Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
255 results about "Respiratory distress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Respiratory distress is difficulty in breathing, and the psychological experience associated with such difficulty, even if there is no physiological basis for experiencing such distress. The physical presentation of respiratory distress is generally referred to as labored breathing, while the sensation of respiratory distress is called shortness of breath or dyspnea. Respiratory distress occurs in connection with various physical ailments, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung, and infant respiratory distress syndrome, a syndrome in premature infants caused by developmental insufficiency of surfactant production and structural immaturity in the lungs. Symptoms may be outwardly evident, physically labored ventilation or respiratory efforts; clinically evident inability to adequately ventilate and/or oxygenate. "Respiratory distress" is the preferred term to use in referring to veterinary patients who present with severe respiratory difficulty.
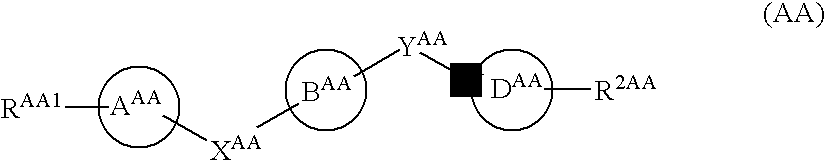
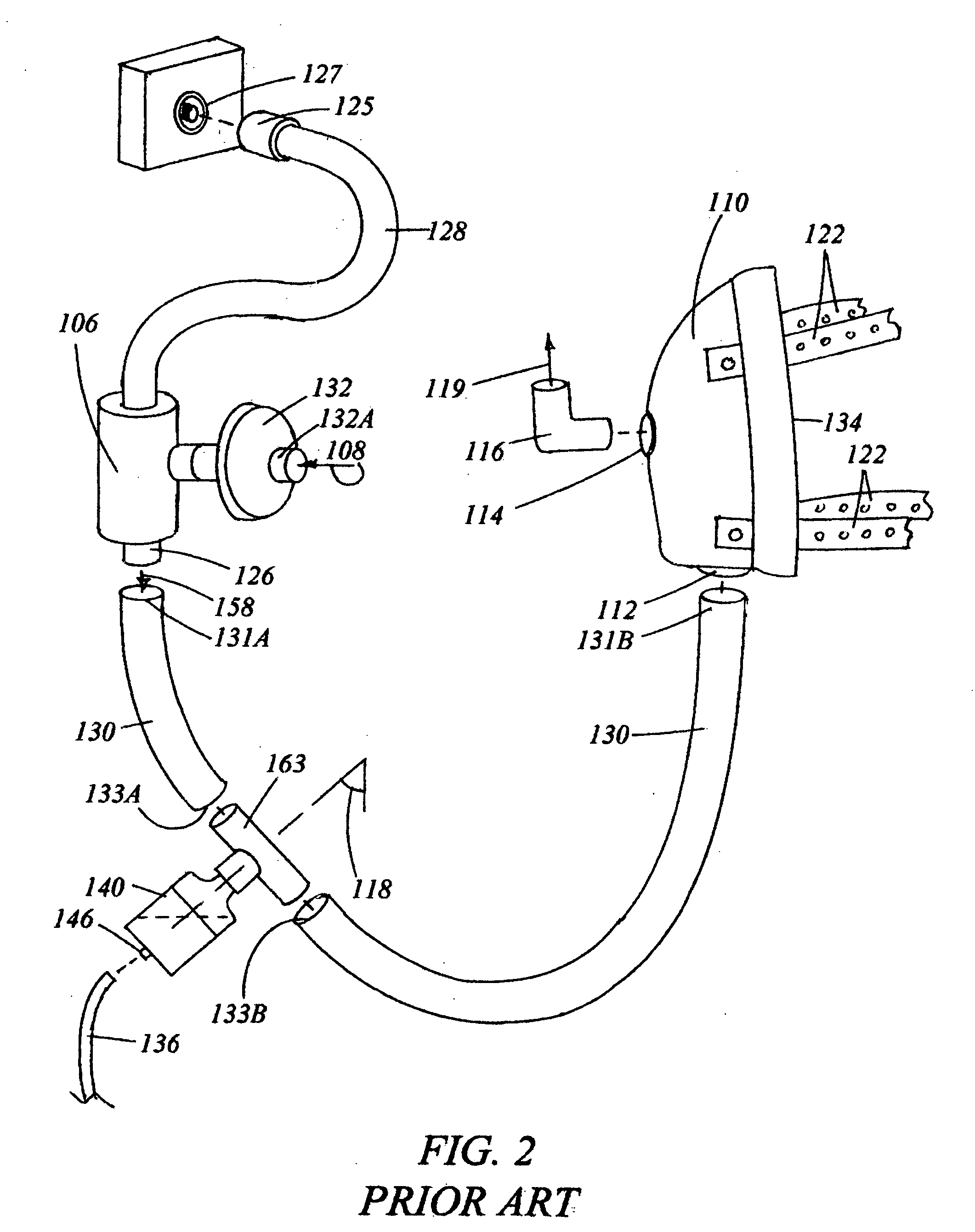
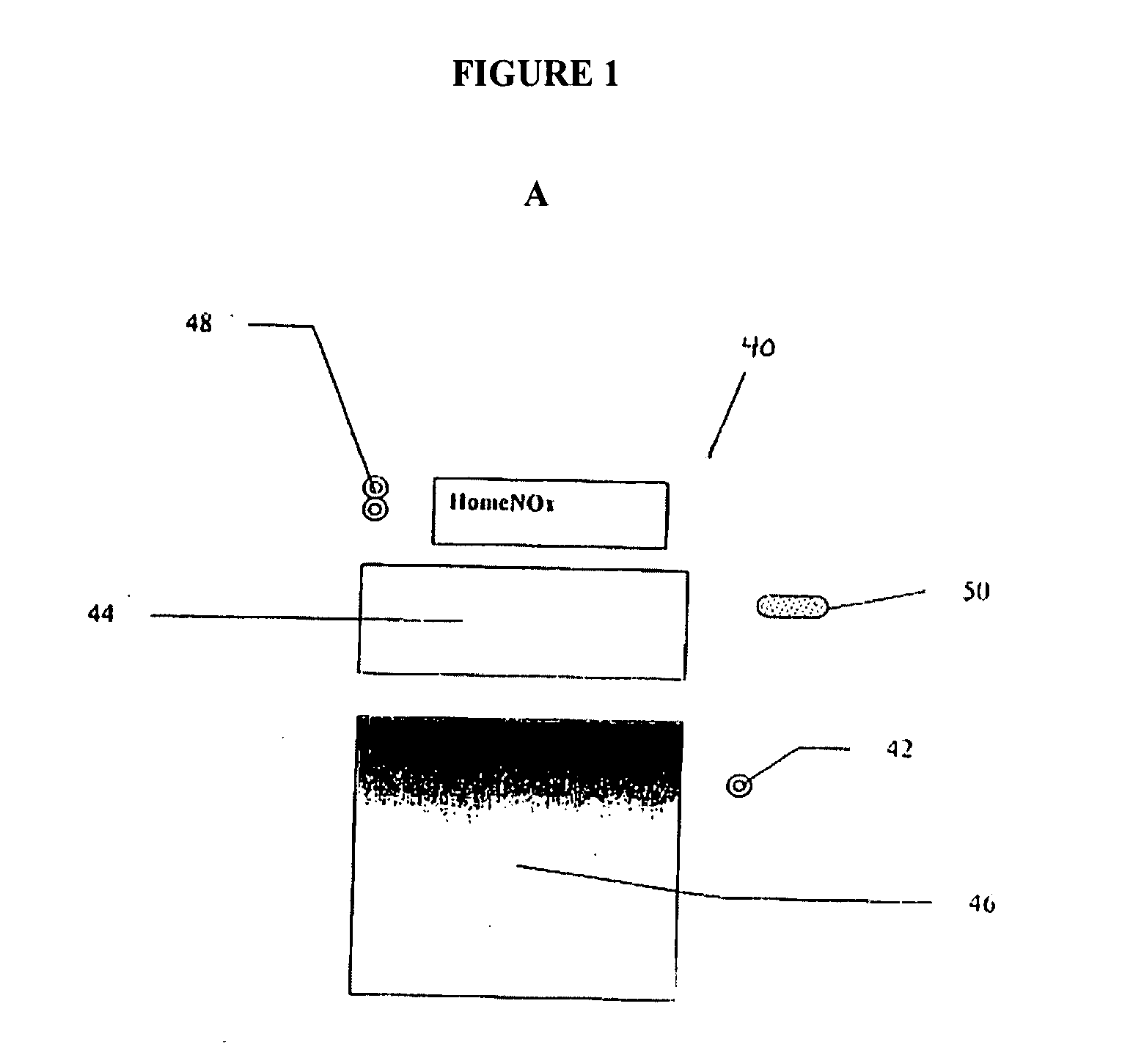
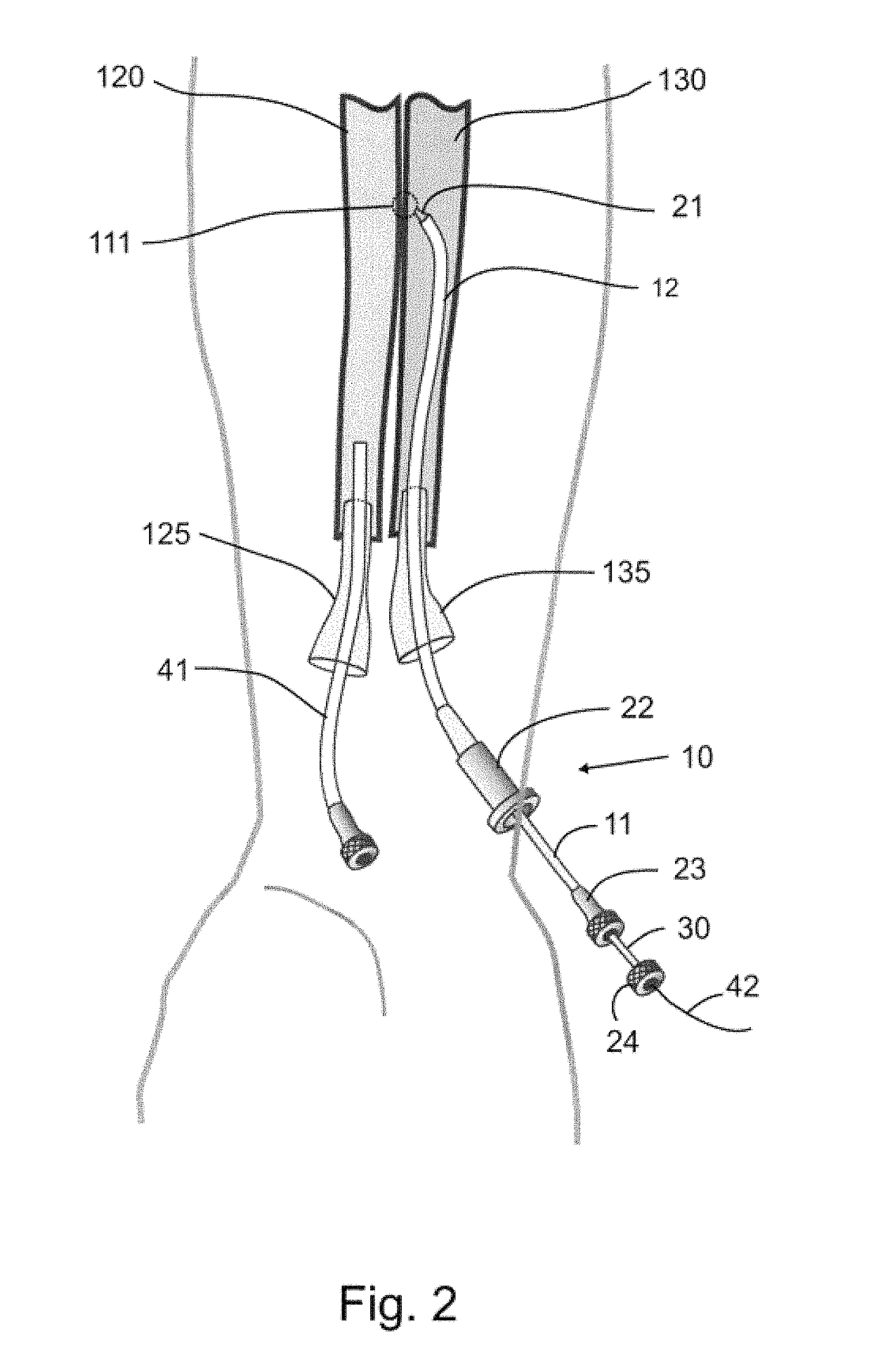
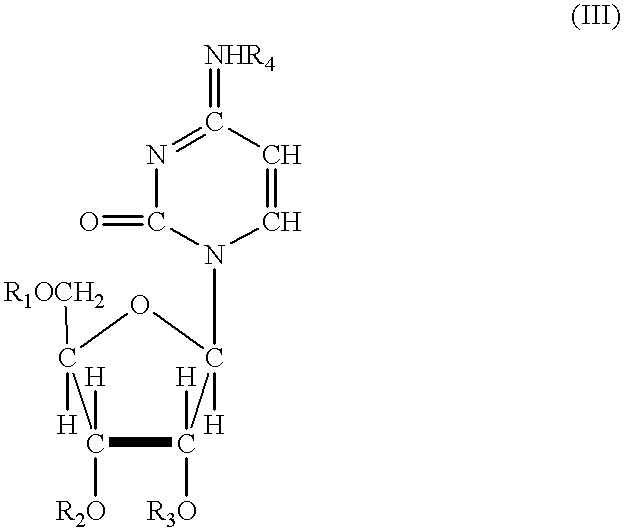
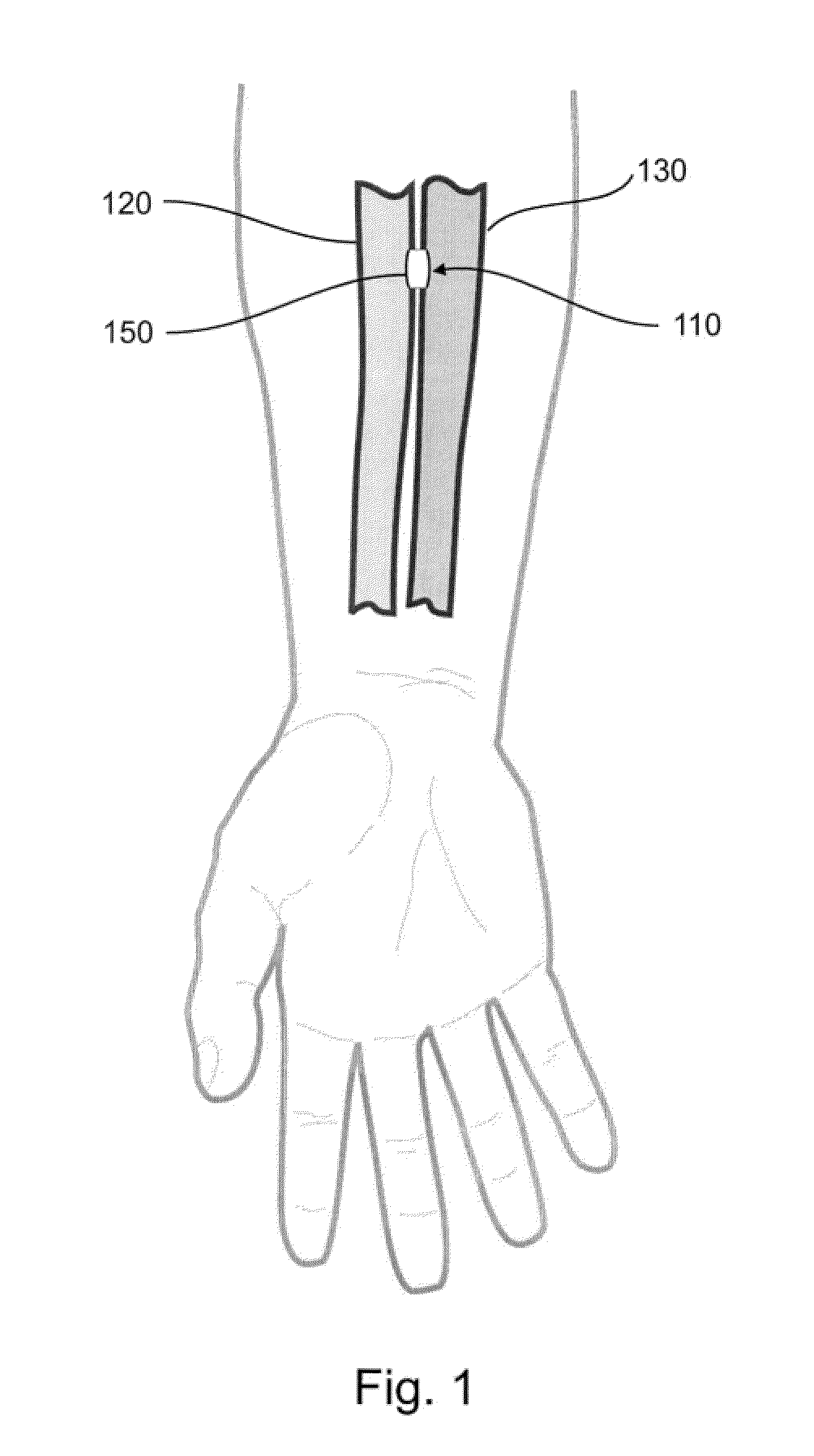
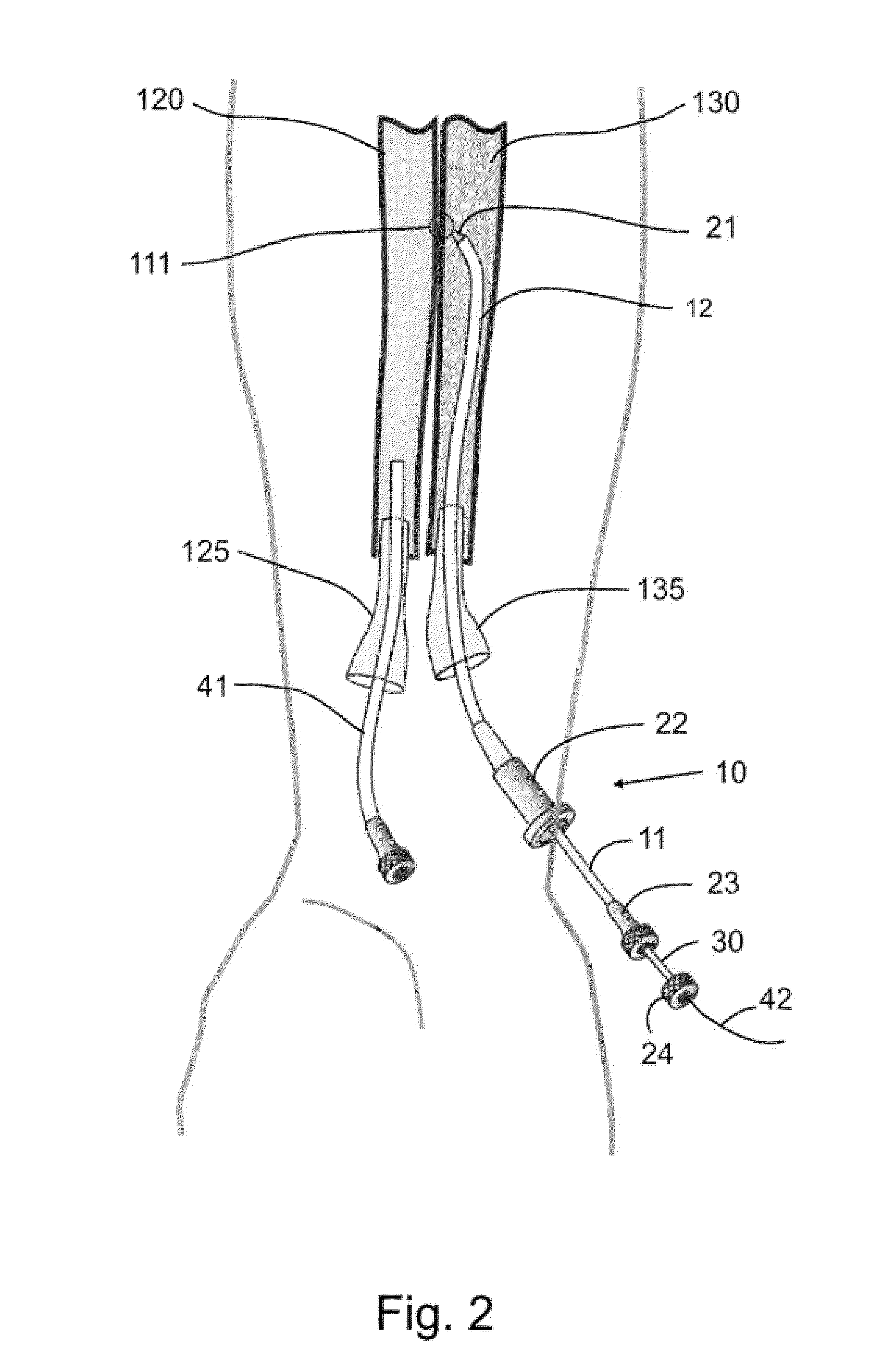
Devices, systems, and methods for energy assisted arterio-venous fistula creation
InactiveUS20060111704A1Avoid bleedingProviding tensionStentsSurgical instruments for heatingRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTDisease
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for the formation of an arteriovenous fistula. Embodiments include catheter apparatus including an ablation element for creating and / or modifying the fistula. The devices, systems and methods can be used to treat patients with one or more numerous ailments including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, hypertension, hypotension, respiratory failure, pulmonary arterial hypertension, lung fibrosis and adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
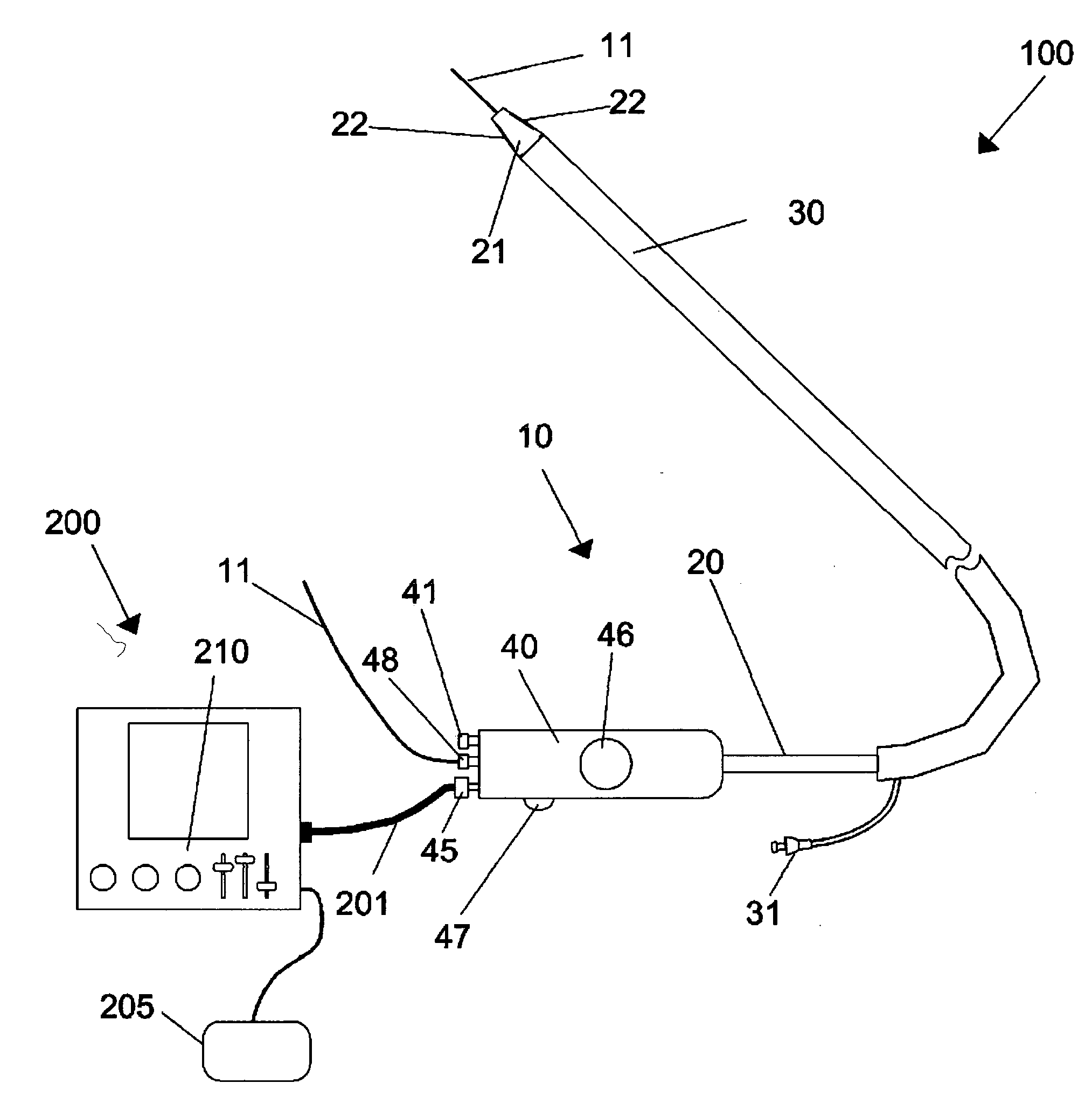
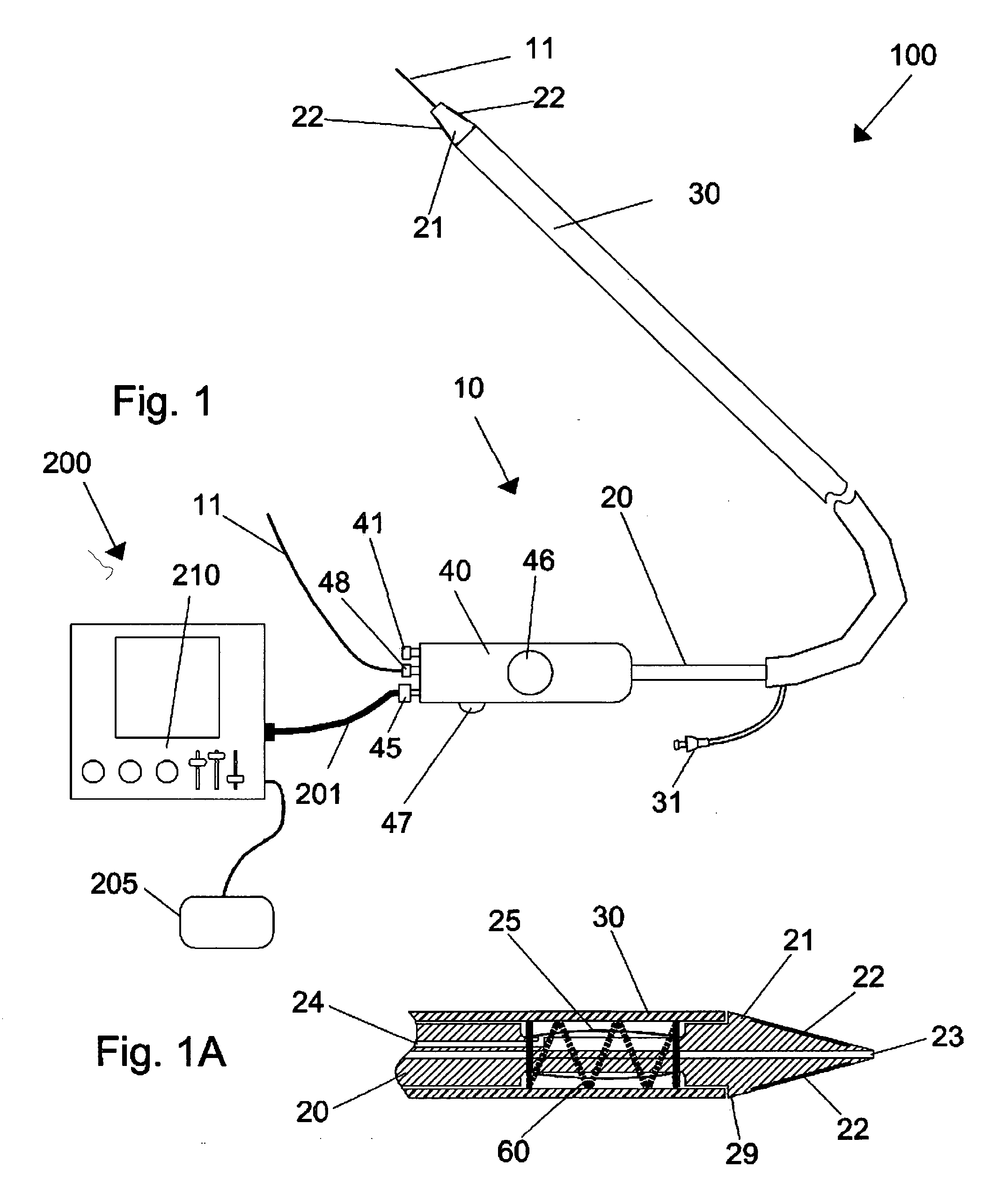
