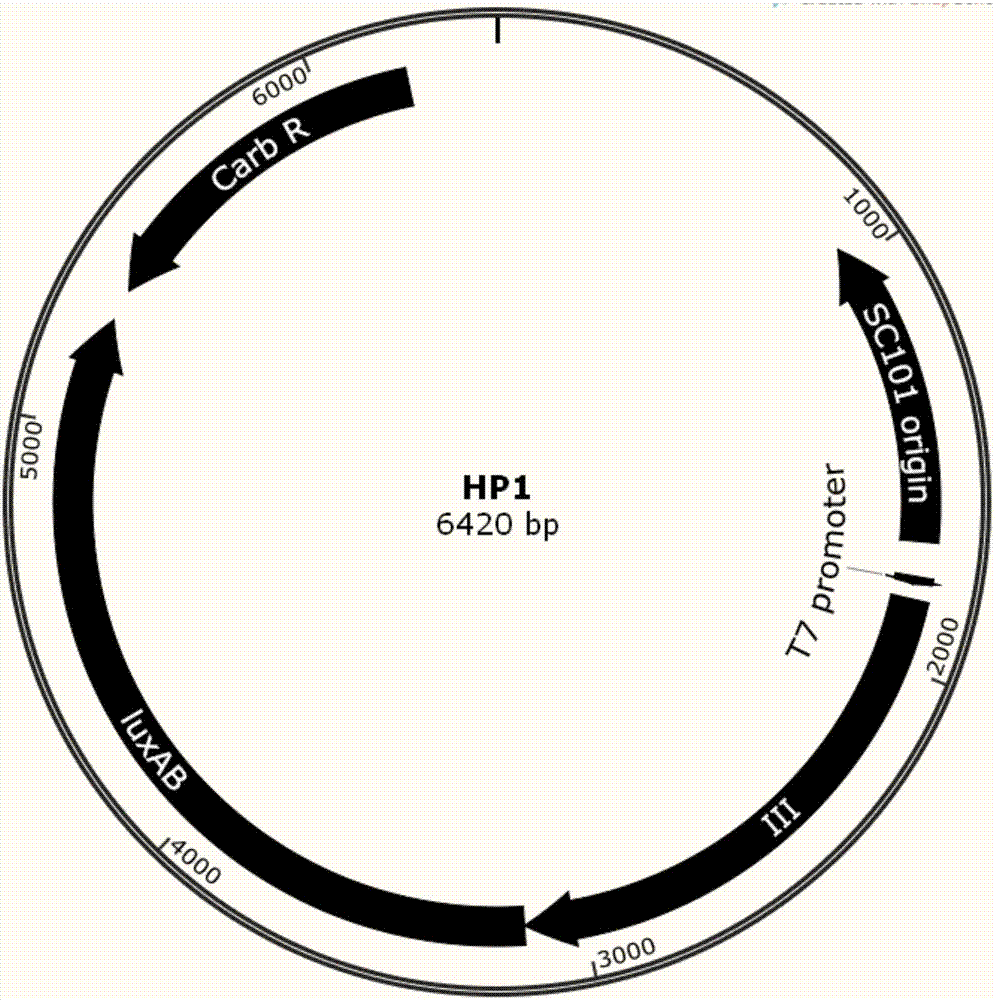
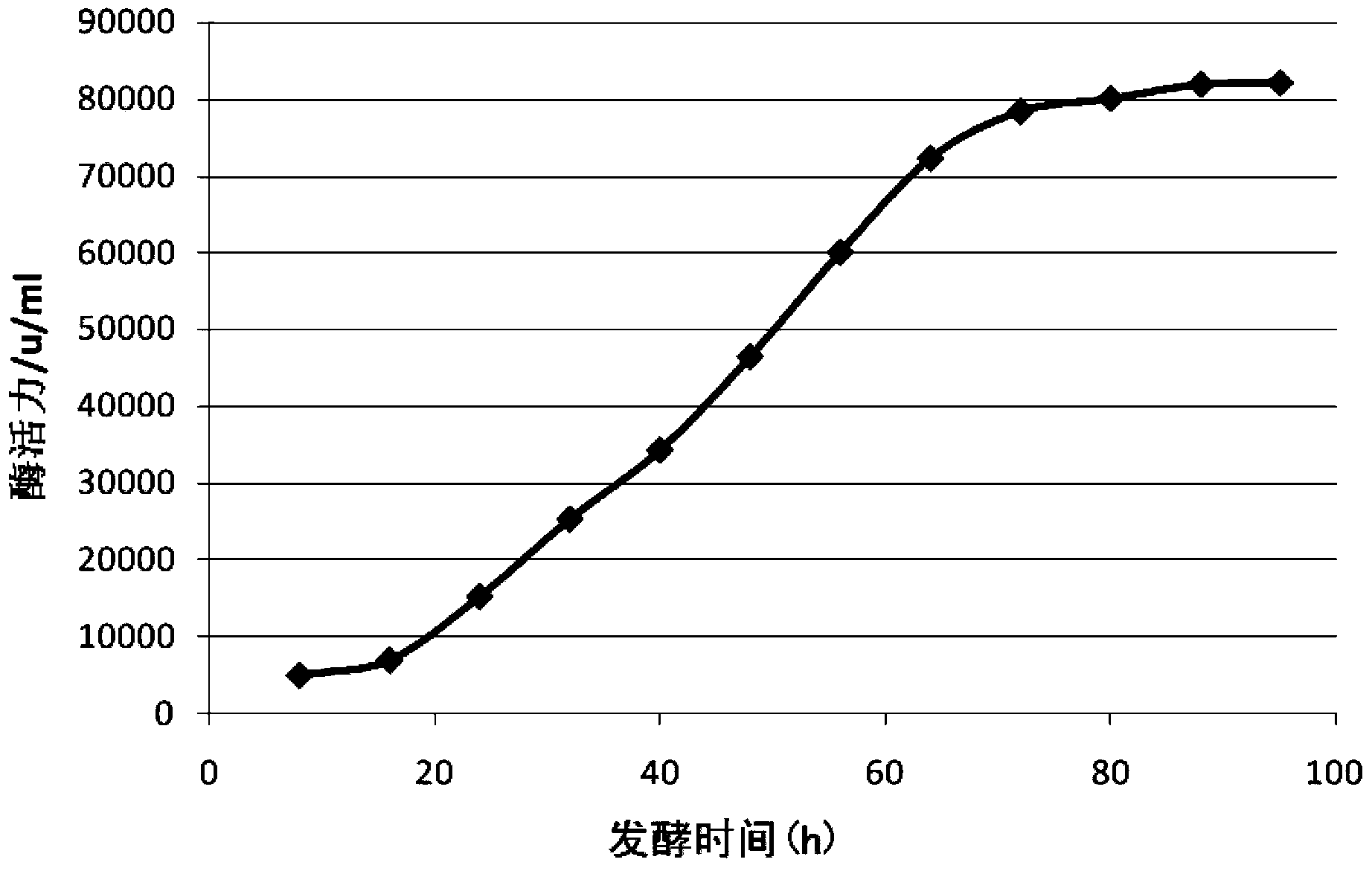
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
145 results about "Induced mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
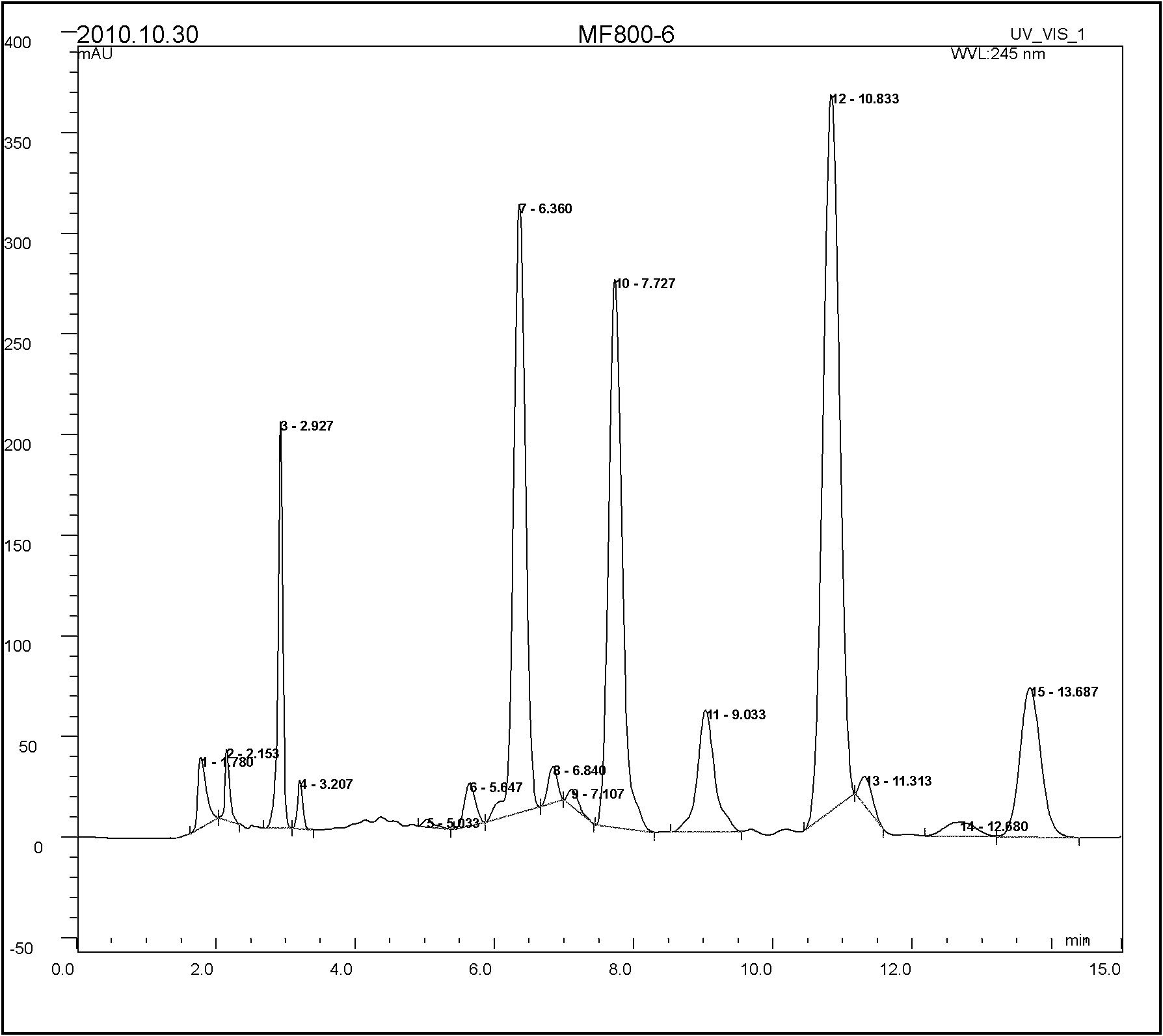
Microalga strain with high CO2 tolerance and high fixation rate and breeding method thereof
InactiveCN102703326AImprove toleranceEasy to fixUnicellular algaeMutant preparationHigh concentrationOrganism
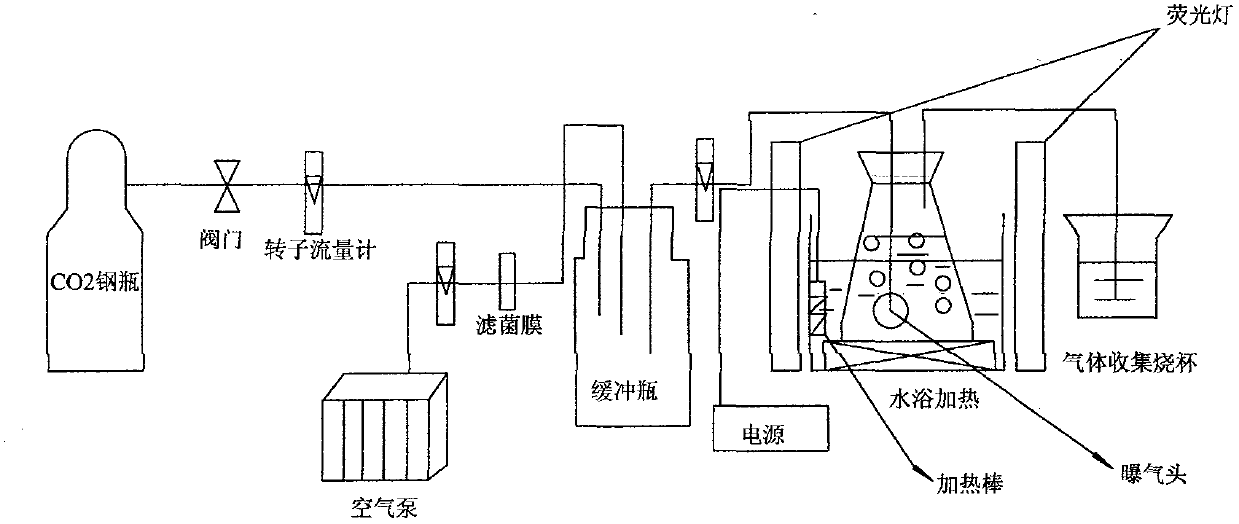
The invention belongs to the technical field of microalga biology, and particularly relates to a microalga strain with high CO2 tolerance and high fixation rate and a breeding method thereof. The microalga is named Chlorella sp.Y-1, and is collected into Common Microorganism Center of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Committee; and collection number is CGMCC No.5429. The invention has the following characteristics: the initial strain is separated from natural environment; after high-CO2-concentration enrichment culture, gene cloning, induced mutation breeding and other operations, the carbon content of the target strain is increased to 56.981%, the optimal fixation concentration is up to 20% (v / v), the fixation rate is up to 5.762g / (L.d), and the maximum tolerance concentration is 100% (v / v); and the target strain has high adaptability to a series of physical and chemical culture conditions, has high culture transfer stability, and high better overall properties than the like research findings at present. The invention aims to solve the bottleneck problem in high concentration CO2 biological fixation technology, cultures an efficient organism capable of efficiently fixing high concentration CO2, implements effective fixation of CO2 in high concentration flue gas and other complex environments, and meanwhile, generates beneficial biological substances.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system of radiation profiling
InactiveUS20170199979A1Improve accuracyImprove completenessMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHealth-index calculationMedical recordWhole body
