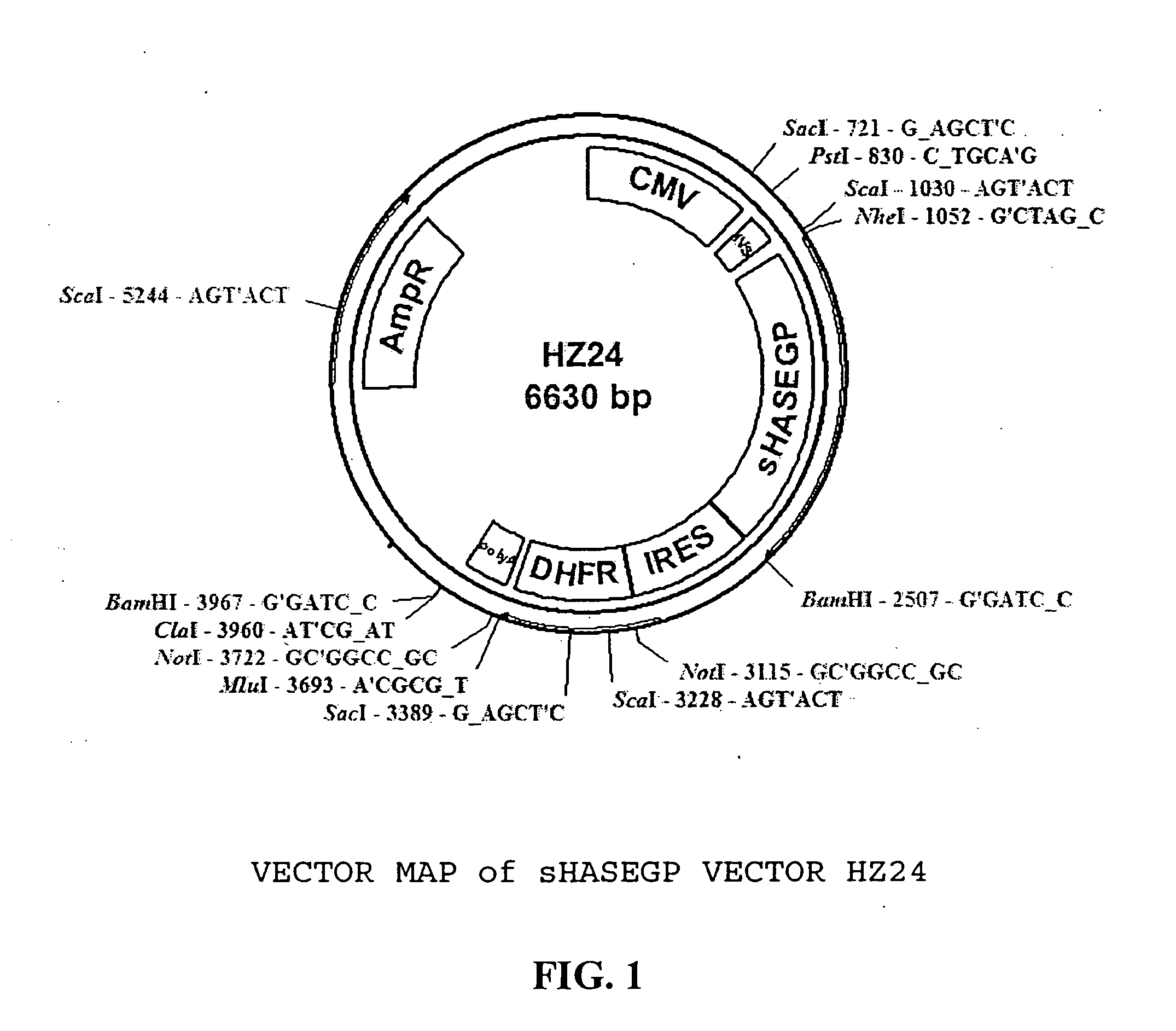
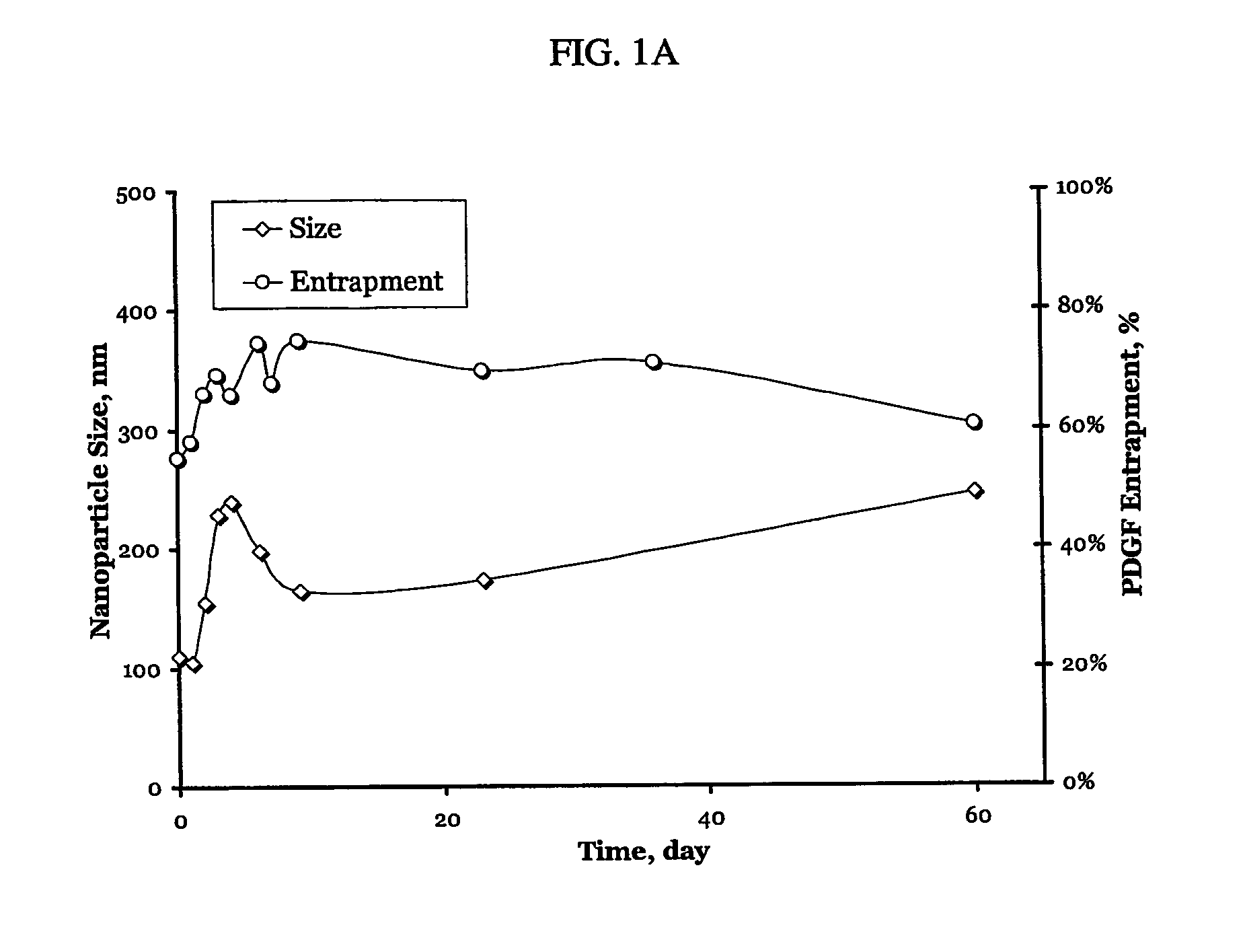
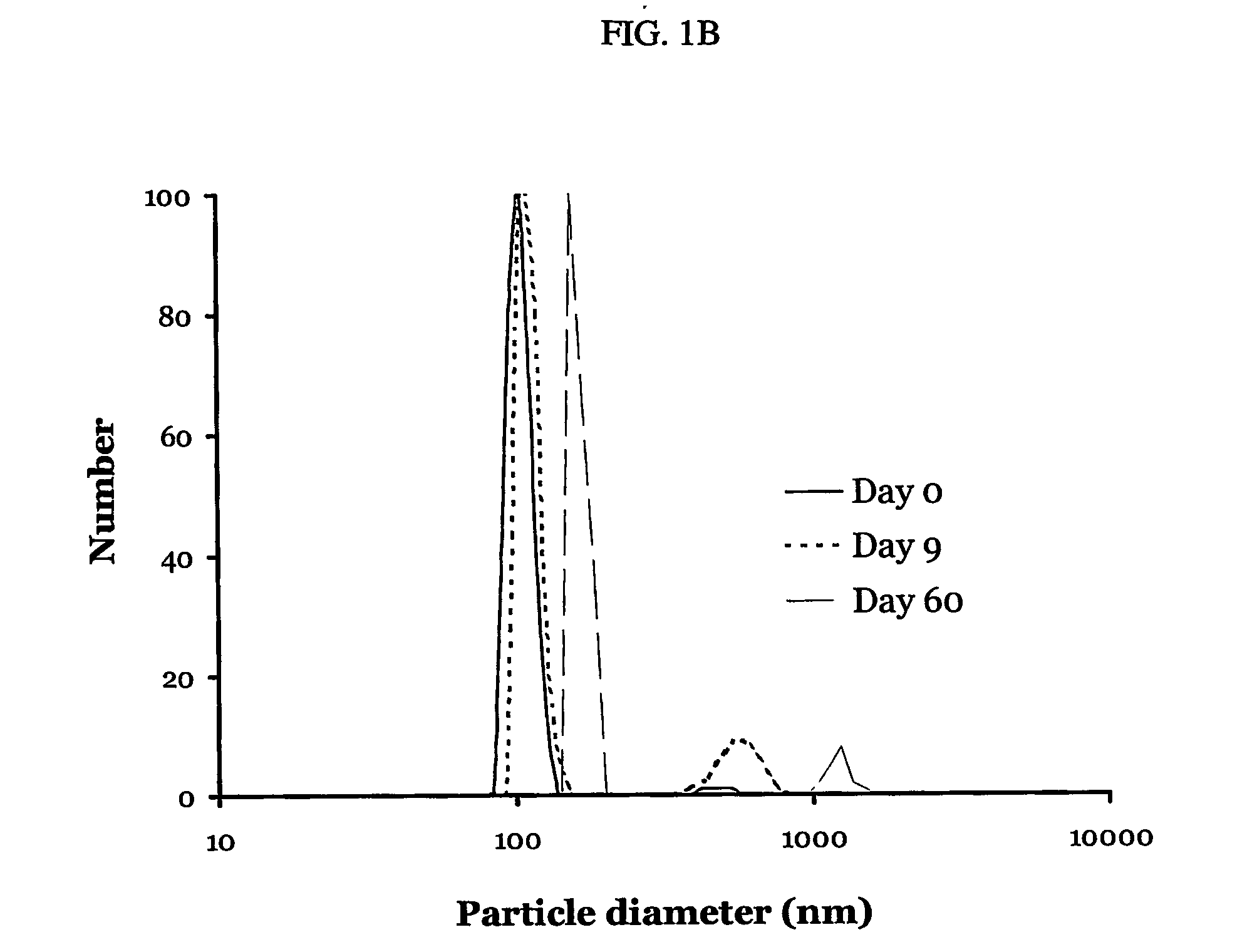
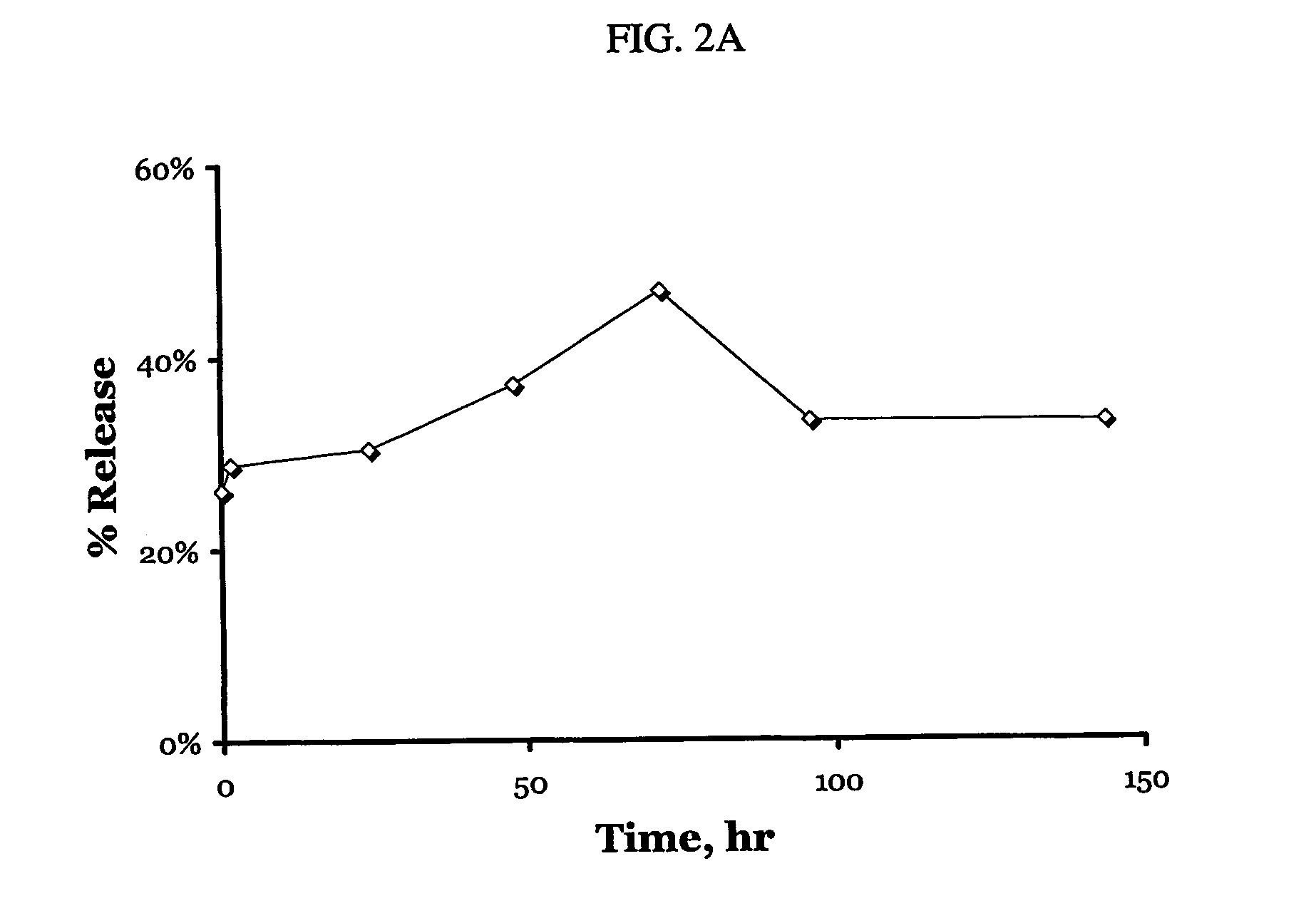
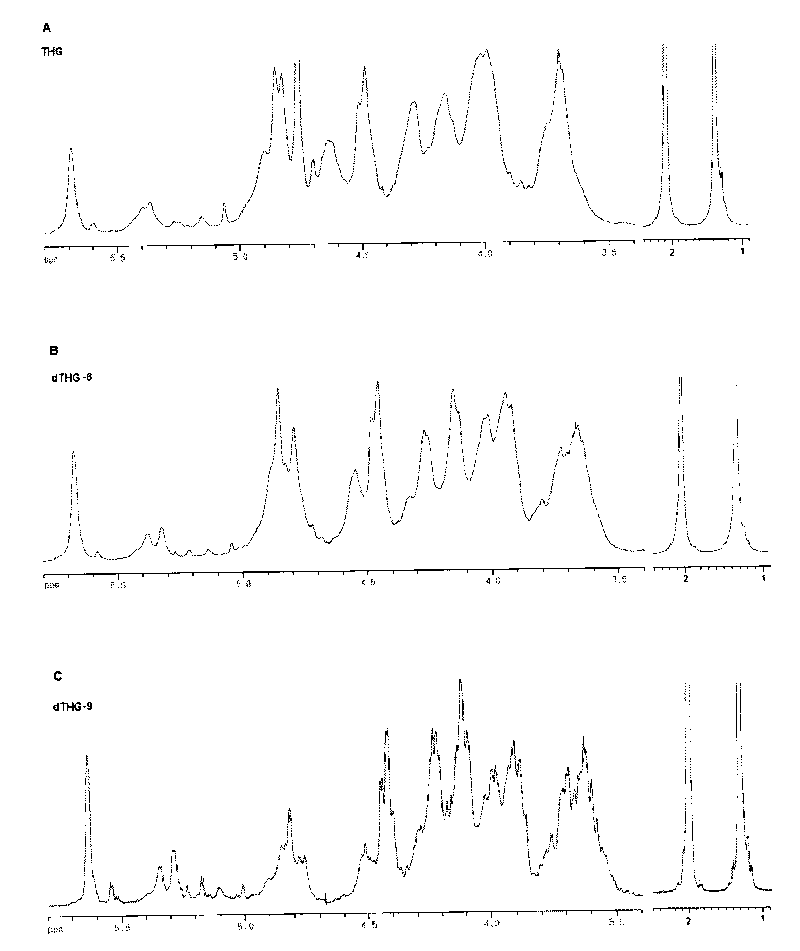
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
554 results about "Glycosaminoglycan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
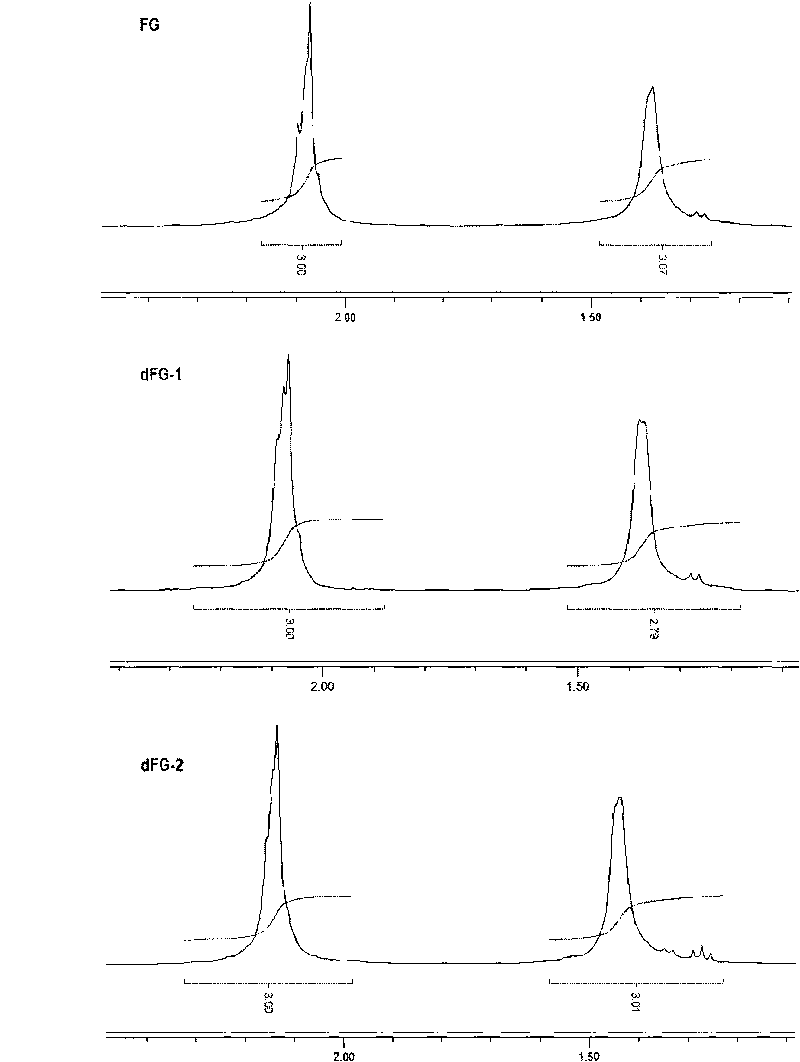
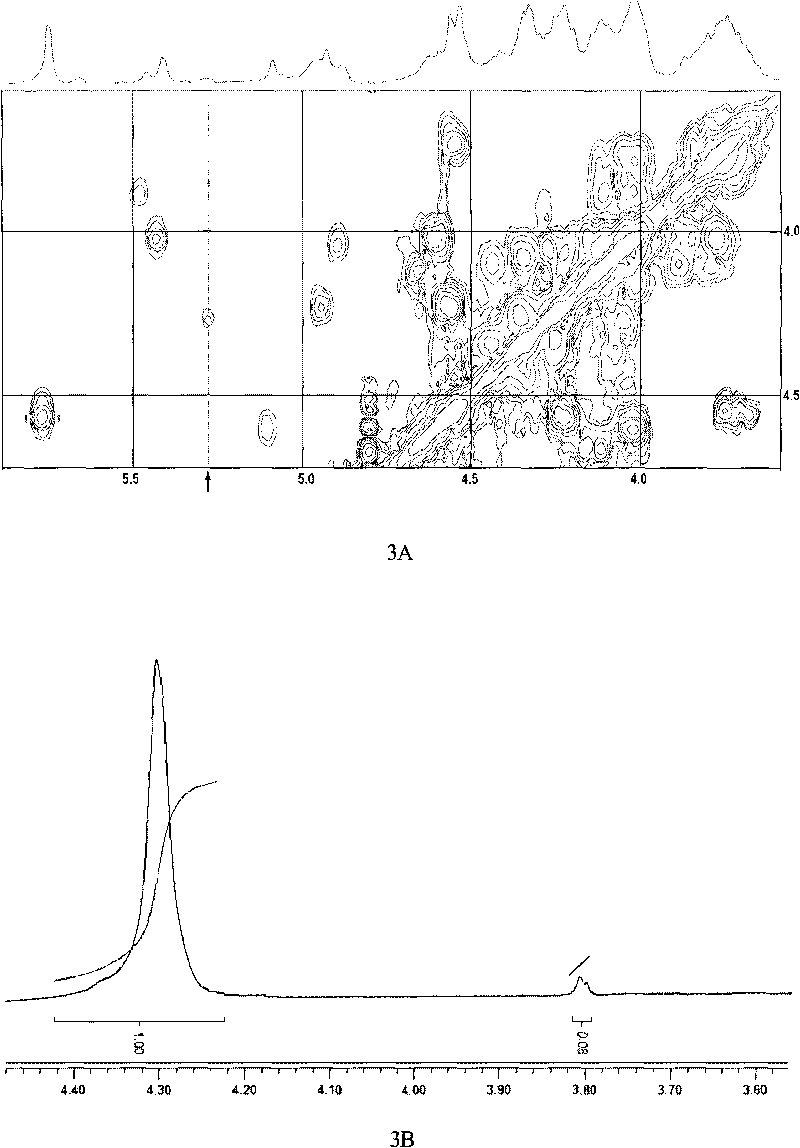
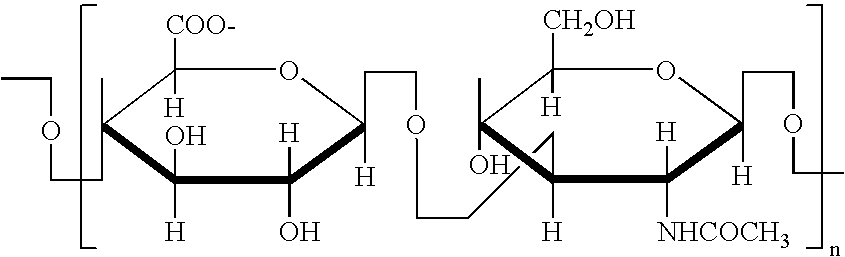
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long linear (unbranched) polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide (double sugar) units. The repeating unit (except for keratan) consists of an amino sugar (N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine) along with a uronic sugar (glucuronic acid or iduronic acid) or galactose. Glycosaminoglycans are highly polar and attract water; they are therefore useful to the body as a lubricant or as a shock absorber.
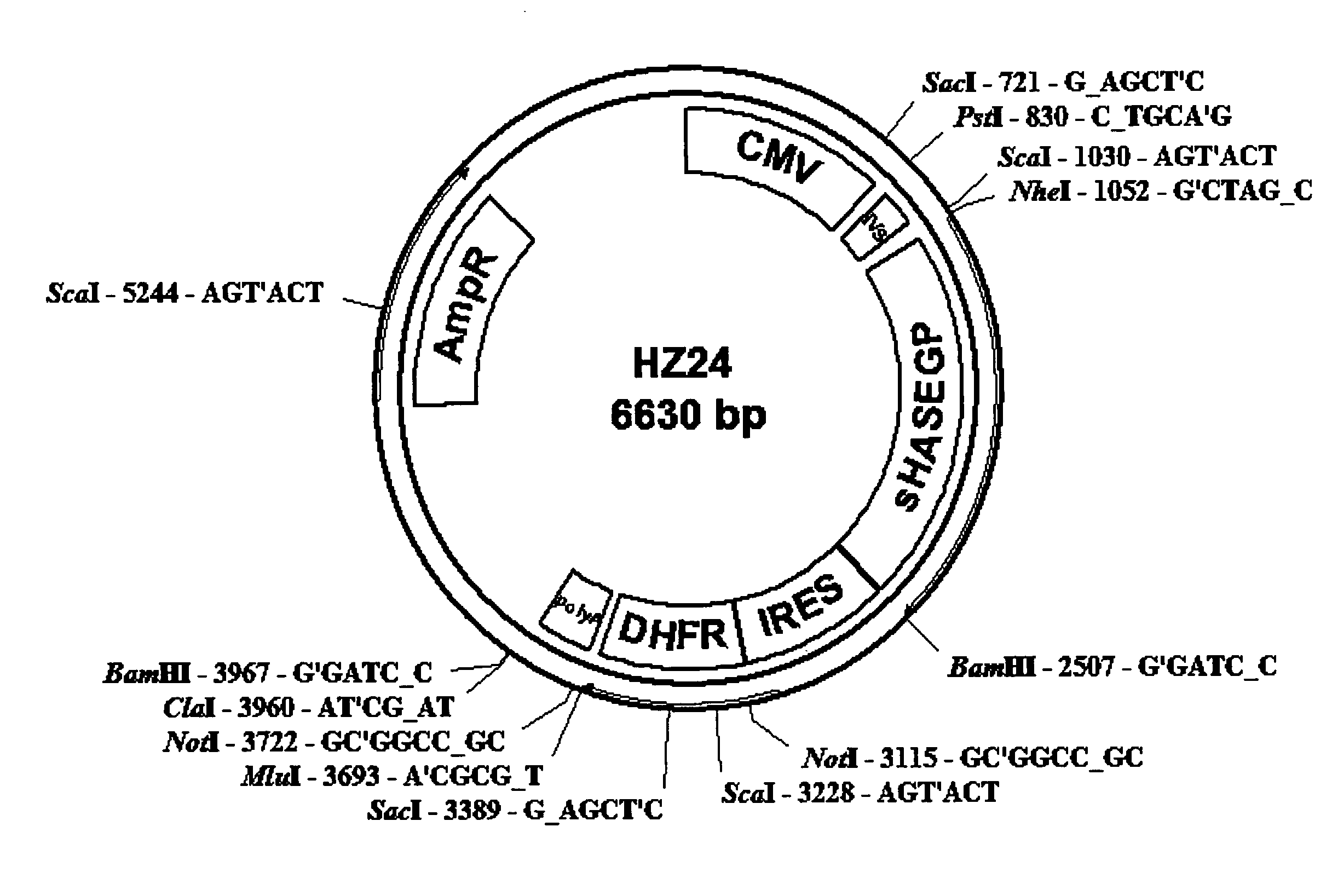
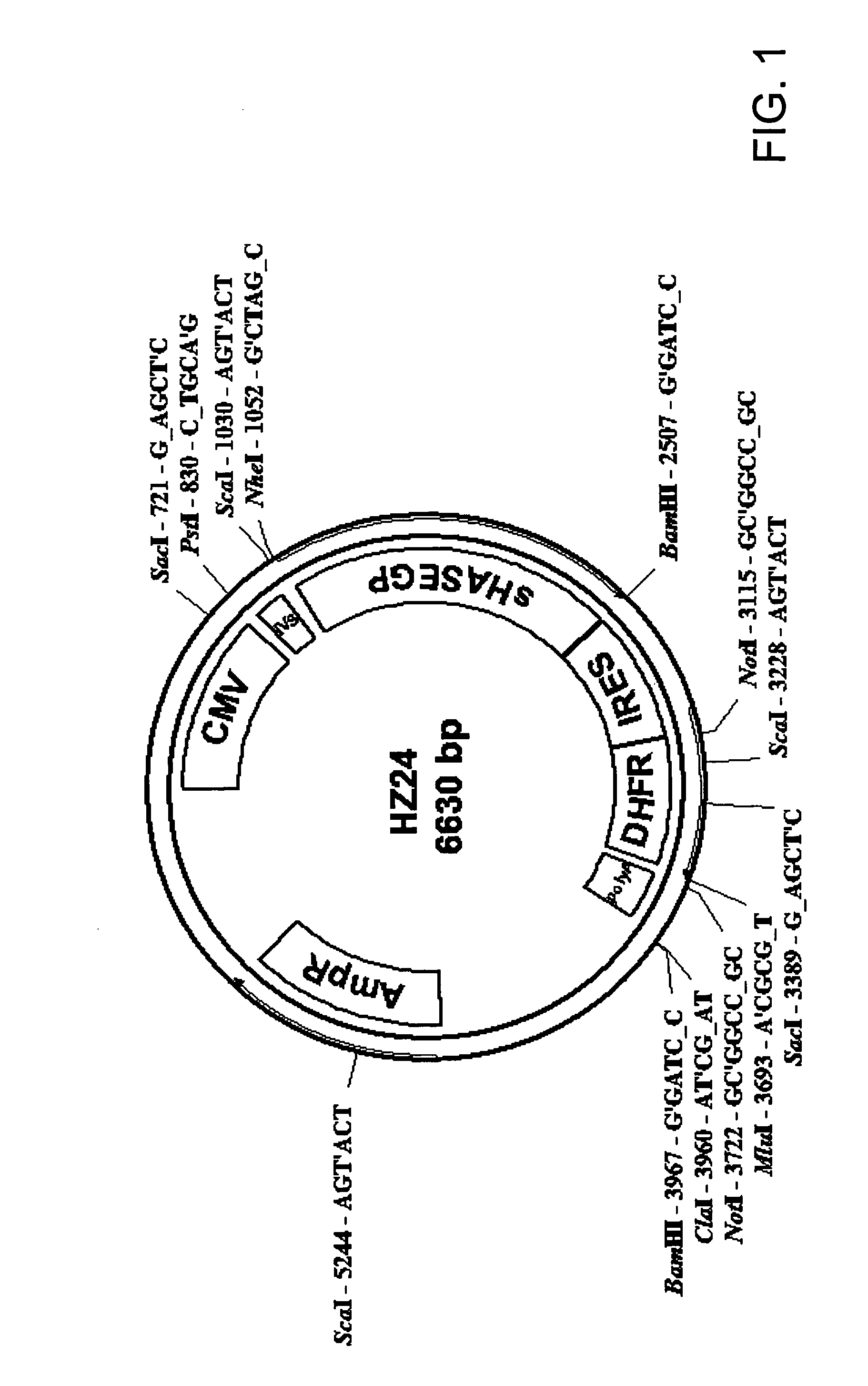
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
