Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
868 results about "Genetic stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic Stability Testing. The term genetic stability is applied to the characterization of the cells used in the production of a biologic. The cells have been genetically modified to contain a number of transgene insertion sequences which code for the protein of interest.
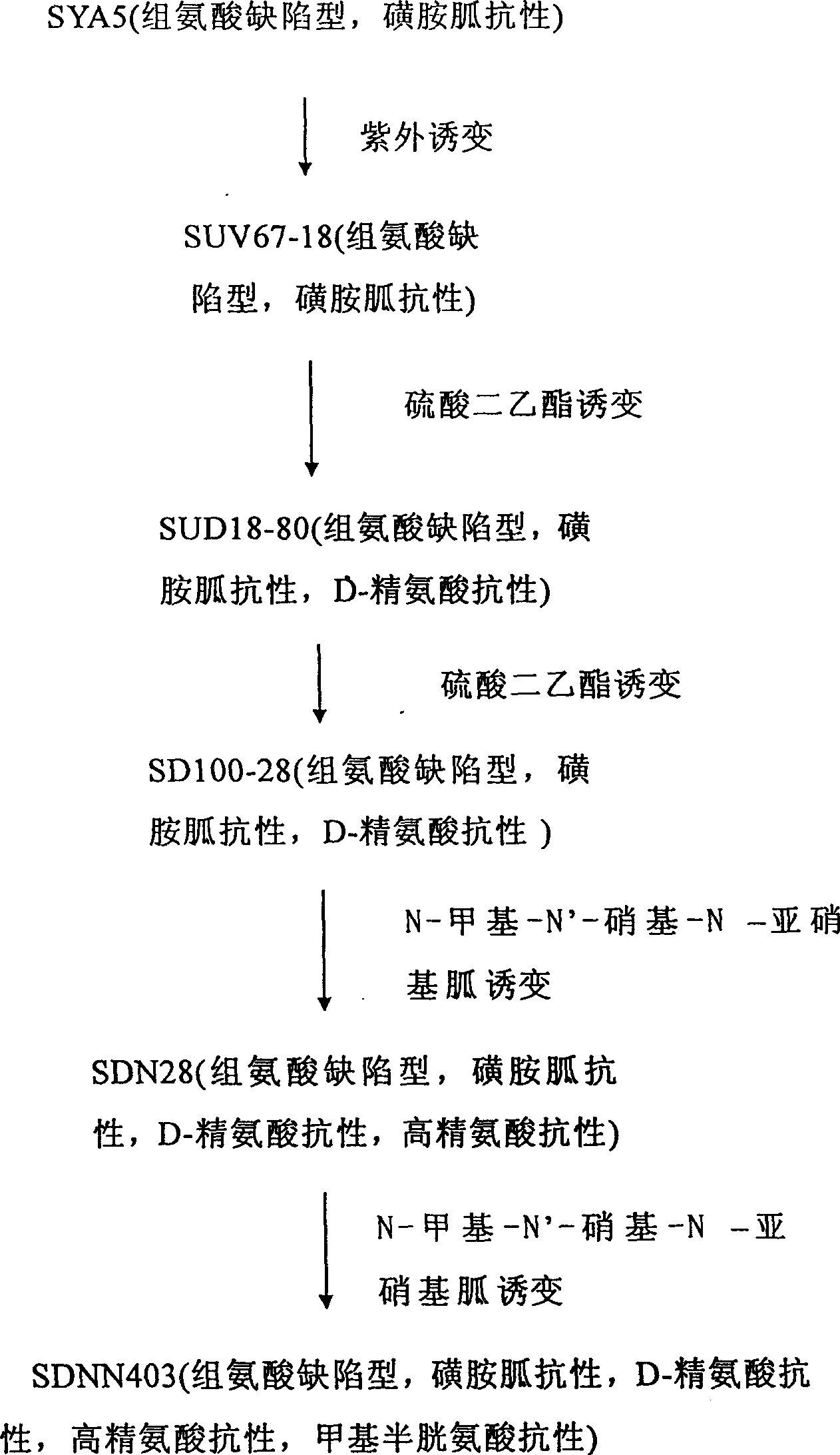
L-arginine producing strain and its mutation method and usage in producing L-arginine
InactiveCN1441055AHigh genetic stabilityGood genetic stabilityBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyArginine
The present invention relates to the fermentation process of producing L-arginine. By using Corynebacterium crenatum SYA5 screened and preserved by the present lab as parent and through conventional physical and chemical mutation process and multiple structural analog resistance screening, mutant strain SDNN403 is obtained. Through culturing of the mutant strain under optimized condition, L-arginine is produced in the yield level of 30-35 g / L. The strain has high genetic stability, stable yield characteristic, high L-arginine yield level, less produced hetero acids and easy technological amplification, and is suitable four industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
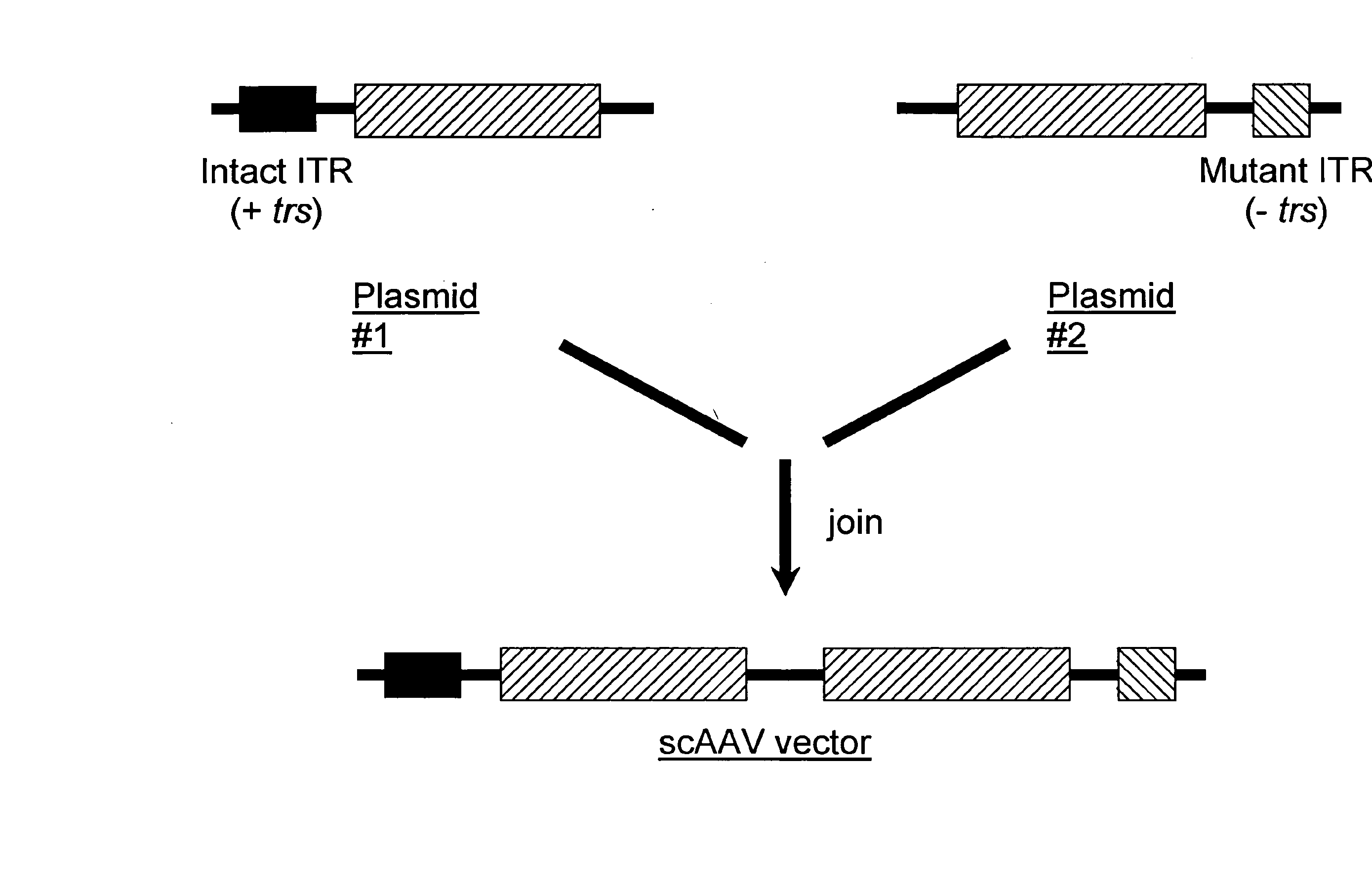
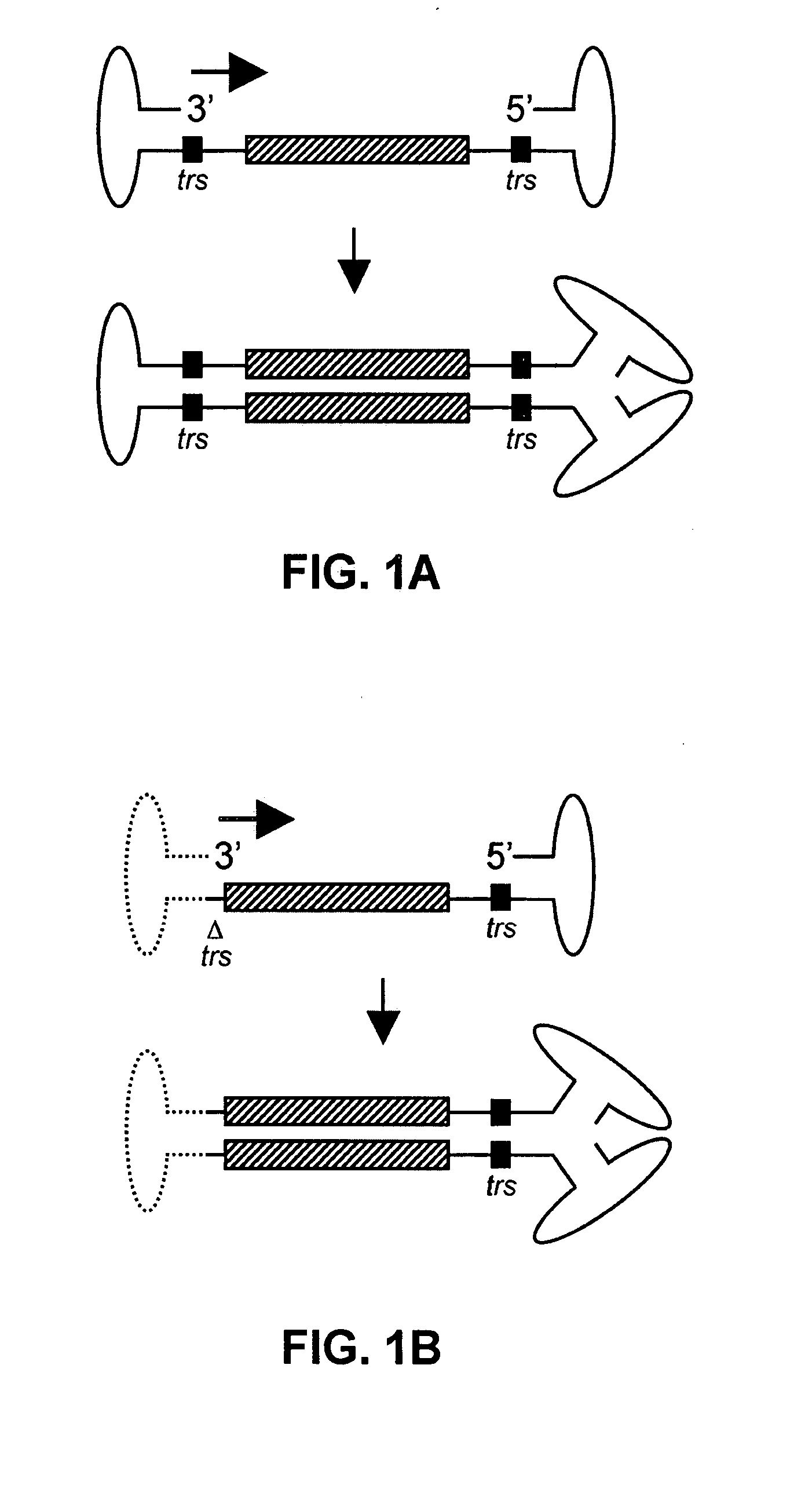
Self-complementary parvoviral vectors, and methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20070253936A1High genetic stabilityStabilized parvovirus vector is more stableBiocideAnimal repellantsGene transferTiter
The teachings herein are generally directed to a method of enhancing the genetic stability of parvovirus vectors. The stability of conventional ss or dsAAV vector constructs can be enhanced, for example, to obtain a concurrent increase in vector titer and purity, as well as an improvement in vector safety, due at least in part to the elimination