The present invention relates to a method and system of risk assessment, by profiling individuals to quantify radiation or agent sensitivity and risk on both organ specific and collective whole body levels, using data including demographic information, medical records, and data from embedded, mobile or fixed sensors. The risk assessment may include analytics on genetic make-up, family history, occupational history, environmental history, medical history, physical attributes, age / gender, socio-economic status, education, and health awareness. When the data is combined with actual and estimates of radiation or agent dose exposures in a geographic environment, the net result is the creation of a risk score which determines the predicted risk an individual has for developing induced mutation, organ injury, and / or cancer.
Owner:REINER BRUCE
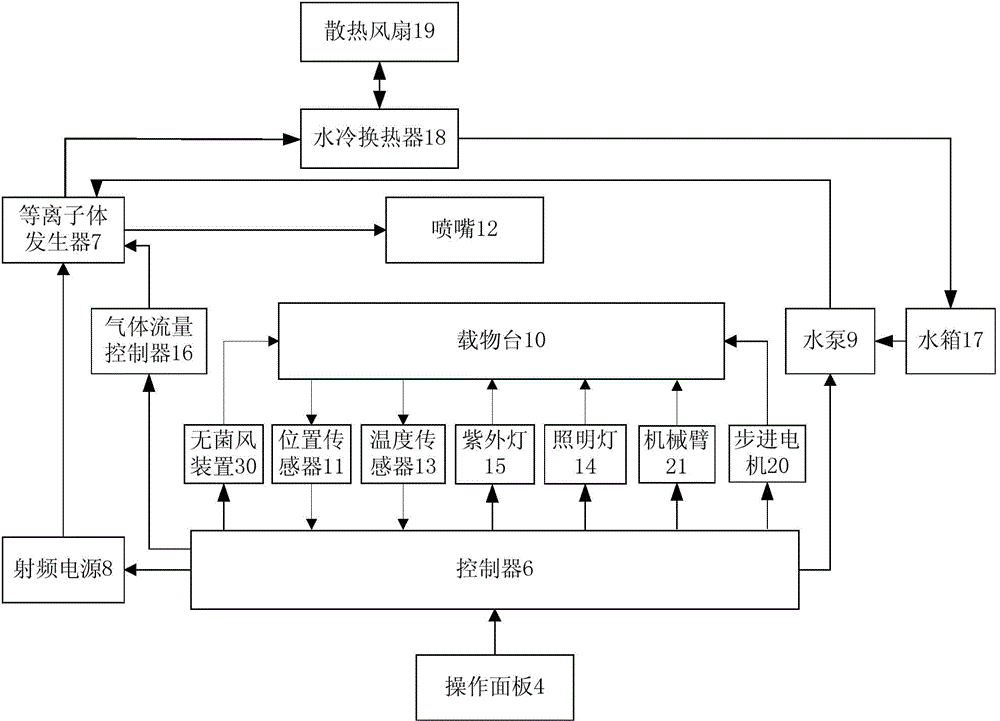
Novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device
ActiveCN103981091ASmooth dischargeEnables continuous automated processingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInduced mutationControl system
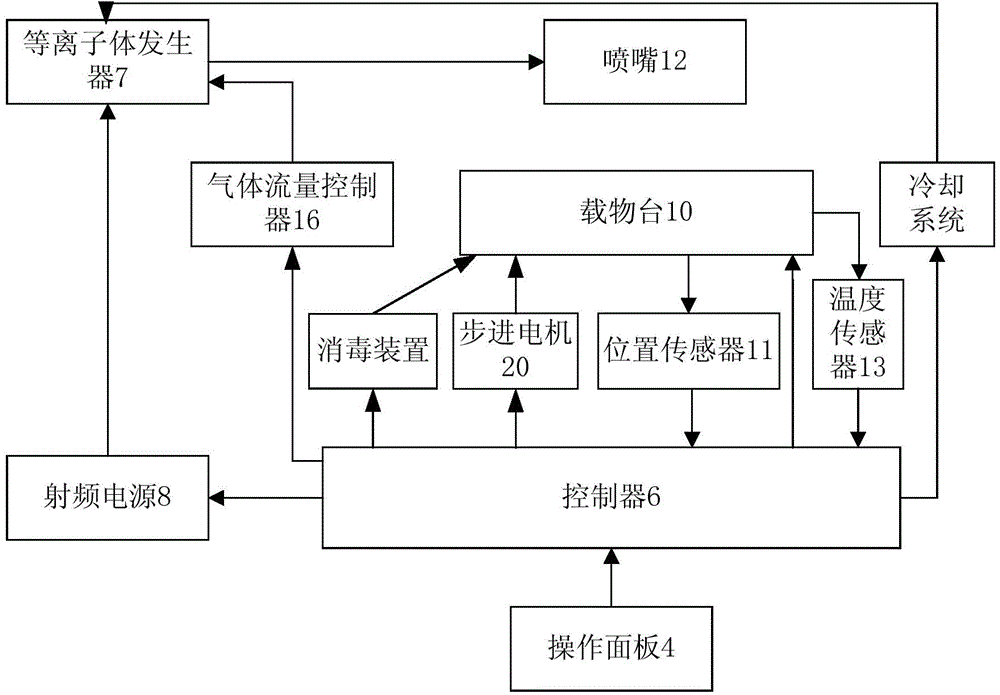
The invention relates to a novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device. The novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device comprises a sample processing system, a cooling system, a control system and a detection system; the sample processing system comprises a clean working chamber without bioactive contaminants; a step motor and an object stage are arranged in the clean working chamber; the object stage is arranged on the step motor; at least one sterilizing device mounting position is reserved in the inner cavity or on the wall of the clean working chamber; the detection system comprises a gas flow controller, a temperature sensor and a position sensor; and the control system comprises an operating panel and a controller, and the controller is used for controlling the step motor to realize rising and falling or horizontal rotation of the object stage so as to automatically process a plurality of samples. The novel normal-pressure room-temperature plasma induced mutation breeding device is capable of realizing the functions of continuous automatic processing, automatic sterilization, automatic monitoring and control on the samples, and also capable of completing the plasma induced mutation breeding in the normal pressure and room temperature environment at higher efficiency.