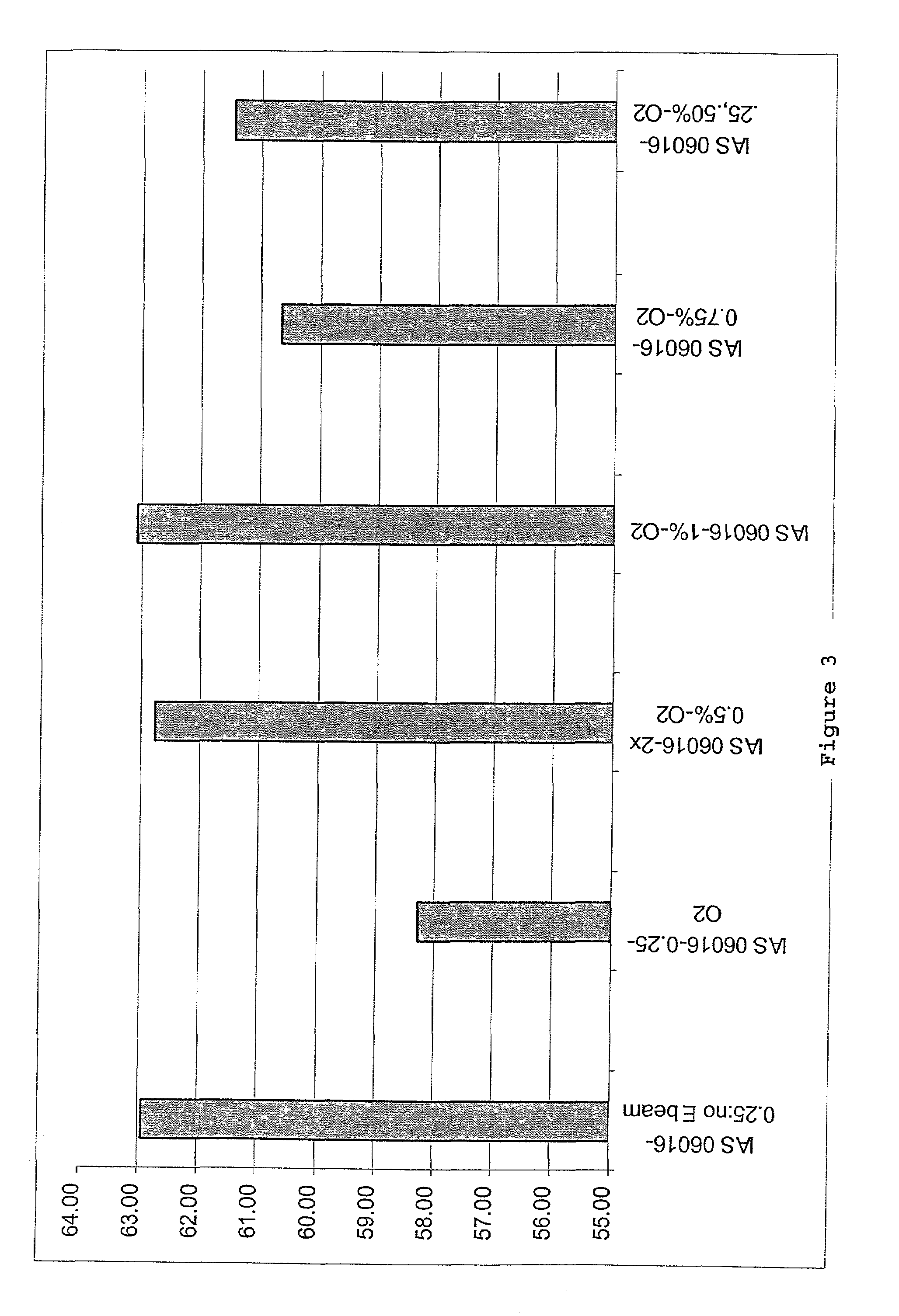
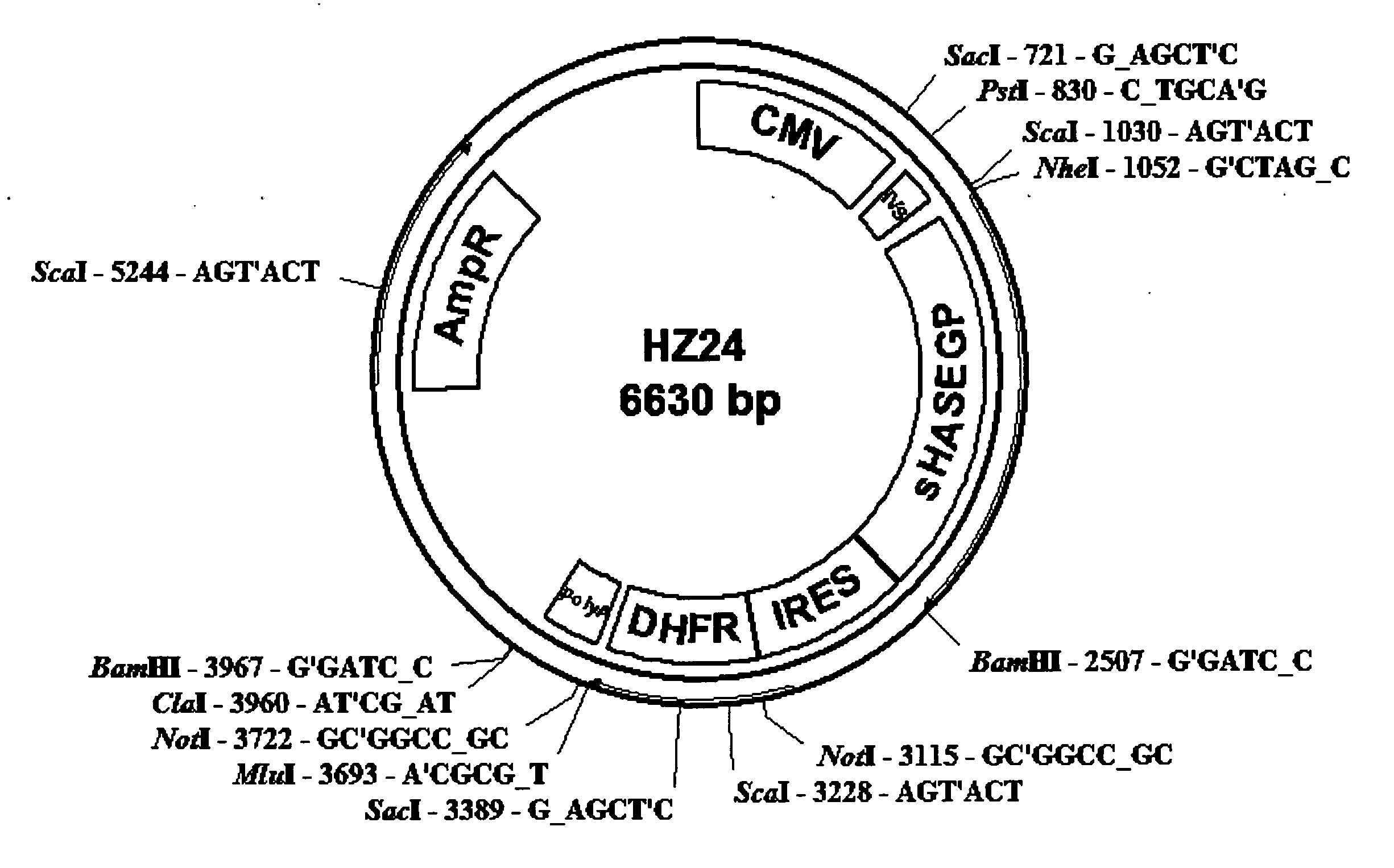
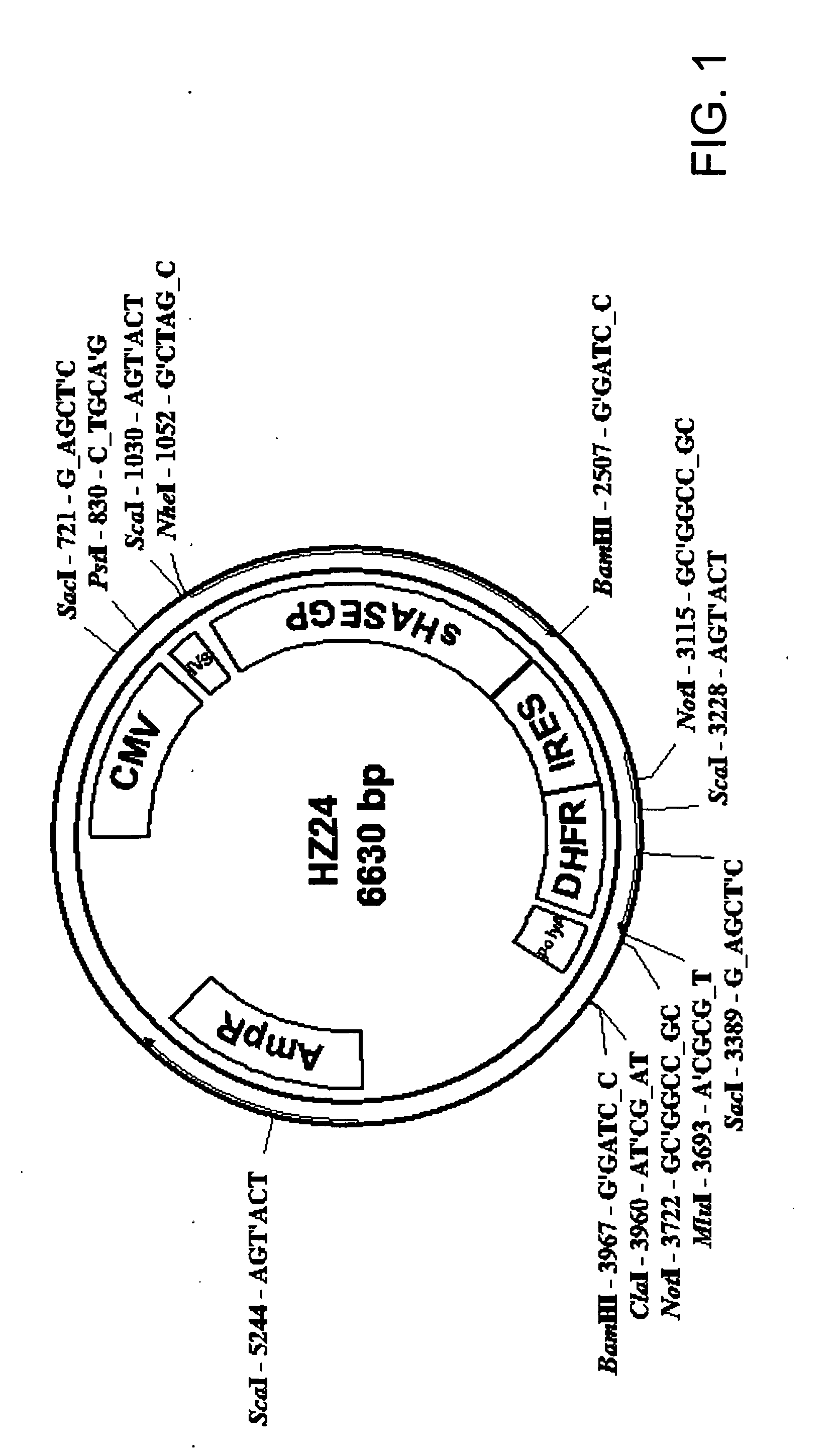
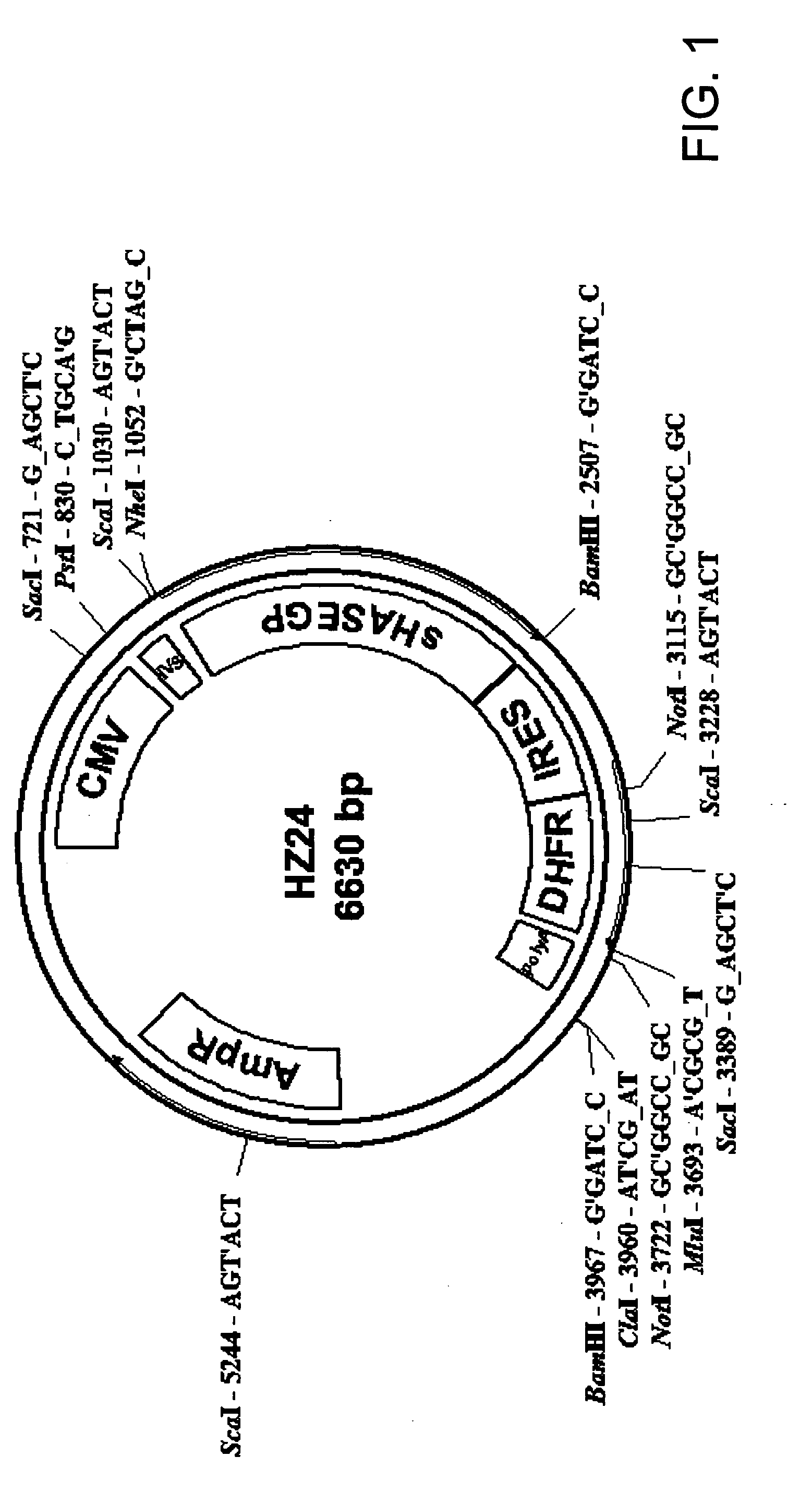
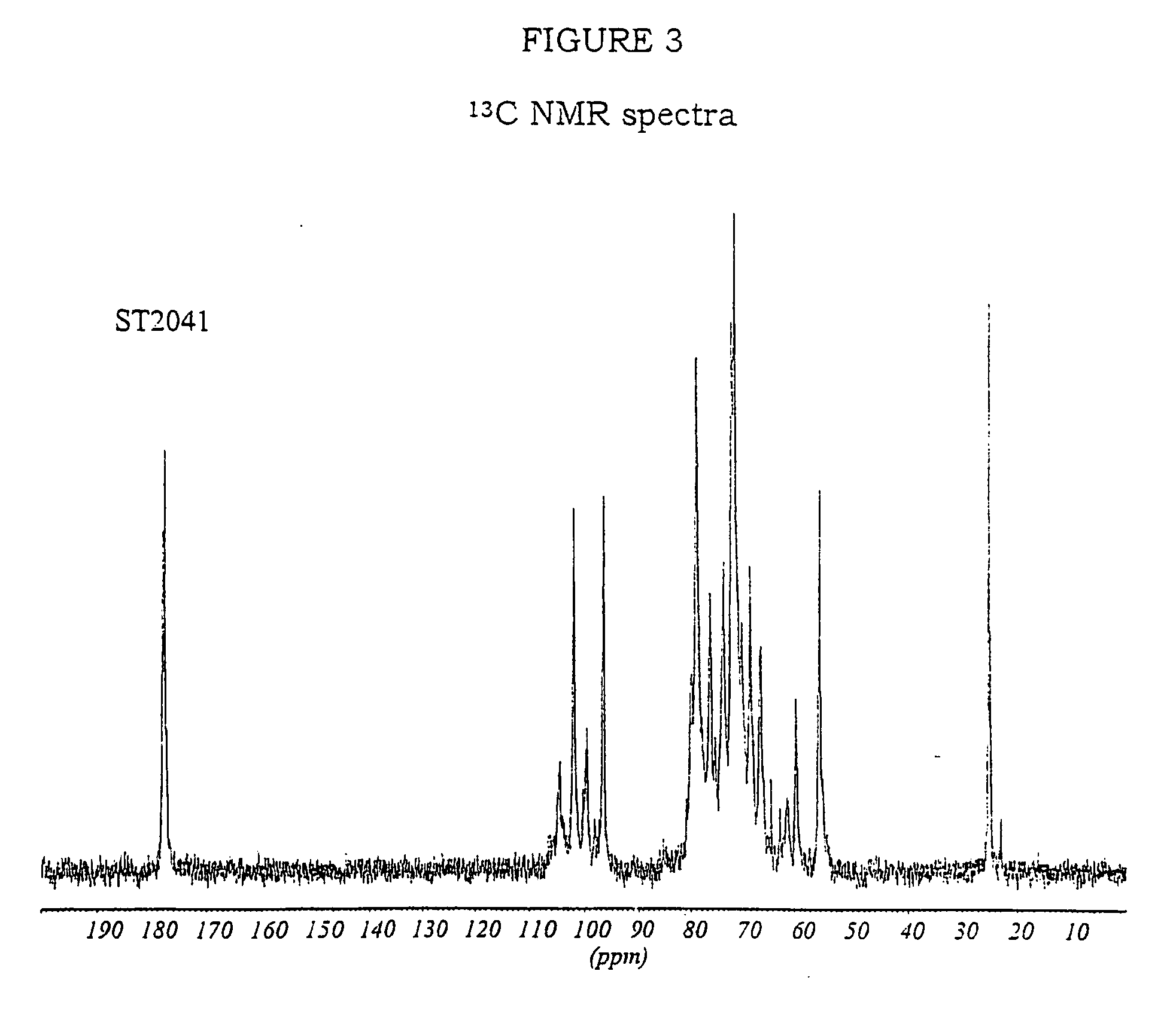
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
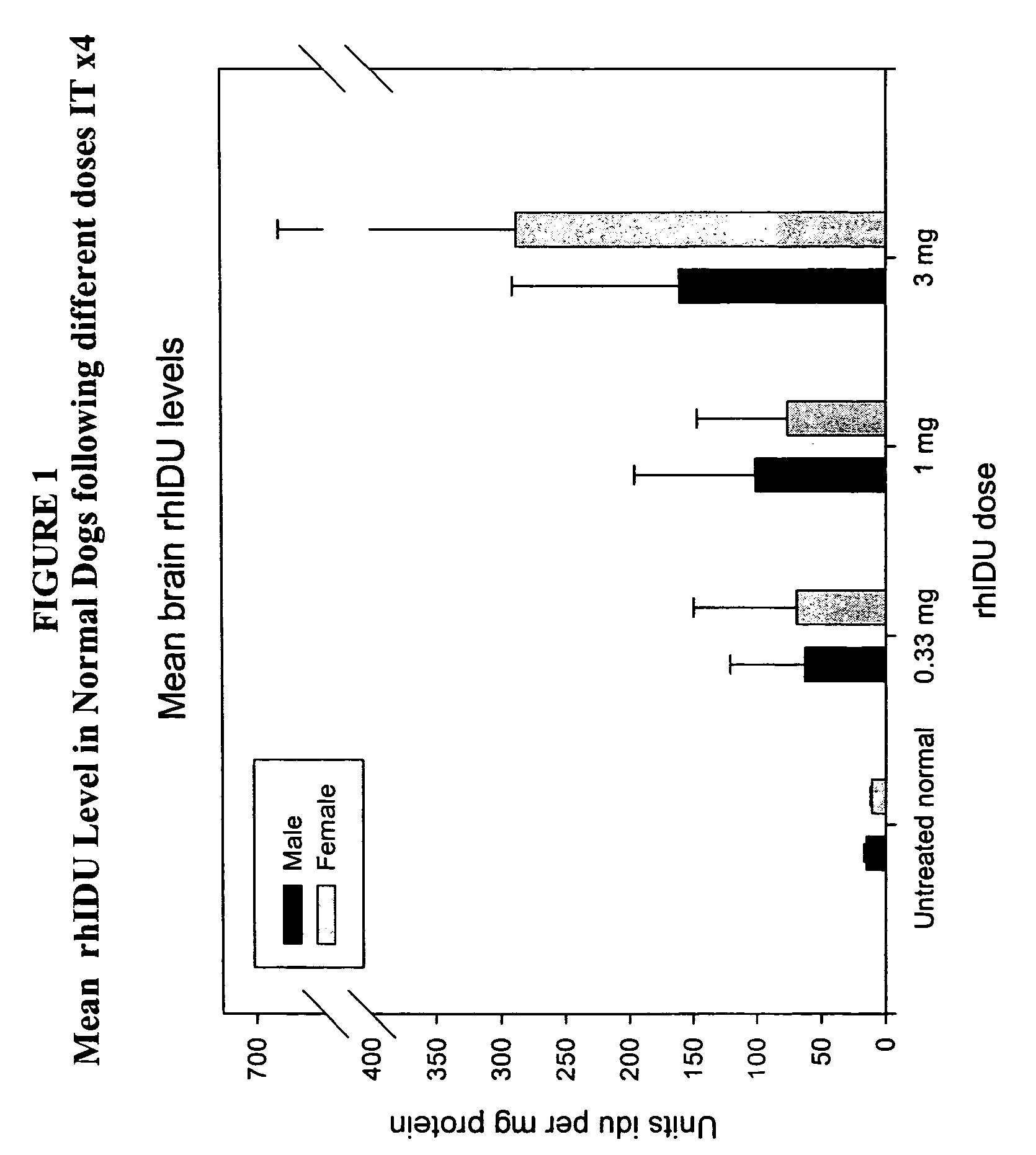
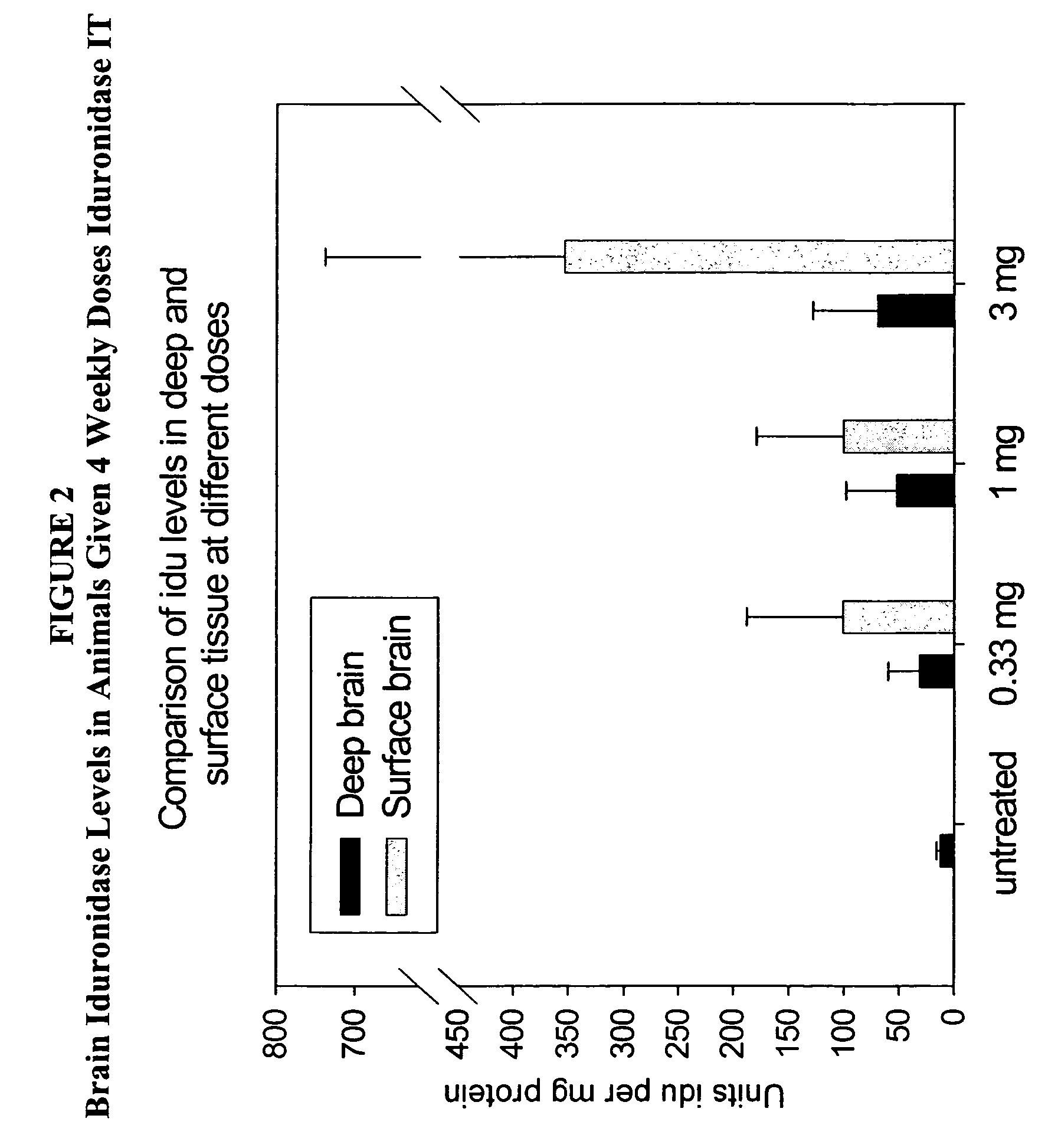
Delivery of therapeutic compounds to the brain and other tissues
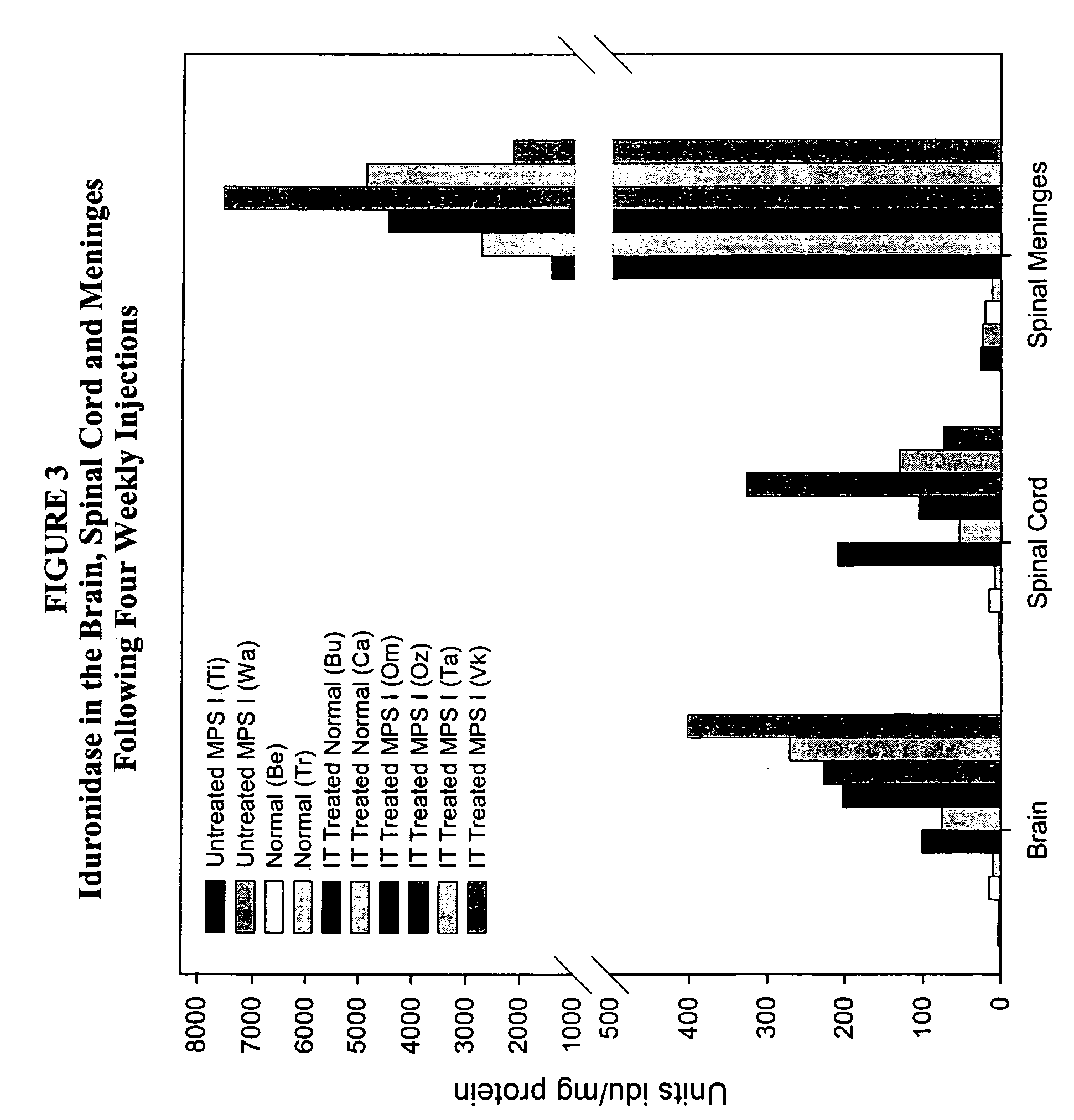
ActiveUS20050048047A1Reduces and eliminates glycogen storage granuleReduce eliminateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMeningesIntrathecal use
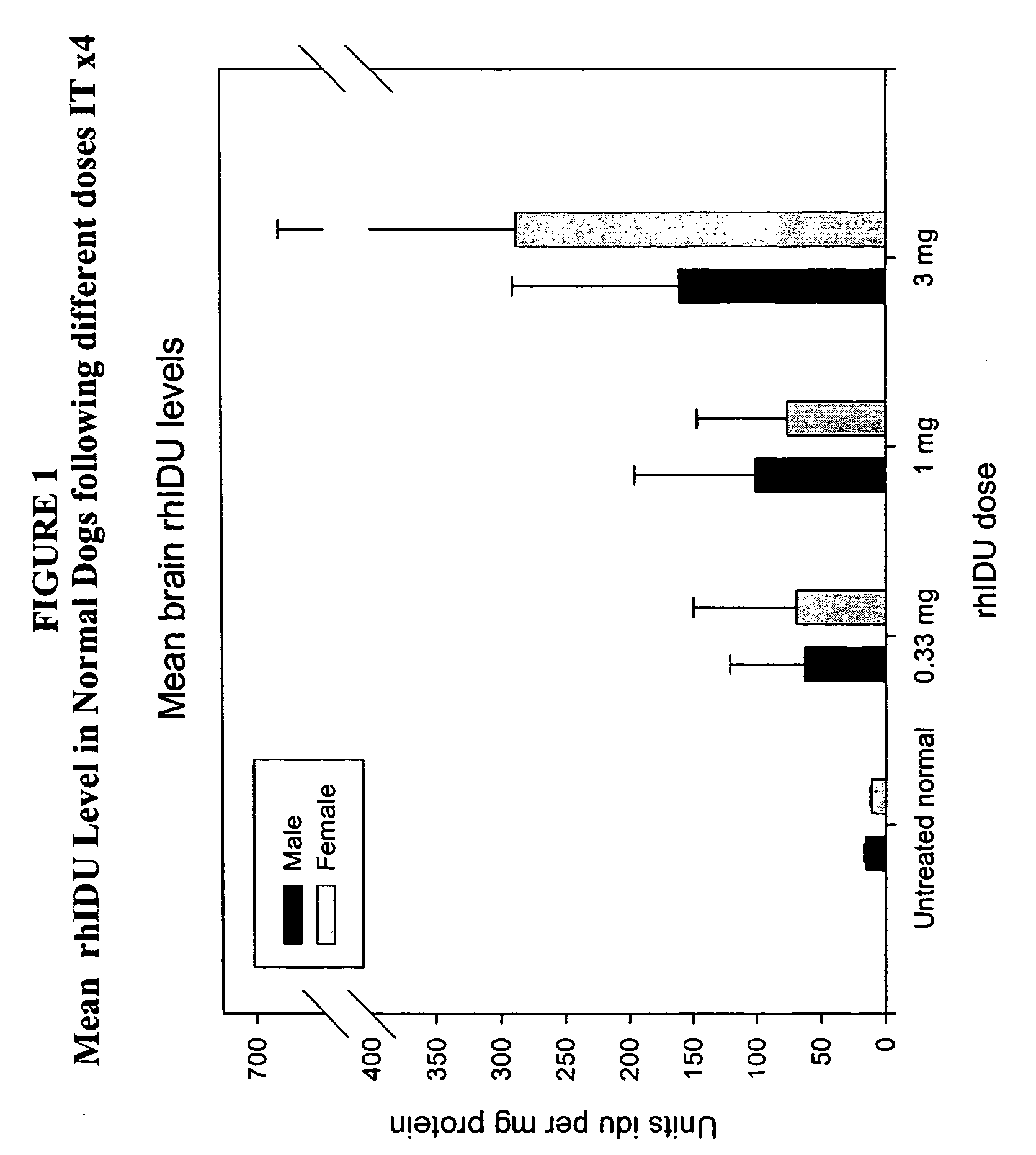
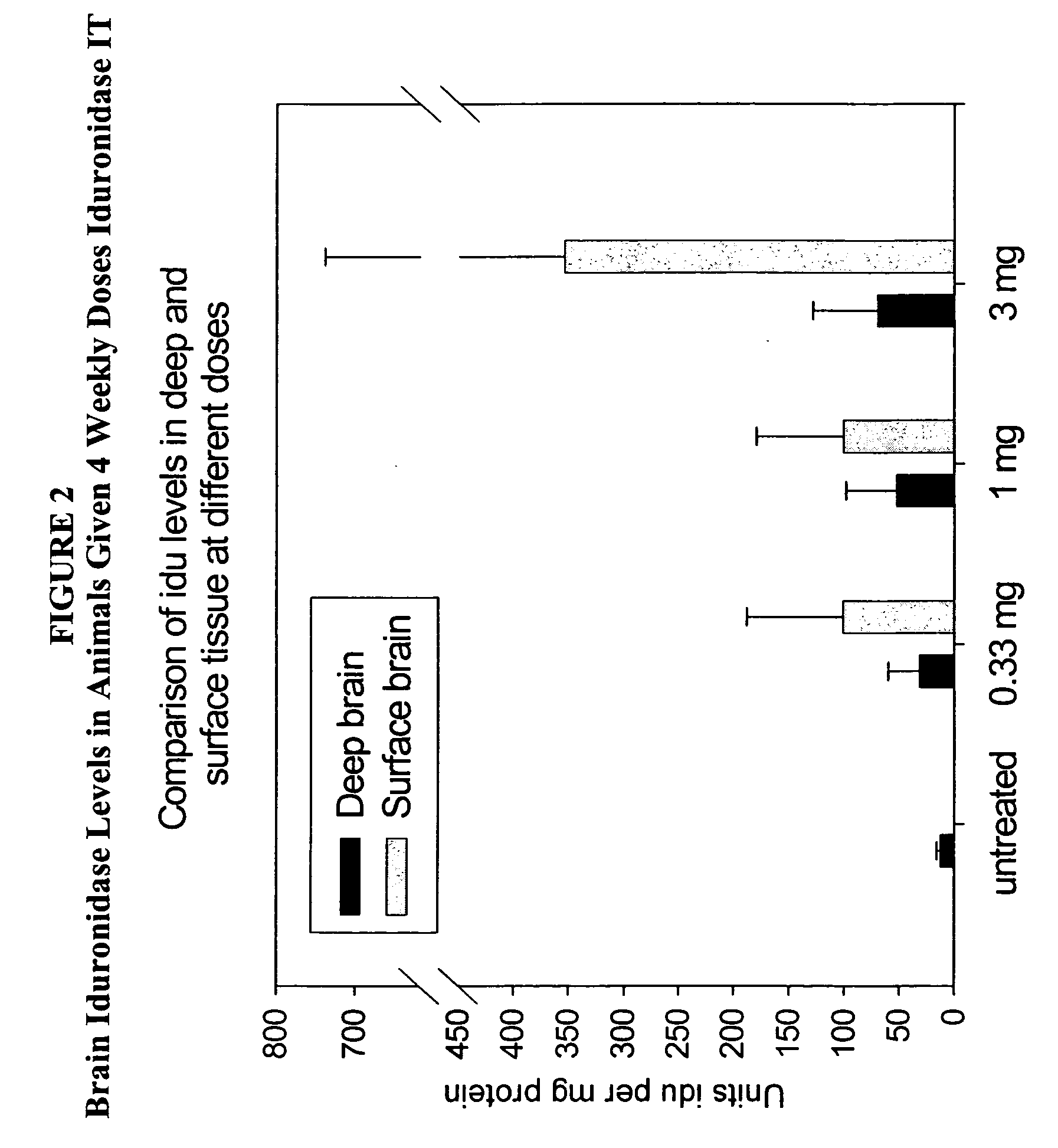
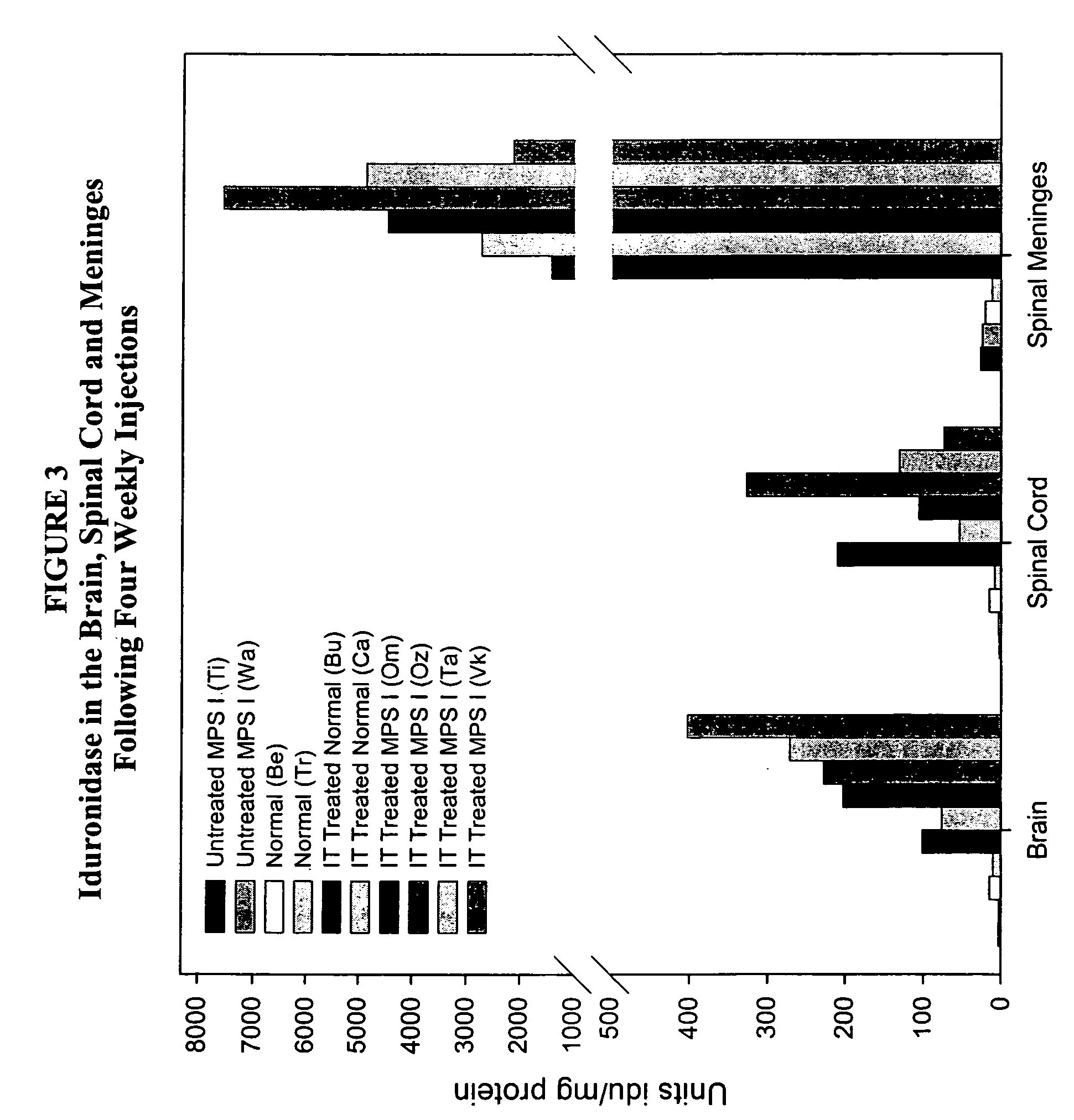
The present invention relates to the intrathecal (IT) administration of recombinant enzyme to treat lysosomal storage disorders. In an exemplary embodiment, intrathecal administration of human α-L-iduronidase (rhIDU) injections in MPS I affected animals resulted in significant enzyme uptake, significant rh-iduronidase activity in brain and