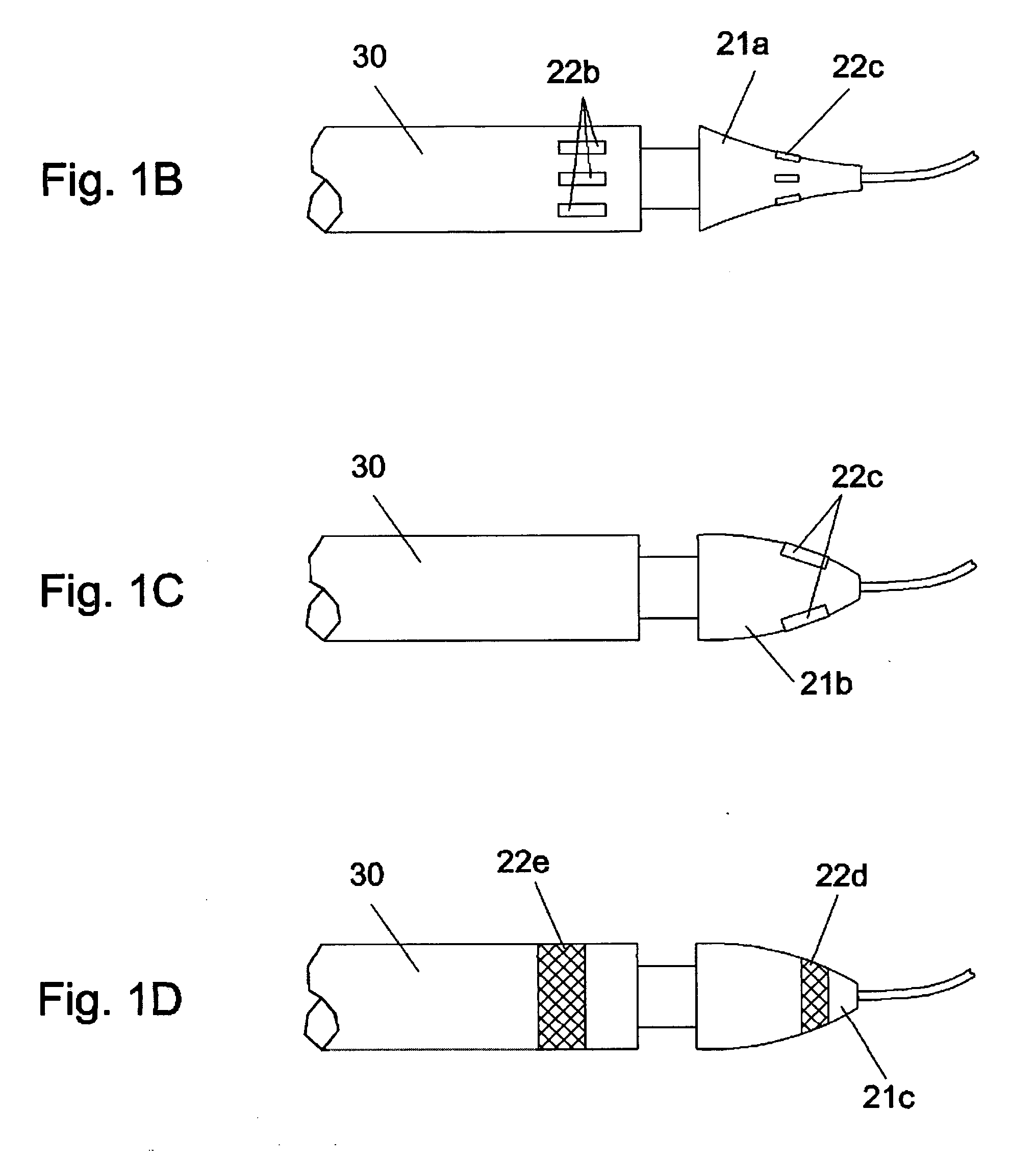
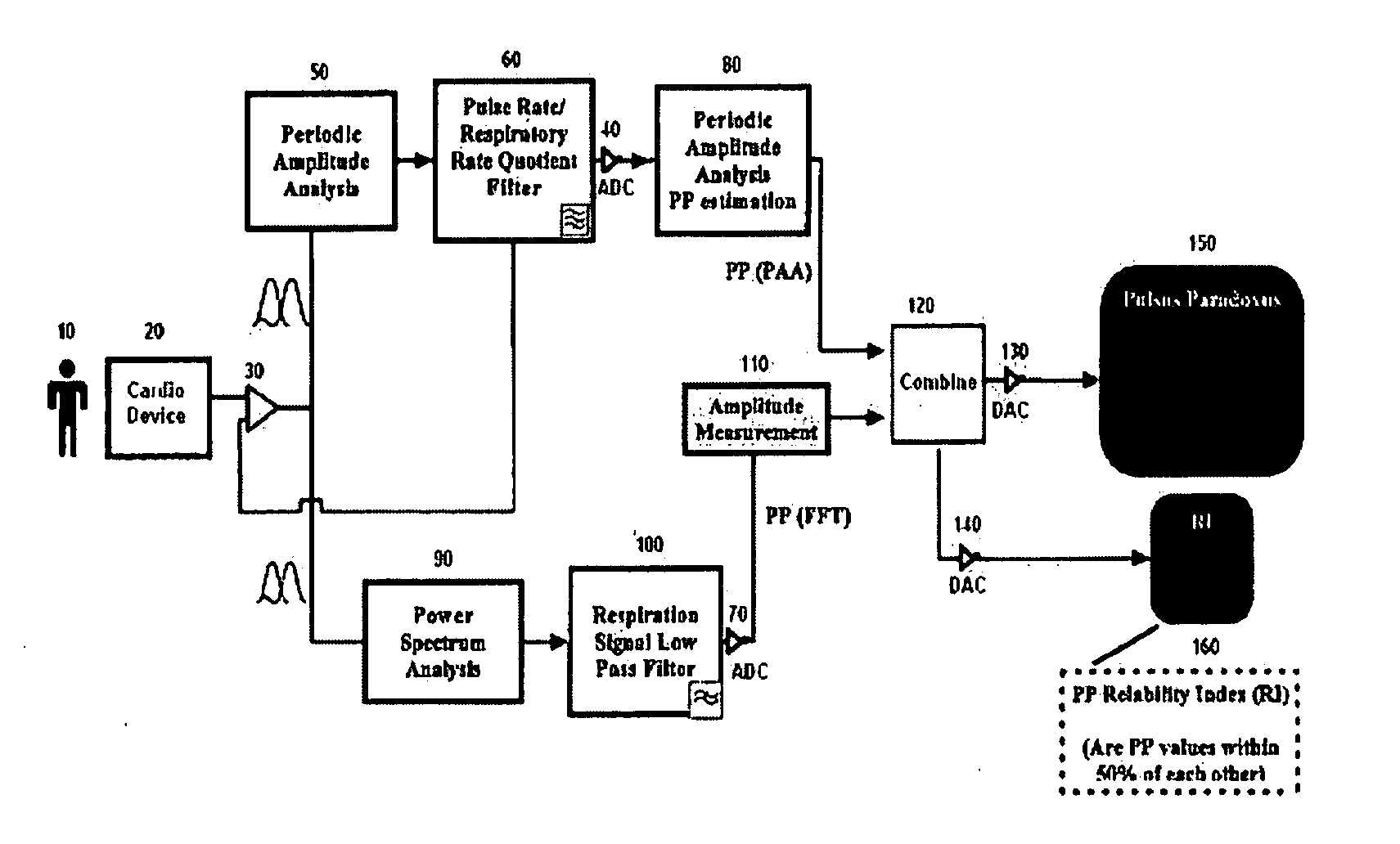
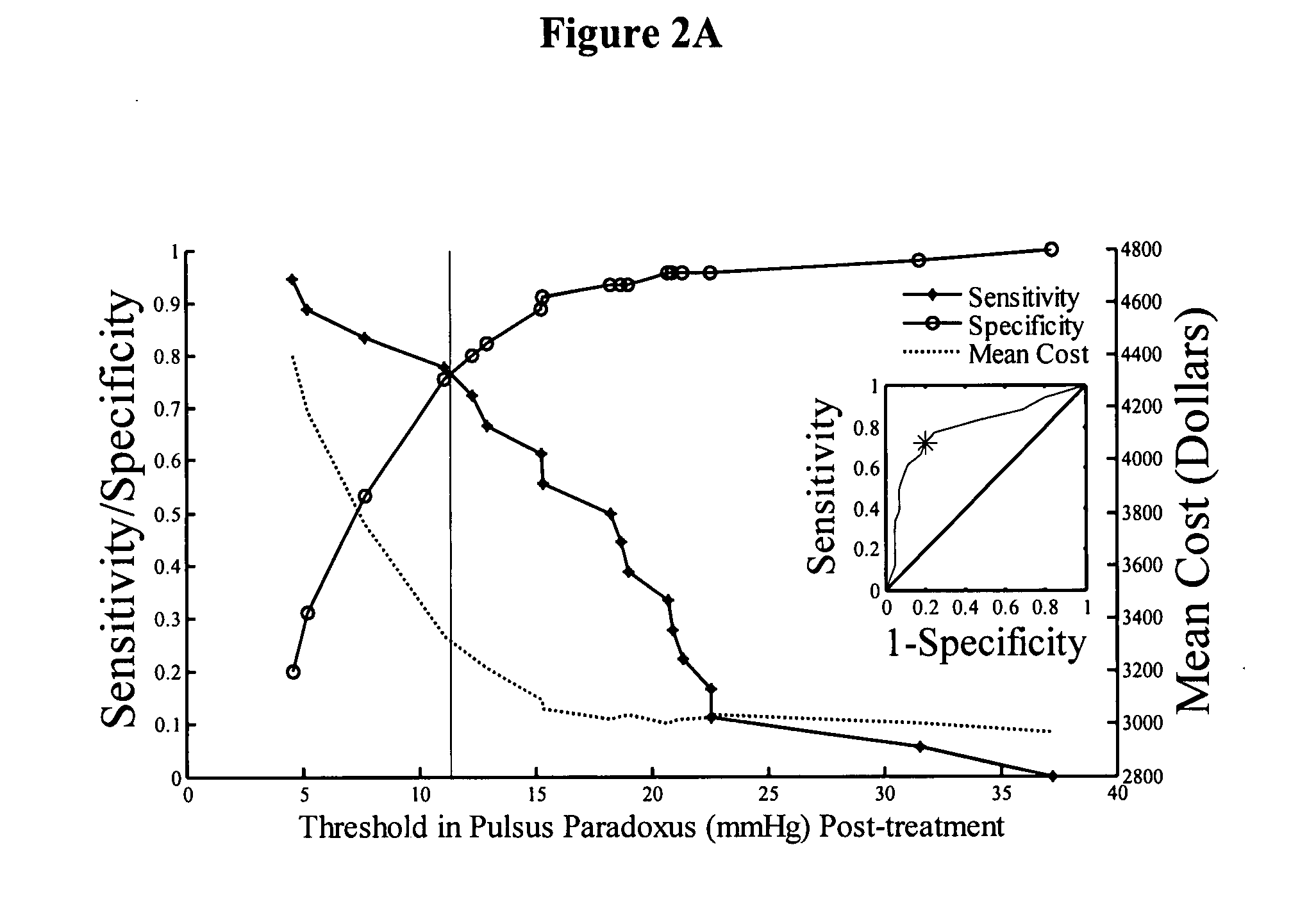
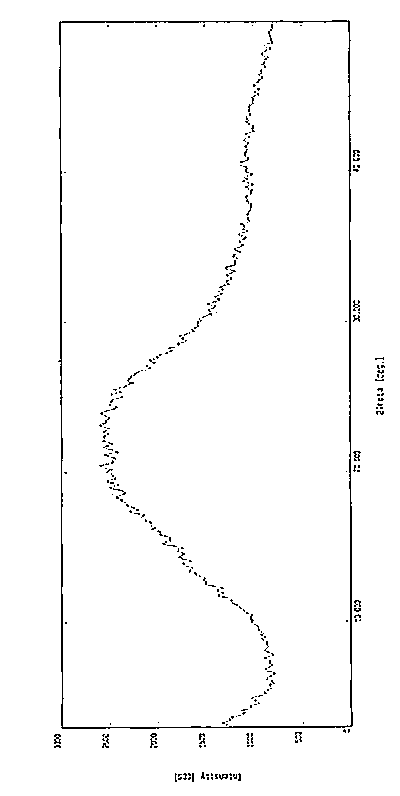
Devices and methods for measuring pulsus paradoxus
The invention relates to methods and devices for measuring pulsus paradoxus. The methods herein employ a combination of one or more forms of waveform analysis for the purpose of measuring pulsus paradoxus and diagnosing respiratory distress. The methods also combine measurements of pulsus paradoxus and physician assessments to diagnose respiratory distress. The methods also combine measurements of pulsus paradoxus and percentage oxygenated hemoglobin to diagnose respiratory distress. The devices of this invention employ pulse oximeters, arterial tonometers, finometers, or processors for the purpose of implementing the methods of the invention.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
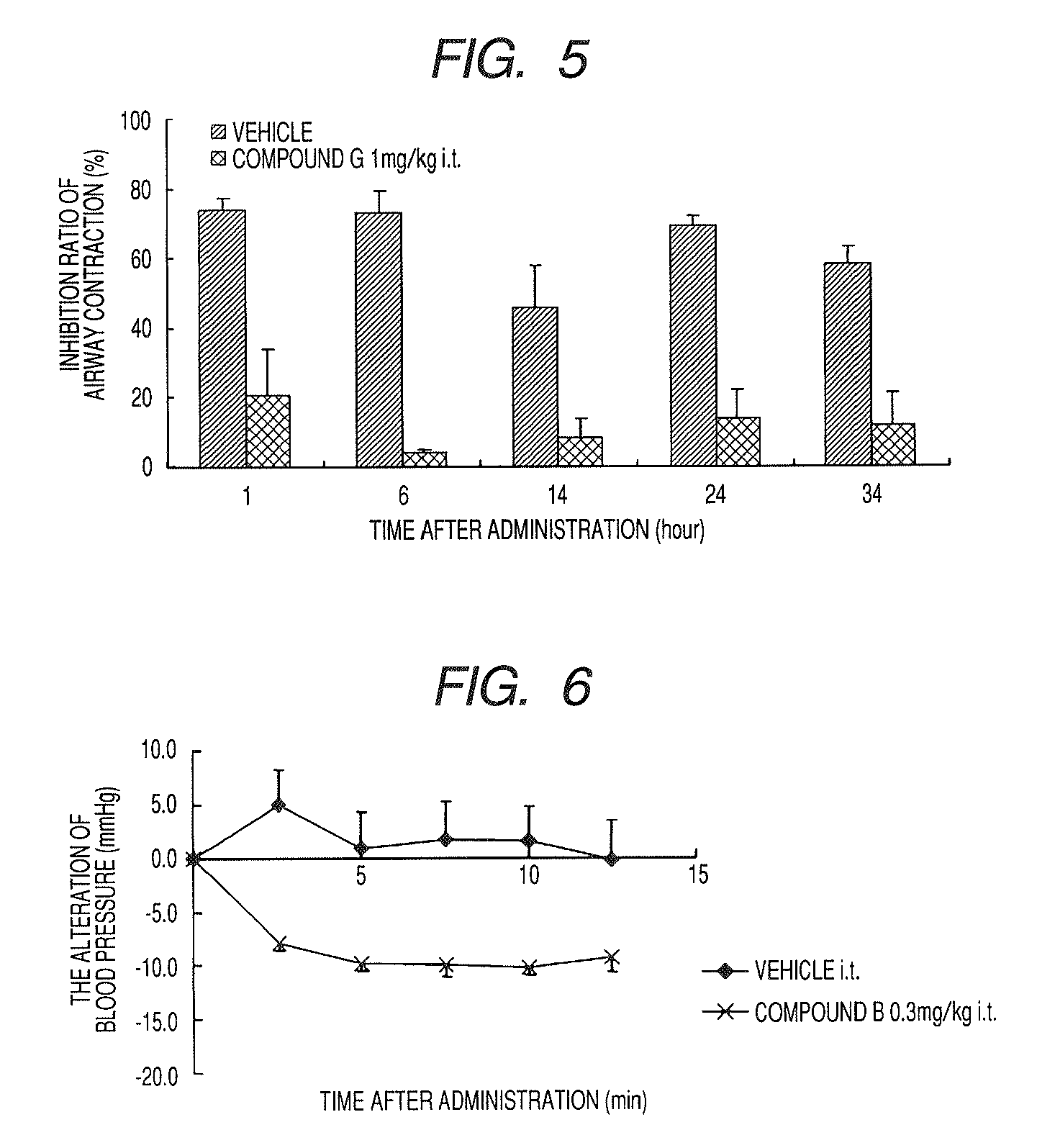
Nitrogenated heterocyclic derivative , and pharmaceutical agent comprising the derivative as active ingredient
InactiveUS20090131403A1Prevention and/or treatmentEasy to useBiocideSenses disorderAcquired immunodeficiencyAutoimmune condition
The compound represented by formula (I), a salt thereof, an N-oxide thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof specifically binds CCR5, so it is useful for preventing and / or treating CCR5-related diseases, for example, various inflammatory diseases (asthma, nephritis, nephropathy, hepatitis, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, ulcerative colitis, etc.), immunological diseases (autoimmune diseases, rejection in organ transplantation, immunosuppression, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, etc.), infectious diseases (infection with human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, urticaria, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, allergic eosinophilic gastroenteritis, etc.), ischemic reperfusion injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock accompanying bacterial infection diabetes cancer metastasis and so on.Wherein all symbols in formula are as defined in the specification
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Carbon monoxide as a biomarker and therapeutic agent