of stuffer DNA from the AAV vector. The method is broadly applicable to all gene transfer / therapy applications, such as those requiring delivery of foreign DNA containing recombinant gene expression cassettes. Such foreign DNA can range, for example, from about 0.2 up to about 5.2 kb in length. The enhanced vector constructs are highly flexible, user-friendly, and can be easily modified (via routine DNA cloning) and utilized (via standard AAV vector technology) by anyone skilled in the art.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
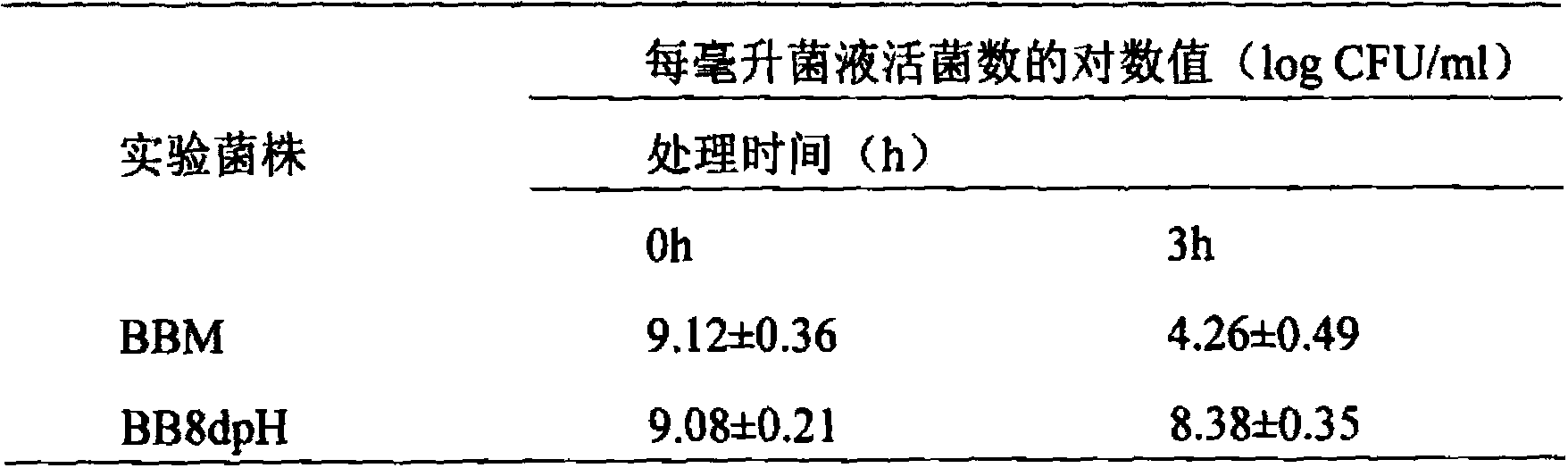
Acid-resistant bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH and application thereof
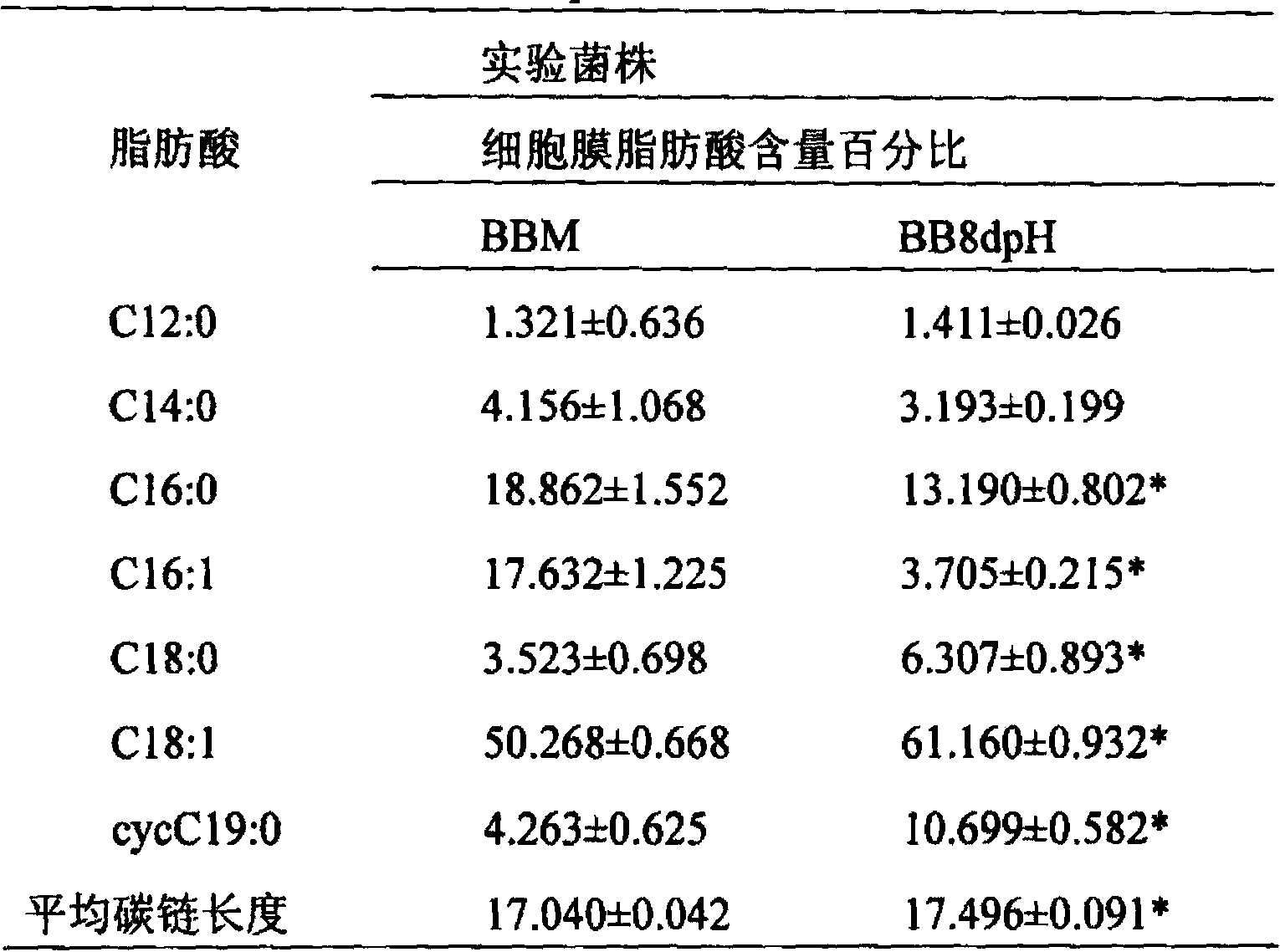
InactiveCN103849590AExcellent acid resistanceGenetically stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFecesCell membrane
The invention provides an acid-resistant bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the 16SrRNA gene part of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and is stored with the preservation number of CGMCCNo.8370. The bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is a strain obtained by separating from the dejecta of healthy young people and further screening under the pH 3.2 acid condition. According to the fermentation and culturing process, anaerobic culture at 37 DEG C is carried out in a BL liquid substrate (containing 0.05% cysteine hydrochloride) for 24 hours. The bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH has remarkably better acid resistance than the common strains, and the acid resistance has genetic stability; the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH has different percent contents of cell membrane fatty acids from the common strains, the average carbon chain length of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is remarkably longer than that of the common strains, and the cell membrane fluidity of the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is remarkably lower than that of the common strains; and the bifidobacterium breve BB8dpH is used in the production field of daily fermented food, health-care food and medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