meninges and a decrease of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) storage in cells of MPS I subjects to that of normal subjects. Intrathecal administration proved more effective than intravenous treatment at alleviating MPS I symptoms, indicating it is a useful method of treating lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Flowable wound matrix and its preparation and use
ActiveUS20090092674A1Efficient deliveryPromote resultsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGlycosaminoglycanBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to a flowable collagen / glycosaminoglycan (GAG) material including particles of collagen / GAG matrix that, when hydrated, can be effectively delivered to wounds having varying depths and geometries. The flowable collagen / GAG matrix allows a more intimate contact between the wound matrix and the wound bed, and provides a structural framework that serves as a scaffold for cell ingrowth.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI +1
Delivery of therapeutic compounds to the brain and other tissues
ActiveUS7442372B2Reduces and eliminates glycogen storage granuleReduce eliminateNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMeningesIntrathecal use
The present invention relates to the intrathecal (IT) administration of recombinant enzyme to treat lysosomal storage disorders. In an exemplary embodiment, intrathecal administration of human α-L-iduronidase (rhIDU) injections in MPS I affected animals resulted in significant enzyme uptake, significant rh-iduronidase activity in brain and meninges and a decrease of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) storage in cells of MPS I subjects to that of normal subjects. Intrathecal administration proved more effective than intravenous treatment at alleviating MPS I symptoms, indicating it is a useful method of treating lysosomal storage disorders.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
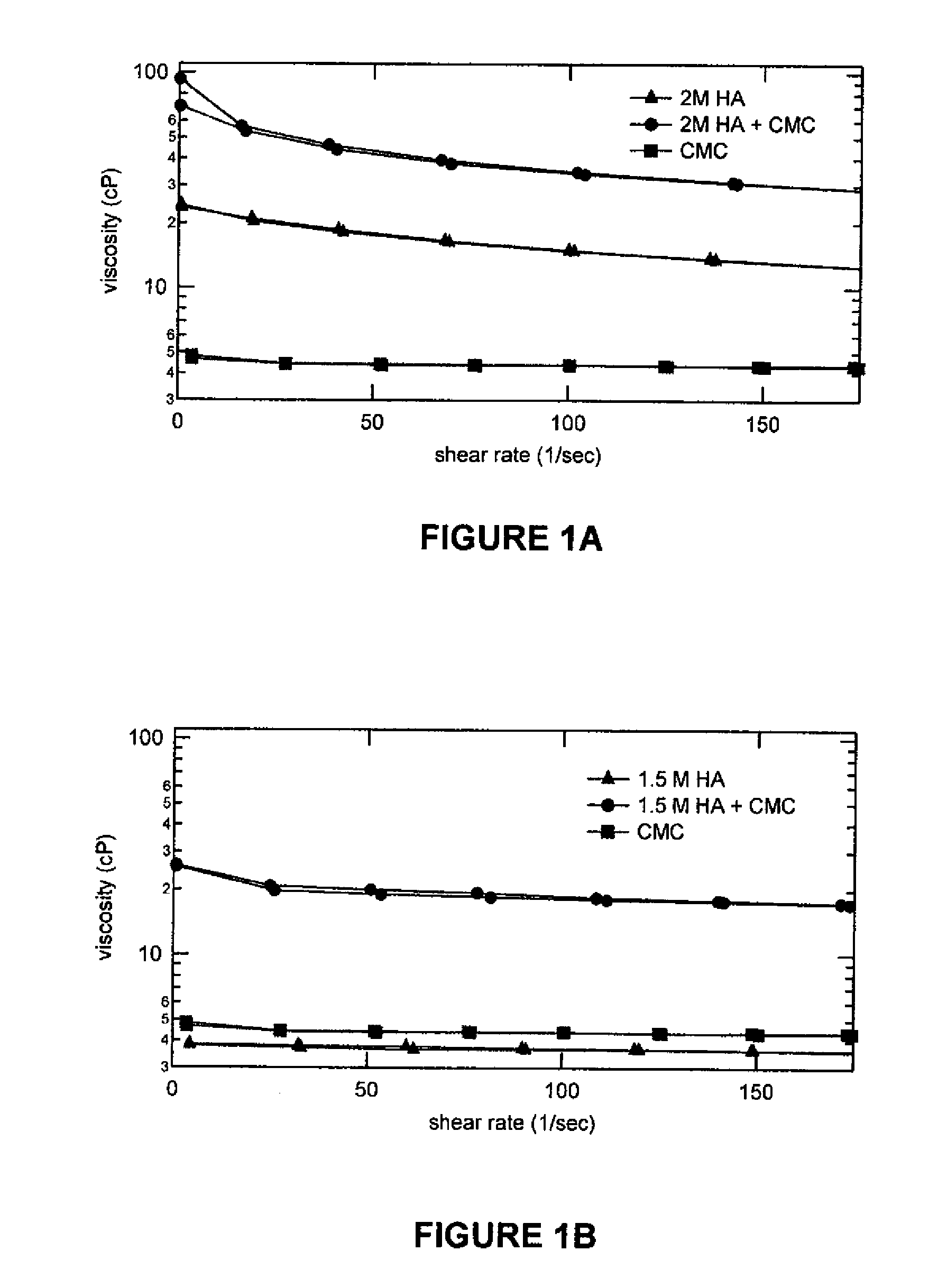
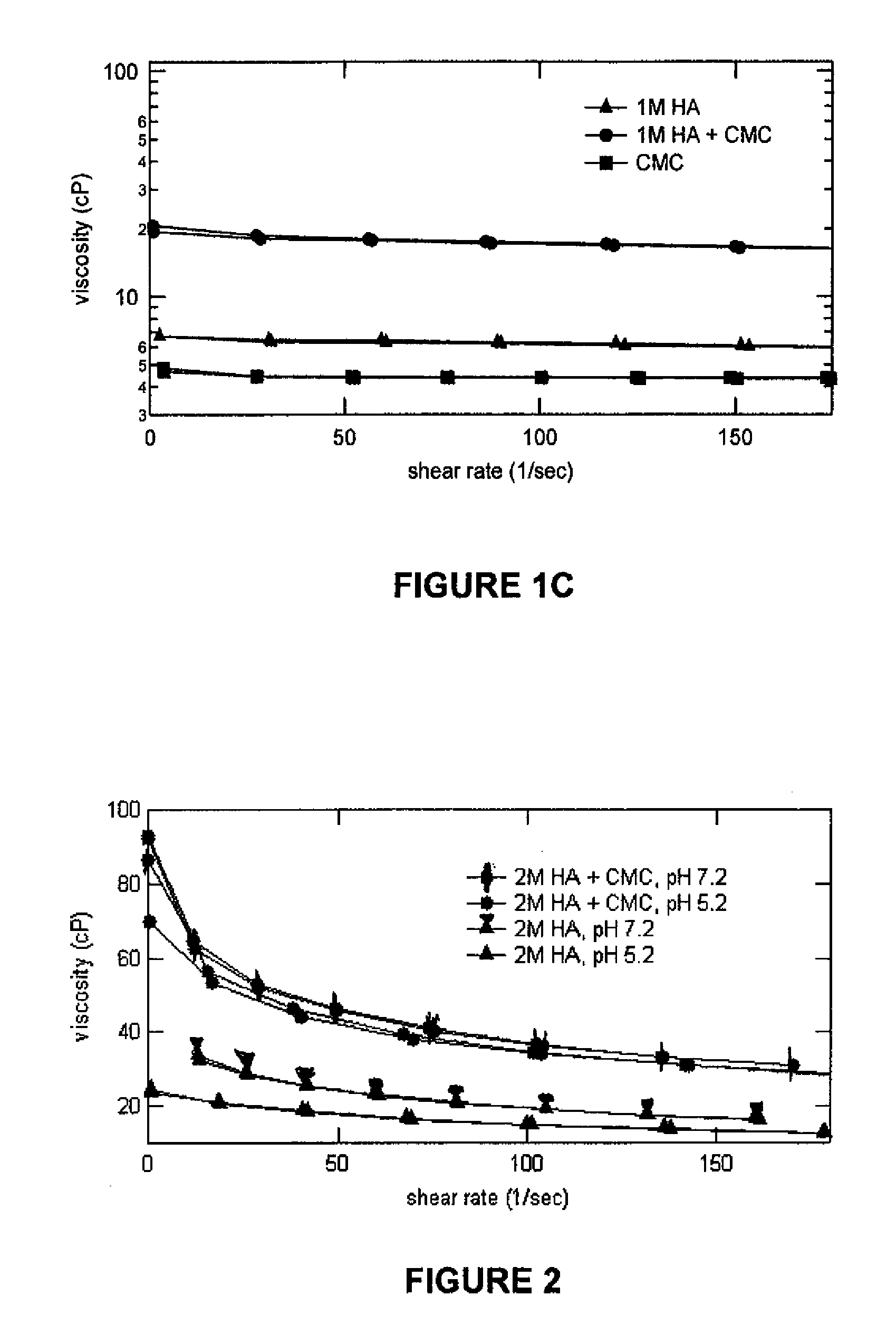
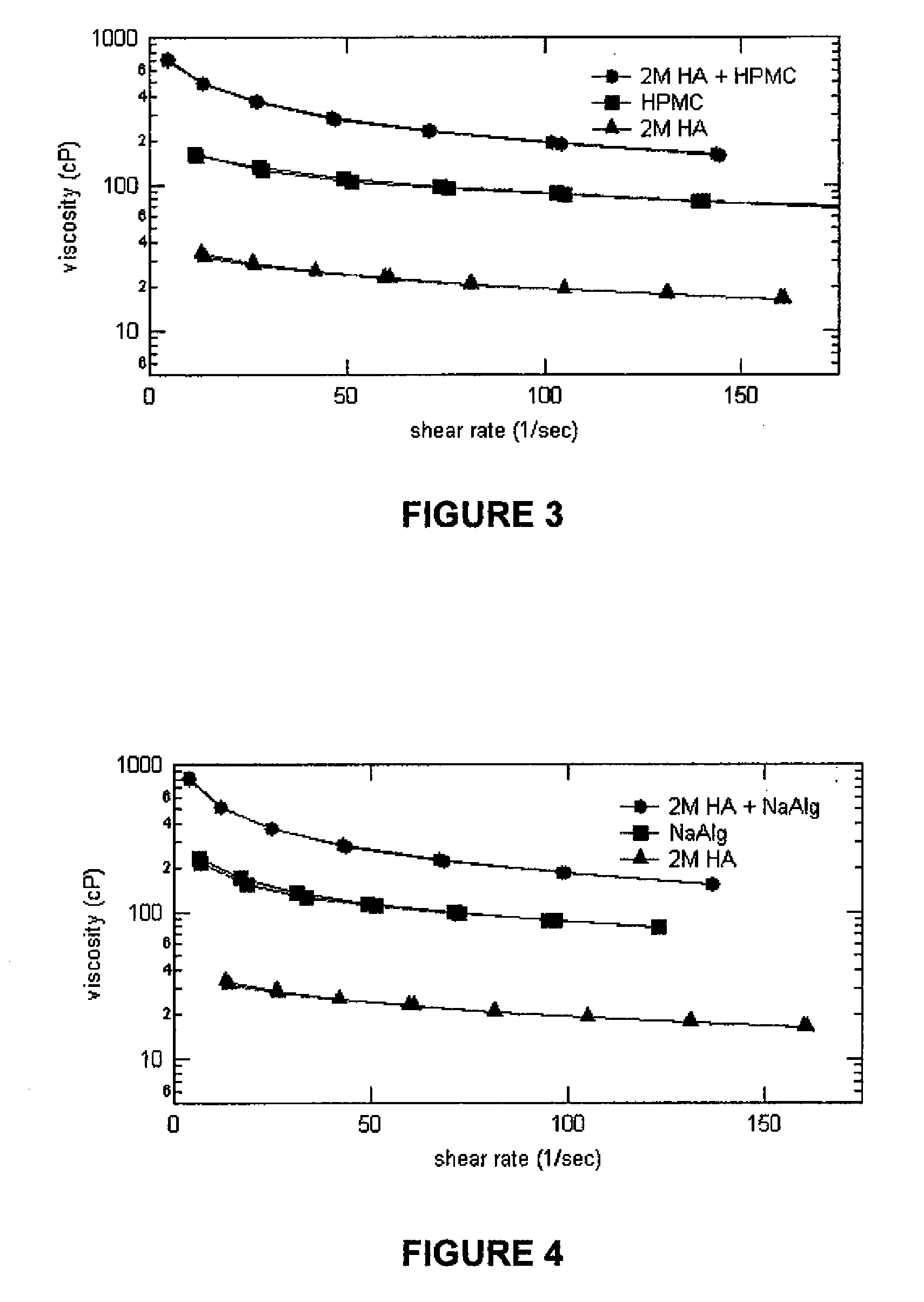
Stabilized Glycosaminoglycan Preparations and Related Methods
Compositions comprising a glycosaminoglycan (e.g., a hyaluronan, hyaluronic acid, hyaluronate, sodium hyaluronate, dermatan sulfate, karatan sulfate, chondroitin 6-sulfate, heparin, etc.) in combination with at least one component selected from; i) polyglycols (e.g., polyethylene glycol), ii) long chain hydroxy polyanionic polysaccharides (e.g., dextran, sodium alginate, alginic acid, propylene glycol alginate, carboxymethyl cellulose and carboxyethyl cellulose, hydroxyl ethyl starch, hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl ethyl cellulose, hydroxy propyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, polylysine, polyhistidine, polyhydroxy proline, poly ornithine, polyvinyl pyrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol, chitosan, etc.) and iii) long chain Nitrogen containing polymers (e.g., Polylysine, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, and polyvinyl alcohol). The invention also includes methods for using such compositions (e.g., as substance delivery materials, tissue fillers or bulking agents, as moistening or hydrating agents, etc.)
