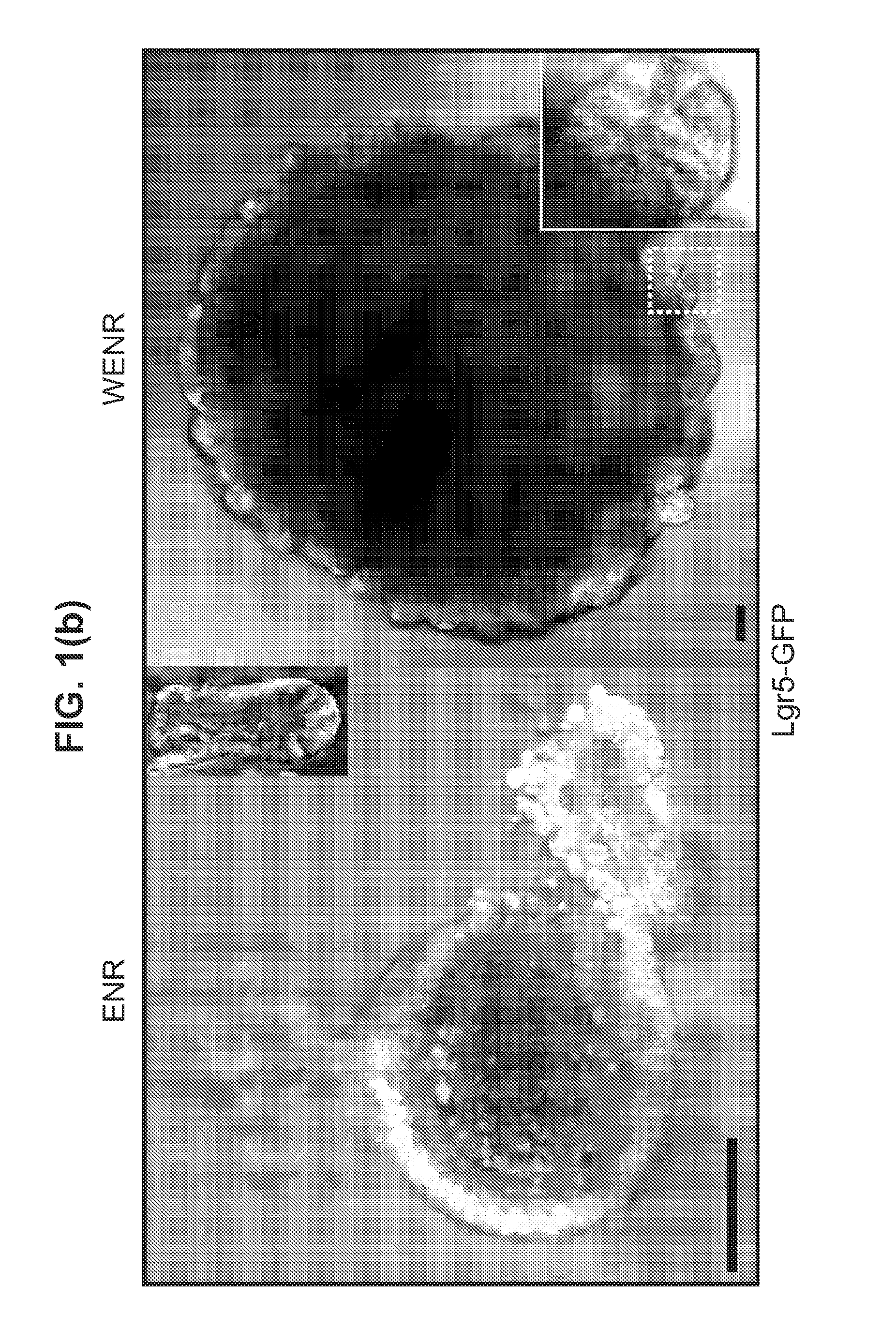
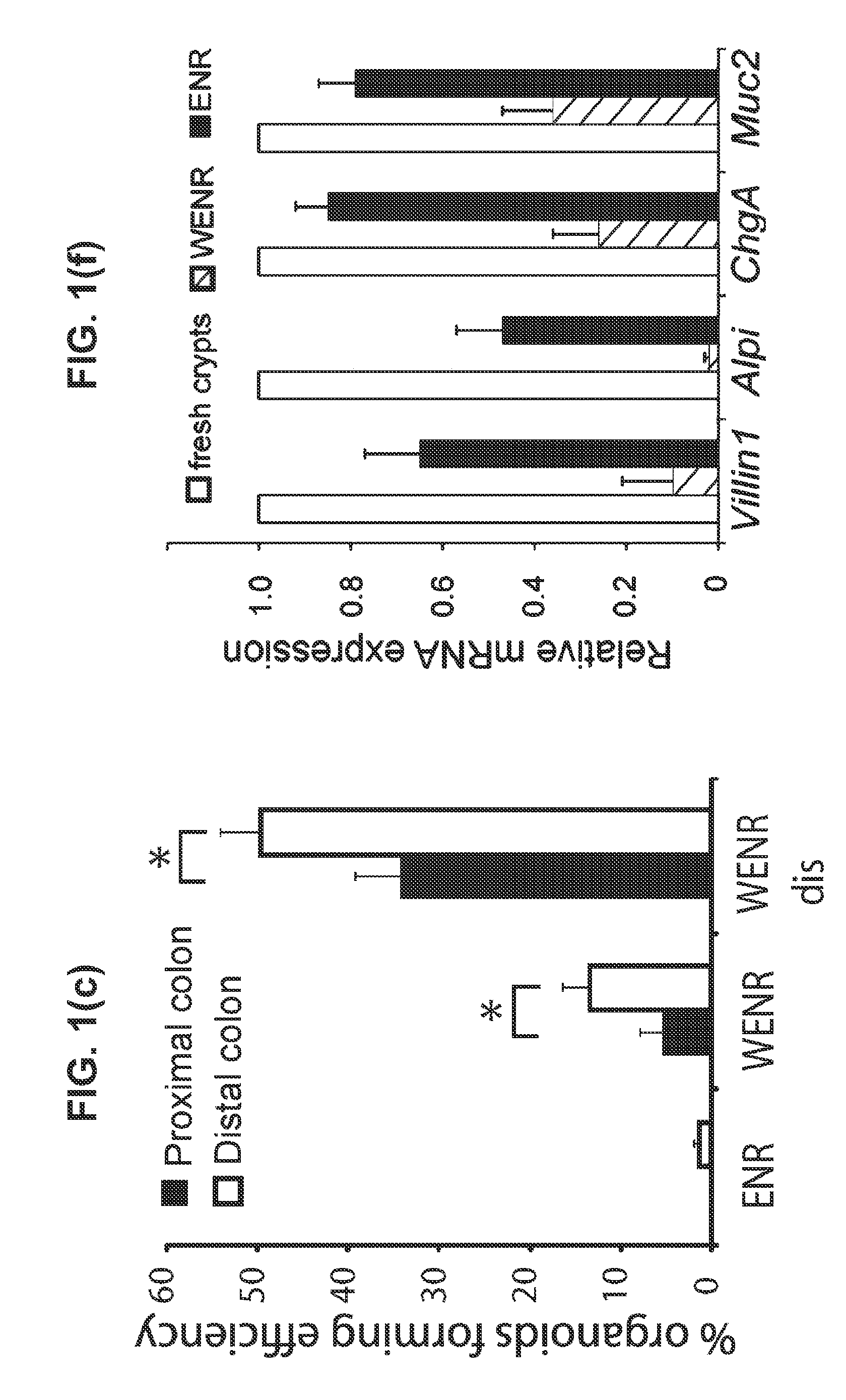
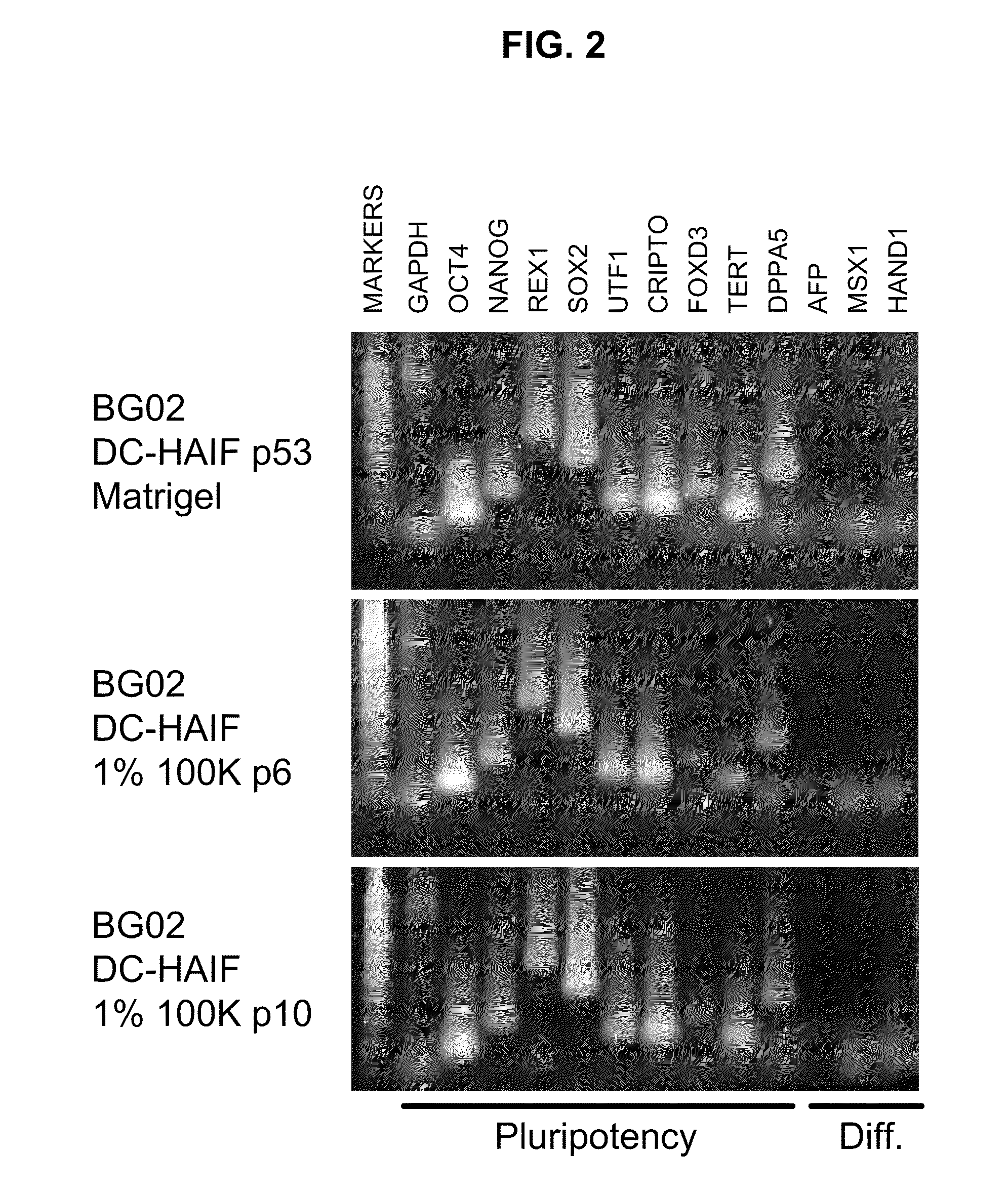
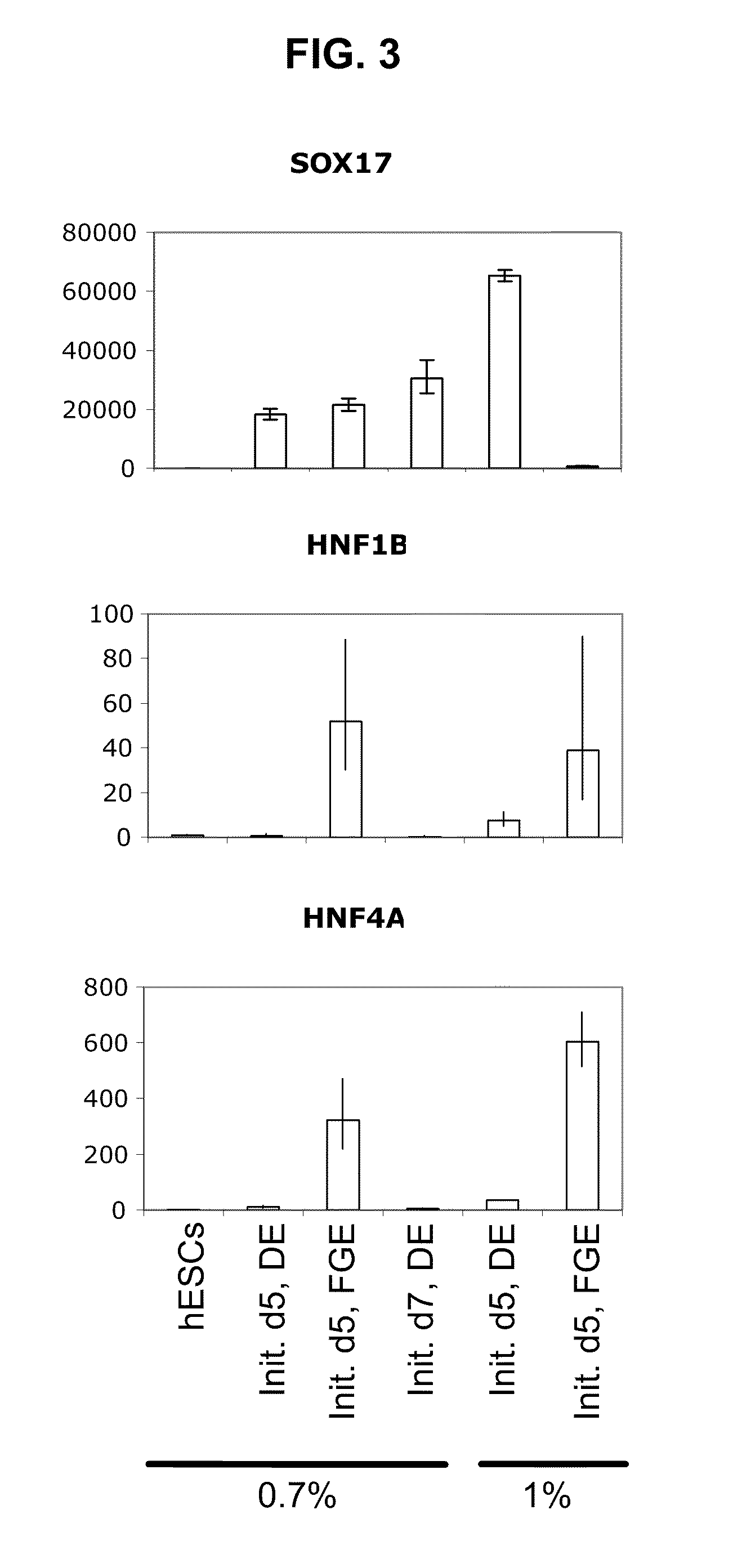
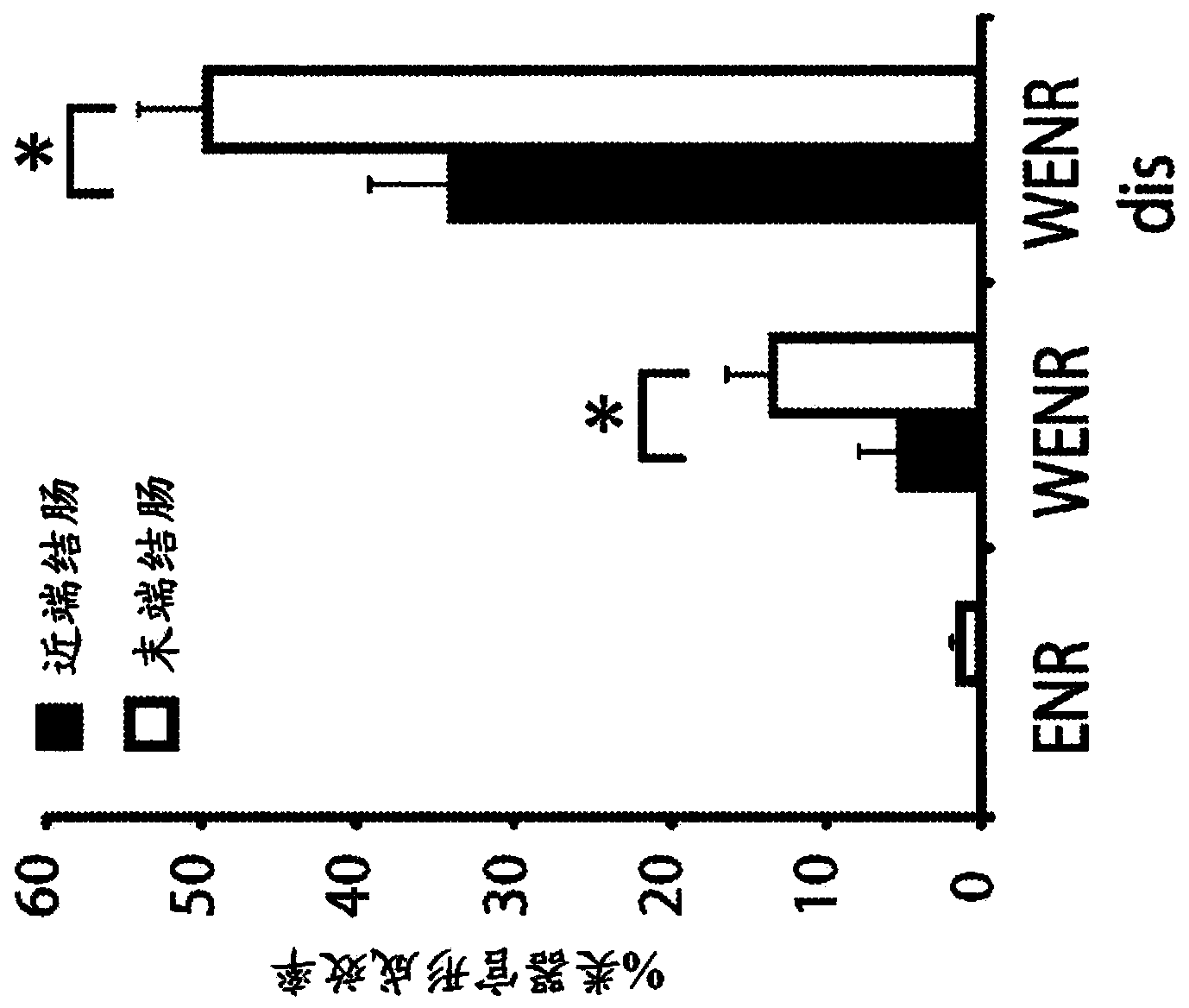
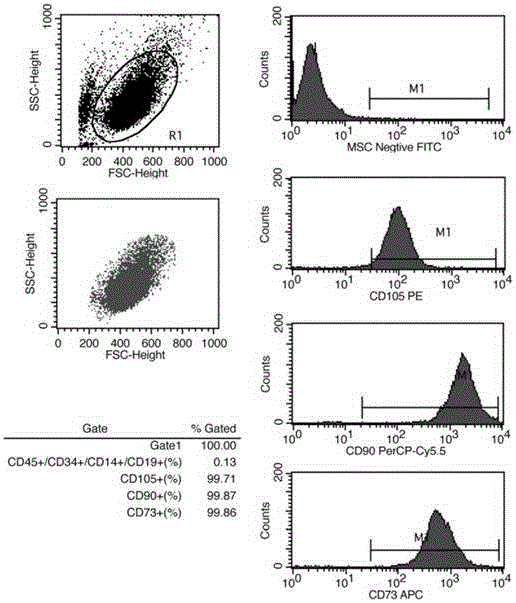
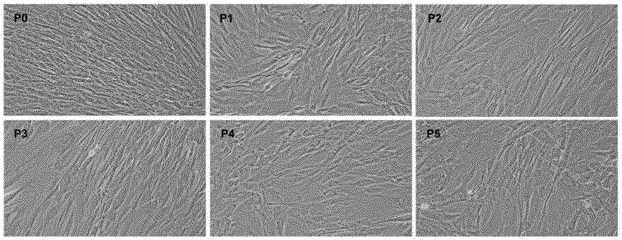
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1026 results about "Stem cell culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A stem cell culture refers to cells that are removed from source material and grown under laboratory conditions. The use of stem cells is still in infancy as of the early 21st century, and human stem cell culture research remains an area of considerable ethical debate.
Defined media for stem cell culture
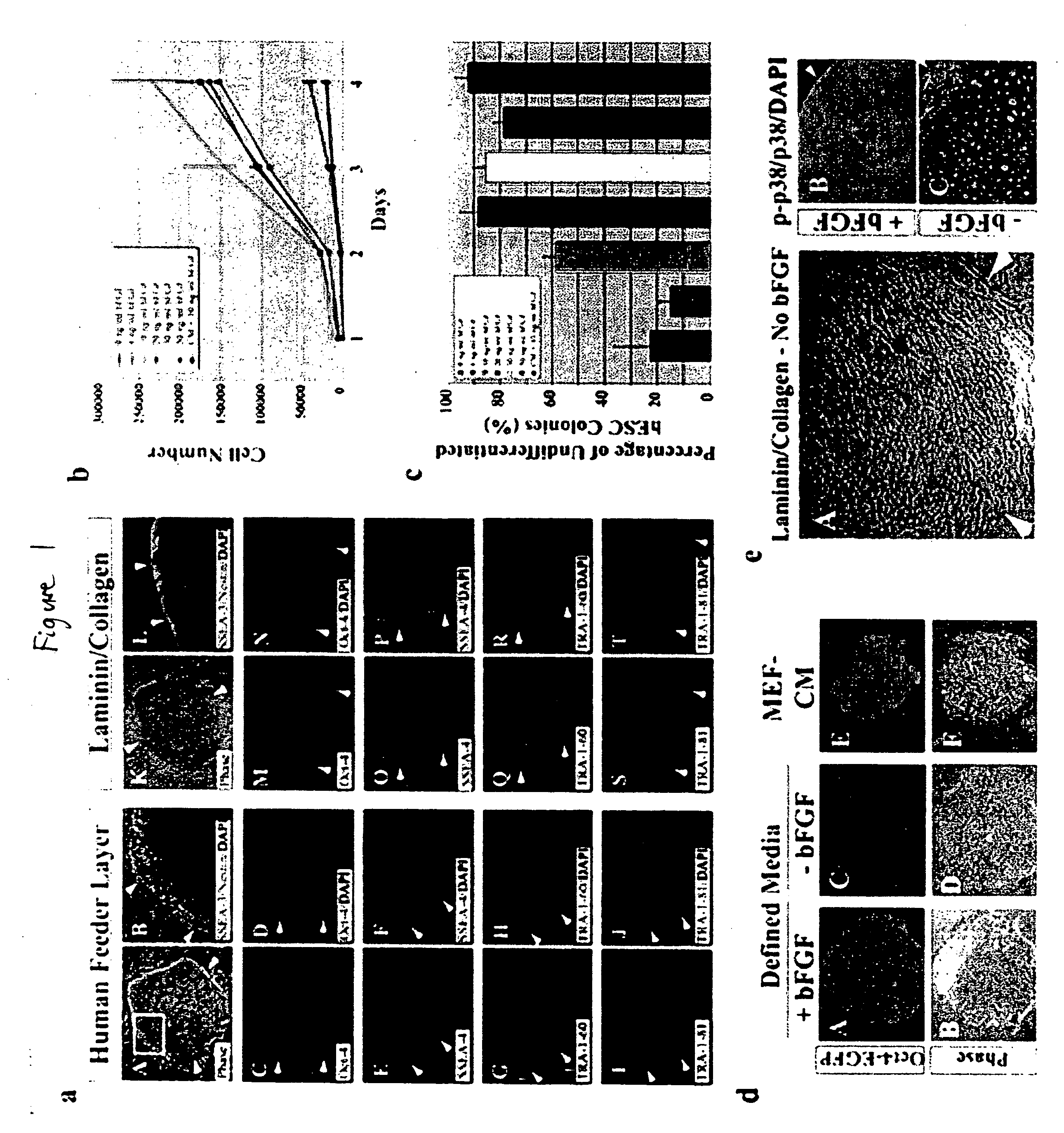
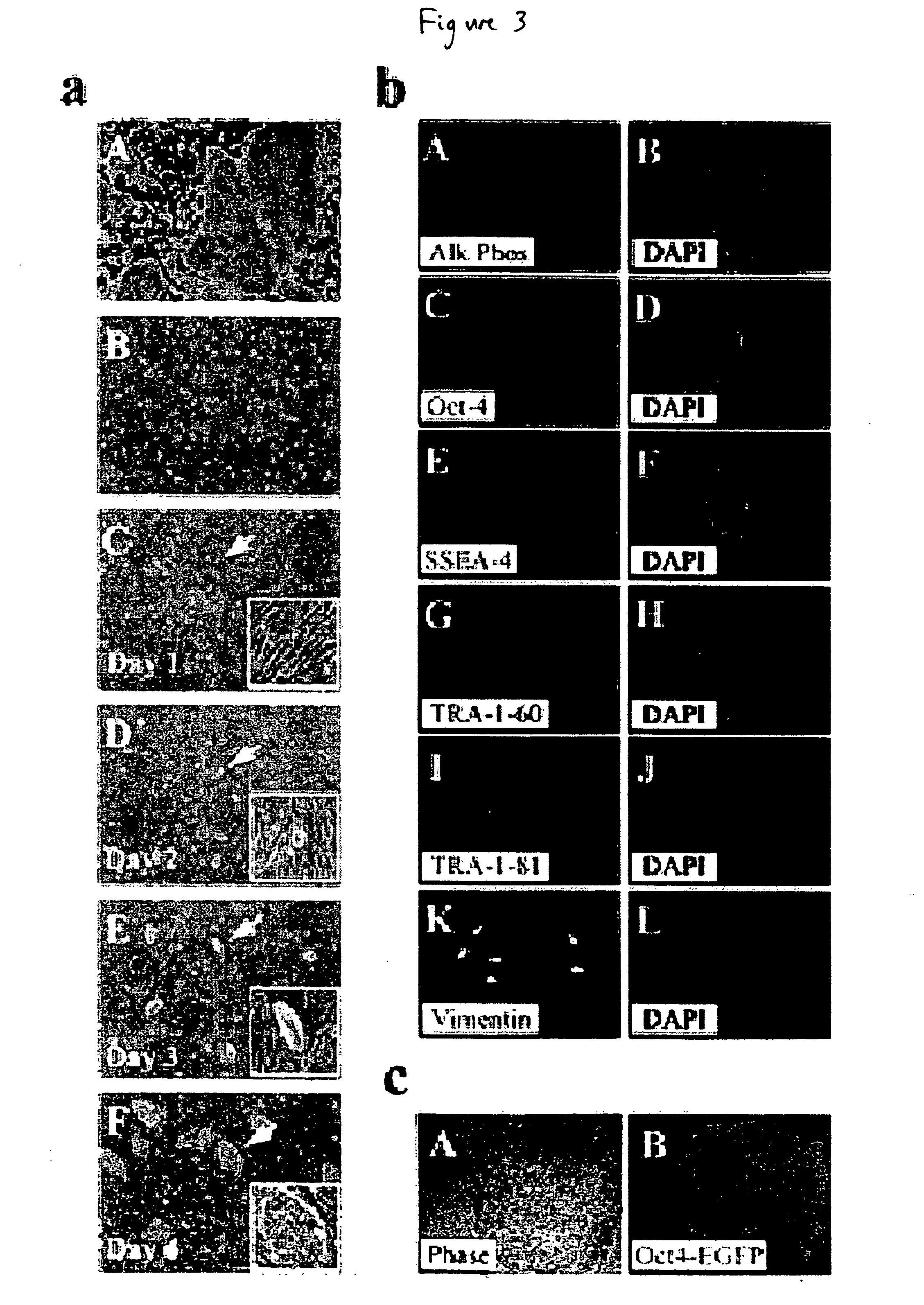
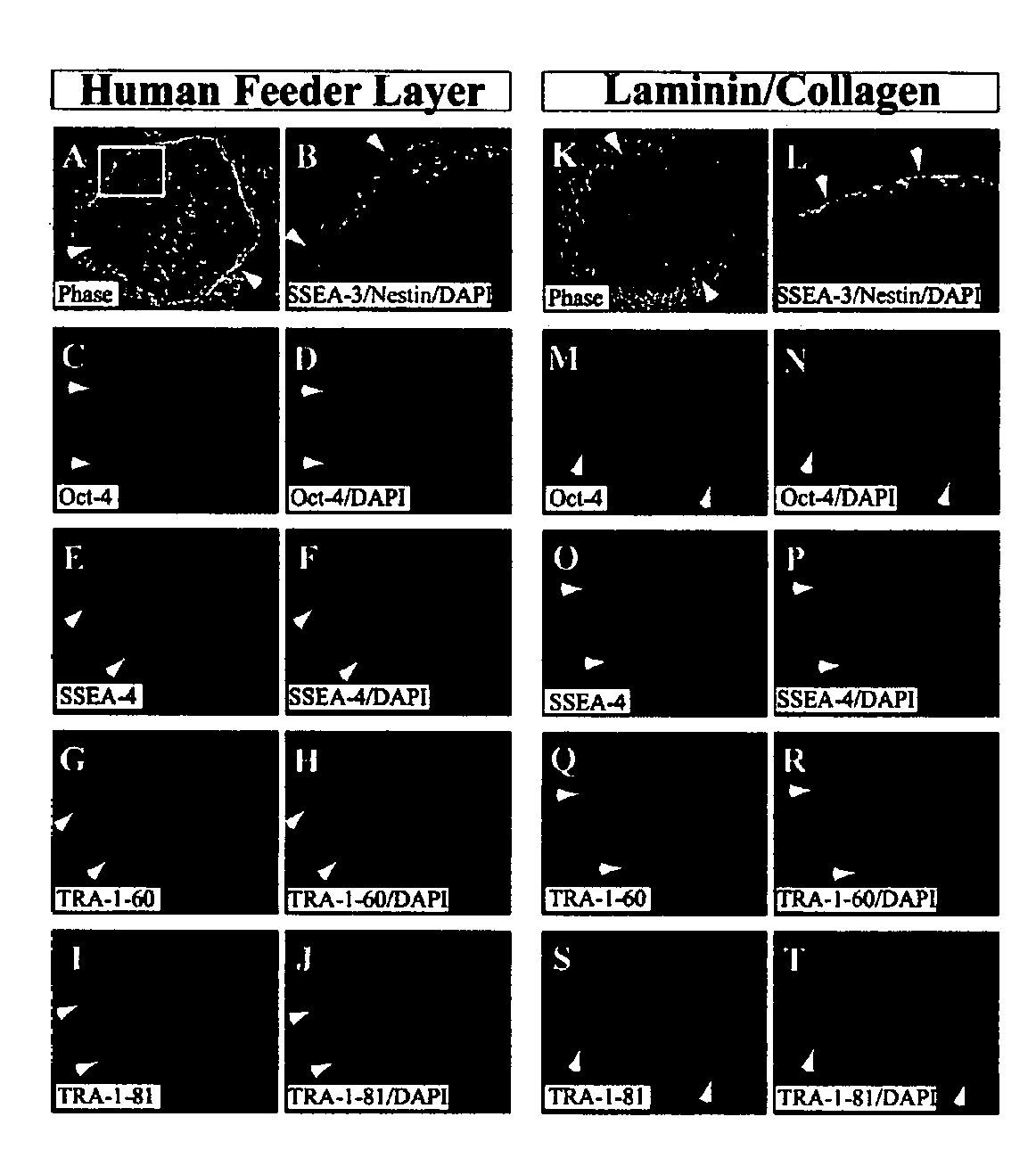
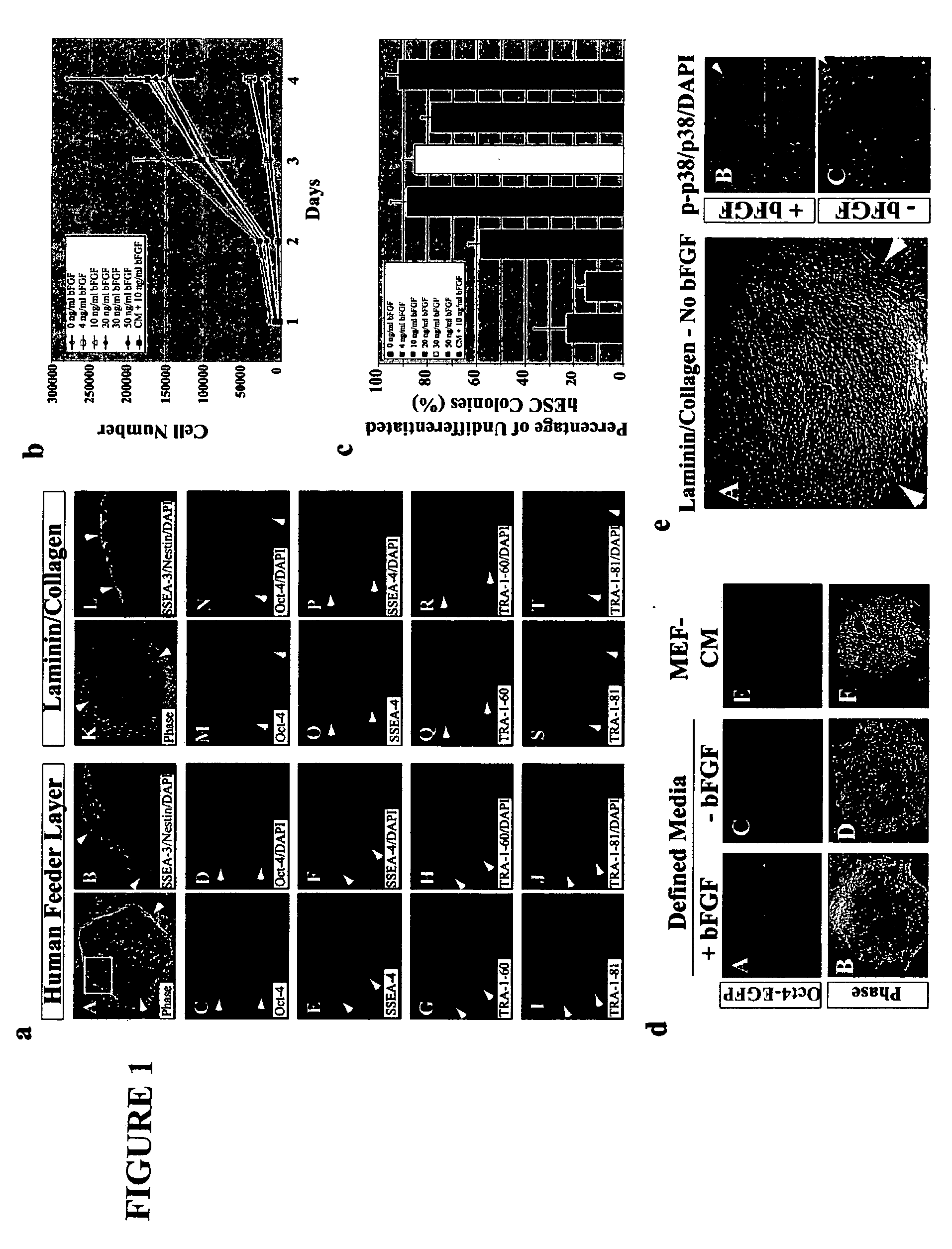
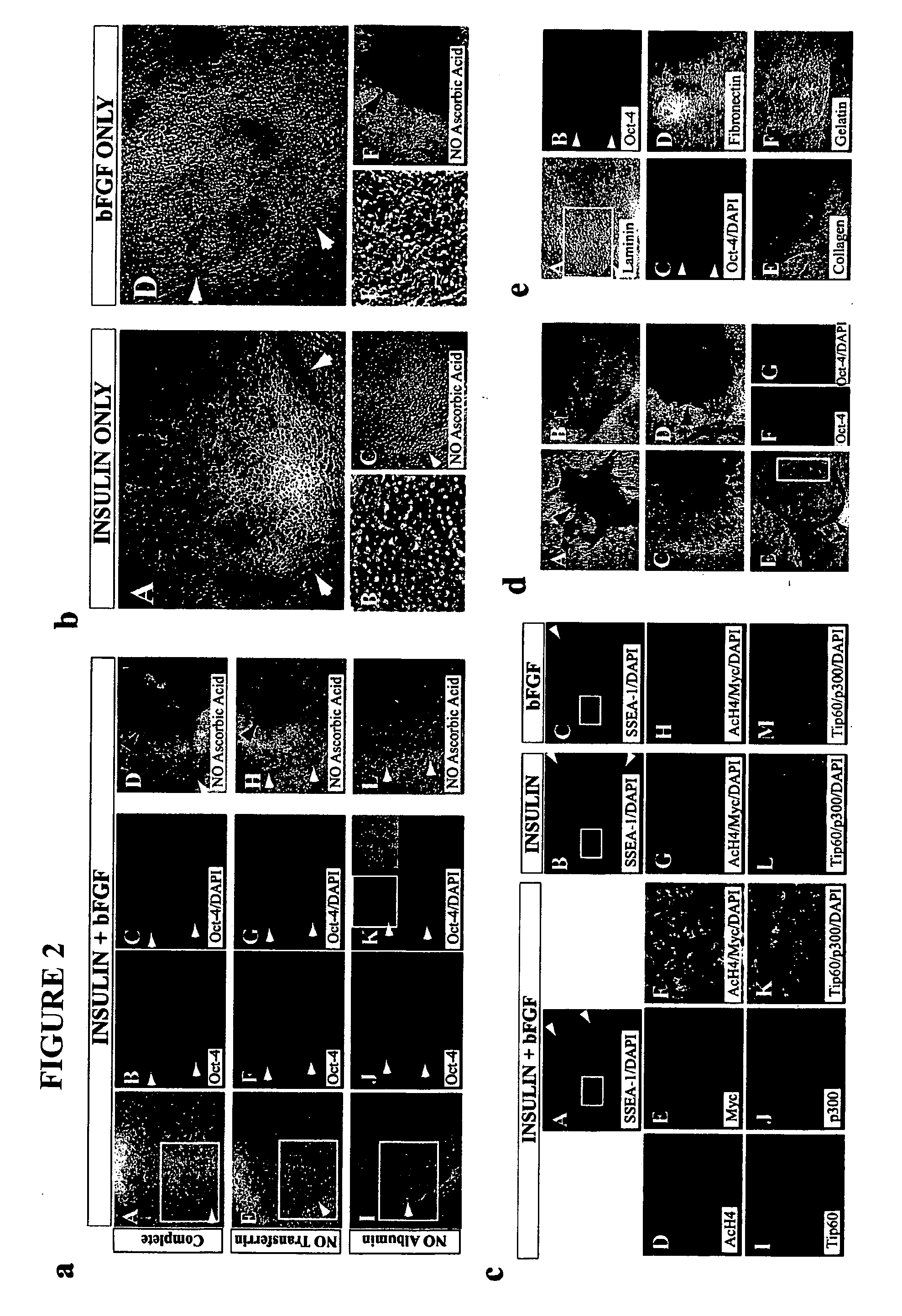
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Defined media for pluripotent stem cell culture
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Cultivation of primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050148070A1Improve cloning efficiencyAvoid variabilityOrganic active ingredientsCulture processMammalFeeder Layer
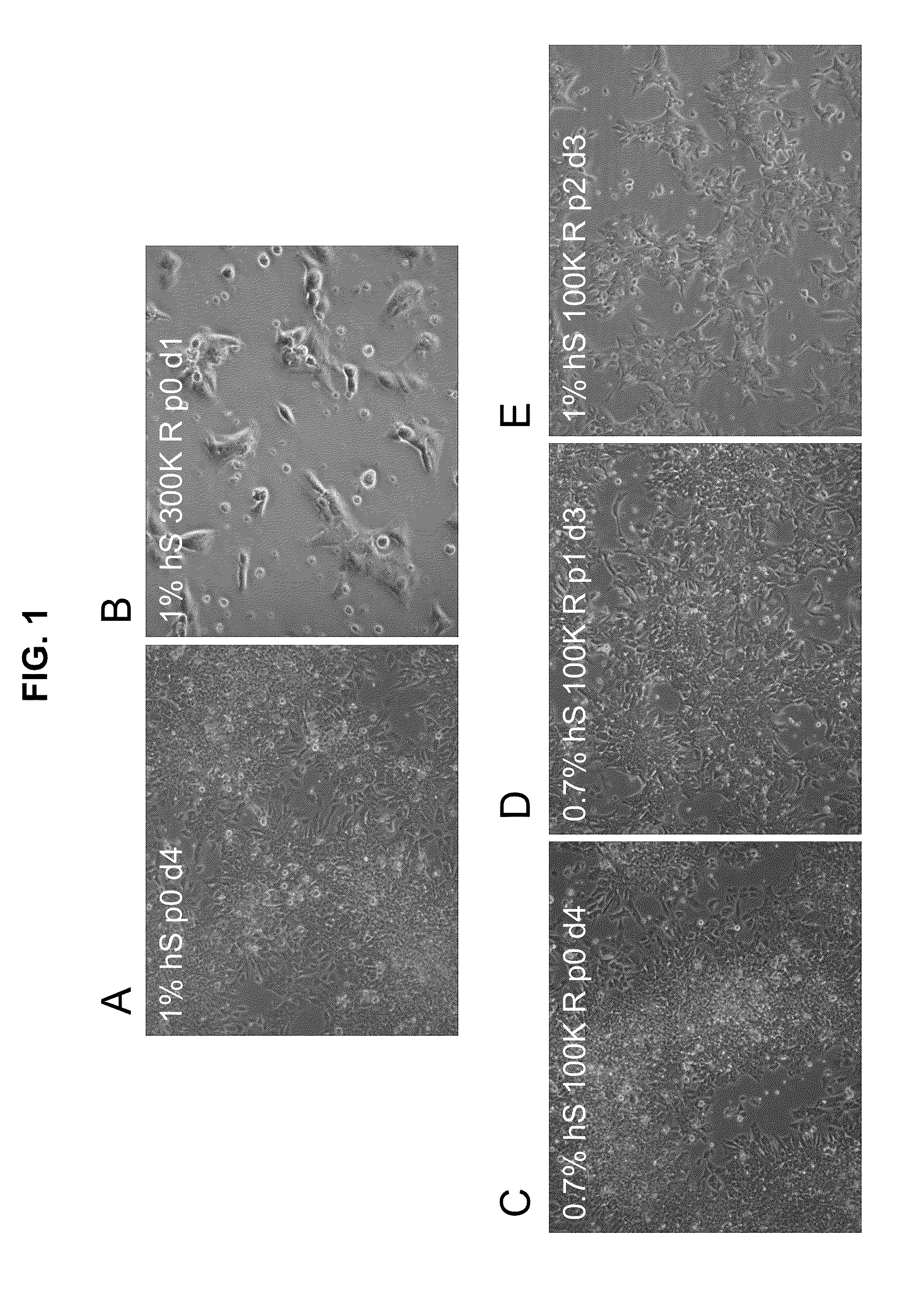
The invention relates to methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells by culturing the stem cells in an environment essentially free of mammalian fetal serum and in a stem cell culture medium including amino acids, vitamins, salts, minerals, transferring, insulin, albumin, and a fibroblast growth factor that is supplied from a source other than just a feeder layer the medium. Also disclosed are compositions capable of supporting the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells without the need for feeder cells or for exposure of the medium to feeder cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cultivation of primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050244962A1Maintain normalMaintaining the karyotype of the stem cellsCulture processArtificial cell constructsFeeder LayerStem cell culture
The invention relates to methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells by culturing the stem cells in an environment essentially free of mammalian fetal serum and in a stem cell culture medium including amino acids, vitamins, salts, minerals, transferring, insulin, albumin, and a fibroblast growth factor that is supplied from a source other than just a feeder layer the medium. Also disclosed are compositions capable of supporting the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells without the need for feeder cells or for exposure of the medium to feeder cells.
Owner:WICELL RES INST
Alternative compositions and methods for the culture of stem cells
InactiveUS20050037488A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Stem cell culture medium and application thereof and stem cell cultivation method
ActiveCN103060264AHigh speedRapid expansionCulture processCell culture mediaMesenchymeCell culture media
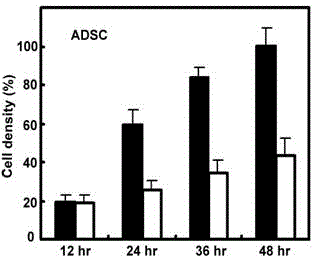
