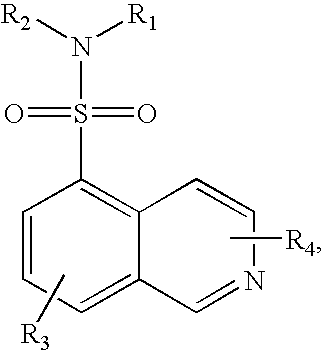
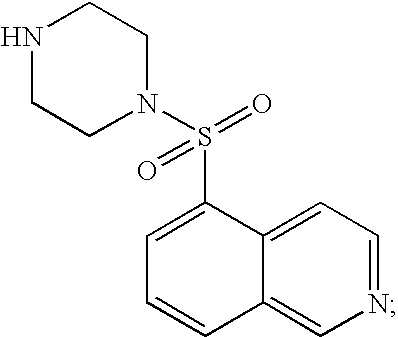
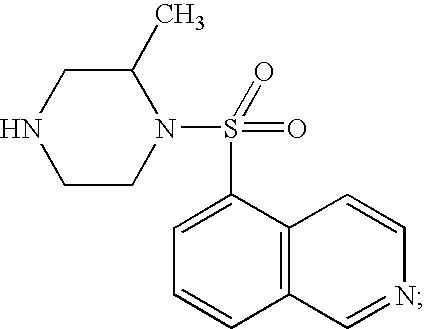
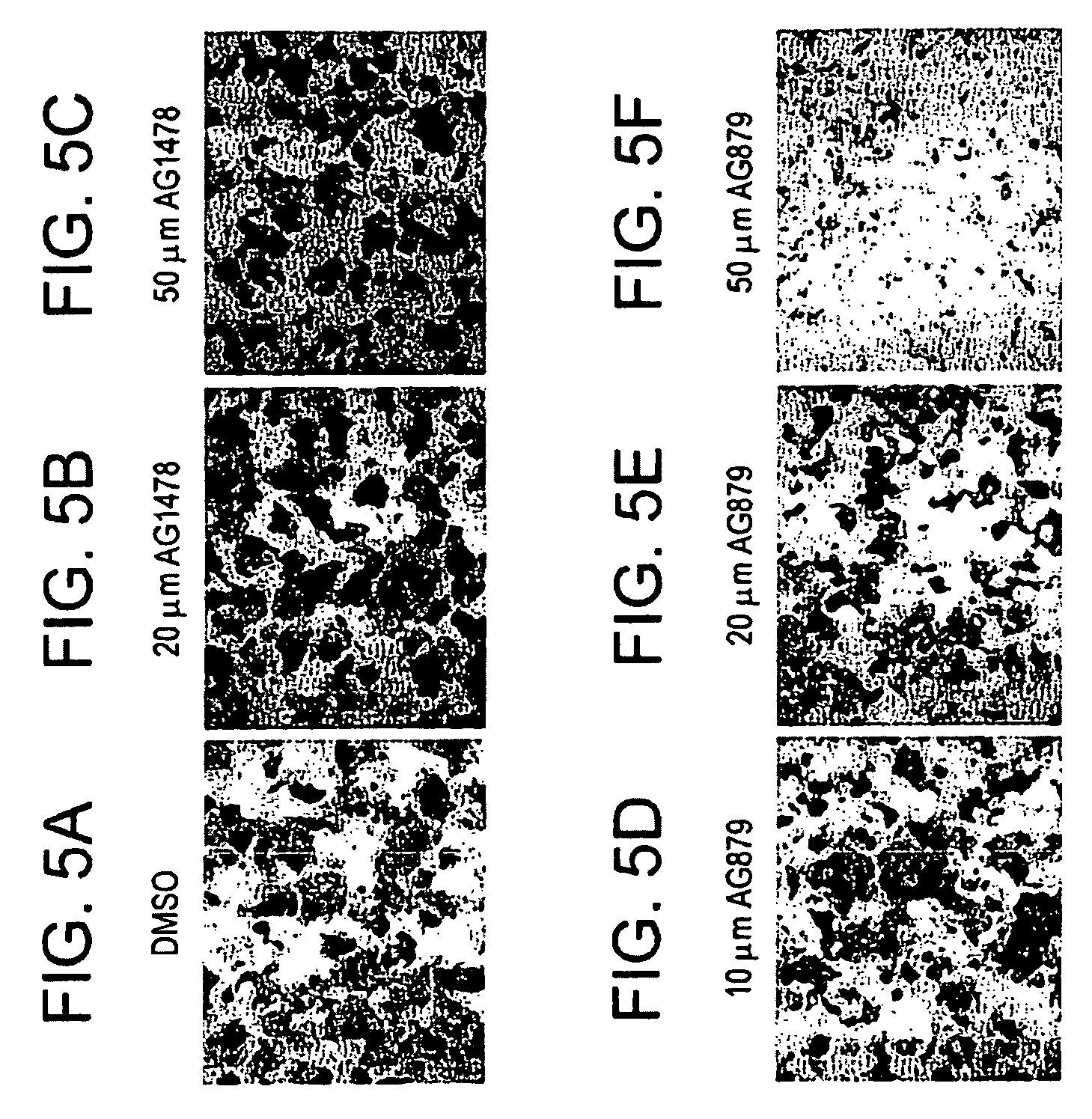
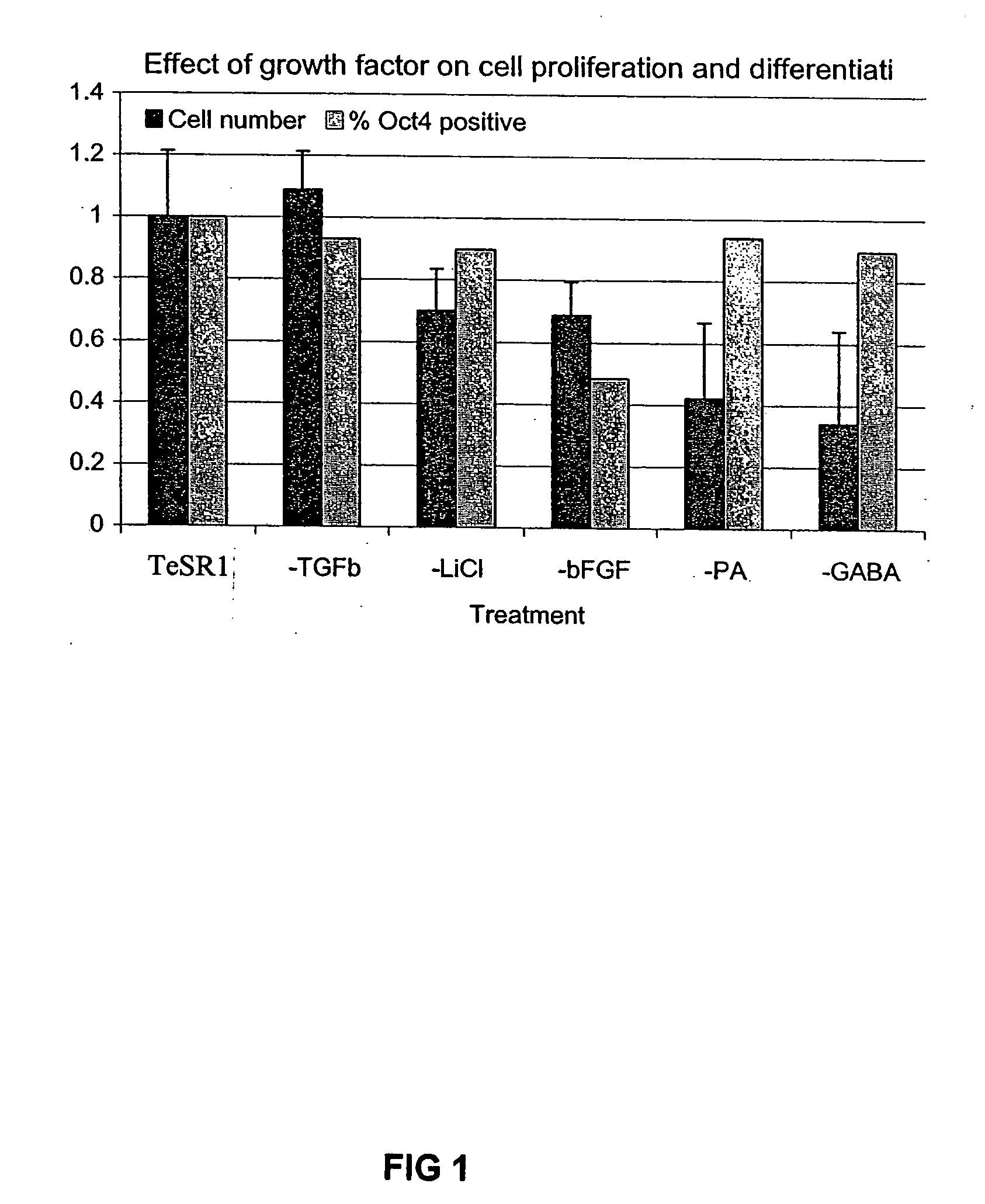
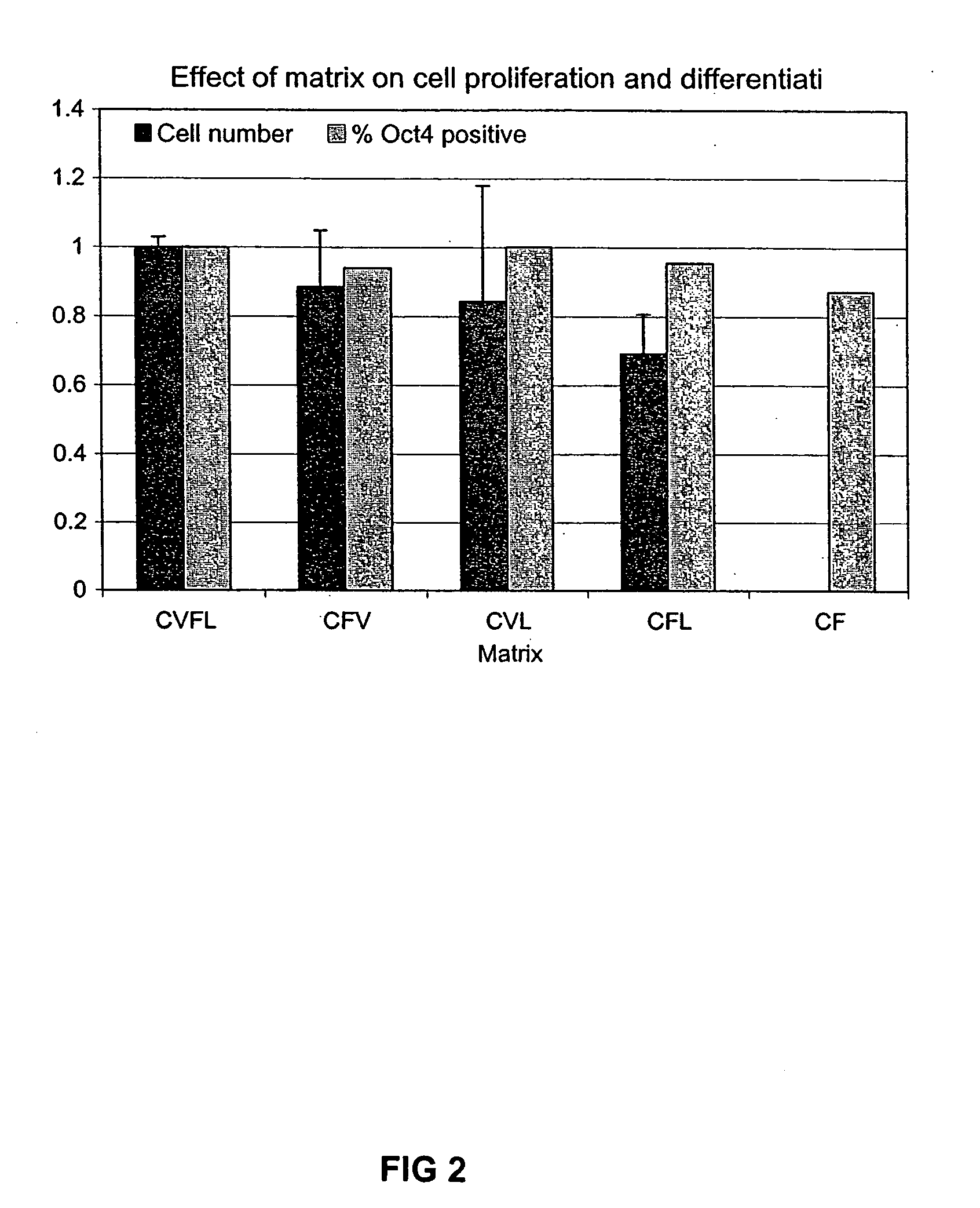
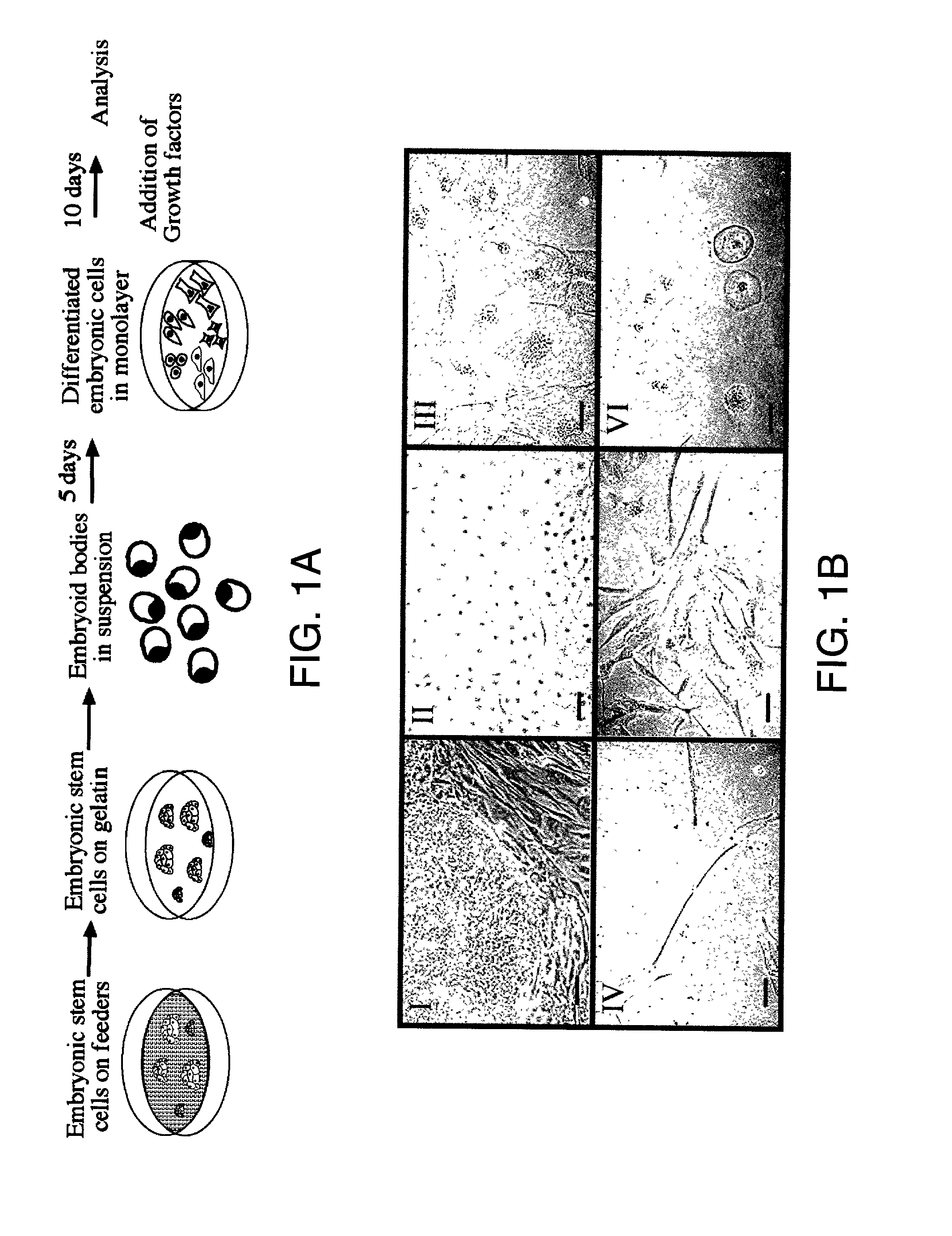
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
982 results about "Embryonic stem cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
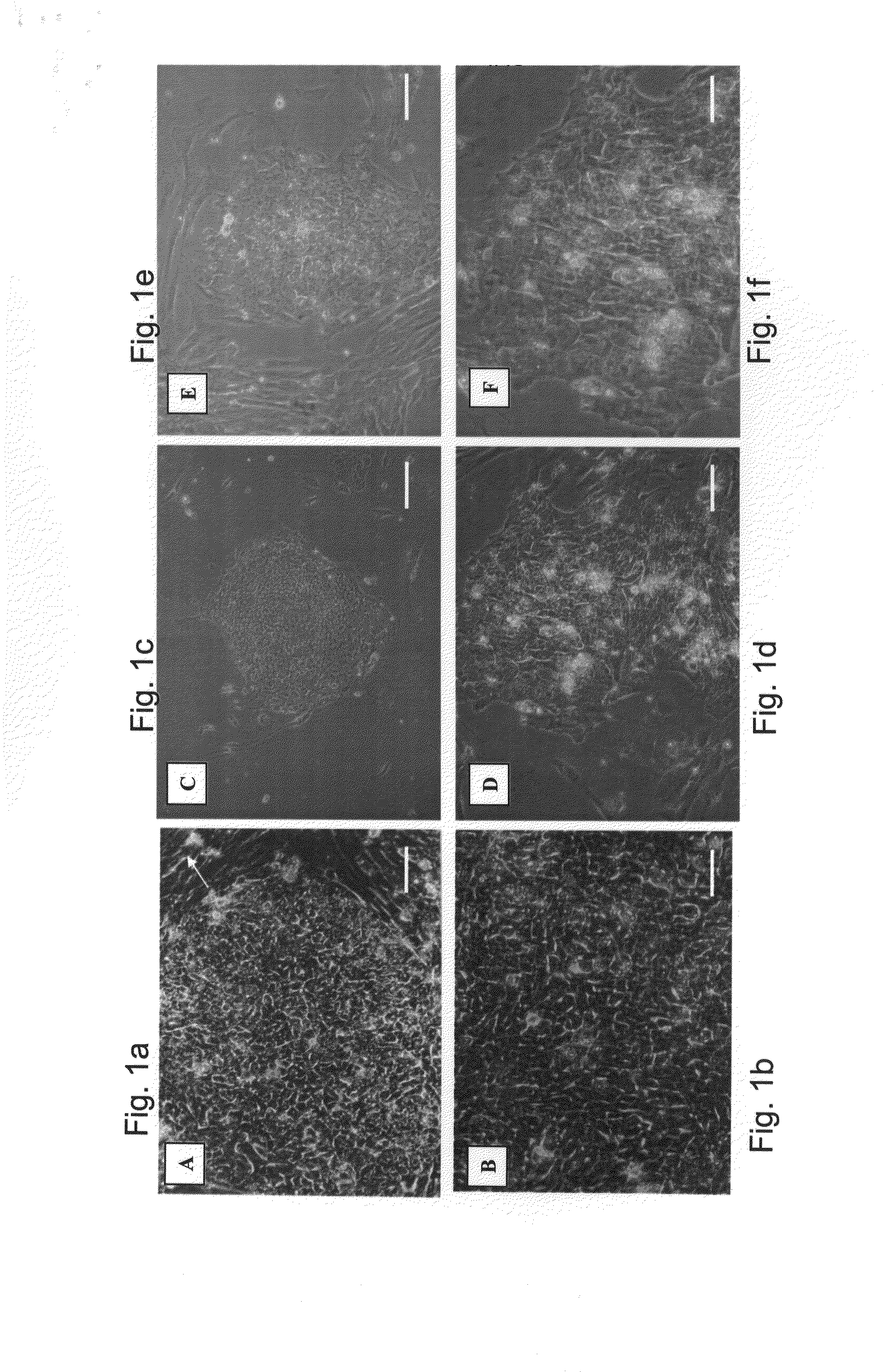
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells or ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast, or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, a process which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should have the same moral considerations as embryos in the post-implantation stage of development.
