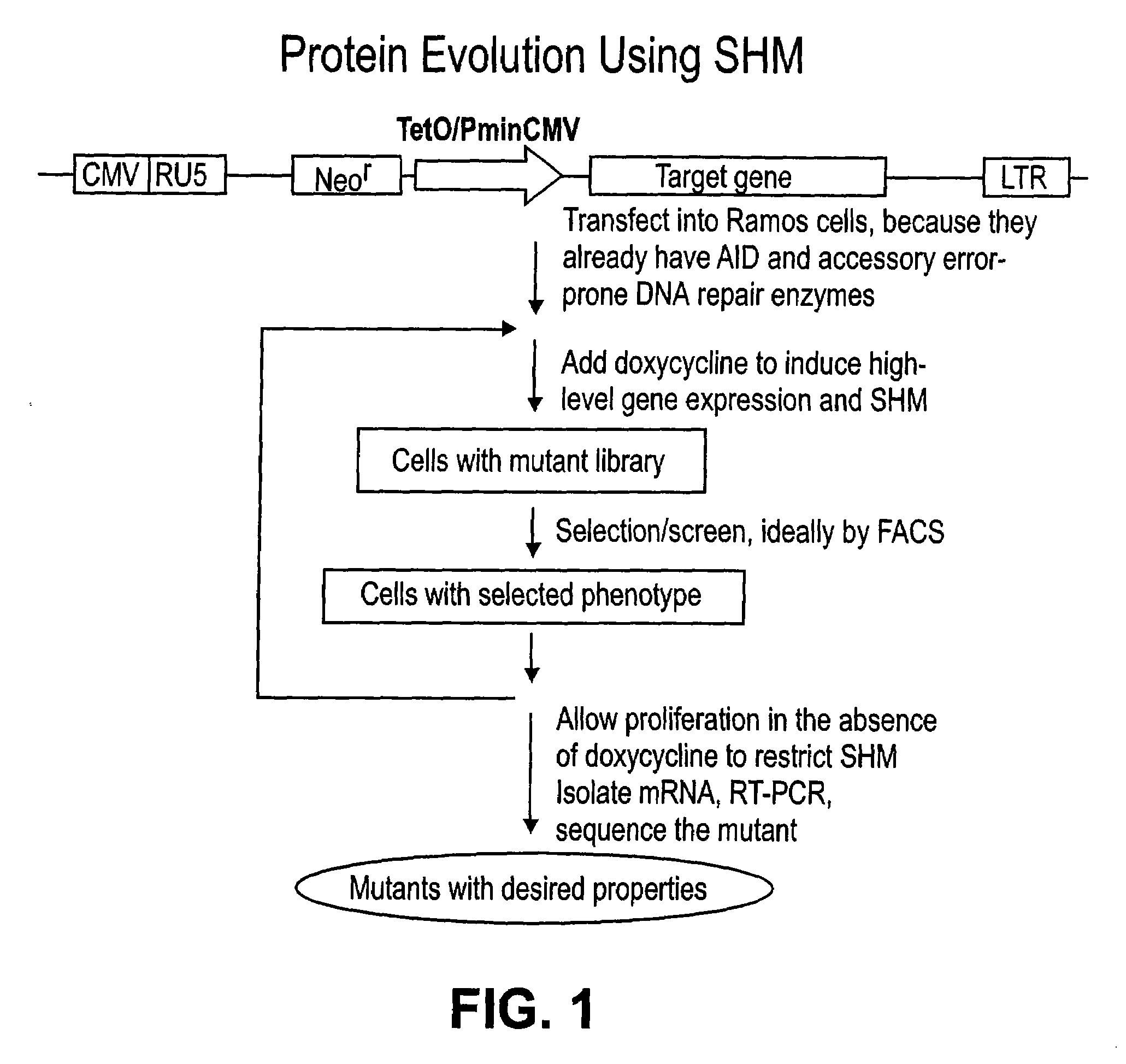
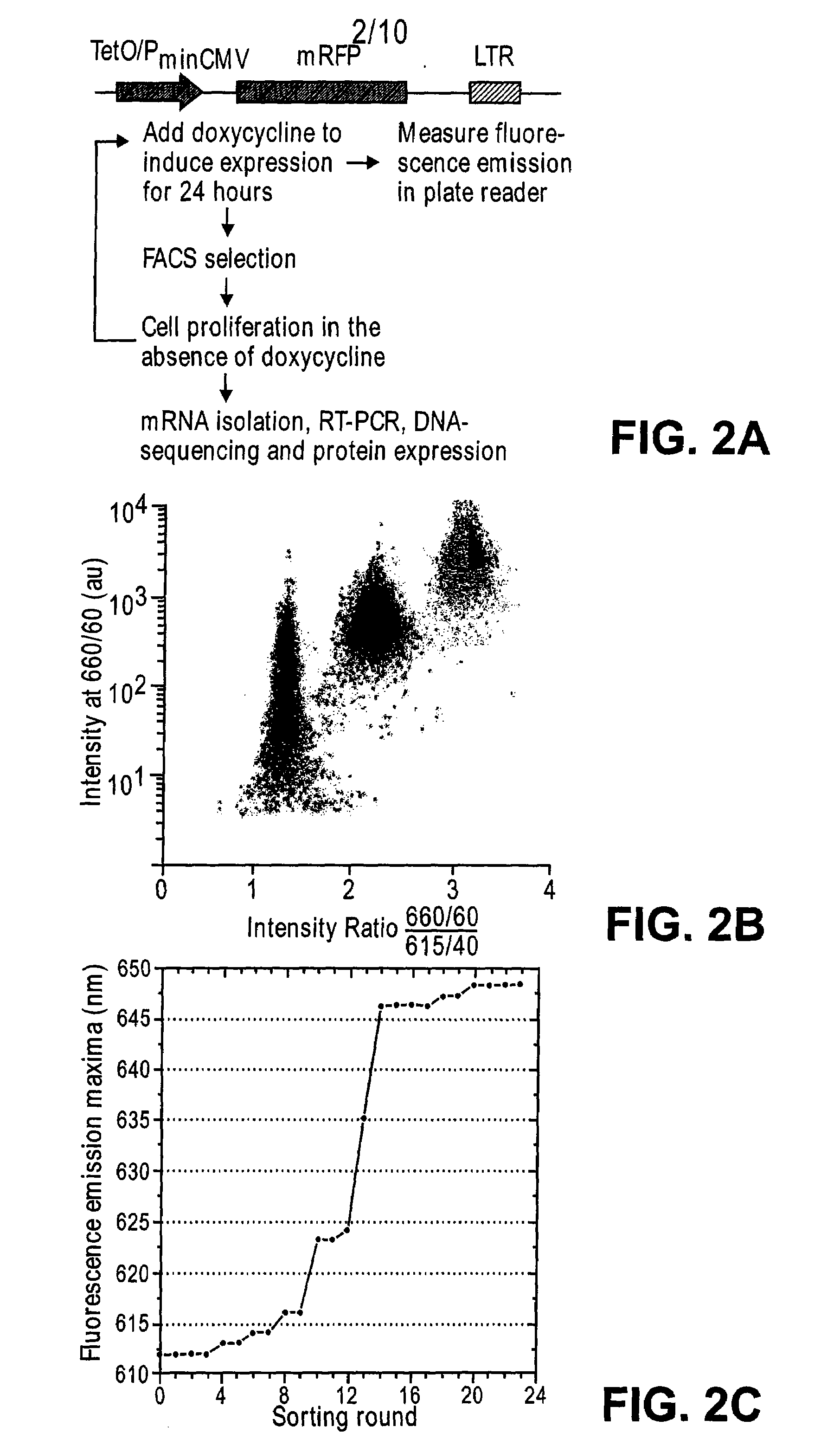
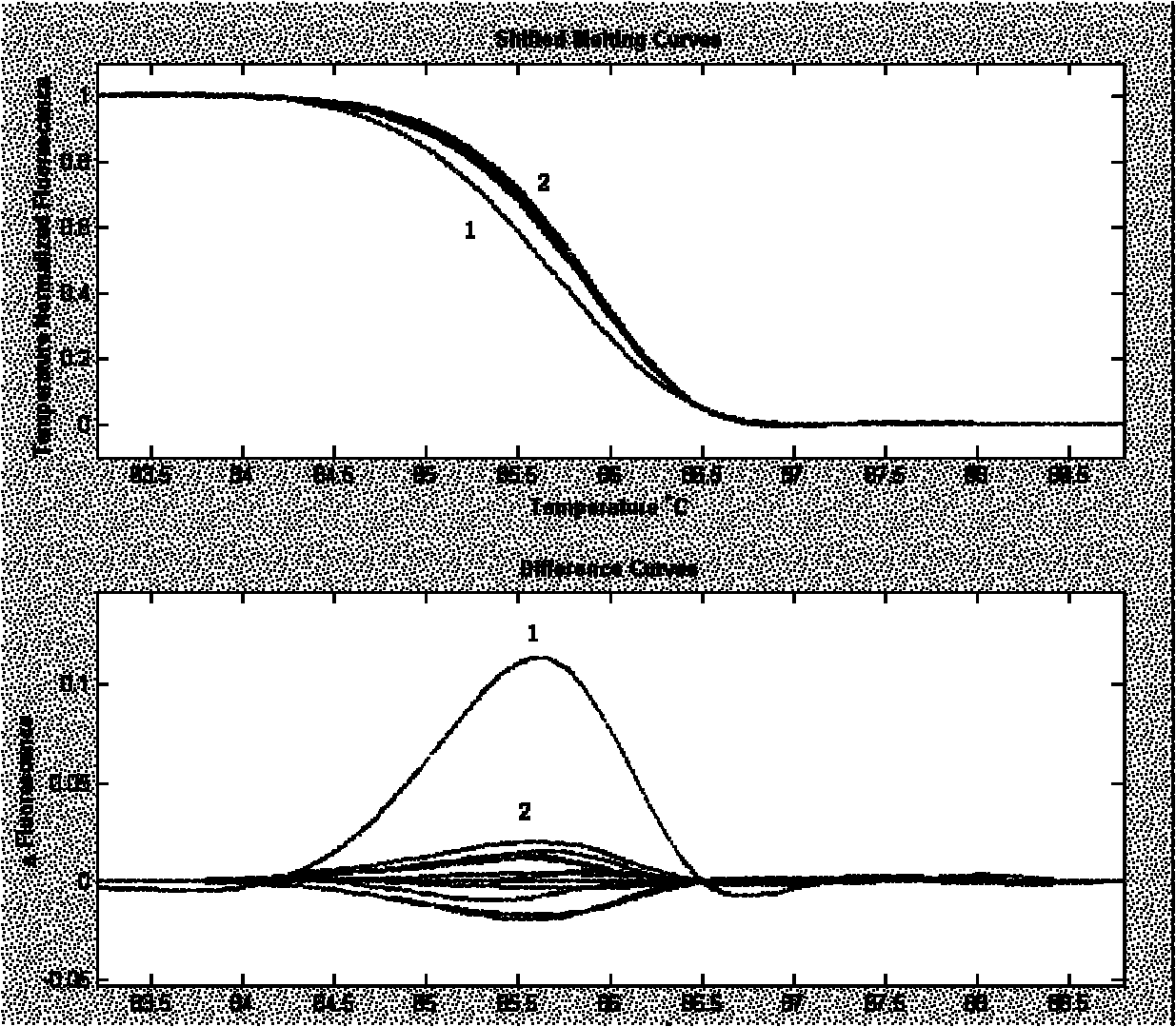
Methods for engineering polypeptide variants via somatic hypermutation and polypeptide made thereby
ActiveUS20080293068A1Improve light resistanceDesired propertyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFluorescent proteinSomatic hypermutation
Methods using somatic hypermutation (SHM) for producing polypeptide and nucleic acid variants, and nucleic acids encoding such polypeptide variants are disclosed. Such variants may have desired properties. Also disclosed are novel polypeptides, such as improved fluorescent proteins, produced by the novel methods, and nucleic acids, vectors, and host cells comprising such vectors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20110230433A1Reduced viabilityIncrease mutation frequencyBiocideMutant preparationCancer cellNucleoside Analogs
Described herein are novel methods and compositions for treatment of cancer by increasing the mutation rate of cancer cells beyond an error threshold, over which the cancer cells are no longer viable. In particular, mutagenic compounds such as nucleoside analogs for treatment of cancer are also described herein.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Mismatch repair gene MLH1 mutation detection kit and application thereof
InactiveCN101974642AIncreased susceptibilityHigh mutation rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDissolutionRFLP - Restriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention relates to a mismatch repair gene MLH1 mutation detection kit and application thereof. The kit comprises the main components: firstly, 20 pairs of MLH1 gene PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and sequencing primers; and secondly, a reagent for PCR amplification. A PCR amplification