InactiveUS20020155166A1Reduce concentrationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsInterstitial lung diseaseRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULT
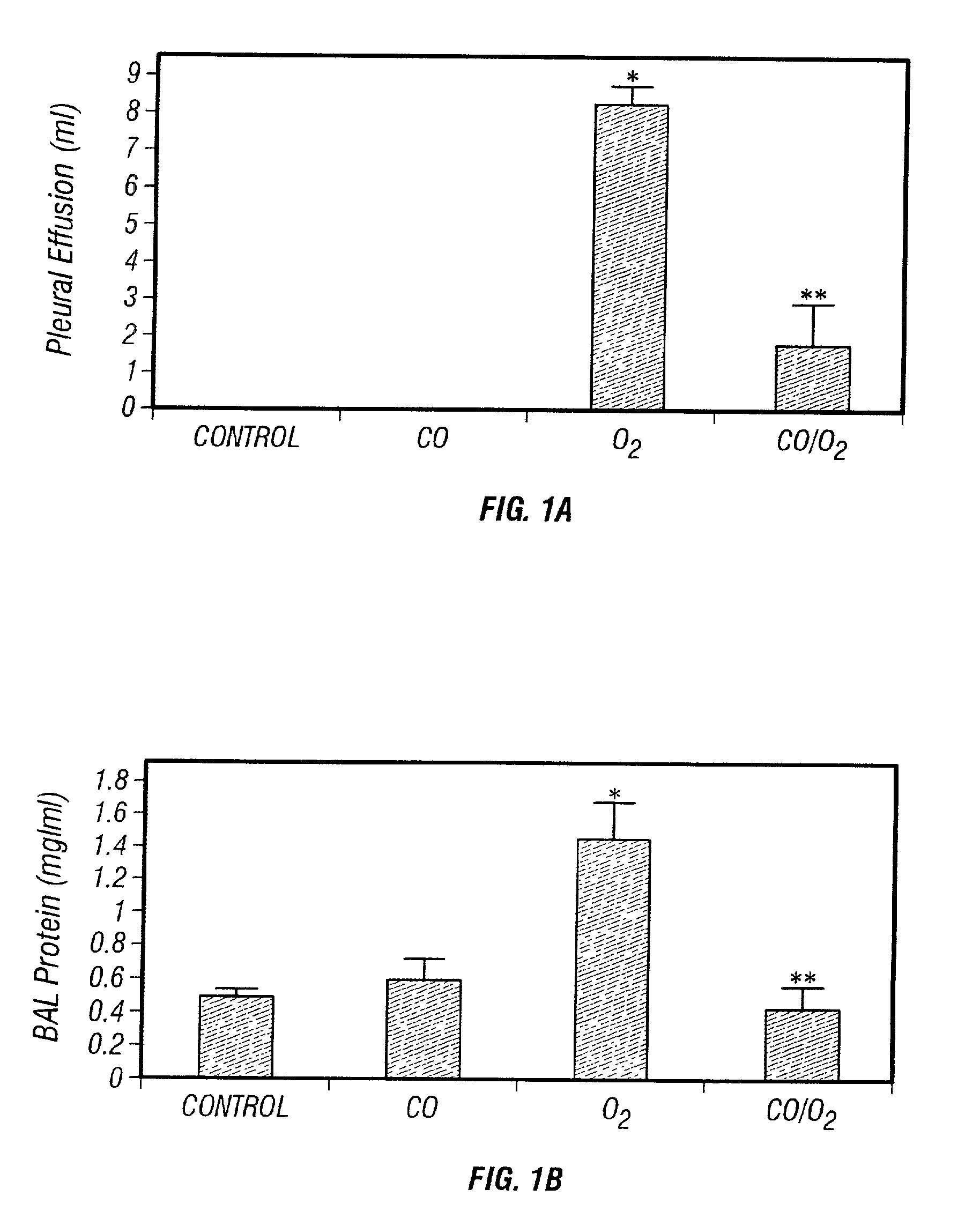
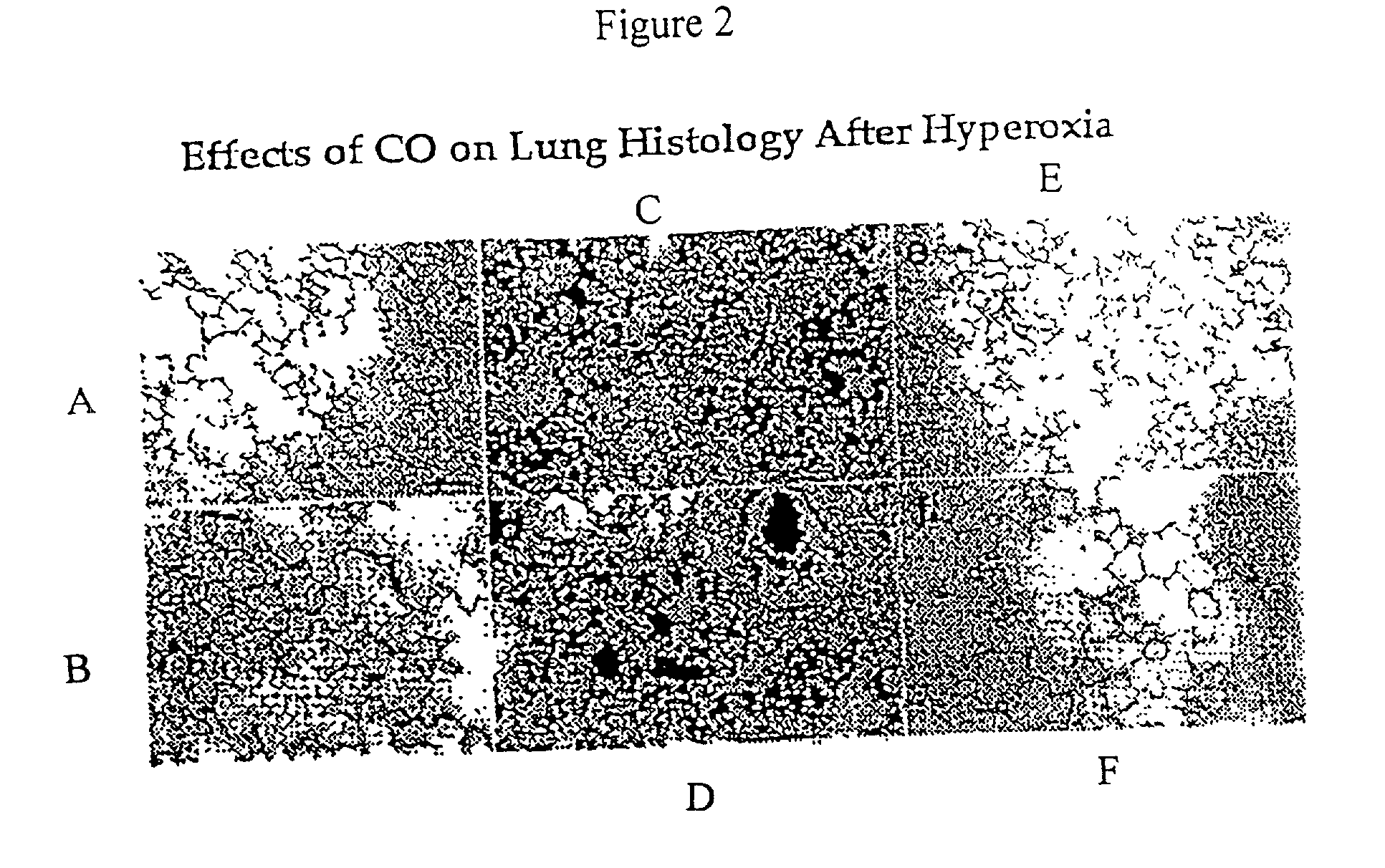
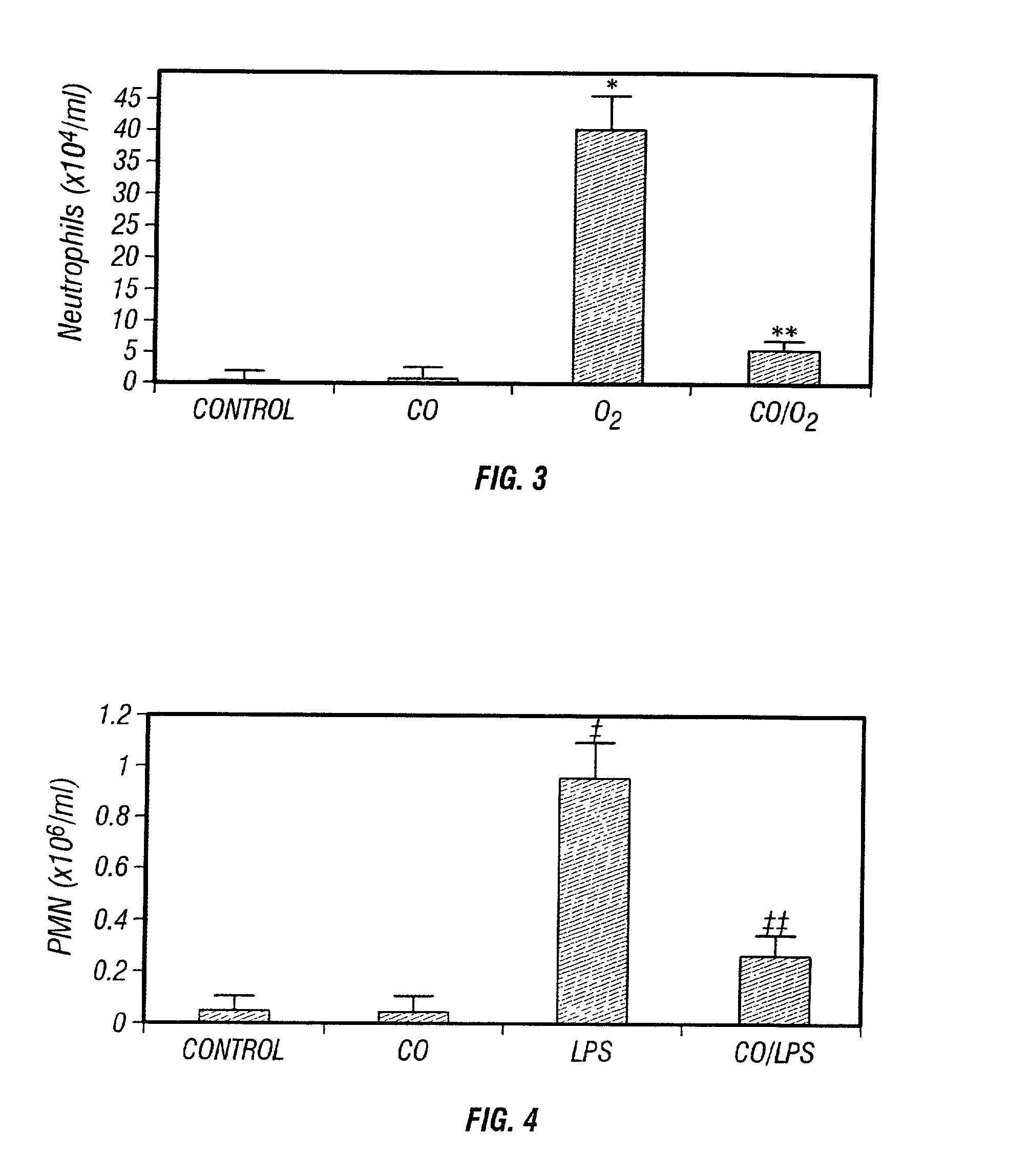
The present invention relates to the use of carbon monoxide (CO) as a biomarker and therapeutic agent of heart, lung, liver, spleen, brain, skin and kidney diseases and other conditions and disease states including, for example, asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, interstitial lung diseases, idiopathic pulmonary diseases, other lung diseases including primary pulmonary hypertension, secondary pulmonary hypertension, cancers, including lung, larynx and throat cancer, arthritis, wound healing, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, peripheral vascular disease and pulmonary vascular thrombotic diseases such as pulmonary embolism. CO may be used to provide anti-inflammatory relief in patients suffering from oxidative stress and other conditions especially including sepsis and septic shock. In addition, carbon monoxide may be used as a biomarker or therapeutic agent for reducing respiratory distress in lung transplant patients and to reduce or inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation in transplant patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
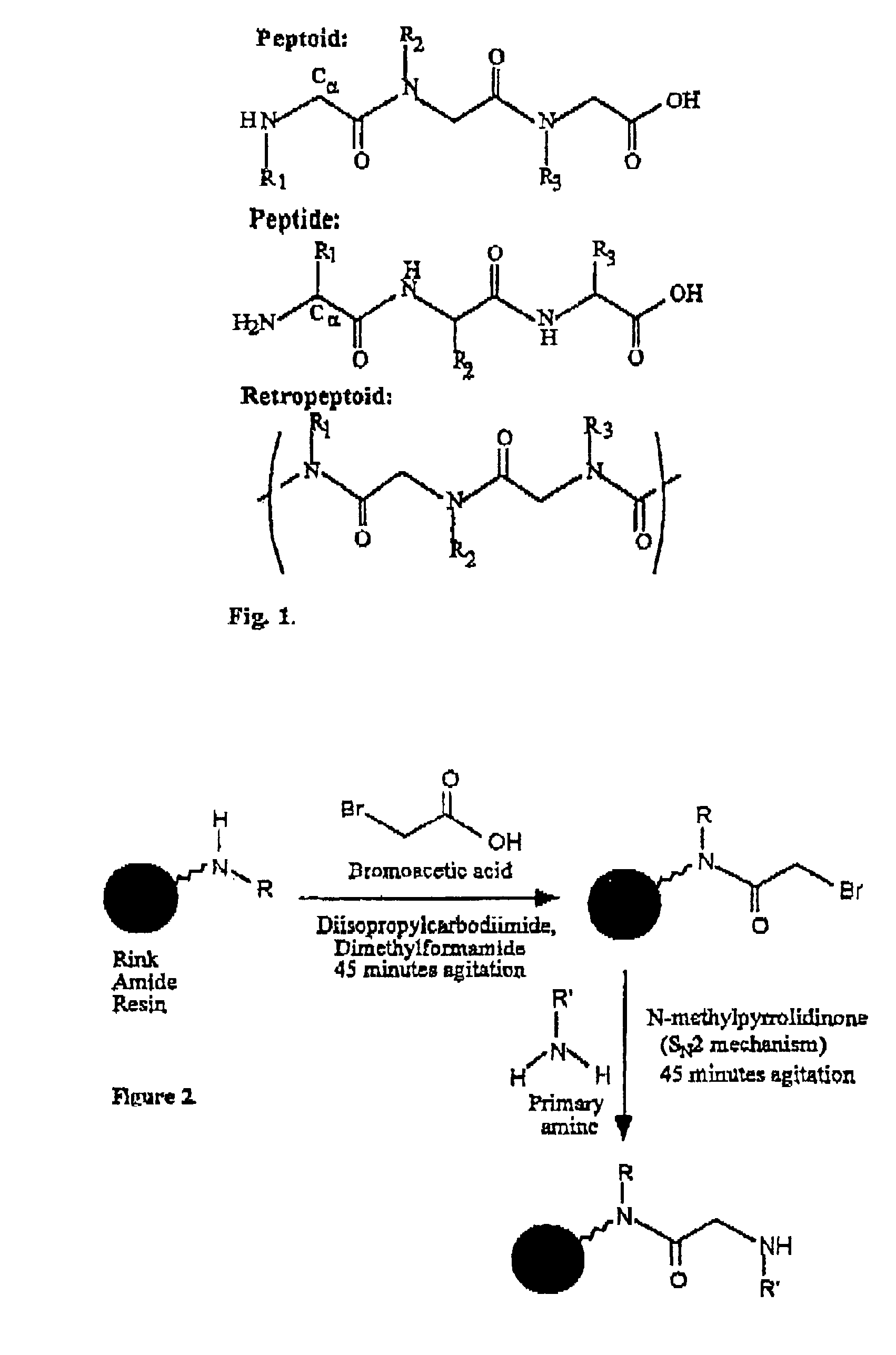
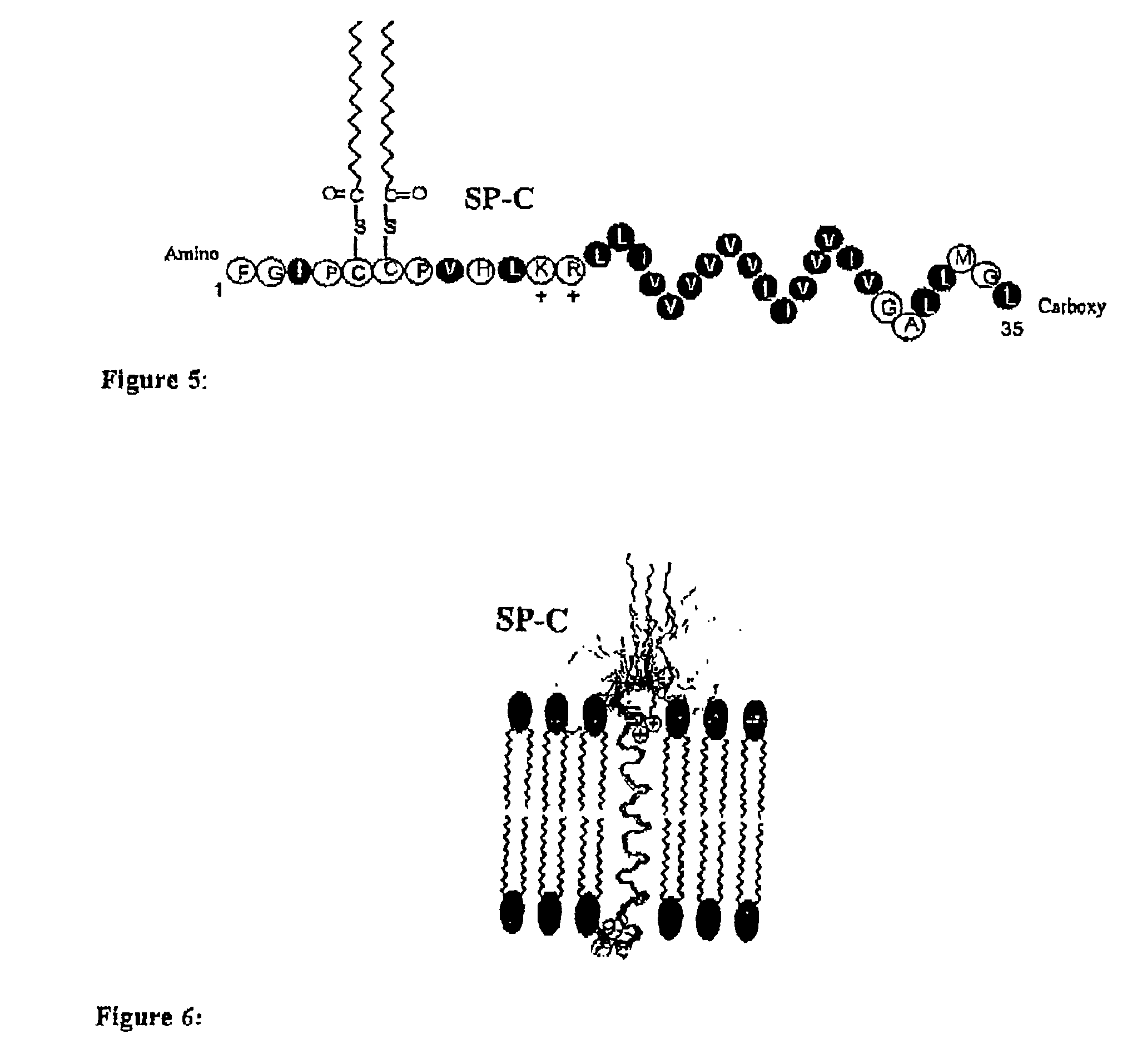
Polypeptoid pulmonary surfactants
InactiveUS6887845B2Low immunogenicityImprove bioavailabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerReverse transcriptase
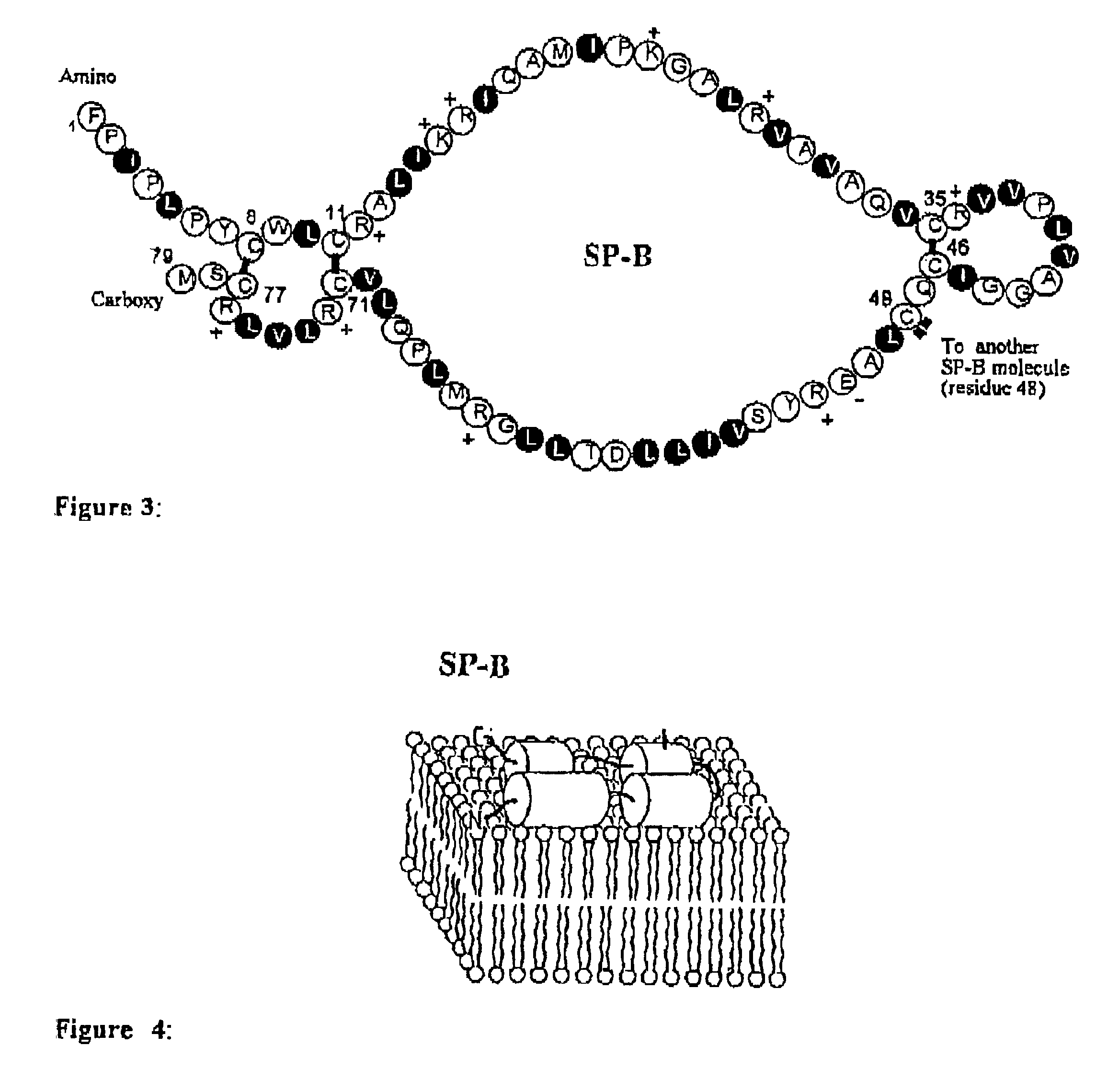
The present invention provides spreading agents based on sequence-specific oligomers comprising a peptoid, a peptide-peptoid chimera, a retropeptoid or a retro(peptoid-peptide) chimera, and methods for using the same, including for the treatment of respiratory distress of the lungs. The spreading agents are sequence-specific oligomers, including retrosequence-specific oligomers, based on a peptide backbone, that are designed as analogs of surfactant protein-B or surfactant protein-C.