Methods of making conditioned cell culture medium compositions
InactiveUS6372494B1Eliminate wrinklesEliminate frown lineCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsReserve CellCell culture media
Novel products comprising conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use are described. The conditioned cell medium compositions of the invention may be comprised of any known defined or undefined medium and may be conditioned using any eukaryotic cell type. The medium may be conditioned by stromal cells, parenchymal cells, mesenchymal stem cells, liver reserve cells, neural stem cells, pancreatic stem cells and / or embryonic stem cells. Additionally, the cells may be genetically modified. A three-dimensional tissue construct is preferred. Once the cell medium of the invention is conditioned, it may be used in any state. Physical embodiments of the conditioned medium include, but are not limited to, liquid or solid, frozen, lyophilized or dried into a powder. Additionally, the medium is formulated with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier as a vehicle for internal administration, applied directly to a food item or product, formulated with a salve or ointment for topical applications, or, for example, made into or added to surgical glue to accelerate healing of sutures following invasive procedures. Also, the medium may be further processed to concentrate or reduce one or more factors or components contained within the medium.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Defined media for stem cell culture
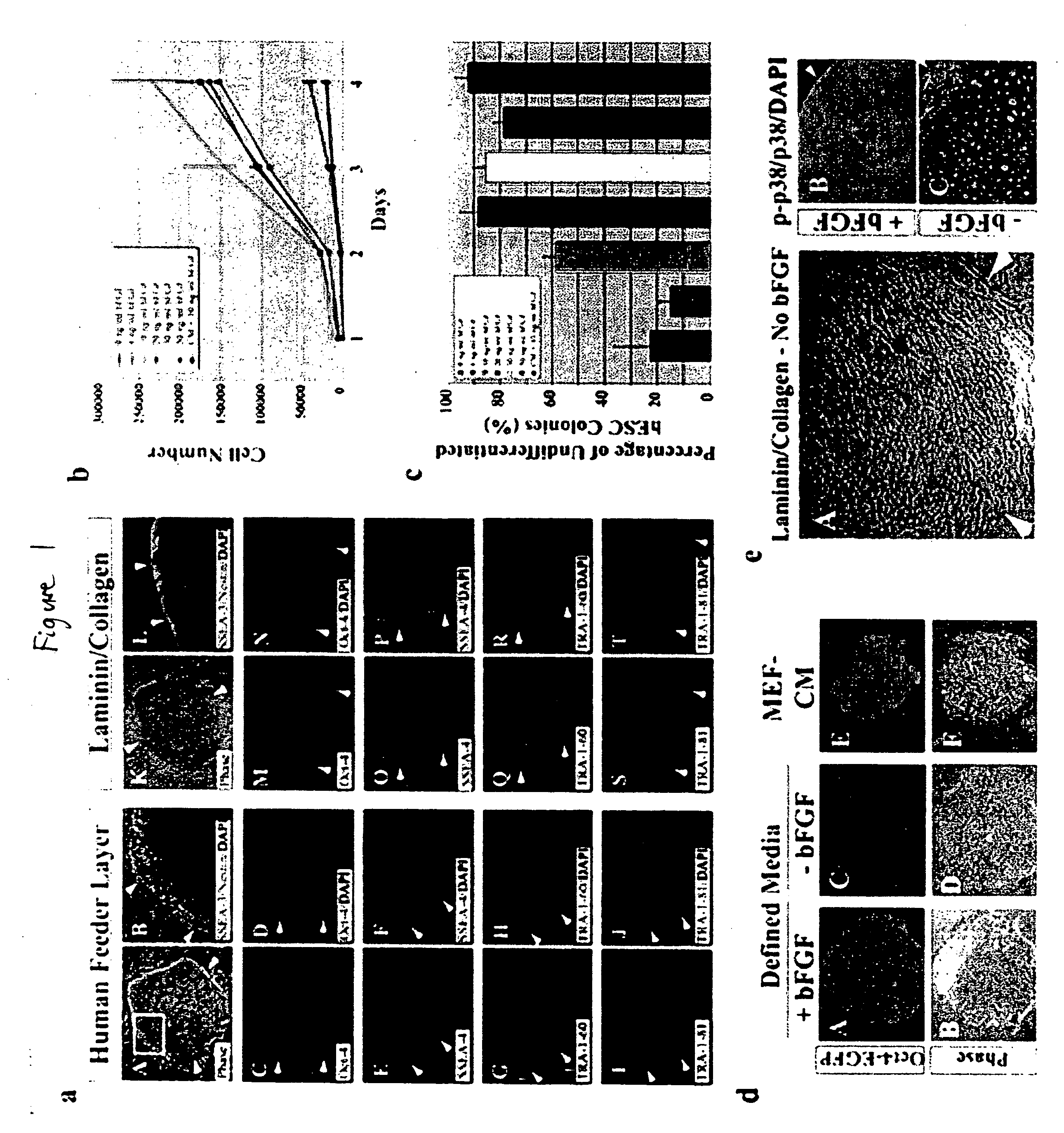
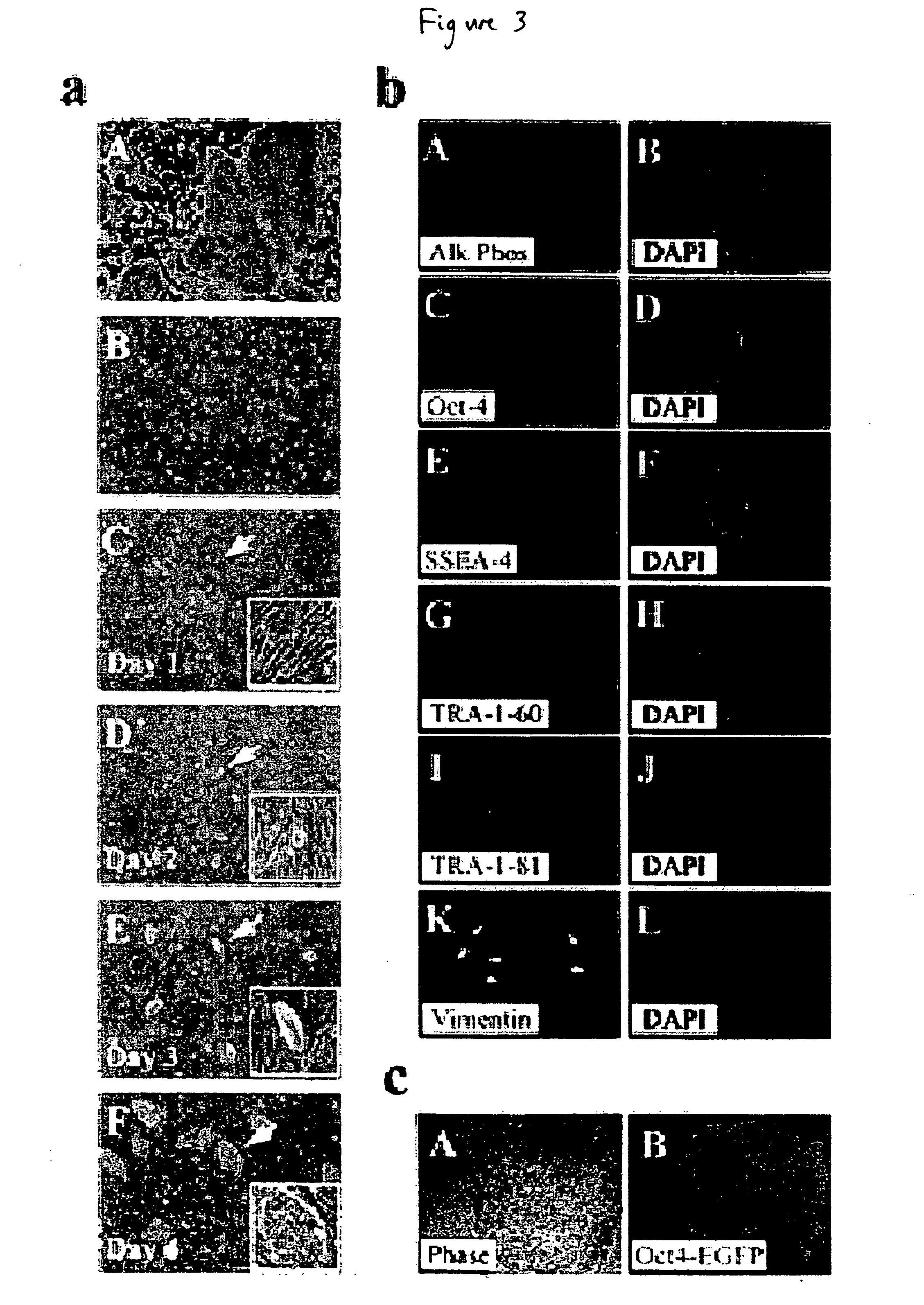
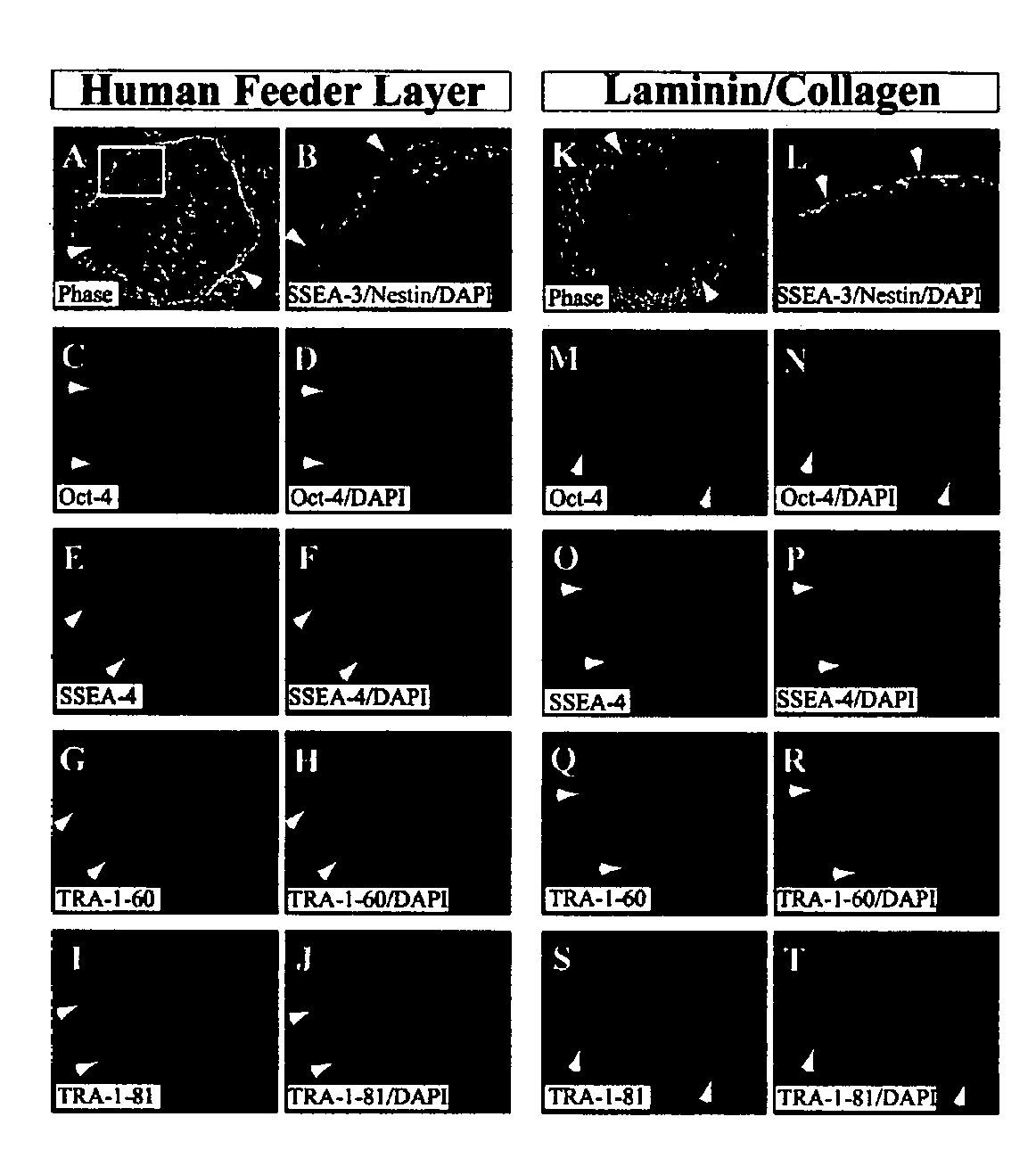
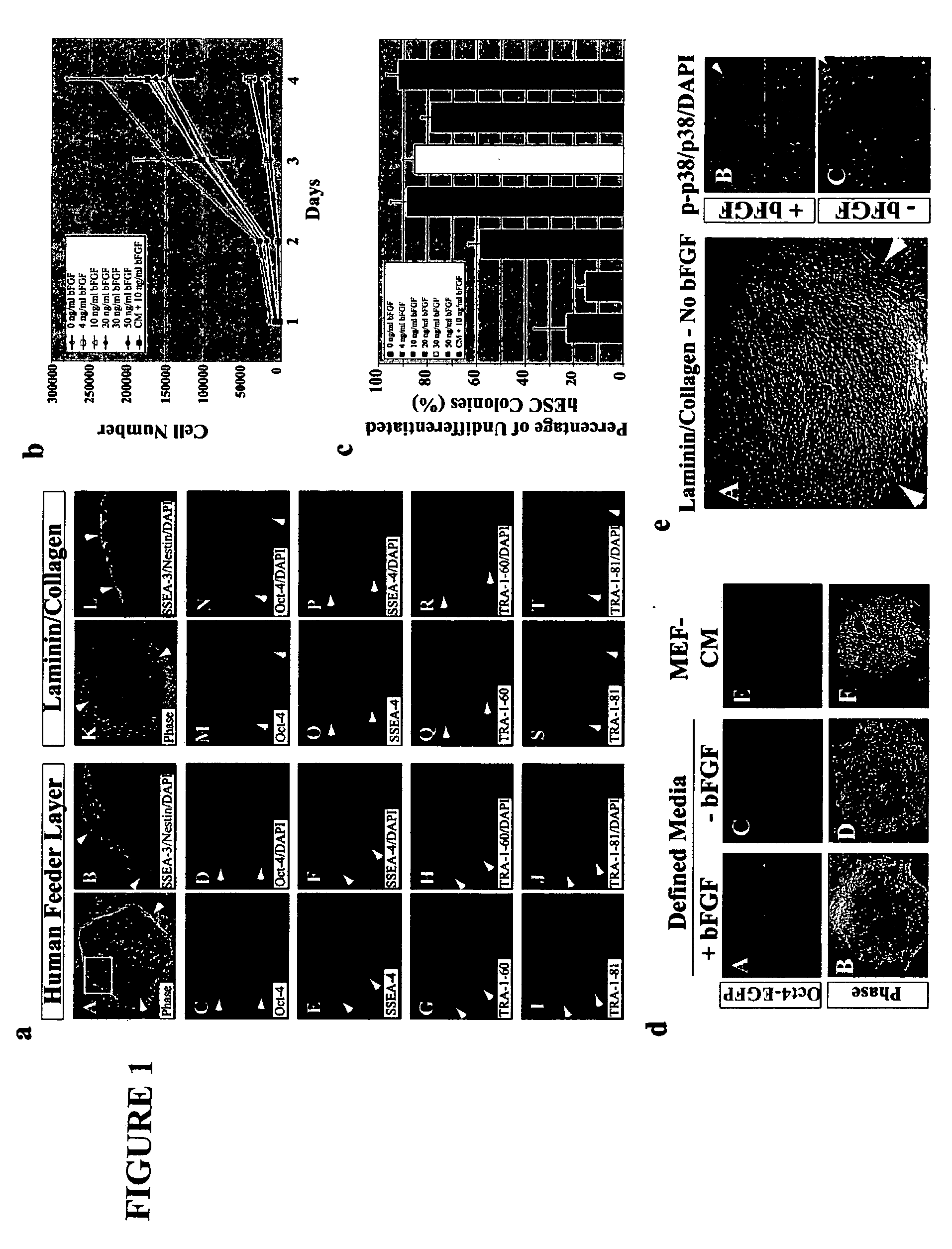
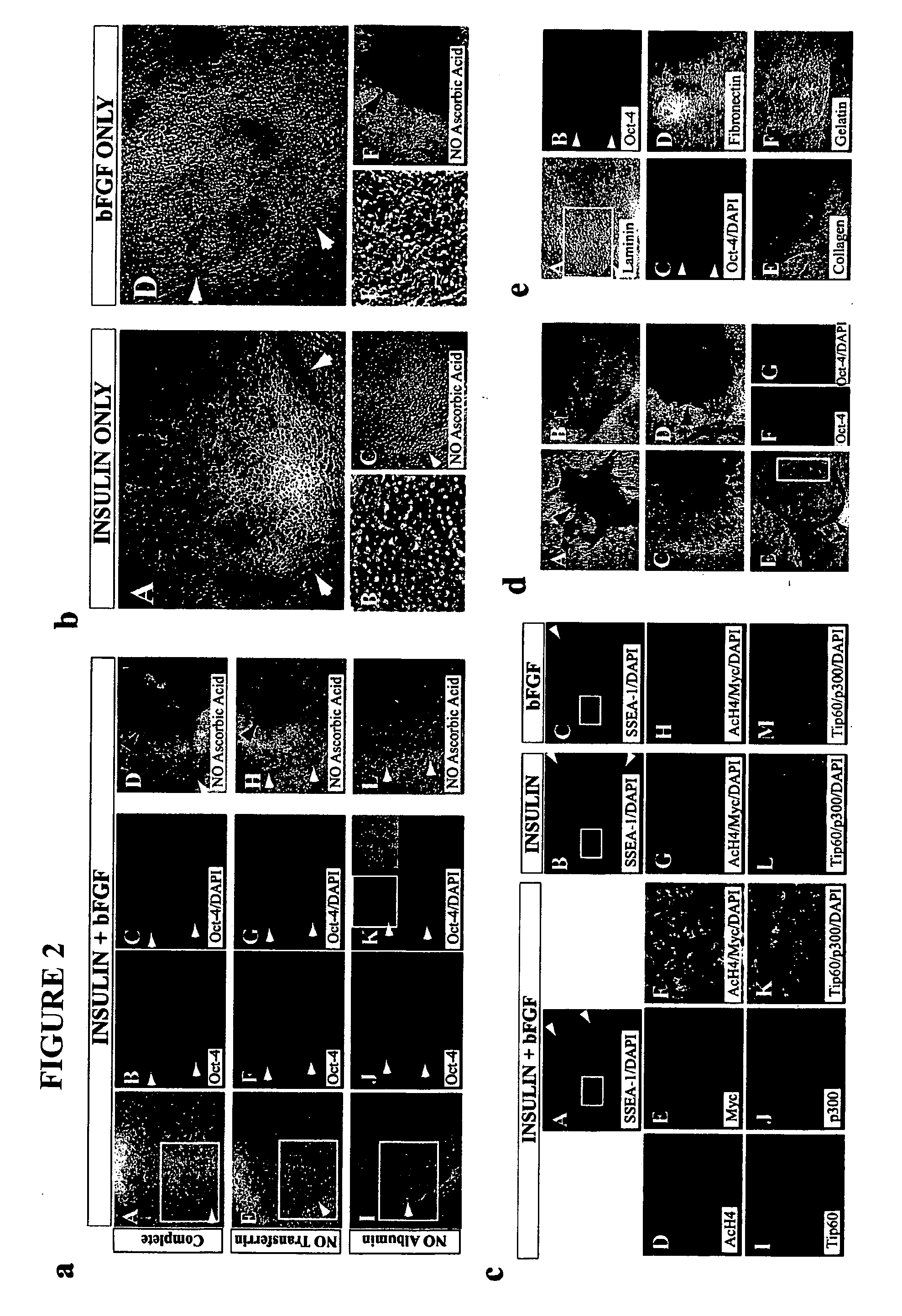
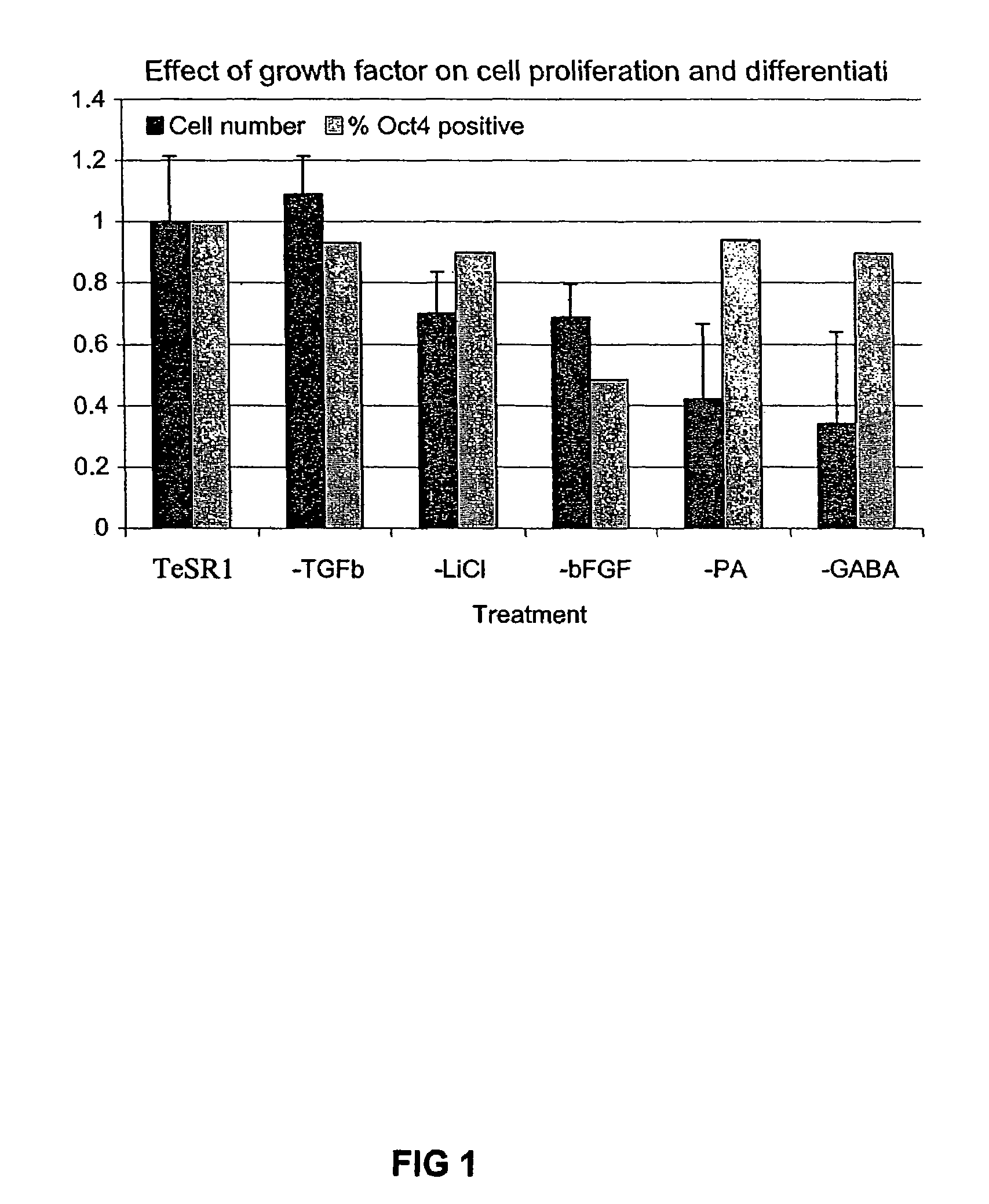
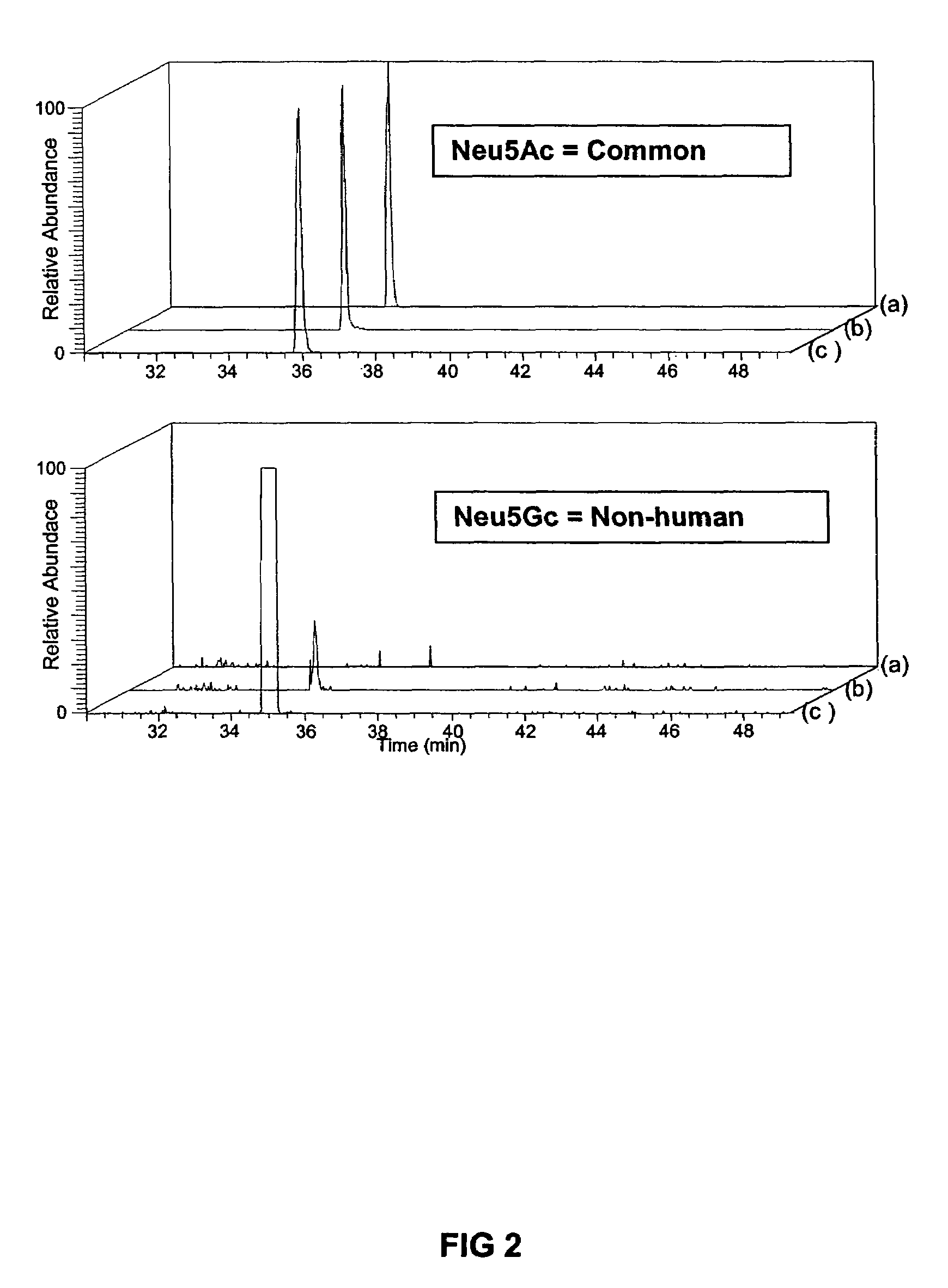
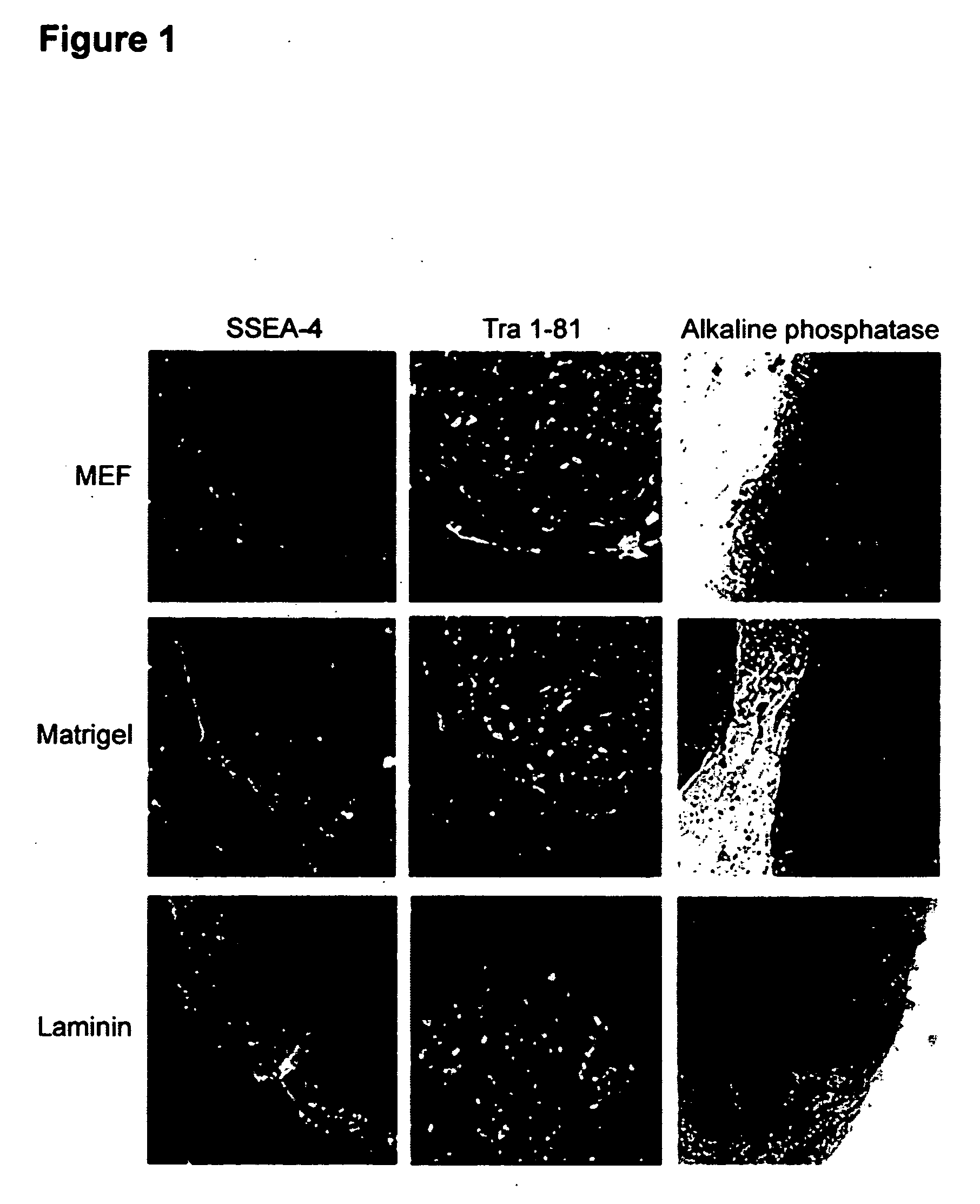
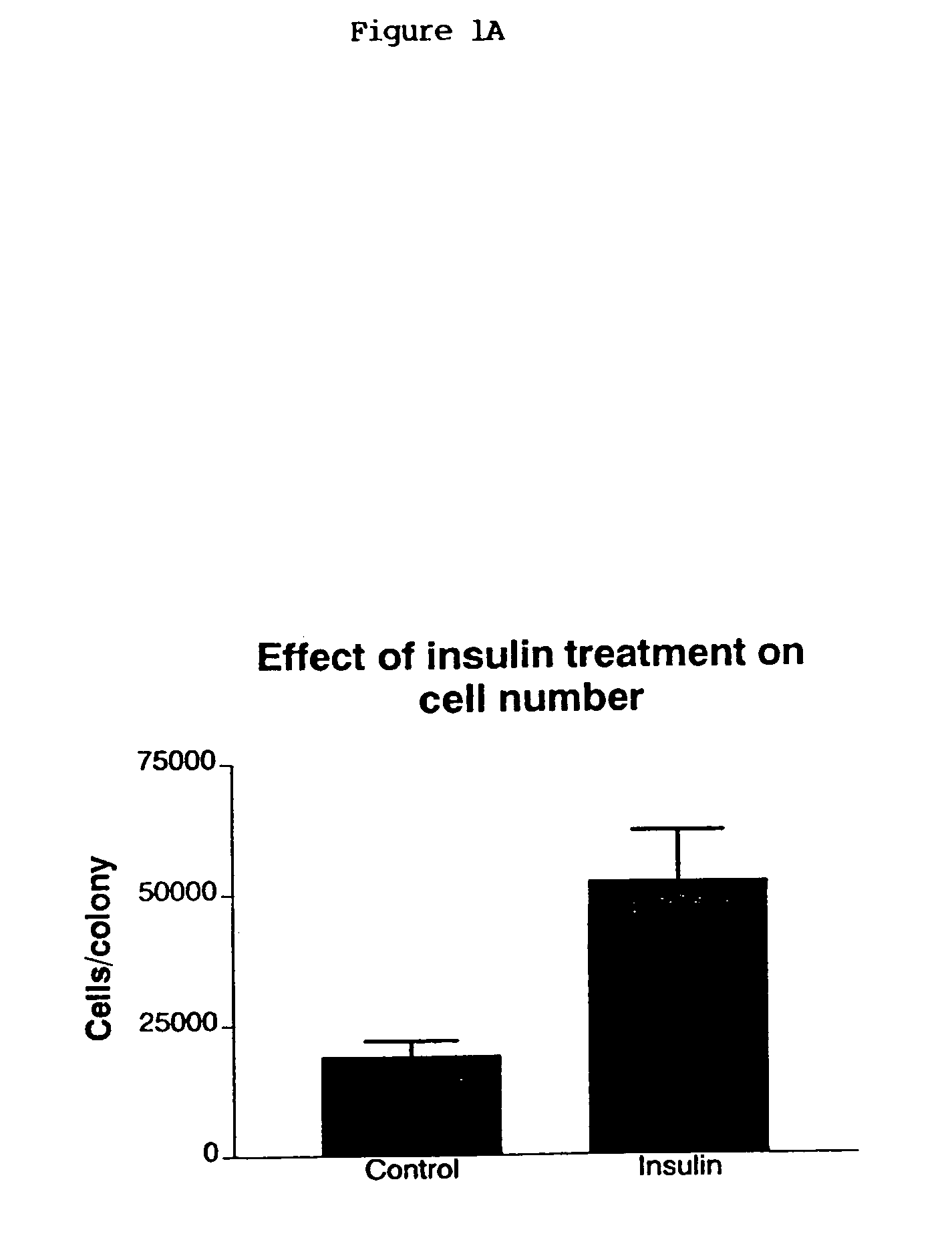
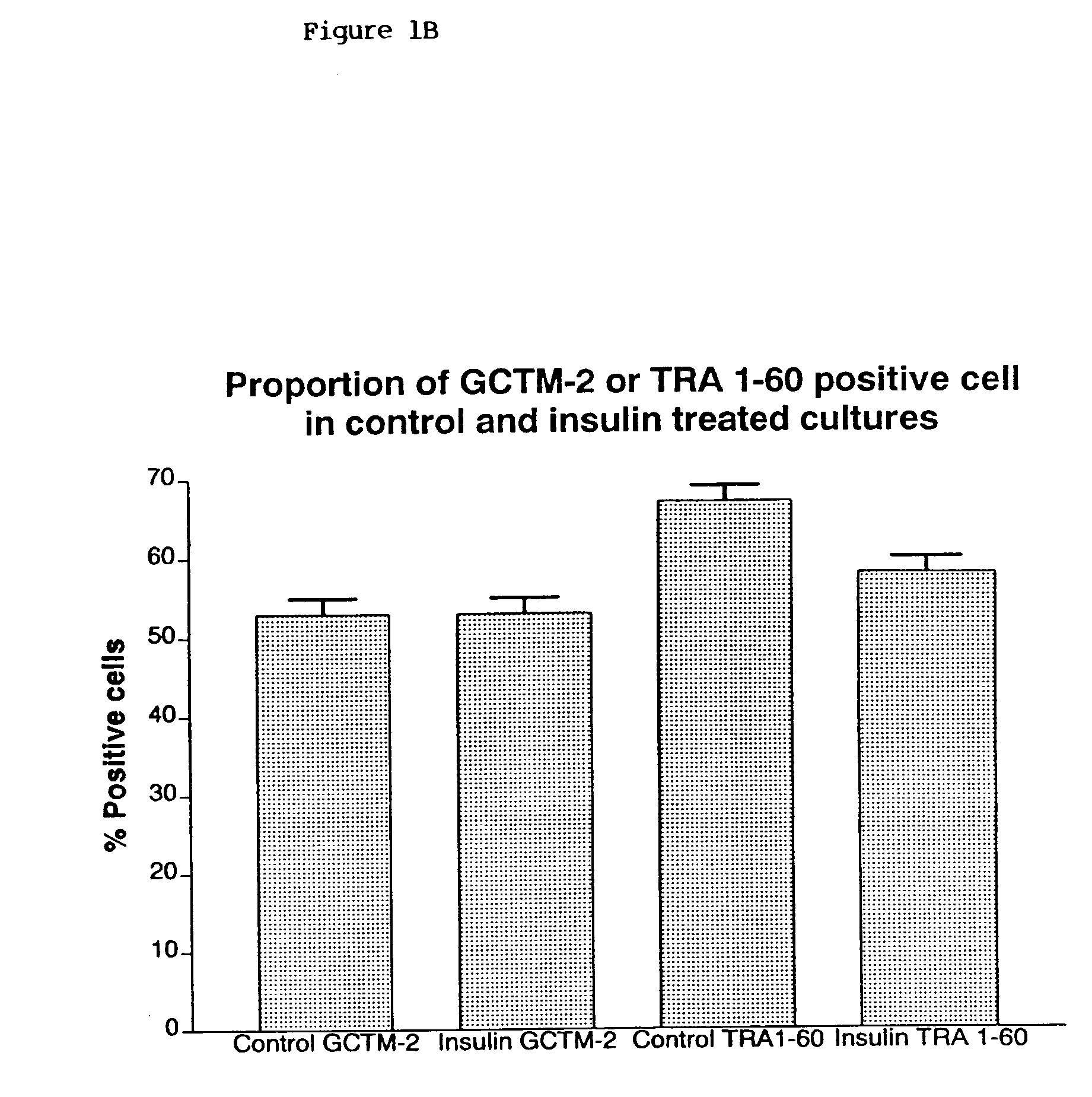
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Defined media for pluripotent stem cell culture
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Isolation, cultivation and uses of stem/progenitor cells
The present invention relates to a method for isolating stem / progenitor cells from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord, wherein the method comprises separating the amniotic membrane from the other components of the umbilical cord in vitro, culturing the amniotic membrane tissue under conditions allowing cell proliferation, and isolating the stem / progenitor cells from the tissue cultures. The isolated stem cell cells can have embryonic stem cell-like properties and can be used for various therapeutic purposes. In one embodiment, the invention relates to the isolation and cultivation of stem cells such as epithelial and / or mesenchymal stem / progenitor cells under conditions allowing the cells to undergo mitotic expansion. Furthermore, the invention is directed to a method for the differentiation of the isolated stem / progenitor cells into epithelial and / or mesenchymal cells.