product obtained through the kit can be used for screening gene micromutation through a high resolution dissolution curve method or carrying out restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. The kit has high efficient MLH1 gene mutation detection and function evaluation actions and is used for mismatch repair gene MLH1 mutation detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method and kit for Coxsackie virus
InactiveCN102312017AShorten the lengthHigh variabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReverse transcription polymerase chain reactionBiology
The invention relates to a real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection method and a kit for a Coxsackie virus. Specifically, the invention discloses a method for detecting the Coxsackie virus, which is characterized in that a polymerase chain reaction is carried out in a polymerase reaction system. The polymerase reaction system comprises an amplification Coxsackie virus-contained specific primer pair and a Coxsackie virus specific probe. The invention also provides the corresponding kit. The invention is capable of sensitively, simply and conveniently detecting and verifying the Coxsackie virus.
Owner:PLANTS & ANIMALS & FOOD TESTING QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Novel attenuated virus strains and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090117149A1Reducing glycosylationReduce probabilityOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseVaccinationVirulent characteristics
Methods and compositions concerning mutant flaviviruses with reduced virulence. In some embodiments the invention concerns nucleotide sequences that encode mutant flaviviral proteins. Viruses comprising mutant NS1 and NS4B genes display reduced virulence are provided. In further aspects of the invention, flavivirus vaccine compositions such as West Nile virus vaccines are provided. In another embodiment the invention provides methods for vaccination against flavivirus infection.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for generating hypermutable organisms
InactiveUS20050188428A1Restore stabilityEnhance mutation rateMutant preparationTissue cultureGenetically modified animalOrganism
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. The enhanced rate of mutation can be further augmented using mutagens. Moreover, the hypermutability of mismatch repair deficient cells can be remedied to stabilize cells or mammals with useful mutations.
Owner:EISAI INC
Red-shifted fluorescent proteins mPlum and mRaspberry and polynucleotides encoding the same
ActiveUS7393923B2Improve light resistanceDesired propertyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
Methods using somatic hypermutation (SHM) for producing polypeptide and nucleic acid variants, and nucleic acids encoding such polypeptide variants are disclosed. Such variants may have desired properties. Also disclosed are novel polypeptides, such as improved fluorescent proteins, produced by the novel methods, and nucleic acids, vectors, and host cells comprising such vectors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for generating hypermutable microbes
InactiveUS7026119B2Decrease endogenous mmr activityRendering hypermutableBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMismatch Repair ProteinDominant negative
Bacteria are manipulated to create desirable output traits using dominant negative alleles of mismatch repair proteins. Enhanced hypermutation is achieved by combination of mismatch repair deficiency and exogenously applied mutagens. Stable bacteria containing desirable output traits are obtained by restoring mismatch repair activity to the bacteria.