Owner:BARRON PH D ANNELISE E +1
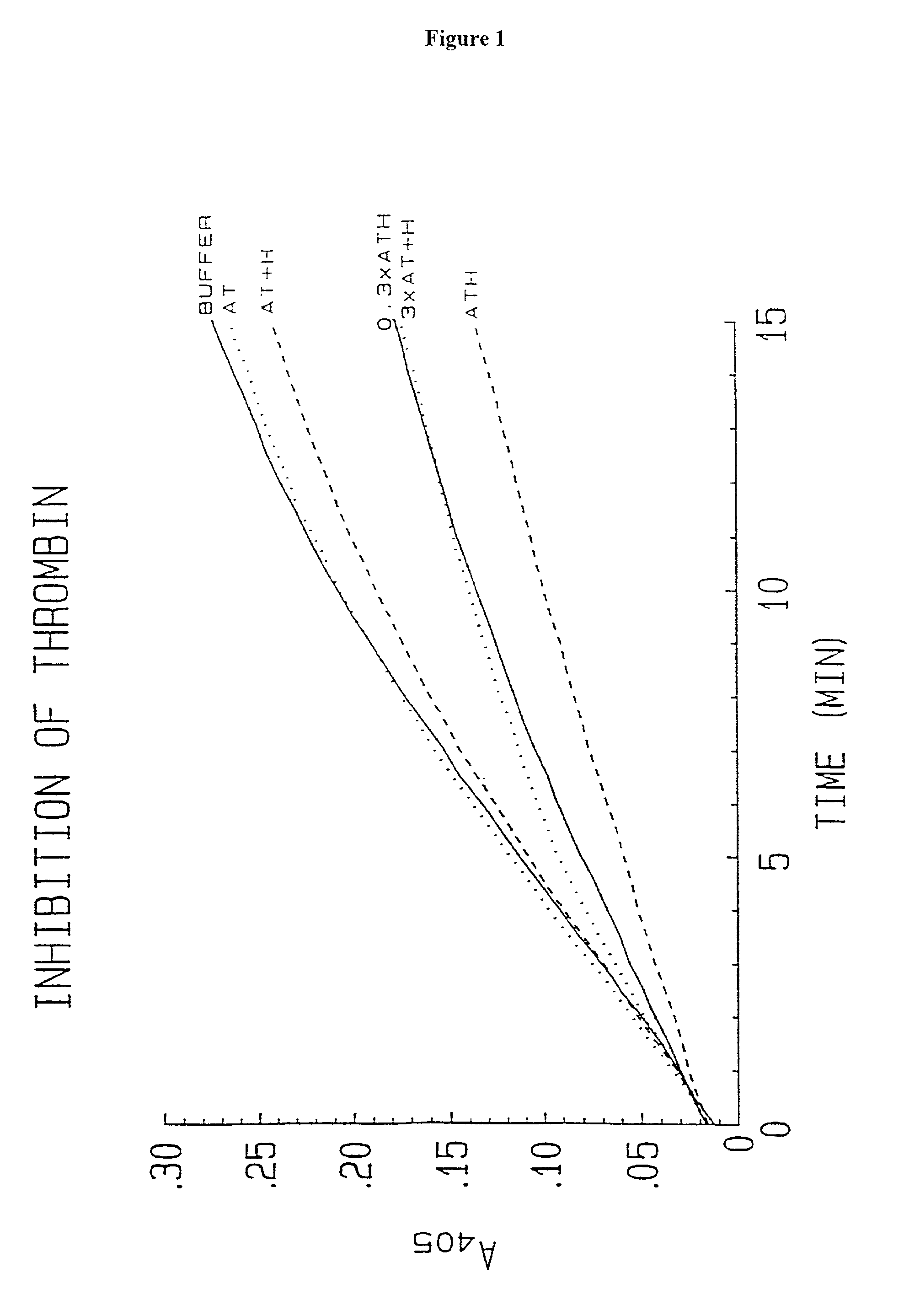
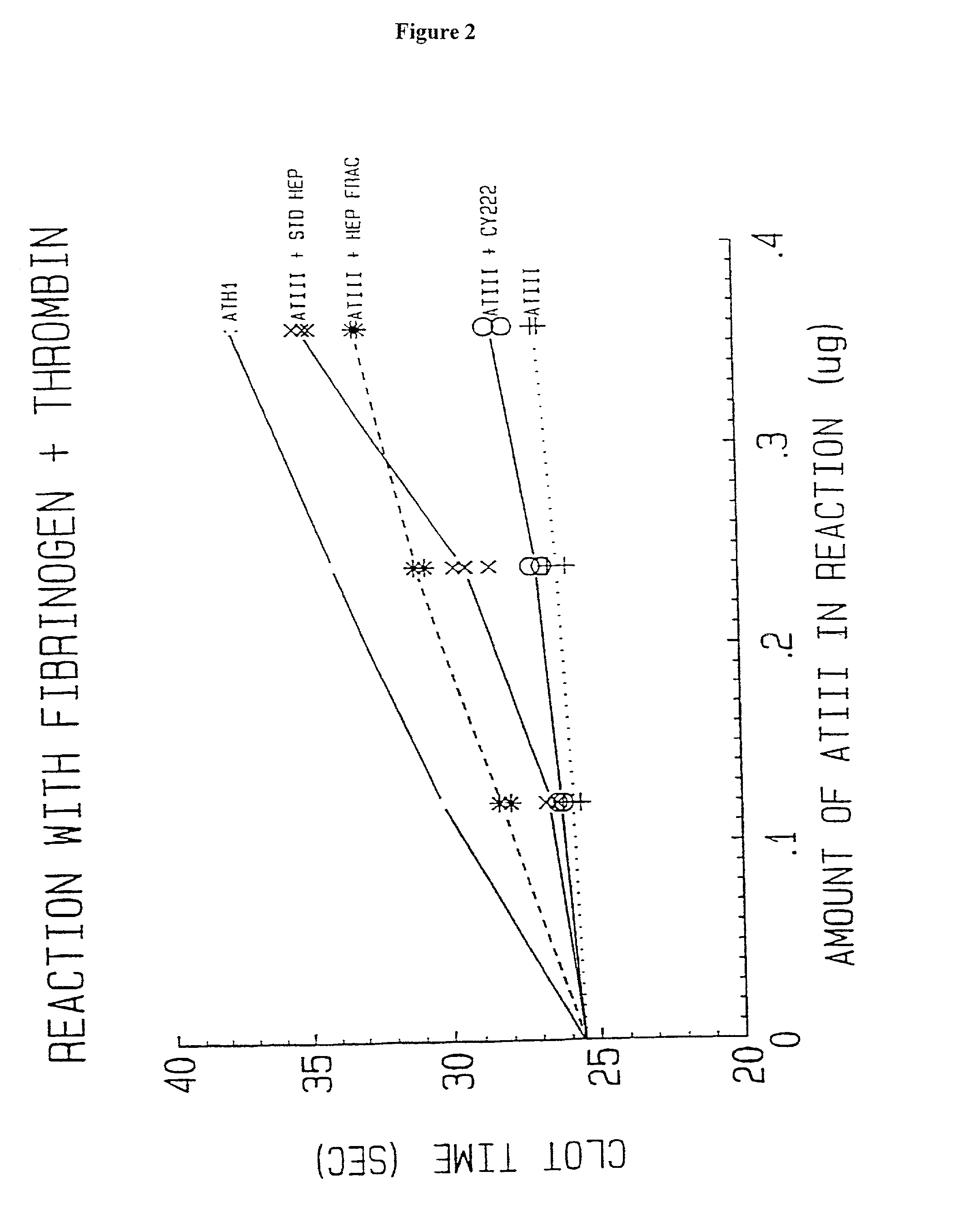
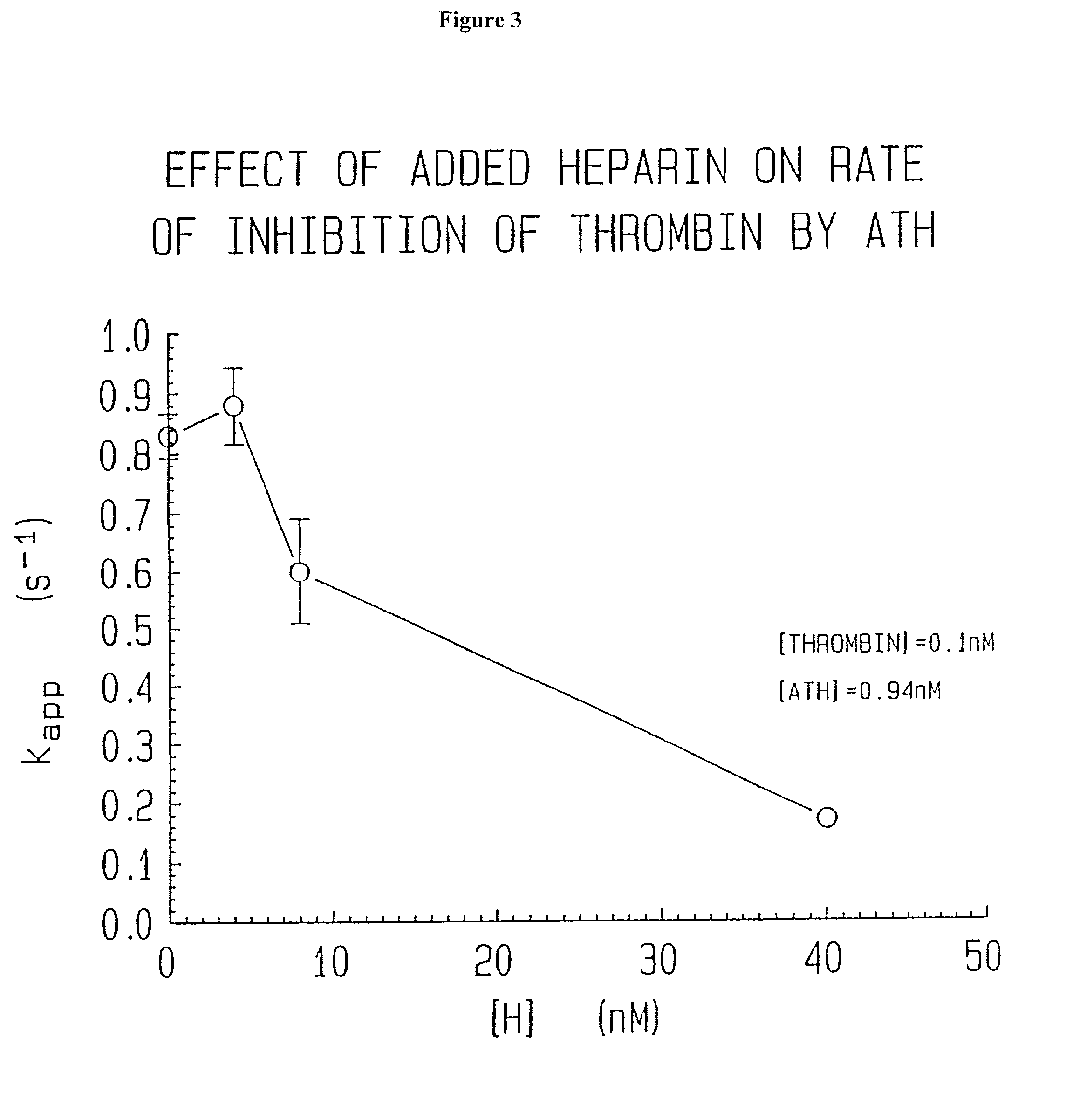
Methods of coating a device using anti-thrombin heparin
Novel conjugates of glycosaminoglycans, particularly heparin and dermatan sulfate, and amine containing species and therapeutic uses thereof are described. In particular, mild methods of conjugating heparins to proteins, such as antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II, which provide covalent conjugates which retain maximal biological activity are described. Uses of these conjugates to prevent thrombogenesis, in particular in lung airways, such as found in infant and adult respiratory distress syndrome, and on surfaces in contact with blood are also described.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
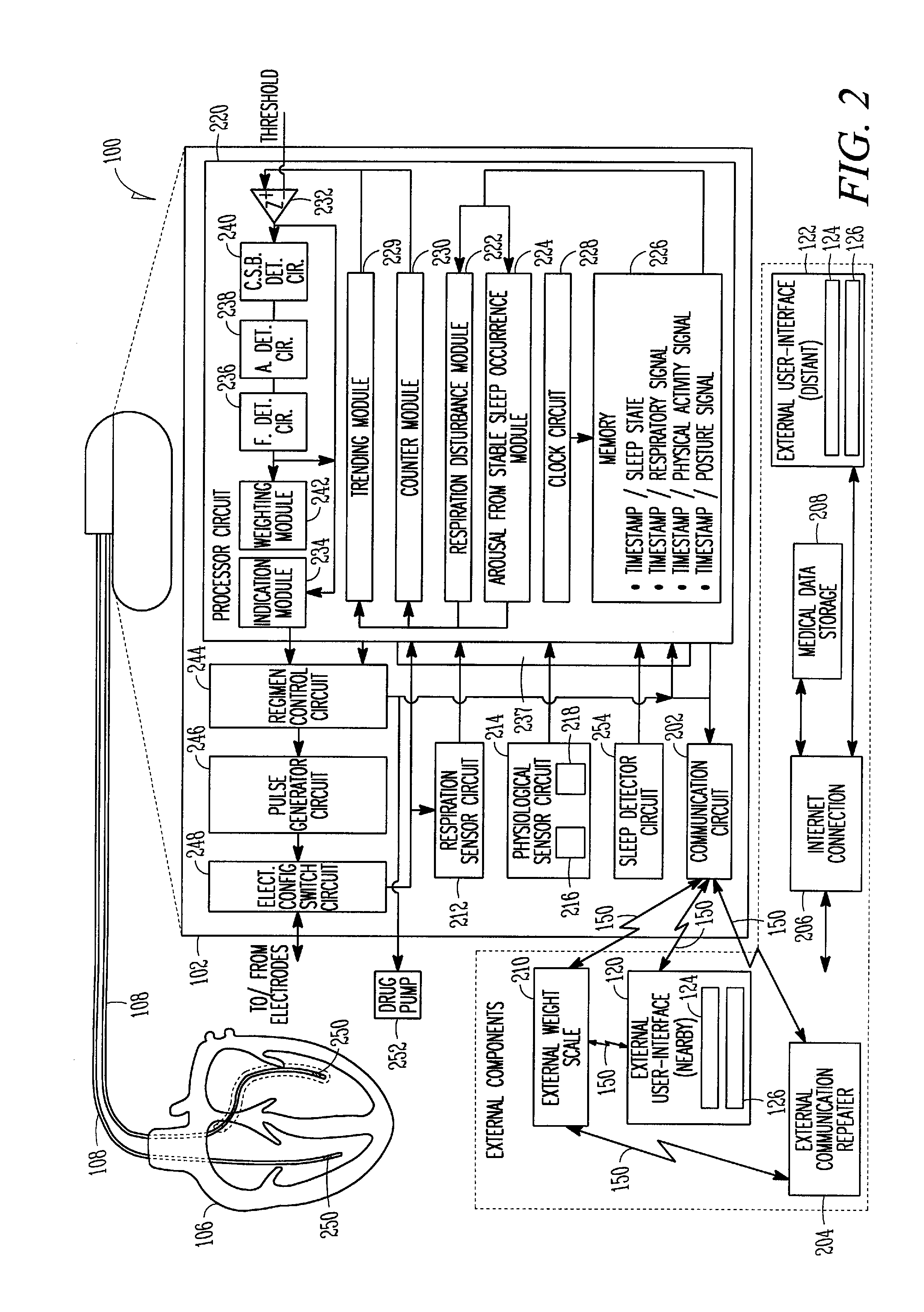
Using respiration distress manifestations for heart failure detection
Systems and methods for diagnosing one or more respiration distress manifestations by implantably recognizing their occurrence and evaluating information about the same to provide an indication of present or impending worsening heart failure are discussed. Using information produced by an implantable respiration sensor circuit and an implantable physiological sensor circuit, such as at least one of a physical activity sensor circuit or a posture sensor circuit, an implantable or external processor circuit may detect a respiration disturbance and an associated subsequent arousal from stable state occurrence and thereafter evaluate over time arousal from stable state occurrences to provide the indication of present or impending worsening heart failure. In one example, information about a fluid level within a subject is used in determining the indication of worsening heart failure. In various examples, a regimen is initiated or adjusted in response to the indication of present or impending worsening heart failure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Ventilator for Rapid Response to Respiratory Disease Conditions
The present invention relates generally to the field of ventilators, and, more specifically, to a ventilator system that addresses respiratory distress due to the onset of an epidemic or pandemic disease state. In particular, the present invention is a ventilator system that can be manufactured quickly with minimal skill requirements and employed rapidly in response to epidemic respiratory disease conditions.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE INC
Acylated uridine and cytidine and uses thereof
ActiveUS6258795B1No untoward pharmaceutical effectEfficient managementBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
The invention relates to compositions comprising acyl derivatives of cytidine and uridine. The invention also relates to methods of treating hepatopathies, diabetes, heart disease, cerebrovascular disorders, Parkinson's disease, infant respiratory distress syndrome and for enhancement of phospholipid biosynthesis comprising administering the acyl derivatives of the invention to an animal.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
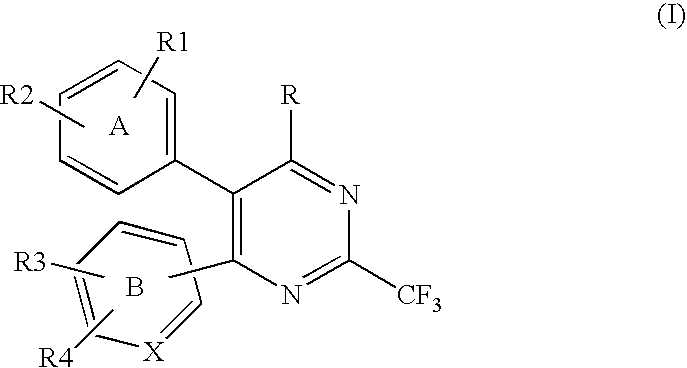
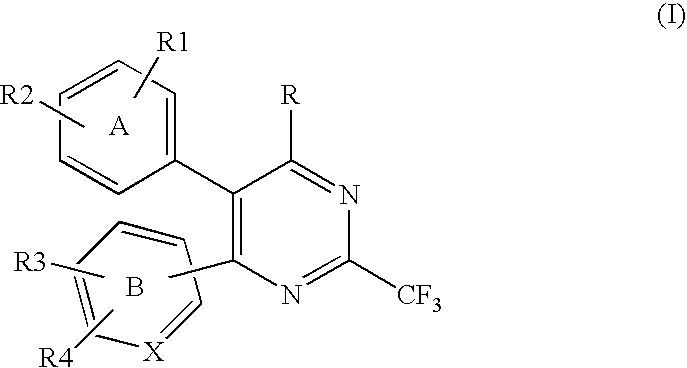
Substituted heterocyclic compounds and methods of use
The present invention relates to pyridines, pyrimidines and derivatives thereof, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. Also included is a method of treatment of inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, Pagets disease, osteoporosis, multiple myeloma, uveititis, acute or chronic myelogenous leukemia, pancreatic β cell destruction, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis, gouty arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), psoriasis, Crohn's disease, allergic rhinitis, ulcerative colitis, anaphylaxis, contact dermatitis, asthma, muscle degeneration, cachexia, Reiter's syndrome, type I diabetes, type II diabetes, bone resorption diseases, graft vs. host reaction, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, myocardial infarction, ischemia reperfusion injury, atherosclerosis, brain trauma, multiple sclerosis, cerebral malaria, sepsis, septic shock, toxic shock syndrome, fever, myalgias due to HIV-1, HIV-2, HIV-3, cytomegalovirus (CMV), influenza, adenovirus, the herpes viruses or herpes zoster infection in a mammal comprising administering an effective amount a compound as described above.
Owner:AMGEN INC