Owner:WUXI TMAXTREE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Rhamnolipid high-yielding bacterial strain, and applications thereof
InactiveCN106987545APromote growthIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycerolBacterial strain
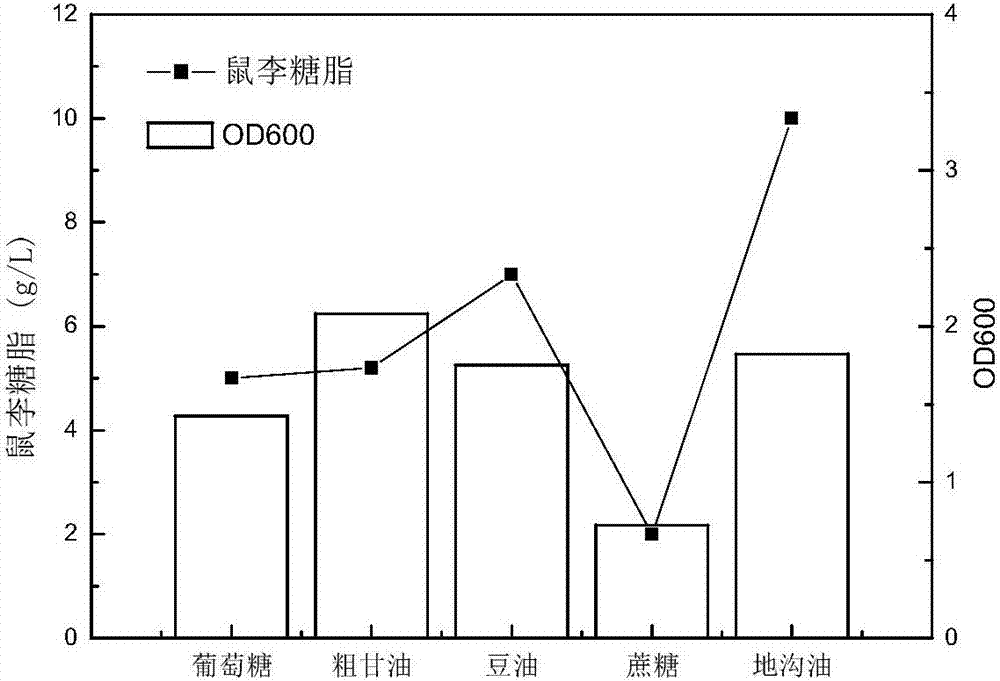
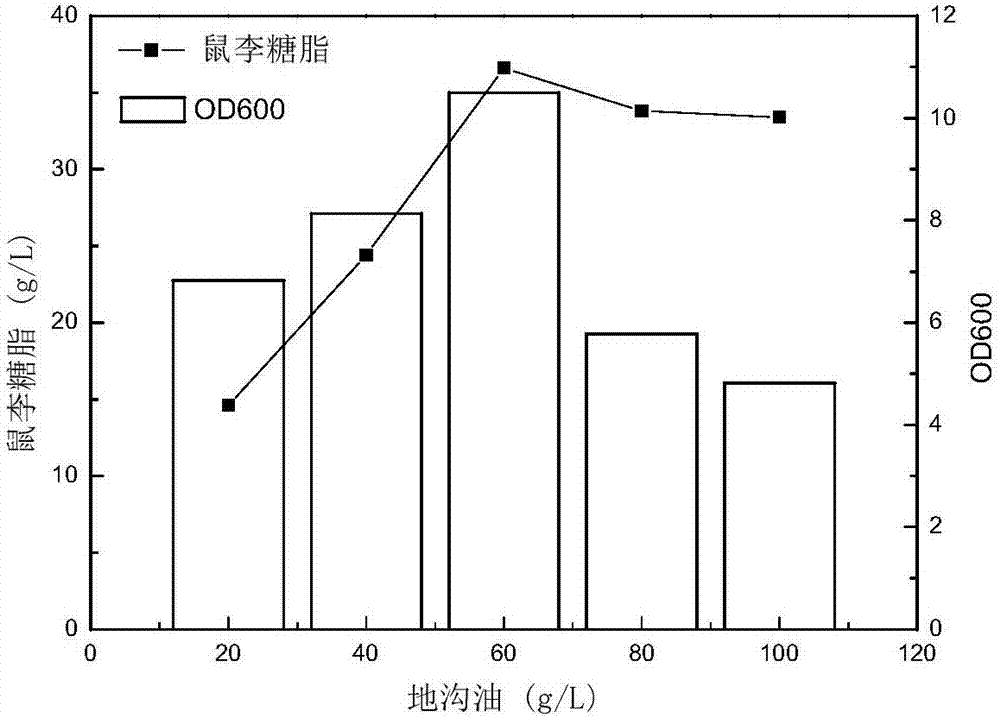
The invention discloses a rhamnolipid high-yielding bacterial strain, and applications thereof. The rhamnolipid high-yielding bacterial strain is named as pseudomonas aeruginosa KT1115, is preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016686. The rhamnolipid high-yielding bacterial strain is stable in hereditary features and high in rhamnolipid yield, and is obtained via ARTP induced mutation, blue gel plate screening, and secondary screening. According to fermentation broth of pseudomonas aeruginosa KT1115, liquid surface tension is reduced to 24.8mN / m<2>, and emulsification value is as high as 80%. Optimization of fermentation conditions including carbon source and nitrogen source single factors, cheap crude glycerine and swill-cooked dirty oil are taken as a composite carbon source, so that production cost is reduced greatly. The rhamnolipid yield of pseudomonas aeruginosa KT1115 is 50.7g / L, is increased by 18.1 times compared with that of a starting strain, conversion rate is 0.75g / g, and is relatively high. Application prospect of pseudomonas aeruginosa KT1115 in further industrialized application is promising.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Plant lactobacillus M1-UVs29 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101402923AImprove securitySmall side effectsMilk preparationBacteriaFood additiveMetabolite
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 with an accession number of CGMCC No.2591. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 can be isolated from fermented meat products of various resources, such as preserved ham, sausage, salami, Xuanwei ham and the like, and is obtained after induced mutation and optimization. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 is a new strain of the induced mutation and isolation and has superior safety and minimal toxic and side effects, and can relieve classical clinical symptoms of coronary heart diseases, atherosclerosis, hyperlipemia and the like and treat cardiovascular diseases of various coronary heart diseases, atherosclerosis, hyperlipemia and the like incurred by hyperlipemia in a safe and effective way. The Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 is applied to the production of beverages, and health products of dairy products, fermented milk, acidsoy milk and the like and food additives. The obtained products of beverages, health products and food additives, containing the fermented Lactobacillus plantarum M1-UVs29 or metabolins, cell debris or secretions thereof, can effectively degrade cholesterol self-cumulated by human bodies and self-contained by food.
Owner:于长青
Microbial bacterial strain for producing sphingolipid alkali
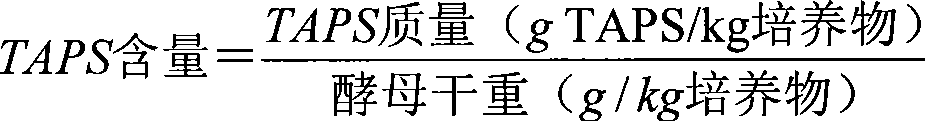
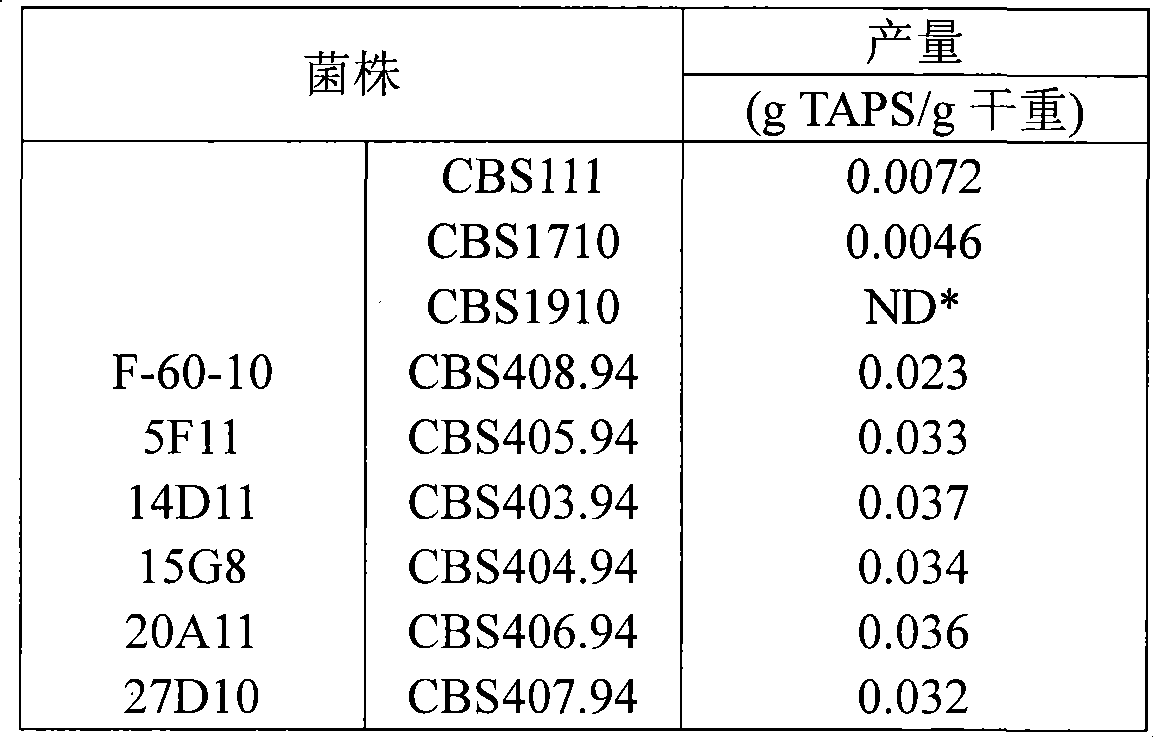
The invention relates to a microbial strain which can produce sphingosine, dihydrosphingosine, phytosphingosine and / or the derivatives thereof with improved level. In addition, the invention further discloses a method which is based on induced mutation or other selection technologies, and the strain is prepared accordingly. As an example, a mutant strain of pichia pastris is provided; and compared with the wild-type strain, compounds produced by the mutant strain are higher by about 50 percent.