Owner:EISAI INC +1
Method for preparing glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and mutant thereof
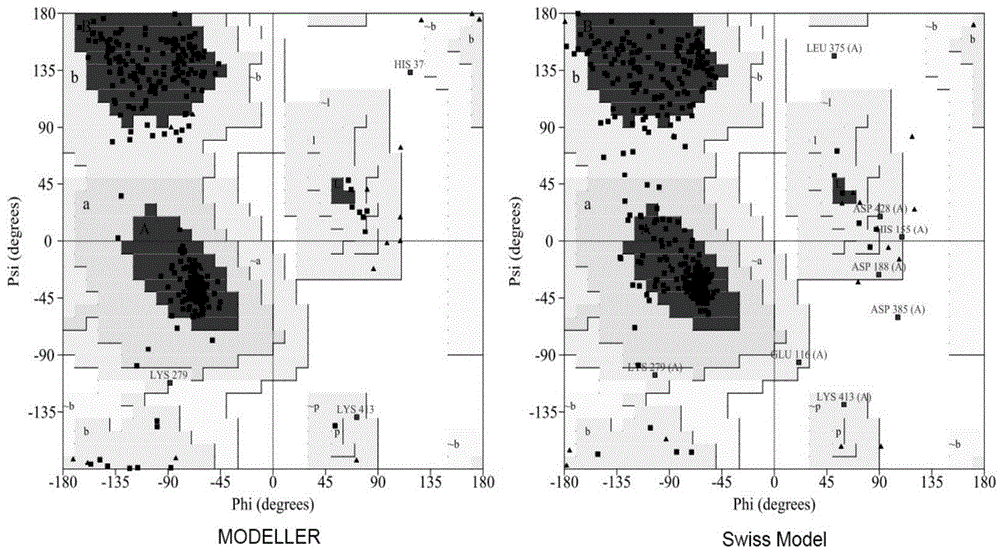
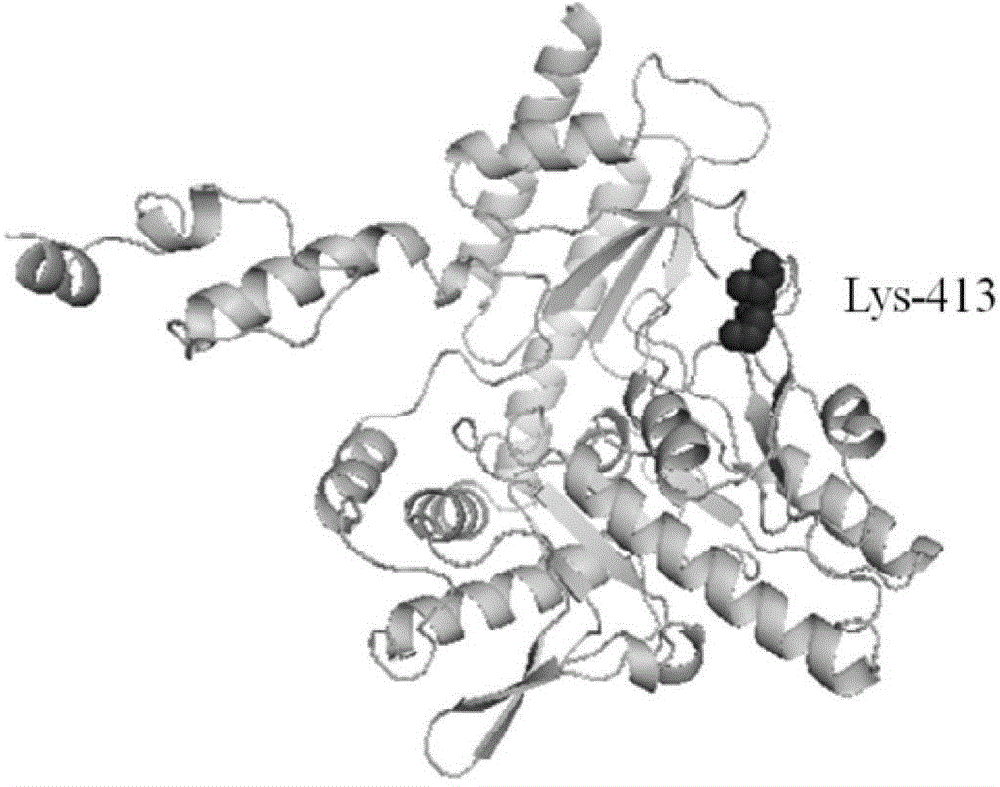
InactiveCN104694524AIncrease reaction rateEase of industrial productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for preparing a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and a mutant thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a three-dimensional structural model of glutamic acid decarboxylase, carrying out dihedral angle reasonable evaluation to generate a ramachandran map, and determining an amino acid residue site in an unreasonable conformation area from the ramachandran map; designing a site-specific mutation primer aiming at the site, and carrying out site-specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene as a template so as to obtain a site-specific mutation library; and screening the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant from the site-specific mutation library. Enzyme is rationally designed through structural information provided by the ramachandran map; in combination with a site-specific mutation technology, the mutation probability is effectively increased; the time is saved; the experimental efficiency is increased; mutant enzyme the catalytic activity of which is superior to wild type enzyme can be obtained by screening; the mutant enzyme is capable of increasing the reaction rate for generating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof; and thus, industrial production of GABA is easily carried out.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Method for increasing EMS induced mutation rate of wheat
PendingCN109729972AHigh mutagenesis rateHigh mutation ratePlant genotype modificationSeed immunisationInduced mutationGermination
The invention discloses a method for increasing the EMS induced mutation rate of wheat. The method comprises the following steps: seed pretreatment, soaking, cleaning, germination treatment, induced mutation treatment, termination, plantation and screening. Based on the characteristic that tender tissues and growth sites are most sensitive to EMS, whitened seeds are subjected to induced mutation treatment by virtue of an EMS solution, so that the mutation rate of the seeds is effectively increased, and the working efficiency of the seeds is effectively improved.