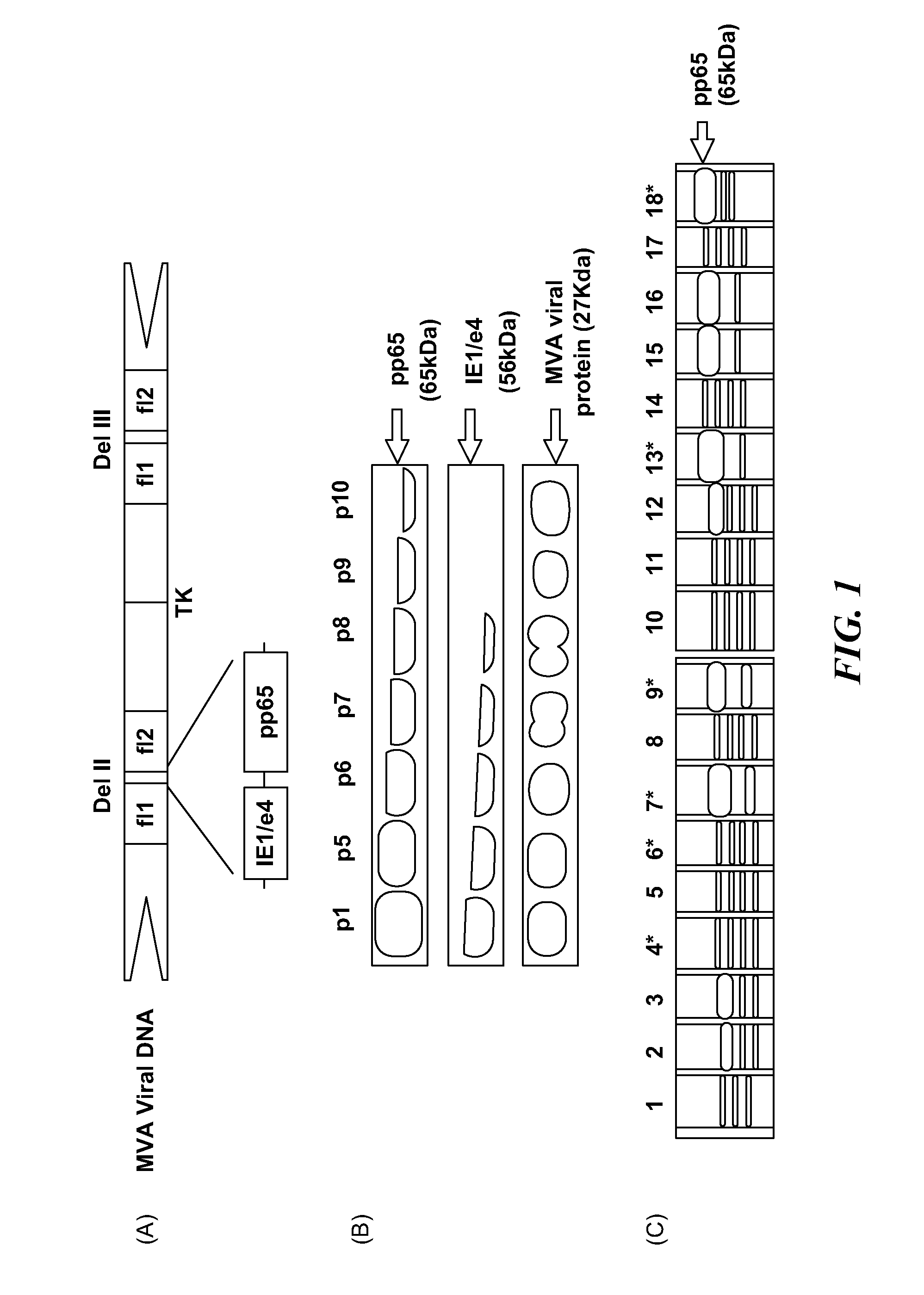
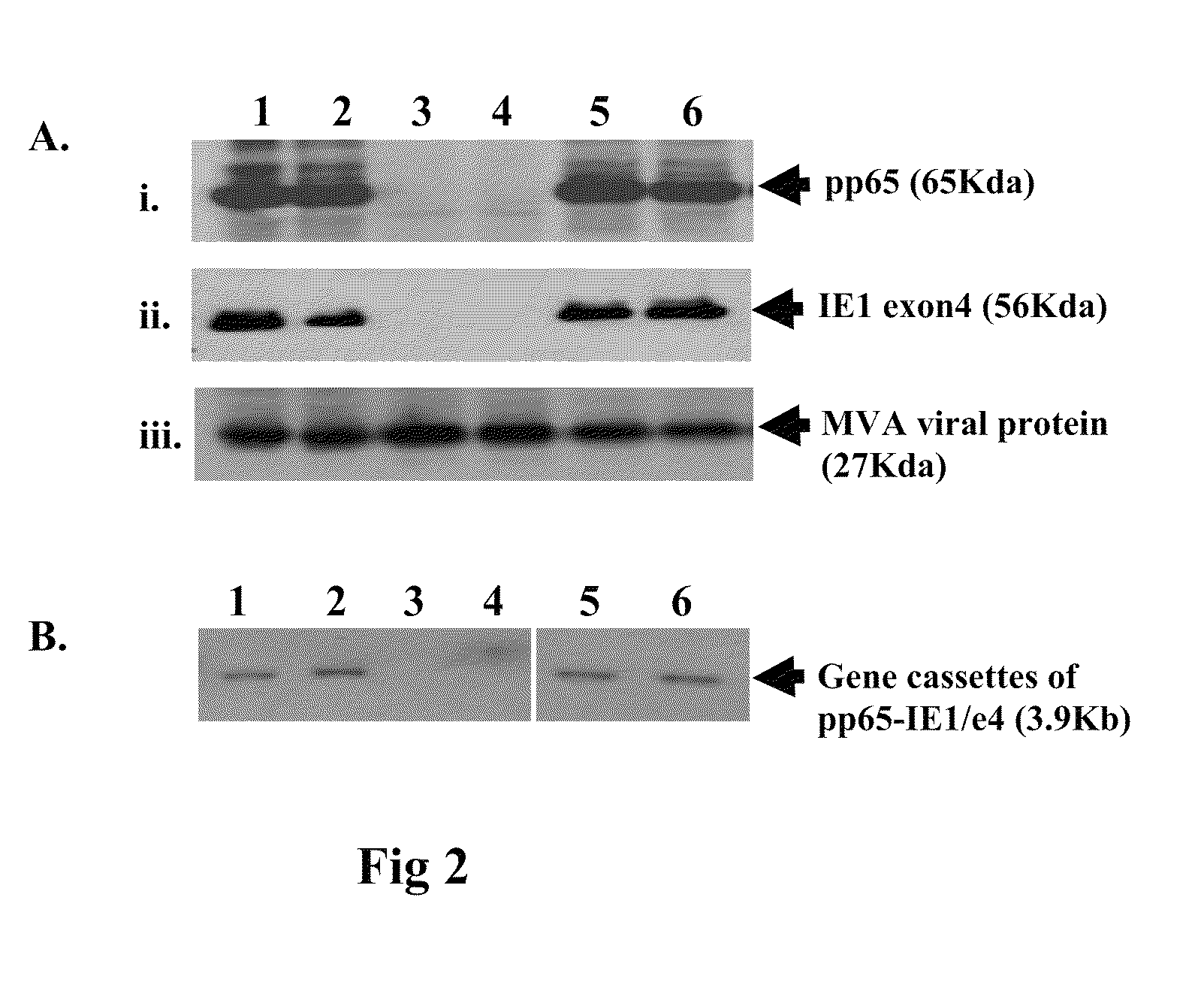
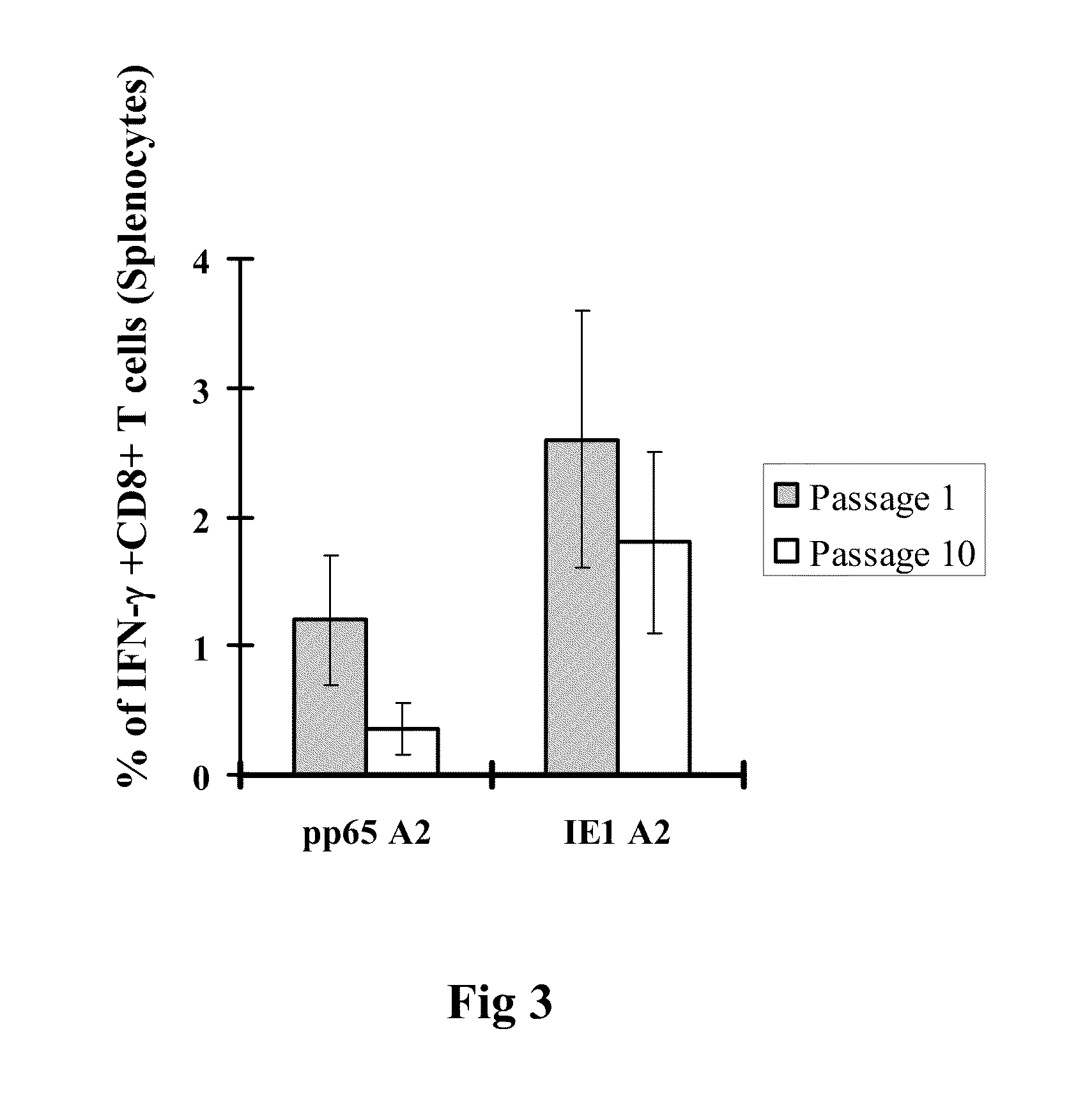
Genetically stable recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (RMVA) vaccines and methods of preparation thereof
ActiveUS20100316667A1Elicit immune responseVectorsSugar derivativesHeterologousModified vaccinia Ankara
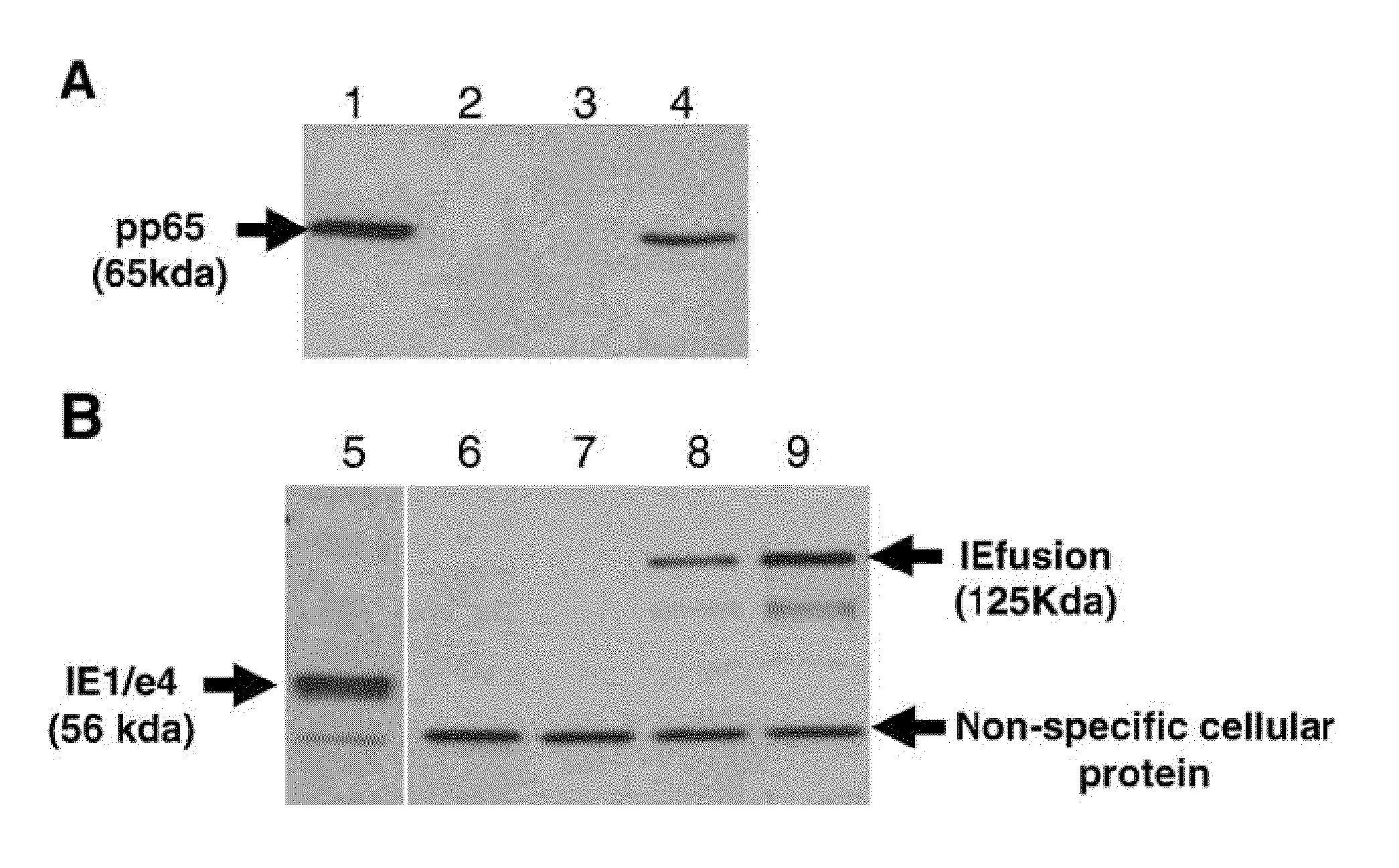
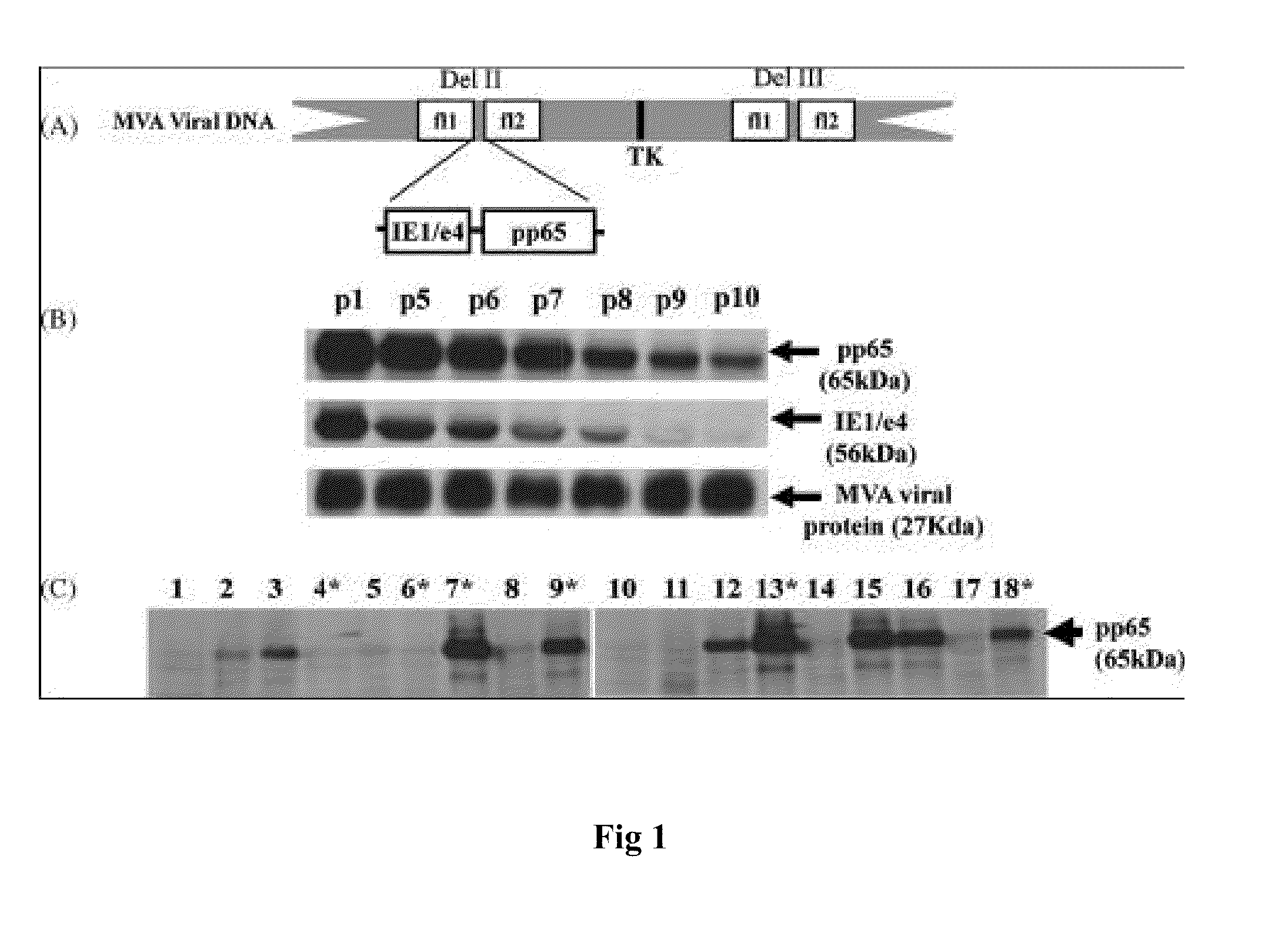
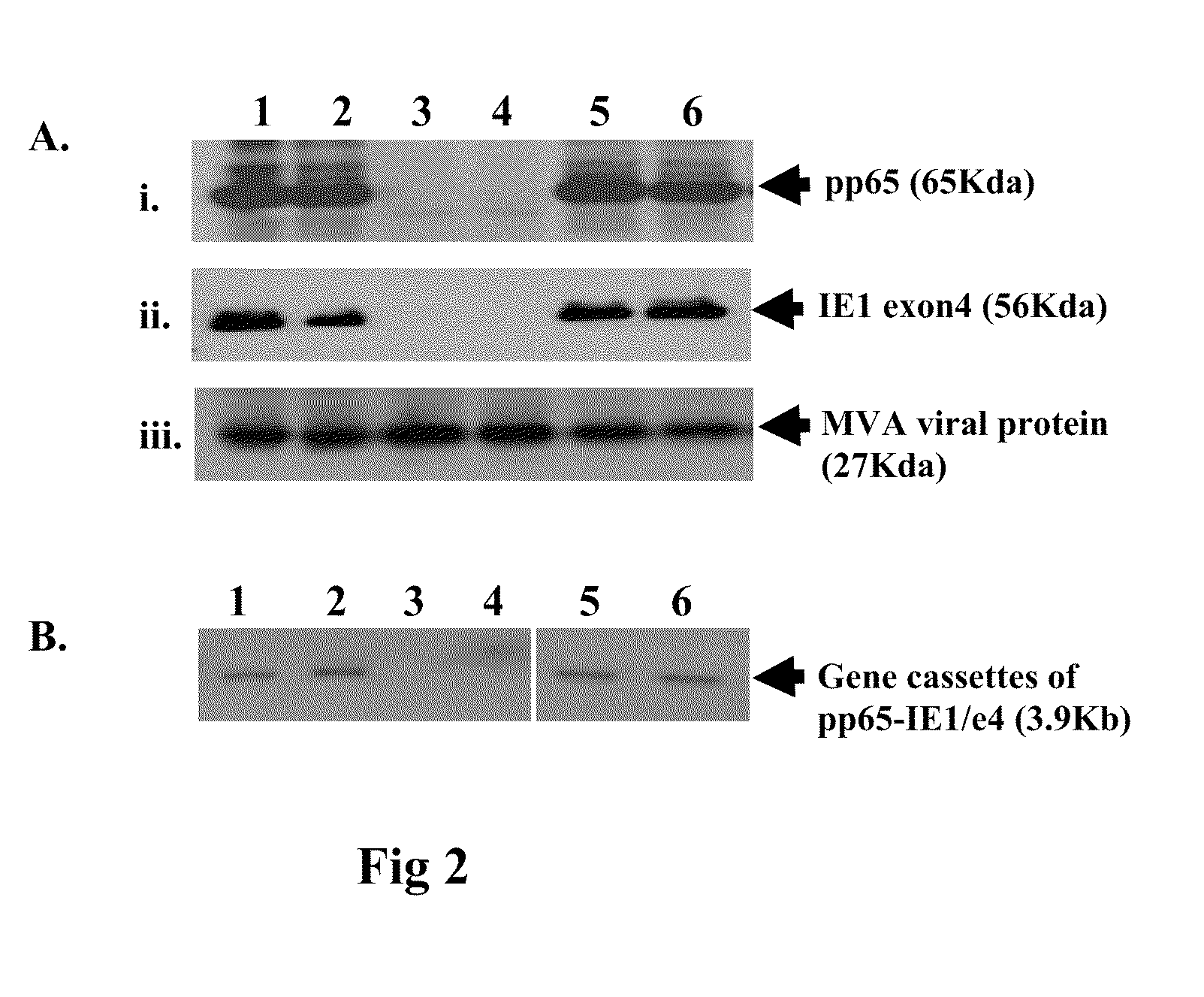
A vaccine comprising an immunologically effective amount of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (rMVA) virus which is genetically stable after serial passage and produced by a) constructing a transfer plasmid vector comprising a modified H5 (mH5) promoter operably linked to a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous foreign protein antigen, wherein the expression of said DNA sequence is under the control of the mH5 promoter; b) generating rMVA virus by transfecting one or more plasmid vectors obtained from step a) into wild type MVA virus; c) identifying rMVA virus expressing one or more heterologous foreign protein antigens using one or more selection methods for serial passage; d) conducting serial passage; e) expanding an rMVA virus strain identified by step d); and f) purifying the rMVA viruses from step e) to form the vaccine. One embodiment is directed to a fusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) protein antigen comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding two or more antigenic portions of Immediate-Early Gene-1 or Immediate-Early Gene-2 (IEfusion), wherein the antigenic portions elicit an immune response when expressed by a vaccine.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