Owner:科兹莫弗姆有限公司
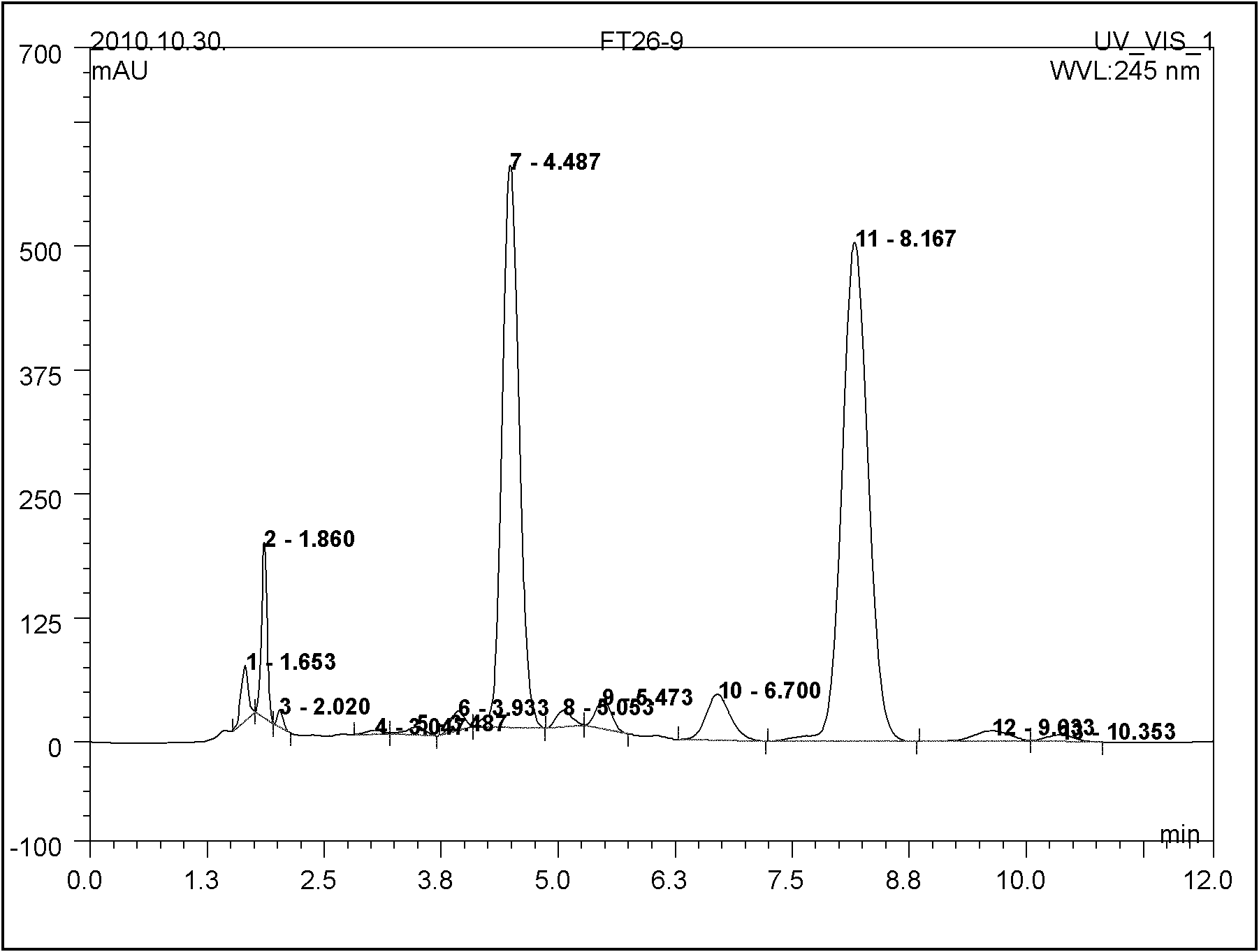
Abamectin producing bacterium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102154168AImprove Abamectin B ComponentLess componentsBacteriaMutant preparationLithium chlorideHydroxylamine
The invention discloses abamectin producing bacterium and a preparation method thereof. The collection name of the bacterium is FT26-9 and the collection number of the bacterium is CGMCC No.4341. The bacterium was collected on November 12th, 2010. The preparation method comprises: performing ultraviolet and lithium chloride combined mutation induction treatment of a starting strain; screening an induced-mutation strain; performing mutation induction by nitrosoguanidine and screening; performing mutation induction by diethyl sulfate and screening; performing mutation induction by hydroxylamine and screening; performing mutation induction by 5-bromouracil and ultraviolet and screening; and finally obtaining the FT26-9 strain which can greatly improve the abamectin B component content in a fermentation product and reduce the abamectin A component content in the fermentation product. When the bacterium is used in industrial production of abamectin, the fermentation unit is improved by about 40 percent, and the product cost is reduced by about 35 percent.
Owner:HEBEI XINGBAI AGRI SCI & TECH CO LTD
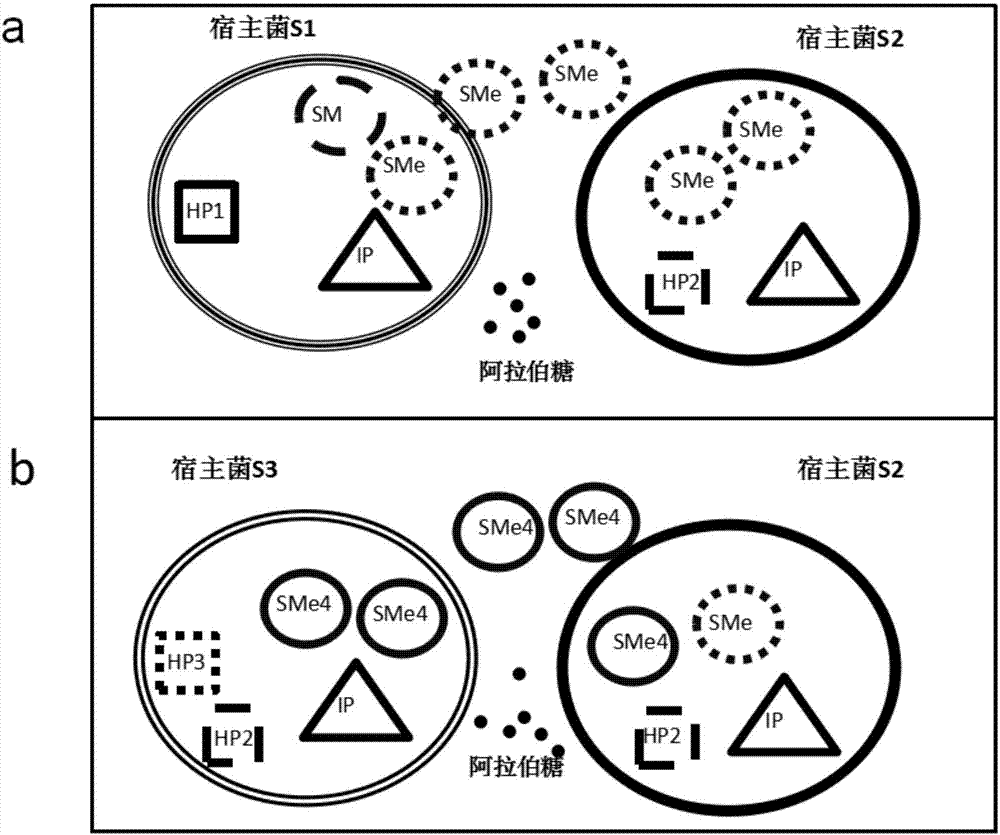
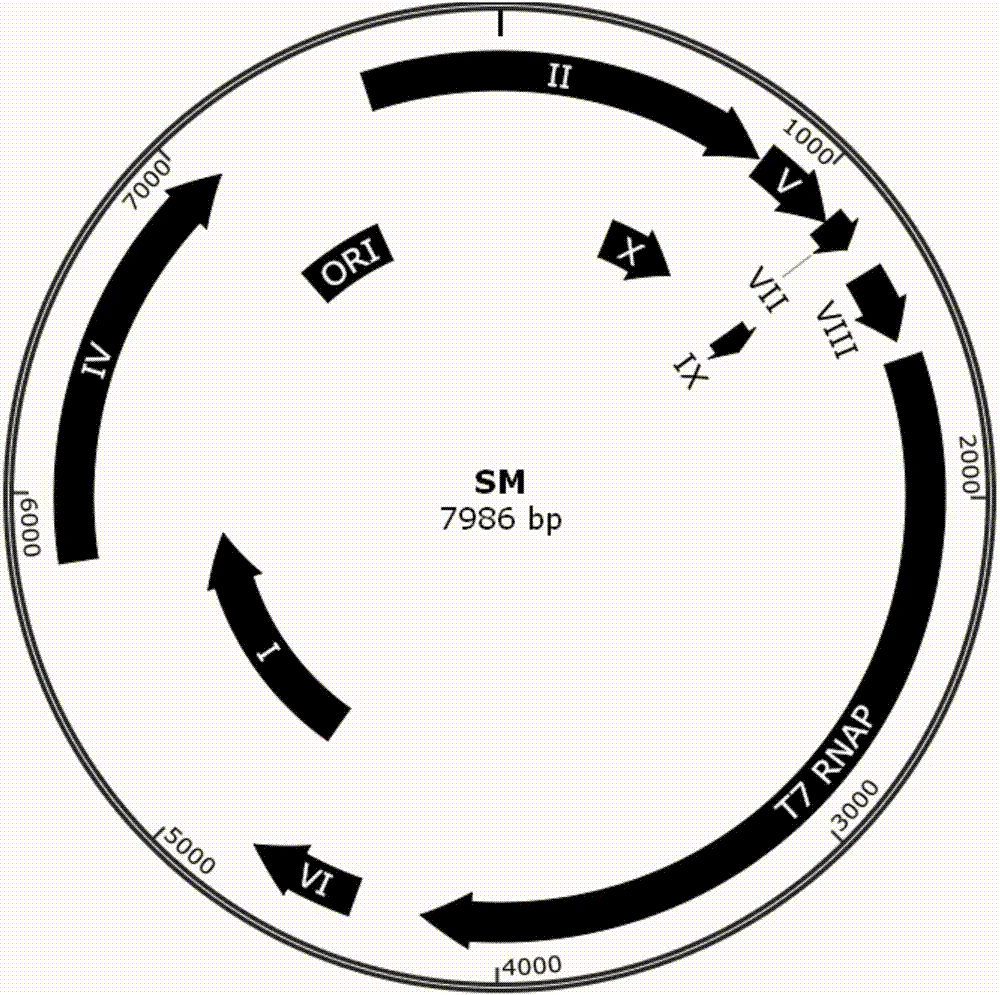
Phage-assisted multi-bacterial continuous directed evolution system and method
ActiveCN107418964AImprove evolutionary efficiencyBacteriaNucleic acid vectorGene ComponentBacteriophage
The invention discloses phage-assisted multi-bacterial continuous directed evolution system and method. The system includes: a phage SM which carries an evolution target gene, a plurality of assistant plasmids HP which support different SM proliferations before and after the evolution, and a plasmid IP which induces mutation. In the system, the different HPs are arranged in different host bacteria, so that proliferation and evolution efficiencies of the phage are effectively improved, and meanwhile, mutual interference between different gene components is avoided. The system and method have great practicability and can be applied to directed evolution of various genes.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Trichoderma reesei capable of producing cellulase in high yield and application of trichoderma reesei
ActiveCN104328056AMany branchesLow viscosityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyInduced mutation
The invention provides a trichoderma reesei mutant strain VLKDN-1. The preservation number of the stain VLKDN-1 is CCTCC NO:M 2014506. A trichoderma reesei mutant strain capable of producing cellulase in high yield is obtained by adopting an ultraviolet-induced mutation technology combined with shake flask selection. Compared with a starting strain, the enzyme activity of the fermentation supernatant of mutant strain trichoderma reesei VLKDN-1 is increased by 235%, the content of protein is increased by 157%, the colonial morphology of the mutant strain is obviously smaller than that of the starting strain; the hyphae are shorter than that of the starting strain; the branches are more than that of the starting strain. The viscosity of a fermentation strain solution is remarkably reduced by virtue of the characteristics of short hyphae and more branches of the small colonial morphology of the mutant strain in the production process; the purposes of reducing the stirring rate and improving the dissolved oxygen are achieved; the production cost is reduced; the trichoderma reesei mutant strain VLKDN-1 is wide in application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP +1
Bacterial strain capable of producing alkali protease and industrialized liquid fermentation method of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103409347AReduce manufacturing costOptimizing the fermentation mechanismBacteriaHydrolasesLeather industryAlkaline protease
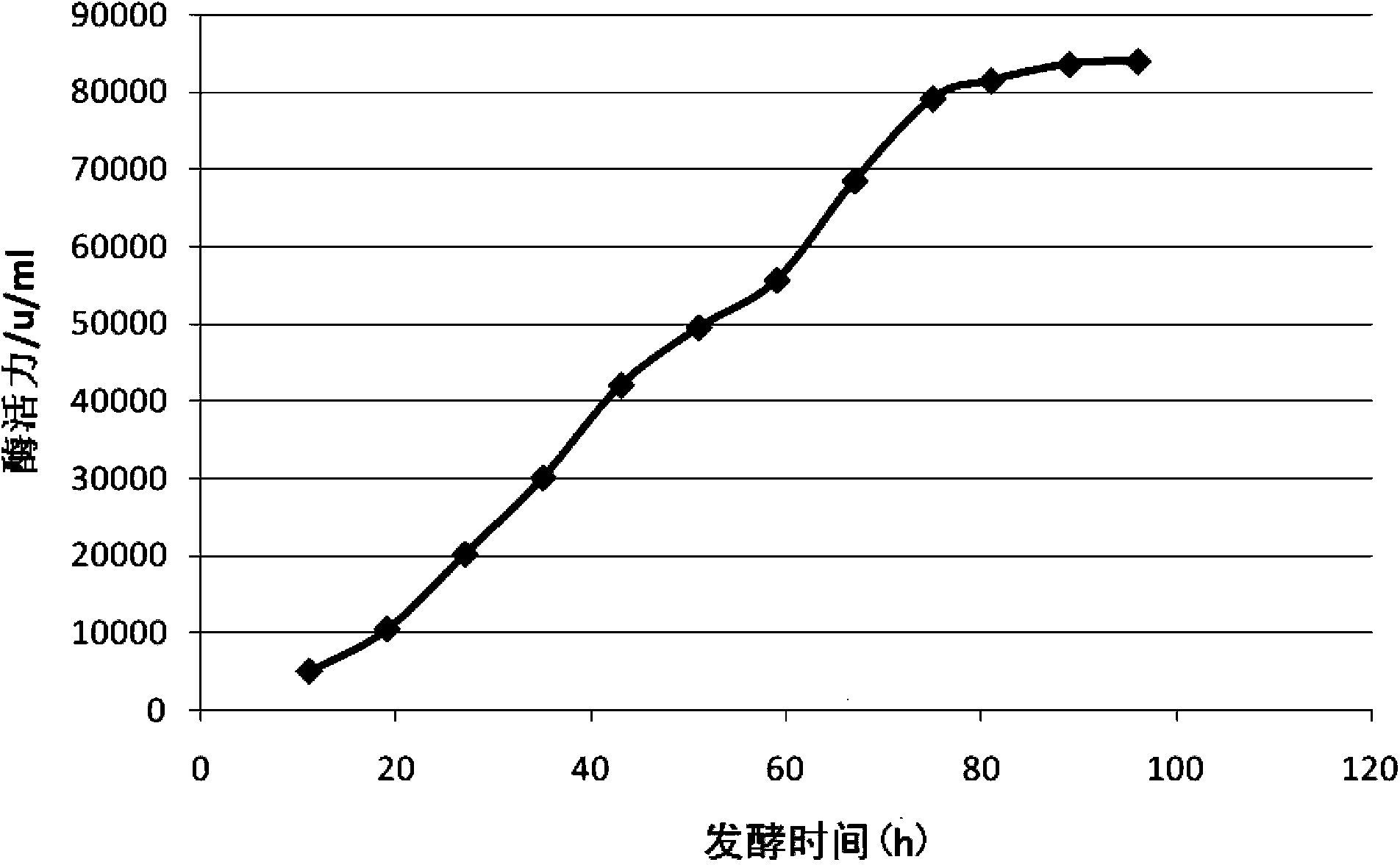
The invention discloses a bacterial strain capable of producing alkali protease and an industrialized liquid fermentation method of the bacterial strain, and belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. The bacterial strain is mutant strain Ap180 of Bacillus alcalophilus, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.7545. The bacterial strain is obtained by repeat UV-induced mutation, nitrosoguanidine-induced mutation and selection of a wild bacterial strain obtained from saline lands. Characteristics of the bacterial strain are that: efficiency of alkali protease production is high, and stability is excellent. The Bacillus alcalophilus strain, which is capable of producing alkali protease and is suitable for industrialized production , is provided in the invention, and related fermentation mechanism is optimized. According to the fermentation mechanism, operation processes are simple, cultivating conditions are mild, fermenting enzyme activity is more than 80000u / ml, production cost of enzyme activity per unit is reduced, and the requirements of market are met. Applications of the alkali protease in fields such as washing agent, forage, and leather industry are more extensive.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGKETE ENZYME PREPARATION