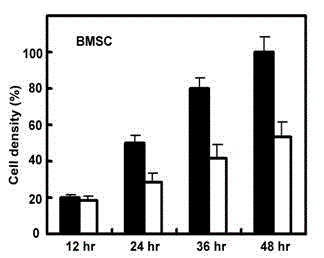
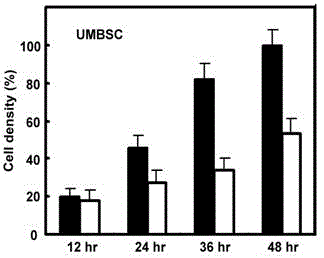
The invention discloses a stem cell culture medium, an application of the stem cell culture medium and a stem cell cultivation method. Blood serum does not exist in the stem cell culture medium. The stem cell culture medium comprises amino acid, vitamin, salt, lipoid, cytokines and egg white polypeptide. The stem cell culture medium is suitable for fast cultivating stem cells which are tissue sources of human and mammal, and comprises but not is limited by fat mesenchyme stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood stem cells. The culture medium enables increasing speed of the cells to be improved by 3-5 times, and differential potentials of the cells can not be affected. Compared with an ordinary stem cell culture medium, stem cells from different sources can be fast expanded, passage number is prolonged, and proficiency properties of the stem cells can be well kept.
Owner:苏州博棠再生医学科技有限公司
Culture of stem cells
ActiveUS20080171385A1Improve cloning efficiencyEconomical and effectiveArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsAnimal productStem cell culture
While culture medium and systems have been described that permit the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells in feeder free and animal product free conditions, these conditions will not readily support cloning of an embryonic stem cell culture meaning, at least here, the initiation of a sub-culture using one or a very few originating cells. It has been found here that a class of small molecules that are inhibitors of kinase enzymes will increase the efficiency of cloning of stem cell cultures sufficiently to make such cloning practical in the defined medium and in other media as well.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Culture media for stem cells
PendingUS20140243227A1Slow proliferationIncrease surface areaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStem cell cultureBiology
Culture media and methods for expanding and differentiating populations of stem cells and for obtaining organoids. Expanded cell populations and organoids obtainable by methods of the invention and their use in drug screening, toxicity assays and regenerative medicine.
Owner:KONINK NEDERLANDSE AKADE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN
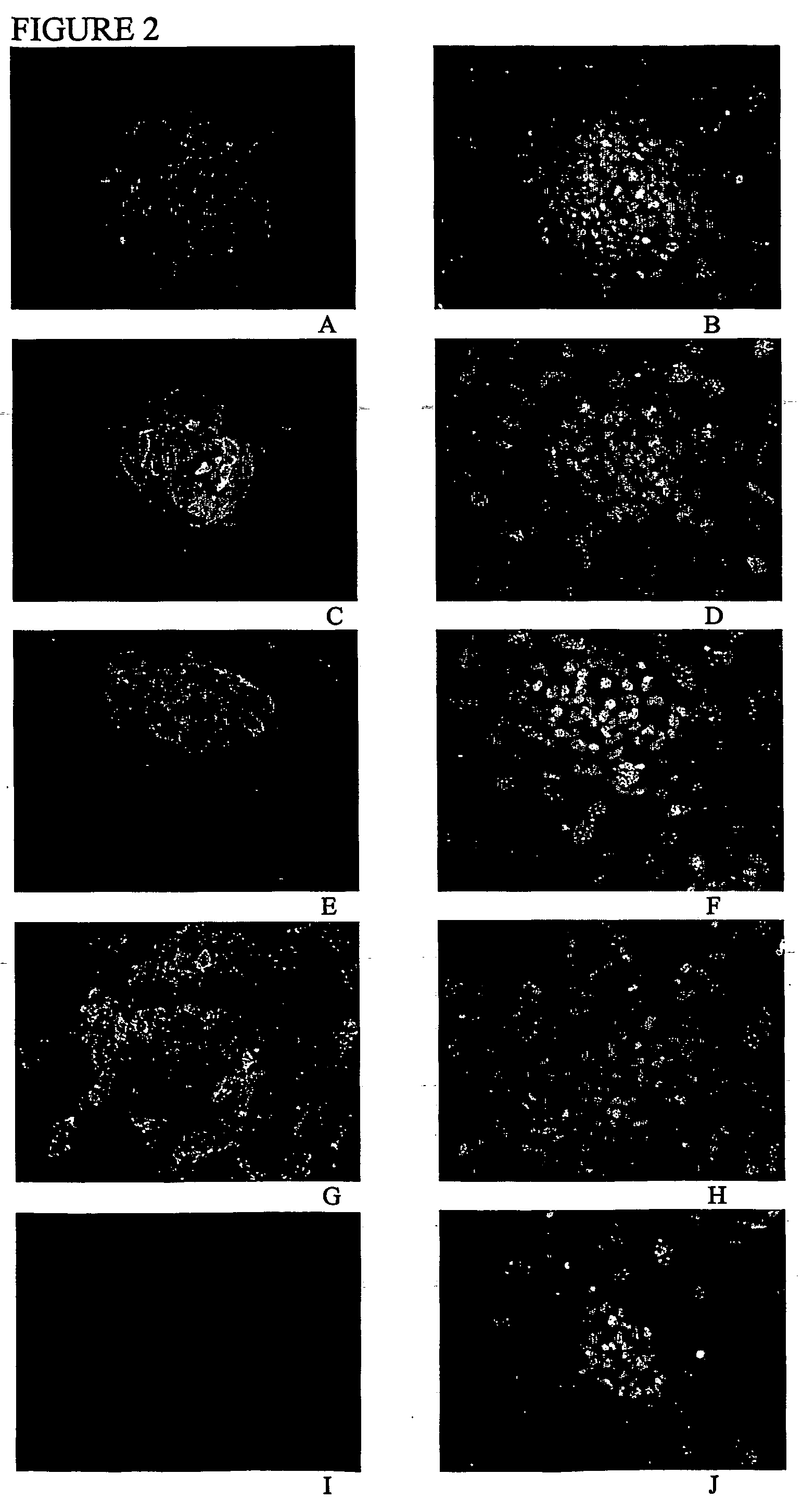
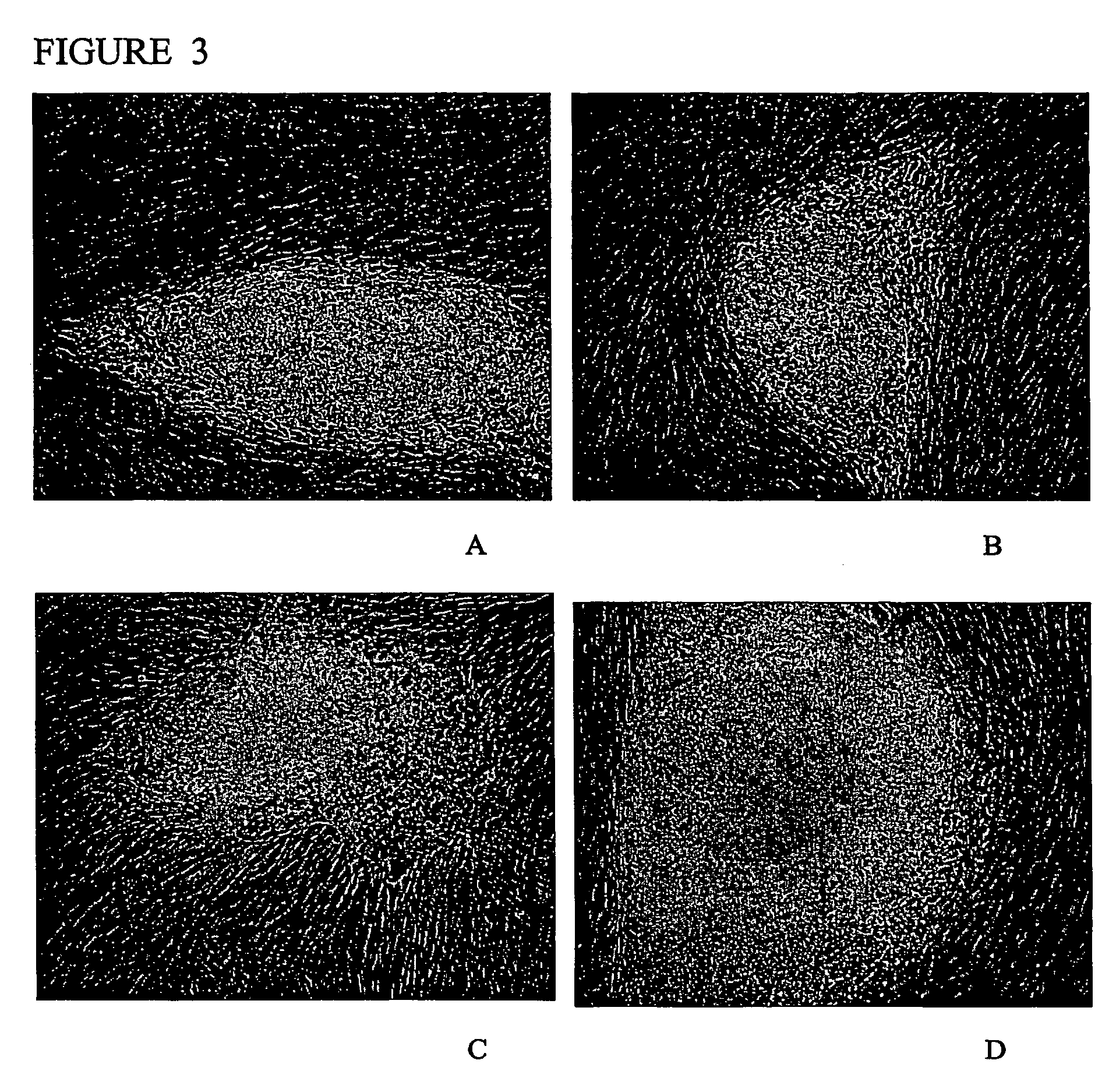
Methods and compositions for feeder-free pluripotent stem cell media containing human serum
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the culture and maintenance of pluripotent stem cells. More particularly, the present invention provides for compositions and methods for culturing, maintaining, growing and stabilizing primate pluripotent stem cells in a feeder-free defined media further comprising human serum, or a soluble attachment component of the human serum, for promoting cell attachment.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Methods and Compositions for Feeder-Free Pluripotent Stem Cell Media Containing Human Serum