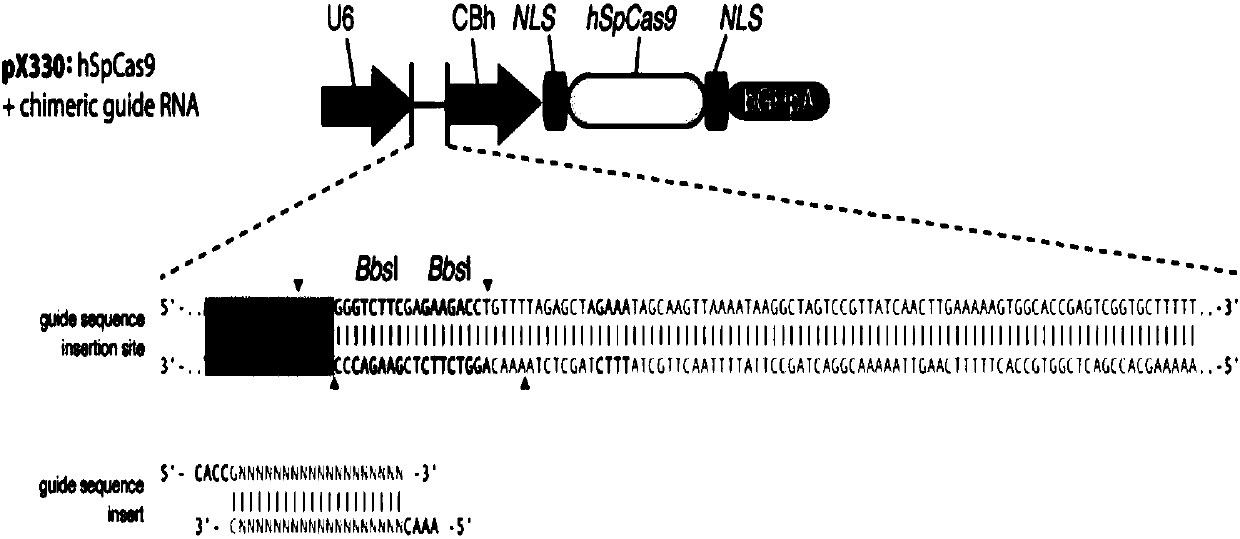
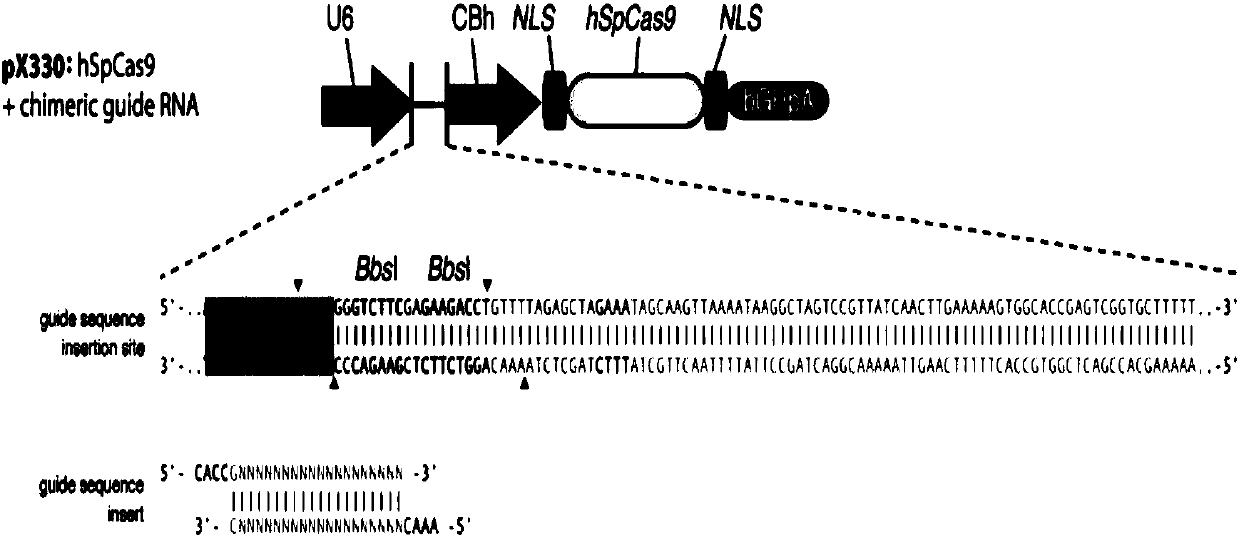
Method for performing GINS2 gene knockout on mesenchymal stem cells by using CRISPR-CAS system
ActiveCN107619829AGood sgRNAHigh knockout efficiencyStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionMesenchymal stem cellPlasmid
The invention provides a method for performing GINS2 gene editing on mesenchymal stem cells by adopting a CRISPR-cas 9 system, and particularly relates to a method for constructing a GINS2 gene-knocked mesenchymal stem cell line. A new enhancin CREnhancer 1.0 is used, so that the editing efficiency of the CRISPR-cas 9 gene in cells can be remarkably improved. The GINS2 knockout plasmid for the mesenchymal stem cells provided by the invention has high genetic stability.
Owner:南京平港生物技术有限公司
Method using CRISPR-Cas system to perform GING2 gene knockout on epidermal stem cell
ActiveCN108715850AStrong knockout effectGood sgRNAGenetically modified cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPlasmidGenetic stability
The invention provides a method using a CRISPR-Cas system to perform GING2 gene editing on an epidermal stem cell and particularly relates to a method for building an epidermal stem cell line with theGING2 gene being knocked out. Two specific gRNAs are built and acquired, and the GINS2 gene editing efficiency of CRISPR / Cas9 in the epidermal stem cell can be increased evidently. An epidermal stemcell GINS2 knockout plasmid is good in hereditary stability and high in targeting efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG AIE BIOSCIENCE CO LTD
Method for knocking out RBM17 gene of mesenchymal stem cells by using CRISPR-CAS system
ActiveCN107760684AGood sgRNAHigh knockout efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMesenchymal stem cellPlasmid