Liquid-state composite bacterial microbe fertilizer and its preparing process
InactiveCN1397521AMeet nutritional requirementsLower unit costBacteriaMutant preparationMicroorganismBacillus megaterium
A liquid-state compound microbial fertilizer is prepared from azotobacteria, bacillus megaterium, silicate bacteria and trace elements through physical and chemical induced mutation, mixing and diluting by water. Its advantages are high yield and quality of agricultural crops, and long quality guarantee period.
Owner:福建省尤溪县绿地生物制品有限公司
Method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation
InactiveCN101624591ARich varietySimplified typesMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesPlasma jetActive particles
The invention discloses a method for breeding microorganisms by plasma-induced mutation, which radiates microorganisms to be induced to mutate with a plasma jet flow that uses neutral active particles as acting particles to obtain mutated microorganisms. The method in which the neutral active particles in the plasma jet flow play a main induction role has the advantages of: ensuring the high activity of forward mutant strains and the high capability and genetic stability of produced target products, reducing mutagenesis period and improving mutagenesis efficiency, inducing a great variety of microorganisms such as prokaryotic microorganisms, eukaryotic microorganisms and archaebacteria in form of microbial community, bacterial suspension or spore suspension, simplifying experimental operation by avoiding culturing the processed microorganisms in the dark, having the characteristics of simple, safe and pollution-free whole operation, low equipment and experiment cost and the like and having great potential role in the field of industrial microorganism induced mutation breeding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Rice CYP704B2 gene mutant, as well as molecule identification method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104894144ABreeding benefitsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The invention provides a rice CYP704B2 gene mutant and applications thereof, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. A nonglutinous rice variety 93-11 is subjected to induced mutation by cobalt 60 radiation, so as to cause deletion of two G basic groups behind 1267 basic groups of a rice CYP704B2 gene; the rice CYP704B2 gene mutant is named as cyp704B2-2, and a nucleotide sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID No.1 and further verifies that the mutant causes rice recessive genic male sterility; the rice CYP704B2 gene mutant can be used for preparing transgenic rice with recessive genic male sterility, and plays an important role in genetic improvement and breeding of rice germplasm resources. The invention also provides a molecular marker identification method of the mutant and applications of the method in breeding and seed production.
Owner:HAINAN BOLIAN RICE GENE TECH CO LTD
In-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium
InactiveCN103039369AEasy to operateHigh mutation frequencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsInduced mutationShoot apex
The invention relates to a chemical mutation breeding technology in the field of biotechnologies, and particularly relates to an in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology of dendranthema morifolium. The in-vitro NaN3 mutation breeding technology comprises the following steps of: performing culture in vitro on an immature stem, a stem tip or a leaf of the dendranthema morifolium to form an aseptic seedling; processing the stem tip and a stem segment of the aseptic seedling, which are taken as explants, by sodium azide (NaN3) in a breeding process to carry out induced mutation; rooting and transplanting a test-tube plantlet; and finally breeding excellent mutant in a field at a flowering phase. The in-vitro sodium azide (NaN3) mutation breeding technology can effectively overcome the obstacle of breed improvement of a clonal plant and the constraints of low bud-variation frequency and small mutational range under natural conditions, can be used for obtaining the excellent mutant within a short period of time, ensures high induced mutation efficiency, and has an important value to the genetic improvement of asexual propagation of the dendranthema morifolium with medicinal and ornamental values.