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the culture and maintenance of pluripotent stem cells. More particularly, the present invention provides for compositions and methods for culturing, maintaining, growing and stabilizing primate pluripotent stem cells in a feeder-free defined media further comprising human serum, or a soluble attachment component of the human serum, for promoting cell attachment.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Method for freezing and reviving umbilical cord tissues and for separating and increasing stem cells
ActiveCN102660497AEfficient in vitro expansionAvoid churnDead animal preservationArtificial cell constructsMedicineUmbilical cord tissue
The invention relates to a method for freezing and reviving umbilical cord tissues and for separating and increasing stem cells after reviving the umbilical cord, and the step comprises the following steps of preparing umbilical cord tissue freezing liquid; sterilizing and washing the umbilical cord tissues; cutting the tissues into blocks; placing the tissue blocks and the freezing liquid into afreezing tube, cold storing the tissue blocks for 0.5 hour under the temperature condition of 4 DEG C and then storing the tissue blocks for one day under the temperature condition of minus 80 DEG C,and then freezing the tissue blocks in liquefied nitrogen; and taking the umbilical cord tissues out of the liquefied nitrogen to use, thawing the umbilical cord tissues in constant-temperature waterbath, utilizing mesenchymal stem cell culture base to washing the umbilical cord tissues through a drop method, and separating and increasing the mesenchymal stem cells of the revived umbilical cord tissues through a tissue attachment method. The method can effectively protect the frozen umbilical cord tissue, so that the umbilical cord tissues can be revived to use, and the method is particularly suitable for separating and increasing the mesenchymal stem cells after the umbilical cord tissue is revived.
Owner:BOYALIFE
Neuronal progenitors from feeder-free human embryonic stem cell culture
The present invention relates to methods for producing feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells (preferably adherent) from embryonic stems cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells, the feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells, preferably human cells themselves, as well as methods for producing feeder cell-free samples of neuronal cells, preferably adherent human neuronal cells and the feeder cell-free neuronal cells themselves. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating neurodegenerative diseases as well as the use of the described cells in assay systems is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Clinical-grade human mesenchymal stem cell serum-free complete medium
ActiveCN103243071APromote growthLow toxicitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin-like growth factorCuticle