Owner:WHEAT RES INST OF AGRI SCI
Schizochytrium limacinum strain as well as mutagenesis method and application thereof
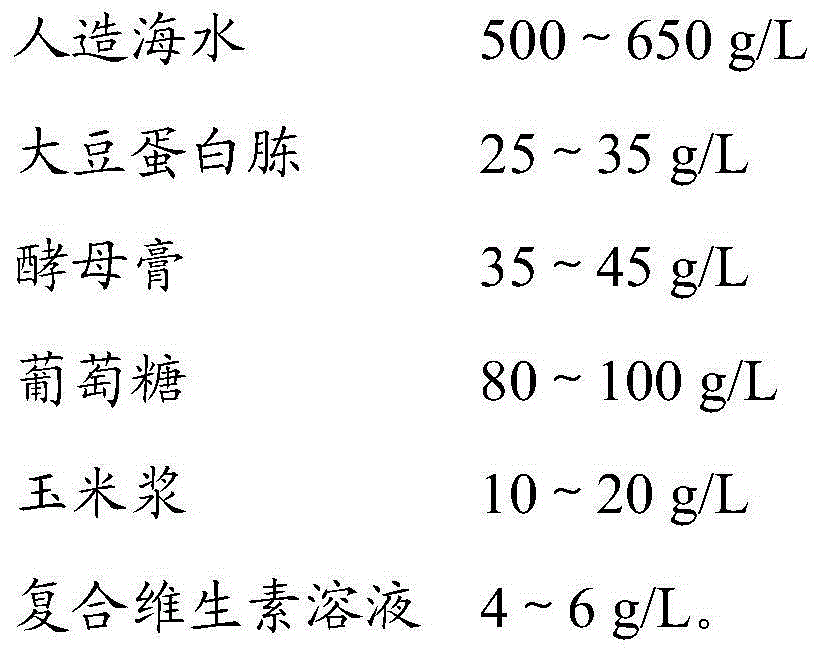
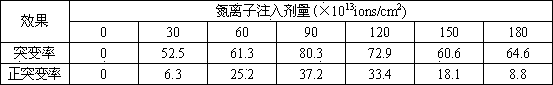
InactiveCN104450529AImprove reproductive abilityGenetically stableFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIon beam
The invention provides a schizochytrium limacinum strain as well as a mutagenesis method and an application thereof. In the prior art, although how to improve the content of DHA in a strain is reported, since the consideration factor is often single, how to significantly improve the content of DHA in the strain is not comprehensively explored which also is a key to achieve the industrialization of schizochytrium limacinum. Schizochytrium limacinum TC5-2 is obtained by virtue of an ion beam mutagenesis method, by combining a culture medium, optimizing a fermentation process and adding an exogenous factor clethodim, the content of DHA in the strain is significantly improved which is conductive to achieving the industrialization of production of DHA by virtue of schizochytrium limacinum.
Owner:郭星
Method for injecting low-energy N<+> for mutation breeding hericium erinaceus strain and bred strain
ActiveCN103805593AIncrease productionNot easy to degradeFungiMutant preparationBiotechnologyGenetic traits
The invention discloses a method for injecting low-energy N<+> for mutation breeding a hericium erinaceus strain and the bred strain. The preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.8610. The breeding method comprises the following steps: screening a hericium erinaceus starting strain subjected to mutagenesis; selecting a protoplast of the hericium erinaceus starting strain as a material for mutagenesis by injecting low-energy nitrogen ions; injecting nitrogen ions for mutagenesis; screening a mutant strain; verifying genetic trait stability, and the like. A novel hericium erinaceus strain of which the fruiting body yield is higher than that of the parent strain is mutated by the invention, the yield of the hericium erinaceus is improved, and good economic benefits can be created.