Owner:ANHUI SCI & TECH UNIV
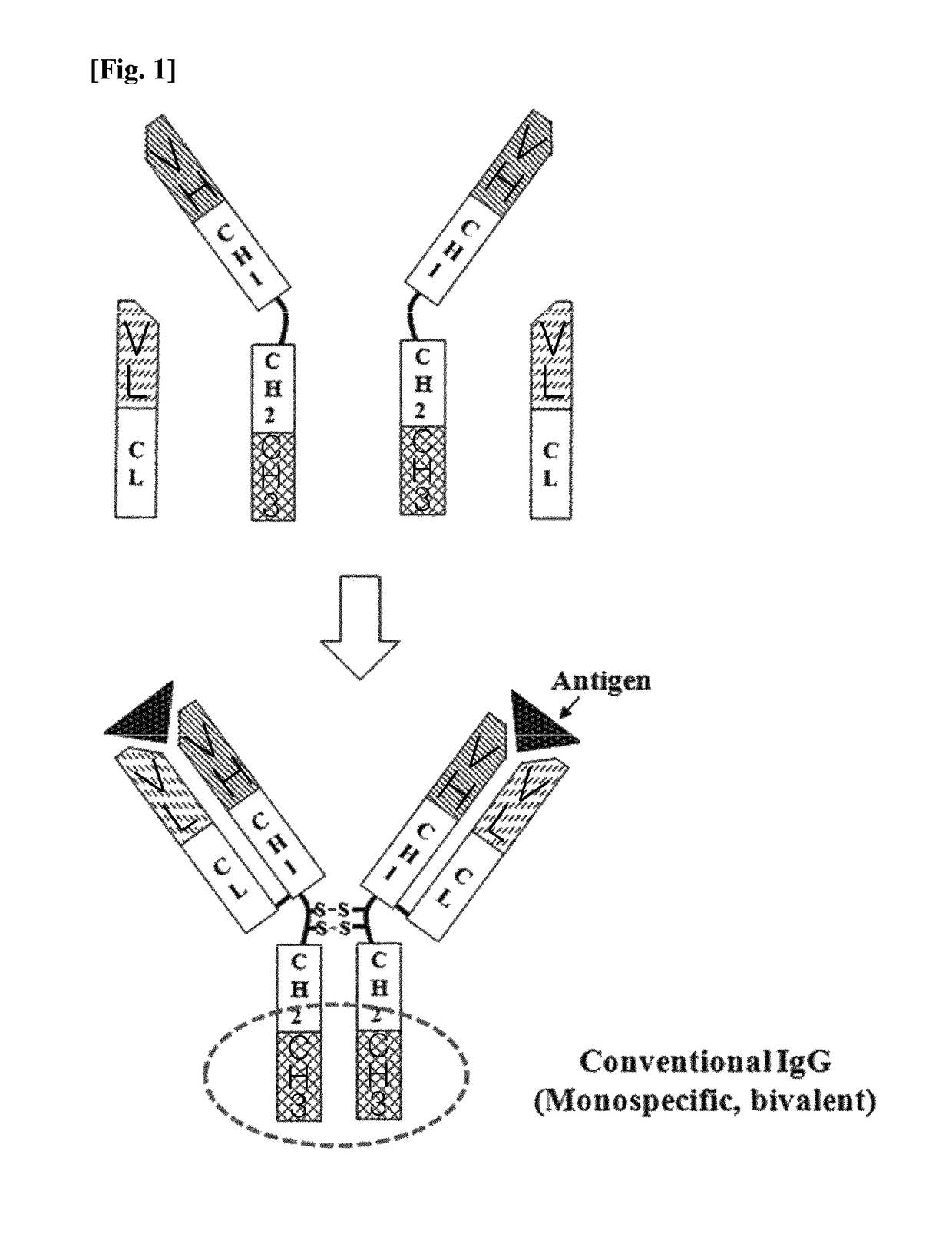
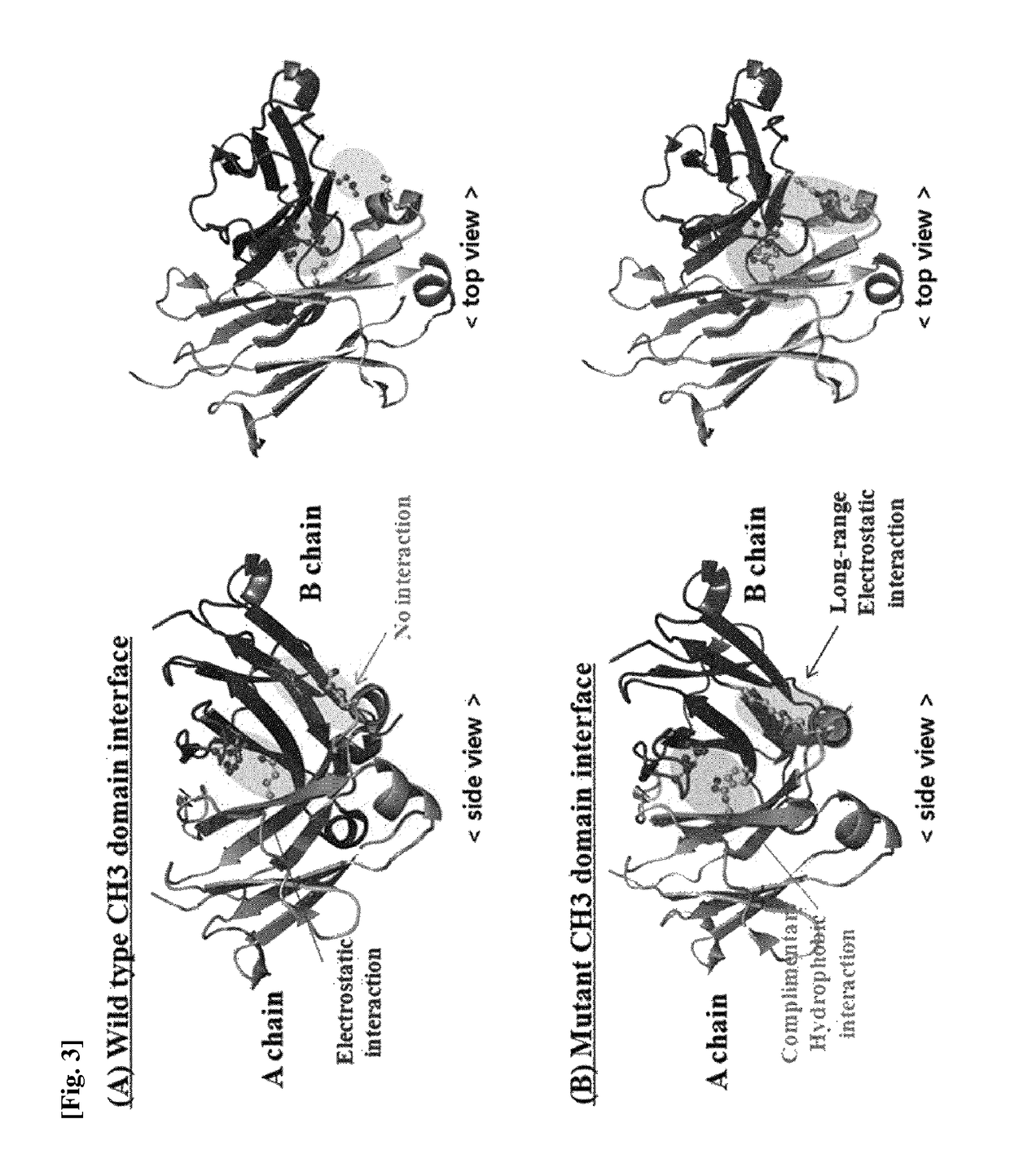
CH3 domain variant pair inducing formation of heterodimer of heavy chain constant region of antibody at high efficiency, method for preparing same, and use thereof
ActiveUS9951145B2High yieldMinimize formationHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseProtein target
Disclosed are a CH3 domain variant pair of an antibody, a method for preparing same, and a use thereof. A mutation is induced in the CH3 domain so as to improve a yield of forming a heterodimer heavy chain constant region of an antibody. The CH3 domain heterodimer forms a heterodimer heavy chain constant region with a high efficiency of 90 to 95% or more and also has outstanding heat stability. A heterodimer heavy chain constant region including the CH3 domain heterodimer can construct a bispecific monoclonal antibody which simultaneously recognizes two kinds of antigens. The CH3 domain heterodimer and the bispecific antibody or fusion protein of an antibody constant region comprising same can be usefully applied to the treatment or prevention of a disease associated with a target antigen or a target protein.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Method for increasing growth speed of ganoderma lucidum mycelia and liquid fermentation biomass
InactiveCN102972211AIncreased sensitivityGood characterMutant preparationHorticultureMicrobial geneticsPeanut meal
The invention discloses a method for increasing the growth speed of ganoderma lucidum mycelia and the liquid fermentation biomass, and belongs to microbial genetics and breeding methods. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) preparing a ganoderma lucidum protoplast; (2) carrying out induced mutation on the ganoderma lucidum protoplast by nitrous acid and regenerating the protoplast; (3) inoculating peanut meal and culturing by a slant culture medium comprising maize, the peanut meal, KH2PO4, MgSO4.7H20 and VB2; (4) inoculating the peanut meal and culturing by a liquid fermentation culture medium comprising the maize, the peanut meal, peptone, glucose, yeast cream, KH2PO4 and MgSO4.7H20; and (5) obtaining active products such as biomasses and polysaccharides, triterpenoids and the like. The method has the benefits as follows: (1) a ganoderma lucidum strain with high mycelial growth speed and high biomass is obtained through induced mutation for the first time; (2) the adopted slant culture medium for the peanut meal is more favorable for quick growth of the ganoderma lucidum mycelia in comparison with a slant culture medium for potato dextrose agar; and (3) the adopted liquid fermentation culture medium for the peanut meal is more favorable for acquisition of higher biomass.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
Nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104232535ASignificantly low toxicityImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmune effectsVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to a nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bacterial strain induced mutation. Particularly, the nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain, named NSX1 (Nocardia seriolae NSX1), of which the culture preservation number is CGMCCNO.9437. An immune compound comprises the nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain used as an immune an immunogenicity component, wherein the concentration of the nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain is 10<3>-10<9>CFU / ml; the nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain is used for preparing drugs for resisting fish nocardiosis and has significant low toxicity effect; meanwhile, the fish can be effectively protected from the invasion of nocardia seriolae caused by nocardia seriolae pathogenic strains or virulence strains; therefore, the nocardia seriolae induced low virulent strain has significant immune effect and good nocardia seriolae disease control effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIV +2
Trichoderma strain capable of generating cellulase and application of trichoderma strain
The invention discloses a Trichoderma strain capable of generating cellulase. The Trichoderma strain is obtained by ultraviolet-induced mutation of Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30, named as Trichoderma reesei CU7-4, collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 10th July, 2015 and numbered as CGMCC N0.11065. The invention further discloses application of the Trichoderma strain to fermenting production of cellulase liquid. Experiments confirm that highest filter paper activity of the strain is 8.28IU / mL which is 3.43 times that of an original strain, highest total protein is 4.14mg / mL which is 1.92 times that of the original strain, and it is indicated that the strain has good application prospect in cellulase production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Strain producing pullulan, application thereof and pullulan production method