The invention relates to a human mesenchymal stem cell culture medium. According to the culture medium, the basal culture medium comprises the following components based on the final concentration: 1-2g / L of human serum albumin, 5-10mg / L of transferring, 2-8mg / L of fibronectin, 1-4mg / L of laminin, 50g / L of Fe(NO3)3.9H2O, 417g / L of FeSO4.7H2O, 1-3mu g / L of estradiol, 2-5mu g / L of testosterone, 1-3mu g / L of progesterone, 39.25-117.74 mu g / L of dexamethasone, 5-10mg / L of insulin, 376.36mg / L of riboflavin, 80.96-242.87mg / L of coenzyme A, 4.41-6.17mg / L of butanediamine, 1-2mg / L of taurine, 0.61-1.85mg / L of aminoethanol, 8.81-26.42mg / L of pyruvic acid, 3.78-7.56mu g / L of sodium selenate, 292.3-584.6mg / L of L-glutamine, 2-8mu g / L of vascular endothelial growth factor, 4-10mu g / L of epidermal growth factor, 4-10mu g / L of basic fibroblast growth factor, 1-5mu g / L of leukaemia inhibitory factor, 1-5mu g / L of insulin-like growth factor-I and 2-8mu g / L of stem cell factor. The culture medium does not contain the animal serum, the potential animal endogenous endotoxin or virus of the animal serum is eliminated, and the culture medium is conveniently applied to clinics.
Owner:QINGDAO RESTORE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Cultivation of human embryonic stem cells in the absence of feeder cells or without conditioned medium
InactiveUS7439064B2Maintain normalMaintaining the karyotype of the stem cellsCulture processArtificial cell constructsFeeder LayerStem cell culture
The invention relates to methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells by culturing the stem cells in an environment essentially free of mammalian fetal serum and in a stem cell culture medium including amino acids, vitamins, salts, minerals, transferring, insulin, albumin, and a fibroblast growth factor that is supplied from a source other than just a feeder layer the medium. Also disclosed are compositions capable of supporting the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells without the need for feeder cells or for exposure of the medium to feeder cells.
Owner:WICELL RES INST
Culture media for stem cells
Culture media and methods for expanding and differentiating populations of stem cells and for obtaining organoids. Expanded cell populations and organoids obtainable by methods of the invention and their use in drug screening, toxicity assays and regenerative medicine.
Owner:KONINK NEDERLANDSE AKADE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN
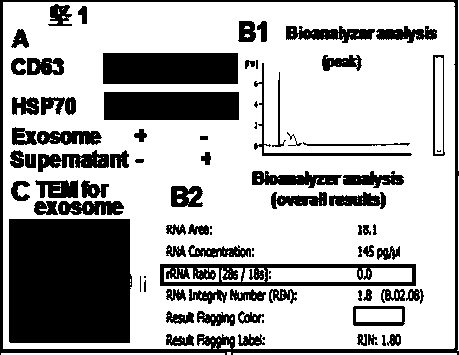
Method for separating exosome from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell source and application thereof
PendingCN106282107AImprove acquisitionEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsFiltrationCentrifugation
The invention relates to a method for separating exosome from a human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell source. The method comprises the following steps: when the P2-P3 placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell convergence rate reaches 85-90%, obtaining a cell culture supernate, carrying out membrane filtration, and collecting the filtrate; centrifugating the filtrate, collecting the centrifugal supernate, adding a 10w / v%-12w / v% polyethyleneglycol culture