The invention provides RBM17 gene edition carried out on mesenchymal stem cells by adopting a CRISPR-CAS system and in particular relates to construction of a mesenchymal stem cell line with the RBM17gene knocked out. A new enhancing CREnhancer1.0 is used, and intracellular CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing efficiency can be obviously improved. The mesenchymal stem cell RBM17 knockout plasmid provided bythe invention has better genetic stability.
Owner:上海启肽智能科技有限公司
Tea source eurotium cristatum strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103275876AImprove processing qualityAvoid pollutionFungiPre-extraction tea treatmentMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a tea source eurotium cristatum strain which is named as eurotium cristatum XU08 and is preserved in the CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on March 13, 2012 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.5891. Researches on the morphological feature, the physiological property, the genetic stability and the growing conditions of the strain during the production of the Fuzhuan tea and industrial trial production of the strain prove that the strain is available as a special leavening agent for the production of the Fuzhuan tea, so that the production cycle can be shortened and the product quality can be improved, and therefore, the strain is very suitable for modern production needs of the Fuzhuan tea.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
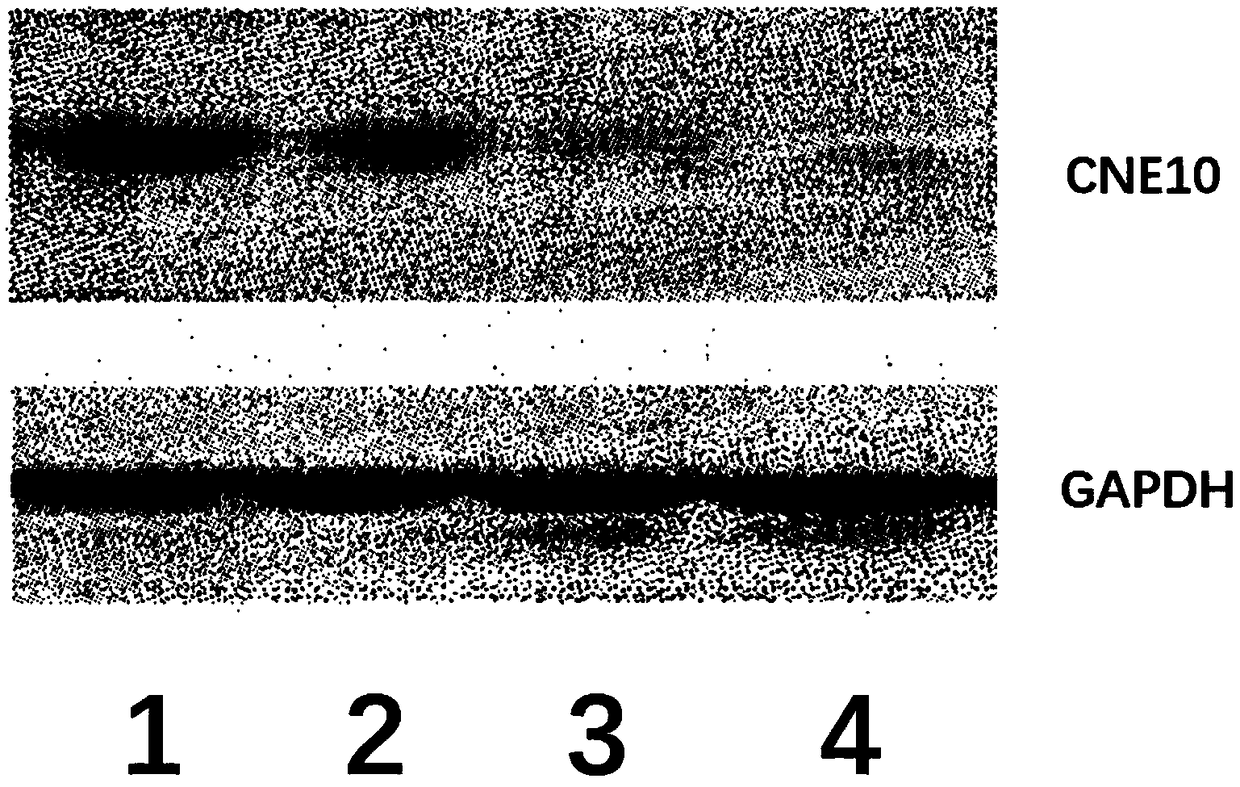
CNE10 gene knockout in epidermal stem cells by using CRISPR-Cas system
The invention provides CNE10 gene editing for epidermal stem cells by using a CRISPR-Cas system, and particularly relates to establishment of an epidermal stem cell system with GNE10 gene knocked out.Through the establishment, two specific gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acids) are obtained, editing efficiency of the CRISPR-Cas system aiming at the GNE10 gene in the epidermal stem cells can be increased remarkably. An obtained epidermal stem cell plasmid with CNE10 gene knockout is good in hereditary stability and high in targeting efficiency.