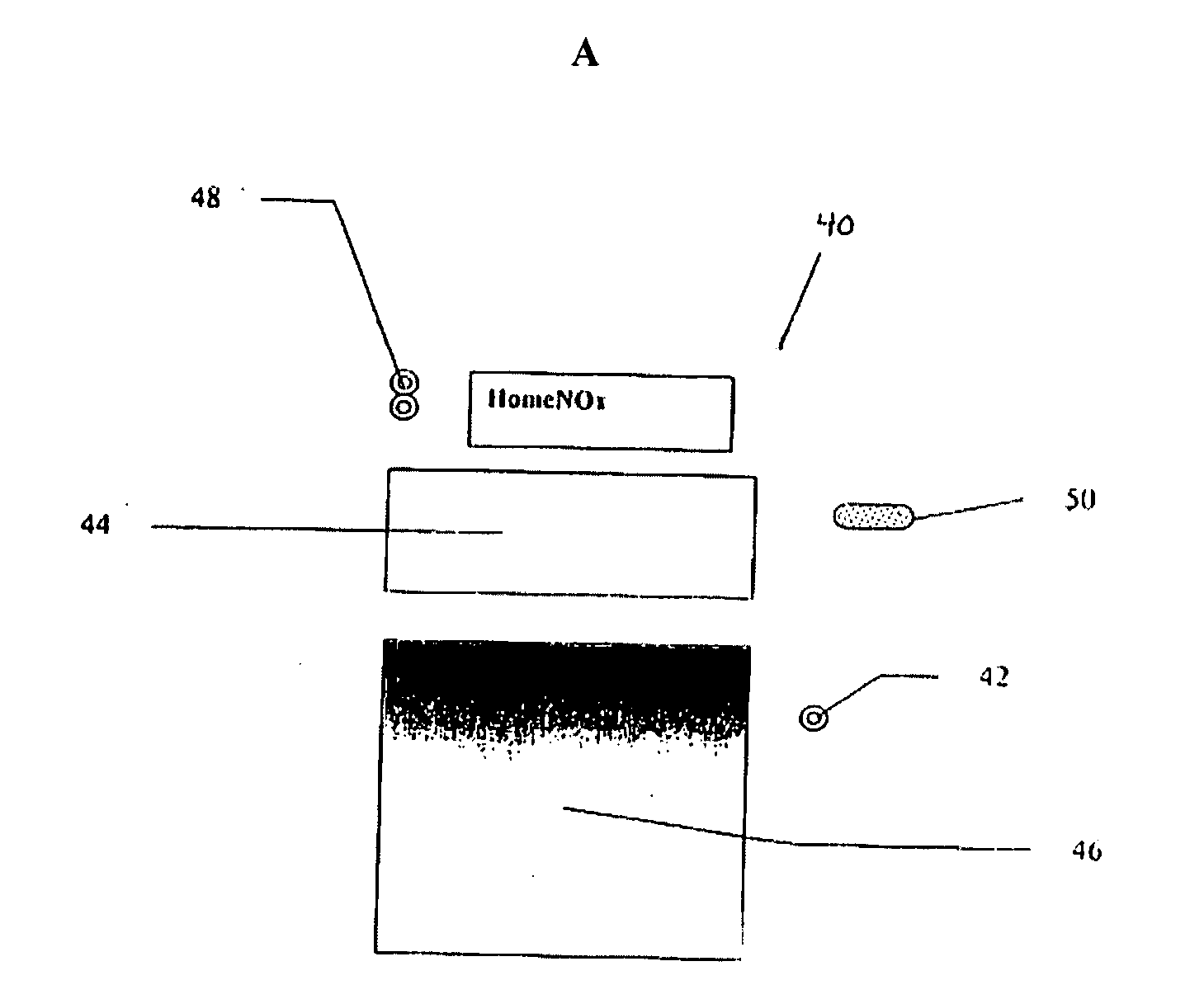
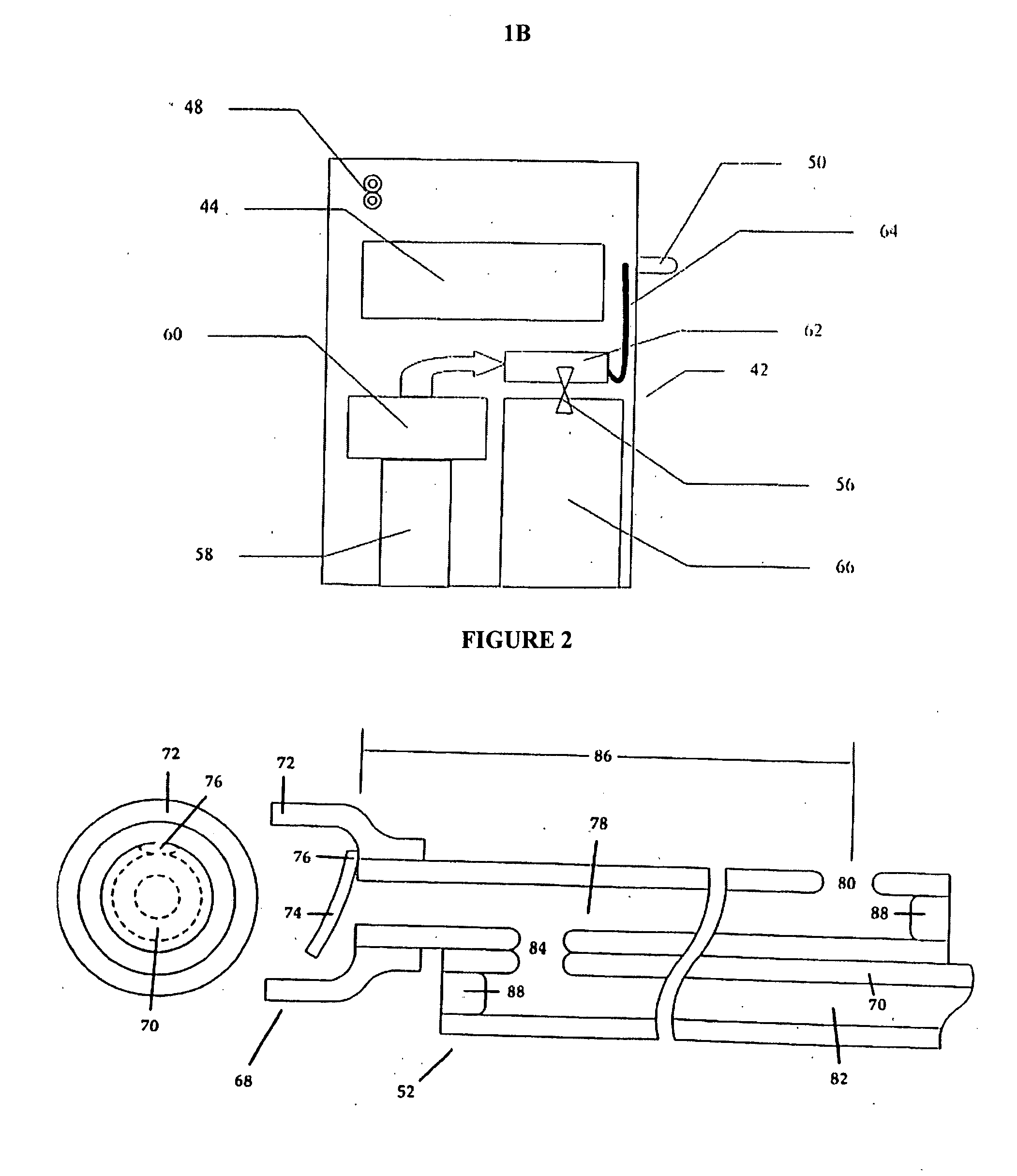
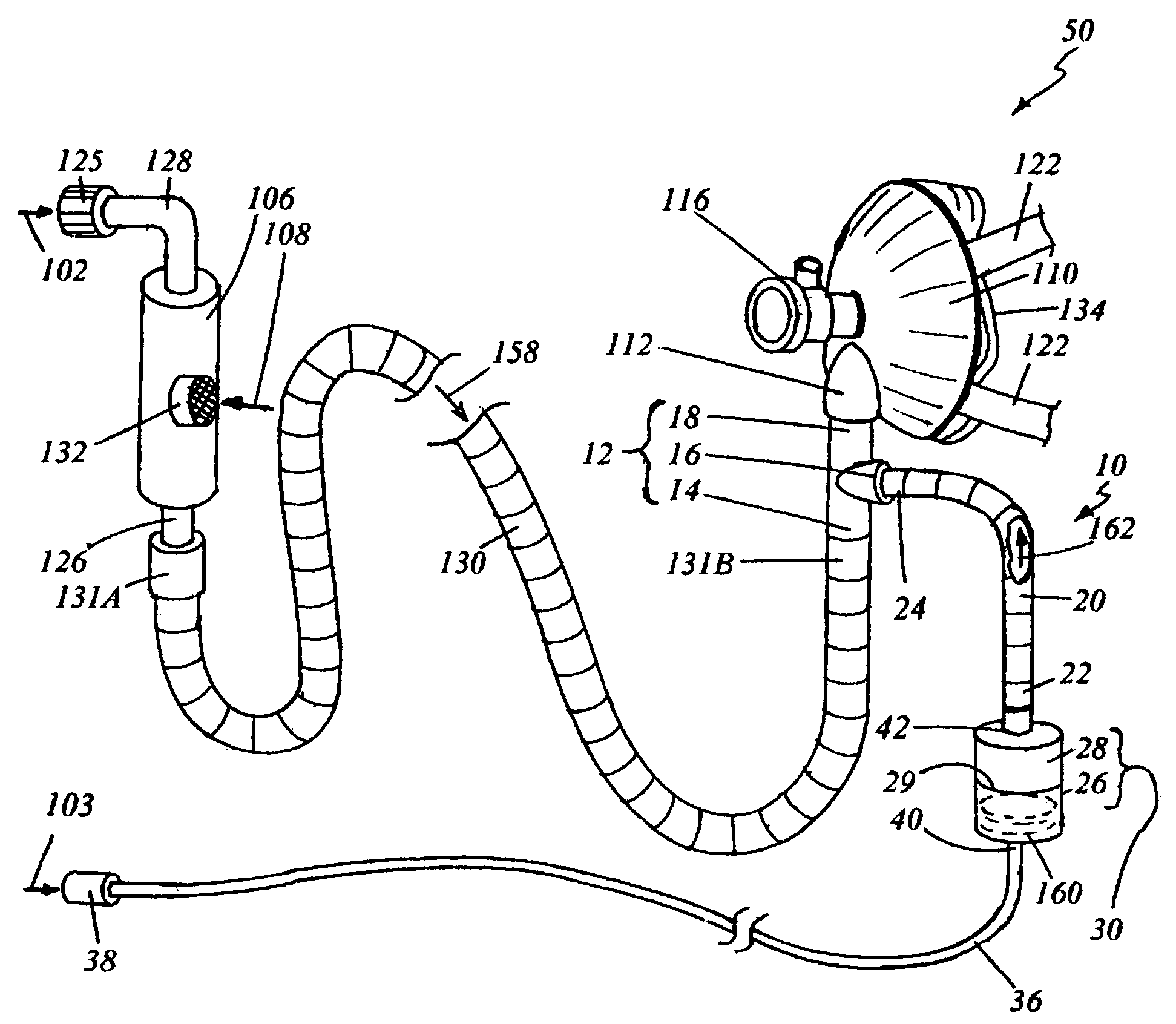
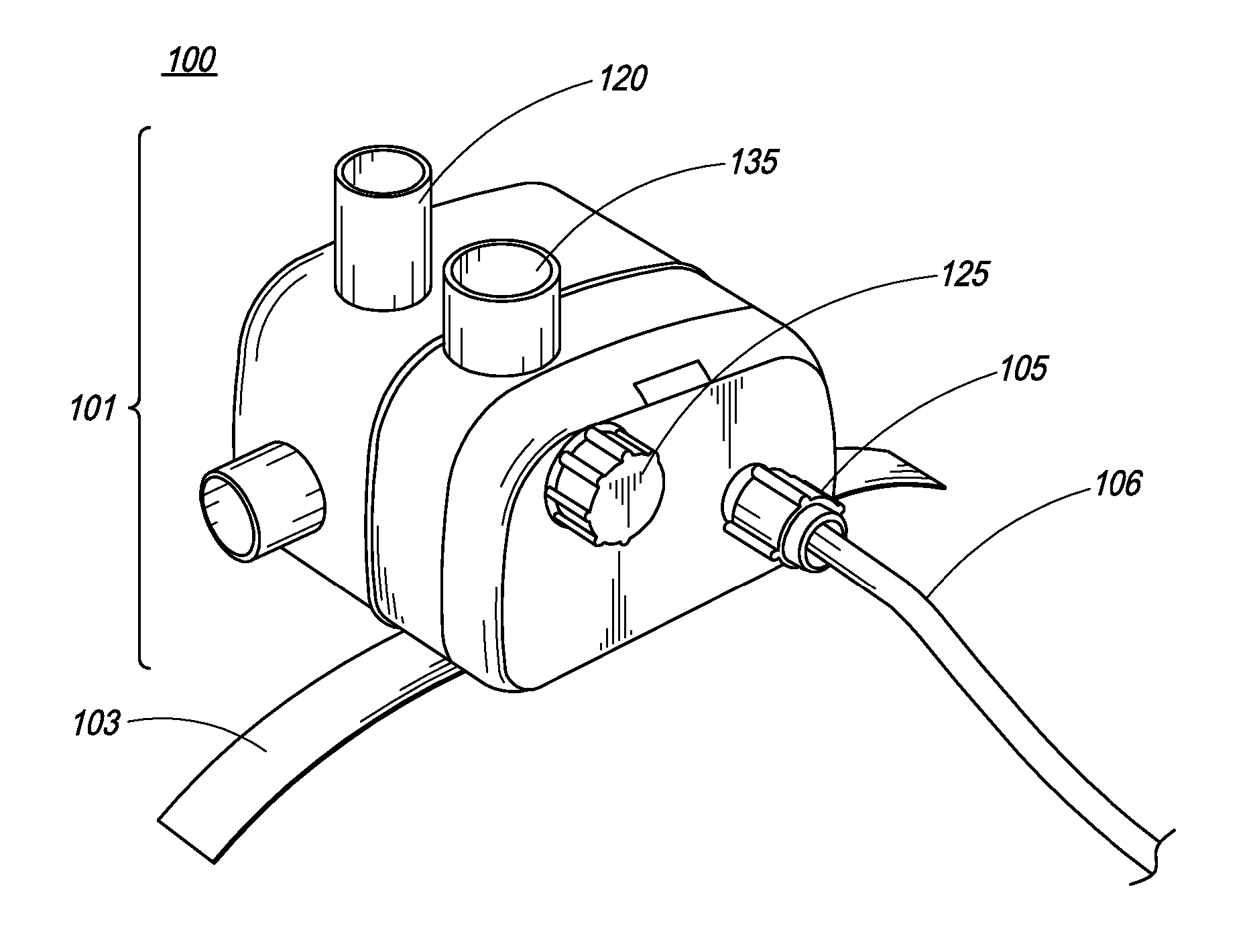
Medication delivery device and method
InactiveUS20070049841A1Highly controllableIncrease chanceRespiratory masksBreathing masksEmergency medicineOxygen
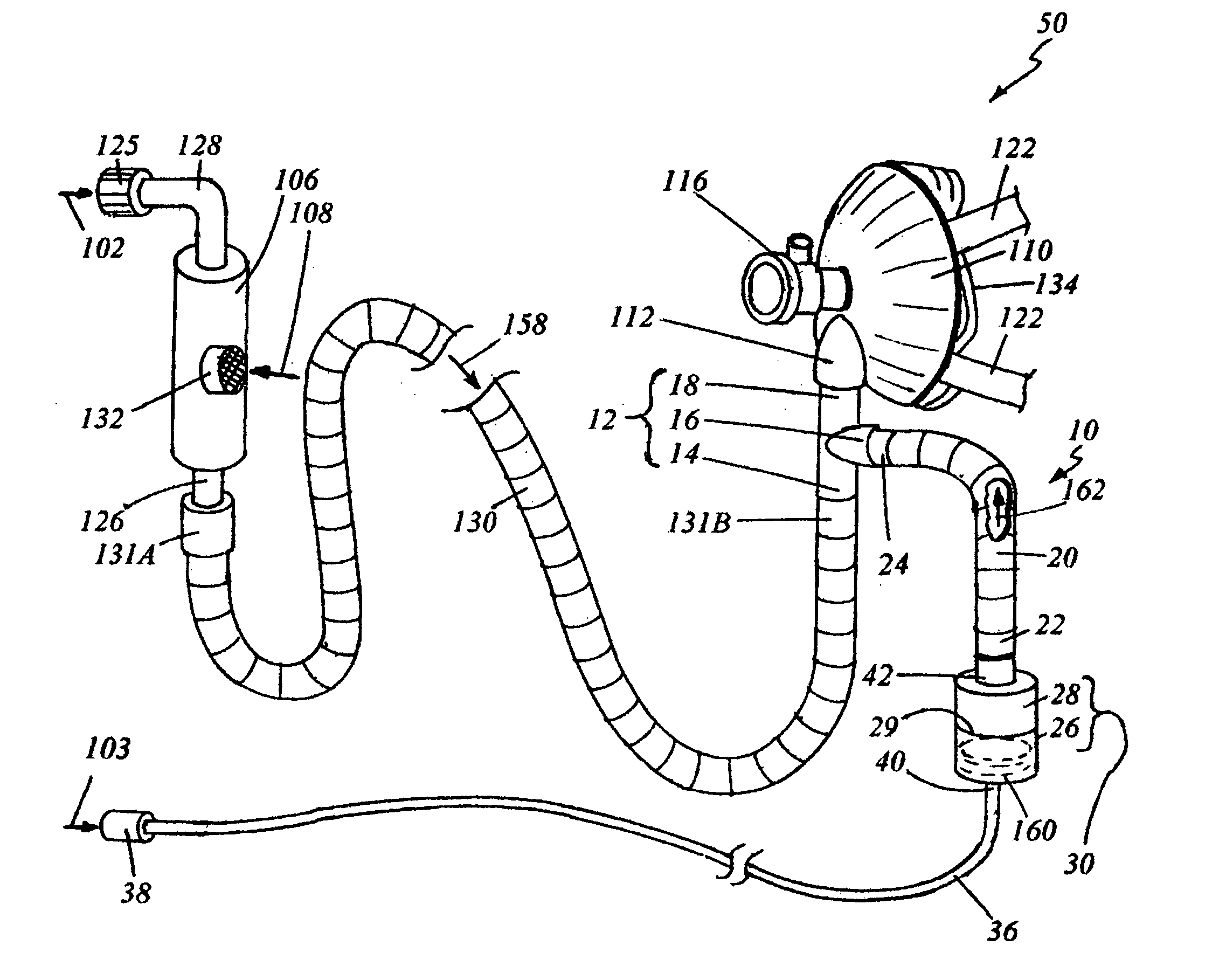
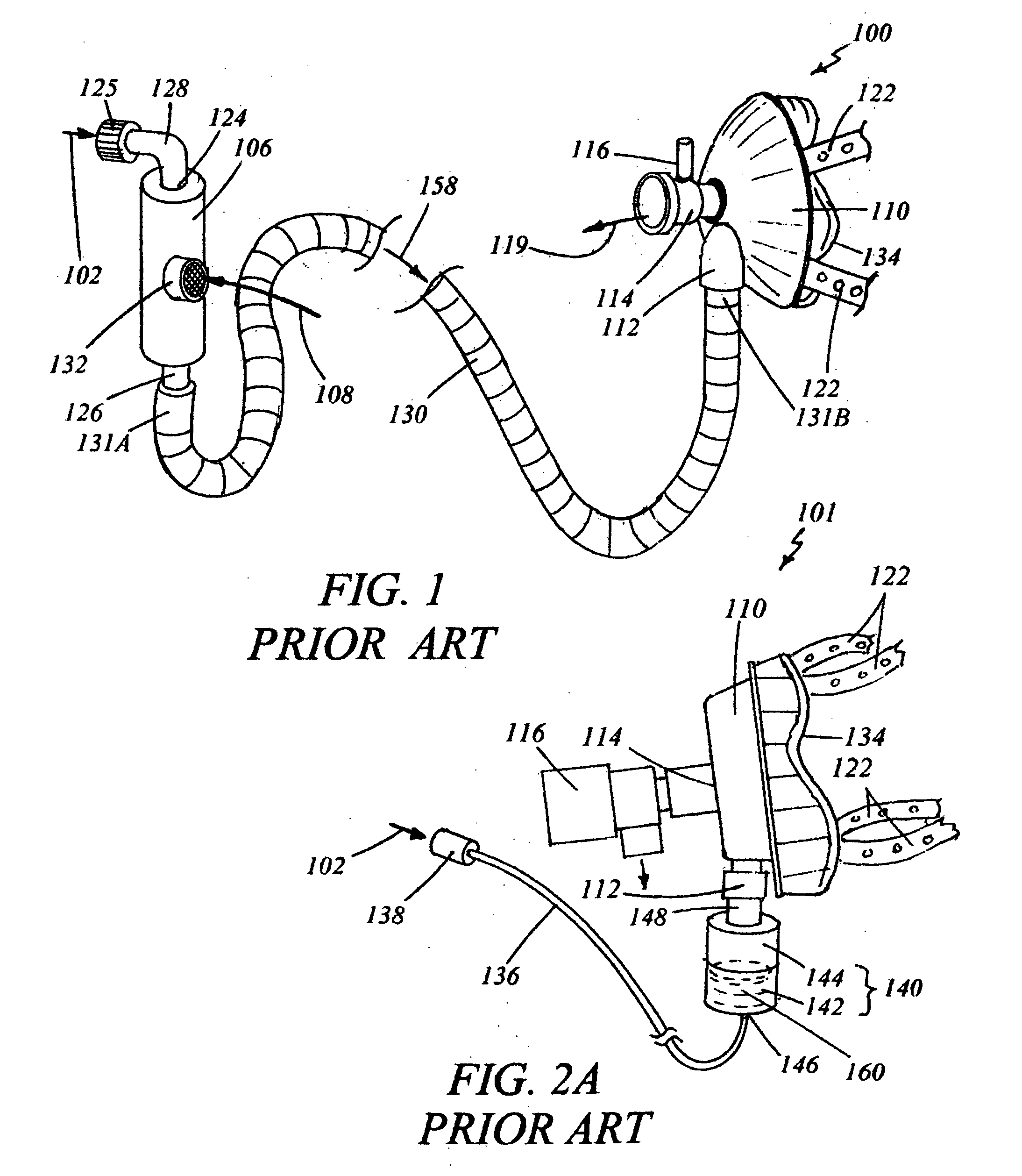
A medication delivery apparatus and method for a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system such as used in emergency treatment of severe respiratory distress. The apparatus of the invention includes a 3-port Tee fitting, one port of which is connected to the inlet port of a CPAP face mask operable at an elevated pressure. A second port is connected to a CPAP gas conduit supplying an oxygen-containing gas at a pressure above atmospheric. The third port is connected to a flexible tube receiving aerosolized medication from an upper outlet of an openable / refillable lightweight nebulizer. The flexible tubing is only long enough to bend vertically downward to support a lightweight nebulizer in a vertical attitude, whereby full nebulization takes place, no medication is spilled, and the tubing length is minimized for maximal transfer of medication to a patient. In addition, cutting of the CPAP gas supply tube and placement of a T fitting between the cut ends, with its concomitant wastage of condensed medication, is avoided. The patient head does not need to be in an upright position. The patient's airway is continuously maintained at an elevated pressure to maintain an open airway and oxygenate the patient, permitting repeated doses of nebulized medications at independently controlled nebulization rates, minimizing downtime of both the pressurized oxygen and aerosolized medication.
Owner:LEPEL PAMELA
Stable amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and particularly relates to an amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound and a preparation method thereof. The amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound has high purity and stability, does not have obvious moisture absorption and weight increase even under the condition of high humidity, ensures that relative substances do not grow, and has higher dissolution rate than crystalline ambroxol hydrochloride. The invention also relates to an application of the amorphous ambroxol hydrochloride compound in preparation of medicine for the treatment of acute and chronic pulmonary diseases with the symptom of ropy sputum and difficult expectoration, phlegm eliminating treatment of acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, asthmatic bronchitis and bronchial asthma, prophylactic treatment of lung complication after an operation, and treatment of infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS) of premature infants and neonates.
Owner:天津梅花生物医药科技有限公司
Use of high dose concentrations of gaseous nitric oxide
InactiveUS20080193566A1Efficient procedureBiocideBronchoscopesRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTArteriolar Vasoconstriction
The invention relates to a methods and devices of delivering gaseous nitric oxide to a mammal or surface at a concentration ranging from about 1000 ppm to about 50,000 ppm of gaseous nitric oxide. Different conditions which can be treated by high dosage administration of gNO include but are not limited to: topical treatments with gNO, cosmetic applications of gNO, vasodilation conditions with gNO, inhalation treatments with gNO, treatments of the blood with gNO, treatment of the skin or tissue with gNO, treatment of infections with gNO, treatment of inflammation on or within the body, and treatments of biofilms with gNO. Other conditions, aliments, or symptoms that may be treated with high dosage gNO include bronchoconstriction, reversible pulmonary vasoconstriction, asthma, pulmonary hypertension, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN).
Owner:PULMONOX TECH
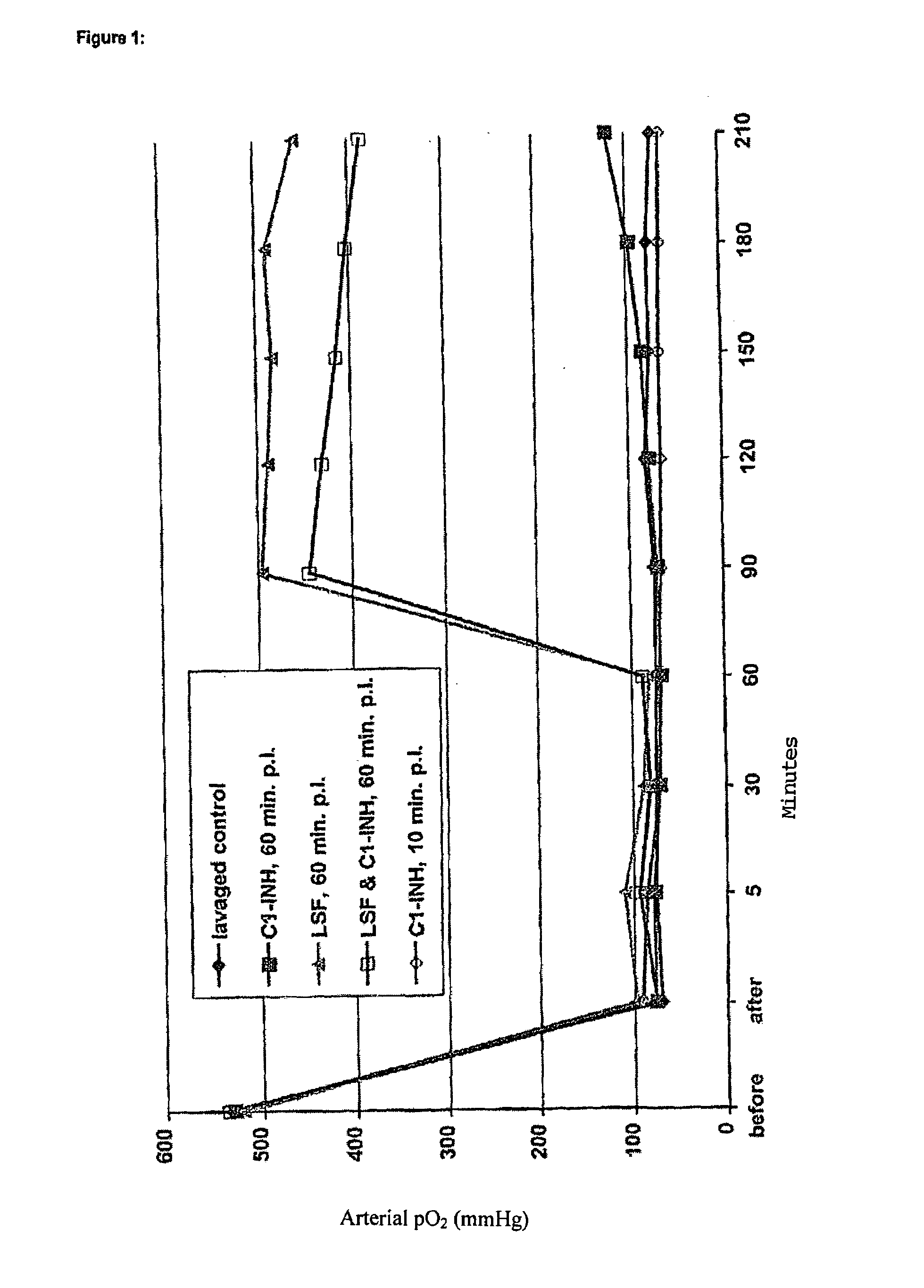
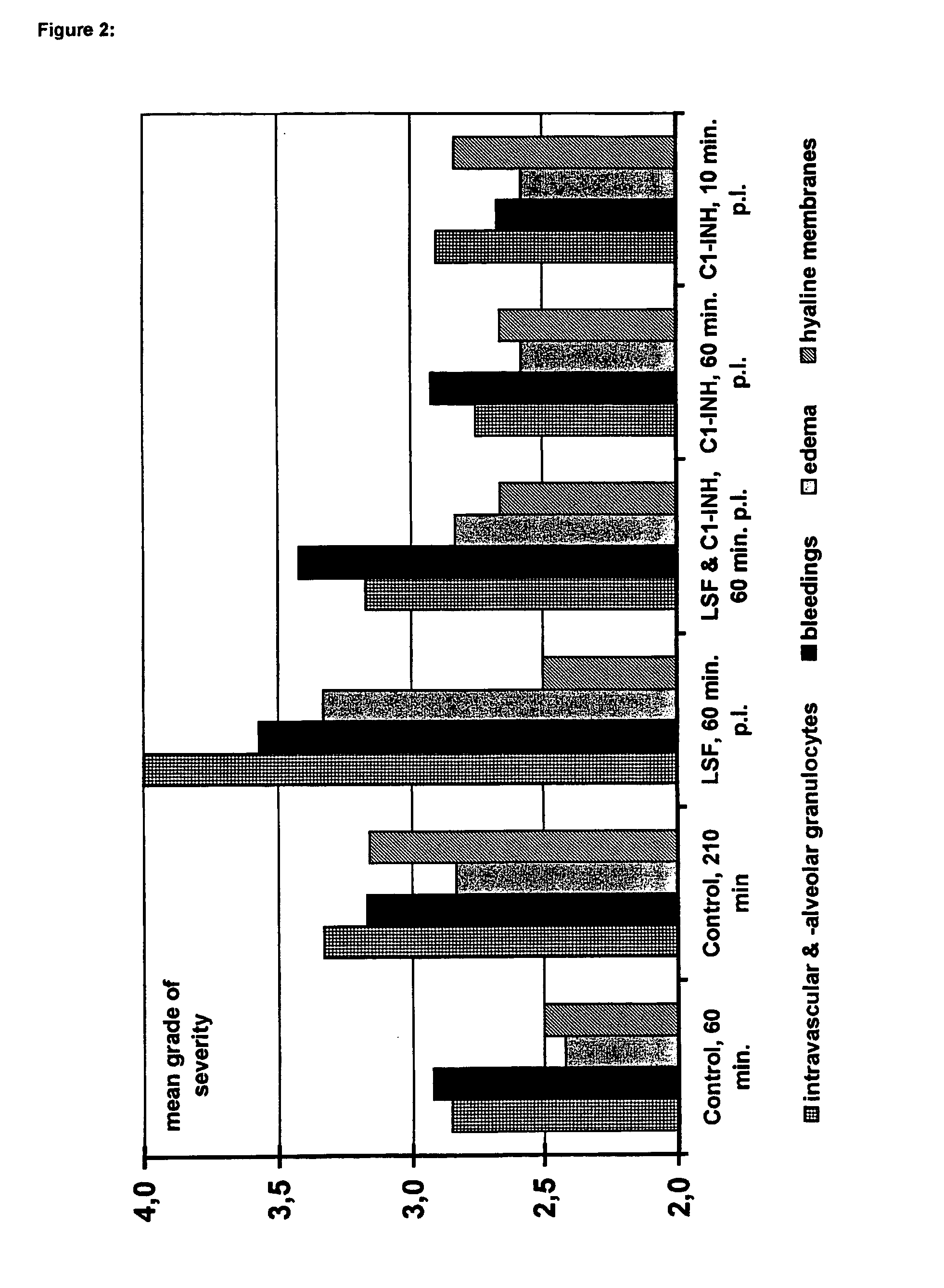
Combination of C1-INH and lung surfactant for the treatment of respiratory disorders
InactiveUS7053176B1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULT
Pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of infant respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury (including adult respiratory distress syndrome) which contains C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) and lung surfactant which comprises a lung surfactant protein.