Owner:JIANGSU ANHUI BIO TECH +1
Transformed CRISPR/SaCas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat/streptococcus pyogenes Cas9) system targeting at hepatitis B virus and application of system
ActiveCN111139240AAntiproliferative activityStrong specificityHydrolasesDigestive systemStreptococcus pyogenesHepatitis B immunization
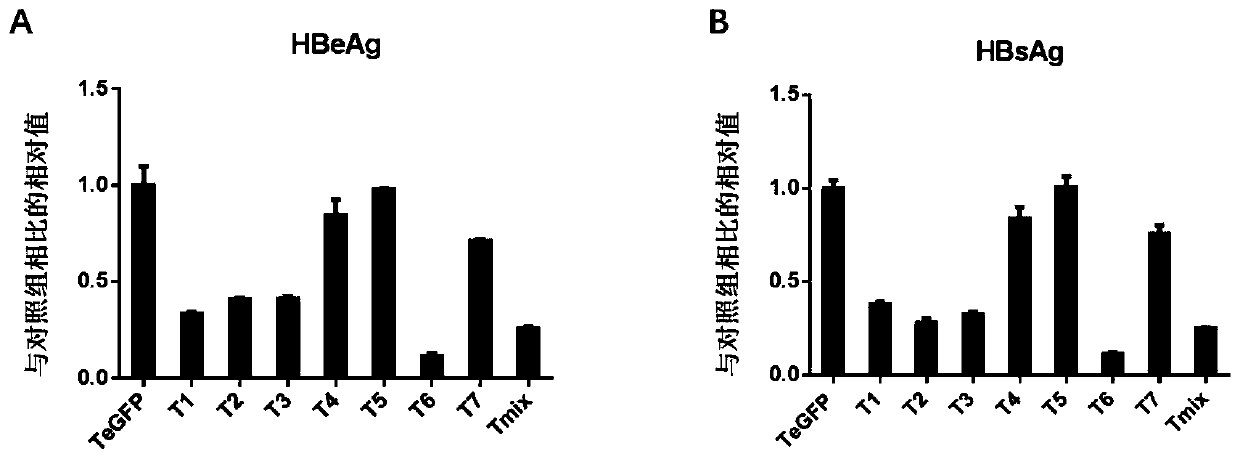
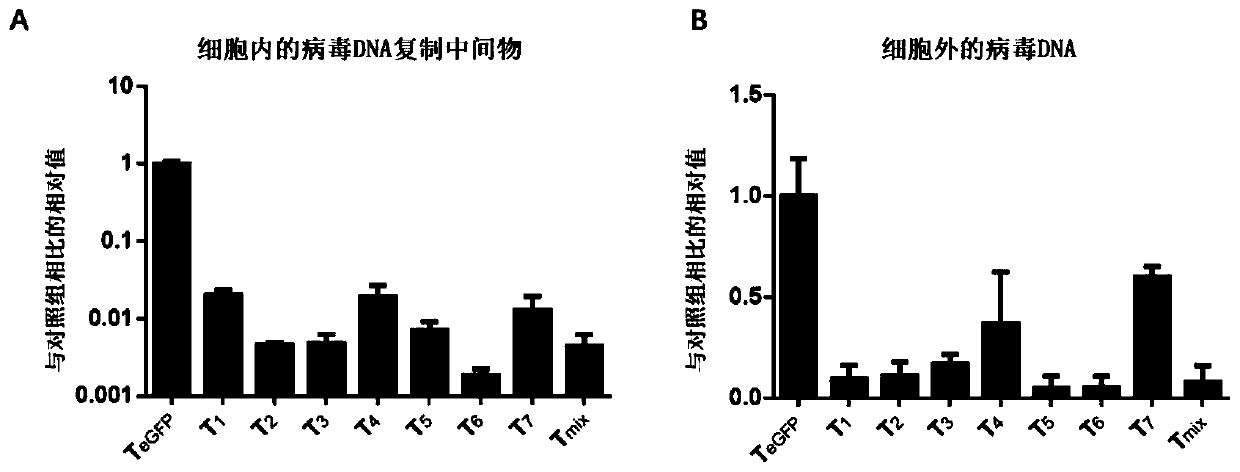
The invention discloses a transformed CRISPR / SaCas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat / streptococcus pyogenes Cas9) system targeting at hepatitis B virus and application of thesystem. According to designing principles of gRNA (guide ribonucleic acid) of CRISPR and conservative regions of HBV (hepatitis B virus) sequences of different genotypes, three gRNAs are screened andconstructed on a PX601expression vector, meanwhile, different specific liver promoters are selected and combined with an enhancer of an HBV genome, and two promoter combinations are screened to transform the expression vector PX601. When the rRNA guided CRISPR transformation system is applied to cell models and mouse models, expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genes can be effectivelyinhibited while liver tissue expression specificity of SaCas9 is remarkably improved. The system is easy to operate, high in security and high in HBV replication. The transformed CRISPR / SaCas9 systemhas the potential of being a novel treatment medicine for treating hepatitis B virus.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods of generating high-production of antibodies from hybridomas created by in vitro immunization