Owner:江西汉氏联合干细胞科技有限公司
Microbial compound preparation and preparation method
The invention discloses a microbial compound preparation, a preparation method and a method for treating kitchen garbage. The method for treating kitchen garbage is to separate out mixed bacteria of bacteria and fungi with a certain ratio from the natural world and fermented food, and then prepare the mixed bacteria preparation to effectively treat the kitchen garbage. The preparation comprises the mixed bacteria including various bacteria, actinomycetes, yeast and mycetes. The preparation is characterized in that the mixed bacteria further comprise bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, high-temperature monad, streptomycete, lactobacillus plantarum, lactobacillus acidophilus, brewer's yeast, pichia pastoris, aroma-producing yeast, rhizopus chinensis, rhizopus oryzae and mucor indicus. The preparation is good for treating the kitchen garbage, non-toxic, harmless, and of genetic stability.
Owner:深圳市三盛环保科技有限公司
Genetically stable recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (rMVA) vaccines and methods of preparation thereof
A vaccine comprising an immunologically effective amount of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (rMVA) virus which is genetically stable after serial passage and produced by a) constructing a transfer plasmid vector comprising a modified H5 (mH5) promoter operably linked to a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous foreign protein antigen, wherein the expression of said DNA sequence is under the control of the mH5 promoter; b) generating rMVA virus by transfecting one or more plasmid vectors obtained from step a) into wild type MVA virus; c) identifying rMVA virus expressing one or more heterologous foreign protein antigens using one or more selection methods for serial passage; d) conducting serial passage; e) expanding an rMVA virus strain identified by step d); and f) purifying the rMVA viruses from step e) to form the vaccine. One embodiment is directed to a fusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) protein antigen comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding two or more antigenic portions of Immediate-Early Gene-1 or Immediate-Early Gene-2 (IEfusion), wherein the antigenic portions elicit an immune response when expressed by a vaccine.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
In vitro conservation method of churysanthemum by reducing macroelements in the medium
InactiveCN101006774ANormal growthKeep material stableDead plant preservationHorticulture methodsAxillary budNormal growth
The invention relates to a method for conserving chrysanthemum in vitro through reducing major element in the medium, which is special for the in vitro conservation of the chrysanthemum germplasm resource. The invention comprises the steps of: taking the suckers of the chrysanthemum as the explants, and axillary buds for subculture, and conserving on the 1 / 2MS, 1 / 2MS (1 / 2NH4+) or 1 / 4MS medium containing 6-BA0.3mg / L and NAA0.1mg / L. The survival rate for a 12-month conservation is 100%, 8 months longer than that of conservation on the normal MS medium. After the conservation material recovers to normal growth, the descendant is proved to have no genetic variance through the detection of POD, EST and ISSR. The invention uses the method of conserving chrysanthemum test-tube plantlet through reducing major element in the medium and identifies the genetic stability of the descendant, which proves that the plants grow normally after one-year conservation and the descendant has no genetic variation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets
ActiveCN101810140AIncrease profitGrow neatlyMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsAxillary budShoot
The invention provides a mthod for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets, which comprises the following steps: a. adopting dendrobium candidum stem sections or stem section axillary buds as explants, wherein chloroplasts of the stem sections or the stem section axillary buds have gene sequences with the GenBank login number of FJ530946; and b. carrying out the processes of axillary bud survival and growth, cespitose shoot inducement and multiplication, and plantlet formation, wherein the culture conditions include the culture room temperature of 26+ / -2 DEG C, the illumination intensity of 20001x, the pH value between 5.8 and 6.0, the light source of a fluorescent lamp or an LED light source, and the illumination time of 12 h per day. The method of the invention aims at the defects of the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, improves the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, and provides a fast propagation method of the dendrobium candidum germchits. The method can meet the requirements of germchits required by large-scale production in a short time, and has the characteristics of low cost, regular germchit growth, simplicity and easy implementation of a domestication method, good inheritance stability and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN WANAN DENDROBIUM IND DEV
Avermectin B1a high-yielding strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102634471AHigh compositionReduce other componentsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLithium chlorideUltraviolet
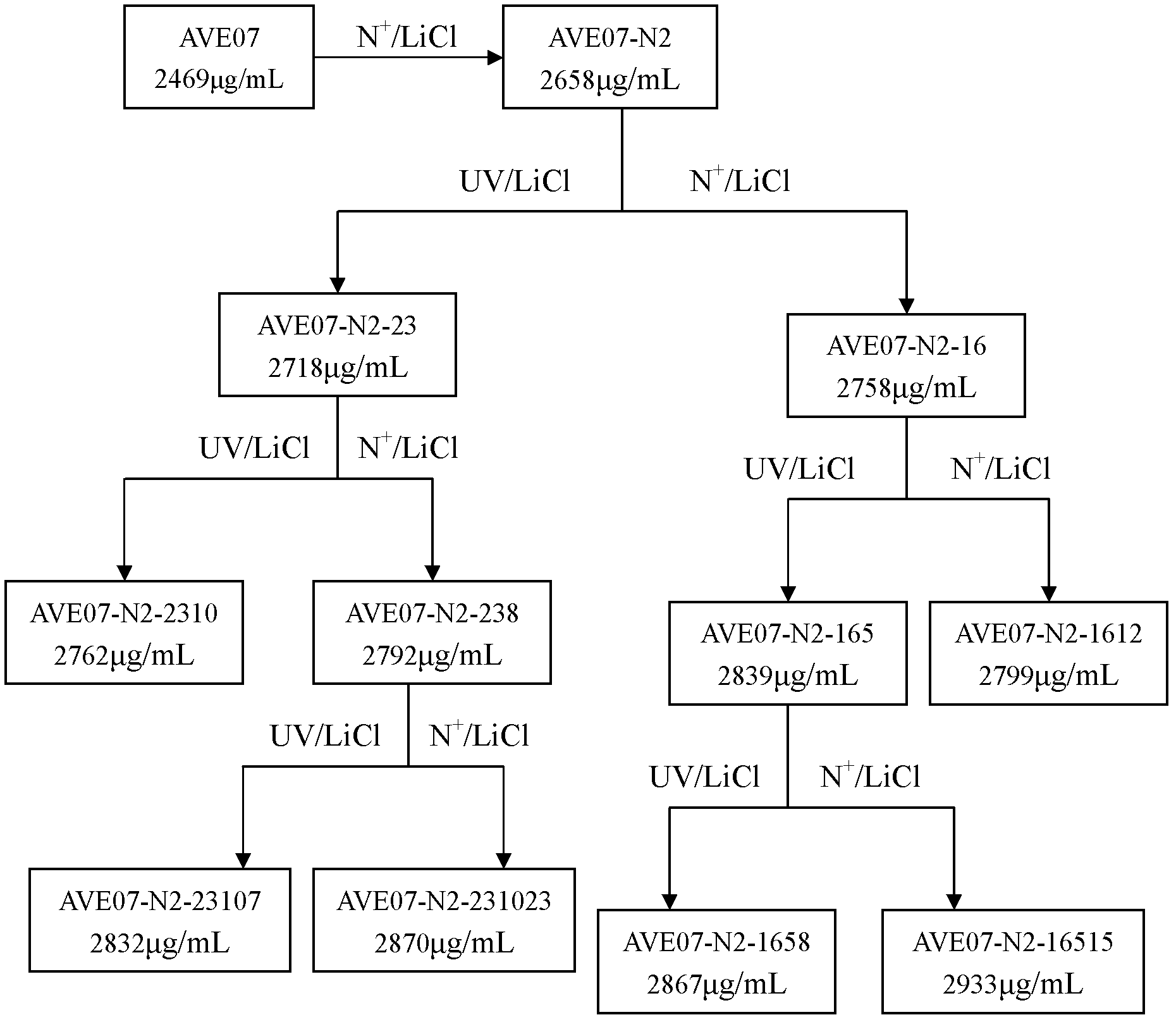
The invention discloses an avermectin B1a high-yielding strain, which is classified and named streptomyces avermitilis AVE 07-N2-16515, and is preserved in a China type culture preservation centre (CCTCC) with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2012094. The avermectin B1a high-yielding strain disclosed by the invention is obtained by combining low-energy nitrogen ion implantation-lithium chloride (N<+>-LiCl) compound mutation with ultraviolet ray-lithium chloride (UV-LiCl) compound mutation, primarily screening, and performing shake-flask fermentation secondary screening, and is used as a starting strain for next mutation, so that the target strain AVE07-N2-16515 is finally screened. The obtained strain can greatly increase the avermectin B1a component and reduce other components in fermentation products, and is good in hereditary stability. The strain is fermented in a 5L fermentation tank to produce avermectin B1a by utilizing glucose as a quick-acting carbon source and cornstarch as a delayed-action carbon source, the titer can achieve 3048 mu g / m, which is improved by 23.4% as compared with the original starting strain AVE07; and the strain can be applied on industrial production, greatly improves a fermenting unit, and has great economic application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof
ActiveCN101935637ANon-pathogenicGood spiritsViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtective antigenOrganism
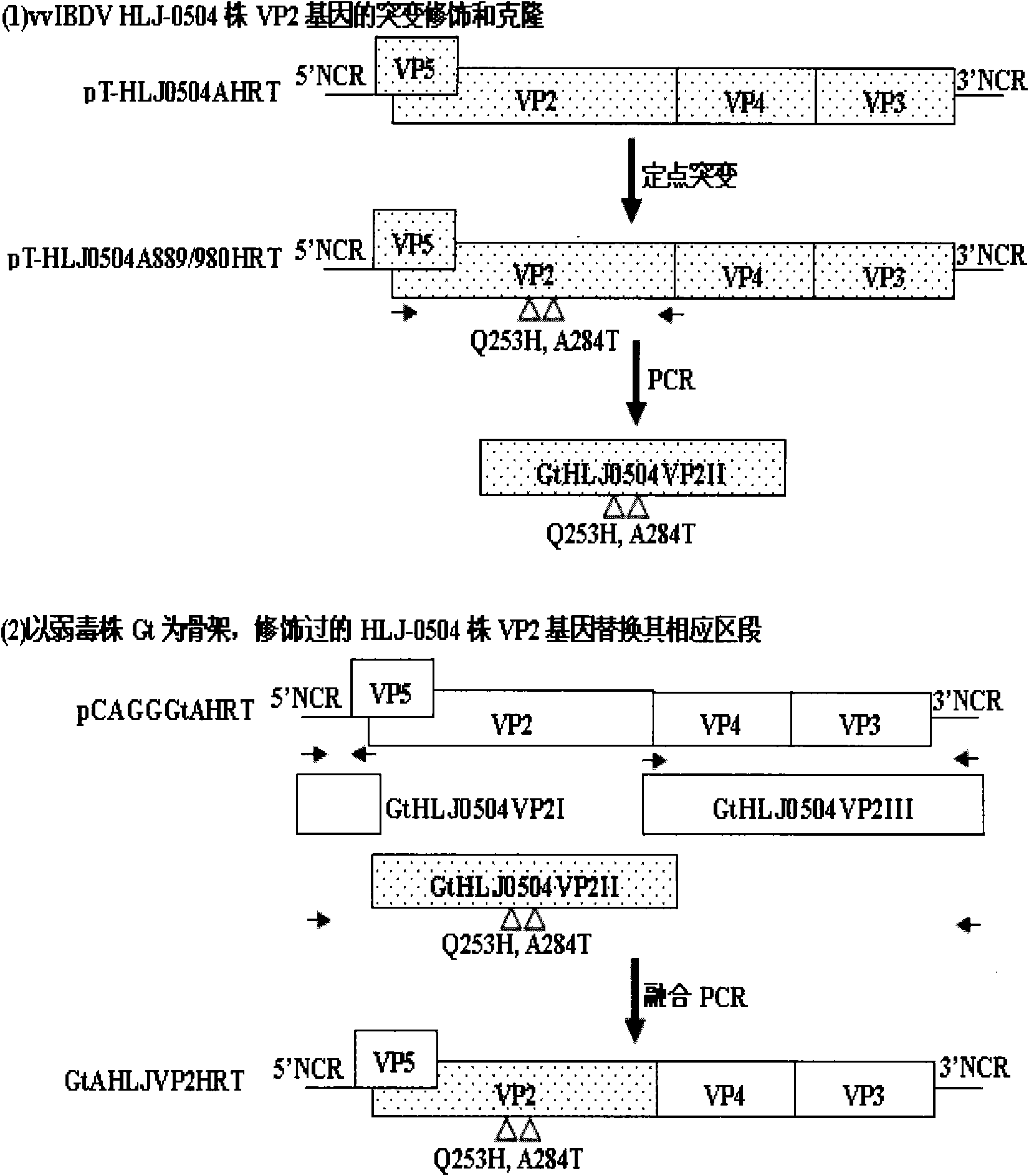
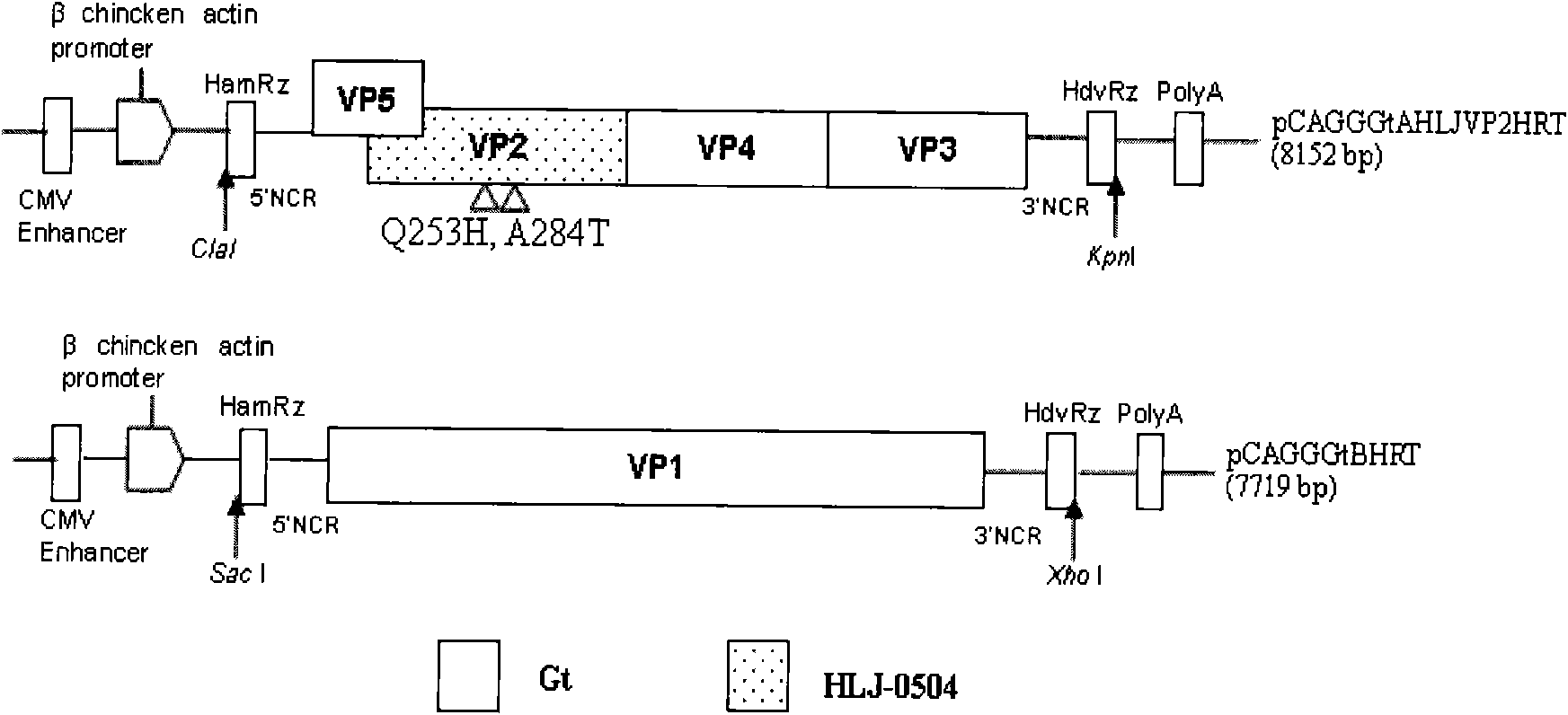
The invention discloses a recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof. In the invention, a major protective antigen gene VP2 of an epidemic superhigh virulent strain is cloned, the nucleotide of the gene VP2 is modified by mutation and then used for replacing a corresponding segment of a Gt genome of a low-virulent strain of the IBDV, so that the infectious clone of a recombinant genome of the IBDV is constructed, and the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain is saved and identified by using an IBDV reverse genetic operation system. The microbial collection number of the vaccine strain is CGMCC No.3749. The recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has high replicability, genetic stability and safety. The immune effect of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is as good as that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain, but is superior to that of the low-virulent vaccine strain. The biological safety of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is superior to that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain. As the vaccine strain, the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency and low toxicity, is a good candidate vaccine strain and can be used for controlling chicken infectious bursal disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Quick propagation seedling-breeding method for reducing vitrifaction in multiple times of subculture of rosaceous plant
InactiveCN101965797AShorten the cycle of selection and breedingEase of mass productionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePlant hormoneVitrification
The invention provides a quick propagation seedling-breeding method for reducing vitrifaction in multiple times of subculture of a rosaceous plant. The method comprises disinfection of explants, induction of buds, sub propagation and rooting induction. The method is characterized in that: in the sub propagation process, test tube seedlings are subjected to rejuvenation culture alternately, and then vigorous test tube seedlings with height of 1 to 3 centimeters are selected and transferred into a rooting culture medium for induced rooting so as to obtain complete test tube plants, wherein a starting culture medium without containing any exogenous plant hormone for rejuvenation is adopted in the rejuvenation culture. The method is quick, efficient, low in cost and convenient for popularization, has good genetic stability and low vitrifaction ratio in the culture process, keeps the propagation coefficient in a high level, and is suitable for tissue culture and quick propagation of the rosaceous plant.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and breeding method
InactiveCN101690463AGenetically stableIncrease productionFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyDry weight
The invention provides a mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and a breeding method. A new high-yield strain of cordyceps militaris is obtained by chemical mutagenesis, the preservation number thereof is CGMCC NO. 2909, and compared with original starting strain, the dry weight of mycelium is increased by 103%, the content of adenosine is increased by 536%, the content of polysaccharide is increased by 22.2%, the content of protein is increased by 55.5%, and the content of mannitol is increased by 37.5 %. The new strain of cordyceps militaris does not degenerate after more than 20 times of subculturing, has genetic stability, and utilizes the research of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to verify the difference on DNA level between the strain and the original starting strain. The invention also discloses the optimum process condition for extracting polysaccharide and adenosine of cordyceps militaris.
Owner:CHANGCHUN SHENGJINNUO BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
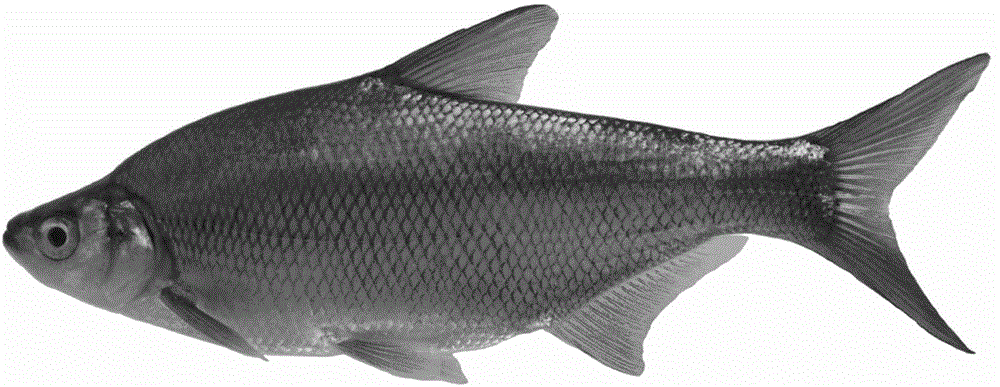
Method for establishment of hybrid strain between bluntsnout bream and topmouth culter and breeding method of topmouth bream
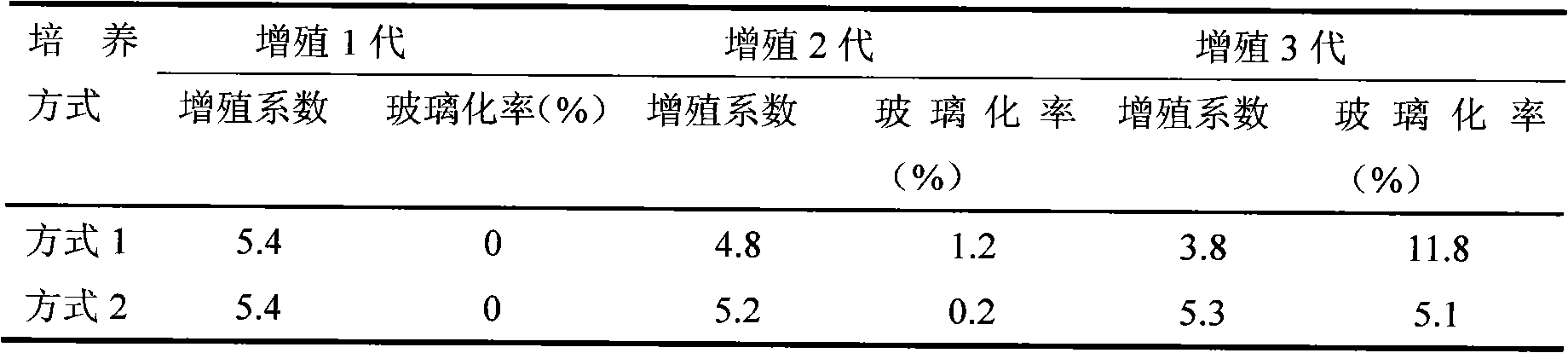
ActiveCN102972319AGenetic stabilityFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPloidyGenetic stability
The invention discloses a method for establishment of a hybrid strain between bluntsnout bream and topmouth culter. The bluntsnout bream is used as a female parent, the topmouth culter is used as a male parent, the hybrid strain F1 of the bluntsnout bream and the topmouth culter is obtained through distant hybridization and is then bred and tested to obtain a bisexual fertile F1; then F1 is cultured as an object, selfing of the bisexual fertile F1 is performed, and a diploid F2 of the bluntsnout bream and the topmouth culter is obtained through incubation and breeding; and the ploidy and sterility of F2 are tested to obtain a bisexual fertile F2, and thus the heterologous bream and culter stain with genetic stability and bisexual sterility is obtained. The invention also discloses a breeding method of topmouth bream. The bisexual fertile diploid hybrid strain F1 of the bluntsnout bream and the topmouth culter and the bisexual fertile F2 of the bluntsnout bream and the topmouth culter are obtained by the establishment method, and backcross breeding is performed with the bluntsnout bream to obtain the hybrid topmouth bream. By adopting the breeding method, the novel hybrid topmouth bream with characteristics of high growth speed, high resistance, high meat quality, attractive shape and the like can be prepared.