Owner:TAKEDA GMBH +1
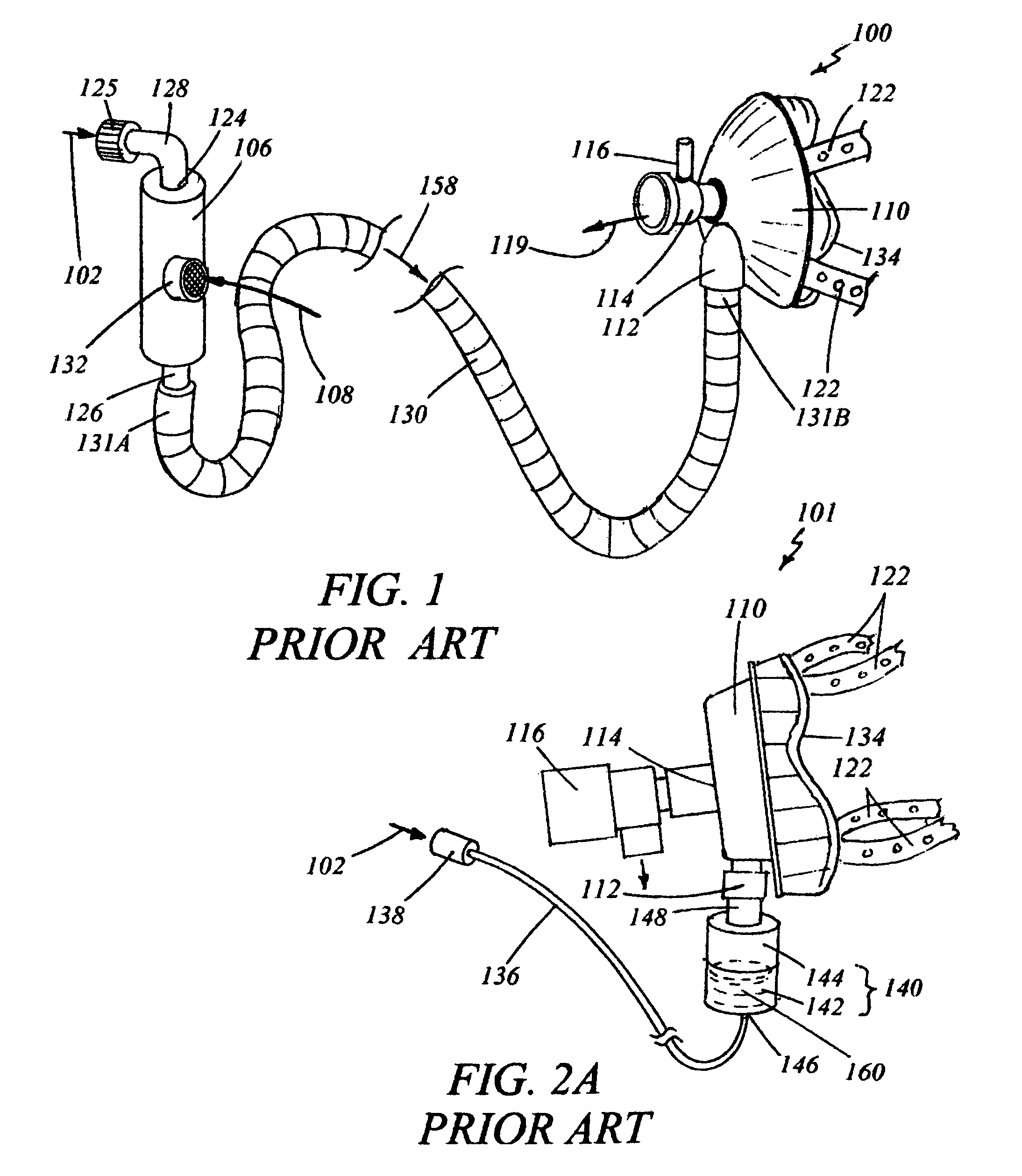
Medication delivery device and method
InactiveUS7448376B2Eliminate and minimize leakageHighly controllableBreathing masksRespiratory masksEmergency medicineOxygen
A medication delivery apparatus and method for a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system such as used in emergency treatment of severe respiratory distress. The apparatus of the invention includes a 3-port Tee fitting, one port of which is connected to the inlet port of a CPAP full face mask operable at a continuous elevated pressure. A second port is connected to a CPAP gas conduit supplying a pressurized oxygen-containing gas. The third port is connected to a flexible tube receiving aerosolized medication from an upper outlet of an openable / refillable lightweight nebulizer. The flexible tube is of a length to support a nebulizer in a vertical attitude.
Owner:LEPEL PAMELA
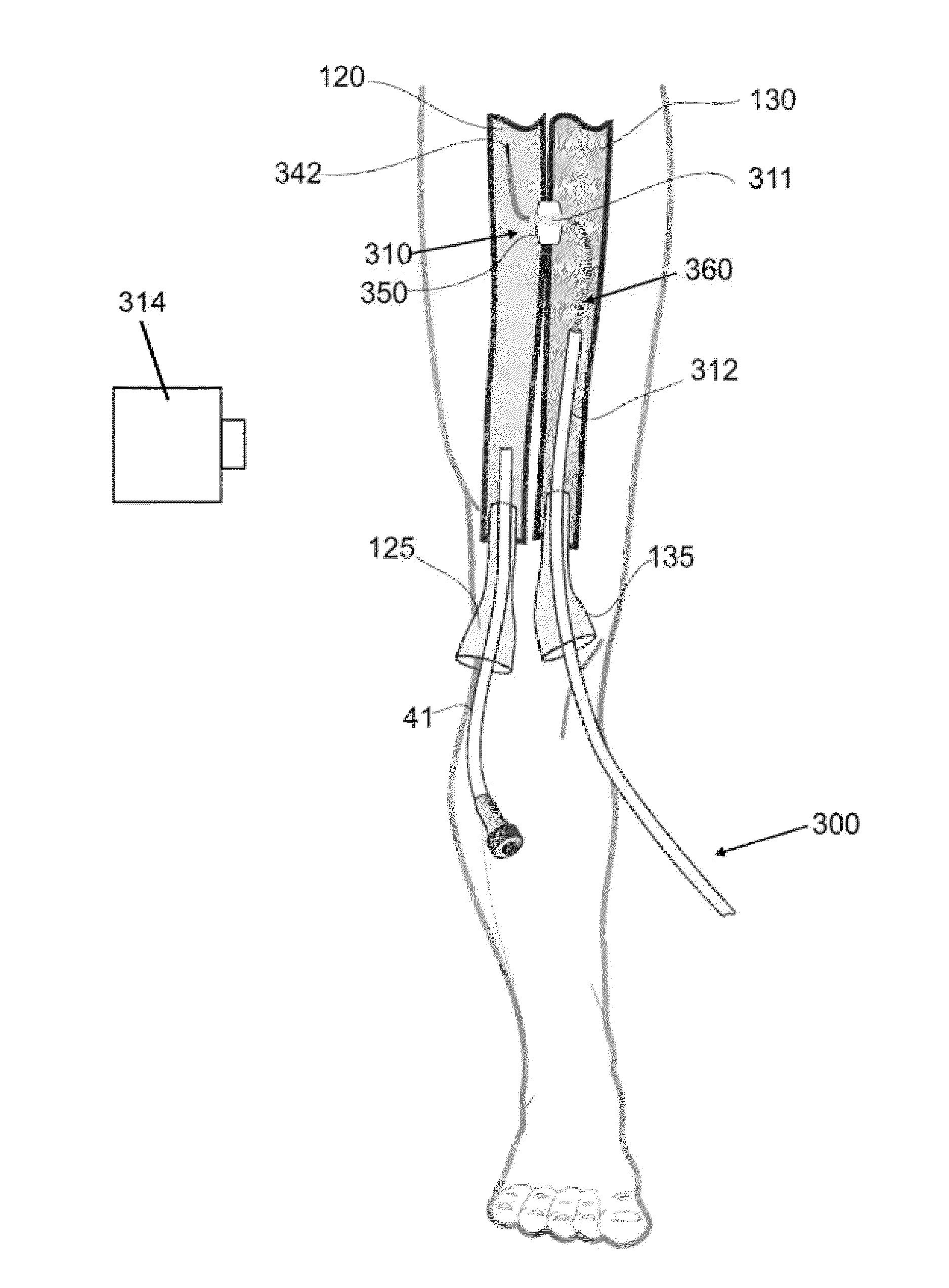
Devices, systems, and methods for peripheral arteriovenous fistula creation
ActiveUS9782533B2Good treatment effectReduce risk and adverse eventOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTDisease
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
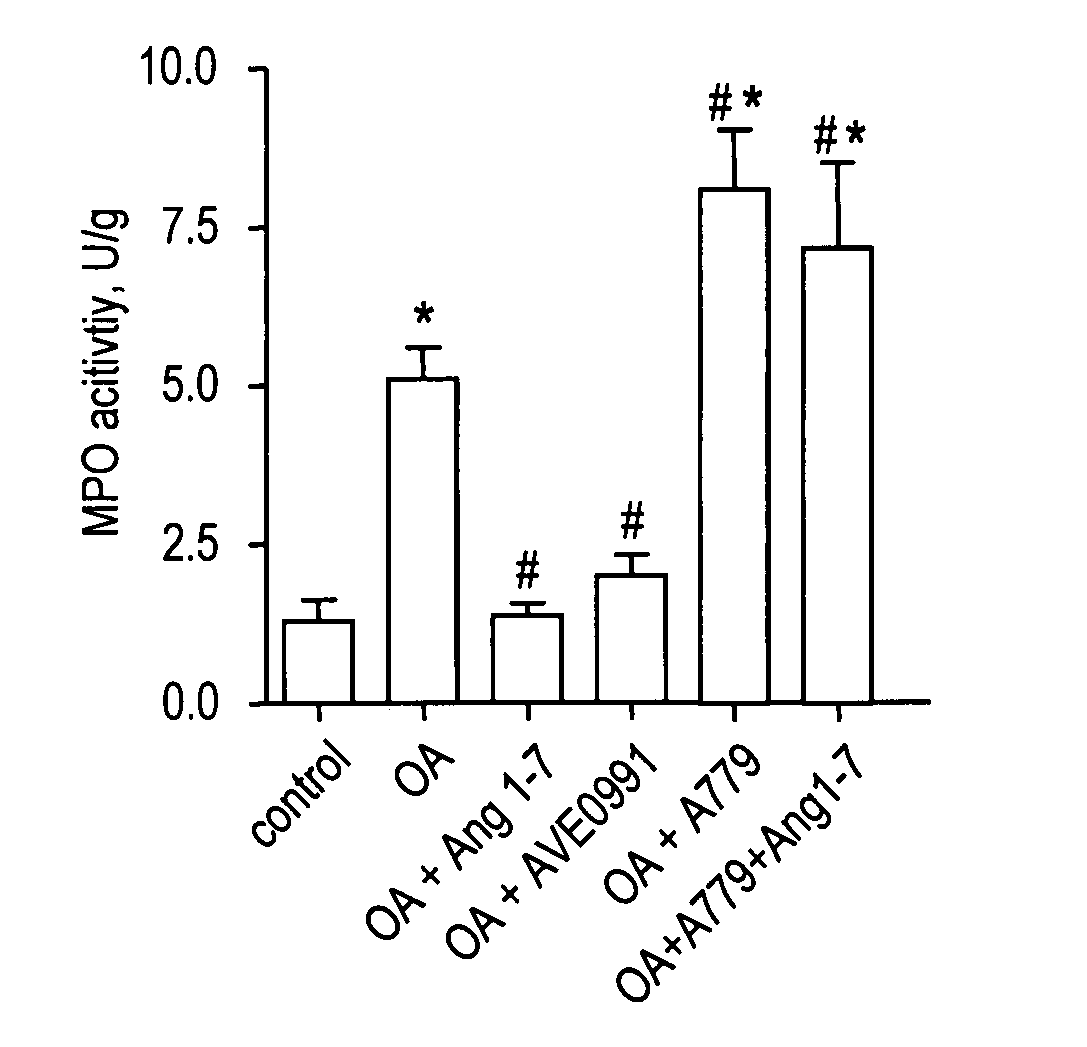
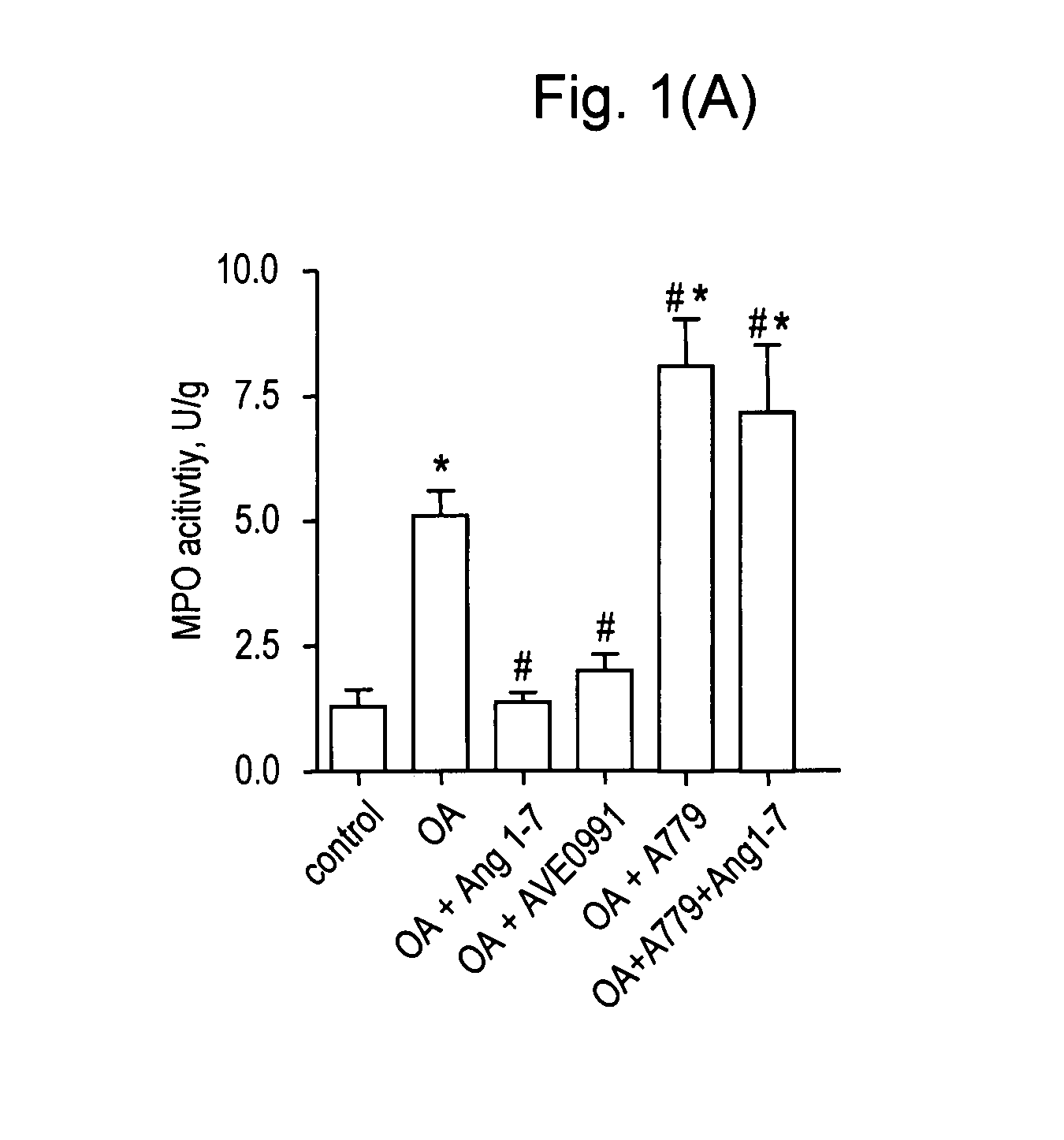
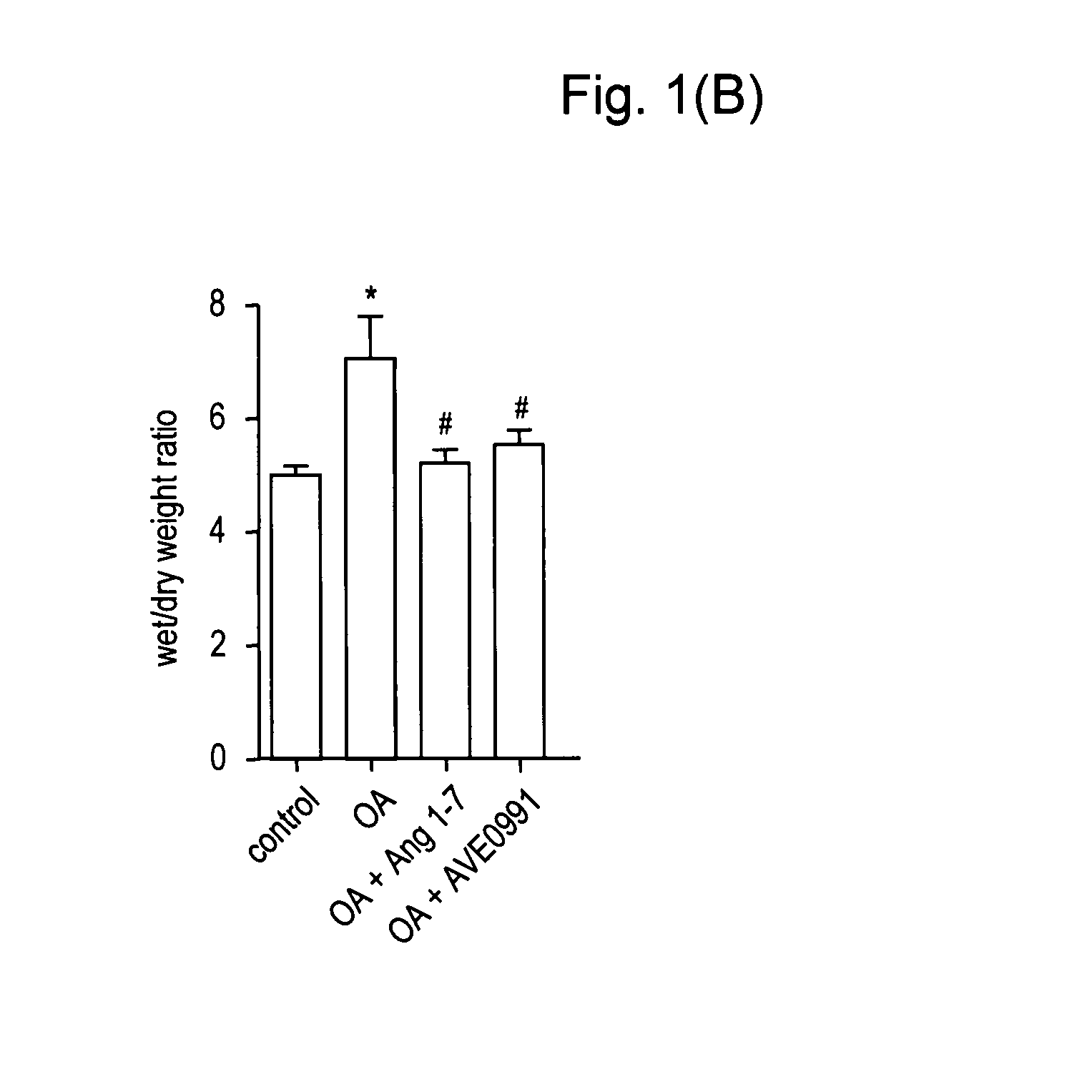
Use of an ang-(1-7) receptor agonist in acute lung injury
InactiveUS20110281805A1Conserved and agonistic propertyIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsALI - Acute lung injuryAgonist
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN
Methods and compositions for the reduction of neutrophil influx and for the treatment of bronchpulmonary dysplasia, respiratory distress syndrome, chronic lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis, asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20060281681A1Suppress immune responseIncrease frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsRespiratory disorderNeutrophil granulocyteObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
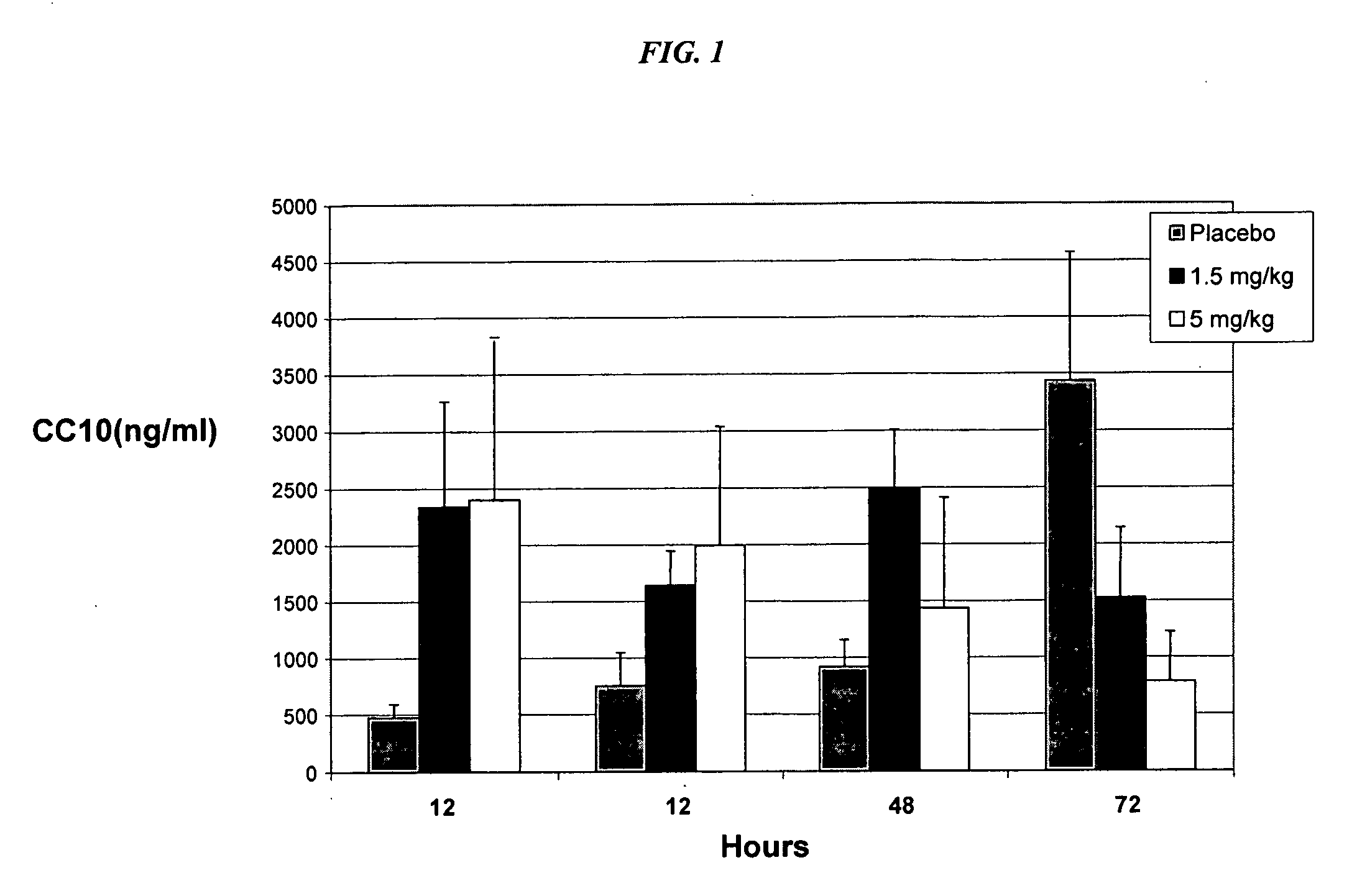
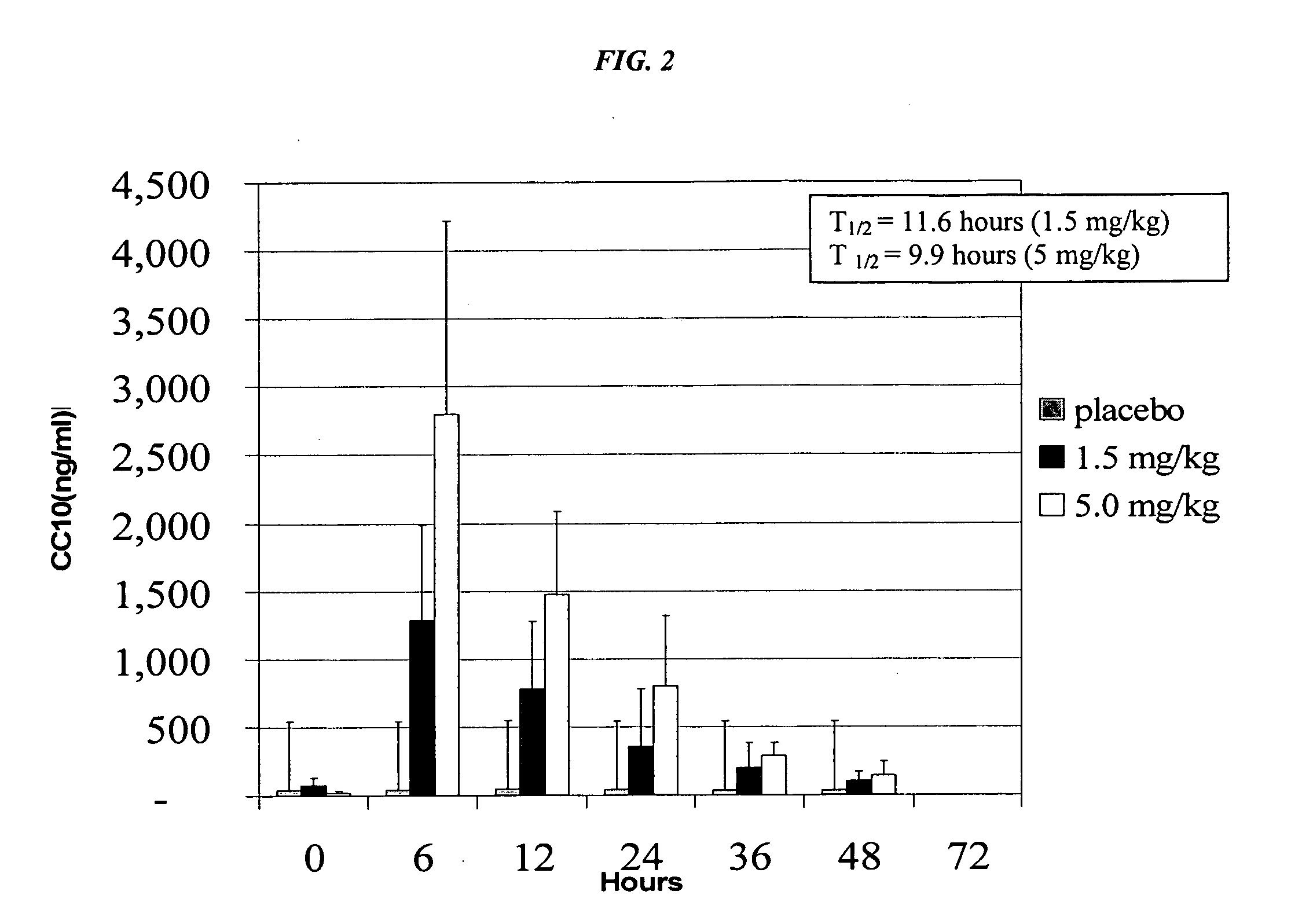
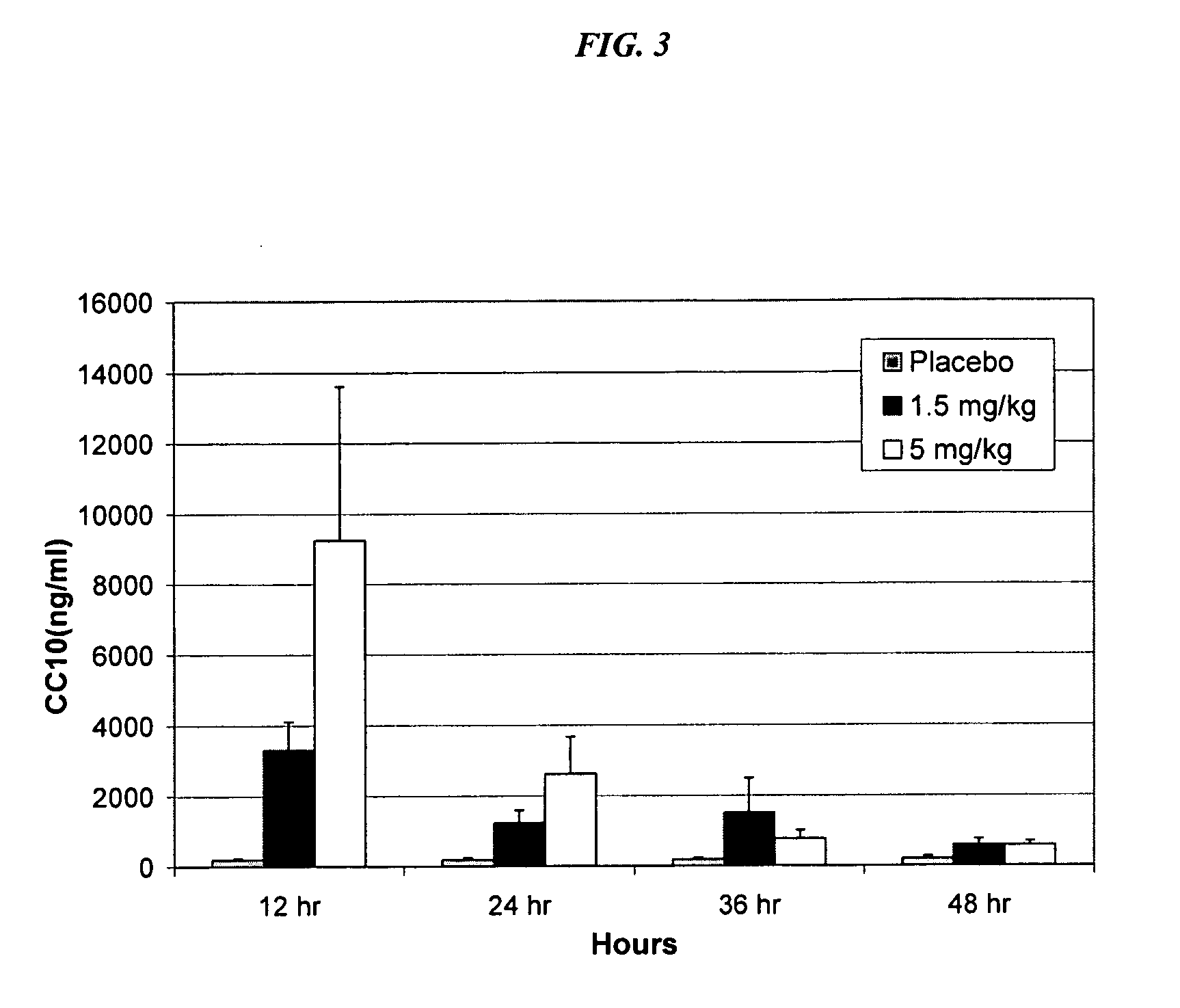
The present invention relates generally to the use of recombinant human CC10 (rhCC10), also known as recombinant human uteroglobin, for use as a therapeutic in the treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS), Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), chronic lung disease and / or pulmonary fibrosis, Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). More particularly, the invention provides methods, including broadly the critical dosage ranges of rhCC10, which may be administered to safely and effectively treat the aforementioned conditions. The invention further provides a composition useful in administering rhCC10 to humans.