InactiveCN105695347AQuality improvementIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and discloses aureobasidium pullulans.The preservation number of the aureobasidium pullulans is CGMCC No.11937.The aureobasidium pullulans with the preservation number being CGMCC No.11937 uses wild aureobasidium pullulans with the preservation number being CGMCC No.3.4580 as an original strain, chemical induced mutation is performed, the aureobasidium pullulans is obtained through screening, the capacity that the aureobasidium pullulans ferments to generate pullulans is remarkably improved, compared with the original strain, the yield of the pullulans is increased by 80%, and the glucose conversion rate is increased by 68%.The color of the finished pullulans becomes lighter obviously.Thus, the aureobasidium pullulans with the preservation number being CGMCC No.11937 can be widely applied to pullulans fermentation.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Strain for producing cellulase and application of strain
InactiveCN103555595AIncrease hydrolysis rateIncrease enzyme activityFungiMutant preparationHigh activityTrichoderma reesei
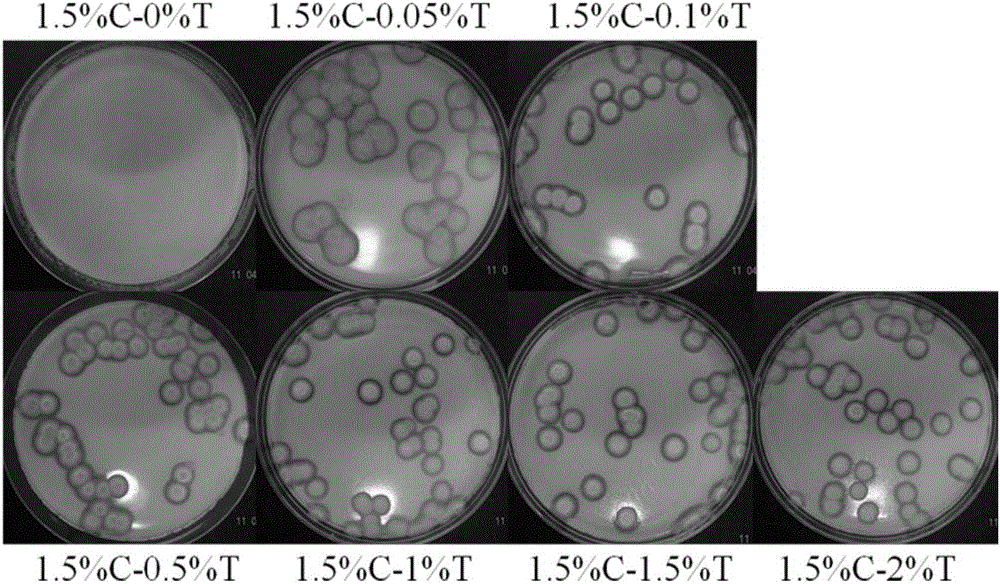
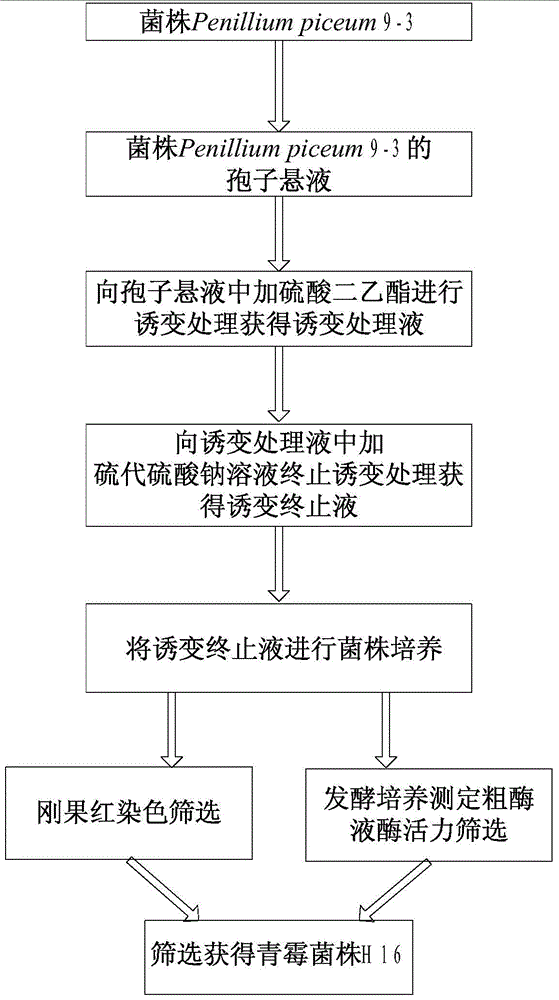
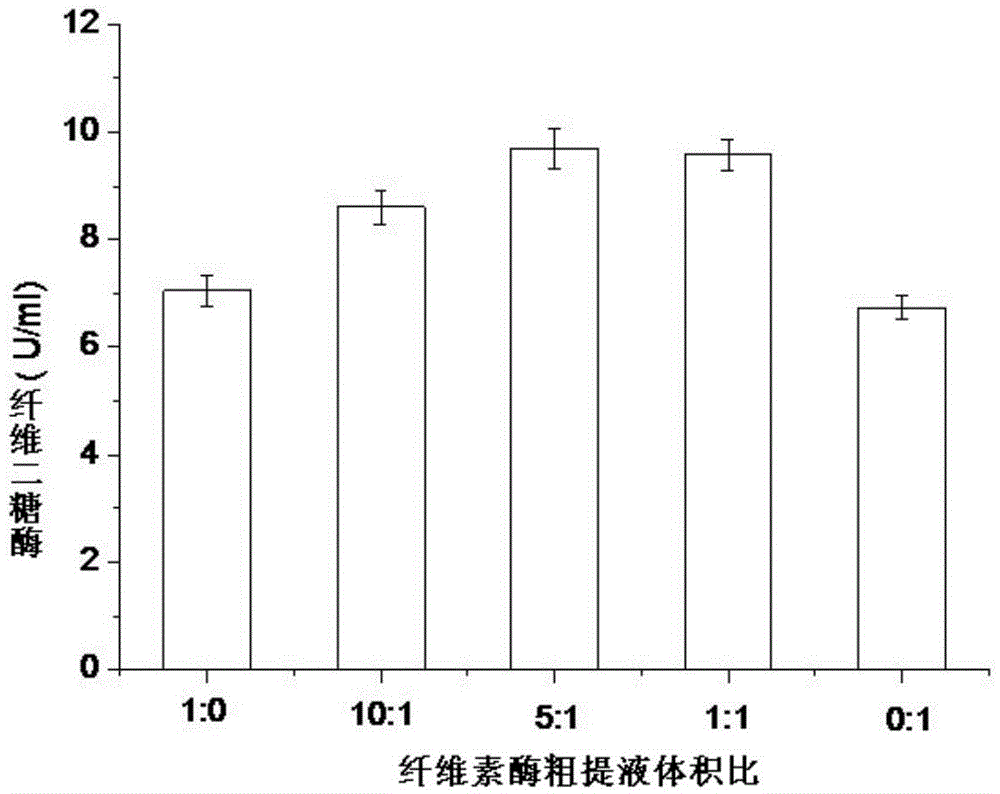
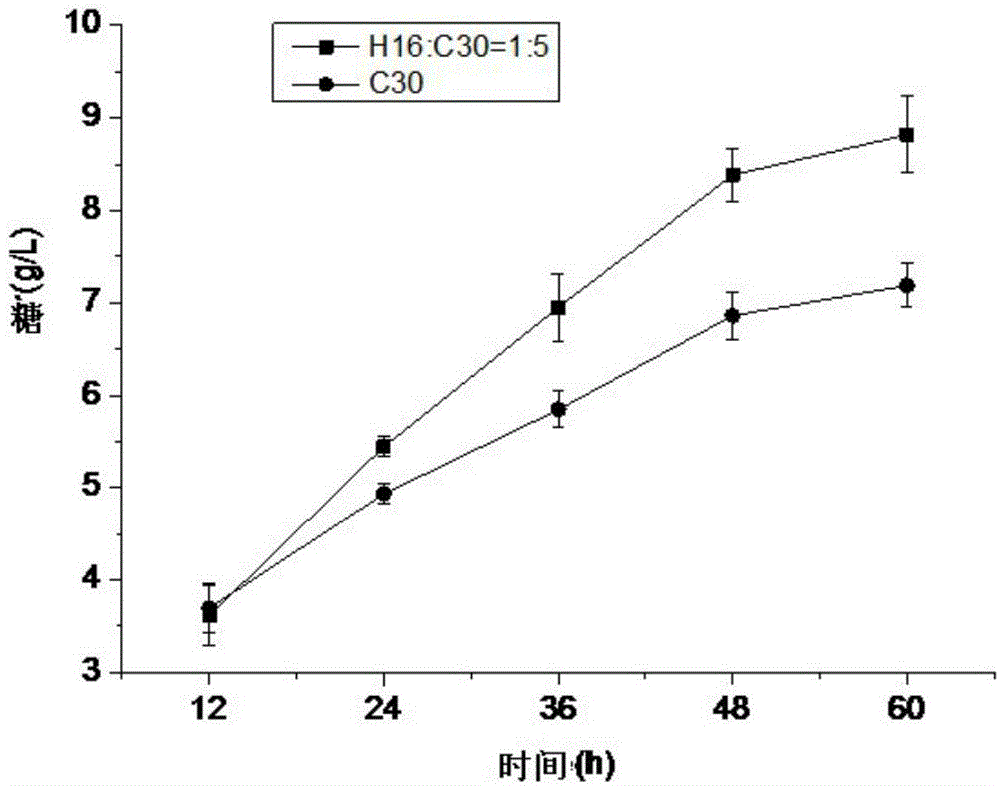
The invention discloses a strain for producing cellulase. The strain has a collection number of CGMCC No.8339 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the classification name of the strain is Penillium piceum H16. The Penillium piceum is obtained through induced mutation treatment by taking a strain Penillium piceum 9-3 screened from straws as an original strain. The Penillium piceum 9-3 serves as the original strain for mutation breeding, the Penillium piceum H16 for producing high-activity cellulase is obtained through breeding, the enzyme activity of filter paperof cellulase crude enzyme liquid obtained by fermenting the Penillium piceum H16 reaches 7IU / mL, and the enzyme activity of beta-glucosidase reaches 50IU / mL. Different cellulase systems of the Penillium piceum H16 and Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 are researched according to different proportions, the enzyme activity and the hydrolysis rate of microcrystalline celluloses are greatly improved at an optimal proportion, and the enzyme cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
SNP markers closely linked with height trait of cabbage type rape, and application of SNP markers
ActiveCN110578015AAccurate distinctionEnables high-throughput screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationInduced mutation
The invention discloses SNP markers closely linked with a height trait of cabbage type rape, and application of the SNP markers. By using an EMS induced mutation technology, a dwarf mutant DF09 with the plant height being 65 cm is obtained. The dwarf mutant DF09 is taken as a research material, a method of map-based cloning is adopted, and a dwarf trait control locus BnDwf.C9 is subjected to finemapping in the 132 Kb interval of a C09 chromosome. In the fine mapping interval, three SNP molecule markers of BnaC09-42, BnaC09-46 and BnaC09-54 which are closely linked with a dwarf trait are obtained. According to the SNP markers closely linked with the height trait of the cabbage type rape, and application of the SNP markers, through a five primer amplification blocked mutation system technology (the BnaC09-42, the BnaC09-46 and the BnaC09-54) or a conventional PCR amplification technology (BnaC09-46pcr), a dwarf material can be accurately screened according to gene types, thus the dwarfmaterial is applied to molecular identification of early target traits, the progress of dwarf breeding is accelerated, and a foundation is laid for clone of dwarf genes.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
Bacillus marinus capable of inducing disease resistance and stress tolerance of plant
InactiveCN105018367ANo pollution in the processStable biological propertiesBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentBeef extract
The invention discloses bacillus marinus capable of inducing disease resistance and stress tolerance of a plant. The bacillus marinus CT2628 (Bacillus sp.) is obtained from an ocean ecological environment through artificial induced mutation breeding and culture condition optimization; the proper artificial culture and fermentation condition is as follows: a proper fermentation culture solution of the CT2628 with the collection number of CGMCC No.8921 is prepared according to the following formula: 1-3g of a beef extract, 2-3g of peptone, 1-3g of yeast powder, 1-3g of glucose, 20-25g of NaCl, 0.3-0.5g of KCl, 1.9-2.5g of MgCl2.7H2O, 0.01-0.02g of FePO4 and 1000ml of water and has the pH value of 7.0-8.0. The invention discloses bacillus marinus capable of inducing disease resistance, salt resistance and cold resistance of the plant and application of the bacillus marinus to agriculture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Method for increasing EMS induced mutation rate of wheat
PendingCN109729972AHigh mutagenesis rateHigh mutation ratePlant genotype modificationSeed immunisationInduced mutationGermination
The invention discloses a method for increasing the EMS induced mutation rate of wheat. The method comprises the following steps: seed pretreatment, soaking, cleaning, germination treatment, induced mutation treatment, termination, plantation and screening. Based on the characteristic that tender tissues and growth sites are most sensitive to EMS, whitened seeds are subjected to induced mutation treatment by virtue of an EMS solution, so that the mutation rate of the seeds is effectively increased, and the working efficiency of the seeds is effectively improved.