Owner:S K PHARMA INC
Prion-free collagen and collagen-derived products and implants for multiple biomedical applications; methods of making thereof
InactiveUS6197935B1Preserve integrityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsIn vivo biocompatibilityCollagen VI
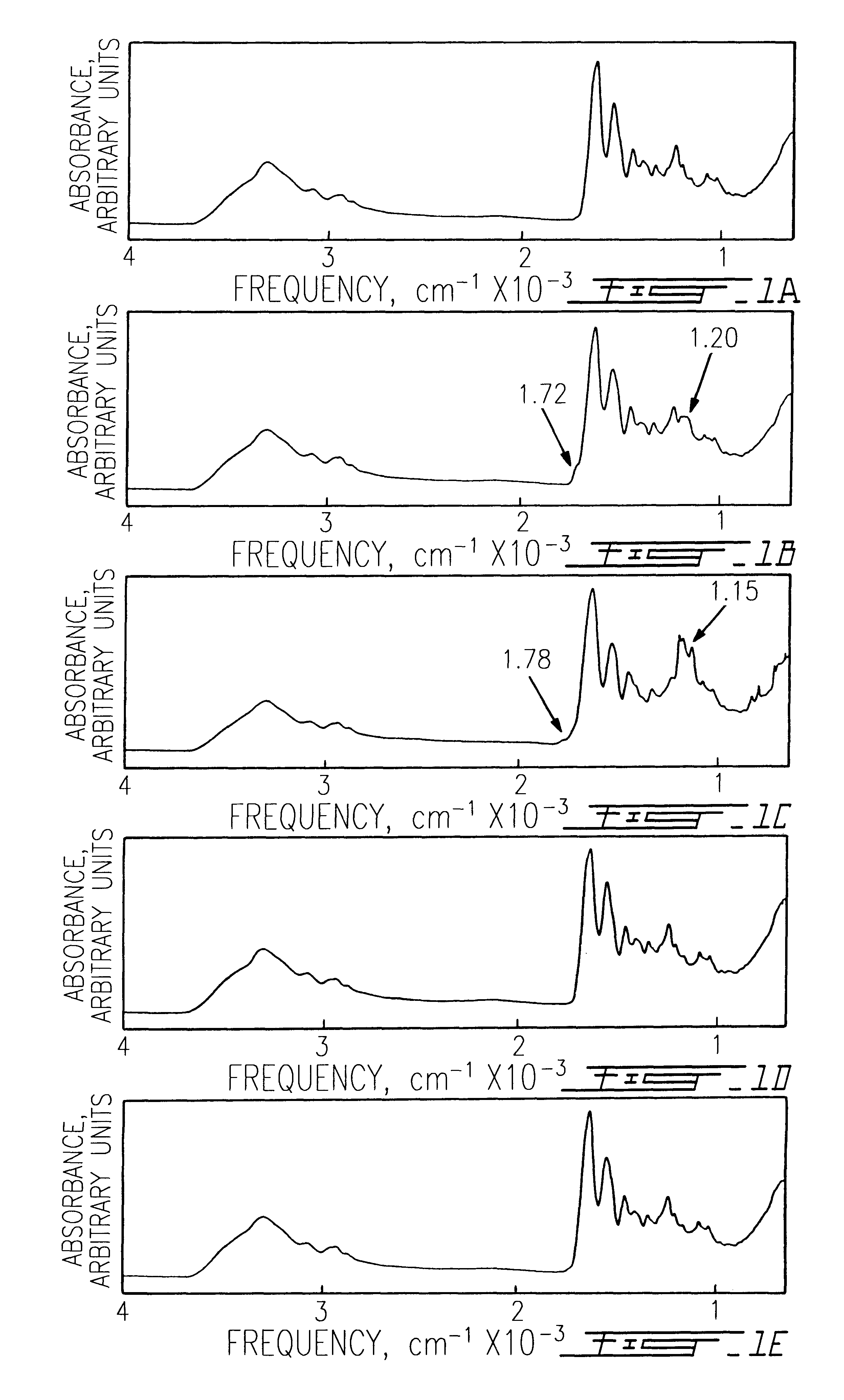
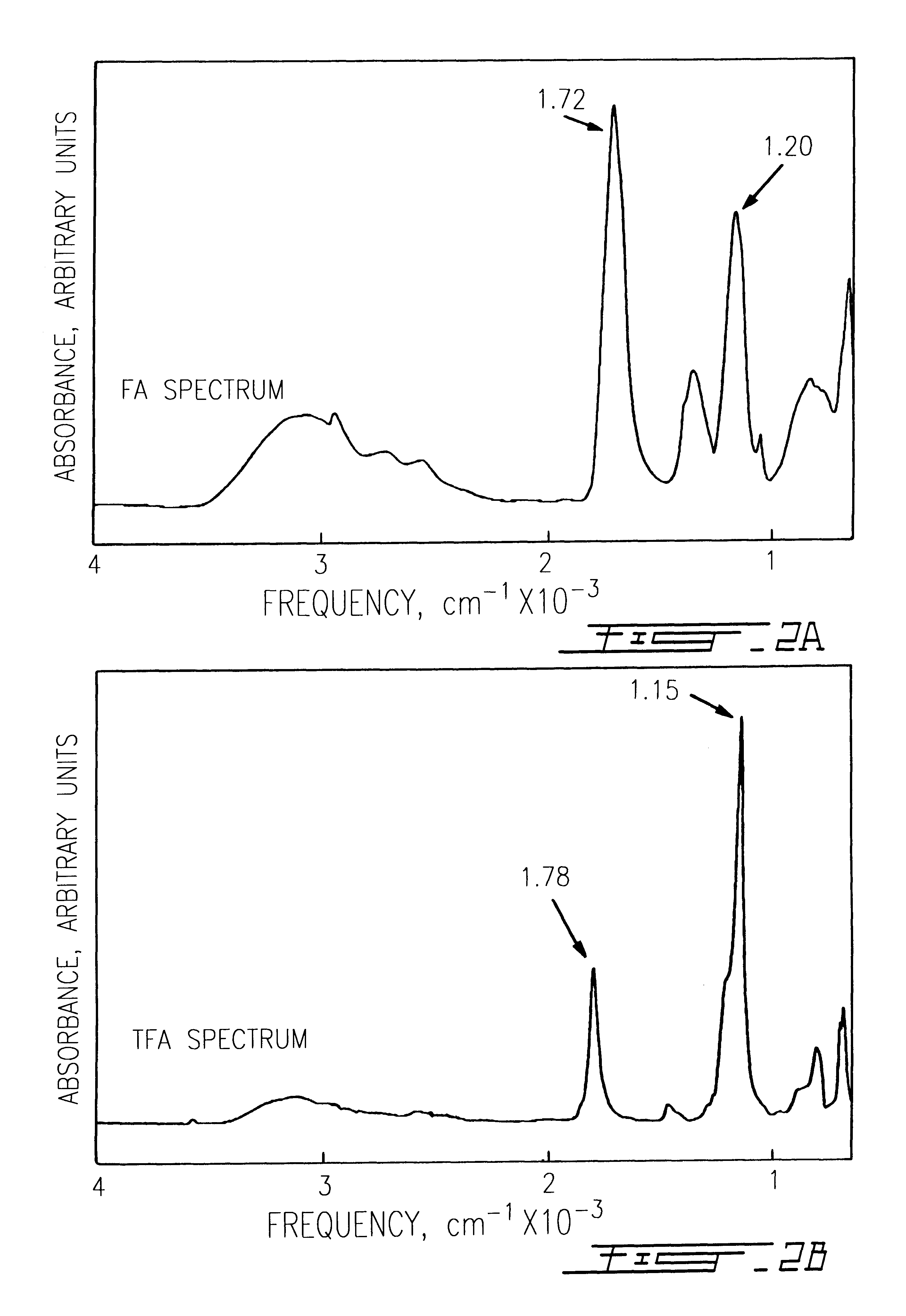
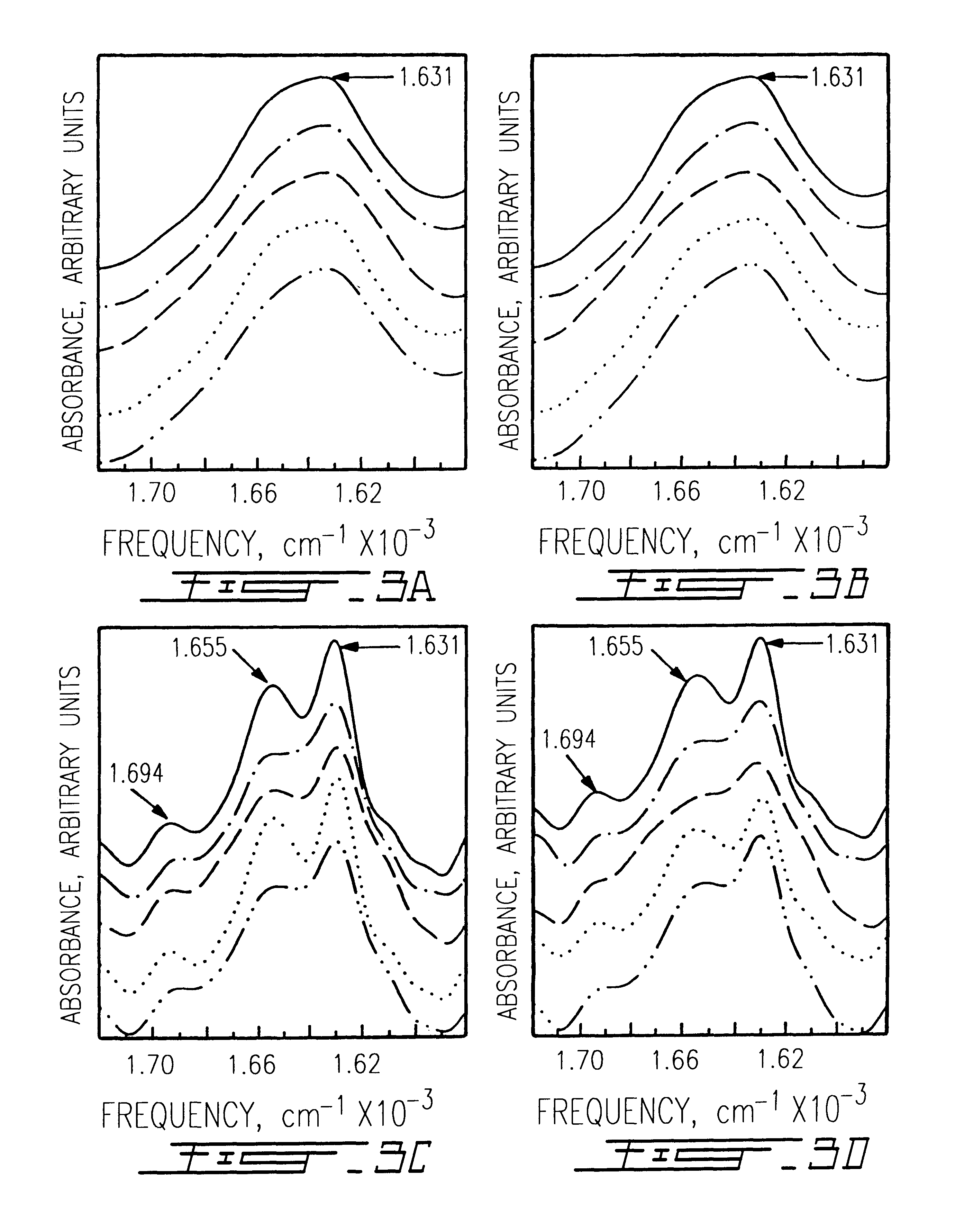
The use of collagen as a biomedical implant raises safety issues towards viruses and prions. The physicochemical changes and the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of collagen treated with heat, and by formic acid (FA), trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), tetrafluoroethanol (TFE) and hexafluoroiso-propanol (HFIP) were investigated. FA and TFA resulted in extensive depurination of nucleic acids while HFIP and TFE did so to a lesser degree. The molecules of FA, and most importantly of TFA, remained within collagen. Although these two acids induced modification in the secondary structure of collagen, resistance to collagenase was not affected and, in vitro, cell growth was not impaired. Severe dehydrothermal treatment, for example 110° C. for 1-3 days under high vacuum, also succeeded in removing completely nucleic acids. Since this treatment also leads to slight cross-linking, it could be advantageously used to eliminate prion and to stabilize gelatin products. Finally, prolonged treatment with TFA provides a transparent collagen, which transparency is further enhanced by adding glycosaminoglycans or proteoglycans, particularly hyaluronic acid. All the above treatments could offer a safe and biocompatible collagen-derived material for diverse biomedical uses, by providing a virus or prion-free product.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Defined serumfree medical solution for ophthalmology
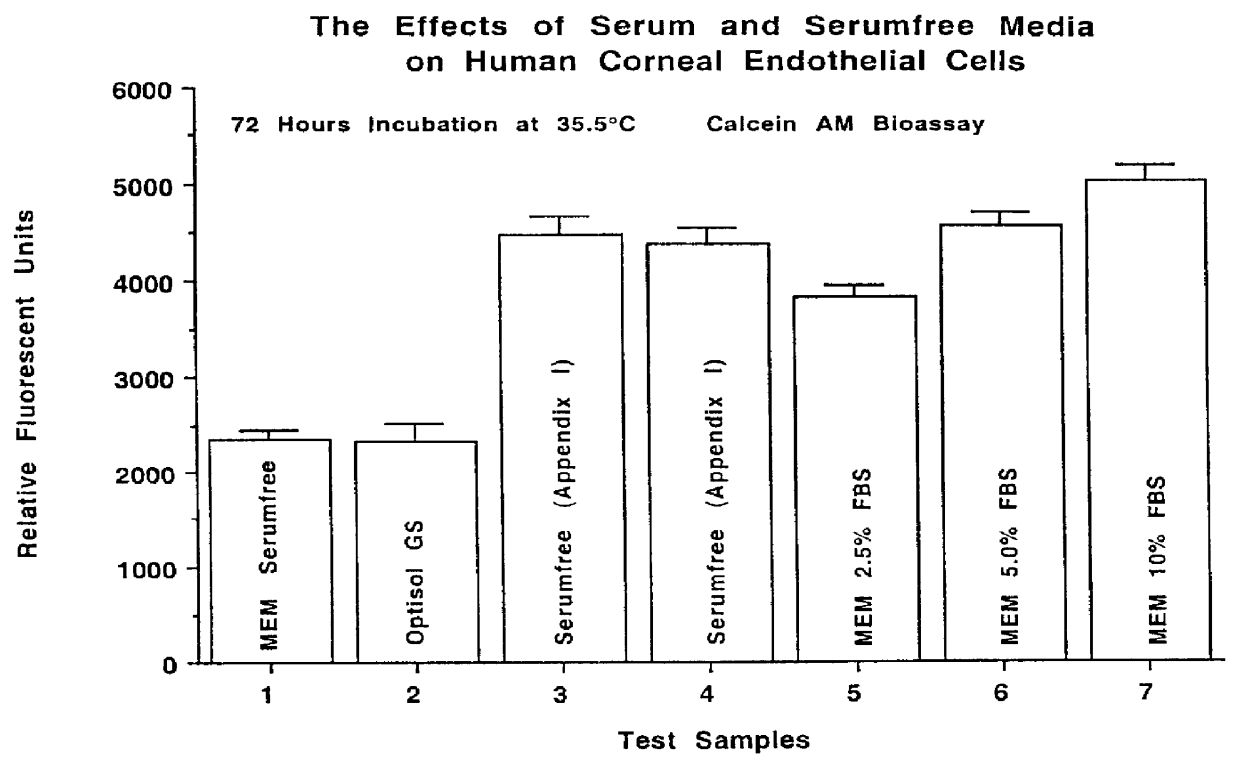
A defined serumfree medical solution for applications in Ophthalmology, that contains one or more cell nutrient supplements, and a growth factor(s) which maintains and enhances the preservation of eye tissues, including human corneal, retinal and corneal epithelial tissues at low to physiological temperatures (2 DEG C. to 38 DEG C.). This solution is composed of a defined aqueous nutrient and electrolyte solution, supplemented with a glycosaminoglycan(s), a deturgescent agent(s), an energy source(s), a buffer system(s), an antioxidant(s), membrane stabilizing agents, an antibiotic(s) and / or antimycotic agent(s), ATP or energy precursors, nutrient cell supplements, coenzymes and enzyme supplements, nucleotide precursors, hormonal supplements, non-essential amino acids, trace minerals, trace elements and a growth factor(s).
Owner:SKELNIK DEBRA L
Glycosaminoglycan and Synthetic Polymer Material for Blood-Contacting Applications
ActiveUS20150196688A1Improve surface chemistryFeasible at commercial productionSuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
Provided herein is a composite, comprising: a polymer host selected from the group consisting of low-density polyethylene (LDPE), linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and polypropylene (PP), polyurethane, polycaprolactone (PCL), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), and polyoxymethylene (POM); and a guest molecule comprising hyaluronic acid; wherein the guest molecule is disposed within the polymer host, and wherein the guest molecule is covalently bonded to at least one other guest molecule. Also provided herein are methods for forming the composite, and blood-contracting devices made from the composite, such as heart valves and vascular grafts.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions based on inhibition of cell invasion and fibrosis by anionic polymers
Owner:TRIAD
Collagen/glycosaminoglycan matrix stable to sterilizing by electron beam radiation
InactiveUS6969523B1Facilitate cross-linkingImprove performanceBiocideMechanical working/deformationCross-linkGlycosaminoglycan
Compositions of cross-linked collagen and a glycosaminoglycan are provided which retain characteristics rendering them useful as tissue engineering matrices or scaffolds following terminal sterilization. Also provided are methods for producing these compositions and terminally sterilized matrices or scaffolds from these compositions as well as methods of using these matrices or scaffolds as tissue engineering devices.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090214505A1Extended half-lifeOptimize allocationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
Provided are soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. Sialated and pegylated forms of the sHASEGPs also are provided. Methods of treatment by administering sHASEGPs and modified forms thereof also are provided.
Owner:HALOZYME
Use Of A Mixture For The Production Of An Agent For Treating Defective Or Degenerated Cartilage In The Production Of Natural Cartilage Replacement In Vitro
InactiveUS20070275032A1Improve the lubrication effectImprove actionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipidPerylene derivatives
A mixture of one or several substances from group A) lubricin, proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) and phosphollipid (SAPL); with one or several substances from group B) hyaluronic acid, glycosaminoglycan and derivatives of said substances; dissolved in a solvent, used for the production of an agent for treating defective or degenerated cartilage in vivo. Said mixture can also be used to produce natural cartilage replacement in vitro.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181032A1Extended half-lifeImprove distributionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods for managing connective tissue ailments
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for managing connective tissue disorders in a patient, a sugar compound that is converted to a glycosaminoglycan, a primary antioxidant component, at least one amino acid component, at least one transition metal component, at least one moisturizing agent, at least one fatty acid. In a preferred embodiment, the composition for topical administration to the patient's skin further included hydrogen peroxide in an amount sufficient to cleanse the skin.