Owner:湖南岳麓山水产育种科技有限公司
Induction and in-vitro culture method of plant stem cells derived from apical meristem of catharanthus roseus roots
InactiveCN111876368AStable subcultureNo epigenetic variationCell culture mediaPlant cellsBiotechnologyStem cell line
The invention discloses an induction and in-vitro culture method of plant stem cells derived from apical meristem of catharanthus roseus roots. The induction method comprises the following steps: cutting off a root cap from the root tip of the catharanthus roseus, performing inoculating to an induction culture medium, performing culturing in dark, and proliferating and growing a stem cell layer inan explant to form a cell cluster; transferring the layered stem cell layer to a subculture medium for culturing for 10-15 days, and performing complete culturing in dark; and performing transferringto a new subculture medium, and performing culturing for 10-15 days under the same condition to obtain a catharanthus roseus stem cell line with stable cell morphology. A catharanthus roseus stem cell culture system is established by inducing apical meristem of the catharanthus roseus roots, stable subculture can be performed under certain conditions, and epigenetic variation is avoided. The catharanthus roseus stem cell culture system established by the invention has the characteristics of being high in growth speed, high in genetic stability and the like, and culture with a 10L bioreactor is preliminarily realized.
Owner:LINGNAN INST OF TECH
Method for dislocation storage of germ resource of chrysanthemum
InactiveCN101002541ANormal growthKeep material stableDead plant preservationPlant tissue cultureAxillary budGermplasm
An in vitro storage method for the germplasm resource of chrysanthemum includes such steps as taking the root bud of chrysanthemum as explant, secondary culture of auxiliary bud, and storing in the MS culture medium containing abscisic acid, 6-BA and NAA. Its survival rate after 10 months is 100%.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
High quality germchit tissure culturing and rapid breeding method of Dendrobium sp.
InactiveCN1631109AStable traitsHigh genetic stabilityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudZoology
Disclosed is the high quality germchit tissure culturing and rapid breeding method of Dendrobium sp., wherein a large amount of test tube seedlings with stabilized performance are obtained through fine breed tissue culture by adopting the path of clumping buds. The produced Dendrobium sp. has the advantages of high genetic stability, quick emergence of seedlings, strong seedlings, good seedling quality, strong resistance, and fine growth status.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Feruloyl-esterase-producing Bacillus licheniformis strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104894017ALow carbon sourceLower requirementBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisSerial passage
The invention discloses a feruloyl-esterase-producing Bacillus licheniformis strain and application thereof. The collection number of the Bacillus licheniformis DBM12 strain is CGMCC No.8672. The Bacillus licheniformis strain has the advantages of lower requirements for the carbon source and nitrogen source, short fermentation time, high safety and no toxicity, and can be used in food / feed industry. The Bacillus licheniformis strain has favorable hereditary stability, and is simple to operate. The feruloyl esterase synthesis capacity is basically unchanged after serial passage by more than 10 generations.
Owner:QINGDAO BEIBAO OCEAN TECH CO LTD
Method for producing momordica grosvenori group seedling with single culture medium
InactiveCN101218896AEasy to operateQuality improvementHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budMomordica
A method for producing a grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling by a single culture medium uses an MS solid medium during the producing process and is characterized in that the angustimycin of 0.1 to 0.5mg L<1> is added into a normal MS solid medium to produce the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling. As the medium singly prepared by the angustimycin can be simultaneously used on each technical tache of 'axillary bud explant starting', 'proliferation and expanding propagation' and 'proliferated seedling rooting', thereby greatly simplifying the producing operation procedures of the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling. In particular, the angustimycin can effectively control the generation of a callus during the culturing process of the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling in particular, which is beneficial to the genetic stability; thereby improving the quality of the tissue culture seedling.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Enterovirus type 71 and use thereof
ActiveCN101717754AViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsHybrid cell preparationEnterovirusHand-foot-and-mouth disease
The invention relates to an enterovirus type 71 (abbreviated as EV71) and use thereof, in particular to a monoclonal virus strain which is separated by a plaque assay method. The progeny viruses of the monoclonal virus strain show genetic stability. The monoclonal virus strain can be used in the production of a vaccine (particularly the production of a vaccine for infant). The virus strain or the vaccine produced by using the same can be used in the prevention of diseases (such as hand-foot-and-mouth diseases, particularly hand-foot-and-mouth diseases in children) caused by the EV71 and has the characteristics of stable titer, high immunogenicity and small immunizing dose.
Owner:SINOVAC BIOTECH
Method for cultivating subcultured bud of upright crown tissue culture seedling of fir wood
ActiveCN104145824AGrowth inhibitionRemove position effectClimate change adaptationAfforestationSocial benefitsEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a subcultured bud of an upright crown tissue culture seedling of fir wood. The method comprises the following steps: an excellent clonal annual burgeon of the fir wood is used as an explant, a breeding bud is obtained through disinfection, sterilization and tissue culture, the breeding bud is innoculated in a proliferation culture medium comprising 1 / 2MS, 1.0mg / L of 6-BA and 0.5mg / L of IBA for inducing the cluster buds to sprout, the subcultured bud which is germinated at the base of the breeding bud and is healthy in growth is selected and is cut in a common rooting culture medium, seedlings are exercised and transplanted, and when the height of the seedlings of the fir wood is 15-30 cm, the seedlings are taken out of a garden for forestation. When the method is used, the proliferation rate of the subcultured bud of the fir wood is as high as 4-6, the breeding speed is high, the seedling culturing number is large, the tissue culture subcultured bud with high genetic stability, 100% of the upright crown rate of the tissue culture seedling and more than 96% of the rooting rate can be in batch production in a short period, and the requirements of the construction and the development of a fir wood reserving base of China for good seedlings can be met, so that the method has better economic benefits, social benefits and ecological benefits.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Protoplast mutation breeding method for improving cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN103215250AGood mutagenic effectEasy to operateFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention relates to a protoplast mutation breeding method for improving the cordycepin content of cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps of activated culture of bacterial strains, solid culture of mycelia, liquid mycelia culture, mycelia enzymolysis, protoplast nitrosoguanidine (NTG) mutation, protoplast regeneration culture, regenerated bacteria subculture, fermentation culture, filtering, further washing of mycelia, measurement of cordycepin content in the mycelia, preservation of the bacteria strain with high cordycepin content, measurement of the genetic stability and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the cordycepin content of the cordyceps militaris can be increased.
Owner:XUZHOU HONGYU AGRI TECH
Tissue-culture rapid propagation method for pyrus betulaefolia bunge
ActiveCN103380730AImprove the efficiency of rapid propagationHigh rooting rateCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue culturePyrus betulaefoliaBud
The invention discloses a tissue-culture rapid propagation method for pyrus betulaefolia bunge. The tissue-culture rapid propagation method for the pyrus betulaefolia bunge comprises disinfecting on explants, inducing buds, propagating test tube seedlings, inducing calluses, inducing rooting and transplanting exercising seedlings. During the process of inducing rooting, the calluses are firstly induced and then the rooting is induced; obtained rooting test tube seedlings are performed seedling exercising in a triangular flask, then transferred to perlite to domesticate the exercising seedling and finally transplanted. Compared with the traditional method, the tissue-culture rapid propagation method for the pyrus betulaefolia bunge has the advantages of being high in rooting rate and survival rate of transplanting, high in propagation rate, low in cost, convenient to popularize, good in genetic stability and suitable for the pyrus betulaefolia bunge.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla
InactiveCN102228001AImprove proliferation efficiencyRealize automated productionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFraxinusCotyledon plant
The invention discloses a micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla and relates to the micropropagation method. The problems of long reproductive cycle, low reproduction efficiency and poor offspring genetic stability in nursery stock propagation of fraxinus rhynchophylla are solved. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, sterilizing fraxinus rhynchophylla seeds, and culturing single cotyledons of zygotic embryos to obtain cotyledonal cell embryos; 2, performing maturation cultivation on the cotyledonal cell embryos; 3, performing sprouting cultivation on the cotyledonal cellembryos subjected to maturation cultivation to obtain regenerated plants; and 4, transplanting the regenerated plants into a culture medium to culture until new leaves are completely unfolded, and removing a covered plastic thin film. The micropropagation method has the advantages of short nursery stock reproductive cycle, high reproductive rate (culturing for 60 to 70 days) and high reproductionefficiency (each explant can generate 15 to 20 somatic embryos); the germination rate of the somatic embryos is up to 87 to 89.55 percent; the transplanting survival rate of the regenerated plants isup to 75 to 80 percent; and the regeneration plants with the same good characteristics as female parents can be generated in mass.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
Hansenula polymorpha expression system, hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha
ActiveCN103045492AThe mutation site is clearLow back mutation rateFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh level expressionGenetic engineering
The invention provides a hansenula polymorpha expression system, a hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha. The expression system contains uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501, of which the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7013. The uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501 provided by the invention has the advantages of definite mutation site, low reverse mutation frequency, good hereditary stability, high biological expression quantity and the like, plays a significant role in researching and producing gene engineering vaccine, has the advantages of higher yield and low cost as compared with other eukaryotic expression systems adopted at present. The invention further provides an expression vector applied to the hansenula polymorpha expression system and a construction method of the expression vector. Two or more genes can be expressed simultaneously through the expression vector. Two target genes can be expressed in a hansenula polymorpha auxotroph cell at a high level without interference.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
Screening preparation for superior enterococcus faecalis and application thereof
InactiveCN101275158AImprove moisture functionImprove oil functionSenses disorderNervous disorderMetaboliteEnterococcus avium
The present invention provides a screen preparing method of excellent enterococcus faecalis and its application. Enterococcus faecalis is the most common representative species in the Enterococcus, living in human intestinal, having no hazard to human, and having benefits. But Enterococcus faecali arises server infection some time, and having resistance to antibiotics. The invention repeatedly cultures and screens enterococcus faecalis, selecting out a strain which has exuberant life, quick growth speed, high fermentation unit, short fermentation cycle, high content of fermentation product, strength production adaptability as a producing strain by researching the contents of morphological characteristics, culture characteristics, physiological and biochemical response, metabolites, genetic character and protein expression, genetic stability, pilot producing index etc, forming a scale production. The broth has functions of immunity adjustment, antitumor etc.
Owner:孙卫
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com