medium supernate solution into the centrifugal supernate according to the volume ratio of 1:1, sufficiently and uniformly mixing, and carrying out secondary centrifugation, wherein the finally obtained precipitate is the exosome. The method is convenient for taking materials, is easy for enrichment amplification culture, reutilizes the P2-P3 placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell culture medium supernatant to obtain the exosome, and does not refer to the problem of medical ethics. In the exosome separation process, membrane filtration, centrifugation, polyethyleneglycol solution addition and other means are adopted to effectively increase the exosome enrichment, so the method has the advantages of short time consumption and low cost.
Owner:章毅 +7
Preparation and application of exosome secreted by human derived blood or mesenchymal stem cell
InactiveCN103767985AAvoid blocking, not easily absorbed by cellsProtection stabilityCosmetic preparationsSenses disorderStem cell cultureSomatic cell
The invention discloses preparation and application of exosome secreted by human derived blood or mesenchymal stem cell. The preparation process of exosome comprises: extracting mesenchymal stem cells from health-human body blood or a stem cell culture supernatant, performing in-vitro culture and amplification, and utilizing means such as low-temperature separation, purification and the like to prepare high-purity high-bioactivity exosome. The blood or mesenchymal stem cell secreted exosome is added into medicines, health-care products and cosmetics according to ratios for developing of products with bioactivity, is capable of effectively regulating and controlling body cell signal transduction, activating cell regeneration, enhancing health cell proliferation and differentiation capacity, further regulating physiologic restoration or removing damaged, pathologic and aged cells of a body, fundamentally changing body physiologic functions, and helping to generate anti-tumor treatment effect by adjusting cellular immunity. The blood or mesenchymal stem cell secreted exosome is applicable to fields of medical science, health care and beauty treatment, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:珠海霍普金斯医药研究院股份有限公司
Stem cell tissue culture seedling raising technique
The invention discloses a stem cell tissue culture seedling raising technique. The technique comprises the steps of 1, taking a fresh plant, conducting sterilization on the surface and cutting the plant; 2, conducting tissue differentiation and reserving a cambium; 3, culturing the cambium on an isolation medium. According to the technique, existing methods are improved based on a traditional tissue culture technique, plant stem cells are taken as a target, induction, separation and explant culture are conducted, and a corresponding stem cell culture system is established. By the adoption of the plant stem cell culture technique, the plant culture technique is enriched, and a novel research direction and opportunity is provided for commercialized production of natural products and development of the plant biotechnology.