Owner:CELLRESEARCH CORP PTE LTD
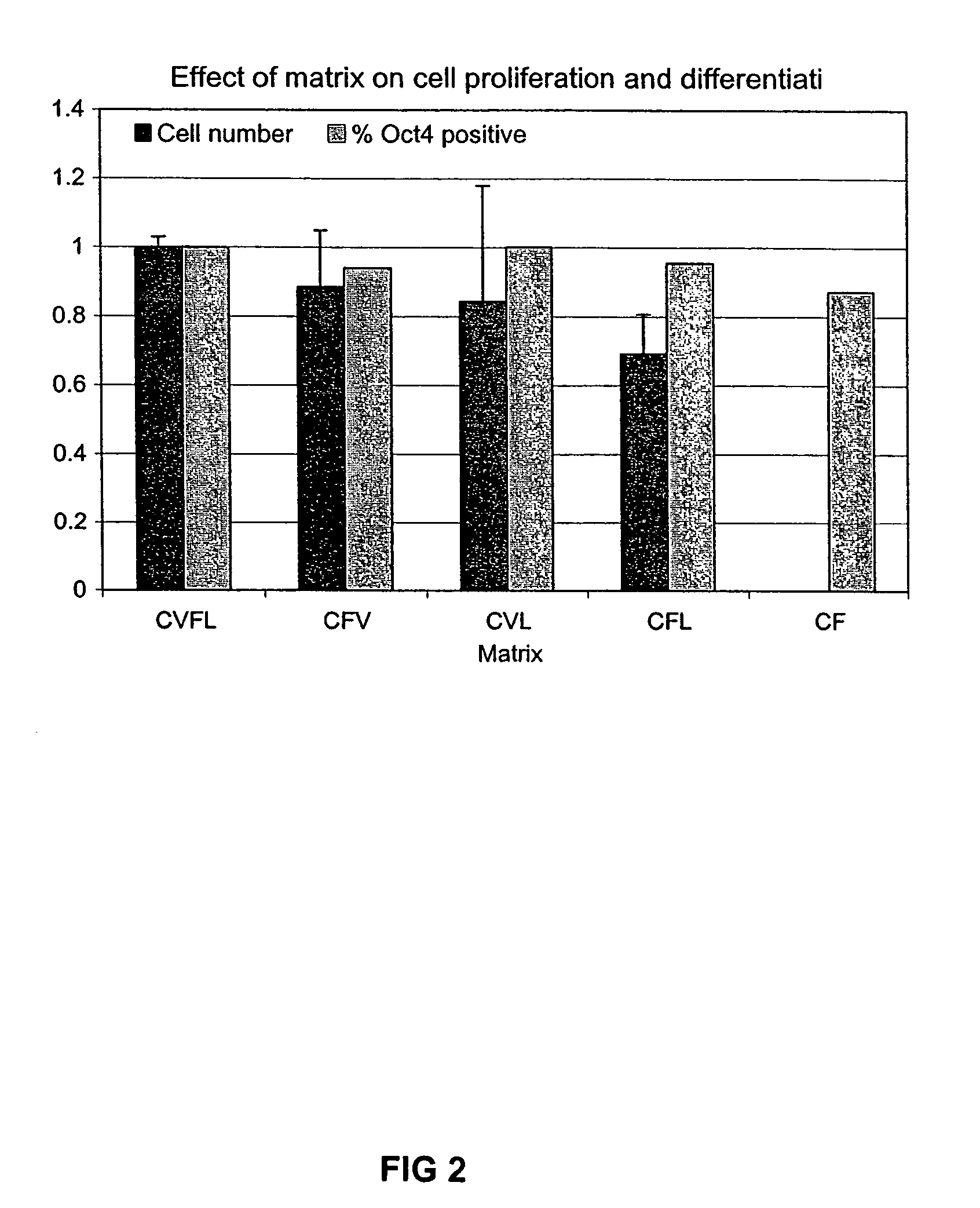
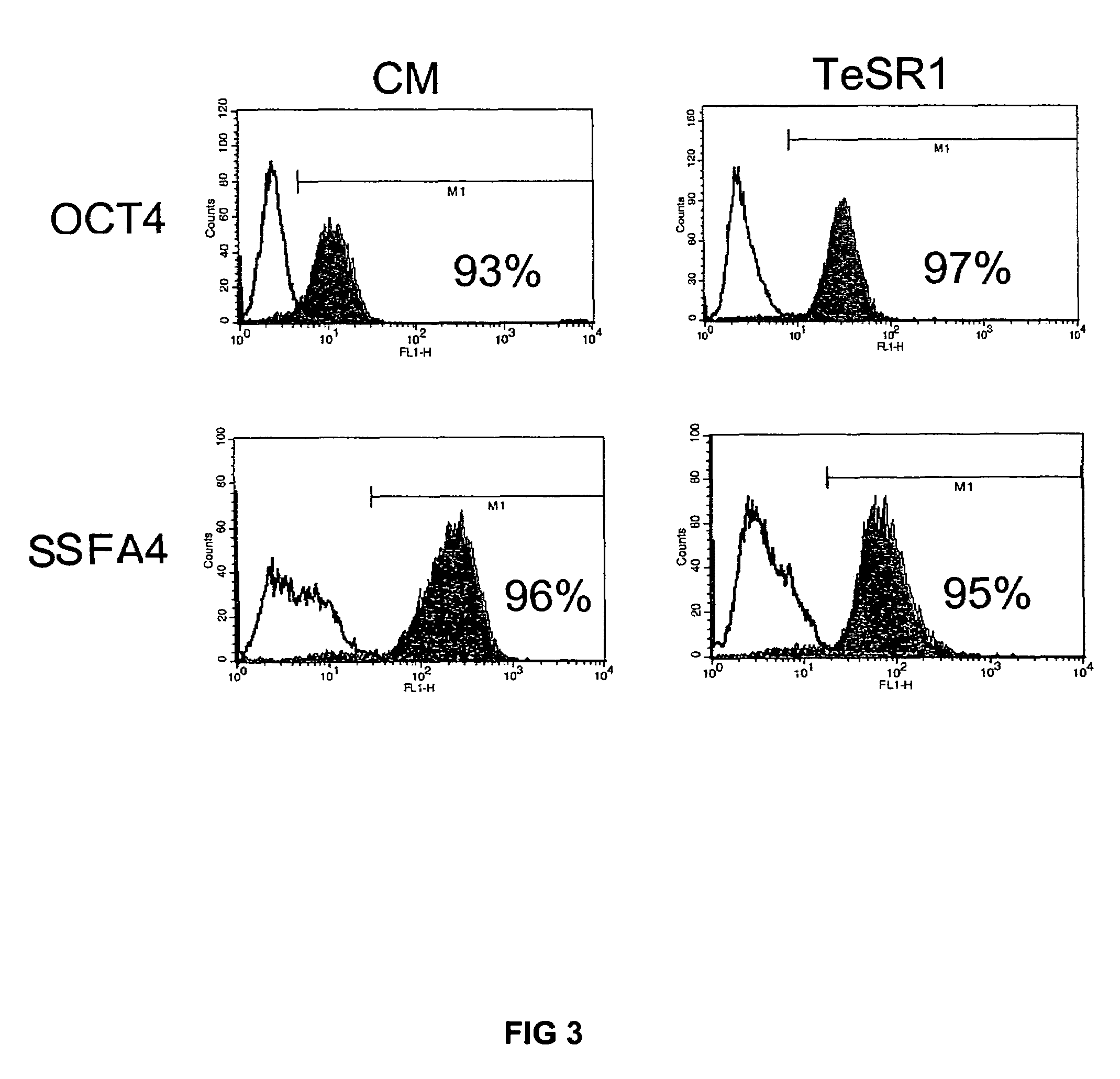
Culturing human embryonic stem cells in medium containing pipecholic acid and gamma amino butyric acid
Previous methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells have required either fibroblast feeder cells or a medium which has been exposed to fibroblast feeder cells in order to maintain the stem cells in an undifferentiated state. It has now been found that if high levels of fibroblast growth factor are used in a medium with gamma amino butyric acid, pipecholic acid, lithium and lipids, the stem cells will remain undifferentiated indefinitely through multiple passages, even without feeder cells or conditioned medium. A humanized matrix of human proteins can be used as a basement matrix to culture the cells. New lines of human embryonic stem cells made using these culture conditions, the medium and the matrix, will never have been exposed to animal cells, animal products, feeder cells or conditioned medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Placental niche and use thereof to culture stem cells
The present invention provides methods for culturing, expanding and differentiating stem cells, particularly human embryonic stem cells. The methods comprise culturing the stem cells for a period of time on a collagen biofabric, particularly a collagen biofabric derived from the amniotic membrane, chorion, or both, from mammalian placenta.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Medium containing pipecholic acid and gamma amino butyric acid and culture of embryonic stem cells
Previous methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells have required either fibroblast feeder cells or a medium which has been exposed to fibroblast feeder cells in order to maintain the stem cells in an undifferentiated state. It has now been found that if high levels of fibroblast growth factor, gamma amino butyric acid, pipecholic acid, lithium and transforming growth factor beta are added to the medium in which the stem cells are cultured, the stem cells will remain undifferentiated indefinitely through multiple passages, even without feeder cells or conditioned medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Stem Cell Aggregate Suspension Compositions and Methods of Differentiation Thereof
The present invention relates to methods for production of undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell aggregate suspension cultures from undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell single cell suspensions and methods of differentiation thereof.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
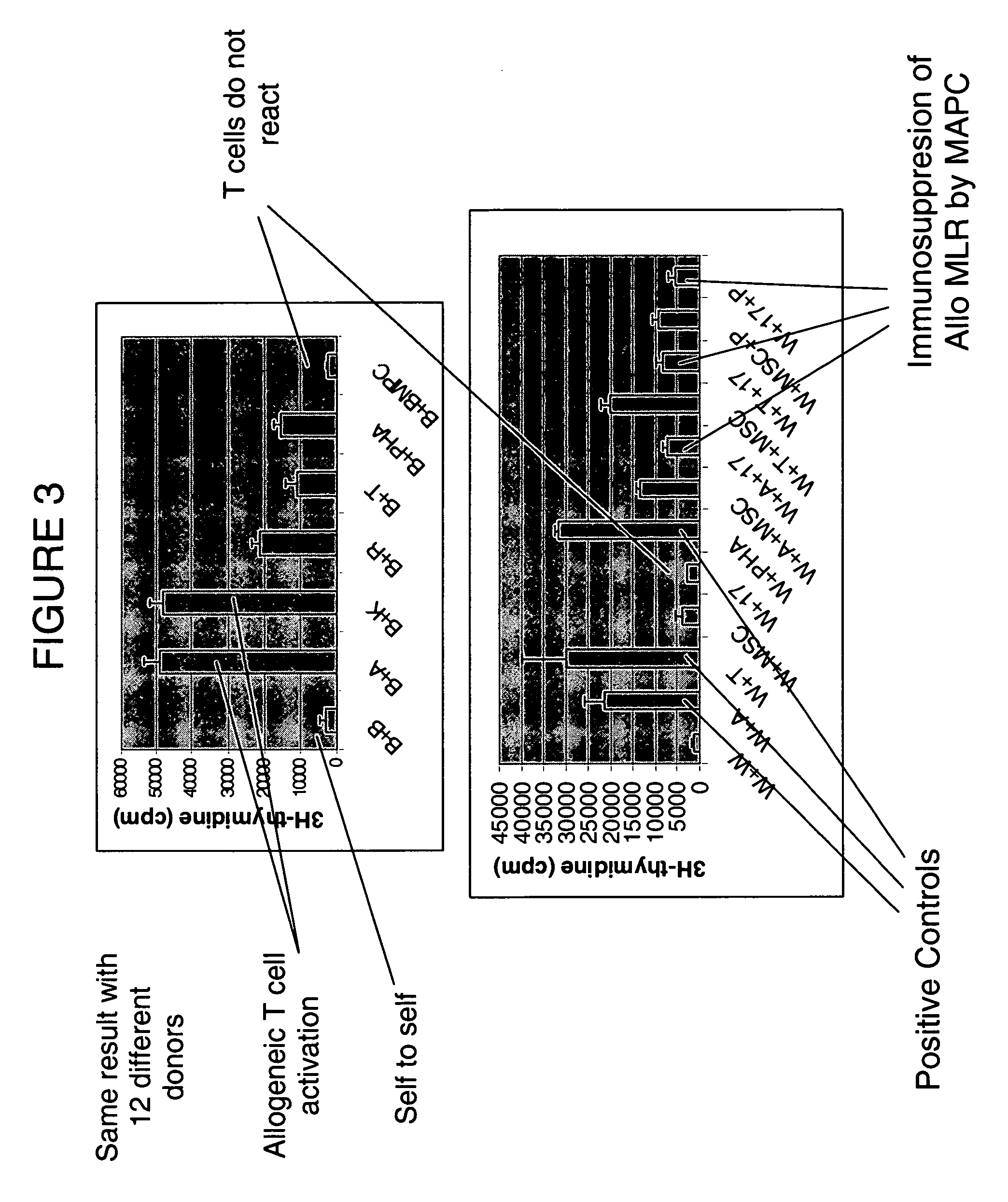
Immunomodulatory properties of multipotent adult progenitor cells and uses thereof
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Renovation and repopulation of decellularized tissues and cadaveric organs by stem cells
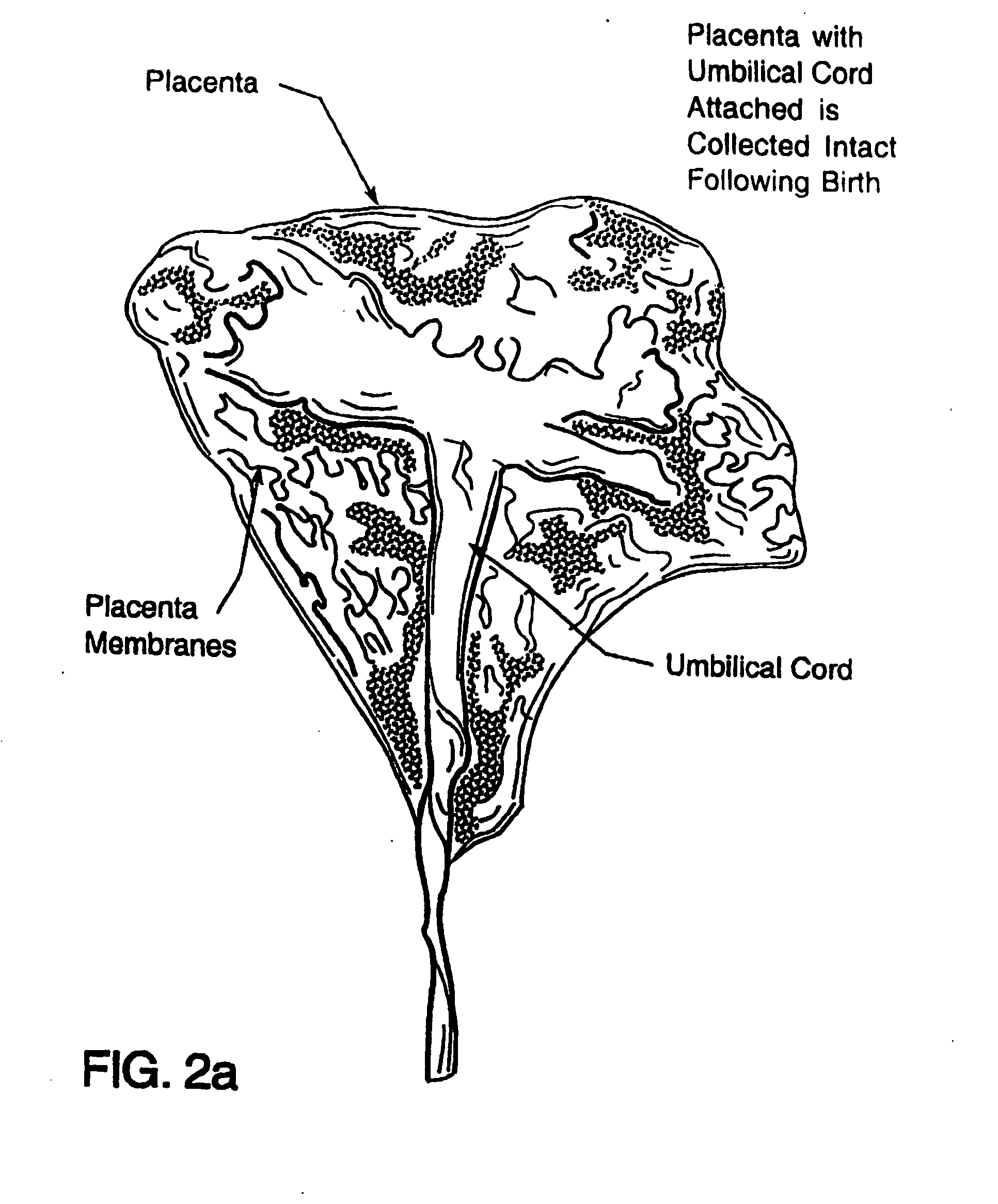
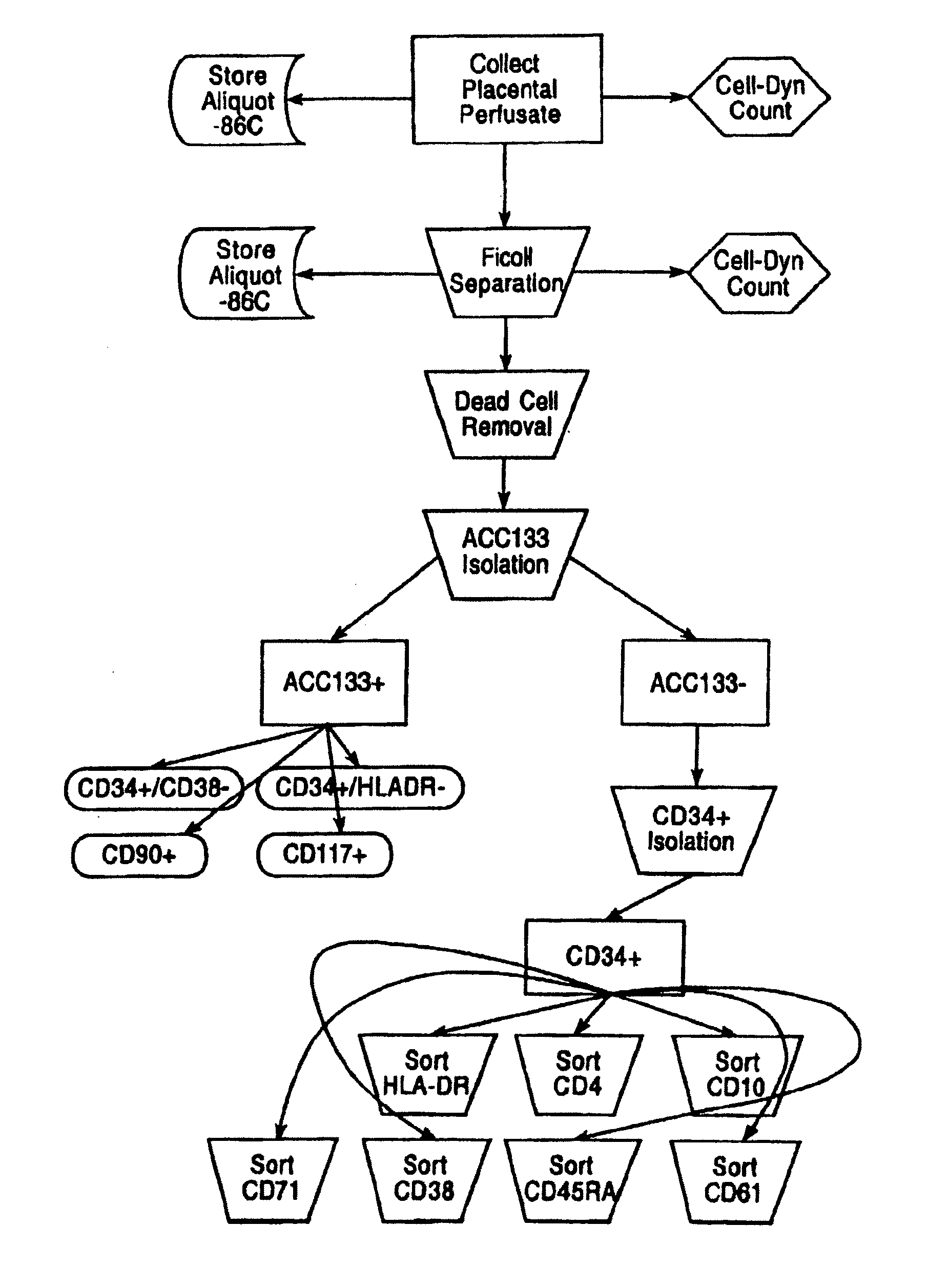
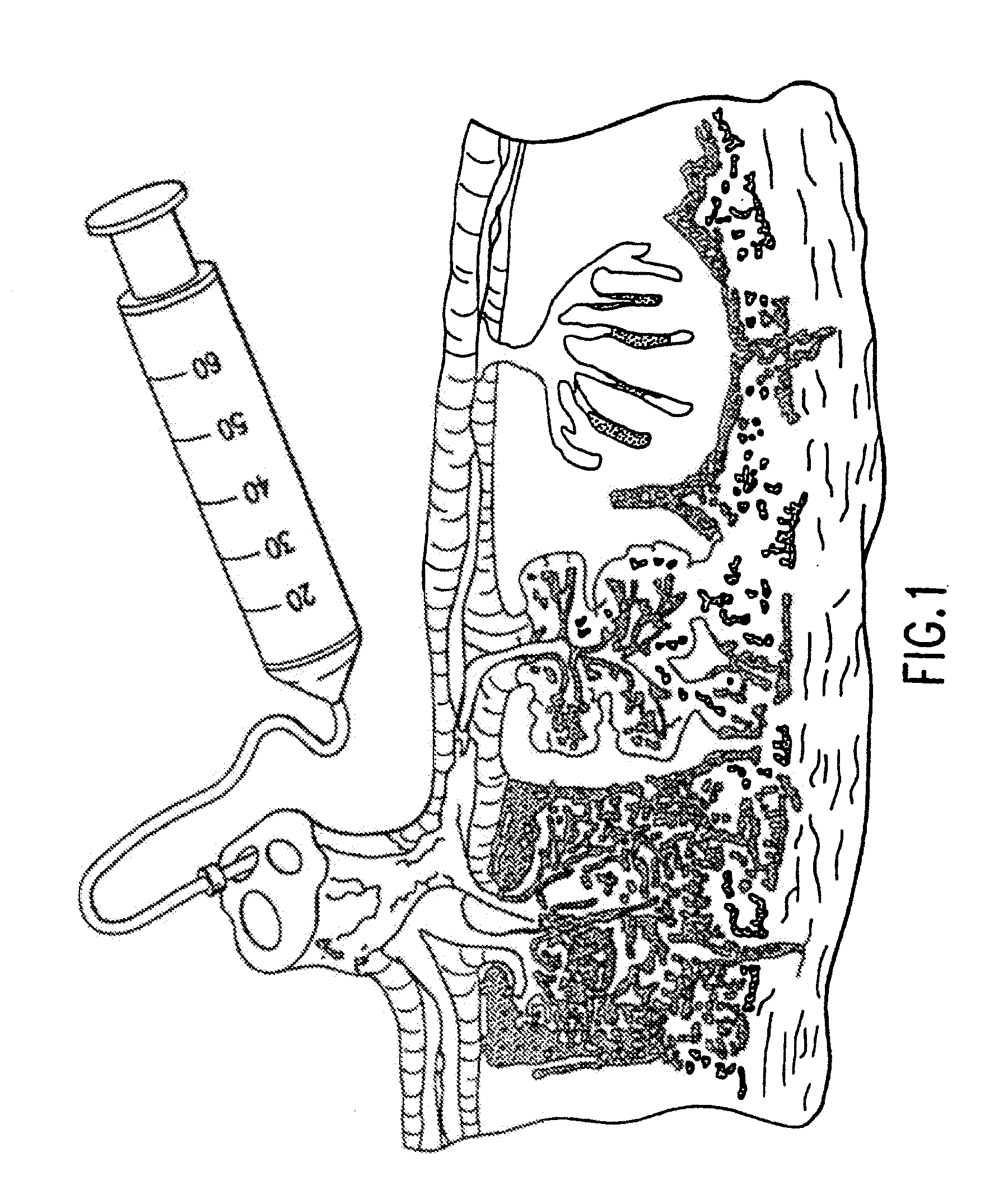
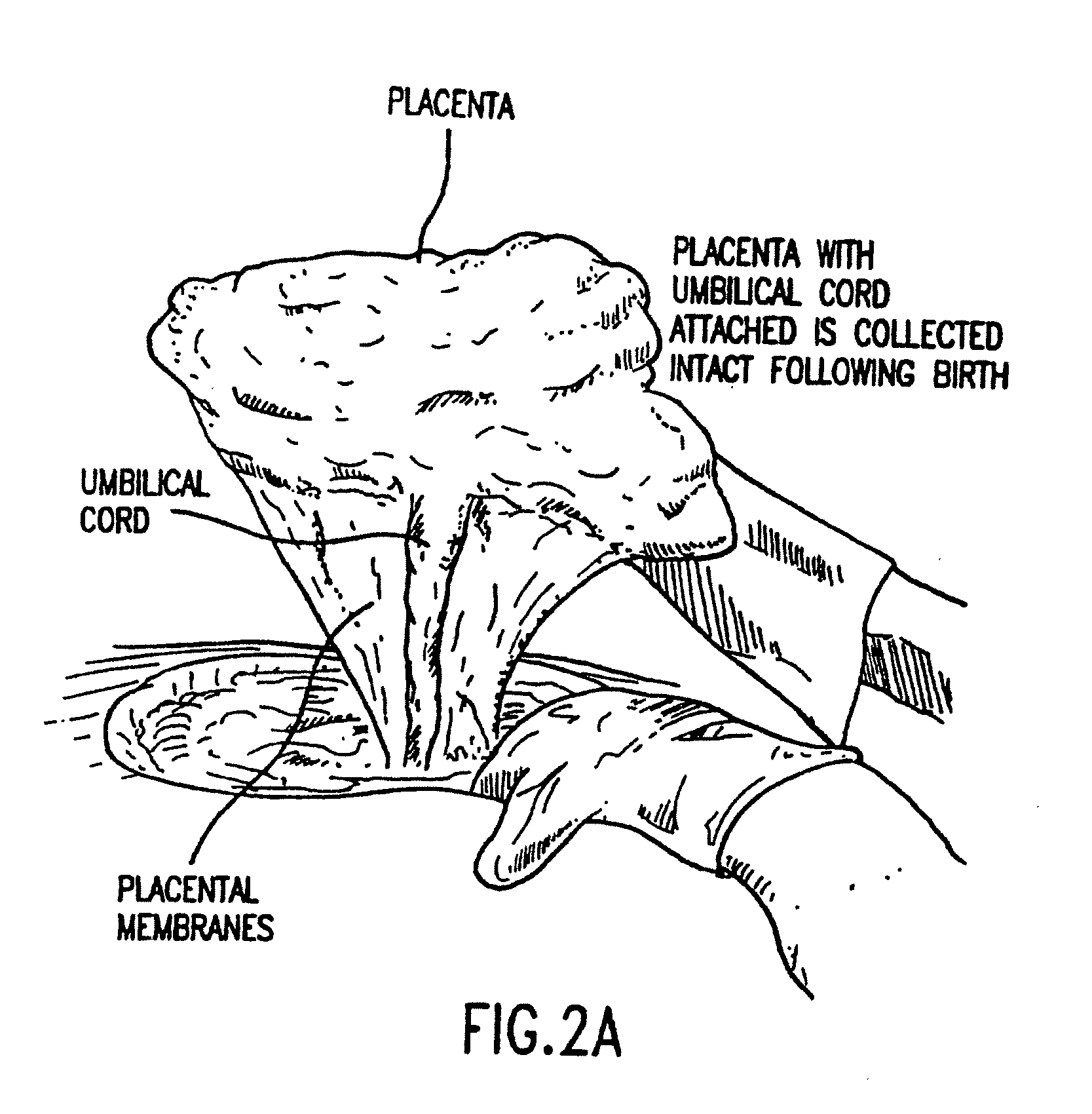
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Alternative compositions and methods for the culture of stem cells
InactiveUS20050037488A1Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
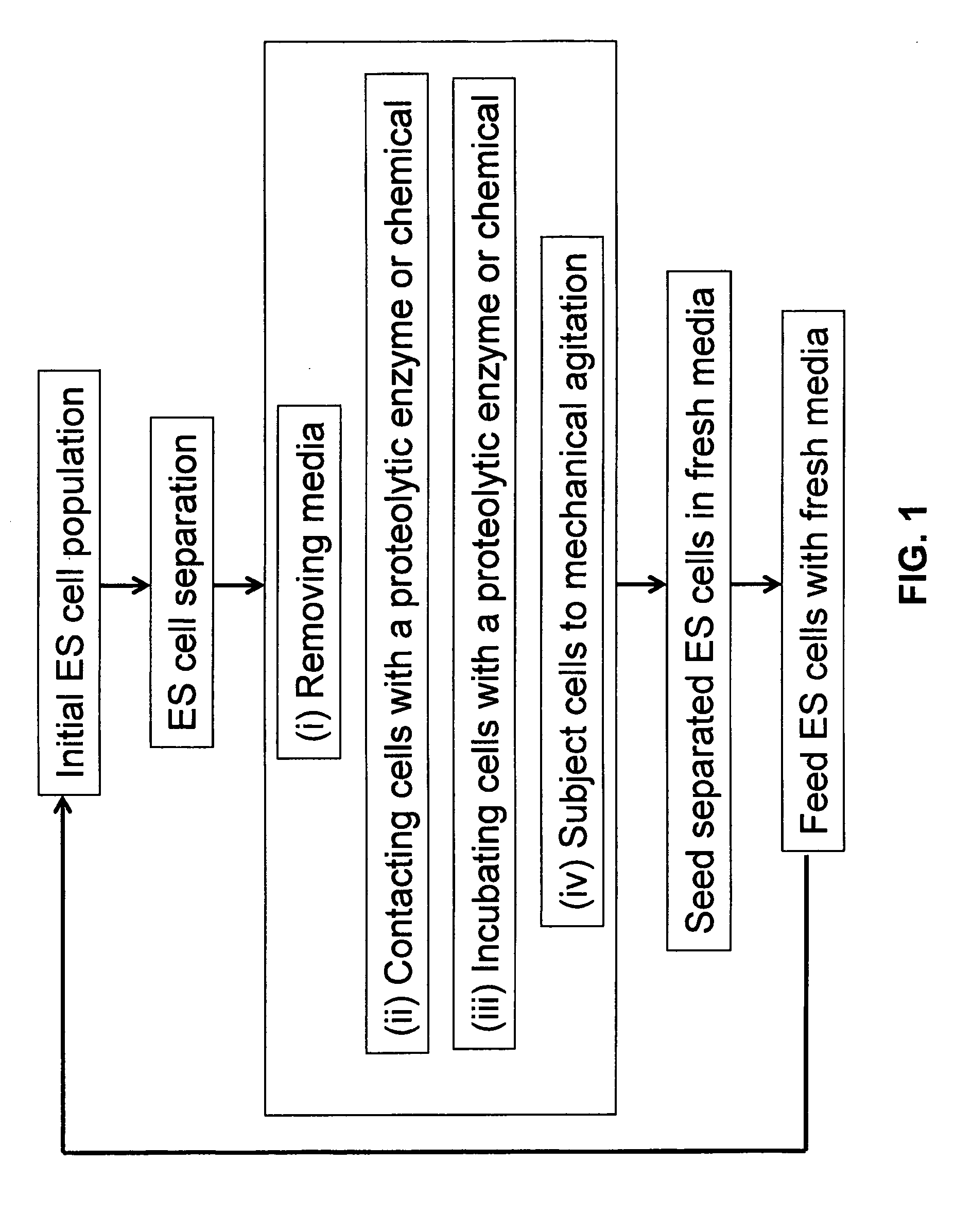
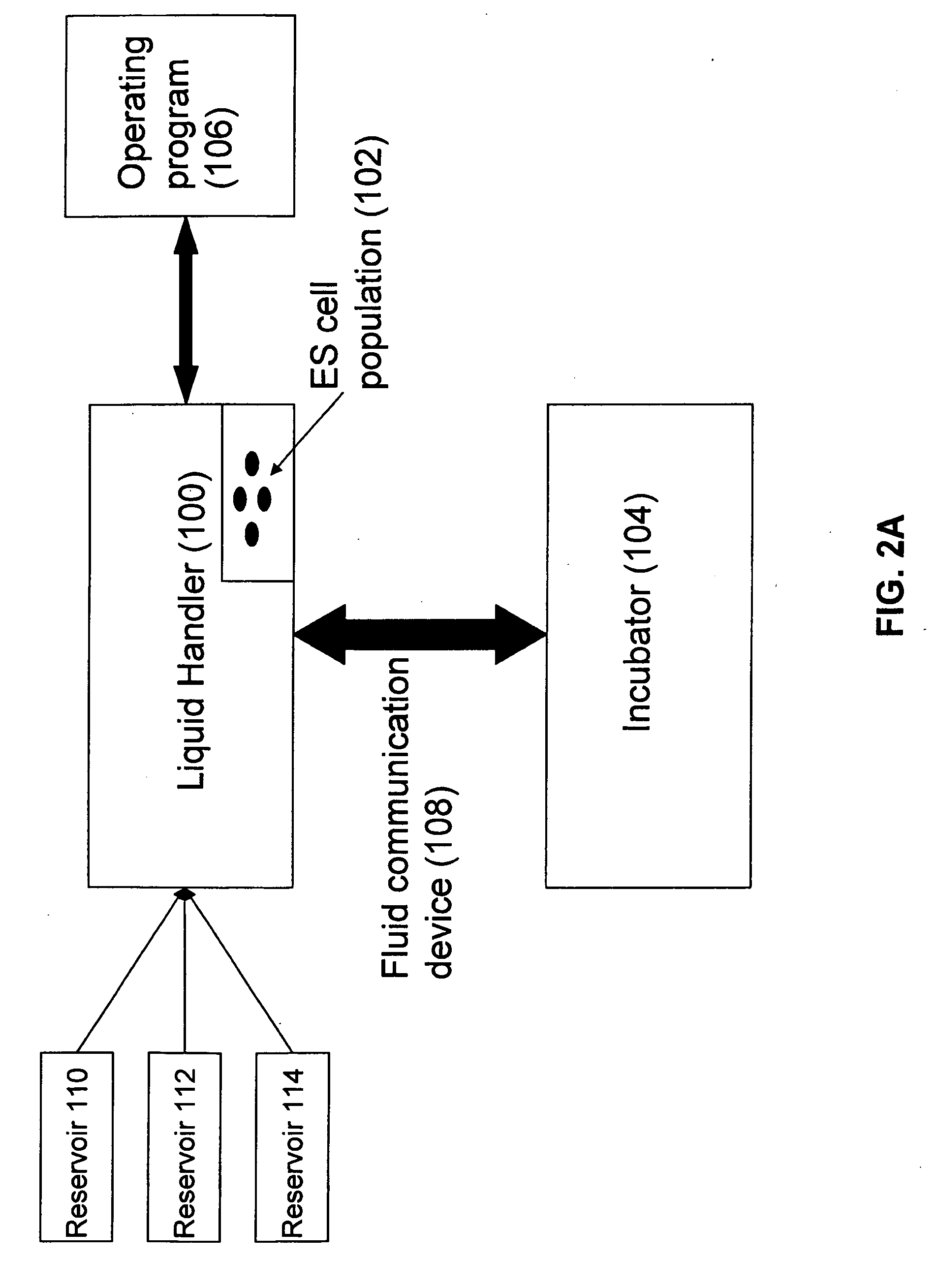
Automated method and apparatus for embryonic stem cell culture
ActiveUS20090029462A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyCell cluster