Owner:WHEAT RES INST OF AGRI SCI
Astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of bioengineering, particularly to an astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof. According to the astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof,compared with an existing single induced mutation technique, a method for simultaneously applying double induced mutation to astaxanthin production saccharomyces cerevisiae strains can produce an extensive variety of mutants, and from a large number of libraries produced by the mutants, the astaxanthin strain with significant increase in yield of astaxanthin can be screened out.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Giant embryo black kerneled rice and method for breeding giant embryo black kerneled rice
InactiveCN102524085AImprove breeding efficiencyShort cycleSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationAdditive ingredientEmbryo
The invention discloses giant embryo black kerneled rice and a method for breeding the giant embryo black kerneled rice. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting giant embryo mutation coarse rice grains by naked eyes from coarse rice of black kerneled rice M2 seeds by irradiating the black kerneled rice seeds which serve as a material by 60Co-gamma rays with a 380Gy dose according to the characteristic that the giant embryo character of rice is controlled by a single recessive gene, and the rice can be obtained by induced mutation, and breeding to form giant embryo black kerneled rice varieties by the selection of an agricultural technology and yield characters. By the method, the specific rice varieties which have the giant embryo character and a black seed coat character simultaneously can be bred simply and quickly, and the coarse rice of the giant embryo black kerneled rice is rich in special nutritional ingredients such as protein, fat, essential amino acid, anthocyanin, carotene, cardiac glycoside, dietary fibers, vitamins, gamma-aminobutyric acid and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for producing seed source of Cordyceps militaris with high-yield cordycepin by radiation breeding
A method for producing a seed source of Cordyceps militaris with high-yield cordycepin to improve the yield of the cordycepin is designed to solve the technical problem that improvement on the content of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris by adding a certain amount of protein sources into culture medium is low and unsatisfactory. The method is used for breeding target strains by radiation, induced mutation and screening. A target strain ycc Gy 1016 is obtained by subjecting an original strain ycc-01 to characteristic parameter radiation treatment, subjecting a varied colony to screening and purification, scientifically testing indicators of generated cordycepin and estimating culture stability, and accordingly the method for producing new strains of Cordyceps militaris with high-yield cordycepin is achieved. Testing show that cordycepin productivity of the strain ycc GY 1016 is 3.8 times of that of the original strain ycc-01. The method has important value on artificial production of functional Cordyceps militaris and has bright application prospect.
Owner:SHENYANG NORMAL UNIV
Construction and application of H9N2-subtype avian influenza virus cell high-yield vaccine strain
ActiveCN105671002AHigh titerImprove adaptabilityAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesAnimals vaccinesEmbryo
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal vaccine preparation and particularly relates to construction and application of an H9N2-subtype avian influenza virus cell high-yield vaccine strain. The cell vaccine strain is prepared through artificially induced mutation screening of an avian influenza isolate and is named H9N2-subtype avian influenza virus W1-HA358 strain, of which an original isolate is A / duck / Hubei / W1 / 2004 (H9N2) strain. The 3rd, 5th and 8th loca of a 3'-terminal of an HA gene non-coding region of the isolate are subjected to artificial site-specific mutagenesis, and a mutation strain is saved through reverse genetic operation, wherein the mutation strain is subjected to passage on an MDCK cell until a stable generation to obtain a high-proliferation-titer virus strain, thereby producing the H9N2-subtype avian influenza virus cell vaccine. The invention solves the problem of instable proliferation of the H9N2-subtype avian influenza on the MDCK cell, and overcomes a defect of shortage of large quantity of chick embryo during outbreak of the avian influenza, thereby increasing preparation efficiency of the vaccine.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for mutagenesis breeding neuter protease high yield bacterial strain by hypophrenia N+ion injection technology
InactiveCN101182513AImprove enzyme production capacityReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMutant preparationNeutral proteinaseBacterial strain
The invention relates to an inducing and breeding method of high yield neutral proteinase strain by using low energy N <+> ion injection technology. The steps are that (1) the initial strain is screened; (2) the N <+> ion is injected for the induced mutation; (3) the high yield strain is screened; (4) the N <+> ion is injected for the induced mutation; (5) the high yield neutral proteinase strain is determined. The invention uses the N <+> ion injection technology for the induced mutation of Bacillus Subtilis AS1.398 of neutral proteinase; after the injection of different dosage of N <+> ion, the survival rate of the strain takes a typical saddle shape dose-effect curve; a high yield mutant strain with good genetic stability can be screened at the best injection dosage of 50*10 <14> ions / cm <2>; the shaking flask activity of the neutral proteinase is about 8230U / mL, which is improved by 81.3 percent. The ion injection technology can be applied into the mutation and selection of high yield neutral proteinase strain; the invention has a higher mutation rate and a wider mutation spectrum for the microorganism; the invention has good mutation effects, which is an ideal breeding method for the microorganism.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving yield of baicalin from hairy roots of scutellaria baicalensis
InactiveCN103918550AIncrease the content of baicalinEasy to operateSugar derivativesHorticulture methodsInduced mutationThree stage
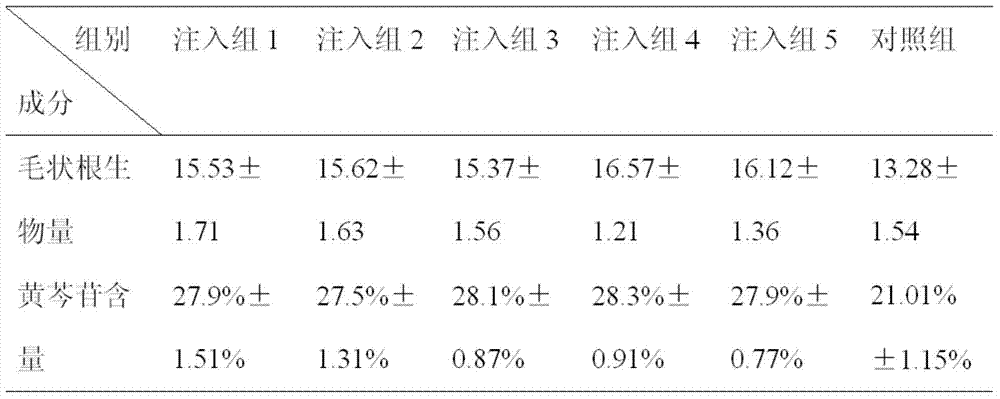
The invention provides a method for improving the yield of baicalin from hairy roots of scutellaria baicalensis. The method mainly comprises the following steps: processing the hairy roots of scutellaria baicalensis by using a low-energy ion beam injection technology, with the processed hairy roots of scutellaria baicalensis as seeds, performing enlarge culturing by using a three-stage culture method, and measuring baicalin content by high efficiency liquid chromatography; the result shows that, compared with a control group, the hairy roots which are subjected to induced mutation by the low-energy ions have the advantages of high growing speed, high capability of biosynthesizing baicalin, genetic stability and the like, when the hairy roots of scutellaria baicalensis grow for 45 days, the biomass and the baicalin content of the hairy roots respectively are 16.57g / L and 28.3g / L, which are improved by 24.77% and 35.03% respectively than those of the hairy roots, respectively being 13.28g / L and 21.01%, which are not injected with the low-energy ions.
Owner:西藏欧塞曼洛医药科技有限公司
Culture method for improving yield of botryococcus polysaccharides
InactiveCN104726445AIncrease biomassImprove antibacterial propertiesUnicellular algaeMutant preparationLiquid mediumUltrasonic radiation
The invention discloses a culture method for improving the yield of botryococcus polysaccharides, comprising the following steps: culturing purified botryococcus to a logarithmic growth period, selecting botryococcus liquid in logarithmic growth, performing induced mutation under the irradiation of argon ion laser, then inoculating to a BG11 liquid medium, and culturing under the conditions that the temperature is 28-33 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 43-86mumol.m<-2>.s<-1> and the illumination period is 14 hours every day; performing ultrasonic radiation treatment after culturing 2-3 days, continuously culturing the botryococcus subjected to the ultrasonic radiation treatment for 12-13 days under the conditions that the culture temperature is 28-33 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 43-86mumol.m<-2>.s<-1> and the illumination period is 14 hours every day, and performing centrifugal separation and sterile water washing on the obtained culture solution to obtain botryococcus rich in polysaccharides. By combining the argon ion laser induced mutation with the ultrasonic treatment, the yield of the cultured botryococcus is high, many polysaccharides are accumulated, and the polysaccharide content of the botryococcus can reach 35.99% of the dry weight.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com