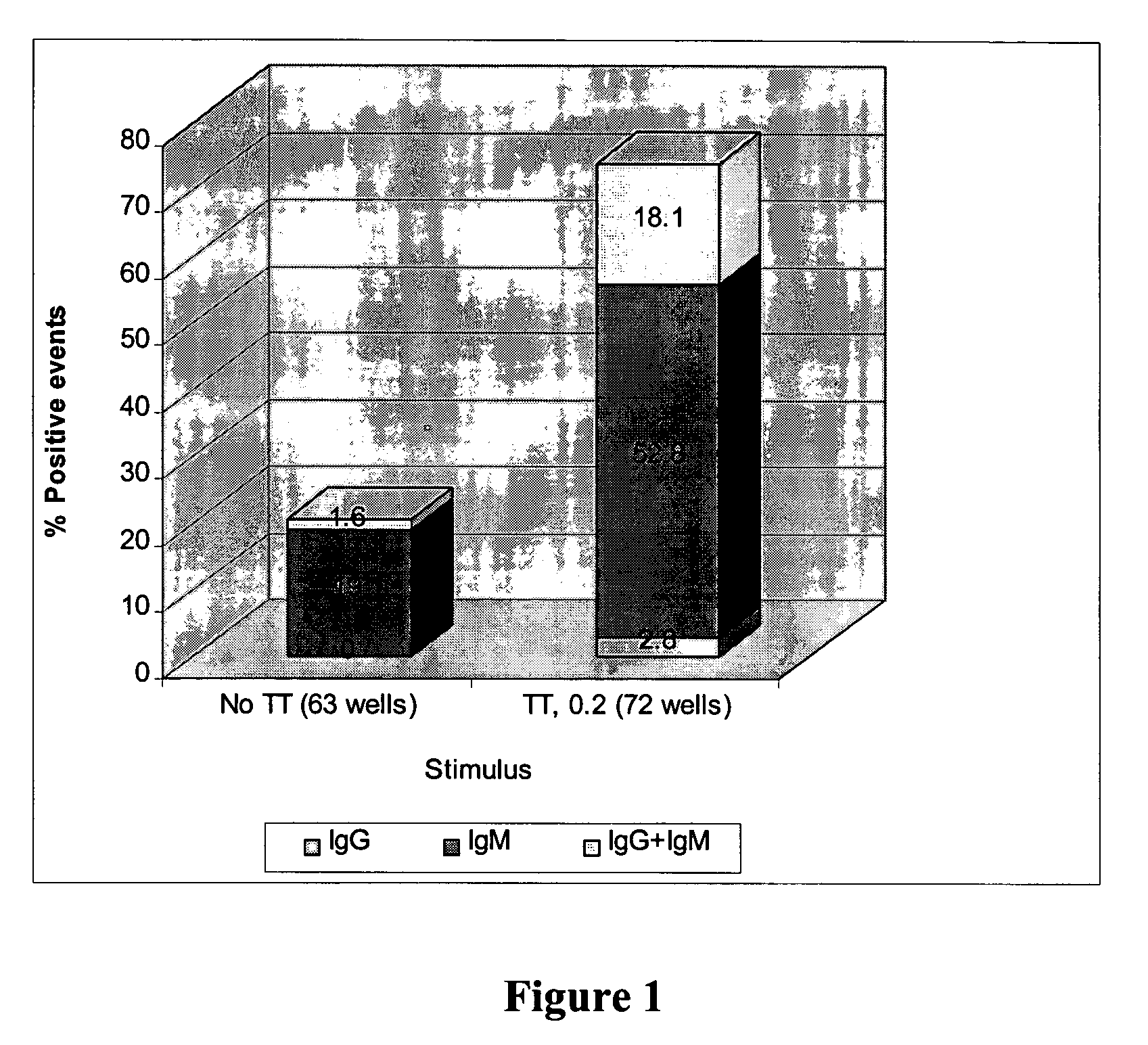
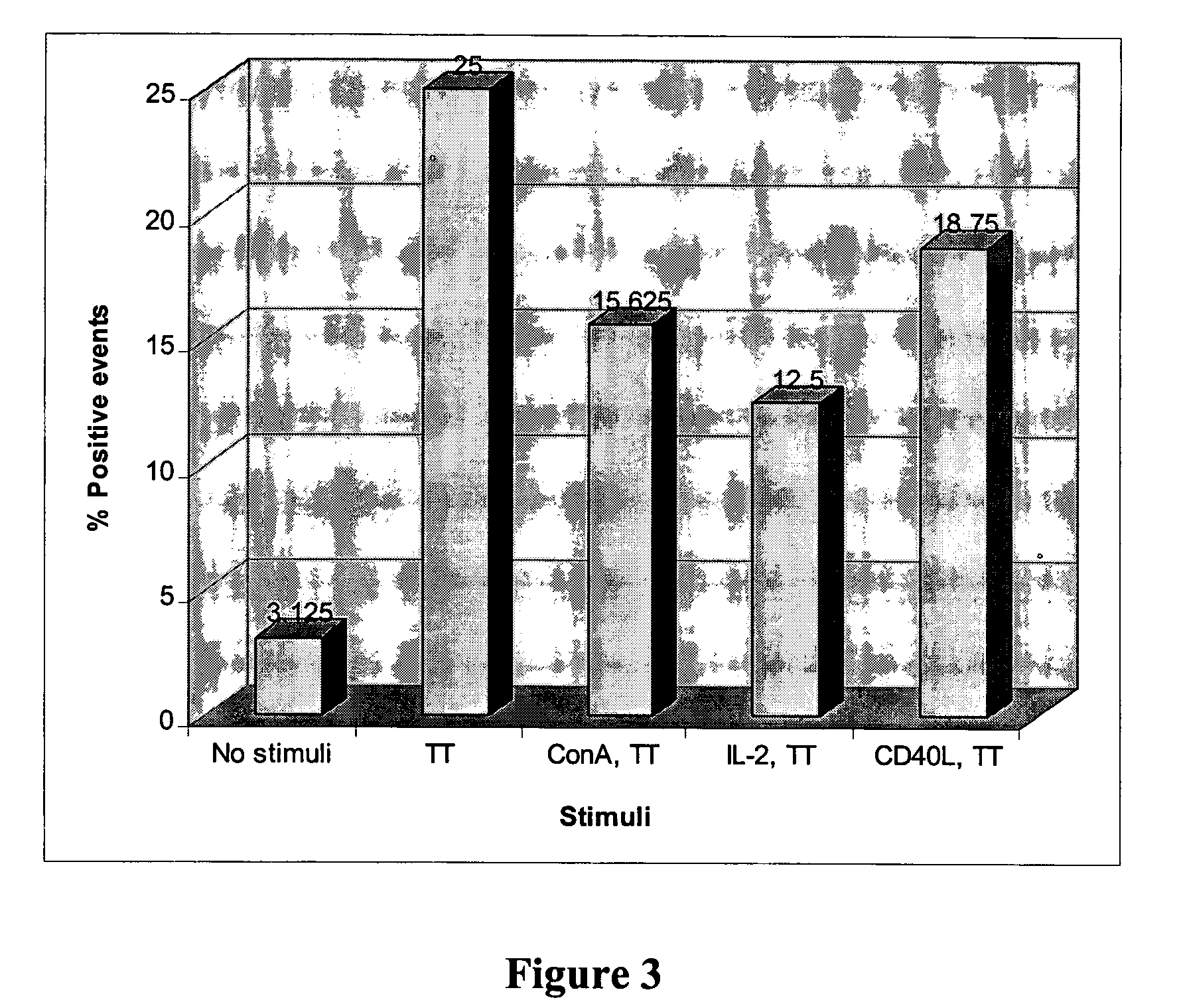
InactiveUS7754450B2Stabilizing genomeHigh mutation rateImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMutant preparationAlleleMammalian expression
The invention provides methods for generating high titers of high-affinity antibodies from hybridoma cells produced by fusing myeloma cells with in vitro immunized donor cells. The hybridoma cells or mammalian expression cells with cloned antibody genes from the hybridomas producing the high-affinity antibodies may be mismatch repair defective due to defects of endogenous mismatch repair subunits of through expression of a dominant negative allele of a mismatch repair gene which allows the hybridoma cell to be hypermutable, may be rendered hypermutable by chemical means, or may be naturally mismatch repair deficient. High-affinity antibodies and high titer producer cells producing antibodies may be prepared by the methods of the invention.
Owner:EISAI INC
Breeding method for colored-leaf-variety of Portulacaria afra
InactiveCN106900548AImprove mutation rate and transplant survival rateShorten the breeding periodPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMutagenic ProcessPortulacaria afra
The invention relates to the technical field of plant tissue culture, in particular to a breeding method of a golden branch jade leaf color leaf variety. The present invention combines tissue culture technology with two mutagenesis methods of colchicine chemical mutagenesis and radiation induction, which significantly improves the mutation rate of golden