Owner:MURAD HOWARD
Bioresorbable and biocompatible compounds for surgical use
A bioresorbable and biocompatible compound for surgical use is composed of functionalized collagen cross-linked with a glycosaminoglycan.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
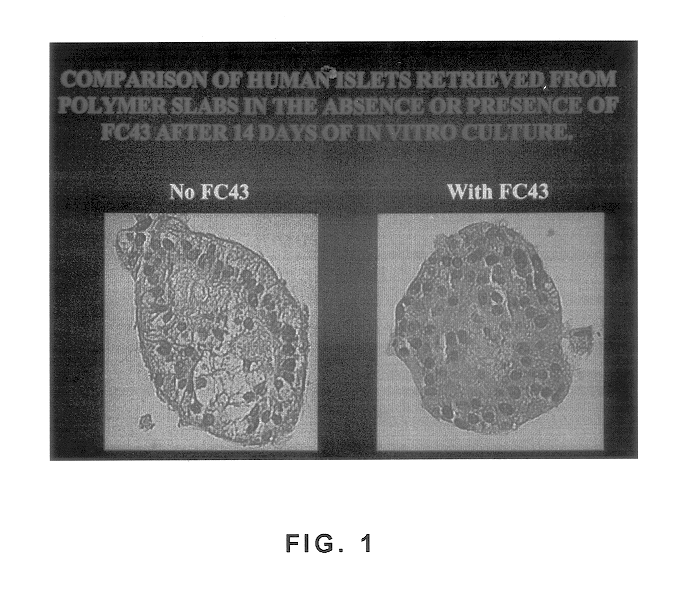
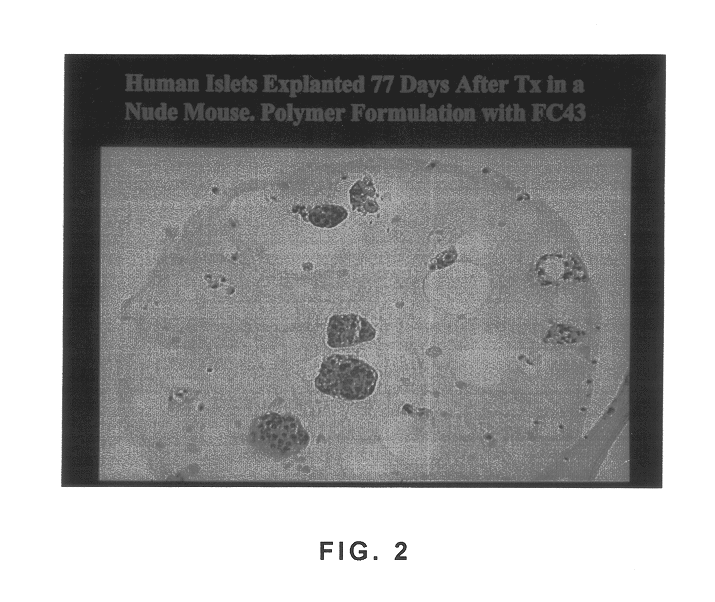
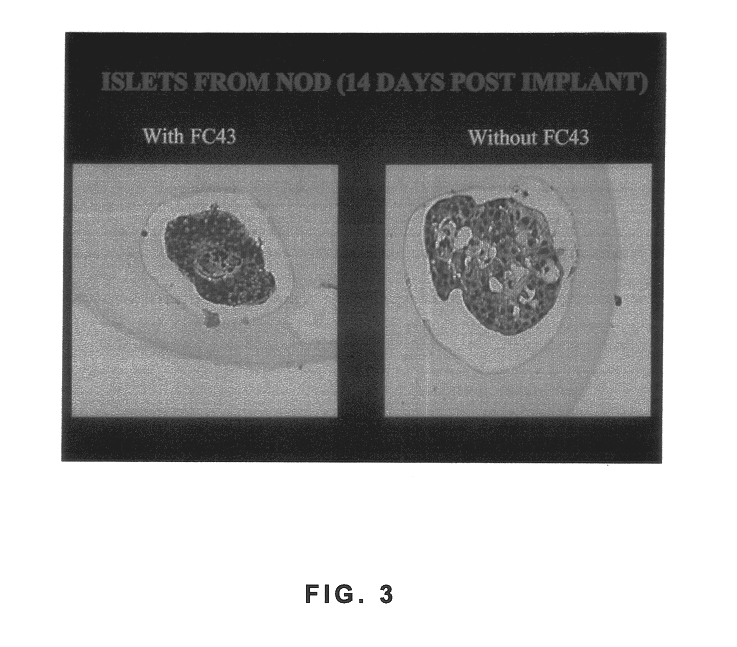
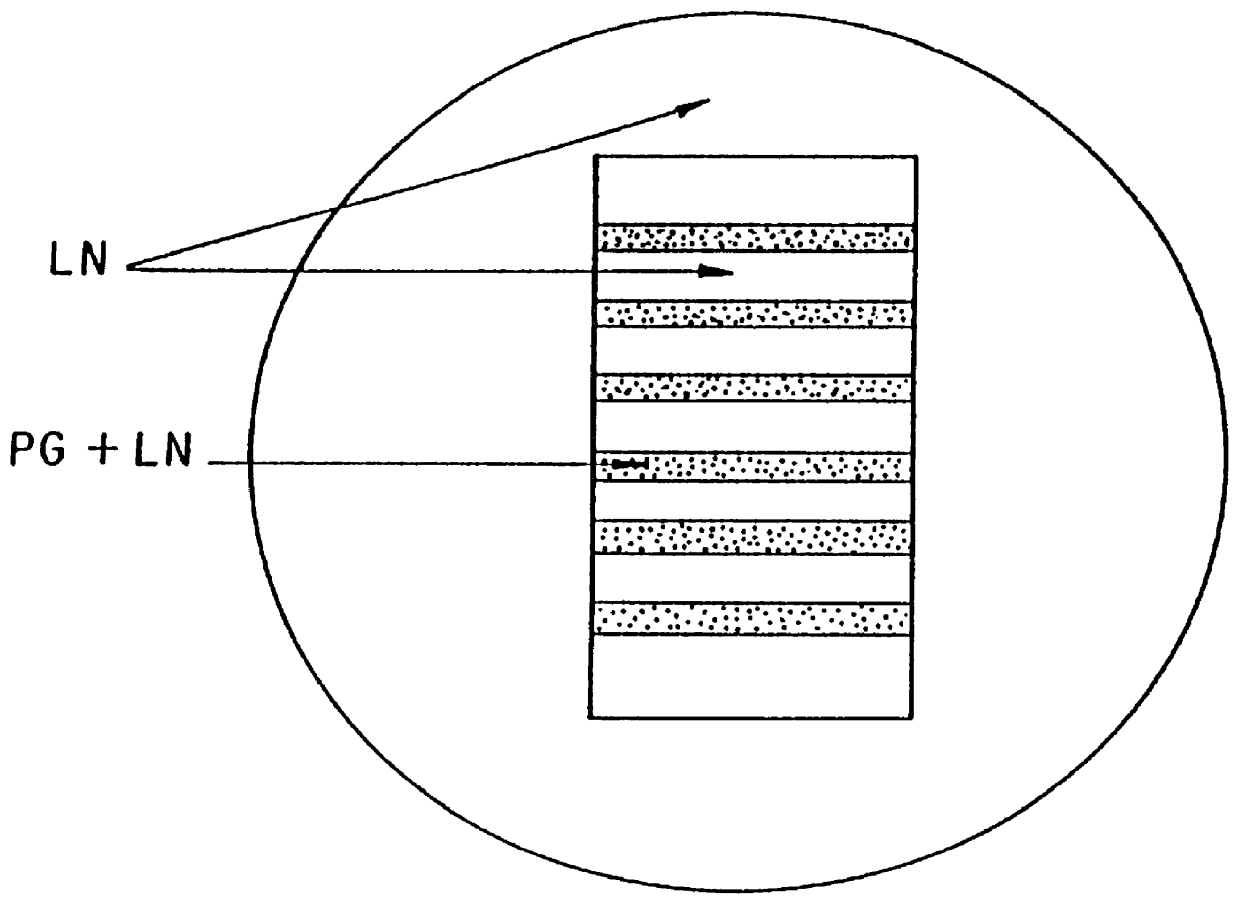
Polymer formulations containing perfluorinated compounds for the engineering of cells and tissues for transplantation that improves cell metabolism and survival, and methods for making same
InactiveUS6630154B1High viscosityMedium viscosity alginatesPowder deliveryBiocideCross-linkInorganic salts
Disclosed and claimed are: a composition including at least one glycosaminoglycan, e.g., CIS, at least one perfluorinated substance and at least one alginate, e.g., sodium alginate, wherein:the at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the perfluorinated substance and / or the alginate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan, the perfluorinated substance and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the perfluorinated substance and / or the alginate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt, and the at least one glycosaminoglycan and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS, and the covalent binding can have been performed prior to cross-linking or polymerizing or vice versa; and,gels comprising the composition; mixtures of such gels or of at least one such gel and at least one such composition; and,methods for making and using such compositions and gels, including products therefrom such as "paints", sprays, matrices, beads, microcapsules.
Owner:BIOMM +1
Method for inhibition of bone growth by anionic polymers
InactiveUS6020326AInhibit bone growthPrevent invasionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell invasionFibrosis
The present invention relates to the discovery that biocompatible anionic polymers can effectively inhibit fibrosis, scar formation, and surgical adhesions. The invention is predicated on the discovery that anionic polymers effectively inhibit invasion of cells associated with detrimental healing processes, and in particular, that the effectiveness of an anionic polymer at inhibiting cell invasion correlates with the anionic charge density of the polymer. Thus the present invention provides a large number of materials for use in methods of inhibiting fibrosis and fibroblast invasion. Anionic polymers for use in the invention include but are not limited to natural proteoglycans, and the glycosaminoglycan moieties of proteoglycans. Additionally, anionic carbohydrates and other anionic polymers may be used. The anionic polymers dextran sulfate and pentosan polysulfate are preferred. In a more preferred embodiment, dextran sulfate, in which the sulfur content is greater than about 10% by weight, may be used. In a more preferred embodiment, the average molecular weight is about 40,000 to 500,000 Daltons. The present invention provides compositions and methods to inhibit fibrosis and scarring associated with surgery. The invention further provides compositions and methods to inhibit glial cell invasion, detrimental bone growth and neurite outgrowth. In a preferred embodiment, the inhibitory compositions further comprise an adhesive protein.
Owner:TRIAD
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181013A1Reduce deliveryImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Methods of coating a device using anti-thrombin heparin
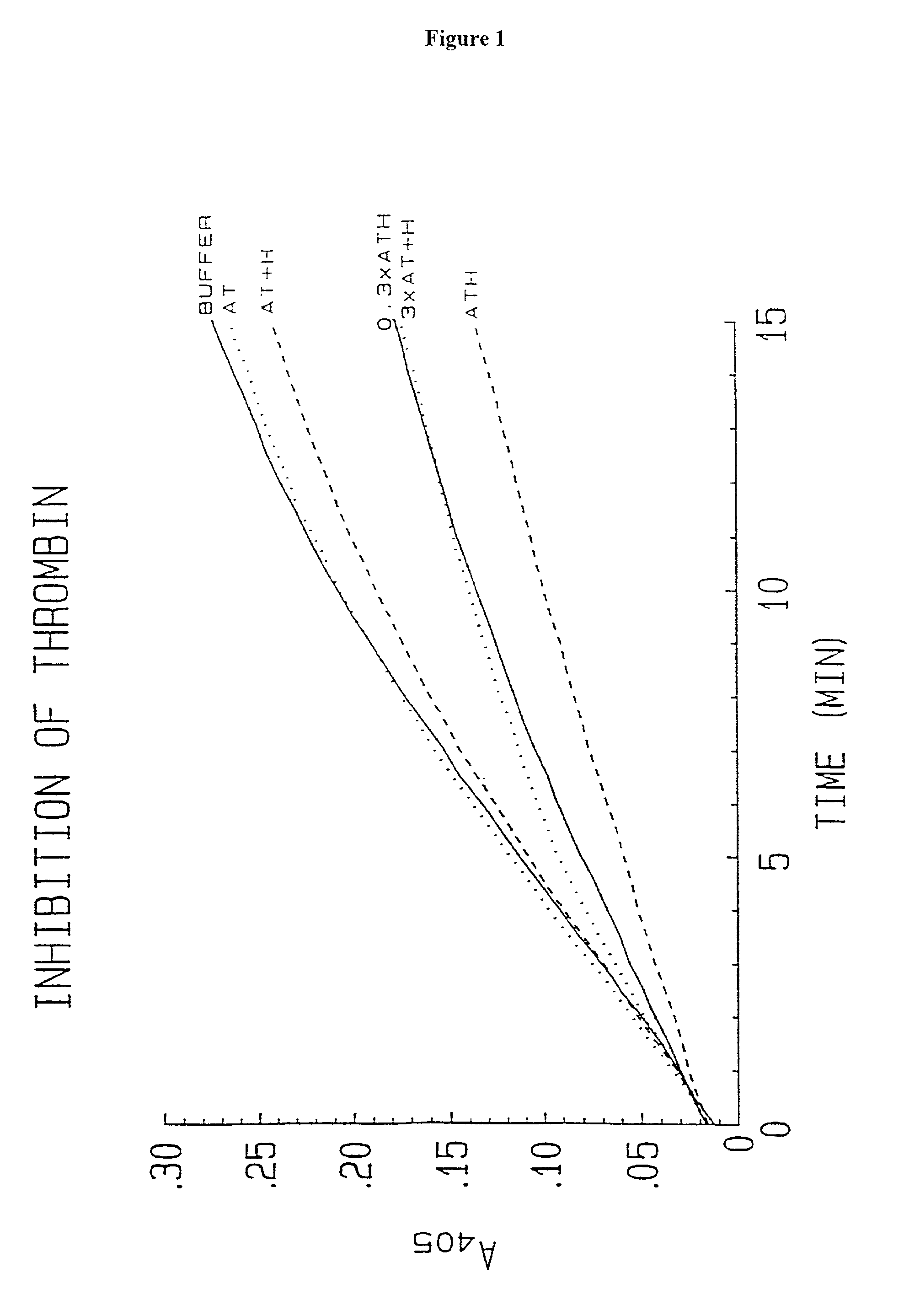
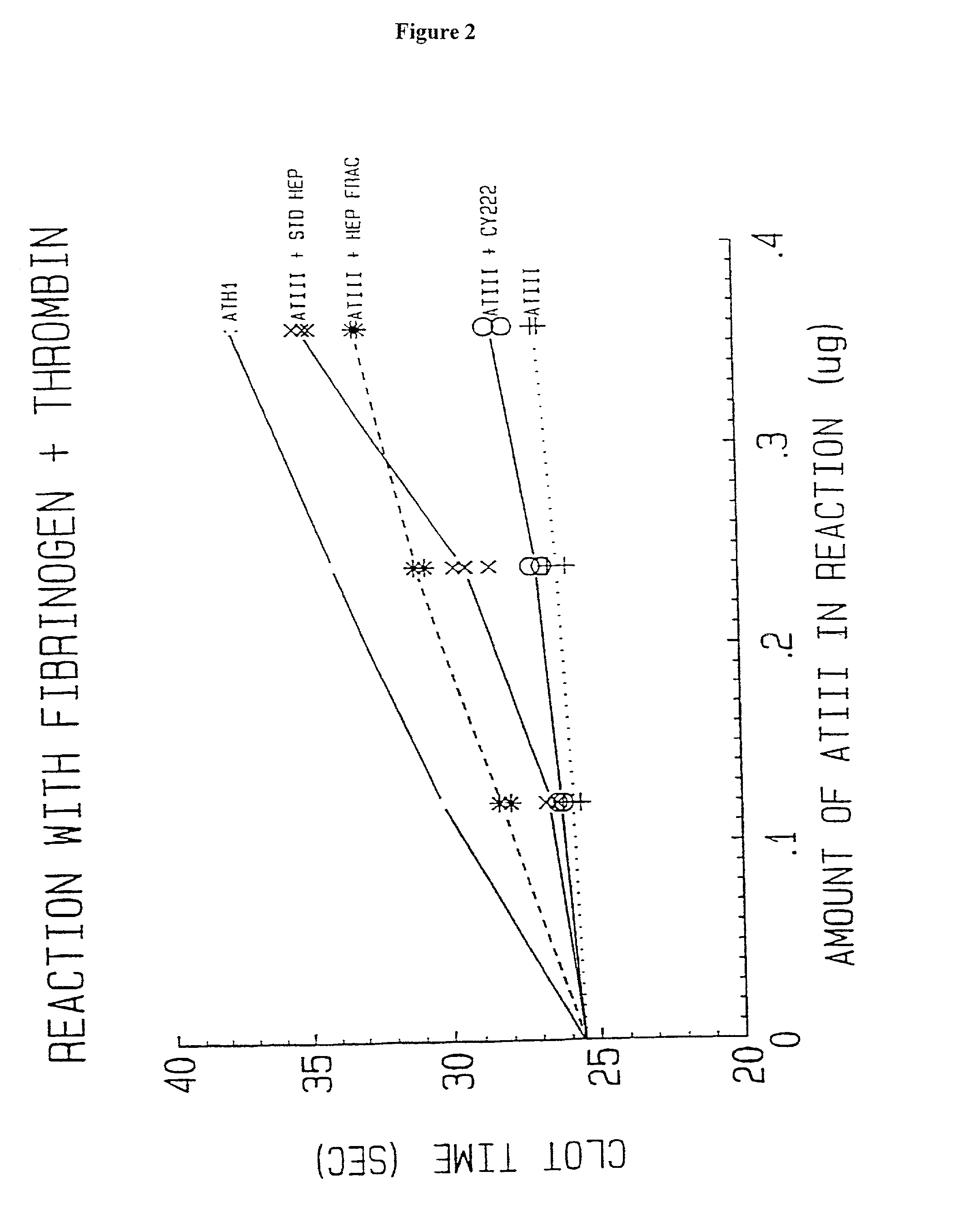
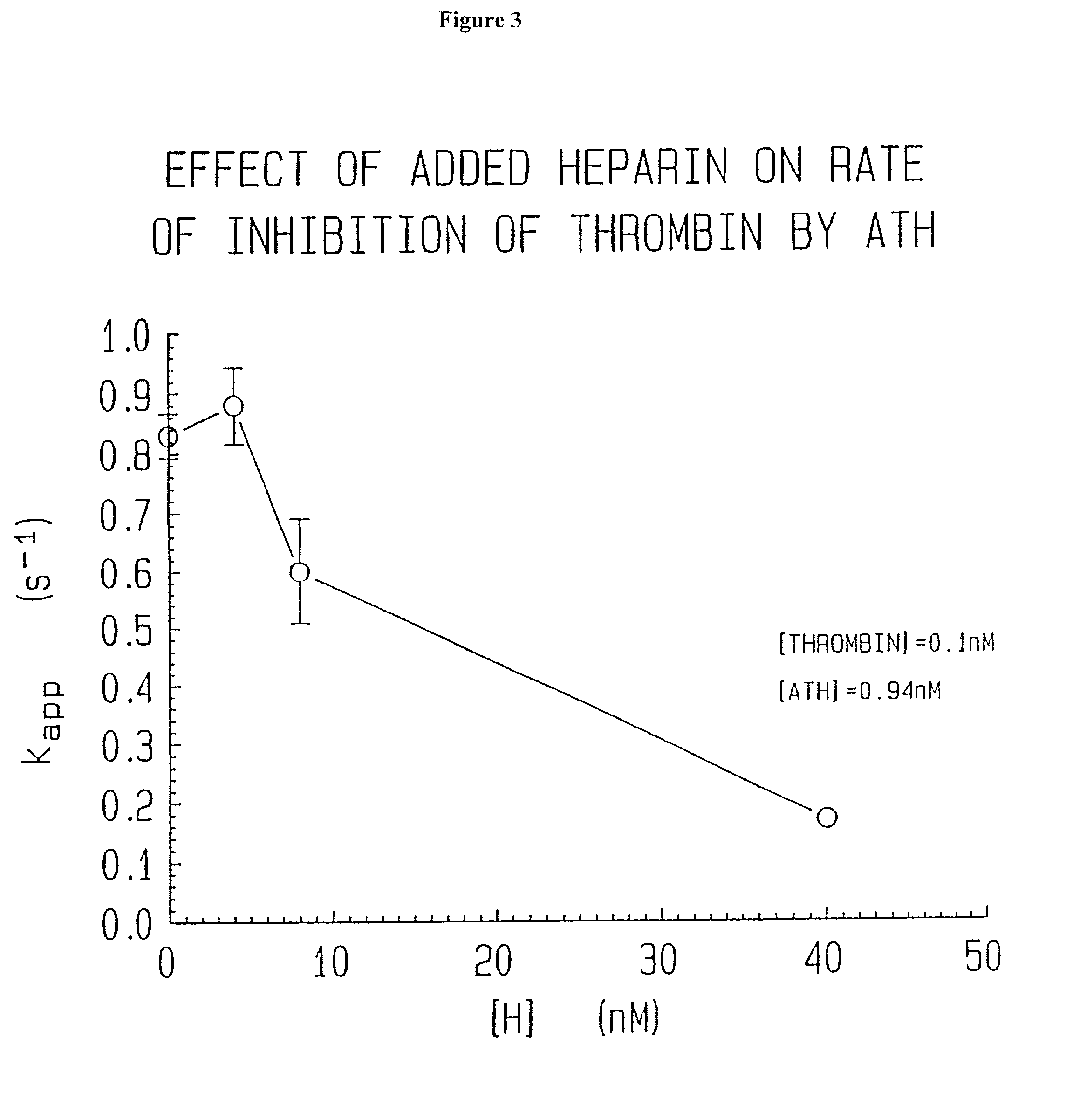
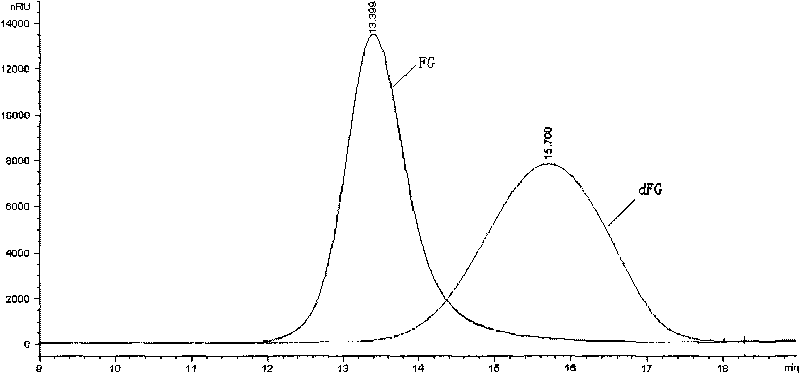
Novel conjugates of glycosaminoglycans, particularly heparin and dermatan sulfate, and amine containing species and therapeutic uses thereof are described. In particular, mild methods of conjugating heparins to proteins, such as antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II, which provide covalent conjugates which retain maximal biological activity are described. Uses of these conjugates to prevent thrombogenesis, in particular in lung airways, such as found in infant and adult respiratory distress syndrome, and on surfaces in contact with blood are also described.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
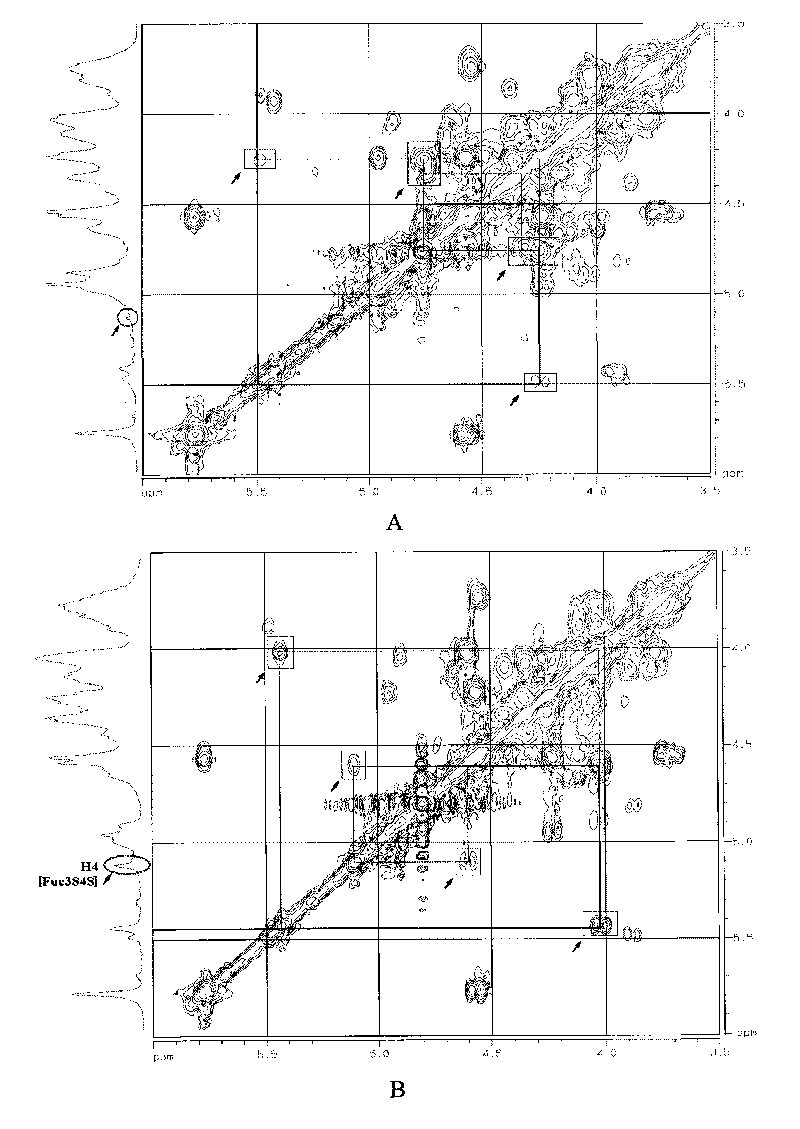
Oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101735336ASimple reaction conditionsQuick responseOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderDepolymerizationGlycan
The invention discloses a method for preparing oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan which is prepared by depolymerizing fucosylated glycosaminoglycan by a depolymerization method of peroxide catalyzed by a 4th period transition metal ion in an aqueous medium, and the preparation method has mild reaction condition, good reproducibility and stability, high pyrolysis selectivity and uniform and controllable product quality. The polysaccharide molecule number of the obtained oligomeric fucosylated glycosaminoglycan using GalNAc as a reducing end is not less than 80 percent, the weight average molecular weight is about 6, 000-20, 000Da, and the protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) is 1.0-2.0.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARMA RES INST CO LTD
Liposomal encapsulation of glycosaminoglycans for the treatment of arthritic joints
Owner:THOMPSON JONATHAN +1
Sustained release preparations composed of biocompatible complex microparticles
A particle includes a complex between a bioactive agent and a complexing agent, provided that the bioactive agent is other than a polynucleotide and an oligonucleotide, and wherein the particle has a bioactive function. The particle has a diameter from about 5 nm to about 100 microns. In certain embodiments, the bioactive agent is a member selected from the group consisting of a growth factor, a hormone, a peptide, a protein, and polysaccharide. In certain embodiments, the complexing agent is a member selected from the group consisting of polysaccharides, glycosaminoglycans, complex carbohydrates, polyacids, modifications and derivatives thereof. Also provided is a method of making the particle. Further provided is a method of administering the particle, including providing the particle, which is adapted to gradually release the bioactive agent; and thereby administering the particle.