The invention concerns methods for automated culture of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) such as human ESCs. In some aspects, methods of the invention employ optimized culture media and limited proteolytic treatment of cells to separate cell clusters for expansion. Automated systems for passage and expansion of ESCs are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
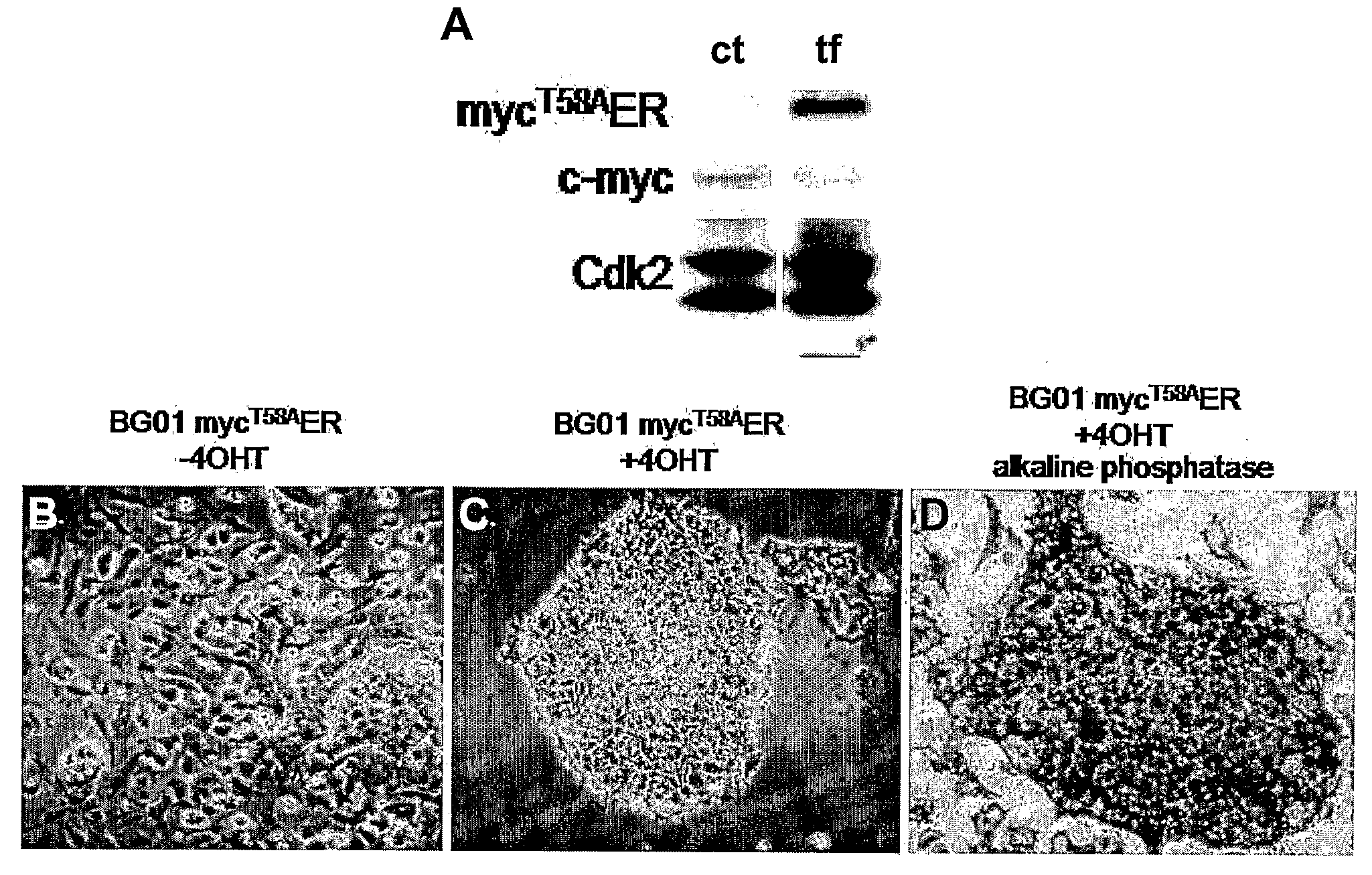
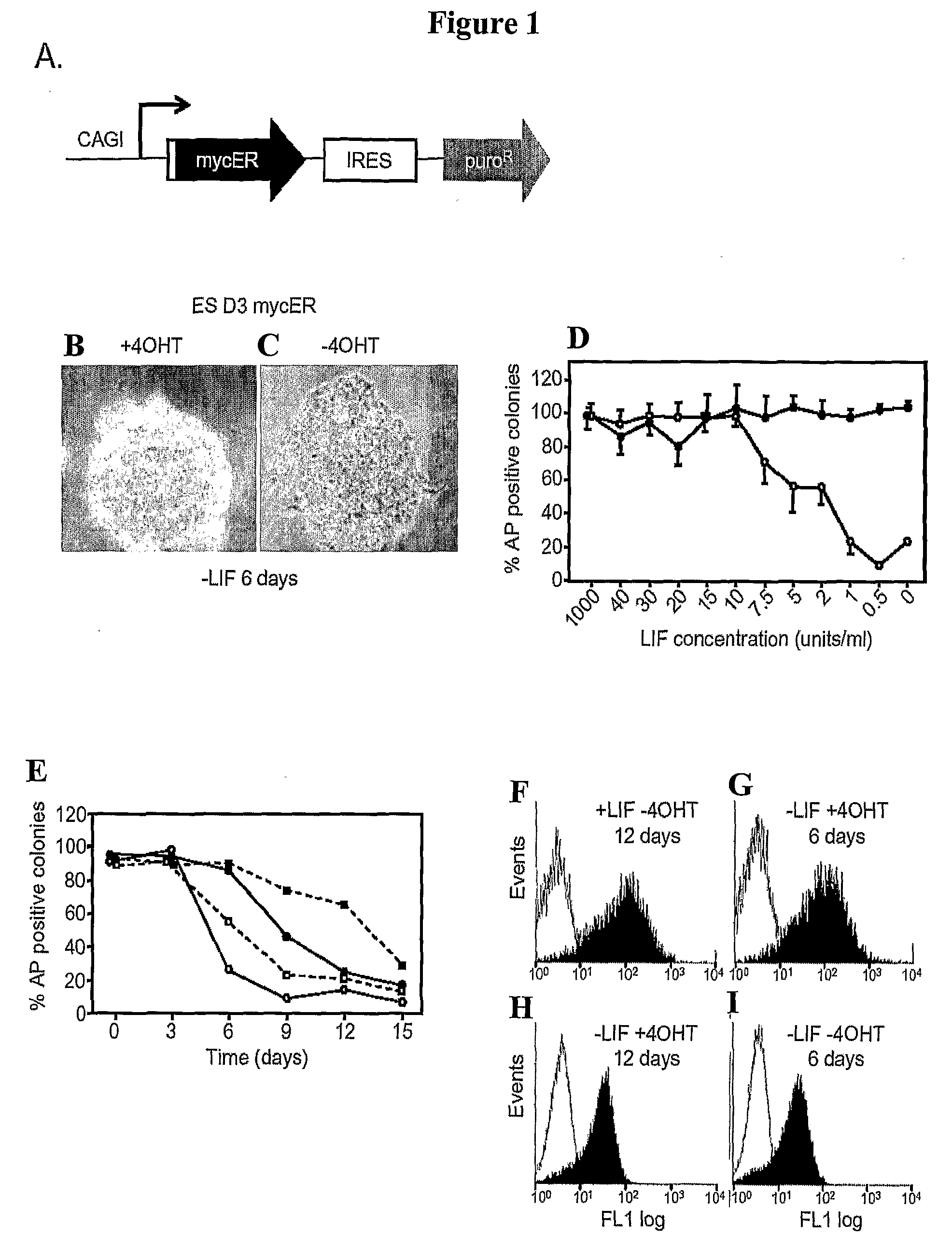
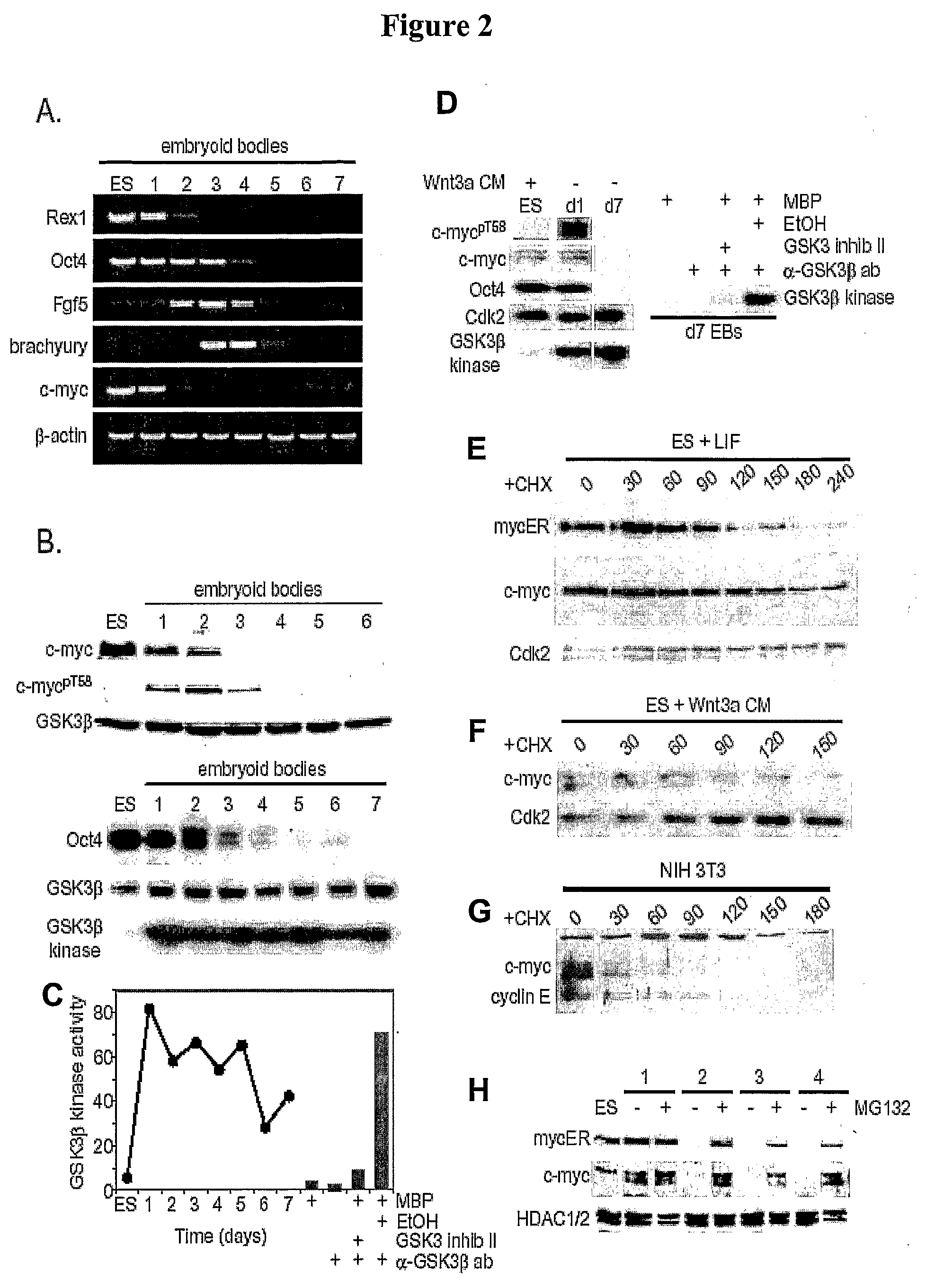
Methods and Compositions Utilizing Myc and Gsk3Beta to Manipulate the Pluripotency of Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20080268533A1Process stabilityReduce phosphorylationArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsMyc proteinsBiological activation
The present invention provides methods for stabilizing pluripotent cells through the transcriptional activation of c-myc. Alternatively, the cells are stabilized through the transcriptional activation of c-myc, and the stabilization of c-myc protein levels. c-myc protein can be stabilized through the inhibition of GSK3β or through other components of the cellular machinery that impact on c-myc stability. The invention contemplates the stabilized pluripotent cells produced using the methods described herein. Methods for the identification of compounds that modulate the stabilization of pluripotent cells through modulating transcriptional activation of c-myc, stabilization of c-myc protein levels, and / or inhibition of GSK3β activity are also contemplated.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158852A1Improve breeding conditionsImprove survival rateGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixIn vitro growth
The present invention discloses a method for improving growth and survival of single human embryonic stem cells. The method includes the step of obtaining a single undifferentiated HES cell; mixing the single undifferentiated cell with an extracellular matrix (ECM) to encompass the cell; and inoculating the mixture onto feeder cells with a nutrient medium in a growth environment. Therefore the single cells can survive, proliferate and grow in vitro.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Conditionally immortalized long-term stem cells and methods of making and using such cells
ActiveUS20070116691A1Inhibit apoptosisPromotes proliferationVirusesGenetic material ingredientsMyeloid leukemiaStudy methods
Disclosed are methods for conditionally immortalizing stem cells, including adult and embryonic stem cells, the cells produced by such methods, therapeutic and laboratory or research methods of using such cells, and methods to identify compounds related to cell differentiation and development or to treat diseases, using such cells. A mouse model of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and cells and methods related to such mouse model are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Culture of stem cells
ActiveUS20080171385A1Improve cloning efficiencyEconomical and effectiveArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsAnimal productStem cell culture
While culture medium and systems have been described that permit the culture and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells in feeder free and animal product free conditions, these conditions will not readily support cloning of an embryonic stem cell culture meaning, at least here, the initiation of a sub-culture using one or a very few originating cells. It has been found here that a class of small molecules that are inhibitors of kinase enzymes will increase the efficiency of cloning of stem cell cultures sufficiently to make such cloning practical in the defined medium and in other media as well.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