Owner:广东融和生态农业集团有限公司
Stem cell cultures
ActiveUS8044201B2Maintain cell survivalImprove survivalNervous disorderOrganic chemistryStem cell cultureCell culture
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Apple stem cell culture method and apple stem cells cultured by method
InactiveCN104711215AShort cycleHigh yieldDead plant preservationPlant cellsFreeze-dryingStem cell culture
The invention relates to the technical field of plant stem cell culture, particularly an apple stem cell culture method and apple stem cells cultured by the method. The method comprises the following steps: by using an apple new branch as a raw material, inducing to form callus, and carrying out enrichment culture and amplification culture to obtain the apple stem cells. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of shorter period and high yield. The method can obtain abundant apple stem cells within about 48 days. The induction culture medium used in the apple stem cell culture process and the variety of the phytohormones contained in the enrichment culture medium are proper and suitable in proportion, and can ensure fast dedifferentiation and abundant reproduction of apple branch cells. The apple stem cells can be freeze-dried or extracted and used for preparing food, drugs, health products or cosmetics. The apple stem cell extraction method provided by the invention is simple and easy to implement and has higher extraction efficiency. The prepared extract contains abundant flavones and polyphenols.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN105420182AOvercoming pollutionOvercoming Cell Expansion NumbersSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPancreatic hormoneStem cell culture
The invention provides a serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and belongs to the technical field of cell culture. The serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells comprises a basal culture medium body and added ingredients, wherein the basal culture medium body is a DMEM culture medium; the added ingredients include a basic fibroblast growth factor hFGF, a epidermal growth factor hEGF, insulin hI, a leukaemia inhibitory factor hLIF and astragalus polysaccharide. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are subjected to subculture and amplification in the medium, and the surfaces of the cultured cells are marked and analyzed. The serum-free medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overcomes the defect of exogenous pollution of serum and solves the problem of contradiction between the cell expansion number and cost reduction. The medium is free of serum, thereby preventing influence of animal-derived serum ingredients on cell culture. The medium can be used for studying the differentiation and proliferation adjusting mechanism of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:SHANDONG JINGYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
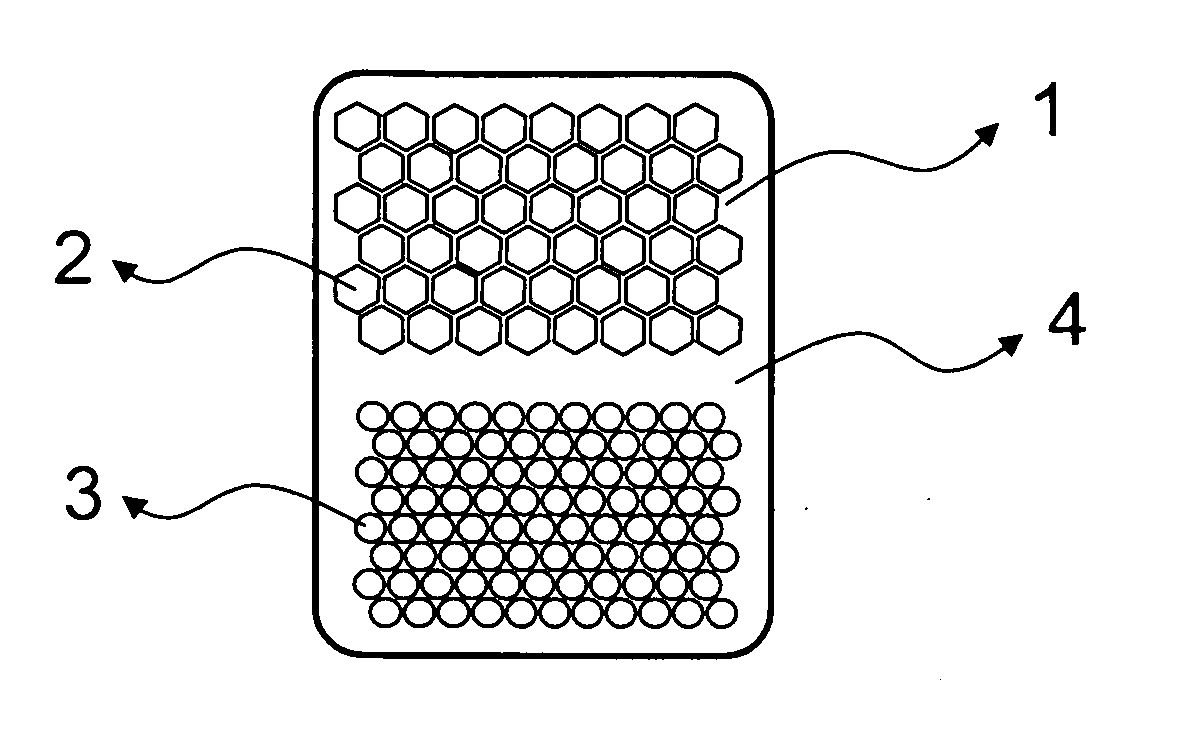
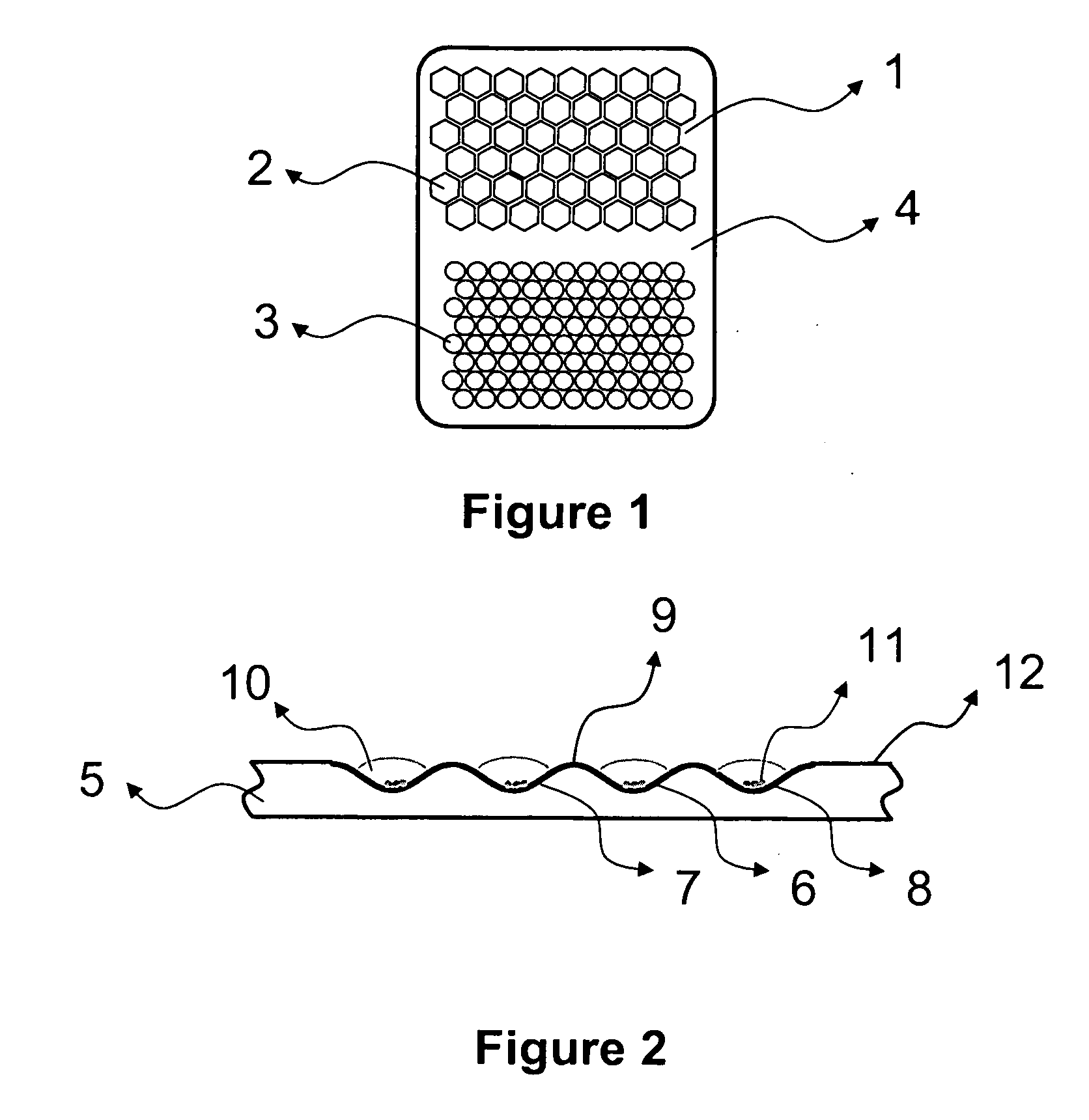
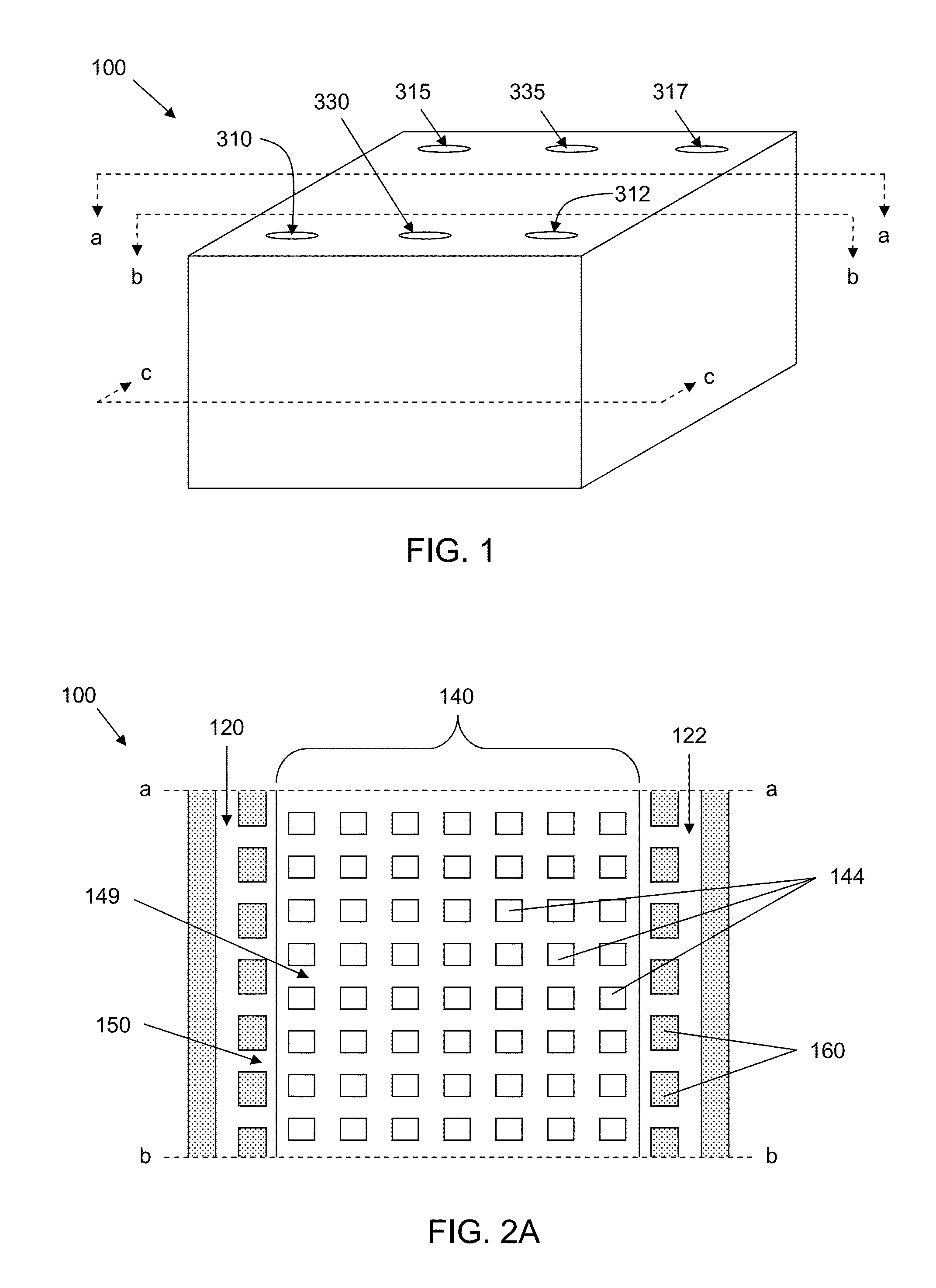
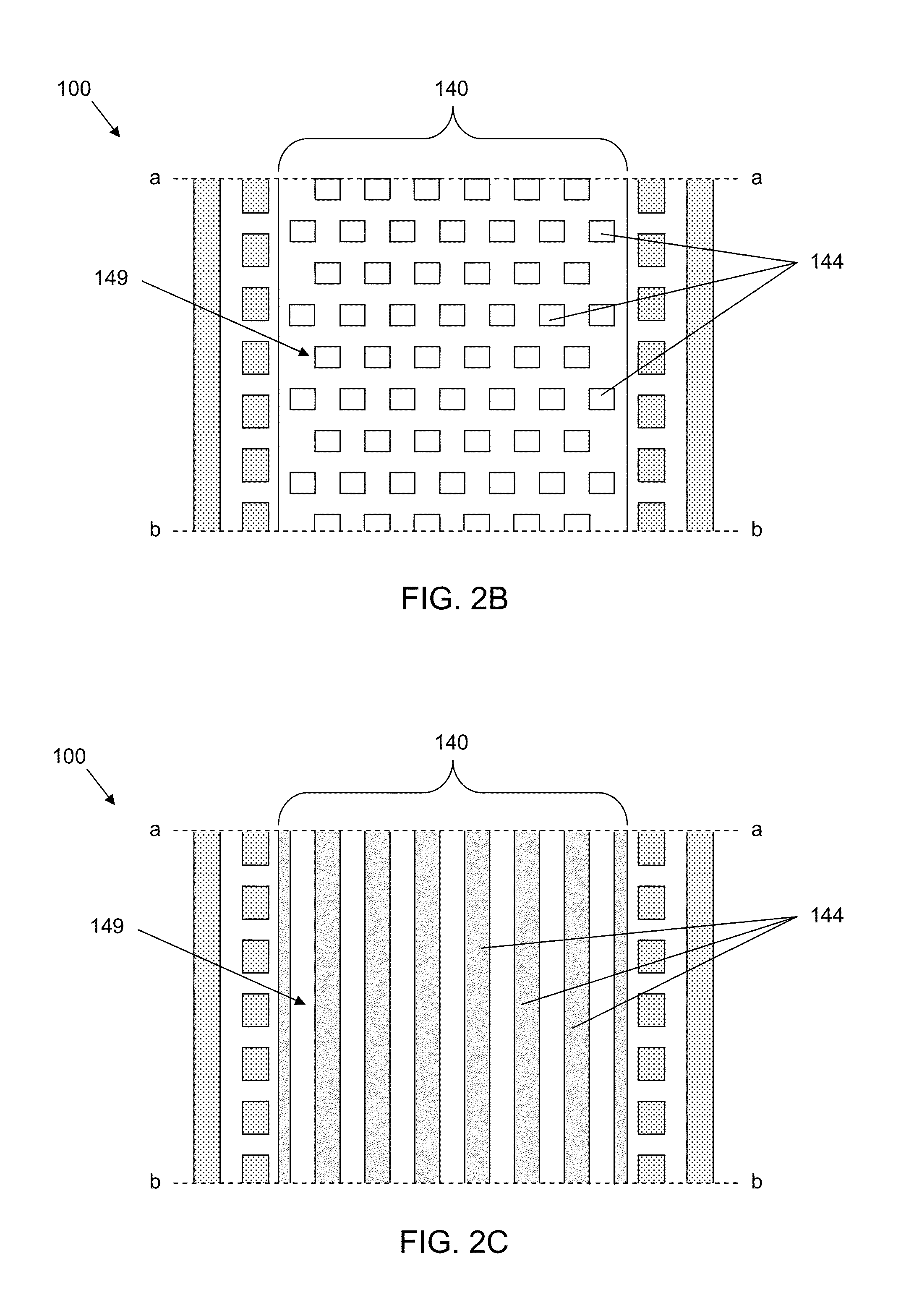
Honeycomb shrink wells for stem cell culture
InactiveUS20120129208A1Small surface areaSignificant effects on stem cell differentiationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHoneycombEngineering
This invention provides a microwell array having a plurality of microwells on a hydrophobic surface wherein the microwells each is substantially proximate to each of its adjacent microwells, as well as methods to prepare arrays. Also provided is a plate that comprises at least one microarray, at least one input channel, at least one output channel, and a channel connecting the input and output channel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Stem cell culture medium and method
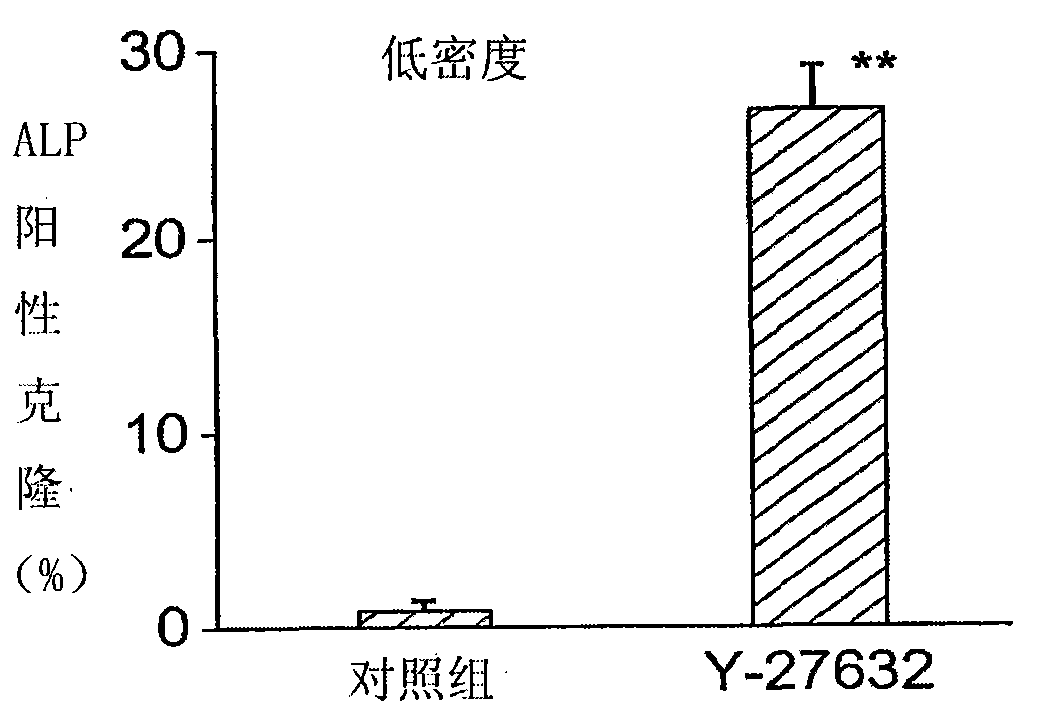
The present invention discloses a stem cell medium and a culturing method. Stem cells such as embryonic stem cells (ES cells), including human ES cells, are cultured in a medium comprising a ROCK inhibitor, and a stem cell culture medium, optionally serum free, comprises a ROCK inhibitor.
Owner:RIKEN
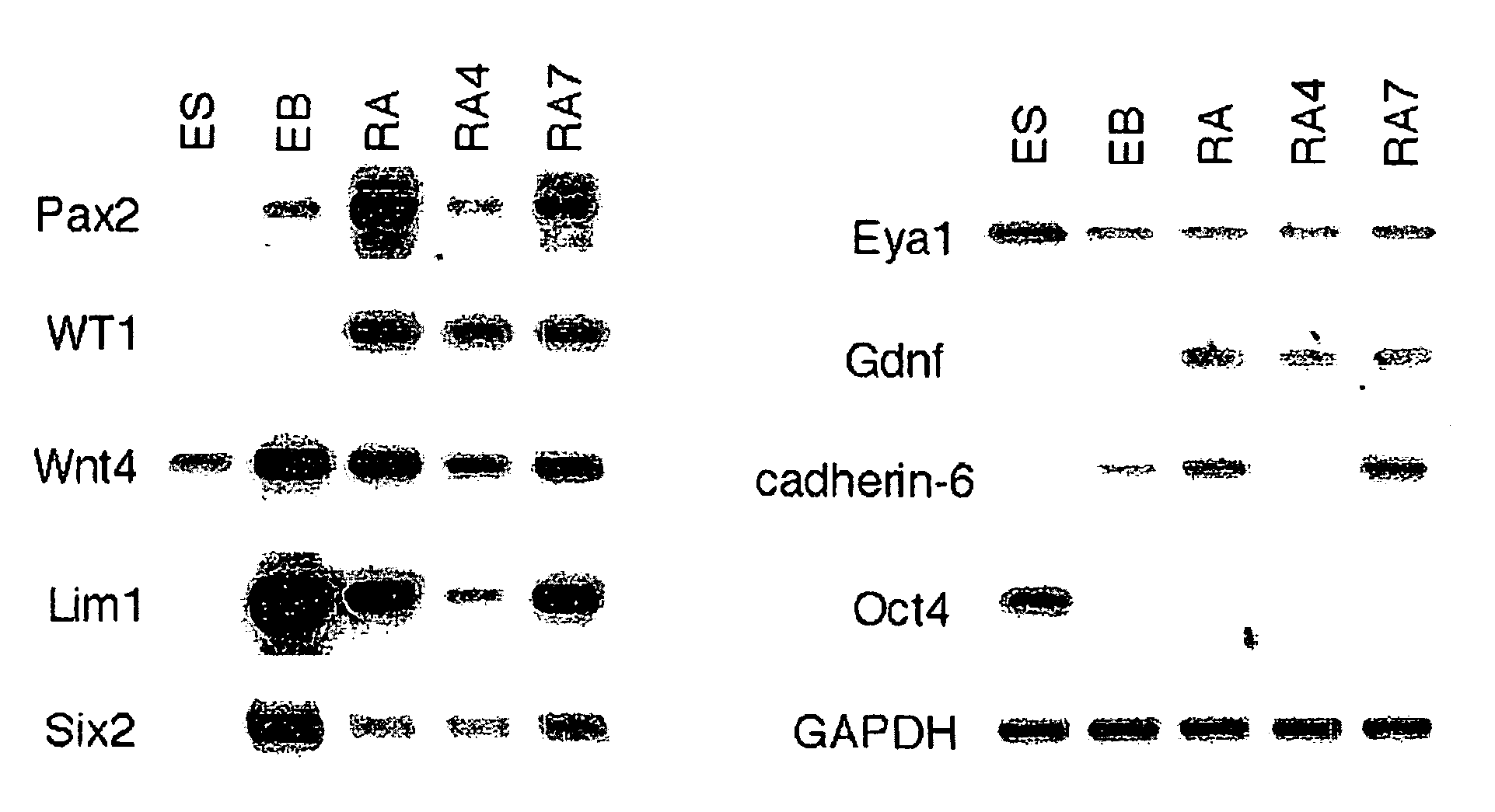
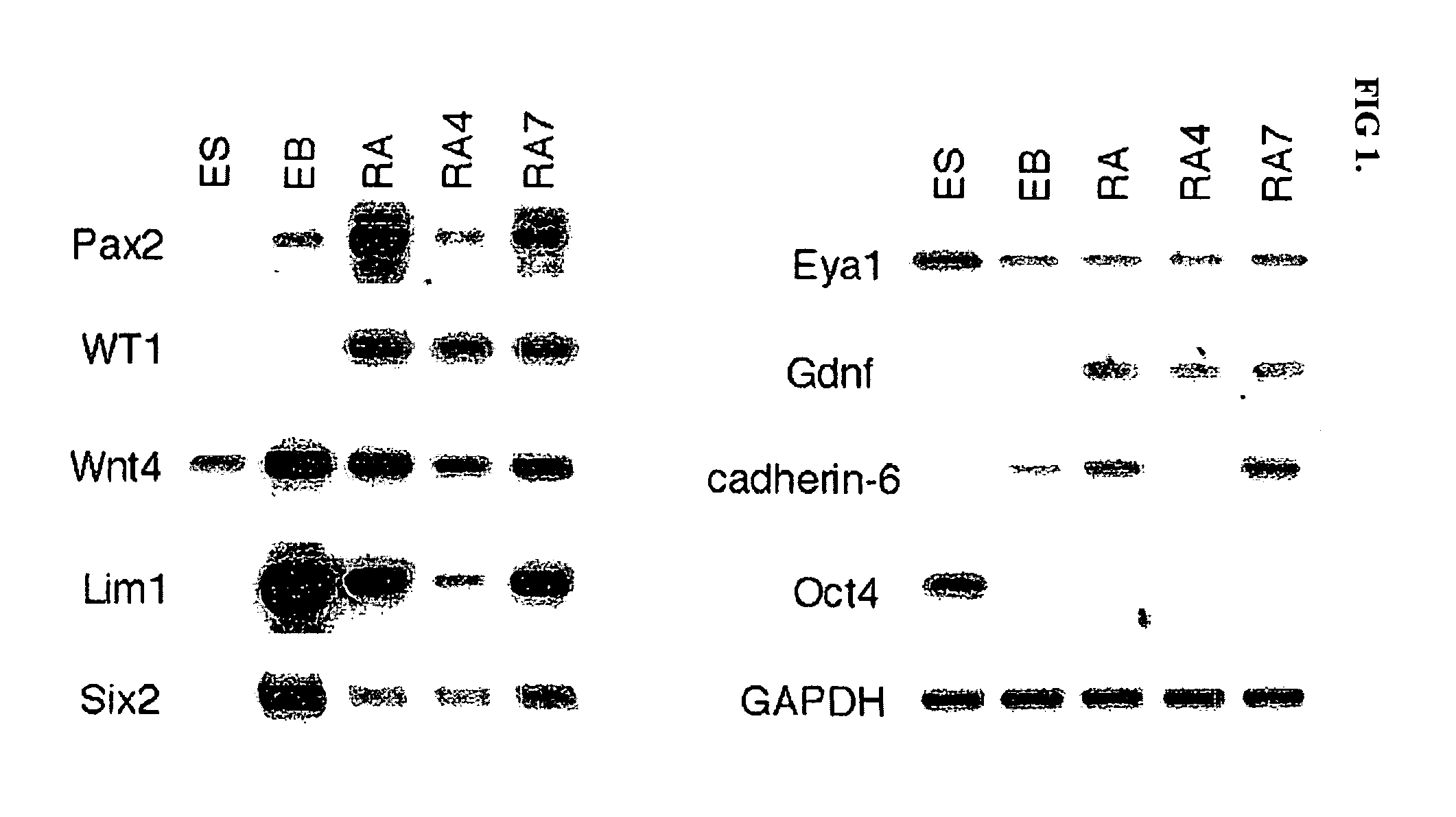
Renal progenitor cells from embryonic stem cells