Owner:CHORNY MICHAEL +1
Acellular matrix with natural level of glycosaminoglycan and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104888274AGuaranteed sterilityImprove decellularization efficiencyProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an acellular matrix with natural level of glycosaminoglycan and preparation and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out acellular disposal on natural biological tissue to obtain an acellular matrix; detecting missing amount of glycosaminoglycan in the acellular matrix; and supplementing glycosaminoglycan by means of natural ingredients in the acellular matrix to obtain the acellular matrix with natural level of glycosaminoglycan. Through the method, a lot of the glycosaminoglycan component in the acellular matrix is recovered. The acellular matrix has good biocompatibility. The natural biological structure is recovered, and the acellular matrix is beneficial to cell growth. glycosaminoglycan is supplemented for the acellular matrix, and a tissue engineering carrier is constructed. According to the invention, a biological carrier which meets cell growth requirement and mechanical strength requirement and has similar structural components as a natural extracellular matrix can be prepared rapidly. The invention is a great breakthrough of the tissue engineering construction technology. Meanwhile, principle of the invention is reliable, the technology is simple and flexible, product reproducibility is good, and industrialization is easy to realize.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
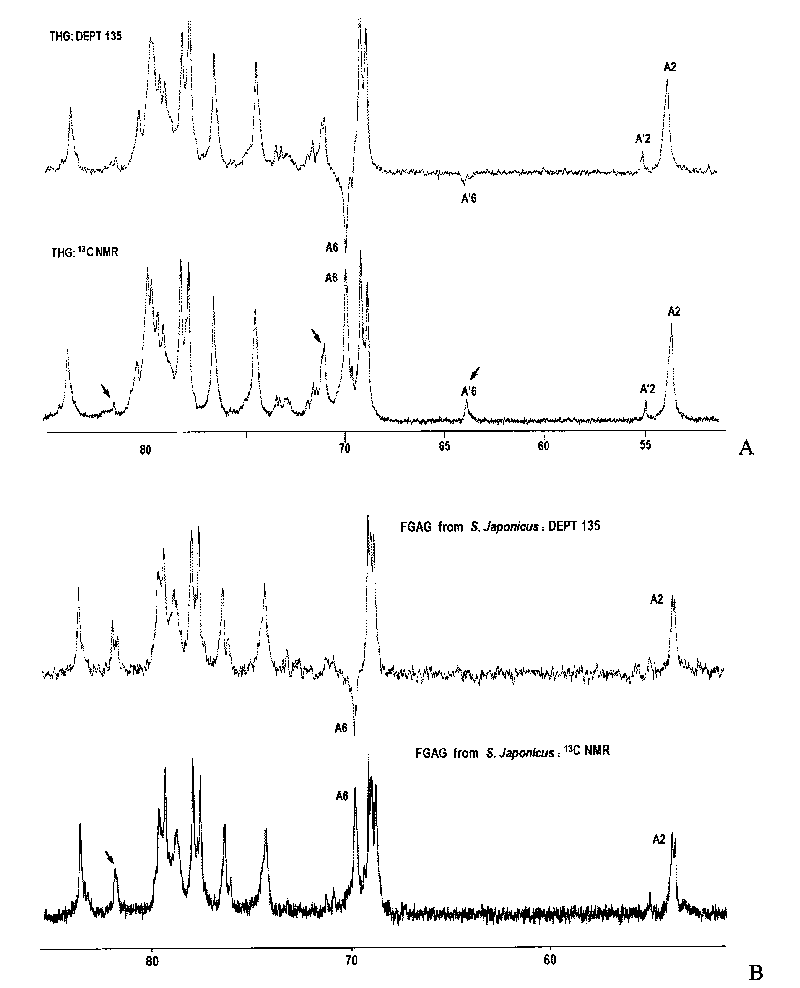
Oligomerization pineapple ginseng glycosaminoglycan and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101724086AGood anticoagulant and antithrombotic activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderMonosaccharide compositionEnzyme inhibitor
The invention discloses oligomerization pineapple ginseng glycosaminoglycan (dTHG). The weight-average molecular weight of the glycosaminoglycan is 8,000-20,000Da, and monosaccharide constituents comprise acetylgalactosaminyl (GaLNAc), glucuronic acid (GLcUA), fucose (Fuc) or sulfuric ester thereof (expressed by -OSO3-), wherein the molar ratio of the GaLNAc to the GLcUA to the Fuc to the -OSO3- is about 1:(+ / -0.3):(1+ / -0.3):(3.5+ / -0.5). The dTHG is a powerful endogenous factor X enzyme inhibitor, has good anticoagulation and anti-thrombus activity and can be used for preventing and / or treating thrombotic diseases. The invention also provides a method for preparing the dTHG, comprising the following steps of: (1) extracting and obtaining fucose glycosaminoglycan (THG) from the walls of pineapple ginseng bodies; (2) adopting a peroxide method or a peroxide method under the catalysis of an ionic catalyst of transition metal of the fourth period to depolymerize the THF so as to obtain dTHG; and (3) removing low molecular and / or high molecular impurity constituents in the dTHG.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEPTUNUS PHARM CO LTD
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20080051567A1Loss of anticoagulant activityImprove propertiesOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPerylene derivativesGlycosaminoglycan
Owner:LEADIANT BIOSCI SA
Method for use of hyaluronic acid in wound management
InactiveUS20030021834A1Minimize tissue damageReduce drynessBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWound healingSurgical site
A method for decreasing or shortening the length of time required to complete a surgical procedure by the application of hyaluronic acid to the surgical site, and for wound management by topical application of hyaluronic acid to a wound by syringe through a thin film dressing. The method of wound management results in accelerated wound healing time. The solution of hyaluronic acid may include an effective amount of a polysulfated glycosaminoglycan for stimulating macrophage activity at the surgical wound site.
Owner:PETITO GEORGE D
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20100196423A1Reduce sensitivityGreater serum half-livesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated form of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
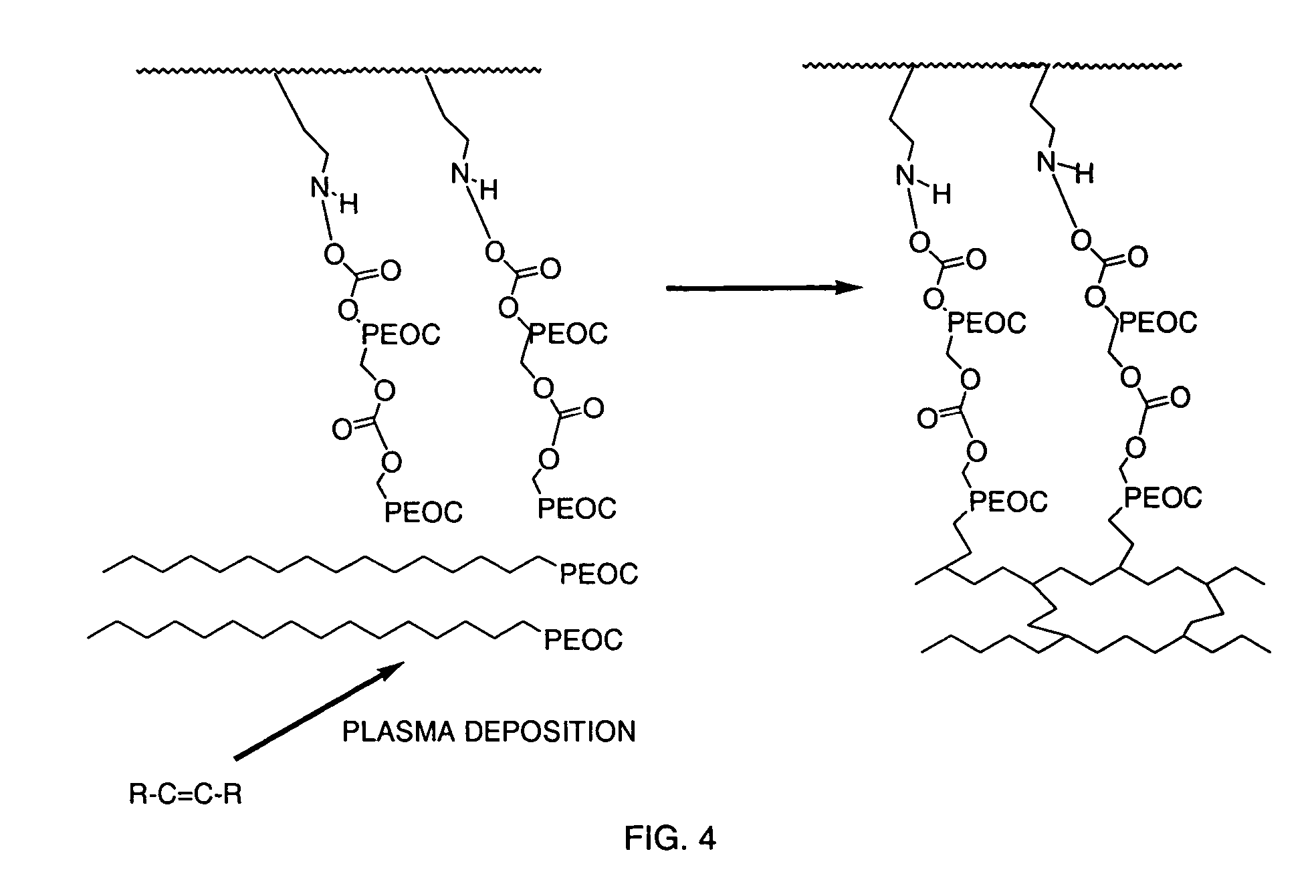
Medical device with plasma cross-linked hydrophilic coating
InactiveUS7217769B2Increased wear and resistance characteristicLubricity be alteredChiropractic devicesPretreated surfacesCross-linkPlasma deposition
A medical device with a hydrophilic and lubricious coating, wherein the coating includes a hydrophilic polymeric unit layer deposited on the medical device and cross-linked with a plasma deposited double bond monomer. The hydrophilic polymeric unit can include ethylene oxide with one or more primary or secondary alcohol groups or glycosaminoglycans such as hyaluronic acid, and the double bond monomer includes monomers containing at least one double bond, preferably a C═C, C═N or C═O bond, including N-trimethylsilyl-allylamine, ethylene, propylene and allyl alcohol.
Owner:BIOSURFACE ENG TECH
Derivatives of partially desulphated glycosaminoglycans as heparanase inhibitors, endowed with antiangiogenic activity and devoid of anticoagulating effect
InactiveUS20060172968A1Avoiding and reducing side effectLoss of anticoagulant activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicinal chemistryAnticoagulant activity
Partially desulphated glycosaminoglycan derivatives are described, particularly heparin, and more particularly a compound of formula (I) where the U, R and R1 groups have the meanings indicated in the description. These glycosaminoglycan derivatives have antiangiogenic and heparanase-inhibiting activity and are devoid of anticoagulant activity.
Owner:LEADIANT BIOSCI SA
Modified biodegradable polymers, preparation and use thereof for making biomaterials and dressings
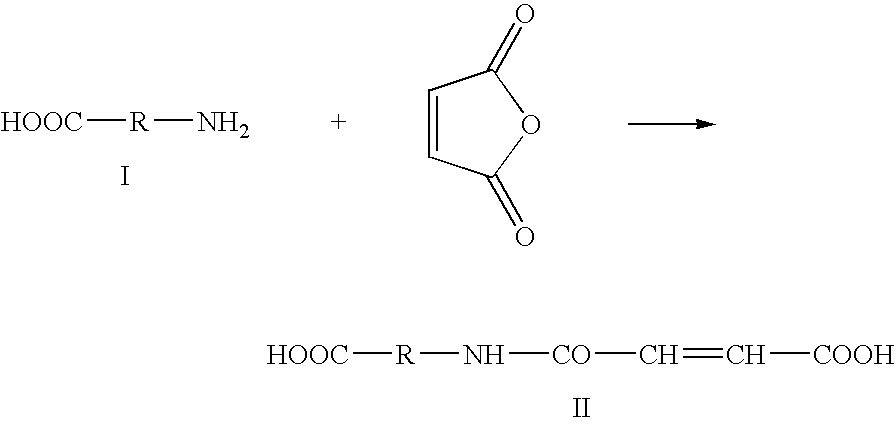
InactiveUS20090035356A1Overcome difficultiesLimit presenceCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceCarboxylic acid
The invention concerns a method for preparing a modified biodegradable polymer in aqueous medium comprising at least two steps. The first step is a reaction between an amino acid, a peptide or a polypeptide and maleic anhydride to form a compound having an unsaturated vinyl-carboxylic acid function. In the second reaction step, the unsaturated diacid obtained in the first step is reacted with a biodegradable polymer having at least one primary amine function, such as a fibrous protein or a glycosaminoglycan. The preferred polymer used is collagen or chitosan. The invention also concerns the modified biodegradable polymer obtained by the method. The invention further concerns a biomaterial or a dressing containing the modified biodegradable polymer having biocompatible, cytocompatible, hemostatic, bactericidal and wound healing properties, and its medical, biomedical, pharmaceutical or cosmetic use.
Owner:BUI KHAC TRUNG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com