branch and jade leaves, shortens the breeding period, expands the variation range of plants at the same time, and reduces the impact of parents on The limitation of variation types provides a simple and efficient method for the breeding of new varieties of Jinzhiyuyecai, which enriches the planting resources of Euonymus.
Owner:河南红枫生物高科股份有限公司
Selection methods
A rational method for obtaining a novel molecule capable of a desired interaction with a substrate of interest comprising selecting hosts or replicators which encode said novel molecules based upon cell or replicator growth caused by the desired interaction of the novel molecule and a selection molecule expressed by said host.
Owner:WOHLSTADTER JACOB NATHANIEL
Ion beam injection mutation breeding method for cordyceps militaris strains and cordyceps militaris strains bred therethrough
ActiveCN104885931AExcellent productivityPromote growthFungi productsLichen productsMicroorganismCordyceps
The invention relates to a cordyceps militaris strain preserved in CGMCC on Oct. 22th, 2014, with the preservation number thereof to be CGMCC No. 9818. The invention also provides the application of the above strain in the liquid fermentation and production of cordycepin and cordyceps militaris mycelium and the solid culture and production of cordycepin, and the ion beam injection mutation breeding method for cordyceps militaris strains. The cordyceps militaris strain is excellent in cordycepin production performance, and the cordycepin yield of the above strain is higher than that of an original strain by 8.85 times.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com