Owner:CC10 SWEDEN
Respiratory stress detection
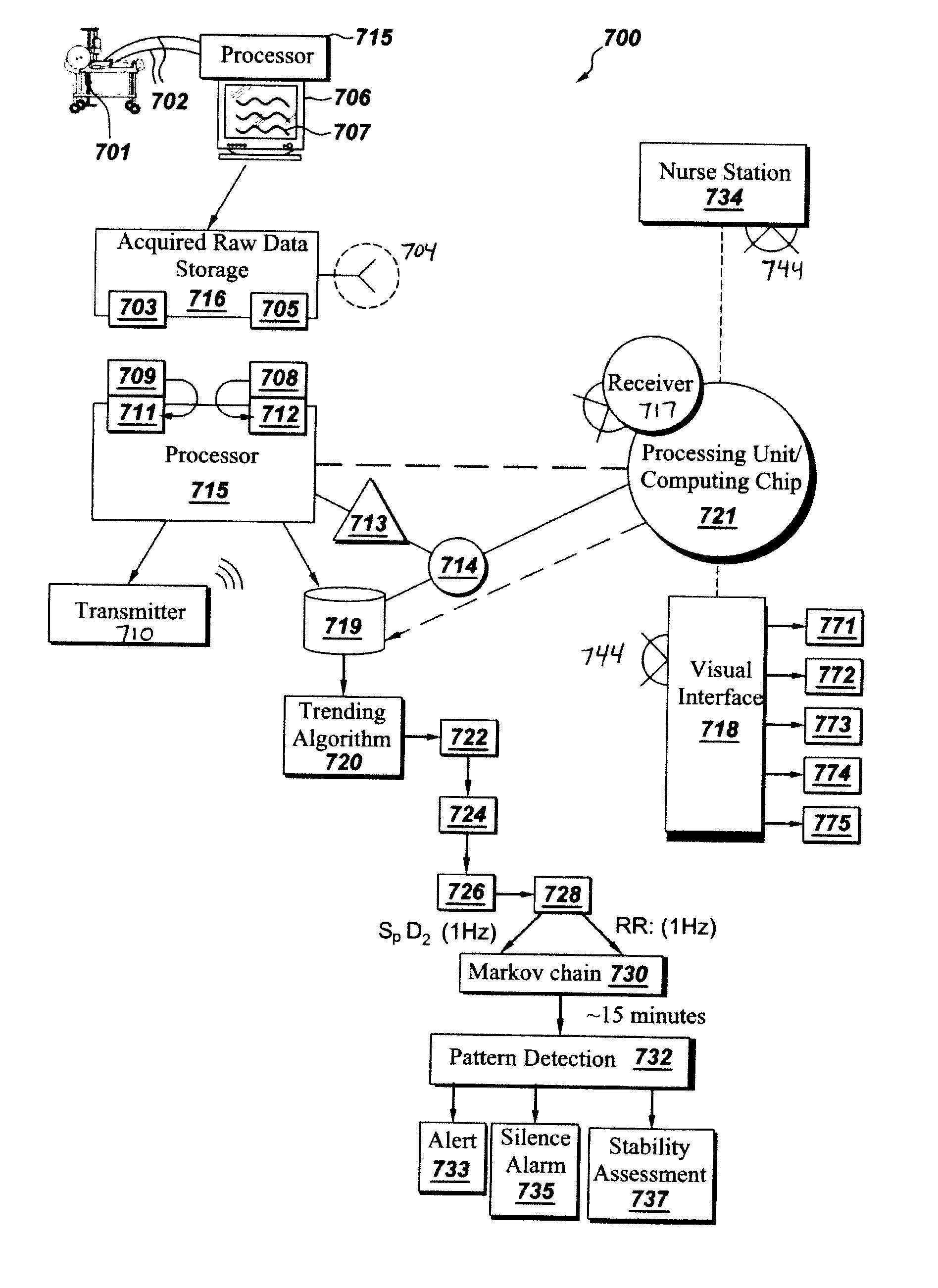
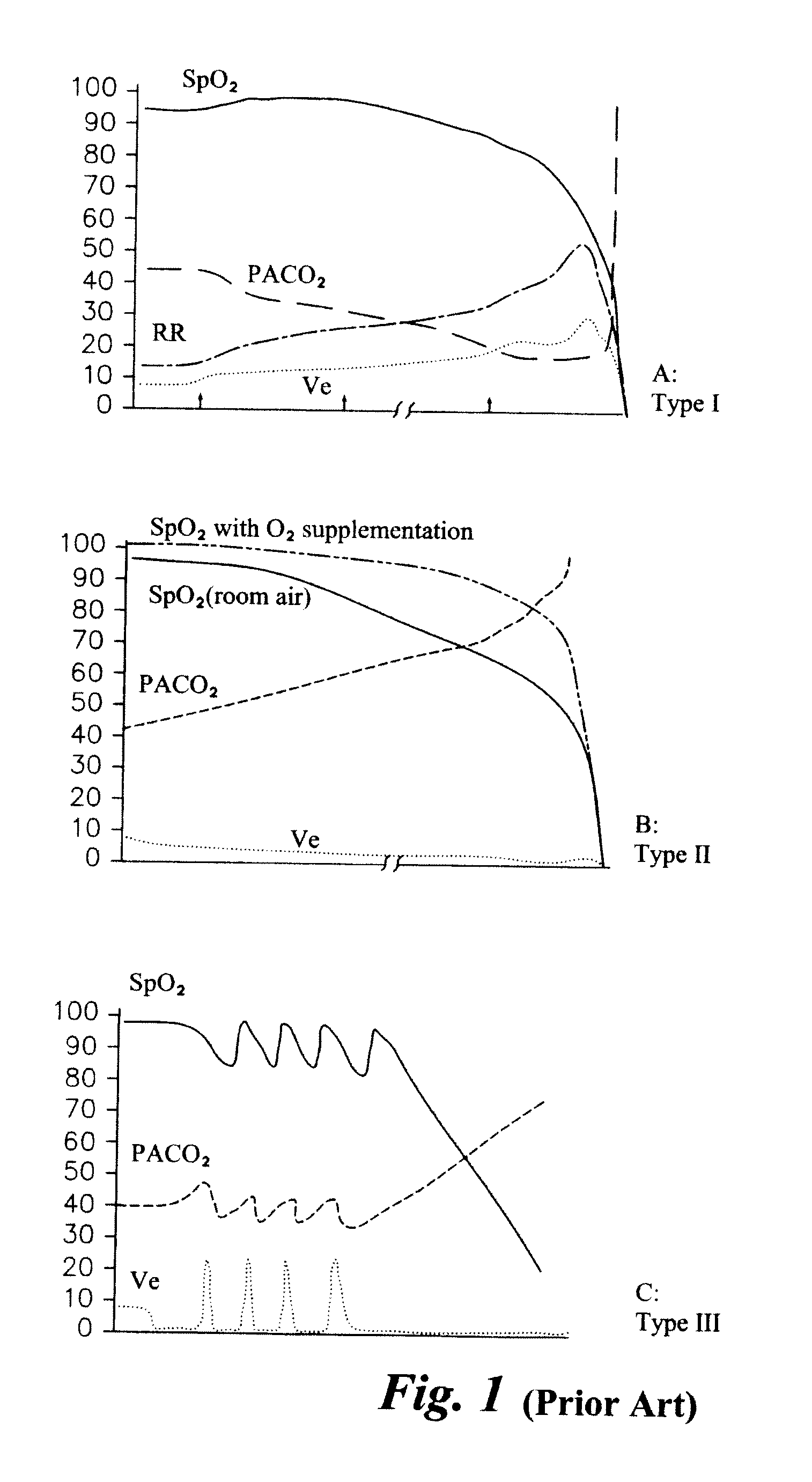
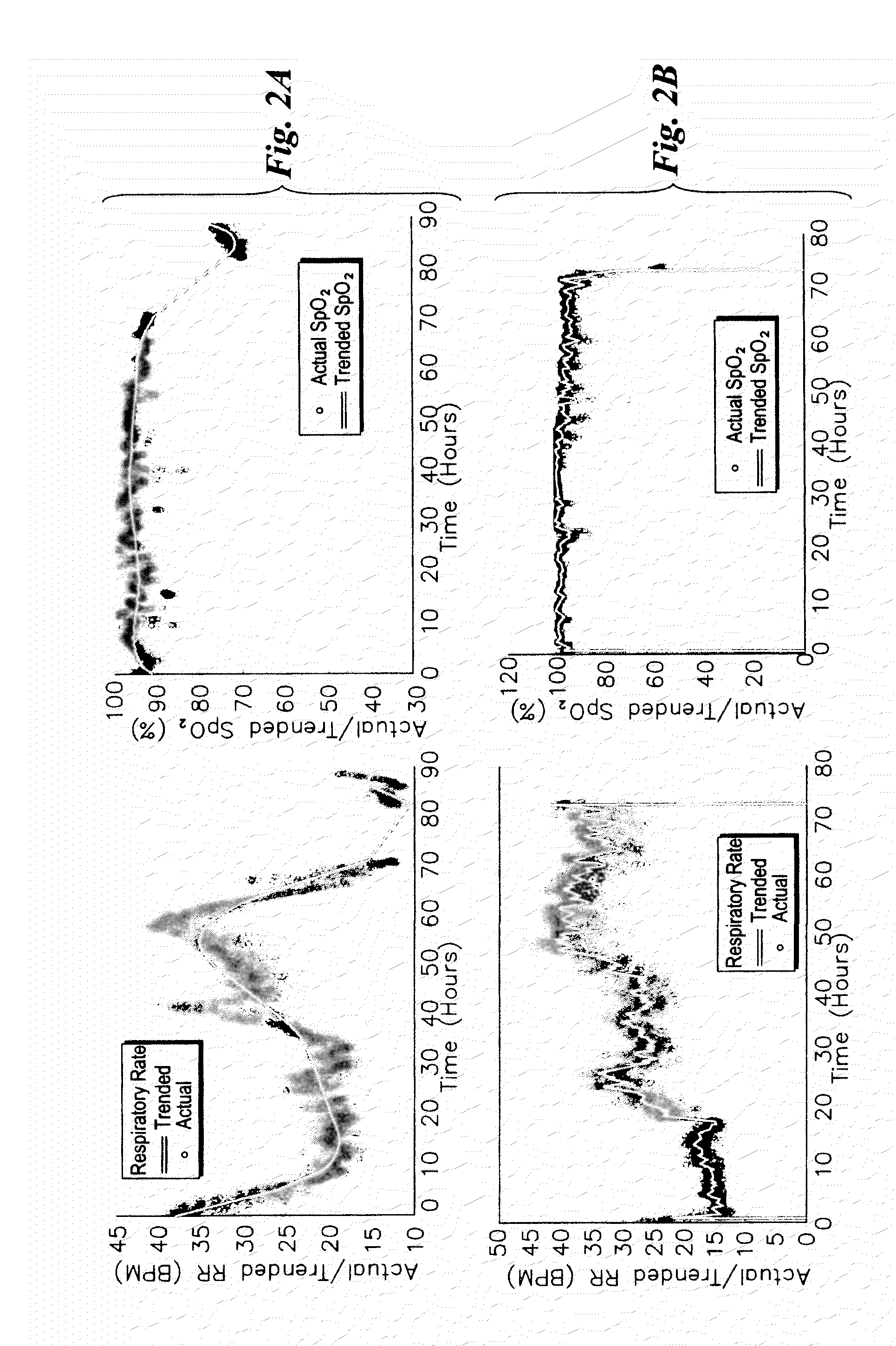
ActiveUS20150157275A1Accurately estimate trends in RRAvoid fatigueHealth-index calculationEvaluation of blood vesselsPatient roomHospitalized patients
Embodiments of the disclosure are directed to a system for analysis of respiratory distress in hospitalized patients. The system performs multi-parametric simultaneous analysis of respiration rate (RR) and pulse oximetry (SpO2) data trends in order to gauge patterns of patient instability pertaining to respiratory distress. Three patterns in SpO2 and RR are used along with LOWESS algorithm and Chauvenets criteria for outlier rejection to obtain robust short term and long term trends in RR and SpO2. Pattern analysis detects the presence of any one of three pattern types proposed. Further, a learning paradigm is introduced to find unknown instances of respiratory distress. This algorithm in conjunction with the learning model allows early detection of respiratory distress in hospital ward and ICU patients.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Acylated uridine and cytidine and uses thereof
InactiveUS6274563B1No untoward pharmaceutical effectEfficient managementBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
The invention relates to compositions comprising acyl derivatives of cytidine and uridine. The invention also relates to methods of treating hepatopathies, diabetes, heart disease, cerebrovascular disorders, Parkinson's disease, infant respiratory distress syndrome and for enhancement of phospholipid biosynthesis comprising administering the acyl derivatives of the invention to an animal.