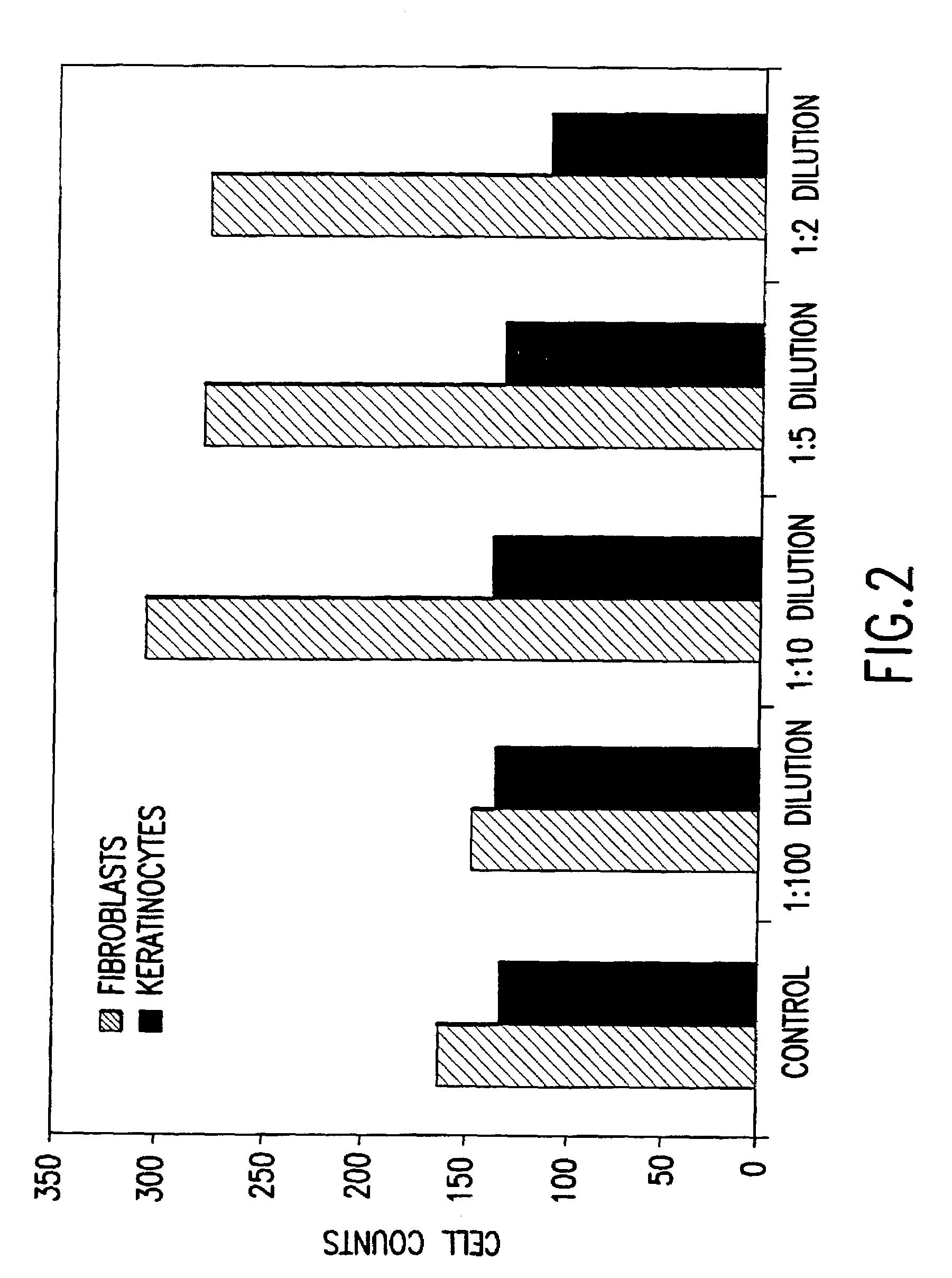
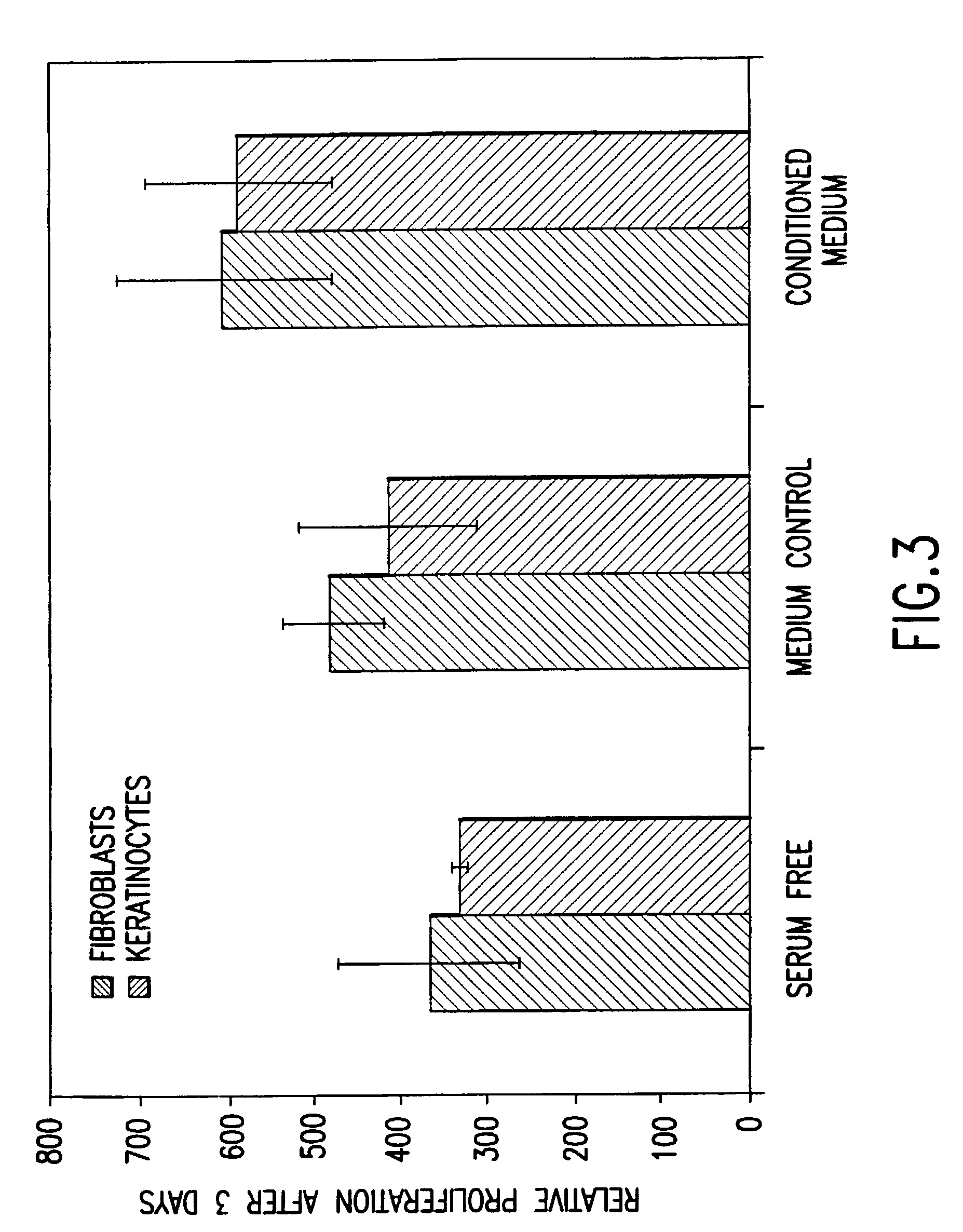
Conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS7118746B1Eliminate wrinkles, frown lines, scarringCondition the skinOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsReserve CellCell culture media
Novel products comprising conditioned cell culture medium compositions and methods of use are described. The conditioned cell medium compositions of the invention may be comprised of any known defined or undefined medium and may be conditioned using any eukaryotic cell type. The medium may be conditioned by stromal cells, parenchymal cells, mesenchymal stem cells, liver reserve cells, neural stem cells, pancreatic stem cells and / or embryonic stem cells. Additionally, the cells may be genetically modified. A three-dimensional tissue construct is preferred. Once the cell medium of the invention is conditioned, it may be used in any state. Physical embodiments of the conditioned medium include, but are not limited to, liquid or solid, frozen, lyophilized or dried into a powder. Additionally, the medium is formulated with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier as a vehicle for internal administration, applied directly to a food item or product, formulated with a salve or ointment for topical applications, or, for example, made into or added to surgical glue to accelerate healing of sutures following invasive procedures. Also, the medium may be further processed to concentrate or reduce one or more factors or components contained within the medium.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
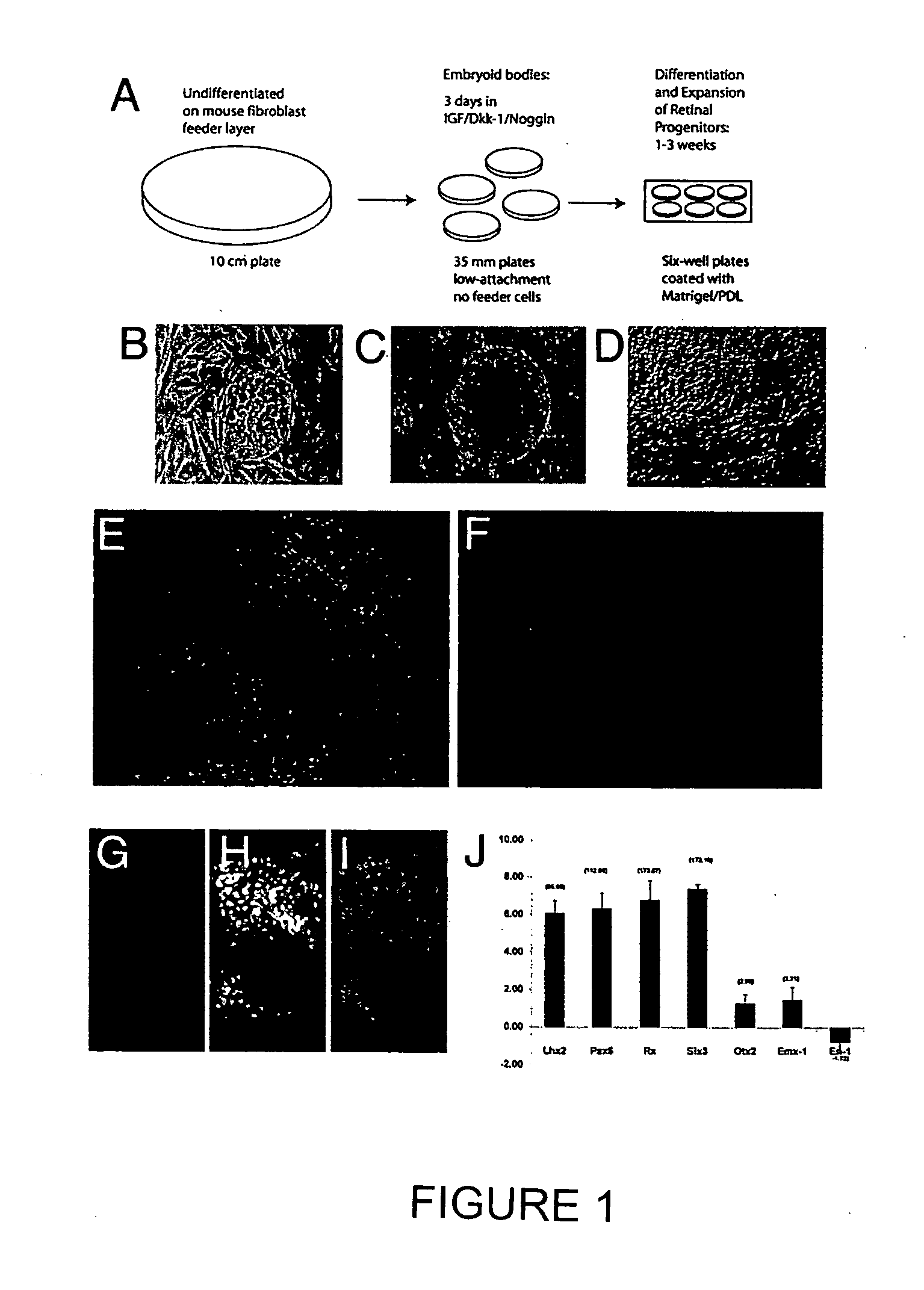
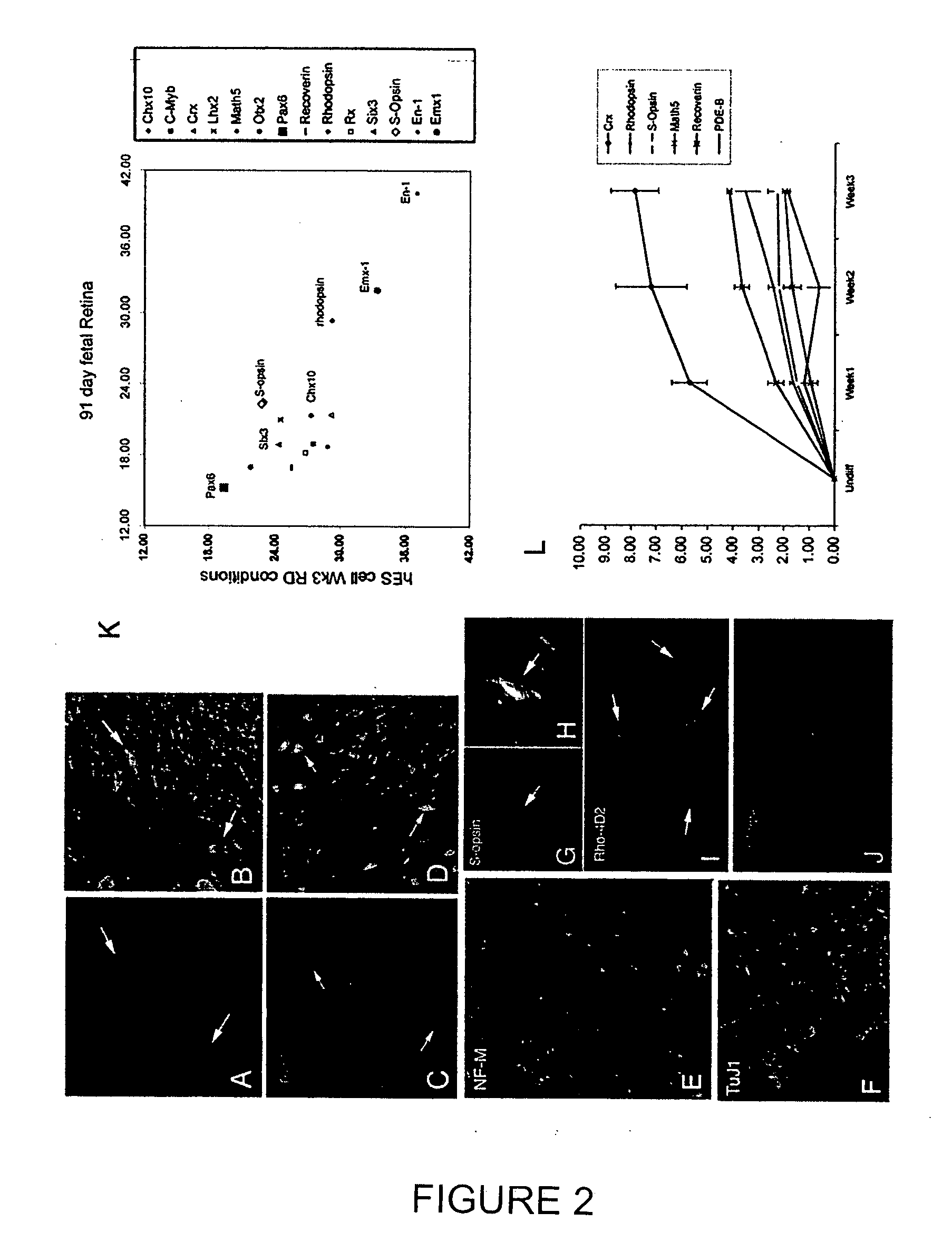
Method of generating human retinal progenitors from embryonic stem cells
Methods are provided for the in vitro differentiation of human retinal progenitor cells from embryonic stem cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Tissue matrices comprising placental stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
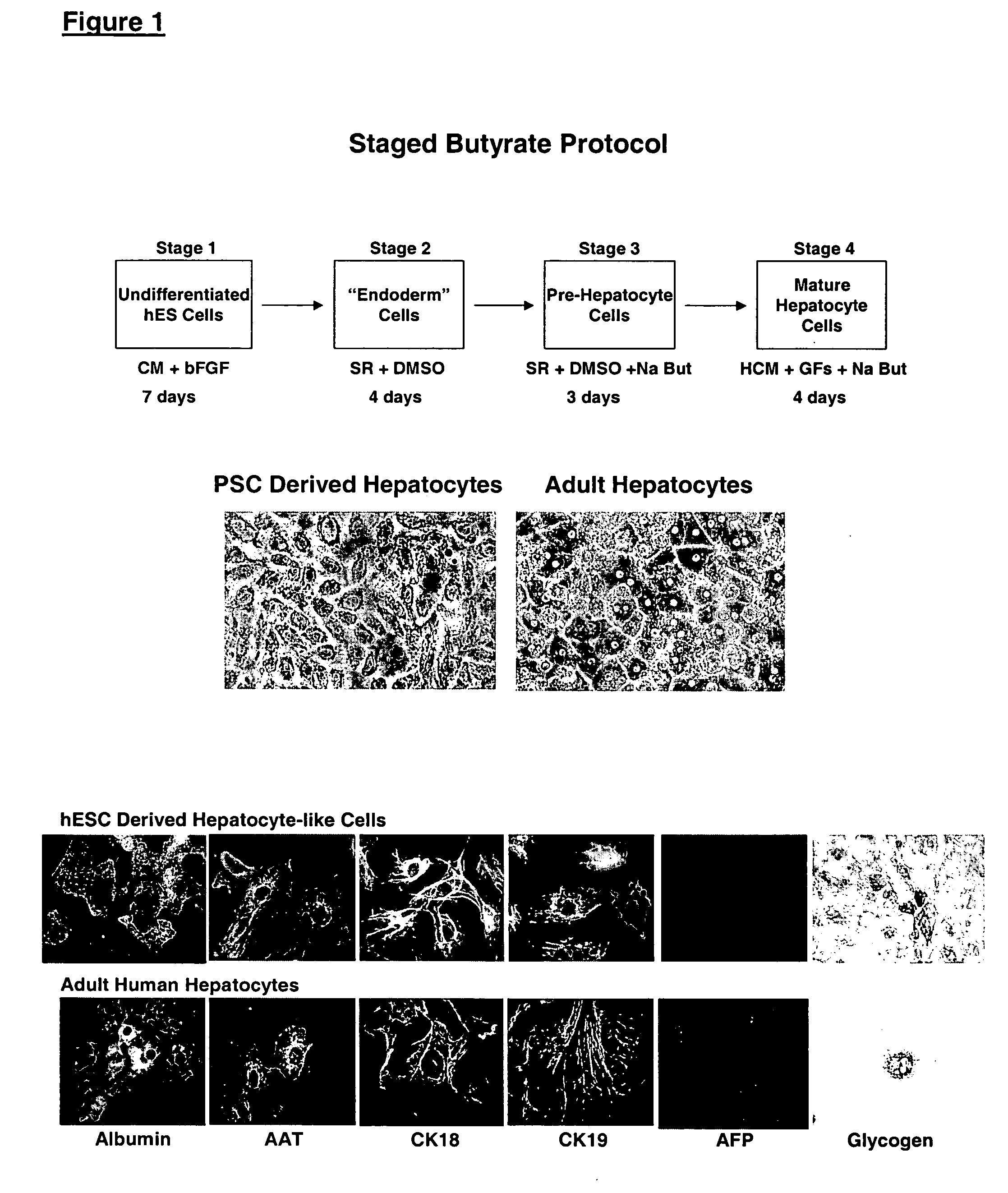
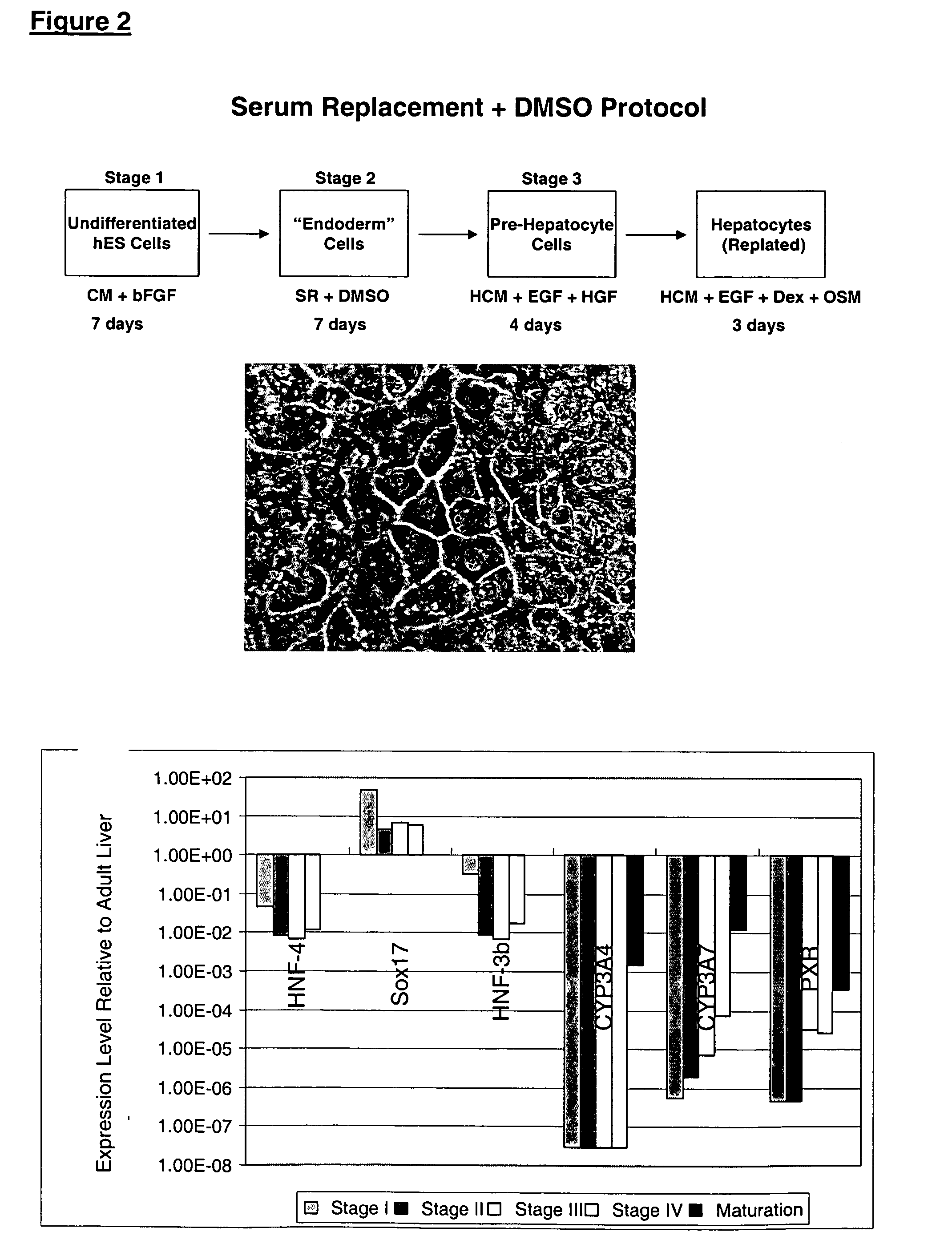
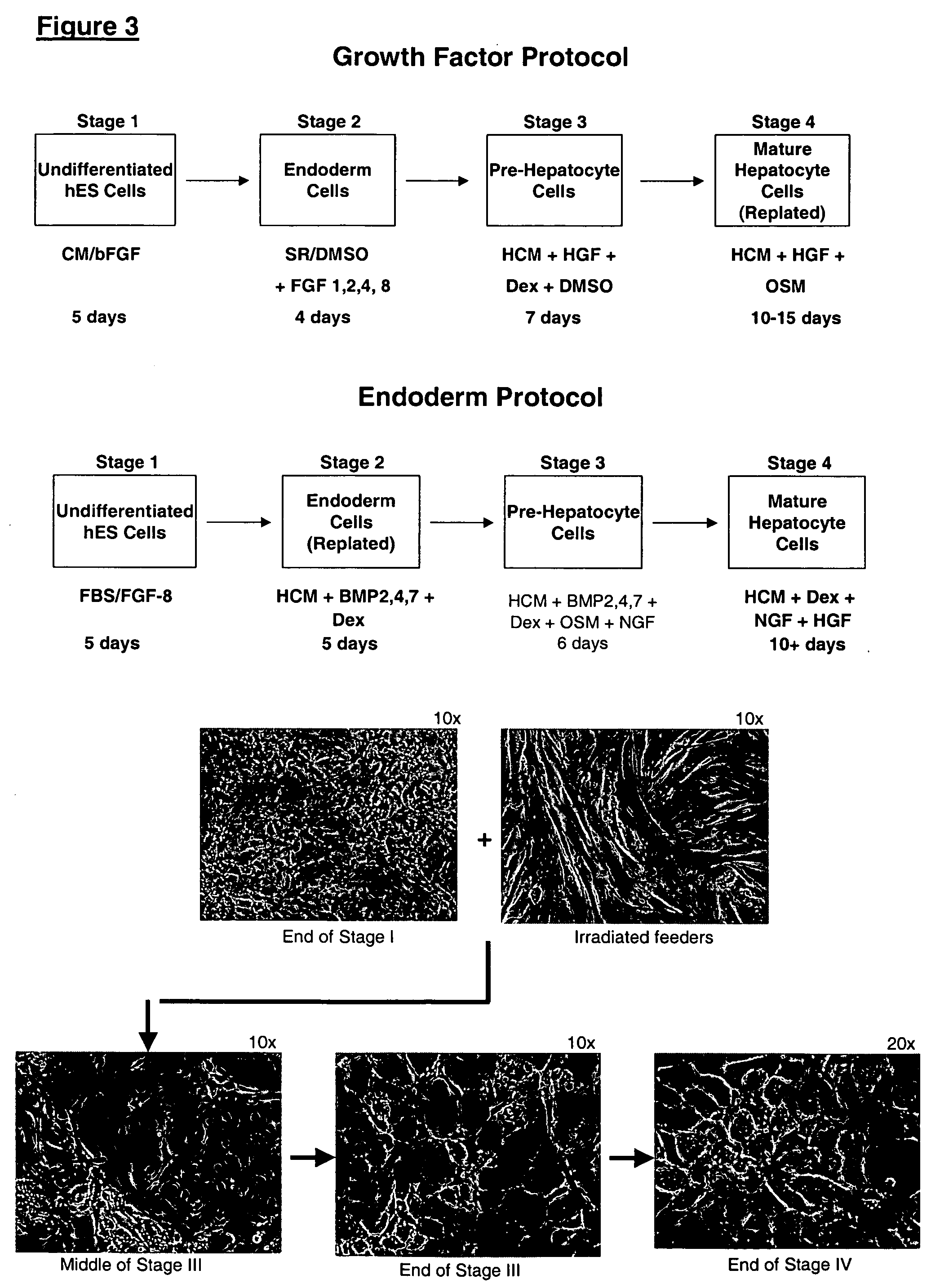
Protocols for making hepatocytes from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050037493A1Promote cell differentiationCulture processDrug screeningGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides a newly developed strategy and particular options for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the hepatocyte lineage. Many of the protocols are based on a strategy in which the cells are first differentiated into early germ layer cells, then into hepatocyte precursors, and then into mature cells. The cells obtained have morphological features and phenotypic markers characteristic of human adult hepatocytes. They also show evidence of cytochrome p450 enzyme activity, validating their utility for commercial applications such as drug screening, or use in the manufacture of medicaments and medical devices for clinical therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Stem cell aggregate suspension compositions and methods of differentiation thereof