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inducing the differentiation of stem cells into renal progenitor cells. In particular, the present invention provides compositions containing activin-a, retinoic acid, and bmp-7, and variants thereof, for differentiating stem cells into renal cells containing tubular epithelia. In certain embodiments, the present invention provides stem cells cultured with compositions used to treat renal disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Cell differntiation inhibiting agent, cell culture method using the same, culture medium, and cultured cell line
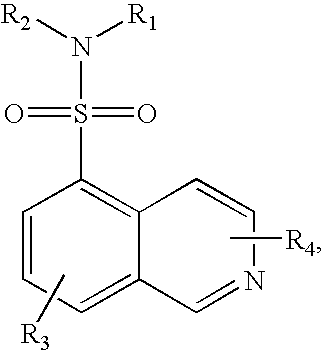
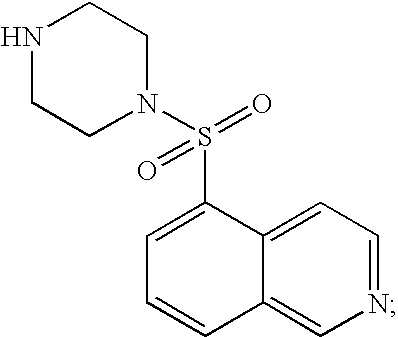
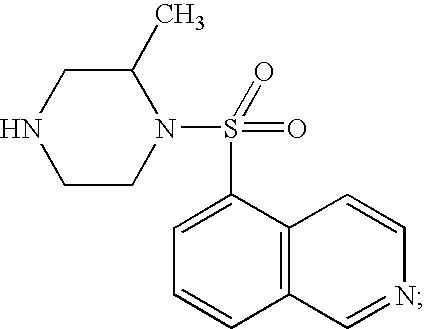
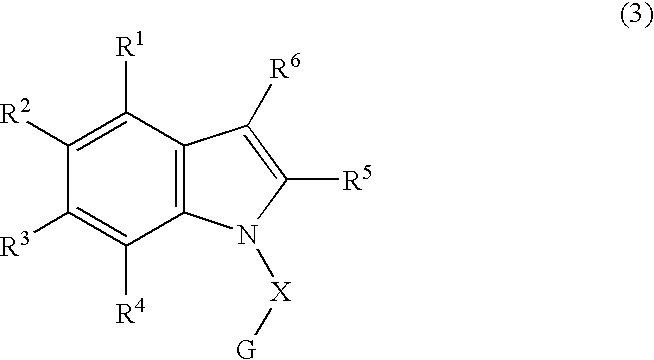
The object of the present invention is to provide a differentiation inhibiting agent which allows culture of a stem cell or an embryonic stem cell in an undifferentiated state without use of any feeder cell, a method for culturing using the same, a cell culture liquid using the same, and a cell prepared by culturing using this differentiation inhibiting agent. The present invention provides a differentiation inhibiting agent which comprises a low molecular weight compound, especially a tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative, as an active ingredient; a method for safely culturing a stem cell in large scale in undifferentiated state in the absence of feeder cell which comprises culturing a stem cell by using a tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative; a culture liquid for stem cells comprising a tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative; and a cell which is obtained by culture using a tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative as a differentiation inhibiting agent.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Microcarriers for Stem Cell Culture
InactiveUS20110143433A1Stable and long-term culturingIncrease differentiationCulture processArtificial cell constructsMatrigelORDER PRIMATES
We disclose a particle comprising a matrix coated thereon and having a positive charge, the particle being of a size to allow aggregation of primate or human stem cells attached thereto. The particle may comprise a substantially elongate, cylindrical or rod shaped particle having a longest dimension of between 50 μm and 400 μm, such as about 200 μm. It may have a cross sectional dimension of between 20 μm and 30 μm. The particle may comprise a substantially compact or spherical shaped particle having a size of between about 20 μm and about 120 μm, for example about 65 μm. We also disclose a method of propagating primate or human stem cells, the method comprising: providing first and second primate or human stem cells attached to first and second respective particles, allowing the first primate or human stem cell to contact the second primate or human stem cell to form an aggregate of cells and culturing the aggregate to propagate the primate or human stem cells for at least one passage. A method of propagating human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) in long term suspension culture using microcarriers coated in Matrigel or hyaluronic acid is also disclosed. We also disclose a method for differentiating stem cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for separating exosome from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell source and reagent used by method
The invention relates to a method for separating exosome from a human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell source and a reagent used by the method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cultivating umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; and (2) extracting umbilical cord blood MSC exosome, wherein the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are cultivated to P3 generation; and extraction forthe umbilical cord blood MSC exosome comprises the following steps: pre-treating exosome suspension; and extracting exosome. The reagent used by the method realtes to a solution which has a special formula and is used as a buffer pad. The method has the excellent technical effects as described in the specification.