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Devices, systems, and methods for peripheral arteriovenous fistula creation
ActiveUS20140188028A1Reduce spreadPromote healingOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTFibrosis
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for the formation of an arteriovenous fistula in the limb of the patient. Embodiments include an apparatus for the creation, modification and maintenance of a fistula, including the modification of an existing dialysis fistula; and a method of supplying oxygenated blood to the venous circulation of a patient. A kit of anastomotic implants is described which supports a broad base of patient anatomies and fistula locations. The devices, systems and methods can be used to treat patients with one or more numerous ailments including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, hypertension, hypotension, respiratory failure, pulmonary arterial hypertension, lung fibrosis and adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Substituted heterocyclic compounds and methods of use
The present invention relates to compounds having the general formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1 is a saturated or unsaturated 5-, 6- or 7-membered, ring containing 0, 1, 2 or 3 atoms selected from N, O and S, wherein the ring may be fused with a benzo group, and is substituted by 0, 1 or 2 oxo groups, and wherein R1 is additionally substituted; and R2 is a substituted C1-6alkyl. Also included is a method of prophylaxis or treatment of inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, Pagets disease, osteoporosis, multiple myeloma, uveititis, acute or chronic myelogenous leukemia, pancreatic β cell destruction, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis, gouty arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), psoriasis, Crohn's disease, allergic rhinitis, ulcerative colitis, anaphylaxis, contact dermatitis, asthma, muscle degeneration, cachexia, Reiter's syndrome, type I diabetes, type II diabetes, bone resorption diseases, graft vs. host reaction, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, myocardial infarction, ischemia reperfusion injury, atherosclerosis, brain trauma, multiple sclerosis, cerebral malaria, sepsis, septic shock, toxic shock syndrome, fever, myalgias due to HIV-1, HIV-2, HIV-3, cytomegalovirus (CMV), influenza, adenovirus, the herpes viruses or herpes zoster infection in a mammal comprising administering an effective amount a compound as described above.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Ventilator for Rapid Response to Respiratory Disease Conditions
The present invention relates generally to the field of ventilators, and, more specifically, to a ventilator system that addresses respiratory distress due to the onset of an epidemic or pandemic disease state. In particular, the present invention is a ventilator system that can be manufactured quickly with minimal skill requirements and employed rapidly in response to epidemic respiratory disease conditions. In one embodiment, the present invention is directed toward a ventilator having a gas input, an inhalation conduit connected to the gas input, a patient flow control valve, operably connected to the gas input via the inhalation conduit, a patient interface, separated from the inhalation conduit by the flow control valve, and a gas shut-off mechanism that senses a pressure state in the inhalation conduit.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
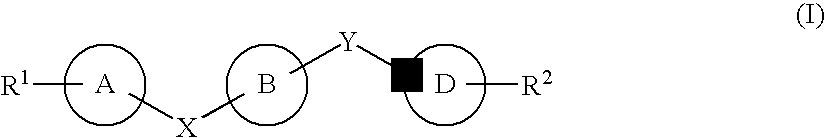
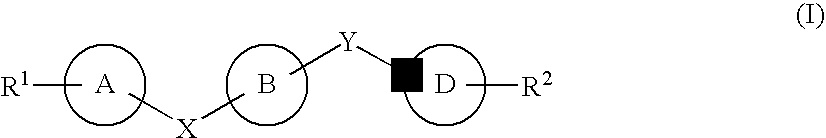
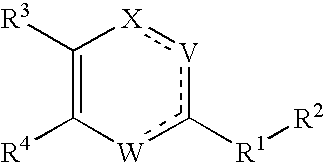
Novel heterocycles
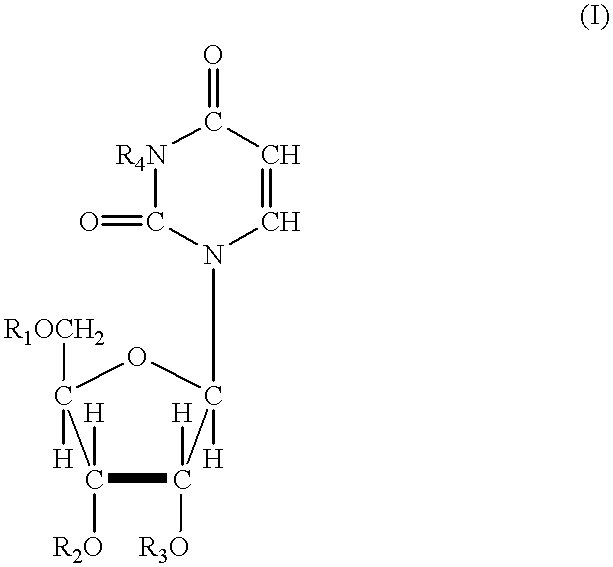
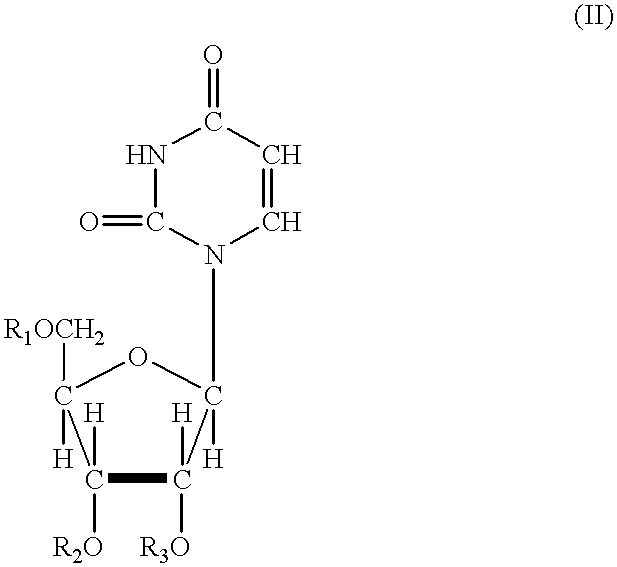
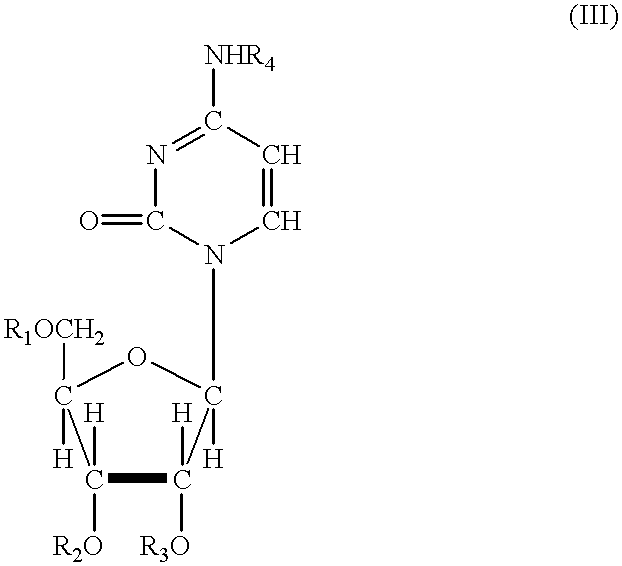
InactiveUS20070167413A1Useful in treatmentOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTContact dermatitis
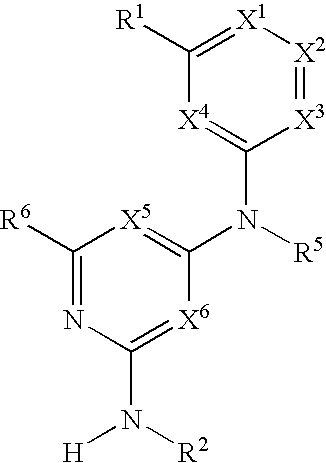
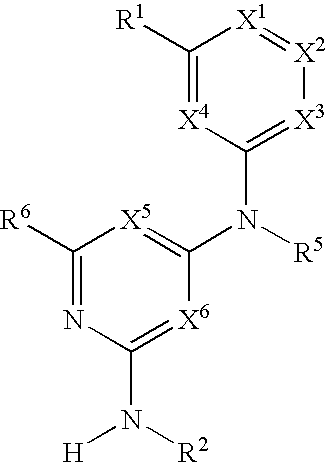
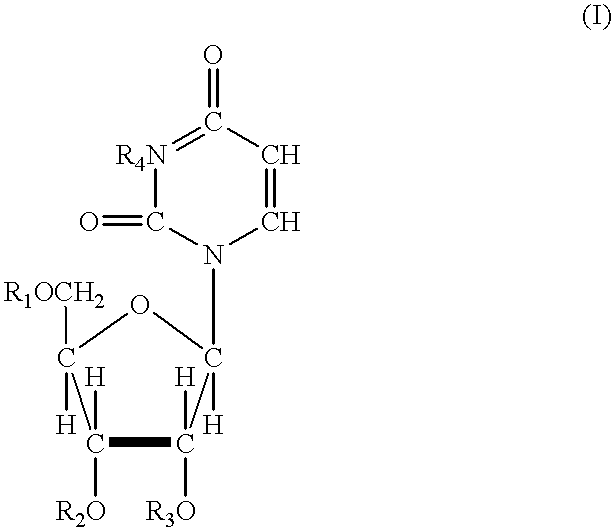
The present invention relates to novel heterocyclic compounds of the general formula (I), their derivatives, analogs, tautomeric forms, stereoisomers, polymorphs, hydrates, solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts and compositions, metabolites and prodrugs thereof. The present invention more particularly provides novel hetereocycles of the general formula (I). Also included is a method of treatment of immunological diseases, inflammation, pain disorder, rheumatoid arthritis; osteoporosis; multiple myeloma; uveititis; acute and chronic myelogenous leukemia; ischemic heart disease; atherosclerosis; cancer; ischemic-induced cell damage; pancreatic beta cell destruction; osteoarthritis; rheumatoid spondylitis; gouty arthritis; inflammatory bowel disease; adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); psoriasis; Crohn's disease; allergic rhinitis; ulcerative colitis; anaphylaxis; contact dermatitis; muscle degeneration; cachexia; asthma; bone resorption diseases; ischemia reperfusion injury; brain trauma; multiple sclerosis; sepsis; septic shock; toxic shock syndrome; fever, and myalgias due to infection in a mammal comprising administering an effective amount of a compound of formula (I) as described above.
Owner:ORCHID RES LAB +1
Substituted heterocyclic compounds and methods of use
The present invention relates to compounds having the general formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1 is a saturated or unsaturated 5-, 6- or 7-membered, ring containing 0, 1, 2 or 3 atoms selected from N, O and S, wherein the ring may be fused with a benzo group, and is substituted by 0, 1 or 2 oxo groups, and wherein R1 is additionally substituted; and R2 is a substituted C1-6alkyl. Also included is a method of prophylaxis or treatment of inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, Pagets disease, osteoporosis, multiple myeloma, uveititis, acute or chronic myelogenous leukemia, pancreatic β cell destruction, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid spondylitis, gouty arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), psoriasis, Crohn's disease, allergic rhinitis, ulcerative colitis, anaphylaxis, contact dermatitis, asthma, muscle degeneration, cachexia, Reiter's syndrome, type I diabetes, type II diabetes, bone resorption diseases, graft vs. host reaction, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, myocardial infarction, ischemia reperfusion injury, atherosclerosis, brain trauma, multiple sclerosis, cerebral malaria, sepsis, septic shock, toxic shock syndrome, fever, myalgias due to HIV-1, HIV-2, HIV-3, cytomegalovirus (CMV), influenza, adenovirus, the herpes viruses or herpes zoster infection in a mammal comprising administering an effective amount a compound as described above.
Owner:AMGEN INC
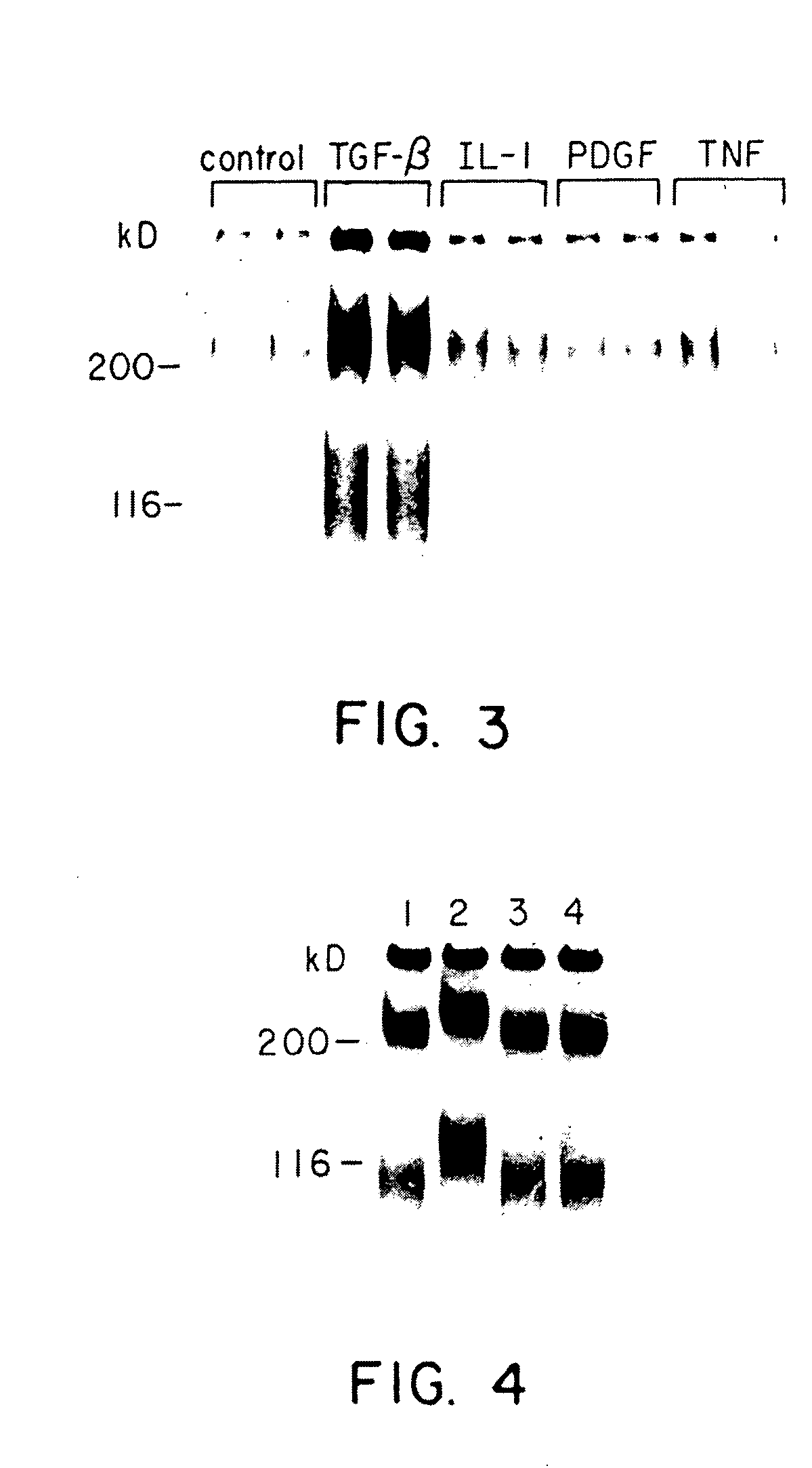
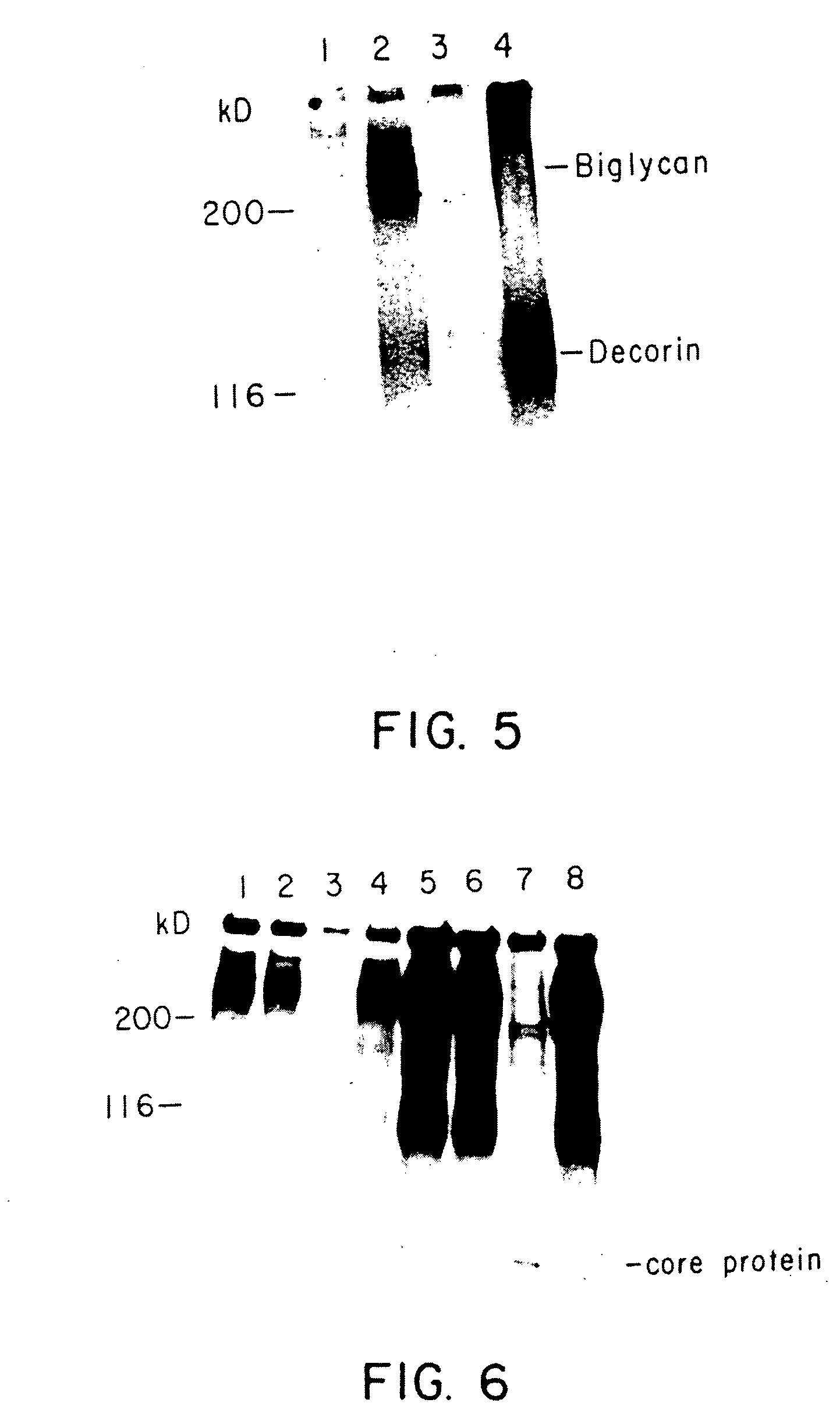
Inhibiting transforming growth factor beta to prevent accumulation of extracellular matrix
InactiveUS20040028682A1Connective tissue peptidesTetrapeptide ingredientsRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTCell-Extracellular Matrix
The present invention provides a method for treating or arresting the progress of pathologies characterized by an accumulation of extracellular matrix components by providing an agent to suppress the activity of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) a peptide growth factor which is anabolic and leads to fibrosis and angiogenesis. In one embodiment, such agent is anti-TGF-beta antibody. Pathologies which can be so treated include, but are not limited to, glomerulonephritis, adult respiratory distress syndrome and cirrhosis of the liver. The invention further provides a method for the diagnosis of pathologies, or incipient pathologies, which are characterized by the accumulation of extracellular matrix components in tissues by determining the levels of TGF-beta in the tissues, a high level being indicative of such pathologies.
Owner:BORDER WAYNE A +1
Medicinal composition for inhalation
InactiveUS7858650B2Prolonged bronchodilating and antiinflammatory effectInhibitionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME ADULTPulmonary Injury
A medicinal composition for inhalation containing a continuous-release type prodrug of an EP2 agonist topically exhibits a prolonged bronchodilating and antiinflammatory effects. Namely, the medicinal composition for inhalation containing a continuous-release type prodrug of an EP2 agonist is useful as a safe preventive and / or a remedy for respiratory diseases (for example, asthma, pulmonary injury, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary emphysema, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, adult respiratory distress syndrome, cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension or the like) without causing any systemic effect such as lowering blood pressure. Thus, a safe and useful remedy for respiratory diseases is provided.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Food and feed compositions including resistant starch
ActiveUS7252836B2Increase the content of dietary fiberReduce morbidityDough treatmentFood processingWeight gainingResistant starch
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC +1
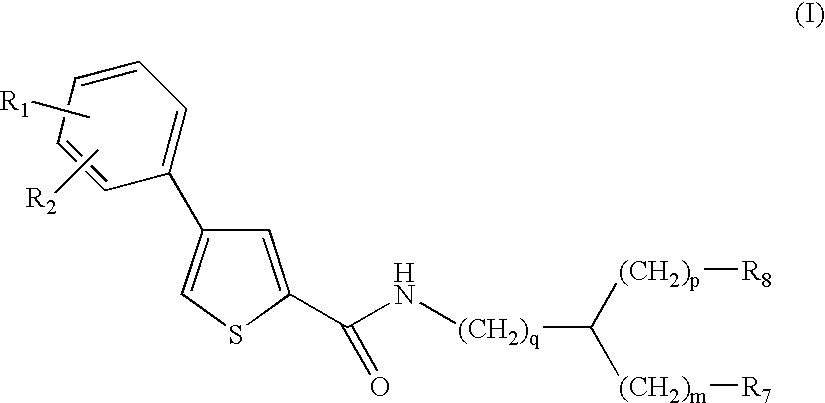
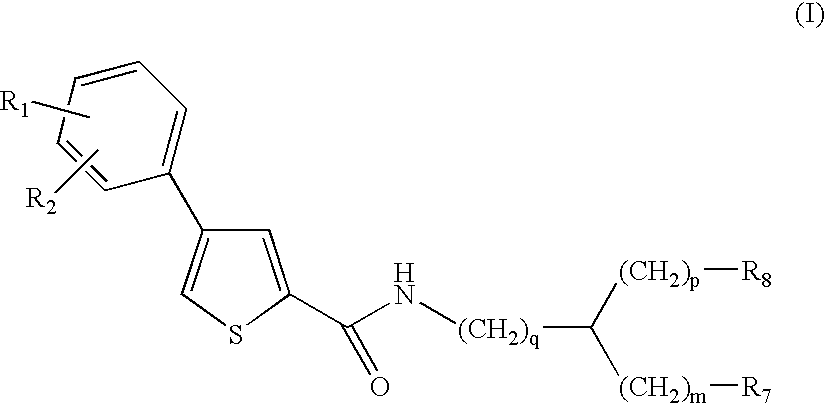
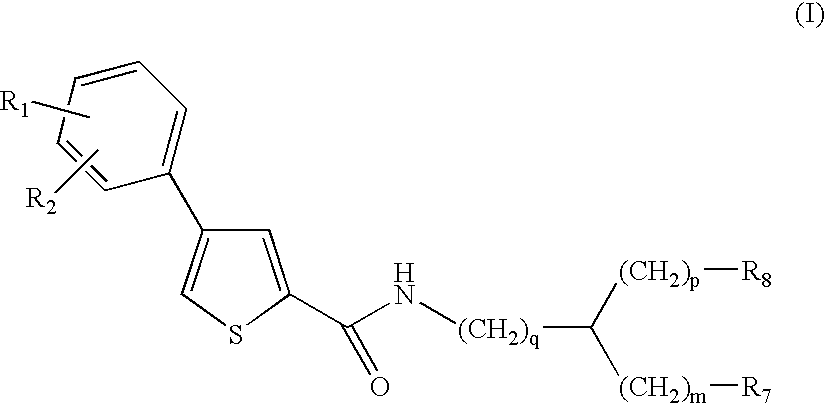
Thiophene amino acid derivatives, process for preparing them and pharmaceutical compositions containing them
The invention provides compounds of Formula (I), stereoisomers thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts of said compounds or stereoisomers, wherein R1, R2, m, p, q, R7 and R8 are as defined below, as well as compositions comprising the same, processes for making the same, and methods of using the same to treat a variety of diseases, including, those requiring interaction with metalloproteases, and more specifically with macrophage metalloelastase (MMP-12), and for the prevention and treatment of respiratory pathologies such as chronic obstructive bronchopneumopathy (COPD), emphysema, chronic bronchitis, chronic pulmonary inflammation, asthma, cystic fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), respiratory allergies including allergic rhinitis, and also diseases associated with the production of TNFα including severe fibrotic pulmonary disease, pulmonary sarcoidosis and silicosis. The compounds of the present invention also show inhibitory activity on metalloprotease-13 (MMP-13), making them useful for the treatment of pathologies involving this enzyme, such as cancer, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis and cardiac insufficiency.
Owner:PFIZER INC
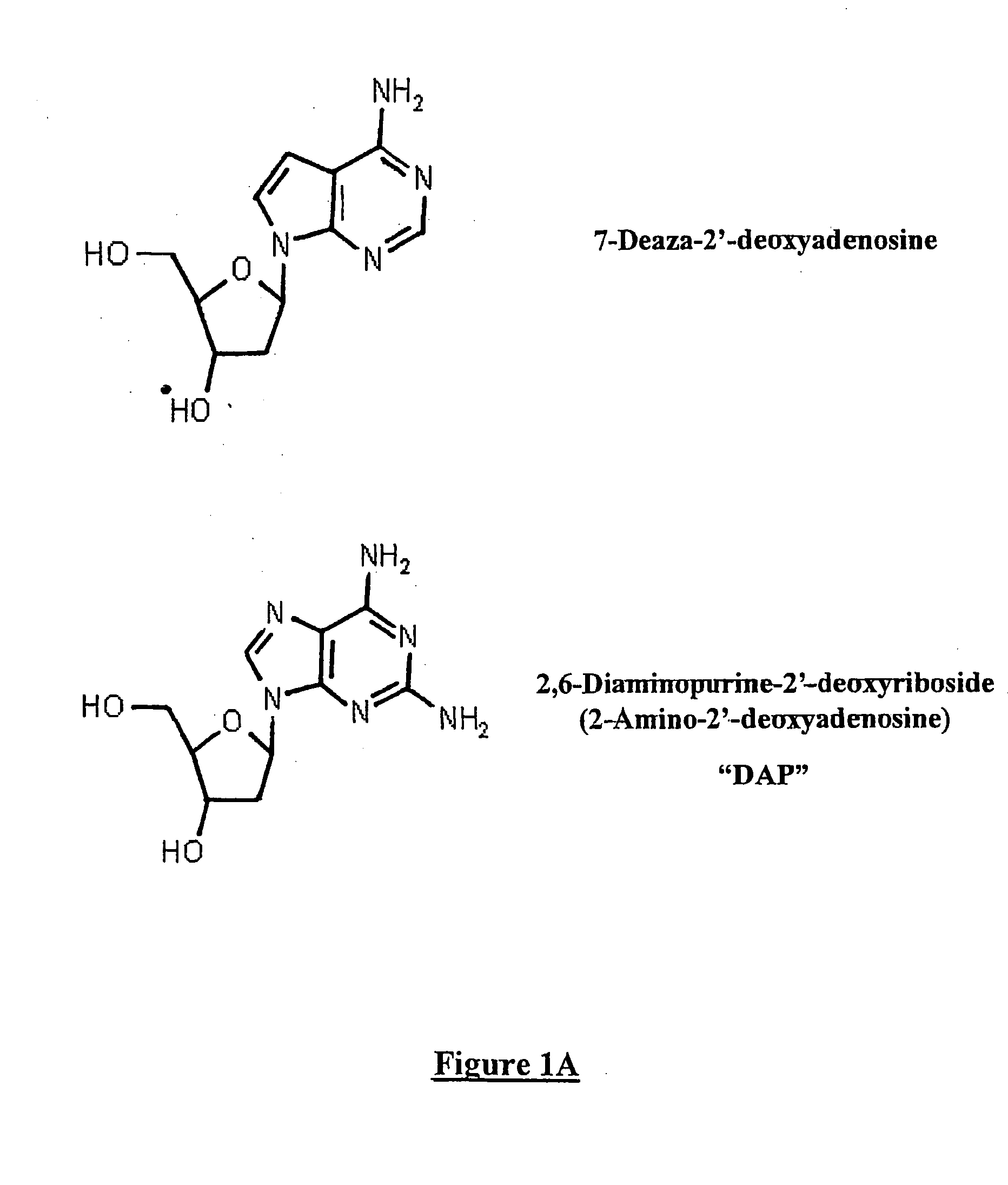
Methods for increasing in vivo efficacy of oligonucleotides and inhibiting inflammation in mammals
The invention relates to the use of nucleotide substitutes for increasing the in vivo efficacy of nucleic acid molecules and also for inhibiting inflammation in mammals. More particularly, the present invention relates to the use of 2′6′diaminopurine (DAP) and analogs thereof per se in anti-inflammatory compositions, and also for preparing nucleic acid molecules having an increased in vivo physiological efficiency and a reduced toxicity as compared to conventional oligos. The invention is particularly useful for the preparation of antisense oligonucleotides for treating pulmonary / respiratory diseases such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive lung disease, eosinophilic bronchitis, allergies, allergic rhinitis, pulmonary fibrosis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, sinusitis, respiratory syncytial virus or other viral respiratory tract infection and cancer.
Owner:PHARMAXIS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com