The present invention relates to methods for production of undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell aggregate suspension cultures from undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell single cell suspensions and methods of differentiation thereof.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Culturing human embryonic stem cells
Previous methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells have required either fibroblast feeder cells or a medium which has been exposed to fibroblast feeder cells in order to maintain the stem cells in an undifferentiated state. It has now been found that if high levels of fibroblast growth factor are used in a medium with gamma amino butyric acid, pipecholic acid, lithium and lipids, the stem cells will remain undifferentiated indefinitely through multiple passages, even without feeder cells or conditioned medium. A humanized matrix of human proteins can be used as a basement matrix to culture the cells. New lines of human embryonic stem cells made using these culture conditions, the medium and the matrix, will never have been exposed to animal cells, animal products, feeder cells or conditioned medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Directed differentiation of embryonic cells
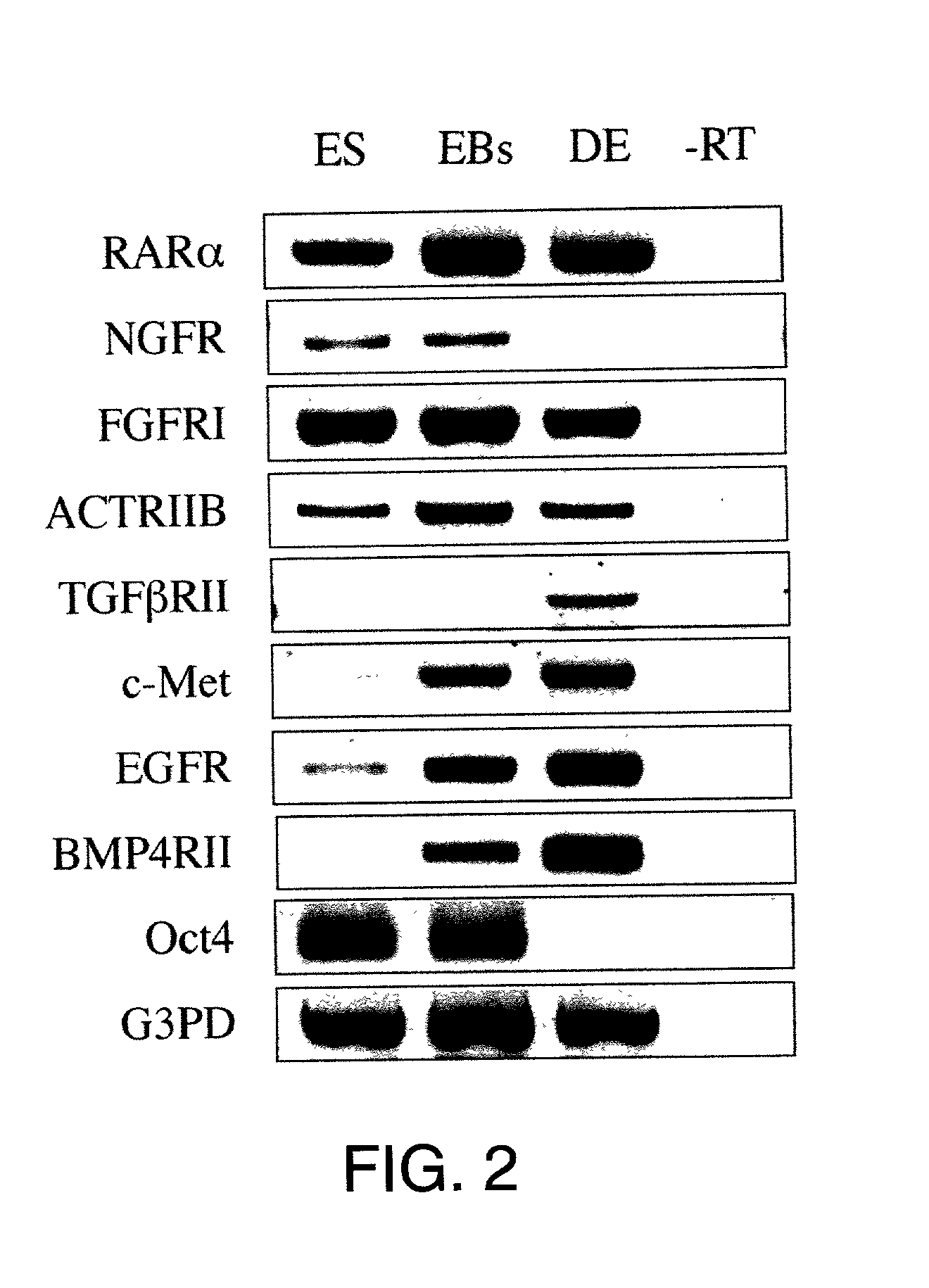
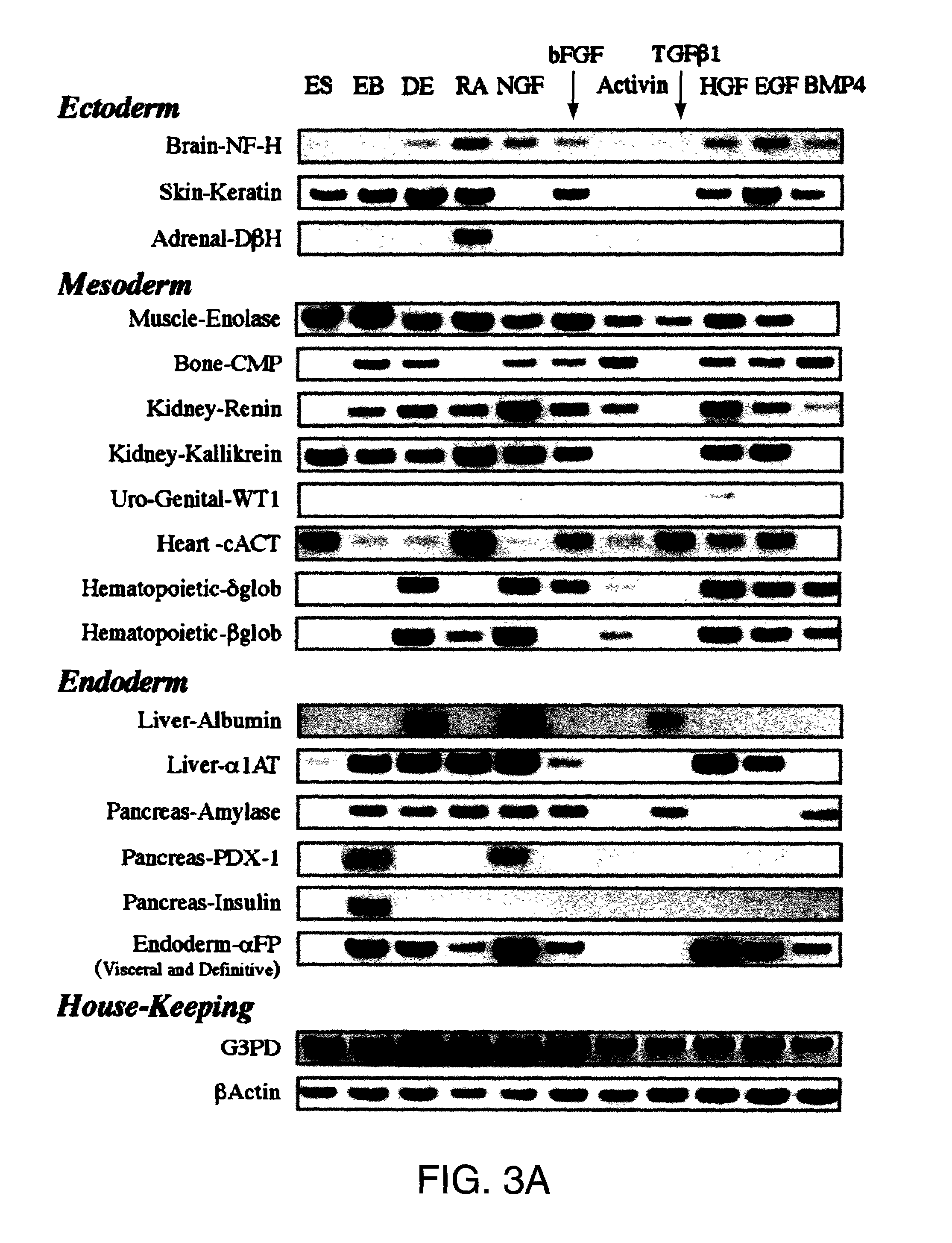
Methods are described for mapping a pathway of differentiation of a population of embryonic cells which includes exposing the cells to an exogenous factor and measuring gene expression products that are characteristic of a particular cell type or lineage. Directing differentiation of human embryonic cells relies on dissociated embryoid bodies which are then exposed to one or more exogenous factors to enrich a culture for a particular cell type. The differentiated cells may be used for treating a medical condition in a human. Kits for determining differentiation pathways and screening exogenous factors for their utility in differentiation are provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Cultured human pancreatic islets, and uses thereof
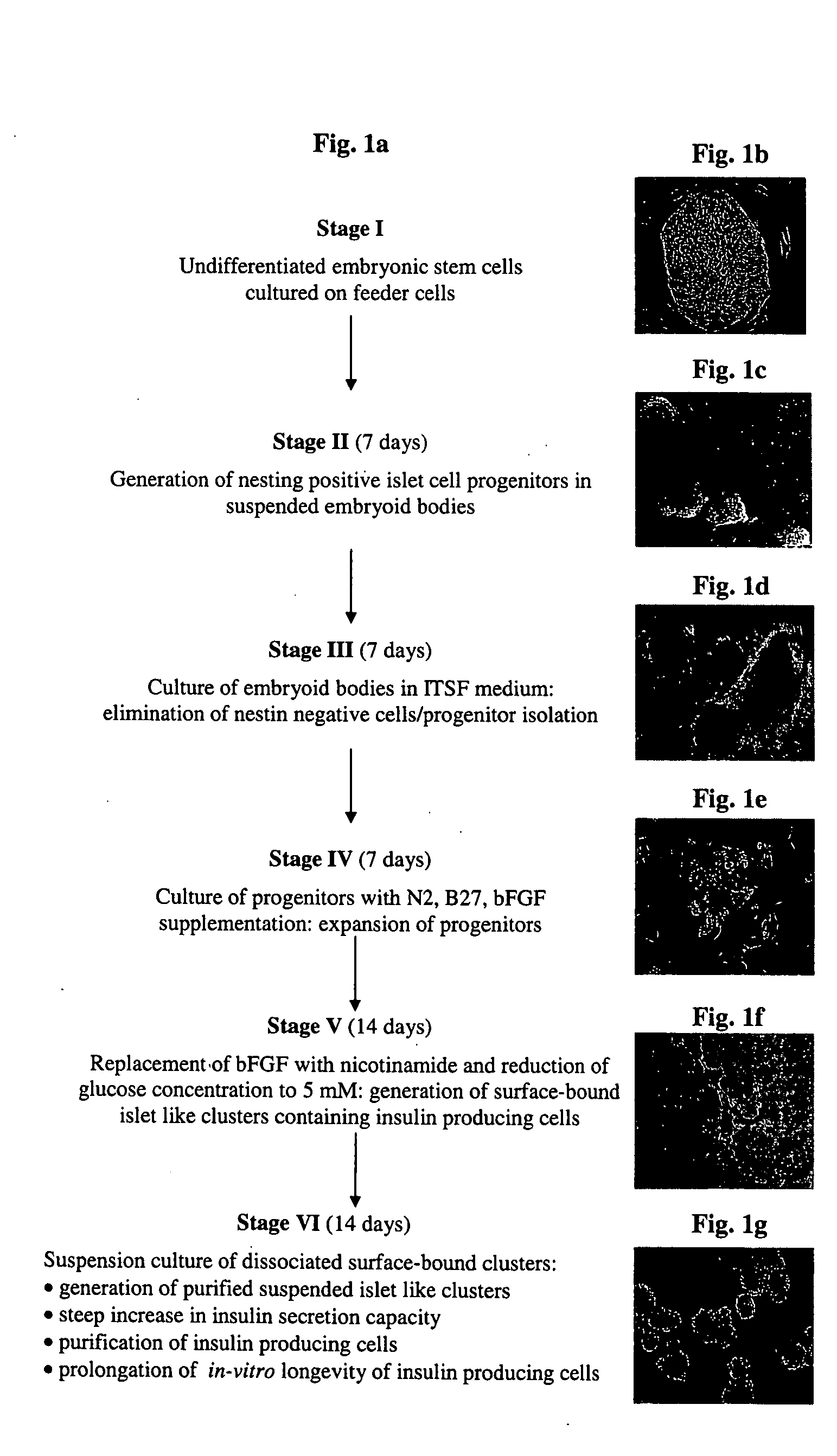
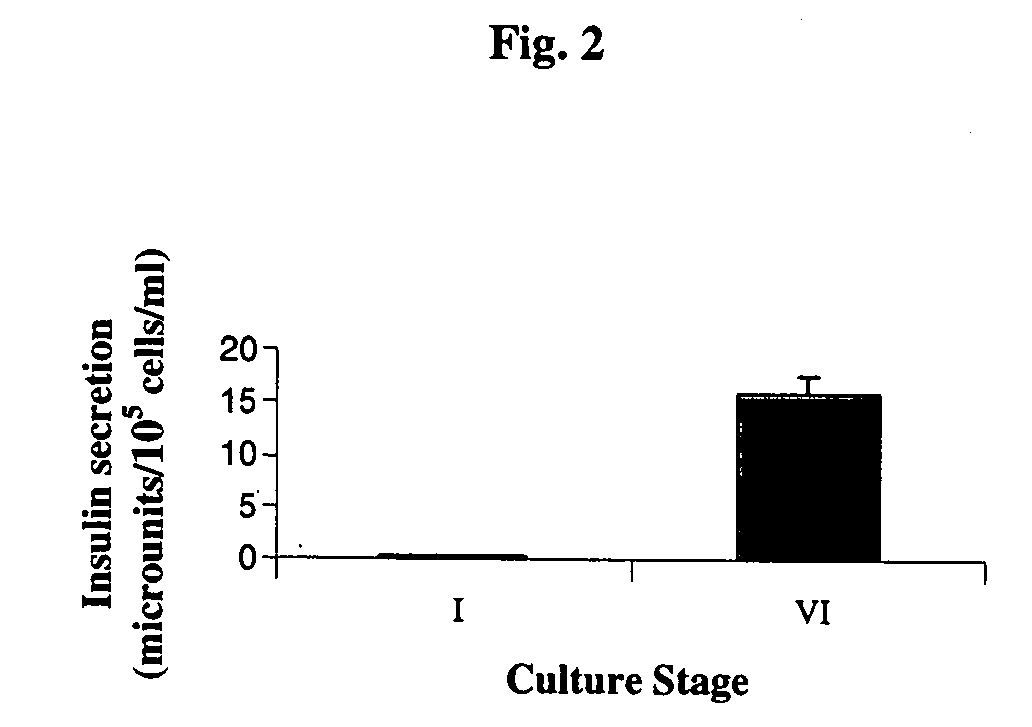
A method of generating cells capable of secreting insulin is disclosed. The method comprises subjecting mammalian embryonic stem cells to set of culturing conditions suitable for differentiation of at least a portion thereof into cells displaying at least one characteristic associated with a pancreatic islet cell progenitor phenotype, and subjecting such differentiated cells to a set of culturing conditions suitable for formation of surface bound cell clusters including insulin producing cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
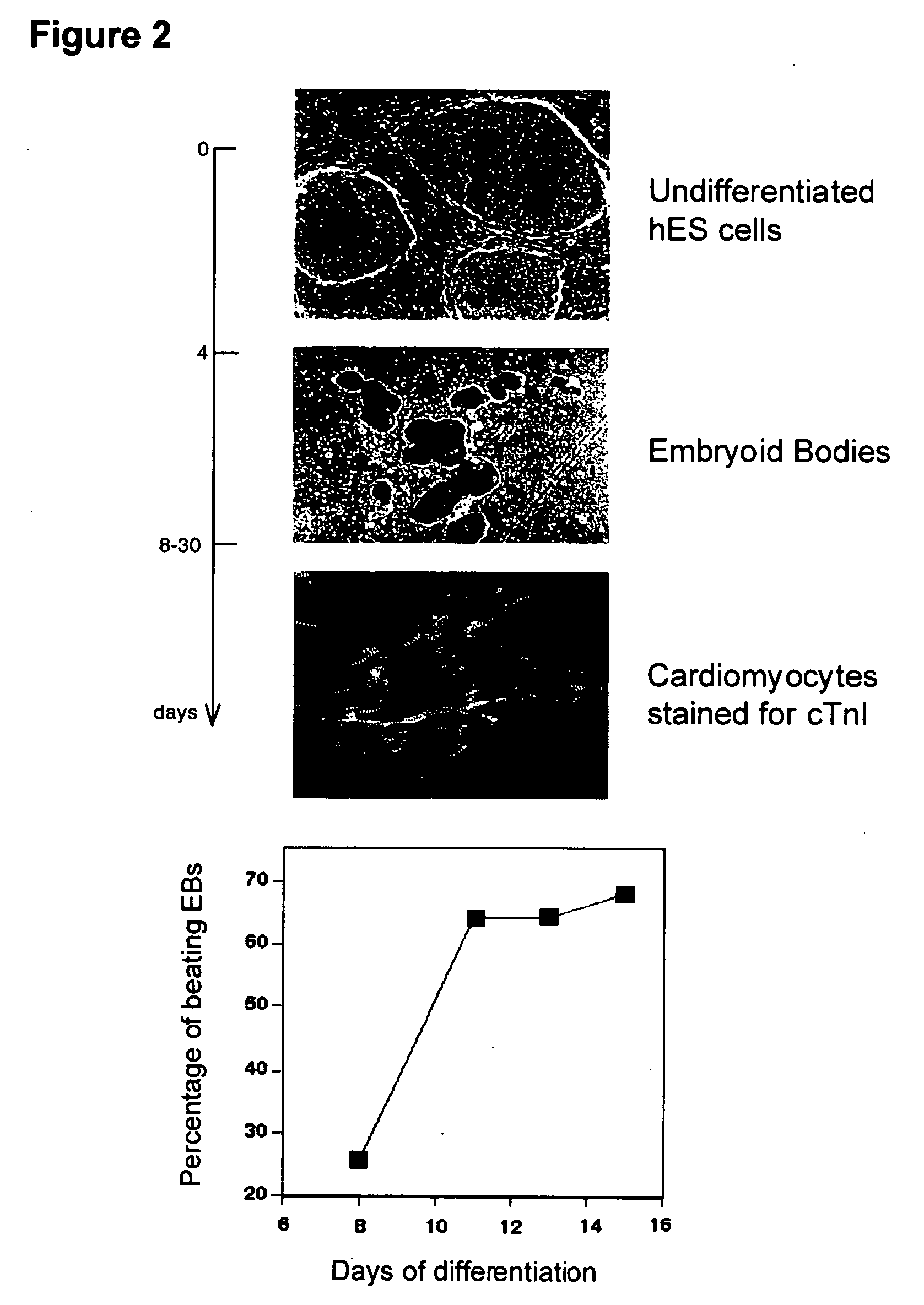
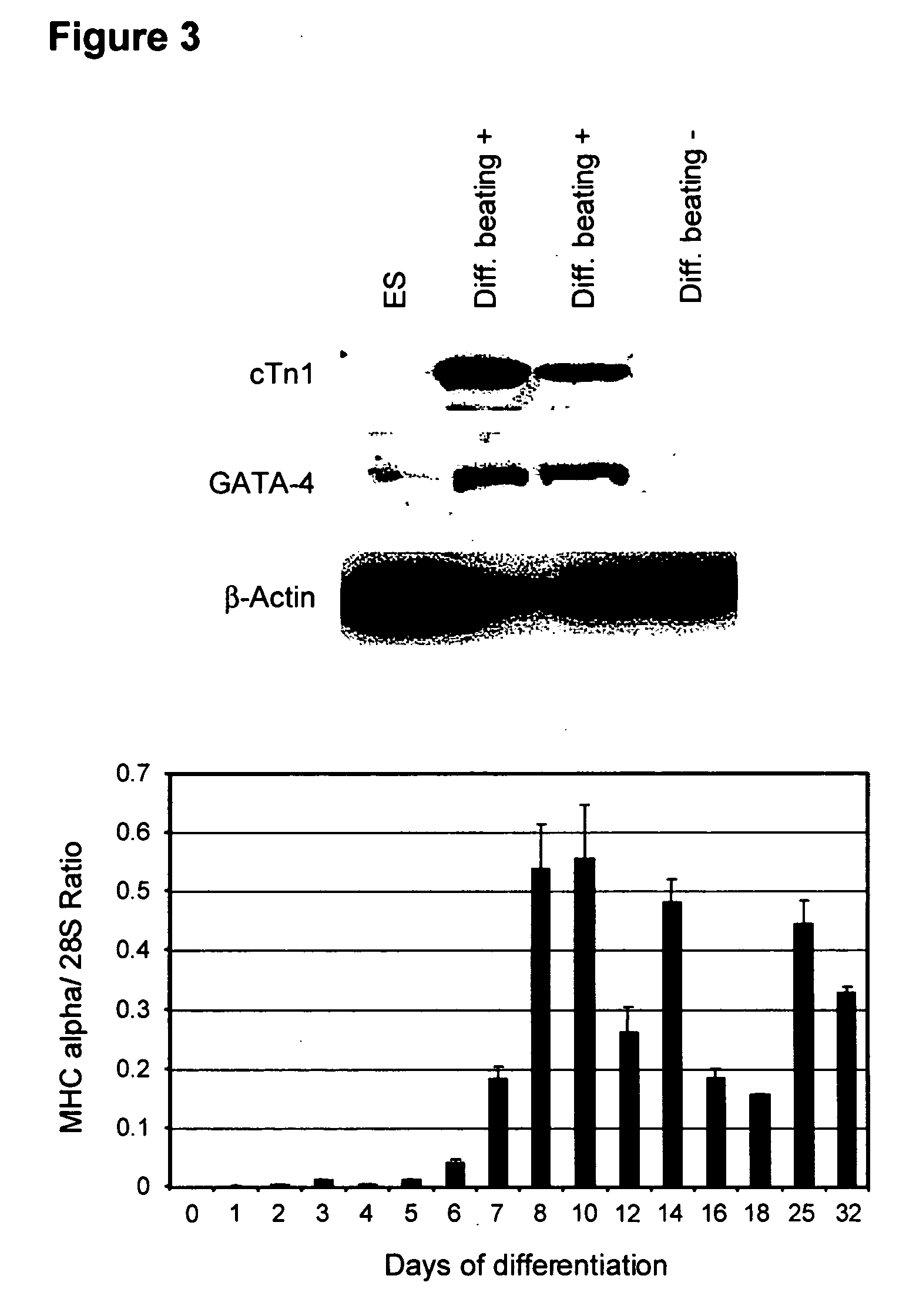
Process for making transplantable cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050054092A1Efficient productionGenetically modified cellsDrug screeningDiseaseHuman cell
This invention provides populations human cells of the cardiomyocyte lineage. The cells are obtained by causing cultures of pluripotent stem cells to differentiate in vitro, and then harvesting cells with certain phenotypic features. Differentiated cells bear cell surface and morphologic markers characteristic of cardiomyocytes, and a proportion of them undergo spontaneous periodic contraction. Highly enriched populations of cardiomyocytes and their replicating precursors can be obtained, suitable for use in a variety of applications, such as drug screening and therapy for cardiac disease.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions related to modulating the extracellular stem cell environment