Owner:FIVE DIMENSION BY INCOSC HEALTH MANAGEMENT JIANGSU
Stem Cells Culture Systems
InactiveUS20090104695A1Inhibiting and preventing differentiationCulture processNervous system cellsHuman cellStem cell culture
The present invention concerns systems and methods for providing human cell cultures. Specific embodiments of the invention relate to cultures of feeder cells for use in stem cell technology, as well as cultures, culture systems and methods for maintenance and propagating of stem cells in an undifferentiated state as well as for the development of somatic cells cultures from stem cells, the somatic cell cultures being free of extraembryonic cells.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT
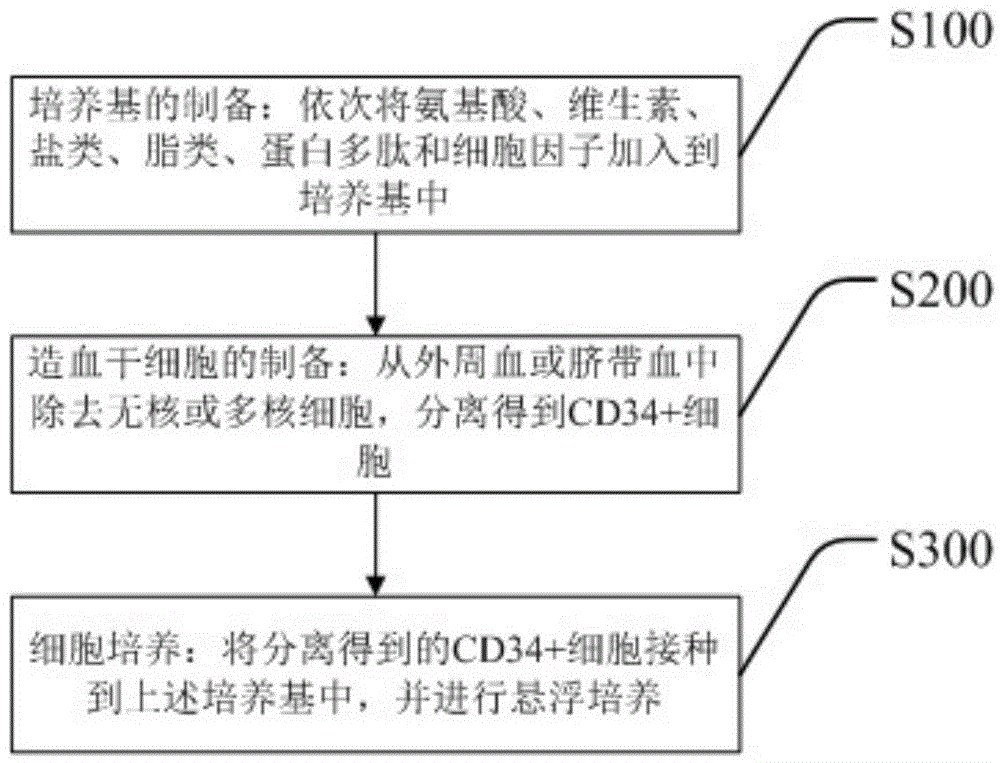
Hematopoietic stem cell culture medium and its application and stem cell cultivation method based on hematopoietic stem cell culture medium
InactiveCN104830772AHigh speedLower blood sugarCulture processCell culture mediaHematopoietic Stem Cell MobilizationTrace element
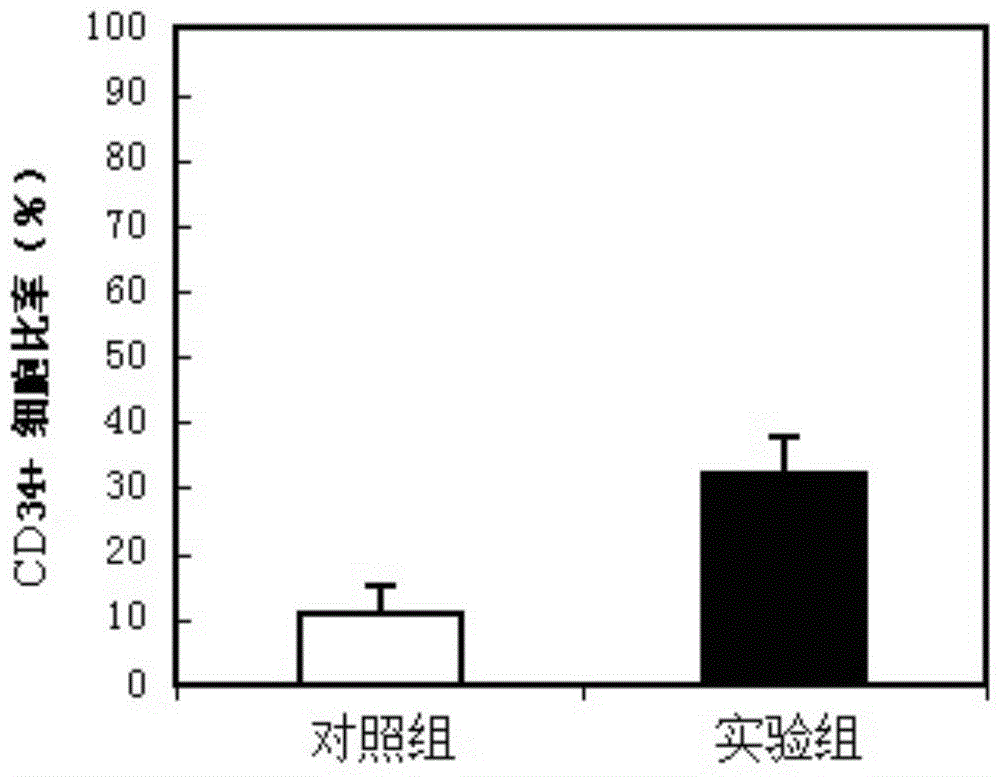
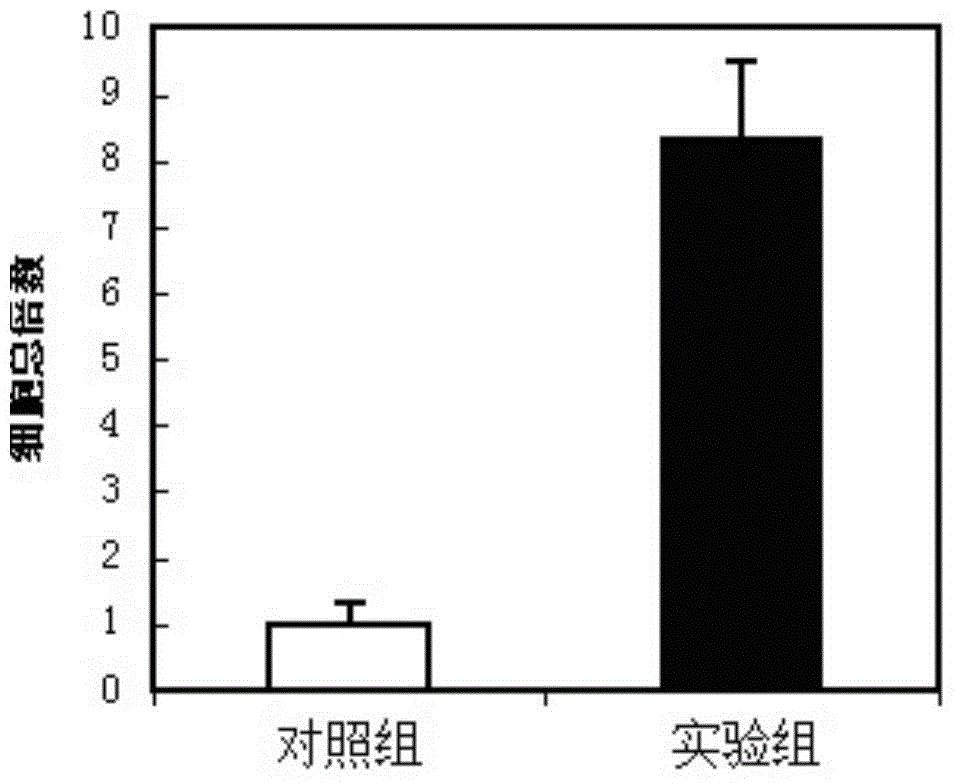
The invention discloses a hematopoietic stem cell culture medium and its application and a stem cell cultivation method based on the hematopoietic stem cell culture medium. The hematopoietic stem cell culture medium is made from amino acids, vitamins, salts, fats, phaseolin polypeptide and cytokines, with one or any of trace elements, organic small molecules, hematopoietic stem cell proliferator, plant extract and animal extract; the hematopoietic stem cell culture medium can quickly proliferate CD34+ cells different in species, and proliferating speed and telomere length of the CD34+ cells is evidently increased; hematopoietic stem cells cultivated via the hematopoietic stem cell culture medium have constant good cell functions, the hematopoietic stem cell culture medium has the functions, including, but not limited to, anticancer action, anti-ageing action and life prolonging, and has promising application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN FULIXIN HEALTH IND DEV LTD +1
Microfluidic device for cell culture
ActiveUS8481303B2Encourage cell polarityEffective simulationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringStem cell culture
A microfluidic cell culture apparatus includes a cell retention chamber and a perfusion channel. The cell retention chamber has a structured surface. The structured surface includes a major surface from which a plurality of projections extends into the chamber. The plurality of projections are arranged to suspend cells cultured in the chamber above the major surface. The first perfusion channel is configured to provide laminar flow of a fluid through the channel and forms a plurality of openings in communication with the cell retention chamber. The openings are configured to prevent cells from the retention chamber from entering the perfusion channel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com