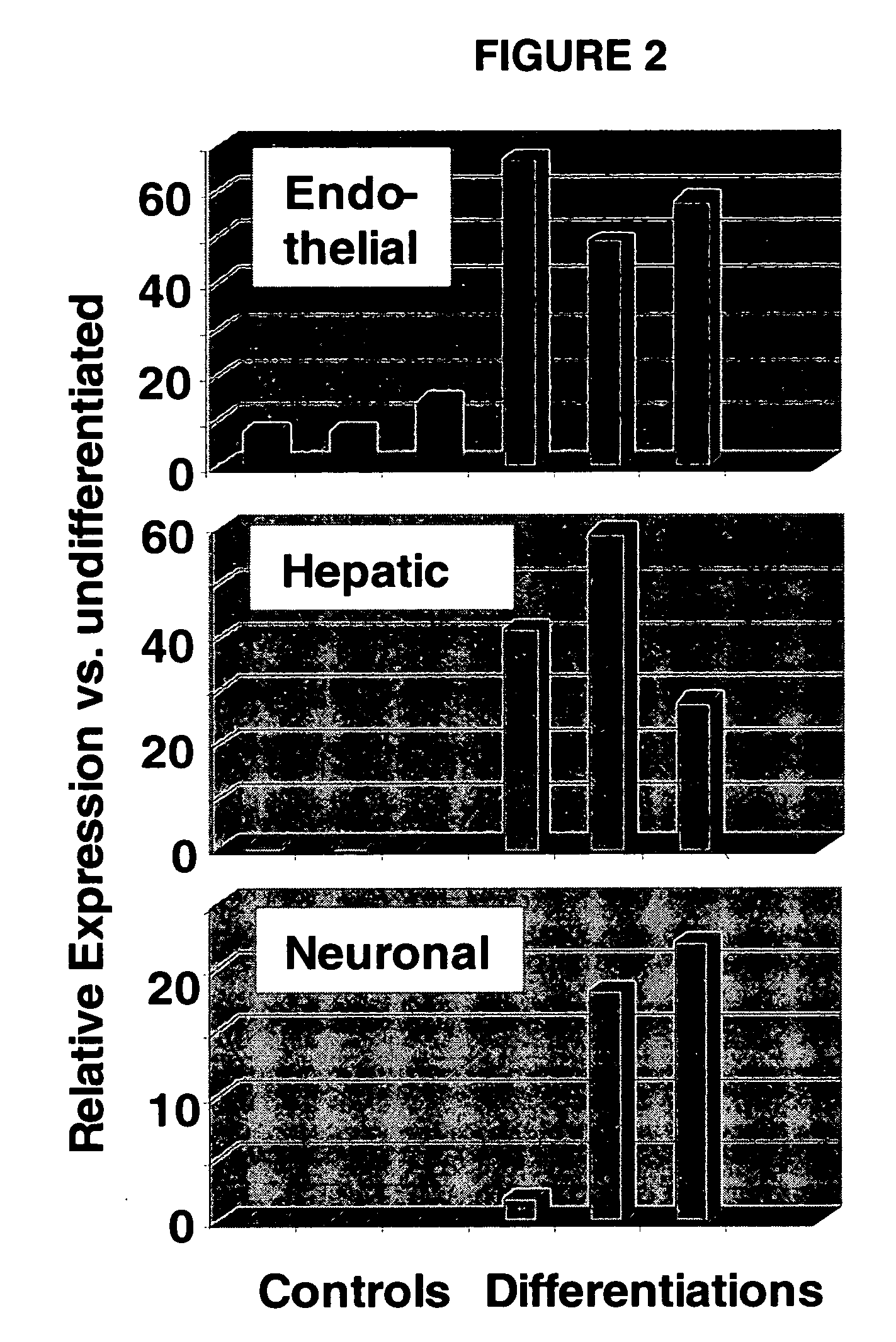
This invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions that modulate the stem cell environment. More specifically, the invention relates, in part, to methods and compositions for modulating stem cell differentiation. Such modulation, in some aspects of the invention, is accomplished by agents that modulate glycosaminoglycans in the stem cell microenvironment (i.e., at or on the cell surface and / or in the extracellular matrix). Therefore, methods and compositions are provide for modulating glycosaminoglycan moieties, e.g., heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (HSGAG) moieties, in the microenvironment of stem cells. Methods and compositions for promoting or inhibiting embryonic stem cell differentiation (e.g., differentiation into endothelial cells) are also provided. This invention also relates, therefore, in part, to cell populations (e.g., endothelial cell populations or impoverished endothelial cell populations) that can be produced with the methods and compositions provided. Furthermore, the invention relates, in part, to tissues, and uses thereof, formed by the methods and compositions provided. Moreover, the invention also relates, in part, to methods of treatment using the methods and compositions provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods of culturing embryonic stem cells and controlled differentiation
InactiveUS7112437B2Enhance cell survivalPromote growthNervous system cellsDead animal preservationDirected differentiationEmbryo
The present invention provides a preparation of undifferentiated embryonic stem (ES) cells sustainable for a prolonged period in an undifferentiated state which will undergo stem cell renewal or somatic differentiation. Preferably the cells are capable of somatic differentiation in vitro and are inclined to differentiate away from an extraembryonic lineage. The present invention also provides method of culturing embryonic stem (ES) cells to improve stem cell maintenance and persistence in culture. The method also provides a culture of ES cells prepared by the method as well as differentiated cells derived from the embryonic cells resulting from directed differentiation procedures provided by the present invention.
Owner:SINGAPORE NAT UNIV OF +1
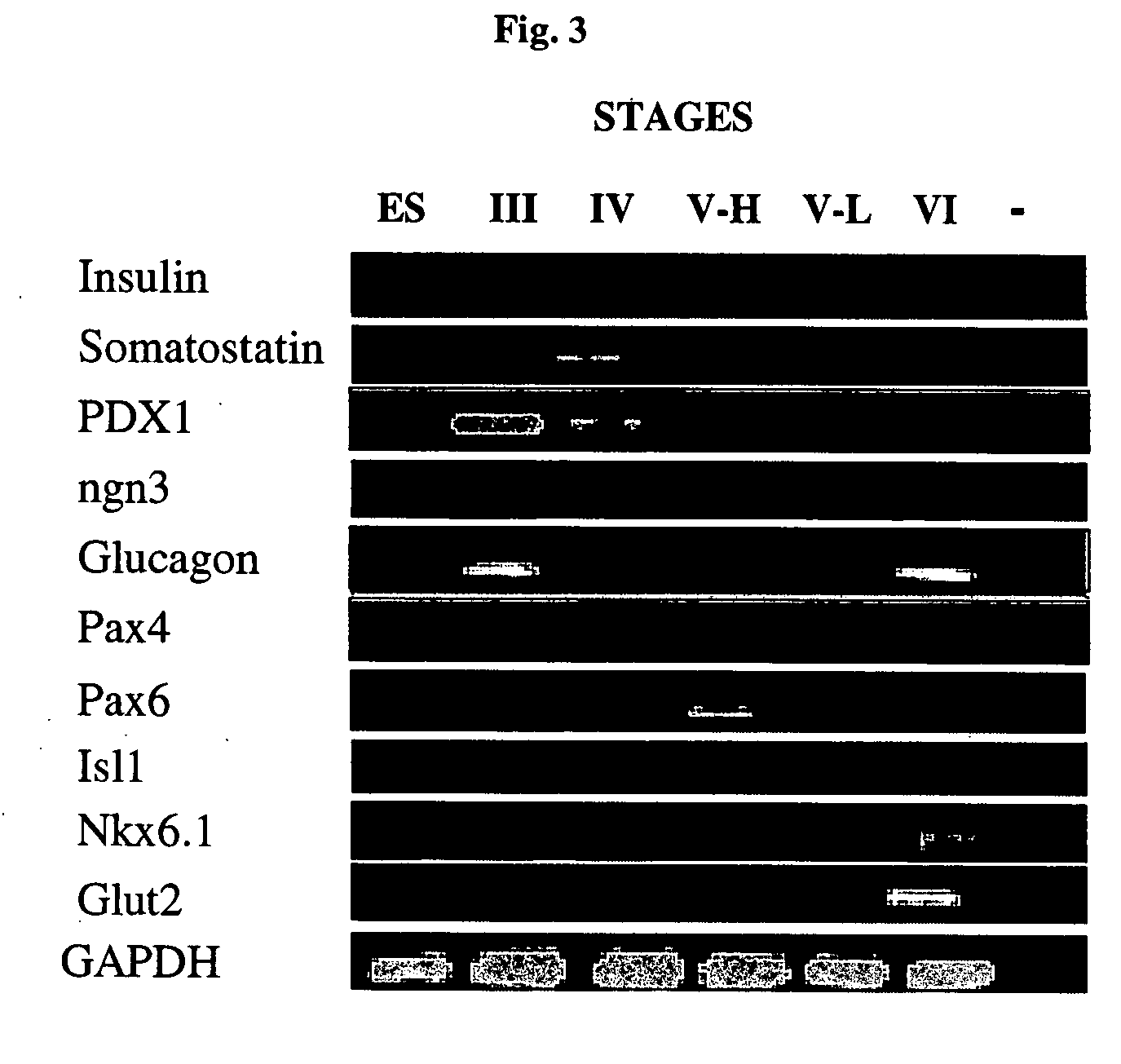
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20110151561A1High expressionPancreatic cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPluripotential stem cellIntracrine
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into insulin producing cells. In particular, the present invention provides a method to increase the expression of NGN3 and NKX6.1 in populations of cells expressing markers characteristic of the pancreatic endocrine lineage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Media for culturing stem cells
Well-defined, xeno-free culture media which comprise a TGF-beta isoform or the chimera formed between IL6 and the soluble IL6 receptor (IL6RIL6), which are capable of maintaining stem cells, and particularly, human embryonic stem cells, in an undifferentiated state are provided. Also provided are cell cultures comprising the culture media and the stem cells and methods of expanding and deriving embryonic stem cells in such well-defined, xeno-free culture media. In addition, the present invention provides methods of differentiating ESCs or EBs formed therefrom for the generation of lineage specific cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com